User login
Bringing you the latest news, research and reviews, exclusive interviews, podcasts, quizzes, and more.
div[contains(@class, 'read-next-article')]
div[contains(@class, 'nav-primary')]
nav[contains(@class, 'nav-primary')]
section[contains(@class, 'footer-nav-section-wrapper')]
nav[contains(@class, 'nav-ce-stack nav-ce-stack__large-screen')]
header[@id='header']
div[contains(@class, 'header__large-screen')]
div[contains(@class, 'main-prefix')]
footer[@id='footer']
section[contains(@class, 'nav-hidden')]
div[contains(@class, 'ce-card-content')]
nav[contains(@class, 'nav-ce-stack')]
div[contains(@class, 'view-medstat-quiz-listing-panes')]
The hateful patient
A 64-year-old White woman with very few medical problems complains of bug bites. She had seen no bugs and had no visible bites. There is no rash. “So what bit me?” she asked, pulling her mask down for emphasis. How should I know? I thought, but didn’t say. She and I have been through this many times.
Before I could respond, she filled the pause with her usual complaints including how hard it is to get an appointment with me and how every appointment with me is a waste of her time. Ignoring the contradistinction of her charges, I took some satisfaction realizing she has just given me a topic to write about: The hateful patient.
They are frustrating, troublesome, rude, sometimes racist, misogynistic, depressing, hopeless, and disheartening. They call you, email you, and come to see you just to annoy you (so it seems). And they’re everywhere. According to one study, nearly one in six are “difficult patients.” It feels like more lately because the vaccine has brought haters back into clinic, just to get us.
But hateful patients aren’t new. In 1978, James E. Groves, MD, a Harvard psychiatrist, wrote a now-classic New England Journal of Medicine article about them called: Taking Care of the Hateful Patient. Even Osler, back in 1889, covered these patients in his lecture to University of Pennsylvania students, advising us to “deal gently with this deliciously credulous old human nature in which we work ... restrain your indignation.” But like much of Osler’s advice, it is easier said than done.
Dr. Groves is more helpful, and presents a model to understand them. Difficult patients, as we’d now call them, fall into four stereotypes: dependent clingers, entitled demanders, manipulative help-rejectors, and self-destructive deniers. It’s Dr. Groves’s bottom line I found insightful. He says that, when patients create negative feelings in us, we’re more likely to make errors. He then gives sound advice: Set firm boundaries and learn to counter the countertransference these patients provoke. Don’t disavow or discharge, Dr. Groves advises, redirect these emotions to motivate you to dig deeper. There you’ll find clinical data that will facilitate understanding and enable better patient management. Yes, easier said.
In addition to Dr. Groves’s analysis of how we harm these patients, I’d add that these disagreeable, malingering patients also harm us doctors. The hangover from a difficult patient encounter can linger for several appointments later or, worse, carryover to home. And now with patient emails proliferating, demanding patients behave as if we have an inexhaustible ability to engage them. We don’t. Many physicians are struggling to care at all; their low empathy battery warnings are blinking red, less than 1% remaining.
What is toxic to us doctors is the maelstrom of cognitive dissonance these patients create in us. Have you ever felt relief to learn a difficult patient has “finally” died? How could we think such a thing?! Didn’t we choose medicine instead of Wall Street because we care about people? But manipulative patients can make us care less. We even use secret language with each other to protect ourselves from them, those GOMERs (get out of my emergency room), bouncebacks, patients with status dramaticus, and those ornery FTDs (failure to die). Save yourself, we say to each other, this patient will kill you.
Caring for my somatizing 64-year-old patient has been difficult, but writing this has helped me reframe our interaction. Unsurprisingly, at the end of her failed visit she asked when she could see me again. “I need to schedule now because I have to find a neighbor to watch my dogs. It takes two buses to come here and I can’t take them with me.” Ah, there’s the clinical data Dr. Groves said I’d find – she’s not here to hurt me, she’s here because I’m all she’s got. At least for this difficult patient, I have a plan. At the bottom of my note I type “RTC 3 mo.”
Dr. Benabio is director of healthcare transformation and chief of dermatology at Kaiser Permanente San Diego. The opinions expressed in this column are his own and do not represent those of Kaiser Permanente. Dr. Benabio is @Dermdoc on Twitter. Write to him at [email protected].
A 64-year-old White woman with very few medical problems complains of bug bites. She had seen no bugs and had no visible bites. There is no rash. “So what bit me?” she asked, pulling her mask down for emphasis. How should I know? I thought, but didn’t say. She and I have been through this many times.
Before I could respond, she filled the pause with her usual complaints including how hard it is to get an appointment with me and how every appointment with me is a waste of her time. Ignoring the contradistinction of her charges, I took some satisfaction realizing she has just given me a topic to write about: The hateful patient.
They are frustrating, troublesome, rude, sometimes racist, misogynistic, depressing, hopeless, and disheartening. They call you, email you, and come to see you just to annoy you (so it seems). And they’re everywhere. According to one study, nearly one in six are “difficult patients.” It feels like more lately because the vaccine has brought haters back into clinic, just to get us.
But hateful patients aren’t new. In 1978, James E. Groves, MD, a Harvard psychiatrist, wrote a now-classic New England Journal of Medicine article about them called: Taking Care of the Hateful Patient. Even Osler, back in 1889, covered these patients in his lecture to University of Pennsylvania students, advising us to “deal gently with this deliciously credulous old human nature in which we work ... restrain your indignation.” But like much of Osler’s advice, it is easier said than done.
Dr. Groves is more helpful, and presents a model to understand them. Difficult patients, as we’d now call them, fall into four stereotypes: dependent clingers, entitled demanders, manipulative help-rejectors, and self-destructive deniers. It’s Dr. Groves’s bottom line I found insightful. He says that, when patients create negative feelings in us, we’re more likely to make errors. He then gives sound advice: Set firm boundaries and learn to counter the countertransference these patients provoke. Don’t disavow or discharge, Dr. Groves advises, redirect these emotions to motivate you to dig deeper. There you’ll find clinical data that will facilitate understanding and enable better patient management. Yes, easier said.
In addition to Dr. Groves’s analysis of how we harm these patients, I’d add that these disagreeable, malingering patients also harm us doctors. The hangover from a difficult patient encounter can linger for several appointments later or, worse, carryover to home. And now with patient emails proliferating, demanding patients behave as if we have an inexhaustible ability to engage them. We don’t. Many physicians are struggling to care at all; their low empathy battery warnings are blinking red, less than 1% remaining.
What is toxic to us doctors is the maelstrom of cognitive dissonance these patients create in us. Have you ever felt relief to learn a difficult patient has “finally” died? How could we think such a thing?! Didn’t we choose medicine instead of Wall Street because we care about people? But manipulative patients can make us care less. We even use secret language with each other to protect ourselves from them, those GOMERs (get out of my emergency room), bouncebacks, patients with status dramaticus, and those ornery FTDs (failure to die). Save yourself, we say to each other, this patient will kill you.
Caring for my somatizing 64-year-old patient has been difficult, but writing this has helped me reframe our interaction. Unsurprisingly, at the end of her failed visit she asked when she could see me again. “I need to schedule now because I have to find a neighbor to watch my dogs. It takes two buses to come here and I can’t take them with me.” Ah, there’s the clinical data Dr. Groves said I’d find – she’s not here to hurt me, she’s here because I’m all she’s got. At least for this difficult patient, I have a plan. At the bottom of my note I type “RTC 3 mo.”
Dr. Benabio is director of healthcare transformation and chief of dermatology at Kaiser Permanente San Diego. The opinions expressed in this column are his own and do not represent those of Kaiser Permanente. Dr. Benabio is @Dermdoc on Twitter. Write to him at [email protected].
A 64-year-old White woman with very few medical problems complains of bug bites. She had seen no bugs and had no visible bites. There is no rash. “So what bit me?” she asked, pulling her mask down for emphasis. How should I know? I thought, but didn’t say. She and I have been through this many times.
Before I could respond, she filled the pause with her usual complaints including how hard it is to get an appointment with me and how every appointment with me is a waste of her time. Ignoring the contradistinction of her charges, I took some satisfaction realizing she has just given me a topic to write about: The hateful patient.
They are frustrating, troublesome, rude, sometimes racist, misogynistic, depressing, hopeless, and disheartening. They call you, email you, and come to see you just to annoy you (so it seems). And they’re everywhere. According to one study, nearly one in six are “difficult patients.” It feels like more lately because the vaccine has brought haters back into clinic, just to get us.
But hateful patients aren’t new. In 1978, James E. Groves, MD, a Harvard psychiatrist, wrote a now-classic New England Journal of Medicine article about them called: Taking Care of the Hateful Patient. Even Osler, back in 1889, covered these patients in his lecture to University of Pennsylvania students, advising us to “deal gently with this deliciously credulous old human nature in which we work ... restrain your indignation.” But like much of Osler’s advice, it is easier said than done.
Dr. Groves is more helpful, and presents a model to understand them. Difficult patients, as we’d now call them, fall into four stereotypes: dependent clingers, entitled demanders, manipulative help-rejectors, and self-destructive deniers. It’s Dr. Groves’s bottom line I found insightful. He says that, when patients create negative feelings in us, we’re more likely to make errors. He then gives sound advice: Set firm boundaries and learn to counter the countertransference these patients provoke. Don’t disavow or discharge, Dr. Groves advises, redirect these emotions to motivate you to dig deeper. There you’ll find clinical data that will facilitate understanding and enable better patient management. Yes, easier said.
In addition to Dr. Groves’s analysis of how we harm these patients, I’d add that these disagreeable, malingering patients also harm us doctors. The hangover from a difficult patient encounter can linger for several appointments later or, worse, carryover to home. And now with patient emails proliferating, demanding patients behave as if we have an inexhaustible ability to engage them. We don’t. Many physicians are struggling to care at all; their low empathy battery warnings are blinking red, less than 1% remaining.
What is toxic to us doctors is the maelstrom of cognitive dissonance these patients create in us. Have you ever felt relief to learn a difficult patient has “finally” died? How could we think such a thing?! Didn’t we choose medicine instead of Wall Street because we care about people? But manipulative patients can make us care less. We even use secret language with each other to protect ourselves from them, those GOMERs (get out of my emergency room), bouncebacks, patients with status dramaticus, and those ornery FTDs (failure to die). Save yourself, we say to each other, this patient will kill you.
Caring for my somatizing 64-year-old patient has been difficult, but writing this has helped me reframe our interaction. Unsurprisingly, at the end of her failed visit she asked when she could see me again. “I need to schedule now because I have to find a neighbor to watch my dogs. It takes two buses to come here and I can’t take them with me.” Ah, there’s the clinical data Dr. Groves said I’d find – she’s not here to hurt me, she’s here because I’m all she’s got. At least for this difficult patient, I have a plan. At the bottom of my note I type “RTC 3 mo.”
Dr. Benabio is director of healthcare transformation and chief of dermatology at Kaiser Permanente San Diego. The opinions expressed in this column are his own and do not represent those of Kaiser Permanente. Dr. Benabio is @Dermdoc on Twitter. Write to him at [email protected].
FDA OKs stimulation device for anxiety in depression
The U.S. Food and Drug Administration has expanded the indication for the noninvasive BrainsWay Deep Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation (Deep TMS) System to include treatment of comorbid anxiety symptoms in adult patients with depression, the company has announced.
As reported by this news organization, the neurostimulation system has previously received FDA approval for treatment-resistant major depression, obsessive-compulsive disorder, and smoking addiction.
In the August 18 announcement, BrainsWay reported that it has also received 510(k) clearance from the FDA to market its TMS system for the reduction of anxious depression symptoms.
“This clearance is confirmation of what many have believed anecdotally for years – that Deep TMS is a unique form of therapy that can address comorbid anxiety symptoms using the same depression treatment protocol,” Aron Tendler, MD, chief medical officer at BrainsWay, said in a press release.
‘Consistent, robust’ effect
, which included both randomized controlled trials and open-label studies.
“The data demonstrated a treatment effect that was consistent, robust, and clinically meaningful for decreasing anxiety symptoms in adult patients suffering from major depressive disorder [MDD],” the company said in its release.
Data from three of the randomized trials showed an effect size of 0.3 when compared with a sham device and an effect size of 0.9 when compared with medication. The overall, weighted, pooled effect size was 0.55.
The company noted that in more than 70 published studies with about 16,000 total participants, effect sizes have ranged from 0.2-0.37 for drug-based anxiety treatments.
“The expanded FDA labeling now allows BrainsWay to market its Deep TMS System for the treatment of depressive episodes and for decreasing anxiety symptoms for those who may exhibit comorbid anxiety symptoms in adult patients suffering from [MDD] and who failed to achieve satisfactory improvement from previous antidepressant medication treatment in the current episode,” the company said.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The U.S. Food and Drug Administration has expanded the indication for the noninvasive BrainsWay Deep Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation (Deep TMS) System to include treatment of comorbid anxiety symptoms in adult patients with depression, the company has announced.
As reported by this news organization, the neurostimulation system has previously received FDA approval for treatment-resistant major depression, obsessive-compulsive disorder, and smoking addiction.
In the August 18 announcement, BrainsWay reported that it has also received 510(k) clearance from the FDA to market its TMS system for the reduction of anxious depression symptoms.
“This clearance is confirmation of what many have believed anecdotally for years – that Deep TMS is a unique form of therapy that can address comorbid anxiety symptoms using the same depression treatment protocol,” Aron Tendler, MD, chief medical officer at BrainsWay, said in a press release.
‘Consistent, robust’ effect
, which included both randomized controlled trials and open-label studies.
“The data demonstrated a treatment effect that was consistent, robust, and clinically meaningful for decreasing anxiety symptoms in adult patients suffering from major depressive disorder [MDD],” the company said in its release.
Data from three of the randomized trials showed an effect size of 0.3 when compared with a sham device and an effect size of 0.9 when compared with medication. The overall, weighted, pooled effect size was 0.55.
The company noted that in more than 70 published studies with about 16,000 total participants, effect sizes have ranged from 0.2-0.37 for drug-based anxiety treatments.
“The expanded FDA labeling now allows BrainsWay to market its Deep TMS System for the treatment of depressive episodes and for decreasing anxiety symptoms for those who may exhibit comorbid anxiety symptoms in adult patients suffering from [MDD] and who failed to achieve satisfactory improvement from previous antidepressant medication treatment in the current episode,” the company said.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The U.S. Food and Drug Administration has expanded the indication for the noninvasive BrainsWay Deep Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation (Deep TMS) System to include treatment of comorbid anxiety symptoms in adult patients with depression, the company has announced.
As reported by this news organization, the neurostimulation system has previously received FDA approval for treatment-resistant major depression, obsessive-compulsive disorder, and smoking addiction.
In the August 18 announcement, BrainsWay reported that it has also received 510(k) clearance from the FDA to market its TMS system for the reduction of anxious depression symptoms.
“This clearance is confirmation of what many have believed anecdotally for years – that Deep TMS is a unique form of therapy that can address comorbid anxiety symptoms using the same depression treatment protocol,” Aron Tendler, MD, chief medical officer at BrainsWay, said in a press release.
‘Consistent, robust’ effect
, which included both randomized controlled trials and open-label studies.
“The data demonstrated a treatment effect that was consistent, robust, and clinically meaningful for decreasing anxiety symptoms in adult patients suffering from major depressive disorder [MDD],” the company said in its release.
Data from three of the randomized trials showed an effect size of 0.3 when compared with a sham device and an effect size of 0.9 when compared with medication. The overall, weighted, pooled effect size was 0.55.
The company noted that in more than 70 published studies with about 16,000 total participants, effect sizes have ranged from 0.2-0.37 for drug-based anxiety treatments.
“The expanded FDA labeling now allows BrainsWay to market its Deep TMS System for the treatment of depressive episodes and for decreasing anxiety symptoms for those who may exhibit comorbid anxiety symptoms in adult patients suffering from [MDD] and who failed to achieve satisfactory improvement from previous antidepressant medication treatment in the current episode,” the company said.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
COVID-19 booster shots to start in September: Officials
at a press briefing August 18.
Those who received the Pfizer-BioNTech and Moderna vaccines would be eligible to get a booster shot 8 months after they received the second dose of those vaccines, officials said. Information on boosters for those who got the one-dose Johnson & Johnson vaccine will be forthcoming.
