User login
News and Views that Matter to Pediatricians
The leading independent newspaper covering news and commentary in pediatrics.
Eosinophilic Esophagitis: 5 Things to Know
Eosinophilic esophagitis (EoE) is a chronic inflammatory disease of the esophagus that affects both children and adults. EoE is defined by symptoms of esophageal dysfunction (eg, dysphagia, vomiting, difficulty in feeding), with presentation varying depending on patient age.
The global incidence of EoE has increased in recent decades. In the United States alone, EoE is estimated to affect approximately 150,000 people and result in as much as $1.4 billion in annual healthcare costs.
There currently is no clear treatment hierarchy for EoE, and long delays between symptom onset and diagnoses are common.
Still, the knowledge base surrounding the disease is growing, and existing interventions have shown tremendous success at curbing symptoms and disease progression.
To help clinicians stay up to date on the latest information on this debilitating disease, here are five things to know about EoE.
1. EoE prevalence is increasing although not consistently around the globe.
EoE was first recognized as a distinct clinical entity in the early 1990s, when it was considered a relatively rare disease. Now, the incidence and prevalence rates of EoE are escalating at rates that cannot be explained by increased disease awareness and detection.
Although EoE has been diagnosed in Latin America, the Middle East, and Asia, such instances are relatively uncommon in comparison with the spiking rates noted in the United States; in Western Europe, including Denmark, the Netherlands, and Switzerland; and in Australia.
Emerging data suggest that climate and location may be a factor in the varying incidence rates of EoE. An analysis of 233,649 patients in a US pathology database reported that EoE was more common in cold and arid climate zones than in tropical zones. Another study suggests that EoE is more common in low-density, rural environments compared with urban settings.
2. Environmental and food exposures may trigger EoE, and genetics probably play a role.
The unequal geographic distribution of EoE lends credence to the theory that external triggers, which naturally differ in various locales, play an outsized role in its development.
Mice studies have indicated that the inhalation of allergens induces notable eosinophil infiltration and degranulation, and a pilot study conducted in New York City found that EoE symptoms peaked during the July-to-September period when grass pollen counts were at their highest.
Early-life factors that can result in alteration to the microbiome have also been identified as possibly influencing EoE development. They include cesarean delivery, preterm delivery, admission to a neonatal intensive care unit, infant formula use, and maternal or infant use of antibiotics. Conversely, evidence suggests that Helicobacter pylori infection may be protective against EoE due to immunomodulating effects that have not yet been sufficiently identified in the literature.
Yet, the clearest association between EoE and outside triggers is found with food exposures. In one analysis of pediatric patients, the items that were most commonly associated with elevated food-specific serum immunoglobulin E antibodies in patients with EoE were milk (78%), wheat (69%), eggs (64%), peanuts (54%), and soy (51%). Food allergies are also on the uptick in countries with rising EoE rates, suggesting that the two trends may be interrelated.
From a genetic standpoint, EoE is more likely to develop in those with first-degree relatives with the disease than in the general population. Thirty independent genes thought to be associated with EoE have been identified. EoE is also significantly more common in men than in women.
3. Diagnosis requires knowing the symptoms, excluding other disorders, and performing biopsy.
EoE can occur early in life, with approximately one third of children with the disease presenting under age 5 years. The prevalence rises with age, eventually peaking in those aged 35-45 years.
The presentation of EoE can be quite variable depending on patient age. Pediatric patients are significantly more likely to experience failure to thrive, vomiting, and heartburn, whereas their adult counterparts more often present with food impaction and dysphagia.
At the 2018 AGREE international consensus conference, researchers defined diagnostic criteria as presence of esophageal dysfunction symptoms; exclusion of non-EoE disorders, such as gastroesophageal reflux disease and achalasia; and esophageal biopsy findings of at least 15 eosinophils per high-power field (or approximately 60 eosinophils per mm2).
Endoscopic findings can also be crucial in diagnosing EoE because patients with this disease often present with inflammatory patterns recognizable in the form of exudates, furrows, and edema and/or fibrotic phenotypes such as the presence of rings and stenosis. Clinicians are advised to refer to the Endoscopic Reference Score proposed by Hirano and colleagues.
4. Treatment approaches rely on the ‘3 Ds.’
Although there is currently no leading strategy for the primary treatment of EoE, clinicians can avail themselves of suggested pathways.
The lack of a treatment hierarchy means that patients typically are very involved in selecting the therapy that works best for them. Physicians should be aware that patients researching EoE on their own might not find the information they need. A recent study found that the artificial intelligence tool ChatGPT was highly inaccurate when it came to providing answers about EoE.
The treatment strategies that clinicians and their patients can choose from revolve around the “3 Ds”: diet, drugs, and dilation.
Diet:
Three dietary interventions are available for EoE treatment:
- Elemental diet, in which patients consume only an amino-acid based formula that does not include any intact proteins
- Empiric elimination diet, which removes foods more commonly associated with food allergy regardless of whether there has been a positive allergy testing result
- Allergy testing-directed food elimination, which involves avoidance of all foods for which specific antibodies were detected or that tested positive on skin-prick tests
Each of these dietary interventions has clear advantages and drawbacks that should be discussed with patients. Elemental diets achieve robust histologic responses, yet their highly restrictive nature makes compliance difficult and can greatly impair patients’ quality of life.
Empiric elimination diets are the most popular choice and have shown high response rates. A common approach is to begin by removing six common foods (milk, wheat, egg, soy, nuts, and fish/seafood), which are then gradually reintroduced to identify the culprits. However, patients must be motivated to follow this process, and the likelihood it will be successful is greatly enhanced with assistance from a dietitian, which may not always be possible.
Last, allergy testing-guided food elimination diets have been reported to produce remissions rates of just under 50%, and the skin allergy tests they primarily rely on have been criticized for being unreliable.
Drugs:
The treatment of EoE experienced a significant advance in 2022 when dupilumab, a monoclonal antibody that binds to the interleukin (IL)–4 receptor alpha, became the first drug approved by the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) for treating EoE in adults and pediatric patients aged 12 years or older. The drug was approved by the European Commission in 2023. In late January 2024, the FDA expanded dupilumab’s approval to children aged 1-11 years and weighing ≥ 15 kg after positive histologic remission and safety results were reported in the two-part phase 3 EoE KIDS trial.
In addition, the FDA approved budesonide, the first oral treatment for EoE, in February 2024.
These approvals have expanded treatment options beyond proton pump inhibitors (PPIs) and topical glucocorticosteroids, both of which received only nuanced recommendations for use under US and UK clinical guidelines.
A recent meta-analysis found that PPIs, off-label and EoE-specific topical steroids, and biologics had greater efficacy than did placebo in achieving histological remission. However, significant heterogeneity in the included studies’ eligibility criteria and outcome measures prevented development of a “solid therapeutic hierarchy,” the authors noted.
In addition, researchers are investigating therapies targeting IL-5 (eg, mepolizumab, reslizumab, and benralizumab) and other key inflammatory mediators in EoE, such as Siglec-8 (lirentelimab), IL-13 (cendakimab), and the sphingosine 1–phosphate receptor (etrasimod).
Dilation:
Finally, patients with significant strictures can benefit from dilation performed via through-the-scope balloons or Savary-Gilliard bougies, which can significantly and immediately improve symptoms even if they cannot address the underlying inflammation. Concerns that dilation would lead to increased complications, such as perforation and mucosal tears, do not appear to be borne out by recent data.
5. Reducing diagnosis delays is crucial for limiting EoE-associated morbidity.
Despite efforts to bring attention to EoE, evidence suggests that delays between symptom onset and diagnosis are common, and result in treatment delays. One study found a median lag time of 6 years.
The longer the delay in treatment, the more likely patients are to develop esophageal rings, a long narrowing in the esophageal caliber, or focal strictures. For example, diagnostic delays of more than 20 years result in prevalence rates of 70.8% for esophageal strictures, compared with 17.2% with delays of 0-2 years.
Simply put, the sooner one can identify EoE and begin treatment, the more likely patients are to be spared its worst effects.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Eosinophilic esophagitis (EoE) is a chronic inflammatory disease of the esophagus that affects both children and adults. EoE is defined by symptoms of esophageal dysfunction (eg, dysphagia, vomiting, difficulty in feeding), with presentation varying depending on patient age.
The global incidence of EoE has increased in recent decades. In the United States alone, EoE is estimated to affect approximately 150,000 people and result in as much as $1.4 billion in annual healthcare costs.
There currently is no clear treatment hierarchy for EoE, and long delays between symptom onset and diagnoses are common.
Still, the knowledge base surrounding the disease is growing, and existing interventions have shown tremendous success at curbing symptoms and disease progression.
To help clinicians stay up to date on the latest information on this debilitating disease, here are five things to know about EoE.
1. EoE prevalence is increasing although not consistently around the globe.
EoE was first recognized as a distinct clinical entity in the early 1990s, when it was considered a relatively rare disease. Now, the incidence and prevalence rates of EoE are escalating at rates that cannot be explained by increased disease awareness and detection.
Although EoE has been diagnosed in Latin America, the Middle East, and Asia, such instances are relatively uncommon in comparison with the spiking rates noted in the United States; in Western Europe, including Denmark, the Netherlands, and Switzerland; and in Australia.
Emerging data suggest that climate and location may be a factor in the varying incidence rates of EoE. An analysis of 233,649 patients in a US pathology database reported that EoE was more common in cold and arid climate zones than in tropical zones. Another study suggests that EoE is more common in low-density, rural environments compared with urban settings.
2. Environmental and food exposures may trigger EoE, and genetics probably play a role.
The unequal geographic distribution of EoE lends credence to the theory that external triggers, which naturally differ in various locales, play an outsized role in its development.
Mice studies have indicated that the inhalation of allergens induces notable eosinophil infiltration and degranulation, and a pilot study conducted in New York City found that EoE symptoms peaked during the July-to-September period when grass pollen counts were at their highest.
Early-life factors that can result in alteration to the microbiome have also been identified as possibly influencing EoE development. They include cesarean delivery, preterm delivery, admission to a neonatal intensive care unit, infant formula use, and maternal or infant use of antibiotics. Conversely, evidence suggests that Helicobacter pylori infection may be protective against EoE due to immunomodulating effects that have not yet been sufficiently identified in the literature.
Yet, the clearest association between EoE and outside triggers is found with food exposures. In one analysis of pediatric patients, the items that were most commonly associated with elevated food-specific serum immunoglobulin E antibodies in patients with EoE were milk (78%), wheat (69%), eggs (64%), peanuts (54%), and soy (51%). Food allergies are also on the uptick in countries with rising EoE rates, suggesting that the two trends may be interrelated.
From a genetic standpoint, EoE is more likely to develop in those with first-degree relatives with the disease than in the general population. Thirty independent genes thought to be associated with EoE have been identified. EoE is also significantly more common in men than in women.
3. Diagnosis requires knowing the symptoms, excluding other disorders, and performing biopsy.
EoE can occur early in life, with approximately one third of children with the disease presenting under age 5 years. The prevalence rises with age, eventually peaking in those aged 35-45 years.
The presentation of EoE can be quite variable depending on patient age. Pediatric patients are significantly more likely to experience failure to thrive, vomiting, and heartburn, whereas their adult counterparts more often present with food impaction and dysphagia.
At the 2018 AGREE international consensus conference, researchers defined diagnostic criteria as presence of esophageal dysfunction symptoms; exclusion of non-EoE disorders, such as gastroesophageal reflux disease and achalasia; and esophageal biopsy findings of at least 15 eosinophils per high-power field (or approximately 60 eosinophils per mm2).
Endoscopic findings can also be crucial in diagnosing EoE because patients with this disease often present with inflammatory patterns recognizable in the form of exudates, furrows, and edema and/or fibrotic phenotypes such as the presence of rings and stenosis. Clinicians are advised to refer to the Endoscopic Reference Score proposed by Hirano and colleagues.
4. Treatment approaches rely on the ‘3 Ds.’
Although there is currently no leading strategy for the primary treatment of EoE, clinicians can avail themselves of suggested pathways.
The lack of a treatment hierarchy means that patients typically are very involved in selecting the therapy that works best for them. Physicians should be aware that patients researching EoE on their own might not find the information they need. A recent study found that the artificial intelligence tool ChatGPT was highly inaccurate when it came to providing answers about EoE.
The treatment strategies that clinicians and their patients can choose from revolve around the “3 Ds”: diet, drugs, and dilation.
Diet:
Three dietary interventions are available for EoE treatment:
- Elemental diet, in which patients consume only an amino-acid based formula that does not include any intact proteins
- Empiric elimination diet, which removes foods more commonly associated with food allergy regardless of whether there has been a positive allergy testing result
- Allergy testing-directed food elimination, which involves avoidance of all foods for which specific antibodies were detected or that tested positive on skin-prick tests
Each of these dietary interventions has clear advantages and drawbacks that should be discussed with patients. Elemental diets achieve robust histologic responses, yet their highly restrictive nature makes compliance difficult and can greatly impair patients’ quality of life.
Empiric elimination diets are the most popular choice and have shown high response rates. A common approach is to begin by removing six common foods (milk, wheat, egg, soy, nuts, and fish/seafood), which are then gradually reintroduced to identify the culprits. However, patients must be motivated to follow this process, and the likelihood it will be successful is greatly enhanced with assistance from a dietitian, which may not always be possible.
Last, allergy testing-guided food elimination diets have been reported to produce remissions rates of just under 50%, and the skin allergy tests they primarily rely on have been criticized for being unreliable.
Drugs:
The treatment of EoE experienced a significant advance in 2022 when dupilumab, a monoclonal antibody that binds to the interleukin (IL)–4 receptor alpha, became the first drug approved by the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) for treating EoE in adults and pediatric patients aged 12 years or older. The drug was approved by the European Commission in 2023. In late January 2024, the FDA expanded dupilumab’s approval to children aged 1-11 years and weighing ≥ 15 kg after positive histologic remission and safety results were reported in the two-part phase 3 EoE KIDS trial.
In addition, the FDA approved budesonide, the first oral treatment for EoE, in February 2024.
These approvals have expanded treatment options beyond proton pump inhibitors (PPIs) and topical glucocorticosteroids, both of which received only nuanced recommendations for use under US and UK clinical guidelines.
A recent meta-analysis found that PPIs, off-label and EoE-specific topical steroids, and biologics had greater efficacy than did placebo in achieving histological remission. However, significant heterogeneity in the included studies’ eligibility criteria and outcome measures prevented development of a “solid therapeutic hierarchy,” the authors noted.
In addition, researchers are investigating therapies targeting IL-5 (eg, mepolizumab, reslizumab, and benralizumab) and other key inflammatory mediators in EoE, such as Siglec-8 (lirentelimab), IL-13 (cendakimab), and the sphingosine 1–phosphate receptor (etrasimod).
Dilation:
Finally, patients with significant strictures can benefit from dilation performed via through-the-scope balloons or Savary-Gilliard bougies, which can significantly and immediately improve symptoms even if they cannot address the underlying inflammation. Concerns that dilation would lead to increased complications, such as perforation and mucosal tears, do not appear to be borne out by recent data.
5. Reducing diagnosis delays is crucial for limiting EoE-associated morbidity.
Despite efforts to bring attention to EoE, evidence suggests that delays between symptom onset and diagnosis are common, and result in treatment delays. One study found a median lag time of 6 years.
The longer the delay in treatment, the more likely patients are to develop esophageal rings, a long narrowing in the esophageal caliber, or focal strictures. For example, diagnostic delays of more than 20 years result in prevalence rates of 70.8% for esophageal strictures, compared with 17.2% with delays of 0-2 years.
Simply put, the sooner one can identify EoE and begin treatment, the more likely patients are to be spared its worst effects.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Eosinophilic esophagitis (EoE) is a chronic inflammatory disease of the esophagus that affects both children and adults. EoE is defined by symptoms of esophageal dysfunction (eg, dysphagia, vomiting, difficulty in feeding), with presentation varying depending on patient age.
