User login
Fragmented readmission after liver transplant linked to adverse outcomes
CORONADO, CALIF. – Postdischarge surgical care fragmentation significantly increases the risk of both 30-day mortality and subsequent readmission in the first year following orthotopic liver transplantation, results from a study of national data showed.
“In an era of regionalization and centers of excellence, the likelihood for postdischarge fragmentation, defined as readmission to any hospital other than the hospital at which the surgery was performed, is an increasing reality,” Anai N. Kothari, MD, said at the annual meeting of the Western Surgical Association. “In many different surgical subspecialties – major vascular operations, bariatric surgery, oncologic resections – it’s known to be a risk factor for adverse events and poor quality. Postdischarge fragmentation is common, [and related to] as often as one in four readmissions. It increases the risk for short- and long-term morbidity and mortality, decreases survival, and increases cost.”
Dr. Kothari reported results from 2,996 patients with 7,485 readmission encounters at 299 hospitals. Of the 7,485 readmissions, 6,249 (83.5%) were nonfragmented, and 1,236 (16.5%) were fragmented. The mean age of patients was 55 years. There were no significant differences in baseline characteristics between patients with nonfragmented and fragmented admissions in terms of patient age, sex, preoperative and postoperative length of stay, Charlson comorbidity index, and comorbidities, with the exception of renal failure, which was more common among patients in the fragmented admission group.
Compared with the patients in the nonfragmented admission group, those in the fragmented admission group had a greater number of average readmissions per patient (3.3 vs. 2.5, respectively; P less than .0001) and a greater number of average days to readmission (168 vs. 105; P less than .0001). Reasons for readmission differed among the two groups. Patients readmitted to the index transplant center were more likely to have a biliary, hematologic, or neurologic complication, while those in the fragmented admissions group were more likely to be readmitted for things like electrolyte disturbances, respiratory issues, gastrointestinal issues, or hematologic-related issues. There was no difference in overall cost of care between the two groups (an average of $11,621.68 vs. $11.585.39, respectively).
After the investigators adjusted for age, sex, reason for readmission, cost of the index liver transplant, readmission length of stay, number of previous readmissions, and time from transplant, postdischarge fragmentation increased the odds of both 30-day mortality (OR, 1.75) and 30-day readmission (OR, 2.14). “It looks like just having a fragmented readmission is an independent predictor for an adverse event,” Dr. Kothari said.
Significant predictors of adverse events following a fragmented readmission included an increased number of previous readmissions (OR, 1.07) and readmission within 90 days of orthotopic liver transplant (OR, 2.19). “These two factors may be important for guiding providers to say, ‘If you have these things, this patient should likely come back to their index transplant center,’” Dr. Kothari said.
He reported having no relevant financial disclosures.
CORONADO, CALIF. – Postdischarge surgical care fragmentation significantly increases the risk of both 30-day mortality and subsequent readmission in the first year following orthotopic liver transplantation, results from a study of national data showed.
“In an era of regionalization and centers of excellence, the likelihood for postdischarge fragmentation, defined as readmission to any hospital other than the hospital at which the surgery was performed, is an increasing reality,” Anai N. Kothari, MD, said at the annual meeting of the Western Surgical Association. “In many different surgical subspecialties – major vascular operations, bariatric surgery, oncologic resections – it’s known to be a risk factor for adverse events and poor quality. Postdischarge fragmentation is common, [and related to] as often as one in four readmissions. It increases the risk for short- and long-term morbidity and mortality, decreases survival, and increases cost.”
Dr. Kothari reported results from 2,996 patients with 7,485 readmission encounters at 299 hospitals. Of the 7,485 readmissions, 6,249 (83.5%) were nonfragmented, and 1,236 (16.5%) were fragmented. The mean age of patients was 55 years. There were no significant differences in baseline characteristics between patients with nonfragmented and fragmented admissions in terms of patient age, sex, preoperative and postoperative length of stay, Charlson comorbidity index, and comorbidities, with the exception of renal failure, which was more common among patients in the fragmented admission group.
Compared with the patients in the nonfragmented admission group, those in the fragmented admission group had a greater number of average readmissions per patient (3.3 vs. 2.5, respectively; P less than .0001) and a greater number of average days to readmission (168 vs. 105; P less than .0001). Reasons for readmission differed among the two groups. Patients readmitted to the index transplant center were more likely to have a biliary, hematologic, or neurologic complication, while those in the fragmented admissions group were more likely to be readmitted for things like electrolyte disturbances, respiratory issues, gastrointestinal issues, or hematologic-related issues. There was no difference in overall cost of care between the two groups (an average of $11,621.68 vs. $11.585.39, respectively).
After the investigators adjusted for age, sex, reason for readmission, cost of the index liver transplant, readmission length of stay, number of previous readmissions, and time from transplant, postdischarge fragmentation increased the odds of both 30-day mortality (OR, 1.75) and 30-day readmission (OR, 2.14). “It looks like just having a fragmented readmission is an independent predictor for an adverse event,” Dr. Kothari said.
Significant predictors of adverse events following a fragmented readmission included an increased number of previous readmissions (OR, 1.07) and readmission within 90 days of orthotopic liver transplant (OR, 2.19). “These two factors may be important for guiding providers to say, ‘If you have these things, this patient should likely come back to their index transplant center,’” Dr. Kothari said.
He reported having no relevant financial disclosures.
CORONADO, CALIF. – Postdischarge surgical care fragmentation significantly increases the risk of both 30-day mortality and subsequent readmission in the first year following orthotopic liver transplantation, results from a study of national data showed.
“In an era of regionalization and centers of excellence, the likelihood for postdischarge fragmentation, defined as readmission to any hospital other than the hospital at which the surgery was performed, is an increasing reality,” Anai N. Kothari, MD, said at the annual meeting of the Western Surgical Association. “In many different surgical subspecialties – major vascular operations, bariatric surgery, oncologic resections – it’s known to be a risk factor for adverse events and poor quality. Postdischarge fragmentation is common, [and related to] as often as one in four readmissions. It increases the risk for short- and long-term morbidity and mortality, decreases survival, and increases cost.”
Dr. Kothari reported results from 2,996 patients with 7,485 readmission encounters at 299 hospitals. Of the 7,485 readmissions, 6,249 (83.5%) were nonfragmented, and 1,236 (16.5%) were fragmented. The mean age of patients was 55 years. There were no significant differences in baseline characteristics between patients with nonfragmented and fragmented admissions in terms of patient age, sex, preoperative and postoperative length of stay, Charlson comorbidity index, and comorbidities, with the exception of renal failure, which was more common among patients in the fragmented admission group.
Compared with the patients in the nonfragmented admission group, those in the fragmented admission group had a greater number of average readmissions per patient (3.3 vs. 2.5, respectively; P less than .0001) and a greater number of average days to readmission (168 vs. 105; P less than .0001). Reasons for readmission differed among the two groups. Patients readmitted to the index transplant center were more likely to have a biliary, hematologic, or neurologic complication, while those in the fragmented admissions group were more likely to be readmitted for things like electrolyte disturbances, respiratory issues, gastrointestinal issues, or hematologic-related issues. There was no difference in overall cost of care between the two groups (an average of $11,621.68 vs. $11.585.39, respectively).
After the investigators adjusted for age, sex, reason for readmission, cost of the index liver transplant, readmission length of stay, number of previous readmissions, and time from transplant, postdischarge fragmentation increased the odds of both 30-day mortality (OR, 1.75) and 30-day readmission (OR, 2.14). “It looks like just having a fragmented readmission is an independent predictor for an adverse event,” Dr. Kothari said.
Significant predictors of adverse events following a fragmented readmission included an increased number of previous readmissions (OR, 1.07) and readmission within 90 days of orthotopic liver transplant (OR, 2.19). “These two factors may be important for guiding providers to say, ‘If you have these things, this patient should likely come back to their index transplant center,’” Dr. Kothari said.
He reported having no relevant financial disclosures.
AT WSA 2016
Key clinical point:
Major finding: After investigators adjusted for numerous variables, postdischarge fragmentation following orthotopic liver transplantation increased the odds of both 30-day mortality (OR, 1.75) and 30-day readmission (OR, 2.14).
Data source: An analysis of data from the Healthcare Cost and Utilization Project State Inpatient Databases for Florida and California between 2006 and 2011 to identify 2,996 patients who underwent orthotopic liver transplantation.
Disclosures: Dr. Kothari reported having no relevant financial disclosures.
Factor VIII microcapsules eyed for eluding neutralizing antibodies
Using platelet microcapsules to deliver factor VIII, a process that is expected to increase factor VIII efficacy and avoid the development of neutralizing antibodies, is being examined via in vitro testing, according to an abstract to be featured during a press conference at the annual meeting of the American Society of Hematology.
Caroline E. Hansen of the Georgia Institute of Technology, Atlanta, and her colleagues performed in vitro experiments that show this technology has the potential to increase factor VIII efficacy for hemophilia A patients with inhibitors.
“Current work evaluating localized thrombin generation due to the factor VIII–loaded microcapsules and the effect of platelet contraction force via pharmacologic agents, such as blebbistatin, ROCK, and myosin inhibitors, [is] ongoing,” the researchers wrote in their abstract.
