User login
Hot Flashes: Do They Predict CVD and Dementia?
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
I’d like to talk about a recent report in the journal Menopause linking menopausal symptoms to increased risk for cognitive impairment. I’d also like to discuss some of the recent studies that have addressed whether hot flashes are linked to increased risk for heart disease and other forms of cardiovascular disease (CVD).
Given that 75%-80% of perimenopausal and postmenopausal women have hot flashes and vasomotor symptoms, it’s undoubtedly a more complex relationship between hot flashes and these outcomes than a simple one-size-fits-all, yes-or-no question.
Increasing evidence shows that several additional factors are important, including the age at which the symptoms are occurring, the time since menopause, the severity of the symptoms, whether they co-occur with night sweats and sleep disruption, and the cardiovascular status of the woman.
Several studies suggest that women who have more severe hot flashes and vasomotor symptoms are more likely to have prevalent cardiovascular risk factors — hypertension, dyslipidemia, high body mass index, endothelial dysfunction — as measured by flow-mediated vasodilation and other measures.
It is quite plausible that hot flashes could be a marker for increased risk for cognitive impairment. But the question remains, are hot flashes associated with cognitive impairment independent of these other risk factors? It appears that the associations between hot flashes, vasomotor symptoms, and CVD, and other adverse outcomes, may be more likely when hot flashes persist after age 60 or are newly occurring in later menopause. In the Women’s Health Initiative observational study, the presence of hot flashes and vasomotor symptoms in early menopause was not linked to any increased risk for heart attack, stroke, total CVD, or all-cause mortality.
However, the onset of these symptoms, especially new onset of these symptoms after age 60 or in later menopause, was in fact linked to increased risk for CVD and all-cause mortality. With respect to cognitive impairment, if a woman is having hot flashes and night sweats with regular sleep disruption, performance on cognitive testing would not be as favorable as it would be in the absence of these symptoms.
This brings us to the new study in Menopause that included approximately 1300 Latino women in nine Latin American countries, with an average age of 55 years. Looking at the association between severe menopausal symptoms and cognitive impairment, researchers found that women with severe symptoms were more likely to have cognitive impairment.
Conversely, they found that the women who had a favorable CVD risk factor status (physically active, lower BMI, healthier) and were ever users of estrogen were less likely to have cognitive impairment.
Clearly, for estrogen therapy, we need randomized clinical trials of the presence or absence of vasomotor symptoms and cognitive and CVD outcomes. Such analyses are ongoing, and new randomized trials focused specifically on women in early menopause would be very beneficial.
At the present time, it’s important that we not alarm women about the associations seen in some of these studies because often they are not independent associations; they aren’t independent of other risk factors that are commonly linked to hot flashes and night sweats. There are many other complexities in the relationship between hot flashes and cognitive impairment.
We need to appreciate that women who have moderate to severe hot flashes (especially when associated with disrupted sleep) do have impaired quality of life. It’s important to treat these symptoms, especially in early menopause, and very effective hormonal and nonhormonal treatments are available.
For women with symptoms that persist into later menopause or who have new onset of symptoms in later menopause, it’s important to prioritize cardiovascular health. For example, be more vigilant about behavioral lifestyle counseling to lower risk, and be even more aggressive in treating dyslipidemia and diabetes.
JoAnn E. Manson, Professor of Medicine and the Michael and Lee Bell Professor of Women’s Health, Harvard Medical School; Chief, Division of Preventive Medicine, Brigham and Women’s Hospital, Boston, Massachusetts; and Past President, North American Menopause Society, 2011-2012, has disclosed the following relevant financial relationships: Received study pill donation and infrastructure support from Mars Symbioscience (for the COSMOS trial).
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
I’d like to talk about a recent report in the journal Menopause linking menopausal symptoms to increased risk for cognitive impairment. I’d also like to discuss some of the recent studies that have addressed whether hot flashes are linked to increased risk for heart disease and other forms of cardiovascular disease (CVD).
Given that 75%-80% of perimenopausal and postmenopausal women have hot flashes and vasomotor symptoms, it’s undoubtedly a more complex relationship between hot flashes and these outcomes than a simple one-size-fits-all, yes-or-no question.
Increasing evidence shows that several additional factors are important, including the age at which the symptoms are occurring, the time since menopause, the severity of the symptoms, whether they co-occur with night sweats and sleep disruption, and the cardiovascular status of the woman.
Several studies suggest that women who have more severe hot flashes and vasomotor symptoms are more likely to have prevalent cardiovascular risk factors — hypertension, dyslipidemia, high body mass index, endothelial dysfunction — as measured by flow-mediated vasodilation and other measures.
It is quite plausible that hot flashes could be a marker for increased risk for cognitive impairment. But the question remains, are hot flashes associated with cognitive impairment independent of these other risk factors? It appears that the associations between hot flashes, vasomotor symptoms, and CVD, and other adverse outcomes, may be more likely when hot flashes persist after age 60 or are newly occurring in later menopause. In the Women’s Health Initiative observational study, the presence of hot flashes and vasomotor symptoms in early menopause was not linked to any increased risk for heart attack, stroke, total CVD, or all-cause mortality.
However, the onset of these symptoms, especially new onset of these symptoms after age 60 or in later menopause, was in fact linked to increased risk for CVD and all-cause mortality. With respect to cognitive impairment, if a woman is having hot flashes and night sweats with regular sleep disruption, performance on cognitive testing would not be as favorable as it would be in the absence of these symptoms.
This brings us to the new study in Menopause that included approximately 1300 Latino women in nine Latin American countries, with an average age of 55 years. Looking at the association between severe menopausal symptoms and cognitive impairment, researchers found that women with severe symptoms were more likely to have cognitive impairment.
Conversely, they found that the women who had a favorable CVD risk factor status (physically active, lower BMI, healthier) and were ever users of estrogen were less likely to have cognitive impairment.
Clearly, for estrogen therapy, we need randomized clinical trials of the presence or absence of vasomotor symptoms and cognitive and CVD outcomes. Such analyses are ongoing, and new randomized trials focused specifically on women in early menopause would be very beneficial.
At the present time, it’s important that we not alarm women about the associations seen in some of these studies because often they are not independent associations; they aren’t independent of other risk factors that are commonly linked to hot flashes and night sweats. There are many other complexities in the relationship between hot flashes and cognitive impairment.
We need to appreciate that women who have moderate to severe hot flashes (especially when associated with disrupted sleep) do have impaired quality of life. It’s important to treat these symptoms, especially in early menopause, and very effective hormonal and nonhormonal treatments are available.
For women with symptoms that persist into later menopause or who have new onset of symptoms in later menopause, it’s important to prioritize cardiovascular health. For example, be more vigilant about behavioral lifestyle counseling to lower risk, and be even more aggressive in treating dyslipidemia and diabetes.
JoAnn E. Manson, Professor of Medicine and the Michael and Lee Bell Professor of Women’s Health, Harvard Medical School; Chief, Division of Preventive Medicine, Brigham and Women’s Hospital, Boston, Massachusetts; and Past President, North American Menopause Society, 2011-2012, has disclosed the following relevant financial relationships: Received study pill donation and infrastructure support from Mars Symbioscience (for the COSMOS trial).
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
I’d like to talk about a recent report in the journal Menopause linking menopausal symptoms to increased risk for cognitive impairment. I’d also like to discuss some of the recent studies that have addressed whether hot flashes are linked to increased risk for heart disease and other forms of cardiovascular disease (CVD).
Given that 75%-80% of perimenopausal and postmenopausal women have hot flashes and vasomotor symptoms, it’s undoubtedly a more complex relationship between hot flashes and these outcomes than a simple one-size-fits-all, yes-or-no question.
Increasing evidence shows that several additional factors are important, including the age at which the symptoms are occurring, the time since menopause, the severity of the symptoms, whether they co-occur with night sweats and sleep disruption, and the cardiovascular status of the woman.
Several studies suggest that women who have more severe hot flashes and vasomotor symptoms are more likely to have prevalent cardiovascular risk factors — hypertension, dyslipidemia, high body mass index, endothelial dysfunction — as measured by flow-mediated vasodilation and other measures.
It is quite plausible that hot flashes could be a marker for increased risk for cognitive impairment. But the question remains, are hot flashes associated with cognitive impairment independent of these other risk factors? It appears that the associations between hot flashes, vasomotor symptoms, and CVD, and other adverse outcomes, may be more likely when hot flashes persist after age 60 or are newly occurring in later menopause. In the Women’s Health Initiative observational study, the presence of hot flashes and vasomotor symptoms in early menopause was not linked to any increased risk for heart attack, stroke, total CVD, or all-cause mortality.
However, the onset of these symptoms, especially new onset of these symptoms after age 60 or in later menopause, was in fact linked to increased risk for CVD and all-cause mortality. With respect to cognitive impairment, if a woman is having hot flashes and night sweats with regular sleep disruption, performance on cognitive testing would not be as favorable as it would be in the absence of these symptoms.
This brings us to the new study in Menopause that included approximately 1300 Latino women in nine Latin American countries, with an average age of 55 years. Looking at the association between severe menopausal symptoms and cognitive impairment, researchers found that women with severe symptoms were more likely to have cognitive impairment.
Conversely, they found that the women who had a favorable CVD risk factor status (physically active, lower BMI, healthier) and were ever users of estrogen were less likely to have cognitive impairment.
Clearly, for estrogen therapy, we need randomized clinical trials of the presence or absence of vasomotor symptoms and cognitive and CVD outcomes. Such analyses are ongoing, and new randomized trials focused specifically on women in early menopause would be very beneficial.
At the present time, it’s important that we not alarm women about the associations seen in some of these studies because often they are not independent associations; they aren’t independent of other risk factors that are commonly linked to hot flashes and night sweats. There are many other complexities in the relationship between hot flashes and cognitive impairment.
We need to appreciate that women who have moderate to severe hot flashes (especially when associated with disrupted sleep) do have impaired quality of life. It’s important to treat these symptoms, especially in early menopause, and very effective hormonal and nonhormonal treatments are available.
For women with symptoms that persist into later menopause or who have new onset of symptoms in later menopause, it’s important to prioritize cardiovascular health. For example, be more vigilant about behavioral lifestyle counseling to lower risk, and be even more aggressive in treating dyslipidemia and diabetes.
JoAnn E. Manson, Professor of Medicine and the Michael and Lee Bell Professor of Women’s Health, Harvard Medical School; Chief, Division of Preventive Medicine, Brigham and Women’s Hospital, Boston, Massachusetts; and Past President, North American Menopause Society, 2011-2012, has disclosed the following relevant financial relationships: Received study pill donation and infrastructure support from Mars Symbioscience (for the COSMOS trial).
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The Rebuilding of Military Medicine
It is the neglect of timely repair that makes rebuilding necessary.
Richard Whately, economist and theologian (1787-1863)
US Congressional inquiry and media attention are so frequently directed at the trials and tribulations of the US Department of Veterans Affairs (VA) that we forget the US Department of Defense (DoD) medical system also shares the federal practitioner space. The focus of the government and press recently has shifted to examine the weaknesses and woes of military medicine. This editorial reviews what that examination discovered about the decline of the DoD house of medicine, why it is in disrepair, proposals for its rebuilding, and reflects on what this trajectory can tell us about maintaining the structure of federal practice.
My father never tired of telling me that he and his medical colleagues returned from the Second World War with knowledge and skills gained in combat theaters that, in many respects, surpassed those of the civilian sector. Though he was biased as a career military physician and combat veteran, there is strong evidence backing the assertion that from World War I to Operations Enduring Freedom and Iraqi Freedom, American military medicine has been the glory of the world.1
A November 2023 report from the DoD Office of the Inspector General (OIG) warned that military medicine was in trouble. The report’s emphasis on access and staffing problems that endanger the availability and quality of health care services will likely strike a chord with VA clinicians. The document is based on data from OIG reports, hotline calls, and audits from the last several years; however, the OIG acknowledges that it did not conduct on-the-ground investigations to confirm the findings.2
When we hear the term military medicine, many immediately think of active duty service members. However, the patient population of DoD is far larger and more diverse. The Military Health System (MHS) provides care to > 9.5 million beneficiaries, including dependents and retirees, veterans, civilian DoD employees, and even contractors. Those who most heavily rely on the MHS are individuals in uniform and their families are experiencing the greatest difficulty with accessing care.3 This includes crucial mental health treatment at a time when rates of military suicide continue to climb.4
The lack of access and dearth of health care practitioners (HCPs) spans both military facilities and the civilian clinics and hospitals where current and former service members and their dependents use the TRICARE beneficiary insurance. Reminiscent of recent challenges at the VA, DoD members are encountering long wait times and the frustrating bureaucracy of inefficient and, at times, inept referral networks. Additionally, many institutions and HCPs will not accept TRICARE because it pays less and has more paperwork than other insurance plans. What is worse, there is currently no governmental leverage to compel them to participate.
The lack of access and dearth of health care practitioners (HCPs) spans both military facilities and the civilian clinics and hospitals where current and former service members and their dependents use the TRICARE beneficiary insurance. Reminiscent of recent challenges at the VA, DoD members are encountering long wait times and the frustrating bureaucracy of inefficient and, at times, inept referral networks. Additionally, many institutions and HCPs will not accept TRICARE because it pays less and has more paperwork than other insurance plans. What is worse, there is currently no governmental leverage to compel them to participate.
As with both the VA and civilian health care spheres, rural areas are the most impacted. Resource shortfalls adversely affect all aspects of care, especially the highly paid specialties like gastroenterology and urology, as well as primary care practitioners essential to ensure the health of military families. The deficits are widespread—all branches report similar obstacles to providing responsive, appropriate care. As if this was not enough to complete the mirror image of the VA’s struggles, there is a rising tide of complaints about the military’s electronic health record system.5 How did the preeminent MHS so rapidly decay? Experts in and out of uniform offer several explanations.
As with most forms of managed care, the need to cut costs drove the Pentagon to send military members and dependents to civilian health care systems to have their medical needs addressed. However, this outsourcing strategy was based on a false assumption that the community had enough capacity to deliver services to the many beneficiaries needing them. Nearly every sector of contemporary American medicine is experiencing a drastic shortage of HCPs. Though the resource allocation problems began before the pandemic, COVID-19 only exacerbated and accelerated them.6
This downsizing of military hospitals and clinics led to another predictable and seemingly unheeded consequence. A decrease in complex cases (particularly surgical cases) led to a reduction in the skills of military HCPs and a further flight of highly trained specialists who require a reasonable volume of complicated cases to retain and sharpen their expertise. The losses of those experienced clinicians further drain the pool of specialists the military can muster to sustain the readiness of troops for war and the health of their families in peace.7
The OIG recommended that the Defense Health Agency address MHS staffing and access deficiencies noted in its report, including identifying poorly performing TRICARE specialty networks and requiring them to meet their access obligation.2 As is customary, the OIG asked for DoD comment. It is unclear whether the DoD responded to that formal request; however, it is more certain it heard the message the OIG and beneficiaries conveyed. In December 2023, the Deputy Secretary of the DoD published a memorandum ordering the stabilization of the MHS. It instructs the MHS to address each of the 3 problem areas outlined in this article: (1) to reclaim patients and beneficiaries who had been outsourced or whose resources were constrained to seek care in the community; (2) to improve access to and staffing for military hospitals and clinics for active duty members and families; and (3) to restore and maintain the military readiness of the clinical forces.8 Several other documents have been issued that emphasize the crucial need to recruit and retain qualified HCPs and support staff if these aims are to be actualized, including the 2024 to 2029 MHS strategic plan.9 As the VA and US Public Health Service know, the current health care environment may be a near impossible mission.10 Although what we know from the history of military medicine is that they have a track record of achieving the impossible.
- Barr J, Podolsky SH. A national medical response to crisis - the legacy of World War II. N Engl J Med. 2020;383(7):613-615. doi:10.1056/NEJMp2008512
- US Department of Defense, Office of the Inspector General. Management advisory: concerns with access to care and staffing shortages in the Military Health System. November 29, 2023. Accessed August 26, 2024. https://www.dodig.mil/reports.html/Article/3602650/management-advisory-concerns-with-access-to-care-and-staffing-shortages-in-the/
- Management advisory: concerns with access to care and staffing shortages in the Military Health System. News release. US Department of Defense, Office of the Inspector General. November 29, 2023. Accessed August 26, 2024. https://www.dodig.mil/In-the-Spotlight/Article/3602662/press-release-management-advisory-concerns-with-access-to-care-and-staffing-sho
- US Department of Defense. Annual report on suicide in the military: calendar year 2022. Accessed August 26, 2024. https://www.dspo.mil/Portals/113/Documents/ARSM_CY22.pdf
- American Hospital Association. Strengthening the Health Care Work Force. November 2021. Accessed August 26, 2024. https://www.aha.org/system/files/media/file/2021/05/fact-sheet-workforce-infrastructure-0521.pdf
- Ziezulewicz G. DOD watchdog report warns of issues across military health system. Military Times. December 6, 2023. Accessed August 26, 2024. https://www.militarytimes.com/news/your-military/2023/12/07/dod-watchdog-report-warns-of-issues-across-military-health-care-system/
- Lawrence Q. It’s time to stop downsizing health care, the Pentagon says. This couple can’t wait. National Public Radio. April 3, 2024. Accessed August 26, 2024. https://www.npr.org/transcripts/1240724195
- Mincher R. Military Health System stabilization: rebuilding health care access is critical to patient’s well-being. January 22, 2024. Accessed August 26, 2024. https://www.defense.gov/News/News-Stories/Article/article/3652092/military-health-system-stabilization-rebuilding-health-care-access-is-critical/
- US Department of Defense, Defense Health Agency. Military Health System strategy fiscal years 2024-2029. Accessed August 26, 2024. https://www.health.mil/Reference-Center/Publications/2023/12/15/MHS_Strategic_Plan_FY24_29
- Jowers K. Pentagon plans to fix ‘chronically understaffed’ medical facilities. Military Times. January 25, 2024. Accessed August 26, 2024. https://www.militarytimes.com/news/your-military/2024/01/25/pentagon-plans-to-fix-chronically-understaffed-medical-facilities/
It is the neglect of timely repair that makes rebuilding necessary.
Richard Whately, economist and theologian (1787-1863)
US Congressional inquiry and media attention are so frequently directed at the trials and tribulations of the US Department of Veterans Affairs (VA) that we forget the US Department of Defense (DoD) medical system also shares the federal practitioner space. The focus of the government and press recently has shifted to examine the weaknesses and woes of military medicine. This editorial reviews what that examination discovered about the decline of the DoD house of medicine, why it is in disrepair, proposals for its rebuilding, and reflects on what this trajectory can tell us about maintaining the structure of federal practice.
My father never tired of telling me that he and his medical colleagues returned from the Second World War with knowledge and skills gained in combat theaters that, in many respects, surpassed those of the civilian sector. Though he was biased as a career military physician and combat veteran, there is strong evidence backing the assertion that from World War I to Operations Enduring Freedom and Iraqi Freedom, American military medicine has been the glory of the world.1
A November 2023 report from the DoD Office of the Inspector General (OIG) warned that military medicine was in trouble. The report’s emphasis on access and staffing problems that endanger the availability and quality of health care services will likely strike a chord with VA clinicians. The document is based on data from OIG reports, hotline calls, and audits from the last several years; however, the OIG acknowledges that it did not conduct on-the-ground investigations to confirm the findings.2
When we hear the term military medicine, many immediately think of active duty service members. However, the patient population of DoD is far larger and more diverse. The Military Health System (MHS) provides care to > 9.5 million beneficiaries, including dependents and retirees, veterans, civilian DoD employees, and even contractors. Those who most heavily rely on the MHS are individuals in uniform and their families are experiencing the greatest difficulty with accessing care.3 This includes crucial mental health treatment at a time when rates of military suicide continue to climb.4
The lack of access and dearth of health care practitioners (HCPs) spans both military facilities and the civilian clinics and hospitals where current and former service members and their dependents use the TRICARE beneficiary insurance. Reminiscent of recent challenges at the VA, DoD members are encountering long wait times and the frustrating bureaucracy of inefficient and, at times, inept referral networks. Additionally, many institutions and HCPs will not accept TRICARE because it pays less and has more paperwork than other insurance plans. What is worse, there is currently no governmental leverage to compel them to participate.
The lack of access and dearth of health care practitioners (HCPs) spans both military facilities and the civilian clinics and hospitals where current and former service members and their dependents use the TRICARE beneficiary insurance. Reminiscent of recent challenges at the VA, DoD members are encountering long wait times and the frustrating bureaucracy of inefficient and, at times, inept referral networks. Additionally, many institutions and HCPs will not accept TRICARE because it pays less and has more paperwork than other insurance plans. What is worse, there is currently no governmental leverage to compel them to participate.
As with both the VA and civilian health care spheres, rural areas are the most impacted. Resource shortfalls adversely affect all aspects of care, especially the highly paid specialties like gastroenterology and urology, as well as primary care practitioners essential to ensure the health of military families. The deficits are widespread—all branches report similar obstacles to providing responsive, appropriate care. As if this was not enough to complete the mirror image of the VA’s struggles, there is a rising tide of complaints about the military’s electronic health record system.5 How did the preeminent MHS so rapidly decay? Experts in and out of uniform offer several explanations.
As with most forms of managed care, the need to cut costs drove the Pentagon to send military members and dependents to civilian health care systems to have their medical needs addressed. However, this outsourcing strategy was based on a false assumption that the community had enough capacity to deliver services to the many beneficiaries needing them. Nearly every sector of contemporary American medicine is experiencing a drastic shortage of HCPs. Though the resource allocation problems began before the pandemic, COVID-19 only exacerbated and accelerated them.6
This downsizing of military hospitals and clinics led to another predictable and seemingly unheeded consequence. A decrease in complex cases (particularly surgical cases) led to a reduction in the skills of military HCPs and a further flight of highly trained specialists who require a reasonable volume of complicated cases to retain and sharpen their expertise. The losses of those experienced clinicians further drain the pool of specialists the military can muster to sustain the readiness of troops for war and the health of their families in peace.7
The OIG recommended that the Defense Health Agency address MHS staffing and access deficiencies noted in its report, including identifying poorly performing TRICARE specialty networks and requiring them to meet their access obligation.2 As is customary, the OIG asked for DoD comment. It is unclear whether the DoD responded to that formal request; however, it is more certain it heard the message the OIG and beneficiaries conveyed. In December 2023, the Deputy Secretary of the DoD published a memorandum ordering the stabilization of the MHS. It instructs the MHS to address each of the 3 problem areas outlined in this article: (1) to reclaim patients and beneficiaries who had been outsourced or whose resources were constrained to seek care in the community; (2) to improve access to and staffing for military hospitals and clinics for active duty members and families; and (3) to restore and maintain the military readiness of the clinical forces.8 Several other documents have been issued that emphasize the crucial need to recruit and retain qualified HCPs and support staff if these aims are to be actualized, including the 2024 to 2029 MHS strategic plan.9 As the VA and US Public Health Service know, the current health care environment may be a near impossible mission.10 Although what we know from the history of military medicine is that they have a track record of achieving the impossible.
It is the neglect of timely repair that makes rebuilding necessary.
Richard Whately, economist and theologian (1787-1863)
US Congressional inquiry and media attention are so frequently directed at the trials and tribulations of the US Department of Veterans Affairs (VA) that we forget the US Department of Defense (DoD) medical system also shares the federal practitioner space. The focus of the government and press recently has shifted to examine the weaknesses and woes of military medicine. This editorial reviews what that examination discovered about the decline of the DoD house of medicine, why it is in disrepair, proposals for its rebuilding, and reflects on what this trajectory can tell us about maintaining the structure of federal practice.
My father never tired of telling me that he and his medical colleagues returned from the Second World War with knowledge and skills gained in combat theaters that, in many respects, surpassed those of the civilian sector. Though he was biased as a career military physician and combat veteran, there is strong evidence backing the assertion that from World War I to Operations Enduring Freedom and Iraqi Freedom, American military medicine has been the glory of the world.1
A November 2023 report from the DoD Office of the Inspector General (OIG) warned that military medicine was in trouble. The report’s emphasis on access and staffing problems that endanger the availability and quality of health care services will likely strike a chord with VA clinicians. The document is based on data from OIG reports, hotline calls, and audits from the last several years; however, the OIG acknowledges that it did not conduct on-the-ground investigations to confirm the findings.2
When we hear the term military medicine, many immediately think of active duty service members. However, the patient population of DoD is far larger and more diverse. The Military Health System (MHS) provides care to > 9.5 million beneficiaries, including dependents and retirees, veterans, civilian DoD employees, and even contractors. Those who most heavily rely on the MHS are individuals in uniform and their families are experiencing the greatest difficulty with accessing care.3 This includes crucial mental health treatment at a time when rates of military suicide continue to climb.4
The lack of access and dearth of health care practitioners (HCPs) spans both military facilities and the civilian clinics and hospitals where current and former service members and their dependents use the TRICARE beneficiary insurance. Reminiscent of recent challenges at the VA, DoD members are encountering long wait times and the frustrating bureaucracy of inefficient and, at times, inept referral networks. Additionally, many institutions and HCPs will not accept TRICARE because it pays less and has more paperwork than other insurance plans. What is worse, there is currently no governmental leverage to compel them to participate.
The lack of access and dearth of health care practitioners (HCPs) spans both military facilities and the civilian clinics and hospitals where current and former service members and their dependents use the TRICARE beneficiary insurance. Reminiscent of recent challenges at the VA, DoD members are encountering long wait times and the frustrating bureaucracy of inefficient and, at times, inept referral networks. Additionally, many institutions and HCPs will not accept TRICARE because it pays less and has more paperwork than other insurance plans. What is worse, there is currently no governmental leverage to compel them to participate.
As with both the VA and civilian health care spheres, rural areas are the most impacted. Resource shortfalls adversely affect all aspects of care, especially the highly paid specialties like gastroenterology and urology, as well as primary care practitioners essential to ensure the health of military families. The deficits are widespread—all branches report similar obstacles to providing responsive, appropriate care. As if this was not enough to complete the mirror image of the VA’s struggles, there is a rising tide of complaints about the military’s electronic health record system.5 How did the preeminent MHS so rapidly decay? Experts in and out of uniform offer several explanations.