The global incidence of EoE has increased in recent decades. In the United States alone, EoE is estimated to affect approximately 150,000 people and result in as much as $1.4 billion in annual healthcare costs.
There currently is no clear treatment hierarchy for EoE, and long delays between symptom onset and diagnoses are common.
Still, the knowledge base surrounding the disease is growing, and existing interventions have shown tremendous success at curbing symptoms and disease progression.
To help clinicians stay up to date on the latest information on this debilitating disease, here are five things to know about EoE.
1. EoE prevalence is increasing although not consistently around the globe.
EoE was first recognized as a distinct clinical entity in the early 1990s, when it was considered a relatively rare disease. Now, the incidence and prevalence rates of EoE are escalating at rates that cannot be explained by increased disease awareness and detection.
Although EoE has been diagnosed in Latin America, the Middle East, and Asia, such instances are relatively uncommon in comparison with the spiking rates noted in the United States; in Western Europe, including Denmark, the Netherlands, and Switzerland; and in Australia.
Emerging data suggest that climate and location may be a factor in the varying incidence rates of EoE. An analysis of 233,649 patients in a US pathology database reported that EoE was more common in cold and arid climate zones than in tropical zones. Another study suggests that EoE is more common in low-density, rural environments compared with urban settings.
2. Environmental and food exposures may trigger EoE, and genetics probably play a role.
The unequal geographic distribution of EoE lends credence to the theory that external triggers, which naturally differ in various locales, play an outsized role in its development.
Mice studies have indicated that the inhalation of allergens induces notable eosinophil infiltration and degranulation, and a pilot study conducted in New York City found that EoE symptoms peaked during the July-to-September period when grass pollen counts were at their highest.
Early-life factors that can result in alteration to the microbiome have also been identified as possibly influencing EoE development. They include cesarean delivery, preterm delivery, admission to a neonatal intensive care unit, infant formula use, and maternal or infant use of antibiotics. Conversely, evidence suggests that Helicobacter pylori infection may be protective against EoE due to immunomodulating effects that have not yet been sufficiently identified in the literature.
Yet, the clearest association between EoE and outside triggers is found with food exposures. In one analysis of pediatric patients, the items that were most commonly associated with elevated food-specific serum immunoglobulin E antibodies in patients with EoE were milk (78%), wheat (69%), eggs (64%), peanuts (54%), and soy (51%). Food allergies are also on the uptick in countries with rising EoE rates, suggesting that the two trends may be interrelated.
From a genetic standpoint, EoE is more likely to develop in those with first-degree relatives with the disease than in the general population. Thirty independent genes thought to be associated with EoE have been identified. EoE is also significantly more common in men than in women.
3. Diagnosis requires knowing the symptoms, excluding other disorders, and performing biopsy.
EoE can occur early in life, with approximately one third of children with the disease presenting under age 5 years. The prevalence rises with age, eventually peaking in those aged 35-45 years.
The presentation of EoE can be quite variable depending on patient age. Pediatric patients are significantly more likely to experience failure to thrive, vomiting, and heartburn, whereas their adult counterparts more often present with food impaction and dysphagia.
At the 2018 AGREE international consensus conference, researchers defined diagnostic criteria as presence of esophageal dysfunction symptoms; exclusion of non-EoE disorders, such as gastroesophageal reflux disease and achalasia; and esophageal biopsy findings of at least 15 eosinophils per high-power field (or approximately 60 eosinophils per mm2).
Endoscopic findings can also be crucial in diagnosing EoE because patients with this disease often present with inflammatory patterns recognizable in the form of exudates, furrows, and edema and/or fibrotic phenotypes such as the presence of rings and stenosis. Clinicians are advised to refer to the Endoscopic Reference Score proposed by Hirano and colleagues.
4. Treatment approaches rely on the ‘3 Ds.’
Although there is currently no leading strategy for the primary treatment of EoE, clinicians can avail themselves of suggested pathways.
The lack of a treatment hierarchy means that patients typically are very involved in selecting the therapy that works best for them. Physicians should be aware that patients researching EoE on their own might not find the information they need. A recent study found that the artificial intelligence tool ChatGPT was highly inaccurate when it came to providing answers about EoE.
The treatment strategies that clinicians and their patients can choose from revolve around the “3 Ds”: diet, drugs, and dilation.
Diet:
Three dietary interventions are available for EoE treatment:
- Elemental diet, in which patients consume only an amino-acid based formula that does not include any intact proteins
- Empiric elimination diet, which removes foods more commonly associated with food allergy regardless of whether there has been a positive allergy testing result
- Allergy testing-directed food elimination, which involves avoidance of all foods for which specific antibodies were detected or that tested positive on skin-prick tests
Each of these dietary interventions has clear advantages and drawbacks that should be discussed with patients. Elemental diets achieve robust histologic responses, yet their highly restrictive nature makes compliance difficult and can greatly impair patients’ quality of life.
Empiric elimination diets are the most popular choice and have shown high response rates. A common approach is to begin by removing six common foods (milk, wheat, egg, soy, nuts, and fish/seafood), which are then gradually reintroduced to identify the culprits. However, patients must be motivated to follow this process, and the likelihood it will be successful is greatly enhanced with assistance from a dietitian, which may not always be possible.
Last, allergy testing-guided food elimination diets have been reported to produce remissions rates of just under 50%, and the skin allergy tests they primarily rely on have been criticized for being unreliable.
Drugs:
The treatment of EoE experienced a significant advance in 2022 when dupilumab, a monoclonal antibody that binds to the interleukin (IL)–4 receptor alpha, became the first drug approved by the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) for treating EoE in adults and pediatric patients aged 12 years or older. The drug was approved by the European Commission in 2023. In late January 2024, the FDA expanded dupilumab’s approval to children aged 1-11 years and weighing ≥ 15 kg after positive histologic remission and safety results were reported in the two-part phase 3 EoE KIDS trial.
In addition, the FDA approved budesonide, the first oral treatment for EoE, in February 2024.
These approvals have expanded treatment options beyond proton pump inhibitors (PPIs) and topical glucocorticosteroids, both of which received only nuanced recommendations for use under US and UK clinical guidelines.
A recent meta-analysis found that PPIs, off-label and EoE-specific topical steroids, and biologics had greater efficacy than did placebo in achieving histological remission. However, significant heterogeneity in the included studies’ eligibility criteria and outcome measures prevented development of a “solid therapeutic hierarchy,” the authors noted.
In addition, researchers are investigating therapies targeting IL-5 (eg, mepolizumab, reslizumab, and benralizumab) and other key inflammatory mediators in EoE, such as Siglec-8 (lirentelimab), IL-13 (cendakimab), and the sphingosine 1–phosphate receptor (etrasimod).
Dilation:
Finally, patients with significant strictures can benefit from dilation performed via through-the-scope balloons or Savary-Gilliard bougies, which can significantly and immediately improve symptoms even if they cannot address the underlying inflammation. Concerns that dilation would lead to increased complications, such as perforation and mucosal tears, do not appear to be borne out by recent data.
5. Reducing diagnosis delays is crucial for limiting EoE-associated morbidity.
Despite efforts to bring attention to EoE, evidence suggests that delays between symptom onset and diagnosis are common, and result in treatment delays. One study found a median lag time of 6 years.
The longer the delay in treatment, the more likely patients are to develop esophageal rings, a long narrowing in the esophageal caliber, or focal strictures. For example, diagnostic delays of more than 20 years result in prevalence rates of 70.8% for esophageal strictures, compared with 17.2% with delays of 0-2 years.
Simply put, the sooner one can identify EoE and begin treatment, the more likely patients are to be spared its worst effects.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Postinfectious Cough: Are Treatments Ever Warranted?
Lingering postinfectious cough has been a concern across Canada this winter. , according to an overview published on February 12 in the Canadian Medical Association Journal
“It’s something a lot of patients are worried about: That lingering cough after a common cold or flu,” lead author Kevin Liang, MD, of the Department of Family Medicine at The University of British Columbia in Vancouver, British Columbia, Canada, told this news organization. He added that some studies show that as much as a quarter of adult patients have this complaint.
Dr. Liang and his colleagues emphasized that the diagnosis of postinfectious cough is one of exclusion. It relies on the absence of concerning physical examination findings and other “subacute cough mimics” such as asthma, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), gastroesophageal reflux disease, or use of angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors.
“Pertussis should be considered in patients with a paroxysmal cough, post-tussive vomiting, and inspiratory whoop,” they added. Coughs that persist beyond 8 weeks warrant further workup such as a pulmonary function test to rule out asthma or COPD. Coughs accompanied by hemoptysis, systemic symptoms, dysphagia, excessive dyspnea, or hoarseness also warrant further workup, they added. And patients with a history of smoking or recurrent pneumonia should be followed more closely.
In the absence of red flags, Dr. Liang and coauthors advised that there is no evidence supporting pharmacologic treatment, “which is associated with harms,” such as medication adverse effects, cost, strain on the medical supply chain, and the fact that pressurized metered-dose inhalers emit powerful greenhouse gases. “A lot of patients come in looking for solutions, but really, all the evidence says the over-the-counter cough syrup just doesn’t work. Or I see clinicians prescribing inhalers or different medication that can cost hundreds of dollars, and their efficacy, at least from the literature, shows that there’s really no improvement. Time and patience are the two keys to solving this,” Dr. Liang told this news organization.
Moreover, there is a distinct absence of guidelines on this topic. The College of Family Physicians of Canada’s recent literature review cited limited data supporting a trial of inhaled corticosteroids, a bronchodilator such as ipratropium-salbutamol, or an intranasal steroid if postnasal drip is suspected. However, “there’s a high risk of bias in the study they cite from using the short-acting bronchodilators, and what it ultimately says is that in most cases, this is self-resolving by around the 20-day mark,” said Dr. Liang. “Our advice is just to err on the side of caution and just provide that information piece to the patient.”
‘Significant Nuance’
Imran Satia, MD, assistant professor of respirology at McMaster University in Hamilton, Ontario, Canada, agreed that “most people who get a viral or bacterial upper or lower respiratory tract infection will get better with time, and there is very little evidence that giving steroids, antibiotics, or cough suppressants is better than waiting it out.” There is “significant nuance” in how to manage this situation, however.
“In some patients with underlying lung disease like asthma or COPD, increasing the frequency of regular inhaled steroids, bronchodilators, oral steroids, antibiotics, and chest imaging with breathing tests may be clinically warranted, and many physicians will do this,” he told this news organization. “In some patients with refractory chronic cough, there is no underlying identifiable disease, despite completing the necessary investigations. Or coughing persists despite trials of treatment for lung diseases, nasal diseases, and stomach reflux disease. This is commonly described as cough hypersensitivity syndrome, for which therapies targeting the neuronal pathways that control coughing are needed.”
Physicians should occasionally consider trying a temporary course of a short-acting bronchodilator inhaler, said Nicholas Vozoris, MD, assistant professor and clinician investigator in respirology at the University of Toronto, Toronto, Ontario, Canada. “I think that would be a reasonable first step in a case of really bad postinfectious cough,” he told this news organization. “But in general, drug treatments are not indicated.”
Environmental Concerns
Yet some things should raise clinicians’ suspicion of more complex issues.
“A pattern of recurrent colds or bronchitis with protracted coughing afterward raises strong suspicion for asthma, which can present as repeated, prolonged respiratory exacerbations,” he said. “Unless asthma is treated with appropriate inhaler therapy on a regular basis, it will unlikely come under control.”
Dr. Vozoris added that the environmental concerns over the use of metered dose inhalers (MDIs) are minimal compared with the other sources of pollution and the risks for undertreatment. “The authors are overplaying the environmental impact of MDI, in my opinion,” he said. “Physicians already have to deal with the challenging issue of suboptimal patient adherence to inhalers, and I fear that such comments may further drive that up. Furthermore, there is also an environmental footprint with not using inhalers, as patients can then experience suboptimally controlled lung disease as a result — and then present to the ER and get admitted to hospital for exacerbations of disease, where more resources and medications are used up.”
“In addition, in patients who are immunocompromised, protracted coughing after what was thought to be a cold may be associated with an “atypical” respiratory infection, such as tuberculosis, that will require special medical treatment,” Dr. Vozoris concluded.
No funding for the review of postinfectious cough was reported. Dr. Liang and Dr. Vozoris disclosed no competing interests. Dr. Satia reported receiving funding from the ERS Respire 3 Fellowship Award, BMA James Trust Award, North-West Lung Centre Charity (Manchester), NIHR CRF Manchester, Merck MSD, AstraZeneca, and GSK. Dr. Satia also has received consulting fees from Merck MSD, Genentech, and Respiplus; as well as speaker fees from AstraZeneca, GSK, Merck MSD, Sanofi-Regeneron. Satia has served on the following task force committees: Chronic Cough (ERS), Asthma Diagnosis and Management (ERS), NEUROCOUGH (ERS CRC), and the CTS Chronic Cough working group.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Lingering postinfectious cough has been a concern across Canada this winter. , according to an overview published on February 12 in the Canadian Medical Association Journal
“It’s something a lot of patients are worried about: That lingering cough after a common cold or flu,” lead author Kevin Liang, MD, of the Department of Family Medicine at The University of British Columbia in Vancouver, British Columbia, Canada, told this news organization. He added that some studies show that as much as a quarter of adult patients have this complaint.
Dr. Liang and his colleagues emphasized that the diagnosis of postinfectious cough is one of exclusion. It relies on the absence of concerning physical examination findings and other “subacute cough mimics” such as asthma, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), gastroesophageal reflux disease, or use of angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors.
“Pertussis should be considered in patients with a paroxysmal cough, post-tussive vomiting, and inspiratory whoop,” they added. Coughs that persist beyond 8 weeks warrant further workup such as a pulmonary function test to rule out asthma or COPD. Coughs accompanied by hemoptysis, systemic symptoms, dysphagia, excessive dyspnea, or hoarseness also warrant further workup, they added. And patients with a history of smoking or recurrent pneumonia should be followed more closely.
In the absence of red flags, Dr. Liang and coauthors advised that there is no evidence supporting pharmacologic treatment, “which is associated with harms,” such as medication adverse effects, cost, strain on the medical supply chain, and the fact that pressurized metered-dose inhalers emit powerful greenhouse gases. “A lot of patients come in looking for solutions, but really, all the evidence says the over-the-counter cough syrup just doesn’t work. Or I see clinicians prescribing inhalers or different medication that can cost hundreds of dollars, and their efficacy, at least from the literature, shows that there’s really no improvement. Time and patience are the two keys to solving this,” Dr. Liang told this news organization.
Moreover, there is a distinct absence of guidelines on this topic. The College of Family Physicians of Canada’s recent literature review cited limited data supporting a trial of inhaled corticosteroids, a bronchodilator such as ipratropium-salbutamol, or an intranasal steroid if postnasal drip is suspected. However, “there’s a high risk of bias in the study they cite from using the short-acting bronchodilators, and what it ultimately says is that in most cases, this is self-resolving by around the 20-day mark,” said Dr. Liang. “Our advice is just to err on the side of caution and just provide that information piece to the patient.”
‘Significant Nuance’
Imran Satia, MD, assistant professor of respirology at McMaster University in Hamilton, Ontario, Canada, agreed that “most people who get a viral or bacterial upper or lower respiratory tract infection will get better with time, and there is very little evidence that giving steroids, antibiotics, or cough suppressants is better than waiting it out.” There is “significant nuance” in how to manage this situation, however.