They fabricated polyelectrolyte layers onto calcium carbonate cores and incorporated fibrinogen into the final layer to facilitate binding with platelets. The microcapsule’s inner core contains factor VIII separated from the polyelectrolyte layers by a dextran core.
In the in vitro model, platelets adhered to the microcapsules, which were incorporated into fibrin networks upon platelet activation. During clot contraction, the microcapsules ruptured only in the vicinity of contracting platelets, ensuring drug delivery was targeted at sites of active clot formation.
The researchers perfused recalcified whole blood and platelet poor plasma into in vitro microfluidic models of vascular injury, which consisted of a collagen/tissue factor patch. The efficacy of systemic and microcapsular factor VIII was quantitatively evaluated by comparing fibrin fluorescence intensity on the patch, which was normalized to platelet number.
Fibrin formation was comparable using microcapsules without dextran, fibrinogen, and loaded factor VIII. Compared with standard systemic infusion of 0.05 U/mL factor VIII, however, microcapsules loaded with 0.01 U/mL factor VIII produced four times as much fibrin.
To mimic hemophilia A blood with inhibitors, a factor VIII inhibitory antibody was introduced into healthy blood samples. Again, significantly more fibrin was produced in samples with microcapsules loaded with 0.01 U/mL factor VIII than with systemic factor VIII infusions at clinically relevant high and low dosages of 0.05 and 0.5 U/mL (P less than .05).
This increased efficacy is likely due to the microcapsule shielding effect on factor VIII, preventing exposure to inhibitory antibodies, the researchers reported.
Ms. Hansen had no relevant financial disclosures. One of her colleagues, Shannon L. Meeks, MD, disclosed adviser relationships with Biogen, Genentech, Bayer Healthcare, Grifols, CSL Behring, and Shire. Another, Wilbur A Lam, MD, PhD, disclosed equity ownership in Sanguina.
Abstract 81: Leveraging the Contractile Force of Platelets for Targeted Factor VIII Delivery in Hemophilia With Inhibitors.
[email protected]
On Twitter @maryjodales
Using platelet microcapsules to deliver factor VIII, a process that is expected to increase factor VIII efficacy and avoid the development of neutralizing antibodies, is being examined via in vitro testing, according to an abstract to be featured during a press conference at the annual meeting of the American Society of Hematology.
Caroline E. Hansen of the Georgia Institute of Technology, Atlanta, and her colleagues performed in vitro experiments that show this technology has the potential to increase factor VIII efficacy for hemophilia A patients with inhibitors.
“Current work evaluating localized thrombin generation due to the factor VIII–loaded microcapsules and the effect of platelet contraction force via pharmacologic agents, such as blebbistatin, ROCK, and myosin inhibitors, [is] ongoing,” the researchers wrote in their abstract.
They fabricated polyelectrolyte layers onto calcium carbonate cores and incorporated fibrinogen into the final layer to facilitate binding with platelets. The microcapsule’s inner core contains factor VIII separated from the polyelectrolyte layers by a dextran core.
In the in vitro model, platelets adhered to the microcapsules, which were incorporated into fibrin networks upon platelet activation. During clot contraction, the microcapsules ruptured only in the vicinity of contracting platelets, ensuring drug delivery was targeted at sites of active clot formation.
The researchers perfused recalcified whole blood and platelet poor plasma into in vitro microfluidic models of vascular injury, which consisted of a collagen/tissue factor patch. The efficacy of systemic and microcapsular factor VIII was quantitatively evaluated by comparing fibrin fluorescence intensity on the patch, which was normalized to platelet number.
Fibrin formation was comparable using microcapsules without dextran, fibrinogen, and loaded factor VIII. Compared with standard systemic infusion of 0.05 U/mL factor VIII, however, microcapsules loaded with 0.01 U/mL factor VIII produced four times as much fibrin.
To mimic hemophilia A blood with inhibitors, a factor VIII inhibitory antibody was introduced into healthy blood samples. Again, significantly more fibrin was produced in samples with microcapsules loaded with 0.01 U/mL factor VIII than with systemic factor VIII infusions at clinically relevant high and low dosages of 0.05 and 0.5 U/mL (P less than .05).
This increased efficacy is likely due to the microcapsule shielding effect on factor VIII, preventing exposure to inhibitory antibodies, the researchers reported.
Ms. Hansen had no relevant financial disclosures. One of her colleagues, Shannon L. Meeks, MD, disclosed adviser relationships with Biogen, Genentech, Bayer Healthcare, Grifols, CSL Behring, and Shire. Another, Wilbur A Lam, MD, PhD, disclosed equity ownership in Sanguina.
Abstract 81: Leveraging the Contractile Force of Platelets for Targeted Factor VIII Delivery in Hemophilia With Inhibitors.
[email protected]
On Twitter @maryjodales
Using platelet microcapsules to deliver factor VIII, a process that is expected to increase factor VIII efficacy and avoid the development of neutralizing antibodies, is being examined via in vitro testing, according to an abstract to be featured during a press conference at the annual meeting of the American Society of Hematology.
Caroline E. Hansen of the Georgia Institute of Technology, Atlanta, and her colleagues performed in vitro experiments that show this technology has the potential to increase factor VIII efficacy for hemophilia A patients with inhibitors.
“Current work evaluating localized thrombin generation due to the factor VIII–loaded microcapsules and the effect of platelet contraction force via pharmacologic agents, such as blebbistatin, ROCK, and myosin inhibitors, [is] ongoing,” the researchers wrote in their abstract.
They fabricated polyelectrolyte layers onto calcium carbonate cores and incorporated fibrinogen into the final layer to facilitate binding with platelets. The microcapsule’s inner core contains factor VIII separated from the polyelectrolyte layers by a dextran core.
In the in vitro model, platelets adhered to the microcapsules, which were incorporated into fibrin networks upon platelet activation. During clot contraction, the microcapsules ruptured only in the vicinity of contracting platelets, ensuring drug delivery was targeted at sites of active clot formation.
The researchers perfused recalcified whole blood and platelet poor plasma into in vitro microfluidic models of vascular injury, which consisted of a collagen/tissue factor patch. The efficacy of systemic and microcapsular factor VIII was quantitatively evaluated by comparing fibrin fluorescence intensity on the patch, which was normalized to platelet number.
Fibrin formation was comparable using microcapsules without dextran, fibrinogen, and loaded factor VIII. Compared with standard systemic infusion of 0.05 U/mL factor VIII, however, microcapsules loaded with 0.01 U/mL factor VIII produced four times as much fibrin.
To mimic hemophilia A blood with inhibitors, a factor VIII inhibitory antibody was introduced into healthy blood samples. Again, significantly more fibrin was produced in samples with microcapsules loaded with 0.01 U/mL factor VIII than with systemic factor VIII infusions at clinically relevant high and low dosages of 0.05 and 0.5 U/mL (P less than .05).
This increased efficacy is likely due to the microcapsule shielding effect on factor VIII, preventing exposure to inhibitory antibodies, the researchers reported.
Ms. Hansen had no relevant financial disclosures. One of her colleagues, Shannon L. Meeks, MD, disclosed adviser relationships with Biogen, Genentech, Bayer Healthcare, Grifols, CSL Behring, and Shire. Another, Wilbur A Lam, MD, PhD, disclosed equity ownership in Sanguina.
Abstract 81: Leveraging the Contractile Force of Platelets for Targeted Factor VIII Delivery in Hemophilia With Inhibitors.
[email protected]
On Twitter @maryjodales
ASH 2016 PREVIEW
FDA approves tenofovir alafenamide for patients with chronic hepatitis B and liver disease
The Food and Drug Administration has approved tenofovir alafenamide (marketed as Vemlidy by Gilead Sciences) for the treatment of adults with chronic hepatitis B virus infection with compensated liver disease.
Tenofovir alafenamide is a novel, targeted prodrug of tenofovir that has demonstrated antiviral efficacy similar to tenofovir disoproxil fumarate (Viread) at significantly lower doses.
Compared with tenofovir disoproxil fumarate, tenofovir alafenamide has “greater plasma stability and more efficiently delivers tenofovir to hepatocytes” which allows tenofovir alafenamide to be administered in daily doses of 25mg while tenofovir disoproxil fumarate requires a dose of 300 mg to be as effective.
In addition, patients treated with tenofovir alafenamide demonstrated “improvements in certain bone and renal laboratory parameters.”
Overall, tenofovir alafenamide was well tolerated. Only 1% of patients discontinued treatment because of adverse events, and the most common adverse events were headache, abdominal pain, fatigue, cough, nausea, and back pain. Vemlidy has a boxed warning in its product label regarding the risks of lactic acidosis/severe hepatomegaly with steatosis and severe acute exacerbation of hepatitis B with discontinuation.
“Vemlidy is the first medication approved to treat this disease in nearly a decade,” said President and Chief Executive Officer of Gilead Sciences John Milligan. “We are excited to offer a new, effective option to help advance long-term care for patients.”
[email protected]
On Twitter @jessnicolecraig
The Food and Drug Administration has approved tenofovir alafenamide (marketed as Vemlidy by Gilead Sciences) for the treatment of adults with chronic hepatitis B virus infection with compensated liver disease.
Tenofovir alafenamide is a novel, targeted prodrug of tenofovir that has demonstrated antiviral efficacy similar to tenofovir disoproxil fumarate (Viread) at significantly lower doses.