As with most forms of managed care, the need to cut costs drove the Pentagon to send military members and dependents to civilian health care systems to have their medical needs addressed. However, this outsourcing strategy was based on a false assumption that the community had enough capacity to deliver services to the many beneficiaries needing them. Nearly every sector of contemporary American medicine is experiencing a drastic shortage of HCPs. Though the resource allocation problems began before the pandemic, COVID-19 only exacerbated and accelerated them.6
This downsizing of military hospitals and clinics led to another predictable and seemingly unheeded consequence. A decrease in complex cases (particularly surgical cases) led to a reduction in the skills of military HCPs and a further flight of highly trained specialists who require a reasonable volume of complicated cases to retain and sharpen their expertise. The losses of those experienced clinicians further drain the pool of specialists the military can muster to sustain the readiness of troops for war and the health of their families in peace.7
The OIG recommended that the Defense Health Agency address MHS staffing and access deficiencies noted in its report, including identifying poorly performing TRICARE specialty networks and requiring them to meet their access obligation.2 As is customary, the OIG asked for DoD comment. It is unclear whether the DoD responded to that formal request; however, it is more certain it heard the message the OIG and beneficiaries conveyed. In December 2023, the Deputy Secretary of the DoD published a memorandum ordering the stabilization of the MHS. It instructs the MHS to address each of the 3 problem areas outlined in this article: (1) to reclaim patients and beneficiaries who had been outsourced or whose resources were constrained to seek care in the community; (2) to improve access to and staffing for military hospitals and clinics for active duty members and families; and (3) to restore and maintain the military readiness of the clinical forces.8 Several other documents have been issued that emphasize the crucial need to recruit and retain qualified HCPs and support staff if these aims are to be actualized, including the 2024 to 2029 MHS strategic plan.9 As the VA and US Public Health Service know, the current health care environment may be a near impossible mission.10 Although what we know from the history of military medicine is that they have a track record of achieving the impossible.
- Barr J, Podolsky SH. A national medical response to crisis - the legacy of World War II. N Engl J Med. 2020;383(7):613-615. doi:10.1056/NEJMp2008512
- US Department of Defense, Office of the Inspector General. Management advisory: concerns with access to care and staffing shortages in the Military Health System. November 29, 2023. Accessed August 26, 2024. https://www.dodig.mil/reports.html/Article/3602650/management-advisory-concerns-with-access-to-care-and-staffing-shortages-in-the/
- Management advisory: concerns with access to care and staffing shortages in the Military Health System. News release. US Department of Defense, Office of the Inspector General. November 29, 2023. Accessed August 26, 2024. https://www.dodig.mil/In-the-Spotlight/Article/3602662/press-release-management-advisory-concerns-with-access-to-care-and-staffing-sho
- US Department of Defense. Annual report on suicide in the military: calendar year 2022. Accessed August 26, 2024. https://www.dspo.mil/Portals/113/Documents/ARSM_CY22.pdf
- American Hospital Association. Strengthening the Health Care Work Force. November 2021. Accessed August 26, 2024. https://www.aha.org/system/files/media/file/2021/05/fact-sheet-workforce-infrastructure-0521.pdf
- Ziezulewicz G. DOD watchdog report warns of issues across military health system. Military Times. December 6, 2023. Accessed August 26, 2024. https://www.militarytimes.com/news/your-military/2023/12/07/dod-watchdog-report-warns-of-issues-across-military-health-care-system/
- Lawrence Q. It’s time to stop downsizing health care, the Pentagon says. This couple can’t wait. National Public Radio. April 3, 2024. Accessed August 26, 2024. https://www.npr.org/transcripts/1240724195
- Mincher R. Military Health System stabilization: rebuilding health care access is critical to patient’s well-being. January 22, 2024. Accessed August 26, 2024. https://www.defense.gov/News/News-Stories/Article/article/3652092/military-health-system-stabilization-rebuilding-health-care-access-is-critical/
- US Department of Defense, Defense Health Agency. Military Health System strategy fiscal years 2024-2029. Accessed August 26, 2024. https://www.health.mil/Reference-Center/Publications/2023/12/15/MHS_Strategic_Plan_FY24_29
- Jowers K. Pentagon plans to fix ‘chronically understaffed’ medical facilities. Military Times. January 25, 2024. Accessed August 26, 2024. https://www.militarytimes.com/news/your-military/2024/01/25/pentagon-plans-to-fix-chronically-understaffed-medical-facilities/
- Barr J, Podolsky SH. A national medical response to crisis - the legacy of World War II. N Engl J Med. 2020;383(7):613-615. doi:10.1056/NEJMp2008512
- US Department of Defense, Office of the Inspector General. Management advisory: concerns with access to care and staffing shortages in the Military Health System. November 29, 2023. Accessed August 26, 2024. https://www.dodig.mil/reports.html/Article/3602650/management-advisory-concerns-with-access-to-care-and-staffing-shortages-in-the/
- Management advisory: concerns with access to care and staffing shortages in the Military Health System. News release. US Department of Defense, Office of the Inspector General. November 29, 2023. Accessed August 26, 2024. https://www.dodig.mil/In-the-Spotlight/Article/3602662/press-release-management-advisory-concerns-with-access-to-care-and-staffing-sho
- US Department of Defense. Annual report on suicide in the military: calendar year 2022. Accessed August 26, 2024. https://www.dspo.mil/Portals/113/Documents/ARSM_CY22.pdf
- American Hospital Association. Strengthening the Health Care Work Force. November 2021. Accessed August 26, 2024. https://www.aha.org/system/files/media/file/2021/05/fact-sheet-workforce-infrastructure-0521.pdf
- Ziezulewicz G. DOD watchdog report warns of issues across military health system. Military Times. December 6, 2023. Accessed August 26, 2024. https://www.militarytimes.com/news/your-military/2023/12/07/dod-watchdog-report-warns-of-issues-across-military-health-care-system/
- Lawrence Q. It’s time to stop downsizing health care, the Pentagon says. This couple can’t wait. National Public Radio. April 3, 2024. Accessed August 26, 2024. https://www.npr.org/transcripts/1240724195
- Mincher R. Military Health System stabilization: rebuilding health care access is critical to patient’s well-being. January 22, 2024. Accessed August 26, 2024. https://www.defense.gov/News/News-Stories/Article/article/3652092/military-health-system-stabilization-rebuilding-health-care-access-is-critical/
- US Department of Defense, Defense Health Agency. Military Health System strategy fiscal years 2024-2029. Accessed August 26, 2024. https://www.health.mil/Reference-Center/Publications/2023/12/15/MHS_Strategic_Plan_FY24_29
- Jowers K. Pentagon plans to fix ‘chronically understaffed’ medical facilities. Military Times. January 25, 2024. Accessed August 26, 2024. https://www.militarytimes.com/news/your-military/2024/01/25/pentagon-plans-to-fix-chronically-understaffed-medical-facilities/
‘Reform School’ for Pharmacy Benefit Managers: How Might Legislation Help Patients?
The term “reform school” is a bit outdated. It used to refer to institutions where young offenders were sent instead of prison. Some argue that pharmacy benefit managers (PBMs) should bypass reform school and go straight to prison. “PBM reform” has become a ubiquitous term, encompassing any legislative or regulatory efforts aimed at curbing PBMs’ bad behavior. When discussing PBM reform, it’s crucial to understand the various segments of the healthcare system affected by PBMs. This complexity often makes it challenging to determine what these reform packages would actually achieve and who they would benefit.
Pharmacists have long been vocal critics of PBMs, and while their issues are extremely important, it is essential to remember that the ultimate victims of PBM misconduct, in terms of access to care, are patients. At some point, we will all be patients, making this issue universally relevant. It has been quite challenging to follow federal legislation on this topic as these packages attempt to address a number of bad behaviors by PBMs affecting a variety of victims. This discussion will examine those reforms that would directly improve patient’s access to available and affordable medications.
Policy Categories of PBM Reform
There are five policy categories of PBM reform legislation overall, including three that have the greatest potential to directly address patient needs. The first is patient access to medications (utilization management, copay assistance, prior authorization, etc.), followed by delinking drug list prices from PBM income and pass-through of price concessions from the manufacturer. The remaining two categories involve transparency and pharmacy-facing reform, both of which are very important. However, this discussion will revolve around the first three categories. It should be noted that many of the legislation packages addressing the categories of patient access, delinking, and pass-through also include transparency issues, particularly as they relate to pharmacy-facing issues.
Patient Access to Medications — Step Therapy Legislation
One of the major obstacles to patient access to medications is the use of PBM utilization management tools such as step therapy (“fail first”), prior authorizations, nonmedical switching, and formulary exclusions. These tools dictate when patients can obtain necessary medications and for how long patients who are stable on their current treatments can remain on them.
While many states have enacted step therapy reforms to prevent stable patients from being whip-sawed between medications that maximize PBM profits (often labeled as “savings”), these state protections apply only to state-regulated health plans. These include fully insured health plans and those offered through the Affordable Care Act’s Health Insurance Marketplace. It also includes state employees, state corrections, and, in some cases, state labor unions. State legislation does not extend to patients covered by employer self-insured health plans, called ERISA plans for the federal law that governs employee benefit plans, the Employee Retirement Income Security Act. These ERISA plans include nearly 35 million people nationwide.
This is where the Safe Step Act (S.652/H.R.2630) becomes crucial, as it allows employees to request exceptions to harmful fail-first protocols. The bill has gained significant momentum, having been reported out of the Senate HELP Committee and discussed in House markups. The Safe Step Act would mandate that an exception to a step therapy protocol must be granted if:
- The required treatment has been ineffective
- The treatment is expected to be ineffective, and delaying effective treatment would lead to irreversible consequences
- The treatment will cause or is likely to cause an adverse reaction
- The treatment is expected to prevent the individual from performing daily activities or occupational responsibilities
- The individual is stable on their current prescription drugs
- There are other circumstances as determined by the Employee Benefits Security Administration
This legislation is vital for ensuring that patients have timely access to the medications they need without unnecessary delays or disruptions.
Patient Access to Medications — Prior Authorizations
Another significant issue affecting patient access to medications is prior authorizations (PAs). According to an American Medical Association survey, nearly one in four physicians (24%) report that a PA has led to a serious adverse event for a patient in their care. In rheumatology, PAs often result in delays in care (even for those initially approved) and a significant increase in steroid usage. In particular, PAs in Medicare Advantage (MA) plans are harmful to Medicare beneficiaries.
The Improving Seniors’ Timely Access to Care Act (H.R.8702 / S.4532) aims to reform PAs used in MA plans, making the process more efficient and transparent to improve access to care for seniors. Unfortunately, it does not cover Part D drugs and may only cover Part B drugs depending on the MA plan’s benefit package. Here are the key provisions of the act:
- Electronic PA: Implementing real-time decisions for routinely approved items and services.
- Transparency: Requiring annual publication of PA information, such as the percentage of requests approved and the average response time.
- Quality and Timeliness Standards: The Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS) will set standards for the quality and timeliness of PA determinations.
- Streamlining Approvals: Simplifying the approval process and reducing the time allowed for health plans to consider PA requests.
This bill passed the House in September 2022 but stalled in the Senate because of an unfavorable Congressional Budget Office score. CMS has since finalized portions of this bill via regulation, zeroing out the CBO score and increasing the chances of its passage.
Delinking Drug Prices from PBM Income and Pass-Through of Price Concessions
Affordability is a crucial aspect of accessibility, especially when it comes to medications. Over the years, we’ve learned that PBMs often favor placing the highest list price drugs on formularies because the rebates and various fees they receive from manufacturers are based on a percentage of the list price. In other words, the higher the medication’s price, the more money the PBM makes.
This practice is evident in both commercial and government formularies, where brand-name drugs are often preferred, while lower-priced generics are either excluded or placed on higher tiers. As a result, while major PBMs benefit from these rebates and fees, patients continue to pay their cost share based on the list price of the medication.
To improve the affordability of medications, a key aspect of PBM reform should be to disincentivize PBMs from selecting higher-priced medications and/or require the pass-through of manufacturer price concessions to patients.
Several major PBM reform bills are currently being considered that address either the delinking of price concessions from the list price of the drug or some form of pass-through of these concessions. These reforms are essential to ensure that patients can access affordable medications without being burdened by inflated costs.
The legislation includes the Pharmacy Benefit Manager Reform Act (S.1339); the Modernizing & Ensuring PBM Accountability Act (S.2973); the Better Mental Health Care, Lower Cost Drugs, and Extenders Act (S.3430); the Protecting Patients Against PBM Abuses Act (H.R. 2880); the DRUG Act (S.2474 / H.R.6283); and the Share the Savings with Seniors Act (S.2474 / H.R.5376).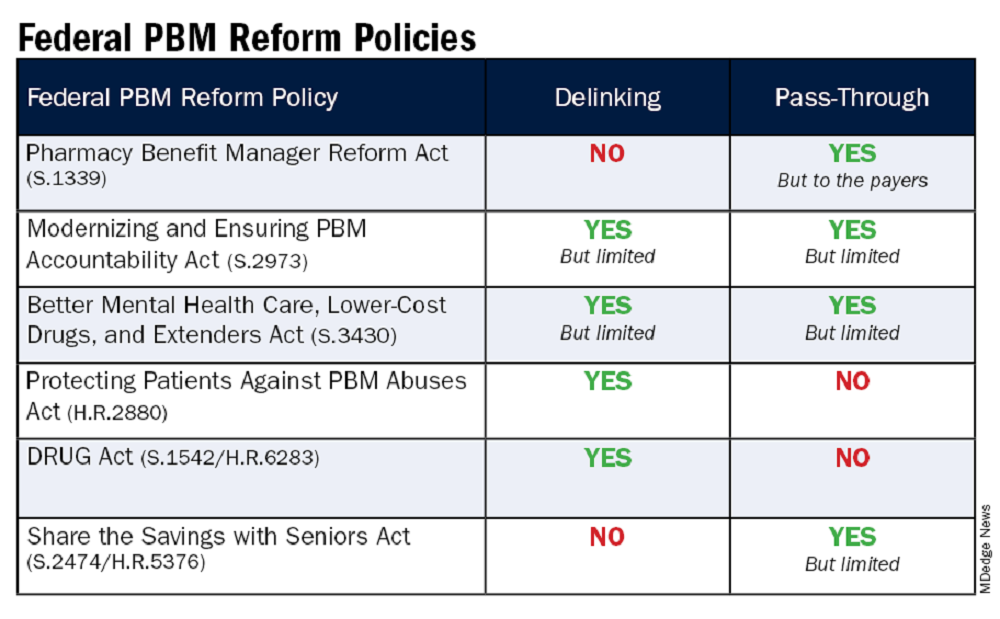
As with all legislation, there are limitations and compromises in each of these. However, these bills are a good first step in addressing PBM remuneration (rebates and fees) based on the list price of the drug and/or passing through to the patient the benefit of manufacturer price concessions. By focusing on key areas like utilization management, delinking drug prices from PBM income, and allowing patients to directly benefit from manufacturer price concessions, we can work toward a more equitable and efficient healthcare system. Reigning in PBM bad behavior is a challenge, but the potential benefits for patient care and access make it a crucial fight worth pursuing.
Please help in efforts to improve patients’ access to available and affordable medications by contacting your representatives in Congress to impart to them the importance of passing legislation. The CSRO’s legislative map tool can help to inform you of the latest information on these and other bills and assist you in engaging with your representatives on them.
Dr. Feldman is a rheumatologist in private practice with The Rheumatology Group in New Orleans. She is the CSRO’s vice president of Advocacy and Government Affairs and its immediate past president, as well as past chair of the Alliance for Safe Biologic Medicines and a past member of the American College of Rheumatology insurance subcommittee. She has no relevant conflicts of interest to disclose. You can reach her at [email protected].
The term “reform school” is a bit outdated. It used to refer to institutions where young offenders were sent instead of prison. Some argue that pharmacy benefit managers (PBMs) should bypass reform school and go straight to prison. “PBM reform” has become a ubiquitous term, encompassing any legislative or regulatory efforts aimed at curbing PBMs’ bad behavior. When discussing PBM reform, it’s crucial to understand the various segments of the healthcare system affected by PBMs. This complexity often makes it challenging to determine what these reform packages would actually achieve and who they would benefit.
Pharmacists have long been vocal critics of PBMs, and while their issues are extremely important, it is essential to remember that the ultimate victims of PBM misconduct, in terms of access to care, are patients. At some point, we will all be patients, making this issue universally relevant. It has been quite challenging to follow federal legislation on this topic as these packages attempt to address a number of bad behaviors by PBMs affecting a variety of victims. This discussion will examine those reforms that would directly improve patient’s access to available and affordable medications.
Policy Categories of PBM Reform
There are five policy categories of PBM reform legislation overall, including three that have the greatest potential to directly address patient needs. The first is patient access to medications (utilization management, copay assistance, prior authorization, etc.), followed by delinking drug list prices from PBM income and pass-through of price concessions from the manufacturer. The remaining two categories involve transparency and pharmacy-facing reform, both of which are very important. However, this discussion will revolve around the first three categories. It should be noted that many of the legislation packages addressing the categories of patient access, delinking, and pass-through also include transparency issues, particularly as they relate to pharmacy-facing issues.
Patient Access to Medications — Step Therapy Legislation
One of the major obstacles to patient access to medications is the use of PBM utilization management tools such as step therapy (“fail first”), prior authorizations, nonmedical switching, and formulary exclusions. These tools dictate when patients can obtain necessary medications and for how long patients who are stable on their current treatments can remain on them.
While many states have enacted step therapy reforms to prevent stable patients from being whip-sawed between medications that maximize PBM profits (often labeled as “savings”), these state protections apply only to state-regulated health plans. These include fully insured health plans and those offered through the Affordable Care Act’s Health Insurance Marketplace. It also includes state employees, state corrections, and, in some cases, state labor unions. State legislation does not extend to patients covered by employer self-insured health plans, called ERISA plans for the federal law that governs employee benefit plans, the Employee Retirement Income Security Act. These ERISA plans include nearly 35 million people nationwide.
This is where the Safe Step Act (S.652/H.R.2630) becomes crucial, as it allows employees to request exceptions to harmful fail-first protocols. The bill has gained significant momentum, having been reported out of the Senate HELP Committee and discussed in House markups. The Safe Step Act would mandate that an exception to a step therapy protocol must be granted if:
- The required treatment has been ineffective
- The treatment is expected to be ineffective, and delaying effective treatment would lead to irreversible consequences
- The treatment will cause or is likely to cause an adverse reaction
- The treatment is expected to prevent the individual from performing daily activities or occupational responsibilities
- The individual is stable on their current prescription drugs
- There are other circumstances as determined by the Employee Benefits Security Administration
This legislation is vital for ensuring that patients have timely access to the medications they need without unnecessary delays or disruptions.
Patient Access to Medications — Prior Authorizations
Another significant issue affecting patient access to medications is prior authorizations (PAs). According to an American Medical Association survey, nearly one in four physicians (24%) report that a PA has led to a serious adverse event for a patient in their care. In rheumatology, PAs often result in delays in care (even for those initially approved) and a significant increase in steroid usage. In particular, PAs in Medicare Advantage (MA) plans are harmful to Medicare beneficiaries.
The Improving Seniors’ Timely Access to Care Act (H.R.8702 / S.4532) aims to reform PAs used in MA plans, making the process more efficient and transparent to improve access to care for seniors. Unfortunately, it does not cover Part D drugs and may only cover Part B drugs depending on the MA plan’s benefit package. Here are the key provisions of the act:
- Electronic PA: Implementing real-time decisions for routinely approved items and services.
- Transparency: Requiring annual publication of PA information, such as the percentage of requests approved and the average response time.
- Quality and Timeliness Standards: The Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS) will set standards for the quality and timeliness of PA determinations.
- Streamlining Approvals: Simplifying the approval process and reducing the time allowed for health plans to consider PA requests.
This bill passed the House in September 2022 but stalled in the Senate because of an unfavorable Congressional Budget Office score. CMS has since finalized portions of this bill via regulation, zeroing out the CBO score and increasing the chances of its passage.
Delinking Drug Prices from PBM Income and Pass-Through of Price Concessions
Affordability is a crucial aspect of accessibility, especially when it comes to medications. Over the years, we’ve learned that PBMs often favor placing the highest list price drugs on formularies because the rebates and various fees they receive from manufacturers are based on a percentage of the list price. In other words, the higher the medication’s price, the more money the PBM makes.
This practice is evident in both commercial and government formularies, where brand-name drugs are often preferred, while lower-priced generics are either excluded or placed on higher tiers. As a result, while major PBMs benefit from these rebates and fees, patients continue to pay their cost share based on the list price of the medication.
To improve the affordability of medications, a key aspect of PBM reform should be to disincentivize PBMs from selecting higher-priced medications and/or require the pass-through of manufacturer price concessions to patients.
Several major PBM reform bills are currently being considered that address either the delinking of price concessions from the list price of the drug or some form of pass-through of these concessions. These reforms are essential to ensure that patients can access affordable medications without being burdened by inflated costs.
The legislation includes the Pharmacy Benefit Manager Reform Act (S.1339); the Modernizing & Ensuring PBM Accountability Act (S.2973); the Better Mental Health Care, Lower Cost Drugs, and Extenders Act (S.3430); the Protecting Patients Against PBM Abuses Act (H.R. 2880); the DRUG Act (S.2474 / H.R.6283); and the Share the Savings with Seniors Act (S.2474 / H.R.5376).
As with all legislation, there are limitations and compromises in each of these. However, these bills are a good first step in addressing PBM remuneration (rebates and fees) based on the list price of the drug and/or passing through to the patient the benefit of manufacturer price concessions. By focusing on key areas like utilization management, delinking drug prices from PBM income, and allowing patients to directly benefit from manufacturer price concessions, we can work toward a more equitable and efficient healthcare system. Reigning in PBM bad behavior is a challenge, but the potential benefits for patient care and access make it a crucial fight worth pursuing.
Please help in efforts to improve patients’ access to available and affordable medications by contacting your representatives in Congress to impart to them the importance of passing legislation. The CSRO’s legislative map tool can help to inform you of the latest information on these and other bills and assist you in engaging with your representatives on them.
Dr. Feldman is a rheumatologist in private practice with The Rheumatology Group in New Orleans. She is the CSRO’s vice president of Advocacy and Government Affairs and its immediate past president, as well as past chair of the Alliance for Safe Biologic Medicines and a past member of the American College of Rheumatology insurance subcommittee. She has no relevant conflicts of interest to disclose. You can reach her at [email protected].
The term “reform school” is a bit outdated. It used to refer to institutions where young offenders were sent instead of prison. Some argue that pharmacy benefit managers (PBMs) should bypass reform school and go straight to prison. “PBM reform” has become a ubiquitous term, encompassing any legislative or regulatory efforts aimed at curbing PBMs’ bad behavior. When discussing PBM reform, it’s crucial to understand the various segments of the healthcare system affected by PBMs. This complexity often makes it challenging to determine what these reform packages would actually achieve and who they would benefit.
Pharmacists have long been vocal critics of PBMs, and while their issues are extremely important, it is essential to remember that the ultimate victims of PBM misconduct, in terms of access to care, are patients. At some point, we will all be patients, making this issue universally relevant. It has been quite challenging to follow federal legislation on this topic as these packages attempt to address a number of bad behaviors by PBMs affecting a variety of victims. This discussion will examine those reforms that would directly improve patient’s access to available and affordable medications.
Policy Categories of PBM Reform
There are five policy categories of PBM reform legislation overall, including three that have the greatest potential to directly address patient needs. The first is patient access to medications (utilization management, copay assistance, prior authorization, etc.), followed by delinking drug list prices from PBM income and pass-through of price concessions from the manufacturer. The remaining two categories involve transparency and pharmacy-facing reform, both of which are very important. However, this discussion will revolve around the first three categories. It should be noted that many of the legislation packages addressing the categories of patient access, delinking, and pass-through also include transparency issues, particularly as they relate to pharmacy-facing issues.
Patient Access to Medications — Step Therapy Legislation
One of the major obstacles to patient access to medications is the use of PBM utilization management tools such as step therapy (“fail first”), prior authorizations, nonmedical switching, and formulary exclusions. These tools dictate when patients can obtain necessary medications and for how long patients who are stable on their current treatments can remain on them.
While many states have enacted step therapy reforms to prevent stable patients from being whip-sawed between medications that maximize PBM profits (often labeled as “savings”), these state protections apply only to state-regulated health plans. These include fully insured health plans and those offered through the Affordable Care Act’s Health Insurance Marketplace. It also includes state employees, state corrections, and, in some cases, state labor unions. State legislation does not extend to patients covered by employer self-insured health plans, called ERISA plans for the federal law that governs employee benefit plans, the Employee Retirement Income Security Act. These ERISA plans include nearly 35 million people nationwide.
This is where the Safe Step Act (S.652/H.R.2630) becomes crucial, as it allows employees to request exceptions to harmful fail-first protocols. The bill has gained significant momentum, having been reported out of the Senate HELP Committee and discussed in House markups. The Safe Step Act would mandate that an exception to a step therapy protocol must be granted if:
- The required treatment has been ineffective
- The treatment is expected to be ineffective, and delaying effective treatment would lead to irreversible consequences
- The treatment will cause or is likely to cause an adverse reaction
- The treatment is expected to prevent the individual from performing daily activities or occupational responsibilities
- The individual is stable on their current prescription drugs
- There are other circumstances as determined by the Employee Benefits Security Administration
This legislation is vital for ensuring that patients have timely access to the medications they need without unnecessary delays or disruptions.
