User login
Bringing you the latest news, research and reviews, exclusive interviews, podcasts, quizzes, and more.
div[contains(@class, 'read-next-article')]
div[contains(@class, 'nav-primary')]
nav[contains(@class, 'nav-primary')]
section[contains(@class, 'footer-nav-section-wrapper')]
nav[contains(@class, 'nav-ce-stack nav-ce-stack__large-screen')]
header[@id='header']
div[contains(@class, 'header__large-screen')]
div[contains(@class, 'read-next-article')]
div[contains(@class, 'main-prefix')]
div[contains(@class, 'nav-primary')]
nav[contains(@class, 'nav-primary')]
section[contains(@class, 'footer-nav-section-wrapper')]
footer[@id='footer']
section[contains(@class, 'nav-hidden')]
div[contains(@class, 'ce-card-content')]
nav[contains(@class, 'nav-ce-stack')]
div[contains(@class, 'view-medstat-quiz-listing-panes')]
div[contains(@class, 'pane-article-sidebar-latest-news')]
New Omicron COVID boosters coming soon: What to know now
– a month ahead of schedule, the Biden administration announced this week.
Moderna has signed a $1.74 billion federal contract to supply 66 million initial doses of the “bivalent” booster, which includes the original “ancestral” virus strain and elements of the Omicron BA.4 and BA.5 variants. Pfizer also announced a $3.2 billion U.S. agreement for another 105 million shots. Both vaccine suppliers have signed options to provide millions more boosters in the months ahead.
About 83.5% of Americans have received at least one COVID-19 shot, with 71.5% fully vaccinated with the initial series, 48% receiving one booster shot, and 31% two boosters, according to the CDC. With about 130,000 new COVID cases per day, and about 440 deaths, officials say the updated boosters may help rein in those figures by targeting the highly transmissible and widely circulating Omicron strains.
Federal health officials are still hammering out details of guidelines and recommendations of who should get the boosters, which are expected to come from the CDC and FDA. For now, authorities have decided not to expand eligibility for second boosters of the existing vaccines – now recommended only for adults over 50 and those 12 and older with immune deficiencies. Children 5 through 11 are advised to receive a single booster, 5 months after their initial vaccine series.
For a preview of what to expect from the CDC and FDA, this news organization spoke with Keri Althoff, PhD, an epidemiologist at Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore.
Q: Based on what we know now, who should be getting one of these new bivalent boosters?A: Of course, there is a process here regarding the specific recommendations, but it appears there will likely be a recommendation for all individuals to get this bivalent booster, similar to the first booster. And there will likely be a recommended time frame as to time since the last booster.
Right now, we have a recommendation for adults over the age of 50 or adults who are at higher risk for severe COVID-related illness [to get] a second booster. For them, there will probably be a timeline that says you should get the booster if you’re X amount of months or more from your second booster; or X amount of months or more from your first booster, if you’ve only had one.
Q: What about pregnant women or those being treated for chronic health conditions?A: I would imagine that once this bivalent booster becomes available, it will be recommended for all adults.
Q: And for children?A: That’s a good question. It’s something I have been digging into, [and] I think parents are really interested in this. Most kids, 5 and above, are supposed to be boosted with one shot right now, if they’re X amount of days from their primary vaccine series. Of course those 6 months to 4.99 years are not yet eligible [for boosters].
As a parent, I would love to see my children become eligible for the bivalent booster. It would be great if these boosters are conveying some additional protection that the kids could get access to before we send them off to school this fall. But there are questions as to whether or not that is going to happen.
Q: If you never received a booster, but only the preliminary vaccine series, do you need to get those earlier boosters before having the new bivalent booster shot?A: I don’t think they will likely make that a requirement – to restrict the bivalent booster only to those who are already boosted or up to date on their vaccines at the time the bivalent booster becomes available. But that will be up to the [CDC] vaccine recommendation committee to decide.
Q: Are there any new risks associated with these boosters, since they were developed so rapidly?A: No. We continue to monitor this technology, and with all the mRNA vaccines that have been delivered, you have seen all that monitoring play out with the detection, for example, of different forms of inflammation of the heart tissue and who that may impact. So, those monitoring systems work, and they work really, really well, so we can detect those things. And we know these vaccines are definitely safe.
Q: Some health experts are concerned “vaccine fatigue” will have an impact on the booster campaign. What’s your take?A: We have seen this fatigue in the proportion of individuals who are boosted with a first booster and even boosted with a second. But having those earlier boosters along with this new bivalent booster is important, because essentially, what we’re doing is really priming the immune system.
We’re trying to expedite the process of getting people’s immune system up to speed so that when the virus comes our way – as we know it will, because [of] these Omicron strains that are highly infectious and really whipping through our communities – we’re able to get the highest level of population immunity, you don’t end up in the hospital.
Q: What other challenges do you see in persuading Americans to get another round of boosters?A: One of the things that I’ve been hearing a lot, which I get very nervous about, is people saying: “Oh, I got fully vaccinated, I did or did not get the booster, and I had COVID anyway and it was really nothing, it didn’t feel like much to me, and so I’m not going to be boosted anymore.” We are not in a place quite yet where those guidelines are being rolled back in any way, shape, or form. We still have highly vulnerable people to severe disease and death in our communities, and we’re seeing hundreds of deaths every day.
There are consequences, even if it isn’t in severity of disease, meaning hospitalization and death. And let’s not let the actual quality of the vaccine being so successful that it can keep you out of the hospital. Don’t mistake that for “I don’t need another one.”
Q: Unlike the flu shot, which is reformulated each year to match circulating strains, the new COVID boosters offer protection against older strains as well as the newer ones. Why?A: It’s all about creating a broader immune response in individuals so that as more strains emerge, which they likely will, we can create a broader population immune response [to all strains]. Our individual bodies are seeing differences in these strains through vaccination that helps everyone stay healthy.
Q: There haven’t been clinical trials of these new mRNA boosters. How strong is the evidence that they will be effective against the emerging Omicron variants?A: There have been some studies – some great studies – looking at things like neutralizing antibodies, which we use as a surrogate for clinical trials. But that is not the same as studying the outcome of interest, which would be hospitalizations. So, part of the challenge is to be able to say: “Okay, this is what we know about the safety and effectiveness of the prior vaccines ... and how can we relate that to outcomes with these new boosters at an earlier stage [before] clinical data is available?”
Q: How long will the new boosters’ protections last – do we know yet?A: That timing is still a question, but of course what plays a big role in that is what COVID strains are circulating. If we prep these boosters that are Omicron specific, and then we have something totally new emerge ... we have to be more nimble because the variants are outpacing what we’re able to do.
This turns out to be a bit of a game of probability – the more infection we have, the more replication of the virus; the more replication, the more opportunity for mutations and subsequent variants.
Q: What about a combined flu-COVID vaccine; is that on the horizon?A: My children, who like most children do not like vaccines, always tell me: “Mom, why can’t they just put the influenza vaccine and the COVID vaccine into the same shot?” And I’m like: “Oh, from your lips to some scientist’s ears.”
At a time like this, where mRNA technology has totally disrupted what we can do with vaccines, in such a good way, I think we should push for the limits, because that would be incredible.
Q: If you’ve received a non-mRNA COVID vaccine, like those produced by Johnson & Johnson and Novavax, should you also get an mRNA booster?A: Right now, the CDC guidelines do state that if your primary vaccine series was not with an mRNA vaccine then being boosted with an mRNA is a fine thing to do, and it’s actually encouraged. So that’s not going to change with the bivalent booster.
Q: Is it okay to get a flu shot and a COVID booster at the same time, as the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention has recommended with past vaccines?A: I don’t anticipate there being recommendations against that. But I would also say watch for the recommendations that come out this fall on the bivalent boosters.
I do hope in the recommendations the CDC makes about the COVID boosters, they will say think about also getting your influenza vaccine, too. You could also get your COVID booster first, then by October get your influenza vaccine.
Q: Once you’re fully boosted, is it safe to stop wearing a mask, social distancing, avoiding crowded indoor spaces, and taking other precautions to avoid COVID-19?A: The virus is going to do what it does, which is infect whomever it can, and make them sick. So, if you see a lot of community transmission – you know who is ill with COVID in your kids’ schools, you know in your workplace and when people go out – that still signals there’s some increases in the circulation of virus. So, look at that to understand what your risk is.
If you know someone or have a colleague who is currently pregnant or immune suppressed, think about how you can protect them with mask-wearing, even if it’s just when you’re in one-on-one closed-door meetings with that individual.
So, your masking question is an important one, and it’s important for people to continue to hang onto those masks and wear them the week before you go see Grandma, for instance, to further reduce your risk so you don’t bring anything to here.
The high-level community risk nationwide is high right now. COVID is here.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMd.com.
– a month ahead of schedule, the Biden administration announced this week.
Moderna has signed a $1.74 billion federal contract to supply 66 million initial doses of the “bivalent” booster, which includes the original “ancestral” virus strain and elements of the Omicron BA.4 and BA.5 variants. Pfizer also announced a $3.2 billion U.S. agreement for another 105 million shots. Both vaccine suppliers have signed options to provide millions more boosters in the months ahead.
About 83.5% of Americans have received at least one COVID-19 shot, with 71.5% fully vaccinated with the initial series, 48% receiving one booster shot, and 31% two boosters, according to the CDC. With about 130,000 new COVID cases per day, and about 440 deaths, officials say the updated boosters may help rein in those figures by targeting the highly transmissible and widely circulating Omicron strains.
Federal health officials are still hammering out details of guidelines and recommendations of who should get the boosters, which are expected to come from the CDC and FDA. For now, authorities have decided not to expand eligibility for second boosters of the existing vaccines – now recommended only for adults over 50 and those 12 and older with immune deficiencies. Children 5 through 11 are advised to receive a single booster, 5 months after their initial vaccine series.
For a preview of what to expect from the CDC and FDA, this news organization spoke with Keri Althoff, PhD, an epidemiologist at Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore.
Q: Based on what we know now, who should be getting one of these new bivalent boosters?A: Of course, there is a process here regarding the specific recommendations, but it appears there will likely be a recommendation for all individuals to get this bivalent booster, similar to the first booster. And there will likely be a recommended time frame as to time since the last booster.
Right now, we have a recommendation for adults over the age of 50 or adults who are at higher risk for severe COVID-related illness [to get] a second booster. For them, there will probably be a timeline that says you should get the booster if you’re X amount of months or more from your second booster; or X amount of months or more from your first booster, if you’ve only had one.
Q: What about pregnant women or those being treated for chronic health conditions?A: I would imagine that once this bivalent booster becomes available, it will be recommended for all adults.
Q: And for children?A: That’s a good question. It’s something I have been digging into, [and] I think parents are really interested in this. Most kids, 5 and above, are supposed to be boosted with one shot right now, if they’re X amount of days from their primary vaccine series. Of course those 6 months to 4.99 years are not yet eligible [for boosters].
As a parent, I would love to see my children become eligible for the bivalent booster. It would be great if these boosters are conveying some additional protection that the kids could get access to before we send them off to school this fall. But there are questions as to whether or not that is going to happen.
Q: If you never received a booster, but only the preliminary vaccine series, do you need to get those earlier boosters before having the new bivalent booster shot?A: I don’t think they will likely make that a requirement – to restrict the bivalent booster only to those who are already boosted or up to date on their vaccines at the time the bivalent booster becomes available. But that will be up to the [CDC] vaccine recommendation committee to decide.
Q: Are there any new risks associated with these boosters, since they were developed so rapidly?A: No. We continue to monitor this technology, and with all the mRNA vaccines that have been delivered, you have seen all that monitoring play out with the detection, for example, of different forms of inflammation of the heart tissue and who that may impact. So, those monitoring systems work, and they work really, really well, so we can detect those things. And we know these vaccines are definitely safe.
Q: Some health experts are concerned “vaccine fatigue” will have an impact on the booster campaign. What’s your take?A: We have seen this fatigue in the proportion of individuals who are boosted with a first booster and even boosted with a second. But having those earlier boosters along with this new bivalent booster is important, because essentially, what we’re doing is really priming the immune system.
We’re trying to expedite the process of getting people’s immune system up to speed so that when the virus comes our way – as we know it will, because [of] these Omicron strains that are highly infectious and really whipping through our communities – we’re able to get the highest level of population immunity, you don’t end up in the hospital.
Q: What other challenges do you see in persuading Americans to get another round of boosters?A: One of the things that I’ve been hearing a lot, which I get very nervous about, is people saying: “Oh, I got fully vaccinated, I did or did not get the booster, and I had COVID anyway and it was really nothing, it didn’t feel like much to me, and so I’m not going to be boosted anymore.” We are not in a place quite yet where those guidelines are being rolled back in any way, shape, or form. We still have highly vulnerable people to severe disease and death in our communities, and we’re seeing hundreds of deaths every day.
There are consequences, even if it isn’t in severity of disease, meaning hospitalization and death. And let’s not let the actual quality of the vaccine being so successful that it can keep you out of the hospital. Don’t mistake that for “I don’t need another one.”
Q: Unlike the flu shot, which is reformulated each year to match circulating strains, the new COVID boosters offer protection against older strains as well as the newer ones. Why?A: It’s all about creating a broader immune response in individuals so that as more strains emerge, which they likely will, we can create a broader population immune response [to all strains]. Our individual bodies are seeing differences in these strains through vaccination that helps everyone stay healthy.
Q: There haven’t been clinical trials of these new mRNA boosters. How strong is the evidence that they will be effective against the emerging Omicron variants?A: There have been some studies – some great studies – looking at things like neutralizing antibodies, which we use as a surrogate for clinical trials. But that is not the same as studying the outcome of interest, which would be hospitalizations. So, part of the challenge is to be able to say: “Okay, this is what we know about the safety and effectiveness of the prior vaccines ... and how can we relate that to outcomes with these new boosters at an earlier stage [before] clinical data is available?”
Q: How long will the new boosters’ protections last – do we know yet?A: That timing is still a question, but of course what plays a big role in that is what COVID strains are circulating. If we prep these boosters that are Omicron specific, and then we have something totally new emerge ... we have to be more nimble because the variants are outpacing what we’re able to do.
This turns out to be a bit of a game of probability – the more infection we have, the more replication of the virus; the more replication, the more opportunity for mutations and subsequent variants.
Q: What about a combined flu-COVID vaccine; is that on the horizon?A: My children, who like most children do not like vaccines, always tell me: “Mom, why can’t they just put the influenza vaccine and the COVID vaccine into the same shot?” And I’m like: “Oh, from your lips to some scientist’s ears.”
At a time like this, where mRNA technology has totally disrupted what we can do with vaccines, in such a good way, I think we should push for the limits, because that would be incredible.
Q: If you’ve received a non-mRNA COVID vaccine, like those produced by Johnson & Johnson and Novavax, should you also get an mRNA booster?A: Right now, the CDC guidelines do state that if your primary vaccine series was not with an mRNA vaccine then being boosted with an mRNA is a fine thing to do, and it’s actually encouraged. So that’s not going to change with the bivalent booster.
Q: Is it okay to get a flu shot and a COVID booster at the same time, as the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention has recommended with past vaccines?A: I don’t anticipate there being recommendations against that. But I would also say watch for the recommendations that come out this fall on the bivalent boosters.
I do hope in the recommendations the CDC makes about the COVID boosters, they will say think about also getting your influenza vaccine, too. You could also get your COVID booster first, then by October get your influenza vaccine.
Q: Once you’re fully boosted, is it safe to stop wearing a mask, social distancing, avoiding crowded indoor spaces, and taking other precautions to avoid COVID-19?A: The virus is going to do what it does, which is infect whomever it can, and make them sick. So, if you see a lot of community transmission – you know who is ill with COVID in your kids’ schools, you know in your workplace and when people go out – that still signals there’s some increases in the circulation of virus. So, look at that to understand what your risk is.
If you know someone or have a colleague who is currently pregnant or immune suppressed, think about how you can protect them with mask-wearing, even if it’s just when you’re in one-on-one closed-door meetings with that individual.
So, your masking question is an important one, and it’s important for people to continue to hang onto those masks and wear them the week before you go see Grandma, for instance, to further reduce your risk so you don’t bring anything to here.
The high-level community risk nationwide is high right now. COVID is here.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMd.com.
– a month ahead of schedule, the Biden administration announced this week.
Moderna has signed a $1.74 billion federal contract to supply 66 million initial doses of the “bivalent” booster, which includes the original “ancestral” virus strain and elements of the Omicron BA.4 and BA.5 variants. Pfizer also announced a $3.2 billion U.S. agreement for another 105 million shots. Both vaccine suppliers have signed options to provide millions more boosters in the months ahead.
About 83.5% of Americans have received at least one COVID-19 shot, with 71.5% fully vaccinated with the initial series, 48% receiving one booster shot, and 31% two boosters, according to the CDC. With about 130,000 new COVID cases per day, and about 440 deaths, officials say the updated boosters may help rein in those figures by targeting the highly transmissible and widely circulating Omicron strains.
Federal health officials are still hammering out details of guidelines and recommendations of who should get the boosters, which are expected to come from the CDC and FDA. For now, authorities have decided not to expand eligibility for second boosters of the existing vaccines – now recommended only for adults over 50 and those 12 and older with immune deficiencies. Children 5 through 11 are advised to receive a single booster, 5 months after their initial vaccine series.
For a preview of what to expect from the CDC and FDA, this news organization spoke with Keri Althoff, PhD, an epidemiologist at Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore.
Q: Based on what we know now, who should be getting one of these new bivalent boosters?A: Of course, there is a process here regarding the specific recommendations, but it appears there will likely be a recommendation for all individuals to get this bivalent booster, similar to the first booster. And there will likely be a recommended time frame as to time since the last booster.
Right now, we have a recommendation for adults over the age of 50 or adults who are at higher risk for severe COVID-related illness [to get] a second booster. For them, there will probably be a timeline that says you should get the booster if you’re X amount of months or more from your second booster; or X amount of months or more from your first booster, if you’ve only had one.
Q: What about pregnant women or those being treated for chronic health conditions?A: I would imagine that once this bivalent booster becomes available, it will be recommended for all adults.
Q: And for children?A: That’s a good question. It’s something I have been digging into, [and] I think parents are really interested in this. Most kids, 5 and above, are supposed to be boosted with one shot right now, if they’re X amount of days from their primary vaccine series. Of course those 6 months to 4.99 years are not yet eligible [for boosters].
As a parent, I would love to see my children become eligible for the bivalent booster. It would be great if these boosters are conveying some additional protection that the kids could get access to before we send them off to school this fall. But there are questions as to whether or not that is going to happen.
Q: If you never received a booster, but only the preliminary vaccine series, do you need to get those earlier boosters before having the new bivalent booster shot?A: I don’t think they will likely make that a requirement – to restrict the bivalent booster only to those who are already boosted or up to date on their vaccines at the time the bivalent booster becomes available. But that will be up to the [CDC] vaccine recommendation committee to decide.
Q: Are there any new risks associated with these boosters, since they were developed so rapidly?A: No. We continue to monitor this technology, and with all the mRNA vaccines that have been delivered, you have seen all that monitoring play out with the detection, for example, of different forms of inflammation of the heart tissue and who that may impact. So, those monitoring systems work, and they work really, really well, so we can detect those things. And we know these vaccines are definitely safe.
Q: Some health experts are concerned “vaccine fatigue” will have an impact on the booster campaign. What’s your take?A: We have seen this fatigue in the proportion of individuals who are boosted with a first booster and even boosted with a second. But having those earlier boosters along with this new bivalent booster is important, because essentially, what we’re doing is really priming the immune system.
We’re trying to expedite the process of getting people’s immune system up to speed so that when the virus comes our way – as we know it will, because [of] these Omicron strains that are highly infectious and really whipping through our communities – we’re able to get the highest level of population immunity, you don’t end up in the hospital.
Q: What other challenges do you see in persuading Americans to get another round of boosters?A: One of the things that I’ve been hearing a lot, which I get very nervous about, is people saying: “Oh, I got fully vaccinated, I did or did not get the booster, and I had COVID anyway and it was really nothing, it didn’t feel like much to me, and so I’m not going to be boosted anymore.” We are not in a place quite yet where those guidelines are being rolled back in any way, shape, or form. We still have highly vulnerable people to severe disease and death in our communities, and we’re seeing hundreds of deaths every day.
There are consequences, even if it isn’t in severity of disease, meaning hospitalization and death. And let’s not let the actual quality of the vaccine being so successful that it can keep you out of the hospital. Don’t mistake that for “I don’t need another one.”
Q: Unlike the flu shot, which is reformulated each year to match circulating strains, the new COVID boosters offer protection against older strains as well as the newer ones. Why?A: It’s all about creating a broader immune response in individuals so that as more strains emerge, which they likely will, we can create a broader population immune response [to all strains]. Our individual bodies are seeing differences in these strains through vaccination that helps everyone stay healthy.
Q: There haven’t been clinical trials of these new mRNA boosters. How strong is the evidence that they will be effective against the emerging Omicron variants?A: There have been some studies – some great studies – looking at things like neutralizing antibodies, which we use as a surrogate for clinical trials. But that is not the same as studying the outcome of interest, which would be hospitalizations. So, part of the challenge is to be able to say: “Okay, this is what we know about the safety and effectiveness of the prior vaccines ... and how can we relate that to outcomes with these new boosters at an earlier stage [before] clinical data is available?”
Q: How long will the new boosters’ protections last – do we know yet?A: That timing is still a question, but of course what plays a big role in that is what COVID strains are circulating. If we prep these boosters that are Omicron specific, and then we have something totally new emerge ... we have to be more nimble because the variants are outpacing what we’re able to do.
This turns out to be a bit of a game of probability – the more infection we have, the more replication of the virus; the more replication, the more opportunity for mutations and subsequent variants.
Q: What about a combined flu-COVID vaccine; is that on the horizon?A: My children, who like most children do not like vaccines, always tell me: “Mom, why can’t they just put the influenza vaccine and the COVID vaccine into the same shot?” And I’m like: “Oh, from your lips to some scientist’s ears.”
At a time like this, where mRNA technology has totally disrupted what we can do with vaccines, in such a good way, I think we should push for the limits, because that would be incredible.
Q: If you’ve received a non-mRNA COVID vaccine, like those produced by Johnson & Johnson and Novavax, should you also get an mRNA booster?A: Right now, the CDC guidelines do state that if your primary vaccine series was not with an mRNA vaccine then being boosted with an mRNA is a fine thing to do, and it’s actually encouraged. So that’s not going to change with the bivalent booster.
Q: Is it okay to get a flu shot and a COVID booster at the same time, as the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention has recommended with past vaccines?A: I don’t anticipate there being recommendations against that. But I would also say watch for the recommendations that come out this fall on the bivalent boosters.
I do hope in the recommendations the CDC makes about the COVID boosters, they will say think about also getting your influenza vaccine, too. You could also get your COVID booster first, then by October get your influenza vaccine.
Q: Once you’re fully boosted, is it safe to stop wearing a mask, social distancing, avoiding crowded indoor spaces, and taking other precautions to avoid COVID-19?A: The virus is going to do what it does, which is infect whomever it can, and make them sick. So, if you see a lot of community transmission – you know who is ill with COVID in your kids’ schools, you know in your workplace and when people go out – that still signals there’s some increases in the circulation of virus. So, look at that to understand what your risk is.
If you know someone or have a colleague who is currently pregnant or immune suppressed, think about how you can protect them with mask-wearing, even if it’s just when you’re in one-on-one closed-door meetings with that individual.
So, your masking question is an important one, and it’s important for people to continue to hang onto those masks and wear them the week before you go see Grandma, for instance, to further reduce your risk so you don’t bring anything to here.
The high-level community risk nationwide is high right now. COVID is here.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMd.com.
Should patients undergoing surgical treatment for cervical lesions also receive an HPV vaccination?
Human papillomavirus (HPV) vaccine given around the time women have surgery for precancerous cervical lesions might lead to a reduction in the risk of lesions returning, as well as other HPV-related diseases, but the effects of this remain unclear.
