User login
Why young hemophiliacs skip prophylaxis
Some young hemophilia patients may not be sticking to their prophylaxis regimens for psychosocial reasons, according to research published in PLOS ONE.
The study included 78 hemophilia patients, ages 12 to 25, treated at 13 centers in England and Wales.
“This research has a specific focus on young people rather than including patients of all age groups,” said study author Sandra Van Os, a PhD student at the University of Hertfordshire in Hatfield, UK.
“This is important since young people are likely to have had a very different experience than the older generations due to the revolutionary improvements in treatment achieved during the past 2 decades. Another key issue is rather than asking parents or healthcare professionals to estimate adherence as previous studies have done, this study asked young people directly.”
The results showed that 18% of the patients did not adhere to their prophylaxis regimens. Most non-adherence was due to forgetting treatment rather than intentionally skipping it.
But there were a few psychosocial reasons for non-adherence. Patients reported non-adherence due to a lack of social support and the perceived impact of prophylaxis on their everyday lives.
Patients also lacked understanding about the effectiveness of prophylaxis and its importance in treating hemophilia.
The patients were more likely to adhere to treatment when they perceived the need for prophylaxis to be greater than their concern over taking it.
And the study suggested a strong emotional reaction to a bleed may encourage young people to adhere to their treatment regimen.
“Interestingly, the findings suggest that, in addition to social support and treatment beliefs, emotional responses in relation to hemophilia, such as fear, anger, or distress, may also contribute to better adherence,” van Os said.
“It is important that patients receive sufficient and appropriate social support in order to stay on track with their treatment. It will also be beneficial to reduce potential concerns about prophylaxis and to assess whether patients understand their treatment sufficiently well and the role they themselves have to play in its effectiveness.”
This research was supported by external, peer-reviewed funding from the Bayer Haemophilia Awards Programme (Caregiver Award awarded to van Os). ![]()

Some young hemophilia patients may not be sticking to their prophylaxis regimens for psychosocial reasons, according to research published in PLOS ONE.
The study included 78 hemophilia patients, ages 12 to 25, treated at 13 centers in England and Wales.
“This research has a specific focus on young people rather than including patients of all age groups,” said study author Sandra Van Os, a PhD student at the University of Hertfordshire in Hatfield, UK.
“This is important since young people are likely to have had a very different experience than the older generations due to the revolutionary improvements in treatment achieved during the past 2 decades. Another key issue is rather than asking parents or healthcare professionals to estimate adherence as previous studies have done, this study asked young people directly.”
The results showed that 18% of the patients did not adhere to their prophylaxis regimens. Most non-adherence was due to forgetting treatment rather than intentionally skipping it.
But there were a few psychosocial reasons for non-adherence. Patients reported non-adherence due to a lack of social support and the perceived impact of prophylaxis on their everyday lives.
Patients also lacked understanding about the effectiveness of prophylaxis and its importance in treating hemophilia.
The patients were more likely to adhere to treatment when they perceived the need for prophylaxis to be greater than their concern over taking it.
And the study suggested a strong emotional reaction to a bleed may encourage young people to adhere to their treatment regimen.
“Interestingly, the findings suggest that, in addition to social support and treatment beliefs, emotional responses in relation to hemophilia, such as fear, anger, or distress, may also contribute to better adherence,” van Os said.
“It is important that patients receive sufficient and appropriate social support in order to stay on track with their treatment. It will also be beneficial to reduce potential concerns about prophylaxis and to assess whether patients understand their treatment sufficiently well and the role they themselves have to play in its effectiveness.”
This research was supported by external, peer-reviewed funding from the Bayer Haemophilia Awards Programme (Caregiver Award awarded to van Os). ![]()

Some young hemophilia patients may not be sticking to their prophylaxis regimens for psychosocial reasons, according to research published in PLOS ONE.
The study included 78 hemophilia patients, ages 12 to 25, treated at 13 centers in England and Wales.
“This research has a specific focus on young people rather than including patients of all age groups,” said study author Sandra Van Os, a PhD student at the University of Hertfordshire in Hatfield, UK.
“This is important since young people are likely to have had a very different experience than the older generations due to the revolutionary improvements in treatment achieved during the past 2 decades. Another key issue is rather than asking parents or healthcare professionals to estimate adherence as previous studies have done, this study asked young people directly.”
The results showed that 18% of the patients did not adhere to their prophylaxis regimens. Most non-adherence was due to forgetting treatment rather than intentionally skipping it.
But there were a few psychosocial reasons for non-adherence. Patients reported non-adherence due to a lack of social support and the perceived impact of prophylaxis on their everyday lives.
Patients also lacked understanding about the effectiveness of prophylaxis and its importance in treating hemophilia.
The patients were more likely to adhere to treatment when they perceived the need for prophylaxis to be greater than their concern over taking it.
And the study suggested a strong emotional reaction to a bleed may encourage young people to adhere to their treatment regimen.
“Interestingly, the findings suggest that, in addition to social support and treatment beliefs, emotional responses in relation to hemophilia, such as fear, anger, or distress, may also contribute to better adherence,” van Os said.
“It is important that patients receive sufficient and appropriate social support in order to stay on track with their treatment. It will also be beneficial to reduce potential concerns about prophylaxis and to assess whether patients understand their treatment sufficiently well and the role they themselves have to play in its effectiveness.”
This research was supported by external, peer-reviewed funding from the Bayer Haemophilia Awards Programme (Caregiver Award awarded to van Os). ![]()
Donor CAR T cells bridge to HSCT in infants with ALL
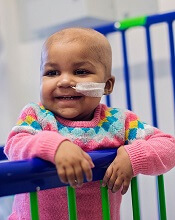
treated with UCART19
Photo courtesy of GOSH
New research suggests that “universal,” donor-derived, chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T cells may be a viable treatment option for very young children who do not have sufficient healthy T cells for autologous CAR T-cell therapy.
The universal CAR T-cell therapy, known as UCART19, was given to 2 infants with relapsed/refractory B-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL) who had previously
exhausted all other treatment options.
Both infants achieved remission after UCART19 and were able to proceed to transplant.
Both were still alive and leukemia-free at last follow-up—12 months and 18 months after UCART19, respectively.
Waseem Qasim, MBBS, PhD, of University College London’s Institute of Child Health and Great Ormond Street Hospital (GOSH) in London, UK, and his colleagues reported these results in Science Translational Medicine.
About the therapy
UCART19 consists of donor T cells modified using transcription activator-like effector nucleases. The cells are programmed to target CD19 and be insensitive to alemtuzumab. That way, a patient can receive alemtuzumab to prevent rejection of HLA-mismatched cells.
UCART19 was under development by Cellectis but is now being developed by Servier and Pfizer Inc. Pfizer has exclusive rights to develop and commercialize UCART19 in the US, while Servier retains exclusive rights for all other countries.
In Science Translational Medicine, Dr Qasim and his colleagues reported results in the first patients ever treated with UCART19. That research was funded, in part, by Cellectis.
Subject 1
The first patient was an 11-month-old, mixed-race infant with high-risk, t(11;19), CD19+ B-ALL. She had already failed chemotherapy, an allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplant (HSCT), and blinatumomab.
Prior to UCART19, she received a dose of vincristine and asparaginase and 7 days of dexamethasone, followed by cytoreduction with fludarabine, cyclophosphamide, and alemtuzumab. She then received a single dose of UCART19 (4.6 × 106/kg).
The patient had neutrophil recovery by day 30, although this was dependent on granulocyte colony-stimulating factor. After that, she developed multilineage cytopenia that persisted until she underwent a second allogeneic HSCT.
Prior to the second HSCT, the patient achieved cytogenetic and molecular remission but also developed grade 2 skin graft-vs-host disease. This was managed with systemic steroids.
The child received rituximab and conditioning with antithymocyte globulin, fludarabine, cyclophosphamide, thiotepa, and total body irradiation, followed by an HSCT from the original mismatched, unrelated donor.
The child achieved a complete remission and has remained minimal residual disease-negative, with full donor chimerism and normalized lymphocyte profiles, at 18 months after UCART19.
Results with this patient were previously reported by GOSH in November 2015 and at the 2015 ASH Annual Meeting.
Subject 2
The second patient was a 16-month-old Caucasian infant who had been diagnosed at 4 weeks of age with high-risk, congenital, mixed lineage leukemia–rearranged B-ALL.
She had already undergone HSCT from a matched, unrelated donor but relapsed. She did not respond to subsequent blinatumomab.
After these failed treatments, the patient received fludarabine, cyclophosphamide, and alemtuzumab, followed by a single infusion of UCART19 (4.0 × 106/kg).
She developed an erythematous rash after treatment, but this was immediately responsive to topical steroids.
The child achieved donor-derived neutrophil recovery and went on to receive a transplant from the same matched, unrelated donor as her previous HSCT.
The child received the transplant within 10 weeks of UCART19 therapy, after receiving rituximab and conditioning with antithymocyte globulin, fludarabine, cyclophosphamide, and total body irradiation.
At 12 months after UCART19, the child remains minimal residual disease-negative and “clinically well.”
“Both infants who have had this treatment have been at home for some time and are doing well,” Dr Qasim said. “We continue to monitor them closely, and, while we have reduced the frequency of their hospital visits and checks, we will still need to keep an eye on them for some time.”
