User login
Bringing you the latest news, research and reviews, exclusive interviews, podcasts, quizzes, and more.
div[contains(@class, 'header__large-screen')]
div[contains(@class, 'read-next-article')]
div[contains(@class, 'nav-primary')]
nav[contains(@class, 'nav-primary')]
section[contains(@class, 'footer-nav-section-wrapper')]
footer[@id='footer']
div[contains(@class, 'main-prefix')]
section[contains(@class, 'nav-hidden')]
div[contains(@class, 'ce-card-content')]
nav[contains(@class, 'nav-ce-stack')]
Is Mental Illness ‘Transmissible’?
Teens with classmates who have a mental illness have a significantly greater risk for a psychiatric diagnosis later in life, even after controlling for parents’ mental health history and other factors, a new study suggested.
The research provides new evidence that adolescents within a specific peer network may possibly “transmit” mental disorders such as depression and anxiety to each other, the investigators noted.
The study is said to the be the largest to date on the topic, including data on more than 700,000 ninth graders in Finland who were followed for up to 18 years.
At least one expert noted that the numbers are higher than he would have expected, but the investigators were quick to caution the study doesn’t prove having a classmate with a mental illness leads to later psychiatric diagnosis among peers.
“The associations observed in the study are not necessarily causal,” lead investigator Jussi Alho, PhD, a postdoctoral researcher at the University of Helsinki, Finland, told this news organization. “The study did not investigate the mechanisms that explain the observed associations.”
The results were published online on May 22 in JAMA Psychiatry.
Few Data
Previous studies have reported a clustering of mood symptoms, eating disorders, and other psychiatric illnesses among adolescent and adult social networks. But most involve self-selected peer groups.
“Investigating the transmission of mental disorders is especially important in childhood and adolescence,” the authors noted. “Yet, despite a few survey studies reporting that adolescents may experience increased mental health symptoms when exposed to friends or peers with mental health problems, large-scale studies on the potential peer influences of mental disorders in youth are lacking,” the authors wrote.
Researchers used a database of 713,809 students in the ninth grade, about half boys and half girls. All were born between January 1, 1985, and December 31, 1997. About 47,000 were excluded as they had a mental disorder diagnosis before the study began.
Some 666,000 students in 860 schools were followed from ninth grade until the first diagnosed mental disorder, death, emigration, or the end of the study in 2019. Median follow-up was 11.4 years.
Diagnoses were gathered from Finnish registries for inpatient, outpatient, and primary care and included ICD-9 and ICD-10 diagnoses for substance misuse disorders, schizophrenia spectrum disorders, mood disorders, anxiety disorders, eating disorders, emotional and social-functioning disorders, and hyperkinetic and conduct disorders.
The authors adjusted for sex, birth year, school and ninth-grade class size, area-level urbanicity, area-level morbidity, area-level education, area-level employment rate, parental educational level, and parental mental health, with a random intercept per school.
Dose-Response Relationship
Overall, a quarter (167,227) of the students were diagnosed with a mental disorder.
The risk of being diagnosed with any mental disorder was 3% higher during the entire follow-up period (hazard ratio [HR], 1.03; 95% CI, 1.02-1.04). Risk was highest in the first year of follow-up (HR, 1.13; 95% CI, 1.08-1.18) and then rose again in years 4 and 5, when the risk was 5% higher with one diagnosed classmate and 10% higher with more than one diagnosed classmate.
The risk was significantly increased for mood, anxiety, and eating disorders in each follow-up time window. Investigators also noted a dose-response relationship: The more classmates with a psychiatric illness, the greater the risk for later mental illness.
“These findings suggest that mental disorders may be transmitted within adolescent peer networks,” the authors wrote.
The researchers chose to describe the spread of mental disorders among peer classmates as “transmission” in part because it has been previously used in the literature, Dr. Alho said.
Alho said the researchers also believe that transmission is an accurate term to describe the potential mechanisms by which mental disorders may spread.
The authors hypothesized that more students might be diagnosed when disorders are normalized, through increased awareness and receptivity to diagnosis and treatment.
Conversely, the rate of disorders might also have increased — especially in the first year of follow-up — if there were no students in the peer network who had been diagnosed, the authors added. Without an example, it might discourage a student to seek help.
The authors also noted that it’s “conceivable that long-term exposure to a depressive individual could lead to gradual development of depressive symptoms through the well-established neural mechanisms of emotional contagion.”
New Direction for Treatment?
Commenting on the findings, Madhukar H. Trivedi, MD, the Betty Jo Hay Distinguished Chair in Mental Health at UT Southwestern Medical School, Dallas, said that the theory that having classmates with psychiatric illness could normalize these conditions has merit.
Once someone is diagnosed or receives treatment, “their peers kind of get implicit permission to be able to then express their own symptoms or express their own problems, which they may have been hiding or not recognized,” he said.
However, Dr. Trivedi disagreed with the authors’ suggestion that the rate of disorders might also have increased if no classmates had received a psychiatric diagnosis, noting that it was unlikely that a student would not have been exposed to depression, anxiety, or another mood disorder — through a peer or family member — given how common those illnesses are.
“The numbers are slightly higher than I would have expected,” Dr. Trivedi said, adding that peer influence having that type of impact “is something that has not been shown before.”
The study is notable for its use of comprehensive registries, which helped solidify the data integrity, Trivedi said, and the results offer some potential new directions for treatment, such as adding peer support. That has been found useful in adult treatment but has been less utilized with adolescents, he said.
The study was funded by the European Union and the Academy of Finland. The authors reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Teens with classmates who have a mental illness have a significantly greater risk for a psychiatric diagnosis later in life, even after controlling for parents’ mental health history and other factors, a new study suggested.
The research provides new evidence that adolescents within a specific peer network may possibly “transmit” mental disorders such as depression and anxiety to each other, the investigators noted.
The study is said to the be the largest to date on the topic, including data on more than 700,000 ninth graders in Finland who were followed for up to 18 years.
At least one expert noted that the numbers are higher than he would have expected, but the investigators were quick to caution the study doesn’t prove having a classmate with a mental illness leads to later psychiatric diagnosis among peers.
“The associations observed in the study are not necessarily causal,” lead investigator Jussi Alho, PhD, a postdoctoral researcher at the University of Helsinki, Finland, told this news organization. “The study did not investigate the mechanisms that explain the observed associations.”
The results were published online on May 22 in JAMA Psychiatry.
Few Data
Previous studies have reported a clustering of mood symptoms, eating disorders, and other psychiatric illnesses among adolescent and adult social networks. But most involve self-selected peer groups.
“Investigating the transmission of mental disorders is especially important in childhood and adolescence,” the authors noted. “Yet, despite a few survey studies reporting that adolescents may experience increased mental health symptoms when exposed to friends or peers with mental health problems, large-scale studies on the potential peer influences of mental disorders in youth are lacking,” the authors wrote.
Researchers used a database of 713,809 students in the ninth grade, about half boys and half girls. All were born between January 1, 1985, and December 31, 1997. About 47,000 were excluded as they had a mental disorder diagnosis before the study began.
Some 666,000 students in 860 schools were followed from ninth grade until the first diagnosed mental disorder, death, emigration, or the end of the study in 2019. Median follow-up was 11.4 years.
Diagnoses were gathered from Finnish registries for inpatient, outpatient, and primary care and included ICD-9 and ICD-10 diagnoses for substance misuse disorders, schizophrenia spectrum disorders, mood disorders, anxiety disorders, eating disorders, emotional and social-functioning disorders, and hyperkinetic and conduct disorders.
The authors adjusted for sex, birth year, school and ninth-grade class size, area-level urbanicity, area-level morbidity, area-level education, area-level employment rate, parental educational level, and parental mental health, with a random intercept per school.
Dose-Response Relationship
Overall, a quarter (167,227) of the students were diagnosed with a mental disorder.
The risk of being diagnosed with any mental disorder was 3% higher during the entire follow-up period (hazard ratio [HR], 1.03; 95% CI, 1.02-1.04). Risk was highest in the first year of follow-up (HR, 1.13; 95% CI, 1.08-1.18) and then rose again in years 4 and 5, when the risk was 5% higher with one diagnosed classmate and 10% higher with more than one diagnosed classmate.
The risk was significantly increased for mood, anxiety, and eating disorders in each follow-up time window. Investigators also noted a dose-response relationship: The more classmates with a psychiatric illness, the greater the risk for later mental illness.
“These findings suggest that mental disorders may be transmitted within adolescent peer networks,” the authors wrote.
The researchers chose to describe the spread of mental disorders among peer classmates as “transmission” in part because it has been previously used in the literature, Dr. Alho said.
Alho said the researchers also believe that transmission is an accurate term to describe the potential mechanisms by which mental disorders may spread.
The authors hypothesized that more students might be diagnosed when disorders are normalized, through increased awareness and receptivity to diagnosis and treatment.
Conversely, the rate of disorders might also have increased — especially in the first year of follow-up — if there were no students in the peer network who had been diagnosed, the authors added. Without an example, it might discourage a student to seek help.
The authors also noted that it’s “conceivable that long-term exposure to a depressive individual could lead to gradual development of depressive symptoms through the well-established neural mechanisms of emotional contagion.”
New Direction for Treatment?
Commenting on the findings, Madhukar H. Trivedi, MD, the Betty Jo Hay Distinguished Chair in Mental Health at UT Southwestern Medical School, Dallas, said that the theory that having classmates with psychiatric illness could normalize these conditions has merit.
Once someone is diagnosed or receives treatment, “their peers kind of get implicit permission to be able to then express their own symptoms or express their own problems, which they may have been hiding or not recognized,” he said.
However, Dr. Trivedi disagreed with the authors’ suggestion that the rate of disorders might also have increased if no classmates had received a psychiatric diagnosis, noting that it was unlikely that a student would not have been exposed to depression, anxiety, or another mood disorder — through a peer or family member — given how common those illnesses are.
“The numbers are slightly higher than I would have expected,” Dr. Trivedi said, adding that peer influence having that type of impact “is something that has not been shown before.”
The study is notable for its use of comprehensive registries, which helped solidify the data integrity, Trivedi said, and the results offer some potential new directions for treatment, such as adding peer support. That has been found useful in adult treatment but has been less utilized with adolescents, he said.
The study was funded by the European Union and the Academy of Finland. The authors reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Teens with classmates who have a mental illness have a significantly greater risk for a psychiatric diagnosis later in life, even after controlling for parents’ mental health history and other factors, a new study suggested.
The research provides new evidence that adolescents within a specific peer network may possibly “transmit” mental disorders such as depression and anxiety to each other, the investigators noted.
The study is said to the be the largest to date on the topic, including data on more than 700,000 ninth graders in Finland who were followed for up to 18 years.
At least one expert noted that the numbers are higher than he would have expected, but the investigators were quick to caution the study doesn’t prove having a classmate with a mental illness leads to later psychiatric diagnosis among peers.
“The associations observed in the study are not necessarily causal,” lead investigator Jussi Alho, PhD, a postdoctoral researcher at the University of Helsinki, Finland, told this news organization. “The study did not investigate the mechanisms that explain the observed associations.”
The results were published online on May 22 in JAMA Psychiatry.
Few Data
Previous studies have reported a clustering of mood symptoms, eating disorders, and other psychiatric illnesses among adolescent and adult social networks. But most involve self-selected peer groups.
“Investigating the transmission of mental disorders is especially important in childhood and adolescence,” the authors noted. “Yet, despite a few survey studies reporting that adolescents may experience increased mental health symptoms when exposed to friends or peers with mental health problems, large-scale studies on the potential peer influences of mental disorders in youth are lacking,” the authors wrote.
Researchers used a database of 713,809 students in the ninth grade, about half boys and half girls. All were born between January 1, 1985, and December 31, 1997. About 47,000 were excluded as they had a mental disorder diagnosis before the study began.
Some 666,000 students in 860 schools were followed from ninth grade until the first diagnosed mental disorder, death, emigration, or the end of the study in 2019. Median follow-up was 11.4 years.
Diagnoses were gathered from Finnish registries for inpatient, outpatient, and primary care and included ICD-9 and ICD-10 diagnoses for substance misuse disorders, schizophrenia spectrum disorders, mood disorders, anxiety disorders, eating disorders, emotional and social-functioning disorders, and hyperkinetic and conduct disorders.
The authors adjusted for sex, birth year, school and ninth-grade class size, area-level urbanicity, area-level morbidity, area-level education, area-level employment rate, parental educational level, and parental mental health, with a random intercept per school.
Dose-Response Relationship
Overall, a quarter (167,227) of the students were diagnosed with a mental disorder.
The risk of being diagnosed with any mental disorder was 3% higher during the entire follow-up period (hazard ratio [HR], 1.03; 95% CI, 1.02-1.04). Risk was highest in the first year of follow-up (HR, 1.13; 95% CI, 1.08-1.18) and then rose again in years 4 and 5, when the risk was 5% higher with one diagnosed classmate and 10% higher with more than one diagnosed classmate.
The risk was significantly increased for mood, anxiety, and eating disorders in each follow-up time window. Investigators also noted a dose-response relationship: The more classmates with a psychiatric illness, the greater the risk for later mental illness.
“These findings suggest that mental disorders may be transmitted within adolescent peer networks,” the authors wrote.
The researchers chose to describe the spread of mental disorders among peer classmates as “transmission” in part because it has been previously used in the literature, Dr. Alho said.
Alho said the researchers also believe that transmission is an accurate term to describe the potential mechanisms by which mental disorders may spread.
The authors hypothesized that more students might be diagnosed when disorders are normalized, through increased awareness and receptivity to diagnosis and treatment.
Conversely, the rate of disorders might also have increased — especially in the first year of follow-up — if there were no students in the peer network who had been diagnosed, the authors added. Without an example, it might discourage a student to seek help.
The authors also noted that it’s “conceivable that long-term exposure to a depressive individual could lead to gradual development of depressive symptoms through the well-established neural mechanisms of emotional contagion.”
New Direction for Treatment?
Commenting on the findings, Madhukar H. Trivedi, MD, the Betty Jo Hay Distinguished Chair in Mental Health at UT Southwestern Medical School, Dallas, said that the theory that having classmates with psychiatric illness could normalize these conditions has merit.
Once someone is diagnosed or receives treatment, “their peers kind of get implicit permission to be able to then express their own symptoms or express their own problems, which they may have been hiding or not recognized,” he said.
However, Dr. Trivedi disagreed with the authors’ suggestion that the rate of disorders might also have increased if no classmates had received a psychiatric diagnosis, noting that it was unlikely that a student would not have been exposed to depression, anxiety, or another mood disorder — through a peer or family member — given how common those illnesses are.
“The numbers are slightly higher than I would have expected,” Dr. Trivedi said, adding that peer influence having that type of impact “is something that has not been shown before.”
The study is notable for its use of comprehensive registries, which helped solidify the data integrity, Trivedi said, and the results offer some potential new directions for treatment, such as adding peer support. That has been found useful in adult treatment but has been less utilized with adolescents, he said.
The study was funded by the European Union and the Academy of Finland. The authors reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Obesity and Cancer: Untangling a Complex Web
According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), over 684,000 Americans are diagnosed with an “obesity-associated” cancer each year.
The incidence of many of these cancers has been rising in recent years, particularly among younger people — a trend that sits in contrast with the overall decline in cancers with no established relationship to excess weight, such as lung and skin cancers.
Is obesity the new smoking? Not exactly.
While about 42% of cancers — including common ones such as colorectal and postmenopausal breast cancers — are considered obesity-related, only about 8% of incident cancers are attributed to excess body weight. People often develop those diseases regardless of weight.
Although plenty of evidence points to excess body fat as a cancer risk factor, it’s unclear at what point excess weight has an effect. Is gaining weight later in life, for instance, better or worse for cancer risk than being overweight or obese from a young age?
There’s another glaring knowledge gap: Does losing weight at some point in adulthood change the picture? In other words, how many of those 684,000 diagnoses might have been prevented if people shed excess pounds?
When it comes to weight and cancer risk, “there’s a lot we don’t know,” said Jennifer W. Bea, PhD, associate professor, health promotion sciences, University of Arizona, Tucson.
A Consistent but Complicated Relationship
Given the growing incidence of obesity — which currently affects about 42% of US adults and 20% of children and teenagers — it’s no surprise that many studies have delved into the potential effects of excess weight on cancer rates.
Although virtually all the evidence comes from large cohort studies, leaving the cause-effect question open, certain associations keep showing up.
“What we know is that, consistently, a higher body mass index [BMI] — particularly in the obese category — leads to a higher risk of multiple cancers,” said Jeffrey A. Meyerhardt, MD, MPH, codirector, Colon and Rectal Cancer Center, Dana-Farber Cancer Institute, Boston.
In a widely cited report published in The New England Journal of Medicine in 2016, the International Agency for Research on Cancer (IARC) analyzed over 1000 epidemiologic studies on body fat and cancer. The agency pointed to over a dozen cancers, including some of the most common and deadly, linked to excess body weight.
That list includes esophageal adenocarcinoma and endometrial cancer — associated with the highest risk — along with kidney, liver, stomach (gastric cardia), pancreatic, colorectal, postmenopausal breast, gallbladder, ovarian, and thyroid cancers, plus multiple myeloma and meningioma. There’s also “limited” evidence linking excess weight to additional cancer types, including aggressive prostate cancer and certain head and neck cancers.
At the same time, Dr. Meyerhardt said, many of those same cancers are also associated with issues that lead to, or coexist with, overweight and obesity, including poor diet, lack of exercise, and metabolic conditions such as diabetes.
It’s a complicated web, and it’s likely, Dr. Meyerhardt said, that high BMI both directly affects cancer risk and is part of a “causal pathway” of other factors that do.
Regarding direct effects, preclinical research has pointed to multiple ways in which excess body fat could contribute to cancer, said Karen M. Basen-Engquist, PhD, MPH, professor, Division of Cancer Prevention and Population Services, The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center, Houston.
One broad mechanism to help explain the obesity-cancer link is chronic systemic inflammation because excess fat tissue can raise levels of substances in the body, such as tumor necrosis factor alpha and interleukin 6, which fuel inflammation. Excess fat also contributes to hyperinsulinemia — too much insulin in the blood — which can help promote the growth and spread of tumor cells.