“In some patients with underlying lung disease like asthma or COPD, increasing the frequency of regular inhaled steroids, bronchodilators, oral steroids, antibiotics, and chest imaging with breathing tests may be clinically warranted, and many physicians will do this,” he told this news organization. “In some patients with refractory chronic cough, there is no underlying identifiable disease, despite completing the necessary investigations. Or coughing persists despite trials of treatment for lung diseases, nasal diseases, and stomach reflux disease. This is commonly described as cough hypersensitivity syndrome, for which therapies targeting the neuronal pathways that control coughing are needed.”
Physicians should occasionally consider trying a temporary course of a short-acting bronchodilator inhaler, said Nicholas Vozoris, MD, assistant professor and clinician investigator in respirology at the University of Toronto, Toronto, Ontario, Canada. “I think that would be a reasonable first step in a case of really bad postinfectious cough,” he told this news organization. “But in general, drug treatments are not indicated.”
Environmental Concerns
Yet some things should raise clinicians’ suspicion of more complex issues.
“A pattern of recurrent colds or bronchitis with protracted coughing afterward raises strong suspicion for asthma, which can present as repeated, prolonged respiratory exacerbations,” he said. “Unless asthma is treated with appropriate inhaler therapy on a regular basis, it will unlikely come under control.”
Dr. Vozoris added that the environmental concerns over the use of metered dose inhalers (MDIs) are minimal compared with the other sources of pollution and the risks for undertreatment. “The authors are overplaying the environmental impact of MDI, in my opinion,” he said. “Physicians already have to deal with the challenging issue of suboptimal patient adherence to inhalers, and I fear that such comments may further drive that up. Furthermore, there is also an environmental footprint with not using inhalers, as patients can then experience suboptimally controlled lung disease as a result — and then present to the ER and get admitted to hospital for exacerbations of disease, where more resources and medications are used up.”
“In addition, in patients who are immunocompromised, protracted coughing after what was thought to be a cold may be associated with an “atypical” respiratory infection, such as tuberculosis, that will require special medical treatment,” Dr. Vozoris concluded.
No funding for the review of postinfectious cough was reported. Dr. Liang and Dr. Vozoris disclosed no competing interests. Dr. Satia reported receiving funding from the ERS Respire 3 Fellowship Award, BMA James Trust Award, North-West Lung Centre Charity (Manchester), NIHR CRF Manchester, Merck MSD, AstraZeneca, and GSK. Dr. Satia also has received consulting fees from Merck MSD, Genentech, and Respiplus; as well as speaker fees from AstraZeneca, GSK, Merck MSD, Sanofi-Regeneron. Satia has served on the following task force committees: Chronic Cough (ERS), Asthma Diagnosis and Management (ERS), NEUROCOUGH (ERS CRC), and the CTS Chronic Cough working group.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Lingering postinfectious cough has been a concern across Canada this winter. , according to an overview published on February 12 in the Canadian Medical Association Journal
“It’s something a lot of patients are worried about: That lingering cough after a common cold or flu,” lead author Kevin Liang, MD, of the Department of Family Medicine at The University of British Columbia in Vancouver, British Columbia, Canada, told this news organization. He added that some studies show that as much as a quarter of adult patients have this complaint.
Dr. Liang and his colleagues emphasized that the diagnosis of postinfectious cough is one of exclusion. It relies on the absence of concerning physical examination findings and other “subacute cough mimics” such as asthma, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), gastroesophageal reflux disease, or use of angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors.
“Pertussis should be considered in patients with a paroxysmal cough, post-tussive vomiting, and inspiratory whoop,” they added. Coughs that persist beyond 8 weeks warrant further workup such as a pulmonary function test to rule out asthma or COPD. Coughs accompanied by hemoptysis, systemic symptoms, dysphagia, excessive dyspnea, or hoarseness also warrant further workup, they added. And patients with a history of smoking or recurrent pneumonia should be followed more closely.
In the absence of red flags, Dr. Liang and coauthors advised that there is no evidence supporting pharmacologic treatment, “which is associated with harms,” such as medication adverse effects, cost, strain on the medical supply chain, and the fact that pressurized metered-dose inhalers emit powerful greenhouse gases. “A lot of patients come in looking for solutions, but really, all the evidence says the over-the-counter cough syrup just doesn’t work. Or I see clinicians prescribing inhalers or different medication that can cost hundreds of dollars, and their efficacy, at least from the literature, shows that there’s really no improvement. Time and patience are the two keys to solving this,” Dr. Liang told this news organization.
Moreover, there is a distinct absence of guidelines on this topic. The College of Family Physicians of Canada’s recent literature review cited limited data supporting a trial of inhaled corticosteroids, a bronchodilator such as ipratropium-salbutamol, or an intranasal steroid if postnasal drip is suspected. However, “there’s a high risk of bias in the study they cite from using the short-acting bronchodilators, and what it ultimately says is that in most cases, this is self-resolving by around the 20-day mark,” said Dr. Liang. “Our advice is just to err on the side of caution and just provide that information piece to the patient.”
‘Significant Nuance’
Imran Satia, MD, assistant professor of respirology at McMaster University in Hamilton, Ontario, Canada, agreed that “most people who get a viral or bacterial upper or lower respiratory tract infection will get better with time, and there is very little evidence that giving steroids, antibiotics, or cough suppressants is better than waiting it out.” There is “significant nuance” in how to manage this situation, however.
“In some patients with underlying lung disease like asthma or COPD, increasing the frequency of regular inhaled steroids, bronchodilators, oral steroids, antibiotics, and chest imaging with breathing tests may be clinically warranted, and many physicians will do this,” he told this news organization. “In some patients with refractory chronic cough, there is no underlying identifiable disease, despite completing the necessary investigations. Or coughing persists despite trials of treatment for lung diseases, nasal diseases, and stomach reflux disease. This is commonly described as cough hypersensitivity syndrome, for which therapies targeting the neuronal pathways that control coughing are needed.”
Physicians should occasionally consider trying a temporary course of a short-acting bronchodilator inhaler, said Nicholas Vozoris, MD, assistant professor and clinician investigator in respirology at the University of Toronto, Toronto, Ontario, Canada. “I think that would be a reasonable first step in a case of really bad postinfectious cough,” he told this news organization. “But in general, drug treatments are not indicated.”
Environmental Concerns
Yet some things should raise clinicians’ suspicion of more complex issues.
“A pattern of recurrent colds or bronchitis with protracted coughing afterward raises strong suspicion for asthma, which can present as repeated, prolonged respiratory exacerbations,” he said. “Unless asthma is treated with appropriate inhaler therapy on a regular basis, it will unlikely come under control.”
Dr. Vozoris added that the environmental concerns over the use of metered dose inhalers (MDIs) are minimal compared with the other sources of pollution and the risks for undertreatment. “The authors are overplaying the environmental impact of MDI, in my opinion,” he said. “Physicians already have to deal with the challenging issue of suboptimal patient adherence to inhalers, and I fear that such comments may further drive that up. Furthermore, there is also an environmental footprint with not using inhalers, as patients can then experience suboptimally controlled lung disease as a result — and then present to the ER and get admitted to hospital for exacerbations of disease, where more resources and medications are used up.”
“In addition, in patients who are immunocompromised, protracted coughing after what was thought to be a cold may be associated with an “atypical” respiratory infection, such as tuberculosis, that will require special medical treatment,” Dr. Vozoris concluded.
No funding for the review of postinfectious cough was reported. Dr. Liang and Dr. Vozoris disclosed no competing interests. Dr. Satia reported receiving funding from the ERS Respire 3 Fellowship Award, BMA James Trust Award, North-West Lung Centre Charity (Manchester), NIHR CRF Manchester, Merck MSD, AstraZeneca, and GSK. Dr. Satia also has received consulting fees from Merck MSD, Genentech, and Respiplus; as well as speaker fees from AstraZeneca, GSK, Merck MSD, Sanofi-Regeneron. Satia has served on the following task force committees: Chronic Cough (ERS), Asthma Diagnosis and Management (ERS), NEUROCOUGH (ERS CRC), and the CTS Chronic Cough working group.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM THE CANADIAN MEDICAL ASSOCIATION JOURNAL
Tapinarof Cream Under FDA Review for Atopic Dermatitis Indication
On February 14, Dermavant Sciences announced that the company had submitted a supplemental New Drug Application (sNDA) to the Food and Drug Administration for tapinarof cream, 1%, for treating atopic dermatitis (AD) in adults and children 2 years of age and older.
Tapinarof cream, 1%, is an aryl hydrocarbon receptor agonist marketed under the brand name VTAMA that was approved in 2022 for treating plaque psoriasis in adults.
According to a Dermavant press release, the sNDA is based on positive data from the phase 3 ADORING 1 and ADORING 2 pivotal trials and interim results from the phase 3 ADORING 3 open-label, long-term extension 48-week trial. In ADORING 1 and ADORING 2, tapinarof cream demonstrated statistically significant improvements in the primary endpoint of Validated Investigator Global Assessment for Atopic Dermatitis (vIGA-AD) treatment success, defined as a vIGA-AD score of 0 (clear) or 1 (almost clear) with at least a 2-grade improvement from baseline; demonstrated treatment success over vehicle at week 8; and met all key secondary endpoints with statistical significance, according to the company.
The most common adverse reactions in patients treated with VTAMA cream include folliculitis, nasopharyngitis, contact dermatitis, headache, and pruritus.
On February 14, Dermavant Sciences announced that the company had submitted a supplemental New Drug Application (sNDA) to the Food and Drug Administration for tapinarof cream, 1%, for treating atopic dermatitis (AD) in adults and children 2 years of age and older.
Tapinarof cream, 1%, is an aryl hydrocarbon receptor agonist marketed under the brand name VTAMA that was approved in 2022 for treating plaque psoriasis in adults.
According to a Dermavant press release, the sNDA is based on positive data from the phase 3 ADORING 1 and ADORING 2 pivotal trials and interim results from the phase 3 ADORING 3 open-label, long-term extension 48-week trial. In ADORING 1 and ADORING 2, tapinarof cream demonstrated statistically significant improvements in the primary endpoint of Validated Investigator Global Assessment for Atopic Dermatitis (vIGA-AD) treatment success, defined as a vIGA-AD score of 0 (clear) or 1 (almost clear) with at least a 2-grade improvement from baseline; demonstrated treatment success over vehicle at week 8; and met all key secondary endpoints with statistical significance, according to the company.
The most common adverse reactions in patients treated with VTAMA cream include folliculitis, nasopharyngitis, contact dermatitis, headache, and pruritus.
On February 14, Dermavant Sciences announced that the company had submitted a supplemental New Drug Application (sNDA) to the Food and Drug Administration for tapinarof cream, 1%, for treating atopic dermatitis (AD) in adults and children 2 years of age and older.
Tapinarof cream, 1%, is an aryl hydrocarbon receptor agonist marketed under the brand name VTAMA that was approved in 2022 for treating plaque psoriasis in adults.
According to a Dermavant press release, the sNDA is based on positive data from the phase 3 ADORING 1 and ADORING 2 pivotal trials and interim results from the phase 3 ADORING 3 open-label, long-term extension 48-week trial. In ADORING 1 and ADORING 2, tapinarof cream demonstrated statistically significant improvements in the primary endpoint of Validated Investigator Global Assessment for Atopic Dermatitis (vIGA-AD) treatment success, defined as a vIGA-AD score of 0 (clear) or 1 (almost clear) with at least a 2-grade improvement from baseline; demonstrated treatment success over vehicle at week 8; and met all key secondary endpoints with statistical significance, according to the company.
The most common adverse reactions in patients treated with VTAMA cream include folliculitis, nasopharyngitis, contact dermatitis, headache, and pruritus.
Physicians as First Responders II
I recently wrote about a fledgling program here in Maine in which some emergency room physicians were being outfitted with equipment and communications gear that would allow them to respond on the fly to emergencies in the field when they weren’t working in the hospital. I questioned the rationale of using in-house personnel, already in short supply, for the few situations in which trained EMT personnel would usually be called. At the same time, I promised to return to the broader subject of the role of physicians as first responders in a future letter. And, here it is.
Have you ever been on a plane or at a large public gathering and the public addressed system crackled, “Is there a doctor on board” or in the audience? Or have you been on the highway and come upon a fresh accident in which it appears that there may have been injuries? Or at a youth soccer game in which a player has been injured and is still on the ground?
How do you usually respond in situations like this? Do you immediately identify yourself as a physician? Or, do you routinely shy away from involvement? What thoughts run through your head?
Do you feel your training and experience with emergencies is so outdated that you doubt you could be of any assistance? Has your practice become so specialized that you aren’t comfortable with anything outside of your specialty? Maybe getting involved is likely to throw your already tight travel schedule into disarray? Or are you afraid that should something go wrong while you were helping out you could be sued?
Keeping in mind that I am a retired septuagenarian pediatrician more than a decade removed from active practice, I would describe my usual response to these situations as “attentive hovering.” I position myself to have a good view of the victim and watch to see if there are any other responders. Either because of their personality or their experience, often there is someone who steps forward to help. Trained EMTs seem to have no hesitancy going into action. If I sense things aren’t going well, or the victim is a child, I will identify myself as a retired pediatrician and offer my assistance. Even if the response given by others seems appropriate, I may still eventually identify myself, maybe to lend an air of legitimacy to the process.
What are the roots of my hesitancy? I have found that I generally have little to add when there is a trained first responder on hand. They have been-there-and-done-that far more recently than I have. They know how to stabilize potential or obvious fractures. They know how to position the victim for transport. Even when I am in an environment where my medical background is already known, I yield to the more recently experienced first responders.
I don’t particularly worry about being sued. Every state has Good Samaritan laws. Although the laws vary from state to state, here in Maine I feel comfortable with the good sense of my fellow citizens. I understand if you live or practice in a more litigious environment you may be more concerned. On an airplane there is the Aviation Medical Assistant Act, which became law in 1998, and provides us with some extra protection.
What if there is a situation in which even with my outdated skills I seem to be the only show in town? Fortunately, that situation hasn’t occurred for me in quite a few years, but the odds are that one might occur. In almost 1 out of 600 airline flights, there is an inflight emergency. I tend to hang out with other septuagenarians and octogenarians doing active things. And I frequent youth athletic events where there is unlikely to be a first responder assigned to the event.
Should I be doing more to update my skills? It’s been a while since I refreshed by CPR techniques. I can’t recall the last time I handled a defibrillator. Should I be learning more about exsanguination prevention techniques?
Every so often there are some rumblings to mandate that all physicians should be required to update these first responder skills to maintain their license or certification. That wouldn’t cover those of us who are retired or who no longer practice medicine. And, I’m not sure we need to add another layer to the system. I think there are enough of us out there who would like to add ourselves to the first responder population, maybe not as fully trained experts but as folks who would like to be more ready to help by updating old or seldom-used skills.
Dr. Wilkoff practiced primary care pediatrics in Brunswick, Maine, for nearly 40 years. He has authored several books on behavioral pediatrics, including “How to Say No to Your Toddler.” Other than a Littman stethoscope he accepted as a first-year medical student in 1966, Dr. Wilkoff reports having nothing to disclose. Email him at [email protected].
I recently wrote about a fledgling program here in Maine in which some emergency room physicians were being outfitted with equipment and communications gear that would allow them to respond on the fly to emergencies in the field when they weren’t working in the hospital. I questioned the rationale of using in-house personnel, already in short supply, for the few situations in which trained EMT personnel would usually be called. At the same time, I promised to return to the broader subject of the role of physicians as first responders in a future letter. And, here it is.
Have you ever been on a plane or at a large public gathering and the public addressed system crackled, “Is there a doctor on board” or in the audience? Or have you been on the highway and come upon a fresh accident in which it appears that there may have been injuries? Or at a youth soccer game in which a player has been injured and is still on the ground?
How do you usually respond in situations like this? Do you immediately identify yourself as a physician? Or, do you routinely shy away from involvement? What thoughts run through your head?