Patient Access to Medications — Prior Authorizations
Another significant issue affecting patient access to medications is prior authorizations (PAs). According to an American Medical Association survey, nearly one in four physicians (24%) report that a PA has led to a serious adverse event for a patient in their care. In rheumatology, PAs often result in delays in care (even for those initially approved) and a significant increase in steroid usage. In particular, PAs in Medicare Advantage (MA) plans are harmful to Medicare beneficiaries.
The Improving Seniors’ Timely Access to Care Act (H.R.8702 / S.4532) aims to reform PAs used in MA plans, making the process more efficient and transparent to improve access to care for seniors. Unfortunately, it does not cover Part D drugs and may only cover Part B drugs depending on the MA plan’s benefit package. Here are the key provisions of the act:
- Electronic PA: Implementing real-time decisions for routinely approved items and services.
- Transparency: Requiring annual publication of PA information, such as the percentage of requests approved and the average response time.
- Quality and Timeliness Standards: The Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS) will set standards for the quality and timeliness of PA determinations.
- Streamlining Approvals: Simplifying the approval process and reducing the time allowed for health plans to consider PA requests.
This bill passed the House in September 2022 but stalled in the Senate because of an unfavorable Congressional Budget Office score. CMS has since finalized portions of this bill via regulation, zeroing out the CBO score and increasing the chances of its passage.
Delinking Drug Prices from PBM Income and Pass-Through of Price Concessions
Affordability is a crucial aspect of accessibility, especially when it comes to medications. Over the years, we’ve learned that PBMs often favor placing the highest list price drugs on formularies because the rebates and various fees they receive from manufacturers are based on a percentage of the list price. In other words, the higher the medication’s price, the more money the PBM makes.
This practice is evident in both commercial and government formularies, where brand-name drugs are often preferred, while lower-priced generics are either excluded or placed on higher tiers. As a result, while major PBMs benefit from these rebates and fees, patients continue to pay their cost share based on the list price of the medication.
To improve the affordability of medications, a key aspect of PBM reform should be to disincentivize PBMs from selecting higher-priced medications and/or require the pass-through of manufacturer price concessions to patients.
Several major PBM reform bills are currently being considered that address either the delinking of price concessions from the list price of the drug or some form of pass-through of these concessions. These reforms are essential to ensure that patients can access affordable medications without being burdened by inflated costs.
The legislation includes the Pharmacy Benefit Manager Reform Act (S.1339); the Modernizing & Ensuring PBM Accountability Act (S.2973); the Better Mental Health Care, Lower Cost Drugs, and Extenders Act (S.3430); the Protecting Patients Against PBM Abuses Act (H.R. 2880); the DRUG Act (S.2474 / H.R.6283); and the Share the Savings with Seniors Act (S.2474 / H.R.5376).
As with all legislation, there are limitations and compromises in each of these. However, these bills are a good first step in addressing PBM remuneration (rebates and fees) based on the list price of the drug and/or passing through to the patient the benefit of manufacturer price concessions. By focusing on key areas like utilization management, delinking drug prices from PBM income, and allowing patients to directly benefit from manufacturer price concessions, we can work toward a more equitable and efficient healthcare system. Reigning in PBM bad behavior is a challenge, but the potential benefits for patient care and access make it a crucial fight worth pursuing.
Please help in efforts to improve patients’ access to available and affordable medications by contacting your representatives in Congress to impart to them the importance of passing legislation. The CSRO’s legislative map tool can help to inform you of the latest information on these and other bills and assist you in engaging with your representatives on them.
Dr. Feldman is a rheumatologist in private practice with The Rheumatology Group in New Orleans. She is the CSRO’s vice president of Advocacy and Government Affairs and its immediate past president, as well as past chair of the Alliance for Safe Biologic Medicines and a past member of the American College of Rheumatology insurance subcommittee. She has no relevant conflicts of interest to disclose. You can reach her at [email protected].
Stones, Bones, Groans, and Moans: Could This Be Primary Hyperparathyroidism?
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
Matthew F. Watto, MD: Welcome back to The Curbsiders. I’m Dr Matthew Frank Watto, here with my great friend and America’s primary care physician, Dr. Paul Nelson Williams.
Paul, we’re going to talk about our primary hyperparathyroidism podcast with Dr. Lindsay Kuo. It’s a topic that I feel much more clear on now.
Now, Paul, in primary care, you see a lot of calcium that is just slightly high. Can we just blame that on thiazide diuretics?
Paul N. Williams, MD: It’s a place to start. As you’re starting to think about the possible etiologies, primary hyperparathyroidism and malignancy are the two that roll right off the tongue, but it is worth going back to the patient’s medication list and making sure you’re not missing something.
Thiazides famously cause hypercalcemia, but in some of the reading I did for this episode, they may just uncover it a little bit early. Patients who are on thiazides who become hypercalcemic seem to go on to develop primary hyperthyroidism anyway. So I don’t think you can solely blame the thiazide.
Another medication that can be causative is lithium. So a good place to look first after you’ve repeated the labs and confirmed hypercalcemia is the patient’s medication list.
Dr. Watto: We’ve talked before about the basic workup for hypercalcemia, and determining whether it’s PTH dependent or PTH independent. On the podcast, we talk more about the full workup, but I wanted to talk about the classic symptoms. Our expert made the point that we don’t see them as much anymore, although we do see kidney stones. People used to present very late in the disease because they weren’t having labs done routinely.
The classic symptoms include osteoporosis and bone tumors. People can get nephrocalcinosis and kidney stones. I hadn’t really thought of it this way because we’re used to diagnosing it early now. Do you feel the same?
Dr. Williams: As labs have started routinely reporting calcium levels, this is more and more often how it’s picked up. The other aspect is that as we are screening for and finding osteoporosis, part of the workup almost always involves getting a parathyroid hormone and a calcium level. We’re seeing these lab abnormalities before we’re seeing symptoms, which is good.
But it also makes things more diagnostically thorny.
Dr. Watto: Dr. Lindsay Kuo made the point that when she sees patients before and after surgery, she’s aware of these nonclassic symptoms — the stones, bones, groans, and the psychiatric overtones that can be anything from fatigue or irritability to dysphoria.
Some people have a generalized weakness that’s very nonspecific. Dr. Kuo said that sometimes these symptoms will disappear after surgery. The patients may just have gotten used to them, or they thought these symptoms were caused by something else, but after surgery they went away.
There are these nonclassic symptoms that are harder to pin down. I was surprised by that.
Dr. Williams: She mentioned polydipsia and polyuria, which have been reported in other studies. It seems like it can be anything. You have to take a good history, but none of those things in and of themselves is an indication for operating unless the patient has the classic renal or bone manifestations.
Dr. Watto: The other thing we talked about is a normal calcium level in a patient with primary hyperparathyroidism, or the finding of a PTH level in the normal range but with a high calcium level that is inappropriate. Can you talk a little bit about those two situations?
Dr. Williams: They’re hard to say but kind of easy to manage because you treat them the same way as someone who has elevated calcium and PTH levels.
The normocalcemic patient is something we might stumble across with osteoporosis screening. Initially the calcium level is elevated, so you repeat it and it’s normal but with an elevated PTH level. You’re like, shoot. Now what?
It turns out that most endocrine surgeons say that the indications for surgery for the classic form of primary hyperparathyroidism apply to these patients as well, and it probably helps with the bone outcomes, which is one of the things they follow most closely. If you have hypercalcemia, you should have a suppressed PTH level, the so-called normohormonal hyperparathyroidism, which is not normal at all. So even if the PTH is in the normal range, it’s still relatively elevated compared with what it should be. That situation is treated in the same way as the classic elevated PTH and elevated calcium levels.
Dr. Watto: If the calcium is abnormal and the PTH is not quite what you’d expect it to be, you can always ask your friendly neighborhood endocrinologist to help you figure out whether the patient really has one of these conditions. You have to make sure that they don’t have a simple secondary cause like a low vitamin D level. In that case, you fix the vitamin D and then recheck the numbers to see if they’ve normalized. But I have found a bunch of these edge cases in which it has been helpful to confer with an endocrinologist, especially before you send someone to a surgeon to take out their parathyroid gland.
This was a really fantastic conversation. If you want to hear the full podcast episode, click here.
Dr. Watto, Clinical Assistant Professor, Department of Medicine, Perelman School of Medicine at University of Pennsylvania; Internist, Department of Medicine, Hospital Medicine Section, Pennsylvania Hospital, Philadelphia, Pennsylvania, has disclosed no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Williams, Associate Professor of Clinical Medicine, Department of General Internal Medicine, Lewis Katz School of Medicine; Staff Physician, Department of General Internal Medicine, Temple Internal Medicine Associates, Philadelphia, Pennsylvania, served as a director, officer, partner, employee, adviser, consultant, or trustee for The Curbsiders, and has received income in an amount equal to or greater than $250 from The Curbsiders.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
Matthew F. Watto, MD: Welcome back to The Curbsiders. I’m Dr Matthew Frank Watto, here with my great friend and America’s primary care physician, Dr. Paul Nelson Williams.
Paul, we’re going to talk about our primary hyperparathyroidism podcast with Dr. Lindsay Kuo. It’s a topic that I feel much more clear on now.
Now, Paul, in primary care, you see a lot of calcium that is just slightly high. Can we just blame that on thiazide diuretics?
Paul N. Williams, MD: It’s a place to start. As you’re starting to think about the possible etiologies, primary hyperparathyroidism and malignancy are the two that roll right off the tongue, but it is worth going back to the patient’s medication list and making sure you’re not missing something.
Thiazides famously cause hypercalcemia, but in some of the reading I did for this episode, they may just uncover it a little bit early. Patients who are on thiazides who become hypercalcemic seem to go on to develop primary hyperthyroidism anyway. So I don’t think you can solely blame the thiazide.
Another medication that can be causative is lithium. So a good place to look first after you’ve repeated the labs and confirmed hypercalcemia is the patient’s medication list.
Dr. Watto: We’ve talked before about the basic workup for hypercalcemia, and determining whether it’s PTH dependent or PTH independent. On the podcast, we talk more about the full workup, but I wanted to talk about the classic symptoms. Our expert made the point that we don’t see them as much anymore, although we do see kidney stones. People used to present very late in the disease because they weren’t having labs done routinely.
The classic symptoms include osteoporosis and bone tumors. People can get nephrocalcinosis and kidney stones. I hadn’t really thought of it this way because we’re used to diagnosing it early now. Do you feel the same?
Dr. Williams: As labs have started routinely reporting calcium levels, this is more and more often how it’s picked up. The other aspect is that as we are screening for and finding osteoporosis, part of the workup almost always involves getting a parathyroid hormone and a calcium level. We’re seeing these lab abnormalities before we’re seeing symptoms, which is good.
But it also makes things more diagnostically thorny.
Dr. Watto: Dr. Lindsay Kuo made the point that when she sees patients before and after surgery, she’s aware of these nonclassic symptoms — the stones, bones, groans, and the psychiatric overtones that can be anything from fatigue or irritability to dysphoria.
Some people have a generalized weakness that’s very nonspecific. Dr. Kuo said that sometimes these symptoms will disappear after surgery. The patients may just have gotten used to them, or they thought these symptoms were caused by something else, but after surgery they went away.
There are these nonclassic symptoms that are harder to pin down. I was surprised by that.
Dr. Williams: She mentioned polydipsia and polyuria, which have been reported in other studies. It seems like it can be anything. You have to take a good history, but none of those things in and of themselves is an indication for operating unless the patient has the classic renal or bone manifestations.
Dr. Watto: The other thing we talked about is a normal calcium level in a patient with primary hyperparathyroidism, or the finding of a PTH level in the normal range but with a high calcium level that is inappropriate. Can you talk a little bit about those two situations?
Dr. Williams: They’re hard to say but kind of easy to manage because you treat them the same way as someone who has elevated calcium and PTH levels.
The normocalcemic patient is something we might stumble across with osteoporosis screening. Initially the calcium level is elevated, so you repeat it and it’s normal but with an elevated PTH level. You’re like, shoot. Now what?
It turns out that most endocrine surgeons say that the indications for surgery for the classic form of primary hyperparathyroidism apply to these patients as well, and it probably helps with the bone outcomes, which is one of the things they follow most closely. If you have hypercalcemia, you should have a suppressed PTH level, the so-called normohormonal hyperparathyroidism, which is not normal at all. So even if the PTH is in the normal range, it’s still relatively elevated compared with what it should be. That situation is treated in the same way as the classic elevated PTH and elevated calcium levels.
Dr. Watto: If the calcium is abnormal and the PTH is not quite what you’d expect it to be, you can always ask your friendly neighborhood endocrinologist to help you figure out whether the patient really has one of these conditions. You have to make sure that they don’t have a simple secondary cause like a low vitamin D level. In that case, you fix the vitamin D and then recheck the numbers to see if they’ve normalized. But I have found a bunch of these edge cases in which it has been helpful to confer with an endocrinologist, especially before you send someone to a surgeon to take out their parathyroid gland.
This was a really fantastic conversation. If you want to hear the full podcast episode, click here.
Dr. Watto, Clinical Assistant Professor, Department of Medicine, Perelman School of Medicine at University of Pennsylvania; Internist, Department of Medicine, Hospital Medicine Section, Pennsylvania Hospital, Philadelphia, Pennsylvania, has disclosed no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Williams, Associate Professor of Clinical Medicine, Department of General Internal Medicine, Lewis Katz School of Medicine; Staff Physician, Department of General Internal Medicine, Temple Internal Medicine Associates, Philadelphia, Pennsylvania, served as a director, officer, partner, employee, adviser, consultant, or trustee for The Curbsiders, and has received income in an amount equal to or greater than $250 from The Curbsiders.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
Matthew F. Watto, MD: Welcome back to The Curbsiders. I’m Dr Matthew Frank Watto, here with my great friend and America’s primary care physician, Dr. Paul Nelson Williams.
Paul, we’re going to talk about our primary hyperparathyroidism podcast with Dr. Lindsay Kuo. It’s a topic that I feel much more clear on now.
Now, Paul, in primary care, you see a lot of calcium that is just slightly high. Can we just blame that on thiazide diuretics?
Paul N. Williams, MD: It’s a place to start. As you’re starting to think about the possible etiologies, primary hyperparathyroidism and malignancy are the two that roll right off the tongue, but it is worth going back to the patient’s medication list and making sure you’re not missing something.
Thiazides famously cause hypercalcemia, but in some of the reading I did for this episode, they may just uncover it a little bit early. Patients who are on thiazides who become hypercalcemic seem to go on to develop primary hyperthyroidism anyway. So I don’t think you can solely blame the thiazide.
Another medication that can be causative is lithium. So a good place to look first after you’ve repeated the labs and confirmed hypercalcemia is the patient’s medication list.
Dr. Watto: We’ve talked before about the basic workup for hypercalcemia, and determining whether it’s PTH dependent or PTH independent. On the podcast, we talk more about the full workup, but I wanted to talk about the classic symptoms. Our expert made the point that we don’t see them as much anymore, although we do see kidney stones. People used to present very late in the disease because they weren’t having labs done routinely.
The classic symptoms include osteoporosis and bone tumors. People can get nephrocalcinosis and kidney stones. I hadn’t really thought of it this way because we’re used to diagnosing it early now. Do you feel the same?
Dr. Williams: As labs have started routinely reporting calcium levels, this is more and more often how it’s picked up. The other aspect is that as we are screening for and finding osteoporosis, part of the workup almost always involves getting a parathyroid hormone and a calcium level. We’re seeing these lab abnormalities before we’re seeing symptoms, which is good.
But it also makes things more diagnostically thorny.
Dr. Watto: Dr. Lindsay Kuo made the point that when she sees patients before and after surgery, she’s aware of these nonclassic symptoms — the stones, bones, groans, and the psychiatric overtones that can be anything from fatigue or irritability to dysphoria.
Some people have a generalized weakness that’s very nonspecific. Dr. Kuo said that sometimes these symptoms will disappear after surgery. The patients may just have gotten used to them, or they thought these symptoms were caused by something else, but after surgery they went away.
There are these nonclassic symptoms that are harder to pin down. I was surprised by that.
Dr. Williams: She mentioned polydipsia and polyuria, which have been reported in other studies. It seems like it can be anything. You have to take a good history, but none of those things in and of themselves is an indication for operating unless the patient has the classic renal or bone manifestations.
Dr. Watto: The other thing we talked about is a normal calcium level in a patient with primary hyperparathyroidism, or the finding of a PTH level in the normal range but with a high calcium level that is inappropriate. Can you talk a little bit about those two situations?
Dr. Williams: They’re hard to say but kind of easy to manage because you treat them the same way as someone who has elevated calcium and PTH levels.
The normocalcemic patient is something we might stumble across with osteoporosis screening. Initially the calcium level is elevated, so you repeat it and it’s normal but with an elevated PTH level. You’re like, shoot. Now what?
It turns out that most endocrine surgeons say that the indications for surgery for the classic form of primary hyperparathyroidism apply to these patients as well, and it probably helps with the bone outcomes, which is one of the things they follow most closely. If you have hypercalcemia, you should have a suppressed PTH level, the so-called normohormonal hyperparathyroidism, which is not normal at all. So even if the PTH is in the normal range, it’s still relatively elevated compared with what it should be. That situation is treated in the same way as the classic elevated PTH and elevated calcium levels.
Dr. Watto: If the calcium is abnormal and the PTH is not quite what you’d expect it to be, you can always ask your friendly neighborhood endocrinologist to help you figure out whether the patient really has one of these conditions. You have to make sure that they don’t have a simple secondary cause like a low vitamin D level. In that case, you fix the vitamin D and then recheck the numbers to see if they’ve normalized. But I have found a bunch of these edge cases in which it has been helpful to confer with an endocrinologist, especially before you send someone to a surgeon to take out their parathyroid gland.
This was a really fantastic conversation. If you want to hear the full podcast episode, click here.
Dr. Watto, Clinical Assistant Professor, Department of Medicine, Perelman School of Medicine at University of Pennsylvania; Internist, Department of Medicine, Hospital Medicine Section, Pennsylvania Hospital, Philadelphia, Pennsylvania, has disclosed no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Williams, Associate Professor of Clinical Medicine, Department of General Internal Medicine, Lewis Katz School of Medicine; Staff Physician, Department of General Internal Medicine, Temple Internal Medicine Associates, Philadelphia, Pennsylvania, served as a director, officer, partner, employee, adviser, consultant, or trustee for The Curbsiders, and has received income in an amount equal to or greater than $250 from The Curbsiders.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Old, Frail Patients: Study More, Intervene Less?
Lessons From SENIOR-RITA
The ability to save cardiac muscle during an acute coronary syndrome with percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI) made cardiology one of the most popular fields in medicine.
But acute coronary syndromes come in different categories. While rapid PCI clearly benefits patients with ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction (STEMI), the best use of angiography and PCI for patients with non–ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction (NSTEMI) is more complex.
There have been many trials and meta-analyses, and generally, outcomes are similar with either approach. Perhaps if one looks with enough optimism, there is a benefit for the more aggressive approach in higher-risk patients.
Despite the similar outcomes with the two strategies, most patients are treated with the early invasive approach. Early and invasive fit the spirit of modern cardiology.
Yet, older patients with acute coronary syndromes present a different challenge. NSTEMI trials, like most trials, enrolled mostly younger adults.
Whether evidence obtained in young people applies to older patients is one of the most common and important questions in all of medical practice. Older patients may be at higher risk for a primary outcome, but they also have greater risks for harm from therapy as well as more competing causes of morbidity and mortality.
Only a handful of smaller trials have enrolled older patients with NSTEMI. These trials have produced little evidence that an early invasive approach should be preferred.
The SENIOR-RITA Trial
At ESC, Vijay Kunadian, MD, from Newcastle, England, presented results of SENIOR-RITA, a large trial comparing an invasive vs conservative strategy in NSTEMI patients 75 years of age or older.
In the conservative arm, coronary angiography was allowed if the patient deteriorated and the procedure was clinically indicated in the judgment of the treating physicians.
Slightly more than 1500 patients with NSTEMI were randomly assigned to either strategy in 48 centers in the United Kingdom. Their mean age was 82 years, nearly half were women, and about a third were frail.
Over 4 years of follow-up, the primary outcome of cardiovascular (CV) death or MI occurred at a similar rate in both arms: 25.6% vs 26.3% for invasive vs conservative, respectively (HR, 0.94; 95% CI, 0.77-1.14; P =.53).
Rates of CV death were also not significantly different (15.8% vs 14.2%; HR, 1.11; 95% CI, 0.86-1.44).
The rate of nonfatal MI was slightly lower in the invasive arm (11.7% vs 15.0%; HR, 0.75; 95% CI, 0.57-0.99).
Some other notable findings: Fewer than half of patients in the invasive arm underwent revascularization. Coronary angiography was done in about a quarter of patients in the conservative arm, and revascularization in only 14%.
Comments
Because medicine has improved and patients live longer, cardiologists increasingly see older adults with frailty. It’s important to study these patients.
The authors tell us that 1 in 5 patients screened were enrolled, and those not enrolled were similar in age and were treated nearly equally with either strategy. Not all trials offer this information; it’s important because knowing that patients in a trial are representative helps us translate evidence to our actual patients.
Another positive was the investigators’ smart choice of cardiovascular death and MI as their primary outcome. Strategy trials are usually open label. If they had included an outcome that requires a decision from a clinician, such as unplanned revascularization, then bias becomes a possibility when patients and clinicians are aware of the treatment assignment. (I wrote about poor endpoint choice in the ABYSS trial.)
The most notable finding in SENIOR-RITA was that approximately 76% of patients in the conservative arm did not have a coronary angiogram and 86% were not revascularized.
Yet, the rate of CV death and MI were similar during 4 years of follow-up. This observation is nearly identical to the findings in chronic stable disease, seen in the ISCHEMIA trial. (See Figure 6a in the paper’s supplement.)
I take two messages from this consistent observation: One is that medical therapy is quite good at treating coronary artery disease not associated with acute vessel closure in STEMI.
The other is that using coronary angiography and revascularization as a bailout, in only a fraction of cases, achieves the same result, so the conservative strategy should be preferred.
I am not sure that the SENIOR-RITA researchers see it this way. They write in their discussion that “clinicians are often reluctant to offer an invasive strategy to frail older adults.” They then remind readers that modern PCI techniques (radial approach) have low rates of adverse events.
Perhaps I misread their message, but that paragraph seemed like it was reinforcing our tendency to offer invasive approaches to patients with NSTEMI.
I feel differently. When a trial reports similar outcomes with two strategies, I think we should favor the one with less intervention. I feel even more strongly about this philosophy in older patients with frailty.
Are we not in the business of helping people with the least amount of intervention?
The greatest challenge for the cardiologist of today is not a lack of treatment options, but whether we should use all options in older, frailer adults.
Good on the SENIOR-RITA investigators, for they have shown that we can avoid intervention in the vast majority of older adults presenting with NSTEMI.
Dr. Mandrola practices cardiac electrophysiology in Louisville, Kentucky, and is a writer and podcaster for Medscape. He espouses a conservative approach to medical practice. He participates in clinical research and writes often about the state of medical evidence. He has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Lessons From SENIOR-RITA
Lessons From SENIOR-RITA
The ability to save cardiac muscle during an acute coronary syndrome with percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI) made cardiology one of the most popular fields in medicine.
But acute coronary syndromes come in different categories. While rapid PCI clearly benefits patients with ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction (STEMI), the best use of angiography and PCI for patients with non–ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction (NSTEMI) is more complex.
There have been many trials and meta-analyses, and generally, outcomes are similar with either approach. Perhaps if one looks with enough optimism, there is a benefit for the more aggressive approach in higher-risk patients.
Despite the similar outcomes with the two strategies, most patients are treated with the early invasive approach. Early and invasive fit the spirit of modern cardiology.
Yet, older patients with acute coronary syndromes present a different challenge. NSTEMI trials, like most trials, enrolled mostly younger adults.
Whether evidence obtained in young people applies to older patients is one of the most common and important questions in all of medical practice. Older patients may be at higher risk for a primary outcome, but they also have greater risks for harm from therapy as well as more competing causes of morbidity and mortality.
Only a handful of smaller trials have enrolled older patients with NSTEMI. These trials have produced little evidence that an early invasive approach should be preferred.
The SENIOR-RITA Trial
At ESC, Vijay Kunadian, MD, from Newcastle, England, presented results of SENIOR-RITA, a large trial comparing an invasive vs conservative strategy in NSTEMI patients 75 years of age or older.
In the conservative arm, coronary angiography was allowed if the patient deteriorated and the procedure was clinically indicated in the judgment of the treating physicians.
Slightly more than 1500 patients with NSTEMI were randomly assigned to either strategy in 48 centers in the United Kingdom. Their mean age was 82 years, nearly half were women, and about a third were frail.
Over 4 years of follow-up, the primary outcome of cardiovascular (CV) death or MI occurred at a similar rate in both arms: 25.6% vs 26.3% for invasive vs conservative, respectively (HR, 0.94; 95% CI, 0.77-1.14; P =.53).
Rates of CV death were also not significantly different (15.8% vs 14.2%; HR, 1.11; 95% CI, 0.86-1.44).
The rate of nonfatal MI was slightly lower in the invasive arm (11.7% vs 15.0%; HR, 0.75; 95% CI, 0.57-0.99).
Some other notable findings: Fewer than half of patients in the invasive arm underwent revascularization. Coronary angiography was done in about a quarter of patients in the conservative arm, and revascularization in only 14%.
Comments
Because medicine has improved and patients live longer, cardiologists increasingly see older adults with frailty. It’s important to study these patients.
The authors tell us that 1 in 5 patients screened were enrolled, and those not enrolled were similar in age and were treated nearly equally with either strategy. Not all trials offer this information; it’s important because knowing that patients in a trial are representative helps us translate evidence to our actual patients.
Another positive was the investigators’ smart choice of cardiovascular death and MI as their primary outcome. Strategy trials are usually open label. If they had included an outcome that requires a decision from a clinician, such as unplanned revascularization, then bias becomes a possibility when patients and clinicians are aware of the treatment assignment. (I wrote about poor endpoint choice in the ABYSS trial.)
