User login
CDC confirms 13th case of coronavirus in U.S.
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention announced the number of confirmed cases of the 2019 Novel Coronavirus (2019-nCoV) in the United States has reached 13.
The latest case, announced Feb. 11, 2020, by the CDC, was in a person in California who was previously under federal quarantine because the patient had traveled to Wuhan, China.
The CDC is currently looking into who the patient may have come in contact with to understand the potential for further spread of the coronavirus.
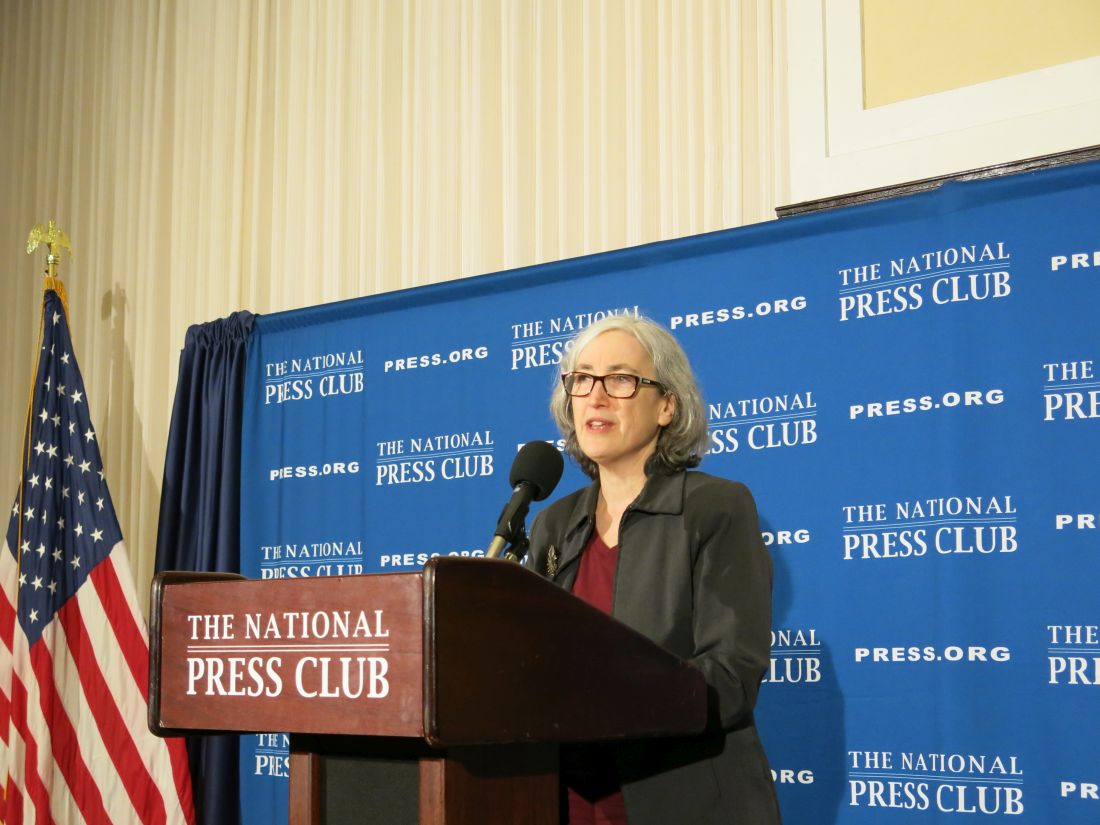
“The contact investigation is ongoing,” CDC principal deputy director Anne Schuchat, MD, said during a Feb. 11 press conference to provide an update on coronavirus containment activities being taken by the CDC.
Dr. Schuchat also addressed issues related to the laboratory test, as the patient in California was initially thought to be negative for the coronavirus.
“With other cases around the country that we are evaluating, we have been doing serial tests to understand whether they are still infectious” and to gather other information about how results change over time, Dr. Schuchat said.
She noted that the CDC does not “have as much information as we would like on the severity of the virus,” noting that there are many cases in China with severe reactions, while the 13 cases in the United States represent a much more mild reaction to the virus so far.
With the latest case in California, she noted that there was “probably a mix-up and the original test wasn’t negative,” although she did not elaborate on what the nature of the mix-up was, stating that was all the information that she had.
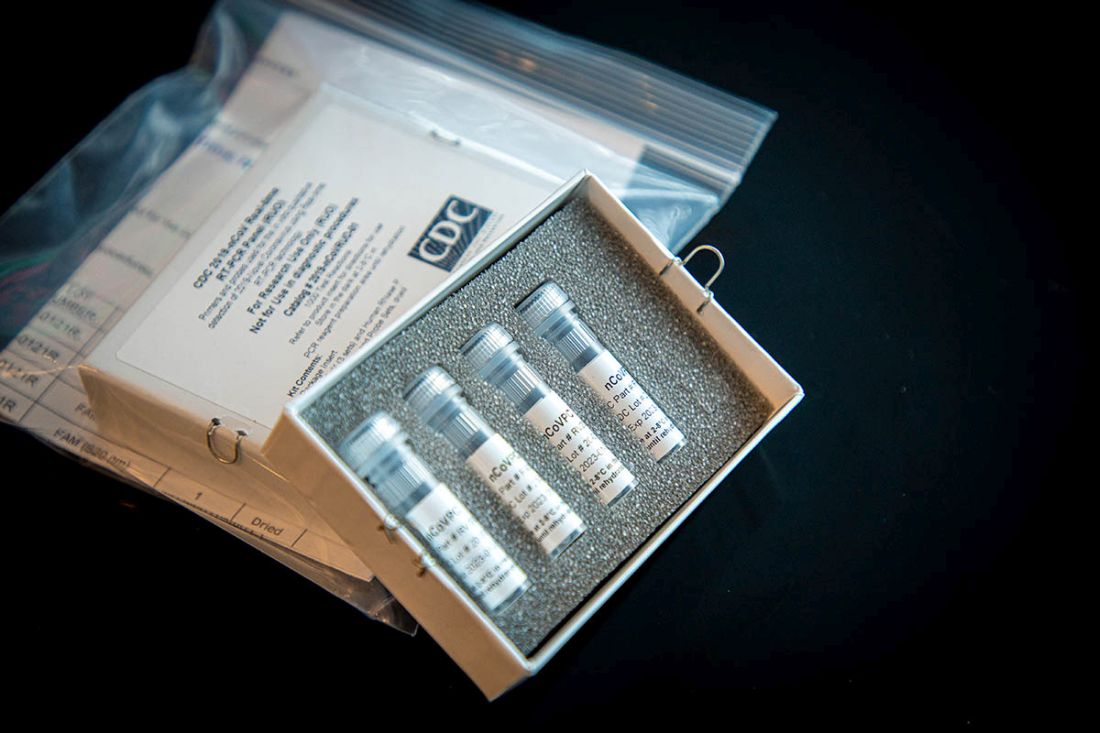
In general, Dr. Schuchat touted the actions taken by the CDC and the federal government focused primarily on containing the spread of the virus in the United States, including the implementation of travel advisories, quarantining passengers returning from China, as well as the new test kits that are being distributed by the agency across the nation and around the world. She also mentioned CDC staff are being deployed around the world to monitor the spreading of the disease and highlighted the outreach efforts to keep the public informed.
Dr. Schuchat highlighted the fact that, of the 13 cases in the United States, 11 were with patients that were in Wuhan, and only 2 were because of close contact with a patient, something that she attributed to the actions being taken.
She also noted that cases in the United States have not been as severe as they have been in China, where deaths have been attributed to the coronavirus outbreak. She added that there have been only two deaths outside of mainland China attributed to the coronavirus.
“Some of the steps the CDC has taken have really put us in better shape should widespread transmission occur in the United States,” she said.
Dr. Schuchat also highlighted that the first charter flight of people quarantined after returning from Wuhan have reached the 14-day milestone and should be on their way home beginning today.
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention announced the number of confirmed cases of the 2019 Novel Coronavirus (2019-nCoV) in the United States has reached 13.
The latest case, announced Feb. 11, 2020, by the CDC, was in a person in California who was previously under federal quarantine because the patient had traveled to Wuhan, China.
The CDC is currently looking into who the patient may have come in contact with to understand the potential for further spread of the coronavirus.
“The contact investigation is ongoing,” CDC principal deputy director Anne Schuchat, MD, said during a Feb. 11 press conference to provide an update on coronavirus containment activities being taken by the CDC.
Dr. Schuchat also addressed issues related to the laboratory test, as the patient in California was initially thought to be negative for the coronavirus.
“With other cases around the country that we are evaluating, we have been doing serial tests to understand whether they are still infectious” and to gather other information about how results change over time, Dr. Schuchat said.
She noted that the CDC does not “have as much information as we would like on the severity of the virus,” noting that there are many cases in China with severe reactions, while the 13 cases in the United States represent a much more mild reaction to the virus so far.
With the latest case in California, she noted that there was “probably a mix-up and the original test wasn’t negative,” although she did not elaborate on what the nature of the mix-up was, stating that was all the information that she had.
In general, Dr. Schuchat touted the actions taken by the CDC and the federal government focused primarily on containing the spread of the virus in the United States, including the implementation of travel advisories, quarantining passengers returning from China, as well as the new test kits that are being distributed by the agency across the nation and around the world. She also mentioned CDC staff are being deployed around the world to monitor the spreading of the disease and highlighted the outreach efforts to keep the public informed.
Dr. Schuchat highlighted the fact that, of the 13 cases in the United States, 11 were with patients that were in Wuhan, and only 2 were because of close contact with a patient, something that she attributed to the actions being taken.
She also noted that cases in the United States have not been as severe as they have been in China, where deaths have been attributed to the coronavirus outbreak. She added that there have been only two deaths outside of mainland China attributed to the coronavirus.
“Some of the steps the CDC has taken have really put us in better shape should widespread transmission occur in the United States,” she said.
Dr. Schuchat also highlighted that the first charter flight of people quarantined after returning from Wuhan have reached the 14-day milestone and should be on their way home beginning today.
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention announced the number of confirmed cases of the 2019 Novel Coronavirus (2019-nCoV) in the United States has reached 13.
The latest case, announced Feb. 11, 2020, by the CDC, was in a person in California who was previously under federal quarantine because the patient had traveled to Wuhan, China.
The CDC is currently looking into who the patient may have come in contact with to understand the potential for further spread of the coronavirus.
“The contact investigation is ongoing,” CDC principal deputy director Anne Schuchat, MD, said during a Feb. 11 press conference to provide an update on coronavirus containment activities being taken by the CDC.
Dr. Schuchat also addressed issues related to the laboratory test, as the patient in California was initially thought to be negative for the coronavirus.
“With other cases around the country that we are evaluating, we have been doing serial tests to understand whether they are still infectious” and to gather other information about how results change over time, Dr. Schuchat said.
She noted that the CDC does not “have as much information as we would like on the severity of the virus,” noting that there are many cases in China with severe reactions, while the 13 cases in the United States represent a much more mild reaction to the virus so far.
With the latest case in California, she noted that there was “probably a mix-up and the original test wasn’t negative,” although she did not elaborate on what the nature of the mix-up was, stating that was all the information that she had.
In general, Dr. Schuchat touted the actions taken by the CDC and the federal government focused primarily on containing the spread of the virus in the United States, including the implementation of travel advisories, quarantining passengers returning from China, as well as the new test kits that are being distributed by the agency across the nation and around the world. She also mentioned CDC staff are being deployed around the world to monitor the spreading of the disease and highlighted the outreach efforts to keep the public informed.
Dr. Schuchat highlighted the fact that, of the 13 cases in the United States, 11 were with patients that were in Wuhan, and only 2 were because of close contact with a patient, something that she attributed to the actions being taken.
She also noted that cases in the United States have not been as severe as they have been in China, where deaths have been attributed to the coronavirus outbreak. She added that there have been only two deaths outside of mainland China attributed to the coronavirus.
“Some of the steps the CDC has taken have really put us in better shape should widespread transmission occur in the United States,” she said.
Dr. Schuchat also highlighted that the first charter flight of people quarantined after returning from Wuhan have reached the 14-day milestone and should be on their way home beginning today.
Consider PET/CT when infectious source is a puzzler
CHICAGO – Dual positron emission tomography-computed tomography (PET/CT) scans changed the treatment course of nearly half of patients whose scans were positive for infection. In a single-center systematic review of 18fluorodeoxyglucose (FDG)–PET/CT scans, 55 of the 138 scans (40%) changed clinical management.
Presenting the findings at the annual meeting of the Radiological Society of North America, Benjamin Viglianti, MD, PhD, said that PET/CT had particular utility in cases of bacteremia and endocarditis, in which the scans changed treatment in 46% of those cases.
Dr. Viglianti, a radiologist at the University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, explained that medical student and first author Anitha Menon, himself, and their collaborators deliberately used a broad definition of clinical management change. The management course was considered to change not only if an unknown infection site was discovered or if a new intervention was initiated after the scan, but also if antibiotic choice or duration was changed or an additional specialty was consulted.
Scans were included in the study if an infectious etiology was found in the scan and if the patient received an infectious disease consult. Bacteremia and endocarditis were the most frequent indications for scans and also the indications for which management was most frequently changed. When a vascular cause was the indication for the scan, management changed 41% of the time. For fevers of unknown origin, the scan changed management in 30% of the cases, while for osteomyelitis, management was changed for 28% of patients.
The investigators identified several broad themes from their review that pointed toward when clinicians might consider FDG-PET/CT imaging in infectious disease management.
The first, said Dr. Viglianti, was that “for patients with suspected vascular graft infection, PET/CT using FDG may be a good first-choice imaging modality.” He pointed to an illustrative case of a patient who was 1 month out from open repair of a thoracoabdominal aortic aneurysm. The patient had abdominal pain, epigastric tenderness and nausea, as well as an erythematous incision site. A CT scan just revealed an abdominal fluid collection, but the PET/CT scan showed radiotracer uptake at the prior repair site, indicating infection.
For patients with bacteremia, the investigators judged that FDG-PET/CT might be particularly useful in patients who have a graft, prosthetic valve, or cardiac device. Here, Dr. Viglianti and his collaborators highlighted the scan of a woman with DiGeorge syndrome who had received aortic root replacement for truncus arteriosis. She had been found to have persistent enterococcal bacteremia at high levels, but had been symptom free. To take a close look at the suspected infectious nidus, a transesophageal echocardiogram had been obtained, but this study didn’t turn up any clear masses or vegetations. The PET/CT scan, though, revealed avid FDG uptake in the area of the prosthesis.
Management course was not likely to be changed for patients with fever of unknown origin, but the investigators did note that whole-body PET/CT was useful to distinguish infectious etiologies from hematologic and oncologic processes. Their review included a patient who had Crohn’s disease and fever, myalgias, and upper abdominal pain, as well as liver enzyme elevation. The PET/CT showed radiotracer uptake within the spleen, which was enlarged. The scan also showed bone marrow uptake; these findings pointed toward hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis rather than an infectious etiology.
For osteomyelitis, said Dr. Viglianti, FDG-PET may have limited utility; it might be most useful when MRI is contraindicated. Within the study population, the investigators identified a patient who had chills and fever along with focal tenderness over the lumbar spine in the context of recent pyelonephritis of a graft kidney. Here, MRI findings were suspicious for osteomyelitis and diskitis, and the FDG uptake at the L4-L5 vertebral levels confirmed the MRI results.
When a patient with a prosthetic valve is suspected of having endocarditis, “cardiac PET/CT may be of high diagnostic value,” said Dr. Viglianti. For patients with endocarditis of native valves, though, a full-body FDG-PET/CT scan may spot septic emboli. A patient identified in the investigators’ review had been admitted for methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus endocarditis. The patient, who had a history of intravenous drug use, received a transesophageal echocardiogram that found severe tricuspid valve regurgitation and vegetations. The whole-body PET/CT scan, though, revealed avid uptake in both buttocks, as well as thigh, ankle and calf muscles – a pattern “suspicious for infectious myositis,” said the researchers.
In discussion during the poster session, Dr. Viglianti said that, although reimbursement for PET/CT scans for infectious etiologies might not be feasible, it can still be a reasonable and even cost-effective choice. At his institution, he said, the requisite radioisotope is made in-house, twice daily, so it’s relatively easy to arrange scans. Since PET/CT scans can be acquired relatively quickly and there’s no delay while waiting for radiotracer uptake, clinical decisions can be made more quickly than when waiting for bone uptake for a technetium-99 scan, he said. This can have the effect of saving a night of hospitalization in many cases.
Dr. Viglianti and Ms. Menon reported that they had no relevant conflicts of interest. No outside sources of funding were reported.
SOURCE: Menon A et al. RSNA 2019, Abstract NM203-SDSUB1.
CHICAGO – Dual positron emission tomography-computed tomography (PET/CT) scans changed the treatment course of nearly half of patients whose scans were positive for infection. In a single-center systematic review of 18fluorodeoxyglucose (FDG)–PET/CT scans, 55 of the 138 scans (40%) changed clinical management.
Presenting the findings at the annual meeting of the Radiological Society of North America, Benjamin Viglianti, MD, PhD, said that PET/CT had particular utility in cases of bacteremia and endocarditis, in which the scans changed treatment in 46% of those cases.
Dr. Viglianti, a radiologist at the University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, explained that medical student and first author Anitha Menon, himself, and their collaborators deliberately used a broad definition of clinical management change. The management course was considered to change not only if an unknown infection site was discovered or if a new intervention was initiated after the scan, but also if antibiotic choice or duration was changed or an additional specialty was consulted.
Scans were included in the study if an infectious etiology was found in the scan and if the patient received an infectious disease consult. Bacteremia and endocarditis were the most frequent indications for scans and also the indications for which management was most frequently changed. When a vascular cause was the indication for the scan, management changed 41% of the time. For fevers of unknown origin, the scan changed management in 30% of the cases, while for osteomyelitis, management was changed for 28% of patients.
The investigators identified several broad themes from their review that pointed toward when clinicians might consider FDG-PET/CT imaging in infectious disease management.
The first, said Dr. Viglianti, was that “for patients with suspected vascular graft infection, PET/CT using FDG may be a good first-choice imaging modality.” He pointed to an illustrative case of a patient who was 1 month out from open repair of a thoracoabdominal aortic aneurysm. The patient had abdominal pain, epigastric tenderness and nausea, as well as an erythematous incision site. A CT scan just revealed an abdominal fluid collection, but the PET/CT scan showed radiotracer uptake at the prior repair site, indicating infection.
For patients with bacteremia, the investigators judged that FDG-PET/CT might be particularly useful in patients who have a graft, prosthetic valve, or cardiac device. Here, Dr. Viglianti and his collaborators highlighted the scan of a woman with DiGeorge syndrome who had received aortic root replacement for truncus arteriosis. She had been found to have persistent enterococcal bacteremia at high levels, but had been symptom free. To take a close look at the suspected infectious nidus, a transesophageal echocardiogram had been obtained, but this study didn’t turn up any clear masses or vegetations. The PET/CT scan, though, revealed avid FDG uptake in the area of the prosthesis.
Management course was not likely to be changed for patients with fever of unknown origin, but the investigators did note that whole-body PET/CT was useful to distinguish infectious etiologies from hematologic and oncologic processes. Their review included a patient who had Crohn’s disease and fever, myalgias, and upper abdominal pain, as well as liver enzyme elevation. The PET/CT showed radiotracer uptake within the spleen, which was enlarged. The scan also showed bone marrow uptake; these findings pointed toward hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis rather than an infectious etiology.
For osteomyelitis, said Dr. Viglianti, FDG-PET may have limited utility; it might be most useful when MRI is contraindicated. Within the study population, the investigators identified a patient who had chills and fever along with focal tenderness over the lumbar spine in the context of recent pyelonephritis of a graft kidney. Here, MRI findings were suspicious for osteomyelitis and diskitis, and the FDG uptake at the L4-L5 vertebral levels confirmed the MRI results.
When a patient with a prosthetic valve is suspected of having endocarditis, “cardiac PET/CT may be of high diagnostic value,” said Dr. Viglianti. For patients with endocarditis of native valves, though, a full-body FDG-PET/CT scan may spot septic emboli. A patient identified in the investigators’ review had been admitted for methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus endocarditis. The patient, who had a history of intravenous drug use, received a transesophageal echocardiogram that found severe tricuspid valve regurgitation and vegetations. The whole-body PET/CT scan, though, revealed avid uptake in both buttocks, as well as thigh, ankle and calf muscles – a pattern “suspicious for infectious myositis,” said the researchers.
In discussion during the poster session, Dr. Viglianti said that, although reimbursement for PET/CT scans for infectious etiologies might not be feasible, it can still be a reasonable and even cost-effective choice. At his institution, he said, the requisite radioisotope is made in-house, twice daily, so it’s relatively easy to arrange scans. Since PET/CT scans can be acquired relatively quickly and there’s no delay while waiting for radiotracer uptake, clinical decisions can be made more quickly than when waiting for bone uptake for a technetium-99 scan, he said. This can have the effect of saving a night of hospitalization in many cases.
