User login
Bringing you the latest news, research and reviews, exclusive interviews, podcasts, quizzes, and more.
div[contains(@class, 'header__large-screen')]
div[contains(@class, 'read-next-article')]
div[contains(@class, 'nav-primary')]
nav[contains(@class, 'nav-primary')]
section[contains(@class, 'footer-nav-section-wrapper')]
footer[@id='footer']
div[contains(@class, 'main-prefix')]
section[contains(@class, 'nav-hidden')]
div[contains(@class, 'ce-card-content')]
nav[contains(@class, 'nav-ce-stack')]
Research Highlights From ESMO Breast Cancer
Among the topics the speakers addressed were breast cancer prevention, early breast cancer, advanced breast cancer, and supportive care.
In recent years, the way clinicians look at carcinogenesis in breast cancer has changed, and many new targets for potential early detection and prevention have emerged, said Suzette Delaloge, MD, of Gustave Roussy, Paris, France, in her presentation at the meeting.
Instant risk assessment at different time points could potentially intercept cancer among high-risk individuals, she said.
A study by Mikael Eriksson, PhD, and colleagues focused on external validation of the Profound AI tool to identify breast cancer risk in the general population. The researchers showed an area under the curve of 0.72 in their AI risk model, which has the potential to be clinically meaningful, although it must be prospectively validated, Dr. Delaloge said in her presentation.
She also reviewed two studies on the use of genes to further refine breast cancer risk among carriers. One of these, a prospective study presented in a session by Kelly-Anne Phillips, MD, of Peter MacCallum Cancer Center, Melbourne, Australia, used the CANRISK online risk assessment tool and validated increased breast cancer risk in BRCA1 and BRCA2 carriers, with AUCs of 0.79 and 0.78, respectively. The other study, which was by Maria Rezqallah Aron, MD, and colleagues examined polygenic scores as a way to refine breast cancer risk stratification among carriers of the ALM and PALB2 genes as well. These genes might be useful in identifying individuals who could benefit from early intervention, including surgery, Dr. Delaloge said.
Translational Research
“Preparing my talk, I felt like a kid in a candy store,” because of the amount of new translational research presented, including several studies of endocrine treatment–based approaches to therapy, said Marleen Kok, MD, of the Netherlands Cancer Institute, Amsterdam.
In her presentation, Dr. Kok highlighted findings from an analysis of patients in the monarchE study (a trial of high-risk patients) showing a consistent improvement in invasive disease-free survival for the subset of patients with germline BRCA1 and BRCA2 mutations who received abemaciclib plus endocrine therapy.
The value of tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes (TILs) on patients who are not receiving chemotherapy is important because of the focus on prognosis, and prospective trials are underway, she said.
A poster on the impact of chemotherapy and stromal tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes (sTILs) in stage I triple-negative breast cancer showed no association between chemotherapy and better outcomes regardless of sTILs in patients who did and did not receive chemotherapy, which has implications for potential treatment sparing in this population, Dr. Kok noted.
Artificial Intelligence (AI) was the subject of several posters at the meeting, and Dr. Kok identified a multisite European study of an automated HER2 scoring system as notable for its size and accuracy. In the study, the accuracy among pathologists was much higher with the assistance of AI, she said. Using AI for more complex analysis has shown success, she said.
Dr. Kok ended her talk with a poster that surveyed breast cancer patients about their understanding of their disease. The results showed that less than half (44%) of patients reported that their healthcare providers had given them enough information to learn about their breast cancer type, and less than one third could recall terminology about biomarkers; the study is important because it shows that clinicians need to do better in explaining these terms to patients, Dr. Kok said.
Early Breast Cancer
Right-sizing therapy, meaning identifying the right treatment for every patient, is a key element of new research in early breast cancer, said Erika Hamilton, MD, of the Sarah Cannon Research Institute, Nashville, Tenn.
She highlighted safety and treatment duration updates from the NATALEE study, which compared adjuvant ribociclib plus nonsteroidal aromatase inhibitor (NSAI) to NSAI alone for ER+/HER2- breast cancer. The current analysis presented at the meeting showed significant benefits with the addition of ribociclib and no evidence of new safety signals or adverse event exacerbations at 3 years, she said. Dose modifications had no significant impact on efficacy, she added.
The findings of no impact of dose reduction on efficacy in both the NATALEE and monarchE studies provide important information on whether dosage can be reduced in patients, which will increase the odds that patients will tolerate extended therapy with good outcomes and stay on their prescribed therapies, Dr. Hamilton emphasized.
The CARABELA study, a phase 2 trial of neoadjuvant letrozole plus abemaciclib vs adriamycin and cyclophosphamide (AC), showed clinically similar response rates but did not meet its endpoint for residual cancer burden (RCB) scores. These data add to results from other studies and show that it is too soon to universally replace neoadjuvant chemotherapy as first-line treatment for highly proliferative ER+ breast cancer, Dr. Hamilton said in her presentation.
Advanced Breast Cancer
Take-home messages about advanced breast cancer include growing evidence for the potential benefits of antibody drug conjugates (ADCs), said Eva Ciruelos, MD, of University Hospital, Madrid, Spain. The TROPION-BREAST01 study, a phase 3 randomized trial, showed significant and clinically meaningful improvement in progression-free survival in patients with previously treated, inoperable, or metastatic HR+/HER2- breast cancer who received datopotamab deruxtecan (Dato-DXd) compared with those who received chemotherapy.
Data from an additional safety analysis were presented at the meeting; although Dato-DXd, a trophoblast cell-surface antigen 2 (TROP2)–directed antibody-drug conjugate, was well-tolerated, it is important to remain aware of toxicities, notably oral mucositis, which occurred in 55.6% of the patients in the study across all grades, and ocular surface toxicity, which occurred in 40% of patients across all grades, Dr. Ciruelos emphasized.
Key research in the area of advanced triple-negative breast cancer included data from the IMPASSION 132 study. This study is “specifically centered on early relapsers,” a population often excluded from other trials, Dr. Ciruelos said. In this study, patients with advanced triple-negative breast cancer were randomized to chemotherapy with or without atezolizumab, and the study showed no benefits with atezolizumab for overall survival, progression-free survival, or overall response rate, she said. “This is something to work with, because this is a very refractory population,” Dr. Ciruelos noted.
New immunotherapy combinations are needed to improve survival in advanced breast cancer patients, Dr. Ciruelos said. At the meeting, researchers presented interim data from a subset of patients in the MORPHEUS-pan breast cancer trial, a phase 1B/2 study involving multiple treatment combinations in locally advanced/metastatic breast cancer patients.
The interim analysis included 18-week data from triple-negative breast cancer patients and compared outcomes for patients randomized to atezolizumab with or without sacituzumab govitecan (SG).
The study was small, with only 31 patients in the combination arm and 11 controls, but the results were promising, with an overall response rate of 76.7% in the combination arm vs 66.7% in the control arm, Dr. Ciruelos said.
Supportive Care
Key supportive care takeaways included data on pregnancy in young breast cancer survivors and the safety of vaginal estrogen therapy in breast cancer patients with genitourinary symptoms, said Anne May, MD, of the University Medical Center Utrecht, Utrecht, Netherlands.
A study previously published in JAMA including nearly 5000 BRCA carriers who were diagnosed with invasive breast cancer at age 40 years or younger showed no association between pregnancy after breast cancer and adverse maternal or fetal outcomes, and pregnancy had no significant impact on overall survival. The authors presented new data on the safety of assisted reproductive techniques (ART) based on the 543 pregnancies in the original study, at the meeting. Of these, 436 conceived naturally, and 107 used ART. After a median of 9.1 years, ART had no effect on disease-free survival compared to natural conception (hazard ratio [HR], 0.64). Based on these findings, fertility preservation should be offered to all women who receive a breast cancer diagnosis and are interested in future fertility, Dr. May said.
Conceiving after breast cancer treatment and follow-up should not be contraindicated for young BRCA carriers, she added.No trial data are available for the effects of vaginal estrogen therapy (VET) on disease-free survival in breast cancer survivors with genitourinary symptoms caused by declining estrogen levels, Dr. May said. However, researchers in France and Switzerland conducted an emulation of a hypothetical target trial using data from the French National social security system for more than 130,000 individuals. Although VET therapy had no impact on disease-free survival in most breast cancer survivors overall, it did have a negative impact in a subset of patients with HR-positive and HR-negative tumors who were treated with aromatase inhibitors. The study was hypothetical, but important because the results suggest that clinicians can safely propose VTE to patients who report genitourinary symptoms after treatment for early-stage breast cancer with tamoxifen, but VTE should be avoided in patients treated with aromatase inhibitors, Dr. May said.
Dr. Delaloge disclosed research support to her institution from AstraZeneca, MSD, Bristol Myers Squibb, Sanofi, Taiho, Novartis, European Commission, INCa, Banque des Territoires, and Fondation Philanthropia. She also disclosed honoraria to her institution from AstraZeneca, Gilead, Novartis, Elsan, Besins, Sanofi, Exact Sciences, and Lilly, as well as travel support from Novartis.
Dr. Kok disclosed research funding from AstraZeneca, Bristol Myers Squibb, Daichi, and Roche, and advisory board membership/speaker’s fees from Alderaan Biotechnology, BIONTECH, Domain Therapeutics, AstraZeneca, Daichi, Bristol Myers Squibb, Gilead, Medscape, MSD, and Roche.
Dr. Hamilton disclosed a consulting advisory role (to her institution) for Accutar Biotechology, AstraZeneca, Daiichi Sankyo, Ellipses Pharma, Entos, Forsum Pharma, Gilead Sciences, Greenwich LifeSciences, Jazz Pharmaceuticals, Lilly, Medical Pharma Services, Mersana, Novartis, Olema Pharmaceuticals, Orum Therapeutics, Roche/Genentech, Stemline Therapeutics, ands others. She also disclosed contracted research/grant support to her institution only from Abbvie, Acerta Pharma, Accutar Biotechnology , ADC Therapeutics, AKESOBIO Australia , Amgen, Aravive, ArQule, Artios, Arvinas, AstraZeneca, AtlasMedx, BeiGene, Black Diamond and others.
Dr. Ciruelos disclosed serving as an external advisor for Roche, MSD, Gilead, AstraZeneca, Daichii Sankyo, Reveal Genomics, Pfizer, Novartis, and Lilly, as well as serving as a speaker for Roche, MSD, Gilead, AstraZeneca, Daichii Sankyo, Reveal Genomics, Pfizer, Novartis, Lilly, and Pierre Fabre. She also disclosed travel grants from Roche, Pfizer, and AstraZeneca, and research grants from Seagen and Roche.
Dr. May had no financial conflicts to disclose.
Among the topics the speakers addressed were breast cancer prevention, early breast cancer, advanced breast cancer, and supportive care.
In recent years, the way clinicians look at carcinogenesis in breast cancer has changed, and many new targets for potential early detection and prevention have emerged, said Suzette Delaloge, MD, of Gustave Roussy, Paris, France, in her presentation at the meeting.
Instant risk assessment at different time points could potentially intercept cancer among high-risk individuals, she said.
A study by Mikael Eriksson, PhD, and colleagues focused on external validation of the Profound AI tool to identify breast cancer risk in the general population. The researchers showed an area under the curve of 0.72 in their AI risk model, which has the potential to be clinically meaningful, although it must be prospectively validated, Dr. Delaloge said in her presentation.
She also reviewed two studies on the use of genes to further refine breast cancer risk among carriers. One of these, a prospective study presented in a session by Kelly-Anne Phillips, MD, of Peter MacCallum Cancer Center, Melbourne, Australia, used the CANRISK online risk assessment tool and validated increased breast cancer risk in BRCA1 and BRCA2 carriers, with AUCs of 0.79 and 0.78, respectively. The other study, which was by Maria Rezqallah Aron, MD, and colleagues examined polygenic scores as a way to refine breast cancer risk stratification among carriers of the ALM and PALB2 genes as well. These genes might be useful in identifying individuals who could benefit from early intervention, including surgery, Dr. Delaloge said.
Translational Research
“Preparing my talk, I felt like a kid in a candy store,” because of the amount of new translational research presented, including several studies of endocrine treatment–based approaches to therapy, said Marleen Kok, MD, of the Netherlands Cancer Institute, Amsterdam.
In her presentation, Dr. Kok highlighted findings from an analysis of patients in the monarchE study (a trial of high-risk patients) showing a consistent improvement in invasive disease-free survival for the subset of patients with germline BRCA1 and BRCA2 mutations who received abemaciclib plus endocrine therapy.
The value of tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes (TILs) on patients who are not receiving chemotherapy is important because of the focus on prognosis, and prospective trials are underway, she said.
A poster on the impact of chemotherapy and stromal tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes (sTILs) in stage I triple-negative breast cancer showed no association between chemotherapy and better outcomes regardless of sTILs in patients who did and did not receive chemotherapy, which has implications for potential treatment sparing in this population, Dr. Kok noted.
Artificial Intelligence (AI) was the subject of several posters at the meeting, and Dr. Kok identified a multisite European study of an automated HER2 scoring system as notable for its size and accuracy. In the study, the accuracy among pathologists was much higher with the assistance of AI, she said. Using AI for more complex analysis has shown success, she said.
Dr. Kok ended her talk with a poster that surveyed breast cancer patients about their understanding of their disease. The results showed that less than half (44%) of patients reported that their healthcare providers had given them enough information to learn about their breast cancer type, and less than one third could recall terminology about biomarkers; the study is important because it shows that clinicians need to do better in explaining these terms to patients, Dr. Kok said.
Early Breast Cancer
Right-sizing therapy, meaning identifying the right treatment for every patient, is a key element of new research in early breast cancer, said Erika Hamilton, MD, of the Sarah Cannon Research Institute, Nashville, Tenn.
She highlighted safety and treatment duration updates from the NATALEE study, which compared adjuvant ribociclib plus nonsteroidal aromatase inhibitor (NSAI) to NSAI alone for ER+/HER2- breast cancer. The current analysis presented at the meeting showed significant benefits with the addition of ribociclib and no evidence of new safety signals or adverse event exacerbations at 3 years, she said. Dose modifications had no significant impact on efficacy, she added.
The findings of no impact of dose reduction on efficacy in both the NATALEE and monarchE studies provide important information on whether dosage can be reduced in patients, which will increase the odds that patients will tolerate extended therapy with good outcomes and stay on their prescribed therapies, Dr. Hamilton emphasized.
The CARABELA study, a phase 2 trial of neoadjuvant letrozole plus abemaciclib vs adriamycin and cyclophosphamide (AC), showed clinically similar response rates but did not meet its endpoint for residual cancer burden (RCB) scores. These data add to results from other studies and show that it is too soon to universally replace neoadjuvant chemotherapy as first-line treatment for highly proliferative ER+ breast cancer, Dr. Hamilton said in her presentation.
Advanced Breast Cancer
Take-home messages about advanced breast cancer include growing evidence for the potential benefits of antibody drug conjugates (ADCs), said Eva Ciruelos, MD, of University Hospital, Madrid, Spain. The TROPION-BREAST01 study, a phase 3 randomized trial, showed significant and clinically meaningful improvement in progression-free survival in patients with previously treated, inoperable, or metastatic HR+/HER2- breast cancer who received datopotamab deruxtecan (Dato-DXd) compared with those who received chemotherapy.
Data from an additional safety analysis were presented at the meeting; although Dato-DXd, a trophoblast cell-surface antigen 2 (TROP2)–directed antibody-drug conjugate, was well-tolerated, it is important to remain aware of toxicities, notably oral mucositis, which occurred in 55.6% of the patients in the study across all grades, and ocular surface toxicity, which occurred in 40% of patients across all grades, Dr. Ciruelos emphasized.
Key research in the area of advanced triple-negative breast cancer included data from the IMPASSION 132 study. This study is “specifically centered on early relapsers,” a population often excluded from other trials, Dr. Ciruelos said. In this study, patients with advanced triple-negative breast cancer were randomized to chemotherapy with or without atezolizumab, and the study showed no benefits with atezolizumab for overall survival, progression-free survival, or overall response rate, she said. “This is something to work with, because this is a very refractory population,” Dr. Ciruelos noted.
New immunotherapy combinations are needed to improve survival in advanced breast cancer patients, Dr. Ciruelos said. At the meeting, researchers presented interim data from a subset of patients in the MORPHEUS-pan breast cancer trial, a phase 1B/2 study involving multiple treatment combinations in locally advanced/metastatic breast cancer patients.
The interim analysis included 18-week data from triple-negative breast cancer patients and compared outcomes for patients randomized to atezolizumab with or without sacituzumab govitecan (SG).
The study was small, with only 31 patients in the combination arm and 11 controls, but the results were promising, with an overall response rate of 76.7% in the combination arm vs 66.7% in the control arm, Dr. Ciruelos said.
Supportive Care
Key supportive care takeaways included data on pregnancy in young breast cancer survivors and the safety of vaginal estrogen therapy in breast cancer patients with genitourinary symptoms, said Anne May, MD, of the University Medical Center Utrecht, Utrecht, Netherlands.
A study previously published in JAMA including nearly 5000 BRCA carriers who were diagnosed with invasive breast cancer at age 40 years or younger showed no association between pregnancy after breast cancer and adverse maternal or fetal outcomes, and pregnancy had no significant impact on overall survival. The authors presented new data on the safety of assisted reproductive techniques (ART) based on the 543 pregnancies in the original study, at the meeting. Of these, 436 conceived naturally, and 107 used ART. After a median of 9.1 years, ART had no effect on disease-free survival compared to natural conception (hazard ratio [HR], 0.64). Based on these findings, fertility preservation should be offered to all women who receive a breast cancer diagnosis and are interested in future fertility, Dr. May said.
Conceiving after breast cancer treatment and follow-up should not be contraindicated for young BRCA carriers, she added.No trial data are available for the effects of vaginal estrogen therapy (VET) on disease-free survival in breast cancer survivors with genitourinary symptoms caused by declining estrogen levels, Dr. May said. However, researchers in France and Switzerland conducted an emulation of a hypothetical target trial using data from the French National social security system for more than 130,000 individuals. Although VET therapy had no impact on disease-free survival in most breast cancer survivors overall, it did have a negative impact in a subset of patients with HR-positive and HR-negative tumors who were treated with aromatase inhibitors. The study was hypothetical, but important because the results suggest that clinicians can safely propose VTE to patients who report genitourinary symptoms after treatment for early-stage breast cancer with tamoxifen, but VTE should be avoided in patients treated with aromatase inhibitors, Dr. May said.
Dr. Delaloge disclosed research support to her institution from AstraZeneca, MSD, Bristol Myers Squibb, Sanofi, Taiho, Novartis, European Commission, INCa, Banque des Territoires, and Fondation Philanthropia. She also disclosed honoraria to her institution from AstraZeneca, Gilead, Novartis, Elsan, Besins, Sanofi, Exact Sciences, and Lilly, as well as travel support from Novartis.
Dr. Kok disclosed research funding from AstraZeneca, Bristol Myers Squibb, Daichi, and Roche, and advisory board membership/speaker’s fees from Alderaan Biotechnology, BIONTECH, Domain Therapeutics, AstraZeneca, Daichi, Bristol Myers Squibb, Gilead, Medscape, MSD, and Roche.
Dr. Hamilton disclosed a consulting advisory role (to her institution) for Accutar Biotechology, AstraZeneca, Daiichi Sankyo, Ellipses Pharma, Entos, Forsum Pharma, Gilead Sciences, Greenwich LifeSciences, Jazz Pharmaceuticals, Lilly, Medical Pharma Services, Mersana, Novartis, Olema Pharmaceuticals, Orum Therapeutics, Roche/Genentech, Stemline Therapeutics, ands others. She also disclosed contracted research/grant support to her institution only from Abbvie, Acerta Pharma, Accutar Biotechnology , ADC Therapeutics, AKESOBIO Australia , Amgen, Aravive, ArQule, Artios, Arvinas, AstraZeneca, AtlasMedx, BeiGene, Black Diamond and others.
Dr. Ciruelos disclosed serving as an external advisor for Roche, MSD, Gilead, AstraZeneca, Daichii Sankyo, Reveal Genomics, Pfizer, Novartis, and Lilly, as well as serving as a speaker for Roche, MSD, Gilead, AstraZeneca, Daichii Sankyo, Reveal Genomics, Pfizer, Novartis, Lilly, and Pierre Fabre. She also disclosed travel grants from Roche, Pfizer, and AstraZeneca, and research grants from Seagen and Roche.
Dr. May had no financial conflicts to disclose.
Among the topics the speakers addressed were breast cancer prevention, early breast cancer, advanced breast cancer, and supportive care.
In recent years, the way clinicians look at carcinogenesis in breast cancer has changed, and many new targets for potential early detection and prevention have emerged, said Suzette Delaloge, MD, of Gustave Roussy, Paris, France, in her presentation at the meeting.
Instant risk assessment at different time points could potentially intercept cancer among high-risk individuals, she said.
A study by Mikael Eriksson, PhD, and colleagues focused on external validation of the Profound AI tool to identify breast cancer risk in the general population. The researchers showed an area under the curve of 0.72 in their AI risk model, which has the potential to be clinically meaningful, although it must be prospectively validated, Dr. Delaloge said in her presentation.
She also reviewed two studies on the use of genes to further refine breast cancer risk among carriers. One of these, a prospective study presented in a session by Kelly-Anne Phillips, MD, of Peter MacCallum Cancer Center, Melbourne, Australia, used the CANRISK online risk assessment tool and validated increased breast cancer risk in BRCA1 and BRCA2 carriers, with AUCs of 0.79 and 0.78, respectively. The other study, which was by Maria Rezqallah Aron, MD, and colleagues examined polygenic scores as a way to refine breast cancer risk stratification among carriers of the ALM and PALB2 genes as well. These genes might be useful in identifying individuals who could benefit from early intervention, including surgery, Dr. Delaloge said.
Translational Research
“Preparing my talk, I felt like a kid in a candy store,” because of the amount of new translational research presented, including several studies of endocrine treatment–based approaches to therapy, said Marleen Kok, MD, of the Netherlands Cancer Institute, Amsterdam.
In her presentation, Dr. Kok highlighted findings from an analysis of patients in the monarchE study (a trial of high-risk patients) showing a consistent improvement in invasive disease-free survival for the subset of patients with germline BRCA1 and BRCA2 mutations who received abemaciclib plus endocrine therapy.
The value of tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes (TILs) on patients who are not receiving chemotherapy is important because of the focus on prognosis, and prospective trials are underway, she said.
A poster on the impact of chemotherapy and stromal tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes (sTILs) in stage I triple-negative breast cancer showed no association between chemotherapy and better outcomes regardless of sTILs in patients who did and did not receive chemotherapy, which has implications for potential treatment sparing in this population, Dr. Kok noted.
Artificial Intelligence (AI) was the subject of several posters at the meeting, and Dr. Kok identified a multisite European study of an automated HER2 scoring system as notable for its size and accuracy. In the study, the accuracy among pathologists was much higher with the assistance of AI, she said. Using AI for more complex analysis has shown success, she said.