The authors of the new study, published in The BMJ, explained that women who have been treated for high-grade cervical intra-epithelial neoplasia (CIN) have a “lifelong residual high risk of cervical cancer and other malignancies related to HPV infection,” and some research suggests that giving a preventive HPV vaccine alongside treatment for CIN might help to “reduce the risk in these women.”
HPV vaccination is highly effective at preventing the development of precancerous cervical lesions, CIN, and in the U.K., HPV vaccination is offered to girls and boys around the age of 12 or 13.
Eluned Hughes, head of information and engagement at Jo’s Cervical Cancer Trust, said: “Recent evidence has found that cases of cervical cancer have fallen 87% since the introduction of the HPV vaccine program in U.K. schools in 2008.”
“However, women over the age of 27, for whom the vaccine was not available, remain at increased risk of cervical cancer,” she highlighted.
Significant risk of bias and scarcity of data
In the study, researchers set out to explore the efficacy of HPV vaccination on the risk of HPV infection and recurrent diseases related to HPV infection in individuals undergoing local surgical treatment of preinvasive genital disease.
The systematic review and meta-analysis, led by researchers at Imperial College London, screened data from PubMed (Medline), Scopus, Cochrane, Web of Science, and ClinicalTrials.gov from inception to March 31, 2021.
The researchers analyzed the results of 18 studies – two randomized controlled trials (RCTs), 12 observational studies, and four post-hoc analyses of RCTs.
The authors said that the two RCTs were classified as low risk of bias, while in the observational studies and post-hoc analyses, risk of bias was moderate for seven, serious for seven, and critical for two. Average length of follow-up was 36 months.
There was a reduction of 57% in the risk of recurrence of high-grade pre-invasive disease (CIN2+) in individuals who were vaccinated, compared with those who were not vaccinated. “The effect estimate was “even more pronounced” – a relative 74% reduction – when the risk of recurrence of CIN2+ was assessed for disease related to the two high-risk HPV types – HPV16 and HPV18,” explained the authors.
However, the researchers noted that these effects are unclear because of the “scarcity of data” and the “moderate to high overall risk of bias” of the available studies.
Quality of evidence inconclusive – more trials needed
With regards to CIN3, the risk of recurrence of was also reduced in patients who were vaccinated, but there was a high level of uncertainty about the quality of this evidence, cautioned the authors.
Evidence was also lacking on the benefit of HPV vaccination for recurrence of vulvar, vaginal, and anal lesions, as well as genital warts.
Analysis of the post-hoc studies from randomized controlled trial data with historic vaccination at randomization before the development of the disease reported inconsistent results, the authors said.
Several study limitations were acknowledged by the authors, including that most of the studies were observational, of low to moderate quality, and with relatively short follow-up times, which they pointed out prevented assessment of long-term effects. In addition, the average age of participants was not provided in most studies, and factors such as smoking – associated with a higher risk of recurrence – were not controlled for in many studies.
“HPV vaccination might reduce the risk of recurrence of CIN, in particular when related to HPV16 or HPV18, in women treated with local excision,” they concluded. However, they cautioned that “quality of evidence indicated that the data were inconclusive.”
“Large, appropriately powered, randomized controlled trials are required to establish the effectiveness of adjuvant HPV vaccination at the time of local surgical treatment of CIN,” they recommended.
“Given that the incidence of recurrence of high-grade disease is low in quality assured national screening programs, such as in the United Kingdom, absolute risks and a cost effectiveness analysis would be important in determining the implementation strategy of HPV vaccination after treatment,” the authors said.
Ms. Hughes said that the charity was pleased to see emerging research into the value of using the HPV vaccine to prevent the recurrence of cervical cell changes. She said that the charity looks forward to seeing “further large-scale studies into the effectiveness of this method.”
In the meantime, the charity encourages all women and other people with a cervix to attend their cervical screening and for young people to have the HPV vaccination when invited, as “these are the best tools we currently have to prevent cervical cancer,” she said.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape UK.
Human papillomavirus (HPV) vaccine given around the time women have surgery for precancerous cervical lesions might lead to a reduction in the risk of lesions returning, as well as other HPV-related diseases, but the effects of this remain unclear.
The authors of the new study, published in The BMJ, explained that women who have been treated for high-grade cervical intra-epithelial neoplasia (CIN) have a “lifelong residual high risk of cervical cancer and other malignancies related to HPV infection,” and some research suggests that giving a preventive HPV vaccine alongside treatment for CIN might help to “reduce the risk in these women.”
HPV vaccination is highly effective at preventing the development of precancerous cervical lesions, CIN, and in the U.K., HPV vaccination is offered to girls and boys around the age of 12 or 13.
Eluned Hughes, head of information and engagement at Jo’s Cervical Cancer Trust, said: “Recent evidence has found that cases of cervical cancer have fallen 87% since the introduction of the HPV vaccine program in U.K. schools in 2008.”
“However, women over the age of 27, for whom the vaccine was not available, remain at increased risk of cervical cancer,” she highlighted.
Significant risk of bias and scarcity of data
In the study, researchers set out to explore the efficacy of HPV vaccination on the risk of HPV infection and recurrent diseases related to HPV infection in individuals undergoing local surgical treatment of preinvasive genital disease.
The systematic review and meta-analysis, led by researchers at Imperial College London, screened data from PubMed (Medline), Scopus, Cochrane, Web of Science, and ClinicalTrials.gov from inception to March 31, 2021.
The researchers analyzed the results of 18 studies – two randomized controlled trials (RCTs), 12 observational studies, and four post-hoc analyses of RCTs.
The authors said that the two RCTs were classified as low risk of bias, while in the observational studies and post-hoc analyses, risk of bias was moderate for seven, serious for seven, and critical for two. Average length of follow-up was 36 months.
There was a reduction of 57% in the risk of recurrence of high-grade pre-invasive disease (CIN2+) in individuals who were vaccinated, compared with those who were not vaccinated. “The effect estimate was “even more pronounced” – a relative 74% reduction – when the risk of recurrence of CIN2+ was assessed for disease related to the two high-risk HPV types – HPV16 and HPV18,” explained the authors.
However, the researchers noted that these effects are unclear because of the “scarcity of data” and the “moderate to high overall risk of bias” of the available studies.
Quality of evidence inconclusive – more trials needed
With regards to CIN3, the risk of recurrence of was also reduced in patients who were vaccinated, but there was a high level of uncertainty about the quality of this evidence, cautioned the authors.
Evidence was also lacking on the benefit of HPV vaccination for recurrence of vulvar, vaginal, and anal lesions, as well as genital warts.
Analysis of the post-hoc studies from randomized controlled trial data with historic vaccination at randomization before the development of the disease reported inconsistent results, the authors said.
Several study limitations were acknowledged by the authors, including that most of the studies were observational, of low to moderate quality, and with relatively short follow-up times, which they pointed out prevented assessment of long-term effects. In addition, the average age of participants was not provided in most studies, and factors such as smoking – associated with a higher risk of recurrence – were not controlled for in many studies.
“HPV vaccination might reduce the risk of recurrence of CIN, in particular when related to HPV16 or HPV18, in women treated with local excision,” they concluded. However, they cautioned that “quality of evidence indicated that the data were inconclusive.”
“Large, appropriately powered, randomized controlled trials are required to establish the effectiveness of adjuvant HPV vaccination at the time of local surgical treatment of CIN,” they recommended.
“Given that the incidence of recurrence of high-grade disease is low in quality assured national screening programs, such as in the United Kingdom, absolute risks and a cost effectiveness analysis would be important in determining the implementation strategy of HPV vaccination after treatment,” the authors said.
Ms. Hughes said that the charity was pleased to see emerging research into the value of using the HPV vaccine to prevent the recurrence of cervical cell changes. She said that the charity looks forward to seeing “further large-scale studies into the effectiveness of this method.”
In the meantime, the charity encourages all women and other people with a cervix to attend their cervical screening and for young people to have the HPV vaccination when invited, as “these are the best tools we currently have to prevent cervical cancer,” she said.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape UK.
Human papillomavirus (HPV) vaccine given around the time women have surgery for precancerous cervical lesions might lead to a reduction in the risk of lesions returning, as well as other HPV-related diseases, but the effects of this remain unclear.
The authors of the new study, published in The BMJ, explained that women who have been treated for high-grade cervical intra-epithelial neoplasia (CIN) have a “lifelong residual high risk of cervical cancer and other malignancies related to HPV infection,” and some research suggests that giving a preventive HPV vaccine alongside treatment for CIN might help to “reduce the risk in these women.”
HPV vaccination is highly effective at preventing the development of precancerous cervical lesions, CIN, and in the U.K., HPV vaccination is offered to girls and boys around the age of 12 or 13.
Eluned Hughes, head of information and engagement at Jo’s Cervical Cancer Trust, said: “Recent evidence has found that cases of cervical cancer have fallen 87% since the introduction of the HPV vaccine program in U.K. schools in 2008.”
“However, women over the age of 27, for whom the vaccine was not available, remain at increased risk of cervical cancer,” she highlighted.
Significant risk of bias and scarcity of data
In the study, researchers set out to explore the efficacy of HPV vaccination on the risk of HPV infection and recurrent diseases related to HPV infection in individuals undergoing local surgical treatment of preinvasive genital disease.
The systematic review and meta-analysis, led by researchers at Imperial College London, screened data from PubMed (Medline), Scopus, Cochrane, Web of Science, and ClinicalTrials.gov from inception to March 31, 2021.
The researchers analyzed the results of 18 studies – two randomized controlled trials (RCTs), 12 observational studies, and four post-hoc analyses of RCTs.
The authors said that the two RCTs were classified as low risk of bias, while in the observational studies and post-hoc analyses, risk of bias was moderate for seven, serious for seven, and critical for two. Average length of follow-up was 36 months.
There was a reduction of 57% in the risk of recurrence of high-grade pre-invasive disease (CIN2+) in individuals who were vaccinated, compared with those who were not vaccinated. “The effect estimate was “even more pronounced” – a relative 74% reduction – when the risk of recurrence of CIN2+ was assessed for disease related to the two high-risk HPV types – HPV16 and HPV18,” explained the authors.
However, the researchers noted that these effects are unclear because of the “scarcity of data” and the “moderate to high overall risk of bias” of the available studies.
Quality of evidence inconclusive – more trials needed
With regards to CIN3, the risk of recurrence of was also reduced in patients who were vaccinated, but there was a high level of uncertainty about the quality of this evidence, cautioned the authors.
Evidence was also lacking on the benefit of HPV vaccination for recurrence of vulvar, vaginal, and anal lesions, as well as genital warts.
Analysis of the post-hoc studies from randomized controlled trial data with historic vaccination at randomization before the development of the disease reported inconsistent results, the authors said.
Several study limitations were acknowledged by the authors, including that most of the studies were observational, of low to moderate quality, and with relatively short follow-up times, which they pointed out prevented assessment of long-term effects. In addition, the average age of participants was not provided in most studies, and factors such as smoking – associated with a higher risk of recurrence – were not controlled for in many studies.
“HPV vaccination might reduce the risk of recurrence of CIN, in particular when related to HPV16 or HPV18, in women treated with local excision,” they concluded. However, they cautioned that “quality of evidence indicated that the data were inconclusive.”
“Large, appropriately powered, randomized controlled trials are required to establish the effectiveness of adjuvant HPV vaccination at the time of local surgical treatment of CIN,” they recommended.
“Given that the incidence of recurrence of high-grade disease is low in quality assured national screening programs, such as in the United Kingdom, absolute risks and a cost effectiveness analysis would be important in determining the implementation strategy of HPV vaccination after treatment,” the authors said.
Ms. Hughes said that the charity was pleased to see emerging research into the value of using the HPV vaccine to prevent the recurrence of cervical cell changes. She said that the charity looks forward to seeing “further large-scale studies into the effectiveness of this method.”
In the meantime, the charity encourages all women and other people with a cervix to attend their cervical screening and for young people to have the HPV vaccination when invited, as “these are the best tools we currently have to prevent cervical cancer,” she said.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape UK.
Why exercise doesn’t help people with long COVID
When Joel Fram woke up on the morning of March 12, 2020, he had a pretty good idea why he felt so lousy.
He lives in New York, where the first wave of the coronavirus was tearing through the city. “I instantly knew,” said the 55-year-old Broadway music director. It was COVID-19.
What started with a general sense of having been hit by a truck soon included a sore throat and such severe fatigue that he once fell asleep in the middle of sending a text to his sister. The final symptoms were chest tightness and trouble breathing.
And then he started to feel better. “By mid-April, my body was feeling essentially back to normal,” he said.
So he did what would have been smart after almost any other illness: He began working out. That didn’t last long. “It felt like someone pulled the carpet out from under me,” he remembered. “I couldn’t walk three blocks without getting breathless and fatigued.”
That was the first indication Mr. Fram had long COVID.
According to the National Center for Health Statistics, at least 7.5% of American adults – close to 20 million people – have symptoms of long COVID.
COVID-19 patients who had the most severe illness will struggle the most with exercise later, according to a review published in June from researchers at the University of California, San Francisco. But even people with mild symptoms can struggle to regain their previous levels of fitness.
“We have participants in our study who had relatively mild acute symptoms and went on to have really profound decreases in their ability to exercise,” said Matthew S. Durstenfeld, MD, a cardiologist at UCSF and principal author of the review.
Most people with long COVID will have lower-than-expected scores on tests of aerobic fitness, as shown by Yale researchers in a study published in August 2021.
“Some amount of that is due to deconditioning,” Dr. Durstenfeld said. “You’re not feeling well, so you’re not exercising to the same degree you might have been before you got infected.”
In a study published in April, people with long COVID told researchers at Britain’s University of Leeds they spent 93% less time in physical activity than they did before their infection.
But multiple studies have found deconditioning is not entirely – or even mostly – to blame.
A 2021 study found that 89% of participants with long COVID had postexertional malaise (PEM), which happens when a patient’s symptoms get worse after they do even minor physical or mental activities. According to the CDC, postexertional malaise can hit as long as 12-48 hours after the activity, and it can take people up to 2 weeks to fully recover.
Unfortunately, the advice patients get from their doctors sometimes makes the problem worse.
How long COVID defies simple solutions
Long COVID is a “dynamic disability” that requires health professionals to go off script when a patient’s symptoms don’t respond in a predictable way to treatment, said David Putrino, PhD, a neuroscientist, physical therapist, and director of rehabilitation innovation for the Mount Sinai Health System in New York.
“We’re not so good at dealing with somebody who, for all intents and purposes, can appear healthy and nondisabled on one day and be completely debilitated the next day,” he said.
Dr. Putrino said more than half of his clinic’s long-COVID patients told his team they had at least one of these persistent problems:
- Fatigue (82%).
- Brain fog (67%).
- Headache (60%).
- Sleep problems (59%).
- Dizziness (54%).
And 86% said exercise worsened their symptoms.
The symptoms are similar to what doctors see with illnesses such as lupus, Lyme disease, and chronic fatigue syndrome – something many experts compare long COVID to. Researchers and medical professionals still don’t know exactly how COVID-19 causes those symptoms. But there are some theories.
Potential causes of long-COVID symptoms
Dr. Putrino said it is possible the virus enters a patient’s cells and hijacks the mitochondria – a part of the cell that provides energy. It can linger there for weeks or months – something known as viral persistence.
“All of a sudden, the body’s getting less energy for itself, even though it’s producing the same amount, or even a little more,” he said. And there is a consequence to this extra stress on the cells. “Creating energy isn’t free. You’re producing more waste products, which puts your body in a state of oxidative stress,” Dr. Putrino said. Oxidative stress damages cells as molecules interact with oxygen in harmful ways.
“The other big mechanism is autonomic dysfunction,” Dr. Putrino said. It’s marked by breathing problems, heart palpitations, and other glitches in areas most healthy people never have to think about. About 70% of long-COVID patients at Mount Sinai’s clinic have some degree of autonomic dysfunction, he said.
For a person with autonomic dysfunction, something as basic as changing posture can trigger a storm of cytokines, a chemical messenger that tells the immune system where and how to respond to challenges like an injury or infection.
“Suddenly, you have this on-off switch,” Dr. Putrino said. “You go straight to ‘fight or flight,’ ” with a surge of adrenaline and a spiking heart rate, “then plunge back to ‘rest or digest.’ You go from fired up to so sleepy, you can’t keep your eyes open.”
A patient with viral persistence and one with autonomic dysfunction may have the same negative reaction to exercise, even though the triggers are completely different.
So how can doctors help long-COVID patients?
The first step, Dr. Putrino said, is to understand the difference between long COVID and a long recovery from COVID-19 infection.
Many of the patients in the latter group still have symptoms 4 weeks after their first infection. “At 4 weeks, yeah, they’re still feeling symptoms, but that’s not long COVID,” he said. “That’s just taking a while to get over a viral infection.”
Fitness advice is simple for those people: Take it easy at first, and gradually increase the amount and intensity of aerobic exercise and strength training.
But that advice would be disastrous for someone who meets Dr. Putrino’s stricter definition of long COVID: “Three to 4 months out from initial infection, they’re experiencing severe fatigue, exertional symptoms, cognitive symptoms, heart palpitations, shortness of breath,” he said.
“Our clinic is extraordinarily cautious with exercise” for those patients, he said.
In Dr. Putrino’s experience, about 20%-30% of patients will make significant progress after 12 weeks. “They’re feeling more or less like they felt pre-COVID,” he said.
The unluckiest 10%-20% won’t make any progress at all. Any type of therapy, even if it’s as simple as moving their legs from a flat position, worsens their symptoms.
The majority – 50%-60% – will have some improvement in their symptoms. But then progress will stop, for reasons researchers are still trying to figure out.
“My sense is that gradually increasing your exercise is still good advice for the vast majority of people,” UCSF’s Dr. Durstenfeld said.
Ideally, that exercise will be supervised by someone trained in cardiac, pulmonary, and/or autonomic rehabilitation – a specialized type of therapy aimed at resyncing the autonomic nervous system that governs breathing and other unconscious functions, he said. But those therapies are rarely covered by insurance, which means most long-COVID patients are on their own.
Dr. Durstenfeld said it’s important that patients keep trying and not give up. “With slow and steady progress, a lot of people can get profoundly better,” he said.
Mr. Fram, who’s worked with careful supervision, says he’s getting closer to something like his pre-COVID-19 life.
But he’s not there yet. Long COVID, he said, “affects my life every single day.”
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
When Joel Fram woke up on the morning of March 12, 2020, he had a pretty good idea why he felt so lousy.
He lives in New York, where the first wave of the coronavirus was tearing through the city. “I instantly knew,” said the 55-year-old Broadway music director. It was COVID-19.
What started with a general sense of having been hit by a truck soon included a sore throat and such severe fatigue that he once fell asleep in the middle of sending a text to his sister. The final symptoms were chest tightness and trouble breathing.
And then he started to feel better. “By mid-April, my body was feeling essentially back to normal,” he said.
So he did what would have been smart after almost any other illness: He began working out. That didn’t last long. “It felt like someone pulled the carpet out from under me,” he remembered. “I couldn’t walk three blocks without getting breathless and fatigued.”
That was the first indication Mr. Fram had long COVID.
According to the National Center for Health Statistics, at least 7.5% of American adults – close to 20 million people – have symptoms of long COVID.
COVID-19 patients who had the most severe illness will struggle the most with exercise later, according to a review published in June from researchers at the University of California, San Francisco. But even people with mild symptoms can struggle to regain their previous levels of fitness.
“We have participants in our study who had relatively mild acute symptoms and went on to have really profound decreases in their ability to exercise,” said Matthew S. Durstenfeld, MD, a cardiologist at UCSF and principal author of the review.
Most people with long COVID will have lower-than-expected scores on tests of aerobic fitness, as shown by Yale researchers in a study published in August 2021.
“Some amount of that is due to deconditioning,” Dr. Durstenfeld said. “You’re not feeling well, so you’re not exercising to the same degree you might have been before you got infected.”
In a study published in April, people with long COVID told researchers at Britain’s University of Leeds they spent 93% less time in physical activity than they did before their infection.
But multiple studies have found deconditioning is not entirely – or even mostly – to blame.
A 2021 study found that 89% of participants with long COVID had postexertional malaise (PEM), which happens when a patient’s symptoms get worse after they do even minor physical or mental activities. According to the CDC, postexertional malaise can hit as long as 12-48 hours after the activity, and it can take people up to 2 weeks to fully recover.
Unfortunately, the advice patients get from their doctors sometimes makes the problem worse.
How long COVID defies simple solutions
Long COVID is a “dynamic disability” that requires health professionals to go off script when a patient’s symptoms don’t respond in a predictable way to treatment, said David Putrino, PhD, a neuroscientist, physical therapist, and director of rehabilitation innovation for the Mount Sinai Health System in New York.
“We’re not so good at dealing with somebody who, for all intents and purposes, can appear healthy and nondisabled on one day and be completely debilitated the next day,” he said.
Dr. Putrino said more than half of his clinic’s long-COVID patients told his team they had at least one of these persistent problems:
- Fatigue (82%).
- Brain fog (67%).
- Headache (60%).
- Sleep problems (59%).
- Dizziness (54%).
And 86% said exercise worsened their symptoms.
The symptoms are similar to what doctors see with illnesses such as lupus, Lyme disease, and chronic fatigue syndrome – something many experts compare long COVID to. Researchers and medical professionals still don’t know exactly how COVID-19 causes those symptoms. But there are some theories.
Potential causes of long-COVID symptoms
Dr. Putrino said it is possible the virus enters a patient’s cells and hijacks the mitochondria – a part of the cell that provides energy. It can linger there for weeks or months – something known as viral persistence.
“All of a sudden, the body’s getting less energy for itself, even though it’s producing the same amount, or even a little more,” he said. And there is a consequence to this extra stress on the cells. “Creating energy isn’t free. You’re producing more waste products, which puts your body in a state of oxidative stress,” Dr. Putrino said. Oxidative stress damages cells as molecules interact with oxygen in harmful ways.
“The other big mechanism is autonomic dysfunction,” Dr. Putrino said. It’s marked by breathing problems, heart palpitations, and other glitches in areas most healthy people never have to think about. About 70% of long-COVID patients at Mount Sinai’s clinic have some degree of autonomic dysfunction, he said.
For a person with autonomic dysfunction, something as basic as changing posture can trigger a storm of cytokines, a chemical messenger that tells the immune system where and how to respond to challenges like an injury or infection.
“Suddenly, you have this on-off switch,” Dr. Putrino said. “You go straight to ‘fight or flight,’ ” with a surge of adrenaline and a spiking heart rate, “then plunge back to ‘rest or digest.’ You go from fired up to so sleepy, you can’t keep your eyes open.”
A patient with viral persistence and one with autonomic dysfunction may have the same negative reaction to exercise, even though the triggers are completely different.
So how can doctors help long-COVID patients?
The first step, Dr. Putrino said, is to understand the difference between long COVID and a long recovery from COVID-19 infection.
Many of the patients in the latter group still have symptoms 4 weeks after their first infection. “At 4 weeks, yeah, they’re still feeling symptoms, but that’s not long COVID,” he said. “That’s just taking a while to get over a viral infection.”
Fitness advice is simple for those people: Take it easy at first, and gradually increase the amount and intensity of aerobic exercise and strength training.
But that advice would be disastrous for someone who meets Dr. Putrino’s stricter definition of long COVID: “Three to 4 months out from initial infection, they’re experiencing severe fatigue, exertional symptoms, cognitive symptoms, heart palpitations, shortness of breath,” he said.
“Our clinic is extraordinarily cautious with exercise” for those patients, he said.
In Dr. Putrino’s experience, about 20%-30% of patients will make significant progress after 12 weeks. “They’re feeling more or less like they felt pre-COVID,” he said.
The unluckiest 10%-20% won’t make any progress at all. Any type of therapy, even if it’s as simple as moving their legs from a flat position, worsens their symptoms.
The majority – 50%-60% – will have some improvement in their symptoms. But then progress will stop, for reasons researchers are still trying to figure out.
“My sense is that gradually increasing your exercise is still good advice for the vast majority of people,” UCSF’s Dr. Durstenfeld said.
