User login
Little Less Talk and a Lot More Action
No matter where one looks for the statistics, no matter what words one chooses to describe it, this country has a child and adolescent mental health crisis. Almost 20% of young people in the 3-17 age bracket have a mental, emotional, developmental, or behavioral disorder. COVID-19 has certainly exacerbated the problem, but the downward trend in the mental health of this nation has been going on for decades.
The voices calling for more services to address the problem are getting more numerous and louder. But, what exactly should those services look like and who should be delivering them?
When considered together, two recent research papers suggest that we should be venturing well beyond the usual mental health strategies if we are going to be successful in addressing the current crisis.
The first paper is an analysis by two psychologists who contend that our efforts to raise the awareness of mental issues may be contributing to the increase in reported mental health problems. The authors agree that more attention paid to mental health conditions can result in “more accurate reporting of previous under-recognized symptoms” and would seem to be a positive. However, the investigators also observe that when exposed to this flood of information, some individuals who are only experiencing minor distress may report their symptoms as mental problems. The authors of the paper have coined the term for this phenomenon as “prevalence inflation.” Their preliminary investigation suggests it may be much more common than once believed and they present numerous situations in which prevalence inflation seems to have occurred.
A New York Times article about this hypothesis reports on a British study in which nearly 30,000 teenagers were instructed by their teachers to “direct their attentions to the present moment” and utilize other mindfulness strategies. The educators had hoped that after 8 years of this indoctrination, the students’ mental health would have improved. The bottom line was that this mindfulness-based program was of no help and may have actually made things worse for a subgroup of students who were at greatest risk for mental health challenges.
Dr. Jack Andrews, one of the authors, feels that mindfulness training may encourage what he calls “co-rumination,” which he describes as “the kind of long, unresolved group discussion that churns up problems without finding solutions.” One has to wonder if “prevalence inflation” and “co-rumination,” if they do exist, may be playing a role in the hotly debated phenomenon some have termed “late-onset gender dysphoria.”
Never having been a fan of mindfulness training as an effective strategy, I am relieved to learn that serious investigators are finding evidence that supports my gut reaction.
If raising awareness, “education,” and group discussion aren’t working, and in some cases are actually contributing to the crisis, or at least making the data difficult to interpret, what should we be doing to turn this foundering ship around?
A second paper, coming from Taiwan, may provide an answer. Huey-Ling Chiang and fellow investigators have reported on a study of nearly two million children and adolescents in which they found improved performance in a variety of physical fitness challenges “was linked with a lower risk of mental health disorder.” The dose-dependent effect resulted in less anxiety and depressive disorders as well as less attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder when cardio-respiratory, muscle endurance, and power indices improved.
There have been other observers who have suggested a link between physical fitness and improved mental health, but this Taiwanese study is by far one of the largest. And, the discovery of a dose-dependent effect makes it particularly convincing.
As I reviewed these two papers, I became increasingly frustrated because this is another example in which one of the answers is staring us in the face and we continue to do nothing more than talk about it.
We already know that physically active people are healthier both physically and mentally, but we do little more than talk. It may be helpful for some people to become a bit more self-aware. However, it is becoming increasingly clear that you can’t talk yourself into being mentally healthy without a concurrent effort to actually do the things that can improve your overall health, such as being physically active and adopting healthy sleep habits. A political advisor once said, “It’s the economy, stupid.” As a community interested in the health of our children and the adults they will become, we need to remind ourselves again, “It’s the old Mind-Body Thing, Stupid.” Our children need a little less talk and a lot more action.
Dr. Wilkoff practiced primary care pediatrics in Brunswick, Maine, for nearly 40 years. He has authored several books on behavioral pediatrics, including “How to Say No to Your Toddler.” Other than a Littman stethoscope he accepted as a first-year medical student in 1966, Dr. Wilkoff reports having nothing to disclose. Email him at [email protected].
No matter where one looks for the statistics, no matter what words one chooses to describe it, this country has a child and adolescent mental health crisis. Almost 20% of young people in the 3-17 age bracket have a mental, emotional, developmental, or behavioral disorder. COVID-19 has certainly exacerbated the problem, but the downward trend in the mental health of this nation has been going on for decades.
The voices calling for more services to address the problem are getting more numerous and louder. But, what exactly should those services look like and who should be delivering them?
When considered together, two recent research papers suggest that we should be venturing well beyond the usual mental health strategies if we are going to be successful in addressing the current crisis.
The first paper is an analysis by two psychologists who contend that our efforts to raise the awareness of mental issues may be contributing to the increase in reported mental health problems. The authors agree that more attention paid to mental health conditions can result in “more accurate reporting of previous under-recognized symptoms” and would seem to be a positive. However, the investigators also observe that when exposed to this flood of information, some individuals who are only experiencing minor distress may report their symptoms as mental problems. The authors of the paper have coined the term for this phenomenon as “prevalence inflation.” Their preliminary investigation suggests it may be much more common than once believed and they present numerous situations in which prevalence inflation seems to have occurred.
A New York Times article about this hypothesis reports on a British study in which nearly 30,000 teenagers were instructed by their teachers to “direct their attentions to the present moment” and utilize other mindfulness strategies. The educators had hoped that after 8 years of this indoctrination, the students’ mental health would have improved. The bottom line was that this mindfulness-based program was of no help and may have actually made things worse for a subgroup of students who were at greatest risk for mental health challenges.
Dr. Jack Andrews, one of the authors, feels that mindfulness training may encourage what he calls “co-rumination,” which he describes as “the kind of long, unresolved group discussion that churns up problems without finding solutions.” One has to wonder if “prevalence inflation” and “co-rumination,” if they do exist, may be playing a role in the hotly debated phenomenon some have termed “late-onset gender dysphoria.”
Never having been a fan of mindfulness training as an effective strategy, I am relieved to learn that serious investigators are finding evidence that supports my gut reaction.
If raising awareness, “education,” and group discussion aren’t working, and in some cases are actually contributing to the crisis, or at least making the data difficult to interpret, what should we be doing to turn this foundering ship around?
A second paper, coming from Taiwan, may provide an answer. Huey-Ling Chiang and fellow investigators have reported on a study of nearly two million children and adolescents in which they found improved performance in a variety of physical fitness challenges “was linked with a lower risk of mental health disorder.” The dose-dependent effect resulted in less anxiety and depressive disorders as well as less attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder when cardio-respiratory, muscle endurance, and power indices improved.
There have been other observers who have suggested a link between physical fitness and improved mental health, but this Taiwanese study is by far one of the largest. And, the discovery of a dose-dependent effect makes it particularly convincing.
As I reviewed these two papers, I became increasingly frustrated because this is another example in which one of the answers is staring us in the face and we continue to do nothing more than talk about it.
We already know that physically active people are healthier both physically and mentally, but we do little more than talk. It may be helpful for some people to become a bit more self-aware. However, it is becoming increasingly clear that you can’t talk yourself into being mentally healthy without a concurrent effort to actually do the things that can improve your overall health, such as being physically active and adopting healthy sleep habits. A political advisor once said, “It’s the economy, stupid.” As a community interested in the health of our children and the adults they will become, we need to remind ourselves again, “It’s the old Mind-Body Thing, Stupid.” Our children need a little less talk and a lot more action.
Dr. Wilkoff practiced primary care pediatrics in Brunswick, Maine, for nearly 40 years. He has authored several books on behavioral pediatrics, including “How to Say No to Your Toddler.” Other than a Littman stethoscope he accepted as a first-year medical student in 1966, Dr. Wilkoff reports having nothing to disclose. Email him at [email protected].
No matter where one looks for the statistics, no matter what words one chooses to describe it, this country has a child and adolescent mental health crisis. Almost 20% of young people in the 3-17 age bracket have a mental, emotional, developmental, or behavioral disorder. COVID-19 has certainly exacerbated the problem, but the downward trend in the mental health of this nation has been going on for decades.
The voices calling for more services to address the problem are getting more numerous and louder. But, what exactly should those services look like and who should be delivering them?
When considered together, two recent research papers suggest that we should be venturing well beyond the usual mental health strategies if we are going to be successful in addressing the current crisis.
The first paper is an analysis by two psychologists who contend that our efforts to raise the awareness of mental issues may be contributing to the increase in reported mental health problems. The authors agree that more attention paid to mental health conditions can result in “more accurate reporting of previous under-recognized symptoms” and would seem to be a positive. However, the investigators also observe that when exposed to this flood of information, some individuals who are only experiencing minor distress may report their symptoms as mental problems. The authors of the paper have coined the term for this phenomenon as “prevalence inflation.” Their preliminary investigation suggests it may be much more common than once believed and they present numerous situations in which prevalence inflation seems to have occurred.
A New York Times article about this hypothesis reports on a British study in which nearly 30,000 teenagers were instructed by their teachers to “direct their attentions to the present moment” and utilize other mindfulness strategies. The educators had hoped that after 8 years of this indoctrination, the students’ mental health would have improved. The bottom line was that this mindfulness-based program was of no help and may have actually made things worse for a subgroup of students who were at greatest risk for mental health challenges.
Dr. Jack Andrews, one of the authors, feels that mindfulness training may encourage what he calls “co-rumination,” which he describes as “the kind of long, unresolved group discussion that churns up problems without finding solutions.” One has to wonder if “prevalence inflation” and “co-rumination,” if they do exist, may be playing a role in the hotly debated phenomenon some have termed “late-onset gender dysphoria.”
Never having been a fan of mindfulness training as an effective strategy, I am relieved to learn that serious investigators are finding evidence that supports my gut reaction.
If raising awareness, “education,” and group discussion aren’t working, and in some cases are actually contributing to the crisis, or at least making the data difficult to interpret, what should we be doing to turn this foundering ship around?
A second paper, coming from Taiwan, may provide an answer. Huey-Ling Chiang and fellow investigators have reported on a study of nearly two million children and adolescents in which they found improved performance in a variety of physical fitness challenges “was linked with a lower risk of mental health disorder.” The dose-dependent effect resulted in less anxiety and depressive disorders as well as less attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder when cardio-respiratory, muscle endurance, and power indices improved.
There have been other observers who have suggested a link between physical fitness and improved mental health, but this Taiwanese study is by far one of the largest. And, the discovery of a dose-dependent effect makes it particularly convincing.
As I reviewed these two papers, I became increasingly frustrated because this is another example in which one of the answers is staring us in the face and we continue to do nothing more than talk about it.
We already know that physically active people are healthier both physically and mentally, but we do little more than talk. It may be helpful for some people to become a bit more self-aware. However, it is becoming increasingly clear that you can’t talk yourself into being mentally healthy without a concurrent effort to actually do the things that can improve your overall health, such as being physically active and adopting healthy sleep habits. A political advisor once said, “It’s the economy, stupid.” As a community interested in the health of our children and the adults they will become, we need to remind ourselves again, “It’s the old Mind-Body Thing, Stupid.” Our children need a little less talk and a lot more action.
Dr. Wilkoff practiced primary care pediatrics in Brunswick, Maine, for nearly 40 years. He has authored several books on behavioral pediatrics, including “How to Say No to Your Toddler.” Other than a Littman stethoscope he accepted as a first-year medical student in 1966, Dr. Wilkoff reports having nothing to disclose. Email him at [email protected].
Hypopigmented Cutaneous Langerhans Cell Histiocytosis in a Hispanic Infant
To the Editor:
Langerhans cell histiocytosis (LCH) is a rare inflammatory neoplasia caused by accumulation of clonal Langerhans cells in 1 or more organs. The clinical spectrum is diverse, ranging from mild, single-organ involvement that may resolve spontaneously to severe progressive multisystem disease that can be fatal. It is most prevalent in children, affecting an estimated 4 to 5 children for every 1 million annually, with male predominance.1 The pathogenesis is driven by activating mutations in the mitogen-activated protein kinase pathway, with the BRAF V600E mutation detected in most LCH patients, resulting in proliferation of pathologic Langerhans cells and dysregulated expression of inflammatory cytokines in LCH lesions.2 A biopsy of lesional tissue is required for definitive diagnosis. Histopathology reveals a mixed inflammatory infiltrate and characteristic mononuclear cells with reniform nuclei that are positive for CD1a and CD207 proteins on immunohistochemical staining.3
Langerhans cell histiocytosis is categorized by the extent of organ involvement. It commonly affects the bones, skin, pituitary gland, liver, lungs, bone marrow, and lymph nodes.4 Single-system LCH involves a single organ with unifocal or multifocal lesions; multisystem LCH involves 2 or more organs and has a worse prognosis if risk organs (eg, liver, spleen, bone marrow) are involved.4
Skin lesions are reported in more than half of LCH cases and are the most common initial manifestation in patients younger than 2 years.4 Cutaneous findings are highly variable, which poses a diagnostic challenge. Common morphologies include erythematous papules, pustules, papulovesicles, scaly plaques, erosions, and petechiae. Lesions can be solitary or widespread and favor the trunk, head, and face.4 We describe an atypical case of hypopigmented cutaneous LCH and review the literature on this morphology in patients with skin of color.
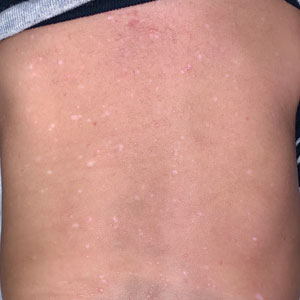
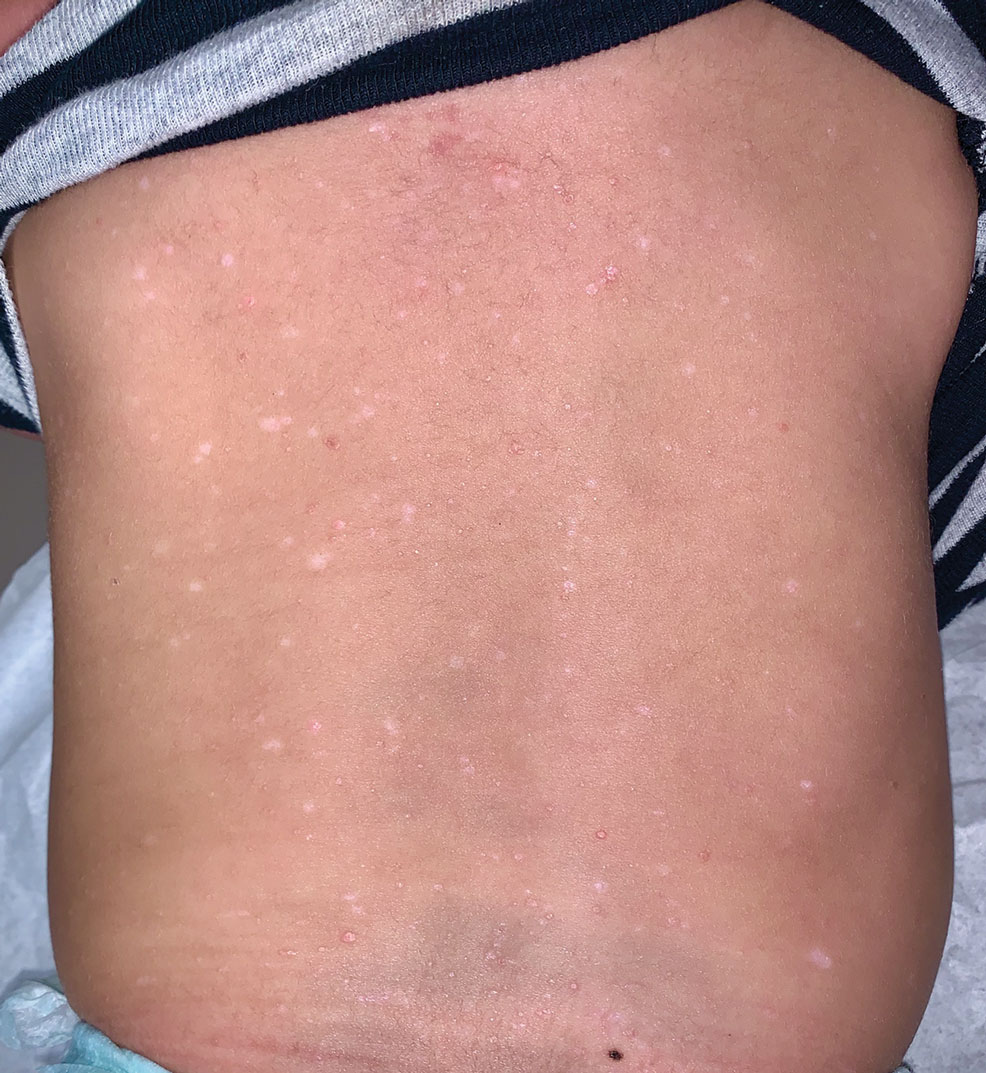
A 7-month-old Hispanic male infant who was otherwise healthy presented with numerous hypopigmented macules and pink papules on the trunk and groin that had progressed since birth. A review of systems was unremarkable. Physical examination revealed 1- to 3-mm, discrete, hypopigmented macules intermixed with 1- to 2-mm pearly pink papules scattered on the back, chest, abdomen, and inguinal folds (Figure 1). Some lesions appeared koebnerized; however, the parents denied a history of scratching or trauma.
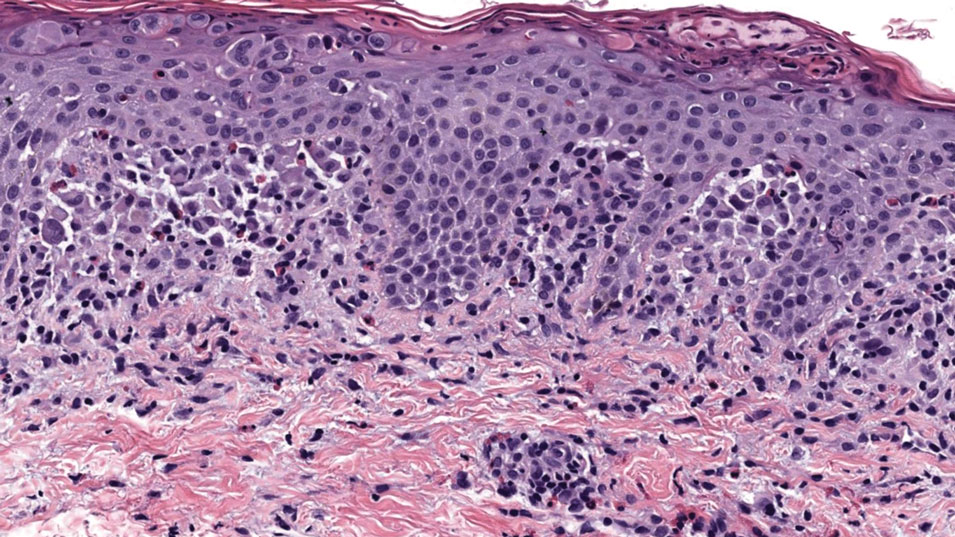
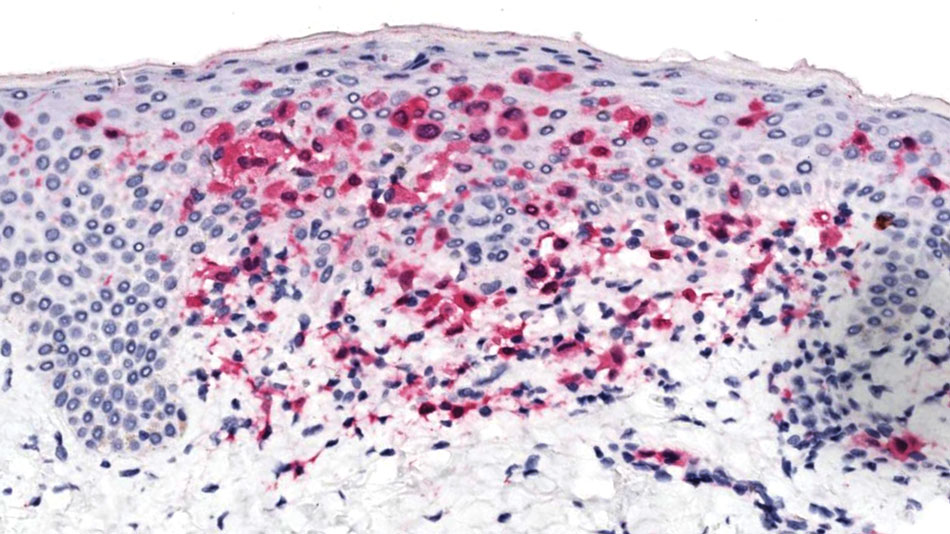
Histopathology of a lesion in the inguinal fold showed aggregates of mononuclear cells with reniform nuclei and abundant amphophilic cytoplasm in the papillary dermis, with focal extension into the epidermis. Scattered eosinophils and multinucleated giant cells were present in the dermal inflammatory infiltrate (Figure 2). Immunohistochemical staining was positive for CD1a (Figure 3) and S-100 protein (Figure 4). Although epidermal Langerhans cell collections also can be seen in allergic contact dermatitis,5 predominant involvement of the papillary dermis and the presence of multinucleated giant cells are characteristic of LCH.4 Given these findings, which were consistent with LCH, the dermatopathology deemed BRAF V600E immunostaining unnecessary for diagnostic purposes.
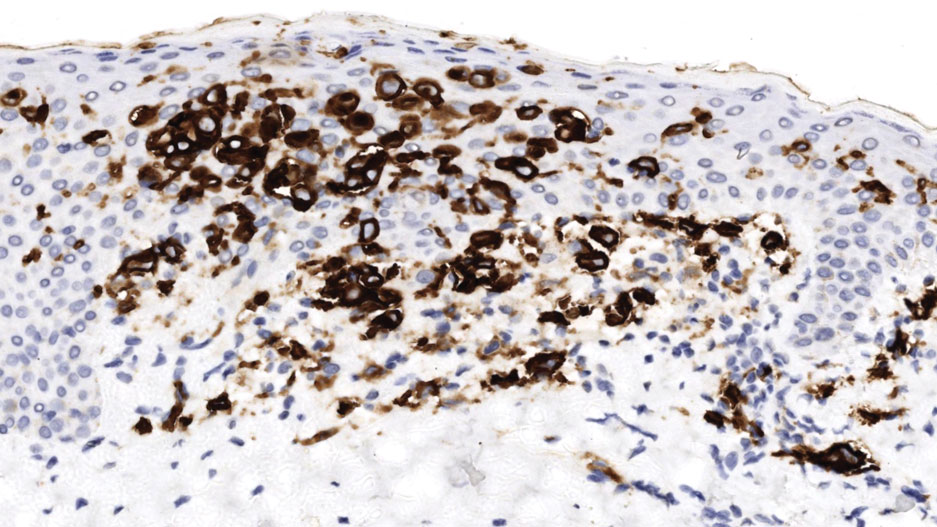
The patient was referred to the hematology and oncology department to undergo thorough evaluation for extracutaneous involvement. The workup included a complete blood cell count, liver function testing, electrolyte assessment, skeletal survey, chest radiography, and ultrasonography of the liver and spleen. All results were negative, suggesting a diagnosis of single-system cutaneous LCH.
Three months later, the patient presented to dermatology with spontaneous regression of all skin lesions. Continued follow-up—every 6 months for 5 years—was recommended to monitor for disease recurrence or progression to multisystem disease.
Cutaneous LCH is a clinically heterogeneous disease with the potential for multisystem involvement and long-term sequelae; therefore, timely diagnosis is paramount to optimize outcomes. However, delayed diagnosis is common because of the spectrum of skin findings that can mimic common pediatric dermatoses, such as seborrheic dermatitis, atopic dermatitis, and diaper dermatitis.4 In one study, the median time from onset of skin lesions to diagnostic biopsy was longer than 3 months (maximum, 5 years).6 Our patient was referred to dermatology 7 months after onset of hypopigmented macules, a rarely reported cutaneous manifestation of LCH.
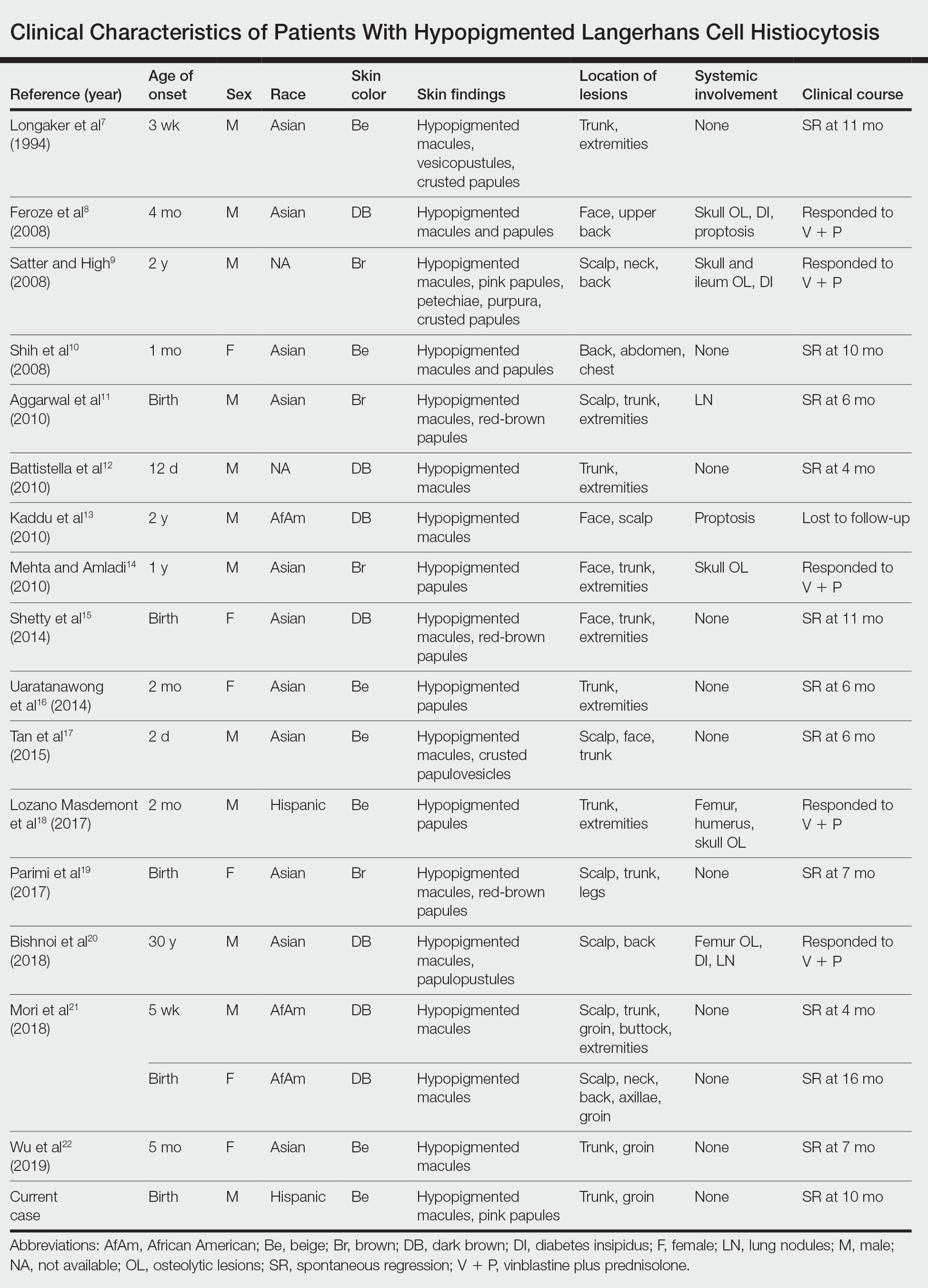
A PubMed search of articles indexed for MEDLINE from 1994 to 2019 using the terms Langerhans cell histiocytotis and hypopigmented yielded 17 cases of LCH presenting as hypopigmented skin lesions (Table).7-22 All cases occurred in patients with skin of color (ie, patients of Asian, Hispanic, or African descent). Hypopigmented macules were the only cutaneous manifestation in 10 (59%) cases. Lesions most commonly were distributed on the trunk (16/17 [94%]) and extremities (8/17 [47%]). The median age of onset was 1 month; 76% (13/17) of patients developed skin lesions before 1 year of age, indicating that this morphology may be more common in newborns. In most patients, the diagnosis was single-system cutaneous LCH; they exhibited spontaneous regression by 8 months of age on average, suggesting that this variant may be associated with a better prognosis. Mori and colleagues21 hypothesized that hypopigmented lesions may represent the resolving stage of active LCH based on histopathologic findings of dermal pallor and fibrosis in a hypopigmented LCH lesion. However, systemic involvement was reported in 7 cases of hypopigmented LCH, highlighting the importance of assessing for multisystem disease regardless of cutaneous morphology.21Langerhans cell histiocytosis should be considered in the differential diagnosis when evaluating hypopigmented skin eruptions in infants with darker skin types. Prompt diagnosis of this atypical variant requires a higher index of suspicion because of its rarity and the polymorphic nature of cutaneous LCH. This morphology may go undiagnosed in the setting of mild or spontaneously resolving disease; notwithstanding, accurate diagnosis and longitudinal surveillance are necessary given the potential for progressive systemic involvement.