Dr Qasim added that there are phase 1 trials of UCART19 underway for children and adults with chronic lymphocytic leukemia and acute lymphoblastic leukemia. ![]()

treated with UCART19
Photo courtesy of GOSH
New research suggests that “universal,” donor-derived, chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T cells may be a viable treatment option for very young children who do not have sufficient healthy T cells for autologous CAR T-cell therapy.
The universal CAR T-cell therapy, known as UCART19, was given to 2 infants with relapsed/refractory B-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL) who had previously
exhausted all other treatment options.
Both infants achieved remission after UCART19 and were able to proceed to transplant.
Both were still alive and leukemia-free at last follow-up—12 months and 18 months after UCART19, respectively.
Waseem Qasim, MBBS, PhD, of University College London’s Institute of Child Health and Great Ormond Street Hospital (GOSH) in London, UK, and his colleagues reported these results in Science Translational Medicine.
About the therapy
UCART19 consists of donor T cells modified using transcription activator-like effector nucleases. The cells are programmed to target CD19 and be insensitive to alemtuzumab. That way, a patient can receive alemtuzumab to prevent rejection of HLA-mismatched cells.
UCART19 was under development by Cellectis but is now being developed by Servier and Pfizer Inc. Pfizer has exclusive rights to develop and commercialize UCART19 in the US, while Servier retains exclusive rights for all other countries.
In Science Translational Medicine, Dr Qasim and his colleagues reported results in the first patients ever treated with UCART19. That research was funded, in part, by Cellectis.
Subject 1
The first patient was an 11-month-old, mixed-race infant with high-risk, t(11;19), CD19+ B-ALL. She had already failed chemotherapy, an allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplant (HSCT), and blinatumomab.
Prior to UCART19, she received a dose of vincristine and asparaginase and 7 days of dexamethasone, followed by cytoreduction with fludarabine, cyclophosphamide, and alemtuzumab. She then received a single dose of UCART19 (4.6 × 106/kg).
The patient had neutrophil recovery by day 30, although this was dependent on granulocyte colony-stimulating factor. After that, she developed multilineage cytopenia that persisted until she underwent a second allogeneic HSCT.
Prior to the second HSCT, the patient achieved cytogenetic and molecular remission but also developed grade 2 skin graft-vs-host disease. This was managed with systemic steroids.
The child received rituximab and conditioning with antithymocyte globulin, fludarabine, cyclophosphamide, thiotepa, and total body irradiation, followed by an HSCT from the original mismatched, unrelated donor.
The child achieved a complete remission and has remained minimal residual disease-negative, with full donor chimerism and normalized lymphocyte profiles, at 18 months after UCART19.
Results with this patient were previously reported by GOSH in November 2015 and at the 2015 ASH Annual Meeting.
Subject 2
The second patient was a 16-month-old Caucasian infant who had been diagnosed at 4 weeks of age with high-risk, congenital, mixed lineage leukemia–rearranged B-ALL.
She had already undergone HSCT from a matched, unrelated donor but relapsed. She did not respond to subsequent blinatumomab.
After these failed treatments, the patient received fludarabine, cyclophosphamide, and alemtuzumab, followed by a single infusion of UCART19 (4.0 × 106/kg).
She developed an erythematous rash after treatment, but this was immediately responsive to topical steroids.
The child achieved donor-derived neutrophil recovery and went on to receive a transplant from the same matched, unrelated donor as her previous HSCT.
The child received the transplant within 10 weeks of UCART19 therapy, after receiving rituximab and conditioning with antithymocyte globulin, fludarabine, cyclophosphamide, and total body irradiation.
At 12 months after UCART19, the child remains minimal residual disease-negative and “clinically well.”
“Both infants who have had this treatment have been at home for some time and are doing well,” Dr Qasim said. “We continue to monitor them closely, and, while we have reduced the frequency of their hospital visits and checks, we will still need to keep an eye on them for some time.”
Dr Qasim added that there are phase 1 trials of UCART19 underway for children and adults with chronic lymphocytic leukemia and acute lymphoblastic leukemia. ![]()

treated with UCART19
Photo courtesy of GOSH
New research suggests that “universal,” donor-derived, chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T cells may be a viable treatment option for very young children who do not have sufficient healthy T cells for autologous CAR T-cell therapy.
The universal CAR T-cell therapy, known as UCART19, was given to 2 infants with relapsed/refractory B-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL) who had previously
exhausted all other treatment options.
Both infants achieved remission after UCART19 and were able to proceed to transplant.
Both were still alive and leukemia-free at last follow-up—12 months and 18 months after UCART19, respectively.
Waseem Qasim, MBBS, PhD, of University College London’s Institute of Child Health and Great Ormond Street Hospital (GOSH) in London, UK, and his colleagues reported these results in Science Translational Medicine.
About the therapy
UCART19 consists of donor T cells modified using transcription activator-like effector nucleases. The cells are programmed to target CD19 and be insensitive to alemtuzumab. That way, a patient can receive alemtuzumab to prevent rejection of HLA-mismatched cells.
UCART19 was under development by Cellectis but is now being developed by Servier and Pfizer Inc. Pfizer has exclusive rights to develop and commercialize UCART19 in the US, while Servier retains exclusive rights for all other countries.
In Science Translational Medicine, Dr Qasim and his colleagues reported results in the first patients ever treated with UCART19. That research was funded, in part, by Cellectis.
Subject 1
The first patient was an 11-month-old, mixed-race infant with high-risk, t(11;19), CD19+ B-ALL. She had already failed chemotherapy, an allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplant (HSCT), and blinatumomab.
Prior to UCART19, she received a dose of vincristine and asparaginase and 7 days of dexamethasone, followed by cytoreduction with fludarabine, cyclophosphamide, and alemtuzumab. She then received a single dose of UCART19 (4.6 × 106/kg).
The patient had neutrophil recovery by day 30, although this was dependent on granulocyte colony-stimulating factor. After that, she developed multilineage cytopenia that persisted until she underwent a second allogeneic HSCT.
Prior to the second HSCT, the patient achieved cytogenetic and molecular remission but also developed grade 2 skin graft-vs-host disease. This was managed with systemic steroids.
The child received rituximab and conditioning with antithymocyte globulin, fludarabine, cyclophosphamide, thiotepa, and total body irradiation, followed by an HSCT from the original mismatched, unrelated donor.
The child achieved a complete remission and has remained minimal residual disease-negative, with full donor chimerism and normalized lymphocyte profiles, at 18 months after UCART19.
Results with this patient were previously reported by GOSH in November 2015 and at the 2015 ASH Annual Meeting.
Subject 2
The second patient was a 16-month-old Caucasian infant who had been diagnosed at 4 weeks of age with high-risk, congenital, mixed lineage leukemia–rearranged B-ALL.
She had already undergone HSCT from a matched, unrelated donor but relapsed. She did not respond to subsequent blinatumomab.
After these failed treatments, the patient received fludarabine, cyclophosphamide, and alemtuzumab, followed by a single infusion of UCART19 (4.0 × 106/kg).
She developed an erythematous rash after treatment, but this was immediately responsive to topical steroids.
The child achieved donor-derived neutrophil recovery and went on to receive a transplant from the same matched, unrelated donor as her previous HSCT.
The child received the transplant within 10 weeks of UCART19 therapy, after receiving rituximab and conditioning with antithymocyte globulin, fludarabine, cyclophosphamide, and total body irradiation.
At 12 months after UCART19, the child remains minimal residual disease-negative and “clinically well.”
“Both infants who have had this treatment have been at home for some time and are doing well,” Dr Qasim said. “We continue to monitor them closely, and, while we have reduced the frequency of their hospital visits and checks, we will still need to keep an eye on them for some time.”
Dr Qasim added that there are phase 1 trials of UCART19 underway for children and adults with chronic lymphocytic leukemia and acute lymphoblastic leukemia. ![]()
Roche launches new blood analyzer
Photo by Graham Colm
Roche has announced the launch of its cobas m 511 integrated hematology analyzer in countries that recognize the CE mark.*
The cobas m 511 combines 3 components of the hematology testing process—a digital morphology analyzer, cell counter, and classifier—into a single system that prepares, stains, and analyzes microscopy blood slides.
Roche said cobas m 511 provides greater accuracy and consistency than current technologies by identifying, counting, isolating, and categorizing blood cells, then presenting the digital images of all these cell types.
The company said this automation and digitalization reduces the need for resource-intensive manual microscope reviews, supports clinicians to share challenging cases around the world, and enables the delivery of quicker results, which ultimately aid patient diagnoses.
The cobas m 511 uses Bloodhound® technology for printing, staining, and imaging. This technology uses 30 µL of blood to print a monolayer onto the slide, stains for further analysis of the morphology, and enables classification of cells displayed on a viewing station.
Unlike the indirect methods commonly used in blood analysis today, the cobas m 511 images individual cells directly.
Based on these direct images, the Bloodhound® technology counts, analyzes morphology, and then classifies every cell in the viewing area to provide a standard complete blood count and 5-part differential and reticulocyte count.
While hematologists will continue to have the option of looking at slides under their microscopes, the cobas m 511 provides cell-by-cell images that, in many cases, may eliminate the need for microscopic review.