Do you feel your training and experience with emergencies is so outdated that you doubt you could be of any assistance? Has your practice become so specialized that you aren’t comfortable with anything outside of your specialty? Maybe getting involved is likely to throw your already tight travel schedule into disarray? Or are you afraid that should something go wrong while you were helping out you could be sued?
Keeping in mind that I am a retired septuagenarian pediatrician more than a decade removed from active practice, I would describe my usual response to these situations as “attentive hovering.” I position myself to have a good view of the victim and watch to see if there are any other responders. Either because of their personality or their experience, often there is someone who steps forward to help. Trained EMTs seem to have no hesitancy going into action. If I sense things aren’t going well, or the victim is a child, I will identify myself as a retired pediatrician and offer my assistance. Even if the response given by others seems appropriate, I may still eventually identify myself, maybe to lend an air of legitimacy to the process.
What are the roots of my hesitancy? I have found that I generally have little to add when there is a trained first responder on hand. They have been-there-and-done-that far more recently than I have. They know how to stabilize potential or obvious fractures. They know how to position the victim for transport. Even when I am in an environment where my medical background is already known, I yield to the more recently experienced first responders.
I don’t particularly worry about being sued. Every state has Good Samaritan laws. Although the laws vary from state to state, here in Maine I feel comfortable with the good sense of my fellow citizens. I understand if you live or practice in a more litigious environment you may be more concerned. On an airplane there is the Aviation Medical Assistant Act, which became law in 1998, and provides us with some extra protection.
What if there is a situation in which even with my outdated skills I seem to be the only show in town? Fortunately, that situation hasn’t occurred for me in quite a few years, but the odds are that one might occur. In almost 1 out of 600 airline flights, there is an inflight emergency. I tend to hang out with other septuagenarians and octogenarians doing active things. And I frequent youth athletic events where there is unlikely to be a first responder assigned to the event.
Should I be doing more to update my skills? It’s been a while since I refreshed by CPR techniques. I can’t recall the last time I handled a defibrillator. Should I be learning more about exsanguination prevention techniques?
Every so often there are some rumblings to mandate that all physicians should be required to update these first responder skills to maintain their license or certification. That wouldn’t cover those of us who are retired or who no longer practice medicine. And, I’m not sure we need to add another layer to the system. I think there are enough of us out there who would like to add ourselves to the first responder population, maybe not as fully trained experts but as folks who would like to be more ready to help by updating old or seldom-used skills.
Dr. Wilkoff practiced primary care pediatrics in Brunswick, Maine, for nearly 40 years. He has authored several books on behavioral pediatrics, including “How to Say No to Your Toddler.” Other than a Littman stethoscope he accepted as a first-year medical student in 1966, Dr. Wilkoff reports having nothing to disclose. Email him at [email protected].
I recently wrote about a fledgling program here in Maine in which some emergency room physicians were being outfitted with equipment and communications gear that would allow them to respond on the fly to emergencies in the field when they weren’t working in the hospital. I questioned the rationale of using in-house personnel, already in short supply, for the few situations in which trained EMT personnel would usually be called. At the same time, I promised to return to the broader subject of the role of physicians as first responders in a future letter. And, here it is.
Have you ever been on a plane or at a large public gathering and the public addressed system crackled, “Is there a doctor on board” or in the audience? Or have you been on the highway and come upon a fresh accident in which it appears that there may have been injuries? Or at a youth soccer game in which a player has been injured and is still on the ground?
How do you usually respond in situations like this? Do you immediately identify yourself as a physician? Or, do you routinely shy away from involvement? What thoughts run through your head?
Do you feel your training and experience with emergencies is so outdated that you doubt you could be of any assistance? Has your practice become so specialized that you aren’t comfortable with anything outside of your specialty? Maybe getting involved is likely to throw your already tight travel schedule into disarray? Or are you afraid that should something go wrong while you were helping out you could be sued?
Keeping in mind that I am a retired septuagenarian pediatrician more than a decade removed from active practice, I would describe my usual response to these situations as “attentive hovering.” I position myself to have a good view of the victim and watch to see if there are any other responders. Either because of their personality or their experience, often there is someone who steps forward to help. Trained EMTs seem to have no hesitancy going into action. If I sense things aren’t going well, or the victim is a child, I will identify myself as a retired pediatrician and offer my assistance. Even if the response given by others seems appropriate, I may still eventually identify myself, maybe to lend an air of legitimacy to the process.
What are the roots of my hesitancy? I have found that I generally have little to add when there is a trained first responder on hand. They have been-there-and-done-that far more recently than I have. They know how to stabilize potential or obvious fractures. They know how to position the victim for transport. Even when I am in an environment where my medical background is already known, I yield to the more recently experienced first responders.
I don’t particularly worry about being sued. Every state has Good Samaritan laws. Although the laws vary from state to state, here in Maine I feel comfortable with the good sense of my fellow citizens. I understand if you live or practice in a more litigious environment you may be more concerned. On an airplane there is the Aviation Medical Assistant Act, which became law in 1998, and provides us with some extra protection.
What if there is a situation in which even with my outdated skills I seem to be the only show in town? Fortunately, that situation hasn’t occurred for me in quite a few years, but the odds are that one might occur. In almost 1 out of 600 airline flights, there is an inflight emergency. I tend to hang out with other septuagenarians and octogenarians doing active things. And I frequent youth athletic events where there is unlikely to be a first responder assigned to the event.
Should I be doing more to update my skills? It’s been a while since I refreshed by CPR techniques. I can’t recall the last time I handled a defibrillator. Should I be learning more about exsanguination prevention techniques?
Every so often there are some rumblings to mandate that all physicians should be required to update these first responder skills to maintain their license or certification. That wouldn’t cover those of us who are retired or who no longer practice medicine. And, I’m not sure we need to add another layer to the system. I think there are enough of us out there who would like to add ourselves to the first responder population, maybe not as fully trained experts but as folks who would like to be more ready to help by updating old or seldom-used skills.
Dr. Wilkoff practiced primary care pediatrics in Brunswick, Maine, for nearly 40 years. He has authored several books on behavioral pediatrics, including “How to Say No to Your Toddler.” Other than a Littman stethoscope he accepted as a first-year medical student in 1966, Dr. Wilkoff reports having nothing to disclose. Email him at [email protected].
Management of Tinea Capitis in Children Varies, Survey Finds
TOPLINE:
METHODOLOGY:
- The fungal scalp infection tinea capitis affects an estimated 3%-13% of children.
- While international guidelines exist for the treatment of tinea capitis in infants and children, no such document has been developed in the United States.
- Researchers distributed a survey by email to dermatologists through the and the Society for Pediatric Dermatology in the United States, asking about how they treated and managed pediatric patients with tinea capitis; 56 dermatologists participated.
TAKEAWAY:
- Most respondents (88.2%) said they felt comfortable prescribing oral medications prior to confirmation for those aged 2-18 years ( was the most common choice in 60.4% of cases), compared with 81.6% for those aged 2 months to 2 years ( was the most common treatment choice in 41.5% of cases), and 48.7% for those aged 0-2 months ( was the most common choice in 28.6% of cases).
- When asked what topical medication they would start prior to confirmation, most respondents said shampoo (62.3% for those aged 0-2 months and 75.5% each for those aged 2 months to 2 years and those aged 2-18 years), yet between 11.3% and 13% said they would use none.
- The most common form of confirmatory testing was , followed by potassium hydroxide preparation, trichoscopy, and Wood’s lamp.
- More than half of survey respondents would alter their choice of oral medication based on culture results, but most would not change their topical medication preference.
IN PRACTICE:
“The management of tinea capitis in the United States is currently variable, particularly with the introduction of newer antifungals,” the authors wrote. “Future steps involve establishing evidence-based clinical practice guidelines that consider drug efficacy, safety profiles, and costs.”
SOURCE:
Bernard Cohen, MD, of the Departments of Pediatrics and Dermatology at Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore, Maryland, led the research, which was published in Pediatric Dermatology.
LIMITATIONS:
Lower response rates associated with online surveys and predefined age groups restrict the granularity of responses.
DISCLOSURES:
The authors reported having no financial disclosures.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
METHODOLOGY:
- The fungal scalp infection tinea capitis affects an estimated 3%-13% of children.
- While international guidelines exist for the treatment of tinea capitis in infants and children, no such document has been developed in the United States.
- Researchers distributed a survey by email to dermatologists through the and the Society for Pediatric Dermatology in the United States, asking about how they treated and managed pediatric patients with tinea capitis; 56 dermatologists participated.
TAKEAWAY:
- Most respondents (88.2%) said they felt comfortable prescribing oral medications prior to confirmation for those aged 2-18 years ( was the most common choice in 60.4% of cases), compared with 81.6% for those aged 2 months to 2 years ( was the most common treatment choice in 41.5% of cases), and 48.7% for those aged 0-2 months ( was the most common choice in 28.6% of cases).
- When asked what topical medication they would start prior to confirmation, most respondents said shampoo (62.3% for those aged 0-2 months and 75.5% each for those aged 2 months to 2 years and those aged 2-18 years), yet between 11.3% and 13% said they would use none.
- The most common form of confirmatory testing was , followed by potassium hydroxide preparation, trichoscopy, and Wood’s lamp.
- More than half of survey respondents would alter their choice of oral medication based on culture results, but most would not change their topical medication preference.
IN PRACTICE:
“The management of tinea capitis in the United States is currently variable, particularly with the introduction of newer antifungals,” the authors wrote. “Future steps involve establishing evidence-based clinical practice guidelines that consider drug efficacy, safety profiles, and costs.”
SOURCE:
Bernard Cohen, MD, of the Departments of Pediatrics and Dermatology at Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore, Maryland, led the research, which was published in Pediatric Dermatology.
LIMITATIONS:
Lower response rates associated with online surveys and predefined age groups restrict the granularity of responses.
DISCLOSURES:
The authors reported having no financial disclosures.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
METHODOLOGY:
- The fungal scalp infection tinea capitis affects an estimated 3%-13% of children.
- While international guidelines exist for the treatment of tinea capitis in infants and children, no such document has been developed in the United States.
- Researchers distributed a survey by email to dermatologists through the and the Society for Pediatric Dermatology in the United States, asking about how they treated and managed pediatric patients with tinea capitis; 56 dermatologists participated.
TAKEAWAY:
- Most respondents (88.2%) said they felt comfortable prescribing oral medications prior to confirmation for those aged 2-18 years ( was the most common choice in 60.4% of cases), compared with 81.6% for those aged 2 months to 2 years ( was the most common treatment choice in 41.5% of cases), and 48.7% for those aged 0-2 months ( was the most common choice in 28.6% of cases).
- When asked what topical medication they would start prior to confirmation, most respondents said shampoo (62.3% for those aged 0-2 months and 75.5% each for those aged 2 months to 2 years and those aged 2-18 years), yet between 11.3% and 13% said they would use none.
- The most common form of confirmatory testing was , followed by potassium hydroxide preparation, trichoscopy, and Wood’s lamp.
- More than half of survey respondents would alter their choice of oral medication based on culture results, but most would not change their topical medication preference.
IN PRACTICE:
“The management of tinea capitis in the United States is currently variable, particularly with the introduction of newer antifungals,” the authors wrote. “Future steps involve establishing evidence-based clinical practice guidelines that consider drug efficacy, safety profiles, and costs.”
SOURCE:
Bernard Cohen, MD, of the Departments of Pediatrics and Dermatology at Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore, Maryland, led the research, which was published in Pediatric Dermatology.
LIMITATIONS:
Lower response rates associated with online surveys and predefined age groups restrict the granularity of responses.
DISCLOSURES:
The authors reported having no financial disclosures.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Bivalent Vaccines Protect Even Children Who’ve Had COVID
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
It was only 3 years ago when we called the pathogen we now refer to as the coronavirus “nCOV-19.” It was, in many ways, more descriptive than what we have today. The little “n” there stood for “novel” — and it was really that little “n” that caused us all the trouble.
You see, coronaviruses themselves were not really new to us. Understudied, perhaps, but with four strains running around the globe at any time giving rise to the common cold, these were viruses our bodies understood.
But Instead of acting like a cold, it acted like nothing we had seen before, at least in our lifetime. The story of the pandemic is very much a bildungsroman of our immune systems — a story of how our immunity grew up.
The difference between the start of 2020 and now, when infections with the coronavirus remain common but not as deadly, can be measured in terms of immune education. Some of our immune systems were educated by infection, some by vaccination, and many by both.
When the first vaccines emerged in December 2020, the opportunity to educate our immune systems was still huge. Though, at the time, an estimated 20 million had been infected in the US and 350,000 had died, there was a large population that remained immunologically naive. I was one of them.
If 2020 into early 2021 was the era of immune education, the postvaccine period was the era of the variant. From one COVID strain to two, to five, to innumerable, our immune memory — trained on a specific version of the virus or its spike protein — became imperfect again. Not naive; these variants were not “novel” in the way COVID-19 was novel, but they were different. And different enough to cause infection.
Following the playbook of another virus that loves to come dressed up in different outfits, the flu virus, we find ourselves in the booster era — a world where yearly doses of a vaccine, ideally matched to the variants circulating when the vaccine is given, are the recommendation if not the norm.
But questions remain about the vaccination program, particularly around who should get it. And two populations with big question marks over their heads are (1) people who have already been infected and (2) kids, because their risk for bad outcomes is so much lower.
This week, we finally have some evidence that can shed light on these questions. The study under the spotlight is this one, appearing in JAMA, which tries to analyze the ability of the bivalent vaccine — that’s the second one to come out, around September 2022 — to protect kids from COVID-19.
Now, right off the bat, this was not a randomized trial. The studies that established the viability of the mRNA vaccine platform were; they happened before the vaccine was authorized. But trials of the bivalent vaccine were mostly limited to proving immune response, not protection from disease.
Nevertheless, with some good observational methods and some statistics, we can try to tease out whether bivalent vaccines in kids worked.
The study combines three prospective cohort studies. The details are in the paper, but what you need to know is that the special sauce of these studies was that the kids were tested for COVID-19 on a weekly basis, whether they had symptoms or not. This is critical because asymptomatic infections can transmit COVID-19.
Let’s do the variables of interest. First and foremost, the bivalent vaccine. Some of these kids got the bivalent vaccine, some didn’t. Other key variables include prior vaccination with the monovalent vaccine. Some had been vaccinated with the monovalent vaccine before, some hadn’t. And, of course, prior infection. Some had been infected before (based on either nasal swabs or blood tests).
Let’s focus first on the primary exposure of interest: getting that bivalent vaccine. Again, this was not randomly assigned; kids who got the bivalent vaccine were different from those who did not. In general, they lived in smaller households, they were more likely to be White, less likely to have had a prior COVID infection, and quite a bit more likely to have at least one chronic condition.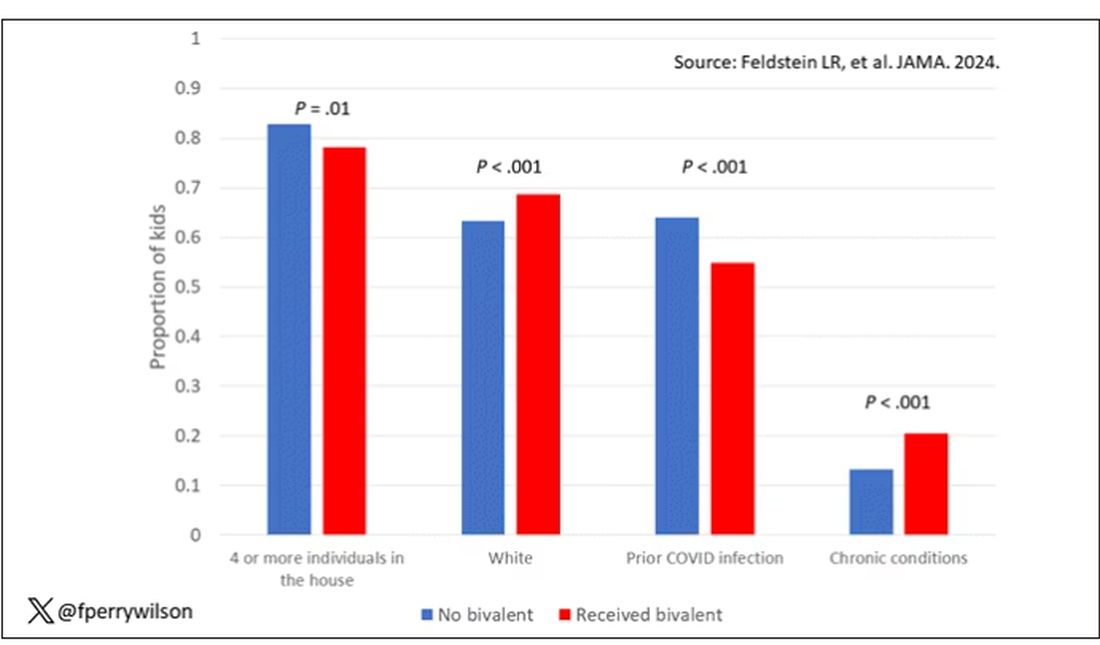
To me, this constellation of factors describes a slightly higher-risk group; it makes sense that they were more likely to get the second vaccine.