Dr. Kok ended her talk with a poster that surveyed breast cancer patients about their understanding of their disease. The results showed that less than half (44%) of patients reported that their healthcare providers had given them enough information to learn about their breast cancer type, and less than one third could recall terminology about biomarkers; the study is important because it shows that clinicians need to do better in explaining these terms to patients, Dr. Kok said.
Early Breast Cancer
Right-sizing therapy, meaning identifying the right treatment for every patient, is a key element of new research in early breast cancer, said Erika Hamilton, MD, of the Sarah Cannon Research Institute, Nashville, Tenn.
She highlighted safety and treatment duration updates from the NATALEE study, which compared adjuvant ribociclib plus nonsteroidal aromatase inhibitor (NSAI) to NSAI alone for ER+/HER2- breast cancer. The current analysis presented at the meeting showed significant benefits with the addition of ribociclib and no evidence of new safety signals or adverse event exacerbations at 3 years, she said. Dose modifications had no significant impact on efficacy, she added.
The findings of no impact of dose reduction on efficacy in both the NATALEE and monarchE studies provide important information on whether dosage can be reduced in patients, which will increase the odds that patients will tolerate extended therapy with good outcomes and stay on their prescribed therapies, Dr. Hamilton emphasized.
The CARABELA study, a phase 2 trial of neoadjuvant letrozole plus abemaciclib vs adriamycin and cyclophosphamide (AC), showed clinically similar response rates but did not meet its endpoint for residual cancer burden (RCB) scores. These data add to results from other studies and show that it is too soon to universally replace neoadjuvant chemotherapy as first-line treatment for highly proliferative ER+ breast cancer, Dr. Hamilton said in her presentation.
Advanced Breast Cancer
Take-home messages about advanced breast cancer include growing evidence for the potential benefits of antibody drug conjugates (ADCs), said Eva Ciruelos, MD, of University Hospital, Madrid, Spain. The TROPION-BREAST01 study, a phase 3 randomized trial, showed significant and clinically meaningful improvement in progression-free survival in patients with previously treated, inoperable, or metastatic HR+/HER2- breast cancer who received datopotamab deruxtecan (Dato-DXd) compared with those who received chemotherapy.
Data from an additional safety analysis were presented at the meeting; although Dato-DXd, a trophoblast cell-surface antigen 2 (TROP2)–directed antibody-drug conjugate, was well-tolerated, it is important to remain aware of toxicities, notably oral mucositis, which occurred in 55.6% of the patients in the study across all grades, and ocular surface toxicity, which occurred in 40% of patients across all grades, Dr. Ciruelos emphasized.
Key research in the area of advanced triple-negative breast cancer included data from the IMPASSION 132 study. This study is “specifically centered on early relapsers,” a population often excluded from other trials, Dr. Ciruelos said. In this study, patients with advanced triple-negative breast cancer were randomized to chemotherapy with or without atezolizumab, and the study showed no benefits with atezolizumab for overall survival, progression-free survival, or overall response rate, she said. “This is something to work with, because this is a very refractory population,” Dr. Ciruelos noted.
New immunotherapy combinations are needed to improve survival in advanced breast cancer patients, Dr. Ciruelos said. At the meeting, researchers presented interim data from a subset of patients in the MORPHEUS-pan breast cancer trial, a phase 1B/2 study involving multiple treatment combinations in locally advanced/metastatic breast cancer patients.
The interim analysis included 18-week data from triple-negative breast cancer patients and compared outcomes for patients randomized to atezolizumab with or without sacituzumab govitecan (SG).
The study was small, with only 31 patients in the combination arm and 11 controls, but the results were promising, with an overall response rate of 76.7% in the combination arm vs 66.7% in the control arm, Dr. Ciruelos said.
Supportive Care
Key supportive care takeaways included data on pregnancy in young breast cancer survivors and the safety of vaginal estrogen therapy in breast cancer patients with genitourinary symptoms, said Anne May, MD, of the University Medical Center Utrecht, Utrecht, Netherlands.
A study previously published in JAMA including nearly 5000 BRCA carriers who were diagnosed with invasive breast cancer at age 40 years or younger showed no association between pregnancy after breast cancer and adverse maternal or fetal outcomes, and pregnancy had no significant impact on overall survival. The authors presented new data on the safety of assisted reproductive techniques (ART) based on the 543 pregnancies in the original study, at the meeting. Of these, 436 conceived naturally, and 107 used ART. After a median of 9.1 years, ART had no effect on disease-free survival compared to natural conception (hazard ratio [HR], 0.64). Based on these findings, fertility preservation should be offered to all women who receive a breast cancer diagnosis and are interested in future fertility, Dr. May said.
Conceiving after breast cancer treatment and follow-up should not be contraindicated for young BRCA carriers, she added.No trial data are available for the effects of vaginal estrogen therapy (VET) on disease-free survival in breast cancer survivors with genitourinary symptoms caused by declining estrogen levels, Dr. May said. However, researchers in France and Switzerland conducted an emulation of a hypothetical target trial using data from the French National social security system for more than 130,000 individuals. Although VET therapy had no impact on disease-free survival in most breast cancer survivors overall, it did have a negative impact in a subset of patients with HR-positive and HR-negative tumors who were treated with aromatase inhibitors. The study was hypothetical, but important because the results suggest that clinicians can safely propose VTE to patients who report genitourinary symptoms after treatment for early-stage breast cancer with tamoxifen, but VTE should be avoided in patients treated with aromatase inhibitors, Dr. May said.
Dr. Delaloge disclosed research support to her institution from AstraZeneca, MSD, Bristol Myers Squibb, Sanofi, Taiho, Novartis, European Commission, INCa, Banque des Territoires, and Fondation Philanthropia. She also disclosed honoraria to her institution from AstraZeneca, Gilead, Novartis, Elsan, Besins, Sanofi, Exact Sciences, and Lilly, as well as travel support from Novartis.
Dr. Kok disclosed research funding from AstraZeneca, Bristol Myers Squibb, Daichi, and Roche, and advisory board membership/speaker’s fees from Alderaan Biotechnology, BIONTECH, Domain Therapeutics, AstraZeneca, Daichi, Bristol Myers Squibb, Gilead, Medscape, MSD, and Roche.
Dr. Hamilton disclosed a consulting advisory role (to her institution) for Accutar Biotechology, AstraZeneca, Daiichi Sankyo, Ellipses Pharma, Entos, Forsum Pharma, Gilead Sciences, Greenwich LifeSciences, Jazz Pharmaceuticals, Lilly, Medical Pharma Services, Mersana, Novartis, Olema Pharmaceuticals, Orum Therapeutics, Roche/Genentech, Stemline Therapeutics, ands others. She also disclosed contracted research/grant support to her institution only from Abbvie, Acerta Pharma, Accutar Biotechnology , ADC Therapeutics, AKESOBIO Australia , Amgen, Aravive, ArQule, Artios, Arvinas, AstraZeneca, AtlasMedx, BeiGene, Black Diamond and others.
Dr. Ciruelos disclosed serving as an external advisor for Roche, MSD, Gilead, AstraZeneca, Daichii Sankyo, Reveal Genomics, Pfizer, Novartis, and Lilly, as well as serving as a speaker for Roche, MSD, Gilead, AstraZeneca, Daichii Sankyo, Reveal Genomics, Pfizer, Novartis, Lilly, and Pierre Fabre. She also disclosed travel grants from Roche, Pfizer, and AstraZeneca, and research grants from Seagen and Roche.
Dr. May had no financial conflicts to disclose.
FROM ESMO BREAST CANCER 2024
Urine Tests Could Be ‘Enormous Step’ in Diagnosing Cancer
Emerging science suggests that the body’s “liquid gold” could be particularly useful for liquid biopsies, offering a convenient, pain-free, and cost-effective way to spot otherwise hard-to-detect cancers.
“The search for cancer biomarkers that can be detected in urine could provide an enormous step forward to decrease cancer patient mortality,” said Kenneth R. Shroyer, MD, PhD, a pathologist at Stony Brook University, Stony Brook, New York, who studies cancer biomarkers.
Physicians have long known that urine can reveal a lot about our health — that’s why urinalysis has been part of medicine for 6000 years. Urine tests can detect diabetes, pregnancy, drug use, and urinary or kidney conditions.
But other conditions leave clues in urine, too, and cancer may be one of the most promising. “Urine testing could detect biomarkers of early-stage cancers, not only from local but also distant sites,” Dr. Shroyer said. It could also help flag recurrence in cancer survivors who have undergone treatment.
Granted, cancer biomarkers in urine are not nearly as widely studied as those in the blood, Dr. Shroyer noted. But a new wave of urine tests suggests research is gaining pace.
“The recent availability of high-throughput screening technologies has enabled researchers to investigate cancer from a top-down, comprehensive approach,” said Pak Kin Wong, PhD, professor of mechanical engineering, biomedical engineering, and surgery at The Pennsylvania State University. “We are starting to understand the rich information that can be obtained from urine.”
Urine is mostly water (about 95%) and urea, a metabolic byproduct that imparts that signature yellow color (about 2%). The other 3% is a mix of waste products, minerals, and other compounds the kidneys removed from the blood. Even in trace amounts, these substances say a lot.
Among them are “exfoliated cancer cells, cell-free DNA, hormones, and the urine microbiota — the collection of microbes in our urinary tract system,” Dr. Wong said.
“It is highly promising to be one of the major biological fluids used for screening, diagnosis, prognosis, and monitoring treatment efficiency in the era of precision medicine,” Dr. Wong said.
How Urine Testing Could Reveal Cancer
Still, as exciting as the prospect is, there’s a lot to consider in the hunt for cancer biomarkers in urine. These biomarkers must be able to pass through the renal nephrons (filtering units), remain stable in urine, and have high-level sensitivity, Dr. Shroyer said. They should also have high specificity for cancer vs benign conditions and be expressed at early stages, before the primary tumor has spread.
“At this stage, few circulating biomarkers have been found that are both sensitive and specific for early-stage disease,” said Dr. Shroyer.
But there are a few promising examples under investigation in humans:
Prostate cancer. Researchers at the University of Michigan have developed a urine test that detects high-grade prostate cancer more accurately than existing tests, including PHI, SelectMDx, 4Kscore, EPI, MPS, and IsoPSA.
The MyProstateScore 2.0 (MPS2) test, which looks for 18 genes associated with high-grade tumors, could reduce unnecessary biopsies in men with elevated prostate-specific antigen levels, according to a paper published in JAMA Oncology.
It makes sense. The prostate gland secretes fluid that becomes part of the semen, traces of which enter urine. After a digital rectal exam, even more prostate fluid enters the urine. If a patient has prostate cancer, genetic material from the cancer cells will infiltrate the urine.
In the MPS2 test, researchers used polymerase chain reaction (PCR) testing in urine. “The technology used for COVID PCR is essentially the same as the PCR used to detect transcripts associated with high-grade prostate cancer in urine,” said study author Arul Chinnaiyan, MD, PhD, director of the Michigan Center for Translational Pathology at the University of Michigan, Ann Arbor. “In the case of the MPS2 test, we are doing PCR on 18 genes simultaneously on urine samples.”
A statistical model uses levels of that genetic material to predict the risk for high-grade disease, helping doctors decide what to do next. At 95% sensitivity, the MPS2 model could eliminate 35%-45% of unnecessary biopsies, compared with 15%-30% for the other tests, and reduce repeat biopsies by 46%-51%, compared with 9%-21% for the other tests.
Head and neck cancer. In a paper published in JCI Insight, researchers described a test that finds ultra-short fragments of DNA in urine to enable early detection of head and neck cancers caused by human papillomavirus.
“Our data show that a relatively small volume of urine (30-60 mL) gives overall detection results comparable to a tube of blood,” said study author Muneesh Tewari, MD, PhD, professor of hematology and oncology at the University of Michigan .
A larger volume of urine could potentially “make cancer detection even more sensitive than blood,” Dr. Tewari said, “allowing cancers to be detected at the earliest stages when they are more curable.”
The team used a technique called droplet digital PCR to detect DNA fragments that are “ultra-short” (less than 50 base pairs long) and usually missed by conventional PCR testing. This transrenal cell-free tumor DNA, which travels from the tumor into the bloodstream, is broken down small enough to pass through the kidneys and into the urine. But the fragments are still long enough to carry information about the tumor’s genetic signature.
This test could spot cancer before a tumor grows big enough — about a centimeter wide and carrying a billion cells — to spot on a CT scan or other imaging test. “When we are instead detecting fragments of DNA released from a tumor,” said Dr. Tewari, “our testing methods are very sensitive and can detect DNA in urine that came from just 5-10 cells in a tumor that died and released their DNA into the blood, which then made its way into the urine.”
Pancreatic cancer. Pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma is one of the deadliest cancers, largely because it is diagnosed so late. A urine panel now in clinical trials could help doctors diagnose the cancer before it has spread so more people can have the tumor surgically removed, improving prognosis.
Using enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay test, a common lab method that detects antibodies and other proteins, the team measured expression levels for three genes (LYVE1, REG1B, and TFF1) in urine samples collected from people up to 5 years before they were diagnosed with pancreatic cancer. The researchers combined this result with patients’ urinary creatinine levels, a common component of existing urinalysis, and their age to develop a risk score.
This score performed similarly to an existing blood test, CA19-9, in predicting patients’ risk for pancreatic cancer up to 1 year before diagnosis. When combined with CA19-9, the urinary panel helped spot cancer up to 2 years before diagnosis.
According to a paper in the International Journal of Cancer, “the urine panel and affiliated PancRISK are currently being validated in a prospective clinical study (UroPanc).” If all goes well, they could be implemented in clinical practice in a few years as a “noninvasive stratification tool” to identify patients for further testing, speeding up diagnosis, and saving lives.
Limitations and Promises
Each cancer type is different, and more research is needed to map out which substances in urine predict which cancers and to develop tests for mass adoption. “There are medical and technological hurdles to the large-scale implementation of urine analysis for complex diseases such as cancer,” said Dr. Wong.
One possibility: Scientists and clinicians could collaborate and use artificial intelligence techniques to combine urine test results with other data.
“It is likely that future diagnostics may combine urine with other biological samples such as feces and saliva, among others,” said Dr. Wong. “This is especially true when novel data science and machine learning techniques can integrate comprehensive data from patients that span genetic, proteomic, metabolic, microbiomic, and even behavioral data to evaluate a patient’s condition.”
One thing that excites Dr. Tewari about urine-based cancer testing: “We think it could be especially impactful for patients living in rural areas or other areas with less access to healthcare services,” he said.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Emerging science suggests that the body’s “liquid gold” could be particularly useful for liquid biopsies, offering a convenient, pain-free, and cost-effective way to spot otherwise hard-to-detect cancers.
“The search for cancer biomarkers that can be detected in urine could provide an enormous step forward to decrease cancer patient mortality,” said Kenneth R. Shroyer, MD, PhD, a pathologist at Stony Brook University, Stony Brook, New York, who studies cancer biomarkers.
Physicians have long known that urine can reveal a lot about our health — that’s why urinalysis has been part of medicine for 6000 years. Urine tests can detect diabetes, pregnancy, drug use, and urinary or kidney conditions.
But other conditions leave clues in urine, too, and cancer may be one of the most promising. “Urine testing could detect biomarkers of early-stage cancers, not only from local but also distant sites,” Dr. Shroyer said. It could also help flag recurrence in cancer survivors who have undergone treatment.
Granted, cancer biomarkers in urine are not nearly as widely studied as those in the blood, Dr. Shroyer noted. But a new wave of urine tests suggests research is gaining pace.
“The recent availability of high-throughput screening technologies has enabled researchers to investigate cancer from a top-down, comprehensive approach,” said Pak Kin Wong, PhD, professor of mechanical engineering, biomedical engineering, and surgery at The Pennsylvania State University. “We are starting to understand the rich information that can be obtained from urine.”
Urine is mostly water (about 95%) and urea, a metabolic byproduct that imparts that signature yellow color (about 2%). The other 3% is a mix of waste products, minerals, and other compounds the kidneys removed from the blood. Even in trace amounts, these substances say a lot.
Among them are “exfoliated cancer cells, cell-free DNA, hormones, and the urine microbiota — the collection of microbes in our urinary tract system,” Dr. Wong said.
“It is highly promising to be one of the major biological fluids used for screening, diagnosis, prognosis, and monitoring treatment efficiency in the era of precision medicine,” Dr. Wong said.
How Urine Testing Could Reveal Cancer
Still, as exciting as the prospect is, there’s a lot to consider in the hunt for cancer biomarkers in urine. These biomarkers must be able to pass through the renal nephrons (filtering units), remain stable in urine, and have high-level sensitivity, Dr. Shroyer said. They should also have high specificity for cancer vs benign conditions and be expressed at early stages, before the primary tumor has spread.
“At this stage, few circulating biomarkers have been found that are both sensitive and specific for early-stage disease,” said Dr. Shroyer.
But there are a few promising examples under investigation in humans:
Prostate cancer. Researchers at the University of Michigan have developed a urine test that detects high-grade prostate cancer more accurately than existing tests, including PHI, SelectMDx, 4Kscore, EPI, MPS, and IsoPSA.
The MyProstateScore 2.0 (MPS2) test, which looks for 18 genes associated with high-grade tumors, could reduce unnecessary biopsies in men with elevated prostate-specific antigen levels, according to a paper published in JAMA Oncology.
It makes sense. The prostate gland secretes fluid that becomes part of the semen, traces of which enter urine. After a digital rectal exam, even more prostate fluid enters the urine. If a patient has prostate cancer, genetic material from the cancer cells will infiltrate the urine.
In the MPS2 test, researchers used polymerase chain reaction (PCR) testing in urine. “The technology used for COVID PCR is essentially the same as the PCR used to detect transcripts associated with high-grade prostate cancer in urine,” said study author Arul Chinnaiyan, MD, PhD, director of the Michigan Center for Translational Pathology at the University of Michigan, Ann Arbor. “In the case of the MPS2 test, we are doing PCR on 18 genes simultaneously on urine samples.”
A statistical model uses levels of that genetic material to predict the risk for high-grade disease, helping doctors decide what to do next. At 95% sensitivity, the MPS2 model could eliminate 35%-45% of unnecessary biopsies, compared with 15%-30% for the other tests, and reduce repeat biopsies by 46%-51%, compared with 9%-21% for the other tests.
Head and neck cancer. In a paper published in JCI Insight, researchers described a test that finds ultra-short fragments of DNA in urine to enable early detection of head and neck cancers caused by human papillomavirus.
“Our data show that a relatively small volume of urine (30-60 mL) gives overall detection results comparable to a tube of blood,” said study author Muneesh Tewari, MD, PhD, professor of hematology and oncology at the University of Michigan .
A larger volume of urine could potentially “make cancer detection even more sensitive than blood,” Dr. Tewari said, “allowing cancers to be detected at the earliest stages when they are more curable.”
The team used a technique called droplet digital PCR to detect DNA fragments that are “ultra-short” (less than 50 base pairs long) and usually missed by conventional PCR testing. This transrenal cell-free tumor DNA, which travels from the tumor into the bloodstream, is broken down small enough to pass through the kidneys and into the urine. But the fragments are still long enough to carry information about the tumor’s genetic signature.
This test could spot cancer before a tumor grows big enough — about a centimeter wide and carrying a billion cells — to spot on a CT scan or other imaging test. “When we are instead detecting fragments of DNA released from a tumor,” said Dr. Tewari, “our testing methods are very sensitive and can detect DNA in urine that came from just 5-10 cells in a tumor that died and released their DNA into the blood, which then made its way into the urine.”
Pancreatic cancer. Pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma is one of the deadliest cancers, largely because it is diagnosed so late. A urine panel now in clinical trials could help doctors diagnose the cancer before it has spread so more people can have the tumor surgically removed, improving prognosis.
Using enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay test, a common lab method that detects antibodies and other proteins, the team measured expression levels for three genes (LYVE1, REG1B, and TFF1) in urine samples collected from people up to 5 years before they were diagnosed with pancreatic cancer. The researchers combined this result with patients’ urinary creatinine levels, a common component of existing urinalysis, and their age to develop a risk score.
This score performed similarly to an existing blood test, CA19-9, in predicting patients’ risk for pancreatic cancer up to 1 year before diagnosis. When combined with CA19-9, the urinary panel helped spot cancer up to 2 years before diagnosis.
According to a paper in the International Journal of Cancer, “the urine panel and affiliated PancRISK are currently being validated in a prospective clinical study (UroPanc).” If all goes well, they could be implemented in clinical practice in a few years as a “noninvasive stratification tool” to identify patients for further testing, speeding up diagnosis, and saving lives.
Limitations and Promises
Each cancer type is different, and more research is needed to map out which substances in urine predict which cancers and to develop tests for mass adoption. “There are medical and technological hurdles to the large-scale implementation of urine analysis for complex diseases such as cancer,” said Dr. Wong.
One possibility: Scientists and clinicians could collaborate and use artificial intelligence techniques to combine urine test results with other data.
“It is likely that future diagnostics may combine urine with other biological samples such as feces and saliva, among others,” said Dr. Wong. “This is especially true when novel data science and machine learning techniques can integrate comprehensive data from patients that span genetic, proteomic, metabolic, microbiomic, and even behavioral data to evaluate a patient’s condition.”
One thing that excites Dr. Tewari about urine-based cancer testing: “We think it could be especially impactful for patients living in rural areas or other areas with less access to healthcare services,” he said.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Emerging science suggests that the body’s “liquid gold” could be particularly useful for liquid biopsies, offering a convenient, pain-free, and cost-effective way to spot otherwise hard-to-detect cancers.
“The search for cancer biomarkers that can be detected in urine could provide an enormous step forward to decrease cancer patient mortality,” said Kenneth R. Shroyer, MD, PhD, a pathologist at Stony Brook University, Stony Brook, New York, who studies cancer biomarkers.
Physicians have long known that urine can reveal a lot about our health — that’s why urinalysis has been part of medicine for 6000 years. Urine tests can detect diabetes, pregnancy, drug use, and urinary or kidney conditions.
But other conditions leave clues in urine, too, and cancer may be one of the most promising. “Urine testing could detect biomarkers of early-stage cancers, not only from local but also distant sites,” Dr. Shroyer said. It could also help flag recurrence in cancer survivors who have undergone treatment.
Granted, cancer biomarkers in urine are not nearly as widely studied as those in the blood, Dr. Shroyer noted. But a new wave of urine tests suggests research is gaining pace.
“The recent availability of high-throughput screening technologies has enabled researchers to investigate cancer from a top-down, comprehensive approach,” said Pak Kin Wong, PhD, professor of mechanical engineering, biomedical engineering, and surgery at The Pennsylvania State University. “We are starting to understand the rich information that can be obtained from urine.”
Urine is mostly water (about 95%) and urea, a metabolic byproduct that imparts that signature yellow color (about 2%). The other 3% is a mix of waste products, minerals, and other compounds the kidneys removed from the blood. Even in trace amounts, these substances say a lot.