Ideally, that exercise will be supervised by someone trained in cardiac, pulmonary, and/or autonomic rehabilitation – a specialized type of therapy aimed at resyncing the autonomic nervous system that governs breathing and other unconscious functions, he said. But those therapies are rarely covered by insurance, which means most long-COVID patients are on their own.
Dr. Durstenfeld said it’s important that patients keep trying and not give up. “With slow and steady progress, a lot of people can get profoundly better,” he said.
Mr. Fram, who’s worked with careful supervision, says he’s getting closer to something like his pre-COVID-19 life.
But he’s not there yet. Long COVID, he said, “affects my life every single day.”
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
When Joel Fram woke up on the morning of March 12, 2020, he had a pretty good idea why he felt so lousy.
He lives in New York, where the first wave of the coronavirus was tearing through the city. “I instantly knew,” said the 55-year-old Broadway music director. It was COVID-19.
What started with a general sense of having been hit by a truck soon included a sore throat and such severe fatigue that he once fell asleep in the middle of sending a text to his sister. The final symptoms were chest tightness and trouble breathing.
And then he started to feel better. “By mid-April, my body was feeling essentially back to normal,” he said.
So he did what would have been smart after almost any other illness: He began working out. That didn’t last long. “It felt like someone pulled the carpet out from under me,” he remembered. “I couldn’t walk three blocks without getting breathless and fatigued.”
That was the first indication Mr. Fram had long COVID.
According to the National Center for Health Statistics, at least 7.5% of American adults – close to 20 million people – have symptoms of long COVID.
COVID-19 patients who had the most severe illness will struggle the most with exercise later, according to a review published in June from researchers at the University of California, San Francisco. But even people with mild symptoms can struggle to regain their previous levels of fitness.
“We have participants in our study who had relatively mild acute symptoms and went on to have really profound decreases in their ability to exercise,” said Matthew S. Durstenfeld, MD, a cardiologist at UCSF and principal author of the review.
Most people with long COVID will have lower-than-expected scores on tests of aerobic fitness, as shown by Yale researchers in a study published in August 2021.
“Some amount of that is due to deconditioning,” Dr. Durstenfeld said. “You’re not feeling well, so you’re not exercising to the same degree you might have been before you got infected.”
In a study published in April, people with long COVID told researchers at Britain’s University of Leeds they spent 93% less time in physical activity than they did before their infection.
But multiple studies have found deconditioning is not entirely – or even mostly – to blame.
A 2021 study found that 89% of participants with long COVID had postexertional malaise (PEM), which happens when a patient’s symptoms get worse after they do even minor physical or mental activities. According to the CDC, postexertional malaise can hit as long as 12-48 hours after the activity, and it can take people up to 2 weeks to fully recover.
Unfortunately, the advice patients get from their doctors sometimes makes the problem worse.
How long COVID defies simple solutions
Long COVID is a “dynamic disability” that requires health professionals to go off script when a patient’s symptoms don’t respond in a predictable way to treatment, said David Putrino, PhD, a neuroscientist, physical therapist, and director of rehabilitation innovation for the Mount Sinai Health System in New York.
“We’re not so good at dealing with somebody who, for all intents and purposes, can appear healthy and nondisabled on one day and be completely debilitated the next day,” he said.
Dr. Putrino said more than half of his clinic’s long-COVID patients told his team they had at least one of these persistent problems:
- Fatigue (82%).
- Brain fog (67%).
- Headache (60%).
- Sleep problems (59%).
- Dizziness (54%).
And 86% said exercise worsened their symptoms.
The symptoms are similar to what doctors see with illnesses such as lupus, Lyme disease, and chronic fatigue syndrome – something many experts compare long COVID to. Researchers and medical professionals still don’t know exactly how COVID-19 causes those symptoms. But there are some theories.
Potential causes of long-COVID symptoms
Dr. Putrino said it is possible the virus enters a patient’s cells and hijacks the mitochondria – a part of the cell that provides energy. It can linger there for weeks or months – something known as viral persistence.
“All of a sudden, the body’s getting less energy for itself, even though it’s producing the same amount, or even a little more,” he said. And there is a consequence to this extra stress on the cells. “Creating energy isn’t free. You’re producing more waste products, which puts your body in a state of oxidative stress,” Dr. Putrino said. Oxidative stress damages cells as molecules interact with oxygen in harmful ways.
“The other big mechanism is autonomic dysfunction,” Dr. Putrino said. It’s marked by breathing problems, heart palpitations, and other glitches in areas most healthy people never have to think about. About 70% of long-COVID patients at Mount Sinai’s clinic have some degree of autonomic dysfunction, he said.
For a person with autonomic dysfunction, something as basic as changing posture can trigger a storm of cytokines, a chemical messenger that tells the immune system where and how to respond to challenges like an injury or infection.
“Suddenly, you have this on-off switch,” Dr. Putrino said. “You go straight to ‘fight or flight,’ ” with a surge of adrenaline and a spiking heart rate, “then plunge back to ‘rest or digest.’ You go from fired up to so sleepy, you can’t keep your eyes open.”
A patient with viral persistence and one with autonomic dysfunction may have the same negative reaction to exercise, even though the triggers are completely different.
So how can doctors help long-COVID patients?
The first step, Dr. Putrino said, is to understand the difference between long COVID and a long recovery from COVID-19 infection.
Many of the patients in the latter group still have symptoms 4 weeks after their first infection. “At 4 weeks, yeah, they’re still feeling symptoms, but that’s not long COVID,” he said. “That’s just taking a while to get over a viral infection.”
Fitness advice is simple for those people: Take it easy at first, and gradually increase the amount and intensity of aerobic exercise and strength training.
But that advice would be disastrous for someone who meets Dr. Putrino’s stricter definition of long COVID: “Three to 4 months out from initial infection, they’re experiencing severe fatigue, exertional symptoms, cognitive symptoms, heart palpitations, shortness of breath,” he said.
“Our clinic is extraordinarily cautious with exercise” for those patients, he said.
In Dr. Putrino’s experience, about 20%-30% of patients will make significant progress after 12 weeks. “They’re feeling more or less like they felt pre-COVID,” he said.
The unluckiest 10%-20% won’t make any progress at all. Any type of therapy, even if it’s as simple as moving their legs from a flat position, worsens their symptoms.
The majority – 50%-60% – will have some improvement in their symptoms. But then progress will stop, for reasons researchers are still trying to figure out.
“My sense is that gradually increasing your exercise is still good advice for the vast majority of people,” UCSF’s Dr. Durstenfeld said.
Ideally, that exercise will be supervised by someone trained in cardiac, pulmonary, and/or autonomic rehabilitation – a specialized type of therapy aimed at resyncing the autonomic nervous system that governs breathing and other unconscious functions, he said. But those therapies are rarely covered by insurance, which means most long-COVID patients are on their own.
Dr. Durstenfeld said it’s important that patients keep trying and not give up. “With slow and steady progress, a lot of people can get profoundly better,” he said.
Mr. Fram, who’s worked with careful supervision, says he’s getting closer to something like his pre-COVID-19 life.
But he’s not there yet. Long COVID, he said, “affects my life every single day.”
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
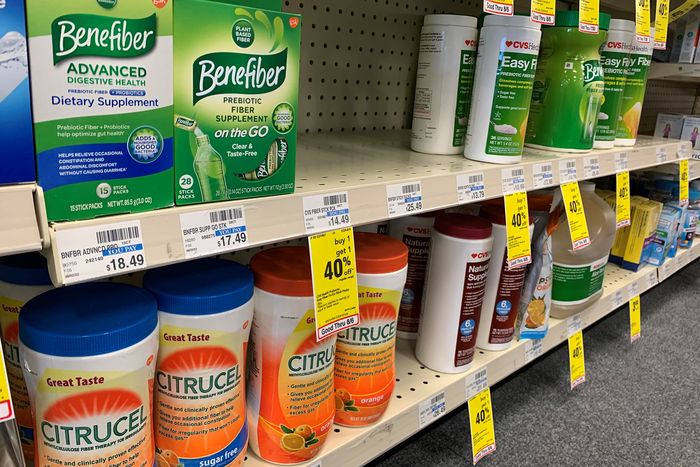
The gut microbes have spoken: All fiber is good fiber
Finding a fiber of good moral fiber
If you’ve ever wandered into the supplement aisle at your local grocery store, you’ve probably noticed an overabundance of fiber supplements that claim to do this for you and benefit that. Since there’s no Food and Drug Administration regulation on fiber supplements, manufacturers are free to (and do) make whatever wild claims they like. And much like choosing which of 500 shows to watch on Netflix, when you’re spoiled for choice, it can be difficult to pick.
Enter a team of molecular geneticists and microbiologists from Duke University. They can’t tell you what show to watch next, but they can tell you which fiber to choose, thanks to their new study. And the answer? Yes.
Well that’s not very helpful, but let us explain. For their study, a group of 28 received three of the main fiber supplements (inulin, dextrin, and galactooligosaccharides) for a week each, followed by a week off of fibers for their gut to return to baseline until they’d received all three. Those who consumed the least fiber at baseline saw the greatest benefit from fiber supplementation, with no appreciable difference between the three types. It was the same story for study participants who already consumed enough fiber; because their guts already hosted a more-optimal microbiome, the type of supplement didn’t matter. The benefits were the same across the board.
In an additional study, the Duke researchers found that gut microbiomes reacted to new fiber within a day, being primed to consume fiber on the first dose and digesting it more quickly on the second fiber dose.
The results, the researchers pointed out, make sense, since the average American only consumes 20%-40% of their daily recommended supply of fiber. Our digestive systems aren’t picky; they just want more, so go out there and choose whatever fiber you’d like. Do that, and then feel free to eat as many double bacon cheeseburgers as you’d like. That is the pinnacle of diet right there. Dietitians literally could not complain about it.
Jarlsberg vs. Camembert: This time it’s skeletal
Fiber is fabulous, of course, but the road to dietary health and wellness fulfillment takes us to many other, equally wondrous places. Hey, look! This next exit is covered with cheese.
All the cheeses are here, from Abbaye de Belloc to Zwitser, and there, right between the jalapeno cheddar and the Jermi tortes you’ll find Jarlsberg, a mild, semisoft, nutty-flavored cheese that comes from Jarlsberg in eastern Norway. A recent study also suggests that Jarlsberg may help to prevent osteopenia and osteoporosis.
A group of Norwegian investigators gathered together 66 healthy women and gave them a daily portion of either Jarlsberg or Camembert for 6 weeks, at which point the Camembert group was switched to Jarlsberg for another 6 weeks.
The research team choose Camembert because of its similarity to Jarlsberg in fat and protein content. Jarlsberg, however, also is rich in vitamin K2, which is important for bone health, and a substance known as DHNA, which “might combat bone thinning and increase bone tissue formation,” they said in a Eurekalert release.
After the first 6 weeks, blood levels of osteocalcin; vitamin K2; and PINP, a peptide involved in bone turnover, were significantly higher in the Jarlsberg group only. All those measures rose significantly after the switch from Camembert to Jarlsberg, while levels of total and LDL cholesterol “fell significantly in the Camembert group after they switched to Jarlsberg,” the team added.
But wait! There’s more! HbA1c fell significantly among those initially eating the Jarlsberg but rose sharply in those eating Camembert. Do you see where this is going? After the Camembert group made the switch to Jarlsberg, their HbA1c levels fell significantly as well.
So it’s not just a cheese thing: The effects are specific to Jarlsberg. Can you guess what we’re having for lunch? Double bacon and fiber Jarlsbergers. Mmm, Jarlsburgers.
Luck be a lady: The mother of twins
It’s widely believed that women who have twins must be more fertile, giving birth to more than one child at a time. Some studies have supported the idea, but more recent work is refuting that claim. In actuality, it might just be more statistics and luck than fertility after all.
Those earlier studies supporting fertility didn’t specify whether the chances of twin births were based on the ability to produce more than one egg at a time or on the number of births that women had overall. Looking at 100,000 preindustrial European births, before contraception was available, researchers from Norway, Germany, France, and the United Kingdom found that the number of total births, twins included, makes all the difference.
“When a woman gives birth several times, the chances increase that at least one of these births will be a twin birth,” investigator Gine Roll Skjærvø of the Norwegian University of Science and Technology said in a written statement.
Since twins occur in 1%-3% of all births, the more births that a woman has, the better her chances of giving birth to twins. The researchers compared it to playing the lottery. You buy enough tickets, eventually your numbers are going to come up. Despite that, however, they found that women who give birth to twins give birth less often than those who don’t have twins. Which raises the idea of sheer luck.
The researchers said that there’s still a lot to uncover in twin births, noting that “uncritically comparing groups of women with and without twins can trick us into believing the opposite of what is really true. These groupings may either hide the effects of twinning and fertility genes where they exist, or vice versa, create the illusion of these if they do not exist.”
For now, this new research claims that it’s basically a lottery. And women who give birth to twins hit the jackpot.
Those with low wages may be earning future memory loss
Not only are low wages detrimental to our souls, hopes, and dreams, but a new study shows that low wages also are linked to quicker memory decline later in life. Sustained low wages not only cause stress and food insecurity in the lives of many, but they also can cause diseases such as depression, obesity, and high blood pressure, which are risk factors for cognitive aging.
The study was conducted using records from the Health and Retirement Study for the years 1992-2016 and focused on 2,879 adults born between 1936 and 1941. The participants were divided into three groups: those who never earned low wages, those who sometimes did, and those who always did.
The investigators found that workers who earned sustained low wages – defined as an hourly wage lower than two-thirds of the federal median wage for the corresponding year – “experienced significantly faster memory decline in older age” than did those who never earned low wages.
There are signs of inflation everywhere we look these days, but many people are not earning higher wages to compensate for the extra expenses. “Increasing the federal minimum wage, for example to $15 per hour, remains a gridlock issue in Congress,” lead author Katrina Kezios of the Columbia University Mailman School of Public Health, said in a statement released by the university.
If only salaries would rise instead of prices for once.
Finding a fiber of good moral fiber
If you’ve ever wandered into the supplement aisle at your local grocery store, you’ve probably noticed an overabundance of fiber supplements that claim to do this for you and benefit that. Since there’s no Food and Drug Administration regulation on fiber supplements, manufacturers are free to (and do) make whatever wild claims they like. And much like choosing which of 500 shows to watch on Netflix, when you’re spoiled for choice, it can be difficult to pick.
Enter a team of molecular geneticists and microbiologists from Duke University. They can’t tell you what show to watch next, but they can tell you which fiber to choose, thanks to their new study. And the answer? Yes.
Well that’s not very helpful, but let us explain. For their study, a group of 28 received three of the main fiber supplements (inulin, dextrin, and galactooligosaccharides) for a week each, followed by a week off of fibers for their gut to return to baseline until they’d received all three. Those who consumed the least fiber at baseline saw the greatest benefit from fiber supplementation, with no appreciable difference between the three types. It was the same story for study participants who already consumed enough fiber; because their guts already hosted a more-optimal microbiome, the type of supplement didn’t matter. The benefits were the same across the board.
In an additional study, the Duke researchers found that gut microbiomes reacted to new fiber within a day, being primed to consume fiber on the first dose and digesting it more quickly on the second fiber dose.
The results, the researchers pointed out, make sense, since the average American only consumes 20%-40% of their daily recommended supply of fiber. Our digestive systems aren’t picky; they just want more, so go out there and choose whatever fiber you’d like. Do that, and then feel free to eat as many double bacon cheeseburgers as you’d like. That is the pinnacle of diet right there. Dietitians literally could not complain about it.
Jarlsberg vs. Camembert: This time it’s skeletal
Fiber is fabulous, of course, but the road to dietary health and wellness fulfillment takes us to many other, equally wondrous places. Hey, look! This next exit is covered with cheese.
All the cheeses are here, from Abbaye de Belloc to Zwitser, and there, right between the jalapeno cheddar and the Jermi tortes you’ll find Jarlsberg, a mild, semisoft, nutty-flavored cheese that comes from Jarlsberg in eastern Norway. A recent study also suggests that Jarlsberg may help to prevent osteopenia and osteoporosis.
A group of Norwegian investigators gathered together 66 healthy women and gave them a daily portion of either Jarlsberg or Camembert for 6 weeks, at which point the Camembert group was switched to Jarlsberg for another 6 weeks.
The research team choose Camembert because of its similarity to Jarlsberg in fat and protein content. Jarlsberg, however, also is rich in vitamin K2, which is important for bone health, and a substance known as DHNA, which “might combat bone thinning and increase bone tissue formation,” they said in a Eurekalert release.
After the first 6 weeks, blood levels of osteocalcin; vitamin K2; and PINP, a peptide involved in bone turnover, were significantly higher in the Jarlsberg group only. All those measures rose significantly after the switch from Camembert to Jarlsberg, while levels of total and LDL cholesterol “fell significantly in the Camembert group after they switched to Jarlsberg,” the team added.
But wait! There’s more! HbA1c fell significantly among those initially eating the Jarlsberg but rose sharply in those eating Camembert. Do you see where this is going? After the Camembert group made the switch to Jarlsberg, their HbA1c levels fell significantly as well.
So it’s not just a cheese thing: The effects are specific to Jarlsberg. Can you guess what we’re having for lunch? Double bacon and fiber Jarlsbergers. Mmm, Jarlsburgers.
Luck be a lady: The mother of twins
It’s widely believed that women who have twins must be more fertile, giving birth to more than one child at a time. Some studies have supported the idea, but more recent work is refuting that claim. In actuality, it might just be more statistics and luck than fertility after all.
Those earlier studies supporting fertility didn’t specify whether the chances of twin births were based on the ability to produce more than one egg at a time or on the number of births that women had overall. Looking at 100,000 preindustrial European births, before contraception was available, researchers from Norway, Germany, France, and the United Kingdom found that the number of total births, twins included, makes all the difference.
“When a woman gives birth several times, the chances increase that at least one of these births will be a twin birth,” investigator Gine Roll Skjærvø of the Norwegian University of Science and Technology said in a written statement.
Since twins occur in 1%-3% of all births, the more births that a woman has, the better her chances of giving birth to twins. The researchers compared it to playing the lottery. You buy enough tickets, eventually your numbers are going to come up. Despite that, however, they found that women who give birth to twins give birth less often than those who don’t have twins. Which raises the idea of sheer luck.
The researchers said that there’s still a lot to uncover in twin births, noting that “uncritically comparing groups of women with and without twins can trick us into believing the opposite of what is really true. These groupings may either hide the effects of twinning and fertility genes where they exist, or vice versa, create the illusion of these if they do not exist.”
For now, this new research claims that it’s basically a lottery. And women who give birth to twins hit the jackpot.
Those with low wages may be earning future memory loss
Not only are low wages detrimental to our souls, hopes, and dreams, but a new study shows that low wages also are linked to quicker memory decline later in life. Sustained low wages not only cause stress and food insecurity in the lives of many, but they also can cause diseases such as depression, obesity, and high blood pressure, which are risk factors for cognitive aging.
The study was conducted using records from the Health and Retirement Study for the years 1992-2016 and focused on 2,879 adults born between 1936 and 1941. The participants were divided into three groups: those who never earned low wages, those who sometimes did, and those who always did.
The investigators found that workers who earned sustained low wages – defined as an hourly wage lower than two-thirds of the federal median wage for the corresponding year – “experienced significantly faster memory decline in older age” than did those who never earned low wages.
There are signs of inflation everywhere we look these days, but many people are not earning higher wages to compensate for the extra expenses. “Increasing the federal minimum wage, for example to $15 per hour, remains a gridlock issue in Congress,” lead author Katrina Kezios of the Columbia University Mailman School of Public Health, said in a statement released by the university.
If only salaries would rise instead of prices for once.
Finding a fiber of good moral fiber
If you’ve ever wandered into the supplement aisle at your local grocery store, you’ve probably noticed an overabundance of fiber supplements that claim to do this for you and benefit that. Since there’s no Food and Drug Administration regulation on fiber supplements, manufacturers are free to (and do) make whatever wild claims they like. And much like choosing which of 500 shows to watch on Netflix, when you’re spoiled for choice, it can be difficult to pick.
Enter a team of molecular geneticists and microbiologists from Duke University. They can’t tell you what show to watch next, but they can tell you which fiber to choose, thanks to their new study. And the answer? Yes.
Well that’s not very helpful, but let us explain. For their study, a group of 28 received three of the main fiber supplements (inulin, dextrin, and galactooligosaccharides) for a week each, followed by a week off of fibers for their gut to return to baseline until they’d received all three. Those who consumed the least fiber at baseline saw the greatest benefit from fiber supplementation, with no appreciable difference between the three types. It was the same story for study participants who already consumed enough fiber; because their guts already hosted a more-optimal microbiome, the type of supplement didn’t matter. The benefits were the same across the board.
In an additional study, the Duke researchers found that gut microbiomes reacted to new fiber within a day, being primed to consume fiber on the first dose and digesting it more quickly on the second fiber dose.
The results, the researchers pointed out, make sense, since the average American only consumes 20%-40% of their daily recommended supply of fiber. Our digestive systems aren’t picky; they just want more, so go out there and choose whatever fiber you’d like. Do that, and then feel free to eat as many double bacon cheeseburgers as you’d like. That is the pinnacle of diet right there. Dietitians literally could not complain about it.
Jarlsberg vs. Camembert: This time it’s skeletal
Fiber is fabulous, of course, but the road to dietary health and wellness fulfillment takes us to many other, equally wondrous places. Hey, look! This next exit is covered with cheese.
All the cheeses are here, from Abbaye de Belloc to Zwitser, and there, right between the jalapeno cheddar and the Jermi tortes you’ll find Jarlsberg, a mild, semisoft, nutty-flavored cheese that comes from Jarlsberg in eastern Norway. A recent study also suggests that Jarlsberg may help to prevent osteopenia and osteoporosis.
A group of Norwegian investigators gathered together 66 healthy women and gave them a daily portion of either Jarlsberg or Camembert for 6 weeks, at which point the Camembert group was switched to Jarlsberg for another 6 weeks.
The research team choose Camembert because of its similarity to Jarlsberg in fat and protein content. Jarlsberg, however, also is rich in vitamin K2, which is important for bone health, and a substance known as DHNA, which “might combat bone thinning and increase bone tissue formation,” they said in a Eurekalert release.
After the first 6 weeks, blood levels of osteocalcin; vitamin K2; and PINP, a peptide involved in bone turnover, were significantly higher in the Jarlsberg group only. All those measures rose significantly after the switch from Camembert to Jarlsberg, while levels of total and LDL cholesterol “fell significantly in the Camembert group after they switched to Jarlsberg,” the team added.
But wait! There’s more! HbA1c fell significantly among those initially eating the Jarlsberg but rose sharply in those eating Camembert. Do you see where this is going? After the Camembert group made the switch to Jarlsberg, their HbA1c levels fell significantly as well.
So it’s not just a cheese thing: The effects are specific to Jarlsberg. Can you guess what we’re having for lunch? Double bacon and fiber Jarlsbergers. Mmm, Jarlsburgers.
Luck be a lady: The mother of twins
It’s widely believed that women who have twins must be more fertile, giving birth to more than one child at a time. Some studies have supported the idea, but more recent work is refuting that claim. In actuality, it might just be more statistics and luck than fertility after all.
Those earlier studies supporting fertility didn’t specify whether the chances of twin births were based on the ability to produce more than one egg at a time or on the number of births that women had overall. Looking at 100,000 preindustrial European births, before contraception was available, researchers from Norway, Germany, France, and the United Kingdom found that the number of total births, twins included, makes all the difference.
“When a woman gives birth several times, the chances increase that at least one of these births will be a twin birth,” investigator Gine Roll Skjærvø of the Norwegian University of Science and Technology said in a written statement.
Since twins occur in 1%-3% of all births, the more births that a woman has, the better her chances of giving birth to twins. The researchers compared it to playing the lottery. You buy enough tickets, eventually your numbers are going to come up. Despite that, however, they found that women who give birth to twins give birth less often than those who don’t have twins. Which raises the idea of sheer luck.
The researchers said that there’s still a lot to uncover in twin births, noting that “uncritically comparing groups of women with and without twins can trick us into believing the opposite of what is really true. These groupings may either hide the effects of twinning and fertility genes where they exist, or vice versa, create the illusion of these if they do not exist.”
