User login
New developments on the forefront of intermediate-risk pulmonary embolism
PULMONARY VASCULAR AND CARDIOVASCULAR NETWORK
Cardiovascular Medicine and Surgery Section
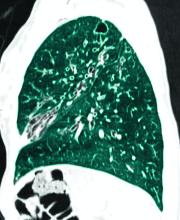
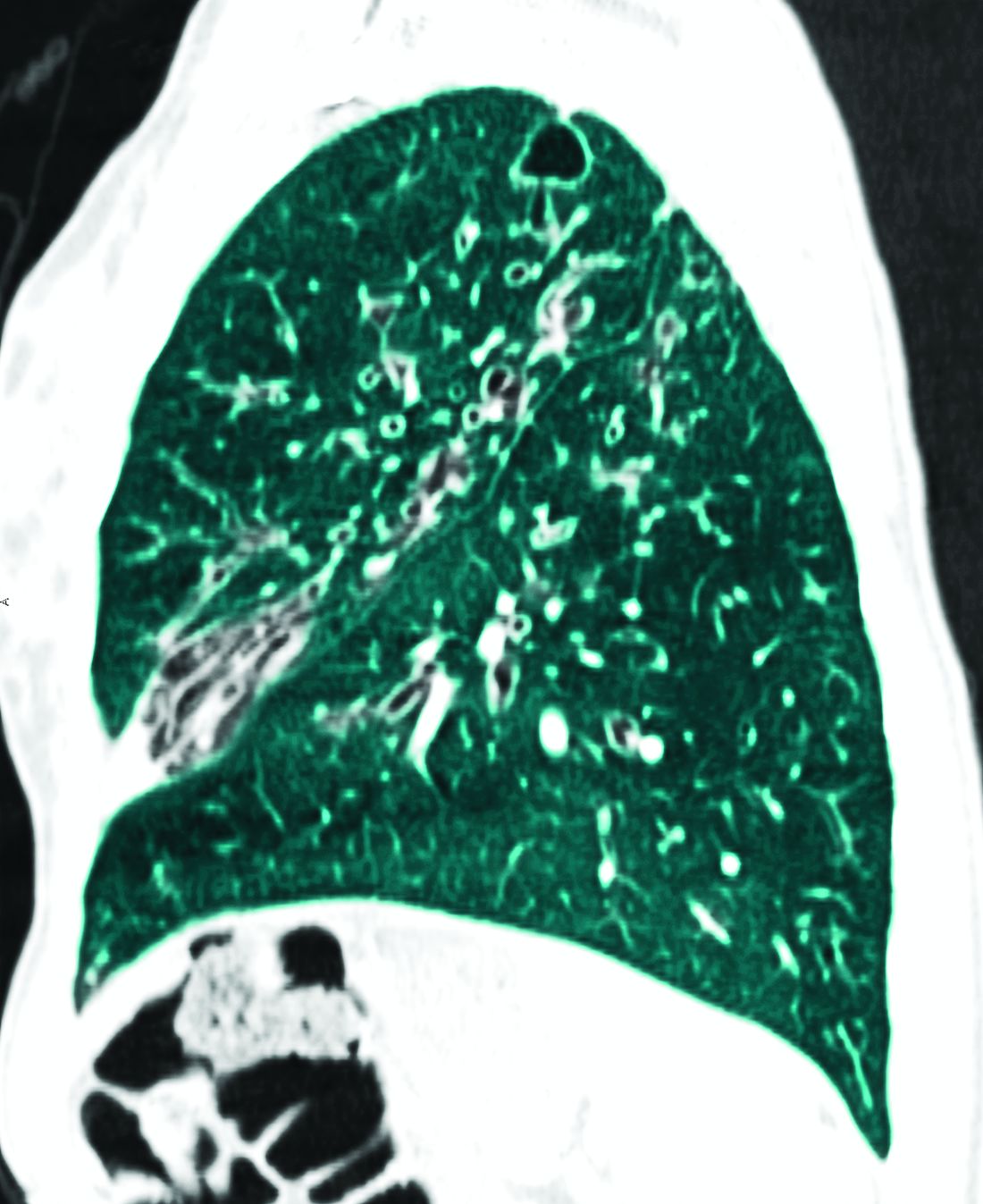
Patients with intermediate-risk pulmonary embolism (IRPE), or those with right ventricular dysfunction without overt hemodynamic instability, represent a heterogenous population with short-term mortality ranging from 2% to 17%.1 While systemic anticoagulation is the mainstay therapy, select individuals may benefit from more immediate reperfusion. Unfortunately, only small, randomized trials exploring surrogate outcomes are available to guide modality and patient selection.2
To better define which patients with IRPE are best managed with which therapy, several large-scale randomized controlled trials are underway. PE-TRACT, a study funded by the National Institutes of Health, aims to randomize 500 patients with IRPE to anticoagulation alone vs one of several modalities of CBT with a focus on long-term functional outcomes, including peak oxygen consumption at 3 months and functional class at 1 year. Aspiration thrombectomy with the FlowTriever® device is being compared with anticoagulation alone in a study of 1,200 patients examining short-term composite end points.
While full-dose thrombolysis may decrease the composite outcome of death or hemodynamic deterioration in this population, the benefit is counterbalanced by the risk of significant bleeding. Whether reduced-dose thrombolysis is associated with improved outcomes has been questioned in several small studies. The PEITHO-3 trial plans to randomize 650 patients with IRPE to reduced-dose thrombolytics vs placebo, exploring several outcomes at 30 days. With multiple large trials ongoing, we anticipate important changes to the landscape of IRPE care over the coming years.
References
1. Fernández C, Bova C, Sanchez O, et al. Validation of a model for identification of patients at intermediate to high risk for complications associated with acute symptomatic pulmonary embolism. Chest. 2015;148(1):211-218. doi:10.1378/chest.14-2551
2. Yuriditsky E, Horowitz JM. The role of the PERT in the management and therapeutic decision-making in pulmonary embolism. Eur Heart J Acute Cardiovasc Care. 2022;11(9):693-694. doi:10.1093/ehjacc/zuac102
3. National Library of Medicine (US). A Randomized Trial of Ultrasound-facilitated, Catheter-directed, Thrombolysis Versus Anticoagulation for Acute Intermediate-high Risk Pulmonary Embolism: The Higher-risk Pulmonary Embolism Thrombolysis Study. Updated July 16, 2024. https://clinicaltrials.gov/study/NCT04790370
4. National Library of Medicine (US). PEERLESS II: RCT of FlowTriever vs. Anticoagulation Alone in Pulmonary Embolism. Updated July 17, 2024. https://clinicaltrials.gov/study/NCT06055920
5. National Library of Medicine (US). A Reduced Dose of Thrombolytic Treatment for Patients With Intermediate High-risk Acute Pulmonary Embolism: a Randomized Controled Trial. Updated July 17, 2024. https://clinicaltrials.gov/study/NCT04430569
PULMONARY VASCULAR AND CARDIOVASCULAR NETWORK
Cardiovascular Medicine and Surgery Section
Patients with intermediate-risk pulmonary embolism (IRPE), or those with right ventricular dysfunction without overt hemodynamic instability, represent a heterogenous population with short-term mortality ranging from 2% to 17%.1 While systemic anticoagulation is the mainstay therapy, select individuals may benefit from more immediate reperfusion. Unfortunately, only small, randomized trials exploring surrogate outcomes are available to guide modality and patient selection.2
To better define which patients with IRPE are best managed with which therapy, several large-scale randomized controlled trials are underway. PE-TRACT, a study funded by the National Institutes of Health, aims to randomize 500 patients with IRPE to anticoagulation alone vs one of several modalities of CBT with a focus on long-term functional outcomes, including peak oxygen consumption at 3 months and functional class at 1 year. Aspiration thrombectomy with the FlowTriever® device is being compared with anticoagulation alone in a study of 1,200 patients examining short-term composite end points.
While full-dose thrombolysis may decrease the composite outcome of death or hemodynamic deterioration in this population, the benefit is counterbalanced by the risk of significant bleeding. Whether reduced-dose thrombolysis is associated with improved outcomes has been questioned in several small studies. The PEITHO-3 trial plans to randomize 650 patients with IRPE to reduced-dose thrombolytics vs placebo, exploring several outcomes at 30 days. With multiple large trials ongoing, we anticipate important changes to the landscape of IRPE care over the coming years.
References
1. Fernández C, Bova C, Sanchez O, et al. Validation of a model for identification of patients at intermediate to high risk for complications associated with acute symptomatic pulmonary embolism. Chest. 2015;148(1):211-218. doi:10.1378/chest.14-2551
2. Yuriditsky E, Horowitz JM. The role of the PERT in the management and therapeutic decision-making in pulmonary embolism. Eur Heart J Acute Cardiovasc Care. 2022;11(9):693-694. doi:10.1093/ehjacc/zuac102
3. National Library of Medicine (US). A Randomized Trial of Ultrasound-facilitated, Catheter-directed, Thrombolysis Versus Anticoagulation for Acute Intermediate-high Risk Pulmonary Embolism: The Higher-risk Pulmonary Embolism Thrombolysis Study. Updated July 16, 2024. https://clinicaltrials.gov/study/NCT04790370
4. National Library of Medicine (US). PEERLESS II: RCT of FlowTriever vs. Anticoagulation Alone in Pulmonary Embolism. Updated July 17, 2024. https://clinicaltrials.gov/study/NCT06055920
5. National Library of Medicine (US). A Reduced Dose of Thrombolytic Treatment for Patients With Intermediate High-risk Acute Pulmonary Embolism: a Randomized Controled Trial. Updated July 17, 2024. https://clinicaltrials.gov/study/NCT04430569
PULMONARY VASCULAR AND CARDIOVASCULAR NETWORK
Cardiovascular Medicine and Surgery Section
Patients with intermediate-risk pulmonary embolism (IRPE), or those with right ventricular dysfunction without overt hemodynamic instability, represent a heterogenous population with short-term mortality ranging from 2% to 17%.1 While systemic anticoagulation is the mainstay therapy, select individuals may benefit from more immediate reperfusion. Unfortunately, only small, randomized trials exploring surrogate outcomes are available to guide modality and patient selection.2
To better define which patients with IRPE are best managed with which therapy, several large-scale randomized controlled trials are underway. PE-TRACT, a study funded by the National Institutes of Health, aims to randomize 500 patients with IRPE to anticoagulation alone vs one of several modalities of CBT with a focus on long-term functional outcomes, including peak oxygen consumption at 3 months and functional class at 1 year. Aspiration thrombectomy with the FlowTriever® device is being compared with anticoagulation alone in a study of 1,200 patients examining short-term composite end points.
While full-dose thrombolysis may decrease the composite outcome of death or hemodynamic deterioration in this population, the benefit is counterbalanced by the risk of significant bleeding. Whether reduced-dose thrombolysis is associated with improved outcomes has been questioned in several small studies. The PEITHO-3 trial plans to randomize 650 patients with IRPE to reduced-dose thrombolytics vs placebo, exploring several outcomes at 30 days. With multiple large trials ongoing, we anticipate important changes to the landscape of IRPE care over the coming years.
References
1. Fernández C, Bova C, Sanchez O, et al. Validation of a model for identification of patients at intermediate to high risk for complications associated with acute symptomatic pulmonary embolism. Chest. 2015;148(1):211-218. doi:10.1378/chest.14-2551
2. Yuriditsky E, Horowitz JM. The role of the PERT in the management and therapeutic decision-making in pulmonary embolism. Eur Heart J Acute Cardiovasc Care. 2022;11(9):693-694. doi:10.1093/ehjacc/zuac102
3. National Library of Medicine (US). A Randomized Trial of Ultrasound-facilitated, Catheter-directed, Thrombolysis Versus Anticoagulation for Acute Intermediate-high Risk Pulmonary Embolism: The Higher-risk Pulmonary Embolism Thrombolysis Study. Updated July 16, 2024. https://clinicaltrials.gov/study/NCT04790370
4. National Library of Medicine (US). PEERLESS II: RCT of FlowTriever vs. Anticoagulation Alone in Pulmonary Embolism. Updated July 17, 2024. https://clinicaltrials.gov/study/NCT06055920
5. National Library of Medicine (US). A Reduced Dose of Thrombolytic Treatment for Patients With Intermediate High-risk Acute Pulmonary Embolism: a Randomized Controled Trial. Updated July 17, 2024. https://clinicaltrials.gov/study/NCT04430569
Bronchiectasis: A call to action
AIRWAYS DISORDERS NETWORK
Bronchiectasis Section
For years, the noncystic fibrosis (CF) bronchiectasis community has been trying to organize to provide better care for more than half a million adults with bronchiectasis in the United States. Internationally, the Europeans created the European Bronchiectasis Registry, which has been a powerful tool including nearly 20,000 patients, to answer important epidemiologic and management questions. We must do more for the bronchiectasis community.
Clinicaltrials.gov indicates that there are 8 international phase 3 or 4 clinical trials that are currently enrolling; 3 of those have enrollment sites in the United States. One such study from University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill is looking at the use of nebulized hypertonic saline in patients with non-CF bronchiectasis to understand the effect it has on mucociliary clearance. Emory University is looking at the use of elexacaftor/tezacaftor/ivacaftor (Trikafta) in patients with non-CF bronchiectasis; these patients have only 1 targetable mutation and a phenotype that resembles CF. This 8-week, open-label, single-center study aims to measure both clinical and biomarker outcomes after treatment with Trikafta. Finally, a phase 3 trial out of Florida, the ICoN-1 study, is examining the efficacy and safety of inhaled clofazimine in the treatment of nontuberculous mycobacteria (NTM). This double-blind, randomized trial will look at culture conversion and quality of life measures. Additionally, the COPD Foundation has created the Bronchiectasis and NTM Research Registry, an American cohort containing more than 5,000 patients and data from 22 different sites, to answer some of the most important questions for clinicians and patients.