“We anticipate a booster will [also] likely be needed,” said U.S. Surgeon General Vivek Murthy, MD. The J&J vaccine was not available in the U.S. until March, he said, and ‘’we expect more data on J&J in the coming weeks, so that plan is coming.”
The plan for boosters for the two mRNA vaccines is pending the FDA’s conducting of an independent review and authorizing the third dose of the Moderna and Pfizer-BioNTech vaccines, as well as an advisory committee of the CDC making the recommendation.
“We know that even highly effective vaccines become less effective over time,” Dr. Murthy said. “Having reviewed the most current data, it is now our clinical judgment that the time to lay out a plan for the COVID-19 boosters is now.”
Research released Aug. 18 shows waning effectiveness of the two mRNA vaccines.
At the briefing, Dr. Murthy and others continually reassured listeners that while effectiveness against infection declines, the vaccines continue to protect against severe infections, hospitalizations, and death.
“If you are fully vaccinated, you still have a high degree of protection against the worst outcomes,” Dr. Murthy said.
Data driving the plan
CDC Director Rochelle Walensky, MD, cited three research studies published Aug. 18 in the CDC’s Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report that helped to drive the decision to recommend boosters.
Analysis of nursing home COVID-19 data from the CDC’s National Healthcare Safety Network showed a significant decline in the effectiveness of the full mRNA vaccine against lab-confirmed COVID-19 infection, from 74.7% before the Delta variant (March 1-May 9, 2021) to 53% when the Delta variant became predominant in the United States. The analysis during the Delta dominant period included 85,000 weekly reports from nearly 15,000 facilities.
Another study looked at more than 10 million New York adults who had been fully vaccinated with either the Moderna, Pfizer, or J&J vaccine by July 25. During the period from May 3 to July 25, overall, the age-adjusted vaccine effectiveness against infection decreased from 91.7% to 79.8%.
Vaccine effectiveness against hospitalization remains high, another study found. An analysis of 1,129 patients who had gotten two doses of an mRNA vaccine showed vaccine effectiveness against hospitalization after 24 weeks. It was 86% at weeks 2-12 and 84% at weeks 13-24.
Immunologic facts
Immunologic information also points to the need for a booster, said Anthony Fauci, MD, the chief medical advisor to the president and director of the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases.
“Antibody levels decline over time,” he said, “and higher antibody levels are associated with higher efficacy of the vaccine. Higher levels of antibody may be needed to protect against Delta.”
A booster increased antibody levels by ‘’at least tenfold and possibly more,” he said. And higher levels of antibody may be required to protect against Delta. Taken together, he said, the data support the use of a booster to increase the overall level of protection.
Booster details
“We will make sure it is convenient and easy to get the booster shot,” said Jeff Zients, the White House COVID-19 response coordinator. As with the previous immunization, he said, the booster will be free, and no one will be asked about immigration status.
The plan for booster shots is an attempt to stay ahead of the virus, officials stressed
Big picture
Not everyone agrees with the booster dose idea. At a World Health Organization briefing Aug. 18, WHO’s Chief Scientist Soumya Swaminathan, MD, an Indian pediatrician, said that the right thing to do right now ‘’is to wait for the science to tell us when boosters, which groups of people, and which vaccines need boosters.”
Like others, she also broached the ‘’moral and ethical argument of giving people third doses, when they’re already well protected and while the rest of the world is waiting for their primary immunization.”
Dr. Swaminathan does see a role for boosters to protect immunocompromised people but noted that ‘’that’s a small number of people.” Widespread boosters ‘’will only lead to more variants, to more escape variants, and perhaps we’re heading into more dire situations.”
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
at a press briefing August 18.
Those who received the Pfizer-BioNTech and Moderna vaccines would be eligible to get a booster shot 8 months after they received the second dose of those vaccines, officials said. Information on boosters for those who got the one-dose Johnson & Johnson vaccine will be forthcoming.
“We anticipate a booster will [also] likely be needed,” said U.S. Surgeon General Vivek Murthy, MD. The J&J vaccine was not available in the U.S. until March, he said, and ‘’we expect more data on J&J in the coming weeks, so that plan is coming.”
The plan for boosters for the two mRNA vaccines is pending the FDA’s conducting of an independent review and authorizing the third dose of the Moderna and Pfizer-BioNTech vaccines, as well as an advisory committee of the CDC making the recommendation.
“We know that even highly effective vaccines become less effective over time,” Dr. Murthy said. “Having reviewed the most current data, it is now our clinical judgment that the time to lay out a plan for the COVID-19 boosters is now.”
Research released Aug. 18 shows waning effectiveness of the two mRNA vaccines.
At the briefing, Dr. Murthy and others continually reassured listeners that while effectiveness against infection declines, the vaccines continue to protect against severe infections, hospitalizations, and death.
“If you are fully vaccinated, you still have a high degree of protection against the worst outcomes,” Dr. Murthy said.
Data driving the plan
CDC Director Rochelle Walensky, MD, cited three research studies published Aug. 18 in the CDC’s Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report that helped to drive the decision to recommend boosters.
Analysis of nursing home COVID-19 data from the CDC’s National Healthcare Safety Network showed a significant decline in the effectiveness of the full mRNA vaccine against lab-confirmed COVID-19 infection, from 74.7% before the Delta variant (March 1-May 9, 2021) to 53% when the Delta variant became predominant in the United States. The analysis during the Delta dominant period included 85,000 weekly reports from nearly 15,000 facilities.
Another study looked at more than 10 million New York adults who had been fully vaccinated with either the Moderna, Pfizer, or J&J vaccine by July 25. During the period from May 3 to July 25, overall, the age-adjusted vaccine effectiveness against infection decreased from 91.7% to 79.8%.
Vaccine effectiveness against hospitalization remains high, another study found. An analysis of 1,129 patients who had gotten two doses of an mRNA vaccine showed vaccine effectiveness against hospitalization after 24 weeks. It was 86% at weeks 2-12 and 84% at weeks 13-24.
Immunologic facts
Immunologic information also points to the need for a booster, said Anthony Fauci, MD, the chief medical advisor to the president and director of the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases.
“Antibody levels decline over time,” he said, “and higher antibody levels are associated with higher efficacy of the vaccine. Higher levels of antibody may be needed to protect against Delta.”
A booster increased antibody levels by ‘’at least tenfold and possibly more,” he said. And higher levels of antibody may be required to protect against Delta. Taken together, he said, the data support the use of a booster to increase the overall level of protection.
Booster details
“We will make sure it is convenient and easy to get the booster shot,” said Jeff Zients, the White House COVID-19 response coordinator. As with the previous immunization, he said, the booster will be free, and no one will be asked about immigration status.
The plan for booster shots is an attempt to stay ahead of the virus, officials stressed
Big picture
Not everyone agrees with the booster dose idea. At a World Health Organization briefing Aug. 18, WHO’s Chief Scientist Soumya Swaminathan, MD, an Indian pediatrician, said that the right thing to do right now ‘’is to wait for the science to tell us when boosters, which groups of people, and which vaccines need boosters.”
Like others, she also broached the ‘’moral and ethical argument of giving people third doses, when they’re already well protected and while the rest of the world is waiting for their primary immunization.”
Dr. Swaminathan does see a role for boosters to protect immunocompromised people but noted that ‘’that’s a small number of people.” Widespread boosters ‘’will only lead to more variants, to more escape variants, and perhaps we’re heading into more dire situations.”
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
at a press briefing August 18.
Those who received the Pfizer-BioNTech and Moderna vaccines would be eligible to get a booster shot 8 months after they received the second dose of those vaccines, officials said. Information on boosters for those who got the one-dose Johnson & Johnson vaccine will be forthcoming.
“We anticipate a booster will [also] likely be needed,” said U.S. Surgeon General Vivek Murthy, MD. The J&J vaccine was not available in the U.S. until March, he said, and ‘’we expect more data on J&J in the coming weeks, so that plan is coming.”
The plan for boosters for the two mRNA vaccines is pending the FDA’s conducting of an independent review and authorizing the third dose of the Moderna and Pfizer-BioNTech vaccines, as well as an advisory committee of the CDC making the recommendation.
“We know that even highly effective vaccines become less effective over time,” Dr. Murthy said. “Having reviewed the most current data, it is now our clinical judgment that the time to lay out a plan for the COVID-19 boosters is now.”
Research released Aug. 18 shows waning effectiveness of the two mRNA vaccines.
At the briefing, Dr. Murthy and others continually reassured listeners that while effectiveness against infection declines, the vaccines continue to protect against severe infections, hospitalizations, and death.
“If you are fully vaccinated, you still have a high degree of protection against the worst outcomes,” Dr. Murthy said.
Data driving the plan
CDC Director Rochelle Walensky, MD, cited three research studies published Aug. 18 in the CDC’s Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report that helped to drive the decision to recommend boosters.
Analysis of nursing home COVID-19 data from the CDC’s National Healthcare Safety Network showed a significant decline in the effectiveness of the full mRNA vaccine against lab-confirmed COVID-19 infection, from 74.7% before the Delta variant (March 1-May 9, 2021) to 53% when the Delta variant became predominant in the United States. The analysis during the Delta dominant period included 85,000 weekly reports from nearly 15,000 facilities.
Another study looked at more than 10 million New York adults who had been fully vaccinated with either the Moderna, Pfizer, or J&J vaccine by July 25. During the period from May 3 to July 25, overall, the age-adjusted vaccine effectiveness against infection decreased from 91.7% to 79.8%.
Vaccine effectiveness against hospitalization remains high, another study found. An analysis of 1,129 patients who had gotten two doses of an mRNA vaccine showed vaccine effectiveness against hospitalization after 24 weeks. It was 86% at weeks 2-12 and 84% at weeks 13-24.
Immunologic facts
Immunologic information also points to the need for a booster, said Anthony Fauci, MD, the chief medical advisor to the president and director of the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases.
“Antibody levels decline over time,” he said, “and higher antibody levels are associated with higher efficacy of the vaccine. Higher levels of antibody may be needed to protect against Delta.”
A booster increased antibody levels by ‘’at least tenfold and possibly more,” he said. And higher levels of antibody may be required to protect against Delta. Taken together, he said, the data support the use of a booster to increase the overall level of protection.
Booster details
“We will make sure it is convenient and easy to get the booster shot,” said Jeff Zients, the White House COVID-19 response coordinator. As with the previous immunization, he said, the booster will be free, and no one will be asked about immigration status.
The plan for booster shots is an attempt to stay ahead of the virus, officials stressed
Big picture
Not everyone agrees with the booster dose idea. At a World Health Organization briefing Aug. 18, WHO’s Chief Scientist Soumya Swaminathan, MD, an Indian pediatrician, said that the right thing to do right now ‘’is to wait for the science to tell us when boosters, which groups of people, and which vaccines need boosters.”
Like others, she also broached the ‘’moral and ethical argument of giving people third doses, when they’re already well protected and while the rest of the world is waiting for their primary immunization.”
Dr. Swaminathan does see a role for boosters to protect immunocompromised people but noted that ‘’that’s a small number of people.” Widespread boosters ‘’will only lead to more variants, to more escape variants, and perhaps we’re heading into more dire situations.”
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
Pfizer recalls four more lots of smoking cessation drug Chantix
Pfizer has recalled four more lots of the smoking cessation drug varenicline (Chantix), according to an Aug. 16 update on the U.S. Food and Drug Administration website.
In a new FDA MedWatch, the agency notes that these 0.5 mg/1 mg tablets are being recalled because of the presence of N-nitroso-varenicline, a nitrosamine impurity, at a level higher than Pfizer’s acceptable intake limit.
On July 2, the FDA reported that Pfizer had voluntarily recalled nine lots of the drug for this reason. As reported by this news organization, the company added three more lots to the recall a few weeks later.
In the update, the FDA noted that, although long-term ingestion of the impurity “may be associated with a theoretical potential increased cancer risk in humans,” there is no immediate risk in taking this medication. The agency added that no related adverse events (AEs) have been reported.
The four additional lots included in the newest recall are as follows:
- 00018522 (expiration date: August 2021).
- 00018523 (expiration date: August 2021).
- 00018739 (expiration date: August 2021).
- 00018740 (expiration date: August 2021).
The recalled lots were distributed in the United States and Puerto Rico from June 2019 to June 2021.
As before, the FDA noted that the benefits of stopping smoking “outweigh the theoretical potential cancer risk” from varenicline’s impurity.
It added that, although the impurities may increase risk for cancer if a high level of exposure continues over a long period, the drug is intended as a short-term treatment to aid in smoking cessation.
For now, clinicians should report any AEs from varenicline to the FDA’s MedWatch program, and patients taking this treatment should consult with their health care practitioner or pharmacy, the update notes.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Pfizer has recalled four more lots of the smoking cessation drug varenicline (Chantix), according to an Aug. 16 update on the U.S. Food and Drug Administration website.
In a new FDA MedWatch, the agency notes that these 0.5 mg/1 mg tablets are being recalled because of the presence of N-nitroso-varenicline, a nitrosamine impurity, at a level higher than Pfizer’s acceptable intake limit.
On July 2, the FDA reported that Pfizer had voluntarily recalled nine lots of the drug for this reason. As reported by this news organization, the company added three more lots to the recall a few weeks later.
In the update, the FDA noted that, although long-term ingestion of the impurity “may be associated with a theoretical potential increased cancer risk in humans,” there is no immediate risk in taking this medication. The agency added that no related adverse events (AEs) have been reported.
The four additional lots included in the newest recall are as follows:
- 00018522 (expiration date: August 2021).
- 00018523 (expiration date: August 2021).
- 00018739 (expiration date: August 2021).
- 00018740 (expiration date: August 2021).
The recalled lots were distributed in the United States and Puerto Rico from June 2019 to June 2021.
As before, the FDA noted that the benefits of stopping smoking “outweigh the theoretical potential cancer risk” from varenicline’s impurity.
It added that, although the impurities may increase risk for cancer if a high level of exposure continues over a long period, the drug is intended as a short-term treatment to aid in smoking cessation.
For now, clinicians should report any AEs from varenicline to the FDA’s MedWatch program, and patients taking this treatment should consult with their health care practitioner or pharmacy, the update notes.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Pfizer has recalled four more lots of the smoking cessation drug varenicline (Chantix), according to an Aug. 16 update on the U.S. Food and Drug Administration website.
In a new FDA MedWatch, the agency notes that these 0.5 mg/1 mg tablets are being recalled because of the presence of N-nitroso-varenicline, a nitrosamine impurity, at a level higher than Pfizer’s acceptable intake limit.
On July 2, the FDA reported that Pfizer had voluntarily recalled nine lots of the drug for this reason. As reported by this news organization, the company added three more lots to the recall a few weeks later.
In the update, the FDA noted that, although long-term ingestion of the impurity “may be associated with a theoretical potential increased cancer risk in humans,” there is no immediate risk in taking this medication. The agency added that no related adverse events (AEs) have been reported.
The four additional lots included in the newest recall are as follows:
- 00018522 (expiration date: August 2021).
- 00018523 (expiration date: August 2021).
- 00018739 (expiration date: August 2021).
- 00018740 (expiration date: August 2021).
The recalled lots were distributed in the United States and Puerto Rico from June 2019 to June 2021.
As before, the FDA noted that the benefits of stopping smoking “outweigh the theoretical potential cancer risk” from varenicline’s impurity.
It added that, although the impurities may increase risk for cancer if a high level of exposure continues over a long period, the drug is intended as a short-term treatment to aid in smoking cessation.
For now, clinicians should report any AEs from varenicline to the FDA’s MedWatch program, and patients taking this treatment should consult with their health care practitioner or pharmacy, the update notes.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Mental health after ICU: It’s complicated
It is well known that survivors of critical care are at heightened risk of mental health disorders even months afterward they are discharged, but it’s less clear what factors might contribute to those outcomes. A new attempt to identify risk factors for post-ICU depression, anxiety, or posttraumatic stress disorder, as well as worse quality of life, paints a complex picture.
Age, mental preexisting mental health concerns, acute emotional stress at the time of critical care, and post-care physical impairment all may play a role, according to the multicenter, prospective cohort study conducted in Brazil, which was published in CHEST .
Previous systematic reviews have shown raised frequencies mental health disorders following ICU discharge, including anxiety (32%-40%), depression (29%-34%), and PTSD (16%-23%). Few studies have looked at the potential impact of preexisting conditions or post-ICU disability on these outcomes, yet that information is critical to key to designing effective prevention and rehabilitation interventions.