Compared with tenofovir disoproxil fumarate, tenofovir alafenamide has “greater plasma stability and more efficiently delivers tenofovir to hepatocytes” which allows tenofovir alafenamide to be administered in daily doses of 25mg while tenofovir disoproxil fumarate requires a dose of 300 mg to be as effective.
In addition, patients treated with tenofovir alafenamide demonstrated “improvements in certain bone and renal laboratory parameters.”
Overall, tenofovir alafenamide was well tolerated. Only 1% of patients discontinued treatment because of adverse events, and the most common adverse events were headache, abdominal pain, fatigue, cough, nausea, and back pain. Vemlidy has a boxed warning in its product label regarding the risks of lactic acidosis/severe hepatomegaly with steatosis and severe acute exacerbation of hepatitis B with discontinuation.
“Vemlidy is the first medication approved to treat this disease in nearly a decade,” said President and Chief Executive Officer of Gilead Sciences John Milligan. “We are excited to offer a new, effective option to help advance long-term care for patients.”
[email protected]
On Twitter @jessnicolecraig
The Food and Drug Administration has approved tenofovir alafenamide (marketed as Vemlidy by Gilead Sciences) for the treatment of adults with chronic hepatitis B virus infection with compensated liver disease.
Tenofovir alafenamide is a novel, targeted prodrug of tenofovir that has demonstrated antiviral efficacy similar to tenofovir disoproxil fumarate (Viread) at significantly lower doses.
Compared with tenofovir disoproxil fumarate, tenofovir alafenamide has “greater plasma stability and more efficiently delivers tenofovir to hepatocytes” which allows tenofovir alafenamide to be administered in daily doses of 25mg while tenofovir disoproxil fumarate requires a dose of 300 mg to be as effective.
In addition, patients treated with tenofovir alafenamide demonstrated “improvements in certain bone and renal laboratory parameters.”
Overall, tenofovir alafenamide was well tolerated. Only 1% of patients discontinued treatment because of adverse events, and the most common adverse events were headache, abdominal pain, fatigue, cough, nausea, and back pain. Vemlidy has a boxed warning in its product label regarding the risks of lactic acidosis/severe hepatomegaly with steatosis and severe acute exacerbation of hepatitis B with discontinuation.
“Vemlidy is the first medication approved to treat this disease in nearly a decade,” said President and Chief Executive Officer of Gilead Sciences John Milligan. “We are excited to offer a new, effective option to help advance long-term care for patients.”
[email protected]
On Twitter @jessnicolecraig
Detecting PH in IPF ‘more art than science’
LOS ANGELES – When it comes to the optimal management of pulmonary hypertension (PH) in patients with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF), there are more questions than definitive answers, according to Brett E. Fenster, MD, FACC.
“Is PH in IPF a disease marker, an independent treatment target, or both?” he asked attendees at the annual meeting of the American College of Chest Physicians. “I think we have conflicting information about that.”
The prevalence of PH is estimated to be 10% in patients with mild to moderate IPF and tends to progress slowly. Common features of PH in IPF patients include shortness of breath, a greater degree of exertional desaturation, and an increased mortality rate.
Dr. Fenster described the ability to detect PH in IPF patients as “more art than science. A lot of different work has been done to look at different testing to get at the patients that may have PH that is a comorbid disease to their IPF. But a lot of times it comes down to assessing their level of dyspnea proportional to their level of disease. In those patients where we think there is something else going on besides their IPF, we’ll oftentimes get an echocardiogram and try to look at their right heart to see if they have features of PH. If it looks like they do, we will circle back and look at the amount of lung disease they have as characterized by their chest imaging, by their pulmonary function testing, and getting a blood gas. If this patient has findings of right heart enlargement, systolic dysfunction, et cetera, that clues us more into looking at PH and referring them to a center that has expertise in that version of PH.”
According to the most recent European Society of Cardiology/European Respiratory Society guidelines, the diagnosis of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD)/IPF/combined pulmonary fibrosis and emphysema (CPFE) without PH can be considered when the mean pulmonary artery pressure (mPAP) on right heart catheterization is less than 25 mm Hg. The diagnosis of COPD/IPF/CPFE with PH, based on these same guidelines, can be considered when the mPAP is 25 mm Hg or more. A patient may have COPD/IPF/CPFE with severe PH when his or her mPAP exceeds 35 mm Hg, or is 25 mm Hg or greater in the presence of a low cardiac output, the guidelines says (Eur Heart J. 2016;37:67-119). “That begins to separate out a group that may potentially benefit from targeted PH therapy,” Dr. Fenster said.
Current treatment approaches include long-term oxygen, diuretics, transplant, and pulmonary rehabilitation, but Dr. Fenster said there is sparse data on the optimal treatment approach. A study of sildenafil in IPF known as STEP-IPF failed to increase 6-minute walking test distance but improved diffusion capacity of carbon monoxide, quality of life, and arterial oxygenation (N Engl J Med. 2010;363:620-8). A study evaluating riociguat for idiopathic interstitial pneumonitis PH was discontinued early because of increased risk of death and adverse events. More recently, the drug ambrisentan was found to be ineffective at reducing the rate of IPF progression and was linked to an increase in disease progression events, including a decline in pulmonary function test values, hospitalization, and death, in the ARTEMIS-IPF trial (Ann Intern Med. 2013;158:641-9).
Randomized, placebo-controlled studies of bosentan in IPF give researchers pause for hope, Dr. Fenster said. BUILD-1 demonstrated a trend toward delayed time to death, delayed disease progression, improved quality of life, and no clear worsening of IPF (Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2008;177[1]:75-81), while BUILD-3 showed a significant improvement in forced vital capacity (FVC) and carbon monoxide diffusing capacity (Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2011;184[1]:92-9). A more recent trial evaluated IV treprostinil in 15 patients with interstitial lung disease and PH (Thorax 2014;69[2]:123-9). Eight of the patients had IPF. “After 12 weeks of treprostinil therapy, almost all of them experienced some degree of improvement in their walk distance,” said Dr. Fenster, who was not involved with the study. “Perhaps more importantly there were significant improvements in almost all parameters from their right heart catheterizations. So when we think about how to treat these patients, we have to weigh the risks and benefits of what we make potentially worse with our IPF therapy, such as worsening hypoxia, V/Q mismatch, disease progression, and volume overload. On the flip side, we might be improving right heart hemodynamics and RV function, which are prognostic in this disease. What’s the net balance of these things in terms of how it translates into functional capacity, quality of life, hospitalization, and mortality? We don’t know.”
According to Dr. Fenster, current data suggest that future IPF PH research should focus on prostanoid pathways and not on the estrogen-receptor and riociguat pathways to determine effective treatments. “We have numerous studies showing potential harm with IPF PH therapy, so we need to very much wade cautiously into this arena,” he said. “There is a potential role for PH therapy in IPF, but we will likely need to study patients with severe PH and IPF to show benefit. I think that’s where we’ll have the most success.”
Dr. Fenster reported having no relevant financial disclosures.
LOS ANGELES – When it comes to the optimal management of pulmonary hypertension (PH) in patients with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF), there are more questions than definitive answers, according to Brett E. Fenster, MD, FACC.
“Is PH in IPF a disease marker, an independent treatment target, or both?” he asked attendees at the annual meeting of the American College of Chest Physicians. “I think we have conflicting information about that.”
The prevalence of PH is estimated to be 10% in patients with mild to moderate IPF and tends to progress slowly. Common features of PH in IPF patients include shortness of breath, a greater degree of exertional desaturation, and an increased mortality rate.
Dr. Fenster described the ability to detect PH in IPF patients as “more art than science. A lot of different work has been done to look at different testing to get at the patients that may have PH that is a comorbid disease to their IPF. But a lot of times it comes down to assessing their level of dyspnea proportional to their level of disease. In those patients where we think there is something else going on besides their IPF, we’ll oftentimes get an echocardiogram and try to look at their right heart to see if they have features of PH. If it looks like they do, we will circle back and look at the amount of lung disease they have as characterized by their chest imaging, by their pulmonary function testing, and getting a blood gas. If this patient has findings of right heart enlargement, systolic dysfunction, et cetera, that clues us more into looking at PH and referring them to a center that has expertise in that version of PH.”
According to the most recent European Society of Cardiology/European Respiratory Society guidelines, the diagnosis of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD)/IPF/combined pulmonary fibrosis and emphysema (CPFE) without PH can be considered when the mean pulmonary artery pressure (mPAP) on right heart catheterization is less than 25 mm Hg. The diagnosis of COPD/IPF/CPFE with PH, based on these same guidelines, can be considered when the mPAP is 25 mm Hg or more. A patient may have COPD/IPF/CPFE with severe PH when his or her mPAP exceeds 35 mm Hg, or is 25 mm Hg or greater in the presence of a low cardiac output, the guidelines says (Eur Heart J. 2016;37:67-119). “That begins to separate out a group that may potentially benefit from targeted PH therapy,” Dr. Fenster said.