Given those factors, what were the rates of COVID infection? After nearly a year of follow-up, around 15% of the kids who hadn’t received the bivalent vaccine got infected compared with 5% of the vaccinated kids. Symptomatic infections represented roughly half of all infections in both groups.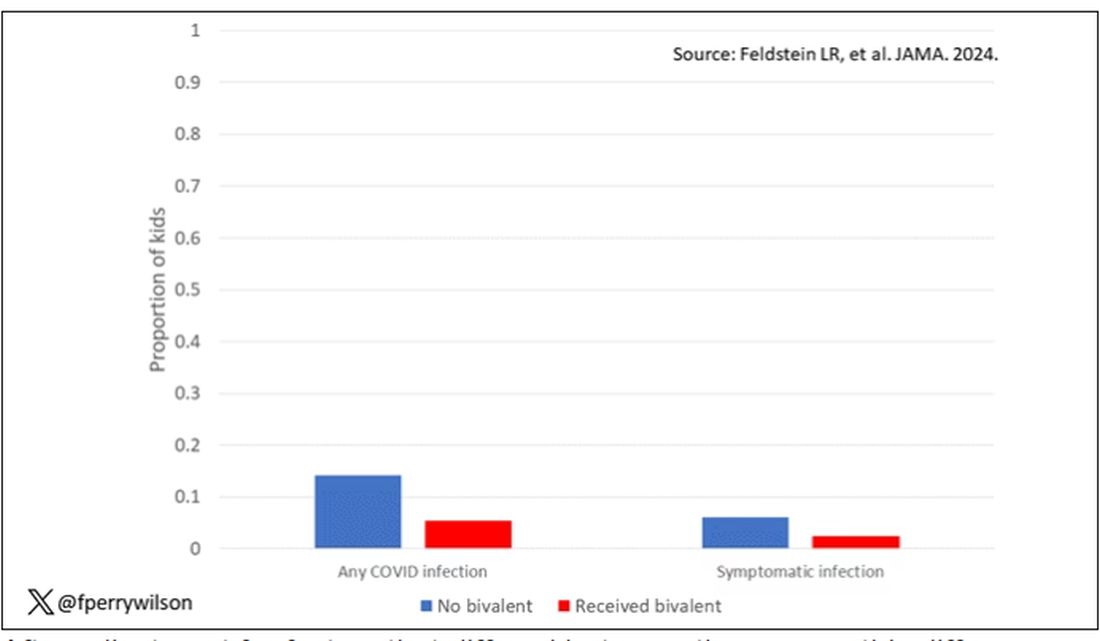
After adjustment for factors that differed between the groups, this difference translated into a vaccine efficacy of about 50% in this population. That’s our first data point. Yes, the bivalent vaccine worked. Not amazingly, of course. But it worked.
What about the kids who had had a prior COVID infection? Somewhat surprisingly, the vaccine was just as effective in this population, despite the fact that their immune systems already had some knowledge of COVID. Ten percent of unvaccinated kids got infected, even though they had been infected before. Just 2.5% of kids who received the bivalent vaccine got infected, suggesting some synergy between prior infection and vaccination.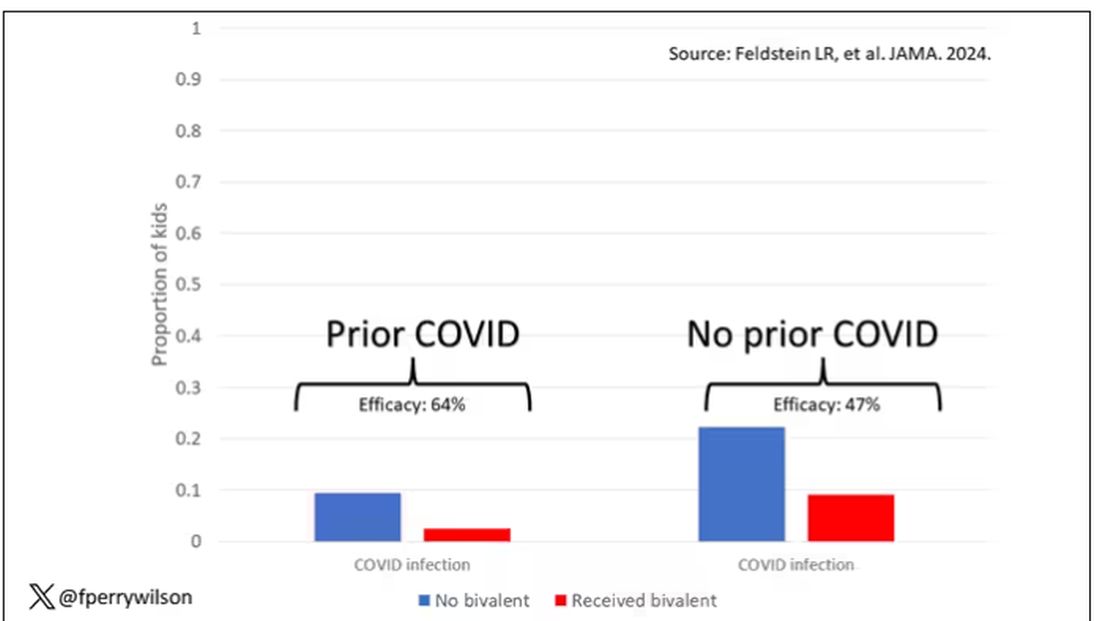
These data suggest that the bivalent vaccine did reduce the risk for COVID infection in kids. All good. But the piece still missing is how severe these infections were. It doesn’t appear that any of the 426 infections documented in this study resulted in hospitalization or death, fortunately. And no data are presented on the incidence of multisystem inflammatory syndrome of children, though given the rarity, I’d be surprised if any of these kids have this either.
So where are we? Well, it seems that the narrative out there that says “the vaccines don’t work” or “the vaccines don’t work if you’ve already been infected” is probably not true. They do work. This study and others in adults show that. If they work to reduce infections, as this study shows, they will also work to reduce deaths. It’s just that death is fortunately so rare in children that the number needed to vaccinate to prevent one death is very large. In that situation, the decision to vaccinate comes down to the risks associated with vaccination. So far, those risk seem very minimal.
Perhaps falling into a flu-like yearly vaccination schedule is not simply the result of old habits dying hard. Maybe it’s actually not a bad idea.
Dr. F. Perry Wilson is associate professor of medicine and public health and director of the Clinical and Translational Research Accelerator at Yale University, New Haven, Conn. He has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
It was only 3 years ago when we called the pathogen we now refer to as the coronavirus “nCOV-19.” It was, in many ways, more descriptive than what we have today. The little “n” there stood for “novel” — and it was really that little “n” that caused us all the trouble.
You see, coronaviruses themselves were not really new to us. Understudied, perhaps, but with four strains running around the globe at any time giving rise to the common cold, these were viruses our bodies understood.
But Instead of acting like a cold, it acted like nothing we had seen before, at least in our lifetime. The story of the pandemic is very much a bildungsroman of our immune systems — a story of how our immunity grew up.
The difference between the start of 2020 and now, when infections with the coronavirus remain common but not as deadly, can be measured in terms of immune education. Some of our immune systems were educated by infection, some by vaccination, and many by both.
When the first vaccines emerged in December 2020, the opportunity to educate our immune systems was still huge. Though, at the time, an estimated 20 million had been infected in the US and 350,000 had died, there was a large population that remained immunologically naive. I was one of them.
If 2020 into early 2021 was the era of immune education, the postvaccine period was the era of the variant. From one COVID strain to two, to five, to innumerable, our immune memory — trained on a specific version of the virus or its spike protein — became imperfect again. Not naive; these variants were not “novel” in the way COVID-19 was novel, but they were different. And different enough to cause infection.
Following the playbook of another virus that loves to come dressed up in different outfits, the flu virus, we find ourselves in the booster era — a world where yearly doses of a vaccine, ideally matched to the variants circulating when the vaccine is given, are the recommendation if not the norm.
But questions remain about the vaccination program, particularly around who should get it. And two populations with big question marks over their heads are (1) people who have already been infected and (2) kids, because their risk for bad outcomes is so much lower.
This week, we finally have some evidence that can shed light on these questions. The study under the spotlight is this one, appearing in JAMA, which tries to analyze the ability of the bivalent vaccine — that’s the second one to come out, around September 2022 — to protect kids from COVID-19.
Now, right off the bat, this was not a randomized trial. The studies that established the viability of the mRNA vaccine platform were; they happened before the vaccine was authorized. But trials of the bivalent vaccine were mostly limited to proving immune response, not protection from disease.
Nevertheless, with some good observational methods and some statistics, we can try to tease out whether bivalent vaccines in kids worked.
The study combines three prospective cohort studies. The details are in the paper, but what you need to know is that the special sauce of these studies was that the kids were tested for COVID-19 on a weekly basis, whether they had symptoms or not. This is critical because asymptomatic infections can transmit COVID-19.
Let’s do the variables of interest. First and foremost, the bivalent vaccine. Some of these kids got the bivalent vaccine, some didn’t. Other key variables include prior vaccination with the monovalent vaccine. Some had been vaccinated with the monovalent vaccine before, some hadn’t. And, of course, prior infection. Some had been infected before (based on either nasal swabs or blood tests).
Let’s focus first on the primary exposure of interest: getting that bivalent vaccine. Again, this was not randomly assigned; kids who got the bivalent vaccine were different from those who did not. In general, they lived in smaller households, they were more likely to be White, less likely to have had a prior COVID infection, and quite a bit more likely to have at least one chronic condition.
To me, this constellation of factors describes a slightly higher-risk group; it makes sense that they were more likely to get the second vaccine.
Given those factors, what were the rates of COVID infection? After nearly a year of follow-up, around 15% of the kids who hadn’t received the bivalent vaccine got infected compared with 5% of the vaccinated kids. Symptomatic infections represented roughly half of all infections in both groups.
After adjustment for factors that differed between the groups, this difference translated into a vaccine efficacy of about 50% in this population. That’s our first data point. Yes, the bivalent vaccine worked. Not amazingly, of course. But it worked.
What about the kids who had had a prior COVID infection? Somewhat surprisingly, the vaccine was just as effective in this population, despite the fact that their immune systems already had some knowledge of COVID. Ten percent of unvaccinated kids got infected, even though they had been infected before. Just 2.5% of kids who received the bivalent vaccine got infected, suggesting some synergy between prior infection and vaccination.
These data suggest that the bivalent vaccine did reduce the risk for COVID infection in kids. All good. But the piece still missing is how severe these infections were. It doesn’t appear that any of the 426 infections documented in this study resulted in hospitalization or death, fortunately. And no data are presented on the incidence of multisystem inflammatory syndrome of children, though given the rarity, I’d be surprised if any of these kids have this either.
So where are we? Well, it seems that the narrative out there that says “the vaccines don’t work” or “the vaccines don’t work if you’ve already been infected” is probably not true. They do work. This study and others in adults show that. If they work to reduce infections, as this study shows, they will also work to reduce deaths. It’s just that death is fortunately so rare in children that the number needed to vaccinate to prevent one death is very large. In that situation, the decision to vaccinate comes down to the risks associated with vaccination. So far, those risk seem very minimal.
Perhaps falling into a flu-like yearly vaccination schedule is not simply the result of old habits dying hard. Maybe it’s actually not a bad idea.
Dr. F. Perry Wilson is associate professor of medicine and public health and director of the Clinical and Translational Research Accelerator at Yale University, New Haven, Conn. He has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
It was only 3 years ago when we called the pathogen we now refer to as the coronavirus “nCOV-19.” It was, in many ways, more descriptive than what we have today. The little “n” there stood for “novel” — and it was really that little “n” that caused us all the trouble.
You see, coronaviruses themselves were not really new to us. Understudied, perhaps, but with four strains running around the globe at any time giving rise to the common cold, these were viruses our bodies understood.
But Instead of acting like a cold, it acted like nothing we had seen before, at least in our lifetime. The story of the pandemic is very much a bildungsroman of our immune systems — a story of how our immunity grew up.
The difference between the start of 2020 and now, when infections with the coronavirus remain common but not as deadly, can be measured in terms of immune education. Some of our immune systems were educated by infection, some by vaccination, and many by both.
When the first vaccines emerged in December 2020, the opportunity to educate our immune systems was still huge. Though, at the time, an estimated 20 million had been infected in the US and 350,000 had died, there was a large population that remained immunologically naive. I was one of them.
If 2020 into early 2021 was the era of immune education, the postvaccine period was the era of the variant. From one COVID strain to two, to five, to innumerable, our immune memory — trained on a specific version of the virus or its spike protein — became imperfect again. Not naive; these variants were not “novel” in the way COVID-19 was novel, but they were different. And different enough to cause infection.
Following the playbook of another virus that loves to come dressed up in different outfits, the flu virus, we find ourselves in the booster era — a world where yearly doses of a vaccine, ideally matched to the variants circulating when the vaccine is given, are the recommendation if not the norm.
But questions remain about the vaccination program, particularly around who should get it. And two populations with big question marks over their heads are (1) people who have already been infected and (2) kids, because their risk for bad outcomes is so much lower.
This week, we finally have some evidence that can shed light on these questions. The study under the spotlight is this one, appearing in JAMA, which tries to analyze the ability of the bivalent vaccine — that’s the second one to come out, around September 2022 — to protect kids from COVID-19.
Now, right off the bat, this was not a randomized trial. The studies that established the viability of the mRNA vaccine platform were; they happened before the vaccine was authorized. But trials of the bivalent vaccine were mostly limited to proving immune response, not protection from disease.
Nevertheless, with some good observational methods and some statistics, we can try to tease out whether bivalent vaccines in kids worked.
The study combines three prospective cohort studies. The details are in the paper, but what you need to know is that the special sauce of these studies was that the kids were tested for COVID-19 on a weekly basis, whether they had symptoms or not. This is critical because asymptomatic infections can transmit COVID-19.
Let’s do the variables of interest. First and foremost, the bivalent vaccine. Some of these kids got the bivalent vaccine, some didn’t. Other key variables include prior vaccination with the monovalent vaccine. Some had been vaccinated with the monovalent vaccine before, some hadn’t. And, of course, prior infection. Some had been infected before (based on either nasal swabs or blood tests).
Let’s focus first on the primary exposure of interest: getting that bivalent vaccine. Again, this was not randomly assigned; kids who got the bivalent vaccine were different from those who did not. In general, they lived in smaller households, they were more likely to be White, less likely to have had a prior COVID infection, and quite a bit more likely to have at least one chronic condition.