The most notable finding in SENIOR-RITA was that approximately 76% of patients in the conservative arm did not have a coronary angiogram and 86% were not revascularized.
Yet, the rate of CV death and MI were similar during 4 years of follow-up. This observation is nearly identical to the findings in chronic stable disease, seen in the ISCHEMIA trial. (See Figure 6a in the paper’s supplement.)
I take two messages from this consistent observation: One is that medical therapy is quite good at treating coronary artery disease not associated with acute vessel closure in STEMI.
The other is that using coronary angiography and revascularization as a bailout, in only a fraction of cases, achieves the same result, so the conservative strategy should be preferred.
I am not sure that the SENIOR-RITA researchers see it this way. They write in their discussion that “clinicians are often reluctant to offer an invasive strategy to frail older adults.” They then remind readers that modern PCI techniques (radial approach) have low rates of adverse events.
Perhaps I misread their message, but that paragraph seemed like it was reinforcing our tendency to offer invasive approaches to patients with NSTEMI.
I feel differently. When a trial reports similar outcomes with two strategies, I think we should favor the one with less intervention. I feel even more strongly about this philosophy in older patients with frailty.
Are we not in the business of helping people with the least amount of intervention?
The greatest challenge for the cardiologist of today is not a lack of treatment options, but whether we should use all options in older, frailer adults.
Good on the SENIOR-RITA investigators, for they have shown that we can avoid intervention in the vast majority of older adults presenting with NSTEMI.
Dr. Mandrola practices cardiac electrophysiology in Louisville, Kentucky, and is a writer and podcaster for Medscape. He espouses a conservative approach to medical practice. He participates in clinical research and writes often about the state of medical evidence. He has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The ability to save cardiac muscle during an acute coronary syndrome with percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI) made cardiology one of the most popular fields in medicine.
But acute coronary syndromes come in different categories. While rapid PCI clearly benefits patients with ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction (STEMI), the best use of angiography and PCI for patients with non–ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction (NSTEMI) is more complex.
There have been many trials and meta-analyses, and generally, outcomes are similar with either approach. Perhaps if one looks with enough optimism, there is a benefit for the more aggressive approach in higher-risk patients.
Despite the similar outcomes with the two strategies, most patients are treated with the early invasive approach. Early and invasive fit the spirit of modern cardiology.
Yet, older patients with acute coronary syndromes present a different challenge. NSTEMI trials, like most trials, enrolled mostly younger adults.
Whether evidence obtained in young people applies to older patients is one of the most common and important questions in all of medical practice. Older patients may be at higher risk for a primary outcome, but they also have greater risks for harm from therapy as well as more competing causes of morbidity and mortality.
Only a handful of smaller trials have enrolled older patients with NSTEMI. These trials have produced little evidence that an early invasive approach should be preferred.
The SENIOR-RITA Trial
At ESC, Vijay Kunadian, MD, from Newcastle, England, presented results of SENIOR-RITA, a large trial comparing an invasive vs conservative strategy in NSTEMI patients 75 years of age or older.
In the conservative arm, coronary angiography was allowed if the patient deteriorated and the procedure was clinically indicated in the judgment of the treating physicians.
Slightly more than 1500 patients with NSTEMI were randomly assigned to either strategy in 48 centers in the United Kingdom. Their mean age was 82 years, nearly half were women, and about a third were frail.
Over 4 years of follow-up, the primary outcome of cardiovascular (CV) death or MI occurred at a similar rate in both arms: 25.6% vs 26.3% for invasive vs conservative, respectively (HR, 0.94; 95% CI, 0.77-1.14; P =.53).
Rates of CV death were also not significantly different (15.8% vs 14.2%; HR, 1.11; 95% CI, 0.86-1.44).
The rate of nonfatal MI was slightly lower in the invasive arm (11.7% vs 15.0%; HR, 0.75; 95% CI, 0.57-0.99).
Some other notable findings: Fewer than half of patients in the invasive arm underwent revascularization. Coronary angiography was done in about a quarter of patients in the conservative arm, and revascularization in only 14%.
Comments
Because medicine has improved and patients live longer, cardiologists increasingly see older adults with frailty. It’s important to study these patients.
The authors tell us that 1 in 5 patients screened were enrolled, and those not enrolled were similar in age and were treated nearly equally with either strategy. Not all trials offer this information; it’s important because knowing that patients in a trial are representative helps us translate evidence to our actual patients.
Another positive was the investigators’ smart choice of cardiovascular death and MI as their primary outcome. Strategy trials are usually open label. If they had included an outcome that requires a decision from a clinician, such as unplanned revascularization, then bias becomes a possibility when patients and clinicians are aware of the treatment assignment. (I wrote about poor endpoint choice in the ABYSS trial.)
The most notable finding in SENIOR-RITA was that approximately 76% of patients in the conservative arm did not have a coronary angiogram and 86% were not revascularized.
Yet, the rate of CV death and MI were similar during 4 years of follow-up. This observation is nearly identical to the findings in chronic stable disease, seen in the ISCHEMIA trial. (See Figure 6a in the paper’s supplement.)
I take two messages from this consistent observation: One is that medical therapy is quite good at treating coronary artery disease not associated with acute vessel closure in STEMI.
The other is that using coronary angiography and revascularization as a bailout, in only a fraction of cases, achieves the same result, so the conservative strategy should be preferred.
I am not sure that the SENIOR-RITA researchers see it this way. They write in their discussion that “clinicians are often reluctant to offer an invasive strategy to frail older adults.” They then remind readers that modern PCI techniques (radial approach) have low rates of adverse events.
Perhaps I misread their message, but that paragraph seemed like it was reinforcing our tendency to offer invasive approaches to patients with NSTEMI.
I feel differently. When a trial reports similar outcomes with two strategies, I think we should favor the one with less intervention. I feel even more strongly about this philosophy in older patients with frailty.
Are we not in the business of helping people with the least amount of intervention?
The greatest challenge for the cardiologist of today is not a lack of treatment options, but whether we should use all options in older, frailer adults.
Good on the SENIOR-RITA investigators, for they have shown that we can avoid intervention in the vast majority of older adults presenting with NSTEMI.
Dr. Mandrola practices cardiac electrophysiology in Louisville, Kentucky, and is a writer and podcaster for Medscape. He espouses a conservative approach to medical practice. He participates in clinical research and writes often about the state of medical evidence. He has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Navigating Ethical and Clinical Considerations Relating to Percutaneous Gastrostomy (PEG) Tubes
Cases
Consults for percutaneous gastrostomy (PEG) tube placement for a patient ...
- With dysphagia after stroke: A 70-year-old female with a history of hypertension presented to the hospital with altered mental status and left-sided weakness. She was previously active and independently living. MRI of the brain revealed a right basal ganglia infarct. As a result, she developed dysphagia. She was evaluated by speech and language pathology and underwent a modified barium swallow. Given concerns for aspiration, the recommendation was made for gastroenterology (GI) consultation to place PEG tube for nutrition and medication administration.
- With advanced dementia: An 85-year-old male with an extensive medical history including advanced dementia was admitted from his nursing home for decreased oral intake. His baseline mental status is awake and alert, but he is nonverbal and does not follow commands. Upon 72-hour calorie count, the nutrition consultants determined that he cannot independently meet his nutrition goals. His family wants “everything done” and are asking about a “feeding tube.” The primary team has now consulted GI for PEG tube placement.
- Who is being discharged to a long-term care facility: A 45-year-old male was admitted to the ICU after a heroin overdose. CPR was initiated in the field and return of spontaneous circulation was obtained after 25 minutes. The patient has minimal brainstem reflexes. He is ventilator dependent. He has no family, and now is status-post tracheostomy placement by two-physician consent. The patient is ready for discharge to a long-term care facility that will not accept patients with nasogastric tubes. GI is consulted for PEG tube placement.
Discussion
Gastroenterologists are often consulted for PEG tube placement. However, This is rooted in the fact that, as one expert wrote, “feeding, unlike any other medical treatment, has a moral and emotional significance derived from culture.”1 Understanding the evidence, ethical considerations, and team dynamic behind PEG tube placement is critical for every gastroenterologist. Herein we review these topics and offer guidelines for having patient-centered conversations involving these fundamental concepts.
First, the gastroenterologist should understand the evidence to debunk myths and clarify truths surrounding PEG tube placement. While PEG tubes may help patients with amyotrophic lateral sclerosis stabilize their weight and can even be prophylactically placed in select patients with head and neck cancer,2,3 they are not always appropriate in patients in early recovery from stroke and have not been shown to improve outcomes in patients with advanced dementia. At least 50% of stroke-related dysphagia resolves within 1-2 weeks, and so the American Heart Association Stroke Council recommends continuing nasogastric tube feeding for 2-3 weeks in patients such as the one presented in case 1 before considering PEG tube placement.4
In situations of advanced dementia such as in case,2 several studies demonstrate that PEG tubes do not reduce or prevent aspiration pneumonia, prevent consequences of malnutrition, prolong life, reduce pressure ulcers, reduce urinary of gastrointestinal tract infections, lead to functional improvement, mitigate decline, or even improve comfort or quality of life for patients or their caregivers.5-7 Despite this evidence, as demonstrated in case,3 it is true that many American skilled nursing facilities will not accept a patient without a PEG if enteral feeding is needed. This restriction may vary by state: One study found that skilled nursing facilities in New York City are much less likely to accept patients with nasogastric feeding tubes than randomly selected skilled nursing facilities throughout the country.6 Nonetheless, gastroenterologists should look to the literature to understand the outcomes of populations of patients after PEG tube placement and use that data to guide decision-making.
Secondly, the five ethical principles that inform all medical decision making – autonomy, beneficence, nonmaleficence, justice, and futility – should also inform the gastroenterologist’s rationale in offering PEG placement.8
Autonomy implies that the medical team has determined who is able to make the decision regarding PEG tube placement for the patient. Beneficence connects the patient’s medical diagnosis and technical parameters of PEG tube placement with his or her goals of care. Nonmaleficence ensures the decision-making party understands the benefits and risks of the procedure, including anticipatory guidance on possible PEG tube management, complications, risks, and need for replacement. Justice incorporates the context of the patient’s life, including family dynamics, religious, cultural, and financial factors. Futility connects the patient’s prognosis with practical aspects of having a PEG tube.
The complexity of PEG placement lies in the fact that these ethical principles are often at odds with each other. For example, case 2 highlights the conflicting principles of autonomy and futility for elderly dementia patients: While PEG tube placements do not improve comfort or quality of life in advanced dementia (futility), the family representing the patient has stated they want everything done for his care, including PEG tube placement (autonomy). Navigating these ethical principles can be difficult, but having a framework to organize the different factors offers sound guidance for the gastroenterologist.
Finally, the gastroenterologist should recognize the roles of the multidisciplinary team members, including the patient and their representatives, regarding PEG tube placement consults. While gastroenterologists can be viewed as the technicians consulted to simply “place the tube,” they must seek to understand the members of the team representing the patient to be stewards of their skill set. Consulting team physicians carry great responsibility in organizing the medical and psychosocial aspects of each patient’s care, and their proper goals to relieve suffering and prevent death may color their judgment regarding who they believe is a candidate for a PEG tube. Nutritionists, speech therapists, and case managers can help provide objective data on the practicality and feasibility of a PEG tube in their patients. The healthcare system may influence the decision to consult heavily, as seen in the rules of the long-term care facility in case.3 While it is the job of the multidisciplinary medical team to explain the evidence and ethical considerations of PEG tube placement in a patient-centered manner, ultimately the decision belongs to the patient and their family or representatives.
The moral burden of not pursuing PEG placement may supersede the medical advice in many situations. There is an emotionally taxing perception that withholding nutrition via PEG is “starving the patient,” despite literature showing many terminally ill patients do not experience thirst or hunger, and those who do have alleviation of these symptoms with small amounts of food or liquid, not with PEG placement.5 As every patient is unique, PEG tube consultation guidelines created with input from all stakeholders have been utilized to ensure that patients are medically optimized for PEG tube placement and that evidence and ethics-based considerations are evaluated by the multidisciplinary team. An example of such a guideline is shown in Figure 1.
If the gastroenterologist encounters more contentious consultations, there are ways to build consensus to both alleviate patient and family suffering as well as elevate the discussions between teams.
First, identify the type of consult that is repeatedly bringing differing viewpoints and differing ethical principles into play. Second, get representatives from teams together in a neutral environment to understand stakeholders needs. New data suggest, in stroke cases like case 1, there may be dramatic benefit in long-term ability to recover if patients can get early intensive rehabilitation.9 This intense daily rehabilitation is not available within the hospital setting at many locations, and facilitation of discharge may be requested earlier than usually advised tube placement. Third, build a common language for requests and responses between teams. For instance, neurologists can identify and document which patients have less likelihood of early spontaneous recovery, and this can allow gastroenterologists to understand that those patients with little potential for early swallowing recovery can safely be targeted for PEG earlier during the hospital course. Other patients described as having a potential for spontaneous improvement should be given time to recover before an intervention is considered.10 Having a common understanding of goals and a better-informed decision pathway helps each team member feel fulfilled and rewarded, which will ultimately help reduce compassion fatigue and moral burden on providers.
In conclusion, PEG tube placement can be a challenging consultation for gastroenterologists because of the clinical, social, and ethical ramifications at stake for the patient. Even when PEG tube placement is technically feasible, the gastroenterologist should feel empowered to address the evidence-based outcomes of PEG tube placement, discuss the ethical principles of the decision-making process, and communicate with a multidisciplinary team using guidelines as set forth by this paper to best serve the patient.
Dr. Seltzer is based in the Department of Internal Medicine, Mount Sinai Morningside-West, New York City. Dr. Pusateri is based in the Division of Gastroenterology, Hepatology and Nutrition, Ohio State University Wexner Medical Center, Columbus. Dr. Nguyen is based in the Division of Gastroenterology and Center for Esophageal Diseases, Baylor Scott & White Health, Dallas, Texas. Dr. Stein is based in the Division of Gastroenterology, Robert Wood Johnson University Hospital, Rutgers University, New Brunswick, New Jersey. All authors contributed equally to this manuscript, and have no disclosures related to this article.
References
1. Mackie S. Gastroenterol Nurs. 2001 May-Jun;24(3):138-42.
2. Miller RG et al. Neurology. 2009 Oct. doi: 10.1212/WNL.0b013e3181bc0141.
3. Colevas AD et al. J Natl Compr Canc Netw. 2018 May. doi: 10.6004/jnccn.2018.0026.
4. Holloway RG et al. Stroke. 2014 Jun. doi: 10.1161/STR.0000000000000015.
5. Finucane TE et al. JAMA. 1999 Oct. doi: 10.1001/jama.282.14.1365.
6. Burgermaster M et al. Nutr Clin Pract. 2016 Jun. doi: 10.1177/0884533616629636.
7. American Geriatrics Society Ethics C, Clinical P, Models of Care C. J Am Geriatr Soc. 2014 Aug. doi: 10.1111/jgs.12924.
8. Beauchamp TL. Principlism in Bioethics. In: Serna P, eds. Bioethical Decision Making and Argumentation. International Library of Ethics, Law, and the New Medicine, vol 70. Springer; Cham. 2016 Sept:1-16. doi: 10.1007/978-3-319-43419-3_1.
9. Powers WJ et al. Stroke. 2019 Oct. doi: 10.1161/STR.0000000000000211.
10. Galovic M et al. JAMA Neurol. 2019 May. doi: 10.1001/jamaneurol.2018.4858.
Cases
Consults for percutaneous gastrostomy (PEG) tube placement for a patient ...
- With dysphagia after stroke: A 70-year-old female with a history of hypertension presented to the hospital with altered mental status and left-sided weakness. She was previously active and independently living. MRI of the brain revealed a right basal ganglia infarct. As a result, she developed dysphagia. She was evaluated by speech and language pathology and underwent a modified barium swallow. Given concerns for aspiration, the recommendation was made for gastroenterology (GI) consultation to place PEG tube for nutrition and medication administration.
- With advanced dementia: An 85-year-old male with an extensive medical history including advanced dementia was admitted from his nursing home for decreased oral intake. His baseline mental status is awake and alert, but he is nonverbal and does not follow commands. Upon 72-hour calorie count, the nutrition consultants determined that he cannot independently meet his nutrition goals. His family wants “everything done” and are asking about a “feeding tube.” The primary team has now consulted GI for PEG tube placement.
- Who is being discharged to a long-term care facility: A 45-year-old male was admitted to the ICU after a heroin overdose. CPR was initiated in the field and return of spontaneous circulation was obtained after 25 minutes. The patient has minimal brainstem reflexes. He is ventilator dependent. He has no family, and now is status-post tracheostomy placement by two-physician consent. The patient is ready for discharge to a long-term care facility that will not accept patients with nasogastric tubes. GI is consulted for PEG tube placement.
Discussion
Gastroenterologists are often consulted for PEG tube placement. However, This is rooted in the fact that, as one expert wrote, “feeding, unlike any other medical treatment, has a moral and emotional significance derived from culture.”1 Understanding the evidence, ethical considerations, and team dynamic behind PEG tube placement is critical for every gastroenterologist. Herein we review these topics and offer guidelines for having patient-centered conversations involving these fundamental concepts.
First, the gastroenterologist should understand the evidence to debunk myths and clarify truths surrounding PEG tube placement. While PEG tubes may help patients with amyotrophic lateral sclerosis stabilize their weight and can even be prophylactically placed in select patients with head and neck cancer,2,3 they are not always appropriate in patients in early recovery from stroke and have not been shown to improve outcomes in patients with advanced dementia. At least 50% of stroke-related dysphagia resolves within 1-2 weeks, and so the American Heart Association Stroke Council recommends continuing nasogastric tube feeding for 2-3 weeks in patients such as the one presented in case 1 before considering PEG tube placement.4
In situations of advanced dementia such as in case,2 several studies demonstrate that PEG tubes do not reduce or prevent aspiration pneumonia, prevent consequences of malnutrition, prolong life, reduce pressure ulcers, reduce urinary of gastrointestinal tract infections, lead to functional improvement, mitigate decline, or even improve comfort or quality of life for patients or their caregivers.5-7 Despite this evidence, as demonstrated in case,3 it is true that many American skilled nursing facilities will not accept a patient without a PEG if enteral feeding is needed. This restriction may vary by state: One study found that skilled nursing facilities in New York City are much less likely to accept patients with nasogastric feeding tubes than randomly selected skilled nursing facilities throughout the country.6 Nonetheless, gastroenterologists should look to the literature to understand the outcomes of populations of patients after PEG tube placement and use that data to guide decision-making.
Secondly, the five ethical principles that inform all medical decision making – autonomy, beneficence, nonmaleficence, justice, and futility – should also inform the gastroenterologist’s rationale in offering PEG placement.8
Autonomy implies that the medical team has determined who is able to make the decision regarding PEG tube placement for the patient. Beneficence connects the patient’s medical diagnosis and technical parameters of PEG tube placement with his or her goals of care. Nonmaleficence ensures the decision-making party understands the benefits and risks of the procedure, including anticipatory guidance on possible PEG tube management, complications, risks, and need for replacement. Justice incorporates the context of the patient’s life, including family dynamics, religious, cultural, and financial factors. Futility connects the patient’s prognosis with practical aspects of having a PEG tube.
The complexity of PEG placement lies in the fact that these ethical principles are often at odds with each other. For example, case 2 highlights the conflicting principles of autonomy and futility for elderly dementia patients: While PEG tube placements do not improve comfort or quality of life in advanced dementia (futility), the family representing the patient has stated they want everything done for his care, including PEG tube placement (autonomy). Navigating these ethical principles can be difficult, but having a framework to organize the different factors offers sound guidance for the gastroenterologist.
Finally, the gastroenterologist should recognize the roles of the multidisciplinary team members, including the patient and their representatives, regarding PEG tube placement consults. While gastroenterologists can be viewed as the technicians consulted to simply “place the tube,” they must seek to understand the members of the team representing the patient to be stewards of their skill set. Consulting team physicians carry great responsibility in organizing the medical and psychosocial aspects of each patient’s care, and their proper goals to relieve suffering and prevent death may color their judgment regarding who they believe is a candidate for a PEG tube. Nutritionists, speech therapists, and case managers can help provide objective data on the practicality and feasibility of a PEG tube in their patients. The healthcare system may influence the decision to consult heavily, as seen in the rules of the long-term care facility in case.3 While it is the job of the multidisciplinary medical team to explain the evidence and ethical considerations of PEG tube placement in a patient-centered manner, ultimately the decision belongs to the patient and their family or representatives.
The moral burden of not pursuing PEG placement may supersede the medical advice in many situations. There is an emotionally taxing perception that withholding nutrition via PEG is “starving the patient,” despite literature showing many terminally ill patients do not experience thirst or hunger, and those who do have alleviation of these symptoms with small amounts of food or liquid, not with PEG placement.5 As every patient is unique, PEG tube consultation guidelines created with input from all stakeholders have been utilized to ensure that patients are medically optimized for PEG tube placement and that evidence and ethics-based considerations are evaluated by the multidisciplinary team. An example of such a guideline is shown in Figure 1.
If the gastroenterologist encounters more contentious consultations, there are ways to build consensus to both alleviate patient and family suffering as well as elevate the discussions between teams.
First, identify the type of consult that is repeatedly bringing differing viewpoints and differing ethical principles into play. Second, get representatives from teams together in a neutral environment to understand stakeholders needs. New data suggest, in stroke cases like case 1, there may be dramatic benefit in long-term ability to recover if patients can get early intensive rehabilitation.9 This intense daily rehabilitation is not available within the hospital setting at many locations, and facilitation of discharge may be requested earlier than usually advised tube placement. Third, build a common language for requests and responses between teams. For instance, neurologists can identify and document which patients have less likelihood of early spontaneous recovery, and this can allow gastroenterologists to understand that those patients with little potential for early swallowing recovery can safely be targeted for PEG earlier during the hospital course. Other patients described as having a potential for spontaneous improvement should be given time to recover before an intervention is considered.10 Having a common understanding of goals and a better-informed decision pathway helps each team member feel fulfilled and rewarded, which will ultimately help reduce compassion fatigue and moral burden on providers.
In conclusion, PEG tube placement can be a challenging consultation for gastroenterologists because of the clinical, social, and ethical ramifications at stake for the patient. Even when PEG tube placement is technically feasible, the gastroenterologist should feel empowered to address the evidence-based outcomes of PEG tube placement, discuss the ethical principles of the decision-making process, and communicate with a multidisciplinary team using guidelines as set forth by this paper to best serve the patient.
Dr. Seltzer is based in the Department of Internal Medicine, Mount Sinai Morningside-West, New York City. Dr. Pusateri is based in the Division of Gastroenterology, Hepatology and Nutrition, Ohio State University Wexner Medical Center, Columbus. Dr. Nguyen is based in the Division of Gastroenterology and Center for Esophageal Diseases, Baylor Scott & White Health, Dallas, Texas. Dr. Stein is based in the Division of Gastroenterology, Robert Wood Johnson University Hospital, Rutgers University, New Brunswick, New Jersey. All authors contributed equally to this manuscript, and have no disclosures related to this article.
References
1. Mackie S. Gastroenterol Nurs. 2001 May-Jun;24(3):138-42.
2. Miller RG et al. Neurology. 2009 Oct. doi: 10.1212/WNL.0b013e3181bc0141.
3. Colevas AD et al. J Natl Compr Canc Netw. 2018 May. doi: 10.6004/jnccn.2018.0026.
4. Holloway RG et al. Stroke. 2014 Jun. doi: 10.1161/STR.0000000000000015.
5. Finucane TE et al. JAMA. 1999 Oct. doi: 10.1001/jama.282.14.1365.
6. Burgermaster M et al. Nutr Clin Pract. 2016 Jun. doi: 10.1177/0884533616629636.
7. American Geriatrics Society Ethics C, Clinical P, Models of Care C. J Am Geriatr Soc. 2014 Aug. doi: 10.1111/jgs.12924.
8. Beauchamp TL. Principlism in Bioethics. In: Serna P, eds. Bioethical Decision Making and Argumentation. International Library of Ethics, Law, and the New Medicine, vol 70. Springer; Cham. 2016 Sept:1-16. doi: 10.1007/978-3-319-43419-3_1.
9. Powers WJ et al. Stroke. 2019 Oct. doi: 10.1161/STR.0000000000000211.
10. Galovic M et al. JAMA Neurol. 2019 May. doi: 10.1001/jamaneurol.2018.4858.
Cases
Consults for percutaneous gastrostomy (PEG) tube placement for a patient ...
- With dysphagia after stroke: A 70-year-old female with a history of hypertension presented to the hospital with altered mental status and left-sided weakness. She was previously active and independently living. MRI of the brain revealed a right basal ganglia infarct. As a result, she developed dysphagia. She was evaluated by speech and language pathology and underwent a modified barium swallow. Given concerns for aspiration, the recommendation was made for gastroenterology (GI) consultation to place PEG tube for nutrition and medication administration.
- With advanced dementia: An 85-year-old male with an extensive medical history including advanced dementia was admitted from his nursing home for decreased oral intake. His baseline mental status is awake and alert, but he is nonverbal and does not follow commands. Upon 72-hour calorie count, the nutrition consultants determined that he cannot independently meet his nutrition goals. His family wants “everything done” and are asking about a “feeding tube.” The primary team has now consulted GI for PEG tube placement.
- Who is being discharged to a long-term care facility: A 45-year-old male was admitted to the ICU after a heroin overdose. CPR was initiated in the field and return of spontaneous circulation was obtained after 25 minutes. The patient has minimal brainstem reflexes. He is ventilator dependent. He has no family, and now is status-post tracheostomy placement by two-physician consent. The patient is ready for discharge to a long-term care facility that will not accept patients with nasogastric tubes. GI is consulted for PEG tube placement.
Discussion
Gastroenterologists are often consulted for PEG tube placement. However, This is rooted in the fact that, as one expert wrote, “feeding, unlike any other medical treatment, has a moral and emotional significance derived from culture.”1 Understanding the evidence, ethical considerations, and team dynamic behind PEG tube placement is critical for every gastroenterologist. Herein we review these topics and offer guidelines for having patient-centered conversations involving these fundamental concepts.
