User login
High-Dose Psilocybin Shows Promising Results for Depression
TOPLINE:
, a new meta-analysis suggests.
METHODOLOGY:
- Researchers conducted a network meta-analysis to evaluate the comparative effectiveness of oral monotherapy with psychedelics versus escitalopram in patients with clinically diagnosed depression.
- The meta-analysis included 811 participants (mean age, 42.49 years; 54.2% women) with clinically diagnosed depression across 15 psychedelic trials and 1968 participants (mean age, 39.35 years; 62.5% women) across five escitalopram trials.
- Trials evaluated oral monotherapy with psychedelics (psilocybin, lysergic acid diethylamide, 3,4-methylenedioxymethamphetamine [MDMA], and ayahuasca), fixed-dose escitalopram (up to 20 mg/d) versus placebo, and psychedelic versus escitalopram monotherapy.
- The primary outcome was a change in depressive symptoms from baseline.
TAKEAWAY:
- Placebo responses in antidepressant trials (mean difference, 3.79; 95% CI, 0.77-6.80) and extremely low-dose psilocybin (mean difference, 3.96; 95% CI, 0.61-7.17) were better than those in psychedelic trials.
- High-dose psilocybin (20 mg or more) performed better than placebo in the antidepressant trials (mean difference, > 3). However, when comparing high-dose psilocybin with the placebo used in antidepressant trials, the effect size was smaller. The standardized mean difference dropped from 0.88 to 0.31, indicating that the effect of high-dose psilocybin was similar to that of current antidepressants.
- High-dose psilocybin was associated with a greater response than escitalopram at 10 mg (4.66; 95% CI, 1.36-7.74) and 20 mg (4.69; 95% CI, 1.64-7.54).
- No interventions were associated with an increased risk for all-cause discontinuation or severe adverse events.
IN PRACTICE:
“Taken together, our study findings suggest that among psychedelic treatments, high-dose psilocybin is more likely to reach the minimal important difference for depressive symptoms in studies with adequate blinding design, while the effect size of psilocybin was similar to that of current antidepressant drugs, showing a mean standardized mean difference of 0.3,” the authors wrote.
SOURCE:
The study was led by Tien-Wei Hsu, MD, I-Shou University and Kaohsiung Medical University, Kaohsiung City, Taiwan. It was published online in The BMJ.
LIMITATIONS:
The study did not assess long-term effects of the interventions. Participants in the MDMA trials were primarily diagnosed with posttraumatic stress disorder, which may not be representative of the general population with depressive symptoms. Moreover, the sample size of the psychedelic trials was small. Using extremely low-dose psychedelics as a reference group may have eliminated some pharmacologic effects as these doses cannot be considered a placebo.
DISCLOSURES:
The study was supported by grants from the National Science and Technology Council. The authors declared no financial relationships with any organizations outside the submitted work in the past 3 years. Full disclosures are available in the original article.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
, a new meta-analysis suggests.
METHODOLOGY:
- Researchers conducted a network meta-analysis to evaluate the comparative effectiveness of oral monotherapy with psychedelics versus escitalopram in patients with clinically diagnosed depression.
- The meta-analysis included 811 participants (mean age, 42.49 years; 54.2% women) with clinically diagnosed depression across 15 psychedelic trials and 1968 participants (mean age, 39.35 years; 62.5% women) across five escitalopram trials.
- Trials evaluated oral monotherapy with psychedelics (psilocybin, lysergic acid diethylamide, 3,4-methylenedioxymethamphetamine [MDMA], and ayahuasca), fixed-dose escitalopram (up to 20 mg/d) versus placebo, and psychedelic versus escitalopram monotherapy.
- The primary outcome was a change in depressive symptoms from baseline.
TAKEAWAY:
- Placebo responses in antidepressant trials (mean difference, 3.79; 95% CI, 0.77-6.80) and extremely low-dose psilocybin (mean difference, 3.96; 95% CI, 0.61-7.17) were better than those in psychedelic trials.
- High-dose psilocybin (20 mg or more) performed better than placebo in the antidepressant trials (mean difference, > 3). However, when comparing high-dose psilocybin with the placebo used in antidepressant trials, the effect size was smaller. The standardized mean difference dropped from 0.88 to 0.31, indicating that the effect of high-dose psilocybin was similar to that of current antidepressants.
- High-dose psilocybin was associated with a greater response than escitalopram at 10 mg (4.66; 95% CI, 1.36-7.74) and 20 mg (4.69; 95% CI, 1.64-7.54).
- No interventions were associated with an increased risk for all-cause discontinuation or severe adverse events.
IN PRACTICE:
“Taken together, our study findings suggest that among psychedelic treatments, high-dose psilocybin is more likely to reach the minimal important difference for depressive symptoms in studies with adequate blinding design, while the effect size of psilocybin was similar to that of current antidepressant drugs, showing a mean standardized mean difference of 0.3,” the authors wrote.
SOURCE:
The study was led by Tien-Wei Hsu, MD, I-Shou University and Kaohsiung Medical University, Kaohsiung City, Taiwan. It was published online in The BMJ.
LIMITATIONS:
The study did not assess long-term effects of the interventions. Participants in the MDMA trials were primarily diagnosed with posttraumatic stress disorder, which may not be representative of the general population with depressive symptoms. Moreover, the sample size of the psychedelic trials was small. Using extremely low-dose psychedelics as a reference group may have eliminated some pharmacologic effects as these doses cannot be considered a placebo.
DISCLOSURES:
The study was supported by grants from the National Science and Technology Council. The authors declared no financial relationships with any organizations outside the submitted work in the past 3 years. Full disclosures are available in the original article.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
, a new meta-analysis suggests.
METHODOLOGY:
- Researchers conducted a network meta-analysis to evaluate the comparative effectiveness of oral monotherapy with psychedelics versus escitalopram in patients with clinically diagnosed depression.
- The meta-analysis included 811 participants (mean age, 42.49 years; 54.2% women) with clinically diagnosed depression across 15 psychedelic trials and 1968 participants (mean age, 39.35 years; 62.5% women) across five escitalopram trials.
- Trials evaluated oral monotherapy with psychedelics (psilocybin, lysergic acid diethylamide, 3,4-methylenedioxymethamphetamine [MDMA], and ayahuasca), fixed-dose escitalopram (up to 20 mg/d) versus placebo, and psychedelic versus escitalopram monotherapy.
- The primary outcome was a change in depressive symptoms from baseline.
TAKEAWAY:
- Placebo responses in antidepressant trials (mean difference, 3.79; 95% CI, 0.77-6.80) and extremely low-dose psilocybin (mean difference, 3.96; 95% CI, 0.61-7.17) were better than those in psychedelic trials.
- High-dose psilocybin (20 mg or more) performed better than placebo in the antidepressant trials (mean difference, > 3). However, when comparing high-dose psilocybin with the placebo used in antidepressant trials, the effect size was smaller. The standardized mean difference dropped from 0.88 to 0.31, indicating that the effect of high-dose psilocybin was similar to that of current antidepressants.
- High-dose psilocybin was associated with a greater response than escitalopram at 10 mg (4.66; 95% CI, 1.36-7.74) and 20 mg (4.69; 95% CI, 1.64-7.54).
- No interventions were associated with an increased risk for all-cause discontinuation or severe adverse events.
IN PRACTICE:
“Taken together, our study findings suggest that among psychedelic treatments, high-dose psilocybin is more likely to reach the minimal important difference for depressive symptoms in studies with adequate blinding design, while the effect size of psilocybin was similar to that of current antidepressant drugs, showing a mean standardized mean difference of 0.3,” the authors wrote.
SOURCE:
The study was led by Tien-Wei Hsu, MD, I-Shou University and Kaohsiung Medical University, Kaohsiung City, Taiwan. It was published online in The BMJ.
LIMITATIONS:
The study did not assess long-term effects of the interventions. Participants in the MDMA trials were primarily diagnosed with posttraumatic stress disorder, which may not be representative of the general population with depressive symptoms. Moreover, the sample size of the psychedelic trials was small. Using extremely low-dose psychedelics as a reference group may have eliminated some pharmacologic effects as these doses cannot be considered a placebo.
DISCLOSURES:
The study was supported by grants from the National Science and Technology Council. The authors declared no financial relationships with any organizations outside the submitted work in the past 3 years. Full disclosures are available in the original article.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Prurigo Nodularis Mechanisms and Current Management Options
Prurigo nodularis (PN)(also called chronic nodular prurigo, prurigo nodularis of Hyde, or picker’s nodules) was first characterized by James Hyde in 1909.1-3 Prurigo nodularis manifests with symmetrical, intensely pruritic, eroded, or hyperkeratotic nodules or papules on the extremities and trunk.1,2,4,5 Studies have shown that individuals with PN experience pruritus, sleep loss, decreased social functioning from the appearance of the nodules, and a higher incidence of anxiety and depression, causing a negative impact on their quality of life.2,6 In addition, the manifestation of PN has been linked to neurologic and psychiatric disorders; however, PN also can be idiopathic and manifest without underlying illnesses.2,6,7
Prurigo nodularis has been associated with other dermatologic conditions such as atopic dermatitis (up to 50%), lichen planus, keratoacanthomas (KAs), and bullous pemphigoid.7-9 It also has been linked to systemic diseases in 38% to 50% of cases, including chronic kidney disease, liver disease, type 2 diabetes mellitus, malignancies (hematopoietic, liver, and skin), and HIV infection.6,8,10
The pathophysiology of PN is highly complex and has yet to be fully elucidated. It is thought to be due to dysregulation and interaction of the increase in neural and immunologic responses of proinflammatory and pruritogenic cytokines.2,11 Treatments aim to break the itch-scratch cycle that perpetuates this disorder; however, this proves difficult, as PN is associated with a higher itch intensity than atopic dermatitis and psoriasis.10 Therefore, most patients attempt multiple forms of treatment for PN, ranging from topical therapies, oral immunosuppressants, and phototherapy to the newest and only medication approved by the US Food and Drug Administration for the treatment of PN—dupilumab.1,7,11 Herein, we provide an updated review of PN with a focus on its epidemiology, histopathology and pathophysiology, comorbidities, clinical presentation, differential diagnosis, and current treatment options.
Epidemiology
There are few studies on the epidemiology of PN; however, middle-aged populations with underlying dermatologic or psychiatric disorders tend to be impacted most frequently.2,12,13 In 2016, it was estimated that almost 88,000 individuals had PN in the United States, with the majority being female; however, this estimate only took into account those aged 18 to 64 years and utilized data from IBM MarketScan Commercial Claims and Encounters Database (IBM Watson Health) from October 2015 to December 2016.14 More recently, a retrospective database analysis estimated the prevalence of PN in the United States to be anywhere from 36.7 to 43.9 cases per 100,000 individuals. However, this retrospective review utilized the International Classification of Diseases, Tenth Revision code; PN has 2 codes associated with the diagnosis, and the coding accuracy is unknown.15 Sutaria et al16 looked at racial disparities in patients with PN utilizing data from TriNetX and found that patients who received a diagnosis of PN were more likely to be women, non-Hispanic, and Black compared with control patients. However, these estimates are restricted to the health care organizations within this database.
In 2018, Poland reported an annual prevalence of 6.52 cases per 100,000 individuals,17 while England reported a yearly prevalence of 3.27 cases per 100,000 individuals.18 Both countries reported most cases were female. However, these studies are not without limitations. Poland only uses the primary diagnosis code for medical billing to simplify clinical coding, thus underestimating the actual prevalence; furthermore, clinical codes more often than not are assigned by someone other than the diagnosing physician, leaving room for error.17 In addition, England’s PN estimate utilized diagnosis data from primary care and inpatient datasets, leaving out outpatient datasets in which patients with PN may have been referred and obtained the diagnosis, potentially underestimating the prevalence in this population.18
In contrast, Korea estimated the annual prevalence of PN to be 4.82 cases per 1000 dermatology outpatients, with the majority being men, based on results from a cross-sectional study among outpatients from the Catholic Medical Center. Although this is the largest health organization in Korea, the scope of this study is limited and lacks data from other medical centers in Korea.19
Histopathology and Pathophysiology
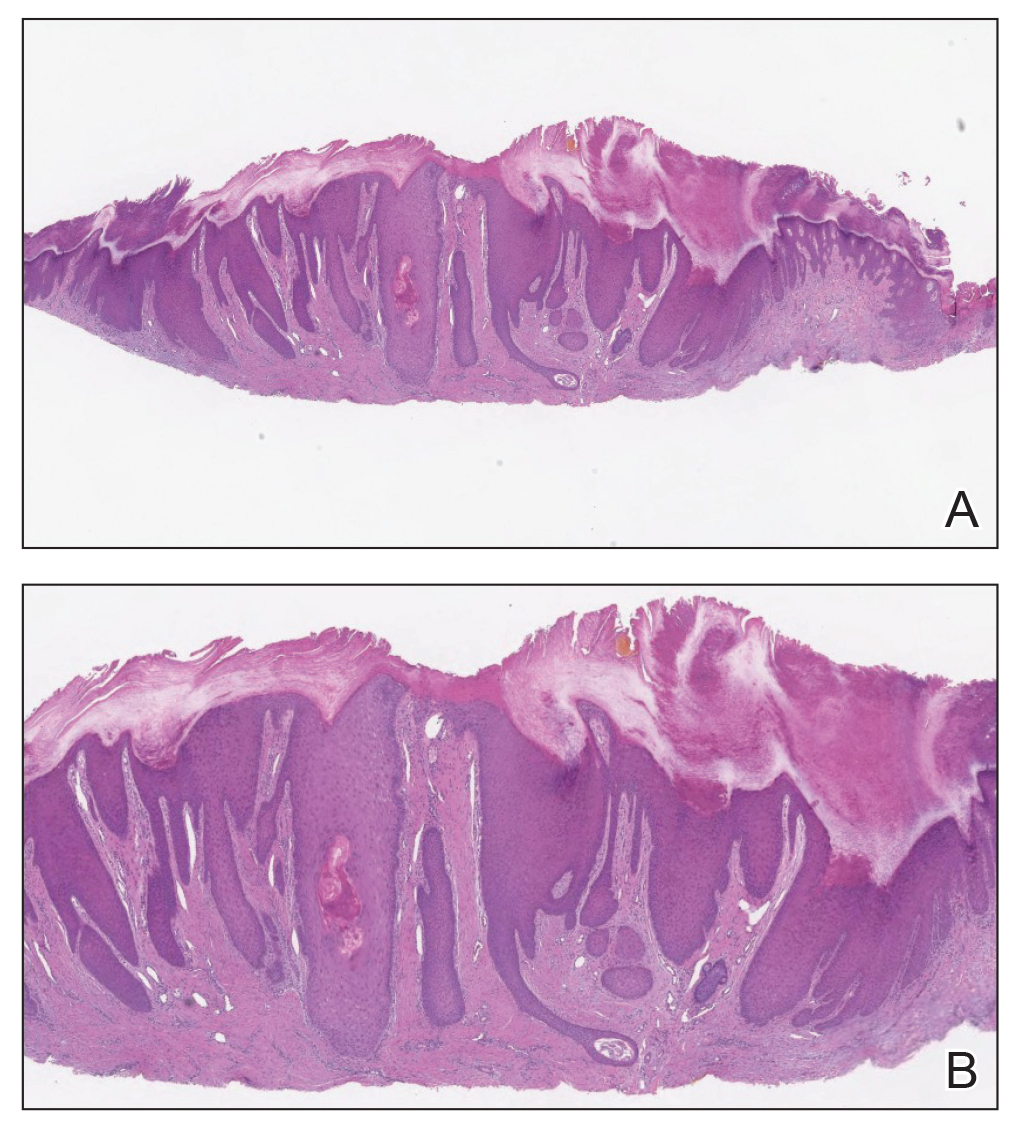
Almost all cells in the skin are involved in PN: keratinocytes, mast cells, dendritic cells, endothelial cells, lymphocytes, eosinophils, collagen fibers, and nerve fibers.11,20 Classically, PN manifests as a dome-shaped lesion with hyperkeratosis, hypergranulosis, and psoriasiform epidermal hyperplasia with increased thickness of the papillary dermis consisting of coarse collagen with compact interstitial and circumvascular infiltration as well as increased lymphocytes and histocytes in the superficial dermis (Figure 1).20 Hyperkeratosis is thought to be due to either the alteration of keratinocyte structures from scratching or keratinocyte abnormalities triggering PN.21 However, the increase in keratinocytes, which secrete nerve growth factor, allows for neuronal hyperplasia within the dermis.22 Nerve growth factor can stimulate keratinocyte proliferation23 in addition to the upregulation of substance P (SP), a tachykinin that triggers vascular dilation and pruritus in the skin.24 The density of SP nerve fibers in the dermis increases in PN, causing proinflammatory effects, upregulating the immune response to promote endothelial hyperplasia and increased vascularization.25 The increase in these fibers may lead to pruritus associated with PN.2,26
Many inflammatory cytokines and mediators also have been implicated in PN. Increased messenger RNA expression of IL-4, IL-17, IL-22, and IL-31 has been described in PN lesions.3,27 Furthermore, studies also have reported increased helper T cell (TH2) cytokines, including IL-4, IL-5, IL-10, and IL-13, in the dermis of PN lesions in patients without a history of atopy.3,28 These pruritogenic cytokines in conjunction with the SP fibers may create an intractable itch for those with PN. The interaction and culmination of the neural and immune responses make PN a complex condition to treat with the multifactorial interaction of systems.
Comorbidities
Prurigo nodularis has been associated with a wide array of comorbidities; however, the direction of the relationship between PN and these conditions makes it difficult to discern if PN is a primary or secondary condition.29 Prurigo nodularis commonly has been connected to other inflammatory dermatoses, with a link to atopic dermatitis being the strongest.5,29 However, PN also has been linked to other pruritic inflammatory cutaneous disorders, including psoriasis, cutaneous T-cell lymphoma, lichen planus, and dermatitis herpetiformis.14,29
Huang et al14 found an increased likelihood of psychiatric illnesses in patients with PN, including eating disorders, nonsuicidal self-injury disorder, attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder, schizophrenia, mood disorders, anxiety, and substance abuse disorders. Treatments directed at the neural aspect of PN have included selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs), which also are utilized to treat these mental health disorders.
Furthermore, systemic diseases also have been found to be associated with PN, including hypertension, type 2 diabetes mellitus, chronic kidney disease, heart failure, cerebrovascular disease, coronary heart disease, and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease.14 The relationship between PN and systemic conditions may be due to increased systemic inflammation and dysregulation of neural and metabolic functions implicated in these conditions from increased pruritic manifestations.29,30 However, studies also have connected PN to infectious conditions such as HIV. One study found that patients with PN had 2.68 higher odds of infection with HIV compared to age- and sex-matched controls.14 It is unknown if these conditions contributed to the development of PN or PN contributed to the development of these disorders.
Clinical Presentations
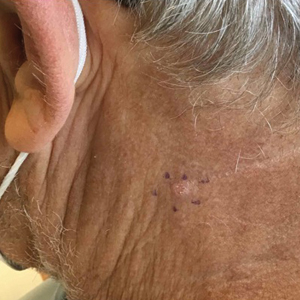
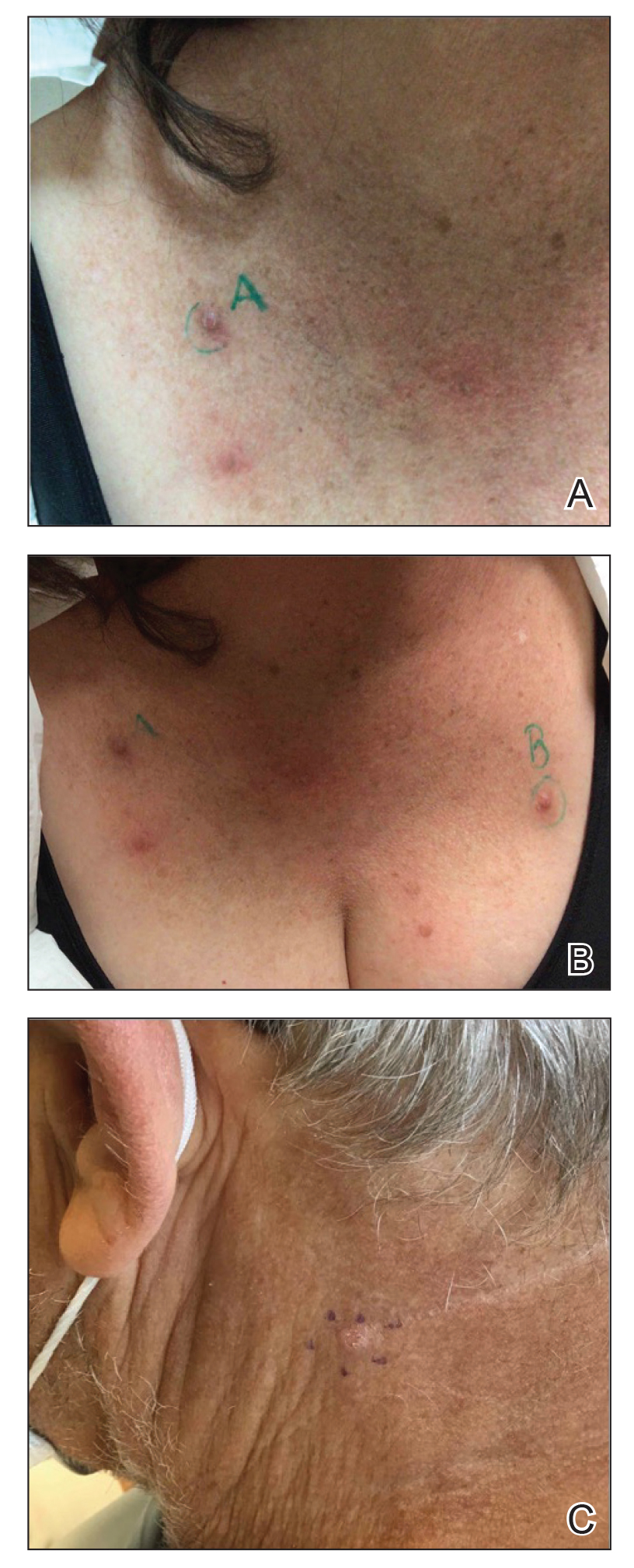
Prurigo nodularis is a chronic inflammatory skin disease that typically manifests with multiple severely pruritic, dome-shaped, firm, hyperpigmented papulonodules with central scale or crust, often with erosion, due to chronic repetitive scratching and picking secondary to pruritic systemic or dermatologic diseases or psychological disorders (Figure 2).1,2,4,5,8,31 Most often, diagnosis of PN is based on history and physical examination of the lesion; however, biopsies may be performed. These nodules commonly manifest with ulceration distributed symmetrically on extensor extremities in easy-to-reach places, sparing the mid back (called the butterfly sign).8 Lesions—either a few or hundreds—can range from a few millimeters to 2 to 3 cm.8,32 The lesions differ in appearance depending on the pigment in the patient’s skin. In patients with darker skin tones, hyperpigmented or hypopigmented papulonodules are not uncommon, while those with fairer skin tones tend to present with erythema.31
Differential Diagnosis
Because of the variation in manifestation of PN, these lesions may resemble other cutaneous conditions. If the lesions are hyperkeratotic, they can mimic hypertrophic lichen planus, which mainfests with hyperkeratotic plaques or nodules on the lower extremities.8,29 In addition, the histopathology of lichen planus resembles the appearance of PN, with epidermal hyperplasia, hypergranulosis, hyperkeratosis, and increased fibroblasts and capillaries.8,29
Pemphigoid nodularis is a rare subtype of bullous pemphigoid that exhibits characteristics of PN with pruritic plaques and erosions.8,29,33 The patient population for pemphigoid nodularis tends to be aged 50 to 60 years, and females are affected more frequently than males. However, pemphigoid nodularis may manifest with blistering and large plaques, which are not seen commonly with PN.29 On histopathology, pemphigoid nodularis deposits IgG and C3 on the basement membrane and has subepidermal clefting, unlike PN.7,29
Actinic prurigo manifests with pruritic papules or nodules post–UV exposure to unprotected skin.8,29,33 This rare condition usually manifests with cheilitis and conjunctivitis. Unlike PN, which commonly affects elderly populations, actinic prurigo typically is found in young females.8,29 Cytologic examination shows hyperkeratosis, spongiosis, and acanthosis of the epidermis with lymphocytic perivascular infiltration of the dermis.34
Neurotic excoriations also tend to mimic PN with raised excoriated lesions; however, this disorder is due to neurotic picking of the skin without associated pruritus or true hyperkeratosis.8,29,33 Histopathology shows epidermal crusting with inflammation of the upper dermis.35
Infiltrative cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma (SCC) may imitate PN in appearance. It manifests as tender, ulcerated, scaly plaques or nodules. Histopathology shows cytologic atypia with an infiltrative architectural pattern and presence of collections of compact keratin and parakeratin (called keratin pearls).
Keratoacanthomas can resemble PN lesions. They usually manifest as nodules measuring 1 to 2 cm in diameter and 0.5 cm thick, resembling crateriform tumors.36 On histopathology, KAs can resemble SCCs; however, KAs tend to manifest more frequently with a keratin-filled crater with a ground-glass appearance.36
Inverted follicular keratosis commonly manifests on the face in elderly men as a single, flesh-colored, verrucous papule that may resemble PN. However, cytology of inverted follicular keratosis is characterized by proliferation and squamous eddies.37 Consideration of the histologic findings and clinical appearance are important to differentiate between PN and cutaneous SCC.
Pseudoepitheliomatous hyperplasia is a benign condition that manifests as a plaque or nodule with crust, scale, or ulceration. Histologically, this condition presents with hyperplastic proliferation of the epidermis and adnexal epithelium.38 The clinical and histologic appearance can mimic PN and other cutaneous eruptions with epidermal hyperplasia.
In clinical cases that are resistant to treatment, biopsy is the best approach to diagnose the lesion. Due to similarities in physical appearance and superficial histologic presentation of PN, KAs from SCC, hypertrophic lichen planus, and other hyperkeratotic lesions, the biopsy should be taken at the base of the lesion to sample deeper layers of skin to differentiate these dermatologic disorders.
Management
Current treatments for PN yield varied results. Many patients with moderate to severe PN attempt multiple therapies before seeing improvement.31 Treatments include topical, oral, and injectable medications and are either directed at the neural or immune components of PN due to the interplay between increased nerve fibers in the lesions (neural axis) as well as increases in cytokines and other immunologic mediators (immune axis) of this condition. However, the FDA recently approved the first treatment for PN—dupilumab—which is an injectable IL-4 receptor antagonist directed at the immunologic interactions affiliated with PN.
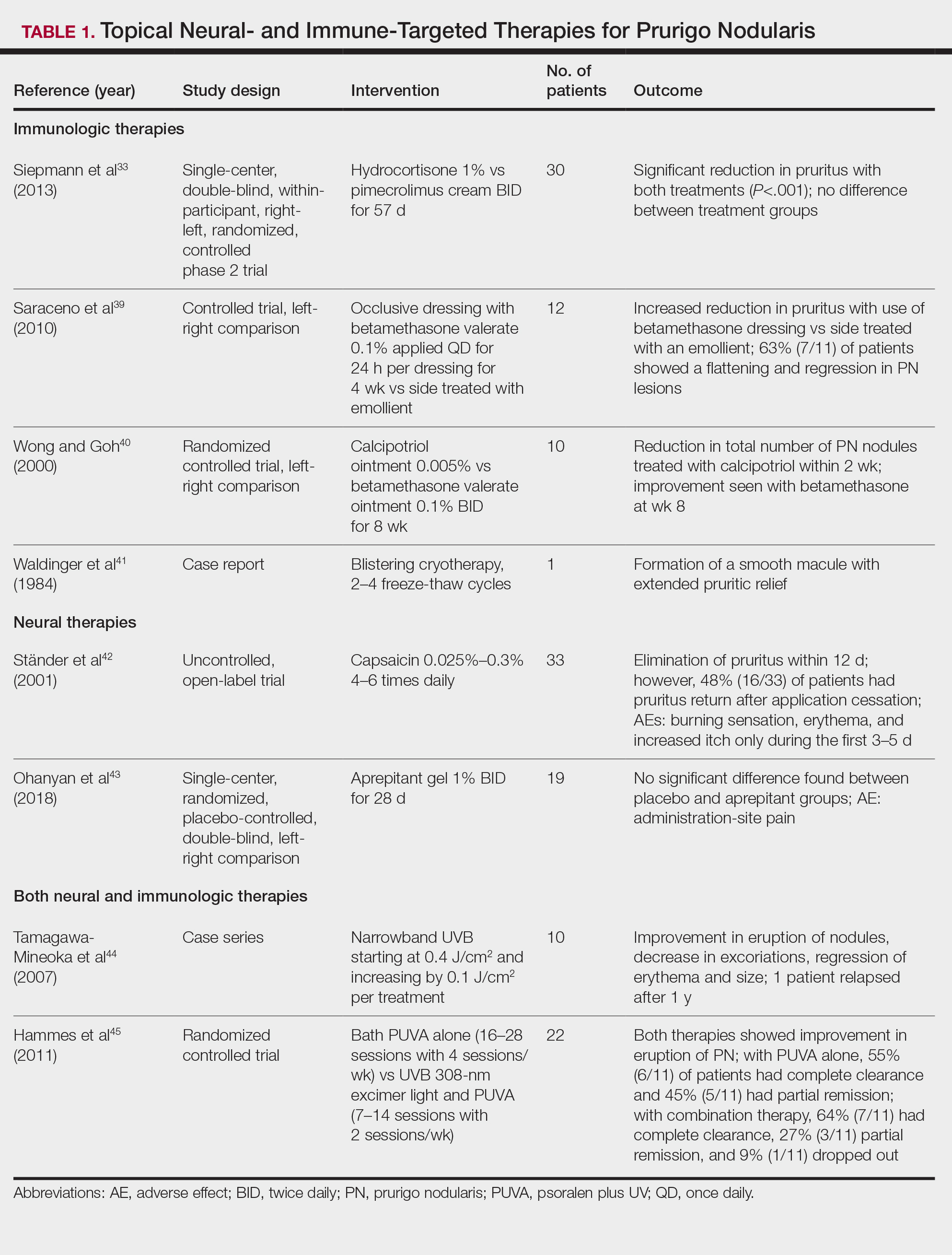
Immune-Mediated Topical Therapies—Immunologic topical therapies include corticosteroids, calcipotriol, and calcineurin inhibitors. Studies that have analyzed these treatments are limited to case reports and small intraindividual and randomized controlled trials (Table 1). Topical therapies usually are first-line agents for most patients. Adverse effects include transient irritation of the skin.40,42,43
Cryotherapy is another topical and immunologic therapy for those with PN; however, this treatment is more appropriate for patients with fewer lesions due to the pain that accompanies lesions treated with liquid nitrogen. In addition, this therapy can cause dyspigmentation of the skin in the treated areas.41
Similar to cryotherapy, intralesional corticosteroid injections are appropriate for patients with few PN lesions. A recent report described intralesional corticosteroid injections of 2.5 mg/mL for a PN nodule with high efficacy.46,47 This treatment has not undergone trials, but success with this modality has been documented, with adverse effects including hyperpigmentation or hypopigmentation in the treated area and transient pain.46
Neural-Mediated Topical Therapies—Neural topical therapies include capsaicin and neurokinin-1 receptor antagonists, aprepitant43 and serlopitant. These treatment studies are limited to small open-label and randomized controlled trials. Adverse effects of these treatments include transient cutaneous pain at the site of topical administration. In addition, neural-mediated topical therapies have shown either limited improvements from baseline or return of symptoms after treatment cessation.42,43
Supplements—N-acetyl cysteine is an over-the-counter supplement that has been reported to improve symptoms in patients with skin-picking disorders.48 The mechanism of action includes antioxidant effects such as decreasing reactive oxygen species, decreasing inflammatory markers, regulating neurotransmitters, and inhibiting hyperkeratosis.49 N-acetyl cysteine has been poorly studied for its application in PN. A small study of 3 patients with subacute PN receiving 1200 mg of oral N-acetyl cysteine reported varying levels of improvement in skin appearance and reduction in skin picking.50
Phototherapy—Phototherapy, a typical first- or second-line treatment modality for PN, targets both the neural- and immune-mediated aspects associated with pruritus in PN (Table 1).51 UV light can penetrate through the epidermal layer of the skin and reach the keratinocytes, which play a role in the immune-related response of PN. In addition, the cutaneous sensory nerves are located in the upper dermal layer, from which nerve fibers grow and penetrate into the epidermis, thereby interacting with the keratinocytes where pruritic signals are transmitted from the periphery up to the brain.51
Studies analyzing the effects of phototherapy on PN are limited to case series and a small randomized controlled trial. However, this trial has shown improvements in pruritus in the participants. Adverse effects include transient burning and erythema at the treated sites.44,45
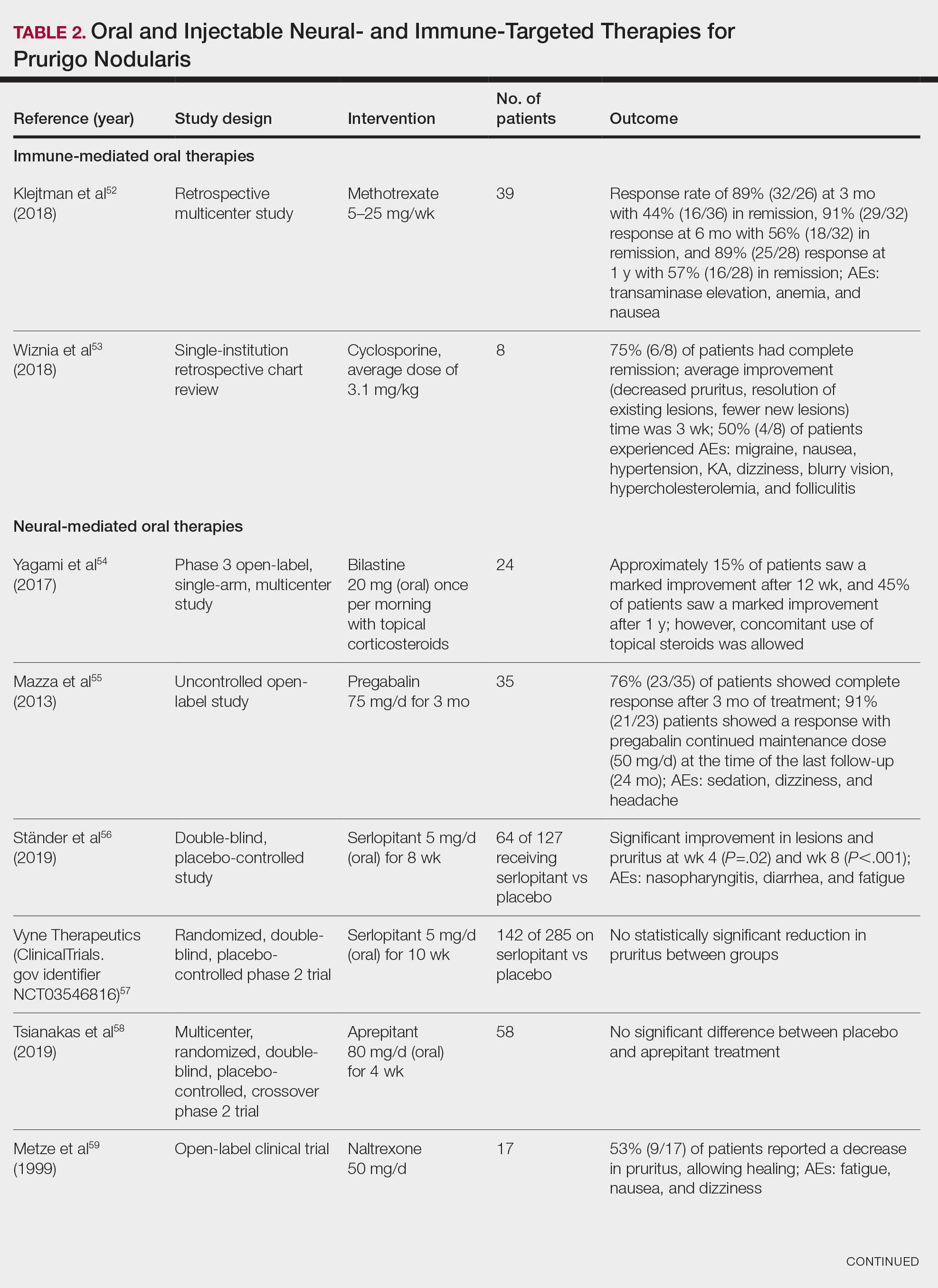
Immune-Mediated Oral Therapies—Immunologic-targeted oral therapies include bilastine, methotrexate, and cyclosporine (Table 2).52,53 Bilastine efficacy was analyzed in a small phase 3, open-label, multicenter study in Japan; however, patients were allowed to use topical steroids in conjunction with the oral antihistamine.54 Methotrexate and cyclosporine are immunosuppressive medications and were analyzed in small retrospective studies. Both treatments yielded notable relief for patients; however, 38.5% (15/39) of patients receiving methotrexate experienced adverse events, and 50.0% (4/8) experienced adverse events with cyclosporine.52,53
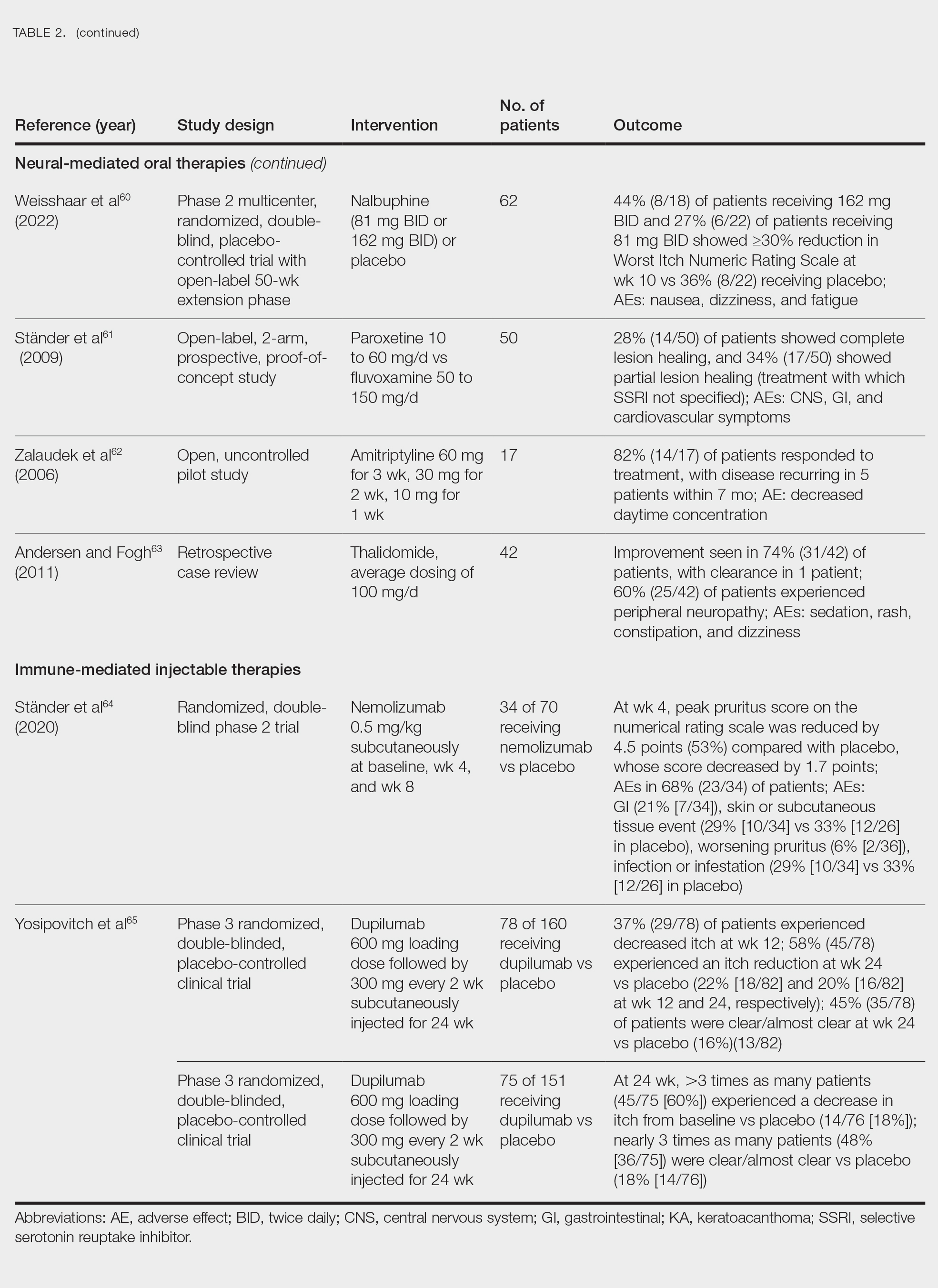
Neural-Mediated Oral Therapies—Neural-targeted oral therapies include pregabalin, serlopitant, aprepitant, naltrexone, nalbuphine, SSRIs (paroxetine and fluvoxamine), amitriptyline, and thalidomide. The research on these treatments ranges from case reviews to randomized controlled trials and open-label trials (Table 2).55-63
Thalidomide was studied in a small retrospective case review that showed notable improvement in PN. Dosages of thalidomide varied, but on average the dose was 100 mg/d. However, greater than 50% of patients experienced at least 1 adverse effect with this treatment.63
A study performed in Italy showed promising results for patients treated with pregabalin, with 70.0% (21/30) continuing to take pregabalin for almost 2 years following completion of the initial 3-month trial.55 Naltrexone decreased pruritus in more than half of patients (9/17).59 Amitriptyline yielded improvements in patients with PN; however, disease recurred in 5 patients (29%) after 7 months.62 A study performed in Germany reported promising results for paroxetine and fluvoxamine; however, some patients enrolled in the study had some form of psychiatric disorder.61
Serlopitant, aprepitant, and nalbuphine were studied in randomized controlled trials. The serlopitant trials were the largest of the neurally mediated oral medication studies; one showed substantial improvement in patients with PN,56 while the most recent trial did not show significant improvement (ClinicalTrials.gov identifier NCT03546816).57 On the other hand, aprepitant showed no major difference between the experimental and placebo groups.58 Nalbuphine 162 mg twice daily showed greater improvement in PN than nalbuphine 81 mg twice daily.60
Immune-Mediated Injectable Therapies—Immune-targeted injectables include nemolizumab and dupilumab (Table 2). Nemolizumab is an IL-31 antagonist that has been studied in a small randomized controlled trial that showed great success in decreasing pruritus associated with PN.64 IL-31 has been implicated in PN, and inhibition of the IL-31 receptor has been shown to disrupt the itch-scratch cycle of PN. Dupilumab is a monoclonal antibody against the IL-4 and IL-13 receptors, and it is the only FDA-approved treatment for PN.65 Blockage of these protein receptors decreases type 2 inflammation and chronic pruritus.66,67 Dupilumab is FDA approved for the treatment of atopic dermatitis and recently was approved for adults with PN. Dupilumab acts to block the shared α-subunit of the pruritogenic cytokines IL-4 and IL-13 pathways,29 thereby breaking the itch-scratch cycle associated with PN and allowing for the healing of these lesions. Results from 2 clinical trials showed substantially reduced itch in patients with PN.65 Dupilumab also was approved by the European Medicines Agency for moderate to severe PN.68
Conclusion
Prurigo nodularis is a chronic condition that affects patient quality of life and can mimic various dermatologic conditions. The epidemiology and pathophysiology of PN have not been fully expounded. More research should be conducted to determine the underpinnings of PN to help identify more consistently effective therapies for this complex condition.
- Durmaz K, Ataseven A, Ozer I, et al. Prurigo nodularis responding to intravenous immunoglobulins. Przegl Dermatol. 2022;109:159-162. doi:10.5114/dr.2022.117988
- Kowalski EH, Kneiber D, Valdebran M, et al. Treatment-resistant prurigo nodularis: challenges and solutions. Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol. 2019;12:163-172. doi:10.2147/CCID.S188070
- Wong LS, Yen YT. Chronic nodular prurigo: an update on the pathogenesis and treatment. Int J Mol Sci. 2022;23:12390. doi:10.3390/ijms232012390
- Janmohamed SR, Gwillim EC, Yousaf M, et al. The impact of prurigo nodularis on quality of life: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Arch Dermatol Res. 2021;313:669-677. doi:10.1007/s00403-020-02148-0
- Zeidler C, Ständer S. The pathogenesis of prurigo nodularis - ‘super-itch’ in exploration. Eur J Pain. 2016;20:37-40. doi:10.1002/ejp.767
- Kwatra SG. Breaking the itch–scratch cycle in prurigo nodularis. N Engl J Med. 2020;382:757-758. doi:10.1056/NEJMe1916733
- Frølunde AS, Wiis MAK, Ben Abdallah H, et al. Non-atopic chronic nodular prurigo (prurigo nodularis hyde): a systematic review of best-evidenced treatment options. Dermatology. 2022;238:950-960. doi:10.1159/000523700
- Kwon CD, Khanna R, Williams KA, et al. Diagnostic workup and evaluation of patients with prurigo nodularis. Medicines (Basel). 2019;6:97. doi:10.3390/medicines6040097
- Kowalski EH, Kneiber D, Valdebran M, et al. Distinguishing truly recalcitrant prurigo nodularis from poor treatment adherence: a response to treatment-resistant prurigo nodularis [Response to letter]. Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol. 2019;12:371-372. doi:10.2147/CCID.S214195
- Whang KA, Le TK, Khanna R, et al. Health-related quality of life and economic burden of prurigo nodularis. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2022;86:573-580. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2021.05.036
- Labib A, Ju T, Vander Does A, et al. Immunotargets and therapy for prurigo nodularis. Immunotargets Ther. 2022;11:11-21. doi:10.2147/ITT.S316602
- Belzberg M, Alphonse MP, Brown I, et al. Prurigo nodularis is characterized by systemic and cutaneous T helper 22 immune polarization. J Invest Dermatol. 2021;141:2208-2218.e14. doi:10.1016/j.jid.2021.02.749
- Ständer S, Pereira MP, Berger T, et al. IFSI-guideline on chronic prurigo including prurigo nodularis. Itch. 2020;5:e42. doi:10.1097/itx.0000000000000042
- Huang AH, Canner JK, Khanna R, et al. Real-world prevalence of prurigo nodularis and burden of associated diseases. J Invest Dermatol. 2020;140:480-483.e4. doi:10.1016/j.jid.2019.07.697
- Ständer S, Augustin M, Berger T, et al. Prevalence of prurigo nodularis in the United States of America: a retrospective database analysis. JAAD Int. 2021;2:28-30. doi:10.1016/j.jdin.2020.10.009
- Sutaria N, Adawi W, Brown I, et al. Racial disparities in mortality among patients with prurigo nodularis: a multi-center cohort study. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2022;86:487-490. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2021.09.028
- Ryczek A, Reich A. Prevalence of prurigo nodularis in Poland. Acta Derm Venereol. 2020;100:adv00155. doi:10.2340/00015555-3518
- Morgan CL, Thomas M, Ständer S, et al. Epidemiology of prurigo nodularis in England: a retrospective database analysis. Br J Dermatol. 2022;187:188-195. doi:10.1111/bjd.21032
- Woo YR, Wang S, Sohn KA, et al. Epidemiology, comorbidities, and prescription patterns of Korean prurigo nodularis patients: a multi-institution study. J Clin Med Res. 2021;11:95. doi:10.3390/jcm11010095
- Weigelt N, Metze D, Ständer S. Prurigo nodularis: systematic analysis of 58 histological criteria in 136 patients. J Cutan Pathol. 2010;37:578-586. doi:10.1111/j.1600-0560.2009.01484.x
- Yang LL, Jiang B, Chen SH, et al. Abnormal keratin expression pattern in prurigo nodularis epidermis. Skin Health Dis. 2022;2:e75. doi:10.1002/ski2.75
- Nockher WA, Renz H. Neurotrophins in allergic diseases: from neuronal growth factors to intercellular signaling molecules. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2006;117:583-589. doi:10.1016/j.jaci.2005.11.049
- Di Marco E, Mathor M, Bondanza S, et al. Nerve growth factor binds to normal human keratinocytes through high and low affinity receptors and stimulates their growth by a novel autocrine loop. J Biol Chem. 1993;268:22838-22846.
- Hägermark O, Hökfelt T, Pernow B. Flare and itch induced by substance P in human skin. J Invest Dermatol. 1978;71:233-235. doi:10.1111/1523-1747.ep12515092
- Choi JE, Di Nardo A. Skin neurogenic inflammation. Semin Immunopathol. 2018;40:249-259. doi:10.1007/s00281-018-0675-z
- Haas S, Capellino S, Phan NQ, et al. Low density of sympathetic nerve fibers relative to substance P-positive nerve fibers in lesional skin of chronic pruritus and prurigo nodularis. J Dermatol Sci. 2010;58:193-197. doi:10.1016/j.jdermsci.2010.03.020
- Park K, Mori T, Nakamura M, et al. Increased expression of mRNAs for IL-4, IL-17, IL-22 and IL-31 in skin lesions of subacute and chronic forms of prurigo. Eur J Dermatol. 2011;21:135-136.
- Tokura Y, Yagi H, Hanaoka K, et al. Subacute and chronic prurigo effectively treated with recombination interferon-gamma: implications for participation of Th2 cells in the pathogenesis of prurigo. Acta Derm Venereol. 1997;77:231-234. doi:10.2340/0001555577231234
- Williams KA, Roh YS, Brown I, et al. Pathophysiology, diagnosis, and pharmacological treatment of prurigo nodularis. Expert Rev Clin Pharmacol. 2021;14:67-77. doi:10.1080/17512433.2021.1852080
- Huang AH, Williams KA, Kwatra SG. Prurigo nodularis: epidemiology and clinical features. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2020;83:1559-1565. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2020.04.183
- Bewley A, Homey B, Pink A. Prurigo nodularis: a review of IL-31RA blockade and other potential treatments. Dermatol Ther. 2022;12:2039-2048. doi:10.1007/s13555-022-00782-2
- Zeidler C, Yosipovitch G, Ständer S. Prurigo nodularis and its management. Dermatol Clin. 2018;36:189-197. doi:10.1016/j.det.2018.02.003
- Siepmann D, Lotts T, Blome C, et al. Evaluation of the antipruritic effects of topical pimecrolimus in non-atopic prurigo nodularis: results of a randomized, hydrocortisone-controlled, double-blind phase II trial. Dermatology. 2013;227:353-360. doi:10.1159/000355671
- Valbuena MC, Muvdi S, Lim HW. Actinic prurigo. Dermatol Clin. 2014;32:335-344, viii. doi:10.1016/j.det.2014.03.010
- Aldhahwani R, Al Hawsawi KA. Neurotic excoriation presenting as solitary papule: case report. J Dermatol Dermatolog Surg. 2022;26:45. doi:10.4103/jdds.jdds_59_21
- Kwiek B, Schwartz RA. Keratoacanthoma (KA): an update and review. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2016;74:1220-1233. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2015.11.033
- Karadag AS, Ozlu E, Uzuncakmak TK, et al. Inverted follicular keratosis successfully treated with imiquimod. Indian Dermatol Online J. 2016;7:177-179. doi:10.4103/2229-5178.182354
- Nayak VN, Uma K, Girish HC, et al. Pseudoepitheliomatous hyperplasia in oral lesions: a review. J Int Oral Health. 2015;7:148-152.
- Saraceno R, Chiricozzi A, Nisticò SP, et al. An occlusive dressing containing betamethasone valerate 0.1% for the treatment of prurigo nodularis. J Dermatolog Treat. 2010;21:363-366. doi:10.3109/09546630903386606
- Wong SS, Goh CL. Double-blind, right/left comparison of calcipotriol ointment and betamethasone ointment in the treatment of prurigo nodularis. Arch Dermatol. 2000;136:807-808. doi:10.1001/archderm.136.6.807
- Waldinger TP, Wong RC, Taylor WB, et al. Cryotherapy improves prurigo nodularis. Arch Dermatol. 1984;120:1598-1600.
- Ständer S, Luger T, Metze D. Treatment of prurigo nodularis with topical capsaicin. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2001;44:471-478. doi:10.1067/mjd.2001.110059
- Ohanyan T, Schoepke N, Eirefelt S, et al. Role of substance P and its receptor neurokinin 1 in chronic prurigo: a randomized, proof-of-concept, controlled trial with topical aprepitant. Acta Derm Venereol. 2018;98:26-31. doi:10.2340/00015555-2780
- Tamagawa-Mineoka R, Katoh N, Ueda E, et al. Narrow-band ultraviolet B phototherapy in patients with recalcitrant nodular prurigo. J Dermatol. 2007;34:691-695. doi:10.1111/j.1346-8138.2007.00360.x
- Hammes S, Hermann J, Roos S, et al. UVB 308-nm excimer light and bath PUVA: combination therapy is very effective in the treatment of prurigo nodularis. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2011;25:799-803. doi:10.1111/j.1468-3083.2010.03865.x
- Richards RN. Update on intralesional steroid: focus on dermatoses. J Cutan Med Surg. 2010;14:19-23. doi:10.2310/7750.2009.08082
- Elmariah S, Kim B, Berger T, et al. Practical approaches for diagnosis and management of prurigo nodularis: United States expert panel consensus. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2021;84:747-760. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2020.07.025
- Grant JE Chamberlain SR Redden SA et al. N-Acetylcysteine in the treatment of excoriation disorder: a randomized clinical trial. JAMA Psychiatry. 2016;73:490-496. doi:10.1001/jamapsychiatry.2016.0060
- Adil M, Amin SS, Mohtashim M. N-acetylcysteine in dermatology. Indian J Dermatol Venereol Leprol. 2018;84:652-659. doi: 10.4103/ijdvl.IJDVL_33_18.
- Taylor M, Bhagwandas K. Trichotillosis, skin picking and N-acetylcysteine. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2015;72(suppl 1):AB117. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jaad.2015.02.482
- Legat FJ. The antipruritic effect of phototherapy. Front Med (Lausanne). 2018;5:333. doi:10.3389/fmed.2018.00333
- Klejtman T, Beylot-Barry M, Joly P, et al. Treatment of prurigo with methotrexate: a multicentre retrospective study of 39 cases. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2018;32:437-440. doi:10.1111/jdv.14646
- Wiznia LE, Callahan SW, Cohen DE, et al. Rapid improvement of prurigo nodularis with cyclosporine treatment. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2018;78:1209-1211. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2018.02.024
- Yagami A, Furue M, Togawa M, et al. One-year safety and efficacy study of bilastine treatment in Japanese patients with chronic spontaneous urticaria or pruritus associated with skin diseases. J Dermatol. 2017;44:375-385. doi:10.1111/1346-8138.13644
- Mazza M, Guerriero G, Marano G, et al. Treatment of prurigo nodularis with pregabalin. J Clin Pharm Ther. 2013;38:16-18. doi:10.1111/jcpt.12005
- Ständer S, Kwon P, Hirman J, et al. Serlopitant reduced pruritus in patients with prurigo nodularis in a phase 2, randomized, placebo-controlled trial. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2019;80:1395-1402. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2019.01.052
- Study of the efficacy, safety and tolerability of serlopitant for the treatment of pruritus (itch) with prurigo nodularis. ClinicalTrials.gov identifier: NCT03546816. Updated May 20, 2021. Accessed August 8, 2024. https://clinicaltrials.gov/study/NCT03546816
- Tsianakas A, Zeidler C, Riepe C, et al. Aprepitant in anti-histamine-refractory chronic nodular prurigo: a multicentre, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, cross-over, phase-II trial (APREPRU). Acta Derm Venereol. 2019;99:379-385. doi:10.2340/00015555-3120
- Metze D, Reimann S, Beissert S, et al. Efficacy and safety of naltrexone, an oral opiate receptor antagonist, in the treatment of pruritus in internal and dermatological diseases. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1999;41:533-539.
- Weisshaar E, Szepietowski JC, Bernhard JD, et al. Efficacy and safety of oral nalbuphine extended release in prurigo nodularis: results of a phase 2 randomized controlled trial with an open‐label extension phase. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2022;36:453-461. doi:10.1111/jdv.17816
- Ständer S, Böckenholt B, Schürmeyer-Horst F, et al. Treatment of chronic pruritus with the selective serotonin re-uptake inhibitors paroxetine and fluvoxamine: results of an open-labelled, two-arm proof-of-concept study. Acta Derm Venereol. 2009;89:45-51. doi:10.2340/00015555-0553
- Zalaudek I, Petrillo G, Baldassarre MA, et al. Amitriptyline as therapeutic and not symptomatic approach in the treatment of prurigo nodularis. G Ital Dermatol Venereol. 2006;141:433-437.
- Andersen TP, Fogh K. Thalidomide in 42 patients with prurigo nodularis Hyde. Dermatology. 2011;223:107-112. doi:10.1159/000331577
- Ständer S, Yosipovitch G, Legat FJ, et al. Trial of nemolizumab in moderate-to-severe prurigo nodularis. N Engl J Med. 2020;382:706-716. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa1908316
- Yosipovitch G, Mollanazar N, Ständer S, et al. Dupilumab in patients with prurigo nodularis: two randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled phase 3 trials. Nat Med. 2023;29:1180-1190. doi:10.1038/s41591-023-02320-9
- Mastorino L, Rosset F, Gelato F, et al. Chronic pruritus in atopic patients treated with dupilumab: real life response and related parameters in 354 patients. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2022;15:883. doi: 10.3390/ph15070883
- Kishi R, Toyama S, Tominaga M, et al. Effects of dupilumab on itch-related events in atopic dermatitis: implications for assessing treatment efficacy in clinical practice. Cells. 2023;12:239. doi: 10.3390/cells12020239
- Dupixent. European Medicines Agency website. Updated July 15, 2024. Accessed August 27, 2024. https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/medicines/human/EPAR/dupixent
Prurigo nodularis (PN)(also called chronic nodular prurigo, prurigo nodularis of Hyde, or picker’s nodules) was first characterized by James Hyde in 1909.1-3 Prurigo nodularis manifests with symmetrical, intensely pruritic, eroded, or hyperkeratotic nodules or papules on the extremities and trunk.1,2,4,5 Studies have shown that individuals with PN experience pruritus, sleep loss, decreased social functioning from the appearance of the nodules, and a higher incidence of anxiety and depression, causing a negative impact on their quality of life.2,6 In addition, the manifestation of PN has been linked to neurologic and psychiatric disorders; however, PN also can be idiopathic and manifest without underlying illnesses.2,6,7
Prurigo nodularis has been associated with other dermatologic conditions such as atopic dermatitis (up to 50%), lichen planus, keratoacanthomas (KAs), and bullous pemphigoid.7-9 It also has been linked to systemic diseases in 38% to 50% of cases, including chronic kidney disease, liver disease, type 2 diabetes mellitus, malignancies (hematopoietic, liver, and skin), and HIV infection.6,8,10
The pathophysiology of PN is highly complex and has yet to be fully elucidated. It is thought to be due to dysregulation and interaction of the increase in neural and immunologic responses of proinflammatory and pruritogenic cytokines.2,11 Treatments aim to break the itch-scratch cycle that perpetuates this disorder; however, this proves difficult, as PN is associated with a higher itch intensity than atopic dermatitis and psoriasis.10 Therefore, most patients attempt multiple forms of treatment for PN, ranging from topical therapies, oral immunosuppressants, and phototherapy to the newest and only medication approved by the US Food and Drug Administration for the treatment of PN—dupilumab.1,7,11 Herein, we provide an updated review of PN with a focus on its epidemiology, histopathology and pathophysiology, comorbidities, clinical presentation, differential diagnosis, and current treatment options.
Epidemiology
There are few studies on the epidemiology of PN; however, middle-aged populations with underlying dermatologic or psychiatric disorders tend to be impacted most frequently.2,12,13 In 2016, it was estimated that almost 88,000 individuals had PN in the United States, with the majority being female; however, this estimate only took into account those aged 18 to 64 years and utilized data from IBM MarketScan Commercial Claims and Encounters Database (IBM Watson Health) from October 2015 to December 2016.14 More recently, a retrospective database analysis estimated the prevalence of PN in the United States to be anywhere from 36.7 to 43.9 cases per 100,000 individuals. However, this retrospective review utilized the International Classification of Diseases, Tenth Revision code; PN has 2 codes associated with the diagnosis, and the coding accuracy is unknown.15 Sutaria et al16 looked at racial disparities in patients with PN utilizing data from TriNetX and found that patients who received a diagnosis of PN were more likely to be women, non-Hispanic, and Black compared with control patients. However, these estimates are restricted to the health care organizations within this database.
In 2018, Poland reported an annual prevalence of 6.52 cases per 100,000 individuals,17 while England reported a yearly prevalence of 3.27 cases per 100,000 individuals.18 Both countries reported most cases were female. However, these studies are not without limitations. Poland only uses the primary diagnosis code for medical billing to simplify clinical coding, thus underestimating the actual prevalence; furthermore, clinical codes more often than not are assigned by someone other than the diagnosing physician, leaving room for error.17 In addition, England’s PN estimate utilized diagnosis data from primary care and inpatient datasets, leaving out outpatient datasets in which patients with PN may have been referred and obtained the diagnosis, potentially underestimating the prevalence in this population.18
In contrast, Korea estimated the annual prevalence of PN to be 4.82 cases per 1000 dermatology outpatients, with the majority being men, based on results from a cross-sectional study among outpatients from the Catholic Medical Center. Although this is the largest health organization in Korea, the scope of this study is limited and lacks data from other medical centers in Korea.19
Histopathology and Pathophysiology
Almost all cells in the skin are involved in PN: keratinocytes, mast cells, dendritic cells, endothelial cells, lymphocytes, eosinophils, collagen fibers, and nerve fibers.11,20 Classically, PN manifests as a dome-shaped lesion with hyperkeratosis, hypergranulosis, and psoriasiform epidermal hyperplasia with increased thickness of the papillary dermis consisting of coarse collagen with compact interstitial and circumvascular infiltration as well as increased lymphocytes and histocytes in the superficial dermis (Figure 1).20 Hyperkeratosis is thought to be due to either the alteration of keratinocyte structures from scratching or keratinocyte abnormalities triggering PN.21 However, the increase in keratinocytes, which secrete nerve growth factor, allows for neuronal hyperplasia within the dermis.22 Nerve growth factor can stimulate keratinocyte proliferation23 in addition to the upregulation of substance P (SP), a tachykinin that triggers vascular dilation and pruritus in the skin.24 The density of SP nerve fibers in the dermis increases in PN, causing proinflammatory effects, upregulating the immune response to promote endothelial hyperplasia and increased vascularization.25 The increase in these fibers may lead to pruritus associated with PN.2,26