We have made significant progress in bronchiectasis research; however, there is still much to learn. Together, we must make a concerted effort to enroll patients in clinical trials. Doing so will allow us to define our epidemiologic profile more precisely and explore new treatments and airway clearance techniques.
AIRWAYS DISORDERS NETWORK
Bronchiectasis Section
For years, the noncystic fibrosis (CF) bronchiectasis community has been trying to organize to provide better care for more than half a million adults with bronchiectasis in the United States. Internationally, the Europeans created the European Bronchiectasis Registry, which has been a powerful tool including nearly 20,000 patients, to answer important epidemiologic and management questions. We must do more for the bronchiectasis community.
Clinicaltrials.gov indicates that there are 8 international phase 3 or 4 clinical trials that are currently enrolling; 3 of those have enrollment sites in the United States. One such study from University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill is looking at the use of nebulized hypertonic saline in patients with non-CF bronchiectasis to understand the effect it has on mucociliary clearance. Emory University is looking at the use of elexacaftor/tezacaftor/ivacaftor (Trikafta) in patients with non-CF bronchiectasis; these patients have only 1 targetable mutation and a phenotype that resembles CF. This 8-week, open-label, single-center study aims to measure both clinical and biomarker outcomes after treatment with Trikafta. Finally, a phase 3 trial out of Florida, the ICoN-1 study, is examining the efficacy and safety of inhaled clofazimine in the treatment of nontuberculous mycobacteria (NTM). This double-blind, randomized trial will look at culture conversion and quality of life measures. Additionally, the COPD Foundation has created the Bronchiectasis and NTM Research Registry, an American cohort containing more than 5,000 patients and data from 22 different sites, to answer some of the most important questions for clinicians and patients.
We have made significant progress in bronchiectasis research; however, there is still much to learn. Together, we must make a concerted effort to enroll patients in clinical trials. Doing so will allow us to define our epidemiologic profile more precisely and explore new treatments and airway clearance techniques.
AIRWAYS DISORDERS NETWORK
Bronchiectasis Section
For years, the noncystic fibrosis (CF) bronchiectasis community has been trying to organize to provide better care for more than half a million adults with bronchiectasis in the United States. Internationally, the Europeans created the European Bronchiectasis Registry, which has been a powerful tool including nearly 20,000 patients, to answer important epidemiologic and management questions. We must do more for the bronchiectasis community.
Clinicaltrials.gov indicates that there are 8 international phase 3 or 4 clinical trials that are currently enrolling; 3 of those have enrollment sites in the United States. One such study from University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill is looking at the use of nebulized hypertonic saline in patients with non-CF bronchiectasis to understand the effect it has on mucociliary clearance. Emory University is looking at the use of elexacaftor/tezacaftor/ivacaftor (Trikafta) in patients with non-CF bronchiectasis; these patients have only 1 targetable mutation and a phenotype that resembles CF. This 8-week, open-label, single-center study aims to measure both clinical and biomarker outcomes after treatment with Trikafta. Finally, a phase 3 trial out of Florida, the ICoN-1 study, is examining the efficacy and safety of inhaled clofazimine in the treatment of nontuberculous mycobacteria (NTM). This double-blind, randomized trial will look at culture conversion and quality of life measures. Additionally, the COPD Foundation has created the Bronchiectasis and NTM Research Registry, an American cohort containing more than 5,000 patients and data from 22 different sites, to answer some of the most important questions for clinicians and patients.
We have made significant progress in bronchiectasis research; however, there is still much to learn. Together, we must make a concerted effort to enroll patients in clinical trials. Doing so will allow us to define our epidemiologic profile more precisely and explore new treatments and airway clearance techniques.
Black Children With Vitiligo at Increased Risk for Psychiatric Disorders: Study
TOPLINE:
Black children with vitiligo are significantly more likely to be diagnosed with psychiatric disorders, including depression, suicidal ideation, and disruptive behavior disorders, than matched controls who did not have vitiligo, according to a case-control study.
METHODOLOGY:
- Researchers conducted a retrospective, single-center, case-control study at Texas Children’s Hospital in Houston on 327 Black children with vitiligo and 981 matched controls without vitiligo.
- The average age of participants was 11.7 years, and 62% were girls.
- The study outcome was the prevalence of psychiatric conditions and rates of treatment (pharmacotherapy and/or psychotherapy) initiation for those conditions.
TAKEAWAY:
- Black children with vitiligo were more likely to be diagnosed with depression (odds ratio [OR], 3.63; P < .001), suicidal ideation (OR, 2.88; P = .005), disruptive behavior disorders (OR, 7.68; P < .001), eating disorders (OR, 15.22; P = .013), generalized anxiety disorder (OR, 2.61; P < .001), and substance abuse (OR, 2.67; P = .011).
- The likelihood of having a psychiatric comorbidity was not significantly different between children with segmental vitiligo and those with generalized vitiligo or between girls and boys.
- Among the patients with vitiligo and psychiatric comorbidities, treatment initiation rates were higher for depression (76.5%), disruptive behavior disorders (82.1%), and eating disorders (100%).
- Treatment initiation rates were lower in patients with vitiligo diagnosed with generalized anxiety disorder (55.3%) and substance abuse (61.5%). Treatment was not initiated in 14% patients with suicidal ideation.
IN PRACTICE:
“Pediatric dermatologists have an important role in screening for psychiatric comorbidities, and implementation of appropriate screening tools while treating vitiligo is likely to have a bidirectional positive impact,” the authors wrote, adding: “By better understanding psychiatric comorbidities of African American children with vitiligo, dermatologists can be more aware of pediatric mental health needs and provide appropriate referrals.”
SOURCE:
This study was led by Emily Strouphauer, BSA, Baylor College of Medicine, Houston, and was published online in JAAD International.
LIMITATIONS:
The study limitations were the retrospective design, small sample size, and heterogeneity in the control group.
DISCLOSURES:
The study did not receive any funding. The authors declared no competing interests.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
Black children with vitiligo are significantly more likely to be diagnosed with psychiatric disorders, including depression, suicidal ideation, and disruptive behavior disorders, than matched controls who did not have vitiligo, according to a case-control study.
METHODOLOGY:
- Researchers conducted a retrospective, single-center, case-control study at Texas Children’s Hospital in Houston on 327 Black children with vitiligo and 981 matched controls without vitiligo.
- The average age of participants was 11.7 years, and 62% were girls.
- The study outcome was the prevalence of psychiatric conditions and rates of treatment (pharmacotherapy and/or psychotherapy) initiation for those conditions.
TAKEAWAY:
- Black children with vitiligo were more likely to be diagnosed with depression (odds ratio [OR], 3.63; P < .001), suicidal ideation (OR, 2.88; P = .005), disruptive behavior disorders (OR, 7.68; P < .001), eating disorders (OR, 15.22; P = .013), generalized anxiety disorder (OR, 2.61; P < .001), and substance abuse (OR, 2.67; P = .011).
- The likelihood of having a psychiatric comorbidity was not significantly different between children with segmental vitiligo and those with generalized vitiligo or between girls and boys.
- Among the patients with vitiligo and psychiatric comorbidities, treatment initiation rates were higher for depression (76.5%), disruptive behavior disorders (82.1%), and eating disorders (100%).
- Treatment initiation rates were lower in patients with vitiligo diagnosed with generalized anxiety disorder (55.3%) and substance abuse (61.5%). Treatment was not initiated in 14% patients with suicidal ideation.
IN PRACTICE:
“Pediatric dermatologists have an important role in screening for psychiatric comorbidities, and implementation of appropriate screening tools while treating vitiligo is likely to have a bidirectional positive impact,” the authors wrote, adding: “By better understanding psychiatric comorbidities of African American children with vitiligo, dermatologists can be more aware of pediatric mental health needs and provide appropriate referrals.”
SOURCE:
This study was led by Emily Strouphauer, BSA, Baylor College of Medicine, Houston, and was published online in JAAD International.
LIMITATIONS:
The study limitations were the retrospective design, small sample size, and heterogeneity in the control group.
DISCLOSURES:
The study did not receive any funding. The authors declared no competing interests.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
Black children with vitiligo are significantly more likely to be diagnosed with psychiatric disorders, including depression, suicidal ideation, and disruptive behavior disorders, than matched controls who did not have vitiligo, according to a case-control study.
METHODOLOGY:
- Researchers conducted a retrospective, single-center, case-control study at Texas Children’s Hospital in Houston on 327 Black children with vitiligo and 981 matched controls without vitiligo.
- The average age of participants was 11.7 years, and 62% were girls.
- The study outcome was the prevalence of psychiatric conditions and rates of treatment (pharmacotherapy and/or psychotherapy) initiation for those conditions.
TAKEAWAY:
- Black children with vitiligo were more likely to be diagnosed with depression (odds ratio [OR], 3.63; P < .001), suicidal ideation (OR, 2.88; P = .005), disruptive behavior disorders (OR, 7.68; P < .001), eating disorders (OR, 15.22; P = .013), generalized anxiety disorder (OR, 2.61; P < .001), and substance abuse (OR, 2.67; P = .011).
- The likelihood of having a psychiatric comorbidity was not significantly different between children with segmental vitiligo and those with generalized vitiligo or between girls and boys.
- Among the patients with vitiligo and psychiatric comorbidities, treatment initiation rates were higher for depression (76.5%), disruptive behavior disorders (82.1%), and eating disorders (100%).
- Treatment initiation rates were lower in patients with vitiligo diagnosed with generalized anxiety disorder (55.3%) and substance abuse (61.5%). Treatment was not initiated in 14% patients with suicidal ideation.
IN PRACTICE:
“Pediatric dermatologists have an important role in screening for psychiatric comorbidities, and implementation of appropriate screening tools while treating vitiligo is likely to have a bidirectional positive impact,” the authors wrote, adding: “By better understanding psychiatric comorbidities of African American children with vitiligo, dermatologists can be more aware of pediatric mental health needs and provide appropriate referrals.”
SOURCE:
This study was led by Emily Strouphauer, BSA, Baylor College of Medicine, Houston, and was published online in JAAD International.
LIMITATIONS:
The study limitations were the retrospective design, small sample size, and heterogeneity in the control group.
DISCLOSURES:
The study did not receive any funding. The authors declared no competing interests.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The countdown to CHEST 2024 begins
As we find ourselves in September, I cannot help but dedicate my column to the upcoming CHEST Annual Meeting quickly approaching, October 6 to 9, in Boston.
If you haven’t yet been to a CHEST Annual Meeting, it’s an unmatched experience.
For those who have attended, there’s always something new to see. Every year is different, with the culture of the location guiding the way and new opportunities to network while engaging in activity. No matter how many times you have been, attending the CHEST Annual Meeting never gets old.
Leveraging CHEST 2024’s location, we’ll be hosting a Grand Rounds event days before the meeting starts with pulmonary and critical care medicine fellows from the regional Boston programs to learn from visiting CHEST leadership on a variety of influential topics. These fellowship programs held events like this prepandemic, so I’m truly excited we could help restart the tradition and give the local fellows an opportunity to interact with each other from both an academic and social perspective. Personally, I am very much looking forward to meeting and getting to know the fellows from the Boston area.
The meeting has a lot of notable opportunities lined up (see my official “President’s checklist”), including the third year of CHEST After Hours (Monday, October 7)—a unique storytelling event focusing on the humanities of medicine in partnership with The Nocturnists podcast. And for the first time in recent years, CHEST 2024 will feature a 5K run/walk (Tuesday, October 8) in support of CHEST philanthropy and its work to fuel breakthroughs, empower innovation, and drive toward a future where every patient’s well-being is safeguarded. I encourage you to register in advance of the meeting to secure your space and snag a souvenir T-shirt.
First thing Sunday morning (October 6), the meeting kicks off with the Opening Session where we will be celebrating the new fellows of the college (FCCP), honoring trailblazers in chest medicine, and welcoming this year’s keynote speaker.
This year’s keynote address will come from Vanessa Kerry, MD, who will speak on environmental issues and her work to raise awareness of the impact of climate change on health.
With so many things to look forward to, this meeting will be one to remember for all in attendance.
I look forward to seeing you in Boston,
Jack
As we find ourselves in September, I cannot help but dedicate my column to the upcoming CHEST Annual Meeting quickly approaching, October 6 to 9, in Boston.
If you haven’t yet been to a CHEST Annual Meeting, it’s an unmatched experience.
For those who have attended, there’s always something new to see. Every year is different, with the culture of the location guiding the way and new opportunities to network while engaging in activity. No matter how many times you have been, attending the CHEST Annual Meeting never gets old.
Leveraging CHEST 2024’s location, we’ll be hosting a Grand Rounds event days before the meeting starts with pulmonary and critical care medicine fellows from the regional Boston programs to learn from visiting CHEST leadership on a variety of influential topics. These fellowship programs held events like this prepandemic, so I’m truly excited we could help restart the tradition and give the local fellows an opportunity to interact with each other from both an academic and social perspective. Personally, I am very much looking forward to meeting and getting to know the fellows from the Boston area.