First, the gastroenterologist should understand the evidence to debunk myths and clarify truths surrounding PEG tube placement. While PEG tubes may help patients with amyotrophic lateral sclerosis stabilize their weight and can even be prophylactically placed in select patients with head and neck cancer,2,3 they are not always appropriate in patients in early recovery from stroke and have not been shown to improve outcomes in patients with advanced dementia. At least 50% of stroke-related dysphagia resolves within 1-2 weeks, and so the American Heart Association Stroke Council recommends continuing nasogastric tube feeding for 2-3 weeks in patients such as the one presented in case 1 before considering PEG tube placement.4
In situations of advanced dementia such as in case,2 several studies demonstrate that PEG tubes do not reduce or prevent aspiration pneumonia, prevent consequences of malnutrition, prolong life, reduce pressure ulcers, reduce urinary of gastrointestinal tract infections, lead to functional improvement, mitigate decline, or even improve comfort or quality of life for patients or their caregivers.5-7 Despite this evidence, as demonstrated in case,3 it is true that many American skilled nursing facilities will not accept a patient without a PEG if enteral feeding is needed. This restriction may vary by state: One study found that skilled nursing facilities in New York City are much less likely to accept patients with nasogastric feeding tubes than randomly selected skilled nursing facilities throughout the country.6 Nonetheless, gastroenterologists should look to the literature to understand the outcomes of populations of patients after PEG tube placement and use that data to guide decision-making.
Secondly, the five ethical principles that inform all medical decision making – autonomy, beneficence, nonmaleficence, justice, and futility – should also inform the gastroenterologist’s rationale in offering PEG placement.8
Autonomy implies that the medical team has determined who is able to make the decision regarding PEG tube placement for the patient. Beneficence connects the patient’s medical diagnosis and technical parameters of PEG tube placement with his or her goals of care. Nonmaleficence ensures the decision-making party understands the benefits and risks of the procedure, including anticipatory guidance on possible PEG tube management, complications, risks, and need for replacement. Justice incorporates the context of the patient’s life, including family dynamics, religious, cultural, and financial factors. Futility connects the patient’s prognosis with practical aspects of having a PEG tube.
The complexity of PEG placement lies in the fact that these ethical principles are often at odds with each other. For example, case 2 highlights the conflicting principles of autonomy and futility for elderly dementia patients: While PEG tube placements do not improve comfort or quality of life in advanced dementia (futility), the family representing the patient has stated they want everything done for his care, including PEG tube placement (autonomy). Navigating these ethical principles can be difficult, but having a framework to organize the different factors offers sound guidance for the gastroenterologist.
Finally, the gastroenterologist should recognize the roles of the multidisciplinary team members, including the patient and their representatives, regarding PEG tube placement consults. While gastroenterologists can be viewed as the technicians consulted to simply “place the tube,” they must seek to understand the members of the team representing the patient to be stewards of their skill set. Consulting team physicians carry great responsibility in organizing the medical and psychosocial aspects of each patient’s care, and their proper goals to relieve suffering and prevent death may color their judgment regarding who they believe is a candidate for a PEG tube. Nutritionists, speech therapists, and case managers can help provide objective data on the practicality and feasibility of a PEG tube in their patients. The healthcare system may influence the decision to consult heavily, as seen in the rules of the long-term care facility in case.3 While it is the job of the multidisciplinary medical team to explain the evidence and ethical considerations of PEG tube placement in a patient-centered manner, ultimately the decision belongs to the patient and their family or representatives.
The moral burden of not pursuing PEG placement may supersede the medical advice in many situations. There is an emotionally taxing perception that withholding nutrition via PEG is “starving the patient,” despite literature showing many terminally ill patients do not experience thirst or hunger, and those who do have alleviation of these symptoms with small amounts of food or liquid, not with PEG placement.5 As every patient is unique, PEG tube consultation guidelines created with input from all stakeholders have been utilized to ensure that patients are medically optimized for PEG tube placement and that evidence and ethics-based considerations are evaluated by the multidisciplinary team. An example of such a guideline is shown in Figure 1.
If the gastroenterologist encounters more contentious consultations, there are ways to build consensus to both alleviate patient and family suffering as well as elevate the discussions between teams.
First, identify the type of consult that is repeatedly bringing differing viewpoints and differing ethical principles into play. Second, get representatives from teams together in a neutral environment to understand stakeholders needs. New data suggest, in stroke cases like case 1, there may be dramatic benefit in long-term ability to recover if patients can get early intensive rehabilitation.9 This intense daily rehabilitation is not available within the hospital setting at many locations, and facilitation of discharge may be requested earlier than usually advised tube placement. Third, build a common language for requests and responses between teams. For instance, neurologists can identify and document which patients have less likelihood of early spontaneous recovery, and this can allow gastroenterologists to understand that those patients with little potential for early swallowing recovery can safely be targeted for PEG earlier during the hospital course. Other patients described as having a potential for spontaneous improvement should be given time to recover before an intervention is considered.10 Having a common understanding of goals and a better-informed decision pathway helps each team member feel fulfilled and rewarded, which will ultimately help reduce compassion fatigue and moral burden on providers.
In conclusion, PEG tube placement can be a challenging consultation for gastroenterologists because of the clinical, social, and ethical ramifications at stake for the patient. Even when PEG tube placement is technically feasible, the gastroenterologist should feel empowered to address the evidence-based outcomes of PEG tube placement, discuss the ethical principles of the decision-making process, and communicate with a multidisciplinary team using guidelines as set forth by this paper to best serve the patient.
Dr. Seltzer is based in the Department of Internal Medicine, Mount Sinai Morningside-West, New York City. Dr. Pusateri is based in the Division of Gastroenterology, Hepatology and Nutrition, Ohio State University Wexner Medical Center, Columbus. Dr. Nguyen is based in the Division of Gastroenterology and Center for Esophageal Diseases, Baylor Scott & White Health, Dallas, Texas. Dr. Stein is based in the Division of Gastroenterology, Robert Wood Johnson University Hospital, Rutgers University, New Brunswick, New Jersey. All authors contributed equally to this manuscript, and have no disclosures related to this article.
References
1. Mackie S. Gastroenterol Nurs. 2001 May-Jun;24(3):138-42.
2. Miller RG et al. Neurology. 2009 Oct. doi: 10.1212/WNL.0b013e3181bc0141.
3. Colevas AD et al. J Natl Compr Canc Netw. 2018 May. doi: 10.6004/jnccn.2018.0026.
4. Holloway RG et al. Stroke. 2014 Jun. doi: 10.1161/STR.0000000000000015.
5. Finucane TE et al. JAMA. 1999 Oct. doi: 10.1001/jama.282.14.1365.
6. Burgermaster M et al. Nutr Clin Pract. 2016 Jun. doi: 10.1177/0884533616629636.
7. American Geriatrics Society Ethics C, Clinical P, Models of Care C. J Am Geriatr Soc. 2014 Aug. doi: 10.1111/jgs.12924.
8. Beauchamp TL. Principlism in Bioethics. In: Serna P, eds. Bioethical Decision Making and Argumentation. International Library of Ethics, Law, and the New Medicine, vol 70. Springer; Cham. 2016 Sept:1-16. doi: 10.1007/978-3-319-43419-3_1.
9. Powers WJ et al. Stroke. 2019 Oct. doi: 10.1161/STR.0000000000000211.
10. Galovic M et al. JAMA Neurol. 2019 May. doi: 10.1001/jamaneurol.2018.4858.
ANA Testing: When to Tap the Brakes
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
There are five reasons you do not want to order that notorious antinuclear antibody (ANA) test — when a patient comes into your office and you say, “Let’s just run a wellness check” and you order the ANA test, or the patient comes in and says, “Hey doc, order everything, okay?” — without really thinking these things through.
1. I’m sure you know that the ANA test, if positive, does not exclude other conditions. For instance, older women could have a positive ANA test; it’s very common in this group.
2. There’s a high false-positive rate for an ANA test. For instance, cancers and viral infections can cause an ANA test to be positive, and certain medications can cause a false-positive ANA test.
3. Context matters. If you have a patient that has particular symptoms, joint swelling, a strong family history of autoimmune disease, a luminal rash that you can’t understand, hair loss, those kind of things, then yes, when you order that ANA test, it’s going to be valuable. If the patient does not have those symptoms, you are just running down this rabbit hole that causes worry for you and your patient.
4. The ANA test on its own is not helpful until you order the subtypes. Double-stranded DNA and anti-SSA or anti-SSB antibodies are just a few examples of the subtypes of the ANA test that really help you understand what you ordered.
5. The elephant in the room: What is the pretest probability of your diagnostic test — all the symptoms, the hair loss, the malar rash, the sores in the mouth, the joint swelling, the blood in the urine? Fluid around the heart, pericarditis, pleurisy, those kinds of symptoms, right? When you have those symptoms and you order an ANA test, then you have basically put directions into your GPS. So now you know that if the test is positive, these are the things you’re going to do with the test going forward.
I hope that these five things have told you: Hey, before you order that ANA test, let’s make sure that we’re not causing unnecessary stress for our patients and also minimizing unnecessary testing.
Dr. Dada, CEO, Overlake Arthritis and Osteoporosis Center, Bellevue, Washington, disclosed ties with Horizon Pharmaceuticals.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
There are five reasons you do not want to order that notorious antinuclear antibody (ANA) test — when a patient comes into your office and you say, “Let’s just run a wellness check” and you order the ANA test, or the patient comes in and says, “Hey doc, order everything, okay?” — without really thinking these things through.
1. I’m sure you know that the ANA test, if positive, does not exclude other conditions. For instance, older women could have a positive ANA test; it’s very common in this group.
2. There’s a high false-positive rate for an ANA test. For instance, cancers and viral infections can cause an ANA test to be positive, and certain medications can cause a false-positive ANA test.
3. Context matters. If you have a patient that has particular symptoms, joint swelling, a strong family history of autoimmune disease, a luminal rash that you can’t understand, hair loss, those kind of things, then yes, when you order that ANA test, it’s going to be valuable. If the patient does not have those symptoms, you are just running down this rabbit hole that causes worry for you and your patient.
4. The ANA test on its own is not helpful until you order the subtypes. Double-stranded DNA and anti-SSA or anti-SSB antibodies are just a few examples of the subtypes of the ANA test that really help you understand what you ordered.
5. The elephant in the room: What is the pretest probability of your diagnostic test — all the symptoms, the hair loss, the malar rash, the sores in the mouth, the joint swelling, the blood in the urine? Fluid around the heart, pericarditis, pleurisy, those kinds of symptoms, right? When you have those symptoms and you order an ANA test, then you have basically put directions into your GPS. So now you know that if the test is positive, these are the things you’re going to do with the test going forward.
I hope that these five things have told you: Hey, before you order that ANA test, let’s make sure that we’re not causing unnecessary stress for our patients and also minimizing unnecessary testing.
Dr. Dada, CEO, Overlake Arthritis and Osteoporosis Center, Bellevue, Washington, disclosed ties with Horizon Pharmaceuticals.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
There are five reasons you do not want to order that notorious antinuclear antibody (ANA) test — when a patient comes into your office and you say, “Let’s just run a wellness check” and you order the ANA test, or the patient comes in and says, “Hey doc, order everything, okay?” — without really thinking these things through.
1. I’m sure you know that the ANA test, if positive, does not exclude other conditions. For instance, older women could have a positive ANA test; it’s very common in this group.
2. There’s a high false-positive rate for an ANA test. For instance, cancers and viral infections can cause an ANA test to be positive, and certain medications can cause a false-positive ANA test.
3. Context matters. If you have a patient that has particular symptoms, joint swelling, a strong family history of autoimmune disease, a luminal rash that you can’t understand, hair loss, those kind of things, then yes, when you order that ANA test, it’s going to be valuable. If the patient does not have those symptoms, you are just running down this rabbit hole that causes worry for you and your patient.
4. The ANA test on its own is not helpful until you order the subtypes. Double-stranded DNA and anti-SSA or anti-SSB antibodies are just a few examples of the subtypes of the ANA test that really help you understand what you ordered.
5. The elephant in the room: What is the pretest probability of your diagnostic test — all the symptoms, the hair loss, the malar rash, the sores in the mouth, the joint swelling, the blood in the urine? Fluid around the heart, pericarditis, pleurisy, those kinds of symptoms, right? When you have those symptoms and you order an ANA test, then you have basically put directions into your GPS. So now you know that if the test is positive, these are the things you’re going to do with the test going forward.
I hope that these five things have told you: Hey, before you order that ANA test, let’s make sure that we’re not causing unnecessary stress for our patients and also minimizing unnecessary testing.
Dr. Dada, CEO, Overlake Arthritis and Osteoporosis Center, Bellevue, Washington, disclosed ties with Horizon Pharmaceuticals.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Diabetes Increases Injury Risk: A Troubling Trend
In 2024, a record number of people are celebrating their 65th birthdays. Increasing age is associated with a higher risk for falls, fractures, and other injuries that may require hospitalization.
In older adults with type 1 and type 2 diabetes, the risk for falls is double that seen in older people without these conditions. Increased clinician awareness of the many factors that result in this higher risk in people with diabetes, and timely implementation of strategies to prevent falls, are essential.
The annual incidence of falls in people with diabetes older than 65 years is about 39%, compared with 19% among those without diabetes. People with diabetes on insulin face an even greater increased risk for falls compared with those who are not using insulin (94% vs 27% increased risk).
Many well-known aspects of diabetes contribute to this greater risk. These include decreased sensorimotor function, musculoskeletal and neuromuscular deficits, foot and body pain, poor vision, hypoglycemic episodes, pharmacologic complications, and problems with hearing and balance.
Optimal management of diabetes and its complications is essential, and the American Diabetes Association has developed clear guidelines for clinicians to follow to reduce the risk for diabetes related complications and manage these conditions.
The prevalence of diabetic peripheral neuropathy increases with age and duration of diabetes. People with diabetic peripheral neuropathy and diminished sensation on their feet are at increased risk for loss of postural control. Loss of proprioceptive feedback (the ability to sense movement, action and location) during standing and walking leads increases the risk for falls.
In addition, less physical activity, impaired muscle strength, and suboptimal postural control all influence gait patterns and increase the risk for falling. Adults with diabetes have a two to three times higher risk for sarcopenia (decreased muscle strength and muscle mass). They also have low plantar flexion strength, causing increased displacement of their center of gravity, which in turn reduces their maximum forward stride and may result in falls and injury.
Many people with diabetes experience neuropathic foot and body pain, requiring psychotropic and other medications that may exacerbate the risk, such as amitriptyline and duloxetine. Furthermore, older adults with diabetes are more likely to take more prescription medications and may be more sensitive to effects of multiple medications than are individuals without diabetes.
A hazard of managing diabetes, particularly with insulin, is the increased risk for unexpected low blood glucose levels. These episodes can also occur in patients taking certain kinds of oral diabetes medications, but they are more common in those on insulin. Low blood glucose can cause dizziness, confusion, and postural instability, increasing the risk for falling.
Diabetic eye complications include retinopathy, macular edema, cataracts, and glaucoma. In a study of close to 10,000 middle-aged and older adults with diabetes, those with moderate eye complications had almost double the risk of falls as those without eye complications.
Another concern with diabetes is its effect on nerves and blood vessels in the inner ear, leading to a negative effect on balance and hearing loss, both of which are also associated with a higher risk for falling and injury.
Clinicians can reduce the risk for falls in patients by taking measures to improve diabetes control and reduce the risk for microvascular disease affecting the nerves, eyes, and ears.
In addition, exercises that optimize muscle mass, bone strength, gait, and balance, and use of specialized footwear in people with neuropathy, may reduce fall risk. Chair yoga and tai chi have also been shown to be helpful. Clinicians can also advise patients on commonsense strategies to implement in their homes, such as ensuring proper lighting, reducing, clutter and minimizing the use of floor rugs.
The risk for falls and the associated risk for fracture and possible hospitalization are of significant concern in older adults — particularly those with diabetes, and even more so in those with diabetes who are on insulin. It is our responsibility as clinicians to implement strategies to optimize diabetes control in our patients and monitor them for microvascular and other complications that may increase this risk, and manage them appropriately if and when these complications occur.
Madhusmita Misra, Professor, Chair, Physician-in-Chief, Department of Pediatrics, University of Virginia and UVA Health Children’s, Charlottesville, has disclosed being a key opinion leader for Lumos Pharma. Sidhartha Pani, Assistant Professor, Department of Internal Medicine, UVA School of Medicine; Medical Director, Department of General Medicine, Same Day Care Clinic, Charlottesville, disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
In 2024, a record number of people are celebrating their 65th birthdays. Increasing age is associated with a higher risk for falls, fractures, and other injuries that may require hospitalization.
In older adults with type 1 and type 2 diabetes, the risk for falls is double that seen in older people without these conditions. Increased clinician awareness of the many factors that result in this higher risk in people with diabetes, and timely implementation of strategies to prevent falls, are essential.
The annual incidence of falls in people with diabetes older than 65 years is about 39%, compared with 19% among those without diabetes. People with diabetes on insulin face an even greater increased risk for falls compared with those who are not using insulin (94% vs 27% increased risk).
Many well-known aspects of diabetes contribute to this greater risk. These include decreased sensorimotor function, musculoskeletal and neuromuscular deficits, foot and body pain, poor vision, hypoglycemic episodes, pharmacologic complications, and problems with hearing and balance.
Optimal management of diabetes and its complications is essential, and the American Diabetes Association has developed clear guidelines for clinicians to follow to reduce the risk for diabetes related complications and manage these conditions.
The prevalence of diabetic peripheral neuropathy increases with age and duration of diabetes. People with diabetic peripheral neuropathy and diminished sensation on their feet are at increased risk for loss of postural control. Loss of proprioceptive feedback (the ability to sense movement, action and location) during standing and walking leads increases the risk for falls.
In addition, less physical activity, impaired muscle strength, and suboptimal postural control all influence gait patterns and increase the risk for falling. Adults with diabetes have a two to three times higher risk for sarcopenia (decreased muscle strength and muscle mass). They also have low plantar flexion strength, causing increased displacement of their center of gravity, which in turn reduces their maximum forward stride and may result in falls and injury.
Many people with diabetes experience neuropathic foot and body pain, requiring psychotropic and other medications that may exacerbate the risk, such as amitriptyline and duloxetine. Furthermore, older adults with diabetes are more likely to take more prescription medications and may be more sensitive to effects of multiple medications than are individuals without diabetes.
A hazard of managing diabetes, particularly with insulin, is the increased risk for unexpected low blood glucose levels. These episodes can also occur in patients taking certain kinds of oral diabetes medications, but they are more common in those on insulin. Low blood glucose can cause dizziness, confusion, and postural instability, increasing the risk for falling.
Diabetic eye complications include retinopathy, macular edema, cataracts, and glaucoma. In a study of close to 10,000 middle-aged and older adults with diabetes, those with moderate eye complications had almost double the risk of falls as those without eye complications.
Another concern with diabetes is its effect on nerves and blood vessels in the inner ear, leading to a negative effect on balance and hearing loss, both of which are also associated with a higher risk for falling and injury.
Clinicians can reduce the risk for falls in patients by taking measures to improve diabetes control and reduce the risk for microvascular disease affecting the nerves, eyes, and ears.
In addition, exercises that optimize muscle mass, bone strength, gait, and balance, and use of specialized footwear in people with neuropathy, may reduce fall risk. Chair yoga and tai chi have also been shown to be helpful. Clinicians can also advise patients on commonsense strategies to implement in their homes, such as ensuring proper lighting, reducing, clutter and minimizing the use of floor rugs.
The risk for falls and the associated risk for fracture and possible hospitalization are of significant concern in older adults — particularly those with diabetes, and even more so in those with diabetes who are on insulin. It is our responsibility as clinicians to implement strategies to optimize diabetes control in our patients and monitor them for microvascular and other complications that may increase this risk, and manage them appropriately if and when these complications occur.
Madhusmita Misra, Professor, Chair, Physician-in-Chief, Department of Pediatrics, University of Virginia and UVA Health Children’s, Charlottesville, has disclosed being a key opinion leader for Lumos Pharma. Sidhartha Pani, Assistant Professor, Department of Internal Medicine, UVA School of Medicine; Medical Director, Department of General Medicine, Same Day Care Clinic, Charlottesville, disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
In 2024, a record number of people are celebrating their 65th birthdays. Increasing age is associated with a higher risk for falls, fractures, and other injuries that may require hospitalization.
In older adults with type 1 and type 2 diabetes, the risk for falls is double that seen in older people without these conditions. Increased clinician awareness of the many factors that result in this higher risk in people with diabetes, and timely implementation of strategies to prevent falls, are essential.
The annual incidence of falls in people with diabetes older than 65 years is about 39%, compared with 19% among those without diabetes. People with diabetes on insulin face an even greater increased risk for falls compared with those who are not using insulin (94% vs 27% increased risk).
Many well-known aspects of diabetes contribute to this greater risk. These include decreased sensorimotor function, musculoskeletal and neuromuscular deficits, foot and body pain, poor vision, hypoglycemic episodes, pharmacologic complications, and problems with hearing and balance.
Optimal management of diabetes and its complications is essential, and the American Diabetes Association has developed clear guidelines for clinicians to follow to reduce the risk for diabetes related complications and manage these conditions.
The prevalence of diabetic peripheral neuropathy increases with age and duration of diabetes. People with diabetic peripheral neuropathy and diminished sensation on their feet are at increased risk for loss of postural control. Loss of proprioceptive feedback (the ability to sense movement, action and location) during standing and walking leads increases the risk for falls.
In addition, less physical activity, impaired muscle strength, and suboptimal postural control all influence gait patterns and increase the risk for falling. Adults with diabetes have a two to three times higher risk for sarcopenia (decreased muscle strength and muscle mass). They also have low plantar flexion strength, causing increased displacement of their center of gravity, which in turn reduces their maximum forward stride and may result in falls and injury.
Many people with diabetes experience neuropathic foot and body pain, requiring psychotropic and other medications that may exacerbate the risk, such as amitriptyline and duloxetine. Furthermore, older adults with diabetes are more likely to take more prescription medications and may be more sensitive to effects of multiple medications than are individuals without diabetes.
A hazard of managing diabetes, particularly with insulin, is the increased risk for unexpected low blood glucose levels. These episodes can also occur in patients taking certain kinds of oral diabetes medications, but they are more common in those on insulin. Low blood glucose can cause dizziness, confusion, and postural instability, increasing the risk for falling.
Diabetic eye complications include retinopathy, macular edema, cataracts, and glaucoma. In a study of close to 10,000 middle-aged and older adults with diabetes, those with moderate eye complications had almost double the risk of falls as those without eye complications.
Another concern with diabetes is its effect on nerves and blood vessels in the inner ear, leading to a negative effect on balance and hearing loss, both of which are also associated with a higher risk for falling and injury.
Clinicians can reduce the risk for falls in patients by taking measures to improve diabetes control and reduce the risk for microvascular disease affecting the nerves, eyes, and ears.
In addition, exercises that optimize muscle mass, bone strength, gait, and balance, and use of specialized footwear in people with neuropathy, may reduce fall risk. Chair yoga and tai chi have also been shown to be helpful. Clinicians can also advise patients on commonsense strategies to implement in their homes, such as ensuring proper lighting, reducing, clutter and minimizing the use of floor rugs.
The risk for falls and the associated risk for fracture and possible hospitalization are of significant concern in older adults — particularly those with diabetes, and even more so in those with diabetes who are on insulin. It is our responsibility as clinicians to implement strategies to optimize diabetes control in our patients and monitor them for microvascular and other complications that may increase this risk, and manage them appropriately if and when these complications occur.
Madhusmita Misra, Professor, Chair, Physician-in-Chief, Department of Pediatrics, University of Virginia and UVA Health Children’s, Charlottesville, has disclosed being a key opinion leader for Lumos Pharma. Sidhartha Pani, Assistant Professor, Department of Internal Medicine, UVA School of Medicine; Medical Director, Department of General Medicine, Same Day Care Clinic, Charlottesville, disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
GLP-1 RA Therapy for Alcohol Use Disorder?
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
Akshay B. Jain, MD: Today we are very excited to have Dr. Leggio join us all the way from the National Institutes of Health (NIH). He is an addiction physician scientist in the intramural research program at NIH. Welcome, Dr. Leggio. Thanks for joining us.
Lorenzo Leggio, MD, PhD: Thank you so much.
Dr. Jain: We’ll get right into this. Your session was, in my mind, extremely informative. The session looked at glucagon-like peptide 1 receptor agonist (GLP-1 RA) therapy and its potential effects on mitigating alcohol misuse syndrome, so, reduction of alcohol addiction potentially.
We’ve seen in some previous clinical trials, including many from your group, that alcohol use is known to be reduced — the overall risk of incidence, as well as recurrence of alcohol use — in individuals who are on GLP-1 RA therapy.
Can you share more insights about the data already out there?
Dr. Leggio: At the preclinical level, we have a very robust line of studies, experiments, and publications looking at the effect of GLP-1 RAs, starting from exenatide up to, more recently, semaglutide. They show that these GLP-1 RAs do reduce alcohol drinking. They used different animal models of excessive alcohol drinking, using different species — for example, mice, rats, nonhuman primates — models that reflect the excessive alcohol drinking behavior that we see in patients, like physical alcohol dependence or binge-like alcohol drinking, and other behaviors in animal models that reflect the human condition.
In addition to that, we recently have seen an increase in human evidence that GLP-1 RAs may reduce alcohol drinking. For example, there is some anecdotal evidence and some analyses using social media showing that people on GLP-1 RAs report drinking less alcohol.
There are also some pharmacoepidemiology studies which are very intriguing and quite promising. In this case, people have been looking at electronic medical records; they have used the pharmacoepidemiology approaches to match patients on GLP-1 RAs because of diabetes or obesity, and have compared and matched to patients on different drugs as the controls.
