User login
Positive topline results for antihypertensive zilebesiran
Zilebesiran (Alnylam Pharmaceuticals), an investigational, subcutaneously administered small-interfering RNA (siRNA) therapeutic in development for the treatment of hypertension, met the primary and secondary endpoints, with an “encouraging” safety profile in the phase 2 KARDIA-1 study, the company announced.
KARDIA-1 is a phase 2 randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, dose-ranging study evaluating the efficacy and safety of zilebesiran as monotherapy in 394 adults with mild to moderate untreated hypertension or on stable therapy with one or more antihypertensive drugs.
Patients were randomly assigned to one of five treatment arms during a 12-month double-blind period and double-blind extension period: 150 mg or 300 mg zilebesiran subcutaneously once every 6 months, 300 mg or 600 mg zilebesiran subcutaneously once every 3 months, or placebo. Patients taking placebo were randomly assigned to one of the four initial zilebesiran dose regimens beginning at month 6.
The primary endpoint was change from baseline in systolic blood pressure (SBP) at 3 months assessed by 24-hour ambulatory blood pressure monitoring.
Topline data show a dose-dependent, clinically significant reduction in 24-hour mean SBP, with a placebo-subtracted reduction greater than 15 mm Hg (P < .0001) with both the 300 mg and 600 mg doses.
The study also met key secondary endpoints, showing “consistent and sustained reductions” in SBP at 6 months, which supports quarterly or biannual dosing, the company said.
There was one death due to cardiopulmonary arrest in a zilebesiran-treated patient that was considered unrelated to the drug. Serious adverse events were reported in 3.6% of zilebesiran-treated patients and 6.7% of placebo-treated patients. None was considered related to the study drug.
Adverse events occurring in 5% or more of zilebesiran-treated patients in any dose arm included COVID-19, injection-site reaction, hyperkalemia, hypertension, upper respiratory tract infection, arthralgia, and headache.
“As a physician, I believe these KARDIA-1 results, which demonstrate clinically significant reductions in systolic blood pressure of greater than 15 mm Hg, along with the ability to achieve durable tonic blood pressure control, provide hope that we may one day have access to a novel therapy with the potential to address the significant unmet needs of patients with uncontrolled hypertension who are at high risk of future cardiovascular events,” study investigator George L. Bakris, MD, director, American Heart Association Comprehensive Hypertension Center, University of Chicago Medicine, said in a statement.
The phase 2 results “further validate” the phase 1 results, published in the New England Journal of Medicine, Simon Fox, PhD, vice president, zilebesiran program lead at Alnylam, said in the statement.
The full KARDIA-1 results will be reported at an upcoming scientific conference, the statement notes. Topline results from the KARDIA-2 phase 2 study of zilebesiran in combination with one of three standard classes of antihypertensive medications in patients with mild to moderate hypertension are expected in early 2024.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Zilebesiran (Alnylam Pharmaceuticals), an investigational, subcutaneously administered small-interfering RNA (siRNA) therapeutic in development for the treatment of hypertension, met the primary and secondary endpoints, with an “encouraging” safety profile in the phase 2 KARDIA-1 study, the company announced.
KARDIA-1 is a phase 2 randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, dose-ranging study evaluating the efficacy and safety of zilebesiran as monotherapy in 394 adults with mild to moderate untreated hypertension or on stable therapy with one or more antihypertensive drugs.
Patients were randomly assigned to one of five treatment arms during a 12-month double-blind period and double-blind extension period: 150 mg or 300 mg zilebesiran subcutaneously once every 6 months, 300 mg or 600 mg zilebesiran subcutaneously once every 3 months, or placebo. Patients taking placebo were randomly assigned to one of the four initial zilebesiran dose regimens beginning at month 6.
The primary endpoint was change from baseline in systolic blood pressure (SBP) at 3 months assessed by 24-hour ambulatory blood pressure monitoring.
Topline data show a dose-dependent, clinically significant reduction in 24-hour mean SBP, with a placebo-subtracted reduction greater than 15 mm Hg (P < .0001) with both the 300 mg and 600 mg doses.
The study also met key secondary endpoints, showing “consistent and sustained reductions” in SBP at 6 months, which supports quarterly or biannual dosing, the company said.
There was one death due to cardiopulmonary arrest in a zilebesiran-treated patient that was considered unrelated to the drug. Serious adverse events were reported in 3.6% of zilebesiran-treated patients and 6.7% of placebo-treated patients. None was considered related to the study drug.
Adverse events occurring in 5% or more of zilebesiran-treated patients in any dose arm included COVID-19, injection-site reaction, hyperkalemia, hypertension, upper respiratory tract infection, arthralgia, and headache.
“As a physician, I believe these KARDIA-1 results, which demonstrate clinically significant reductions in systolic blood pressure of greater than 15 mm Hg, along with the ability to achieve durable tonic blood pressure control, provide hope that we may one day have access to a novel therapy with the potential to address the significant unmet needs of patients with uncontrolled hypertension who are at high risk of future cardiovascular events,” study investigator George L. Bakris, MD, director, American Heart Association Comprehensive Hypertension Center, University of Chicago Medicine, said in a statement.
The phase 2 results “further validate” the phase 1 results, published in the New England Journal of Medicine, Simon Fox, PhD, vice president, zilebesiran program lead at Alnylam, said in the statement.
The full KARDIA-1 results will be reported at an upcoming scientific conference, the statement notes. Topline results from the KARDIA-2 phase 2 study of zilebesiran in combination with one of three standard classes of antihypertensive medications in patients with mild to moderate hypertension are expected in early 2024.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Zilebesiran (Alnylam Pharmaceuticals), an investigational, subcutaneously administered small-interfering RNA (siRNA) therapeutic in development for the treatment of hypertension, met the primary and secondary endpoints, with an “encouraging” safety profile in the phase 2 KARDIA-1 study, the company announced.
KARDIA-1 is a phase 2 randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, dose-ranging study evaluating the efficacy and safety of zilebesiran as monotherapy in 394 adults with mild to moderate untreated hypertension or on stable therapy with one or more antihypertensive drugs.
Patients were randomly assigned to one of five treatment arms during a 12-month double-blind period and double-blind extension period: 150 mg or 300 mg zilebesiran subcutaneously once every 6 months, 300 mg or 600 mg zilebesiran subcutaneously once every 3 months, or placebo. Patients taking placebo were randomly assigned to one of the four initial zilebesiran dose regimens beginning at month 6.
The primary endpoint was change from baseline in systolic blood pressure (SBP) at 3 months assessed by 24-hour ambulatory blood pressure monitoring.
Topline data show a dose-dependent, clinically significant reduction in 24-hour mean SBP, with a placebo-subtracted reduction greater than 15 mm Hg (P < .0001) with both the 300 mg and 600 mg doses.
The study also met key secondary endpoints, showing “consistent and sustained reductions” in SBP at 6 months, which supports quarterly or biannual dosing, the company said.
There was one death due to cardiopulmonary arrest in a zilebesiran-treated patient that was considered unrelated to the drug. Serious adverse events were reported in 3.6% of zilebesiran-treated patients and 6.7% of placebo-treated patients. None was considered related to the study drug.
Adverse events occurring in 5% or more of zilebesiran-treated patients in any dose arm included COVID-19, injection-site reaction, hyperkalemia, hypertension, upper respiratory tract infection, arthralgia, and headache.
“As a physician, I believe these KARDIA-1 results, which demonstrate clinically significant reductions in systolic blood pressure of greater than 15 mm Hg, along with the ability to achieve durable tonic blood pressure control, provide hope that we may one day have access to a novel therapy with the potential to address the significant unmet needs of patients with uncontrolled hypertension who are at high risk of future cardiovascular events,” study investigator George L. Bakris, MD, director, American Heart Association Comprehensive Hypertension Center, University of Chicago Medicine, said in a statement.
The phase 2 results “further validate” the phase 1 results, published in the New England Journal of Medicine, Simon Fox, PhD, vice president, zilebesiran program lead at Alnylam, said in the statement.
The full KARDIA-1 results will be reported at an upcoming scientific conference, the statement notes. Topline results from the KARDIA-2 phase 2 study of zilebesiran in combination with one of three standard classes of antihypertensive medications in patients with mild to moderate hypertension are expected in early 2024.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Pandemic tied to significant drop in residents’ PTSD rates
TOPLINE
First-year medical residents training during COVID-19 were significantly less likely to have posttraumatic stress disorder and workplace trauma, compared with their counterparts who trained before the pandemic, and reported fewer work hours, higher workload satisfaction, and fewer medical errors, new research shows.
METHODOLOGY
- Studies have reported a high prevalence of PTSD symptoms among residents during the pandemic, but it’s unclear if this prevalence differs from prepandemic levels.
- Using the Intern Health Study, a longitudinal cohort study of 1st-year residents, researchers investigated differences in PTSD symptoms among those training before the pandemic (2018-2019) and during its first wave (March to June, 2020).
- The study included 1,957 first-year residents (48.2% female; mean age, 27.6 years) who completed a baseline survey 2 months before their residency start, and then quarterly surveys during their intern year, with the fourth quarterly survey including a screen for PTSD.
- Researchers assessed differences in nonresidency factors and residency-related factors before and during the pandemic and examined exposure to workplace trauma.
TAKEAWAY
- (7.1% vs. 10.7%; odds ratio, 0.64; 95% confidence interval, 0.46-0.88; P = .01).
- They were also less likely to have workplace trauma exposure (50.9% vs. 56.6%; OR, 0.80; 95% CI, 0.66-0.95; P = .01).
- Residents training during the pandemic compared to prepandemic reported significantly lower weekly duty hours (score mean difference –3.1 hours; 95% CI, –4.1 to −2.0 hours), lower mean reports of medical errors (MD, −0.04; 95% CI, –0.06 to –0.01), and higher workload satisfaction (MD, 0.2; 95% CI, 0.2-0.3).
- However, after accounting for these residency-related factors, training during the pandemic was no longer associated with lower odds of presenting PTSD symptoms.
IN PRACTICE
While the findings show residents training during the first pandemic wave were less likely to have PTSD, future studies should further follow these residents’ PTSD symptoms and investigate whether interventions targeting residency-related factors could reduce their PTSD risk moving forward, the investigators note.
SOURCE
The study was carried out by Michelle K. Ptak, BA, department of psychology, University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, and colleagues. It was published online Aug. 22 in JAMA Network Open.
LIMITATIONS
The study used self-reports and included only the first pandemic wave, 1st-year residents, and prepandemic data for a single academic year. Survey participation decreased during the pandemic, and it’s possible there were unmeasured factors associated with PTSD risk.
DISCLOSURES
The study was supported by the National Institute of Mental Health and the National Institutes of Health. The authors report no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE
First-year medical residents training during COVID-19 were significantly less likely to have posttraumatic stress disorder and workplace trauma, compared with their counterparts who trained before the pandemic, and reported fewer work hours, higher workload satisfaction, and fewer medical errors, new research shows.
METHODOLOGY
- Studies have reported a high prevalence of PTSD symptoms among residents during the pandemic, but it’s unclear if this prevalence differs from prepandemic levels.
- Using the Intern Health Study, a longitudinal cohort study of 1st-year residents, researchers investigated differences in PTSD symptoms among those training before the pandemic (2018-2019) and during its first wave (March to June, 2020).
- The study included 1,957 first-year residents (48.2% female; mean age, 27.6 years) who completed a baseline survey 2 months before their residency start, and then quarterly surveys during their intern year, with the fourth quarterly survey including a screen for PTSD.
- Researchers assessed differences in nonresidency factors and residency-related factors before and during the pandemic and examined exposure to workplace trauma.
TAKEAWAY
- (7.1% vs. 10.7%; odds ratio, 0.64; 95% confidence interval, 0.46-0.88; P = .01).
- They were also less likely to have workplace trauma exposure (50.9% vs. 56.6%; OR, 0.80; 95% CI, 0.66-0.95; P = .01).
- Residents training during the pandemic compared to prepandemic reported significantly lower weekly duty hours (score mean difference –3.1 hours; 95% CI, –4.1 to −2.0 hours), lower mean reports of medical errors (MD, −0.04; 95% CI, –0.06 to –0.01), and higher workload satisfaction (MD, 0.2; 95% CI, 0.2-0.3).
- However, after accounting for these residency-related factors, training during the pandemic was no longer associated with lower odds of presenting PTSD symptoms.
IN PRACTICE
While the findings show residents training during the first pandemic wave were less likely to have PTSD, future studies should further follow these residents’ PTSD symptoms and investigate whether interventions targeting residency-related factors could reduce their PTSD risk moving forward, the investigators note.
SOURCE
The study was carried out by Michelle K. Ptak, BA, department of psychology, University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, and colleagues. It was published online Aug. 22 in JAMA Network Open.
LIMITATIONS
The study used self-reports and included only the first pandemic wave, 1st-year residents, and prepandemic data for a single academic year. Survey participation decreased during the pandemic, and it’s possible there were unmeasured factors associated with PTSD risk.
DISCLOSURES
The study was supported by the National Institute of Mental Health and the National Institutes of Health. The authors report no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE
First-year medical residents training during COVID-19 were significantly less likely to have posttraumatic stress disorder and workplace trauma, compared with their counterparts who trained before the pandemic, and reported fewer work hours, higher workload satisfaction, and fewer medical errors, new research shows.
METHODOLOGY
- Studies have reported a high prevalence of PTSD symptoms among residents during the pandemic, but it’s unclear if this prevalence differs from prepandemic levels.
- Using the Intern Health Study, a longitudinal cohort study of 1st-year residents, researchers investigated differences in PTSD symptoms among those training before the pandemic (2018-2019) and during its first wave (March to June, 2020).
- The study included 1,957 first-year residents (48.2% female; mean age, 27.6 years) who completed a baseline survey 2 months before their residency start, and then quarterly surveys during their intern year, with the fourth quarterly survey including a screen for PTSD.
- Researchers assessed differences in nonresidency factors and residency-related factors before and during the pandemic and examined exposure to workplace trauma.
TAKEAWAY
- (7.1% vs. 10.7%; odds ratio, 0.64; 95% confidence interval, 0.46-0.88; P = .01).
- They were also less likely to have workplace trauma exposure (50.9% vs. 56.6%; OR, 0.80; 95% CI, 0.66-0.95; P = .01).
- Residents training during the pandemic compared to prepandemic reported significantly lower weekly duty hours (score mean difference –3.1 hours; 95% CI, –4.1 to −2.0 hours), lower mean reports of medical errors (MD, −0.04; 95% CI, –0.06 to –0.01), and higher workload satisfaction (MD, 0.2; 95% CI, 0.2-0.3).
- However, after accounting for these residency-related factors, training during the pandemic was no longer associated with lower odds of presenting PTSD symptoms.
IN PRACTICE
While the findings show residents training during the first pandemic wave were less likely to have PTSD, future studies should further follow these residents’ PTSD symptoms and investigate whether interventions targeting residency-related factors could reduce their PTSD risk moving forward, the investigators note.
SOURCE
The study was carried out by Michelle K. Ptak, BA, department of psychology, University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, and colleagues. It was published online Aug. 22 in JAMA Network Open.
LIMITATIONS
The study used self-reports and included only the first pandemic wave, 1st-year residents, and prepandemic data for a single academic year. Survey participation decreased during the pandemic, and it’s possible there were unmeasured factors associated with PTSD risk.
DISCLOSURES
The study was supported by the National Institute of Mental Health and the National Institutes of Health. The authors report no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM JAMA NETWORK OPEN
How ob.gyn. programs provide abortion training post Dobbs
to fulfill required clinical rotations in the procedure.
The Accreditation Council for Graduate Medical Education requires ob.gyn. residents – unless they have a religious or moral exemption – to undergo abortion training to complete their programs. In states with bans or restrictions on family planning services or abortions, resident training must be received at institutions that are out of state.
Some residency programs are just beginning to coordinate out-of-state training, while others are further along in their offerings. There’s no formal matching process, and it remains unclear who will cover the costs of residents training elsewhere for a month.
These uncertainties, along with lack of coordination about malpractice, clinical rotations, and limited faculty, leave some program directors skeptical they’ll be able to keep up with demand for out-of-state slots. They are also wary of harming their own residents’ educational and clinical opportunities.
A 3rd-year ob.gyn. resident, who didn’t want to give her name or residency program for fear of backlash against her home institution, told this news organization that the Catholic-affiliated site is trying to avoid drawing attention to its minimal abortion training in a restrictive Midwest state. She knew after the Supreme Court’s decision in Dobbs v. Jackson she’d have to look outside the program for more complex abortion training.
While she could learn dilation and curettage or other first-trimester or early–second-trimester procedures at the Midwest program, she said she couldn’t learn dilation and evacuation.
A mentor at her program connected her with a residency program at the University of New Mexico, where she recently started a 5-week family planning rotation. She is the first out-of-state resident hosted by UNM. Currently, UNM has six ob.gyn. residents per class year, for a total of 36, and six family planning fellows.
The ob.gyn. resident is staying with a friend at no cost, and her home institution still pays her salary. But she still must pay the mortgage on a home she can’t live in while away and misses being part of a community where she’s built a life over the past 2 years.
“There’s a part of you that’s just angry that you can’t do this for the women ... in your state,” she said. “Unfortunately, there isn’t a formalized program for ob.gyn. residents interested in more advanced training to be matched with a program that has the ability to offer that training. It’s very much a word-of-mouth and who-you-know situation. For people without those connections, it can be difficult to obtain this training unless they are interested in a formal fellowship.”
This year, about 1,500 ob.gyn. residents matched into 280 residency programs, according to the National Residency Matching Program.
Alyssa Colwill, MD, assistant professor of obstetrics and gynecology at Oregon Health and Science University and director of the ob.gyn. Ryan Residency Program at OHSU, estimated that 1,000 ob.gyn. residents per year will seek out-of-state abortion training. The estimate is based on the number of residents in programs in states with restrictions.
The Ryan Program, which began in 1999, helps ob.gyn. residency programs provide training in abortion and contraception care (family planning) as a required rotation.
Connecting programs
Ryan-affiliated residencies have been helping connect programs in states with abortion bans and restrictions to programs in states with more liberal laws.
Twelve of the 100 Ryan programs sent residents out of state in the past academic year, and 15 will follow this year. More are expected soon, said Kristin Simonson, MA, director of programs and operations at the Ryan Residency Program, headquartered at the Bixby Center for Global Reproductive Health at the University of California, San Francisco.
Before the Dobbs decision, very few programs considered next steps to train ob.gyn. residents if abortions became illegal, Ms. Simonson said. “I think a lot of people just kind of were waiting and seeing ... and hoping that they wouldn’t have to make any drastic plans. It was hard to motivate people to have a plan B ready to go,” she said.
“Almost all of us working in this field had a really bad feeling,” said Courtney G. Forbis, MD, UNM assistant professor of ob.gyn. and Ryan Residency director. She and colleagues began planning for the future months ahead of the court decision. But the program wasn’t able to begin accepting out-of-state residents until now, she said. “We are trying to use this experience to see what we can accommodate in the future.”
OHSU also began planning for alternative training when it learned of the leaked Supreme Court decision, Dr. Colwill said. “We decided that we had the bandwidth and opportunity to train more individuals that were going to lose access to services and educational opportunities,” she said.
The university ran a 4-week test rotation last fall. So far, six residents and one fellow have come from out of the state, said Dr. Colwill. OHSU hopes to have 10 more in the coming year. The out-of-state learners will join 32 ob.gyn. residents and 12 fellows who were already in the program, she said.
To ease residents’ integration into an away program, the Ryan Program – along with the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists, the Council on Resident Education in Obstetrics and Gynecology, and Innovating Education in Reproductive Health – recently began offering a free, web-based patient-centered abortion education curriculum.
The course supplements in-person clinical training in abortion care and prepares residents traveling and transitioning into another program to begin learning new skills on their first day, AnnaMarie Connolly, MD, ACOG’s chief of education and academic affairs, said in a prepared statement.
