User login
How Effective Is the High-Dose Flu Vaccine in Older Adults?
How can the immunogenicity and effectiveness of flu vaccines be improved in older adults? Several strategies are available, one being the addition of an adjuvant. For example, the MF59-adjuvanted vaccine has shown superior immunogenicity. However, “we do not have data from controlled and randomized clinical trials showing superior clinical effectiveness versus the standard dose,” Professor Odile Launay, an infectious disease specialist at Cochin Hospital in Paris, France, noted during a press conference. Another option is to increase the antigen dose in the vaccine, creating a high-dose (HD) flu vaccine.
Why is there a need for an HD vaccine? “The elderly population bears the greatest burden from the flu,” explained Launay. “This is due to three factors: An aging immune system, a higher number of comorbidities, and increased frailty.” Standard-dose flu vaccines are seen as offering suboptimal protection for those older than 65 years, which led to the development of a quadrivalent vaccine with four times the antigen dose of standard flu vaccines. This HD vaccine was introduced in France during the 2021/2022 flu season. A real-world cohort study has since been conducted to evaluate its effectiveness in the target population — those aged 65 years or older. The results were recently published in Clinical Microbiology and Infection.
Cohort Study
The study included 405,385 noninstitutionalized people aged 65 years or older matched with 1,621,540 individuals in a 1:4 ratio. The first group received the HD vaccine, while the second group received the standard-dose vaccine. Both the groups had an average age of 77 years, with 56% women, and 51% vaccinated in pharmacies. The majority had been previously vaccinated against flu (91%), and 97% had completed a full COVID-19 vaccination schedule. More than half had at least one chronic illness.
Hospitalization rates for flu — the study’s primary outcome — were 69.5 vs 90.5 per 100,000 person-years in the HD vs standard-dose group. This represented a 23.3% reduction (95% CI, 8.4-35.8; P = .003).
Strengths and Limitations
Among the strengths of the study, Launay highlighted the large number of vaccinated participants older than 65 years — more than 7 million — and the widespread use of polymerase chain reaction flu tests in cases of hospitalization for respiratory infections, which improved flu coding in the database used. Additionally, the results were consistent with those of previous studies.
However, limitations included the retrospective design, which did not randomize participants and introduced potential bias. For example, the HD vaccine may have been prioritized for the oldest people or those with multiple comorbidities. Additionally, the 2021/2022 flu season was atypical, with the simultaneous circulation of the flu virus and SARS-CoV-2, as noted by Launay.
Conclusion
In conclusion, this first evaluation of the HD flu vaccine’s effectiveness in France showed a 25% reduction in hospitalizations, consistent with existing data covering 12 flu seasons. The vaccine has been available for a longer period in the United States and Northern Europe.
“The latest unpublished data from the 2022/23 season show a 27% reduction in hospitalizations with the HD vaccine in people over 65,” added Launay.
Note: Due to a pricing disagreement with the French government, Sanofi’s HD flu vaccine Efluelda, intended for people older than 65 years, will not be available this year. (See: Withdrawal of the Efluelda Influenza Vaccine: The Academy of Medicine Reacts). However, the company has submitted a dossier for a trivalent form for a return in the 2025/2026 season and is working on developing mRNA vaccines. Additionally, a combined flu/COVID-19 vaccine is currently in development.
The study was funded by Sanofi. Several authors are Sanofi employees. Odile Launay reported conflicts of interest with Sanofi, MSD, Pfizer, GSK, and Moderna.
This story was translated from Medscape’s French edition using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
How can the immunogenicity and effectiveness of flu vaccines be improved in older adults? Several strategies are available, one being the addition of an adjuvant. For example, the MF59-adjuvanted vaccine has shown superior immunogenicity. However, “we do not have data from controlled and randomized clinical trials showing superior clinical effectiveness versus the standard dose,” Professor Odile Launay, an infectious disease specialist at Cochin Hospital in Paris, France, noted during a press conference. Another option is to increase the antigen dose in the vaccine, creating a high-dose (HD) flu vaccine.
Why is there a need for an HD vaccine? “The elderly population bears the greatest burden from the flu,” explained Launay. “This is due to three factors: An aging immune system, a higher number of comorbidities, and increased frailty.” Standard-dose flu vaccines are seen as offering suboptimal protection for those older than 65 years, which led to the development of a quadrivalent vaccine with four times the antigen dose of standard flu vaccines. This HD vaccine was introduced in France during the 2021/2022 flu season. A real-world cohort study has since been conducted to evaluate its effectiveness in the target population — those aged 65 years or older. The results were recently published in Clinical Microbiology and Infection.
Cohort Study
The study included 405,385 noninstitutionalized people aged 65 years or older matched with 1,621,540 individuals in a 1:4 ratio. The first group received the HD vaccine, while the second group received the standard-dose vaccine. Both the groups had an average age of 77 years, with 56% women, and 51% vaccinated in pharmacies. The majority had been previously vaccinated against flu (91%), and 97% had completed a full COVID-19 vaccination schedule. More than half had at least one chronic illness.
Hospitalization rates for flu — the study’s primary outcome — were 69.5 vs 90.5 per 100,000 person-years in the HD vs standard-dose group. This represented a 23.3% reduction (95% CI, 8.4-35.8; P = .003).
Strengths and Limitations
Among the strengths of the study, Launay highlighted the large number of vaccinated participants older than 65 years — more than 7 million — and the widespread use of polymerase chain reaction flu tests in cases of hospitalization for respiratory infections, which improved flu coding in the database used. Additionally, the results were consistent with those of previous studies.
However, limitations included the retrospective design, which did not randomize participants and introduced potential bias. For example, the HD vaccine may have been prioritized for the oldest people or those with multiple comorbidities. Additionally, the 2021/2022 flu season was atypical, with the simultaneous circulation of the flu virus and SARS-CoV-2, as noted by Launay.
Conclusion
In conclusion, this first evaluation of the HD flu vaccine’s effectiveness in France showed a 25% reduction in hospitalizations, consistent with existing data covering 12 flu seasons. The vaccine has been available for a longer period in the United States and Northern Europe.
“The latest unpublished data from the 2022/23 season show a 27% reduction in hospitalizations with the HD vaccine in people over 65,” added Launay.
Note: Due to a pricing disagreement with the French government, Sanofi’s HD flu vaccine Efluelda, intended for people older than 65 years, will not be available this year. (See: Withdrawal of the Efluelda Influenza Vaccine: The Academy of Medicine Reacts). However, the company has submitted a dossier for a trivalent form for a return in the 2025/2026 season and is working on developing mRNA vaccines. Additionally, a combined flu/COVID-19 vaccine is currently in development.
The study was funded by Sanofi. Several authors are Sanofi employees. Odile Launay reported conflicts of interest with Sanofi, MSD, Pfizer, GSK, and Moderna.
This story was translated from Medscape’s French edition using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
How can the immunogenicity and effectiveness of flu vaccines be improved in older adults? Several strategies are available, one being the addition of an adjuvant. For example, the MF59-adjuvanted vaccine has shown superior immunogenicity. However, “we do not have data from controlled and randomized clinical trials showing superior clinical effectiveness versus the standard dose,” Professor Odile Launay, an infectious disease specialist at Cochin Hospital in Paris, France, noted during a press conference. Another option is to increase the antigen dose in the vaccine, creating a high-dose (HD) flu vaccine.
Why is there a need for an HD vaccine? “The elderly population bears the greatest burden from the flu,” explained Launay. “This is due to three factors: An aging immune system, a higher number of comorbidities, and increased frailty.” Standard-dose flu vaccines are seen as offering suboptimal protection for those older than 65 years, which led to the development of a quadrivalent vaccine with four times the antigen dose of standard flu vaccines. This HD vaccine was introduced in France during the 2021/2022 flu season. A real-world cohort study has since been conducted to evaluate its effectiveness in the target population — those aged 65 years or older. The results were recently published in Clinical Microbiology and Infection.
Cohort Study
The study included 405,385 noninstitutionalized people aged 65 years or older matched with 1,621,540 individuals in a 1:4 ratio. The first group received the HD vaccine, while the second group received the standard-dose vaccine. Both the groups had an average age of 77 years, with 56% women, and 51% vaccinated in pharmacies. The majority had been previously vaccinated against flu (91%), and 97% had completed a full COVID-19 vaccination schedule. More than half had at least one chronic illness.
Hospitalization rates for flu — the study’s primary outcome — were 69.5 vs 90.5 per 100,000 person-years in the HD vs standard-dose group. This represented a 23.3% reduction (95% CI, 8.4-35.8; P = .003).
Strengths and Limitations
Among the strengths of the study, Launay highlighted the large number of vaccinated participants older than 65 years — more than 7 million — and the widespread use of polymerase chain reaction flu tests in cases of hospitalization for respiratory infections, which improved flu coding in the database used. Additionally, the results were consistent with those of previous studies.
However, limitations included the retrospective design, which did not randomize participants and introduced potential bias. For example, the HD vaccine may have been prioritized for the oldest people or those with multiple comorbidities. Additionally, the 2021/2022 flu season was atypical, with the simultaneous circulation of the flu virus and SARS-CoV-2, as noted by Launay.
Conclusion
In conclusion, this first evaluation of the HD flu vaccine’s effectiveness in France showed a 25% reduction in hospitalizations, consistent with existing data covering 12 flu seasons. The vaccine has been available for a longer period in the United States and Northern Europe.
“The latest unpublished data from the 2022/23 season show a 27% reduction in hospitalizations with the HD vaccine in people over 65,” added Launay.
Note: Due to a pricing disagreement with the French government, Sanofi’s HD flu vaccine Efluelda, intended for people older than 65 years, will not be available this year. (See: Withdrawal of the Efluelda Influenza Vaccine: The Academy of Medicine Reacts). However, the company has submitted a dossier for a trivalent form for a return in the 2025/2026 season and is working on developing mRNA vaccines. Additionally, a combined flu/COVID-19 vaccine is currently in development.
The study was funded by Sanofi. Several authors are Sanofi employees. Odile Launay reported conflicts of interest with Sanofi, MSD, Pfizer, GSK, and Moderna.
This story was translated from Medscape’s French edition using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Responses Sustained with Ritlecitinib in Patients with Alopecia Through 48 Weeks
TOPLINE:
, and up to one third of nonresponders at week 24 also achieved responses by week 48.
METHODOLOGY:
- Researchers conducted a post hoc analysis of an international, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase 2b/3 trial (ALLEGRO) and included 718 adults and adolescents aged 12 or older with severe AA (Severity of Alopecia Tool [SALT] score ≥ 50).
- Patients received various doses of the oral Janus kinase inhibitor ritlecitinib, with or without a 4-week loading dose, including 200/50 mg, 200/30 mg, 50 mg, or 30 mg, with or without a 4-week loading dose for up to 24 weeks and continued to receive their assigned maintenance dose.
- Researchers assessed sustained clinical responses at week 48 for those who had achieved SALT scores ≤ 20 and ≤ 10 at 24 weeks, and nonresponders at week 24 were assessed for responses through week 48.
- Adverse events were also evaluated.
TAKEAWAY:
- Among patients on ritlecitinib who had responded at week 24, SALT responses ≤ 20 were sustained in 85.2%-100% of patients through week 48. Similar results were seen among patients who achieved a SALT score ≤ 10 (68.8%-91.7%) and improvements in eyebrow (70.4%-96.9%) or eyelash (52.4%-94.1%) assessment scores.
- Among those who were nonresponders at week 24, 22.2%-33.7% achieved a SALT score ≤ 20 and 19.8%-25.5% achieved a SALT score ≤ 10 by week 48. Similarly, among those with no eyebrow or eyelash responses at week 24, 19.7%-32.8% and 16.7%-30.2% had improved eyebrow or eyelash assessment scores, respectively, at week 48.
- Between weeks 24 and 48, adverse events were reported in 74%-93% of patients who achieved a SALT score ≤ 20, most were mild or moderate; two serious events were reported but deemed unrelated to treatment. The safety profile was similar across all subgroups.
- No deaths, malignancies, major cardiovascular events, opportunistic infections, or herpes zoster infections were observed.
IN PRACTICE:
“The majority of ritlecitinib-treated patients with AA who met target clinical response based on scalp, eyebrow, or eyelash regrowth at week 24 sustained their response through week 48 with continued treatment,” the authors wrote. “Some patients, including those with more extensive hair loss, may require ritlecitinib treatment beyond 6 months to achieve target clinical response,” they added.
SOURCE:
The study was led by Melissa Piliang, MD, of the Department of Dermatology, Cleveland Clinic, and was published online on October 17 in the Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology.
LIMITATIONS:
The analysis was limited by its post hoc nature, small sample size in each treatment group, and a follow-up period of only 48 weeks.
DISCLOSURES:
This study was funded by Pfizer. Piliang disclosed being a consultant or investigator for Pfizer, Eli Lilly, and Procter & Gamble. Six authors were employees or shareholders of or received salary from Pfizer. Other authors also reported financial relationships with pharmaceutical companies outside this work, including Pfizer.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
, and up to one third of nonresponders at week 24 also achieved responses by week 48.
METHODOLOGY:
- Researchers conducted a post hoc analysis of an international, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase 2b/3 trial (ALLEGRO) and included 718 adults and adolescents aged 12 or older with severe AA (Severity of Alopecia Tool [SALT] score ≥ 50).
- Patients received various doses of the oral Janus kinase inhibitor ritlecitinib, with or without a 4-week loading dose, including 200/50 mg, 200/30 mg, 50 mg, or 30 mg, with or without a 4-week loading dose for up to 24 weeks and continued to receive their assigned maintenance dose.
- Researchers assessed sustained clinical responses at week 48 for those who had achieved SALT scores ≤ 20 and ≤ 10 at 24 weeks, and nonresponders at week 24 were assessed for responses through week 48.
- Adverse events were also evaluated.
TAKEAWAY:
- Among patients on ritlecitinib who had responded at week 24, SALT responses ≤ 20 were sustained in 85.2%-100% of patients through week 48. Similar results were seen among patients who achieved a SALT score ≤ 10 (68.8%-91.7%) and improvements in eyebrow (70.4%-96.9%) or eyelash (52.4%-94.1%) assessment scores.
- Among those who were nonresponders at week 24, 22.2%-33.7% achieved a SALT score ≤ 20 and 19.8%-25.5% achieved a SALT score ≤ 10 by week 48. Similarly, among those with no eyebrow or eyelash responses at week 24, 19.7%-32.8% and 16.7%-30.2% had improved eyebrow or eyelash assessment scores, respectively, at week 48.
- Between weeks 24 and 48, adverse events were reported in 74%-93% of patients who achieved a SALT score ≤ 20, most were mild or moderate; two serious events were reported but deemed unrelated to treatment. The safety profile was similar across all subgroups.
- No deaths, malignancies, major cardiovascular events, opportunistic infections, or herpes zoster infections were observed.