A study was recently published Nature Communications by a group in Cleveland in collaboration with Dr. Nora Volkow from the National Institute on Drug Abuse. This study shows the association between being on a GLP-1 RA and the lower incidence of alcohol use disorder and lower drinking.
There is also some promise from prospective randomized clinical trials. In particular, there was one clinical trial from Denmark, a well-known and -conducted clinical trial where they looked at exenatide, and they didn’t see an effect of exenatide compared with placebo in the main analysis. But in a subanalysis, they did see that exenatide reduced alcohol drinking, but only in patients with alcohol use disorder and obesity.
This suggests that these medications may work for some patients and not for other patients. That’s fine, because just like in any other field in medicine, including diabetes, obesity, hypertension, Parkinson’s, and depression, not all medications work for everybody. If these medications will work for alcohol addiction, we do not expect that they will work for everybody.
One ongoing question in the field is to try to identify the phenotypes or the subgroup of people who may be more responsive to these medications.
Dr. Jain: This is such a fascinating field, and all these studies are coming out. In your review of all the literature so far, do you think this is dose dependent? Also, we see that, for instance, with certain individuals, when they take GLP-1 RA therapy, they might have a lot of gastrointestinal (GI) side effects. Recent studies have shown that the rate of these GI side effects does not necessarily correlate with the amount of weight loss. In the alcohol addiction field, do you think that the GI side effects, things like nausea, could also have a potential role in mitigating the alcohol addiction?
Dr. Leggio: This is a great question. They may play a role; they may contribute, too, but we don’t think that they are the driving mechanism of why people drink less, for at least a couple of reasons.
One is that, similar to the obesity field, the data we have so far don’t necessarily show a relationship between the GI side effects and the reduction in drinking. Plus, the reduction in drinking is likely to happen later when many GI side effects are gone or attenuated.
The second reason is from the neuroscience field. We are starting to better understand the mechanism at the brain level as to how these medications work. We don’t see that the nausea or, more generally, not feeling well — malaise, etc. — are driving mechanisms for how these medications work.
Again, it’s not to discount completely that the GI side effects may play a role, but I would say that, if anything, they may be more contributing to. And if they do, that will not be unique to this class of medication. For example, we have three medications approved by the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) for alcohol use disorder.
One challenge we have in the addiction field is that many people don’t know that these medications exist — many primary care providers don’t know — and they are completely underutilized. Everybody here who is listening to us knows that roughly 85% of people with diabetes receive a medication for diabetes. For alcohol use disorder, the number is 2%. These are medications approved by the FDA.
One of them is naltrexone, which does give GI symptoms — in particular, nausea and vomiting. The other medication is acamprosate, which does give diarrhea.
You have medications approved for alcohol disorder where you do have some GI symptoms, but they are not the mechanism either for how these medications help people to curb craving and reduce alcohol drinking.
Dr. Jain: What about the dose-dependent action? Do you think that GLP-1 RAs, at a lower dose, may not have an effect on alcohol use disorder vs at a higher dose, or is everyone a little different?
Dr. Leggio: That’s a wonderful question. The short answer is, we don’t know, to be honest. Now, in some of the animal studies — my team has been in collaboration with other scientists in the NIH intramural research program, and also with scientists in academia, for example, at Scripps, UCLA — we see a dose response where the higher the dose, the higher the effect of the drug. In this case, semaglutide reduced binge drinking in a rat model of a physical alcohol dependence.
That said, I would be very cautious about claiming, based on the rodent data, that humans will have a dose response. It’s an open question. We really don’t know. Some of the pharmacoepidemiology data suggested that even lower doses — for example, using semaglutide for diabetes without going up to the obesity dose — may be just as effective as a higher dose in reducing the incidence of alcohol use disorder.
It’s important also to keep in mind that the pharmacoepidemiology data are always an association. Reduction in alcohol disorder is associated with the prescription GLP-1 RA, but they don’t really replace the more gold-standard, double-blind, placebo-controlled randomized clinical trial. Nonetheless, with the pharmacoepidemiology data, I think there is an argument to at least hypothesize that people may respond well, even to lower doses.
This also may be important from a safety standpoint.
Basically, we need to wait for results in the next years to come from randomized clinical trials to better unfold the question about doses. For example, just anecdotally, I will tell you that in the clinical trial we are conducting right now at the NIH Intramural Research Program, for which I’m the principal investigator (PI), we are going up to 2.4 mg — the highest dose of semaglutide.
We are collaborating with Kyle Simmons, PhD, from Oklahoma State University. Our two studies are not like a two-site clinical trial, but they are harmonized. In Dr. Simmons’ clinical trial, they’re going up to 1.0 mg. We are excited about this team approach because the trials are slightly different, but they’re harmonized to the point that, once the studies are done, we’ll be able to combine and compare data to better answer the question about dosing, and many other questions.
Dr. Jain: From a clinical perspective, we see that many people who are battling alcohol use disorder may not have obesity. They might actually be on the leaner side, and hence, we may not want to use a high dose of GLP-1 RA therapy. It’ll be very exciting to see when these results come out.
This brings me to the next question. I think everyone would love to know why this happens. Why is GLP-1 RA having this effect on alcohol use disorder? I know that your group has done many animal studies, as you pointed out, and one of the postulated theories was the effect on the GABA neurotransmission pathway.
Can you tell us more about what you feel is the underlying mechanism of action here?
Dr. Leggio: I will start by saying that we don’t fully know. There are many open questions. If I can sidetrack for one second: We come up with the idea that, first of all, alcohol use disorder and substance use disorder are addictive behaviors, addictive disorders. We define addiction as a brain disease.
Granted that addiction is a brain disease, it doesn’t mean that addiction works just in the brain in isolation. As we all know, the brain works in concert with the rest of the body. One specific approach my team has been taking is working on the analogy and the similarities between obesity and addiction to try to understand how the body-brain connection, such as the gut-brain-neuroendocrine pathway, may play a role in patients with addiction.
With that in mind, a large amount of work in my lab in the past 20 years — since I’ve been a PI — has been focused on studying this neuroendocrine pathways related to the gut-brain axis. For example, we have done work on insulin and leptin, primarily; we had done work on ghrelin, and since 2015 on the GLP-1 RAs.
With that in mind, the framework we are working on, which is also substantiated by many studies done by our team and other teams in the neuroscience field, kind of supports the idea that, similar to what we see in obesity, these medications may work by affecting what we call reward processing, or the seeking for addictive drugs, such as alcohol, and also the drugs such as the stimulants, opioids, nicotine, and so on.
The idea is that the mechanism is driven by the ability of the medication — semaglutide and all the GLP-1 RAs — to reduce the rewarding properties of alcohol and drugs. To maybe make the example more pragmatic, what does that mean? It means, for example, that a patient who typically has 10 drinks per day in the afternoon and night, while they are on the medication they may feel the lack of need to drink up to 10 to feel the same reward.
They may be able to stop after two or three drinks, which means a significant harm reduction and a beneficial outcome. This also brings us to another mechanism, which may be related to society. We don’t fully understand how much the society mechanism, including society mechanism related to GI motility, may also play a role.
With that said, we don’t think that the effect of the GLP-1 RAs is merely due to alcohol being a calorie-based nutrient because, in fact, we see alcohol as an addictive drug, not as a nutrient. Also, the GLP-1 RAs, at least in animal models, seem to work on other addictive drugs that don’t have calories, such as nicotine, and possibly with cannabis, opioids, and stimulants.
Then on the molecular level, our team recently showed, in collaboration with Dr. Marisa Roberto from Scripps in La Jolla, California, that semaglutide may in fact change the GABA transmission at the level of some brain regions, such as the amygdala and the prefrontal cortex. These are brain regions that are well-established hubs that play a role in the mechanism underlying addiction.
There are also some very exciting recent data showing how these medications may work not just on GABA or just on dopamine, which is the canonical way we conceive of reward processing, but by working on both by modulating GABA transmission — for example, at the ventral tegmental area and dopamine transmission at the nucleus accumbens.
Bottom line, if I summarize all of this, is that the mechanism is not fully understood, but there is definitely a contribution of this medication to effect and reward processing, possibly by altering the balance between GABA and dopamine. There are still some unknown questions, such as, are these mechanisms all brain driven or are they signaling from the periphery to the brain, or maybe both?
Also, as we all know, there are many differences across all these GLP-1 analogs in brain penetrance. Whether the drug needs to go to the brain to have an effect on alcohol drinking, cocaine seeking, or smoking is really an open question.
Dr. Jain: This is so thought-provoking. I guess the more we uncover, the more mesmerized we get with all the potential crosstalk. There is a large amount of overlap in the brain with each of these different things and how it all interplays with each other.
Speaking of interplay, I’m thinking about how many people prone to having alcohol use disorder can potentially develop complications, one of these being chronic pancreatitis. This is a well-known complication that can occur in people having alcohol addiction. Along that same line, we know that previous history of pancreatitis is considered a use-with-caution, or we don’t want to use GLP-1 RA therapy in people who have had pancreatitis.
Now it becomes this quagmire where people may have chronic pancreatitis, but we may want to consider GLP-1 RA therapy for management of alcohol use disorder. What are your thoughts about this, and the safety, potentially, in using it in these patients?
Dr. Leggio: This is another wonderful question. That’s definitely a top priority in our mind, to address these kinds of questions. For example, our RCT does have, as core primary outcomes, not only the efficacy defined as a reduction in alcohol drinking, but also safety.
The reason is exactly what you just explained. There are many unanswered questions, including whether giving a GLP-1 RA and alcohol together may have synergistic effects and increase the likelihood of having pancreatitis.
The good news is that, so far, based on the published literature, including the RCT done with exenatide in Denmark and published in 2022 and also the ongoing clinical trials — including my own clinical trial, but of course we are blind — pancreatitis has not been coming out as an adverse event.
However, it’s also true that it often happens in clinical medication development. Of course, we screen and select our population well. For example, we do exclude people who have a history of pancreatitis. We exclude people with high lipase or with any of the clinical symptomatology that makes us concerned about these people having pancreatitis.
As often happens when you move a medication from clinical trials to clinical practice, we still need to understand whether this medication works in patients. I’m just speculating, but even if the clinical trials do not raise red flags in terms of increased risk for some side effects such as pancreatitis, I think it will be very important for practitioners to keep a close eye on the death risk regardless.
It’s very interesting that it’s similar to alcohol liver disease. With pancreatitis, not every single patient with alcohol addiction has pancreatitis. We don’t really fully understand why some people develop pancreatitis and some people do not. The point being that there are many patients with alcohol addiction who don’t have pancreatitis and may benefit from these medications if they work. Again, we have to prove that in patients.
On the other side, as we all know, pancreatitis is a potentially life-threatening condition for those people who either have it or are at risk for it. I think we have to be very careful before we consider giving them a GLP-1 RA.
One could argue that alcohol is the leading cause of mortality and morbidity in the world. For example, right now, alcohol is the leading cause of liver disease. It’s the main reason for liver transplantation in our country. Alcohol is affecting thousands of people in terms of death and emergency room visits.
You could argue that the downside is not treating these people and they die because of alcohol addiction. A GLP-1 RA is not going to be for everybody. I will remind everybody that (1) we do have FDA-approved medications for alcohol addiction; and (2) there are also other medications not approved by the FDA, but with a proven efficacy in some clinical trials — for example, topiramate and gabapentin — and they’ve been endorsed by the American Psychiatric Association.
There is also some evidence for another medication, baclofen, which has been endorsed by the American College of Gastroenterology for patients with alcohol addiction and liver disease.
The point I’m making is that it’s not that either we use the GLP-1 RAs or we have no other tools. We have other tools. I think we have to personalize the treatment based on the patient’s profile from a safety standpoint and from a phenotypic standpoint.
Dr. Jain: I love that thought. I think individualization is the key here.
We know that people with diabetes have a higher risk for pancreatitis by virtue of having diabetes. People with obesity also have a higher risk for pancreatitis by virtue of having obesity. These are the two conditions where we are using a large amount of GLP-1 RA therapy. Again, the idea is looking at the person in front of us and then deciding, based on their past medical history and their current risk, whether or not a medication is a right fit for them.
I think more individualization here will come as we start using these medications that might be having potential effects on different organ systems. You mentioned a little bit about the liver, so a thought came in my mind. We know that people with diabetes who have alcohol use disorder are at a higher risk for potential hypoglycemia. If they have events when they have increased consumption of alcohol, there can be more hypoglycemia.
We now could potentially be using semaglutide or other GLP-1 RA therapy for management of alcohol use disorder. In your own experience in the studies that you’ve done or the literature that’s out there, has that been associated with an even higher risk for hypoglycemia?
Dr. Leggio: It’s a wonderful question. I’m not aware of any formal and published report of that association. That said, your thinking from a physiopathologist standpoint makes total sense. I could not agree more. The fact that nothing has been published, at least to my knowledge, doesn’t mean that the death risk doesn’t exist. In fact, I agree with you that it does exist.
Alcohol use disorder is interesting and tricky clinically because chronically, alcohol addiction or alcohol use disorder is associated with an increased risk for diabetes. Acutely, as you point out; and this could be with or without alcohol use disorder. An episode of a high volume of binge drinking may lead to hypoglycemia.
This is one of the reasons why people may show up to the emergency room with intoxication, and one of the symptoms detected at the emergency room is that they also have hypoglycemia in addition to vomiting, nausea, and everything else that we see in patients with acute intoxication.
Similar to the discussion about pancreatitis, as we work on understanding the possible role of GLP-1 RA in patients with alcohol use disorder, we do have to keep a close eye on the risk for hypoglycemia. The short answer is that this is not well established, but based on the simple concept of “first, do no harm,” I think we need to track that very carefully.
In the ongoing clinical trial we’re doing in Maryland in my program at the NIH, we do just that. We are tracking glucose levels. Of course, patients come to clinic weekly, so unless they have symptoms, typically we don’t see anything at the time.
More important, we educate our patients when they go through the consent process. We tell them that this medication per se does not give hypoglycemia. In fact, we’re including people with diabetes, so for people on other medications like metformin, we explain to them that technically such a risk should not exist, but because you’re drinking alcohol in excessive amounts, you do have a potential higher risk. We just don’t know how significant that risk could be.
We do a large amount of education at baseline when they enroll in our study. We also educate our patients on how to recognize early on the potential risk for hypoglycemia, exactly for the reasons you said. We explain to them the unknown potential that the GLP-1 RAs and alcohol together may synergize and give hypoglycemia.
Dr. Jain: I don’t know if you got this feeling at the ADA conference, but I felt, when attending all these sessions, that it seems like GLP-1 RA is the gift that keeps giving. We see the effect on diabetes, obesity, metabolic-associated steatotic liver disease, possibly with Alzheimer’s, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, and so many things.
Now, of course, there’s potential use in alcohol use disorder. Do you think that using GLP-1 RA therapy is ready for prime time? Do you think we are now ready to prescribe this in people with alcohol use disorder?
Dr. Leggio: I would say we’re not there yet. As I mentioned at the beginning, the evidence keeps on growing. It’s getting stronger and stronger because the positive data keep on coming up. We have data from animal models, including the different species, ranging from rodents to nonhuman primates. We have anecdotal evidence and machine-learning approaches using, for example, big data and social media data. Now we have pharmacoepidemiology data and some small, initial, but still good randomized clinical trials.
What we are missing is the final step of having a substantial number of prospective, double-blind, placebo-controlled clinical trials to really prove or disprove whether these medications work, and to also better understand which patients may respond to these medications.
The good news is that there are many ongoing clinical trials. We are conducting a clinical trial in Maryland at the NIH. Dr. Simmons is doing a clinical trial at Oklahoma State University. Dr. Christian Hendershot at UNC is conducting a study at Chapel Hill. Dr. Josh Gowin is doing a study in Colorado. Dr. Anders Fink-Jensen is doing a study in Denmark. The momentum is very high.
I’m only mentioning those people who are doing alcohol-semaglutide clinical trials. There are also people doing clinical trials on smoking, stimulants, and opioids. There are actually some very fresh, still unpublished data from Penn State that were presented publicly at conferences, showing how these drugs may reduce opioid craving, which is, of course, critically important, given that we’re in the middle of a fentanyl pandemic that is killing one person every 7 minutes, for example, in Baltimore. It’s very alarming and we need more treatments.
The bottom line is that it’s very promising, but we need to wait for these clinical trials to have a definitive answer. I would say that if you have a patient with diabetes, obesity, and also alcohol addiction, and they are on semaglutide or any other GLP-1 RA, and in addition to using the medication for diabetes and obesity, they also have a beneficial effect on their alcohol drinking, then that’s fantastic. At the end of the day, that’s the mission we all share: helping people.
If it’s someone without obesity and diabetes, personally, at this stage, I will go with other medications that either have FDA approval or at least very solid evidence of efficacy from RCTs rather than going with the GLP-1 RA, at least until I see more definitive data from randomized clinical trials.
There is a large amount of hope. We are hoping that these clinical trials will be positive. We are very enthusiastic and we’re also very thrilled to see that Novo Nordisk recently launched a gigantic multisite clinical trial with — I forgot how many sites, but it’s very large across Europe, America, and maybe other continents as well.
Their primary outcome is improvement in alcohol-related liver disease, but they’re also looking at alcohol drinking as a secondary outcome. That’s very important because, unlike in the diabetes field, in the addiction field, we do struggle to build partnership with the private sector because sometimes the addiction field is not seen as an appetitive field from pharma.
We all know that the best success in any medication development story is when you put academia, the government, and pharma together. Think about the COVID-19 vaccine development. That’s unfortunately the exception rather than rule in the addiction field.
With the company doing a large clinical trial in the alcohol field, although they focus more on the liver but they also looked at drinking, I really hope we’ll see more and more companies in the private sector take more and more interest in addiction. Also, I hope to see more and more partnership between the private sector, the government, and academia.
Dr. Jain: Such exciting times, indeed. We can’t wait enough for the results of these and many other trials to come out. Dr. Leggio, it was an absolute delight chatting with you today. Thank you so much for joining us from ADA 2024.
Akshay B. Jain, MD, Clinical Instructor, Department of Endocrinology, University of British Columbia; Endocrinologist, TLC Diabetes and Endocrinology, Vancouver, British Columbia, Canada, has disclosed the following relevant financial relationships: Serve(d) as a speaker or a member of a speakers bureau for: Abbott; Acerus; AstraZeneca; Amgen; Bausch Healthcare; Bayer; Boehringer Ingelheim; Care to Know; CCRN; Connected in Motion; CPD Network; Dexcom; Diabetes Canada; Eli Lilly; GSK; HLS Therapeutics; Janssen; Master Clinician Alliance; MDBriefcase; Merck; Medtronic; Moderna; Novartis; Novo Nordisk; Partners in Progressive Medical Education; Pfizer; Sanofi Aventis; Timed Right; WebMD. Received research grants/research support from: Abbott; Amgen; Novo Nordisk. Received consulting fees from: Abbott; Acerus; AstraZeneca; Amgen; Bausch Healthcare; Bayer; Boehringer Ingelheim; Dexcom; Eli Lilly; Gilead Sciences; GSK; HLS Therapeutics; Insulet; Janssen; Medtronic; Novo Nordisk; Partners in Progressive Medical Education; PocketPills; Roche; Sanofi Aventis; Takeda. Lorenzo Leggio, MD, PhD, Clinical Director, Deputy Scientific Director, National Institute on Drug Abuse Intramural Research Program, National Institutes of Health, Baltimore, Maryland, has disclosed the following relevant financial relationships: Serve(d) as a US federal employee for: National Institutes of Health. He had received income in an amount equal to or greater than $250 from: UK Medical Council on Alcohol for his service as editor-in-chief for Alcohol and Alcoholism and received royalties from Rutledge as an editor for a textbook.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
Akshay B. Jain, MD: Today we are very excited to have Dr. Leggio join us all the way from the National Institutes of Health (NIH). He is an addiction physician scientist in the intramural research program at NIH. Welcome, Dr. Leggio. Thanks for joining us.
Lorenzo Leggio, MD, PhD: Thank you so much.
Dr. Jain: We’ll get right into this. Your session was, in my mind, extremely informative. The session looked at glucagon-like peptide 1 receptor agonist (GLP-1 RA) therapy and its potential effects on mitigating alcohol misuse syndrome, so, reduction of alcohol addiction potentially.
We’ve seen in some previous clinical trials, including many from your group, that alcohol use is known to be reduced — the overall risk of incidence, as well as recurrence of alcohol use — in individuals who are on GLP-1 RA therapy.
Can you share more insights about the data already out there?
Dr. Leggio: At the preclinical level, we have a very robust line of studies, experiments, and publications looking at the effect of GLP-1 RAs, starting from exenatide up to, more recently, semaglutide. They show that these GLP-1 RAs do reduce alcohol drinking. They used different animal models of excessive alcohol drinking, using different species — for example, mice, rats, nonhuman primates — models that reflect the excessive alcohol drinking behavior that we see in patients, like physical alcohol dependence or binge-like alcohol drinking, and other behaviors in animal models that reflect the human condition.
In addition to that, we recently have seen an increase in human evidence that GLP-1 RAs may reduce alcohol drinking. For example, there is some anecdotal evidence and some analyses using social media showing that people on GLP-1 RAs report drinking less alcohol.
There are also some pharmacoepidemiology studies which are very intriguing and quite promising. In this case, people have been looking at electronic medical records; they have used the pharmacoepidemiology approaches to match patients on GLP-1 RAs because of diabetes or obesity, and have compared and matched to patients on different drugs as the controls.
A study was recently published Nature Communications by a group in Cleveland in collaboration with Dr. Nora Volkow from the National Institute on Drug Abuse. This study shows the association between being on a GLP-1 RA and the lower incidence of alcohol use disorder and lower drinking.
There is also some promise from prospective randomized clinical trials. In particular, there was one clinical trial from Denmark, a well-known and -conducted clinical trial where they looked at exenatide, and they didn’t see an effect of exenatide compared with placebo in the main analysis. But in a subanalysis, they did see that exenatide reduced alcohol drinking, but only in patients with alcohol use disorder and obesity.
This suggests that these medications may work for some patients and not for other patients. That’s fine, because just like in any other field in medicine, including diabetes, obesity, hypertension, Parkinson’s, and depression, not all medications work for everybody. If these medications will work for alcohol addiction, we do not expect that they will work for everybody.
One ongoing question in the field is to try to identify the phenotypes or the subgroup of people who may be more responsive to these medications.
Dr. Jain: This is such a fascinating field, and all these studies are coming out. In your review of all the literature so far, do you think this is dose dependent? Also, we see that, for instance, with certain individuals, when they take GLP-1 RA therapy, they might have a lot of gastrointestinal (GI) side effects. Recent studies have shown that the rate of these GI side effects does not necessarily correlate with the amount of weight loss. In the alcohol addiction field, do you think that the GI side effects, things like nausea, could also have a potential role in mitigating the alcohol addiction?
Dr. Leggio: This is a great question. They may play a role; they may contribute, too, but we don’t think that they are the driving mechanism of why people drink less, for at least a couple of reasons.
One is that, similar to the obesity field, the data we have so far don’t necessarily show a relationship between the GI side effects and the reduction in drinking. Plus, the reduction in drinking is likely to happen later when many GI side effects are gone or attenuated.
The second reason is from the neuroscience field. We are starting to better understand the mechanism at the brain level as to how these medications work. We don’t see that the nausea or, more generally, not feeling well — malaise, etc. — are driving mechanisms for how these medications work.
Again, it’s not to discount completely that the GI side effects may play a role, but I would say that, if anything, they may be more contributing to. And if they do, that will not be unique to this class of medication. For example, we have three medications approved by the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) for alcohol use disorder.
One challenge we have in the addiction field is that many people don’t know that these medications exist — many primary care providers don’t know — and they are completely underutilized. Everybody here who is listening to us knows that roughly 85% of people with diabetes receive a medication for diabetes. For alcohol use disorder, the number is 2%. These are medications approved by the FDA.
One of them is naltrexone, which does give GI symptoms — in particular, nausea and vomiting. The other medication is acamprosate, which does give diarrhea.
You have medications approved for alcohol disorder where you do have some GI symptoms, but they are not the mechanism either for how these medications help people to curb craving and reduce alcohol drinking.
Dr. Jain: What about the dose-dependent action? Do you think that GLP-1 RAs, at a lower dose, may not have an effect on alcohol use disorder vs at a higher dose, or is everyone a little different?
Dr. Leggio: That’s a wonderful question. The short answer is, we don’t know, to be honest. Now, in some of the animal studies — my team has been in collaboration with other scientists in the NIH intramural research program, and also with scientists in academia, for example, at Scripps, UCLA — we see a dose response where the higher the dose, the higher the effect of the drug. In this case, semaglutide reduced binge drinking in a rat model of a physical alcohol dependence.
That said, I would be very cautious about claiming, based on the rodent data, that humans will have a dose response. It’s an open question. We really don’t know. Some of the pharmacoepidemiology data suggested that even lower doses — for example, using semaglutide for diabetes without going up to the obesity dose — may be just as effective as a higher dose in reducing the incidence of alcohol use disorder.
It’s important also to keep in mind that the pharmacoepidemiology data are always an association. Reduction in alcohol disorder is associated with the prescription GLP-1 RA, but they don’t really replace the more gold-standard, double-blind, placebo-controlled randomized clinical trial. Nonetheless, with the pharmacoepidemiology data, I think there is an argument to at least hypothesize that people may respond well, even to lower doses.
This also may be important from a safety standpoint.
Basically, we need to wait for results in the next years to come from randomized clinical trials to better unfold the question about doses. For example, just anecdotally, I will tell you that in the clinical trial we are conducting right now at the NIH Intramural Research Program, for which I’m the principal investigator (PI), we are going up to 2.4 mg — the highest dose of semaglutide.