To me, this constellation of factors describes a slightly higher-risk group; it makes sense that they were more likely to get the second vaccine.
Given those factors, what were the rates of COVID infection? After nearly a year of follow-up, around 15% of the kids who hadn’t received the bivalent vaccine got infected compared with 5% of the vaccinated kids. Symptomatic infections represented roughly half of all infections in both groups.
After adjustment for factors that differed between the groups, this difference translated into a vaccine efficacy of about 50% in this population. That’s our first data point. Yes, the bivalent vaccine worked. Not amazingly, of course. But it worked.
What about the kids who had had a prior COVID infection? Somewhat surprisingly, the vaccine was just as effective in this population, despite the fact that their immune systems already had some knowledge of COVID. Ten percent of unvaccinated kids got infected, even though they had been infected before. Just 2.5% of kids who received the bivalent vaccine got infected, suggesting some synergy between prior infection and vaccination.
These data suggest that the bivalent vaccine did reduce the risk for COVID infection in kids. All good. But the piece still missing is how severe these infections were. It doesn’t appear that any of the 426 infections documented in this study resulted in hospitalization or death, fortunately. And no data are presented on the incidence of multisystem inflammatory syndrome of children, though given the rarity, I’d be surprised if any of these kids have this either.
So where are we? Well, it seems that the narrative out there that says “the vaccines don’t work” or “the vaccines don’t work if you’ve already been infected” is probably not true. They do work. This study and others in adults show that. If they work to reduce infections, as this study shows, they will also work to reduce deaths. It’s just that death is fortunately so rare in children that the number needed to vaccinate to prevent one death is very large. In that situation, the decision to vaccinate comes down to the risks associated with vaccination. So far, those risk seem very minimal.
Perhaps falling into a flu-like yearly vaccination schedule is not simply the result of old habits dying hard. Maybe it’s actually not a bad idea.
Dr. F. Perry Wilson is associate professor of medicine and public health and director of the Clinical and Translational Research Accelerator at Yale University, New Haven, Conn. He has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
OTC Topical Scar Products May Contain Allergens, Study Finds
TOPLINE:
METHODOLOGY:
- OTC topical scar treatments have the potential to cause an allergic reaction, but the prevalence of North American Contact Dermatitis Group (NACDG) core allergens in these products is unclear.
- Researchers used the word scar in a query of Amazon.com and four other retail websites to identify topical scar products for consumers and noted the list of ingredients.
- The investigators also surveyed the American Contact Dermatitis Society’s Contact Allergen Management Program (CAMP), a resource that helps patients with allergies find personal care products that are safe to use, for pertinent products.
TAKEAWAY:
- The search query identified 156 products. Of these, 119 (76.2%) were gels, creams, or oils and 37 (23.7%) were sheets, strips, or tape.
- Of the 125 products that had a list of ingredients, 69 (55.2%) contained at least one NACDG allergen and 45 (36%) contained more than one.
- The top six most common allergens listed in the ingredients were fragrance (16.8%), phenoxyethanol (16.8%), parabens (14.4%), panthenol (12.8%), sodium benzoate (9.60%), and ethylhexylglycerin (8%).
- Analysis of CAMP revealed that the program only had five unique scar products in its list, suggesting that CAMP might not be a reliable source of scar product information for patients with known allergies to pertinent NACDG allergens.
IN PRACTICE:
“Patients can consider trying a ‘use test’ on the inner forearm before applying to the surgical site,” the authors wrote. “It may reveal they are sensitive or sensitized by a product.
SOURCE:
First author Meera Kattapuram, MD, of the Department of Internal Medicine at Mount Sinai Hospital, New York, led the study, published in the February issue of Dermatologic Surgery.
LIMITATIONS:
Limitations include the selection of five retailers and the top 100 products from each website and the potential for ingredient list inaccuracies.
DISCLOSURES:
The authors reported having no financial conflicts of interest. The research was supported by a grant from the National Institutes of Health/National Cancer Institute.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
METHODOLOGY:
- OTC topical scar treatments have the potential to cause an allergic reaction, but the prevalence of North American Contact Dermatitis Group (NACDG) core allergens in these products is unclear.
- Researchers used the word scar in a query of Amazon.com and four other retail websites to identify topical scar products for consumers and noted the list of ingredients.
- The investigators also surveyed the American Contact Dermatitis Society’s Contact Allergen Management Program (CAMP), a resource that helps patients with allergies find personal care products that are safe to use, for pertinent products.
TAKEAWAY:
- The search query identified 156 products. Of these, 119 (76.2%) were gels, creams, or oils and 37 (23.7%) were sheets, strips, or tape.
- Of the 125 products that had a list of ingredients, 69 (55.2%) contained at least one NACDG allergen and 45 (36%) contained more than one.
- The top six most common allergens listed in the ingredients were fragrance (16.8%), phenoxyethanol (16.8%), parabens (14.4%), panthenol (12.8%), sodium benzoate (9.60%), and ethylhexylglycerin (8%).
- Analysis of CAMP revealed that the program only had five unique scar products in its list, suggesting that CAMP might not be a reliable source of scar product information for patients with known allergies to pertinent NACDG allergens.
IN PRACTICE:
“Patients can consider trying a ‘use test’ on the inner forearm before applying to the surgical site,” the authors wrote. “It may reveal they are sensitive or sensitized by a product.
SOURCE:
First author Meera Kattapuram, MD, of the Department of Internal Medicine at Mount Sinai Hospital, New York, led the study, published in the February issue of Dermatologic Surgery.
LIMITATIONS:
Limitations include the selection of five retailers and the top 100 products from each website and the potential for ingredient list inaccuracies.
DISCLOSURES:
The authors reported having no financial conflicts of interest. The research was supported by a grant from the National Institutes of Health/National Cancer Institute.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
METHODOLOGY:
- OTC topical scar treatments have the potential to cause an allergic reaction, but the prevalence of North American Contact Dermatitis Group (NACDG) core allergens in these products is unclear.
- Researchers used the word scar in a query of Amazon.com and four other retail websites to identify topical scar products for consumers and noted the list of ingredients.
- The investigators also surveyed the American Contact Dermatitis Society’s Contact Allergen Management Program (CAMP), a resource that helps patients with allergies find personal care products that are safe to use, for pertinent products.
TAKEAWAY:
- The search query identified 156 products. Of these, 119 (76.2%) were gels, creams, or oils and 37 (23.7%) were sheets, strips, or tape.
- Of the 125 products that had a list of ingredients, 69 (55.2%) contained at least one NACDG allergen and 45 (36%) contained more than one.
- The top six most common allergens listed in the ingredients were fragrance (16.8%), phenoxyethanol (16.8%), parabens (14.4%), panthenol (12.8%), sodium benzoate (9.60%), and ethylhexylglycerin (8%).
- Analysis of CAMP revealed that the program only had five unique scar products in its list, suggesting that CAMP might not be a reliable source of scar product information for patients with known allergies to pertinent NACDG allergens.
IN PRACTICE:
“Patients can consider trying a ‘use test’ on the inner forearm before applying to the surgical site,” the authors wrote. “It may reveal they are sensitive or sensitized by a product.
SOURCE:
First author Meera Kattapuram, MD, of the Department of Internal Medicine at Mount Sinai Hospital, New York, led the study, published in the February issue of Dermatologic Surgery.
LIMITATIONS:
Limitations include the selection of five retailers and the top 100 products from each website and the potential for ingredient list inaccuracies.
DISCLOSURES:
The authors reported having no financial conflicts of interest. The research was supported by a grant from the National Institutes of Health/National Cancer Institute.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
When Babies ‘Stop Breathing,’ Who Needs Admission and a Workup?
Many infants have experienced an episode of apnea, defined as a pause in respiration of 20 seconds or more. Most episodes remain unexplained, and no underlying cause can be found. Historically, these were referred to as “near-miss SIDS,” episodes, but that label suggested that all of these events would have ended in death had someone not intervened. New descriptive terminology was needed.
In the mid-1980s, the term “apparent life-threatening event” (ALTE) was adopted. But that term, too, was an overstatement, because although scary for parents, these brief apnea episodes were not, in most cases, truly life-threatening.
In 2013, authors of a systematic review coined the term “brief resolved unexplained event” (BRUE). This review also addressed the history and physical exam features associated with risk for a subsequent episode. It was felt that hospitalization and testing might be warranted if certain infants could be identified as high risk for recurrence.
What Is Considered a BRUE?
In the current working definition of BRUE, the child must be < 1 year old. The episode must be a sudden, brief, and resolved, with one or more of these characteristics:
- Cyanosis or pallor (but not turning red)
- A change in breathing (absent, decreased, or irregular)
- A change in tone (hypertonia or hypotonia)
- A change in responsiveness.
Furthermore, to qualify as a BRUE, no explanation can be found for the event based on the history and physical examination but before any laboratory testing is done. The definition also excludes children with known potential explanatory diagnoses (such as gastroesophageal reflux or bronchiolitis) and those who are otherwise symptomatically ill at the time of the event.
Decision to Admit and Recurrence Risk
An apnea event in an otherwise healthy infant, regardless of what it’s called, puts providers and parents in a difficult position. Should the infant be hospitalized for further monitoring and potentially more invasive testing to determine the cause of the episode? And what are the chances that the episode will be repeated?
A clinical practice guideline (CPG) for BRUE, widely adopted in 2016, resulted in significant reductions in healthcare utilization. The CPG attempted to identify low-risk infants who could safely be discharged from the emergency department. Although the CPG improved outcomes, experts acknowledged that an underlying problem was not likely to be identified even among infants deemed high risk, and these infants would be hospitalized unnecessarily.
Available data were simply insufficient to support this decision. So, with the goal of identifying factors that could help predict recurrent BRUE risk, a 15-hospital collaborative study was undertaken, followed by the development and validation of a clinical decision rule for predicting the risk for a serious underlying diagnosis or event recurrence among infants presenting with BRUE.
Here’s what we learned from more than 3000 cases of BRUE.
First, it turns out that it’s not easy to determine whether an infant is at low or high risk for recurrence of BRUE. Initially, 91.5% of patients enrolled in the study would have been labeled high risk.
Furthermore, a BRUE recurred in 14.3% of the cohort, and 4.8% of high-risk infants were found to have a serious undiagnosed condition. Seizures, airway anomalies, and gastroesophageal reflux were the top three causes of BRUE, but the spectrum of underlying pathology was quite considerable.
The problem was that 4.6% of the entire cohort were found to have a serious underlying condition, nearly identical to the proportion of high-risk infants with these conditions. This prompted the question of whether simply labeling infants “high risk” was really appropriate any longer.
Revised BRUE Management
Although it hasn’t been possible to group infants neatly in low and high-risk categories, the data from that large cohort led to the development of the BRUE 2.0 criteria, which enabled more focused risk assessment of an infant who experienced a BRUE. With an app on MDCalc, these criteria allow providers to ascertain, and show families, a visual representation of their infant’s individualized risk for a subsequent BRUE and of having a serious underlying condition.
The cohort study also identified red flags from the history or physical exam of infants who experienced a BRUE: weight loss, failure to thrive, or a history of feeding problems. Exam findings such as a bulging fontanelle, forceful or bilious emesis, and evidence of gastrointestinal (GI) bleeding suggest a medical diagnosis rather than a BRUE. If GI-related causes are high on the differential, a feeding evaluation can be helpful. A feeding evaluation can be done in the outpatient setting and does not require hospitalization.
For suspicion of an underlying neurological condition (such as seizures), experts recommend obtaining a short EEG, which is highly sensitive for detecting infantile spasms and encephalopathy. They recommend reserving MRI for infants with abnormalities on EEG or physical exam. Metabolic or genetic testing should be done only if the infant looks ill, because most patients with genetic or inborn errors of metabolism will continue to have symptoms as they become older.
The approach to BRUE has moved into the realm of shared decision-making with families. The likelihood of identifying a serious diagnosis is low for most of these children. And unfortunately, no single test can diagnose the full spectrum of potential explanatory diagnoses. For example, data from 2023 demonstrate that only 1.1% of lab tests following a BRUE contributed to a diagnosis, and most of the time that was a positive viral test. Similarly, imaging was helpful in only 1.5% of cases. So, explaining the evidence and deciding along with parents what is reasonable to do (or not do) is the current state of affairs.
My Take
As I reflect back on two and a half decades of caring for these patients, I believe that recent data have helped us a great deal. We do less testing and admit fewer infants to the hospital than we did 20 years ago, and that’s a good thing. Nevertheless, looking for a few red flags, having a high index of suspicion when the clinical exam is abnormal, and engaging in shared decision-making with families can help make the caring for these challenging patients more bearable and lead to better outcomes for all involved.
Dr. Basco is Professor, Department of Pediatrics, Medical University of South Carolina (MUSC); Director, Division of General Pediatrics, Department of Pediatrics, MUSC Children’s Hospital, Charleston, South Carolina. He has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Many infants have experienced an episode of apnea, defined as a pause in respiration of 20 seconds or more. Most episodes remain unexplained, and no underlying cause can be found. Historically, these were referred to as “near-miss SIDS,” episodes, but that label suggested that all of these events would have ended in death had someone not intervened. New descriptive terminology was needed.
In the mid-1980s, the term “apparent life-threatening event” (ALTE) was adopted. But that term, too, was an overstatement, because although scary for parents, these brief apnea episodes were not, in most cases, truly life-threatening.
In 2013, authors of a systematic review coined the term “brief resolved unexplained event” (BRUE). This review also addressed the history and physical exam features associated with risk for a subsequent episode. It was felt that hospitalization and testing might be warranted if certain infants could be identified as high risk for recurrence.
What Is Considered a BRUE?
In the current working definition of BRUE, the child must be < 1 year old. The episode must be a sudden, brief, and resolved, with one or more of these characteristics:
- Cyanosis or pallor (but not turning red)
- A change in breathing (absent, decreased, or irregular)
- A change in tone (hypertonia or hypotonia)
- A change in responsiveness.
Furthermore, to qualify as a BRUE, no explanation can be found for the event based on the history and physical examination but before any laboratory testing is done. The definition also excludes children with known potential explanatory diagnoses (such as gastroesophageal reflux or bronchiolitis) and those who are otherwise symptomatically ill at the time of the event.
Decision to Admit and Recurrence Risk
An apnea event in an otherwise healthy infant, regardless of what it’s called, puts providers and parents in a difficult position. Should the infant be hospitalized for further monitoring and potentially more invasive testing to determine the cause of the episode? And what are the chances that the episode will be repeated?
A clinical practice guideline (CPG) for BRUE, widely adopted in 2016, resulted in significant reductions in healthcare utilization. The CPG attempted to identify low-risk infants who could safely be discharged from the emergency department. Although the CPG improved outcomes, experts acknowledged that an underlying problem was not likely to be identified even among infants deemed high risk, and these infants would be hospitalized unnecessarily.
Available data were simply insufficient to support this decision. So, with the goal of identifying factors that could help predict recurrent BRUE risk, a 15-hospital collaborative study was undertaken, followed by the development and validation of a clinical decision rule for predicting the risk for a serious underlying diagnosis or event recurrence among infants presenting with BRUE.
Here’s what we learned from more than 3000 cases of BRUE.
First, it turns out that it’s not easy to determine whether an infant is at low or high risk for recurrence of BRUE. Initially, 91.5% of patients enrolled in the study would have been labeled high risk.
Furthermore, a BRUE recurred in 14.3% of the cohort, and 4.8% of high-risk infants were found to have a serious undiagnosed condition. Seizures, airway anomalies, and gastroesophageal reflux were the top three causes of BRUE, but the spectrum of underlying pathology was quite considerable.
The problem was that 4.6% of the entire cohort were found to have a serious underlying condition, nearly identical to the proportion of high-risk infants with these conditions. This prompted the question of whether simply labeling infants “high risk” was really appropriate any longer.