1. Guyot-Goubin A, Donadieu J, Barkaoui M, et al. Descriptive epidemiology of childhood Langerhans cell histiocytosis in France, 2000–2004. Pediatr Blood Cancer. 2008;51:71-75. doi:10.1002/pbc.21498
2. Badalian-Very G, Vergilio J-A, Degar BA, et al. Recurrent BRAF mutations in Langerhans cell histiocytosis. Blood. 2010;116:1919-1923. doi:10.1182/blood-2010-04-279083
3. Haupt R, Minkov M, Astigarraga I, et al; Euro Histio Network. Langerhans cell histiocytosis (LCH): guidelines for diagnosis, clinical work‐up, and treatment for patients till the age of 18 years. Pediatr Blood Cancer. 2013;60:175-184. doi:10.1002/pbc.24367
4. Krooks J, Minkov M, Weatherall AG. Langerhans cell histiocytosis in children: history, classification, pathobiology, clinical manifestations, and prognosis. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2018;78:1035-1044. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2017.05.059
5. Rosa G, Fernandez AP, Vij A, et al. Langerhans cell collections, but not eosinophils, are clues to a diagnosis of allergic contact dermatitis in appropriate skin biopsies. J Cutan Pathol. 2016;43:498-504. doi:10.1111/cup.12707
6. Simko SJ, Garmezy B, Abhyankar H, et al. Differentiating skin-limited and multisystem Langerhans cell histiocytosis. J Pediatr. 2014;165:990-996. doi:10.1016/j.jpeds.2014.07.063
7. Longaker MA, Frieden IJ, LeBoit PE, et al. Congenital “self-healing” Langerhans cell histiocytosis: the need for long-term follow-up. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1994;31(5, pt 2):910-916. doi:10.1016/s0190-9622(94)70258-6
8. Feroze K, Unni M, Jayasree MG, et al. Langerhans cell histiocytosis presenting with hypopigmented macules. Indian J Dermatol Venereol Leprol. 2008;74:670-672. doi:10.4103/0378-6323.45128
9. Satter EK, High WA. Langerhans cell histiocytosis: a case report and summary of the current recommendations of the Histiocyte Society. Dermatol Online J. 2008;14:3.
10. Chang SL, Shih IH, Kuo TT, et al. Congenital self-healing reticulohistiocytosis presenting as hypopigmented macules and papules in a neonate. Dermatologica Sinica 2008;26:80-84.
11. Aggarwal V, Seth A, Jain M, et al. Congenital Langerhans cell histiocytosis with skin and lung involvement: spontaneous regression. Indian J Pediatr. 2010;77:811-812.
12. Battistella M, Fraitag S, Teillac DH, et al. Neonatal and early infantile cutaneous Langerhans cell histiocytosis: comparison of self-regressive and non-self-regressive forms. Arch Dermatol. 2010;146:149-156. doi:10.1001/archdermatol.2009.360
13. Kaddu S, Mulyowa G, Kovarik C. Hypopigmented scaly, scalp and facial lesions and disfiguring exopthalmus. Clin Exp Dermatol. 2010;3:E52-E53. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2230.2009.03336.x
14. Mehta B, Amladi S. Langerhans cell histiocytosis presenting as hypopigmented papules. Pediatr Dermatol. 2010;27:215-217. doi:10.1111/j.1525-1470.2010.01104.x
15. Shetty S, Monappa V, Pai K, et al. Congenital self-healing reticulohistiocytosis: a case report. Our Dermatol Online. 2014;5:264-266.
16. Uaratanawong R, Kootiratrakarn T, Sudtikoonaseth P, et al. Congenital self-healing reticulohistiocytosis presented with multiple hypopigmented flat-topped papules: a case report and review of literatures. J Med Assoc Thai. 2014;97:993-997.
17. Tan Q, Gan LQ, Wang H. Congenital self-healing Langerhans cell histiocytosis in a male neonate. Indian J Dermatol Venereol Leprol. 2015;81:75-77. doi:10.4103/0378-6323.148587
18. Lozano Masdemont B, Gómez‐Recuero Muñoz L, Villanueva Álvarez‐Santullano A, et al. Langerhans cell histiocytosis mimicking lichen nitidus with bone involvement. Australas J Dermatol. 2017;58:231-233. doi:10.1111/ajd.12467
19. Parimi LR, You J, Hong L, et al. Congenital self-healing reticulohistiocytosis with spontaneous regression. An Bras Dermatol. 2017;92:553-555. doi:10.1590/abd1806-4841.20175432
20. Bishnoi A, De D, Khullar G, et al. Hypopigmented and acneiform lesions: an unusual initial presentation of adult-onset multisystem Langerhans cell histiocytosis. Indian J Dermatol Venereol Leprol. 2018;84:621-626. doi:10.4103/ijdvl.IJDVL_639_17
21. Mori S, Adar T, Kazlouskaya V, et al. Cutaneous Langerhans cell histiocytosis presenting with hypopigmented lesions: report of two cases and review of literature. Pediatr Dermatol. 2018;35:502-506. doi:10.1111/pde.13509
22. Wu X, Huang J, Jiang L, et al. Congenital self‐healing reticulohistiocytosis with BRAF V600E mutation in an infant. Clin Exp Dermatol. 2019;44:647-650. doi:10.1111/ced.13880
To the Editor:
Langerhans cell histiocytosis (LCH) is a rare inflammatory neoplasia caused by accumulation of clonal Langerhans cells in 1 or more organs. The clinical spectrum is diverse, ranging from mild, single-organ involvement that may resolve spontaneously to severe progressive multisystem disease that can be fatal. It is most prevalent in children, affecting an estimated 4 to 5 children for every 1 million annually, with male predominance.1 The pathogenesis is driven by activating mutations in the mitogen-activated protein kinase pathway, with the BRAF V600E mutation detected in most LCH patients, resulting in proliferation of pathologic Langerhans cells and dysregulated expression of inflammatory cytokines in LCH lesions.2 A biopsy of lesional tissue is required for definitive diagnosis. Histopathology reveals a mixed inflammatory infiltrate and characteristic mononuclear cells with reniform nuclei that are positive for CD1a and CD207 proteins on immunohistochemical staining.3
Langerhans cell histiocytosis is categorized by the extent of organ involvement. It commonly affects the bones, skin, pituitary gland, liver, lungs, bone marrow, and lymph nodes.4 Single-system LCH involves a single organ with unifocal or multifocal lesions; multisystem LCH involves 2 or more organs and has a worse prognosis if risk organs (eg, liver, spleen, bone marrow) are involved.4
Skin lesions are reported in more than half of LCH cases and are the most common initial manifestation in patients younger than 2 years.4 Cutaneous findings are highly variable, which poses a diagnostic challenge. Common morphologies include erythematous papules, pustules, papulovesicles, scaly plaques, erosions, and petechiae. Lesions can be solitary or widespread and favor the trunk, head, and face.4 We describe an atypical case of hypopigmented cutaneous LCH and review the literature on this morphology in patients with skin of color.
A 7-month-old Hispanic male infant who was otherwise healthy presented with numerous hypopigmented macules and pink papules on the trunk and groin that had progressed since birth. A review of systems was unremarkable. Physical examination revealed 1- to 3-mm, discrete, hypopigmented macules intermixed with 1- to 2-mm pearly pink papules scattered on the back, chest, abdomen, and inguinal folds (Figure 1). Some lesions appeared koebnerized; however, the parents denied a history of scratching or trauma.
Histopathology of a lesion in the inguinal fold showed aggregates of mononuclear cells with reniform nuclei and abundant amphophilic cytoplasm in the papillary dermis, with focal extension into the epidermis. Scattered eosinophils and multinucleated giant cells were present in the dermal inflammatory infiltrate (Figure 2). Immunohistochemical staining was positive for CD1a (Figure 3) and S-100 protein (Figure 4). Although epidermal Langerhans cell collections also can be seen in allergic contact dermatitis,5 predominant involvement of the papillary dermis and the presence of multinucleated giant cells are characteristic of LCH.4 Given these findings, which were consistent with LCH, the dermatopathology deemed BRAF V600E immunostaining unnecessary for diagnostic purposes.





The patient was referred to the hematology and oncology department to undergo thorough evaluation for extracutaneous involvement. The workup included a complete blood cell count, liver function testing, electrolyte assessment, skeletal survey, chest radiography, and ultrasonography of the liver and spleen. All results were negative, suggesting a diagnosis of single-system cutaneous LCH.
Three months later, the patient presented to dermatology with spontaneous regression of all skin lesions. Continued follow-up—every 6 months for 5 years—was recommended to monitor for disease recurrence or progression to multisystem disease.
Cutaneous LCH is a clinically heterogeneous disease with the potential for multisystem involvement and long-term sequelae; therefore, timely diagnosis is paramount to optimize outcomes. However, delayed diagnosis is common because of the spectrum of skin findings that can mimic common pediatric dermatoses, such as seborrheic dermatitis, atopic dermatitis, and diaper dermatitis.4 In one study, the median time from onset of skin lesions to diagnostic biopsy was longer than 3 months (maximum, 5 years).6 Our patient was referred to dermatology 7 months after onset of hypopigmented macules, a rarely reported cutaneous manifestation of LCH.
A PubMed search of articles indexed for MEDLINE from 1994 to 2019 using the terms Langerhans cell histiocytotis and hypopigmented yielded 17 cases of LCH presenting as hypopigmented skin lesions (Table).7-22 All cases occurred in patients with skin of color (ie, patients of Asian, Hispanic, or African descent). Hypopigmented macules were the only cutaneous manifestation in 10 (59%) cases. Lesions most commonly were distributed on the trunk (16/17 [94%]) and extremities (8/17 [47%]). The median age of onset was 1 month; 76% (13/17) of patients developed skin lesions before 1 year of age, indicating that this morphology may be more common in newborns. In most patients, the diagnosis was single-system cutaneous LCH; they exhibited spontaneous regression by 8 months of age on average, suggesting that this variant may be associated with a better prognosis. Mori and colleagues21 hypothesized that hypopigmented lesions may represent the resolving stage of active LCH based on histopathologic findings of dermal pallor and fibrosis in a hypopigmented LCH lesion. However, systemic involvement was reported in 7 cases of hypopigmented LCH, highlighting the importance of assessing for multisystem disease regardless of cutaneous morphology.21Langerhans cell histiocytosis should be considered in the differential diagnosis when evaluating hypopigmented skin eruptions in infants with darker skin types. Prompt diagnosis of this atypical variant requires a higher index of suspicion because of its rarity and the polymorphic nature of cutaneous LCH. This morphology may go undiagnosed in the setting of mild or spontaneously resolving disease; notwithstanding, accurate diagnosis and longitudinal surveillance are necessary given the potential for progressive systemic involvement.
To the Editor:
Langerhans cell histiocytosis (LCH) is a rare inflammatory neoplasia caused by accumulation of clonal Langerhans cells in 1 or more organs. The clinical spectrum is diverse, ranging from mild, single-organ involvement that may resolve spontaneously to severe progressive multisystem disease that can be fatal. It is most prevalent in children, affecting an estimated 4 to 5 children for every 1 million annually, with male predominance.1 The pathogenesis is driven by activating mutations in the mitogen-activated protein kinase pathway, with the BRAF V600E mutation detected in most LCH patients, resulting in proliferation of pathologic Langerhans cells and dysregulated expression of inflammatory cytokines in LCH lesions.2 A biopsy of lesional tissue is required for definitive diagnosis. Histopathology reveals a mixed inflammatory infiltrate and characteristic mononuclear cells with reniform nuclei that are positive for CD1a and CD207 proteins on immunohistochemical staining.3
Langerhans cell histiocytosis is categorized by the extent of organ involvement. It commonly affects the bones, skin, pituitary gland, liver, lungs, bone marrow, and lymph nodes.4 Single-system LCH involves a single organ with unifocal or multifocal lesions; multisystem LCH involves 2 or more organs and has a worse prognosis if risk organs (eg, liver, spleen, bone marrow) are involved.4
Skin lesions are reported in more than half of LCH cases and are the most common initial manifestation in patients younger than 2 years.4 Cutaneous findings are highly variable, which poses a diagnostic challenge. Common morphologies include erythematous papules, pustules, papulovesicles, scaly plaques, erosions, and petechiae. Lesions can be solitary or widespread and favor the trunk, head, and face.4 We describe an atypical case of hypopigmented cutaneous LCH and review the literature on this morphology in patients with skin of color.
A 7-month-old Hispanic male infant who was otherwise healthy presented with numerous hypopigmented macules and pink papules on the trunk and groin that had progressed since birth. A review of systems was unremarkable. Physical examination revealed 1- to 3-mm, discrete, hypopigmented macules intermixed with 1- to 2-mm pearly pink papules scattered on the back, chest, abdomen, and inguinal folds (Figure 1). Some lesions appeared koebnerized; however, the parents denied a history of scratching or trauma.
Histopathology of a lesion in the inguinal fold showed aggregates of mononuclear cells with reniform nuclei and abundant amphophilic cytoplasm in the papillary dermis, with focal extension into the epidermis. Scattered eosinophils and multinucleated giant cells were present in the dermal inflammatory infiltrate (Figure 2). Immunohistochemical staining was positive for CD1a (Figure 3) and S-100 protein (Figure 4). Although epidermal Langerhans cell collections also can be seen in allergic contact dermatitis,5 predominant involvement of the papillary dermis and the presence of multinucleated giant cells are characteristic of LCH.4 Given these findings, which were consistent with LCH, the dermatopathology deemed BRAF V600E immunostaining unnecessary for diagnostic purposes.





The patient was referred to the hematology and oncology department to undergo thorough evaluation for extracutaneous involvement. The workup included a complete blood cell count, liver function testing, electrolyte assessment, skeletal survey, chest radiography, and ultrasonography of the liver and spleen. All results were negative, suggesting a diagnosis of single-system cutaneous LCH.
Three months later, the patient presented to dermatology with spontaneous regression of all skin lesions. Continued follow-up—every 6 months for 5 years—was recommended to monitor for disease recurrence or progression to multisystem disease.
Cutaneous LCH is a clinically heterogeneous disease with the potential for multisystem involvement and long-term sequelae; therefore, timely diagnosis is paramount to optimize outcomes. However, delayed diagnosis is common because of the spectrum of skin findings that can mimic common pediatric dermatoses, such as seborrheic dermatitis, atopic dermatitis, and diaper dermatitis.4 In one study, the median time from onset of skin lesions to diagnostic biopsy was longer than 3 months (maximum, 5 years).6 Our patient was referred to dermatology 7 months after onset of hypopigmented macules, a rarely reported cutaneous manifestation of LCH.
A PubMed search of articles indexed for MEDLINE from 1994 to 2019 using the terms Langerhans cell histiocytotis and hypopigmented yielded 17 cases of LCH presenting as hypopigmented skin lesions (Table).7-22 All cases occurred in patients with skin of color (ie, patients of Asian, Hispanic, or African descent). Hypopigmented macules were the only cutaneous manifestation in 10 (59%) cases. Lesions most commonly were distributed on the trunk (16/17 [94%]) and extremities (8/17 [47%]). The median age of onset was 1 month; 76% (13/17) of patients developed skin lesions before 1 year of age, indicating that this morphology may be more common in newborns. In most patients, the diagnosis was single-system cutaneous LCH; they exhibited spontaneous regression by 8 months of age on average, suggesting that this variant may be associated with a better prognosis. Mori and colleagues21 hypothesized that hypopigmented lesions may represent the resolving stage of active LCH based on histopathologic findings of dermal pallor and fibrosis in a hypopigmented LCH lesion. However, systemic involvement was reported in 7 cases of hypopigmented LCH, highlighting the importance of assessing for multisystem disease regardless of cutaneous morphology.21Langerhans cell histiocytosis should be considered in the differential diagnosis when evaluating hypopigmented skin eruptions in infants with darker skin types. Prompt diagnosis of this atypical variant requires a higher index of suspicion because of its rarity and the polymorphic nature of cutaneous LCH. This morphology may go undiagnosed in the setting of mild or spontaneously resolving disease; notwithstanding, accurate diagnosis and longitudinal surveillance are necessary given the potential for progressive systemic involvement.
1. Guyot-Goubin A, Donadieu J, Barkaoui M, et al. Descriptive epidemiology of childhood Langerhans cell histiocytosis in France, 2000–2004. Pediatr Blood Cancer. 2008;51:71-75. doi:10.1002/pbc.21498
2. Badalian-Very G, Vergilio J-A, Degar BA, et al. Recurrent BRAF mutations in Langerhans cell histiocytosis. Blood. 2010;116:1919-1923. doi:10.1182/blood-2010-04-279083
3. Haupt R, Minkov M, Astigarraga I, et al; Euro Histio Network. Langerhans cell histiocytosis (LCH): guidelines for diagnosis, clinical work‐up, and treatment for patients till the age of 18 years. Pediatr Blood Cancer. 2013;60:175-184. doi:10.1002/pbc.24367
4. Krooks J, Minkov M, Weatherall AG. Langerhans cell histiocytosis in children: history, classification, pathobiology, clinical manifestations, and prognosis. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2018;78:1035-1044. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2017.05.059
5. Rosa G, Fernandez AP, Vij A, et al. Langerhans cell collections, but not eosinophils, are clues to a diagnosis of allergic contact dermatitis in appropriate skin biopsies. J Cutan Pathol. 2016;43:498-504. doi:10.1111/cup.12707
6. Simko SJ, Garmezy B, Abhyankar H, et al. Differentiating skin-limited and multisystem Langerhans cell histiocytosis. J Pediatr. 2014;165:990-996. doi:10.1016/j.jpeds.2014.07.063
7. Longaker MA, Frieden IJ, LeBoit PE, et al. Congenital “self-healing” Langerhans cell histiocytosis: the need for long-term follow-up. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1994;31(5, pt 2):910-916. doi:10.1016/s0190-9622(94)70258-6
8. Feroze K, Unni M, Jayasree MG, et al. Langerhans cell histiocytosis presenting with hypopigmented macules. Indian J Dermatol Venereol Leprol. 2008;74:670-672. doi:10.4103/0378-6323.45128
9. Satter EK, High WA. Langerhans cell histiocytosis: a case report and summary of the current recommendations of the Histiocyte Society. Dermatol Online J. 2008;14:3.
10. Chang SL, Shih IH, Kuo TT, et al. Congenital self-healing reticulohistiocytosis presenting as hypopigmented macules and papules in a neonate. Dermatologica Sinica 2008;26:80-84.
11. Aggarwal V, Seth A, Jain M, et al. Congenital Langerhans cell histiocytosis with skin and lung involvement: spontaneous regression. Indian J Pediatr. 2010;77:811-812.
12. Battistella M, Fraitag S, Teillac DH, et al. Neonatal and early infantile cutaneous Langerhans cell histiocytosis: comparison of self-regressive and non-self-regressive forms. Arch Dermatol. 2010;146:149-156. doi:10.1001/archdermatol.2009.360
13. Kaddu S, Mulyowa G, Kovarik C. Hypopigmented scaly, scalp and facial lesions and disfiguring exopthalmus. Clin Exp Dermatol. 2010;3:E52-E53. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2230.2009.03336.x
14. Mehta B, Amladi S. Langerhans cell histiocytosis presenting as hypopigmented papules. Pediatr Dermatol. 2010;27:215-217. doi:10.1111/j.1525-1470.2010.01104.x
15. Shetty S, Monappa V, Pai K, et al. Congenital self-healing reticulohistiocytosis: a case report. Our Dermatol Online. 2014;5:264-266.
16. Uaratanawong R, Kootiratrakarn T, Sudtikoonaseth P, et al. Congenital self-healing reticulohistiocytosis presented with multiple hypopigmented flat-topped papules: a case report and review of literatures. J Med Assoc Thai. 2014;97:993-997.
17. Tan Q, Gan LQ, Wang H. Congenital self-healing Langerhans cell histiocytosis in a male neonate. Indian J Dermatol Venereol Leprol. 2015;81:75-77. doi:10.4103/0378-6323.148587
18. Lozano Masdemont B, Gómez‐Recuero Muñoz L, Villanueva Álvarez‐Santullano A, et al. Langerhans cell histiocytosis mimicking lichen nitidus with bone involvement. Australas J Dermatol. 2017;58:231-233. doi:10.1111/ajd.12467
19. Parimi LR, You J, Hong L, et al. Congenital self-healing reticulohistiocytosis with spontaneous regression. An Bras Dermatol. 2017;92:553-555. doi:10.1590/abd1806-4841.20175432
20. Bishnoi A, De D, Khullar G, et al. Hypopigmented and acneiform lesions: an unusual initial presentation of adult-onset multisystem Langerhans cell histiocytosis. Indian J Dermatol Venereol Leprol. 2018;84:621-626. doi:10.4103/ijdvl.IJDVL_639_17
21. Mori S, Adar T, Kazlouskaya V, et al. Cutaneous Langerhans cell histiocytosis presenting with hypopigmented lesions: report of two cases and review of literature. Pediatr Dermatol. 2018;35:502-506. doi:10.1111/pde.13509
22. Wu X, Huang J, Jiang L, et al. Congenital self‐healing reticulohistiocytosis with BRAF V600E mutation in an infant. Clin Exp Dermatol. 2019;44:647-650. doi:10.1111/ced.13880
1. Guyot-Goubin A, Donadieu J, Barkaoui M, et al. Descriptive epidemiology of childhood Langerhans cell histiocytosis in France, 2000–2004. Pediatr Blood Cancer. 2008;51:71-75. doi:10.1002/pbc.21498
2. Badalian-Very G, Vergilio J-A, Degar BA, et al. Recurrent BRAF mutations in Langerhans cell histiocytosis. Blood. 2010;116:1919-1923. doi:10.1182/blood-2010-04-279083
3. Haupt R, Minkov M, Astigarraga I, et al; Euro Histio Network. Langerhans cell histiocytosis (LCH): guidelines for diagnosis, clinical work‐up, and treatment for patients till the age of 18 years. Pediatr Blood Cancer. 2013;60:175-184. doi:10.1002/pbc.24367
4. Krooks J, Minkov M, Weatherall AG. Langerhans cell histiocytosis in children: history, classification, pathobiology, clinical manifestations, and prognosis. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2018;78:1035-1044. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2017.05.059
5. Rosa G, Fernandez AP, Vij A, et al. Langerhans cell collections, but not eosinophils, are clues to a diagnosis of allergic contact dermatitis in appropriate skin biopsies. J Cutan Pathol. 2016;43:498-504. doi:10.1111/cup.12707
6. Simko SJ, Garmezy B, Abhyankar H, et al. Differentiating skin-limited and multisystem Langerhans cell histiocytosis. J Pediatr. 2014;165:990-996. doi:10.1016/j.jpeds.2014.07.063
7. Longaker MA, Frieden IJ, LeBoit PE, et al. Congenital “self-healing” Langerhans cell histiocytosis: the need for long-term follow-up. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1994;31(5, pt 2):910-916. doi:10.1016/s0190-9622(94)70258-6
8. Feroze K, Unni M, Jayasree MG, et al. Langerhans cell histiocytosis presenting with hypopigmented macules. Indian J Dermatol Venereol Leprol. 2008;74:670-672. doi:10.4103/0378-6323.45128
9. Satter EK, High WA. Langerhans cell histiocytosis: a case report and summary of the current recommendations of the Histiocyte Society. Dermatol Online J. 2008;14:3.
10. Chang SL, Shih IH, Kuo TT, et al. Congenital self-healing reticulohistiocytosis presenting as hypopigmented macules and papules in a neonate. Dermatologica Sinica 2008;26:80-84.
11. Aggarwal V, Seth A, Jain M, et al. Congenital Langerhans cell histiocytosis with skin and lung involvement: spontaneous regression. Indian J Pediatr. 2010;77:811-812.
12. Battistella M, Fraitag S, Teillac DH, et al. Neonatal and early infantile cutaneous Langerhans cell histiocytosis: comparison of self-regressive and non-self-regressive forms. Arch Dermatol. 2010;146:149-156. doi:10.1001/archdermatol.2009.360
13. Kaddu S, Mulyowa G, Kovarik C. Hypopigmented scaly, scalp and facial lesions and disfiguring exopthalmus. Clin Exp Dermatol. 2010;3:E52-E53. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2230.2009.03336.x
14. Mehta B, Amladi S. Langerhans cell histiocytosis presenting as hypopigmented papules. Pediatr Dermatol. 2010;27:215-217. doi:10.1111/j.1525-1470.2010.01104.x
15. Shetty S, Monappa V, Pai K, et al. Congenital self-healing reticulohistiocytosis: a case report. Our Dermatol Online. 2014;5:264-266.
16. Uaratanawong R, Kootiratrakarn T, Sudtikoonaseth P, et al. Congenital self-healing reticulohistiocytosis presented with multiple hypopigmented flat-topped papules: a case report and review of literatures. J Med Assoc Thai. 2014;97:993-997.
17. Tan Q, Gan LQ, Wang H. Congenital self-healing Langerhans cell histiocytosis in a male neonate. Indian J Dermatol Venereol Leprol. 2015;81:75-77. doi:10.4103/0378-6323.148587
18. Lozano Masdemont B, Gómez‐Recuero Muñoz L, Villanueva Álvarez‐Santullano A, et al. Langerhans cell histiocytosis mimicking lichen nitidus with bone involvement. Australas J Dermatol. 2017;58:231-233. doi:10.1111/ajd.12467
19. Parimi LR, You J, Hong L, et al. Congenital self-healing reticulohistiocytosis with spontaneous regression. An Bras Dermatol. 2017;92:553-555. doi:10.1590/abd1806-4841.20175432
20. Bishnoi A, De D, Khullar G, et al. Hypopigmented and acneiform lesions: an unusual initial presentation of adult-onset multisystem Langerhans cell histiocytosis. Indian J Dermatol Venereol Leprol. 2018;84:621-626. doi:10.4103/ijdvl.IJDVL_639_17
21. Mori S, Adar T, Kazlouskaya V, et al. Cutaneous Langerhans cell histiocytosis presenting with hypopigmented lesions: report of two cases and review of literature. Pediatr Dermatol. 2018;35:502-506. doi:10.1111/pde.13509
22. Wu X, Huang J, Jiang L, et al. Congenital self‐healing reticulohistiocytosis with BRAF V600E mutation in an infant. Clin Exp Dermatol. 2019;44:647-650. doi:10.1111/ced.13880
Practice Points
- Dermatologists should be aware of the hypopigmented variant of cutaneous Langerhans cell histiocytosis (LCH), which has been reported exclusively in patients with skin of color.
- Langerhans cell histiocytosis should be included in the differential diagnosis of hypopigmented macules, which may be the only cutaneous manifestation or may coincide with typical lesions of LCH.
- Hypopigmented cutaneous LCH may be more common in newborns and associated with a better prognosis.
Arthroscopy Doesn’t Delay Total Knee Replacement in Knee Osteoarthritis
TOPLINE:
Adding arthroscopic surgery to nonoperative management neither delays nor accelerates the timing of total knee arthroplasty (TKA) in patients with knee osteoarthritis (OA).
METHODOLOGY:
- Some case series show that arthroscopic surgery for knee OA may delay more invasive procedures, such as TKA or osteotomy, while longitudinal cohort studies often contradict this. Current OA guidelines are yet to address this issue.
- This secondary analysis of a randomized trial compared the long-term incidence of TKA in 178 patients (mean age, 59 years; 64.3% women) with knee OA who were referred for potential arthroscopic surgery at a tertiary care center in Canada.
- The patients received nonoperative care with or without additional arthroscopic surgery.
- Patients in the arthroscopic surgery group had specific knee procedures (resection of degenerative knee tissues) along with nonoperative management (physical therapy plus medications as required), while the control group received nonoperative management alone.
- The primary outcome was TKA on the knee being studied, and the secondary outcome was TKA or osteotomy on either knee.
TAKEAWAY:
- During a median follow-up of 13.8 years, 37.6% of patients underwent TKA, with comparable proportions of patients in the arthroscopic surgery and control groups undergoing TKA (adjusted hazard ratio [aHR], 0.85; 95% CI, 0.52-1.40).
- The rates of TKA or osteotomy on either knee were similar in both groups (aHR, 0.91; 95% CI, 0.59-1.41).
- A time-stratified analysis done for 0-5 years, 5-10 years, and beyond 10 years of follow-up also showed a consistent interpretation.
- When patients with crossover to arthroscopic surgery during the follow-up were included, the results remained similar for both the primary (HR, 0.88; 95% CI, 0.53-1.44) and secondary (HR, 1.08; 95% CI, 0.69-1.68) outcomes.
IN PRACTICE:
“Our study findings do not support the use of arthroscopic surgery for OA of the knee.” “Arthroscopic surgery does not provide additional benefit to nonoperative management for improving pain, stiffness, and function and is likely not cost-effective at 2 years of follow-up,” the authors wrote.