The results suggest that preexisting mental health and factors associated with the critical illness, which have gained attention as potential factors, aren’t sufficient to explain these outcomes. “Our data suggest that the network of potential risk factors for mental illness among patients who have been discharged from the ICU is much more complex and may involve risk factors from multiple domains. ... Long-term mental health disorders after critical illness may be the result of the interaction among stressors before ICU stay, during ICU stay, and after ICU stay, calling attention to the need for interdisciplinary and multifaceted strategies aimed at preventing and screening for mental health disorders after ICU discharge,” Cassiano Teixeira, MD, PhD, of the Postgraduation of Pulmonology–Federal University of Rio Grande do Sul, Brazil, and colleagues wrote.
The researchers also noted that some risk factors could be screened and may be modifiable, including anxiety and depression symptoms at ICU discharge, as well as reduced physical function status.
Complications or risk factors?
The findings are significant, though they may represent complications of emotional distress following ICU stays, rather than risk factors that predict it, according to an accompanying editorial. The author, O. Joseph Bienvenu III, MD, PhD, who is a professor of psychiatry and behavioral sciences at Johns Hopkins Medicine, Baltimore. He called for prospective studies to determine the predictive value of these factors. “If we are to improve long-term mental health after critical illnesses, this predictive information will be vital to selective prevention efforts.”
Potential interventions could include psychological treatment in the ICU, ICU follow-up clinics, support groups, and cognitive-behavioral therapy, among others. Whichever approach is used, it should be targeted, according to Dr. Bienvenu, since patients who have greater emotional distress seem to gain the most benefit from such interventions.
The researchers examined outcomes among 579 adults who had spent at least 72 hours in the ICU. The median age was 61 years, and 47% were women.
Six months after release from the ICU, telephone assessments by trained researchers revealed that 48% had impairment in physical function, compared with the time preceding ICU admission. 36.2% of participants had a mental health disorder: 24.2% reported anxiety, 20.9% had depression, and 15.4% had PTSD.
Increasing numbers of psychiatric syndromes, from 0 to 3, was associated with worse scores on the mental dimension on the health-related quality of life (HRQoL) score, but there was no relationship with scores on the physical dimension.
Risks to mental health
Clinical characteristics associated with risk of anxiety at 6 months post discharge included being 65 years or older (prevalence ratio, 0.63; P = .009), a history of depression (PR, 1.52; P = .009), anxiety at discharge (PR, 1.65; P = .003), depression at discharge (HR, 1.44; P = .02), physical dependence (PR, 1.48; P = .01), and reduced physical functional status at 6 months post discharge (PR, 1.38; P = .04).
Characteristics associated with depression at 6 months post discharge included a history of depression (PR, 1.78; P = .001), symptoms of depression at discharge (PR, 3.04; P < .001), and reduced physical functional status at 6 months (PR, 1.53; P = .01).
Characteristics associated with PTSD at 6 months post discharge were depression symptoms at discharge (PR, 1.70; P = .01), physical dependence (PR, 1.79; P = .01), and reduced physical status at 6 months (PR, 1.62; P = .02).
Characteristics associated with any mental health disorder included higher education (PR, 0.74; P = .04), a history of depression (PR, 1.32; P = .02), anxiety symptoms at discharge (PR, 1.55; P = .001), depression symptoms at discharge (PR, 1.50; P = .001), and physical dependence at 6 months following discharge (PR, 1.66; P < .001).
“The lower HRQoL found in ICU survivors with mental health disorders in comparison with those without is a reason for concern. This finding, in association with the higher prevalence of psychiatric syndromes among ICU survivors, reinforces the importance of assessing anxiety, depression, and PTSD symptoms among ICU survivors, because these syndromes typically are long lasting and underdiagnosed, and their occurrence may affect quality of life, survival, and costs in the context of care after ICU discharge,” according to the researchers.
The authors of the study and Dr. Bienvenu have no relevant financial disclosures.
It is well known that survivors of critical care are at heightened risk of mental health disorders even months afterward they are discharged, but it’s less clear what factors might contribute to those outcomes. A new attempt to identify risk factors for post-ICU depression, anxiety, or posttraumatic stress disorder, as well as worse quality of life, paints a complex picture.
Age, mental preexisting mental health concerns, acute emotional stress at the time of critical care, and post-care physical impairment all may play a role, according to the multicenter, prospective cohort study conducted in Brazil, which was published in CHEST .
Previous systematic reviews have shown raised frequencies mental health disorders following ICU discharge, including anxiety (32%-40%), depression (29%-34%), and PTSD (16%-23%). Few studies have looked at the potential impact of preexisting conditions or post-ICU disability on these outcomes, yet that information is critical to key to designing effective prevention and rehabilitation interventions.
The results suggest that preexisting mental health and factors associated with the critical illness, which have gained attention as potential factors, aren’t sufficient to explain these outcomes. “Our data suggest that the network of potential risk factors for mental illness among patients who have been discharged from the ICU is much more complex and may involve risk factors from multiple domains. ... Long-term mental health disorders after critical illness may be the result of the interaction among stressors before ICU stay, during ICU stay, and after ICU stay, calling attention to the need for interdisciplinary and multifaceted strategies aimed at preventing and screening for mental health disorders after ICU discharge,” Cassiano Teixeira, MD, PhD, of the Postgraduation of Pulmonology–Federal University of Rio Grande do Sul, Brazil, and colleagues wrote.
The researchers also noted that some risk factors could be screened and may be modifiable, including anxiety and depression symptoms at ICU discharge, as well as reduced physical function status.
Complications or risk factors?
The findings are significant, though they may represent complications of emotional distress following ICU stays, rather than risk factors that predict it, according to an accompanying editorial. The author, O. Joseph Bienvenu III, MD, PhD, who is a professor of psychiatry and behavioral sciences at Johns Hopkins Medicine, Baltimore. He called for prospective studies to determine the predictive value of these factors. “If we are to improve long-term mental health after critical illnesses, this predictive information will be vital to selective prevention efforts.”
Potential interventions could include psychological treatment in the ICU, ICU follow-up clinics, support groups, and cognitive-behavioral therapy, among others. Whichever approach is used, it should be targeted, according to Dr. Bienvenu, since patients who have greater emotional distress seem to gain the most benefit from such interventions.
The researchers examined outcomes among 579 adults who had spent at least 72 hours in the ICU. The median age was 61 years, and 47% were women.
Six months after release from the ICU, telephone assessments by trained researchers revealed that 48% had impairment in physical function, compared with the time preceding ICU admission. 36.2% of participants had a mental health disorder: 24.2% reported anxiety, 20.9% had depression, and 15.4% had PTSD.
Increasing numbers of psychiatric syndromes, from 0 to 3, was associated with worse scores on the mental dimension on the health-related quality of life (HRQoL) score, but there was no relationship with scores on the physical dimension.
Risks to mental health
Clinical characteristics associated with risk of anxiety at 6 months post discharge included being 65 years or older (prevalence ratio, 0.63; P = .009), a history of depression (PR, 1.52; P = .009), anxiety at discharge (PR, 1.65; P = .003), depression at discharge (HR, 1.44; P = .02), physical dependence (PR, 1.48; P = .01), and reduced physical functional status at 6 months post discharge (PR, 1.38; P = .04).
Characteristics associated with depression at 6 months post discharge included a history of depression (PR, 1.78; P = .001), symptoms of depression at discharge (PR, 3.04; P < .001), and reduced physical functional status at 6 months (PR, 1.53; P = .01).
Characteristics associated with PTSD at 6 months post discharge were depression symptoms at discharge (PR, 1.70; P = .01), physical dependence (PR, 1.79; P = .01), and reduced physical status at 6 months (PR, 1.62; P = .02).
Characteristics associated with any mental health disorder included higher education (PR, 0.74; P = .04), a history of depression (PR, 1.32; P = .02), anxiety symptoms at discharge (PR, 1.55; P = .001), depression symptoms at discharge (PR, 1.50; P = .001), and physical dependence at 6 months following discharge (PR, 1.66; P < .001).
“The lower HRQoL found in ICU survivors with mental health disorders in comparison with those without is a reason for concern. This finding, in association with the higher prevalence of psychiatric syndromes among ICU survivors, reinforces the importance of assessing anxiety, depression, and PTSD symptoms among ICU survivors, because these syndromes typically are long lasting and underdiagnosed, and their occurrence may affect quality of life, survival, and costs in the context of care after ICU discharge,” according to the researchers.
The authors of the study and Dr. Bienvenu have no relevant financial disclosures.
It is well known that survivors of critical care are at heightened risk of mental health disorders even months afterward they are discharged, but it’s less clear what factors might contribute to those outcomes. A new attempt to identify risk factors for post-ICU depression, anxiety, or posttraumatic stress disorder, as well as worse quality of life, paints a complex picture.
Age, mental preexisting mental health concerns, acute emotional stress at the time of critical care, and post-care physical impairment all may play a role, according to the multicenter, prospective cohort study conducted in Brazil, which was published in CHEST .
Previous systematic reviews have shown raised frequencies mental health disorders following ICU discharge, including anxiety (32%-40%), depression (29%-34%), and PTSD (16%-23%). Few studies have looked at the potential impact of preexisting conditions or post-ICU disability on these outcomes, yet that information is critical to key to designing effective prevention and rehabilitation interventions.
The results suggest that preexisting mental health and factors associated with the critical illness, which have gained attention as potential factors, aren’t sufficient to explain these outcomes. “Our data suggest that the network of potential risk factors for mental illness among patients who have been discharged from the ICU is much more complex and may involve risk factors from multiple domains. ... Long-term mental health disorders after critical illness may be the result of the interaction among stressors before ICU stay, during ICU stay, and after ICU stay, calling attention to the need for interdisciplinary and multifaceted strategies aimed at preventing and screening for mental health disorders after ICU discharge,” Cassiano Teixeira, MD, PhD, of the Postgraduation of Pulmonology–Federal University of Rio Grande do Sul, Brazil, and colleagues wrote.
The researchers also noted that some risk factors could be screened and may be modifiable, including anxiety and depression symptoms at ICU discharge, as well as reduced physical function status.
Complications or risk factors?
The findings are significant, though they may represent complications of emotional distress following ICU stays, rather than risk factors that predict it, according to an accompanying editorial. The author, O. Joseph Bienvenu III, MD, PhD, who is a professor of psychiatry and behavioral sciences at Johns Hopkins Medicine, Baltimore. He called for prospective studies to determine the predictive value of these factors. “If we are to improve long-term mental health after critical illnesses, this predictive information will be vital to selective prevention efforts.”
Potential interventions could include psychological treatment in the ICU, ICU follow-up clinics, support groups, and cognitive-behavioral therapy, among others. Whichever approach is used, it should be targeted, according to Dr. Bienvenu, since patients who have greater emotional distress seem to gain the most benefit from such interventions.
The researchers examined outcomes among 579 adults who had spent at least 72 hours in the ICU. The median age was 61 years, and 47% were women.
Six months after release from the ICU, telephone assessments by trained researchers revealed that 48% had impairment in physical function, compared with the time preceding ICU admission. 36.2% of participants had a mental health disorder: 24.2% reported anxiety, 20.9% had depression, and 15.4% had PTSD.
Increasing numbers of psychiatric syndromes, from 0 to 3, was associated with worse scores on the mental dimension on the health-related quality of life (HRQoL) score, but there was no relationship with scores on the physical dimension.
Risks to mental health
Clinical characteristics associated with risk of anxiety at 6 months post discharge included being 65 years or older (prevalence ratio, 0.63; P = .009), a history of depression (PR, 1.52; P = .009), anxiety at discharge (PR, 1.65; P = .003), depression at discharge (HR, 1.44; P = .02), physical dependence (PR, 1.48; P = .01), and reduced physical functional status at 6 months post discharge (PR, 1.38; P = .04).
Characteristics associated with depression at 6 months post discharge included a history of depression (PR, 1.78; P = .001), symptoms of depression at discharge (PR, 3.04; P < .001), and reduced physical functional status at 6 months (PR, 1.53; P = .01).
Characteristics associated with PTSD at 6 months post discharge were depression symptoms at discharge (PR, 1.70; P = .01), physical dependence (PR, 1.79; P = .01), and reduced physical status at 6 months (PR, 1.62; P = .02).
Characteristics associated with any mental health disorder included higher education (PR, 0.74; P = .04), a history of depression (PR, 1.32; P = .02), anxiety symptoms at discharge (PR, 1.55; P = .001), depression symptoms at discharge (PR, 1.50; P = .001), and physical dependence at 6 months following discharge (PR, 1.66; P < .001).
“The lower HRQoL found in ICU survivors with mental health disorders in comparison with those without is a reason for concern. This finding, in association with the higher prevalence of psychiatric syndromes among ICU survivors, reinforces the importance of assessing anxiety, depression, and PTSD symptoms among ICU survivors, because these syndromes typically are long lasting and underdiagnosed, and their occurrence may affect quality of life, survival, and costs in the context of care after ICU discharge,” according to the researchers.
The authors of the study and Dr. Bienvenu have no relevant financial disclosures.
FROM CHEST
‘Reassuring’ findings for second-generation antipsychotics during pregnancy
Second-generation antipsychotics (SGAs) taken by pregnant women are linked to a low rate of adverse effects in their children, new research suggests.
Data from a large registry study of almost 2,000 women showed that 2.5% of the live births in a group that had been exposed to antipsychotics had confirmed major malformations compared with 2% of the live births in a non-exposed group. This translated into an estimated odds ratio of 1.5 for major malformations.
“The 2.5% absolute risk for major malformations is consistent with the estimates of the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention’s national baseline rate of major malformations in the general population,” lead author Adele Viguera, MD, MPH, director of research for women’s mental health, Cleveland Clinic Neurological Institute, told this news organization.
“Our results are reassuring and suggest that second-generation antipsychotics, as a class, do not substantially increase the risk of major malformations,” Dr. Viguera said.
The findings were published online August 3 in the Journal of Clinical Psychiatry.
Safety data scarce
Despite the increasing use of SGAs to treat a “spectrum of psychiatric disorders,” relatively little data are available on the reproductive safety of these agents, Dr. Viguera said.
The National Pregnancy Registry for Atypical Antipsychotics (NPRAA) was established in 2008 to determine risk for major malformation among infants exposed to these medications during the first trimester, relative to a comparison group of unexposed infants of mothers with histories of psychiatric morbidity.
The NPRAA follows pregnant women (aged 18 to 45 years) with psychiatric illness who are exposed or unexposed to SGAs during pregnancy. Participants are recruited through nationwide provider referral, self-referral, and advertisement through the Massachusetts General Hospital Center for Women’s Mental Health website.
Specific data collected are shown in the following table.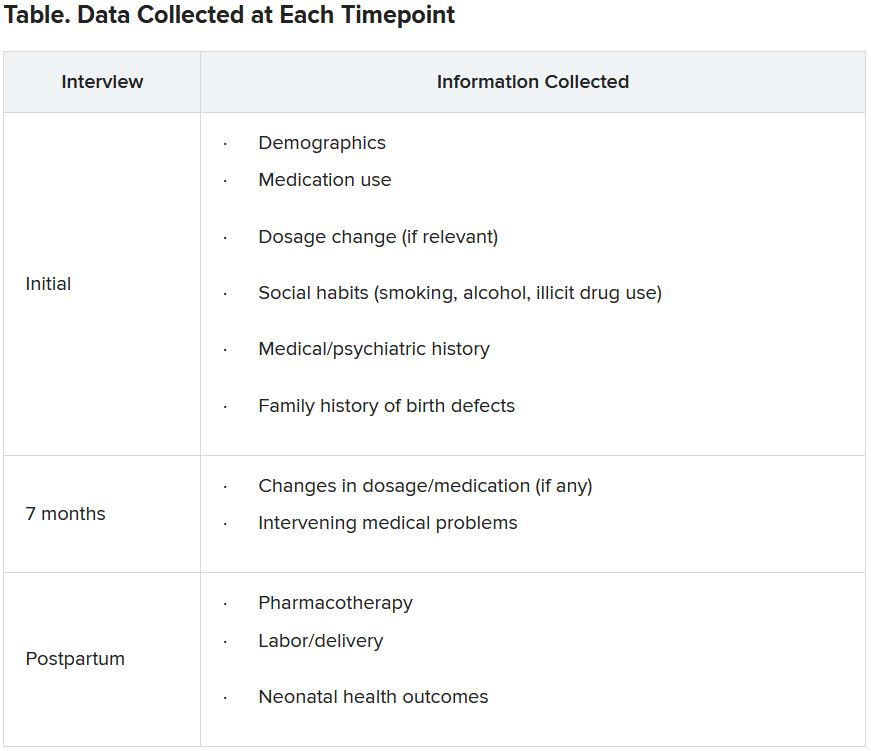
Since publication of the first results in 2015, the sample size for the trial has increased – and the absolute and relative risk for major malformations observed in the study population are “more precise,” the investigators note. The current study presented updated previous findings.