For now, this new research claims that it’s basically a lottery. And women who give birth to twins hit the jackpot.
Those with low wages may be earning future memory loss
Not only are low wages detrimental to our souls, hopes, and dreams, but a new study shows that low wages also are linked to quicker memory decline later in life. Sustained low wages not only cause stress and food insecurity in the lives of many, but they also can cause diseases such as depression, obesity, and high blood pressure, which are risk factors for cognitive aging.
The study was conducted using records from the Health and Retirement Study for the years 1992-2016 and focused on 2,879 adults born between 1936 and 1941. The participants were divided into three groups: those who never earned low wages, those who sometimes did, and those who always did.
The investigators found that workers who earned sustained low wages – defined as an hourly wage lower than two-thirds of the federal median wage for the corresponding year – “experienced significantly faster memory decline in older age” than did those who never earned low wages.
There are signs of inflation everywhere we look these days, but many people are not earning higher wages to compensate for the extra expenses. “Increasing the federal minimum wage, for example to $15 per hour, remains a gridlock issue in Congress,” lead author Katrina Kezios of the Columbia University Mailman School of Public Health, said in a statement released by the university.
If only salaries would rise instead of prices for once.
Medical assistants identify strategies and barriers to clinic efficiency
ABSTRACT
Background: Medical assistant (MA) roles have expanded rapidly as primary care has evolved and MAs take on new patient care duties. Research that looks at the MA experience and factors that enhance or reduce efficiency among MAs is limited.
Methods: We surveyed all MAs working in 6 clinics run by a large academic family medicine department in Ann Arbor, Michigan. MAs deemed by peers as “most efficient” were selected for follow-up interviews. We evaluated personal strategies for efficiency, barriers to efficient care, impact of physician actions on efficiency, and satisfaction.
Results: A total of 75/86 MAs (87%) responded to at least some survey questions and 61/86 (71%) completed the full survey. We interviewed 18 MAs face to face. Most saw their role as essential to clinic functioning and viewed health care as a personal calling. MAs identified common strategies to improve efficiency and described the MA role to orchestrate the flow of the clinic day. Staff recognized differing priorities of patients, staff, and physicians and articulated frustrations with hierarchy and competing priorities as well as behaviors that impeded clinic efficiency. Respondents emphasized the importance of feeling valued by others on their team.
Conclusions: With the evolving demands made on MAs’ time, it is critical to understand how the most effective staff members manage their role and highlight the strategies they employ to provide efficient clinical care. Understanding factors that increase or decrease MA job satisfaction can help identify high-efficiency practices and promote a clinic culture that values and supports all staff.
As primary care continues to evolve into more team-based practice, the role of the medical assistant (MA) has rapidly transformed.1 Staff may assist with patient management, documentation in the electronic medical record, order entry, pre-visit planning, and fulfillment of quality metrics, particularly in a Primary Care Medical Home (PCMH).2 From 2012 through 2014, MA job postings per graduate increased from 1.3 to 2.3, suggesting twice as many job postings as graduates.3 As the demand for experienced MAs increases, the ability to recruit and retain high-performing staff members will be critical.
MAs are referenced in medical literature as early as the 1800s.4 The American Association of Medical Assistants was founded in 1956, which led to educational standardization and certifications.5 Despite the important role that MAs have long played in the proper functioning of a medical clinic—and the knowledge that team configurations impact a clinic’s efficiency and quality6,7—few investigations have sought out the MA’s perspective.8,9 Given the increasing clinical demands placed on all members of the primary care team (and the burnout that often results), it seems that MA insights into clinic efficiency could be valuable.
Continue to: Methods...
METHODS
This cross-sectional study was conducted from February to April 2019 at a large academic institution with 6 regional ambulatory care family medicine clinics, each one with 11,000 to 18,000 patient visits annually. Faculty work at all 6 clinics and residents at 2 of them. All MAs are hired, paid, and managed by a central administrative department rather than by the family medicine department. The family medicine clinics are currently PCMH certified, with a mix of fee-for-service and capitated reimbursement.
We developed and piloted a voluntary, anonymous 39-question (29 closed-ended and 10 brief open-ended) online Qualtrics survey, which we distributed via an email link to all the MAs in the department. The survey included clinic site, years as an MA, perceptions of the clinic environment, perception of teamwork at their site, identification of efficient practices, and feedback for physicians to improve efficiency and flow. Most questions were Likert-style with 5 choices ranging from “strongly agree” to “strongly disagree” or short answer. Age and gender were omitted to protect confidentiality, as most MAs in the department are female. Participants could opt to enter in a drawing for three $25 gift cards. The survey was reviewed by the University of Michigan Institutional Review Board and deemed exempt.
We asked MAs to nominate peers in their clinic who were “especially efficient and do their jobs well—people that others can learn from.” The staff members who were nominated most frequently by their peers were invited to share additional perspectives via a 10- to 30-minute semi-structured interview with the first author. Interviews covered highly efficient practices, barriers and facilitators to efficient care, and physician behaviors that impaired efficiency. We interviewed a minimum of 2 MAs per clinic and increased the number of interviews through snowball sampling, as needed, to reach data saturation (eg, the point at which we were no longer hearing new content). MAs were assured that all comments would be anonymized. There was no monetary incentive for the interviews. The interviewer had previously met only 3 of the 18 MAs interviewed.
Analysis. Summary statistics were calculated for quantitative data. To compare subgroups (such as individual clinics), a chi-square test was used. In cases when there were small cell sizes (< 5 subjects), we used the Fisher’s Exact test. Qualitative data was collected with real-time typewritten notes during the interviews to capture ideas and verbatim quotes when possible. We also included open-ended comments shared on the Qualtrics survey. Data were organized by theme using a deductive coding approach. Both authors reviewed and discussed observations, and coding was conducted by the first author. Reporting followed the STROBE Statement checklist for cross-sectional studies.10 Results were shared with MAs, supervisory staff, and physicians, which allowed for feedback and comments and served as “member-checking.” MAs reported that the data reflected their lived experiences.
Continue to: RESULTS...
RESULTS
Surveys were distributed to all 86 MAs working in family medicine clinics. A total of 75 (87%) responded to at least some questions (typically just demographics). We used those who completed the full survey (n = 61; 71%) for data analysis. Eighteen MAs participated in face-to-face interviews. Among respondents, 35 (47%) had worked at least 10 years as an MA and 21 (28%) had worked at least a decade in the family medicine department.
Perception of role
All respondents (n = 61; 100%) somewhat or strongly agreed that the MA role was “very important to keep the clinic functioning” and 58 (95%) reported that working in health care was “a calling” for them. Only 7 (11%) agreed that family medicine was an easier environment for MAs compared to a specialty clinic; 30 (49%) disagreed with this. Among respondents, 32 (53%) strongly or somewhat agreed that their work was very stressful and just half (n = 28; 46%) agreed there were adequate MA staff at their clinic.
Efficiency and competing priorities
MAs described important work values that increased their efficiency. These included clinic culture (good communication and strong teamwork), as well as individual strategies such as multitasking, limiting patient conversations, and doing tasks in a consistent way to improve accuracy. (See TABLE 1.) They identified ways physicians bolster or hurt efficiency and ways in which the relationship between the physician and the MA shapes the MA’s perception of their value in clinic.
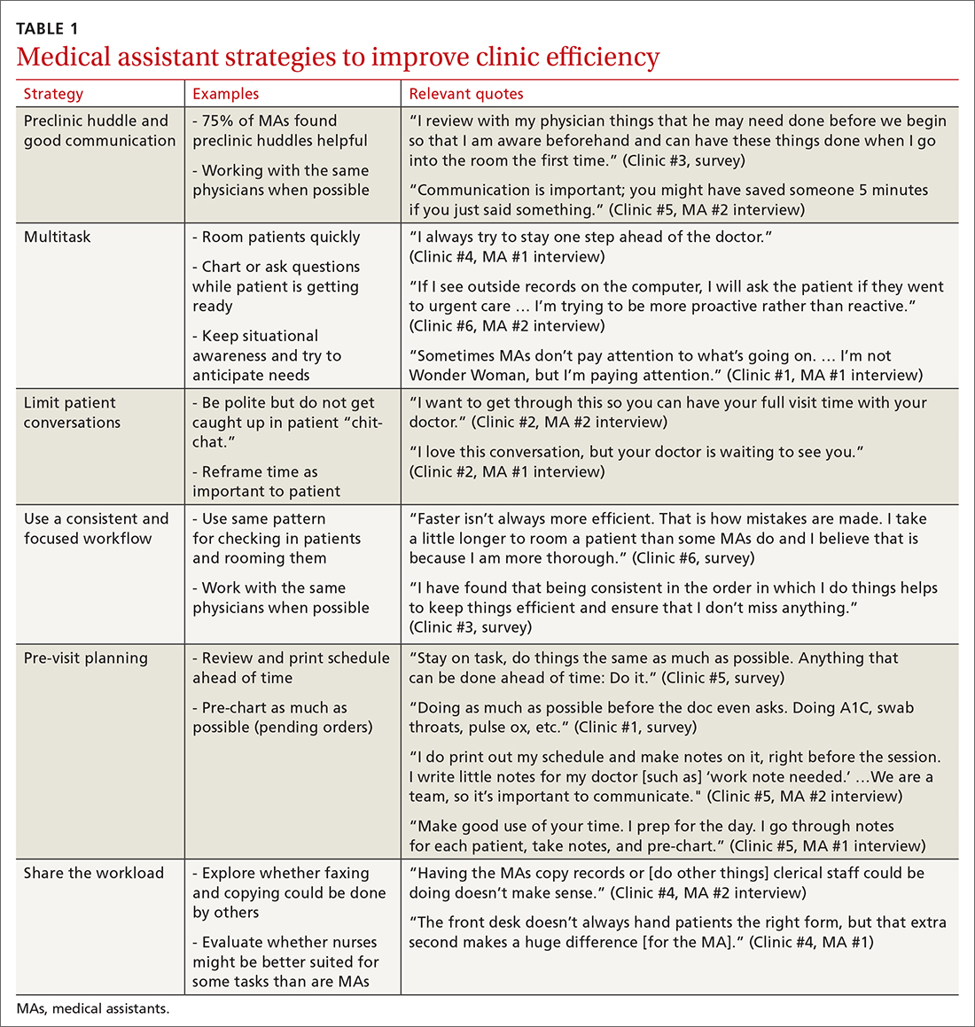
Communication was emphasized as critical for efficient care, and MAs encouraged the use of preclinic huddles and communication as priorities. Seventy-five percent of MAs reported preclinic huddles to plan for patient care were helpful, but only half said huddles took place “always” or “most of the time.” Many described reviewing the schedule and completing tasks ahead of patient arrival as critical to efficiency.
Participants described the tension between their identified role of orchestrating clinic flow and responding to directives by others that disrupted the flow. Several MAs found it challenging when physicians agreed to see very late patients and felt frustrated when decisions that changed the flow were made by the physician or front desk staff without including the MA. MAs were also able to articulate how they managed competing priorities within the clinic, such as when a patient- or physician-driven need to extend appointments was at odds with maintaining a timely schedule. They were eager to share personal tips for time management and prided themselves on careful and accurate performance and skills they had learned on the job. MAs also described how efficiency could be adversely affected by the behaviors or attitudes of physicians. (See TABLE 2.)
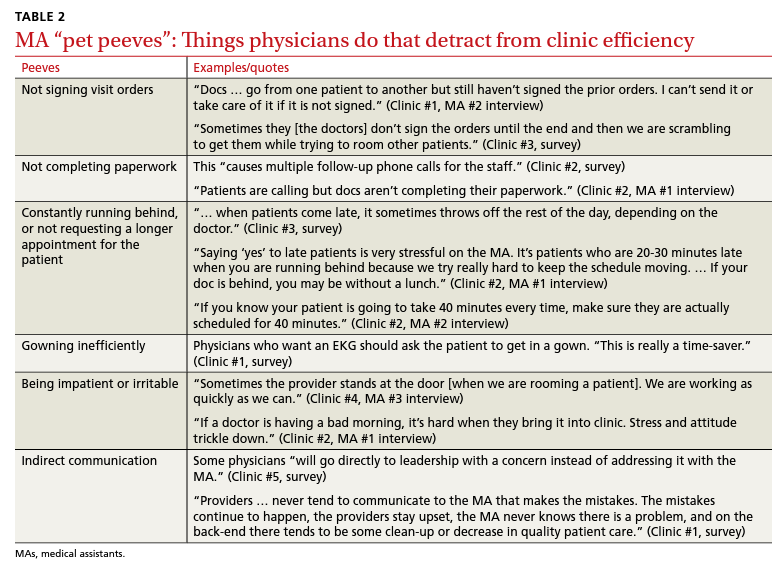
Continue to: Clinic environment...
Clinic environment
Thirty-six MAs (59%) reported that other MAs on their team were willing to help them out in clinic “a great deal” or “a lot” of the time, by helping to room a patient, acting as a chaperone for an exam, or doing a point-of-care lab. This sense of support varied across clinics (38% to 91% reported good support), suggesting that cultures vary by site. Some MAs expressed frustration at peers they saw as resistant to helping, exemplified by this verbatim quote from an interview:
“Some don’t want to help out. They may sigh. It’s how they react—you just know.” (Clinic #1, MA #2 interview)
Efficient MAs stressed the need for situational awareness to recognize when co-workers need help:
“[Peers often] are not aware that another MA is drowning. There’s 5 people who could have done that, and here I am running around and nobody budged.” (Clinic #5, MA #2 interview)
A minority of staff used the open-ended survey sections to describe clinic hierarchy. When asked about “pet peeves,” a few advised that physicians should not “talk down” to staff and should try to teach rather than criticize. Another asked that physicians not “bark orders” or have “low gratitude” for staff work. MAs found micromanaging stressful—particularly when the physician prompted the MA about patient arrivals:
“[I don’t like] when providers will make a comment about a patient arriving when you already know this information. You then rush to put [the] patient in [a] room, then [the] provider ends up making [the] patient wait an extensive amount of time. I’m perfectly capable of knowing when a patient arrives.” (Clinic #6, survey)
MAs did not like physicians “talking bad about us” or blaming the MA if the clinic is running behind.
Despite these concerns, most MAs reported feeling appreciated for the job they do. Only 10 (16%) reported that the people they work with rarely say “thank you,” and 2 (3%) stated they were not well supported by the physicians in clinic. Most (n = 38; 62%) strongly agreed or agreed that they felt part of the team and that their opinions matter. In the interviews, many expanded on this idea:
“I really feel like I’m valued, so I want to do everything I can to make [my doctor’s] day go better. If you want a good clinic, the best thing a doc can do is make the MA feel valued.” (Clinic #1, MA #1 interview)
Continue to: DISCUSSION...
DISCUSSION
Participants described their role much as an orchestra director, with MAs as the key to clinic flow and timeliness.9 Respondents articulated multiple common strategies used to increase their own efficiency and clinic flow; these may be considered best practices and incorporated as part of the basic training. Most MAs reported their day-to-day jobs were stressful and believed this was underrecognized, so efficiency strategies are critical. With staff completing multiple time-sensitive tasks during clinic, consistent co-worker support is crucial and may impact efficiency.8 Proper training of managers to provide that support and ensure equitable workloads may be one strategy to ensure that staff members feel the workplace is fair and collegial.
Several comments reflected the power differential within medical offices. One study reported that MAs and physicians “occupy roles at opposite ends of social and occupational hierarchies.”11 It’s important for physicians to be cognizant of these patterns and clinic culture, as reducing a hierarchy-based environment will be appreciated by MAs.9 Prior research has found that MAs have higher perceptions of their own competence than do the physicians working with them.12 If there is a fundamental lack of trust between the 2 groups, this will undoubtedly hinder team-building. Attention to this issue is key to a more favorable work environment.
Almost all respondents reported health care was a “calling,” which mirrors physician research that suggests seeing work as a “calling” is protective against burnout.13,14 Open-ended comments indicated great pride in contributions, and most staff members felt appreciated by their teams. Many described the working relationships with physicians as critical to their satisfaction at work and indicated that strong partnerships motivated them to do their best to make the physician’s day easier. Staff job satisfaction is linked to improved quality of care, so treating staff well contributes to high-value care for patients.15 We also uncovered some MA “pet peeves” that hinder efficiency and could be shared with physicians to emphasize the importance of patience and civility.
One barrier to expansion of MA roles within PCMH practices is the limited pay and career ladder for MAs who adopt new job responsibilities that require advanced skills or training.1,2 The mean MA salary at our institution ($37,372) is higher than in our state overall ($33,760), which may impact satisfaction.16 In addition, 93% of MAs are women; thus, they may continue to struggle more with lower pay than do workers in male- dominated professions.17,18 Expected job growth from 2018-2028 is predicted at 23%, which may help to boost salaries. 19 Prior studies describe the lack of a job ladder or promotion opportunities as a challenge1,20; this was not formally assessed in our study.
MAs see work in family medicine as much harder than it is in other specialty clinics. Being trusted with more responsibility, greater autonomy,21-23 and expanded patient care roles can boost MA self-efficacy, which can reduce burnout for both physicians and MAs. 8,24 However, new responsibilities should include appropriate training, support, and compensation, and match staff interests.7
Study limitations. The study was limited to 6 clinics in 1 department at a large academic medical center. Interviewed participants were selected by convenience and snowball sampling and thus, the results cannot be generalized to the population of MAs as a whole. As the initial interview goal was simply to gather efficiency tips, the project was not designed to be formal qualitative research. However, the discussions built on open-ended comments from the written survey helped contextualize our quantitative findings about efficiency. Notes were documented in real time by a single interviewer with rapid typing skills, which allowed capture of quotes verbatim. Subsequent studies would benefit from more formal qualitative research methods (recording and transcribing interviews, multiple coders to reduce risk of bias, and more complex thematic analysis).
Our research demonstrated how MAs perceive their roles in primary care and the facilitators and barriers to high efficiency in the workplace, which begins to fill an important knowledge gap in primary care. Disseminating practices that staff members themselves have identified as effective, and being attentive to how staff members are treated, may increase individual efficiency while improving staff retention and satisfaction.
CORRESPONDENCE Katherine J. Gold, MD, MSW, MS, Department of Family Medicine and Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology, University of Michigan, 1018 Fuller Street, Ann Arbor, MI 48104-1213; [email protected]
- Chapman SA, Blash LK. New roles for medical assistants in innovative primary care practices. Health Serv Res. 2017;52(suppl 1):383-406.
- Ferrante JM, Shaw EK, Bayly JE, et al. Barriers and facilitators to expanding roles of medical assistants in patient-centered medical homes (PCMHs). J Am Board Fam Med. 2018;31:226-235.
- Atkins B. The outlook for medical assisting in 2016 and beyond. Accessed January 27, 2022. www.medicalassistantdegrees.net/ articles/medical-assisting-trends/
- Unqualified medical “assistants.” Hospital (Lond 1886). 1897;23:163-164.
- Ameritech College of Healthcare. The origins of the AAMA. Accessed January 27, 2022. www.ameritech.edu/blog/medicalassisting-history/
- Dai M, Willard-Grace R, Knox M, et al. Team configurations, efficiency, and family physician burnout. J Am Board Fam Med. 2020;33:368-377.
- Harper PG, Van Riper K, Ramer T, et al. Team-based care: an expanded medical assistant role—enhanced rooming and visit assistance. J Interprof Care. 2018:1-7.
- Sheridan B, Chien AT, Peters AS, et al. Team-based primary care: the medical assistant perspective. Health Care Manage Rev. 2018;43:115-125.
- Tache S, Hill-Sakurai L. Medical assistants: the invisible “glue” of primary health care practices in the United States? J Health Organ Manag. 2010;24:288-305.
- STROBE checklist for cohort, case-control, and cross-sectional studies. Accessed January 27, 2022. www.strobe-statement.org/ fileadmin/Strobe/uploads/checklists/STROBE_checklist_v4_ combined.pdf
- Gray CP, Harrison MI, Hung D. Medical assistants as flow managers in primary care: challenges and recommendations. J Healthc Manag. 2016;61:181-191.
- Elder NC, Jacobson CJ, Bolon SK, et al. Patterns of relating between physicians and medical assistants in small family medicine offices. Ann Fam Med. 2014;12:150-157.
- Jager AJ, Tutty MA, Kao AC. Association between physician burnout and identification with medicine as a calling. Mayo Clinic Proc. 2017;92:415-422.
- Yoon JD, Daley BM, Curlin FA. The association between a sense of calling and physician well-being: a national study of primary care physicians and psychiatrists. Acad Psychiatry. 2017;41:167-173.
- Mohr DC, Young GJ, Meterko M, et al. Job satisfaction of primary care team members and quality of care. Am J Med Qual. 2011;26:18-25.
- US Bureau of Labor Statistics. Occupational employment and wage statistics. Accessed January 27, 2022. https://www.bls.gov/ oes/current/oes319092.htm
- Chapman SA, Marks A, Dower C. Positioning medical assistants for a greater role in the era of health reform. Acad Med. 2015;90:1347-1352.
- Mandel H. The role of occupational attributes in gender earnings inequality, 1970-2010. Soc Sci Res. 2016;55:122-138.
- US Bureau of Labor Statistics. Occupational outlook handbook: medical assistants. Accessed January 27, 2022. www.bls.gov/ooh/ healthcare/medical-assistants.htm
- Skillman SM, Dahal A, Frogner BK, et al. Frontline workers’ career pathways: a detailed look at Washington state’s medical assistant workforce. Med Care Res Rev. 2018:1077558718812950.
- Morse G, Salyers MP, Rollins AL, et al. Burnout in mental health services: a review of the problem and its remediation. Adm Policy Ment Health. 2012;39:341-352.
- Dubois CA, Bentein K, Ben Mansour JB, et al. Why some employees adopt or resist reorganization of work practices in health care: associations between perceived loss of resources, burnout, and attitudes to change. Int J Environ Res Pub Health. 2014;11: 187-201.
- Aronsson G, Theorell T, Grape T, et al. A systematic review including meta-analysis of work environment and burnout symptoms. BMC Public Health. 2017;17:264.
- O’Malley AS, Gourevitch R, Draper K, et al. Overcoming challenges to teamwork in patient-centered medical homes: a qualitative study. J Gen Intern Med. 2015;30:183-192.
ABSTRACT
Background: Medical assistant (MA) roles have expanded rapidly as primary care has evolved and MAs take on new patient care duties. Research that looks at the MA experience and factors that enhance or reduce efficiency among MAs is limited.
Methods: We surveyed all MAs working in 6 clinics run by a large academic family medicine department in Ann Arbor, Michigan. MAs deemed by peers as “most efficient” were selected for follow-up interviews. We evaluated personal strategies for efficiency, barriers to efficient care, impact of physician actions on efficiency, and satisfaction.
Results: A total of 75/86 MAs (87%) responded to at least some survey questions and 61/86 (71%) completed the full survey. We interviewed 18 MAs face to face. Most saw their role as essential to clinic functioning and viewed health care as a personal calling. MAs identified common strategies to improve efficiency and described the MA role to orchestrate the flow of the clinic day. Staff recognized differing priorities of patients, staff, and physicians and articulated frustrations with hierarchy and competing priorities as well as behaviors that impeded clinic efficiency. Respondents emphasized the importance of feeling valued by others on their team.
Conclusions: With the evolving demands made on MAs’ time, it is critical to understand how the most effective staff members manage their role and highlight the strategies they employ to provide efficient clinical care. Understanding factors that increase or decrease MA job satisfaction can help identify high-efficiency practices and promote a clinic culture that values and supports all staff.
As primary care continues to evolve into more team-based practice, the role of the medical assistant (MA) has rapidly transformed.1 Staff may assist with patient management, documentation in the electronic medical record, order entry, pre-visit planning, and fulfillment of quality metrics, particularly in a Primary Care Medical Home (PCMH).2 From 2012 through 2014, MA job postings per graduate increased from 1.3 to 2.3, suggesting twice as many job postings as graduates.3 As the demand for experienced MAs increases, the ability to recruit and retain high-performing staff members will be critical.