SOURCE:
This study was led by Trevor B. Birmingham, PhD, Fowler Kennedy Sport Medicine Clinic, University of Western Ontario, London, Ontario, Canada. It was published online in JAMA Network Open
LIMITATIONS:
The study was designed to assess differences in 2-year patient-reported outcomes rather than long-term TKA incidence. Factors influencing decisions to undergo TKA or osteotomy were not considered. Moreover, the effects observed in this study should be evaluated considering the estimated confidence intervals.
DISCLOSURES:
This study was supported by the ICES, which is funded by an annual grant from the Ontario Ministry of Health and the Ministry of Long-Term Care. Some authors declared consulting, performing contracted services, or receiving grant funding, royalties, and nonfinancial support from various sources.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
Adding arthroscopic surgery to nonoperative management neither delays nor accelerates the timing of total knee arthroplasty (TKA) in patients with knee osteoarthritis (OA).
METHODOLOGY:
- Some case series show that arthroscopic surgery for knee OA may delay more invasive procedures, such as TKA or osteotomy, while longitudinal cohort studies often contradict this. Current OA guidelines are yet to address this issue.
- This secondary analysis of a randomized trial compared the long-term incidence of TKA in 178 patients (mean age, 59 years; 64.3% women) with knee OA who were referred for potential arthroscopic surgery at a tertiary care center in Canada.
- The patients received nonoperative care with or without additional arthroscopic surgery.
- Patients in the arthroscopic surgery group had specific knee procedures (resection of degenerative knee tissues) along with nonoperative management (physical therapy plus medications as required), while the control group received nonoperative management alone.
- The primary outcome was TKA on the knee being studied, and the secondary outcome was TKA or osteotomy on either knee.
TAKEAWAY:
- During a median follow-up of 13.8 years, 37.6% of patients underwent TKA, with comparable proportions of patients in the arthroscopic surgery and control groups undergoing TKA (adjusted hazard ratio [aHR], 0.85; 95% CI, 0.52-1.40).
- The rates of TKA or osteotomy on either knee were similar in both groups (aHR, 0.91; 95% CI, 0.59-1.41).
- A time-stratified analysis done for 0-5 years, 5-10 years, and beyond 10 years of follow-up also showed a consistent interpretation.
- When patients with crossover to arthroscopic surgery during the follow-up were included, the results remained similar for both the primary (HR, 0.88; 95% CI, 0.53-1.44) and secondary (HR, 1.08; 95% CI, 0.69-1.68) outcomes.
IN PRACTICE:
“Our study findings do not support the use of arthroscopic surgery for OA of the knee.” “Arthroscopic surgery does not provide additional benefit to nonoperative management for improving pain, stiffness, and function and is likely not cost-effective at 2 years of follow-up,” the authors wrote.
SOURCE:
This study was led by Trevor B. Birmingham, PhD, Fowler Kennedy Sport Medicine Clinic, University of Western Ontario, London, Ontario, Canada. It was published online in JAMA Network Open
LIMITATIONS:
The study was designed to assess differences in 2-year patient-reported outcomes rather than long-term TKA incidence. Factors influencing decisions to undergo TKA or osteotomy were not considered. Moreover, the effects observed in this study should be evaluated considering the estimated confidence intervals.
DISCLOSURES:
This study was supported by the ICES, which is funded by an annual grant from the Ontario Ministry of Health and the Ministry of Long-Term Care. Some authors declared consulting, performing contracted services, or receiving grant funding, royalties, and nonfinancial support from various sources.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
Adding arthroscopic surgery to nonoperative management neither delays nor accelerates the timing of total knee arthroplasty (TKA) in patients with knee osteoarthritis (OA).
METHODOLOGY:
- Some case series show that arthroscopic surgery for knee OA may delay more invasive procedures, such as TKA or osteotomy, while longitudinal cohort studies often contradict this. Current OA guidelines are yet to address this issue.
- This secondary analysis of a randomized trial compared the long-term incidence of TKA in 178 patients (mean age, 59 years; 64.3% women) with knee OA who were referred for potential arthroscopic surgery at a tertiary care center in Canada.
- The patients received nonoperative care with or without additional arthroscopic surgery.
- Patients in the arthroscopic surgery group had specific knee procedures (resection of degenerative knee tissues) along with nonoperative management (physical therapy plus medications as required), while the control group received nonoperative management alone.
- The primary outcome was TKA on the knee being studied, and the secondary outcome was TKA or osteotomy on either knee.
TAKEAWAY:
- During a median follow-up of 13.8 years, 37.6% of patients underwent TKA, with comparable proportions of patients in the arthroscopic surgery and control groups undergoing TKA (adjusted hazard ratio [aHR], 0.85; 95% CI, 0.52-1.40).
- The rates of TKA or osteotomy on either knee were similar in both groups (aHR, 0.91; 95% CI, 0.59-1.41).
- A time-stratified analysis done for 0-5 years, 5-10 years, and beyond 10 years of follow-up also showed a consistent interpretation.
- When patients with crossover to arthroscopic surgery during the follow-up were included, the results remained similar for both the primary (HR, 0.88; 95% CI, 0.53-1.44) and secondary (HR, 1.08; 95% CI, 0.69-1.68) outcomes.
IN PRACTICE:
“Our study findings do not support the use of arthroscopic surgery for OA of the knee.” “Arthroscopic surgery does not provide additional benefit to nonoperative management for improving pain, stiffness, and function and is likely not cost-effective at 2 years of follow-up,” the authors wrote.
SOURCE:
This study was led by Trevor B. Birmingham, PhD, Fowler Kennedy Sport Medicine Clinic, University of Western Ontario, London, Ontario, Canada. It was published online in JAMA Network Open
LIMITATIONS:
The study was designed to assess differences in 2-year patient-reported outcomes rather than long-term TKA incidence. Factors influencing decisions to undergo TKA or osteotomy were not considered. Moreover, the effects observed in this study should be evaluated considering the estimated confidence intervals.
DISCLOSURES:
This study was supported by the ICES, which is funded by an annual grant from the Ontario Ministry of Health and the Ministry of Long-Term Care. Some authors declared consulting, performing contracted services, or receiving grant funding, royalties, and nonfinancial support from various sources.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Vigilance Needed in Gout Treatment to Reduce CVD Risks
NEW YORK — Urate, the culprit of gout, affects the vasculature in multiple ways that can raise cardiovascular risk (CV) in an individual with gout, and following guidelines for gout treatment, including the use of colchicine, can be the key to reducing those risks.
“Guideline-concordant gout treatment, which is essentially an anti-inflammatory urate-lowering strategy, at least improves arterial physiology and likely reduces cardiovascular risk,” Michael H. Pillinger, MD, told attendees at the 4th Annual Cardiometabolic Risk in Inflammatory Conditions conference. Dr. Pillinger is professor of medicine and biochemistry and molecular pharmacology at New York University Grossman School of Medicine, New York City, who has published multiple studies on gout.
He cited evidence that has shown soluble urate stimulates the production of C-reactive protein (CRP), which is a predictor of cardiovascular disease (CVD). Another study, in which Dr. Pillinger participated, demonstrated that gout patients have impaired vascular endothelial function associated with a chronic, low-level inflammatory state, he said.
“There’s good evidence that urate itself affects the vasculature in multiple ways, and I suspect this may be a model for other metabolic effects on vasculature,” Dr. Pillinger said. “Patients with gout have abnormal endothelium in ways that really convey vascular risk.”
Gout, Inflammation, and CVD
However, for rheumatologists to study the association between gout-related inflammation and CVD is “very, very hard,” Dr. Pillinger added. “But I do think that the mechanisms by which gout induces biological changes in the vasculature may provide insights into cardiovascular disease in general.”
One way to evaluate the effects of gout on the endothelium in the clinic is to measure flow-mediated dilation. This technique involves placing an ultrasound probe over the brachial artery and measuring the baseline artery diameter. Then, with the blood pressure cuff over the forearm, inflate it to reduce flow, then release the cuff and measure the brachial artery diameter after the endothelium releases vasodilators.
Dr. Pillinger and colleagues evaluated this technique in 34 patients with gout and 64 controls and found that patients with gout had an almost 50% decrease in flow-mediated dilation, he said. “Interestingly, the higher the urate, the worse the flow; the more the inflammation, the worse the flow, so seemingly corresponding with the severity of the gout,” he said. That raised an obvious question, Dr. Pillinger continued: “If you can treat the gout, can you improve the flow-mediated dilation?”
His group answered that question with a study in 38 previously untreated patients with gout, giving them colchicine 0.6 mg twice daily for a month plus a urate-lowering xanthine oxidase inhibitor (allopurinol or febuxostat) to treat them to a target urate level of < 6 mg/dL. “We saw an increase in endothelial function, and it normalized,” Dr. Pillinger said.
However, some study participants didn’t respond. “They were people with well-established other cardiovascular comorbidities — hypertension, hyperlipidemia,” he said. “I think some people just have vessels that are too damaged to get at them just by fixing their gout problem or their inflammation.”
That means patients with gout need to be treated with colchicine early on to avoid CV problems, Dr. Pillinger added. “We ought to get to them before they have the other problems,” he said.
Managing gout, and the concomitant CV problems, requires vigilance both during and in between flares, Dr. Pillinger said after his presentation.
“We have always taught that patients between flares basically look like people with no gout, but we do know now that patients with gout between flares tend to have what you might call ‘subclinical’ inflammation: CRPs and ESRs [erythrocyte sedimentation rates] that are higher than those of the general population, though not so excessive that they might grab attention,” he said. “We also know that many, if not all, patients between flares have urate deposited in or around their joints, but how these two relate is not fully established.”
Better treatment within 3 months of an acute gout flare may reduce the risk for CV events, he said, but that’s based on speculation more so than clinical data.
Potential Benefits of Targeting Inflammation
“More chronically, we know from the cardiologists’ studies that anti-inflammatory therapy should reduce risk in the high-risk general population,” Dr. Pillinger said. “There are no prospective studies confirming that this approach will work among gout patients, but there is no reason why it shouldn’t work — except perhaps that gout patients may have higher inflammation than the general population and also have more comorbidities, so they could perhaps be more resistant.”
Dr. Pillinger said that his group’s studies and another led by Daniel Solomon, MD, at Brigham and Women’s Hospital in Boston, have indicated that anti-inflammatory strategies in gout will lower CV risk.
“And interestingly,” he added, “our data suggest that colchicine use may lower risk not only in high-risk gout patients but also in gout patients who start with no CAD [coronary artery disease] but who seem to have less incident CAD on colchicine. I see this as identifying that gout patients are intrinsically at high risk for CAD, even if they don’t actually have any, so they represent a population for whom lowering chronic inflammation may help prevent incident disease.”
Dr. Pillinger provided more evidence that the understanding of the relationship between gout, gout flares, and CV risk is evolving, said Michael S. Garshick, MD, who attended the conference and is head of the Cardio-Rheumatology Program at NYU Langone, New York City.
“There’s epidemiologic evidence supporting the association,” Dr. Garshick told this news organization after the conference. “We think that most conditions with immune system activation do tend to have an increased risk of some form of cardiovascular disease, but I think the relationship with gout has been highly underpublicized.”
Many patients with gout tend to have a higher prevalence of traditional cardiometabolic issues, which may compound the relationship, Dr. Garshick added. “However, I would argue that with this patient subset that it doesn’t matter because gout patients have a higher risk of traditional risk factors, and you have to [treat-to-target] those traditional risk factors.”
While the clinical evidence of a link between gout and atherosclerosis may not be conclusive, enough circumstantial evidence exists to believe that treating gout will reduce CV risks, he said. “Some of the imaging techniques do suggest that gouty crystals [are] in the atherosclerotic plaque of gout patients,” Dr. Garshick added. Dr. Pillinger’s work, he said, “is showing us that there are different pathways to develop atherosclerosis.”
Dr. Pillinger disclosed relationships with Federation Bio, Fortress Biotech, Amgen, Scilex, Hikma Pharmaceuticals, LG Chem, and Olatec Therapeutics. Dr. Garshick disclosed relationships with Kiniksa Pharmaceuticals, Agepha Pharma, Bristol Myers Squibb, and Horizon Therapeutics.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
NEW YORK — Urate, the culprit of gout, affects the vasculature in multiple ways that can raise cardiovascular risk (CV) in an individual with gout, and following guidelines for gout treatment, including the use of colchicine, can be the key to reducing those risks.
“Guideline-concordant gout treatment, which is essentially an anti-inflammatory urate-lowering strategy, at least improves arterial physiology and likely reduces cardiovascular risk,” Michael H. Pillinger, MD, told attendees at the 4th Annual Cardiometabolic Risk in Inflammatory Conditions conference. Dr. Pillinger is professor of medicine and biochemistry and molecular pharmacology at New York University Grossman School of Medicine, New York City, who has published multiple studies on gout.
He cited evidence that has shown soluble urate stimulates the production of C-reactive protein (CRP), which is a predictor of cardiovascular disease (CVD). Another study, in which Dr. Pillinger participated, demonstrated that gout patients have impaired vascular endothelial function associated with a chronic, low-level inflammatory state, he said.
“There’s good evidence that urate itself affects the vasculature in multiple ways, and I suspect this may be a model for other metabolic effects on vasculature,” Dr. Pillinger said. “Patients with gout have abnormal endothelium in ways that really convey vascular risk.”
Gout, Inflammation, and CVD
However, for rheumatologists to study the association between gout-related inflammation and CVD is “very, very hard,” Dr. Pillinger added. “But I do think that the mechanisms by which gout induces biological changes in the vasculature may provide insights into cardiovascular disease in general.”
One way to evaluate the effects of gout on the endothelium in the clinic is to measure flow-mediated dilation. This technique involves placing an ultrasound probe over the brachial artery and measuring the baseline artery diameter. Then, with the blood pressure cuff over the forearm, inflate it to reduce flow, then release the cuff and measure the brachial artery diameter after the endothelium releases vasodilators.
Dr. Pillinger and colleagues evaluated this technique in 34 patients with gout and 64 controls and found that patients with gout had an almost 50% decrease in flow-mediated dilation, he said. “Interestingly, the higher the urate, the worse the flow; the more the inflammation, the worse the flow, so seemingly corresponding with the severity of the gout,” he said. That raised an obvious question, Dr. Pillinger continued: “If you can treat the gout, can you improve the flow-mediated dilation?”
His group answered that question with a study in 38 previously untreated patients with gout, giving them colchicine 0.6 mg twice daily for a month plus a urate-lowering xanthine oxidase inhibitor (allopurinol or febuxostat) to treat them to a target urate level of < 6 mg/dL. “We saw an increase in endothelial function, and it normalized,” Dr. Pillinger said.
However, some study participants didn’t respond. “They were people with well-established other cardiovascular comorbidities — hypertension, hyperlipidemia,” he said. “I think some people just have vessels that are too damaged to get at them just by fixing their gout problem or their inflammation.”
That means patients with gout need to be treated with colchicine early on to avoid CV problems, Dr. Pillinger added. “We ought to get to them before they have the other problems,” he said.
Managing gout, and the concomitant CV problems, requires vigilance both during and in between flares, Dr. Pillinger said after his presentation.
“We have always taught that patients between flares basically look like people with no gout, but we do know now that patients with gout between flares tend to have what you might call ‘subclinical’ inflammation: CRPs and ESRs [erythrocyte sedimentation rates] that are higher than those of the general population, though not so excessive that they might grab attention,” he said. “We also know that many, if not all, patients between flares have urate deposited in or around their joints, but how these two relate is not fully established.”
Better treatment within 3 months of an acute gout flare may reduce the risk for CV events, he said, but that’s based on speculation more so than clinical data.
Potential Benefits of Targeting Inflammation
“More chronically, we know from the cardiologists’ studies that anti-inflammatory therapy should reduce risk in the high-risk general population,” Dr. Pillinger said. “There are no prospective studies confirming that this approach will work among gout patients, but there is no reason why it shouldn’t work — except perhaps that gout patients may have higher inflammation than the general population and also have more comorbidities, so they could perhaps be more resistant.”
Dr. Pillinger said that his group’s studies and another led by Daniel Solomon, MD, at Brigham and Women’s Hospital in Boston, have indicated that anti-inflammatory strategies in gout will lower CV risk.
“And interestingly,” he added, “our data suggest that colchicine use may lower risk not only in high-risk gout patients but also in gout patients who start with no CAD [coronary artery disease] but who seem to have less incident CAD on colchicine. I see this as identifying that gout patients are intrinsically at high risk for CAD, even if they don’t actually have any, so they represent a population for whom lowering chronic inflammation may help prevent incident disease.”
Dr. Pillinger provided more evidence that the understanding of the relationship between gout, gout flares, and CV risk is evolving, said Michael S. Garshick, MD, who attended the conference and is head of the Cardio-Rheumatology Program at NYU Langone, New York City.
“There’s epidemiologic evidence supporting the association,” Dr. Garshick told this news organization after the conference. “We think that most conditions with immune system activation do tend to have an increased risk of some form of cardiovascular disease, but I think the relationship with gout has been highly underpublicized.”
Many patients with gout tend to have a higher prevalence of traditional cardiometabolic issues, which may compound the relationship, Dr. Garshick added. “However, I would argue that with this patient subset that it doesn’t matter because gout patients have a higher risk of traditional risk factors, and you have to [treat-to-target] those traditional risk factors.”
While the clinical evidence of a link between gout and atherosclerosis may not be conclusive, enough circumstantial evidence exists to believe that treating gout will reduce CV risks, he said. “Some of the imaging techniques do suggest that gouty crystals [are] in the atherosclerotic plaque of gout patients,” Dr. Garshick added. Dr. Pillinger’s work, he said, “is showing us that there are different pathways to develop atherosclerosis.”
Dr. Pillinger disclosed relationships with Federation Bio, Fortress Biotech, Amgen, Scilex, Hikma Pharmaceuticals, LG Chem, and Olatec Therapeutics. Dr. Garshick disclosed relationships with Kiniksa Pharmaceuticals, Agepha Pharma, Bristol Myers Squibb, and Horizon Therapeutics.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
NEW YORK — Urate, the culprit of gout, affects the vasculature in multiple ways that can raise cardiovascular risk (CV) in an individual with gout, and following guidelines for gout treatment, including the use of colchicine, can be the key to reducing those risks.
“Guideline-concordant gout treatment, which is essentially an anti-inflammatory urate-lowering strategy, at least improves arterial physiology and likely reduces cardiovascular risk,” Michael H. Pillinger, MD, told attendees at the 4th Annual Cardiometabolic Risk in Inflammatory Conditions conference. Dr. Pillinger is professor of medicine and biochemistry and molecular pharmacology at New York University Grossman School of Medicine, New York City, who has published multiple studies on gout.
He cited evidence that has shown soluble urate stimulates the production of C-reactive protein (CRP), which is a predictor of cardiovascular disease (CVD). Another study, in which Dr. Pillinger participated, demonstrated that gout patients have impaired vascular endothelial function associated with a chronic, low-level inflammatory state, he said.
“There’s good evidence that urate itself affects the vasculature in multiple ways, and I suspect this may be a model for other metabolic effects on vasculature,” Dr. Pillinger said. “Patients with gout have abnormal endothelium in ways that really convey vascular risk.”
Gout, Inflammation, and CVD
However, for rheumatologists to study the association between gout-related inflammation and CVD is “very, very hard,” Dr. Pillinger added. “But I do think that the mechanisms by which gout induces biological changes in the vasculature may provide insights into cardiovascular disease in general.”
One way to evaluate the effects of gout on the endothelium in the clinic is to measure flow-mediated dilation. This technique involves placing an ultrasound probe over the brachial artery and measuring the baseline artery diameter. Then, with the blood pressure cuff over the forearm, inflate it to reduce flow, then release the cuff and measure the brachial artery diameter after the endothelium releases vasodilators.
Dr. Pillinger and colleagues evaluated this technique in 34 patients with gout and 64 controls and found that patients with gout had an almost 50% decrease in flow-mediated dilation, he said. “Interestingly, the higher the urate, the worse the flow; the more the inflammation, the worse the flow, so seemingly corresponding with the severity of the gout,” he said. That raised an obvious question, Dr. Pillinger continued: “If you can treat the gout, can you improve the flow-mediated dilation?”
His group answered that question with a study in 38 previously untreated patients with gout, giving them colchicine 0.6 mg twice daily for a month plus a urate-lowering xanthine oxidase inhibitor (allopurinol or febuxostat) to treat them to a target urate level of < 6 mg/dL. “We saw an increase in endothelial function, and it normalized,” Dr. Pillinger said.
However, some study participants didn’t respond. “They were people with well-established other cardiovascular comorbidities — hypertension, hyperlipidemia,” he said. “I think some people just have vessels that are too damaged to get at them just by fixing their gout problem or their inflammation.”
That means patients with gout need to be treated with colchicine early on to avoid CV problems, Dr. Pillinger added. “We ought to get to them before they have the other problems,” he said.
Managing gout, and the concomitant CV problems, requires vigilance both during and in between flares, Dr. Pillinger said after his presentation.
“We have always taught that patients between flares basically look like people with no gout, but we do know now that patients with gout between flares tend to have what you might call ‘subclinical’ inflammation: CRPs and ESRs [erythrocyte sedimentation rates] that are higher than those of the general population, though not so excessive that they might grab attention,” he said. “We also know that many, if not all, patients between flares have urate deposited in or around their joints, but how these two relate is not fully established.”
Better treatment within 3 months of an acute gout flare may reduce the risk for CV events, he said, but that’s based on speculation more so than clinical data.
Potential Benefits of Targeting Inflammation
“More chronically, we know from the cardiologists’ studies that anti-inflammatory therapy should reduce risk in the high-risk general population,” Dr. Pillinger said. “There are no prospective studies confirming that this approach will work among gout patients, but there is no reason why it shouldn’t work — except perhaps that gout patients may have higher inflammation than the general population and also have more comorbidities, so they could perhaps be more resistant.”
Dr. Pillinger said that his group’s studies and another led by Daniel Solomon, MD, at Brigham and Women’s Hospital in Boston, have indicated that anti-inflammatory strategies in gout will lower CV risk.
“And interestingly,” he added, “our data suggest that colchicine use may lower risk not only in high-risk gout patients but also in gout patients who start with no CAD [coronary artery disease] but who seem to have less incident CAD on colchicine. I see this as identifying that gout patients are intrinsically at high risk for CAD, even if they don’t actually have any, so they represent a population for whom lowering chronic inflammation may help prevent incident disease.”
Dr. Pillinger provided more evidence that the understanding of the relationship between gout, gout flares, and CV risk is evolving, said Michael S. Garshick, MD, who attended the conference and is head of the Cardio-Rheumatology Program at NYU Langone, New York City.
“There’s epidemiologic evidence supporting the association,” Dr. Garshick told this news organization after the conference. “We think that most conditions with immune system activation do tend to have an increased risk of some form of cardiovascular disease, but I think the relationship with gout has been highly underpublicized.”
Many patients with gout tend to have a higher prevalence of traditional cardiometabolic issues, which may compound the relationship, Dr. Garshick added. “However, I would argue that with this patient subset that it doesn’t matter because gout patients have a higher risk of traditional risk factors, and you have to [treat-to-target] those traditional risk factors.”
While the clinical evidence of a link between gout and atherosclerosis may not be conclusive, enough circumstantial evidence exists to believe that treating gout will reduce CV risks, he said. “Some of the imaging techniques do suggest that gouty crystals [are] in the atherosclerotic plaque of gout patients,” Dr. Garshick added. Dr. Pillinger’s work, he said, “is showing us that there are different pathways to develop atherosclerosis.”
Dr. Pillinger disclosed relationships with Federation Bio, Fortress Biotech, Amgen, Scilex, Hikma Pharmaceuticals, LG Chem, and Olatec Therapeutics. Dr. Garshick disclosed relationships with Kiniksa Pharmaceuticals, Agepha Pharma, Bristol Myers Squibb, and Horizon Therapeutics.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Exploring Skin Pigmentation Adaptation: A Systematic Review on the Vitamin D Adaptation Hypothesis
The risk for developing skin cancer can be somewhat attributed to variations in skin pigmentation. Historically, lighter skin pigmentation has been observed in populations living in higher latitudes and darker pigmentation in populations near the equator. Although skin pigmentation is a conglomeration of genetic and environmental factors, anthropologic studies have demonstrated an association of human skin lightening with historic human migratory patterns.1 It is postulated that migration to latitudes with less UVB light penetration has resulted in a compensatory natural selection of lighter skin types. Furthermore, the driving force behind this migration-associated skin lightening has remained unclear.1
The need for folate metabolism, vitamin D synthesis, and barrier protection, as well as cultural practices, has been postulated as driving factors for skin pigmentation variation. Synthesis of vitamin D is a UV radiation (UVR)–dependent process and has remained a prominent theoretical driver for the basis of evolutionary skin lightening. Vitamin D can be acquired both exogenously or endogenously via dietary supplementation or sunlight; however, historically it has been obtained through UVB exposure primarily. Once UVB is absorbed by the skin, it catalyzes conversion of 7-dehydrocholesterol to previtamin D3, which is converted to vitamin D in the kidneys.2,3 It is suggested that lighter skin tones have an advantage over darker skin tones in synthesizing vitamin D at higher latitudes where there is less UVB, thus leading to the adaptation process.1 In this systematic review, we analyzed the evolutionary vitamin D adaptation hypothesis and assessed the validity of evidence supporting this theory in the literature.
Methods
A search of PubMed, Embase, and the Cochrane Reviews database was conducted using the terms evolution, vitamin D, and skin to generate articles published from 2010 to 2022 that evaluated the influence of UVR-dependent production of vitamin D on skin pigmentation through historical migration patterns (Figure). Studies were excluded during an initial screening of abstracts followed by full-text assessment if they only had abstracts and if articles were inaccessible for review or in the form of case reports and commentaries.
The following data were extracted from each included study: reference citation, affiliated institutions of authors, author specialties, journal name, year of publication, study period, type of article, type of study, mechanism of adaptation, data concluding or supporting vitamin D as the driver, and data concluding or suggesting against vitamin D as the driver. Data concluding or supporting vitamin D as the driver were recorded from statistically significant results, study conclusions, and direct quotations. Data concluding or suggesting against vitamin D as the driver also were recorded from significant results, study conclusions, and direct quotes. The mechanism of adaptation was based on vitamin D synthesis modulation, melanin upregulation, genetic selections, genetic drift, mating patterns, increased vitamin D sensitivity, interbreeding, and diet.
Studies included in the analysis were placed into 1 of 3 categories: supporting, neutral, and against. Strength of Recommendation Taxonomy (SORT) criteria were used to classify the level of evidence of each article.4 Each article’s level of evidence was then graded (Table 1). The SORT grading levels were based on quality and evidence type: level 1 signified good-quality, patient-oriented evidence; level 2 signified limited-quality, patient-oriented evidence; and level 3 signified other evidence.4
Results
Article Selection—A total of 229 articles were identified for screening, and 39 studies met inclusion criteria.1-3,5-40 Systematic and retrospective reviews were the most common types of studies. Genomic analysis/sequencing/genome-wide association studies (GWAS) were the most common methods of analysis. Of these 39 articles, 26 were classified as supporting the evolutionary vitamin D adaptation hypothesis, 10 were classified as neutral, and 3 were classified as against (Table 1).
Of the articles classified as supporting the vitamin D hypothesis, 13 articles were level 1 evidence, 9 were level 2, and 4 were level 3. Key findings supporting the vitamin D hypothesis included genetic natural selection favoring vitamin D synthesis genes at higher latitudes with lower UVR and the skin lightening that occurred to protect against vitamin D deficiency (Table 1). Specific genes supporting these findings included 7-dehydrocholesterol reductase (DHCR7), vitamin D receptor (VDR), tyrosinase (TYR), tyrosinase-related protein 1 (TYRP1), oculocutaneous albinism type 2 melanosomal transmembrane protein (OCA2), solute carrier family 45 member 2 (SLC45A2), solute carrier family 4 member 5 (SLC24A5), Kit ligand (KITLG), melanocortin 1 receptor (MC1R), and HECT and RLD domain containing E3 ubiquitin protein ligase 2 (HERC2)(Table 2).
Of the articles classified as being against the vitamin D hypothesis, 1 article was level 1 evidence, 1 was level 2, and 1 was level 3. Key findings refuting the vitamin D hypothesis included similar amounts of vitamin D synthesis in contemporary dark- and light-pigmented individuals, vitamin D–rich diets in the late Paleolithic period and in early agriculturalists, and metabolic conservation being the primary driver (Table 1).
Of the articles classified as neutral to the hypothesis, 7 articles were level 1 evidence and 3 were level 2. Key findings of these articles included genetic selection favoring vitamin D synthesis only for populations at extremely northern latitudes, skin lightening that was sustained in northern latitudes from the neighboring human ancestor the chimpanzee, and evidence for long-term evolutionary pressures and short-term plastic adaptations in vitamin D genes (Table 1).