The meeting has a lot of notable opportunities lined up (see my official “President’s checklist”), including the third year of CHEST After Hours (Monday, October 7)—a unique storytelling event focusing on the humanities of medicine in partnership with The Nocturnists podcast. And for the first time in recent years, CHEST 2024 will feature a 5K run/walk (Tuesday, October 8) in support of CHEST philanthropy and its work to fuel breakthroughs, empower innovation, and drive toward a future where every patient’s well-being is safeguarded. I encourage you to register in advance of the meeting to secure your space and snag a souvenir T-shirt.
First thing Sunday morning (October 6), the meeting kicks off with the Opening Session where we will be celebrating the new fellows of the college (FCCP), honoring trailblazers in chest medicine, and welcoming this year’s keynote speaker.
This year’s keynote address will come from Vanessa Kerry, MD, who will speak on environmental issues and her work to raise awareness of the impact of climate change on health.
With so many things to look forward to, this meeting will be one to remember for all in attendance.
I look forward to seeing you in Boston,
Jack
As we find ourselves in September, I cannot help but dedicate my column to the upcoming CHEST Annual Meeting quickly approaching, October 6 to 9, in Boston.
If you haven’t yet been to a CHEST Annual Meeting, it’s an unmatched experience.
For those who have attended, there’s always something new to see. Every year is different, with the culture of the location guiding the way and new opportunities to network while engaging in activity. No matter how many times you have been, attending the CHEST Annual Meeting never gets old.
Leveraging CHEST 2024’s location, we’ll be hosting a Grand Rounds event days before the meeting starts with pulmonary and critical care medicine fellows from the regional Boston programs to learn from visiting CHEST leadership on a variety of influential topics. These fellowship programs held events like this prepandemic, so I’m truly excited we could help restart the tradition and give the local fellows an opportunity to interact with each other from both an academic and social perspective. Personally, I am very much looking forward to meeting and getting to know the fellows from the Boston area.
The meeting has a lot of notable opportunities lined up (see my official “President’s checklist”), including the third year of CHEST After Hours (Monday, October 7)—a unique storytelling event focusing on the humanities of medicine in partnership with The Nocturnists podcast. And for the first time in recent years, CHEST 2024 will feature a 5K run/walk (Tuesday, October 8) in support of CHEST philanthropy and its work to fuel breakthroughs, empower innovation, and drive toward a future where every patient’s well-being is safeguarded. I encourage you to register in advance of the meeting to secure your space and snag a souvenir T-shirt.
First thing Sunday morning (October 6), the meeting kicks off with the Opening Session where we will be celebrating the new fellows of the college (FCCP), honoring trailblazers in chest medicine, and welcoming this year’s keynote speaker.
This year’s keynote address will come from Vanessa Kerry, MD, who will speak on environmental issues and her work to raise awareness of the impact of climate change on health.
With so many things to look forward to, this meeting will be one to remember for all in attendance.
I look forward to seeing you in Boston,
Jack
Neurofibromatosis: What Affects Quality of Life Most?
TOPLINE:
Mobile images may be reliable for assessing cutaneous neurofibroma (cNF) features in patients with neurofibromatosis type 1 (NF1), according to a crowd-sourced .
METHODOLOGY:
- To learn more about the association of cNFs with QoL, pain, and itch in patients with this rare disease, researchers enrolled 1016 individuals aged 40 years and older with NF1 who had at least one cNF, from May 2021 to December 2023, after reaching out to patient-led or NF1 advocacy organizations in 13 countries, including the United States.
- Participants provided demographic data, detailed photographs, and saliva samples for genetic sequencing, with 583 participants (mean age, 51.7 years; 65.9% women) submitting high-quality photographs from seven body regions at the time of the study analysis.
- A subset of 50 participants also underwent whole-body imaging.
- Four researchers independently rated the photographs for various cNF features, including general severity, number, size, facial severity, and subtypes.
TAKEAWAY:
- Based on evaluations by NF1 specialists, the agreement between mobile and whole-body images was “substantial” (74%-88% agreement) for the number of cNFs, general severity, and facial severity. Agreement between self-reported numbers of cNFs and investigator-rated numbers based on photographs was “minimal to fair.”
- Female sex, the number of cNFs, severity of cNFs on the face, and globular cNFs were associated with worse QoL (based on Skindex scores); severity of cNFs on the face had the strongest impact on overall QoL (P < .001).
- An increasing number of cNFs and worsening facial severity were strongly correlated with higher emotion subdomain scores.
- A higher number of cNFs, more severe cNFs on the face, and larger cNFs were all slightly associated with increased itch and pain (P < .01).
IN PRACTICE:
“To develop effective therapeutics, meaningful clinical outcomes that are tied with improvement in QoL for persons with NF1 must be clearly defined,” the authors wrote. The results of this study, they added, “suggested the benefit of this crowd-sourced resource by identifying the features of cNFs with the greatest association with QoL and symptoms of pain and itch in persons with NF1, highlighting new intervention strategies and features to target to most improve QoL in NF1.”
SOURCE:
The study was led by Michelle Jade Lin, BS, Stanford University School of Medicine, Redwood City, California, and was published online in JAMA Dermatology.
LIMITATIONS:
The study included only a small number of individuals from racial and ethnic minority groups and did not capture ethnicity information, which could have provided further insights into disease impact across different demographics.
DISCLOSURES:
This study was supported by Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore, and the Bloomberg Family Foundation. Ms. Lin reported support from the Stanford Medical Scholars Research Program. Three authors reported personal fees or grants outside this work. Other authors reported no competing interests.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
Mobile images may be reliable for assessing cutaneous neurofibroma (cNF) features in patients with neurofibromatosis type 1 (NF1), according to a crowd-sourced .
METHODOLOGY:
- To learn more about the association of cNFs with QoL, pain, and itch in patients with this rare disease, researchers enrolled 1016 individuals aged 40 years and older with NF1 who had at least one cNF, from May 2021 to December 2023, after reaching out to patient-led or NF1 advocacy organizations in 13 countries, including the United States.
- Participants provided demographic data, detailed photographs, and saliva samples for genetic sequencing, with 583 participants (mean age, 51.7 years; 65.9% women) submitting high-quality photographs from seven body regions at the time of the study analysis.
- A subset of 50 participants also underwent whole-body imaging.
- Four researchers independently rated the photographs for various cNF features, including general severity, number, size, facial severity, and subtypes.
TAKEAWAY:
- Based on evaluations by NF1 specialists, the agreement between mobile and whole-body images was “substantial” (74%-88% agreement) for the number of cNFs, general severity, and facial severity. Agreement between self-reported numbers of cNFs and investigator-rated numbers based on photographs was “minimal to fair.”
- Female sex, the number of cNFs, severity of cNFs on the face, and globular cNFs were associated with worse QoL (based on Skindex scores); severity of cNFs on the face had the strongest impact on overall QoL (P < .001).
- An increasing number of cNFs and worsening facial severity were strongly correlated with higher emotion subdomain scores.
- A higher number of cNFs, more severe cNFs on the face, and larger cNFs were all slightly associated with increased itch and pain (P < .01).
IN PRACTICE:
“To develop effective therapeutics, meaningful clinical outcomes that are tied with improvement in QoL for persons with NF1 must be clearly defined,” the authors wrote. The results of this study, they added, “suggested the benefit of this crowd-sourced resource by identifying the features of cNFs with the greatest association with QoL and symptoms of pain and itch in persons with NF1, highlighting new intervention strategies and features to target to most improve QoL in NF1.”
SOURCE:
The study was led by Michelle Jade Lin, BS, Stanford University School of Medicine, Redwood City, California, and was published online in JAMA Dermatology.
LIMITATIONS:
The study included only a small number of individuals from racial and ethnic minority groups and did not capture ethnicity information, which could have provided further insights into disease impact across different demographics.
DISCLOSURES:
This study was supported by Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore, and the Bloomberg Family Foundation. Ms. Lin reported support from the Stanford Medical Scholars Research Program. Three authors reported personal fees or grants outside this work. Other authors reported no competing interests.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
Mobile images may be reliable for assessing cutaneous neurofibroma (cNF) features in patients with neurofibromatosis type 1 (NF1), according to a crowd-sourced .
METHODOLOGY:
- To learn more about the association of cNFs with QoL, pain, and itch in patients with this rare disease, researchers enrolled 1016 individuals aged 40 years and older with NF1 who had at least one cNF, from May 2021 to December 2023, after reaching out to patient-led or NF1 advocacy organizations in 13 countries, including the United States.
- Participants provided demographic data, detailed photographs, and saliva samples for genetic sequencing, with 583 participants (mean age, 51.7 years; 65.9% women) submitting high-quality photographs from seven body regions at the time of the study analysis.
- A subset of 50 participants also underwent whole-body imaging.
- Four researchers independently rated the photographs for various cNF features, including general severity, number, size, facial severity, and subtypes.
TAKEAWAY:
- Based on evaluations by NF1 specialists, the agreement between mobile and whole-body images was “substantial” (74%-88% agreement) for the number of cNFs, general severity, and facial severity. Agreement between self-reported numbers of cNFs and investigator-rated numbers based on photographs was “minimal to fair.”
- Female sex, the number of cNFs, severity of cNFs on the face, and globular cNFs were associated with worse QoL (based on Skindex scores); severity of cNFs on the face had the strongest impact on overall QoL (P < .001).
- An increasing number of cNFs and worsening facial severity were strongly correlated with higher emotion subdomain scores.
- A higher number of cNFs, more severe cNFs on the face, and larger cNFs were all slightly associated with increased itch and pain (P < .01).
IN PRACTICE:
“To develop effective therapeutics, meaningful clinical outcomes that are tied with improvement in QoL for persons with NF1 must be clearly defined,” the authors wrote. The results of this study, they added, “suggested the benefit of this crowd-sourced resource by identifying the features of cNFs with the greatest association with QoL and symptoms of pain and itch in persons with NF1, highlighting new intervention strategies and features to target to most improve QoL in NF1.”
SOURCE:
The study was led by Michelle Jade Lin, BS, Stanford University School of Medicine, Redwood City, California, and was published online in JAMA Dermatology.
LIMITATIONS:
The study included only a small number of individuals from racial and ethnic minority groups and did not capture ethnicity information, which could have provided further insights into disease impact across different demographics.
DISCLOSURES:
This study was supported by Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore, and the Bloomberg Family Foundation. Ms. Lin reported support from the Stanford Medical Scholars Research Program. Three authors reported personal fees or grants outside this work. Other authors reported no competing interests.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Parents’ Technology Use May Shape Adolescents’ Mental Health
, according to a new study based in Canada.
In fact, this parental “technoference” is associated with higher levels of inattention and hyperactivity symptoms later in the child’s development, the researchers found.
“We hear a lot about children’s and adolescents’ screen time in the media, but we forget that parents are also on their screens a lot. In fact, past research shows that when parents are with their children, they spend 1 in 3 minutes on a screen,” said lead author Audrey-Ann Deneault, PhD, assistant professor of social psychology at the University of Montreal, Montreal, Quebec, Canada.
“We’ve all experienced moments when we’re on the phone and not hearing someone call us or don’t notice something happening right before our eyes,” she said. “We think that’s why it’s important to look at technoference. When parents use screens, they are more likely to miss when their child needs them.”
The study was published online in JAMA Network Open.
Analyzing Parental Technoference
As part of the All Our Families study, Dr. Deneault and colleagues analyzed a cohort of mothers and 1303 emerging adolescents between ages 9 and 11 years in Calgary, with the aim of understanding long-term associations between perceived parental interruptions (or technoference) and their children’s mental health.
Women were recruited during pregnancy between May 2008 and December 2010. For this study, the adolescents were assessed three times — at ages 9 years (in 2020), 10 years (in 2021), and 11 years (in 2021 and 2022). The mothers gave consent for their children to participate, and the children gave assent as well.
During the assessments, the adolescents completed questionnaires about their perceptions of parental technoference and their mental health symptoms, such as anxiety, depression, inattention, and hyperactivity. The study focused on the magnitude of effect sizes rather than statistical significance.
Overall, higher levels of anxiety symptoms at ages 9 and 10 years were prospectively associated with higher levels of perceived parental technoference at ages 10 and 11 years. The effect size was small.
In addition, higher levels of perceived parental technoference at ages 9 and 10 years were prospectively associated with higher levels of hyperactivity at ages 10 and 11 years and higher levels of inattention at age 11 years. There were no significant differences by gender.
“Technoference and youth mental health interact in complex ways. We found that when emerging adolescents have higher rates of anxiety, this can prompt parents to engage in more technoference,” Dr. Deneault said. “This latter bit highlights that parents may be struggling when their youths have mental health difficulties.”
Considering Healthy Changes
The findings call for a multitiered approach, Dr. Deneault said, in which adolescents and parents receive support related to mental health concerns, technology use, and healthy parent-child interactions.
“The key takeaway is that parents’ screen time matters and should begin to be a part of the conversation when we think about child and adolescent mental health,” she said.
Future research should look at the direction of associations between adolescent mental health and parental technoference, as well as underlying mechanisms, specific activities linked to technoference, and different age groups and stages of development, the study authors wrote.
“As a society, we need to understand how parents’ use of technology can interfere or not with youths’ mental health,” said Nicole Letourneau, PhD, a research professor of pediatrics, psychiatry, and community health sciences focused on parent and child health at the University of Calgary, Calgary, Alberta, Canada.
Dr. Letourneau, who wasn’t involved in this study, has researched the effects of parental technoference on parent-child relationships and child health and developmental outcomes. She and her colleagues found that parents recognized changes in their child’s behavior.