Many inflammatory cytokines and mediators also have been implicated in PN. Increased messenger RNA expression of IL-4, IL-17, IL-22, and IL-31 has been described in PN lesions.3,27 Furthermore, studies also have reported increased helper T cell (TH2) cytokines, including IL-4, IL-5, IL-10, and IL-13, in the dermis of PN lesions in patients without a history of atopy.3,28 These pruritogenic cytokines in conjunction with the SP fibers may create an intractable itch for those with PN. The interaction and culmination of the neural and immune responses make PN a complex condition to treat with the multifactorial interaction of systems.
Comorbidities
Prurigo nodularis has been associated with a wide array of comorbidities; however, the direction of the relationship between PN and these conditions makes it difficult to discern if PN is a primary or secondary condition.29 Prurigo nodularis commonly has been connected to other inflammatory dermatoses, with a link to atopic dermatitis being the strongest.5,29 However, PN also has been linked to other pruritic inflammatory cutaneous disorders, including psoriasis, cutaneous T-cell lymphoma, lichen planus, and dermatitis herpetiformis.14,29
Huang et al14 found an increased likelihood of psychiatric illnesses in patients with PN, including eating disorders, nonsuicidal self-injury disorder, attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder, schizophrenia, mood disorders, anxiety, and substance abuse disorders. Treatments directed at the neural aspect of PN have included selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs), which also are utilized to treat these mental health disorders.
Furthermore, systemic diseases also have been found to be associated with PN, including hypertension, type 2 diabetes mellitus, chronic kidney disease, heart failure, cerebrovascular disease, coronary heart disease, and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease.14 The relationship between PN and systemic conditions may be due to increased systemic inflammation and dysregulation of neural and metabolic functions implicated in these conditions from increased pruritic manifestations.29,30 However, studies also have connected PN to infectious conditions such as HIV. One study found that patients with PN had 2.68 higher odds of infection with HIV compared to age- and sex-matched controls.14 It is unknown if these conditions contributed to the development of PN or PN contributed to the development of these disorders.
Clinical Presentations
Prurigo nodularis is a chronic inflammatory skin disease that typically manifests with multiple severely pruritic, dome-shaped, firm, hyperpigmented papulonodules with central scale or crust, often with erosion, due to chronic repetitive scratching and picking secondary to pruritic systemic or dermatologic diseases or psychological disorders (Figure 2).1,2,4,5,8,31 Most often, diagnosis of PN is based on history and physical examination of the lesion; however, biopsies may be performed. These nodules commonly manifest with ulceration distributed symmetrically on extensor extremities in easy-to-reach places, sparing the mid back (called the butterfly sign).8 Lesions—either a few or hundreds—can range from a few millimeters to 2 to 3 cm.8,32 The lesions differ in appearance depending on the pigment in the patient’s skin. In patients with darker skin tones, hyperpigmented or hypopigmented papulonodules are not uncommon, while those with fairer skin tones tend to present with erythema.31

Differential Diagnosis
Because of the variation in manifestation of PN, these lesions may resemble other cutaneous conditions. If the lesions are hyperkeratotic, they can mimic hypertrophic lichen planus, which mainfests with hyperkeratotic plaques or nodules on the lower extremities.8,29 In addition, the histopathology of lichen planus resembles the appearance of PN, with epidermal hyperplasia, hypergranulosis, hyperkeratosis, and increased fibroblasts and capillaries.8,29
Pemphigoid nodularis is a rare subtype of bullous pemphigoid that exhibits characteristics of PN with pruritic plaques and erosions.8,29,33 The patient population for pemphigoid nodularis tends to be aged 50 to 60 years, and females are affected more frequently than males. However, pemphigoid nodularis may manifest with blistering and large plaques, which are not seen commonly with PN.29 On histopathology, pemphigoid nodularis deposits IgG and C3 on the basement membrane and has subepidermal clefting, unlike PN.7,29
Actinic prurigo manifests with pruritic papules or nodules post–UV exposure to unprotected skin.8,29,33 This rare condition usually manifests with cheilitis and conjunctivitis. Unlike PN, which commonly affects elderly populations, actinic prurigo typically is found in young females.8,29 Cytologic examination shows hyperkeratosis, spongiosis, and acanthosis of the epidermis with lymphocytic perivascular infiltration of the dermis.34
Neurotic excoriations also tend to mimic PN with raised excoriated lesions; however, this disorder is due to neurotic picking of the skin without associated pruritus or true hyperkeratosis.8,29,33 Histopathology shows epidermal crusting with inflammation of the upper dermis.35
Infiltrative cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma (SCC) may imitate PN in appearance. It manifests as tender, ulcerated, scaly plaques or nodules. Histopathology shows cytologic atypia with an infiltrative architectural pattern and presence of collections of compact keratin and parakeratin (called keratin pearls).
Keratoacanthomas can resemble PN lesions. They usually manifest as nodules measuring 1 to 2 cm in diameter and 0.5 cm thick, resembling crateriform tumors.36 On histopathology, KAs can resemble SCCs; however, KAs tend to manifest more frequently with a keratin-filled crater with a ground-glass appearance.36
Inverted follicular keratosis commonly manifests on the face in elderly men as a single, flesh-colored, verrucous papule that may resemble PN. However, cytology of inverted follicular keratosis is characterized by proliferation and squamous eddies.37 Consideration of the histologic findings and clinical appearance are important to differentiate between PN and cutaneous SCC.
Pseudoepitheliomatous hyperplasia is a benign condition that manifests as a plaque or nodule with crust, scale, or ulceration. Histologically, this condition presents with hyperplastic proliferation of the epidermis and adnexal epithelium.38 The clinical and histologic appearance can mimic PN and other cutaneous eruptions with epidermal hyperplasia.
In clinical cases that are resistant to treatment, biopsy is the best approach to diagnose the lesion. Due to similarities in physical appearance and superficial histologic presentation of PN, KAs from SCC, hypertrophic lichen planus, and other hyperkeratotic lesions, the biopsy should be taken at the base of the lesion to sample deeper layers of skin to differentiate these dermatologic disorders.
Management
Current treatments for PN yield varied results. Many patients with moderate to severe PN attempt multiple therapies before seeing improvement.31 Treatments include topical, oral, and injectable medications and are either directed at the neural or immune components of PN due to the interplay between increased nerve fibers in the lesions (neural axis) as well as increases in cytokines and other immunologic mediators (immune axis) of this condition. However, the FDA recently approved the first treatment for PN—dupilumab—which is an injectable IL-4 receptor antagonist directed at the immunologic interactions affiliated with PN.
Immune-Mediated Topical Therapies—Immunologic topical therapies include corticosteroids, calcipotriol, and calcineurin inhibitors. Studies that have analyzed these treatments are limited to case reports and small intraindividual and randomized controlled trials (Table 1). Topical therapies usually are first-line agents for most patients. Adverse effects include transient irritation of the skin.40,42,43

Cryotherapy is another topical and immunologic therapy for those with PN; however, this treatment is more appropriate for patients with fewer lesions due to the pain that accompanies lesions treated with liquid nitrogen. In addition, this therapy can cause dyspigmentation of the skin in the treated areas.41
Similar to cryotherapy, intralesional corticosteroid injections are appropriate for patients with few PN lesions. A recent report described intralesional corticosteroid injections of 2.5 mg/mL for a PN nodule with high efficacy.46,47 This treatment has not undergone trials, but success with this modality has been documented, with adverse effects including hyperpigmentation or hypopigmentation in the treated area and transient pain.46
Neural-Mediated Topical Therapies—Neural topical therapies include capsaicin and neurokinin-1 receptor antagonists, aprepitant43 and serlopitant. These treatment studies are limited to small open-label and randomized controlled trials. Adverse effects of these treatments include transient cutaneous pain at the site of topical administration. In addition, neural-mediated topical therapies have shown either limited improvements from baseline or return of symptoms after treatment cessation.42,43
Supplements—N-acetyl cysteine is an over-the-counter supplement that has been reported to improve symptoms in patients with skin-picking disorders.48 The mechanism of action includes antioxidant effects such as decreasing reactive oxygen species, decreasing inflammatory markers, regulating neurotransmitters, and inhibiting hyperkeratosis.49 N-acetyl cysteine has been poorly studied for its application in PN. A small study of 3 patients with subacute PN receiving 1200 mg of oral N-acetyl cysteine reported varying levels of improvement in skin appearance and reduction in skin picking.50
Phototherapy—Phototherapy, a typical first- or second-line treatment modality for PN, targets both the neural- and immune-mediated aspects associated with pruritus in PN (Table 1).51 UV light can penetrate through the epidermal layer of the skin and reach the keratinocytes, which play a role in the immune-related response of PN. In addition, the cutaneous sensory nerves are located in the upper dermal layer, from which nerve fibers grow and penetrate into the epidermis, thereby interacting with the keratinocytes where pruritic signals are transmitted from the periphery up to the brain.51
Studies analyzing the effects of phototherapy on PN are limited to case series and a small randomized controlled trial. However, this trial has shown improvements in pruritus in the participants. Adverse effects include transient burning and erythema at the treated sites.44,45
Immune-Mediated Oral Therapies—Immunologic-targeted oral therapies include bilastine, methotrexate, and cyclosporine (Table 2).52,53 Bilastine efficacy was analyzed in a small phase 3, open-label, multicenter study in Japan; however, patients were allowed to use topical steroids in conjunction with the oral antihistamine.54 Methotrexate and cyclosporine are immunosuppressive medications and were analyzed in small retrospective studies. Both treatments yielded notable relief for patients; however, 38.5% (15/39) of patients receiving methotrexate experienced adverse events, and 50.0% (4/8) experienced adverse events with cyclosporine.52,53


Neural-Mediated Oral Therapies—Neural-targeted oral therapies include pregabalin, serlopitant, aprepitant, naltrexone, nalbuphine, SSRIs (paroxetine and fluvoxamine), amitriptyline, and thalidomide. The research on these treatments ranges from case reviews to randomized controlled trials and open-label trials (Table 2).55-63
Thalidomide was studied in a small retrospective case review that showed notable improvement in PN. Dosages of thalidomide varied, but on average the dose was 100 mg/d. However, greater than 50% of patients experienced at least 1 adverse effect with this treatment.63
A study performed in Italy showed promising results for patients treated with pregabalin, with 70.0% (21/30) continuing to take pregabalin for almost 2 years following completion of the initial 3-month trial.55 Naltrexone decreased pruritus in more than half of patients (9/17).59 Amitriptyline yielded improvements in patients with PN; however, disease recurred in 5 patients (29%) after 7 months.62 A study performed in Germany reported promising results for paroxetine and fluvoxamine; however, some patients enrolled in the study had some form of psychiatric disorder.61
Serlopitant, aprepitant, and nalbuphine were studied in randomized controlled trials. The serlopitant trials were the largest of the neurally mediated oral medication studies; one showed substantial improvement in patients with PN,56 while the most recent trial did not show significant improvement (ClinicalTrials.gov identifier NCT03546816).57 On the other hand, aprepitant showed no major difference between the experimental and placebo groups.58 Nalbuphine 162 mg twice daily showed greater improvement in PN than nalbuphine 81 mg twice daily.60
Immune-Mediated Injectable Therapies—Immune-targeted injectables include nemolizumab and dupilumab (Table 2). Nemolizumab is an IL-31 antagonist that has been studied in a small randomized controlled trial that showed great success in decreasing pruritus associated with PN.64 IL-31 has been implicated in PN, and inhibition of the IL-31 receptor has been shown to disrupt the itch-scratch cycle of PN. Dupilumab is a monoclonal antibody against the IL-4 and IL-13 receptors, and it is the only FDA-approved treatment for PN.65 Blockage of these protein receptors decreases type 2 inflammation and chronic pruritus.66,67 Dupilumab is FDA approved for the treatment of atopic dermatitis and recently was approved for adults with PN. Dupilumab acts to block the shared α-subunit of the pruritogenic cytokines IL-4 and IL-13 pathways,29 thereby breaking the itch-scratch cycle associated with PN and allowing for the healing of these lesions. Results from 2 clinical trials showed substantially reduced itch in patients with PN.65 Dupilumab also was approved by the European Medicines Agency for moderate to severe PN.68
Conclusion
Prurigo nodularis is a chronic condition that affects patient quality of life and can mimic various dermatologic conditions. The epidemiology and pathophysiology of PN have not been fully expounded. More research should be conducted to determine the underpinnings of PN to help identify more consistently effective therapies for this complex condition.
Prurigo nodularis (PN)(also called chronic nodular prurigo, prurigo nodularis of Hyde, or picker’s nodules) was first characterized by James Hyde in 1909.1-3 Prurigo nodularis manifests with symmetrical, intensely pruritic, eroded, or hyperkeratotic nodules or papules on the extremities and trunk.1,2,4,5 Studies have shown that individuals with PN experience pruritus, sleep loss, decreased social functioning from the appearance of the nodules, and a higher incidence of anxiety and depression, causing a negative impact on their quality of life.2,6 In addition, the manifestation of PN has been linked to neurologic and psychiatric disorders; however, PN also can be idiopathic and manifest without underlying illnesses.2,6,7
Prurigo nodularis has been associated with other dermatologic conditions such as atopic dermatitis (up to 50%), lichen planus, keratoacanthomas (KAs), and bullous pemphigoid.7-9 It also has been linked to systemic diseases in 38% to 50% of cases, including chronic kidney disease, liver disease, type 2 diabetes mellitus, malignancies (hematopoietic, liver, and skin), and HIV infection.6,8,10
The pathophysiology of PN is highly complex and has yet to be fully elucidated. It is thought to be due to dysregulation and interaction of the increase in neural and immunologic responses of proinflammatory and pruritogenic cytokines.2,11 Treatments aim to break the itch-scratch cycle that perpetuates this disorder; however, this proves difficult, as PN is associated with a higher itch intensity than atopic dermatitis and psoriasis.10 Therefore, most patients attempt multiple forms of treatment for PN, ranging from topical therapies, oral immunosuppressants, and phototherapy to the newest and only medication approved by the US Food and Drug Administration for the treatment of PN—dupilumab.1,7,11 Herein, we provide an updated review of PN with a focus on its epidemiology, histopathology and pathophysiology, comorbidities, clinical presentation, differential diagnosis, and current treatment options.
Epidemiology
There are few studies on the epidemiology of PN; however, middle-aged populations with underlying dermatologic or psychiatric disorders tend to be impacted most frequently.2,12,13 In 2016, it was estimated that almost 88,000 individuals had PN in the United States, with the majority being female; however, this estimate only took into account those aged 18 to 64 years and utilized data from IBM MarketScan Commercial Claims and Encounters Database (IBM Watson Health) from October 2015 to December 2016.14 More recently, a retrospective database analysis estimated the prevalence of PN in the United States to be anywhere from 36.7 to 43.9 cases per 100,000 individuals. However, this retrospective review utilized the International Classification of Diseases, Tenth Revision code; PN has 2 codes associated with the diagnosis, and the coding accuracy is unknown.15 Sutaria et al16 looked at racial disparities in patients with PN utilizing data from TriNetX and found that patients who received a diagnosis of PN were more likely to be women, non-Hispanic, and Black compared with control patients. However, these estimates are restricted to the health care organizations within this database.
In 2018, Poland reported an annual prevalence of 6.52 cases per 100,000 individuals,17 while England reported a yearly prevalence of 3.27 cases per 100,000 individuals.18 Both countries reported most cases were female. However, these studies are not without limitations. Poland only uses the primary diagnosis code for medical billing to simplify clinical coding, thus underestimating the actual prevalence; furthermore, clinical codes more often than not are assigned by someone other than the diagnosing physician, leaving room for error.17 In addition, England’s PN estimate utilized diagnosis data from primary care and inpatient datasets, leaving out outpatient datasets in which patients with PN may have been referred and obtained the diagnosis, potentially underestimating the prevalence in this population.18
In contrast, Korea estimated the annual prevalence of PN to be 4.82 cases per 1000 dermatology outpatients, with the majority being men, based on results from a cross-sectional study among outpatients from the Catholic Medical Center. Although this is the largest health organization in Korea, the scope of this study is limited and lacks data from other medical centers in Korea.19
Histopathology and Pathophysiology
Almost all cells in the skin are involved in PN: keratinocytes, mast cells, dendritic cells, endothelial cells, lymphocytes, eosinophils, collagen fibers, and nerve fibers.11,20 Classically, PN manifests as a dome-shaped lesion with hyperkeratosis, hypergranulosis, and psoriasiform epidermal hyperplasia with increased thickness of the papillary dermis consisting of coarse collagen with compact interstitial and circumvascular infiltration as well as increased lymphocytes and histocytes in the superficial dermis (Figure 1).20 Hyperkeratosis is thought to be due to either the alteration of keratinocyte structures from scratching or keratinocyte abnormalities triggering PN.21 However, the increase in keratinocytes, which secrete nerve growth factor, allows for neuronal hyperplasia within the dermis.22 Nerve growth factor can stimulate keratinocyte proliferation23 in addition to the upregulation of substance P (SP), a tachykinin that triggers vascular dilation and pruritus in the skin.24 The density of SP nerve fibers in the dermis increases in PN, causing proinflammatory effects, upregulating the immune response to promote endothelial hyperplasia and increased vascularization.25 The increase in these fibers may lead to pruritus associated with PN.2,26

Many inflammatory cytokines and mediators also have been implicated in PN. Increased messenger RNA expression of IL-4, IL-17, IL-22, and IL-31 has been described in PN lesions.3,27 Furthermore, studies also have reported increased helper T cell (TH2) cytokines, including IL-4, IL-5, IL-10, and IL-13, in the dermis of PN lesions in patients without a history of atopy.3,28 These pruritogenic cytokines in conjunction with the SP fibers may create an intractable itch for those with PN. The interaction and culmination of the neural and immune responses make PN a complex condition to treat with the multifactorial interaction of systems.
Comorbidities
Prurigo nodularis has been associated with a wide array of comorbidities; however, the direction of the relationship between PN and these conditions makes it difficult to discern if PN is a primary or secondary condition.29 Prurigo nodularis commonly has been connected to other inflammatory dermatoses, with a link to atopic dermatitis being the strongest.5,29 However, PN also has been linked to other pruritic inflammatory cutaneous disorders, including psoriasis, cutaneous T-cell lymphoma, lichen planus, and dermatitis herpetiformis.14,29
Huang et al14 found an increased likelihood of psychiatric illnesses in patients with PN, including eating disorders, nonsuicidal self-injury disorder, attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder, schizophrenia, mood disorders, anxiety, and substance abuse disorders. Treatments directed at the neural aspect of PN have included selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs), which also are utilized to treat these mental health disorders.
Furthermore, systemic diseases also have been found to be associated with PN, including hypertension, type 2 diabetes mellitus, chronic kidney disease, heart failure, cerebrovascular disease, coronary heart disease, and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease.14 The relationship between PN and systemic conditions may be due to increased systemic inflammation and dysregulation of neural and metabolic functions implicated in these conditions from increased pruritic manifestations.29,30 However, studies also have connected PN to infectious conditions such as HIV. One study found that patients with PN had 2.68 higher odds of infection with HIV compared to age- and sex-matched controls.14 It is unknown if these conditions contributed to the development of PN or PN contributed to the development of these disorders.
Clinical Presentations
Prurigo nodularis is a chronic inflammatory skin disease that typically manifests with multiple severely pruritic, dome-shaped, firm, hyperpigmented papulonodules with central scale or crust, often with erosion, due to chronic repetitive scratching and picking secondary to pruritic systemic or dermatologic diseases or psychological disorders (Figure 2).1,2,4,5,8,31 Most often, diagnosis of PN is based on history and physical examination of the lesion; however, biopsies may be performed. These nodules commonly manifest with ulceration distributed symmetrically on extensor extremities in easy-to-reach places, sparing the mid back (called the butterfly sign).8 Lesions—either a few or hundreds—can range from a few millimeters to 2 to 3 cm.8,32 The lesions differ in appearance depending on the pigment in the patient’s skin. In patients with darker skin tones, hyperpigmented or hypopigmented papulonodules are not uncommon, while those with fairer skin tones tend to present with erythema.31