MAs are referenced in medical literature as early as the 1800s.4 The American Association of Medical Assistants was founded in 1956, which led to educational standardization and certifications.5 Despite the important role that MAs have long played in the proper functioning of a medical clinic—and the knowledge that team configurations impact a clinic’s efficiency and quality6,7—few investigations have sought out the MA’s perspective.8,9 Given the increasing clinical demands placed on all members of the primary care team (and the burnout that often results), it seems that MA insights into clinic efficiency could be valuable.
Continue to: Methods...
METHODS
This cross-sectional study was conducted from February to April 2019 at a large academic institution with 6 regional ambulatory care family medicine clinics, each one with 11,000 to 18,000 patient visits annually. Faculty work at all 6 clinics and residents at 2 of them. All MAs are hired, paid, and managed by a central administrative department rather than by the family medicine department. The family medicine clinics are currently PCMH certified, with a mix of fee-for-service and capitated reimbursement.
We developed and piloted a voluntary, anonymous 39-question (29 closed-ended and 10 brief open-ended) online Qualtrics survey, which we distributed via an email link to all the MAs in the department. The survey included clinic site, years as an MA, perceptions of the clinic environment, perception of teamwork at their site, identification of efficient practices, and feedback for physicians to improve efficiency and flow. Most questions were Likert-style with 5 choices ranging from “strongly agree” to “strongly disagree” or short answer. Age and gender were omitted to protect confidentiality, as most MAs in the department are female. Participants could opt to enter in a drawing for three $25 gift cards. The survey was reviewed by the University of Michigan Institutional Review Board and deemed exempt.
We asked MAs to nominate peers in their clinic who were “especially efficient and do their jobs well—people that others can learn from.” The staff members who were nominated most frequently by their peers were invited to share additional perspectives via a 10- to 30-minute semi-structured interview with the first author. Interviews covered highly efficient practices, barriers and facilitators to efficient care, and physician behaviors that impaired efficiency. We interviewed a minimum of 2 MAs per clinic and increased the number of interviews through snowball sampling, as needed, to reach data saturation (eg, the point at which we were no longer hearing new content). MAs were assured that all comments would be anonymized. There was no monetary incentive for the interviews. The interviewer had previously met only 3 of the 18 MAs interviewed.
Analysis. Summary statistics were calculated for quantitative data. To compare subgroups (such as individual clinics), a chi-square test was used. In cases when there were small cell sizes (< 5 subjects), we used the Fisher’s Exact test. Qualitative data was collected with real-time typewritten notes during the interviews to capture ideas and verbatim quotes when possible. We also included open-ended comments shared on the Qualtrics survey. Data were organized by theme using a deductive coding approach. Both authors reviewed and discussed observations, and coding was conducted by the first author. Reporting followed the STROBE Statement checklist for cross-sectional studies.10 Results were shared with MAs, supervisory staff, and physicians, which allowed for feedback and comments and served as “member-checking.” MAs reported that the data reflected their lived experiences.
Continue to: RESULTS...
RESULTS
Surveys were distributed to all 86 MAs working in family medicine clinics. A total of 75 (87%) responded to at least some questions (typically just demographics). We used those who completed the full survey (n = 61; 71%) for data analysis. Eighteen MAs participated in face-to-face interviews. Among respondents, 35 (47%) had worked at least 10 years as an MA and 21 (28%) had worked at least a decade in the family medicine department.
Perception of role
All respondents (n = 61; 100%) somewhat or strongly agreed that the MA role was “very important to keep the clinic functioning” and 58 (95%) reported that working in health care was “a calling” for them. Only 7 (11%) agreed that family medicine was an easier environment for MAs compared to a specialty clinic; 30 (49%) disagreed with this. Among respondents, 32 (53%) strongly or somewhat agreed that their work was very stressful and just half (n = 28; 46%) agreed there were adequate MA staff at their clinic.
Efficiency and competing priorities
MAs described important work values that increased their efficiency. These included clinic culture (good communication and strong teamwork), as well as individual strategies such as multitasking, limiting patient conversations, and doing tasks in a consistent way to improve accuracy. (See TABLE 1.) They identified ways physicians bolster or hurt efficiency and ways in which the relationship between the physician and the MA shapes the MA’s perception of their value in clinic.

Communication was emphasized as critical for efficient care, and MAs encouraged the use of preclinic huddles and communication as priorities. Seventy-five percent of MAs reported preclinic huddles to plan for patient care were helpful, but only half said huddles took place “always” or “most of the time.” Many described reviewing the schedule and completing tasks ahead of patient arrival as critical to efficiency.
Participants described the tension between their identified role of orchestrating clinic flow and responding to directives by others that disrupted the flow. Several MAs found it challenging when physicians agreed to see very late patients and felt frustrated when decisions that changed the flow were made by the physician or front desk staff without including the MA. MAs were also able to articulate how they managed competing priorities within the clinic, such as when a patient- or physician-driven need to extend appointments was at odds with maintaining a timely schedule. They were eager to share personal tips for time management and prided themselves on careful and accurate performance and skills they had learned on the job. MAs also described how efficiency could be adversely affected by the behaviors or attitudes of physicians. (See TABLE 2.)

Continue to: Clinic environment...
Clinic environment
Thirty-six MAs (59%) reported that other MAs on their team were willing to help them out in clinic “a great deal” or “a lot” of the time, by helping to room a patient, acting as a chaperone for an exam, or doing a point-of-care lab. This sense of support varied across clinics (38% to 91% reported good support), suggesting that cultures vary by site. Some MAs expressed frustration at peers they saw as resistant to helping, exemplified by this verbatim quote from an interview:
“Some don’t want to help out. They may sigh. It’s how they react—you just know.” (Clinic #1, MA #2 interview)
Efficient MAs stressed the need for situational awareness to recognize when co-workers need help:
“[Peers often] are not aware that another MA is drowning. There’s 5 people who could have done that, and here I am running around and nobody budged.” (Clinic #5, MA #2 interview)
A minority of staff used the open-ended survey sections to describe clinic hierarchy. When asked about “pet peeves,” a few advised that physicians should not “talk down” to staff and should try to teach rather than criticize. Another asked that physicians not “bark orders” or have “low gratitude” for staff work. MAs found micromanaging stressful—particularly when the physician prompted the MA about patient arrivals:
“[I don’t like] when providers will make a comment about a patient arriving when you already know this information. You then rush to put [the] patient in [a] room, then [the] provider ends up making [the] patient wait an extensive amount of time. I’m perfectly capable of knowing when a patient arrives.” (Clinic #6, survey)
MAs did not like physicians “talking bad about us” or blaming the MA if the clinic is running behind.
Despite these concerns, most MAs reported feeling appreciated for the job they do. Only 10 (16%) reported that the people they work with rarely say “thank you,” and 2 (3%) stated they were not well supported by the physicians in clinic. Most (n = 38; 62%) strongly agreed or agreed that they felt part of the team and that their opinions matter. In the interviews, many expanded on this idea:
“I really feel like I’m valued, so I want to do everything I can to make [my doctor’s] day go better. If you want a good clinic, the best thing a doc can do is make the MA feel valued.” (Clinic #1, MA #1 interview)
Continue to: DISCUSSION...
DISCUSSION
Participants described their role much as an orchestra director, with MAs as the key to clinic flow and timeliness.9 Respondents articulated multiple common strategies used to increase their own efficiency and clinic flow; these may be considered best practices and incorporated as part of the basic training. Most MAs reported their day-to-day jobs were stressful and believed this was underrecognized, so efficiency strategies are critical. With staff completing multiple time-sensitive tasks during clinic, consistent co-worker support is crucial and may impact efficiency.8 Proper training of managers to provide that support and ensure equitable workloads may be one strategy to ensure that staff members feel the workplace is fair and collegial.
Several comments reflected the power differential within medical offices. One study reported that MAs and physicians “occupy roles at opposite ends of social and occupational hierarchies.”11 It’s important for physicians to be cognizant of these patterns and clinic culture, as reducing a hierarchy-based environment will be appreciated by MAs.9 Prior research has found that MAs have higher perceptions of their own competence than do the physicians working with them.12 If there is a fundamental lack of trust between the 2 groups, this will undoubtedly hinder team-building. Attention to this issue is key to a more favorable work environment.
Almost all respondents reported health care was a “calling,” which mirrors physician research that suggests seeing work as a “calling” is protective against burnout.13,14 Open-ended comments indicated great pride in contributions, and most staff members felt appreciated by their teams. Many described the working relationships with physicians as critical to their satisfaction at work and indicated that strong partnerships motivated them to do their best to make the physician’s day easier. Staff job satisfaction is linked to improved quality of care, so treating staff well contributes to high-value care for patients.15 We also uncovered some MA “pet peeves” that hinder efficiency and could be shared with physicians to emphasize the importance of patience and civility.
One barrier to expansion of MA roles within PCMH practices is the limited pay and career ladder for MAs who adopt new job responsibilities that require advanced skills or training.1,2 The mean MA salary at our institution ($37,372) is higher than in our state overall ($33,760), which may impact satisfaction.16 In addition, 93% of MAs are women; thus, they may continue to struggle more with lower pay than do workers in male- dominated professions.17,18 Expected job growth from 2018-2028 is predicted at 23%, which may help to boost salaries. 19 Prior studies describe the lack of a job ladder or promotion opportunities as a challenge1,20; this was not formally assessed in our study.
MAs see work in family medicine as much harder than it is in other specialty clinics. Being trusted with more responsibility, greater autonomy,21-23 and expanded patient care roles can boost MA self-efficacy, which can reduce burnout for both physicians and MAs. 8,24 However, new responsibilities should include appropriate training, support, and compensation, and match staff interests.7
Study limitations. The study was limited to 6 clinics in 1 department at a large academic medical center. Interviewed participants were selected by convenience and snowball sampling and thus, the results cannot be generalized to the population of MAs as a whole. As the initial interview goal was simply to gather efficiency tips, the project was not designed to be formal qualitative research. However, the discussions built on open-ended comments from the written survey helped contextualize our quantitative findings about efficiency. Notes were documented in real time by a single interviewer with rapid typing skills, which allowed capture of quotes verbatim. Subsequent studies would benefit from more formal qualitative research methods (recording and transcribing interviews, multiple coders to reduce risk of bias, and more complex thematic analysis).
Our research demonstrated how MAs perceive their roles in primary care and the facilitators and barriers to high efficiency in the workplace, which begins to fill an important knowledge gap in primary care. Disseminating practices that staff members themselves have identified as effective, and being attentive to how staff members are treated, may increase individual efficiency while improving staff retention and satisfaction.
CORRESPONDENCE Katherine J. Gold, MD, MSW, MS, Department of Family Medicine and Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology, University of Michigan, 1018 Fuller Street, Ann Arbor, MI 48104-1213; [email protected]
ABSTRACT
Background: Medical assistant (MA) roles have expanded rapidly as primary care has evolved and MAs take on new patient care duties. Research that looks at the MA experience and factors that enhance or reduce efficiency among MAs is limited.
Methods: We surveyed all MAs working in 6 clinics run by a large academic family medicine department in Ann Arbor, Michigan. MAs deemed by peers as “most efficient” were selected for follow-up interviews. We evaluated personal strategies for efficiency, barriers to efficient care, impact of physician actions on efficiency, and satisfaction.
Results: A total of 75/86 MAs (87%) responded to at least some survey questions and 61/86 (71%) completed the full survey. We interviewed 18 MAs face to face. Most saw their role as essential to clinic functioning and viewed health care as a personal calling. MAs identified common strategies to improve efficiency and described the MA role to orchestrate the flow of the clinic day. Staff recognized differing priorities of patients, staff, and physicians and articulated frustrations with hierarchy and competing priorities as well as behaviors that impeded clinic efficiency. Respondents emphasized the importance of feeling valued by others on their team.
Conclusions: With the evolving demands made on MAs’ time, it is critical to understand how the most effective staff members manage their role and highlight the strategies they employ to provide efficient clinical care. Understanding factors that increase or decrease MA job satisfaction can help identify high-efficiency practices and promote a clinic culture that values and supports all staff.
As primary care continues to evolve into more team-based practice, the role of the medical assistant (MA) has rapidly transformed.1 Staff may assist with patient management, documentation in the electronic medical record, order entry, pre-visit planning, and fulfillment of quality metrics, particularly in a Primary Care Medical Home (PCMH).2 From 2012 through 2014, MA job postings per graduate increased from 1.3 to 2.3, suggesting twice as many job postings as graduates.3 As the demand for experienced MAs increases, the ability to recruit and retain high-performing staff members will be critical.
MAs are referenced in medical literature as early as the 1800s.4 The American Association of Medical Assistants was founded in 1956, which led to educational standardization and certifications.5 Despite the important role that MAs have long played in the proper functioning of a medical clinic—and the knowledge that team configurations impact a clinic’s efficiency and quality6,7—few investigations have sought out the MA’s perspective.8,9 Given the increasing clinical demands placed on all members of the primary care team (and the burnout that often results), it seems that MA insights into clinic efficiency could be valuable.
Continue to: Methods...
METHODS
This cross-sectional study was conducted from February to April 2019 at a large academic institution with 6 regional ambulatory care family medicine clinics, each one with 11,000 to 18,000 patient visits annually. Faculty work at all 6 clinics and residents at 2 of them. All MAs are hired, paid, and managed by a central administrative department rather than by the family medicine department. The family medicine clinics are currently PCMH certified, with a mix of fee-for-service and capitated reimbursement.
We developed and piloted a voluntary, anonymous 39-question (29 closed-ended and 10 brief open-ended) online Qualtrics survey, which we distributed via an email link to all the MAs in the department. The survey included clinic site, years as an MA, perceptions of the clinic environment, perception of teamwork at their site, identification of efficient practices, and feedback for physicians to improve efficiency and flow. Most questions were Likert-style with 5 choices ranging from “strongly agree” to “strongly disagree” or short answer. Age and gender were omitted to protect confidentiality, as most MAs in the department are female. Participants could opt to enter in a drawing for three $25 gift cards. The survey was reviewed by the University of Michigan Institutional Review Board and deemed exempt.
We asked MAs to nominate peers in their clinic who were “especially efficient and do their jobs well—people that others can learn from.” The staff members who were nominated most frequently by their peers were invited to share additional perspectives via a 10- to 30-minute semi-structured interview with the first author. Interviews covered highly efficient practices, barriers and facilitators to efficient care, and physician behaviors that impaired efficiency. We interviewed a minimum of 2 MAs per clinic and increased the number of interviews through snowball sampling, as needed, to reach data saturation (eg, the point at which we were no longer hearing new content). MAs were assured that all comments would be anonymized. There was no monetary incentive for the interviews. The interviewer had previously met only 3 of the 18 MAs interviewed.
Analysis. Summary statistics were calculated for quantitative data. To compare subgroups (such as individual clinics), a chi-square test was used. In cases when there were small cell sizes (< 5 subjects), we used the Fisher’s Exact test. Qualitative data was collected with real-time typewritten notes during the interviews to capture ideas and verbatim quotes when possible. We also included open-ended comments shared on the Qualtrics survey. Data were organized by theme using a deductive coding approach. Both authors reviewed and discussed observations, and coding was conducted by the first author. Reporting followed the STROBE Statement checklist for cross-sectional studies.10 Results were shared with MAs, supervisory staff, and physicians, which allowed for feedback and comments and served as “member-checking.” MAs reported that the data reflected their lived experiences.
Continue to: RESULTS...
RESULTS
Surveys were distributed to all 86 MAs working in family medicine clinics. A total of 75 (87%) responded to at least some questions (typically just demographics). We used those who completed the full survey (n = 61; 71%) for data analysis. Eighteen MAs participated in face-to-face interviews. Among respondents, 35 (47%) had worked at least 10 years as an MA and 21 (28%) had worked at least a decade in the family medicine department.
Perception of role
All respondents (n = 61; 100%) somewhat or strongly agreed that the MA role was “very important to keep the clinic functioning” and 58 (95%) reported that working in health care was “a calling” for them. Only 7 (11%) agreed that family medicine was an easier environment for MAs compared to a specialty clinic; 30 (49%) disagreed with this. Among respondents, 32 (53%) strongly or somewhat agreed that their work was very stressful and just half (n = 28; 46%) agreed there were adequate MA staff at their clinic.
Efficiency and competing priorities
MAs described important work values that increased their efficiency. These included clinic culture (good communication and strong teamwork), as well as individual strategies such as multitasking, limiting patient conversations, and doing tasks in a consistent way to improve accuracy. (See TABLE 1.) They identified ways physicians bolster or hurt efficiency and ways in which the relationship between the physician and the MA shapes the MA’s perception of their value in clinic.

Communication was emphasized as critical for efficient care, and MAs encouraged the use of preclinic huddles and communication as priorities. Seventy-five percent of MAs reported preclinic huddles to plan for patient care were helpful, but only half said huddles took place “always” or “most of the time.” Many described reviewing the schedule and completing tasks ahead of patient arrival as critical to efficiency.
Participants described the tension between their identified role of orchestrating clinic flow and responding to directives by others that disrupted the flow. Several MAs found it challenging when physicians agreed to see very late patients and felt frustrated when decisions that changed the flow were made by the physician or front desk staff without including the MA. MAs were also able to articulate how they managed competing priorities within the clinic, such as when a patient- or physician-driven need to extend appointments was at odds with maintaining a timely schedule. They were eager to share personal tips for time management and prided themselves on careful and accurate performance and skills they had learned on the job. MAs also described how efficiency could be adversely affected by the behaviors or attitudes of physicians. (See TABLE 2.)

Continue to: Clinic environment...
Clinic environment
Thirty-six MAs (59%) reported that other MAs on their team were willing to help them out in clinic “a great deal” or “a lot” of the time, by helping to room a patient, acting as a chaperone for an exam, or doing a point-of-care lab. This sense of support varied across clinics (38% to 91% reported good support), suggesting that cultures vary by site. Some MAs expressed frustration at peers they saw as resistant to helping, exemplified by this verbatim quote from an interview:
“Some don’t want to help out. They may sigh. It’s how they react—you just know.” (Clinic #1, MA #2 interview)
Efficient MAs stressed the need for situational awareness to recognize when co-workers need help:
“[Peers often] are not aware that another MA is drowning. There’s 5 people who could have done that, and here I am running around and nobody budged.” (Clinic #5, MA #2 interview)
A minority of staff used the open-ended survey sections to describe clinic hierarchy. When asked about “pet peeves,” a few advised that physicians should not “talk down” to staff and should try to teach rather than criticize. Another asked that physicians not “bark orders” or have “low gratitude” for staff work. MAs found micromanaging stressful—particularly when the physician prompted the MA about patient arrivals:
“[I don’t like] when providers will make a comment about a patient arriving when you already know this information. You then rush to put [the] patient in [a] room, then [the] provider ends up making [the] patient wait an extensive amount of time. I’m perfectly capable of knowing when a patient arrives.” (Clinic #6, survey)
MAs did not like physicians “talking bad about us” or blaming the MA if the clinic is running behind.
Despite these concerns, most MAs reported feeling appreciated for the job they do. Only 10 (16%) reported that the people they work with rarely say “thank you,” and 2 (3%) stated they were not well supported by the physicians in clinic. Most (n = 38; 62%) strongly agreed or agreed that they felt part of the team and that their opinions matter. In the interviews, many expanded on this idea:
“I really feel like I’m valued, so I want to do everything I can to make [my doctor’s] day go better. If you want a good clinic, the best thing a doc can do is make the MA feel valued.” (Clinic #1, MA #1 interview)
Continue to: DISCUSSION...
DISCUSSION
Participants described their role much as an orchestra director, with MAs as the key to clinic flow and timeliness.9 Respondents articulated multiple common strategies used to increase their own efficiency and clinic flow; these may be considered best practices and incorporated as part of the basic training. Most MAs reported their day-to-day jobs were stressful and believed this was underrecognized, so efficiency strategies are critical. With staff completing multiple time-sensitive tasks during clinic, consistent co-worker support is crucial and may impact efficiency.8 Proper training of managers to provide that support and ensure equitable workloads may be one strategy to ensure that staff members feel the workplace is fair and collegial.
Several comments reflected the power differential within medical offices. One study reported that MAs and physicians “occupy roles at opposite ends of social and occupational hierarchies.”11 It’s important for physicians to be cognizant of these patterns and clinic culture, as reducing a hierarchy-based environment will be appreciated by MAs.9 Prior research has found that MAs have higher perceptions of their own competence than do the physicians working with them.12 If there is a fundamental lack of trust between the 2 groups, this will undoubtedly hinder team-building. Attention to this issue is key to a more favorable work environment.
Almost all respondents reported health care was a “calling,” which mirrors physician research that suggests seeing work as a “calling” is protective against burnout.13,14 Open-ended comments indicated great pride in contributions, and most staff members felt appreciated by their teams. Many described the working relationships with physicians as critical to their satisfaction at work and indicated that strong partnerships motivated them to do their best to make the physician’s day easier. Staff job satisfaction is linked to improved quality of care, so treating staff well contributes to high-value care for patients.15 We also uncovered some MA “pet peeves” that hinder efficiency and could be shared with physicians to emphasize the importance of patience and civility.
One barrier to expansion of MA roles within PCMH practices is the limited pay and career ladder for MAs who adopt new job responsibilities that require advanced skills or training.1,2 The mean MA salary at our institution ($37,372) is higher than in our state overall ($33,760), which may impact satisfaction.16 In addition, 93% of MAs are women; thus, they may continue to struggle more with lower pay than do workers in male- dominated professions.17,18 Expected job growth from 2018-2028 is predicted at 23%, which may help to boost salaries. 19 Prior studies describe the lack of a job ladder or promotion opportunities as a challenge1,20; this was not formally assessed in our study.
MAs see work in family medicine as much harder than it is in other specialty clinics. Being trusted with more responsibility, greater autonomy,21-23 and expanded patient care roles can boost MA self-efficacy, which can reduce burnout for both physicians and MAs. 8,24 However, new responsibilities should include appropriate training, support, and compensation, and match staff interests.7
Study limitations. The study was limited to 6 clinics in 1 department at a large academic medical center. Interviewed participants were selected by convenience and snowball sampling and thus, the results cannot be generalized to the population of MAs as a whole. As the initial interview goal was simply to gather efficiency tips, the project was not designed to be formal qualitative research. However, the discussions built on open-ended comments from the written survey helped contextualize our quantitative findings about efficiency. Notes were documented in real time by a single interviewer with rapid typing skills, which allowed capture of quotes verbatim. Subsequent studies would benefit from more formal qualitative research methods (recording and transcribing interviews, multiple coders to reduce risk of bias, and more complex thematic analysis).
Our research demonstrated how MAs perceive their roles in primary care and the facilitators and barriers to high efficiency in the workplace, which begins to fill an important knowledge gap in primary care. Disseminating practices that staff members themselves have identified as effective, and being attentive to how staff members are treated, may increase individual efficiency while improving staff retention and satisfaction.
CORRESPONDENCE Katherine J. Gold, MD, MSW, MS, Department of Family Medicine and Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology, University of Michigan, 1018 Fuller Street, Ann Arbor, MI 48104-1213; [email protected]
- Chapman SA, Blash LK. New roles for medical assistants in innovative primary care practices. Health Serv Res. 2017;52(suppl 1):383-406.
- Ferrante JM, Shaw EK, Bayly JE, et al. Barriers and facilitators to expanding roles of medical assistants in patient-centered medical homes (PCMHs). J Am Board Fam Med. 2018;31:226-235.
- Atkins B. The outlook for medical assisting in 2016 and beyond. Accessed January 27, 2022. www.medicalassistantdegrees.net/ articles/medical-assisting-trends/
- Unqualified medical “assistants.” Hospital (Lond 1886). 1897;23:163-164.
- Ameritech College of Healthcare. The origins of the AAMA. Accessed January 27, 2022. www.ameritech.edu/blog/medicalassisting-history/
- Dai M, Willard-Grace R, Knox M, et al. Team configurations, efficiency, and family physician burnout. J Am Board Fam Med. 2020;33:368-377.