“Parental support is important for healthy development, and if parents are distracted by their devices, they can miss important but subtle cues that youth are using to signal their needs,” she said. “Given the troubling rise in youth mental health problems, we need to understand potential contributors so we can offer ways to reduce risks and promote youth mental health.”
Communication with parents should be considered as well. For instance, healthcare providers can address the positive and negative aspects of technology use.
“There is enough research out now that we should be more concerned than we currently are about how parents’ own technology habits might influence child and teen well-being. Yet, taking an overall negative lens to parent technology and smartphone habits may not prove very fruitful,” said Brandon McDaniel, PhD, a senior research scientist at the Parkview Mirro Center for Research & Innovation in Fort Wayne, Indiana.
Dr. McDaniel, who also wasn’t involved with this study, has researched technoference and associations with child behavior problems, as well as parents’ desires to change phone use. He noted that parents may use their devices for positive reasons, such as finding support from others, regulating their own emotions, and escaping from stress, so they can be more emotionally available for their children soon after using their phone.
“Many parents already feel an immense amount of guilt surrounding smartphone use in the presence of their child,” he said. “I suggest that practitioners address parent technology use in ways that validate parents in their positive uses of technology while helping them identify areas of their tech habits that may be counterproductive for their own or their child’s health and mental health.”
The All Our Families study was supported by an Alberta Innovates–Health Solutions Interdisciplinary Team Grant and the Alberta Children’s Hospital Foundation. The current analysis received funding from the Canadian Institutes of Health Research, a Children and Screens: Institute of Digital Media and Child Development COVID-19 grant, an Alberta Innovates grant, and a Banting Postdoctoral Fellowship. Dr. Deneault, Dr. Letourneau, and Dr. McDaniel reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
, according to a new study based in Canada.
In fact, this parental “technoference” is associated with higher levels of inattention and hyperactivity symptoms later in the child’s development, the researchers found.
“We hear a lot about children’s and adolescents’ screen time in the media, but we forget that parents are also on their screens a lot. In fact, past research shows that when parents are with their children, they spend 1 in 3 minutes on a screen,” said lead author Audrey-Ann Deneault, PhD, assistant professor of social psychology at the University of Montreal, Montreal, Quebec, Canada.
“We’ve all experienced moments when we’re on the phone and not hearing someone call us or don’t notice something happening right before our eyes,” she said. “We think that’s why it’s important to look at technoference. When parents use screens, they are more likely to miss when their child needs them.”
The study was published online in JAMA Network Open.
Analyzing Parental Technoference
As part of the All Our Families study, Dr. Deneault and colleagues analyzed a cohort of mothers and 1303 emerging adolescents between ages 9 and 11 years in Calgary, with the aim of understanding long-term associations between perceived parental interruptions (or technoference) and their children’s mental health.
Women were recruited during pregnancy between May 2008 and December 2010. For this study, the adolescents were assessed three times — at ages 9 years (in 2020), 10 years (in 2021), and 11 years (in 2021 and 2022). The mothers gave consent for their children to participate, and the children gave assent as well.
During the assessments, the adolescents completed questionnaires about their perceptions of parental technoference and their mental health symptoms, such as anxiety, depression, inattention, and hyperactivity. The study focused on the magnitude of effect sizes rather than statistical significance.
Overall, higher levels of anxiety symptoms at ages 9 and 10 years were prospectively associated with higher levels of perceived parental technoference at ages 10 and 11 years. The effect size was small.
In addition, higher levels of perceived parental technoference at ages 9 and 10 years were prospectively associated with higher levels of hyperactivity at ages 10 and 11 years and higher levels of inattention at age 11 years. There were no significant differences by gender.
“Technoference and youth mental health interact in complex ways. We found that when emerging adolescents have higher rates of anxiety, this can prompt parents to engage in more technoference,” Dr. Deneault said. “This latter bit highlights that parents may be struggling when their youths have mental health difficulties.”
Considering Healthy Changes
The findings call for a multitiered approach, Dr. Deneault said, in which adolescents and parents receive support related to mental health concerns, technology use, and healthy parent-child interactions.
“The key takeaway is that parents’ screen time matters and should begin to be a part of the conversation when we think about child and adolescent mental health,” she said.
Future research should look at the direction of associations between adolescent mental health and parental technoference, as well as underlying mechanisms, specific activities linked to technoference, and different age groups and stages of development, the study authors wrote.
“As a society, we need to understand how parents’ use of technology can interfere or not with youths’ mental health,” said Nicole Letourneau, PhD, a research professor of pediatrics, psychiatry, and community health sciences focused on parent and child health at the University of Calgary, Calgary, Alberta, Canada.
Dr. Letourneau, who wasn’t involved in this study, has researched the effects of parental technoference on parent-child relationships and child health and developmental outcomes. She and her colleagues found that parents recognized changes in their child’s behavior.
“Parental support is important for healthy development, and if parents are distracted by their devices, they can miss important but subtle cues that youth are using to signal their needs,” she said. “Given the troubling rise in youth mental health problems, we need to understand potential contributors so we can offer ways to reduce risks and promote youth mental health.”
Communication with parents should be considered as well. For instance, healthcare providers can address the positive and negative aspects of technology use.
“There is enough research out now that we should be more concerned than we currently are about how parents’ own technology habits might influence child and teen well-being. Yet, taking an overall negative lens to parent technology and smartphone habits may not prove very fruitful,” said Brandon McDaniel, PhD, a senior research scientist at the Parkview Mirro Center for Research & Innovation in Fort Wayne, Indiana.
Dr. McDaniel, who also wasn’t involved with this study, has researched technoference and associations with child behavior problems, as well as parents’ desires to change phone use. He noted that parents may use their devices for positive reasons, such as finding support from others, regulating their own emotions, and escaping from stress, so they can be more emotionally available for their children soon after using their phone.
“Many parents already feel an immense amount of guilt surrounding smartphone use in the presence of their child,” he said. “I suggest that practitioners address parent technology use in ways that validate parents in their positive uses of technology while helping them identify areas of their tech habits that may be counterproductive for their own or their child’s health and mental health.”
The All Our Families study was supported by an Alberta Innovates–Health Solutions Interdisciplinary Team Grant and the Alberta Children’s Hospital Foundation. The current analysis received funding from the Canadian Institutes of Health Research, a Children and Screens: Institute of Digital Media and Child Development COVID-19 grant, an Alberta Innovates grant, and a Banting Postdoctoral Fellowship. Dr. Deneault, Dr. Letourneau, and Dr. McDaniel reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
, according to a new study based in Canada.
In fact, this parental “technoference” is associated with higher levels of inattention and hyperactivity symptoms later in the child’s development, the researchers found.
“We hear a lot about children’s and adolescents’ screen time in the media, but we forget that parents are also on their screens a lot. In fact, past research shows that when parents are with their children, they spend 1 in 3 minutes on a screen,” said lead author Audrey-Ann Deneault, PhD, assistant professor of social psychology at the University of Montreal, Montreal, Quebec, Canada.
“We’ve all experienced moments when we’re on the phone and not hearing someone call us or don’t notice something happening right before our eyes,” she said. “We think that’s why it’s important to look at technoference. When parents use screens, they are more likely to miss when their child needs them.”
The study was published online in JAMA Network Open.
Analyzing Parental Technoference
As part of the All Our Families study, Dr. Deneault and colleagues analyzed a cohort of mothers and 1303 emerging adolescents between ages 9 and 11 years in Calgary, with the aim of understanding long-term associations between perceived parental interruptions (or technoference) and their children’s mental health.
Women were recruited during pregnancy between May 2008 and December 2010. For this study, the adolescents were assessed three times — at ages 9 years (in 2020), 10 years (in 2021), and 11 years (in 2021 and 2022). The mothers gave consent for their children to participate, and the children gave assent as well.
During the assessments, the adolescents completed questionnaires about their perceptions of parental technoference and their mental health symptoms, such as anxiety, depression, inattention, and hyperactivity. The study focused on the magnitude of effect sizes rather than statistical significance.
Overall, higher levels of anxiety symptoms at ages 9 and 10 years were prospectively associated with higher levels of perceived parental technoference at ages 10 and 11 years. The effect size was small.
In addition, higher levels of perceived parental technoference at ages 9 and 10 years were prospectively associated with higher levels of hyperactivity at ages 10 and 11 years and higher levels of inattention at age 11 years. There were no significant differences by gender.
“Technoference and youth mental health interact in complex ways. We found that when emerging adolescents have higher rates of anxiety, this can prompt parents to engage in more technoference,” Dr. Deneault said. “This latter bit highlights that parents may be struggling when their youths have mental health difficulties.”
Considering Healthy Changes
The findings call for a multitiered approach, Dr. Deneault said, in which adolescents and parents receive support related to mental health concerns, technology use, and healthy parent-child interactions.
“The key takeaway is that parents’ screen time matters and should begin to be a part of the conversation when we think about child and adolescent mental health,” she said.
Future research should look at the direction of associations between adolescent mental health and parental technoference, as well as underlying mechanisms, specific activities linked to technoference, and different age groups and stages of development, the study authors wrote.
“As a society, we need to understand how parents’ use of technology can interfere or not with youths’ mental health,” said Nicole Letourneau, PhD, a research professor of pediatrics, psychiatry, and community health sciences focused on parent and child health at the University of Calgary, Calgary, Alberta, Canada.
Dr. Letourneau, who wasn’t involved in this study, has researched the effects of parental technoference on parent-child relationships and child health and developmental outcomes. She and her colleagues found that parents recognized changes in their child’s behavior.
“Parental support is important for healthy development, and if parents are distracted by their devices, they can miss important but subtle cues that youth are using to signal their needs,” she said. “Given the troubling rise in youth mental health problems, we need to understand potential contributors so we can offer ways to reduce risks and promote youth mental health.”
Communication with parents should be considered as well. For instance, healthcare providers can address the positive and negative aspects of technology use.
“There is enough research out now that we should be more concerned than we currently are about how parents’ own technology habits might influence child and teen well-being. Yet, taking an overall negative lens to parent technology and smartphone habits may not prove very fruitful,” said Brandon McDaniel, PhD, a senior research scientist at the Parkview Mirro Center for Research & Innovation in Fort Wayne, Indiana.
Dr. McDaniel, who also wasn’t involved with this study, has researched technoference and associations with child behavior problems, as well as parents’ desires to change phone use. He noted that parents may use their devices for positive reasons, such as finding support from others, regulating their own emotions, and escaping from stress, so they can be more emotionally available for their children soon after using their phone.
“Many parents already feel an immense amount of guilt surrounding smartphone use in the presence of their child,” he said. “I suggest that practitioners address parent technology use in ways that validate parents in their positive uses of technology while helping them identify areas of their tech habits that may be counterproductive for their own or their child’s health and mental health.”
The All Our Families study was supported by an Alberta Innovates–Health Solutions Interdisciplinary Team Grant and the Alberta Children’s Hospital Foundation. The current analysis received funding from the Canadian Institutes of Health Research, a Children and Screens: Institute of Digital Media and Child Development COVID-19 grant, an Alberta Innovates grant, and a Banting Postdoctoral Fellowship. Dr. Deneault, Dr. Letourneau, and Dr. McDaniel reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM JAMA NETWORK OPEN
PTSD: The Basics
Editor's Note: This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication.
Editor's Note: This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication.
Editor's Note: This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication.
OSA in pregnancy: Who to test, how to screen, and does treatment help?
The increased prevalence in pregnancy can be explained by physiologic changes impacting the upper airway such as increases in maternal blood volume and reductions in oncotic pressure, as well as increases in circulating levels of estrogen and progesterone. OSA in pregnancy is associated with adverse perinatal outcomes such as hypertensive disorders of pregnancy, gestational diabetes, severe maternal morbidity abnormalities in fetal growth, preterm birth, and congenital abnormalities in the offspring.2,3 Despite this evidence, guidelines on the screening, diagnosis, and treatment of OSA in pregnancy have only recently been published and will be reviewed here.1
The obstetric subcommittee of the Society of Anesthesia and Sleep Medicine that produced these guidelines had expertise in obstetric anesthesiology, sleep medicine and sleep research, high-risk obstetrics, and obstetric medicine. The guideline aimed to answer 3 questions: 1) Who should be screened in pregnancy for OSA, 2) how to make a diagnosis of OSA in pregnancy and the postpartum period, and 3) what is the treatment for OSA in pregnancy and the postpartum period. Although the estimated number of annual pregnancies in the US declined between 2010 to 2019, these clinical questions remain critical considering the obesity epidemic, the ability to conceive despite advanced maternal age and chronic illnesses with the use of fertility treatments, and the crisis of severe maternal morbidity and mortality. As sleep disordered breathing (SDB) has been associated with many conditions linked to maternal mortality, better management of SDB in this population is key.
Screening for OSA in the pregnant population
The guideline does not support universal screening of all people who are pregnant, but rather suggests that people who are pregnant and at high risk for OSA, such as those with a body mass index (BMI) ≥30 kg/m2 and those with hypertensive disorders of pregnancy, or diabetes, in the index pregnancy or a prior pregnancy, be screened for OSA in the first or second trimester.1 Screening for OSA in pregnancy in limited populations is recommended due to the lower yield of universal screening and its potential burden on the health care system. Furthermore, screening for OSA in early pregnancy is suggested given the practical challenges of arranging testing, initiating, and allowing time for patients to become acclimated to therapy in later stages of pregnancy. However, even when timing of diagnosis may not allow for appropriate treatment of OSA during pregnancy, knowing a person’s OSA status before delivery is beneficial, particularly for patients at risk for Cesarean delivery who may require intubation and exposure to sedative medications, as well as those receiving epidural anesthesia, as OSA is a risk factor for respiratory depression.