IN PRACTICE:
“The majority of ritlecitinib-treated patients with AA who met target clinical response based on scalp, eyebrow, or eyelash regrowth at week 24 sustained their response through week 48 with continued treatment,” the authors wrote. “Some patients, including those with more extensive hair loss, may require ritlecitinib treatment beyond 6 months to achieve target clinical response,” they added.
SOURCE:
The study was led by Melissa Piliang, MD, of the Department of Dermatology, Cleveland Clinic, and was published online on October 17 in the Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology.
LIMITATIONS:
The analysis was limited by its post hoc nature, small sample size in each treatment group, and a follow-up period of only 48 weeks.
DISCLOSURES:
This study was funded by Pfizer. Piliang disclosed being a consultant or investigator for Pfizer, Eli Lilly, and Procter & Gamble. Six authors were employees or shareholders of or received salary from Pfizer. Other authors also reported financial relationships with pharmaceutical companies outside this work, including Pfizer.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
, and up to one third of nonresponders at week 24 also achieved responses by week 48.
METHODOLOGY:
- Researchers conducted a post hoc analysis of an international, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase 2b/3 trial (ALLEGRO) and included 718 adults and adolescents aged 12 or older with severe AA (Severity of Alopecia Tool [SALT] score ≥ 50).
- Patients received various doses of the oral Janus kinase inhibitor ritlecitinib, with or without a 4-week loading dose, including 200/50 mg, 200/30 mg, 50 mg, or 30 mg, with or without a 4-week loading dose for up to 24 weeks and continued to receive their assigned maintenance dose.
- Researchers assessed sustained clinical responses at week 48 for those who had achieved SALT scores ≤ 20 and ≤ 10 at 24 weeks, and nonresponders at week 24 were assessed for responses through week 48.
- Adverse events were also evaluated.
TAKEAWAY:
- Among patients on ritlecitinib who had responded at week 24, SALT responses ≤ 20 were sustained in 85.2%-100% of patients through week 48. Similar results were seen among patients who achieved a SALT score ≤ 10 (68.8%-91.7%) and improvements in eyebrow (70.4%-96.9%) or eyelash (52.4%-94.1%) assessment scores.
- Among those who were nonresponders at week 24, 22.2%-33.7% achieved a SALT score ≤ 20 and 19.8%-25.5% achieved a SALT score ≤ 10 by week 48. Similarly, among those with no eyebrow or eyelash responses at week 24, 19.7%-32.8% and 16.7%-30.2% had improved eyebrow or eyelash assessment scores, respectively, at week 48.
- Between weeks 24 and 48, adverse events were reported in 74%-93% of patients who achieved a SALT score ≤ 20, most were mild or moderate; two serious events were reported but deemed unrelated to treatment. The safety profile was similar across all subgroups.
- No deaths, malignancies, major cardiovascular events, opportunistic infections, or herpes zoster infections were observed.
IN PRACTICE:
“The majority of ritlecitinib-treated patients with AA who met target clinical response based on scalp, eyebrow, or eyelash regrowth at week 24 sustained their response through week 48 with continued treatment,” the authors wrote. “Some patients, including those with more extensive hair loss, may require ritlecitinib treatment beyond 6 months to achieve target clinical response,” they added.
SOURCE:
The study was led by Melissa Piliang, MD, of the Department of Dermatology, Cleveland Clinic, and was published online on October 17 in the Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology.
LIMITATIONS:
The analysis was limited by its post hoc nature, small sample size in each treatment group, and a follow-up period of only 48 weeks.
DISCLOSURES:
This study was funded by Pfizer. Piliang disclosed being a consultant or investigator for Pfizer, Eli Lilly, and Procter & Gamble. Six authors were employees or shareholders of or received salary from Pfizer. Other authors also reported financial relationships with pharmaceutical companies outside this work, including Pfizer.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
New Clinician Tool Aims to Stop ALS Diagnosis Delays
SAVANNAH, GEORGIA —
The one-page “thinkALS” tool, designed for clinicians who don’t specialize in neuromuscular disorders, offers a guide to recognize ALS symptoms and determine when it’s time to refer patients to ALS clinics.
“Time is of the essence. It’s really important because the paradigm of looking at ALS is shifting from this being a fatal disease that nobody can do anything about,” said Suma Babu, MBBS, MPH, assistant professor of neurology at Massachusetts General Hospital/Harvard Medical School in Boston, in a presentation at American Association of Neuromuscular & Electrodiagnostic Medicine (AANEM) 2024. “As a community, we need to think about how can get to the diagnosis point early and get patients started on therapies.”
On Average, ALS Diagnosis Takes 12-15 Months
As Babu noted, the percentage of patients initially diagnosed with something else may be as high as 52%. The time to diagnosis in ALS remained steady at a mean 12-15 months from 1996-1998 to 2000-2018.
“If you keep in mind that an average ALS patient lives only 3-5 years from symptom onset, they’re spending one third of their survival time in just trying to figure out what the diagnosis is,” Babu said. “Often, they may even undergo unnecessary testing and unnecessary surgeries — carpal tunnel releases, spinal surgeries, and so on.”
Babu’s own research, which is under review for publication, examined 2011-2021 Medicare claims to determine the typical time from first neurologist consult to confirmed ALS diagnosis. The mean for ALS/neuromuscular specialists is 9.6 months, while it’s 16.7 months for nonspecialist neurologists.
“It’s a hard pill to swallow,” Babu said, referring to the fact that neurologists are contributing to some of this situation. “But it is a challenge because ALS does not have a definitive diagnostic test, and you’re ruling out other possibilities.”
A ‘Sense of Nihilism’ About Prognoses
She added that “unless you’re seeing a lot of ALS patients, this is not going to be on a neurologist’s or a nurse practitioner’s radar to think about ALS early and then refer them to the right place.”
There’s also an unwarranted “sense of nihilism” about prognoses for patients, she said. “Sometimes people do not understand what’s going on within the ALS field in terms of ‘What are we going to do about it if it’s diagnosed?’ ”
The new one-page tool will be helpful in making diagnoses, she said. “If you have a patient who has asymmetric, progressive weakness, there is an instrument you can turn to that will walk you through the most common symptoms. It’ll also walk you through what to do next.”
The tool lists features of ALS and factors that support — or don’t support — an ALS diagnosis. Users are told to “think ALS” if features in two categories are present and no features in a third category are present.
Referral Wording Is Crucial
Babu added that the “important key feature of this instrument” is guidance for non-neurologists regarding what to write on a referral to neurology so the patient is channeled directly to an ALS clinic. The recommended wording: “CLINICAL SUSPICION FOR ALS.”
Neurologist Ximena Arcila-Londono, MD, of Henry Ford Health in Detroit, spoke after Babu’s presentation and agreed that wording is crucial in referrals. “Please include in your words ‘Rule out motor neuron disorder’ or ‘Rule out ALS,’ ” she said. “Some people in the community are very reluctant to use those words in their referral. If you don’t use the referral and you send them [regarding] weakness, that person is going to get stuck in the general neurology pile. The moment you use the word ‘motor neuron disorder’ or ALS, most of us will get to those patients within a month.”
The tool’s wording adds that “most ALS centers can accommodate urgent ALS referrals within 2 weeks.”
Babu disclosed receiving research funding from the AANEM Foundation, American Academy of Neurology, Muscular Dystrophy Association, OrphAI, Biogen, Ionis, Novartis, Denali, uniQure, and MarvelBiome. Arcila-Londono had no disclosures.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
SAVANNAH, GEORGIA —
The one-page “thinkALS” tool, designed for clinicians who don’t specialize in neuromuscular disorders, offers a guide to recognize ALS symptoms and determine when it’s time to refer patients to ALS clinics.
“Time is of the essence. It’s really important because the paradigm of looking at ALS is shifting from this being a fatal disease that nobody can do anything about,” said Suma Babu, MBBS, MPH, assistant professor of neurology at Massachusetts General Hospital/Harvard Medical School in Boston, in a presentation at American Association of Neuromuscular & Electrodiagnostic Medicine (AANEM) 2024. “As a community, we need to think about how can get to the diagnosis point early and get patients started on therapies.”
On Average, ALS Diagnosis Takes 12-15 Months
As Babu noted, the percentage of patients initially diagnosed with something else may be as high as 52%. The time to diagnosis in ALS remained steady at a mean 12-15 months from 1996-1998 to 2000-2018.
“If you keep in mind that an average ALS patient lives only 3-5 years from symptom onset, they’re spending one third of their survival time in just trying to figure out what the diagnosis is,” Babu said. “Often, they may even undergo unnecessary testing and unnecessary surgeries — carpal tunnel releases, spinal surgeries, and so on.”
Babu’s own research, which is under review for publication, examined 2011-2021 Medicare claims to determine the typical time from first neurologist consult to confirmed ALS diagnosis. The mean for ALS/neuromuscular specialists is 9.6 months, while it’s 16.7 months for nonspecialist neurologists.
“It’s a hard pill to swallow,” Babu said, referring to the fact that neurologists are contributing to some of this situation. “But it is a challenge because ALS does not have a definitive diagnostic test, and you’re ruling out other possibilities.”
A ‘Sense of Nihilism’ About Prognoses
She added that “unless you’re seeing a lot of ALS patients, this is not going to be on a neurologist’s or a nurse practitioner’s radar to think about ALS early and then refer them to the right place.”
There’s also an unwarranted “sense of nihilism” about prognoses for patients, she said. “Sometimes people do not understand what’s going on within the ALS field in terms of ‘What are we going to do about it if it’s diagnosed?’ ”
The new one-page tool will be helpful in making diagnoses, she said. “If you have a patient who has asymmetric, progressive weakness, there is an instrument you can turn to that will walk you through the most common symptoms. It’ll also walk you through what to do next.”
The tool lists features of ALS and factors that support — or don’t support — an ALS diagnosis. Users are told to “think ALS” if features in two categories are present and no features in a third category are present.
Referral Wording Is Crucial
Babu added that the “important key feature of this instrument” is guidance for non-neurologists regarding what to write on a referral to neurology so the patient is channeled directly to an ALS clinic. The recommended wording: “CLINICAL SUSPICION FOR ALS.”
Neurologist Ximena Arcila-Londono, MD, of Henry Ford Health in Detroit, spoke after Babu’s presentation and agreed that wording is crucial in referrals. “Please include in your words ‘Rule out motor neuron disorder’ or ‘Rule out ALS,’ ” she said. “Some people in the community are very reluctant to use those words in their referral. If you don’t use the referral and you send them [regarding] weakness, that person is going to get stuck in the general neurology pile. The moment you use the word ‘motor neuron disorder’ or ALS, most of us will get to those patients within a month.”
The tool’s wording adds that “most ALS centers can accommodate urgent ALS referrals within 2 weeks.”
Babu disclosed receiving research funding from the AANEM Foundation, American Academy of Neurology, Muscular Dystrophy Association, OrphAI, Biogen, Ionis, Novartis, Denali, uniQure, and MarvelBiome. Arcila-Londono had no disclosures.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
SAVANNAH, GEORGIA —
The one-page “thinkALS” tool, designed for clinicians who don’t specialize in neuromuscular disorders, offers a guide to recognize ALS symptoms and determine when it’s time to refer patients to ALS clinics.
“Time is of the essence. It’s really important because the paradigm of looking at ALS is shifting from this being a fatal disease that nobody can do anything about,” said Suma Babu, MBBS, MPH, assistant professor of neurology at Massachusetts General Hospital/Harvard Medical School in Boston, in a presentation at American Association of Neuromuscular & Electrodiagnostic Medicine (AANEM) 2024. “As a community, we need to think about how can get to the diagnosis point early and get patients started on therapies.”
On Average, ALS Diagnosis Takes 12-15 Months
As Babu noted, the percentage of patients initially diagnosed with something else may be as high as 52%. The time to diagnosis in ALS remained steady at a mean 12-15 months from 1996-1998 to 2000-2018.
“If you keep in mind that an average ALS patient lives only 3-5 years from symptom onset, they’re spending one third of their survival time in just trying to figure out what the diagnosis is,” Babu said. “Often, they may even undergo unnecessary testing and unnecessary surgeries — carpal tunnel releases, spinal surgeries, and so on.”
Babu’s own research, which is under review for publication, examined 2011-2021 Medicare claims to determine the typical time from first neurologist consult to confirmed ALS diagnosis. The mean for ALS/neuromuscular specialists is 9.6 months, while it’s 16.7 months for nonspecialist neurologists.
“It’s a hard pill to swallow,” Babu said, referring to the fact that neurologists are contributing to some of this situation. “But it is a challenge because ALS does not have a definitive diagnostic test, and you’re ruling out other possibilities.”
A ‘Sense of Nihilism’ About Prognoses
She added that “unless you’re seeing a lot of ALS patients, this is not going to be on a neurologist’s or a nurse practitioner’s radar to think about ALS early and then refer them to the right place.”
There’s also an unwarranted “sense of nihilism” about prognoses for patients, she said. “Sometimes people do not understand what’s going on within the ALS field in terms of ‘What are we going to do about it if it’s diagnosed?’ ”
The new one-page tool will be helpful in making diagnoses, she said. “If you have a patient who has asymmetric, progressive weakness, there is an instrument you can turn to that will walk you through the most common symptoms. It’ll also walk you through what to do next.”
The tool lists features of ALS and factors that support — or don’t support — an ALS diagnosis. Users are told to “think ALS” if features in two categories are present and no features in a third category are present.
Referral Wording Is Crucial
Babu added that the “important key feature of this instrument” is guidance for non-neurologists regarding what to write on a referral to neurology so the patient is channeled directly to an ALS clinic. The recommended wording: “CLINICAL SUSPICION FOR ALS.”
Neurologist Ximena Arcila-Londono, MD, of Henry Ford Health in Detroit, spoke after Babu’s presentation and agreed that wording is crucial in referrals. “Please include in your words ‘Rule out motor neuron disorder’ or ‘Rule out ALS,’ ” she said. “Some people in the community are very reluctant to use those words in their referral. If you don’t use the referral and you send them [regarding] weakness, that person is going to get stuck in the general neurology pile. The moment you use the word ‘motor neuron disorder’ or ALS, most of us will get to those patients within a month.”
The tool’s wording adds that “most ALS centers can accommodate urgent ALS referrals within 2 weeks.”
Babu disclosed receiving research funding from the AANEM Foundation, American Academy of Neurology, Muscular Dystrophy Association, OrphAI, Biogen, Ionis, Novartis, Denali, uniQure, and MarvelBiome. Arcila-Londono had no disclosures.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM AANEM 2024
Contraceptive Users in the United States Show Preference for Alternative Sources
TOPLINE:
Individuals using contraceptive pills, patches, and rings must frequently interact with the healthcare system for continued use. More than half of US contraceptive users prefer alternative sources over traditional in-person care. Only 35.6% of respondents selected in-person care as their most preferred source.
METHODOLOGY:
- Researchers conducted a cross-sectional nationally representative survey in the United States in 2022 through NORC’s AmeriSpeak panel.
- A total of 3059 eligible panelists, aged 15-44 years, completed the survey, with 595 individuals currently using a pill, patch, or ring contraceptive included in the analysis.