But the underlying reasons also appear to vary by cancer type, Dr. Basen-Engquist said. With hormonally driven cancer types, such as breast and endometrial, excess body fat may alter hormone levels in ways that spur tumor growth. Extra fat tissue may, for example, convert androgens into estrogens, which could help feed estrogen-dependent tumors.
That, Dr. Basen-Engquist noted, could be why excess weight is associated with postmenopausal, not premenopausal, breast cancer: Before menopause, body fat is a relatively minor contributor to estrogen levels but becomes more important after menopause.
How Big Is the Effect?
While more than a dozen cancers have been consistently linked to excess weight, the strength of those associations varies considerably.
Endometrial and esophageal cancers are two that stand out. In the 2016 IARC analysis, people with severe obesity had a seven-times greater risk for endometrial cancer and 4.8-times greater risk for esophageal adenocarcinoma vs people with a normal BMI.
With other cancers, the risk increases for those with severe obesity compared with a normal BMI were far more modest: 10% for ovarian cancer, 30% for colorectal cancer, and 80% for kidney and stomach cancers, for example. For postmenopausal breast cancer, every five-unit increase in BMI was associated with a 10% relative risk increase.
A 2018 study from the American Cancer Society, which attempted to estimate the proportion of cancers in the United States attributable to modifiable risk factors — including alcohol consumption, ultraviolet rays exposure, and physical inactivity — found that smoking accounted for the highest proportion of cancer cases by a wide margin (19%), but excess weight came in second (7.8%).
Again, weight appeared to play a bigger role in certain cancers than others: An estimated 60% of endometrial cancers were linked to excess weight, as were roughly one third of esophageal, kidney, and liver cancers. At the other end of the spectrum, just over 11% of breast, 5% of colorectal, and 4% of ovarian cancers were attributable to excess weight.
Even at the lower end, those rates could make a big difference on the population level, especially for groups with higher rates of obesity.
CDC data show that obesity-related cancers are rising among women younger than 50 years, most rapidly among Hispanic women, and some less common obesity-related cancers, such as stomach, thyroid and pancreatic, are also rising among Black individuals and Hispanic Americans.
Obesity may be one reason for growing cancer disparities, said Leah Ferrucci, PhD, MPH, assistant professor, epidemiology, Yale School of Public Health, New Haven, Connecticut. But, she added, the evidence is limited because Black individuals and Hispanic Americans are understudied.
When Do Extra Pounds Matter?
When it comes to cancer risk, at what point in life does excess weight, or weight gain, matter? Is the standard weight gain in middle age, for instance, as hazardous as being overweight or obese from a young age?
Some evidence suggests there’s no “safe” time for putting on excess pounds.
A recent meta-analysis concluded that weight gain at any point after age 18 years is associated with incremental increases in the risk for postmenopausal breast cancer. A 2023 study in JAMA Network Open found a similar pattern with colorectal and other gastrointestinal cancers: People who had sustained overweight or obesity from age 20 years through middle age faced an increased risk of developing those cancers after age 55 years.
The timing of weight gain didn’t seem to matter either. The same elevated risk held among people who were normal weight in their younger years but became overweight after age 55 years.
Those studies focused on later-onset disease. But, in recent years, experts have tracked a troubling rise in early-onset cancers — those diagnosed before age 50 years — particularly gastrointestinal cancers.
An obvious question, Dr. Meyerhardt said, is whether the growing prevalence of obesity among young people is partly to blame.
There’s some data to support that, he said. An analysis from the Nurses’ Health Study II found that women with obesity had double the risk for early-onset colorectal cancer as those with a normal BMI. And every 5-kg increase in weight after age 18 years was associated with a 9% increase in colorectal cancer risk.
But while obesity trends probably partly explain the rise in early-onset cancers, there is likely more to the story, Dr. Meyerhardt said.
“I think all of us who see an increasing number of patients under 50 with colorectal cancer know there’s a fair number who do not fit that [high BMI] profile,” he said. “There’s a fair number over 50 who don’t either.”
Does Weight Loss Help?
With all the evidence pointing to high BMI as a cancer risk factor, a logical conclusion is that weight loss should reduce that excess risk. However, Dr. Bea said, there’s actually little data to support that, and what exists comes from observational studies.
Some research has focused on people who had substantial weight loss after bariatric surgery, with encouraging results. A study published in JAMA found that among 5053 people who underwent bariatric surgery, 2.9% developed an obesity-related cancer over 10 years compared with 4.9% in the nonsurgery group.
Most people, however, aim for less dramatic weight loss, with the help of diet and exercise or sometimes medication. Some evidence shows that a modest degree of weight loss may lower the risks for postmenopausal breast and endometrial cancers.
A 2020 pooled analysis found, for instance, that among women aged ≥ 50 years, those who lost as little as 2.0-4.5 kg, or 4.4-10.0 pounds, and kept it off for 10 years had a lower risk for breast cancer than women whose weight remained stable. And losing more weight — 9 kg, or about 20 pounds, or more — was even better for lowering cancer risk.
But other research suggests the opposite. A recent analysis found that people who lost weight within the past 2 years through diet and exercise had a higher risk for a range of cancers compared with those who did not lose weight. Overall, though, the increased risk was quite low.
Whatever the research does, or doesn’t, show about weight and cancer risk, Dr. Basen-Engquist said, it’s important that risk factors, obesity and otherwise, aren’t “used as blame tools.”
“With obesity, behavior certainly plays into it,” she said. “But there are so many influences on our behavior that are socially determined.”
Both Dr. Basen-Engquist and Dr. Meyerhardt said it’s important for clinicians to consider the individual in front of them and for everyone to set realistic expectations.
People with obesity should not feel they have to become thin to be healthier, and no one has to leap from being sedentary to exercising several hours a week.
“We don’t want patients to feel that if they don’t get to a stated goal in a guideline, it’s all for naught,” Dr. Meyerhardt said.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), over 684,000 Americans are diagnosed with an “obesity-associated” cancer each year.
The incidence of many of these cancers has been rising in recent years, particularly among younger people — a trend that sits in contrast with the overall decline in cancers with no established relationship to excess weight, such as lung and skin cancers.
Is obesity the new smoking? Not exactly.
While about 42% of cancers — including common ones such as colorectal and postmenopausal breast cancers — are considered obesity-related, only about 8% of incident cancers are attributed to excess body weight. People often develop those diseases regardless of weight.
Although plenty of evidence points to excess body fat as a cancer risk factor, it’s unclear at what point excess weight has an effect. Is gaining weight later in life, for instance, better or worse for cancer risk than being overweight or obese from a young age?
There’s another glaring knowledge gap: Does losing weight at some point in adulthood change the picture? In other words, how many of those 684,000 diagnoses might have been prevented if people shed excess pounds?
When it comes to weight and cancer risk, “there’s a lot we don’t know,” said Jennifer W. Bea, PhD, associate professor, health promotion sciences, University of Arizona, Tucson.
A Consistent but Complicated Relationship
Given the growing incidence of obesity — which currently affects about 42% of US adults and 20% of children and teenagers — it’s no surprise that many studies have delved into the potential effects of excess weight on cancer rates.
Although virtually all the evidence comes from large cohort studies, leaving the cause-effect question open, certain associations keep showing up.
“What we know is that, consistently, a higher body mass index [BMI] — particularly in the obese category — leads to a higher risk of multiple cancers,” said Jeffrey A. Meyerhardt, MD, MPH, codirector, Colon and Rectal Cancer Center, Dana-Farber Cancer Institute, Boston.
In a widely cited report published in The New England Journal of Medicine in 2016, the International Agency for Research on Cancer (IARC) analyzed over 1000 epidemiologic studies on body fat and cancer. The agency pointed to over a dozen cancers, including some of the most common and deadly, linked to excess body weight.
That list includes esophageal adenocarcinoma and endometrial cancer — associated with the highest risk — along with kidney, liver, stomach (gastric cardia), pancreatic, colorectal, postmenopausal breast, gallbladder, ovarian, and thyroid cancers, plus multiple myeloma and meningioma. There’s also “limited” evidence linking excess weight to additional cancer types, including aggressive prostate cancer and certain head and neck cancers.
At the same time, Dr. Meyerhardt said, many of those same cancers are also associated with issues that lead to, or coexist with, overweight and obesity, including poor diet, lack of exercise, and metabolic conditions such as diabetes.
It’s a complicated web, and it’s likely, Dr. Meyerhardt said, that high BMI both directly affects cancer risk and is part of a “causal pathway” of other factors that do.
Regarding direct effects, preclinical research has pointed to multiple ways in which excess body fat could contribute to cancer, said Karen M. Basen-Engquist, PhD, MPH, professor, Division of Cancer Prevention and Population Services, The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center, Houston.
One broad mechanism to help explain the obesity-cancer link is chronic systemic inflammation because excess fat tissue can raise levels of substances in the body, such as tumor necrosis factor alpha and interleukin 6, which fuel inflammation. Excess fat also contributes to hyperinsulinemia — too much insulin in the blood — which can help promote the growth and spread of tumor cells.
But the underlying reasons also appear to vary by cancer type, Dr. Basen-Engquist said. With hormonally driven cancer types, such as breast and endometrial, excess body fat may alter hormone levels in ways that spur tumor growth. Extra fat tissue may, for example, convert androgens into estrogens, which could help feed estrogen-dependent tumors.
That, Dr. Basen-Engquist noted, could be why excess weight is associated with postmenopausal, not premenopausal, breast cancer: Before menopause, body fat is a relatively minor contributor to estrogen levels but becomes more important after menopause.
How Big Is the Effect?
While more than a dozen cancers have been consistently linked to excess weight, the strength of those associations varies considerably.
Endometrial and esophageal cancers are two that stand out. In the 2016 IARC analysis, people with severe obesity had a seven-times greater risk for endometrial cancer and 4.8-times greater risk for esophageal adenocarcinoma vs people with a normal BMI.
With other cancers, the risk increases for those with severe obesity compared with a normal BMI were far more modest: 10% for ovarian cancer, 30% for colorectal cancer, and 80% for kidney and stomach cancers, for example. For postmenopausal breast cancer, every five-unit increase in BMI was associated with a 10% relative risk increase.
A 2018 study from the American Cancer Society, which attempted to estimate the proportion of cancers in the United States attributable to modifiable risk factors — including alcohol consumption, ultraviolet rays exposure, and physical inactivity — found that smoking accounted for the highest proportion of cancer cases by a wide margin (19%), but excess weight came in second (7.8%).
Again, weight appeared to play a bigger role in certain cancers than others: An estimated 60% of endometrial cancers were linked to excess weight, as were roughly one third of esophageal, kidney, and liver cancers. At the other end of the spectrum, just over 11% of breast, 5% of colorectal, and 4% of ovarian cancers were attributable to excess weight.
Even at the lower end, those rates could make a big difference on the population level, especially for groups with higher rates of obesity.
CDC data show that obesity-related cancers are rising among women younger than 50 years, most rapidly among Hispanic women, and some less common obesity-related cancers, such as stomach, thyroid and pancreatic, are also rising among Black individuals and Hispanic Americans.
Obesity may be one reason for growing cancer disparities, said Leah Ferrucci, PhD, MPH, assistant professor, epidemiology, Yale School of Public Health, New Haven, Connecticut. But, she added, the evidence is limited because Black individuals and Hispanic Americans are understudied.
When Do Extra Pounds Matter?
When it comes to cancer risk, at what point in life does excess weight, or weight gain, matter? Is the standard weight gain in middle age, for instance, as hazardous as being overweight or obese from a young age?
Some evidence suggests there’s no “safe” time for putting on excess pounds.
A recent meta-analysis concluded that weight gain at any point after age 18 years is associated with incremental increases in the risk for postmenopausal breast cancer. A 2023 study in JAMA Network Open found a similar pattern with colorectal and other gastrointestinal cancers: People who had sustained overweight or obesity from age 20 years through middle age faced an increased risk of developing those cancers after age 55 years.
The timing of weight gain didn’t seem to matter either. The same elevated risk held among people who were normal weight in their younger years but became overweight after age 55 years.
Those studies focused on later-onset disease. But, in recent years, experts have tracked a troubling rise in early-onset cancers — those diagnosed before age 50 years — particularly gastrointestinal cancers.
An obvious question, Dr. Meyerhardt said, is whether the growing prevalence of obesity among young people is partly to blame.
There’s some data to support that, he said. An analysis from the Nurses’ Health Study II found that women with obesity had double the risk for early-onset colorectal cancer as those with a normal BMI. And every 5-kg increase in weight after age 18 years was associated with a 9% increase in colorectal cancer risk.
But while obesity trends probably partly explain the rise in early-onset cancers, there is likely more to the story, Dr. Meyerhardt said.
“I think all of us who see an increasing number of patients under 50 with colorectal cancer know there’s a fair number who do not fit that [high BMI] profile,” he said. “There’s a fair number over 50 who don’t either.”
Does Weight Loss Help?
With all the evidence pointing to high BMI as a cancer risk factor, a logical conclusion is that weight loss should reduce that excess risk. However, Dr. Bea said, there’s actually little data to support that, and what exists comes from observational studies.
Some research has focused on people who had substantial weight loss after bariatric surgery, with encouraging results. A study published in JAMA found that among 5053 people who underwent bariatric surgery, 2.9% developed an obesity-related cancer over 10 years compared with 4.9% in the nonsurgery group.
Most people, however, aim for less dramatic weight loss, with the help of diet and exercise or sometimes medication. Some evidence shows that a modest degree of weight loss may lower the risks for postmenopausal breast and endometrial cancers.
A 2020 pooled analysis found, for instance, that among women aged ≥ 50 years, those who lost as little as 2.0-4.5 kg, or 4.4-10.0 pounds, and kept it off for 10 years had a lower risk for breast cancer than women whose weight remained stable. And losing more weight — 9 kg, or about 20 pounds, or more — was even better for lowering cancer risk.
But other research suggests the opposite. A recent analysis found that people who lost weight within the past 2 years through diet and exercise had a higher risk for a range of cancers compared with those who did not lose weight. Overall, though, the increased risk was quite low.
Whatever the research does, or doesn’t, show about weight and cancer risk, Dr. Basen-Engquist said, it’s important that risk factors, obesity and otherwise, aren’t “used as blame tools.”
“With obesity, behavior certainly plays into it,” she said. “But there are so many influences on our behavior that are socially determined.”
Both Dr. Basen-Engquist and Dr. Meyerhardt said it’s important for clinicians to consider the individual in front of them and for everyone to set realistic expectations.
People with obesity should not feel they have to become thin to be healthier, and no one has to leap from being sedentary to exercising several hours a week.
“We don’t want patients to feel that if they don’t get to a stated goal in a guideline, it’s all for naught,” Dr. Meyerhardt said.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), over 684,000 Americans are diagnosed with an “obesity-associated” cancer each year.
The incidence of many of these cancers has been rising in recent years, particularly among younger people — a trend that sits in contrast with the overall decline in cancers with no established relationship to excess weight, such as lung and skin cancers.
Is obesity the new smoking? Not exactly.
While about 42% of cancers — including common ones such as colorectal and postmenopausal breast cancers — are considered obesity-related, only about 8% of incident cancers are attributed to excess body weight. People often develop those diseases regardless of weight.
Although plenty of evidence points to excess body fat as a cancer risk factor, it’s unclear at what point excess weight has an effect. Is gaining weight later in life, for instance, better or worse for cancer risk than being overweight or obese from a young age?
There’s another glaring knowledge gap: Does losing weight at some point in adulthood change the picture? In other words, how many of those 684,000 diagnoses might have been prevented if people shed excess pounds?
When it comes to weight and cancer risk, “there’s a lot we don’t know,” said Jennifer W. Bea, PhD, associate professor, health promotion sciences, University of Arizona, Tucson.
A Consistent but Complicated Relationship
Given the growing incidence of obesity — which currently affects about 42% of US adults and 20% of children and teenagers — it’s no surprise that many studies have delved into the potential effects of excess weight on cancer rates.
Although virtually all the evidence comes from large cohort studies, leaving the cause-effect question open, certain associations keep showing up.
“What we know is that, consistently, a higher body mass index [BMI] — particularly in the obese category — leads to a higher risk of multiple cancers,” said Jeffrey A. Meyerhardt, MD, MPH, codirector, Colon and Rectal Cancer Center, Dana-Farber Cancer Institute, Boston.
In a widely cited report published in The New England Journal of Medicine in 2016, the International Agency for Research on Cancer (IARC) analyzed over 1000 epidemiologic studies on body fat and cancer. The agency pointed to over a dozen cancers, including some of the most common and deadly, linked to excess body weight.
That list includes esophageal adenocarcinoma and endometrial cancer — associated with the highest risk — along with kidney, liver, stomach (gastric cardia), pancreatic, colorectal, postmenopausal breast, gallbladder, ovarian, and thyroid cancers, plus multiple myeloma and meningioma. There’s also “limited” evidence linking excess weight to additional cancer types, including aggressive prostate cancer and certain head and neck cancers.
At the same time, Dr. Meyerhardt said, many of those same cancers are also associated with issues that lead to, or coexist with, overweight and obesity, including poor diet, lack of exercise, and metabolic conditions such as diabetes.
It’s a complicated web, and it’s likely, Dr. Meyerhardt said, that high BMI both directly affects cancer risk and is part of a “causal pathway” of other factors that do.
Regarding direct effects, preclinical research has pointed to multiple ways in which excess body fat could contribute to cancer, said Karen M. Basen-Engquist, PhD, MPH, professor, Division of Cancer Prevention and Population Services, The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center, Houston.
One broad mechanism to help explain the obesity-cancer link is chronic systemic inflammation because excess fat tissue can raise levels of substances in the body, such as tumor necrosis factor alpha and interleukin 6, which fuel inflammation. Excess fat also contributes to hyperinsulinemia — too much insulin in the blood — which can help promote the growth and spread of tumor cells.
But the underlying reasons also appear to vary by cancer type, Dr. Basen-Engquist said. With hormonally driven cancer types, such as breast and endometrial, excess body fat may alter hormone levels in ways that spur tumor growth. Extra fat tissue may, for example, convert androgens into estrogens, which could help feed estrogen-dependent tumors.