Demographic differences
Of the 1,906 women who enrolled as of April 2020, 1,311 (mean age, 32.6 years; 81.3% White) completed the study and were eligible for inclusion in the analysis.
Although the groups had a virtually identical mean age, fewer women in the exposure group were married compared with those in the non-exposure group (77% vs. 90%, respectively) and fewer had a college education (71.2% vs. 87.8%). There was also a higher percentage of first-trimester cigarette smokers in the exposure group (18.4% vs. 5.1%).
On the other hand, more women in the non-exposure group used alcohol than in the exposure group (28.6% vs. 21.4%, respectively).
The most frequent psychiatric disorder in the exposure group was bipolar disorder (63.9%), followed by major depression (12.9%), anxiety (5.8%), and schizophrenia (4.5%). Only 11.4% of women in the non-exposure group were diagnosed with bipolar disorder, whereas 34.1% were diagnosed with major depression, 31.3% with anxiety, and none with schizophrenia.
Notably, a large percentage of women in both groups had a history of postpartum depression and/or psychosis (41.4% and 35.5%, respectively).
The most frequently used SGAs in the exposure group were quetiapine (Seroquel), aripiprazole (Abilify), and lurasidone (Latuda).
Participants in the exposure group had a higher age at initial onset of primary psychiatric diagnosis and a lower proportion of lifetime illness compared with those in the non-exposure group.
Major clinical implication?
Among 640 live births in the exposure group, which included 17 twin pregnancies and 1 triplet pregnancy, 2.5% reported major malformations. Among 704 live births in the control group, which included 14 twin pregnancies, 1.99% reported major malformations.
The estimated OR for major malformations comparing exposed and unexposed infants was 1.48 (95% confidence interval, 0.625-3.517).
The authors note that their findings were consistent with one of the largest studies to date, which included a nationwide sample of more than 1 million women. Its results showed that, among infants exposed to SGAs versus those who were not exposed, the estimated risk ratio after adjusting for psychiatric conditions was 1.05 (95% CI, 0.96-1.16).
Additionally, “a hallmark of a teratogen is that it tends to cause a specific type or pattern of malformations, and we found no preponderance of one single type of major malformation or specific pattern of malformations among the exposed and unexposed groups,” Dr. Viguera said
“A major clinical implication of these findings is that for women with major mood and/or psychotic disorders, treatment with an atypical antipsychotic during pregnancy may be the most prudent clinical decision, much as continued treatment is recommended for pregnant women with other serious and chronic medical conditions, such as epilepsy,” she added.
The concept of ‘satisficing’
Commenting on the study, Vivien Burt, MD, PhD, founder and director/consultant of the Women’s Life Center at the Resnick University of California, Los Angeles (UCLA) Neuropsychiatric Hospital, called the findings “reassuring.”
The results “support the conclusion that in pregnant women with serious psychiatric illnesses, the use of SGAs is often a better option than avoiding these medications and exposing both the women and their offspring to the adverse consequences of maternal mental illness,” she said.
An accompanying editorial co-authored by Dr. Burt and colleague Sonya Rasminsky, MD, introduced the concept of “satisficing” – a term coined by Herbert Simon, a behavioral economist and Nobel Laureate. “Satisficing” is a “decision-making strategy that aims for a satisfactory (‘good enough’) outcome rather than a perfect one.”
The concept applies to decision-making beyond the field of economics “and is critical to how physicians help patients make decisions when they are faced with multiple treatment options,” said Dr. Burt, a professor emeritus of psychiatry at UCLA.
“The goal of ‘satisficing’ is to plan for the most satisfactory outcome, knowing that there are always unknowns, so in an uncertain world, clinicians should carefully help their patients make decisions that will allow them to achieve an outcome they can best live with,” she noted.
The investigators note that their findings may not be generalizable to the larger population of women taking SGAs, given that their participants were “overwhelmingly White, married, and well-educated women.”
They add that enrollment into the NPRAA registry is ongoing and larger sample sizes will “further narrow the confidence interval around the risk estimates and allow for adjustment of likely sources of confounding.”
The NPRAA is supported by Alkermes, Johnson & Johnson/Janssen Pharmaceuticals, Otsuka America Pharmaceutical, Sunovion Pharmaceuticals, SAGE Therapeutics, Teva Pharmaceuticals, and Aurobindo Pharma. Past sponsors of the NPRAA are listed in the original paper. Dr. Viguera receives research support from the NPRAA, Alkermes Biopharmaceuticals, Aurobindo Pharma, Janssen Pharmaceuticals, Otsuka Pharmaceutical, Sunovion Pharmaceuticals, Teva Pharmaceuticals, and SAGE Therapeutics and receives adviser/consulting fees from Up-to-Date. Dr. Burt has been a consultant/speaker for Sage Therapeutics. Dr. Rasminsky has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Second-generation antipsychotics (SGAs) taken by pregnant women are linked to a low rate of adverse effects in their children, new research suggests.
Data from a large registry study of almost 2,000 women showed that 2.5% of the live births in a group that had been exposed to antipsychotics had confirmed major malformations compared with 2% of the live births in a non-exposed group. This translated into an estimated odds ratio of 1.5 for major malformations.
“The 2.5% absolute risk for major malformations is consistent with the estimates of the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention’s national baseline rate of major malformations in the general population,” lead author Adele Viguera, MD, MPH, director of research for women’s mental health, Cleveland Clinic Neurological Institute, told this news organization.
“Our results are reassuring and suggest that second-generation antipsychotics, as a class, do not substantially increase the risk of major malformations,” Dr. Viguera said.
The findings were published online August 3 in the Journal of Clinical Psychiatry.
Safety data scarce
Despite the increasing use of SGAs to treat a “spectrum of psychiatric disorders,” relatively little data are available on the reproductive safety of these agents, Dr. Viguera said.
The National Pregnancy Registry for Atypical Antipsychotics (NPRAA) was established in 2008 to determine risk for major malformation among infants exposed to these medications during the first trimester, relative to a comparison group of unexposed infants of mothers with histories of psychiatric morbidity.
The NPRAA follows pregnant women (aged 18 to 45 years) with psychiatric illness who are exposed or unexposed to SGAs during pregnancy. Participants are recruited through nationwide provider referral, self-referral, and advertisement through the Massachusetts General Hospital Center for Women’s Mental Health website.
Specific data collected are shown in the following table.
Since publication of the first results in 2015, the sample size for the trial has increased – and the absolute and relative risk for major malformations observed in the study population are “more precise,” the investigators note. The current study presented updated previous findings.
Demographic differences
Of the 1,906 women who enrolled as of April 2020, 1,311 (mean age, 32.6 years; 81.3% White) completed the study and were eligible for inclusion in the analysis.
Although the groups had a virtually identical mean age, fewer women in the exposure group were married compared with those in the non-exposure group (77% vs. 90%, respectively) and fewer had a college education (71.2% vs. 87.8%). There was also a higher percentage of first-trimester cigarette smokers in the exposure group (18.4% vs. 5.1%).
On the other hand, more women in the non-exposure group used alcohol than in the exposure group (28.6% vs. 21.4%, respectively).
The most frequent psychiatric disorder in the exposure group was bipolar disorder (63.9%), followed by major depression (12.9%), anxiety (5.8%), and schizophrenia (4.5%). Only 11.4% of women in the non-exposure group were diagnosed with bipolar disorder, whereas 34.1% were diagnosed with major depression, 31.3% with anxiety, and none with schizophrenia.
Notably, a large percentage of women in both groups had a history of postpartum depression and/or psychosis (41.4% and 35.5%, respectively).
The most frequently used SGAs in the exposure group were quetiapine (Seroquel), aripiprazole (Abilify), and lurasidone (Latuda).
Participants in the exposure group had a higher age at initial onset of primary psychiatric diagnosis and a lower proportion of lifetime illness compared with those in the non-exposure group.
Major clinical implication?
Among 640 live births in the exposure group, which included 17 twin pregnancies and 1 triplet pregnancy, 2.5% reported major malformations. Among 704 live births in the control group, which included 14 twin pregnancies, 1.99% reported major malformations.
The estimated OR for major malformations comparing exposed and unexposed infants was 1.48 (95% confidence interval, 0.625-3.517).
The authors note that their findings were consistent with one of the largest studies to date, which included a nationwide sample of more than 1 million women. Its results showed that, among infants exposed to SGAs versus those who were not exposed, the estimated risk ratio after adjusting for psychiatric conditions was 1.05 (95% CI, 0.96-1.16).
Additionally, “a hallmark of a teratogen is that it tends to cause a specific type or pattern of malformations, and we found no preponderance of one single type of major malformation or specific pattern of malformations among the exposed and unexposed groups,” Dr. Viguera said
“A major clinical implication of these findings is that for women with major mood and/or psychotic disorders, treatment with an atypical antipsychotic during pregnancy may be the most prudent clinical decision, much as continued treatment is recommended for pregnant women with other serious and chronic medical conditions, such as epilepsy,” she added.
The concept of ‘satisficing’
Commenting on the study, Vivien Burt, MD, PhD, founder and director/consultant of the Women’s Life Center at the Resnick University of California, Los Angeles (UCLA) Neuropsychiatric Hospital, called the findings “reassuring.”
The results “support the conclusion that in pregnant women with serious psychiatric illnesses, the use of SGAs is often a better option than avoiding these medications and exposing both the women and their offspring to the adverse consequences of maternal mental illness,” she said.
An accompanying editorial co-authored by Dr. Burt and colleague Sonya Rasminsky, MD, introduced the concept of “satisficing” – a term coined by Herbert Simon, a behavioral economist and Nobel Laureate. “Satisficing” is a “decision-making strategy that aims for a satisfactory (‘good enough’) outcome rather than a perfect one.”
The concept applies to decision-making beyond the field of economics “and is critical to how physicians help patients make decisions when they are faced with multiple treatment options,” said Dr. Burt, a professor emeritus of psychiatry at UCLA.
“The goal of ‘satisficing’ is to plan for the most satisfactory outcome, knowing that there are always unknowns, so in an uncertain world, clinicians should carefully help their patients make decisions that will allow them to achieve an outcome they can best live with,” she noted.
The investigators note that their findings may not be generalizable to the larger population of women taking SGAs, given that their participants were “overwhelmingly White, married, and well-educated women.”
They add that enrollment into the NPRAA registry is ongoing and larger sample sizes will “further narrow the confidence interval around the risk estimates and allow for adjustment of likely sources of confounding.”
The NPRAA is supported by Alkermes, Johnson & Johnson/Janssen Pharmaceuticals, Otsuka America Pharmaceutical, Sunovion Pharmaceuticals, SAGE Therapeutics, Teva Pharmaceuticals, and Aurobindo Pharma. Past sponsors of the NPRAA are listed in the original paper. Dr. Viguera receives research support from the NPRAA, Alkermes Biopharmaceuticals, Aurobindo Pharma, Janssen Pharmaceuticals, Otsuka Pharmaceutical, Sunovion Pharmaceuticals, Teva Pharmaceuticals, and SAGE Therapeutics and receives adviser/consulting fees from Up-to-Date. Dr. Burt has been a consultant/speaker for Sage Therapeutics. Dr. Rasminsky has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Second-generation antipsychotics (SGAs) taken by pregnant women are linked to a low rate of adverse effects in their children, new research suggests.
Data from a large registry study of almost 2,000 women showed that 2.5% of the live births in a group that had been exposed to antipsychotics had confirmed major malformations compared with 2% of the live births in a non-exposed group. This translated into an estimated odds ratio of 1.5 for major malformations.
“The 2.5% absolute risk for major malformations is consistent with the estimates of the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention’s national baseline rate of major malformations in the general population,” lead author Adele Viguera, MD, MPH, director of research for women’s mental health, Cleveland Clinic Neurological Institute, told this news organization.
“Our results are reassuring and suggest that second-generation antipsychotics, as a class, do not substantially increase the risk of major malformations,” Dr. Viguera said.
The findings were published online August 3 in the Journal of Clinical Psychiatry.
Safety data scarce
Despite the increasing use of SGAs to treat a “spectrum of psychiatric disorders,” relatively little data are available on the reproductive safety of these agents, Dr. Viguera said.
The National Pregnancy Registry for Atypical Antipsychotics (NPRAA) was established in 2008 to determine risk for major malformation among infants exposed to these medications during the first trimester, relative to a comparison group of unexposed infants of mothers with histories of psychiatric morbidity.
The NPRAA follows pregnant women (aged 18 to 45 years) with psychiatric illness who are exposed or unexposed to SGAs during pregnancy. Participants are recruited through nationwide provider referral, self-referral, and advertisement through the Massachusetts General Hospital Center for Women’s Mental Health website.
Specific data collected are shown in the following table.
Since publication of the first results in 2015, the sample size for the trial has increased – and the absolute and relative risk for major malformations observed in the study population are “more precise,” the investigators note. The current study presented updated previous findings.
Demographic differences
Of the 1,906 women who enrolled as of April 2020, 1,311 (mean age, 32.6 years; 81.3% White) completed the study and were eligible for inclusion in the analysis.
Although the groups had a virtually identical mean age, fewer women in the exposure group were married compared with those in the non-exposure group (77% vs. 90%, respectively) and fewer had a college education (71.2% vs. 87.8%). There was also a higher percentage of first-trimester cigarette smokers in the exposure group (18.4% vs. 5.1%).
On the other hand, more women in the non-exposure group used alcohol than in the exposure group (28.6% vs. 21.4%, respectively).
The most frequent psychiatric disorder in the exposure group was bipolar disorder (63.9%), followed by major depression (12.9%), anxiety (5.8%), and schizophrenia (4.5%). Only 11.4% of women in the non-exposure group were diagnosed with bipolar disorder, whereas 34.1% were diagnosed with major depression, 31.3% with anxiety, and none with schizophrenia.
Notably, a large percentage of women in both groups had a history of postpartum depression and/or psychosis (41.4% and 35.5%, respectively).
The most frequently used SGAs in the exposure group were quetiapine (Seroquel), aripiprazole (Abilify), and lurasidone (Latuda).
Participants in the exposure group had a higher age at initial onset of primary psychiatric diagnosis and a lower proportion of lifetime illness compared with those in the non-exposure group.
Major clinical implication?
Among 640 live births in the exposure group, which included 17 twin pregnancies and 1 triplet pregnancy, 2.5% reported major malformations. Among 704 live births in the control group, which included 14 twin pregnancies, 1.99% reported major malformations.
The estimated OR for major malformations comparing exposed and unexposed infants was 1.48 (95% confidence interval, 0.625-3.517).
The authors note that their findings were consistent with one of the largest studies to date, which included a nationwide sample of more than 1 million women. Its results showed that, among infants exposed to SGAs versus those who were not exposed, the estimated risk ratio after adjusting for psychiatric conditions was 1.05 (95% CI, 0.96-1.16).
Additionally, “a hallmark of a teratogen is that it tends to cause a specific type or pattern of malformations, and we found no preponderance of one single type of major malformation or specific pattern of malformations among the exposed and unexposed groups,” Dr. Viguera said
“A major clinical implication of these findings is that for women with major mood and/or psychotic disorders, treatment with an atypical antipsychotic during pregnancy may be the most prudent clinical decision, much as continued treatment is recommended for pregnant women with other serious and chronic medical conditions, such as epilepsy,” she added.
The concept of ‘satisficing’
Commenting on the study, Vivien Burt, MD, PhD, founder and director/consultant of the Women’s Life Center at the Resnick University of California, Los Angeles (UCLA) Neuropsychiatric Hospital, called the findings “reassuring.”
The results “support the conclusion that in pregnant women with serious psychiatric illnesses, the use of SGAs is often a better option than avoiding these medications and exposing both the women and their offspring to the adverse consequences of maternal mental illness,” she said.