Comment
The importance of appropriate vitamin D levels is hypothesized as a potent driver in skin lightening because the vitamin is essential for many biochemical processes within the human body. Proper calcification of bones requires activated vitamin D to prevent rickets in childhood. Pelvic deformation in women with rickets can obstruct childbirth in primitive medical environments.15 This direct reproductive impairment suggests a strong selective pressure for skin lightening in populations that migrated northward to enhance vitamin D synthesis.
Of the 39 articles that we reviewed, the majority (n=26 [66.7%]) supported the hypothesis that vitamin D synthesis was the main driver behind skin lightening, whereas 3 (7.7%) did not support the hypothesis and 10 (25.6%) were neutral. Other leading theories explaining skin lightening included the idea that enhanced melanogenesis protected against folate degradation; genetic selection for light-skin alleles due to genetic drift; skin lightening being the result of sexual selection; and a combination of factors, including dietary choices, clothing preferences, and skin permeability barriers.
Articles With Supporting Evidence for the Vitamin D Theory—As Homo sapiens migrated out of Africa, migration patterns demonstrated the correlation between distance from the equator and skin pigmentation from natural selection. Individuals with darker skin pigment required higher levels of UVR to synthesize vitamin D. According to Beleza et al,1 as humans migrated to areas of higher latitudes with lower levels of UVR, natural selection favored the development of lighter skin to maximize vitamin D production. Vitamin D is linked to calcium metabolism, and its deficiency can lead to bone malformations and poor immune function.35 Several genes affecting melanogenesis and skin pigment have been found to have geospatial patterns that map to different geographic locations of various populations, indicating how human migration patterns out of Africa created this natural selection for skin lightening. The gene KITLG—associated with lighter skin pigmentation—has been found in high frequencies in both European and East Asian populations and is proposed to have increased in frequency after the migration out of Africa. However, the genes TYRP1, SLC24A5, and SLC45A2 were found at high frequencies only in European populations, and this selection occurred 11,000 to 19,000 years ago during the Last Glacial Maximum (15,000–20,000 years ago), demonstrating the selection for European over East Asian characteristics. During this period, seasonal changes increased the risk for vitamin D deficiency and provided an urgency for selection to a lighter skin pigment.1
The migration of H sapiens to northern latitudes prompted the selection of alleles that would increasevitamin D synthesis to counteract the reduced UV exposure. Genetic analysis studies have found key associations between genes encoding for the metabolism of vitamin D and pigmentation. Among this complex network are the essential downstream enzymes in the melanocortin receptor 1 pathway, including TYR and TYRP1. Forty-six of 960 single-nucleotide polymorphisms located in 29 different genes involved in skin pigmentation that were analyzed in a cohort of 2970 individuals were significantly associated with serum vitamin D levels (P<.05). The exocyst complex component 2 (EXOC2), TYR, and TYRP1 gene variants were shown to have the greatest influence on vitamin D status.9 These data reveal how pigment genotypes are predictive of vitamin D levels and the epistatic potential among many genes in this complex network.
Gene variation plays an important role in vitamin D status when comparing genetic polymorphisms in populations in northern latitudes to African populations. Vitamin D3 precursor availability is decreased by 7-DHCR catalyzing the precursors substrate to cholesterol. In a study using GWAS, it was found that “variations in DHCR7 may aid vitamin D production by conserving cutaneous 7-DHC levels. A high prevalence of DHCR7 variants were found in European and Northeast Asian populations but not in African populations, suggesting that selection occurred for these DHCR7 mutations in populations who migrated to more northern latitudes.5 Multilocus networks have been established between the VDR promotor and skin color genes (Table 2) that exhibit a strong in-Africa vs out-of-Africa frequency pattern. It also has been shown that genetic variation (suggesting a long-term evolutionary inclination) and epigenetic modification (indicative of short-term exposure) of VDR lends support to the vitamin D hypothesis. As latitude decreases, prevalence of VDR FokI (F allele), BsmI (B allele), ApaI (A allele), and TaqI (T allele) also decreases in a linear manner, linking latitude to VDR polymorphisms. Plasma vitamin D levels and photoperiod of conception—UV exposure during the periconceptional period—also were extrapolative of VDR methylation in a study involving 80 participants, where these 2 factors accounted for 17% of variance in methylation.6
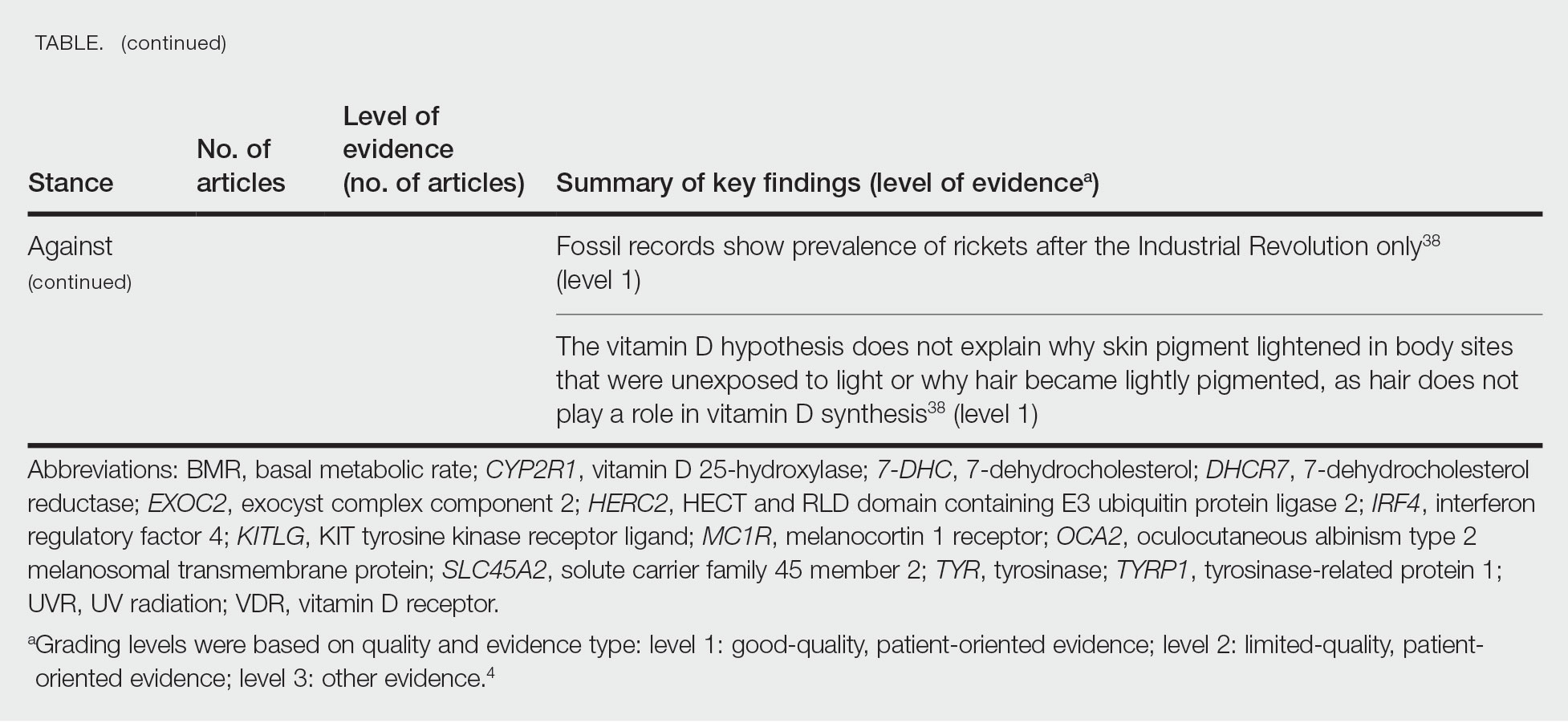
Other noteworthy genes included HERC2, which has implications in the expression of OCA2 (melanocyte-specific transporter protein), and IRF4, which encodes for an important enzyme in folate-dependent melanin production. In an Australian cross-sectional study that analyzed vitamin D and pigmentation gene polymorphisms in conjunction with plasma vitamin D levels, the most notable rate of vitamin D loss occurred in individuals with the darkest pigmentation HERC2 (AA) genotype.31 In contrast, the lightest pigmentation HERC2 (GG) genotypes had increased vitamin D3 photosynthesis. Interestingly, the lightest interferon regulatory factor 4 (IRF4) TT genotype and the darkest HERC2 AA genotype, rendering the greatest folate loss and largest synthesis of vitamin D3, were not seen in combination in any of the participants.30 In addition to HERC2, derived alleles from pigment-associated genes SLC24A5*A and SLC45A2*G demonstrated greater frequencies in Europeans (>90%) compared to Africans and East Asians, where the allelic frequencies were either rare or absent.1 This evidence delineates not only the complexity but also the strong relationship between skin pigmentation, latitude, and vitamin D status. The GWAS also have supported this concept. In comparing European populations to African populations, there was a 4-fold increase in the frequencies of “derived alleles of the vitamin D transport protein (GC, rs3755967), the 25(OH)D3 synthesizing enzyme (CYP2R1, rs10741657), VDR (rs2228570 (commonly known as FokI polymorphism), rs1544410 (Bsm1), and rs731236 (Taq1) and the VDR target genes CYP24A1 (rs17216707), CD14 (rs2569190), and CARD9 (rs4077515).”32
Articles With Evidence Against the Vitamin D Theory—This review analyzed the level of support for the theory that vitamin D was the main driver for skin lightening. Although most articles supported this theory, there were articles that listed other plausible counterarguments. Jablonski and Chaplin3 suggested that humans living in higher latitudes compensated for increased demand of vitamin D by placing cultural importance on a diet of vitamin D–rich foods and thus would not have experienced decreased vitamin D levels, which we hypothesize were the driver for skin lightening. Elias et al39 argued that initial pigment dilution may have instead served to improve metabolic conservation, as the authors found no evidence of rickets—the sequelae of vitamin D deficiency—in pre–industrial age human fossils. Elias and Williams38 proposed that differences in skin pigment are due to a more intact skin permeability barrier as “a requirement for life in a desiccating terrestrial environment,” which is seen in darker skin tones compared to lighter skin tones and thus can survive better in warmer climates with less risk of infections or dehydration.
Articles With Neutral Evidence for the Vitamin D Theory—Greaves41 argued against the idea that skin evolved to become lighter to protect against vitamin D deficiency. They proposed that the chimpanzee, which is the human’s most closely related species, had light skin covered by hair, and the loss of this hair led to exposed pale skin that created a need for increased melanin production for protection from UVR. Greaves41 stated that the MC1R gene (associated with darker pigmentation) was selected for in African populations, and those with pale skin retained their original pigment as they migrated to higher latitudes. Further research has demonstrated that the genetic natural selection for skin pigment is a complex process that involves multiple gene variants found throughout cultures across the globe.
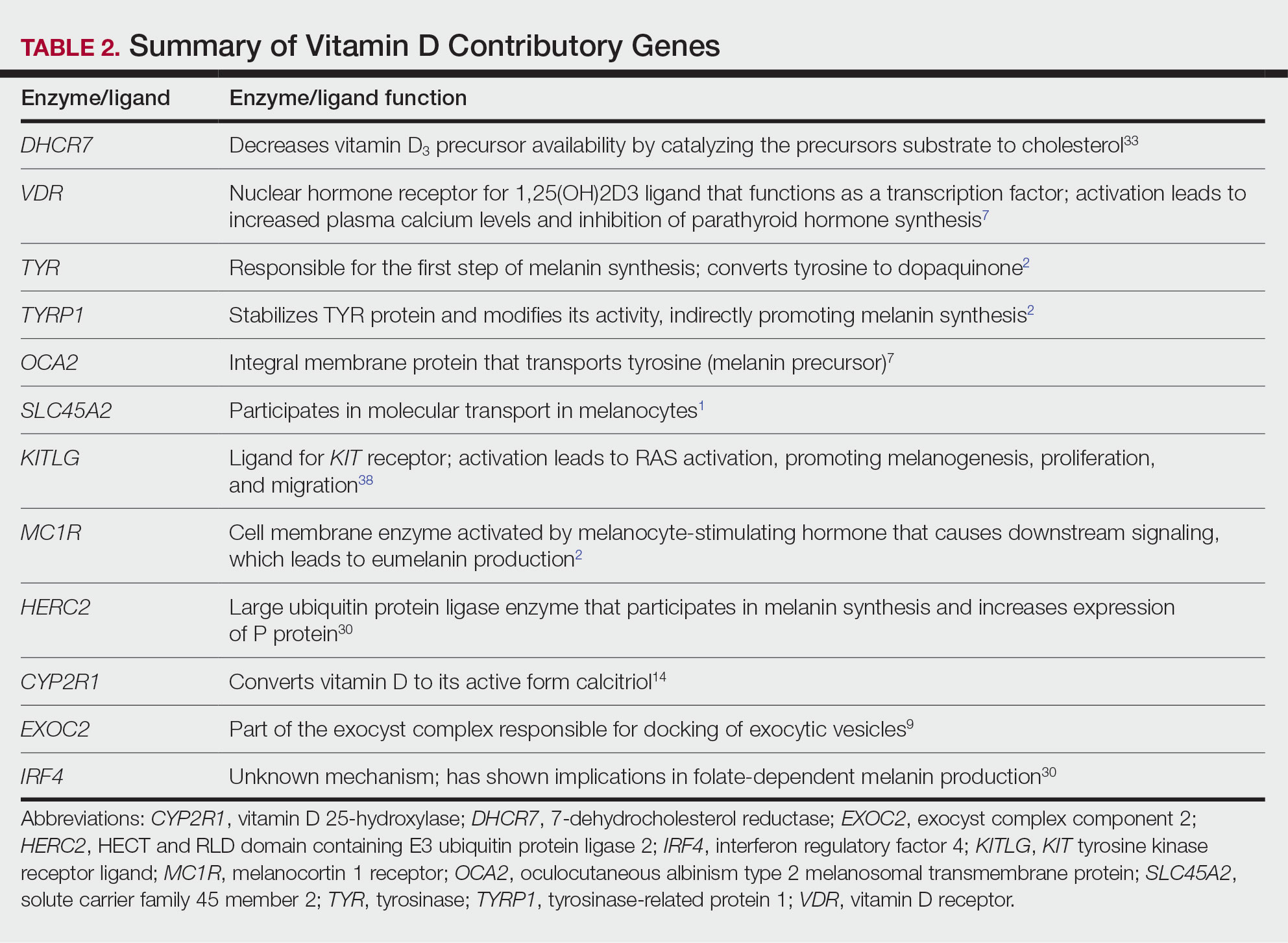
Conclusion
Skin pigmentation has continuously evolved alongside humans. Genetic selection for lighter skin coincides with a favorable selection for genes involved in vitamin D synthesis as humans migrated to northern latitudes, which enabled humans to produce adequate levels of exogenous vitamin D in low-UVR areas and in turn promoted survival. Early humans without access to supplementation or foods rich in vitamin D acquired vitamin D primarily through sunlight. In comparison to modern society, where vitamin D supplementation is accessible and human lifespans are prolonged, lighter skin tone is now a risk factor for malignant cancers of the skin rather than being a protective adaptation. Current sun behavior recommendations conclude that the body’s need for vitamin D is satisfied by UV exposure to the arms, legs, hands, and/or face for only 5 to 30 minutes between 10
The hypothesis that skin lightening primarily was driven by the need for vitamin D can only be partially supported by our review. Studies have shown that there is a corresponding complex network of genes that determines skin pigmentation as well as vitamin D synthesis and conservation. However, there is sufficient evidence that skin lightening is multifactorial in nature, and vitamin D alone may not be the sole driver. The information in this review can be used by health care providers to educate patients on sun protection, given the lesser threat of severe vitamin D deficiency in developed communities today that have access to adequate nutrition and supplementation.
Skin lightening and its coinciding evolutionary drivers are a rather neglected area of research. Due to heterogeneous cohorts and conservative data analysis, GWAS studies run the risk of type II error, yielding a limitation in our data analysis.9 Furthermore, the data regarding specific time frames in evolutionary skin lightening as well as the intensity of gene polymorphisms are limited.1 Further studies are needed to determine the interconnectedness of the current skin-lightening theories to identify other important factors that may play a role in the process. Determining the key event can help us better understand skin-adaptation mechanisms and create a framework for understanding the vital process involved in adaptation, survival, and disease manifestation in different patient populations.
- Beleza S, Santos AM, McEvoy B, et al. The timing of pigmentation lightening in Europeans. Mol Biol Evol. 2013;30:24-35. doi:10.1093/molbev/mss207
- Carlberg C. Nutrigenomics of vitamin D. Nutrients. 2019;11:676. doi:10.3390/nu11030676
- Jablonski NG, Chaplin G. The roles of vitamin D and cutaneous vitamin D production in human evolution and health. Int J Paleopathol. 2018;23:54-59. doi:10.1016/j.ijpp.2018.01.005
- Weiss BD. SORT: strength of recommendation taxonomy. Fam Med. 2004;36:141-143.
- Wolf ST, Kenney WL. The vitamin D–folate hypothesis in human vascular health. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiology. 2019;317:R491-R501. doi:10.1152/ajpregu.00136.2019
- Lucock M, Jones P, Martin C, et al. Photobiology of vitamins. Nutr Rev. 2018;76:512-525. doi:10.1093/nutrit/nuy013
- Hochberg Z, Hochberg I. Evolutionary perspective in rickets and vitamin D. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2019;10:306. doi:10.3389/fendo.2019.00306
- Rossberg W, Saternus R, Wagenpfeil S, et al. Human pigmentation, cutaneous vitamin D synthesis and evolution: variants of genes (SNPs) involved in skin pigmentation are associated with 25(OH)D serum concentration. Anticancer Res. 2016;36:1429-1437.
- Saternus R, Pilz S, Gräber S, et al. A closer look at evolution: variants (SNPs) of genes involved in skin pigmentation, including EXOC2, TYR, TYRP1, and DCT, are associated with 25(OH)D serum concentration. Endocrinology. 2015;156:39-47. doi:10.1210/en.2014-1238
- López S, García Ó, Yurrebaso I, et al. The interplay between natural selection and susceptibility to melanoma on allele 374F of SLC45A2 gene in a south European population. PloS One. 2014;9:E104367. doi:1371/journal.pone.0104367
- Lucock M, Yates Z, Martin C, et al. Vitamin D, folate, and potential early lifecycle environmental origin of significant adult phenotypes. Evol Med Public Health. 2014;2014:69-91. doi:10.1093/emph/eou013
- Hudjashov G, Villems R, Kivisild T. Global patterns of diversity and selection in human tyrosinase gene. PloS One. 2013;8:E74307. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0074307
- Khan R, Khan BSR. Diet, disease and pigment variation in humans. Med Hypotheses. 2010;75:363-367. doi:10.1016/j.mehy.2010.03.033
- Kuan V, Martineau AR, Griffiths CJ, et al. DHCR7 mutations linked to higher vitamin D status allowed early human migration to northern latitudes. BMC Evol Biol. 2013;13:144. doi:10.1186/1471-2148-13-144
- Omenn GS. Evolution and public health. Proc National Acad Sci. 2010;107(suppl 1):1702-1709. doi:10.1073/pnas.0906198106
- Yuen AWC, Jablonski NG. Vitamin D: in the evolution of human skin colour. Med Hypotheses. 2010;74:39-44. doi:10.1016/j.mehy.2009.08.007
- Vieth R. Weaker bones and white skin as adaptions to improve anthropological “fitness” for northern environments. Osteoporosis Int. 2020;31:617-624. doi:10.1007/s00198-019-05167-4
- Carlberg C. Vitamin D: a micronutrient regulating genes. Curr Pharm Des. 2019;25:1740-1746. doi:10.2174/1381612825666190705193227
- Haddadeen C, Lai C, Cho SY, et al. Variants of the melanocortin‐1 receptor: do they matter clinically? Exp Dermatol. 2015;1:5-9. doi:10.1111/exd.12540
- Yao S, Ambrosone CB. Associations between vitamin D deficiency and risk of aggressive breast cancer in African-American women. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 2013;136:337-341. doi:10.1016/j.jsbmb.2012.09.010
- Jablonski N. The evolution of human skin colouration and its relevance to health in the modern world. J Royal Coll Physicians Edinb. 2012;42:58-63. doi:10.4997/jrcpe.2012.114
- Jablonski NG, Chaplin G. Human skin pigmentation as an adaptation to UV radiation. Proc National Acad Sci. 2010;107(suppl 2):8962-8968. doi:10.1073/pnas.0914628107
- Hochberg Z, Templeton AR. Evolutionary perspective in skin color, vitamin D and its receptor. Hormones. 2010;9:307-311. doi:10.14310/horm.2002.1281
- Jones P, Lucock M, Veysey M, et al. The vitamin D–folate hypothesis as an evolutionary model for skin pigmentation: an update and integration of current ideas. Nutrients. 2018;10:554. doi:10.3390/nu10050554
- Lindqvist PG, Epstein E, Landin-Olsson M, et al. Women with fair phenotypes seem to confer a survival advantage in a low UV milieu. a nested matched case control study. PloS One. 2020;15:E0228582. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0228582
- Holick MF. Shedding new light on the role of the sunshine vitamin D for skin health: the lncRNA–skin cancer connection. Exp Dermatol. 2014;23:391-392. doi:10.1111/exd.12386
- Jablonski NG, Chaplin G. Epidermal pigmentation in the human lineage is an adaptation to ultraviolet radiation. J Hum Evol. 2013;65:671-675. doi:10.1016/j.jhevol.2013.06.004
- Jablonski NG, Chaplin G. The evolution of skin pigmentation and hair texture in people of African ancestry. Dermatol Clin. 2014;32:113-121. doi:10.1016/j.det.2013.11.003
- Jablonski NG. The evolution of human skin pigmentation involved the interactions of genetic, environmental, and cultural variables. Pigment Cell Melanoma Res. 2021;34:707-7 doi:10.1111/pcmr.12976
- Lucock MD, Jones PR, Veysey M, et al. Biophysical evidence to support and extend the vitamin D‐folate hypothesis as a paradigm for the evolution of human skin pigmentation. Am J Hum Biol. 2022;34:E23667. doi:10.1002/ajhb.23667
- Missaggia BO, Reales G, Cybis GB, et al. Adaptation and co‐adaptation of skin pigmentation and vitamin D genes in native Americans. Am J Med Genet C Semin Med Genet. 2020;184:1060-1077. doi:10.1002/ajmg.c.31873
- Hanel A, Carlberg C. Skin colour and vitamin D: an update. Exp Dermatol. 2020;29:864-875. doi:10.1111/exd.14142
- Hanel A, Carlberg C. Vitamin D and evolution: pharmacologic implications. Biochem Pharmacol. 2020;173:113595. doi:10.1016/j.bcp.2019.07.024
- Flegr J, Sýkorová K, Fiala V, et al. Increased 25(OH)D3 level in redheaded people: could redheadedness be an adaptation to temperate climate? Exp Dermatol. 2020;29:598-609. doi:10.1111/exd.14119
- James WPT, Johnson RJ, Speakman JR, et al. Nutrition and its role in human evolution. J Intern Med. 2019;285:533-549. doi:10.1111/joim.12878
- Lucock M, Jones P, Martin C, et al. Vitamin D: beyond metabolism. J Evid Based Complementary Altern Med. 2015;20:310-322. doi:10.1177/2156587215580491
- Jarrett P, Scragg R. Evolution, prehistory and vitamin D. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2020;17:646. doi:10.3390/ijerph17020646
- Elias PM, Williams ML. Re-appraisal of current theories for thedevelopment and loss of epidermal pigmentation in hominins and modern humans. J Hum Evol. 2013;64:687-692. doi:10.1016/j.jhevol.2013.02.003
- Elias PM, Williams ML. Basis for the gain and subsequent dilution of epidermal pigmentation during human evolution: the barrier and metabolic conservation hypotheses revisited. Am J Phys Anthropol. 2016;161:189-207. doi:10.1002/ajpa.23030
- Williams JD, Jacobson EL, Kim H, et al. Water soluble vitamins, clinical research and future application. Subcell Biochem. 2011;56:181-197. doi:10.1007/978-94-007-2199-9_10
- Greaves M. Was skin cancer a selective force for black pigmentation in early hominin evolution [published online February 26, 2014]? Proc Biol Sci. 2014;281:20132955. doi:10.1098/rspb.2013.2955
- Holick MF. Vitamin D deficiency. N Engl J Med. 2007;357:266-281. doi:10.1056/nejmra070553
- Bouillon R. Comparative analysis of nutritional guidelines for vitamin D. Nat Rev Endocrinol. 2017;13:466-479. doi:10.1038/nrendo.2017.31
- US Department of Health and Human Services. The Surgeon General’s Call to Action to Prevent Skin Cancer. US Dept of Health and Human Services, Office of the Surgeon General; 2014. Accessed April 29, 2024. https://www.hhs.gov/sites/default/files/call-to-action-prevent-skin-cancer.pdf
- Institute of Medicine (US) Committee to Review Dietary Reference Intakes for Vitamin D and Calcium; Ross AC, Taylor CL, Yaktine AL, et al, eds. Dietary Reference Intakes for Calcium and Vitamin D. National Academies Press; 2011. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK56070/
The risk for developing skin cancer can be somewhat attributed to variations in skin pigmentation. Historically, lighter skin pigmentation has been observed in populations living in higher latitudes and darker pigmentation in populations near the equator. Although skin pigmentation is a conglomeration of genetic and environmental factors, anthropologic studies have demonstrated an association of human skin lightening with historic human migratory patterns.1 It is postulated that migration to latitudes with less UVB light penetration has resulted in a compensatory natural selection of lighter skin types. Furthermore, the driving force behind this migration-associated skin lightening has remained unclear.1
The need for folate metabolism, vitamin D synthesis, and barrier protection, as well as cultural practices, has been postulated as driving factors for skin pigmentation variation. Synthesis of vitamin D is a UV radiation (UVR)–dependent process and has remained a prominent theoretical driver for the basis of evolutionary skin lightening. Vitamin D can be acquired both exogenously or endogenously via dietary supplementation or sunlight; however, historically it has been obtained through UVB exposure primarily. Once UVB is absorbed by the skin, it catalyzes conversion of 7-dehydrocholesterol to previtamin D3, which is converted to vitamin D in the kidneys.2,3 It is suggested that lighter skin tones have an advantage over darker skin tones in synthesizing vitamin D at higher latitudes where there is less UVB, thus leading to the adaptation process.1 In this systematic review, we analyzed the evolutionary vitamin D adaptation hypothesis and assessed the validity of evidence supporting this theory in the literature.
Methods
A search of PubMed, Embase, and the Cochrane Reviews database was conducted using the terms evolution, vitamin D, and skin to generate articles published from 2010 to 2022 that evaluated the influence of UVR-dependent production of vitamin D on skin pigmentation through historical migration patterns (Figure). Studies were excluded during an initial screening of abstracts followed by full-text assessment if they only had abstracts and if articles were inaccessible for review or in the form of case reports and commentaries.
The following data were extracted from each included study: reference citation, affiliated institutions of authors, author specialties, journal name, year of publication, study period, type of article, type of study, mechanism of adaptation, data concluding or supporting vitamin D as the driver, and data concluding or suggesting against vitamin D as the driver. Data concluding or supporting vitamin D as the driver were recorded from statistically significant results, study conclusions, and direct quotations. Data concluding or suggesting against vitamin D as the driver also were recorded from significant results, study conclusions, and direct quotes. The mechanism of adaptation was based on vitamin D synthesis modulation, melanin upregulation, genetic selections, genetic drift, mating patterns, increased vitamin D sensitivity, interbreeding, and diet.
Studies included in the analysis were placed into 1 of 3 categories: supporting, neutral, and against. Strength of Recommendation Taxonomy (SORT) criteria were used to classify the level of evidence of each article.4 Each article’s level of evidence was then graded (Table 1). The SORT grading levels were based on quality and evidence type: level 1 signified good-quality, patient-oriented evidence; level 2 signified limited-quality, patient-oriented evidence; and level 3 signified other evidence.4
Results
Article Selection—A total of 229 articles were identified for screening, and 39 studies met inclusion criteria.1-3,5-40 Systematic and retrospective reviews were the most common types of studies. Genomic analysis/sequencing/genome-wide association studies (GWAS) were the most common methods of analysis. Of these 39 articles, 26 were classified as supporting the evolutionary vitamin D adaptation hypothesis, 10 were classified as neutral, and 3 were classified as against (Table 1).