Revised BRUE Management
Although it hasn’t been possible to group infants neatly in low and high-risk categories, the data from that large cohort led to the development of the BRUE 2.0 criteria, which enabled more focused risk assessment of an infant who experienced a BRUE. With an app on MDCalc, these criteria allow providers to ascertain, and show families, a visual representation of their infant’s individualized risk for a subsequent BRUE and of having a serious underlying condition.
The cohort study also identified red flags from the history or physical exam of infants who experienced a BRUE: weight loss, failure to thrive, or a history of feeding problems. Exam findings such as a bulging fontanelle, forceful or bilious emesis, and evidence of gastrointestinal (GI) bleeding suggest a medical diagnosis rather than a BRUE. If GI-related causes are high on the differential, a feeding evaluation can be helpful. A feeding evaluation can be done in the outpatient setting and does not require hospitalization.
For suspicion of an underlying neurological condition (such as seizures), experts recommend obtaining a short EEG, which is highly sensitive for detecting infantile spasms and encephalopathy. They recommend reserving MRI for infants with abnormalities on EEG or physical exam. Metabolic or genetic testing should be done only if the infant looks ill, because most patients with genetic or inborn errors of metabolism will continue to have symptoms as they become older.
The approach to BRUE has moved into the realm of shared decision-making with families. The likelihood of identifying a serious diagnosis is low for most of these children. And unfortunately, no single test can diagnose the full spectrum of potential explanatory diagnoses. For example, data from 2023 demonstrate that only 1.1% of lab tests following a BRUE contributed to a diagnosis, and most of the time that was a positive viral test. Similarly, imaging was helpful in only 1.5% of cases. So, explaining the evidence and deciding along with parents what is reasonable to do (or not do) is the current state of affairs.
My Take
As I reflect back on two and a half decades of caring for these patients, I believe that recent data have helped us a great deal. We do less testing and admit fewer infants to the hospital than we did 20 years ago, and that’s a good thing. Nevertheless, looking for a few red flags, having a high index of suspicion when the clinical exam is abnormal, and engaging in shared decision-making with families can help make the caring for these challenging patients more bearable and lead to better outcomes for all involved.
Dr. Basco is Professor, Department of Pediatrics, Medical University of South Carolina (MUSC); Director, Division of General Pediatrics, Department of Pediatrics, MUSC Children’s Hospital, Charleston, South Carolina. He has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Many infants have experienced an episode of apnea, defined as a pause in respiration of 20 seconds or more. Most episodes remain unexplained, and no underlying cause can be found. Historically, these were referred to as “near-miss SIDS,” episodes, but that label suggested that all of these events would have ended in death had someone not intervened. New descriptive terminology was needed.
In the mid-1980s, the term “apparent life-threatening event” (ALTE) was adopted. But that term, too, was an overstatement, because although scary for parents, these brief apnea episodes were not, in most cases, truly life-threatening.
In 2013, authors of a systematic review coined the term “brief resolved unexplained event” (BRUE). This review also addressed the history and physical exam features associated with risk for a subsequent episode. It was felt that hospitalization and testing might be warranted if certain infants could be identified as high risk for recurrence.
What Is Considered a BRUE?
In the current working definition of BRUE, the child must be < 1 year old. The episode must be a sudden, brief, and resolved, with one or more of these characteristics:
- Cyanosis or pallor (but not turning red)
- A change in breathing (absent, decreased, or irregular)
- A change in tone (hypertonia or hypotonia)
- A change in responsiveness.
Furthermore, to qualify as a BRUE, no explanation can be found for the event based on the history and physical examination but before any laboratory testing is done. The definition also excludes children with known potential explanatory diagnoses (such as gastroesophageal reflux or bronchiolitis) and those who are otherwise symptomatically ill at the time of the event.
Decision to Admit and Recurrence Risk
An apnea event in an otherwise healthy infant, regardless of what it’s called, puts providers and parents in a difficult position. Should the infant be hospitalized for further monitoring and potentially more invasive testing to determine the cause of the episode? And what are the chances that the episode will be repeated?
A clinical practice guideline (CPG) for BRUE, widely adopted in 2016, resulted in significant reductions in healthcare utilization. The CPG attempted to identify low-risk infants who could safely be discharged from the emergency department. Although the CPG improved outcomes, experts acknowledged that an underlying problem was not likely to be identified even among infants deemed high risk, and these infants would be hospitalized unnecessarily.
Available data were simply insufficient to support this decision. So, with the goal of identifying factors that could help predict recurrent BRUE risk, a 15-hospital collaborative study was undertaken, followed by the development and validation of a clinical decision rule for predicting the risk for a serious underlying diagnosis or event recurrence among infants presenting with BRUE.
Here’s what we learned from more than 3000 cases of BRUE.
First, it turns out that it’s not easy to determine whether an infant is at low or high risk for recurrence of BRUE. Initially, 91.5% of patients enrolled in the study would have been labeled high risk.
Furthermore, a BRUE recurred in 14.3% of the cohort, and 4.8% of high-risk infants were found to have a serious undiagnosed condition. Seizures, airway anomalies, and gastroesophageal reflux were the top three causes of BRUE, but the spectrum of underlying pathology was quite considerable.
The problem was that 4.6% of the entire cohort were found to have a serious underlying condition, nearly identical to the proportion of high-risk infants with these conditions. This prompted the question of whether simply labeling infants “high risk” was really appropriate any longer.
Revised BRUE Management
Although it hasn’t been possible to group infants neatly in low and high-risk categories, the data from that large cohort led to the development of the BRUE 2.0 criteria, which enabled more focused risk assessment of an infant who experienced a BRUE. With an app on MDCalc, these criteria allow providers to ascertain, and show families, a visual representation of their infant’s individualized risk for a subsequent BRUE and of having a serious underlying condition.
The cohort study also identified red flags from the history or physical exam of infants who experienced a BRUE: weight loss, failure to thrive, or a history of feeding problems. Exam findings such as a bulging fontanelle, forceful or bilious emesis, and evidence of gastrointestinal (GI) bleeding suggest a medical diagnosis rather than a BRUE. If GI-related causes are high on the differential, a feeding evaluation can be helpful. A feeding evaluation can be done in the outpatient setting and does not require hospitalization.
For suspicion of an underlying neurological condition (such as seizures), experts recommend obtaining a short EEG, which is highly sensitive for detecting infantile spasms and encephalopathy. They recommend reserving MRI for infants with abnormalities on EEG or physical exam. Metabolic or genetic testing should be done only if the infant looks ill, because most patients with genetic or inborn errors of metabolism will continue to have symptoms as they become older.
The approach to BRUE has moved into the realm of shared decision-making with families. The likelihood of identifying a serious diagnosis is low for most of these children. And unfortunately, no single test can diagnose the full spectrum of potential explanatory diagnoses. For example, data from 2023 demonstrate that only 1.1% of lab tests following a BRUE contributed to a diagnosis, and most of the time that was a positive viral test. Similarly, imaging was helpful in only 1.5% of cases. So, explaining the evidence and deciding along with parents what is reasonable to do (or not do) is the current state of affairs.
My Take
As I reflect back on two and a half decades of caring for these patients, I believe that recent data have helped us a great deal. We do less testing and admit fewer infants to the hospital than we did 20 years ago, and that’s a good thing. Nevertheless, looking for a few red flags, having a high index of suspicion when the clinical exam is abnormal, and engaging in shared decision-making with families can help make the caring for these challenging patients more bearable and lead to better outcomes for all involved.
Dr. Basco is Professor, Department of Pediatrics, Medical University of South Carolina (MUSC); Director, Division of General Pediatrics, Department of Pediatrics, MUSC Children’s Hospital, Charleston, South Carolina. He has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Study: Lifetime Cost of Vyjuvek Gene Therapy for DEB Could Be $15-$22 Million
according to the authors of a new study.
The US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approved Vyjuvek (Krystal Biotech) in May 2023 for the treatment of wounds in patients ages 6 months and older with dystrophic epidermolysis bullosa (DEB), which includes two types, the most severe form (autosomal recessive, or RDEB) and the autosomal dominant form of DEB (DDEB), which tends to be milder.
Treatment with Vyjuvek “represents an important advance in the treatment of RDEB,” wrote Adam J.N. Raymakers, PhD, and colleagues at the Program on Regulation, Therapeutics, and Law; the Department of Dermatology; and the Division of Pulmonary and Critical Care Medicine at Brigham & Women’s Hospital in Boston, Massachusetts, in their paper, published in JAMA Dermatology. But the price “will be high, potentially limiting patients’ access to it,” they added. Evidence to support it in DDEB “is less conclusive,” they wrote, noting that the pivotal phase 3 study that led to approval included one patient with DDEB.
“The wider indication granted by the FDA may lead to friction between payers on the one hand and patients and physicians on the other,” they wrote, noting a potential minimum price of $300,000 per patient a year, which was based on Krystal’s regulatory filings.
There is no cure for DEB. Vyjuvek, applied as a gel on an ongoing basis, uses a nonreplicating herpes simplex virus type 1 vector to deliver the COL7A1 gene directly to skin cells, restoring the COL7 protein fibrils that stabilize skin structure.
The authors estimated that in the United States, 894 individuals – largely children – with both forms of the disease would be eligible for Vyjuvek treatment in the first year. Based on the $300,000 price, spending on gene therapy could range from $179 million to $357 million for those 894 patients, they reported in the study.
Over the first 3 years, spending could range as high as $1 billion, the authors estimated. Even if patients with only the most severe disease (RDEB) — an estimated 442 patients — received treatment, spending could be $132 million and up to $400 million or more over the first 3 years, they wrote.
Some media outlets have reported that Vyjuvek could cost as much as $600,000, said Dr. Raymakers, a research fellow. That price “would double all of our estimates,” he told this news organization.
The study assumed that patients with RDEB would only live to age 50, which led to a lifetime cost estimate of $15 million. But that is likely a conservative estimate, he and his coauthors wrote, noting that many patients with RDEB die from squamous cell carcinoma, but that Vyjuvek could, by attenuating skin damage, also potentially prevent skin cancer.
Dr. Raymakers said he and his colleagues began their study when Vyjuvek was approved, and thus they did not have any real-world data on the price or payer responses. Their estimates also did not include differing dosing regimens, which also could change their spending figures.
Krystal Biotech recently reported that in its third quarter of 2023 – representing just 1 month of Vyjuvek availability – it received requests to begin treatment for 284 patients from 136 unique clinicians. Twenty percent of the start requests were for patients with the milder form (DDEB), and a third of all the requests were for patients 10 years of age or younger. The company also said that it had “received positive coverage determinations from all major commercial national health plans” and that it was on track to receive approval from most state Medicaid plans.
In 1 month, Krystal reported net Vyjuvek revenues of $8.6 million.
The authors suggested that one way to evaluate Vyjuvek’s value — especially for those with DDEB — would be through a cost-effectiveness study. While important, a cost-effectiveness study would not get at the impact on a payer, said Dr. Raymakers. “Something can be cost-effective but unaffordable to the system,” he said.
“When there’s one of these very expensive therapies, that’s one thing,” he said. “But when there’s more and more coming to market, you wonder how much can be tolerated,” said Dr. Raymakers.
CMS Launching Gene Therapy Program
The Biden administration recently announced that it was launching a program aimed at increasing access, curbing costs, and ensuring value of gene therapies, starting with sickle cell disease. The program will begin in early 2025. Among other aspects, the federal government will negotiate the price of the product with the manufacturer.
“The goal of the Cell and Gene Therapy Access Model is to increase access to innovative cell and gene therapies for people with Medicaid by making it easier for states to pay for these therapies,” said Liz Fowler, CMS Deputy Administrator and Director of the CMS Innovation Center, in a statement announcing the program.
Whether the new program takes a look at Vyjuvek – and when – is not clear.
But the authors of the study noted that the lifetime costs of treating a patient with Vyjuvek “exceed the costs of all other one-time gene therapies for other diseases.” And they wrote, even at the most conservative estimates, Vyjuvek “will be the most expensive gene therapy currently marketed in the US.”
The study was funded by a grant from Arnold Ventures, grants from the Kaiser Permanente Institute for Health Policy, the Commonwealth Fund, and the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute. Dr. Raymakers and co-authors reported no financial relationships relevant to the work.
according to the authors of a new study.
The US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approved Vyjuvek (Krystal Biotech) in May 2023 for the treatment of wounds in patients ages 6 months and older with dystrophic epidermolysis bullosa (DEB), which includes two types, the most severe form (autosomal recessive, or RDEB) and the autosomal dominant form of DEB (DDEB), which tends to be milder.
Treatment with Vyjuvek “represents an important advance in the treatment of RDEB,” wrote Adam J.N. Raymakers, PhD, and colleagues at the Program on Regulation, Therapeutics, and Law; the Department of Dermatology; and the Division of Pulmonary and Critical Care Medicine at Brigham & Women’s Hospital in Boston, Massachusetts, in their paper, published in JAMA Dermatology. But the price “will be high, potentially limiting patients’ access to it,” they added. Evidence to support it in DDEB “is less conclusive,” they wrote, noting that the pivotal phase 3 study that led to approval included one patient with DDEB.
“The wider indication granted by the FDA may lead to friction between payers on the one hand and patients and physicians on the other,” they wrote, noting a potential minimum price of $300,000 per patient a year, which was based on Krystal’s regulatory filings.
There is no cure for DEB. Vyjuvek, applied as a gel on an ongoing basis, uses a nonreplicating herpes simplex virus type 1 vector to deliver the COL7A1 gene directly to skin cells, restoring the COL7 protein fibrils that stabilize skin structure.
The authors estimated that in the United States, 894 individuals – largely children – with both forms of the disease would be eligible for Vyjuvek treatment in the first year. Based on the $300,000 price, spending on gene therapy could range from $179 million to $357 million for those 894 patients, they reported in the study.
Over the first 3 years, spending could range as high as $1 billion, the authors estimated. Even if patients with only the most severe disease (RDEB) — an estimated 442 patients — received treatment, spending could be $132 million and up to $400 million or more over the first 3 years, they wrote.
Some media outlets have reported that Vyjuvek could cost as much as $600,000, said Dr. Raymakers, a research fellow. That price “would double all of our estimates,” he told this news organization.
The study assumed that patients with RDEB would only live to age 50, which led to a lifetime cost estimate of $15 million. But that is likely a conservative estimate, he and his coauthors wrote, noting that many patients with RDEB die from squamous cell carcinoma, but that Vyjuvek could, by attenuating skin damage, also potentially prevent skin cancer.
Dr. Raymakers said he and his colleagues began their study when Vyjuvek was approved, and thus they did not have any real-world data on the price or payer responses. Their estimates also did not include differing dosing regimens, which also could change their spending figures.
Krystal Biotech recently reported that in its third quarter of 2023 – representing just 1 month of Vyjuvek availability – it received requests to begin treatment for 284 patients from 136 unique clinicians. Twenty percent of the start requests were for patients with the milder form (DDEB), and a third of all the requests were for patients 10 years of age or younger. The company also said that it had “received positive coverage determinations from all major commercial national health plans” and that it was on track to receive approval from most state Medicaid plans.
In 1 month, Krystal reported net Vyjuvek revenues of $8.6 million.
The authors suggested that one way to evaluate Vyjuvek’s value — especially for those with DDEB — would be through a cost-effectiveness study. While important, a cost-effectiveness study would not get at the impact on a payer, said Dr. Raymakers. “Something can be cost-effective but unaffordable to the system,” he said.
“When there’s one of these very expensive therapies, that’s one thing,” he said. “But when there’s more and more coming to market, you wonder how much can be tolerated,” said Dr. Raymakers.
CMS Launching Gene Therapy Program
The Biden administration recently announced that it was launching a program aimed at increasing access, curbing costs, and ensuring value of gene therapies, starting with sickle cell disease. The program will begin in early 2025. Among other aspects, the federal government will negotiate the price of the product with the manufacturer.