Among them are “exfoliated cancer cells, cell-free DNA, hormones, and the urine microbiota — the collection of microbes in our urinary tract system,” Dr. Wong said.
“It is highly promising to be one of the major biological fluids used for screening, diagnosis, prognosis, and monitoring treatment efficiency in the era of precision medicine,” Dr. Wong said.
How Urine Testing Could Reveal Cancer
Still, as exciting as the prospect is, there’s a lot to consider in the hunt for cancer biomarkers in urine. These biomarkers must be able to pass through the renal nephrons (filtering units), remain stable in urine, and have high-level sensitivity, Dr. Shroyer said. They should also have high specificity for cancer vs benign conditions and be expressed at early stages, before the primary tumor has spread.
“At this stage, few circulating biomarkers have been found that are both sensitive and specific for early-stage disease,” said Dr. Shroyer.
But there are a few promising examples under investigation in humans:
Prostate cancer. Researchers at the University of Michigan have developed a urine test that detects high-grade prostate cancer more accurately than existing tests, including PHI, SelectMDx, 4Kscore, EPI, MPS, and IsoPSA.
The MyProstateScore 2.0 (MPS2) test, which looks for 18 genes associated with high-grade tumors, could reduce unnecessary biopsies in men with elevated prostate-specific antigen levels, according to a paper published in JAMA Oncology.
It makes sense. The prostate gland secretes fluid that becomes part of the semen, traces of which enter urine. After a digital rectal exam, even more prostate fluid enters the urine. If a patient has prostate cancer, genetic material from the cancer cells will infiltrate the urine.
In the MPS2 test, researchers used polymerase chain reaction (PCR) testing in urine. “The technology used for COVID PCR is essentially the same as the PCR used to detect transcripts associated with high-grade prostate cancer in urine,” said study author Arul Chinnaiyan, MD, PhD, director of the Michigan Center for Translational Pathology at the University of Michigan, Ann Arbor. “In the case of the MPS2 test, we are doing PCR on 18 genes simultaneously on urine samples.”
A statistical model uses levels of that genetic material to predict the risk for high-grade disease, helping doctors decide what to do next. At 95% sensitivity, the MPS2 model could eliminate 35%-45% of unnecessary biopsies, compared with 15%-30% for the other tests, and reduce repeat biopsies by 46%-51%, compared with 9%-21% for the other tests.
Head and neck cancer. In a paper published in JCI Insight, researchers described a test that finds ultra-short fragments of DNA in urine to enable early detection of head and neck cancers caused by human papillomavirus.
“Our data show that a relatively small volume of urine (30-60 mL) gives overall detection results comparable to a tube of blood,” said study author Muneesh Tewari, MD, PhD, professor of hematology and oncology at the University of Michigan .
A larger volume of urine could potentially “make cancer detection even more sensitive than blood,” Dr. Tewari said, “allowing cancers to be detected at the earliest stages when they are more curable.”
The team used a technique called droplet digital PCR to detect DNA fragments that are “ultra-short” (less than 50 base pairs long) and usually missed by conventional PCR testing. This transrenal cell-free tumor DNA, which travels from the tumor into the bloodstream, is broken down small enough to pass through the kidneys and into the urine. But the fragments are still long enough to carry information about the tumor’s genetic signature.
This test could spot cancer before a tumor grows big enough — about a centimeter wide and carrying a billion cells — to spot on a CT scan or other imaging test. “When we are instead detecting fragments of DNA released from a tumor,” said Dr. Tewari, “our testing methods are very sensitive and can detect DNA in urine that came from just 5-10 cells in a tumor that died and released their DNA into the blood, which then made its way into the urine.”
Pancreatic cancer. Pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma is one of the deadliest cancers, largely because it is diagnosed so late. A urine panel now in clinical trials could help doctors diagnose the cancer before it has spread so more people can have the tumor surgically removed, improving prognosis.
Using enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay test, a common lab method that detects antibodies and other proteins, the team measured expression levels for three genes (LYVE1, REG1B, and TFF1) in urine samples collected from people up to 5 years before they were diagnosed with pancreatic cancer. The researchers combined this result with patients’ urinary creatinine levels, a common component of existing urinalysis, and their age to develop a risk score.
This score performed similarly to an existing blood test, CA19-9, in predicting patients’ risk for pancreatic cancer up to 1 year before diagnosis. When combined with CA19-9, the urinary panel helped spot cancer up to 2 years before diagnosis.
According to a paper in the International Journal of Cancer, “the urine panel and affiliated PancRISK are currently being validated in a prospective clinical study (UroPanc).” If all goes well, they could be implemented in clinical practice in a few years as a “noninvasive stratification tool” to identify patients for further testing, speeding up diagnosis, and saving lives.
Limitations and Promises
Each cancer type is different, and more research is needed to map out which substances in urine predict which cancers and to develop tests for mass adoption. “There are medical and technological hurdles to the large-scale implementation of urine analysis for complex diseases such as cancer,” said Dr. Wong.
One possibility: Scientists and clinicians could collaborate and use artificial intelligence techniques to combine urine test results with other data.
“It is likely that future diagnostics may combine urine with other biological samples such as feces and saliva, among others,” said Dr. Wong. “This is especially true when novel data science and machine learning techniques can integrate comprehensive data from patients that span genetic, proteomic, metabolic, microbiomic, and even behavioral data to evaluate a patient’s condition.”
One thing that excites Dr. Tewari about urine-based cancer testing: “We think it could be especially impactful for patients living in rural areas or other areas with less access to healthcare services,” he said.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Treatments for Early HS Range From Topical Therapies to Laser Hair Removal
This can be challenging because to date, no Food and Drug Administration–approved treatments exist for early-stage HS and only two biologics exist for moderate to severe disease.
“For someone with occasional nodules and abscesses, we often use antibiotics and topical antiseptics,” Christopher Sayed, MD, a dermatologist at the HS and Follicular Disorders Clinic at the University of North Carolina, Chapel Hill, told this news organization. “We may use these daily for weeks or months or just provide them to use for 1-2 weeks at a time for intermittent flares if a patient doesn’t want to take a pill every day,” he said. “For women, hormonal options like oral contraceptive pills and spironolactone can be a great option” if they don’t mind taking a daily pill.
Topical options that Jennifer L. Hsiao, MD, reaches for in her role as director of the HS clinic at the University of Southern California, Los Angeles, include chlorhexidine wash, topical clindamycin, and topical resorcinol. Systemic medications include oral antibiotics such as doxycycline or clindamycin, while hormonal options include oral contraceptives and/or spironolactone for women and finasteride for men.
Laser hair removal for both men and women can also help treat lesions and abscesses in the groin and axillae, since reducing hair follicles tends to result in fewer follicles that become inflamed and form nodules and abscesses over time, “but it requires multiple visits and not all patients have access to it,” Dr. Sayed said. “Once patients start to develop tunnels or scars or fail to respond to some of these other treatments, I am quick to open the conversation on biologics to help avoid progression and long-term need for surgery.”
Metformin Among Options to Consider
According to Dr. Hsiao, other treatment options to consider trying in patients with mild HS include metformin, “especially in patients who also have prediabetes, PCOS, or obesity;” isotretinoin if the patient has concomitant severe acne; botulinum toxin injections; apremilast or topical roflumilast, and antihyperhidrosis medications such as prescription aluminum chloride topicals, glycopyrronium wipes, and glycopyrrolate.
Recommending lifestyle modifications such as smoking cessation and weight loss for patients diagnosed with early-stage HS is “challenging,” Dr. Sayed said, “because the evidence on different triggers and lifestyle modifications isn’t very strong. There can also be a lot of stigmas around weight and smoking in HS, and it can alienate patients to go straight to these topics in the first visit.”
Many patients also ask what dietary changes they can make to improve their HS. “The most common things patients tend to bring up are dairy avoidance and reducing carbohydrates,” he said. “Supplements like zinc and turmeric are also frequently brought up by patients and some find them helpful. Once rapport is built, I may discuss smoking cessation as potentially helping prevent as much activity over time or weight loss as possibly helping improve response to treatments, but I don’t promise that these things always help since modifying them doesn’t always lead to improvement.”
Dr. Hsiao noted that existing research suggests that following a Mediterranean diet may benefit HS symptoms.
Early Data on Ruxolitinib Cream Promising
At the 2024 annual meeting of the American Academy of Dermatology, researchers reported on the results of a phase 2 study, which found that topical 1.5% ruxolitinib, a Janus kinase (JAK) inhibitor (currently FDA-approved for atopic dermatitis) was effective in reducing abscess and inflammatory nodule count in patients with mild HS. “There is a major need for this kind of option, and the early results are promising,” said Dr. Sayed, who was not involved with the study. “It’s very difficult to get this covered for patients currently since it is off label for HS. We’ve gotten it for a few patients, and one has really liked it, but it’s unclear how consistent the others were with their use, and their level of improvement was not clear to me.”
For mild HS, he added, “the most important area in which we’ve seen growing evidence is around hair removal lasers such as Nd:YAG and alexandrite lasers. Improving access for patients is a major priority in the coming years.”
According to Dr. Hsiao, other approaches being studied for treating mild HS include a topical aryl hydrocarbon receptor agonist known as AT193, and oral medications, such as phosphodiesterase-4 inhibitors. Laser therapies are also being studied, “such as fractional ablative CO2 laser therapy combined with topical triamcinolone,” she said. “However, the majority of ongoing HS trials are for moderate to severe disease, so there is certainly a need for more investigation into mild HS treatment approaches.”
Dr. Sayed disclosed that he is secretary of the HS Foundation and a member of the European HS Foundation. He has served as a consultant for AbbVie, Alumis, AstraZeneca, Incyte, InflaRx, Novartis, Sanofi, Sonoma Biotherapeutics, and UCB; as a speaker for AbbVie, Novartis, and UCB; and as an investigator for Chemocentryx, Incyte, InflaRx, Novartis, and UCB. Dr. Hsiao disclosed that she is a member of the board of directors for the HS Foundation and has served as a consultant for AbbVie, Aclaris, Boehringer Ingelheim, Incyte, Novartis, and UCB; as a speaker for AbbVie, Novartis, Sanofi Regeneron, and UCB; and as an investigator for Amgen, Boehringer Ingelheim, and Incyte.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
This can be challenging because to date, no Food and Drug Administration–approved treatments exist for early-stage HS and only two biologics exist for moderate to severe disease.
“For someone with occasional nodules and abscesses, we often use antibiotics and topical antiseptics,” Christopher Sayed, MD, a dermatologist at the HS and Follicular Disorders Clinic at the University of North Carolina, Chapel Hill, told this news organization. “We may use these daily for weeks or months or just provide them to use for 1-2 weeks at a time for intermittent flares if a patient doesn’t want to take a pill every day,” he said. “For women, hormonal options like oral contraceptive pills and spironolactone can be a great option” if they don’t mind taking a daily pill.
Topical options that Jennifer L. Hsiao, MD, reaches for in her role as director of the HS clinic at the University of Southern California, Los Angeles, include chlorhexidine wash, topical clindamycin, and topical resorcinol. Systemic medications include oral antibiotics such as doxycycline or clindamycin, while hormonal options include oral contraceptives and/or spironolactone for women and finasteride for men.
Laser hair removal for both men and women can also help treat lesions and abscesses in the groin and axillae, since reducing hair follicles tends to result in fewer follicles that become inflamed and form nodules and abscesses over time, “but it requires multiple visits and not all patients have access to it,” Dr. Sayed said. “Once patients start to develop tunnels or scars or fail to respond to some of these other treatments, I am quick to open the conversation on biologics to help avoid progression and long-term need for surgery.”
Metformin Among Options to Consider
According to Dr. Hsiao, other treatment options to consider trying in patients with mild HS include metformin, “especially in patients who also have prediabetes, PCOS, or obesity;” isotretinoin if the patient has concomitant severe acne; botulinum toxin injections; apremilast or topical roflumilast, and antihyperhidrosis medications such as prescription aluminum chloride topicals, glycopyrronium wipes, and glycopyrrolate.
Recommending lifestyle modifications such as smoking cessation and weight loss for patients diagnosed with early-stage HS is “challenging,” Dr. Sayed said, “because the evidence on different triggers and lifestyle modifications isn’t very strong. There can also be a lot of stigmas around weight and smoking in HS, and it can alienate patients to go straight to these topics in the first visit.”
Many patients also ask what dietary changes they can make to improve their HS. “The most common things patients tend to bring up are dairy avoidance and reducing carbohydrates,” he said. “Supplements like zinc and turmeric are also frequently brought up by patients and some find them helpful. Once rapport is built, I may discuss smoking cessation as potentially helping prevent as much activity over time or weight loss as possibly helping improve response to treatments, but I don’t promise that these things always help since modifying them doesn’t always lead to improvement.”
Dr. Hsiao noted that existing research suggests that following a Mediterranean diet may benefit HS symptoms.
Early Data on Ruxolitinib Cream Promising
At the 2024 annual meeting of the American Academy of Dermatology, researchers reported on the results of a phase 2 study, which found that topical 1.5% ruxolitinib, a Janus kinase (JAK) inhibitor (currently FDA-approved for atopic dermatitis) was effective in reducing abscess and inflammatory nodule count in patients with mild HS. “There is a major need for this kind of option, and the early results are promising,” said Dr. Sayed, who was not involved with the study. “It’s very difficult to get this covered for patients currently since it is off label for HS. We’ve gotten it for a few patients, and one has really liked it, but it’s unclear how consistent the others were with their use, and their level of improvement was not clear to me.”
For mild HS, he added, “the most important area in which we’ve seen growing evidence is around hair removal lasers such as Nd:YAG and alexandrite lasers. Improving access for patients is a major priority in the coming years.”
According to Dr. Hsiao, other approaches being studied for treating mild HS include a topical aryl hydrocarbon receptor agonist known as AT193, and oral medications, such as phosphodiesterase-4 inhibitors. Laser therapies are also being studied, “such as fractional ablative CO2 laser therapy combined with topical triamcinolone,” she said. “However, the majority of ongoing HS trials are for moderate to severe disease, so there is certainly a need for more investigation into mild HS treatment approaches.”
Dr. Sayed disclosed that he is secretary of the HS Foundation and a member of the European HS Foundation. He has served as a consultant for AbbVie, Alumis, AstraZeneca, Incyte, InflaRx, Novartis, Sanofi, Sonoma Biotherapeutics, and UCB; as a speaker for AbbVie, Novartis, and UCB; and as an investigator for Chemocentryx, Incyte, InflaRx, Novartis, and UCB. Dr. Hsiao disclosed that she is a member of the board of directors for the HS Foundation and has served as a consultant for AbbVie, Aclaris, Boehringer Ingelheim, Incyte, Novartis, and UCB; as a speaker for AbbVie, Novartis, Sanofi Regeneron, and UCB; and as an investigator for Amgen, Boehringer Ingelheim, and Incyte.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
This can be challenging because to date, no Food and Drug Administration–approved treatments exist for early-stage HS and only two biologics exist for moderate to severe disease.
“For someone with occasional nodules and abscesses, we often use antibiotics and topical antiseptics,” Christopher Sayed, MD, a dermatologist at the HS and Follicular Disorders Clinic at the University of North Carolina, Chapel Hill, told this news organization. “We may use these daily for weeks or months or just provide them to use for 1-2 weeks at a time for intermittent flares if a patient doesn’t want to take a pill every day,” he said. “For women, hormonal options like oral contraceptive pills and spironolactone can be a great option” if they don’t mind taking a daily pill.
Topical options that Jennifer L. Hsiao, MD, reaches for in her role as director of the HS clinic at the University of Southern California, Los Angeles, include chlorhexidine wash, topical clindamycin, and topical resorcinol. Systemic medications include oral antibiotics such as doxycycline or clindamycin, while hormonal options include oral contraceptives and/or spironolactone for women and finasteride for men.
Laser hair removal for both men and women can also help treat lesions and abscesses in the groin and axillae, since reducing hair follicles tends to result in fewer follicles that become inflamed and form nodules and abscesses over time, “but it requires multiple visits and not all patients have access to it,” Dr. Sayed said. “Once patients start to develop tunnels or scars or fail to respond to some of these other treatments, I am quick to open the conversation on biologics to help avoid progression and long-term need for surgery.”
Metformin Among Options to Consider
According to Dr. Hsiao, other treatment options to consider trying in patients with mild HS include metformin, “especially in patients who also have prediabetes, PCOS, or obesity;” isotretinoin if the patient has concomitant severe acne; botulinum toxin injections; apremilast or topical roflumilast, and antihyperhidrosis medications such as prescription aluminum chloride topicals, glycopyrronium wipes, and glycopyrrolate.
Recommending lifestyle modifications such as smoking cessation and weight loss for patients diagnosed with early-stage HS is “challenging,” Dr. Sayed said, “because the evidence on different triggers and lifestyle modifications isn’t very strong. There can also be a lot of stigmas around weight and smoking in HS, and it can alienate patients to go straight to these topics in the first visit.”
Many patients also ask what dietary changes they can make to improve their HS. “The most common things patients tend to bring up are dairy avoidance and reducing carbohydrates,” he said. “Supplements like zinc and turmeric are also frequently brought up by patients and some find them helpful. Once rapport is built, I may discuss smoking cessation as potentially helping prevent as much activity over time or weight loss as possibly helping improve response to treatments, but I don’t promise that these things always help since modifying them doesn’t always lead to improvement.”
Dr. Hsiao noted that existing research suggests that following a Mediterranean diet may benefit HS symptoms.
Early Data on Ruxolitinib Cream Promising
At the 2024 annual meeting of the American Academy of Dermatology, researchers reported on the results of a phase 2 study, which found that topical 1.5% ruxolitinib, a Janus kinase (JAK) inhibitor (currently FDA-approved for atopic dermatitis) was effective in reducing abscess and inflammatory nodule count in patients with mild HS. “There is a major need for this kind of option, and the early results are promising,” said Dr. Sayed, who was not involved with the study. “It’s very difficult to get this covered for patients currently since it is off label for HS. We’ve gotten it for a few patients, and one has really liked it, but it’s unclear how consistent the others were with their use, and their level of improvement was not clear to me.”
For mild HS, he added, “the most important area in which we’ve seen growing evidence is around hair removal lasers such as Nd:YAG and alexandrite lasers. Improving access for patients is a major priority in the coming years.”
According to Dr. Hsiao, other approaches being studied for treating mild HS include a topical aryl hydrocarbon receptor agonist known as AT193, and oral medications, such as phosphodiesterase-4 inhibitors. Laser therapies are also being studied, “such as fractional ablative CO2 laser therapy combined with topical triamcinolone,” she said. “However, the majority of ongoing HS trials are for moderate to severe disease, so there is certainly a need for more investigation into mild HS treatment approaches.”
Dr. Sayed disclosed that he is secretary of the HS Foundation and a member of the European HS Foundation. He has served as a consultant for AbbVie, Alumis, AstraZeneca, Incyte, InflaRx, Novartis, Sanofi, Sonoma Biotherapeutics, and UCB; as a speaker for AbbVie, Novartis, and UCB; and as an investigator for Chemocentryx, Incyte, InflaRx, Novartis, and UCB. Dr. Hsiao disclosed that she is a member of the board of directors for the HS Foundation and has served as a consultant for AbbVie, Aclaris, Boehringer Ingelheim, Incyte, Novartis, and UCB; as a speaker for AbbVie, Novartis, Sanofi Regeneron, and UCB; and as an investigator for Amgen, Boehringer Ingelheim, and Incyte.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
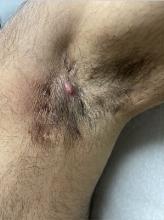
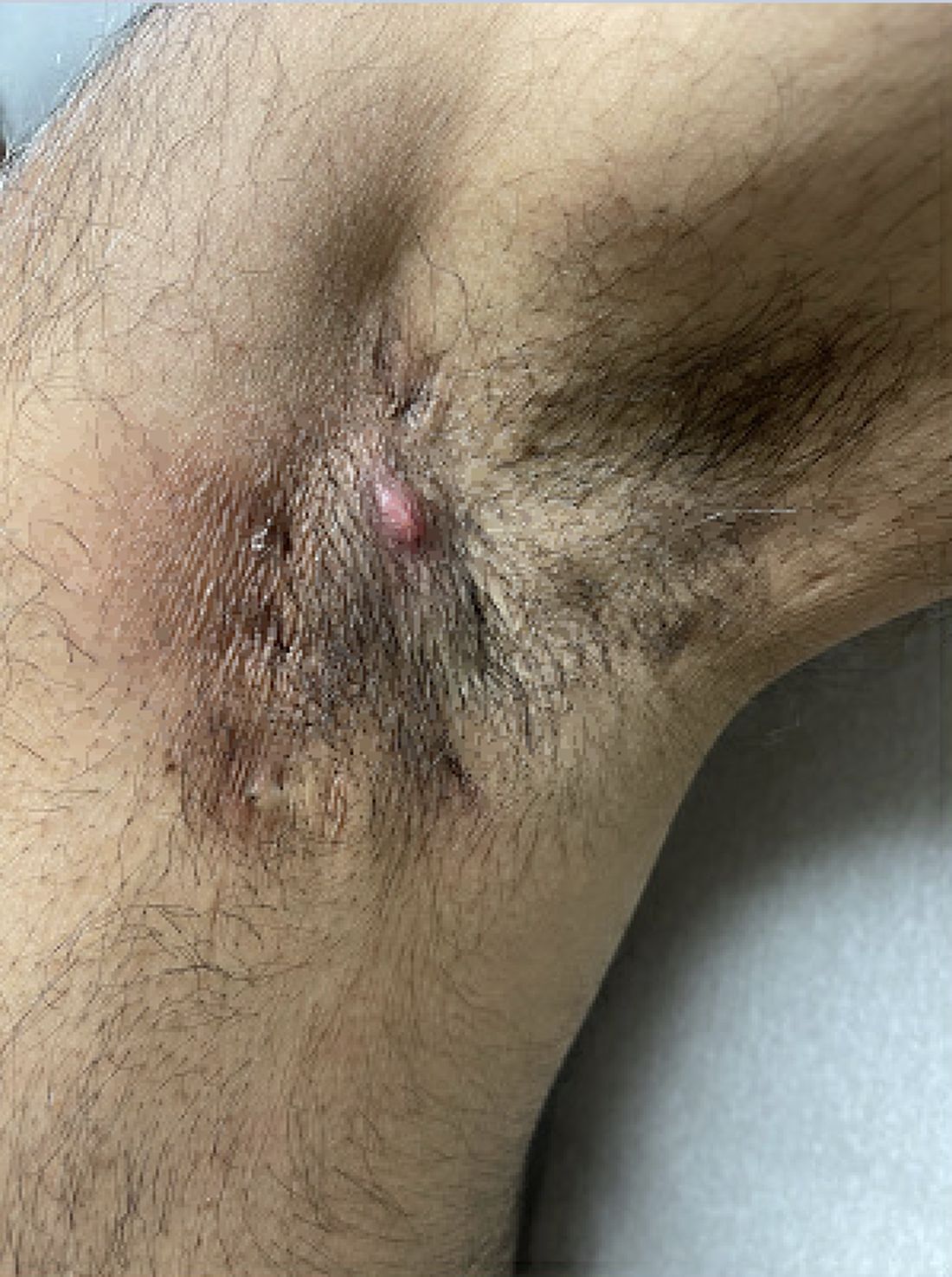
Diagnosing Mild Hidradenitis Suppurativa: Early Stage Can Mimic Other Diseases
, such as an infection, folliculitis, and acne.
