User login
Local Anesthetics in Cosmetic Dermatology
Local anesthesia is a central component of successful interventions in cosmetic dermatology. The number of anesthetic medications and administration techniques has grown in recent years as outpatient cosmetic procedures continue to expand. Pain is a common barrier to cosmetic procedures, and alleviating the fear of painful interventions is critical to patient satisfaction and future visits. To accommodate a multitude of cosmetic interventions, it is important for clinicians to be well versed in applications of topical and regional anesthesia. In this article, we review pain management strategies for use in cosmetic practice.
Local Anesthetics
The sensation of pain is carried to the central nervous system by unmyelinated C nerve fibers. Local anesthetics (LAs) act by blocking fast voltage-gated sodium channels in the cell membrane of the nerve, thereby inhibiting downstream propagation of an action potential and the transmission of painful stimuli.1 The chemical structure of LAs is fundamental to their mechanism of action and metabolism. Local anesthetics contain a lipophilic aromatic group, an intermediate chain, and a hydrophilic amine group. Broadly, agents are classified as amides or esters depending on the chemical group attached to the intermediate chain.2 Amides (eg, lidocaine, bupivacaine, articaine, mepivacaine, prilocaine, levobupivacaine) are metabolized by the hepatic system; esters (eg, procaine, proparacaine, benzocaine, chlorprocaine, tetracaine, cocaine) are metabolized by plasma cholinesterase, which produces para-aminobenzoic acid, a potentially dangerous metabolite that has been implicated in allergic reactions.3
Lidocaine is the most prevalent LA used in dermatology practices. Importantly, lidocaine is a class IB antiarrhythmic agent used in cardiology to treat ventricular arrhythmias.4 As an anesthetic, a maximum dose of 4.5 mg/kg can be administered, increasing to 7.0 mg/kg when mixed with epinephrine; with higher doses, there is a risk for central nervous system and cardiovascular toxicity.5 Initial symptoms of lidocaine toxicity include dizziness, tinnitus, circumoral paresthesia, blurred vision, and a metallic taste in the mouth.6 Systemic absorption of topical anesthetics is heightened across mucosal membranes, and care should be taken when applying over large surface areas.
Allergic reactions to LAs may be local or less frequently systemic. It is important to note that LAs tend to show cross-reactivity within their class rather than across different classes.7 Reactions can be classified as type I or type IV. Type I (IgE-mediated) reactions evolve in minutes to hours, affecting the skin and possibly leading to respiratory and circulatory collapse. Delayed reactions to LAs have increased in recent years, with type IV contact allergy most frequently found in connection with benzocaine and lidocaine.8
Topical Anesthesia
Topical anesthetics are effective and easy to use and are particularly valuable in patients with needle phobia. In certain cases, these medications may be applied by the patient prior to arrival, thereby reducing visit time. Topical agents act on nerve fibers running through the dermis; therefore, efficacy is dependent on successful penetration through the stratum corneum and viable epidermis. To enhance absorption, agents may be applied under an occlusive dressing.
Topical anesthetics are most commonly used for injectable fillers, ablative and nonablative laser resurfacing, laser hair removal, and tattoo removal. The eutectic mixture of 2.5% lidocaine and 2.5% prilocaine as well as topical 4% or 5% lidocaine are the most commonly used US Food and Drug Administration–approved products for topical anesthesia. In addition, several compounded pharmacy products are available.
After 60 minutes of application of the eutectic mixture of 2.5% lidocaine and 2.5% prilocaine, a 3-mm depth of analgesia is reached, and after 120 minutes, a 4.5-mm depth is reached.9 It elicits a biphasic vascular response of vasoconstriction and blanching followed by vasodilation and erythema.10 Most adverse events are mild and transient, but allergic contact dermatitis and contact urticaria have been reported.11-13 In older children and adults, the maximum application area is 200 cm2, with a maximum dose of 20 g used for no longer than 4 hours.
The 4% or 5% lidocaine cream uses a liposomal delivery system, which is designed to improve cutaneous penetration and has been shown to provide longer durations of anesthesia than nonliposomal lidocaine preparations.14 Application should be performed 30 to 60 minutes prior to a procedure. In a study comparing the eutectic mixture of 2.5% lidocaine and 2.5% prilocaine versus lidocaine cream 5% for pain control during laser hair removal with a 1064-nm Nd:YAG laser, no significant differences were found.15 The maximum application area is 100 cm2 in children weighing less than 20 kg. A study of healthy adults demonstrated safety with the use of 30 to 60 g of occluded liposomal lidocaine cream 4%.16
In addition to US Food and Drug Administration–approved products, several compounded pharmacy products are available for topical anesthesia. These formulations include benzocaine-lidocaine-tetracaine gel, tetracaine-adrenaline-cocaine solution, and lidocaine-epinephrine-tetracaine solution. A triple-anesthetic gel, benzocaine-lidocaine-tetracaine is widely used in cosmetic practice. The product has been shown to provide adequate anesthesia for laser resurfacing after 20 minutes without occlusion.17 Of note, compounded anesthetics lack standardization, and different pharmacies may follow their own individual protocols.
Regional Anesthesia
Regional nerve blockade is a useful option for more widespread or complex interventions. Using regional nerve blockade, effective analgesia can be delivered to a target area while avoiding the toxicity and pain associated with numerous anesthetic infiltrations. In addition, there is no distortion of the tissue architecture, allowing for improved visual evaluation during the procedure. Recently, hyaluronic acid fillers have been compounded with lidocaine as a means of reducing procedural pain.
Blocks for Dermal Fillers
Forehead
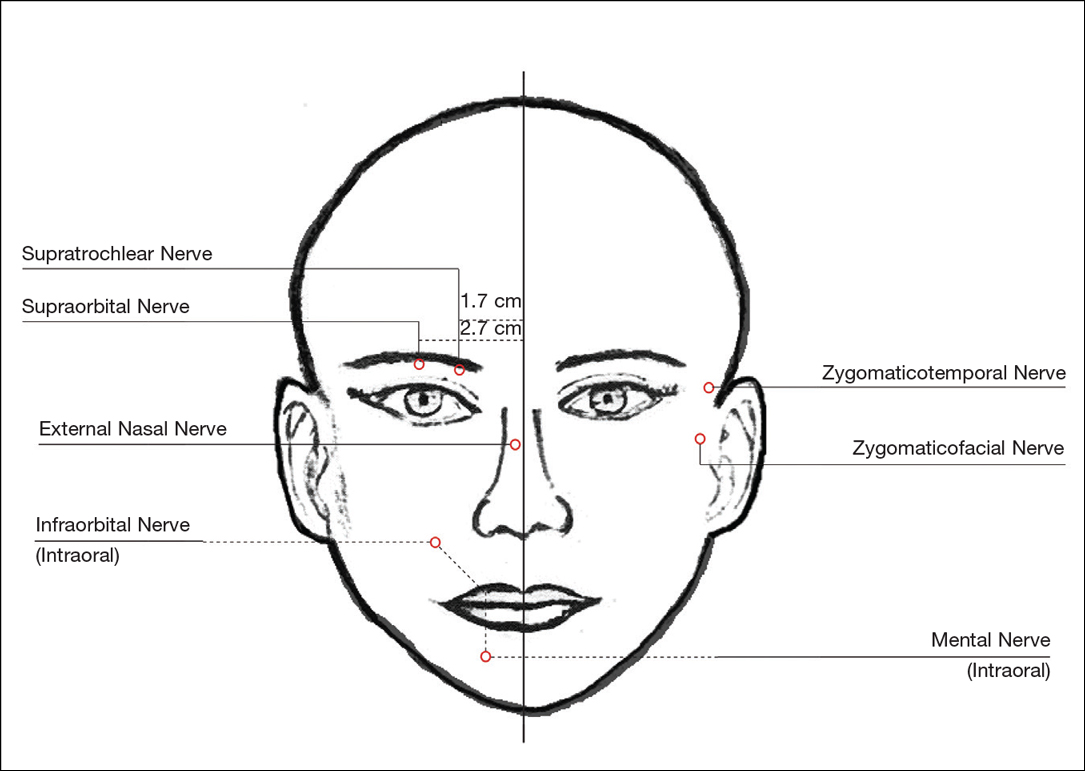
For dermal filler injections of the glabellar and frontalis lines, anesthesia of the forehead may be desired. The supraorbital and supratrochlear nerves supply this area. The supraorbital nerve can be injected at the supraorbital notch, which is measured roughly 2.7 cm from the glabella. The orbital rim should be palpated with the nondominant hand, and 1 to 2 mL of anesthetic should be injected just below the rim (Figure 1). The supratrochlear nerve is located roughly 1.7 cm from the midline and can be similarly injected under the orbital rim with 1 to 2 mL of anesthetic (Figure 1).
Lateral Temple Region
Anesthesia of the zygomaticotemporal nerve can be used to reduce pain from dermal filler injections of the lateral canthal and temporal areas. The nerve is identified by first palpating the zygomaticofrontal suture. A long needle is then inserted posteriorly, immediately behind the concave surface of the lateral orbital rim, and 1 to 2 mL of anesthetic is injected (Figure 1).
Malar Region
Blockade of the zygomaticofacial nerve is commonly performed in conjunction with the zygomaticotemporal nerve and provides anesthesia to the malar region for cheek augmentation procedures. To identify the target area, the junction of the lateral and inferior orbital rim should be palpated. With the needle placed just lateral to this point, 1 to 2 mL of anesthetic is injected (Figure 1).
Blocks for Perioral Fillers
Upper Lips/Nasolabial Folds
Bilateral blockade of the infraorbital nerves provides anesthesia to the upper lip and nasolabial folds prior to filler injections. The infraorbital nerve can be targeted via an intraoral route where it exits the maxilla at the infraorbital foramen. The nerve is anesthetized by palpating the infraorbital ridge and injecting 3 to 5 mL of anesthetic roughly 1 cm below this point on the vertical axis of the midpupillary line (Figure 1). The external nasal nerve, thought to be a branch of cranial nerve V, also may be targeted if there is inadequate anesthesia from the infraorbital block. This nerve is reached by injecting at the osseocartilaginous junction of the nasal bones (Figure 1).
Lower Lips
Blockade of the mental nerve provides anesthesia to the lower lips for augmentation procedures. The mental nerve can be targeted on each side at the mental foramen, which is located below the root of the lower second premolar. Aiming roughly 1 cm below the gumline, 3 to 5 mL of anesthetic is injected intraorally (Figure 1). A transcutaneous approach toward the same target also is possible, though this technique risks visible bruising. Alternatively, the upper or lower lips can be anesthetized using 4 to 5 submucosal injections at evenly spaced intervals between the canine teeth.18
Blocks for Palmoplantar Hyperhidrosis
The treatment of palmoplantar hyperhidrosis benefits from regional blocks. Botulinum toxin has been well established as an effective therapy for the condition.19-21 Given the sensitivity of palmoplantar sites, it is valuable to achieve effective analgesia of the region prior to dermal injections of botulinum toxin.
Wrists
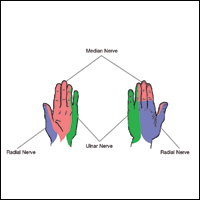
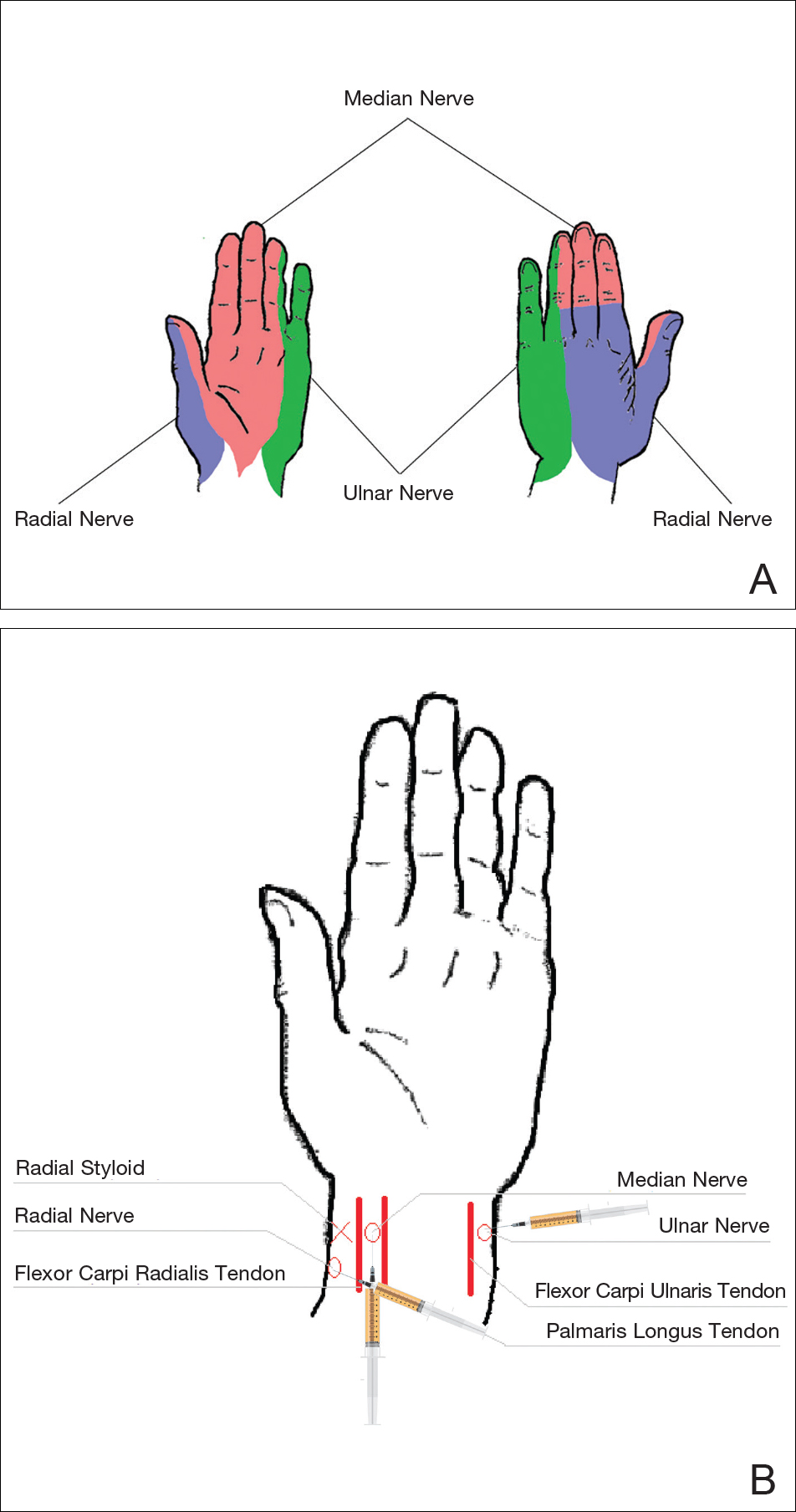
Sensory innervation of the palm is provided by the median, ulnar, and radial nerves (Figure 2A).
The ulnar nerve is anesthetized between the ulnar artery and the flexor carpi ulnaris muscle. The artery is identified by palpation, and special care should be taken to avoid intra-arterial injection. The needle is directed toward the radial styloid, and 3 to 5 mL of anesthetic is injected roughly 1 cm proximal to the wrist crease (Figure 2B).
Anesthesia of the radial nerve can be considered a field block given the numerous small branches that supply the hand. These branches are reached by injecting anesthetic roughly 2 to 3 cm proximal to the radial styloid with the needle aimed medially and extending the injection dorsally (Figure 2B). A total of 4 to 6 mL of anesthetic is used.
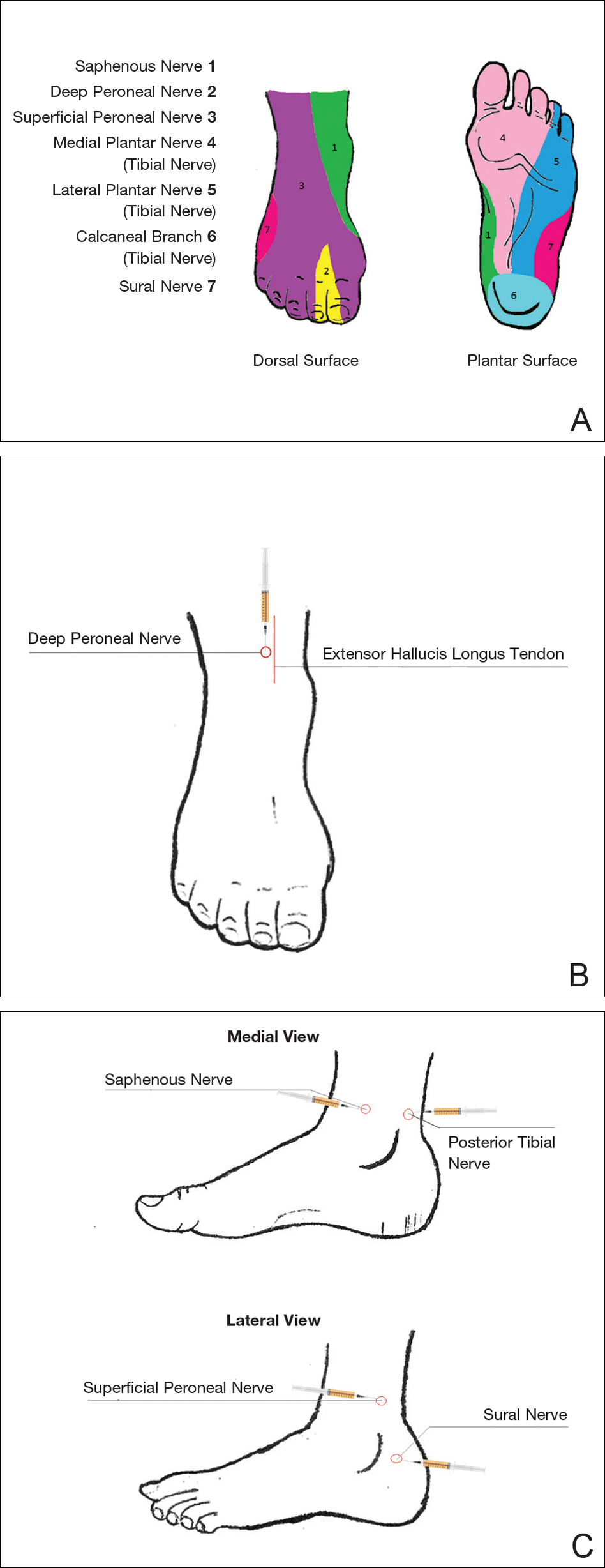
Ankles
An ankle block provides anesthesia to the dorsal and plantar surfaces of the foot.22 The region is supplied by the superficial peroneal nerve, deep peroneal nerve, sural nerve, saphenous nerve, and branches of the posterior tibial nerve (Figure 3A).