Differential Diagnosis
Because of the variation in manifestation of PN, these lesions may resemble other cutaneous conditions. If the lesions are hyperkeratotic, they can mimic hypertrophic lichen planus, which mainfests with hyperkeratotic plaques or nodules on the lower extremities.8,29 In addition, the histopathology of lichen planus resembles the appearance of PN, with epidermal hyperplasia, hypergranulosis, hyperkeratosis, and increased fibroblasts and capillaries.8,29
Pemphigoid nodularis is a rare subtype of bullous pemphigoid that exhibits characteristics of PN with pruritic plaques and erosions.8,29,33 The patient population for pemphigoid nodularis tends to be aged 50 to 60 years, and females are affected more frequently than males. However, pemphigoid nodularis may manifest with blistering and large plaques, which are not seen commonly with PN.29 On histopathology, pemphigoid nodularis deposits IgG and C3 on the basement membrane and has subepidermal clefting, unlike PN.7,29
Actinic prurigo manifests with pruritic papules or nodules post–UV exposure to unprotected skin.8,29,33 This rare condition usually manifests with cheilitis and conjunctivitis. Unlike PN, which commonly affects elderly populations, actinic prurigo typically is found in young females.8,29 Cytologic examination shows hyperkeratosis, spongiosis, and acanthosis of the epidermis with lymphocytic perivascular infiltration of the dermis.34
Neurotic excoriations also tend to mimic PN with raised excoriated lesions; however, this disorder is due to neurotic picking of the skin without associated pruritus or true hyperkeratosis.8,29,33 Histopathology shows epidermal crusting with inflammation of the upper dermis.35
Infiltrative cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma (SCC) may imitate PN in appearance. It manifests as tender, ulcerated, scaly plaques or nodules. Histopathology shows cytologic atypia with an infiltrative architectural pattern and presence of collections of compact keratin and parakeratin (called keratin pearls).
Keratoacanthomas can resemble PN lesions. They usually manifest as nodules measuring 1 to 2 cm in diameter and 0.5 cm thick, resembling crateriform tumors.36 On histopathology, KAs can resemble SCCs; however, KAs tend to manifest more frequently with a keratin-filled crater with a ground-glass appearance.36
Inverted follicular keratosis commonly manifests on the face in elderly men as a single, flesh-colored, verrucous papule that may resemble PN. However, cytology of inverted follicular keratosis is characterized by proliferation and squamous eddies.37 Consideration of the histologic findings and clinical appearance are important to differentiate between PN and cutaneous SCC.
Pseudoepitheliomatous hyperplasia is a benign condition that manifests as a plaque or nodule with crust, scale, or ulceration. Histologically, this condition presents with hyperplastic proliferation of the epidermis and adnexal epithelium.38 The clinical and histologic appearance can mimic PN and other cutaneous eruptions with epidermal hyperplasia.
In clinical cases that are resistant to treatment, biopsy is the best approach to diagnose the lesion. Due to similarities in physical appearance and superficial histologic presentation of PN, KAs from SCC, hypertrophic lichen planus, and other hyperkeratotic lesions, the biopsy should be taken at the base of the lesion to sample deeper layers of skin to differentiate these dermatologic disorders.
Management
Current treatments for PN yield varied results. Many patients with moderate to severe PN attempt multiple therapies before seeing improvement.31 Treatments include topical, oral, and injectable medications and are either directed at the neural or immune components of PN due to the interplay between increased nerve fibers in the lesions (neural axis) as well as increases in cytokines and other immunologic mediators (immune axis) of this condition. However, the FDA recently approved the first treatment for PN—dupilumab—which is an injectable IL-4 receptor antagonist directed at the immunologic interactions affiliated with PN.
Immune-Mediated Topical Therapies—Immunologic topical therapies include corticosteroids, calcipotriol, and calcineurin inhibitors. Studies that have analyzed these treatments are limited to case reports and small intraindividual and randomized controlled trials (Table 1). Topical therapies usually are first-line agents for most patients. Adverse effects include transient irritation of the skin.40,42,43

Cryotherapy is another topical and immunologic therapy for those with PN; however, this treatment is more appropriate for patients with fewer lesions due to the pain that accompanies lesions treated with liquid nitrogen. In addition, this therapy can cause dyspigmentation of the skin in the treated areas.41
Similar to cryotherapy, intralesional corticosteroid injections are appropriate for patients with few PN lesions. A recent report described intralesional corticosteroid injections of 2.5 mg/mL for a PN nodule with high efficacy.46,47 This treatment has not undergone trials, but success with this modality has been documented, with adverse effects including hyperpigmentation or hypopigmentation in the treated area and transient pain.46
Neural-Mediated Topical Therapies—Neural topical therapies include capsaicin and neurokinin-1 receptor antagonists, aprepitant43 and serlopitant. These treatment studies are limited to small open-label and randomized controlled trials. Adverse effects of these treatments include transient cutaneous pain at the site of topical administration. In addition, neural-mediated topical therapies have shown either limited improvements from baseline or return of symptoms after treatment cessation.42,43
Supplements—N-acetyl cysteine is an over-the-counter supplement that has been reported to improve symptoms in patients with skin-picking disorders.48 The mechanism of action includes antioxidant effects such as decreasing reactive oxygen species, decreasing inflammatory markers, regulating neurotransmitters, and inhibiting hyperkeratosis.49 N-acetyl cysteine has been poorly studied for its application in PN. A small study of 3 patients with subacute PN receiving 1200 mg of oral N-acetyl cysteine reported varying levels of improvement in skin appearance and reduction in skin picking.50
Phototherapy—Phototherapy, a typical first- or second-line treatment modality for PN, targets both the neural- and immune-mediated aspects associated with pruritus in PN (Table 1).51 UV light can penetrate through the epidermal layer of the skin and reach the keratinocytes, which play a role in the immune-related response of PN. In addition, the cutaneous sensory nerves are located in the upper dermal layer, from which nerve fibers grow and penetrate into the epidermis, thereby interacting with the keratinocytes where pruritic signals are transmitted from the periphery up to the brain.51
Studies analyzing the effects of phototherapy on PN are limited to case series and a small randomized controlled trial. However, this trial has shown improvements in pruritus in the participants. Adverse effects include transient burning and erythema at the treated sites.44,45
Immune-Mediated Oral Therapies—Immunologic-targeted oral therapies include bilastine, methotrexate, and cyclosporine (Table 2).52,53 Bilastine efficacy was analyzed in a small phase 3, open-label, multicenter study in Japan; however, patients were allowed to use topical steroids in conjunction with the oral antihistamine.54 Methotrexate and cyclosporine are immunosuppressive medications and were analyzed in small retrospective studies. Both treatments yielded notable relief for patients; however, 38.5% (15/39) of patients receiving methotrexate experienced adverse events, and 50.0% (4/8) experienced adverse events with cyclosporine.52,53