According to 2019 guidelines from the United States and Canadian hidradenitis suppurativa foundations, the diagnostic criteria for HS in general are the presence of typical lesions such as abscesses, nodules, and tunnels in classic locations such as underarms, groins, and buttocks that recur over the course of at least 6 months. “There is no need for additional testing or imaging to make the diagnosis,” said Dr. Sayed, co-chair of the 2019 guidelines work group, who sees patients at the HS and Follicular Disorders Clinic at the University of North Carolina, Chapel Hill. “In many ways, the diagnosis should be very simple since the presentation is classic in most cases, though it can be confusing in the first 6 months or so.”
Persistence, Recurrence Major Clues
Prior to being diagnosed with Hurley stage I HS — characterized by recurrent nodules and abscesses with minimal scars, according to the guidelines — most people figure they’ve been getting recurrent Staphylococcus aureus infections or are having trouble with ingrown hairs from shaving, he continued. They may also say they get “boils” without an understanding of what has been causing them.
“Early HS can mimic an intense folliculitis or furuncles that can sometimes be caused by Staphylococcus infections, but the history of persistence or recurrence for months, despite treatment that should cover something like a Staph infection is a major clue,” Dr. Sayed said. “Thanks to improved resources on the internet, more patients, compared to several years ago, come in asking about HS after they’ve done their own research. As public awareness improves, hopefully this trend will grow, and patients will be diagnosed and treated earlier.” Family history is also a strong predictor of HS, since about half of patients have first-degree relatives who have a history of HS, he noted.
Clinicians can use the Hurley staging system to characterize the extent of disease and the Dermatology Life Quality Index to measure the impact of HS on quality of life. “We perform these assessments in our specialty clinic at each visit, but they are not necessary for diagnosis,” Dr. Sayed told this news organization.
The ‘2-2-6 Rule’
When she sees a patient who might have HS, Jennifer L. Hsiao, MD, a dermatologist who directs the HS clinic at the University of Southern California, Los Angeles, follows the “2-2-6 rule,” which involves asking patients if they have had 2 episodes of 2 or more abscesses in 6 months. “If the patient answers yes, there’s a high likelihood that person has HS,” she said.
Hurley stage I HS is defined as nodules and abscesses without sinus tracts (tunnels) or scarring. But in Dr. Hsiao’s opinion, the Hurley staging system “is not the best way to characterize disease activity” because some patients meet criteria for Hurley stage I disease, meaning they do not have any scars or sinus tracts/tunnels, “but they have high disease activity with several inflammatory nodules and large painful abscesses that are limiting their quality of life and ability to function.”
Most cases of early-stage HS can be diagnosed in a single clinic visit, but some patients may present with a limited history of disease. For example, they may report having only had one episode of an axillary abscess or one episode of a few folliculitis-like papules in the groin. “In the absence of other physical exam findings suggestive of HS, such as open or double-headed comedones in flexural regions, I tell the patient that it is too early to call their condition HS, and I recommend that if they have another episode to call the office for an appointment for evaluation,” Dr. Hsiao said in an interview.
“What sets HS apart from an isolated incidence of a Staphylococcus aureus furuncle is the history of recurrence,” she added. To better characterize HS disease severity, she uses the six-point HS Physician Global Assessment score, a scale from 0 to 5, which classifies a patient as having moderate HS if they have five or more inflammatory nodules, or one abscess and one or more inflammatory nodule(s), without the requirement of demonstrating a scar or tunnel on a physical exam.
To help guide management decisions, Dr. Hsiao also considers asking patients with early-stage HS the following questions:
- Do you have a primary care provider (PCP)? PCPs are important care partners for patients with HS doctor to help screen for the comorbidities associated with the condition.
- What seems to make your HS worse? This can help identify potential triggers to avoid.
- What other medical conditions do you have?
- How would you describe the impact HS has on your quality of life?
- For women: Does your HS get worse around your period? “This can help to identify a potential hormonal trigger,” she said. “If the patient answers ‘yes,’ I would strongly consider a combined oral contraceptive pill and/or spironolactone as part of the patient’s treatment regimen.”
‘Window of Opportunity’ to Intervene
According to Dr. Hsiao, there has been a paradigm shift in the approach to HS management that emphasizes a “window of opportunity,” where earlier initiation of appropriate long-term immunomodulator therapy is recommended to try to mitigate disease progression. The development of tunnels and scars is a telltale sign that permanent tissue destruction is occurring, and the patient’s HS is no longer mild.
Ideally, a conversation about adalimumab, a tumor necrosis factor inhibitor, and secukinumab, an interleukin-17A antagonist (the two currently Food and Drug Administration–approved medications for HS, for moderate to severe disease/Hurley stage II/III) will have already been started with patients prior to development of a high tunnel or scar burden, signs of later-stage disease.
“Medications like this have the potential to slow and prevent that progression and reduce the surgical burden patients face over time, which is a major priority,” Dr. Sayed said. He noted that while comfort level with managing HS can vary among clinicians, “I’d encourage dermatologists to stay engaged with these patients because our training in the medical and surgical management of complex diseases like this is unmatched among other specialties,” he said. “Education of colleagues in other specialties should also be a big priority, especially for those in urgent care, emergency medicine, surgery, and ob.gyn. who often encounter these patients and may be less familiar” with HS.
Besides the North American clinical management guidelines for HS, which are expected to be updated in the next 18-24 months, as well as comorbidity screening recommendations for HS published in 2022, another resource Dr. Sayed and Dr. Hsiao recommend is the HS Foundation website, which features a link to Continuing Medical Education video lectures. The foundation also hosts an annual Symposium on HS Advances. This year’s event is scheduled in November in Austin, Texas.
Dr. Sayed disclosed that he is secretary of the HS Foundation and a member of the European HS Foundation. He has served as a consultant for AbbVie, Alumis, AstraZeneca, Incyte, InflaRx, Novartis, Sanofi, Sonoma Biotherapeutics, and UCB; as a speaker for AbbVie, Novartis, and UCB; and as an investigator for Chemocentryx, Incyte, InflaRx, Novartis, and UCB. Dr. Hsiao disclosed that she is a member of the board of directors for the HS Foundation and has served as a consultant for AbbVie, Aclaris, Boehringer Ingelheim, Incyte, Novartis, and UCB; as a speaker for AbbVie, Novartis, Sanofi Regeneron, and UCB; and as an investigator for Amgen, Boehringer Ingelheim, and Incyte.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
, such as an infection, folliculitis, and acne.
According to 2019 guidelines from the United States and Canadian hidradenitis suppurativa foundations, the diagnostic criteria for HS in general are the presence of typical lesions such as abscesses, nodules, and tunnels in classic locations such as underarms, groins, and buttocks that recur over the course of at least 6 months. “There is no need for additional testing or imaging to make the diagnosis,” said Dr. Sayed, co-chair of the 2019 guidelines work group, who sees patients at the HS and Follicular Disorders Clinic at the University of North Carolina, Chapel Hill. “In many ways, the diagnosis should be very simple since the presentation is classic in most cases, though it can be confusing in the first 6 months or so.”
Persistence, Recurrence Major Clues
Prior to being diagnosed with Hurley stage I HS — characterized by recurrent nodules and abscesses with minimal scars, according to the guidelines — most people figure they’ve been getting recurrent Staphylococcus aureus infections or are having trouble with ingrown hairs from shaving, he continued. They may also say they get “boils” without an understanding of what has been causing them.
“Early HS can mimic an intense folliculitis or furuncles that can sometimes be caused by Staphylococcus infections, but the history of persistence or recurrence for months, despite treatment that should cover something like a Staph infection is a major clue,” Dr. Sayed said. “Thanks to improved resources on the internet, more patients, compared to several years ago, come in asking about HS after they’ve done their own research. As public awareness improves, hopefully this trend will grow, and patients will be diagnosed and treated earlier.” Family history is also a strong predictor of HS, since about half of patients have first-degree relatives who have a history of HS, he noted.
Clinicians can use the Hurley staging system to characterize the extent of disease and the Dermatology Life Quality Index to measure the impact of HS on quality of life. “We perform these assessments in our specialty clinic at each visit, but they are not necessary for diagnosis,” Dr. Sayed told this news organization.
The ‘2-2-6 Rule’
When she sees a patient who might have HS, Jennifer L. Hsiao, MD, a dermatologist who directs the HS clinic at the University of Southern California, Los Angeles, follows the “2-2-6 rule,” which involves asking patients if they have had 2 episodes of 2 or more abscesses in 6 months. “If the patient answers yes, there’s a high likelihood that person has HS,” she said.
Hurley stage I HS is defined as nodules and abscesses without sinus tracts (tunnels) or scarring. But in Dr. Hsiao’s opinion, the Hurley staging system “is not the best way to characterize disease activity” because some patients meet criteria for Hurley stage I disease, meaning they do not have any scars or sinus tracts/tunnels, “but they have high disease activity with several inflammatory nodules and large painful abscesses that are limiting their quality of life and ability to function.”
Most cases of early-stage HS can be diagnosed in a single clinic visit, but some patients may present with a limited history of disease. For example, they may report having only had one episode of an axillary abscess or one episode of a few folliculitis-like papules in the groin. “In the absence of other physical exam findings suggestive of HS, such as open or double-headed comedones in flexural regions, I tell the patient that it is too early to call their condition HS, and I recommend that if they have another episode to call the office for an appointment for evaluation,” Dr. Hsiao said in an interview.
“What sets HS apart from an isolated incidence of a Staphylococcus aureus furuncle is the history of recurrence,” she added. To better characterize HS disease severity, she uses the six-point HS Physician Global Assessment score, a scale from 0 to 5, which classifies a patient as having moderate HS if they have five or more inflammatory nodules, or one abscess and one or more inflammatory nodule(s), without the requirement of demonstrating a scar or tunnel on a physical exam.
To help guide management decisions, Dr. Hsiao also considers asking patients with early-stage HS the following questions:
- Do you have a primary care provider (PCP)? PCPs are important care partners for patients with HS doctor to help screen for the comorbidities associated with the condition.
- What seems to make your HS worse? This can help identify potential triggers to avoid.
- What other medical conditions do you have?
- How would you describe the impact HS has on your quality of life?
- For women: Does your HS get worse around your period? “This can help to identify a potential hormonal trigger,” she said. “If the patient answers ‘yes,’ I would strongly consider a combined oral contraceptive pill and/or spironolactone as part of the patient’s treatment regimen.”
‘Window of Opportunity’ to Intervene
According to Dr. Hsiao, there has been a paradigm shift in the approach to HS management that emphasizes a “window of opportunity,” where earlier initiation of appropriate long-term immunomodulator therapy is recommended to try to mitigate disease progression. The development of tunnels and scars is a telltale sign that permanent tissue destruction is occurring, and the patient’s HS is no longer mild.
Ideally, a conversation about adalimumab, a tumor necrosis factor inhibitor, and secukinumab, an interleukin-17A antagonist (the two currently Food and Drug Administration–approved medications for HS, for moderate to severe disease/Hurley stage II/III) will have already been started with patients prior to development of a high tunnel or scar burden, signs of later-stage disease.
“Medications like this have the potential to slow and prevent that progression and reduce the surgical burden patients face over time, which is a major priority,” Dr. Sayed said. He noted that while comfort level with managing HS can vary among clinicians, “I’d encourage dermatologists to stay engaged with these patients because our training in the medical and surgical management of complex diseases like this is unmatched among other specialties,” he said. “Education of colleagues in other specialties should also be a big priority, especially for those in urgent care, emergency medicine, surgery, and ob.gyn. who often encounter these patients and may be less familiar” with HS.
Besides the North American clinical management guidelines for HS, which are expected to be updated in the next 18-24 months, as well as comorbidity screening recommendations for HS published in 2022, another resource Dr. Sayed and Dr. Hsiao recommend is the HS Foundation website, which features a link to Continuing Medical Education video lectures. The foundation also hosts an annual Symposium on HS Advances. This year’s event is scheduled in November in Austin, Texas.
Dr. Sayed disclosed that he is secretary of the HS Foundation and a member of the European HS Foundation. He has served as a consultant for AbbVie, Alumis, AstraZeneca, Incyte, InflaRx, Novartis, Sanofi, Sonoma Biotherapeutics, and UCB; as a speaker for AbbVie, Novartis, and UCB; and as an investigator for Chemocentryx, Incyte, InflaRx, Novartis, and UCB. Dr. Hsiao disclosed that she is a member of the board of directors for the HS Foundation and has served as a consultant for AbbVie, Aclaris, Boehringer Ingelheim, Incyte, Novartis, and UCB; as a speaker for AbbVie, Novartis, Sanofi Regeneron, and UCB; and as an investigator for Amgen, Boehringer Ingelheim, and Incyte.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
, such as an infection, folliculitis, and acne.
According to 2019 guidelines from the United States and Canadian hidradenitis suppurativa foundations, the diagnostic criteria for HS in general are the presence of typical lesions such as abscesses, nodules, and tunnels in classic locations such as underarms, groins, and buttocks that recur over the course of at least 6 months. “There is no need for additional testing or imaging to make the diagnosis,” said Dr. Sayed, co-chair of the 2019 guidelines work group, who sees patients at the HS and Follicular Disorders Clinic at the University of North Carolina, Chapel Hill. “In many ways, the diagnosis should be very simple since the presentation is classic in most cases, though it can be confusing in the first 6 months or so.”
Persistence, Recurrence Major Clues
Prior to being diagnosed with Hurley stage I HS — characterized by recurrent nodules and abscesses with minimal scars, according to the guidelines — most people figure they’ve been getting recurrent Staphylococcus aureus infections or are having trouble with ingrown hairs from shaving, he continued. They may also say they get “boils” without an understanding of what has been causing them.
“Early HS can mimic an intense folliculitis or furuncles that can sometimes be caused by Staphylococcus infections, but the history of persistence or recurrence for months, despite treatment that should cover something like a Staph infection is a major clue,” Dr. Sayed said. “Thanks to improved resources on the internet, more patients, compared to several years ago, come in asking about HS after they’ve done their own research. As public awareness improves, hopefully this trend will grow, and patients will be diagnosed and treated earlier.” Family history is also a strong predictor of HS, since about half of patients have first-degree relatives who have a history of HS, he noted.
Clinicians can use the Hurley staging system to characterize the extent of disease and the Dermatology Life Quality Index to measure the impact of HS on quality of life. “We perform these assessments in our specialty clinic at each visit, but they are not necessary for diagnosis,” Dr. Sayed told this news organization.
The ‘2-2-6 Rule’
When she sees a patient who might have HS, Jennifer L. Hsiao, MD, a dermatologist who directs the HS clinic at the University of Southern California, Los Angeles, follows the “2-2-6 rule,” which involves asking patients if they have had 2 episodes of 2 or more abscesses in 6 months. “If the patient answers yes, there’s a high likelihood that person has HS,” she said.
Hurley stage I HS is defined as nodules and abscesses without sinus tracts (tunnels) or scarring. But in Dr. Hsiao’s opinion, the Hurley staging system “is not the best way to characterize disease activity” because some patients meet criteria for Hurley stage I disease, meaning they do not have any scars or sinus tracts/tunnels, “but they have high disease activity with several inflammatory nodules and large painful abscesses that are limiting their quality of life and ability to function.”
Most cases of early-stage HS can be diagnosed in a single clinic visit, but some patients may present with a limited history of disease. For example, they may report having only had one episode of an axillary abscess or one episode of a few folliculitis-like papules in the groin. “In the absence of other physical exam findings suggestive of HS, such as open or double-headed comedones in flexural regions, I tell the patient that it is too early to call their condition HS, and I recommend that if they have another episode to call the office for an appointment for evaluation,” Dr. Hsiao said in an interview.
“What sets HS apart from an isolated incidence of a Staphylococcus aureus furuncle is the history of recurrence,” she added. To better characterize HS disease severity, she uses the six-point HS Physician Global Assessment score, a scale from 0 to 5, which classifies a patient as having moderate HS if they have five or more inflammatory nodules, or one abscess and one or more inflammatory nodule(s), without the requirement of demonstrating a scar or tunnel on a physical exam.
To help guide management decisions, Dr. Hsiao also considers asking patients with early-stage HS the following questions:
- Do you have a primary care provider (PCP)? PCPs are important care partners for patients with HS doctor to help screen for the comorbidities associated with the condition.
- What seems to make your HS worse? This can help identify potential triggers to avoid.
- What other medical conditions do you have?
- How would you describe the impact HS has on your quality of life?
- For women: Does your HS get worse around your period? “This can help to identify a potential hormonal trigger,” she said. “If the patient answers ‘yes,’ I would strongly consider a combined oral contraceptive pill and/or spironolactone as part of the patient’s treatment regimen.”
‘Window of Opportunity’ to Intervene
According to Dr. Hsiao, there has been a paradigm shift in the approach to HS management that emphasizes a “window of opportunity,” where earlier initiation of appropriate long-term immunomodulator therapy is recommended to try to mitigate disease progression. The development of tunnels and scars is a telltale sign that permanent tissue destruction is occurring, and the patient’s HS is no longer mild.
Ideally, a conversation about adalimumab, a tumor necrosis factor inhibitor, and secukinumab, an interleukin-17A antagonist (the two currently Food and Drug Administration–approved medications for HS, for moderate to severe disease/Hurley stage II/III) will have already been started with patients prior to development of a high tunnel or scar burden, signs of later-stage disease.
“Medications like this have the potential to slow and prevent that progression and reduce the surgical burden patients face over time, which is a major priority,” Dr. Sayed said. He noted that while comfort level with managing HS can vary among clinicians, “I’d encourage dermatologists to stay engaged with these patients because our training in the medical and surgical management of complex diseases like this is unmatched among other specialties,” he said. “Education of colleagues in other specialties should also be a big priority, especially for those in urgent care, emergency medicine, surgery, and ob.gyn. who often encounter these patients and may be less familiar” with HS.
Besides the North American clinical management guidelines for HS, which are expected to be updated in the next 18-24 months, as well as comorbidity screening recommendations for HS published in 2022, another resource Dr. Sayed and Dr. Hsiao recommend is the HS Foundation website, which features a link to Continuing Medical Education video lectures. The foundation also hosts an annual Symposium on HS Advances. This year’s event is scheduled in November in Austin, Texas.
Dr. Sayed disclosed that he is secretary of the HS Foundation and a member of the European HS Foundation. He has served as a consultant for AbbVie, Alumis, AstraZeneca, Incyte, InflaRx, Novartis, Sanofi, Sonoma Biotherapeutics, and UCB; as a speaker for AbbVie, Novartis, and UCB; and as an investigator for Chemocentryx, Incyte, InflaRx, Novartis, and UCB. Dr. Hsiao disclosed that she is a member of the board of directors for the HS Foundation and has served as a consultant for AbbVie, Aclaris, Boehringer Ingelheim, Incyte, Novartis, and UCB; as a speaker for AbbVie, Novartis, Sanofi Regeneron, and UCB; and as an investigator for Amgen, Boehringer Ingelheim, and Incyte.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The Lure of Specialty Medicine Pulls Nurse Practitioners From Primary Care
For many patients, seeing a nurse practitioner has become a routine part of primary care, in which these “NPs” often perform the same tasks that patients have relied on doctors for.
But NPs in specialty care? That’s not routine, at least not yet. Increasingly, though, nurse practitioners and physician assistants are joining cardiology, dermatology, and other specialty practices, broadening their skills and increasing their income.
This development worries some people who track the health workforce, because current trends suggest primary care, which has counted on nurse practitioners to backstop physician shortages, soon might not be able to rely on them to the same extent.
“They’re succumbing to the same challenges that we have with physicians,” said Atul Grover, MD, PhD, executive director of the Research and Action Institute at the Association of American Medical Colleges. The rates NPs can command in a specialty practice “are quite a bit higher” than practice salaries in primary care, he said.
When nurse practitioner programs began to proliferate in the 1970s, “at first it looked great, producing all these nurse practitioners that go to work with primary care physicians,” said Yalda Jabbarpour, MD, director of the American Academy of Family Physicians’ Robert Graham Center for Policy Studies. “But now only 30% are going into primary care.”
Dr. Jabbarpour was referring to the 2024 primary care scorecard by the Milbank Memorial Fund, which found that from 2016 to 2021 the proportion of nurse practitioners who worked in primary care practices hovered between 32% and 34%, even though their numbers grew rapidly. The proportion of physician assistants, also known as physician associates, in primary care ranged from 27% to 30%, the study found.
Both nurse practitioners and physician assistants are advanced practice clinicians who, in addition to graduate degrees, must complete distinct education, training, and certification steps. NPs can practice without a doctor’s supervision in more than two dozen states, while PAs have similar independence in only a handful of states.
About 88% of nurse practitioners are certified in an area of primary care, according to the American Association of Nurse Practitioners. But it is difficult to track exactly how many work in primary care or in specialty practices. Unlike physicians, they’re generally not required to be endorsed by a national standard-setting body to practice in specialties like oncology or cardiology, for example. The AANP declined to answer questions about its annual workforce survey or the extent to which primary care NPs are moving toward specialties.
Though data tracking the change is sparse, specialty practices are adding these advanced practice clinicians at almost the same rate as primary care practices, according to frequently cited research published in 2018.
The clearest evidence of the shift: From 2008 to 2016, there was a 22% increase in the number of specialty practices that employed nurse practitioners and physician assistants, according to that study. The increase in the number of primary care practices that employed these professionals was 24%.
Once more, the most recent projections by the Association of American Medical Colleges predict a dearth of at least 20,200 primary care physicians by 2036. There will also be a shortfall of non-primary care specialists, including a deficiency of at least 10,100 surgical physicians and up to 25,000 physicians in other specialties.
When it comes to the actual work performed, the lines between primary and specialty care are often blurred, said Candice Chen, MD, MPH, associate professor of health policy and management at George Washington University.
“You might be a nurse practitioner working in a gastroenterology clinic or cardiology clinic, but the scope of what you do is starting to overlap with primary care,” she said.
Nurse practitioners’ salaries vary widely by location, type of facility, and experience. Still, according to data from health care recruiter AMN Healthcare Physician Solutions, formerly known as Merritt Hawkins, the total annual average starting compensation, including signing bonus, for nurse practitioners and physician assistants in specialty practice was $172,544 in the year that ended March 31, slightly higher than the $166,544 for those in primary care.
According to forecasts from the federal Bureau of Labor Statistics, nurse practitioner jobs will increase faster than jobs in almost any other occupation in the decade leading up to 2032, growing by 123,600 jobs or 45%. (Wind turbine service technician is the only other occupation projected to grow as fast.) The growth rate for physician assistants is also much faster than average, at 27%. There are more than twice as many nurse practitioners as physician assistants, however: 323,900 versus 148,000, in 2022.