To anesthetize the deep peroneal nerve, the extensor hallucis longus tendon is first identified on the anterior surface of the ankle through dorsiflexion of the toes; the dorsalis pedis artery runs in close proximity. The injection should be placed lateral to the tendon and artery (Figure 3B). The needle should be inserted until bone is reached, withdrawn slightly, and then 3 to 5 mL of anesthetic should be injected. To block the saphenous nerve, the needle can then be directed superficially toward the medial malleolus, and 3 to 5 mL should be injected in a subcutaneous wheal (Figure 3C). To block the superficial peroneal nerve, the needle should then be directed toward the lateral malleolus, and 3 to 5 mL should be injected in a subcutaneous wheal (Figure 3C).
The posterior tibial nerve is located posterior to the medial malleolus. The dorsalis pedis artery can be palpated near this location. The needle should be inserted posterior to the artery, extending until bone is reached (Figure 3C). The needle is then withdrawn slightly, and 3 to 5 mL of anesthetic is injected. Finally, the sural nerve is anesthetized between the Achilles tendon and the lateral malleolus, using 5 mL of anesthetic to raise a subcutaneous wheal (Figure 3C).
Conclusion
Proper pain management is integral to ensuring a positive experience for cosmetic patients. Enhanced knowledge of local anesthetic techniques allows the clinician to provide for a variety of procedural indications and patient preferences. As anesthetic strategies are continually evolving, it is important for practitioners to remain informed of these developments.
- Scholz A. Mechanisms of (local) anaesthetics on voltage-gated sodium and other ion channels. Br J Anaesth. 2002;89:52-61.
- Auletta MJ. Local anesthesia for dermatologic surgery. Semin Dermatol. 1994;13:35-42.
- Park KK, Sharon VR. A review of local anesthetics: minimizing risk and side effects in cutaneous surgery. Dermatol Surg. 2017;43:173-187.
- Reiz S, Nath S. Cardiotoxicity of local anaesthetic agents. Br J Anaesth. 1986;58:736-746.
- Klein JA, Kassarjdian N. Lidocaine toxicity with tumescent liposuction. a case report of probable drug interactions. Dermatol Surg. 1997;23:1169-1174.
- Minkis K, Whittington A, Alam M. Dermatologic surgery emergencies: complications caused by systemic reactions, high-energy systems, and trauma. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2016;75:265-284.
- Morais-Almeida M, Gaspar A, Marinho S, et al. Allergy to local anesthetics of the amide group with tolerance to procaine. Allergy. 2003;58:827-828.
- To D, Kossintseva I, de Gannes G. Lidocaine contact allergy is becoming more prevalent. Dermatol Surg. 2014;40:1367-1372.
- Wahlgren CF, Quiding H. Depth of cutaneous analgesia after application of a eutectic mixture of the local anesthetics lidocaine and prilocaine (EMLA cream). J Am Acad Dermatol. 2000;42:584-588.
- Bjerring P, Andersen PH, Arendt-Nielsen L. Vascular response of human skin after analgesia with EMLA cream. Br J Anaesth. 1989;63:655-660.
- Ismail F, Goldsmith PC. EMLA cream-induced allergic contact dermatitis in a child with thalassaemia major. Contact Dermatitis. 2005;52:111.
- Thakur BK, Murali MR. EMLA cream-induced allergic contact dermatitis: a role for prilocaine as an immunogen. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1995;95:776-778.
- Waton J, Boulanger A, Trechot PH, et al. Contact urticaria from EMLA cream. Contact Dermatitis. 2004;51:284-287.
- Bucalo BD, Mirikitani EJ, Moy RL. Comparison of skin anesthetic effect of liposomal lidocaine, nonliposomal lidocaine, and EMLA using 30-minute application time. Dermatol Surg. 1998;24:537-541.
- Guardiano RA, Norwood CW. Direct comparison of EMLA versus lidocaine for pain control in Nd:YAG 1,064 nm laser hair removal. Dermatol Surg. 2005;31:396-398.
- Nestor MS. Safety of occluded 4% liposomal lidocaine cream. J Drugs Dermatol. 2006;5:618-620.
- Oni G, Rasko Y, Kenkel J. Topical lidocaine enhanced by laser pretreatment: a safe and effective method of analgesia for facial rejuvenation. Aesthet Surg J. 2013;33:854-861.
- Niamtu J 3rd. Simple technique for lip and nasolabial fold anesthesia for injectable fillers. Dermatol Surg. 2005;31:1330-1332.
- Naumann M, Flachenecker P, Brocker EB, et al. Botulinum toxin for palmar hyperhidrosis. Lancet. 1997;349:252.
- Naumann M, Hofmann U, Bergmann I, et al. Focal hyperhidrosis: effective treatment with intracutaneous botulinum toxin. Arch Dermatol. 1998;134:301-304.
- Shelley WB, Talanin NY, Shelley ED. Botulinum toxin therapy for palmar hyperhidrosis. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1998;38(2, pt 1):227-229.
- Davies T, Karanovic S, Shergill B. Essential regional nerve blocks for the dermatologist: part 2. Clin Exp Dermatol. 2014;39:861-867.
Local anesthesia is a central component of successful interventions in cosmetic dermatology. The number of anesthetic medications and administration techniques has grown in recent years as outpatient cosmetic procedures continue to expand. Pain is a common barrier to cosmetic procedures, and alleviating the fear of painful interventions is critical to patient satisfaction and future visits. To accommodate a multitude of cosmetic interventions, it is important for clinicians to be well versed in applications of topical and regional anesthesia. In this article, we review pain management strategies for use in cosmetic practice.
Local Anesthetics
The sensation of pain is carried to the central nervous system by unmyelinated C nerve fibers. Local anesthetics (LAs) act by blocking fast voltage-gated sodium channels in the cell membrane of the nerve, thereby inhibiting downstream propagation of an action potential and the transmission of painful stimuli.1 The chemical structure of LAs is fundamental to their mechanism of action and metabolism. Local anesthetics contain a lipophilic aromatic group, an intermediate chain, and a hydrophilic amine group. Broadly, agents are classified as amides or esters depending on the chemical group attached to the intermediate chain.2 Amides (eg, lidocaine, bupivacaine, articaine, mepivacaine, prilocaine, levobupivacaine) are metabolized by the hepatic system; esters (eg, procaine, proparacaine, benzocaine, chlorprocaine, tetracaine, cocaine) are metabolized by plasma cholinesterase, which produces para-aminobenzoic acid, a potentially dangerous metabolite that has been implicated in allergic reactions.3
Lidocaine is the most prevalent LA used in dermatology practices. Importantly, lidocaine is a class IB antiarrhythmic agent used in cardiology to treat ventricular arrhythmias.4 As an anesthetic, a maximum dose of 4.5 mg/kg can be administered, increasing to 7.0 mg/kg when mixed with epinephrine; with higher doses, there is a risk for central nervous system and cardiovascular toxicity.5 Initial symptoms of lidocaine toxicity include dizziness, tinnitus, circumoral paresthesia, blurred vision, and a metallic taste in the mouth.6 Systemic absorption of topical anesthetics is heightened across mucosal membranes, and care should be taken when applying over large surface areas.
Allergic reactions to LAs may be local or less frequently systemic. It is important to note that LAs tend to show cross-reactivity within their class rather than across different classes.7 Reactions can be classified as type I or type IV. Type I (IgE-mediated) reactions evolve in minutes to hours, affecting the skin and possibly leading to respiratory and circulatory collapse. Delayed reactions to LAs have increased in recent years, with type IV contact allergy most frequently found in connection with benzocaine and lidocaine.8
Topical Anesthesia
Topical anesthetics are effective and easy to use and are particularly valuable in patients with needle phobia. In certain cases, these medications may be applied by the patient prior to arrival, thereby reducing visit time. Topical agents act on nerve fibers running through the dermis; therefore, efficacy is dependent on successful penetration through the stratum corneum and viable epidermis. To enhance absorption, agents may be applied under an occlusive dressing.
Topical anesthetics are most commonly used for injectable fillers, ablative and nonablative laser resurfacing, laser hair removal, and tattoo removal. The eutectic mixture of 2.5% lidocaine and 2.5% prilocaine as well as topical 4% or 5% lidocaine are the most commonly used US Food and Drug Administration–approved products for topical anesthesia. In addition, several compounded pharmacy products are available.
After 60 minutes of application of the eutectic mixture of 2.5% lidocaine and 2.5% prilocaine, a 3-mm depth of analgesia is reached, and after 120 minutes, a 4.5-mm depth is reached.9 It elicits a biphasic vascular response of vasoconstriction and blanching followed by vasodilation and erythema.10 Most adverse events are mild and transient, but allergic contact dermatitis and contact urticaria have been reported.11-13 In older children and adults, the maximum application area is 200 cm2, with a maximum dose of 20 g used for no longer than 4 hours.
The 4% or 5% lidocaine cream uses a liposomal delivery system, which is designed to improve cutaneous penetration and has been shown to provide longer durations of anesthesia than nonliposomal lidocaine preparations.14 Application should be performed 30 to 60 minutes prior to a procedure. In a study comparing the eutectic mixture of 2.5% lidocaine and 2.5% prilocaine versus lidocaine cream 5% for pain control during laser hair removal with a 1064-nm Nd:YAG laser, no significant differences were found.15 The maximum application area is 100 cm2 in children weighing less than 20 kg. A study of healthy adults demonstrated safety with the use of 30 to 60 g of occluded liposomal lidocaine cream 4%.16
In addition to US Food and Drug Administration–approved products, several compounded pharmacy products are available for topical anesthesia. These formulations include benzocaine-lidocaine-tetracaine gel, tetracaine-adrenaline-cocaine solution, and lidocaine-epinephrine-tetracaine solution. A triple-anesthetic gel, benzocaine-lidocaine-tetracaine is widely used in cosmetic practice. The product has been shown to provide adequate anesthesia for laser resurfacing after 20 minutes without occlusion.17 Of note, compounded anesthetics lack standardization, and different pharmacies may follow their own individual protocols.
Regional Anesthesia
Regional nerve blockade is a useful option for more widespread or complex interventions. Using regional nerve blockade, effective analgesia can be delivered to a target area while avoiding the toxicity and pain associated with numerous anesthetic infiltrations. In addition, there is no distortion of the tissue architecture, allowing for improved visual evaluation during the procedure. Recently, hyaluronic acid fillers have been compounded with lidocaine as a means of reducing procedural pain.
Blocks for Dermal Fillers
Forehead
For dermal filler injections of the glabellar and frontalis lines, anesthesia of the forehead may be desired. The supraorbital and supratrochlear nerves supply this area. The supraorbital nerve can be injected at the supraorbital notch, which is measured roughly 2.7 cm from the glabella. The orbital rim should be palpated with the nondominant hand, and 1 to 2 mL of anesthetic should be injected just below the rim (Figure 1). The supratrochlear nerve is located roughly 1.7 cm from the midline and can be similarly injected under the orbital rim with 1 to 2 mL of anesthetic (Figure 1).
Lateral Temple Region
Anesthesia of the zygomaticotemporal nerve can be used to reduce pain from dermal filler injections of the lateral canthal and temporal areas. The nerve is identified by first palpating the zygomaticofrontal suture. A long needle is then inserted posteriorly, immediately behind the concave surface of the lateral orbital rim, and 1 to 2 mL of anesthetic is injected (Figure 1).
Malar Region
Blockade of the zygomaticofacial nerve is commonly performed in conjunction with the zygomaticotemporal nerve and provides anesthesia to the malar region for cheek augmentation procedures. To identify the target area, the junction of the lateral and inferior orbital rim should be palpated. With the needle placed just lateral to this point, 1 to 2 mL of anesthetic is injected (Figure 1).

Blocks for Perioral Fillers
Upper Lips/Nasolabial Folds
Bilateral blockade of the infraorbital nerves provides anesthesia to the upper lip and nasolabial folds prior to filler injections. The infraorbital nerve can be targeted via an intraoral route where it exits the maxilla at the infraorbital foramen. The nerve is anesthetized by palpating the infraorbital ridge and injecting 3 to 5 mL of anesthetic roughly 1 cm below this point on the vertical axis of the midpupillary line (Figure 1). The external nasal nerve, thought to be a branch of cranial nerve V, also may be targeted if there is inadequate anesthesia from the infraorbital block. This nerve is reached by injecting at the osseocartilaginous junction of the nasal bones (Figure 1).
Lower Lips
Blockade of the mental nerve provides anesthesia to the lower lips for augmentation procedures. The mental nerve can be targeted on each side at the mental foramen, which is located below the root of the lower second premolar. Aiming roughly 1 cm below the gumline, 3 to 5 mL of anesthetic is injected intraorally (Figure 1). A transcutaneous approach toward the same target also is possible, though this technique risks visible bruising. Alternatively, the upper or lower lips can be anesthetized using 4 to 5 submucosal injections at evenly spaced intervals between the canine teeth.18
Blocks for Palmoplantar Hyperhidrosis
The treatment of palmoplantar hyperhidrosis benefits from regional blocks. Botulinum toxin has been well established as an effective therapy for the condition.19-21 Given the sensitivity of palmoplantar sites, it is valuable to achieve effective analgesia of the region prior to dermal injections of botulinum toxin.
Wrists
Sensory innervation of the palm is provided by the median, ulnar, and radial nerves (Figure 2A).
The ulnar nerve is anesthetized between the ulnar artery and the flexor carpi ulnaris muscle. The artery is identified by palpation, and special care should be taken to avoid intra-arterial injection. The needle is directed toward the radial styloid, and 3 to 5 mL of anesthetic is injected roughly 1 cm proximal to the wrist crease (Figure 2B).
Anesthesia of the radial nerve can be considered a field block given the numerous small branches that supply the hand. These branches are reached by injecting anesthetic roughly 2 to 3 cm proximal to the radial styloid with the needle aimed medially and extending the injection dorsally (Figure 2B). A total of 4 to 6 mL of anesthetic is used.

Ankles
An ankle block provides anesthesia to the dorsal and plantar surfaces of the foot.22 The region is supplied by the superficial peroneal nerve, deep peroneal nerve, sural nerve, saphenous nerve, and branches of the posterior tibial nerve (Figure 3A).
To anesthetize the deep peroneal nerve, the extensor hallucis longus tendon is first identified on the anterior surface of the ankle through dorsiflexion of the toes; the dorsalis pedis artery runs in close proximity. The injection should be placed lateral to the tendon and artery (Figure 3B). The needle should be inserted until bone is reached, withdrawn slightly, and then 3 to 5 mL of anesthetic should be injected. To block the saphenous nerve, the needle can then be directed superficially toward the medial malleolus, and 3 to 5 mL should be injected in a subcutaneous wheal (Figure 3C). To block the superficial peroneal nerve, the needle should then be directed toward the lateral malleolus, and 3 to 5 mL should be injected in a subcutaneous wheal (Figure 3C).
The posterior tibial nerve is located posterior to the medial malleolus. The dorsalis pedis artery can be palpated near this location. The needle should be inserted posterior to the artery, extending until bone is reached (Figure 3C). The needle is then withdrawn slightly, and 3 to 5 mL of anesthetic is injected. Finally, the sural nerve is anesthetized between the Achilles tendon and the lateral malleolus, using 5 mL of anesthetic to raise a subcutaneous wheal (Figure 3C).

Conclusion
Proper pain management is integral to ensuring a positive experience for cosmetic patients. Enhanced knowledge of local anesthetic techniques allows the clinician to provide for a variety of procedural indications and patient preferences. As anesthetic strategies are continually evolving, it is important for practitioners to remain informed of these developments.
Local anesthesia is a central component of successful interventions in cosmetic dermatology. The number of anesthetic medications and administration techniques has grown in recent years as outpatient cosmetic procedures continue to expand. Pain is a common barrier to cosmetic procedures, and alleviating the fear of painful interventions is critical to patient satisfaction and future visits. To accommodate a multitude of cosmetic interventions, it is important for clinicians to be well versed in applications of topical and regional anesthesia. In this article, we review pain management strategies for use in cosmetic practice.
Local Anesthetics
The sensation of pain is carried to the central nervous system by unmyelinated C nerve fibers. Local anesthetics (LAs) act by blocking fast voltage-gated sodium channels in the cell membrane of the nerve, thereby inhibiting downstream propagation of an action potential and the transmission of painful stimuli.1 The chemical structure of LAs is fundamental to their mechanism of action and metabolism. Local anesthetics contain a lipophilic aromatic group, an intermediate chain, and a hydrophilic amine group. Broadly, agents are classified as amides or esters depending on the chemical group attached to the intermediate chain.2 Amides (eg, lidocaine, bupivacaine, articaine, mepivacaine, prilocaine, levobupivacaine) are metabolized by the hepatic system; esters (eg, procaine, proparacaine, benzocaine, chlorprocaine, tetracaine, cocaine) are metabolized by plasma cholinesterase, which produces para-aminobenzoic acid, a potentially dangerous metabolite that has been implicated in allergic reactions.3
Lidocaine is the most prevalent LA used in dermatology practices. Importantly, lidocaine is a class IB antiarrhythmic agent used in cardiology to treat ventricular arrhythmias.4 As an anesthetic, a maximum dose of 4.5 mg/kg can be administered, increasing to 7.0 mg/kg when mixed with epinephrine; with higher doses, there is a risk for central nervous system and cardiovascular toxicity.5 Initial symptoms of lidocaine toxicity include dizziness, tinnitus, circumoral paresthesia, blurred vision, and a metallic taste in the mouth.6 Systemic absorption of topical anesthetics is heightened across mucosal membranes, and care should be taken when applying over large surface areas.