Although screening was thought to be beneficial in specific populations, there is insufficient evidence to recommend any one screening tool. The guideline made recommendations against the use of the Berlin questionnaire, STOP-BANG questionnaire, Epworth Sleepiness Scale, or the ASA checklist.1 These screening tools were developed and validated in nonpregnant patient populations and their pooled sensitivity and specificity to detect OSA in pregnancy is low. Individual components of these screening tools, such as prepregnancy BMI, frequency and volume of snoring, hypertension, and neck circumference ≥16 inches have, however, been associated with OSA status.
Pregnancy-specific OSA screening tools have been proposed.4,5 The guideline suggests these pregnancy-specific tools may be considered for screening for OSA in pregnancy but still require external validation, especially in high-risk populations. The committee agreed that individuals with BMI >30kg/m2, hypertension, diabetes, and those with a history of difficult intubation or Mallampati score III or IV are considered at risk for OSA in pregnancy.
Diagnosis of OSA in the pregnant population
In the general population, in-laboratory polysomnogram (PSG) is the gold standard diagnostic test. However, for patients in whom uncomplicated OSA is suspected with a moderate to high pretest probability, unattended home sleep apnea testing (HSAT) is a reasonable initial study. On the other hand, in-lab PSG is recommended in mission-critical workers and when coexisting respiratory sleep disorders, or nonrespiratory sleep disorders, are suspected. For individuals who are pregnant and suspected of having OSA, the guideline suggests that HSAT is a reasonable diagnostic tool, as many level III devices have demonstrated good agreement between the respiratory disturbance index (RDI) and apnea-hypopnea index (AHI) measured by PSG.6 Notably, most studies have examined the performance of level III devices in late pregnancy in populations with obesity; hence, the performance of these devices in early pregnancy when risk for OSA is lower, or more subtle forms of SDB may be more common, is less clear but may be an acceptable first-line test.
The guideline did not provide recommendations for next steps following an inconclusive, technically inadequate, or negative HSAT. However, recommendations to proceed with in-lab PSG in individuals with clinical suspicion for OSA and a negative HSAT is a reasonable approach, keeping in mind the time restrictions of pregnancy. The more delayed the diagnosis, the less time there will be for initiation of and acclimation to therapy to maximize potential benefits during pregnancy. HSAT is especially practical and convenient for individuals with young families. The guideline does not recommend the use of overnight oximetry for diagnostic purposes.1
The postpartum period is usually associated with weight loss and reversal of pregnancy physiology. Generally, the decision to perform a repeat sleep study following weight loss is individualized, based on factors such as improved symptoms or sustained, significant weight loss. Though data show improvement in AHI following delivery, small studies show persistent OSA in nearly half of individuals diagnosed in pregnancy. Hence, as pregnancy increases the risk for OSA, and given that the postpartum status is not always associated with resolution of OSA, the guideline recommends considering repeat diagnostic testing in the postpartum period.1 The decision to repeat testing also depends on whether OSA or OSA symptoms predated pregnancy, on the persistence of symptoms, and the degree of weight loss with delivery and the postpartum body habitus.
Treatment of OSA in the pregnant population
The guideline recommends behavior modification in OSA similarly to individuals who are not pregnant (avoidance of sedatives, smoking, and alcohol).1 However, weight loss is not recommended in pregnancy due to the potential for harm to the fetus.
The gold standard treatment for people who are pregnant and have OSA is continuous positive airway pressure (CPAP). Treatment of OSA in pregnancy is complicated by the fact that very few women are referred to sleep practices due to time restrictions and logistical reasons, and that data demonstrating improved pregnancy outcomes with CPAP are scarce, limiting the prioritization of OSA management. However, expert consensus considers a theoretical benefit in the context of lack of current evidence of harm from treatment. Hence, at this point, the guideline recommends counseling around CPAP therapy be aimed at improvement in symptoms, AHI, and quality of life, rather than pregnancy-specific outcomes.1 This recommendation was based on observations from small case series that demonstrated improved breathing parameters during sleep and symptoms, and small randomized controlled trials (RCT), limited by short-term exposure to the intervention. However, since the publication of this guideline, a large RCT that randomized pregnant women with SDB to CPAP or usual care has demonstrated significantly lower diastolic blood pressure, an altered diastolic blood pressure trajectory, and a lower rate of preeclampsia in the group treated with CPAP compared with usual care.7
This guideline provides helpful insight on who to screen and how to manage OSA in pregnancy but additional research is needed to elucidate benefits of treatment and its effects on maternal and neonatal outcomes. Multidisciplinary collaborations between obstetric and sleep teams are necessary to ensure that screening and diagnostic strategies result in management change for improved outcomes.
References
1. Dominguez JE, Cantrell S, Habib AS, et al. Society of Anesthesia and Sleep Medicine and the Society for Obstetric Anesthesia and Perinatology Consensus Guideline on the screening, diagnosis and treatment of obstructive sleep apnea in pregnancy. Obstet Gynecol. 2023;142(2):403-423.
2. Bourjeily, G, Danilack C, Bublitz M, Muri J, Rosene-Montella K, Lipkind H. Maternal obstructive sleep apnea and neonatal birth outcomes in a population based sample. Sleep Med. 2000;66:233-240.
3. Malhamé I, Bublitz MH, Wilson D, Sanapo L, Rochin E, Bourjeily G. Sleep disordered breathing and the risk of severe maternal morbidity in women with preeclampsia: a population-based study. Pregnancy Hypertens. 2022;30:215-220.
4. Izci-Balserak B, Zhu B, Gurubhagavatula I, Keenan BT, Pien GW. A screening algorithm for obstructive sleep apnea in pregnancy. Ann Am Thorac Soc. 2019;16(10):1286-1294.
5. Louis J, Koch MA, Reddy UM, et al. Predictors of sleep-disordered breathing in pregnancy. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2018;218(5):521.e1.e12.
6. Sharkey K, Waters K, Millman R, Moore R, Martin SM, Bourjeily. Validation of the Apnea Risk Evaluation System (ARES) device against laboratory polysomnogram in pregnant women at risk for obstructive sleep apnea syndrome. J Clin Sleep Med. 2014;10(5):497-502.
7. Tantrakul V, Ingsathit A, Liamsombut S, et al. Treatment of obstructive sleep apnea in high-risk pregnancy: a multicenter randomized controlled trial. Respir Res. 2023;24(1):171.
The increased prevalence in pregnancy can be explained by physiologic changes impacting the upper airway such as increases in maternal blood volume and reductions in oncotic pressure, as well as increases in circulating levels of estrogen and progesterone. OSA in pregnancy is associated with adverse perinatal outcomes such as hypertensive disorders of pregnancy, gestational diabetes, severe maternal morbidity abnormalities in fetal growth, preterm birth, and congenital abnormalities in the offspring.2,3 Despite this evidence, guidelines on the screening, diagnosis, and treatment of OSA in pregnancy have only recently been published and will be reviewed here.1
The obstetric subcommittee of the Society of Anesthesia and Sleep Medicine that produced these guidelines had expertise in obstetric anesthesiology, sleep medicine and sleep research, high-risk obstetrics, and obstetric medicine. The guideline aimed to answer 3 questions: 1) Who should be screened in pregnancy for OSA, 2) how to make a diagnosis of OSA in pregnancy and the postpartum period, and 3) what is the treatment for OSA in pregnancy and the postpartum period. Although the estimated number of annual pregnancies in the US declined between 2010 to 2019, these clinical questions remain critical considering the obesity epidemic, the ability to conceive despite advanced maternal age and chronic illnesses with the use of fertility treatments, and the crisis of severe maternal morbidity and mortality. As sleep disordered breathing (SDB) has been associated with many conditions linked to maternal mortality, better management of SDB in this population is key.
Screening for OSA in the pregnant population
The guideline does not support universal screening of all people who are pregnant, but rather suggests that people who are pregnant and at high risk for OSA, such as those with a body mass index (BMI) ≥30 kg/m2 and those with hypertensive disorders of pregnancy, or diabetes, in the index pregnancy or a prior pregnancy, be screened for OSA in the first or second trimester.1 Screening for OSA in pregnancy in limited populations is recommended due to the lower yield of universal screening and its potential burden on the health care system. Furthermore, screening for OSA in early pregnancy is suggested given the practical challenges of arranging testing, initiating, and allowing time for patients to become acclimated to therapy in later stages of pregnancy. However, even when timing of diagnosis may not allow for appropriate treatment of OSA during pregnancy, knowing a person’s OSA status before delivery is beneficial, particularly for patients at risk for Cesarean delivery who may require intubation and exposure to sedative medications, as well as those receiving epidural anesthesia, as OSA is a risk factor for respiratory depression.
Although screening was thought to be beneficial in specific populations, there is insufficient evidence to recommend any one screening tool. The guideline made recommendations against the use of the Berlin questionnaire, STOP-BANG questionnaire, Epworth Sleepiness Scale, or the ASA checklist.1 These screening tools were developed and validated in nonpregnant patient populations and their pooled sensitivity and specificity to detect OSA in pregnancy is low. Individual components of these screening tools, such as prepregnancy BMI, frequency and volume of snoring, hypertension, and neck circumference ≥16 inches have, however, been associated with OSA status.
Pregnancy-specific OSA screening tools have been proposed.4,5 The guideline suggests these pregnancy-specific tools may be considered for screening for OSA in pregnancy but still require external validation, especially in high-risk populations. The committee agreed that individuals with BMI >30kg/m2, hypertension, diabetes, and those with a history of difficult intubation or Mallampati score III or IV are considered at risk for OSA in pregnancy.
Diagnosis of OSA in the pregnant population
In the general population, in-laboratory polysomnogram (PSG) is the gold standard diagnostic test. However, for patients in whom uncomplicated OSA is suspected with a moderate to high pretest probability, unattended home sleep apnea testing (HSAT) is a reasonable initial study. On the other hand, in-lab PSG is recommended in mission-critical workers and when coexisting respiratory sleep disorders, or nonrespiratory sleep disorders, are suspected. For individuals who are pregnant and suspected of having OSA, the guideline suggests that HSAT is a reasonable diagnostic tool, as many level III devices have demonstrated good agreement between the respiratory disturbance index (RDI) and apnea-hypopnea index (AHI) measured by PSG.6 Notably, most studies have examined the performance of level III devices in late pregnancy in populations with obesity; hence, the performance of these devices in early pregnancy when risk for OSA is lower, or more subtle forms of SDB may be more common, is less clear but may be an acceptable first-line test.
The guideline did not provide recommendations for next steps following an inconclusive, technically inadequate, or negative HSAT. However, recommendations to proceed with in-lab PSG in individuals with clinical suspicion for OSA and a negative HSAT is a reasonable approach, keeping in mind the time restrictions of pregnancy. The more delayed the diagnosis, the less time there will be for initiation of and acclimation to therapy to maximize potential benefits during pregnancy. HSAT is especially practical and convenient for individuals with young families. The guideline does not recommend the use of overnight oximetry for diagnostic purposes.1
The postpartum period is usually associated with weight loss and reversal of pregnancy physiology. Generally, the decision to perform a repeat sleep study following weight loss is individualized, based on factors such as improved symptoms or sustained, significant weight loss. Though data show improvement in AHI following delivery, small studies show persistent OSA in nearly half of individuals diagnosed in pregnancy. Hence, as pregnancy increases the risk for OSA, and given that the postpartum status is not always associated with resolution of OSA, the guideline recommends considering repeat diagnostic testing in the postpartum period.1 The decision to repeat testing also depends on whether OSA or OSA symptoms predated pregnancy, on the persistence of symptoms, and the degree of weight loss with delivery and the postpartum body habitus.
Treatment of OSA in the pregnant population
The guideline recommends behavior modification in OSA similarly to individuals who are not pregnant (avoidance of sedatives, smoking, and alcohol).1 However, weight loss is not recommended in pregnancy due to the potential for harm to the fetus.
The gold standard treatment for people who are pregnant and have OSA is continuous positive airway pressure (CPAP). Treatment of OSA in pregnancy is complicated by the fact that very few women are referred to sleep practices due to time restrictions and logistical reasons, and that data demonstrating improved pregnancy outcomes with CPAP are scarce, limiting the prioritization of OSA management. However, expert consensus considers a theoretical benefit in the context of lack of current evidence of harm from treatment. Hence, at this point, the guideline recommends counseling around CPAP therapy be aimed at improvement in symptoms, AHI, and quality of life, rather than pregnancy-specific outcomes.1 This recommendation was based on observations from small case series that demonstrated improved breathing parameters during sleep and symptoms, and small randomized controlled trials (RCT), limited by short-term exposure to the intervention. However, since the publication of this guideline, a large RCT that randomized pregnant women with SDB to CPAP or usual care has demonstrated significantly lower diastolic blood pressure, an altered diastolic blood pressure trajectory, and a lower rate of preeclampsia in the group treated with CPAP compared with usual care.7
This guideline provides helpful insight on who to screen and how to manage OSA in pregnancy but additional research is needed to elucidate benefits of treatment and its effects on maternal and neonatal outcomes. Multidisciplinary collaborations between obstetric and sleep teams are necessary to ensure that screening and diagnostic strategies result in management change for improved outcomes.