- Harper PG, Van Riper K, Ramer T, et al. Team-based care: an expanded medical assistant role—enhanced rooming and visit assistance. J Interprof Care. 2018:1-7.
- Sheridan B, Chien AT, Peters AS, et al. Team-based primary care: the medical assistant perspective. Health Care Manage Rev. 2018;43:115-125.
- Tache S, Hill-Sakurai L. Medical assistants: the invisible “glue” of primary health care practices in the United States? J Health Organ Manag. 2010;24:288-305.
- STROBE checklist for cohort, case-control, and cross-sectional studies. Accessed January 27, 2022. www.strobe-statement.org/ fileadmin/Strobe/uploads/checklists/STROBE_checklist_v4_ combined.pdf
- Gray CP, Harrison MI, Hung D. Medical assistants as flow managers in primary care: challenges and recommendations. J Healthc Manag. 2016;61:181-191.
- Elder NC, Jacobson CJ, Bolon SK, et al. Patterns of relating between physicians and medical assistants in small family medicine offices. Ann Fam Med. 2014;12:150-157.
- Jager AJ, Tutty MA, Kao AC. Association between physician burnout and identification with medicine as a calling. Mayo Clinic Proc. 2017;92:415-422.
- Yoon JD, Daley BM, Curlin FA. The association between a sense of calling and physician well-being: a national study of primary care physicians and psychiatrists. Acad Psychiatry. 2017;41:167-173.
- Mohr DC, Young GJ, Meterko M, et al. Job satisfaction of primary care team members and quality of care. Am J Med Qual. 2011;26:18-25.
- US Bureau of Labor Statistics. Occupational employment and wage statistics. Accessed January 27, 2022. https://www.bls.gov/ oes/current/oes319092.htm
- Chapman SA, Marks A, Dower C. Positioning medical assistants for a greater role in the era of health reform. Acad Med. 2015;90:1347-1352.
- Mandel H. The role of occupational attributes in gender earnings inequality, 1970-2010. Soc Sci Res. 2016;55:122-138.
- US Bureau of Labor Statistics. Occupational outlook handbook: medical assistants. Accessed January 27, 2022. www.bls.gov/ooh/ healthcare/medical-assistants.htm
- Skillman SM, Dahal A, Frogner BK, et al. Frontline workers’ career pathways: a detailed look at Washington state’s medical assistant workforce. Med Care Res Rev. 2018:1077558718812950.
- Morse G, Salyers MP, Rollins AL, et al. Burnout in mental health services: a review of the problem and its remediation. Adm Policy Ment Health. 2012;39:341-352.
- Dubois CA, Bentein K, Ben Mansour JB, et al. Why some employees adopt or resist reorganization of work practices in health care: associations between perceived loss of resources, burnout, and attitudes to change. Int J Environ Res Pub Health. 2014;11: 187-201.
- Aronsson G, Theorell T, Grape T, et al. A systematic review including meta-analysis of work environment and burnout symptoms. BMC Public Health. 2017;17:264.
- O’Malley AS, Gourevitch R, Draper K, et al. Overcoming challenges to teamwork in patient-centered medical homes: a qualitative study. J Gen Intern Med. 2015;30:183-192.
- Chapman SA, Blash LK. New roles for medical assistants in innovative primary care practices. Health Serv Res. 2017;52(suppl 1):383-406.
- Ferrante JM, Shaw EK, Bayly JE, et al. Barriers and facilitators to expanding roles of medical assistants in patient-centered medical homes (PCMHs). J Am Board Fam Med. 2018;31:226-235.
- Atkins B. The outlook for medical assisting in 2016 and beyond. Accessed January 27, 2022. www.medicalassistantdegrees.net/ articles/medical-assisting-trends/
- Unqualified medical “assistants.” Hospital (Lond 1886). 1897;23:163-164.
- Ameritech College of Healthcare. The origins of the AAMA. Accessed January 27, 2022. www.ameritech.edu/blog/medicalassisting-history/
- Dai M, Willard-Grace R, Knox M, et al. Team configurations, efficiency, and family physician burnout. J Am Board Fam Med. 2020;33:368-377.
- Harper PG, Van Riper K, Ramer T, et al. Team-based care: an expanded medical assistant role—enhanced rooming and visit assistance. J Interprof Care. 2018:1-7.
- Sheridan B, Chien AT, Peters AS, et al. Team-based primary care: the medical assistant perspective. Health Care Manage Rev. 2018;43:115-125.
- Tache S, Hill-Sakurai L. Medical assistants: the invisible “glue” of primary health care practices in the United States? J Health Organ Manag. 2010;24:288-305.
- STROBE checklist for cohort, case-control, and cross-sectional studies. Accessed January 27, 2022. www.strobe-statement.org/ fileadmin/Strobe/uploads/checklists/STROBE_checklist_v4_ combined.pdf
- Gray CP, Harrison MI, Hung D. Medical assistants as flow managers in primary care: challenges and recommendations. J Healthc Manag. 2016;61:181-191.
- Elder NC, Jacobson CJ, Bolon SK, et al. Patterns of relating between physicians and medical assistants in small family medicine offices. Ann Fam Med. 2014;12:150-157.
- Jager AJ, Tutty MA, Kao AC. Association between physician burnout and identification with medicine as a calling. Mayo Clinic Proc. 2017;92:415-422.
- Yoon JD, Daley BM, Curlin FA. The association between a sense of calling and physician well-being: a national study of primary care physicians and psychiatrists. Acad Psychiatry. 2017;41:167-173.
- Mohr DC, Young GJ, Meterko M, et al. Job satisfaction of primary care team members and quality of care. Am J Med Qual. 2011;26:18-25.
- US Bureau of Labor Statistics. Occupational employment and wage statistics. Accessed January 27, 2022. https://www.bls.gov/ oes/current/oes319092.htm
- Chapman SA, Marks A, Dower C. Positioning medical assistants for a greater role in the era of health reform. Acad Med. 2015;90:1347-1352.
- Mandel H. The role of occupational attributes in gender earnings inequality, 1970-2010. Soc Sci Res. 2016;55:122-138.
- US Bureau of Labor Statistics. Occupational outlook handbook: medical assistants. Accessed January 27, 2022. www.bls.gov/ooh/ healthcare/medical-assistants.htm
- Skillman SM, Dahal A, Frogner BK, et al. Frontline workers’ career pathways: a detailed look at Washington state’s medical assistant workforce. Med Care Res Rev. 2018:1077558718812950.
- Morse G, Salyers MP, Rollins AL, et al. Burnout in mental health services: a review of the problem and its remediation. Adm Policy Ment Health. 2012;39:341-352.
- Dubois CA, Bentein K, Ben Mansour JB, et al. Why some employees adopt or resist reorganization of work practices in health care: associations between perceived loss of resources, burnout, and attitudes to change. Int J Environ Res Pub Health. 2014;11: 187-201.
- Aronsson G, Theorell T, Grape T, et al. A systematic review including meta-analysis of work environment and burnout symptoms. BMC Public Health. 2017;17:264.
- O’Malley AS, Gourevitch R, Draper K, et al. Overcoming challenges to teamwork in patient-centered medical homes: a qualitative study. J Gen Intern Med. 2015;30:183-192.
Haven’t had COVID yet? Wanna bet?
We all have friends or relatives who, somehow, have managed to avoid catching COVID-19, which has infected more than 91.5 million Americans. You may even be one of the lucky ones yourself.
But health experts are saying: Not so fast. because they didn’t have symptoms or had mild cases they mistook for a cold or allergies.
The upshot: These silent COVID-19 cases reflect a hidden side of the pandemic that may be helping to drive new surges and viral variants.
Still, infectious disease experts say there is little doubt that some people have indeed managed to avoid COVID-19 infection altogether, and they are trying to understand why.
Several recent studies have suggested certain genetic and immune system traits may better protect this group of people against the coronavirus, making them less likely than others to be infected or seriously sickened. Researchers around the world are now studying these seemingly super-immune people for clues to what makes them so special, with an eye toward better vaccines, treatments, and prevention strategies.
Infectious disease specialists say both types of cases – those unknowingly infected by COVID-19 and people who’ve avoided the virus altogether – matter greatly to public health, more than 2 years into the pandemic.
“It’s definitely true that some people have had COVID and don’t realize it,” says Stephen Kissler, PhD, an infectious disease researcher with the Harvard T.H. Chan School of Public Health, Boston. “It is potentially good news if there’s more immunity in the population than we realize.”
But he says that being able to identify genetic and other factors that may offer some people protection against COVID-19 is an “exciting prospect” that could help find out who’s most at risk and improve efforts to get the pandemic under control.
Some studies have found a person’s genetic profile, past exposure to other COVID-like viruses, allergies, and even drugs they take for other conditions may all provide some defense – even for people who have not been vaccinated, don’t use masks, or don’t practice social distancing.
A person’s medical history and genetics may help decide their risk from new diseases, meaning “we may be able to help identify people who are at especially high risk from infection,” Dr. Kissler says. “That knowledge could help those people better shield themselves from infection and get quicker access to treatment and vaccines, if necessary. … We don’t yet know, but studies are ongoing for these things.”
Amesh Adalja, MD, an infectious disease specialist with the Johns Hopkins Center for Health Security, Baltimore, agrees that emerging research on people who’ve avoided infection offers the chance of new public health strategies to combat COVID-19.
“I’m sure there is some subset of people who are [COVID] negative,” he says. “So what explains that phenomenon, especially if that person was out there getting significant exposures?”
Have you had COVID without knowing it?
In a media briefing late last month, White House COVID-19 Response Coordinator Ashish Jha, MD, said more than 70% of the U.S. population has had the virus, according to the latest CDC data. That’s up from 33.5% in December.
But the actual number of people in the U.S. who have been infected with SARS-CoV-2, the scientific name for the virus that causes COVID-19, is likely to be much higher due to cases without symptoms that are unreported, experts say.
Since the early days of the pandemic, researchers have tried to put a number on these hidden cases, but that figure has been evolving and a clear consensus has not emerged.
In September 2020, a study published in the Annals of Internal Medicine said “approximately 40% to 45% of those infected with SARS-CoV-2 will remain asymptomatic.”
A follow-up analysis of 95 studies, published last December, reached similar findings, estimating that more than 40% of COVID-19 infections didn’t come with symptoms.
To get a better handle on the issue, CDC officials have been working with the American Red Cross and other blood banks to track COVID-19 antibodies – proteins your body makes after exposure to the virus to fight off an infection – in donors who said they have never had COVID-19.
While that joint effort is still ongoing, early findings say the number of donors with antibodies from COVID-19 infection increased in blood donors from 3.5% in July 2020 to at least 20.2% in May 2021. Since then, those percentages have soared, in part due to the introduction of vaccines, which also make the body produce COVID-19 antibodies.
The most current findings show that 83.3% of donors have combined COVID infection– and vaccine-induced antibodies in their blood. Those findings are based on 1.4 million blood donations.
Health experts say all of these studies are strong evidence that many COVID-19 cases continue to go undetected. In fact, the University of Washington Institute for Health Metrics and Evaluation estimates that only 7% of positive COVID-19 cases in the U.S. are being detected. That means case rates are actually 14.5 times higher than the official count of 131,000 new COVID infections each day, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, which reports the virus is still killing about 440 Americans daily.
So, why is all this important, in terms of public health?
Experts say people are more likely to be cautious if they know COVID-19 cases are high where they live, work, and play. On the other hand, if they believe case rates in their communities are lower than they actually are, they may be less likely to get vaccinated and boosted, wear masks indoors, avoid crowded indoor spaces, and take other precautions to fend off infection.
How do some avoid infection altogether?
In addition to tracking cases that go unreported and don’t have symptoms, infectious disease experts have also been trying to figure out why some people have managed to avoid getting the highly contagious virus.
Several leading lines of research have produced promising early results – suggesting that a person’s genetic makeup, past exposure to less-lethal coronaviruses, allergies, and even certain drugs they take for other conditions may all provide at least some protection against COVID.
“Our study showed that there are many human genes – hundreds of genes – that can impact SARS-CoV-2 infection,” says Neville Sanjana, PhD, a geneticist at New York University and the New York Genome Center who co-led the study. “With a better understanding of host genetic factors, we can find new kinds of therapies that target these host factors to block infection.”
In addition, he says several studies show some drugs that regulate genes, such as the breast cancer drug tamoxifen, also appear to knock down COVID-19 risk. He suggests such drugs, already approved by the Food and Drug Administration, might be “repurposed” to target the virus.
Studies in other countries show that patients taking tamoxifen before the pandemic were protected against severe COVID-19, Dr. Sanjana says. “That was a really cool thing, highlighting the power of harnessing host genetics. The virus critically depends on our genes to complete key parts of its life cycle.”
The NYU research findings echo other studies that have been published in recent months.
In July, a team of researchers led by the National Cancer Institute identified a genetic factor that appears to determine how severe an infection will be. In a study involving 3,000 people, they found that two gene changes, or mutations, that decrease the expression of a gene called OAS1 boosted the risk of hospitalization from COVID-19. OAS1 is part of the immune system’s response to viral infections.
As a result, developing a genetic therapy designed to increase the OAS1 gene’s expression might reduce the risk of severe disease.
“It’s very natural to get infected once you are exposed. There’s no magic bullet for that. But after you get infected, how you’re going to respond to this infection, that’s what is going to be affected by your genetic variants,” said Ludmila Prokunina-Olsson, PhD, the study’s lead researcher and chief of the National Cancer Institute’s Laboratory of Translational Genomics, Bethesda, Md., in an interview with NBC News.
Benjamin tenOever, PhD, a New York University virologist who co-authored the 2020 research, says the new genetic research is promising, but he believes it’s unlikely scientists will be able to identify a single gene responsible for actually preventing a COVID-19 infection.
“On the flip side, we have identified many genes that makes the disease worse,” he says.
T cells ‘remember’ past viral infections
As Dr. tenOever and Dr. Sanjana suggest, another intriguing line of research has found that prior viral infections may prime the body’s immune system to fight COVID-19.
Four other common coronaviruses – aside from SARS-CoV-2 – infect people worldwide, typically causing mild to moderate upper respiratory illnesses like the common cold, says Alessandro Sette, PhD, an infectious disease expert and vaccine researcher with the La Jolla (Calif.) Institute for Immunology.
In a recent study published in Science, he and his team found past infection with these other coronaviruses may give some protection against SARS-CoV-2.
T cells – white blood cells that act like immunological ninjas to ferret out and fight infections – appear to maintain a kind of “biological memory” of coronaviruses they have seen before and can mount an attack on similar pathogens, such SARS-CoV-2, Dr. Sette says.
The new work builds on a prior research he helped lead that found 40%-60% of people never exposed to SARS-CoV-2 had T cells that reacted to the virus – with their immune systems recognizing fragments of a virus they had never seen before.
Dr. Sette says his research shows that people whose T cells have this “preexisting memory” of past coronavirus exposures also tend to respond better to vaccination for reasons not yet well understood.
“The question is, at which point will there be enough immunity from vaccination, repeated infections from other coronaviruses, but also some of the variants of the SARS-CoV-2 … where infections become less frequent? We’re not there yet,” he says.
In addition to these exciting genetic and T-cell findings, other research has suggested low-grade inflammation from allergies – a key part of the body’s immune response to foreign substances – may also give some people an extra leg up, in terms of avoiding COVID infection.
Last May, a study of 1,400 households published in The Journal of Allergy and Clinical Immunology found that having a food allergy cut the risk of COVID-19 infection in half.
The researchers said it’s unclear why allergies may reduce the risk of infection, but they noted that people with food allergies express fewer ACE2 receptors on the surface of their airway cells, making it harder for the virus to enter cells.
The big picture: Prevention still your best bet
So, what’s the takeaway from all of this emerging research?
New York University’s Dr. tenOever says that while genes, T cells and allergies may offer some protection against COVID, tried-and-true precautions – vaccination, wearing masks, avoiding crowded indoor spaces, and social distancing – are likely to provide a greater defense.
He believes these precautions are likely why he and his family have never contracted COVID-19.
“I was tested weekly, as were my kids at school,” he says. “We definitely never got COVID, despite the fact that we live in New York City and I worked in a hospital every single day of the pandemic.”
Ziyad Al-Aly, MD, an infectious disease specialist and director of clinical epidemiology at Washington University in St. Louis, agrees that the new research on COVID-19 is intriguing but won’t likely result in practical changes in the approach to fighting the virus in the near term.
“Getting a deeper understanding of potential genetic factors or other characteristics – that could really help us understand why the virus just comes and goes without any ill effects in some people, and in other people it produces really serious disease,” he says. “That will really help us eventually to design better vaccines to prevent it or reduce severity or even [treat] people who get severe disease.”
In the meantime, Dr. Al-Aly says, “it’s still best to do everything you can to avoid infection in the first place – even if you’re vaccinated or previously infected, you should really try to avoid reinfection.”
That means sit outside if you can when visiting a restaurant. Wear a mask on a plane, even though it’s not required. And get vaccinated and boosted.
“In the future, there may be more tools to address this pandemic, but that’s really the best advice for now,” Dr. Al-Aly says.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
We all have friends or relatives who, somehow, have managed to avoid catching COVID-19, which has infected more than 91.5 million Americans. You may even be one of the lucky ones yourself.
But health experts are saying: Not so fast. because they didn’t have symptoms or had mild cases they mistook for a cold or allergies.
The upshot: These silent COVID-19 cases reflect a hidden side of the pandemic that may be helping to drive new surges and viral variants.
Still, infectious disease experts say there is little doubt that some people have indeed managed to avoid COVID-19 infection altogether, and they are trying to understand why.
Several recent studies have suggested certain genetic and immune system traits may better protect this group of people against the coronavirus, making them less likely than others to be infected or seriously sickened. Researchers around the world are now studying these seemingly super-immune people for clues to what makes them so special, with an eye toward better vaccines, treatments, and prevention strategies.
Infectious disease specialists say both types of cases – those unknowingly infected by COVID-19 and people who’ve avoided the virus altogether – matter greatly to public health, more than 2 years into the pandemic.
“It’s definitely true that some people have had COVID and don’t realize it,” says Stephen Kissler, PhD, an infectious disease researcher with the Harvard T.H. Chan School of Public Health, Boston. “It is potentially good news if there’s more immunity in the population than we realize.”
But he says that being able to identify genetic and other factors that may offer some people protection against COVID-19 is an “exciting prospect” that could help find out who’s most at risk and improve efforts to get the pandemic under control.
Some studies have found a person’s genetic profile, past exposure to other COVID-like viruses, allergies, and even drugs they take for other conditions may all provide some defense – even for people who have not been vaccinated, don’t use masks, or don’t practice social distancing.
A person’s medical history and genetics may help decide their risk from new diseases, meaning “we may be able to help identify people who are at especially high risk from infection,” Dr. Kissler says. “That knowledge could help those people better shield themselves from infection and get quicker access to treatment and vaccines, if necessary. … We don’t yet know, but studies are ongoing for these things.”
Amesh Adalja, MD, an infectious disease specialist with the Johns Hopkins Center for Health Security, Baltimore, agrees that emerging research on people who’ve avoided infection offers the chance of new public health strategies to combat COVID-19.
“I’m sure there is some subset of people who are [COVID] negative,” he says. “So what explains that phenomenon, especially if that person was out there getting significant exposures?”
Have you had COVID without knowing it?
In a media briefing late last month, White House COVID-19 Response Coordinator Ashish Jha, MD, said more than 70% of the U.S. population has had the virus, according to the latest CDC data. That’s up from 33.5% in December.
But the actual number of people in the U.S. who have been infected with SARS-CoV-2, the scientific name for the virus that causes COVID-19, is likely to be much higher due to cases without symptoms that are unreported, experts say.
Since the early days of the pandemic, researchers have tried to put a number on these hidden cases, but that figure has been evolving and a clear consensus has not emerged.
In September 2020, a study published in the Annals of Internal Medicine said “approximately 40% to 45% of those infected with SARS-CoV-2 will remain asymptomatic.”
A follow-up analysis of 95 studies, published last December, reached similar findings, estimating that more than 40% of COVID-19 infections didn’t come with symptoms.
To get a better handle on the issue, CDC officials have been working with the American Red Cross and other blood banks to track COVID-19 antibodies – proteins your body makes after exposure to the virus to fight off an infection – in donors who said they have never had COVID-19.
While that joint effort is still ongoing, early findings say the number of donors with antibodies from COVID-19 infection increased in blood donors from 3.5% in July 2020 to at least 20.2% in May 2021. Since then, those percentages have soared, in part due to the introduction of vaccines, which also make the body produce COVID-19 antibodies.
The most current findings show that 83.3% of donors have combined COVID infection– and vaccine-induced antibodies in their blood. Those findings are based on 1.4 million blood donations.
Health experts say all of these studies are strong evidence that many COVID-19 cases continue to go undetected. In fact, the University of Washington Institute for Health Metrics and Evaluation estimates that only 7% of positive COVID-19 cases in the U.S. are being detected. That means case rates are actually 14.5 times higher than the official count of 131,000 new COVID infections each day, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, which reports the virus is still killing about 440 Americans daily.
So, why is all this important, in terms of public health?
Experts say people are more likely to be cautious if they know COVID-19 cases are high where they live, work, and play. On the other hand, if they believe case rates in their communities are lower than they actually are, they may be less likely to get vaccinated and boosted, wear masks indoors, avoid crowded indoor spaces, and take other precautions to fend off infection.
How do some avoid infection altogether?
In addition to tracking cases that go unreported and don’t have symptoms, infectious disease experts have also been trying to figure out why some people have managed to avoid getting the highly contagious virus.
Several leading lines of research have produced promising early results – suggesting that a person’s genetic makeup, past exposure to less-lethal coronaviruses, allergies, and even certain drugs they take for other conditions may all provide at least some protection against COVID.
“Our study showed that there are many human genes – hundreds of genes – that can impact SARS-CoV-2 infection,” says Neville Sanjana, PhD, a geneticist at New York University and the New York Genome Center who co-led the study. “With a better understanding of host genetic factors, we can find new kinds of therapies that target these host factors to block infection.”
In addition, he says several studies show some drugs that regulate genes, such as the breast cancer drug tamoxifen, also appear to knock down COVID-19 risk. He suggests such drugs, already approved by the Food and Drug Administration, might be “repurposed” to target the virus.
Studies in other countries show that patients taking tamoxifen before the pandemic were protected against severe COVID-19, Dr. Sanjana says. “That was a really cool thing, highlighting the power of harnessing host genetics. The virus critically depends on our genes to complete key parts of its life cycle.”
The NYU research findings echo other studies that have been published in recent months.
In July, a team of researchers led by the National Cancer Institute identified a genetic factor that appears to determine how severe an infection will be. In a study involving 3,000 people, they found that two gene changes, or mutations, that decrease the expression of a gene called OAS1 boosted the risk of hospitalization from COVID-19. OAS1 is part of the immune system’s response to viral infections.
As a result, developing a genetic therapy designed to increase the OAS1 gene’s expression might reduce the risk of severe disease.
“It’s very natural to get infected once you are exposed. There’s no magic bullet for that. But after you get infected, how you’re going to respond to this infection, that’s what is going to be affected by your genetic variants,” said Ludmila Prokunina-Olsson, PhD, the study’s lead researcher and chief of the National Cancer Institute’s Laboratory of Translational Genomics, Bethesda, Md., in an interview with NBC News.
Benjamin tenOever, PhD, a New York University virologist who co-authored the 2020 research, says the new genetic research is promising, but he believes it’s unlikely scientists will be able to identify a single gene responsible for actually preventing a COVID-19 infection.
“On the flip side, we have identified many genes that makes the disease worse,” he says.
T cells ‘remember’ past viral infections
As Dr. tenOever and Dr. Sanjana suggest, another intriguing line of research has found that prior viral infections may prime the body’s immune system to fight COVID-19.
Four other common coronaviruses – aside from SARS-CoV-2 – infect people worldwide, typically causing mild to moderate upper respiratory illnesses like the common cold, says Alessandro Sette, PhD, an infectious disease expert and vaccine researcher with the La Jolla (Calif.) Institute for Immunology.