“The goal of the Cell and Gene Therapy Access Model is to increase access to innovative cell and gene therapies for people with Medicaid by making it easier for states to pay for these therapies,” said Liz Fowler, CMS Deputy Administrator and Director of the CMS Innovation Center, in a statement announcing the program.
Whether the new program takes a look at Vyjuvek – and when – is not clear.
But the authors of the study noted that the lifetime costs of treating a patient with Vyjuvek “exceed the costs of all other one-time gene therapies for other diseases.” And they wrote, even at the most conservative estimates, Vyjuvek “will be the most expensive gene therapy currently marketed in the US.”
The study was funded by a grant from Arnold Ventures, grants from the Kaiser Permanente Institute for Health Policy, the Commonwealth Fund, and the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute. Dr. Raymakers and co-authors reported no financial relationships relevant to the work.
according to the authors of a new study.
The US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approved Vyjuvek (Krystal Biotech) in May 2023 for the treatment of wounds in patients ages 6 months and older with dystrophic epidermolysis bullosa (DEB), which includes two types, the most severe form (autosomal recessive, or RDEB) and the autosomal dominant form of DEB (DDEB), which tends to be milder.
Treatment with Vyjuvek “represents an important advance in the treatment of RDEB,” wrote Adam J.N. Raymakers, PhD, and colleagues at the Program on Regulation, Therapeutics, and Law; the Department of Dermatology; and the Division of Pulmonary and Critical Care Medicine at Brigham & Women’s Hospital in Boston, Massachusetts, in their paper, published in JAMA Dermatology. But the price “will be high, potentially limiting patients’ access to it,” they added. Evidence to support it in DDEB “is less conclusive,” they wrote, noting that the pivotal phase 3 study that led to approval included one patient with DDEB.
“The wider indication granted by the FDA may lead to friction between payers on the one hand and patients and physicians on the other,” they wrote, noting a potential minimum price of $300,000 per patient a year, which was based on Krystal’s regulatory filings.
There is no cure for DEB. Vyjuvek, applied as a gel on an ongoing basis, uses a nonreplicating herpes simplex virus type 1 vector to deliver the COL7A1 gene directly to skin cells, restoring the COL7 protein fibrils that stabilize skin structure.
The authors estimated that in the United States, 894 individuals – largely children – with both forms of the disease would be eligible for Vyjuvek treatment in the first year. Based on the $300,000 price, spending on gene therapy could range from $179 million to $357 million for those 894 patients, they reported in the study.
Over the first 3 years, spending could range as high as $1 billion, the authors estimated. Even if patients with only the most severe disease (RDEB) — an estimated 442 patients — received treatment, spending could be $132 million and up to $400 million or more over the first 3 years, they wrote.
Some media outlets have reported that Vyjuvek could cost as much as $600,000, said Dr. Raymakers, a research fellow. That price “would double all of our estimates,” he told this news organization.
The study assumed that patients with RDEB would only live to age 50, which led to a lifetime cost estimate of $15 million. But that is likely a conservative estimate, he and his coauthors wrote, noting that many patients with RDEB die from squamous cell carcinoma, but that Vyjuvek could, by attenuating skin damage, also potentially prevent skin cancer.
Dr. Raymakers said he and his colleagues began their study when Vyjuvek was approved, and thus they did not have any real-world data on the price or payer responses. Their estimates also did not include differing dosing regimens, which also could change their spending figures.
Krystal Biotech recently reported that in its third quarter of 2023 – representing just 1 month of Vyjuvek availability – it received requests to begin treatment for 284 patients from 136 unique clinicians. Twenty percent of the start requests were for patients with the milder form (DDEB), and a third of all the requests were for patients 10 years of age or younger. The company also said that it had “received positive coverage determinations from all major commercial national health plans” and that it was on track to receive approval from most state Medicaid plans.
In 1 month, Krystal reported net Vyjuvek revenues of $8.6 million.
The authors suggested that one way to evaluate Vyjuvek’s value — especially for those with DDEB — would be through a cost-effectiveness study. While important, a cost-effectiveness study would not get at the impact on a payer, said Dr. Raymakers. “Something can be cost-effective but unaffordable to the system,” he said.
“When there’s one of these very expensive therapies, that’s one thing,” he said. “But when there’s more and more coming to market, you wonder how much can be tolerated,” said Dr. Raymakers.
CMS Launching Gene Therapy Program
The Biden administration recently announced that it was launching a program aimed at increasing access, curbing costs, and ensuring value of gene therapies, starting with sickle cell disease. The program will begin in early 2025. Among other aspects, the federal government will negotiate the price of the product with the manufacturer.
“The goal of the Cell and Gene Therapy Access Model is to increase access to innovative cell and gene therapies for people with Medicaid by making it easier for states to pay for these therapies,” said Liz Fowler, CMS Deputy Administrator and Director of the CMS Innovation Center, in a statement announcing the program.
Whether the new program takes a look at Vyjuvek – and when – is not clear.
But the authors of the study noted that the lifetime costs of treating a patient with Vyjuvek “exceed the costs of all other one-time gene therapies for other diseases.” And they wrote, even at the most conservative estimates, Vyjuvek “will be the most expensive gene therapy currently marketed in the US.”
The study was funded by a grant from Arnold Ventures, grants from the Kaiser Permanente Institute for Health Policy, the Commonwealth Fund, and the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute. Dr. Raymakers and co-authors reported no financial relationships relevant to the work.
FROM JAMA DERMATOLOGY
Youth Mental Health in ‘Dire Straits’
, suggests a new report that shines a light on the global mental health crisis among young people.
The burden is high in this population, with around one-fifth of all disease-related disability attributable to mental disorders. The data, drawn from the 2019 Global Burden of Disease (GBD) study, examines mental health in the 293 million people worldwide in this age group.
“This concentration of disability burden at an early age raises concern about the potential lifetime impact of these conditions,” wrote the authors, led by Christian Kieling, MD, PhD, Universidade Federal do Rio Grande do Sul, Porto Alegre, Brazil.
The study was published online in JAMA Psychiatry.
State of Emergency
Soaring rates of mental health disorders among young people, intensified by the COVID-19 pandemic, have led the American Academy of Child and Adolescent Psychiatry and the American Academy of Pediatrics to declare a state of emergency.
Using the GBD study, Dr. Kieling and colleagues estimated the global prevalence and years lived with disability associated with mental disorders and substance use disorders in people aged 5-24 years.
In 2019, individuals in this age range had at least one mental disorder and 31 million had a substance use disorder — an average prevalence of 11.6% and 1.2%, respectively.
The prevalence of mental disorders doubled from the age range of 5-9 years (6.8%) to 20-24 years (13.6%).
Among mental disorders analyzed, anxiety disorders were most common in the overall population (84 million; 3.35%) and schizophrenia the least common (2 million; 0.08%).
Notably, the researchers said, there was a steep increase in mood disorders, particularly anxiety and substance use disorders, across early to late adolescence and from late adolescence to young adulthood.
Mental disorders and substance use disorders were the leading cause of nonfatal disability in children and youths in 2019, accounting for 31 million and 4.3 million years lived with disability (YLDs), respectively. That represents roughly 20% and 3% of YLDs, respectively, from all causes.
Youth Mental Health Is Not a Monolith
“That youth mental health is in such dire straits is particularly striking given that many measures of global physical health in young people are improving,” wrote the authors of an accompanying editorial.
In their editorial, Jeremy Veenstra-VanderWeele, MD, Department of Psychiatry, Columbia University, New York, and co-authors noted that these and other age- and gender-related findings “represent a meaningful contribution to the literature.”
The granular data underscore that youth mental health is “not a monolith” but rather involves considerable variation in prevalence and morbidity across both age and gender, they wrote.
Therefore, mental health screening, promotion, and prevention efforts may benefit from an age-based approach that targets specific disorders during “high prevalence developmental intervals, with keen attention also paid to gender,” they suggested.
On the basis of the findings in this analysis, healthcare and education resource allocation may need to be adjusted for specific disorders, they added.
“One might propose a community- or school-based mental health initiative that screens for and educates parents and teachers on ADHD and anxiety disorders from kindergarten through third grade (ages 5-9 years, when prevalence and resulting disability grow markedly),” Dr. Veenstra-VanderWeele and colleagues wrote. “Later initiatives could then focus on mood and substance use disorders during high school and college (ages 15-19 years and 20-24 years).”
The study was partially funded by a research grant from the Cundill Centre for Child and Youth Depression. Dr. Kieling is the founder of Wida. Dr. Veenstra-VanderWeele reported receiving grants from the National Institutes of Health and Simon’s Foundation and research support/advisory board/editorial fees from Autism Speaks, Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality, Health Resources and Services Administration Maternal and Child Health Bureau, American Academy of Child and Adolescent Psychiatry, Forest, Janssen, Yamo, MapLight, Acadia, Roche, Novartis, Seaside Therapeutics, Springer, SynapDx, and Wiley.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
, suggests a new report that shines a light on the global mental health crisis among young people.
The burden is high in this population, with around one-fifth of all disease-related disability attributable to mental disorders. The data, drawn from the 2019 Global Burden of Disease (GBD) study, examines mental health in the 293 million people worldwide in this age group.
“This concentration of disability burden at an early age raises concern about the potential lifetime impact of these conditions,” wrote the authors, led by Christian Kieling, MD, PhD, Universidade Federal do Rio Grande do Sul, Porto Alegre, Brazil.
The study was published online in JAMA Psychiatry.
State of Emergency
Soaring rates of mental health disorders among young people, intensified by the COVID-19 pandemic, have led the American Academy of Child and Adolescent Psychiatry and the American Academy of Pediatrics to declare a state of emergency.
Using the GBD study, Dr. Kieling and colleagues estimated the global prevalence and years lived with disability associated with mental disorders and substance use disorders in people aged 5-24 years.
In 2019, individuals in this age range had at least one mental disorder and 31 million had a substance use disorder — an average prevalence of 11.6% and 1.2%, respectively.
The prevalence of mental disorders doubled from the age range of 5-9 years (6.8%) to 20-24 years (13.6%).
Among mental disorders analyzed, anxiety disorders were most common in the overall population (84 million; 3.35%) and schizophrenia the least common (2 million; 0.08%).
Notably, the researchers said, there was a steep increase in mood disorders, particularly anxiety and substance use disorders, across early to late adolescence and from late adolescence to young adulthood.
Mental disorders and substance use disorders were the leading cause of nonfatal disability in children and youths in 2019, accounting for 31 million and 4.3 million years lived with disability (YLDs), respectively. That represents roughly 20% and 3% of YLDs, respectively, from all causes.
Youth Mental Health Is Not a Monolith
“That youth mental health is in such dire straits is particularly striking given that many measures of global physical health in young people are improving,” wrote the authors of an accompanying editorial.
In their editorial, Jeremy Veenstra-VanderWeele, MD, Department of Psychiatry, Columbia University, New York, and co-authors noted that these and other age- and gender-related findings “represent a meaningful contribution to the literature.”
The granular data underscore that youth mental health is “not a monolith” but rather involves considerable variation in prevalence and morbidity across both age and gender, they wrote.
Therefore, mental health screening, promotion, and prevention efforts may benefit from an age-based approach that targets specific disorders during “high prevalence developmental intervals, with keen attention also paid to gender,” they suggested.
On the basis of the findings in this analysis, healthcare and education resource allocation may need to be adjusted for specific disorders, they added.
“One might propose a community- or school-based mental health initiative that screens for and educates parents and teachers on ADHD and anxiety disorders from kindergarten through third grade (ages 5-9 years, when prevalence and resulting disability grow markedly),” Dr. Veenstra-VanderWeele and colleagues wrote. “Later initiatives could then focus on mood and substance use disorders during high school and college (ages 15-19 years and 20-24 years).”
The study was partially funded by a research grant from the Cundill Centre for Child and Youth Depression. Dr. Kieling is the founder of Wida. Dr. Veenstra-VanderWeele reported receiving grants from the National Institutes of Health and Simon’s Foundation and research support/advisory board/editorial fees from Autism Speaks, Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality, Health Resources and Services Administration Maternal and Child Health Bureau, American Academy of Child and Adolescent Psychiatry, Forest, Janssen, Yamo, MapLight, Acadia, Roche, Novartis, Seaside Therapeutics, Springer, SynapDx, and Wiley.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
, suggests a new report that shines a light on the global mental health crisis among young people.
The burden is high in this population, with around one-fifth of all disease-related disability attributable to mental disorders. The data, drawn from the 2019 Global Burden of Disease (GBD) study, examines mental health in the 293 million people worldwide in this age group.
“This concentration of disability burden at an early age raises concern about the potential lifetime impact of these conditions,” wrote the authors, led by Christian Kieling, MD, PhD, Universidade Federal do Rio Grande do Sul, Porto Alegre, Brazil.
The study was published online in JAMA Psychiatry.
State of Emergency
Soaring rates of mental health disorders among young people, intensified by the COVID-19 pandemic, have led the American Academy of Child and Adolescent Psychiatry and the American Academy of Pediatrics to declare a state of emergency.
Using the GBD study, Dr. Kieling and colleagues estimated the global prevalence and years lived with disability associated with mental disorders and substance use disorders in people aged 5-24 years.
In 2019, individuals in this age range had at least one mental disorder and 31 million had a substance use disorder — an average prevalence of 11.6% and 1.2%, respectively.
The prevalence of mental disorders doubled from the age range of 5-9 years (6.8%) to 20-24 years (13.6%).
Among mental disorders analyzed, anxiety disorders were most common in the overall population (84 million; 3.35%) and schizophrenia the least common (2 million; 0.08%).
Notably, the researchers said, there was a steep increase in mood disorders, particularly anxiety and substance use disorders, across early to late adolescence and from late adolescence to young adulthood.
Mental disorders and substance use disorders were the leading cause of nonfatal disability in children and youths in 2019, accounting for 31 million and 4.3 million years lived with disability (YLDs), respectively. That represents roughly 20% and 3% of YLDs, respectively, from all causes.
Youth Mental Health Is Not a Monolith
“That youth mental health is in such dire straits is particularly striking given that many measures of global physical health in young people are improving,” wrote the authors of an accompanying editorial.
In their editorial, Jeremy Veenstra-VanderWeele, MD, Department of Psychiatry, Columbia University, New York, and co-authors noted that these and other age- and gender-related findings “represent a meaningful contribution to the literature.”
The granular data underscore that youth mental health is “not a monolith” but rather involves considerable variation in prevalence and morbidity across both age and gender, they wrote.
Therefore, mental health screening, promotion, and prevention efforts may benefit from an age-based approach that targets specific disorders during “high prevalence developmental intervals, with keen attention also paid to gender,” they suggested.
On the basis of the findings in this analysis, healthcare and education resource allocation may need to be adjusted for specific disorders, they added.
“One might propose a community- or school-based mental health initiative that screens for and educates parents and teachers on ADHD and anxiety disorders from kindergarten through third grade (ages 5-9 years, when prevalence and resulting disability grow markedly),” Dr. Veenstra-VanderWeele and colleagues wrote. “Later initiatives could then focus on mood and substance use disorders during high school and college (ages 15-19 years and 20-24 years).”
The study was partially funded by a research grant from the Cundill Centre for Child and Youth Depression. Dr. Kieling is the founder of Wida. Dr. Veenstra-VanderWeele reported receiving grants from the National Institutes of Health and Simon’s Foundation and research support/advisory board/editorial fees from Autism Speaks, Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality, Health Resources and Services Administration Maternal and Child Health Bureau, American Academy of Child and Adolescent Psychiatry, Forest, Janssen, Yamo, MapLight, Acadia, Roche, Novartis, Seaside Therapeutics, Springer, SynapDx, and Wiley.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.