Current treatment approaches include long-term oxygen, diuretics, transplant, and pulmonary rehabilitation, but Dr. Fenster said there is sparse data on the optimal treatment approach. A study of sildenafil in IPF known as STEP-IPF failed to increase 6-minute walking test distance but improved diffusion capacity of carbon monoxide, quality of life, and arterial oxygenation (N Engl J Med. 2010;363:620-8). A study evaluating riociguat for idiopathic interstitial pneumonitis PH was discontinued early because of increased risk of death and adverse events. More recently, the drug ambrisentan was found to be ineffective at reducing the rate of IPF progression and was linked to an increase in disease progression events, including a decline in pulmonary function test values, hospitalization, and death, in the ARTEMIS-IPF trial (Ann Intern Med. 2013;158:641-9).
Randomized, placebo-controlled studies of bosentan in IPF give researchers pause for hope, Dr. Fenster said. BUILD-1 demonstrated a trend toward delayed time to death, delayed disease progression, improved quality of life, and no clear worsening of IPF (Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2008;177[1]:75-81), while BUILD-3 showed a significant improvement in forced vital capacity (FVC) and carbon monoxide diffusing capacity (Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2011;184[1]:92-9). A more recent trial evaluated IV treprostinil in 15 patients with interstitial lung disease and PH (Thorax 2014;69[2]:123-9). Eight of the patients had IPF. “After 12 weeks of treprostinil therapy, almost all of them experienced some degree of improvement in their walk distance,” said Dr. Fenster, who was not involved with the study. “Perhaps more importantly there were significant improvements in almost all parameters from their right heart catheterizations. So when we think about how to treat these patients, we have to weigh the risks and benefits of what we make potentially worse with our IPF therapy, such as worsening hypoxia, V/Q mismatch, disease progression, and volume overload. On the flip side, we might be improving right heart hemodynamics and RV function, which are prognostic in this disease. What’s the net balance of these things in terms of how it translates into functional capacity, quality of life, hospitalization, and mortality? We don’t know.”
According to Dr. Fenster, current data suggest that future IPF PH research should focus on prostanoid pathways and not on the estrogen-receptor and riociguat pathways to determine effective treatments. “We have numerous studies showing potential harm with IPF PH therapy, so we need to very much wade cautiously into this arena,” he said. “There is a potential role for PH therapy in IPF, but we will likely need to study patients with severe PH and IPF to show benefit. I think that’s where we’ll have the most success.”
Dr. Fenster reported having no relevant financial disclosures.
LOS ANGELES – When it comes to the optimal management of pulmonary hypertension (PH) in patients with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF), there are more questions than definitive answers, according to Brett E. Fenster, MD, FACC.
“Is PH in IPF a disease marker, an independent treatment target, or both?” he asked attendees at the annual meeting of the American College of Chest Physicians. “I think we have conflicting information about that.”
The prevalence of PH is estimated to be 10% in patients with mild to moderate IPF and tends to progress slowly. Common features of PH in IPF patients include shortness of breath, a greater degree of exertional desaturation, and an increased mortality rate.
Dr. Fenster described the ability to detect PH in IPF patients as “more art than science. A lot of different work has been done to look at different testing to get at the patients that may have PH that is a comorbid disease to their IPF. But a lot of times it comes down to assessing their level of dyspnea proportional to their level of disease. In those patients where we think there is something else going on besides their IPF, we’ll oftentimes get an echocardiogram and try to look at their right heart to see if they have features of PH. If it looks like they do, we will circle back and look at the amount of lung disease they have as characterized by their chest imaging, by their pulmonary function testing, and getting a blood gas. If this patient has findings of right heart enlargement, systolic dysfunction, et cetera, that clues us more into looking at PH and referring them to a center that has expertise in that version of PH.”
According to the most recent European Society of Cardiology/European Respiratory Society guidelines, the diagnosis of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD)/IPF/combined pulmonary fibrosis and emphysema (CPFE) without PH can be considered when the mean pulmonary artery pressure (mPAP) on right heart catheterization is less than 25 mm Hg. The diagnosis of COPD/IPF/CPFE with PH, based on these same guidelines, can be considered when the mPAP is 25 mm Hg or more. A patient may have COPD/IPF/CPFE with severe PH when his or her mPAP exceeds 35 mm Hg, or is 25 mm Hg or greater in the presence of a low cardiac output, the guidelines says (Eur Heart J. 2016;37:67-119). “That begins to separate out a group that may potentially benefit from targeted PH therapy,” Dr. Fenster said.
Current treatment approaches include long-term oxygen, diuretics, transplant, and pulmonary rehabilitation, but Dr. Fenster said there is sparse data on the optimal treatment approach. A study of sildenafil in IPF known as STEP-IPF failed to increase 6-minute walking test distance but improved diffusion capacity of carbon monoxide, quality of life, and arterial oxygenation (N Engl J Med. 2010;363:620-8). A study evaluating riociguat for idiopathic interstitial pneumonitis PH was discontinued early because of increased risk of death and adverse events. More recently, the drug ambrisentan was found to be ineffective at reducing the rate of IPF progression and was linked to an increase in disease progression events, including a decline in pulmonary function test values, hospitalization, and death, in the ARTEMIS-IPF trial (Ann Intern Med. 2013;158:641-9).
Randomized, placebo-controlled studies of bosentan in IPF give researchers pause for hope, Dr. Fenster said. BUILD-1 demonstrated a trend toward delayed time to death, delayed disease progression, improved quality of life, and no clear worsening of IPF (Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2008;177[1]:75-81), while BUILD-3 showed a significant improvement in forced vital capacity (FVC) and carbon monoxide diffusing capacity (Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2011;184[1]:92-9). A more recent trial evaluated IV treprostinil in 15 patients with interstitial lung disease and PH (Thorax 2014;69[2]:123-9). Eight of the patients had IPF. “After 12 weeks of treprostinil therapy, almost all of them experienced some degree of improvement in their walk distance,” said Dr. Fenster, who was not involved with the study. “Perhaps more importantly there were significant improvements in almost all parameters from their right heart catheterizations. So when we think about how to treat these patients, we have to weigh the risks and benefits of what we make potentially worse with our IPF therapy, such as worsening hypoxia, V/Q mismatch, disease progression, and volume overload. On the flip side, we might be improving right heart hemodynamics and RV function, which are prognostic in this disease. What’s the net balance of these things in terms of how it translates into functional capacity, quality of life, hospitalization, and mortality? We don’t know.”
According to Dr. Fenster, current data suggest that future IPF PH research should focus on prostanoid pathways and not on the estrogen-receptor and riociguat pathways to determine effective treatments. “We have numerous studies showing potential harm with IPF PH therapy, so we need to very much wade cautiously into this arena,” he said. “There is a potential role for PH therapy in IPF, but we will likely need to study patients with severe PH and IPF to show benefit. I think that’s where we’ll have the most success.”
Dr. Fenster reported having no relevant financial disclosures.
Toddler gaze patterns heritable, stable over time
NEW YORK – A team of autism researchers has found that patterns of social-visual engagement are markedly more similar among identical twin toddlers than among fraternal twins.
Social-visual engagement (SVE), which can be measured using eye-tracking technology, is how humans give preferential attention to social stimuli – in particular, people’s eyes and mouths, which provide important information for communication.
Lower levels of SVE have been shown to be associated with the later development of autism, even in children just a few months old (Nature. 2013 Dec 19;504:427-31). “But what hasn’t been shown until now is that this measure relates to genetics,” said Natasha Marrus, MD, PhD, of the department of psychiatry at Washington University in St. Louis.
The identical twins, who share 100% of their genes, “showed much more similar levels of social-visual engagement than fraternal twins,” Dr. Marrus said, with an intraclass correlation coefficient (ICC) of 0.91 (95% confidence interval, 0.85-0.95) for time spent looking at eyes, compared with 0.35 (95% CI, 0.07-0.59) for fraternal twins. Similar results were obtained for the caregiver questionnaire, suggesting strong genetic influences on both early reciprocal social behavior and SVE, said Dr. Marrus, also of Washington University.
At 36 months, 69 of the twin pairs were reevaluated. The investigators again found significantly greater SVE concordance for the identical twins: ICC, 0.93 (95% CI, 0.75-0.98), compared with ICC, 0.25 (95% CI, 0.0-0.60) for fraternal twins. They also found SVE patterns strongly correlated between 21 and 36 months for individual twins, indicating traitlike stability of this behavior over time.
“These two measures that are heritable, like autism, can be measured in a general population sample, which means they show good variability – potentially allowing the detection of subtle differences that may correspond to levels of risk for autism,” Dr. Marrus said. “By 18-21 months, the risk markers for later autism are already there – if you use a nuanced enough measure to detect them.”
Dr. Marrus said that while some practitioners have been able to reliably diagnose autism in children younger than 24 months, “it’s usually with the most severe cases,” she said. “But 18 months is a big time for social as well as language development, which becomes easier to measure at that point.”
A future direction for study, she said, “would be to go earlier. If we’re seeing this at 18 months, maybe we’d see it at 12.”
With autism, “early intervention is key, and even 6 months could make a difference,” Dr. Marrus said. “These two measures stand a really good chance of telling us important things about autism – which at early ages means better diagnostic prediction, measurement of severity and risk, and the potential to monitor responses to interventions.”
The National Institutes of Health supported the study through a grant to Dr. Constantino, and Dr. Marrus’s work was supported with a postdoctoral fellowship from the Autism Science Foundation. The investigators declared no relevant financial conflicts.
NEW YORK – A team of autism researchers has found that patterns of social-visual engagement are markedly more similar among identical twin toddlers than among fraternal twins.