Neural-Mediated Oral Therapies—Neural-targeted oral therapies include pregabalin, serlopitant, aprepitant, naltrexone, nalbuphine, SSRIs (paroxetine and fluvoxamine), amitriptyline, and thalidomide. The research on these treatments ranges from case reviews to randomized controlled trials and open-label trials (Table 2).55-63
Thalidomide was studied in a small retrospective case review that showed notable improvement in PN. Dosages of thalidomide varied, but on average the dose was 100 mg/d. However, greater than 50% of patients experienced at least 1 adverse effect with this treatment.63
A study performed in Italy showed promising results for patients treated with pregabalin, with 70.0% (21/30) continuing to take pregabalin for almost 2 years following completion of the initial 3-month trial.55 Naltrexone decreased pruritus in more than half of patients (9/17).59 Amitriptyline yielded improvements in patients with PN; however, disease recurred in 5 patients (29%) after 7 months.62 A study performed in Germany reported promising results for paroxetine and fluvoxamine; however, some patients enrolled in the study had some form of psychiatric disorder.61
Serlopitant, aprepitant, and nalbuphine were studied in randomized controlled trials. The serlopitant trials were the largest of the neurally mediated oral medication studies; one showed substantial improvement in patients with PN,56 while the most recent trial did not show significant improvement (ClinicalTrials.gov identifier NCT03546816).57 On the other hand, aprepitant showed no major difference between the experimental and placebo groups.58 Nalbuphine 162 mg twice daily showed greater improvement in PN than nalbuphine 81 mg twice daily.60
Immune-Mediated Injectable Therapies—Immune-targeted injectables include nemolizumab and dupilumab (Table 2). Nemolizumab is an IL-31 antagonist that has been studied in a small randomized controlled trial that showed great success in decreasing pruritus associated with PN.64 IL-31 has been implicated in PN, and inhibition of the IL-31 receptor has been shown to disrupt the itch-scratch cycle of PN. Dupilumab is a monoclonal antibody against the IL-4 and IL-13 receptors, and it is the only FDA-approved treatment for PN.65 Blockage of these protein receptors decreases type 2 inflammation and chronic pruritus.66,67 Dupilumab is FDA approved for the treatment of atopic dermatitis and recently was approved for adults with PN. Dupilumab acts to block the shared α-subunit of the pruritogenic cytokines IL-4 and IL-13 pathways,29 thereby breaking the itch-scratch cycle associated with PN and allowing for the healing of these lesions. Results from 2 clinical trials showed substantially reduced itch in patients with PN.65 Dupilumab also was approved by the European Medicines Agency for moderate to severe PN.68
Conclusion
Prurigo nodularis is a chronic condition that affects patient quality of life and can mimic various dermatologic conditions. The epidemiology and pathophysiology of PN have not been fully expounded. More research should be conducted to determine the underpinnings of PN to help identify more consistently effective therapies for this complex condition.
- Durmaz K, Ataseven A, Ozer I, et al. Prurigo nodularis responding to intravenous immunoglobulins. Przegl Dermatol. 2022;109:159-162. doi:10.5114/dr.2022.117988
- Kowalski EH, Kneiber D, Valdebran M, et al. Treatment-resistant prurigo nodularis: challenges and solutions. Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol. 2019;12:163-172. doi:10.2147/CCID.S188070
- Wong LS, Yen YT. Chronic nodular prurigo: an update on the pathogenesis and treatment. Int J Mol Sci. 2022;23:12390. doi:10.3390/ijms232012390
- Janmohamed SR, Gwillim EC, Yousaf M, et al. The impact of prurigo nodularis on quality of life: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Arch Dermatol Res. 2021;313:669-677. doi:10.1007/s00403-020-02148-0
- Zeidler C, Ständer S. The pathogenesis of prurigo nodularis - ‘super-itch’ in exploration. Eur J Pain. 2016;20:37-40. doi:10.1002/ejp.767
- Kwatra SG. Breaking the itch–scratch cycle in prurigo nodularis. N Engl J Med. 2020;382:757-758. doi:10.1056/NEJMe1916733
- Frølunde AS, Wiis MAK, Ben Abdallah H, et al. Non-atopic chronic nodular prurigo (prurigo nodularis hyde): a systematic review of best-evidenced treatment options. Dermatology. 2022;238:950-960. doi:10.1159/000523700
- Kwon CD, Khanna R, Williams KA, et al. Diagnostic workup and evaluation of patients with prurigo nodularis. Medicines (Basel). 2019;6:97. doi:10.3390/medicines6040097
- Kowalski EH, Kneiber D, Valdebran M, et al. Distinguishing truly recalcitrant prurigo nodularis from poor treatment adherence: a response to treatment-resistant prurigo nodularis [Response to letter]. Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol. 2019;12:371-372. doi:10.2147/CCID.S214195
- Whang KA, Le TK, Khanna R, et al. Health-related quality of life and economic burden of prurigo nodularis. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2022;86:573-580. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2021.05.036
- Labib A, Ju T, Vander Does A, et al. Immunotargets and therapy for prurigo nodularis. Immunotargets Ther. 2022;11:11-21. doi:10.2147/ITT.S316602
- Belzberg M, Alphonse MP, Brown I, et al. Prurigo nodularis is characterized by systemic and cutaneous T helper 22 immune polarization. J Invest Dermatol. 2021;141:2208-2218.e14. doi:10.1016/j.jid.2021.02.749
- Ständer S, Pereira MP, Berger T, et al. IFSI-guideline on chronic prurigo including prurigo nodularis. Itch. 2020;5:e42. doi:10.1097/itx.0000000000000042
- Huang AH, Canner JK, Khanna R, et al. Real-world prevalence of prurigo nodularis and burden of associated diseases. J Invest Dermatol. 2020;140:480-483.e4. doi:10.1016/j.jid.2019.07.697
- Ständer S, Augustin M, Berger T, et al. Prevalence of prurigo nodularis in the United States of America: a retrospective database analysis. JAAD Int. 2021;2:28-30. doi:10.1016/j.jdin.2020.10.009
- Sutaria N, Adawi W, Brown I, et al. Racial disparities in mortality among patients with prurigo nodularis: a multi-center cohort study. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2022;86:487-490. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2021.09.028
- Ryczek A, Reich A. Prevalence of prurigo nodularis in Poland. Acta Derm Venereol. 2020;100:adv00155. doi:10.2340/00015555-3518
- Morgan CL, Thomas M, Ständer S, et al. Epidemiology of prurigo nodularis in England: a retrospective database analysis. Br J Dermatol. 2022;187:188-195. doi:10.1111/bjd.21032
- Woo YR, Wang S, Sohn KA, et al. Epidemiology, comorbidities, and prescription patterns of Korean prurigo nodularis patients: a multi-institution study. J Clin Med Res. 2021;11:95. doi:10.3390/jcm11010095
- Weigelt N, Metze D, Ständer S. Prurigo nodularis: systematic analysis of 58 histological criteria in 136 patients. J Cutan Pathol. 2010;37:578-586. doi:10.1111/j.1600-0560.2009.01484.x
- Yang LL, Jiang B, Chen SH, et al. Abnormal keratin expression pattern in prurigo nodularis epidermis. Skin Health Dis. 2022;2:e75. doi:10.1002/ski2.75
- Nockher WA, Renz H. Neurotrophins in allergic diseases: from neuronal growth factors to intercellular signaling molecules. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2006;117:583-589. doi:10.1016/j.jaci.2005.11.049
- Di Marco E, Mathor M, Bondanza S, et al. Nerve growth factor binds to normal human keratinocytes through high and low affinity receptors and stimulates their growth by a novel autocrine loop. J Biol Chem. 1993;268:22838-22846.
- Hägermark O, Hökfelt T, Pernow B. Flare and itch induced by substance P in human skin. J Invest Dermatol. 1978;71:233-235. doi:10.1111/1523-1747.ep12515092
- Choi JE, Di Nardo A. Skin neurogenic inflammation. Semin Immunopathol. 2018;40:249-259. doi:10.1007/s00281-018-0675-z
- Haas S, Capellino S, Phan NQ, et al. Low density of sympathetic nerve fibers relative to substance P-positive nerve fibers in lesional skin of chronic pruritus and prurigo nodularis. J Dermatol Sci. 2010;58:193-197. doi:10.1016/j.jdermsci.2010.03.020
- Park K, Mori T, Nakamura M, et al. Increased expression of mRNAs for IL-4, IL-17, IL-22 and IL-31 in skin lesions of subacute and chronic forms of prurigo. Eur J Dermatol. 2011;21:135-136.
- Tokura Y, Yagi H, Hanaoka K, et al. Subacute and chronic prurigo effectively treated with recombination interferon-gamma: implications for participation of Th2 cells in the pathogenesis of prurigo. Acta Derm Venereol. 1997;77:231-234. doi:10.2340/0001555577231234
- Williams KA, Roh YS, Brown I, et al. Pathophysiology, diagnosis, and pharmacological treatment of prurigo nodularis. Expert Rev Clin Pharmacol. 2021;14:67-77. doi:10.1080/17512433.2021.1852080
- Huang AH, Williams KA, Kwatra SG. Prurigo nodularis: epidemiology and clinical features. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2020;83:1559-1565. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2020.04.183
- Bewley A, Homey B, Pink A. Prurigo nodularis: a review of IL-31RA blockade and other potential treatments. Dermatol Ther. 2022;12:2039-2048. doi:10.1007/s13555-022-00782-2
- Zeidler C, Yosipovitch G, Ständer S. Prurigo nodularis and its management. Dermatol Clin. 2018;36:189-197. doi:10.1016/j.det.2018.02.003
- Siepmann D, Lotts T, Blome C, et al. Evaluation of the antipruritic effects of topical pimecrolimus in non-atopic prurigo nodularis: results of a randomized, hydrocortisone-controlled, double-blind phase II trial. Dermatology. 2013;227:353-360. doi:10.1159/000355671
- Valbuena MC, Muvdi S, Lim HW. Actinic prurigo. Dermatol Clin. 2014;32:335-344, viii. doi:10.1016/j.det.2014.03.010
- Aldhahwani R, Al Hawsawi KA. Neurotic excoriation presenting as solitary papule: case report. J Dermatol Dermatolog Surg. 2022;26:45. doi:10.4103/jdds.jdds_59_21
- Kwiek B, Schwartz RA. Keratoacanthoma (KA): an update and review. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2016;74:1220-1233. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2015.11.033
- Karadag AS, Ozlu E, Uzuncakmak TK, et al. Inverted follicular keratosis successfully treated with imiquimod. Indian Dermatol Online J. 2016;7:177-179. doi:10.4103/2229-5178.182354
- Nayak VN, Uma K, Girish HC, et al. Pseudoepitheliomatous hyperplasia in oral lesions: a review. J Int Oral Health. 2015;7:148-152.
- Saraceno R, Chiricozzi A, Nisticò SP, et al. An occlusive dressing containing betamethasone valerate 0.1% for the treatment of prurigo nodularis. J Dermatolog Treat. 2010;21:363-366. doi:10.3109/09546630903386606
- Wong SS, Goh CL. Double-blind, right/left comparison of calcipotriol ointment and betamethasone ointment in the treatment of prurigo nodularis. Arch Dermatol. 2000;136:807-808. doi:10.1001/archderm.136.6.807
- Waldinger TP, Wong RC, Taylor WB, et al. Cryotherapy improves prurigo nodularis. Arch Dermatol. 1984;120:1598-1600.
- Ständer S, Luger T, Metze D. Treatment of prurigo nodularis with topical capsaicin. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2001;44:471-478. doi:10.1067/mjd.2001.110059
- Ohanyan T, Schoepke N, Eirefelt S, et al. Role of substance P and its receptor neurokinin 1 in chronic prurigo: a randomized, proof-of-concept, controlled trial with topical aprepitant. Acta Derm Venereol. 2018;98:26-31. doi:10.2340/00015555-2780
- Tamagawa-Mineoka R, Katoh N, Ueda E, et al. Narrow-band ultraviolet B phototherapy in patients with recalcitrant nodular prurigo. J Dermatol. 2007;34:691-695. doi:10.1111/j.1346-8138.2007.00360.x
- Hammes S, Hermann J, Roos S, et al. UVB 308-nm excimer light and bath PUVA: combination therapy is very effective in the treatment of prurigo nodularis. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2011;25:799-803. doi:10.1111/j.1468-3083.2010.03865.x
- Richards RN. Update on intralesional steroid: focus on dermatoses. J Cutan Med Surg. 2010;14:19-23. doi:10.2310/7750.2009.08082
- Elmariah S, Kim B, Berger T, et al. Practical approaches for diagnosis and management of prurigo nodularis: United States expert panel consensus. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2021;84:747-760. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2020.07.025
- Grant JE Chamberlain SR Redden SA et al. N-Acetylcysteine in the treatment of excoriation disorder: a randomized clinical trial. JAMA Psychiatry. 2016;73:490-496. doi:10.1001/jamapsychiatry.2016.0060
- Adil M, Amin SS, Mohtashim M. N-acetylcysteine in dermatology. Indian J Dermatol Venereol Leprol. 2018;84:652-659. doi: 10.4103/ijdvl.IJDVL_33_18.
- Taylor M, Bhagwandas K. Trichotillosis, skin picking and N-acetylcysteine. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2015;72(suppl 1):AB117. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jaad.2015.02.482
- Legat FJ. The antipruritic effect of phototherapy. Front Med (Lausanne). 2018;5:333. doi:10.3389/fmed.2018.00333
- Klejtman T, Beylot-Barry M, Joly P, et al. Treatment of prurigo with methotrexate: a multicentre retrospective study of 39 cases. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2018;32:437-440. doi:10.1111/jdv.14646
- Wiznia LE, Callahan SW, Cohen DE, et al. Rapid improvement of prurigo nodularis with cyclosporine treatment. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2018;78:1209-1211. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2018.02.024
- Yagami A, Furue M, Togawa M, et al. One-year safety and efficacy study of bilastine treatment in Japanese patients with chronic spontaneous urticaria or pruritus associated with skin diseases. J Dermatol. 2017;44:375-385. doi:10.1111/1346-8138.13644
- Mazza M, Guerriero G, Marano G, et al. Treatment of prurigo nodularis with pregabalin. J Clin Pharm Ther. 2013;38:16-18. doi:10.1111/jcpt.12005
- Ständer S, Kwon P, Hirman J, et al. Serlopitant reduced pruritus in patients with prurigo nodularis in a phase 2, randomized, placebo-controlled trial. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2019;80:1395-1402. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2019.01.052
- Study of the efficacy, safety and tolerability of serlopitant for the treatment of pruritus (itch) with prurigo nodularis. ClinicalTrials.gov identifier: NCT03546816. Updated May 20, 2021. Accessed August 8, 2024. https://clinicaltrials.gov/study/NCT03546816
- Tsianakas A, Zeidler C, Riepe C, et al. Aprepitant in anti-histamine-refractory chronic nodular prurigo: a multicentre, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, cross-over, phase-II trial (APREPRU). Acta Derm Venereol. 2019;99:379-385. doi:10.2340/00015555-3120
- Metze D, Reimann S, Beissert S, et al. Efficacy and safety of naltrexone, an oral opiate receptor antagonist, in the treatment of pruritus in internal and dermatological diseases. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1999;41:533-539.
- Weisshaar E, Szepietowski JC, Bernhard JD, et al. Efficacy and safety of oral nalbuphine extended release in prurigo nodularis: results of a phase 2 randomized controlled trial with an open‐label extension phase. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2022;36:453-461. doi:10.1111/jdv.17816
- Ständer S, Böckenholt B, Schürmeyer-Horst F, et al. Treatment of chronic pruritus with the selective serotonin re-uptake inhibitors paroxetine and fluvoxamine: results of an open-labelled, two-arm proof-of-concept study. Acta Derm Venereol. 2009;89:45-51. doi:10.2340/00015555-0553
- Zalaudek I, Petrillo G, Baldassarre MA, et al. Amitriptyline as therapeutic and not symptomatic approach in the treatment of prurigo nodularis. G Ital Dermatol Venereol. 2006;141:433-437.
- Andersen TP, Fogh K. Thalidomide in 42 patients with prurigo nodularis Hyde. Dermatology. 2011;223:107-112. doi:10.1159/000331577
- Ständer S, Yosipovitch G, Legat FJ, et al. Trial of nemolizumab in moderate-to-severe prurigo nodularis. N Engl J Med. 2020;382:706-716. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa1908316
- Yosipovitch G, Mollanazar N, Ständer S, et al. Dupilumab in patients with prurigo nodularis: two randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled phase 3 trials. Nat Med. 2023;29:1180-1190. doi:10.1038/s41591-023-02320-9
- Mastorino L, Rosset F, Gelato F, et al. Chronic pruritus in atopic patients treated with dupilumab: real life response and related parameters in 354 patients. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2022;15:883. doi: 10.3390/ph15070883
- Kishi R, Toyama S, Tominaga M, et al. Effects of dupilumab on itch-related events in atopic dermatitis: implications for assessing treatment efficacy in clinical practice. Cells. 2023;12:239. doi: 10.3390/cells12020239
- Dupixent. European Medicines Agency website. Updated July 15, 2024. Accessed August 27, 2024. https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/medicines/human/EPAR/dupixent
- Durmaz K, Ataseven A, Ozer I, et al. Prurigo nodularis responding to intravenous immunoglobulins. Przegl Dermatol. 2022;109:159-162. doi:10.5114/dr.2022.117988
- Kowalski EH, Kneiber D, Valdebran M, et al. Treatment-resistant prurigo nodularis: challenges and solutions. Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol. 2019;12:163-172. doi:10.2147/CCID.S188070
- Wong LS, Yen YT. Chronic nodular prurigo: an update on the pathogenesis and treatment. Int J Mol Sci. 2022;23:12390. doi:10.3390/ijms232012390
- Janmohamed SR, Gwillim EC, Yousaf M, et al. The impact of prurigo nodularis on quality of life: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Arch Dermatol Res. 2021;313:669-677. doi:10.1007/s00403-020-02148-0
- Zeidler C, Ständer S. The pathogenesis of prurigo nodularis - ‘super-itch’ in exploration. Eur J Pain. 2016;20:37-40. doi:10.1002/ejp.767
- Kwatra SG. Breaking the itch–scratch cycle in prurigo nodularis. N Engl J Med. 2020;382:757-758. doi:10.1056/NEJMe1916733
- Frølunde AS, Wiis MAK, Ben Abdallah H, et al. Non-atopic chronic nodular prurigo (prurigo nodularis hyde): a systematic review of best-evidenced treatment options. Dermatology. 2022;238:950-960. doi:10.1159/000523700
- Kwon CD, Khanna R, Williams KA, et al. Diagnostic workup and evaluation of patients with prurigo nodularis. Medicines (Basel). 2019;6:97. doi:10.3390/medicines6040097
- Kowalski EH, Kneiber D, Valdebran M, et al. Distinguishing truly recalcitrant prurigo nodularis from poor treatment adherence: a response to treatment-resistant prurigo nodularis [Response to letter]. Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol. 2019;12:371-372. doi:10.2147/CCID.S214195
- Whang KA, Le TK, Khanna R, et al. Health-related quality of life and economic burden of prurigo nodularis. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2022;86:573-580. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2021.05.036
- Labib A, Ju T, Vander Does A, et al. Immunotargets and therapy for prurigo nodularis. Immunotargets Ther. 2022;11:11-21. doi:10.2147/ITT.S316602
- Belzberg M, Alphonse MP, Brown I, et al. Prurigo nodularis is characterized by systemic and cutaneous T helper 22 immune polarization. J Invest Dermatol. 2021;141:2208-2218.e14. doi:10.1016/j.jid.2021.02.749
- Ständer S, Pereira MP, Berger T, et al. IFSI-guideline on chronic prurigo including prurigo nodularis. Itch. 2020;5:e42. doi:10.1097/itx.0000000000000042
- Huang AH, Canner JK, Khanna R, et al. Real-world prevalence of prurigo nodularis and burden of associated diseases. J Invest Dermatol. 2020;140:480-483.e4. doi:10.1016/j.jid.2019.07.697
- Ständer S, Augustin M, Berger T, et al. Prevalence of prurigo nodularis in the United States of America: a retrospective database analysis. JAAD Int. 2021;2:28-30. doi:10.1016/j.jdin.2020.10.009
- Sutaria N, Adawi W, Brown I, et al. Racial disparities in mortality among patients with prurigo nodularis: a multi-center cohort study. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2022;86:487-490. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2021.09.028
- Ryczek A, Reich A. Prevalence of prurigo nodularis in Poland. Acta Derm Venereol. 2020;100:adv00155. doi:10.2340/00015555-3518
- Morgan CL, Thomas M, Ständer S, et al. Epidemiology of prurigo nodularis in England: a retrospective database analysis. Br J Dermatol. 2022;187:188-195. doi:10.1111/bjd.21032
- Woo YR, Wang S, Sohn KA, et al. Epidemiology, comorbidities, and prescription patterns of Korean prurigo nodularis patients: a multi-institution study. J Clin Med Res. 2021;11:95. doi:10.3390/jcm11010095
- Weigelt N, Metze D, Ständer S. Prurigo nodularis: systematic analysis of 58 histological criteria in 136 patients. J Cutan Pathol. 2010;37:578-586. doi:10.1111/j.1600-0560.2009.01484.x
- Yang LL, Jiang B, Chen SH, et al. Abnormal keratin expression pattern in prurigo nodularis epidermis. Skin Health Dis. 2022;2:e75. doi:10.1002/ski2.75
- Nockher WA, Renz H. Neurotrophins in allergic diseases: from neuronal growth factors to intercellular signaling molecules. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2006;117:583-589. doi:10.1016/j.jaci.2005.11.049
- Di Marco E, Mathor M, Bondanza S, et al. Nerve growth factor binds to normal human keratinocytes through high and low affinity receptors and stimulates their growth by a novel autocrine loop. J Biol Chem. 1993;268:22838-22846.
- Hägermark O, Hökfelt T, Pernow B. Flare and itch induced by substance P in human skin. J Invest Dermatol. 1978;71:233-235. doi:10.1111/1523-1747.ep12515092
- Choi JE, Di Nardo A. Skin neurogenic inflammation. Semin Immunopathol. 2018;40:249-259. doi:10.1007/s00281-018-0675-z
- Haas S, Capellino S, Phan NQ, et al. Low density of sympathetic nerve fibers relative to substance P-positive nerve fibers in lesional skin of chronic pruritus and prurigo nodularis. J Dermatol Sci. 2010;58:193-197. doi:10.1016/j.jdermsci.2010.03.020
- Park K, Mori T, Nakamura M, et al. Increased expression of mRNAs for IL-4, IL-17, IL-22 and IL-31 in skin lesions of subacute and chronic forms of prurigo. Eur J Dermatol. 2011;21:135-136.
- Tokura Y, Yagi H, Hanaoka K, et al. Subacute and chronic prurigo effectively treated with recombination interferon-gamma: implications for participation of Th2 cells in the pathogenesis of prurigo. Acta Derm Venereol. 1997;77:231-234. doi:10.2340/0001555577231234
- Williams KA, Roh YS, Brown I, et al. Pathophysiology, diagnosis, and pharmacological treatment of prurigo nodularis. Expert Rev Clin Pharmacol. 2021;14:67-77. doi:10.1080/17512433.2021.1852080
- Huang AH, Williams KA, Kwatra SG. Prurigo nodularis: epidemiology and clinical features. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2020;83:1559-1565. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2020.04.183
- Bewley A, Homey B, Pink A. Prurigo nodularis: a review of IL-31RA blockade and other potential treatments. Dermatol Ther. 2022;12:2039-2048. doi:10.1007/s13555-022-00782-2
- Zeidler C, Yosipovitch G, Ständer S. Prurigo nodularis and its management. Dermatol Clin. 2018;36:189-197. doi:10.1016/j.det.2018.02.003
- Siepmann D, Lotts T, Blome C, et al. Evaluation of the antipruritic effects of topical pimecrolimus in non-atopic prurigo nodularis: results of a randomized, hydrocortisone-controlled, double-blind phase II trial. Dermatology. 2013;227:353-360. doi:10.1159/000355671
- Valbuena MC, Muvdi S, Lim HW. Actinic prurigo. Dermatol Clin. 2014;32:335-344, viii. doi:10.1016/j.det.2014.03.010
- Aldhahwani R, Al Hawsawi KA. Neurotic excoriation presenting as solitary papule: case report. J Dermatol Dermatolog Surg. 2022;26:45. doi:10.4103/jdds.jdds_59_21
- Kwiek B, Schwartz RA. Keratoacanthoma (KA): an update and review. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2016;74:1220-1233. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2015.11.033
- Karadag AS, Ozlu E, Uzuncakmak TK, et al. Inverted follicular keratosis successfully treated with imiquimod. Indian Dermatol Online J. 2016;7:177-179. doi:10.4103/2229-5178.182354
- Nayak VN, Uma K, Girish HC, et al. Pseudoepitheliomatous hyperplasia in oral lesions: a review. J Int Oral Health. 2015;7:148-152.
- Saraceno R, Chiricozzi A, Nisticò SP, et al. An occlusive dressing containing betamethasone valerate 0.1% for the treatment of prurigo nodularis. J Dermatolog Treat. 2010;21:363-366. doi:10.3109/09546630903386606
- Wong SS, Goh CL. Double-blind, right/left comparison of calcipotriol ointment and betamethasone ointment in the treatment of prurigo nodularis. Arch Dermatol. 2000;136:807-808. doi:10.1001/archderm.136.6.807
- Waldinger TP, Wong RC, Taylor WB, et al. Cryotherapy improves prurigo nodularis. Arch Dermatol. 1984;120:1598-1600.
- Ständer S, Luger T, Metze D. Treatment of prurigo nodularis with topical capsaicin. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2001;44:471-478. doi:10.1067/mjd.2001.110059
- Ohanyan T, Schoepke N, Eirefelt S, et al. Role of substance P and its receptor neurokinin 1 in chronic prurigo: a randomized, proof-of-concept, controlled trial with topical aprepitant. Acta Derm Venereol. 2018;98:26-31. doi:10.2340/00015555-2780
- Tamagawa-Mineoka R, Katoh N, Ueda E, et al. Narrow-band ultraviolet B phototherapy in patients with recalcitrant nodular prurigo. J Dermatol. 2007;34:691-695. doi:10.1111/j.1346-8138.2007.00360.x
- Hammes S, Hermann J, Roos S, et al. UVB 308-nm excimer light and bath PUVA: combination therapy is very effective in the treatment of prurigo nodularis. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2011;25:799-803. doi:10.1111/j.1468-3083.2010.03865.x
- Richards RN. Update on intralesional steroid: focus on dermatoses. J Cutan Med Surg. 2010;14:19-23. doi:10.2310/7750.2009.08082
- Elmariah S, Kim B, Berger T, et al. Practical approaches for diagnosis and management of prurigo nodularis: United States expert panel consensus. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2021;84:747-760. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2020.07.025
- Grant JE Chamberlain SR Redden SA et al. N-Acetylcysteine in the treatment of excoriation disorder: a randomized clinical trial. JAMA Psychiatry. 2016;73:490-496. doi:10.1001/jamapsychiatry.2016.0060
- Adil M, Amin SS, Mohtashim M. N-acetylcysteine in dermatology. Indian J Dermatol Venereol Leprol. 2018;84:652-659. doi: 10.4103/ijdvl.IJDVL_33_18.
- Taylor M, Bhagwandas K. Trichotillosis, skin picking and N-acetylcysteine. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2015;72(suppl 1):AB117. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jaad.2015.02.482
- Legat FJ. The antipruritic effect of phototherapy. Front Med (Lausanne). 2018;5:333. doi:10.3389/fmed.2018.00333
- Klejtman T, Beylot-Barry M, Joly P, et al. Treatment of prurigo with methotrexate: a multicentre retrospective study of 39 cases. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2018;32:437-440. doi:10.1111/jdv.14646
- Wiznia LE, Callahan SW, Cohen DE, et al. Rapid improvement of prurigo nodularis with cyclosporine treatment. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2018;78:1209-1211. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2018.02.024
- Yagami A, Furue M, Togawa M, et al. One-year safety and efficacy study of bilastine treatment in Japanese patients with chronic spontaneous urticaria or pruritus associated with skin diseases. J Dermatol. 2017;44:375-385. doi:10.1111/1346-8138.13644
- Mazza M, Guerriero G, Marano G, et al. Treatment of prurigo nodularis with pregabalin. J Clin Pharm Ther. 2013;38:16-18. doi:10.1111/jcpt.12005
- Ständer S, Kwon P, Hirman J, et al. Serlopitant reduced pruritus in patients with prurigo nodularis in a phase 2, randomized, placebo-controlled trial. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2019;80:1395-1402. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2019.01.052
- Study of the efficacy, safety and tolerability of serlopitant for the treatment of pruritus (itch) with prurigo nodularis. ClinicalTrials.gov identifier: NCT03546816. Updated May 20, 2021. Accessed August 8, 2024. https://clinicaltrials.gov/study/NCT03546816
- Tsianakas A, Zeidler C, Riepe C, et al. Aprepitant in anti-histamine-refractory chronic nodular prurigo: a multicentre, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, cross-over, phase-II trial (APREPRU). Acta Derm Venereol. 2019;99:379-385. doi:10.2340/00015555-3120
- Metze D, Reimann S, Beissert S, et al. Efficacy and safety of naltrexone, an oral opiate receptor antagonist, in the treatment of pruritus in internal and dermatological diseases. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1999;41:533-539.
- Weisshaar E, Szepietowski JC, Bernhard JD, et al. Efficacy and safety of oral nalbuphine extended release in prurigo nodularis: results of a phase 2 randomized controlled trial with an open‐label extension phase. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2022;36:453-461. doi:10.1111/jdv.17816
- Ständer S, Böckenholt B, Schürmeyer-Horst F, et al. Treatment of chronic pruritus with the selective serotonin re-uptake inhibitors paroxetine and fluvoxamine: results of an open-labelled, two-arm proof-of-concept study. Acta Derm Venereol. 2009;89:45-51. doi:10.2340/00015555-0553
- Zalaudek I, Petrillo G, Baldassarre MA, et al. Amitriptyline as therapeutic and not symptomatic approach in the treatment of prurigo nodularis. G Ital Dermatol Venereol. 2006;141:433-437.
- Andersen TP, Fogh K. Thalidomide in 42 patients with prurigo nodularis Hyde. Dermatology. 2011;223:107-112. doi:10.1159/000331577
- Ständer S, Yosipovitch G, Legat FJ, et al. Trial of nemolizumab in moderate-to-severe prurigo nodularis. N Engl J Med. 2020;382:706-716. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa1908316
- Yosipovitch G, Mollanazar N, Ständer S, et al. Dupilumab in patients with prurigo nodularis: two randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled phase 3 trials. Nat Med. 2023;29:1180-1190. doi:10.1038/s41591-023-02320-9
- Mastorino L, Rosset F, Gelato F, et al. Chronic pruritus in atopic patients treated with dupilumab: real life response and related parameters in 354 patients. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2022;15:883. doi: 10.3390/ph15070883
- Kishi R, Toyama S, Tominaga M, et al. Effects of dupilumab on itch-related events in atopic dermatitis: implications for assessing treatment efficacy in clinical practice. Cells. 2023;12:239. doi: 10.3390/cells12020239
- Dupixent. European Medicines Agency website. Updated July 15, 2024. Accessed August 27, 2024. https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/medicines/human/EPAR/dupixent
Practice Points
- Clinically, prurigo nodularis can mimic an array of dermatologic skin conditions and may be diagnosed more frequently in patients with comorbidities.
- Dupilumab is the first and only treatment for prurigo nodularis approved by the US Food and Drug Administration; however, many topical treatments are currently used as first-line therapies.
New Associations Identified Between IBD and Extraintestinal Manifestations
, according to a recent study.
For instance, antinuclear cytoplastic antibody is associated with primary sclerosing cholangitis (PSC) in Crohn’s disease, and CPEB4 genetic variation is associated with skin manifestations.
“Up to 40% of people with IBD suffer with symptoms from inflammation that occurs outside the gut, particularly affecting the liver, skin, and joints. These symptoms can often have a bigger impact on quality of life than the gut inflammation itself and can actually be life-threatening,” said senior author Dermot McGovern, MD, PhD, AGAF, director of translational medicine at the F. Widjaja Foundation Inflammatory Bowel Disease and Immunobiology Research Institute at Cedars-Sinai Medical Center, Los Angeles.
“With the advances in therapies for IBD, including availability of gut-selective agents, treatment choices often incorporate whether a patient has one of these manifestations or not,” he said. “We need to understand who is at increased risk of these and why.”
The study was published in Gastroenterology .
Analyzing Associations
Dr. McGovern and colleagues analyzed data for 12,083 unrelated European ancestry IBD cases with presence or absence of EIMs across four cohorts in the Cedars-Sinai Medical Center IBD Research Repository, National Institute for Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases IBD Genetics Consortium, Sinai Helmsley Alliance for Research Excellence Consortium, and Risk Stratification and Identification of Immunogenetic and Microbial Markers of Rapid Disease Progression in Children with Crohn’s Disease.
In particular, the researchers looked at EIM phenotypes such as ankylosing spondylitis and sacroiliitis, PSC, peripheral arthritis, and skin and ocular manifestations. They analyzed clinical and serologic parameters through regression analyses using a mixed-effects model, as well as within-case logistic regression for genetic associations.
Overall, 14% of patients had at least one EIM. Contrary to previous reports, only 2% had multiple EIMs, and most co-occurrences were negatively correlated. Nearly all EIMs were more common in Crohn’s disease, except for PSC, which was more common in ulcerative colitis.
In general, EIMs occurred more often in women, particularly with Crohn’s disease and colonic disease location, and in patients who required surgery. Jewish ancestry was associated with psoriasis and overall skin manifestations.
Smoking increased the risk for multiple EIMs, except for PSC, where there appeared to be a “protective” effect. Older age at diagnosis and a family history of IBD were associated with increased risk for certain EIMs as well.
In addition, the research team noted multiple serologic associations, such as immunoglobulin (Ig) G and IgA, perinuclear antinuclear cytoplastic antibodies, and anti–Pseudomonas fluorescens–associated sequences with any EIM, as well as particular associations with PSC, such as anti-Saccharomyces cerevisiae antibodies and anti-flagellin.
There were also genome-wide significant associations within the major histocompatibility complex and CPEB4. Genetic associations implicated tumor necrosis factor, Janus kinase-signal transducer and activator of transcription, and interleukin 6 as potential targets for EIMs.
“We are working with colleagues across the world to increase the sample size, as we believe there is more to find,” Dr. McGovern said. “Importantly, this includes non-European ancestry subjects, as there is an urgent need to increase the diversity of populations we study so advances in clinical care are available to all communities.”
Considering Target Therapies
As medicine becomes more specialized, physicians should remember to consider the whole patient while choosing treatment strategies.
“Sometimes doctors wear blinders to the whole person, and it’s important to be aware of a holistic approach, where a gastroenterologist also asks about potential joint inflammation or a rheumatologist asks about bowel inflammation,” said David Rubin, MD, AGAF, chief of the Section of Gastroenterology, Hepatology and Nutrition at the University of Chicago Medicine, Chicago.
Dr. Rubin, who wasn’t involved with this study, has researched and published on EIMs in IBD. He and colleagues analyzed the prevalence, pathophysiology, and clinical presentation of EIMs to better understand possibilities for disease management.
“As we’ve gotten a better understanding of the immune system, we’ve learned that an EIM can sometimes provide a clue to the treatment we might use,” he said. “Given a similar amount of bowel inflammation, if one patient also has joint pain and another doesn’t, we might choose different treatments based on the immune pathway that might be involved.”
In future studies, researchers may consider whether these genetic or serologic markers could predict EIM manifestation before it occurs clinically, Dr. Rubin said. He and colleagues are also studying the links between IBD and mental health associations.
“So far, we don’t have a blood test or biopsy test that tells you which treatment is more or less likely to work, so we need to think carefully as clinicians and look to other organ systems for clues,” he said. “It’s not only more efficient to pick a single therapy to treat both the skin and bowel, but it may actually be more effective if both have a particular dominant pathway.”
The study was supported by internal funds from the F. Widjaja Foundation Inflammatory Bowel and Immunobiology Research Institute. Several authors reported consultant roles or other associations with pharmaceutical companies. Dr. Rubin reported no relevant disclosures.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
, according to a recent study.
For instance, antinuclear cytoplastic antibody is associated with primary sclerosing cholangitis (PSC) in Crohn’s disease, and CPEB4 genetic variation is associated with skin manifestations.
“Up to 40% of people with IBD suffer with symptoms from inflammation that occurs outside the gut, particularly affecting the liver, skin, and joints. These symptoms can often have a bigger impact on quality of life than the gut inflammation itself and can actually be life-threatening,” said senior author Dermot McGovern, MD, PhD, AGAF, director of translational medicine at the F. Widjaja Foundation Inflammatory Bowel Disease and Immunobiology Research Institute at Cedars-Sinai Medical Center, Los Angeles.
“With the advances in therapies for IBD, including availability of gut-selective agents, treatment choices often incorporate whether a patient has one of these manifestations or not,” he said. “We need to understand who is at increased risk of these and why.”
The study was published in Gastroenterology .
Analyzing Associations
Dr. McGovern and colleagues analyzed data for 12,083 unrelated European ancestry IBD cases with presence or absence of EIMs across four cohorts in the Cedars-Sinai Medical Center IBD Research Repository, National Institute for Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases IBD Genetics Consortium, Sinai Helmsley Alliance for Research Excellence Consortium, and Risk Stratification and Identification of Immunogenetic and Microbial Markers of Rapid Disease Progression in Children with Crohn’s Disease.
In particular, the researchers looked at EIM phenotypes such as ankylosing spondylitis and sacroiliitis, PSC, peripheral arthritis, and skin and ocular manifestations. They analyzed clinical and serologic parameters through regression analyses using a mixed-effects model, as well as within-case logistic regression for genetic associations.
Overall, 14% of patients had at least one EIM. Contrary to previous reports, only 2% had multiple EIMs, and most co-occurrences were negatively correlated. Nearly all EIMs were more common in Crohn’s disease, except for PSC, which was more common in ulcerative colitis.
In general, EIMs occurred more often in women, particularly with Crohn’s disease and colonic disease location, and in patients who required surgery. Jewish ancestry was associated with psoriasis and overall skin manifestations.
Smoking increased the risk for multiple EIMs, except for PSC, where there appeared to be a “protective” effect. Older age at diagnosis and a family history of IBD were associated with increased risk for certain EIMs as well.
In addition, the research team noted multiple serologic associations, such as immunoglobulin (Ig) G and IgA, perinuclear antinuclear cytoplastic antibodies, and anti–Pseudomonas fluorescens–associated sequences with any EIM, as well as particular associations with PSC, such as anti-Saccharomyces cerevisiae antibodies and anti-flagellin.
There were also genome-wide significant associations within the major histocompatibility complex and CPEB4. Genetic associations implicated tumor necrosis factor, Janus kinase-signal transducer and activator of transcription, and interleukin 6 as potential targets for EIMs.
“We are working with colleagues across the world to increase the sample size, as we believe there is more to find,” Dr. McGovern said. “Importantly, this includes non-European ancestry subjects, as there is an urgent need to increase the diversity of populations we study so advances in clinical care are available to all communities.”
Considering Target Therapies
As medicine becomes more specialized, physicians should remember to consider the whole patient while choosing treatment strategies.
“Sometimes doctors wear blinders to the whole person, and it’s important to be aware of a holistic approach, where a gastroenterologist also asks about potential joint inflammation or a rheumatologist asks about bowel inflammation,” said David Rubin, MD, AGAF, chief of the Section of Gastroenterology, Hepatology and Nutrition at the University of Chicago Medicine, Chicago.
Dr. Rubin, who wasn’t involved with this study, has researched and published on EIMs in IBD. He and colleagues analyzed the prevalence, pathophysiology, and clinical presentation of EIMs to better understand possibilities for disease management.
“As we’ve gotten a better understanding of the immune system, we’ve learned that an EIM can sometimes provide a clue to the treatment we might use,” he said. “Given a similar amount of bowel inflammation, if one patient also has joint pain and another doesn’t, we might choose different treatments based on the immune pathway that might be involved.”
In future studies, researchers may consider whether these genetic or serologic markers could predict EIM manifestation before it occurs clinically, Dr. Rubin said. He and colleagues are also studying the links between IBD and mental health associations.
“So far, we don’t have a blood test or biopsy test that tells you which treatment is more or less likely to work, so we need to think carefully as clinicians and look to other organ systems for clues,” he said. “It’s not only more efficient to pick a single therapy to treat both the skin and bowel, but it may actually be more effective if both have a particular dominant pathway.”
The study was supported by internal funds from the F. Widjaja Foundation Inflammatory Bowel and Immunobiology Research Institute. Several authors reported consultant roles or other associations with pharmaceutical companies. Dr. Rubin reported no relevant disclosures.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
, according to a recent study.
For instance, antinuclear cytoplastic antibody is associated with primary sclerosing cholangitis (PSC) in Crohn’s disease, and CPEB4 genetic variation is associated with skin manifestations.
“Up to 40% of people with IBD suffer with symptoms from inflammation that occurs outside the gut, particularly affecting the liver, skin, and joints. These symptoms can often have a bigger impact on quality of life than the gut inflammation itself and can actually be life-threatening,” said senior author Dermot McGovern, MD, PhD, AGAF, director of translational medicine at the F. Widjaja Foundation Inflammatory Bowel Disease and Immunobiology Research Institute at Cedars-Sinai Medical Center, Los Angeles.
“With the advances in therapies for IBD, including availability of gut-selective agents, treatment choices often incorporate whether a patient has one of these manifestations or not,” he said. “We need to understand who is at increased risk of these and why.”
The study was published in Gastroenterology .
Analyzing Associations
Dr. McGovern and colleagues analyzed data for 12,083 unrelated European ancestry IBD cases with presence or absence of EIMs across four cohorts in the Cedars-Sinai Medical Center IBD Research Repository, National Institute for Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases IBD Genetics Consortium, Sinai Helmsley Alliance for Research Excellence Consortium, and Risk Stratification and Identification of Immunogenetic and Microbial Markers of Rapid Disease Progression in Children with Crohn’s Disease.
In particular, the researchers looked at EIM phenotypes such as ankylosing spondylitis and sacroiliitis, PSC, peripheral arthritis, and skin and ocular manifestations. They analyzed clinical and serologic parameters through regression analyses using a mixed-effects model, as well as within-case logistic regression for genetic associations.
Overall, 14% of patients had at least one EIM. Contrary to previous reports, only 2% had multiple EIMs, and most co-occurrences were negatively correlated. Nearly all EIMs were more common in Crohn’s disease, except for PSC, which was more common in ulcerative colitis.
In general, EIMs occurred more often in women, particularly with Crohn’s disease and colonic disease location, and in patients who required surgery. Jewish ancestry was associated with psoriasis and overall skin manifestations.
Smoking increased the risk for multiple EIMs, except for PSC, where there appeared to be a “protective” effect. Older age at diagnosis and a family history of IBD were associated with increased risk for certain EIMs as well.
In addition, the research team noted multiple serologic associations, such as immunoglobulin (Ig) G and IgA, perinuclear antinuclear cytoplastic antibodies, and anti–Pseudomonas fluorescens–associated sequences with any EIM, as well as particular associations with PSC, such as anti-Saccharomyces cerevisiae antibodies and anti-flagellin.
There were also genome-wide significant associations within the major histocompatibility complex and CPEB4. Genetic associations implicated tumor necrosis factor, Janus kinase-signal transducer and activator of transcription, and interleukin 6 as potential targets for EIMs.
“We are working with colleagues across the world to increase the sample size, as we believe there is more to find,” Dr. McGovern said. “Importantly, this includes non-European ancestry subjects, as there is an urgent need to increase the diversity of populations we study so advances in clinical care are available to all communities.”
Considering Target Therapies
As medicine becomes more specialized, physicians should remember to consider the whole patient while choosing treatment strategies.
“Sometimes doctors wear blinders to the whole person, and it’s important to be aware of a holistic approach, where a gastroenterologist also asks about potential joint inflammation or a rheumatologist asks about bowel inflammation,” said David Rubin, MD, AGAF, chief of the Section of Gastroenterology, Hepatology and Nutrition at the University of Chicago Medicine, Chicago.
Dr. Rubin, who wasn’t involved with this study, has researched and published on EIMs in IBD. He and colleagues analyzed the prevalence, pathophysiology, and clinical presentation of EIMs to better understand possibilities for disease management.
“As we’ve gotten a better understanding of the immune system, we’ve learned that an EIM can sometimes provide a clue to the treatment we might use,” he said. “Given a similar amount of bowel inflammation, if one patient also has joint pain and another doesn’t, we might choose different treatments based on the immune pathway that might be involved.”
In future studies, researchers may consider whether these genetic or serologic markers could predict EIM manifestation before it occurs clinically, Dr. Rubin said. He and colleagues are also studying the links between IBD and mental health associations.
“So far, we don’t have a blood test or biopsy test that tells you which treatment is more or less likely to work, so we need to think carefully as clinicians and look to other organ systems for clues,” he said. “It’s not only more efficient to pick a single therapy to treat both the skin and bowel, but it may actually be more effective if both have a particular dominant pathway.”
The study was supported by internal funds from the F. Widjaja Foundation Inflammatory Bowel and Immunobiology Research Institute. Several authors reported consultant roles or other associations with pharmaceutical companies. Dr. Rubin reported no relevant disclosures.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Successful Treatment of Refractory Extensive Pityriasis Rubra Pilaris With Risankizumab and Acitretin
To the Editor:
Pityriasis rubra pilaris (PRP) is a rare papulosquamous condition with an unknown pathogenesis and limited efficacy data, which can make treatment challenging. Some cases of PRP spontaneously resolve in a few months, which is most common in the pediatric population.1 Pityriasis rubra pilaris in adults is likely to persist for years, and spontaneous resolution is unpredictable. Randomized clinical trials are difficult to perform due to the rarity of PRP.
Although there is no cure and no standard protocol for treating PRP, systemic retinoids historically are considered first-line therapy for moderate to severe cases.2 Additional management approaches include symptomatic control with moisturizers and psychological support. Alternative systemic treatments for moderate to severe cases include methotrexate, phototherapy, and cyclosporine.2
Pityriasis rubra pilaris demonstrates a favorable response to methotrexate treatment, especially in type I cases; however, patients on this alternative therapy should be monitored for severe adverse effects (eg, hepatotoxicity, pancytopenia, pneumonitis).2 Phototherapy should be approached with caution. Narrowband UVB, UVA1, and psoralen plus UVA therapy have successfully treated PRP; however, the response is variable. In some cases, the opposite effect can occur, in which the condition is photoaggravated. Phototherapy is a valid alternative form of treatment when used in combination with acitretin, and a phototest should be performed prior to starting this regimen. Cyclosporine is another immunosuppressant that can be considered for PRP treatment, though there are limited data demonstrating its efficacy.2
The introduction of biologic agents has changed the treatment approach for many dermatologic diseases, including PRP. Given the similar features between psoriasis and PRP, the biologics prescribed for psoriasis therapy also are used for patients with PRP that is challenging to treat, such as anti–tumor necrosis factor α inhibitors and IL inhibitors—specifically IL-17 and IL-23. Remission has been achieved with the use of biologics in combination with retinoid therapy.2
Biologic therapies used for PRP effectively inhibit cytokines and reduce the overall inflammatory processes involved in the development of the scaly patches and plaques seen in this condition. However, most reported clinical experiences are case studies, and more research in the form of randomized clinical trials is needed to understand the efficacy and long-term effects of this form of treatment in PRP. We present a case of a patient with refractory adult subtype I PRP that was successfully treated with the IL-23 inhibitor risankizumab.
A 65-year-old man was referred to Florida Academic Dermatology Center (Coral Gables, Florida) with biopsy-proven PRP diagnosed 1 year prior. The patient reported experiencing a debilitating quality of life in the year since diagnosis (Figure 1). Treatment attempts with dupilumab, tralokinumab, intramuscular steroid injections, and topical corticosteroids had failed (Figure 2). Following evaluation at Florida Academic Dermatology Center, the patient was started on acitretin 25 mg every other day and received an initial subcutaneous injection of ixekizumab 160 mg (an IL-17 inhibitor) followed 2 weeks later by a second injection of 80 mg. After the 2 doses of ixekizumab, the patient’s condition worsened with the development of pinpoint hemorrhagic lesions. The medication was discontinued, and he was started on risankizumab 150 mg at the approved dosing regimen for plaque psoriasis in combination with the acitretin therapy. Prior to starting risankizumab, the affected body surface area (BSA) was 80%. At 1-month follow-up, he showed improvement with reduction in scaling and erythema and an affected BSA of 30% (Figure 3). At 4-month follow-up, he continued showing improvement with an affected BSA of 10% (Figure 4). Acitretin was discontinued, and the patient has been successfully maintained on risankizumab 150 mg/mL subcutaneous injections every 12 weeks since.
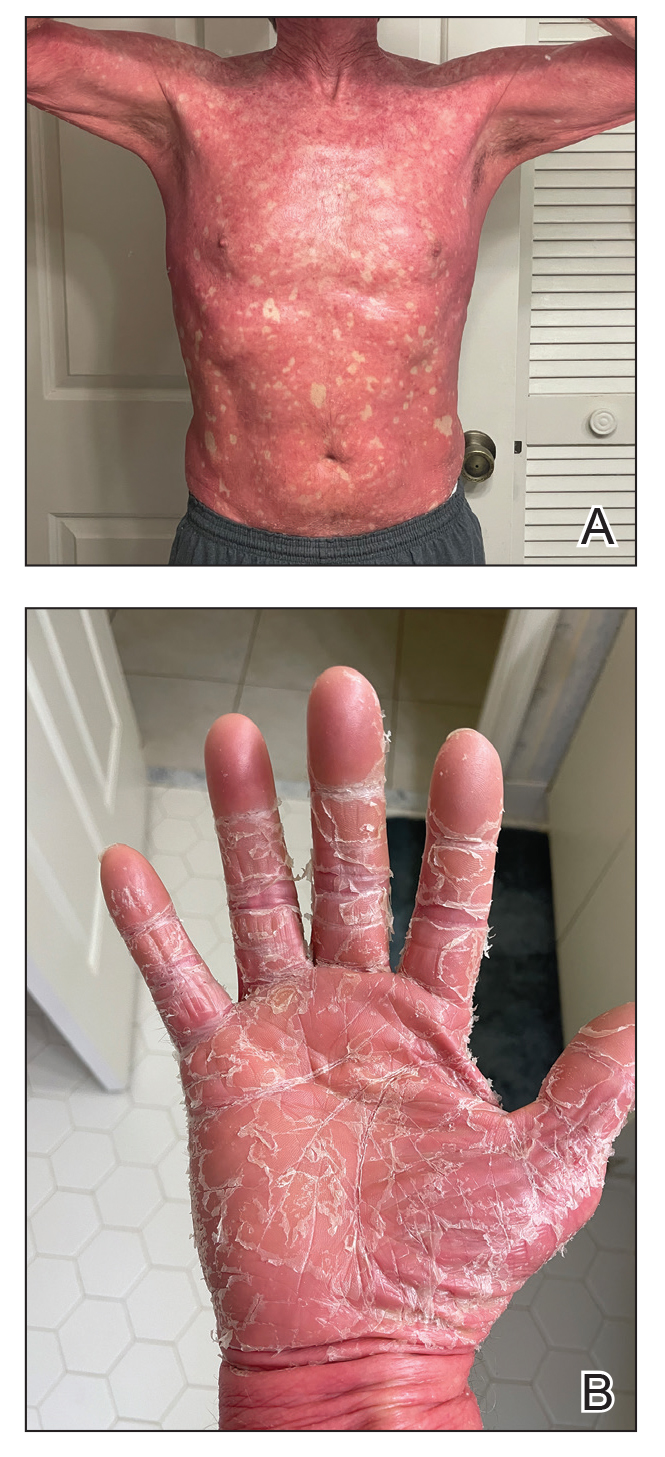
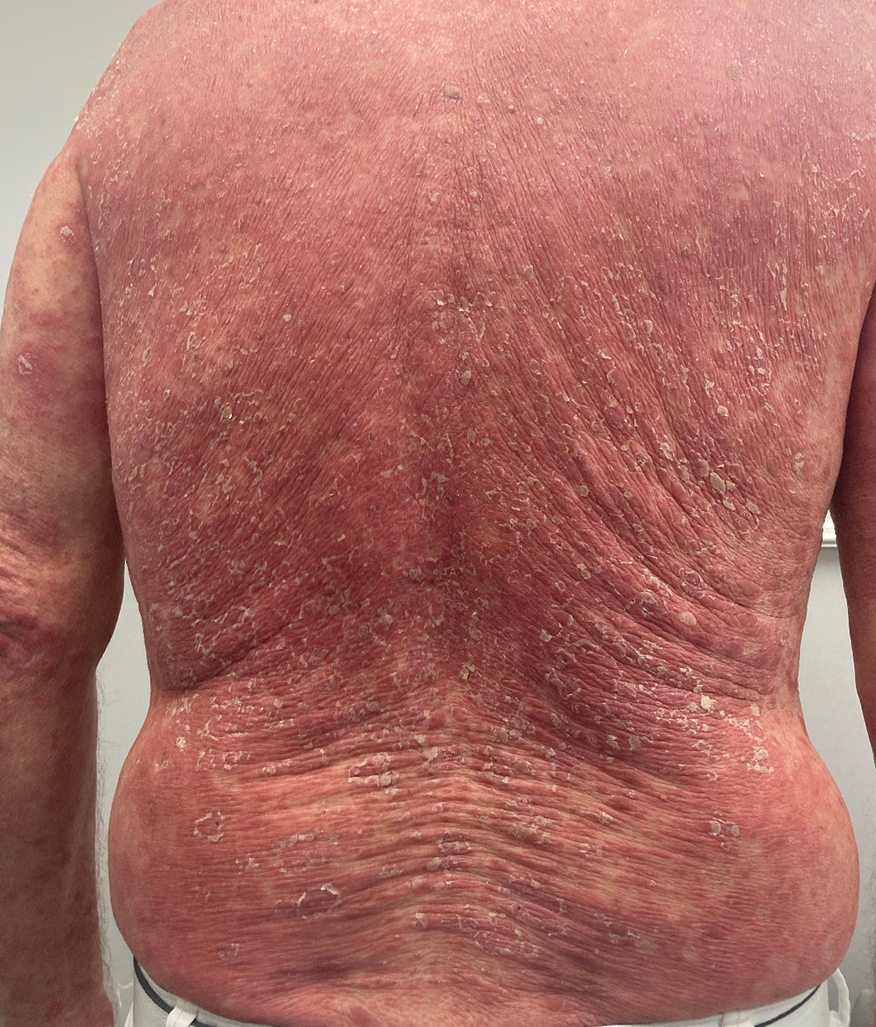
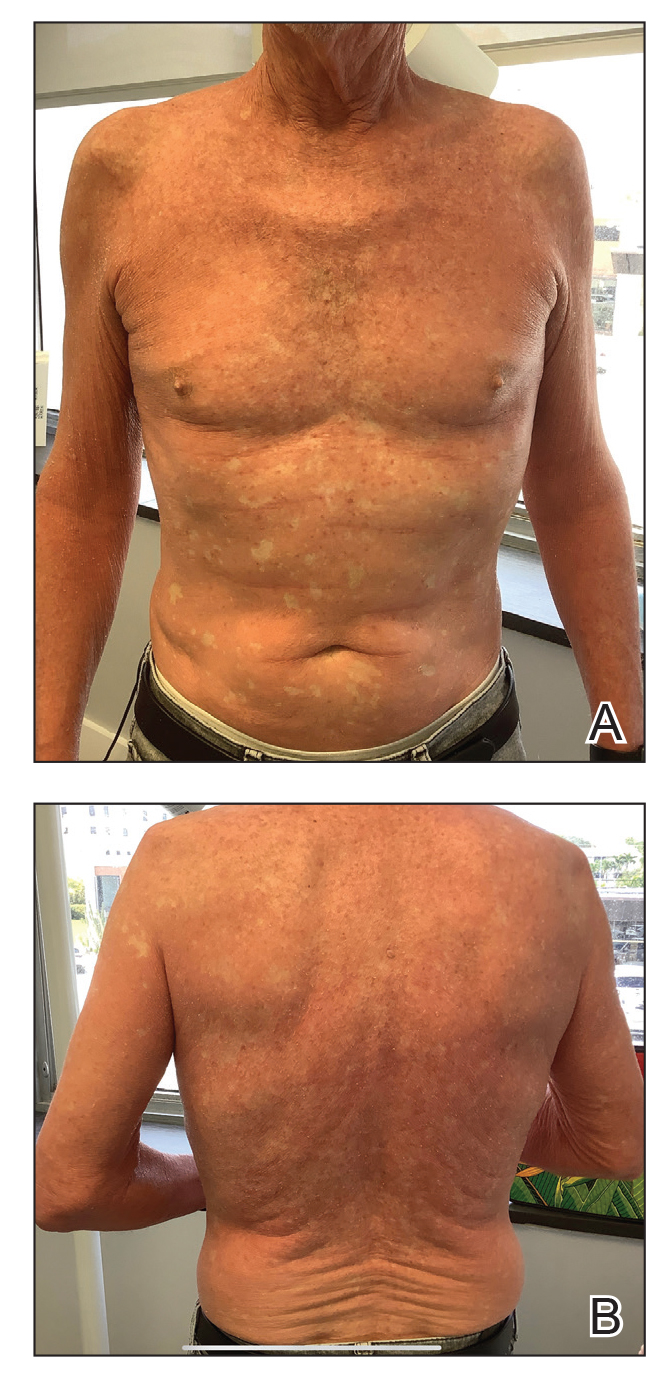
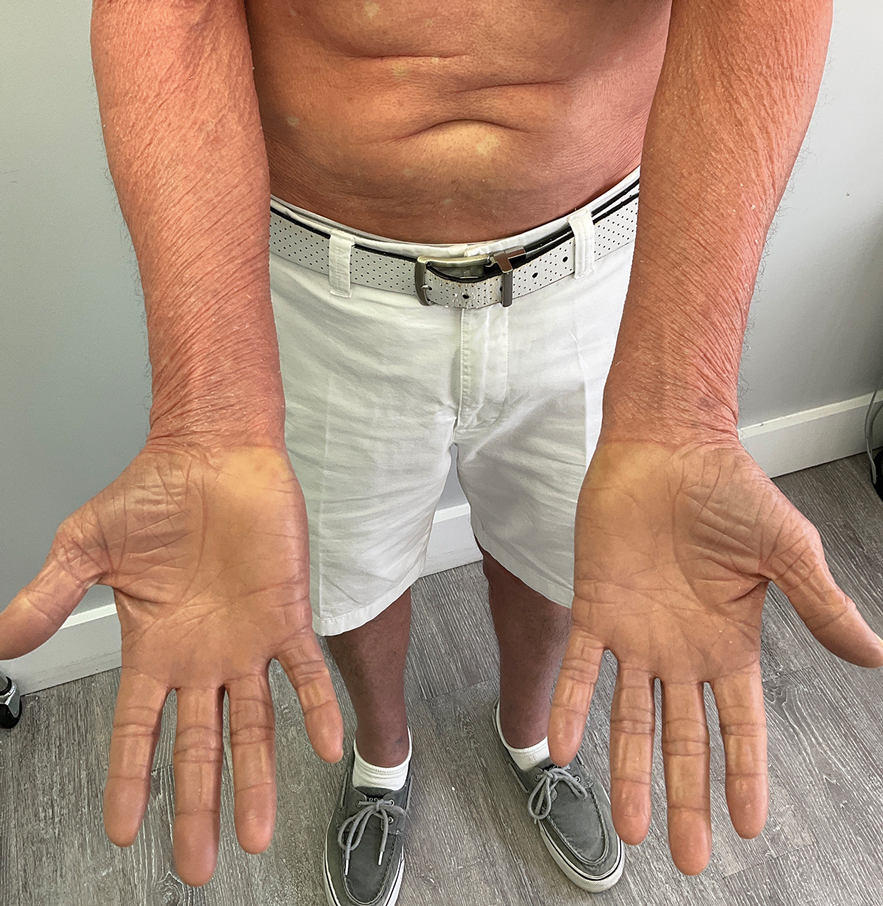
Oral retinoid therapy historically was considered first-line therapy for moderate to severe PRP. A systematic review (N=105) of retinoid therapies showed 83% of patients with PRP who were treated with acitretin plus biologic therapy had a favorable response, whereas only 36% of patients treated with acitretin as monotherapy had the same response, highlighting the importance of dual therapy.3 The use of ustekinumab, ixekizumab, and secukinumab (IL-17 inhibitors) for refractory PRP has been well documented, but a PubMed search of articles indexed for MEDLINE using the search terms risankizumab and pityriasis rubra pilaris yielded only 8 published cases of risankizumab for treatment of PRP.4-8 All patients were diagnosed with refractory PRP, and multiple treatment modalities failed.
Ustekinumab has been shown to create a rapid response and maintain it long term, especially in patients with type 1 PRP who did not respond to systemic therapies or anti–tumor necrosis factor α agents.2 An open-label, single-arm clinical trial found secukinumab was an effective therapy for PRP and demonstrated transcription heterogeneity of this dermatologic condition.9 The researchers proposed that some patients may respond to IL-17 inhibitors but others may not due to the differences in RNA molecules transcribed.9 Our patient demonstrated worsening of his condition with an IL-17 inhibitor but experienced remarkable improvement with risankizumab, an IL-23 inhibitor.
Risankizumab is indicated for the treatment of adults with moderate to severe plaque psoriasis. This humanized IgG1 monoclonal antibody targets the p19 subunit of IL-23, inhibiting its role in the pathogenic helper T cell (TH17) pathway. Research has shown that it is an efficacious and well-tolerated treatment modality for psoriatic conditions.10 It is well known that PRP and psoriasis have similar cytokine activations; therefore, we propose that combination therapy with risankizumab and acitretin may show promise for refractory PRP.
- Gelmetti C, Schiuma AA, Cerri D, et al. Pityriasis rubra pilaris in childhood: a long-term study of 29 cases. Pediatr Dermatol. 1986;3:446-451. doi:10.1111/j.1525-1470.1986.tb00648.x
- Moretta G, De Luca EV, Di Stefani A. Management of refractory pityriasis rubra pilaris: challenges and solutions. Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol. 2017;10:451-457. doi:10.2147/CCID.S124351
- Engelmann C, Elsner P, Miguel D. Treatment of pityriasis rubra pilaris type I: a systematic review. Eur J Dermatol. 2019;29:524-537. doi:10.1684/ejd.2019.3641
- Ricar J, Cetkovska P. Successful treatment of refractory extensive pityriasis rubra pilaris with risankizumab. Br J Dermatol. 2021;184:E148. doi:10.1111/bjd.19681
- Brocco E, Laffitte E. Risankizumab for pityriasis rubra pilaris. Clin Exp Dermatol. 2021;46:1322-1324. doi:10.1111/ced.14715
- Duarte B, Paiva Lopes MJ. Response to: ‘Successful treatment of refractory extensive pityriasis rubra pilaris with risankizumab.’ Br J Dermatol. 2021;185:235-236. doi:10.1111/bjd.20061
- Kromer C, Schön MP, Mössner R. Treatment of pityriasis rubra pilaris with risankizumab in two cases. J Dtsch Dermatol Ges. 2021;19:1207-1209. doi:10.1111/ddg.14504
- Kołt-Kamińska M, Osińska A, Kaznowska E, et al. Successful treatment of pityriasis rubra pilaris with risankizumab in children. Dermatol Ther (Heidelb). 2023;13:2431-2441. doi:10.1007/s13555-023-01005-y
- Boudreaux BW, Pincelli TP, Bhullar PK, et al. Secukinumab for the treatment of adult-onset pityriasis rubra pilaris: a single-arm clinical trial with transcriptomic analysis. Br J Dermatol. 2022;187:650-658. doi:10.1111/bjd.21708
- Blauvelt A, Leonardi CL, Gooderham M, et al. Efficacy and safety of continuous risankizumab therapy vs treatment withdrawal in patients with moderate to severe plaque psoriasis: a phase 3 randomized clinical trial. JAMA Dermatol. 2020;156:649-658. doi:10.1001/jamadermatol.2020.0723
To the Editor:
Pityriasis rubra pilaris (PRP) is a rare papulosquamous condition with an unknown pathogenesis and limited efficacy data, which can make treatment challenging. Some cases of PRP spontaneously resolve in a few months, which is most common in the pediatric population.1 Pityriasis rubra pilaris in adults is likely to persist for years, and spontaneous resolution is unpredictable. Randomized clinical trials are difficult to perform due to the rarity of PRP.
Although there is no cure and no standard protocol for treating PRP, systemic retinoids historically are considered first-line therapy for moderate to severe cases.2 Additional management approaches include symptomatic control with moisturizers and psychological support. Alternative systemic treatments for moderate to severe cases include methotrexate, phototherapy, and cyclosporine.2
Pityriasis rubra pilaris demonstrates a favorable response to methotrexate treatment, especially in type I cases; however, patients on this alternative therapy should be monitored for severe adverse effects (eg, hepatotoxicity, pancytopenia, pneumonitis).2 Phototherapy should be approached with caution. Narrowband UVB, UVA1, and psoralen plus UVA therapy have successfully treated PRP; however, the response is variable. In some cases, the opposite effect can occur, in which the condition is photoaggravated. Phototherapy is a valid alternative form of treatment when used in combination with acitretin, and a phototest should be performed prior to starting this regimen. Cyclosporine is another immunosuppressant that can be considered for PRP treatment, though there are limited data demonstrating its efficacy.2
The introduction of biologic agents has changed the treatment approach for many dermatologic diseases, including PRP. Given the similar features between psoriasis and PRP, the biologics prescribed for psoriasis therapy also are used for patients with PRP that is challenging to treat, such as anti–tumor necrosis factor α inhibitors and IL inhibitors—specifically IL-17 and IL-23. Remission has been achieved with the use of biologics in combination with retinoid therapy.2
Biologic therapies used for PRP effectively inhibit cytokines and reduce the overall inflammatory processes involved in the development of the scaly patches and plaques seen in this condition. However, most reported clinical experiences are case studies, and more research in the form of randomized clinical trials is needed to understand the efficacy and long-term effects of this form of treatment in PRP. We present a case of a patient with refractory adult subtype I PRP that was successfully treated with the IL-23 inhibitor risankizumab.
A 65-year-old man was referred to Florida Academic Dermatology Center (Coral Gables, Florida) with biopsy-proven PRP diagnosed 1 year prior. The patient reported experiencing a debilitating quality of life in the year since diagnosis (Figure 1). Treatment attempts with dupilumab, tralokinumab, intramuscular steroid injections, and topical corticosteroids had failed (Figure 2). Following evaluation at Florida Academic Dermatology Center, the patient was started on acitretin 25 mg every other day and received an initial subcutaneous injection of ixekizumab 160 mg (an IL-17 inhibitor) followed 2 weeks later by a second injection of 80 mg. After the 2 doses of ixekizumab, the patient’s condition worsened with the development of pinpoint hemorrhagic lesions. The medication was discontinued, and he was started on risankizumab 150 mg at the approved dosing regimen for plaque psoriasis in combination with the acitretin therapy. Prior to starting risankizumab, the affected body surface area (BSA) was 80%. At 1-month follow-up, he showed improvement with reduction in scaling and erythema and an affected BSA of 30% (Figure 3). At 4-month follow-up, he continued showing improvement with an affected BSA of 10% (Figure 4). Acitretin was discontinued, and the patient has been successfully maintained on risankizumab 150 mg/mL subcutaneous injections every 12 weeks since.




Oral retinoid therapy historically was considered first-line therapy for moderate to severe PRP. A systematic review (N=105) of retinoid therapies showed 83% of patients with PRP who were treated with acitretin plus biologic therapy had a favorable response, whereas only 36% of patients treated with acitretin as monotherapy had the same response, highlighting the importance of dual therapy.3 The use of ustekinumab, ixekizumab, and secukinumab (IL-17 inhibitors) for refractory PRP has been well documented, but a PubMed search of articles indexed for MEDLINE using the search terms risankizumab and pityriasis rubra pilaris yielded only 8 published cases of risankizumab for treatment of PRP.4-8 All patients were diagnosed with refractory PRP, and multiple treatment modalities failed.
Ustekinumab has been shown to create a rapid response and maintain it long term, especially in patients with type 1 PRP who did not respond to systemic therapies or anti–tumor necrosis factor α agents.2 An open-label, single-arm clinical trial found secukinumab was an effective therapy for PRP and demonstrated transcription heterogeneity of this dermatologic condition.9 The researchers proposed that some patients may respond to IL-17 inhibitors but others may not due to the differences in RNA molecules transcribed.9 Our patient demonstrated worsening of his condition with an IL-17 inhibitor but experienced remarkable improvement with risankizumab, an IL-23 inhibitor.
Risankizumab is indicated for the treatment of adults with moderate to severe plaque psoriasis. This humanized IgG1 monoclonal antibody targets the p19 subunit of IL-23, inhibiting its role in the pathogenic helper T cell (TH17) pathway. Research has shown that it is an efficacious and well-tolerated treatment modality for psoriatic conditions.10 It is well known that PRP and psoriasis have similar cytokine activations; therefore, we propose that combination therapy with risankizumab and acitretin may show promise for refractory PRP.
To the Editor:
Pityriasis rubra pilaris (PRP) is a rare papulosquamous condition with an unknown pathogenesis and limited efficacy data, which can make treatment challenging. Some cases of PRP spontaneously resolve in a few months, which is most common in the pediatric population.1 Pityriasis rubra pilaris in adults is likely to persist for years, and spontaneous resolution is unpredictable. Randomized clinical trials are difficult to perform due to the rarity of PRP.
Although there is no cure and no standard protocol for treating PRP, systemic retinoids historically are considered first-line therapy for moderate to severe cases.2 Additional management approaches include symptomatic control with moisturizers and psychological support. Alternative systemic treatments for moderate to severe cases include methotrexate, phototherapy, and cyclosporine.2
Pityriasis rubra pilaris demonstrates a favorable response to methotrexate treatment, especially in type I cases; however, patients on this alternative therapy should be monitored for severe adverse effects (eg, hepatotoxicity, pancytopenia, pneumonitis).2 Phototherapy should be approached with caution. Narrowband UVB, UVA1, and psoralen plus UVA therapy have successfully treated PRP; however, the response is variable. In some cases, the opposite effect can occur, in which the condition is photoaggravated. Phototherapy is a valid alternative form of treatment when used in combination with acitretin, and a phototest should be performed prior to starting this regimen. Cyclosporine is another immunosuppressant that can be considered for PRP treatment, though there are limited data demonstrating its efficacy.2
The introduction of biologic agents has changed the treatment approach for many dermatologic diseases, including PRP. Given the similar features between psoriasis and PRP, the biologics prescribed for psoriasis therapy also are used for patients with PRP that is challenging to treat, such as anti–tumor necrosis factor α inhibitors and IL inhibitors—specifically IL-17 and IL-23. Remission has been achieved with the use of biologics in combination with retinoid therapy.2
Biologic therapies used for PRP effectively inhibit cytokines and reduce the overall inflammatory processes involved in the development of the scaly patches and plaques seen in this condition. However, most reported clinical experiences are case studies, and more research in the form of randomized clinical trials is needed to understand the efficacy and long-term effects of this form of treatment in PRP. We present a case of a patient with refractory adult subtype I PRP that was successfully treated with the IL-23 inhibitor risankizumab.
A 65-year-old man was referred to Florida Academic Dermatology Center (Coral Gables, Florida) with biopsy-proven PRP diagnosed 1 year prior. The patient reported experiencing a debilitating quality of life in the year since diagnosis (Figure 1). Treatment attempts with dupilumab, tralokinumab, intramuscular steroid injections, and topical corticosteroids had failed (Figure 2). Following evaluation at Florida Academic Dermatology Center, the patient was started on acitretin 25 mg every other day and received an initial subcutaneous injection of ixekizumab 160 mg (an IL-17 inhibitor) followed 2 weeks later by a second injection of 80 mg. After the 2 doses of ixekizumab, the patient’s condition worsened with the development of pinpoint hemorrhagic lesions. The medication was discontinued, and he was started on risankizumab 150 mg at the approved dosing regimen for plaque psoriasis in combination with the acitretin therapy. Prior to starting risankizumab, the affected body surface area (BSA) was 80%. At 1-month follow-up, he showed improvement with reduction in scaling and erythema and an affected BSA of 30% (Figure 3). At 4-month follow-up, he continued showing improvement with an affected BSA of 10% (Figure 4). Acitretin was discontinued, and the patient has been successfully maintained on risankizumab 150 mg/mL subcutaneous injections every 12 weeks since.