That, Dr. Basen-Engquist noted, could be why excess weight is associated with postmenopausal, not premenopausal, breast cancer: Before menopause, body fat is a relatively minor contributor to estrogen levels but becomes more important after menopause.
How Big Is the Effect?
While more than a dozen cancers have been consistently linked to excess weight, the strength of those associations varies considerably.
Endometrial and esophageal cancers are two that stand out. In the 2016 IARC analysis, people with severe obesity had a seven-times greater risk for endometrial cancer and 4.8-times greater risk for esophageal adenocarcinoma vs people with a normal BMI.
With other cancers, the risk increases for those with severe obesity compared with a normal BMI were far more modest: 10% for ovarian cancer, 30% for colorectal cancer, and 80% for kidney and stomach cancers, for example. For postmenopausal breast cancer, every five-unit increase in BMI was associated with a 10% relative risk increase.
A 2018 study from the American Cancer Society, which attempted to estimate the proportion of cancers in the United States attributable to modifiable risk factors — including alcohol consumption, ultraviolet rays exposure, and physical inactivity — found that smoking accounted for the highest proportion of cancer cases by a wide margin (19%), but excess weight came in second (7.8%).
Again, weight appeared to play a bigger role in certain cancers than others: An estimated 60% of endometrial cancers were linked to excess weight, as were roughly one third of esophageal, kidney, and liver cancers. At the other end of the spectrum, just over 11% of breast, 5% of colorectal, and 4% of ovarian cancers were attributable to excess weight.
Even at the lower end, those rates could make a big difference on the population level, especially for groups with higher rates of obesity.
CDC data show that obesity-related cancers are rising among women younger than 50 years, most rapidly among Hispanic women, and some less common obesity-related cancers, such as stomach, thyroid and pancreatic, are also rising among Black individuals and Hispanic Americans.
Obesity may be one reason for growing cancer disparities, said Leah Ferrucci, PhD, MPH, assistant professor, epidemiology, Yale School of Public Health, New Haven, Connecticut. But, she added, the evidence is limited because Black individuals and Hispanic Americans are understudied.
When Do Extra Pounds Matter?
When it comes to cancer risk, at what point in life does excess weight, or weight gain, matter? Is the standard weight gain in middle age, for instance, as hazardous as being overweight or obese from a young age?
Some evidence suggests there’s no “safe” time for putting on excess pounds.
A recent meta-analysis concluded that weight gain at any point after age 18 years is associated with incremental increases in the risk for postmenopausal breast cancer. A 2023 study in JAMA Network Open found a similar pattern with colorectal and other gastrointestinal cancers: People who had sustained overweight or obesity from age 20 years through middle age faced an increased risk of developing those cancers after age 55 years.
The timing of weight gain didn’t seem to matter either. The same elevated risk held among people who were normal weight in their younger years but became overweight after age 55 years.
Those studies focused on later-onset disease. But, in recent years, experts have tracked a troubling rise in early-onset cancers — those diagnosed before age 50 years — particularly gastrointestinal cancers.
An obvious question, Dr. Meyerhardt said, is whether the growing prevalence of obesity among young people is partly to blame.
There’s some data to support that, he said. An analysis from the Nurses’ Health Study II found that women with obesity had double the risk for early-onset colorectal cancer as those with a normal BMI. And every 5-kg increase in weight after age 18 years was associated with a 9% increase in colorectal cancer risk.
But while obesity trends probably partly explain the rise in early-onset cancers, there is likely more to the story, Dr. Meyerhardt said.
“I think all of us who see an increasing number of patients under 50 with colorectal cancer know there’s a fair number who do not fit that [high BMI] profile,” he said. “There’s a fair number over 50 who don’t either.”
Does Weight Loss Help?
With all the evidence pointing to high BMI as a cancer risk factor, a logical conclusion is that weight loss should reduce that excess risk. However, Dr. Bea said, there’s actually little data to support that, and what exists comes from observational studies.
Some research has focused on people who had substantial weight loss after bariatric surgery, with encouraging results. A study published in JAMA found that among 5053 people who underwent bariatric surgery, 2.9% developed an obesity-related cancer over 10 years compared with 4.9% in the nonsurgery group.
Most people, however, aim for less dramatic weight loss, with the help of diet and exercise or sometimes medication. Some evidence shows that a modest degree of weight loss may lower the risks for postmenopausal breast and endometrial cancers.
A 2020 pooled analysis found, for instance, that among women aged ≥ 50 years, those who lost as little as 2.0-4.5 kg, or 4.4-10.0 pounds, and kept it off for 10 years had a lower risk for breast cancer than women whose weight remained stable. And losing more weight — 9 kg, or about 20 pounds, or more — was even better for lowering cancer risk.
But other research suggests the opposite. A recent analysis found that people who lost weight within the past 2 years through diet and exercise had a higher risk for a range of cancers compared with those who did not lose weight. Overall, though, the increased risk was quite low.
Whatever the research does, or doesn’t, show about weight and cancer risk, Dr. Basen-Engquist said, it’s important that risk factors, obesity and otherwise, aren’t “used as blame tools.”
“With obesity, behavior certainly plays into it,” she said. “But there are so many influences on our behavior that are socially determined.”
Both Dr. Basen-Engquist and Dr. Meyerhardt said it’s important for clinicians to consider the individual in front of them and for everyone to set realistic expectations.
People with obesity should not feel they have to become thin to be healthier, and no one has to leap from being sedentary to exercising several hours a week.
“We don’t want patients to feel that if they don’t get to a stated goal in a guideline, it’s all for naught,” Dr. Meyerhardt said.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Parental e-Cigarette Use Linked to Atopic Dermatitis Risk in Children
TOPLINE:
METHODOLOGY:
- AD is one of the most common inflammatory conditions in children and is linked to environmental risk factors, such as exposure to secondhand smoke and prenatal exposure to tobacco.
- To address the effect of e-cigarettes use on children, researchers conducted a cross-sectional analysis of data from the 2014-2018 National Health Interview Survey, a nationally representative sample of the US population.
- The analysis included 48,637,111 individuals (mean age, 8.4 years), with 6,354,515 (13%) indicating a history of AD (mean age, 8 years).
TAKEAWAY:
- The prevalence of parental e-cigarette use was 18.0% among individuals with AD, compared with 14.4% among those without AD.
- This corresponded to a 24% higher risk for AD associated with parental e-cigarette use (adjusted odds ratio, 1.24; 95% CI, 1.08-1.42).
- The association between e-cigarette use and AD in children held regardless of parent’s sex.
IN PRACTICE:
“Our results suggest that parental e-cigarette use was associated with pediatric AD,” the authors concluded. They noted that the authors of a previous study that associated e-cigarette use with AD in adults postulated that the cause was “the inflammatory state created by” e-cigarettes.
SOURCE:
This study, led by Gun Min Youn, Department of Dermatology, Stanford University School of Medicine, Stanford, California, was published online in JAMA Dermatology.
LIMITATIONS:
The cross-sectional survey design limited the ability to draw causal inferences. Defining e-cigarette use as a single past instance could affect the strength of the findings. Only past-year e-cigarette use was considered. Furthermore, data on pediatric cigarette or e-cigarette use, a potential confounder, were unavailable.
DISCLOSURES:
The study did not disclose funding information. One author reported receiving consultation fees outside the submitted work. No other disclosures were reported.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
METHODOLOGY:
- AD is one of the most common inflammatory conditions in children and is linked to environmental risk factors, such as exposure to secondhand smoke and prenatal exposure to tobacco.
- To address the effect of e-cigarettes use on children, researchers conducted a cross-sectional analysis of data from the 2014-2018 National Health Interview Survey, a nationally representative sample of the US population.
- The analysis included 48,637,111 individuals (mean age, 8.4 years), with 6,354,515 (13%) indicating a history of AD (mean age, 8 years).
TAKEAWAY:
- The prevalence of parental e-cigarette use was 18.0% among individuals with AD, compared with 14.4% among those without AD.
- This corresponded to a 24% higher risk for AD associated with parental e-cigarette use (adjusted odds ratio, 1.24; 95% CI, 1.08-1.42).
- The association between e-cigarette use and AD in children held regardless of parent’s sex.
IN PRACTICE:
“Our results suggest that parental e-cigarette use was associated with pediatric AD,” the authors concluded. They noted that the authors of a previous study that associated e-cigarette use with AD in adults postulated that the cause was “the inflammatory state created by” e-cigarettes.
SOURCE:
This study, led by Gun Min Youn, Department of Dermatology, Stanford University School of Medicine, Stanford, California, was published online in JAMA Dermatology.
LIMITATIONS:
The cross-sectional survey design limited the ability to draw causal inferences. Defining e-cigarette use as a single past instance could affect the strength of the findings. Only past-year e-cigarette use was considered. Furthermore, data on pediatric cigarette or e-cigarette use, a potential confounder, were unavailable.
DISCLOSURES:
The study did not disclose funding information. One author reported receiving consultation fees outside the submitted work. No other disclosures were reported.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
METHODOLOGY:
- AD is one of the most common inflammatory conditions in children and is linked to environmental risk factors, such as exposure to secondhand smoke and prenatal exposure to tobacco.
- To address the effect of e-cigarettes use on children, researchers conducted a cross-sectional analysis of data from the 2014-2018 National Health Interview Survey, a nationally representative sample of the US population.
- The analysis included 48,637,111 individuals (mean age, 8.4 years), with 6,354,515 (13%) indicating a history of AD (mean age, 8 years).
TAKEAWAY:
- The prevalence of parental e-cigarette use was 18.0% among individuals with AD, compared with 14.4% among those without AD.
- This corresponded to a 24% higher risk for AD associated with parental e-cigarette use (adjusted odds ratio, 1.24; 95% CI, 1.08-1.42).
- The association between e-cigarette use and AD in children held regardless of parent’s sex.
IN PRACTICE:
“Our results suggest that parental e-cigarette use was associated with pediatric AD,” the authors concluded. They noted that the authors of a previous study that associated e-cigarette use with AD in adults postulated that the cause was “the inflammatory state created by” e-cigarettes.
SOURCE:
This study, led by Gun Min Youn, Department of Dermatology, Stanford University School of Medicine, Stanford, California, was published online in JAMA Dermatology.
LIMITATIONS:
The cross-sectional survey design limited the ability to draw causal inferences. Defining e-cigarette use as a single past instance could affect the strength of the findings. Only past-year e-cigarette use was considered. Furthermore, data on pediatric cigarette or e-cigarette use, a potential confounder, were unavailable.
DISCLOSURES:
The study did not disclose funding information. One author reported receiving consultation fees outside the submitted work. No other disclosures were reported.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Decision-Making Help for Kids With Disabilities Entering Adulthood
About one in six children (17%) between 3 and 17 years have a disability, which may affect their ability to make decisions when they transition to adulthood.
Typically, at age 18, a young adult assumes rights such as the legal right to make medical decisions (including reproductive decisions), and mental health, financial, and education decisions.
.
Several Options in the Continuum
The AAP describes a continuum of decision-making for youth with IDD from fully autonomous decisions to decisions made by an appointed guardian.
Highlighting an array of options is one way this paper is helpful, said Matthew Siegel, MD, chief of clinical enterprise with the Department of Psychiatry & Behavioral Sciences at Boston Children’s Hospital in Massachusetts. “I suspect that for a lot of practitioners what they’re aware of is guardianship or no guardianship.” These authors highlight that the options are more nuanced, he said.
Pediatricians have widely different ideas about what their role should be in facilitating decision-making in the transition period, he said, so this paper helps clarify what advocacy and discussion are needed.
The paper, written by first author Renee M. Turchi, MD, MPH, and colleagues on behalf of the Council on Children with Disabilities’ Committee on Medical Liability and Risk Management, states that, “The goal should always be the least restrictive decision-making that balances autonomy with safety and supports.”
One Alternative Is Supported Decision-Making
Supported decision-making is one alternative to guardianship. Authors explain that under that framework, a patient can choose a trusted support person and create an agreement with that person on what kinds of decisions the person needs help with and how much assistance is needed. The individual makes the final decision, not the support person.
Authors explain the benefits of that approach: “Individuals with IDD who use supported decision-making report increased confidence in themselves and their decision-making, improved decision-making skills, increased engagement with their community, and perceived more control of their lives,” the authors wrote.
Another option for people with IDD might be, rather than formally naming a substitute decision-maker, allowing a parent or caregiver access to their electronic health record or allowing that person to have independent discussions with their physician.
With guardianship, also called conservatorship in some states, a court requires clear and convincing evidence that the youth is not competent to make his or her own decisions. The court may order evaluations by many professionals, including pediatricians.
State-Specific Legal Information Is Available
Many states have recently enacted laws surrounding supported decision-making and guardianship. The authors reference a national resource center website that details the legislation for each state and points to resources and tools for pediatricians, families, and patients.
“Historically, pediatricians have rarely discussed the legal aspects of transition to adult-oriented services with the youth with IDD and subsequently, their families,” the authors wrote.
Discussions Should Start Early
Ideally, the authors wrote, the discussions about what level of supports might be necessary in the transition to adulthood should start at age 12-14 and include the youth, teachers, parents, and the medical team.
That’s earlier than some of the previous guidance, Dr. Siegel said, and it will be important to evaluate future evidence on the best age to start planning “both from a cognitive development standpoint and from a practicality standpoint.”
The authors point out that the needs for level of support may change and “pediatricians can reevaluate the decision-making arrangement as part of the annual physical/mental examinations to align with the youth’s desires, needs, and decision-making abilities over time.”
The authors and Dr. Siegel report no relevant financial relationships.
About one in six children (17%) between 3 and 17 years have a disability, which may affect their ability to make decisions when they transition to adulthood.
Typically, at age 18, a young adult assumes rights such as the legal right to make medical decisions (including reproductive decisions), and mental health, financial, and education decisions.
.
Several Options in the Continuum
The AAP describes a continuum of decision-making for youth with IDD from fully autonomous decisions to decisions made by an appointed guardian.
Highlighting an array of options is one way this paper is helpful, said Matthew Siegel, MD, chief of clinical enterprise with the Department of Psychiatry & Behavioral Sciences at Boston Children’s Hospital in Massachusetts. “I suspect that for a lot of practitioners what they’re aware of is guardianship or no guardianship.” These authors highlight that the options are more nuanced, he said.
Pediatricians have widely different ideas about what their role should be in facilitating decision-making in the transition period, he said, so this paper helps clarify what advocacy and discussion are needed.
The paper, written by first author Renee M. Turchi, MD, MPH, and colleagues on behalf of the Council on Children with Disabilities’ Committee on Medical Liability and Risk Management, states that, “The goal should always be the least restrictive decision-making that balances autonomy with safety and supports.”
One Alternative Is Supported Decision-Making
Supported decision-making is one alternative to guardianship. Authors explain that under that framework, a patient can choose a trusted support person and create an agreement with that person on what kinds of decisions the person needs help with and how much assistance is needed. The individual makes the final decision, not the support person.
Authors explain the benefits of that approach: “Individuals with IDD who use supported decision-making report increased confidence in themselves and their decision-making, improved decision-making skills, increased engagement with their community, and perceived more control of their lives,” the authors wrote.
Another option for people with IDD might be, rather than formally naming a substitute decision-maker, allowing a parent or caregiver access to their electronic health record or allowing that person to have independent discussions with their physician.
With guardianship, also called conservatorship in some states, a court requires clear and convincing evidence that the youth is not competent to make his or her own decisions. The court may order evaluations by many professionals, including pediatricians.
State-Specific Legal Information Is Available
Many states have recently enacted laws surrounding supported decision-making and guardianship. The authors reference a national resource center website that details the legislation for each state and points to resources and tools for pediatricians, families, and patients.
“Historically, pediatricians have rarely discussed the legal aspects of transition to adult-oriented services with the youth with IDD and subsequently, their families,” the authors wrote.
Discussions Should Start Early
Ideally, the authors wrote, the discussions about what level of supports might be necessary in the transition to adulthood should start at age 12-14 and include the youth, teachers, parents, and the medical team.
That’s earlier than some of the previous guidance, Dr. Siegel said, and it will be important to evaluate future evidence on the best age to start planning “both from a cognitive development standpoint and from a practicality standpoint.”
The authors point out that the needs for level of support may change and “pediatricians can reevaluate the decision-making arrangement as part of the annual physical/mental examinations to align with the youth’s desires, needs, and decision-making abilities over time.”
The authors and Dr. Siegel report no relevant financial relationships.
About one in six children (17%) between 3 and 17 years have a disability, which may affect their ability to make decisions when they transition to adulthood.
Typically, at age 18, a young adult assumes rights such as the legal right to make medical decisions (including reproductive decisions), and mental health, financial, and education decisions.
.
Several Options in the Continuum
The AAP describes a continuum of decision-making for youth with IDD from fully autonomous decisions to decisions made by an appointed guardian.
Highlighting an array of options is one way this paper is helpful, said Matthew Siegel, MD, chief of clinical enterprise with the Department of Psychiatry & Behavioral Sciences at Boston Children’s Hospital in Massachusetts. “I suspect that for a lot of practitioners what they’re aware of is guardianship or no guardianship.” These authors highlight that the options are more nuanced, he said.
Pediatricians have widely different ideas about what their role should be in facilitating decision-making in the transition period, he said, so this paper helps clarify what advocacy and discussion are needed.
The paper, written by first author Renee M. Turchi, MD, MPH, and colleagues on behalf of the Council on Children with Disabilities’ Committee on Medical Liability and Risk Management, states that, “The goal should always be the least restrictive decision-making that balances autonomy with safety and supports.”
One Alternative Is Supported Decision-Making
Supported decision-making is one alternative to guardianship. Authors explain that under that framework, a patient can choose a trusted support person and create an agreement with that person on what kinds of decisions the person needs help with and how much assistance is needed. The individual makes the final decision, not the support person.
Authors explain the benefits of that approach: “Individuals with IDD who use supported decision-making report increased confidence in themselves and their decision-making, improved decision-making skills, increased engagement with their community, and perceived more control of their lives,” the authors wrote.
Another option for people with IDD might be, rather than formally naming a substitute decision-maker, allowing a parent or caregiver access to their electronic health record or allowing that person to have independent discussions with their physician.