We are collaborating with Kyle Simmons, PhD, from Oklahoma State University. Our two studies are not like a two-site clinical trial, but they are harmonized. In Dr. Simmons’ clinical trial, they’re going up to 1.0 mg. We are excited about this team approach because the trials are slightly different, but they’re harmonized to the point that, once the studies are done, we’ll be able to combine and compare data to better answer the question about dosing, and many other questions.
Dr. Jain: From a clinical perspective, we see that many people who are battling alcohol use disorder may not have obesity. They might actually be on the leaner side, and hence, we may not want to use a high dose of GLP-1 RA therapy. It’ll be very exciting to see when these results come out.
This brings me to the next question. I think everyone would love to know why this happens. Why is GLP-1 RA having this effect on alcohol use disorder? I know that your group has done many animal studies, as you pointed out, and one of the postulated theories was the effect on the GABA neurotransmission pathway.
Can you tell us more about what you feel is the underlying mechanism of action here?
Dr. Leggio: I will start by saying that we don’t fully know. There are many open questions. If I can sidetrack for one second: We come up with the idea that, first of all, alcohol use disorder and substance use disorder are addictive behaviors, addictive disorders. We define addiction as a brain disease.
Granted that addiction is a brain disease, it doesn’t mean that addiction works just in the brain in isolation. As we all know, the brain works in concert with the rest of the body. One specific approach my team has been taking is working on the analogy and the similarities between obesity and addiction to try to understand how the body-brain connection, such as the gut-brain-neuroendocrine pathway, may play a role in patients with addiction.
With that in mind, a large amount of work in my lab in the past 20 years — since I’ve been a PI — has been focused on studying this neuroendocrine pathways related to the gut-brain axis. For example, we have done work on insulin and leptin, primarily; we had done work on ghrelin, and since 2015 on the GLP-1 RAs.
With that in mind, the framework we are working on, which is also substantiated by many studies done by our team and other teams in the neuroscience field, kind of supports the idea that, similar to what we see in obesity, these medications may work by affecting what we call reward processing, or the seeking for addictive drugs, such as alcohol, and also the drugs such as the stimulants, opioids, nicotine, and so on.
The idea is that the mechanism is driven by the ability of the medication — semaglutide and all the GLP-1 RAs — to reduce the rewarding properties of alcohol and drugs. To maybe make the example more pragmatic, what does that mean? It means, for example, that a patient who typically has 10 drinks per day in the afternoon and night, while they are on the medication they may feel the lack of need to drink up to 10 to feel the same reward.
They may be able to stop after two or three drinks, which means a significant harm reduction and a beneficial outcome. This also brings us to another mechanism, which may be related to society. We don’t fully understand how much the society mechanism, including society mechanism related to GI motility, may also play a role.
With that said, we don’t think that the effect of the GLP-1 RAs is merely due to alcohol being a calorie-based nutrient because, in fact, we see alcohol as an addictive drug, not as a nutrient. Also, the GLP-1 RAs, at least in animal models, seem to work on other addictive drugs that don’t have calories, such as nicotine, and possibly with cannabis, opioids, and stimulants.
Then on the molecular level, our team recently showed, in collaboration with Dr. Marisa Roberto from Scripps in La Jolla, California, that semaglutide may in fact change the GABA transmission at the level of some brain regions, such as the amygdala and the prefrontal cortex. These are brain regions that are well-established hubs that play a role in the mechanism underlying addiction.
There are also some very exciting recent data showing how these medications may work not just on GABA or just on dopamine, which is the canonical way we conceive of reward processing, but by working on both by modulating GABA transmission — for example, at the ventral tegmental area and dopamine transmission at the nucleus accumbens.
Bottom line, if I summarize all of this, is that the mechanism is not fully understood, but there is definitely a contribution of this medication to effect and reward processing, possibly by altering the balance between GABA and dopamine. There are still some unknown questions, such as, are these mechanisms all brain driven or are they signaling from the periphery to the brain, or maybe both?
Also, as we all know, there are many differences across all these GLP-1 analogs in brain penetrance. Whether the drug needs to go to the brain to have an effect on alcohol drinking, cocaine seeking, or smoking is really an open question.
Dr. Jain: This is so thought-provoking. I guess the more we uncover, the more mesmerized we get with all the potential crosstalk. There is a large amount of overlap in the brain with each of these different things and how it all interplays with each other.
Speaking of interplay, I’m thinking about how many people prone to having alcohol use disorder can potentially develop complications, one of these being chronic pancreatitis. This is a well-known complication that can occur in people having alcohol addiction. Along that same line, we know that previous history of pancreatitis is considered a use-with-caution, or we don’t want to use GLP-1 RA therapy in people who have had pancreatitis.
Now it becomes this quagmire where people may have chronic pancreatitis, but we may want to consider GLP-1 RA therapy for management of alcohol use disorder. What are your thoughts about this, and the safety, potentially, in using it in these patients?
Dr. Leggio: This is another wonderful question. That’s definitely a top priority in our mind, to address these kinds of questions. For example, our RCT does have, as core primary outcomes, not only the efficacy defined as a reduction in alcohol drinking, but also safety.
The reason is exactly what you just explained. There are many unanswered questions, including whether giving a GLP-1 RA and alcohol together may have synergistic effects and increase the likelihood of having pancreatitis.
The good news is that, so far, based on the published literature, including the RCT done with exenatide in Denmark and published in 2022 and also the ongoing clinical trials — including my own clinical trial, but of course we are blind — pancreatitis has not been coming out as an adverse event.
However, it’s also true that it often happens in clinical medication development. Of course, we screen and select our population well. For example, we do exclude people who have a history of pancreatitis. We exclude people with high lipase or with any of the clinical symptomatology that makes us concerned about these people having pancreatitis.
As often happens when you move a medication from clinical trials to clinical practice, we still need to understand whether this medication works in patients. I’m just speculating, but even if the clinical trials do not raise red flags in terms of increased risk for some side effects such as pancreatitis, I think it will be very important for practitioners to keep a close eye on the death risk regardless.
It’s very interesting that it’s similar to alcohol liver disease. With pancreatitis, not every single patient with alcohol addiction has pancreatitis. We don’t really fully understand why some people develop pancreatitis and some people do not. The point being that there are many patients with alcohol addiction who don’t have pancreatitis and may benefit from these medications if they work. Again, we have to prove that in patients.
On the other side, as we all know, pancreatitis is a potentially life-threatening condition for those people who either have it or are at risk for it. I think we have to be very careful before we consider giving them a GLP-1 RA.
One could argue that alcohol is the leading cause of mortality and morbidity in the world. For example, right now, alcohol is the leading cause of liver disease. It’s the main reason for liver transplantation in our country. Alcohol is affecting thousands of people in terms of death and emergency room visits.
You could argue that the downside is not treating these people and they die because of alcohol addiction. A GLP-1 RA is not going to be for everybody. I will remind everybody that (1) we do have FDA-approved medications for alcohol addiction; and (2) there are also other medications not approved by the FDA, but with a proven efficacy in some clinical trials — for example, topiramate and gabapentin — and they’ve been endorsed by the American Psychiatric Association.
There is also some evidence for another medication, baclofen, which has been endorsed by the American College of Gastroenterology for patients with alcohol addiction and liver disease.
The point I’m making is that it’s not that either we use the GLP-1 RAs or we have no other tools. We have other tools. I think we have to personalize the treatment based on the patient’s profile from a safety standpoint and from a phenotypic standpoint.
Dr. Jain: I love that thought. I think individualization is the key here.
We know that people with diabetes have a higher risk for pancreatitis by virtue of having diabetes. People with obesity also have a higher risk for pancreatitis by virtue of having obesity. These are the two conditions where we are using a large amount of GLP-1 RA therapy. Again, the idea is looking at the person in front of us and then deciding, based on their past medical history and their current risk, whether or not a medication is a right fit for them.
I think more individualization here will come as we start using these medications that might be having potential effects on different organ systems. You mentioned a little bit about the liver, so a thought came in my mind. We know that people with diabetes who have alcohol use disorder are at a higher risk for potential hypoglycemia. If they have events when they have increased consumption of alcohol, there can be more hypoglycemia.
We now could potentially be using semaglutide or other GLP-1 RA therapy for management of alcohol use disorder. In your own experience in the studies that you’ve done or the literature that’s out there, has that been associated with an even higher risk for hypoglycemia?
Dr. Leggio: It’s a wonderful question. I’m not aware of any formal and published report of that association. That said, your thinking from a physiopathologist standpoint makes total sense. I could not agree more. The fact that nothing has been published, at least to my knowledge, doesn’t mean that the death risk doesn’t exist. In fact, I agree with you that it does exist.
Alcohol use disorder is interesting and tricky clinically because chronically, alcohol addiction or alcohol use disorder is associated with an increased risk for diabetes. Acutely, as you point out; and this could be with or without alcohol use disorder. An episode of a high volume of binge drinking may lead to hypoglycemia.
This is one of the reasons why people may show up to the emergency room with intoxication, and one of the symptoms detected at the emergency room is that they also have hypoglycemia in addition to vomiting, nausea, and everything else that we see in patients with acute intoxication.
Similar to the discussion about pancreatitis, as we work on understanding the possible role of GLP-1 RA in patients with alcohol use disorder, we do have to keep a close eye on the risk for hypoglycemia. The short answer is that this is not well established, but based on the simple concept of “first, do no harm,” I think we need to track that very carefully.
In the ongoing clinical trial we’re doing in Maryland in my program at the NIH, we do just that. We are tracking glucose levels. Of course, patients come to clinic weekly, so unless they have symptoms, typically we don’t see anything at the time.
More important, we educate our patients when they go through the consent process. We tell them that this medication per se does not give hypoglycemia. In fact, we’re including people with diabetes, so for people on other medications like metformin, we explain to them that technically such a risk should not exist, but because you’re drinking alcohol in excessive amounts, you do have a potential higher risk. We just don’t know how significant that risk could be.
We do a large amount of education at baseline when they enroll in our study. We also educate our patients on how to recognize early on the potential risk for hypoglycemia, exactly for the reasons you said. We explain to them the unknown potential that the GLP-1 RAs and alcohol together may synergize and give hypoglycemia.
Dr. Jain: I don’t know if you got this feeling at the ADA conference, but I felt, when attending all these sessions, that it seems like GLP-1 RA is the gift that keeps giving. We see the effect on diabetes, obesity, metabolic-associated steatotic liver disease, possibly with Alzheimer’s, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, and so many things.
Now, of course, there’s potential use in alcohol use disorder. Do you think that using GLP-1 RA therapy is ready for prime time? Do you think we are now ready to prescribe this in people with alcohol use disorder?
Dr. Leggio: I would say we’re not there yet. As I mentioned at the beginning, the evidence keeps on growing. It’s getting stronger and stronger because the positive data keep on coming up. We have data from animal models, including the different species, ranging from rodents to nonhuman primates. We have anecdotal evidence and machine-learning approaches using, for example, big data and social media data. Now we have pharmacoepidemiology data and some small, initial, but still good randomized clinical trials.
What we are missing is the final step of having a substantial number of prospective, double-blind, placebo-controlled clinical trials to really prove or disprove whether these medications work, and to also better understand which patients may respond to these medications.
The good news is that there are many ongoing clinical trials. We are conducting a clinical trial in Maryland at the NIH. Dr. Simmons is doing a clinical trial at Oklahoma State University. Dr. Christian Hendershot at UNC is conducting a study at Chapel Hill. Dr. Josh Gowin is doing a study in Colorado. Dr. Anders Fink-Jensen is doing a study in Denmark. The momentum is very high.
I’m only mentioning those people who are doing alcohol-semaglutide clinical trials. There are also people doing clinical trials on smoking, stimulants, and opioids. There are actually some very fresh, still unpublished data from Penn State that were presented publicly at conferences, showing how these drugs may reduce opioid craving, which is, of course, critically important, given that we’re in the middle of a fentanyl pandemic that is killing one person every 7 minutes, for example, in Baltimore. It’s very alarming and we need more treatments.
The bottom line is that it’s very promising, but we need to wait for these clinical trials to have a definitive answer. I would say that if you have a patient with diabetes, obesity, and also alcohol addiction, and they are on semaglutide or any other GLP-1 RA, and in addition to using the medication for diabetes and obesity, they also have a beneficial effect on their alcohol drinking, then that’s fantastic. At the end of the day, that’s the mission we all share: helping people.
If it’s someone without obesity and diabetes, personally, at this stage, I will go with other medications that either have FDA approval or at least very solid evidence of efficacy from RCTs rather than going with the GLP-1 RA, at least until I see more definitive data from randomized clinical trials.
There is a large amount of hope. We are hoping that these clinical trials will be positive. We are very enthusiastic and we’re also very thrilled to see that Novo Nordisk recently launched a gigantic multisite clinical trial with — I forgot how many sites, but it’s very large across Europe, America, and maybe other continents as well.
Their primary outcome is improvement in alcohol-related liver disease, but they’re also looking at alcohol drinking as a secondary outcome. That’s very important because, unlike in the diabetes field, in the addiction field, we do struggle to build partnership with the private sector because sometimes the addiction field is not seen as an appetitive field from pharma.
We all know that the best success in any medication development story is when you put academia, the government, and pharma together. Think about the COVID-19 vaccine development. That’s unfortunately the exception rather than rule in the addiction field.
With the company doing a large clinical trial in the alcohol field, although they focus more on the liver but they also looked at drinking, I really hope we’ll see more and more companies in the private sector take more and more interest in addiction. Also, I hope to see more and more partnership between the private sector, the government, and academia.
Dr. Jain: Such exciting times, indeed. We can’t wait enough for the results of these and many other trials to come out. Dr. Leggio, it was an absolute delight chatting with you today. Thank you so much for joining us from ADA 2024.
Akshay B. Jain, MD, Clinical Instructor, Department of Endocrinology, University of British Columbia; Endocrinologist, TLC Diabetes and Endocrinology, Vancouver, British Columbia, Canada, has disclosed the following relevant financial relationships: Serve(d) as a speaker or a member of a speakers bureau for: Abbott; Acerus; AstraZeneca; Amgen; Bausch Healthcare; Bayer; Boehringer Ingelheim; Care to Know; CCRN; Connected in Motion; CPD Network; Dexcom; Diabetes Canada; Eli Lilly; GSK; HLS Therapeutics; Janssen; Master Clinician Alliance; MDBriefcase; Merck; Medtronic; Moderna; Novartis; Novo Nordisk; Partners in Progressive Medical Education; Pfizer; Sanofi Aventis; Timed Right; WebMD. Received research grants/research support from: Abbott; Amgen; Novo Nordisk. Received consulting fees from: Abbott; Acerus; AstraZeneca; Amgen; Bausch Healthcare; Bayer; Boehringer Ingelheim; Dexcom; Eli Lilly; Gilead Sciences; GSK; HLS Therapeutics; Insulet; Janssen; Medtronic; Novo Nordisk; Partners in Progressive Medical Education; PocketPills; Roche; Sanofi Aventis; Takeda. Lorenzo Leggio, MD, PhD, Clinical Director, Deputy Scientific Director, National Institute on Drug Abuse Intramural Research Program, National Institutes of Health, Baltimore, Maryland, has disclosed the following relevant financial relationships: Serve(d) as a US federal employee for: National Institutes of Health. He had received income in an amount equal to or greater than $250 from: UK Medical Council on Alcohol for his service as editor-in-chief for Alcohol and Alcoholism and received royalties from Rutledge as an editor for a textbook.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
Akshay B. Jain, MD: Today we are very excited to have Dr. Leggio join us all the way from the National Institutes of Health (NIH). He is an addiction physician scientist in the intramural research program at NIH. Welcome, Dr. Leggio. Thanks for joining us.
Lorenzo Leggio, MD, PhD: Thank you so much.
Dr. Jain: We’ll get right into this. Your session was, in my mind, extremely informative. The session looked at glucagon-like peptide 1 receptor agonist (GLP-1 RA) therapy and its potential effects on mitigating alcohol misuse syndrome, so, reduction of alcohol addiction potentially.
We’ve seen in some previous clinical trials, including many from your group, that alcohol use is known to be reduced — the overall risk of incidence, as well as recurrence of alcohol use — in individuals who are on GLP-1 RA therapy.
Can you share more insights about the data already out there?
Dr. Leggio: At the preclinical level, we have a very robust line of studies, experiments, and publications looking at the effect of GLP-1 RAs, starting from exenatide up to, more recently, semaglutide. They show that these GLP-1 RAs do reduce alcohol drinking. They used different animal models of excessive alcohol drinking, using different species — for example, mice, rats, nonhuman primates — models that reflect the excessive alcohol drinking behavior that we see in patients, like physical alcohol dependence or binge-like alcohol drinking, and other behaviors in animal models that reflect the human condition.
In addition to that, we recently have seen an increase in human evidence that GLP-1 RAs may reduce alcohol drinking. For example, there is some anecdotal evidence and some analyses using social media showing that people on GLP-1 RAs report drinking less alcohol.
There are also some pharmacoepidemiology studies which are very intriguing and quite promising. In this case, people have been looking at electronic medical records; they have used the pharmacoepidemiology approaches to match patients on GLP-1 RAs because of diabetes or obesity, and have compared and matched to patients on different drugs as the controls.
A study was recently published Nature Communications by a group in Cleveland in collaboration with Dr. Nora Volkow from the National Institute on Drug Abuse. This study shows the association between being on a GLP-1 RA and the lower incidence of alcohol use disorder and lower drinking.
There is also some promise from prospective randomized clinical trials. In particular, there was one clinical trial from Denmark, a well-known and -conducted clinical trial where they looked at exenatide, and they didn’t see an effect of exenatide compared with placebo in the main analysis. But in a subanalysis, they did see that exenatide reduced alcohol drinking, but only in patients with alcohol use disorder and obesity.
This suggests that these medications may work for some patients and not for other patients. That’s fine, because just like in any other field in medicine, including diabetes, obesity, hypertension, Parkinson’s, and depression, not all medications work for everybody. If these medications will work for alcohol addiction, we do not expect that they will work for everybody.
One ongoing question in the field is to try to identify the phenotypes or the subgroup of people who may be more responsive to these medications.
Dr. Jain: This is such a fascinating field, and all these studies are coming out. In your review of all the literature so far, do you think this is dose dependent? Also, we see that, for instance, with certain individuals, when they take GLP-1 RA therapy, they might have a lot of gastrointestinal (GI) side effects. Recent studies have shown that the rate of these GI side effects does not necessarily correlate with the amount of weight loss. In the alcohol addiction field, do you think that the GI side effects, things like nausea, could also have a potential role in mitigating the alcohol addiction?
Dr. Leggio: This is a great question. They may play a role; they may contribute, too, but we don’t think that they are the driving mechanism of why people drink less, for at least a couple of reasons.
One is that, similar to the obesity field, the data we have so far don’t necessarily show a relationship between the GI side effects and the reduction in drinking. Plus, the reduction in drinking is likely to happen later when many GI side effects are gone or attenuated.
The second reason is from the neuroscience field. We are starting to better understand the mechanism at the brain level as to how these medications work. We don’t see that the nausea or, more generally, not feeling well — malaise, etc. — are driving mechanisms for how these medications work.
Again, it’s not to discount completely that the GI side effects may play a role, but I would say that, if anything, they may be more contributing to. And if they do, that will not be unique to this class of medication. For example, we have three medications approved by the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) for alcohol use disorder.
One challenge we have in the addiction field is that many people don’t know that these medications exist — many primary care providers don’t know — and they are completely underutilized. Everybody here who is listening to us knows that roughly 85% of people with diabetes receive a medication for diabetes. For alcohol use disorder, the number is 2%. These are medications approved by the FDA.
One of them is naltrexone, which does give GI symptoms — in particular, nausea and vomiting. The other medication is acamprosate, which does give diarrhea.
You have medications approved for alcohol disorder where you do have some GI symptoms, but they are not the mechanism either for how these medications help people to curb craving and reduce alcohol drinking.
Dr. Jain: What about the dose-dependent action? Do you think that GLP-1 RAs, at a lower dose, may not have an effect on alcohol use disorder vs at a higher dose, or is everyone a little different?
Dr. Leggio: That’s a wonderful question. The short answer is, we don’t know, to be honest. Now, in some of the animal studies — my team has been in collaboration with other scientists in the NIH intramural research program, and also with scientists in academia, for example, at Scripps, UCLA — we see a dose response where the higher the dose, the higher the effect of the drug. In this case, semaglutide reduced binge drinking in a rat model of a physical alcohol dependence.
That said, I would be very cautious about claiming, based on the rodent data, that humans will have a dose response. It’s an open question. We really don’t know. Some of the pharmacoepidemiology data suggested that even lower doses — for example, using semaglutide for diabetes without going up to the obesity dose — may be just as effective as a higher dose in reducing the incidence of alcohol use disorder.
It’s important also to keep in mind that the pharmacoepidemiology data are always an association. Reduction in alcohol disorder is associated with the prescription GLP-1 RA, but they don’t really replace the more gold-standard, double-blind, placebo-controlled randomized clinical trial. Nonetheless, with the pharmacoepidemiology data, I think there is an argument to at least hypothesize that people may respond well, even to lower doses.
This also may be important from a safety standpoint.
Basically, we need to wait for results in the next years to come from randomized clinical trials to better unfold the question about doses. For example, just anecdotally, I will tell you that in the clinical trial we are conducting right now at the NIH Intramural Research Program, for which I’m the principal investigator (PI), we are going up to 2.4 mg — the highest dose of semaglutide.
We are collaborating with Kyle Simmons, PhD, from Oklahoma State University. Our two studies are not like a two-site clinical trial, but they are harmonized. In Dr. Simmons’ clinical trial, they’re going up to 1.0 mg. We are excited about this team approach because the trials are slightly different, but they’re harmonized to the point that, once the studies are done, we’ll be able to combine and compare data to better answer the question about dosing, and many other questions.
Dr. Jain: From a clinical perspective, we see that many people who are battling alcohol use disorder may not have obesity. They might actually be on the leaner side, and hence, we may not want to use a high dose of GLP-1 RA therapy. It’ll be very exciting to see when these results come out.
This brings me to the next question. I think everyone would love to know why this happens. Why is GLP-1 RA having this effect on alcohol use disorder? I know that your group has done many animal studies, as you pointed out, and one of the postulated theories was the effect on the GABA neurotransmission pathway.
Can you tell us more about what you feel is the underlying mechanism of action here?
Dr. Leggio: I will start by saying that we don’t fully know. There are many open questions. If I can sidetrack for one second: We come up with the idea that, first of all, alcohol use disorder and substance use disorder are addictive behaviors, addictive disorders. We define addiction as a brain disease.
Granted that addiction is a brain disease, it doesn’t mean that addiction works just in the brain in isolation. As we all know, the brain works in concert with the rest of the body. One specific approach my team has been taking is working on the analogy and the similarities between obesity and addiction to try to understand how the body-brain connection, such as the gut-brain-neuroendocrine pathway, may play a role in patients with addiction.
With that in mind, a large amount of work in my lab in the past 20 years — since I’ve been a PI — has been focused on studying this neuroendocrine pathways related to the gut-brain axis. For example, we have done work on insulin and leptin, primarily; we had done work on ghrelin, and since 2015 on the GLP-1 RAs.
With that in mind, the framework we are working on, which is also substantiated by many studies done by our team and other teams in the neuroscience field, kind of supports the idea that, similar to what we see in obesity, these medications may work by affecting what we call reward processing, or the seeking for addictive drugs, such as alcohol, and also the drugs such as the stimulants, opioids, nicotine, and so on.
The idea is that the mechanism is driven by the ability of the medication — semaglutide and all the GLP-1 RAs — to reduce the rewarding properties of alcohol and drugs. To maybe make the example more pragmatic, what does that mean? It means, for example, that a patient who typically has 10 drinks per day in the afternoon and night, while they are on the medication they may feel the lack of need to drink up to 10 to feel the same reward.
They may be able to stop after two or three drinks, which means a significant harm reduction and a beneficial outcome. This also brings us to another mechanism, which may be related to society. We don’t fully understand how much the society mechanism, including society mechanism related to GI motility, may also play a role.
With that said, we don’t think that the effect of the GLP-1 RAs is merely due to alcohol being a calorie-based nutrient because, in fact, we see alcohol as an addictive drug, not as a nutrient. Also, the GLP-1 RAs, at least in animal models, seem to work on other addictive drugs that don’t have calories, such as nicotine, and possibly with cannabis, opioids, and stimulants.
Then on the molecular level, our team recently showed, in collaboration with Dr. Marisa Roberto from Scripps in La Jolla, California, that semaglutide may in fact change the GABA transmission at the level of some brain regions, such as the amygdala and the prefrontal cortex. These are brain regions that are well-established hubs that play a role in the mechanism underlying addiction.
There are also some very exciting recent data showing how these medications may work not just on GABA or just on dopamine, which is the canonical way we conceive of reward processing, but by working on both by modulating GABA transmission — for example, at the ventral tegmental area and dopamine transmission at the nucleus accumbens.
Bottom line, if I summarize all of this, is that the mechanism is not fully understood, but there is definitely a contribution of this medication to effect and reward processing, possibly by altering the balance between GABA and dopamine. There are still some unknown questions, such as, are these mechanisms all brain driven or are they signaling from the periphery to the brain, or maybe both?
Also, as we all know, there are many differences across all these GLP-1 analogs in brain penetrance. Whether the drug needs to go to the brain to have an effect on alcohol drinking, cocaine seeking, or smoking is really an open question.
Dr. Jain: This is so thought-provoking. I guess the more we uncover, the more mesmerized we get with all the potential crosstalk. There is a large amount of overlap in the brain with each of these different things and how it all interplays with each other.
Speaking of interplay, I’m thinking about how many people prone to having alcohol use disorder can potentially develop complications, one of these being chronic pancreatitis. This is a well-known complication that can occur in people having alcohol addiction. Along that same line, we know that previous history of pancreatitis is considered a use-with-caution, or we don’t want to use GLP-1 RA therapy in people who have had pancreatitis.