Oral retinoid therapy historically was considered first-line therapy for moderate to severe PRP. A systematic review (N=105) of retinoid therapies showed 83% of patients with PRP who were treated with acitretin plus biologic therapy had a favorable response, whereas only 36% of patients treated with acitretin as monotherapy had the same response, highlighting the importance of dual therapy.3 The use of ustekinumab, ixekizumab, and secukinumab (IL-17 inhibitors) for refractory PRP has been well documented, but a PubMed search of articles indexed for MEDLINE using the search terms risankizumab and pityriasis rubra pilaris yielded only 8 published cases of risankizumab for treatment of PRP.4-8 All patients were diagnosed with refractory PRP, and multiple treatment modalities failed.
Ustekinumab has been shown to create a rapid response and maintain it long term, especially in patients with type 1 PRP who did not respond to systemic therapies or anti–tumor necrosis factor α agents.2 An open-label, single-arm clinical trial found secukinumab was an effective therapy for PRP and demonstrated transcription heterogeneity of this dermatologic condition.9 The researchers proposed that some patients may respond to IL-17 inhibitors but others may not due to the differences in RNA molecules transcribed.9 Our patient demonstrated worsening of his condition with an IL-17 inhibitor but experienced remarkable improvement with risankizumab, an IL-23 inhibitor.
Risankizumab is indicated for the treatment of adults with moderate to severe plaque psoriasis. This humanized IgG1 monoclonal antibody targets the p19 subunit of IL-23, inhibiting its role in the pathogenic helper T cell (TH17) pathway. Research has shown that it is an efficacious and well-tolerated treatment modality for psoriatic conditions.10 It is well known that PRP and psoriasis have similar cytokine activations; therefore, we propose that combination therapy with risankizumab and acitretin may show promise for refractory PRP.
- Gelmetti C, Schiuma AA, Cerri D, et al. Pityriasis rubra pilaris in childhood: a long-term study of 29 cases. Pediatr Dermatol. 1986;3:446-451. doi:10.1111/j.1525-1470.1986.tb00648.x
- Moretta G, De Luca EV, Di Stefani A. Management of refractory pityriasis rubra pilaris: challenges and solutions. Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol. 2017;10:451-457. doi:10.2147/CCID.S124351
- Engelmann C, Elsner P, Miguel D. Treatment of pityriasis rubra pilaris type I: a systematic review. Eur J Dermatol. 2019;29:524-537. doi:10.1684/ejd.2019.3641
- Ricar J, Cetkovska P. Successful treatment of refractory extensive pityriasis rubra pilaris with risankizumab. Br J Dermatol. 2021;184:E148. doi:10.1111/bjd.19681
- Brocco E, Laffitte E. Risankizumab for pityriasis rubra pilaris. Clin Exp Dermatol. 2021;46:1322-1324. doi:10.1111/ced.14715
- Duarte B, Paiva Lopes MJ. Response to: ‘Successful treatment of refractory extensive pityriasis rubra pilaris with risankizumab.’ Br J Dermatol. 2021;185:235-236. doi:10.1111/bjd.20061
- Kromer C, Schön MP, Mössner R. Treatment of pityriasis rubra pilaris with risankizumab in two cases. J Dtsch Dermatol Ges. 2021;19:1207-1209. doi:10.1111/ddg.14504
- Kołt-Kamińska M, Osińska A, Kaznowska E, et al. Successful treatment of pityriasis rubra pilaris with risankizumab in children. Dermatol Ther (Heidelb). 2023;13:2431-2441. doi:10.1007/s13555-023-01005-y
- Boudreaux BW, Pincelli TP, Bhullar PK, et al. Secukinumab for the treatment of adult-onset pityriasis rubra pilaris: a single-arm clinical trial with transcriptomic analysis. Br J Dermatol. 2022;187:650-658. doi:10.1111/bjd.21708
- Blauvelt A, Leonardi CL, Gooderham M, et al. Efficacy and safety of continuous risankizumab therapy vs treatment withdrawal in patients with moderate to severe plaque psoriasis: a phase 3 randomized clinical trial. JAMA Dermatol. 2020;156:649-658. doi:10.1001/jamadermatol.2020.0723
- Gelmetti C, Schiuma AA, Cerri D, et al. Pityriasis rubra pilaris in childhood: a long-term study of 29 cases. Pediatr Dermatol. 1986;3:446-451. doi:10.1111/j.1525-1470.1986.tb00648.x
- Moretta G, De Luca EV, Di Stefani A. Management of refractory pityriasis rubra pilaris: challenges and solutions. Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol. 2017;10:451-457. doi:10.2147/CCID.S124351
- Engelmann C, Elsner P, Miguel D. Treatment of pityriasis rubra pilaris type I: a systematic review. Eur J Dermatol. 2019;29:524-537. doi:10.1684/ejd.2019.3641
- Ricar J, Cetkovska P. Successful treatment of refractory extensive pityriasis rubra pilaris with risankizumab. Br J Dermatol. 2021;184:E148. doi:10.1111/bjd.19681
- Brocco E, Laffitte E. Risankizumab for pityriasis rubra pilaris. Clin Exp Dermatol. 2021;46:1322-1324. doi:10.1111/ced.14715
- Duarte B, Paiva Lopes MJ. Response to: ‘Successful treatment of refractory extensive pityriasis rubra pilaris with risankizumab.’ Br J Dermatol. 2021;185:235-236. doi:10.1111/bjd.20061
- Kromer C, Schön MP, Mössner R. Treatment of pityriasis rubra pilaris with risankizumab in two cases. J Dtsch Dermatol Ges. 2021;19:1207-1209. doi:10.1111/ddg.14504
- Kołt-Kamińska M, Osińska A, Kaznowska E, et al. Successful treatment of pityriasis rubra pilaris with risankizumab in children. Dermatol Ther (Heidelb). 2023;13:2431-2441. doi:10.1007/s13555-023-01005-y
- Boudreaux BW, Pincelli TP, Bhullar PK, et al. Secukinumab for the treatment of adult-onset pityriasis rubra pilaris: a single-arm clinical trial with transcriptomic analysis. Br J Dermatol. 2022;187:650-658. doi:10.1111/bjd.21708
- Blauvelt A, Leonardi CL, Gooderham M, et al. Efficacy and safety of continuous risankizumab therapy vs treatment withdrawal in patients with moderate to severe plaque psoriasis: a phase 3 randomized clinical trial. JAMA Dermatol. 2020;156:649-658. doi:10.1001/jamadermatol.2020.0723
Practice Points
- Pityriasis rubra pilaris (PRP) is a rare condition that is challenging to treat due to its unknown pathogenesis and limited efficacy data. Systemic retinoids historically were considered first-line therapy for moderate to severe cases of PRP.
- Biologics may be useful for refractory cases of PRP.
- Risankizumab is approved for moderate to severe plaque psoriasis and can be considered off-label for refractory PRP.
A Roadmap to Research Opportunities for Dermatology Residents
Dermatology remains one of the most competitive specialties in the residency match, with successful applicants demonstrating a well-rounded application reflecting not only their academic excellence but also their dedication to research, community service, and hands-on clinical experience.1 A growing emphasis on scholarly activities has made it crucial for applicants to stand out, with an increasing number opting to take gap years to engage in focused research endeavors.2 In highly competitive specialties such as dermatology, successful applicants now report more than 20 research items on average.3,4 This trend also is evident in primary care specialties, which have seen a 2- to 3-fold increase in reported research activities. The average unmatched applicant today lists more research items than the average matched applicant did a decade ago, underscoring the growing emphasis on scholarly activity.3
Ideally, graduate medical education should foster an environment of inquiry and scholarship, where residents develop new knowledge, evaluate research findings, and cultivate lifelong habits of inquiry. The Accreditation Council for Graduate Medical Education requires residents to engage in scholarship, such as case reports, research reviews, and original research.5 Research during residency has been linked to several benefits, including enhanced patient care through improved critical appraisal skills, clinical reasoning, and lifelong learning.6,7 Additionally, students and residents who publish research are more likely to achieve higher rank during residency and pursue careers in academic medicine, potentially helping to address the decline in clinician investigators.8,9 Publishing and presenting research also can enhance a residency program’s reputation, making it more attractive to competitive applicants, and may be beneficial for residents seeking jobs or fellowships.6
Dermatology residency programs vary in their structure and support for resident research. One survey revealed that many programs lack the necessary support, structure, and resources to effectively promote and maintain research training.1 Additionally, residents have less exposure to researchers who could serve as mentors due to the growing demands placed on attending physicians in teaching hospitals.10
The Research Arms Race
The growing emphasis on scholarly activity for residency and fellowship applicants coupled with the use of research productivity to differentiate candidates has led some to declare a “research arms race” in residency selection.3 As one author stated, “We need less research, better research, and research done for the right reasons.”11 Indeed, most articles authored by medical students are short reviews or case reports, with the majority (59% [207/350]) being cited zero times, according to one analysis.12 Given the variable research infrastructure between programs and the decreasing availability of research mentors despite the growing emphasis on scholarly activity, applicants face an unfortunate dilemma. Until the system changes, those who protest this research arms race by not engaging in substantial scholarly activity are less likely to match into competitive specialties. Thus, the race continues.
The Value of Mentorship
Resident research success is impacted by having an effective faculty research mentor.13 Although all medical research at the student or resident levels should be conducted with a faculty mentor to oversee it, finding a mentor can be challenging. If a resident’s program boasts a strong research infrastructure or prolific faculty, building relationships with potential mentors is a logical first step for residents wishing to engage in research; however, if suitable mentors are lacking, efforts should be made by residents to establish these connections elsewhere, such as attending society meetings to network with potential mentors and applying to formal mentorship programs (eg, the American Society for Dermatologic Surgery’s Preceptor Program, the Women’s Dermatologic Society’s Mentorship Award). Unsolicited email inquiries asking, “Hi Dr. X, my name is Y, and I was wondering if you have any research projects I could help with?” often go unanswered. Instead, consider emailing or approaching potential mentors with a more developed proposition, such as the following example:
Hello Dr. X, my name is Y. I have enjoyed reading your publications on A, which inspired me to think about B. I reviewed the literature and noticed a potential to enhance our current understanding on the topic. My team and I conducted a systematic review of the available literature and drafted a manuscript summarizing our findings. Given your expertise in this field, would you be willing to collaborate on this paper? We would be grateful for your critical eye, suggestions for improvement, and overall thoughts.
This approach demonstrates initiative, provides a clear plan, and shows respect for the mentor’s expertise, increasing the likelihood of a positive response and fruitful collaboration. Assuming the resident’s working draft meets the potential mentor’s basic expectations, such a display of initiative is likely to impress them, and they may then offer opportunities to engage in meaningful research projects in the future. Everyone benefits! These efforts to establish connections with mentors can pave the way to further collaboration and meaningful research opportunities for dermatology residents.
The Systematic Review: An Attractive Option For Residents
There are several potential avenues for students or residents interested in pursuing research. Case reports and case series are relatively easy to compile, can be completed quickly, and often require minimal guidance from a faculty mentor; however, case reports rank low in the research hierarchy. Conversely, prospective blinded clinical trials provide some of the highest-quality evidence available but are challenging to conduct without a practicing faculty member to provide a patient cohort, often require extensive funding, and may involve complex statistical analyses beyond the expertise of most students or residents. Additionally, they may take years to complete, often extending beyond residency or fellowship application deadlines.
Most medical applicants likely hold at least some hesitation in churning out vast amounts of low-quality research merely to boost their publication count for the match process. Ideally, those who pursue scholarly activity should be driven by a genuine desire to contribute meaningfully to the medical literature. One particularly valuable avenue for trainees wishing to engage in research is the systematic review, which aims to identify, evaluate, and summarize the findings of all relevant individual studies regarding a research topic and answer a focused question. If performed thoughtfully, a systematic review can meaningfully contribute to the medical literature without requiring access to a prospectively followed cohort of patients or the constant supervision of a faculty mentor. Sure, systematic reviews may not be as robust as prospective cohort clinical trials, but they often provide comprehensive insights and are considered valuable contributions to evidence-based medicine. With the help of co-residents or medical students, a medical reference librarian, and a statistician—along with a working understanding of universally accepted quality measures—a resident physician and their team can produce a systematic review that ultimately may merit publication in a top-tier medical journal.
The remainder of this column will outline a streamlined approach to the systematic review writing process, specifically tailored for medical residents who may not have affiliations to a prolific research department or established relationships with faculty mentors in their field of interest. The aim is to offer a basic framework to help residents navigate the complexities of conducting and writing a high-quality, impactful systematic review. It is important to emphasize that resident research should always be conducted under the guidance of a faculty mentor, and this approach is not intended to encourage independent research and publication by residents. Instead, it provides steps that can be undertaken with a foundational understanding of accepted principles, allowing residents to compile a working draft of a manuscript in collaboration with a trusted faculty mentor.
The Systematic Review: A Simple Approach
Step 1: Choose a Topic—Once a resident has decided to embark on conducting a systematic review, the first step is to choose a topic, which requires consideration of several factors to ensure relevance, feasibility, and impact. Begin by identifying areas of clinical uncertainty or controversy in which a comprehensive synthesis of the literature could provide valuable insights. Often, such a topic can be gleaned from the conclusion section of other primary studies; statements such as “further study is needed to determine the efficacy of X” or “systematic reviews would be beneficial to ascertaining the impact of Y” may be a great place to start.
Next, ensure that sufficient primary studies exist to support a robust review or meta-analysis by conducting a preliminary literature search, which will confirm that the chosen topic is both researchable and relevant. A narrow, focused, well-defined topic likely will prove more feasible to review than a broad, ill-defined one. Once a topic is selected, it is advisable to discuss it with a faculty mentor before starting the literature search to ensure the topic’s feasibility and clinical relevance, helping to guide your research in a meaningful direction.
When deciding between a systematic review and a meta-analysis, the nature of the research question is an influential factor. A systematic review is particularly suitable for addressing broad questions or topics when the aim is to summarize and synthesize all relevant research studies; for example, a systematic review may investigate the various treatment options for atopic dermatitis and their efficacy, which allows for a comprehensive overview of the available treatments—both the interventions and the outcomes. In contrast, a meta-analysis is ideal for collecting and statistically combining quantitative data from multiple primary studies, provided there are enough relevant studies available in the literature.
Step 2: Build a Team—Recruiting a skilled librarian to assist with Medical Subject Headings (MeSH) terms and retrieving relevant papers is crucial for conducting a high-quality systematic review or meta-analysis. Medical librarians specializing in health sciences enhance the efficiency, comprehensiveness, and reliability of your literature search, substantially boosting your work’s credibility. These librarians are well versed in medical databases such as PubMed and Embase. Begin by contacting your institution’s library services, as there often are valuable resources and personnel available to assist you. Personally, I was surprised to find a librarian at my institution specifically dedicated to helping medical residents with such projects! These professionals are eager to help, and if provided with the scope and goal of your project, they can deliver literature search results in a digestible format. Similarly, seeking the expertise of a medical statistician is crucial to the accuracy and legitimacy of your study. In your final paper, it is important to recognize the contributions of the librarian and statistician, either as co-authors or in the acknowledgments section.
In addition, recruiting colleagues or medical students can be an effective strategy to make the project more feasible and offer collaborative benefits for all parties involved. Given the growing emphasis on research for residency and fellowship admissions, there usually is no shortage of motivated volunteers.
Next, identify the software tool you will use for your systematic review. Options range from simple spreadsheets such as Microsoft Excel to reference managers such as EndNote or Mendeley or dedicated systematic review tools. Academic institutions may subscribe to paid services such as Covidence (https://www.covidence.org), or you can utilize free alternatives such as Rayyan (https://www.rayyan.ai). Investing time in learning to navigate dedicated systematic review software can greatly enhance efficiency and reduce frustrations compared to more basic methods. Ultimately, staying organized, thorough, and committed is key.
Step 3: Conduct the Literature Review—At this point, your research topic has been decided, a medical reference librarian has provided the results of a comprehensive literature search, and a software tool has been chosen. The next task is to read hundreds or thousands of papers—easy, right? With your dedicated team assembled, the workload can be divided and conquered. The first step involves screening out duplicate and irrelevant studies based on titles and abstracts. Next, review the remaining papers in more detail. Those that pass this preliminary screen should be read in their entirety, and only the papers relevant to the research topic should be included in the final synthesis. If there are uncertainties about a study’s relevance, consulting a faculty mentor is advisable. To ensure the systematic review is as thorough as possible, pay special attention to the references section of each paper, as cited references can reveal relevant studies that may have been missed in the literature search.
Once all relevant papers are compiled and read, the relevant data points should be extracted and imputed into a data sheet. Collaborating with a medical statistician is crucial at this stage, as they can provide guidance on the most effective ways to structure and input data. After all studies are included, the relevant statistical analyses on the resultant dataset can be run.
Step 4: Write the Paper—In 2020, the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses (PRISMA) statement was developed to ensure transparent and complete reporting of systematic reviews. A full discussion of PRISMA guidelines is beyond the scope of this paper; Page et al14 provided a summary, checklist, and flow diagram that is available online (https://www.prisma-statement.org). Following the PRISMA checklist and guidelines ensures a high-quality, transparent, and reliable systematic review. These guidelines not only help streamline and simplify the writing process but also enhance its efficiency and effectiveness. Discovering the PRISMA checklist can be transformative, providing a valuable roadmap that guides the author through each step of the reporting process, helping to avoid common pitfalls. This structured approach ultimately leads to a more comprehensive and trustworthy review.
Step 5: Make Finishing Touches—At this stage in the systematic review process, the studies have been compiled and thoroughly analyzed and the statistical analysis has been conducted. The results have been organized within a structured framework following the PRISMA checklist. With these steps completed, the next task is to finalize the manuscript and seek a final review from the senior author or faculty mentor. To streamline this process, it is beneficial to adhere to the formatting guidelines of the specific medical journal you intend to submit to. Check the author guidelines on the journal’s website and review recent systematic reviews published there as a reference. Even if you have not chosen a journal yet, formatting your manuscript according to a prestigious journal’s general style provides a strong foundation that can be easily adapted to fit another journal’s requirements if necessary.
Final Thoughts
Designing and conducting a systematic review is no easy task, but it can be a valuable skill for dermatology residents aiming to contribute meaningfully to the medical literature. The process of compiling a systematic review offers an opportunity for developing critical research skills, from formulating a research question to synthesizing evidence and presenting findings in a clear methodical way. Engaging in systematic review writing not only enhances the resident’s understanding of a particular topic but also demonstrates a commitment to scholarly activity—a key factor in an increasingly competitive residency and fellowship application environment.
The basic steps outlined in this article are just one way in which residents can begin to navigate the complexities of medical research, specifically the systematic review process. By assembling a supportive team, utilizing available resources, and adhering to established guidelines such as PRISMA, one can produce a high-quality, impactful review. Ultimately, the systematic review process is not just about publication—it is about fostering a habit of inquiry, improving patient care, and contributing to the ever-evolving field of medicine. With dedication and collaboration, even the most challenging aspects of research can be tackled, paving the way for future opportunities and professional growth. In this way, perhaps one day the spirit of the “research race” can shift from a frantic sprint to a graceful marathon, where each mile is run with heart and every step is filled with purpose.
- Anand P, Szeto MD, Flaten H, et al. Dermatology residency research policies: a 2021 national survey. Int J Womens Dermatol. 2021;7:787-792.
- Costello CM, Harvey JA, Besch-Stokes JG, et al. The role research gap years play in a successful dermatology match. Int J Dermatol. 2022;61:226-230.
- Elliott B, Carmody JB. Publish or perish: the research arms race in residency selection. J Grad Med Educ. 2023;15:524-527.
- MedSchoolCoach. How competitive is a dermatology residency? Updated in 2023. ProspectiveDoctor website. Accessed August 22, 2024. https://www.prospectivedoctor.com/how-competitive-is-a-dermatology-residency/#:~:text=Statistics%20on%20the%20Dermatology%20Match,applied%2C%20169%20did%20not%20match
- ACGME program requirements for graduate medical education in dermatology. Accreditation Council for Graduate Medical Education Updated July 1, 2023. Accessed August 22, 2024. https://www.acgme.org/globalassets/pfassets/programrequirements/080_dermatology_2023.pdf
- Bhuiya T, Makaryus AN. The importance of engaging in scientific research during medical training. Int J Angiol. 2023;32:153-157.
- Seaburg LA, Wang AT, West CP, et al. Associations between resident physicians’ publications and clinical performance during residency training. BMC Med Educ. 2016;16:22.
- West CP, Halvorsen AJ, McDonald FS. Scholarship during residency training: a controlled comparison study. Am J Med. 2011;124:983-987.e1.
- Bhattacharya SD, Williams JB, De La Fuente SG, et al. Does protected research time during general surgery training contribute to graduates’ career choice? Am Surg. 2011;77:907-910.
- Kralovec PD, Miller JA, Wellikson L, et al. The status of hospital medicine groups in the United States. J Hosp Med. 2006;1:75-80.
- Altman DG. The scandal of poor medical research. BMJ. 1994;308:283-284.
- Wickramasinghe DP, Perera CS, Senarathna S, et al. Patterns and trends of medical student research. BMC Med Educ. 2013;13:175.
- Ercan-Fang NG, Mahmoud MA, Cottrell C, et al. Best practices in resident research—a national survey of high functioning internal medicine residency programs in resident research in USA. Am J Med Sci. 2021;361:23-29.
- Page MJ, Moher D, Bossuyt PM, et al. PRISMA 2020 explanation and elaboration: updated guidance and exemplars for reporting systematic reviews. BMJ. 2021;372.
Dermatology remains one of the most competitive specialties in the residency match, with successful applicants demonstrating a well-rounded application reflecting not only their academic excellence but also their dedication to research, community service, and hands-on clinical experience.1 A growing emphasis on scholarly activities has made it crucial for applicants to stand out, with an increasing number opting to take gap years to engage in focused research endeavors.2 In highly competitive specialties such as dermatology, successful applicants now report more than 20 research items on average.3,4 This trend also is evident in primary care specialties, which have seen a 2- to 3-fold increase in reported research activities. The average unmatched applicant today lists more research items than the average matched applicant did a decade ago, underscoring the growing emphasis on scholarly activity.3
Ideally, graduate medical education should foster an environment of inquiry and scholarship, where residents develop new knowledge, evaluate research findings, and cultivate lifelong habits of inquiry. The Accreditation Council for Graduate Medical Education requires residents to engage in scholarship, such as case reports, research reviews, and original research.5 Research during residency has been linked to several benefits, including enhanced patient care through improved critical appraisal skills, clinical reasoning, and lifelong learning.6,7 Additionally, students and residents who publish research are more likely to achieve higher rank during residency and pursue careers in academic medicine, potentially helping to address the decline in clinician investigators.8,9 Publishing and presenting research also can enhance a residency program’s reputation, making it more attractive to competitive applicants, and may be beneficial for residents seeking jobs or fellowships.6
Dermatology residency programs vary in their structure and support for resident research. One survey revealed that many programs lack the necessary support, structure, and resources to effectively promote and maintain research training.1 Additionally, residents have less exposure to researchers who could serve as mentors due to the growing demands placed on attending physicians in teaching hospitals.10
The Research Arms Race
The growing emphasis on scholarly activity for residency and fellowship applicants coupled with the use of research productivity to differentiate candidates has led some to declare a “research arms race” in residency selection.3 As one author stated, “We need less research, better research, and research done for the right reasons.”11 Indeed, most articles authored by medical students are short reviews or case reports, with the majority (59% [207/350]) being cited zero times, according to one analysis.12 Given the variable research infrastructure between programs and the decreasing availability of research mentors despite the growing emphasis on scholarly activity, applicants face an unfortunate dilemma. Until the system changes, those who protest this research arms race by not engaging in substantial scholarly activity are less likely to match into competitive specialties. Thus, the race continues.
The Value of Mentorship
Resident research success is impacted by having an effective faculty research mentor.13 Although all medical research at the student or resident levels should be conducted with a faculty mentor to oversee it, finding a mentor can be challenging. If a resident’s program boasts a strong research infrastructure or prolific faculty, building relationships with potential mentors is a logical first step for residents wishing to engage in research; however, if suitable mentors are lacking, efforts should be made by residents to establish these connections elsewhere, such as attending society meetings to network with potential mentors and applying to formal mentorship programs (eg, the American Society for Dermatologic Surgery’s Preceptor Program, the Women’s Dermatologic Society’s Mentorship Award). Unsolicited email inquiries asking, “Hi Dr. X, my name is Y, and I was wondering if you have any research projects I could help with?” often go unanswered. Instead, consider emailing or approaching potential mentors with a more developed proposition, such as the following example:
Hello Dr. X, my name is Y. I have enjoyed reading your publications on A, which inspired me to think about B. I reviewed the literature and noticed a potential to enhance our current understanding on the topic. My team and I conducted a systematic review of the available literature and drafted a manuscript summarizing our findings. Given your expertise in this field, would you be willing to collaborate on this paper? We would be grateful for your critical eye, suggestions for improvement, and overall thoughts.
This approach demonstrates initiative, provides a clear plan, and shows respect for the mentor’s expertise, increasing the likelihood of a positive response and fruitful collaboration. Assuming the resident’s working draft meets the potential mentor’s basic expectations, such a display of initiative is likely to impress them, and they may then offer opportunities to engage in meaningful research projects in the future. Everyone benefits! These efforts to establish connections with mentors can pave the way to further collaboration and meaningful research opportunities for dermatology residents.
The Systematic Review: An Attractive Option For Residents
There are several potential avenues for students or residents interested in pursuing research. Case reports and case series are relatively easy to compile, can be completed quickly, and often require minimal guidance from a faculty mentor; however, case reports rank low in the research hierarchy. Conversely, prospective blinded clinical trials provide some of the highest-quality evidence available but are challenging to conduct without a practicing faculty member to provide a patient cohort, often require extensive funding, and may involve complex statistical analyses beyond the expertise of most students or residents. Additionally, they may take years to complete, often extending beyond residency or fellowship application deadlines.
Most medical applicants likely hold at least some hesitation in churning out vast amounts of low-quality research merely to boost their publication count for the match process. Ideally, those who pursue scholarly activity should be driven by a genuine desire to contribute meaningfully to the medical literature. One particularly valuable avenue for trainees wishing to engage in research is the systematic review, which aims to identify, evaluate, and summarize the findings of all relevant individual studies regarding a research topic and answer a focused question. If performed thoughtfully, a systematic review can meaningfully contribute to the medical literature without requiring access to a prospectively followed cohort of patients or the constant supervision of a faculty mentor. Sure, systematic reviews may not be as robust as prospective cohort clinical trials, but they often provide comprehensive insights and are considered valuable contributions to evidence-based medicine. With the help of co-residents or medical students, a medical reference librarian, and a statistician—along with a working understanding of universally accepted quality measures—a resident physician and their team can produce a systematic review that ultimately may merit publication in a top-tier medical journal.
The remainder of this column will outline a streamlined approach to the systematic review writing process, specifically tailored for medical residents who may not have affiliations to a prolific research department or established relationships with faculty mentors in their field of interest. The aim is to offer a basic framework to help residents navigate the complexities of conducting and writing a high-quality, impactful systematic review. It is important to emphasize that resident research should always be conducted under the guidance of a faculty mentor, and this approach is not intended to encourage independent research and publication by residents. Instead, it provides steps that can be undertaken with a foundational understanding of accepted principles, allowing residents to compile a working draft of a manuscript in collaboration with a trusted faculty mentor.
The Systematic Review: A Simple Approach
Step 1: Choose a Topic—Once a resident has decided to embark on conducting a systematic review, the first step is to choose a topic, which requires consideration of several factors to ensure relevance, feasibility, and impact. Begin by identifying areas of clinical uncertainty or controversy in which a comprehensive synthesis of the literature could provide valuable insights. Often, such a topic can be gleaned from the conclusion section of other primary studies; statements such as “further study is needed to determine the efficacy of X” or “systematic reviews would be beneficial to ascertaining the impact of Y” may be a great place to start.
Next, ensure that sufficient primary studies exist to support a robust review or meta-analysis by conducting a preliminary literature search, which will confirm that the chosen topic is both researchable and relevant. A narrow, focused, well-defined topic likely will prove more feasible to review than a broad, ill-defined one. Once a topic is selected, it is advisable to discuss it with a faculty mentor before starting the literature search to ensure the topic’s feasibility and clinical relevance, helping to guide your research in a meaningful direction.
When deciding between a systematic review and a meta-analysis, the nature of the research question is an influential factor. A systematic review is particularly suitable for addressing broad questions or topics when the aim is to summarize and synthesize all relevant research studies; for example, a systematic review may investigate the various treatment options for atopic dermatitis and their efficacy, which allows for a comprehensive overview of the available treatments—both the interventions and the outcomes. In contrast, a meta-analysis is ideal for collecting and statistically combining quantitative data from multiple primary studies, provided there are enough relevant studies available in the literature.
Step 2: Build a Team—Recruiting a skilled librarian to assist with Medical Subject Headings (MeSH) terms and retrieving relevant papers is crucial for conducting a high-quality systematic review or meta-analysis. Medical librarians specializing in health sciences enhance the efficiency, comprehensiveness, and reliability of your literature search, substantially boosting your work’s credibility. These librarians are well versed in medical databases such as PubMed and Embase. Begin by contacting your institution’s library services, as there often are valuable resources and personnel available to assist you. Personally, I was surprised to find a librarian at my institution specifically dedicated to helping medical residents with such projects! These professionals are eager to help, and if provided with the scope and goal of your project, they can deliver literature search results in a digestible format. Similarly, seeking the expertise of a medical statistician is crucial to the accuracy and legitimacy of your study. In your final paper, it is important to recognize the contributions of the librarian and statistician, either as co-authors or in the acknowledgments section.
In addition, recruiting colleagues or medical students can be an effective strategy to make the project more feasible and offer collaborative benefits for all parties involved. Given the growing emphasis on research for residency and fellowship admissions, there usually is no shortage of motivated volunteers.
Next, identify the software tool you will use for your systematic review. Options range from simple spreadsheets such as Microsoft Excel to reference managers such as EndNote or Mendeley or dedicated systematic review tools. Academic institutions may subscribe to paid services such as Covidence (https://www.covidence.org), or you can utilize free alternatives such as Rayyan (https://www.rayyan.ai). Investing time in learning to navigate dedicated systematic review software can greatly enhance efficiency and reduce frustrations compared to more basic methods. Ultimately, staying organized, thorough, and committed is key.
Step 3: Conduct the Literature Review—At this point, your research topic has been decided, a medical reference librarian has provided the results of a comprehensive literature search, and a software tool has been chosen. The next task is to read hundreds or thousands of papers—easy, right? With your dedicated team assembled, the workload can be divided and conquered. The first step involves screening out duplicate and irrelevant studies based on titles and abstracts. Next, review the remaining papers in more detail. Those that pass this preliminary screen should be read in their entirety, and only the papers relevant to the research topic should be included in the final synthesis. If there are uncertainties about a study’s relevance, consulting a faculty mentor is advisable. To ensure the systematic review is as thorough as possible, pay special attention to the references section of each paper, as cited references can reveal relevant studies that may have been missed in the literature search.
Once all relevant papers are compiled and read, the relevant data points should be extracted and imputed into a data sheet. Collaborating with a medical statistician is crucial at this stage, as they can provide guidance on the most effective ways to structure and input data. After all studies are included, the relevant statistical analyses on the resultant dataset can be run.
Step 4: Write the Paper—In 2020, the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses (PRISMA) statement was developed to ensure transparent and complete reporting of systematic reviews. A full discussion of PRISMA guidelines is beyond the scope of this paper; Page et al14 provided a summary, checklist, and flow diagram that is available online (https://www.prisma-statement.org). Following the PRISMA checklist and guidelines ensures a high-quality, transparent, and reliable systematic review. These guidelines not only help streamline and simplify the writing process but also enhance its efficiency and effectiveness. Discovering the PRISMA checklist can be transformative, providing a valuable roadmap that guides the author through each step of the reporting process, helping to avoid common pitfalls. This structured approach ultimately leads to a more comprehensive and trustworthy review.
Step 5: Make Finishing Touches—At this stage in the systematic review process, the studies have been compiled and thoroughly analyzed and the statistical analysis has been conducted. The results have been organized within a structured framework following the PRISMA checklist. With these steps completed, the next task is to finalize the manuscript and seek a final review from the senior author or faculty mentor. To streamline this process, it is beneficial to adhere to the formatting guidelines of the specific medical journal you intend to submit to. Check the author guidelines on the journal’s website and review recent systematic reviews published there as a reference. Even if you have not chosen a journal yet, formatting your manuscript according to a prestigious journal’s general style provides a strong foundation that can be easily adapted to fit another journal’s requirements if necessary.
Final Thoughts
Designing and conducting a systematic review is no easy task, but it can be a valuable skill for dermatology residents aiming to contribute meaningfully to the medical literature. The process of compiling a systematic review offers an opportunity for developing critical research skills, from formulating a research question to synthesizing evidence and presenting findings in a clear methodical way. Engaging in systematic review writing not only enhances the resident’s understanding of a particular topic but also demonstrates a commitment to scholarly activity—a key factor in an increasingly competitive residency and fellowship application environment.
The basic steps outlined in this article are just one way in which residents can begin to navigate the complexities of medical research, specifically the systematic review process. By assembling a supportive team, utilizing available resources, and adhering to established guidelines such as PRISMA, one can produce a high-quality, impactful review. Ultimately, the systematic review process is not just about publication—it is about fostering a habit of inquiry, improving patient care, and contributing to the ever-evolving field of medicine. With dedication and collaboration, even the most challenging aspects of research can be tackled, paving the way for future opportunities and professional growth. In this way, perhaps one day the spirit of the “research race” can shift from a frantic sprint to a graceful marathon, where each mile is run with heart and every step is filled with purpose.
Dermatology remains one of the most competitive specialties in the residency match, with successful applicants demonstrating a well-rounded application reflecting not only their academic excellence but also their dedication to research, community service, and hands-on clinical experience.1 A growing emphasis on scholarly activities has made it crucial for applicants to stand out, with an increasing number opting to take gap years to engage in focused research endeavors.2 In highly competitive specialties such as dermatology, successful applicants now report more than 20 research items on average.3,4 This trend also is evident in primary care specialties, which have seen a 2- to 3-fold increase in reported research activities. The average unmatched applicant today lists more research items than the average matched applicant did a decade ago, underscoring the growing emphasis on scholarly activity.3
Ideally, graduate medical education should foster an environment of inquiry and scholarship, where residents develop new knowledge, evaluate research findings, and cultivate lifelong habits of inquiry. The Accreditation Council for Graduate Medical Education requires residents to engage in scholarship, such as case reports, research reviews, and original research.5 Research during residency has been linked to several benefits, including enhanced patient care through improved critical appraisal skills, clinical reasoning, and lifelong learning.6,7 Additionally, students and residents who publish research are more likely to achieve higher rank during residency and pursue careers in academic medicine, potentially helping to address the decline in clinician investigators.8,9 Publishing and presenting research also can enhance a residency program’s reputation, making it more attractive to competitive applicants, and may be beneficial for residents seeking jobs or fellowships.6
Dermatology residency programs vary in their structure and support for resident research. One survey revealed that many programs lack the necessary support, structure, and resources to effectively promote and maintain research training.1 Additionally, residents have less exposure to researchers who could serve as mentors due to the growing demands placed on attending physicians in teaching hospitals.10
The Research Arms Race
The growing emphasis on scholarly activity for residency and fellowship applicants coupled with the use of research productivity to differentiate candidates has led some to declare a “research arms race” in residency selection.3 As one author stated, “We need less research, better research, and research done for the right reasons.”11 Indeed, most articles authored by medical students are short reviews or case reports, with the majority (59% [207/350]) being cited zero times, according to one analysis.12 Given the variable research infrastructure between programs and the decreasing availability of research mentors despite the growing emphasis on scholarly activity, applicants face an unfortunate dilemma. Until the system changes, those who protest this research arms race by not engaging in substantial scholarly activity are less likely to match into competitive specialties. Thus, the race continues.
The Value of Mentorship
Resident research success is impacted by having an effective faculty research mentor.13 Although all medical research at the student or resident levels should be conducted with a faculty mentor to oversee it, finding a mentor can be challenging. If a resident’s program boasts a strong research infrastructure or prolific faculty, building relationships with potential mentors is a logical first step for residents wishing to engage in research; however, if suitable mentors are lacking, efforts should be made by residents to establish these connections elsewhere, such as attending society meetings to network with potential mentors and applying to formal mentorship programs (eg, the American Society for Dermatologic Surgery’s Preceptor Program, the Women’s Dermatologic Society’s Mentorship Award). Unsolicited email inquiries asking, “Hi Dr. X, my name is Y, and I was wondering if you have any research projects I could help with?” often go unanswered. Instead, consider emailing or approaching potential mentors with a more developed proposition, such as the following example:
Hello Dr. X, my name is Y. I have enjoyed reading your publications on A, which inspired me to think about B. I reviewed the literature and noticed a potential to enhance our current understanding on the topic. My team and I conducted a systematic review of the available literature and drafted a manuscript summarizing our findings. Given your expertise in this field, would you be willing to collaborate on this paper? We would be grateful for your critical eye, suggestions for improvement, and overall thoughts.
This approach demonstrates initiative, provides a clear plan, and shows respect for the mentor’s expertise, increasing the likelihood of a positive response and fruitful collaboration. Assuming the resident’s working draft meets the potential mentor’s basic expectations, such a display of initiative is likely to impress them, and they may then offer opportunities to engage in meaningful research projects in the future. Everyone benefits! These efforts to establish connections with mentors can pave the way to further collaboration and meaningful research opportunities for dermatology residents.
The Systematic Review: An Attractive Option For Residents
There are several potential avenues for students or residents interested in pursuing research. Case reports and case series are relatively easy to compile, can be completed quickly, and often require minimal guidance from a faculty mentor; however, case reports rank low in the research hierarchy. Conversely, prospective blinded clinical trials provide some of the highest-quality evidence available but are challenging to conduct without a practicing faculty member to provide a patient cohort, often require extensive funding, and may involve complex statistical analyses beyond the expertise of most students or residents. Additionally, they may take years to complete, often extending beyond residency or fellowship application deadlines.