Of the articles classified as supporting the vitamin D hypothesis, 13 articles were level 1 evidence, 9 were level 2, and 4 were level 3. Key findings supporting the vitamin D hypothesis included genetic natural selection favoring vitamin D synthesis genes at higher latitudes with lower UVR and the skin lightening that occurred to protect against vitamin D deficiency (Table 1). Specific genes supporting these findings included 7-dehydrocholesterol reductase (DHCR7), vitamin D receptor (VDR), tyrosinase (TYR), tyrosinase-related protein 1 (TYRP1), oculocutaneous albinism type 2 melanosomal transmembrane protein (OCA2), solute carrier family 45 member 2 (SLC45A2), solute carrier family 4 member 5 (SLC24A5), Kit ligand (KITLG), melanocortin 1 receptor (MC1R), and HECT and RLD domain containing E3 ubiquitin protein ligase 2 (HERC2)(Table 2).

Of the articles classified as being against the vitamin D hypothesis, 1 article was level 1 evidence, 1 was level 2, and 1 was level 3. Key findings refuting the vitamin D hypothesis included similar amounts of vitamin D synthesis in contemporary dark- and light-pigmented individuals, vitamin D–rich diets in the late Paleolithic period and in early agriculturalists, and metabolic conservation being the primary driver (Table 1).
Of the articles classified as neutral to the hypothesis, 7 articles were level 1 evidence and 3 were level 2. Key findings of these articles included genetic selection favoring vitamin D synthesis only for populations at extremely northern latitudes, skin lightening that was sustained in northern latitudes from the neighboring human ancestor the chimpanzee, and evidence for long-term evolutionary pressures and short-term plastic adaptations in vitamin D genes (Table 1).
Comment
The importance of appropriate vitamin D levels is hypothesized as a potent driver in skin lightening because the vitamin is essential for many biochemical processes within the human body. Proper calcification of bones requires activated vitamin D to prevent rickets in childhood. Pelvic deformation in women with rickets can obstruct childbirth in primitive medical environments.15 This direct reproductive impairment suggests a strong selective pressure for skin lightening in populations that migrated northward to enhance vitamin D synthesis.
Of the 39 articles that we reviewed, the majority (n=26 [66.7%]) supported the hypothesis that vitamin D synthesis was the main driver behind skin lightening, whereas 3 (7.7%) did not support the hypothesis and 10 (25.6%) were neutral. Other leading theories explaining skin lightening included the idea that enhanced melanogenesis protected against folate degradation; genetic selection for light-skin alleles due to genetic drift; skin lightening being the result of sexual selection; and a combination of factors, including dietary choices, clothing preferences, and skin permeability barriers.
Articles With Supporting Evidence for the Vitamin D Theory—As Homo sapiens migrated out of Africa, migration patterns demonstrated the correlation between distance from the equator and skin pigmentation from natural selection. Individuals with darker skin pigment required higher levels of UVR to synthesize vitamin D. According to Beleza et al,1 as humans migrated to areas of higher latitudes with lower levels of UVR, natural selection favored the development of lighter skin to maximize vitamin D production. Vitamin D is linked to calcium metabolism, and its deficiency can lead to bone malformations and poor immune function.35 Several genes affecting melanogenesis and skin pigment have been found to have geospatial patterns that map to different geographic locations of various populations, indicating how human migration patterns out of Africa created this natural selection for skin lightening. The gene KITLG—associated with lighter skin pigmentation—has been found in high frequencies in both European and East Asian populations and is proposed to have increased in frequency after the migration out of Africa. However, the genes TYRP1, SLC24A5, and SLC45A2 were found at high frequencies only in European populations, and this selection occurred 11,000 to 19,000 years ago during the Last Glacial Maximum (15,000–20,000 years ago), demonstrating the selection for European over East Asian characteristics. During this period, seasonal changes increased the risk for vitamin D deficiency and provided an urgency for selection to a lighter skin pigment.1
The migration of H sapiens to northern latitudes prompted the selection of alleles that would increasevitamin D synthesis to counteract the reduced UV exposure. Genetic analysis studies have found key associations between genes encoding for the metabolism of vitamin D and pigmentation. Among this complex network are the essential downstream enzymes in the melanocortin receptor 1 pathway, including TYR and TYRP1. Forty-six of 960 single-nucleotide polymorphisms located in 29 different genes involved in skin pigmentation that were analyzed in a cohort of 2970 individuals were significantly associated with serum vitamin D levels (P<.05). The exocyst complex component 2 (EXOC2), TYR, and TYRP1 gene variants were shown to have the greatest influence on vitamin D status.9 These data reveal how pigment genotypes are predictive of vitamin D levels and the epistatic potential among many genes in this complex network.
Gene variation plays an important role in vitamin D status when comparing genetic polymorphisms in populations in northern latitudes to African populations. Vitamin D3 precursor availability is decreased by 7-DHCR catalyzing the precursors substrate to cholesterol. In a study using GWAS, it was found that “variations in DHCR7 may aid vitamin D production by conserving cutaneous 7-DHC levels. A high prevalence of DHCR7 variants were found in European and Northeast Asian populations but not in African populations, suggesting that selection occurred for these DHCR7 mutations in populations who migrated to more northern latitudes.5 Multilocus networks have been established between the VDR promotor and skin color genes (Table 2) that exhibit a strong in-Africa vs out-of-Africa frequency pattern. It also has been shown that genetic variation (suggesting a long-term evolutionary inclination) and epigenetic modification (indicative of short-term exposure) of VDR lends support to the vitamin D hypothesis. As latitude decreases, prevalence of VDR FokI (F allele), BsmI (B allele), ApaI (A allele), and TaqI (T allele) also decreases in a linear manner, linking latitude to VDR polymorphisms. Plasma vitamin D levels and photoperiod of conception—UV exposure during the periconceptional period—also were extrapolative of VDR methylation in a study involving 80 participants, where these 2 factors accounted for 17% of variance in methylation.6


Other noteworthy genes included HERC2, which has implications in the expression of OCA2 (melanocyte-specific transporter protein), and IRF4, which encodes for an important enzyme in folate-dependent melanin production. In an Australian cross-sectional study that analyzed vitamin D and pigmentation gene polymorphisms in conjunction with plasma vitamin D levels, the most notable rate of vitamin D loss occurred in individuals with the darkest pigmentation HERC2 (AA) genotype.31 In contrast, the lightest pigmentation HERC2 (GG) genotypes had increased vitamin D3 photosynthesis. Interestingly, the lightest interferon regulatory factor 4 (IRF4) TT genotype and the darkest HERC2 AA genotype, rendering the greatest folate loss and largest synthesis of vitamin D3, were not seen in combination in any of the participants.30 In addition to HERC2, derived alleles from pigment-associated genes SLC24A5*A and SLC45A2*G demonstrated greater frequencies in Europeans (>90%) compared to Africans and East Asians, where the allelic frequencies were either rare or absent.1 This evidence delineates not only the complexity but also the strong relationship between skin pigmentation, latitude, and vitamin D status. The GWAS also have supported this concept. In comparing European populations to African populations, there was a 4-fold increase in the frequencies of “derived alleles of the vitamin D transport protein (GC, rs3755967), the 25(OH)D3 synthesizing enzyme (CYP2R1, rs10741657), VDR (rs2228570 (commonly known as FokI polymorphism), rs1544410 (Bsm1), and rs731236 (Taq1) and the VDR target genes CYP24A1 (rs17216707), CD14 (rs2569190), and CARD9 (rs4077515).”32
Articles With Evidence Against the Vitamin D Theory—This review analyzed the level of support for the theory that vitamin D was the main driver for skin lightening. Although most articles supported this theory, there were articles that listed other plausible counterarguments. Jablonski and Chaplin3 suggested that humans living in higher latitudes compensated for increased demand of vitamin D by placing cultural importance on a diet of vitamin D–rich foods and thus would not have experienced decreased vitamin D levels, which we hypothesize were the driver for skin lightening. Elias et al39 argued that initial pigment dilution may have instead served to improve metabolic conservation, as the authors found no evidence of rickets—the sequelae of vitamin D deficiency—in pre–industrial age human fossils. Elias and Williams38 proposed that differences in skin pigment are due to a more intact skin permeability barrier as “a requirement for life in a desiccating terrestrial environment,” which is seen in darker skin tones compared to lighter skin tones and thus can survive better in warmer climates with less risk of infections or dehydration.
Articles With Neutral Evidence for the Vitamin D Theory—Greaves41 argued against the idea that skin evolved to become lighter to protect against vitamin D deficiency. They proposed that the chimpanzee, which is the human’s most closely related species, had light skin covered by hair, and the loss of this hair led to exposed pale skin that created a need for increased melanin production for protection from UVR. Greaves41 stated that the MC1R gene (associated with darker pigmentation) was selected for in African populations, and those with pale skin retained their original pigment as they migrated to higher latitudes. Further research has demonstrated that the genetic natural selection for skin pigment is a complex process that involves multiple gene variants found throughout cultures across the globe.

Conclusion
Skin pigmentation has continuously evolved alongside humans. Genetic selection for lighter skin coincides with a favorable selection for genes involved in vitamin D synthesis as humans migrated to northern latitudes, which enabled humans to produce adequate levels of exogenous vitamin D in low-UVR areas and in turn promoted survival. Early humans without access to supplementation or foods rich in vitamin D acquired vitamin D primarily through sunlight. In comparison to modern society, where vitamin D supplementation is accessible and human lifespans are prolonged, lighter skin tone is now a risk factor for malignant cancers of the skin rather than being a protective adaptation. Current sun behavior recommendations conclude that the body’s need for vitamin D is satisfied by UV exposure to the arms, legs, hands, and/or face for only 5 to 30 minutes between 10
The hypothesis that skin lightening primarily was driven by the need for vitamin D can only be partially supported by our review. Studies have shown that there is a corresponding complex network of genes that determines skin pigmentation as well as vitamin D synthesis and conservation. However, there is sufficient evidence that skin lightening is multifactorial in nature, and vitamin D alone may not be the sole driver. The information in this review can be used by health care providers to educate patients on sun protection, given the lesser threat of severe vitamin D deficiency in developed communities today that have access to adequate nutrition and supplementation.
Skin lightening and its coinciding evolutionary drivers are a rather neglected area of research. Due to heterogeneous cohorts and conservative data analysis, GWAS studies run the risk of type II error, yielding a limitation in our data analysis.9 Furthermore, the data regarding specific time frames in evolutionary skin lightening as well as the intensity of gene polymorphisms are limited.1 Further studies are needed to determine the interconnectedness of the current skin-lightening theories to identify other important factors that may play a role in the process. Determining the key event can help us better understand skin-adaptation mechanisms and create a framework for understanding the vital process involved in adaptation, survival, and disease manifestation in different patient populations.
The risk for developing skin cancer can be somewhat attributed to variations in skin pigmentation. Historically, lighter skin pigmentation has been observed in populations living in higher latitudes and darker pigmentation in populations near the equator. Although skin pigmentation is a conglomeration of genetic and environmental factors, anthropologic studies have demonstrated an association of human skin lightening with historic human migratory patterns.1 It is postulated that migration to latitudes with less UVB light penetration has resulted in a compensatory natural selection of lighter skin types. Furthermore, the driving force behind this migration-associated skin lightening has remained unclear.1
The need for folate metabolism, vitamin D synthesis, and barrier protection, as well as cultural practices, has been postulated as driving factors for skin pigmentation variation. Synthesis of vitamin D is a UV radiation (UVR)–dependent process and has remained a prominent theoretical driver for the basis of evolutionary skin lightening. Vitamin D can be acquired both exogenously or endogenously via dietary supplementation or sunlight; however, historically it has been obtained through UVB exposure primarily. Once UVB is absorbed by the skin, it catalyzes conversion of 7-dehydrocholesterol to previtamin D3, which is converted to vitamin D in the kidneys.2,3 It is suggested that lighter skin tones have an advantage over darker skin tones in synthesizing vitamin D at higher latitudes where there is less UVB, thus leading to the adaptation process.1 In this systematic review, we analyzed the evolutionary vitamin D adaptation hypothesis and assessed the validity of evidence supporting this theory in the literature.
Methods
A search of PubMed, Embase, and the Cochrane Reviews database was conducted using the terms evolution, vitamin D, and skin to generate articles published from 2010 to 2022 that evaluated the influence of UVR-dependent production of vitamin D on skin pigmentation through historical migration patterns (Figure). Studies were excluded during an initial screening of abstracts followed by full-text assessment if they only had abstracts and if articles were inaccessible for review or in the form of case reports and commentaries.
The following data were extracted from each included study: reference citation, affiliated institutions of authors, author specialties, journal name, year of publication, study period, type of article, type of study, mechanism of adaptation, data concluding or supporting vitamin D as the driver, and data concluding or suggesting against vitamin D as the driver. Data concluding or supporting vitamin D as the driver were recorded from statistically significant results, study conclusions, and direct quotations. Data concluding or suggesting against vitamin D as the driver also were recorded from significant results, study conclusions, and direct quotes. The mechanism of adaptation was based on vitamin D synthesis modulation, melanin upregulation, genetic selections, genetic drift, mating patterns, increased vitamin D sensitivity, interbreeding, and diet.
Studies included in the analysis were placed into 1 of 3 categories: supporting, neutral, and against. Strength of Recommendation Taxonomy (SORT) criteria were used to classify the level of evidence of each article.4 Each article’s level of evidence was then graded (Table 1). The SORT grading levels were based on quality and evidence type: level 1 signified good-quality, patient-oriented evidence; level 2 signified limited-quality, patient-oriented evidence; and level 3 signified other evidence.4
Results
Article Selection—A total of 229 articles were identified for screening, and 39 studies met inclusion criteria.1-3,5-40 Systematic and retrospective reviews were the most common types of studies. Genomic analysis/sequencing/genome-wide association studies (GWAS) were the most common methods of analysis. Of these 39 articles, 26 were classified as supporting the evolutionary vitamin D adaptation hypothesis, 10 were classified as neutral, and 3 were classified as against (Table 1).
Of the articles classified as supporting the vitamin D hypothesis, 13 articles were level 1 evidence, 9 were level 2, and 4 were level 3. Key findings supporting the vitamin D hypothesis included genetic natural selection favoring vitamin D synthesis genes at higher latitudes with lower UVR and the skin lightening that occurred to protect against vitamin D deficiency (Table 1). Specific genes supporting these findings included 7-dehydrocholesterol reductase (DHCR7), vitamin D receptor (VDR), tyrosinase (TYR), tyrosinase-related protein 1 (TYRP1), oculocutaneous albinism type 2 melanosomal transmembrane protein (OCA2), solute carrier family 45 member 2 (SLC45A2), solute carrier family 4 member 5 (SLC24A5), Kit ligand (KITLG), melanocortin 1 receptor (MC1R), and HECT and RLD domain containing E3 ubiquitin protein ligase 2 (HERC2)(Table 2).

Of the articles classified as being against the vitamin D hypothesis, 1 article was level 1 evidence, 1 was level 2, and 1 was level 3. Key findings refuting the vitamin D hypothesis included similar amounts of vitamin D synthesis in contemporary dark- and light-pigmented individuals, vitamin D–rich diets in the late Paleolithic period and in early agriculturalists, and metabolic conservation being the primary driver (Table 1).
Of the articles classified as neutral to the hypothesis, 7 articles were level 1 evidence and 3 were level 2. Key findings of these articles included genetic selection favoring vitamin D synthesis only for populations at extremely northern latitudes, skin lightening that was sustained in northern latitudes from the neighboring human ancestor the chimpanzee, and evidence for long-term evolutionary pressures and short-term plastic adaptations in vitamin D genes (Table 1).
Comment
The importance of appropriate vitamin D levels is hypothesized as a potent driver in skin lightening because the vitamin is essential for many biochemical processes within the human body. Proper calcification of bones requires activated vitamin D to prevent rickets in childhood. Pelvic deformation in women with rickets can obstruct childbirth in primitive medical environments.15 This direct reproductive impairment suggests a strong selective pressure for skin lightening in populations that migrated northward to enhance vitamin D synthesis.
Of the 39 articles that we reviewed, the majority (n=26 [66.7%]) supported the hypothesis that vitamin D synthesis was the main driver behind skin lightening, whereas 3 (7.7%) did not support the hypothesis and 10 (25.6%) were neutral. Other leading theories explaining skin lightening included the idea that enhanced melanogenesis protected against folate degradation; genetic selection for light-skin alleles due to genetic drift; skin lightening being the result of sexual selection; and a combination of factors, including dietary choices, clothing preferences, and skin permeability barriers.
Articles With Supporting Evidence for the Vitamin D Theory—As Homo sapiens migrated out of Africa, migration patterns demonstrated the correlation between distance from the equator and skin pigmentation from natural selection. Individuals with darker skin pigment required higher levels of UVR to synthesize vitamin D. According to Beleza et al,1 as humans migrated to areas of higher latitudes with lower levels of UVR, natural selection favored the development of lighter skin to maximize vitamin D production. Vitamin D is linked to calcium metabolism, and its deficiency can lead to bone malformations and poor immune function.35 Several genes affecting melanogenesis and skin pigment have been found to have geospatial patterns that map to different geographic locations of various populations, indicating how human migration patterns out of Africa created this natural selection for skin lightening. The gene KITLG—associated with lighter skin pigmentation—has been found in high frequencies in both European and East Asian populations and is proposed to have increased in frequency after the migration out of Africa. However, the genes TYRP1, SLC24A5, and SLC45A2 were found at high frequencies only in European populations, and this selection occurred 11,000 to 19,000 years ago during the Last Glacial Maximum (15,000–20,000 years ago), demonstrating the selection for European over East Asian characteristics. During this period, seasonal changes increased the risk for vitamin D deficiency and provided an urgency for selection to a lighter skin pigment.1
The migration of H sapiens to northern latitudes prompted the selection of alleles that would increasevitamin D synthesis to counteract the reduced UV exposure. Genetic analysis studies have found key associations between genes encoding for the metabolism of vitamin D and pigmentation. Among this complex network are the essential downstream enzymes in the melanocortin receptor 1 pathway, including TYR and TYRP1. Forty-six of 960 single-nucleotide polymorphisms located in 29 different genes involved in skin pigmentation that were analyzed in a cohort of 2970 individuals were significantly associated with serum vitamin D levels (P<.05). The exocyst complex component 2 (EXOC2), TYR, and TYRP1 gene variants were shown to have the greatest influence on vitamin D status.9 These data reveal how pigment genotypes are predictive of vitamin D levels and the epistatic potential among many genes in this complex network.
Gene variation plays an important role in vitamin D status when comparing genetic polymorphisms in populations in northern latitudes to African populations. Vitamin D3 precursor availability is decreased by 7-DHCR catalyzing the precursors substrate to cholesterol. In a study using GWAS, it was found that “variations in DHCR7 may aid vitamin D production by conserving cutaneous 7-DHC levels. A high prevalence of DHCR7 variants were found in European and Northeast Asian populations but not in African populations, suggesting that selection occurred for these DHCR7 mutations in populations who migrated to more northern latitudes.5 Multilocus networks have been established between the VDR promotor and skin color genes (Table 2) that exhibit a strong in-Africa vs out-of-Africa frequency pattern. It also has been shown that genetic variation (suggesting a long-term evolutionary inclination) and epigenetic modification (indicative of short-term exposure) of VDR lends support to the vitamin D hypothesis. As latitude decreases, prevalence of VDR FokI (F allele), BsmI (B allele), ApaI (A allele), and TaqI (T allele) also decreases in a linear manner, linking latitude to VDR polymorphisms. Plasma vitamin D levels and photoperiod of conception—UV exposure during the periconceptional period—also were extrapolative of VDR methylation in a study involving 80 participants, where these 2 factors accounted for 17% of variance in methylation.6


Other noteworthy genes included HERC2, which has implications in the expression of OCA2 (melanocyte-specific transporter protein), and IRF4, which encodes for an important enzyme in folate-dependent melanin production. In an Australian cross-sectional study that analyzed vitamin D and pigmentation gene polymorphisms in conjunction with plasma vitamin D levels, the most notable rate of vitamin D loss occurred in individuals with the darkest pigmentation HERC2 (AA) genotype.31 In contrast, the lightest pigmentation HERC2 (GG) genotypes had increased vitamin D3 photosynthesis. Interestingly, the lightest interferon regulatory factor 4 (IRF4) TT genotype and the darkest HERC2 AA genotype, rendering the greatest folate loss and largest synthesis of vitamin D3, were not seen in combination in any of the participants.30 In addition to HERC2, derived alleles from pigment-associated genes SLC24A5*A and SLC45A2*G demonstrated greater frequencies in Europeans (>90%) compared to Africans and East Asians, where the allelic frequencies were either rare or absent.1 This evidence delineates not only the complexity but also the strong relationship between skin pigmentation, latitude, and vitamin D status. The GWAS also have supported this concept. In comparing European populations to African populations, there was a 4-fold increase in the frequencies of “derived alleles of the vitamin D transport protein (GC, rs3755967), the 25(OH)D3 synthesizing enzyme (CYP2R1, rs10741657), VDR (rs2228570 (commonly known as FokI polymorphism), rs1544410 (Bsm1), and rs731236 (Taq1) and the VDR target genes CYP24A1 (rs17216707), CD14 (rs2569190), and CARD9 (rs4077515).”32
Articles With Evidence Against the Vitamin D Theory—This review analyzed the level of support for the theory that vitamin D was the main driver for skin lightening. Although most articles supported this theory, there were articles that listed other plausible counterarguments. Jablonski and Chaplin3 suggested that humans living in higher latitudes compensated for increased demand of vitamin D by placing cultural importance on a diet of vitamin D–rich foods and thus would not have experienced decreased vitamin D levels, which we hypothesize were the driver for skin lightening. Elias et al39 argued that initial pigment dilution may have instead served to improve metabolic conservation, as the authors found no evidence of rickets—the sequelae of vitamin D deficiency—in pre–industrial age human fossils. Elias and Williams38 proposed that differences in skin pigment are due to a more intact skin permeability barrier as “a requirement for life in a desiccating terrestrial environment,” which is seen in darker skin tones compared to lighter skin tones and thus can survive better in warmer climates with less risk of infections or dehydration.
Articles With Neutral Evidence for the Vitamin D Theory—Greaves41 argued against the idea that skin evolved to become lighter to protect against vitamin D deficiency. They proposed that the chimpanzee, which is the human’s most closely related species, had light skin covered by hair, and the loss of this hair led to exposed pale skin that created a need for increased melanin production for protection from UVR. Greaves41 stated that the MC1R gene (associated with darker pigmentation) was selected for in African populations, and those with pale skin retained their original pigment as they migrated to higher latitudes. Further research has demonstrated that the genetic natural selection for skin pigment is a complex process that involves multiple gene variants found throughout cultures across the globe.

Conclusion
Skin pigmentation has continuously evolved alongside humans. Genetic selection for lighter skin coincides with a favorable selection for genes involved in vitamin D synthesis as humans migrated to northern latitudes, which enabled humans to produce adequate levels of exogenous vitamin D in low-UVR areas and in turn promoted survival. Early humans without access to supplementation or foods rich in vitamin D acquired vitamin D primarily through sunlight. In comparison to modern society, where vitamin D supplementation is accessible and human lifespans are prolonged, lighter skin tone is now a risk factor for malignant cancers of the skin rather than being a protective adaptation. Current sun behavior recommendations conclude that the body’s need for vitamin D is satisfied by UV exposure to the arms, legs, hands, and/or face for only 5 to 30 minutes between 10
The hypothesis that skin lightening primarily was driven by the need for vitamin D can only be partially supported by our review. Studies have shown that there is a corresponding complex network of genes that determines skin pigmentation as well as vitamin D synthesis and conservation. However, there is sufficient evidence that skin lightening is multifactorial in nature, and vitamin D alone may not be the sole driver. The information in this review can be used by health care providers to educate patients on sun protection, given the lesser threat of severe vitamin D deficiency in developed communities today that have access to adequate nutrition and supplementation.
Skin lightening and its coinciding evolutionary drivers are a rather neglected area of research. Due to heterogeneous cohorts and conservative data analysis, GWAS studies run the risk of type II error, yielding a limitation in our data analysis.9 Furthermore, the data regarding specific time frames in evolutionary skin lightening as well as the intensity of gene polymorphisms are limited.1 Further studies are needed to determine the interconnectedness of the current skin-lightening theories to identify other important factors that may play a role in the process. Determining the key event can help us better understand skin-adaptation mechanisms and create a framework for understanding the vital process involved in adaptation, survival, and disease manifestation in different patient populations.
- Beleza S, Santos AM, McEvoy B, et al. The timing of pigmentation lightening in Europeans. Mol Biol Evol. 2013;30:24-35. doi:10.1093/molbev/mss207
- Carlberg C. Nutrigenomics of vitamin D. Nutrients. 2019;11:676. doi:10.3390/nu11030676
- Jablonski NG, Chaplin G. The roles of vitamin D and cutaneous vitamin D production in human evolution and health. Int J Paleopathol. 2018;23:54-59. doi:10.1016/j.ijpp.2018.01.005
- Weiss BD. SORT: strength of recommendation taxonomy. Fam Med. 2004;36:141-143.
- Wolf ST, Kenney WL. The vitamin D–folate hypothesis in human vascular health. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiology. 2019;317:R491-R501. doi:10.1152/ajpregu.00136.2019
- Lucock M, Jones P, Martin C, et al. Photobiology of vitamins. Nutr Rev. 2018;76:512-525. doi:10.1093/nutrit/nuy013
- Hochberg Z, Hochberg I. Evolutionary perspective in rickets and vitamin D. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2019;10:306. doi:10.3389/fendo.2019.00306
- Rossberg W, Saternus R, Wagenpfeil S, et al. Human pigmentation, cutaneous vitamin D synthesis and evolution: variants of genes (SNPs) involved in skin pigmentation are associated with 25(OH)D serum concentration. Anticancer Res. 2016;36:1429-1437.