“With this launch, patients will benefit from a faster and more accurate diagnosis of blood diseases as diverse as anemia and leukemia,” said Roland Diggelmann, CEO of Roche Diagnostics.
“We are entering a new area of innovation with Roche in hematology testing, supporting customers with integrated and efficient laboratory solutions, which deliver increased medical value.” ![]()
*Local product availability may vary independently from CE mark approval. The cobas m 511 integrated hematology analyzer is not available in countries with previously agreed third-party vendor agreements.

Photo by Graham Colm
Roche has announced the launch of its cobas m 511 integrated hematology analyzer in countries that recognize the CE mark.*
The cobas m 511 combines 3 components of the hematology testing process—a digital morphology analyzer, cell counter, and classifier—into a single system that prepares, stains, and analyzes microscopy blood slides.
Roche said cobas m 511 provides greater accuracy and consistency than current technologies by identifying, counting, isolating, and categorizing blood cells, then presenting the digital images of all these cell types.
The company said this automation and digitalization reduces the need for resource-intensive manual microscope reviews, supports clinicians to share challenging cases around the world, and enables the delivery of quicker results, which ultimately aid patient diagnoses.
The cobas m 511 uses Bloodhound® technology for printing, staining, and imaging. This technology uses 30 µL of blood to print a monolayer onto the slide, stains for further analysis of the morphology, and enables classification of cells displayed on a viewing station.
Unlike the indirect methods commonly used in blood analysis today, the cobas m 511 images individual cells directly.
Based on these direct images, the Bloodhound® technology counts, analyzes morphology, and then classifies every cell in the viewing area to provide a standard complete blood count and 5-part differential and reticulocyte count.
While hematologists will continue to have the option of looking at slides under their microscopes, the cobas m 511 provides cell-by-cell images that, in many cases, may eliminate the need for microscopic review.
“With this launch, patients will benefit from a faster and more accurate diagnosis of blood diseases as diverse as anemia and leukemia,” said Roland Diggelmann, CEO of Roche Diagnostics.
“We are entering a new area of innovation with Roche in hematology testing, supporting customers with integrated and efficient laboratory solutions, which deliver increased medical value.” ![]()
*Local product availability may vary independently from CE mark approval. The cobas m 511 integrated hematology analyzer is not available in countries with previously agreed third-party vendor agreements.

Photo by Graham Colm
Roche has announced the launch of its cobas m 511 integrated hematology analyzer in countries that recognize the CE mark.*
The cobas m 511 combines 3 components of the hematology testing process—a digital morphology analyzer, cell counter, and classifier—into a single system that prepares, stains, and analyzes microscopy blood slides.
Roche said cobas m 511 provides greater accuracy and consistency than current technologies by identifying, counting, isolating, and categorizing blood cells, then presenting the digital images of all these cell types.
The company said this automation and digitalization reduces the need for resource-intensive manual microscope reviews, supports clinicians to share challenging cases around the world, and enables the delivery of quicker results, which ultimately aid patient diagnoses.
The cobas m 511 uses Bloodhound® technology for printing, staining, and imaging. This technology uses 30 µL of blood to print a monolayer onto the slide, stains for further analysis of the morphology, and enables classification of cells displayed on a viewing station.
Unlike the indirect methods commonly used in blood analysis today, the cobas m 511 images individual cells directly.
Based on these direct images, the Bloodhound® technology counts, analyzes morphology, and then classifies every cell in the viewing area to provide a standard complete blood count and 5-part differential and reticulocyte count.
While hematologists will continue to have the option of looking at slides under their microscopes, the cobas m 511 provides cell-by-cell images that, in many cases, may eliminate the need for microscopic review.
“With this launch, patients will benefit from a faster and more accurate diagnosis of blood diseases as diverse as anemia and leukemia,” said Roland Diggelmann, CEO of Roche Diagnostics.
“We are entering a new area of innovation with Roche in hematology testing, supporting customers with integrated and efficient laboratory solutions, which deliver increased medical value.” ![]()
*Local product availability may vary independently from CE mark approval. The cobas m 511 integrated hematology analyzer is not available in countries with previously agreed third-party vendor agreements.
Surgeon General Issues ‘Call to Action’ on Substance Abuse Crisis
Before he assumed his position as U.S. Surgeon General, Vivek Murthy, MD, says, he stopped by to say good-bye to his colleagues. The nurses had 1 parting request: If you can only do 1 thing as Surgeon General, please do something about the addiction crisis in America.
Thus, for the first time, a U.S. Surgeon General has dedicated a report to substance misuse and related disorders, calling these issues one of America’s most pressing public health concerns. “I am issuing a new call to action,” he says in the foreword, “to end the public health crisis of addiction.” Nearly 21 million Americans suffer from substance use disorders—more than the number of people who have all cancers combined.
Facing Addiction in America: The Surgeon General’s Report on Alcohol, Drugs, and Health offers an in-depth look at the science of substance use disorders and addiction, with chapters on neurobiology, prevention, treatment, recovery, health systems integration, and recommendations for the future.
One of the findings is that substance use disorder treatment in the U.S. remains “largely separate” from the rest of health care and serves only a fraction of those in need of treatment. An estimated 1 in 7 people in the U.S. develops a substance use disorder at some point in their lives, yet only 1 in 10 receives treatment. Many factors contribute to this treatment gap, including the stigma associated with drug and alcohol addiction.
There has been progress: The Obama administration has invested in research, development, and evaluation of programs to prevent and treat substance misuse and substance use disorders, as well as support recovery, the report says.
“It’s time to change how we view addiction,” said Dr. Murthy. “Not as a moral failing, but as a chronic illness that must be treated with skill, urgency and compassion. The way we address this crisis is a test for America.”
Before he assumed his position as U.S. Surgeon General, Vivek Murthy, MD, says, he stopped by to say good-bye to his colleagues. The nurses had 1 parting request: If you can only do 1 thing as Surgeon General, please do something about the addiction crisis in America.
Thus, for the first time, a U.S. Surgeon General has dedicated a report to substance misuse and related disorders, calling these issues one of America’s most pressing public health concerns. “I am issuing a new call to action,” he says in the foreword, “to end the public health crisis of addiction.” Nearly 21 million Americans suffer from substance use disorders—more than the number of people who have all cancers combined.
Facing Addiction in America: The Surgeon General’s Report on Alcohol, Drugs, and Health offers an in-depth look at the science of substance use disorders and addiction, with chapters on neurobiology, prevention, treatment, recovery, health systems integration, and recommendations for the future.
One of the findings is that substance use disorder treatment in the U.S. remains “largely separate” from the rest of health care and serves only a fraction of those in need of treatment. An estimated 1 in 7 people in the U.S. develops a substance use disorder at some point in their lives, yet only 1 in 10 receives treatment. Many factors contribute to this treatment gap, including the stigma associated with drug and alcohol addiction.
There has been progress: The Obama administration has invested in research, development, and evaluation of programs to prevent and treat substance misuse and substance use disorders, as well as support recovery, the report says.
“It’s time to change how we view addiction,” said Dr. Murthy. “Not as a moral failing, but as a chronic illness that must be treated with skill, urgency and compassion. The way we address this crisis is a test for America.”
Before he assumed his position as U.S. Surgeon General, Vivek Murthy, MD, says, he stopped by to say good-bye to his colleagues. The nurses had 1 parting request: If you can only do 1 thing as Surgeon General, please do something about the addiction crisis in America.
Thus, for the first time, a U.S. Surgeon General has dedicated a report to substance misuse and related disorders, calling these issues one of America’s most pressing public health concerns. “I am issuing a new call to action,” he says in the foreword, “to end the public health crisis of addiction.” Nearly 21 million Americans suffer from substance use disorders—more than the number of people who have all cancers combined.
Facing Addiction in America: The Surgeon General’s Report on Alcohol, Drugs, and Health offers an in-depth look at the science of substance use disorders and addiction, with chapters on neurobiology, prevention, treatment, recovery, health systems integration, and recommendations for the future.
One of the findings is that substance use disorder treatment in the U.S. remains “largely separate” from the rest of health care and serves only a fraction of those in need of treatment. An estimated 1 in 7 people in the U.S. develops a substance use disorder at some point in their lives, yet only 1 in 10 receives treatment. Many factors contribute to this treatment gap, including the stigma associated with drug and alcohol addiction.
There has been progress: The Obama administration has invested in research, development, and evaluation of programs to prevent and treat substance misuse and substance use disorders, as well as support recovery, the report says.
“It’s time to change how we view addiction,” said Dr. Murthy. “Not as a moral failing, but as a chronic illness that must be treated with skill, urgency and compassion. The way we address this crisis is a test for America.”
A Call for Optimizing the Research Portfolio for Glioblastoma
The past 10 years have seen a rise in clinical trials for the treatment of primary and recurrent glioblastoma—but the “slightly positive trend” has been due to an increase in phase 2, not phase 3, studies, say researchers from University of Bern in Switzerland. Moreover, the majority of these trials focus on drugs designed for central nervous system (CNS) malignancies; trials addressing radiotherapy, surgery, imaging, and other therapeutic or diagnostic methods “appear to be rare.”