Social-visual engagement (SVE), which can be measured using eye-tracking technology, is how humans give preferential attention to social stimuli – in particular, people’s eyes and mouths, which provide important information for communication.
Lower levels of SVE have been shown to be associated with the later development of autism, even in children just a few months old (Nature. 2013 Dec 19;504:427-31). “But what hasn’t been shown until now is that this measure relates to genetics,” said Natasha Marrus, MD, PhD, of the department of psychiatry at Washington University in St. Louis.
The identical twins, who share 100% of their genes, “showed much more similar levels of social-visual engagement than fraternal twins,” Dr. Marrus said, with an intraclass correlation coefficient (ICC) of 0.91 (95% confidence interval, 0.85-0.95) for time spent looking at eyes, compared with 0.35 (95% CI, 0.07-0.59) for fraternal twins. Similar results were obtained for the caregiver questionnaire, suggesting strong genetic influences on both early reciprocal social behavior and SVE, said Dr. Marrus, also of Washington University.
At 36 months, 69 of the twin pairs were reevaluated. The investigators again found significantly greater SVE concordance for the identical twins: ICC, 0.93 (95% CI, 0.75-0.98), compared with ICC, 0.25 (95% CI, 0.0-0.60) for fraternal twins. They also found SVE patterns strongly correlated between 21 and 36 months for individual twins, indicating traitlike stability of this behavior over time.
“These two measures that are heritable, like autism, can be measured in a general population sample, which means they show good variability – potentially allowing the detection of subtle differences that may correspond to levels of risk for autism,” Dr. Marrus said. “By 18-21 months, the risk markers for later autism are already there – if you use a nuanced enough measure to detect them.”
Dr. Marrus said that while some practitioners have been able to reliably diagnose autism in children younger than 24 months, “it’s usually with the most severe cases,” she said. “But 18 months is a big time for social as well as language development, which becomes easier to measure at that point.”
A future direction for study, she said, “would be to go earlier. If we’re seeing this at 18 months, maybe we’d see it at 12.”
With autism, “early intervention is key, and even 6 months could make a difference,” Dr. Marrus said. “These two measures stand a really good chance of telling us important things about autism – which at early ages means better diagnostic prediction, measurement of severity and risk, and the potential to monitor responses to interventions.”
The National Institutes of Health supported the study through a grant to Dr. Constantino, and Dr. Marrus’s work was supported with a postdoctoral fellowship from the Autism Science Foundation. The investigators declared no relevant financial conflicts.
NEW YORK – A team of autism researchers has found that patterns of social-visual engagement are markedly more similar among identical twin toddlers than among fraternal twins.
Social-visual engagement (SVE), which can be measured using eye-tracking technology, is how humans give preferential attention to social stimuli – in particular, people’s eyes and mouths, which provide important information for communication.
Lower levels of SVE have been shown to be associated with the later development of autism, even in children just a few months old (Nature. 2013 Dec 19;504:427-31). “But what hasn’t been shown until now is that this measure relates to genetics,” said Natasha Marrus, MD, PhD, of the department of psychiatry at Washington University in St. Louis.
The identical twins, who share 100% of their genes, “showed much more similar levels of social-visual engagement than fraternal twins,” Dr. Marrus said, with an intraclass correlation coefficient (ICC) of 0.91 (95% confidence interval, 0.85-0.95) for time spent looking at eyes, compared with 0.35 (95% CI, 0.07-0.59) for fraternal twins. Similar results were obtained for the caregiver questionnaire, suggesting strong genetic influences on both early reciprocal social behavior and SVE, said Dr. Marrus, also of Washington University.
At 36 months, 69 of the twin pairs were reevaluated. The investigators again found significantly greater SVE concordance for the identical twins: ICC, 0.93 (95% CI, 0.75-0.98), compared with ICC, 0.25 (95% CI, 0.0-0.60) for fraternal twins. They also found SVE patterns strongly correlated between 21 and 36 months for individual twins, indicating traitlike stability of this behavior over time.
“These two measures that are heritable, like autism, can be measured in a general population sample, which means they show good variability – potentially allowing the detection of subtle differences that may correspond to levels of risk for autism,” Dr. Marrus said. “By 18-21 months, the risk markers for later autism are already there – if you use a nuanced enough measure to detect them.”
Dr. Marrus said that while some practitioners have been able to reliably diagnose autism in children younger than 24 months, “it’s usually with the most severe cases,” she said. “But 18 months is a big time for social as well as language development, which becomes easier to measure at that point.”
A future direction for study, she said, “would be to go earlier. If we’re seeing this at 18 months, maybe we’d see it at 12.”
With autism, “early intervention is key, and even 6 months could make a difference,” Dr. Marrus said. “These two measures stand a really good chance of telling us important things about autism – which at early ages means better diagnostic prediction, measurement of severity and risk, and the potential to monitor responses to interventions.”
The National Institutes of Health supported the study through a grant to Dr. Constantino, and Dr. Marrus’s work was supported with a postdoctoral fellowship from the Autism Science Foundation. The investigators declared no relevant financial conflicts.
AT AACAP 2016
Weekly number of Zika-infected pregnancies drops by half
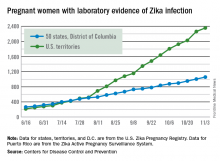
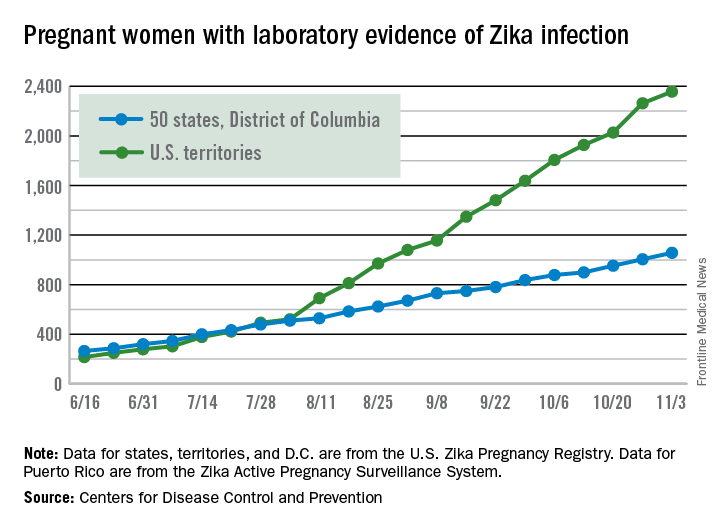
There were 146 new cases of pregnant women with laboratory evidence of Zika infection reported in the United States for the week ending Nov. 3 – just about half of the 288-case increase reported the week before, according to Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
For the year so far, there have been 1,057 cases of pregnant women with Zika in the states and the District of Columbia – 52 for the week ending Nov. 3 – and 2,357 cases in the territories, the CDC announced, with 94 reported in the most recent week. The total number of U.S. cases – 3,414 – is up by 4.4% over the previous week.
The CDC also reported one new infant born with Zika-related birth defects for the week ending Nov. 3, bringing the total for the year to 26 in the states/D.C. There were no new Zika-related pregnancy losses reported, so the total remains at five. State-level data are not being reported to protect the privacy of affected women and children.
The CDC is no longer reporting adverse pregnancy outcomes for the territories because Puerto Rico is not using the same “inclusion criteria to monitor brain abnormalities and other adverse pregnancy outcomes.” As of Sept. 29 – the date of the last territorial report – there had been one liveborn infant and one pregnancy loss related to Zika.
Zika-related birth defects reported by the CDC could include microcephaly, calcium deposits in the brain indicating possible brain damage, excess fluid in the brain cavities and surrounding the brain, absent or poorly formed brain structures, abnormal eye development, or other problems resulting from brain damage that affect nerves, muscles, and bones. The pregnancy losses encompass any miscarriage, stillbirth, and termination with evidence of birth defects.
The pregnancy-related figures for states, territories, and D.C. reflect reporting to the U.S. Zika Pregnancy Registry; data for Puerto Rico are reported to the U.S. Zika Active Pregnancy Surveillance System.
There were 146 new cases of pregnant women with laboratory evidence of Zika infection reported in the United States for the week ending Nov. 3 – just about half of the 288-case increase reported the week before, according to Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
For the year so far, there have been 1,057 cases of pregnant women with Zika in the states and the District of Columbia – 52 for the week ending Nov. 3 – and 2,357 cases in the territories, the CDC announced, with 94 reported in the most recent week. The total number of U.S. cases – 3,414 – is up by 4.4% over the previous week.
The CDC also reported one new infant born with Zika-related birth defects for the week ending Nov. 3, bringing the total for the year to 26 in the states/D.C. There were no new Zika-related pregnancy losses reported, so the total remains at five. State-level data are not being reported to protect the privacy of affected women and children.
The CDC is no longer reporting adverse pregnancy outcomes for the territories because Puerto Rico is not using the same “inclusion criteria to monitor brain abnormalities and other adverse pregnancy outcomes.” As of Sept. 29 – the date of the last territorial report – there had been one liveborn infant and one pregnancy loss related to Zika.
Zika-related birth defects reported by the CDC could include microcephaly, calcium deposits in the brain indicating possible brain damage, excess fluid in the brain cavities and surrounding the brain, absent or poorly formed brain structures, abnormal eye development, or other problems resulting from brain damage that affect nerves, muscles, and bones. The pregnancy losses encompass any miscarriage, stillbirth, and termination with evidence of birth defects.