In a recent study published in Science, he and his team found past infection with these other coronaviruses may give some protection against SARS-CoV-2.
T cells – white blood cells that act like immunological ninjas to ferret out and fight infections – appear to maintain a kind of “biological memory” of coronaviruses they have seen before and can mount an attack on similar pathogens, such SARS-CoV-2, Dr. Sette says.
The new work builds on a prior research he helped lead that found 40%-60% of people never exposed to SARS-CoV-2 had T cells that reacted to the virus – with their immune systems recognizing fragments of a virus they had never seen before.
Dr. Sette says his research shows that people whose T cells have this “preexisting memory” of past coronavirus exposures also tend to respond better to vaccination for reasons not yet well understood.
“The question is, at which point will there be enough immunity from vaccination, repeated infections from other coronaviruses, but also some of the variants of the SARS-CoV-2 … where infections become less frequent? We’re not there yet,” he says.
In addition to these exciting genetic and T-cell findings, other research has suggested low-grade inflammation from allergies – a key part of the body’s immune response to foreign substances – may also give some people an extra leg up, in terms of avoiding COVID infection.
Last May, a study of 1,400 households published in The Journal of Allergy and Clinical Immunology found that having a food allergy cut the risk of COVID-19 infection in half.
The researchers said it’s unclear why allergies may reduce the risk of infection, but they noted that people with food allergies express fewer ACE2 receptors on the surface of their airway cells, making it harder for the virus to enter cells.
The big picture: Prevention still your best bet
So, what’s the takeaway from all of this emerging research?
New York University’s Dr. tenOever says that while genes, T cells and allergies may offer some protection against COVID, tried-and-true precautions – vaccination, wearing masks, avoiding crowded indoor spaces, and social distancing – are likely to provide a greater defense.
He believes these precautions are likely why he and his family have never contracted COVID-19.
“I was tested weekly, as were my kids at school,” he says. “We definitely never got COVID, despite the fact that we live in New York City and I worked in a hospital every single day of the pandemic.”
Ziyad Al-Aly, MD, an infectious disease specialist and director of clinical epidemiology at Washington University in St. Louis, agrees that the new research on COVID-19 is intriguing but won’t likely result in practical changes in the approach to fighting the virus in the near term.
“Getting a deeper understanding of potential genetic factors or other characteristics – that could really help us understand why the virus just comes and goes without any ill effects in some people, and in other people it produces really serious disease,” he says. “That will really help us eventually to design better vaccines to prevent it or reduce severity or even [treat] people who get severe disease.”
In the meantime, Dr. Al-Aly says, “it’s still best to do everything you can to avoid infection in the first place – even if you’re vaccinated or previously infected, you should really try to avoid reinfection.”
That means sit outside if you can when visiting a restaurant. Wear a mask on a plane, even though it’s not required. And get vaccinated and boosted.
“In the future, there may be more tools to address this pandemic, but that’s really the best advice for now,” Dr. Al-Aly says.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
We all have friends or relatives who, somehow, have managed to avoid catching COVID-19, which has infected more than 91.5 million Americans. You may even be one of the lucky ones yourself.
But health experts are saying: Not so fast. because they didn’t have symptoms or had mild cases they mistook for a cold or allergies.
The upshot: These silent COVID-19 cases reflect a hidden side of the pandemic that may be helping to drive new surges and viral variants.
Still, infectious disease experts say there is little doubt that some people have indeed managed to avoid COVID-19 infection altogether, and they are trying to understand why.
Several recent studies have suggested certain genetic and immune system traits may better protect this group of people against the coronavirus, making them less likely than others to be infected or seriously sickened. Researchers around the world are now studying these seemingly super-immune people for clues to what makes them so special, with an eye toward better vaccines, treatments, and prevention strategies.
Infectious disease specialists say both types of cases – those unknowingly infected by COVID-19 and people who’ve avoided the virus altogether – matter greatly to public health, more than 2 years into the pandemic.
“It’s definitely true that some people have had COVID and don’t realize it,” says Stephen Kissler, PhD, an infectious disease researcher with the Harvard T.H. Chan School of Public Health, Boston. “It is potentially good news if there’s more immunity in the population than we realize.”
But he says that being able to identify genetic and other factors that may offer some people protection against COVID-19 is an “exciting prospect” that could help find out who’s most at risk and improve efforts to get the pandemic under control.
Some studies have found a person’s genetic profile, past exposure to other COVID-like viruses, allergies, and even drugs they take for other conditions may all provide some defense – even for people who have not been vaccinated, don’t use masks, or don’t practice social distancing.
A person’s medical history and genetics may help decide their risk from new diseases, meaning “we may be able to help identify people who are at especially high risk from infection,” Dr. Kissler says. “That knowledge could help those people better shield themselves from infection and get quicker access to treatment and vaccines, if necessary. … We don’t yet know, but studies are ongoing for these things.”
Amesh Adalja, MD, an infectious disease specialist with the Johns Hopkins Center for Health Security, Baltimore, agrees that emerging research on people who’ve avoided infection offers the chance of new public health strategies to combat COVID-19.
“I’m sure there is some subset of people who are [COVID] negative,” he says. “So what explains that phenomenon, especially if that person was out there getting significant exposures?”
Have you had COVID without knowing it?
In a media briefing late last month, White House COVID-19 Response Coordinator Ashish Jha, MD, said more than 70% of the U.S. population has had the virus, according to the latest CDC data. That’s up from 33.5% in December.
But the actual number of people in the U.S. who have been infected with SARS-CoV-2, the scientific name for the virus that causes COVID-19, is likely to be much higher due to cases without symptoms that are unreported, experts say.
Since the early days of the pandemic, researchers have tried to put a number on these hidden cases, but that figure has been evolving and a clear consensus has not emerged.
In September 2020, a study published in the Annals of Internal Medicine said “approximately 40% to 45% of those infected with SARS-CoV-2 will remain asymptomatic.”
A follow-up analysis of 95 studies, published last December, reached similar findings, estimating that more than 40% of COVID-19 infections didn’t come with symptoms.
To get a better handle on the issue, CDC officials have been working with the American Red Cross and other blood banks to track COVID-19 antibodies – proteins your body makes after exposure to the virus to fight off an infection – in donors who said they have never had COVID-19.
While that joint effort is still ongoing, early findings say the number of donors with antibodies from COVID-19 infection increased in blood donors from 3.5% in July 2020 to at least 20.2% in May 2021. Since then, those percentages have soared, in part due to the introduction of vaccines, which also make the body produce COVID-19 antibodies.
The most current findings show that 83.3% of donors have combined COVID infection– and vaccine-induced antibodies in their blood. Those findings are based on 1.4 million blood donations.
Health experts say all of these studies are strong evidence that many COVID-19 cases continue to go undetected. In fact, the University of Washington Institute for Health Metrics and Evaluation estimates that only 7% of positive COVID-19 cases in the U.S. are being detected. That means case rates are actually 14.5 times higher than the official count of 131,000 new COVID infections each day, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, which reports the virus is still killing about 440 Americans daily.
So, why is all this important, in terms of public health?
Experts say people are more likely to be cautious if they know COVID-19 cases are high where they live, work, and play. On the other hand, if they believe case rates in their communities are lower than they actually are, they may be less likely to get vaccinated and boosted, wear masks indoors, avoid crowded indoor spaces, and take other precautions to fend off infection.
How do some avoid infection altogether?
In addition to tracking cases that go unreported and don’t have symptoms, infectious disease experts have also been trying to figure out why some people have managed to avoid getting the highly contagious virus.
Several leading lines of research have produced promising early results – suggesting that a person’s genetic makeup, past exposure to less-lethal coronaviruses, allergies, and even certain drugs they take for other conditions may all provide at least some protection against COVID.
“Our study showed that there are many human genes – hundreds of genes – that can impact SARS-CoV-2 infection,” says Neville Sanjana, PhD, a geneticist at New York University and the New York Genome Center who co-led the study. “With a better understanding of host genetic factors, we can find new kinds of therapies that target these host factors to block infection.”
In addition, he says several studies show some drugs that regulate genes, such as the breast cancer drug tamoxifen, also appear to knock down COVID-19 risk. He suggests such drugs, already approved by the Food and Drug Administration, might be “repurposed” to target the virus.
Studies in other countries show that patients taking tamoxifen before the pandemic were protected against severe COVID-19, Dr. Sanjana says. “That was a really cool thing, highlighting the power of harnessing host genetics. The virus critically depends on our genes to complete key parts of its life cycle.”
The NYU research findings echo other studies that have been published in recent months.
In July, a team of researchers led by the National Cancer Institute identified a genetic factor that appears to determine how severe an infection will be. In a study involving 3,000 people, they found that two gene changes, or mutations, that decrease the expression of a gene called OAS1 boosted the risk of hospitalization from COVID-19. OAS1 is part of the immune system’s response to viral infections.
As a result, developing a genetic therapy designed to increase the OAS1 gene’s expression might reduce the risk of severe disease.
“It’s very natural to get infected once you are exposed. There’s no magic bullet for that. But after you get infected, how you’re going to respond to this infection, that’s what is going to be affected by your genetic variants,” said Ludmila Prokunina-Olsson, PhD, the study’s lead researcher and chief of the National Cancer Institute’s Laboratory of Translational Genomics, Bethesda, Md., in an interview with NBC News.
Benjamin tenOever, PhD, a New York University virologist who co-authored the 2020 research, says the new genetic research is promising, but he believes it’s unlikely scientists will be able to identify a single gene responsible for actually preventing a COVID-19 infection.
“On the flip side, we have identified many genes that makes the disease worse,” he says.
T cells ‘remember’ past viral infections
As Dr. tenOever and Dr. Sanjana suggest, another intriguing line of research has found that prior viral infections may prime the body’s immune system to fight COVID-19.
Four other common coronaviruses – aside from SARS-CoV-2 – infect people worldwide, typically causing mild to moderate upper respiratory illnesses like the common cold, says Alessandro Sette, PhD, an infectious disease expert and vaccine researcher with the La Jolla (Calif.) Institute for Immunology.
In a recent study published in Science, he and his team found past infection with these other coronaviruses may give some protection against SARS-CoV-2.
T cells – white blood cells that act like immunological ninjas to ferret out and fight infections – appear to maintain a kind of “biological memory” of coronaviruses they have seen before and can mount an attack on similar pathogens, such SARS-CoV-2, Dr. Sette says.
The new work builds on a prior research he helped lead that found 40%-60% of people never exposed to SARS-CoV-2 had T cells that reacted to the virus – with their immune systems recognizing fragments of a virus they had never seen before.
Dr. Sette says his research shows that people whose T cells have this “preexisting memory” of past coronavirus exposures also tend to respond better to vaccination for reasons not yet well understood.
“The question is, at which point will there be enough immunity from vaccination, repeated infections from other coronaviruses, but also some of the variants of the SARS-CoV-2 … where infections become less frequent? We’re not there yet,” he says.
In addition to these exciting genetic and T-cell findings, other research has suggested low-grade inflammation from allergies – a key part of the body’s immune response to foreign substances – may also give some people an extra leg up, in terms of avoiding COVID infection.
Last May, a study of 1,400 households published in The Journal of Allergy and Clinical Immunology found that having a food allergy cut the risk of COVID-19 infection in half.
The researchers said it’s unclear why allergies may reduce the risk of infection, but they noted that people with food allergies express fewer ACE2 receptors on the surface of their airway cells, making it harder for the virus to enter cells.
The big picture: Prevention still your best bet
So, what’s the takeaway from all of this emerging research?
New York University’s Dr. tenOever says that while genes, T cells and allergies may offer some protection against COVID, tried-and-true precautions – vaccination, wearing masks, avoiding crowded indoor spaces, and social distancing – are likely to provide a greater defense.
He believes these precautions are likely why he and his family have never contracted COVID-19.
“I was tested weekly, as were my kids at school,” he says. “We definitely never got COVID, despite the fact that we live in New York City and I worked in a hospital every single day of the pandemic.”
Ziyad Al-Aly, MD, an infectious disease specialist and director of clinical epidemiology at Washington University in St. Louis, agrees that the new research on COVID-19 is intriguing but won’t likely result in practical changes in the approach to fighting the virus in the near term.
“Getting a deeper understanding of potential genetic factors or other characteristics – that could really help us understand why the virus just comes and goes without any ill effects in some people, and in other people it produces really serious disease,” he says. “That will really help us eventually to design better vaccines to prevent it or reduce severity or even [treat] people who get severe disease.”
In the meantime, Dr. Al-Aly says, “it’s still best to do everything you can to avoid infection in the first place – even if you’re vaccinated or previously infected, you should really try to avoid reinfection.”
That means sit outside if you can when visiting a restaurant. Wear a mask on a plane, even though it’s not required. And get vaccinated and boosted.
“In the future, there may be more tools to address this pandemic, but that’s really the best advice for now,” Dr. Al-Aly says.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
Long COVID comes in three forms: Study
, according to a new preprint study published on MedRxiv that hasn’t yet been peer-reviewed.
Long COVID has been hard to define due to its large number of symptoms, but researchers at King’s College London have identified three distinct profiles – with long-term symptoms focused on neurological, respiratory, or physical conditions. So far, they also found patterns among people infected with the original coronavirus strain, the Alpha variant, and the Delta variant.
“These data show clearly that post-COVID syndrome is not just one condition but appears to have several subtypes,” Claire Steves, PhD, one of the study authors and a senior clinical lecturer in King’s College London’s School of Life Course & Population Sciences, said in a statement.
“Understanding the root causes of these subtypes may help in finding treatment strategies,” she said. “Moreover, these data emphasize the need for long-COVID services to incorporate a personalized approach sensitive to the issues of each individual.”
The research team analyzed ZOE COVID app data for 1,459 people who have had symptoms for more than 84 days, or 12 weeks, according to their definition of long COVID or post-COVID syndrome.
They found that the largest group had a cluster of symptoms in the nervous system, such as fatigue, brain fog, and headaches. It was the most common subtype among the Alpha variant, which was dominant in winter 2020-2021, and the Delta variant, which was dominant in 2021.
The second group had respiratory symptoms, such as chest pain and severe shortness of breath, which could suggest lung damage, the researchers wrote. It was the largest cluster for the original coronavirus strain in spring 2020, when people were unvaccinated.
The third group included people who reported a diverse range of physical symptoms, including heart palpitations, muscle aches and pain, and changes to their skin and hair. This group had some of the “most severe and debilitating multi-organ symptoms,” the researchers wrote.
The researchers found that the subtypes were similar in vaccinated and unvaccinated people based on the variants investigated so far. But the data showed that the risk of long COVID was reduced by vaccination.
In addition, although the three subtypes were present in all the variants, other symptom clusters had subtle differences among the variants, such as symptoms in the stomach and intestines. The differences could be due to other things that changed during the pandemic, such as the time of year, social behaviors, and treatments, the researchers said.
“Machine learning approaches, such as clustering analysis, have made it possible to start exploring and identifying different profiles of post-COVID syndrome,” Marc Modat, PhD, who led the analysis and is a senior lecturer at King’s College London’s School of Biomedical Engineering & Imaging Sciences, said in the statement.
“This opens new avenues of research to better understand COVID-19 and to motivate clinical research that might mitigate the long-term effects of the disease,” he said.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
, according to a new preprint study published on MedRxiv that hasn’t yet been peer-reviewed.
Long COVID has been hard to define due to its large number of symptoms, but researchers at King’s College London have identified three distinct profiles – with long-term symptoms focused on neurological, respiratory, or physical conditions. So far, they also found patterns among people infected with the original coronavirus strain, the Alpha variant, and the Delta variant.
“These data show clearly that post-COVID syndrome is not just one condition but appears to have several subtypes,” Claire Steves, PhD, one of the study authors and a senior clinical lecturer in King’s College London’s School of Life Course & Population Sciences, said in a statement.
“Understanding the root causes of these subtypes may help in finding treatment strategies,” she said. “Moreover, these data emphasize the need for long-COVID services to incorporate a personalized approach sensitive to the issues of each individual.”
The research team analyzed ZOE COVID app data for 1,459 people who have had symptoms for more than 84 days, or 12 weeks, according to their definition of long COVID or post-COVID syndrome.
They found that the largest group had a cluster of symptoms in the nervous system, such as fatigue, brain fog, and headaches. It was the most common subtype among the Alpha variant, which was dominant in winter 2020-2021, and the Delta variant, which was dominant in 2021.
The second group had respiratory symptoms, such as chest pain and severe shortness of breath, which could suggest lung damage, the researchers wrote. It was the largest cluster for the original coronavirus strain in spring 2020, when people were unvaccinated.
The third group included people who reported a diverse range of physical symptoms, including heart palpitations, muscle aches and pain, and changes to their skin and hair. This group had some of the “most severe and debilitating multi-organ symptoms,” the researchers wrote.
The researchers found that the subtypes were similar in vaccinated and unvaccinated people based on the variants investigated so far. But the data showed that the risk of long COVID was reduced by vaccination.
In addition, although the three subtypes were present in all the variants, other symptom clusters had subtle differences among the variants, such as symptoms in the stomach and intestines. The differences could be due to other things that changed during the pandemic, such as the time of year, social behaviors, and treatments, the researchers said.
“Machine learning approaches, such as clustering analysis, have made it possible to start exploring and identifying different profiles of post-COVID syndrome,” Marc Modat, PhD, who led the analysis and is a senior lecturer at King’s College London’s School of Biomedical Engineering & Imaging Sciences, said in the statement.
“This opens new avenues of research to better understand COVID-19 and to motivate clinical research that might mitigate the long-term effects of the disease,” he said.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
, according to a new preprint study published on MedRxiv that hasn’t yet been peer-reviewed.
Long COVID has been hard to define due to its large number of symptoms, but researchers at King’s College London have identified three distinct profiles – with long-term symptoms focused on neurological, respiratory, or physical conditions. So far, they also found patterns among people infected with the original coronavirus strain, the Alpha variant, and the Delta variant.
“These data show clearly that post-COVID syndrome is not just one condition but appears to have several subtypes,” Claire Steves, PhD, one of the study authors and a senior clinical lecturer in King’s College London’s School of Life Course & Population Sciences, said in a statement.
“Understanding the root causes of these subtypes may help in finding treatment strategies,” she said. “Moreover, these data emphasize the need for long-COVID services to incorporate a personalized approach sensitive to the issues of each individual.”
The research team analyzed ZOE COVID app data for 1,459 people who have had symptoms for more than 84 days, or 12 weeks, according to their definition of long COVID or post-COVID syndrome.
They found that the largest group had a cluster of symptoms in the nervous system, such as fatigue, brain fog, and headaches. It was the most common subtype among the Alpha variant, which was dominant in winter 2020-2021, and the Delta variant, which was dominant in 2021.
The second group had respiratory symptoms, such as chest pain and severe shortness of breath, which could suggest lung damage, the researchers wrote. It was the largest cluster for the original coronavirus strain in spring 2020, when people were unvaccinated.
The third group included people who reported a diverse range of physical symptoms, including heart palpitations, muscle aches and pain, and changes to their skin and hair. This group had some of the “most severe and debilitating multi-organ symptoms,” the researchers wrote.
The researchers found that the subtypes were similar in vaccinated and unvaccinated people based on the variants investigated so far. But the data showed that the risk of long COVID was reduced by vaccination.
In addition, although the three subtypes were present in all the variants, other symptom clusters had subtle differences among the variants, such as symptoms in the stomach and intestines. The differences could be due to other things that changed during the pandemic, such as the time of year, social behaviors, and treatments, the researchers said.
“Machine learning approaches, such as clustering analysis, have made it possible to start exploring and identifying different profiles of post-COVID syndrome,” Marc Modat, PhD, who led the analysis and is a senior lecturer at King’s College London’s School of Biomedical Engineering & Imaging Sciences, said in the statement.
“This opens new avenues of research to better understand COVID-19 and to motivate clinical research that might mitigate the long-term effects of the disease,” he said.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
Resection of five-centimeter cesarean scar ectopic pregnancy and isthmocele repair using vascular clamps
Burnout and stress of today: How do we cope?
Interestingly, the group that seems to be least impacted by this was health care administrators (with 12% of them planning on leaving their jobs).
I couldn’t stop thinking about these percentages.
I am reminded every day of the commitment and excellence of my colleagues in the health care field, and I do not want to lose them. I am hoping the following information and my thoughts on this topic will be helpful for those thinking about leaving health care.
Surgeon general’s burnout report
The surgeon general recently released a report on addressing health care worker burnout.2 It includes several very interesting and appropriate observations. I will summarize the most important ones here:
1. Our health depends on the well-being of our health workforce.
2. Direct harm to health care workers can lead to anxiety, depression, insomnia, and interpersonal and relationship struggles.
3. Health care workers experience exhaustion from providing overwhelming care and empathy.
4. Health care workers spend less time with patients and too much time with EHRs.
5. There are health workforce shortages.
The report is comprehensive, and everything in it is correct. The real issue is how does it go from being a report to true actionable items that we as health care professionals benefit from? I think in regards to exhaustion from overwhelming care responsibilities, and empathy fatigue, we need better boundaries.
Those who go into medicine, and especially those who go into primary care, always put the patients’ needs first. When operating in a broken system, it stays broken when individuals cover for the deficiencies in the system. Adding four extra patients every day because there is no one to refer them to with availability is injurious to the health care provider, and those providers who accept these additional patients will eventually be part of the 23% who want to leave their jobs. It feels awful to say no, but until the system stops accommodating there will not be substantial change.
The empathy drain
One of the unreported stresses of open access for patients through EHR communications is the empathy drain on physicians. When I see a patient in clinic with chronic symptoms or issues, I spend important time making sure we have a plan and an agreed upon time frame.
With the EHR, patients frequently send multiple messages for the same symptoms between visits. It is okay to redirect the patient and share that these issues will be discussed at length at appointments. My reasoning on this is that I think it is better for me to better care for myself and stay as the doctor for my patients, than always say yes to limitless needs and soon be looking for the off ramp.
The following statistic in the surgeon general’s report really hit home. For every hour of direct patient care, physicians currently spend 2 hours on the EHR system. Most practices allow 10%-20% of time for catch up, where with statistics like this it should be 50%. This concept is fully lost on administrators, or ignored.
It is only when we refuse to continue to accept and follow a broken system that it will change. A minority of internal medicine and family doctors (4.5% in 2018) practice in direct primary care models, where these issues are addressed. Unfortunately, this model as it is currently available is not an option for lower income patients.
A major theme in the surgeon general’s report was that administrative burdens need to be reduced by 75% by 2025. When I look at the report, I see the suggestions, I just don’t see how it will be achieved. Despite almost all clinics moving to the EHR, paperwork in the form of faxes and forms has increased.
A sweeping reform would be needed to eliminate daily faxes from PT offices, visiting nurse services, prior authorization, patients reminders from insurance companies, and disability forms from patients. I am glad that there is acknowledgment of the problem, but this change will take more than 3 years.
Takeaways
So what do we do?
Be good to yourself, and your colleagues. The pandemic has isolated us, which accelerates burnout.
Reach out to people you care about.
We are all feeling this. Set boundaries that allow you to care for yourself, and accept that you are doing your best, even if you can’t meet the needs of all your patients all the time.
Dr. Paauw is professor of medicine in the division of general internal medicine at the University of Washington, Seattle, and he serves as third-year medical student clerkship director at the University of Washington. He is a member of the editorial advisory board of Internal Medicine News. Dr. Paauw has no conflicts to disclose. Contact him at [email protected].
References
1. Sinsky CA et al. Covid-related stress and work intentions in a sample of US health care workers. Mayo Clin Proc Innov Qual Outcomes. 2021 Dec;5(6):1165-73.
2. Addressing health worker burnout. The U.S. Surgeon General’s advisory on building a thriving health workforce.
Interestingly, the group that seems to be least impacted by this was health care administrators (with 12% of them planning on leaving their jobs).
I couldn’t stop thinking about these percentages.
I am reminded every day of the commitment and excellence of my colleagues in the health care field, and I do not want to lose them. I am hoping the following information and my thoughts on this topic will be helpful for those thinking about leaving health care.