With guardianship, also called conservatorship in some states, a court requires clear and convincing evidence that the youth is not competent to make his or her own decisions. The court may order evaluations by many professionals, including pediatricians.
State-Specific Legal Information Is Available
Many states have recently enacted laws surrounding supported decision-making and guardianship. The authors reference a national resource center website that details the legislation for each state and points to resources and tools for pediatricians, families, and patients.
“Historically, pediatricians have rarely discussed the legal aspects of transition to adult-oriented services with the youth with IDD and subsequently, their families,” the authors wrote.
Discussions Should Start Early
Ideally, the authors wrote, the discussions about what level of supports might be necessary in the transition to adulthood should start at age 12-14 and include the youth, teachers, parents, and the medical team.
That’s earlier than some of the previous guidance, Dr. Siegel said, and it will be important to evaluate future evidence on the best age to start planning “both from a cognitive development standpoint and from a practicality standpoint.”
The authors point out that the needs for level of support may change and “pediatricians can reevaluate the decision-making arrangement as part of the annual physical/mental examinations to align with the youth’s desires, needs, and decision-making abilities over time.”
The authors and Dr. Siegel report no relevant financial relationships.
FROM PEDIATRICS
New Administration Routes for Adrenaline in Anaphylaxis
PARIS — While anaphylaxis requires immediate adrenaline administration through autoinjection, the use of this treatment is not optimal. Therefore, the development of new adrenaline formulations (such as for intranasal, sublingual, and transcutaneous routes) aims to facilitate the drug’s use and reduce persistent delays in administration by patients and caregivers. An overview of the research was presented at the 19th French-speaking Congress of Allergology.
Anaphylaxis is a severe and potentially fatal immediate hypersensitivity reaction with highly variable and dynamic clinical presentations. It requires prompt recognition for immediate treatment with intramuscular (IM) adrenaline (at the anterolateral aspect of the mid-thigh).
One might think that this reflex is acquired, but in France, while the number of prescribed adrenaline autoinjection (AAI) devices has been increasing for a decade, reaching 965,944 units in 2022, this first-line treatment is underused. Anapen (150, 300, and 500 µg), EpiPen (150 and 300 µg), Jext (150 µg and 300 µg), and Emerade (150, 300, and 500 µg) are the four products marketed in France in 2024.
“Only 17.3% of individuals presenting to the emergency department in the Lorraine region used it in 2015,” said Catherine Neukirch, MD, a pneumologist at Hôpital Bichat–Claude Bernard in Paris, France, with rates of 11.3% for children and 20.3% for adults.
Anaphylaxis Incidence Increasing
Approximately 0.3% (95% CI, 0.1-0.5) of the population will experience an anaphylaxis episode in their lifetime. Incidence in Europe, across all causes, is estimated between 1.5 and 7.9 cases per 100,000 inhabitants per year. Although anaphylaxis is on the rise, its associated mortality remains low, ranging between 0.05 and 0.51 per million per year for drugs, between 0.03 and 0.32 per million per year for foods, and between 0.09 and 0.13 per million per year for hymenopteran venoms.
Data from the European Anaphylaxis Registry indicate that anaphylaxis manifests rapidly after allergen exposure: 55% of cases occur within 10 minutes and 80% within 30 minutes. In addition, a biphasic reaction, which can occur up to 72 hours after exposure, is observed in < 5% of cases.
While a delay in adrenaline use is associated with risk for increased morbidity and mortality, AAI significantly reduces error rates compared with manual treatments involving ampoules, needles, and syringes. It also reduces the associated panic risks. However, there are multiple barriers to adrenaline use. The clinical symptoms of anaphylaxis may be misleading, especially if it occurs without cutaneous and urticarial manifestations but with only acute bronchospasm. It may present as isolated laryngeal edema without digestive involvement, hypotension, or other respiratory problems.
Other limitations to adrenaline use include technical difficulties and the possibility of incorrect administration, the need for appropriate needle sizes for patients with obesity, needle phobia, potential adverse effects of adrenaline injections, failure to carry two autoinjectors, constraints related to storage and bulky transport, as well as the need for training and practice.
“These factors contribute to underuse of adrenaline by patients and caregivers,” said Dr. Neukirch, which results in delays in necessary administration.
Adrenaline Treatment Criteria?
An analysis published in 2023 based on pharmacovigilance data from 30 regional French centers from 1984 to 2022 included 42 reported cases (average age, 33 years; 26% children) of reactions to AAI, which probably is an underestimate. About 40% of AAI uses occurred during anaphylaxis. The remaining 60% were triggered outside of reactions. The main reasons were accidental injections, mainly in the fingers, and cases of not triggering the autoinjector, underlining the importance of patient education.
In 2015, the European Medicines Agency required pharmacological studies for injectable adrenaline on healthy volunteers. These studies include ultrasound measurements of bolus injection, pharmacokinetics (ie, absorption, distribution, metabolism, and excretion), and pharmacodynamics (ie, the effect of the drug and the mechanism of action in the body), with precise evaluation of cardiovascular effects (eg, systolic and diastolic blood pressures and heart rate).
Among the information collected with the different products, ultrasound studies have shown a different localization of the adrenaline bolus (ie, in muscle in patients with normal BMI and mostly in adipose tissue in patients with BMI indicating overweight and obesity). The consequences of this finding are still unknown.
In a study with 500 µg Anapen, women with overweight or obesity showed different pharmacokinetic or pharmacodynamic profiles from those in men with normal weight, with an increase in the area under the curve (0-240 min) and marked changes in the heart rate time curve.
IM administration of 0.5 mg produces rapid pharmacokinetic effects in patients with normal weight, overweight, or obesity, with a delay for the second peak in the latter case. This delay perhaps results from initial local vasoconstriction due to adrenaline.
The early peak plasma concentration occurs at 5-10 minutes for AAI, with a faster speed for Anapen and EpiPen.
Moreover, needle size is not the most important factor. Rather, it is the strength and speed of injection, which can vary depending on the AAI.
Also, the optimal plasma concentration of adrenaline to treat anaphylaxis is not known; studies cannot be conducted during anaphylaxis. In terms of pharmacokinetics, a small series discovered that increased skin or muscle thickness delays the absorption of EpiPen AAI.
Intranasal Adrenaline
To facilitate rapid adrenaline use and convince reluctant patients to carry and use adrenaline, intranasal, sublingual, or transcutaneous forms are under development.
Three intranasal forms of adrenaline are already well advanced, including Neffy from ARS Pharma, epinephrine sprays from Bryn Pharma and Hikma, and Oxero from Oragoo, which contains dry powder.
A comparison of intranasal adrenaline Neffy and AAI shows that the former has satisfactory pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic effects.
In a phase 1 randomized crossover study of 42 healthy adults comparing the pharmacokinetic effects of Neffy adrenaline (2 mg) and EpiPen (0.3 mg), as well as IM epinephrine 0.3 mg, several observations were made. For a single dose, the maximum concentration (Cmax) of Neffy was lower than that of EpiPen.
However, with repeated doses administered 10 minutes apart, the Cmax of Neffy was higher than that of EpiPen. At this stage, pharmacodynamic responses to intranasal products are at least comparable with those of approved injectable products.
A comparison of the pharmacodynamic effects, such as systolic and diastolic blood pressures and heart rate, of Neffy adrenaline and AAI concluded that the profile of Neffy is comparable with that of EpiPen and superior to that of IM epinephrine.
In patients with a history of allergic rhinitis, adrenaline Cmax appears to be increased, while time to peak plasma concentration (Tmax) is reduced. Low blood pressure does not prevent Neffy absorption. Neffy is currently under review by the American and European health authorities.
Intranasal absorption of dry powder adrenaline appears to be faster than that of EpiPen, thus offering a clinical advantage in the short therapeutic window for anaphylaxis treatment.
In an open-label trial conducted on 12 adults with seasonal allergic rhinitis without asthma, the pharmacokinetics, pharmacodynamics, and safety of adrenaline were compared between FMXIN002 (1.6 and 3.2 mg), which was administered intranasally with or without nasal allergen challenge, and IM EpiPen 0.3 mg. Pharmacokinetics varied by patient. Nevertheless, nasal FMXIN002 had a shorter Tmax, a doubled Cmax after the allergen challenge peak, and a higher area under the curve in the 8 hours following administration compared with EpiPen. Pharmacodynamic effects comparable with those of EpiPen were noted at 15 minutes to 4 hours after administration. The tolerance was good, with mild and local side effects. The powder seems to deposit slightly better in the nasal cavity. It remains stable for 6 months at a temperature of 40 °C and relative humidity of 75% and for 2 years at a temperature of 25 °C and relative humidity of 60%.
Sublingual Adrenaline Film
AQST-109 is a sublingual film that is intended to allow rapid administration of epinephrine 1, which is a prodrug of adrenaline. The product is the size of a postage stamp, weighs < 30 g, and dissolves on contact with the tongue.
The EPIPHAST II study was a phase 1, multiperiod, crossover study conducted on 24 healthy adults (age, 24-49 years) who were randomly assigned to receive either 12 or 0.3 mg of AQST-109 of manual IM adrenaline in the first two periods. All participants received 0.3 mg of EpiPen in the last period.
EpiPen 0.3 mg resulted in a higher Cmax than AQST-109 12 mg. AQST-109 12 mg had the fastest median Tmax of 12 minutes. The areas under the curve of AQST-109 12 mg fell between those of EpiPen 0.3 mg and manual IM adrenaline 0.3 mg.
Early increases in systolic blood pressure, diastolic blood pressure, and heart rate were observed with AQST-109 12 mg. Changes were more pronounced with AQST-109 12 mg despite a higher Cmax with EpiPen 0.3 mg.
Part 3 of the EPIPHAST study evaluated the impact of food exposure (ie, a peanut butter sandwich) on the pharmacokinetics of AQST-109 12 mg in 24 healthy adults. Oral food residues did not significantly affect pharmacodynamic parameters, and no treatment-related adverse events were reported.
Researchers concluded that AQST-109 12 mg absorption would not be altered by “real” situations if used during meals. “These results suggest that the sublingual adrenaline film could be promising in real situations,” said Dr. Neukirch, especially in cases of food allergy with recent ingestion of the allergenic food.
Transcutaneous Adrenaline
A transcutaneous form of adrenaline that uses the Zeneo device developed by Crossject, a company based in Dijon, France, comes in the form of an AAI that requires no needle. This project, funded by the European Union, uses a gas generator to propel the drug at very high speed through the skin in 50 milliseconds. This method allows for extended drug storage.
Dr. Neukirch reported financial relationships with Viatris, Stallergènes, ALK, Astrazeneca, Sanofi, GSK, and Novartis.
This story was translated from the Medscape French edition using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
PARIS — While anaphylaxis requires immediate adrenaline administration through autoinjection, the use of this treatment is not optimal. Therefore, the development of new adrenaline formulations (such as for intranasal, sublingual, and transcutaneous routes) aims to facilitate the drug’s use and reduce persistent delays in administration by patients and caregivers. An overview of the research was presented at the 19th French-speaking Congress of Allergology.
Anaphylaxis is a severe and potentially fatal immediate hypersensitivity reaction with highly variable and dynamic clinical presentations. It requires prompt recognition for immediate treatment with intramuscular (IM) adrenaline (at the anterolateral aspect of the mid-thigh).
One might think that this reflex is acquired, but in France, while the number of prescribed adrenaline autoinjection (AAI) devices has been increasing for a decade, reaching 965,944 units in 2022, this first-line treatment is underused. Anapen (150, 300, and 500 µg), EpiPen (150 and 300 µg), Jext (150 µg and 300 µg), and Emerade (150, 300, and 500 µg) are the four products marketed in France in 2024.
“Only 17.3% of individuals presenting to the emergency department in the Lorraine region used it in 2015,” said Catherine Neukirch, MD, a pneumologist at Hôpital Bichat–Claude Bernard in Paris, France, with rates of 11.3% for children and 20.3% for adults.
Anaphylaxis Incidence Increasing
Approximately 0.3% (95% CI, 0.1-0.5) of the population will experience an anaphylaxis episode in their lifetime. Incidence in Europe, across all causes, is estimated between 1.5 and 7.9 cases per 100,000 inhabitants per year. Although anaphylaxis is on the rise, its associated mortality remains low, ranging between 0.05 and 0.51 per million per year for drugs, between 0.03 and 0.32 per million per year for foods, and between 0.09 and 0.13 per million per year for hymenopteran venoms.
Data from the European Anaphylaxis Registry indicate that anaphylaxis manifests rapidly after allergen exposure: 55% of cases occur within 10 minutes and 80% within 30 minutes. In addition, a biphasic reaction, which can occur up to 72 hours after exposure, is observed in < 5% of cases.
While a delay in adrenaline use is associated with risk for increased morbidity and mortality, AAI significantly reduces error rates compared with manual treatments involving ampoules, needles, and syringes. It also reduces the associated panic risks. However, there are multiple barriers to adrenaline use. The clinical symptoms of anaphylaxis may be misleading, especially if it occurs without cutaneous and urticarial manifestations but with only acute bronchospasm. It may present as isolated laryngeal edema without digestive involvement, hypotension, or other respiratory problems.
Other limitations to adrenaline use include technical difficulties and the possibility of incorrect administration, the need for appropriate needle sizes for patients with obesity, needle phobia, potential adverse effects of adrenaline injections, failure to carry two autoinjectors, constraints related to storage and bulky transport, as well as the need for training and practice.
“These factors contribute to underuse of adrenaline by patients and caregivers,” said Dr. Neukirch, which results in delays in necessary administration.
Adrenaline Treatment Criteria?
An analysis published in 2023 based on pharmacovigilance data from 30 regional French centers from 1984 to 2022 included 42 reported cases (average age, 33 years; 26% children) of reactions to AAI, which probably is an underestimate. About 40% of AAI uses occurred during anaphylaxis. The remaining 60% were triggered outside of reactions. The main reasons were accidental injections, mainly in the fingers, and cases of not triggering the autoinjector, underlining the importance of patient education.
In 2015, the European Medicines Agency required pharmacological studies for injectable adrenaline on healthy volunteers. These studies include ultrasound measurements of bolus injection, pharmacokinetics (ie, absorption, distribution, metabolism, and excretion), and pharmacodynamics (ie, the effect of the drug and the mechanism of action in the body), with precise evaluation of cardiovascular effects (eg, systolic and diastolic blood pressures and heart rate).
Among the information collected with the different products, ultrasound studies have shown a different localization of the adrenaline bolus (ie, in muscle in patients with normal BMI and mostly in adipose tissue in patients with BMI indicating overweight and obesity). The consequences of this finding are still unknown.
In a study with 500 µg Anapen, women with overweight or obesity showed different pharmacokinetic or pharmacodynamic profiles from those in men with normal weight, with an increase in the area under the curve (0-240 min) and marked changes in the heart rate time curve.
IM administration of 0.5 mg produces rapid pharmacokinetic effects in patients with normal weight, overweight, or obesity, with a delay for the second peak in the latter case. This delay perhaps results from initial local vasoconstriction due to adrenaline.
The early peak plasma concentration occurs at 5-10 minutes for AAI, with a faster speed for Anapen and EpiPen.
Moreover, needle size is not the most important factor. Rather, it is the strength and speed of injection, which can vary depending on the AAI.
Also, the optimal plasma concentration of adrenaline to treat anaphylaxis is not known; studies cannot be conducted during anaphylaxis. In terms of pharmacokinetics, a small series discovered that increased skin or muscle thickness delays the absorption of EpiPen AAI.
Intranasal Adrenaline
To facilitate rapid adrenaline use and convince reluctant patients to carry and use adrenaline, intranasal, sublingual, or transcutaneous forms are under development.
Three intranasal forms of adrenaline are already well advanced, including Neffy from ARS Pharma, epinephrine sprays from Bryn Pharma and Hikma, and Oxero from Oragoo, which contains dry powder.
A comparison of intranasal adrenaline Neffy and AAI shows that the former has satisfactory pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic effects.
In a phase 1 randomized crossover study of 42 healthy adults comparing the pharmacokinetic effects of Neffy adrenaline (2 mg) and EpiPen (0.3 mg), as well as IM epinephrine 0.3 mg, several observations were made. For a single dose, the maximum concentration (Cmax) of Neffy was lower than that of EpiPen.
However, with repeated doses administered 10 minutes apart, the Cmax of Neffy was higher than that of EpiPen. At this stage, pharmacodynamic responses to intranasal products are at least comparable with those of approved injectable products.
A comparison of the pharmacodynamic effects, such as systolic and diastolic blood pressures and heart rate, of Neffy adrenaline and AAI concluded that the profile of Neffy is comparable with that of EpiPen and superior to that of IM epinephrine.
In patients with a history of allergic rhinitis, adrenaline Cmax appears to be increased, while time to peak plasma concentration (Tmax) is reduced. Low blood pressure does not prevent Neffy absorption. Neffy is currently under review by the American and European health authorities.
Intranasal absorption of dry powder adrenaline appears to be faster than that of EpiPen, thus offering a clinical advantage in the short therapeutic window for anaphylaxis treatment.
In an open-label trial conducted on 12 adults with seasonal allergic rhinitis without asthma, the pharmacokinetics, pharmacodynamics, and safety of adrenaline were compared between FMXIN002 (1.6 and 3.2 mg), which was administered intranasally with or without nasal allergen challenge, and IM EpiPen 0.3 mg. Pharmacokinetics varied by patient. Nevertheless, nasal FMXIN002 had a shorter Tmax, a doubled Cmax after the allergen challenge peak, and a higher area under the curve in the 8 hours following administration compared with EpiPen. Pharmacodynamic effects comparable with those of EpiPen were noted at 15 minutes to 4 hours after administration. The tolerance was good, with mild and local side effects. The powder seems to deposit slightly better in the nasal cavity. It remains stable for 6 months at a temperature of 40 °C and relative humidity of 75% and for 2 years at a temperature of 25 °C and relative humidity of 60%.
Sublingual Adrenaline Film
AQST-109 is a sublingual film that is intended to allow rapid administration of epinephrine 1, which is a prodrug of adrenaline. The product is the size of a postage stamp, weighs < 30 g, and dissolves on contact with the tongue.