Dr. Viglianti and Ms. Menon reported that they had no relevant conflicts of interest. No outside sources of funding were reported.
SOURCE: Menon A et al. RSNA 2019, Abstract NM203-SDSUB1.
CHICAGO – Dual positron emission tomography-computed tomography (PET/CT) scans changed the treatment course of nearly half of patients whose scans were positive for infection. In a single-center systematic review of 18fluorodeoxyglucose (FDG)–PET/CT scans, 55 of the 138 scans (40%) changed clinical management.
Presenting the findings at the annual meeting of the Radiological Society of North America, Benjamin Viglianti, MD, PhD, said that PET/CT had particular utility in cases of bacteremia and endocarditis, in which the scans changed treatment in 46% of those cases.
Dr. Viglianti, a radiologist at the University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, explained that medical student and first author Anitha Menon, himself, and their collaborators deliberately used a broad definition of clinical management change. The management course was considered to change not only if an unknown infection site was discovered or if a new intervention was initiated after the scan, but also if antibiotic choice or duration was changed or an additional specialty was consulted.
Scans were included in the study if an infectious etiology was found in the scan and if the patient received an infectious disease consult. Bacteremia and endocarditis were the most frequent indications for scans and also the indications for which management was most frequently changed. When a vascular cause was the indication for the scan, management changed 41% of the time. For fevers of unknown origin, the scan changed management in 30% of the cases, while for osteomyelitis, management was changed for 28% of patients.
The investigators identified several broad themes from their review that pointed toward when clinicians might consider FDG-PET/CT imaging in infectious disease management.
The first, said Dr. Viglianti, was that “for patients with suspected vascular graft infection, PET/CT using FDG may be a good first-choice imaging modality.” He pointed to an illustrative case of a patient who was 1 month out from open repair of a thoracoabdominal aortic aneurysm. The patient had abdominal pain, epigastric tenderness and nausea, as well as an erythematous incision site. A CT scan just revealed an abdominal fluid collection, but the PET/CT scan showed radiotracer uptake at the prior repair site, indicating infection.
For patients with bacteremia, the investigators judged that FDG-PET/CT might be particularly useful in patients who have a graft, prosthetic valve, or cardiac device. Here, Dr. Viglianti and his collaborators highlighted the scan of a woman with DiGeorge syndrome who had received aortic root replacement for truncus arteriosis. She had been found to have persistent enterococcal bacteremia at high levels, but had been symptom free. To take a close look at the suspected infectious nidus, a transesophageal echocardiogram had been obtained, but this study didn’t turn up any clear masses or vegetations. The PET/CT scan, though, revealed avid FDG uptake in the area of the prosthesis.
Management course was not likely to be changed for patients with fever of unknown origin, but the investigators did note that whole-body PET/CT was useful to distinguish infectious etiologies from hematologic and oncologic processes. Their review included a patient who had Crohn’s disease and fever, myalgias, and upper abdominal pain, as well as liver enzyme elevation. The PET/CT showed radiotracer uptake within the spleen, which was enlarged. The scan also showed bone marrow uptake; these findings pointed toward hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis rather than an infectious etiology.
For osteomyelitis, said Dr. Viglianti, FDG-PET may have limited utility; it might be most useful when MRI is contraindicated. Within the study population, the investigators identified a patient who had chills and fever along with focal tenderness over the lumbar spine in the context of recent pyelonephritis of a graft kidney. Here, MRI findings were suspicious for osteomyelitis and diskitis, and the FDG uptake at the L4-L5 vertebral levels confirmed the MRI results.
When a patient with a prosthetic valve is suspected of having endocarditis, “cardiac PET/CT may be of high diagnostic value,” said Dr. Viglianti. For patients with endocarditis of native valves, though, a full-body FDG-PET/CT scan may spot septic emboli. A patient identified in the investigators’ review had been admitted for methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus endocarditis. The patient, who had a history of intravenous drug use, received a transesophageal echocardiogram that found severe tricuspid valve regurgitation and vegetations. The whole-body PET/CT scan, though, revealed avid uptake in both buttocks, as well as thigh, ankle and calf muscles – a pattern “suspicious for infectious myositis,” said the researchers.
In discussion during the poster session, Dr. Viglianti said that, although reimbursement for PET/CT scans for infectious etiologies might not be feasible, it can still be a reasonable and even cost-effective choice. At his institution, he said, the requisite radioisotope is made in-house, twice daily, so it’s relatively easy to arrange scans. Since PET/CT scans can be acquired relatively quickly and there’s no delay while waiting for radiotracer uptake, clinical decisions can be made more quickly than when waiting for bone uptake for a technetium-99 scan, he said. This can have the effect of saving a night of hospitalization in many cases.
Dr. Viglianti and Ms. Menon reported that they had no relevant conflicts of interest. No outside sources of funding were reported.
SOURCE: Menon A et al. RSNA 2019, Abstract NM203-SDSUB1.
REPORTING FROM RSNA 2019
What you absolutely need to know about tail coverage
A 28-year-old pediatrician working in a large group practice in California found a new job in Pennsylvania. The job would allow her to live with her husband, who was a nonphysician.
On her last day of work at the California job, the practice’s office manager asked her, “Do you know about the tail coverage?”
He explained that it is malpractice insurance for any cases filed against her after leaving the job. Without it, he said, she would not be covered for those claims.
The physician (who asked not to be identified) had very little savings and suddenly had to pay a five-figure bill for tail coverage. To provide the extra malpractice coverage, she and her husband had to use savings they’d set aside to buy a house.
Getting tail coverage, known formally as an extended reporting endorsement, often comes as a complete and costly surprise for new doctors, says Dennis Hursh, Esq, a health care attorney based in Middletown, Penn., who deals with physicians’ employment contracts.
“Having to pay for a tail can disrupt lives,” Hursh said. “A tail can cost about one third of a young doctor’s salary. If you don’t feel you can afford to pay that, you may be forced to stay with a job you don’t like.”
Most medical residents don’t think about tail coverage until they apply for their first job, but last year, residents at Hahnemann University Hospital in Philadelphia got a painful early lesson.
In the summer, the hospital went out of business because of financial problems. Hundreds of medical residents and fellows not only were forced to find new programs but also had to prepare to buy tail coverage for their training years at Hahnemann.
“All the guarantees have been yanked out from under us,” said Tom Sibert, MD, a former internal medicine resident at the hospital, who is now finishing his training in California. “Residents don’t have that kind of money.”
Hahnemann trainees have asked the judge in the bankruptcy proceedings to put them ahead of other creditors and to ensure their tail coverage is paid. As of early February, the issue had not been resolved.
Meanwhile, Sibert and many other former trainees were trying to get quotes for purchasing tail coverage. They have been shocked by the amounts they would have to pay.
How tail coverage works
Medical malpractice tail coverage protects from incidents that took place when doctors were at their previous jobs but that later resulted in malpractice claims after they had left that employer.
One type of malpractice insurance, an occurrence policy, does not need tail coverage. Occurrence policies cover any incident that occurred when the policy was in force, no matter when a claim was filed – even if it is filed many years after the claims-filing period of the policy ends.
However, most malpractice policies – as many as 85%, according to one estimate – are claims-made policies. Claims-made policies are more much common because they’re significantly less expensive than occurrence policies.
Under a claims-made policy, coverage for malpractice claims completely stops when the policy ends. It does not cover incidents that occurred when the policy was in force but for which the patients later filed claims, as the occurrence policy does. So a tail is needed to cover these claims.
Physicians in all stages of their career may need tail coverage when they leave a job, change malpractice carriers, or retire.
But young physicians often have greater problems with tail coverage, for several reasons. They tend to be employed, and as such, they cannot choose the coverage they want. As a result, they most likely get claims-made coverage. In addition, the job turnover tends to be higher for these doctors. When leaving a job, the tail comes into play. More than half of new physicians leave their first job within 5 years, and of those, more than half leave after only 1 or 2 years.
Young physicians have no experience with tails and may not even know what they are. “In training, malpractice coverage is not a problem because the program handles it,” Mr. Hursh said. Accreditation standards require that teaching hospitals buy coverage, including a tail when residents leave.
So when young physicians are offered their first job and are handed an employment contract to sign, they may not even look for tail coverage, says Mr. Hursh, who wrote The Final Hurdle, a Physician’s Guide to Negotiating a Fair Employment Agreement. Instead, “young physicians tend to focus on issues like salary, benefits, and signing bonuses,” he said.
Mr. Hursh says the tail is usually the most expensive potential cost in the contract.
There’s no easy way to get out of paying the tail coverage once it is enshrined in the contract. The full tail can cost five or even six figures, depending on the physicians’ specialty, the local malpractice premium, and the physician’s own claims history.
Can you negotiate your tail coverage?
Negotiating tail coverage in the employment contract involves some familiarity with medical malpractice insurance and a close reading of the contract. First, you have to determine that the employer is providing claims-made coverage, which would require a tail if you leave. Then you have to determine whether the employer will pay for the tail coverage.
Often, the contract does not even mention tail coverage. “It could merely state that the practice will be responsible for malpractice coverage while you are working there,” Mr. Hursh said. Although it never specifies the tail, this language indicates that you will be paying for it, he says.
Therefore, it’s wise to have a conversation with your prospective employer about the tail. “Some new doctors never ask the question ‘What happens if I leave? Do I get tail coverage?’ ” said Israel Teitelbaum, an attorney who is chairman of Contemporary Insurance Services, an insurance broker in Silver Spring, Md.
Talking about the tail, however, can be a touchy subject for many young doctors applying for their first job. The tail matters only if you leave the job, and you may not want to imply that you would ever want to leave. Too much money, however, is on the line for you not to ask, Mr. Teitelbaum said.
Even if the employer verbally agrees to pay for the tail coverage, experts advise that you try to get the employer’s commitment in writing and have it put it into the contract.
Getting the employer to cover the tail in the initial contract is crucial because once you have agreed to work there, “it’s much more difficult to get it changed,” Mr. Teitelbaum said. However, even if tail coverage is not in the first contract, you shouldn’t give up, he says. You should try again in the next contract a few years later.
“It’s never too late to bring it up,” Mr. Teitelbaum said. After a few years of employment, you have a track record at the job. “A doctor who is very desirable to the employer may be able to get tail coverage on contract renewal.”
Coverage: Large employers vs. small employers
Willingness to pay for an employee’s tail coverage varies depending on the size of the employer. Large employers – systems, hospitals, and large practices – are much more likely to cover the tail than small and medium-sized practices.
Large employers tend to pay for at least part of the tail because they realize that it is in their interest to do so. Since they have the deepest pockets, they’re often the first to be named in a lawsuit. They might have to pay the whole claim if the physician did not have tail coverage.
However, many large employers want to use tail coverage as a bargaining chip to make sure doctors stay for a while at least. One typical arrangement, Mr. Hursh says, is to pay only one-fifth of the tail if the physician leaves in the first year of employment and then to pay one fifth more in each succeeding year until year five, when the employer assumes the entire cost of the tail.
Smaller practices, on the other hand, are usually close-fisted about tail coverage. “They tend to view the tail as an unnecessary expense,” Mr. Hursh said. “They don’t want to pay for a doctor who is not generating revenue for them any more.”
Traditionally, when physicians become partners, practices are more generous and agree to pay their tails if they leave, Mr. Hursh says. But he thinks this is changing, too – recent partnership contracts he has reviewed did not provide for tail coverage.
Times you don’t need to pay for tail coverage
Even if you’re responsible for the tail coverage, your insurance arrangement may be such that you don’t have to pay for it, says Michelle Perron, a malpractice insurance broker in North Hampton, N.H.
For example, if the carrier at your new job is the same as the one at your old job, your coverage would continue with no break, and you would not need a tail, she says. Even if you move to another state, your old carrier might also sell policies there, and you would then likely have seamless coverage, Ms. Perron says. This would be handy if you could choose your new carrier.
Even when you change carriers, Ms. Perron says, the new one might agree to pick up the old carrier’s coverage in return for getting your business, assuming you are an independent physician buying your own coverage. The new carrier would issue prior acts coverage, also known as nose coverage.
Older doctors going into retirement also have a potential tail coverage problem, but their tail coverage premium is often waived, Ms. Perron says. The need for a tail has to do with claims arising post retirement, after your coverage has ended. Typically, if you have been with the carrier for at least 5 years and you are age 55 years or older, your carrier will waive the tail coverage premium, she says.
However, if the retired doctor starts practicing again, even part time, the carrier may want to take back the free tail, she says. Some retired doctors get around this by buying a lower-priced tail from another company, but the former carrier may still want its money back, Ms. Perron says.
Can you just go without tail coverage?
What happens if physicians with a tail commitment choose to wing it and not pay for the tail? If a claim was never made against them, they may believe that the expense is unnecessary. The situation, however, is not so simple.
Some states require having tail coverage. Malpractice coverage is required in seven states, and at least some of those states explicitly extend this requirement to tails. They are Colorado, Connecticut, Kansas, Massachusetts, New Jersey, Rhode Island, and Wisconsin. Eleven more states tie malpractice coverage, perhaps including tails, to some benefit for the doctor, such as tort reform. These states include Indiana, Nebraska, New Mexico, New York, and Pennsylvania.
Many hospitals require tail coverage for privileges, and some insurers do as well. In addition, Ms. Perron says a missing tail reduces your prospects when looking for a job. “For the employer, having to pay coverage for a new hire will cost more than starting fresh with someone else,” she said.
Still, it’s important to remember the risk of being sued. “If you don’t buy the tail coverage, you are at risk for a lawsuit for many years to come,” Mr. Teitelbaum said.
Doctors should consider their potential lifetime risk, not just their current risk. Although only 8% of doctors younger than age 40 have been sued for malpractice, that figure climbs to almost half by the time doctors reach age 55.
The risks are higher in some specialties. About 63% of general surgeons and ob.gyns. have been sued.
Many of these claims are without merit, and doctors pay only the legal expenses of defending the case. Some doctors may think they could risk frivolous suits and cover legal expenses out of pocket. An American Medical Association survey showed that 68% of closed claims against doctors were dropped, dismissed, or withdrawn. It said these claims cost an average of more than $30,000 to defend.
However, Mr. Teitelbaum puts the defense costs for so-called frivolous suits much higher than the AMA, at $250,000 or more. “Even if you’re sure you won’t have to pay a claim, you still have to defend yourself against frivolous suits,” he said. “You won’t recover those expenses.”
How to lower your tail coverage cost
Physicians typically have 60 days to buy tail coverage after their regular coverage has ended. Specialized brokers such as Mr. Teitelbaum and Ms. Perron help physicians look for the best tails to buy.
The cost of the tail depends on how long you’ve been at your job when you leave it, Ms. Perron says. If you leave in the first 1 or 2 years of the policy, she says, the tail price will be lower because the coverage period is shorter.
Usually the most expensive tail available is from the carrier that issued the original policy. Why is this? “Carriers rarely sell a tail that undercuts their retail price,” Mr. Teitelbaum said. “They don’t want to compete with themselves, and in fact doing so could pose regulatory problems for them.”
Instead of buying from their own carrier, doctors can purchase stand-alone tails from competitors, which Mr. Teitelbaum says are 10%-30% less expensive than the policy the original carrier issues. However, stand-alone tails are not always easy to find, especially for high-cost specialties such as neurosurgery and ob.gyn., he says.
Some physicians try to bring down the cost of the tail by limiting the duration of the tail. You can buy tails that only cover claims filed 1-5 years after the incident took place, rather than indefinitely. These limits mirror the typical statute of limitations – the time limit to file a claim in each state. This limit is as little as 2 years in some states, though it can be as long as 6 years in others.
However, some states make exceptions to the statute of limitations. The 2- to 6-year clock doesn’t start ticking until the mistake is discovered or, in the case of children, when they reach adulthood. “This means that with a limited tail, you always have risk,” Perron said.
And yet some doctors insist on these time-limited tails. “If a doctor opts for 3 years’ coverage, that’s better than no years,” Mr. Teitelbaum said. “But I would advise them to take at least 5 years because that gives you coverage for the basic statute of limitations in most states. Three-year tails do yield savings, but often they’re not enough to warrant the risk.”
Another way to reduce costs is to lower the coverage limits of the tail. The standard coverage limit is $1 million per case and $3 million per year, so doctors might be able to save money on the premium by buying limits of $200,000/$600,000. But Mr. Teitelbaum says most companies would refuse to sell a policy with a limit lower than that of the expiring policy.
Further ways to reduce the cost of the tail include buying tail coverage that doesn’t give the physician the right to approve a settlement or that doesn’t include legal fees in the coverage limits. But these options, too, raise the physician’s risks. Whichever option you choose, the important thing is to protect yourself against costly lawsuits.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
A 28-year-old pediatrician working in a large group practice in California found a new job in Pennsylvania. The job would allow her to live with her husband, who was a nonphysician.
On her last day of work at the California job, the practice’s office manager asked her, “Do you know about the tail coverage?”
He explained that it is malpractice insurance for any cases filed against her after leaving the job. Without it, he said, she would not be covered for those claims.
The physician (who asked not to be identified) had very little savings and suddenly had to pay a five-figure bill for tail coverage. To provide the extra malpractice coverage, she and her husband had to use savings they’d set aside to buy a house.
Getting tail coverage, known formally as an extended reporting endorsement, often comes as a complete and costly surprise for new doctors, says Dennis Hursh, Esq, a health care attorney based in Middletown, Penn., who deals with physicians’ employment contracts.
“Having to pay for a tail can disrupt lives,” Hursh said. “A tail can cost about one third of a young doctor’s salary. If you don’t feel you can afford to pay that, you may be forced to stay with a job you don’t like.”
Most medical residents don’t think about tail coverage until they apply for their first job, but last year, residents at Hahnemann University Hospital in Philadelphia got a painful early lesson.
In the summer, the hospital went out of business because of financial problems. Hundreds of medical residents and fellows not only were forced to find new programs but also had to prepare to buy tail coverage for their training years at Hahnemann.
“All the guarantees have been yanked out from under us,” said Tom Sibert, MD, a former internal medicine resident at the hospital, who is now finishing his training in California. “Residents don’t have that kind of money.”
Hahnemann trainees have asked the judge in the bankruptcy proceedings to put them ahead of other creditors and to ensure their tail coverage is paid. As of early February, the issue had not been resolved.
Meanwhile, Sibert and many other former trainees were trying to get quotes for purchasing tail coverage. They have been shocked by the amounts they would have to pay.
How tail coverage works
Medical malpractice tail coverage protects from incidents that took place when doctors were at their previous jobs but that later resulted in malpractice claims after they had left that employer.
One type of malpractice insurance, an occurrence policy, does not need tail coverage. Occurrence policies cover any incident that occurred when the policy was in force, no matter when a claim was filed – even if it is filed many years after the claims-filing period of the policy ends.
However, most malpractice policies – as many as 85%, according to one estimate – are claims-made policies. Claims-made policies are more much common because they’re significantly less expensive than occurrence policies.
Under a claims-made policy, coverage for malpractice claims completely stops when the policy ends. It does not cover incidents that occurred when the policy was in force but for which the patients later filed claims, as the occurrence policy does. So a tail is needed to cover these claims.
Physicians in all stages of their career may need tail coverage when they leave a job, change malpractice carriers, or retire.
But young physicians often have greater problems with tail coverage, for several reasons. They tend to be employed, and as such, they cannot choose the coverage they want. As a result, they most likely get claims-made coverage. In addition, the job turnover tends to be higher for these doctors. When leaving a job, the tail comes into play. More than half of new physicians leave their first job within 5 years, and of those, more than half leave after only 1 or 2 years.
Young physicians have no experience with tails and may not even know what they are. “In training, malpractice coverage is not a problem because the program handles it,” Mr. Hursh said. Accreditation standards require that teaching hospitals buy coverage, including a tail when residents leave.
So when young physicians are offered their first job and are handed an employment contract to sign, they may not even look for tail coverage, says Mr. Hursh, who wrote The Final Hurdle, a Physician’s Guide to Negotiating a Fair Employment Agreement. Instead, “young physicians tend to focus on issues like salary, benefits, and signing bonuses,” he said.
Mr. Hursh says the tail is usually the most expensive potential cost in the contract.
There’s no easy way to get out of paying the tail coverage once it is enshrined in the contract. The full tail can cost five or even six figures, depending on the physicians’ specialty, the local malpractice premium, and the physician’s own claims history.
Can you negotiate your tail coverage?
Negotiating tail coverage in the employment contract involves some familiarity with medical malpractice insurance and a close reading of the contract. First, you have to determine that the employer is providing claims-made coverage, which would require a tail if you leave. Then you have to determine whether the employer will pay for the tail coverage.