Training costs
Residents and their institutions also face additional costs. The home institution that loses a resident for a few weeks to a month has to determine how to cover the care not provided while they are away, Ms. Simonson said. Residents may incur expenses for transportation, housing, food, and other things while out of state.
OHSU covers transportation and housing through its abortion care and training fund, but there are other factors to consider, Dr. Colwill said. For example, the home and host programs have to coordinate licensing, malpractice, and line up rotation dates, she said.
Among other complications, UNM wasn’t able to set up an agreement so that its new resident could participate in a rotation at Planned Parenthood. “We have the clinical volume to accommodate another learner,” Dr. Forbis said. But the program has to balance resources, such as “trying to make sure we don’t have one faculty [member] assigned to too many learners at one time,” she said.
Given the logistic and financial challenges, programs may not be able to ensure that all residents who need abortion training receive it, said Ms. Simonson.
The Ryan Program, for instance, can’t help the more than 100 residency programs in states where abortions are currently illegal, she said.
UNM is trying to partner with specific programs, such as those in the state of Texas where abortion is banned, to train its residents each year, Dr. Forbis said.
OHSU also will look for opportunities to train as many residents as possible, Dr. Colwill said, “but I don’t think we’ll ever be able to fill that gap of 1,000 residents that need this training.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
to fulfill required clinical rotations in the procedure.
The Accreditation Council for Graduate Medical Education requires ob.gyn. residents – unless they have a religious or moral exemption – to undergo abortion training to complete their programs. In states with bans or restrictions on family planning services or abortions, resident training must be received at institutions that are out of state.
Some residency programs are just beginning to coordinate out-of-state training, while others are further along in their offerings. There’s no formal matching process, and it remains unclear who will cover the costs of residents training elsewhere for a month.
These uncertainties, along with lack of coordination about malpractice, clinical rotations, and limited faculty, leave some program directors skeptical they’ll be able to keep up with demand for out-of-state slots. They are also wary of harming their own residents’ educational and clinical opportunities.
A 3rd-year ob.gyn. resident, who didn’t want to give her name or residency program for fear of backlash against her home institution, told this news organization that the Catholic-affiliated site is trying to avoid drawing attention to its minimal abortion training in a restrictive Midwest state. She knew after the Supreme Court’s decision in Dobbs v. Jackson she’d have to look outside the program for more complex abortion training.
While she could learn dilation and curettage or other first-trimester or early–second-trimester procedures at the Midwest program, she said she couldn’t learn dilation and evacuation.
A mentor at her program connected her with a residency program at the University of New Mexico, where she recently started a 5-week family planning rotation. She is the first out-of-state resident hosted by UNM. Currently, UNM has six ob.gyn. residents per class year, for a total of 36, and six family planning fellows.
The ob.gyn. resident is staying with a friend at no cost, and her home institution still pays her salary. But she still must pay the mortgage on a home she can’t live in while away and misses being part of a community where she’s built a life over the past 2 years.
“There’s a part of you that’s just angry that you can’t do this for the women ... in your state,” she said. “Unfortunately, there isn’t a formalized program for ob.gyn. residents interested in more advanced training to be matched with a program that has the ability to offer that training. It’s very much a word-of-mouth and who-you-know situation. For people without those connections, it can be difficult to obtain this training unless they are interested in a formal fellowship.”
This year, about 1,500 ob.gyn. residents matched into 280 residency programs, according to the National Residency Matching Program.
Alyssa Colwill, MD, assistant professor of obstetrics and gynecology at Oregon Health and Science University and director of the ob.gyn. Ryan Residency Program at OHSU, estimated that 1,000 ob.gyn. residents per year will seek out-of-state abortion training. The estimate is based on the number of residents in programs in states with restrictions.
The Ryan Program, which began in 1999, helps ob.gyn. residency programs provide training in abortion and contraception care (family planning) as a required rotation.
Connecting programs
Ryan-affiliated residencies have been helping connect programs in states with abortion bans and restrictions to programs in states with more liberal laws.
Twelve of the 100 Ryan programs sent residents out of state in the past academic year, and 15 will follow this year. More are expected soon, said Kristin Simonson, MA, director of programs and operations at the Ryan Residency Program, headquartered at the Bixby Center for Global Reproductive Health at the University of California, San Francisco.
Before the Dobbs decision, very few programs considered next steps to train ob.gyn. residents if abortions became illegal, Ms. Simonson said. “I think a lot of people just kind of were waiting and seeing ... and hoping that they wouldn’t have to make any drastic plans. It was hard to motivate people to have a plan B ready to go,” she said.
“Almost all of us working in this field had a really bad feeling,” said Courtney G. Forbis, MD, UNM assistant professor of ob.gyn. and Ryan Residency director. She and colleagues began planning for the future months ahead of the court decision. But the program wasn’t able to begin accepting out-of-state residents until now, she said. “We are trying to use this experience to see what we can accommodate in the future.”
OHSU also began planning for alternative training when it learned of the leaked Supreme Court decision, Dr. Colwill said. “We decided that we had the bandwidth and opportunity to train more individuals that were going to lose access to services and educational opportunities,” she said.
The university ran a 4-week test rotation last fall. So far, six residents and one fellow have come from out of the state, said Dr. Colwill. OHSU hopes to have 10 more in the coming year. The out-of-state learners will join 32 ob.gyn. residents and 12 fellows who were already in the program, she said.
To ease residents’ integration into an away program, the Ryan Program – along with the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists, the Council on Resident Education in Obstetrics and Gynecology, and Innovating Education in Reproductive Health – recently began offering a free, web-based patient-centered abortion education curriculum.
The course supplements in-person clinical training in abortion care and prepares residents traveling and transitioning into another program to begin learning new skills on their first day, AnnaMarie Connolly, MD, ACOG’s chief of education and academic affairs, said in a prepared statement.
Training costs
Residents and their institutions also face additional costs. The home institution that loses a resident for a few weeks to a month has to determine how to cover the care not provided while they are away, Ms. Simonson said. Residents may incur expenses for transportation, housing, food, and other things while out of state.
OHSU covers transportation and housing through its abortion care and training fund, but there are other factors to consider, Dr. Colwill said. For example, the home and host programs have to coordinate licensing, malpractice, and line up rotation dates, she said.
Among other complications, UNM wasn’t able to set up an agreement so that its new resident could participate in a rotation at Planned Parenthood. “We have the clinical volume to accommodate another learner,” Dr. Forbis said. But the program has to balance resources, such as “trying to make sure we don’t have one faculty [member] assigned to too many learners at one time,” she said.
Given the logistic and financial challenges, programs may not be able to ensure that all residents who need abortion training receive it, said Ms. Simonson.
The Ryan Program, for instance, can’t help the more than 100 residency programs in states where abortions are currently illegal, she said.
UNM is trying to partner with specific programs, such as those in the state of Texas where abortion is banned, to train its residents each year, Dr. Forbis said.
OHSU also will look for opportunities to train as many residents as possible, Dr. Colwill said, “but I don’t think we’ll ever be able to fill that gap of 1,000 residents that need this training.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
to fulfill required clinical rotations in the procedure.
The Accreditation Council for Graduate Medical Education requires ob.gyn. residents – unless they have a religious or moral exemption – to undergo abortion training to complete their programs. In states with bans or restrictions on family planning services or abortions, resident training must be received at institutions that are out of state.
Some residency programs are just beginning to coordinate out-of-state training, while others are further along in their offerings. There’s no formal matching process, and it remains unclear who will cover the costs of residents training elsewhere for a month.
These uncertainties, along with lack of coordination about malpractice, clinical rotations, and limited faculty, leave some program directors skeptical they’ll be able to keep up with demand for out-of-state slots. They are also wary of harming their own residents’ educational and clinical opportunities.
A 3rd-year ob.gyn. resident, who didn’t want to give her name or residency program for fear of backlash against her home institution, told this news organization that the Catholic-affiliated site is trying to avoid drawing attention to its minimal abortion training in a restrictive Midwest state. She knew after the Supreme Court’s decision in Dobbs v. Jackson she’d have to look outside the program for more complex abortion training.
While she could learn dilation and curettage or other first-trimester or early–second-trimester procedures at the Midwest program, she said she couldn’t learn dilation and evacuation.
A mentor at her program connected her with a residency program at the University of New Mexico, where she recently started a 5-week family planning rotation. She is the first out-of-state resident hosted by UNM. Currently, UNM has six ob.gyn. residents per class year, for a total of 36, and six family planning fellows.
The ob.gyn. resident is staying with a friend at no cost, and her home institution still pays her salary. But she still must pay the mortgage on a home she can’t live in while away and misses being part of a community where she’s built a life over the past 2 years.
“There’s a part of you that’s just angry that you can’t do this for the women ... in your state,” she said. “Unfortunately, there isn’t a formalized program for ob.gyn. residents interested in more advanced training to be matched with a program that has the ability to offer that training. It’s very much a word-of-mouth and who-you-know situation. For people without those connections, it can be difficult to obtain this training unless they are interested in a formal fellowship.”
This year, about 1,500 ob.gyn. residents matched into 280 residency programs, according to the National Residency Matching Program.
Alyssa Colwill, MD, assistant professor of obstetrics and gynecology at Oregon Health and Science University and director of the ob.gyn. Ryan Residency Program at OHSU, estimated that 1,000 ob.gyn. residents per year will seek out-of-state abortion training. The estimate is based on the number of residents in programs in states with restrictions.
The Ryan Program, which began in 1999, helps ob.gyn. residency programs provide training in abortion and contraception care (family planning) as a required rotation.
Connecting programs
Ryan-affiliated residencies have been helping connect programs in states with abortion bans and restrictions to programs in states with more liberal laws.
Twelve of the 100 Ryan programs sent residents out of state in the past academic year, and 15 will follow this year. More are expected soon, said Kristin Simonson, MA, director of programs and operations at the Ryan Residency Program, headquartered at the Bixby Center for Global Reproductive Health at the University of California, San Francisco.
Before the Dobbs decision, very few programs considered next steps to train ob.gyn. residents if abortions became illegal, Ms. Simonson said. “I think a lot of people just kind of were waiting and seeing ... and hoping that they wouldn’t have to make any drastic plans. It was hard to motivate people to have a plan B ready to go,” she said.
“Almost all of us working in this field had a really bad feeling,” said Courtney G. Forbis, MD, UNM assistant professor of ob.gyn. and Ryan Residency director. She and colleagues began planning for the future months ahead of the court decision. But the program wasn’t able to begin accepting out-of-state residents until now, she said. “We are trying to use this experience to see what we can accommodate in the future.”
OHSU also began planning for alternative training when it learned of the leaked Supreme Court decision, Dr. Colwill said. “We decided that we had the bandwidth and opportunity to train more individuals that were going to lose access to services and educational opportunities,” she said.
The university ran a 4-week test rotation last fall. So far, six residents and one fellow have come from out of the state, said Dr. Colwill. OHSU hopes to have 10 more in the coming year. The out-of-state learners will join 32 ob.gyn. residents and 12 fellows who were already in the program, she said.
To ease residents’ integration into an away program, the Ryan Program – along with the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists, the Council on Resident Education in Obstetrics and Gynecology, and Innovating Education in Reproductive Health – recently began offering a free, web-based patient-centered abortion education curriculum.
The course supplements in-person clinical training in abortion care and prepares residents traveling and transitioning into another program to begin learning new skills on their first day, AnnaMarie Connolly, MD, ACOG’s chief of education and academic affairs, said in a prepared statement.
Training costs
Residents and their institutions also face additional costs. The home institution that loses a resident for a few weeks to a month has to determine how to cover the care not provided while they are away, Ms. Simonson said. Residents may incur expenses for transportation, housing, food, and other things while out of state.
OHSU covers transportation and housing through its abortion care and training fund, but there are other factors to consider, Dr. Colwill said. For example, the home and host programs have to coordinate licensing, malpractice, and line up rotation dates, she said.
Among other complications, UNM wasn’t able to set up an agreement so that its new resident could participate in a rotation at Planned Parenthood. “We have the clinical volume to accommodate another learner,” Dr. Forbis said. But the program has to balance resources, such as “trying to make sure we don’t have one faculty [member] assigned to too many learners at one time,” she said.
Given the logistic and financial challenges, programs may not be able to ensure that all residents who need abortion training receive it, said Ms. Simonson.
The Ryan Program, for instance, can’t help the more than 100 residency programs in states where abortions are currently illegal, she said.
UNM is trying to partner with specific programs, such as those in the state of Texas where abortion is banned, to train its residents each year, Dr. Forbis said.
OHSU also will look for opportunities to train as many residents as possible, Dr. Colwill said, “but I don’t think we’ll ever be able to fill that gap of 1,000 residents that need this training.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Can this device take on enlarged prostates?
Inflating a drug-coated balloon in the prostate is the latest approach to treating a common cause of frequent or difficult urination in older men.
As the prostate naturally grows with age, the gland can obstruct the flow of urine – leading to frequent trips to the bathroom and disrupted nights. An estimated 50% of men aged 60 years and older have benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH). That figure rises to more than 80% by age 70 and to 90% by age 80.
Transurethral resection of the prostate was the main surgical treatment for symptomatic BPH for much of the 20th century.
More recently, researchers have developed various minimally invasive surgical therapy (MIST) devices to treat the obstruction while limiting effects on sexual function. Some newer devices use lasers or water vapor to remove prostate tissue. Another approach uses implants to move and hold prostate tissue out of the way.
Now drug-coated balloons have entered the picture.
, paclitaxel – best known as a chemotherapy medication – to limit further growth and keep the lobes apart.
The Food and Drug Administration approved Optilume BPH in June. The results from a randomized controlled trial of the device were published in The Journal of Urology.
Uptake of MIST devices for BPH “has been variable due to a host of factors including mixed results, complexity of equipment, and costs,” the journal’s editor, D. Robert Siemens, MD, noted in the issue.
The developer of the device, Urotronic, said it expects that the newest treatment will be commercially available in the near future. Discussions about cost, insurance coverage, and how to train urologists to use it are ongoing, said Ian Schorn, the company’s vice president of clinical affairs.
Raevti Bole, MD, a urologic surgeon at Cleveland Clinic’s Glickman Urological and Kidney Institute, said BPH treatments ideally benefit patients for years, so she is eager to see how patients are doing 5 and 10 years after the Optilume BPH procedure. Studies should also examine its effects on fertility.
But given the safety and efficacy results reported 1 year after treatment, “I think this is something that a lot of people are going to be able to use in their practice and that their patients are going to benefit from,” Dr. Bole told this news organization.
She said she expects most urologists will be able to master the technology. The procedure’s minimal effect on sexual issues and the relatively short time needed to perform it are other advantages.
“All of those things are very positive in terms of whether patients are going to want to consider it and also whether surgeons are going to be able to realistically learn it and offer it at their centers,” Dr. Bole said.
In choosing a particular treatment, Dr. Bole discusses options with patients and takes into account factors such as trial data, the nature and severity of symptoms, treatment goals, comorbidities, and the size of the prostate.
Available MIST devices can vary by institution, and urologists can have different levels of experience with each device. If a patient is interested in an approach a surgeon does not offer, the surgeon can refer the patient to a colleague who does.
Active vs. sham treatment
Urologists may be familiar with another Optilume device, the Optilume urethral drug-coated balloon, that is used for urethral strictures.
The devices have similar names, and the underlying technology is similar, but there are major differences, Mr. Schorn said.
The BPH device expands between the lobes of the prostate, creating an anterior commissurotomy. A double-lobe balloon locks the device in place during inflation.
For the PINNACLE trial of the BPH device, which was conducted at 18 sites in the United States and Canada, Steven A. Kaplan, MD, of the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York, and colleagues enrolled 148 men with symptomatic BPH who were experiencing urinary flow obstruction.
The average age of the patients was 65 years; 100 of them were assigned to undergo active treatment with Optilume BPH. The rest received a sham procedure that mimicked active treatment.
At 3 months, men who received active treatment had an average improvement in the International Prostate Symptom Score of about 11 points. This improvement was maintained at 1 year. Those who received sham treatment experienced an 8-point improvement at 3 months that dissipated over time.
The rate of urine flow increased dramatically with Optilume BPH, the researchers reported.
Five serious adverse events were considered to be possibly related to the device. There were four cases of postprocedural hematuria that required cystoscopic management or extended observation, and one case of urethral false passage that required extended catheterization.
Nonserious adverse events in the men who underwent the Optilume procedure typically resolved in about a month and included hematuria (40%), urinary tract infection (14%), dysuria (9.2%), urge or mixed incontinence (8.2%), mild stress incontinence (7.1%), bladder spasms (6.1%), elevated prostate-specific antigen levels (6.1%), and urinary urgency (6.1%), according to the researchers.
In a subset of participants for whom pharmacokinetic data were available, systemic exposure to paclitaxel was minimal.
Four participants in the Optilume BPH arm (4.1%) reported ejaculatory dysfunction, compared with one man in the sham treatment arm (2.1%). There were no cases of treatment-related erectile dysfunction.
Most patients were treated under deep sedation or general anesthesia, and the average procedure time was 26 minutes.
After the procedure, patients received a Foley catheter, which remained in place for about 2 days, “which is not significantly different from water vapor thermal therapy, holmium laser enucleation of the prostate, or laser photovaporization in similar gland sizes,” Dr. Bole and Petar Bajic, MD, also with Cleveland Clinic, noted in a commentary accompanying the article in The Journal of Urology.
MIST devices can be ideal for patients who prioritize sexual function, but the need for a temporary catheter after the procedure can be a “major postoperative source of patient dissatisfaction,” they acknowledged.
“Consistent with other minimally invasive technologies, the Optilume BPH procedure is a straightforward procedure that can be conducted in an ambulatory or office outpatient setting with pain management at physician and patient discretion,” Dr. Kaplan and his coauthors wrote.
The study was featured on the cover of the journal, which the research team saw as an unusual but welcome spotlight for a treatment for BPH.
“We were thrilled that we got on the cover of The Journal of Urology, which is not a common thing for BPH technology,” Mr. Schorn said.
Urotronic funded the PINNACLE study. Dr. Bole has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Inflating a drug-coated balloon in the prostate is the latest approach to treating a common cause of frequent or difficult urination in older men.
As the prostate naturally grows with age, the gland can obstruct the flow of urine – leading to frequent trips to the bathroom and disrupted nights. An estimated 50% of men aged 60 years and older have benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH). That figure rises to more than 80% by age 70 and to 90% by age 80.
Transurethral resection of the prostate was the main surgical treatment for symptomatic BPH for much of the 20th century.
More recently, researchers have developed various minimally invasive surgical therapy (MIST) devices to treat the obstruction while limiting effects on sexual function. Some newer devices use lasers or water vapor to remove prostate tissue. Another approach uses implants to move and hold prostate tissue out of the way.
Now drug-coated balloons have entered the picture.
, paclitaxel – best known as a chemotherapy medication – to limit further growth and keep the lobes apart.
The Food and Drug Administration approved Optilume BPH in June. The results from a randomized controlled trial of the device were published in The Journal of Urology.
Uptake of MIST devices for BPH “has been variable due to a host of factors including mixed results, complexity of equipment, and costs,” the journal’s editor, D. Robert Siemens, MD, noted in the issue.
The developer of the device, Urotronic, said it expects that the newest treatment will be commercially available in the near future. Discussions about cost, insurance coverage, and how to train urologists to use it are ongoing, said Ian Schorn, the company’s vice president of clinical affairs.
Raevti Bole, MD, a urologic surgeon at Cleveland Clinic’s Glickman Urological and Kidney Institute, said BPH treatments ideally benefit patients for years, so she is eager to see how patients are doing 5 and 10 years after the Optilume BPH procedure. Studies should also examine its effects on fertility.
But given the safety and efficacy results reported 1 year after treatment, “I think this is something that a lot of people are going to be able to use in their practice and that their patients are going to benefit from,” Dr. Bole told this news organization.