An accompanying editorial co-authored by Dr. Burt and colleague Sonya Rasminsky, MD, introduced the concept of “satisficing” – a term coined by Herbert Simon, a behavioral economist and Nobel Laureate. “Satisficing” is a “decision-making strategy that aims for a satisfactory (‘good enough’) outcome rather than a perfect one.”
The concept applies to decision-making beyond the field of economics “and is critical to how physicians help patients make decisions when they are faced with multiple treatment options,” said Dr. Burt, a professor emeritus of psychiatry at UCLA.
“The goal of ‘satisficing’ is to plan for the most satisfactory outcome, knowing that there are always unknowns, so in an uncertain world, clinicians should carefully help their patients make decisions that will allow them to achieve an outcome they can best live with,” she noted.
The investigators note that their findings may not be generalizable to the larger population of women taking SGAs, given that their participants were “overwhelmingly White, married, and well-educated women.”
They add that enrollment into the NPRAA registry is ongoing and larger sample sizes will “further narrow the confidence interval around the risk estimates and allow for adjustment of likely sources of confounding.”
The NPRAA is supported by Alkermes, Johnson & Johnson/Janssen Pharmaceuticals, Otsuka America Pharmaceutical, Sunovion Pharmaceuticals, SAGE Therapeutics, Teva Pharmaceuticals, and Aurobindo Pharma. Past sponsors of the NPRAA are listed in the original paper. Dr. Viguera receives research support from the NPRAA, Alkermes Biopharmaceuticals, Aurobindo Pharma, Janssen Pharmaceuticals, Otsuka Pharmaceutical, Sunovion Pharmaceuticals, Teva Pharmaceuticals, and SAGE Therapeutics and receives adviser/consulting fees from Up-to-Date. Dr. Burt has been a consultant/speaker for Sage Therapeutics. Dr. Rasminsky has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Psychiatrists’ income, wealth gain ground despite COVID-19 challenges
Although many physicians endured pandemic-related income struggles in 2020, psychiatrists are doing fairly well with building their nest egg and paying down debt, according to the Medscape Psychiatrist Wealth and Debt Report 2021.
Surprisingly, despite COVID-19, psychiatrists’ income improved somewhat this year – from $268,000 in 2020 to $275,000 in 2021.
However, that still puts psychiatrists among the lower-paid specialists.
The highest-paying specialty is plastic surgery ($526,000), followed by orthopedics and orthopedic surgery ($511,000) and cardiology ($459,000), according to the overall Medscape Physician Wealth and Debt Report 2021. The report is based on responses from nearly 18,000 physicians in 29 specialties. All were surveyed between Oct. 6, 2020, and Feb. 11, 2021.
Psychiatrists’ overall wealth gained some ground over the past year, with 40% reporting a net worth of $1 million to $5 million this year – up from 38% last year. Just 6% of psychiatrists have a net worth north of $5 million, up slightly from 5% last year.
Keeping up with bills
based in St. Louis Park, Minn. He noted that the rise in the stock market also played a role, with the S&P 500 finishing the year up over 18%.
“I’ve seen clients accumulate cash, which has added to their net worth. They cut back on spending because they were worried about big declines in income and also because there was simply less to spend money on,” Dr. Greenwald said.
The percentage of psychiatrists with a net worth under $500,000 decreased from 37% last year to 32% this year. Psychiatry is still among the specialties reporting a high percentage of members with net worth below $500,000.
But gender matters. Earnings overall are higher for male than female psychiatrists, and that is reflected in net worth. Fewer female than male psychiatrists are worth more than $5 million (4% vs. 7%), and more female psychiatrists have a net worth of less than $500,000 (41% vs. 26%).
As in prior years, most psychiatrists are paying down a home mortgage on their primary residence (66%). Psychiatrists’ mortgage payments span a wide range, from less than $100,000 (23%) to more than $500,000 (15%). However, 27% report having no mortgage.
Mortgage aside, other top expenses or debts for psychiatrists are car loan payments (36%), paying off college and medical school debt (26%), credit card debt (25%), and medical expenses for self or loved ones (19%).
Other expenses include college tuition for children (16%), car lease payments (14%), mortgage on a second home (13%), private-school tuition for a child (12%), and child care (12%).
Despite some financially challenging months, the vast majority of psychiatrists (94%) kept up with paying their bills.
That’s better than what much of America experienced. According to a U.S. Census Bureau survey conducted last July, roughly 25% of adults missed a mortgage or rent payment because of COVID-related difficulties.
About half of psychiatrists pool their income to pay for bills. One-quarter do not have joint accounts with a spouse or partner.
Spender or saver?
About three-quarters of psychiatrists continued to spend as usual in 2020. About one-quarter took significant steps to lower their expenses, such as refinancing their home or moving to a less costly home.
In line with prior Medscape surveys, about half of psychiatrists have a general idea of how much they spend and on what, but they do not track or formalize it.
According to a recent survey by Intuit, only 35% of Americans say they know how much they spent last month. Viewed by age, 27% of millennials, 34% of Gen Xers, and 46% of baby boomers knew how much they spent.
Many psychiatrists have a higher-than-average number of credit cards; 42% have at least five. By comparison, the average American has four.
Savings was mixed for psychiatrists this past year; 61% put in the same amount or more each month into their 401(k) plans, but 33% put in less money, compared with last year.
For taxable savings accounts, half of psychiatrists put the same amount or more into after-tax accounts – but 22% put in less money, compared with last year. Another one-quarter did not use these savings accounts at all.
The percentage of psychiatrists who experienced losses because of practice problems rose from 6% to 9% in the past year. Much of that was likely because of COVID. However, about the same percentage reported no financial losses this year (76%), compared with last year (75%).
The vast majority of psychiatrists report living within or below their means; only 5% live above their means.
“There are certainly folks who believe that, as long as they pay off their credit card each month and contribute to their 401(k) enough to get their employer match, they’re doing okay,” Dr. Greenwald said.
However, “living within one’s means is having a 3-6 months’ emergency fund; saving at least 20% of gross income toward retirement; adequately funding 529 college accounts; and, for younger docs, paying down high-interest-rate debt at a good clip,” he added.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Although many physicians endured pandemic-related income struggles in 2020, psychiatrists are doing fairly well with building their nest egg and paying down debt, according to the Medscape Psychiatrist Wealth and Debt Report 2021.
Surprisingly, despite COVID-19, psychiatrists’ income improved somewhat this year – from $268,000 in 2020 to $275,000 in 2021.
However, that still puts psychiatrists among the lower-paid specialists.
The highest-paying specialty is plastic surgery ($526,000), followed by orthopedics and orthopedic surgery ($511,000) and cardiology ($459,000), according to the overall Medscape Physician Wealth and Debt Report 2021. The report is based on responses from nearly 18,000 physicians in 29 specialties. All were surveyed between Oct. 6, 2020, and Feb. 11, 2021.
Psychiatrists’ overall wealth gained some ground over the past year, with 40% reporting a net worth of $1 million to $5 million this year – up from 38% last year. Just 6% of psychiatrists have a net worth north of $5 million, up slightly from 5% last year.
Keeping up with bills
based in St. Louis Park, Minn. He noted that the rise in the stock market also played a role, with the S&P 500 finishing the year up over 18%.
“I’ve seen clients accumulate cash, which has added to their net worth. They cut back on spending because they were worried about big declines in income and also because there was simply less to spend money on,” Dr. Greenwald said.
The percentage of psychiatrists with a net worth under $500,000 decreased from 37% last year to 32% this year. Psychiatry is still among the specialties reporting a high percentage of members with net worth below $500,000.
But gender matters. Earnings overall are higher for male than female psychiatrists, and that is reflected in net worth. Fewer female than male psychiatrists are worth more than $5 million (4% vs. 7%), and more female psychiatrists have a net worth of less than $500,000 (41% vs. 26%).
As in prior years, most psychiatrists are paying down a home mortgage on their primary residence (66%). Psychiatrists’ mortgage payments span a wide range, from less than $100,000 (23%) to more than $500,000 (15%). However, 27% report having no mortgage.
Mortgage aside, other top expenses or debts for psychiatrists are car loan payments (36%), paying off college and medical school debt (26%), credit card debt (25%), and medical expenses for self or loved ones (19%).
Other expenses include college tuition for children (16%), car lease payments (14%), mortgage on a second home (13%), private-school tuition for a child (12%), and child care (12%).
Despite some financially challenging months, the vast majority of psychiatrists (94%) kept up with paying their bills.
That’s better than what much of America experienced. According to a U.S. Census Bureau survey conducted last July, roughly 25% of adults missed a mortgage or rent payment because of COVID-related difficulties.
About half of psychiatrists pool their income to pay for bills. One-quarter do not have joint accounts with a spouse or partner.
Spender or saver?
About three-quarters of psychiatrists continued to spend as usual in 2020. About one-quarter took significant steps to lower their expenses, such as refinancing their home or moving to a less costly home.
In line with prior Medscape surveys, about half of psychiatrists have a general idea of how much they spend and on what, but they do not track or formalize it.
According to a recent survey by Intuit, only 35% of Americans say they know how much they spent last month. Viewed by age, 27% of millennials, 34% of Gen Xers, and 46% of baby boomers knew how much they spent.
Many psychiatrists have a higher-than-average number of credit cards; 42% have at least five. By comparison, the average American has four.
Savings was mixed for psychiatrists this past year; 61% put in the same amount or more each month into their 401(k) plans, but 33% put in less money, compared with last year.
For taxable savings accounts, half of psychiatrists put the same amount or more into after-tax accounts – but 22% put in less money, compared with last year. Another one-quarter did not use these savings accounts at all.
The percentage of psychiatrists who experienced losses because of practice problems rose from 6% to 9% in the past year. Much of that was likely because of COVID. However, about the same percentage reported no financial losses this year (76%), compared with last year (75%).
The vast majority of psychiatrists report living within or below their means; only 5% live above their means.
“There are certainly folks who believe that, as long as they pay off their credit card each month and contribute to their 401(k) enough to get their employer match, they’re doing okay,” Dr. Greenwald said.
However, “living within one’s means is having a 3-6 months’ emergency fund; saving at least 20% of gross income toward retirement; adequately funding 529 college accounts; and, for younger docs, paying down high-interest-rate debt at a good clip,” he added.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Although many physicians endured pandemic-related income struggles in 2020, psychiatrists are doing fairly well with building their nest egg and paying down debt, according to the Medscape Psychiatrist Wealth and Debt Report 2021.
Surprisingly, despite COVID-19, psychiatrists’ income improved somewhat this year – from $268,000 in 2020 to $275,000 in 2021.
However, that still puts psychiatrists among the lower-paid specialists.
The highest-paying specialty is plastic surgery ($526,000), followed by orthopedics and orthopedic surgery ($511,000) and cardiology ($459,000), according to the overall Medscape Physician Wealth and Debt Report 2021. The report is based on responses from nearly 18,000 physicians in 29 specialties. All were surveyed between Oct. 6, 2020, and Feb. 11, 2021.
Psychiatrists’ overall wealth gained some ground over the past year, with 40% reporting a net worth of $1 million to $5 million this year – up from 38% last year. Just 6% of psychiatrists have a net worth north of $5 million, up slightly from 5% last year.
Keeping up with bills
based in St. Louis Park, Minn. He noted that the rise in the stock market also played a role, with the S&P 500 finishing the year up over 18%.
“I’ve seen clients accumulate cash, which has added to their net worth. They cut back on spending because they were worried about big declines in income and also because there was simply less to spend money on,” Dr. Greenwald said.
The percentage of psychiatrists with a net worth under $500,000 decreased from 37% last year to 32% this year. Psychiatry is still among the specialties reporting a high percentage of members with net worth below $500,000.
But gender matters. Earnings overall are higher for male than female psychiatrists, and that is reflected in net worth. Fewer female than male psychiatrists are worth more than $5 million (4% vs. 7%), and more female psychiatrists have a net worth of less than $500,000 (41% vs. 26%).
As in prior years, most psychiatrists are paying down a home mortgage on their primary residence (66%). Psychiatrists’ mortgage payments span a wide range, from less than $100,000 (23%) to more than $500,000 (15%). However, 27% report having no mortgage.
Mortgage aside, other top expenses or debts for psychiatrists are car loan payments (36%), paying off college and medical school debt (26%), credit card debt (25%), and medical expenses for self or loved ones (19%).
Other expenses include college tuition for children (16%), car lease payments (14%), mortgage on a second home (13%), private-school tuition for a child (12%), and child care (12%).
Despite some financially challenging months, the vast majority of psychiatrists (94%) kept up with paying their bills.
That’s better than what much of America experienced. According to a U.S. Census Bureau survey conducted last July, roughly 25% of adults missed a mortgage or rent payment because of COVID-related difficulties.
About half of psychiatrists pool their income to pay for bills. One-quarter do not have joint accounts with a spouse or partner.
Spender or saver?
About three-quarters of psychiatrists continued to spend as usual in 2020. About one-quarter took significant steps to lower their expenses, such as refinancing their home or moving to a less costly home.
In line with prior Medscape surveys, about half of psychiatrists have a general idea of how much they spend and on what, but they do not track or formalize it.
According to a recent survey by Intuit, only 35% of Americans say they know how much they spent last month. Viewed by age, 27% of millennials, 34% of Gen Xers, and 46% of baby boomers knew how much they spent.
Many psychiatrists have a higher-than-average number of credit cards; 42% have at least five. By comparison, the average American has four.
Savings was mixed for psychiatrists this past year; 61% put in the same amount or more each month into their 401(k) plans, but 33% put in less money, compared with last year.
For taxable savings accounts, half of psychiatrists put the same amount or more into after-tax accounts – but 22% put in less money, compared with last year. Another one-quarter did not use these savings accounts at all.
The percentage of psychiatrists who experienced losses because of practice problems rose from 6% to 9% in the past year. Much of that was likely because of COVID. However, about the same percentage reported no financial losses this year (76%), compared with last year (75%).
The vast majority of psychiatrists report living within or below their means; only 5% live above their means.
“There are certainly folks who believe that, as long as they pay off their credit card each month and contribute to their 401(k) enough to get their employer match, they’re doing okay,” Dr. Greenwald said.
However, “living within one’s means is having a 3-6 months’ emergency fund; saving at least 20% of gross income toward retirement; adequately funding 529 college accounts; and, for younger docs, paying down high-interest-rate debt at a good clip,” he added.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Shedding the super-doctor myth requires an honest look at systemic racism
An overwhelmingly loud and high-pitched screech rattles against your hip. You startle and groan into the pillow as your thoughts settle into conscious awareness. It is 3 a.m. You are a 2nd-year resident trudging through the night shift, alerted to the presence of a new patient awaiting an emergency assessment. You are the only in-house physician. Walking steadfastly toward the emergency unit, you enter and greet the patient. Immediately, you observe a look of surprise followed immediately by a scowl.
You extend a hand, but your greeting is abruptly cut short with: “I want to see a doctor!” You pace your breaths to quell annoyance and resume your introduction, asserting that you are a doctor and indeed the only doctor on duty. After moments of deep sighs and questions regarding your credentials, you persuade the patient to start the interview.
It is now 8 a.m. The frustration of the night starts to ease as you prepare to leave. While gathering your things, a visitor is overheard inquiring the whereabouts of a hospital unit. Volunteering as a guide, you walk the person toward the opposite end of the hospital. Bleary eyed, muscle laxed, and bone weary, you point out the entrance, then turn to leave. The steady rhythm of your steps suddenly halts as you hear from behind: “Thank you! You speak English really well!” Blankly, you stare. Your voice remains mute while your brain screams: “What is that supposed to mean?” But you do not utter a sound, because intuitively, you know the answer.
While reading this scenario, what did you feel? Pride in knowing that the physician was able to successfully navigate a busy night? Relief in the physician’s ability to maintain a professional demeanor despite belittling microaggressions? Are you angry? Would you replay those moments like reruns of a bad TV show? Can you imagine entering your home and collapsing onto the bed as your tears of fury pool over your rumpled sheets?
The emotional release of that morning is seared into my memory. Over the years, I questioned my reactions. Was I too passive? Should I have schooled them on their ignorance? Had I done so, would I have incurred reprimands? Would standing up for myself cause years of hard work to fall away? Moreover, had I defended myself, would I forever have been viewed as “The Angry Black Woman?”