Allergic reactions to LAs may be local or less frequently systemic. It is important to note that LAs tend to show cross-reactivity within their class rather than across different classes.7 Reactions can be classified as type I or type IV. Type I (IgE-mediated) reactions evolve in minutes to hours, affecting the skin and possibly leading to respiratory and circulatory collapse. Delayed reactions to LAs have increased in recent years, with type IV contact allergy most frequently found in connection with benzocaine and lidocaine.8
Topical Anesthesia
Topical anesthetics are effective and easy to use and are particularly valuable in patients with needle phobia. In certain cases, these medications may be applied by the patient prior to arrival, thereby reducing visit time. Topical agents act on nerve fibers running through the dermis; therefore, efficacy is dependent on successful penetration through the stratum corneum and viable epidermis. To enhance absorption, agents may be applied under an occlusive dressing.
Topical anesthetics are most commonly used for injectable fillers, ablative and nonablative laser resurfacing, laser hair removal, and tattoo removal. The eutectic mixture of 2.5% lidocaine and 2.5% prilocaine as well as topical 4% or 5% lidocaine are the most commonly used US Food and Drug Administration–approved products for topical anesthesia. In addition, several compounded pharmacy products are available.
After 60 minutes of application of the eutectic mixture of 2.5% lidocaine and 2.5% prilocaine, a 3-mm depth of analgesia is reached, and after 120 minutes, a 4.5-mm depth is reached.9 It elicits a biphasic vascular response of vasoconstriction and blanching followed by vasodilation and erythema.10 Most adverse events are mild and transient, but allergic contact dermatitis and contact urticaria have been reported.11-13 In older children and adults, the maximum application area is 200 cm2, with a maximum dose of 20 g used for no longer than 4 hours.
The 4% or 5% lidocaine cream uses a liposomal delivery system, which is designed to improve cutaneous penetration and has been shown to provide longer durations of anesthesia than nonliposomal lidocaine preparations.14 Application should be performed 30 to 60 minutes prior to a procedure. In a study comparing the eutectic mixture of 2.5% lidocaine and 2.5% prilocaine versus lidocaine cream 5% for pain control during laser hair removal with a 1064-nm Nd:YAG laser, no significant differences were found.15 The maximum application area is 100 cm2 in children weighing less than 20 kg. A study of healthy adults demonstrated safety with the use of 30 to 60 g of occluded liposomal lidocaine cream 4%.16
In addition to US Food and Drug Administration–approved products, several compounded pharmacy products are available for topical anesthesia. These formulations include benzocaine-lidocaine-tetracaine gel, tetracaine-adrenaline-cocaine solution, and lidocaine-epinephrine-tetracaine solution. A triple-anesthetic gel, benzocaine-lidocaine-tetracaine is widely used in cosmetic practice. The product has been shown to provide adequate anesthesia for laser resurfacing after 20 minutes without occlusion.17 Of note, compounded anesthetics lack standardization, and different pharmacies may follow their own individual protocols.
Regional Anesthesia
Regional nerve blockade is a useful option for more widespread or complex interventions. Using regional nerve blockade, effective analgesia can be delivered to a target area while avoiding the toxicity and pain associated with numerous anesthetic infiltrations. In addition, there is no distortion of the tissue architecture, allowing for improved visual evaluation during the procedure. Recently, hyaluronic acid fillers have been compounded with lidocaine as a means of reducing procedural pain.
Blocks for Dermal Fillers
Forehead
For dermal filler injections of the glabellar and frontalis lines, anesthesia of the forehead may be desired. The supraorbital and supratrochlear nerves supply this area. The supraorbital nerve can be injected at the supraorbital notch, which is measured roughly 2.7 cm from the glabella. The orbital rim should be palpated with the nondominant hand, and 1 to 2 mL of anesthetic should be injected just below the rim (Figure 1). The supratrochlear nerve is located roughly 1.7 cm from the midline and can be similarly injected under the orbital rim with 1 to 2 mL of anesthetic (Figure 1).
Lateral Temple Region
Anesthesia of the zygomaticotemporal nerve can be used to reduce pain from dermal filler injections of the lateral canthal and temporal areas. The nerve is identified by first palpating the zygomaticofrontal suture. A long needle is then inserted posteriorly, immediately behind the concave surface of the lateral orbital rim, and 1 to 2 mL of anesthetic is injected (Figure 1).
Malar Region
Blockade of the zygomaticofacial nerve is commonly performed in conjunction with the zygomaticotemporal nerve and provides anesthesia to the malar region for cheek augmentation procedures. To identify the target area, the junction of the lateral and inferior orbital rim should be palpated. With the needle placed just lateral to this point, 1 to 2 mL of anesthetic is injected (Figure 1).

Blocks for Perioral Fillers
Upper Lips/Nasolabial Folds
Bilateral blockade of the infraorbital nerves provides anesthesia to the upper lip and nasolabial folds prior to filler injections. The infraorbital nerve can be targeted via an intraoral route where it exits the maxilla at the infraorbital foramen. The nerve is anesthetized by palpating the infraorbital ridge and injecting 3 to 5 mL of anesthetic roughly 1 cm below this point on the vertical axis of the midpupillary line (Figure 1). The external nasal nerve, thought to be a branch of cranial nerve V, also may be targeted if there is inadequate anesthesia from the infraorbital block. This nerve is reached by injecting at the osseocartilaginous junction of the nasal bones (Figure 1).
Lower Lips
Blockade of the mental nerve provides anesthesia to the lower lips for augmentation procedures. The mental nerve can be targeted on each side at the mental foramen, which is located below the root of the lower second premolar. Aiming roughly 1 cm below the gumline, 3 to 5 mL of anesthetic is injected intraorally (Figure 1). A transcutaneous approach toward the same target also is possible, though this technique risks visible bruising. Alternatively, the upper or lower lips can be anesthetized using 4 to 5 submucosal injections at evenly spaced intervals between the canine teeth.18
Blocks for Palmoplantar Hyperhidrosis
The treatment of palmoplantar hyperhidrosis benefits from regional blocks. Botulinum toxin has been well established as an effective therapy for the condition.19-21 Given the sensitivity of palmoplantar sites, it is valuable to achieve effective analgesia of the region prior to dermal injections of botulinum toxin.
Wrists
Sensory innervation of the palm is provided by the median, ulnar, and radial nerves (Figure 2A).
The ulnar nerve is anesthetized between the ulnar artery and the flexor carpi ulnaris muscle. The artery is identified by palpation, and special care should be taken to avoid intra-arterial injection. The needle is directed toward the radial styloid, and 3 to 5 mL of anesthetic is injected roughly 1 cm proximal to the wrist crease (Figure 2B).
Anesthesia of the radial nerve can be considered a field block given the numerous small branches that supply the hand. These branches are reached by injecting anesthetic roughly 2 to 3 cm proximal to the radial styloid with the needle aimed medially and extending the injection dorsally (Figure 2B). A total of 4 to 6 mL of anesthetic is used.

Ankles
An ankle block provides anesthesia to the dorsal and plantar surfaces of the foot.22 The region is supplied by the superficial peroneal nerve, deep peroneal nerve, sural nerve, saphenous nerve, and branches of the posterior tibial nerve (Figure 3A).
To anesthetize the deep peroneal nerve, the extensor hallucis longus tendon is first identified on the anterior surface of the ankle through dorsiflexion of the toes; the dorsalis pedis artery runs in close proximity. The injection should be placed lateral to the tendon and artery (Figure 3B). The needle should be inserted until bone is reached, withdrawn slightly, and then 3 to 5 mL of anesthetic should be injected. To block the saphenous nerve, the needle can then be directed superficially toward the medial malleolus, and 3 to 5 mL should be injected in a subcutaneous wheal (Figure 3C). To block the superficial peroneal nerve, the needle should then be directed toward the lateral malleolus, and 3 to 5 mL should be injected in a subcutaneous wheal (Figure 3C).
The posterior tibial nerve is located posterior to the medial malleolus. The dorsalis pedis artery can be palpated near this location. The needle should be inserted posterior to the artery, extending until bone is reached (Figure 3C). The needle is then withdrawn slightly, and 3 to 5 mL of anesthetic is injected. Finally, the sural nerve is anesthetized between the Achilles tendon and the lateral malleolus, using 5 mL of anesthetic to raise a subcutaneous wheal (Figure 3C).

Conclusion
Proper pain management is integral to ensuring a positive experience for cosmetic patients. Enhanced knowledge of local anesthetic techniques allows the clinician to provide for a variety of procedural indications and patient preferences. As anesthetic strategies are continually evolving, it is important for practitioners to remain informed of these developments.
- Scholz A. Mechanisms of (local) anaesthetics on voltage-gated sodium and other ion channels. Br J Anaesth. 2002;89:52-61.
- Auletta MJ. Local anesthesia for dermatologic surgery. Semin Dermatol. 1994;13:35-42.
- Park KK, Sharon VR. A review of local anesthetics: minimizing risk and side effects in cutaneous surgery. Dermatol Surg. 2017;43:173-187.
- Reiz S, Nath S. Cardiotoxicity of local anaesthetic agents. Br J Anaesth. 1986;58:736-746.
- Klein JA, Kassarjdian N. Lidocaine toxicity with tumescent liposuction. a case report of probable drug interactions. Dermatol Surg. 1997;23:1169-1174.
- Minkis K, Whittington A, Alam M. Dermatologic surgery emergencies: complications caused by systemic reactions, high-energy systems, and trauma. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2016;75:265-284.
- Morais-Almeida M, Gaspar A, Marinho S, et al. Allergy to local anesthetics of the amide group with tolerance to procaine. Allergy. 2003;58:827-828.
- To D, Kossintseva I, de Gannes G. Lidocaine contact allergy is becoming more prevalent. Dermatol Surg. 2014;40:1367-1372.
- Wahlgren CF, Quiding H. Depth of cutaneous analgesia after application of a eutectic mixture of the local anesthetics lidocaine and prilocaine (EMLA cream). J Am Acad Dermatol. 2000;42:584-588.
- Bjerring P, Andersen PH, Arendt-Nielsen L. Vascular response of human skin after analgesia with EMLA cream. Br J Anaesth. 1989;63:655-660.
- Ismail F, Goldsmith PC. EMLA cream-induced allergic contact dermatitis in a child with thalassaemia major. Contact Dermatitis. 2005;52:111.
- Thakur BK, Murali MR. EMLA cream-induced allergic contact dermatitis: a role for prilocaine as an immunogen. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1995;95:776-778.
- Waton J, Boulanger A, Trechot PH, et al. Contact urticaria from EMLA cream. Contact Dermatitis. 2004;51:284-287.
- Bucalo BD, Mirikitani EJ, Moy RL. Comparison of skin anesthetic effect of liposomal lidocaine, nonliposomal lidocaine, and EMLA using 30-minute application time. Dermatol Surg. 1998;24:537-541.
- Guardiano RA, Norwood CW. Direct comparison of EMLA versus lidocaine for pain control in Nd:YAG 1,064 nm laser hair removal. Dermatol Surg. 2005;31:396-398.
- Nestor MS. Safety of occluded 4% liposomal lidocaine cream. J Drugs Dermatol. 2006;5:618-620.
- Oni G, Rasko Y, Kenkel J. Topical lidocaine enhanced by laser pretreatment: a safe and effective method of analgesia for facial rejuvenation. Aesthet Surg J. 2013;33:854-861.
- Niamtu J 3rd. Simple technique for lip and nasolabial fold anesthesia for injectable fillers. Dermatol Surg. 2005;31:1330-1332.
- Naumann M, Flachenecker P, Brocker EB, et al. Botulinum toxin for palmar hyperhidrosis. Lancet. 1997;349:252.
- Naumann M, Hofmann U, Bergmann I, et al. Focal hyperhidrosis: effective treatment with intracutaneous botulinum toxin. Arch Dermatol. 1998;134:301-304.
- Shelley WB, Talanin NY, Shelley ED. Botulinum toxin therapy for palmar hyperhidrosis. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1998;38(2, pt 1):227-229.
- Davies T, Karanovic S, Shergill B. Essential regional nerve blocks for the dermatologist: part 2. Clin Exp Dermatol. 2014;39:861-867.
- Scholz A. Mechanisms of (local) anaesthetics on voltage-gated sodium and other ion channels. Br J Anaesth. 2002;89:52-61.
- Auletta MJ. Local anesthesia for dermatologic surgery. Semin Dermatol. 1994;13:35-42.
- Park KK, Sharon VR. A review of local anesthetics: minimizing risk and side effects in cutaneous surgery. Dermatol Surg. 2017;43:173-187.
- Reiz S, Nath S. Cardiotoxicity of local anaesthetic agents. Br J Anaesth. 1986;58:736-746.
- Klein JA, Kassarjdian N. Lidocaine toxicity with tumescent liposuction. a case report of probable drug interactions. Dermatol Surg. 1997;23:1169-1174.
- Minkis K, Whittington A, Alam M. Dermatologic surgery emergencies: complications caused by systemic reactions, high-energy systems, and trauma. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2016;75:265-284.
- Morais-Almeida M, Gaspar A, Marinho S, et al. Allergy to local anesthetics of the amide group with tolerance to procaine. Allergy. 2003;58:827-828.
- To D, Kossintseva I, de Gannes G. Lidocaine contact allergy is becoming more prevalent. Dermatol Surg. 2014;40:1367-1372.
- Wahlgren CF, Quiding H. Depth of cutaneous analgesia after application of a eutectic mixture of the local anesthetics lidocaine and prilocaine (EMLA cream). J Am Acad Dermatol. 2000;42:584-588.
- Bjerring P, Andersen PH, Arendt-Nielsen L. Vascular response of human skin after analgesia with EMLA cream. Br J Anaesth. 1989;63:655-660.
- Ismail F, Goldsmith PC. EMLA cream-induced allergic contact dermatitis in a child with thalassaemia major. Contact Dermatitis. 2005;52:111.
- Thakur BK, Murali MR. EMLA cream-induced allergic contact dermatitis: a role for prilocaine as an immunogen. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1995;95:776-778.
- Waton J, Boulanger A, Trechot PH, et al. Contact urticaria from EMLA cream. Contact Dermatitis. 2004;51:284-287.
- Bucalo BD, Mirikitani EJ, Moy RL. Comparison of skin anesthetic effect of liposomal lidocaine, nonliposomal lidocaine, and EMLA using 30-minute application time. Dermatol Surg. 1998;24:537-541.
- Guardiano RA, Norwood CW. Direct comparison of EMLA versus lidocaine for pain control in Nd:YAG 1,064 nm laser hair removal. Dermatol Surg. 2005;31:396-398.
- Nestor MS. Safety of occluded 4% liposomal lidocaine cream. J Drugs Dermatol. 2006;5:618-620.
- Oni G, Rasko Y, Kenkel J. Topical lidocaine enhanced by laser pretreatment: a safe and effective method of analgesia for facial rejuvenation. Aesthet Surg J. 2013;33:854-861.
- Niamtu J 3rd. Simple technique for lip and nasolabial fold anesthesia for injectable fillers. Dermatol Surg. 2005;31:1330-1332.
- Naumann M, Flachenecker P, Brocker EB, et al. Botulinum toxin for palmar hyperhidrosis. Lancet. 1997;349:252.
- Naumann M, Hofmann U, Bergmann I, et al. Focal hyperhidrosis: effective treatment with intracutaneous botulinum toxin. Arch Dermatol. 1998;134:301-304.
- Shelley WB, Talanin NY, Shelley ED. Botulinum toxin therapy for palmar hyperhidrosis. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1998;38(2, pt 1):227-229.
- Davies T, Karanovic S, Shergill B. Essential regional nerve blocks for the dermatologist: part 2. Clin Exp Dermatol. 2014;39:861-867.
Practice Points
- The proper delivery of local anesthesia is integral to successful cosmetic interventions.
- Regional nerve blocks can provide effective analgesia while reducing the number of injections and preserving the architecture of the cosmetic field.
Product News: 06 2017
Avène Complexion Correcting Shield SPF 50+
Pierre Fabre Dermo-Cosmetique USA adds the Avène Complexion Correcting Shield SPF 50+ mineral sunscreen to its physician-dispensed sun care line. This tinted moisturizer, available in 3 shades, provides 24-hour hydration and an effective antioxidant defense against sun-induced free radicals. Avène Complexion Correcting Shield provides an instant blurring effect to camouflage skin imperfections such as large pores, uneven skin tone, redness, fine lines, and wrinkles. For more information, visit www.aveneusa.com.
Coppertone Clearly Sheer Whipped Sunscreen
Bayer introduces Coppertone Clearly Sheer Whipped Sunscreen, a rich and creamy formula available in sun protection factor 30 and 50. Coppertone Clearly Sheer Whipped Sunscreen absorbs quickly to leave skin feeling soft and smooth. It offers broad-spectrum UVA/UVB protection and is water resistant for up to 80 minutes.For more information, visit www.coppertone.com.
DerMend Mature Skin Solutions
Ferndale Healthcare launches DerMend Mature Skin Solutions, an over-the-counter line consisting of 3 products specifically designed for patients aged 50 years and older. The Fragile Skin Moisturizing Formula rejuvenates thin and fragile skin with hyaluronic acid, retinol, glycolic acid, niacinaminde, and 5 ceramides. The Moisturizing Anti-Itch Lotion is steroid free and contains
Jan Marini Sunscreens
Jan Marini Skin Research, Inc, introduces Antioxidant Daily Face Protectant SPF 33 and Marini Physical Protectant SPF 45, both providing broad-spectrum UVA/UVB protection. Antioxidant Daily Face Protectant provides oil control and advanced hydration for daily use to reduce and address damage caused by sun exposure. Marini Physical Protectant utilizes purely physical filters to decrease the risk of premature skin aging and features a universal tint with a sheer matte finish. For more information, visit www.janmarini.com.