She said she expects most urologists will be able to master the technology. The procedure’s minimal effect on sexual issues and the relatively short time needed to perform it are other advantages.
“All of those things are very positive in terms of whether patients are going to want to consider it and also whether surgeons are going to be able to realistically learn it and offer it at their centers,” Dr. Bole said.
In choosing a particular treatment, Dr. Bole discusses options with patients and takes into account factors such as trial data, the nature and severity of symptoms, treatment goals, comorbidities, and the size of the prostate.
Available MIST devices can vary by institution, and urologists can have different levels of experience with each device. If a patient is interested in an approach a surgeon does not offer, the surgeon can refer the patient to a colleague who does.
Active vs. sham treatment
Urologists may be familiar with another Optilume device, the Optilume urethral drug-coated balloon, that is used for urethral strictures.
The devices have similar names, and the underlying technology is similar, but there are major differences, Mr. Schorn said.
The BPH device expands between the lobes of the prostate, creating an anterior commissurotomy. A double-lobe balloon locks the device in place during inflation.
For the PINNACLE trial of the BPH device, which was conducted at 18 sites in the United States and Canada, Steven A. Kaplan, MD, of the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York, and colleagues enrolled 148 men with symptomatic BPH who were experiencing urinary flow obstruction.
The average age of the patients was 65 years; 100 of them were assigned to undergo active treatment with Optilume BPH. The rest received a sham procedure that mimicked active treatment.
At 3 months, men who received active treatment had an average improvement in the International Prostate Symptom Score of about 11 points. This improvement was maintained at 1 year. Those who received sham treatment experienced an 8-point improvement at 3 months that dissipated over time.
The rate of urine flow increased dramatically with Optilume BPH, the researchers reported.
Five serious adverse events were considered to be possibly related to the device. There were four cases of postprocedural hematuria that required cystoscopic management or extended observation, and one case of urethral false passage that required extended catheterization.
Nonserious adverse events in the men who underwent the Optilume procedure typically resolved in about a month and included hematuria (40%), urinary tract infection (14%), dysuria (9.2%), urge or mixed incontinence (8.2%), mild stress incontinence (7.1%), bladder spasms (6.1%), elevated prostate-specific antigen levels (6.1%), and urinary urgency (6.1%), according to the researchers.
In a subset of participants for whom pharmacokinetic data were available, systemic exposure to paclitaxel was minimal.
Four participants in the Optilume BPH arm (4.1%) reported ejaculatory dysfunction, compared with one man in the sham treatment arm (2.1%). There were no cases of treatment-related erectile dysfunction.
Most patients were treated under deep sedation or general anesthesia, and the average procedure time was 26 minutes.
After the procedure, patients received a Foley catheter, which remained in place for about 2 days, “which is not significantly different from water vapor thermal therapy, holmium laser enucleation of the prostate, or laser photovaporization in similar gland sizes,” Dr. Bole and Petar Bajic, MD, also with Cleveland Clinic, noted in a commentary accompanying the article in The Journal of Urology.
MIST devices can be ideal for patients who prioritize sexual function, but the need for a temporary catheter after the procedure can be a “major postoperative source of patient dissatisfaction,” they acknowledged.
“Consistent with other minimally invasive technologies, the Optilume BPH procedure is a straightforward procedure that can be conducted in an ambulatory or office outpatient setting with pain management at physician and patient discretion,” Dr. Kaplan and his coauthors wrote.
The study was featured on the cover of the journal, which the research team saw as an unusual but welcome spotlight for a treatment for BPH.
“We were thrilled that we got on the cover of The Journal of Urology, which is not a common thing for BPH technology,” Mr. Schorn said.
Urotronic funded the PINNACLE study. Dr. Bole has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Inflating a drug-coated balloon in the prostate is the latest approach to treating a common cause of frequent or difficult urination in older men.
As the prostate naturally grows with age, the gland can obstruct the flow of urine – leading to frequent trips to the bathroom and disrupted nights. An estimated 50% of men aged 60 years and older have benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH). That figure rises to more than 80% by age 70 and to 90% by age 80.
Transurethral resection of the prostate was the main surgical treatment for symptomatic BPH for much of the 20th century.
More recently, researchers have developed various minimally invasive surgical therapy (MIST) devices to treat the obstruction while limiting effects on sexual function. Some newer devices use lasers or water vapor to remove prostate tissue. Another approach uses implants to move and hold prostate tissue out of the way.
Now drug-coated balloons have entered the picture.
, paclitaxel – best known as a chemotherapy medication – to limit further growth and keep the lobes apart.
The Food and Drug Administration approved Optilume BPH in June. The results from a randomized controlled trial of the device were published in The Journal of Urology.
Uptake of MIST devices for BPH “has been variable due to a host of factors including mixed results, complexity of equipment, and costs,” the journal’s editor, D. Robert Siemens, MD, noted in the issue.
The developer of the device, Urotronic, said it expects that the newest treatment will be commercially available in the near future. Discussions about cost, insurance coverage, and how to train urologists to use it are ongoing, said Ian Schorn, the company’s vice president of clinical affairs.
Raevti Bole, MD, a urologic surgeon at Cleveland Clinic’s Glickman Urological and Kidney Institute, said BPH treatments ideally benefit patients for years, so she is eager to see how patients are doing 5 and 10 years after the Optilume BPH procedure. Studies should also examine its effects on fertility.
But given the safety and efficacy results reported 1 year after treatment, “I think this is something that a lot of people are going to be able to use in their practice and that their patients are going to benefit from,” Dr. Bole told this news organization.
She said she expects most urologists will be able to master the technology. The procedure’s minimal effect on sexual issues and the relatively short time needed to perform it are other advantages.
“All of those things are very positive in terms of whether patients are going to want to consider it and also whether surgeons are going to be able to realistically learn it and offer it at their centers,” Dr. Bole said.
In choosing a particular treatment, Dr. Bole discusses options with patients and takes into account factors such as trial data, the nature and severity of symptoms, treatment goals, comorbidities, and the size of the prostate.
Available MIST devices can vary by institution, and urologists can have different levels of experience with each device. If a patient is interested in an approach a surgeon does not offer, the surgeon can refer the patient to a colleague who does.
Active vs. sham treatment
Urologists may be familiar with another Optilume device, the Optilume urethral drug-coated balloon, that is used for urethral strictures.
The devices have similar names, and the underlying technology is similar, but there are major differences, Mr. Schorn said.
The BPH device expands between the lobes of the prostate, creating an anterior commissurotomy. A double-lobe balloon locks the device in place during inflation.
For the PINNACLE trial of the BPH device, which was conducted at 18 sites in the United States and Canada, Steven A. Kaplan, MD, of the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York, and colleagues enrolled 148 men with symptomatic BPH who were experiencing urinary flow obstruction.
The average age of the patients was 65 years; 100 of them were assigned to undergo active treatment with Optilume BPH. The rest received a sham procedure that mimicked active treatment.
At 3 months, men who received active treatment had an average improvement in the International Prostate Symptom Score of about 11 points. This improvement was maintained at 1 year. Those who received sham treatment experienced an 8-point improvement at 3 months that dissipated over time.
The rate of urine flow increased dramatically with Optilume BPH, the researchers reported.
Five serious adverse events were considered to be possibly related to the device. There were four cases of postprocedural hematuria that required cystoscopic management or extended observation, and one case of urethral false passage that required extended catheterization.
Nonserious adverse events in the men who underwent the Optilume procedure typically resolved in about a month and included hematuria (40%), urinary tract infection (14%), dysuria (9.2%), urge or mixed incontinence (8.2%), mild stress incontinence (7.1%), bladder spasms (6.1%), elevated prostate-specific antigen levels (6.1%), and urinary urgency (6.1%), according to the researchers.
In a subset of participants for whom pharmacokinetic data were available, systemic exposure to paclitaxel was minimal.
Four participants in the Optilume BPH arm (4.1%) reported ejaculatory dysfunction, compared with one man in the sham treatment arm (2.1%). There were no cases of treatment-related erectile dysfunction.
Most patients were treated under deep sedation or general anesthesia, and the average procedure time was 26 minutes.
After the procedure, patients received a Foley catheter, which remained in place for about 2 days, “which is not significantly different from water vapor thermal therapy, holmium laser enucleation of the prostate, or laser photovaporization in similar gland sizes,” Dr. Bole and Petar Bajic, MD, also with Cleveland Clinic, noted in a commentary accompanying the article in The Journal of Urology.
MIST devices can be ideal for patients who prioritize sexual function, but the need for a temporary catheter after the procedure can be a “major postoperative source of patient dissatisfaction,” they acknowledged.
“Consistent with other minimally invasive technologies, the Optilume BPH procedure is a straightforward procedure that can be conducted in an ambulatory or office outpatient setting with pain management at physician and patient discretion,” Dr. Kaplan and his coauthors wrote.
The study was featured on the cover of the journal, which the research team saw as an unusual but welcome spotlight for a treatment for BPH.
“We were thrilled that we got on the cover of The Journal of Urology, which is not a common thing for BPH technology,” Mr. Schorn said.
Urotronic funded the PINNACLE study. Dr. Bole has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Medication treatment of opioid use disorder in primary care practice: Opportunities and limitations
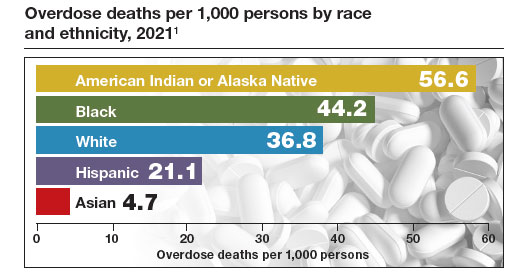
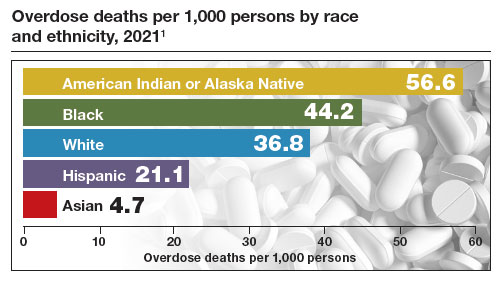
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) reported 106,699 deaths in 2021 from drug overdose, with the majority being linked to synthetic opioids, including fentanyl and tramadol.1 This number compares with 42,795 deaths due to motor vehicle accidents and 48,183 deaths due to suicide in 2021.2,3 Most of the opioid overdose deaths occurred among people aged 25 to 64 years, the peak age of patients cared for by obstetrician-gynecologists. Among pregnant and postpartum persons, mortality due to drug overdose has increased by 81% between 2017 and 2020.4
Among pregnant and postpartum patients, drug overdose death is more common than suicide, and the risk for drug overdose death appears to be greatest in the year following delivery.5,6 In many cases, postpartum patients with OUD have had multiple contacts with the health care system prior to their death, showing that there is an opportunity for therapeutic intervention before the death occurred.7 Medication-assisted recovery for OUD involves a comprehensive array of interventions including medication, counseling, and social support. Medication treatment of OUD with BUP or methadone reduces the risk for death but is underutilized among patients with OUD.6,8 Recent federal legislation has removed restrictions on the use of BUP, increasing the opportunity for primary care clinicians to prescribe it for the treatment of OUD.9
Screening and diagnosis of OUD
Screening for OUD is recommended for patients who are at risk for opioid misuse (ie, those who are taking/have taken opioid medications). The OWLS (Overuse, Worrying, Losing interest, and feeling Slowed down, sluggish, or sedated) screening tool is used to detect prescription medication OUD and has 4 questions10:
1. In the past 3 months did you use your opioid medicines for other purposes—for example, to help you sleep or to help with stress or worry?
2. In the past 3 months did opioid medicines cause you to feel slowed down, sluggish, or sedated?
3. In the past 3 months did opioid medicines cause you to lose interest in your usual activities?
4. In the past 3 months did you worry about your use of opioid medicines?
Patient agreement with 3 or 4 questions indicates a positive screening test.
If the patient has a positive screening test, a formal diagnosis of OUD can be made using the 11 symptoms outlined in the American Psychiatric Association’s Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, Fifth Edition.11 The diagnosis of mild (2 to 3 symptoms), moderate (4 to 5 symptoms), or severe OUD (6 or more symptoms) is made based on the number of symptoms the patient reports.
Buprenorphine treatment of OUD in primary care
The role of primary care clinicians in the medication treatment of OUD is increasing. Using a nationwide system that tracks prescription medications, investigators reported that, in 2004, psychiatrists wrote 32.2% of all BUP prescriptions; in 2021, however, only 10% of such prescriptions were provided by psychiatrists, with most prescriptions written by non-psychiatrist physicians, nurse practitioners, and physician assistants that year.12 Innovative telehealth approaches to consultation and medication treatment of OUD are now available—one example is QuickMD.13 Such sites are designed to remove barriers to initiating medication treatment of OUD.
The role of primary care clinicians in the management of OUD using BUP and buprenorphine-naloxone (BUP-NAL) has increased due to many factors, including:
- the removal of US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) barriers to prescribing BUP
- the epidemic of OUD and the small size of the addiction specialist workforce, necessitating that primary care clinicians become engaged in the treatment of OUD
- an increase in unobserved initiation of BUP among ambulatory patients, and a parallel decrease in cases of observed initiation in addiction center settings
- the reframing of OUD as a chronic medical problem, with many similarities to diabetes, obesity, dyslipidemia, and hypertension.
Similar to other diseases managed by primary care clinicians, OUD requires long-term chronic treatment with a medicine that, if taken as directed, provides excellent outcomes. Primary care clinicians who prescribe BUP also can optimize longitudinal care for comorbid disorders such as hypertension and diabetes, which are prevalent in people with OUD.
In 2019, New Jersey implemented new guidelines for the treatment of OUD, removing prior authorization barriers, increasing reimbursement for office-based OUD treatment, and establishing regional centers of excellence. The implementation of the new guidelines was followed by a marked increase in BUP prescribers among primary care clinicians, emergency medicine physicians, and advanced practice clinicians.14
To estimate the public health impact of BUP prescribing by primary care clinicians, investigators simulated patient outcomes in 3 scenarios15:
1. primary care clinicians refer patients to addiction specialists for OUD treatment
2. primary care clinicians provide BUP services in their practice
3. primary care clinicians provide BUP and harm reduction kits containing syringes and wound care supplies in their practice.
Strategies 2 and 3 resulted in 14% fewer deaths due to opioid overdose, an increased life expectancy of approximately 2.7 years, and reduced hospital costs. For strategy 3, the incremental cost per life-year saved was $34,400. The investigators noted that prescribing BUP in primary care practice increases practice costs.15
Treatment with BUP reduces death from opioid overdose, improves patient health, decreases use of illicit opioids, and reduces patient cravings for opioids. BUP is a safe medication and is associated with fewer adverse effects than insulin or warfarin.16
Continue to: Methadone treatment of OUD...
Methadone treatment of OUD
Methadone is a full opioid agonist approved by the FDA for the treatment of severe pain or OUD. Methadone treatment of OUD is strictly regulated and typically is ordered and administered at an opioid treatment program that is federally licensed. Methadone for OUD treatment cannot be prescribed by a physician to a pharmacy, limiting its use in primary care practice. Methadone used to treat OUD is ordered and dispensed at opioid-treatment programs. Take-home doses of methadone may be available to patients after adherence to the regimen has been established. When used long-term, higher doses of methadone are associated with better adherence, but these higher doses can cause respiratory depression. In a study of 189 pregnant patients taking methadone to treat OUD, daily doses of 60 mg or greater were associated with better treatment retention at delivery and 60 days postpartum, as well as less use of nonprescription opioids.17 Under limited circumstances methadone can be ordered and dispensed for hospitalized patients with OUD.
Methadone is a pure opioid receptor agonist. Naloxone (NAL) is an opioid receptor antagonist. Buprenorphine (BUP) is a partial opioid receptor agonist-antagonist, which limits overdose risk. BUP often is combined with NAL as a combination formulation, which is thought to reduce the repurposing of BUP for non-prescribed uses. At appropriate treatment dosages, both methadone (≥60 mg) and BUP (≥ 16 mg) are highly effective for the treatment of OUD.1 For patients with health insurance, pharmacy benefits often provide some coverage for preferred products but no coverage for other products. Not all pharmacies carry BUP products. In a study of more than 5,000 pharmacies, approximately 60% reported that they carry and can dispense BUP medications.2
BUP monotherapy is available as generic sublingual tablets, buccal films (Belbuca), formulations for injection (Sublocade), and subcutaneous implants (Probuphine). BUPNAL is available as buccal films (Bunavail), sublingual films (Suboxone), and sublingual tablets (Zubsolv). For BUP-NAL combination productions, the following dose combinations have been reported to have similar effects: BUP-NAL 8 mg/2 mg sublingual film, BUP-NAL 5.7 mg/1.4 mg sublingual tablet, and BUP-NAL 4.2 mg/0.7 mg buccal film.3
When initiating BUP-monotherapy or BUP-NAL treatment for OUD, one approach for unobserved initiation is to instruct the patient to discontinue using opioid agonist drugs and wait for the onset of mild to moderate withdrawal symptoms. The purpose of this step is to avoid precipitating severe withdrawal symptoms caused by giving BUP or BUP-NAL to a patient who has recently used opioid drugs.
If BUP-NAL sublingual films (Suboxone) are prescribed following the onset of mild to moderate withdrawal symptoms, the patient can initiate therapy with a dose of 2 mg BUP/0.5 mg NAL or 4 mg BUP/1 mg NAL. At 60 to 120 minutes following the initial dose, if withdrawal symptoms persist, an additional dose of 4 mg BUP/1 mg NAL can be given. Thereafter, symptoms can be assessed every 60 to 120 minutes and additional doses administered to control symptoms. On the second day of therapy, a maximum of 16 mg of BUP is administered. Over the following days and weeks, if symptoms and cravings persist at a BUP dose of 16 mg, the total daily dose of BUP can be titrated up to 24 mg. For long-term treatment, a commonly prescribed daily dose is 16 mg BUP/4 mg NAL or 24 mg BUP/6 mg NAL. An absolute contraindication to BUP or BUP/NAL treatment is an allergy to the medication, and a relative contraindication is liver failure.
One potential complication of transmucosal BUP or BUP-NAL treatment is a dry mouth (xerostomia), which may contribute to dental disease.4 However, some experts question the quality of the data that contributed to the warning.5,6 Potential dental complications might be prevented by regular oral health examinations, daily flossing and teeth brushing, and stimulation of saliva by sugar-free gum or lozenges.
Primary care clinicians who initiate BUP or BUPNAL treatment for OUD often have a weekly visit with the patient during the initial phase of treatment and then every 3 to 4 weeks during maintenance therapy. Most patients need long-term treatment to achieve the goals of therapy, which include prevention of opioid overdose, reduction of cravings for nonprescription narcotics, and improvement in overall health. BUP and BUP-NAL treatment are effective without formal counseling, but counseling and social work support improve long-term adherence with treatment. Primary care clinicians who have experience with medication treatment of OUD report that their experience convinces them that medication treatment of OUD has similarities to the long-term treatment of diabetes, with antihyperglycemia medicines or the treatment of HIV infection with antiviral medications.
References
1. Mattick RP, Breen C, Kimber J, et al. Buprenorphine maintenance versus placebo or methadone maintenance for opioid dependence. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2014;CD002207.
2. Weiner SG, Qato DM, Faust JS, et al. Pharmacy availability of buprenorphine for opioid use disorder treatment in the U.S. JAMA Netw Open. 2023;6:E2316089.
3. Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration (SAMHSA). Medications for opioid use disorder. SAMHSA website. Accessed August 21, 2023. https ://store.samhsa.gov/sites/default/files/SAMHSA_Digital_Download/PEP 21-02-01-002.pdf
4. FDA warns about dental problems with buprenorphine medicines dissolved in the mouth. FDA website. Accessed August 21, 2023. https ://www.fda.gov/drugs/drug-safety-and-availability/fda-warns-about-dental-problems-buprenorphine-medicines-dissolved-mouth-treat-opioiduse-disorder#:~:text=What%20did%20FDA%20find%3F,medicines%20 dissolved%20in%20the%20mouth
5. Watson DP, Etmian S, Gastala N. Sublingual buprenorphine-naloxone exposure and dental disease. JAMA. 2023;329:1223-1224.