- Primary outcomes measured were the use of any preferred source and the most preferred source when obtaining contraception.
- Sources included in-person care, telehealth, pharmacist-prescribed, online service, and over the counter.
- Data were analyzed from January 25, 2023, to August 15, 2024.
TAKEAWAY:
- Only 35.6% of respondents selected in-person care as their most preferred source of contraception.
- Only 49.7% of respondents obtained their method from a preferred source, while 39.8% received it from their most preferred source.
- Respondents who previously reported being unable to get their method on time had higher odds of preferring an alternative source (adjusted odds ratio [AOR], 2.57; 95% CI, 1.36-4.87).
- Those who recently received person-centered contraceptive counseling had lower odds of preferring an alternative source (AOR, 0.59; 95% CI, 0.35-0.98).
IN PRACTICE:
“The low level of preference for in-person care suggests that expanding contraceptive sources outside of traditional healthcare settings has a role in ameliorating barriers to access and can promote reproductive autonomy,” wrote the authors of the study.
SOURCE:
The study was led by Anu Manchikanti Gómez, PhD, Sexual Health and Reproductive Equity Program, School of Social Welfare, University of California, Berkeley. It was published online in JAMA Network Open.
LIMITATIONS:
The study’s cross-sectional design limited the ability to establish causality. The sample was limited to individuals aged 15-44 years, which may not represent all contraceptive users. Self-reported data may be subject to recall bias. The study did not distinguish between synchronous and asynchronous telehealth preferences.
DISCLOSURES:
The study was supported by Arnold Ventures. Gómez disclosed receiving personal fees from various organizations outside the submitted work. Additional disclosures are noted in the original article.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
Individuals using contraceptive pills, patches, and rings must frequently interact with the healthcare system for continued use. More than half of US contraceptive users prefer alternative sources over traditional in-person care. Only 35.6% of respondents selected in-person care as their most preferred source.
METHODOLOGY:
- Researchers conducted a cross-sectional nationally representative survey in the United States in 2022 through NORC’s AmeriSpeak panel.
- A total of 3059 eligible panelists, aged 15-44 years, completed the survey, with 595 individuals currently using a pill, patch, or ring contraceptive included in the analysis.
- Primary outcomes measured were the use of any preferred source and the most preferred source when obtaining contraception.
- Sources included in-person care, telehealth, pharmacist-prescribed, online service, and over the counter.
- Data were analyzed from January 25, 2023, to August 15, 2024.
TAKEAWAY:
- Only 35.6% of respondents selected in-person care as their most preferred source of contraception.
- Only 49.7% of respondents obtained their method from a preferred source, while 39.8% received it from their most preferred source.
- Respondents who previously reported being unable to get their method on time had higher odds of preferring an alternative source (adjusted odds ratio [AOR], 2.57; 95% CI, 1.36-4.87).
- Those who recently received person-centered contraceptive counseling had lower odds of preferring an alternative source (AOR, 0.59; 95% CI, 0.35-0.98).
IN PRACTICE:
“The low level of preference for in-person care suggests that expanding contraceptive sources outside of traditional healthcare settings has a role in ameliorating barriers to access and can promote reproductive autonomy,” wrote the authors of the study.
SOURCE:
The study was led by Anu Manchikanti Gómez, PhD, Sexual Health and Reproductive Equity Program, School of Social Welfare, University of California, Berkeley. It was published online in JAMA Network Open.
LIMITATIONS:
The study’s cross-sectional design limited the ability to establish causality. The sample was limited to individuals aged 15-44 years, which may not represent all contraceptive users. Self-reported data may be subject to recall bias. The study did not distinguish between synchronous and asynchronous telehealth preferences.
DISCLOSURES:
The study was supported by Arnold Ventures. Gómez disclosed receiving personal fees from various organizations outside the submitted work. Additional disclosures are noted in the original article.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
Individuals using contraceptive pills, patches, and rings must frequently interact with the healthcare system for continued use. More than half of US contraceptive users prefer alternative sources over traditional in-person care. Only 35.6% of respondents selected in-person care as their most preferred source.
METHODOLOGY:
- Researchers conducted a cross-sectional nationally representative survey in the United States in 2022 through NORC’s AmeriSpeak panel.
- A total of 3059 eligible panelists, aged 15-44 years, completed the survey, with 595 individuals currently using a pill, patch, or ring contraceptive included in the analysis.
- Primary outcomes measured were the use of any preferred source and the most preferred source when obtaining contraception.
- Sources included in-person care, telehealth, pharmacist-prescribed, online service, and over the counter.
- Data were analyzed from January 25, 2023, to August 15, 2024.
TAKEAWAY:
- Only 35.6% of respondents selected in-person care as their most preferred source of contraception.
- Only 49.7% of respondents obtained their method from a preferred source, while 39.8% received it from their most preferred source.
- Respondents who previously reported being unable to get their method on time had higher odds of preferring an alternative source (adjusted odds ratio [AOR], 2.57; 95% CI, 1.36-4.87).
- Those who recently received person-centered contraceptive counseling had lower odds of preferring an alternative source (AOR, 0.59; 95% CI, 0.35-0.98).
IN PRACTICE:
“The low level of preference for in-person care suggests that expanding contraceptive sources outside of traditional healthcare settings has a role in ameliorating barriers to access and can promote reproductive autonomy,” wrote the authors of the study.
SOURCE:
The study was led by Anu Manchikanti Gómez, PhD, Sexual Health and Reproductive Equity Program, School of Social Welfare, University of California, Berkeley. It was published online in JAMA Network Open.
LIMITATIONS:
The study’s cross-sectional design limited the ability to establish causality. The sample was limited to individuals aged 15-44 years, which may not represent all contraceptive users. Self-reported data may be subject to recall bias. The study did not distinguish between synchronous and asynchronous telehealth preferences.
DISCLOSURES:
The study was supported by Arnold Ventures. Gómez disclosed receiving personal fees from various organizations outside the submitted work. Additional disclosures are noted in the original article.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
PCOS Linked to Hypertensive Blood Pressure in Teens
TOPLINE:
Adolescent girls with polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) have an increased risk for hypertension, according to a new study which underscores the importance of blood pressure surveillance in this population.
METHODOLOGY:
- The retrospective cohort study examined the association between PCOS and hypertension in adolescent girls within a diverse community-based US healthcare population.
- The researchers analyzed data from 224,418 adolescent girls (mean age at index visit, 14.9 years; 15.8% classified as having obesity) who had a well-child visit between 2013 and 2019, during which their systolic blood pressure and diastolic blood pressure were measured.
- Blood pressure in the hypertensive range was classified using the 2017 American Academy of Pediatrics Practice Guideline, with thresholds of 130/80 mm Hg or greater.
TAKEAWAY:
- The proportion of adolescent girls with high blood pressure was significantly greater among those with PCOS than among those without the condition (18.2% vs 7.1%; P < .001).
- Adolescent girls with PCOS had a 25% higher risk for hypertension than those without the disorder (adjusted odds ratio [aOR], 1.25; 95% CI, 1.10-1.42).
- Similarly, adolescent girls with obesity and PCOS had a 23% higher risk for high blood pressure than those without PCOS (aOR, 1.23; 95% CI, 1.06-1.42).
IN PRACTICE:
“The high prevalence of [hypertension] associated with PCOS emphasizes the key role of early [blood pressure] monitoring in this high-risk group,” the authors of the study wrote.
SOURCE:
The study was led by Sherry Zhang, MD, Kaiser Permanente Oakland Medical Center, Oakland, California, and was published online in the American Journal of Preventive Medicine.
LIMITATIONS:
The study relied on coded diagnoses of PCOS from clinical settings, which may have led to detection and referral biases. The findings may not be generalizable to an unselected population in which adolescent girls are systematically screened for both PCOS and hypertension.
DISCLOSURES:
This study was funded by the Cardiovascular and Metabolic Conditions Research Section and the Biostatistical Consulting Unit at the Division of Research, Kaiser Permanente Northern California and by the Kaiser Permanente Northern California Community Health Program. The authors declared having no conflicts of interest.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
Adolescent girls with polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) have an increased risk for hypertension, according to a new study which underscores the importance of blood pressure surveillance in this population.
METHODOLOGY:
- The retrospective cohort study examined the association between PCOS and hypertension in adolescent girls within a diverse community-based US healthcare population.
- The researchers analyzed data from 224,418 adolescent girls (mean age at index visit, 14.9 years; 15.8% classified as having obesity) who had a well-child visit between 2013 and 2019, during which their systolic blood pressure and diastolic blood pressure were measured.
- Blood pressure in the hypertensive range was classified using the 2017 American Academy of Pediatrics Practice Guideline, with thresholds of 130/80 mm Hg or greater.
TAKEAWAY:
- The proportion of adolescent girls with high blood pressure was significantly greater among those with PCOS than among those without the condition (18.2% vs 7.1%; P < .001).
- Adolescent girls with PCOS had a 25% higher risk for hypertension than those without the disorder (adjusted odds ratio [aOR], 1.25; 95% CI, 1.10-1.42).
- Similarly, adolescent girls with obesity and PCOS had a 23% higher risk for high blood pressure than those without PCOS (aOR, 1.23; 95% CI, 1.06-1.42).
IN PRACTICE:
“The high prevalence of [hypertension] associated with PCOS emphasizes the key role of early [blood pressure] monitoring in this high-risk group,” the authors of the study wrote.
SOURCE:
The study was led by Sherry Zhang, MD, Kaiser Permanente Oakland Medical Center, Oakland, California, and was published online in the American Journal of Preventive Medicine.
LIMITATIONS:
The study relied on coded diagnoses of PCOS from clinical settings, which may have led to detection and referral biases. The findings may not be generalizable to an unselected population in which adolescent girls are systematically screened for both PCOS and hypertension.
DISCLOSURES:
This study was funded by the Cardiovascular and Metabolic Conditions Research Section and the Biostatistical Consulting Unit at the Division of Research, Kaiser Permanente Northern California and by the Kaiser Permanente Northern California Community Health Program. The authors declared having no conflicts of interest.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
Adolescent girls with polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) have an increased risk for hypertension, according to a new study which underscores the importance of blood pressure surveillance in this population.
METHODOLOGY:
- The retrospective cohort study examined the association between PCOS and hypertension in adolescent girls within a diverse community-based US healthcare population.
- The researchers analyzed data from 224,418 adolescent girls (mean age at index visit, 14.9 years; 15.8% classified as having obesity) who had a well-child visit between 2013 and 2019, during which their systolic blood pressure and diastolic blood pressure were measured.
- Blood pressure in the hypertensive range was classified using the 2017 American Academy of Pediatrics Practice Guideline, with thresholds of 130/80 mm Hg or greater.
TAKEAWAY:
- The proportion of adolescent girls with high blood pressure was significantly greater among those with PCOS than among those without the condition (18.2% vs 7.1%; P < .001).
- Adolescent girls with PCOS had a 25% higher risk for hypertension than those without the disorder (adjusted odds ratio [aOR], 1.25; 95% CI, 1.10-1.42).
- Similarly, adolescent girls with obesity and PCOS had a 23% higher risk for high blood pressure than those without PCOS (aOR, 1.23; 95% CI, 1.06-1.42).
IN PRACTICE:
“The high prevalence of [hypertension] associated with PCOS emphasizes the key role of early [blood pressure] monitoring in this high-risk group,” the authors of the study wrote.
SOURCE:
The study was led by Sherry Zhang, MD, Kaiser Permanente Oakland Medical Center, Oakland, California, and was published online in the American Journal of Preventive Medicine.
LIMITATIONS:
The study relied on coded diagnoses of PCOS from clinical settings, which may have led to detection and referral biases. The findings may not be generalizable to an unselected population in which adolescent girls are systematically screened for both PCOS and hypertension.
DISCLOSURES:
This study was funded by the Cardiovascular and Metabolic Conditions Research Section and the Biostatistical Consulting Unit at the Division of Research, Kaiser Permanente Northern California and by the Kaiser Permanente Northern California Community Health Program. The authors declared having no conflicts of interest.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Dry Eye Linked to Increased Risk for Mental Health Disorders
TOPLINE:
Patients with dry eye disease are more than three times as likely to have mental health conditions, such as depression and anxiety, as those without the condition.
METHODOLOGY:
- Researchers used a database from the National Institutes of Health to investigate the association between dry eye disease and mental health disorders in a large and diverse nationwide population of American adults.
- They identified 18,257 patients (mean age, 64.9 years; 67% women) with dry eye disease who were propensity score–matched with 54,765 participants without the condition.
- The cases of dry eye disease were identified using Systematized Nomenclature of Medicine codes for dry eyes, meibomian gland dysfunction, and tear film insufficiency.
- The outcome measures for mental health conditions were clinical diagnoses of depressive disorders, anxiety-related disorders, bipolar disorder, and schizophrenia spectrum disorders.
TAKEAWAY:
- Patients with dry eye disease had more than triple the risk for mental health conditions than participants without the condition (adjusted odds ratio [aOR], 3.21; P < .001).
- Patients with dry eye disease had a higher risk for a depressive disorder (aOR, 3.47), anxiety-related disorder (aOR, 2.74), bipolar disorder (aOR, 2.23), and schizophrenia spectrum disorder (aOR, 2.48; P < .001 for all) than participants without the condition.
- The associations between dry eye disease and mental health conditions were significantly stronger among Black individuals than among White individuals, except for bipolar disorder.
- Dry eye disease was associated with two- to threefold higher odds of depressive disorders, anxiety-related disorders, bipolar disorder, and schizophrenia spectrum disorders even in participants who never used medications for mental health (P < .001 for all).
IN PRACTICE:
“Greater efforts should be undertaken to screen patients with DED [dry eye disease] for mental health conditions, particularly in historically medically underserved populations,” the authors of the study wrote.
SOURCE:
This study was led by Aaron T. Zhao, of the Perelman School of Medicine at the University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, and was published online on October 15, 2024, in the American Journal of Ophthalmology.
LIMITATIONS:
This study relied on electronic health record data, which may have led to the inclusion of participants with undiagnosed dry eye disease as control participants. Moreover, the study did not evaluate the severity of dry eye disease or the severity and duration of mental health conditions, which may have affected the results. The database analyzed in this study may not have fully captured the complete demographic profile of the nationwide population, which may have affected the generalizability of the findings.
DISCLOSURES:
This study was supported by funding from the National Institutes of Health and Research to Prevent Blindness. The authors declared having no conflicts of interest.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
Patients with dry eye disease are more than three times as likely to have mental health conditions, such as depression and anxiety, as those without the condition.
METHODOLOGY:
- Researchers used a database from the National Institutes of Health to investigate the association between dry eye disease and mental health disorders in a large and diverse nationwide population of American adults.
- They identified 18,257 patients (mean age, 64.9 years; 67% women) with dry eye disease who were propensity score–matched with 54,765 participants without the condition.