If you would like your product included in Product News, please email a press release to the Editorial Office at [email protected].
Avène Complexion Correcting Shield SPF 50+
Pierre Fabre Dermo-Cosmetique USA adds the Avène Complexion Correcting Shield SPF 50+ mineral sunscreen to its physician-dispensed sun care line. This tinted moisturizer, available in 3 shades, provides 24-hour hydration and an effective antioxidant defense against sun-induced free radicals. Avène Complexion Correcting Shield provides an instant blurring effect to camouflage skin imperfections such as large pores, uneven skin tone, redness, fine lines, and wrinkles. For more information, visit www.aveneusa.com.
Coppertone Clearly Sheer Whipped Sunscreen
Bayer introduces Coppertone Clearly Sheer Whipped Sunscreen, a rich and creamy formula available in sun protection factor 30 and 50. Coppertone Clearly Sheer Whipped Sunscreen absorbs quickly to leave skin feeling soft and smooth. It offers broad-spectrum UVA/UVB protection and is water resistant for up to 80 minutes.For more information, visit www.coppertone.com.
DerMend Mature Skin Solutions
Ferndale Healthcare launches DerMend Mature Skin Solutions, an over-the-counter line consisting of 3 products specifically designed for patients aged 50 years and older. The Fragile Skin Moisturizing Formula rejuvenates thin and fragile skin with hyaluronic acid, retinol, glycolic acid, niacinaminde, and 5 ceramides. The Moisturizing Anti-Itch Lotion is steroid free and contains
Jan Marini Sunscreens
Jan Marini Skin Research, Inc, introduces Antioxidant Daily Face Protectant SPF 33 and Marini Physical Protectant SPF 45, both providing broad-spectrum UVA/UVB protection. Antioxidant Daily Face Protectant provides oil control and advanced hydration for daily use to reduce and address damage caused by sun exposure. Marini Physical Protectant utilizes purely physical filters to decrease the risk of premature skin aging and features a universal tint with a sheer matte finish. For more information, visit www.janmarini.com.
If you would like your product included in Product News, please email a press release to the Editorial Office at [email protected].
Avène Complexion Correcting Shield SPF 50+
Pierre Fabre Dermo-Cosmetique USA adds the Avène Complexion Correcting Shield SPF 50+ mineral sunscreen to its physician-dispensed sun care line. This tinted moisturizer, available in 3 shades, provides 24-hour hydration and an effective antioxidant defense against sun-induced free radicals. Avène Complexion Correcting Shield provides an instant blurring effect to camouflage skin imperfections such as large pores, uneven skin tone, redness, fine lines, and wrinkles. For more information, visit www.aveneusa.com.
Coppertone Clearly Sheer Whipped Sunscreen
Bayer introduces Coppertone Clearly Sheer Whipped Sunscreen, a rich and creamy formula available in sun protection factor 30 and 50. Coppertone Clearly Sheer Whipped Sunscreen absorbs quickly to leave skin feeling soft and smooth. It offers broad-spectrum UVA/UVB protection and is water resistant for up to 80 minutes.For more information, visit www.coppertone.com.
DerMend Mature Skin Solutions
Ferndale Healthcare launches DerMend Mature Skin Solutions, an over-the-counter line consisting of 3 products specifically designed for patients aged 50 years and older. The Fragile Skin Moisturizing Formula rejuvenates thin and fragile skin with hyaluronic acid, retinol, glycolic acid, niacinaminde, and 5 ceramides. The Moisturizing Anti-Itch Lotion is steroid free and contains
Jan Marini Sunscreens
Jan Marini Skin Research, Inc, introduces Antioxidant Daily Face Protectant SPF 33 and Marini Physical Protectant SPF 45, both providing broad-spectrum UVA/UVB protection. Antioxidant Daily Face Protectant provides oil control and advanced hydration for daily use to reduce and address damage caused by sun exposure. Marini Physical Protectant utilizes purely physical filters to decrease the risk of premature skin aging and features a universal tint with a sheer matte finish. For more information, visit www.janmarini.com.
If you would like your product included in Product News, please email a press release to the Editorial Office at [email protected].
Predicting functional outcome after pediatric osteomyelitis
MADRID – Ninety percent of children with acute hematogenous osteomyelitis will do fine after their initial course of antibiotics and don’t require long-term follow-up; and the other 10% can be identified within the first few days of hospitalization, Lawson A. Copley, MD, said at the annual meeting of the European Society for Paediatric Infectious Diseases.
The tool that enables physicians to distinguish the 10% of children at high risk for severe orthopedic sequelae is a validated severity of illness score that can be determined within the first several days of hospitalization. The 0-10 score, developed by Dr. Copley and his coinvestigators (J Pediatr Orthop. 2016 Oct 12. doi: 10.1097/BPO.0000000000000879), awards points for the patient’s initial C-reactive protein level, the C-reactive protein levels on hospital days 2-3 and 4-5, the number of febrile days on antibiotic therapy, the band percentage of WBC, ICU admission, and disseminated disease such as endocarditis, septic pulmonary embolism, and deep venous thrombosis.
There is a dearth of long-term follow-up studies of pediatric osteomyelitis. To address this unmet need, he and his coinvestigators have enrolled 198 children with acute hematogenous osteomyelitis in an ongoing prospective study. All were treated with antibiotics until clinical and laboratory resolution of the infection and achievement of a normal erythrocyte sedimentation rate. All patients are being followed in a specialized multidisciplinary clinic at Texas Scottish Rite Hospital for Children directed by Dr. Copley. To date, 118 patients have been seen for their 2-year follow-up visit, which includes radiographs of the previous infection site, an orthopedic exam, and completion of the Pediatric Quality of Life Inventory and the Pediatric Outcomes Data Collection Instrument.
At follow-up, the children fell into three broad categories. Ten percent had severe radiographic and/or clinical sequelae such as limb length discrepancy, visible deformity, limited range of motion, osteonecrosis, physeal arrest, or joint destruction. Roughly 40% had complete resolution with normal function and no growth disturbance or other sequelae. And 50% had clinical resolution with a completely normal physical exam and excellent outcome measures, but minimal radiographic sequelae, mainly consisting of central physeal tenting.
“We think that they’re probably a low-risk group,” he said of that last group.
Children with severe sequelae had greater severity of illness at presentation and a more complicated course of initial therapy than those with complete resolution at 2 years of follow-up. Their mean severity of illness score was 4.9, compared with 1.8 in the 40% of children with complete resolution and 3.4 in those with mild radiographic sequelae.
In a univariate logistic regression analysis, each point increase in initial disease severity score was associated with a 20% bump in the risk of developing severe sequelae, with a predictive area under the curve of 0.67. A multivariate logistic regression analysis identified other independent predictors of severe sequelae: age below 6 years, being culture positive for methicillin-resistant Streptococcus aureus, and osteomyelitis contiguous with septic arthritis or abscess, which ultimately led to osteonecrosis and destruction. Incorporating these additional risk factors along with the initial severity of illness score improved the predictive area under the curve to 0.85.
About one-half of patients seen in the pediatric osteomyelitis clinic were bacteremic on admission, and of those, roughly half continued to be bacteremic despite antibiotic therapy. However, there was no difference in the prevalence of bacteremia between the groups with mild versus severe illness.
Asked how introduction of the severity-of-illness score has affected his surgical approach, Dr. Copley said he has become selectively more surgically aggressive.
“A lot of our children have abscesses that are pretty substantial,” he noted. “We’ve learned the hard way. I’ve been doing this for about 14 years now, and initially I used to do a lot of simple debridement of the infection. Now we’re much more extensive in our approach, so we do fewer surgeries, but those surgeries are more extensive.”
Dr. Copley reported having no financial conflicts regarding his study.
MADRID – Ninety percent of children with acute hematogenous osteomyelitis will do fine after their initial course of antibiotics and don’t require long-term follow-up; and the other 10% can be identified within the first few days of hospitalization, Lawson A. Copley, MD, said at the annual meeting of the European Society for Paediatric Infectious Diseases.
The tool that enables physicians to distinguish the 10% of children at high risk for severe orthopedic sequelae is a validated severity of illness score that can be determined within the first several days of hospitalization. The 0-10 score, developed by Dr. Copley and his coinvestigators (J Pediatr Orthop. 2016 Oct 12. doi: 10.1097/BPO.0000000000000879), awards points for the patient’s initial C-reactive protein level, the C-reactive protein levels on hospital days 2-3 and 4-5, the number of febrile days on antibiotic therapy, the band percentage of WBC, ICU admission, and disseminated disease such as endocarditis, septic pulmonary embolism, and deep venous thrombosis.
There is a dearth of long-term follow-up studies of pediatric osteomyelitis. To address this unmet need, he and his coinvestigators have enrolled 198 children with acute hematogenous osteomyelitis in an ongoing prospective study. All were treated with antibiotics until clinical and laboratory resolution of the infection and achievement of a normal erythrocyte sedimentation rate. All patients are being followed in a specialized multidisciplinary clinic at Texas Scottish Rite Hospital for Children directed by Dr. Copley. To date, 118 patients have been seen for their 2-year follow-up visit, which includes radiographs of the previous infection site, an orthopedic exam, and completion of the Pediatric Quality of Life Inventory and the Pediatric Outcomes Data Collection Instrument.
At follow-up, the children fell into three broad categories. Ten percent had severe radiographic and/or clinical sequelae such as limb length discrepancy, visible deformity, limited range of motion, osteonecrosis, physeal arrest, or joint destruction. Roughly 40% had complete resolution with normal function and no growth disturbance or other sequelae. And 50% had clinical resolution with a completely normal physical exam and excellent outcome measures, but minimal radiographic sequelae, mainly consisting of central physeal tenting.
“We think that they’re probably a low-risk group,” he said of that last group.
Children with severe sequelae had greater severity of illness at presentation and a more complicated course of initial therapy than those with complete resolution at 2 years of follow-up. Their mean severity of illness score was 4.9, compared with 1.8 in the 40% of children with complete resolution and 3.4 in those with mild radiographic sequelae.
In a univariate logistic regression analysis, each point increase in initial disease severity score was associated with a 20% bump in the risk of developing severe sequelae, with a predictive area under the curve of 0.67. A multivariate logistic regression analysis identified other independent predictors of severe sequelae: age below 6 years, being culture positive for methicillin-resistant Streptococcus aureus, and osteomyelitis contiguous with septic arthritis or abscess, which ultimately led to osteonecrosis and destruction. Incorporating these additional risk factors along with the initial severity of illness score improved the predictive area under the curve to 0.85.
About one-half of patients seen in the pediatric osteomyelitis clinic were bacteremic on admission, and of those, roughly half continued to be bacteremic despite antibiotic therapy. However, there was no difference in the prevalence of bacteremia between the groups with mild versus severe illness.
Asked how introduction of the severity-of-illness score has affected his surgical approach, Dr. Copley said he has become selectively more surgically aggressive.
“A lot of our children have abscesses that are pretty substantial,” he noted. “We’ve learned the hard way. I’ve been doing this for about 14 years now, and initially I used to do a lot of simple debridement of the infection. Now we’re much more extensive in our approach, so we do fewer surgeries, but those surgeries are more extensive.”
Dr. Copley reported having no financial conflicts regarding his study.
MADRID – Ninety percent of children with acute hematogenous osteomyelitis will do fine after their initial course of antibiotics and don’t require long-term follow-up; and the other 10% can be identified within the first few days of hospitalization, Lawson A. Copley, MD, said at the annual meeting of the European Society for Paediatric Infectious Diseases.
The tool that enables physicians to distinguish the 10% of children at high risk for severe orthopedic sequelae is a validated severity of illness score that can be determined within the first several days of hospitalization. The 0-10 score, developed by Dr. Copley and his coinvestigators (J Pediatr Orthop. 2016 Oct 12. doi: 10.1097/BPO.0000000000000879), awards points for the patient’s initial C-reactive protein level, the C-reactive protein levels on hospital days 2-3 and 4-5, the number of febrile days on antibiotic therapy, the band percentage of WBC, ICU admission, and disseminated disease such as endocarditis, septic pulmonary embolism, and deep venous thrombosis.
There is a dearth of long-term follow-up studies of pediatric osteomyelitis. To address this unmet need, he and his coinvestigators have enrolled 198 children with acute hematogenous osteomyelitis in an ongoing prospective study. All were treated with antibiotics until clinical and laboratory resolution of the infection and achievement of a normal erythrocyte sedimentation rate. All patients are being followed in a specialized multidisciplinary clinic at Texas Scottish Rite Hospital for Children directed by Dr. Copley. To date, 118 patients have been seen for their 2-year follow-up visit, which includes radiographs of the previous infection site, an orthopedic exam, and completion of the Pediatric Quality of Life Inventory and the Pediatric Outcomes Data Collection Instrument.
At follow-up, the children fell into three broad categories. Ten percent had severe radiographic and/or clinical sequelae such as limb length discrepancy, visible deformity, limited range of motion, osteonecrosis, physeal arrest, or joint destruction. Roughly 40% had complete resolution with normal function and no growth disturbance or other sequelae. And 50% had clinical resolution with a completely normal physical exam and excellent outcome measures, but minimal radiographic sequelae, mainly consisting of central physeal tenting.
“We think that they’re probably a low-risk group,” he said of that last group.
Children with severe sequelae had greater severity of illness at presentation and a more complicated course of initial therapy than those with complete resolution at 2 years of follow-up. Their mean severity of illness score was 4.9, compared with 1.8 in the 40% of children with complete resolution and 3.4 in those with mild radiographic sequelae.
In a univariate logistic regression analysis, each point increase in initial disease severity score was associated with a 20% bump in the risk of developing severe sequelae, with a predictive area under the curve of 0.67. A multivariate logistic regression analysis identified other independent predictors of severe sequelae: age below 6 years, being culture positive for methicillin-resistant Streptococcus aureus, and osteomyelitis contiguous with septic arthritis or abscess, which ultimately led to osteonecrosis and destruction. Incorporating these additional risk factors along with the initial severity of illness score improved the predictive area under the curve to 0.85.
About one-half of patients seen in the pediatric osteomyelitis clinic were bacteremic on admission, and of those, roughly half continued to be bacteremic despite antibiotic therapy. However, there was no difference in the prevalence of bacteremia between the groups with mild versus severe illness.
Asked how introduction of the severity-of-illness score has affected his surgical approach, Dr. Copley said he has become selectively more surgically aggressive.
“A lot of our children have abscesses that are pretty substantial,” he noted. “We’ve learned the hard way. I’ve been doing this for about 14 years now, and initially I used to do a lot of simple debridement of the infection. Now we’re much more extensive in our approach, so we do fewer surgeries, but those surgeries are more extensive.”
Dr. Copley reported having no financial conflicts regarding his study.
AT ESPID 2017
Key clinical point:
Major finding: Ninety percent of children with acute hematogenous osteomyelitis require no long-term follow-up after their initial antibiotic therapy.
Data source: An ongoing prospective study of 118 children followed for 2 years after initial treatment of acute hematogenous osteomyelitis.
Disclosures: The study presenter reported having no financial conflicts.
TRK inhibitor shows ‘striking’ activity, durability across diverse adult and pediatric cancers
CHICAGO – Larotrectinib, an oral inhibitor of tropomyosin receptor kinase (TRK), has durable efficacy across diverse adult and pediatric cancers that harbor a genetic aberration known as TRK fusion, finds an analysis of three trials reported at the annual meeting of the American Society of Clinical Oncology.
Fusion of a TRK gene with an unrelated gene leads to uncontrolled signaling in the TRK pathway, potentially causing tumor growth and addiction to this input, lead author David Hyman, MD, chief of early drug development at Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center in New York explained in a press briefing.
Dr. Hyman and his colleagues analyzed data from 55 patients having 17 discrete types of advanced cancer harboring TRK fusions who were treated with larotrectinib in phase I and II trials. Results showed an overall response rate of 76%, and the large majority of responses were still ongoing at 12 months.
“I believe these data support larotrectinib as a potential new standard of care for these patients,” he said. “However, I want to emphasize that really recognizing this benefit in the community will require that we test patients more universally for the presence of TRK fusions or other tumor-agnostic biomarkers, such as microsatellite instability.”
On the basis of these promising data, the drug’s manufacturer, Loxo Oncology, plans to submit a New Drug Application to the Food and Drug Administration later this year or early next year. Larotrectinib has already been granted both orphan drug designation (for drugs used to treat rare conditions) and breakthrough therapy designation (for drugs used to treat serious conditions showing greater efficacy than available therapies).
A randomized trial pitting larotrectinib against other therapies is unlikely given the low prevalence of TRK fusions, the lack of treatment options for the fairly heavily pretreated trial patients, and the drug’s impressive performance, according to Dr. Hyman.
“The efficacy is so striking that it really exceeds almost any existing standard of care for solid tumors,” he elaborated. “There is hardly any chemotherapy or targeted therapy that has a response rate or durability that looks like larotrectinib in these patients.”
Expert perspective
The data for larotrectinib “really bring us into a new era where treatment is truly based on mutation, not location,” said Sumanta Kumar Pal, MD, a medical oncologist at City of Hope, in Duarte, Calif. “When I was in training, which was not too long ago, it really would have been a pipe dream to think that we could have treated cancers independent of their site of origin. … With the data presented by Dr. Hyman for larotrectinib, we may now be poised to treat many cancers in a manner that is agnostic of their site of origin and that is instead based on molecular criteria.
TRK testing
Several next-generation sequencing–based tests already available clinically can pick up TRK fusions, Dr. Hyman pointed out. “But it is important for the ordering physician to understand whether the tests they are ordering includes fusion detection and, if it’s an option, to select it. Otherwise, they will not find TRK fusions.
“The list price for these tests is in the kind of low thousands of dollars, which equates essentially to a PET scan for the cancer patient,” he noted. In cancers where sequential single-gene testing is already being done as standard of care, there is “minimal” incremental cost of instead using comprehensive testing that would detect TRK fusions.