Often, the contract does not even mention tail coverage. “It could merely state that the practice will be responsible for malpractice coverage while you are working there,” Mr. Hursh said. Although it never specifies the tail, this language indicates that you will be paying for it, he says.
Therefore, it’s wise to have a conversation with your prospective employer about the tail. “Some new doctors never ask the question ‘What happens if I leave? Do I get tail coverage?’ ” said Israel Teitelbaum, an attorney who is chairman of Contemporary Insurance Services, an insurance broker in Silver Spring, Md.
Talking about the tail, however, can be a touchy subject for many young doctors applying for their first job. The tail matters only if you leave the job, and you may not want to imply that you would ever want to leave. Too much money, however, is on the line for you not to ask, Mr. Teitelbaum said.
Even if the employer verbally agrees to pay for the tail coverage, experts advise that you try to get the employer’s commitment in writing and have it put it into the contract.
Getting the employer to cover the tail in the initial contract is crucial because once you have agreed to work there, “it’s much more difficult to get it changed,” Mr. Teitelbaum said. However, even if tail coverage is not in the first contract, you shouldn’t give up, he says. You should try again in the next contract a few years later.
“It’s never too late to bring it up,” Mr. Teitelbaum said. After a few years of employment, you have a track record at the job. “A doctor who is very desirable to the employer may be able to get tail coverage on contract renewal.”
Coverage: Large employers vs. small employers
Willingness to pay for an employee’s tail coverage varies depending on the size of the employer. Large employers – systems, hospitals, and large practices – are much more likely to cover the tail than small and medium-sized practices.
Large employers tend to pay for at least part of the tail because they realize that it is in their interest to do so. Since they have the deepest pockets, they’re often the first to be named in a lawsuit. They might have to pay the whole claim if the physician did not have tail coverage.
However, many large employers want to use tail coverage as a bargaining chip to make sure doctors stay for a while at least. One typical arrangement, Mr. Hursh says, is to pay only one-fifth of the tail if the physician leaves in the first year of employment and then to pay one fifth more in each succeeding year until year five, when the employer assumes the entire cost of the tail.
Smaller practices, on the other hand, are usually close-fisted about tail coverage. “They tend to view the tail as an unnecessary expense,” Mr. Hursh said. “They don’t want to pay for a doctor who is not generating revenue for them any more.”
Traditionally, when physicians become partners, practices are more generous and agree to pay their tails if they leave, Mr. Hursh says. But he thinks this is changing, too – recent partnership contracts he has reviewed did not provide for tail coverage.
Times you don’t need to pay for tail coverage
Even if you’re responsible for the tail coverage, your insurance arrangement may be such that you don’t have to pay for it, says Michelle Perron, a malpractice insurance broker in North Hampton, N.H.
For example, if the carrier at your new job is the same as the one at your old job, your coverage would continue with no break, and you would not need a tail, she says. Even if you move to another state, your old carrier might also sell policies there, and you would then likely have seamless coverage, Ms. Perron says. This would be handy if you could choose your new carrier.
Even when you change carriers, Ms. Perron says, the new one might agree to pick up the old carrier’s coverage in return for getting your business, assuming you are an independent physician buying your own coverage. The new carrier would issue prior acts coverage, also known as nose coverage.
Older doctors going into retirement also have a potential tail coverage problem, but their tail coverage premium is often waived, Ms. Perron says. The need for a tail has to do with claims arising post retirement, after your coverage has ended. Typically, if you have been with the carrier for at least 5 years and you are age 55 years or older, your carrier will waive the tail coverage premium, she says.
However, if the retired doctor starts practicing again, even part time, the carrier may want to take back the free tail, she says. Some retired doctors get around this by buying a lower-priced tail from another company, but the former carrier may still want its money back, Ms. Perron says.
Can you just go without tail coverage?
What happens if physicians with a tail commitment choose to wing it and not pay for the tail? If a claim was never made against them, they may believe that the expense is unnecessary. The situation, however, is not so simple.
Some states require having tail coverage. Malpractice coverage is required in seven states, and at least some of those states explicitly extend this requirement to tails. They are Colorado, Connecticut, Kansas, Massachusetts, New Jersey, Rhode Island, and Wisconsin. Eleven more states tie malpractice coverage, perhaps including tails, to some benefit for the doctor, such as tort reform. These states include Indiana, Nebraska, New Mexico, New York, and Pennsylvania.
Many hospitals require tail coverage for privileges, and some insurers do as well. In addition, Ms. Perron says a missing tail reduces your prospects when looking for a job. “For the employer, having to pay coverage for a new hire will cost more than starting fresh with someone else,” she said.
Still, it’s important to remember the risk of being sued. “If you don’t buy the tail coverage, you are at risk for a lawsuit for many years to come,” Mr. Teitelbaum said.
Doctors should consider their potential lifetime risk, not just their current risk. Although only 8% of doctors younger than age 40 have been sued for malpractice, that figure climbs to almost half by the time doctors reach age 55.
The risks are higher in some specialties. About 63% of general surgeons and ob.gyns. have been sued.
Many of these claims are without merit, and doctors pay only the legal expenses of defending the case. Some doctors may think they could risk frivolous suits and cover legal expenses out of pocket. An American Medical Association survey showed that 68% of closed claims against doctors were dropped, dismissed, or withdrawn. It said these claims cost an average of more than $30,000 to defend.
However, Mr. Teitelbaum puts the defense costs for so-called frivolous suits much higher than the AMA, at $250,000 or more. “Even if you’re sure you won’t have to pay a claim, you still have to defend yourself against frivolous suits,” he said. “You won’t recover those expenses.”
How to lower your tail coverage cost
Physicians typically have 60 days to buy tail coverage after their regular coverage has ended. Specialized brokers such as Mr. Teitelbaum and Ms. Perron help physicians look for the best tails to buy.
The cost of the tail depends on how long you’ve been at your job when you leave it, Ms. Perron says. If you leave in the first 1 or 2 years of the policy, she says, the tail price will be lower because the coverage period is shorter.
Usually the most expensive tail available is from the carrier that issued the original policy. Why is this? “Carriers rarely sell a tail that undercuts their retail price,” Mr. Teitelbaum said. “They don’t want to compete with themselves, and in fact doing so could pose regulatory problems for them.”
Instead of buying from their own carrier, doctors can purchase stand-alone tails from competitors, which Mr. Teitelbaum says are 10%-30% less expensive than the policy the original carrier issues. However, stand-alone tails are not always easy to find, especially for high-cost specialties such as neurosurgery and ob.gyn., he says.
Some physicians try to bring down the cost of the tail by limiting the duration of the tail. You can buy tails that only cover claims filed 1-5 years after the incident took place, rather than indefinitely. These limits mirror the typical statute of limitations – the time limit to file a claim in each state. This limit is as little as 2 years in some states, though it can be as long as 6 years in others.
However, some states make exceptions to the statute of limitations. The 2- to 6-year clock doesn’t start ticking until the mistake is discovered or, in the case of children, when they reach adulthood. “This means that with a limited tail, you always have risk,” Perron said.
And yet some doctors insist on these time-limited tails. “If a doctor opts for 3 years’ coverage, that’s better than no years,” Mr. Teitelbaum said. “But I would advise them to take at least 5 years because that gives you coverage for the basic statute of limitations in most states. Three-year tails do yield savings, but often they’re not enough to warrant the risk.”
Another way to reduce costs is to lower the coverage limits of the tail. The standard coverage limit is $1 million per case and $3 million per year, so doctors might be able to save money on the premium by buying limits of $200,000/$600,000. But Mr. Teitelbaum says most companies would refuse to sell a policy with a limit lower than that of the expiring policy.
Further ways to reduce the cost of the tail include buying tail coverage that doesn’t give the physician the right to approve a settlement or that doesn’t include legal fees in the coverage limits. But these options, too, raise the physician’s risks. Whichever option you choose, the important thing is to protect yourself against costly lawsuits.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
A 28-year-old pediatrician working in a large group practice in California found a new job in Pennsylvania. The job would allow her to live with her husband, who was a nonphysician.
On her last day of work at the California job, the practice’s office manager asked her, “Do you know about the tail coverage?”
He explained that it is malpractice insurance for any cases filed against her after leaving the job. Without it, he said, she would not be covered for those claims.
The physician (who asked not to be identified) had very little savings and suddenly had to pay a five-figure bill for tail coverage. To provide the extra malpractice coverage, she and her husband had to use savings they’d set aside to buy a house.
Getting tail coverage, known formally as an extended reporting endorsement, often comes as a complete and costly surprise for new doctors, says Dennis Hursh, Esq, a health care attorney based in Middletown, Penn., who deals with physicians’ employment contracts.
“Having to pay for a tail can disrupt lives,” Hursh said. “A tail can cost about one third of a young doctor’s salary. If you don’t feel you can afford to pay that, you may be forced to stay with a job you don’t like.”
Most medical residents don’t think about tail coverage until they apply for their first job, but last year, residents at Hahnemann University Hospital in Philadelphia got a painful early lesson.
In the summer, the hospital went out of business because of financial problems. Hundreds of medical residents and fellows not only were forced to find new programs but also had to prepare to buy tail coverage for their training years at Hahnemann.
“All the guarantees have been yanked out from under us,” said Tom Sibert, MD, a former internal medicine resident at the hospital, who is now finishing his training in California. “Residents don’t have that kind of money.”
Hahnemann trainees have asked the judge in the bankruptcy proceedings to put them ahead of other creditors and to ensure their tail coverage is paid. As of early February, the issue had not been resolved.
Meanwhile, Sibert and many other former trainees were trying to get quotes for purchasing tail coverage. They have been shocked by the amounts they would have to pay.
How tail coverage works
Medical malpractice tail coverage protects from incidents that took place when doctors were at their previous jobs but that later resulted in malpractice claims after they had left that employer.
One type of malpractice insurance, an occurrence policy, does not need tail coverage. Occurrence policies cover any incident that occurred when the policy was in force, no matter when a claim was filed – even if it is filed many years after the claims-filing period of the policy ends.
However, most malpractice policies – as many as 85%, according to one estimate – are claims-made policies. Claims-made policies are more much common because they’re significantly less expensive than occurrence policies.
Under a claims-made policy, coverage for malpractice claims completely stops when the policy ends. It does not cover incidents that occurred when the policy was in force but for which the patients later filed claims, as the occurrence policy does. So a tail is needed to cover these claims.
Physicians in all stages of their career may need tail coverage when they leave a job, change malpractice carriers, or retire.
But young physicians often have greater problems with tail coverage, for several reasons. They tend to be employed, and as such, they cannot choose the coverage they want. As a result, they most likely get claims-made coverage. In addition, the job turnover tends to be higher for these doctors. When leaving a job, the tail comes into play. More than half of new physicians leave their first job within 5 years, and of those, more than half leave after only 1 or 2 years.
Young physicians have no experience with tails and may not even know what they are. “In training, malpractice coverage is not a problem because the program handles it,” Mr. Hursh said. Accreditation standards require that teaching hospitals buy coverage, including a tail when residents leave.
So when young physicians are offered their first job and are handed an employment contract to sign, they may not even look for tail coverage, says Mr. Hursh, who wrote The Final Hurdle, a Physician’s Guide to Negotiating a Fair Employment Agreement. Instead, “young physicians tend to focus on issues like salary, benefits, and signing bonuses,” he said.
Mr. Hursh says the tail is usually the most expensive potential cost in the contract.
There’s no easy way to get out of paying the tail coverage once it is enshrined in the contract. The full tail can cost five or even six figures, depending on the physicians’ specialty, the local malpractice premium, and the physician’s own claims history.
Can you negotiate your tail coverage?
Negotiating tail coverage in the employment contract involves some familiarity with medical malpractice insurance and a close reading of the contract. First, you have to determine that the employer is providing claims-made coverage, which would require a tail if you leave. Then you have to determine whether the employer will pay for the tail coverage.
Often, the contract does not even mention tail coverage. “It could merely state that the practice will be responsible for malpractice coverage while you are working there,” Mr. Hursh said. Although it never specifies the tail, this language indicates that you will be paying for it, he says.
Therefore, it’s wise to have a conversation with your prospective employer about the tail. “Some new doctors never ask the question ‘What happens if I leave? Do I get tail coverage?’ ” said Israel Teitelbaum, an attorney who is chairman of Contemporary Insurance Services, an insurance broker in Silver Spring, Md.
Talking about the tail, however, can be a touchy subject for many young doctors applying for their first job. The tail matters only if you leave the job, and you may not want to imply that you would ever want to leave. Too much money, however, is on the line for you not to ask, Mr. Teitelbaum said.
Even if the employer verbally agrees to pay for the tail coverage, experts advise that you try to get the employer’s commitment in writing and have it put it into the contract.
Getting the employer to cover the tail in the initial contract is crucial because once you have agreed to work there, “it’s much more difficult to get it changed,” Mr. Teitelbaum said. However, even if tail coverage is not in the first contract, you shouldn’t give up, he says. You should try again in the next contract a few years later.
“It’s never too late to bring it up,” Mr. Teitelbaum said. After a few years of employment, you have a track record at the job. “A doctor who is very desirable to the employer may be able to get tail coverage on contract renewal.”
Coverage: Large employers vs. small employers
Willingness to pay for an employee’s tail coverage varies depending on the size of the employer. Large employers – systems, hospitals, and large practices – are much more likely to cover the tail than small and medium-sized practices.
Large employers tend to pay for at least part of the tail because they realize that it is in their interest to do so. Since they have the deepest pockets, they’re often the first to be named in a lawsuit. They might have to pay the whole claim if the physician did not have tail coverage.
However, many large employers want to use tail coverage as a bargaining chip to make sure doctors stay for a while at least. One typical arrangement, Mr. Hursh says, is to pay only one-fifth of the tail if the physician leaves in the first year of employment and then to pay one fifth more in each succeeding year until year five, when the employer assumes the entire cost of the tail.
Smaller practices, on the other hand, are usually close-fisted about tail coverage. “They tend to view the tail as an unnecessary expense,” Mr. Hursh said. “They don’t want to pay for a doctor who is not generating revenue for them any more.”
Traditionally, when physicians become partners, practices are more generous and agree to pay their tails if they leave, Mr. Hursh says. But he thinks this is changing, too – recent partnership contracts he has reviewed did not provide for tail coverage.
Times you don’t need to pay for tail coverage
Even if you’re responsible for the tail coverage, your insurance arrangement may be such that you don’t have to pay for it, says Michelle Perron, a malpractice insurance broker in North Hampton, N.H.
For example, if the carrier at your new job is the same as the one at your old job, your coverage would continue with no break, and you would not need a tail, she says. Even if you move to another state, your old carrier might also sell policies there, and you would then likely have seamless coverage, Ms. Perron says. This would be handy if you could choose your new carrier.
Even when you change carriers, Ms. Perron says, the new one might agree to pick up the old carrier’s coverage in return for getting your business, assuming you are an independent physician buying your own coverage. The new carrier would issue prior acts coverage, also known as nose coverage.
Older doctors going into retirement also have a potential tail coverage problem, but their tail coverage premium is often waived, Ms. Perron says. The need for a tail has to do with claims arising post retirement, after your coverage has ended. Typically, if you have been with the carrier for at least 5 years and you are age 55 years or older, your carrier will waive the tail coverage premium, she says.
However, if the retired doctor starts practicing again, even part time, the carrier may want to take back the free tail, she says. Some retired doctors get around this by buying a lower-priced tail from another company, but the former carrier may still want its money back, Ms. Perron says.
Can you just go without tail coverage?
What happens if physicians with a tail commitment choose to wing it and not pay for the tail? If a claim was never made against them, they may believe that the expense is unnecessary. The situation, however, is not so simple.
Some states require having tail coverage. Malpractice coverage is required in seven states, and at least some of those states explicitly extend this requirement to tails. They are Colorado, Connecticut, Kansas, Massachusetts, New Jersey, Rhode Island, and Wisconsin. Eleven more states tie malpractice coverage, perhaps including tails, to some benefit for the doctor, such as tort reform. These states include Indiana, Nebraska, New Mexico, New York, and Pennsylvania.
Many hospitals require tail coverage for privileges, and some insurers do as well. In addition, Ms. Perron says a missing tail reduces your prospects when looking for a job. “For the employer, having to pay coverage for a new hire will cost more than starting fresh with someone else,” she said.
Still, it’s important to remember the risk of being sued. “If you don’t buy the tail coverage, you are at risk for a lawsuit for many years to come,” Mr. Teitelbaum said.
Doctors should consider their potential lifetime risk, not just their current risk. Although only 8% of doctors younger than age 40 have been sued for malpractice, that figure climbs to almost half by the time doctors reach age 55.
The risks are higher in some specialties. About 63% of general surgeons and ob.gyns. have been sued.
Many of these claims are without merit, and doctors pay only the legal expenses of defending the case. Some doctors may think they could risk frivolous suits and cover legal expenses out of pocket. An American Medical Association survey showed that 68% of closed claims against doctors were dropped, dismissed, or withdrawn. It said these claims cost an average of more than $30,000 to defend.
However, Mr. Teitelbaum puts the defense costs for so-called frivolous suits much higher than the AMA, at $250,000 or more. “Even if you’re sure you won’t have to pay a claim, you still have to defend yourself against frivolous suits,” he said. “You won’t recover those expenses.”
How to lower your tail coverage cost
Physicians typically have 60 days to buy tail coverage after their regular coverage has ended. Specialized brokers such as Mr. Teitelbaum and Ms. Perron help physicians look for the best tails to buy.
The cost of the tail depends on how long you’ve been at your job when you leave it, Ms. Perron says. If you leave in the first 1 or 2 years of the policy, she says, the tail price will be lower because the coverage period is shorter.
Usually the most expensive tail available is from the carrier that issued the original policy. Why is this? “Carriers rarely sell a tail that undercuts their retail price,” Mr. Teitelbaum said. “They don’t want to compete with themselves, and in fact doing so could pose regulatory problems for them.”
Instead of buying from their own carrier, doctors can purchase stand-alone tails from competitors, which Mr. Teitelbaum says are 10%-30% less expensive than the policy the original carrier issues. However, stand-alone tails are not always easy to find, especially for high-cost specialties such as neurosurgery and ob.gyn., he says.
Some physicians try to bring down the cost of the tail by limiting the duration of the tail. You can buy tails that only cover claims filed 1-5 years after the incident took place, rather than indefinitely. These limits mirror the typical statute of limitations – the time limit to file a claim in each state. This limit is as little as 2 years in some states, though it can be as long as 6 years in others.
However, some states make exceptions to the statute of limitations. The 2- to 6-year clock doesn’t start ticking until the mistake is discovered or, in the case of children, when they reach adulthood. “This means that with a limited tail, you always have risk,” Perron said.
And yet some doctors insist on these time-limited tails. “If a doctor opts for 3 years’ coverage, that’s better than no years,” Mr. Teitelbaum said. “But I would advise them to take at least 5 years because that gives you coverage for the basic statute of limitations in most states. Three-year tails do yield savings, but often they’re not enough to warrant the risk.”
Another way to reduce costs is to lower the coverage limits of the tail. The standard coverage limit is $1 million per case and $3 million per year, so doctors might be able to save money on the premium by buying limits of $200,000/$600,000. But Mr. Teitelbaum says most companies would refuse to sell a policy with a limit lower than that of the expiring policy.
Further ways to reduce the cost of the tail include buying tail coverage that doesn’t give the physician the right to approve a settlement or that doesn’t include legal fees in the coverage limits. But these options, too, raise the physician’s risks. Whichever option you choose, the important thing is to protect yourself against costly lawsuits.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Medicare study evaluates impact of U.S. Hospital Readmissions Reduction Program
Research offers evidence against calls to curtail the program
Among Medicare beneficiaries admitted to the hospital between 2008 and 2016, there was an increase in postdischarge 30-day mortality for patients with heart failure, but not for those with acute myocardial infarction or pneumonia.
The finding comes from an effort to evaluate the use of services soon after discharge for conditions targeted in the U.S. Hospital Readmissions Reduction Program (HRRP), and patients’ outcomes.
“The announcement and implementation of the HRRP were associated with a reduction in readmissions within 30 days of discharge for heart failure, acute myocardial infarction, and pneumonia, as shown by a decrease in the overall national rate of readmissions,” first author Rohan Khera, MD, and colleagues wrote in a study published online Jan. 15, 2020, in the British Medical Journal (doi:10.1136/bmj.l6831).
“Concerns existed that pressures to reduce readmissions had led to the evolution of care patterns that may have adverse consequences through reducing access to care in appropriate settings. Therefore, determining whether patients who are seen in acute care settings, but not admitted to hospital, experience an increased risk of mortality is essential.”