The researchers analyzed records of 208,777 studies registered at ClinicalTrials.gov. They classified trials according to disease setting (newly diagnosed glioblastoma, recurrent disease, and no differentiation) and by intervention (standard or experimental). All surgical approaches were considered experimental as were all radiotherapy approaches in the recurrent setting.
Related: Death Rates for Brain Cancer Trend Downward
Nearly all the trials (91%) evaluated forms of systemic therapy, with 44% in primary and 54% in recurrent disease. The majority of trials were phase 2 studies (88%); only 11% were phase 3.
Researchers identified 100 different molecular agents or biologics of which 40 had initially been approved for indications other than glioblastoma or CNS malignancies. Two agents (carmustine and lomustine) were approved for glioblastoma or other CNS or solid malignancies. Only 1 (temozolomide) was approved for glioblastoma. Of 57 compounds with investigational status, 19 were developed specifically for glioblastoma.
By contrast, the researchers say that surgery, radiotherapy, and imaging are “heavily underrepresented,” being the focus of > 10% of all phase 1 and 2 glioblastoma trials.
Industry “has displayed a strong interest in sponsoring trials for glioblastoma,” the researchers note. The fact that industry was a primary sponsor of one-fourth of the trials and a leading source of monetary support in 44% “indicates that glioblastoma is an attractive target even financially.” But the authors find “reason for concern” in the lack of industrial funding for research beyond forms of systemic therapy.
Related: Role of Radiosurgery in the Treatment of Brain Metastasis
They suggest, for instance, that learning more about alternative radiotherapy schedules along with dose or volume alterations could be of interest for glioblastoma treatment. They also note that imaging modalities rarely are evaluated in the prospective setting, and the size and role of the optimal radiotherapy margins are “a matter of debate”—of particular importance in recurrent glioblastoma.
The most probable cause for the upward trend of phase 2 trials in glioblastoma, the researchers say, is the failure of previous early investigative treatments to show a clinically significant advantage. Instead of starting more trials “unselectively,” they suggest, it might be better to enroll patients with glioblastoma in early phase trials with novel designs.
Source:
Cihoric N, Tsikkinis A, Minniti G, et al. Radiat Oncol. 2017;12(1):1.
doi: 10.1186/s13014-016-0740-5.
The past 10 years have seen a rise in clinical trials for the treatment of primary and recurrent glioblastoma—but the “slightly positive trend” has been due to an increase in phase 2, not phase 3, studies, say researchers from University of Bern in Switzerland. Moreover, the majority of these trials focus on drugs designed for central nervous system (CNS) malignancies; trials addressing radiotherapy, surgery, imaging, and other therapeutic or diagnostic methods “appear to be rare.”
The researchers analyzed records of 208,777 studies registered at ClinicalTrials.gov. They classified trials according to disease setting (newly diagnosed glioblastoma, recurrent disease, and no differentiation) and by intervention (standard or experimental). All surgical approaches were considered experimental as were all radiotherapy approaches in the recurrent setting.
Related: Death Rates for Brain Cancer Trend Downward
Nearly all the trials (91%) evaluated forms of systemic therapy, with 44% in primary and 54% in recurrent disease. The majority of trials were phase 2 studies (88%); only 11% were phase 3.
Researchers identified 100 different molecular agents or biologics of which 40 had initially been approved for indications other than glioblastoma or CNS malignancies. Two agents (carmustine and lomustine) were approved for glioblastoma or other CNS or solid malignancies. Only 1 (temozolomide) was approved for glioblastoma. Of 57 compounds with investigational status, 19 were developed specifically for glioblastoma.
By contrast, the researchers say that surgery, radiotherapy, and imaging are “heavily underrepresented,” being the focus of > 10% of all phase 1 and 2 glioblastoma trials.
Industry “has displayed a strong interest in sponsoring trials for glioblastoma,” the researchers note. The fact that industry was a primary sponsor of one-fourth of the trials and a leading source of monetary support in 44% “indicates that glioblastoma is an attractive target even financially.” But the authors find “reason for concern” in the lack of industrial funding for research beyond forms of systemic therapy.
Related: Role of Radiosurgery in the Treatment of Brain Metastasis
They suggest, for instance, that learning more about alternative radiotherapy schedules along with dose or volume alterations could be of interest for glioblastoma treatment. They also note that imaging modalities rarely are evaluated in the prospective setting, and the size and role of the optimal radiotherapy margins are “a matter of debate”—of particular importance in recurrent glioblastoma.
The most probable cause for the upward trend of phase 2 trials in glioblastoma, the researchers say, is the failure of previous early investigative treatments to show a clinically significant advantage. Instead of starting more trials “unselectively,” they suggest, it might be better to enroll patients with glioblastoma in early phase trials with novel designs.
Source:
Cihoric N, Tsikkinis A, Minniti G, et al. Radiat Oncol. 2017;12(1):1.
doi: 10.1186/s13014-016-0740-5.
The past 10 years have seen a rise in clinical trials for the treatment of primary and recurrent glioblastoma—but the “slightly positive trend” has been due to an increase in phase 2, not phase 3, studies, say researchers from University of Bern in Switzerland. Moreover, the majority of these trials focus on drugs designed for central nervous system (CNS) malignancies; trials addressing radiotherapy, surgery, imaging, and other therapeutic or diagnostic methods “appear to be rare.”
The researchers analyzed records of 208,777 studies registered at ClinicalTrials.gov. They classified trials according to disease setting (newly diagnosed glioblastoma, recurrent disease, and no differentiation) and by intervention (standard or experimental). All surgical approaches were considered experimental as were all radiotherapy approaches in the recurrent setting.
Related: Death Rates for Brain Cancer Trend Downward
Nearly all the trials (91%) evaluated forms of systemic therapy, with 44% in primary and 54% in recurrent disease. The majority of trials were phase 2 studies (88%); only 11% were phase 3.
Researchers identified 100 different molecular agents or biologics of which 40 had initially been approved for indications other than glioblastoma or CNS malignancies. Two agents (carmustine and lomustine) were approved for glioblastoma or other CNS or solid malignancies. Only 1 (temozolomide) was approved for glioblastoma. Of 57 compounds with investigational status, 19 were developed specifically for glioblastoma.
By contrast, the researchers say that surgery, radiotherapy, and imaging are “heavily underrepresented,” being the focus of > 10% of all phase 1 and 2 glioblastoma trials.
Industry “has displayed a strong interest in sponsoring trials for glioblastoma,” the researchers note. The fact that industry was a primary sponsor of one-fourth of the trials and a leading source of monetary support in 44% “indicates that glioblastoma is an attractive target even financially.” But the authors find “reason for concern” in the lack of industrial funding for research beyond forms of systemic therapy.
Related: Role of Radiosurgery in the Treatment of Brain Metastasis
They suggest, for instance, that learning more about alternative radiotherapy schedules along with dose or volume alterations could be of interest for glioblastoma treatment. They also note that imaging modalities rarely are evaluated in the prospective setting, and the size and role of the optimal radiotherapy margins are “a matter of debate”—of particular importance in recurrent glioblastoma.
The most probable cause for the upward trend of phase 2 trials in glioblastoma, the researchers say, is the failure of previous early investigative treatments to show a clinically significant advantage. Instead of starting more trials “unselectively,” they suggest, it might be better to enroll patients with glioblastoma in early phase trials with novel designs.
Source:
Cihoric N, Tsikkinis A, Minniti G, et al. Radiat Oncol. 2017;12(1):1.
doi: 10.1186/s13014-016-0740-5.
The Itch That Won't Quit
A 68-year-old woman with a very itchy rash is referred to dermatology for evaluation. She reports the itching to be constant—24 hours a day, seven days a week—but particularly severe at bedtime.
The rash has been totally unresponsive to numerous treatment attempts over the past year, including topical steroids (triamcinolone 0.1% cream bid), oral antibiotics (trimethoprim/sulfa), and oral steroids (prednisone).
The patient lives alone, apart from the occasional overnight visit from her grandchild.
EXAMINATION
The widespread rash spares only the patient’s legs below the knees. It is comprised of sparsely distributed excoriated foci, some surrounded by oval-to-round scales. The patient scratches the sites throughout the examination.
During a shave biopsy of one of the lesions on the patient’s arm, she mentions that occasionally lesions also manifest on her hands and fingers. Closer examination reveals a few unremarkable, scaly, 1- to 3-mm papules on her volar wrists. These are scraped with a #10 blade and placed on a slide, which is covered, filled with potassium hydroxide 10%, and examined under 10x magnification.

What is the diagnosis?
DISCUSSION
After a lengthy search, a single scabies adult (scabies sarcoptei var humanus) was found embedded in the scales. Scabies is one of the two most common ectoparasitic infestations in this country (the other being head lice).
Paradoxically, it is one of the most over- and under-diagnosed medical conditions worldwide. It is transmitted from person to person and can only be acquired from close, prolonged contact with another human who has the condition. This case illustrates some of the difficulties involved in making the diagnosis.
While it is vital to consider scabies in the differential for constant, severe itching, there are situations in which it can be ruled out. People who live alone and/or avoid physical contact with other people cannot get scabies. It can only be acquired from an infected person—not from a dog, cat, or inanimate object. In this case, the patient lived alone, but she hosted sleepovers with her grandchild—the likely source of this infestation.