Most medical applicants likely hold at least some hesitation in churning out vast amounts of low-quality research merely to boost their publication count for the match process. Ideally, those who pursue scholarly activity should be driven by a genuine desire to contribute meaningfully to the medical literature. One particularly valuable avenue for trainees wishing to engage in research is the systematic review, which aims to identify, evaluate, and summarize the findings of all relevant individual studies regarding a research topic and answer a focused question. If performed thoughtfully, a systematic review can meaningfully contribute to the medical literature without requiring access to a prospectively followed cohort of patients or the constant supervision of a faculty mentor. Sure, systematic reviews may not be as robust as prospective cohort clinical trials, but they often provide comprehensive insights and are considered valuable contributions to evidence-based medicine. With the help of co-residents or medical students, a medical reference librarian, and a statistician—along with a working understanding of universally accepted quality measures—a resident physician and their team can produce a systematic review that ultimately may merit publication in a top-tier medical journal.
The remainder of this column will outline a streamlined approach to the systematic review writing process, specifically tailored for medical residents who may not have affiliations to a prolific research department or established relationships with faculty mentors in their field of interest. The aim is to offer a basic framework to help residents navigate the complexities of conducting and writing a high-quality, impactful systematic review. It is important to emphasize that resident research should always be conducted under the guidance of a faculty mentor, and this approach is not intended to encourage independent research and publication by residents. Instead, it provides steps that can be undertaken with a foundational understanding of accepted principles, allowing residents to compile a working draft of a manuscript in collaboration with a trusted faculty mentor.
The Systematic Review: A Simple Approach
Step 1: Choose a Topic—Once a resident has decided to embark on conducting a systematic review, the first step is to choose a topic, which requires consideration of several factors to ensure relevance, feasibility, and impact. Begin by identifying areas of clinical uncertainty or controversy in which a comprehensive synthesis of the literature could provide valuable insights. Often, such a topic can be gleaned from the conclusion section of other primary studies; statements such as “further study is needed to determine the efficacy of X” or “systematic reviews would be beneficial to ascertaining the impact of Y” may be a great place to start.
Next, ensure that sufficient primary studies exist to support a robust review or meta-analysis by conducting a preliminary literature search, which will confirm that the chosen topic is both researchable and relevant. A narrow, focused, well-defined topic likely will prove more feasible to review than a broad, ill-defined one. Once a topic is selected, it is advisable to discuss it with a faculty mentor before starting the literature search to ensure the topic’s feasibility and clinical relevance, helping to guide your research in a meaningful direction.
When deciding between a systematic review and a meta-analysis, the nature of the research question is an influential factor. A systematic review is particularly suitable for addressing broad questions or topics when the aim is to summarize and synthesize all relevant research studies; for example, a systematic review may investigate the various treatment options for atopic dermatitis and their efficacy, which allows for a comprehensive overview of the available treatments—both the interventions and the outcomes. In contrast, a meta-analysis is ideal for collecting and statistically combining quantitative data from multiple primary studies, provided there are enough relevant studies available in the literature.
Step 2: Build a Team—Recruiting a skilled librarian to assist with Medical Subject Headings (MeSH) terms and retrieving relevant papers is crucial for conducting a high-quality systematic review or meta-analysis. Medical librarians specializing in health sciences enhance the efficiency, comprehensiveness, and reliability of your literature search, substantially boosting your work’s credibility. These librarians are well versed in medical databases such as PubMed and Embase. Begin by contacting your institution’s library services, as there often are valuable resources and personnel available to assist you. Personally, I was surprised to find a librarian at my institution specifically dedicated to helping medical residents with such projects! These professionals are eager to help, and if provided with the scope and goal of your project, they can deliver literature search results in a digestible format. Similarly, seeking the expertise of a medical statistician is crucial to the accuracy and legitimacy of your study. In your final paper, it is important to recognize the contributions of the librarian and statistician, either as co-authors or in the acknowledgments section.
In addition, recruiting colleagues or medical students can be an effective strategy to make the project more feasible and offer collaborative benefits for all parties involved. Given the growing emphasis on research for residency and fellowship admissions, there usually is no shortage of motivated volunteers.
Next, identify the software tool you will use for your systematic review. Options range from simple spreadsheets such as Microsoft Excel to reference managers such as EndNote or Mendeley or dedicated systematic review tools. Academic institutions may subscribe to paid services such as Covidence (https://www.covidence.org), or you can utilize free alternatives such as Rayyan (https://www.rayyan.ai). Investing time in learning to navigate dedicated systematic review software can greatly enhance efficiency and reduce frustrations compared to more basic methods. Ultimately, staying organized, thorough, and committed is key.
Step 3: Conduct the Literature Review—At this point, your research topic has been decided, a medical reference librarian has provided the results of a comprehensive literature search, and a software tool has been chosen. The next task is to read hundreds or thousands of papers—easy, right? With your dedicated team assembled, the workload can be divided and conquered. The first step involves screening out duplicate and irrelevant studies based on titles and abstracts. Next, review the remaining papers in more detail. Those that pass this preliminary screen should be read in their entirety, and only the papers relevant to the research topic should be included in the final synthesis. If there are uncertainties about a study’s relevance, consulting a faculty mentor is advisable. To ensure the systematic review is as thorough as possible, pay special attention to the references section of each paper, as cited references can reveal relevant studies that may have been missed in the literature search.
Once all relevant papers are compiled and read, the relevant data points should be extracted and imputed into a data sheet. Collaborating with a medical statistician is crucial at this stage, as they can provide guidance on the most effective ways to structure and input data. After all studies are included, the relevant statistical analyses on the resultant dataset can be run.
Step 4: Write the Paper—In 2020, the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses (PRISMA) statement was developed to ensure transparent and complete reporting of systematic reviews. A full discussion of PRISMA guidelines is beyond the scope of this paper; Page et al14 provided a summary, checklist, and flow diagram that is available online (https://www.prisma-statement.org). Following the PRISMA checklist and guidelines ensures a high-quality, transparent, and reliable systematic review. These guidelines not only help streamline and simplify the writing process but also enhance its efficiency and effectiveness. Discovering the PRISMA checklist can be transformative, providing a valuable roadmap that guides the author through each step of the reporting process, helping to avoid common pitfalls. This structured approach ultimately leads to a more comprehensive and trustworthy review.
Step 5: Make Finishing Touches—At this stage in the systematic review process, the studies have been compiled and thoroughly analyzed and the statistical analysis has been conducted. The results have been organized within a structured framework following the PRISMA checklist. With these steps completed, the next task is to finalize the manuscript and seek a final review from the senior author or faculty mentor. To streamline this process, it is beneficial to adhere to the formatting guidelines of the specific medical journal you intend to submit to. Check the author guidelines on the journal’s website and review recent systematic reviews published there as a reference. Even if you have not chosen a journal yet, formatting your manuscript according to a prestigious journal’s general style provides a strong foundation that can be easily adapted to fit another journal’s requirements if necessary.
Final Thoughts
Designing and conducting a systematic review is no easy task, but it can be a valuable skill for dermatology residents aiming to contribute meaningfully to the medical literature. The process of compiling a systematic review offers an opportunity for developing critical research skills, from formulating a research question to synthesizing evidence and presenting findings in a clear methodical way. Engaging in systematic review writing not only enhances the resident’s understanding of a particular topic but also demonstrates a commitment to scholarly activity—a key factor in an increasingly competitive residency and fellowship application environment.
The basic steps outlined in this article are just one way in which residents can begin to navigate the complexities of medical research, specifically the systematic review process. By assembling a supportive team, utilizing available resources, and adhering to established guidelines such as PRISMA, one can produce a high-quality, impactful review. Ultimately, the systematic review process is not just about publication—it is about fostering a habit of inquiry, improving patient care, and contributing to the ever-evolving field of medicine. With dedication and collaboration, even the most challenging aspects of research can be tackled, paving the way for future opportunities and professional growth. In this way, perhaps one day the spirit of the “research race” can shift from a frantic sprint to a graceful marathon, where each mile is run with heart and every step is filled with purpose.
- Anand P, Szeto MD, Flaten H, et al. Dermatology residency research policies: a 2021 national survey. Int J Womens Dermatol. 2021;7:787-792.
- Costello CM, Harvey JA, Besch-Stokes JG, et al. The role research gap years play in a successful dermatology match. Int J Dermatol. 2022;61:226-230.
- Elliott B, Carmody JB. Publish or perish: the research arms race in residency selection. J Grad Med Educ. 2023;15:524-527.
- MedSchoolCoach. How competitive is a dermatology residency? Updated in 2023. ProspectiveDoctor website. Accessed August 22, 2024. https://www.prospectivedoctor.com/how-competitive-is-a-dermatology-residency/#:~:text=Statistics%20on%20the%20Dermatology%20Match,applied%2C%20169%20did%20not%20match
- ACGME program requirements for graduate medical education in dermatology. Accreditation Council for Graduate Medical Education Updated July 1, 2023. Accessed August 22, 2024. https://www.acgme.org/globalassets/pfassets/programrequirements/080_dermatology_2023.pdf
- Bhuiya T, Makaryus AN. The importance of engaging in scientific research during medical training. Int J Angiol. 2023;32:153-157.
- Seaburg LA, Wang AT, West CP, et al. Associations between resident physicians’ publications and clinical performance during residency training. BMC Med Educ. 2016;16:22.
- West CP, Halvorsen AJ, McDonald FS. Scholarship during residency training: a controlled comparison study. Am J Med. 2011;124:983-987.e1.
- Bhattacharya SD, Williams JB, De La Fuente SG, et al. Does protected research time during general surgery training contribute to graduates’ career choice? Am Surg. 2011;77:907-910.
- Kralovec PD, Miller JA, Wellikson L, et al. The status of hospital medicine groups in the United States. J Hosp Med. 2006;1:75-80.
- Altman DG. The scandal of poor medical research. BMJ. 1994;308:283-284.
- Wickramasinghe DP, Perera CS, Senarathna S, et al. Patterns and trends of medical student research. BMC Med Educ. 2013;13:175.
- Ercan-Fang NG, Mahmoud MA, Cottrell C, et al. Best practices in resident research—a national survey of high functioning internal medicine residency programs in resident research in USA. Am J Med Sci. 2021;361:23-29.
- Page MJ, Moher D, Bossuyt PM, et al. PRISMA 2020 explanation and elaboration: updated guidance and exemplars for reporting systematic reviews. BMJ. 2021;372.
- Anand P, Szeto MD, Flaten H, et al. Dermatology residency research policies: a 2021 national survey. Int J Womens Dermatol. 2021;7:787-792.
- Costello CM, Harvey JA, Besch-Stokes JG, et al. The role research gap years play in a successful dermatology match. Int J Dermatol. 2022;61:226-230.
- Elliott B, Carmody JB. Publish or perish: the research arms race in residency selection. J Grad Med Educ. 2023;15:524-527.
- MedSchoolCoach. How competitive is a dermatology residency? Updated in 2023. ProspectiveDoctor website. Accessed August 22, 2024. https://www.prospectivedoctor.com/how-competitive-is-a-dermatology-residency/#:~:text=Statistics%20on%20the%20Dermatology%20Match,applied%2C%20169%20did%20not%20match
- ACGME program requirements for graduate medical education in dermatology. Accreditation Council for Graduate Medical Education Updated July 1, 2023. Accessed August 22, 2024. https://www.acgme.org/globalassets/pfassets/programrequirements/080_dermatology_2023.pdf
- Bhuiya T, Makaryus AN. The importance of engaging in scientific research during medical training. Int J Angiol. 2023;32:153-157.
- Seaburg LA, Wang AT, West CP, et al. Associations between resident physicians’ publications and clinical performance during residency training. BMC Med Educ. 2016;16:22.
- West CP, Halvorsen AJ, McDonald FS. Scholarship during residency training: a controlled comparison study. Am J Med. 2011;124:983-987.e1.
- Bhattacharya SD, Williams JB, De La Fuente SG, et al. Does protected research time during general surgery training contribute to graduates’ career choice? Am Surg. 2011;77:907-910.
- Kralovec PD, Miller JA, Wellikson L, et al. The status of hospital medicine groups in the United States. J Hosp Med. 2006;1:75-80.
- Altman DG. The scandal of poor medical research. BMJ. 1994;308:283-284.
- Wickramasinghe DP, Perera CS, Senarathna S, et al. Patterns and trends of medical student research. BMC Med Educ. 2013;13:175.
- Ercan-Fang NG, Mahmoud MA, Cottrell C, et al. Best practices in resident research—a national survey of high functioning internal medicine residency programs in resident research in USA. Am J Med Sci. 2021;361:23-29.
- Page MJ, Moher D, Bossuyt PM, et al. PRISMA 2020 explanation and elaboration: updated guidance and exemplars for reporting systematic reviews. BMJ. 2021;372.
Resident Pearls
- Establishing a strong relationship with a research mentor is crucial for success in resident research. If your program lacks the necessary infrastructure, take the initiative to network at society meetings or apply for formal mentorship programs.
- For residents facing limited access to patient cohorts and large datasets or those without access to a robust research infrastructure, conducting a systematic review is a valuable and feasible research option, allowing for meaningful contributions to the medical literature.
How Intermittent Fasting Could Transform Adolescent Obesity
TOPLINE:
METHODOLOGY:
- Researchers conducted a 52-week randomized clinical trial at two pediatric centers in Australia that involved 141 adolescents aged 13-17 years with obesity and at least one associated complication.
- Participants were divided into two groups: IER and CER, with three phases: Very low-energy diet (weeks 0-4), intensive intervention (weeks 5-16), and continued intervention/maintenance (weeks 17-52).
- Interventions included a very low-energy diet of 3350 kJ/d (800 kcal/d) for the first 4 weeks, followed by either IER intervention (2500-2950 kJ [600-700 kcal 3 days/wk]) or a daily CER intervention (6000-8000 kJ/d based on age; 1430-1670 kcal/d for teens aged 13-14 years and 1670-1900 kcal/d for teens aged 15-17 years).
- Participants were provided with multivitamins and met with dietitians regularly, with additional support via telephone, text message, or email.
TAKEAWAY:
- Teens in both the IER and CER groups showed a 0.28 reduction in BMI z-scores at 52 weeks with no significant differences between the two.
- The researchers observed no differences in body composition or cardiometabolic outcomes between the IER and CER groups.
- The occurrence of insulin resistance was reduced in both groups at week 16, but this effect was maintained only in the CER group at week 52.
- The study found no significant differences in the occurrence of dyslipidemia or impaired hepatic function between the IER and CER groups.
IN PRACTICE:
“These findings suggest that for adolescents with obesity-associated complications, IER can be incorporated into a behavioral weight management program, providing an option in addition to CER and offering participants more choice,” the authors of the study wrote.
SOURCE:
The study was led by Natalie B. Lister, PhD, of the University of Sydney in Australia and was published online in JAMA Pediatrics.
LIMITATIONS:
The COVID-19 pandemic and subsequent lockdowns limited the sample size. Some dietitian visits were conducted via telehealth.
DISCLOSURES:
Dr. Lister received grants from the National Health and Medical Research Council of Australia. A coauthor, Louise A. Baur, MBBS, PhD, received speakers’ fees from Novo Nordisk and served as a member of the Eli Lilly Advisory Committee.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
METHODOLOGY:
- Researchers conducted a 52-week randomized clinical trial at two pediatric centers in Australia that involved 141 adolescents aged 13-17 years with obesity and at least one associated complication.
- Participants were divided into two groups: IER and CER, with three phases: Very low-energy diet (weeks 0-4), intensive intervention (weeks 5-16), and continued intervention/maintenance (weeks 17-52).
- Interventions included a very low-energy diet of 3350 kJ/d (800 kcal/d) for the first 4 weeks, followed by either IER intervention (2500-2950 kJ [600-700 kcal 3 days/wk]) or a daily CER intervention (6000-8000 kJ/d based on age; 1430-1670 kcal/d for teens aged 13-14 years and 1670-1900 kcal/d for teens aged 15-17 years).
- Participants were provided with multivitamins and met with dietitians regularly, with additional support via telephone, text message, or email.
TAKEAWAY:
- Teens in both the IER and CER groups showed a 0.28 reduction in BMI z-scores at 52 weeks with no significant differences between the two.
- The researchers observed no differences in body composition or cardiometabolic outcomes between the IER and CER groups.
- The occurrence of insulin resistance was reduced in both groups at week 16, but this effect was maintained only in the CER group at week 52.
- The study found no significant differences in the occurrence of dyslipidemia or impaired hepatic function between the IER and CER groups.
IN PRACTICE:
“These findings suggest that for adolescents with obesity-associated complications, IER can be incorporated into a behavioral weight management program, providing an option in addition to CER and offering participants more choice,” the authors of the study wrote.
SOURCE:
The study was led by Natalie B. Lister, PhD, of the University of Sydney in Australia and was published online in JAMA Pediatrics.
LIMITATIONS:
The COVID-19 pandemic and subsequent lockdowns limited the sample size. Some dietitian visits were conducted via telehealth.
DISCLOSURES:
Dr. Lister received grants from the National Health and Medical Research Council of Australia. A coauthor, Louise A. Baur, MBBS, PhD, received speakers’ fees from Novo Nordisk and served as a member of the Eli Lilly Advisory Committee.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
METHODOLOGY:
- Researchers conducted a 52-week randomized clinical trial at two pediatric centers in Australia that involved 141 adolescents aged 13-17 years with obesity and at least one associated complication.
- Participants were divided into two groups: IER and CER, with three phases: Very low-energy diet (weeks 0-4), intensive intervention (weeks 5-16), and continued intervention/maintenance (weeks 17-52).
- Interventions included a very low-energy diet of 3350 kJ/d (800 kcal/d) for the first 4 weeks, followed by either IER intervention (2500-2950 kJ [600-700 kcal 3 days/wk]) or a daily CER intervention (6000-8000 kJ/d based on age; 1430-1670 kcal/d for teens aged 13-14 years and 1670-1900 kcal/d for teens aged 15-17 years).
- Participants were provided with multivitamins and met with dietitians regularly, with additional support via telephone, text message, or email.
TAKEAWAY:
- Teens in both the IER and CER groups showed a 0.28 reduction in BMI z-scores at 52 weeks with no significant differences between the two.
- The researchers observed no differences in body composition or cardiometabolic outcomes between the IER and CER groups.
- The occurrence of insulin resistance was reduced in both groups at week 16, but this effect was maintained only in the CER group at week 52.
- The study found no significant differences in the occurrence of dyslipidemia or impaired hepatic function between the IER and CER groups.
IN PRACTICE:
“These findings suggest that for adolescents with obesity-associated complications, IER can be incorporated into a behavioral weight management program, providing an option in addition to CER and offering participants more choice,” the authors of the study wrote.
SOURCE:
The study was led by Natalie B. Lister, PhD, of the University of Sydney in Australia and was published online in JAMA Pediatrics.
LIMITATIONS:
The COVID-19 pandemic and subsequent lockdowns limited the sample size. Some dietitian visits were conducted via telehealth.
DISCLOSURES:
Dr. Lister received grants from the National Health and Medical Research Council of Australia. A coauthor, Louise A. Baur, MBBS, PhD, received speakers’ fees from Novo Nordisk and served as a member of the Eli Lilly Advisory Committee.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Trends in Industry Payments to Dermatologists: A 5-Year Analysis of Open Payments Data (2017-2021)
Financial relationships between physicians and industry are prevalent and complex and may have implications for patient care. A 2007 study reported that 94% of 3167 physicians surveyed had established some form of paid relationship with companies in the pharmaceutical industry.1 To facilitate increased transparency around these relationships, lawmakers passed the Physician Payments Sunshine Act in 2010, which requires pharmaceutical companies and device manufacturers to report all payments made to physicians.2 Mandatory disclosures include meals, honoraria, travel expenses, grants, and ownership or investment interests greater than $10. The information is displayed publicly in the Open Payments database (OPD)(https://openpayments-data.cms.gov/), a platform run by the Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services.
The OPD allows for in-depth analyses of industry payments made to physicians. Many medical specialties—including orthopedics,3-5 plastic surgery,6,7 ophthalmology,8 and gastroenterology9—have published extensive literature characterizing the nature of these payments and disparities in the distribution of payments based on sex, geographic distribution, and other factors. After the first full year of OPD data collection for dermatology in 2014, Feng et al10 examined the number, amount, and nature of industry payments to dermatologists, as well as their geographic distribution for that year. As a follow-up to this initial research, Schlager et al11 characterized payments made to dermatologists for the year 2016 and found an increase in the total payments, mean payments, and number of dermatologists receiving payments compared with the 2014 data.
Our study aimed to characterize the last 5 years of available OPD data—from January 1, 2017, to December 31, 2021—to further explore trends in industry payments made to dermatologists. In particular, we examined the effects of the COVID-19 pandemic on payments as well as sex disparities and the distribution of industry payments.
Methods
We performed a retrospective analysis of the OPD for the general payment datasets from January 1, 2017, to December 31, 2021. The results were filtered to include only payments made to dermatologists, excluding physicians from other specialties, physician assistants, and other types of practitioners. Data for each physician were grouped by National Provider Identifier (NPI) for providers included in the set, allowing for analysis at the individual level. Data on sex were extracted from the National Plan & Provider Enumeration System’s monthly data dissemination for NPIs for July 2023 (when the study was conducted) and were joined to the OPD data using the NPI number reported for each physician. All data were extracted, transformed, and analyzed using R software (version 4.2.1). Figures and visualizations were produced using Microsoft Excel 2016.
Results
In 2017, a total of 358,884 payments were made by industry to dermatologists, accounting for nearly $58.0 million. The mean total value of payments received per dermatologist was $5231.74, and the mean payment amount was $161.49. In 2018, the total number of payments increased year-over-year by 5.5% (378,509 payments), the total value of payments received increased by 7.5% (approximately $62.3 million), and the mean total value of payments received per dermatologist increased by 5.3% ($5508.98). In 2019, the total number of payments increased by 3.0% (389,670 total payments), the total value of payments recieved increased by 13.2% (approximately $70.5 million), and the mean total value of payments received per dermatologist increased by 11.3% ($6133.45). All of these values decreased in 2020, likely due to COVID-19–related restrictions on travel and meetings (total number of payments, 208,470 [−46.5%]; total value of payments received, approximately $37.5 million [−46.9%], mean total value of payments received per dermatologist, $3757.27 [−38.7%]), but the mean payment amount remained stable at $179.47. In 2021, the total number of payments (295,808 [+41.9%]), total value of payments received (approximately $50.3 million [+34.4%]), and mean total value of payments received per dermatologist ($4707.88 [+25.3%]) all rebounded, but not to pre-2020 levels (Table 1). When looking at the geographic distribution of payments, the top 5 states receiving the highest total value of payments during the study period included California ($41.51 million), New York ($32.26 million), Florida ($21.38 million), Texas ($19.93 million), and Pennsylvania ($11.69 million).
For each year from 2017 to 2021, more than 80% of payments made to dermatologists were less than $50. The majority (60.7%–75.8%) were in the $10 to $50 range. Between 4% and 5% of payments were more than $1000 for each year. Fewer than 10% of dermatologists received more than $5000 in total payments per year. Most dermatologists (33.3%–36.9%) received $100 to $500 per year. The distribution of payments stratified by number of payments made by amount and payment amount per dermatologist is further delineated in Table 2.
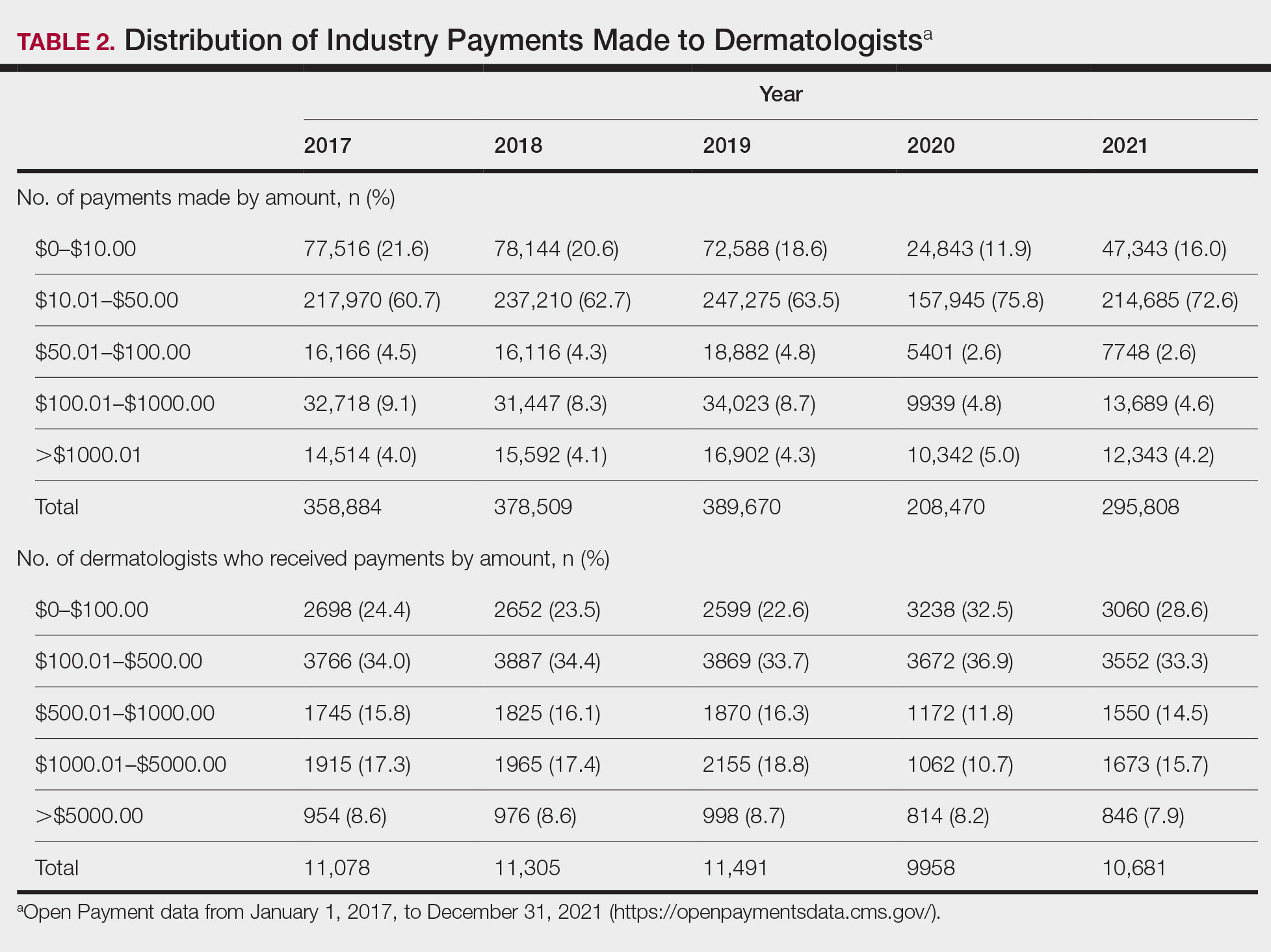
Among dermatologists who received industry payments in 2017, slightly more than half (50.9%) were male; however, male dermatologists accounted for more than $40.1 million of the more than $57.6 million total payments made to dermatologists (69.6%) that year. Male dermatologists received a mean payment amount of $198.26, while female dermatologists received a significantly smaller amount of $113.52 (P<.001). The mean total value of payments received per male dermatologist was $7204.36, while the mean total value for female dermatologists was $3272.16 (P<.001). The same statistically significant disparities in mean payment amount and mean total value of payments received by male vs female dermatologists were observed for every year from 2017 through 2021 (Table 3).
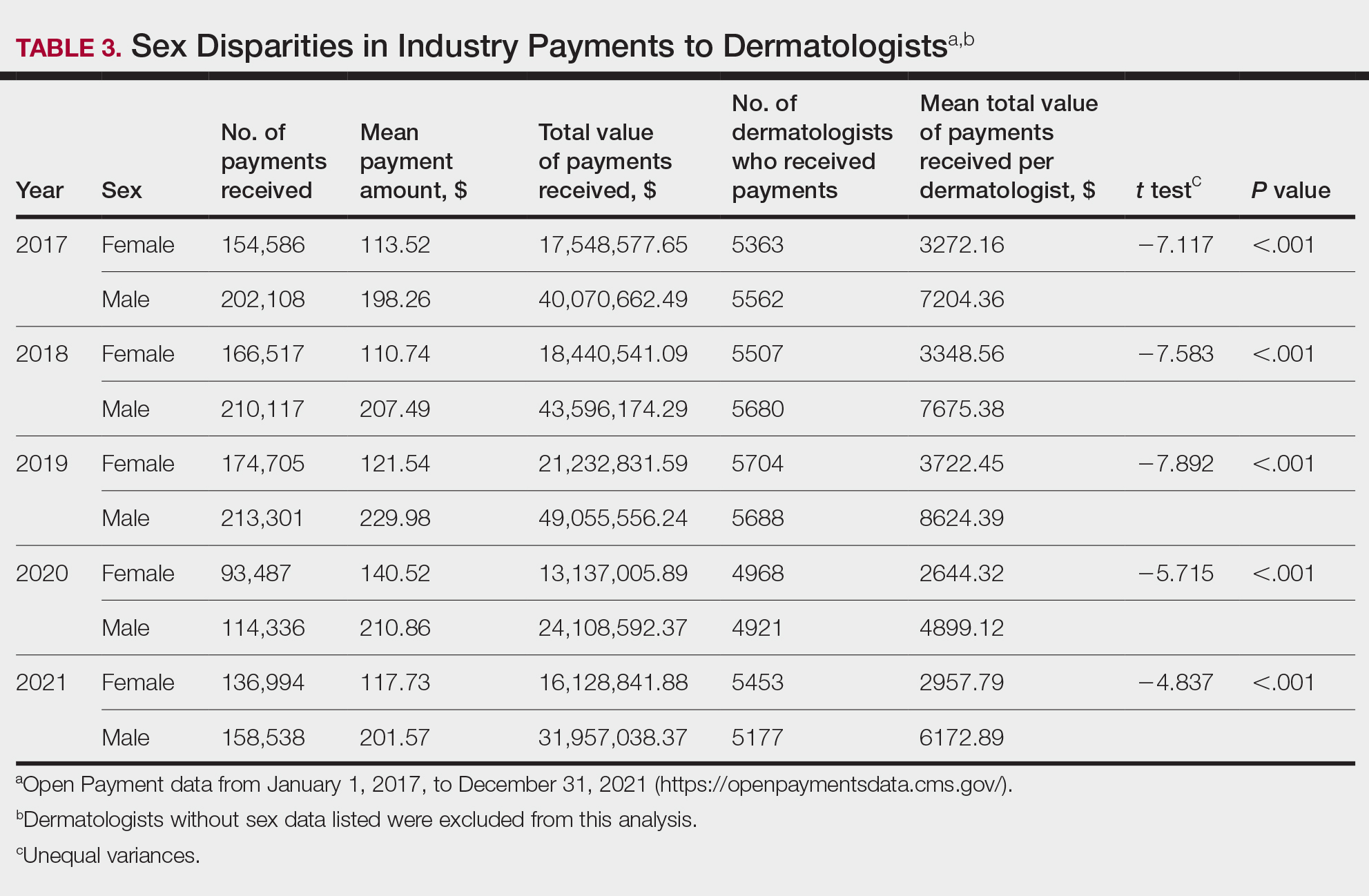
Comment
Benefits of Physician Relationships With Industry—The Physician Payments Sunshine Act increased transparency of industry payments to physicians by creating the OPD through which these relationships can be reported.12 The effects of these relationships on treatment practices have been the subject of many studies in recent years. Some have suggested that industry ties may impact prescription patterns of endorsed medications.13 It also has been reported that the chance of a research study identifying a positive outcome for a particular treatment is higher when the study is funded by a pharmaceutical company compared to other sponsors.14 On the other hand, some researchers have argued that, when established and maintained in an ethical manner, industry-physician relationships may help practitioners stay updated on the newest treatment paradigms and benefit patient care.15 Industry relationships may help drive innovation of new products with direct input from frontline physicians who take care of the patients these products aim to help.
Limitations of the OPD—Critics of the OPD have argued that the reported data lack sufficient context and are not easily interpretable by most patients.16 In addition, many patients might not know about the existence of the database. Indeed, one national survey-based study showed that only 12% of 3542 respondents knew that this information was publicly available, and only 5% knew whether their own physician had received industry payments.17
Increased Payments From Industry—Our analysis builds on previously reported data in dermatology from 2014 to 2016.10,11 We found that the trends of increasing numbers and dollar amounts of payments made by industry to dermatologists continued from 2017 to 2019, which may reflect the intended effects of the Physician Payments Sunshine Act, as more payments are being reported in a transparent manner. It also shows that relationships between industry and dermatologists have become more commonplace over time.
It is important to consider these trends in the context of overall Medicare expenditures and prescription volumes. Between 2008 and 2021, prescription volumes have been increasing at a rate of 1% to 4% per year, with 2020 being an exception as the volume decreased slightly from the year prior due to COVID-19 (−3%). Similarly, total Medicare and Medicaid expenditures have been growing at a rate of almost 5% per year.18 Based on our study results, it appears the total value of payments made between 2017 and 2021 increased at a rate that outpaced prescription volume and expenditures; however, it is difficult to draw conclusions about the relationship between payments made to dermatologists and spending without examining prescriptions specific to dermatologists in the OPD dataset. This relationship could be further explored in future studies.
COVID-19 Restrictions Impacted Payments in 2021—We hypothesize that COVID-19–related restrictions on traveling and in-person meetings led to a decrease in the number of payments, total payment amount, and mean total value of payments received per dermatologist. Notably, compensation for services other than consulting, including speaking fees, had the most precipitous decrease in total payment amount. On the other hand, honoraria and consulting fees were least impacted, as many dermatologists were still able to maintain relationships with industry on an advisory basis without traveling. From 2020 to 2021, the number of total payments and dollar amounts increased with easing of COVID-19 restrictions; however, they had not yet rebounded to 2019 levels during the study period. It will be interesting to continue monitoring these trends once data from future years become available.
Top-Compensated Dermatologists—Our study results also show that for all years from 2017 through 2021, the majority of industry payments were made to a small concentrated percentage of top-compensated dermatologists, which may reflect larger and more frequent payments to those identified by pharmaceutical companies as thought leaders and key opinion leaders in the field or those who are more willing to establish extensive ties with industry. Similarly skewed distributions in payments have been shown in other medical subspecialties including neurosurgery, plastic surgery, otolaryngology, and orthopedics.4,6,19,20 It also is apparent that the majority of compensated dermatologists in the OPD maintain relatively small ties with industry. For every year from 2017 to 2021, more than half of compensated dermatologists received total payments of less than $500 per year, most of which stemmed from the food and beverage category. Interestingly, a prior study showed that patient perceptions of industry-physician ties may be more strongly impacted by the payment category than the amount.21 For example, respondents viewed payments for meals and lodging more negatively, as they were seen more as personal gifts without direct benefit to patients. Conversely, respondents held more positive views of physicians who received free drug samples, which were perceived as benefiting patients, as well as those receiving consulting fees, which were perceived as a signal of physician expertise. Notably, in the same study, physicians who received no payments from industry were seen as honest but also were viewed by some respondents as being inexperienced or uninformed about new treatments.21
The contribution and public perception of dermatologists who conduct investigator-initiated research utilizing other types of funding (eg, government grants) also are important to consider but were not directly assessed within the scope of the current study.
Sex Disparities in Compensation—Multiple studies in the literature have demonstrated that sex inequities exist across medical specialties.22,23 In dermatology, although women make up slightly more than 50% of board-certified dermatologists, they continue to be underrepresented compared with men in leadership positions, academic rank, research funding, and lectureships at national meetings.24-27 In survey-based studies specifically examining gender-based physician compensation, male dermatologists were found to earn higher salaries than their female counterparts in both private practice and academic settings, even after adjusting for work hours, practice characteristics, and academic rank.28,29
Our study contributes to the growing body of evidence suggesting that sex inequities also may exist with regard to financial payments from industry. Our results showed that, although the number of male and female dermatologists with industry relationships was similar each year, the number of payments made and total payment amount were both significantly (P<.001) higher for male dermatologists from 2017 through 2021. In 2021, the mean payment amount ($201.57 for male dermatologists; $117.73 for female dermatologists) and mean total amount of payments received ($6172.89 and $2957.79, respectively) also were significantly higher for male compared with female dermatologists (P<.001). The cause of this disparity likely is multifactorial and warrants additional studies in the future. One hypothesis in the existing literature is that male physicians may be more inclined to seek out relationships with industry; it also is possible that disparities in research funding, academic rank, and speaking opportunities at national conferences detailed previously may contribute to inequities in industry payments as companies seek out perceived leaders in the field.30
Limitations and Future Directions—Several important limitations of our study warrant further consideration. As with any database study, the accuracy of the results presented and the conclusions drawn are highly dependent on the precision of the available data, which is reliant on transparent documentation by pharmaceutical companies and physicians. There are no independent methods of verifying the information reported. There have been reports in the literature questioning the utility of the OPD data and risk for misinterpretation.16,31 Furthermore, the OPD only includes companies whose products are covered by government-sponsored programs, such as Medicare and Medicaid, and therefore does not encompass the totality of industry-dermatologist relationships. We also focused specifically on board-certified dermatologists and did not analyze the extent of industry relationships involving residents, nurses, physician assistants, and other critical members of health care teams that may impact patient care. Differences between academic and private practice payments also could not be examined using the OPD but could present an interesting area for future studies.
Despite these limitations, our study was extensive, using the publicly available OPD to analyze trends and disparities in financial relationships between dermatologists and industry partners from 2017 through 2021. Notably, these findings are not intended to provide judgment or seek to tease out financial relationships that are beneficial for patient care from those that are not; rather, they are intended only to lend additional transparency, provoke thought, and encourage future studies and discussion surrounding this important topic.
Conclusion
Financial relationships between dermatologists and industry are complex and are becoming more prevalent, as shown in our study. These relationships may be critical to facilitate novel patient-centered research and growth in the field of dermatology; however, they also have the potential to be seen as bias in patient care. Transparent reporting of these relationships is an important step in future research regarding the effects of different payment types and serves as the basis for further understanding industry-dermatologist relationships as well as any inequities that exist in the distribution of payments. We encourage all dermatologists to review their public profiles in the OPD. Physicians have the opportunity to review all payment data reported by companies and challenge the accuracy of the data if necessary.
- Campbell EG, Gruen RL, Mountford J, et al. A national survey of physician-industry relationships. N Engl J Med. 2007;356:1742-1750.
- Kirschner NM, Sulmasy LS, Kesselheim AS. Health policy basics: the Physician Payment Sunshine Act and the Open Payments program. Ann Intern Med. 2014;161:519-521.
- Braithwaite J, Frane N, Partan MJ, et al. Review of industry payments to general orthopaedic surgeons reported by the open payments database: 2014 to 2019. J Am Acad Orthop Surg Glob Res Rev. 2021;5:E21.00060.
- Pathak N, Mercier MR, Galivanche AR, et al. Industry payments to orthopedic spine surgeons reported by the open payments database: 2014-2017. Clin Spine Surg. 2020;33:E572-E578.
- Almaguer AM, Wills BW, Robin JX, et al. Open payments reporting of industry compensation for orthopedic residents. J Surg Educ. 2020;77:1632-1637.
- Chao AH, Gangopadhyay N. Industry financial relationships in plastic surgery: analysis of the sunshine act open payments database. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2016;138:341E-348E.
- Khetpal S, Mets EJ, Ahmad M, et al. The open payments sunshine act database revisited: a 5-year analysis of industry payments to plastic surgeons. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2021;148:877E-878E.
- Slentz DH, Nelson CC, Lichter PR. Characteristics of industry payments to ophthalmologists in the open payments database. JAMA Ophthalmol. 2019;137:1038-1044.
- Gangireddy VGR, Amin R, Yu K, et al. Analysis of payments to GI physicians in the United States: open payments data study. JGH Open. 2020;4:1031-1036.
- Feng H, Wu P, Leger M. Exploring the industry-dermatologist financial relationship: insight from the open payment data. JAMA Dermatol. 2016;152:1307-1313.
- Schlager E, Flaten H, St Claire C, et al. Industry payments to dermatologists: updates from the 2016 open payment data. Dermatol Online J. 2018;24:13030/qt8r74w3c4.
- Agrawal S, Brennan N, Budetti P. The Sunshine Act—effects on physicians. N Engl J Med. 2013;368:2054-2057.
- DeJong C, Aguilar T, Tseng CW, et al. Pharmaceutical industry-sponsored meals and physician prescribing patterns for Medicare beneficiaries. JAMA Intern Med. 2016;176:1114-1122.
- Lexchin J, Bero LA, Djulbegovic B, et al. Pharmaceutical industry sponsorship and research outcome and quality: systematic review. BMJ. 2003;326:1167-1170.
- Nakayama DK. In defense of industry-physician relationships. Am Surg. 2010;76:987-994.
- Chimonas S, DeVito NJ, Rothman DJ. Bringing transparency to medicine: exploring physicians’ views and experiences of the sunshine act. Am J Bioeth. 2017;17:4-18.
- Pham-Kanter G, Mello MM, Lehmann LS, et la. Public awareness of and contact with physicians who receive industry payments: a national survey. J Gen Intern Med. 2017;32:767-774.
- National Health Expenditure Fact Sheet. Updated December 13, 2023 Accessed August 9, 2024. https://www.cms.gov/data-research/statistics-trends-and-reports/national-health-expenditure-data/nhe-fact-sheet
- de Lotbiniere-Bassett MP, McDonald PJ. Industry financial relationships in neurosurgery in 2015: analysis of the Sunshine Act Open Payments database. World Neurosurg. 2018;114:E920-E925.
- Pathak N, Fujiwara RJT, Mehra S. Assessment of nonresearch industry payments to otolaryngologists in 2014 and 2015. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2018;158:1028-1034.
- Perry JE, Cox D, Cox AD. Trust and transparency: patient perceptions of physicians’ financial relationships with pharmaceutical companies. J Law Med Ethics. 2014;42:475-491.
- Freund KM, Raj A, Kaplan SE, et al. Inequities in academic compensation by gender: a follow-up to the national faculty survey cohort study. Acad Med. 2016;91:1068-1073.
- Seabury SA, Chandra A, Jena AB. Trends in the earnings of male and female health care professionals in the United States, 1987 to 2010. JAMA Intern Med. 2013;173:1748-1750.
- Flaten HK, Goodman L, Wong E, et al. Analysis of speaking opportunities by gender at national dermatologic surgery conferences. Dermatol Surg. 2020;46:1195-1201.
- Lobl M, Grinnell M, Higgins S, et al. Representation of women as editors in dermatology journals: a comprehensive review. Int J Womens Dermatol. 2020;6:20-24.
- Stratman H, Stratman EJ. Assessment of percentage of women in the dermatology workforce presenting at American Academy of Dermatology annual meetings, 1992-2017. JAMA Dermatol. 2019;155:384-386.
- Wu AG, Lipner SR. Sex trends in leadership of the American Academy of Dermatology: a cross-sectional study. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2020;83:592-594.
- Weeks WB, Wallace AE. Gender differences in dermatologists’ annual incomes. Cutis. 2007;80:325-332.
- Sachdeva M, Price KN, Hsiao JL, et al. Gender and rank salary trends among academic dermatologists. Int J Womens Dermatol. 2020;6:324-326.
- Rose SL, Sanghani RM, Schmidt C, et al. Gender differences in physicians’ financial ties to industry: a study of national disclosure data. PLoS One. 2015;10:E0129197.
- Santhakumar S, Adashi EY. The physician payment sunshine act: testing the value of transparency. JAMA. 2015;313:23-24.
Financial relationships between physicians and industry are prevalent and complex and may have implications for patient care. A 2007 study reported that 94% of 3167 physicians surveyed had established some form of paid relationship with companies in the pharmaceutical industry.1 To facilitate increased transparency around these relationships, lawmakers passed the Physician Payments Sunshine Act in 2010, which requires pharmaceutical companies and device manufacturers to report all payments made to physicians.2 Mandatory disclosures include meals, honoraria, travel expenses, grants, and ownership or investment interests greater than $10. The information is displayed publicly in the Open Payments database (OPD)(https://openpayments-data.cms.gov/), a platform run by the Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services.
The OPD allows for in-depth analyses of industry payments made to physicians. Many medical specialties—including orthopedics,3-5 plastic surgery,6,7 ophthalmology,8 and gastroenterology9—have published extensive literature characterizing the nature of these payments and disparities in the distribution of payments based on sex, geographic distribution, and other factors. After the first full year of OPD data collection for dermatology in 2014, Feng et al10 examined the number, amount, and nature of industry payments to dermatologists, as well as their geographic distribution for that year. As a follow-up to this initial research, Schlager et al11 characterized payments made to dermatologists for the year 2016 and found an increase in the total payments, mean payments, and number of dermatologists receiving payments compared with the 2014 data.
Our study aimed to characterize the last 5 years of available OPD data—from January 1, 2017, to December 31, 2021—to further explore trends in industry payments made to dermatologists. In particular, we examined the effects of the COVID-19 pandemic on payments as well as sex disparities and the distribution of industry payments.
Methods
We performed a retrospective analysis of the OPD for the general payment datasets from January 1, 2017, to December 31, 2021. The results were filtered to include only payments made to dermatologists, excluding physicians from other specialties, physician assistants, and other types of practitioners. Data for each physician were grouped by National Provider Identifier (NPI) for providers included in the set, allowing for analysis at the individual level. Data on sex were extracted from the National Plan & Provider Enumeration System’s monthly data dissemination for NPIs for July 2023 (when the study was conducted) and were joined to the OPD data using the NPI number reported for each physician. All data were extracted, transformed, and analyzed using R software (version 4.2.1). Figures and visualizations were produced using Microsoft Excel 2016.
Results
In 2017, a total of 358,884 payments were made by industry to dermatologists, accounting for nearly $58.0 million. The mean total value of payments received per dermatologist was $5231.74, and the mean payment amount was $161.49. In 2018, the total number of payments increased year-over-year by 5.5% (378,509 payments), the total value of payments received increased by 7.5% (approximately $62.3 million), and the mean total value of payments received per dermatologist increased by 5.3% ($5508.98). In 2019, the total number of payments increased by 3.0% (389,670 total payments), the total value of payments recieved increased by 13.2% (approximately $70.5 million), and the mean total value of payments received per dermatologist increased by 11.3% ($6133.45). All of these values decreased in 2020, likely due to COVID-19–related restrictions on travel and meetings (total number of payments, 208,470 [−46.5%]; total value of payments received, approximately $37.5 million [−46.9%], mean total value of payments received per dermatologist, $3757.27 [−38.7%]), but the mean payment amount remained stable at $179.47. In 2021, the total number of payments (295,808 [+41.9%]), total value of payments received (approximately $50.3 million [+34.4%]), and mean total value of payments received per dermatologist ($4707.88 [+25.3%]) all rebounded, but not to pre-2020 levels (Table 1). When looking at the geographic distribution of payments, the top 5 states receiving the highest total value of payments during the study period included California ($41.51 million), New York ($32.26 million), Florida ($21.38 million), Texas ($19.93 million), and Pennsylvania ($11.69 million).