Dr. Khera, a cardiologist at the University of Texas Southwestern Medical Center, Dallas, and colleagues limited the analysis to Medicare claims data from patients who were admitted to the hospital with heart failure, acute myocardial infarction (MI), or pneumonia between 2008 and 2016. Key outcomes of interest were: (1) postdischarge 30-day mortality; and (2) acute care utilization in inpatient units, observation units, and the ED during the postdischarge period.
During the study period there were 3,772,924 hospital admissions for heart failure, 1,570,113 for acute MI, and 3,131,162 for pneumonia. The greatest number of readmissions within 30 days of discharge was for heart failure patients (22.5%), followed by acute MI (17.5%), and pneumonia (17.2%).
The overall rates of observation stays were 1.7% for heart failure, 2.6% for acute MI, and 1.4% for pneumonia, while the overall rates of emergency department visits were 6.4% for heart failure, 6.8% for acute MI, and 6.3% for pneumonia. Cumulatively, about one-third of all admissions – 30.7% for heart failure, 26.9% for acute MI, and 24.8% for pneumonia – received postdischarge care in any acute care setting.
Dr. Khera and colleagues found that overall postdischarge 30-day mortality was 8.7% for heart failure, 7.3% for acute MI, and 8.4% for pneumonia. At the same time, postdischarge 30-day mortality was higher in patients with readmissions (13.2% for heart failure, 12.7% for acute MI, and 15.3% for pneumonia), compared with those who had observation stays (4.5% for heart failure, 2.7% for acute MI, and 4.6% for pneumonia), emergency department visits (9.7% for heart failure, 8.8% for acute MI, and 7.8% for pneumonia), or no postdischarge acute care (7.2% for heart failure, 6.0% for acute MI, and 6.9% for pneumonia). Risk adjusted mortality increased annually by 0.05% only for heart failure, while it decreased by 0.06% for acute MI, and did not significantly change for pneumonia.
“The study strongly suggests that the HRRP did not lead to harm through inappropriate triage of patients at high risk to observation units and the emergency department, and therefore provides evidence against calls to curtail the program owing to this theoretical concern (see JAMA 2018;320:2539-41),” the researchers concluded.
They acknowledged certain limitations of the study, including the fact that they were “unable to identify patterns of acute care during the index hospital admission that would be associated with a higher rate of postdischarge acute care in observation units and emergency departments and whether these visits represented avenues for planned postdischarge follow-up care. Moreover, the proportion of these care encounters that were preventable remains poorly understood.”
Dr. Khera disclosed that he is supported by the National Center for Advancing Translational Sciences of the National Institutes of Health. His coauthors reported having numerous disclosures.
SOURCE: Khera et al. BMJ 2020;368:l6831.
Research offers evidence against calls to curtail the program
Research offers evidence against calls to curtail the program
Among Medicare beneficiaries admitted to the hospital between 2008 and 2016, there was an increase in postdischarge 30-day mortality for patients with heart failure, but not for those with acute myocardial infarction or pneumonia.
The finding comes from an effort to evaluate the use of services soon after discharge for conditions targeted in the U.S. Hospital Readmissions Reduction Program (HRRP), and patients’ outcomes.
“The announcement and implementation of the HRRP were associated with a reduction in readmissions within 30 days of discharge for heart failure, acute myocardial infarction, and pneumonia, as shown by a decrease in the overall national rate of readmissions,” first author Rohan Khera, MD, and colleagues wrote in a study published online Jan. 15, 2020, in the British Medical Journal (doi:10.1136/bmj.l6831).
“Concerns existed that pressures to reduce readmissions had led to the evolution of care patterns that may have adverse consequences through reducing access to care in appropriate settings. Therefore, determining whether patients who are seen in acute care settings, but not admitted to hospital, experience an increased risk of mortality is essential.”
Dr. Khera, a cardiologist at the University of Texas Southwestern Medical Center, Dallas, and colleagues limited the analysis to Medicare claims data from patients who were admitted to the hospital with heart failure, acute myocardial infarction (MI), or pneumonia between 2008 and 2016. Key outcomes of interest were: (1) postdischarge 30-day mortality; and (2) acute care utilization in inpatient units, observation units, and the ED during the postdischarge period.
During the study period there were 3,772,924 hospital admissions for heart failure, 1,570,113 for acute MI, and 3,131,162 for pneumonia. The greatest number of readmissions within 30 days of discharge was for heart failure patients (22.5%), followed by acute MI (17.5%), and pneumonia (17.2%).
The overall rates of observation stays were 1.7% for heart failure, 2.6% for acute MI, and 1.4% for pneumonia, while the overall rates of emergency department visits were 6.4% for heart failure, 6.8% for acute MI, and 6.3% for pneumonia. Cumulatively, about one-third of all admissions – 30.7% for heart failure, 26.9% for acute MI, and 24.8% for pneumonia – received postdischarge care in any acute care setting.
Dr. Khera and colleagues found that overall postdischarge 30-day mortality was 8.7% for heart failure, 7.3% for acute MI, and 8.4% for pneumonia. At the same time, postdischarge 30-day mortality was higher in patients with readmissions (13.2% for heart failure, 12.7% for acute MI, and 15.3% for pneumonia), compared with those who had observation stays (4.5% for heart failure, 2.7% for acute MI, and 4.6% for pneumonia), emergency department visits (9.7% for heart failure, 8.8% for acute MI, and 7.8% for pneumonia), or no postdischarge acute care (7.2% for heart failure, 6.0% for acute MI, and 6.9% for pneumonia). Risk adjusted mortality increased annually by 0.05% only for heart failure, while it decreased by 0.06% for acute MI, and did not significantly change for pneumonia.
“The study strongly suggests that the HRRP did not lead to harm through inappropriate triage of patients at high risk to observation units and the emergency department, and therefore provides evidence against calls to curtail the program owing to this theoretical concern (see JAMA 2018;320:2539-41),” the researchers concluded.
They acknowledged certain limitations of the study, including the fact that they were “unable to identify patterns of acute care during the index hospital admission that would be associated with a higher rate of postdischarge acute care in observation units and emergency departments and whether these visits represented avenues for planned postdischarge follow-up care. Moreover, the proportion of these care encounters that were preventable remains poorly understood.”
Dr. Khera disclosed that he is supported by the National Center for Advancing Translational Sciences of the National Institutes of Health. His coauthors reported having numerous disclosures.
SOURCE: Khera et al. BMJ 2020;368:l6831.
Among Medicare beneficiaries admitted to the hospital between 2008 and 2016, there was an increase in postdischarge 30-day mortality for patients with heart failure, but not for those with acute myocardial infarction or pneumonia.
The finding comes from an effort to evaluate the use of services soon after discharge for conditions targeted in the U.S. Hospital Readmissions Reduction Program (HRRP), and patients’ outcomes.
“The announcement and implementation of the HRRP were associated with a reduction in readmissions within 30 days of discharge for heart failure, acute myocardial infarction, and pneumonia, as shown by a decrease in the overall national rate of readmissions,” first author Rohan Khera, MD, and colleagues wrote in a study published online Jan. 15, 2020, in the British Medical Journal (doi:10.1136/bmj.l6831).
“Concerns existed that pressures to reduce readmissions had led to the evolution of care patterns that may have adverse consequences through reducing access to care in appropriate settings. Therefore, determining whether patients who are seen in acute care settings, but not admitted to hospital, experience an increased risk of mortality is essential.”
Dr. Khera, a cardiologist at the University of Texas Southwestern Medical Center, Dallas, and colleagues limited the analysis to Medicare claims data from patients who were admitted to the hospital with heart failure, acute myocardial infarction (MI), or pneumonia between 2008 and 2016. Key outcomes of interest were: (1) postdischarge 30-day mortality; and (2) acute care utilization in inpatient units, observation units, and the ED during the postdischarge period.
During the study period there were 3,772,924 hospital admissions for heart failure, 1,570,113 for acute MI, and 3,131,162 for pneumonia. The greatest number of readmissions within 30 days of discharge was for heart failure patients (22.5%), followed by acute MI (17.5%), and pneumonia (17.2%).
The overall rates of observation stays were 1.7% for heart failure, 2.6% for acute MI, and 1.4% for pneumonia, while the overall rates of emergency department visits were 6.4% for heart failure, 6.8% for acute MI, and 6.3% for pneumonia. Cumulatively, about one-third of all admissions – 30.7% for heart failure, 26.9% for acute MI, and 24.8% for pneumonia – received postdischarge care in any acute care setting.
Dr. Khera and colleagues found that overall postdischarge 30-day mortality was 8.7% for heart failure, 7.3% for acute MI, and 8.4% for pneumonia. At the same time, postdischarge 30-day mortality was higher in patients with readmissions (13.2% for heart failure, 12.7% for acute MI, and 15.3% for pneumonia), compared with those who had observation stays (4.5% for heart failure, 2.7% for acute MI, and 4.6% for pneumonia), emergency department visits (9.7% for heart failure, 8.8% for acute MI, and 7.8% for pneumonia), or no postdischarge acute care (7.2% for heart failure, 6.0% for acute MI, and 6.9% for pneumonia). Risk adjusted mortality increased annually by 0.05% only for heart failure, while it decreased by 0.06% for acute MI, and did not significantly change for pneumonia.
“The study strongly suggests that the HRRP did not lead to harm through inappropriate triage of patients at high risk to observation units and the emergency department, and therefore provides evidence against calls to curtail the program owing to this theoretical concern (see JAMA 2018;320:2539-41),” the researchers concluded.
They acknowledged certain limitations of the study, including the fact that they were “unable to identify patterns of acute care during the index hospital admission that would be associated with a higher rate of postdischarge acute care in observation units and emergency departments and whether these visits represented avenues for planned postdischarge follow-up care. Moreover, the proportion of these care encounters that were preventable remains poorly understood.”
Dr. Khera disclosed that he is supported by the National Center for Advancing Translational Sciences of the National Institutes of Health. His coauthors reported having numerous disclosures.
SOURCE: Khera et al. BMJ 2020;368:l6831.
FROM BMJ
Flu activity increases for third straight week
For the second time during the 2019-2020 flu season, activity measures have climbed into noteworthy territory.
The proportion of outpatient visits for influenza-like illness (ILI) reached its highest December level, 7.1%, since 2003 and then dropped for 2 weeks. Three weeks of increases since then, however, have the outpatient-visit rate at 6.7% for the week ending Feb. 1, 2020, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention reported. The baseline rate for the United States is 2.4%.
That rate of 6.7% is already above the highest rates recorded in eight of the last nine flu seasons, and another increase could mean a second, separate trip above 7.0% in the 2019-2020 season – something that has not occurred since national tracking began in 1997, CDC data show.
Those same data also show that,
Another important measure on the rise, the proportion of respiratory specimens testing positive for influenza, reached a new high for the season, 29.8%, during the week of Feb. 1, the CDC’s influenza division said.
Tests at clinical laboratories also show that predominance is continuing to switch from type B (45.6%) to type A (54.4%), the influenza division noted. Overall predominance for the season, however, continues to favor type B, 59.3% to 40.7%.
The percentage of deaths caused by pneumonia and influenza, which passed the threshold for epidemic of 7.2% back in early January, has been trending downward for the last 3 weeks and was 7.1% as of Feb. 1, according to the influenza division.
ILI-related deaths among children continue to remain high, with a total count of 78 for the season after another 10 deaths were reported during the week ending Feb. 1, the CDC reported. Comparable numbers for the last three seasons are 44 (2018-2019), 97 (2017-2018), and 35 (2016-2017).
The CDC estimates put the total number of ILIs at around 22 million for the season so far, leading to 210,000 hospitalizations. The agency said that it expects to release estimates of vaccine effectiveness later this month.
For the second time during the 2019-2020 flu season, activity measures have climbed into noteworthy territory.

The proportion of outpatient visits for influenza-like illness (ILI) reached its highest December level, 7.1%, since 2003 and then dropped for 2 weeks. Three weeks of increases since then, however, have the outpatient-visit rate at 6.7% for the week ending Feb. 1, 2020, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention reported. The baseline rate for the United States is 2.4%.
That rate of 6.7% is already above the highest rates recorded in eight of the last nine flu seasons, and another increase could mean a second, separate trip above 7.0% in the 2019-2020 season – something that has not occurred since national tracking began in 1997, CDC data show.
Those same data also show that,
Another important measure on the rise, the proportion of respiratory specimens testing positive for influenza, reached a new high for the season, 29.8%, during the week of Feb. 1, the CDC’s influenza division said.
Tests at clinical laboratories also show that predominance is continuing to switch from type B (45.6%) to type A (54.4%), the influenza division noted. Overall predominance for the season, however, continues to favor type B, 59.3% to 40.7%.
The percentage of deaths caused by pneumonia and influenza, which passed the threshold for epidemic of 7.2% back in early January, has been trending downward for the last 3 weeks and was 7.1% as of Feb. 1, according to the influenza division.
ILI-related deaths among children continue to remain high, with a total count of 78 for the season after another 10 deaths were reported during the week ending Feb. 1, the CDC reported. Comparable numbers for the last three seasons are 44 (2018-2019), 97 (2017-2018), and 35 (2016-2017).
The CDC estimates put the total number of ILIs at around 22 million for the season so far, leading to 210,000 hospitalizations. The agency said that it expects to release estimates of vaccine effectiveness later this month.
For the second time during the 2019-2020 flu season, activity measures have climbed into noteworthy territory.

The proportion of outpatient visits for influenza-like illness (ILI) reached its highest December level, 7.1%, since 2003 and then dropped for 2 weeks. Three weeks of increases since then, however, have the outpatient-visit rate at 6.7% for the week ending Feb. 1, 2020, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention reported. The baseline rate for the United States is 2.4%.
That rate of 6.7% is already above the highest rates recorded in eight of the last nine flu seasons, and another increase could mean a second, separate trip above 7.0% in the 2019-2020 season – something that has not occurred since national tracking began in 1997, CDC data show.
Those same data also show that,
Another important measure on the rise, the proportion of respiratory specimens testing positive for influenza, reached a new high for the season, 29.8%, during the week of Feb. 1, the CDC’s influenza division said.
Tests at clinical laboratories also show that predominance is continuing to switch from type B (45.6%) to type A (54.4%), the influenza division noted. Overall predominance for the season, however, continues to favor type B, 59.3% to 40.7%.
The percentage of deaths caused by pneumonia and influenza, which passed the threshold for epidemic of 7.2% back in early January, has been trending downward for the last 3 weeks and was 7.1% as of Feb. 1, according to the influenza division.
ILI-related deaths among children continue to remain high, with a total count of 78 for the season after another 10 deaths were reported during the week ending Feb. 1, the CDC reported. Comparable numbers for the last three seasons are 44 (2018-2019), 97 (2017-2018), and 35 (2016-2017).
The CDC estimates put the total number of ILIs at around 22 million for the season so far, leading to 210,000 hospitalizations. The agency said that it expects to release estimates of vaccine effectiveness later this month.
Remdesivir under study as treatment for novel coronavirus

“What they’re looking at is the effect of this drug -- either the drug plus standard of care versus standard of care alone,” Anthony S. Fauci, MD, reported Feb. 7 during a press briefing held by members of President Trump’s Coronavirus Task Force. “I think pretty soon we are going to get a definitive answer, whether one of these among several drugs works.”
Dr. Fauci, director of the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases, added that several organizations and individual investigators are developing vaccines for 2019-nCoV. In one such effort, the National Institutes of Health is working with Moderna Inc. to develop a vaccine built on a messenger RNA platform. “One of the first steps is to successfully get that [novel coronavirus] gene and insert it into the messenger RNA platform successfully and allow it to express proteins,” Dr. Fauci explained. “We’ve succeeded in that. The next [step] is to put it in a mouse animal model to induce immunogenicity, and to get the company to make [gold nanoparticle] products. All of those have been successfully implemented. There have been no glitches so far. If that continues, we will be in Phase 1 trials in people within the next two-and-a-half months.”
In another development on the same day, Robert R. Redfield, MD, director of the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, announced that Heath & Human Services issued an interim final rule to amend foreign quarantine regulations in the wake of the public health threat posed by the 2019-nCoV. “This will enable CDC to collect certain contact information data regarding airline passengers and crew when they arrive from other countries. . .and may be exposed to communicable disease,” Dr. Redfield said. “This action is part of our multi-layered approach to the U.S. response and demonstrates our commitment to take all necessary actions to protect the American people.”
According to Alex Azar, secretary of Health and Human Services, and chair of President Trump’s Coronavirus Task Force, there are 12 confirmed cases of the novel coronavirus in the United States, including two cases of transmission to people who had not recently been in China. “Although the virus represents a potentially very serious public health threat, and we expect to continue seeing more cases here, the immediate risk to the American public is low at this time,” Mr. Azar said. “We are working as quickly as possible on the many unanswered questions about this virus. That includes exactly how it spreads, how deadly it is, whether it’s commonly transmitted by patients who are not yet displaying symptoms, and other issues.”

“What they’re looking at is the effect of this drug -- either the drug plus standard of care versus standard of care alone,” Anthony S. Fauci, MD, reported Feb. 7 during a press briefing held by members of President Trump’s Coronavirus Task Force. “I think pretty soon we are going to get a definitive answer, whether one of these among several drugs works.”
Dr. Fauci, director of the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases, added that several organizations and individual investigators are developing vaccines for 2019-nCoV. In one such effort, the National Institutes of Health is working with Moderna Inc. to develop a vaccine built on a messenger RNA platform. “One of the first steps is to successfully get that [novel coronavirus] gene and insert it into the messenger RNA platform successfully and allow it to express proteins,” Dr. Fauci explained. “We’ve succeeded in that. The next [step] is to put it in a mouse animal model to induce immunogenicity, and to get the company to make [gold nanoparticle] products. All of those have been successfully implemented. There have been no glitches so far. If that continues, we will be in Phase 1 trials in people within the next two-and-a-half months.”
In another development on the same day, Robert R. Redfield, MD, director of the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, announced that Heath & Human Services issued an interim final rule to amend foreign quarantine regulations in the wake of the public health threat posed by the 2019-nCoV. “This will enable CDC to collect certain contact information data regarding airline passengers and crew when they arrive from other countries. . .and may be exposed to communicable disease,” Dr. Redfield said. “This action is part of our multi-layered approach to the U.S. response and demonstrates our commitment to take all necessary actions to protect the American people.”
According to Alex Azar, secretary of Health and Human Services, and chair of President Trump’s Coronavirus Task Force, there are 12 confirmed cases of the novel coronavirus in the United States, including two cases of transmission to people who had not recently been in China. “Although the virus represents a potentially very serious public health threat, and we expect to continue seeing more cases here, the immediate risk to the American public is low at this time,” Mr. Azar said. “We are working as quickly as possible on the many unanswered questions about this virus. That includes exactly how it spreads, how deadly it is, whether it’s commonly transmitted by patients who are not yet displaying symptoms, and other issues.”

“What they’re looking at is the effect of this drug -- either the drug plus standard of care versus standard of care alone,” Anthony S. Fauci, MD, reported Feb. 7 during a press briefing held by members of President Trump’s Coronavirus Task Force. “I think pretty soon we are going to get a definitive answer, whether one of these among several drugs works.”
Dr. Fauci, director of the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases, added that several organizations and individual investigators are developing vaccines for 2019-nCoV. In one such effort, the National Institutes of Health is working with Moderna Inc. to develop a vaccine built on a messenger RNA platform. “One of the first steps is to successfully get that [novel coronavirus] gene and insert it into the messenger RNA platform successfully and allow it to express proteins,” Dr. Fauci explained. “We’ve succeeded in that. The next [step] is to put it in a mouse animal model to induce immunogenicity, and to get the company to make [gold nanoparticle] products. All of those have been successfully implemented. There have been no glitches so far. If that continues, we will be in Phase 1 trials in people within the next two-and-a-half months.”
In another development on the same day, Robert R. Redfield, MD, director of the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, announced that Heath & Human Services issued an interim final rule to amend foreign quarantine regulations in the wake of the public health threat posed by the 2019-nCoV. “This will enable CDC to collect certain contact information data regarding airline passengers and crew when they arrive from other countries. . .and may be exposed to communicable disease,” Dr. Redfield said. “This action is part of our multi-layered approach to the U.S. response and demonstrates our commitment to take all necessary actions to protect the American people.”
According to Alex Azar, secretary of Health and Human Services, and chair of President Trump’s Coronavirus Task Force, there are 12 confirmed cases of the novel coronavirus in the United States, including two cases of transmission to people who had not recently been in China. “Although the virus represents a potentially very serious public health threat, and we expect to continue seeing more cases here, the immediate risk to the American public is low at this time,” Mr. Azar said. “We are working as quickly as possible on the many unanswered questions about this virus. That includes exactly how it spreads, how deadly it is, whether it’s commonly transmitted by patients who are not yet displaying symptoms, and other issues.”
Social determinants of health and the hospitalist
Are access to housing and food as important as therapeutics?