Oncologists should be aware that obtaining test results can take weeks, Dr. Hyman stressed. “My personal opinion is that this [testing] should be more broadly adopted and should be adopted at a point in the patient’s treatment … [so that they] don’t become too sick, as we see in our own experience as well, and don’t have an opportunity to be treated even when the test results come back positive. So I would generally advocate early testing.”
Study details
For the study, which was funded by Loxo Oncology, the investigators analyzed data from three trials in which patients with advanced TRK fusion–positive solid cancers received larotrectinib (LOXO-101): a phase I trial among 8 adult patients, a phase I/II trial among 12 pediatric patients (SCOUT), and a phase II “basket” trial among 35 adult and adolescent patients (NAVIGATE).
“I want to emphasize that these patients were identified by local testing,” Dr. Hyman noted. “We did not perform central screening to find the TRK fusions, and in fact, 50 different laboratories identified the 55 patients. So this in a sense really represents the real-world identification of these patients.”
In an integrated analysis, the overall rate of confirmed response as assessed by investigators was 76%, with complete response in 12% of patients and partial response in 64%. Two patients had such deep tumor regression that they experienced downstaging enabling them to undergo potentially curative surgery. Efficacy was consistent regardless of tumor type, which TRK gene was affected, and the fusion partner gene.
Median time to response was 1.8 months. “This is actually just a reflection of when the first scan was obtained. But in the clinic, patients reported dramatic improvement of their symptoms within days of beginning therapy,” Dr. Hyman said.
With a median follow-up of 5.8 months, the median duration of response was not yet reached. Fully 79% of responses were still ongoing at 12 months. Median progression-free survival was likewise not reached; the 12-month rate was 63%.
The leading treatment-emergent adverse events were fatigue (38%), dizziness (27%), nausea (26%), and anemia (26%). “This is an extremely well tolerated therapy with only 13% of patients requiring any form of dose modification and not a single patient discontinuing due to adverse events,” he said.
It is unclear why some patients had apparent primary resistance to larotrectinib, but their TRK fusion test results may have been incorrect, Dr. Hyman speculated. Six patients developed acquired resistance to larotrectinib; five of them were found to have an identical resistance mutation, and two went on to receive and have a response to LOXO-195, a next-generation TRK inhibitor that appears to retain activity in the presence of this mutation (Cancer Discov. 2017 June 3. doi: 10.1158/2159-8290.CD-17-0507).
Dr. Hyman disclosed that he has a consulting or advisory role with Atara Biotherapeutics, Chugai Pharma, and CytomX Therapeutics, and that he receives research funding from AstraZeneca and Puma Biotechnology.
CHICAGO – Larotrectinib, an oral inhibitor of tropomyosin receptor kinase (TRK), has durable efficacy across diverse adult and pediatric cancers that harbor a genetic aberration known as TRK fusion, finds an analysis of three trials reported at the annual meeting of the American Society of Clinical Oncology.
Fusion of a TRK gene with an unrelated gene leads to uncontrolled signaling in the TRK pathway, potentially causing tumor growth and addiction to this input, lead author David Hyman, MD, chief of early drug development at Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center in New York explained in a press briefing.
Dr. Hyman and his colleagues analyzed data from 55 patients having 17 discrete types of advanced cancer harboring TRK fusions who were treated with larotrectinib in phase I and II trials. Results showed an overall response rate of 76%, and the large majority of responses were still ongoing at 12 months.
“I believe these data support larotrectinib as a potential new standard of care for these patients,” he said. “However, I want to emphasize that really recognizing this benefit in the community will require that we test patients more universally for the presence of TRK fusions or other tumor-agnostic biomarkers, such as microsatellite instability.”
On the basis of these promising data, the drug’s manufacturer, Loxo Oncology, plans to submit a New Drug Application to the Food and Drug Administration later this year or early next year. Larotrectinib has already been granted both orphan drug designation (for drugs used to treat rare conditions) and breakthrough therapy designation (for drugs used to treat serious conditions showing greater efficacy than available therapies).
A randomized trial pitting larotrectinib against other therapies is unlikely given the low prevalence of TRK fusions, the lack of treatment options for the fairly heavily pretreated trial patients, and the drug’s impressive performance, according to Dr. Hyman.
“The efficacy is so striking that it really exceeds almost any existing standard of care for solid tumors,” he elaborated. “There is hardly any chemotherapy or targeted therapy that has a response rate or durability that looks like larotrectinib in these patients.”
Expert perspective
The data for larotrectinib “really bring us into a new era where treatment is truly based on mutation, not location,” said Sumanta Kumar Pal, MD, a medical oncologist at City of Hope, in Duarte, Calif. “When I was in training, which was not too long ago, it really would have been a pipe dream to think that we could have treated cancers independent of their site of origin. … With the data presented by Dr. Hyman for larotrectinib, we may now be poised to treat many cancers in a manner that is agnostic of their site of origin and that is instead based on molecular criteria.
TRK testing
Several next-generation sequencing–based tests already available clinically can pick up TRK fusions, Dr. Hyman pointed out. “But it is important for the ordering physician to understand whether the tests they are ordering includes fusion detection and, if it’s an option, to select it. Otherwise, they will not find TRK fusions.
“The list price for these tests is in the kind of low thousands of dollars, which equates essentially to a PET scan for the cancer patient,” he noted. In cancers where sequential single-gene testing is already being done as standard of care, there is “minimal” incremental cost of instead using comprehensive testing that would detect TRK fusions.
Oncologists should be aware that obtaining test results can take weeks, Dr. Hyman stressed. “My personal opinion is that this [testing] should be more broadly adopted and should be adopted at a point in the patient’s treatment … [so that they] don’t become too sick, as we see in our own experience as well, and don’t have an opportunity to be treated even when the test results come back positive. So I would generally advocate early testing.”
Study details
For the study, which was funded by Loxo Oncology, the investigators analyzed data from three trials in which patients with advanced TRK fusion–positive solid cancers received larotrectinib (LOXO-101): a phase I trial among 8 adult patients, a phase I/II trial among 12 pediatric patients (SCOUT), and a phase II “basket” trial among 35 adult and adolescent patients (NAVIGATE).
“I want to emphasize that these patients were identified by local testing,” Dr. Hyman noted. “We did not perform central screening to find the TRK fusions, and in fact, 50 different laboratories identified the 55 patients. So this in a sense really represents the real-world identification of these patients.”
In an integrated analysis, the overall rate of confirmed response as assessed by investigators was 76%, with complete response in 12% of patients and partial response in 64%. Two patients had such deep tumor regression that they experienced downstaging enabling them to undergo potentially curative surgery. Efficacy was consistent regardless of tumor type, which TRK gene was affected, and the fusion partner gene.
Median time to response was 1.8 months. “This is actually just a reflection of when the first scan was obtained. But in the clinic, patients reported dramatic improvement of their symptoms within days of beginning therapy,” Dr. Hyman said.
With a median follow-up of 5.8 months, the median duration of response was not yet reached. Fully 79% of responses were still ongoing at 12 months. Median progression-free survival was likewise not reached; the 12-month rate was 63%.
The leading treatment-emergent adverse events were fatigue (38%), dizziness (27%), nausea (26%), and anemia (26%). “This is an extremely well tolerated therapy with only 13% of patients requiring any form of dose modification and not a single patient discontinuing due to adverse events,” he said.
It is unclear why some patients had apparent primary resistance to larotrectinib, but their TRK fusion test results may have been incorrect, Dr. Hyman speculated. Six patients developed acquired resistance to larotrectinib; five of them were found to have an identical resistance mutation, and two went on to receive and have a response to LOXO-195, a next-generation TRK inhibitor that appears to retain activity in the presence of this mutation (Cancer Discov. 2017 June 3. doi: 10.1158/2159-8290.CD-17-0507).
Dr. Hyman disclosed that he has a consulting or advisory role with Atara Biotherapeutics, Chugai Pharma, and CytomX Therapeutics, and that he receives research funding from AstraZeneca and Puma Biotechnology.
CHICAGO – Larotrectinib, an oral inhibitor of tropomyosin receptor kinase (TRK), has durable efficacy across diverse adult and pediatric cancers that harbor a genetic aberration known as TRK fusion, finds an analysis of three trials reported at the annual meeting of the American Society of Clinical Oncology.
Fusion of a TRK gene with an unrelated gene leads to uncontrolled signaling in the TRK pathway, potentially causing tumor growth and addiction to this input, lead author David Hyman, MD, chief of early drug development at Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center in New York explained in a press briefing.
Dr. Hyman and his colleagues analyzed data from 55 patients having 17 discrete types of advanced cancer harboring TRK fusions who were treated with larotrectinib in phase I and II trials. Results showed an overall response rate of 76%, and the large majority of responses were still ongoing at 12 months.
“I believe these data support larotrectinib as a potential new standard of care for these patients,” he said. “However, I want to emphasize that really recognizing this benefit in the community will require that we test patients more universally for the presence of TRK fusions or other tumor-agnostic biomarkers, such as microsatellite instability.”
On the basis of these promising data, the drug’s manufacturer, Loxo Oncology, plans to submit a New Drug Application to the Food and Drug Administration later this year or early next year. Larotrectinib has already been granted both orphan drug designation (for drugs used to treat rare conditions) and breakthrough therapy designation (for drugs used to treat serious conditions showing greater efficacy than available therapies).
A randomized trial pitting larotrectinib against other therapies is unlikely given the low prevalence of TRK fusions, the lack of treatment options for the fairly heavily pretreated trial patients, and the drug’s impressive performance, according to Dr. Hyman.
“The efficacy is so striking that it really exceeds almost any existing standard of care for solid tumors,” he elaborated. “There is hardly any chemotherapy or targeted therapy that has a response rate or durability that looks like larotrectinib in these patients.”
Expert perspective
The data for larotrectinib “really bring us into a new era where treatment is truly based on mutation, not location,” said Sumanta Kumar Pal, MD, a medical oncologist at City of Hope, in Duarte, Calif. “When I was in training, which was not too long ago, it really would have been a pipe dream to think that we could have treated cancers independent of their site of origin. … With the data presented by Dr. Hyman for larotrectinib, we may now be poised to treat many cancers in a manner that is agnostic of their site of origin and that is instead based on molecular criteria.
TRK testing
Several next-generation sequencing–based tests already available clinically can pick up TRK fusions, Dr. Hyman pointed out. “But it is important for the ordering physician to understand whether the tests they are ordering includes fusion detection and, if it’s an option, to select it. Otherwise, they will not find TRK fusions.
“The list price for these tests is in the kind of low thousands of dollars, which equates essentially to a PET scan for the cancer patient,” he noted. In cancers where sequential single-gene testing is already being done as standard of care, there is “minimal” incremental cost of instead using comprehensive testing that would detect TRK fusions.
Oncologists should be aware that obtaining test results can take weeks, Dr. Hyman stressed. “My personal opinion is that this [testing] should be more broadly adopted and should be adopted at a point in the patient’s treatment … [so that they] don’t become too sick, as we see in our own experience as well, and don’t have an opportunity to be treated even when the test results come back positive. So I would generally advocate early testing.”
Study details
For the study, which was funded by Loxo Oncology, the investigators analyzed data from three trials in which patients with advanced TRK fusion–positive solid cancers received larotrectinib (LOXO-101): a phase I trial among 8 adult patients, a phase I/II trial among 12 pediatric patients (SCOUT), and a phase II “basket” trial among 35 adult and adolescent patients (NAVIGATE).
“I want to emphasize that these patients were identified by local testing,” Dr. Hyman noted. “We did not perform central screening to find the TRK fusions, and in fact, 50 different laboratories identified the 55 patients. So this in a sense really represents the real-world identification of these patients.”
In an integrated analysis, the overall rate of confirmed response as assessed by investigators was 76%, with complete response in 12% of patients and partial response in 64%. Two patients had such deep tumor regression that they experienced downstaging enabling them to undergo potentially curative surgery. Efficacy was consistent regardless of tumor type, which TRK gene was affected, and the fusion partner gene.
Median time to response was 1.8 months. “This is actually just a reflection of when the first scan was obtained. But in the clinic, patients reported dramatic improvement of their symptoms within days of beginning therapy,” Dr. Hyman said.
With a median follow-up of 5.8 months, the median duration of response was not yet reached. Fully 79% of responses were still ongoing at 12 months. Median progression-free survival was likewise not reached; the 12-month rate was 63%.
The leading treatment-emergent adverse events were fatigue (38%), dizziness (27%), nausea (26%), and anemia (26%). “This is an extremely well tolerated therapy with only 13% of patients requiring any form of dose modification and not a single patient discontinuing due to adverse events,” he said.
It is unclear why some patients had apparent primary resistance to larotrectinib, but their TRK fusion test results may have been incorrect, Dr. Hyman speculated. Six patients developed acquired resistance to larotrectinib; five of them were found to have an identical resistance mutation, and two went on to receive and have a response to LOXO-195, a next-generation TRK inhibitor that appears to retain activity in the presence of this mutation (Cancer Discov. 2017 June 3. doi: 10.1158/2159-8290.CD-17-0507).
Dr. Hyman disclosed that he has a consulting or advisory role with Atara Biotherapeutics, Chugai Pharma, and CytomX Therapeutics, and that he receives research funding from AstraZeneca and Puma Biotechnology.
AT ASCO 2017
Key clinical point:
Major finding: The overall response rate was 76%, and 79% of responses were still ongoing at 12 months.
Data source: An integrated analysis of phase I and II trials among 55 children and adults having 17 discrete types of advanced cancer with TRK fusions.
Disclosures: Dr. Hyman disclosed that he has a consulting or advisory role with Atara Biotherapeutics, Chugai Pharma, and CytomX Therapeutics, and that he receives research funding from AstraZeneca and Puma Biotechnology. The study was funded by Loxo Oncology.
VIDEO: Survival improves when cancer patients self-report symptoms
CHICAGO – Patients with metastatic cancer who self-reported symptoms during routine cancer treatment experienced a number of benefits, including a statistically significant improvement in overall survival, according to findings from a randomized, controlled clinical trial.
The median overall survival among 441 patients receiving treatment for metastatic breast, lung, genitourinary, or gynecologic cancer who were randomized to the intervention arm was more than 5 months longer – a nearly 20% increase – than in 325 patients who received standard care (31.2 vs. 26 months), Ethan Basch, MD, reported at the annual meeting of the American Society of Clinical Oncology.
Additionally, 31% of patients in the intervention arm had better quality of life/physical functioning, compared with those in the control arm, and 7% fewer patients in the intervention arm visited an emergency room during the course of the study. The duration of potentially life-prolonging chemotherapy was increased by an average of 2 months in the intervention arm, he said.
The findings were simultaneously published online in a research letter in JAMA (2017 Jun 4. doi: 10.1001/jama.2017.7156).
Symptoms such as nausea, pain, and fatigue are common among patients with metastatic cancer, Dr. Basch said. “Unfortunately, they often go undetected by doctors and nurses until they become severe and physically debilitating,” he added, explaining that patients are often hesitant to call the office to report symptoms between visits.
Even at office visits, competing topics can interfere with communication about symptoms, he noted.
He and his colleagues hypothesized that self-reporting of patient symptoms between visits or prior to a visit while in the clinic waiting area would prompt earlier intervention and improve symptom control and outcomes.
Study subjects were patients at Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center who had advanced solid genitourinary, gynecologic, breast, or lung tumors and who were receiving outpatient chemotherapy. Those assigned to the intervention group used tablet computers and an online web survey system to report on 12 symptoms commonly experienced during chemotherapy. The system triggers an alert to a nurse when a severe or worsening symptom is reported. Patients in the usual care group discussed symptoms during office visits and were encouraged to call the office between visits if they experienced concerning symptoms.
Patients remained on the study until discontinuation of all cancer treatment, hospice, or death.
One possible explanation for the findings is that this self-reporting approach prompts clinicians to manage symptoms before they cause serious downstream complications, Dr. Basch said.
The approach may also keep patients more physically functional, which is known from prior studies to have a strong association with better survival, and the approach may also improve management of chemotherapy side effects, enabling longer duration of beneficial cancer treatment, he said, explaining that, “in oncology, we often are limited in our ability to give life-prolonging treatment because people don’t tolerate it well.”
“This approach should be considered for inclusion in standard symptoms management as a component of high quality cancer care,” he concluded, noting that efforts are underway to test the next generation of systems to improve communication between patients and care teams and to figure out how best to integrate these tools into oncology practice.
The system used in the this study was designed for research, but a number of companies have tools currently available for patient-reported outcomes, and others are being developed, Dr. Basch said, noting that a National Cancer Institute questionnaire – the PRO-CTCAE – is publicly available and could be loaded into patients’ electronic health records for this purpose as well.
ASCO’s chief medical officer, Richard L. Schilsky, MD, said the findings demonstrate that “these frequent touches between the patient and their health care providers obviously can make a huge difference in their outcomes.”
Additionally, ASCO expert Harold J. Burstein, MD, of Dana-Farber Cancer Institute, Boston, said this “exciting and compelling study” validates the feeling among many clinicians that patient-focused, team-based care can improve outcomes in a meaningful way for patients. In a video interview, he further discusses the challenges with implementing a system like this and particularly with obtaining funding to support implementation.
“If this was a drug, if it was iPad-olizumab, it would be worth tens, if not hundreds of thousands, of dollars per year to have something that improved overall survival. We don’t have those same kinds of dollars to help implement these into our electronic health records or our systems. We need to find ways to support that and make it happen,” he said.
This study was supported by the National Institutes of Health and the Conquer Cancer Foundation of the American Society of Clinical Oncology. Dr. Basch and Dr. Burstein each reported having no disclosures.
The video associated with this article is no longer available on this site. Please view all of our videos on the MDedge YouTube channel
The video associated with this article is no longer available on this site. Please view all of our videos on the MDedge YouTube channel
The video associated with this article is no longer available on this site. Please view all of our videos on the MDedge YouTube channel
CHICAGO – Patients with metastatic cancer who self-reported symptoms during routine cancer treatment experienced a number of benefits, including a statistically significant improvement in overall survival, according to findings from a randomized, controlled clinical trial.