6. Brothers TD, Lewer D, Bonn M. Sublingual buprenorphine-naloxone exposure and dental disease. JAMA. 2023;329:1224.
Medication treatment of OUD in obstetrics
In the United States, the prevalence of OUD among pregnant patients hospitalized for delivery more than quadrupled from 1999 through 2014.18 BUP and methadone commonly are used to treat OUD during pregnancy.19 Among pregnant patients about 5% of buprenorphine prescriptions are written by obstetricians.20 An innovative approach to initiating BUP for pregnant patients with OUD is to use unobserved initiation, which involves outpatient discontinuation of nonprescription opioids to induce mild to moderate withdrawal symptoms followed by initiation of BUP treatment. In one cohort study, 55 pregnant patients used an unobserved outpatient protocol to initiate BUP treatment; 80% of the patients previously had used methadone or BUP. No patient experienced a precipitated withdrawal and 96% of patients returned for their office visit 1 week after initiation of treatment. Eighty-six percent of patients remained in treatment 3 months following initiation of BUP.21
Compared with methadone, BUP treatment during pregnancy may result in lower rates of neonatal abstinence syndrome. In one study of pregnant patients who were using methadone (n = 5,056) or BUP (n = 11,272) in late pregnancy, neonatal abstinence syndrome was diagnosed in 69.2% and 52.0% of newborns, respectively (adjusted relative risk, 0.73; 95% confidence interval, 0.71–0.75).22 In addition, compared with methadone, the use of BUP was associated with a reduced risk for low birth weight (14.9% vs 8.3%) and a lower risk for preterm birth (24.9% vs 14.4%). In this study, there were no differences in maternal obstetric outcomes when comparing BUP versus methadone treatment. Similar results have been reported in a meta-analysis analyzing the use of methadone and BUP during pregnancy.23 Studies performed to date have not shown an increased risk of congenital anomalies with the use of BUP-NAL during pregnancy.24,25
Although there may be differences in newborn outcomes with BUP and methadone, the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists does not recommend switching from methadone to BUP during pregnancy because precipitated withdrawal may occur.26 Based on recent studies, the American Society of Addiction Medicine has advised that it is safe to prescribe pregnant patients either BUP or BUP-NAL.27,28
Medication treatment of OUD with or without intensive counseling
The FDA recently reviewed literature related to the advantages and challenges of combining intensive counseling with medication treatment of OUD.29 The FDA noted that treatment saves lives and encouraged clinicians to initiate medication treatment of OUD or refer the patient to an appropriate clinician or treatment center. Combining medication treatment of OUD with intensive counseling is associated with greater treatment adherence and reduced health care costs. For example, in one study of 4,987 patients with OUD, initiation of counseling within 8 weeks of the start of medication treatment and a BUP dose of 16 mg or greater daily were associated with increased adherence to treatment.30 For patients receiving a BUP dose of less than 16 mg daily, treatment adherence with and without counseling was approximately 325 and 230 days, respectively. When the dose of BUP was 16 mg or greater, treatment adherence with and without counseling was approximately 405 and 320 days, respectively.30
Counseling should always be offered to patients initiating medication treatment of OUD. It should be noted that counseling alone is not a highly effective treatment for OUD.31 The FDA recently advised that the lack of availability of intensive counseling should not prevent clinicians from initiating BUP for the treatment of OUD.29 OUD is associated with a high mortalityrate and if counseling is not possible, medication treatment should be initiated. Substantial evidence demonstrates that medication treatment of OUD is associated with many benefits.16 The FDA advisory committee concluded that OUD treatment decisions should use shared decision making and be supportive and patient centered.29
The opportunities for medication treatment of OUD in primary care practice have expanded due to the recent FDA removal of restrictions on the use of BUP and heightened awareness of the positive public health impact of medication treatment. Challenges to the medication treatment of OUD remain, including stigmatization of OUD, barriers to insurance coverage for BUP, practice costs of treating OUD, and gaps in clinical education. For many pregnant patients, their main point of contact with health care is their obstetrician. By incorporating OUD treatment in pregnancy care, obstetricians will improve the health of the mother and newborn, contributing to the well-being of current and future generations. ●
Experts have recommended several interventions that may help reduce opioid overdose death.1 A consensus recommendation is that people who use drugs should be provided naloxone rescue medication and educated on the proper use of naloxone. Naloxone rescue medication is available in formulations for nasal or parenteral administration. The US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) recently has approved naloxone for over-the-counter status. The American Medical Association has provided a short web video on how to administer nasal naloxone.2 In a small pilot study, obstetricians offered every postpartum patient with naloxone administration education and a 2-dose nasal naloxone pack, with 76% of patients accepting the nasal naloxone pack.3
Many experts recommend that people who use drugs should be advised to never use them alone and to test a small amount of the drug to assess its potency. Many patients who use opioid drugs also take benzodiazepines, which can contribute to respiratory depression.4 Patients should avoid mixing drugs (eg, opioids and benzodiazepines). Some experts recommend that patients who use drugs should be provided take-home fentanyl test strips so they can evaluate their drugs for the presence of fentanyl, a medication that suppresses respiration and contributes to many overdose deaths. In addition, people who use drugs and are interested in reducing their use of drugs or managing overdose risk can be offered initiation of medication treatment of OUD.1
References
1. Wood E, Solomon ED, Hadland SE. Universal precautions for people at risk of opioid overdose in North America. JAMA Int Med. 2023;183:401-402.
2. How to administer Naloxone. AMA website. Accessed August 28, 2023. https://www.ama-assn.org /delivering-care/overdose-epidemic/how-administer-naloxone
3. Naliboff JA, Tharpe N. Universal postpartum naloxone provision: a harm reduction quality improvement project. J Addict Med. 2022;17:360-362.
4. Kelly JC, Raghuraman N, Stout MJ, et al. Home induction of buprenorphine for treatment of opioid use disorder in pregnancy. Obstet Gynecol. 2021;138:655-659.
- Spencer MR, Miniño AM, Warner M. Drug overdose deaths in the United States, 20012021. NCHS Data Brief no 457. Hyattsville, MD, National Center for Health Statistics. 2022. NCHS Data Brief No. 457. Published December 2022. Accessed August 21, 2023. https://www.cdc.gov /nchs/products/databriefs/db457.htm
- US traffic deaths drop slightly in 2022 but still a ‘crisis.’ AP News website. Published April 20, 2023. Accessed August 21, 2023. https://apnews.com /article/traffic-deaths-distracted-driving-crisis -6db6471e273b275920b6c4f9eb7e493b
- Suicide statistics. American Foundation for Suicide Prevention website. Accessed August 21, 2023. https://afsp.org/suicide-statistics/
- Bruzelius E, Martins SS. US Trends in drug overdose mortality among pregnant and postpartum persons, 2017-2020. JAMA. 2022;328:2159-2161.
- Metz TD, Rovner P, Hoffman MC, et al. Maternal deaths from suicide and overdose in Colorado, 2004-2012. Obstet Gynecol. 2016;128:1233-1240.
- Schiff DM, Nielsen T, Terplan M, et al. Fatal and nonfatal overdose among pregnant and postpartum women in Massachusetts. Obstet Gynecol. 2018;132:466-474.
- Goldman-Mellor S, Margerison CE. Maternal drug-related death and suicide are leading causes of postpartum death in California. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2019;221:489.e1-489.e9.
- Sordo L, Barrio G, Bravo MJ, et al. Mortality risk during and after opioid substitution treatment: systematic review and meta-analysis of cohort studies. BMJ. 2017;357:j1550.
- Waiver elimination (MAT Act). SAMHSA website. Accessed August 21, 2023. https://www .samhsa.gov/medications-substance-use- disorders/removal-data-waiver-requirement
- Picco L, Middleton M, Bruno R, et al. Validation of the OWLS, a Screening Tool for Measuring Prescription Opioid Use Disorder in Primary Care. Pain Med. 2020;21:2757-2764.
- American Psychiatric Association. Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders. 5th ed. American Psychiatric Association; 2013.
- Creedon TB, Ali MM, Schuman-Olivier Z. Trends in buprenorphine prescribing for opioid use disorder by psychiatrists in the US from 2003 to 2021. JAMA Health Forum. 2023;4:E230221.
- Quick MD website. Accessed August 21, 2023. https://quick.md/
- Treitler P, Nowels M, Samples H, et al. BUP utilization and prescribing among New Jersey Medicaid beneficiaries after adoption of initiatives designed to improve treatment access. JAMA Netw Open. 2023;6:E2312030.
- Jawa R, Tin Y, Nall S, et al. Estimated clinical outcomes and cost-effectiveness associated with provision of addiction treatment in US primary care clinics. JAMA Netw Open. 2023;6:E237888.
- Wakeman SE, Larochelle MR, Ameli O, et al. Comparative effectiveness of different treatment pathways of opioid use disorder. JAMA Netw Open. 2020;3:E1920622.
- Wilder CM, Hosta D, Winhusen T. Association of methadone dose with substance use and treatment retention in pregnant and postpartum women with opioid use disorder. J Subst Abuse Treat. 2017;80:33-36.
- Haight SC, Ko JY, Tong VT, et al. Opioid use disorder documented at delivery hospitalization - United States, 1999-2014. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2018;67:845-849.
- Xu KY, Jones HE, Schiff DM, et al. Initiation and treatment discontinuation of medications for opioid use disorder in pregnant people compared with nonpregnant people. Obstet Gynecol. 2023;141:845-853.
- Kelly D, Krans EE. Medical specialty of buprenorphine prescribers for pregnant women with opioid use disorder. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2019;220:502-503.
- Kelly JC, Raghuraman N, Stout MJ, et al. Home induction of buprenorphine for treatment of opioid use disorder in pregnancy. Obstet Gynecol. 2021;138:655-659.
- Suarez EA, Huybrechts KF, Straub L, et al. Buprenorphine versus methadone for opioid use disorder in pregnancy. N Engl J Med. 2022;387:2033-2044.
- Kinsella M, Halliday LO, Shaw M, et al. Buprenorphine compared with methadone in pregnancy: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Subst Use Misuse. 2022;57:1400-1416.
- Jumah NA, Edwards C, Balfour-Boehm J, et al. Observational study of the safety of buprenorphine-naloxone in pregnancy in a rural and remote population. BMJ Open. 2016;6:E011774.
- Mullins N, Galvin SL, Ramage M, et al. Buprenorphine and naloxone versus buprenorphine for opioid use disorder in pregnancy: a cohort study. J Addict Med. 2020;14:185-192.
- Opioid use and opioid use disorder in pregnancy. Committee Opinion No. 711. American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists. Obstet Gynecol. 2017;130:E81-E94.
- The ASAM National Practice Guideline for the Treatment of Opioid Use Disorder: 2020 Focused Update. J Addict Med. 2020;14(2S suppl 1):1-91.
- Link HM, Jones H, Miller L, et al. Buprenorphinenaloxone use in pregnancy: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Am J Obstet Gynecol MFM. 2020;2:100179.
- Delphin-Rittmon ME, Cavazzoni P. US Food and Drug Administration website. https://www.fda .gov/media/168027/download
- Eren K, Schuster J, Herschell A, et al. Association of Counseling and Psychotherapy on retention in medication for addiction treatment within a large Medicaid population. J Addict Med. 2022;16:346353.
- Kakko J, Dybrandt Svanborg K, Kreek MJ, et al. 1-year retention and social function after buprenorphine-assisted relapse prevention treatment for heroin dependence in Sweden: a randomized, placebo-controlled trial. Lancet. 2003;361:662-668.
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) reported 106,699 deaths in 2021 from drug overdose, with the majority being linked to synthetic opioids, including fentanyl and tramadol.1 This number compares with 42,795 deaths due to motor vehicle accidents and 48,183 deaths due to suicide in 2021.2,3 Most of the opioid overdose deaths occurred among people aged 25 to 64 years, the peak age of patients cared for by obstetrician-gynecologists. Among pregnant and postpartum persons, mortality due to drug overdose has increased by 81% between 2017 and 2020.4
Among pregnant and postpartum patients, drug overdose death is more common than suicide, and the risk for drug overdose death appears to be greatest in the year following delivery.5,6 In many cases, postpartum patients with OUD have had multiple contacts with the health care system prior to their death, showing that there is an opportunity for therapeutic intervention before the death occurred.7 Medication-assisted recovery for OUD involves a comprehensive array of interventions including medication, counseling, and social support. Medication treatment of OUD with BUP or methadone reduces the risk for death but is underutilized among patients with OUD.6,8 Recent federal legislation has removed restrictions on the use of BUP, increasing the opportunity for primary care clinicians to prescribe it for the treatment of OUD.9
Screening and diagnosis of OUD
Screening for OUD is recommended for patients who are at risk for opioid misuse (ie, those who are taking/have taken opioid medications). The OWLS (Overuse, Worrying, Losing interest, and feeling Slowed down, sluggish, or sedated) screening tool is used to detect prescription medication OUD and has 4 questions10:
1. In the past 3 months did you use your opioid medicines for other purposes—for example, to help you sleep or to help with stress or worry?
2. In the past 3 months did opioid medicines cause you to feel slowed down, sluggish, or sedated?
3. In the past 3 months did opioid medicines cause you to lose interest in your usual activities?
4. In the past 3 months did you worry about your use of opioid medicines?
Patient agreement with 3 or 4 questions indicates a positive screening test.
If the patient has a positive screening test, a formal diagnosis of OUD can be made using the 11 symptoms outlined in the American Psychiatric Association’s Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, Fifth Edition.11 The diagnosis of mild (2 to 3 symptoms), moderate (4 to 5 symptoms), or severe OUD (6 or more symptoms) is made based on the number of symptoms the patient reports.

Buprenorphine treatment of OUD in primary care
The role of primary care clinicians in the medication treatment of OUD is increasing. Using a nationwide system that tracks prescription medications, investigators reported that, in 2004, psychiatrists wrote 32.2% of all BUP prescriptions; in 2021, however, only 10% of such prescriptions were provided by psychiatrists, with most prescriptions written by non-psychiatrist physicians, nurse practitioners, and physician assistants that year.12 Innovative telehealth approaches to consultation and medication treatment of OUD are now available—one example is QuickMD.13 Such sites are designed to remove barriers to initiating medication treatment of OUD.
The role of primary care clinicians in the management of OUD using BUP and buprenorphine-naloxone (BUP-NAL) has increased due to many factors, including:
- the removal of US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) barriers to prescribing BUP
- the epidemic of OUD and the small size of the addiction specialist workforce, necessitating that primary care clinicians become engaged in the treatment of OUD
- an increase in unobserved initiation of BUP among ambulatory patients, and a parallel decrease in cases of observed initiation in addiction center settings
- the reframing of OUD as a chronic medical problem, with many similarities to diabetes, obesity, dyslipidemia, and hypertension.
Similar to other diseases managed by primary care clinicians, OUD requires long-term chronic treatment with a medicine that, if taken as directed, provides excellent outcomes. Primary care clinicians who prescribe BUP also can optimize longitudinal care for comorbid disorders such as hypertension and diabetes, which are prevalent in people with OUD.
In 2019, New Jersey implemented new guidelines for the treatment of OUD, removing prior authorization barriers, increasing reimbursement for office-based OUD treatment, and establishing regional centers of excellence. The implementation of the new guidelines was followed by a marked increase in BUP prescribers among primary care clinicians, emergency medicine physicians, and advanced practice clinicians.14
To estimate the public health impact of BUP prescribing by primary care clinicians, investigators simulated patient outcomes in 3 scenarios15:
1. primary care clinicians refer patients to addiction specialists for OUD treatment
2. primary care clinicians provide BUP services in their practice
3. primary care clinicians provide BUP and harm reduction kits containing syringes and wound care supplies in their practice.
Strategies 2 and 3 resulted in 14% fewer deaths due to opioid overdose, an increased life expectancy of approximately 2.7 years, and reduced hospital costs. For strategy 3, the incremental cost per life-year saved was $34,400. The investigators noted that prescribing BUP in primary care practice increases practice costs.15
Treatment with BUP reduces death from opioid overdose, improves patient health, decreases use of illicit opioids, and reduces patient cravings for opioids. BUP is a safe medication and is associated with fewer adverse effects than insulin or warfarin.16
Continue to: Methadone treatment of OUD...
Methadone treatment of OUD
Methadone is a full opioid agonist approved by the FDA for the treatment of severe pain or OUD. Methadone treatment of OUD is strictly regulated and typically is ordered and administered at an opioid treatment program that is federally licensed. Methadone for OUD treatment cannot be prescribed by a physician to a pharmacy, limiting its use in primary care practice. Methadone used to treat OUD is ordered and dispensed at opioid-treatment programs. Take-home doses of methadone may be available to patients after adherence to the regimen has been established. When used long-term, higher doses of methadone are associated with better adherence, but these higher doses can cause respiratory depression. In a study of 189 pregnant patients taking methadone to treat OUD, daily doses of 60 mg or greater were associated with better treatment retention at delivery and 60 days postpartum, as well as less use of nonprescription opioids.17 Under limited circumstances methadone can be ordered and dispensed for hospitalized patients with OUD.
Methadone is a pure opioid receptor agonist. Naloxone (NAL) is an opioid receptor antagonist. Buprenorphine (BUP) is a partial opioid receptor agonist-antagonist, which limits overdose risk. BUP often is combined with NAL as a combination formulation, which is thought to reduce the repurposing of BUP for non-prescribed uses. At appropriate treatment dosages, both methadone (≥60 mg) and BUP (≥ 16 mg) are highly effective for the treatment of OUD.1 For patients with health insurance, pharmacy benefits often provide some coverage for preferred products but no coverage for other products. Not all pharmacies carry BUP products. In a study of more than 5,000 pharmacies, approximately 60% reported that they carry and can dispense BUP medications.2
BUP monotherapy is available as generic sublingual tablets, buccal films (Belbuca), formulations for injection (Sublocade), and subcutaneous implants (Probuphine). BUPNAL is available as buccal films (Bunavail), sublingual films (Suboxone), and sublingual tablets (Zubsolv). For BUP-NAL combination productions, the following dose combinations have been reported to have similar effects: BUP-NAL 8 mg/2 mg sublingual film, BUP-NAL 5.7 mg/1.4 mg sublingual tablet, and BUP-NAL 4.2 mg/0.7 mg buccal film.3
When initiating BUP-monotherapy or BUP-NAL treatment for OUD, one approach for unobserved initiation is to instruct the patient to discontinue using opioid agonist drugs and wait for the onset of mild to moderate withdrawal symptoms. The purpose of this step is to avoid precipitating severe withdrawal symptoms caused by giving BUP or BUP-NAL to a patient who has recently used opioid drugs.
If BUP-NAL sublingual films (Suboxone) are prescribed following the onset of mild to moderate withdrawal symptoms, the patient can initiate therapy with a dose of 2 mg BUP/0.5 mg NAL or 4 mg BUP/1 mg NAL. At 60 to 120 minutes following the initial dose, if withdrawal symptoms persist, an additional dose of 4 mg BUP/1 mg NAL can be given. Thereafter, symptoms can be assessed every 60 to 120 minutes and additional doses administered to control symptoms. On the second day of therapy, a maximum of 16 mg of BUP is administered. Over the following days and weeks, if symptoms and cravings persist at a BUP dose of 16 mg, the total daily dose of BUP can be titrated up to 24 mg. For long-term treatment, a commonly prescribed daily dose is 16 mg BUP/4 mg NAL or 24 mg BUP/6 mg NAL. An absolute contraindication to BUP or BUP/NAL treatment is an allergy to the medication, and a relative contraindication is liver failure.