Scabies can manifest as an eczematoid rash that will not respond to topical or systemic steroids. Conversely, when eczema patients are misdiagnosed with scabies, permethrin cream worsens the condition. Therefore, once scabies is considered in the differential, a KOH prep is indicated for a definitive diagnosis.
In terms of treatment, it does little good to simply treat the patient in question. The entire family (and/or close contacts) needs to be treated simultaneously—but before that, the source of the scabies needs to be identified. Failure to address all of these factors often leads to “treatment failure.”
The case patient was successfully treated with a combination of permethrin cream and oral ivermectin, according to the standard regimen (two treatments, seven to 10 days apart).
TAKE-HOME LEARNING POINTS
- Scabies can only be acquired from close, prolonged contact with another human who has the condition.
- Intractable itching and failure to respond to treatment (ie, topical and systemic steroids) are its dependable diagnostic features.
- Scraping suspected scabetic lesions (tiny vesicles, dried papules, or—if you’re lucky—a burrow) and examining them under 10x microscopy is preferable for confirmation of the diagnosis.
- The whole family must be treated in synchrony with the patient.
- It is essential to identify the source of the scabies (eg, spouse, boyfriend/girlfriend, child) to successfully eradicate the problem.
A 68-year-old woman with a very itchy rash is referred to dermatology for evaluation. She reports the itching to be constant—24 hours a day, seven days a week—but particularly severe at bedtime.
The rash has been totally unresponsive to numerous treatment attempts over the past year, including topical steroids (triamcinolone 0.1% cream bid), oral antibiotics (trimethoprim/sulfa), and oral steroids (prednisone).
The patient lives alone, apart from the occasional overnight visit from her grandchild.
EXAMINATION
The widespread rash spares only the patient’s legs below the knees. It is comprised of sparsely distributed excoriated foci, some surrounded by oval-to-round scales. The patient scratches the sites throughout the examination.
During a shave biopsy of one of the lesions on the patient’s arm, she mentions that occasionally lesions also manifest on her hands and fingers. Closer examination reveals a few unremarkable, scaly, 1- to 3-mm papules on her volar wrists. These are scraped with a #10 blade and placed on a slide, which is covered, filled with potassium hydroxide 10%, and examined under 10x magnification.

What is the diagnosis?
DISCUSSION
After a lengthy search, a single scabies adult (scabies sarcoptei var humanus) was found embedded in the scales. Scabies is one of the two most common ectoparasitic infestations in this country (the other being head lice).
Paradoxically, it is one of the most over- and under-diagnosed medical conditions worldwide. It is transmitted from person to person and can only be acquired from close, prolonged contact with another human who has the condition. This case illustrates some of the difficulties involved in making the diagnosis.
While it is vital to consider scabies in the differential for constant, severe itching, there are situations in which it can be ruled out. People who live alone and/or avoid physical contact with other people cannot get scabies. It can only be acquired from an infected person—not from a dog, cat, or inanimate object. In this case, the patient lived alone, but she hosted sleepovers with her grandchild—the likely source of this infestation.
Scabies can manifest as an eczematoid rash that will not respond to topical or systemic steroids. Conversely, when eczema patients are misdiagnosed with scabies, permethrin cream worsens the condition. Therefore, once scabies is considered in the differential, a KOH prep is indicated for a definitive diagnosis.
In terms of treatment, it does little good to simply treat the patient in question. The entire family (and/or close contacts) needs to be treated simultaneously—but before that, the source of the scabies needs to be identified. Failure to address all of these factors often leads to “treatment failure.”
The case patient was successfully treated with a combination of permethrin cream and oral ivermectin, according to the standard regimen (two treatments, seven to 10 days apart).
TAKE-HOME LEARNING POINTS
- Scabies can only be acquired from close, prolonged contact with another human who has the condition.
- Intractable itching and failure to respond to treatment (ie, topical and systemic steroids) are its dependable diagnostic features.
- Scraping suspected scabetic lesions (tiny vesicles, dried papules, or—if you’re lucky—a burrow) and examining them under 10x microscopy is preferable for confirmation of the diagnosis.
- The whole family must be treated in synchrony with the patient.
- It is essential to identify the source of the scabies (eg, spouse, boyfriend/girlfriend, child) to successfully eradicate the problem.
A 68-year-old woman with a very itchy rash is referred to dermatology for evaluation. She reports the itching to be constant—24 hours a day, seven days a week—but particularly severe at bedtime.
The rash has been totally unresponsive to numerous treatment attempts over the past year, including topical steroids (triamcinolone 0.1% cream bid), oral antibiotics (trimethoprim/sulfa), and oral steroids (prednisone).
The patient lives alone, apart from the occasional overnight visit from her grandchild.
EXAMINATION
The widespread rash spares only the patient’s legs below the knees. It is comprised of sparsely distributed excoriated foci, some surrounded by oval-to-round scales. The patient scratches the sites throughout the examination.
During a shave biopsy of one of the lesions on the patient’s arm, she mentions that occasionally lesions also manifest on her hands and fingers. Closer examination reveals a few unremarkable, scaly, 1- to 3-mm papules on her volar wrists. These are scraped with a #10 blade and placed on a slide, which is covered, filled with potassium hydroxide 10%, and examined under 10x magnification.

What is the diagnosis?
DISCUSSION
After a lengthy search, a single scabies adult (scabies sarcoptei var humanus) was found embedded in the scales. Scabies is one of the two most common ectoparasitic infestations in this country (the other being head lice).
Paradoxically, it is one of the most over- and under-diagnosed medical conditions worldwide. It is transmitted from person to person and can only be acquired from close, prolonged contact with another human who has the condition. This case illustrates some of the difficulties involved in making the diagnosis.
While it is vital to consider scabies in the differential for constant, severe itching, there are situations in which it can be ruled out. People who live alone and/or avoid physical contact with other people cannot get scabies. It can only be acquired from an infected person—not from a dog, cat, or inanimate object. In this case, the patient lived alone, but she hosted sleepovers with her grandchild—the likely source of this infestation.
Scabies can manifest as an eczematoid rash that will not respond to topical or systemic steroids. Conversely, when eczema patients are misdiagnosed with scabies, permethrin cream worsens the condition. Therefore, once scabies is considered in the differential, a KOH prep is indicated for a definitive diagnosis.
In terms of treatment, it does little good to simply treat the patient in question. The entire family (and/or close contacts) needs to be treated simultaneously—but before that, the source of the scabies needs to be identified. Failure to address all of these factors often leads to “treatment failure.”
The case patient was successfully treated with a combination of permethrin cream and oral ivermectin, according to the standard regimen (two treatments, seven to 10 days apart).
TAKE-HOME LEARNING POINTS
- Scabies can only be acquired from close, prolonged contact with another human who has the condition.
- Intractable itching and failure to respond to treatment (ie, topical and systemic steroids) are its dependable diagnostic features.
- Scraping suspected scabetic lesions (tiny vesicles, dried papules, or—if you’re lucky—a burrow) and examining them under 10x microscopy is preferable for confirmation of the diagnosis.
- The whole family must be treated in synchrony with the patient.
- It is essential to identify the source of the scabies (eg, spouse, boyfriend/girlfriend, child) to successfully eradicate the problem.
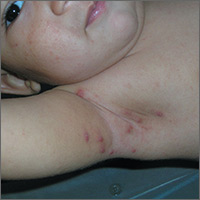
Pruritic nodules in axillae
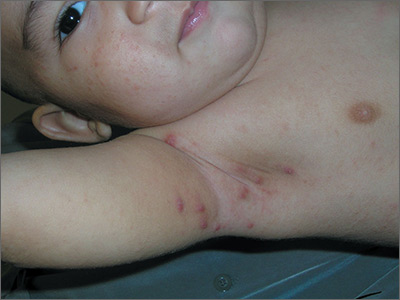
The FP suspected scabies, realizing that in addition to the classic burrows seen between the fingers, scabies may present with pruritic nodules in the axilla or genital region. This child did not have any visible burrows between his fingers and there was no involvement of the genital area. Using dermoscopy, scabies mites were seen as triangular structures with trailing burrows over some of the nodules. The mother agreed to have her hands examined and scabies mites were seen between her fingers.
The child weighed less than 33 pounds, so he was not an appropriate candidate for oral ivermectin. The physician prescribed 5% permethrin cream for the child, mother, and other household members. The FP explained the importance of applying the cream from the neck down to the toes overnight and washing it off in the morning. Toddlers often have the scabies mites above the neck, so the mother was counseled to apply the 5% permethrin cream on her son’s head and face, being careful to avoid his mouth and eyes. The FP also gave the family directions to wash their clothes and bedclothes.
Photos and text for Photo Rounds Friday courtesy of Richard P. Usatine, MD. This case was adapted from: Usatine R, Chanoine P, Smith M. Scabies. In: Usatine R, Smith M, Mayeaux EJ, et al, eds. Color Atlas of Family Medicine. 2nd ed. New York, NY: McGraw-Hill; 2013:575-580.