To Dr. Grover of the AAMC, numbers like this signal that there will probably be enough NPs, PAs, and physicians to meet primary care needs. At the same time, “expect more NPs and PAs to also flow out into other specialties,” he said.
When Pamela Ograbisz started working as a registered nurse 27 years ago, she worked in a cardiothoracic intensive care unit. After she became a family nurse practitioner a few years later, she found a job with a similar specialty practice, which trained her to take on a bigger role, first running their outpatient clinic, then working on the floor, and later in the intensive care unit.
If nurse practitioners want to specialize, often “the doctors mentor them just like they would with a physician residency,” said Ms. Ograbisz, now vice president of clinical operations at temporary placement recruiter LocumTenens.com.
If physician assistants want to specialize, they also can do so through mentoring, or they can receive “certificates of added qualifications” in 10 specialties to demonstrate their expertise. Most employers don’t “encourage or require” these certificates, however, said Jennifer Orozco, DMSc, PA-C, DFAAPA, chief medical officer at the American Academy of Physician Associates.
There are a number of training programs for family nurse practitioners who want to develop skills in other areas.
Raina Hoebelheinrich, 40, a family nurse practitioner at a regional medical center in Yankton, South Dakota, recently enrolled in a three-semester post-master’s endocrinology training program at Mount Marty University. She lives on a farm in nearby northeastern Nebraska with her husband and five sons.
Ms. Hoebelheinrich’s new skills could be helpful in her current hospital job, in which she sees a lot of patients with acute diabetes, or in a clinic setting like the one in Sioux Falls, South Dakota, where she is doing her clinical endocrinology training.
Lack of access to endocrinology care in rural areas is a real problem, and many people may travel hundreds of miles to see a specialist.
“There aren’t a lot of options,” she said.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
For many patients, seeing a nurse practitioner has become a routine part of primary care, in which these “NPs” often perform the same tasks that patients have relied on doctors for.
But NPs in specialty care? That’s not routine, at least not yet. Increasingly, though, nurse practitioners and physician assistants are joining cardiology, dermatology, and other specialty practices, broadening their skills and increasing their income.
This development worries some people who track the health workforce, because current trends suggest primary care, which has counted on nurse practitioners to backstop physician shortages, soon might not be able to rely on them to the same extent.
“They’re succumbing to the same challenges that we have with physicians,” said Atul Grover, MD, PhD, executive director of the Research and Action Institute at the Association of American Medical Colleges. The rates NPs can command in a specialty practice “are quite a bit higher” than practice salaries in primary care, he said.
When nurse practitioner programs began to proliferate in the 1970s, “at first it looked great, producing all these nurse practitioners that go to work with primary care physicians,” said Yalda Jabbarpour, MD, director of the American Academy of Family Physicians’ Robert Graham Center for Policy Studies. “But now only 30% are going into primary care.”
Dr. Jabbarpour was referring to the 2024 primary care scorecard by the Milbank Memorial Fund, which found that from 2016 to 2021 the proportion of nurse practitioners who worked in primary care practices hovered between 32% and 34%, even though their numbers grew rapidly. The proportion of physician assistants, also known as physician associates, in primary care ranged from 27% to 30%, the study found.
Both nurse practitioners and physician assistants are advanced practice clinicians who, in addition to graduate degrees, must complete distinct education, training, and certification steps. NPs can practice without a doctor’s supervision in more than two dozen states, while PAs have similar independence in only a handful of states.
About 88% of nurse practitioners are certified in an area of primary care, according to the American Association of Nurse Practitioners. But it is difficult to track exactly how many work in primary care or in specialty practices. Unlike physicians, they’re generally not required to be endorsed by a national standard-setting body to practice in specialties like oncology or cardiology, for example. The AANP declined to answer questions about its annual workforce survey or the extent to which primary care NPs are moving toward specialties.
Though data tracking the change is sparse, specialty practices are adding these advanced practice clinicians at almost the same rate as primary care practices, according to frequently cited research published in 2018.
The clearest evidence of the shift: From 2008 to 2016, there was a 22% increase in the number of specialty practices that employed nurse practitioners and physician assistants, according to that study. The increase in the number of primary care practices that employed these professionals was 24%.
Once more, the most recent projections by the Association of American Medical Colleges predict a dearth of at least 20,200 primary care physicians by 2036. There will also be a shortfall of non-primary care specialists, including a deficiency of at least 10,100 surgical physicians and up to 25,000 physicians in other specialties.
When it comes to the actual work performed, the lines between primary and specialty care are often blurred, said Candice Chen, MD, MPH, associate professor of health policy and management at George Washington University.
“You might be a nurse practitioner working in a gastroenterology clinic or cardiology clinic, but the scope of what you do is starting to overlap with primary care,” she said.
Nurse practitioners’ salaries vary widely by location, type of facility, and experience. Still, according to data from health care recruiter AMN Healthcare Physician Solutions, formerly known as Merritt Hawkins, the total annual average starting compensation, including signing bonus, for nurse practitioners and physician assistants in specialty practice was $172,544 in the year that ended March 31, slightly higher than the $166,544 for those in primary care.
According to forecasts from the federal Bureau of Labor Statistics, nurse practitioner jobs will increase faster than jobs in almost any other occupation in the decade leading up to 2032, growing by 123,600 jobs or 45%. (Wind turbine service technician is the only other occupation projected to grow as fast.) The growth rate for physician assistants is also much faster than average, at 27%. There are more than twice as many nurse practitioners as physician assistants, however: 323,900 versus 148,000, in 2022.
To Dr. Grover of the AAMC, numbers like this signal that there will probably be enough NPs, PAs, and physicians to meet primary care needs. At the same time, “expect more NPs and PAs to also flow out into other specialties,” he said.
When Pamela Ograbisz started working as a registered nurse 27 years ago, she worked in a cardiothoracic intensive care unit. After she became a family nurse practitioner a few years later, she found a job with a similar specialty practice, which trained her to take on a bigger role, first running their outpatient clinic, then working on the floor, and later in the intensive care unit.
If nurse practitioners want to specialize, often “the doctors mentor them just like they would with a physician residency,” said Ms. Ograbisz, now vice president of clinical operations at temporary placement recruiter LocumTenens.com.
If physician assistants want to specialize, they also can do so through mentoring, or they can receive “certificates of added qualifications” in 10 specialties to demonstrate their expertise. Most employers don’t “encourage or require” these certificates, however, said Jennifer Orozco, DMSc, PA-C, DFAAPA, chief medical officer at the American Academy of Physician Associates.
There are a number of training programs for family nurse practitioners who want to develop skills in other areas.
Raina Hoebelheinrich, 40, a family nurse practitioner at a regional medical center in Yankton, South Dakota, recently enrolled in a three-semester post-master’s endocrinology training program at Mount Marty University. She lives on a farm in nearby northeastern Nebraska with her husband and five sons.
Ms. Hoebelheinrich’s new skills could be helpful in her current hospital job, in which she sees a lot of patients with acute diabetes, or in a clinic setting like the one in Sioux Falls, South Dakota, where she is doing her clinical endocrinology training.
Lack of access to endocrinology care in rural areas is a real problem, and many people may travel hundreds of miles to see a specialist.
“There aren’t a lot of options,” she said.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
For many patients, seeing a nurse practitioner has become a routine part of primary care, in which these “NPs” often perform the same tasks that patients have relied on doctors for.
But NPs in specialty care? That’s not routine, at least not yet. Increasingly, though, nurse practitioners and physician assistants are joining cardiology, dermatology, and other specialty practices, broadening their skills and increasing their income.
This development worries some people who track the health workforce, because current trends suggest primary care, which has counted on nurse practitioners to backstop physician shortages, soon might not be able to rely on them to the same extent.
“They’re succumbing to the same challenges that we have with physicians,” said Atul Grover, MD, PhD, executive director of the Research and Action Institute at the Association of American Medical Colleges. The rates NPs can command in a specialty practice “are quite a bit higher” than practice salaries in primary care, he said.
When nurse practitioner programs began to proliferate in the 1970s, “at first it looked great, producing all these nurse practitioners that go to work with primary care physicians,” said Yalda Jabbarpour, MD, director of the American Academy of Family Physicians’ Robert Graham Center for Policy Studies. “But now only 30% are going into primary care.”
Dr. Jabbarpour was referring to the 2024 primary care scorecard by the Milbank Memorial Fund, which found that from 2016 to 2021 the proportion of nurse practitioners who worked in primary care practices hovered between 32% and 34%, even though their numbers grew rapidly. The proportion of physician assistants, also known as physician associates, in primary care ranged from 27% to 30%, the study found.
Both nurse practitioners and physician assistants are advanced practice clinicians who, in addition to graduate degrees, must complete distinct education, training, and certification steps. NPs can practice without a doctor’s supervision in more than two dozen states, while PAs have similar independence in only a handful of states.
About 88% of nurse practitioners are certified in an area of primary care, according to the American Association of Nurse Practitioners. But it is difficult to track exactly how many work in primary care or in specialty practices. Unlike physicians, they’re generally not required to be endorsed by a national standard-setting body to practice in specialties like oncology or cardiology, for example. The AANP declined to answer questions about its annual workforce survey or the extent to which primary care NPs are moving toward specialties.
Though data tracking the change is sparse, specialty practices are adding these advanced practice clinicians at almost the same rate as primary care practices, according to frequently cited research published in 2018.
The clearest evidence of the shift: From 2008 to 2016, there was a 22% increase in the number of specialty practices that employed nurse practitioners and physician assistants, according to that study. The increase in the number of primary care practices that employed these professionals was 24%.
Once more, the most recent projections by the Association of American Medical Colleges predict a dearth of at least 20,200 primary care physicians by 2036. There will also be a shortfall of non-primary care specialists, including a deficiency of at least 10,100 surgical physicians and up to 25,000 physicians in other specialties.
When it comes to the actual work performed, the lines between primary and specialty care are often blurred, said Candice Chen, MD, MPH, associate professor of health policy and management at George Washington University.
“You might be a nurse practitioner working in a gastroenterology clinic or cardiology clinic, but the scope of what you do is starting to overlap with primary care,” she said.
Nurse practitioners’ salaries vary widely by location, type of facility, and experience. Still, according to data from health care recruiter AMN Healthcare Physician Solutions, formerly known as Merritt Hawkins, the total annual average starting compensation, including signing bonus, for nurse practitioners and physician assistants in specialty practice was $172,544 in the year that ended March 31, slightly higher than the $166,544 for those in primary care.
According to forecasts from the federal Bureau of Labor Statistics, nurse practitioner jobs will increase faster than jobs in almost any other occupation in the decade leading up to 2032, growing by 123,600 jobs or 45%. (Wind turbine service technician is the only other occupation projected to grow as fast.) The growth rate for physician assistants is also much faster than average, at 27%. There are more than twice as many nurse practitioners as physician assistants, however: 323,900 versus 148,000, in 2022.
To Dr. Grover of the AAMC, numbers like this signal that there will probably be enough NPs, PAs, and physicians to meet primary care needs. At the same time, “expect more NPs and PAs to also flow out into other specialties,” he said.
When Pamela Ograbisz started working as a registered nurse 27 years ago, she worked in a cardiothoracic intensive care unit. After she became a family nurse practitioner a few years later, she found a job with a similar specialty practice, which trained her to take on a bigger role, first running their outpatient clinic, then working on the floor, and later in the intensive care unit.
If nurse practitioners want to specialize, often “the doctors mentor them just like they would with a physician residency,” said Ms. Ograbisz, now vice president of clinical operations at temporary placement recruiter LocumTenens.com.
If physician assistants want to specialize, they also can do so through mentoring, or they can receive “certificates of added qualifications” in 10 specialties to demonstrate their expertise. Most employers don’t “encourage or require” these certificates, however, said Jennifer Orozco, DMSc, PA-C, DFAAPA, chief medical officer at the American Academy of Physician Associates.
There are a number of training programs for family nurse practitioners who want to develop skills in other areas.
Raina Hoebelheinrich, 40, a family nurse practitioner at a regional medical center in Yankton, South Dakota, recently enrolled in a three-semester post-master’s endocrinology training program at Mount Marty University. She lives on a farm in nearby northeastern Nebraska with her husband and five sons.
Ms. Hoebelheinrich’s new skills could be helpful in her current hospital job, in which she sees a lot of patients with acute diabetes, or in a clinic setting like the one in Sioux Falls, South Dakota, where she is doing her clinical endocrinology training.
Lack of access to endocrinology care in rural areas is a real problem, and many people may travel hundreds of miles to see a specialist.
“There aren’t a lot of options,” she said.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Do You Really Know a UTI When You See It?
An updated clinical approach to diagnosing urinary tract infections (UTIs) that considers five potential phenotype categories instead of the usual three could aid clinical management and better center patient needs, according to the authors of a new study in The Journal of Urology.
The current diagnostic paradigm includes UTI, asymptomatic bacteriuria (ASB), or not UTI, but the researchers believe these categories exclude for more ambiguous clinical cases, such as patients whose bacteria counts are low but who are symptomatic, or when nonspecific symptoms make it difficult to determine whether treatment with antibiotics is appropriate.
“Our findings suggest the need to reframe our conceptual model of UTI vs ASB to recognize clinical uncertainty and reflect the full spectrum of clinical presentations,” Sonali D. Advani, MBBS, MPH, an associate professor of medicine in infectious disease at Duke University School of Medicine, in Durham, North Carolina, and her colleagues wrote. “Recent data suggest that UTI may present as a bidirectional continuum from asymptomatic bladder colonization to a symptomatic bladder infection,” and some populations may lack the signs or symptoms specific to urinary tract or have chronic lower urinary tract symptoms (LUTS) that make it difficult to distinguish between ASB and UTI, they wrote.
Nitya E. Abraham, MD, an associate professor of urology at Albert Einstein College of Medicine and Montefiore Einstein in New York City, agreed the current paradigm has room for refinement.
“The current classification system doesn’t account for certain patients such as patients who have bothersome urinary symptoms, but urine testing comes back negative, or patients with positive urine testing, but who aren’t able to report the presence or absence of symptoms,” Dr. Abraham, who was not involved in the new research, told this news organization.
Boback Berookhim, MD, a urologist at Northwell Health in New Hyde Park, New York, who was also not involved in the research, said the goal with this study appears to be better identifying who will need antibiotics.
“I think this is more of a forward-looking study in terms of trying to identify patients who currently may not be treated or may be over treated and better identifying subsets,” Dr. Berookhim told this news organization.
However, he said the relevance of the work is far greater in hospitals than in outpatient settings.
“I think it’s much more relevant in inpatient environments where a patient is in hospital and whatever antibiotics are being written are going to be overseen and you’re going to see higher resistance patterns,” Dr. Berookhim said. “For the average doctor who’s seeing patients in the office and writing them prescriptions in the office, this doesn’t really affect them.”
Antibiotic Dilemma
A key issue in determining the best approach to UTI diagnosis is assessing the appropriateness of antibiotic treatment. Up to half of hospitalized patients have ASB, for which current practice guidelines advise against antibiotics, Dr. Advani and her colleagues noted. Yet many of these patients receive antibiotics regardless, and research has shown links between treatment and longer length of stay, antibiotic resistance, and infection with Clostridioides difficile.
The challenge comes with patients who do not fit easily into the existing categories. One includes patients who have positive urine cultures but whose symptoms, such as hypotension or fever, are not specific to the genitourinary tract.
While current guidelines advise against treating these patients with antibiotics, the patients are often older adults with cognitive impairment or delirium, and frontline physicians may err on the side of prescribing antibiotics because of their clinical uncertainty. That treatment can lead to tension with hospital antibiotic stewardship teams that recommend withholding antibiotics for those patients.
“These clinical scenarios highlight differences between the frontline clinicians’ and antibiotic stewardship teams’ definitions of ‘asymptomatic,’ highlighting the ambiguity of the term ‘asymptomatic bacteriuria,’” Dr. Advani and her colleagues wrote.
A fever, for example, could signal a viral or bacterial infection or result from a nonurinary source, Dr. Abraham said. “The antibiotic stewardship team likely prefers to observe the clinical course and wait for more data to demonstrate need for antibiotics,” she said. “Hence, there are conflicting priorities and confusion of when to treat with antibiotics for this common dilemma in patients presenting to the ER or urgent care.”
Meanwhile, other patients, particularly women, may present with urinary symptoms and pyuria but have lab results revealing a colony count below the 100,000 CFU/mL threshold that would indicate antibiotic treatment.
“Some of these women are likely suffering from a UTI and may not receive treatment if clinicians focus primarily on the urine culture results,” Dr. Abraham said. She pointed out the existence of other options than urine culture for better identifying UTI, such as urinary cell-free DNA or next-generation DNA testing of the urine. But she also said the 100,000 CFU/mL threshold should not be absolute.
“For example, I will treat patients for UTI with 10,000-50,000 CFU/mL if they also have UTI symptoms like blood in the urine, burning with urination, bladder pain, increased urgency or frequency, and the urinalysis shows a high white blood cell count,” Dr. Abraham said.
Dr. Abraham also noted a third group outside the scope of the new study: People with urinary symptoms who don’t undergo urine tests or who are treated empirically with antibiotics. “It is unclear whether those in this group truly have a UTI, but it is a common scenario that patients are unable to get urine tests and are treated with over-the-phone prescriptions to expedite treatment,” she said.
Get on the BUS
The researchers conducted a retrospective study across one academic medical center and four community hospitals in three states to assess the feasibility of using five categories of UTI diagnosis: The three existing ones plus LUTS/other urologic symptoms (OUS) and bacteriuria of unclear significance (BUS). These additional categories arose out of an hour-long discussion with a focus group of experts across several disciplines.
The analysis covered the charts of 3392 randomly selected encounters out of 220,531 total inpatient or emergency department encounters between January 2017 and December 2019 in which adults received a urinalysis and urine culture order within the same 24-hour period. The patients’ median age was 67 years, over half (59.6%) were women, and nearly a quarter (24.2%) had an underlying immunocompromising condition.
Most of the cultures were obtained from inpatients. Nearly a third (30.6%) were negative for culture, while 42.1% grew at least 100,000 CFU/mL of bacteria and 17% grew mixed flora.
Based on current criteria, 21.3% of the patients had a UTI, 20.8% had ASB, and 47.6% had no UTI. The remaining 10.3% had culture growth under 100,000 CFU/mL and, therefore, did not fit in any of these categories, “as there is no consistent guidance on whether to classify them as no UTI or ASB or contamination,” the authors wrote.
When the researchers applied the new criteria, more than half of the cases of ASB (68%) were reclassified as BUS, and 28.9% of the no-UTI cases were reclassified as LUTS/OUS.
In a sensitivity analysis that examined samples with bacteriuria below the 100,000 CFU/mL threshold, nearly half the unclassified cases (43.3%) were reassigned as a UTI, increasing the proportion of patients with a diagnosed UTI from 21.3% to 25.8% of the total population. Of the remaining patients who had originally been unclassified, 14.2% were newly defined as ASB, and 42.5% became BUS.
Dr. Abraham said the addition of the BUS and LUTS/OUS categories has the potential to improve and individualize patient care. Clinicians can consider nonantibiotic therapies for the patients who had LUTS/OUS while they look into possible causes, while the BUS cases enable frontline clinicians and antibiotic stewardship teams to “meet in the middle” by monitoring those patients more closely in case symptoms worsen, she said.
The authors highlighted three key takeaways from their study, starting with the fact that nearly two thirds of patients who underwent testing for a UTI did not have signs or symptoms localized to the urinary tract — the ones reclassified as BUS.
“Hence, reclassifying patients as BUS may provide an opportunity to acknowledge diagnostic uncertainty and need for additional monitoring than ASB patients so as to promote a nuanced and patient-centered approach to diagnosis and management,” the authors wrote.
Second, a third of patients initially classified as not having a UTI were reclassified into the new LUTS/OUS category because of their symptoms, such as a poor or intermittent stream, dribbling, hesitancy, frequency, urge incontinence, and nocturia. These patients would need further workup to determine the best approach to management.
Finally, the sensitivity analysis “suggested that lowering the bacterial threshold in some symptomatic patients may capture additional patients with UTI whose symptoms may be dismissed due to concern for contamination or attributed to LUTS rather than infection.” Given that the 100,000 CFU/mL threshold is based on a single study in 1956, the authors suggested more research may help define better CFU thresholds to improve clinical care.
Dr. Berookhim said the study authors took a reasonable and thorough approach in how they tried to consider the best way to update the current diagnostic classification schema.
“I think using this as a jumping off point to look deeper is worthwhile,” such as conducting randomized controlled trials to assess the use of new categories, he said. “Getting more granular than this, I think, would just muddy the waters and make it more difficult to make clinical decisions.”
The research was funded by the National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases. Dr. Advani reported consulting fees from Locus Biosciences, Sysmex America, GlaxoSmithKline, and bioMérieux. Dr. Abraham and Dr. Berookhim reported no relevant financial conflicts of interest.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
An updated clinical approach to diagnosing urinary tract infections (UTIs) that considers five potential phenotype categories instead of the usual three could aid clinical management and better center patient needs, according to the authors of a new study in The Journal of Urology.
The current diagnostic paradigm includes UTI, asymptomatic bacteriuria (ASB), or not UTI, but the researchers believe these categories exclude for more ambiguous clinical cases, such as patients whose bacteria counts are low but who are symptomatic, or when nonspecific symptoms make it difficult to determine whether treatment with antibiotics is appropriate.
“Our findings suggest the need to reframe our conceptual model of UTI vs ASB to recognize clinical uncertainty and reflect the full spectrum of clinical presentations,” Sonali D. Advani, MBBS, MPH, an associate professor of medicine in infectious disease at Duke University School of Medicine, in Durham, North Carolina, and her colleagues wrote. “Recent data suggest that UTI may present as a bidirectional continuum from asymptomatic bladder colonization to a symptomatic bladder infection,” and some populations may lack the signs or symptoms specific to urinary tract or have chronic lower urinary tract symptoms (LUTS) that make it difficult to distinguish between ASB and UTI, they wrote.
Nitya E. Abraham, MD, an associate professor of urology at Albert Einstein College of Medicine and Montefiore Einstein in New York City, agreed the current paradigm has room for refinement.
“The current classification system doesn’t account for certain patients such as patients who have bothersome urinary symptoms, but urine testing comes back negative, or patients with positive urine testing, but who aren’t able to report the presence or absence of symptoms,” Dr. Abraham, who was not involved in the new research, told this news organization.
Boback Berookhim, MD, a urologist at Northwell Health in New Hyde Park, New York, who was also not involved in the research, said the goal with this study appears to be better identifying who will need antibiotics.
“I think this is more of a forward-looking study in terms of trying to identify patients who currently may not be treated or may be over treated and better identifying subsets,” Dr. Berookhim told this news organization.
However, he said the relevance of the work is far greater in hospitals than in outpatient settings.