While physicians acknowledge that the social determinants of health can impact outcomes from medical care, some may feel that trying to address factors such as homelessness, food insecurity, or lack of ready access to transportation or pharmacy services is just not part of the doctor’s job. A majority of 621 physicians surveyed in the summer of 2017 by Salt Lake City–based health care intelligence firm Leavitt Partners say they are neither capable of nor responsible for addressing such issues.1
But that view may become unsustainable as the U.S. health care system continues to advance toward value- and population-based models of health care and as evidence mounts that social factors are important contributors to costly outcomes, such as avoidable hospital readmissions or emergency room visits. A recent report from the Robert Wood Johnson Foundation estimates that at least 40% of health outcomes are the result of social and economic factors, while only 20% can be attributed to medical care.2
“This is a hot topic – getting a lot of attention these days,” said hospitalist and care transitions expert Ramon Jacobs-Shaw, MD, MPA, regional medical officer for CareMore Health, a California-based physician-led health delivery organization and subsidiary of Anthem. “If you go around the country, some doctors still see social factors as the realm of the social worker. But large health care organizations are coming to recognize that social determinants are huge contributors to the health of their members and to the outcomes of their care.”
Hospitalists could be the natural providers to delve into the specific psychosocial aspects of their patients’ lives, or try to figure out how those factors contribute to health care needs, Dr. Jacobs-Shaw said. They typically confront such issues while the patient is in the hospital bed, but what are the steps that led to the hospitalization in the first place? What will happen after the patient is discharged?
“For example, if patients lack transportation, how can they get to their follow-up medical appointment in the primary care office in order to manage their diabetes? If you can’t follow up with them, their diabetes could get out of control, with complications as a result, such as an infected wound,” he said. Another big issue is access to affordable medications. “CareMore has pharmacists embedded on our care teams. They try to figure out the best medicine for the patient but at the lowest cost. They meet individually with patients and do medication counseling, particularly for those with polypharmacy issues.”
Making health care more equitable
Dr. Jacobs-Shaw has long held a personal interest in issues of inclusiveness, diversity, and how to make health care more equitable for historically underserved groups. Asking how to have a bigger impact on these issues is what brought him, after 13 years as a hospitalist on the East Coast, to CareMore, a company that has made addressing social needs central to its care model. “In California, where I am based, we are a wrap-around for patients who are covered by Medicare Advantage plans. We are whatever the patient needs us to be.”
He oversees a group of hospitalists, dubbed extensivists, who provide advanced patient care and chronic disease management. In the extensivist model, physicians and advanced practice nurses provide comprehensive and coordinated care to patients with complex medical issues, taking their scope of practice beyond the hospital into homes, post-acute care facilities, and other settings, with a focus on keeping patients healthier and reducing readmission.3
“Our patients get access to extra services and resources, some of which are available at our care centers – which are one-stop outpatient facilities. We also focus on a lot of things physicians didn’t historically think were within their wheelhouse. Hospitalists deal with these kinds of issues every day, but may not label them as social determinants of health,” Dr. Jacobs-Shaw said. He emphasized that hospitalists should realize that they are not powerless to address these issues, working in partnership with other groups in and out of the hospital. They should also know that health care payers increasingly are dedicating resources to these issues.
“We just started trying to address homelessness through a pilot in Orange County, working with nonprofit organizations and philanthropy to offer a transitional site of care for our patients who are being discharged from the hospital and have housing insecurity issues, to get them transitioned into more secure housing,” Dr. Jacobs-Shaw said. CareMore also has a transportation collaborative that offers no-cost, nonemergency transportation to medical appointments. “That’s meeting them where they are at, based on an assessment of their needs and resources.”
What are social determinants?
The social determinants of health – social, environmental, and other nonmedical factors that contribute to overall health status and medical need – have been defined by the World Health Organization as: “conditions in which people are born, grow, live, work, and age.” That is a broad complex of overlapping social and systems issues, but it provides a context for a broader understanding of the patient’s health and response to medical interventions.
Socioeconomic status is a huge determinant. Level of education may be more important than income if the person lacks the health literacy to navigate the system and access needed care. Housing instability may include poor sanitation, substandard dwellings, or unsafe neighborhoods – all of which can affect a person’s well-being. Environmental health may include compromised air quality – which can impact pulmonary health. Other issues include access to employment and child care, utility needs, and interpersonal violence.
A 2014 paper in Annals of Internal Medicine found that residence within a disadvantaged neighborhood was a factor in hospital readmission rates as often as was chronic pulmonary disease.4 A recent report on social determinants of health by the National Institute for Health Care Management notes that patients with food insecurity are 2.4 times more likely to go to the emergency room, while those with transportation needs are 2.6 times more likely.5
What can health care leaders do to better equip their clinicians and teams to help patients deal with this array of complex needs? Intermountain Healthcare, based in Salt Lake City, spearheaded in 2018 the development of the Alliance for the Determinants of Health, starting in the communities of Ogden and St. George, Utah. The Alliance seeks to promote health, improve access to care, and decrease health care costs through a charitable contribution of $12 million over 3 years to seed collaborative demonstration projects.
Lisa Nichols, assistant vice president for community health at Intermountain, said that, while hospitalists were not directly involved in planning the Alliance, hospitalists and ED physicians have become essential to the patient-screening process for health and social needs.
“We met with hospitalists, emergency departments, and hospital administrators, because we wanted their feedback on how to raise awareness of the social needs of patients,” she said. “They have good ideas. They see the patients who come in from the homeless shelters.”
Other hospitals are subsidizing apartments for homeless patients being discharged from the hospital. CommonSpirit Health, the new national Catholic health care organization formed by the 2019 merger of Dignity Health and Catholic Health Initiatives, has explored how to help create and sustain affordable housing in the communities it serves. Investments like this have inspired others, such as Kaiser Permanente, to get involved in supporting housing initiatives.6
Comprehensive community care
David Meltzer, MD, PhD, a hospitalist and professor of medicine at the University of Chicago, said most hospitalists these days believe social determinants of health are part of their job responsibilities.
“That’s not to say we all do it well. We may fail at addressing some of the barriers our patients face. But I don’t know anyone who still says it’s not their job,” he said.
Since 2012, Dr. Meltzer has led a pilot called Comprehensive Care Physicians (CCP), in which the same physician cares for patients with chronic health problems in the clinic and in the hospital, working with a team of nurse practitioners, social workers, care coordinators, and other specialists. A total of 2,000 patients with chronic health problems were enrolled in the study from 2012 to 2016, half assigned to standard care and half assigned to five CCP doctors. The result: The CCP model has shown large improvements in outcomes – particularly among the more vulnerable, less activated patients, is preferred by patients, and has significantly reduced health care utilization.
The next step for the research team is another randomized controlled trial called Comprehensive Care, Community, and Culture, designed to address unmet social needs. Study group patients will also be screened for unmet social needs and have access to a community health worker and to the initiative’s Artful Living Program, which includes community and cultural activities like yoga and dance classes, cooking classes, art classes, and music concerts. To address the complex dimensions and determinants of health, Dr. Meltzer explained, efforts to improve health must extend to sectors far beyond traditional health care.
“I think trying to understand your patients’ social and nonmedical needs starts with getting to know them, and asking about their needs,” he said. “The better you know them, the better you are able to make medical decisions that will promote positive outcomes.”
Sound Physicians, a national hospitalist company based in Tacoma, Wash., and working in 350 hospitals in 41 states, recently published a blog post on its website about the importance of social determinants of health.7 Sound Physicians participates in value-based care through bundled Medicare/Medicaid contracts based on episodes of care for hospitalized patients with certain diagnoses or DRGs, explained John Dickey, MD, the company’s chief medical officer for population health.
“We’ve been heavily involved in trying to improve cost and outcomes of care since 2015. Social determinants absolutely play into trying to lower costs of care and reduce rates of readmissions, which are often multifactorial in cause,” he said. Hospitalists are uniquely equipped to impact post-acute outcomes, Dr. Dickey said, working in partnership with a position Sound Physicians calls the clinical performance nurse.
“We can also partner with primary care providers, provide education for our hospitalist staff, and work with in-home care supports for patients such as these, who otherwise might end up in a skilled nursing facility – even though they’d rather be at home,” he said.
Innovations at Northwell Health
Northwell Health, a multihospital comprehensive health system serving the New York City metro area and Long Island, has shown innovative leadership in addressing social factors. The 23-hospital system initiated in early 2019 a 15-item Self-Reported Social Determinants Screening Tool, which is now used with hospitalized patients to connect them with the support they need to fully recover and avoid readmissions.
Northwell is also providing professional education on social determinants for different constituencies across its system, said Johanna Martinez, MD, MS, a hospitalist and GME Director of Diversity and Health Equity at the Zucker School of Medicine at Hofstra/Northwell. A day-long training retreat was offered to GME faculty, and learning platforms have been developed for physicians, social workers, nurses, and others.
“One of the questions that comes up is that if you find social needs, what do you do about them?” Dr. Martinez explained. That’s more a difficult challenge, she said, so at Northwell, orthopedic surgeons are now asking patients questions like: “What’s going to happen when you go home? What are your social supports? Can you get to the physical therapist’s office?”
Another example of Northwell’s innovations is its Food as Health Program, initially piloted at Long Island Jewish Hospital in Valley Stream, N.Y. Hospitalized patients are asked two questions using a validated screening tool called the Hunger Vital Sign to identify their food insecurities.8 Those who answer yes are referred to a dietitian, and if they have a nutrition-related diagnosis, they enter the multidisciplinary wraparound program.
A key element is the food and health center, located on the hospital campus, where they can get food to take home and referrals to other services, with culturally tailored, disease-specific food education incorporated into the discharge plan. One of the partnering organizations is Island Harvest Food Bank, which helps about 1 in every 10 residents of Long Island with their food insecurity issues.
“When I talk to clinicians, most of us went into medicine to save lives and cure people. Yet the research shows that no matter who we are, we can’t do the best work that our patients need unless we consider their social determinants,” Dr. Martinez said. Ultimately, she noted, there is a need to change the culture of health care. “We have to create system change, reimbursement change, policy change.”
Omolara Uwemedimo, MD, MPH, associate professor of pediatrics and occupational medicine at Northwell and a former nocturnist, said the treatment of illness and health improvement don’t begin in the hospital, they begin in the community. Identifying where people are struggling and what communities they come from requires a broader view of the provider’s role. “Are patients who are readmitted to the hospital generally coming from certain demographics or from certain zip codes?” she asked. “Start there. How can we better connect with those communities?”
Education is key
In 2020 and beyond, hospitalists will hear more about the social determinants of health, Dr. Jacobs-Shaw concluded. “Without addressing those social determinants, we aren’t going to be able to meaningfully impact outcomes or be effective stewards of health care costs – addressing the psychosocial factors and root causes of patients coming in and out of the hospital.”
He added that self-education is key for hospitalists and the teams they work with – to be more aware of the link between health outcomes and social determinants. Guidelines and other resources on social determinants of health are available from the American College of Physicians and the American Association of Family Physicians. ACP issued a position paper on addressing social determinants of health to improve patient care,while AAFP has a research page on its website dedicated to social determinants of health, highlighting a number of initiatives and resources for physicians and others.9
The American Hospital Association has produced fact sheets on ICD-10CM code categories for social determinants of health, including 11 ICD-10 “Z” codes, numbered Z55-Z65, which can be used for coding interventions to address social determinants of health. Other experts are looking at how to adapt the electronic health record to capture sociodemographic and behavioral factors, and then trigger referrals to resources in the hospital and the broader community, and how to mobilize artificial intelligence and machine learning to better identify social needs.
“Our doctors really want to be able to take care of the whole patient, while being stewards of health care resources. But sometimes we feel powerless and wonder how we can have a bigger impact on people, on populations” Dr. Jacobs-Shaw said. “Remember it only takes one voice within an organization to start to elevate this topic.”
References
1. Rappleye E. Physicians say social determinants of health are not their responsibility. Becker’s Hospital Review. 2018 May 15.
2. Robert Wood Johnson Foundation, University of Wisconsin Population Health Institute. County Health Rankings, 2014.
3. Freeman, GA. The extensivist model. Health Leaders Magazine, 2016 Sep 15.
4. Kind AJ et al. Neighborhood socioeconomic disadvantage and 30-day rehospitalization: A retrospective cohort study. Ann Intern Med. 2014 Dec 2;161(11):765-74.
5. National Institute for Health Care Management. Addressing social determinants of health can improve community health & reduce costs.
6. Vial PB. Boundless collaboration: A philosophy for sustainable and stabilizing housing investment strategies. Health Progress: Journal of the Catholic Health Association of the United States. September-October 2019.
7. Social determinants of health: New solutions for growing complexities. Op-Med, a blog by Sound Physicians. 2019 Aug 1.
8. The hunger vital sign: A new standard of care for preventive health.
9. Daniel H et al. Addressing social determinants to improve patient care and promote health equity: An American College of Physicians position paper. Ann Intern Med. 2018;168:557-578.
Are access to housing and food as important as therapeutics?
Are access to housing and food as important as therapeutics?
While physicians acknowledge that the social determinants of health can impact outcomes from medical care, some may feel that trying to address factors such as homelessness, food insecurity, or lack of ready access to transportation or pharmacy services is just not part of the doctor’s job. A majority of 621 physicians surveyed in the summer of 2017 by Salt Lake City–based health care intelligence firm Leavitt Partners say they are neither capable of nor responsible for addressing such issues.1
But that view may become unsustainable as the U.S. health care system continues to advance toward value- and population-based models of health care and as evidence mounts that social factors are important contributors to costly outcomes, such as avoidable hospital readmissions or emergency room visits. A recent report from the Robert Wood Johnson Foundation estimates that at least 40% of health outcomes are the result of social and economic factors, while only 20% can be attributed to medical care.2
“This is a hot topic – getting a lot of attention these days,” said hospitalist and care transitions expert Ramon Jacobs-Shaw, MD, MPA, regional medical officer for CareMore Health, a California-based physician-led health delivery organization and subsidiary of Anthem. “If you go around the country, some doctors still see social factors as the realm of the social worker. But large health care organizations are coming to recognize that social determinants are huge contributors to the health of their members and to the outcomes of their care.”
Hospitalists could be the natural providers to delve into the specific psychosocial aspects of their patients’ lives, or try to figure out how those factors contribute to health care needs, Dr. Jacobs-Shaw said. They typically confront such issues while the patient is in the hospital bed, but what are the steps that led to the hospitalization in the first place? What will happen after the patient is discharged?
“For example, if patients lack transportation, how can they get to their follow-up medical appointment in the primary care office in order to manage their diabetes? If you can’t follow up with them, their diabetes could get out of control, with complications as a result, such as an infected wound,” he said. Another big issue is access to affordable medications. “CareMore has pharmacists embedded on our care teams. They try to figure out the best medicine for the patient but at the lowest cost. They meet individually with patients and do medication counseling, particularly for those with polypharmacy issues.”
Making health care more equitable
Dr. Jacobs-Shaw has long held a personal interest in issues of inclusiveness, diversity, and how to make health care more equitable for historically underserved groups. Asking how to have a bigger impact on these issues is what brought him, after 13 years as a hospitalist on the East Coast, to CareMore, a company that has made addressing social needs central to its care model. “In California, where I am based, we are a wrap-around for patients who are covered by Medicare Advantage plans. We are whatever the patient needs us to be.”
He oversees a group of hospitalists, dubbed extensivists, who provide advanced patient care and chronic disease management. In the extensivist model, physicians and advanced practice nurses provide comprehensive and coordinated care to patients with complex medical issues, taking their scope of practice beyond the hospital into homes, post-acute care facilities, and other settings, with a focus on keeping patients healthier and reducing readmission.3
“Our patients get access to extra services and resources, some of which are available at our care centers – which are one-stop outpatient facilities. We also focus on a lot of things physicians didn’t historically think were within their wheelhouse. Hospitalists deal with these kinds of issues every day, but may not label them as social determinants of health,” Dr. Jacobs-Shaw said. He emphasized that hospitalists should realize that they are not powerless to address these issues, working in partnership with other groups in and out of the hospital. They should also know that health care payers increasingly are dedicating resources to these issues.
“We just started trying to address homelessness through a pilot in Orange County, working with nonprofit organizations and philanthropy to offer a transitional site of care for our patients who are being discharged from the hospital and have housing insecurity issues, to get them transitioned into more secure housing,” Dr. Jacobs-Shaw said. CareMore also has a transportation collaborative that offers no-cost, nonemergency transportation to medical appointments. “That’s meeting them where they are at, based on an assessment of their needs and resources.”
What are social determinants?
The social determinants of health – social, environmental, and other nonmedical factors that contribute to overall health status and medical need – have been defined by the World Health Organization as: “conditions in which people are born, grow, live, work, and age.” That is a broad complex of overlapping social and systems issues, but it provides a context for a broader understanding of the patient’s health and response to medical interventions.
Socioeconomic status is a huge determinant. Level of education may be more important than income if the person lacks the health literacy to navigate the system and access needed care. Housing instability may include poor sanitation, substandard dwellings, or unsafe neighborhoods – all of which can affect a person’s well-being. Environmental health may include compromised air quality – which can impact pulmonary health. Other issues include access to employment and child care, utility needs, and interpersonal violence.
A 2014 paper in Annals of Internal Medicine found that residence within a disadvantaged neighborhood was a factor in hospital readmission rates as often as was chronic pulmonary disease.4 A recent report on social determinants of health by the National Institute for Health Care Management notes that patients with food insecurity are 2.4 times more likely to go to the emergency room, while those with transportation needs are 2.6 times more likely.5
What can health care leaders do to better equip their clinicians and teams to help patients deal with this array of complex needs? Intermountain Healthcare, based in Salt Lake City, spearheaded in 2018 the development of the Alliance for the Determinants of Health, starting in the communities of Ogden and St. George, Utah. The Alliance seeks to promote health, improve access to care, and decrease health care costs through a charitable contribution of $12 million over 3 years to seed collaborative demonstration projects.
Lisa Nichols, assistant vice president for community health at Intermountain, said that, while hospitalists were not directly involved in planning the Alliance, hospitalists and ED physicians have become essential to the patient-screening process for health and social needs.
“We met with hospitalists, emergency departments, and hospital administrators, because we wanted their feedback on how to raise awareness of the social needs of patients,” she said. “They have good ideas. They see the patients who come in from the homeless shelters.”
Other hospitals are subsidizing apartments for homeless patients being discharged from the hospital. CommonSpirit Health, the new national Catholic health care organization formed by the 2019 merger of Dignity Health and Catholic Health Initiatives, has explored how to help create and sustain affordable housing in the communities it serves. Investments like this have inspired others, such as Kaiser Permanente, to get involved in supporting housing initiatives.6
Comprehensive community care
David Meltzer, MD, PhD, a hospitalist and professor of medicine at the University of Chicago, said most hospitalists these days believe social determinants of health are part of their job responsibilities.
“That’s not to say we all do it well. We may fail at addressing some of the barriers our patients face. But I don’t know anyone who still says it’s not their job,” he said.
Since 2012, Dr. Meltzer has led a pilot called Comprehensive Care Physicians (CCP), in which the same physician cares for patients with chronic health problems in the clinic and in the hospital, working with a team of nurse practitioners, social workers, care coordinators, and other specialists. A total of 2,000 patients with chronic health problems were enrolled in the study from 2012 to 2016, half assigned to standard care and half assigned to five CCP doctors. The result: The CCP model has shown large improvements in outcomes – particularly among the more vulnerable, less activated patients, is preferred by patients, and has significantly reduced health care utilization.
The next step for the research team is another randomized controlled trial called Comprehensive Care, Community, and Culture, designed to address unmet social needs. Study group patients will also be screened for unmet social needs and have access to a community health worker and to the initiative’s Artful Living Program, which includes community and cultural activities like yoga and dance classes, cooking classes, art classes, and music concerts. To address the complex dimensions and determinants of health, Dr. Meltzer explained, efforts to improve health must extend to sectors far beyond traditional health care.
“I think trying to understand your patients’ social and nonmedical needs starts with getting to know them, and asking about their needs,” he said. “The better you know them, the better you are able to make medical decisions that will promote positive outcomes.”
Sound Physicians, a national hospitalist company based in Tacoma, Wash., and working in 350 hospitals in 41 states, recently published a blog post on its website about the importance of social determinants of health.7 Sound Physicians participates in value-based care through bundled Medicare/Medicaid contracts based on episodes of care for hospitalized patients with certain diagnoses or DRGs, explained John Dickey, MD, the company’s chief medical officer for population health.
“We’ve been heavily involved in trying to improve cost and outcomes of care since 2015. Social determinants absolutely play into trying to lower costs of care and reduce rates of readmissions, which are often multifactorial in cause,” he said. Hospitalists are uniquely equipped to impact post-acute outcomes, Dr. Dickey said, working in partnership with a position Sound Physicians calls the clinical performance nurse.