The EPIPHAST II study was a phase 1, multiperiod, crossover study conducted on 24 healthy adults (age, 24-49 years) who were randomly assigned to receive either 12 or 0.3 mg of AQST-109 of manual IM adrenaline in the first two periods. All participants received 0.3 mg of EpiPen in the last period.
EpiPen 0.3 mg resulted in a higher Cmax than AQST-109 12 mg. AQST-109 12 mg had the fastest median Tmax of 12 minutes. The areas under the curve of AQST-109 12 mg fell between those of EpiPen 0.3 mg and manual IM adrenaline 0.3 mg.
Early increases in systolic blood pressure, diastolic blood pressure, and heart rate were observed with AQST-109 12 mg. Changes were more pronounced with AQST-109 12 mg despite a higher Cmax with EpiPen 0.3 mg.
Part 3 of the EPIPHAST study evaluated the impact of food exposure (ie, a peanut butter sandwich) on the pharmacokinetics of AQST-109 12 mg in 24 healthy adults. Oral food residues did not significantly affect pharmacodynamic parameters, and no treatment-related adverse events were reported.
Researchers concluded that AQST-109 12 mg absorption would not be altered by “real” situations if used during meals. “These results suggest that the sublingual adrenaline film could be promising in real situations,” said Dr. Neukirch, especially in cases of food allergy with recent ingestion of the allergenic food.
Transcutaneous Adrenaline
A transcutaneous form of adrenaline that uses the Zeneo device developed by Crossject, a company based in Dijon, France, comes in the form of an AAI that requires no needle. This project, funded by the European Union, uses a gas generator to propel the drug at very high speed through the skin in 50 milliseconds. This method allows for extended drug storage.
Dr. Neukirch reported financial relationships with Viatris, Stallergènes, ALK, Astrazeneca, Sanofi, GSK, and Novartis.
This story was translated from the Medscape French edition using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
PARIS — While anaphylaxis requires immediate adrenaline administration through autoinjection, the use of this treatment is not optimal. Therefore, the development of new adrenaline formulations (such as for intranasal, sublingual, and transcutaneous routes) aims to facilitate the drug’s use and reduce persistent delays in administration by patients and caregivers. An overview of the research was presented at the 19th French-speaking Congress of Allergology.
Anaphylaxis is a severe and potentially fatal immediate hypersensitivity reaction with highly variable and dynamic clinical presentations. It requires prompt recognition for immediate treatment with intramuscular (IM) adrenaline (at the anterolateral aspect of the mid-thigh).
One might think that this reflex is acquired, but in France, while the number of prescribed adrenaline autoinjection (AAI) devices has been increasing for a decade, reaching 965,944 units in 2022, this first-line treatment is underused. Anapen (150, 300, and 500 µg), EpiPen (150 and 300 µg), Jext (150 µg and 300 µg), and Emerade (150, 300, and 500 µg) are the four products marketed in France in 2024.
“Only 17.3% of individuals presenting to the emergency department in the Lorraine region used it in 2015,” said Catherine Neukirch, MD, a pneumologist at Hôpital Bichat–Claude Bernard in Paris, France, with rates of 11.3% for children and 20.3% for adults.
Anaphylaxis Incidence Increasing
Approximately 0.3% (95% CI, 0.1-0.5) of the population will experience an anaphylaxis episode in their lifetime. Incidence in Europe, across all causes, is estimated between 1.5 and 7.9 cases per 100,000 inhabitants per year. Although anaphylaxis is on the rise, its associated mortality remains low, ranging between 0.05 and 0.51 per million per year for drugs, between 0.03 and 0.32 per million per year for foods, and between 0.09 and 0.13 per million per year for hymenopteran venoms.
Data from the European Anaphylaxis Registry indicate that anaphylaxis manifests rapidly after allergen exposure: 55% of cases occur within 10 minutes and 80% within 30 minutes. In addition, a biphasic reaction, which can occur up to 72 hours after exposure, is observed in < 5% of cases.
While a delay in adrenaline use is associated with risk for increased morbidity and mortality, AAI significantly reduces error rates compared with manual treatments involving ampoules, needles, and syringes. It also reduces the associated panic risks. However, there are multiple barriers to adrenaline use. The clinical symptoms of anaphylaxis may be misleading, especially if it occurs without cutaneous and urticarial manifestations but with only acute bronchospasm. It may present as isolated laryngeal edema without digestive involvement, hypotension, or other respiratory problems.
Other limitations to adrenaline use include technical difficulties and the possibility of incorrect administration, the need for appropriate needle sizes for patients with obesity, needle phobia, potential adverse effects of adrenaline injections, failure to carry two autoinjectors, constraints related to storage and bulky transport, as well as the need for training and practice.
“These factors contribute to underuse of adrenaline by patients and caregivers,” said Dr. Neukirch, which results in delays in necessary administration.
Adrenaline Treatment Criteria?
An analysis published in 2023 based on pharmacovigilance data from 30 regional French centers from 1984 to 2022 included 42 reported cases (average age, 33 years; 26% children) of reactions to AAI, which probably is an underestimate. About 40% of AAI uses occurred during anaphylaxis. The remaining 60% were triggered outside of reactions. The main reasons were accidental injections, mainly in the fingers, and cases of not triggering the autoinjector, underlining the importance of patient education.
In 2015, the European Medicines Agency required pharmacological studies for injectable adrenaline on healthy volunteers. These studies include ultrasound measurements of bolus injection, pharmacokinetics (ie, absorption, distribution, metabolism, and excretion), and pharmacodynamics (ie, the effect of the drug and the mechanism of action in the body), with precise evaluation of cardiovascular effects (eg, systolic and diastolic blood pressures and heart rate).
Among the information collected with the different products, ultrasound studies have shown a different localization of the adrenaline bolus (ie, in muscle in patients with normal BMI and mostly in adipose tissue in patients with BMI indicating overweight and obesity). The consequences of this finding are still unknown.
In a study with 500 µg Anapen, women with overweight or obesity showed different pharmacokinetic or pharmacodynamic profiles from those in men with normal weight, with an increase in the area under the curve (0-240 min) and marked changes in the heart rate time curve.
IM administration of 0.5 mg produces rapid pharmacokinetic effects in patients with normal weight, overweight, or obesity, with a delay for the second peak in the latter case. This delay perhaps results from initial local vasoconstriction due to adrenaline.
The early peak plasma concentration occurs at 5-10 minutes for AAI, with a faster speed for Anapen and EpiPen.
Moreover, needle size is not the most important factor. Rather, it is the strength and speed of injection, which can vary depending on the AAI.
Also, the optimal plasma concentration of adrenaline to treat anaphylaxis is not known; studies cannot be conducted during anaphylaxis. In terms of pharmacokinetics, a small series discovered that increased skin or muscle thickness delays the absorption of EpiPen AAI.
Intranasal Adrenaline
To facilitate rapid adrenaline use and convince reluctant patients to carry and use adrenaline, intranasal, sublingual, or transcutaneous forms are under development.
Three intranasal forms of adrenaline are already well advanced, including Neffy from ARS Pharma, epinephrine sprays from Bryn Pharma and Hikma, and Oxero from Oragoo, which contains dry powder.
A comparison of intranasal adrenaline Neffy and AAI shows that the former has satisfactory pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic effects.
In a phase 1 randomized crossover study of 42 healthy adults comparing the pharmacokinetic effects of Neffy adrenaline (2 mg) and EpiPen (0.3 mg), as well as IM epinephrine 0.3 mg, several observations were made. For a single dose, the maximum concentration (Cmax) of Neffy was lower than that of EpiPen.
However, with repeated doses administered 10 minutes apart, the Cmax of Neffy was higher than that of EpiPen. At this stage, pharmacodynamic responses to intranasal products are at least comparable with those of approved injectable products.
A comparison of the pharmacodynamic effects, such as systolic and diastolic blood pressures and heart rate, of Neffy adrenaline and AAI concluded that the profile of Neffy is comparable with that of EpiPen and superior to that of IM epinephrine.
In patients with a history of allergic rhinitis, adrenaline Cmax appears to be increased, while time to peak plasma concentration (Tmax) is reduced. Low blood pressure does not prevent Neffy absorption. Neffy is currently under review by the American and European health authorities.
Intranasal absorption of dry powder adrenaline appears to be faster than that of EpiPen, thus offering a clinical advantage in the short therapeutic window for anaphylaxis treatment.
In an open-label trial conducted on 12 adults with seasonal allergic rhinitis without asthma, the pharmacokinetics, pharmacodynamics, and safety of adrenaline were compared between FMXIN002 (1.6 and 3.2 mg), which was administered intranasally with or without nasal allergen challenge, and IM EpiPen 0.3 mg. Pharmacokinetics varied by patient. Nevertheless, nasal FMXIN002 had a shorter Tmax, a doubled Cmax after the allergen challenge peak, and a higher area under the curve in the 8 hours following administration compared with EpiPen. Pharmacodynamic effects comparable with those of EpiPen were noted at 15 minutes to 4 hours after administration. The tolerance was good, with mild and local side effects. The powder seems to deposit slightly better in the nasal cavity. It remains stable for 6 months at a temperature of 40 °C and relative humidity of 75% and for 2 years at a temperature of 25 °C and relative humidity of 60%.
Sublingual Adrenaline Film
AQST-109 is a sublingual film that is intended to allow rapid administration of epinephrine 1, which is a prodrug of adrenaline. The product is the size of a postage stamp, weighs < 30 g, and dissolves on contact with the tongue.
The EPIPHAST II study was a phase 1, multiperiod, crossover study conducted on 24 healthy adults (age, 24-49 years) who were randomly assigned to receive either 12 or 0.3 mg of AQST-109 of manual IM adrenaline in the first two periods. All participants received 0.3 mg of EpiPen in the last period.
EpiPen 0.3 mg resulted in a higher Cmax than AQST-109 12 mg. AQST-109 12 mg had the fastest median Tmax of 12 minutes. The areas under the curve of AQST-109 12 mg fell between those of EpiPen 0.3 mg and manual IM adrenaline 0.3 mg.
Early increases in systolic blood pressure, diastolic blood pressure, and heart rate were observed with AQST-109 12 mg. Changes were more pronounced with AQST-109 12 mg despite a higher Cmax with EpiPen 0.3 mg.
Part 3 of the EPIPHAST study evaluated the impact of food exposure (ie, a peanut butter sandwich) on the pharmacokinetics of AQST-109 12 mg in 24 healthy adults. Oral food residues did not significantly affect pharmacodynamic parameters, and no treatment-related adverse events were reported.
Researchers concluded that AQST-109 12 mg absorption would not be altered by “real” situations if used during meals. “These results suggest that the sublingual adrenaline film could be promising in real situations,” said Dr. Neukirch, especially in cases of food allergy with recent ingestion of the allergenic food.
Transcutaneous Adrenaline
A transcutaneous form of adrenaline that uses the Zeneo device developed by Crossject, a company based in Dijon, France, comes in the form of an AAI that requires no needle. This project, funded by the European Union, uses a gas generator to propel the drug at very high speed through the skin in 50 milliseconds. This method allows for extended drug storage.
Dr. Neukirch reported financial relationships with Viatris, Stallergènes, ALK, Astrazeneca, Sanofi, GSK, and Novartis.
This story was translated from the Medscape French edition using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
PCPs May Have a New Tool to Help Identify Autism in Young Children
Incorporating eye-tracking biomarkers into pediatric autism assessments may make identifying the condition easier, according to new findings published in JAMA Network Open.
Researchers created an artificial intelligence–based tool to help primary care clinicians and pediatricians spot potential cases of the neurological condition, according to Brandon Keehn, PhD, associate professor in the Department of Speech, Language, and Hearing Sciences at Purdue University in West Lafayette, Indiana, and an author of the study.
Most primary care clinicians do not receive specialized training in identifying autism, and around a third diagnose the condition with uncertainty, according to Dr. Keehn. The tool helps clinicians by incorporating their diagnosis and self-reported level of certainty with eye-tracking biomarkers. A clinical psychologist also assessed children, either verifying or confuting the earlier results.
The tool produced the same diagnosis as that from a psychologist in 90% of cases. When children were assessed using eye biomarkers alone, the diagnosis was aligned with that of a psychologist 77% of the time.
“This is the first step in demonstrating both that eye-tracking biomarkers are sensitive to autism and whether or not these biomarkers provide extra clinical information for primary care physicians to more accurately diagnose autism,” Dr. Keehn told this news organization.
The study took place between 2019 and 2022 and included 146 children between 14 and 48 months old who were treated at seven primary care practices in Indiana. Dr. Keehn and colleagues asked primary care clinicians to rate their level of certainty in their diagnosis.
During the biomarker test, toddlers watched cartoons while researchers tracked their eye movements. Six biomarkers included in the test were based on previous research linking eye movements to autism, according to Dr. Keehn.
These included whether toddlers looked more at images of people or geometric patterns and the speed and size of pupil dilation when exposed to bright light.
Most toddlers produced a positive result for autism in only one biomarker test. Dr. Keehn said this confirms that children should be tested for a variety of biomarkers because each patient’s condition manifests differently.
Dr. Keehn said his team is still a few steps away from determining how the model would work in a real clinical setting and that they are planning more research with a larger study population.
Alice Kuo, MD, a pediatrician specializing in autism at the University of California, Los Angeles (UCLA), said primary care clinicians should feel comfortable making an autism diagnosis.
“Any tool that helps them to do that can be useful, since wait times for a specialist can take years,” Dr. Kuo, also the director of the Autism Intervention Research Network on Physical Health at UCLA, said.
However, Dr. Kuo said she is concerned about the cases that were falsely identified as positive or negative.
“To be told your kid is autistic when he’s not, or to be told your kid is not when he clinically is, has huge ramifications,” she said.
The study was funded by the National Institute of Mental Health, the Riley Children’s Foundation, and the Indiana Clinical and Translational Sciences Institute. Dr. Keehn reported payments for workshops on the use of the Autism Diagnostic Observation Schedule.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com .
Incorporating eye-tracking biomarkers into pediatric autism assessments may make identifying the condition easier, according to new findings published in JAMA Network Open.
Researchers created an artificial intelligence–based tool to help primary care clinicians and pediatricians spot potential cases of the neurological condition, according to Brandon Keehn, PhD, associate professor in the Department of Speech, Language, and Hearing Sciences at Purdue University in West Lafayette, Indiana, and an author of the study.
Most primary care clinicians do not receive specialized training in identifying autism, and around a third diagnose the condition with uncertainty, according to Dr. Keehn. The tool helps clinicians by incorporating their diagnosis and self-reported level of certainty with eye-tracking biomarkers. A clinical psychologist also assessed children, either verifying or confuting the earlier results.
The tool produced the same diagnosis as that from a psychologist in 90% of cases. When children were assessed using eye biomarkers alone, the diagnosis was aligned with that of a psychologist 77% of the time.
“This is the first step in demonstrating both that eye-tracking biomarkers are sensitive to autism and whether or not these biomarkers provide extra clinical information for primary care physicians to more accurately diagnose autism,” Dr. Keehn told this news organization.
The study took place between 2019 and 2022 and included 146 children between 14 and 48 months old who were treated at seven primary care practices in Indiana. Dr. Keehn and colleagues asked primary care clinicians to rate their level of certainty in their diagnosis.
During the biomarker test, toddlers watched cartoons while researchers tracked their eye movements. Six biomarkers included in the test were based on previous research linking eye movements to autism, according to Dr. Keehn.
These included whether toddlers looked more at images of people or geometric patterns and the speed and size of pupil dilation when exposed to bright light.
Most toddlers produced a positive result for autism in only one biomarker test. Dr. Keehn said this confirms that children should be tested for a variety of biomarkers because each patient’s condition manifests differently.
Dr. Keehn said his team is still a few steps away from determining how the model would work in a real clinical setting and that they are planning more research with a larger study population.
Alice Kuo, MD, a pediatrician specializing in autism at the University of California, Los Angeles (UCLA), said primary care clinicians should feel comfortable making an autism diagnosis.
“Any tool that helps them to do that can be useful, since wait times for a specialist can take years,” Dr. Kuo, also the director of the Autism Intervention Research Network on Physical Health at UCLA, said.
However, Dr. Kuo said she is concerned about the cases that were falsely identified as positive or negative.
“To be told your kid is autistic when he’s not, or to be told your kid is not when he clinically is, has huge ramifications,” she said.
The study was funded by the National Institute of Mental Health, the Riley Children’s Foundation, and the Indiana Clinical and Translational Sciences Institute. Dr. Keehn reported payments for workshops on the use of the Autism Diagnostic Observation Schedule.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com .
Incorporating eye-tracking biomarkers into pediatric autism assessments may make identifying the condition easier, according to new findings published in JAMA Network Open.
Researchers created an artificial intelligence–based tool to help primary care clinicians and pediatricians spot potential cases of the neurological condition, according to Brandon Keehn, PhD, associate professor in the Department of Speech, Language, and Hearing Sciences at Purdue University in West Lafayette, Indiana, and an author of the study.
Most primary care clinicians do not receive specialized training in identifying autism, and around a third diagnose the condition with uncertainty, according to Dr. Keehn. The tool helps clinicians by incorporating their diagnosis and self-reported level of certainty with eye-tracking biomarkers. A clinical psychologist also assessed children, either verifying or confuting the earlier results.
The tool produced the same diagnosis as that from a psychologist in 90% of cases. When children were assessed using eye biomarkers alone, the diagnosis was aligned with that of a psychologist 77% of the time.
“This is the first step in demonstrating both that eye-tracking biomarkers are sensitive to autism and whether or not these biomarkers provide extra clinical information for primary care physicians to more accurately diagnose autism,” Dr. Keehn told this news organization.
The study took place between 2019 and 2022 and included 146 children between 14 and 48 months old who were treated at seven primary care practices in Indiana. Dr. Keehn and colleagues asked primary care clinicians to rate their level of certainty in their diagnosis.
During the biomarker test, toddlers watched cartoons while researchers tracked their eye movements. Six biomarkers included in the test were based on previous research linking eye movements to autism, according to Dr. Keehn.
These included whether toddlers looked more at images of people or geometric patterns and the speed and size of pupil dilation when exposed to bright light.