For each year from 2017 to 2021, more than 80% of payments made to dermatologists were less than $50. The majority (60.7%–75.8%) were in the $10 to $50 range. Between 4% and 5% of payments were more than $1000 for each year. Fewer than 10% of dermatologists received more than $5000 in total payments per year. Most dermatologists (33.3%–36.9%) received $100 to $500 per year. The distribution of payments stratified by number of payments made by amount and payment amount per dermatologist is further delineated in Table 2.

Among dermatologists who received industry payments in 2017, slightly more than half (50.9%) were male; however, male dermatologists accounted for more than $40.1 million of the more than $57.6 million total payments made to dermatologists (69.6%) that year. Male dermatologists received a mean payment amount of $198.26, while female dermatologists received a significantly smaller amount of $113.52 (P<.001). The mean total value of payments received per male dermatologist was $7204.36, while the mean total value for female dermatologists was $3272.16 (P<.001). The same statistically significant disparities in mean payment amount and mean total value of payments received by male vs female dermatologists were observed for every year from 2017 through 2021 (Table 3).

Comment
Benefits of Physician Relationships With Industry—The Physician Payments Sunshine Act increased transparency of industry payments to physicians by creating the OPD through which these relationships can be reported.12 The effects of these relationships on treatment practices have been the subject of many studies in recent years. Some have suggested that industry ties may impact prescription patterns of endorsed medications.13 It also has been reported that the chance of a research study identifying a positive outcome for a particular treatment is higher when the study is funded by a pharmaceutical company compared to other sponsors.14 On the other hand, some researchers have argued that, when established and maintained in an ethical manner, industry-physician relationships may help practitioners stay updated on the newest treatment paradigms and benefit patient care.15 Industry relationships may help drive innovation of new products with direct input from frontline physicians who take care of the patients these products aim to help.
Limitations of the OPD—Critics of the OPD have argued that the reported data lack sufficient context and are not easily interpretable by most patients.16 In addition, many patients might not know about the existence of the database. Indeed, one national survey-based study showed that only 12% of 3542 respondents knew that this information was publicly available, and only 5% knew whether their own physician had received industry payments.17
Increased Payments From Industry—Our analysis builds on previously reported data in dermatology from 2014 to 2016.10,11 We found that the trends of increasing numbers and dollar amounts of payments made by industry to dermatologists continued from 2017 to 2019, which may reflect the intended effects of the Physician Payments Sunshine Act, as more payments are being reported in a transparent manner. It also shows that relationships between industry and dermatologists have become more commonplace over time.
It is important to consider these trends in the context of overall Medicare expenditures and prescription volumes. Between 2008 and 2021, prescription volumes have been increasing at a rate of 1% to 4% per year, with 2020 being an exception as the volume decreased slightly from the year prior due to COVID-19 (−3%). Similarly, total Medicare and Medicaid expenditures have been growing at a rate of almost 5% per year.18 Based on our study results, it appears the total value of payments made between 2017 and 2021 increased at a rate that outpaced prescription volume and expenditures; however, it is difficult to draw conclusions about the relationship between payments made to dermatologists and spending without examining prescriptions specific to dermatologists in the OPD dataset. This relationship could be further explored in future studies.
COVID-19 Restrictions Impacted Payments in 2021—We hypothesize that COVID-19–related restrictions on traveling and in-person meetings led to a decrease in the number of payments, total payment amount, and mean total value of payments received per dermatologist. Notably, compensation for services other than consulting, including speaking fees, had the most precipitous decrease in total payment amount. On the other hand, honoraria and consulting fees were least impacted, as many dermatologists were still able to maintain relationships with industry on an advisory basis without traveling. From 2020 to 2021, the number of total payments and dollar amounts increased with easing of COVID-19 restrictions; however, they had not yet rebounded to 2019 levels during the study period. It will be interesting to continue monitoring these trends once data from future years become available.
Top-Compensated Dermatologists—Our study results also show that for all years from 2017 through 2021, the majority of industry payments were made to a small concentrated percentage of top-compensated dermatologists, which may reflect larger and more frequent payments to those identified by pharmaceutical companies as thought leaders and key opinion leaders in the field or those who are more willing to establish extensive ties with industry. Similarly skewed distributions in payments have been shown in other medical subspecialties including neurosurgery, plastic surgery, otolaryngology, and orthopedics.4,6,19,20 It also is apparent that the majority of compensated dermatologists in the OPD maintain relatively small ties with industry. For every year from 2017 to 2021, more than half of compensated dermatologists received total payments of less than $500 per year, most of which stemmed from the food and beverage category. Interestingly, a prior study showed that patient perceptions of industry-physician ties may be more strongly impacted by the payment category than the amount.21 For example, respondents viewed payments for meals and lodging more negatively, as they were seen more as personal gifts without direct benefit to patients. Conversely, respondents held more positive views of physicians who received free drug samples, which were perceived as benefiting patients, as well as those receiving consulting fees, which were perceived as a signal of physician expertise. Notably, in the same study, physicians who received no payments from industry were seen as honest but also were viewed by some respondents as being inexperienced or uninformed about new treatments.21
The contribution and public perception of dermatologists who conduct investigator-initiated research utilizing other types of funding (eg, government grants) also are important to consider but were not directly assessed within the scope of the current study.
Sex Disparities in Compensation—Multiple studies in the literature have demonstrated that sex inequities exist across medical specialties.22,23 In dermatology, although women make up slightly more than 50% of board-certified dermatologists, they continue to be underrepresented compared with men in leadership positions, academic rank, research funding, and lectureships at national meetings.24-27 In survey-based studies specifically examining gender-based physician compensation, male dermatologists were found to earn higher salaries than their female counterparts in both private practice and academic settings, even after adjusting for work hours, practice characteristics, and academic rank.28,29
Our study contributes to the growing body of evidence suggesting that sex inequities also may exist with regard to financial payments from industry. Our results showed that, although the number of male and female dermatologists with industry relationships was similar each year, the number of payments made and total payment amount were both significantly (P<.001) higher for male dermatologists from 2017 through 2021. In 2021, the mean payment amount ($201.57 for male dermatologists; $117.73 for female dermatologists) and mean total amount of payments received ($6172.89 and $2957.79, respectively) also were significantly higher for male compared with female dermatologists (P<.001). The cause of this disparity likely is multifactorial and warrants additional studies in the future. One hypothesis in the existing literature is that male physicians may be more inclined to seek out relationships with industry; it also is possible that disparities in research funding, academic rank, and speaking opportunities at national conferences detailed previously may contribute to inequities in industry payments as companies seek out perceived leaders in the field.30
Limitations and Future Directions—Several important limitations of our study warrant further consideration. As with any database study, the accuracy of the results presented and the conclusions drawn are highly dependent on the precision of the available data, which is reliant on transparent documentation by pharmaceutical companies and physicians. There are no independent methods of verifying the information reported. There have been reports in the literature questioning the utility of the OPD data and risk for misinterpretation.16,31 Furthermore, the OPD only includes companies whose products are covered by government-sponsored programs, such as Medicare and Medicaid, and therefore does not encompass the totality of industry-dermatologist relationships. We also focused specifically on board-certified dermatologists and did not analyze the extent of industry relationships involving residents, nurses, physician assistants, and other critical members of health care teams that may impact patient care. Differences between academic and private practice payments also could not be examined using the OPD but could present an interesting area for future studies.
Despite these limitations, our study was extensive, using the publicly available OPD to analyze trends and disparities in financial relationships between dermatologists and industry partners from 2017 through 2021. Notably, these findings are not intended to provide judgment or seek to tease out financial relationships that are beneficial for patient care from those that are not; rather, they are intended only to lend additional transparency, provoke thought, and encourage future studies and discussion surrounding this important topic.
Conclusion
Financial relationships between dermatologists and industry are complex and are becoming more prevalent, as shown in our study. These relationships may be critical to facilitate novel patient-centered research and growth in the field of dermatology; however, they also have the potential to be seen as bias in patient care. Transparent reporting of these relationships is an important step in future research regarding the effects of different payment types and serves as the basis for further understanding industry-dermatologist relationships as well as any inequities that exist in the distribution of payments. We encourage all dermatologists to review their public profiles in the OPD. Physicians have the opportunity to review all payment data reported by companies and challenge the accuracy of the data if necessary.
Financial relationships between physicians and industry are prevalent and complex and may have implications for patient care. A 2007 study reported that 94% of 3167 physicians surveyed had established some form of paid relationship with companies in the pharmaceutical industry.1 To facilitate increased transparency around these relationships, lawmakers passed the Physician Payments Sunshine Act in 2010, which requires pharmaceutical companies and device manufacturers to report all payments made to physicians.2 Mandatory disclosures include meals, honoraria, travel expenses, grants, and ownership or investment interests greater than $10. The information is displayed publicly in the Open Payments database (OPD)(https://openpayments-data.cms.gov/), a platform run by the Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services.
The OPD allows for in-depth analyses of industry payments made to physicians. Many medical specialties—including orthopedics,3-5 plastic surgery,6,7 ophthalmology,8 and gastroenterology9—have published extensive literature characterizing the nature of these payments and disparities in the distribution of payments based on sex, geographic distribution, and other factors. After the first full year of OPD data collection for dermatology in 2014, Feng et al10 examined the number, amount, and nature of industry payments to dermatologists, as well as their geographic distribution for that year. As a follow-up to this initial research, Schlager et al11 characterized payments made to dermatologists for the year 2016 and found an increase in the total payments, mean payments, and number of dermatologists receiving payments compared with the 2014 data.
Our study aimed to characterize the last 5 years of available OPD data—from January 1, 2017, to December 31, 2021—to further explore trends in industry payments made to dermatologists. In particular, we examined the effects of the COVID-19 pandemic on payments as well as sex disparities and the distribution of industry payments.
Methods
We performed a retrospective analysis of the OPD for the general payment datasets from January 1, 2017, to December 31, 2021. The results were filtered to include only payments made to dermatologists, excluding physicians from other specialties, physician assistants, and other types of practitioners. Data for each physician were grouped by National Provider Identifier (NPI) for providers included in the set, allowing for analysis at the individual level. Data on sex were extracted from the National Plan & Provider Enumeration System’s monthly data dissemination for NPIs for July 2023 (when the study was conducted) and were joined to the OPD data using the NPI number reported for each physician. All data were extracted, transformed, and analyzed using R software (version 4.2.1). Figures and visualizations were produced using Microsoft Excel 2016.
Results
In 2017, a total of 358,884 payments were made by industry to dermatologists, accounting for nearly $58.0 million. The mean total value of payments received per dermatologist was $5231.74, and the mean payment amount was $161.49. In 2018, the total number of payments increased year-over-year by 5.5% (378,509 payments), the total value of payments received increased by 7.5% (approximately $62.3 million), and the mean total value of payments received per dermatologist increased by 5.3% ($5508.98). In 2019, the total number of payments increased by 3.0% (389,670 total payments), the total value of payments recieved increased by 13.2% (approximately $70.5 million), and the mean total value of payments received per dermatologist increased by 11.3% ($6133.45). All of these values decreased in 2020, likely due to COVID-19–related restrictions on travel and meetings (total number of payments, 208,470 [−46.5%]; total value of payments received, approximately $37.5 million [−46.9%], mean total value of payments received per dermatologist, $3757.27 [−38.7%]), but the mean payment amount remained stable at $179.47. In 2021, the total number of payments (295,808 [+41.9%]), total value of payments received (approximately $50.3 million [+34.4%]), and mean total value of payments received per dermatologist ($4707.88 [+25.3%]) all rebounded, but not to pre-2020 levels (Table 1). When looking at the geographic distribution of payments, the top 5 states receiving the highest total value of payments during the study period included California ($41.51 million), New York ($32.26 million), Florida ($21.38 million), Texas ($19.93 million), and Pennsylvania ($11.69 million).

For each year from 2017 to 2021, more than 80% of payments made to dermatologists were less than $50. The majority (60.7%–75.8%) were in the $10 to $50 range. Between 4% and 5% of payments were more than $1000 for each year. Fewer than 10% of dermatologists received more than $5000 in total payments per year. Most dermatologists (33.3%–36.9%) received $100 to $500 per year. The distribution of payments stratified by number of payments made by amount and payment amount per dermatologist is further delineated in Table 2.

Among dermatologists who received industry payments in 2017, slightly more than half (50.9%) were male; however, male dermatologists accounted for more than $40.1 million of the more than $57.6 million total payments made to dermatologists (69.6%) that year. Male dermatologists received a mean payment amount of $198.26, while female dermatologists received a significantly smaller amount of $113.52 (P<.001). The mean total value of payments received per male dermatologist was $7204.36, while the mean total value for female dermatologists was $3272.16 (P<.001). The same statistically significant disparities in mean payment amount and mean total value of payments received by male vs female dermatologists were observed for every year from 2017 through 2021 (Table 3).