- The cases of dry eye disease were identified using Systematized Nomenclature of Medicine codes for dry eyes, meibomian gland dysfunction, and tear film insufficiency.
- The outcome measures for mental health conditions were clinical diagnoses of depressive disorders, anxiety-related disorders, bipolar disorder, and schizophrenia spectrum disorders.
TAKEAWAY:
- Patients with dry eye disease had more than triple the risk for mental health conditions than participants without the condition (adjusted odds ratio [aOR], 3.21; P < .001).
- Patients with dry eye disease had a higher risk for a depressive disorder (aOR, 3.47), anxiety-related disorder (aOR, 2.74), bipolar disorder (aOR, 2.23), and schizophrenia spectrum disorder (aOR, 2.48; P < .001 for all) than participants without the condition.
- The associations between dry eye disease and mental health conditions were significantly stronger among Black individuals than among White individuals, except for bipolar disorder.
- Dry eye disease was associated with two- to threefold higher odds of depressive disorders, anxiety-related disorders, bipolar disorder, and schizophrenia spectrum disorders even in participants who never used medications for mental health (P < .001 for all).
IN PRACTICE:
“Greater efforts should be undertaken to screen patients with DED [dry eye disease] for mental health conditions, particularly in historically medically underserved populations,” the authors of the study wrote.
SOURCE:
This study was led by Aaron T. Zhao, of the Perelman School of Medicine at the University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, and was published online on October 15, 2024, in the American Journal of Ophthalmology.
LIMITATIONS:
This study relied on electronic health record data, which may have led to the inclusion of participants with undiagnosed dry eye disease as control participants. Moreover, the study did not evaluate the severity of dry eye disease or the severity and duration of mental health conditions, which may have affected the results. The database analyzed in this study may not have fully captured the complete demographic profile of the nationwide population, which may have affected the generalizability of the findings.
DISCLOSURES:
This study was supported by funding from the National Institutes of Health and Research to Prevent Blindness. The authors declared having no conflicts of interest.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
Patients with dry eye disease are more than three times as likely to have mental health conditions, such as depression and anxiety, as those without the condition.
METHODOLOGY:
- Researchers used a database from the National Institutes of Health to investigate the association between dry eye disease and mental health disorders in a large and diverse nationwide population of American adults.
- They identified 18,257 patients (mean age, 64.9 years; 67% women) with dry eye disease who were propensity score–matched with 54,765 participants without the condition.
- The cases of dry eye disease were identified using Systematized Nomenclature of Medicine codes for dry eyes, meibomian gland dysfunction, and tear film insufficiency.
- The outcome measures for mental health conditions were clinical diagnoses of depressive disorders, anxiety-related disorders, bipolar disorder, and schizophrenia spectrum disorders.
TAKEAWAY:
- Patients with dry eye disease had more than triple the risk for mental health conditions than participants without the condition (adjusted odds ratio [aOR], 3.21; P < .001).
- Patients with dry eye disease had a higher risk for a depressive disorder (aOR, 3.47), anxiety-related disorder (aOR, 2.74), bipolar disorder (aOR, 2.23), and schizophrenia spectrum disorder (aOR, 2.48; P < .001 for all) than participants without the condition.
- The associations between dry eye disease and mental health conditions were significantly stronger among Black individuals than among White individuals, except for bipolar disorder.
- Dry eye disease was associated with two- to threefold higher odds of depressive disorders, anxiety-related disorders, bipolar disorder, and schizophrenia spectrum disorders even in participants who never used medications for mental health (P < .001 for all).
IN PRACTICE:
“Greater efforts should be undertaken to screen patients with DED [dry eye disease] for mental health conditions, particularly in historically medically underserved populations,” the authors of the study wrote.
SOURCE:
This study was led by Aaron T. Zhao, of the Perelman School of Medicine at the University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, and was published online on October 15, 2024, in the American Journal of Ophthalmology.
LIMITATIONS:
This study relied on electronic health record data, which may have led to the inclusion of participants with undiagnosed dry eye disease as control participants. Moreover, the study did not evaluate the severity of dry eye disease or the severity and duration of mental health conditions, which may have affected the results. The database analyzed in this study may not have fully captured the complete demographic profile of the nationwide population, which may have affected the generalizability of the findings.
DISCLOSURES:
This study was supported by funding from the National Institutes of Health and Research to Prevent Blindness. The authors declared having no conflicts of interest.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Higher Doses of Vitamin D3 Do Not Reduce Cardiac Biomarkers in Older Adults
TOPLINE:
Higher doses of vitamin D3 supplementation did not significantly reduce cardiac biomarkers in older adults with low serum vitamin D levels. The STURDY trial found no significant differences in high-sensitivity cardiac troponin I (hs-cTnI) and N-terminal pro-B-type natriuretic peptide (NT-proBNP) between low- and high-dose groups.
METHODOLOGY:
- A total of 688 participants aged 70 years or older with low serum 25-hydroxy vitamin D levels (10-29 ng/mL) were included in the STURDY trial.
- Participants were randomized to receive one of four doses of vitamin D3 supplementation: 200, 1000, 2000, or 4000 IU/d, with 200 IU/d as the reference dose.
- Cardiac biomarkers, including hs-cTnI and NT-proBNP, were measured at baseline, 3 months, 12 months, and 24 months.
- The trial was conducted at two community-based research institutions in the United States between July 2015 and March 2019.
- The effects of vitamin D3 dose on biomarkers were assessed via mixed-effects tobit models, with participants followed up to 24 months or until study termination.
TAKEAWAY:
- Higher doses of vitamin D3 supplementation did not significantly affect hs-cTnI levels compared with the low-dose group (1.6% difference; 95% CI, −5.3 to 8.9).
- No significant differences were observed in NT-proBNP levels between the high-dose and low-dose groups (−1.8% difference; 95% CI, −9.3 to 6.3).
- Both hs-cTnI and NT-proBNP levels increased in both low- and high-dose groups over time, with hs-cTnI increasing by 5.2% and 7.0%, respectively, and NT-proBNP increasing by 11.3% and 9.3%, respectively.
- The findings suggest that higher doses of vitamin D3 supplementation do not reduce markers of subclinical cardiovascular disease in older adults with low serum vitamin D levels.
IN PRACTICE:
“We can speculate that the systemic effects of vitamin D deficiency are more profound among the very old, and there may be an inverse relationship between supplementation and inflammation. It is also possible that serum vitamin D level is a risk marker but not a risk factor for CVD risk and related underlying mechanisms,” wrote the authors of the study.
SOURCE:
The study was led by Katharine W. Rainer, MD, Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center in Boston. It was published online in the Journal of the American College of Cardiology.
LIMITATIONS:
The study’s community-based population may limit the generalizability of the findings to populations at higher risk for cardiovascular disease. Additionally, the baseline cardiac biomarkers were lower than those in some high-risk populations, which may affect the precision of the assay performance. The study may not have had adequate power for cross-sectional and subgroup analyses. Both groups received some vitamin D3 supplementation, making it difficult to determine the impact of lower-dose supplementation vs no supplementation.
DISCLOSURES:
The study was supported by grants from the National Institute on Aging, the Office of Dietary Supplements, the Mid-Atlantic Nutrition Obesity Research Center, and the Johns Hopkins Institute for Clinical and Translational Research. Rainer disclosed receiving grants from these organizations.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
Higher doses of vitamin D3 supplementation did not significantly reduce cardiac biomarkers in older adults with low serum vitamin D levels. The STURDY trial found no significant differences in high-sensitivity cardiac troponin I (hs-cTnI) and N-terminal pro-B-type natriuretic peptide (NT-proBNP) between low- and high-dose groups.
METHODOLOGY:
- A total of 688 participants aged 70 years or older with low serum 25-hydroxy vitamin D levels (10-29 ng/mL) were included in the STURDY trial.
- Participants were randomized to receive one of four doses of vitamin D3 supplementation: 200, 1000, 2000, or 4000 IU/d, with 200 IU/d as the reference dose.
- Cardiac biomarkers, including hs-cTnI and NT-proBNP, were measured at baseline, 3 months, 12 months, and 24 months.
- The trial was conducted at two community-based research institutions in the United States between July 2015 and March 2019.
- The effects of vitamin D3 dose on biomarkers were assessed via mixed-effects tobit models, with participants followed up to 24 months or until study termination.
TAKEAWAY:
- Higher doses of vitamin D3 supplementation did not significantly affect hs-cTnI levels compared with the low-dose group (1.6% difference; 95% CI, −5.3 to 8.9).
- No significant differences were observed in NT-proBNP levels between the high-dose and low-dose groups (−1.8% difference; 95% CI, −9.3 to 6.3).
- Both hs-cTnI and NT-proBNP levels increased in both low- and high-dose groups over time, with hs-cTnI increasing by 5.2% and 7.0%, respectively, and NT-proBNP increasing by 11.3% and 9.3%, respectively.
- The findings suggest that higher doses of vitamin D3 supplementation do not reduce markers of subclinical cardiovascular disease in older adults with low serum vitamin D levels.
IN PRACTICE:
“We can speculate that the systemic effects of vitamin D deficiency are more profound among the very old, and there may be an inverse relationship between supplementation and inflammation. It is also possible that serum vitamin D level is a risk marker but not a risk factor for CVD risk and related underlying mechanisms,” wrote the authors of the study.
SOURCE:
The study was led by Katharine W. Rainer, MD, Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center in Boston. It was published online in the Journal of the American College of Cardiology.
LIMITATIONS:
The study’s community-based population may limit the generalizability of the findings to populations at higher risk for cardiovascular disease. Additionally, the baseline cardiac biomarkers were lower than those in some high-risk populations, which may affect the precision of the assay performance. The study may not have had adequate power for cross-sectional and subgroup analyses. Both groups received some vitamin D3 supplementation, making it difficult to determine the impact of lower-dose supplementation vs no supplementation.
DISCLOSURES:
The study was supported by grants from the National Institute on Aging, the Office of Dietary Supplements, the Mid-Atlantic Nutrition Obesity Research Center, and the Johns Hopkins Institute for Clinical and Translational Research. Rainer disclosed receiving grants from these organizations.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
Higher doses of vitamin D3 supplementation did not significantly reduce cardiac biomarkers in older adults with low serum vitamin D levels. The STURDY trial found no significant differences in high-sensitivity cardiac troponin I (hs-cTnI) and N-terminal pro-B-type natriuretic peptide (NT-proBNP) between low- and high-dose groups.
METHODOLOGY:
- A total of 688 participants aged 70 years or older with low serum 25-hydroxy vitamin D levels (10-29 ng/mL) were included in the STURDY trial.
- Participants were randomized to receive one of four doses of vitamin D3 supplementation: 200, 1000, 2000, or 4000 IU/d, with 200 IU/d as the reference dose.
- Cardiac biomarkers, including hs-cTnI and NT-proBNP, were measured at baseline, 3 months, 12 months, and 24 months.
- The trial was conducted at two community-based research institutions in the United States between July 2015 and March 2019.
- The effects of vitamin D3 dose on biomarkers were assessed via mixed-effects tobit models, with participants followed up to 24 months or until study termination.
TAKEAWAY:
- Higher doses of vitamin D3 supplementation did not significantly affect hs-cTnI levels compared with the low-dose group (1.6% difference; 95% CI, −5.3 to 8.9).
- No significant differences were observed in NT-proBNP levels between the high-dose and low-dose groups (−1.8% difference; 95% CI, −9.3 to 6.3).
- Both hs-cTnI and NT-proBNP levels increased in both low- and high-dose groups over time, with hs-cTnI increasing by 5.2% and 7.0%, respectively, and NT-proBNP increasing by 11.3% and 9.3%, respectively.
- The findings suggest that higher doses of vitamin D3 supplementation do not reduce markers of subclinical cardiovascular disease in older adults with low serum vitamin D levels.
IN PRACTICE:
“We can speculate that the systemic effects of vitamin D deficiency are more profound among the very old, and there may be an inverse relationship between supplementation and inflammation. It is also possible that serum vitamin D level is a risk marker but not a risk factor for CVD risk and related underlying mechanisms,” wrote the authors of the study.
SOURCE:
The study was led by Katharine W. Rainer, MD, Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center in Boston. It was published online in the Journal of the American College of Cardiology.
LIMITATIONS:
The study’s community-based population may limit the generalizability of the findings to populations at higher risk for cardiovascular disease. Additionally, the baseline cardiac biomarkers were lower than those in some high-risk populations, which may affect the precision of the assay performance. The study may not have had adequate power for cross-sectional and subgroup analyses. Both groups received some vitamin D3 supplementation, making it difficult to determine the impact of lower-dose supplementation vs no supplementation.
DISCLOSURES:
The study was supported by grants from the National Institute on Aging, the Office of Dietary Supplements, the Mid-Atlantic Nutrition Obesity Research Center, and the Johns Hopkins Institute for Clinical and Translational Research. Rainer disclosed receiving grants from these organizations.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Projected 2023 Cost Reduction From Tumor Necrosis Factor α Inhibitor Biosimilars in Dermatology: A National Medicare Analysis
To the Editor:
Although biologics provide major therapeutic benefits for dermatologic conditions, they also come with a substantial cost, making them among the most expensive medications available. Medicare and Medicaid spending on biologics for dermatologic conditions increased by 320% from 2012 to 2018, reaching a staggering $10.6 billion in 2018 alone.1 Biosimilars show promise in reducing health care spending for dermatologic conditions; however, their utilization has been limited due to multiple factors, including delayed market entry from patent thickets, exclusionary formulary contracts, and prescriber skepticism regarding their safety and efficacy.2 For instance, a national survey of 1201 US physicians in specialties that are high prescribers of biologics reported that 55% doubted the safety and appropriateness of biosimilars.3
US Food and Drug Administration approval of biosimilars for adalimumab and etanercept offers the potential to reduce health care spending for dermatologic conditions. However, this cost reduction is dependent on utilization rates among dermatologists. In this national cross-sectional review of Medicare data, we predicted the impact of these biosimilars on dermatologic Medicare costs and demonstrated how differing utilization rates among dermatologists can influence potential savings.
To model 2023 utilization and cost reduction from biosimilars, we analyzed Medicare Part D data from 2020 on existing biosimilars, including granulocyte colony–stimulating factors, erythropoiesis-stimulating agents, and tumor necrosis factor α inhibitors.4 Methods in line with a 2021 report from the US Department of Health and Human Services5 as well as those of Yazdany et al6 were used. For each class, we calculated the 2020 distribution of biosimilar and originator drug claims as well as biosimilar cost reduction per 30-day claim. We utilized 2018-2021 annual growth rates for branded adalimumab and etanercept to estimate 30-day claims for 2023 and the cost of these branded agents in the absence of biosimilars. The hypothetical 2023 cost reduction from adalimumab and etanercept biosimilars was estimated by assuming 2020 biosimilar utilization rates and mean cost reduction per claim. This study utilized publicly available or aggregate summary data (not attributable to specific patients) and did not qualify as human subject research; therefore, institutional review board approval was not required.