Most toddlers produced a positive result for autism in only one biomarker test. Dr. Keehn said this confirms that children should be tested for a variety of biomarkers because each patient’s condition manifests differently.
Dr. Keehn said his team is still a few steps away from determining how the model would work in a real clinical setting and that they are planning more research with a larger study population.
Alice Kuo, MD, a pediatrician specializing in autism at the University of California, Los Angeles (UCLA), said primary care clinicians should feel comfortable making an autism diagnosis.
“Any tool that helps them to do that can be useful, since wait times for a specialist can take years,” Dr. Kuo, also the director of the Autism Intervention Research Network on Physical Health at UCLA, said.
However, Dr. Kuo said she is concerned about the cases that were falsely identified as positive or negative.
“To be told your kid is autistic when he’s not, or to be told your kid is not when he clinically is, has huge ramifications,” she said.
The study was funded by the National Institute of Mental Health, the Riley Children’s Foundation, and the Indiana Clinical and Translational Sciences Institute. Dr. Keehn reported payments for workshops on the use of the Autism Diagnostic Observation Schedule.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com .
FROM JAMA NETWORK OPEN
Will the Federal Non-Compete Ban Take Effect?
(with very limited exceptions). The final rule will not go into effect until 120 days after its publication in the Federal Register, which took place on May 7, and numerous legal challenges appear to be on the horizon.
The principal components of the rule are as follows:
- After the effective date, most non-compete agreements (which prevent departing employees from signing with a new employer for a defined period within a specific geographic area) are banned nationwide.
- The rule exempts certain “senior executives,” ie individuals who earn more than $151,164 annually and serve in policy-making positions.
- There is another major exception for non-competes connected with a sale of a business.
- While not explicitly stated, the rule arguably exempts non-profits, tax-exempt hospitals, and other tax-exempt entities.
- Employers must provide verbal and written notice to employees regarding existing agreements, which would be voided under the rule.
The final rule is the latest skirmish in an ongoing, years-long debate. Twelve states have already put non-compete bans in place, according to a recent paper, and they may serve as a harbinger of things to come should the federal ban go into effect. Each state rule varies in its specifics as states respond to local market conditions. While some states ban all non-compete agreements outright, others limit them based on variables, such as income and employment circumstances. Of course, should the federal ban take effect, it will supersede whatever rules the individual states have in place.
In drafting the rule, the FTC reasoned that non-compete clauses constitute restraint of trade, and eliminating them could potentially increase worker earnings as well as lower health care costs by billions of dollars. In its statements on the proposed ban, the FTC claimed that it could lower health spending across the board by almost $150 billion per year and return $300 million to workers each year in earnings. The agency cited a large body of research that non-competes make it harder for workers to move between jobs and can raise prices for goods and services, while suppressing wages for workers and inhibiting the creation of new businesses.
Most physicians affected by non-compete agreements heavily favor the new rule, because it would give them more control over their careers and expand their practice and income opportunities. It would allow them to get a new job with a competing organization, bucking a long-standing trend that hospitals and health care systems have heavily relied on to keep staff in place.
The rule would, however, keep in place “non-solicitation” rules that many health care organizations have put in place. That means that if a physician leaves an employer, he or she cannot reach out to former patients and colleagues to bring them along or invite them to join him or her at the new employment venue.
Within that clause, however, the FTC has specified that if such non-solicitation agreement has the “equivalent effect” of a non-compete, the agency would deem it such. That means, even if that rule stands, it could be contested and may be interpreted as violating the non-compete provision. So, there is value in reading all the fine print should the rule move forward.
Physicians in independent practices who employ physician assistants and nurse practitioners have expressed concerns that their expensively trained employees might be tempted to accept a nearby, higher-paying position. The “non-solicitation” clause would theoretically prevent them from taking patients and co-workers with them — unless it were successfully contested. Many questions remain.
Further complicating the non-compete ban issue is how it might impact nonprofit institutions. Most hospitals structured as nonprofits would theoretically be exempt from the rule, although it is not specifically stated in the rule itself, because the FTC Act gives the Commission jurisdiction over for-profit companies only. This would obviously create an unfair advantage for nonprofits, who could continue writing non-compete clauses with impunity.
All of these questions may be moot, of course, because a number of powerful entities with deep pockets have lined up in opposition to the rule. Some of them have even questioned the FTC’s authority to pass the rule at all, on the grounds that Section 5 of the FTC Act does not give it the authority to police labor markets. A lawsuit has already been filed by the US Chamber of Commerce. Other large groups in opposition are the American Medical Group Association, the American Hospital Association, and numerous large hospital and healthcare networks.
Only time will tell whether this issue will be regulated on a national level or remain the purview of each individual state.
Dr. Eastern practices dermatology and dermatologic surgery in Belleville, N.J. He is the author of numerous articles and textbook chapters, and is a longtime monthly columnist for Dermatology News. Write to him at [email protected].
(with very limited exceptions). The final rule will not go into effect until 120 days after its publication in the Federal Register, which took place on May 7, and numerous legal challenges appear to be on the horizon.
The principal components of the rule are as follows:
- After the effective date, most non-compete agreements (which prevent departing employees from signing with a new employer for a defined period within a specific geographic area) are banned nationwide.
- The rule exempts certain “senior executives,” ie individuals who earn more than $151,164 annually and serve in policy-making positions.
- There is another major exception for non-competes connected with a sale of a business.
- While not explicitly stated, the rule arguably exempts non-profits, tax-exempt hospitals, and other tax-exempt entities.
- Employers must provide verbal and written notice to employees regarding existing agreements, which would be voided under the rule.
The final rule is the latest skirmish in an ongoing, years-long debate. Twelve states have already put non-compete bans in place, according to a recent paper, and they may serve as a harbinger of things to come should the federal ban go into effect. Each state rule varies in its specifics as states respond to local market conditions. While some states ban all non-compete agreements outright, others limit them based on variables, such as income and employment circumstances. Of course, should the federal ban take effect, it will supersede whatever rules the individual states have in place.
In drafting the rule, the FTC reasoned that non-compete clauses constitute restraint of trade, and eliminating them could potentially increase worker earnings as well as lower health care costs by billions of dollars. In its statements on the proposed ban, the FTC claimed that it could lower health spending across the board by almost $150 billion per year and return $300 million to workers each year in earnings. The agency cited a large body of research that non-competes make it harder for workers to move between jobs and can raise prices for goods and services, while suppressing wages for workers and inhibiting the creation of new businesses.
Most physicians affected by non-compete agreements heavily favor the new rule, because it would give them more control over their careers and expand their practice and income opportunities. It would allow them to get a new job with a competing organization, bucking a long-standing trend that hospitals and health care systems have heavily relied on to keep staff in place.
The rule would, however, keep in place “non-solicitation” rules that many health care organizations have put in place. That means that if a physician leaves an employer, he or she cannot reach out to former patients and colleagues to bring them along or invite them to join him or her at the new employment venue.
Within that clause, however, the FTC has specified that if such non-solicitation agreement has the “equivalent effect” of a non-compete, the agency would deem it such. That means, even if that rule stands, it could be contested and may be interpreted as violating the non-compete provision. So, there is value in reading all the fine print should the rule move forward.
Physicians in independent practices who employ physician assistants and nurse practitioners have expressed concerns that their expensively trained employees might be tempted to accept a nearby, higher-paying position. The “non-solicitation” clause would theoretically prevent them from taking patients and co-workers with them — unless it were successfully contested. Many questions remain.
Further complicating the non-compete ban issue is how it might impact nonprofit institutions. Most hospitals structured as nonprofits would theoretically be exempt from the rule, although it is not specifically stated in the rule itself, because the FTC Act gives the Commission jurisdiction over for-profit companies only. This would obviously create an unfair advantage for nonprofits, who could continue writing non-compete clauses with impunity.
All of these questions may be moot, of course, because a number of powerful entities with deep pockets have lined up in opposition to the rule. Some of them have even questioned the FTC’s authority to pass the rule at all, on the grounds that Section 5 of the FTC Act does not give it the authority to police labor markets. A lawsuit has already been filed by the US Chamber of Commerce. Other large groups in opposition are the American Medical Group Association, the American Hospital Association, and numerous large hospital and healthcare networks.
Only time will tell whether this issue will be regulated on a national level or remain the purview of each individual state.
Dr. Eastern practices dermatology and dermatologic surgery in Belleville, N.J. He is the author of numerous articles and textbook chapters, and is a longtime monthly columnist for Dermatology News. Write to him at [email protected].
(with very limited exceptions). The final rule will not go into effect until 120 days after its publication in the Federal Register, which took place on May 7, and numerous legal challenges appear to be on the horizon.
The principal components of the rule are as follows:
- After the effective date, most non-compete agreements (which prevent departing employees from signing with a new employer for a defined period within a specific geographic area) are banned nationwide.
- The rule exempts certain “senior executives,” ie individuals who earn more than $151,164 annually and serve in policy-making positions.
- There is another major exception for non-competes connected with a sale of a business.
- While not explicitly stated, the rule arguably exempts non-profits, tax-exempt hospitals, and other tax-exempt entities.
- Employers must provide verbal and written notice to employees regarding existing agreements, which would be voided under the rule.
The final rule is the latest skirmish in an ongoing, years-long debate. Twelve states have already put non-compete bans in place, according to a recent paper, and they may serve as a harbinger of things to come should the federal ban go into effect. Each state rule varies in its specifics as states respond to local market conditions. While some states ban all non-compete agreements outright, others limit them based on variables, such as income and employment circumstances. Of course, should the federal ban take effect, it will supersede whatever rules the individual states have in place.
In drafting the rule, the FTC reasoned that non-compete clauses constitute restraint of trade, and eliminating them could potentially increase worker earnings as well as lower health care costs by billions of dollars. In its statements on the proposed ban, the FTC claimed that it could lower health spending across the board by almost $150 billion per year and return $300 million to workers each year in earnings. The agency cited a large body of research that non-competes make it harder for workers to move between jobs and can raise prices for goods and services, while suppressing wages for workers and inhibiting the creation of new businesses.
Most physicians affected by non-compete agreements heavily favor the new rule, because it would give them more control over their careers and expand their practice and income opportunities. It would allow them to get a new job with a competing organization, bucking a long-standing trend that hospitals and health care systems have heavily relied on to keep staff in place.
The rule would, however, keep in place “non-solicitation” rules that many health care organizations have put in place. That means that if a physician leaves an employer, he or she cannot reach out to former patients and colleagues to bring them along or invite them to join him or her at the new employment venue.
Within that clause, however, the FTC has specified that if such non-solicitation agreement has the “equivalent effect” of a non-compete, the agency would deem it such. That means, even if that rule stands, it could be contested and may be interpreted as violating the non-compete provision. So, there is value in reading all the fine print should the rule move forward.
Physicians in independent practices who employ physician assistants and nurse practitioners have expressed concerns that their expensively trained employees might be tempted to accept a nearby, higher-paying position. The “non-solicitation” clause would theoretically prevent them from taking patients and co-workers with them — unless it were successfully contested. Many questions remain.
Further complicating the non-compete ban issue is how it might impact nonprofit institutions. Most hospitals structured as nonprofits would theoretically be exempt from the rule, although it is not specifically stated in the rule itself, because the FTC Act gives the Commission jurisdiction over for-profit companies only. This would obviously create an unfair advantage for nonprofits, who could continue writing non-compete clauses with impunity.
All of these questions may be moot, of course, because a number of powerful entities with deep pockets have lined up in opposition to the rule. Some of them have even questioned the FTC’s authority to pass the rule at all, on the grounds that Section 5 of the FTC Act does not give it the authority to police labor markets. A lawsuit has already been filed by the US Chamber of Commerce. Other large groups in opposition are the American Medical Group Association, the American Hospital Association, and numerous large hospital and healthcare networks.
Only time will tell whether this issue will be regulated on a national level or remain the purview of each individual state.
Dr. Eastern practices dermatology and dermatologic surgery in Belleville, N.J. He is the author of numerous articles and textbook chapters, and is a longtime monthly columnist for Dermatology News. Write to him at [email protected].
Fluoride, Water, and Kids’ Brains: It’s Complicated
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
I recently looked back at my folder full of these medical study commentaries, this weekly video series we call Impact Factor, and realized that I’ve been doing this for a long time. More than 400 articles, believe it or not.
I’ve learned a lot in that time — about medicine, of course — but also about how people react to certain topics. If you’ve been with me this whole time, or even for just a chunk of it, you’ll know that I tend to take a measured approach to most topics. No one study is ever truly definitive, after all. But regardless of how even-keeled I may be, there are some topics that I just know in advance are going to be a bit divisive: studies about gun control; studies about vitamin D; and, of course, studies about fluoride.
Shall We Shake This Hornet’s Nest?
The fluoridation of the US water system began in 1945 with the goal of reducing cavities in the population. The CDC named water fluoridation one of the 10 great public health achievements of the 20th century, along with such inarguable achievements as the recognition of tobacco as a health hazard.
But fluoridation has never been without its detractors. One problem is that the spectrum of beliefs about the potential harm of fluoridation is huge. On one end, you have science-based concerns such as the recognition that excessive fluoride intake can cause fluorosis and stain tooth enamel. I’ll note that the EPA regulates fluoride levels — there is a fair amount of naturally occurring fluoride in water tables around the world — to prevent this. And, of course, on the other end of the spectrum, you have beliefs that are essentially conspiracy theories: “They” add fluoride to the water supply to control us.
The challenge for me is that when one “side” of a scientific debate includes the crazy theories, it can be hard to discuss that whole spectrum, since there are those who will see evidence of any adverse fluoride effect as confirmation that the conspiracy theory is true.
I can’t help this. So I’ll just say this up front: I am about to tell you about a study that shows some potential risk from fluoride exposure. I will tell you up front that there are some significant caveats to the study that call the results into question. And I will tell you up front that no one is controlling your mind, or my mind, with fluoride; they do it with social media.
Let’s Dive Into These Shark-Infested, Fluoridated Waters
We’re talking about the study, “Maternal Urinary Fluoride and Child Neurobehavior at Age 36 Months,” which appears in JAMA Network Open.
It’s a study of 229 mother-child pairs from the Los Angeles area. The moms had their urinary fluoride level measured once before 30 weeks of gestation. A neurobehavioral battery called the Preschool Child Behavior Checklist was administered to the children at age 36 months.
The main thing you’ll hear about this study — in headlines, Facebook posts, and manifestos locked in drawers somewhere — is the primary result: A 0.68-mg/L increase in urinary fluoride in the mothers, about 25 percentile points, was associated with a doubling of the risk for neurobehavioral problems in their kids when they were 3 years old.
Yikes.
But this is not a randomized trial. Researchers didn’t randomly assign some women to have high fluoride intake and some women to have low fluoride intake. They knew that other factors that might lead to neurobehavioral problems could also lead to higher fluoride intake. They represent these factors in what’s known as a directed acyclic graph, as seen here, and account for them statistically using a regression equation.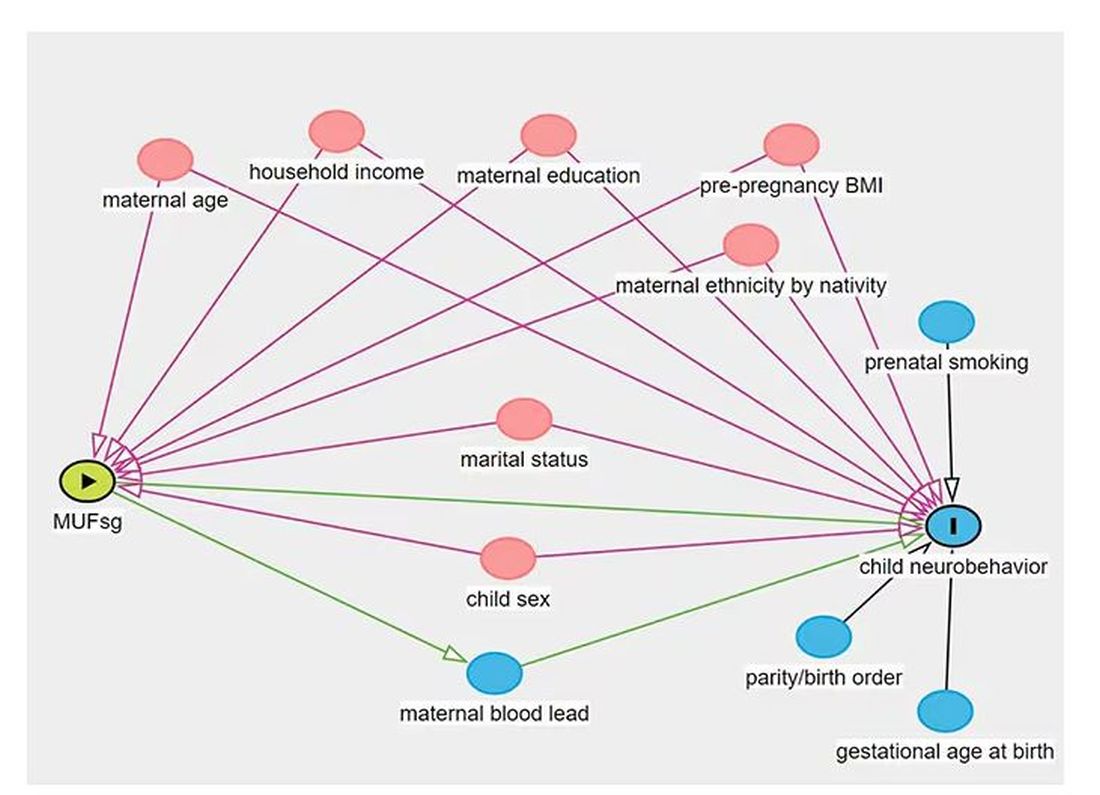
Not represented here are neighborhood characteristics. Los Angeles does not have uniformly fluoridated water, and neurobehavioral problems in kids are strongly linked to stressors in their environments. Fluoride level could be an innocent bystander.
I’m really just describing the classic issue of correlation versus causation here, the bane of all observational research and — let’s be honest — a bit of a crutch that allows us to disregard the results of studies we don’t like, provided the study wasn’t a randomized trial.
But I have a deeper issue with this study than the old “failure to adjust for relevant confounders” thing, as important as that is.