To learn more about the Color Atlas of Family Medicine, see: www.amazon.com/Color-Family-Medicine-Richard-Usatine/dp/0071769641/
You can now get the second edition of the Color Atlas of Family Medicine as an app by clicking on this link: usatinemedia.com

The FP suspected scabies, realizing that in addition to the classic burrows seen between the fingers, scabies may present with pruritic nodules in the axilla or genital region. This child did not have any visible burrows between his fingers and there was no involvement of the genital area. Using dermoscopy, scabies mites were seen as triangular structures with trailing burrows over some of the nodules. The mother agreed to have her hands examined and scabies mites were seen between her fingers.
The child weighed less than 33 pounds, so he was not an appropriate candidate for oral ivermectin. The physician prescribed 5% permethrin cream for the child, mother, and other household members. The FP explained the importance of applying the cream from the neck down to the toes overnight and washing it off in the morning. Toddlers often have the scabies mites above the neck, so the mother was counseled to apply the 5% permethrin cream on her son’s head and face, being careful to avoid his mouth and eyes. The FP also gave the family directions to wash their clothes and bedclothes.
Photos and text for Photo Rounds Friday courtesy of Richard P. Usatine, MD. This case was adapted from: Usatine R, Chanoine P, Smith M. Scabies. In: Usatine R, Smith M, Mayeaux EJ, et al, eds. Color Atlas of Family Medicine. 2nd ed. New York, NY: McGraw-Hill; 2013:575-580.
To learn more about the Color Atlas of Family Medicine, see: www.amazon.com/Color-Family-Medicine-Richard-Usatine/dp/0071769641/
You can now get the second edition of the Color Atlas of Family Medicine as an app by clicking on this link: usatinemedia.com

The FP suspected scabies, realizing that in addition to the classic burrows seen between the fingers, scabies may present with pruritic nodules in the axilla or genital region. This child did not have any visible burrows between his fingers and there was no involvement of the genital area. Using dermoscopy, scabies mites were seen as triangular structures with trailing burrows over some of the nodules. The mother agreed to have her hands examined and scabies mites were seen between her fingers.
The child weighed less than 33 pounds, so he was not an appropriate candidate for oral ivermectin. The physician prescribed 5% permethrin cream for the child, mother, and other household members. The FP explained the importance of applying the cream from the neck down to the toes overnight and washing it off in the morning. Toddlers often have the scabies mites above the neck, so the mother was counseled to apply the 5% permethrin cream on her son’s head and face, being careful to avoid his mouth and eyes. The FP also gave the family directions to wash their clothes and bedclothes.
Photos and text for Photo Rounds Friday courtesy of Richard P. Usatine, MD. This case was adapted from: Usatine R, Chanoine P, Smith M. Scabies. In: Usatine R, Smith M, Mayeaux EJ, et al, eds. Color Atlas of Family Medicine. 2nd ed. New York, NY: McGraw-Hill; 2013:575-580.
To learn more about the Color Atlas of Family Medicine, see: www.amazon.com/Color-Family-Medicine-Richard-Usatine/dp/0071769641/
You can now get the second edition of the Color Atlas of Family Medicine as an app by clicking on this link: usatinemedia.com
Hospital-acquired VTE with high risk of recurrence
Clinical question: Is the risk of recurrence for a venous thromboembolism (VTE) acquired as an inpatient higher than other reversible risk factors?
Background: In patients with acute VTE, transient provoking factors place patients at lower risks for recurrent VTE, while persistent factors (that is, cancer) increase risk for recurrence. Unprovoked VTE places patients at intermediate to high risk, but few data are present for VTE experienced while in the hospital.
Study design: Single-center, population-based, prospective cohort study.
Setting: Tromso, Norway.
Synopsis: Using repeat health surveys from 1994 to 2012, researchers followed 822 patients with a validated, first-lifetime VTE. Hospital-related VTE was defined as a VTE within 8 weeks of hospitalization related to medical illness, surgery, or in patients with active cancer.
This global definition of hospital-related VTE was not associated with an increased risk of recurrent VTE (hazard ratio, 0.99; 0.69-1.41). However, in separate groups, the cumulative risk of recurrence after 5 years in hospital-related VTE due to medical illness was similar to nonhospital-related VTE (20.1% vs. 18.4%), higher than VTE related to surgery (11%), and lower than VTE related to cancer (27.4%).
Risk-adjusted analyses maintained these differences in recurrence risk dependent on reason for hospitalization (cancer, medical illness, surgery). When compared with non-hospital VTE, however, hospital-related VTE was associated with a threefold higher risk of death.
Study limitations included being from a single center, possibly underpowered due to low number of events.
Bottom line: Hospital-related VTE has a high risk of recurrence, but risk level is variable and dependent on the reason for hospitalization.
Citation: Bjøri E, Arshad N, Johnsen HS, Hansen J-B, Brækkan SK. Hospital-related first venous thromboembolism and risk of recurrence [published online ahead of print, Sept. 2, 2016]. J Thromb Haemost. doi: 10.1111/jth.13492
Dr. Ciarkowski is a clinical instructor at the University of Utah School of Medicine and an academic hospitalist at the University of Utah Hospital.
Clinical question: Is the risk of recurrence for a venous thromboembolism (VTE) acquired as an inpatient higher than other reversible risk factors?
Background: In patients with acute VTE, transient provoking factors place patients at lower risks for recurrent VTE, while persistent factors (that is, cancer) increase risk for recurrence. Unprovoked VTE places patients at intermediate to high risk, but few data are present for VTE experienced while in the hospital.
Study design: Single-center, population-based, prospective cohort study.
Setting: Tromso, Norway.
Synopsis: Using repeat health surveys from 1994 to 2012, researchers followed 822 patients with a validated, first-lifetime VTE. Hospital-related VTE was defined as a VTE within 8 weeks of hospitalization related to medical illness, surgery, or in patients with active cancer.
This global definition of hospital-related VTE was not associated with an increased risk of recurrent VTE (hazard ratio, 0.99; 0.69-1.41). However, in separate groups, the cumulative risk of recurrence after 5 years in hospital-related VTE due to medical illness was similar to nonhospital-related VTE (20.1% vs. 18.4%), higher than VTE related to surgery (11%), and lower than VTE related to cancer (27.4%).
Risk-adjusted analyses maintained these differences in recurrence risk dependent on reason for hospitalization (cancer, medical illness, surgery). When compared with non-hospital VTE, however, hospital-related VTE was associated with a threefold higher risk of death.
Study limitations included being from a single center, possibly underpowered due to low number of events.
Bottom line: Hospital-related VTE has a high risk of recurrence, but risk level is variable and dependent on the reason for hospitalization.
Citation: Bjøri E, Arshad N, Johnsen HS, Hansen J-B, Brækkan SK. Hospital-related first venous thromboembolism and risk of recurrence [published online ahead of print, Sept. 2, 2016]. J Thromb Haemost. doi: 10.1111/jth.13492
Dr. Ciarkowski is a clinical instructor at the University of Utah School of Medicine and an academic hospitalist at the University of Utah Hospital.
Clinical question: Is the risk of recurrence for a venous thromboembolism (VTE) acquired as an inpatient higher than other reversible risk factors?
Background: In patients with acute VTE, transient provoking factors place patients at lower risks for recurrent VTE, while persistent factors (that is, cancer) increase risk for recurrence. Unprovoked VTE places patients at intermediate to high risk, but few data are present for VTE experienced while in the hospital.
Study design: Single-center, population-based, prospective cohort study.
Setting: Tromso, Norway.
Synopsis: Using repeat health surveys from 1994 to 2012, researchers followed 822 patients with a validated, first-lifetime VTE. Hospital-related VTE was defined as a VTE within 8 weeks of hospitalization related to medical illness, surgery, or in patients with active cancer.
This global definition of hospital-related VTE was not associated with an increased risk of recurrent VTE (hazard ratio, 0.99; 0.69-1.41). However, in separate groups, the cumulative risk of recurrence after 5 years in hospital-related VTE due to medical illness was similar to nonhospital-related VTE (20.1% vs. 18.4%), higher than VTE related to surgery (11%), and lower than VTE related to cancer (27.4%).
Risk-adjusted analyses maintained these differences in recurrence risk dependent on reason for hospitalization (cancer, medical illness, surgery). When compared with non-hospital VTE, however, hospital-related VTE was associated with a threefold higher risk of death.
Study limitations included being from a single center, possibly underpowered due to low number of events.
Bottom line: Hospital-related VTE has a high risk of recurrence, but risk level is variable and dependent on the reason for hospitalization.
Citation: Bjøri E, Arshad N, Johnsen HS, Hansen J-B, Brækkan SK. Hospital-related first venous thromboembolism and risk of recurrence [published online ahead of print, Sept. 2, 2016]. J Thromb Haemost. doi: 10.1111/jth.13492
Dr. Ciarkowski is a clinical instructor at the University of Utah School of Medicine and an academic hospitalist at the University of Utah Hospital.
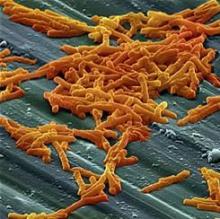
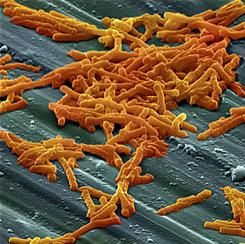
Bezlotoxumab prevents recurrent C. difficile infection
Adding bezlotoxumab to standard antibiotic treatment of primary or recurrent Clostridium difficile infection reduces recurrences by 38% (10 percentage points), according to a report published in the New England Journal of Medicine.