“We can also partner with primary care providers, provide education for our hospitalist staff, and work with in-home care supports for patients such as these, who otherwise might end up in a skilled nursing facility – even though they’d rather be at home,” he said.
Innovations at Northwell Health
Northwell Health, a multihospital comprehensive health system serving the New York City metro area and Long Island, has shown innovative leadership in addressing social factors. The 23-hospital system initiated in early 2019 a 15-item Self-Reported Social Determinants Screening Tool, which is now used with hospitalized patients to connect them with the support they need to fully recover and avoid readmissions.
Northwell is also providing professional education on social determinants for different constituencies across its system, said Johanna Martinez, MD, MS, a hospitalist and GME Director of Diversity and Health Equity at the Zucker School of Medicine at Hofstra/Northwell. A day-long training retreat was offered to GME faculty, and learning platforms have been developed for physicians, social workers, nurses, and others.
“One of the questions that comes up is that if you find social needs, what do you do about them?” Dr. Martinez explained. That’s more a difficult challenge, she said, so at Northwell, orthopedic surgeons are now asking patients questions like: “What’s going to happen when you go home? What are your social supports? Can you get to the physical therapist’s office?”
Another example of Northwell’s innovations is its Food as Health Program, initially piloted at Long Island Jewish Hospital in Valley Stream, N.Y. Hospitalized patients are asked two questions using a validated screening tool called the Hunger Vital Sign to identify their food insecurities.8 Those who answer yes are referred to a dietitian, and if they have a nutrition-related diagnosis, they enter the multidisciplinary wraparound program.
A key element is the food and health center, located on the hospital campus, where they can get food to take home and referrals to other services, with culturally tailored, disease-specific food education incorporated into the discharge plan. One of the partnering organizations is Island Harvest Food Bank, which helps about 1 in every 10 residents of Long Island with their food insecurity issues.
“When I talk to clinicians, most of us went into medicine to save lives and cure people. Yet the research shows that no matter who we are, we can’t do the best work that our patients need unless we consider their social determinants,” Dr. Martinez said. Ultimately, she noted, there is a need to change the culture of health care. “We have to create system change, reimbursement change, policy change.”
Omolara Uwemedimo, MD, MPH, associate professor of pediatrics and occupational medicine at Northwell and a former nocturnist, said the treatment of illness and health improvement don’t begin in the hospital, they begin in the community. Identifying where people are struggling and what communities they come from requires a broader view of the provider’s role. “Are patients who are readmitted to the hospital generally coming from certain demographics or from certain zip codes?” she asked. “Start there. How can we better connect with those communities?”
Education is key
In 2020 and beyond, hospitalists will hear more about the social determinants of health, Dr. Jacobs-Shaw concluded. “Without addressing those social determinants, we aren’t going to be able to meaningfully impact outcomes or be effective stewards of health care costs – addressing the psychosocial factors and root causes of patients coming in and out of the hospital.”
He added that self-education is key for hospitalists and the teams they work with – to be more aware of the link between health outcomes and social determinants. Guidelines and other resources on social determinants of health are available from the American College of Physicians and the American Association of Family Physicians. ACP issued a position paper on addressing social determinants of health to improve patient care,while AAFP has a research page on its website dedicated to social determinants of health, highlighting a number of initiatives and resources for physicians and others.9
The American Hospital Association has produced fact sheets on ICD-10CM code categories for social determinants of health, including 11 ICD-10 “Z” codes, numbered Z55-Z65, which can be used for coding interventions to address social determinants of health. Other experts are looking at how to adapt the electronic health record to capture sociodemographic and behavioral factors, and then trigger referrals to resources in the hospital and the broader community, and how to mobilize artificial intelligence and machine learning to better identify social needs.
“Our doctors really want to be able to take care of the whole patient, while being stewards of health care resources. But sometimes we feel powerless and wonder how we can have a bigger impact on people, on populations” Dr. Jacobs-Shaw said. “Remember it only takes one voice within an organization to start to elevate this topic.”
References
1. Rappleye E. Physicians say social determinants of health are not their responsibility. Becker’s Hospital Review. 2018 May 15.
2. Robert Wood Johnson Foundation, University of Wisconsin Population Health Institute. County Health Rankings, 2014.
3. Freeman, GA. The extensivist model. Health Leaders Magazine, 2016 Sep 15.
4. Kind AJ et al. Neighborhood socioeconomic disadvantage and 30-day rehospitalization: A retrospective cohort study. Ann Intern Med. 2014 Dec 2;161(11):765-74.
5. National Institute for Health Care Management. Addressing social determinants of health can improve community health & reduce costs.
6. Vial PB. Boundless collaboration: A philosophy for sustainable and stabilizing housing investment strategies. Health Progress: Journal of the Catholic Health Association of the United States. September-October 2019.
7. Social determinants of health: New solutions for growing complexities. Op-Med, a blog by Sound Physicians. 2019 Aug 1.
8. The hunger vital sign: A new standard of care for preventive health.
9. Daniel H et al. Addressing social determinants to improve patient care and promote health equity: An American College of Physicians position paper. Ann Intern Med. 2018;168:557-578.
While physicians acknowledge that the social determinants of health can impact outcomes from medical care, some may feel that trying to address factors such as homelessness, food insecurity, or lack of ready access to transportation or pharmacy services is just not part of the doctor’s job. A majority of 621 physicians surveyed in the summer of 2017 by Salt Lake City–based health care intelligence firm Leavitt Partners say they are neither capable of nor responsible for addressing such issues.1
But that view may become unsustainable as the U.S. health care system continues to advance toward value- and population-based models of health care and as evidence mounts that social factors are important contributors to costly outcomes, such as avoidable hospital readmissions or emergency room visits. A recent report from the Robert Wood Johnson Foundation estimates that at least 40% of health outcomes are the result of social and economic factors, while only 20% can be attributed to medical care.2
“This is a hot topic – getting a lot of attention these days,” said hospitalist and care transitions expert Ramon Jacobs-Shaw, MD, MPA, regional medical officer for CareMore Health, a California-based physician-led health delivery organization and subsidiary of Anthem. “If you go around the country, some doctors still see social factors as the realm of the social worker. But large health care organizations are coming to recognize that social determinants are huge contributors to the health of their members and to the outcomes of their care.”
Hospitalists could be the natural providers to delve into the specific psychosocial aspects of their patients’ lives, or try to figure out how those factors contribute to health care needs, Dr. Jacobs-Shaw said. They typically confront such issues while the patient is in the hospital bed, but what are the steps that led to the hospitalization in the first place? What will happen after the patient is discharged?
“For example, if patients lack transportation, how can they get to their follow-up medical appointment in the primary care office in order to manage their diabetes? If you can’t follow up with them, their diabetes could get out of control, with complications as a result, such as an infected wound,” he said. Another big issue is access to affordable medications. “CareMore has pharmacists embedded on our care teams. They try to figure out the best medicine for the patient but at the lowest cost. They meet individually with patients and do medication counseling, particularly for those with polypharmacy issues.”
Making health care more equitable
Dr. Jacobs-Shaw has long held a personal interest in issues of inclusiveness, diversity, and how to make health care more equitable for historically underserved groups. Asking how to have a bigger impact on these issues is what brought him, after 13 years as a hospitalist on the East Coast, to CareMore, a company that has made addressing social needs central to its care model. “In California, where I am based, we are a wrap-around for patients who are covered by Medicare Advantage plans. We are whatever the patient needs us to be.”
He oversees a group of hospitalists, dubbed extensivists, who provide advanced patient care and chronic disease management. In the extensivist model, physicians and advanced practice nurses provide comprehensive and coordinated care to patients with complex medical issues, taking their scope of practice beyond the hospital into homes, post-acute care facilities, and other settings, with a focus on keeping patients healthier and reducing readmission.3
“Our patients get access to extra services and resources, some of which are available at our care centers – which are one-stop outpatient facilities. We also focus on a lot of things physicians didn’t historically think were within their wheelhouse. Hospitalists deal with these kinds of issues every day, but may not label them as social determinants of health,” Dr. Jacobs-Shaw said. He emphasized that hospitalists should realize that they are not powerless to address these issues, working in partnership with other groups in and out of the hospital. They should also know that health care payers increasingly are dedicating resources to these issues.
“We just started trying to address homelessness through a pilot in Orange County, working with nonprofit organizations and philanthropy to offer a transitional site of care for our patients who are being discharged from the hospital and have housing insecurity issues, to get them transitioned into more secure housing,” Dr. Jacobs-Shaw said. CareMore also has a transportation collaborative that offers no-cost, nonemergency transportation to medical appointments. “That’s meeting them where they are at, based on an assessment of their needs and resources.”
What are social determinants?
The social determinants of health – social, environmental, and other nonmedical factors that contribute to overall health status and medical need – have been defined by the World Health Organization as: “conditions in which people are born, grow, live, work, and age.” That is a broad complex of overlapping social and systems issues, but it provides a context for a broader understanding of the patient’s health and response to medical interventions.
Socioeconomic status is a huge determinant. Level of education may be more important than income if the person lacks the health literacy to navigate the system and access needed care. Housing instability may include poor sanitation, substandard dwellings, or unsafe neighborhoods – all of which can affect a person’s well-being. Environmental health may include compromised air quality – which can impact pulmonary health. Other issues include access to employment and child care, utility needs, and interpersonal violence.
A 2014 paper in Annals of Internal Medicine found that residence within a disadvantaged neighborhood was a factor in hospital readmission rates as often as was chronic pulmonary disease.4 A recent report on social determinants of health by the National Institute for Health Care Management notes that patients with food insecurity are 2.4 times more likely to go to the emergency room, while those with transportation needs are 2.6 times more likely.5
What can health care leaders do to better equip their clinicians and teams to help patients deal with this array of complex needs? Intermountain Healthcare, based in Salt Lake City, spearheaded in 2018 the development of the Alliance for the Determinants of Health, starting in the communities of Ogden and St. George, Utah. The Alliance seeks to promote health, improve access to care, and decrease health care costs through a charitable contribution of $12 million over 3 years to seed collaborative demonstration projects.
Lisa Nichols, assistant vice president for community health at Intermountain, said that, while hospitalists were not directly involved in planning the Alliance, hospitalists and ED physicians have become essential to the patient-screening process for health and social needs.
“We met with hospitalists, emergency departments, and hospital administrators, because we wanted their feedback on how to raise awareness of the social needs of patients,” she said. “They have good ideas. They see the patients who come in from the homeless shelters.”
Other hospitals are subsidizing apartments for homeless patients being discharged from the hospital. CommonSpirit Health, the new national Catholic health care organization formed by the 2019 merger of Dignity Health and Catholic Health Initiatives, has explored how to help create and sustain affordable housing in the communities it serves. Investments like this have inspired others, such as Kaiser Permanente, to get involved in supporting housing initiatives.6
Comprehensive community care
David Meltzer, MD, PhD, a hospitalist and professor of medicine at the University of Chicago, said most hospitalists these days believe social determinants of health are part of their job responsibilities.
“That’s not to say we all do it well. We may fail at addressing some of the barriers our patients face. But I don’t know anyone who still says it’s not their job,” he said.
Since 2012, Dr. Meltzer has led a pilot called Comprehensive Care Physicians (CCP), in which the same physician cares for patients with chronic health problems in the clinic and in the hospital, working with a team of nurse practitioners, social workers, care coordinators, and other specialists. A total of 2,000 patients with chronic health problems were enrolled in the study from 2012 to 2016, half assigned to standard care and half assigned to five CCP doctors. The result: The CCP model has shown large improvements in outcomes – particularly among the more vulnerable, less activated patients, is preferred by patients, and has significantly reduced health care utilization.
The next step for the research team is another randomized controlled trial called Comprehensive Care, Community, and Culture, designed to address unmet social needs. Study group patients will also be screened for unmet social needs and have access to a community health worker and to the initiative’s Artful Living Program, which includes community and cultural activities like yoga and dance classes, cooking classes, art classes, and music concerts. To address the complex dimensions and determinants of health, Dr. Meltzer explained, efforts to improve health must extend to sectors far beyond traditional health care.
“I think trying to understand your patients’ social and nonmedical needs starts with getting to know them, and asking about their needs,” he said. “The better you know them, the better you are able to make medical decisions that will promote positive outcomes.”
Sound Physicians, a national hospitalist company based in Tacoma, Wash., and working in 350 hospitals in 41 states, recently published a blog post on its website about the importance of social determinants of health.7 Sound Physicians participates in value-based care through bundled Medicare/Medicaid contracts based on episodes of care for hospitalized patients with certain diagnoses or DRGs, explained John Dickey, MD, the company’s chief medical officer for population health.
“We’ve been heavily involved in trying to improve cost and outcomes of care since 2015. Social determinants absolutely play into trying to lower costs of care and reduce rates of readmissions, which are often multifactorial in cause,” he said. Hospitalists are uniquely equipped to impact post-acute outcomes, Dr. Dickey said, working in partnership with a position Sound Physicians calls the clinical performance nurse.
“We can also partner with primary care providers, provide education for our hospitalist staff, and work with in-home care supports for patients such as these, who otherwise might end up in a skilled nursing facility – even though they’d rather be at home,” he said.
Innovations at Northwell Health
Northwell Health, a multihospital comprehensive health system serving the New York City metro area and Long Island, has shown innovative leadership in addressing social factors. The 23-hospital system initiated in early 2019 a 15-item Self-Reported Social Determinants Screening Tool, which is now used with hospitalized patients to connect them with the support they need to fully recover and avoid readmissions.
Northwell is also providing professional education on social determinants for different constituencies across its system, said Johanna Martinez, MD, MS, a hospitalist and GME Director of Diversity and Health Equity at the Zucker School of Medicine at Hofstra/Northwell. A day-long training retreat was offered to GME faculty, and learning platforms have been developed for physicians, social workers, nurses, and others.
“One of the questions that comes up is that if you find social needs, what do you do about them?” Dr. Martinez explained. That’s more a difficult challenge, she said, so at Northwell, orthopedic surgeons are now asking patients questions like: “What’s going to happen when you go home? What are your social supports? Can you get to the physical therapist’s office?”
Another example of Northwell’s innovations is its Food as Health Program, initially piloted at Long Island Jewish Hospital in Valley Stream, N.Y. Hospitalized patients are asked two questions using a validated screening tool called the Hunger Vital Sign to identify their food insecurities.8 Those who answer yes are referred to a dietitian, and if they have a nutrition-related diagnosis, they enter the multidisciplinary wraparound program.
A key element is the food and health center, located on the hospital campus, where they can get food to take home and referrals to other services, with culturally tailored, disease-specific food education incorporated into the discharge plan. One of the partnering organizations is Island Harvest Food Bank, which helps about 1 in every 10 residents of Long Island with their food insecurity issues.
“When I talk to clinicians, most of us went into medicine to save lives and cure people. Yet the research shows that no matter who we are, we can’t do the best work that our patients need unless we consider their social determinants,” Dr. Martinez said. Ultimately, she noted, there is a need to change the culture of health care. “We have to create system change, reimbursement change, policy change.”
Omolara Uwemedimo, MD, MPH, associate professor of pediatrics and occupational medicine at Northwell and a former nocturnist, said the treatment of illness and health improvement don’t begin in the hospital, they begin in the community. Identifying where people are struggling and what communities they come from requires a broader view of the provider’s role. “Are patients who are readmitted to the hospital generally coming from certain demographics or from certain zip codes?” she asked. “Start there. How can we better connect with those communities?”
Education is key
In 2020 and beyond, hospitalists will hear more about the social determinants of health, Dr. Jacobs-Shaw concluded. “Without addressing those social determinants, we aren’t going to be able to meaningfully impact outcomes or be effective stewards of health care costs – addressing the psychosocial factors and root causes of patients coming in and out of the hospital.”
He added that self-education is key for hospitalists and the teams they work with – to be more aware of the link between health outcomes and social determinants. Guidelines and other resources on social determinants of health are available from the American College of Physicians and the American Association of Family Physicians. ACP issued a position paper on addressing social determinants of health to improve patient care,while AAFP has a research page on its website dedicated to social determinants of health, highlighting a number of initiatives and resources for physicians and others.9
The American Hospital Association has produced fact sheets on ICD-10CM code categories for social determinants of health, including 11 ICD-10 “Z” codes, numbered Z55-Z65, which can be used for coding interventions to address social determinants of health. Other experts are looking at how to adapt the electronic health record to capture sociodemographic and behavioral factors, and then trigger referrals to resources in the hospital and the broader community, and how to mobilize artificial intelligence and machine learning to better identify social needs.
“Our doctors really want to be able to take care of the whole patient, while being stewards of health care resources. But sometimes we feel powerless and wonder how we can have a bigger impact on people, on populations” Dr. Jacobs-Shaw said. “Remember it only takes one voice within an organization to start to elevate this topic.”
References
1. Rappleye E. Physicians say social determinants of health are not their responsibility. Becker’s Hospital Review. 2018 May 15.
2. Robert Wood Johnson Foundation, University of Wisconsin Population Health Institute. County Health Rankings, 2014.
3. Freeman, GA. The extensivist model. Health Leaders Magazine, 2016 Sep 15.
4. Kind AJ et al. Neighborhood socioeconomic disadvantage and 30-day rehospitalization: A retrospective cohort study. Ann Intern Med. 2014 Dec 2;161(11):765-74.
5. National Institute for Health Care Management. Addressing social determinants of health can improve community health & reduce costs.
6. Vial PB. Boundless collaboration: A philosophy for sustainable and stabilizing housing investment strategies. Health Progress: Journal of the Catholic Health Association of the United States. September-October 2019.
7. Social determinants of health: New solutions for growing complexities. Op-Med, a blog by Sound Physicians. 2019 Aug 1.
8. The hunger vital sign: A new standard of care for preventive health.
9. Daniel H et al. Addressing social determinants to improve patient care and promote health equity: An American College of Physicians position paper. Ann Intern Med. 2018;168:557-578.
Cardiac arrest: Targeted temperature management a game changer
SNOWMASS, COLO. – Targeted temperature management maintained at 32-36 degrees Celsius is now a strong class I recommendation for all comatose patients who experience return of spontaneous circulation after out-of-hospital cardiac arrest, including those with nonshockable rhythms, Erin A. Bohula, MD, PhD, said at the annual Cardiovascular Conference at Snowmass sponsored by the American College of Cardiology.
“Our practice is that ,” said Dr. Bohula, a cardiologist and critical care specialist at Brigham and Women’s Hospital and Harvard Medical School, Boston.
The current ACC/AHA guidelines declare: “There are essentially no patients for whom temperature control somewhere in the range between 32 degrees C [89.6 F) and 36 degrees C [96.8 F] is contraindicated.” The writing committee cited “recent clinical trial data enrolling patients with all rhythms, the rarity of adverse effects in trials, the high neurologic morbidity and mortality without any specific interventions, and the preponderance of data suggesting that temperature is an important variable for neurologic recovery” (Circulation. 2015 Nov 3;132[18 Suppl 2]:S465-82).
“That’s a pretty strong statement,” Dr. Bohula observed.
The current guidelines, which date back to 2015, give a class I, level of evidence B recommendation for targeted temperature management (TTM) in patients who are comatose with return of spontaneous circulation (ROSC) after out-of-hospital cardiac arrest involving ventricular fibrillation or pulseless ventricular fibrillation. The bedside definition of comatose is lack of meaningful response to verbal commands to squeeze hands, blink, or move toes.
The current recommendation for TTM in patients resuscitated from out-of-hospital cardiac arrest with a nonshockable rhythm is class I, level of evidence C, meaning it’s based on expert consensus. However, that recommendation is now out of date and due for a level-of-evidence upgrade in light of the recent results of the French HYPERION trial, an open-label randomized trial of 584 patients resuscitated from cardiac arrest with a nonshockable rhythm. Although 90-day mortality was similarly high in the TTM and targeted normothermia groups, the rate of favorable neurologic outcome as assessed by a Cerebral Performance Category scale score of 1 or 2 was 10.2% in the TTM group, significantly better than the 5.7% rate in controls (N Engl J Med. 2019 Dec 12;381[24]:2327-37).
The 2010, ACC/AHA guidelines recommended a TTM range of 32-34 degrees C, but on the basis of subsequent persuasive randomized trial data, that range was broadened to 32-36 degrees C in the 2015 guidelines, with a class IB recommendation. Maintenance of TTM for at least 24 hours has a IIa, level of evidence C recommendation in the current guidelines.
The guidelines emphasize that specific features may favor selection of one temperature for TTM over another. For example, patients with seizures or cerebral edema might be better off with TTM at a lower temperature, while a higher temperature may be best for those with bleeding or severe bradycardia. At Brigham and Women’s Hospital, the default temperature is 33 degrees C. However, TTM with a goal of 36 degrees C is seriously considered in patients with recent head trauma, major surgery within the past 2 weeks, refractory hypotension, severe sepsis, pregnancy, or high bleeding risk. Rewarming is done at a rate of 0.25 degrees C per hour, with sedation maintained until the patient has been returned to 98.6 degrees F, according to Dr. Bohula.