The pregnancy-related figures for states, territories, and D.C. reflect reporting to the U.S. Zika Pregnancy Registry; data for Puerto Rico are reported to the U.S. Zika Active Pregnancy Surveillance System.
There were 146 new cases of pregnant women with laboratory evidence of Zika infection reported in the United States for the week ending Nov. 3 – just about half of the 288-case increase reported the week before, according to Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
For the year so far, there have been 1,057 cases of pregnant women with Zika in the states and the District of Columbia – 52 for the week ending Nov. 3 – and 2,357 cases in the territories, the CDC announced, with 94 reported in the most recent week. The total number of U.S. cases – 3,414 – is up by 4.4% over the previous week.
The CDC also reported one new infant born with Zika-related birth defects for the week ending Nov. 3, bringing the total for the year to 26 in the states/D.C. There were no new Zika-related pregnancy losses reported, so the total remains at five. State-level data are not being reported to protect the privacy of affected women and children.
The CDC is no longer reporting adverse pregnancy outcomes for the territories because Puerto Rico is not using the same “inclusion criteria to monitor brain abnormalities and other adverse pregnancy outcomes.” As of Sept. 29 – the date of the last territorial report – there had been one liveborn infant and one pregnancy loss related to Zika.
Zika-related birth defects reported by the CDC could include microcephaly, calcium deposits in the brain indicating possible brain damage, excess fluid in the brain cavities and surrounding the brain, absent or poorly formed brain structures, abnormal eye development, or other problems resulting from brain damage that affect nerves, muscles, and bones. The pregnancy losses encompass any miscarriage, stillbirth, and termination with evidence of birth defects.
The pregnancy-related figures for states, territories, and D.C. reflect reporting to the U.S. Zika Pregnancy Registry; data for Puerto Rico are reported to the U.S. Zika Active Pregnancy Surveillance System.
Biologic-naive psoriasis patients get biggest boost with treatment
LAS VEGAS – Biologic-naive psoriasis patients had stronger responses to treatment than those who were previously treated and switched from one biologic to another, according to a systematic review of 15 studies in adults with psoriasis.
In a real-world setting, patients who fail treatment with a tumor necrosis factor–alfa (TNF-alfa) inhibitor or ustekinumab may be switched from one treatment to another, Steven R. Feldman, MD, professor of dermatology at Wake Forest University, Winston-Salem, N.C., said in a poster presented at the Skin Disease Education Foundation’s annual Las Vegas Dermatology Seminar. “However, there is conflicting evidence of reduced effectiveness in later lines of treatment,” he added.
In four of the studies, biologic-naive patients showed significantly better responses when given anti-TNF agents than patients who had been treated with a biologic. Another study showed that the reduced effectiveness of adalimumab treatment was associated with the number of previous treatments with anti-TNFs (hazard ratio, 1.63). Another study found an association between previous treatment with etanercept and loss of response and serious adverse effects (HR, 4.32).
The other nine studies suggested some evidence of effectiveness for treatment with anti-TNFs or ustekinumab as later lines of treatment for psoriasis patients, but most of the studies (six of nine) did not include information on whether the results were statistically significant.
“More real-world evidence and future research in studies with large sample sizes are needed to further understand the role of anti-TNF and ustekinumab as later-line treatment in psoriasis management,” Dr. Feldman said.
He disclosed relationships with multiple companies, including study sponsor Novartis; one of the study coauthors is affiliated with Novartis. SDEF and this organization are owned by the same parent company.
LAS VEGAS – Biologic-naive psoriasis patients had stronger responses to treatment than those who were previously treated and switched from one biologic to another, according to a systematic review of 15 studies in adults with psoriasis.
In a real-world setting, patients who fail treatment with a tumor necrosis factor–alfa (TNF-alfa) inhibitor or ustekinumab may be switched from one treatment to another, Steven R. Feldman, MD, professor of dermatology at Wake Forest University, Winston-Salem, N.C., said in a poster presented at the Skin Disease Education Foundation’s annual Las Vegas Dermatology Seminar. “However, there is conflicting evidence of reduced effectiveness in later lines of treatment,” he added.
In four of the studies, biologic-naive patients showed significantly better responses when given anti-TNF agents than patients who had been treated with a biologic. Another study showed that the reduced effectiveness of adalimumab treatment was associated with the number of previous treatments with anti-TNFs (hazard ratio, 1.63). Another study found an association between previous treatment with etanercept and loss of response and serious adverse effects (HR, 4.32).
The other nine studies suggested some evidence of effectiveness for treatment with anti-TNFs or ustekinumab as later lines of treatment for psoriasis patients, but most of the studies (six of nine) did not include information on whether the results were statistically significant.
“More real-world evidence and future research in studies with large sample sizes are needed to further understand the role of anti-TNF and ustekinumab as later-line treatment in psoriasis management,” Dr. Feldman said.
He disclosed relationships with multiple companies, including study sponsor Novartis; one of the study coauthors is affiliated with Novartis. SDEF and this organization are owned by the same parent company.
LAS VEGAS – Biologic-naive psoriasis patients had stronger responses to treatment than those who were previously treated and switched from one biologic to another, according to a systematic review of 15 studies in adults with psoriasis.
In a real-world setting, patients who fail treatment with a tumor necrosis factor–alfa (TNF-alfa) inhibitor or ustekinumab may be switched from one treatment to another, Steven R. Feldman, MD, professor of dermatology at Wake Forest University, Winston-Salem, N.C., said in a poster presented at the Skin Disease Education Foundation’s annual Las Vegas Dermatology Seminar. “However, there is conflicting evidence of reduced effectiveness in later lines of treatment,” he added.
In four of the studies, biologic-naive patients showed significantly better responses when given anti-TNF agents than patients who had been treated with a biologic. Another study showed that the reduced effectiveness of adalimumab treatment was associated with the number of previous treatments with anti-TNFs (hazard ratio, 1.63). Another study found an association between previous treatment with etanercept and loss of response and serious adverse effects (HR, 4.32).
The other nine studies suggested some evidence of effectiveness for treatment with anti-TNFs or ustekinumab as later lines of treatment for psoriasis patients, but most of the studies (six of nine) did not include information on whether the results were statistically significant.
“More real-world evidence and future research in studies with large sample sizes are needed to further understand the role of anti-TNF and ustekinumab as later-line treatment in psoriasis management,” Dr. Feldman said.
He disclosed relationships with multiple companies, including study sponsor Novartis; one of the study coauthors is affiliated with Novartis. SDEF and this organization are owned by the same parent company.
AT SDEF LAS VEGAS DERMATOLOGY SEMINAR
Key clinical point:
Major finding: Biologic-naive psoriasis patients had stronger responses to treatment than those who were previously treated and switched from one biologic to another.
Data source: A systematic review of 15 observational studies of adults with psoriasis evaluating anti-TNF agents or ustekinumab as second-line or later-line treatments.
Disclosures: Dr. Feldman disclosed relationships with multiple companies, including study sponsor Novartis; one of the study coauthors is affiliated with Novartis.
Therapeutic alternative to liver transplantation could be on horizon in NASH
BOSTON – A novel therapeutic approach to nonalcoholic steatohepatitis could one day mean sufferers of this severe form of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease have an alternative to transplantation.
Preclinical findings from a study using mesenchymal stem cells adapted from unsuitable organs for transplant have shown promise in suppressing inflammation in nonalcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH).
By adding an inflammatory cocktail to cell cultures, with or without immunosuppression with cyclosporine, Dr. Gellynck and his colleagues were able to provoke secretion of anti-inflammatory and antifibrotic cytokines. HepaStem was shown to inhibit the T-lymphocyte response to the inflammation and also suppress the dendritic cell generation and function in co-culture experiments. In a NASH disease model culture, the immunosuppression did not solely affect disease progression, but cell-based treatment significantly and dose-dependently decreased collagen levels. A single HepaStem injection “significantly” decreased the nonalcoholic fatty liver disease activity disease score, supporting the proposed mechanism of action, namely reduced inflammation.
Dr. Gellynck and his colleagues believe their findings warrant phase I/II studies in humans with NASH.
All study workers are employed by Promethera Biosciences.
[email protected]
On Twitter @whitneymcknight
BOSTON – A novel therapeutic approach to nonalcoholic steatohepatitis could one day mean sufferers of this severe form of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease have an alternative to transplantation.
Preclinical findings from a study using mesenchymal stem cells adapted from unsuitable organs for transplant have shown promise in suppressing inflammation in nonalcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH).
By adding an inflammatory cocktail to cell cultures, with or without immunosuppression with cyclosporine, Dr. Gellynck and his colleagues were able to provoke secretion of anti-inflammatory and antifibrotic cytokines. HepaStem was shown to inhibit the T-lymphocyte response to the inflammation and also suppress the dendritic cell generation and function in co-culture experiments. In a NASH disease model culture, the immunosuppression did not solely affect disease progression, but cell-based treatment significantly and dose-dependently decreased collagen levels. A single HepaStem injection “significantly” decreased the nonalcoholic fatty liver disease activity disease score, supporting the proposed mechanism of action, namely reduced inflammation.