“I think it’s much more relevant in inpatient environments where a patient is in hospital and whatever antibiotics are being written are going to be overseen and you’re going to see higher resistance patterns,” Dr. Berookhim said. “For the average doctor who’s seeing patients in the office and writing them prescriptions in the office, this doesn’t really affect them.”
Antibiotic Dilemma
A key issue in determining the best approach to UTI diagnosis is assessing the appropriateness of antibiotic treatment. Up to half of hospitalized patients have ASB, for which current practice guidelines advise against antibiotics, Dr. Advani and her colleagues noted. Yet many of these patients receive antibiotics regardless, and research has shown links between treatment and longer length of stay, antibiotic resistance, and infection with Clostridioides difficile.
The challenge comes with patients who do not fit easily into the existing categories. One includes patients who have positive urine cultures but whose symptoms, such as hypotension or fever, are not specific to the genitourinary tract.
While current guidelines advise against treating these patients with antibiotics, the patients are often older adults with cognitive impairment or delirium, and frontline physicians may err on the side of prescribing antibiotics because of their clinical uncertainty. That treatment can lead to tension with hospital antibiotic stewardship teams that recommend withholding antibiotics for those patients.
“These clinical scenarios highlight differences between the frontline clinicians’ and antibiotic stewardship teams’ definitions of ‘asymptomatic,’ highlighting the ambiguity of the term ‘asymptomatic bacteriuria,’” Dr. Advani and her colleagues wrote.
A fever, for example, could signal a viral or bacterial infection or result from a nonurinary source, Dr. Abraham said. “The antibiotic stewardship team likely prefers to observe the clinical course and wait for more data to demonstrate need for antibiotics,” she said. “Hence, there are conflicting priorities and confusion of when to treat with antibiotics for this common dilemma in patients presenting to the ER or urgent care.”
Meanwhile, other patients, particularly women, may present with urinary symptoms and pyuria but have lab results revealing a colony count below the 100,000 CFU/mL threshold that would indicate antibiotic treatment.
“Some of these women are likely suffering from a UTI and may not receive treatment if clinicians focus primarily on the urine culture results,” Dr. Abraham said. She pointed out the existence of other options than urine culture for better identifying UTI, such as urinary cell-free DNA or next-generation DNA testing of the urine. But she also said the 100,000 CFU/mL threshold should not be absolute.
“For example, I will treat patients for UTI with 10,000-50,000 CFU/mL if they also have UTI symptoms like blood in the urine, burning with urination, bladder pain, increased urgency or frequency, and the urinalysis shows a high white blood cell count,” Dr. Abraham said.
Dr. Abraham also noted a third group outside the scope of the new study: People with urinary symptoms who don’t undergo urine tests or who are treated empirically with antibiotics. “It is unclear whether those in this group truly have a UTI, but it is a common scenario that patients are unable to get urine tests and are treated with over-the-phone prescriptions to expedite treatment,” she said.
Get on the BUS
The researchers conducted a retrospective study across one academic medical center and four community hospitals in three states to assess the feasibility of using five categories of UTI diagnosis: The three existing ones plus LUTS/other urologic symptoms (OUS) and bacteriuria of unclear significance (BUS). These additional categories arose out of an hour-long discussion with a focus group of experts across several disciplines.
The analysis covered the charts of 3392 randomly selected encounters out of 220,531 total inpatient or emergency department encounters between January 2017 and December 2019 in which adults received a urinalysis and urine culture order within the same 24-hour period. The patients’ median age was 67 years, over half (59.6%) were women, and nearly a quarter (24.2%) had an underlying immunocompromising condition.
Most of the cultures were obtained from inpatients. Nearly a third (30.6%) were negative for culture, while 42.1% grew at least 100,000 CFU/mL of bacteria and 17% grew mixed flora.
Based on current criteria, 21.3% of the patients had a UTI, 20.8% had ASB, and 47.6% had no UTI. The remaining 10.3% had culture growth under 100,000 CFU/mL and, therefore, did not fit in any of these categories, “as there is no consistent guidance on whether to classify them as no UTI or ASB or contamination,” the authors wrote.
When the researchers applied the new criteria, more than half of the cases of ASB (68%) were reclassified as BUS, and 28.9% of the no-UTI cases were reclassified as LUTS/OUS.
In a sensitivity analysis that examined samples with bacteriuria below the 100,000 CFU/mL threshold, nearly half the unclassified cases (43.3%) were reassigned as a UTI, increasing the proportion of patients with a diagnosed UTI from 21.3% to 25.8% of the total population. Of the remaining patients who had originally been unclassified, 14.2% were newly defined as ASB, and 42.5% became BUS.
Dr. Abraham said the addition of the BUS and LUTS/OUS categories has the potential to improve and individualize patient care. Clinicians can consider nonantibiotic therapies for the patients who had LUTS/OUS while they look into possible causes, while the BUS cases enable frontline clinicians and antibiotic stewardship teams to “meet in the middle” by monitoring those patients more closely in case symptoms worsen, she said.
The authors highlighted three key takeaways from their study, starting with the fact that nearly two thirds of patients who underwent testing for a UTI did not have signs or symptoms localized to the urinary tract — the ones reclassified as BUS.
“Hence, reclassifying patients as BUS may provide an opportunity to acknowledge diagnostic uncertainty and need for additional monitoring than ASB patients so as to promote a nuanced and patient-centered approach to diagnosis and management,” the authors wrote.
Second, a third of patients initially classified as not having a UTI were reclassified into the new LUTS/OUS category because of their symptoms, such as a poor or intermittent stream, dribbling, hesitancy, frequency, urge incontinence, and nocturia. These patients would need further workup to determine the best approach to management.
Finally, the sensitivity analysis “suggested that lowering the bacterial threshold in some symptomatic patients may capture additional patients with UTI whose symptoms may be dismissed due to concern for contamination or attributed to LUTS rather than infection.” Given that the 100,000 CFU/mL threshold is based on a single study in 1956, the authors suggested more research may help define better CFU thresholds to improve clinical care.
Dr. Berookhim said the study authors took a reasonable and thorough approach in how they tried to consider the best way to update the current diagnostic classification schema.
“I think using this as a jumping off point to look deeper is worthwhile,” such as conducting randomized controlled trials to assess the use of new categories, he said. “Getting more granular than this, I think, would just muddy the waters and make it more difficult to make clinical decisions.”
The research was funded by the National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases. Dr. Advani reported consulting fees from Locus Biosciences, Sysmex America, GlaxoSmithKline, and bioMérieux. Dr. Abraham and Dr. Berookhim reported no relevant financial conflicts of interest.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
An updated clinical approach to diagnosing urinary tract infections (UTIs) that considers five potential phenotype categories instead of the usual three could aid clinical management and better center patient needs, according to the authors of a new study in The Journal of Urology.
The current diagnostic paradigm includes UTI, asymptomatic bacteriuria (ASB), or not UTI, but the researchers believe these categories exclude for more ambiguous clinical cases, such as patients whose bacteria counts are low but who are symptomatic, or when nonspecific symptoms make it difficult to determine whether treatment with antibiotics is appropriate.
“Our findings suggest the need to reframe our conceptual model of UTI vs ASB to recognize clinical uncertainty and reflect the full spectrum of clinical presentations,” Sonali D. Advani, MBBS, MPH, an associate professor of medicine in infectious disease at Duke University School of Medicine, in Durham, North Carolina, and her colleagues wrote. “Recent data suggest that UTI may present as a bidirectional continuum from asymptomatic bladder colonization to a symptomatic bladder infection,” and some populations may lack the signs or symptoms specific to urinary tract or have chronic lower urinary tract symptoms (LUTS) that make it difficult to distinguish between ASB and UTI, they wrote.
Nitya E. Abraham, MD, an associate professor of urology at Albert Einstein College of Medicine and Montefiore Einstein in New York City, agreed the current paradigm has room for refinement.
“The current classification system doesn’t account for certain patients such as patients who have bothersome urinary symptoms, but urine testing comes back negative, or patients with positive urine testing, but who aren’t able to report the presence or absence of symptoms,” Dr. Abraham, who was not involved in the new research, told this news organization.
Boback Berookhim, MD, a urologist at Northwell Health in New Hyde Park, New York, who was also not involved in the research, said the goal with this study appears to be better identifying who will need antibiotics.
“I think this is more of a forward-looking study in terms of trying to identify patients who currently may not be treated or may be over treated and better identifying subsets,” Dr. Berookhim told this news organization.
However, he said the relevance of the work is far greater in hospitals than in outpatient settings.
“I think it’s much more relevant in inpatient environments where a patient is in hospital and whatever antibiotics are being written are going to be overseen and you’re going to see higher resistance patterns,” Dr. Berookhim said. “For the average doctor who’s seeing patients in the office and writing them prescriptions in the office, this doesn’t really affect them.”
Antibiotic Dilemma
A key issue in determining the best approach to UTI diagnosis is assessing the appropriateness of antibiotic treatment. Up to half of hospitalized patients have ASB, for which current practice guidelines advise against antibiotics, Dr. Advani and her colleagues noted. Yet many of these patients receive antibiotics regardless, and research has shown links between treatment and longer length of stay, antibiotic resistance, and infection with Clostridioides difficile.
The challenge comes with patients who do not fit easily into the existing categories. One includes patients who have positive urine cultures but whose symptoms, such as hypotension or fever, are not specific to the genitourinary tract.
While current guidelines advise against treating these patients with antibiotics, the patients are often older adults with cognitive impairment or delirium, and frontline physicians may err on the side of prescribing antibiotics because of their clinical uncertainty. That treatment can lead to tension with hospital antibiotic stewardship teams that recommend withholding antibiotics for those patients.
“These clinical scenarios highlight differences between the frontline clinicians’ and antibiotic stewardship teams’ definitions of ‘asymptomatic,’ highlighting the ambiguity of the term ‘asymptomatic bacteriuria,’” Dr. Advani and her colleagues wrote.
A fever, for example, could signal a viral or bacterial infection or result from a nonurinary source, Dr. Abraham said. “The antibiotic stewardship team likely prefers to observe the clinical course and wait for more data to demonstrate need for antibiotics,” she said. “Hence, there are conflicting priorities and confusion of when to treat with antibiotics for this common dilemma in patients presenting to the ER or urgent care.”
Meanwhile, other patients, particularly women, may present with urinary symptoms and pyuria but have lab results revealing a colony count below the 100,000 CFU/mL threshold that would indicate antibiotic treatment.
“Some of these women are likely suffering from a UTI and may not receive treatment if clinicians focus primarily on the urine culture results,” Dr. Abraham said. She pointed out the existence of other options than urine culture for better identifying UTI, such as urinary cell-free DNA or next-generation DNA testing of the urine. But she also said the 100,000 CFU/mL threshold should not be absolute.
“For example, I will treat patients for UTI with 10,000-50,000 CFU/mL if they also have UTI symptoms like blood in the urine, burning with urination, bladder pain, increased urgency or frequency, and the urinalysis shows a high white blood cell count,” Dr. Abraham said.
Dr. Abraham also noted a third group outside the scope of the new study: People with urinary symptoms who don’t undergo urine tests or who are treated empirically with antibiotics. “It is unclear whether those in this group truly have a UTI, but it is a common scenario that patients are unable to get urine tests and are treated with over-the-phone prescriptions to expedite treatment,” she said.
Get on the BUS
The researchers conducted a retrospective study across one academic medical center and four community hospitals in three states to assess the feasibility of using five categories of UTI diagnosis: The three existing ones plus LUTS/other urologic symptoms (OUS) and bacteriuria of unclear significance (BUS). These additional categories arose out of an hour-long discussion with a focus group of experts across several disciplines.
The analysis covered the charts of 3392 randomly selected encounters out of 220,531 total inpatient or emergency department encounters between January 2017 and December 2019 in which adults received a urinalysis and urine culture order within the same 24-hour period. The patients’ median age was 67 years, over half (59.6%) were women, and nearly a quarter (24.2%) had an underlying immunocompromising condition.
Most of the cultures were obtained from inpatients. Nearly a third (30.6%) were negative for culture, while 42.1% grew at least 100,000 CFU/mL of bacteria and 17% grew mixed flora.
Based on current criteria, 21.3% of the patients had a UTI, 20.8% had ASB, and 47.6% had no UTI. The remaining 10.3% had culture growth under 100,000 CFU/mL and, therefore, did not fit in any of these categories, “as there is no consistent guidance on whether to classify them as no UTI or ASB or contamination,” the authors wrote.
When the researchers applied the new criteria, more than half of the cases of ASB (68%) were reclassified as BUS, and 28.9% of the no-UTI cases were reclassified as LUTS/OUS.
In a sensitivity analysis that examined samples with bacteriuria below the 100,000 CFU/mL threshold, nearly half the unclassified cases (43.3%) were reassigned as a UTI, increasing the proportion of patients with a diagnosed UTI from 21.3% to 25.8% of the total population. Of the remaining patients who had originally been unclassified, 14.2% were newly defined as ASB, and 42.5% became BUS.
Dr. Abraham said the addition of the BUS and LUTS/OUS categories has the potential to improve and individualize patient care. Clinicians can consider nonantibiotic therapies for the patients who had LUTS/OUS while they look into possible causes, while the BUS cases enable frontline clinicians and antibiotic stewardship teams to “meet in the middle” by monitoring those patients more closely in case symptoms worsen, she said.
The authors highlighted three key takeaways from their study, starting with the fact that nearly two thirds of patients who underwent testing for a UTI did not have signs or symptoms localized to the urinary tract — the ones reclassified as BUS.
“Hence, reclassifying patients as BUS may provide an opportunity to acknowledge diagnostic uncertainty and need for additional monitoring than ASB patients so as to promote a nuanced and patient-centered approach to diagnosis and management,” the authors wrote.
Second, a third of patients initially classified as not having a UTI were reclassified into the new LUTS/OUS category because of their symptoms, such as a poor or intermittent stream, dribbling, hesitancy, frequency, urge incontinence, and nocturia. These patients would need further workup to determine the best approach to management.
Finally, the sensitivity analysis “suggested that lowering the bacterial threshold in some symptomatic patients may capture additional patients with UTI whose symptoms may be dismissed due to concern for contamination or attributed to LUTS rather than infection.” Given that the 100,000 CFU/mL threshold is based on a single study in 1956, the authors suggested more research may help define better CFU thresholds to improve clinical care.
Dr. Berookhim said the study authors took a reasonable and thorough approach in how they tried to consider the best way to update the current diagnostic classification schema.
“I think using this as a jumping off point to look deeper is worthwhile,” such as conducting randomized controlled trials to assess the use of new categories, he said. “Getting more granular than this, I think, would just muddy the waters and make it more difficult to make clinical decisions.”
The research was funded by the National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases. Dr. Advani reported consulting fees from Locus Biosciences, Sysmex America, GlaxoSmithKline, and bioMérieux. Dr. Abraham and Dr. Berookhim reported no relevant financial conflicts of interest.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM THE JOURNAL OF UROLOGY
Former UCLA Doctor Receives $14 Million in Gender Discrimination Retrial
A California jury has awarded $14 million to a former University of California, Los Angeles (UCLA) oncologist who claimed she was paid thousands less than her male colleagues and wrongfully terminated after her complaints of gender-based harassment and intimidation were ignored by program leadership.
The decision comes after a lengthy 8-year legal battle in which an appellate judge reversed a previous jury decision in her favor.
Lauren Pinter-Brown, MD, a hematologic oncologist, was hired in 2005 by the University of California, Los Angeles School of Medicine — now called UCLA’s David Geffen School of Medicine. As the school’s lymphoma program director, she conducted clinical research alongside other oncology doctors, including Sven de Vos, MD.
She claimed that her professional relationship with Dr. de Vos became contentious after he demonstrated “oppositional” and “disrespectful” behavior at team meetings, such as talking over her and turning his chair so Dr. Pinter-Brown faced his back. Court documents indicated that Dr. de Vos refused to use Dr. Pinter-Brown’s title in front of colleagues despite doing so for male counterparts.
Dr. Pinter-Brown argued that she was treated as the “butt of a joke” by Dr. de Vos and other male colleagues. In 2016, she sued Dr. de Vos, the university, and its governing body, the Board of Regents, for wrongful termination.
She was awarded a $13 million verdict in 2018. However, the California Court of Appeals overturned it in 2020 after concluding that several mistakes during the court proceedings impeded the school’s right to a fair and impartial trial. The case was retried, culminating in the even higher award of $14 million issued on May 9.
“Two juries have come to virtually identical findings showing multiple problems at UCLA involving gender discrimination,” Dr. Pinter-Brown’s attorney, Carney R. Shegerian, JD, told this news organization.
A spokesperson from UCLA’s David Geffen School of Medicine said administrators are carefully reviewing the new decision.
The spokesperson told this news organization that the medical school and its health system remain “deeply committed to maintaining a workplace free from discrimination, intimidation, retaliation, or harassment of any kind” and fostering a “respectful and inclusive environment ... in research, medical education, and patient care.”
Gender Pay Disparities Persist in Medicine
The gender pay gap in medicine is well documented. The 2024 Medscape Physician Compensation Report found that male doctors earn about 29% more than their female counterparts, with the disparity growing larger among specialists. In addition, a recent JAMA Health Forum study found that male physicians earned 21%-24% more per hour than female physicians.
Dr. Pinter-Brown, who now works at the University of California, Irvine, alleged that she was paid $200,000 less annually, on average, than her male colleagues.
That’s not surprising, says Martha Gulati, MD, professor and director of preventive cardiology at Cedars-Sinai Smidt Heart Institute, Los Angeles. She coauthored a commentary about gender disparities in JAMA Network Open. Dr. Gulati told this news organization that even a “small” pay disparity of $100,000 annually adds up.
“Let’s say the [male physician] invests it at 3% and adds to it yearly. Even without a raise, in 20 years, that is approximately $3 million,” Dr. Gulati explained. “Once you find out you are paid less than your male colleagues, you are upset. Your sense of value and self-worth disappears.”
Eileen Barrett, MD, MPH, president-elect of the American Medical Women’s Association, said that gender discrimination is likely more prevalent than research indicates. She told this news organization that self-doubt and fear of retaliation keep many from exposing the mistreatment.
Although more women are entering medicine, too few rise to the highest positions, Dr. Barrett said.
“Unfortunately, many are pulled and pushed into specialties and subspecialties that have lower compensation and are not promoted to leadership, so just having numbers isn’t enough to achieve equity,” Dr. Barrett said.
Dr. Pinter-Brown claimed she was repeatedly harassed and intimidated by Dr. de Vos from 2008 to 2015. Despite voicing concerns multiple times about the discriminatory behavior, the only resolutions offered by the male-dominated program leadership were for her to separate from the group and conduct lymphoma research independently or to avoid interacting with Dr. de Vos, court records said.
Even the school’s male Title IX officer, Jan Tillisch, MD, who handled gender-based discrimination complaints, reportedly made sexist comments. When Dr. Pinter-Brown sought his help, he allegedly told her that she had a reputation as an “angry woman” and “diva,” court records showed.
According to court documents, Dr. Pinter-Brown endured nitpicking and research audits as retaliation for speaking out, temporarily suspending her research privileges. She said she was subsequently removed from the director position and replaced by Dr. de Vos.
Female physicians who report discriminatory behavior often have unfavorable outcomes and risk future career prospects, Dr. Gulati said.
To shift this dynamic, she said institutions must increase transparency and practices that support female doctors receiving “equal pay for equal work.”
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
A California jury has awarded $14 million to a former University of California, Los Angeles (UCLA) oncologist who claimed she was paid thousands less than her male colleagues and wrongfully terminated after her complaints of gender-based harassment and intimidation were ignored by program leadership.
The decision comes after a lengthy 8-year legal battle in which an appellate judge reversed a previous jury decision in her favor.
Lauren Pinter-Brown, MD, a hematologic oncologist, was hired in 2005 by the University of California, Los Angeles School of Medicine — now called UCLA’s David Geffen School of Medicine. As the school’s lymphoma program director, she conducted clinical research alongside other oncology doctors, including Sven de Vos, MD.
She claimed that her professional relationship with Dr. de Vos became contentious after he demonstrated “oppositional” and “disrespectful” behavior at team meetings, such as talking over her and turning his chair so Dr. Pinter-Brown faced his back. Court documents indicated that Dr. de Vos refused to use Dr. Pinter-Brown’s title in front of colleagues despite doing so for male counterparts.
Dr. Pinter-Brown argued that she was treated as the “butt of a joke” by Dr. de Vos and other male colleagues. In 2016, she sued Dr. de Vos, the university, and its governing body, the Board of Regents, for wrongful termination.
She was awarded a $13 million verdict in 2018. However, the California Court of Appeals overturned it in 2020 after concluding that several mistakes during the court proceedings impeded the school’s right to a fair and impartial trial. The case was retried, culminating in the even higher award of $14 million issued on May 9.
“Two juries have come to virtually identical findings showing multiple problems at UCLA involving gender discrimination,” Dr. Pinter-Brown’s attorney, Carney R. Shegerian, JD, told this news organization.
A spokesperson from UCLA’s David Geffen School of Medicine said administrators are carefully reviewing the new decision.
The spokesperson told this news organization that the medical school and its health system remain “deeply committed to maintaining a workplace free from discrimination, intimidation, retaliation, or harassment of any kind” and fostering a “respectful and inclusive environment ... in research, medical education, and patient care.”
Gender Pay Disparities Persist in Medicine
The gender pay gap in medicine is well documented. The 2024 Medscape Physician Compensation Report found that male doctors earn about 29% more than their female counterparts, with the disparity growing larger among specialists. In addition, a recent JAMA Health Forum study found that male physicians earned 21%-24% more per hour than female physicians.
Dr. Pinter-Brown, who now works at the University of California, Irvine, alleged that she was paid $200,000 less annually, on average, than her male colleagues.
That’s not surprising, says Martha Gulati, MD, professor and director of preventive cardiology at Cedars-Sinai Smidt Heart Institute, Los Angeles. She coauthored a commentary about gender disparities in JAMA Network Open. Dr. Gulati told this news organization that even a “small” pay disparity of $100,000 annually adds up.
“Let’s say the [male physician] invests it at 3% and adds to it yearly. Even without a raise, in 20 years, that is approximately $3 million,” Dr. Gulati explained. “Once you find out you are paid less than your male colleagues, you are upset. Your sense of value and self-worth disappears.”
Eileen Barrett, MD, MPH, president-elect of the American Medical Women’s Association, said that gender discrimination is likely more prevalent than research indicates. She told this news organization that self-doubt and fear of retaliation keep many from exposing the mistreatment.
Although more women are entering medicine, too few rise to the highest positions, Dr. Barrett said.
“Unfortunately, many are pulled and pushed into specialties and subspecialties that have lower compensation and are not promoted to leadership, so just having numbers isn’t enough to achieve equity,” Dr. Barrett said.