This story is more than a vignette. For me, it is another reminder that, despite how far we have come, we have much further to go. As a Black woman in a professional sphere, I stand upon the shoulders of those who sacrificed for a dream, a greater purpose. My foremothers and forefathers fought bravely and tirelessly so that we could attain levels of success that were only once but a dream. Despite this progress, a grimace, carelessly spoken words, or a mindless gesture remind me that, no matter how much I toil and what levels of success I achieve, when I meet someone for the first time or encounter someone from my past, I find myself wondering whether I am remembered for me or because I am “The Black One.”
Honest look at medicine is imperative
It is important to consider multiple facets of the super-doctor myth. We are dedicated, fearless, authoritative, ambitious individuals. We do not yield to sickness, family obligations, or fatigue. Medicine is a calling, and the patient deserves the utmost respect and professional behavior. Impervious to ethnicity, race, nationality, or creed, we are unbiased and always in service of the greater good. Often, however, I wonder how the expectations of patient-focused, patient-centered care can prevail without an honest look at the vicissitudes facing medicine.
We find ourselves amid a tumultuous year overshadowed by a devastating pandemic that skews heavily toward Black and Brown communities, in addition to political turmoil and racial reckoning that sprang forth from fear, anger, and determination ignited by the murders of Breonna Taylor and George Floyd – communities united in outrage lamenting the cries of Black Lives Matter.
I remember the tears briskly falling upon my blouse as I watched Mr. Floyd’s life violently ripped from this Earth. Shortly thereafter, I remember the phone calls, emails, and texts from close friends, acquaintances, and colleagues offering support, listening ears, pledging to learn and endeavoring to understand the struggle for recognition and the fight for human rights. Even so, the deafening support was clouded by the preternatural silence of some medical organizations. Within the Black physician community, outrage was palpable. We reflected upon years of sacrifice and perseverance despite the challenge of bigotry, ignorance, and racism – not only from patients and their families – but also colleagues and administrators. Yet, in our time of horror and need, in those moments of vulnerability ... silence. Eventually, lengthy proclamations of support were expressed through various media. However, it felt too safe, too corporate, and too generic and inauthentic. As a result, an exodus of Black physicians from leadership positions and academic medicine took hold as the blatant continuation of rhetoric – coupled with ineffective outreach and support – finally took its toll.
Frequently, I question how the obstacles of medical school, residency, and beyond are expected to be traversed while living in a world that consistently affords additional challenges to those who look, act, or speak in a manner that varies from the perceived standard. In a culture where the myth of the super doctor reigns, how do we reconcile attainment of a false and detrimental narrative while the overarching pressure acutely felt by Black physicians magnifies in the setting of stereotypes, sociopolitical turbulence, bigotry, and racism? How can one sacrifice for an entity that is unwilling to acknowledge the psychological implications of that sacrifice?
For instance, while in medical school, I transitioned my hair to its natural state but was counseled against doing so because of the risk of losing residency opportunities as a direct result of my “unprofessional” appearance. Throughout residency, multiple incidents come to mind, including frequent demands to see my hospital badge despite the same not being of asked of my White cohorts; denial of entry into physician entrance within the residency building because, despite my professional attire, I was presumed to be a member of the custodial staff; and patients being confused and asking for a doctor despite my long white coat and clear introductions.
Furthermore, the fluency of my speech and the absence of regional dialect or vernacular are quite often lauded by patients. Inquiries to touch my hair as well as hypotheses regarding my nationality or degree of “blackness” with respect to the shape of my nose, eyes, and lips are openly questioned. Unfortunately, those uncomfortable incidents have not been limited to patient encounters.
In one instance, while presenting a patient in the presence of my attending and a 3rd-year medical student, I was sternly admonished for disclosing the race of the patient. I sat still and resolute as this doctor spoke on increased risk of bias in diagnosis and treatment when race is identified. Outwardly, I projected patience but inside, I seethed. In that moment, I realized that I would never have the luxury of ignorance or denial. Although I desire to be valued for my prowess in medicine, the mythical status was not created with my skin color in mind. For is avoidance not but a reflection of denial?
In these chaotic and uncertain times, how can we continue to promote a pathological ideal when the roads traveled are so fundamentally skewed? If a White physician faces a belligerent and argumentative patient, there is opportunity for debriefing both individually and among a larger cohort via classes, conferences, and supervisions. Conversely, when a Black physician is derided with racist sentiment, will they have the same opportunity for reflection and support? Despite identical expectations of professionalism and growth, how can one be successful in a system that either directly or indirectly encourages the opposite?
As we try to shed the super-doctor myth, we must recognize that this unattainable and detrimental persona hinders progress. This myth undermines our ability to understand our fragility, the limitations of our capabilities, and the strength of our vulnerability. We must take an honest look at the manner in which our individual biases and the deeply ingrained (and potentially unconscious) systemic biases are counterintuitive to the success and support of physicians of color.
Dr. Thomas is a board-certified adult psychiatrist with an interest in chronic illness, women’s behavioral health, and minority mental health. She currently practices in North Kingstown and East Providence, R.I. She has no conflicts of interest.
An overwhelmingly loud and high-pitched screech rattles against your hip. You startle and groan into the pillow as your thoughts settle into conscious awareness. It is 3 a.m. You are a 2nd-year resident trudging through the night shift, alerted to the presence of a new patient awaiting an emergency assessment. You are the only in-house physician. Walking steadfastly toward the emergency unit, you enter and greet the patient. Immediately, you observe a look of surprise followed immediately by a scowl.
You extend a hand, but your greeting is abruptly cut short with: “I want to see a doctor!” You pace your breaths to quell annoyance and resume your introduction, asserting that you are a doctor and indeed the only doctor on duty. After moments of deep sighs and questions regarding your credentials, you persuade the patient to start the interview.
It is now 8 a.m. The frustration of the night starts to ease as you prepare to leave. While gathering your things, a visitor is overheard inquiring the whereabouts of a hospital unit. Volunteering as a guide, you walk the person toward the opposite end of the hospital. Bleary eyed, muscle laxed, and bone weary, you point out the entrance, then turn to leave. The steady rhythm of your steps suddenly halts as you hear from behind: “Thank you! You speak English really well!” Blankly, you stare. Your voice remains mute while your brain screams: “What is that supposed to mean?” But you do not utter a sound, because intuitively, you know the answer.
While reading this scenario, what did you feel? Pride in knowing that the physician was able to successfully navigate a busy night? Relief in the physician’s ability to maintain a professional demeanor despite belittling microaggressions? Are you angry? Would you replay those moments like reruns of a bad TV show? Can you imagine entering your home and collapsing onto the bed as your tears of fury pool over your rumpled sheets?
The emotional release of that morning is seared into my memory. Over the years, I questioned my reactions. Was I too passive? Should I have schooled them on their ignorance? Had I done so, would I have incurred reprimands? Would standing up for myself cause years of hard work to fall away? Moreover, had I defended myself, would I forever have been viewed as “The Angry Black Woman?”
This story is more than a vignette. For me, it is another reminder that, despite how far we have come, we have much further to go. As a Black woman in a professional sphere, I stand upon the shoulders of those who sacrificed for a dream, a greater purpose. My foremothers and forefathers fought bravely and tirelessly so that we could attain levels of success that were only once but a dream. Despite this progress, a grimace, carelessly spoken words, or a mindless gesture remind me that, no matter how much I toil and what levels of success I achieve, when I meet someone for the first time or encounter someone from my past, I find myself wondering whether I am remembered for me or because I am “The Black One.”
Honest look at medicine is imperative
It is important to consider multiple facets of the super-doctor myth. We are dedicated, fearless, authoritative, ambitious individuals. We do not yield to sickness, family obligations, or fatigue. Medicine is a calling, and the patient deserves the utmost respect and professional behavior. Impervious to ethnicity, race, nationality, or creed, we are unbiased and always in service of the greater good. Often, however, I wonder how the expectations of patient-focused, patient-centered care can prevail without an honest look at the vicissitudes facing medicine.
We find ourselves amid a tumultuous year overshadowed by a devastating pandemic that skews heavily toward Black and Brown communities, in addition to political turmoil and racial reckoning that sprang forth from fear, anger, and determination ignited by the murders of Breonna Taylor and George Floyd – communities united in outrage lamenting the cries of Black Lives Matter.
I remember the tears briskly falling upon my blouse as I watched Mr. Floyd’s life violently ripped from this Earth. Shortly thereafter, I remember the phone calls, emails, and texts from close friends, acquaintances, and colleagues offering support, listening ears, pledging to learn and endeavoring to understand the struggle for recognition and the fight for human rights. Even so, the deafening support was clouded by the preternatural silence of some medical organizations. Within the Black physician community, outrage was palpable. We reflected upon years of sacrifice and perseverance despite the challenge of bigotry, ignorance, and racism – not only from patients and their families – but also colleagues and administrators. Yet, in our time of horror and need, in those moments of vulnerability ... silence. Eventually, lengthy proclamations of support were expressed through various media. However, it felt too safe, too corporate, and too generic and inauthentic. As a result, an exodus of Black physicians from leadership positions and academic medicine took hold as the blatant continuation of rhetoric – coupled with ineffective outreach and support – finally took its toll.
Frequently, I question how the obstacles of medical school, residency, and beyond are expected to be traversed while living in a world that consistently affords additional challenges to those who look, act, or speak in a manner that varies from the perceived standard. In a culture where the myth of the super doctor reigns, how do we reconcile attainment of a false and detrimental narrative while the overarching pressure acutely felt by Black physicians magnifies in the setting of stereotypes, sociopolitical turbulence, bigotry, and racism? How can one sacrifice for an entity that is unwilling to acknowledge the psychological implications of that sacrifice?
For instance, while in medical school, I transitioned my hair to its natural state but was counseled against doing so because of the risk of losing residency opportunities as a direct result of my “unprofessional” appearance. Throughout residency, multiple incidents come to mind, including frequent demands to see my hospital badge despite the same not being of asked of my White cohorts; denial of entry into physician entrance within the residency building because, despite my professional attire, I was presumed to be a member of the custodial staff; and patients being confused and asking for a doctor despite my long white coat and clear introductions.
Furthermore, the fluency of my speech and the absence of regional dialect or vernacular are quite often lauded by patients. Inquiries to touch my hair as well as hypotheses regarding my nationality or degree of “blackness” with respect to the shape of my nose, eyes, and lips are openly questioned. Unfortunately, those uncomfortable incidents have not been limited to patient encounters.
In one instance, while presenting a patient in the presence of my attending and a 3rd-year medical student, I was sternly admonished for disclosing the race of the patient. I sat still and resolute as this doctor spoke on increased risk of bias in diagnosis and treatment when race is identified. Outwardly, I projected patience but inside, I seethed. In that moment, I realized that I would never have the luxury of ignorance or denial. Although I desire to be valued for my prowess in medicine, the mythical status was not created with my skin color in mind. For is avoidance not but a reflection of denial?
In these chaotic and uncertain times, how can we continue to promote a pathological ideal when the roads traveled are so fundamentally skewed? If a White physician faces a belligerent and argumentative patient, there is opportunity for debriefing both individually and among a larger cohort via classes, conferences, and supervisions. Conversely, when a Black physician is derided with racist sentiment, will they have the same opportunity for reflection and support? Despite identical expectations of professionalism and growth, how can one be successful in a system that either directly or indirectly encourages the opposite?
As we try to shed the super-doctor myth, we must recognize that this unattainable and detrimental persona hinders progress. This myth undermines our ability to understand our fragility, the limitations of our capabilities, and the strength of our vulnerability. We must take an honest look at the manner in which our individual biases and the deeply ingrained (and potentially unconscious) systemic biases are counterintuitive to the success and support of physicians of color.
Dr. Thomas is a board-certified adult psychiatrist with an interest in chronic illness, women’s behavioral health, and minority mental health. She currently practices in North Kingstown and East Providence, R.I. She has no conflicts of interest.
An overwhelmingly loud and high-pitched screech rattles against your hip. You startle and groan into the pillow as your thoughts settle into conscious awareness. It is 3 a.m. You are a 2nd-year resident trudging through the night shift, alerted to the presence of a new patient awaiting an emergency assessment. You are the only in-house physician. Walking steadfastly toward the emergency unit, you enter and greet the patient. Immediately, you observe a look of surprise followed immediately by a scowl.
You extend a hand, but your greeting is abruptly cut short with: “I want to see a doctor!” You pace your breaths to quell annoyance and resume your introduction, asserting that you are a doctor and indeed the only doctor on duty. After moments of deep sighs and questions regarding your credentials, you persuade the patient to start the interview.
It is now 8 a.m. The frustration of the night starts to ease as you prepare to leave. While gathering your things, a visitor is overheard inquiring the whereabouts of a hospital unit. Volunteering as a guide, you walk the person toward the opposite end of the hospital. Bleary eyed, muscle laxed, and bone weary, you point out the entrance, then turn to leave. The steady rhythm of your steps suddenly halts as you hear from behind: “Thank you! You speak English really well!” Blankly, you stare. Your voice remains mute while your brain screams: “What is that supposed to mean?” But you do not utter a sound, because intuitively, you know the answer.
While reading this scenario, what did you feel? Pride in knowing that the physician was able to successfully navigate a busy night? Relief in the physician’s ability to maintain a professional demeanor despite belittling microaggressions? Are you angry? Would you replay those moments like reruns of a bad TV show? Can you imagine entering your home and collapsing onto the bed as your tears of fury pool over your rumpled sheets?
The emotional release of that morning is seared into my memory. Over the years, I questioned my reactions. Was I too passive? Should I have schooled them on their ignorance? Had I done so, would I have incurred reprimands? Would standing up for myself cause years of hard work to fall away? Moreover, had I defended myself, would I forever have been viewed as “The Angry Black Woman?”
This story is more than a vignette. For me, it is another reminder that, despite how far we have come, we have much further to go. As a Black woman in a professional sphere, I stand upon the shoulders of those who sacrificed for a dream, a greater purpose. My foremothers and forefathers fought bravely and tirelessly so that we could attain levels of success that were only once but a dream. Despite this progress, a grimace, carelessly spoken words, or a mindless gesture remind me that, no matter how much I toil and what levels of success I achieve, when I meet someone for the first time or encounter someone from my past, I find myself wondering whether I am remembered for me or because I am “The Black One.”
Honest look at medicine is imperative
It is important to consider multiple facets of the super-doctor myth. We are dedicated, fearless, authoritative, ambitious individuals. We do not yield to sickness, family obligations, or fatigue. Medicine is a calling, and the patient deserves the utmost respect and professional behavior. Impervious to ethnicity, race, nationality, or creed, we are unbiased and always in service of the greater good. Often, however, I wonder how the expectations of patient-focused, patient-centered care can prevail without an honest look at the vicissitudes facing medicine.
We find ourselves amid a tumultuous year overshadowed by a devastating pandemic that skews heavily toward Black and Brown communities, in addition to political turmoil and racial reckoning that sprang forth from fear, anger, and determination ignited by the murders of Breonna Taylor and George Floyd – communities united in outrage lamenting the cries of Black Lives Matter.
I remember the tears briskly falling upon my blouse as I watched Mr. Floyd’s life violently ripped from this Earth. Shortly thereafter, I remember the phone calls, emails, and texts from close friends, acquaintances, and colleagues offering support, listening ears, pledging to learn and endeavoring to understand the struggle for recognition and the fight for human rights. Even so, the deafening support was clouded by the preternatural silence of some medical organizations. Within the Black physician community, outrage was palpable. We reflected upon years of sacrifice and perseverance despite the challenge of bigotry, ignorance, and racism – not only from patients and their families – but also colleagues and administrators. Yet, in our time of horror and need, in those moments of vulnerability ... silence. Eventually, lengthy proclamations of support were expressed through various media. However, it felt too safe, too corporate, and too generic and inauthentic. As a result, an exodus of Black physicians from leadership positions and academic medicine took hold as the blatant continuation of rhetoric – coupled with ineffective outreach and support – finally took its toll.
Frequently, I question how the obstacles of medical school, residency, and beyond are expected to be traversed while living in a world that consistently affords additional challenges to those who look, act, or speak in a manner that varies from the perceived standard. In a culture where the myth of the super doctor reigns, how do we reconcile attainment of a false and detrimental narrative while the overarching pressure acutely felt by Black physicians magnifies in the setting of stereotypes, sociopolitical turbulence, bigotry, and racism? How can one sacrifice for an entity that is unwilling to acknowledge the psychological implications of that sacrifice?