As many as 35% of patients who complete initial antibiotic treatment have at least one recurrence of C. difficile infection, and the rate of repeat recurrence rate jumps to 60% after the initial recurrence. Researchers performed two parallel international phase III trials to assess the efficacy and safety of bezlotoxumab, alone or in combination with actoxumab, for preventing such recurrences. Both monoclonal antibodies work by binding to and neutralizing C. difficile toxins; bezlotoxumab targets toxin B and actoxumab targets toxin A, said Mark H. Wilcox, MD, of the division of microbiology, Leeds (England) General Infirmary, and his associates.
The primary efficacy endpoint – the proportion of patients with recurrent C. difficile infection during 12 weeks of follow-up – was substantially lower with bezlotoxumab (17%) than with placebo (28%) in the first trial and in the second trial (16% vs. 26%). This treatment benefit was evident as early as 2 weeks after infusion and persisted throughout follow-up, the investigators said (N Engl J Med. 2017 Jan 25. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1602615).
The agent’s persistent effect through 12 weeks is important to note because approximately 30% of the recurrences in this study “occurred beyond the conventional 4-week assessment period for treatment efficacy. The number needed to treat to prevent one episode of recurrent C. difficile infection was 10; it was 6 among participants 65 years of age or older and those with previous C. difficile infection,” Dr. Wilcox and his associates noted.
Bezlotoxumab was consistently effective in several sensitivity analyses. It also was effective in both trials individually as well as in pooled results. And the choice of oral antibiotic appeared to have no effect on bezlotoxumab’s efficacy.
In a post hoc analysis, bezlotoxumab was also effective in the subgroup of 1,964 patients at highest risk for C. difficile recurrence because they were elderly, had compromised immunity, had the most severe infections, had a history of C. difficile infection, or carried a strain of the organism associated with particularly poor outcomes. In this subgroup, 17% of patients given bezlotoxumab and 16% of those given bezlotoxumab plus actoxumab developed recurrences, compared with 30% of those given placebo.
Regarding adverse events, the agent had “a generally favorable safety profile,” and the rates of adverse events “were generally as expected, given the underlying disease severity, baseline coexisting conditions, and ages of the participants.” Two participants discontinued the infusion because of an adverse event. Drug-related adverse events occurred in 7% of the entire study population, serious drug-related adverse events occurred in 1%, and both occurred at similar rates across the study groups.
Both trials were funded by Merck, which also was involved in study design, data analysis and interpretation, and writing the reports. Dr. Wilcox and his associates reported ties to Merck and numerous other industry sources.
Bezlotoxumab must be placed in perspective, seen within the context of alternative options currently being evaluated in clinical trials.
These include recently developed drugs such as ridinilazole, surotomycin, cadazolid, RBX2660, and SER-109. Also under assessment is the oral administration of nontoxigenic C. difficile strains to compete with toxigenic strains, as well as three vaccines against the organism. Stool transplantation also is known to be highly successful in preventing recurrent C. difficile infection.
In addition, the cost-effectiveness of bezlotoxumab, especially in relation to these alternative treatments, hasn’t yet been determined.
John G. Bartlett, MD, is in the department of medicine at Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore. He reported having no relevant financial disclosures. Dr. Bartlett made these remarks in an editorial accompanying Dr. Wilcox’s report (N Engl J Med. 2017 Jan 25. doi: 10.1056/NEJMe1614726).
Bezlotoxumab must be placed in perspective, seen within the context of alternative options currently being evaluated in clinical trials.
These include recently developed drugs such as ridinilazole, surotomycin, cadazolid, RBX2660, and SER-109. Also under assessment is the oral administration of nontoxigenic C. difficile strains to compete with toxigenic strains, as well as three vaccines against the organism. Stool transplantation also is known to be highly successful in preventing recurrent C. difficile infection.
In addition, the cost-effectiveness of bezlotoxumab, especially in relation to these alternative treatments, hasn’t yet been determined.
John G. Bartlett, MD, is in the department of medicine at Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore. He reported having no relevant financial disclosures. Dr. Bartlett made these remarks in an editorial accompanying Dr. Wilcox’s report (N Engl J Med. 2017 Jan 25. doi: 10.1056/NEJMe1614726).
Bezlotoxumab must be placed in perspective, seen within the context of alternative options currently being evaluated in clinical trials.
These include recently developed drugs such as ridinilazole, surotomycin, cadazolid, RBX2660, and SER-109. Also under assessment is the oral administration of nontoxigenic C. difficile strains to compete with toxigenic strains, as well as three vaccines against the organism. Stool transplantation also is known to be highly successful in preventing recurrent C. difficile infection.
In addition, the cost-effectiveness of bezlotoxumab, especially in relation to these alternative treatments, hasn’t yet been determined.
John G. Bartlett, MD, is in the department of medicine at Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore. He reported having no relevant financial disclosures. Dr. Bartlett made these remarks in an editorial accompanying Dr. Wilcox’s report (N Engl J Med. 2017 Jan 25. doi: 10.1056/NEJMe1614726).
Adding bezlotoxumab to standard antibiotic treatment of primary or recurrent Clostridium difficile infection reduces recurrences by 38% (10 percentage points), according to a report published in the New England Journal of Medicine.
As many as 35% of patients who complete initial antibiotic treatment have at least one recurrence of C. difficile infection, and the rate of repeat recurrence rate jumps to 60% after the initial recurrence. Researchers performed two parallel international phase III trials to assess the efficacy and safety of bezlotoxumab, alone or in combination with actoxumab, for preventing such recurrences. Both monoclonal antibodies work by binding to and neutralizing C. difficile toxins; bezlotoxumab targets toxin B and actoxumab targets toxin A, said Mark H. Wilcox, MD, of the division of microbiology, Leeds (England) General Infirmary, and his associates.
The primary efficacy endpoint – the proportion of patients with recurrent C. difficile infection during 12 weeks of follow-up – was substantially lower with bezlotoxumab (17%) than with placebo (28%) in the first trial and in the second trial (16% vs. 26%). This treatment benefit was evident as early as 2 weeks after infusion and persisted throughout follow-up, the investigators said (N Engl J Med. 2017 Jan 25. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1602615).
The agent’s persistent effect through 12 weeks is important to note because approximately 30% of the recurrences in this study “occurred beyond the conventional 4-week assessment period for treatment efficacy. The number needed to treat to prevent one episode of recurrent C. difficile infection was 10; it was 6 among participants 65 years of age or older and those with previous C. difficile infection,” Dr. Wilcox and his associates noted.
Bezlotoxumab was consistently effective in several sensitivity analyses. It also was effective in both trials individually as well as in pooled results. And the choice of oral antibiotic appeared to have no effect on bezlotoxumab’s efficacy.
In a post hoc analysis, bezlotoxumab was also effective in the subgroup of 1,964 patients at highest risk for C. difficile recurrence because they were elderly, had compromised immunity, had the most severe infections, had a history of C. difficile infection, or carried a strain of the organism associated with particularly poor outcomes. In this subgroup, 17% of patients given bezlotoxumab and 16% of those given bezlotoxumab plus actoxumab developed recurrences, compared with 30% of those given placebo.
Regarding adverse events, the agent had “a generally favorable safety profile,” and the rates of adverse events “were generally as expected, given the underlying disease severity, baseline coexisting conditions, and ages of the participants.” Two participants discontinued the infusion because of an adverse event. Drug-related adverse events occurred in 7% of the entire study population, serious drug-related adverse events occurred in 1%, and both occurred at similar rates across the study groups.
Both trials were funded by Merck, which also was involved in study design, data analysis and interpretation, and writing the reports. Dr. Wilcox and his associates reported ties to Merck and numerous other industry sources.
Adding bezlotoxumab to standard antibiotic treatment of primary or recurrent Clostridium difficile infection reduces recurrences by 38% (10 percentage points), according to a report published in the New England Journal of Medicine.
As many as 35% of patients who complete initial antibiotic treatment have at least one recurrence of C. difficile infection, and the rate of repeat recurrence rate jumps to 60% after the initial recurrence. Researchers performed two parallel international phase III trials to assess the efficacy and safety of bezlotoxumab, alone or in combination with actoxumab, for preventing such recurrences. Both monoclonal antibodies work by binding to and neutralizing C. difficile toxins; bezlotoxumab targets toxin B and actoxumab targets toxin A, said Mark H. Wilcox, MD, of the division of microbiology, Leeds (England) General Infirmary, and his associates.
The primary efficacy endpoint – the proportion of patients with recurrent C. difficile infection during 12 weeks of follow-up – was substantially lower with bezlotoxumab (17%) than with placebo (28%) in the first trial and in the second trial (16% vs. 26%). This treatment benefit was evident as early as 2 weeks after infusion and persisted throughout follow-up, the investigators said (N Engl J Med. 2017 Jan 25. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1602615).
The agent’s persistent effect through 12 weeks is important to note because approximately 30% of the recurrences in this study “occurred beyond the conventional 4-week assessment period for treatment efficacy. The number needed to treat to prevent one episode of recurrent C. difficile infection was 10; it was 6 among participants 65 years of age or older and those with previous C. difficile infection,” Dr. Wilcox and his associates noted.