The median overall survival among 441 patients receiving treatment for metastatic breast, lung, genitourinary, or gynecologic cancer who were randomized to the intervention arm was more than 5 months longer – a nearly 20% increase – than in 325 patients who received standard care (31.2 vs. 26 months), Ethan Basch, MD, reported at the annual meeting of the American Society of Clinical Oncology.
Additionally, 31% of patients in the intervention arm had better quality of life/physical functioning, compared with those in the control arm, and 7% fewer patients in the intervention arm visited an emergency room during the course of the study. The duration of potentially life-prolonging chemotherapy was increased by an average of 2 months in the intervention arm, he said.
The findings were simultaneously published online in a research letter in JAMA (2017 Jun 4. doi: 10.1001/jama.2017.7156).
Symptoms such as nausea, pain, and fatigue are common among patients with metastatic cancer, Dr. Basch said. “Unfortunately, they often go undetected by doctors and nurses until they become severe and physically debilitating,” he added, explaining that patients are often hesitant to call the office to report symptoms between visits.
Even at office visits, competing topics can interfere with communication about symptoms, he noted.
He and his colleagues hypothesized that self-reporting of patient symptoms between visits or prior to a visit while in the clinic waiting area would prompt earlier intervention and improve symptom control and outcomes.
Study subjects were patients at Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center who had advanced solid genitourinary, gynecologic, breast, or lung tumors and who were receiving outpatient chemotherapy. Those assigned to the intervention group used tablet computers and an online web survey system to report on 12 symptoms commonly experienced during chemotherapy. The system triggers an alert to a nurse when a severe or worsening symptom is reported. Patients in the usual care group discussed symptoms during office visits and were encouraged to call the office between visits if they experienced concerning symptoms.
Patients remained on the study until discontinuation of all cancer treatment, hospice, or death.
One possible explanation for the findings is that this self-reporting approach prompts clinicians to manage symptoms before they cause serious downstream complications, Dr. Basch said.
The approach may also keep patients more physically functional, which is known from prior studies to have a strong association with better survival, and the approach may also improve management of chemotherapy side effects, enabling longer duration of beneficial cancer treatment, he said, explaining that, “in oncology, we often are limited in our ability to give life-prolonging treatment because people don’t tolerate it well.”
“This approach should be considered for inclusion in standard symptoms management as a component of high quality cancer care,” he concluded, noting that efforts are underway to test the next generation of systems to improve communication between patients and care teams and to figure out how best to integrate these tools into oncology practice.
The system used in the this study was designed for research, but a number of companies have tools currently available for patient-reported outcomes, and others are being developed, Dr. Basch said, noting that a National Cancer Institute questionnaire – the PRO-CTCAE – is publicly available and could be loaded into patients’ electronic health records for this purpose as well.
ASCO’s chief medical officer, Richard L. Schilsky, MD, said the findings demonstrate that “these frequent touches between the patient and their health care providers obviously can make a huge difference in their outcomes.”
Additionally, ASCO expert Harold J. Burstein, MD, of Dana-Farber Cancer Institute, Boston, said this “exciting and compelling study” validates the feeling among many clinicians that patient-focused, team-based care can improve outcomes in a meaningful way for patients. In a video interview, he further discusses the challenges with implementing a system like this and particularly with obtaining funding to support implementation.
“If this was a drug, if it was iPad-olizumab, it would be worth tens, if not hundreds of thousands, of dollars per year to have something that improved overall survival. We don’t have those same kinds of dollars to help implement these into our electronic health records or our systems. We need to find ways to support that and make it happen,” he said.
This study was supported by the National Institutes of Health and the Conquer Cancer Foundation of the American Society of Clinical Oncology. Dr. Basch and Dr. Burstein each reported having no disclosures.
CHICAGO – Patients with metastatic cancer who self-reported symptoms during routine cancer treatment experienced a number of benefits, including a statistically significant improvement in overall survival, according to findings from a randomized, controlled clinical trial.
The median overall survival among 441 patients receiving treatment for metastatic breast, lung, genitourinary, or gynecologic cancer who were randomized to the intervention arm was more than 5 months longer – a nearly 20% increase – than in 325 patients who received standard care (31.2 vs. 26 months), Ethan Basch, MD, reported at the annual meeting of the American Society of Clinical Oncology.
Additionally, 31% of patients in the intervention arm had better quality of life/physical functioning, compared with those in the control arm, and 7% fewer patients in the intervention arm visited an emergency room during the course of the study. The duration of potentially life-prolonging chemotherapy was increased by an average of 2 months in the intervention arm, he said.
The findings were simultaneously published online in a research letter in JAMA (2017 Jun 4. doi: 10.1001/jama.2017.7156).
Symptoms such as nausea, pain, and fatigue are common among patients with metastatic cancer, Dr. Basch said. “Unfortunately, they often go undetected by doctors and nurses until they become severe and physically debilitating,” he added, explaining that patients are often hesitant to call the office to report symptoms between visits.
Even at office visits, competing topics can interfere with communication about symptoms, he noted.
He and his colleagues hypothesized that self-reporting of patient symptoms between visits or prior to a visit while in the clinic waiting area would prompt earlier intervention and improve symptom control and outcomes.
Study subjects were patients at Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center who had advanced solid genitourinary, gynecologic, breast, or lung tumors and who were receiving outpatient chemotherapy. Those assigned to the intervention group used tablet computers and an online web survey system to report on 12 symptoms commonly experienced during chemotherapy. The system triggers an alert to a nurse when a severe or worsening symptom is reported. Patients in the usual care group discussed symptoms during office visits and were encouraged to call the office between visits if they experienced concerning symptoms.
Patients remained on the study until discontinuation of all cancer treatment, hospice, or death.
One possible explanation for the findings is that this self-reporting approach prompts clinicians to manage symptoms before they cause serious downstream complications, Dr. Basch said.
The approach may also keep patients more physically functional, which is known from prior studies to have a strong association with better survival, and the approach may also improve management of chemotherapy side effects, enabling longer duration of beneficial cancer treatment, he said, explaining that, “in oncology, we often are limited in our ability to give life-prolonging treatment because people don’t tolerate it well.”
“This approach should be considered for inclusion in standard symptoms management as a component of high quality cancer care,” he concluded, noting that efforts are underway to test the next generation of systems to improve communication between patients and care teams and to figure out how best to integrate these tools into oncology practice.
The system used in the this study was designed for research, but a number of companies have tools currently available for patient-reported outcomes, and others are being developed, Dr. Basch said, noting that a National Cancer Institute questionnaire – the PRO-CTCAE – is publicly available and could be loaded into patients’ electronic health records for this purpose as well.
ASCO’s chief medical officer, Richard L. Schilsky, MD, said the findings demonstrate that “these frequent touches between the patient and their health care providers obviously can make a huge difference in their outcomes.”
Additionally, ASCO expert Harold J. Burstein, MD, of Dana-Farber Cancer Institute, Boston, said this “exciting and compelling study” validates the feeling among many clinicians that patient-focused, team-based care can improve outcomes in a meaningful way for patients. In a video interview, he further discusses the challenges with implementing a system like this and particularly with obtaining funding to support implementation.
“If this was a drug, if it was iPad-olizumab, it would be worth tens, if not hundreds of thousands, of dollars per year to have something that improved overall survival. We don’t have those same kinds of dollars to help implement these into our electronic health records or our systems. We need to find ways to support that and make it happen,” he said.
This study was supported by the National Institutes of Health and the Conquer Cancer Foundation of the American Society of Clinical Oncology. Dr. Basch and Dr. Burstein each reported having no disclosures.
AT THE 2017 ASCO ANNUAL MEETING
Key clinical point:
Major finding: Median overall survival was 31.2, vs. 26 months, with self-reporting of symptoms, vs. usual care.
Data source: A randomized controlled clinical trial of 766 patients.
Disclosures: This study was supported by the National Institutes of Health and the Conquer Cancer Foundation of the American Society of Clinical Oncology. Dr. Basch and Dr. Burstein each reported having no disclosures.
VIDEO: Routine genomic testing identifies actionable alterations in 52% of tumors
CHICAGO –
Molecular profiling, including genetic sequencing and copy number variation analysis, was performed in 1944 tumors from patients with advanced tumors enrolled in the profiLER study. Of the tumors screened, mutations deemed actionable were identified in 1,004 (52%), with 394 patients having two or more actionable targets, and the remainder having one identified targeted treatment. A molecular targeted treatment was recommended for 676 patients (35% of those tested).
“We showed that the patients who did receive the molecular targeted agents were doing better in terms of overall survival,” said Olivier Tredan, MD, PhD, the study’s lead investigator. Noting that these are trends as the trial was not randomized, he reported that the overall survival (OS) for those receiving targeted treatments was 53.7% at 3 years, compared with 46.1% for those who did not receive targeted treatment. The trend continued out to 5 years, with the OS for the targeted treatment group at 34.8%, compared with 28.1% OS for those who did not receive targeted treatment, he said at the annual meeting of the American Society of Clinical Oncology.
The video associated with this article is no longer available on this site. Please view all of our videos on the MDedge YouTube channel
Many patients either were too sick to receive the recommended treatment or died before they could be treated, Dr. Tredan said in a video interview.
Of the patients who did receive targeted treatment, over 60% received mTOR inhibitors. The next most common therapies were multitarget tyrosine kinase receptor (TKR)–inhibiting/antiangiogenic therapies, received by about one-third of patients. Fewer than one in five patients received any other therapies. Tumor types were colorectal, gynecological, breast, head and neck carcinomas, sarcomas, and brain tumors.
A new randomized clinical study, profiLER 2, is planned. The new study will pit a 315-gene commercial test against the 69-gene test used in profiLER 1, to see whether casting a wider net yields more targets for therapy.
Still, knowing that a treatment might help is useful only if the patient can actually receive the drug, said Dr. Tredan. “What we want is more molecular targeted agent initiation, so we need to have larger screening programs, but we need also to have access to novel targeted agents.”
Dr. Tredan reported financial relationships with Bayer, GlaxoSmithKline, and Novartis.
[email protected]
On Twitter @karioakes
CHICAGO –
Molecular profiling, including genetic sequencing and copy number variation analysis, was performed in 1944 tumors from patients with advanced tumors enrolled in the profiLER study. Of the tumors screened, mutations deemed actionable were identified in 1,004 (52%), with 394 patients having two or more actionable targets, and the remainder having one identified targeted treatment. A molecular targeted treatment was recommended for 676 patients (35% of those tested).
“We showed that the patients who did receive the molecular targeted agents were doing better in terms of overall survival,” said Olivier Tredan, MD, PhD, the study’s lead investigator. Noting that these are trends as the trial was not randomized, he reported that the overall survival (OS) for those receiving targeted treatments was 53.7% at 3 years, compared with 46.1% for those who did not receive targeted treatment. The trend continued out to 5 years, with the OS for the targeted treatment group at 34.8%, compared with 28.1% OS for those who did not receive targeted treatment, he said at the annual meeting of the American Society of Clinical Oncology.
The video associated with this article is no longer available on this site. Please view all of our videos on the MDedge YouTube channel
Many patients either were too sick to receive the recommended treatment or died before they could be treated, Dr. Tredan said in a video interview.
Of the patients who did receive targeted treatment, over 60% received mTOR inhibitors. The next most common therapies were multitarget tyrosine kinase receptor (TKR)–inhibiting/antiangiogenic therapies, received by about one-third of patients. Fewer than one in five patients received any other therapies. Tumor types were colorectal, gynecological, breast, head and neck carcinomas, sarcomas, and brain tumors.
A new randomized clinical study, profiLER 2, is planned. The new study will pit a 315-gene commercial test against the 69-gene test used in profiLER 1, to see whether casting a wider net yields more targets for therapy.
Still, knowing that a treatment might help is useful only if the patient can actually receive the drug, said Dr. Tredan. “What we want is more molecular targeted agent initiation, so we need to have larger screening programs, but we need also to have access to novel targeted agents.”
Dr. Tredan reported financial relationships with Bayer, GlaxoSmithKline, and Novartis.
[email protected]
On Twitter @karioakes
CHICAGO –
Molecular profiling, including genetic sequencing and copy number variation analysis, was performed in 1944 tumors from patients with advanced tumors enrolled in the profiLER study. Of the tumors screened, mutations deemed actionable were identified in 1,004 (52%), with 394 patients having two or more actionable targets, and the remainder having one identified targeted treatment. A molecular targeted treatment was recommended for 676 patients (35% of those tested).
“We showed that the patients who did receive the molecular targeted agents were doing better in terms of overall survival,” said Olivier Tredan, MD, PhD, the study’s lead investigator. Noting that these are trends as the trial was not randomized, he reported that the overall survival (OS) for those receiving targeted treatments was 53.7% at 3 years, compared with 46.1% for those who did not receive targeted treatment. The trend continued out to 5 years, with the OS for the targeted treatment group at 34.8%, compared with 28.1% OS for those who did not receive targeted treatment, he said at the annual meeting of the American Society of Clinical Oncology.
The video associated with this article is no longer available on this site. Please view all of our videos on the MDedge YouTube channel
Many patients either were too sick to receive the recommended treatment or died before they could be treated, Dr. Tredan said in a video interview.
Of the patients who did receive targeted treatment, over 60% received mTOR inhibitors. The next most common therapies were multitarget tyrosine kinase receptor (TKR)–inhibiting/antiangiogenic therapies, received by about one-third of patients. Fewer than one in five patients received any other therapies. Tumor types were colorectal, gynecological, breast, head and neck carcinomas, sarcomas, and brain tumors.
A new randomized clinical study, profiLER 2, is planned. The new study will pit a 315-gene commercial test against the 69-gene test used in profiLER 1, to see whether casting a wider net yields more targets for therapy.
Still, knowing that a treatment might help is useful only if the patient can actually receive the drug, said Dr. Tredan. “What we want is more molecular targeted agent initiation, so we need to have larger screening programs, but we need also to have access to novel targeted agents.”
Dr. Tredan reported financial relationships with Bayer, GlaxoSmithKline, and Novartis.
[email protected]
On Twitter @karioakes
AT ASCO 2017
Immune-agonist combo has activity against several tumor types
CHICAGO – A combination of the programmed death 1 (PD-1) inhibitor nivolumab (Opdivo) with an experimental immune-enhancing monoclonal antibody induced clinical responses in patients with several different solid tumor types, including some patients who had disease progression on a PD-1 inhibitor, investigators reported.
The investigational agent, euphoniously named BMS-986156 (986156), is a fully human immunoglobulin G1 agonist monoclonal antibody with high affinity binding for the glucocorticoid-induced tumor necrosis factor receptor–related gene (GITR).
BMS-986156156 “induces potent antitumor immunity by several mechanisms. First, it increases T-effector cell survival and function. Second, it promotes T-regulatory cell depletion and reduction through its conversion to other immune cells. As well, it reduces T-reg-mediated suppression of T-effector cells,” said Lillian L Siu, MD, from the Princess Margaret Hospital in Toronto.
In preclinical studies, the combination of an anti-GITR and an anti-PD-1 agent showed synergistic activity against murine tumor models.
Dr. Siu and colleagues conducted a phase I/IIa study of BMS-986156 with or without nivolumab in 66 patients with advanced solid tumors.
The 29 patients assigned to BMS-986156 monotherapy were started at 10 mg every 2 weeks, which was gradually titrated upward to find the maximum tolerated dose of 240 mg Q2 weeks.
The 37 patients assigned to the combination were started on a dose of 30-mg nivolumab and 240-mg BMS-986156. The nivolumab dose but not the BMS-986156 dose was then titrated upward to a maximum tolerated dose of 240 mg for each agent. This dose was based on pharmacodynamic and pharmacokinetic studies.
Tumor types included melanoma, cervical, colon, breast, renal, pancreatic, and ovarian cancers and cholangiocarcinoma.
Approximately one-third of patients in the monotherapy arm and nearly half of those in the combination arm had undergone three or more prior therapies for cancer. Seven patients in the monotherapy group and five in the combination group had previously received a PD-1 or PD-L1 inhibitor.
The median duration of treatment ranged from 7 to 15.5 weeks for 156 monotherapy and 8 to 18 weeks for the combination.
Safe and well tolerated
There were no dose-limiting toxicities or treatment-related deaths in either study arm, and patients tolerated both BMS-986156 monotherapy and the combination well. There were no grade 3 or 4 adverse events in the monotherapy arm.
“In the combination arm, the toxicity is very consistent with that observed with nivolumab monotherapy alone,” Dr. Siu said.
The only grade 4 event in this group was an increase in blood creatine phosphokinase. In this group, there were six grade 3 adverse events, including one each of colitis, dehydration, fatigue and increases in hepatic enzymes, lipase increase, and lung infection.
In pharmacokinetic studies, the action of the combinations was linear, with dose-related increases in exposure, and the combination had low immunogenicity, with no patients developing persistent antidrug antibodies.
The combination was also associated with increases in natural killer and CD8 cells in peripheral blood. Immunophenotyping of patients treated with the 240/240-mg dose of the combination showed increased proliferation and activation of CD8 effector cells, central memory cells, and CD4 cells.
Early promise
Dr. Siu reviewed interim efficacy results for the five patients treated with the combination who had responses.
For example, a 44-year-old woman with metastatic cervical cancer – a tumor type known to have high levels of GITR expression – had received more than three prior lines of therapy, including chemotherapy with a vascular endothelial growth factor inhibitor. She had a partial response with the combination, with an approximately 62% reduction in tumor burden. She had an ongoing response to the combination at the time of data cutoff in March 2017.
Two other patients had partial responses after progression on an anti-PD-1 agents, including one with nasopharyngeal cancer who had received three prior lines of therapy, including chemotherapy and a PD-1 inhibitor. This patient had an approximately 43% reduction in tumor burden, with a 17-week duration of response and ongoing response at data cutoff.