The exposure of interest in this study is maternal urinary fluoride, as measured in a spot sample. It’s not often that I get to go deep on nephrology in this space, but let’s think about that for a second. Let’s assume for a moment that fluoride is toxic to the developing fetal brain, the main concern raised by the results of the study. How would that work? Presumably, mom would be ingesting fluoride from various sources (like the water supply), and that fluoride would get into her blood, and from her blood across the placenta to the baby’s blood, and into the baby’s brain.
Is Urinary Fluoride a Good Measure of Blood Fluoride?
It’s not great. Empirically, we have data that tell us that levels of urine fluoride are not all that similar to levels of serum fluoride. In 2014, a study investigated the correlation between urine and serum fluoride in a cohort of 60 schoolchildren and found a correlation coefficient of around 0.5.
Why isn’t urine fluoride a great proxy for serum fluoride? The most obvious reason is the urine concentration. Human urine concentration can range from about 50 mmol to 1200 mmol (a 24-fold difference) depending on hydration status. Over the course of 24 hours, for example, the amount of fluoride you put out in your urine may be fairly stable in relation to intake, but for a spot urine sample it would be wildly variable. The authors know this, of course, and so they divide the measured urine fluoride by the specific gravity of the urine to give a sort of “dilution adjusted” value. That’s what is actually used in this study. But specific gravity is, itself, an imperfect measure of how dilute the urine is.
This is something that comes up a lot in urinary biomarker research and it’s not that hard to get around. The best thing would be to just measure blood levels of fluoride. The second best option is 24-hour fluoride excretion. After that, the next best thing would be to adjust the spot concentration by other markers of urinary dilution — creatinine or osmolality — as sensitivity analyses. Any of these approaches would lend credence to the results of the study.
Urinary fluoride excretion is pH dependent. The more acidic the urine, the less fluoride is excreted. Many things — including, importantly, diet — affect urine pH. And it is not a stretch to think that diet may also affect the developing fetus. Neither urine pH nor dietary habits were accounted for in this study.
So, here we are. We have an observational study suggesting a harm that may be associated with fluoride. There may be a causal link here, in which case we need further studies to weigh the harm against the more well-established public health benefit. Or, this is all correlation — an illusion created by the limitations of observational data, and the unique challenges of estimating intake from a single urine sample. In other words, this study has something for everyone, fluoride boosters and skeptics alike. Let the arguments begin. But, if possible, leave me out of it.
Dr. Wilson is associate professor of medicine and public health and director of the Clinical and Translational Research Accelerator at Yale University, New Haven, Conn. He has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
I recently looked back at my folder full of these medical study commentaries, this weekly video series we call Impact Factor, and realized that I’ve been doing this for a long time. More than 400 articles, believe it or not.
I’ve learned a lot in that time — about medicine, of course — but also about how people react to certain topics. If you’ve been with me this whole time, or even for just a chunk of it, you’ll know that I tend to take a measured approach to most topics. No one study is ever truly definitive, after all. But regardless of how even-keeled I may be, there are some topics that I just know in advance are going to be a bit divisive: studies about gun control; studies about vitamin D; and, of course, studies about fluoride.
Shall We Shake This Hornet’s Nest?
The fluoridation of the US water system began in 1945 with the goal of reducing cavities in the population. The CDC named water fluoridation one of the 10 great public health achievements of the 20th century, along with such inarguable achievements as the recognition of tobacco as a health hazard.
But fluoridation has never been without its detractors. One problem is that the spectrum of beliefs about the potential harm of fluoridation is huge. On one end, you have science-based concerns such as the recognition that excessive fluoride intake can cause fluorosis and stain tooth enamel. I’ll note that the EPA regulates fluoride levels — there is a fair amount of naturally occurring fluoride in water tables around the world — to prevent this. And, of course, on the other end of the spectrum, you have beliefs that are essentially conspiracy theories: “They” add fluoride to the water supply to control us.
The challenge for me is that when one “side” of a scientific debate includes the crazy theories, it can be hard to discuss that whole spectrum, since there are those who will see evidence of any adverse fluoride effect as confirmation that the conspiracy theory is true.
I can’t help this. So I’ll just say this up front: I am about to tell you about a study that shows some potential risk from fluoride exposure. I will tell you up front that there are some significant caveats to the study that call the results into question. And I will tell you up front that no one is controlling your mind, or my mind, with fluoride; they do it with social media.
Let’s Dive Into These Shark-Infested, Fluoridated Waters
We’re talking about the study, “Maternal Urinary Fluoride and Child Neurobehavior at Age 36 Months,” which appears in JAMA Network Open.
It’s a study of 229 mother-child pairs from the Los Angeles area. The moms had their urinary fluoride level measured once before 30 weeks of gestation. A neurobehavioral battery called the Preschool Child Behavior Checklist was administered to the children at age 36 months.
The main thing you’ll hear about this study — in headlines, Facebook posts, and manifestos locked in drawers somewhere — is the primary result: A 0.68-mg/L increase in urinary fluoride in the mothers, about 25 percentile points, was associated with a doubling of the risk for neurobehavioral problems in their kids when they were 3 years old.
Yikes.
But this is not a randomized trial. Researchers didn’t randomly assign some women to have high fluoride intake and some women to have low fluoride intake. They knew that other factors that might lead to neurobehavioral problems could also lead to higher fluoride intake. They represent these factors in what’s known as a directed acyclic graph, as seen here, and account for them statistically using a regression equation.
Not represented here are neighborhood characteristics. Los Angeles does not have uniformly fluoridated water, and neurobehavioral problems in kids are strongly linked to stressors in their environments. Fluoride level could be an innocent bystander.
I’m really just describing the classic issue of correlation versus causation here, the bane of all observational research and — let’s be honest — a bit of a crutch that allows us to disregard the results of studies we don’t like, provided the study wasn’t a randomized trial.
But I have a deeper issue with this study than the old “failure to adjust for relevant confounders” thing, as important as that is.
The exposure of interest in this study is maternal urinary fluoride, as measured in a spot sample. It’s not often that I get to go deep on nephrology in this space, but let’s think about that for a second. Let’s assume for a moment that fluoride is toxic to the developing fetal brain, the main concern raised by the results of the study. How would that work? Presumably, mom would be ingesting fluoride from various sources (like the water supply), and that fluoride would get into her blood, and from her blood across the placenta to the baby’s blood, and into the baby’s brain.
Is Urinary Fluoride a Good Measure of Blood Fluoride?
It’s not great. Empirically, we have data that tell us that levels of urine fluoride are not all that similar to levels of serum fluoride. In 2014, a study investigated the correlation between urine and serum fluoride in a cohort of 60 schoolchildren and found a correlation coefficient of around 0.5.
Why isn’t urine fluoride a great proxy for serum fluoride? The most obvious reason is the urine concentration. Human urine concentration can range from about 50 mmol to 1200 mmol (a 24-fold difference) depending on hydration status. Over the course of 24 hours, for example, the amount of fluoride you put out in your urine may be fairly stable in relation to intake, but for a spot urine sample it would be wildly variable. The authors know this, of course, and so they divide the measured urine fluoride by the specific gravity of the urine to give a sort of “dilution adjusted” value. That’s what is actually used in this study. But specific gravity is, itself, an imperfect measure of how dilute the urine is.
This is something that comes up a lot in urinary biomarker research and it’s not that hard to get around. The best thing would be to just measure blood levels of fluoride. The second best option is 24-hour fluoride excretion. After that, the next best thing would be to adjust the spot concentration by other markers of urinary dilution — creatinine or osmolality — as sensitivity analyses. Any of these approaches would lend credence to the results of the study.
Urinary fluoride excretion is pH dependent. The more acidic the urine, the less fluoride is excreted. Many things — including, importantly, diet — affect urine pH. And it is not a stretch to think that diet may also affect the developing fetus. Neither urine pH nor dietary habits were accounted for in this study.
So, here we are. We have an observational study suggesting a harm that may be associated with fluoride. There may be a causal link here, in which case we need further studies to weigh the harm against the more well-established public health benefit. Or, this is all correlation — an illusion created by the limitations of observational data, and the unique challenges of estimating intake from a single urine sample. In other words, this study has something for everyone, fluoride boosters and skeptics alike. Let the arguments begin. But, if possible, leave me out of it.
Dr. Wilson is associate professor of medicine and public health and director of the Clinical and Translational Research Accelerator at Yale University, New Haven, Conn. He has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
I recently looked back at my folder full of these medical study commentaries, this weekly video series we call Impact Factor, and realized that I’ve been doing this for a long time. More than 400 articles, believe it or not.
I’ve learned a lot in that time — about medicine, of course — but also about how people react to certain topics. If you’ve been with me this whole time, or even for just a chunk of it, you’ll know that I tend to take a measured approach to most topics. No one study is ever truly definitive, after all. But regardless of how even-keeled I may be, there are some topics that I just know in advance are going to be a bit divisive: studies about gun control; studies about vitamin D; and, of course, studies about fluoride.
Shall We Shake This Hornet’s Nest?
The fluoridation of the US water system began in 1945 with the goal of reducing cavities in the population. The CDC named water fluoridation one of the 10 great public health achievements of the 20th century, along with such inarguable achievements as the recognition of tobacco as a health hazard.
But fluoridation has never been without its detractors. One problem is that the spectrum of beliefs about the potential harm of fluoridation is huge. On one end, you have science-based concerns such as the recognition that excessive fluoride intake can cause fluorosis and stain tooth enamel. I’ll note that the EPA regulates fluoride levels — there is a fair amount of naturally occurring fluoride in water tables around the world — to prevent this. And, of course, on the other end of the spectrum, you have beliefs that are essentially conspiracy theories: “They” add fluoride to the water supply to control us.
The challenge for me is that when one “side” of a scientific debate includes the crazy theories, it can be hard to discuss that whole spectrum, since there are those who will see evidence of any adverse fluoride effect as confirmation that the conspiracy theory is true.
I can’t help this. So I’ll just say this up front: I am about to tell you about a study that shows some potential risk from fluoride exposure. I will tell you up front that there are some significant caveats to the study that call the results into question. And I will tell you up front that no one is controlling your mind, or my mind, with fluoride; they do it with social media.
Let’s Dive Into These Shark-Infested, Fluoridated Waters
We’re talking about the study, “Maternal Urinary Fluoride and Child Neurobehavior at Age 36 Months,” which appears in JAMA Network Open.
It’s a study of 229 mother-child pairs from the Los Angeles area. The moms had their urinary fluoride level measured once before 30 weeks of gestation. A neurobehavioral battery called the Preschool Child Behavior Checklist was administered to the children at age 36 months.
The main thing you’ll hear about this study — in headlines, Facebook posts, and manifestos locked in drawers somewhere — is the primary result: A 0.68-mg/L increase in urinary fluoride in the mothers, about 25 percentile points, was associated with a doubling of the risk for neurobehavioral problems in their kids when they were 3 years old.
Yikes.
But this is not a randomized trial. Researchers didn’t randomly assign some women to have high fluoride intake and some women to have low fluoride intake. They knew that other factors that might lead to neurobehavioral problems could also lead to higher fluoride intake. They represent these factors in what’s known as a directed acyclic graph, as seen here, and account for them statistically using a regression equation.
Not represented here are neighborhood characteristics. Los Angeles does not have uniformly fluoridated water, and neurobehavioral problems in kids are strongly linked to stressors in their environments. Fluoride level could be an innocent bystander.
I’m really just describing the classic issue of correlation versus causation here, the bane of all observational research and — let’s be honest — a bit of a crutch that allows us to disregard the results of studies we don’t like, provided the study wasn’t a randomized trial.
But I have a deeper issue with this study than the old “failure to adjust for relevant confounders” thing, as important as that is.
The exposure of interest in this study is maternal urinary fluoride, as measured in a spot sample. It’s not often that I get to go deep on nephrology in this space, but let’s think about that for a second. Let’s assume for a moment that fluoride is toxic to the developing fetal brain, the main concern raised by the results of the study. How would that work? Presumably, mom would be ingesting fluoride from various sources (like the water supply), and that fluoride would get into her blood, and from her blood across the placenta to the baby’s blood, and into the baby’s brain.
Is Urinary Fluoride a Good Measure of Blood Fluoride?
It’s not great. Empirically, we have data that tell us that levels of urine fluoride are not all that similar to levels of serum fluoride. In 2014, a study investigated the correlation between urine and serum fluoride in a cohort of 60 schoolchildren and found a correlation coefficient of around 0.5.
Why isn’t urine fluoride a great proxy for serum fluoride? The most obvious reason is the urine concentration. Human urine concentration can range from about 50 mmol to 1200 mmol (a 24-fold difference) depending on hydration status. Over the course of 24 hours, for example, the amount of fluoride you put out in your urine may be fairly stable in relation to intake, but for a spot urine sample it would be wildly variable. The authors know this, of course, and so they divide the measured urine fluoride by the specific gravity of the urine to give a sort of “dilution adjusted” value. That’s what is actually used in this study. But specific gravity is, itself, an imperfect measure of how dilute the urine is.
This is something that comes up a lot in urinary biomarker research and it’s not that hard to get around. The best thing would be to just measure blood levels of fluoride. The second best option is 24-hour fluoride excretion. After that, the next best thing would be to adjust the spot concentration by other markers of urinary dilution — creatinine or osmolality — as sensitivity analyses. Any of these approaches would lend credence to the results of the study.
Urinary fluoride excretion is pH dependent. The more acidic the urine, the less fluoride is excreted. Many things — including, importantly, diet — affect urine pH. And it is not a stretch to think that diet may also affect the developing fetus. Neither urine pH nor dietary habits were accounted for in this study.
So, here we are. We have an observational study suggesting a harm that may be associated with fluoride. There may be a causal link here, in which case we need further studies to weigh the harm against the more well-established public health benefit. Or, this is all correlation — an illusion created by the limitations of observational data, and the unique challenges of estimating intake from a single urine sample. In other words, this study has something for everyone, fluoride boosters and skeptics alike. Let the arguments begin. But, if possible, leave me out of it.
Dr. Wilson is associate professor of medicine and public health and director of the Clinical and Translational Research Accelerator at Yale University, New Haven, Conn. He has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Recent Evidence for Home Phototherapy Benefits May Improve Access for Patients with Psoriasis
Supporters of home phototherapy for patients with plaque and guttate psoriasis had plenty to cheer about at the annual meeting of the American Academy of Dermatology (AAD) in March. There, Joel M. Gelfand, MD, professor of dermatology and epidemiology at the University of Pennsylvania in Philadelphia, presented results from the LITE study, a trial that tested the hypothesis that narrowband ultraviolet B phototherapy of psoriasis at home is noninferior to office treatment, based on outcomes that matter to patients, clinicians, and payers. While smaller studies have drawn similar conclusions,
The co-primary outcomes in the LITE study were a Physician’s Global Assessment (PGA) score of 0/1 (clear, almost clear) and a Dermatology Life Quality Index (DLQI) score of 5 or less (small, no effect on health-related quality of life).
Dr. Gelfand and colleagues at 42 sites in the United States enrolled 783 patients aged 12 years and older who had plaque or guttate psoriasis and were candidates for phototherapy at home or in an office setting. Following 12 weeks of treatment, 25.6% of patients in the office-based phototherapy group achieved a PGA score of 0/1 compared with 32.8% of patients in the home-based phototherapy group (P > .0001 for noninferiority, non-response imputation for missing data). Similarly, 33.6% of patients in the office-based phototherapy group achieved a DLQI score of 5 or less compared with 52.4% of patients in the home-based phototherapy group (P > .0001 for noninferiority, non-response imputation for missing data).
A Safe and Effective Option
“I think that it’s important for physicians, insurance companies, and patients with psoriasis to understand that this is a very safe and effective form of therapy,” Craig A. Elmets, MD, professor of dermatology at The University of Alabama at Birmingham, said in an interview. “For people who are not interested in systemic medications or who have contraindications to systemic medications, phototherapy would be ideal,” added Dr. Elmets, first author of the joint AAD–National Psoriasis Foundation (NPF) guidelines for the management and treatment of psoriasis with phototherapy, published in 2019.
Factors beyond efficacy support the role of home phototherapy, Dr. Gelfand said, including the fact that it costs 10-100 times less than biologics for psoriasis and that office-based phototherapy is not available in 90% of counties in the United States. However, insurance coverage of home phototherapy “is highly variable because until the LITE study, there was no large-scale US data to support its use,” he told this news organization.
“Also, insurance companies are broken up into two parts: Durable medical goods and the medical side such as pharmacy costs, and they are siloed. The durable medical goods side views phototherapy as expensive, while the pharmacy side views it as dirt cheap. This is part of the problem with our health system. A lot of things are siloed and don’t make any sense,” said Dr. Gelfand, director of the Psoriasis and Phototherapy Treatment Center at the University of Pennsylvania. By working with the NPF and payers, he added, “we’re hoping ... to transform the way insurance companies think about covering home phototherapy.”
In the meantime, he and Dr. Elmets shared practical ways to optimize access to home phototherapy for psoriasis patients:
Have the discussion. Patients “rarely bring this up as an option,” Dr. Elmets said, so the onus is on clinicians to talk about it. In his view, the ideal candidate “is averse to using systemic agents but whose disease is beyond the point where topical medicines alone will work. One of the advantages of phototherapy is that it doesn’t have immunosuppressive effects.”
Clinicians and patients can learn about the efficacy and safety of phototherapy for psoriasis, including home-based options, on the NPF’s web site and by reading the 2019 joint AAD-NPF guidelines.
Shared decision-making is key. “When a patient comes in, I’ll discuss what their treatment options are and [we] will decide upon a course of action based on their unique needs and preferences [and] if it’s medically appropriate, meaning they have the type of psoriasis likely to respond to phototherapy,” Dr. Gelfand said. A patient with psoriasis mainly on the fingernails or genitals “is not a good candidate for phototherapy. If it’s on the trunk or extremities, that patient would be a good candidate.”
Home phototherapy candidates also must be willing and able to operate a machine and have dedicated space in their dwelling for it (most units are about the size of a door). Patients also have to be reliable, follow directions, and come back in person for follow-up appointments “so we can assess their response to treatment and fine-tune things as necessary and make sure they’re not developing any skin damage,” Dr. Gelfand said.