Based on several negative studies of TTM using rapid infusion of chilled fluids in the ambulance en route to the hospital, the guidelines rate that practice class IIIA, meaning don’t do it. Avoidance of a systolic blood pressure below 90 mm Hg and a mean arterial pressure of less than 65 mm Hg gets a class IIb level of evidence C recommendation to lessen the risk of cerebral hypoxia.
TTM a major breakthrough
Prior to the introduction of TTM, comatose patients with ROSC after out-of-hospital cardiac arrest had a dreadful prognosis, with survival rates of 1%-10% in registry studies. In contrast, the survival rate in the landmark TTM clinical trials was 50%-60%. And while that’s a dramatic improvement, ROSC after cardiac arrest remains a high-mortality condition. Dr. Bohula was first author of a report by the Critical Care Cardiology Trials Network, composed of 16 tertiary cardiac intensive care units in the United States and Canada. Cardiac arrest was the primary indication for 8.7% of 3,049 consecutive admissions, and its 38% mortality rate was the highest of all cardiac critical care indications (JAMA Cardiol. 2019 Jul 24;4[9]:928-35).
TTM was developed in response to a recognition that two-thirds of deaths in patients who make it to the hospital after out-of-hospital cardiac arrest are neurologic – the result of brain anoxia – rather than being due to the myocardial ischemia that may have initially brought them to medical attention.
“Time is brain cells, the same way we think of time as cardiac muscle,” Dr. Bohula observed.
The main idea behind therapeutic hypothermia is that it lowers the cerebral metabolic rate of oxygen to reduce the consequences of ongoing anoxia. The brain doesn’t require as much perfusion when cooled.
TTM has other beneficial neurologic effects as well: It reduces cerebral blood volume via autoregulation, decreases intracranial pressure, and blunts the inflammatory response involved in the postcardiac arrest syndrome. In addition, TTM has anticonvulsant properties, an important effect because seizures and/or myoclonus occur in up to 15% of adults who achieve ROSC after cardiac arrest – and in even more of those who are comatose after doing so. And seizures increase the brain’s metabolic rate threefold, resulting in more cerebral ischemic injury, she explained.
Seizure activity can be difficult to distinguish from shivering in a patient on TTM. For this reason Dr. Bohula recommends putting patients on continuous EEG monitoring from the time of admission, as is the routine practice at the Brigham.
She reported serving as a consultant to Daiichi Sankyo, Servier, Lexicon, Kowa, Merck, Novartis, Novo Nordisk, and the National Institutes of Health. In addition, she generates institutional research grants provided by a half-dozen pharmaceutical companies.
SNOWMASS, COLO. – Targeted temperature management maintained at 32-36 degrees Celsius is now a strong class I recommendation for all comatose patients who experience return of spontaneous circulation after out-of-hospital cardiac arrest, including those with nonshockable rhythms, Erin A. Bohula, MD, PhD, said at the annual Cardiovascular Conference at Snowmass sponsored by the American College of Cardiology.
“Our practice is that ,” said Dr. Bohula, a cardiologist and critical care specialist at Brigham and Women’s Hospital and Harvard Medical School, Boston.
The current ACC/AHA guidelines declare: “There are essentially no patients for whom temperature control somewhere in the range between 32 degrees C [89.6 F) and 36 degrees C [96.8 F] is contraindicated.” The writing committee cited “recent clinical trial data enrolling patients with all rhythms, the rarity of adverse effects in trials, the high neurologic morbidity and mortality without any specific interventions, and the preponderance of data suggesting that temperature is an important variable for neurologic recovery” (Circulation. 2015 Nov 3;132[18 Suppl 2]:S465-82).
“That’s a pretty strong statement,” Dr. Bohula observed.
The current guidelines, which date back to 2015, give a class I, level of evidence B recommendation for targeted temperature management (TTM) in patients who are comatose with return of spontaneous circulation (ROSC) after out-of-hospital cardiac arrest involving ventricular fibrillation or pulseless ventricular fibrillation. The bedside definition of comatose is lack of meaningful response to verbal commands to squeeze hands, blink, or move toes.
The current recommendation for TTM in patients resuscitated from out-of-hospital cardiac arrest with a nonshockable rhythm is class I, level of evidence C, meaning it’s based on expert consensus. However, that recommendation is now out of date and due for a level-of-evidence upgrade in light of the recent results of the French HYPERION trial, an open-label randomized trial of 584 patients resuscitated from cardiac arrest with a nonshockable rhythm. Although 90-day mortality was similarly high in the TTM and targeted normothermia groups, the rate of favorable neurologic outcome as assessed by a Cerebral Performance Category scale score of 1 or 2 was 10.2% in the TTM group, significantly better than the 5.7% rate in controls (N Engl J Med. 2019 Dec 12;381[24]:2327-37).
The 2010, ACC/AHA guidelines recommended a TTM range of 32-34 degrees C, but on the basis of subsequent persuasive randomized trial data, that range was broadened to 32-36 degrees C in the 2015 guidelines, with a class IB recommendation. Maintenance of TTM for at least 24 hours has a IIa, level of evidence C recommendation in the current guidelines.
The guidelines emphasize that specific features may favor selection of one temperature for TTM over another. For example, patients with seizures or cerebral edema might be better off with TTM at a lower temperature, while a higher temperature may be best for those with bleeding or severe bradycardia. At Brigham and Women’s Hospital, the default temperature is 33 degrees C. However, TTM with a goal of 36 degrees C is seriously considered in patients with recent head trauma, major surgery within the past 2 weeks, refractory hypotension, severe sepsis, pregnancy, or high bleeding risk. Rewarming is done at a rate of 0.25 degrees C per hour, with sedation maintained until the patient has been returned to 98.6 degrees F, according to Dr. Bohula.
Based on several negative studies of TTM using rapid infusion of chilled fluids in the ambulance en route to the hospital, the guidelines rate that practice class IIIA, meaning don’t do it. Avoidance of a systolic blood pressure below 90 mm Hg and a mean arterial pressure of less than 65 mm Hg gets a class IIb level of evidence C recommendation to lessen the risk of cerebral hypoxia.
TTM a major breakthrough
Prior to the introduction of TTM, comatose patients with ROSC after out-of-hospital cardiac arrest had a dreadful prognosis, with survival rates of 1%-10% in registry studies. In contrast, the survival rate in the landmark TTM clinical trials was 50%-60%. And while that’s a dramatic improvement, ROSC after cardiac arrest remains a high-mortality condition. Dr. Bohula was first author of a report by the Critical Care Cardiology Trials Network, composed of 16 tertiary cardiac intensive care units in the United States and Canada. Cardiac arrest was the primary indication for 8.7% of 3,049 consecutive admissions, and its 38% mortality rate was the highest of all cardiac critical care indications (JAMA Cardiol. 2019 Jul 24;4[9]:928-35).
TTM was developed in response to a recognition that two-thirds of deaths in patients who make it to the hospital after out-of-hospital cardiac arrest are neurologic – the result of brain anoxia – rather than being due to the myocardial ischemia that may have initially brought them to medical attention.
“Time is brain cells, the same way we think of time as cardiac muscle,” Dr. Bohula observed.
The main idea behind therapeutic hypothermia is that it lowers the cerebral metabolic rate of oxygen to reduce the consequences of ongoing anoxia. The brain doesn’t require as much perfusion when cooled.
TTM has other beneficial neurologic effects as well: It reduces cerebral blood volume via autoregulation, decreases intracranial pressure, and blunts the inflammatory response involved in the postcardiac arrest syndrome. In addition, TTM has anticonvulsant properties, an important effect because seizures and/or myoclonus occur in up to 15% of adults who achieve ROSC after cardiac arrest – and in even more of those who are comatose after doing so. And seizures increase the brain’s metabolic rate threefold, resulting in more cerebral ischemic injury, she explained.
Seizure activity can be difficult to distinguish from shivering in a patient on TTM. For this reason Dr. Bohula recommends putting patients on continuous EEG monitoring from the time of admission, as is the routine practice at the Brigham.
She reported serving as a consultant to Daiichi Sankyo, Servier, Lexicon, Kowa, Merck, Novartis, Novo Nordisk, and the National Institutes of Health. In addition, she generates institutional research grants provided by a half-dozen pharmaceutical companies.
SNOWMASS, COLO. – Targeted temperature management maintained at 32-36 degrees Celsius is now a strong class I recommendation for all comatose patients who experience return of spontaneous circulation after out-of-hospital cardiac arrest, including those with nonshockable rhythms, Erin A. Bohula, MD, PhD, said at the annual Cardiovascular Conference at Snowmass sponsored by the American College of Cardiology.
“Our practice is that ,” said Dr. Bohula, a cardiologist and critical care specialist at Brigham and Women’s Hospital and Harvard Medical School, Boston.
The current ACC/AHA guidelines declare: “There are essentially no patients for whom temperature control somewhere in the range between 32 degrees C [89.6 F) and 36 degrees C [96.8 F] is contraindicated.” The writing committee cited “recent clinical trial data enrolling patients with all rhythms, the rarity of adverse effects in trials, the high neurologic morbidity and mortality without any specific interventions, and the preponderance of data suggesting that temperature is an important variable for neurologic recovery” (Circulation. 2015 Nov 3;132[18 Suppl 2]:S465-82).
“That’s a pretty strong statement,” Dr. Bohula observed.
The current guidelines, which date back to 2015, give a class I, level of evidence B recommendation for targeted temperature management (TTM) in patients who are comatose with return of spontaneous circulation (ROSC) after out-of-hospital cardiac arrest involving ventricular fibrillation or pulseless ventricular fibrillation. The bedside definition of comatose is lack of meaningful response to verbal commands to squeeze hands, blink, or move toes.
The current recommendation for TTM in patients resuscitated from out-of-hospital cardiac arrest with a nonshockable rhythm is class I, level of evidence C, meaning it’s based on expert consensus. However, that recommendation is now out of date and due for a level-of-evidence upgrade in light of the recent results of the French HYPERION trial, an open-label randomized trial of 584 patients resuscitated from cardiac arrest with a nonshockable rhythm. Although 90-day mortality was similarly high in the TTM and targeted normothermia groups, the rate of favorable neurologic outcome as assessed by a Cerebral Performance Category scale score of 1 or 2 was 10.2% in the TTM group, significantly better than the 5.7% rate in controls (N Engl J Med. 2019 Dec 12;381[24]:2327-37).
The 2010, ACC/AHA guidelines recommended a TTM range of 32-34 degrees C, but on the basis of subsequent persuasive randomized trial data, that range was broadened to 32-36 degrees C in the 2015 guidelines, with a class IB recommendation. Maintenance of TTM for at least 24 hours has a IIa, level of evidence C recommendation in the current guidelines.
The guidelines emphasize that specific features may favor selection of one temperature for TTM over another. For example, patients with seizures or cerebral edema might be better off with TTM at a lower temperature, while a higher temperature may be best for those with bleeding or severe bradycardia. At Brigham and Women’s Hospital, the default temperature is 33 degrees C. However, TTM with a goal of 36 degrees C is seriously considered in patients with recent head trauma, major surgery within the past 2 weeks, refractory hypotension, severe sepsis, pregnancy, or high bleeding risk. Rewarming is done at a rate of 0.25 degrees C per hour, with sedation maintained until the patient has been returned to 98.6 degrees F, according to Dr. Bohula.
Based on several negative studies of TTM using rapid infusion of chilled fluids in the ambulance en route to the hospital, the guidelines rate that practice class IIIA, meaning don’t do it. Avoidance of a systolic blood pressure below 90 mm Hg and a mean arterial pressure of less than 65 mm Hg gets a class IIb level of evidence C recommendation to lessen the risk of cerebral hypoxia.
TTM a major breakthrough
Prior to the introduction of TTM, comatose patients with ROSC after out-of-hospital cardiac arrest had a dreadful prognosis, with survival rates of 1%-10% in registry studies. In contrast, the survival rate in the landmark TTM clinical trials was 50%-60%. And while that’s a dramatic improvement, ROSC after cardiac arrest remains a high-mortality condition. Dr. Bohula was first author of a report by the Critical Care Cardiology Trials Network, composed of 16 tertiary cardiac intensive care units in the United States and Canada. Cardiac arrest was the primary indication for 8.7% of 3,049 consecutive admissions, and its 38% mortality rate was the highest of all cardiac critical care indications (JAMA Cardiol. 2019 Jul 24;4[9]:928-35).
TTM was developed in response to a recognition that two-thirds of deaths in patients who make it to the hospital after out-of-hospital cardiac arrest are neurologic – the result of brain anoxia – rather than being due to the myocardial ischemia that may have initially brought them to medical attention.
“Time is brain cells, the same way we think of time as cardiac muscle,” Dr. Bohula observed.
The main idea behind therapeutic hypothermia is that it lowers the cerebral metabolic rate of oxygen to reduce the consequences of ongoing anoxia. The brain doesn’t require as much perfusion when cooled.
TTM has other beneficial neurologic effects as well: It reduces cerebral blood volume via autoregulation, decreases intracranial pressure, and blunts the inflammatory response involved in the postcardiac arrest syndrome. In addition, TTM has anticonvulsant properties, an important effect because seizures and/or myoclonus occur in up to 15% of adults who achieve ROSC after cardiac arrest – and in even more of those who are comatose after doing so. And seizures increase the brain’s metabolic rate threefold, resulting in more cerebral ischemic injury, she explained.
Seizure activity can be difficult to distinguish from shivering in a patient on TTM. For this reason Dr. Bohula recommends putting patients on continuous EEG monitoring from the time of admission, as is the routine practice at the Brigham.
She reported serving as a consultant to Daiichi Sankyo, Servier, Lexicon, Kowa, Merck, Novartis, Novo Nordisk, and the National Institutes of Health. In addition, she generates institutional research grants provided by a half-dozen pharmaceutical companies.
EXPERT ANALYSIS FROM ACC SNOWMASS 2020
CDC begins coronavirus diagnostic test kit distribution; new case confirmed in Wisconsin
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention and the Wisconsin Department of Health Services confirmed a new case of the 2019 Novel Coronavirus (2019-nCoV) on Feb. 5, 2020, bringing the total number of cases in the United States to 12.*
Earlier in the day, Nancy Messonnier, MD, director of the CDC National Center for Immunization and Respiratory Diseases, told reporters that 206 individuals under investigation had tested negative for infection with the novel virus and that tests were pending on another 76 individuals.
The agency also announced during a press briefing call that diagnostic test kits will begin shipping on Feb. 5, less than 24 hours after receiving an emergency use authorization from the Food and Drug Administration. Full information is available in an article published in the Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report.
The emergency use authorization will allow for broader use of the CDC’s 2019-nCoV Real Time RT-PCR Diagnostic Panel, which to date has been limited for use at CDC laboratories. Under the emergency use authorization, the diagnostic kit is authorized for patients who meed the CDC criteria for 2019-nCoV testing. The diagnostic test is a reverse transcriptase polymerase chain reaction test that provides presumptive detection of 2019-nCoV from respiratory secretions, such as nasal or oral swabs. A positive test indicates likely infection, although a negative test does not preclude infection and should not be the sole determination for patient management decisions.
“Today, the test kits will start shipping to over 100 U.S. public health labs,” she said. “Each of these labs is required to perform international verification for [Clinical Laboratory Improvement Amendments] compliance prior to reporting out. This process is expected to take a few days.”
Dr. Messonnier said that 200 test kits will be distributed to domestic labs and another 200 test kits will go to select international labs. Each kit can perform diagnostics on 700-800 patient samples.
“What that means is that, by the start of next week, we expect there to be much enhanced capacity for laboratory testing closer to our patients,” she said, adding that additional test kits are being produced and will be available for ordering in the future. Each laboratory that places an order will receive one test kit.
“Distribution of these tests will improve the global capacity to detect and respond to this new virus,” Dr. Messonnier said. “Availability of this test is a starting place for greater commercial availability of diagnostic testing for nCoV.”
The CDC also said that the next batch of passengers arriving from Wuhan, China, will be arriving in one of four locations: Travis Air Force Base, Fairfield, Calif.; Marine Corps Air Station Miramar, San Diego; Lackland Air Force Base, San Antonio; and Eppley Airfield, Omaha, Neb. Passengers will be quarantined for up to 14 days from the day the flight left Wuhan and medical care will be provided if needed.
“We do not believe these people pose a threat to the communities where they are being housed as we are taking measures to minimize any contact,” she said, adding that confirmed infections are expected among these and other returning travelers.
Dr. Messonnier warned that the quarantine measures “may not catch every single returning traveler returning with novel coronavirus, given the nature of this virus and how it is spreading. But if we can catch the majority of them, that will slow the entry of this virus into the United States.”
*This story was updated on 02/05/2020.
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention and the Wisconsin Department of Health Services confirmed a new case of the 2019 Novel Coronavirus (2019-nCoV) on Feb. 5, 2020, bringing the total number of cases in the United States to 12.*
Earlier in the day, Nancy Messonnier, MD, director of the CDC National Center for Immunization and Respiratory Diseases, told reporters that 206 individuals under investigation had tested negative for infection with the novel virus and that tests were pending on another 76 individuals.
The agency also announced during a press briefing call that diagnostic test kits will begin shipping on Feb. 5, less than 24 hours after receiving an emergency use authorization from the Food and Drug Administration. Full information is available in an article published in the Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report.
The emergency use authorization will allow for broader use of the CDC’s 2019-nCoV Real Time RT-PCR Diagnostic Panel, which to date has been limited for use at CDC laboratories. Under the emergency use authorization, the diagnostic kit is authorized for patients who meed the CDC criteria for 2019-nCoV testing. The diagnostic test is a reverse transcriptase polymerase chain reaction test that provides presumptive detection of 2019-nCoV from respiratory secretions, such as nasal or oral swabs. A positive test indicates likely infection, although a negative test does not preclude infection and should not be the sole determination for patient management decisions.
“Today, the test kits will start shipping to over 100 U.S. public health labs,” she said. “Each of these labs is required to perform international verification for [Clinical Laboratory Improvement Amendments] compliance prior to reporting out. This process is expected to take a few days.”
Dr. Messonnier said that 200 test kits will be distributed to domestic labs and another 200 test kits will go to select international labs. Each kit can perform diagnostics on 700-800 patient samples.
“What that means is that, by the start of next week, we expect there to be much enhanced capacity for laboratory testing closer to our patients,” she said, adding that additional test kits are being produced and will be available for ordering in the future. Each laboratory that places an order will receive one test kit.
“Distribution of these tests will improve the global capacity to detect and respond to this new virus,” Dr. Messonnier said. “Availability of this test is a starting place for greater commercial availability of diagnostic testing for nCoV.”
The CDC also said that the next batch of passengers arriving from Wuhan, China, will be arriving in one of four locations: Travis Air Force Base, Fairfield, Calif.; Marine Corps Air Station Miramar, San Diego; Lackland Air Force Base, San Antonio; and Eppley Airfield, Omaha, Neb. Passengers will be quarantined for up to 14 days from the day the flight left Wuhan and medical care will be provided if needed.
“We do not believe these people pose a threat to the communities where they are being housed as we are taking measures to minimize any contact,” she said, adding that confirmed infections are expected among these and other returning travelers.
Dr. Messonnier warned that the quarantine measures “may not catch every single returning traveler returning with novel coronavirus, given the nature of this virus and how it is spreading. But if we can catch the majority of them, that will slow the entry of this virus into the United States.”
*This story was updated on 02/05/2020.
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention and the Wisconsin Department of Health Services confirmed a new case of the 2019 Novel Coronavirus (2019-nCoV) on Feb. 5, 2020, bringing the total number of cases in the United States to 12.*
Earlier in the day, Nancy Messonnier, MD, director of the CDC National Center for Immunization and Respiratory Diseases, told reporters that 206 individuals under investigation had tested negative for infection with the novel virus and that tests were pending on another 76 individuals.
The agency also announced during a press briefing call that diagnostic test kits will begin shipping on Feb. 5, less than 24 hours after receiving an emergency use authorization from the Food and Drug Administration. Full information is available in an article published in the Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report.
The emergency use authorization will allow for broader use of the CDC’s 2019-nCoV Real Time RT-PCR Diagnostic Panel, which to date has been limited for use at CDC laboratories. Under the emergency use authorization, the diagnostic kit is authorized for patients who meed the CDC criteria for 2019-nCoV testing. The diagnostic test is a reverse transcriptase polymerase chain reaction test that provides presumptive detection of 2019-nCoV from respiratory secretions, such as nasal or oral swabs. A positive test indicates likely infection, although a negative test does not preclude infection and should not be the sole determination for patient management decisions.