In 2020, biosimilar utilization proportions ranged from 6.4% (tumor necrosis factor α inhibitors) to 82.7% (granulocyte colony–stimulating factors), with a mean across all classes of 35.7%. On average, the cost per 30-day claim of biosimilars was 66.8% of originator agents (Table 1). In 2021, we identified 57,868 30-day claims for branded adalimumab and etanercept submitted by dermatologists. From 2018 to 2021, 30-day branded adalimumab claims increased by 1.27% annually (cost + 10.62% annually), while claims for branded etanercept decreased by 13.0% annually (cost + 5.68% annually). Assuming these trends, the cost of branded adalimumab and etanercept was estimated to be $539 million in 2023. Applying the aforementioned 35.7% utilization, the introduction of biosimilars in dermatology would yield a cost reduction of approximately $118 million (21.9%). A high utilization rate (82.7%) of biosimilars among dermatologists would increase cost savings to $199 million (36.9%)(Table 2).

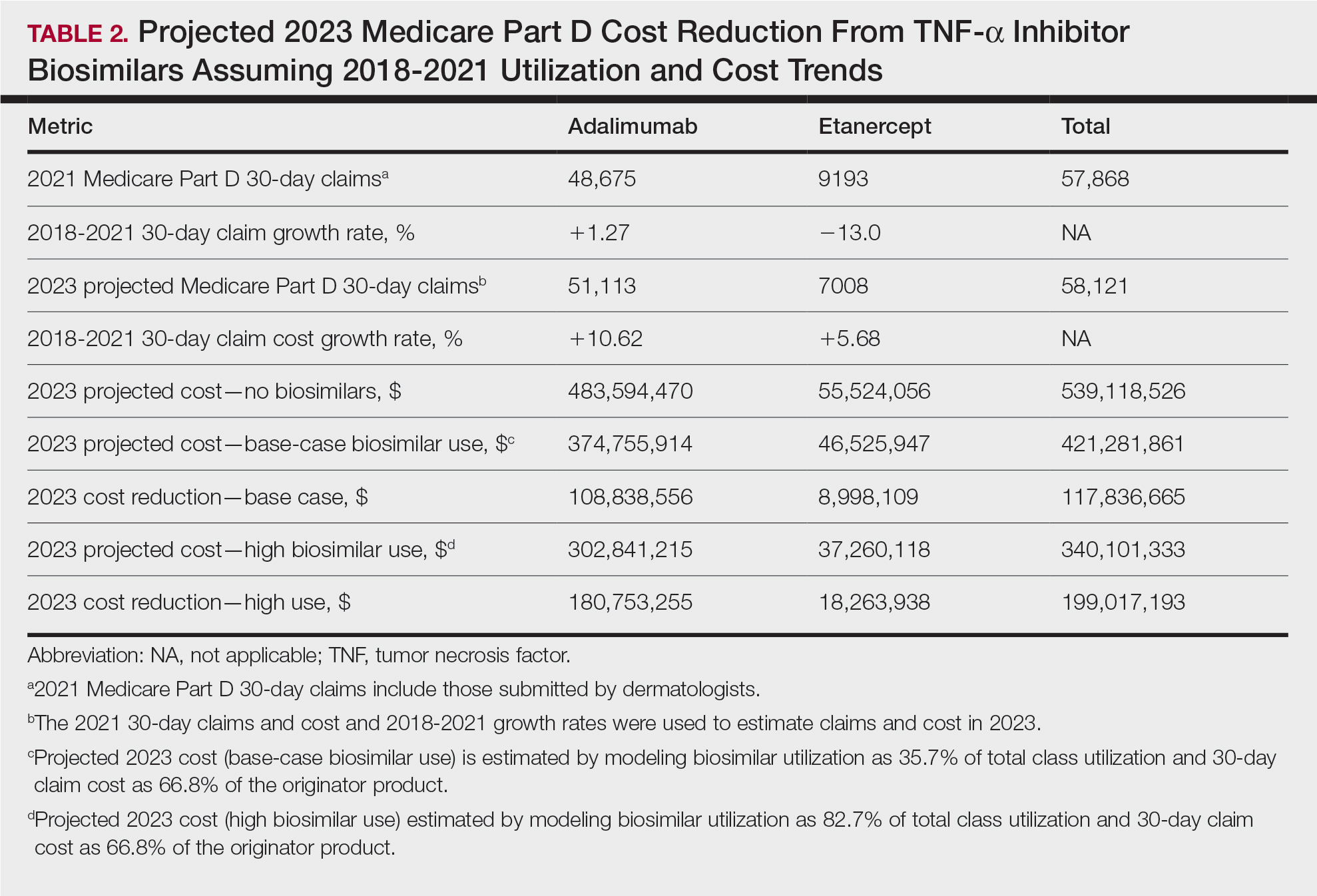
Our study demonstrates that the introduction of 2 biosimilars into dermatology may result in a notable reduction in Medicare expenditures. The savings observed are likely to translate to substantial cost savings for patients. A cross-sectional analysis of 2020 Medicare data indicated that coverage for psoriasis medications was 10.0% to 99.8% across different products and Medicare Part D plans. Consequently, patients faced considerable out-of-pocket expenses, amounting to $5653 and $5714 per year for adalimumab and etanercept, respectively.7
We found that the extent of savings from biosimilars was dependent on the utilization rates among dermatologists, with the highest utilization rate almost doubling the total savings of average utilization rates. Given the impact of high utilization and the wide variation observed, understanding the factors that have influenced uptake of biosimilars is important to increasing utilization as these medications become integrated into dermatology. For instance, limited uptake of infliximab initially may have been influenced by concerns about efficacy and increased adverse events.8,9 In contrast, the high utilization of filgrastim biosimilars (82.7%) may be attributed to its longevity in the market and familiarity to prescribers, as filgrastim was the first biosimilar to be approved in the United States.10
Promoting reasonable utilization of biosimilars may require prescriber education on their safety and approval processes, which could foster increased utilization and reduce skepticism.4 Under the Biologics Price Competition and Innovation Act, the US Food and Drug Administration approves biosimilars only when they exhibit “high similarity” and show no “clinically meaningful differences” compared to the reference biologic, with no added safety risks or reduced efficacy.11 Moreover, a 2023 systematic review of 17 studies found no major difference in efficacy and safety between biosimilars and originators of etanercept, infliximab, and other biologics.12 Understanding these findings may reassure dermatologists and patients about the reliability and safety of biosimilars.
A limitation of our study is that it solely assesses Medicare data and estimates derived from existing (separate) biologic classes. It also does not account for potential expenditure shifts to newer biologic agents (eg, IL-12/17/23 inhibitors) or changes in manufacturer behavior or promotions. Nevertheless, it indicates notable financial savings from new biosimilar agents in dermatology; along with their compelling efficacy and safety profiles, this could represent a substantial benefit to patients and the health care system.
- Price KN, Atluri S, Hsiao JL, et al. Medicare and medicaid spending trends for immunomodulators prescribed for dermatologic conditions. J Dermatolog Treat. 2020;33:575-579.
- Zhai MZ, Sarpatwari A, Kesselheim AS. Why are biosimilars not living up to their promise in the US? AMA J Ethics. 2019;21:E668-E678. doi:10.1001/amajethics.2019.668
- Cohen H, Beydoun D, Chien D, et al. Awareness, knowledge, and perceptions of biosimilars among specialty physicians. Adv Ther. 2017;33:2160-2172.
- Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services. Medicare Part D prescribers— by provider and drug. Accessed September 11, 2024. https://data.cms.gov/provider-summary-by-type-of-service/medicare-part-d-prescribers/medicare-part-d-prescribers-by-provider-and-drug/data
- US Department of Health and Human Services. Office of Inspector General. Medicare Part D and beneficiaries could realize significant spending reductions with increased biosimilar use. Accessed September 11, 2024. https://oig.hhs.gov/oei/reports/OEI-05-20-00480.pdf
- Yazdany J, Dudley RA, Lin GA, et al. Out-of-pocket costs for infliximab and its biosimilar for rheumatoid arthritis under Medicare Part D. JAMA. 2018;320:931-933. doi:10.1001/jama.2018.7316
- Pourali SP, Nshuti L, Dusetzina SB. Out-of-pocket costs of specialty medications for psoriasis and psoriatic arthritis treatment in the medicare population. JAMA Dermatol. 2021;157:1239-1241. doi:10.1001/ jamadermatol.2021.3616
- Lebwohl M. Biosimilars in dermatology. JAMA Dermatol. 2021; 157:641-642. doi:10.1001/jamadermatol.2021.0219
- Westerkam LL, Tackett KJ, Sayed CJ. Comparing the effectiveness and safety associated with infliximab vs infliximab-abda therapy for patients with hidradenitis suppurativa. JAMA Dermatol. 2021;157:708-711. doi:10.1001/jamadermatol.2021.0220
- Awad M, Singh P, Hilas O. Zarxio (Filgrastim-sndz): the first biosimilar approved by the FDA. P T. 2017;42:19-23.
- Development of therapeutic protein biosimilars: comparative analytical assessment and other quality-related considerations guidance for industry. US Department of Health and Human Services website. Updated June 15, 2022. Accessed October 21, 2024. https://www.fda.gov/regulatory-information/search-fda-guidance-documents/development-therapeutic-protein-biosimilars-comparative-analyticalassessment-and-other-quality
- Phan DB, Elyoussfi S, Stevenson M, et al. Biosimilars for the treatment of psoriasis: a systematic review of clinical trials and observational studies. JAMA Dermatol. 2023;159:763-771. doi:10.1001/jamadermatol.2023.1338
To the Editor:
Although biologics provide major therapeutic benefits for dermatologic conditions, they also come with a substantial cost, making them among the most expensive medications available. Medicare and Medicaid spending on biologics for dermatologic conditions increased by 320% from 2012 to 2018, reaching a staggering $10.6 billion in 2018 alone.1 Biosimilars show promise in reducing health care spending for dermatologic conditions; however, their utilization has been limited due to multiple factors, including delayed market entry from patent thickets, exclusionary formulary contracts, and prescriber skepticism regarding their safety and efficacy.2 For instance, a national survey of 1201 US physicians in specialties that are high prescribers of biologics reported that 55% doubted the safety and appropriateness of biosimilars.3
US Food and Drug Administration approval of biosimilars for adalimumab and etanercept offers the potential to reduce health care spending for dermatologic conditions. However, this cost reduction is dependent on utilization rates among dermatologists. In this national cross-sectional review of Medicare data, we predicted the impact of these biosimilars on dermatologic Medicare costs and demonstrated how differing utilization rates among dermatologists can influence potential savings.
To model 2023 utilization and cost reduction from biosimilars, we analyzed Medicare Part D data from 2020 on existing biosimilars, including granulocyte colony–stimulating factors, erythropoiesis-stimulating agents, and tumor necrosis factor α inhibitors.4 Methods in line with a 2021 report from the US Department of Health and Human Services5 as well as those of Yazdany et al6 were used. For each class, we calculated the 2020 distribution of biosimilar and originator drug claims as well as biosimilar cost reduction per 30-day claim. We utilized 2018-2021 annual growth rates for branded adalimumab and etanercept to estimate 30-day claims for 2023 and the cost of these branded agents in the absence of biosimilars. The hypothetical 2023 cost reduction from adalimumab and etanercept biosimilars was estimated by assuming 2020 biosimilar utilization rates and mean cost reduction per claim. This study utilized publicly available or aggregate summary data (not attributable to specific patients) and did not qualify as human subject research; therefore, institutional review board approval was not required.
In 2020, biosimilar utilization proportions ranged from 6.4% (tumor necrosis factor α inhibitors) to 82.7% (granulocyte colony–stimulating factors), with a mean across all classes of 35.7%. On average, the cost per 30-day claim of biosimilars was 66.8% of originator agents (Table 1). In 2021, we identified 57,868 30-day claims for branded adalimumab and etanercept submitted by dermatologists. From 2018 to 2021, 30-day branded adalimumab claims increased by 1.27% annually (cost + 10.62% annually), while claims for branded etanercept decreased by 13.0% annually (cost + 5.68% annually). Assuming these trends, the cost of branded adalimumab and etanercept was estimated to be $539 million in 2023. Applying the aforementioned 35.7% utilization, the introduction of biosimilars in dermatology would yield a cost reduction of approximately $118 million (21.9%). A high utilization rate (82.7%) of biosimilars among dermatologists would increase cost savings to $199 million (36.9%)(Table 2).


Our study demonstrates that the introduction of 2 biosimilars into dermatology may result in a notable reduction in Medicare expenditures. The savings observed are likely to translate to substantial cost savings for patients. A cross-sectional analysis of 2020 Medicare data indicated that coverage for psoriasis medications was 10.0% to 99.8% across different products and Medicare Part D plans. Consequently, patients faced considerable out-of-pocket expenses, amounting to $5653 and $5714 per year for adalimumab and etanercept, respectively.7
We found that the extent of savings from biosimilars was dependent on the utilization rates among dermatologists, with the highest utilization rate almost doubling the total savings of average utilization rates. Given the impact of high utilization and the wide variation observed, understanding the factors that have influenced uptake of biosimilars is important to increasing utilization as these medications become integrated into dermatology. For instance, limited uptake of infliximab initially may have been influenced by concerns about efficacy and increased adverse events.8,9 In contrast, the high utilization of filgrastim biosimilars (82.7%) may be attributed to its longevity in the market and familiarity to prescribers, as filgrastim was the first biosimilar to be approved in the United States.10
Promoting reasonable utilization of biosimilars may require prescriber education on their safety and approval processes, which could foster increased utilization and reduce skepticism.4 Under the Biologics Price Competition and Innovation Act, the US Food and Drug Administration approves biosimilars only when they exhibit “high similarity” and show no “clinically meaningful differences” compared to the reference biologic, with no added safety risks or reduced efficacy.11 Moreover, a 2023 systematic review of 17 studies found no major difference in efficacy and safety between biosimilars and originators of etanercept, infliximab, and other biologics.12 Understanding these findings may reassure dermatologists and patients about the reliability and safety of biosimilars.
A limitation of our study is that it solely assesses Medicare data and estimates derived from existing (separate) biologic classes. It also does not account for potential expenditure shifts to newer biologic agents (eg, IL-12/17/23 inhibitors) or changes in manufacturer behavior or promotions. Nevertheless, it indicates notable financial savings from new biosimilar agents in dermatology; along with their compelling efficacy and safety profiles, this could represent a substantial benefit to patients and the health care system.
To the Editor:
Although biologics provide major therapeutic benefits for dermatologic conditions, they also come with a substantial cost, making them among the most expensive medications available. Medicare and Medicaid spending on biologics for dermatologic conditions increased by 320% from 2012 to 2018, reaching a staggering $10.6 billion in 2018 alone.1 Biosimilars show promise in reducing health care spending for dermatologic conditions; however, their utilization has been limited due to multiple factors, including delayed market entry from patent thickets, exclusionary formulary contracts, and prescriber skepticism regarding their safety and efficacy.2 For instance, a national survey of 1201 US physicians in specialties that are high prescribers of biologics reported that 55% doubted the safety and appropriateness of biosimilars.3
US Food and Drug Administration approval of biosimilars for adalimumab and etanercept offers the potential to reduce health care spending for dermatologic conditions. However, this cost reduction is dependent on utilization rates among dermatologists. In this national cross-sectional review of Medicare data, we predicted the impact of these biosimilars on dermatologic Medicare costs and demonstrated how differing utilization rates among dermatologists can influence potential savings.