One potential complication of transmucosal BUP or BUP-NAL treatment is a dry mouth (xerostomia), which may contribute to dental disease.4 However, some experts question the quality of the data that contributed to the warning.5,6 Potential dental complications might be prevented by regular oral health examinations, daily flossing and teeth brushing, and stimulation of saliva by sugar-free gum or lozenges.
Primary care clinicians who initiate BUP or BUPNAL treatment for OUD often have a weekly visit with the patient during the initial phase of treatment and then every 3 to 4 weeks during maintenance therapy. Most patients need long-term treatment to achieve the goals of therapy, which include prevention of opioid overdose, reduction of cravings for nonprescription narcotics, and improvement in overall health. BUP and BUP-NAL treatment are effective without formal counseling, but counseling and social work support improve long-term adherence with treatment. Primary care clinicians who have experience with medication treatment of OUD report that their experience convinces them that medication treatment of OUD has similarities to the long-term treatment of diabetes, with antihyperglycemia medicines or the treatment of HIV infection with antiviral medications.
References
1. Mattick RP, Breen C, Kimber J, et al. Buprenorphine maintenance versus placebo or methadone maintenance for opioid dependence. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2014;CD002207.
2. Weiner SG, Qato DM, Faust JS, et al. Pharmacy availability of buprenorphine for opioid use disorder treatment in the U.S. JAMA Netw Open. 2023;6:E2316089.
3. Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration (SAMHSA). Medications for opioid use disorder. SAMHSA website. Accessed August 21, 2023. https ://store.samhsa.gov/sites/default/files/SAMHSA_Digital_Download/PEP 21-02-01-002.pdf
4. FDA warns about dental problems with buprenorphine medicines dissolved in the mouth. FDA website. Accessed August 21, 2023. https ://www.fda.gov/drugs/drug-safety-and-availability/fda-warns-about-dental-problems-buprenorphine-medicines-dissolved-mouth-treat-opioiduse-disorder#:~:text=What%20did%20FDA%20find%3F,medicines%20 dissolved%20in%20the%20mouth
5. Watson DP, Etmian S, Gastala N. Sublingual buprenorphine-naloxone exposure and dental disease. JAMA. 2023;329:1223-1224.
6. Brothers TD, Lewer D, Bonn M. Sublingual buprenorphine-naloxone exposure and dental disease. JAMA. 2023;329:1224.
Medication treatment of OUD in obstetrics
In the United States, the prevalence of OUD among pregnant patients hospitalized for delivery more than quadrupled from 1999 through 2014.18 BUP and methadone commonly are used to treat OUD during pregnancy.19 Among pregnant patients about 5% of buprenorphine prescriptions are written by obstetricians.20 An innovative approach to initiating BUP for pregnant patients with OUD is to use unobserved initiation, which involves outpatient discontinuation of nonprescription opioids to induce mild to moderate withdrawal symptoms followed by initiation of BUP treatment. In one cohort study, 55 pregnant patients used an unobserved outpatient protocol to initiate BUP treatment; 80% of the patients previously had used methadone or BUP. No patient experienced a precipitated withdrawal and 96% of patients returned for their office visit 1 week after initiation of treatment. Eighty-six percent of patients remained in treatment 3 months following initiation of BUP.21
Compared with methadone, BUP treatment during pregnancy may result in lower rates of neonatal abstinence syndrome. In one study of pregnant patients who were using methadone (n = 5,056) or BUP (n = 11,272) in late pregnancy, neonatal abstinence syndrome was diagnosed in 69.2% and 52.0% of newborns, respectively (adjusted relative risk, 0.73; 95% confidence interval, 0.71–0.75).22 In addition, compared with methadone, the use of BUP was associated with a reduced risk for low birth weight (14.9% vs 8.3%) and a lower risk for preterm birth (24.9% vs 14.4%). In this study, there were no differences in maternal obstetric outcomes when comparing BUP versus methadone treatment. Similar results have been reported in a meta-analysis analyzing the use of methadone and BUP during pregnancy.23 Studies performed to date have not shown an increased risk of congenital anomalies with the use of BUP-NAL during pregnancy.24,25
Although there may be differences in newborn outcomes with BUP and methadone, the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists does not recommend switching from methadone to BUP during pregnancy because precipitated withdrawal may occur.26 Based on recent studies, the American Society of Addiction Medicine has advised that it is safe to prescribe pregnant patients either BUP or BUP-NAL.27,28
Medication treatment of OUD with or without intensive counseling
The FDA recently reviewed literature related to the advantages and challenges of combining intensive counseling with medication treatment of OUD.29 The FDA noted that treatment saves lives and encouraged clinicians to initiate medication treatment of OUD or refer the patient to an appropriate clinician or treatment center. Combining medication treatment of OUD with intensive counseling is associated with greater treatment adherence and reduced health care costs. For example, in one study of 4,987 patients with OUD, initiation of counseling within 8 weeks of the start of medication treatment and a BUP dose of 16 mg or greater daily were associated with increased adherence to treatment.30 For patients receiving a BUP dose of less than 16 mg daily, treatment adherence with and without counseling was approximately 325 and 230 days, respectively. When the dose of BUP was 16 mg or greater, treatment adherence with and without counseling was approximately 405 and 320 days, respectively.30
Counseling should always be offered to patients initiating medication treatment of OUD. It should be noted that counseling alone is not a highly effective treatment for OUD.31 The FDA recently advised that the lack of availability of intensive counseling should not prevent clinicians from initiating BUP for the treatment of OUD.29 OUD is associated with a high mortalityrate and if counseling is not possible, medication treatment should be initiated. Substantial evidence demonstrates that medication treatment of OUD is associated with many benefits.16 The FDA advisory committee concluded that OUD treatment decisions should use shared decision making and be supportive and patient centered.29
The opportunities for medication treatment of OUD in primary care practice have expanded due to the recent FDA removal of restrictions on the use of BUP and heightened awareness of the positive public health impact of medication treatment. Challenges to the medication treatment of OUD remain, including stigmatization of OUD, barriers to insurance coverage for BUP, practice costs of treating OUD, and gaps in clinical education. For many pregnant patients, their main point of contact with health care is their obstetrician. By incorporating OUD treatment in pregnancy care, obstetricians will improve the health of the mother and newborn, contributing to the well-being of current and future generations. ●
Experts have recommended several interventions that may help reduce opioid overdose death.1 A consensus recommendation is that people who use drugs should be provided naloxone rescue medication and educated on the proper use of naloxone. Naloxone rescue medication is available in formulations for nasal or parenteral administration. The US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) recently has approved naloxone for over-the-counter status. The American Medical Association has provided a short web video on how to administer nasal naloxone.2 In a small pilot study, obstetricians offered every postpartum patient with naloxone administration education and a 2-dose nasal naloxone pack, with 76% of patients accepting the nasal naloxone pack.3
Many experts recommend that people who use drugs should be advised to never use them alone and to test a small amount of the drug to assess its potency. Many patients who use opioid drugs also take benzodiazepines, which can contribute to respiratory depression.4 Patients should avoid mixing drugs (eg, opioids and benzodiazepines). Some experts recommend that patients who use drugs should be provided take-home fentanyl test strips so they can evaluate their drugs for the presence of fentanyl, a medication that suppresses respiration and contributes to many overdose deaths. In addition, people who use drugs and are interested in reducing their use of drugs or managing overdose risk can be offered initiation of medication treatment of OUD.1
References
1. Wood E, Solomon ED, Hadland SE. Universal precautions for people at risk of opioid overdose in North America. JAMA Int Med. 2023;183:401-402.
2. How to administer Naloxone. AMA website. Accessed August 28, 2023. https://www.ama-assn.org /delivering-care/overdose-epidemic/how-administer-naloxone
3. Naliboff JA, Tharpe N. Universal postpartum naloxone provision: a harm reduction quality improvement project. J Addict Med. 2022;17:360-362.
4. Kelly JC, Raghuraman N, Stout MJ, et al. Home induction of buprenorphine for treatment of opioid use disorder in pregnancy. Obstet Gynecol. 2021;138:655-659.
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) reported 106,699 deaths in 2021 from drug overdose, with the majority being linked to synthetic opioids, including fentanyl and tramadol.1 This number compares with 42,795 deaths due to motor vehicle accidents and 48,183 deaths due to suicide in 2021.2,3 Most of the opioid overdose deaths occurred among people aged 25 to 64 years, the peak age of patients cared for by obstetrician-gynecologists. Among pregnant and postpartum persons, mortality due to drug overdose has increased by 81% between 2017 and 2020.4
Among pregnant and postpartum patients, drug overdose death is more common than suicide, and the risk for drug overdose death appears to be greatest in the year following delivery.5,6 In many cases, postpartum patients with OUD have had multiple contacts with the health care system prior to their death, showing that there is an opportunity for therapeutic intervention before the death occurred.7 Medication-assisted recovery for OUD involves a comprehensive array of interventions including medication, counseling, and social support. Medication treatment of OUD with BUP or methadone reduces the risk for death but is underutilized among patients with OUD.6,8 Recent federal legislation has removed restrictions on the use of BUP, increasing the opportunity for primary care clinicians to prescribe it for the treatment of OUD.9
Screening and diagnosis of OUD
Screening for OUD is recommended for patients who are at risk for opioid misuse (ie, those who are taking/have taken opioid medications). The OWLS (Overuse, Worrying, Losing interest, and feeling Slowed down, sluggish, or sedated) screening tool is used to detect prescription medication OUD and has 4 questions10:
1. In the past 3 months did you use your opioid medicines for other purposes—for example, to help you sleep or to help with stress or worry?
2. In the past 3 months did opioid medicines cause you to feel slowed down, sluggish, or sedated?
3. In the past 3 months did opioid medicines cause you to lose interest in your usual activities?
4. In the past 3 months did you worry about your use of opioid medicines?
Patient agreement with 3 or 4 questions indicates a positive screening test.
If the patient has a positive screening test, a formal diagnosis of OUD can be made using the 11 symptoms outlined in the American Psychiatric Association’s Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, Fifth Edition.11 The diagnosis of mild (2 to 3 symptoms), moderate (4 to 5 symptoms), or severe OUD (6 or more symptoms) is made based on the number of symptoms the patient reports.

Buprenorphine treatment of OUD in primary care
The role of primary care clinicians in the medication treatment of OUD is increasing. Using a nationwide system that tracks prescription medications, investigators reported that, in 2004, psychiatrists wrote 32.2% of all BUP prescriptions; in 2021, however, only 10% of such prescriptions were provided by psychiatrists, with most prescriptions written by non-psychiatrist physicians, nurse practitioners, and physician assistants that year.12 Innovative telehealth approaches to consultation and medication treatment of OUD are now available—one example is QuickMD.13 Such sites are designed to remove barriers to initiating medication treatment of OUD.
The role of primary care clinicians in the management of OUD using BUP and buprenorphine-naloxone (BUP-NAL) has increased due to many factors, including:
- the removal of US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) barriers to prescribing BUP
- the epidemic of OUD and the small size of the addiction specialist workforce, necessitating that primary care clinicians become engaged in the treatment of OUD
- an increase in unobserved initiation of BUP among ambulatory patients, and a parallel decrease in cases of observed initiation in addiction center settings
- the reframing of OUD as a chronic medical problem, with many similarities to diabetes, obesity, dyslipidemia, and hypertension.
Similar to other diseases managed by primary care clinicians, OUD requires long-term chronic treatment with a medicine that, if taken as directed, provides excellent outcomes. Primary care clinicians who prescribe BUP also can optimize longitudinal care for comorbid disorders such as hypertension and diabetes, which are prevalent in people with OUD.
In 2019, New Jersey implemented new guidelines for the treatment of OUD, removing prior authorization barriers, increasing reimbursement for office-based OUD treatment, and establishing regional centers of excellence. The implementation of the new guidelines was followed by a marked increase in BUP prescribers among primary care clinicians, emergency medicine physicians, and advanced practice clinicians.14
To estimate the public health impact of BUP prescribing by primary care clinicians, investigators simulated patient outcomes in 3 scenarios15:
1. primary care clinicians refer patients to addiction specialists for OUD treatment
2. primary care clinicians provide BUP services in their practice
3. primary care clinicians provide BUP and harm reduction kits containing syringes and wound care supplies in their practice.
Strategies 2 and 3 resulted in 14% fewer deaths due to opioid overdose, an increased life expectancy of approximately 2.7 years, and reduced hospital costs. For strategy 3, the incremental cost per life-year saved was $34,400. The investigators noted that prescribing BUP in primary care practice increases practice costs.15
Treatment with BUP reduces death from opioid overdose, improves patient health, decreases use of illicit opioids, and reduces patient cravings for opioids. BUP is a safe medication and is associated with fewer adverse effects than insulin or warfarin.16
Continue to: Methadone treatment of OUD...
Methadone treatment of OUD
Methadone is a full opioid agonist approved by the FDA for the treatment of severe pain or OUD. Methadone treatment of OUD is strictly regulated and typically is ordered and administered at an opioid treatment program that is federally licensed. Methadone for OUD treatment cannot be prescribed by a physician to a pharmacy, limiting its use in primary care practice. Methadone used to treat OUD is ordered and dispensed at opioid-treatment programs. Take-home doses of methadone may be available to patients after adherence to the regimen has been established. When used long-term, higher doses of methadone are associated with better adherence, but these higher doses can cause respiratory depression. In a study of 189 pregnant patients taking methadone to treat OUD, daily doses of 60 mg or greater were associated with better treatment retention at delivery and 60 days postpartum, as well as less use of nonprescription opioids.17 Under limited circumstances methadone can be ordered and dispensed for hospitalized patients with OUD.
Methadone is a pure opioid receptor agonist. Naloxone (NAL) is an opioid receptor antagonist. Buprenorphine (BUP) is a partial opioid receptor agonist-antagonist, which limits overdose risk. BUP often is combined with NAL as a combination formulation, which is thought to reduce the repurposing of BUP for non-prescribed uses. At appropriate treatment dosages, both methadone (≥60 mg) and BUP (≥ 16 mg) are highly effective for the treatment of OUD.1 For patients with health insurance, pharmacy benefits often provide some coverage for preferred products but no coverage for other products. Not all pharmacies carry BUP products. In a study of more than 5,000 pharmacies, approximately 60% reported that they carry and can dispense BUP medications.2
BUP monotherapy is available as generic sublingual tablets, buccal films (Belbuca), formulations for injection (Sublocade), and subcutaneous implants (Probuphine). BUPNAL is available as buccal films (Bunavail), sublingual films (Suboxone), and sublingual tablets (Zubsolv). For BUP-NAL combination productions, the following dose combinations have been reported to have similar effects: BUP-NAL 8 mg/2 mg sublingual film, BUP-NAL 5.7 mg/1.4 mg sublingual tablet, and BUP-NAL 4.2 mg/0.7 mg buccal film.3
When initiating BUP-monotherapy or BUP-NAL treatment for OUD, one approach for unobserved initiation is to instruct the patient to discontinue using opioid agonist drugs and wait for the onset of mild to moderate withdrawal symptoms. The purpose of this step is to avoid precipitating severe withdrawal symptoms caused by giving BUP or BUP-NAL to a patient who has recently used opioid drugs.
If BUP-NAL sublingual films (Suboxone) are prescribed following the onset of mild to moderate withdrawal symptoms, the patient can initiate therapy with a dose of 2 mg BUP/0.5 mg NAL or 4 mg BUP/1 mg NAL. At 60 to 120 minutes following the initial dose, if withdrawal symptoms persist, an additional dose of 4 mg BUP/1 mg NAL can be given. Thereafter, symptoms can be assessed every 60 to 120 minutes and additional doses administered to control symptoms. On the second day of therapy, a maximum of 16 mg of BUP is administered. Over the following days and weeks, if symptoms and cravings persist at a BUP dose of 16 mg, the total daily dose of BUP can be titrated up to 24 mg. For long-term treatment, a commonly prescribed daily dose is 16 mg BUP/4 mg NAL or 24 mg BUP/6 mg NAL. An absolute contraindication to BUP or BUP/NAL treatment is an allergy to the medication, and a relative contraindication is liver failure.
One potential complication of transmucosal BUP or BUP-NAL treatment is a dry mouth (xerostomia), which may contribute to dental disease.4 However, some experts question the quality of the data that contributed to the warning.5,6 Potential dental complications might be prevented by regular oral health examinations, daily flossing and teeth brushing, and stimulation of saliva by sugar-free gum or lozenges.
Primary care clinicians who initiate BUP or BUPNAL treatment for OUD often have a weekly visit with the patient during the initial phase of treatment and then every 3 to 4 weeks during maintenance therapy. Most patients need long-term treatment to achieve the goals of therapy, which include prevention of opioid overdose, reduction of cravings for nonprescription narcotics, and improvement in overall health. BUP and BUP-NAL treatment are effective without formal counseling, but counseling and social work support improve long-term adherence with treatment. Primary care clinicians who have experience with medication treatment of OUD report that their experience convinces them that medication treatment of OUD has similarities to the long-term treatment of diabetes, with antihyperglycemia medicines or the treatment of HIV infection with antiviral medications.
References
1. Mattick RP, Breen C, Kimber J, et al. Buprenorphine maintenance versus placebo or methadone maintenance for opioid dependence. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2014;CD002207.
2. Weiner SG, Qato DM, Faust JS, et al. Pharmacy availability of buprenorphine for opioid use disorder treatment in the U.S. JAMA Netw Open. 2023;6:E2316089.
3. Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration (SAMHSA). Medications for opioid use disorder. SAMHSA website. Accessed August 21, 2023. https ://store.samhsa.gov/sites/default/files/SAMHSA_Digital_Download/PEP 21-02-01-002.pdf
4. FDA warns about dental problems with buprenorphine medicines dissolved in the mouth. FDA website. Accessed August 21, 2023. https ://www.fda.gov/drugs/drug-safety-and-availability/fda-warns-about-dental-problems-buprenorphine-medicines-dissolved-mouth-treat-opioiduse-disorder#:~:text=What%20did%20FDA%20find%3F,medicines%20 dissolved%20in%20the%20mouth
5. Watson DP, Etmian S, Gastala N. Sublingual buprenorphine-naloxone exposure and dental disease. JAMA. 2023;329:1223-1224.