For instance, while in medical school, I transitioned my hair to its natural state but was counseled against doing so because of the risk of losing residency opportunities as a direct result of my “unprofessional” appearance. Throughout residency, multiple incidents come to mind, including frequent demands to see my hospital badge despite the same not being of asked of my White cohorts; denial of entry into physician entrance within the residency building because, despite my professional attire, I was presumed to be a member of the custodial staff; and patients being confused and asking for a doctor despite my long white coat and clear introductions.
Furthermore, the fluency of my speech and the absence of regional dialect or vernacular are quite often lauded by patients. Inquiries to touch my hair as well as hypotheses regarding my nationality or degree of “blackness” with respect to the shape of my nose, eyes, and lips are openly questioned. Unfortunately, those uncomfortable incidents have not been limited to patient encounters.
In one instance, while presenting a patient in the presence of my attending and a 3rd-year medical student, I was sternly admonished for disclosing the race of the patient. I sat still and resolute as this doctor spoke on increased risk of bias in diagnosis and treatment when race is identified. Outwardly, I projected patience but inside, I seethed. In that moment, I realized that I would never have the luxury of ignorance or denial. Although I desire to be valued for my prowess in medicine, the mythical status was not created with my skin color in mind. For is avoidance not but a reflection of denial?
In these chaotic and uncertain times, how can we continue to promote a pathological ideal when the roads traveled are so fundamentally skewed? If a White physician faces a belligerent and argumentative patient, there is opportunity for debriefing both individually and among a larger cohort via classes, conferences, and supervisions. Conversely, when a Black physician is derided with racist sentiment, will they have the same opportunity for reflection and support? Despite identical expectations of professionalism and growth, how can one be successful in a system that either directly or indirectly encourages the opposite?
As we try to shed the super-doctor myth, we must recognize that this unattainable and detrimental persona hinders progress. This myth undermines our ability to understand our fragility, the limitations of our capabilities, and the strength of our vulnerability. We must take an honest look at the manner in which our individual biases and the deeply ingrained (and potentially unconscious) systemic biases are counterintuitive to the success and support of physicians of color.
Dr. Thomas is a board-certified adult psychiatrist with an interest in chronic illness, women’s behavioral health, and minority mental health. She currently practices in North Kingstown and East Providence, R.I. She has no conflicts of interest.
‘No justification’ for suicide warning on all antiseizure meds
, new research shows. “There appears to be no justification for the FDA to label every new antiseizure medication with a warning that it may increase risk of suicidality,” said study investigator Michael R. Sperling, MD, professor of neurology, Thomas Jefferson University, Philadelphia.
“How many patients are afraid of their medication and do not take it because of the warning – and are consequently at risk because of that? We do not know, but have anecdotal experience that this is certainly an issue,” Dr. Sperling, who is director of the Jefferson Comprehensive Epilepsy Center, added.
The study was published online August 2 in JAMA Neurology.
Blanket warning
In 2008, the FDA issued an alert stating that antiseizure medications increase suicidality. The alert was based on pooled data from placebo-controlled clinical trials that included 11 antiseizure medications – carbamazepine, felbamate, gabapentin, lamotrigine, levetiracetam, oxcarbazepine, pregabalin, tiagabine, topiramate, valproate, and zonisamide.
The meta-analytic review showed that, compared with placebo, antiseizure medications nearly doubled suicide risk among patients treated for epilepsy, psychiatric disorders, and other diseases. As a result of the FDA study, all antiseizure medications that have been approved since 2008 carry a warning for suicidality.
However, subsequent analyses did not show the same results, Dr. Sperling and colleagues noted.
“Pivotal” antiseizure medication epilepsy trials since 2008 have evaluated suicidality prospectively. Since 2011, trials have included the validated Columbia Suicidality Severity Rating Scale, they noted.
Meta analysis showed no increased risk
Dr. Sperling and colleagues conducted a meta-analysis of 17 randomized placebo-controlled epilepsy trials of five antiseizure medications approved since 2008. These antiseizure medications were eslicarbazepine, perampanel, brivaracetam, cannabidiol, and cenobamate. The trials involved 5,996 patients, including 4,000 who were treated with antiseizure medications and 1,996 who were treated with placebo.
Confining the analysis to epilepsy trials avoids potential confounders, such as possible differences in suicidality risks between different diseases, the researchers noted.
They found no evidence of increased risk for suicidal ideation (overall risk ratio, antiseizure medications vs. placebo: 0.75; 95% confidence interval: 0.35-1.60) or suicide attempt (risk ratio, 0.75; 95% CI: 0.30-1.87) overall or for any individual antiseizure medication.
Suicidal ideation occurred in 12 of 4,000 patients treated with antiseizure medications (0.30%), versus 7 of 1,996 patients treated with placebo (0.35%) (P = .74). Three patients who were treated with antiseizure medications attempted suicide; no patients who were treated with placebo attempted suicide (P = .22). There were no completed suicides.
“There is no current evidence that the five antiseizure medications evaluated in this study increase suicidality in epilepsy and merit a suicidality class warning,” the investigators wrote. When prescribed for epilepsy, “evidence does not support the FDA’s labeling practice of a blanket assumption of increased suicidality,” said Dr. Sperling.
“Our findings indicate the nonspecific suicide warning for all epilepsy drugs is simply not justifiable,” he said. “The results are not surprising. Different drugs affect cells in different ways. So there’s no reason to expect that every drug would increase suicide risk for every patient,” Dr. Sperling said in a statement.
“It’s important to recognize that epilepsy has many causes – perinatal injury, stroke, tumor, head trauma, developmental malformations, genetic causes, and others – and these underlying etiologies may well contribute to the presence of depression and suicidality in this population,” he said in an interview. “Psychodynamic influences also may occur as a consequence of having seizures. This is a complicated area, and drugs are simply one piece of the puzzle,” he added.
Dr. Sperling said the FDA has accomplished “one useful thing with its warning – it highlighted that physicians and other health care providers must pay attention to their patients’ psychological state, ask questions, and treat accordingly.”
The study had no specific funding. Dr. Sperling has received grants from Eisai, Medtronic, Neurelis, SK Life Science, Sunovion, Takeda, Xenon, Cerevel Therapeutics, UCB Pharma, and Engage Pharma; personal fees from Neurelis, Medscape, Neurology Live, International Medical Press, UCB Pharma, Eisai, Oxford University Press, and Projects in Knowledge. He has also consulted for Medtronic outside the submitted work; payments went to Thomas Jefferson University. A complete list of authors’ disclosures is available with the original article.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
, new research shows. “There appears to be no justification for the FDA to label every new antiseizure medication with a warning that it may increase risk of suicidality,” said study investigator Michael R. Sperling, MD, professor of neurology, Thomas Jefferson University, Philadelphia.
“How many patients are afraid of their medication and do not take it because of the warning – and are consequently at risk because of that? We do not know, but have anecdotal experience that this is certainly an issue,” Dr. Sperling, who is director of the Jefferson Comprehensive Epilepsy Center, added.
The study was published online August 2 in JAMA Neurology.
Blanket warning
In 2008, the FDA issued an alert stating that antiseizure medications increase suicidality. The alert was based on pooled data from placebo-controlled clinical trials that included 11 antiseizure medications – carbamazepine, felbamate, gabapentin, lamotrigine, levetiracetam, oxcarbazepine, pregabalin, tiagabine, topiramate, valproate, and zonisamide.
The meta-analytic review showed that, compared with placebo, antiseizure medications nearly doubled suicide risk among patients treated for epilepsy, psychiatric disorders, and other diseases. As a result of the FDA study, all antiseizure medications that have been approved since 2008 carry a warning for suicidality.
However, subsequent analyses did not show the same results, Dr. Sperling and colleagues noted.
“Pivotal” antiseizure medication epilepsy trials since 2008 have evaluated suicidality prospectively. Since 2011, trials have included the validated Columbia Suicidality Severity Rating Scale, they noted.
Meta analysis showed no increased risk
Dr. Sperling and colleagues conducted a meta-analysis of 17 randomized placebo-controlled epilepsy trials of five antiseizure medications approved since 2008. These antiseizure medications were eslicarbazepine, perampanel, brivaracetam, cannabidiol, and cenobamate. The trials involved 5,996 patients, including 4,000 who were treated with antiseizure medications and 1,996 who were treated with placebo.
Confining the analysis to epilepsy trials avoids potential confounders, such as possible differences in suicidality risks between different diseases, the researchers noted.
They found no evidence of increased risk for suicidal ideation (overall risk ratio, antiseizure medications vs. placebo: 0.75; 95% confidence interval: 0.35-1.60) or suicide attempt (risk ratio, 0.75; 95% CI: 0.30-1.87) overall or for any individual antiseizure medication.
Suicidal ideation occurred in 12 of 4,000 patients treated with antiseizure medications (0.30%), versus 7 of 1,996 patients treated with placebo (0.35%) (P = .74). Three patients who were treated with antiseizure medications attempted suicide; no patients who were treated with placebo attempted suicide (P = .22). There were no completed suicides.
“There is no current evidence that the five antiseizure medications evaluated in this study increase suicidality in epilepsy and merit a suicidality class warning,” the investigators wrote. When prescribed for epilepsy, “evidence does not support the FDA’s labeling practice of a blanket assumption of increased suicidality,” said Dr. Sperling.
“Our findings indicate the nonspecific suicide warning for all epilepsy drugs is simply not justifiable,” he said. “The results are not surprising. Different drugs affect cells in different ways. So there’s no reason to expect that every drug would increase suicide risk for every patient,” Dr. Sperling said in a statement.
“It’s important to recognize that epilepsy has many causes – perinatal injury, stroke, tumor, head trauma, developmental malformations, genetic causes, and others – and these underlying etiologies may well contribute to the presence of depression and suicidality in this population,” he said in an interview. “Psychodynamic influences also may occur as a consequence of having seizures. This is a complicated area, and drugs are simply one piece of the puzzle,” he added.
Dr. Sperling said the FDA has accomplished “one useful thing with its warning – it highlighted that physicians and other health care providers must pay attention to their patients’ psychological state, ask questions, and treat accordingly.”
The study had no specific funding. Dr. Sperling has received grants from Eisai, Medtronic, Neurelis, SK Life Science, Sunovion, Takeda, Xenon, Cerevel Therapeutics, UCB Pharma, and Engage Pharma; personal fees from Neurelis, Medscape, Neurology Live, International Medical Press, UCB Pharma, Eisai, Oxford University Press, and Projects in Knowledge. He has also consulted for Medtronic outside the submitted work; payments went to Thomas Jefferson University. A complete list of authors’ disclosures is available with the original article.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
, new research shows. “There appears to be no justification for the FDA to label every new antiseizure medication with a warning that it may increase risk of suicidality,” said study investigator Michael R. Sperling, MD, professor of neurology, Thomas Jefferson University, Philadelphia.
“How many patients are afraid of their medication and do not take it because of the warning – and are consequently at risk because of that? We do not know, but have anecdotal experience that this is certainly an issue,” Dr. Sperling, who is director of the Jefferson Comprehensive Epilepsy Center, added.
The study was published online August 2 in JAMA Neurology.
Blanket warning
In 2008, the FDA issued an alert stating that antiseizure medications increase suicidality. The alert was based on pooled data from placebo-controlled clinical trials that included 11 antiseizure medications – carbamazepine, felbamate, gabapentin, lamotrigine, levetiracetam, oxcarbazepine, pregabalin, tiagabine, topiramate, valproate, and zonisamide.
The meta-analytic review showed that, compared with placebo, antiseizure medications nearly doubled suicide risk among patients treated for epilepsy, psychiatric disorders, and other diseases. As a result of the FDA study, all antiseizure medications that have been approved since 2008 carry a warning for suicidality.
However, subsequent analyses did not show the same results, Dr. Sperling and colleagues noted.
“Pivotal” antiseizure medication epilepsy trials since 2008 have evaluated suicidality prospectively. Since 2011, trials have included the validated Columbia Suicidality Severity Rating Scale, they noted.
Meta analysis showed no increased risk
Dr. Sperling and colleagues conducted a meta-analysis of 17 randomized placebo-controlled epilepsy trials of five antiseizure medications approved since 2008. These antiseizure medications were eslicarbazepine, perampanel, brivaracetam, cannabidiol, and cenobamate. The trials involved 5,996 patients, including 4,000 who were treated with antiseizure medications and 1,996 who were treated with placebo.
Confining the analysis to epilepsy trials avoids potential confounders, such as possible differences in suicidality risks between different diseases, the researchers noted.
They found no evidence of increased risk for suicidal ideation (overall risk ratio, antiseizure medications vs. placebo: 0.75; 95% confidence interval: 0.35-1.60) or suicide attempt (risk ratio, 0.75; 95% CI: 0.30-1.87) overall or for any individual antiseizure medication.
Suicidal ideation occurred in 12 of 4,000 patients treated with antiseizure medications (0.30%), versus 7 of 1,996 patients treated with placebo (0.35%) (P = .74). Three patients who were treated with antiseizure medications attempted suicide; no patients who were treated with placebo attempted suicide (P = .22). There were no completed suicides.
“There is no current evidence that the five antiseizure medications evaluated in this study increase suicidality in epilepsy and merit a suicidality class warning,” the investigators wrote. When prescribed for epilepsy, “evidence does not support the FDA’s labeling practice of a blanket assumption of increased suicidality,” said Dr. Sperling.
“Our findings indicate the nonspecific suicide warning for all epilepsy drugs is simply not justifiable,” he said. “The results are not surprising. Different drugs affect cells in different ways. So there’s no reason to expect that every drug would increase suicide risk for every patient,” Dr. Sperling said in a statement.
“It’s important to recognize that epilepsy has many causes – perinatal injury, stroke, tumor, head trauma, developmental malformations, genetic causes, and others – and these underlying etiologies may well contribute to the presence of depression and suicidality in this population,” he said in an interview. “Psychodynamic influences also may occur as a consequence of having seizures. This is a complicated area, and drugs are simply one piece of the puzzle,” he added.
Dr. Sperling said the FDA has accomplished “one useful thing with its warning – it highlighted that physicians and other health care providers must pay attention to their patients’ psychological state, ask questions, and treat accordingly.”
The study had no specific funding. Dr. Sperling has received grants from Eisai, Medtronic, Neurelis, SK Life Science, Sunovion, Takeda, Xenon, Cerevel Therapeutics, UCB Pharma, and Engage Pharma; personal fees from Neurelis, Medscape, Neurology Live, International Medical Press, UCB Pharma, Eisai, Oxford University Press, and Projects in Knowledge. He has also consulted for Medtronic outside the submitted work; payments went to Thomas Jefferson University. A complete list of authors’ disclosures is available with the original article.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM JAMA NEUROLOGY
Wisdom may counter loneliness, burnout in older adults
Wisdom increases with age, and although this personality trait is regarded as nebulous by many, there is evidence that it has biological and neuropsychiatric underpinnings. It could even hold the key to reducing loneliness and burnout among older people.
Those were some of the key messages delivered by Tanya T. Nguyen, PhD, of the department of psychiatry at the University of California, San Diego, who spoke at a virtual meeting presented by Current Psychiatry and the American Academy of Clinical Psychiatrists.
“To many people, wisdom remains a fuzzy concept that’s difficult to operationalize and measure. It’s analogous to the concepts of consciousness, emotions, and cognitions, which at one point were considered nonscientific, but today we accept them as biological and scientific entities,” Dr. Nguyen said during her talk at the meeting presented by MedscapeLive. MedscapeLive and this news organization are owned by the same parent company.
Interest in quantifying and studying wisdom has picked up in recent years, and Dr. Nguyen gave a definition with six elements that includes prosocial behaviors such as empathy and compassion, as well as emotional regulation, self-reflection, decisiveness, and social decision-making. She also included a spirituality component, though she conceded that this is controversial.
She noted that there are cultural variations in the definition of wisdom, but it has changed little over time, suggesting that it may be biological rather than cultural in nature, and therefore may have a neuropsychiatric underpinning.
Loss of some or all characteristics of wisdom occurs in some behaviors and disorders, including most markedly in the neurodegenerative disorder frontotemporal dementia (FTD), which is characterized by damage only in the prefrontal cortex and anterior temporal lobes. It usually occurs before age 60, and patients exhibit poor social awareness, impulsivity, antisocial behavior, and a lack of insight and empathy.