Dr. Gellynck and his colleagues believe their findings warrant phase I/II studies in humans with NASH.
All study workers are employed by Promethera Biosciences.
[email protected]
On Twitter @whitneymcknight
BOSTON – A novel therapeutic approach to nonalcoholic steatohepatitis could one day mean sufferers of this severe form of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease have an alternative to transplantation.
Preclinical findings from a study using mesenchymal stem cells adapted from unsuitable organs for transplant have shown promise in suppressing inflammation in nonalcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH).
By adding an inflammatory cocktail to cell cultures, with or without immunosuppression with cyclosporine, Dr. Gellynck and his colleagues were able to provoke secretion of anti-inflammatory and antifibrotic cytokines. HepaStem was shown to inhibit the T-lymphocyte response to the inflammation and also suppress the dendritic cell generation and function in co-culture experiments. In a NASH disease model culture, the immunosuppression did not solely affect disease progression, but cell-based treatment significantly and dose-dependently decreased collagen levels. A single HepaStem injection “significantly” decreased the nonalcoholic fatty liver disease activity disease score, supporting the proposed mechanism of action, namely reduced inflammation.
Dr. Gellynck and his colleagues believe their findings warrant phase I/II studies in humans with NASH.
All study workers are employed by Promethera Biosciences.
[email protected]
On Twitter @whitneymcknight
FROM THE LIVER MEETING 2016
Cenicriviroc was well-tolerated but did not outperform placebo across all endpoints
Cenicriviroc, an oral chemokine receptor CCR/5 antagonist, was well tolerated, although it did not best placebo across all study endpoints, according to results of a 1-year phase IIb study released in an abstract in advance of the annual meeting of the American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases.
A correlation between treatment benefit and disease severity was reported by Arun J. Sanyal, MD, of Virginia Commonwealth University in Richmond, and coworkers, however.
In the 2-year, multinational, phase IIb, double-blind CENTAUR (Efficacy and Safety Study of Cenicriviroc for the Treatment of NASH in Adult Subjects With Liver Fibrosis) study, 289 adults with chronic liver disease were randomly assigned to either 150 mg cenicriviroc (CVC) once daily or to placebo. At baseline, study participants had either histologically defined nonalcoholic steatohepatitis, a nonalcoholic fatty liver disease score (NAS) of 4 or greater, or liver fibrosis between stages 1 and 3. Just over half of the cohort were women, 72% had metabolic syndrome, and 53% had diabetes. Three-quarters had an NAS score of 5 or higher, and 67% had fibrosis between stages 2 and 3. The mean body mass index across the study was 34 kg/m2.
At 1 year, liver biopsy showed that 16% of the CVC group had achieved at least a 2-point improvement in NAS, 3% less than controls (P = .519). Resolution of steatohepatitis with no worsening of fibrosis was higher in the study arm, compared with controls: 8% vs. 6% (P = .494). A significant difference was seen in members of the study arm who had advanced disease characteristics at baseline, compared with controls, by at least one stage in fibrosis improvement, with no worsening of steatohepatitis (P = .023). Across the study, improvement in fibrosis by two stages was seen in eight patients given CVC and in three controls. Progression to cirrhosis occurred in two members of the study arm and in five controls.
Adverse treatment-related events were similar across the study. The most commonly reported were fatigue (2.8%) and diarrhea (2.1%) in the study arm and headache (3.5%) in controls.
Most of the researchers associated with this study have industry relationships, including Brian L. Wiens, PhD, Pamela Vig, PhD, Star Seyedkazemi, PharmD, and Eric Lefebvre, MD, all of whom are employed by study sponsor, Tobira Therapeutics.
[email protected]
On Twitter @whitneymcknight
Cenicriviroc, an oral chemokine receptor CCR/5 antagonist, was well tolerated, although it did not best placebo across all study endpoints, according to results of a 1-year phase IIb study released in an abstract in advance of the annual meeting of the American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases.
A correlation between treatment benefit and disease severity was reported by Arun J. Sanyal, MD, of Virginia Commonwealth University in Richmond, and coworkers, however.
In the 2-year, multinational, phase IIb, double-blind CENTAUR (Efficacy and Safety Study of Cenicriviroc for the Treatment of NASH in Adult Subjects With Liver Fibrosis) study, 289 adults with chronic liver disease were randomly assigned to either 150 mg cenicriviroc (CVC) once daily or to placebo. At baseline, study participants had either histologically defined nonalcoholic steatohepatitis, a nonalcoholic fatty liver disease score (NAS) of 4 or greater, or liver fibrosis between stages 1 and 3. Just over half of the cohort were women, 72% had metabolic syndrome, and 53% had diabetes. Three-quarters had an NAS score of 5 or higher, and 67% had fibrosis between stages 2 and 3. The mean body mass index across the study was 34 kg/m2.
At 1 year, liver biopsy showed that 16% of the CVC group had achieved at least a 2-point improvement in NAS, 3% less than controls (P = .519). Resolution of steatohepatitis with no worsening of fibrosis was higher in the study arm, compared with controls: 8% vs. 6% (P = .494). A significant difference was seen in members of the study arm who had advanced disease characteristics at baseline, compared with controls, by at least one stage in fibrosis improvement, with no worsening of steatohepatitis (P = .023). Across the study, improvement in fibrosis by two stages was seen in eight patients given CVC and in three controls. Progression to cirrhosis occurred in two members of the study arm and in five controls.
Adverse treatment-related events were similar across the study. The most commonly reported were fatigue (2.8%) and diarrhea (2.1%) in the study arm and headache (3.5%) in controls.
Most of the researchers associated with this study have industry relationships, including Brian L. Wiens, PhD, Pamela Vig, PhD, Star Seyedkazemi, PharmD, and Eric Lefebvre, MD, all of whom are employed by study sponsor, Tobira Therapeutics.
[email protected]
On Twitter @whitneymcknight
Cenicriviroc, an oral chemokine receptor CCR/5 antagonist, was well tolerated, although it did not best placebo across all study endpoints, according to results of a 1-year phase IIb study released in an abstract in advance of the annual meeting of the American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases.
A correlation between treatment benefit and disease severity was reported by Arun J. Sanyal, MD, of Virginia Commonwealth University in Richmond, and coworkers, however.
In the 2-year, multinational, phase IIb, double-blind CENTAUR (Efficacy and Safety Study of Cenicriviroc for the Treatment of NASH in Adult Subjects With Liver Fibrosis) study, 289 adults with chronic liver disease were randomly assigned to either 150 mg cenicriviroc (CVC) once daily or to placebo. At baseline, study participants had either histologically defined nonalcoholic steatohepatitis, a nonalcoholic fatty liver disease score (NAS) of 4 or greater, or liver fibrosis between stages 1 and 3. Just over half of the cohort were women, 72% had metabolic syndrome, and 53% had diabetes. Three-quarters had an NAS score of 5 or higher, and 67% had fibrosis between stages 2 and 3. The mean body mass index across the study was 34 kg/m2.
At 1 year, liver biopsy showed that 16% of the CVC group had achieved at least a 2-point improvement in NAS, 3% less than controls (P = .519). Resolution of steatohepatitis with no worsening of fibrosis was higher in the study arm, compared with controls: 8% vs. 6% (P = .494). A significant difference was seen in members of the study arm who had advanced disease characteristics at baseline, compared with controls, by at least one stage in fibrosis improvement, with no worsening of steatohepatitis (P = .023). Across the study, improvement in fibrosis by two stages was seen in eight patients given CVC and in three controls. Progression to cirrhosis occurred in two members of the study arm and in five controls.
Adverse treatment-related events were similar across the study. The most commonly reported were fatigue (2.8%) and diarrhea (2.1%) in the study arm and headache (3.5%) in controls.
Most of the researchers associated with this study have industry relationships, including Brian L. Wiens, PhD, Pamela Vig, PhD, Star Seyedkazemi, PharmD, and Eric Lefebvre, MD, all of whom are employed by study sponsor, Tobira Therapeutics.
[email protected]
On Twitter @whitneymcknight
FROM THE LIVER MEETING 2016
MBX-8025 yields ‘striking’ efficacy results but new safety signal in primary biliary cholangitis
The investigational peroxisome proliferator–activated receptor delta agonist MBX-8025 exhibited a “striking anticholestatic effect” without causing pruritus in a phase II trial of 35 patients with primary biliary cholangitis.
But three patients developed grade 3 increases in serum transaminase levels that reversed when they stopped treatment, David Jones, MD, of the University of Newcastle (United Kingdom) and his associates will report at the annual meeting of the American Association of Liver Diseases. The effect seemed dose related, so future studies should explore whether MBX-8025 is effective at lower doses, they concluded in a late-breaking abstract released in advance of the meeting.
Primary biliary cholangitis, an important cause of end-stage liver disease, is initially associated with fatigue and pruritus and often responds inadequately to first-line treatment with ursodeoxycholic acid. MBX-8025 selectively activates the peroxisome proliferator–activated receptor delta, a nuclear receptor that regulates genes involved in lipid storage and transport. In prior studies, MBX-8025 decreased serum alkaline phosphatase (ALP) levels and seemed well tolerated in healthy volunteers and patients with dyslipidemia, the investigators noted.