6. Brothers TD, Lewer D, Bonn M. Sublingual buprenorphine-naloxone exposure and dental disease. JAMA. 2023;329:1224.
Medication treatment of OUD in obstetrics
In the United States, the prevalence of OUD among pregnant patients hospitalized for delivery more than quadrupled from 1999 through 2014.18 BUP and methadone commonly are used to treat OUD during pregnancy.19 Among pregnant patients about 5% of buprenorphine prescriptions are written by obstetricians.20 An innovative approach to initiating BUP for pregnant patients with OUD is to use unobserved initiation, which involves outpatient discontinuation of nonprescription opioids to induce mild to moderate withdrawal symptoms followed by initiation of BUP treatment. In one cohort study, 55 pregnant patients used an unobserved outpatient protocol to initiate BUP treatment; 80% of the patients previously had used methadone or BUP. No patient experienced a precipitated withdrawal and 96% of patients returned for their office visit 1 week after initiation of treatment. Eighty-six percent of patients remained in treatment 3 months following initiation of BUP.21
Compared with methadone, BUP treatment during pregnancy may result in lower rates of neonatal abstinence syndrome. In one study of pregnant patients who were using methadone (n = 5,056) or BUP (n = 11,272) in late pregnancy, neonatal abstinence syndrome was diagnosed in 69.2% and 52.0% of newborns, respectively (adjusted relative risk, 0.73; 95% confidence interval, 0.71–0.75).22 In addition, compared with methadone, the use of BUP was associated with a reduced risk for low birth weight (14.9% vs 8.3%) and a lower risk for preterm birth (24.9% vs 14.4%). In this study, there were no differences in maternal obstetric outcomes when comparing BUP versus methadone treatment. Similar results have been reported in a meta-analysis analyzing the use of methadone and BUP during pregnancy.23 Studies performed to date have not shown an increased risk of congenital anomalies with the use of BUP-NAL during pregnancy.24,25
Although there may be differences in newborn outcomes with BUP and methadone, the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists does not recommend switching from methadone to BUP during pregnancy because precipitated withdrawal may occur.26 Based on recent studies, the American Society of Addiction Medicine has advised that it is safe to prescribe pregnant patients either BUP or BUP-NAL.27,28
Medication treatment of OUD with or without intensive counseling
The FDA recently reviewed literature related to the advantages and challenges of combining intensive counseling with medication treatment of OUD.29 The FDA noted that treatment saves lives and encouraged clinicians to initiate medication treatment of OUD or refer the patient to an appropriate clinician or treatment center. Combining medication treatment of OUD with intensive counseling is associated with greater treatment adherence and reduced health care costs. For example, in one study of 4,987 patients with OUD, initiation of counseling within 8 weeks of the start of medication treatment and a BUP dose of 16 mg or greater daily were associated with increased adherence to treatment.30 For patients receiving a BUP dose of less than 16 mg daily, treatment adherence with and without counseling was approximately 325 and 230 days, respectively. When the dose of BUP was 16 mg or greater, treatment adherence with and without counseling was approximately 405 and 320 days, respectively.30
Counseling should always be offered to patients initiating medication treatment of OUD. It should be noted that counseling alone is not a highly effective treatment for OUD.31 The FDA recently advised that the lack of availability of intensive counseling should not prevent clinicians from initiating BUP for the treatment of OUD.29 OUD is associated with a high mortalityrate and if counseling is not possible, medication treatment should be initiated. Substantial evidence demonstrates that medication treatment of OUD is associated with many benefits.16 The FDA advisory committee concluded that OUD treatment decisions should use shared decision making and be supportive and patient centered.29
The opportunities for medication treatment of OUD in primary care practice have expanded due to the recent FDA removal of restrictions on the use of BUP and heightened awareness of the positive public health impact of medication treatment. Challenges to the medication treatment of OUD remain, including stigmatization of OUD, barriers to insurance coverage for BUP, practice costs of treating OUD, and gaps in clinical education. For many pregnant patients, their main point of contact with health care is their obstetrician. By incorporating OUD treatment in pregnancy care, obstetricians will improve the health of the mother and newborn, contributing to the well-being of current and future generations. ●
Experts have recommended several interventions that may help reduce opioid overdose death.1 A consensus recommendation is that people who use drugs should be provided naloxone rescue medication and educated on the proper use of naloxone. Naloxone rescue medication is available in formulations for nasal or parenteral administration. The US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) recently has approved naloxone for over-the-counter status. The American Medical Association has provided a short web video on how to administer nasal naloxone.2 In a small pilot study, obstetricians offered every postpartum patient with naloxone administration education and a 2-dose nasal naloxone pack, with 76% of patients accepting the nasal naloxone pack.3
Many experts recommend that people who use drugs should be advised to never use them alone and to test a small amount of the drug to assess its potency. Many patients who use opioid drugs also take benzodiazepines, which can contribute to respiratory depression.4 Patients should avoid mixing drugs (eg, opioids and benzodiazepines). Some experts recommend that patients who use drugs should be provided take-home fentanyl test strips so they can evaluate their drugs for the presence of fentanyl, a medication that suppresses respiration and contributes to many overdose deaths. In addition, people who use drugs and are interested in reducing their use of drugs or managing overdose risk can be offered initiation of medication treatment of OUD.1
References
1. Wood E, Solomon ED, Hadland SE. Universal precautions for people at risk of opioid overdose in North America. JAMA Int Med. 2023;183:401-402.
2. How to administer Naloxone. AMA website. Accessed August 28, 2023. https://www.ama-assn.org /delivering-care/overdose-epidemic/how-administer-naloxone
3. Naliboff JA, Tharpe N. Universal postpartum naloxone provision: a harm reduction quality improvement project. J Addict Med. 2022;17:360-362.
4. Kelly JC, Raghuraman N, Stout MJ, et al. Home induction of buprenorphine for treatment of opioid use disorder in pregnancy. Obstet Gynecol. 2021;138:655-659.
- Spencer MR, Miniño AM, Warner M. Drug overdose deaths in the United States, 20012021. NCHS Data Brief no 457. Hyattsville, MD, National Center for Health Statistics. 2022. NCHS Data Brief No. 457. Published December 2022. Accessed August 21, 2023. https://www.cdc.gov /nchs/products/databriefs/db457.htm
- US traffic deaths drop slightly in 2022 but still a ‘crisis.’ AP News website. Published April 20, 2023. Accessed August 21, 2023. https://apnews.com /article/traffic-deaths-distracted-driving-crisis -6db6471e273b275920b6c4f9eb7e493b
- Suicide statistics. American Foundation for Suicide Prevention website. Accessed August 21, 2023. https://afsp.org/suicide-statistics/
- Bruzelius E, Martins SS. US Trends in drug overdose mortality among pregnant and postpartum persons, 2017-2020. JAMA. 2022;328:2159-2161.
- Metz TD, Rovner P, Hoffman MC, et al. Maternal deaths from suicide and overdose in Colorado, 2004-2012. Obstet Gynecol. 2016;128:1233-1240.
- Schiff DM, Nielsen T, Terplan M, et al. Fatal and nonfatal overdose among pregnant and postpartum women in Massachusetts. Obstet Gynecol. 2018;132:466-474.
- Goldman-Mellor S, Margerison CE. Maternal drug-related death and suicide are leading causes of postpartum death in California. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2019;221:489.e1-489.e9.
- Sordo L, Barrio G, Bravo MJ, et al. Mortality risk during and after opioid substitution treatment: systematic review and meta-analysis of cohort studies. BMJ. 2017;357:j1550.
- Waiver elimination (MAT Act). SAMHSA website. Accessed August 21, 2023. https://www .samhsa.gov/medications-substance-use- disorders/removal-data-waiver-requirement
- Picco L, Middleton M, Bruno R, et al. Validation of the OWLS, a Screening Tool for Measuring Prescription Opioid Use Disorder in Primary Care. Pain Med. 2020;21:2757-2764.
- American Psychiatric Association. Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders. 5th ed. American Psychiatric Association; 2013.
- Creedon TB, Ali MM, Schuman-Olivier Z. Trends in buprenorphine prescribing for opioid use disorder by psychiatrists in the US from 2003 to 2021. JAMA Health Forum. 2023;4:E230221.
- Quick MD website. Accessed August 21, 2023. https://quick.md/
- Treitler P, Nowels M, Samples H, et al. BUP utilization and prescribing among New Jersey Medicaid beneficiaries after adoption of initiatives designed to improve treatment access. JAMA Netw Open. 2023;6:E2312030.
- Jawa R, Tin Y, Nall S, et al. Estimated clinical outcomes and cost-effectiveness associated with provision of addiction treatment in US primary care clinics. JAMA Netw Open. 2023;6:E237888.
- Wakeman SE, Larochelle MR, Ameli O, et al. Comparative effectiveness of different treatment pathways of opioid use disorder. JAMA Netw Open. 2020;3:E1920622.
- Wilder CM, Hosta D, Winhusen T. Association of methadone dose with substance use and treatment retention in pregnant and postpartum women with opioid use disorder. J Subst Abuse Treat. 2017;80:33-36.
- Haight SC, Ko JY, Tong VT, et al. Opioid use disorder documented at delivery hospitalization - United States, 1999-2014. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2018;67:845-849.
- Xu KY, Jones HE, Schiff DM, et al. Initiation and treatment discontinuation of medications for opioid use disorder in pregnant people compared with nonpregnant people. Obstet Gynecol. 2023;141:845-853.
- Kelly D, Krans EE. Medical specialty of buprenorphine prescribers for pregnant women with opioid use disorder. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2019;220:502-503.
- Kelly JC, Raghuraman N, Stout MJ, et al. Home induction of buprenorphine for treatment of opioid use disorder in pregnancy. Obstet Gynecol. 2021;138:655-659.
- Suarez EA, Huybrechts KF, Straub L, et al. Buprenorphine versus methadone for opioid use disorder in pregnancy. N Engl J Med. 2022;387:2033-2044.
- Kinsella M, Halliday LO, Shaw M, et al. Buprenorphine compared with methadone in pregnancy: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Subst Use Misuse. 2022;57:1400-1416.
- Jumah NA, Edwards C, Balfour-Boehm J, et al. Observational study of the safety of buprenorphine-naloxone in pregnancy in a rural and remote population. BMJ Open. 2016;6:E011774.
- Mullins N, Galvin SL, Ramage M, et al. Buprenorphine and naloxone versus buprenorphine for opioid use disorder in pregnancy: a cohort study. J Addict Med. 2020;14:185-192.
- Opioid use and opioid use disorder in pregnancy. Committee Opinion No. 711. American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists. Obstet Gynecol. 2017;130:E81-E94.
- The ASAM National Practice Guideline for the Treatment of Opioid Use Disorder: 2020 Focused Update. J Addict Med. 2020;14(2S suppl 1):1-91.
- Link HM, Jones H, Miller L, et al. Buprenorphinenaloxone use in pregnancy: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Am J Obstet Gynecol MFM. 2020;2:100179.
- Delphin-Rittmon ME, Cavazzoni P. US Food and Drug Administration website. https://www.fda .gov/media/168027/download
- Eren K, Schuster J, Herschell A, et al. Association of Counseling and Psychotherapy on retention in medication for addiction treatment within a large Medicaid population. J Addict Med. 2022;16:346353.
- Kakko J, Dybrandt Svanborg K, Kreek MJ, et al. 1-year retention and social function after buprenorphine-assisted relapse prevention treatment for heroin dependence in Sweden: a randomized, placebo-controlled trial. Lancet. 2003;361:662-668.
- Spencer MR, Miniño AM, Warner M. Drug overdose deaths in the United States, 20012021. NCHS Data Brief no 457. Hyattsville, MD, National Center for Health Statistics. 2022. NCHS Data Brief No. 457. Published December 2022. Accessed August 21, 2023. https://www.cdc.gov /nchs/products/databriefs/db457.htm
- US traffic deaths drop slightly in 2022 but still a ‘crisis.’ AP News website. Published April 20, 2023. Accessed August 21, 2023. https://apnews.com /article/traffic-deaths-distracted-driving-crisis -6db6471e273b275920b6c4f9eb7e493b
- Suicide statistics. American Foundation for Suicide Prevention website. Accessed August 21, 2023. https://afsp.org/suicide-statistics/
- Bruzelius E, Martins SS. US Trends in drug overdose mortality among pregnant and postpartum persons, 2017-2020. JAMA. 2022;328:2159-2161.
- Metz TD, Rovner P, Hoffman MC, et al. Maternal deaths from suicide and overdose in Colorado, 2004-2012. Obstet Gynecol. 2016;128:1233-1240.
- Schiff DM, Nielsen T, Terplan M, et al. Fatal and nonfatal overdose among pregnant and postpartum women in Massachusetts. Obstet Gynecol. 2018;132:466-474.
- Goldman-Mellor S, Margerison CE. Maternal drug-related death and suicide are leading causes of postpartum death in California. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2019;221:489.e1-489.e9.
- Sordo L, Barrio G, Bravo MJ, et al. Mortality risk during and after opioid substitution treatment: systematic review and meta-analysis of cohort studies. BMJ. 2017;357:j1550.
- Waiver elimination (MAT Act). SAMHSA website. Accessed August 21, 2023. https://www .samhsa.gov/medications-substance-use- disorders/removal-data-waiver-requirement
- Picco L, Middleton M, Bruno R, et al. Validation of the OWLS, a Screening Tool for Measuring Prescription Opioid Use Disorder in Primary Care. Pain Med. 2020;21:2757-2764.
- American Psychiatric Association. Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders. 5th ed. American Psychiatric Association; 2013.
- Creedon TB, Ali MM, Schuman-Olivier Z. Trends in buprenorphine prescribing for opioid use disorder by psychiatrists in the US from 2003 to 2021. JAMA Health Forum. 2023;4:E230221.
- Quick MD website. Accessed August 21, 2023. https://quick.md/
- Treitler P, Nowels M, Samples H, et al. BUP utilization and prescribing among New Jersey Medicaid beneficiaries after adoption of initiatives designed to improve treatment access. JAMA Netw Open. 2023;6:E2312030.
- Jawa R, Tin Y, Nall S, et al. Estimated clinical outcomes and cost-effectiveness associated with provision of addiction treatment in US primary care clinics. JAMA Netw Open. 2023;6:E237888.
- Wakeman SE, Larochelle MR, Ameli O, et al. Comparative effectiveness of different treatment pathways of opioid use disorder. JAMA Netw Open. 2020;3:E1920622.
- Wilder CM, Hosta D, Winhusen T. Association of methadone dose with substance use and treatment retention in pregnant and postpartum women with opioid use disorder. J Subst Abuse Treat. 2017;80:33-36.
- Haight SC, Ko JY, Tong VT, et al. Opioid use disorder documented at delivery hospitalization - United States, 1999-2014. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2018;67:845-849.
- Xu KY, Jones HE, Schiff DM, et al. Initiation and treatment discontinuation of medications for opioid use disorder in pregnant people compared with nonpregnant people. Obstet Gynecol. 2023;141:845-853.
- Kelly D, Krans EE. Medical specialty of buprenorphine prescribers for pregnant women with opioid use disorder. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2019;220:502-503.
- Kelly JC, Raghuraman N, Stout MJ, et al. Home induction of buprenorphine for treatment of opioid use disorder in pregnancy. Obstet Gynecol. 2021;138:655-659.
- Suarez EA, Huybrechts KF, Straub L, et al. Buprenorphine versus methadone for opioid use disorder in pregnancy. N Engl J Med. 2022;387:2033-2044.
- Kinsella M, Halliday LO, Shaw M, et al. Buprenorphine compared with methadone in pregnancy: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Subst Use Misuse. 2022;57:1400-1416.
- Jumah NA, Edwards C, Balfour-Boehm J, et al. Observational study of the safety of buprenorphine-naloxone in pregnancy in a rural and remote population. BMJ Open. 2016;6:E011774.
- Mullins N, Galvin SL, Ramage M, et al. Buprenorphine and naloxone versus buprenorphine for opioid use disorder in pregnancy: a cohort study. J Addict Med. 2020;14:185-192.
- Opioid use and opioid use disorder in pregnancy. Committee Opinion No. 711. American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists. Obstet Gynecol. 2017;130:E81-E94.
- The ASAM National Practice Guideline for the Treatment of Opioid Use Disorder: 2020 Focused Update. J Addict Med. 2020;14(2S suppl 1):1-91.
- Link HM, Jones H, Miller L, et al. Buprenorphinenaloxone use in pregnancy: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Am J Obstet Gynecol MFM. 2020;2:100179.
- Delphin-Rittmon ME, Cavazzoni P. US Food and Drug Administration website. https://www.fda .gov/media/168027/download
- Eren K, Schuster J, Herschell A, et al. Association of Counseling and Psychotherapy on retention in medication for addiction treatment within a large Medicaid population. J Addict Med. 2022;16:346353.
- Kakko J, Dybrandt Svanborg K, Kreek MJ, et al. 1-year retention and social function after buprenorphine-assisted relapse prevention treatment for heroin dependence in Sweden: a randomized, placebo-controlled trial. Lancet. 2003;361:662-668.
Is this the best screening test for prostate cancer?
In the ReIMAGINE study, a group of researchers from the United Kingdom found that half of men with apparently “safe” levels of prostate-specific antigen (PSA) below 3 ng/mL had clinically significant prostate cancers when multiparametric MRI was added to screening. The researchers, whose paper appeared in BMJ Oncology, also found that one in six screened men had a prostate lesion on MRI.
Meanwhile, a large Swedish population-based study, published in JAMA Network Open, showed that pre-biopsy MRIs combined with PSA testing after adoption of guidelines recommending MRIs led to a decrease in the proportion of men with negative biopsies (28% to 7%) and the number of Gleason score 6 cancers (24% to 6%), while the proportion of Gleason score 7-10 cancers rose from 49% to 86%.
Researchers compared prostate MRI uptake rates in the Jönköping Region in southern Sweden over 9 years – 2011 through 2018 before prostate MRIs were recommended nationally, and 2018-2020 when MRIs became commonly used.
David Robinson, MD, PhD, associate professor at Linköping University and leader of the Swedish study, told this news organization: “MRI is now standard for men before biopsy” in that country. In Sweden, which has a high rate of mortality from prostate cancer – about 50 deaths per 100,000 men vs. 12 and 8 per 100,000 in the United Kingdom and United States, respectively – PSA testing is not routine. “Most men that are diagnosed with prostate cancer have no symptoms. They have asked for a PSA when they have visited their general practitioner,” Dr. Robinson said. “To take a PSA test is not encouraged but it is not discouraged either. It is up to each man to decide.”
PSA screening is not common in the United Kingdom. Caroline Moore, MD, chair of urology at University College London and principal investigator on ReIMAGINE, said only 20% of UK men older than age 50 undergo PSA tests because doctors in the United Kingdom are concerned about the sort of overdiagnosis and overtreatment of prostate cancer that has occurred in the United States since the mid-1990s, when PSA screening was adopted here.
The rate of PSA screening in the United States has declined with controversies over recommendations for screening, though they remain above European rates: 37% in 2019, down from 47% in 2005, according to a 2022 Veterans Administration study published in JAMA Oncology.
In the UK study, Dr. Moore’s hospital-based group asked general practitioners to send letters to 2,096 men aged 50-75 years who had not been diagnosed with prostate cancer, inviting them to undergo prostate health checks combining screening with PSA and 10-minute prostate MRIs.
Of the 457 men who responded to the letters, 303 completed both screening tests. Older White men were more likely to respond, and Black men responded 20% less often.
Of the men who completed screening, 29 (9.6%) were diagnosed with clinically significant cancer and 3 were diagnosed with clinically insignificant cancer, the researchers reported.
Dr. Moore said the PSA and MRI-first approach spared men from biopsies as well as the downsides of active surveillance, which include close monitoring with urology visits and occasional MRIs or biopsies over many years. Biopsies are considered undesirable because of pain and the risk for sepsis and other infections associated with transrectal biopsies.
But urologists in America were less convinced by the international data. William J. Catalona, MD, a urologist at Northwestern University in Chicago, who developed the PSA screening test in the 1990s, said he wasn’t surprised so many men in ReIMAGINE with low PSAs had advanced cancers. “Some of the most aggressive prostate cancers occur in men with a low PSA level – not new news,” he said.
Dr. Catalona also disagreed with the UK researchers’ emphasis on MRIs because the readings often are incorrect. A 2021 study in Prostate Cancer and Prostatic Diseases reported that multiparametric MRI had a false-negative rate of between 10% and 20%.
“MRI alone should not be considered more reliable than PSA. Rather, it should be considered complementary,” he said.
Michael S. Leapman, MD, MHS, associate professor of urology at the Yale Cancer Center, New Haven, Conn., said the UK findings point to a role for MRI as a “triage tool” to help identify men with elevated PSAs who should have a prostate biopsy.
But he said the research to date doesn’t support the use of MRI as a stand-alone test for prostate cancer. “In my opinion, it would have to demonstrate some tangible benefit to patients other than finding a greater number of cancers, such as improvement in cancer control, lower burden from the disease overall, or cancer-specific survival,” he said.
Major U.S. guidelines recommend including MRIs before biopsies. Dr. Leapman also pointed out that 2023 recommendations from the National Comprehensive Cancer Network state that MRI is “strongly recommended if available.” Yet fewer than half of U.S. urologists use MRIs as a screening tool, he said.
“My sense is that MRI is not available everywhere. We have also seen that wait times are too long in some centers, leading physicians and patients to opt for biopsy – particularly in cases with higher suspicion,” he said.
The studies from Sweden and the United Kingdom “demonstrate the strides being made in reducing overdetection of low-grade prostate cancer will increase detection of clinically significant Gleason 3+4 or higher” tumors, Dr. Leapman said. “It is unclear whether such patients in whom their otherwise low-risk disease is recast as ‘intermediate risk’ meaningfully stand to benefit in the long term from this detection.”