Dr. Pinter-Brown claimed she was repeatedly harassed and intimidated by Dr. de Vos from 2008 to 2015. Despite voicing concerns multiple times about the discriminatory behavior, the only resolutions offered by the male-dominated program leadership were for her to separate from the group and conduct lymphoma research independently or to avoid interacting with Dr. de Vos, court records said.
Even the school’s male Title IX officer, Jan Tillisch, MD, who handled gender-based discrimination complaints, reportedly made sexist comments. When Dr. Pinter-Brown sought his help, he allegedly told her that she had a reputation as an “angry woman” and “diva,” court records showed.
According to court documents, Dr. Pinter-Brown endured nitpicking and research audits as retaliation for speaking out, temporarily suspending her research privileges. She said she was subsequently removed from the director position and replaced by Dr. de Vos.
Female physicians who report discriminatory behavior often have unfavorable outcomes and risk future career prospects, Dr. Gulati said.
To shift this dynamic, she said institutions must increase transparency and practices that support female doctors receiving “equal pay for equal work.”
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
A California jury has awarded $14 million to a former University of California, Los Angeles (UCLA) oncologist who claimed she was paid thousands less than her male colleagues and wrongfully terminated after her complaints of gender-based harassment and intimidation were ignored by program leadership.
The decision comes after a lengthy 8-year legal battle in which an appellate judge reversed a previous jury decision in her favor.
Lauren Pinter-Brown, MD, a hematologic oncologist, was hired in 2005 by the University of California, Los Angeles School of Medicine — now called UCLA’s David Geffen School of Medicine. As the school’s lymphoma program director, she conducted clinical research alongside other oncology doctors, including Sven de Vos, MD.
She claimed that her professional relationship with Dr. de Vos became contentious after he demonstrated “oppositional” and “disrespectful” behavior at team meetings, such as talking over her and turning his chair so Dr. Pinter-Brown faced his back. Court documents indicated that Dr. de Vos refused to use Dr. Pinter-Brown’s title in front of colleagues despite doing so for male counterparts.
Dr. Pinter-Brown argued that she was treated as the “butt of a joke” by Dr. de Vos and other male colleagues. In 2016, she sued Dr. de Vos, the university, and its governing body, the Board of Regents, for wrongful termination.
She was awarded a $13 million verdict in 2018. However, the California Court of Appeals overturned it in 2020 after concluding that several mistakes during the court proceedings impeded the school’s right to a fair and impartial trial. The case was retried, culminating in the even higher award of $14 million issued on May 9.
“Two juries have come to virtually identical findings showing multiple problems at UCLA involving gender discrimination,” Dr. Pinter-Brown’s attorney, Carney R. Shegerian, JD, told this news organization.
A spokesperson from UCLA’s David Geffen School of Medicine said administrators are carefully reviewing the new decision.
The spokesperson told this news organization that the medical school and its health system remain “deeply committed to maintaining a workplace free from discrimination, intimidation, retaliation, or harassment of any kind” and fostering a “respectful and inclusive environment ... in research, medical education, and patient care.”
Gender Pay Disparities Persist in Medicine
The gender pay gap in medicine is well documented. The 2024 Medscape Physician Compensation Report found that male doctors earn about 29% more than their female counterparts, with the disparity growing larger among specialists. In addition, a recent JAMA Health Forum study found that male physicians earned 21%-24% more per hour than female physicians.
Dr. Pinter-Brown, who now works at the University of California, Irvine, alleged that she was paid $200,000 less annually, on average, than her male colleagues.
That’s not surprising, says Martha Gulati, MD, professor and director of preventive cardiology at Cedars-Sinai Smidt Heart Institute, Los Angeles. She coauthored a commentary about gender disparities in JAMA Network Open. Dr. Gulati told this news organization that even a “small” pay disparity of $100,000 annually adds up.
“Let’s say the [male physician] invests it at 3% and adds to it yearly. Even without a raise, in 20 years, that is approximately $3 million,” Dr. Gulati explained. “Once you find out you are paid less than your male colleagues, you are upset. Your sense of value and self-worth disappears.”
Eileen Barrett, MD, MPH, president-elect of the American Medical Women’s Association, said that gender discrimination is likely more prevalent than research indicates. She told this news organization that self-doubt and fear of retaliation keep many from exposing the mistreatment.
Although more women are entering medicine, too few rise to the highest positions, Dr. Barrett said.
“Unfortunately, many are pulled and pushed into specialties and subspecialties that have lower compensation and are not promoted to leadership, so just having numbers isn’t enough to achieve equity,” Dr. Barrett said.
Dr. Pinter-Brown claimed she was repeatedly harassed and intimidated by Dr. de Vos from 2008 to 2015. Despite voicing concerns multiple times about the discriminatory behavior, the only resolutions offered by the male-dominated program leadership were for her to separate from the group and conduct lymphoma research independently or to avoid interacting with Dr. de Vos, court records said.
Even the school’s male Title IX officer, Jan Tillisch, MD, who handled gender-based discrimination complaints, reportedly made sexist comments. When Dr. Pinter-Brown sought his help, he allegedly told her that she had a reputation as an “angry woman” and “diva,” court records showed.
According to court documents, Dr. Pinter-Brown endured nitpicking and research audits as retaliation for speaking out, temporarily suspending her research privileges. She said she was subsequently removed from the director position and replaced by Dr. de Vos.
Female physicians who report discriminatory behavior often have unfavorable outcomes and risk future career prospects, Dr. Gulati said.
To shift this dynamic, she said institutions must increase transparency and practices that support female doctors receiving “equal pay for equal work.”
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
How Physician Mortgage Loans Work for Doctors With Debt
Tell someone you’re a doctor, and the reaction is often: “You must be rich.” But physicians who are just finishing medical school or are in their early careers might feel far from it. The average medical school debt is more than $200,000, with total debts including undergrad climbing well north of $250,000.
That leaves house-hunting physicians in a predicament. A key factor for lending institutions is the “debt to income” ratio, a calculation which indicates if you already have too much debt to pay your mortgage. That single equation could eliminate you from lenders’ mortgage requirements.
But young doctors are also in a unique situation. Yes, they carry above-average levels of debt, but they are on a path to substantial income in future years. That’s where the physician mortgage loan (PML) becomes a useful option.
What Is a Physician Mortgage Loan?
, according to Stephen Chang, MD, a radiologist, and a managing director at Acts Financial Advisors in McLean, Virginia.
The key features, according to James M. Dahle, MD, an emergency physician and founder of The White Coat Investor, include:
- No required down payment, which is typically 20% with a conventional loan.
- No private mortgage insurance (PMI). This is often a requirement of traditional loans, designed to protect the lender if the buyer misses payments. PMLs don’t involve PMI even if you don’t put down 20%.
- No pay stubs. With a conventional loan, pay stubs are often required to prove income level and reliability. PMLs will often allow an employment contract in place of those.
- Different consideration of the student loan burden.
Those are the upsides, of course, but there may be downsides. Dr. Dahle said a PML might involve slightly higher rates and fees than a conventional mortgage does but not always.
Who Is Best Suited for a Physician Mortgage Loan?
Financial advisers caution that everyone should first consider their full financial picture before applying for a mortgage, PML or otherwise. “If you don’t have the money saved for a down payment, one can ask if you are financially prepared to purchase a home,” says Cobin Soelberg, MD, an anesthesiologist and owner of Greeley Wealth Management, a financial planning firm serving physician families in Bend, Oregon.
If your savings are slim, you might need to build those accounts further before pursuing home ownership and the expenses that come along with it.
Your credit score can contribute to the equation. “With any loan product, we always recommend working to optimize your personal credit score as soon as possible before applying for a loan,” said Mark P. Eid, MD, a dermatologist and co–managing director (with Dr. Chang) at Act Financial Advisors. “Once you get into the high 700s, you’ve typically qualified for the best interest rates, so while that perfect 850 is nice to achieve, it’s by no means necessary.”
Also, assess your reasons for purchasing a home and whether it will fit your lifestyle in the coming years. “The main reason that [my wife and I] wanted to buy a home was for stability,” said Jordan Frey, MD, founder of The Prudent Plastic Surgeon. “After living in apartments for years, we wanted a place that was truly our own. We definitely felt disappointed and frustrated when worrying that our student debt may limit our ability to do this.”
Like many physicians, Dr. Frey had taken on a huge amount of debt, to the tune of half a million dollars in student loans and credit card debt when he finished training in 2020. The question Dr. Frey and his wife wrestled with was: “How much debt should we take on in addition to what we already have?”
What Are the Risks? What’s in the Fine Print?
The eased limitations of PMLs come with potential pitfalls, and physicians should not imagine that they have unlimited buying power.
“Many physicians buy more expensive or bigger houses than they need simply because banks are willing to lend physicians money,” Dr. Soelberg warns. “So, the doctor gets locked into a large mortgage and cannot build wealth, save for retirement, and repay their student loans.”
As you shop around, beware of omissions and scams. When meeting with lenders, Dr. Frey recalled that some didn’t even present PMLs as an option, and others presented them with unfavorable terms. He was careful to look for disadvantages hidden in the fine print, such as a potential “big hike in the rate a year later.”
But sometimes, a scam is not outright deception but is more like temptation. So it’s important to have your own best interests in mind without relying on lenders’ advice.
“When we were shopping around, some mortgage lenders would [offer] $1.5 million, and we thought ‘that makes no sense,’ ” said Dr. Frey. “[Physicians] have big future income, which makes us attractive to these lenders. No one in their right mind would give a mortgage like this to anyone else. They aren’t worried about whether it’s a smart decision for you or not.”
What Other Red Flags Should You Look Out for?
Dr. Frey recommends medical professionals beware of these red flags when shopping for PMLs:
- A request for any type of collateral, including your medical practice
- A rate that is much higher than others
- A lender is pushing you to borrow a higher amount than you’re comfortable with
- A lender attempts to influence your decision about the size of your down payment
Remember, if you are choosing an adjustable-rate mortgage (ARM), your rate will recalibrate on the basis of the market’s rates — for better or worse. This means that your payment might be higher or lower, taking current interest rates into account, based on the market.
Looking back, Dr. Frey said he might reconsider his decision to use a 10-year ARM. He and his wife chose it because the rate was low at the time, and they planned to pay off the mortgage quickly or move before it went up. But the uncertainty added an element of pressure.
How Can PMLs Contribute to Overall Financial Health?
Dr. Frey says his physician mortgage was “a huge advantage,” allowing him and his wife to put 0% down on their home without PMI. But most importantly, it fit within their overall financial plan, which included investing. “The money that we would have potentially used for a down payment, we used to buy a rental property, which then got us more income,” he says.
Of course, buying a rental property is not the only path to financial health and freedom. Many people approach a home as an investment that will eventually become fully their own. Others might put that down payment toward building a safety net of savings accounts.
Used strategically and intentionally, PMLs can put you on a more predictable financial path. And with less money stress, buying a home can be an exciting milestone as you plan your future and put down roots in a community.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Tell someone you’re a doctor, and the reaction is often: “You must be rich.” But physicians who are just finishing medical school or are in their early careers might feel far from it. The average medical school debt is more than $200,000, with total debts including undergrad climbing well north of $250,000.
That leaves house-hunting physicians in a predicament. A key factor for lending institutions is the “debt to income” ratio, a calculation which indicates if you already have too much debt to pay your mortgage. That single equation could eliminate you from lenders’ mortgage requirements.
But young doctors are also in a unique situation. Yes, they carry above-average levels of debt, but they are on a path to substantial income in future years. That’s where the physician mortgage loan (PML) becomes a useful option.
What Is a Physician Mortgage Loan?
, according to Stephen Chang, MD, a radiologist, and a managing director at Acts Financial Advisors in McLean, Virginia.
The key features, according to James M. Dahle, MD, an emergency physician and founder of The White Coat Investor, include:
- No required down payment, which is typically 20% with a conventional loan.
- No private mortgage insurance (PMI). This is often a requirement of traditional loans, designed to protect the lender if the buyer misses payments. PMLs don’t involve PMI even if you don’t put down 20%.
- No pay stubs. With a conventional loan, pay stubs are often required to prove income level and reliability. PMLs will often allow an employment contract in place of those.
- Different consideration of the student loan burden.
Those are the upsides, of course, but there may be downsides. Dr. Dahle said a PML might involve slightly higher rates and fees than a conventional mortgage does but not always.
Who Is Best Suited for a Physician Mortgage Loan?
Financial advisers caution that everyone should first consider their full financial picture before applying for a mortgage, PML or otherwise. “If you don’t have the money saved for a down payment, one can ask if you are financially prepared to purchase a home,” says Cobin Soelberg, MD, an anesthesiologist and owner of Greeley Wealth Management, a financial planning firm serving physician families in Bend, Oregon.
If your savings are slim, you might need to build those accounts further before pursuing home ownership and the expenses that come along with it.
Your credit score can contribute to the equation. “With any loan product, we always recommend working to optimize your personal credit score as soon as possible before applying for a loan,” said Mark P. Eid, MD, a dermatologist and co–managing director (with Dr. Chang) at Act Financial Advisors. “Once you get into the high 700s, you’ve typically qualified for the best interest rates, so while that perfect 850 is nice to achieve, it’s by no means necessary.”
Also, assess your reasons for purchasing a home and whether it will fit your lifestyle in the coming years. “The main reason that [my wife and I] wanted to buy a home was for stability,” said Jordan Frey, MD, founder of The Prudent Plastic Surgeon. “After living in apartments for years, we wanted a place that was truly our own. We definitely felt disappointed and frustrated when worrying that our student debt may limit our ability to do this.”
Like many physicians, Dr. Frey had taken on a huge amount of debt, to the tune of half a million dollars in student loans and credit card debt when he finished training in 2020. The question Dr. Frey and his wife wrestled with was: “How much debt should we take on in addition to what we already have?”
What Are the Risks? What’s in the Fine Print?
The eased limitations of PMLs come with potential pitfalls, and physicians should not imagine that they have unlimited buying power.
“Many physicians buy more expensive or bigger houses than they need simply because banks are willing to lend physicians money,” Dr. Soelberg warns. “So, the doctor gets locked into a large mortgage and cannot build wealth, save for retirement, and repay their student loans.”
As you shop around, beware of omissions and scams. When meeting with lenders, Dr. Frey recalled that some didn’t even present PMLs as an option, and others presented them with unfavorable terms. He was careful to look for disadvantages hidden in the fine print, such as a potential “big hike in the rate a year later.”
But sometimes, a scam is not outright deception but is more like temptation. So it’s important to have your own best interests in mind without relying on lenders’ advice.
“When we were shopping around, some mortgage lenders would [offer] $1.5 million, and we thought ‘that makes no sense,’ ” said Dr. Frey. “[Physicians] have big future income, which makes us attractive to these lenders. No one in their right mind would give a mortgage like this to anyone else. They aren’t worried about whether it’s a smart decision for you or not.”
What Other Red Flags Should You Look Out for?
Dr. Frey recommends medical professionals beware of these red flags when shopping for PMLs:
- A request for any type of collateral, including your medical practice
- A rate that is much higher than others
- A lender is pushing you to borrow a higher amount than you’re comfortable with
- A lender attempts to influence your decision about the size of your down payment
Remember, if you are choosing an adjustable-rate mortgage (ARM), your rate will recalibrate on the basis of the market’s rates — for better or worse. This means that your payment might be higher or lower, taking current interest rates into account, based on the market.
Looking back, Dr. Frey said he might reconsider his decision to use a 10-year ARM. He and his wife chose it because the rate was low at the time, and they planned to pay off the mortgage quickly or move before it went up. But the uncertainty added an element of pressure.
How Can PMLs Contribute to Overall Financial Health?
Dr. Frey says his physician mortgage was “a huge advantage,” allowing him and his wife to put 0% down on their home without PMI. But most importantly, it fit within their overall financial plan, which included investing. “The money that we would have potentially used for a down payment, we used to buy a rental property, which then got us more income,” he says.
Of course, buying a rental property is not the only path to financial health and freedom. Many people approach a home as an investment that will eventually become fully their own. Others might put that down payment toward building a safety net of savings accounts.
Used strategically and intentionally, PMLs can put you on a more predictable financial path. And with less money stress, buying a home can be an exciting milestone as you plan your future and put down roots in a community.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Tell someone you’re a doctor, and the reaction is often: “You must be rich.” But physicians who are just finishing medical school or are in their early careers might feel far from it. The average medical school debt is more than $200,000, with total debts including undergrad climbing well north of $250,000.
That leaves house-hunting physicians in a predicament. A key factor for lending institutions is the “debt to income” ratio, a calculation which indicates if you already have too much debt to pay your mortgage. That single equation could eliminate you from lenders’ mortgage requirements.
But young doctors are also in a unique situation. Yes, they carry above-average levels of debt, but they are on a path to substantial income in future years. That’s where the physician mortgage loan (PML) becomes a useful option.
What Is a Physician Mortgage Loan?
, according to Stephen Chang, MD, a radiologist, and a managing director at Acts Financial Advisors in McLean, Virginia.
The key features, according to James M. Dahle, MD, an emergency physician and founder of The White Coat Investor, include:
- No required down payment, which is typically 20% with a conventional loan.
- No private mortgage insurance (PMI). This is often a requirement of traditional loans, designed to protect the lender if the buyer misses payments. PMLs don’t involve PMI even if you don’t put down 20%.
- No pay stubs. With a conventional loan, pay stubs are often required to prove income level and reliability. PMLs will often allow an employment contract in place of those.
- Different consideration of the student loan burden.
Those are the upsides, of course, but there may be downsides. Dr. Dahle said a PML might involve slightly higher rates and fees than a conventional mortgage does but not always.
Who Is Best Suited for a Physician Mortgage Loan?
Financial advisers caution that everyone should first consider their full financial picture before applying for a mortgage, PML or otherwise. “If you don’t have the money saved for a down payment, one can ask if you are financially prepared to purchase a home,” says Cobin Soelberg, MD, an anesthesiologist and owner of Greeley Wealth Management, a financial planning firm serving physician families in Bend, Oregon.
If your savings are slim, you might need to build those accounts further before pursuing home ownership and the expenses that come along with it.
Your credit score can contribute to the equation. “With any loan product, we always recommend working to optimize your personal credit score as soon as possible before applying for a loan,” said Mark P. Eid, MD, a dermatologist and co–managing director (with Dr. Chang) at Act Financial Advisors. “Once you get into the high 700s, you’ve typically qualified for the best interest rates, so while that perfect 850 is nice to achieve, it’s by no means necessary.”
Also, assess your reasons for purchasing a home and whether it will fit your lifestyle in the coming years. “The main reason that [my wife and I] wanted to buy a home was for stability,” said Jordan Frey, MD, founder of The Prudent Plastic Surgeon. “After living in apartments for years, we wanted a place that was truly our own. We definitely felt disappointed and frustrated when worrying that our student debt may limit our ability to do this.”
Like many physicians, Dr. Frey had taken on a huge amount of debt, to the tune of half a million dollars in student loans and credit card debt when he finished training in 2020. The question Dr. Frey and his wife wrestled with was: “How much debt should we take on in addition to what we already have?”
What Are the Risks? What’s in the Fine Print?
The eased limitations of PMLs come with potential pitfalls, and physicians should not imagine that they have unlimited buying power.
“Many physicians buy more expensive or bigger houses than they need simply because banks are willing to lend physicians money,” Dr. Soelberg warns. “So, the doctor gets locked into a large mortgage and cannot build wealth, save for retirement, and repay their student loans.”
As you shop around, beware of omissions and scams. When meeting with lenders, Dr. Frey recalled that some didn’t even present PMLs as an option, and others presented them with unfavorable terms. He was careful to look for disadvantages hidden in the fine print, such as a potential “big hike in the rate a year later.”
But sometimes, a scam is not outright deception but is more like temptation. So it’s important to have your own best interests in mind without relying on lenders’ advice.
“When we were shopping around, some mortgage lenders would [offer] $1.5 million, and we thought ‘that makes no sense,’ ” said Dr. Frey. “[Physicians] have big future income, which makes us attractive to these lenders. No one in their right mind would give a mortgage like this to anyone else. They aren’t worried about whether it’s a smart decision for you or not.”
What Other Red Flags Should You Look Out for?
Dr. Frey recommends medical professionals beware of these red flags when shopping for PMLs:
- A request for any type of collateral, including your medical practice
- A rate that is much higher than others
- A lender is pushing you to borrow a higher amount than you’re comfortable with
- A lender attempts to influence your decision about the size of your down payment
Remember, if you are choosing an adjustable-rate mortgage (ARM), your rate will recalibrate on the basis of the market’s rates — for better or worse. This means that your payment might be higher or lower, taking current interest rates into account, based on the market.
Looking back, Dr. Frey said he might reconsider his decision to use a 10-year ARM. He and his wife chose it because the rate was low at the time, and they planned to pay off the mortgage quickly or move before it went up. But the uncertainty added an element of pressure.
How Can PMLs Contribute to Overall Financial Health?
Dr. Frey says his physician mortgage was “a huge advantage,” allowing him and his wife to put 0% down on their home without PMI. But most importantly, it fit within their overall financial plan, which included investing. “The money that we would have potentially used for a down payment, we used to buy a rental property, which then got us more income,” he says.
Of course, buying a rental property is not the only path to financial health and freedom. Many people approach a home as an investment that will eventually become fully their own. Others might put that down payment toward building a safety net of savings accounts.
Used strategically and intentionally, PMLs can put you on a more predictable financial path. And with less money stress, buying a home can be an exciting milestone as you plan your future and put down roots in a community.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Crossing State Lines: PA Licensure Compact Coming Soon
For decades, physicians and nurses who ventured across state lines to practice, particularly in locum tenens roles, have reaped the benefits of medical licensure compacts. Yet, the same courtesy has eluded physician assistants (PAs), until now.
In April, Virginia Governor Glenn Youngkin signed the bill enacting the PA Compact making Virginia the seventh state to join. The legislation opens a cross-state agreement with seven states and finally allows locum tenens PAs to practice across these state’s borders.
How the PA Compact Works
The interstate arrangement recognizes valid, unencumbered PA licenses issued by other states in the compact. PAs working within the seven states won’t need a separate license from any of those states to practice.
The states include Delaware, Nebraska, Utah, Washington, West Virginia, Wisconsin, and Virginia. While the compact has been approved, the American Academy of Physician Associates said it could take an additional 18-24 months for the states to execute it, giving PAs the access they need to work in the compact states.
How the PA Compact Helps
The PA Compact holds the promise of alleviating some of the travel barriers that PAs often encounter, especially when they work locum tenens or in telehealth and must traverse state lines to deliver essential healthcare. This agreement not only enhances healthcare access but also empowers facilities to recruit new PAs, thereby bridging gaps in their healthcare staffing and addressing public health emergencies more effectively.
PAs will also gain increased flexibility and additional opportunities to earn and benefit from the right to practice in more states without requiring a time-consuming and expensive licensure from each state.
One motivating factor behind developing an interstate compact for physician assistants is that the same types of compacts for physicians and nurses are highly successful. The Nurse Licensure Compact and the Interstate Medical Licensure Compact for physicians encompass 37 and 41 states, respectively. While the seven-state PA Compact is in its earliest stages, it will likely be equally beneficial for PAs.