The other patient was a 59-year-old with malignant melanoma that had advanced on pembrolizumab (Keytruda). This patient too had received three prior lines of therapy, including a BRAF inhibitor, anti-PD-1, and BRAF/MEK inhibitor combination.
This patient had a response of 24-week duration at the time of data cutoff. It is ongoing, Dr. Liu said.
“This combination of immune agonists was safe with a low incidence of severe toxicity, and there was no maximum tolerated dose; however, the maximum administered dose may not be the most effective dose to move forward,” commented Siwen Hu-Lieskovan MD, PhD, from the Jonsson Comprehensive Cancer Center at the University of California, Los Angeles, the invited discussant.
She noted that activity of the combination has been seen in a wide range of tumor histologies but added that further biomarker studies will be critical for identifying patients who are likely to respond.
The study was funded by Bristol-Myers Squibb. Dr. Siu disclosed research funding from the company and others and consulting/advising several different companies. Dr. Hu-Lieskovan disclosed institutional research funding from BMS and other companies, as well as honoraria and consulting and serving in an advisory capacity for companies other than BMS. Several coauthors are employees of the company.
CHICAGO – A combination of the programmed death 1 (PD-1) inhibitor nivolumab (Opdivo) with an experimental immune-enhancing monoclonal antibody induced clinical responses in patients with several different solid tumor types, including some patients who had disease progression on a PD-1 inhibitor, investigators reported.
The investigational agent, euphoniously named BMS-986156 (986156), is a fully human immunoglobulin G1 agonist monoclonal antibody with high affinity binding for the glucocorticoid-induced tumor necrosis factor receptor–related gene (GITR).
BMS-986156156 “induces potent antitumor immunity by several mechanisms. First, it increases T-effector cell survival and function. Second, it promotes T-regulatory cell depletion and reduction through its conversion to other immune cells. As well, it reduces T-reg-mediated suppression of T-effector cells,” said Lillian L Siu, MD, from the Princess Margaret Hospital in Toronto.
In preclinical studies, the combination of an anti-GITR and an anti-PD-1 agent showed synergistic activity against murine tumor models.
Dr. Siu and colleagues conducted a phase I/IIa study of BMS-986156 with or without nivolumab in 66 patients with advanced solid tumors.
The 29 patients assigned to BMS-986156 monotherapy were started at 10 mg every 2 weeks, which was gradually titrated upward to find the maximum tolerated dose of 240 mg Q2 weeks.
The 37 patients assigned to the combination were started on a dose of 30-mg nivolumab and 240-mg BMS-986156. The nivolumab dose but not the BMS-986156 dose was then titrated upward to a maximum tolerated dose of 240 mg for each agent. This dose was based on pharmacodynamic and pharmacokinetic studies.
Tumor types included melanoma, cervical, colon, breast, renal, pancreatic, and ovarian cancers and cholangiocarcinoma.
Approximately one-third of patients in the monotherapy arm and nearly half of those in the combination arm had undergone three or more prior therapies for cancer. Seven patients in the monotherapy group and five in the combination group had previously received a PD-1 or PD-L1 inhibitor.
The median duration of treatment ranged from 7 to 15.5 weeks for 156 monotherapy and 8 to 18 weeks for the combination.
Safe and well tolerated
There were no dose-limiting toxicities or treatment-related deaths in either study arm, and patients tolerated both BMS-986156 monotherapy and the combination well. There were no grade 3 or 4 adverse events in the monotherapy arm.
“In the combination arm, the toxicity is very consistent with that observed with nivolumab monotherapy alone,” Dr. Siu said.
The only grade 4 event in this group was an increase in blood creatine phosphokinase. In this group, there were six grade 3 adverse events, including one each of colitis, dehydration, fatigue and increases in hepatic enzymes, lipase increase, and lung infection.
In pharmacokinetic studies, the action of the combinations was linear, with dose-related increases in exposure, and the combination had low immunogenicity, with no patients developing persistent antidrug antibodies.
The combination was also associated with increases in natural killer and CD8 cells in peripheral blood. Immunophenotyping of patients treated with the 240/240-mg dose of the combination showed increased proliferation and activation of CD8 effector cells, central memory cells, and CD4 cells.
Early promise
Dr. Siu reviewed interim efficacy results for the five patients treated with the combination who had responses.
For example, a 44-year-old woman with metastatic cervical cancer – a tumor type known to have high levels of GITR expression – had received more than three prior lines of therapy, including chemotherapy with a vascular endothelial growth factor inhibitor. She had a partial response with the combination, with an approximately 62% reduction in tumor burden. She had an ongoing response to the combination at the time of data cutoff in March 2017.
Two other patients had partial responses after progression on an anti-PD-1 agents, including one with nasopharyngeal cancer who had received three prior lines of therapy, including chemotherapy and a PD-1 inhibitor. This patient had an approximately 43% reduction in tumor burden, with a 17-week duration of response and ongoing response at data cutoff.
The other patient was a 59-year-old with malignant melanoma that had advanced on pembrolizumab (Keytruda). This patient too had received three prior lines of therapy, including a BRAF inhibitor, anti-PD-1, and BRAF/MEK inhibitor combination.
This patient had a response of 24-week duration at the time of data cutoff. It is ongoing, Dr. Liu said.
“This combination of immune agonists was safe with a low incidence of severe toxicity, and there was no maximum tolerated dose; however, the maximum administered dose may not be the most effective dose to move forward,” commented Siwen Hu-Lieskovan MD, PhD, from the Jonsson Comprehensive Cancer Center at the University of California, Los Angeles, the invited discussant.
She noted that activity of the combination has been seen in a wide range of tumor histologies but added that further biomarker studies will be critical for identifying patients who are likely to respond.
The study was funded by Bristol-Myers Squibb. Dr. Siu disclosed research funding from the company and others and consulting/advising several different companies. Dr. Hu-Lieskovan disclosed institutional research funding from BMS and other companies, as well as honoraria and consulting and serving in an advisory capacity for companies other than BMS. Several coauthors are employees of the company.
CHICAGO – A combination of the programmed death 1 (PD-1) inhibitor nivolumab (Opdivo) with an experimental immune-enhancing monoclonal antibody induced clinical responses in patients with several different solid tumor types, including some patients who had disease progression on a PD-1 inhibitor, investigators reported.
The investigational agent, euphoniously named BMS-986156 (986156), is a fully human immunoglobulin G1 agonist monoclonal antibody with high affinity binding for the glucocorticoid-induced tumor necrosis factor receptor–related gene (GITR).
BMS-986156156 “induces potent antitumor immunity by several mechanisms. First, it increases T-effector cell survival and function. Second, it promotes T-regulatory cell depletion and reduction through its conversion to other immune cells. As well, it reduces T-reg-mediated suppression of T-effector cells,” said Lillian L Siu, MD, from the Princess Margaret Hospital in Toronto.
In preclinical studies, the combination of an anti-GITR and an anti-PD-1 agent showed synergistic activity against murine tumor models.
Dr. Siu and colleagues conducted a phase I/IIa study of BMS-986156 with or without nivolumab in 66 patients with advanced solid tumors.
The 29 patients assigned to BMS-986156 monotherapy were started at 10 mg every 2 weeks, which was gradually titrated upward to find the maximum tolerated dose of 240 mg Q2 weeks.
The 37 patients assigned to the combination were started on a dose of 30-mg nivolumab and 240-mg BMS-986156. The nivolumab dose but not the BMS-986156 dose was then titrated upward to a maximum tolerated dose of 240 mg for each agent. This dose was based on pharmacodynamic and pharmacokinetic studies.
Tumor types included melanoma, cervical, colon, breast, renal, pancreatic, and ovarian cancers and cholangiocarcinoma.
Approximately one-third of patients in the monotherapy arm and nearly half of those in the combination arm had undergone three or more prior therapies for cancer. Seven patients in the monotherapy group and five in the combination group had previously received a PD-1 or PD-L1 inhibitor.
The median duration of treatment ranged from 7 to 15.5 weeks for 156 monotherapy and 8 to 18 weeks for the combination.
Safe and well tolerated
There were no dose-limiting toxicities or treatment-related deaths in either study arm, and patients tolerated both BMS-986156 monotherapy and the combination well. There were no grade 3 or 4 adverse events in the monotherapy arm.
“In the combination arm, the toxicity is very consistent with that observed with nivolumab monotherapy alone,” Dr. Siu said.
The only grade 4 event in this group was an increase in blood creatine phosphokinase. In this group, there were six grade 3 adverse events, including one each of colitis, dehydration, fatigue and increases in hepatic enzymes, lipase increase, and lung infection.
In pharmacokinetic studies, the action of the combinations was linear, with dose-related increases in exposure, and the combination had low immunogenicity, with no patients developing persistent antidrug antibodies.
The combination was also associated with increases in natural killer and CD8 cells in peripheral blood. Immunophenotyping of patients treated with the 240/240-mg dose of the combination showed increased proliferation and activation of CD8 effector cells, central memory cells, and CD4 cells.
Early promise
Dr. Siu reviewed interim efficacy results for the five patients treated with the combination who had responses.
For example, a 44-year-old woman with metastatic cervical cancer – a tumor type known to have high levels of GITR expression – had received more than three prior lines of therapy, including chemotherapy with a vascular endothelial growth factor inhibitor. She had a partial response with the combination, with an approximately 62% reduction in tumor burden. She had an ongoing response to the combination at the time of data cutoff in March 2017.
Two other patients had partial responses after progression on an anti-PD-1 agents, including one with nasopharyngeal cancer who had received three prior lines of therapy, including chemotherapy and a PD-1 inhibitor. This patient had an approximately 43% reduction in tumor burden, with a 17-week duration of response and ongoing response at data cutoff.
The other patient was a 59-year-old with malignant melanoma that had advanced on pembrolizumab (Keytruda). This patient too had received three prior lines of therapy, including a BRAF inhibitor, anti-PD-1, and BRAF/MEK inhibitor combination.
This patient had a response of 24-week duration at the time of data cutoff. It is ongoing, Dr. Liu said.
“This combination of immune agonists was safe with a low incidence of severe toxicity, and there was no maximum tolerated dose; however, the maximum administered dose may not be the most effective dose to move forward,” commented Siwen Hu-Lieskovan MD, PhD, from the Jonsson Comprehensive Cancer Center at the University of California, Los Angeles, the invited discussant.
She noted that activity of the combination has been seen in a wide range of tumor histologies but added that further biomarker studies will be critical for identifying patients who are likely to respond.
The study was funded by Bristol-Myers Squibb. Dr. Siu disclosed research funding from the company and others and consulting/advising several different companies. Dr. Hu-Lieskovan disclosed institutional research funding from BMS and other companies, as well as honoraria and consulting and serving in an advisory capacity for companies other than BMS. Several coauthors are employees of the company.
AT ASCO 2017
Key clinical point: A combination of a GITR-agonist and anti-PD-1 agent was safe and produced partial responses in patients with heavily pretreated advanced cancers.
Major finding: Two patients with cancers that had progression on a PD-1 inhibitor had durable partial responses.
Data source: A phase I/IIa dose-finding and safety study of BMS986156 alone or in combination with nivolumab (Opdivo).
Disclosures: The study was funded by Bristol-Myers Squibb. Dr. Siu disclosed research funding from the company and others and consulting/advising for several different companies. Dr. Hu-Lieskovan disclosed institutional research funding from BMS and other companies, as well as honoraria and consulting and serving in an advisory capacity for companies other than BMS. Several coauthors are employees of the company.
Cirrhosis linked to increased risk of stroke
reported online June 5 in JAMA Neurology.
Cirrhosis is known to be associated with “extrahepatic hemorrhagic and thrombotic processes, such as GI bleeding and venous thromboembolism. [But] the cerebrovascular complications of cirrhosis are comparatively less well understood.” Previous studies of the association with stroke have been small and have yielded conflicting results, with some finding a reduced incidence of stroke and others finding an increase among cirrhosis patients, said Neal S. Parikh, MD, of the Fell Family Brain and Mind Research Institute and Weill Cornell Medicine, both in New York, and his associates.
After the data were adjusted to account for stroke risk factors, relevant comorbidities, and demographic traits, the annual incidence of any type of stroke was significantly higher with cirrhosis than without cirrhosis (hazard ratio, 1.4). The association was stronger for intracranial hemorrhage (HR, 1.9) and subarachnoid hemorrhage (HR, 2.4) than for ischemic stroke (HR, 1.3).
The results of several secondary and sensitivity analyses were consistent with those of the primary analysis, regardless of whether the cirrhosis was alcohol-related or the stroke was fatal. The association was strongest among patients who had decompensated cirrhosis and was not evident at all among patients who had mild liver disease, Dr. Parikh and his associates said (JAMA Neurol. 2017 Jun 5 [doi: 10.1001/jamaneurol.2017.0923).
This study was not designed to explore the reasons for an association between cirrhosis and stroke, but the investigators noted many possible explanations. First, “cirrhosis is accompanied by a mixed coagulopathy, with potential implications for hemorrhagic and thrombotic processes.” It has been linked to many bleeding complications, including, most recently, cerebral microhemorrhages detectable on brain MRI. In addition, the underlying causes of cirrhosis, including alcohol abuse, hepatitis infection, and metabolic disease, may also contribute to stroke risk.
Alternatively, clinicians caring for patients with cirrhosis “may limit the aggressiveness of stroke prevention” – for example, by limiting antithrombotic medications or statins – because they are mindful of the patient’s increased risk of bleeding and hepatic toxicity, the investigators said.
reported online June 5 in JAMA Neurology.
Cirrhosis is known to be associated with “extrahepatic hemorrhagic and thrombotic processes, such as GI bleeding and venous thromboembolism. [But] the cerebrovascular complications of cirrhosis are comparatively less well understood.” Previous studies of the association with stroke have been small and have yielded conflicting results, with some finding a reduced incidence of stroke and others finding an increase among cirrhosis patients, said Neal S. Parikh, MD, of the Fell Family Brain and Mind Research Institute and Weill Cornell Medicine, both in New York, and his associates.
After the data were adjusted to account for stroke risk factors, relevant comorbidities, and demographic traits, the annual incidence of any type of stroke was significantly higher with cirrhosis than without cirrhosis (hazard ratio, 1.4). The association was stronger for intracranial hemorrhage (HR, 1.9) and subarachnoid hemorrhage (HR, 2.4) than for ischemic stroke (HR, 1.3).
The results of several secondary and sensitivity analyses were consistent with those of the primary analysis, regardless of whether the cirrhosis was alcohol-related or the stroke was fatal. The association was strongest among patients who had decompensated cirrhosis and was not evident at all among patients who had mild liver disease, Dr. Parikh and his associates said (JAMA Neurol. 2017 Jun 5 [doi: 10.1001/jamaneurol.2017.0923).
This study was not designed to explore the reasons for an association between cirrhosis and stroke, but the investigators noted many possible explanations. First, “cirrhosis is accompanied by a mixed coagulopathy, with potential implications for hemorrhagic and thrombotic processes.” It has been linked to many bleeding complications, including, most recently, cerebral microhemorrhages detectable on brain MRI. In addition, the underlying causes of cirrhosis, including alcohol abuse, hepatitis infection, and metabolic disease, may also contribute to stroke risk.
Alternatively, clinicians caring for patients with cirrhosis “may limit the aggressiveness of stroke prevention” – for example, by limiting antithrombotic medications or statins – because they are mindful of the patient’s increased risk of bleeding and hepatic toxicity, the investigators said.
reported online June 5 in JAMA Neurology.
Cirrhosis is known to be associated with “extrahepatic hemorrhagic and thrombotic processes, such as GI bleeding and venous thromboembolism. [But] the cerebrovascular complications of cirrhosis are comparatively less well understood.” Previous studies of the association with stroke have been small and have yielded conflicting results, with some finding a reduced incidence of stroke and others finding an increase among cirrhosis patients, said Neal S. Parikh, MD, of the Fell Family Brain and Mind Research Institute and Weill Cornell Medicine, both in New York, and his associates.
After the data were adjusted to account for stroke risk factors, relevant comorbidities, and demographic traits, the annual incidence of any type of stroke was significantly higher with cirrhosis than without cirrhosis (hazard ratio, 1.4). The association was stronger for intracranial hemorrhage (HR, 1.9) and subarachnoid hemorrhage (HR, 2.4) than for ischemic stroke (HR, 1.3).
The results of several secondary and sensitivity analyses were consistent with those of the primary analysis, regardless of whether the cirrhosis was alcohol-related or the stroke was fatal. The association was strongest among patients who had decompensated cirrhosis and was not evident at all among patients who had mild liver disease, Dr. Parikh and his associates said (JAMA Neurol. 2017 Jun 5 [doi: 10.1001/jamaneurol.2017.0923).
This study was not designed to explore the reasons for an association between cirrhosis and stroke, but the investigators noted many possible explanations. First, “cirrhosis is accompanied by a mixed coagulopathy, with potential implications for hemorrhagic and thrombotic processes.” It has been linked to many bleeding complications, including, most recently, cerebral microhemorrhages detectable on brain MRI. In addition, the underlying causes of cirrhosis, including alcohol abuse, hepatitis infection, and metabolic disease, may also contribute to stroke risk.
Alternatively, clinicians caring for patients with cirrhosis “may limit the aggressiveness of stroke prevention” – for example, by limiting antithrombotic medications or statins – because they are mindful of the patient’s increased risk of bleeding and hepatic toxicity, the investigators said.
FROM JAMA NEUROLOGY
Key clinical point: Cirrhosis was associated with an increased risk of stroke, especially hemorrhagic stroke, in a large nationally representative cohort study.
Major finding: The annual incidence of any type of stroke was significantly higher with cirrhosis than without cirrhosis (HR, 1.4), and this association was stronger for intracranial hemorrhage (HR, 1.9) and subarachnoid hemorrhage (HR, 2.4) than for ischemic stroke (HR, 1.3).
Data source: A retrospective cohort study involving a nationally representative sample of 1.6 million Medicare patients.
Disclosures: This study was supported by the National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke and the Florence Gould Endowment for Discovery in Stroke. Dr. Parikh and his associates reported having no relevant financial disclosures.