Dr. Robinson reported no relevant financial conflicts of interest. The Swedish Cancer Society, the Swedish Research Council, Region Jönköping, Futurum, and Clinical Cancer Research Foundation in Jönköping supported the Swedish study. Members of the ReIMAGINE study team disclosed research support from the United Kingdom’s National Institute of Health Research and various industry/other sources. The Medical Research Council and Cancer Research UK funded the ReIMAGINE study.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
In the ReIMAGINE study, a group of researchers from the United Kingdom found that half of men with apparently “safe” levels of prostate-specific antigen (PSA) below 3 ng/mL had clinically significant prostate cancers when multiparametric MRI was added to screening. The researchers, whose paper appeared in BMJ Oncology, also found that one in six screened men had a prostate lesion on MRI.
Meanwhile, a large Swedish population-based study, published in JAMA Network Open, showed that pre-biopsy MRIs combined with PSA testing after adoption of guidelines recommending MRIs led to a decrease in the proportion of men with negative biopsies (28% to 7%) and the number of Gleason score 6 cancers (24% to 6%), while the proportion of Gleason score 7-10 cancers rose from 49% to 86%.
Researchers compared prostate MRI uptake rates in the Jönköping Region in southern Sweden over 9 years – 2011 through 2018 before prostate MRIs were recommended nationally, and 2018-2020 when MRIs became commonly used.
David Robinson, MD, PhD, associate professor at Linköping University and leader of the Swedish study, told this news organization: “MRI is now standard for men before biopsy” in that country. In Sweden, which has a high rate of mortality from prostate cancer – about 50 deaths per 100,000 men vs. 12 and 8 per 100,000 in the United Kingdom and United States, respectively – PSA testing is not routine. “Most men that are diagnosed with prostate cancer have no symptoms. They have asked for a PSA when they have visited their general practitioner,” Dr. Robinson said. “To take a PSA test is not encouraged but it is not discouraged either. It is up to each man to decide.”
PSA screening is not common in the United Kingdom. Caroline Moore, MD, chair of urology at University College London and principal investigator on ReIMAGINE, said only 20% of UK men older than age 50 undergo PSA tests because doctors in the United Kingdom are concerned about the sort of overdiagnosis and overtreatment of prostate cancer that has occurred in the United States since the mid-1990s, when PSA screening was adopted here.
The rate of PSA screening in the United States has declined with controversies over recommendations for screening, though they remain above European rates: 37% in 2019, down from 47% in 2005, according to a 2022 Veterans Administration study published in JAMA Oncology.
In the UK study, Dr. Moore’s hospital-based group asked general practitioners to send letters to 2,096 men aged 50-75 years who had not been diagnosed with prostate cancer, inviting them to undergo prostate health checks combining screening with PSA and 10-minute prostate MRIs.
Of the 457 men who responded to the letters, 303 completed both screening tests. Older White men were more likely to respond, and Black men responded 20% less often.
Of the men who completed screening, 29 (9.6%) were diagnosed with clinically significant cancer and 3 were diagnosed with clinically insignificant cancer, the researchers reported.
Dr. Moore said the PSA and MRI-first approach spared men from biopsies as well as the downsides of active surveillance, which include close monitoring with urology visits and occasional MRIs or biopsies over many years. Biopsies are considered undesirable because of pain and the risk for sepsis and other infections associated with transrectal biopsies.
But urologists in America were less convinced by the international data. William J. Catalona, MD, a urologist at Northwestern University in Chicago, who developed the PSA screening test in the 1990s, said he wasn’t surprised so many men in ReIMAGINE with low PSAs had advanced cancers. “Some of the most aggressive prostate cancers occur in men with a low PSA level – not new news,” he said.
Dr. Catalona also disagreed with the UK researchers’ emphasis on MRIs because the readings often are incorrect. A 2021 study in Prostate Cancer and Prostatic Diseases reported that multiparametric MRI had a false-negative rate of between 10% and 20%.
“MRI alone should not be considered more reliable than PSA. Rather, it should be considered complementary,” he said.
Michael S. Leapman, MD, MHS, associate professor of urology at the Yale Cancer Center, New Haven, Conn., said the UK findings point to a role for MRI as a “triage tool” to help identify men with elevated PSAs who should have a prostate biopsy.
But he said the research to date doesn’t support the use of MRI as a stand-alone test for prostate cancer. “In my opinion, it would have to demonstrate some tangible benefit to patients other than finding a greater number of cancers, such as improvement in cancer control, lower burden from the disease overall, or cancer-specific survival,” he said.
Major U.S. guidelines recommend including MRIs before biopsies. Dr. Leapman also pointed out that 2023 recommendations from the National Comprehensive Cancer Network state that MRI is “strongly recommended if available.” Yet fewer than half of U.S. urologists use MRIs as a screening tool, he said.
“My sense is that MRI is not available everywhere. We have also seen that wait times are too long in some centers, leading physicians and patients to opt for biopsy – particularly in cases with higher suspicion,” he said.
The studies from Sweden and the United Kingdom “demonstrate the strides being made in reducing overdetection of low-grade prostate cancer will increase detection of clinically significant Gleason 3+4 or higher” tumors, Dr. Leapman said. “It is unclear whether such patients in whom their otherwise low-risk disease is recast as ‘intermediate risk’ meaningfully stand to benefit in the long term from this detection.”
Dr. Robinson reported no relevant financial conflicts of interest. The Swedish Cancer Society, the Swedish Research Council, Region Jönköping, Futurum, and Clinical Cancer Research Foundation in Jönköping supported the Swedish study. Members of the ReIMAGINE study team disclosed research support from the United Kingdom’s National Institute of Health Research and various industry/other sources. The Medical Research Council and Cancer Research UK funded the ReIMAGINE study.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
In the ReIMAGINE study, a group of researchers from the United Kingdom found that half of men with apparently “safe” levels of prostate-specific antigen (PSA) below 3 ng/mL had clinically significant prostate cancers when multiparametric MRI was added to screening. The researchers, whose paper appeared in BMJ Oncology, also found that one in six screened men had a prostate lesion on MRI.
Meanwhile, a large Swedish population-based study, published in JAMA Network Open, showed that pre-biopsy MRIs combined with PSA testing after adoption of guidelines recommending MRIs led to a decrease in the proportion of men with negative biopsies (28% to 7%) and the number of Gleason score 6 cancers (24% to 6%), while the proportion of Gleason score 7-10 cancers rose from 49% to 86%.
Researchers compared prostate MRI uptake rates in the Jönköping Region in southern Sweden over 9 years – 2011 through 2018 before prostate MRIs were recommended nationally, and 2018-2020 when MRIs became commonly used.
David Robinson, MD, PhD, associate professor at Linköping University and leader of the Swedish study, told this news organization: “MRI is now standard for men before biopsy” in that country. In Sweden, which has a high rate of mortality from prostate cancer – about 50 deaths per 100,000 men vs. 12 and 8 per 100,000 in the United Kingdom and United States, respectively – PSA testing is not routine. “Most men that are diagnosed with prostate cancer have no symptoms. They have asked for a PSA when they have visited their general practitioner,” Dr. Robinson said. “To take a PSA test is not encouraged but it is not discouraged either. It is up to each man to decide.”
PSA screening is not common in the United Kingdom. Caroline Moore, MD, chair of urology at University College London and principal investigator on ReIMAGINE, said only 20% of UK men older than age 50 undergo PSA tests because doctors in the United Kingdom are concerned about the sort of overdiagnosis and overtreatment of prostate cancer that has occurred in the United States since the mid-1990s, when PSA screening was adopted here.
The rate of PSA screening in the United States has declined with controversies over recommendations for screening, though they remain above European rates: 37% in 2019, down from 47% in 2005, according to a 2022 Veterans Administration study published in JAMA Oncology.
In the UK study, Dr. Moore’s hospital-based group asked general practitioners to send letters to 2,096 men aged 50-75 years who had not been diagnosed with prostate cancer, inviting them to undergo prostate health checks combining screening with PSA and 10-minute prostate MRIs.
Of the 457 men who responded to the letters, 303 completed both screening tests. Older White men were more likely to respond, and Black men responded 20% less often.
Of the men who completed screening, 29 (9.6%) were diagnosed with clinically significant cancer and 3 were diagnosed with clinically insignificant cancer, the researchers reported.
Dr. Moore said the PSA and MRI-first approach spared men from biopsies as well as the downsides of active surveillance, which include close monitoring with urology visits and occasional MRIs or biopsies over many years. Biopsies are considered undesirable because of pain and the risk for sepsis and other infections associated with transrectal biopsies.
But urologists in America were less convinced by the international data. William J. Catalona, MD, a urologist at Northwestern University in Chicago, who developed the PSA screening test in the 1990s, said he wasn’t surprised so many men in ReIMAGINE with low PSAs had advanced cancers. “Some of the most aggressive prostate cancers occur in men with a low PSA level – not new news,” he said.
Dr. Catalona also disagreed with the UK researchers’ emphasis on MRIs because the readings often are incorrect. A 2021 study in Prostate Cancer and Prostatic Diseases reported that multiparametric MRI had a false-negative rate of between 10% and 20%.
“MRI alone should not be considered more reliable than PSA. Rather, it should be considered complementary,” he said.
Michael S. Leapman, MD, MHS, associate professor of urology at the Yale Cancer Center, New Haven, Conn., said the UK findings point to a role for MRI as a “triage tool” to help identify men with elevated PSAs who should have a prostate biopsy.
But he said the research to date doesn’t support the use of MRI as a stand-alone test for prostate cancer. “In my opinion, it would have to demonstrate some tangible benefit to patients other than finding a greater number of cancers, such as improvement in cancer control, lower burden from the disease overall, or cancer-specific survival,” he said.
Major U.S. guidelines recommend including MRIs before biopsies. Dr. Leapman also pointed out that 2023 recommendations from the National Comprehensive Cancer Network state that MRI is “strongly recommended if available.” Yet fewer than half of U.S. urologists use MRIs as a screening tool, he said.
“My sense is that MRI is not available everywhere. We have also seen that wait times are too long in some centers, leading physicians and patients to opt for biopsy – particularly in cases with higher suspicion,” he said.
The studies from Sweden and the United Kingdom “demonstrate the strides being made in reducing overdetection of low-grade prostate cancer will increase detection of clinically significant Gleason 3+4 or higher” tumors, Dr. Leapman said. “It is unclear whether such patients in whom their otherwise low-risk disease is recast as ‘intermediate risk’ meaningfully stand to benefit in the long term from this detection.”
Dr. Robinson reported no relevant financial conflicts of interest. The Swedish Cancer Society, the Swedish Research Council, Region Jönköping, Futurum, and Clinical Cancer Research Foundation in Jönköping supported the Swedish study. Members of the ReIMAGINE study team disclosed research support from the United Kingdom’s National Institute of Health Research and various industry/other sources. The Medical Research Council and Cancer Research UK funded the ReIMAGINE study.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Frequency and duration of GERD symptoms associated with poor sleep
of the Nurses’ Health Study II published in JAMA Network Open.
The findings suggest that treating gastroesophageal reflux may do more than offer symptomatic relief, but it could improve the chances of a good night’s rest by addressing comorbidities associated with poor sleep quality, wrote authors who were led by Andrew T. Chan, MD, MPH, of the Clinical and Translational Epidemiology Unit at Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston.
“Approximately 20% of the U.S. population experiences gastroesophageal reflux (GER) symptoms at least once a week, and the worldwide prevalence of GER disease (GERD) has been increasing. Beyond its association with quality of life, GERD is also associated with long-term complications, including Barrett esophagus and esophageal adenocarcinoma,” the authors wrote. “In this prospective cohort study, we found that GER symptoms were associated with an increase in subsequent risk of poor sleep quality. Although risk was somewhat attenuated among women who regularly used PPIs [proton pump inhibitors] and/or H2RAs [histamine2-receptor antagonists], the risk of poor sleep quality remained significantly higher among those who experienced GER symptoms at least once a week.”
A growing body of evidence suggests that GERD may be one of those lesser known risk factors of poor sleep quality (trouble falling asleep, sleep disturbance, daytime sleepiness, or restlessness of sleep). But data on the subject are scarce, compelling researchers to conduct the present investigation.
The analysis drew data from the Nurses’ Health Study II, an ongoing prospective study involving 116,429 female participants. Among the 48,536 women included in this analysis, 7,929 (16.3%) developed poor sleep quality during a 4-year follow-up period.
The multivariable relative risk for poor sleep quality among women who experienced GER symptoms more than once a week was 1.53 (95% confidence interval, 1.45-1.62). For those who experienced GER symptoms more than twice a week, the RR was 1.49 (95% CI, 1.39-1.58) for difficulty in falling asleep, 1.47 (95% CI, 1.39-1.56) for excessive daytime sleepiness, and 1.44 (95% CI, 1.36-1.53) for restlessness of sleep.
GER was more common in women who had higher body mass index, were less physically active, and had asthma and depression. Among women who experienced GER more than once a week, 48.2% regularly used PPIs and/or H2RAs which are commonly prescribed for GERD. However, researchers found that frequent GER symptoms were significantly associated with higher risk of poor sleep quality regardless of whether patients used PPIs and/or H2RAs. But poor sleep quality, in this case, was more common among those who did not use PPIs or H2RAs.
In an interview, Bradley M. Morganstern, MD, medical director of the Inflammatory Bowel Disease Center at NYU Long Island, Mineola, N.Y., brought up the potential for confounding variables. For example, obesity could confound the analysis, he said, as people who are overweight have increased risk of reflux, but also sleep apnea, a strong risk factor for poor sleep.
Despite this possible limitation, Dr. Morganstern said the results are important because they point to a possible practice gap. Physicians typically screen for the classic symptoms of reflux like discomfort and burning, but not sleep quality.
“It’s not something we usually ask about unless the patient volunteers that they’re actually having reflux symptoms at nighttime,” Dr. Morganstern said. This possible link between reflux and poor sleep quality should be on the radar for both gastroenterologists and primary care providers, he added.
“I think different specialties could be asking about it for different reasons,” Dr. Morganstern said, suggesting that it may be worth discussing during diagnosis of reflux or detection of poor sleep quality, and when monitoring symptoms and responses to therapy.
Dr. Chan reported receiving grants from Pfizer, Zoe, and Freenome and receiving personal fees from Pfizer and Boehringer Ingelheim outside the submitted work. Other authors disclosed receiving fees and grants from a number of companies, but outside of the scope of this work.
of the Nurses’ Health Study II published in JAMA Network Open.
The findings suggest that treating gastroesophageal reflux may do more than offer symptomatic relief, but it could improve the chances of a good night’s rest by addressing comorbidities associated with poor sleep quality, wrote authors who were led by Andrew T. Chan, MD, MPH, of the Clinical and Translational Epidemiology Unit at Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston.
“Approximately 20% of the U.S. population experiences gastroesophageal reflux (GER) symptoms at least once a week, and the worldwide prevalence of GER disease (GERD) has been increasing. Beyond its association with quality of life, GERD is also associated with long-term complications, including Barrett esophagus and esophageal adenocarcinoma,” the authors wrote. “In this prospective cohort study, we found that GER symptoms were associated with an increase in subsequent risk of poor sleep quality. Although risk was somewhat attenuated among women who regularly used PPIs [proton pump inhibitors] and/or H2RAs [histamine2-receptor antagonists], the risk of poor sleep quality remained significantly higher among those who experienced GER symptoms at least once a week.”
A growing body of evidence suggests that GERD may be one of those lesser known risk factors of poor sleep quality (trouble falling asleep, sleep disturbance, daytime sleepiness, or restlessness of sleep). But data on the subject are scarce, compelling researchers to conduct the present investigation.
The analysis drew data from the Nurses’ Health Study II, an ongoing prospective study involving 116,429 female participants. Among the 48,536 women included in this analysis, 7,929 (16.3%) developed poor sleep quality during a 4-year follow-up period.
The multivariable relative risk for poor sleep quality among women who experienced GER symptoms more than once a week was 1.53 (95% confidence interval, 1.45-1.62). For those who experienced GER symptoms more than twice a week, the RR was 1.49 (95% CI, 1.39-1.58) for difficulty in falling asleep, 1.47 (95% CI, 1.39-1.56) for excessive daytime sleepiness, and 1.44 (95% CI, 1.36-1.53) for restlessness of sleep.
GER was more common in women who had higher body mass index, were less physically active, and had asthma and depression. Among women who experienced GER more than once a week, 48.2% regularly used PPIs and/or H2RAs which are commonly prescribed for GERD. However, researchers found that frequent GER symptoms were significantly associated with higher risk of poor sleep quality regardless of whether patients used PPIs and/or H2RAs. But poor sleep quality, in this case, was more common among those who did not use PPIs or H2RAs.
In an interview, Bradley M. Morganstern, MD, medical director of the Inflammatory Bowel Disease Center at NYU Long Island, Mineola, N.Y., brought up the potential for confounding variables. For example, obesity could confound the analysis, he said, as people who are overweight have increased risk of reflux, but also sleep apnea, a strong risk factor for poor sleep.
Despite this possible limitation, Dr. Morganstern said the results are important because they point to a possible practice gap. Physicians typically screen for the classic symptoms of reflux like discomfort and burning, but not sleep quality.
“It’s not something we usually ask about unless the patient volunteers that they’re actually having reflux symptoms at nighttime,” Dr. Morganstern said. This possible link between reflux and poor sleep quality should be on the radar for both gastroenterologists and primary care providers, he added.
“I think different specialties could be asking about it for different reasons,” Dr. Morganstern said, suggesting that it may be worth discussing during diagnosis of reflux or detection of poor sleep quality, and when monitoring symptoms and responses to therapy.
Dr. Chan reported receiving grants from Pfizer, Zoe, and Freenome and receiving personal fees from Pfizer and Boehringer Ingelheim outside the submitted work. Other authors disclosed receiving fees and grants from a number of companies, but outside of the scope of this work.
of the Nurses’ Health Study II published in JAMA Network Open.
The findings suggest that treating gastroesophageal reflux may do more than offer symptomatic relief, but it could improve the chances of a good night’s rest by addressing comorbidities associated with poor sleep quality, wrote authors who were led by Andrew T. Chan, MD, MPH, of the Clinical and Translational Epidemiology Unit at Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston.
“Approximately 20% of the U.S. population experiences gastroesophageal reflux (GER) symptoms at least once a week, and the worldwide prevalence of GER disease (GERD) has been increasing. Beyond its association with quality of life, GERD is also associated with long-term complications, including Barrett esophagus and esophageal adenocarcinoma,” the authors wrote. “In this prospective cohort study, we found that GER symptoms were associated with an increase in subsequent risk of poor sleep quality. Although risk was somewhat attenuated among women who regularly used PPIs [proton pump inhibitors] and/or H2RAs [histamine2-receptor antagonists], the risk of poor sleep quality remained significantly higher among those who experienced GER symptoms at least once a week.”
A growing body of evidence suggests that GERD may be one of those lesser known risk factors of poor sleep quality (trouble falling asleep, sleep disturbance, daytime sleepiness, or restlessness of sleep). But data on the subject are scarce, compelling researchers to conduct the present investigation.
The analysis drew data from the Nurses’ Health Study II, an ongoing prospective study involving 116,429 female participants. Among the 48,536 women included in this analysis, 7,929 (16.3%) developed poor sleep quality during a 4-year follow-up period.
The multivariable relative risk for poor sleep quality among women who experienced GER symptoms more than once a week was 1.53 (95% confidence interval, 1.45-1.62). For those who experienced GER symptoms more than twice a week, the RR was 1.49 (95% CI, 1.39-1.58) for difficulty in falling asleep, 1.47 (95% CI, 1.39-1.56) for excessive daytime sleepiness, and 1.44 (95% CI, 1.36-1.53) for restlessness of sleep.