- Saternus R, Pilz S, Gräber S, et al. A closer look at evolution: variants (SNPs) of genes involved in skin pigmentation, including EXOC2, TYR, TYRP1, and DCT, are associated with 25(OH)D serum concentration. Endocrinology. 2015;156:39-47. doi:10.1210/en.2014-1238
- López S, García Ó, Yurrebaso I, et al. The interplay between natural selection and susceptibility to melanoma on allele 374F of SLC45A2 gene in a south European population. PloS One. 2014;9:E104367. doi:1371/journal.pone.0104367
- Lucock M, Yates Z, Martin C, et al. Vitamin D, folate, and potential early lifecycle environmental origin of significant adult phenotypes. Evol Med Public Health. 2014;2014:69-91. doi:10.1093/emph/eou013
- Hudjashov G, Villems R, Kivisild T. Global patterns of diversity and selection in human tyrosinase gene. PloS One. 2013;8:E74307. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0074307
- Khan R, Khan BSR. Diet, disease and pigment variation in humans. Med Hypotheses. 2010;75:363-367. doi:10.1016/j.mehy.2010.03.033
- Kuan V, Martineau AR, Griffiths CJ, et al. DHCR7 mutations linked to higher vitamin D status allowed early human migration to northern latitudes. BMC Evol Biol. 2013;13:144. doi:10.1186/1471-2148-13-144
- Omenn GS. Evolution and public health. Proc National Acad Sci. 2010;107(suppl 1):1702-1709. doi:10.1073/pnas.0906198106
- Yuen AWC, Jablonski NG. Vitamin D: in the evolution of human skin colour. Med Hypotheses. 2010;74:39-44. doi:10.1016/j.mehy.2009.08.007
- Vieth R. Weaker bones and white skin as adaptions to improve anthropological “fitness” for northern environments. Osteoporosis Int. 2020;31:617-624. doi:10.1007/s00198-019-05167-4
- Carlberg C. Vitamin D: a micronutrient regulating genes. Curr Pharm Des. 2019;25:1740-1746. doi:10.2174/1381612825666190705193227
- Haddadeen C, Lai C, Cho SY, et al. Variants of the melanocortin‐1 receptor: do they matter clinically? Exp Dermatol. 2015;1:5-9. doi:10.1111/exd.12540
- Yao S, Ambrosone CB. Associations between vitamin D deficiency and risk of aggressive breast cancer in African-American women. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 2013;136:337-341. doi:10.1016/j.jsbmb.2012.09.010
- Jablonski N. The evolution of human skin colouration and its relevance to health in the modern world. J Royal Coll Physicians Edinb. 2012;42:58-63. doi:10.4997/jrcpe.2012.114
- Jablonski NG, Chaplin G. Human skin pigmentation as an adaptation to UV radiation. Proc National Acad Sci. 2010;107(suppl 2):8962-8968. doi:10.1073/pnas.0914628107
- Hochberg Z, Templeton AR. Evolutionary perspective in skin color, vitamin D and its receptor. Hormones. 2010;9:307-311. doi:10.14310/horm.2002.1281
- Jones P, Lucock M, Veysey M, et al. The vitamin D–folate hypothesis as an evolutionary model for skin pigmentation: an update and integration of current ideas. Nutrients. 2018;10:554. doi:10.3390/nu10050554
- Lindqvist PG, Epstein E, Landin-Olsson M, et al. Women with fair phenotypes seem to confer a survival advantage in a low UV milieu. a nested matched case control study. PloS One. 2020;15:E0228582. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0228582
- Holick MF. Shedding new light on the role of the sunshine vitamin D for skin health: the lncRNA–skin cancer connection. Exp Dermatol. 2014;23:391-392. doi:10.1111/exd.12386
- Jablonski NG, Chaplin G. Epidermal pigmentation in the human lineage is an adaptation to ultraviolet radiation. J Hum Evol. 2013;65:671-675. doi:10.1016/j.jhevol.2013.06.004
- Jablonski NG, Chaplin G. The evolution of skin pigmentation and hair texture in people of African ancestry. Dermatol Clin. 2014;32:113-121. doi:10.1016/j.det.2013.11.003
- Jablonski NG. The evolution of human skin pigmentation involved the interactions of genetic, environmental, and cultural variables. Pigment Cell Melanoma Res. 2021;34:707-7 doi:10.1111/pcmr.12976
- Lucock MD, Jones PR, Veysey M, et al. Biophysical evidence to support and extend the vitamin D‐folate hypothesis as a paradigm for the evolution of human skin pigmentation. Am J Hum Biol. 2022;34:E23667. doi:10.1002/ajhb.23667
- Missaggia BO, Reales G, Cybis GB, et al. Adaptation and co‐adaptation of skin pigmentation and vitamin D genes in native Americans. Am J Med Genet C Semin Med Genet. 2020;184:1060-1077. doi:10.1002/ajmg.c.31873
- Hanel A, Carlberg C. Skin colour and vitamin D: an update. Exp Dermatol. 2020;29:864-875. doi:10.1111/exd.14142
- Hanel A, Carlberg C. Vitamin D and evolution: pharmacologic implications. Biochem Pharmacol. 2020;173:113595. doi:10.1016/j.bcp.2019.07.024
- Flegr J, Sýkorová K, Fiala V, et al. Increased 25(OH)D3 level in redheaded people: could redheadedness be an adaptation to temperate climate? Exp Dermatol. 2020;29:598-609. doi:10.1111/exd.14119
- James WPT, Johnson RJ, Speakman JR, et al. Nutrition and its role in human evolution. J Intern Med. 2019;285:533-549. doi:10.1111/joim.12878
- Lucock M, Jones P, Martin C, et al. Vitamin D: beyond metabolism. J Evid Based Complementary Altern Med. 2015;20:310-322. doi:10.1177/2156587215580491
- Jarrett P, Scragg R. Evolution, prehistory and vitamin D. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2020;17:646. doi:10.3390/ijerph17020646
- Elias PM, Williams ML. Re-appraisal of current theories for thedevelopment and loss of epidermal pigmentation in hominins and modern humans. J Hum Evol. 2013;64:687-692. doi:10.1016/j.jhevol.2013.02.003
- Elias PM, Williams ML. Basis for the gain and subsequent dilution of epidermal pigmentation during human evolution: the barrier and metabolic conservation hypotheses revisited. Am J Phys Anthropol. 2016;161:189-207. doi:10.1002/ajpa.23030
- Williams JD, Jacobson EL, Kim H, et al. Water soluble vitamins, clinical research and future application. Subcell Biochem. 2011;56:181-197. doi:10.1007/978-94-007-2199-9_10
- Greaves M. Was skin cancer a selective force for black pigmentation in early hominin evolution [published online February 26, 2014]? Proc Biol Sci. 2014;281:20132955. doi:10.1098/rspb.2013.2955
- Holick MF. Vitamin D deficiency. N Engl J Med. 2007;357:266-281. doi:10.1056/nejmra070553
- Bouillon R. Comparative analysis of nutritional guidelines for vitamin D. Nat Rev Endocrinol. 2017;13:466-479. doi:10.1038/nrendo.2017.31
- US Department of Health and Human Services. The Surgeon General’s Call to Action to Prevent Skin Cancer. US Dept of Health and Human Services, Office of the Surgeon General; 2014. Accessed April 29, 2024. https://www.hhs.gov/sites/default/files/call-to-action-prevent-skin-cancer.pdf
- Institute of Medicine (US) Committee to Review Dietary Reference Intakes for Vitamin D and Calcium; Ross AC, Taylor CL, Yaktine AL, et al, eds. Dietary Reference Intakes for Calcium and Vitamin D. National Academies Press; 2011. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK56070/
- Beleza S, Santos AM, McEvoy B, et al. The timing of pigmentation lightening in Europeans. Mol Biol Evol. 2013;30:24-35. doi:10.1093/molbev/mss207
- Carlberg C. Nutrigenomics of vitamin D. Nutrients. 2019;11:676. doi:10.3390/nu11030676
- Jablonski NG, Chaplin G. The roles of vitamin D and cutaneous vitamin D production in human evolution and health. Int J Paleopathol. 2018;23:54-59. doi:10.1016/j.ijpp.2018.01.005
- Weiss BD. SORT: strength of recommendation taxonomy. Fam Med. 2004;36:141-143.
- Wolf ST, Kenney WL. The vitamin D–folate hypothesis in human vascular health. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiology. 2019;317:R491-R501. doi:10.1152/ajpregu.00136.2019
- Lucock M, Jones P, Martin C, et al. Photobiology of vitamins. Nutr Rev. 2018;76:512-525. doi:10.1093/nutrit/nuy013
- Hochberg Z, Hochberg I. Evolutionary perspective in rickets and vitamin D. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2019;10:306. doi:10.3389/fendo.2019.00306
- Rossberg W, Saternus R, Wagenpfeil S, et al. Human pigmentation, cutaneous vitamin D synthesis and evolution: variants of genes (SNPs) involved in skin pigmentation are associated with 25(OH)D serum concentration. Anticancer Res. 2016;36:1429-1437.
- Saternus R, Pilz S, Gräber S, et al. A closer look at evolution: variants (SNPs) of genes involved in skin pigmentation, including EXOC2, TYR, TYRP1, and DCT, are associated with 25(OH)D serum concentration. Endocrinology. 2015;156:39-47. doi:10.1210/en.2014-1238
- López S, García Ó, Yurrebaso I, et al. The interplay between natural selection and susceptibility to melanoma on allele 374F of SLC45A2 gene in a south European population. PloS One. 2014;9:E104367. doi:1371/journal.pone.0104367
- Lucock M, Yates Z, Martin C, et al. Vitamin D, folate, and potential early lifecycle environmental origin of significant adult phenotypes. Evol Med Public Health. 2014;2014:69-91. doi:10.1093/emph/eou013
- Hudjashov G, Villems R, Kivisild T. Global patterns of diversity and selection in human tyrosinase gene. PloS One. 2013;8:E74307. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0074307
- Khan R, Khan BSR. Diet, disease and pigment variation in humans. Med Hypotheses. 2010;75:363-367. doi:10.1016/j.mehy.2010.03.033
- Kuan V, Martineau AR, Griffiths CJ, et al. DHCR7 mutations linked to higher vitamin D status allowed early human migration to northern latitudes. BMC Evol Biol. 2013;13:144. doi:10.1186/1471-2148-13-144
- Omenn GS. Evolution and public health. Proc National Acad Sci. 2010;107(suppl 1):1702-1709. doi:10.1073/pnas.0906198106
- Yuen AWC, Jablonski NG. Vitamin D: in the evolution of human skin colour. Med Hypotheses. 2010;74:39-44. doi:10.1016/j.mehy.2009.08.007
- Vieth R. Weaker bones and white skin as adaptions to improve anthropological “fitness” for northern environments. Osteoporosis Int. 2020;31:617-624. doi:10.1007/s00198-019-05167-4
- Carlberg C. Vitamin D: a micronutrient regulating genes. Curr Pharm Des. 2019;25:1740-1746. doi:10.2174/1381612825666190705193227
- Haddadeen C, Lai C, Cho SY, et al. Variants of the melanocortin‐1 receptor: do they matter clinically? Exp Dermatol. 2015;1:5-9. doi:10.1111/exd.12540
- Yao S, Ambrosone CB. Associations between vitamin D deficiency and risk of aggressive breast cancer in African-American women. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 2013;136:337-341. doi:10.1016/j.jsbmb.2012.09.010
- Jablonski N. The evolution of human skin colouration and its relevance to health in the modern world. J Royal Coll Physicians Edinb. 2012;42:58-63. doi:10.4997/jrcpe.2012.114
- Jablonski NG, Chaplin G. Human skin pigmentation as an adaptation to UV radiation. Proc National Acad Sci. 2010;107(suppl 2):8962-8968. doi:10.1073/pnas.0914628107
- Hochberg Z, Templeton AR. Evolutionary perspective in skin color, vitamin D and its receptor. Hormones. 2010;9:307-311. doi:10.14310/horm.2002.1281
- Jones P, Lucock M, Veysey M, et al. The vitamin D–folate hypothesis as an evolutionary model for skin pigmentation: an update and integration of current ideas. Nutrients. 2018;10:554. doi:10.3390/nu10050554
- Lindqvist PG, Epstein E, Landin-Olsson M, et al. Women with fair phenotypes seem to confer a survival advantage in a low UV milieu. a nested matched case control study. PloS One. 2020;15:E0228582. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0228582
- Holick MF. Shedding new light on the role of the sunshine vitamin D for skin health: the lncRNA–skin cancer connection. Exp Dermatol. 2014;23:391-392. doi:10.1111/exd.12386
- Jablonski NG, Chaplin G. Epidermal pigmentation in the human lineage is an adaptation to ultraviolet radiation. J Hum Evol. 2013;65:671-675. doi:10.1016/j.jhevol.2013.06.004
- Jablonski NG, Chaplin G. The evolution of skin pigmentation and hair texture in people of African ancestry. Dermatol Clin. 2014;32:113-121. doi:10.1016/j.det.2013.11.003
- Jablonski NG. The evolution of human skin pigmentation involved the interactions of genetic, environmental, and cultural variables. Pigment Cell Melanoma Res. 2021;34:707-7 doi:10.1111/pcmr.12976
- Lucock MD, Jones PR, Veysey M, et al. Biophysical evidence to support and extend the vitamin D‐folate hypothesis as a paradigm for the evolution of human skin pigmentation. Am J Hum Biol. 2022;34:E23667. doi:10.1002/ajhb.23667
- Missaggia BO, Reales G, Cybis GB, et al. Adaptation and co‐adaptation of skin pigmentation and vitamin D genes in native Americans. Am J Med Genet C Semin Med Genet. 2020;184:1060-1077. doi:10.1002/ajmg.c.31873
- Hanel A, Carlberg C. Skin colour and vitamin D: an update. Exp Dermatol. 2020;29:864-875. doi:10.1111/exd.14142
- Hanel A, Carlberg C. Vitamin D and evolution: pharmacologic implications. Biochem Pharmacol. 2020;173:113595. doi:10.1016/j.bcp.2019.07.024
- Flegr J, Sýkorová K, Fiala V, et al. Increased 25(OH)D3 level in redheaded people: could redheadedness be an adaptation to temperate climate? Exp Dermatol. 2020;29:598-609. doi:10.1111/exd.14119
- James WPT, Johnson RJ, Speakman JR, et al. Nutrition and its role in human evolution. J Intern Med. 2019;285:533-549. doi:10.1111/joim.12878
- Lucock M, Jones P, Martin C, et al. Vitamin D: beyond metabolism. J Evid Based Complementary Altern Med. 2015;20:310-322. doi:10.1177/2156587215580491
- Jarrett P, Scragg R. Evolution, prehistory and vitamin D. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2020;17:646. doi:10.3390/ijerph17020646
- Elias PM, Williams ML. Re-appraisal of current theories for thedevelopment and loss of epidermal pigmentation in hominins and modern humans. J Hum Evol. 2013;64:687-692. doi:10.1016/j.jhevol.2013.02.003
- Elias PM, Williams ML. Basis for the gain and subsequent dilution of epidermal pigmentation during human evolution: the barrier and metabolic conservation hypotheses revisited. Am J Phys Anthropol. 2016;161:189-207. doi:10.1002/ajpa.23030
- Williams JD, Jacobson EL, Kim H, et al. Water soluble vitamins, clinical research and future application. Subcell Biochem. 2011;56:181-197. doi:10.1007/978-94-007-2199-9_10
- Greaves M. Was skin cancer a selective force for black pigmentation in early hominin evolution [published online February 26, 2014]? Proc Biol Sci. 2014;281:20132955. doi:10.1098/rspb.2013.2955
- Holick MF. Vitamin D deficiency. N Engl J Med. 2007;357:266-281. doi:10.1056/nejmra070553
- Bouillon R. Comparative analysis of nutritional guidelines for vitamin D. Nat Rev Endocrinol. 2017;13:466-479. doi:10.1038/nrendo.2017.31
- US Department of Health and Human Services. The Surgeon General’s Call to Action to Prevent Skin Cancer. US Dept of Health and Human Services, Office of the Surgeon General; 2014. Accessed April 29, 2024. https://www.hhs.gov/sites/default/files/call-to-action-prevent-skin-cancer.pdf
- Institute of Medicine (US) Committee to Review Dietary Reference Intakes for Vitamin D and Calcium; Ross AC, Taylor CL, Yaktine AL, et al, eds. Dietary Reference Intakes for Calcium and Vitamin D. National Academies Press; 2011. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK56070/
Practice Points
- Sufficient UV radiation exposure is required to synthesize vitamin D, but excess exposure increases skin cancer risk.
- Genes associated with vitamin D production and melanin synthesis form an interconnected network that explains skin tone polymorphisms and their influence on healthy sun behaviors.
- Adaptations in genetics of skin pigmentation and vitamin D metabolism due to anthropologic patterns of migration to northern latitudes may help explain predisposition to dermatologic diseases such as skin cancer.
AGA Clinical Guideline Stresses Patient Preferences in Barrett’s Treatment
Published in Gastroenterology , the clinical practice guideline makes five main recommendations — one strong and four conditional — based on very low to moderate evidence. It also stresses that providers should practice shared decision making according to patient preferences and risk perception.
For the most part, the new guideline is not a significant departure from the way expert endoscopists are currently practicing EET for BE and related neoplasia, gastroenterologist Joel H. Rubenstein, MD, MSc, AGAF, of the Barrett’s Esophagus Program in the Division of Gastroenterology at University of Michigan Medical School at Ann Arbor, said in an interview. One of three first authors of the guideline, Dr. Rubenstein added, “There is, however, considerable variability in how endoscopists practice, and we hope this guidance will serve as a useful resource to refer to for best practices.”
Added gastroenterologist Tarek Sawas, MD, MPH, assistant professor of internal medicine at UT Southwestern Medical Center in Dallas, “We hope the update will provide some clarity for practice and for implementation, while allowing gastroenterologists the freedom to decide what is best for patients based on lesion characteristics.”
Dr. Sawas added that one of the differences in the new guideline relates to the approach to low-grade dysplasia. While earlier guidance favored treatment over surveillance, patient preferences should now be factored into management. “Some patients are risk-averse and prefer to wait and watch, while others place more value on treatment and just want to get on with it,” he said.
When this guideline was circulated for public comment, “the areas prompting the most feedback was on our current suggestions against the routine use of EET in non-dysplastic BE and for the use of either endoscopic mucosal resection [EMR] or endoscopic submucosal dissection [ESD] for resection — with the expectation that the vast majority may be managed with EMR,” Dr. Rubenstein said.
“We felt that ESD would work best for larger lesions,” explained Dr. Sawas. “There aren’t a lot data in this area, just some observational studies, but we should have more data for comparison in the next few years.”
The incidence of esophageal adenocarcinoma continues to rise and an update was deemed in order since the AGA’s last formal guidance on this subject using the systematic GRADE (Grading of Recommendations Assessment, Development, and Evaluation) methodology was issued in 2011. “In the following time span, there’s been a lot of research, particularly with regard to management of low-grade dysplasia and endoscopic resection techniques,” Dr. Rubenstein said.
Key Recommendations
The 14 guideline panelists made the following suggestions for treatment and implementation based on different levels of certainty of evidence (CoE):
1. If high-grade dysplasia (HGD) is present, EET is recommended over surveillance, with subsequent surveillance performed at 3, 6, and 12 months, and annually thereafter. (Strong recommendation, moderate CoE).
Surveillance endoscopies should obtain targeted tissue samples of visible lesions and random biopsies of the cardia and distal 2 cm of the tubular esophagus.
2. In patients with low-grade dysplasia, EET is also preferred to surveillance. But for those placing a higher value on the certain harms and a lower value on the uncertain benefits of EET for reducing mortality, surveillance endoscopy is a reasonable option. (Conditional recommendation, low CoE).
Following EET, clinicians should perform surveillance at years 1 and 3 after complete eradication of intestinal metaplasia, then revert to the surveillance intervals used in non-dysplastic BE.
3. For non-dysplastic BE, the AGA advises against the routine use of EET. (Conditional recommendation, low CoE).
4. Patients undergoing EET should have resection of visible lesions followed by ablation of the remaining BE segment rather than resection of the entire segment.
In patients with only a small area of BE beyond the visible lesion, endoscopic resection is acceptable and may be preferred over repeated ablation. Radiofrequency ablation is the preferred ablative modality. (Conditional recommendation, very low CoE).
5. For treating visible neoplastic lesions the AGA suggests either EMR or ESD based on lesion characteristics. (Conditional recommendation, very low CoE).
Patients with suspected T1 esophageal adenocarcinoma (EAC) should be considered for EET. Endoscopic resection is recommended over endoscopic ultrasound for distinguishing EAC from HGD and for staging depth of invasion.
The vast majority of neoplastic lesions may be managed with EMR rather than ESD. Patients who have bulky lesions, or lesions highly suspicious of at least T1b invasion and are deemed candidates for endoscopic resection might benefit from ESD over EMR. Those with previously failed EMR might benefit from ESD.
As to the generally low quality of the supporting evidence, Dr. Rubenstein said, “Unfortunately, very few decisions we make in medicine are supported by high certainty of evidence, but we still have to make a decision.” He pointed out that the guideline highlights areas for future research that could help strengthen or change the guideline’s recommendations.
Considering benefits and harms, the panelists concluded that overall CoE across critical desirable outcomes of disease progression to EAC was moderate. Patient-important outcomes informing the harms were strictures, major bleeding perforation, and serious adverse events.
Lifestyle
The guidance also urges providers to counsel BE patients on tobacco cessation and weight loss if needed, and notes the specter of cancer may incentivize patients to make lifestyle changes.
The most common causes of death in EET patients are cardiovascular disease and other cancers, for which tobacco use and obesity are also major risk factors, and tobacco is associated with strictures, the panelists wrote. “The prospect of progression to cancer in patients with dysplastic BE often holds greater valence than prior counseling attempts, and patients may re-commit to such efforts following consultation for EET.”
Going Forward
Areas for future attention include:
- Identifying populations with non-dysplastic BE whose risk warrants EET
- Balancing risk and benefit of EET in low-grade dysplasia
- Randomized controlled trials comparing EMR and ESD in higher-risk lesions
- Optimal management of post-EET pain
- Stricture prevention and control
- Managing resistant/recurrent disease beyond reflux control
- Optimal surveillance and biopsy strategies following EETThis guideline was supported by the National Institutes of Health, the Department of Defense, the Veterans Administration Health Services and Research Division, and the Katy O. and Paul M. Rady Endowed Chair in Esophageal Cancer Research at the University of Colorado.
Dr. Sawas had no competing interests to disclose. Dr. Rubenstein reported research funding from Lucid Diagnostics.
Several other panelists reported research funding or consultation fees from various pharmaceutical and biotechnology companies.
Published in Gastroenterology , the clinical practice guideline makes five main recommendations — one strong and four conditional — based on very low to moderate evidence. It also stresses that providers should practice shared decision making according to patient preferences and risk perception.
For the most part, the new guideline is not a significant departure from the way expert endoscopists are currently practicing EET for BE and related neoplasia, gastroenterologist Joel H. Rubenstein, MD, MSc, AGAF, of the Barrett’s Esophagus Program in the Division of Gastroenterology at University of Michigan Medical School at Ann Arbor, said in an interview. One of three first authors of the guideline, Dr. Rubenstein added, “There is, however, considerable variability in how endoscopists practice, and we hope this guidance will serve as a useful resource to refer to for best practices.”
Added gastroenterologist Tarek Sawas, MD, MPH, assistant professor of internal medicine at UT Southwestern Medical Center in Dallas, “We hope the update will provide some clarity for practice and for implementation, while allowing gastroenterologists the freedom to decide what is best for patients based on lesion characteristics.”
Dr. Sawas added that one of the differences in the new guideline relates to the approach to low-grade dysplasia. While earlier guidance favored treatment over surveillance, patient preferences should now be factored into management. “Some patients are risk-averse and prefer to wait and watch, while others place more value on treatment and just want to get on with it,” he said.
When this guideline was circulated for public comment, “the areas prompting the most feedback was on our current suggestions against the routine use of EET in non-dysplastic BE and for the use of either endoscopic mucosal resection [EMR] or endoscopic submucosal dissection [ESD] for resection — with the expectation that the vast majority may be managed with EMR,” Dr. Rubenstein said.
“We felt that ESD would work best for larger lesions,” explained Dr. Sawas. “There aren’t a lot data in this area, just some observational studies, but we should have more data for comparison in the next few years.”
The incidence of esophageal adenocarcinoma continues to rise and an update was deemed in order since the AGA’s last formal guidance on this subject using the systematic GRADE (Grading of Recommendations Assessment, Development, and Evaluation) methodology was issued in 2011. “In the following time span, there’s been a lot of research, particularly with regard to management of low-grade dysplasia and endoscopic resection techniques,” Dr. Rubenstein said.
Key Recommendations
The 14 guideline panelists made the following suggestions for treatment and implementation based on different levels of certainty of evidence (CoE):
1. If high-grade dysplasia (HGD) is present, EET is recommended over surveillance, with subsequent surveillance performed at 3, 6, and 12 months, and annually thereafter. (Strong recommendation, moderate CoE).
Surveillance endoscopies should obtain targeted tissue samples of visible lesions and random biopsies of the cardia and distal 2 cm of the tubular esophagus.
2. In patients with low-grade dysplasia, EET is also preferred to surveillance. But for those placing a higher value on the certain harms and a lower value on the uncertain benefits of EET for reducing mortality, surveillance endoscopy is a reasonable option. (Conditional recommendation, low CoE).
Following EET, clinicians should perform surveillance at years 1 and 3 after complete eradication of intestinal metaplasia, then revert to the surveillance intervals used in non-dysplastic BE.
3. For non-dysplastic BE, the AGA advises against the routine use of EET. (Conditional recommendation, low CoE).
4. Patients undergoing EET should have resection of visible lesions followed by ablation of the remaining BE segment rather than resection of the entire segment.
In patients with only a small area of BE beyond the visible lesion, endoscopic resection is acceptable and may be preferred over repeated ablation. Radiofrequency ablation is the preferred ablative modality. (Conditional recommendation, very low CoE).
5. For treating visible neoplastic lesions the AGA suggests either EMR or ESD based on lesion characteristics. (Conditional recommendation, very low CoE).
Patients with suspected T1 esophageal adenocarcinoma (EAC) should be considered for EET. Endoscopic resection is recommended over endoscopic ultrasound for distinguishing EAC from HGD and for staging depth of invasion.
The vast majority of neoplastic lesions may be managed with EMR rather than ESD. Patients who have bulky lesions, or lesions highly suspicious of at least T1b invasion and are deemed candidates for endoscopic resection might benefit from ESD over EMR. Those with previously failed EMR might benefit from ESD.
As to the generally low quality of the supporting evidence, Dr. Rubenstein said, “Unfortunately, very few decisions we make in medicine are supported by high certainty of evidence, but we still have to make a decision.” He pointed out that the guideline highlights areas for future research that could help strengthen or change the guideline’s recommendations.
Considering benefits and harms, the panelists concluded that overall CoE across critical desirable outcomes of disease progression to EAC was moderate. Patient-important outcomes informing the harms were strictures, major bleeding perforation, and serious adverse events.
Lifestyle
The guidance also urges providers to counsel BE patients on tobacco cessation and weight loss if needed, and notes the specter of cancer may incentivize patients to make lifestyle changes.
The most common causes of death in EET patients are cardiovascular disease and other cancers, for which tobacco use and obesity are also major risk factors, and tobacco is associated with strictures, the panelists wrote. “The prospect of progression to cancer in patients with dysplastic BE often holds greater valence than prior counseling attempts, and patients may re-commit to such efforts following consultation for EET.”
Going Forward
Areas for future attention include:
- Identifying populations with non-dysplastic BE whose risk warrants EET
- Balancing risk and benefit of EET in low-grade dysplasia
- Randomized controlled trials comparing EMR and ESD in higher-risk lesions
- Optimal management of post-EET pain
- Stricture prevention and control
- Managing resistant/recurrent disease beyond reflux control
- Optimal surveillance and biopsy strategies following EETThis guideline was supported by the National Institutes of Health, the Department of Defense, the Veterans Administration Health Services and Research Division, and the Katy O. and Paul M. Rady Endowed Chair in Esophageal Cancer Research at the University of Colorado.
Dr. Sawas had no competing interests to disclose. Dr. Rubenstein reported research funding from Lucid Diagnostics.
Several other panelists reported research funding or consultation fees from various pharmaceutical and biotechnology companies.
Published in Gastroenterology , the clinical practice guideline makes five main recommendations — one strong and four conditional — based on very low to moderate evidence. It also stresses that providers should practice shared decision making according to patient preferences and risk perception.
For the most part, the new guideline is not a significant departure from the way expert endoscopists are currently practicing EET for BE and related neoplasia, gastroenterologist Joel H. Rubenstein, MD, MSc, AGAF, of the Barrett’s Esophagus Program in the Division of Gastroenterology at University of Michigan Medical School at Ann Arbor, said in an interview. One of three first authors of the guideline, Dr. Rubenstein added, “There is, however, considerable variability in how endoscopists practice, and we hope this guidance will serve as a useful resource to refer to for best practices.”
Added gastroenterologist Tarek Sawas, MD, MPH, assistant professor of internal medicine at UT Southwestern Medical Center in Dallas, “We hope the update will provide some clarity for practice and for implementation, while allowing gastroenterologists the freedom to decide what is best for patients based on lesion characteristics.”
Dr. Sawas added that one of the differences in the new guideline relates to the approach to low-grade dysplasia. While earlier guidance favored treatment over surveillance, patient preferences should now be factored into management. “Some patients are risk-averse and prefer to wait and watch, while others place more value on treatment and just want to get on with it,” he said.
When this guideline was circulated for public comment, “the areas prompting the most feedback was on our current suggestions against the routine use of EET in non-dysplastic BE and for the use of either endoscopic mucosal resection [EMR] or endoscopic submucosal dissection [ESD] for resection — with the expectation that the vast majority may be managed with EMR,” Dr. Rubenstein said.
“We felt that ESD would work best for larger lesions,” explained Dr. Sawas. “There aren’t a lot data in this area, just some observational studies, but we should have more data for comparison in the next few years.”
The incidence of esophageal adenocarcinoma continues to rise and an update was deemed in order since the AGA’s last formal guidance on this subject using the systematic GRADE (Grading of Recommendations Assessment, Development, and Evaluation) methodology was issued in 2011. “In the following time span, there’s been a lot of research, particularly with regard to management of low-grade dysplasia and endoscopic resection techniques,” Dr. Rubenstein said.
Key Recommendations
The 14 guideline panelists made the following suggestions for treatment and implementation based on different levels of certainty of evidence (CoE):
1. If high-grade dysplasia (HGD) is present, EET is recommended over surveillance, with subsequent surveillance performed at 3, 6, and 12 months, and annually thereafter. (Strong recommendation, moderate CoE).
Surveillance endoscopies should obtain targeted tissue samples of visible lesions and random biopsies of the cardia and distal 2 cm of the tubular esophagus.
2. In patients with low-grade dysplasia, EET is also preferred to surveillance. But for those placing a higher value on the certain harms and a lower value on the uncertain benefits of EET for reducing mortality, surveillance endoscopy is a reasonable option. (Conditional recommendation, low CoE).
Following EET, clinicians should perform surveillance at years 1 and 3 after complete eradication of intestinal metaplasia, then revert to the surveillance intervals used in non-dysplastic BE.
3. For non-dysplastic BE, the AGA advises against the routine use of EET. (Conditional recommendation, low CoE).
4. Patients undergoing EET should have resection of visible lesions followed by ablation of the remaining BE segment rather than resection of the entire segment.
In patients with only a small area of BE beyond the visible lesion, endoscopic resection is acceptable and may be preferred over repeated ablation. Radiofrequency ablation is the preferred ablative modality. (Conditional recommendation, very low CoE).
5. For treating visible neoplastic lesions the AGA suggests either EMR or ESD based on lesion characteristics. (Conditional recommendation, very low CoE).
Patients with suspected T1 esophageal adenocarcinoma (EAC) should be considered for EET. Endoscopic resection is recommended over endoscopic ultrasound for distinguishing EAC from HGD and for staging depth of invasion.