Surgeon general’s burnout report
The surgeon general recently released a report on addressing health care worker burnout.2 It includes several very interesting and appropriate observations. I will summarize the most important ones here:
1. Our health depends on the well-being of our health workforce.
2. Direct harm to health care workers can lead to anxiety, depression, insomnia, and interpersonal and relationship struggles.
3. Health care workers experience exhaustion from providing overwhelming care and empathy.
4. Health care workers spend less time with patients and too much time with EHRs.
5. There are health workforce shortages.
The report is comprehensive, and everything in it is correct. The real issue is how does it go from being a report to true actionable items that we as health care professionals benefit from? I think in regards to exhaustion from overwhelming care responsibilities, and empathy fatigue, we need better boundaries.
Those who go into medicine, and especially those who go into primary care, always put the patients’ needs first. When operating in a broken system, it stays broken when individuals cover for the deficiencies in the system. Adding four extra patients every day because there is no one to refer them to with availability is injurious to the health care provider, and those providers who accept these additional patients will eventually be part of the 23% who want to leave their jobs. It feels awful to say no, but until the system stops accommodating there will not be substantial change.
The empathy drain
One of the unreported stresses of open access for patients through EHR communications is the empathy drain on physicians. When I see a patient in clinic with chronic symptoms or issues, I spend important time making sure we have a plan and an agreed upon time frame.
With the EHR, patients frequently send multiple messages for the same symptoms between visits. It is okay to redirect the patient and share that these issues will be discussed at length at appointments. My reasoning on this is that I think it is better for me to better care for myself and stay as the doctor for my patients, than always say yes to limitless needs and soon be looking for the off ramp.
The following statistic in the surgeon general’s report really hit home. For every hour of direct patient care, physicians currently spend 2 hours on the EHR system. Most practices allow 10%-20% of time for catch up, where with statistics like this it should be 50%. This concept is fully lost on administrators, or ignored.
It is only when we refuse to continue to accept and follow a broken system that it will change. A minority of internal medicine and family doctors (4.5% in 2018) practice in direct primary care models, where these issues are addressed. Unfortunately, this model as it is currently available is not an option for lower income patients.
A major theme in the surgeon general’s report was that administrative burdens need to be reduced by 75% by 2025. When I look at the report, I see the suggestions, I just don’t see how it will be achieved. Despite almost all clinics moving to the EHR, paperwork in the form of faxes and forms has increased.
A sweeping reform would be needed to eliminate daily faxes from PT offices, visiting nurse services, prior authorization, patients reminders from insurance companies, and disability forms from patients. I am glad that there is acknowledgment of the problem, but this change will take more than 3 years.
Takeaways
So what do we do?
Be good to yourself, and your colleagues. The pandemic has isolated us, which accelerates burnout.
Reach out to people you care about.
We are all feeling this. Set boundaries that allow you to care for yourself, and accept that you are doing your best, even if you can’t meet the needs of all your patients all the time.
Dr. Paauw is professor of medicine in the division of general internal medicine at the University of Washington, Seattle, and he serves as third-year medical student clerkship director at the University of Washington. He is a member of the editorial advisory board of Internal Medicine News. Dr. Paauw has no conflicts to disclose. Contact him at [email protected].
References
1. Sinsky CA et al. Covid-related stress and work intentions in a sample of US health care workers. Mayo Clin Proc Innov Qual Outcomes. 2021 Dec;5(6):1165-73.
2. Addressing health worker burnout. The U.S. Surgeon General’s advisory on building a thriving health workforce.
Interestingly, the group that seems to be least impacted by this was health care administrators (with 12% of them planning on leaving their jobs).
I couldn’t stop thinking about these percentages.
I am reminded every day of the commitment and excellence of my colleagues in the health care field, and I do not want to lose them. I am hoping the following information and my thoughts on this topic will be helpful for those thinking about leaving health care.
Surgeon general’s burnout report
The surgeon general recently released a report on addressing health care worker burnout.2 It includes several very interesting and appropriate observations. I will summarize the most important ones here:
1. Our health depends on the well-being of our health workforce.
2. Direct harm to health care workers can lead to anxiety, depression, insomnia, and interpersonal and relationship struggles.
3. Health care workers experience exhaustion from providing overwhelming care and empathy.
4. Health care workers spend less time with patients and too much time with EHRs.
5. There are health workforce shortages.
The report is comprehensive, and everything in it is correct. The real issue is how does it go from being a report to true actionable items that we as health care professionals benefit from? I think in regards to exhaustion from overwhelming care responsibilities, and empathy fatigue, we need better boundaries.
Those who go into medicine, and especially those who go into primary care, always put the patients’ needs first. When operating in a broken system, it stays broken when individuals cover for the deficiencies in the system. Adding four extra patients every day because there is no one to refer them to with availability is injurious to the health care provider, and those providers who accept these additional patients will eventually be part of the 23% who want to leave their jobs. It feels awful to say no, but until the system stops accommodating there will not be substantial change.
The empathy drain
One of the unreported stresses of open access for patients through EHR communications is the empathy drain on physicians. When I see a patient in clinic with chronic symptoms or issues, I spend important time making sure we have a plan and an agreed upon time frame.
With the EHR, patients frequently send multiple messages for the same symptoms between visits. It is okay to redirect the patient and share that these issues will be discussed at length at appointments. My reasoning on this is that I think it is better for me to better care for myself and stay as the doctor for my patients, than always say yes to limitless needs and soon be looking for the off ramp.
The following statistic in the surgeon general’s report really hit home. For every hour of direct patient care, physicians currently spend 2 hours on the EHR system. Most practices allow 10%-20% of time for catch up, where with statistics like this it should be 50%. This concept is fully lost on administrators, or ignored.
It is only when we refuse to continue to accept and follow a broken system that it will change. A minority of internal medicine and family doctors (4.5% in 2018) practice in direct primary care models, where these issues are addressed. Unfortunately, this model as it is currently available is not an option for lower income patients.
A major theme in the surgeon general’s report was that administrative burdens need to be reduced by 75% by 2025. When I look at the report, I see the suggestions, I just don’t see how it will be achieved. Despite almost all clinics moving to the EHR, paperwork in the form of faxes and forms has increased.
A sweeping reform would be needed to eliminate daily faxes from PT offices, visiting nurse services, prior authorization, patients reminders from insurance companies, and disability forms from patients. I am glad that there is acknowledgment of the problem, but this change will take more than 3 years.
Takeaways
So what do we do?
Be good to yourself, and your colleagues. The pandemic has isolated us, which accelerates burnout.
Reach out to people you care about.
We are all feeling this. Set boundaries that allow you to care for yourself, and accept that you are doing your best, even if you can’t meet the needs of all your patients all the time.
Dr. Paauw is professor of medicine in the division of general internal medicine at the University of Washington, Seattle, and he serves as third-year medical student clerkship director at the University of Washington. He is a member of the editorial advisory board of Internal Medicine News. Dr. Paauw has no conflicts to disclose. Contact him at [email protected].
References
1. Sinsky CA et al. Covid-related stress and work intentions in a sample of US health care workers. Mayo Clin Proc Innov Qual Outcomes. 2021 Dec;5(6):1165-73.
2. Addressing health worker burnout. The U.S. Surgeon General’s advisory on building a thriving health workforce.
Researcher revisits ‘03 guidance on monkeypox in pregnant women
In creating a guide about monkeypox for ob.gyns., Denise J. Jamieson, MD, MPH, turned to research she relied on during another outbreak of the disease nearly 20 years ago.
Dr. Jamieson, the James Robert McCord Professor and chair of the department of gynecology and obstetrics at Emory Healthcare, Atlanta, had been working for the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention in 2003 when doctors diagnosed monkeypox in several states.
That year, the virus was mainly transmitted by contact with pet prairie dogs, including in childcare and school settings. Of the approximately 70 suspected and confirmed cases, 55% occurred in female patients, according to one study .
Dr. Jamieson, an obstetrician with a focus on emerging infectious diseases, and colleagues at the agency published a commentary in Obstetrics & Gynecology highlighting the need for physicians to stay up to date with relevant information about the virus.
Fast forward to 2022: Dr. Jamieson – again with coauthors from the CDC – is delivering a similar message in the same journal about the need for clinicians to be prepared for this virus.
“Most ob.gyns. have never seen a case of monkeypox virus infection and may not be aware of testing, treatment, or pre-exposure or postexposure vaccine options,” she and her coauthors wrote in a primer published online.
But if a woman were to contract the virus, her ob.gyn. might well be the first clinician she called. “We are often the first people, the first physicians to see and evaluate women with various symptoms,” Dr. Jamieson said.
To promptly diagnose, treat, and prevent further spread of monkeypox, ob.gyns. need up-to-date information, Dr. Jamieson and colleagues said.
Based on data from related viruses like smallpox, monkeypox may be more severe in pregnant women and entail risk for adverse pregnancy outcomes, Dr. Jamieson said.
Outliers
So far this year, monkeypox has predominantly spread among men who have sex with men. Cases have occurred in women, however, some of whom have required hospitalization.
According to the CDC, as of July 25, 1,373 cases of monkeypox in the United States were in men and 13 in women. The total confirmed case count exceeded 5,800 as of Aug. 1. The agency recently announced that it planned to make the disease a reportable condition.
In the United Kingdom, which has been hit hard by the outbreak, researchers are keeping a close eye on the number of cases in women to assess how the disease is spreading.
At least one case of monkeypox in the United States has occurred in a pregnant woman who delivered. The mother and baby, who received immune globulin as a preventive measure, are doing well, according to health officials.
“We know that infection can occur through placental transfer. In the case that we are aware of presently, it does not appear that the virus was transmitted,” said John T. Brooks, MD, the CDC’s chief medical officer in the division of HIV prevention, on a July 23 call with clinicians.
While monkeypox can be transmitted in utero and during sexual activity, it also can spread through any close contact with skin lesions or body fluids and possibly through touching contaminated items like clothing or linens, according to the CDC.
A preferred vaccine and antiviral in pregnancy
One monkeypox vaccine, Jynneos, is preferred for use during pregnancy, while another, ACAM2000, is contraindicated, the CDC advises.
Jynneos can be offered to people who are pregnant or breastfeeding who are eligible for vaccination based on confirmed or likely contact with cases, ideally within 4 days of exposure. People at high risk for exposure, such as laboratory workers, may receive the vaccine in advance.
Developmental toxicity studies in animals showed no evidence of harm with the Jynneos vaccine, Dr. Jamieson said.
ACAM2000, however, can cause fetal vaccinia and should not be used in people who are pregnant or breastfeeding, according to the CDC.
The Society for Maternal-Fetal Medicine notes that, if treatment for monkeypox is warranted, tecovirimat should be considered the first-line antiviral for pregnant, recently pregnant, and breastfeeding people, in line with CDC guidance.
Current outbreak ‘very different,’ but lessons apply
In 2003, some women exposed to monkeypox through contact with infected prairie dogs were pregnant – which is how Dr. Jamieson came to be involved in responding to the outbreak and studying the effects of the virus in pregnancy.
“When this resurfaced this year, of course it caught my attention,” Dr. Jamieson said. The extensive person-to-person transmission and far greater number of cases today make the current outbreak “very different” from the prior one, she said.
But key principles in managing the disease and understanding its potential risks in pregnancy – despite relatively limited information – remain the same.
“Whenever you are looking at an infectious disease, you want to think about, are pregnant persons more susceptible or more likely to have severe disease,” Dr. Jamieson said. Smallpox, a similar orthopoxvirus, “is more severe during pregnancy with a higher case fatality rate,” which is one reason for concern with monkeypox in this population.
In terms of pregnancy outcomes, researchers have data from only a handful of confirmed cases of monkeypox, which makes it difficult to draw conclusions, Dr. Jamieson said. A review of five cases from outside the United States in prior years found that three resulted in loss of the pregnancy. One resulted in preterm delivery of an infant who subsequently died. One child was apparently healthy and born at term.
Addition to the differential diagnosis
A separate team of researchers has proposed a clinical management algorithm for pregnant women with suspected exposure to monkeypox.
“Clinicians must maintain a high index of suspicion for monkeypox virus in any pregnant woman presenting with lymphadenopathy and vesiculopustular rash – including rash localized to the genital or perianal region – even if there are no apparent epidemiological links,” Pradip Dashraath, MBBS, National University Hospital, Singapore, and coauthors wrote in The Lancet.
Jamieson echoed the call for increased vigilance.
“As ob.gyns., people may present to us with genital lesions concerning for sexually transmitted infection. And it is important to include monkeypox in our differential,” Dr. Jamieson said. “We are trying to get the word out that it needs to be part of what you think about when you see a patient with genital ulcers.”
Health care professionals have acquired monkeypox through contact with patients or fomites, so clinicians should be sure to use appropriate precautions when evaluating patients who might have monkeypox, Dr. Jamieson added. Appropriate protective measures include wearing a gown, gloves, eye protection, and an N95.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
In creating a guide about monkeypox for ob.gyns., Denise J. Jamieson, MD, MPH, turned to research she relied on during another outbreak of the disease nearly 20 years ago.
Dr. Jamieson, the James Robert McCord Professor and chair of the department of gynecology and obstetrics at Emory Healthcare, Atlanta, had been working for the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention in 2003 when doctors diagnosed monkeypox in several states.
That year, the virus was mainly transmitted by contact with pet prairie dogs, including in childcare and school settings. Of the approximately 70 suspected and confirmed cases, 55% occurred in female patients, according to one study .
Dr. Jamieson, an obstetrician with a focus on emerging infectious diseases, and colleagues at the agency published a commentary in Obstetrics & Gynecology highlighting the need for physicians to stay up to date with relevant information about the virus.
Fast forward to 2022: Dr. Jamieson – again with coauthors from the CDC – is delivering a similar message in the same journal about the need for clinicians to be prepared for this virus.
“Most ob.gyns. have never seen a case of monkeypox virus infection and may not be aware of testing, treatment, or pre-exposure or postexposure vaccine options,” she and her coauthors wrote in a primer published online.
But if a woman were to contract the virus, her ob.gyn. might well be the first clinician she called. “We are often the first people, the first physicians to see and evaluate women with various symptoms,” Dr. Jamieson said.
To promptly diagnose, treat, and prevent further spread of monkeypox, ob.gyns. need up-to-date information, Dr. Jamieson and colleagues said.
Based on data from related viruses like smallpox, monkeypox may be more severe in pregnant women and entail risk for adverse pregnancy outcomes, Dr. Jamieson said.
Outliers
So far this year, monkeypox has predominantly spread among men who have sex with men. Cases have occurred in women, however, some of whom have required hospitalization.
According to the CDC, as of July 25, 1,373 cases of monkeypox in the United States were in men and 13 in women. The total confirmed case count exceeded 5,800 as of Aug. 1. The agency recently announced that it planned to make the disease a reportable condition.
In the United Kingdom, which has been hit hard by the outbreak, researchers are keeping a close eye on the number of cases in women to assess how the disease is spreading.
At least one case of monkeypox in the United States has occurred in a pregnant woman who delivered. The mother and baby, who received immune globulin as a preventive measure, are doing well, according to health officials.
“We know that infection can occur through placental transfer. In the case that we are aware of presently, it does not appear that the virus was transmitted,” said John T. Brooks, MD, the CDC’s chief medical officer in the division of HIV prevention, on a July 23 call with clinicians.
While monkeypox can be transmitted in utero and during sexual activity, it also can spread through any close contact with skin lesions or body fluids and possibly through touching contaminated items like clothing or linens, according to the CDC.
A preferred vaccine and antiviral in pregnancy
One monkeypox vaccine, Jynneos, is preferred for use during pregnancy, while another, ACAM2000, is contraindicated, the CDC advises.
Jynneos can be offered to people who are pregnant or breastfeeding who are eligible for vaccination based on confirmed or likely contact with cases, ideally within 4 days of exposure. People at high risk for exposure, such as laboratory workers, may receive the vaccine in advance.
Developmental toxicity studies in animals showed no evidence of harm with the Jynneos vaccine, Dr. Jamieson said.
ACAM2000, however, can cause fetal vaccinia and should not be used in people who are pregnant or breastfeeding, according to the CDC.
The Society for Maternal-Fetal Medicine notes that, if treatment for monkeypox is warranted, tecovirimat should be considered the first-line antiviral for pregnant, recently pregnant, and breastfeeding people, in line with CDC guidance.
Current outbreak ‘very different,’ but lessons apply
In 2003, some women exposed to monkeypox through contact with infected prairie dogs were pregnant – which is how Dr. Jamieson came to be involved in responding to the outbreak and studying the effects of the virus in pregnancy.
“When this resurfaced this year, of course it caught my attention,” Dr. Jamieson said. The extensive person-to-person transmission and far greater number of cases today make the current outbreak “very different” from the prior one, she said.
But key principles in managing the disease and understanding its potential risks in pregnancy – despite relatively limited information – remain the same.
“Whenever you are looking at an infectious disease, you want to think about, are pregnant persons more susceptible or more likely to have severe disease,” Dr. Jamieson said. Smallpox, a similar orthopoxvirus, “is more severe during pregnancy with a higher case fatality rate,” which is one reason for concern with monkeypox in this population.
In terms of pregnancy outcomes, researchers have data from only a handful of confirmed cases of monkeypox, which makes it difficult to draw conclusions, Dr. Jamieson said. A review of five cases from outside the United States in prior years found that three resulted in loss of the pregnancy. One resulted in preterm delivery of an infant who subsequently died. One child was apparently healthy and born at term.
Addition to the differential diagnosis
A separate team of researchers has proposed a clinical management algorithm for pregnant women with suspected exposure to monkeypox.
“Clinicians must maintain a high index of suspicion for monkeypox virus in any pregnant woman presenting with lymphadenopathy and vesiculopustular rash – including rash localized to the genital or perianal region – even if there are no apparent epidemiological links,” Pradip Dashraath, MBBS, National University Hospital, Singapore, and coauthors wrote in The Lancet.
Jamieson echoed the call for increased vigilance.
“As ob.gyns., people may present to us with genital lesions concerning for sexually transmitted infection. And it is important to include monkeypox in our differential,” Dr. Jamieson said. “We are trying to get the word out that it needs to be part of what you think about when you see a patient with genital ulcers.”
Health care professionals have acquired monkeypox through contact with patients or fomites, so clinicians should be sure to use appropriate precautions when evaluating patients who might have monkeypox, Dr. Jamieson added. Appropriate protective measures include wearing a gown, gloves, eye protection, and an N95.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
In creating a guide about monkeypox for ob.gyns., Denise J. Jamieson, MD, MPH, turned to research she relied on during another outbreak of the disease nearly 20 years ago.
Dr. Jamieson, the James Robert McCord Professor and chair of the department of gynecology and obstetrics at Emory Healthcare, Atlanta, had been working for the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention in 2003 when doctors diagnosed monkeypox in several states.
That year, the virus was mainly transmitted by contact with pet prairie dogs, including in childcare and school settings. Of the approximately 70 suspected and confirmed cases, 55% occurred in female patients, according to one study .
Dr. Jamieson, an obstetrician with a focus on emerging infectious diseases, and colleagues at the agency published a commentary in Obstetrics & Gynecology highlighting the need for physicians to stay up to date with relevant information about the virus.
Fast forward to 2022: Dr. Jamieson – again with coauthors from the CDC – is delivering a similar message in the same journal about the need for clinicians to be prepared for this virus.
“Most ob.gyns. have never seen a case of monkeypox virus infection and may not be aware of testing, treatment, or pre-exposure or postexposure vaccine options,” she and her coauthors wrote in a primer published online.
But if a woman were to contract the virus, her ob.gyn. might well be the first clinician she called. “We are often the first people, the first physicians to see and evaluate women with various symptoms,” Dr. Jamieson said.
To promptly diagnose, treat, and prevent further spread of monkeypox, ob.gyns. need up-to-date information, Dr. Jamieson and colleagues said.
Based on data from related viruses like smallpox, monkeypox may be more severe in pregnant women and entail risk for adverse pregnancy outcomes, Dr. Jamieson said.
Outliers
So far this year, monkeypox has predominantly spread among men who have sex with men. Cases have occurred in women, however, some of whom have required hospitalization.
According to the CDC, as of July 25, 1,373 cases of monkeypox in the United States were in men and 13 in women. The total confirmed case count exceeded 5,800 as of Aug. 1. The agency recently announced that it planned to make the disease a reportable condition.
In the United Kingdom, which has been hit hard by the outbreak, researchers are keeping a close eye on the number of cases in women to assess how the disease is spreading.
At least one case of monkeypox in the United States has occurred in a pregnant woman who delivered. The mother and baby, who received immune globulin as a preventive measure, are doing well, according to health officials.
“We know that infection can occur through placental transfer. In the case that we are aware of presently, it does not appear that the virus was transmitted,” said John T. Brooks, MD, the CDC’s chief medical officer in the division of HIV prevention, on a July 23 call with clinicians.
While monkeypox can be transmitted in utero and during sexual activity, it also can spread through any close contact with skin lesions or body fluids and possibly through touching contaminated items like clothing or linens, according to the CDC.
A preferred vaccine and antiviral in pregnancy
One monkeypox vaccine, Jynneos, is preferred for use during pregnancy, while another, ACAM2000, is contraindicated, the CDC advises.
Jynneos can be offered to people who are pregnant or breastfeeding who are eligible for vaccination based on confirmed or likely contact with cases, ideally within 4 days of exposure. People at high risk for exposure, such as laboratory workers, may receive the vaccine in advance.
Developmental toxicity studies in animals showed no evidence of harm with the Jynneos vaccine, Dr. Jamieson said.
ACAM2000, however, can cause fetal vaccinia and should not be used in people who are pregnant or breastfeeding, according to the CDC.
The Society for Maternal-Fetal Medicine notes that, if treatment for monkeypox is warranted, tecovirimat should be considered the first-line antiviral for pregnant, recently pregnant, and breastfeeding people, in line with CDC guidance.
Current outbreak ‘very different,’ but lessons apply
In 2003, some women exposed to monkeypox through contact with infected prairie dogs were pregnant – which is how Dr. Jamieson came to be involved in responding to the outbreak and studying the effects of the virus in pregnancy.
“When this resurfaced this year, of course it caught my attention,” Dr. Jamieson said. The extensive person-to-person transmission and far greater number of cases today make the current outbreak “very different” from the prior one, she said.
But key principles in managing the disease and understanding its potential risks in pregnancy – despite relatively limited information – remain the same.
“Whenever you are looking at an infectious disease, you want to think about, are pregnant persons more susceptible or more likely to have severe disease,” Dr. Jamieson said. Smallpox, a similar orthopoxvirus, “is more severe during pregnancy with a higher case fatality rate,” which is one reason for concern with monkeypox in this population.
In terms of pregnancy outcomes, researchers have data from only a handful of confirmed cases of monkeypox, which makes it difficult to draw conclusions, Dr. Jamieson said. A review of five cases from outside the United States in prior years found that three resulted in loss of the pregnancy. One resulted in preterm delivery of an infant who subsequently died. One child was apparently healthy and born at term.
Addition to the differential diagnosis
A separate team of researchers has proposed a clinical management algorithm for pregnant women with suspected exposure to monkeypox.
“Clinicians must maintain a high index of suspicion for monkeypox virus in any pregnant woman presenting with lymphadenopathy and vesiculopustular rash – including rash localized to the genital or perianal region – even if there are no apparent epidemiological links,” Pradip Dashraath, MBBS, National University Hospital, Singapore, and coauthors wrote in The Lancet.
Jamieson echoed the call for increased vigilance.
“As ob.gyns., people may present to us with genital lesions concerning for sexually transmitted infection. And it is important to include monkeypox in our differential,” Dr. Jamieson said. “We are trying to get the word out that it needs to be part of what you think about when you see a patient with genital ulcers.”
Health care professionals have acquired monkeypox through contact with patients or fomites, so clinicians should be sure to use appropriate precautions when evaluating patients who might have monkeypox, Dr. Jamieson added. Appropriate protective measures include wearing a gown, gloves, eye protection, and an N95.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM OBSTETRICS AND GYNECOLOGY