“Today, the test kits will start shipping to over 100 U.S. public health labs,” she said. “Each of these labs is required to perform international verification for [Clinical Laboratory Improvement Amendments] compliance prior to reporting out. This process is expected to take a few days.”
Dr. Messonnier said that 200 test kits will be distributed to domestic labs and another 200 test kits will go to select international labs. Each kit can perform diagnostics on 700-800 patient samples.
“What that means is that, by the start of next week, we expect there to be much enhanced capacity for laboratory testing closer to our patients,” she said, adding that additional test kits are being produced and will be available for ordering in the future. Each laboratory that places an order will receive one test kit.
“Distribution of these tests will improve the global capacity to detect and respond to this new virus,” Dr. Messonnier said. “Availability of this test is a starting place for greater commercial availability of diagnostic testing for nCoV.”
The CDC also said that the next batch of passengers arriving from Wuhan, China, will be arriving in one of four locations: Travis Air Force Base, Fairfield, Calif.; Marine Corps Air Station Miramar, San Diego; Lackland Air Force Base, San Antonio; and Eppley Airfield, Omaha, Neb. Passengers will be quarantined for up to 14 days from the day the flight left Wuhan and medical care will be provided if needed.
“We do not believe these people pose a threat to the communities where they are being housed as we are taking measures to minimize any contact,” she said, adding that confirmed infections are expected among these and other returning travelers.
Dr. Messonnier warned that the quarantine measures “may not catch every single returning traveler returning with novel coronavirus, given the nature of this virus and how it is spreading. But if we can catch the majority of them, that will slow the entry of this virus into the United States.”
*This story was updated on 02/05/2020.
The 2019 novel coronavirus: Case review IDs clinical characteristics
A group of physicians in Wuhan, China, who are treating patients with the 2019 novel coronavirus have gone the extra mile to share their clinical experiences with colleagues around the world.
Nanshan Chen, MD, of Jinyintan Hospital, Wuhan, and his team conducted a retrospective study on 99 cases and, in very short order, published their initial findings in the Lancet online on Jan. 29. These findings could guide action in other cases and help clinicians all over the world create treatment plans for patients of the 2019-nCoV.
The findings show that and characteristics of those with fatal infections align with the MuLBSTA score – an early warning model for predicting viral pneumonia–related mortality, according to a case review.
Of 99 patients who presented with 2019-nCoV pneumonia at Jinyintan Hospital between Jan. 1 and Jan. 20, 67 were men, the mean age was 55.5 years, and 50 patients had chronic diseases.
“All the data of included cases have been shared with [the World Health Organization]. The study was approved by Jinyintan Hospital Ethics Committee and written informed consent was obtained from patients involved before enrollment when data were collected retrospectively,” the researchers noted.
Nearly half of the patients (49%) lived or worked near a specific seafood market, suggesting disease clustering.
Clinical manifestations affecting the majority of patients included fever and cough in 83% and 82% of patients, respectively. Other symptoms included shortness of breath in 31%, muscle aches in 11%, confusion in 9%, headache in 8%, sore throat in 5%, and rhinorrhea, chest pain, diarrhea, and nausea and vomiting in 1%-4% of patients, the investigators found.
Imaging showed bilateral pneumonia in 75% of cases, multiple mottling and ground-glass opacity in 14%, and pneumothorax in 1%. Organ function damage was present in a third of patients at admission: 17% had acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS) – including 11 patients who worsened quickly and died of multiple organ failure. Eight percent had acute respiratory injury, 3% had acute renal injury, 4% had septic shock, and 1% had ventilator-associated pneumonia, they said, noting that all cases were confirmed by real-time polymerase chain reaction.
A notable laboratory finding was reduced absolute lymphocyte counts in most patients, the investigators said.
All patients were treated in isolation and 76% received antiviral treatment with oseltamivir, ganciclovir, lopinavir, or ritonavir for 3-14 days (median, 3 days). Most patients also received antibiotic treatment, including a single antibiotic in 25% of cases and combination therapy in 45%, with most antibiotics used to cover “common pathogens and some atypical pathogens,” they said, adding that “when secondary bacterial infection occurred, medication was administered according to the results of bacterial culture and drug sensitivity.”
Cephalosporins, quinolones, carbapenems, tigecycline against methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus, linezolid, and antifungal drugs were used, and duration ranged from 3 to 17 days (median, 5 days).
Nineteen patients also received steroid treatments.
As of Jan. 25, 31 patients had been discharged and 57 remained hospitalized. Of the 11 who died, the first 2 were a 61-year-old man and a 69-year-old man, each diagnosed with severe pneumonia and ARDS. The first experienced sudden cardiac arrest and died on admission day 11, and the second died of severe pneumonia, septic shock, and respiratory failure on admission day 9. Neither had underlying disease, but both had a long history of smoking, the investigators noted.
“The deaths of these two patients were consistent with the MuLBSTA score,” they wrote, explaining that the scoring system takes into account multilobular infiltration, lymphopenia, bacterial coinfection, smoking history, hypertension, and age.
Eight of the nine other patients who died had lymphopenia, seven had bilateral pneumonia, five were over age 60 years, three had hypertension, and one was a heavy smoker, they added.
Most coronavirus infections cause mild symptoms and have good prognosis, but some patients with the 2019-nCoV, which was identified Jan. 7 following the development of several cases of pneumonia of unknown etiology in Wuhan, develop fatal disease. The paucity of data regarding epidemiology and clinical features of pneumonia associated with 2019-nCoV prompted the current retrospective study at the center where the first cases were admitted, the investigators explained.
They noted that the sequence of 2019-nCoV “is relatively different from the six other coronavirus subtypes, including the highly pathogenic severe acute respiratory syndrome (SARS)-CoV and Middle East Respiratory Syndrome (MERS)-CoV, as well as the human coronaviruses (HCoV)-OC43, -229E, -NL63, and -HKU1 that induce mild upper respiratory disease, but can be classified as a betacoronavirus with evidence of human-to-human transmission.
Mortality associated with SARS-CoV and MERS-CoV have been reported as more than 10% and more than 35%, respectively; at data cutoff for the current study, mortality among the 99 included cases was 11%, which is similar to that in another recent 2019-nCoV report, they said.
The finding of greater risk among older men also has been seen with SARS-CoV and MERS-CoV, and the high rate among individuals with chronic diseases, mainly cerebrovascular disease, cardiovascular disease, and diabetes, also has been reported with MERS-CoV, they added.
“Our results suggest that 2019-nCoV is more likely to infect older adult males with chronic comorbidities as a result of the weaker immune functions of these patients,” they wrote.
Coinfection with bacteria and fungi occurred in some patients, particularly those with severe illness, and cultures most often showed A. baumannii, K. pneumoniae, A. flavus, C. glabrata, and C. albicans, and the findings of reduced absolute lymphocyte values in most patients suggests that “2019-nCoV might mainly act on lymphocytes, especially T lymphocytes, as does SARS-CoV,” they noted.
Given the rapid progression with ARDS and septic shock in some patients in this review, “early identification and timely treatment of critical cases is of crucial importance,” they said.
“Use of intravenous immunoglobulin is recommended to enhance the ability of anti-infection for severely ill patients, and steroids (methylprednisolone 1-2 mg/kg per day) are recommended for patients with ARDS, for as short a duration of treatment as possible,” they added.
Further, since some studies suggest that a substantial decrease in lymphocyte count indicates consumption of many immune cells by coronavirus, thereby inhibiting cellular immune function, damage to T lymphocytes might be “an important factor leading to exacerbations of patients,” they wrote, adding that “[t]he low absolute value of lymphocytes could be used as a reference index in the diagnosis of new coronavirus infections in the clinic.”
The MuLBSTA score also should be investigated to determine its applicability for predicting mortality risk in patients with 2019-nCoV infection, they added.
The current study is limited by its small sample size; additional studies are needed to include “as many patients as possible in Wuhan, in other cities in China, and even in other countries to get a more comprehensive understanding of 2019-nCoV,” they said.
The National Key R&D Program of China funded the study. The authors reported having no conflicts of interest.
SOURCE: Chen N et al. Lancet. 2020 Jan 29. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30211-7.
A group of physicians in Wuhan, China, who are treating patients with the 2019 novel coronavirus have gone the extra mile to share their clinical experiences with colleagues around the world.
Nanshan Chen, MD, of Jinyintan Hospital, Wuhan, and his team conducted a retrospective study on 99 cases and, in very short order, published their initial findings in the Lancet online on Jan. 29. These findings could guide action in other cases and help clinicians all over the world create treatment plans for patients of the 2019-nCoV.
The findings show that and characteristics of those with fatal infections align with the MuLBSTA score – an early warning model for predicting viral pneumonia–related mortality, according to a case review.
Of 99 patients who presented with 2019-nCoV pneumonia at Jinyintan Hospital between Jan. 1 and Jan. 20, 67 were men, the mean age was 55.5 years, and 50 patients had chronic diseases.
“All the data of included cases have been shared with [the World Health Organization]. The study was approved by Jinyintan Hospital Ethics Committee and written informed consent was obtained from patients involved before enrollment when data were collected retrospectively,” the researchers noted.
Nearly half of the patients (49%) lived or worked near a specific seafood market, suggesting disease clustering.
Clinical manifestations affecting the majority of patients included fever and cough in 83% and 82% of patients, respectively. Other symptoms included shortness of breath in 31%, muscle aches in 11%, confusion in 9%, headache in 8%, sore throat in 5%, and rhinorrhea, chest pain, diarrhea, and nausea and vomiting in 1%-4% of patients, the investigators found.
Imaging showed bilateral pneumonia in 75% of cases, multiple mottling and ground-glass opacity in 14%, and pneumothorax in 1%. Organ function damage was present in a third of patients at admission: 17% had acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS) – including 11 patients who worsened quickly and died of multiple organ failure. Eight percent had acute respiratory injury, 3% had acute renal injury, 4% had septic shock, and 1% had ventilator-associated pneumonia, they said, noting that all cases were confirmed by real-time polymerase chain reaction.
A notable laboratory finding was reduced absolute lymphocyte counts in most patients, the investigators said.
All patients were treated in isolation and 76% received antiviral treatment with oseltamivir, ganciclovir, lopinavir, or ritonavir for 3-14 days (median, 3 days). Most patients also received antibiotic treatment, including a single antibiotic in 25% of cases and combination therapy in 45%, with most antibiotics used to cover “common pathogens and some atypical pathogens,” they said, adding that “when secondary bacterial infection occurred, medication was administered according to the results of bacterial culture and drug sensitivity.”
Cephalosporins, quinolones, carbapenems, tigecycline against methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus, linezolid, and antifungal drugs were used, and duration ranged from 3 to 17 days (median, 5 days).
Nineteen patients also received steroid treatments.
As of Jan. 25, 31 patients had been discharged and 57 remained hospitalized. Of the 11 who died, the first 2 were a 61-year-old man and a 69-year-old man, each diagnosed with severe pneumonia and ARDS. The first experienced sudden cardiac arrest and died on admission day 11, and the second died of severe pneumonia, septic shock, and respiratory failure on admission day 9. Neither had underlying disease, but both had a long history of smoking, the investigators noted.
“The deaths of these two patients were consistent with the MuLBSTA score,” they wrote, explaining that the scoring system takes into account multilobular infiltration, lymphopenia, bacterial coinfection, smoking history, hypertension, and age.
Eight of the nine other patients who died had lymphopenia, seven had bilateral pneumonia, five were over age 60 years, three had hypertension, and one was a heavy smoker, they added.
Most coronavirus infections cause mild symptoms and have good prognosis, but some patients with the 2019-nCoV, which was identified Jan. 7 following the development of several cases of pneumonia of unknown etiology in Wuhan, develop fatal disease. The paucity of data regarding epidemiology and clinical features of pneumonia associated with 2019-nCoV prompted the current retrospective study at the center where the first cases were admitted, the investigators explained.
They noted that the sequence of 2019-nCoV “is relatively different from the six other coronavirus subtypes, including the highly pathogenic severe acute respiratory syndrome (SARS)-CoV and Middle East Respiratory Syndrome (MERS)-CoV, as well as the human coronaviruses (HCoV)-OC43, -229E, -NL63, and -HKU1 that induce mild upper respiratory disease, but can be classified as a betacoronavirus with evidence of human-to-human transmission.
Mortality associated with SARS-CoV and MERS-CoV have been reported as more than 10% and more than 35%, respectively; at data cutoff for the current study, mortality among the 99 included cases was 11%, which is similar to that in another recent 2019-nCoV report, they said.
The finding of greater risk among older men also has been seen with SARS-CoV and MERS-CoV, and the high rate among individuals with chronic diseases, mainly cerebrovascular disease, cardiovascular disease, and diabetes, also has been reported with MERS-CoV, they added.
“Our results suggest that 2019-nCoV is more likely to infect older adult males with chronic comorbidities as a result of the weaker immune functions of these patients,” they wrote.
Coinfection with bacteria and fungi occurred in some patients, particularly those with severe illness, and cultures most often showed A. baumannii, K. pneumoniae, A. flavus, C. glabrata, and C. albicans, and the findings of reduced absolute lymphocyte values in most patients suggests that “2019-nCoV might mainly act on lymphocytes, especially T lymphocytes, as does SARS-CoV,” they noted.
Given the rapid progression with ARDS and septic shock in some patients in this review, “early identification and timely treatment of critical cases is of crucial importance,” they said.
“Use of intravenous immunoglobulin is recommended to enhance the ability of anti-infection for severely ill patients, and steroids (methylprednisolone 1-2 mg/kg per day) are recommended for patients with ARDS, for as short a duration of treatment as possible,” they added.
Further, since some studies suggest that a substantial decrease in lymphocyte count indicates consumption of many immune cells by coronavirus, thereby inhibiting cellular immune function, damage to T lymphocytes might be “an important factor leading to exacerbations of patients,” they wrote, adding that “[t]he low absolute value of lymphocytes could be used as a reference index in the diagnosis of new coronavirus infections in the clinic.”
The MuLBSTA score also should be investigated to determine its applicability for predicting mortality risk in patients with 2019-nCoV infection, they added.
The current study is limited by its small sample size; additional studies are needed to include “as many patients as possible in Wuhan, in other cities in China, and even in other countries to get a more comprehensive understanding of 2019-nCoV,” they said.
The National Key R&D Program of China funded the study. The authors reported having no conflicts of interest.
SOURCE: Chen N et al. Lancet. 2020 Jan 29. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30211-7.
A group of physicians in Wuhan, China, who are treating patients with the 2019 novel coronavirus have gone the extra mile to share their clinical experiences with colleagues around the world.
Nanshan Chen, MD, of Jinyintan Hospital, Wuhan, and his team conducted a retrospective study on 99 cases and, in very short order, published their initial findings in the Lancet online on Jan. 29. These findings could guide action in other cases and help clinicians all over the world create treatment plans for patients of the 2019-nCoV.
The findings show that and characteristics of those with fatal infections align with the MuLBSTA score – an early warning model for predicting viral pneumonia–related mortality, according to a case review.
Of 99 patients who presented with 2019-nCoV pneumonia at Jinyintan Hospital between Jan. 1 and Jan. 20, 67 were men, the mean age was 55.5 years, and 50 patients had chronic diseases.
“All the data of included cases have been shared with [the World Health Organization]. The study was approved by Jinyintan Hospital Ethics Committee and written informed consent was obtained from patients involved before enrollment when data were collected retrospectively,” the researchers noted.
Nearly half of the patients (49%) lived or worked near a specific seafood market, suggesting disease clustering.
Clinical manifestations affecting the majority of patients included fever and cough in 83% and 82% of patients, respectively. Other symptoms included shortness of breath in 31%, muscle aches in 11%, confusion in 9%, headache in 8%, sore throat in 5%, and rhinorrhea, chest pain, diarrhea, and nausea and vomiting in 1%-4% of patients, the investigators found.
Imaging showed bilateral pneumonia in 75% of cases, multiple mottling and ground-glass opacity in 14%, and pneumothorax in 1%. Organ function damage was present in a third of patients at admission: 17% had acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS) – including 11 patients who worsened quickly and died of multiple organ failure. Eight percent had acute respiratory injury, 3% had acute renal injury, 4% had septic shock, and 1% had ventilator-associated pneumonia, they said, noting that all cases were confirmed by real-time polymerase chain reaction.
A notable laboratory finding was reduced absolute lymphocyte counts in most patients, the investigators said.
All patients were treated in isolation and 76% received antiviral treatment with oseltamivir, ganciclovir, lopinavir, or ritonavir for 3-14 days (median, 3 days). Most patients also received antibiotic treatment, including a single antibiotic in 25% of cases and combination therapy in 45%, with most antibiotics used to cover “common pathogens and some atypical pathogens,” they said, adding that “when secondary bacterial infection occurred, medication was administered according to the results of bacterial culture and drug sensitivity.”
Cephalosporins, quinolones, carbapenems, tigecycline against methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus, linezolid, and antifungal drugs were used, and duration ranged from 3 to 17 days (median, 5 days).
Nineteen patients also received steroid treatments.
As of Jan. 25, 31 patients had been discharged and 57 remained hospitalized. Of the 11 who died, the first 2 were a 61-year-old man and a 69-year-old man, each diagnosed with severe pneumonia and ARDS. The first experienced sudden cardiac arrest and died on admission day 11, and the second died of severe pneumonia, septic shock, and respiratory failure on admission day 9. Neither had underlying disease, but both had a long history of smoking, the investigators noted.
“The deaths of these two patients were consistent with the MuLBSTA score,” they wrote, explaining that the scoring system takes into account multilobular infiltration, lymphopenia, bacterial coinfection, smoking history, hypertension, and age.
Eight of the nine other patients who died had lymphopenia, seven had bilateral pneumonia, five were over age 60 years, three had hypertension, and one was a heavy smoker, they added.
Most coronavirus infections cause mild symptoms and have good prognosis, but some patients with the 2019-nCoV, which was identified Jan. 7 following the development of several cases of pneumonia of unknown etiology in Wuhan, develop fatal disease. The paucity of data regarding epidemiology and clinical features of pneumonia associated with 2019-nCoV prompted the current retrospective study at the center where the first cases were admitted, the investigators explained.
They noted that the sequence of 2019-nCoV “is relatively different from the six other coronavirus subtypes, including the highly pathogenic severe acute respiratory syndrome (SARS)-CoV and Middle East Respiratory Syndrome (MERS)-CoV, as well as the human coronaviruses (HCoV)-OC43, -229E, -NL63, and -HKU1 that induce mild upper respiratory disease, but can be classified as a betacoronavirus with evidence of human-to-human transmission.
Mortality associated with SARS-CoV and MERS-CoV have been reported as more than 10% and more than 35%, respectively; at data cutoff for the current study, mortality among the 99 included cases was 11%, which is similar to that in another recent 2019-nCoV report, they said.
The finding of greater risk among older men also has been seen with SARS-CoV and MERS-CoV, and the high rate among individuals with chronic diseases, mainly cerebrovascular disease, cardiovascular disease, and diabetes, also has been reported with MERS-CoV, they added.
“Our results suggest that 2019-nCoV is more likely to infect older adult males with chronic comorbidities as a result of the weaker immune functions of these patients,” they wrote.
Coinfection with bacteria and fungi occurred in some patients, particularly those with severe illness, and cultures most often showed A. baumannii, K. pneumoniae, A. flavus, C. glabrata, and C. albicans, and the findings of reduced absolute lymphocyte values in most patients suggests that “2019-nCoV might mainly act on lymphocytes, especially T lymphocytes, as does SARS-CoV,” they noted.
Given the rapid progression with ARDS and septic shock in some patients in this review, “early identification and timely treatment of critical cases is of crucial importance,” they said.
“Use of intravenous immunoglobulin is recommended to enhance the ability of anti-infection for severely ill patients, and steroids (methylprednisolone 1-2 mg/kg per day) are recommended for patients with ARDS, for as short a duration of treatment as possible,” they added.
Further, since some studies suggest that a substantial decrease in lymphocyte count indicates consumption of many immune cells by coronavirus, thereby inhibiting cellular immune function, damage to T lymphocytes might be “an important factor leading to exacerbations of patients,” they wrote, adding that “[t]he low absolute value of lymphocytes could be used as a reference index in the diagnosis of new coronavirus infections in the clinic.”
The MuLBSTA score also should be investigated to determine its applicability for predicting mortality risk in patients with 2019-nCoV infection, they added.
The current study is limited by its small sample size; additional studies are needed to include “as many patients as possible in Wuhan, in other cities in China, and even in other countries to get a more comprehensive understanding of 2019-nCoV,” they said.
The National Key R&D Program of China funded the study. The authors reported having no conflicts of interest.
SOURCE: Chen N et al. Lancet. 2020 Jan 29. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30211-7.
FROM THE LANCET