Bezlotoxumab was consistently effective in several sensitivity analyses. It also was effective in both trials individually as well as in pooled results. And the choice of oral antibiotic appeared to have no effect on bezlotoxumab’s efficacy.
In a post hoc analysis, bezlotoxumab was also effective in the subgroup of 1,964 patients at highest risk for C. difficile recurrence because they were elderly, had compromised immunity, had the most severe infections, had a history of C. difficile infection, or carried a strain of the organism associated with particularly poor outcomes. In this subgroup, 17% of patients given bezlotoxumab and 16% of those given bezlotoxumab plus actoxumab developed recurrences, compared with 30% of those given placebo.
Regarding adverse events, the agent had “a generally favorable safety profile,” and the rates of adverse events “were generally as expected, given the underlying disease severity, baseline coexisting conditions, and ages of the participants.” Two participants discontinued the infusion because of an adverse event. Drug-related adverse events occurred in 7% of the entire study population, serious drug-related adverse events occurred in 1%, and both occurred at similar rates across the study groups.
Both trials were funded by Merck, which also was involved in study design, data analysis and interpretation, and writing the reports. Dr. Wilcox and his associates reported ties to Merck and numerous other industry sources.
FROM THE NEW ENGLAND JOURNAL OF MEDICINE
Key clinical point: Adding bezlotoxumab to standard antibiotic treatment of primary or recurrent Clostridium difficile infection reduced recurrences by 38% (10 percentage points).
Major finding: The number needed to treat to prevent one episode of recurrent C. difficile infection was 10; it was 6 among high-risk participants who were 65 years of age or older or who had previous C. difficile infection.
Data source: Two parallel randomized double-blind placebo-controlled international trials involving 2,655 adults followed for 12 weeks.
Disclosures: Both trials were funded by Merck, which also was involved in study design, data analysis and interpretation, and writing the reports. Dr. Wilcox and his associates reported ties to Merck and numerous other industry sources.
1 in 10 youths, 1 in 4 adults in U.S. use tobacco products
More than one in four U.S. adults are current users of at least one type of tobacco product, and nearly 1 in 10 youths report using tobacco in the previous month, according to a report published in the Jan. 26 edition of the New England Journal of Medicine.
Analysis of data from 45,971 adults and youths aged 12 years and older in Wave 1 of the national longitudinal Population Assessment of Tobacco and Health (PATH) study showed 28% of adults were current users of tobacco products, and 20% were daily users. Cigarettes were the most commonly used tobacco product: 18% of adults said they were current users of cigarettes and 16% were daily users. Cigars and e-cigarettes were the next most common tobacco products, with 8% of adults currently using cigars, and 6% currently using e-cigarettes. (N Eng J Med. 2016, Jan 26. doi: 10.1056/NEJMsa1607538).
“Among adults, tobacco use was generally higher among younger adults, men, members of racial minorities, members of sexual minorities, those with lower educational attainment and lower household income, and those living in the South or Midwest than among their counterparts,” wrote Karin A. Kasza of the department of health behavior at the Roswell Park Cancer Institute, Buffalo, N.Y., and coauthors. “Among youths, the prevalences of ever use and use in the previous 30 days were higher among older youths, male youths, and members of sexual minorities than among their counterparts.”
Many also reported using combinations of tobacco products in the previous 30 days, with 23% of adults and 15% of youths using cigarettes and e-cigarettes concurrently.
The authors noted that the estimates of tobacco use among youths obtained from this household-based survey were lower than those seen in previous school-based surveys, and suggested the survey method may have influenced young people’s responses.
“Surveys administered in a school-based environment may overestimate tobacco-use behaviors because of peer influences, whereas youths may underreport tobacco-use behaviors in a home-based survey out of fear that their parents will overhear answers or learn about them from the interviewer,” Ms. Kasza and her associates wrote.
The study was supported by the National Institute on Drug Abuse, National Institutes of Health, and the Food and Drug Administration and U.S. Department of Health and Human Services under a contract to Westat. One author declared grant support from a pharmaceutical company and having acted as an expert witness against the tobacco industry. Another declared advisory board positions and grant support from private industry, and a third declared stock in private industry. No other conflicts of interest were declared.
More than one in four U.S. adults are current users of at least one type of tobacco product, and nearly 1 in 10 youths report using tobacco in the previous month, according to a report published in the Jan. 26 edition of the New England Journal of Medicine.
Analysis of data from 45,971 adults and youths aged 12 years and older in Wave 1 of the national longitudinal Population Assessment of Tobacco and Health (PATH) study showed 28% of adults were current users of tobacco products, and 20% were daily users. Cigarettes were the most commonly used tobacco product: 18% of adults said they were current users of cigarettes and 16% were daily users. Cigars and e-cigarettes were the next most common tobacco products, with 8% of adults currently using cigars, and 6% currently using e-cigarettes. (N Eng J Med. 2016, Jan 26. doi: 10.1056/NEJMsa1607538).
“Among adults, tobacco use was generally higher among younger adults, men, members of racial minorities, members of sexual minorities, those with lower educational attainment and lower household income, and those living in the South or Midwest than among their counterparts,” wrote Karin A. Kasza of the department of health behavior at the Roswell Park Cancer Institute, Buffalo, N.Y., and coauthors. “Among youths, the prevalences of ever use and use in the previous 30 days were higher among older youths, male youths, and members of sexual minorities than among their counterparts.”
Many also reported using combinations of tobacco products in the previous 30 days, with 23% of adults and 15% of youths using cigarettes and e-cigarettes concurrently.
The authors noted that the estimates of tobacco use among youths obtained from this household-based survey were lower than those seen in previous school-based surveys, and suggested the survey method may have influenced young people’s responses.
“Surveys administered in a school-based environment may overestimate tobacco-use behaviors because of peer influences, whereas youths may underreport tobacco-use behaviors in a home-based survey out of fear that their parents will overhear answers or learn about them from the interviewer,” Ms. Kasza and her associates wrote.
The study was supported by the National Institute on Drug Abuse, National Institutes of Health, and the Food and Drug Administration and U.S. Department of Health and Human Services under a contract to Westat. One author declared grant support from a pharmaceutical company and having acted as an expert witness against the tobacco industry. Another declared advisory board positions and grant support from private industry, and a third declared stock in private industry. No other conflicts of interest were declared.
More than one in four U.S. adults are current users of at least one type of tobacco product, and nearly 1 in 10 youths report using tobacco in the previous month, according to a report published in the Jan. 26 edition of the New England Journal of Medicine.
Analysis of data from 45,971 adults and youths aged 12 years and older in Wave 1 of the national longitudinal Population Assessment of Tobacco and Health (PATH) study showed 28% of adults were current users of tobacco products, and 20% were daily users. Cigarettes were the most commonly used tobacco product: 18% of adults said they were current users of cigarettes and 16% were daily users. Cigars and e-cigarettes were the next most common tobacco products, with 8% of adults currently using cigars, and 6% currently using e-cigarettes. (N Eng J Med. 2016, Jan 26. doi: 10.1056/NEJMsa1607538).
“Among adults, tobacco use was generally higher among younger adults, men, members of racial minorities, members of sexual minorities, those with lower educational attainment and lower household income, and those living in the South or Midwest than among their counterparts,” wrote Karin A. Kasza of the department of health behavior at the Roswell Park Cancer Institute, Buffalo, N.Y., and coauthors. “Among youths, the prevalences of ever use and use in the previous 30 days were higher among older youths, male youths, and members of sexual minorities than among their counterparts.”
Many also reported using combinations of tobacco products in the previous 30 days, with 23% of adults and 15% of youths using cigarettes and e-cigarettes concurrently.
The authors noted that the estimates of tobacco use among youths obtained from this household-based survey were lower than those seen in previous school-based surveys, and suggested the survey method may have influenced young people’s responses.
“Surveys administered in a school-based environment may overestimate tobacco-use behaviors because of peer influences, whereas youths may underreport tobacco-use behaviors in a home-based survey out of fear that their parents will overhear answers or learn about them from the interviewer,” Ms. Kasza and her associates wrote.
The study was supported by the National Institute on Drug Abuse, National Institutes of Health, and the Food and Drug Administration and U.S. Department of Health and Human Services under a contract to Westat. One author declared grant support from a pharmaceutical company and having acted as an expert witness against the tobacco industry. Another declared advisory board positions and grant support from private industry, and a third declared stock in private industry. No other conflicts of interest were declared.
FROM THE NEW ENGLAND JOURNAL OF MEDICINE
Key clinical point: More than one in four U.S. adults are current users of at least one type of tobacco product, and nearly 1 in 10 youths report using tobacco in the previous month.
Major finding: The PATH study found 28% of adults are current users of tobacco products, and 20% are daily users.
Data source: Wave 1 of the national longitudinal Population Assessment of Tobacco and Health (PATH) study.
Disclosures: The study was supported by the National Institute on Drug Abuse, National Institutes of Health, and the Food and Drug Administration and U.S. Department of Health and Human Services. One author declared grant support from a pharmaceutical company and having acted as an expert witness against the tobacco industry. Another declared advisory board positions and grant support from private industry, and a third declared stock in private industry. No other conflicts of interest were declared.