References
1. Dominguez JE, Cantrell S, Habib AS, et al. Society of Anesthesia and Sleep Medicine and the Society for Obstetric Anesthesia and Perinatology Consensus Guideline on the screening, diagnosis and treatment of obstructive sleep apnea in pregnancy. Obstet Gynecol. 2023;142(2):403-423.
2. Bourjeily, G, Danilack C, Bublitz M, Muri J, Rosene-Montella K, Lipkind H. Maternal obstructive sleep apnea and neonatal birth outcomes in a population based sample. Sleep Med. 2000;66:233-240.
3. Malhamé I, Bublitz MH, Wilson D, Sanapo L, Rochin E, Bourjeily G. Sleep disordered breathing and the risk of severe maternal morbidity in women with preeclampsia: a population-based study. Pregnancy Hypertens. 2022;30:215-220.
4. Izci-Balserak B, Zhu B, Gurubhagavatula I, Keenan BT, Pien GW. A screening algorithm for obstructive sleep apnea in pregnancy. Ann Am Thorac Soc. 2019;16(10):1286-1294.
5. Louis J, Koch MA, Reddy UM, et al. Predictors of sleep-disordered breathing in pregnancy. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2018;218(5):521.e1.e12.
6. Sharkey K, Waters K, Millman R, Moore R, Martin SM, Bourjeily. Validation of the Apnea Risk Evaluation System (ARES) device against laboratory polysomnogram in pregnant women at risk for obstructive sleep apnea syndrome. J Clin Sleep Med. 2014;10(5):497-502.
7. Tantrakul V, Ingsathit A, Liamsombut S, et al. Treatment of obstructive sleep apnea in high-risk pregnancy: a multicenter randomized controlled trial. Respir Res. 2023;24(1):171.
The increased prevalence in pregnancy can be explained by physiologic changes impacting the upper airway such as increases in maternal blood volume and reductions in oncotic pressure, as well as increases in circulating levels of estrogen and progesterone. OSA in pregnancy is associated with adverse perinatal outcomes such as hypertensive disorders of pregnancy, gestational diabetes, severe maternal morbidity abnormalities in fetal growth, preterm birth, and congenital abnormalities in the offspring.2,3 Despite this evidence, guidelines on the screening, diagnosis, and treatment of OSA in pregnancy have only recently been published and will be reviewed here.1
The obstetric subcommittee of the Society of Anesthesia and Sleep Medicine that produced these guidelines had expertise in obstetric anesthesiology, sleep medicine and sleep research, high-risk obstetrics, and obstetric medicine. The guideline aimed to answer 3 questions: 1) Who should be screened in pregnancy for OSA, 2) how to make a diagnosis of OSA in pregnancy and the postpartum period, and 3) what is the treatment for OSA in pregnancy and the postpartum period. Although the estimated number of annual pregnancies in the US declined between 2010 to 2019, these clinical questions remain critical considering the obesity epidemic, the ability to conceive despite advanced maternal age and chronic illnesses with the use of fertility treatments, and the crisis of severe maternal morbidity and mortality. As sleep disordered breathing (SDB) has been associated with many conditions linked to maternal mortality, better management of SDB in this population is key.
Screening for OSA in the pregnant population
The guideline does not support universal screening of all people who are pregnant, but rather suggests that people who are pregnant and at high risk for OSA, such as those with a body mass index (BMI) ≥30 kg/m2 and those with hypertensive disorders of pregnancy, or diabetes, in the index pregnancy or a prior pregnancy, be screened for OSA in the first or second trimester.1 Screening for OSA in pregnancy in limited populations is recommended due to the lower yield of universal screening and its potential burden on the health care system. Furthermore, screening for OSA in early pregnancy is suggested given the practical challenges of arranging testing, initiating, and allowing time for patients to become acclimated to therapy in later stages of pregnancy. However, even when timing of diagnosis may not allow for appropriate treatment of OSA during pregnancy, knowing a person’s OSA status before delivery is beneficial, particularly for patients at risk for Cesarean delivery who may require intubation and exposure to sedative medications, as well as those receiving epidural anesthesia, as OSA is a risk factor for respiratory depression.
Although screening was thought to be beneficial in specific populations, there is insufficient evidence to recommend any one screening tool. The guideline made recommendations against the use of the Berlin questionnaire, STOP-BANG questionnaire, Epworth Sleepiness Scale, or the ASA checklist.1 These screening tools were developed and validated in nonpregnant patient populations and their pooled sensitivity and specificity to detect OSA in pregnancy is low. Individual components of these screening tools, such as prepregnancy BMI, frequency and volume of snoring, hypertension, and neck circumference ≥16 inches have, however, been associated with OSA status.
Pregnancy-specific OSA screening tools have been proposed.4,5 The guideline suggests these pregnancy-specific tools may be considered for screening for OSA in pregnancy but still require external validation, especially in high-risk populations. The committee agreed that individuals with BMI >30kg/m2, hypertension, diabetes, and those with a history of difficult intubation or Mallampati score III or IV are considered at risk for OSA in pregnancy.
Diagnosis of OSA in the pregnant population
In the general population, in-laboratory polysomnogram (PSG) is the gold standard diagnostic test. However, for patients in whom uncomplicated OSA is suspected with a moderate to high pretest probability, unattended home sleep apnea testing (HSAT) is a reasonable initial study. On the other hand, in-lab PSG is recommended in mission-critical workers and when coexisting respiratory sleep disorders, or nonrespiratory sleep disorders, are suspected. For individuals who are pregnant and suspected of having OSA, the guideline suggests that HSAT is a reasonable diagnostic tool, as many level III devices have demonstrated good agreement between the respiratory disturbance index (RDI) and apnea-hypopnea index (AHI) measured by PSG.6 Notably, most studies have examined the performance of level III devices in late pregnancy in populations with obesity; hence, the performance of these devices in early pregnancy when risk for OSA is lower, or more subtle forms of SDB may be more common, is less clear but may be an acceptable first-line test.
The guideline did not provide recommendations for next steps following an inconclusive, technically inadequate, or negative HSAT. However, recommendations to proceed with in-lab PSG in individuals with clinical suspicion for OSA and a negative HSAT is a reasonable approach, keeping in mind the time restrictions of pregnancy. The more delayed the diagnosis, the less time there will be for initiation of and acclimation to therapy to maximize potential benefits during pregnancy. HSAT is especially practical and convenient for individuals with young families. The guideline does not recommend the use of overnight oximetry for diagnostic purposes.1
The postpartum period is usually associated with weight loss and reversal of pregnancy physiology. Generally, the decision to perform a repeat sleep study following weight loss is individualized, based on factors such as improved symptoms or sustained, significant weight loss. Though data show improvement in AHI following delivery, small studies show persistent OSA in nearly half of individuals diagnosed in pregnancy. Hence, as pregnancy increases the risk for OSA, and given that the postpartum status is not always associated with resolution of OSA, the guideline recommends considering repeat diagnostic testing in the postpartum period.1 The decision to repeat testing also depends on whether OSA or OSA symptoms predated pregnancy, on the persistence of symptoms, and the degree of weight loss with delivery and the postpartum body habitus.
Treatment of OSA in the pregnant population
The guideline recommends behavior modification in OSA similarly to individuals who are not pregnant (avoidance of sedatives, smoking, and alcohol).1 However, weight loss is not recommended in pregnancy due to the potential for harm to the fetus.
The gold standard treatment for people who are pregnant and have OSA is continuous positive airway pressure (CPAP). Treatment of OSA in pregnancy is complicated by the fact that very few women are referred to sleep practices due to time restrictions and logistical reasons, and that data demonstrating improved pregnancy outcomes with CPAP are scarce, limiting the prioritization of OSA management. However, expert consensus considers a theoretical benefit in the context of lack of current evidence of harm from treatment. Hence, at this point, the guideline recommends counseling around CPAP therapy be aimed at improvement in symptoms, AHI, and quality of life, rather than pregnancy-specific outcomes.1 This recommendation was based on observations from small case series that demonstrated improved breathing parameters during sleep and symptoms, and small randomized controlled trials (RCT), limited by short-term exposure to the intervention. However, since the publication of this guideline, a large RCT that randomized pregnant women with SDB to CPAP or usual care has demonstrated significantly lower diastolic blood pressure, an altered diastolic blood pressure trajectory, and a lower rate of preeclampsia in the group treated with CPAP compared with usual care.7
This guideline provides helpful insight on who to screen and how to manage OSA in pregnancy but additional research is needed to elucidate benefits of treatment and its effects on maternal and neonatal outcomes. Multidisciplinary collaborations between obstetric and sleep teams are necessary to ensure that screening and diagnostic strategies result in management change for improved outcomes.
References
1. Dominguez JE, Cantrell S, Habib AS, et al. Society of Anesthesia and Sleep Medicine and the Society for Obstetric Anesthesia and Perinatology Consensus Guideline on the screening, diagnosis and treatment of obstructive sleep apnea in pregnancy. Obstet Gynecol. 2023;142(2):403-423.
2. Bourjeily, G, Danilack C, Bublitz M, Muri J, Rosene-Montella K, Lipkind H. Maternal obstructive sleep apnea and neonatal birth outcomes in a population based sample. Sleep Med. 2000;66:233-240.
3. Malhamé I, Bublitz MH, Wilson D, Sanapo L, Rochin E, Bourjeily G. Sleep disordered breathing and the risk of severe maternal morbidity in women with preeclampsia: a population-based study. Pregnancy Hypertens. 2022;30:215-220.
4. Izci-Balserak B, Zhu B, Gurubhagavatula I, Keenan BT, Pien GW. A screening algorithm for obstructive sleep apnea in pregnancy. Ann Am Thorac Soc. 2019;16(10):1286-1294.
5. Louis J, Koch MA, Reddy UM, et al. Predictors of sleep-disordered breathing in pregnancy. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2018;218(5):521.e1.e12.
6. Sharkey K, Waters K, Millman R, Moore R, Martin SM, Bourjeily. Validation of the Apnea Risk Evaluation System (ARES) device against laboratory polysomnogram in pregnant women at risk for obstructive sleep apnea syndrome. J Clin Sleep Med. 2014;10(5):497-502.
7. Tantrakul V, Ingsathit A, Liamsombut S, et al. Treatment of obstructive sleep apnea in high-risk pregnancy: a multicenter randomized controlled trial. Respir Res. 2023;24(1):171.
Cystic fibrosis: Advances, ongoing challenges
After Rena Barrow-Wells, an African American mother, fought mightily to prevent a repeat of her experience of two decades earlier when her first child’s cystic fibrosis (CF) took 4 years to diagnose, her story became the subject of a New York Times feature covering disparities in diagnostic CF screening. The article highlighted not only her struggles, but also the utter transformation of the CF landscape since the introduction of small molecule mutation-specific drugs. These drugs restore function to defective CF transmembrane conductance regulator (CFTR) proteins. By the time Ms. Barrow-Wells’ young son was treated, lung and pancreatic scarring were already significant. So when the 39-mutation variant screening test available in Ms. Barrow-Wells’ Lawrenceville, Georgia, clinic turned out negative for CF, her pediatrician told her to stop worrying despite her new son’s inherent genetic risk, telltale salty skin, foul-smelling diapers, and her pleas to test for sweat chloride. It still took 3 months for a confirmed diagnosis and the initiation of treatment.
Current genetic tests, based largely on older clinical trials that enrolled mostly white children, are highly accurate for identifying CF in white babies (95%), but often fail to identify substantial percentages of mutations originating in Africa, Asia, and Latin America. They miss CF in Asian (44%), Black (22%), and Hispanic, Native American and Alaskan Native babies (14%), the Times article stated. In the United States, the number of CF variants tested for falls into a wide range: from the one variant found mostly in White populations in Mississippi (with a 38% Black populace) to 689 variants in Wisconsin.
Not too far back, CF was thought of as an inherited childhood disease leading often to childhood or adolescent mortality.
Today’s CF challenges
Beyond refinements in screening instruments and policies that broaden access leading to the earliest possible diagnoses, ongoing research needs include finding treatments for other variants, and caring for adult populations living with treated CF and the disease’s multisystem manifestations. “As people with CF live longer, we need to be very focused on optimized adult medical care for this population,” Marc A. Sala, MD, assistant professor of medicine, Adult CF Program, Northwestern University Feinberg School of Medicine, Chicago, said in an interview. “For example, we need higher vigilance for liver, microvascular, coronary artery disease, and various cancer screenings. We do not know exactly how these will manifest differently from the way they do in non-CF populations, so this is where more work needs to be done.”
Emphasis on monitoring
The authors of “Future therapies for cystic fibrosis” (Allen et al. Nature Communications, 2023 Feb 8), after citing the ongoing transformative change for people with CF since the introduction of CFTR drugs, gave voice to important cautions. “Disease will progress, albeit more slowly, and will be more challenging to monitor. Effective CFTR modulators will likely slow or, at best, halt disease progression, but will not reverse a disease that has already become fixed.” They cited pancreatic destruction in the majority, bronchiectasis, and absence of the vas deferens, with still recurring (although less frequently) pulmonary exacerbations along with chronic infections and persistent airway inflammation. “It is essential that we do not become complacent about disease progression in this population,” the researchers stated. They cautioned also that effective surveillance for infection is critical in asymptomatic patients, emphasizing that it underpins the management of young healthy children with CF who demonstrate disease progression despite a lack of symptoms.