Educate yourself about existing options. Home phototherapy units from manufacturers such as Daavlin, National Biological Corporation, and SolRx range between $1200 and $6000 in cost, Dr. Gelfand said. He and his colleagues used the Daavlin 7 series in the LITE study. That unit features an integrated dosimetry system that delivers the correct dose of energy based on parameters that the prescribing clinician recommends. Settings are based on the patient’s skin type and how much the prescriber wants to increase the dose for each treatment. “The machine does the rest,” he said. “It knows what dose to give, so they get the same dosing as they would in an office situation.”
Smaller home-based phototherapy units designed to treat the hands and feet are available. So are handheld units to treat the scalp. “These can be a nice option for patients who have a few spots, but if the disease is moderate to severe, then it’s going to be pretty laborious to [use them],” Dr. Elmets said.
Remember that phototherapy is not a cure-all. According to the joint AAD-NPF guidelines, most phototherapy regimens require treatments two to three times per week for 10-14 weeks. Once patients achieve their home phototherapy treatment goal, Dr. Elmets often recommends treatments one to two times per week for maintenance.
“Patients with psoriasis have a lifetime condition,” he noted. “There are certainly cases where people have gone on phototherapy, cleared, and then stopped for a period of time. If they flare up, they can always go back to phototherapy. Usually, people who are on phototherapy use some type of topical agents to touch up areas that are resistant.”
Expect pushback from insurers on coverage. While Medicare and some integrated health plans cover home phototherapy, expect to spend time writing letters or placing phone calls to insurance companies to convince them why they should cover home phototherapy for candidate psoriasis patients. “Usually there’s a lot of letter writing and a long delay in getting approval,” Dr. Elmets said.
Dr. Elmets and Dr. Gelfand reported no relevant financial relationships. The LITE study was funded by the Patient-Centered Outcomes Research Institute. Research partners included the National Psoriasis Foundation and Daavlin, which provided the home phototherapy machines and covered the cost of shipping the devices.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Supporters of home phototherapy for patients with plaque and guttate psoriasis had plenty to cheer about at the annual meeting of the American Academy of Dermatology (AAD) in March. There, Joel M. Gelfand, MD, professor of dermatology and epidemiology at the University of Pennsylvania in Philadelphia, presented results from the LITE study, a trial that tested the hypothesis that narrowband ultraviolet B phototherapy of psoriasis at home is noninferior to office treatment, based on outcomes that matter to patients, clinicians, and payers. While smaller studies have drawn similar conclusions,
The co-primary outcomes in the LITE study were a Physician’s Global Assessment (PGA) score of 0/1 (clear, almost clear) and a Dermatology Life Quality Index (DLQI) score of 5 or less (small, no effect on health-related quality of life).
Dr. Gelfand and colleagues at 42 sites in the United States enrolled 783 patients aged 12 years and older who had plaque or guttate psoriasis and were candidates for phototherapy at home or in an office setting. Following 12 weeks of treatment, 25.6% of patients in the office-based phototherapy group achieved a PGA score of 0/1 compared with 32.8% of patients in the home-based phototherapy group (P > .0001 for noninferiority, non-response imputation for missing data). Similarly, 33.6% of patients in the office-based phototherapy group achieved a DLQI score of 5 or less compared with 52.4% of patients in the home-based phototherapy group (P > .0001 for noninferiority, non-response imputation for missing data).
A Safe and Effective Option
“I think that it’s important for physicians, insurance companies, and patients with psoriasis to understand that this is a very safe and effective form of therapy,” Craig A. Elmets, MD, professor of dermatology at The University of Alabama at Birmingham, said in an interview. “For people who are not interested in systemic medications or who have contraindications to systemic medications, phototherapy would be ideal,” added Dr. Elmets, first author of the joint AAD–National Psoriasis Foundation (NPF) guidelines for the management and treatment of psoriasis with phototherapy, published in 2019.
Factors beyond efficacy support the role of home phototherapy, Dr. Gelfand said, including the fact that it costs 10-100 times less than biologics for psoriasis and that office-based phototherapy is not available in 90% of counties in the United States. However, insurance coverage of home phototherapy “is highly variable because until the LITE study, there was no large-scale US data to support its use,” he told this news organization.
“Also, insurance companies are broken up into two parts: Durable medical goods and the medical side such as pharmacy costs, and they are siloed. The durable medical goods side views phototherapy as expensive, while the pharmacy side views it as dirt cheap. This is part of the problem with our health system. A lot of things are siloed and don’t make any sense,” said Dr. Gelfand, director of the Psoriasis and Phototherapy Treatment Center at the University of Pennsylvania. By working with the NPF and payers, he added, “we’re hoping ... to transform the way insurance companies think about covering home phototherapy.”
In the meantime, he and Dr. Elmets shared practical ways to optimize access to home phototherapy for psoriasis patients:
Have the discussion. Patients “rarely bring this up as an option,” Dr. Elmets said, so the onus is on clinicians to talk about it. In his view, the ideal candidate “is averse to using systemic agents but whose disease is beyond the point where topical medicines alone will work. One of the advantages of phototherapy is that it doesn’t have immunosuppressive effects.”
Clinicians and patients can learn about the efficacy and safety of phototherapy for psoriasis, including home-based options, on the NPF’s web site and by reading the 2019 joint AAD-NPF guidelines.
Shared decision-making is key. “When a patient comes in, I’ll discuss what their treatment options are and [we] will decide upon a course of action based on their unique needs and preferences [and] if it’s medically appropriate, meaning they have the type of psoriasis likely to respond to phototherapy,” Dr. Gelfand said. A patient with psoriasis mainly on the fingernails or genitals “is not a good candidate for phototherapy. If it’s on the trunk or extremities, that patient would be a good candidate.”
Home phototherapy candidates also must be willing and able to operate a machine and have dedicated space in their dwelling for it (most units are about the size of a door). Patients also have to be reliable, follow directions, and come back in person for follow-up appointments “so we can assess their response to treatment and fine-tune things as necessary and make sure they’re not developing any skin damage,” Dr. Gelfand said.
Educate yourself about existing options. Home phototherapy units from manufacturers such as Daavlin, National Biological Corporation, and SolRx range between $1200 and $6000 in cost, Dr. Gelfand said. He and his colleagues used the Daavlin 7 series in the LITE study. That unit features an integrated dosimetry system that delivers the correct dose of energy based on parameters that the prescribing clinician recommends. Settings are based on the patient’s skin type and how much the prescriber wants to increase the dose for each treatment. “The machine does the rest,” he said. “It knows what dose to give, so they get the same dosing as they would in an office situation.”
Smaller home-based phototherapy units designed to treat the hands and feet are available. So are handheld units to treat the scalp. “These can be a nice option for patients who have a few spots, but if the disease is moderate to severe, then it’s going to be pretty laborious to [use them],” Dr. Elmets said.
Remember that phototherapy is not a cure-all. According to the joint AAD-NPF guidelines, most phototherapy regimens require treatments two to three times per week for 10-14 weeks. Once patients achieve their home phototherapy treatment goal, Dr. Elmets often recommends treatments one to two times per week for maintenance.
“Patients with psoriasis have a lifetime condition,” he noted. “There are certainly cases where people have gone on phototherapy, cleared, and then stopped for a period of time. If they flare up, they can always go back to phototherapy. Usually, people who are on phototherapy use some type of topical agents to touch up areas that are resistant.”
Expect pushback from insurers on coverage. While Medicare and some integrated health plans cover home phototherapy, expect to spend time writing letters or placing phone calls to insurance companies to convince them why they should cover home phototherapy for candidate psoriasis patients. “Usually there’s a lot of letter writing and a long delay in getting approval,” Dr. Elmets said.
Dr. Elmets and Dr. Gelfand reported no relevant financial relationships. The LITE study was funded by the Patient-Centered Outcomes Research Institute. Research partners included the National Psoriasis Foundation and Daavlin, which provided the home phototherapy machines and covered the cost of shipping the devices.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Supporters of home phototherapy for patients with plaque and guttate psoriasis had plenty to cheer about at the annual meeting of the American Academy of Dermatology (AAD) in March. There, Joel M. Gelfand, MD, professor of dermatology and epidemiology at the University of Pennsylvania in Philadelphia, presented results from the LITE study, a trial that tested the hypothesis that narrowband ultraviolet B phototherapy of psoriasis at home is noninferior to office treatment, based on outcomes that matter to patients, clinicians, and payers. While smaller studies have drawn similar conclusions,
The co-primary outcomes in the LITE study were a Physician’s Global Assessment (PGA) score of 0/1 (clear, almost clear) and a Dermatology Life Quality Index (DLQI) score of 5 or less (small, no effect on health-related quality of life).
Dr. Gelfand and colleagues at 42 sites in the United States enrolled 783 patients aged 12 years and older who had plaque or guttate psoriasis and were candidates for phototherapy at home or in an office setting. Following 12 weeks of treatment, 25.6% of patients in the office-based phototherapy group achieved a PGA score of 0/1 compared with 32.8% of patients in the home-based phototherapy group (P > .0001 for noninferiority, non-response imputation for missing data). Similarly, 33.6% of patients in the office-based phototherapy group achieved a DLQI score of 5 or less compared with 52.4% of patients in the home-based phototherapy group (P > .0001 for noninferiority, non-response imputation for missing data).
A Safe and Effective Option
“I think that it’s important for physicians, insurance companies, and patients with psoriasis to understand that this is a very safe and effective form of therapy,” Craig A. Elmets, MD, professor of dermatology at The University of Alabama at Birmingham, said in an interview. “For people who are not interested in systemic medications or who have contraindications to systemic medications, phototherapy would be ideal,” added Dr. Elmets, first author of the joint AAD–National Psoriasis Foundation (NPF) guidelines for the management and treatment of psoriasis with phototherapy, published in 2019.
Factors beyond efficacy support the role of home phototherapy, Dr. Gelfand said, including the fact that it costs 10-100 times less than biologics for psoriasis and that office-based phototherapy is not available in 90% of counties in the United States. However, insurance coverage of home phototherapy “is highly variable because until the LITE study, there was no large-scale US data to support its use,” he told this news organization.
“Also, insurance companies are broken up into two parts: Durable medical goods and the medical side such as pharmacy costs, and they are siloed. The durable medical goods side views phototherapy as expensive, while the pharmacy side views it as dirt cheap. This is part of the problem with our health system. A lot of things are siloed and don’t make any sense,” said Dr. Gelfand, director of the Psoriasis and Phototherapy Treatment Center at the University of Pennsylvania. By working with the NPF and payers, he added, “we’re hoping ... to transform the way insurance companies think about covering home phototherapy.”
In the meantime, he and Dr. Elmets shared practical ways to optimize access to home phototherapy for psoriasis patients:
Have the discussion. Patients “rarely bring this up as an option,” Dr. Elmets said, so the onus is on clinicians to talk about it. In his view, the ideal candidate “is averse to using systemic agents but whose disease is beyond the point where topical medicines alone will work. One of the advantages of phototherapy is that it doesn’t have immunosuppressive effects.”
Clinicians and patients can learn about the efficacy and safety of phototherapy for psoriasis, including home-based options, on the NPF’s web site and by reading the 2019 joint AAD-NPF guidelines.
Shared decision-making is key. “When a patient comes in, I’ll discuss what their treatment options are and [we] will decide upon a course of action based on their unique needs and preferences [and] if it’s medically appropriate, meaning they have the type of psoriasis likely to respond to phototherapy,” Dr. Gelfand said. A patient with psoriasis mainly on the fingernails or genitals “is not a good candidate for phototherapy. If it’s on the trunk or extremities, that patient would be a good candidate.”
Home phototherapy candidates also must be willing and able to operate a machine and have dedicated space in their dwelling for it (most units are about the size of a door). Patients also have to be reliable, follow directions, and come back in person for follow-up appointments “so we can assess their response to treatment and fine-tune things as necessary and make sure they’re not developing any skin damage,” Dr. Gelfand said.
Educate yourself about existing options. Home phototherapy units from manufacturers such as Daavlin, National Biological Corporation, and SolRx range between $1200 and $6000 in cost, Dr. Gelfand said. He and his colleagues used the Daavlin 7 series in the LITE study. That unit features an integrated dosimetry system that delivers the correct dose of energy based on parameters that the prescribing clinician recommends. Settings are based on the patient’s skin type and how much the prescriber wants to increase the dose for each treatment. “The machine does the rest,” he said. “It knows what dose to give, so they get the same dosing as they would in an office situation.”
Smaller home-based phototherapy units designed to treat the hands and feet are available. So are handheld units to treat the scalp. “These can be a nice option for patients who have a few spots, but if the disease is moderate to severe, then it’s going to be pretty laborious to [use them],” Dr. Elmets said.
Remember that phototherapy is not a cure-all. According to the joint AAD-NPF guidelines, most phototherapy regimens require treatments two to three times per week for 10-14 weeks. Once patients achieve their home phototherapy treatment goal, Dr. Elmets often recommends treatments one to two times per week for maintenance.
“Patients with psoriasis have a lifetime condition,” he noted. “There are certainly cases where people have gone on phototherapy, cleared, and then stopped for a period of time. If they flare up, they can always go back to phototherapy. Usually, people who are on phototherapy use some type of topical agents to touch up areas that are resistant.”
Expect pushback from insurers on coverage. While Medicare and some integrated health plans cover home phototherapy, expect to spend time writing letters or placing phone calls to insurance companies to convince them why they should cover home phototherapy for candidate psoriasis patients. “Usually there’s a lot of letter writing and a long delay in getting approval,” Dr. Elmets said.
Dr. Elmets and Dr. Gelfand reported no relevant financial relationships. The LITE study was funded by the Patient-Centered Outcomes Research Institute. Research partners included the National Psoriasis Foundation and Daavlin, which provided the home phototherapy machines and covered the cost of shipping the devices.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Belimumab Autoinjector Approved for Pediatric Lupus
The US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has approved Benlysta (belimumab) autoinjector for patients aged 5 years or older with active systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) on standard therapy. This is the first time that children with SLE can receive this treatment at home, according to a GSK press release.
Prior to this approval, pediatric patients aged 5 years or older could receive belimumab only intravenously via a 1-hour infusion in a hospital or clinic setting.
“Going to the doctor’s office once every 4 weeks can be a logistical hurdle for some children and their caregivers, so having the option to administer Benlysta in the comfort of their home provides much-needed flexibility,” Mary Crimmings, the interim CEO and senior vice president for marketing and communications at the Lupus Foundation of America, said in a statement.
An estimated 5000-10,000 children in the United States are living with SLE.
Belimumab is a B-lymphocyte stimulator–specific inhibitor approved for the treatment of active SLE and active lupus nephritis in patients aged 5 years or older receiving standard therapy. This approval of the subcutaneous administration of belimumab applies only to pediatric patients with SLE.
The 200-mg injection can be administered once every week for children who weigh ≥ 40 kg and should be given once every 2 weeks for children weighing between 15 and 40 kg.
The autoinjector “will be available immediately” for caregivers, the company announcement said.
“Patients are our top priority, and we are always working to innovate solutions that can improve lives and address unmet needs,” Court Horncastle, senior vice president and head of US specialty at GSK, said in the press release. “This approval for an at-home treatment is the first and only of its kind for children with lupus and is a testament to our continued commitment to the lupus community.”
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
The US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has approved Benlysta (belimumab) autoinjector for patients aged 5 years or older with active systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) on standard therapy. This is the first time that children with SLE can receive this treatment at home, according to a GSK press release.
Prior to this approval, pediatric patients aged 5 years or older could receive belimumab only intravenously via a 1-hour infusion in a hospital or clinic setting.
“Going to the doctor’s office once every 4 weeks can be a logistical hurdle for some children and their caregivers, so having the option to administer Benlysta in the comfort of their home provides much-needed flexibility,” Mary Crimmings, the interim CEO and senior vice president for marketing and communications at the Lupus Foundation of America, said in a statement.
An estimated 5000-10,000 children in the United States are living with SLE.
Belimumab is a B-lymphocyte stimulator–specific inhibitor approved for the treatment of active SLE and active lupus nephritis in patients aged 5 years or older receiving standard therapy. This approval of the subcutaneous administration of belimumab applies only to pediatric patients with SLE.
The 200-mg injection can be administered once every week for children who weigh ≥ 40 kg and should be given once every 2 weeks for children weighing between 15 and 40 kg.
The autoinjector “will be available immediately” for caregivers, the company announcement said.
“Patients are our top priority, and we are always working to innovate solutions that can improve lives and address unmet needs,” Court Horncastle, senior vice president and head of US specialty at GSK, said in the press release. “This approval for an at-home treatment is the first and only of its kind for children with lupus and is a testament to our continued commitment to the lupus community.”
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
The US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has approved Benlysta (belimumab) autoinjector for patients aged 5 years or older with active systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) on standard therapy. This is the first time that children with SLE can receive this treatment at home, according to a GSK press release.
Prior to this approval, pediatric patients aged 5 years or older could receive belimumab only intravenously via a 1-hour infusion in a hospital or clinic setting.
“Going to the doctor’s office once every 4 weeks can be a logistical hurdle for some children and their caregivers, so having the option to administer Benlysta in the comfort of their home provides much-needed flexibility,” Mary Crimmings, the interim CEO and senior vice president for marketing and communications at the Lupus Foundation of America, said in a statement.
An estimated 5000-10,000 children in the United States are living with SLE.
Belimumab is a B-lymphocyte stimulator–specific inhibitor approved for the treatment of active SLE and active lupus nephritis in patients aged 5 years or older receiving standard therapy. This approval of the subcutaneous administration of belimumab applies only to pediatric patients with SLE.
The 200-mg injection can be administered once every week for children who weigh ≥ 40 kg and should be given once every 2 weeks for children weighing between 15 and 40 kg.
The autoinjector “will be available immediately” for caregivers, the company announcement said.
“Patients are our top priority, and we are always working to innovate solutions that can improve lives and address unmet needs,” Court Horncastle, senior vice president and head of US specialty at GSK, said in the press release. “This approval for an at-home treatment is the first and only of its kind for children with lupus and is a testament to our continued commitment to the lupus community.”
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.