A survey by Barton Associates found that 95% of PAs said they would be more likely to consider working in a different state if the PA Compact made it more accessible.
Other states have begun legislation to enact a PA Compact, including Colorado, New Hampshire, Maine, Michigan New York, Ohio, Oklahoma, Rhode Island, Tennessee, and Vermont.
If your state still needs to enact a compact or file for compact legislation, let your elected officials know that the PAs in your state want to join a compact.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com .
For decades, physicians and nurses who ventured across state lines to practice, particularly in locum tenens roles, have reaped the benefits of medical licensure compacts. Yet, the same courtesy has eluded physician assistants (PAs), until now.
In April, Virginia Governor Glenn Youngkin signed the bill enacting the PA Compact making Virginia the seventh state to join. The legislation opens a cross-state agreement with seven states and finally allows locum tenens PAs to practice across these state’s borders.
How the PA Compact Works
The interstate arrangement recognizes valid, unencumbered PA licenses issued by other states in the compact. PAs working within the seven states won’t need a separate license from any of those states to practice.
The states include Delaware, Nebraska, Utah, Washington, West Virginia, Wisconsin, and Virginia. While the compact has been approved, the American Academy of Physician Associates said it could take an additional 18-24 months for the states to execute it, giving PAs the access they need to work in the compact states.
How the PA Compact Helps
The PA Compact holds the promise of alleviating some of the travel barriers that PAs often encounter, especially when they work locum tenens or in telehealth and must traverse state lines to deliver essential healthcare. This agreement not only enhances healthcare access but also empowers facilities to recruit new PAs, thereby bridging gaps in their healthcare staffing and addressing public health emergencies more effectively.
PAs will also gain increased flexibility and additional opportunities to earn and benefit from the right to practice in more states without requiring a time-consuming and expensive licensure from each state.
One motivating factor behind developing an interstate compact for physician assistants is that the same types of compacts for physicians and nurses are highly successful. The Nurse Licensure Compact and the Interstate Medical Licensure Compact for physicians encompass 37 and 41 states, respectively. While the seven-state PA Compact is in its earliest stages, it will likely be equally beneficial for PAs.
A survey by Barton Associates found that 95% of PAs said they would be more likely to consider working in a different state if the PA Compact made it more accessible.
Other states have begun legislation to enact a PA Compact, including Colorado, New Hampshire, Maine, Michigan New York, Ohio, Oklahoma, Rhode Island, Tennessee, and Vermont.
If your state still needs to enact a compact or file for compact legislation, let your elected officials know that the PAs in your state want to join a compact.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com .
For decades, physicians and nurses who ventured across state lines to practice, particularly in locum tenens roles, have reaped the benefits of medical licensure compacts. Yet, the same courtesy has eluded physician assistants (PAs), until now.
In April, Virginia Governor Glenn Youngkin signed the bill enacting the PA Compact making Virginia the seventh state to join. The legislation opens a cross-state agreement with seven states and finally allows locum tenens PAs to practice across these state’s borders.
How the PA Compact Works
The interstate arrangement recognizes valid, unencumbered PA licenses issued by other states in the compact. PAs working within the seven states won’t need a separate license from any of those states to practice.
The states include Delaware, Nebraska, Utah, Washington, West Virginia, Wisconsin, and Virginia. While the compact has been approved, the American Academy of Physician Associates said it could take an additional 18-24 months for the states to execute it, giving PAs the access they need to work in the compact states.
How the PA Compact Helps
The PA Compact holds the promise of alleviating some of the travel barriers that PAs often encounter, especially when they work locum tenens or in telehealth and must traverse state lines to deliver essential healthcare. This agreement not only enhances healthcare access but also empowers facilities to recruit new PAs, thereby bridging gaps in their healthcare staffing and addressing public health emergencies more effectively.
PAs will also gain increased flexibility and additional opportunities to earn and benefit from the right to practice in more states without requiring a time-consuming and expensive licensure from each state.
One motivating factor behind developing an interstate compact for physician assistants is that the same types of compacts for physicians and nurses are highly successful. The Nurse Licensure Compact and the Interstate Medical Licensure Compact for physicians encompass 37 and 41 states, respectively. While the seven-state PA Compact is in its earliest stages, it will likely be equally beneficial for PAs.
A survey by Barton Associates found that 95% of PAs said they would be more likely to consider working in a different state if the PA Compact made it more accessible.
Other states have begun legislation to enact a PA Compact, including Colorado, New Hampshire, Maine, Michigan New York, Ohio, Oklahoma, Rhode Island, Tennessee, and Vermont.
If your state still needs to enact a compact or file for compact legislation, let your elected officials know that the PAs in your state want to join a compact.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com .
Follow-Up Outcomes Data Often Missing for FDA Drug Approvals Based on Surrogate Markers
Over the past few decades, the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has increasingly relied on surrogate measures such as blood tests instead of clinical outcomes for medication approvals. But critics say the agency lacks consistent standards to ensure the surrogate aligns with clinical outcomes that matter to patients — things like improvements in symptoms and gains in function.
Sometimes those decisions backfire. Consider: In July 2021, the FDA approved aducanumab for the treatment of Alzheimer’s disease, bucking the advice of an advisory panel for the agency that questioned the effectiveness of the medication. Regulators relied on data from the drugmaker, Biogen, showing the monoclonal antibody could reduce levels of amyloid beta plaques in blood — a surrogate marker officials hoped would translate to clinical benefit.
The FDA’s decision triggered significant controversy, and Biogen in January announced it is pulling it from the market this year, citing disappointing sales.
Although the case of aducanumab might seem extreme, given the stakes — Alzheimer’s remains a disease without an effective treatment — it’s far from unusual.
“When we prescribe a drug, there is an underlying assumption that the FDA has done its due diligence to confirm the drug is safe and of benefit,” said Reshma Ramachandran, MD, MPP, MHS, a researcher at Yale School of Medicine, New Haven, Connecticut, and a coauthor of a recent review of surrogate outcomes. “In fact, we found either no evidence or low-quality evidence.” Such markers are associated with clinical outcomes. “We just don’t know if they work meaningfully to treat the patient’s condition. The results were pretty shocking for us,” she said.
The FDA in 2018 released an Adult Surrogate Endpoint Table listing markers that can be used as substitutes for clinical outcomes to more quickly test, review, and approve new therapies. The analysis found the majority of these endpoints lacked subsequent confirmations, defined as published meta-analyses of clinical studies to validate the association between the marker and a clinical outcome important to patients.
In a paper published in JAMA, Dr. Ramachandran and her colleagues looked at 37 surrogate endpoints for nearly 3 dozen nononcologic diseases in the table.
Approval with surrogate markers implies responsibility for postapproval or validation studies — not just lab measures or imaging findings but mortality, morbidity, or improved quality of life, said Joshua D. Wallach, PhD, MS, assistant professor in the department of epidemiology at the Emory Rollins School of Public Health in Atlanta and lead author of the JAMA review.
Dr. Wallach said surrogate markers are easier to measure and do not require large and long trials. But the FDA has not provided clear rules for what makes a surrogate marker valid in clinical trials.
“They’ve said that at a minimum, it requires meta-analytical evidence from studies that have looked at the correlation or the association between the surrogate and the clinical outcome,” Dr. Wallach said. “Our understanding was that if that’s a minimum expectation, we should be able to find those studies in the literature. And the reality is that we were unable to find evidence from those types of studies supporting the association between the surrogate and the clinical outcome.”
Physicians generally do not receive training about the FDA approval process and the difference between biomarkers, surrogate markers, and clinical endpoints, Dr. Ramachandran said. “Our study shows that things are much more uncertain than we thought when it comes to the prescribing of new drugs,” she said.
Surrogate Markers on the Rise
Dr. Wallach’s group looked for published meta-analyses compiling randomized controlled trials reporting surrogate endpoints for more than 3 dozen chronic nononcologic conditions, including type 2 diabetes, Alzheimer’s, kidney disease, HIV, gout, and lupus. They found no meta-analyses at all for 59% of the surrogate markers, while for those that were studied, few reported high-strength evidence of an association with clinical outcomes.
The findings echo previous research. In a 2020 study in JAMA Network Open, researchers tallied primary endpoints for all FDA approvals of new drugs and therapies during three 3-year periods: 1995-1997, 2005-2007, and 2015-2017. The proportion of products whose approvals were based on the use of clinical endpoints decreased from 43.8% in 1995-1997 to 28.4% in 2005-2007 to 23.3% in 2015-2017. The share based on surrogate endpoints rose from 43.3% to roughly 60% over the same interval.
A 2017 study in the Journal of Health Economics found the use of “imperfect” surrogate endpoints helped support the approval of an average of 16 new drugs per year between 2010 and 2014 compared with six per year from 1998 to 2008.
Similar concerns about weak associations between surrogate markers and drugs used to treat cancer have been documented before, including in a 2020 study published in eClinicalMedicine. The researchers found the surrogate endpoints in the FDA table either were not tested or were tested but proven to be weak surrogates.
“And yet the FDA considered these as good enough not only for accelerated approval but also for regular approval,” said Bishal Gyawali, MD, PhD, associate professor in the department of oncology at Queen’s University, Kingston, Ontario, Canada, who led the group.
The use of surrogate endpoints is also increasing in Europe, said Huseyin Naci, MHS, PhD, associate professor of health policy at the London School of Economics and Political Science in England. He cited a cohort study of 298 randomized clinical trials (RCTs) in JAMA Oncology suggesting “contemporary oncology RCTs now largely measure putative surrogate endpoints.” Dr. Wallach called the FDA’s surrogate table “a great first step toward transparency. But a key column is missing from that table, telling us what is the basis for which the FDA allows drug companies to use the recognized surrogate markers. What is the evidence they are considering?”
If the agency allows companies the flexibility to validate surrogate endpoints, postmarketing studies designed to confirm the clinical utility of those endpoints should follow.
“We obviously want physicians to be guided by evidence when they’re selecting treatments, and they need to be able to interpret the clinical benefits of the drug that they’re prescribing,” he said. “This is really about having the research consumer, patients, and physicians, as well as industry, understand why certain markers are considered and not considered.”
Dr. Wallach reported receiving grants from the FDA (through the Yale University — Mayo Clinic Center of Excellence in Regulatory Science and Innovation), National Institute on Alcohol Abuse and Alcoholism (1K01AA028258), and Johnson & Johnson (through the Yale University Open Data Access Project); and consulting fees from Hagens Berman Sobol Shapiro LLP and Dugan Law Firm APLC outside the submitted work. Dr. Ramachandran reported receiving grants from the Stavros Niarchos Foundation and FDA; receiving consulting fees from ReAct Action on Antibiotic Resistance strategy policy program outside the submitted work; and serving in an unpaid capacity as chair of the FDA task force for the nonprofit organization Doctors for America and in an unpaid capacity as board president for Universities Allied for Essential Medicines North America.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Over the past few decades, the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has increasingly relied on surrogate measures such as blood tests instead of clinical outcomes for medication approvals. But critics say the agency lacks consistent standards to ensure the surrogate aligns with clinical outcomes that matter to patients — things like improvements in symptoms and gains in function.
Sometimes those decisions backfire. Consider: In July 2021, the FDA approved aducanumab for the treatment of Alzheimer’s disease, bucking the advice of an advisory panel for the agency that questioned the effectiveness of the medication. Regulators relied on data from the drugmaker, Biogen, showing the monoclonal antibody could reduce levels of amyloid beta plaques in blood — a surrogate marker officials hoped would translate to clinical benefit.
The FDA’s decision triggered significant controversy, and Biogen in January announced it is pulling it from the market this year, citing disappointing sales.
Although the case of aducanumab might seem extreme, given the stakes — Alzheimer’s remains a disease without an effective treatment — it’s far from unusual.
“When we prescribe a drug, there is an underlying assumption that the FDA has done its due diligence to confirm the drug is safe and of benefit,” said Reshma Ramachandran, MD, MPP, MHS, a researcher at Yale School of Medicine, New Haven, Connecticut, and a coauthor of a recent review of surrogate outcomes. “In fact, we found either no evidence or low-quality evidence.” Such markers are associated with clinical outcomes. “We just don’t know if they work meaningfully to treat the patient’s condition. The results were pretty shocking for us,” she said.
The FDA in 2018 released an Adult Surrogate Endpoint Table listing markers that can be used as substitutes for clinical outcomes to more quickly test, review, and approve new therapies. The analysis found the majority of these endpoints lacked subsequent confirmations, defined as published meta-analyses of clinical studies to validate the association between the marker and a clinical outcome important to patients.
In a paper published in JAMA, Dr. Ramachandran and her colleagues looked at 37 surrogate endpoints for nearly 3 dozen nononcologic diseases in the table.
Approval with surrogate markers implies responsibility for postapproval or validation studies — not just lab measures or imaging findings but mortality, morbidity, or improved quality of life, said Joshua D. Wallach, PhD, MS, assistant professor in the department of epidemiology at the Emory Rollins School of Public Health in Atlanta and lead author of the JAMA review.
Dr. Wallach said surrogate markers are easier to measure and do not require large and long trials. But the FDA has not provided clear rules for what makes a surrogate marker valid in clinical trials.
“They’ve said that at a minimum, it requires meta-analytical evidence from studies that have looked at the correlation or the association between the surrogate and the clinical outcome,” Dr. Wallach said. “Our understanding was that if that’s a minimum expectation, we should be able to find those studies in the literature. And the reality is that we were unable to find evidence from those types of studies supporting the association between the surrogate and the clinical outcome.”
Physicians generally do not receive training about the FDA approval process and the difference between biomarkers, surrogate markers, and clinical endpoints, Dr. Ramachandran said. “Our study shows that things are much more uncertain than we thought when it comes to the prescribing of new drugs,” she said.
Surrogate Markers on the Rise
Dr. Wallach’s group looked for published meta-analyses compiling randomized controlled trials reporting surrogate endpoints for more than 3 dozen chronic nononcologic conditions, including type 2 diabetes, Alzheimer’s, kidney disease, HIV, gout, and lupus. They found no meta-analyses at all for 59% of the surrogate markers, while for those that were studied, few reported high-strength evidence of an association with clinical outcomes.
The findings echo previous research. In a 2020 study in JAMA Network Open, researchers tallied primary endpoints for all FDA approvals of new drugs and therapies during three 3-year periods: 1995-1997, 2005-2007, and 2015-2017. The proportion of products whose approvals were based on the use of clinical endpoints decreased from 43.8% in 1995-1997 to 28.4% in 2005-2007 to 23.3% in 2015-2017. The share based on surrogate endpoints rose from 43.3% to roughly 60% over the same interval.
A 2017 study in the Journal of Health Economics found the use of “imperfect” surrogate endpoints helped support the approval of an average of 16 new drugs per year between 2010 and 2014 compared with six per year from 1998 to 2008.
Similar concerns about weak associations between surrogate markers and drugs used to treat cancer have been documented before, including in a 2020 study published in eClinicalMedicine. The researchers found the surrogate endpoints in the FDA table either were not tested or were tested but proven to be weak surrogates.
“And yet the FDA considered these as good enough not only for accelerated approval but also for regular approval,” said Bishal Gyawali, MD, PhD, associate professor in the department of oncology at Queen’s University, Kingston, Ontario, Canada, who led the group.
The use of surrogate endpoints is also increasing in Europe, said Huseyin Naci, MHS, PhD, associate professor of health policy at the London School of Economics and Political Science in England. He cited a cohort study of 298 randomized clinical trials (RCTs) in JAMA Oncology suggesting “contemporary oncology RCTs now largely measure putative surrogate endpoints.” Dr. Wallach called the FDA’s surrogate table “a great first step toward transparency. But a key column is missing from that table, telling us what is the basis for which the FDA allows drug companies to use the recognized surrogate markers. What is the evidence they are considering?”
If the agency allows companies the flexibility to validate surrogate endpoints, postmarketing studies designed to confirm the clinical utility of those endpoints should follow.
“We obviously want physicians to be guided by evidence when they’re selecting treatments, and they need to be able to interpret the clinical benefits of the drug that they’re prescribing,” he said. “This is really about having the research consumer, patients, and physicians, as well as industry, understand why certain markers are considered and not considered.”
Dr. Wallach reported receiving grants from the FDA (through the Yale University — Mayo Clinic Center of Excellence in Regulatory Science and Innovation), National Institute on Alcohol Abuse and Alcoholism (1K01AA028258), and Johnson & Johnson (through the Yale University Open Data Access Project); and consulting fees from Hagens Berman Sobol Shapiro LLP and Dugan Law Firm APLC outside the submitted work. Dr. Ramachandran reported receiving grants from the Stavros Niarchos Foundation and FDA; receiving consulting fees from ReAct Action on Antibiotic Resistance strategy policy program outside the submitted work; and serving in an unpaid capacity as chair of the FDA task force for the nonprofit organization Doctors for America and in an unpaid capacity as board president for Universities Allied for Essential Medicines North America.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Over the past few decades, the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has increasingly relied on surrogate measures such as blood tests instead of clinical outcomes for medication approvals. But critics say the agency lacks consistent standards to ensure the surrogate aligns with clinical outcomes that matter to patients — things like improvements in symptoms and gains in function.
Sometimes those decisions backfire. Consider: In July 2021, the FDA approved aducanumab for the treatment of Alzheimer’s disease, bucking the advice of an advisory panel for the agency that questioned the effectiveness of the medication. Regulators relied on data from the drugmaker, Biogen, showing the monoclonal antibody could reduce levels of amyloid beta plaques in blood — a surrogate marker officials hoped would translate to clinical benefit.
The FDA’s decision triggered significant controversy, and Biogen in January announced it is pulling it from the market this year, citing disappointing sales.
Although the case of aducanumab might seem extreme, given the stakes — Alzheimer’s remains a disease without an effective treatment — it’s far from unusual.
“When we prescribe a drug, there is an underlying assumption that the FDA has done its due diligence to confirm the drug is safe and of benefit,” said Reshma Ramachandran, MD, MPP, MHS, a researcher at Yale School of Medicine, New Haven, Connecticut, and a coauthor of a recent review of surrogate outcomes. “In fact, we found either no evidence or low-quality evidence.” Such markers are associated with clinical outcomes. “We just don’t know if they work meaningfully to treat the patient’s condition. The results were pretty shocking for us,” she said.
The FDA in 2018 released an Adult Surrogate Endpoint Table listing markers that can be used as substitutes for clinical outcomes to more quickly test, review, and approve new therapies. The analysis found the majority of these endpoints lacked subsequent confirmations, defined as published meta-analyses of clinical studies to validate the association between the marker and a clinical outcome important to patients.
In a paper published in JAMA, Dr. Ramachandran and her colleagues looked at 37 surrogate endpoints for nearly 3 dozen nononcologic diseases in the table.
Approval with surrogate markers implies responsibility for postapproval or validation studies — not just lab measures or imaging findings but mortality, morbidity, or improved quality of life, said Joshua D. Wallach, PhD, MS, assistant professor in the department of epidemiology at the Emory Rollins School of Public Health in Atlanta and lead author of the JAMA review.
Dr. Wallach said surrogate markers are easier to measure and do not require large and long trials. But the FDA has not provided clear rules for what makes a surrogate marker valid in clinical trials.
“They’ve said that at a minimum, it requires meta-analytical evidence from studies that have looked at the correlation or the association between the surrogate and the clinical outcome,” Dr. Wallach said. “Our understanding was that if that’s a minimum expectation, we should be able to find those studies in the literature. And the reality is that we were unable to find evidence from those types of studies supporting the association between the surrogate and the clinical outcome.”
Physicians generally do not receive training about the FDA approval process and the difference between biomarkers, surrogate markers, and clinical endpoints, Dr. Ramachandran said. “Our study shows that things are much more uncertain than we thought when it comes to the prescribing of new drugs,” she said.
Surrogate Markers on the Rise
Dr. Wallach’s group looked for published meta-analyses compiling randomized controlled trials reporting surrogate endpoints for more than 3 dozen chronic nononcologic conditions, including type 2 diabetes, Alzheimer’s, kidney disease, HIV, gout, and lupus. They found no meta-analyses at all for 59% of the surrogate markers, while for those that were studied, few reported high-strength evidence of an association with clinical outcomes.
The findings echo previous research. In a 2020 study in JAMA Network Open, researchers tallied primary endpoints for all FDA approvals of new drugs and therapies during three 3-year periods: 1995-1997, 2005-2007, and 2015-2017. The proportion of products whose approvals were based on the use of clinical endpoints decreased from 43.8% in 1995-1997 to 28.4% in 2005-2007 to 23.3% in 2015-2017. The share based on surrogate endpoints rose from 43.3% to roughly 60% over the same interval.
A 2017 study in the Journal of Health Economics found the use of “imperfect” surrogate endpoints helped support the approval of an average of 16 new drugs per year between 2010 and 2014 compared with six per year from 1998 to 2008.
Similar concerns about weak associations between surrogate markers and drugs used to treat cancer have been documented before, including in a 2020 study published in eClinicalMedicine. The researchers found the surrogate endpoints in the FDA table either were not tested or were tested but proven to be weak surrogates.
“And yet the FDA considered these as good enough not only for accelerated approval but also for regular approval,” said Bishal Gyawali, MD, PhD, associate professor in the department of oncology at Queen’s University, Kingston, Ontario, Canada, who led the group.
The use of surrogate endpoints is also increasing in Europe, said Huseyin Naci, MHS, PhD, associate professor of health policy at the London School of Economics and Political Science in England. He cited a cohort study of 298 randomized clinical trials (RCTs) in JAMA Oncology suggesting “contemporary oncology RCTs now largely measure putative surrogate endpoints.” Dr. Wallach called the FDA’s surrogate table “a great first step toward transparency. But a key column is missing from that table, telling us what is the basis for which the FDA allows drug companies to use the recognized surrogate markers. What is the evidence they are considering?”
If the agency allows companies the flexibility to validate surrogate endpoints, postmarketing studies designed to confirm the clinical utility of those endpoints should follow.
“We obviously want physicians to be guided by evidence when they’re selecting treatments, and they need to be able to interpret the clinical benefits of the drug that they’re prescribing,” he said. “This is really about having the research consumer, patients, and physicians, as well as industry, understand why certain markers are considered and not considered.”
Dr. Wallach reported receiving grants from the FDA (through the Yale University — Mayo Clinic Center of Excellence in Regulatory Science and Innovation), National Institute on Alcohol Abuse and Alcoholism (1K01AA028258), and Johnson & Johnson (through the Yale University Open Data Access Project); and consulting fees from Hagens Berman Sobol Shapiro LLP and Dugan Law Firm APLC outside the submitted work. Dr. Ramachandran reported receiving grants from the Stavros Niarchos Foundation and FDA; receiving consulting fees from ReAct Action on Antibiotic Resistance strategy policy program outside the submitted work; and serving in an unpaid capacity as chair of the FDA task force for the nonprofit organization Doctors for America and in an unpaid capacity as board president for Universities Allied for Essential Medicines North America.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM JAMA