Among the ~90% for whom Trikafta is suitable and approved (those with least one copy of F508del or specific other responsive mutations), improvements include increased percent predicted FEV1 by 10%-15% or more, decreased exacerbations, and improved quality of life,” Dr. Sala said. “Subsequent ‘real world’ experience shows dramatic reductions in sputum production and decreased frequency of lung transplant.”
Mutation agnostic therapy
Unfortunately, CF mutants, outside the population eligible for Trikafta, are prodigious in number and do not fall into just a few major groups. “Furthermore, although CF is a monogenic disease, it has variable phenotypes even for two individuals with the same mutations,” Dr. Sala said. “Current CFTR modulators act on the dysfunctional CFTR protein (either as channel gating potentiators or molecular chaperones to improve misfolding). That leaves about 10% of the CF population, those with little to no protein production (such as in nonsense mutations) ineligible for treatment with CFTR modulators. “The ideal for efficacy and equity, given that some CFTR mutations only exist in a handful of people, would be to develop a ‘mutation agnostic’ strategy — such as with mRNA or gene delivery. Here you could imagine that regardless of the type of mutation, a patient would then be able to receive the technology to increase CFTR channel function,” Dr. Sala said. Many modifiable factors, including host immunity and non-CFTR genes that impact CFTR indirectly, may underlie the fact that one person has a worse trajectory than another. “New therapies may also be found in this area of research,” Dr. Sala said.
Strategies in testing phases
“For patients with class I (nonsense) mutations there is hope that small molecules will be identified that can facilitate premature truncation codon (PTC) read-through and/or impede mRNA decay allowing for clinically relevant levels of functional CFTR,” the researchers noted. While the most extensively developed, ataluren, an oxadiazole, failed in phase 3 trials after initial promise, other ribosomal read-through drugs are in preclinical and early phase clinical trials. Also, early encouraging results support an alternative strategy, engineered transfer RNAs (tRNAs) that introduce an amino acid to an elongating peptide in place of the termination codon.
While these will address specific mutations, DNA or mRNA replacement strategies would be “mutation agnostic,” the researchers stated. The major challenge: delivery to the respiratory epithelium. Approaches currently in early testing include an inhaled aerosolized, lipid-based nanoparticle carrier for mRNA delivery, viral and non-viral DNA transfer, lipid-mediated CFTR gene transfer, pseudotyped lentiviral vector and adeno-associated vector transfer of CFTR DNA.
Adult CF care
“Adult CF care in general is a completely new frontier,” Meilinh Thi, DO, director of the adult cystic fibrosis program and assistant professor at University of Texas Health at San Antonio, said in an interview. “It’s fairly new to have separate pediatric and adult CF centers. There’s been a shift,” she said. “We’re encountering diseases in CF that we have not in the past had to deal with: diabetes that has features of both type 1 and type 2, increased colon cancer risk, bone disease, and mental health issues. Also, while pregnancy was previously discouraged for women with CF because of lung disease, now many are giving birth without complications and living normal lives,” Dr. Thi said.
“We do encourage our patients to talk to us before becoming pregnant so we can discuss the risk of passing on the gene. And, we do encourage their significant others to get testing. Some patients and their others, however, do decline to get tested,” she added.
The lifetime health issues conferred by CF, Dr. Thi noted, include lung disease with chronic inflammation, infection, respiratory failure (still the most common cause of death), gastrointestinal disorders (including of the pancreas) , colon obstruction and colon cancer, sinus disease, and reproductive system effects. Their permanence, she said, depends on how far their disease has progressed. “So the earlier you can provide these newer therapies — the modulators, for example, or the gene therapy whenever that comes out, then the less damage these organ systems will have, and the patients, we hope, will then do better.”
After Rena Barrow-Wells, an African American mother, fought mightily to prevent a repeat of her experience of two decades earlier when her first child’s cystic fibrosis (CF) took 4 years to diagnose, her story became the subject of a New York Times feature covering disparities in diagnostic CF screening. The article highlighted not only her struggles, but also the utter transformation of the CF landscape since the introduction of small molecule mutation-specific drugs. These drugs restore function to defective CF transmembrane conductance regulator (CFTR) proteins. By the time Ms. Barrow-Wells’ young son was treated, lung and pancreatic scarring were already significant. So when the 39-mutation variant screening test available in Ms. Barrow-Wells’ Lawrenceville, Georgia, clinic turned out negative for CF, her pediatrician told her to stop worrying despite her new son’s inherent genetic risk, telltale salty skin, foul-smelling diapers, and her pleas to test for sweat chloride. It still took 3 months for a confirmed diagnosis and the initiation of treatment.
Current genetic tests, based largely on older clinical trials that enrolled mostly white children, are highly accurate for identifying CF in white babies (95%), but often fail to identify substantial percentages of mutations originating in Africa, Asia, and Latin America. They miss CF in Asian (44%), Black (22%), and Hispanic, Native American and Alaskan Native babies (14%), the Times article stated. In the United States, the number of CF variants tested for falls into a wide range: from the one variant found mostly in White populations in Mississippi (with a 38% Black populace) to 689 variants in Wisconsin.
Not too far back, CF was thought of as an inherited childhood disease leading often to childhood or adolescent mortality.
Today’s CF challenges
Beyond refinements in screening instruments and policies that broaden access leading to the earliest possible diagnoses, ongoing research needs include finding treatments for other variants, and caring for adult populations living with treated CF and the disease’s multisystem manifestations. “As people with CF live longer, we need to be very focused on optimized adult medical care for this population,” Marc A. Sala, MD, assistant professor of medicine, Adult CF Program, Northwestern University Feinberg School of Medicine, Chicago, said in an interview. “For example, we need higher vigilance for liver, microvascular, coronary artery disease, and various cancer screenings. We do not know exactly how these will manifest differently from the way they do in non-CF populations, so this is where more work needs to be done.”
Emphasis on monitoring
The authors of “Future therapies for cystic fibrosis” (Allen et al. Nature Communications, 2023 Feb 8), after citing the ongoing transformative change for people with CF since the introduction of CFTR drugs, gave voice to important cautions. “Disease will progress, albeit more slowly, and will be more challenging to monitor. Effective CFTR modulators will likely slow or, at best, halt disease progression, but will not reverse a disease that has already become fixed.” They cited pancreatic destruction in the majority, bronchiectasis, and absence of the vas deferens, with still recurring (although less frequently) pulmonary exacerbations along with chronic infections and persistent airway inflammation. “It is essential that we do not become complacent about disease progression in this population,” the researchers stated. They cautioned also that effective surveillance for infection is critical in asymptomatic patients, emphasizing that it underpins the management of young healthy children with CF who demonstrate disease progression despite a lack of symptoms.
Among the ~90% for whom Trikafta is suitable and approved (those with least one copy of F508del or specific other responsive mutations), improvements include increased percent predicted FEV1 by 10%-15% or more, decreased exacerbations, and improved quality of life,” Dr. Sala said. “Subsequent ‘real world’ experience shows dramatic reductions in sputum production and decreased frequency of lung transplant.”
Mutation agnostic therapy
Unfortunately, CF mutants, outside the population eligible for Trikafta, are prodigious in number and do not fall into just a few major groups. “Furthermore, although CF is a monogenic disease, it has variable phenotypes even for two individuals with the same mutations,” Dr. Sala said. “Current CFTR modulators act on the dysfunctional CFTR protein (either as channel gating potentiators or molecular chaperones to improve misfolding). That leaves about 10% of the CF population, those with little to no protein production (such as in nonsense mutations) ineligible for treatment with CFTR modulators. “The ideal for efficacy and equity, given that some CFTR mutations only exist in a handful of people, would be to develop a ‘mutation agnostic’ strategy — such as with mRNA or gene delivery. Here you could imagine that regardless of the type of mutation, a patient would then be able to receive the technology to increase CFTR channel function,” Dr. Sala said. Many modifiable factors, including host immunity and non-CFTR genes that impact CFTR indirectly, may underlie the fact that one person has a worse trajectory than another. “New therapies may also be found in this area of research,” Dr. Sala said.
Strategies in testing phases
“For patients with class I (nonsense) mutations there is hope that small molecules will be identified that can facilitate premature truncation codon (PTC) read-through and/or impede mRNA decay allowing for clinically relevant levels of functional CFTR,” the researchers noted. While the most extensively developed, ataluren, an oxadiazole, failed in phase 3 trials after initial promise, other ribosomal read-through drugs are in preclinical and early phase clinical trials. Also, early encouraging results support an alternative strategy, engineered transfer RNAs (tRNAs) that introduce an amino acid to an elongating peptide in place of the termination codon.
While these will address specific mutations, DNA or mRNA replacement strategies would be “mutation agnostic,” the researchers stated. The major challenge: delivery to the respiratory epithelium. Approaches currently in early testing include an inhaled aerosolized, lipid-based nanoparticle carrier for mRNA delivery, viral and non-viral DNA transfer, lipid-mediated CFTR gene transfer, pseudotyped lentiviral vector and adeno-associated vector transfer of CFTR DNA.
Adult CF care
“Adult CF care in general is a completely new frontier,” Meilinh Thi, DO, director of the adult cystic fibrosis program and assistant professor at University of Texas Health at San Antonio, said in an interview. “It’s fairly new to have separate pediatric and adult CF centers. There’s been a shift,” she said. “We’re encountering diseases in CF that we have not in the past had to deal with: diabetes that has features of both type 1 and type 2, increased colon cancer risk, bone disease, and mental health issues. Also, while pregnancy was previously discouraged for women with CF because of lung disease, now many are giving birth without complications and living normal lives,” Dr. Thi said.
“We do encourage our patients to talk to us before becoming pregnant so we can discuss the risk of passing on the gene. And, we do encourage their significant others to get testing. Some patients and their others, however, do decline to get tested,” she added.
The lifetime health issues conferred by CF, Dr. Thi noted, include lung disease with chronic inflammation, infection, respiratory failure (still the most common cause of death), gastrointestinal disorders (including of the pancreas) , colon obstruction and colon cancer, sinus disease, and reproductive system effects. Their permanence, she said, depends on how far their disease has progressed. “So the earlier you can provide these newer therapies — the modulators, for example, or the gene therapy whenever that comes out, then the less damage these organ systems will have, and the patients, we hope, will then do better.”
After Rena Barrow-Wells, an African American mother, fought mightily to prevent a repeat of her experience of two decades earlier when her first child’s cystic fibrosis (CF) took 4 years to diagnose, her story became the subject of a New York Times feature covering disparities in diagnostic CF screening. The article highlighted not only her struggles, but also the utter transformation of the CF landscape since the introduction of small molecule mutation-specific drugs. These drugs restore function to defective CF transmembrane conductance regulator (CFTR) proteins. By the time Ms. Barrow-Wells’ young son was treated, lung and pancreatic scarring were already significant. So when the 39-mutation variant screening test available in Ms. Barrow-Wells’ Lawrenceville, Georgia, clinic turned out negative for CF, her pediatrician told her to stop worrying despite her new son’s inherent genetic risk, telltale salty skin, foul-smelling diapers, and her pleas to test for sweat chloride. It still took 3 months for a confirmed diagnosis and the initiation of treatment.
Current genetic tests, based largely on older clinical trials that enrolled mostly white children, are highly accurate for identifying CF in white babies (95%), but often fail to identify substantial percentages of mutations originating in Africa, Asia, and Latin America. They miss CF in Asian (44%), Black (22%), and Hispanic, Native American and Alaskan Native babies (14%), the Times article stated. In the United States, the number of CF variants tested for falls into a wide range: from the one variant found mostly in White populations in Mississippi (with a 38% Black populace) to 689 variants in Wisconsin.
Not too far back, CF was thought of as an inherited childhood disease leading often to childhood or adolescent mortality.
Today’s CF challenges
Beyond refinements in screening instruments and policies that broaden access leading to the earliest possible diagnoses, ongoing research needs include finding treatments for other variants, and caring for adult populations living with treated CF and the disease’s multisystem manifestations. “As people with CF live longer, we need to be very focused on optimized adult medical care for this population,” Marc A. Sala, MD, assistant professor of medicine, Adult CF Program, Northwestern University Feinberg School of Medicine, Chicago, said in an interview. “For example, we need higher vigilance for liver, microvascular, coronary artery disease, and various cancer screenings. We do not know exactly how these will manifest differently from the way they do in non-CF populations, so this is where more work needs to be done.”
Emphasis on monitoring
The authors of “Future therapies for cystic fibrosis” (Allen et al. Nature Communications, 2023 Feb 8), after citing the ongoing transformative change for people with CF since the introduction of CFTR drugs, gave voice to important cautions. “Disease will progress, albeit more slowly, and will be more challenging to monitor. Effective CFTR modulators will likely slow or, at best, halt disease progression, but will not reverse a disease that has already become fixed.” They cited pancreatic destruction in the majority, bronchiectasis, and absence of the vas deferens, with still recurring (although less frequently) pulmonary exacerbations along with chronic infections and persistent airway inflammation. “It is essential that we do not become complacent about disease progression in this population,” the researchers stated. They cautioned also that effective surveillance for infection is critical in asymptomatic patients, emphasizing that it underpins the management of young healthy children with CF who demonstrate disease progression despite a lack of symptoms.
Among the ~90% for whom Trikafta is suitable and approved (those with least one copy of F508del or specific other responsive mutations), improvements include increased percent predicted FEV1 by 10%-15% or more, decreased exacerbations, and improved quality of life,” Dr. Sala said. “Subsequent ‘real world’ experience shows dramatic reductions in sputum production and decreased frequency of lung transplant.”