As a next step, they randomly assigned patients with primary biliary cholangitis whose ALP levels remained at least 1.67 times the upper limit of normal, despite at least 12 months of ursodeoxycholic acid therapy, to receive either placebo or 50 or 200 mg MBX-8026 for 12 weeks. The primary outcome was percent change in ALP levels, which, at baseline, averaged 233 U/L in the placebo group, 312 U/L in the 50 mg group, and 248 U/L in the 200-mg group.
At the end of treatment, ALP levels had dropped by an average of 63% in the 200-mg MBX-8025 group, 53% in the 50-mg group, and 2% in the placebo group (P less than .0001 for each dose effect versus placebo). Percent decreases in gamma-glutamyl transferase averaged 43% for both dose groups and 3% in the placebo group. Median levels of 7-alpha-hydroxy-4-cholesten-3-one, a marker of bile acid synthesis, fell by 77% in the 200-mg group and by 55% in the 50-mg group, but rose by 29% in the placebo group. Both the 50-mg and the 200-mg doses yielded statistically similar effects on all three cholestatic markers.
Although MBX-8025 did not appear to cause or worsen pruritus, 3 of the 35 patients developed rapid, asymptomatic, grade 3 increases in serum levels of alanine aminotransferase, the researchers reported. Two patients were taking 200 mg MBX-8025, and one was taking 50 mg. The effect fully reversed after patients stopped treatment, and was not associated with hyperbilirubinemia. Another patient in the 200-mg group stopped treatment because of what the investigators called “a muscle adverse event [that we] considered drug-related.”
The trial was halted halfway through recruitment, having established proof of concept, the investigators concluded. Because MBX-8025 is primarily excreted in bile, and primary biliary cholangitis obstructs bile flow, affected patients might have had more hepatic exposure to the agent than did those in previous trials, and this might explain the new safety signal, they noted.
CymaBay Therapeutics makes MBX-8025 and funded the trial. Dr. Jones disclosed ties to Intercept, GlaxoSmithKline, Novartis, and Falk. Eight coinvestigators disclosed employment with or other ties to CymaBay Therapeutics. The other three coinvestigators had no relevant disclosures.
The investigational peroxisome proliferator–activated receptor delta agonist MBX-8025 exhibited a “striking anticholestatic effect” without causing pruritus in a phase II trial of 35 patients with primary biliary cholangitis.
But three patients developed grade 3 increases in serum transaminase levels that reversed when they stopped treatment, David Jones, MD, of the University of Newcastle (United Kingdom) and his associates will report at the annual meeting of the American Association of Liver Diseases. The effect seemed dose related, so future studies should explore whether MBX-8025 is effective at lower doses, they concluded in a late-breaking abstract released in advance of the meeting.
Primary biliary cholangitis, an important cause of end-stage liver disease, is initially associated with fatigue and pruritus and often responds inadequately to first-line treatment with ursodeoxycholic acid. MBX-8025 selectively activates the peroxisome proliferator–activated receptor delta, a nuclear receptor that regulates genes involved in lipid storage and transport. In prior studies, MBX-8025 decreased serum alkaline phosphatase (ALP) levels and seemed well tolerated in healthy volunteers and patients with dyslipidemia, the investigators noted.
As a next step, they randomly assigned patients with primary biliary cholangitis whose ALP levels remained at least 1.67 times the upper limit of normal, despite at least 12 months of ursodeoxycholic acid therapy, to receive either placebo or 50 or 200 mg MBX-8026 for 12 weeks. The primary outcome was percent change in ALP levels, which, at baseline, averaged 233 U/L in the placebo group, 312 U/L in the 50 mg group, and 248 U/L in the 200-mg group.
At the end of treatment, ALP levels had dropped by an average of 63% in the 200-mg MBX-8025 group, 53% in the 50-mg group, and 2% in the placebo group (P less than .0001 for each dose effect versus placebo). Percent decreases in gamma-glutamyl transferase averaged 43% for both dose groups and 3% in the placebo group. Median levels of 7-alpha-hydroxy-4-cholesten-3-one, a marker of bile acid synthesis, fell by 77% in the 200-mg group and by 55% in the 50-mg group, but rose by 29% in the placebo group. Both the 50-mg and the 200-mg doses yielded statistically similar effects on all three cholestatic markers.
Although MBX-8025 did not appear to cause or worsen pruritus, 3 of the 35 patients developed rapid, asymptomatic, grade 3 increases in serum levels of alanine aminotransferase, the researchers reported. Two patients were taking 200 mg MBX-8025, and one was taking 50 mg. The effect fully reversed after patients stopped treatment, and was not associated with hyperbilirubinemia. Another patient in the 200-mg group stopped treatment because of what the investigators called “a muscle adverse event [that we] considered drug-related.”
The trial was halted halfway through recruitment, having established proof of concept, the investigators concluded. Because MBX-8025 is primarily excreted in bile, and primary biliary cholangitis obstructs bile flow, affected patients might have had more hepatic exposure to the agent than did those in previous trials, and this might explain the new safety signal, they noted.
CymaBay Therapeutics makes MBX-8025 and funded the trial. Dr. Jones disclosed ties to Intercept, GlaxoSmithKline, Novartis, and Falk. Eight coinvestigators disclosed employment with or other ties to CymaBay Therapeutics. The other three coinvestigators had no relevant disclosures.
The investigational peroxisome proliferator–activated receptor delta agonist MBX-8025 exhibited a “striking anticholestatic effect” without causing pruritus in a phase II trial of 35 patients with primary biliary cholangitis.
But three patients developed grade 3 increases in serum transaminase levels that reversed when they stopped treatment, David Jones, MD, of the University of Newcastle (United Kingdom) and his associates will report at the annual meeting of the American Association of Liver Diseases. The effect seemed dose related, so future studies should explore whether MBX-8025 is effective at lower doses, they concluded in a late-breaking abstract released in advance of the meeting.
Primary biliary cholangitis, an important cause of end-stage liver disease, is initially associated with fatigue and pruritus and often responds inadequately to first-line treatment with ursodeoxycholic acid. MBX-8025 selectively activates the peroxisome proliferator–activated receptor delta, a nuclear receptor that regulates genes involved in lipid storage and transport. In prior studies, MBX-8025 decreased serum alkaline phosphatase (ALP) levels and seemed well tolerated in healthy volunteers and patients with dyslipidemia, the investigators noted.
As a next step, they randomly assigned patients with primary biliary cholangitis whose ALP levels remained at least 1.67 times the upper limit of normal, despite at least 12 months of ursodeoxycholic acid therapy, to receive either placebo or 50 or 200 mg MBX-8026 for 12 weeks. The primary outcome was percent change in ALP levels, which, at baseline, averaged 233 U/L in the placebo group, 312 U/L in the 50 mg group, and 248 U/L in the 200-mg group.
At the end of treatment, ALP levels had dropped by an average of 63% in the 200-mg MBX-8025 group, 53% in the 50-mg group, and 2% in the placebo group (P less than .0001 for each dose effect versus placebo). Percent decreases in gamma-glutamyl transferase averaged 43% for both dose groups and 3% in the placebo group. Median levels of 7-alpha-hydroxy-4-cholesten-3-one, a marker of bile acid synthesis, fell by 77% in the 200-mg group and by 55% in the 50-mg group, but rose by 29% in the placebo group. Both the 50-mg and the 200-mg doses yielded statistically similar effects on all three cholestatic markers.
Although MBX-8025 did not appear to cause or worsen pruritus, 3 of the 35 patients developed rapid, asymptomatic, grade 3 increases in serum levels of alanine aminotransferase, the researchers reported. Two patients were taking 200 mg MBX-8025, and one was taking 50 mg. The effect fully reversed after patients stopped treatment, and was not associated with hyperbilirubinemia. Another patient in the 200-mg group stopped treatment because of what the investigators called “a muscle adverse event [that we] considered drug-related.”
The trial was halted halfway through recruitment, having established proof of concept, the investigators concluded. Because MBX-8025 is primarily excreted in bile, and primary biliary cholangitis obstructs bile flow, affected patients might have had more hepatic exposure to the agent than did those in previous trials, and this might explain the new safety signal, they noted.
CymaBay Therapeutics makes MBX-8025 and funded the trial. Dr. Jones disclosed ties to Intercept, GlaxoSmithKline, Novartis, and Falk. Eight coinvestigators disclosed employment with or other ties to CymaBay Therapeutics. The other three coinvestigators had no relevant disclosures.
FROM THE LIVER MEETING 2016
Key clinical point: In patients with primary biliary cholangitis, the investigational agent MBX-8025 was associated with significant decreases in cholestatic markers, but also with grade 3 increases in serum levels of alanine aminotransferase (ALT).
Major finding: At the end of treatment, alkaline phosphatase levels had dropped by 63% and by 53% in the 200-mg and 50-mg groups, respectively, and by 2% in the placebo group (P less than .0001). Three patients developed fully reversible grade 3 ALT increases.
Data source: A 12-week, double-blind, phase II trial of 35 patients with primary biliary cholangitis who had responded inadequately to ursodeoxycholic acid (NCT02609048).
Disclosures: CymaBay Therapeutics makes MBX-8025 and funded the trial. Dr. Jones disclosed ties to Intercept, GlaxoSmithKline, Novartis, and Falk. Eight coinvestigators disclosed employment with or other ties to CymaBay Therapeutics. The other three researchers had no relevant disclosures.