This and other lines of evidence have led to the suggestion that wisdom may be governed by processes in the prefrontal cortex and the limbic striatum. The prefrontal cortex controls executive functions such as planning, predicting, and anticipating events, as well as managing emotional reactions and impulses. “Thus, wisdom involves parts of the brain that balance cold, hard analytical reasoning with primitive desires and drives, which ultimately leads to self-regulation, social insight, theory of mind, and empathy,” said Dr. Nguyen.
Wisdom has long been associated with age, but age is also linked to cognitive decline. A recent discovery that the brain does not stop evolving at older age may help explain this contradiction. Brains develop in a back to front order, so that the prefrontal cortex is the last to mature. As we age, neural activity shifts from the occipital lobes to the prefrontal cortex and its executive decision-making power.
“The brain may recruit higher-order networks to the prefrontal cortex that are associated with wisdom development,” said Dr. Nguyen. She also pointed out that asymmetry between the left and right hemisphere is reduced with age, as tasks that relied on circuits from one hemisphere or another more often call upon both. “In order to make up for lost synapses and neurons with aging, active older adults use more neuronal networks from both hemispheres to perform the same mental activity,” Dr. Nguyen said.
Some interventions can improve scores in traits associated with wisdom in older adults, and could be an important contributor to improvements in health and longevity, said Dr. Nguyen. Randomized, controlled trials have demonstrated that psychosocial or behavioral interventions can improve elements of wisdom such as prosocial behaviors and emotional regulation, both in people with mental illness and in the general population, with moderate to large effect sizes. But such studies don’t prove an effect on overall wisdom.
The intervention achieved positive results in 89 participants in senior housing communities, though the effect sizes were small, possibly because of high baseline resilience. A subanalysis suggested that reduction in loneliness was mediated by an increase in compassion.
“One of the most striking findings from our research on wisdom is this consistent and very strongly negative correlation between wisdom and loneliness,” Dr. Nguyen said. She highlighted other U.S. nationwide and cross-cultural studies that showed inverse relationships between loneliness and wisdom.
Loneliness is an important topic because it can contribute to burnout and suicide rates.
“Loneliness has a profound effect on how we show up in the workplace, in school, and in our communities. And that leads to anxiety, depression, depersonalization, and emotional fatigue. All are key features of burnout. And together loneliness and burnout have contributed to increased rates of suicide by 30%, and opioid-related deaths almost sixfold since the late 1990s,” Dr. Nguyen said.
Loneliness also is associated with worse physical health, and it may be linked to wisdom. “Loneliness can be conceptualized as being caused and maintained by objective circumstances, such as physical or social distancing, and by thoughts, behaviors, and feelings surrounding those experiences, including biased perceptions of social relations, and a negative assessment of one’s social skills, which then results in a discrepancy between one’s desired and perceived social relationships, which then can contribute to social withdrawal,” Dr. Nguyen said.
Dr. Nguyen highlighted the AARP Foundation’s Experience Corps program, which recruits older adults to act as mentors and tutors for children in kindergarten through third grade. It involves 15 hours per week over an entire school year, with a focus on child literacy, development, and behavioral management skills. A study revealed a significant impact. “It showed improvements in children’s grades and happiness, as well as seniors’ mental and physical health,” Dr. Nguyen said.
Dr. Nguyen concluded that wisdom “may be a vaccine against compassion fatigue and burnout that drive today’s behavioral epidemics of loneliness, opioid abuse, and suicide. It’s a tool for our times. It’s nuanced, flexible, pragmatic, compassionate, and it presents a reasonable framework for getting along in the often messy world that we all share.”
Implications for psychiatrists
Henry A. Nasrallah, MD, who organized the conference, suggested that the benefits of wisdom may not be limited to patients. He pointed out that surgeons often retire at age 60 or 65 because of declining physical skills, while psychiatrists continue to practice.
“We develop more wisdom and better skills, and we can practice into our 60s and 70s. I know psychiatrists who practice sometimes into their 80s. It’s really a wonderful thing to know that what you do in life develops or enhances the neuroplasticity of certain brain regions. In our case, in psychiatry, it is the brain regions involved in wisdom,” commented Dr. Nasrallah, who is a professor of psychiatry, neurology, and neuroscience at the University of Cincinnati.
Dr. Nguyen has no financial disclosures. Dr. Nasrallah has received grants from Abbott, AstraZeneca, Forest, Janssen, Lilly, Pfizer, and Shire, and advises Abbott, AstraZeneca, and Shire.
Wisdom increases with age, and although this personality trait is regarded as nebulous by many, there is evidence that it has biological and neuropsychiatric underpinnings. It could even hold the key to reducing loneliness and burnout among older people.
Those were some of the key messages delivered by Tanya T. Nguyen, PhD, of the department of psychiatry at the University of California, San Diego, who spoke at a virtual meeting presented by Current Psychiatry and the American Academy of Clinical Psychiatrists.
“To many people, wisdom remains a fuzzy concept that’s difficult to operationalize and measure. It’s analogous to the concepts of consciousness, emotions, and cognitions, which at one point were considered nonscientific, but today we accept them as biological and scientific entities,” Dr. Nguyen said during her talk at the meeting presented by MedscapeLive. MedscapeLive and this news organization are owned by the same parent company.
Interest in quantifying and studying wisdom has picked up in recent years, and Dr. Nguyen gave a definition with six elements that includes prosocial behaviors such as empathy and compassion, as well as emotional regulation, self-reflection, decisiveness, and social decision-making. She also included a spirituality component, though she conceded that this is controversial.
She noted that there are cultural variations in the definition of wisdom, but it has changed little over time, suggesting that it may be biological rather than cultural in nature, and therefore may have a neuropsychiatric underpinning.
Loss of some or all characteristics of wisdom occurs in some behaviors and disorders, including most markedly in the neurodegenerative disorder frontotemporal dementia (FTD), which is characterized by damage only in the prefrontal cortex and anterior temporal lobes. It usually occurs before age 60, and patients exhibit poor social awareness, impulsivity, antisocial behavior, and a lack of insight and empathy.
This and other lines of evidence have led to the suggestion that wisdom may be governed by processes in the prefrontal cortex and the limbic striatum. The prefrontal cortex controls executive functions such as planning, predicting, and anticipating events, as well as managing emotional reactions and impulses. “Thus, wisdom involves parts of the brain that balance cold, hard analytical reasoning with primitive desires and drives, which ultimately leads to self-regulation, social insight, theory of mind, and empathy,” said Dr. Nguyen.
Wisdom has long been associated with age, but age is also linked to cognitive decline. A recent discovery that the brain does not stop evolving at older age may help explain this contradiction. Brains develop in a back to front order, so that the prefrontal cortex is the last to mature. As we age, neural activity shifts from the occipital lobes to the prefrontal cortex and its executive decision-making power.
“The brain may recruit higher-order networks to the prefrontal cortex that are associated with wisdom development,” said Dr. Nguyen. She also pointed out that asymmetry between the left and right hemisphere is reduced with age, as tasks that relied on circuits from one hemisphere or another more often call upon both. “In order to make up for lost synapses and neurons with aging, active older adults use more neuronal networks from both hemispheres to perform the same mental activity,” Dr. Nguyen said.
Some interventions can improve scores in traits associated with wisdom in older adults, and could be an important contributor to improvements in health and longevity, said Dr. Nguyen. Randomized, controlled trials have demonstrated that psychosocial or behavioral interventions can improve elements of wisdom such as prosocial behaviors and emotional regulation, both in people with mental illness and in the general population, with moderate to large effect sizes. But such studies don’t prove an effect on overall wisdom.
The intervention achieved positive results in 89 participants in senior housing communities, though the effect sizes were small, possibly because of high baseline resilience. A subanalysis suggested that reduction in loneliness was mediated by an increase in compassion.
“One of the most striking findings from our research on wisdom is this consistent and very strongly negative correlation between wisdom and loneliness,” Dr. Nguyen said. She highlighted other U.S. nationwide and cross-cultural studies that showed inverse relationships between loneliness and wisdom.
Loneliness is an important topic because it can contribute to burnout and suicide rates.
“Loneliness has a profound effect on how we show up in the workplace, in school, and in our communities. And that leads to anxiety, depression, depersonalization, and emotional fatigue. All are key features of burnout. And together loneliness and burnout have contributed to increased rates of suicide by 30%, and opioid-related deaths almost sixfold since the late 1990s,” Dr. Nguyen said.
Loneliness also is associated with worse physical health, and it may be linked to wisdom. “Loneliness can be conceptualized as being caused and maintained by objective circumstances, such as physical or social distancing, and by thoughts, behaviors, and feelings surrounding those experiences, including biased perceptions of social relations, and a negative assessment of one’s social skills, which then results in a discrepancy between one’s desired and perceived social relationships, which then can contribute to social withdrawal,” Dr. Nguyen said.
Dr. Nguyen highlighted the AARP Foundation’s Experience Corps program, which recruits older adults to act as mentors and tutors for children in kindergarten through third grade. It involves 15 hours per week over an entire school year, with a focus on child literacy, development, and behavioral management skills. A study revealed a significant impact. “It showed improvements in children’s grades and happiness, as well as seniors’ mental and physical health,” Dr. Nguyen said.
Dr. Nguyen concluded that wisdom “may be a vaccine against compassion fatigue and burnout that drive today’s behavioral epidemics of loneliness, opioid abuse, and suicide. It’s a tool for our times. It’s nuanced, flexible, pragmatic, compassionate, and it presents a reasonable framework for getting along in the often messy world that we all share.”
Implications for psychiatrists
Henry A. Nasrallah, MD, who organized the conference, suggested that the benefits of wisdom may not be limited to patients. He pointed out that surgeons often retire at age 60 or 65 because of declining physical skills, while psychiatrists continue to practice.
“We develop more wisdom and better skills, and we can practice into our 60s and 70s. I know psychiatrists who practice sometimes into their 80s. It’s really a wonderful thing to know that what you do in life develops or enhances the neuroplasticity of certain brain regions. In our case, in psychiatry, it is the brain regions involved in wisdom,” commented Dr. Nasrallah, who is a professor of psychiatry, neurology, and neuroscience at the University of Cincinnati.
Dr. Nguyen has no financial disclosures. Dr. Nasrallah has received grants from Abbott, AstraZeneca, Forest, Janssen, Lilly, Pfizer, and Shire, and advises Abbott, AstraZeneca, and Shire.
Wisdom increases with age, and although this personality trait is regarded as nebulous by many, there is evidence that it has biological and neuropsychiatric underpinnings. It could even hold the key to reducing loneliness and burnout among older people.
Those were some of the key messages delivered by Tanya T. Nguyen, PhD, of the department of psychiatry at the University of California, San Diego, who spoke at a virtual meeting presented by Current Psychiatry and the American Academy of Clinical Psychiatrists.
“To many people, wisdom remains a fuzzy concept that’s difficult to operationalize and measure. It’s analogous to the concepts of consciousness, emotions, and cognitions, which at one point were considered nonscientific, but today we accept them as biological and scientific entities,” Dr. Nguyen said during her talk at the meeting presented by MedscapeLive. MedscapeLive and this news organization are owned by the same parent company.
Interest in quantifying and studying wisdom has picked up in recent years, and Dr. Nguyen gave a definition with six elements that includes prosocial behaviors such as empathy and compassion, as well as emotional regulation, self-reflection, decisiveness, and social decision-making. She also included a spirituality component, though she conceded that this is controversial.
She noted that there are cultural variations in the definition of wisdom, but it has changed little over time, suggesting that it may be biological rather than cultural in nature, and therefore may have a neuropsychiatric underpinning.
Loss of some or all characteristics of wisdom occurs in some behaviors and disorders, including most markedly in the neurodegenerative disorder frontotemporal dementia (FTD), which is characterized by damage only in the prefrontal cortex and anterior temporal lobes. It usually occurs before age 60, and patients exhibit poor social awareness, impulsivity, antisocial behavior, and a lack of insight and empathy.
This and other lines of evidence have led to the suggestion that wisdom may be governed by processes in the prefrontal cortex and the limbic striatum. The prefrontal cortex controls executive functions such as planning, predicting, and anticipating events, as well as managing emotional reactions and impulses. “Thus, wisdom involves parts of the brain that balance cold, hard analytical reasoning with primitive desires and drives, which ultimately leads to self-regulation, social insight, theory of mind, and empathy,” said Dr. Nguyen.
Wisdom has long been associated with age, but age is also linked to cognitive decline. A recent discovery that the brain does not stop evolving at older age may help explain this contradiction. Brains develop in a back to front order, so that the prefrontal cortex is the last to mature. As we age, neural activity shifts from the occipital lobes to the prefrontal cortex and its executive decision-making power.
“The brain may recruit higher-order networks to the prefrontal cortex that are associated with wisdom development,” said Dr. Nguyen. She also pointed out that asymmetry between the left and right hemisphere is reduced with age, as tasks that relied on circuits from one hemisphere or another more often call upon both. “In order to make up for lost synapses and neurons with aging, active older adults use more neuronal networks from both hemispheres to perform the same mental activity,” Dr. Nguyen said.
Some interventions can improve scores in traits associated with wisdom in older adults, and could be an important contributor to improvements in health and longevity, said Dr. Nguyen. Randomized, controlled trials have demonstrated that psychosocial or behavioral interventions can improve elements of wisdom such as prosocial behaviors and emotional regulation, both in people with mental illness and in the general population, with moderate to large effect sizes. But such studies don’t prove an effect on overall wisdom.
The intervention achieved positive results in 89 participants in senior housing communities, though the effect sizes were small, possibly because of high baseline resilience. A subanalysis suggested that reduction in loneliness was mediated by an increase in compassion.
“One of the most striking findings from our research on wisdom is this consistent and very strongly negative correlation between wisdom and loneliness,” Dr. Nguyen said. She highlighted other U.S. nationwide and cross-cultural studies that showed inverse relationships between loneliness and wisdom.
Loneliness is an important topic because it can contribute to burnout and suicide rates.
“Loneliness has a profound effect on how we show up in the workplace, in school, and in our communities. And that leads to anxiety, depression, depersonalization, and emotional fatigue. All are key features of burnout. And together loneliness and burnout have contributed to increased rates of suicide by 30%, and opioid-related deaths almost sixfold since the late 1990s,” Dr. Nguyen said.
Loneliness also is associated with worse physical health, and it may be linked to wisdom. “Loneliness can be conceptualized as being caused and maintained by objective circumstances, such as physical or social distancing, and by thoughts, behaviors, and feelings surrounding those experiences, including biased perceptions of social relations, and a negative assessment of one’s social skills, which then results in a discrepancy between one’s desired and perceived social relationships, which then can contribute to social withdrawal,” Dr. Nguyen said.
Dr. Nguyen highlighted the AARP Foundation’s Experience Corps program, which recruits older adults to act as mentors and tutors for children in kindergarten through third grade. It involves 15 hours per week over an entire school year, with a focus on child literacy, development, and behavioral management skills. A study revealed a significant impact. “It showed improvements in children’s grades and happiness, as well as seniors’ mental and physical health,” Dr. Nguyen said.
Dr. Nguyen concluded that wisdom “may be a vaccine against compassion fatigue and burnout that drive today’s behavioral epidemics of loneliness, opioid abuse, and suicide. It’s a tool for our times. It’s nuanced, flexible, pragmatic, compassionate, and it presents a reasonable framework for getting along in the often messy world that we all share.”
Implications for psychiatrists
Henry A. Nasrallah, MD, who organized the conference, suggested that the benefits of wisdom may not be limited to patients. He pointed out that surgeons often retire at age 60 or 65 because of declining physical skills, while psychiatrists continue to practice.
“We develop more wisdom and better skills, and we can practice into our 60s and 70s. I know psychiatrists who practice sometimes into their 80s. It’s really a wonderful thing to know that what you do in life develops or enhances the neuroplasticity of certain brain regions. In our case, in psychiatry, it is the brain regions involved in wisdom,” commented Dr. Nasrallah, who is a professor of psychiatry, neurology, and neuroscience at the University of Cincinnati.
Dr. Nguyen has no financial disclosures. Dr. Nasrallah has received grants from Abbott, AstraZeneca, Forest, Janssen, Lilly, Pfizer, and Shire, and advises Abbott, AstraZeneca, and Shire.
REPORTING FROM FOCUS ON NEUROPSYCHIATRY 2021