To model 2023 utilization and cost reduction from biosimilars, we analyzed Medicare Part D data from 2020 on existing biosimilars, including granulocyte colony–stimulating factors, erythropoiesis-stimulating agents, and tumor necrosis factor α inhibitors.4 Methods in line with a 2021 report from the US Department of Health and Human Services5 as well as those of Yazdany et al6 were used. For each class, we calculated the 2020 distribution of biosimilar and originator drug claims as well as biosimilar cost reduction per 30-day claim. We utilized 2018-2021 annual growth rates for branded adalimumab and etanercept to estimate 30-day claims for 2023 and the cost of these branded agents in the absence of biosimilars. The hypothetical 2023 cost reduction from adalimumab and etanercept biosimilars was estimated by assuming 2020 biosimilar utilization rates and mean cost reduction per claim. This study utilized publicly available or aggregate summary data (not attributable to specific patients) and did not qualify as human subject research; therefore, institutional review board approval was not required.
In 2020, biosimilar utilization proportions ranged from 6.4% (tumor necrosis factor α inhibitors) to 82.7% (granulocyte colony–stimulating factors), with a mean across all classes of 35.7%. On average, the cost per 30-day claim of biosimilars was 66.8% of originator agents (Table 1). In 2021, we identified 57,868 30-day claims for branded adalimumab and etanercept submitted by dermatologists. From 2018 to 2021, 30-day branded adalimumab claims increased by 1.27% annually (cost + 10.62% annually), while claims for branded etanercept decreased by 13.0% annually (cost + 5.68% annually). Assuming these trends, the cost of branded adalimumab and etanercept was estimated to be $539 million in 2023. Applying the aforementioned 35.7% utilization, the introduction of biosimilars in dermatology would yield a cost reduction of approximately $118 million (21.9%). A high utilization rate (82.7%) of biosimilars among dermatologists would increase cost savings to $199 million (36.9%)(Table 2).


Our study demonstrates that the introduction of 2 biosimilars into dermatology may result in a notable reduction in Medicare expenditures. The savings observed are likely to translate to substantial cost savings for patients. A cross-sectional analysis of 2020 Medicare data indicated that coverage for psoriasis medications was 10.0% to 99.8% across different products and Medicare Part D plans. Consequently, patients faced considerable out-of-pocket expenses, amounting to $5653 and $5714 per year for adalimumab and etanercept, respectively.7
We found that the extent of savings from biosimilars was dependent on the utilization rates among dermatologists, with the highest utilization rate almost doubling the total savings of average utilization rates. Given the impact of high utilization and the wide variation observed, understanding the factors that have influenced uptake of biosimilars is important to increasing utilization as these medications become integrated into dermatology. For instance, limited uptake of infliximab initially may have been influenced by concerns about efficacy and increased adverse events.8,9 In contrast, the high utilization of filgrastim biosimilars (82.7%) may be attributed to its longevity in the market and familiarity to prescribers, as filgrastim was the first biosimilar to be approved in the United States.10
Promoting reasonable utilization of biosimilars may require prescriber education on their safety and approval processes, which could foster increased utilization and reduce skepticism.4 Under the Biologics Price Competition and Innovation Act, the US Food and Drug Administration approves biosimilars only when they exhibit “high similarity” and show no “clinically meaningful differences” compared to the reference biologic, with no added safety risks or reduced efficacy.11 Moreover, a 2023 systematic review of 17 studies found no major difference in efficacy and safety between biosimilars and originators of etanercept, infliximab, and other biologics.12 Understanding these findings may reassure dermatologists and patients about the reliability and safety of biosimilars.
A limitation of our study is that it solely assesses Medicare data and estimates derived from existing (separate) biologic classes. It also does not account for potential expenditure shifts to newer biologic agents (eg, IL-12/17/23 inhibitors) or changes in manufacturer behavior or promotions. Nevertheless, it indicates notable financial savings from new biosimilar agents in dermatology; along with their compelling efficacy and safety profiles, this could represent a substantial benefit to patients and the health care system.
- Price KN, Atluri S, Hsiao JL, et al. Medicare and medicaid spending trends for immunomodulators prescribed for dermatologic conditions. J Dermatolog Treat. 2020;33:575-579.
- Zhai MZ, Sarpatwari A, Kesselheim AS. Why are biosimilars not living up to their promise in the US? AMA J Ethics. 2019;21:E668-E678. doi:10.1001/amajethics.2019.668
- Cohen H, Beydoun D, Chien D, et al. Awareness, knowledge, and perceptions of biosimilars among specialty physicians. Adv Ther. 2017;33:2160-2172.
- Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services. Medicare Part D prescribers— by provider and drug. Accessed September 11, 2024. https://data.cms.gov/provider-summary-by-type-of-service/medicare-part-d-prescribers/medicare-part-d-prescribers-by-provider-and-drug/data
- US Department of Health and Human Services. Office of Inspector General. Medicare Part D and beneficiaries could realize significant spending reductions with increased biosimilar use. Accessed September 11, 2024. https://oig.hhs.gov/oei/reports/OEI-05-20-00480.pdf
- Yazdany J, Dudley RA, Lin GA, et al. Out-of-pocket costs for infliximab and its biosimilar for rheumatoid arthritis under Medicare Part D. JAMA. 2018;320:931-933. doi:10.1001/jama.2018.7316
- Pourali SP, Nshuti L, Dusetzina SB. Out-of-pocket costs of specialty medications for psoriasis and psoriatic arthritis treatment in the medicare population. JAMA Dermatol. 2021;157:1239-1241. doi:10.1001/ jamadermatol.2021.3616
- Lebwohl M. Biosimilars in dermatology. JAMA Dermatol. 2021; 157:641-642. doi:10.1001/jamadermatol.2021.0219
- Westerkam LL, Tackett KJ, Sayed CJ. Comparing the effectiveness and safety associated with infliximab vs infliximab-abda therapy for patients with hidradenitis suppurativa. JAMA Dermatol. 2021;157:708-711. doi:10.1001/jamadermatol.2021.0220
- Awad M, Singh P, Hilas O. Zarxio (Filgrastim-sndz): the first biosimilar approved by the FDA. P T. 2017;42:19-23.
- Development of therapeutic protein biosimilars: comparative analytical assessment and other quality-related considerations guidance for industry. US Department of Health and Human Services website. Updated June 15, 2022. Accessed October 21, 2024. https://www.fda.gov/regulatory-information/search-fda-guidance-documents/development-therapeutic-protein-biosimilars-comparative-analyticalassessment-and-other-quality
- Phan DB, Elyoussfi S, Stevenson M, et al. Biosimilars for the treatment of psoriasis: a systematic review of clinical trials and observational studies. JAMA Dermatol. 2023;159:763-771. doi:10.1001/jamadermatol.2023.1338
- Price KN, Atluri S, Hsiao JL, et al. Medicare and medicaid spending trends for immunomodulators prescribed for dermatologic conditions. J Dermatolog Treat. 2020;33:575-579.
- Zhai MZ, Sarpatwari A, Kesselheim AS. Why are biosimilars not living up to their promise in the US? AMA J Ethics. 2019;21:E668-E678. doi:10.1001/amajethics.2019.668
- Cohen H, Beydoun D, Chien D, et al. Awareness, knowledge, and perceptions of biosimilars among specialty physicians. Adv Ther. 2017;33:2160-2172.
- Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services. Medicare Part D prescribers— by provider and drug. Accessed September 11, 2024. https://data.cms.gov/provider-summary-by-type-of-service/medicare-part-d-prescribers/medicare-part-d-prescribers-by-provider-and-drug/data
- US Department of Health and Human Services. Office of Inspector General. Medicare Part D and beneficiaries could realize significant spending reductions with increased biosimilar use. Accessed September 11, 2024. https://oig.hhs.gov/oei/reports/OEI-05-20-00480.pdf
- Yazdany J, Dudley RA, Lin GA, et al. Out-of-pocket costs for infliximab and its biosimilar for rheumatoid arthritis under Medicare Part D. JAMA. 2018;320:931-933. doi:10.1001/jama.2018.7316
- Pourali SP, Nshuti L, Dusetzina SB. Out-of-pocket costs of specialty medications for psoriasis and psoriatic arthritis treatment in the medicare population. JAMA Dermatol. 2021;157:1239-1241. doi:10.1001/ jamadermatol.2021.3616
- Lebwohl M. Biosimilars in dermatology. JAMA Dermatol. 2021; 157:641-642. doi:10.1001/jamadermatol.2021.0219
- Westerkam LL, Tackett KJ, Sayed CJ. Comparing the effectiveness and safety associated with infliximab vs infliximab-abda therapy for patients with hidradenitis suppurativa. JAMA Dermatol. 2021;157:708-711. doi:10.1001/jamadermatol.2021.0220
- Awad M, Singh P, Hilas O. Zarxio (Filgrastim-sndz): the first biosimilar approved by the FDA. P T. 2017;42:19-23.
- Development of therapeutic protein biosimilars: comparative analytical assessment and other quality-related considerations guidance for industry. US Department of Health and Human Services website. Updated June 15, 2022. Accessed October 21, 2024. https://www.fda.gov/regulatory-information/search-fda-guidance-documents/development-therapeutic-protein-biosimilars-comparative-analyticalassessment-and-other-quality
- Phan DB, Elyoussfi S, Stevenson M, et al. Biosimilars for the treatment of psoriasis: a systematic review of clinical trials and observational studies. JAMA Dermatol. 2023;159:763-771. doi:10.1001/jamadermatol.2023.1338
Practice Points
- Biosimilars for adalimumab and etanercept are safe and effective alternatives with the potential to reduce health care costs in dermatology by approximately $118 million.
- A high utilization rate of biosimilars by dermatologists would increase cost savings even further.
Phenytoin-Induced DRESS Syndrome: Clinical and Laboratory Characteristics
To the Editor:
Drug reaction with eosinophilia and systemic symptoms (DRESS) syndrome—a severe cutaneous adverse drug reaction—is characterized by a cutaneous rash and systemic upset in the form of various internal organ and hematologic disturbances. This delayed and idiosyncratic syndrome went by several names, including anticonvulsant hypersensitivity syndrome, before Bocquet et al1 proposed the term DRESS syndrome.
Phenytoin, a hydantoin derivative used in neurology, was implicated in 41% of cases of DRESS syndrome in a study of 100 patients conducted in southern India.2,3 While DRESS syndrome is a newer name, the clinical picture of DRESS secondary to phenytoin use remains similar in that it manifests with a morbilliform rash and systemic upset. We sought to describe the clinical and laboratory characteristics of phenytoin-induced DRESS syndrome in this case series.
The analysis included 23 patients with DRESS syndrome secondary to phenytoin use who presented to a tertiary care institution in North India between July 2021 and December 2022, satisfied the European Registry of Severe Cutaneous Adverse Reaction (RegiSCAR) criteria,4 and achieved a DRESS diagnostic score of more than 1. The mean age of the patients was 44 years (range, 14–74 years). There was a slight female predominance with a male to female ratio of 0.9:1. More than half of the patients (52.2% [12/23]) presented directly to the dermatology outpatient department; the remaining patients were referred from other departments (47.8% [11/23]). Patients primarily were receiving phenytoin for neurologic indications. Specific reasons included antiseizure prophylaxis following a traffic accident (34.8% [8/23]); epilepsy (26.1% [6/23]); and neoplastic (17.4% [4/23]), vascular (17.4% [4/23]), and infectious (4.3% [1/23]) causes. The mean latency period from drug intake to symptom onset was 29 days (range, 6–62 days), and the mean illness duration was 9 days (range, 1–45 days).
The majority of patients experienced pruritus (91.3% [21/23]) and fever (74.0% [17/23]), and all initially had a rash. Maculopapular morphology was seen in all patients. Erythema multiforme–like (17.4% [4/23]), erythrodermic (17.4% [4/23]), and vesicular (13.0% [3/23]) rashes also were documented (Figure 1). The trunk (100% [23/23]) and extremities (95.7% [22/23]) were involved most often, followed by the palms and soles (56.5% [13/23]). The mean total body surface area affected was 73.65%. Only 7 patients (30.4%) had mucosal involvement; nonhemorrhagic cheilitis was the most common manifestation.
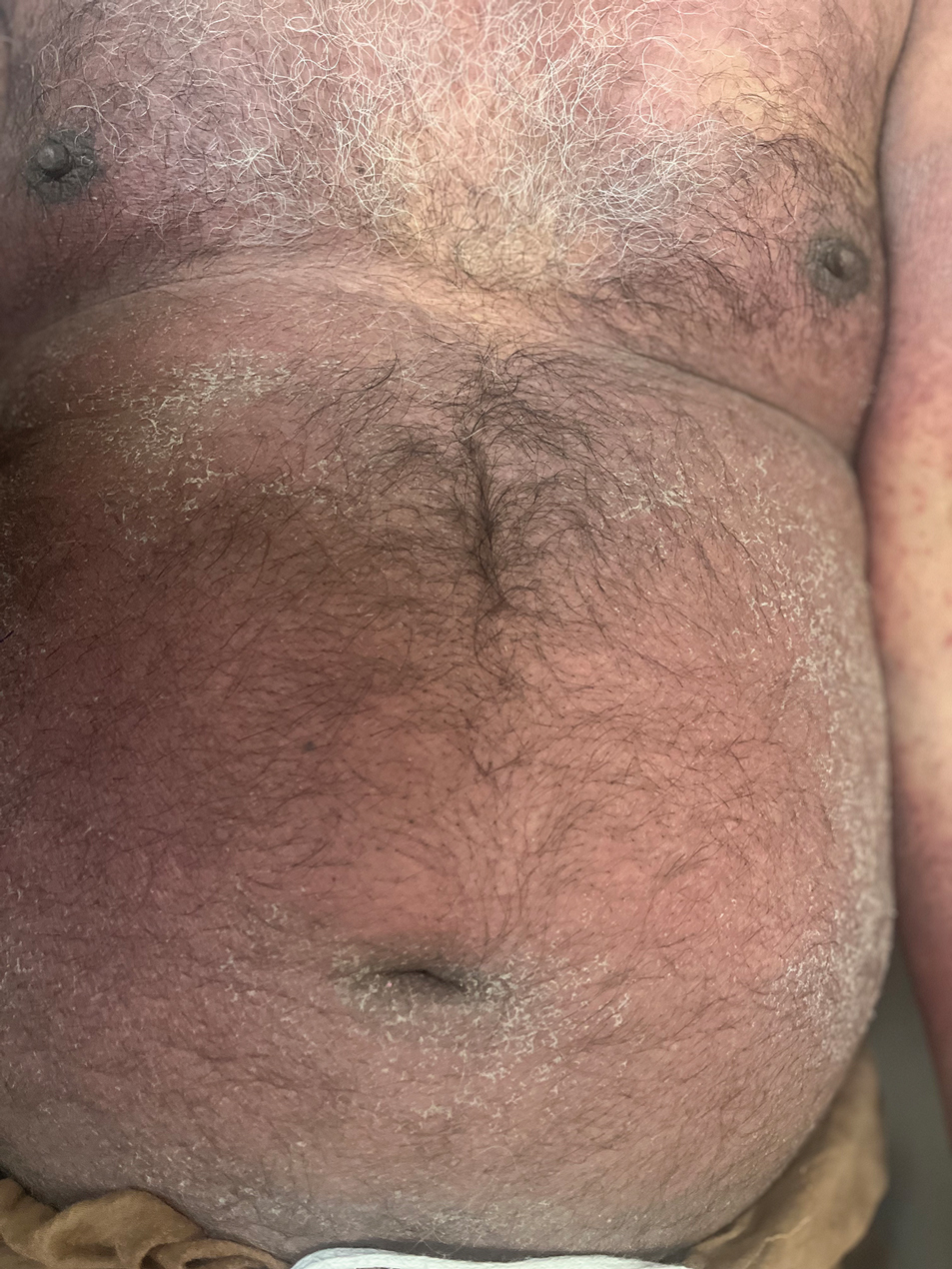
Facial edema, a hallmark feature of DRESS syndrome, was noted in 69.6% (16/23) of patients (Figure 2). Lymphadenopathy was present in 43.5% (10/23) of patients; of those cases, the inguinal (40.0%; n=4) and cervical (30%; n=3) nodes most commonly were involved. Although DRESS syndrome can affect internal organs, this was an issue for only 2 (8.7%) patients who experienced mild hepatomegaly.