VIDEO: Phase III results show promise for erenumab as migraine prevention drug
BOSTON – Two phase III trials of the investigational monoclonal antibody erenumab show promising results in reducing – but not eliminating – days affected by migraines and related disruptions in daily life with limited side effects, representing “an entirely new way forward” in migraine prevention, according to Peter Goadsby, MD.
In May, shortly after the results were released at the annual meeting of the American Academy of Neurology, Amgen filed regulatory documents for erenumab with the Food and Drug Administration.
Erenumab, also known as AMG 334, “is going to be the first mechanism-specific, migraine-targeted preventive treatment approach ever,” Dr. Goadsby, a University of California, San Francisco, neurologist, predicted at the annual meeting of the American Academy of Neurology. Erenumab is a fully human monoclonal antibody that is designed to block the calcitonin gene-related peptide (CGRP) receptor, which is linked to migraine.
Several drug makers are investigating CGRP-modulating treatments for migraine. Results suggest that the medications are “effective for episodic and migraine patients,” said Amaal Starling, MD, of the Mayo Clinic, Scottsdale, Ariz., who spoke about the drugs in a plenary session at the meeting. “They have rapid onset of efficacy, minimal side effects, and infrequent administration. All of these things may improve adherence.”
Dr. Goadsby is the lead author of the study reporting phase III results from the 24-week STRIVE trial, which tested two monthly subcutaneous doses of erenumab (70 mg and 140 mg) against placebo in a 1:1:1 ratio in 955 patients. The patients all had suffered from episodic migraine for at least a year.
“STRIVE has shown that the 70-mg and 140-mg doses are better than placebo at the regulatory endpoint and clinically relevant endpoints,” Dr. Goadsby said, “and there are improvements in function, everyday activities, and physical impairment. The overall frequency of adverse and serious events were comparable, even the same.”
The participants reported an average of 8.3 monthly migraine days (MMDs) at the beginning of the study. At the end, the number declined significantly by an average of 3.2 days (70-mg dose), 3.7 days (140-mg dose), and 1.8 days (placebo; P less than .001).
Half of those in the 140-mg group achieved at least a 50% reduction in MMDs, compared with 43% and 27% for the 70-mg and placebo groups, respectively (P less than .001).
The researchers also examined changes in scores regarding Physical Impairment (PI) and Impact on Everyday Activities (EA) as determined by the Migraine Physical Function Impact Diary. PI scores improved by 4.2, 4.8, and 2.4 points in the 70-mg, 140-mg, and placebo groups, respectively. EA scores improved by 5.5, 5.9, and 3.3 points, respectively (P less than .001).
The study authors reported that tolerability was similar for placebo and the drug. The most common adverse events were nasopharyngitis, upper respiratory tract infection, and sinusitis.
The researchers at the AAN meeting also released the results of a second study known as ARISE, led by David W. Dodick, MD, of the Mayo Clinic, Phoenix, Ariz. This double-blind, 12-week trial randomly assigned 577 adults with episodic migraine to a monthly subcutaneous dose of a placebo or 70 mg of erenumab.
The patients reported an average of 8.3 MMDs at the beginning of the trial. Those who took the medication reported an average 2.9 fewer MMDs while those who took the placebo reported 1.8 fewer MMDs (P less than .001) at 9-12 weeks.
Forty percent of those who took the drug saw a decrease of at least half in MMDs, compared with 30% of those who took placebo (odds ratio, 1.6; P = .010).
The PI levels declined by at least 5 points in 27% of placebo patients and 33% of erenumab patients (P = .13). EA levels declined by at least 5 points in 36% of placebo patients and 40% of erenumab patients (P = .26)
There were similar levels of adverse events in both drug and placebo groups, led by upper respiratory tract infection, injection site pain, and nasopharyngitis.
The Mayo Clinic’s Dr. Starling said anti-CGRP medications may dramatically improve the world of preventive migraine treatments, which are recommended for a third of migraine patients. Only about 3%-13% use them, she said.
In the future, it may be possible to be able to identify and target “super-responders” whose MMDs dip by 75% or more in some cases.
But there are questions, she said. The drugs’ specific mechanism for blocking migraine is not yet clear, and it’s also not clear if the CGRP antagonists could push patients at risk of TIA or cardiac angina to have a stroke instead.
Dr. Starling discussed some of the implications of the CGRP antagonists in development in a video interview.
Both studies were funded by Amgen. Dr. Goadsby reported numerous grants and personal fees from multiple drug makers, including Amgen. Dr. Starling reported support from Amgen, eNeura, and Eli Lilly. Dr. Dodick disclosed many relationships with pharmaceutical companies developing or marketing drugs for headache and migraine, including Amgen.
The video associated with this article is no longer available on this site. Please view all of our videos on the MDedge YouTube channel
BOSTON – Two phase III trials of the investigational monoclonal antibody erenumab show promising results in reducing – but not eliminating – days affected by migraines and related disruptions in daily life with limited side effects, representing “an entirely new way forward” in migraine prevention, according to Peter Goadsby, MD.
In May, shortly after the results were released at the annual meeting of the American Academy of Neurology, Amgen filed regulatory documents for erenumab with the Food and Drug Administration.
Erenumab, also known as AMG 334, “is going to be the first mechanism-specific, migraine-targeted preventive treatment approach ever,” Dr. Goadsby, a University of California, San Francisco, neurologist, predicted at the annual meeting of the American Academy of Neurology. Erenumab is a fully human monoclonal antibody that is designed to block the calcitonin gene-related peptide (CGRP) receptor, which is linked to migraine.
Several drug makers are investigating CGRP-modulating treatments for migraine. Results suggest that the medications are “effective for episodic and migraine patients,” said Amaal Starling, MD, of the Mayo Clinic, Scottsdale, Ariz., who spoke about the drugs in a plenary session at the meeting. “They have rapid onset of efficacy, minimal side effects, and infrequent administration. All of these things may improve adherence.”
Dr. Goadsby is the lead author of the study reporting phase III results from the 24-week STRIVE trial, which tested two monthly subcutaneous doses of erenumab (70 mg and 140 mg) against placebo in a 1:1:1 ratio in 955 patients. The patients all had suffered from episodic migraine for at least a year.
“STRIVE has shown that the 70-mg and 140-mg doses are better than placebo at the regulatory endpoint and clinically relevant endpoints,” Dr. Goadsby said, “and there are improvements in function, everyday activities, and physical impairment. The overall frequency of adverse and serious events were comparable, even the same.”
The participants reported an average of 8.3 monthly migraine days (MMDs) at the beginning of the study. At the end, the number declined significantly by an average of 3.2 days (70-mg dose), 3.7 days (140-mg dose), and 1.8 days (placebo; P less than .001).
Half of those in the 140-mg group achieved at least a 50% reduction in MMDs, compared with 43% and 27% for the 70-mg and placebo groups, respectively (P less than .001).
The researchers also examined changes in scores regarding Physical Impairment (PI) and Impact on Everyday Activities (EA) as determined by the Migraine Physical Function Impact Diary. PI scores improved by 4.2, 4.8, and 2.4 points in the 70-mg, 140-mg, and placebo groups, respectively. EA scores improved by 5.5, 5.9, and 3.3 points, respectively (P less than .001).
The study authors reported that tolerability was similar for placebo and the drug. The most common adverse events were nasopharyngitis, upper respiratory tract infection, and sinusitis.
The researchers at the AAN meeting also released the results of a second study known as ARISE, led by David W. Dodick, MD, of the Mayo Clinic, Phoenix, Ariz. This double-blind, 12-week trial randomly assigned 577 adults with episodic migraine to a monthly subcutaneous dose of a placebo or 70 mg of erenumab.
The patients reported an average of 8.3 MMDs at the beginning of the trial. Those who took the medication reported an average 2.9 fewer MMDs while those who took the placebo reported 1.8 fewer MMDs (P less than .001) at 9-12 weeks.
Forty percent of those who took the drug saw a decrease of at least half in MMDs, compared with 30% of those who took placebo (odds ratio, 1.6; P = .010).
The PI levels declined by at least 5 points in 27% of placebo patients and 33% of erenumab patients (P = .13). EA levels declined by at least 5 points in 36% of placebo patients and 40% of erenumab patients (P = .26)
There were similar levels of adverse events in both drug and placebo groups, led by upper respiratory tract infection, injection site pain, and nasopharyngitis.
The Mayo Clinic’s Dr. Starling said anti-CGRP medications may dramatically improve the world of preventive migraine treatments, which are recommended for a third of migraine patients. Only about 3%-13% use them, she said.
In the future, it may be possible to be able to identify and target “super-responders” whose MMDs dip by 75% or more in some cases.
But there are questions, she said. The drugs’ specific mechanism for blocking migraine is not yet clear, and it’s also not clear if the CGRP antagonists could push patients at risk of TIA or cardiac angina to have a stroke instead.
Dr. Starling discussed some of the implications of the CGRP antagonists in development in a video interview.
Both studies were funded by Amgen. Dr. Goadsby reported numerous grants and personal fees from multiple drug makers, including Amgen. Dr. Starling reported support from Amgen, eNeura, and Eli Lilly. Dr. Dodick disclosed many relationships with pharmaceutical companies developing or marketing drugs for headache and migraine, including Amgen.
The video associated with this article is no longer available on this site. Please view all of our videos on the MDedge YouTube channel
BOSTON – Two phase III trials of the investigational monoclonal antibody erenumab show promising results in reducing – but not eliminating – days affected by migraines and related disruptions in daily life with limited side effects, representing “an entirely new way forward” in migraine prevention, according to Peter Goadsby, MD.
In May, shortly after the results were released at the annual meeting of the American Academy of Neurology, Amgen filed regulatory documents for erenumab with the Food and Drug Administration.
Erenumab, also known as AMG 334, “is going to be the first mechanism-specific, migraine-targeted preventive treatment approach ever,” Dr. Goadsby, a University of California, San Francisco, neurologist, predicted at the annual meeting of the American Academy of Neurology. Erenumab is a fully human monoclonal antibody that is designed to block the calcitonin gene-related peptide (CGRP) receptor, which is linked to migraine.
Several drug makers are investigating CGRP-modulating treatments for migraine. Results suggest that the medications are “effective for episodic and migraine patients,” said Amaal Starling, MD, of the Mayo Clinic, Scottsdale, Ariz., who spoke about the drugs in a plenary session at the meeting. “They have rapid onset of efficacy, minimal side effects, and infrequent administration. All of these things may improve adherence.”
Dr. Goadsby is the lead author of the study reporting phase III results from the 24-week STRIVE trial, which tested two monthly subcutaneous doses of erenumab (70 mg and 140 mg) against placebo in a 1:1:1 ratio in 955 patients. The patients all had suffered from episodic migraine for at least a year.
“STRIVE has shown that the 70-mg and 140-mg doses are better than placebo at the regulatory endpoint and clinically relevant endpoints,” Dr. Goadsby said, “and there are improvements in function, everyday activities, and physical impairment. The overall frequency of adverse and serious events were comparable, even the same.”
The participants reported an average of 8.3 monthly migraine days (MMDs) at the beginning of the study. At the end, the number declined significantly by an average of 3.2 days (70-mg dose), 3.7 days (140-mg dose), and 1.8 days (placebo; P less than .001).
Half of those in the 140-mg group achieved at least a 50% reduction in MMDs, compared with 43% and 27% for the 70-mg and placebo groups, respectively (P less than .001).
The researchers also examined changes in scores regarding Physical Impairment (PI) and Impact on Everyday Activities (EA) as determined by the Migraine Physical Function Impact Diary. PI scores improved by 4.2, 4.8, and 2.4 points in the 70-mg, 140-mg, and placebo groups, respectively. EA scores improved by 5.5, 5.9, and 3.3 points, respectively (P less than .001).
The study authors reported that tolerability was similar for placebo and the drug. The most common adverse events were nasopharyngitis, upper respiratory tract infection, and sinusitis.
The researchers at the AAN meeting also released the results of a second study known as ARISE, led by David W. Dodick, MD, of the Mayo Clinic, Phoenix, Ariz. This double-blind, 12-week trial randomly assigned 577 adults with episodic migraine to a monthly subcutaneous dose of a placebo or 70 mg of erenumab.
The patients reported an average of 8.3 MMDs at the beginning of the trial. Those who took the medication reported an average 2.9 fewer MMDs while those who took the placebo reported 1.8 fewer MMDs (P less than .001) at 9-12 weeks.
Forty percent of those who took the drug saw a decrease of at least half in MMDs, compared with 30% of those who took placebo (odds ratio, 1.6; P = .010).
The PI levels declined by at least 5 points in 27% of placebo patients and 33% of erenumab patients (P = .13). EA levels declined by at least 5 points in 36% of placebo patients and 40% of erenumab patients (P = .26)
There were similar levels of adverse events in both drug and placebo groups, led by upper respiratory tract infection, injection site pain, and nasopharyngitis.
The Mayo Clinic’s Dr. Starling said anti-CGRP medications may dramatically improve the world of preventive migraine treatments, which are recommended for a third of migraine patients. Only about 3%-13% use them, she said.
In the future, it may be possible to be able to identify and target “super-responders” whose MMDs dip by 75% or more in some cases.
But there are questions, she said. The drugs’ specific mechanism for blocking migraine is not yet clear, and it’s also not clear if the CGRP antagonists could push patients at risk of TIA or cardiac angina to have a stroke instead.
Dr. Starling discussed some of the implications of the CGRP antagonists in development in a video interview.
Both studies were funded by Amgen. Dr. Goadsby reported numerous grants and personal fees from multiple drug makers, including Amgen. Dr. Starling reported support from Amgen, eNeura, and Eli Lilly. Dr. Dodick disclosed many relationships with pharmaceutical companies developing or marketing drugs for headache and migraine, including Amgen.
The video associated with this article is no longer available on this site. Please view all of our videos on the MDedge YouTube channel
AT AAN 2017
Female predisposition to anxiety disorders may have prenatal origin
SAN FRANCISCO – Why are anxiety disorders twice as prevalent in women as in men? As in Hawaiian hula dancing, the expressive hands may tell the tale.
The ratio of the length of the index finger to ring finger – known as the 2D:4D ratio – is a physical trait that remains stable across the lifetimes of males and females. It’s also a reliable indicator of prenatal exposure to androgens. In female college students, the higher the 2D:4D ratio, the greater their level of ruminative thinking, which is known to be both a risk factor and maintenance factor for anxiety, Ellie Shuo Jin reported at the annual conference of the Anxiety and Depression Association of America.
The findings shed new light on the relationship between testosterone and anxiety disorders, according to Ms. Jin, a doctoral student at the University of Texas, Austin. The hormone previously has been linked to reduced levels of anxiety, an observation consistent with the lower prevalence of anxiety disorders in men. However, it has been unclear whether prenatal exposure to testosterone, which encourages organizational effects, or the activational effects of postnatal exposure to the hormone is most protective against anxiety disorders.
Ms. Jin found that prenatal testosterone exposure as reflected in a low 2D:4D ratio was associated with a lower level of repetitive negative thinking as measured using the Perseverative Thinking Questionnaire but only in the female students.
She reported having no financial conflicts of interest regarding her study.
SAN FRANCISCO – Why are anxiety disorders twice as prevalent in women as in men? As in Hawaiian hula dancing, the expressive hands may tell the tale.
The ratio of the length of the index finger to ring finger – known as the 2D:4D ratio – is a physical trait that remains stable across the lifetimes of males and females. It’s also a reliable indicator of prenatal exposure to androgens. In female college students, the higher the 2D:4D ratio, the greater their level of ruminative thinking, which is known to be both a risk factor and maintenance factor for anxiety, Ellie Shuo Jin reported at the annual conference of the Anxiety and Depression Association of America.
The findings shed new light on the relationship between testosterone and anxiety disorders, according to Ms. Jin, a doctoral student at the University of Texas, Austin. The hormone previously has been linked to reduced levels of anxiety, an observation consistent with the lower prevalence of anxiety disorders in men. However, it has been unclear whether prenatal exposure to testosterone, which encourages organizational effects, or the activational effects of postnatal exposure to the hormone is most protective against anxiety disorders.
Ms. Jin found that prenatal testosterone exposure as reflected in a low 2D:4D ratio was associated with a lower level of repetitive negative thinking as measured using the Perseverative Thinking Questionnaire but only in the female students.
She reported having no financial conflicts of interest regarding her study.
SAN FRANCISCO – Why are anxiety disorders twice as prevalent in women as in men? As in Hawaiian hula dancing, the expressive hands may tell the tale.
The ratio of the length of the index finger to ring finger – known as the 2D:4D ratio – is a physical trait that remains stable across the lifetimes of males and females. It’s also a reliable indicator of prenatal exposure to androgens. In female college students, the higher the 2D:4D ratio, the greater their level of ruminative thinking, which is known to be both a risk factor and maintenance factor for anxiety, Ellie Shuo Jin reported at the annual conference of the Anxiety and Depression Association of America.
The findings shed new light on the relationship between testosterone and anxiety disorders, according to Ms. Jin, a doctoral student at the University of Texas, Austin. The hormone previously has been linked to reduced levels of anxiety, an observation consistent with the lower prevalence of anxiety disorders in men. However, it has been unclear whether prenatal exposure to testosterone, which encourages organizational effects, or the activational effects of postnatal exposure to the hormone is most protective against anxiety disorders.
Ms. Jin found that prenatal testosterone exposure as reflected in a low 2D:4D ratio was associated with a lower level of repetitive negative thinking as measured using the Perseverative Thinking Questionnaire but only in the female students.
She reported having no financial conflicts of interest regarding her study.
AT THE ANXIETY AND DEPRESSION CONFERENCE 2017
Key clinical point:
Major finding: The higher the ratio of the length of the index finger to the ring finger on the left hand, the greater the predisposition to repetitive negative thinking in women but not in men.
Data source: This cross-sectional study correlated the 2D:4D digit ratio to levels of repetitive negative thinking in 103 college students.
Disclosures: The presenter reported having no financial conflicts regarding her study.