Mutation agnostic therapy
Unfortunately, CF mutants, outside the population eligible for Trikafta, are prodigious in number and do not fall into just a few major groups. “Furthermore, although CF is a monogenic disease, it has variable phenotypes even for two individuals with the same mutations,” Dr. Sala said. “Current CFTR modulators act on the dysfunctional CFTR protein (either as channel gating potentiators or molecular chaperones to improve misfolding). That leaves about 10% of the CF population, those with little to no protein production (such as in nonsense mutations) ineligible for treatment with CFTR modulators. “The ideal for efficacy and equity, given that some CFTR mutations only exist in a handful of people, would be to develop a ‘mutation agnostic’ strategy — such as with mRNA or gene delivery. Here you could imagine that regardless of the type of mutation, a patient would then be able to receive the technology to increase CFTR channel function,” Dr. Sala said. Many modifiable factors, including host immunity and non-CFTR genes that impact CFTR indirectly, may underlie the fact that one person has a worse trajectory than another. “New therapies may also be found in this area of research,” Dr. Sala said.
Strategies in testing phases
“For patients with class I (nonsense) mutations there is hope that small molecules will be identified that can facilitate premature truncation codon (PTC) read-through and/or impede mRNA decay allowing for clinically relevant levels of functional CFTR,” the researchers noted. While the most extensively developed, ataluren, an oxadiazole, failed in phase 3 trials after initial promise, other ribosomal read-through drugs are in preclinical and early phase clinical trials. Also, early encouraging results support an alternative strategy, engineered transfer RNAs (tRNAs) that introduce an amino acid to an elongating peptide in place of the termination codon.
While these will address specific mutations, DNA or mRNA replacement strategies would be “mutation agnostic,” the researchers stated. The major challenge: delivery to the respiratory epithelium. Approaches currently in early testing include an inhaled aerosolized, lipid-based nanoparticle carrier for mRNA delivery, viral and non-viral DNA transfer, lipid-mediated CFTR gene transfer, pseudotyped lentiviral vector and adeno-associated vector transfer of CFTR DNA.
Adult CF care
“Adult CF care in general is a completely new frontier,” Meilinh Thi, DO, director of the adult cystic fibrosis program and assistant professor at University of Texas Health at San Antonio, said in an interview. “It’s fairly new to have separate pediatric and adult CF centers. There’s been a shift,” she said. “We’re encountering diseases in CF that we have not in the past had to deal with: diabetes that has features of both type 1 and type 2, increased colon cancer risk, bone disease, and mental health issues. Also, while pregnancy was previously discouraged for women with CF because of lung disease, now many are giving birth without complications and living normal lives,” Dr. Thi said.
“We do encourage our patients to talk to us before becoming pregnant so we can discuss the risk of passing on the gene. And, we do encourage their significant others to get testing. Some patients and their others, however, do decline to get tested,” she added.
The lifetime health issues conferred by CF, Dr. Thi noted, include lung disease with chronic inflammation, infection, respiratory failure (still the most common cause of death), gastrointestinal disorders (including of the pancreas) , colon obstruction and colon cancer, sinus disease, and reproductive system effects. Their permanence, she said, depends on how far their disease has progressed. “So the earlier you can provide these newer therapies — the modulators, for example, or the gene therapy whenever that comes out, then the less damage these organ systems will have, and the patients, we hope, will then do better.”
Top reads from the CHEST journal portfolio
Covering the frailty scale in ILD, diagnosis of peripheral pulmonary nodules, and platelet mitochondrial function in sepsis.
Journal CHEST®
By Guler, MD, and colleagues
Life expectancy is a very important factor for patients with interstitial lung disease (ILD) and their caregivers. The discussion surrounding prognosis is often wrought with uncertainty and is inherently painful for both patients and clinicians when faced with nonmodifiable traits. This study illustrates the significance of employing a method that succinctly and systematically communicates the degree of functional impairment in patients with fibrotic lung disease. The authors have highlighted the importance of identifying and improving health factors associated with frailty to enhance the survival and quality of life of patients with chronic noncurable fibrotic lung disease. It also presents hope that interventions aimed at improving functional capacity may improve frailty and thus modify prognosis. In the future, longitudinal trends of frailty assessments following interventions aimed at improving both exercise and functional capacity, like pulmonary rehab, should be explored.
– Commentary by Priya Balakrishnan, MD, MS, FCCP, Member of the CHEST Physician Editorial Board
CHEST® Pulmonary
By Michael V. Brown, MD, and colleagues
Brown and colleagues provide a systemic review and meta-analysis of the diagnostic yield of cone beam computed tomography (CBCT) scan combined with radial-endobronchial ultrasound (r-EBUS) for the diagnosis of peripheral pulmonary nodules. They included 14 studies (865 patients with 882 lesions) with pooled diagnostic yield from CBCT scan and r-EBUS for peripheral pulmonary nodules of 80% (95% CI, 76% to 84%) with complication rates of 2.01% for pneumothorax and 1.08% for bleeding. Amongst the studies selected, confounders (including study design, definition of diagnostic yield, use of ROSE, additional equipment, etc) existed. The important takeaway is that 3D imaging guidance with CBCT scan can corroborate “tool in lesion” and thus potentially improve the outcomes of the different bronchoscopic modalities utilized to diagnose peripheral pulmonary nodules. Future prospective investigations with less heterogeneity in study design and outcomes, as well as comparison with newer technologies such as robotic bronchoscopy, are necessary to corroborate these findings.
– Commentary by Saadia A. Faiz, MD, FCCP, Member of the CHEST Physician Editorial Board
CHEST® Critical Care
Platelet Bioenergetics and Associations With Delirium and Coma in Patients With Sepsis
By Chukwudi A. Onyemekwu, DO, and colleagues
The study by Onyemekwu and colleagues explores the link between platelet mitochondrial function and acute brain dysfunction (delirium and coma) in patients with sepsis. The investigators measured various parameters of platelet mitochondrial respiratory bioenergetics and found that increased spare respiratory capacity was significantly associated with coma but not delirium. These findings suggest that systemic mitochondrial function could influence brain health and indicate a potential link between mitochondrial bioenergetics and coma during sepsis. The study did not find a significant association between platelet bioenergetics and delirium, suggesting that coma and delirium may have different underlying pathophysiologic mechanisms. We must interpret the results with caution, as the associations identified in this observational study do not prove causation. It is possible that the changes seen in platelet mitochondria may be a result of coma rather than a mechanism. Nonetheless, the study provides a foundation for future research to explore the mechanistic role of mitochondria in acute brain dysfunction during sepsis and the potential for developing mitochondrial-targeted therapies as a possible treatment approach for patients with sepsis-induced coma.
– Commentary by Angel O. Coz, MD, FCCP, Editor in Chief of CHEST Physician
Covering the frailty scale in ILD, diagnosis of peripheral pulmonary nodules, and platelet mitochondrial function in sepsis.
Covering the frailty scale in ILD, diagnosis of peripheral pulmonary nodules, and platelet mitochondrial function in sepsis.
Journal CHEST®
By Guler, MD, and colleagues
Life expectancy is a very important factor for patients with interstitial lung disease (ILD) and their caregivers. The discussion surrounding prognosis is often wrought with uncertainty and is inherently painful for both patients and clinicians when faced with nonmodifiable traits. This study illustrates the significance of employing a method that succinctly and systematically communicates the degree of functional impairment in patients with fibrotic lung disease. The authors have highlighted the importance of identifying and improving health factors associated with frailty to enhance the survival and quality of life of patients with chronic noncurable fibrotic lung disease. It also presents hope that interventions aimed at improving functional capacity may improve frailty and thus modify prognosis. In the future, longitudinal trends of frailty assessments following interventions aimed at improving both exercise and functional capacity, like pulmonary rehab, should be explored.
– Commentary by Priya Balakrishnan, MD, MS, FCCP, Member of the CHEST Physician Editorial Board
CHEST® Pulmonary
By Michael V. Brown, MD, and colleagues
Brown and colleagues provide a systemic review and meta-analysis of the diagnostic yield of cone beam computed tomography (CBCT) scan combined with radial-endobronchial ultrasound (r-EBUS) for the diagnosis of peripheral pulmonary nodules. They included 14 studies (865 patients with 882 lesions) with pooled diagnostic yield from CBCT scan and r-EBUS for peripheral pulmonary nodules of 80% (95% CI, 76% to 84%) with complication rates of 2.01% for pneumothorax and 1.08% for bleeding. Amongst the studies selected, confounders (including study design, definition of diagnostic yield, use of ROSE, additional equipment, etc) existed. The important takeaway is that 3D imaging guidance with CBCT scan can corroborate “tool in lesion” and thus potentially improve the outcomes of the different bronchoscopic modalities utilized to diagnose peripheral pulmonary nodules. Future prospective investigations with less heterogeneity in study design and outcomes, as well as comparison with newer technologies such as robotic bronchoscopy, are necessary to corroborate these findings.
– Commentary by Saadia A. Faiz, MD, FCCP, Member of the CHEST Physician Editorial Board
CHEST® Critical Care
Platelet Bioenergetics and Associations With Delirium and Coma in Patients With Sepsis
By Chukwudi A. Onyemekwu, DO, and colleagues
The study by Onyemekwu and colleagues explores the link between platelet mitochondrial function and acute brain dysfunction (delirium and coma) in patients with sepsis. The investigators measured various parameters of platelet mitochondrial respiratory bioenergetics and found that increased spare respiratory capacity was significantly associated with coma but not delirium. These findings suggest that systemic mitochondrial function could influence brain health and indicate a potential link between mitochondrial bioenergetics and coma during sepsis. The study did not find a significant association between platelet bioenergetics and delirium, suggesting that coma and delirium may have different underlying pathophysiologic mechanisms. We must interpret the results with caution, as the associations identified in this observational study do not prove causation. It is possible that the changes seen in platelet mitochondria may be a result of coma rather than a mechanism. Nonetheless, the study provides a foundation for future research to explore the mechanistic role of mitochondria in acute brain dysfunction during sepsis and the potential for developing mitochondrial-targeted therapies as a possible treatment approach for patients with sepsis-induced coma.
– Commentary by Angel O. Coz, MD, FCCP, Editor in Chief of CHEST Physician
Journal CHEST®
By Guler, MD, and colleagues
Life expectancy is a very important factor for patients with interstitial lung disease (ILD) and their caregivers. The discussion surrounding prognosis is often wrought with uncertainty and is inherently painful for both patients and clinicians when faced with nonmodifiable traits. This study illustrates the significance of employing a method that succinctly and systematically communicates the degree of functional impairment in patients with fibrotic lung disease. The authors have highlighted the importance of identifying and improving health factors associated with frailty to enhance the survival and quality of life of patients with chronic noncurable fibrotic lung disease. It also presents hope that interventions aimed at improving functional capacity may improve frailty and thus modify prognosis. In the future, longitudinal trends of frailty assessments following interventions aimed at improving both exercise and functional capacity, like pulmonary rehab, should be explored.
– Commentary by Priya Balakrishnan, MD, MS, FCCP, Member of the CHEST Physician Editorial Board
CHEST® Pulmonary
By Michael V. Brown, MD, and colleagues
Brown and colleagues provide a systemic review and meta-analysis of the diagnostic yield of cone beam computed tomography (CBCT) scan combined with radial-endobronchial ultrasound (r-EBUS) for the diagnosis of peripheral pulmonary nodules. They included 14 studies (865 patients with 882 lesions) with pooled diagnostic yield from CBCT scan and r-EBUS for peripheral pulmonary nodules of 80% (95% CI, 76% to 84%) with complication rates of 2.01% for pneumothorax and 1.08% for bleeding. Amongst the studies selected, confounders (including study design, definition of diagnostic yield, use of ROSE, additional equipment, etc) existed. The important takeaway is that 3D imaging guidance with CBCT scan can corroborate “tool in lesion” and thus potentially improve the outcomes of the different bronchoscopic modalities utilized to diagnose peripheral pulmonary nodules. Future prospective investigations with less heterogeneity in study design and outcomes, as well as comparison with newer technologies such as robotic bronchoscopy, are necessary to corroborate these findings.
– Commentary by Saadia A. Faiz, MD, FCCP, Member of the CHEST Physician Editorial Board
CHEST® Critical Care
Platelet Bioenergetics and Associations With Delirium and Coma in Patients With Sepsis
By Chukwudi A. Onyemekwu, DO, and colleagues
The study by Onyemekwu and colleagues explores the link between platelet mitochondrial function and acute brain dysfunction (delirium and coma) in patients with sepsis. The investigators measured various parameters of platelet mitochondrial respiratory bioenergetics and found that increased spare respiratory capacity was significantly associated with coma but not delirium. These findings suggest that systemic mitochondrial function could influence brain health and indicate a potential link between mitochondrial bioenergetics and coma during sepsis. The study did not find a significant association between platelet bioenergetics and delirium, suggesting that coma and delirium may have different underlying pathophysiologic mechanisms. We must interpret the results with caution, as the associations identified in this observational study do not prove causation. It is possible that the changes seen in platelet mitochondria may be a result of coma rather than a mechanism. Nonetheless, the study provides a foundation for future research to explore the mechanistic role of mitochondria in acute brain dysfunction during sepsis and the potential for developing mitochondrial-targeted therapies as a possible treatment approach for patients with sepsis-induced coma.
– Commentary by Angel O. Coz, MD, FCCP, Editor in Chief of CHEST Physician