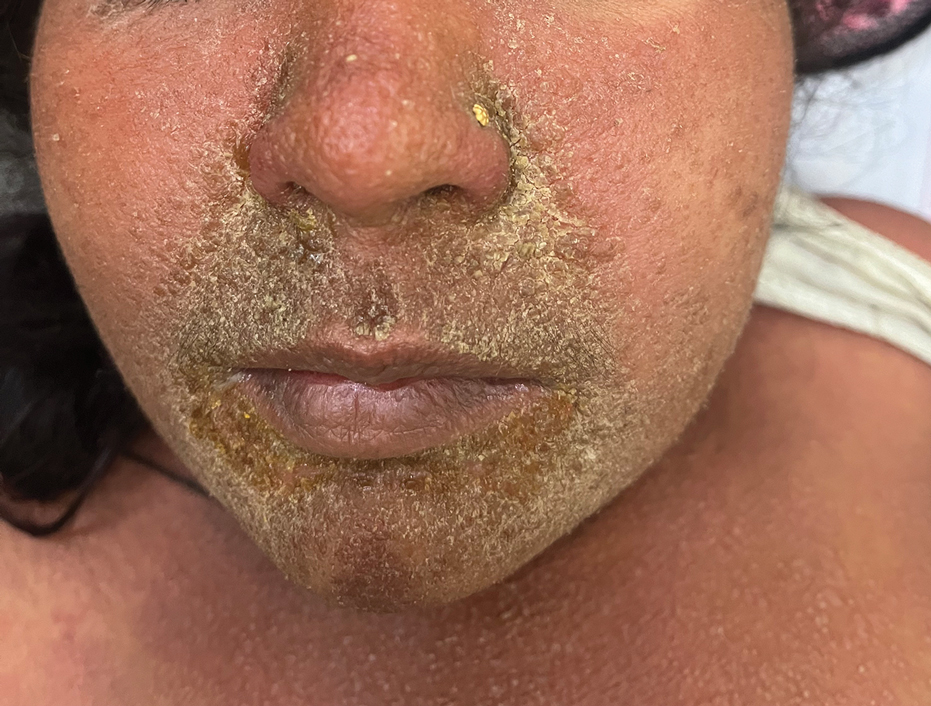
Laboratory investigations revealed a mean differential eosinophil percentage of 10.3% (reference range, 1%–4%), while the mean absolute eosinophil count was 1.0634×109/L (reference range, 0.02–0.5×109/L). Other hematologic findings included the mean percentages of neutrophils (60%; reference range, 50%–60%), lymphocytes (19.95%; reference range, 20%–50%), and monocytes (8.70%; reference range, 2%–8%).
Liver function tests revealed transaminitis5 as the most common finding, with mean aspartate aminotransferase levels of 109 U/L (reference range, 8–33 U/L), mean alanine aminotransferase of 97.9 U/L (reference range, 7–56 U/L), and mean alkaline phosphatase levels of 211.35 U/L (reference range, 44–147 U/L). Half of the patients had notable (>2 times the upper limit of normal) transaminitis.
Renal blood workup revealed slightly elevated blood urea nitrogen levels with a mean value of 28.4 mg/dL (reference range, 6–24 mg/dL), and mean serum creatinine was 0.78 mg/dL (reference range for men, 0.7–1.3 mg/dL; for women, 0.6–1.1 mg/dL).
All patients were treated with oral steroids (prednisolone 1 mg/kg/d) before tapering slowly over the following 6 to 8 weeks. The culprit drug (phenytoin) was stopped on the day of presentation. Resolution of rash and itching was seen in all patients by 3 weeks after presentation without any relapse by follow-up at 6 weeks from presentation to the hospital.
Our case series seeks to discuss the clinical and laboratory features of phenytoin-induced DRESS syndrome. Our patients had more erythrodermic and erythema multiforme–like morphologies, less mucosal involvement, more hepatic involvement, and earlier resolution.
- Bocquet H, Bagot M, Roujeau JC. Drug-induced pseudolymphoma and drug hypersensitivity syndrome (drug rash with eosinophilia and systemic symptoms: DRESS). Semin Cutan Med Surg. 1996;15:250-257. doi:10.1016/s1085-5629(96)80038-1
- Patocka J, Wu Q, Nepovimova E, et al. Phenytoin—an anti-seizure drug: overview of its chemistry, pharmacology and toxicology. Food Chem Toxicol. 2020;142:111393. doi:10.1016/j.fct.2020.111393
- Sasidharanpillai S, Chathoth AT, Khader A, et al. Predictors of disease severity in drug reaction with eosinophilia and systemic symptoms. Indian J Dermatol Venereol Leprol. 2019;85:266-275. doi:10.4103/ijdvl.IJDVL_482_17
- Kardaun SH, Sekula P, Valeyrie-Allanore L, et al. Drug reaction with eosinophilia and systemic symptoms (DRESS): an original multisystem adverse drug reaction. Results from the prospective RegiSCAR study. Brit J Dermatol. 2013;169:1071-1080.
- Morán-Mariños C, Alva-Diaz C, De la Cruz Ramirez W, et al. Drug reaction with eosinophilia and systemic symptoms (DRESS) induced by phenytoin re-exposure: case report and systematic review. Acta Clin Belg. 2022;77:177-185. doi:10.1080/17843286.2020.1767459
To the Editor:
Drug reaction with eosinophilia and systemic symptoms (DRESS) syndrome—a severe cutaneous adverse drug reaction—is characterized by a cutaneous rash and systemic upset in the form of various internal organ and hematologic disturbances. This delayed and idiosyncratic syndrome went by several names, including anticonvulsant hypersensitivity syndrome, before Bocquet et al1 proposed the term DRESS syndrome.
Phenytoin, a hydantoin derivative used in neurology, was implicated in 41% of cases of DRESS syndrome in a study of 100 patients conducted in southern India.2,3 While DRESS syndrome is a newer name, the clinical picture of DRESS secondary to phenytoin use remains similar in that it manifests with a morbilliform rash and systemic upset. We sought to describe the clinical and laboratory characteristics of phenytoin-induced DRESS syndrome in this case series.
The analysis included 23 patients with DRESS syndrome secondary to phenytoin use who presented to a tertiary care institution in North India between July 2021 and December 2022, satisfied the European Registry of Severe Cutaneous Adverse Reaction (RegiSCAR) criteria,4 and achieved a DRESS diagnostic score of more than 1. The mean age of the patients was 44 years (range, 14–74 years). There was a slight female predominance with a male to female ratio of 0.9:1. More than half of the patients (52.2% [12/23]) presented directly to the dermatology outpatient department; the remaining patients were referred from other departments (47.8% [11/23]). Patients primarily were receiving phenytoin for neurologic indications. Specific reasons included antiseizure prophylaxis following a traffic accident (34.8% [8/23]); epilepsy (26.1% [6/23]); and neoplastic (17.4% [4/23]), vascular (17.4% [4/23]), and infectious (4.3% [1/23]) causes. The mean latency period from drug intake to symptom onset was 29 days (range, 6–62 days), and the mean illness duration was 9 days (range, 1–45 days).
The majority of patients experienced pruritus (91.3% [21/23]) and fever (74.0% [17/23]), and all initially had a rash. Maculopapular morphology was seen in all patients. Erythema multiforme–like (17.4% [4/23]), erythrodermic (17.4% [4/23]), and vesicular (13.0% [3/23]) rashes also were documented (Figure 1). The trunk (100% [23/23]) and extremities (95.7% [22/23]) were involved most often, followed by the palms and soles (56.5% [13/23]). The mean total body surface area affected was 73.65%. Only 7 patients (30.4%) had mucosal involvement; nonhemorrhagic cheilitis was the most common manifestation.

Facial edema, a hallmark feature of DRESS syndrome, was noted in 69.6% (16/23) of patients (Figure 2). Lymphadenopathy was present in 43.5% (10/23) of patients; of those cases, the inguinal (40.0%; n=4) and cervical (30%; n=3) nodes most commonly were involved. Although DRESS syndrome can affect internal organs, this was an issue for only 2 (8.7%) patients who experienced mild hepatomegaly.

Laboratory investigations revealed a mean differential eosinophil percentage of 10.3% (reference range, 1%–4%), while the mean absolute eosinophil count was 1.0634×109/L (reference range, 0.02–0.5×109/L). Other hematologic findings included the mean percentages of neutrophils (60%; reference range, 50%–60%), lymphocytes (19.95%; reference range, 20%–50%), and monocytes (8.70%; reference range, 2%–8%).
Liver function tests revealed transaminitis5 as the most common finding, with mean aspartate aminotransferase levels of 109 U/L (reference range, 8–33 U/L), mean alanine aminotransferase of 97.9 U/L (reference range, 7–56 U/L), and mean alkaline phosphatase levels of 211.35 U/L (reference range, 44–147 U/L). Half of the patients had notable (>2 times the upper limit of normal) transaminitis.
Renal blood workup revealed slightly elevated blood urea nitrogen levels with a mean value of 28.4 mg/dL (reference range, 6–24 mg/dL), and mean serum creatinine was 0.78 mg/dL (reference range for men, 0.7–1.3 mg/dL; for women, 0.6–1.1 mg/dL).
All patients were treated with oral steroids (prednisolone 1 mg/kg/d) before tapering slowly over the following 6 to 8 weeks. The culprit drug (phenytoin) was stopped on the day of presentation. Resolution of rash and itching was seen in all patients by 3 weeks after presentation without any relapse by follow-up at 6 weeks from presentation to the hospital.
Our case series seeks to discuss the clinical and laboratory features of phenytoin-induced DRESS syndrome. Our patients had more erythrodermic and erythema multiforme–like morphologies, less mucosal involvement, more hepatic involvement, and earlier resolution.
To the Editor:
Drug reaction with eosinophilia and systemic symptoms (DRESS) syndrome—a severe cutaneous adverse drug reaction—is characterized by a cutaneous rash and systemic upset in the form of various internal organ and hematologic disturbances. This delayed and idiosyncratic syndrome went by several names, including anticonvulsant hypersensitivity syndrome, before Bocquet et al1 proposed the term DRESS syndrome.
Phenytoin, a hydantoin derivative used in neurology, was implicated in 41% of cases of DRESS syndrome in a study of 100 patients conducted in southern India.2,3 While DRESS syndrome is a newer name, the clinical picture of DRESS secondary to phenytoin use remains similar in that it manifests with a morbilliform rash and systemic upset. We sought to describe the clinical and laboratory characteristics of phenytoin-induced DRESS syndrome in this case series.
The analysis included 23 patients with DRESS syndrome secondary to phenytoin use who presented to a tertiary care institution in North India between July 2021 and December 2022, satisfied the European Registry of Severe Cutaneous Adverse Reaction (RegiSCAR) criteria,4 and achieved a DRESS diagnostic score of more than 1. The mean age of the patients was 44 years (range, 14–74 years). There was a slight female predominance with a male to female ratio of 0.9:1. More than half of the patients (52.2% [12/23]) presented directly to the dermatology outpatient department; the remaining patients were referred from other departments (47.8% [11/23]). Patients primarily were receiving phenytoin for neurologic indications. Specific reasons included antiseizure prophylaxis following a traffic accident (34.8% [8/23]); epilepsy (26.1% [6/23]); and neoplastic (17.4% [4/23]), vascular (17.4% [4/23]), and infectious (4.3% [1/23]) causes. The mean latency period from drug intake to symptom onset was 29 days (range, 6–62 days), and the mean illness duration was 9 days (range, 1–45 days).
The majority of patients experienced pruritus (91.3% [21/23]) and fever (74.0% [17/23]), and all initially had a rash. Maculopapular morphology was seen in all patients. Erythema multiforme–like (17.4% [4/23]), erythrodermic (17.4% [4/23]), and vesicular (13.0% [3/23]) rashes also were documented (Figure 1). The trunk (100% [23/23]) and extremities (95.7% [22/23]) were involved most often, followed by the palms and soles (56.5% [13/23]). The mean total body surface area affected was 73.65%. Only 7 patients (30.4%) had mucosal involvement; nonhemorrhagic cheilitis was the most common manifestation.

Facial edema, a hallmark feature of DRESS syndrome, was noted in 69.6% (16/23) of patients (Figure 2). Lymphadenopathy was present in 43.5% (10/23) of patients; of those cases, the inguinal (40.0%; n=4) and cervical (30%; n=3) nodes most commonly were involved. Although DRESS syndrome can affect internal organs, this was an issue for only 2 (8.7%) patients who experienced mild hepatomegaly.

Laboratory investigations revealed a mean differential eosinophil percentage of 10.3% (reference range, 1%–4%), while the mean absolute eosinophil count was 1.0634×109/L (reference range, 0.02–0.5×109/L). Other hematologic findings included the mean percentages of neutrophils (60%; reference range, 50%–60%), lymphocytes (19.95%; reference range, 20%–50%), and monocytes (8.70%; reference range, 2%–8%).