Comment
Benefits of Physician Relationships With Industry—The Physician Payments Sunshine Act increased transparency of industry payments to physicians by creating the OPD through which these relationships can be reported.12 The effects of these relationships on treatment practices have been the subject of many studies in recent years. Some have suggested that industry ties may impact prescription patterns of endorsed medications.13 It also has been reported that the chance of a research study identifying a positive outcome for a particular treatment is higher when the study is funded by a pharmaceutical company compared to other sponsors.14 On the other hand, some researchers have argued that, when established and maintained in an ethical manner, industry-physician relationships may help practitioners stay updated on the newest treatment paradigms and benefit patient care.15 Industry relationships may help drive innovation of new products with direct input from frontline physicians who take care of the patients these products aim to help.
Limitations of the OPD—Critics of the OPD have argued that the reported data lack sufficient context and are not easily interpretable by most patients.16 In addition, many patients might not know about the existence of the database. Indeed, one national survey-based study showed that only 12% of 3542 respondents knew that this information was publicly available, and only 5% knew whether their own physician had received industry payments.17
Increased Payments From Industry—Our analysis builds on previously reported data in dermatology from 2014 to 2016.10,11 We found that the trends of increasing numbers and dollar amounts of payments made by industry to dermatologists continued from 2017 to 2019, which may reflect the intended effects of the Physician Payments Sunshine Act, as more payments are being reported in a transparent manner. It also shows that relationships between industry and dermatologists have become more commonplace over time.
It is important to consider these trends in the context of overall Medicare expenditures and prescription volumes. Between 2008 and 2021, prescription volumes have been increasing at a rate of 1% to 4% per year, with 2020 being an exception as the volume decreased slightly from the year prior due to COVID-19 (−3%). Similarly, total Medicare and Medicaid expenditures have been growing at a rate of almost 5% per year.18 Based on our study results, it appears the total value of payments made between 2017 and 2021 increased at a rate that outpaced prescription volume and expenditures; however, it is difficult to draw conclusions about the relationship between payments made to dermatologists and spending without examining prescriptions specific to dermatologists in the OPD dataset. This relationship could be further explored in future studies.
COVID-19 Restrictions Impacted Payments in 2021—We hypothesize that COVID-19–related restrictions on traveling and in-person meetings led to a decrease in the number of payments, total payment amount, and mean total value of payments received per dermatologist. Notably, compensation for services other than consulting, including speaking fees, had the most precipitous decrease in total payment amount. On the other hand, honoraria and consulting fees were least impacted, as many dermatologists were still able to maintain relationships with industry on an advisory basis without traveling. From 2020 to 2021, the number of total payments and dollar amounts increased with easing of COVID-19 restrictions; however, they had not yet rebounded to 2019 levels during the study period. It will be interesting to continue monitoring these trends once data from future years become available.
Top-Compensated Dermatologists—Our study results also show that for all years from 2017 through 2021, the majority of industry payments were made to a small concentrated percentage of top-compensated dermatologists, which may reflect larger and more frequent payments to those identified by pharmaceutical companies as thought leaders and key opinion leaders in the field or those who are more willing to establish extensive ties with industry. Similarly skewed distributions in payments have been shown in other medical subspecialties including neurosurgery, plastic surgery, otolaryngology, and orthopedics.4,6,19,20 It also is apparent that the majority of compensated dermatologists in the OPD maintain relatively small ties with industry. For every year from 2017 to 2021, more than half of compensated dermatologists received total payments of less than $500 per year, most of which stemmed from the food and beverage category. Interestingly, a prior study showed that patient perceptions of industry-physician ties may be more strongly impacted by the payment category than the amount.21 For example, respondents viewed payments for meals and lodging more negatively, as they were seen more as personal gifts without direct benefit to patients. Conversely, respondents held more positive views of physicians who received free drug samples, which were perceived as benefiting patients, as well as those receiving consulting fees, which were perceived as a signal of physician expertise. Notably, in the same study, physicians who received no payments from industry were seen as honest but also were viewed by some respondents as being inexperienced or uninformed about new treatments.21
The contribution and public perception of dermatologists who conduct investigator-initiated research utilizing other types of funding (eg, government grants) also are important to consider but were not directly assessed within the scope of the current study.
Sex Disparities in Compensation—Multiple studies in the literature have demonstrated that sex inequities exist across medical specialties.22,23 In dermatology, although women make up slightly more than 50% of board-certified dermatologists, they continue to be underrepresented compared with men in leadership positions, academic rank, research funding, and lectureships at national meetings.24-27 In survey-based studies specifically examining gender-based physician compensation, male dermatologists were found to earn higher salaries than their female counterparts in both private practice and academic settings, even after adjusting for work hours, practice characteristics, and academic rank.28,29
Our study contributes to the growing body of evidence suggesting that sex inequities also may exist with regard to financial payments from industry. Our results showed that, although the number of male and female dermatologists with industry relationships was similar each year, the number of payments made and total payment amount were both significantly (P<.001) higher for male dermatologists from 2017 through 2021. In 2021, the mean payment amount ($201.57 for male dermatologists; $117.73 for female dermatologists) and mean total amount of payments received ($6172.89 and $2957.79, respectively) also were significantly higher for male compared with female dermatologists (P<.001). The cause of this disparity likely is multifactorial and warrants additional studies in the future. One hypothesis in the existing literature is that male physicians may be more inclined to seek out relationships with industry; it also is possible that disparities in research funding, academic rank, and speaking opportunities at national conferences detailed previously may contribute to inequities in industry payments as companies seek out perceived leaders in the field.30
Limitations and Future Directions—Several important limitations of our study warrant further consideration. As with any database study, the accuracy of the results presented and the conclusions drawn are highly dependent on the precision of the available data, which is reliant on transparent documentation by pharmaceutical companies and physicians. There are no independent methods of verifying the information reported. There have been reports in the literature questioning the utility of the OPD data and risk for misinterpretation.16,31 Furthermore, the OPD only includes companies whose products are covered by government-sponsored programs, such as Medicare and Medicaid, and therefore does not encompass the totality of industry-dermatologist relationships. We also focused specifically on board-certified dermatologists and did not analyze the extent of industry relationships involving residents, nurses, physician assistants, and other critical members of health care teams that may impact patient care. Differences between academic and private practice payments also could not be examined using the OPD but could present an interesting area for future studies.
Despite these limitations, our study was extensive, using the publicly available OPD to analyze trends and disparities in financial relationships between dermatologists and industry partners from 2017 through 2021. Notably, these findings are not intended to provide judgment or seek to tease out financial relationships that are beneficial for patient care from those that are not; rather, they are intended only to lend additional transparency, provoke thought, and encourage future studies and discussion surrounding this important topic.
Conclusion
Financial relationships between dermatologists and industry are complex and are becoming more prevalent, as shown in our study. These relationships may be critical to facilitate novel patient-centered research and growth in the field of dermatology; however, they also have the potential to be seen as bias in patient care. Transparent reporting of these relationships is an important step in future research regarding the effects of different payment types and serves as the basis for further understanding industry-dermatologist relationships as well as any inequities that exist in the distribution of payments. We encourage all dermatologists to review their public profiles in the OPD. Physicians have the opportunity to review all payment data reported by companies and challenge the accuracy of the data if necessary.
- Campbell EG, Gruen RL, Mountford J, et al. A national survey of physician-industry relationships. N Engl J Med. 2007;356:1742-1750.
- Kirschner NM, Sulmasy LS, Kesselheim AS. Health policy basics: the Physician Payment Sunshine Act and the Open Payments program. Ann Intern Med. 2014;161:519-521.
- Braithwaite J, Frane N, Partan MJ, et al. Review of industry payments to general orthopaedic surgeons reported by the open payments database: 2014 to 2019. J Am Acad Orthop Surg Glob Res Rev. 2021;5:E21.00060.
- Pathak N, Mercier MR, Galivanche AR, et al. Industry payments to orthopedic spine surgeons reported by the open payments database: 2014-2017. Clin Spine Surg. 2020;33:E572-E578.
- Almaguer AM, Wills BW, Robin JX, et al. Open payments reporting of industry compensation for orthopedic residents. J Surg Educ. 2020;77:1632-1637.
- Chao AH, Gangopadhyay N. Industry financial relationships in plastic surgery: analysis of the sunshine act open payments database. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2016;138:341E-348E.
- Khetpal S, Mets EJ, Ahmad M, et al. The open payments sunshine act database revisited: a 5-year analysis of industry payments to plastic surgeons. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2021;148:877E-878E.
- Slentz DH, Nelson CC, Lichter PR. Characteristics of industry payments to ophthalmologists in the open payments database. JAMA Ophthalmol. 2019;137:1038-1044.
- Gangireddy VGR, Amin R, Yu K, et al. Analysis of payments to GI physicians in the United States: open payments data study. JGH Open. 2020;4:1031-1036.
- Feng H, Wu P, Leger M. Exploring the industry-dermatologist financial relationship: insight from the open payment data. JAMA Dermatol. 2016;152:1307-1313.
- Schlager E, Flaten H, St Claire C, et al. Industry payments to dermatologists: updates from the 2016 open payment data. Dermatol Online J. 2018;24:13030/qt8r74w3c4.
- Agrawal S, Brennan N, Budetti P. The Sunshine Act—effects on physicians. N Engl J Med. 2013;368:2054-2057.
- DeJong C, Aguilar T, Tseng CW, et al. Pharmaceutical industry-sponsored meals and physician prescribing patterns for Medicare beneficiaries. JAMA Intern Med. 2016;176:1114-1122.
- Lexchin J, Bero LA, Djulbegovic B, et al. Pharmaceutical industry sponsorship and research outcome and quality: systematic review. BMJ. 2003;326:1167-1170.
- Nakayama DK. In defense of industry-physician relationships. Am Surg. 2010;76:987-994.
- Chimonas S, DeVito NJ, Rothman DJ. Bringing transparency to medicine: exploring physicians’ views and experiences of the sunshine act. Am J Bioeth. 2017;17:4-18.
- Pham-Kanter G, Mello MM, Lehmann LS, et la. Public awareness of and contact with physicians who receive industry payments: a national survey. J Gen Intern Med. 2017;32:767-774.
- National Health Expenditure Fact Sheet. Updated December 13, 2023 Accessed August 9, 2024. https://www.cms.gov/data-research/statistics-trends-and-reports/national-health-expenditure-data/nhe-fact-sheet
- de Lotbiniere-Bassett MP, McDonald PJ. Industry financial relationships in neurosurgery in 2015: analysis of the Sunshine Act Open Payments database. World Neurosurg. 2018;114:E920-E925.
- Pathak N, Fujiwara RJT, Mehra S. Assessment of nonresearch industry payments to otolaryngologists in 2014 and 2015. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2018;158:1028-1034.
- Perry JE, Cox D, Cox AD. Trust and transparency: patient perceptions of physicians’ financial relationships with pharmaceutical companies. J Law Med Ethics. 2014;42:475-491.
- Freund KM, Raj A, Kaplan SE, et al. Inequities in academic compensation by gender: a follow-up to the national faculty survey cohort study. Acad Med. 2016;91:1068-1073.
- Seabury SA, Chandra A, Jena AB. Trends in the earnings of male and female health care professionals in the United States, 1987 to 2010. JAMA Intern Med. 2013;173:1748-1750.
- Flaten HK, Goodman L, Wong E, et al. Analysis of speaking opportunities by gender at national dermatologic surgery conferences. Dermatol Surg. 2020;46:1195-1201.
- Lobl M, Grinnell M, Higgins S, et al. Representation of women as editors in dermatology journals: a comprehensive review. Int J Womens Dermatol. 2020;6:20-24.
- Stratman H, Stratman EJ. Assessment of percentage of women in the dermatology workforce presenting at American Academy of Dermatology annual meetings, 1992-2017. JAMA Dermatol. 2019;155:384-386.
- Wu AG, Lipner SR. Sex trends in leadership of the American Academy of Dermatology: a cross-sectional study. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2020;83:592-594.
- Weeks WB, Wallace AE. Gender differences in dermatologists’ annual incomes. Cutis. 2007;80:325-332.
- Sachdeva M, Price KN, Hsiao JL, et al. Gender and rank salary trends among academic dermatologists. Int J Womens Dermatol. 2020;6:324-326.
- Rose SL, Sanghani RM, Schmidt C, et al. Gender differences in physicians’ financial ties to industry: a study of national disclosure data. PLoS One. 2015;10:E0129197.
- Santhakumar S, Adashi EY. The physician payment sunshine act: testing the value of transparency. JAMA. 2015;313:23-24.
- Campbell EG, Gruen RL, Mountford J, et al. A national survey of physician-industry relationships. N Engl J Med. 2007;356:1742-1750.
- Kirschner NM, Sulmasy LS, Kesselheim AS. Health policy basics: the Physician Payment Sunshine Act and the Open Payments program. Ann Intern Med. 2014;161:519-521.
- Braithwaite J, Frane N, Partan MJ, et al. Review of industry payments to general orthopaedic surgeons reported by the open payments database: 2014 to 2019. J Am Acad Orthop Surg Glob Res Rev. 2021;5:E21.00060.
- Pathak N, Mercier MR, Galivanche AR, et al. Industry payments to orthopedic spine surgeons reported by the open payments database: 2014-2017. Clin Spine Surg. 2020;33:E572-E578.
- Almaguer AM, Wills BW, Robin JX, et al. Open payments reporting of industry compensation for orthopedic residents. J Surg Educ. 2020;77:1632-1637.
- Chao AH, Gangopadhyay N. Industry financial relationships in plastic surgery: analysis of the sunshine act open payments database. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2016;138:341E-348E.
- Khetpal S, Mets EJ, Ahmad M, et al. The open payments sunshine act database revisited: a 5-year analysis of industry payments to plastic surgeons. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2021;148:877E-878E.
- Slentz DH, Nelson CC, Lichter PR. Characteristics of industry payments to ophthalmologists in the open payments database. JAMA Ophthalmol. 2019;137:1038-1044.
- Gangireddy VGR, Amin R, Yu K, et al. Analysis of payments to GI physicians in the United States: open payments data study. JGH Open. 2020;4:1031-1036.
- Feng H, Wu P, Leger M. Exploring the industry-dermatologist financial relationship: insight from the open payment data. JAMA Dermatol. 2016;152:1307-1313.
- Schlager E, Flaten H, St Claire C, et al. Industry payments to dermatologists: updates from the 2016 open payment data. Dermatol Online J. 2018;24:13030/qt8r74w3c4.
- Agrawal S, Brennan N, Budetti P. The Sunshine Act—effects on physicians. N Engl J Med. 2013;368:2054-2057.
- DeJong C, Aguilar T, Tseng CW, et al. Pharmaceutical industry-sponsored meals and physician prescribing patterns for Medicare beneficiaries. JAMA Intern Med. 2016;176:1114-1122.
- Lexchin J, Bero LA, Djulbegovic B, et al. Pharmaceutical industry sponsorship and research outcome and quality: systematic review. BMJ. 2003;326:1167-1170.
- Nakayama DK. In defense of industry-physician relationships. Am Surg. 2010;76:987-994.
- Chimonas S, DeVito NJ, Rothman DJ. Bringing transparency to medicine: exploring physicians’ views and experiences of the sunshine act. Am J Bioeth. 2017;17:4-18.
- Pham-Kanter G, Mello MM, Lehmann LS, et la. Public awareness of and contact with physicians who receive industry payments: a national survey. J Gen Intern Med. 2017;32:767-774.
- National Health Expenditure Fact Sheet. Updated December 13, 2023 Accessed August 9, 2024. https://www.cms.gov/data-research/statistics-trends-and-reports/national-health-expenditure-data/nhe-fact-sheet
- de Lotbiniere-Bassett MP, McDonald PJ. Industry financial relationships in neurosurgery in 2015: analysis of the Sunshine Act Open Payments database. World Neurosurg. 2018;114:E920-E925.
- Pathak N, Fujiwara RJT, Mehra S. Assessment of nonresearch industry payments to otolaryngologists in 2014 and 2015. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2018;158:1028-1034.
- Perry JE, Cox D, Cox AD. Trust and transparency: patient perceptions of physicians’ financial relationships with pharmaceutical companies. J Law Med Ethics. 2014;42:475-491.
- Freund KM, Raj A, Kaplan SE, et al. Inequities in academic compensation by gender: a follow-up to the national faculty survey cohort study. Acad Med. 2016;91:1068-1073.
- Seabury SA, Chandra A, Jena AB. Trends in the earnings of male and female health care professionals in the United States, 1987 to 2010. JAMA Intern Med. 2013;173:1748-1750.
- Flaten HK, Goodman L, Wong E, et al. Analysis of speaking opportunities by gender at national dermatologic surgery conferences. Dermatol Surg. 2020;46:1195-1201.
- Lobl M, Grinnell M, Higgins S, et al. Representation of women as editors in dermatology journals: a comprehensive review. Int J Womens Dermatol. 2020;6:20-24.
- Stratman H, Stratman EJ. Assessment of percentage of women in the dermatology workforce presenting at American Academy of Dermatology annual meetings, 1992-2017. JAMA Dermatol. 2019;155:384-386.
- Wu AG, Lipner SR. Sex trends in leadership of the American Academy of Dermatology: a cross-sectional study. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2020;83:592-594.
- Weeks WB, Wallace AE. Gender differences in dermatologists’ annual incomes. Cutis. 2007;80:325-332.
- Sachdeva M, Price KN, Hsiao JL, et al. Gender and rank salary trends among academic dermatologists. Int J Womens Dermatol. 2020;6:324-326.
- Rose SL, Sanghani RM, Schmidt C, et al. Gender differences in physicians’ financial ties to industry: a study of national disclosure data. PLoS One. 2015;10:E0129197.
- Santhakumar S, Adashi EY. The physician payment sunshine act: testing the value of transparency. JAMA. 2015;313:23-24.
Practice Points
- Industry payments to dermatologists are prevalent and complex and may have implications for patient care.
- To facilitate increased transparency around industry-physician relationships, lawmakers passed the Physician Payments Sunshine Act requiring pharmaceutical companies and device manufacturers to report all payments made to physicians.
- We encourage dermatologists to review their public profiles on the Open Payments database, as physicians have the opportunity to challenge the accuracy of the reported data, if applicable.
From Scrubs to Social Media: How Some Med Students Become Influencers
A medical student’s life is an endless cycle of classes, exams, clinical rotations, and residency preparation. On TikTok and Instagram, among other sites, they share medical school experiences and lessons learned in the classroom and advocate for causes such as increased diversity and gender rights in the medical field.
This news organization caught up with a few social media influencers with a large online following to learn how medical students can effectively use social media to build a professional brand and network. Most of the students interviewed said that their social media platforms offered an opportunity to educate others about significant medical developments, feel part of a community with a like-minded audience, and network with doctors who may lead them to a future residency or career path.
Many med students said that they built their large audiences by creating a platform for people of their ethnic background, nationality, race, gender, or simply what others weren’t already talking about. They said they saw a niche in social media that was missing or others hadn’t tackled in the same way.
When Joel Bervell began med school in 2020, he questioned some of the lessons he learned about how race is used in medical practice, which didn’t make sense to him. So, he began his own research. He had about 2000 followers on Instagram at the time.
Mr. Bervell read a new study about pulse oximeters and how they often produce misleading readings on patients with dark skin.
He wondered why he hadn’t learned this in medical school, so he posted it on TikTok. Within 24 hours, about 500,000 people viewed it. Most of the comments were from doctors, nurses, and physician assistants who said they weren’t aware of the disparity.
While his initial posts detailed his journey to medical school and a day-in-the-life of a medical student, he transitioned to posts primarily about race, health equity, and what he perceives as racial bias in medicine.
Now, the fourth-year Ghanaian-American student at the Elson S. Floyd College of Medicine at Washington State University Spokane has close to 1.2 million followers on Instagram and TikTok combined. He frequently visits the White House to advise on social media’s influence on healthcare and has appeared on the Kelly Clarkson Show, Good Morning America, CNN, and ABC, among others.
He said he also uses social media to translate complex medical information for a general audience, many of whom access health information online so they can manage their own healthcare. He sees his social media work as an extension of his medical education, allowing him to delve deeper into subjects and report on them as if he were publishing research in a medical journal.
“When I came to medical school, yes, I wanted to be a doctor. But I also wanted to impact people.” Social media allows him to educate many more people than individual patients, the 29-year-old told this news organization.
Inspiring Minorities
Tabhata Paulet, 27, started her TikTok presence as a premed student in 2021. She aimed to provide free resources to help low-income, first-generation Latinx students like herself study for standardized exams.
“I always looked online for guidance and resources, and the medical influencers did not share a similar background. So, I shared my story and what I had to do as a first-generation and first person in my family to become a physician. I did not have access to the same resources as my peers,” said Ms. Paulet, who was born in Peru and came to New Jersey as a child.
Students who are Hispanic, Latinx, or of Spanish origin made up 6.8% of total medical school enrollment in 2023-2024, up slightly from 6.7% in 2022-2023, according to the Association of American Medical Colleges (AAMC).
Ms. Paulet’s online presence grew when she began documenting her experiences as a first-year medical student, bridging the language barrier for Spanish-speaking patients so they could understand their diagnosis and treatment. She often posts about health disparity and barriers to care for underserved communities.
Most of her nearly 22,000 followers are Hispanic, said the now fourth-year student at Rutgers New Jersey Medical School in Newark, New Jersey. “I talk a lot about my interesting Spanish-speaking patients ... and how sometimes speaking their native language truly makes a difference in their care.”
She believes that she serves an important role in social media. “It can be very inspirational for those who come after you [in med school] to see someone from a similar culture and upbringing.”
Creating a Community
It was during a therapy session 4 years ago that Jeremy “JP” Scott decided to share Instagram posts about his experiences as a nontraditional medical student. The 37-year-old was studying at Ross University School of Medicine in Barbados and was feeling lonely as an international medical student training to be a doctor as a second career.
Before starting med school, Mr. Scott was an adjunct professor and lab supervisor at the University of Hartford Biology Department, West Hartford, Connecticut, and then a research assistant and lab manager at the Wistar Institute in Philadelphia.
Although he wanted to follow his mother’s path to becoming a doctor, it was more difficult than he envisioned, said the fourth-year student who completed clinical rotations in the United States and is now applying for residencies.
“I talked about how medical school is not what it appears to be ... There are a lot of challenges we are going through,” especially as people of color, he said.
Mr. Scott believes social media helps people feel included and less alone. He said many of his followers are med students and physicians.
His posts often focus on LGBTQIA+ pride and being a minority as a Black man in medicine.
“The pandemic spurred a lot of us. We had a racial reckoning in our country at the time. It inspired us to talk as Black creators and Black medical students.”
Black or African American medical students made up 8.5% of total med school enrollment in 2023-2024, a slight increase from 2022 to 2023, according to AAMC figures. Black men represented 7% of total enrollment in 2023-2024, while Black women represented 9.8%.
After only a handful of online posts in which Mr. Scott candidly discussed his mental health struggles and relationships, he attracted the attention of several medical apparel companies, including the popular FIGS scrubs. He’s now an ambassador for the company, which supports him and his content.
“My association with FIGS has helped attract a wider online audience, increasing my presence.” Today, he has 14,000 Instagram followers. “It opened up so many opportunities,” Mr. Scott said. One example is working with the national LGBTQIA+ community.
“The goal was never to be a social media influencer, to gain sponsorships or photo opportunities,” he said.
“My job, first, is as a medical student. Everything else is second. I am not trying to be a professional social media personality. I’m trying to be an actual physician.” He also tries to separate JP “social media” from Jeremy, the medical student.
“On Instagram, anyone can pull it up and see what you’re doing. The last thing I want is for them to think that I’m not serious about what I’m doing, that I’m not here to learn and become a doctor.”
Benefits and Drawbacks
Ms. Paulet said her social media following helped her connect with leaders in the Latinx medical community, including an obstetrics anesthesiologist, her intended specialty. “I don’t think I’d be able to do that without a social media platform.”
Her online activity also propelled her from regional to national leadership in the Latino Medical Student Association (LMSA). She now also runs their Instagram page, which has 14,000 followers.
Mr. Bervell believes social media is a great way to network. He’s connected with people he wouldn’t have met otherwise, including physicians. “I think it will help me get into a residency,” he said. “It allows people to know who you are ... They will be able to tell in a few videos the type of doctor I want to be.”
On the other hand, Mr. Bervell is aware of the negative impacts of social media on mental health. “You can get lost in social media.” For that reason, he often tries to disconnect. “I can go days without my phone.”
Posting on social media can be time-consuming, Mr. Bervell admitted. He said he spent about 2 hours a day researching, editing, and posting on TikTok when he first started building his following. Now, he spends about 2-3 hours a week creating videos. “I don’t post every day anymore. I don’t have the time.”
When she started building her TikTok presence, Ms. Paulet said she devoted 15 hours a week to the endeavor, but now she spends 10-12 hours a week posting online, including on LMSA’s Instagram page. “Whenever you are done with an exam or have a study break, this is something fun to do.” She also says you never know who you’re going to inspire when you put yourself out there.
“Talk about your journey, rotations, or your experience in your first or second year of medical school. Talk about milestones like board exams.”
Word to the Wise
Some students may be concerned that their posts might affect a potential residency program. But the medical students interviewed say they want to find programs that align with their values and accept them for who they are.
Mr. Scott said he’s not worried about someone not liking him because of who he is. “I am Black and openly gay. If it’s a problem, I don’t need to work with you or your institution.”
Mr. Bervell stressed that medical students should stay professional online. “I reach 5-10 million people a month, and I have to think: Would I want them to see this? You have to know at all times that someone is watching. I’m very careful about how I post. I script out every video.”
Mr. Scott agreed. He advises those interested in becoming medical influencers to know what they can’t post online. For example, to ensure safety and privacy, Mr. Scott doesn’t take photos in the hospital, show his medical badge, or post patient information. “You want to be respectful of your future medical profession,” he said.
“If it’s something my mother would be ashamed of, I don’t need to post about it.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
A medical student’s life is an endless cycle of classes, exams, clinical rotations, and residency preparation. On TikTok and Instagram, among other sites, they share medical school experiences and lessons learned in the classroom and advocate for causes such as increased diversity and gender rights in the medical field.
This news organization caught up with a few social media influencers with a large online following to learn how medical students can effectively use social media to build a professional brand and network. Most of the students interviewed said that their social media platforms offered an opportunity to educate others about significant medical developments, feel part of a community with a like-minded audience, and network with doctors who may lead them to a future residency or career path.
Many med students said that they built their large audiences by creating a platform for people of their ethnic background, nationality, race, gender, or simply what others weren’t already talking about. They said they saw a niche in social media that was missing or others hadn’t tackled in the same way.
When Joel Bervell began med school in 2020, he questioned some of the lessons he learned about how race is used in medical practice, which didn’t make sense to him. So, he began his own research. He had about 2000 followers on Instagram at the time.
Mr. Bervell read a new study about pulse oximeters and how they often produce misleading readings on patients with dark skin.
He wondered why he hadn’t learned this in medical school, so he posted it on TikTok. Within 24 hours, about 500,000 people viewed it. Most of the comments were from doctors, nurses, and physician assistants who said they weren’t aware of the disparity.
While his initial posts detailed his journey to medical school and a day-in-the-life of a medical student, he transitioned to posts primarily about race, health equity, and what he perceives as racial bias in medicine.
Now, the fourth-year Ghanaian-American student at the Elson S. Floyd College of Medicine at Washington State University Spokane has close to 1.2 million followers on Instagram and TikTok combined. He frequently visits the White House to advise on social media’s influence on healthcare and has appeared on the Kelly Clarkson Show, Good Morning America, CNN, and ABC, among others.
He said he also uses social media to translate complex medical information for a general audience, many of whom access health information online so they can manage their own healthcare. He sees his social media work as an extension of his medical education, allowing him to delve deeper into subjects and report on them as if he were publishing research in a medical journal.
“When I came to medical school, yes, I wanted to be a doctor. But I also wanted to impact people.” Social media allows him to educate many more people than individual patients, the 29-year-old told this news organization.
Inspiring Minorities
Tabhata Paulet, 27, started her TikTok presence as a premed student in 2021. She aimed to provide free resources to help low-income, first-generation Latinx students like herself study for standardized exams.
“I always looked online for guidance and resources, and the medical influencers did not share a similar background. So, I shared my story and what I had to do as a first-generation and first person in my family to become a physician. I did not have access to the same resources as my peers,” said Ms. Paulet, who was born in Peru and came to New Jersey as a child.
Students who are Hispanic, Latinx, or of Spanish origin made up 6.8% of total medical school enrollment in 2023-2024, up slightly from 6.7% in 2022-2023, according to the Association of American Medical Colleges (AAMC).
Ms. Paulet’s online presence grew when she began documenting her experiences as a first-year medical student, bridging the language barrier for Spanish-speaking patients so they could understand their diagnosis and treatment. She often posts about health disparity and barriers to care for underserved communities.
Most of her nearly 22,000 followers are Hispanic, said the now fourth-year student at Rutgers New Jersey Medical School in Newark, New Jersey. “I talk a lot about my interesting Spanish-speaking patients ... and how sometimes speaking their native language truly makes a difference in their care.”
She believes that she serves an important role in social media. “It can be very inspirational for those who come after you [in med school] to see someone from a similar culture and upbringing.”
Creating a Community
It was during a therapy session 4 years ago that Jeremy “JP” Scott decided to share Instagram posts about his experiences as a nontraditional medical student. The 37-year-old was studying at Ross University School of Medicine in Barbados and was feeling lonely as an international medical student training to be a doctor as a second career.
Before starting med school, Mr. Scott was an adjunct professor and lab supervisor at the University of Hartford Biology Department, West Hartford, Connecticut, and then a research assistant and lab manager at the Wistar Institute in Philadelphia.
Although he wanted to follow his mother’s path to becoming a doctor, it was more difficult than he envisioned, said the fourth-year student who completed clinical rotations in the United States and is now applying for residencies.
“I talked about how medical school is not what it appears to be ... There are a lot of challenges we are going through,” especially as people of color, he said.
Mr. Scott believes social media helps people feel included and less alone. He said many of his followers are med students and physicians.
His posts often focus on LGBTQIA+ pride and being a minority as a Black man in medicine.
“The pandemic spurred a lot of us. We had a racial reckoning in our country at the time. It inspired us to talk as Black creators and Black medical students.”
Black or African American medical students made up 8.5% of total med school enrollment in 2023-2024, a slight increase from 2022 to 2023, according to AAMC figures. Black men represented 7% of total enrollment in 2023-2024, while Black women represented 9.8%.
After only a handful of online posts in which Mr. Scott candidly discussed his mental health struggles and relationships, he attracted the attention of several medical apparel companies, including the popular FIGS scrubs. He’s now an ambassador for the company, which supports him and his content.
“My association with FIGS has helped attract a wider online audience, increasing my presence.” Today, he has 14,000 Instagram followers. “It opened up so many opportunities,” Mr. Scott said. One example is working with the national LGBTQIA+ community.
“The goal was never to be a social media influencer, to gain sponsorships or photo opportunities,” he said.
“My job, first, is as a medical student. Everything else is second. I am not trying to be a professional social media personality. I’m trying to be an actual physician.” He also tries to separate JP “social media” from Jeremy, the medical student.
“On Instagram, anyone can pull it up and see what you’re doing. The last thing I want is for them to think that I’m not serious about what I’m doing, that I’m not here to learn and become a doctor.”
Benefits and Drawbacks
Ms. Paulet said her social media following helped her connect with leaders in the Latinx medical community, including an obstetrics anesthesiologist, her intended specialty. “I don’t think I’d be able to do that without a social media platform.”
Her online activity also propelled her from regional to national leadership in the Latino Medical Student Association (LMSA). She now also runs their Instagram page, which has 14,000 followers.
Mr. Bervell believes social media is a great way to network. He’s connected with people he wouldn’t have met otherwise, including physicians. “I think it will help me get into a residency,” he said. “It allows people to know who you are ... They will be able to tell in a few videos the type of doctor I want to be.”
On the other hand, Mr. Bervell is aware of the negative impacts of social media on mental health. “You can get lost in social media.” For that reason, he often tries to disconnect. “I can go days without my phone.”
Posting on social media can be time-consuming, Mr. Bervell admitted. He said he spent about 2 hours a day researching, editing, and posting on TikTok when he first started building his following. Now, he spends about 2-3 hours a week creating videos. “I don’t post every day anymore. I don’t have the time.”
When she started building her TikTok presence, Ms. Paulet said she devoted 15 hours a week to the endeavor, but now she spends 10-12 hours a week posting online, including on LMSA’s Instagram page. “Whenever you are done with an exam or have a study break, this is something fun to do.” She also says you never know who you’re going to inspire when you put yourself out there.
“Talk about your journey, rotations, or your experience in your first or second year of medical school. Talk about milestones like board exams.”
Word to the Wise
Some students may be concerned that their posts might affect a potential residency program. But the medical students interviewed say they want to find programs that align with their values and accept them for who they are.
Mr. Scott said he’s not worried about someone not liking him because of who he is. “I am Black and openly gay. If it’s a problem, I don’t need to work with you or your institution.”
Mr. Bervell stressed that medical students should stay professional online. “I reach 5-10 million people a month, and I have to think: Would I want them to see this? You have to know at all times that someone is watching. I’m very careful about how I post. I script out every video.”
Mr. Scott agreed. He advises those interested in becoming medical influencers to know what they can’t post online. For example, to ensure safety and privacy, Mr. Scott doesn’t take photos in the hospital, show his medical badge, or post patient information. “You want to be respectful of your future medical profession,” he said.
“If it’s something my mother would be ashamed of, I don’t need to post about it.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
A medical student’s life is an endless cycle of classes, exams, clinical rotations, and residency preparation. On TikTok and Instagram, among other sites, they share medical school experiences and lessons learned in the classroom and advocate for causes such as increased diversity and gender rights in the medical field.
This news organization caught up with a few social media influencers with a large online following to learn how medical students can effectively use social media to build a professional brand and network. Most of the students interviewed said that their social media platforms offered an opportunity to educate others about significant medical developments, feel part of a community with a like-minded audience, and network with doctors who may lead them to a future residency or career path.
Many med students said that they built their large audiences by creating a platform for people of their ethnic background, nationality, race, gender, or simply what others weren’t already talking about. They said they saw a niche in social media that was missing or others hadn’t tackled in the same way.
When Joel Bervell began med school in 2020, he questioned some of the lessons he learned about how race is used in medical practice, which didn’t make sense to him. So, he began his own research. He had about 2000 followers on Instagram at the time.
Mr. Bervell read a new study about pulse oximeters and how they often produce misleading readings on patients with dark skin.
He wondered why he hadn’t learned this in medical school, so he posted it on TikTok. Within 24 hours, about 500,000 people viewed it. Most of the comments were from doctors, nurses, and physician assistants who said they weren’t aware of the disparity.
While his initial posts detailed his journey to medical school and a day-in-the-life of a medical student, he transitioned to posts primarily about race, health equity, and what he perceives as racial bias in medicine.
Now, the fourth-year Ghanaian-American student at the Elson S. Floyd College of Medicine at Washington State University Spokane has close to 1.2 million followers on Instagram and TikTok combined. He frequently visits the White House to advise on social media’s influence on healthcare and has appeared on the Kelly Clarkson Show, Good Morning America, CNN, and ABC, among others.
He said he also uses social media to translate complex medical information for a general audience, many of whom access health information online so they can manage their own healthcare. He sees his social media work as an extension of his medical education, allowing him to delve deeper into subjects and report on them as if he were publishing research in a medical journal.
“When I came to medical school, yes, I wanted to be a doctor. But I also wanted to impact people.” Social media allows him to educate many more people than individual patients, the 29-year-old told this news organization.
Inspiring Minorities
Tabhata Paulet, 27, started her TikTok presence as a premed student in 2021. She aimed to provide free resources to help low-income, first-generation Latinx students like herself study for standardized exams.
“I always looked online for guidance and resources, and the medical influencers did not share a similar background. So, I shared my story and what I had to do as a first-generation and first person in my family to become a physician. I did not have access to the same resources as my peers,” said Ms. Paulet, who was born in Peru and came to New Jersey as a child.
Students who are Hispanic, Latinx, or of Spanish origin made up 6.8% of total medical school enrollment in 2023-2024, up slightly from 6.7% in 2022-2023, according to the Association of American Medical Colleges (AAMC).
Ms. Paulet’s online presence grew when she began documenting her experiences as a first-year medical student, bridging the language barrier for Spanish-speaking patients so they could understand their diagnosis and treatment. She often posts about health disparity and barriers to care for underserved communities.
Most of her nearly 22,000 followers are Hispanic, said the now fourth-year student at Rutgers New Jersey Medical School in Newark, New Jersey. “I talk a lot about my interesting Spanish-speaking patients ... and how sometimes speaking their native language truly makes a difference in their care.”
She believes that she serves an important role in social media. “It can be very inspirational for those who come after you [in med school] to see someone from a similar culture and upbringing.”
Creating a Community
It was during a therapy session 4 years ago that Jeremy “JP” Scott decided to share Instagram posts about his experiences as a nontraditional medical student. The 37-year-old was studying at Ross University School of Medicine in Barbados and was feeling lonely as an international medical student training to be a doctor as a second career.
Before starting med school, Mr. Scott was an adjunct professor and lab supervisor at the University of Hartford Biology Department, West Hartford, Connecticut, and then a research assistant and lab manager at the Wistar Institute in Philadelphia.
Although he wanted to follow his mother’s path to becoming a doctor, it was more difficult than he envisioned, said the fourth-year student who completed clinical rotations in the United States and is now applying for residencies.
“I talked about how medical school is not what it appears to be ... There are a lot of challenges we are going through,” especially as people of color, he said.
Mr. Scott believes social media helps people feel included and less alone. He said many of his followers are med students and physicians.
His posts often focus on LGBTQIA+ pride and being a minority as a Black man in medicine.
“The pandemic spurred a lot of us. We had a racial reckoning in our country at the time. It inspired us to talk as Black creators and Black medical students.”
Black or African American medical students made up 8.5% of total med school enrollment in 2023-2024, a slight increase from 2022 to 2023, according to AAMC figures. Black men represented 7% of total enrollment in 2023-2024, while Black women represented 9.8%.
After only a handful of online posts in which Mr. Scott candidly discussed his mental health struggles and relationships, he attracted the attention of several medical apparel companies, including the popular FIGS scrubs. He’s now an ambassador for the company, which supports him and his content.
“My association with FIGS has helped attract a wider online audience, increasing my presence.” Today, he has 14,000 Instagram followers. “It opened up so many opportunities,” Mr. Scott said. One example is working with the national LGBTQIA+ community.
“The goal was never to be a social media influencer, to gain sponsorships or photo opportunities,” he said.
“My job, first, is as a medical student. Everything else is second. I am not trying to be a professional social media personality. I’m trying to be an actual physician.” He also tries to separate JP “social media” from Jeremy, the medical student.
“On Instagram, anyone can pull it up and see what you’re doing. The last thing I want is for them to think that I’m not serious about what I’m doing, that I’m not here to learn and become a doctor.”
Benefits and Drawbacks
Ms. Paulet said her social media following helped her connect with leaders in the Latinx medical community, including an obstetrics anesthesiologist, her intended specialty. “I don’t think I’d be able to do that without a social media platform.”
Her online activity also propelled her from regional to national leadership in the Latino Medical Student Association (LMSA). She now also runs their Instagram page, which has 14,000 followers.
Mr. Bervell believes social media is a great way to network. He’s connected with people he wouldn’t have met otherwise, including physicians. “I think it will help me get into a residency,” he said. “It allows people to know who you are ... They will be able to tell in a few videos the type of doctor I want to be.”
On the other hand, Mr. Bervell is aware of the negative impacts of social media on mental health. “You can get lost in social media.” For that reason, he often tries to disconnect. “I can go days without my phone.”
Posting on social media can be time-consuming, Mr. Bervell admitted. He said he spent about 2 hours a day researching, editing, and posting on TikTok when he first started building his following. Now, he spends about 2-3 hours a week creating videos. “I don’t post every day anymore. I don’t have the time.”
When she started building her TikTok presence, Ms. Paulet said she devoted 15 hours a week to the endeavor, but now she spends 10-12 hours a week posting online, including on LMSA’s Instagram page. “Whenever you are done with an exam or have a study break, this is something fun to do.” She also says you never know who you’re going to inspire when you put yourself out there.
“Talk about your journey, rotations, or your experience in your first or second year of medical school. Talk about milestones like board exams.”
Word to the Wise
Some students may be concerned that their posts might affect a potential residency program. But the medical students interviewed say they want to find programs that align with their values and accept them for who they are.
Mr. Scott said he’s not worried about someone not liking him because of who he is. “I am Black and openly gay. If it’s a problem, I don’t need to work with you or your institution.”
Mr. Bervell stressed that medical students should stay professional online. “I reach 5-10 million people a month, and I have to think: Would I want them to see this? You have to know at all times that someone is watching. I’m very careful about how I post. I script out every video.”
Mr. Scott agreed. He advises those interested in becoming medical influencers to know what they can’t post online. For example, to ensure safety and privacy, Mr. Scott doesn’t take photos in the hospital, show his medical badge, or post patient information. “You want to be respectful of your future medical profession,” he said.
“If it’s something my mother would be ashamed of, I don’t need to post about it.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Balloon Catheters May Reduce Blood Loss in Women with Placenta Accreta Spectrum Disorder
Prophylactic placement of balloon catheters or sheaths prior to planned cesarean delivery may reduce blood loss in women with placenta accreta spectrum disorder, according to a new systematic review of more than 5,000 individuals.
Placenta accreta spectrum disorder occurs when the endometrial-myometrial interface of the uterus is damaged, wrote Lisanne R. Bonsen, MD, of Leiden University Medical Center, the Netherlands, and colleagues. As a result, the placenta fails to detach at the time of birth and can result in life-threatening postpartum hemorrhage, the researchers said.
The greater the depth of placental invasiveness, the more severe the maternal outcomes, the researchers noted. Previous cesarean delivery is the primary risk factor for placenta accreta spectrum disorder, and the incidence has increased along with the increased rates of cesarean delivery on a global level, they explained.
More research is needed on intrapartum strategies to improve maternal outcomes, and prophylactic radiologic intervention to reduce perioperative blood loss has been explored, the researchers wrote. However, placenta accreta spectrum disorder remains relatively rare in most pregnancy settings, and data on the effect of prophylactic radiologic interventions to reduce bleeding in this high-risk population are limited they said.
In the review published in Obstetrics & Gynecology, the researchers analyzed data from 50 studies of prophylactic radiologic interventions (48 observational studies and 2 randomized, controlled trials) including 5,962 women.
The primary outcome was perioperative blood loss; secondary outcomes included the number of red blood cells transferred within 24 hours after delivery, maternal mortality, adverse events related to the interventions, and surgical complications.
Blood loss was significantly lower in the intervention groups compared with the control groups for patients who underwent distal balloon occlusion (30 studies), proximal balloon occlusion (14 studies), or uterine artery embolization (5 studies), with mean differences in blood loss of 406 mL, 1,041 mL, and 936 mL, respectively.
Results were similar with lower blood loss for intervention patients compared with controls in subgroup analyses of different types of placenta accreta spectrum disorder and those with placenta accreta spectrum disorder confirmed post partum.
Across the 35 studies that included data on blood transfusions, women who underwent any prophylactic radiologic intervention averaged fewer red blood cell units transferred than women who had no radiologic intervention, with a mean difference of 1.13, 1.90, and 1.86 units for distal prophylactic balloon occlusion, proximal prophylactic balloon occlusion, and prophylactic uterine artery embolization, respectively.
Data on adverse events related to the interventions were limited, but noted in approximately 2% of patients who underwent distal or proximal prophylactic balloon occlusion, and 45% of patients who underwent prophylactic uterine artery embolization. One maternal death was reported and attributed to diffuse intravascular coagulation. Three cardiac arrests occurred in control patients across different studies and all were successfully resuscitated.
Most of the studies did not report data on the researchers’ predefined secondary outcomes, including shock, transfer to a higher level of care, coagulopathy, organ dysfunction, and patient-reported outcomes.
What Works Best
“Our main analysis reveals differences in outcomes among the three interventions, with proximal balloon occlusion demonstrating the strongest effect,” the researchers wrote. “Our results show a blood loss reduction of 406 mL by distal prophylactic balloon occlusion. An explanation for the differences between the results of prophylactic balloon occlusion–distal and prophylactic balloon occlusion–proximal could be that implementing occlusion at a distal level may be less effective because of bleeding from the collateral circulation,” they said.
The findings were limited by several factors including the observational design of most of the studies, variation in measurements of blood loss among studies and in inclusion criteria, and insufficient adverse event data to draw conclusions about safety, the researchers noted. More research is needed to examine efficacy and safety of the interventions according to different sensitivities of placenta accreta spectrum disorder, they added.
Results Support Judicious Intervention
“Although previous studies showed mixed results, our meta-analysis demonstrated that prophylactic radiologic interventions, particularly balloon occlusion (both distal and proximal), were associated with reduced perioperative blood loss and less red blood cell unit transfusion; this was most pronounced in women with confirmed placenta percreta,” Bonsen said in an interview. However, the heterogeneity across the included studies prevents generalizations about the overall effects of the interventions across different severities of placenta accreta spectrum disorder, she said.*
Despite these limitations, the overview of the currently available evidence provides insights for clinical decision making, said Bonsen. “Our study highlights that, if we were to be certain of the diagnosis of placenta accreta spectrum disorder antepartum, prophylactic radiologic intervention could help reduce peripartum blood loss,” she said.
Risks vs Benefits
“Given the challenges in performing randomized surgical trials in a pregnant patient population with an uncommon disorder, this level of evidence provides important data to assist with clinical decision making in patients with placenta accreta spectrum disorder,” despite the limitations of the observational studies, wrote Jocelyn S. Chapman, MD, and Arianna M. Cassidy, MD, both affiliated with the Multidisciplinary Approach to Placenta Accreta Spectrum Disorder Service (MAPS) at the University of California, San Francisco, in an accompanying editorial.
Previous research has shown an increased risk of severe maternal morbidity among women with placenta accreta spectrum disorder and previous intervention strategies have involved protocols, surgical techniques, and management strategies, they wrote.
Uterine artery embolization after cesarean delivery also has been associated with reduced hemorrhage and no adverse events, but this procedure was not included in the studies reviewed and is best conducted in a delivery setup not available in many hospital systems, the editorialists noted.
The current study illustrates the value of prophylactic balloon occlusion and placement of vascular sheaths to reduce blood loss and blood transfusion, but the risk of thrombosis and lumbosacral pain must be considered, they said. These risks may be a reasonable trade-off to avoid severe blood loss and ICU care, and to preserve the uterus, Chapman and Cassidy added.
“However, we would urge continued critical appraisal of each placenta accreta spectrum disorder case with a multidisciplinary team to evaluate the available evidence-based strategies most likely to mitigate clinically relevant complications while minimizing the introduction of new ones,” the editorialists concluded.
The study received no outside funding. The researchers had no financial conflicts to disclose. Dr. Chapman and Dr. Cassidy had no financial conflicts to disclose.
*This story was updated on August 28, 2024.
Prophylactic placement of balloon catheters or sheaths prior to planned cesarean delivery may reduce blood loss in women with placenta accreta spectrum disorder, according to a new systematic review of more than 5,000 individuals.
Placenta accreta spectrum disorder occurs when the endometrial-myometrial interface of the uterus is damaged, wrote Lisanne R. Bonsen, MD, of Leiden University Medical Center, the Netherlands, and colleagues. As a result, the placenta fails to detach at the time of birth and can result in life-threatening postpartum hemorrhage, the researchers said.
The greater the depth of placental invasiveness, the more severe the maternal outcomes, the researchers noted. Previous cesarean delivery is the primary risk factor for placenta accreta spectrum disorder, and the incidence has increased along with the increased rates of cesarean delivery on a global level, they explained.
More research is needed on intrapartum strategies to improve maternal outcomes, and prophylactic radiologic intervention to reduce perioperative blood loss has been explored, the researchers wrote. However, placenta accreta spectrum disorder remains relatively rare in most pregnancy settings, and data on the effect of prophylactic radiologic interventions to reduce bleeding in this high-risk population are limited they said.
In the review published in Obstetrics & Gynecology, the researchers analyzed data from 50 studies of prophylactic radiologic interventions (48 observational studies and 2 randomized, controlled trials) including 5,962 women.
The primary outcome was perioperative blood loss; secondary outcomes included the number of red blood cells transferred within 24 hours after delivery, maternal mortality, adverse events related to the interventions, and surgical complications.
Blood loss was significantly lower in the intervention groups compared with the control groups for patients who underwent distal balloon occlusion (30 studies), proximal balloon occlusion (14 studies), or uterine artery embolization (5 studies), with mean differences in blood loss of 406 mL, 1,041 mL, and 936 mL, respectively.
Results were similar with lower blood loss for intervention patients compared with controls in subgroup analyses of different types of placenta accreta spectrum disorder and those with placenta accreta spectrum disorder confirmed post partum.
Across the 35 studies that included data on blood transfusions, women who underwent any prophylactic radiologic intervention averaged fewer red blood cell units transferred than women who had no radiologic intervention, with a mean difference of 1.13, 1.90, and 1.86 units for distal prophylactic balloon occlusion, proximal prophylactic balloon occlusion, and prophylactic uterine artery embolization, respectively.
Data on adverse events related to the interventions were limited, but noted in approximately 2% of patients who underwent distal or proximal prophylactic balloon occlusion, and 45% of patients who underwent prophylactic uterine artery embolization. One maternal death was reported and attributed to diffuse intravascular coagulation. Three cardiac arrests occurred in control patients across different studies and all were successfully resuscitated.
Most of the studies did not report data on the researchers’ predefined secondary outcomes, including shock, transfer to a higher level of care, coagulopathy, organ dysfunction, and patient-reported outcomes.
What Works Best
“Our main analysis reveals differences in outcomes among the three interventions, with proximal balloon occlusion demonstrating the strongest effect,” the researchers wrote. “Our results show a blood loss reduction of 406 mL by distal prophylactic balloon occlusion. An explanation for the differences between the results of prophylactic balloon occlusion–distal and prophylactic balloon occlusion–proximal could be that implementing occlusion at a distal level may be less effective because of bleeding from the collateral circulation,” they said.
The findings were limited by several factors including the observational design of most of the studies, variation in measurements of blood loss among studies and in inclusion criteria, and insufficient adverse event data to draw conclusions about safety, the researchers noted. More research is needed to examine efficacy and safety of the interventions according to different sensitivities of placenta accreta spectrum disorder, they added.
Results Support Judicious Intervention
“Although previous studies showed mixed results, our meta-analysis demonstrated that prophylactic radiologic interventions, particularly balloon occlusion (both distal and proximal), were associated with reduced perioperative blood loss and less red blood cell unit transfusion; this was most pronounced in women with confirmed placenta percreta,” Bonsen said in an interview. However, the heterogeneity across the included studies prevents generalizations about the overall effects of the interventions across different severities of placenta accreta spectrum disorder, she said.*
Despite these limitations, the overview of the currently available evidence provides insights for clinical decision making, said Bonsen. “Our study highlights that, if we were to be certain of the diagnosis of placenta accreta spectrum disorder antepartum, prophylactic radiologic intervention could help reduce peripartum blood loss,” she said.
Risks vs Benefits
“Given the challenges in performing randomized surgical trials in a pregnant patient population with an uncommon disorder, this level of evidence provides important data to assist with clinical decision making in patients with placenta accreta spectrum disorder,” despite the limitations of the observational studies, wrote Jocelyn S. Chapman, MD, and Arianna M. Cassidy, MD, both affiliated with the Multidisciplinary Approach to Placenta Accreta Spectrum Disorder Service (MAPS) at the University of California, San Francisco, in an accompanying editorial.
Previous research has shown an increased risk of severe maternal morbidity among women with placenta accreta spectrum disorder and previous intervention strategies have involved protocols, surgical techniques, and management strategies, they wrote.
Uterine artery embolization after cesarean delivery also has been associated with reduced hemorrhage and no adverse events, but this procedure was not included in the studies reviewed and is best conducted in a delivery setup not available in many hospital systems, the editorialists noted.
The current study illustrates the value of prophylactic balloon occlusion and placement of vascular sheaths to reduce blood loss and blood transfusion, but the risk of thrombosis and lumbosacral pain must be considered, they said. These risks may be a reasonable trade-off to avoid severe blood loss and ICU care, and to preserve the uterus, Chapman and Cassidy added.
“However, we would urge continued critical appraisal of each placenta accreta spectrum disorder case with a multidisciplinary team to evaluate the available evidence-based strategies most likely to mitigate clinically relevant complications while minimizing the introduction of new ones,” the editorialists concluded.
The study received no outside funding. The researchers had no financial conflicts to disclose. Dr. Chapman and Dr. Cassidy had no financial conflicts to disclose.
*This story was updated on August 28, 2024.
Prophylactic placement of balloon catheters or sheaths prior to planned cesarean delivery may reduce blood loss in women with placenta accreta spectrum disorder, according to a new systematic review of more than 5,000 individuals.
Placenta accreta spectrum disorder occurs when the endometrial-myometrial interface of the uterus is damaged, wrote Lisanne R. Bonsen, MD, of Leiden University Medical Center, the Netherlands, and colleagues. As a result, the placenta fails to detach at the time of birth and can result in life-threatening postpartum hemorrhage, the researchers said.
The greater the depth of placental invasiveness, the more severe the maternal outcomes, the researchers noted. Previous cesarean delivery is the primary risk factor for placenta accreta spectrum disorder, and the incidence has increased along with the increased rates of cesarean delivery on a global level, they explained.
More research is needed on intrapartum strategies to improve maternal outcomes, and prophylactic radiologic intervention to reduce perioperative blood loss has been explored, the researchers wrote. However, placenta accreta spectrum disorder remains relatively rare in most pregnancy settings, and data on the effect of prophylactic radiologic interventions to reduce bleeding in this high-risk population are limited they said.
In the review published in Obstetrics & Gynecology, the researchers analyzed data from 50 studies of prophylactic radiologic interventions (48 observational studies and 2 randomized, controlled trials) including 5,962 women.
The primary outcome was perioperative blood loss; secondary outcomes included the number of red blood cells transferred within 24 hours after delivery, maternal mortality, adverse events related to the interventions, and surgical complications.
Blood loss was significantly lower in the intervention groups compared with the control groups for patients who underwent distal balloon occlusion (30 studies), proximal balloon occlusion (14 studies), or uterine artery embolization (5 studies), with mean differences in blood loss of 406 mL, 1,041 mL, and 936 mL, respectively.
Results were similar with lower blood loss for intervention patients compared with controls in subgroup analyses of different types of placenta accreta spectrum disorder and those with placenta accreta spectrum disorder confirmed post partum.
Across the 35 studies that included data on blood transfusions, women who underwent any prophylactic radiologic intervention averaged fewer red blood cell units transferred than women who had no radiologic intervention, with a mean difference of 1.13, 1.90, and 1.86 units for distal prophylactic balloon occlusion, proximal prophylactic balloon occlusion, and prophylactic uterine artery embolization, respectively.
Data on adverse events related to the interventions were limited, but noted in approximately 2% of patients who underwent distal or proximal prophylactic balloon occlusion, and 45% of patients who underwent prophylactic uterine artery embolization. One maternal death was reported and attributed to diffuse intravascular coagulation. Three cardiac arrests occurred in control patients across different studies and all were successfully resuscitated.
Most of the studies did not report data on the researchers’ predefined secondary outcomes, including shock, transfer to a higher level of care, coagulopathy, organ dysfunction, and patient-reported outcomes.
What Works Best
“Our main analysis reveals differences in outcomes among the three interventions, with proximal balloon occlusion demonstrating the strongest effect,” the researchers wrote. “Our results show a blood loss reduction of 406 mL by distal prophylactic balloon occlusion. An explanation for the differences between the results of prophylactic balloon occlusion–distal and prophylactic balloon occlusion–proximal could be that implementing occlusion at a distal level may be less effective because of bleeding from the collateral circulation,” they said.
The findings were limited by several factors including the observational design of most of the studies, variation in measurements of blood loss among studies and in inclusion criteria, and insufficient adverse event data to draw conclusions about safety, the researchers noted. More research is needed to examine efficacy and safety of the interventions according to different sensitivities of placenta accreta spectrum disorder, they added.
Results Support Judicious Intervention
“Although previous studies showed mixed results, our meta-analysis demonstrated that prophylactic radiologic interventions, particularly balloon occlusion (both distal and proximal), were associated with reduced perioperative blood loss and less red blood cell unit transfusion; this was most pronounced in women with confirmed placenta percreta,” Bonsen said in an interview. However, the heterogeneity across the included studies prevents generalizations about the overall effects of the interventions across different severities of placenta accreta spectrum disorder, she said.*
Despite these limitations, the overview of the currently available evidence provides insights for clinical decision making, said Bonsen. “Our study highlights that, if we were to be certain of the diagnosis of placenta accreta spectrum disorder antepartum, prophylactic radiologic intervention could help reduce peripartum blood loss,” she said.
Risks vs Benefits
“Given the challenges in performing randomized surgical trials in a pregnant patient population with an uncommon disorder, this level of evidence provides important data to assist with clinical decision making in patients with placenta accreta spectrum disorder,” despite the limitations of the observational studies, wrote Jocelyn S. Chapman, MD, and Arianna M. Cassidy, MD, both affiliated with the Multidisciplinary Approach to Placenta Accreta Spectrum Disorder Service (MAPS) at the University of California, San Francisco, in an accompanying editorial.
Previous research has shown an increased risk of severe maternal morbidity among women with placenta accreta spectrum disorder and previous intervention strategies have involved protocols, surgical techniques, and management strategies, they wrote.
Uterine artery embolization after cesarean delivery also has been associated with reduced hemorrhage and no adverse events, but this procedure was not included in the studies reviewed and is best conducted in a delivery setup not available in many hospital systems, the editorialists noted.
The current study illustrates the value of prophylactic balloon occlusion and placement of vascular sheaths to reduce blood loss and blood transfusion, but the risk of thrombosis and lumbosacral pain must be considered, they said. These risks may be a reasonable trade-off to avoid severe blood loss and ICU care, and to preserve the uterus, Chapman and Cassidy added.
“However, we would urge continued critical appraisal of each placenta accreta spectrum disorder case with a multidisciplinary team to evaluate the available evidence-based strategies most likely to mitigate clinically relevant complications while minimizing the introduction of new ones,” the editorialists concluded.
The study received no outside funding. The researchers had no financial conflicts to disclose. Dr. Chapman and Dr. Cassidy had no financial conflicts to disclose.
*This story was updated on August 28, 2024.
FROM OBSTETRICS & GYNECOLOGY
Aspirin for CRC Prevention May Work Best in Adults With Unhealthy Lifestyles
TOPLINE:
METHODOLOGY:
- Aspirin is an established agent for CRC prevention. Whether individuals with more lifestyle risk factors might derive greater benefit from aspirin remains unclear.
- Researchers analyzed regular aspirin use (defined as taking two or more standard 325-mg tablets per week) using long-term follow-up data from 63,957 women in the Nurses’ Health Study and 43,698 men in the Health Professionals Follow-Up Study.
- They calculated a healthy lifestyle score for each participant based on body mass index (BMI), alcohol intake, physical activity, diet, and smoking, with higher scores corresponding to healthier lifestyles.
- Outcomes included multivariable-adjusted 10-year cumulative incidence of CRC, the absolute risk reduction (ARR) with aspirin use, and number needed to treat associated with regular aspirin use by lifestyle score.
TAKEAWAY:
- During more than 3 million person-years of follow-up, 2544 new cases of CRC were documented.
- The 10-year cumulative incidence of CRC was 1.98% among regular aspirin users compared with 2.95% among nonusers, corresponding to an ARR of 0.97%.
- The ARR associated with aspirin use was greatest among individuals with the unhealthiest lifestyle scores and progressively decreased with healthier lifestyle scores (P < .001 for additive interaction).
- Those with the unhealthiest lifestyle scores (0-1) had a 10-year ARR of 1.28% from aspirin use, whereas those with the healthiest lifestyle scores (4-5) had an ARR of 0.11%.
- The number needed to treat with aspirin for 10 years to prevent one CRC case was 78 for those with the unhealthiest lifestyles, compared with 909 for those with the healthiest lifestyles.
- Among the individual components of the healthy lifestyle score, higher BMI and smoking correlated with greater reductions in CRC risk from aspirin use.
IN PRACTICE:
“These results support the use of lifestyle risk factors to identify individuals who may have a more favorable risk-benefit profile for cancer prevention with aspirin,” the authors wrote.
SOURCE:
The study, with first author Daniel R. Sikavi, MD, from Massachusetts General Hospital and Harvard Medical School in Boston, was published online in JAMA Oncology.
LIMITATIONS:
The study population consisted of health professionals who were predominantly White, which may limit generalizability of the findings. Lifestyle factors and aspirin use were self-reported, which may introduce measurement errors. The study did not systematically assess adverse outcomes potentially due to aspirin use or the presence of a known hereditary cancer syndrome.
DISCLOSURES:
The study had no commercial funding. The authors had no relevant conflicts of interest.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
METHODOLOGY:
- Aspirin is an established agent for CRC prevention. Whether individuals with more lifestyle risk factors might derive greater benefit from aspirin remains unclear.
- Researchers analyzed regular aspirin use (defined as taking two or more standard 325-mg tablets per week) using long-term follow-up data from 63,957 women in the Nurses’ Health Study and 43,698 men in the Health Professionals Follow-Up Study.
- They calculated a healthy lifestyle score for each participant based on body mass index (BMI), alcohol intake, physical activity, diet, and smoking, with higher scores corresponding to healthier lifestyles.
- Outcomes included multivariable-adjusted 10-year cumulative incidence of CRC, the absolute risk reduction (ARR) with aspirin use, and number needed to treat associated with regular aspirin use by lifestyle score.
TAKEAWAY:
- During more than 3 million person-years of follow-up, 2544 new cases of CRC were documented.
- The 10-year cumulative incidence of CRC was 1.98% among regular aspirin users compared with 2.95% among nonusers, corresponding to an ARR of 0.97%.
- The ARR associated with aspirin use was greatest among individuals with the unhealthiest lifestyle scores and progressively decreased with healthier lifestyle scores (P < .001 for additive interaction).
- Those with the unhealthiest lifestyle scores (0-1) had a 10-year ARR of 1.28% from aspirin use, whereas those with the healthiest lifestyle scores (4-5) had an ARR of 0.11%.
- The number needed to treat with aspirin for 10 years to prevent one CRC case was 78 for those with the unhealthiest lifestyles, compared with 909 for those with the healthiest lifestyles.
- Among the individual components of the healthy lifestyle score, higher BMI and smoking correlated with greater reductions in CRC risk from aspirin use.
IN PRACTICE:
“These results support the use of lifestyle risk factors to identify individuals who may have a more favorable risk-benefit profile for cancer prevention with aspirin,” the authors wrote.
SOURCE:
The study, with first author Daniel R. Sikavi, MD, from Massachusetts General Hospital and Harvard Medical School in Boston, was published online in JAMA Oncology.
LIMITATIONS:
The study population consisted of health professionals who were predominantly White, which may limit generalizability of the findings. Lifestyle factors and aspirin use were self-reported, which may introduce measurement errors. The study did not systematically assess adverse outcomes potentially due to aspirin use or the presence of a known hereditary cancer syndrome.
DISCLOSURES:
The study had no commercial funding. The authors had no relevant conflicts of interest.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
METHODOLOGY:
- Aspirin is an established agent for CRC prevention. Whether individuals with more lifestyle risk factors might derive greater benefit from aspirin remains unclear.
- Researchers analyzed regular aspirin use (defined as taking two or more standard 325-mg tablets per week) using long-term follow-up data from 63,957 women in the Nurses’ Health Study and 43,698 men in the Health Professionals Follow-Up Study.
- They calculated a healthy lifestyle score for each participant based on body mass index (BMI), alcohol intake, physical activity, diet, and smoking, with higher scores corresponding to healthier lifestyles.
- Outcomes included multivariable-adjusted 10-year cumulative incidence of CRC, the absolute risk reduction (ARR) with aspirin use, and number needed to treat associated with regular aspirin use by lifestyle score.
TAKEAWAY:
- During more than 3 million person-years of follow-up, 2544 new cases of CRC were documented.
- The 10-year cumulative incidence of CRC was 1.98% among regular aspirin users compared with 2.95% among nonusers, corresponding to an ARR of 0.97%.
- The ARR associated with aspirin use was greatest among individuals with the unhealthiest lifestyle scores and progressively decreased with healthier lifestyle scores (P < .001 for additive interaction).
- Those with the unhealthiest lifestyle scores (0-1) had a 10-year ARR of 1.28% from aspirin use, whereas those with the healthiest lifestyle scores (4-5) had an ARR of 0.11%.
- The number needed to treat with aspirin for 10 years to prevent one CRC case was 78 for those with the unhealthiest lifestyles, compared with 909 for those with the healthiest lifestyles.
- Among the individual components of the healthy lifestyle score, higher BMI and smoking correlated with greater reductions in CRC risk from aspirin use.
IN PRACTICE:
“These results support the use of lifestyle risk factors to identify individuals who may have a more favorable risk-benefit profile for cancer prevention with aspirin,” the authors wrote.
SOURCE:
The study, with first author Daniel R. Sikavi, MD, from Massachusetts General Hospital and Harvard Medical School in Boston, was published online in JAMA Oncology.
LIMITATIONS:
The study population consisted of health professionals who were predominantly White, which may limit generalizability of the findings. Lifestyle factors and aspirin use were self-reported, which may introduce measurement errors. The study did not systematically assess adverse outcomes potentially due to aspirin use or the presence of a known hereditary cancer syndrome.
DISCLOSURES:
The study had no commercial funding. The authors had no relevant conflicts of interest.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.