The vast majority of neoplastic lesions may be managed with EMR rather than ESD. Patients who have bulky lesions, or lesions highly suspicious of at least T1b invasion and are deemed candidates for endoscopic resection might benefit from ESD over EMR. Those with previously failed EMR might benefit from ESD.
As to the generally low quality of the supporting evidence, Dr. Rubenstein said, “Unfortunately, very few decisions we make in medicine are supported by high certainty of evidence, but we still have to make a decision.” He pointed out that the guideline highlights areas for future research that could help strengthen or change the guideline’s recommendations.
Considering benefits and harms, the panelists concluded that overall CoE across critical desirable outcomes of disease progression to EAC was moderate. Patient-important outcomes informing the harms were strictures, major bleeding perforation, and serious adverse events.
Lifestyle
The guidance also urges providers to counsel BE patients on tobacco cessation and weight loss if needed, and notes the specter of cancer may incentivize patients to make lifestyle changes.
The most common causes of death in EET patients are cardiovascular disease and other cancers, for which tobacco use and obesity are also major risk factors, and tobacco is associated with strictures, the panelists wrote. “The prospect of progression to cancer in patients with dysplastic BE often holds greater valence than prior counseling attempts, and patients may re-commit to such efforts following consultation for EET.”
Going Forward
Areas for future attention include:
- Identifying populations with non-dysplastic BE whose risk warrants EET
- Balancing risk and benefit of EET in low-grade dysplasia
- Randomized controlled trials comparing EMR and ESD in higher-risk lesions
- Optimal management of post-EET pain
- Stricture prevention and control
- Managing resistant/recurrent disease beyond reflux control
- Optimal surveillance and biopsy strategies following EETThis guideline was supported by the National Institutes of Health, the Department of Defense, the Veterans Administration Health Services and Research Division, and the Katy O. and Paul M. Rady Endowed Chair in Esophageal Cancer Research at the University of Colorado.
Dr. Sawas had no competing interests to disclose. Dr. Rubenstein reported research funding from Lucid Diagnostics.
Several other panelists reported research funding or consultation fees from various pharmaceutical and biotechnology companies.
FROM GASTROENTEROLOGY
Serious Mental Illness Tied to Multiple Physical Illnesses
Serious mental illness (SMI), including bipolar disorder or schizophrenia spectrum disorders, is associated with a twofold increased risk for comorbid physical illness, results of a new meta-analysis showed.
“Although treatment of physical and mental health remains siloed in many health services globally, the high prevalence of physical multimorbidity attests to the urgent need for integrated care models that address both physical and mental health outcomes in people with severe mental illness,” the authors, led by Sean Halstead, MD, of The University of Queensland Medical School in Brisbane, Australia, wrote.
The findings were published online in The Lancet Psychiatry.
Shorter Lifespan?
SMI is associated with reduced life expectancy, and experts speculate that additional chronic illnesses — whether physical or psychiatric — may underlie this association.
While previous research has paired SMI with comorbid physical illnesses, the researchers noted that this study is the first to focus on both physical and psychiatric multimorbidity in individuals with SMI.
The investigators conducted a meta-analysis of 82 observational studies comprising 1.6 million individuals with SMI and 13.2 million control subjects to determine the risk for physical or psychiatric multimorbidity.
Studies were included if participants were diagnosed with either a schizophrenia spectrum disorder or bipolar disorder, and the study assessed either physical multimorbidity (at least two physical health conditions) or psychiatric multimorbidity (at least three psychiatric conditions), including the initial SMI.
Investigators found that individuals with SMI had more than a twofold increased risk for physical multimorbidity than those without SMI (odds ratio [OR], 2.40; 95% CI, 1.57-3.65; P = .0009).
Physical multimorbidity, which included cardiovascular, endocrine, neurological rental, gastrointestinal, musculoskeletal, and infectious disorders, was prevalent at similar rates in both schizophrenia spectrum disorder and bipolar disorder.
The ratio of physical multimorbidity was about four times higher in younger populations with SMI (mean age ≤ 40; OR, 3.99; 95% CI, 1.43-11.10) than in older populations (mean age > 40; OR, 1.55; 95% CI, 0.96-2.51; subgroup differences, P = .0013).
In terms of absolute prevalence, 25% of those with SMI had a physical multimorbidity, and 14% had a psychiatric multimorbidity, which were primarily anxiety and substance use disorders.
Investigators speculated that physical multimorbidity in SMI could stem from side effects of psychotropic medications, which are known to cause rapid cardiometabolic changes, including weight gain. In addition, lifestyle factors or nonmodifiable risk factors could also contribute to physical multimorbidity.
The study’s limitations included its small sample sizes for subgroup analyses and insufficient analysis for significant covariates, including smoking rates and symptom severity.
“While health services and treatment guidelines often operate on the assumption that individuals have a single principal diagnosis, these results attest to the clinical complexity many people with severe mental illness face in relation to burden of chronic disease,” the investigators wrote. They added that a greater understanding of the epidemiological manifestations of multimorbidity in SMI is “imperative.”
There was no source of funding for this study. Dr. Halstead is supported by the Australian Research Training Program scholarship. Other disclosures were noted in the original article.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com .
Serious mental illness (SMI), including bipolar disorder or schizophrenia spectrum disorders, is associated with a twofold increased risk for comorbid physical illness, results of a new meta-analysis showed.
“Although treatment of physical and mental health remains siloed in many health services globally, the high prevalence of physical multimorbidity attests to the urgent need for integrated care models that address both physical and mental health outcomes in people with severe mental illness,” the authors, led by Sean Halstead, MD, of The University of Queensland Medical School in Brisbane, Australia, wrote.
The findings were published online in The Lancet Psychiatry.
Shorter Lifespan?
SMI is associated with reduced life expectancy, and experts speculate that additional chronic illnesses — whether physical or psychiatric — may underlie this association.
While previous research has paired SMI with comorbid physical illnesses, the researchers noted that this study is the first to focus on both physical and psychiatric multimorbidity in individuals with SMI.
The investigators conducted a meta-analysis of 82 observational studies comprising 1.6 million individuals with SMI and 13.2 million control subjects to determine the risk for physical or psychiatric multimorbidity.
Studies were included if participants were diagnosed with either a schizophrenia spectrum disorder or bipolar disorder, and the study assessed either physical multimorbidity (at least two physical health conditions) or psychiatric multimorbidity (at least three psychiatric conditions), including the initial SMI.
Investigators found that individuals with SMI had more than a twofold increased risk for physical multimorbidity than those without SMI (odds ratio [OR], 2.40; 95% CI, 1.57-3.65; P = .0009).
Physical multimorbidity, which included cardiovascular, endocrine, neurological rental, gastrointestinal, musculoskeletal, and infectious disorders, was prevalent at similar rates in both schizophrenia spectrum disorder and bipolar disorder.
The ratio of physical multimorbidity was about four times higher in younger populations with SMI (mean age ≤ 40; OR, 3.99; 95% CI, 1.43-11.10) than in older populations (mean age > 40; OR, 1.55; 95% CI, 0.96-2.51; subgroup differences, P = .0013).
In terms of absolute prevalence, 25% of those with SMI had a physical multimorbidity, and 14% had a psychiatric multimorbidity, which were primarily anxiety and substance use disorders.
Investigators speculated that physical multimorbidity in SMI could stem from side effects of psychotropic medications, which are known to cause rapid cardiometabolic changes, including weight gain. In addition, lifestyle factors or nonmodifiable risk factors could also contribute to physical multimorbidity.
The study’s limitations included its small sample sizes for subgroup analyses and insufficient analysis for significant covariates, including smoking rates and symptom severity.
“While health services and treatment guidelines often operate on the assumption that individuals have a single principal diagnosis, these results attest to the clinical complexity many people with severe mental illness face in relation to burden of chronic disease,” the investigators wrote. They added that a greater understanding of the epidemiological manifestations of multimorbidity in SMI is “imperative.”
There was no source of funding for this study. Dr. Halstead is supported by the Australian Research Training Program scholarship. Other disclosures were noted in the original article.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com .
Serious mental illness (SMI), including bipolar disorder or schizophrenia spectrum disorders, is associated with a twofold increased risk for comorbid physical illness, results of a new meta-analysis showed.
“Although treatment of physical and mental health remains siloed in many health services globally, the high prevalence of physical multimorbidity attests to the urgent need for integrated care models that address both physical and mental health outcomes in people with severe mental illness,” the authors, led by Sean Halstead, MD, of The University of Queensland Medical School in Brisbane, Australia, wrote.
The findings were published online in The Lancet Psychiatry.
Shorter Lifespan?
SMI is associated with reduced life expectancy, and experts speculate that additional chronic illnesses — whether physical or psychiatric — may underlie this association.
While previous research has paired SMI with comorbid physical illnesses, the researchers noted that this study is the first to focus on both physical and psychiatric multimorbidity in individuals with SMI.
The investigators conducted a meta-analysis of 82 observational studies comprising 1.6 million individuals with SMI and 13.2 million control subjects to determine the risk for physical or psychiatric multimorbidity.
Studies were included if participants were diagnosed with either a schizophrenia spectrum disorder or bipolar disorder, and the study assessed either physical multimorbidity (at least two physical health conditions) or psychiatric multimorbidity (at least three psychiatric conditions), including the initial SMI.
Investigators found that individuals with SMI had more than a twofold increased risk for physical multimorbidity than those without SMI (odds ratio [OR], 2.40; 95% CI, 1.57-3.65; P = .0009).
Physical multimorbidity, which included cardiovascular, endocrine, neurological rental, gastrointestinal, musculoskeletal, and infectious disorders, was prevalent at similar rates in both schizophrenia spectrum disorder and bipolar disorder.
The ratio of physical multimorbidity was about four times higher in younger populations with SMI (mean age ≤ 40; OR, 3.99; 95% CI, 1.43-11.10) than in older populations (mean age > 40; OR, 1.55; 95% CI, 0.96-2.51; subgroup differences, P = .0013).
In terms of absolute prevalence, 25% of those with SMI had a physical multimorbidity, and 14% had a psychiatric multimorbidity, which were primarily anxiety and substance use disorders.
Investigators speculated that physical multimorbidity in SMI could stem from side effects of psychotropic medications, which are known to cause rapid cardiometabolic changes, including weight gain. In addition, lifestyle factors or nonmodifiable risk factors could also contribute to physical multimorbidity.
The study’s limitations included its small sample sizes for subgroup analyses and insufficient analysis for significant covariates, including smoking rates and symptom severity.
“While health services and treatment guidelines often operate on the assumption that individuals have a single principal diagnosis, these results attest to the clinical complexity many people with severe mental illness face in relation to burden of chronic disease,” the investigators wrote. They added that a greater understanding of the epidemiological manifestations of multimorbidity in SMI is “imperative.”
There was no source of funding for this study. Dr. Halstead is supported by the Australian Research Training Program scholarship. Other disclosures were noted in the original article.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com .
FROM THE LANCET PSYCHIATRY
Don’t Leave CVD Risk in RA Undertreated Despite Unresolved Questions
NEW YORK — Patients with rheumatoid arthritis (RA) carry a high risk for cardiovascular events, but mounting clinical evidence suggests they’re being undertreated to manage that risk. Rheumatologists should consider a patient with RA’s cardiovascular disease (CVD) status before deciding on RA treatments, a researcher of cardiometabolic disorders advised.
“The ORAL Surveillance trial suggests that we need to consider cardiovascular risk factors and maybe do additional screening in these patients before we use RA therapies,” Jon T. Giles, MD, PhD, director of the Cedars-Sinai Inflammatory Arthritis Clinical Center at Cedars-Sinai in Los Angeles, told attendees at the 4th Annual Cardiometabolic Risk in Inflammatory Conditions conference.
Underuse of Statins
ORAL Surveillance enrolled 4362 patients with RA aged 50 years and older with at least one cardiovascular risk factor. About 23% of all patients were taking statins, as were about half of patients with a history of atherosclerotic CVD (ASCVD).
“A lot of those people should have been on statins,” Dr. Giles said in an interview. “Not because of their RA but because of their risk factors, and then RA brings it up another notch.” In the population with ASCVD, Dr. Giles added, “It should have been more like 70% and 80%. If we’re talking about a disease that has enhanced cardiovascular risk, then the adoption of standard care that you would do for anybody in the general population should be at that standard and maybe above.”
Multiple studies have documented the underlying risk for CVD events, CV mortality, and subclinical atherosclerosis in people with RA, Dr. Giles noted in his presentation. Physiologically, the RA-specific risk factors most linked to CVD risk are systemic inflammation/cytokine excess and specific circulating T-cell and intermediate monocyte subsets, or both, Dr. Giles said.
Disease-Modifying Antirheumatic Drugs (DMARDs) and CVD Risk
Likewise, research in the past decade has linked methotrexate and tumor necrosis factor (TNF) inhibitors to reduced ASCVD events in RA. Another study showed that abatacept had an effect similar to that of etanercept in patients with RA, and the ENTRACTE trial, for which Dr. Giles was the lead author, demonstrated that tocilizumab matched etanercept in reducing CV events.
The ORAL Surveillance investigators also reported that patients with RA who were receiving the Janus kinase (JAK) inhibitor tofacitinib had a higher risk for major adverse cardiovascular events and cancers than those on TNF therapy, Dr. Giles noted. While statins in combination with JAK inhibitors may have the potential to provide a balance for controlling CV risk in patients with RA, he said later that the potential of JAK inhibitors in reducing CVD risk in RA “is still unsettled.”
The ongoing TARGET trial is further evaluating the impact of DMARDs on vascular inflammation in RA, said Dr. Giles, who’s also a trial principal investigator. TARGET is randomizing 115 patients with RA who didn’t respond to methotrexate to a TNF inhibitor or the addition of sulfasalazine and hydroxychloroquine to their methotrexate. Patients can be on low-intensity but not high-intensity statin therapy, Dr. Giles said.
TARGET results reported last year demonstrated an 8% decrease in arterial fluorodeoxyglucose (FDG) uptake on PET-CT in both treatment arms. Previous studies, Dr. Giles noted, have shown a potential link between FDG and histologic markers of inflammation. “An 8% decrease in vascular FDG is in line with what you would expect from statin treatment,” he said.
TARGET results published in April showed that a measure of a cluster of 12 cytokines and other inflammatory mediators, known as the multibiomarker disease activity (MBDA) score and marketed under the brand name Vectra DA, may help determine arterial FDG uptake. “Those who had a low MBDA score at week 24 actually had the greatest reduction in the arterial FDG,” he said.
Those results were driven entirely by low serum amyloid A (SAA) levels, Dr. Giles said. Those same results didn’t hold for patients in whom SAA and C-reactive protein were correlated.
“So, there’s more to come here,” Dr. Giles said. “We’re looking at other, much larger biomarker panels.”
Nonetheless, he said, sufficient evidence exists to conclude that treating RA to target reduces CV events. “The idea is that at every visit that you see an RA patient, you measure their disease activity, and if they’re not at the target of low disease activity or remission, then you change their therapy to improve that,” he said in an interview.
But an evidence-based guideline is needed to improve coverage of CVD risks in patients with RA, Dr. Giles said. “There is a movement afoot” for a guideline, he said. “If you just did what is supposed to happen for a general population, you would make some improvements. The risk-benefit [ratio] for statins for people with RA has been looked at, and it’s very favorable.”
Unanswered Questions
Dr. Giles noted that the ORAL Surveillance trial has left a number of questions unanswered about the role of JAK inhibitors in managing CVD risk in patients with RA. “The issue that we’re trying to ask is, is it just the TNF inhibitors may be better? Is this a subpopulation issue, or was it just bad luck from the purposes of this one trial? Granted, it was a very large trial, but you can still have luck in terms of getting an effect that’s not accurate.”
Dr. Giles’ “gut feeling” on JAK inhibitors is that they’re not causing harm, but that they’re not as effective as TNF inhibitors in ameliorating CV risks in patients with RA.
Michael S. Garshick, MD, who attended the conference and is head of the cardio-rheumatology program at NYU Langone Health, concurred that a number of unanswered questions persist over the treatment of CVD risk in RA — and autoimmune disease in general.
“I think we’re still trying to prove that DMARDs reduce cardiovascular risk in autoimmune conditions,” he said. “The epidemiologic data would suggest, yes, that inflammation prevention is beneficial for cardiovascular disease, but the TARGET trial suggested that vascular inflammation improved by treating RA, but that biologic therapy wasn’t better than traditional triple therapy.”
Other questions remain unanswered, Dr. Garshick said.
“Is there a specific immunotherapy that is most beneficial to reduce heart disease in patients with an autoimmune condition, whether it’s rheumatoid arthritis, psoriasis, or lupus?”
Dr. Garshick said he’s specifically interested in the residual risk that exists after treating the autoimmunity. “Do you still have a higher risk for heart disease, and if so, why? Is there something else going on that we can’t see?”
The biggest unanswered question, he said, is “How can we do a better job of recognizing heart disease risk in these patients? That’s the low-hanging fruit that people are studying, but across many of those studies, patients have higher rates of blood pressure, cholesterol issues, obesity, diabetes, and many times, we’re not adequately treating these comorbidities.”
That, Dr. Garshick said, may be a result of physician fatigue. “And so [treatment of these comorbidities is] kicked down the road for a year or years,” he added.
Dr. Giles disclosed financial relationships with Pfizer, AbbVie, Eli Lilly, and Novartis. Dr. Garshick disclosed relationships with Kiniksa Pharmaceuticals, Agepha Pharma, Bristol Myers Squibb, and Horizon Therapeutics.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
NEW YORK — Patients with rheumatoid arthritis (RA) carry a high risk for cardiovascular events, but mounting clinical evidence suggests they’re being undertreated to manage that risk. Rheumatologists should consider a patient with RA’s cardiovascular disease (CVD) status before deciding on RA treatments, a researcher of cardiometabolic disorders advised.
“The ORAL Surveillance trial suggests that we need to consider cardiovascular risk factors and maybe do additional screening in these patients before we use RA therapies,” Jon T. Giles, MD, PhD, director of the Cedars-Sinai Inflammatory Arthritis Clinical Center at Cedars-Sinai in Los Angeles, told attendees at the 4th Annual Cardiometabolic Risk in Inflammatory Conditions conference.
Underuse of Statins
ORAL Surveillance enrolled 4362 patients with RA aged 50 years and older with at least one cardiovascular risk factor. About 23% of all patients were taking statins, as were about half of patients with a history of atherosclerotic CVD (ASCVD).
“A lot of those people should have been on statins,” Dr. Giles said in an interview. “Not because of their RA but because of their risk factors, and then RA brings it up another notch.” In the population with ASCVD, Dr. Giles added, “It should have been more like 70% and 80%. If we’re talking about a disease that has enhanced cardiovascular risk, then the adoption of standard care that you would do for anybody in the general population should be at that standard and maybe above.”
Multiple studies have documented the underlying risk for CVD events, CV mortality, and subclinical atherosclerosis in people with RA, Dr. Giles noted in his presentation. Physiologically, the RA-specific risk factors most linked to CVD risk are systemic inflammation/cytokine excess and specific circulating T-cell and intermediate monocyte subsets, or both, Dr. Giles said.
Disease-Modifying Antirheumatic Drugs (DMARDs) and CVD Risk
Likewise, research in the past decade has linked methotrexate and tumor necrosis factor (TNF) inhibitors to reduced ASCVD events in RA. Another study showed that abatacept had an effect similar to that of etanercept in patients with RA, and the ENTRACTE trial, for which Dr. Giles was the lead author, demonstrated that tocilizumab matched etanercept in reducing CV events.
The ORAL Surveillance investigators also reported that patients with RA who were receiving the Janus kinase (JAK) inhibitor tofacitinib had a higher risk for major adverse cardiovascular events and cancers than those on TNF therapy, Dr. Giles noted. While statins in combination with JAK inhibitors may have the potential to provide a balance for controlling CV risk in patients with RA, he said later that the potential of JAK inhibitors in reducing CVD risk in RA “is still unsettled.”
The ongoing TARGET trial is further evaluating the impact of DMARDs on vascular inflammation in RA, said Dr. Giles, who’s also a trial principal investigator. TARGET is randomizing 115 patients with RA who didn’t respond to methotrexate to a TNF inhibitor or the addition of sulfasalazine and hydroxychloroquine to their methotrexate. Patients can be on low-intensity but not high-intensity statin therapy, Dr. Giles said.
TARGET results reported last year demonstrated an 8% decrease in arterial fluorodeoxyglucose (FDG) uptake on PET-CT in both treatment arms. Previous studies, Dr. Giles noted, have shown a potential link between FDG and histologic markers of inflammation. “An 8% decrease in vascular FDG is in line with what you would expect from statin treatment,” he said.
TARGET results published in April showed that a measure of a cluster of 12 cytokines and other inflammatory mediators, known as the multibiomarker disease activity (MBDA) score and marketed under the brand name Vectra DA, may help determine arterial FDG uptake. “Those who had a low MBDA score at week 24 actually had the greatest reduction in the arterial FDG,” he said.
Those results were driven entirely by low serum amyloid A (SAA) levels, Dr. Giles said. Those same results didn’t hold for patients in whom SAA and C-reactive protein were correlated.
“So, there’s more to come here,” Dr. Giles said. “We’re looking at other, much larger biomarker panels.”
Nonetheless, he said, sufficient evidence exists to conclude that treating RA to target reduces CV events. “The idea is that at every visit that you see an RA patient, you measure their disease activity, and if they’re not at the target of low disease activity or remission, then you change their therapy to improve that,” he said in an interview.
But an evidence-based guideline is needed to improve coverage of CVD risks in patients with RA, Dr. Giles said. “There is a movement afoot” for a guideline, he said. “If you just did what is supposed to happen for a general population, you would make some improvements. The risk-benefit [ratio] for statins for people with RA has been looked at, and it’s very favorable.”
Unanswered Questions
Dr. Giles noted that the ORAL Surveillance trial has left a number of questions unanswered about the role of JAK inhibitors in managing CVD risk in patients with RA. “The issue that we’re trying to ask is, is it just the TNF inhibitors may be better? Is this a subpopulation issue, or was it just bad luck from the purposes of this one trial? Granted, it was a very large trial, but you can still have luck in terms of getting an effect that’s not accurate.”
Dr. Giles’ “gut feeling” on JAK inhibitors is that they’re not causing harm, but that they’re not as effective as TNF inhibitors in ameliorating CV risks in patients with RA.
Michael S. Garshick, MD, who attended the conference and is head of the cardio-rheumatology program at NYU Langone Health, concurred that a number of unanswered questions persist over the treatment of CVD risk in RA — and autoimmune disease in general.
“I think we’re still trying to prove that DMARDs reduce cardiovascular risk in autoimmune conditions,” he said. “The epidemiologic data would suggest, yes, that inflammation prevention is beneficial for cardiovascular disease, but the TARGET trial suggested that vascular inflammation improved by treating RA, but that biologic therapy wasn’t better than traditional triple therapy.”
Other questions remain unanswered, Dr. Garshick said.
“Is there a specific immunotherapy that is most beneficial to reduce heart disease in patients with an autoimmune condition, whether it’s rheumatoid arthritis, psoriasis, or lupus?”
Dr. Garshick said he’s specifically interested in the residual risk that exists after treating the autoimmunity. “Do you still have a higher risk for heart disease, and if so, why? Is there something else going on that we can’t see?”
The biggest unanswered question, he said, is “How can we do a better job of recognizing heart disease risk in these patients? That’s the low-hanging fruit that people are studying, but across many of those studies, patients have higher rates of blood pressure, cholesterol issues, obesity, diabetes, and many times, we’re not adequately treating these comorbidities.”
That, Dr. Garshick said, may be a result of physician fatigue. “And so [treatment of these comorbidities is] kicked down the road for a year or years,” he added.
Dr. Giles disclosed financial relationships with Pfizer, AbbVie, Eli Lilly, and Novartis. Dr. Garshick disclosed relationships with Kiniksa Pharmaceuticals, Agepha Pharma, Bristol Myers Squibb, and Horizon Therapeutics.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
NEW YORK — Patients with rheumatoid arthritis (RA) carry a high risk for cardiovascular events, but mounting clinical evidence suggests they’re being undertreated to manage that risk. Rheumatologists should consider a patient with RA’s cardiovascular disease (CVD) status before deciding on RA treatments, a researcher of cardiometabolic disorders advised.
“The ORAL Surveillance trial suggests that we need to consider cardiovascular risk factors and maybe do additional screening in these patients before we use RA therapies,” Jon T. Giles, MD, PhD, director of the Cedars-Sinai Inflammatory Arthritis Clinical Center at Cedars-Sinai in Los Angeles, told attendees at the 4th Annual Cardiometabolic Risk in Inflammatory Conditions conference.
Underuse of Statins
ORAL Surveillance enrolled 4362 patients with RA aged 50 years and older with at least one cardiovascular risk factor. About 23% of all patients were taking statins, as were about half of patients with a history of atherosclerotic CVD (ASCVD).
“A lot of those people should have been on statins,” Dr. Giles said in an interview. “Not because of their RA but because of their risk factors, and then RA brings it up another notch.” In the population with ASCVD, Dr. Giles added, “It should have been more like 70% and 80%. If we’re talking about a disease that has enhanced cardiovascular risk, then the adoption of standard care that you would do for anybody in the general population should be at that standard and maybe above.”
Multiple studies have documented the underlying risk for CVD events, CV mortality, and subclinical atherosclerosis in people with RA, Dr. Giles noted in his presentation. Physiologically, the RA-specific risk factors most linked to CVD risk are systemic inflammation/cytokine excess and specific circulating T-cell and intermediate monocyte subsets, or both, Dr. Giles said.
Disease-Modifying Antirheumatic Drugs (DMARDs) and CVD Risk
Likewise, research in the past decade has linked methotrexate and tumor necrosis factor (TNF) inhibitors to reduced ASCVD events in RA. Another study showed that abatacept had an effect similar to that of etanercept in patients with RA, and the ENTRACTE trial, for which Dr. Giles was the lead author, demonstrated that tocilizumab matched etanercept in reducing CV events.
The ORAL Surveillance investigators also reported that patients with RA who were receiving the Janus kinase (JAK) inhibitor tofacitinib had a higher risk for major adverse cardiovascular events and cancers than those on TNF therapy, Dr. Giles noted. While statins in combination with JAK inhibitors may have the potential to provide a balance for controlling CV risk in patients with RA, he said later that the potential of JAK inhibitors in reducing CVD risk in RA “is still unsettled.”
The ongoing TARGET trial is further evaluating the impact of DMARDs on vascular inflammation in RA, said Dr. Giles, who’s also a trial principal investigator. TARGET is randomizing 115 patients with RA who didn’t respond to methotrexate to a TNF inhibitor or the addition of sulfasalazine and hydroxychloroquine to their methotrexate. Patients can be on low-intensity but not high-intensity statin therapy, Dr. Giles said.
TARGET results reported last year demonstrated an 8% decrease in arterial fluorodeoxyglucose (FDG) uptake on PET-CT in both treatment arms. Previous studies, Dr. Giles noted, have shown a potential link between FDG and histologic markers of inflammation. “An 8% decrease in vascular FDG is in line with what you would expect from statin treatment,” he said.
TARGET results published in April showed that a measure of a cluster of 12 cytokines and other inflammatory mediators, known as the multibiomarker disease activity (MBDA) score and marketed under the brand name Vectra DA, may help determine arterial FDG uptake. “Those who had a low MBDA score at week 24 actually had the greatest reduction in the arterial FDG,” he said.
Those results were driven entirely by low serum amyloid A (SAA) levels, Dr. Giles said. Those same results didn’t hold for patients in whom SAA and C-reactive protein were correlated.
“So, there’s more to come here,” Dr. Giles said. “We’re looking at other, much larger biomarker panels.”
Nonetheless, he said, sufficient evidence exists to conclude that treating RA to target reduces CV events. “The idea is that at every visit that you see an RA patient, you measure their disease activity, and if they’re not at the target of low disease activity or remission, then you change their therapy to improve that,” he said in an interview.
But an evidence-based guideline is needed to improve coverage of CVD risks in patients with RA, Dr. Giles said. “There is a movement afoot” for a guideline, he said. “If you just did what is supposed to happen for a general population, you would make some improvements. The risk-benefit [ratio] for statins for people with RA has been looked at, and it’s very favorable.”
Unanswered Questions
Dr. Giles noted that the ORAL Surveillance trial has left a number of questions unanswered about the role of JAK inhibitors in managing CVD risk in patients with RA. “The issue that we’re trying to ask is, is it just the TNF inhibitors may be better? Is this a subpopulation issue, or was it just bad luck from the purposes of this one trial? Granted, it was a very large trial, but you can still have luck in terms of getting an effect that’s not accurate.”
Dr. Giles’ “gut feeling” on JAK inhibitors is that they’re not causing harm, but that they’re not as effective as TNF inhibitors in ameliorating CV risks in patients with RA.