Liver function tests revealed transaminitis5 as the most common finding, with mean aspartate aminotransferase levels of 109 U/L (reference range, 8–33 U/L), mean alanine aminotransferase of 97.9 U/L (reference range, 7–56 U/L), and mean alkaline phosphatase levels of 211.35 U/L (reference range, 44–147 U/L). Half of the patients had notable (>2 times the upper limit of normal) transaminitis.
Renal blood workup revealed slightly elevated blood urea nitrogen levels with a mean value of 28.4 mg/dL (reference range, 6–24 mg/dL), and mean serum creatinine was 0.78 mg/dL (reference range for men, 0.7–1.3 mg/dL; for women, 0.6–1.1 mg/dL).
All patients were treated with oral steroids (prednisolone 1 mg/kg/d) before tapering slowly over the following 6 to 8 weeks. The culprit drug (phenytoin) was stopped on the day of presentation. Resolution of rash and itching was seen in all patients by 3 weeks after presentation without any relapse by follow-up at 6 weeks from presentation to the hospital.
Our case series seeks to discuss the clinical and laboratory features of phenytoin-induced DRESS syndrome. Our patients had more erythrodermic and erythema multiforme–like morphologies, less mucosal involvement, more hepatic involvement, and earlier resolution.
- Bocquet H, Bagot M, Roujeau JC. Drug-induced pseudolymphoma and drug hypersensitivity syndrome (drug rash with eosinophilia and systemic symptoms: DRESS). Semin Cutan Med Surg. 1996;15:250-257. doi:10.1016/s1085-5629(96)80038-1
- Patocka J, Wu Q, Nepovimova E, et al. Phenytoin—an anti-seizure drug: overview of its chemistry, pharmacology and toxicology. Food Chem Toxicol. 2020;142:111393. doi:10.1016/j.fct.2020.111393
- Sasidharanpillai S, Chathoth AT, Khader A, et al. Predictors of disease severity in drug reaction with eosinophilia and systemic symptoms. Indian J Dermatol Venereol Leprol. 2019;85:266-275. doi:10.4103/ijdvl.IJDVL_482_17
- Kardaun SH, Sekula P, Valeyrie-Allanore L, et al. Drug reaction with eosinophilia and systemic symptoms (DRESS): an original multisystem adverse drug reaction. Results from the prospective RegiSCAR study. Brit J Dermatol. 2013;169:1071-1080.
- Morán-Mariños C, Alva-Diaz C, De la Cruz Ramirez W, et al. Drug reaction with eosinophilia and systemic symptoms (DRESS) induced by phenytoin re-exposure: case report and systematic review. Acta Clin Belg. 2022;77:177-185. doi:10.1080/17843286.2020.1767459
- Bocquet H, Bagot M, Roujeau JC. Drug-induced pseudolymphoma and drug hypersensitivity syndrome (drug rash with eosinophilia and systemic symptoms: DRESS). Semin Cutan Med Surg. 1996;15:250-257. doi:10.1016/s1085-5629(96)80038-1
- Patocka J, Wu Q, Nepovimova E, et al. Phenytoin—an anti-seizure drug: overview of its chemistry, pharmacology and toxicology. Food Chem Toxicol. 2020;142:111393. doi:10.1016/j.fct.2020.111393
- Sasidharanpillai S, Chathoth AT, Khader A, et al. Predictors of disease severity in drug reaction with eosinophilia and systemic symptoms. Indian J Dermatol Venereol Leprol. 2019;85:266-275. doi:10.4103/ijdvl.IJDVL_482_17
- Kardaun SH, Sekula P, Valeyrie-Allanore L, et al. Drug reaction with eosinophilia and systemic symptoms (DRESS): an original multisystem adverse drug reaction. Results from the prospective RegiSCAR study. Brit J Dermatol. 2013;169:1071-1080.
- Morán-Mariños C, Alva-Diaz C, De la Cruz Ramirez W, et al. Drug reaction with eosinophilia and systemic symptoms (DRESS) induced by phenytoin re-exposure: case report and systematic review. Acta Clin Belg. 2022;77:177-185. doi:10.1080/17843286.2020.1767459
Practice Points
- Phenytoin has been implicated in drug reaction with eosinophilia and systemic symptoms (DRESS) syndrome, and common symptoms include rash, pruritus, and fever.
- Transaminitis may occur in patients with DRESS syndrome secondary to phenytoin use.
Cardiac Monitoring Is Crucial in Neuromuscular Disorder Care
SAVANNAH, GEORGIA — , a neurologist told an audience of nerve/muscle specialists.
The cardiac conditions can range from asymptomatic to potentially lethal, Nicholas J. Silvestri, MD, professor of neurology at the Jacobs School of Medicine and Biomedical Sciences, University at Buffalo, in New York, said in a presentation at the American Association of Neuromuscular & Electrodiagnostic Medicine (AANEM) 2024. “It’s really important to know when to do tests and refer to cardiology, and it’s really important to find a cardiologist who can work in concert in taking care of these patients.”
Protein Alterations May Disrupt Heart Muscles
In muscular dystrophies, a prevailing theory suggests that alterations to proteins such as dystrophin disrupt structural integrity in both muscle and cardiac cells, he said.
In Duchenne muscular dystrophy (DMD), cardiomyopathy, cardiac conduction abnormalities, or both usually appear in patients by age 10. “It’s important to know that it’s probably present to some degree before that, and it’s not going to get better over time,” he said.
Cardiac problems are universal in DMD by age 18, he said. “Men and boys are living longer, so they have the opportunity to develop the cardiac abnormalities that accrue with time.” Conduction abnormalities typically appear first. “In a lot of these boys, you’ll typically see persistent sinus tachycardia. But they can also develop atrial arrhythmias and bundle branch blocks.”
Sudden cardiac death is responsible for mortality in an estimated 15% patients with DMD. “Very sadly, I lost a patient this way just a few months ago,” Silvestri said.
ECGs and Echos Are Recommended
Screening is crucial. “Make sure that patients get that referral and get these tests done,” he said. “You need an ECG and echo by diagnosis or age 6. This is usually repeated annually or biannually, typically by the cardiologist you’re working with.”
The good news is that there’s evidence of survival benefits from treatment with angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors for dilated cardiomyopathy. “Some cardiac experts feel treatment with angiotensin receptor blockers (ARBs) is equivalent.”
Most boys will get echocardiograms, he said, “but there’s a lot of evidence showing that cardiac MRI is probably preferable for a number of reasons,” including better visualization. But the need for sedation limits access, he said, and cardiac MRI may not be available at some facilities.
Worse Outcomes in Becker Muscular Dystrophy (BMD)
Cardiac involvement is more common and more severe in BMD than in DMD. About 50% of deaths in BMD are attributed to malignant arrhythmias or congestive heart failure, he said.
Screening requirements and treatment options in BMD are similar to those in DMD, with the added option of heart transplantation.
Silvestri cautioned that up to 40% of female carriers of dystrophin mutations can develop cardiac dysfunction similar to that seen in DMD and BMD. Cardiac assessments are recommended every 5 years. “It’s important to genotype Mom,” he said, especially in light of the fact that two thirds of DMD cases may be inherited.
“When I send genetic testing on the mother and find her to be a carrier, I send her to a cardiologist so she has the appropriate screening done,” he said.
Pacemakers May Be Considered in Type 1 Myotonic Dystrophy
In type 1 myotonic dystrophy, cardiac conduction abnormalities are seen in two thirds of patients, and sudden cardiac death in up to 30% of patients. “When it is diagnosed, patients do need an ECG at that time, as well as annually,” he said.
Holter monitoring or implantable loop recorders may be recommended, and permanent pacing via an implantable cardioverter-defibrillator might be appropriate.
“Based on the literature to date, the exact timing is not is not clear,” Silvestri said. “The electrophysiologists in my area tend to be very aggressive, thankfully, and treat them fairly soon with pacemakers when we see the first sign of trouble.”
Silvestri disclosed consultant/advisory relationships with argenx, Alexion, Amgen, UCB, Immunovant, and Janssen.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
SAVANNAH, GEORGIA — , a neurologist told an audience of nerve/muscle specialists.
The cardiac conditions can range from asymptomatic to potentially lethal, Nicholas J. Silvestri, MD, professor of neurology at the Jacobs School of Medicine and Biomedical Sciences, University at Buffalo, in New York, said in a presentation at the American Association of Neuromuscular & Electrodiagnostic Medicine (AANEM) 2024. “It’s really important to know when to do tests and refer to cardiology, and it’s really important to find a cardiologist who can work in concert in taking care of these patients.”
Protein Alterations May Disrupt Heart Muscles
In muscular dystrophies, a prevailing theory suggests that alterations to proteins such as dystrophin disrupt structural integrity in both muscle and cardiac cells, he said.
In Duchenne muscular dystrophy (DMD), cardiomyopathy, cardiac conduction abnormalities, or both usually appear in patients by age 10. “It’s important to know that it’s probably present to some degree before that, and it’s not going to get better over time,” he said.
Cardiac problems are universal in DMD by age 18, he said. “Men and boys are living longer, so they have the opportunity to develop the cardiac abnormalities that accrue with time.” Conduction abnormalities typically appear first. “In a lot of these boys, you’ll typically see persistent sinus tachycardia. But they can also develop atrial arrhythmias and bundle branch blocks.”
Sudden cardiac death is responsible for mortality in an estimated 15% patients with DMD. “Very sadly, I lost a patient this way just a few months ago,” Silvestri said.
ECGs and Echos Are Recommended
Screening is crucial. “Make sure that patients get that referral and get these tests done,” he said. “You need an ECG and echo by diagnosis or age 6. This is usually repeated annually or biannually, typically by the cardiologist you’re working with.”
The good news is that there’s evidence of survival benefits from treatment with angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors for dilated cardiomyopathy. “Some cardiac experts feel treatment with angiotensin receptor blockers (ARBs) is equivalent.”
Most boys will get echocardiograms, he said, “but there’s a lot of evidence showing that cardiac MRI is probably preferable for a number of reasons,” including better visualization. But the need for sedation limits access, he said, and cardiac MRI may not be available at some facilities.
Worse Outcomes in Becker Muscular Dystrophy (BMD)
Cardiac involvement is more common and more severe in BMD than in DMD. About 50% of deaths in BMD are attributed to malignant arrhythmias or congestive heart failure, he said.
Screening requirements and treatment options in BMD are similar to those in DMD, with the added option of heart transplantation.
Silvestri cautioned that up to 40% of female carriers of dystrophin mutations can develop cardiac dysfunction similar to that seen in DMD and BMD. Cardiac assessments are recommended every 5 years. “It’s important to genotype Mom,” he said, especially in light of the fact that two thirds of DMD cases may be inherited.
“When I send genetic testing on the mother and find her to be a carrier, I send her to a cardiologist so she has the appropriate screening done,” he said.
Pacemakers May Be Considered in Type 1 Myotonic Dystrophy
In type 1 myotonic dystrophy, cardiac conduction abnormalities are seen in two thirds of patients, and sudden cardiac death in up to 30% of patients. “When it is diagnosed, patients do need an ECG at that time, as well as annually,” he said.
Holter monitoring or implantable loop recorders may be recommended, and permanent pacing via an implantable cardioverter-defibrillator might be appropriate.
“Based on the literature to date, the exact timing is not is not clear,” Silvestri said. “The electrophysiologists in my area tend to be very aggressive, thankfully, and treat them fairly soon with pacemakers when we see the first sign of trouble.”
Silvestri disclosed consultant/advisory relationships with argenx, Alexion, Amgen, UCB, Immunovant, and Janssen.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
SAVANNAH, GEORGIA — , a neurologist told an audience of nerve/muscle specialists.
The cardiac conditions can range from asymptomatic to potentially lethal, Nicholas J. Silvestri, MD, professor of neurology at the Jacobs School of Medicine and Biomedical Sciences, University at Buffalo, in New York, said in a presentation at the American Association of Neuromuscular & Electrodiagnostic Medicine (AANEM) 2024. “It’s really important to know when to do tests and refer to cardiology, and it’s really important to find a cardiologist who can work in concert in taking care of these patients.”
Protein Alterations May Disrupt Heart Muscles
In muscular dystrophies, a prevailing theory suggests that alterations to proteins such as dystrophin disrupt structural integrity in both muscle and cardiac cells, he said.
In Duchenne muscular dystrophy (DMD), cardiomyopathy, cardiac conduction abnormalities, or both usually appear in patients by age 10. “It’s important to know that it’s probably present to some degree before that, and it’s not going to get better over time,” he said.
Cardiac problems are universal in DMD by age 18, he said. “Men and boys are living longer, so they have the opportunity to develop the cardiac abnormalities that accrue with time.” Conduction abnormalities typically appear first. “In a lot of these boys, you’ll typically see persistent sinus tachycardia. But they can also develop atrial arrhythmias and bundle branch blocks.”
Sudden cardiac death is responsible for mortality in an estimated 15% patients with DMD. “Very sadly, I lost a patient this way just a few months ago,” Silvestri said.
ECGs and Echos Are Recommended
Screening is crucial. “Make sure that patients get that referral and get these tests done,” he said. “You need an ECG and echo by diagnosis or age 6. This is usually repeated annually or biannually, typically by the cardiologist you’re working with.”
The good news is that there’s evidence of survival benefits from treatment with angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors for dilated cardiomyopathy. “Some cardiac experts feel treatment with angiotensin receptor blockers (ARBs) is equivalent.”
Most boys will get echocardiograms, he said, “but there’s a lot of evidence showing that cardiac MRI is probably preferable for a number of reasons,” including better visualization. But the need for sedation limits access, he said, and cardiac MRI may not be available at some facilities.
Worse Outcomes in Becker Muscular Dystrophy (BMD)
Cardiac involvement is more common and more severe in BMD than in DMD. About 50% of deaths in BMD are attributed to malignant arrhythmias or congestive heart failure, he said.
Screening requirements and treatment options in BMD are similar to those in DMD, with the added option of heart transplantation.
Silvestri cautioned that up to 40% of female carriers of dystrophin mutations can develop cardiac dysfunction similar to that seen in DMD and BMD. Cardiac assessments are recommended every 5 years. “It’s important to genotype Mom,” he said, especially in light of the fact that two thirds of DMD cases may be inherited.
“When I send genetic testing on the mother and find her to be a carrier, I send her to a cardiologist so she has the appropriate screening done,” he said.
Pacemakers May Be Considered in Type 1 Myotonic Dystrophy
In type 1 myotonic dystrophy, cardiac conduction abnormalities are seen in two thirds of patients, and sudden cardiac death in up to 30% of patients. “When it is diagnosed, patients do need an ECG at that time, as well as annually,” he said.
Holter monitoring or implantable loop recorders may be recommended, and permanent pacing via an implantable cardioverter-defibrillator might be appropriate.
“Based on the literature to date, the exact timing is not is not clear,” Silvestri said. “The electrophysiologists in my area tend to be very aggressive, thankfully, and treat them fairly soon with pacemakers when we see the first sign of trouble.”
Silvestri disclosed consultant/advisory relationships with argenx, Alexion, Amgen, UCB, Immunovant, and Janssen.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM AANEM 2024