GER was more common in women who had higher body mass index, were less physically active, and had asthma and depression. Among women who experienced GER more than once a week, 48.2% regularly used PPIs and/or H2RAs which are commonly prescribed for GERD. However, researchers found that frequent GER symptoms were significantly associated with higher risk of poor sleep quality regardless of whether patients used PPIs and/or H2RAs. But poor sleep quality, in this case, was more common among those who did not use PPIs or H2RAs.
In an interview, Bradley M. Morganstern, MD, medical director of the Inflammatory Bowel Disease Center at NYU Long Island, Mineola, N.Y., brought up the potential for confounding variables. For example, obesity could confound the analysis, he said, as people who are overweight have increased risk of reflux, but also sleep apnea, a strong risk factor for poor sleep.
Despite this possible limitation, Dr. Morganstern said the results are important because they point to a possible practice gap. Physicians typically screen for the classic symptoms of reflux like discomfort and burning, but not sleep quality.
“It’s not something we usually ask about unless the patient volunteers that they’re actually having reflux symptoms at nighttime,” Dr. Morganstern said. This possible link between reflux and poor sleep quality should be on the radar for both gastroenterologists and primary care providers, he added.
“I think different specialties could be asking about it for different reasons,” Dr. Morganstern said, suggesting that it may be worth discussing during diagnosis of reflux or detection of poor sleep quality, and when monitoring symptoms and responses to therapy.
Dr. Chan reported receiving grants from Pfizer, Zoe, and Freenome and receiving personal fees from Pfizer and Boehringer Ingelheim outside the submitted work. Other authors disclosed receiving fees and grants from a number of companies, but outside of the scope of this work.
FROM JAMA NETWORK OPEN
Demographic Characteristics of Veterans Diagnosed With Breast and Gynecologic Cancers: A Comparative Analysis With the General Population
PURPOSE
This project aims to describe the demographics of Veterans diagnosed with breast and gynecologic cancers and assess differences compared to the general population.
BACKGROUND
With an increasing number of women Veterans enrolling in the VA, it is crucial for oncologists to be prepared to provide care for VeterS32 • SEPTEMBER 2023 www.mdedge.com/fedprac/avaho NOTES ans diagnosed with breast and gynecologic cancers. Despite the rising incidence of these cancers among Veterans, there is limited characterization of the demographic profile of this population. Understanding the unique characteristics of Veterans with these malignancies, distinct from the general population, is essential for the Veterans Administration (VA) to develop programs and enhance care for these patients.
METHODS/DATA ANALYSIS
Consult records from the VA Corporate Data Warehouse between January 1, 2021, and December 31, 2022, were analyzed to identify Veterans with newly diagnosed breast, uterine, ovarian, cervical, and vulvovaginal cancer. Demographic were evaluated. Data on the general population were obtained data from SEER (Surveillance, Epidemiology, and End Results) 19 database for 2020.
RESULTS
A total of 3,304 Veterans diagnosed with breast cancer and 918 Veterans with gynecologic cancers were identified (uterine, n = 365; cervical, n = 344, ovarian, n = 177; vulvovaginal, n = 32). Veterans were found to be younger than the general population, with a mean age at diagnosis of 59 for Veterans with breast cancer to 63 for non-veterans. Among those with gynecologic cancers, the mean age at diagnosis for Veterans was 55 compared to 61 for non-veterans. Male breast cancer cases were more prevalent among Veterans, accounting for 11% in the VA compared to 1% in SEER. The Veteran cohort also displayed a higher proportion of Black patients, with 30% of breast cancer cases in the VA being Black compared to 12% in SEER.
CONCLUSIONS/IMPLICATIONS
Veterans diagnosed with breast and gynecologic cancers exhibit unique demographic characteristics compared to the general population. They tend to be younger and have a higher representation of Black patients. The incidence of male breast cancer is notably higher among Veterans. As the prevalence of these cancer types continue to rise among Veterans, it is vital for oncologists to be aware of and adequately address the unique health needs of this population. These findings emphasize the importance of tailored strategies and programs to provide optimal care for Veterans with breast and gynecologic cancers.
PURPOSE
This project aims to describe the demographics of Veterans diagnosed with breast and gynecologic cancers and assess differences compared to the general population.
BACKGROUND
With an increasing number of women Veterans enrolling in the VA, it is crucial for oncologists to be prepared to provide care for VeterS32 • SEPTEMBER 2023 www.mdedge.com/fedprac/avaho NOTES ans diagnosed with breast and gynecologic cancers. Despite the rising incidence of these cancers among Veterans, there is limited characterization of the demographic profile of this population. Understanding the unique characteristics of Veterans with these malignancies, distinct from the general population, is essential for the Veterans Administration (VA) to develop programs and enhance care for these patients.
METHODS/DATA ANALYSIS
Consult records from the VA Corporate Data Warehouse between January 1, 2021, and December 31, 2022, were analyzed to identify Veterans with newly diagnosed breast, uterine, ovarian, cervical, and vulvovaginal cancer. Demographic were evaluated. Data on the general population were obtained data from SEER (Surveillance, Epidemiology, and End Results) 19 database for 2020.
RESULTS
A total of 3,304 Veterans diagnosed with breast cancer and 918 Veterans with gynecologic cancers were identified (uterine, n = 365; cervical, n = 344, ovarian, n = 177; vulvovaginal, n = 32). Veterans were found to be younger than the general population, with a mean age at diagnosis of 59 for Veterans with breast cancer to 63 for non-veterans. Among those with gynecologic cancers, the mean age at diagnosis for Veterans was 55 compared to 61 for non-veterans. Male breast cancer cases were more prevalent among Veterans, accounting for 11% in the VA compared to 1% in SEER. The Veteran cohort also displayed a higher proportion of Black patients, with 30% of breast cancer cases in the VA being Black compared to 12% in SEER.
CONCLUSIONS/IMPLICATIONS
Veterans diagnosed with breast and gynecologic cancers exhibit unique demographic characteristics compared to the general population. They tend to be younger and have a higher representation of Black patients. The incidence of male breast cancer is notably higher among Veterans. As the prevalence of these cancer types continue to rise among Veterans, it is vital for oncologists to be aware of and adequately address the unique health needs of this population. These findings emphasize the importance of tailored strategies and programs to provide optimal care for Veterans with breast and gynecologic cancers.
PURPOSE
This project aims to describe the demographics of Veterans diagnosed with breast and gynecologic cancers and assess differences compared to the general population.
BACKGROUND
With an increasing number of women Veterans enrolling in the VA, it is crucial for oncologists to be prepared to provide care for VeterS32 • SEPTEMBER 2023 www.mdedge.com/fedprac/avaho NOTES ans diagnosed with breast and gynecologic cancers. Despite the rising incidence of these cancers among Veterans, there is limited characterization of the demographic profile of this population. Understanding the unique characteristics of Veterans with these malignancies, distinct from the general population, is essential for the Veterans Administration (VA) to develop programs and enhance care for these patients.
METHODS/DATA ANALYSIS
Consult records from the VA Corporate Data Warehouse between January 1, 2021, and December 31, 2022, were analyzed to identify Veterans with newly diagnosed breast, uterine, ovarian, cervical, and vulvovaginal cancer. Demographic were evaluated. Data on the general population were obtained data from SEER (Surveillance, Epidemiology, and End Results) 19 database for 2020.
RESULTS
A total of 3,304 Veterans diagnosed with breast cancer and 918 Veterans with gynecologic cancers were identified (uterine, n = 365; cervical, n = 344, ovarian, n = 177; vulvovaginal, n = 32). Veterans were found to be younger than the general population, with a mean age at diagnosis of 59 for Veterans with breast cancer to 63 for non-veterans. Among those with gynecologic cancers, the mean age at diagnosis for Veterans was 55 compared to 61 for non-veterans. Male breast cancer cases were more prevalent among Veterans, accounting for 11% in the VA compared to 1% in SEER. The Veteran cohort also displayed a higher proportion of Black patients, with 30% of breast cancer cases in the VA being Black compared to 12% in SEER.
CONCLUSIONS/IMPLICATIONS
Veterans diagnosed with breast and gynecologic cancers exhibit unique demographic characteristics compared to the general population. They tend to be younger and have a higher representation of Black patients. The incidence of male breast cancer is notably higher among Veterans. As the prevalence of these cancer types continue to rise among Veterans, it is vital for oncologists to be aware of and adequately address the unique health needs of this population. These findings emphasize the importance of tailored strategies and programs to provide optimal care for Veterans with breast and gynecologic cancers.
A Case of Compound Heterozygous Factor V Leiden and Prothrombin G20210A Mutations With Recurrent Arterial Thromboembolism
BACKGROUND
There are 5 germline mutations that lead to hypercoagulability in the general population including: Factor V Leiden (FVL), Prothrombin G20210A (F2A), Protein C Deficiency (PCD), Protein S Deficiency (PSD), and Antithrombin Deficiency (ATD). Typical guidance is to defer testing, as it is thought not to change management.
CASE REPORT
We present a case of a patient who was found to be compound heterozygous mutations for FVL and F2A, who presented with two episodes of arterial thromboembolism resulting in cerebrovascular accident (CVA). A 63-year-old male with past medical history of hypertension, a CVA four years prior, and medication non-compliance presents with new onset left sided hemiparesis after an episode of convulsions. MRI and CT imaging of the head revealed ischemic CVA secondary to thromboembolism in the right posterior cerebral artery’s (PCA), P1 branch. Following administration of tissue plasminogen activator (tPA) he had rapid symptom improvement. This second ischemic CVA prompted a workup which was notable for: negative echocardiogram, negative 30-day cardiac monitor, CT chest negative for malignancy, no significant vascular findings, negative for antiphospholipid syndrome, but genetic testing revealed the patient to be heterozygous for FVL and F2A mutations. He was started on apixaban 5 mg twice daily for ongoing secondary prevention. Though medication compliance continues to be difficult, after being placed on direct anticoagulant (DOAC), he has not had recurrent venous or arterial thrombotic events. A small case series found double heterozygosity for FVL and F2A further increases the risk of venous thromboembolism up to 17% or more in a lifetime.
CONCLUSIONS
Although current recommendations advocate against testing for specific mutations in most cases as it is likely not to change management1, this case suggests that it may be of some benefit in patients that have a workup that does not yield a clear etiology, especially in cryptogenic stroke which is typically managed with aspirin rather than direct oral anticoagulant.
BACKGROUND
There are 5 germline mutations that lead to hypercoagulability in the general population including: Factor V Leiden (FVL), Prothrombin G20210A (F2A), Protein C Deficiency (PCD), Protein S Deficiency (PSD), and Antithrombin Deficiency (ATD). Typical guidance is to defer testing, as it is thought not to change management.
CASE REPORT
We present a case of a patient who was found to be compound heterozygous mutations for FVL and F2A, who presented with two episodes of arterial thromboembolism resulting in cerebrovascular accident (CVA). A 63-year-old male with past medical history of hypertension, a CVA four years prior, and medication non-compliance presents with new onset left sided hemiparesis after an episode of convulsions. MRI and CT imaging of the head revealed ischemic CVA secondary to thromboembolism in the right posterior cerebral artery’s (PCA), P1 branch. Following administration of tissue plasminogen activator (tPA) he had rapid symptom improvement. This second ischemic CVA prompted a workup which was notable for: negative echocardiogram, negative 30-day cardiac monitor, CT chest negative for malignancy, no significant vascular findings, negative for antiphospholipid syndrome, but genetic testing revealed the patient to be heterozygous for FVL and F2A mutations. He was started on apixaban 5 mg twice daily for ongoing secondary prevention. Though medication compliance continues to be difficult, after being placed on direct anticoagulant (DOAC), he has not had recurrent venous or arterial thrombotic events. A small case series found double heterozygosity for FVL and F2A further increases the risk of venous thromboembolism up to 17% or more in a lifetime.
CONCLUSIONS
Although current recommendations advocate against testing for specific mutations in most cases as it is likely not to change management1, this case suggests that it may be of some benefit in patients that have a workup that does not yield a clear etiology, especially in cryptogenic stroke which is typically managed with aspirin rather than direct oral anticoagulant.
BACKGROUND
There are 5 germline mutations that lead to hypercoagulability in the general population including: Factor V Leiden (FVL), Prothrombin G20210A (F2A), Protein C Deficiency (PCD), Protein S Deficiency (PSD), and Antithrombin Deficiency (ATD). Typical guidance is to defer testing, as it is thought not to change management.
CASE REPORT
We present a case of a patient who was found to be compound heterozygous mutations for FVL and F2A, who presented with two episodes of arterial thromboembolism resulting in cerebrovascular accident (CVA). A 63-year-old male with past medical history of hypertension, a CVA four years prior, and medication non-compliance presents with new onset left sided hemiparesis after an episode of convulsions. MRI and CT imaging of the head revealed ischemic CVA secondary to thromboembolism in the right posterior cerebral artery’s (PCA), P1 branch. Following administration of tissue plasminogen activator (tPA) he had rapid symptom improvement. This second ischemic CVA prompted a workup which was notable for: negative echocardiogram, negative 30-day cardiac monitor, CT chest negative for malignancy, no significant vascular findings, negative for antiphospholipid syndrome, but genetic testing revealed the patient to be heterozygous for FVL and F2A mutations. He was started on apixaban 5 mg twice daily for ongoing secondary prevention. Though medication compliance continues to be difficult, after being placed on direct anticoagulant (DOAC), he has not had recurrent venous or arterial thrombotic events. A small case series found double heterozygosity for FVL and F2A further increases the risk of venous thromboembolism up to 17% or more in a lifetime.
CONCLUSIONS
Although current recommendations advocate against testing for specific mutations in most cases as it is likely not to change management1, this case suggests that it may be of some benefit in patients that have a workup that does not yield a clear etiology, especially in cryptogenic stroke which is typically managed with aspirin rather than direct oral anticoagulant.
Impact of Socioeconomic Disparities and Facility Type on Overall Survival in Stage I vs Stage IV Amelanotic Melanoma: An Analysis of the National Cancer Database
PURPOSE
This study addresses a gap in knowledge regarding socioeconomic factors, facility type, and overall survival in stage I vs stage IV Amelanotic Melanoma.
BACKGROUND
Amelanotic Melanoma (AM) is a rare form of melanoma that lacks pigment and accounts for approximately 5% of melanomas. Light skin color and increasing age are important risk factors. Although curable when diagnosed early, it is often missed or mistaken for other benign conditions. A study investigating the impact of facility type on overall survival between stage I vs stage IV AM has yet to be done.
METHODS
This is a retrospective study of patients diagnosed with Amelanotic Melanoma (ICD-8730) between 2004 and 2020 in the National Cancer Database (NCDB) to compare demographic features and overall survival (n = 2147). Exclusion criteria included missing data.
DATA ANALYSIS
Descriptive statistics for all AM patients were collected. Median household income and facility type were compared between patients diagnosed with stage I and stage IV AM using Pearson Chi- Square test. Breslow thickness and overall survival between stage I and stage IV were evaluated using independent t-test and Kaplan-Meier test, respectively. All variables were evaluated for a significance of P < .05.
RESULTS
Most cases analyzed were White (98.1%), male (58.6%), and had Medicare as the primary payor at diagnosis (51.1%). Of 2147 cases, 497 were stage I (23.1%) and 164 were stage IV AM (7.6%) with a mean age at diagnosis of 66.05 and 63.72 years, respectively. There was a significant difference in overall survival between stage I (mean = 118.7 months) and stage 4 (mean = 42.4 months, P < 0.001). The average Breslow thickness was 1.17mm in stage I and 2.59mm in stage IV (P<0.05). More patients diagnosed at stage I used academic facilities than those diagnosed at stage IV (43.9% vs 33.8%, P<0.05). Most patients diagnosed at stage I were high income compared to patients diagnosed at stage IV (55% vs 43.2%, P<0.05).
CONCLUSIONS
With the overall survival of stage IV AM being significantly worse, we hope this study can provide a starting point in the study and prevention of disparities in the early diagnosis of AM.
PURPOSE
This study addresses a gap in knowledge regarding socioeconomic factors, facility type, and overall survival in stage I vs stage IV Amelanotic Melanoma.
BACKGROUND
Amelanotic Melanoma (AM) is a rare form of melanoma that lacks pigment and accounts for approximately 5% of melanomas. Light skin color and increasing age are important risk factors. Although curable when diagnosed early, it is often missed or mistaken for other benign conditions. A study investigating the impact of facility type on overall survival between stage I vs stage IV AM has yet to be done.
METHODS
This is a retrospective study of patients diagnosed with Amelanotic Melanoma (ICD-8730) between 2004 and 2020 in the National Cancer Database (NCDB) to compare demographic features and overall survival (n = 2147). Exclusion criteria included missing data.
DATA ANALYSIS
Descriptive statistics for all AM patients were collected. Median household income and facility type were compared between patients diagnosed with stage I and stage IV AM using Pearson Chi- Square test. Breslow thickness and overall survival between stage I and stage IV were evaluated using independent t-test and Kaplan-Meier test, respectively. All variables were evaluated for a significance of P < .05.
RESULTS
Most cases analyzed were White (98.1%), male (58.6%), and had Medicare as the primary payor at diagnosis (51.1%). Of 2147 cases, 497 were stage I (23.1%) and 164 were stage IV AM (7.6%) with a mean age at diagnosis of 66.05 and 63.72 years, respectively. There was a significant difference in overall survival between stage I (mean = 118.7 months) and stage 4 (mean = 42.4 months, P < 0.001). The average Breslow thickness was 1.17mm in stage I and 2.59mm in stage IV (P<0.05). More patients diagnosed at stage I used academic facilities than those diagnosed at stage IV (43.9% vs 33.8%, P<0.05). Most patients diagnosed at stage I were high income compared to patients diagnosed at stage IV (55% vs 43.2%, P<0.05).
CONCLUSIONS
With the overall survival of stage IV AM being significantly worse, we hope this study can provide a starting point in the study and prevention of disparities in the early diagnosis of AM.
PURPOSE
This study addresses a gap in knowledge regarding socioeconomic factors, facility type, and overall survival in stage I vs stage IV Amelanotic Melanoma.
BACKGROUND
Amelanotic Melanoma (AM) is a rare form of melanoma that lacks pigment and accounts for approximately 5% of melanomas. Light skin color and increasing age are important risk factors. Although curable when diagnosed early, it is often missed or mistaken for other benign conditions. A study investigating the impact of facility type on overall survival between stage I vs stage IV AM has yet to be done.
METHODS
This is a retrospective study of patients diagnosed with Amelanotic Melanoma (ICD-8730) between 2004 and 2020 in the National Cancer Database (NCDB) to compare demographic features and overall survival (n = 2147). Exclusion criteria included missing data.
DATA ANALYSIS
Descriptive statistics for all AM patients were collected. Median household income and facility type were compared between patients diagnosed with stage I and stage IV AM using Pearson Chi- Square test. Breslow thickness and overall survival between stage I and stage IV were evaluated using independent t-test and Kaplan-Meier test, respectively. All variables were evaluated for a significance of P < .05.
RESULTS
Most cases analyzed were White (98.1%), male (58.6%), and had Medicare as the primary payor at diagnosis (51.1%). Of 2147 cases, 497 were stage I (23.1%) and 164 were stage IV AM (7.6%) with a mean age at diagnosis of 66.05 and 63.72 years, respectively. There was a significant difference in overall survival between stage I (mean = 118.7 months) and stage 4 (mean = 42.4 months, P < 0.001). The average Breslow thickness was 1.17mm in stage I and 2.59mm in stage IV (P<0.05). More patients diagnosed at stage I used academic facilities than those diagnosed at stage IV (43.9% vs 33.8%, P<0.05). Most patients diagnosed at stage I were high income compared to patients diagnosed at stage IV (55% vs 43.2%, P<0.05).
CONCLUSIONS
With the overall survival of stage IV AM being significantly worse, we hope this study can provide a starting point in the study and prevention of disparities in the early diagnosis of AM.