Michael S. Garshick, MD, who attended the conference and is head of the cardio-rheumatology program at NYU Langone Health, concurred that a number of unanswered questions persist over the treatment of CVD risk in RA — and autoimmune disease in general.
“I think we’re still trying to prove that DMARDs reduce cardiovascular risk in autoimmune conditions,” he said. “The epidemiologic data would suggest, yes, that inflammation prevention is beneficial for cardiovascular disease, but the TARGET trial suggested that vascular inflammation improved by treating RA, but that biologic therapy wasn’t better than traditional triple therapy.”
Other questions remain unanswered, Dr. Garshick said.
“Is there a specific immunotherapy that is most beneficial to reduce heart disease in patients with an autoimmune condition, whether it’s rheumatoid arthritis, psoriasis, or lupus?”
Dr. Garshick said he’s specifically interested in the residual risk that exists after treating the autoimmunity. “Do you still have a higher risk for heart disease, and if so, why? Is there something else going on that we can’t see?”
The biggest unanswered question, he said, is “How can we do a better job of recognizing heart disease risk in these patients? That’s the low-hanging fruit that people are studying, but across many of those studies, patients have higher rates of blood pressure, cholesterol issues, obesity, diabetes, and many times, we’re not adequately treating these comorbidities.”
That, Dr. Garshick said, may be a result of physician fatigue. “And so [treatment of these comorbidities is] kicked down the road for a year or years,” he added.
Dr. Giles disclosed financial relationships with Pfizer, AbbVie, Eli Lilly, and Novartis. Dr. Garshick disclosed relationships with Kiniksa Pharmaceuticals, Agepha Pharma, Bristol Myers Squibb, and Horizon Therapeutics.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Alcohol to Blame: Weight Regain After Bariatric Surgery
A 50-year-old woman with a history of class 3 obesity, gastroesophageal reflux disease, prediabetes, metabolic dysfunction–associated steatotic liver disease, asthma, and depression returns to our weight management clinic with weight regain 4 years after Roux-en-Y gastric bypass.
Her initial body weight was 389 lb (176.8 kg; body mass index [BMI], 65), and her nadir weight after surgery was 183 lb (83.2 kg; BMI, 30.5), representing a total weight loss of 53%. During the initial 2 years after surgery, she experienced multiple life stressors and was treated with venlafaxine for mild depression. She regained 25 lb (11.4 kg). Over the next 2 years, she gained another 20 lb (9.1 kg), for a total of 45 lb (20.5 kg) above nadir.
The patient reported increased nighttime consumption of alcohol including vodka, wine, and beer of over 20 drinks per week for the past 2 years. Her laboratory profile showed an elevated fasting glucose level (106 mg/dL, formerly 98 mg/dL), an elevated gamma-glutamyl transferase (GGT) level, and iron deficiency anemia. She admitted to regularly missing doses of postbariatric vitamins and minerals.
Ask Patients About Alcohol Use
It’s important to ask patients with significant weight regain after metabolic and bariatric surgery (MBS) about alcohol intake, because patients who have MBS are at an increased risk of developing alcohol use disorder (AUD).
The American Society for Metabolic and Bariatric Surgery recommends screening for alcohol intake both before and after MBS. Underreporting of alcohol consumption is common, but an elevated GGT level or elevated liver enzyme levels can indicate alcohol use. Depression and anxiety exacerbated by life stressors often accompany excessive alcohol intake.
Some antiobesity medications that regulate appetite may also help limit excessive alcohol intake. Naltrexone is used both for the treatment of AUD and for weight management, often in combination with bupropion). In a patient with weight regain and AUD, naltrexone alone would be a reasonable treatment option, although weight loss would probably be modest. The addition of bupropion to naltrexone would probably produce more weight loss; average total body weight loss with bupropion-naltrexone in clinical trials was about 6%. One cautionary note on bupropion: A patient’s seizure history should be elicited, because people with AUD are at increased risk for seizures in the withdrawal stage and bupropion can make those seizures more likely.
Glucagon-like peptide 1 (GLP-1) receptor agonists (eg, liraglutide and semaglutide) and dual GLP-1/GIP (glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide receptor agonists) (eg, tirzepatide) are second-generation antiobesity medications that produce more weight loss than first-generation agents such as bupropion/naltrexone. Of note, prior bariatric surgery was an exclusion criterion in the clinical trials assessing the efficacy of these agents for weight loss. The use of GLP-1 receptor agonists after MBS in people with inadequate weight loss or weight regain has been an area of active research. The BARI-OPTIMISE randomized clinical trial published in 2023 assessed the safety and efficacy of liraglutide 3.0 mg daily in patients with inadequate weight loss after MBS. The mean body weight reduction was 8.82% in the liraglutide group vs 0.54% in the placebo group.
There is also emerging interest in the potential of GLP-1 receptor agonists in AUD. These medications act on the central nervous system to influence reward pathways. In rodents, studies have shown that GLP-1 receptor agonist administration reduces alcohol intake, although most studies have focused on short-term effects.
A series of experiments assessed the effects of semaglutide on alcohol intake in rodents. The authors found that semaglutide lowered the alcohol-induced release of dopamine and enhanced dopamine metabolism within the nucleus accumbens.
Evidence in humans is still limited, with only one published randomized controlled trial to date. In the 26-week study, weekly exenatide was not superior to placebo in reducing the number of heavy drinking days in patients with AUD who also received cognitive-behavioral therapy. An exploratory analysis in a subgroup of patients with obesity and AUD showed that exenatide reduced alcohol consumption. Of note, exenatide is rarely used in clinical practice because it does not produce substantial weight loss.
Liraglutide was chosen for this patient because of the established efficacy for this agent in patients with a history of MBS. In addition, patients often anecdotally report reduced desire for alcohol while taking a GLP-1 receptor agonist. Although GLP-1 receptor agonists have been shown to reduce alcohol intake in animal studies, their efficacy and safety in humans with AUD are not yet well established.
Back to Our Patient:
Given the patient’s weight regain, an upper gastrointestinal series was performed to rule out gastro-gastric fistula or other anatomic abnormalities. After fistula was ruled out, she was prescribed liraglutide for weight management, which was titrated from 0.6 mg/d to 3 mg/d per the prescribing guidelines.
With the use of liraglutide over the next year, the patient maintained a stable weight of 200 lb (90.9 kg) and noted that along with reduced appetite, her cravings for alcohol had diminished and she no longer felt the urge to drink alcohol at night. Her fasting glucose and GGT levels normalized. She began to see a nutritionist regularly and was planning to rejoin a bariatric support group.
Dr. Schmitz is an instructor in the Department of Medicine, Division of Endocrinology, Diabetes, and Metabolism, Weill Cornell Medicine, New York. She has disclosed no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Kashyap is a assistant chief of clinical affairs, Division of Endocrinology, Diabetes and Metabolism, Weill Cornell New York Presbyterian, New York. She disclosed ties to GI Dynamics.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
A 50-year-old woman with a history of class 3 obesity, gastroesophageal reflux disease, prediabetes, metabolic dysfunction–associated steatotic liver disease, asthma, and depression returns to our weight management clinic with weight regain 4 years after Roux-en-Y gastric bypass.
Her initial body weight was 389 lb (176.8 kg; body mass index [BMI], 65), and her nadir weight after surgery was 183 lb (83.2 kg; BMI, 30.5), representing a total weight loss of 53%. During the initial 2 years after surgery, she experienced multiple life stressors and was treated with venlafaxine for mild depression. She regained 25 lb (11.4 kg). Over the next 2 years, she gained another 20 lb (9.1 kg), for a total of 45 lb (20.5 kg) above nadir.
The patient reported increased nighttime consumption of alcohol including vodka, wine, and beer of over 20 drinks per week for the past 2 years. Her laboratory profile showed an elevated fasting glucose level (106 mg/dL, formerly 98 mg/dL), an elevated gamma-glutamyl transferase (GGT) level, and iron deficiency anemia. She admitted to regularly missing doses of postbariatric vitamins and minerals.
Ask Patients About Alcohol Use
It’s important to ask patients with significant weight regain after metabolic and bariatric surgery (MBS) about alcohol intake, because patients who have MBS are at an increased risk of developing alcohol use disorder (AUD).
The American Society for Metabolic and Bariatric Surgery recommends screening for alcohol intake both before and after MBS. Underreporting of alcohol consumption is common, but an elevated GGT level or elevated liver enzyme levels can indicate alcohol use. Depression and anxiety exacerbated by life stressors often accompany excessive alcohol intake.
Some antiobesity medications that regulate appetite may also help limit excessive alcohol intake. Naltrexone is used both for the treatment of AUD and for weight management, often in combination with bupropion). In a patient with weight regain and AUD, naltrexone alone would be a reasonable treatment option, although weight loss would probably be modest. The addition of bupropion to naltrexone would probably produce more weight loss; average total body weight loss with bupropion-naltrexone in clinical trials was about 6%. One cautionary note on bupropion: A patient’s seizure history should be elicited, because people with AUD are at increased risk for seizures in the withdrawal stage and bupropion can make those seizures more likely.
Glucagon-like peptide 1 (GLP-1) receptor agonists (eg, liraglutide and semaglutide) and dual GLP-1/GIP (glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide receptor agonists) (eg, tirzepatide) are second-generation antiobesity medications that produce more weight loss than first-generation agents such as bupropion/naltrexone. Of note, prior bariatric surgery was an exclusion criterion in the clinical trials assessing the efficacy of these agents for weight loss. The use of GLP-1 receptor agonists after MBS in people with inadequate weight loss or weight regain has been an area of active research. The BARI-OPTIMISE randomized clinical trial published in 2023 assessed the safety and efficacy of liraglutide 3.0 mg daily in patients with inadequate weight loss after MBS. The mean body weight reduction was 8.82% in the liraglutide group vs 0.54% in the placebo group.
There is also emerging interest in the potential of GLP-1 receptor agonists in AUD. These medications act on the central nervous system to influence reward pathways. In rodents, studies have shown that GLP-1 receptor agonist administration reduces alcohol intake, although most studies have focused on short-term effects.
A series of experiments assessed the effects of semaglutide on alcohol intake in rodents. The authors found that semaglutide lowered the alcohol-induced release of dopamine and enhanced dopamine metabolism within the nucleus accumbens.
Evidence in humans is still limited, with only one published randomized controlled trial to date. In the 26-week study, weekly exenatide was not superior to placebo in reducing the number of heavy drinking days in patients with AUD who also received cognitive-behavioral therapy. An exploratory analysis in a subgroup of patients with obesity and AUD showed that exenatide reduced alcohol consumption. Of note, exenatide is rarely used in clinical practice because it does not produce substantial weight loss.
Liraglutide was chosen for this patient because of the established efficacy for this agent in patients with a history of MBS. In addition, patients often anecdotally report reduced desire for alcohol while taking a GLP-1 receptor agonist. Although GLP-1 receptor agonists have been shown to reduce alcohol intake in animal studies, their efficacy and safety in humans with AUD are not yet well established.
Back to Our Patient:
Given the patient’s weight regain, an upper gastrointestinal series was performed to rule out gastro-gastric fistula or other anatomic abnormalities. After fistula was ruled out, she was prescribed liraglutide for weight management, which was titrated from 0.6 mg/d to 3 mg/d per the prescribing guidelines.
With the use of liraglutide over the next year, the patient maintained a stable weight of 200 lb (90.9 kg) and noted that along with reduced appetite, her cravings for alcohol had diminished and she no longer felt the urge to drink alcohol at night. Her fasting glucose and GGT levels normalized. She began to see a nutritionist regularly and was planning to rejoin a bariatric support group.
Dr. Schmitz is an instructor in the Department of Medicine, Division of Endocrinology, Diabetes, and Metabolism, Weill Cornell Medicine, New York. She has disclosed no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Kashyap is a assistant chief of clinical affairs, Division of Endocrinology, Diabetes and Metabolism, Weill Cornell New York Presbyterian, New York. She disclosed ties to GI Dynamics.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
A 50-year-old woman with a history of class 3 obesity, gastroesophageal reflux disease, prediabetes, metabolic dysfunction–associated steatotic liver disease, asthma, and depression returns to our weight management clinic with weight regain 4 years after Roux-en-Y gastric bypass.
Her initial body weight was 389 lb (176.8 kg; body mass index [BMI], 65), and her nadir weight after surgery was 183 lb (83.2 kg; BMI, 30.5), representing a total weight loss of 53%. During the initial 2 years after surgery, she experienced multiple life stressors and was treated with venlafaxine for mild depression. She regained 25 lb (11.4 kg). Over the next 2 years, she gained another 20 lb (9.1 kg), for a total of 45 lb (20.5 kg) above nadir.
The patient reported increased nighttime consumption of alcohol including vodka, wine, and beer of over 20 drinks per week for the past 2 years. Her laboratory profile showed an elevated fasting glucose level (106 mg/dL, formerly 98 mg/dL), an elevated gamma-glutamyl transferase (GGT) level, and iron deficiency anemia. She admitted to regularly missing doses of postbariatric vitamins and minerals.
Ask Patients About Alcohol Use
It’s important to ask patients with significant weight regain after metabolic and bariatric surgery (MBS) about alcohol intake, because patients who have MBS are at an increased risk of developing alcohol use disorder (AUD).
The American Society for Metabolic and Bariatric Surgery recommends screening for alcohol intake both before and after MBS. Underreporting of alcohol consumption is common, but an elevated GGT level or elevated liver enzyme levels can indicate alcohol use. Depression and anxiety exacerbated by life stressors often accompany excessive alcohol intake.
Some antiobesity medications that regulate appetite may also help limit excessive alcohol intake. Naltrexone is used both for the treatment of AUD and for weight management, often in combination with bupropion). In a patient with weight regain and AUD, naltrexone alone would be a reasonable treatment option, although weight loss would probably be modest. The addition of bupropion to naltrexone would probably produce more weight loss; average total body weight loss with bupropion-naltrexone in clinical trials was about 6%. One cautionary note on bupropion: A patient’s seizure history should be elicited, because people with AUD are at increased risk for seizures in the withdrawal stage and bupropion can make those seizures more likely.
Glucagon-like peptide 1 (GLP-1) receptor agonists (eg, liraglutide and semaglutide) and dual GLP-1/GIP (glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide receptor agonists) (eg, tirzepatide) are second-generation antiobesity medications that produce more weight loss than first-generation agents such as bupropion/naltrexone. Of note, prior bariatric surgery was an exclusion criterion in the clinical trials assessing the efficacy of these agents for weight loss. The use of GLP-1 receptor agonists after MBS in people with inadequate weight loss or weight regain has been an area of active research. The BARI-OPTIMISE randomized clinical trial published in 2023 assessed the safety and efficacy of liraglutide 3.0 mg daily in patients with inadequate weight loss after MBS. The mean body weight reduction was 8.82% in the liraglutide group vs 0.54% in the placebo group.
There is also emerging interest in the potential of GLP-1 receptor agonists in AUD. These medications act on the central nervous system to influence reward pathways. In rodents, studies have shown that GLP-1 receptor agonist administration reduces alcohol intake, although most studies have focused on short-term effects.
A series of experiments assessed the effects of semaglutide on alcohol intake in rodents. The authors found that semaglutide lowered the alcohol-induced release of dopamine and enhanced dopamine metabolism within the nucleus accumbens.
Evidence in humans is still limited, with only one published randomized controlled trial to date. In the 26-week study, weekly exenatide was not superior to placebo in reducing the number of heavy drinking days in patients with AUD who also received cognitive-behavioral therapy. An exploratory analysis in a subgroup of patients with obesity and AUD showed that exenatide reduced alcohol consumption. Of note, exenatide is rarely used in clinical practice because it does not produce substantial weight loss.
Liraglutide was chosen for this patient because of the established efficacy for this agent in patients with a history of MBS. In addition, patients often anecdotally report reduced desire for alcohol while taking a GLP-1 receptor agonist. Although GLP-1 receptor agonists have been shown to reduce alcohol intake in animal studies, their efficacy and safety in humans with AUD are not yet well established.
Back to Our Patient:
Given the patient’s weight regain, an upper gastrointestinal series was performed to rule out gastro-gastric fistula or other anatomic abnormalities. After fistula was ruled out, she was prescribed liraglutide for weight management, which was titrated from 0.6 mg/d to 3 mg/d per the prescribing guidelines.
With the use of liraglutide over the next year, the patient maintained a stable weight of 200 lb (90.9 kg) and noted that along with reduced appetite, her cravings for alcohol had diminished and she no longer felt the urge to drink alcohol at night. Her fasting glucose and GGT levels normalized. She began to see a nutritionist regularly and was planning to rejoin a bariatric support group.
Dr. Schmitz is an instructor in the Department of Medicine, Division of Endocrinology, Diabetes, and Metabolism, Weill Cornell Medicine, New York. She has disclosed no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Kashyap is a assistant chief of clinical affairs, Division of Endocrinology, Diabetes and Metabolism, Weill Cornell New York Presbyterian, New York. She disclosed ties to GI Dynamics.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Do Antipsychotic Overprescribing Warning Letters Work?
Warning letters to primary care physicians (PCPs) regarding overprescription of quetiapine were helpful in reducing overprescribing of this agent, new research suggested.
Investigators analyzed data from an earlier trial that compared prescribing patterns in 5055 PCPs who receive a placebo letter or three warning letters informing them that their prescribing of quetiapine was high and under review by Medicare. Patients in question all had dementia and were either living in nursing homes or in the community.
The intervention reduced quetiapine use among all patients with dementia, with no detectable adverse effects on cognitive function, behavioral symptoms, depression, metabolic diagnoses, hospitalization, or death.
“This study found that overprescribing warning letters to PCPs safely reduced quetiapine prescribing to their patients with dementia,” wrote investigators led by Adam Sacarny, PhD, of the Department of Health Policy and Management, Mailman School of Public Health, Columbia University, New York.
“This intervention and other[s] like it may be useful for future efforts to promote guideline-concordant care,” they added.
The study was published online in JAMA Network Open.
Off-Label Prescribing Common
The off-label use of antipsychotics in patients with dementia is fairly common, the investigators noted, affecting roughly one in seven nursing home residents and a similar number of community-dwelling older adults with dementia.
The agents are often prescribed to treat behavioral symptoms associated with dementia, including agitation and aggression. Although some evidence supports this use, antipsychotics in dementia patients can also cause an increased risk for weight gain, cognitive decline, falls and other injuries, cerebrovascular events, and mortality.
While some professional societies have called for “judicious use of antipsychotics in dementia care,” there is little evidence that reducing antipsychotic use in people with dementia might result in a benefit, investigators wrote.
The researchers analyzed data from a previous trial that focused on quetiapine, which is the most prescribed antipsychotic in the United States and is frequently used for patients with dementia.
In the original study, 2528 PCPs received a placebo letter and 2527 received three warning letters sent by the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS), which identified the highest-volume PCP prescribers of quetiapine.
The warning letters stated that the recipient’s quetiapine prescribing was high relative to their peers and was under review by Medicare. The placebo letter clarified an unrelated regulation.
The current secondary analysis followed the providers and a cohort of their patients from their first receipt of the letters in 2015 through April 2017. The current evaluation analyzes patients’ outcomes through December 2018, utilizing Medicare fee-for-service claims, Minimum Data Set nursing home assessment, and Medicare enrollment data.
Low-Cost, Effective Intervention
While the original study focused on total quetiapine prescribing by study PCPs, the current analysis focused on patients’ total quetiapine use per 90-day period. Additional secondary outcomes included measures of cognitive function and behavioral symptoms, indicators of depression, metabolic diagnoses, indicators of use of hospital and healthcare services, and death.
PCPs in the study had a total of 84,881 patients with dementia living in nursing homes and 261,288 living in the community. At baseline, there were 92,874 patients (mean age, 82 years; 69% female).
The warning letters were associated with reduced quetiapine use among both nursing home patients and community-dwelling patients (adjusted difference, –0.7 days; P = .02 and adjusted difference, −1.5 days; P < .001, respectively).
Among nursing home patients, there were no statistically significant adverse changes in cognitive of behavioral health measures that coincided with reduction in quetiapine use.
Although a higher percentage of treatment vs control patients reported weight loss, the difference was not significant, and rates of metabolic diagnoses were similar in both groups. There were also no significant differences between the groups in emergency department use, inpatient hospital admission, or use of restraints.
Results were similar for patients living in the community.
Additionally, no adverse effects on more severe health endpoints, including rates of hospital use or entry to nursing facilities, were detected. Importantly, the risk for death was statistically significantly lower for patients whose PCPs had received warning letters vs control patients (P = .04).
The analysis “provides evidence that a low-cost letter intervention informed by behavioral science can reduce prescribing of quetiapine to patients with dementia in nursing home and community settings,” the authors wrote.
Researchers did not directly observe the administration of the medication but instead used prescription drug fills as a proxy. Moreover, they could not observe results for patients enrolled in Medicare Advantage, and claims-based and assessment-based outcomes might have been subject to measurement errors and under-ascertainment of diagnoses.
The authors received support from the National Institute on Aging. They reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Warning letters to primary care physicians (PCPs) regarding overprescription of quetiapine were helpful in reducing overprescribing of this agent, new research suggested.
Investigators analyzed data from an earlier trial that compared prescribing patterns in 5055 PCPs who receive a placebo letter or three warning letters informing them that their prescribing of quetiapine was high and under review by Medicare. Patients in question all had dementia and were either living in nursing homes or in the community.
The intervention reduced quetiapine use among all patients with dementia, with no detectable adverse effects on cognitive function, behavioral symptoms, depression, metabolic diagnoses, hospitalization, or death.
“This study found that overprescribing warning letters to PCPs safely reduced quetiapine prescribing to their patients with dementia,” wrote investigators led by Adam Sacarny, PhD, of the Department of Health Policy and Management, Mailman School of Public Health, Columbia University, New York.
“This intervention and other[s] like it may be useful for future efforts to promote guideline-concordant care,” they added.
The study was published online in JAMA Network Open.
Off-Label Prescribing Common
The off-label use of antipsychotics in patients with dementia is fairly common, the investigators noted, affecting roughly one in seven nursing home residents and a similar number of community-dwelling older adults with dementia.
The agents are often prescribed to treat behavioral symptoms associated with dementia, including agitation and aggression. Although some evidence supports this use, antipsychotics in dementia patients can also cause an increased risk for weight gain, cognitive decline, falls and other injuries, cerebrovascular events, and mortality.
While some professional societies have called for “judicious use of antipsychotics in dementia care,” there is little evidence that reducing antipsychotic use in people with dementia might result in a benefit, investigators wrote.
The researchers analyzed data from a previous trial that focused on quetiapine, which is the most prescribed antipsychotic in the United States and is frequently used for patients with dementia.
In the original study, 2528 PCPs received a placebo letter and 2527 received three warning letters sent by the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS), which identified the highest-volume PCP prescribers of quetiapine.
The warning letters stated that the recipient’s quetiapine prescribing was high relative to their peers and was under review by Medicare. The placebo letter clarified an unrelated regulation.
The current secondary analysis followed the providers and a cohort of their patients from their first receipt of the letters in 2015 through April 2017. The current evaluation analyzes patients’ outcomes through December 2018, utilizing Medicare fee-for-service claims, Minimum Data Set nursing home assessment, and Medicare enrollment data.
Low-Cost, Effective Intervention
While the original study focused on total quetiapine prescribing by study PCPs, the current analysis focused on patients’ total quetiapine use per 90-day period. Additional secondary outcomes included measures of cognitive function and behavioral symptoms, indicators of depression, metabolic diagnoses, indicators of use of hospital and healthcare services, and death.
PCPs in the study had a total of 84,881 patients with dementia living in nursing homes and 261,288 living in the community. At baseline, there were 92,874 patients (mean age, 82 years; 69% female).
The warning letters were associated with reduced quetiapine use among both nursing home patients and community-dwelling patients (adjusted difference, –0.7 days; P = .02 and adjusted difference, −1.5 days; P < .001, respectively).
Among nursing home patients, there were no statistically significant adverse changes in cognitive of behavioral health measures that coincided with reduction in quetiapine use.
Although a higher percentage of treatment vs control patients reported weight loss, the difference was not significant, and rates of metabolic diagnoses were similar in both groups. There were also no significant differences between the groups in emergency department use, inpatient hospital admission, or use of restraints.
Results were similar for patients living in the community.
Additionally, no adverse effects on more severe health endpoints, including rates of hospital use or entry to nursing facilities, were detected. Importantly, the risk for death was statistically significantly lower for patients whose PCPs had received warning letters vs control patients (P = .04).
The analysis “provides evidence that a low-cost letter intervention informed by behavioral science can reduce prescribing of quetiapine to patients with dementia in nursing home and community settings,” the authors wrote.
Researchers did not directly observe the administration of the medication but instead used prescription drug fills as a proxy. Moreover, they could not observe results for patients enrolled in Medicare Advantage, and claims-based and assessment-based outcomes might have been subject to measurement errors and under-ascertainment of diagnoses.
The authors received support from the National Institute on Aging. They reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Warning letters to primary care physicians (PCPs) regarding overprescription of quetiapine were helpful in reducing overprescribing of this agent, new research suggested.
Investigators analyzed data from an earlier trial that compared prescribing patterns in 5055 PCPs who receive a placebo letter or three warning letters informing them that their prescribing of quetiapine was high and under review by Medicare. Patients in question all had dementia and were either living in nursing homes or in the community.
The intervention reduced quetiapine use among all patients with dementia, with no detectable adverse effects on cognitive function, behavioral symptoms, depression, metabolic diagnoses, hospitalization, or death.
“This study found that overprescribing warning letters to PCPs safely reduced quetiapine prescribing to their patients with dementia,” wrote investigators led by Adam Sacarny, PhD, of the Department of Health Policy and Management, Mailman School of Public Health, Columbia University, New York.
“This intervention and other[s] like it may be useful for future efforts to promote guideline-concordant care,” they added.
The study was published online in JAMA Network Open.
Off-Label Prescribing Common
The off-label use of antipsychotics in patients with dementia is fairly common, the investigators noted, affecting roughly one in seven nursing home residents and a similar number of community-dwelling older adults with dementia.
The agents are often prescribed to treat behavioral symptoms associated with dementia, including agitation and aggression. Although some evidence supports this use, antipsychotics in dementia patients can also cause an increased risk for weight gain, cognitive decline, falls and other injuries, cerebrovascular events, and mortality.
While some professional societies have called for “judicious use of antipsychotics in dementia care,” there is little evidence that reducing antipsychotic use in people with dementia might result in a benefit, investigators wrote.
The researchers analyzed data from a previous trial that focused on quetiapine, which is the most prescribed antipsychotic in the United States and is frequently used for patients with dementia.
In the original study, 2528 PCPs received a placebo letter and 2527 received three warning letters sent by the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS), which identified the highest-volume PCP prescribers of quetiapine.
The warning letters stated that the recipient’s quetiapine prescribing was high relative to their peers and was under review by Medicare. The placebo letter clarified an unrelated regulation.
The current secondary analysis followed the providers and a cohort of their patients from their first receipt of the letters in 2015 through April 2017. The current evaluation analyzes patients’ outcomes through December 2018, utilizing Medicare fee-for-service claims, Minimum Data Set nursing home assessment, and Medicare enrollment data.
Low-Cost, Effective Intervention
While the original study focused on total quetiapine prescribing by study PCPs, the current analysis focused on patients’ total quetiapine use per 90-day period. Additional secondary outcomes included measures of cognitive function and behavioral symptoms, indicators of depression, metabolic diagnoses, indicators of use of hospital and healthcare services, and death.
PCPs in the study had a total of 84,881 patients with dementia living in nursing homes and 261,288 living in the community. At baseline, there were 92,874 patients (mean age, 82 years; 69% female).
The warning letters were associated with reduced quetiapine use among both nursing home patients and community-dwelling patients (adjusted difference, –0.7 days; P = .02 and adjusted difference, −1.5 days; P < .001, respectively).
Among nursing home patients, there were no statistically significant adverse changes in cognitive of behavioral health measures that coincided with reduction in quetiapine use.
Although a higher percentage of treatment vs control patients reported weight loss, the difference was not significant, and rates of metabolic diagnoses were similar in both groups. There were also no significant differences between the groups in emergency department use, inpatient hospital admission, or use of restraints.
Results were similar for patients living in the community.
Additionally, no adverse effects on more severe health endpoints, including rates of hospital use or entry to nursing facilities, were detected. Importantly, the risk for death was statistically significantly lower for patients whose PCPs had received warning letters vs control patients (P = .04).
The analysis “provides evidence that a low-cost letter intervention informed by behavioral science can reduce prescribing of quetiapine to patients with dementia in nursing home and community settings,” the authors wrote.
Researchers did not directly observe the administration of the medication but instead used prescription drug fills as a proxy. Moreover, they could not observe results for patients enrolled in Medicare Advantage, and claims-based and assessment-based outcomes might have been subject to measurement errors and under-ascertainment of diagnoses.
The authors received support from the National Institute on Aging. They reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM JAMA NETWORK OPEN