Now it becomes this quagmire where people may have chronic pancreatitis, but we may want to consider GLP-1 RA therapy for management of alcohol use disorder. What are your thoughts about this, and the safety, potentially, in using it in these patients?
Dr. Leggio: This is another wonderful question. That’s definitely a top priority in our mind, to address these kinds of questions. For example, our RCT does have, as core primary outcomes, not only the efficacy defined as a reduction in alcohol drinking, but also safety.
The reason is exactly what you just explained. There are many unanswered questions, including whether giving a GLP-1 RA and alcohol together may have synergistic effects and increase the likelihood of having pancreatitis.
The good news is that, so far, based on the published literature, including the RCT done with exenatide in Denmark and published in 2022 and also the ongoing clinical trials — including my own clinical trial, but of course we are blind — pancreatitis has not been coming out as an adverse event.
However, it’s also true that it often happens in clinical medication development. Of course, we screen and select our population well. For example, we do exclude people who have a history of pancreatitis. We exclude people with high lipase or with any of the clinical symptomatology that makes us concerned about these people having pancreatitis.
As often happens when you move a medication from clinical trials to clinical practice, we still need to understand whether this medication works in patients. I’m just speculating, but even if the clinical trials do not raise red flags in terms of increased risk for some side effects such as pancreatitis, I think it will be very important for practitioners to keep a close eye on the death risk regardless.
It’s very interesting that it’s similar to alcohol liver disease. With pancreatitis, not every single patient with alcohol addiction has pancreatitis. We don’t really fully understand why some people develop pancreatitis and some people do not. The point being that there are many patients with alcohol addiction who don’t have pancreatitis and may benefit from these medications if they work. Again, we have to prove that in patients.
On the other side, as we all know, pancreatitis is a potentially life-threatening condition for those people who either have it or are at risk for it. I think we have to be very careful before we consider giving them a GLP-1 RA.
One could argue that alcohol is the leading cause of mortality and morbidity in the world. For example, right now, alcohol is the leading cause of liver disease. It’s the main reason for liver transplantation in our country. Alcohol is affecting thousands of people in terms of death and emergency room visits.
You could argue that the downside is not treating these people and they die because of alcohol addiction. A GLP-1 RA is not going to be for everybody. I will remind everybody that (1) we do have FDA-approved medications for alcohol addiction; and (2) there are also other medications not approved by the FDA, but with a proven efficacy in some clinical trials — for example, topiramate and gabapentin — and they’ve been endorsed by the American Psychiatric Association.
There is also some evidence for another medication, baclofen, which has been endorsed by the American College of Gastroenterology for patients with alcohol addiction and liver disease.
The point I’m making is that it’s not that either we use the GLP-1 RAs or we have no other tools. We have other tools. I think we have to personalize the treatment based on the patient’s profile from a safety standpoint and from a phenotypic standpoint.
Dr. Jain: I love that thought. I think individualization is the key here.
We know that people with diabetes have a higher risk for pancreatitis by virtue of having diabetes. People with obesity also have a higher risk for pancreatitis by virtue of having obesity. These are the two conditions where we are using a large amount of GLP-1 RA therapy. Again, the idea is looking at the person in front of us and then deciding, based on their past medical history and their current risk, whether or not a medication is a right fit for them.
I think more individualization here will come as we start using these medications that might be having potential effects on different organ systems. You mentioned a little bit about the liver, so a thought came in my mind. We know that people with diabetes who have alcohol use disorder are at a higher risk for potential hypoglycemia. If they have events when they have increased consumption of alcohol, there can be more hypoglycemia.
We now could potentially be using semaglutide or other GLP-1 RA therapy for management of alcohol use disorder. In your own experience in the studies that you’ve done or the literature that’s out there, has that been associated with an even higher risk for hypoglycemia?
Dr. Leggio: It’s a wonderful question. I’m not aware of any formal and published report of that association. That said, your thinking from a physiopathologist standpoint makes total sense. I could not agree more. The fact that nothing has been published, at least to my knowledge, doesn’t mean that the death risk doesn’t exist. In fact, I agree with you that it does exist.
Alcohol use disorder is interesting and tricky clinically because chronically, alcohol addiction or alcohol use disorder is associated with an increased risk for diabetes. Acutely, as you point out; and this could be with or without alcohol use disorder. An episode of a high volume of binge drinking may lead to hypoglycemia.
This is one of the reasons why people may show up to the emergency room with intoxication, and one of the symptoms detected at the emergency room is that they also have hypoglycemia in addition to vomiting, nausea, and everything else that we see in patients with acute intoxication.
Similar to the discussion about pancreatitis, as we work on understanding the possible role of GLP-1 RA in patients with alcohol use disorder, we do have to keep a close eye on the risk for hypoglycemia. The short answer is that this is not well established, but based on the simple concept of “first, do no harm,” I think we need to track that very carefully.
In the ongoing clinical trial we’re doing in Maryland in my program at the NIH, we do just that. We are tracking glucose levels. Of course, patients come to clinic weekly, so unless they have symptoms, typically we don’t see anything at the time.
More important, we educate our patients when they go through the consent process. We tell them that this medication per se does not give hypoglycemia. In fact, we’re including people with diabetes, so for people on other medications like metformin, we explain to them that technically such a risk should not exist, but because you’re drinking alcohol in excessive amounts, you do have a potential higher risk. We just don’t know how significant that risk could be.
We do a large amount of education at baseline when they enroll in our study. We also educate our patients on how to recognize early on the potential risk for hypoglycemia, exactly for the reasons you said. We explain to them the unknown potential that the GLP-1 RAs and alcohol together may synergize and give hypoglycemia.
Dr. Jain: I don’t know if you got this feeling at the ADA conference, but I felt, when attending all these sessions, that it seems like GLP-1 RA is the gift that keeps giving. We see the effect on diabetes, obesity, metabolic-associated steatotic liver disease, possibly with Alzheimer’s, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, and so many things.
Now, of course, there’s potential use in alcohol use disorder. Do you think that using GLP-1 RA therapy is ready for prime time? Do you think we are now ready to prescribe this in people with alcohol use disorder?
Dr. Leggio: I would say we’re not there yet. As I mentioned at the beginning, the evidence keeps on growing. It’s getting stronger and stronger because the positive data keep on coming up. We have data from animal models, including the different species, ranging from rodents to nonhuman primates. We have anecdotal evidence and machine-learning approaches using, for example, big data and social media data. Now we have pharmacoepidemiology data and some small, initial, but still good randomized clinical trials.
What we are missing is the final step of having a substantial number of prospective, double-blind, placebo-controlled clinical trials to really prove or disprove whether these medications work, and to also better understand which patients may respond to these medications.
The good news is that there are many ongoing clinical trials. We are conducting a clinical trial in Maryland at the NIH. Dr. Simmons is doing a clinical trial at Oklahoma State University. Dr. Christian Hendershot at UNC is conducting a study at Chapel Hill. Dr. Josh Gowin is doing a study in Colorado. Dr. Anders Fink-Jensen is doing a study in Denmark. The momentum is very high.
I’m only mentioning those people who are doing alcohol-semaglutide clinical trials. There are also people doing clinical trials on smoking, stimulants, and opioids. There are actually some very fresh, still unpublished data from Penn State that were presented publicly at conferences, showing how these drugs may reduce opioid craving, which is, of course, critically important, given that we’re in the middle of a fentanyl pandemic that is killing one person every 7 minutes, for example, in Baltimore. It’s very alarming and we need more treatments.
The bottom line is that it’s very promising, but we need to wait for these clinical trials to have a definitive answer. I would say that if you have a patient with diabetes, obesity, and also alcohol addiction, and they are on semaglutide or any other GLP-1 RA, and in addition to using the medication for diabetes and obesity, they also have a beneficial effect on their alcohol drinking, then that’s fantastic. At the end of the day, that’s the mission we all share: helping people.
If it’s someone without obesity and diabetes, personally, at this stage, I will go with other medications that either have FDA approval or at least very solid evidence of efficacy from RCTs rather than going with the GLP-1 RA, at least until I see more definitive data from randomized clinical trials.
There is a large amount of hope. We are hoping that these clinical trials will be positive. We are very enthusiastic and we’re also very thrilled to see that Novo Nordisk recently launched a gigantic multisite clinical trial with — I forgot how many sites, but it’s very large across Europe, America, and maybe other continents as well.
Their primary outcome is improvement in alcohol-related liver disease, but they’re also looking at alcohol drinking as a secondary outcome. That’s very important because, unlike in the diabetes field, in the addiction field, we do struggle to build partnership with the private sector because sometimes the addiction field is not seen as an appetitive field from pharma.
We all know that the best success in any medication development story is when you put academia, the government, and pharma together. Think about the COVID-19 vaccine development. That’s unfortunately the exception rather than rule in the addiction field.
With the company doing a large clinical trial in the alcohol field, although they focus more on the liver but they also looked at drinking, I really hope we’ll see more and more companies in the private sector take more and more interest in addiction. Also, I hope to see more and more partnership between the private sector, the government, and academia.
Dr. Jain: Such exciting times, indeed. We can’t wait enough for the results of these and many other trials to come out. Dr. Leggio, it was an absolute delight chatting with you today. Thank you so much for joining us from ADA 2024.
Akshay B. Jain, MD, Clinical Instructor, Department of Endocrinology, University of British Columbia; Endocrinologist, TLC Diabetes and Endocrinology, Vancouver, British Columbia, Canada, has disclosed the following relevant financial relationships: Serve(d) as a speaker or a member of a speakers bureau for: Abbott; Acerus; AstraZeneca; Amgen; Bausch Healthcare; Bayer; Boehringer Ingelheim; Care to Know; CCRN; Connected in Motion; CPD Network; Dexcom; Diabetes Canada; Eli Lilly; GSK; HLS Therapeutics; Janssen; Master Clinician Alliance; MDBriefcase; Merck; Medtronic; Moderna; Novartis; Novo Nordisk; Partners in Progressive Medical Education; Pfizer; Sanofi Aventis; Timed Right; WebMD. Received research grants/research support from: Abbott; Amgen; Novo Nordisk. Received consulting fees from: Abbott; Acerus; AstraZeneca; Amgen; Bausch Healthcare; Bayer; Boehringer Ingelheim; Dexcom; Eli Lilly; Gilead Sciences; GSK; HLS Therapeutics; Insulet; Janssen; Medtronic; Novo Nordisk; Partners in Progressive Medical Education; PocketPills; Roche; Sanofi Aventis; Takeda. Lorenzo Leggio, MD, PhD, Clinical Director, Deputy Scientific Director, National Institute on Drug Abuse Intramural Research Program, National Institutes of Health, Baltimore, Maryland, has disclosed the following relevant financial relationships: Serve(d) as a US federal employee for: National Institutes of Health. He had received income in an amount equal to or greater than $250 from: UK Medical Council on Alcohol for his service as editor-in-chief for Alcohol and Alcoholism and received royalties from Rutledge as an editor for a textbook.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM ADA 2024
Unlocking the Potential of Baricitinib for Vitiligo
Vitiligo, the most common skin pigmentation disorder, has affected patients for thousands of years.1 The psychological and social impacts on patients include sleep and sexual disorders, low self-esteem, low quality of life, anxiety, and depression when compared to those without vitiligo.2,3 There have been substantial therapeutic advancements in the treatment of vitiligo, with the recent approval of ruxolitinib cream 1.5% by the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) in 2022 and by the European Medicines Agency in 2023.4 Ruxolitinib is the first topical Janus kinase (JAK) inhibitor approved by the FDA for the treatment of nonsegmental vitiligo in patients 12 years and older, ushering in the era of JAK inhibitors for patients affected by vitiligo. The efficacy and safety of ruxolitinib was supported by 2 randomized clinical trials.4 It also is FDA approved for the intermittent and short-term treatment of mild to moderate atopic dermatitis in nonimmunocompromised patients 12 years and older whose disease is not adequately controlled with other topical medications.5
Vitiligo is characterized by an important inflammatory component, with the JAK/STAT (signal transducer and activator of transcription) pathway playing a crucial role in transmitting signals of inflammatory cytokines. In particular, IFN-γ and chemokines CXCL9 and CXCL10 are major contributors to the development of vitiligo, acting through the JAK/STAT pathway in local keratinocytes. Inhibiting JAK activity helps mitigate the effects of IFN-γ and downstream chemokines.6
Currently, baricitinib is not FDA approved for the treatment of vitiligo; it is FDA approved for moderate to severe active rheumatoid arthritis, severe alopecia areata, and in specific cases for COVID-19.7 Mumford et al8 first reported the use of oral baricitinib for the treatment of nonsegmental vitiligo. This patient experienced poor improvement using the oral JAK inhibitor tofacitinib for 5 months but achieved near-complete repigmentation after switching to baricitinib for 8 months (4 mg daily).8 Furthermore, a recent study found that in vitro baricitinib could increase tyrosinase activity and melanin content as well as stimulate the expression of genes related to tyrosinase in damaged melanocytes.9
A recent study by Li et al10 has shown satisfactory repigmentation and good tolerance in 2 cases of vitiligo treated with oral baricitinib in combination with narrowband UVB (NB-UVB) phototherapy. These findings are supported by a prior study of oral tofacitinib and NB-UVB phototherapy in 10 cases; the JAK inhibitor treatment demonstrated enhanced effectiveness when combined with light exposure.11
Large-scale randomized clinical trials are needed to evaluate the efficacy and safety of oral baricitinib for vitiligo treatment. Currently, a clinical trial is underway (recruiting phase) to compare the efficacy and safety of combining baricitinib and excimer lamp phototherapy vs phototherapy alone.12 The results of this trial can provide valuable information about whether baricitinib is promising as part of the therapeutic arsenal for vitiligo treatment in the future. A recently completed multicenter, randomized, double-blind clinical trial assessed the efficacy and tolerability of oral baricitinib in combination with NB-UVB phototherapy for the treatment of vitiligo. The trial included 49 patients and may provide valuable insights for the potential future application of baricitinib in the treatment of vitiligo.13 If the results of these clinical trials are favorable, approval of the first orally administered JAK inhibitor for repigmentation treatment in patients with vitiligo could follow, which would be a major breakthrough.
The off-label use of baricitinib—alone or in combination with phototherapy—appears to be promising in studies with a small sample size (an important limitation). The results of clinical trials will help us elucidate the efficacy and safety of baricitinib for vitiligo treatment, which could be a subject of debate. Recently, the FDA issued a warning due to findings showing that the use of tofacitinib has been associated with an increased risk of serious heart-related events, such heart attack, stroke, cancer, blood clots, and death.14 In response, the FDA issued warnings for 2 other JAK inhibitors—baricitinib and upadacitinib. Unlike tofacitinib, baricitinib and upadacitinib have not been studied in large safety clinical trials, and as a result, their risks have not been adequately evaluated. However, due to the shared mechanisms of action of these drugs, the FDA believes that these medications may pose similar risks as those observed in the tofacitinib safety trial.14
Disadvantages of JAK inhibitors include the high cost, immune-related side effects, potential cardiovascular adverse effects, and limited availability worldwide. If current and future clinical trials obtain objective evidence with a large sample size that yields positive outcomes with tolerable or acceptable side effects, and if the drug is affordable for hospitals and patients, the use of oral or topical baricitinib will be embraced and may be approved for vitiligo.
- Berger BJ, Rudolph RI, Leyden JJ. Letter: transient acantholytic dermatosis. Arch Dermatol. 1974;109:913. doi:10.1001/archderm.1974.01630060081033
- Hu Z, Wang T. Beyond skin white spots: vitiligo and associated comorbidities. Front Med (Lausanne). 2023;10:1072837. doi:10.3389/fmed.2023.1072837
- Rzepecki AK, McLellan BN, Elbuluk N. Beyond traditional treatment: the importance of psychosocial therapy in vitiligo. J Drugs Dermatol. 2018;17:688-691.
- Topical ruxolitinib evaluation in vitiligo study 1 (TRuE-V1). ClinicalTrials.gov identifier: NCT04052425. Updated September 21, 2022. Accessed August 16, 2024. https://clinicaltrials.gov/study/NCT04052425
- US Food and Drug Administration. FDA approves topical treatment addressing repigmentation in vitiligo in patients aged 12 and older. July 19, 2022. Accessed August 16, 2024. https://www.fda.gov/drugs/news-events-human-drugs/fda-approves-topical-treatment-addressing-repigmentation-vitiligo-patients-aged-12-and-older
- Harris JE, Harris TH, Weninger W, et al. A mouse model of vitiligo with focused epidermal depigmentation requires IFN-γ for autoreactive CD8+ T-cell accumulation in the skin. J Invest Dermatol. 2012;132:1869-1876. doi:10.1038/jid.2011.463
- Garcia-Melendo C, Cubiró X, Puig L. Janus kinase inhibitors in dermatology: part 1—general considerations and applications in vitiligo and alopecia areata. Actas Dermosifiliogr. 2021;112:503-515. doi:10.1016/j.ad.2020.12.003
- Mumford BP, Gibson A, Chong AH. Repigmentation of vitiligo with oral baricitinib. Australas J Dermatol. 2020;61:374-376. doi:10.1111/ajd.13348
- Dong J, Huang X, Ma LP, et al. Baricitinib is effective in treating progressing vitiligo in vivo and in vitro. Dose Response. 2022;20:15593258221105370. doi:10.1177/15593258221105370
- Li X, Sun Y, Du J, et al. Excellent repigmentation of generalized vitiligo with oral baricitinib combined with NB-UVB phototherapy. Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol. 2023;16:635-638. doi:10.2147/CCID.S396430
- Liu LY, Strassner JP, Refat MA, et al. Repigmentation in vitiligo using the Janus kinase inhibitor tofacitinib may require concomitant light exposure. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2017;77:675-682.e1. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2017.05.043
- Evaluation safety, efficacy baricitinib plus excimer light versus excimer light alone in non segmental vitiligo. ClinicalTrials.gov identifier: NCT05950542. Updated July 18, 2023. Accessed August 16, 2024. https://clinicaltrials.gov/study/NCT05950542
- Evaluation of effect and tolerance of the association of baricitinib and phototherapy versus phototherapy in adults with progressive vitiligo (BARVIT). ClinicalTrials.gov identifier: NCT04822584. Updated June 13, 2023. Accessed August 16, 2024. https://clinicaltrials.gov/study/NCT04822584
- US Food and Drug Administration. FDA requires warnings about increased risk of serious heart-related events, cancer, blood clots, and death for JAK inhibitors that treat certain chronic inflammatory conditions. December 7, 2021. Accessed August 16, 2024. https://www.fda.gov/drugs/drug-safety-and-availability/fda-requires-warnings-about-increased-risk-serious-heart-related-events-cancer-blood-clots-and-death
Vitiligo, the most common skin pigmentation disorder, has affected patients for thousands of years.1 The psychological and social impacts on patients include sleep and sexual disorders, low self-esteem, low quality of life, anxiety, and depression when compared to those without vitiligo.2,3 There have been substantial therapeutic advancements in the treatment of vitiligo, with the recent approval of ruxolitinib cream 1.5% by the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) in 2022 and by the European Medicines Agency in 2023.4 Ruxolitinib is the first topical Janus kinase (JAK) inhibitor approved by the FDA for the treatment of nonsegmental vitiligo in patients 12 years and older, ushering in the era of JAK inhibitors for patients affected by vitiligo. The efficacy and safety of ruxolitinib was supported by 2 randomized clinical trials.4 It also is FDA approved for the intermittent and short-term treatment of mild to moderate atopic dermatitis in nonimmunocompromised patients 12 years and older whose disease is not adequately controlled with other topical medications.5
Vitiligo is characterized by an important inflammatory component, with the JAK/STAT (signal transducer and activator of transcription) pathway playing a crucial role in transmitting signals of inflammatory cytokines. In particular, IFN-γ and chemokines CXCL9 and CXCL10 are major contributors to the development of vitiligo, acting through the JAK/STAT pathway in local keratinocytes. Inhibiting JAK activity helps mitigate the effects of IFN-γ and downstream chemokines.6
Currently, baricitinib is not FDA approved for the treatment of vitiligo; it is FDA approved for moderate to severe active rheumatoid arthritis, severe alopecia areata, and in specific cases for COVID-19.7 Mumford et al8 first reported the use of oral baricitinib for the treatment of nonsegmental vitiligo. This patient experienced poor improvement using the oral JAK inhibitor tofacitinib for 5 months but achieved near-complete repigmentation after switching to baricitinib for 8 months (4 mg daily).8 Furthermore, a recent study found that in vitro baricitinib could increase tyrosinase activity and melanin content as well as stimulate the expression of genes related to tyrosinase in damaged melanocytes.9
A recent study by Li et al10 has shown satisfactory repigmentation and good tolerance in 2 cases of vitiligo treated with oral baricitinib in combination with narrowband UVB (NB-UVB) phototherapy. These findings are supported by a prior study of oral tofacitinib and NB-UVB phototherapy in 10 cases; the JAK inhibitor treatment demonstrated enhanced effectiveness when combined with light exposure.11
Large-scale randomized clinical trials are needed to evaluate the efficacy and safety of oral baricitinib for vitiligo treatment. Currently, a clinical trial is underway (recruiting phase) to compare the efficacy and safety of combining baricitinib and excimer lamp phototherapy vs phototherapy alone.12 The results of this trial can provide valuable information about whether baricitinib is promising as part of the therapeutic arsenal for vitiligo treatment in the future. A recently completed multicenter, randomized, double-blind clinical trial assessed the efficacy and tolerability of oral baricitinib in combination with NB-UVB phototherapy for the treatment of vitiligo. The trial included 49 patients and may provide valuable insights for the potential future application of baricitinib in the treatment of vitiligo.13 If the results of these clinical trials are favorable, approval of the first orally administered JAK inhibitor for repigmentation treatment in patients with vitiligo could follow, which would be a major breakthrough.
The off-label use of baricitinib—alone or in combination with phototherapy—appears to be promising in studies with a small sample size (an important limitation). The results of clinical trials will help us elucidate the efficacy and safety of baricitinib for vitiligo treatment, which could be a subject of debate. Recently, the FDA issued a warning due to findings showing that the use of tofacitinib has been associated with an increased risk of serious heart-related events, such heart attack, stroke, cancer, blood clots, and death.14 In response, the FDA issued warnings for 2 other JAK inhibitors—baricitinib and upadacitinib. Unlike tofacitinib, baricitinib and upadacitinib have not been studied in large safety clinical trials, and as a result, their risks have not been adequately evaluated. However, due to the shared mechanisms of action of these drugs, the FDA believes that these medications may pose similar risks as those observed in the tofacitinib safety trial.14
Disadvantages of JAK inhibitors include the high cost, immune-related side effects, potential cardiovascular adverse effects, and limited availability worldwide. If current and future clinical trials obtain objective evidence with a large sample size that yields positive outcomes with tolerable or acceptable side effects, and if the drug is affordable for hospitals and patients, the use of oral or topical baricitinib will be embraced and may be approved for vitiligo.
Vitiligo, the most common skin pigmentation disorder, has affected patients for thousands of years.1 The psychological and social impacts on patients include sleep and sexual disorders, low self-esteem, low quality of life, anxiety, and depression when compared to those without vitiligo.2,3 There have been substantial therapeutic advancements in the treatment of vitiligo, with the recent approval of ruxolitinib cream 1.5% by the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) in 2022 and by the European Medicines Agency in 2023.4 Ruxolitinib is the first topical Janus kinase (JAK) inhibitor approved by the FDA for the treatment of nonsegmental vitiligo in patients 12 years and older, ushering in the era of JAK inhibitors for patients affected by vitiligo. The efficacy and safety of ruxolitinib was supported by 2 randomized clinical trials.4 It also is FDA approved for the intermittent and short-term treatment of mild to moderate atopic dermatitis in nonimmunocompromised patients 12 years and older whose disease is not adequately controlled with other topical medications.5
Vitiligo is characterized by an important inflammatory component, with the JAK/STAT (signal transducer and activator of transcription) pathway playing a crucial role in transmitting signals of inflammatory cytokines. In particular, IFN-γ and chemokines CXCL9 and CXCL10 are major contributors to the development of vitiligo, acting through the JAK/STAT pathway in local keratinocytes. Inhibiting JAK activity helps mitigate the effects of IFN-γ and downstream chemokines.6
Currently, baricitinib is not FDA approved for the treatment of vitiligo; it is FDA approved for moderate to severe active rheumatoid arthritis, severe alopecia areata, and in specific cases for COVID-19.7 Mumford et al8 first reported the use of oral baricitinib for the treatment of nonsegmental vitiligo. This patient experienced poor improvement using the oral JAK inhibitor tofacitinib for 5 months but achieved near-complete repigmentation after switching to baricitinib for 8 months (4 mg daily).8 Furthermore, a recent study found that in vitro baricitinib could increase tyrosinase activity and melanin content as well as stimulate the expression of genes related to tyrosinase in damaged melanocytes.9
A recent study by Li et al10 has shown satisfactory repigmentation and good tolerance in 2 cases of vitiligo treated with oral baricitinib in combination with narrowband UVB (NB-UVB) phototherapy. These findings are supported by a prior study of oral tofacitinib and NB-UVB phototherapy in 10 cases; the JAK inhibitor treatment demonstrated enhanced effectiveness when combined with light exposure.11
Large-scale randomized clinical trials are needed to evaluate the efficacy and safety of oral baricitinib for vitiligo treatment. Currently, a clinical trial is underway (recruiting phase) to compare the efficacy and safety of combining baricitinib and excimer lamp phototherapy vs phototherapy alone.12 The results of this trial can provide valuable information about whether baricitinib is promising as part of the therapeutic arsenal for vitiligo treatment in the future. A recently completed multicenter, randomized, double-blind clinical trial assessed the efficacy and tolerability of oral baricitinib in combination with NB-UVB phototherapy for the treatment of vitiligo. The trial included 49 patients and may provide valuable insights for the potential future application of baricitinib in the treatment of vitiligo.13 If the results of these clinical trials are favorable, approval of the first orally administered JAK inhibitor for repigmentation treatment in patients with vitiligo could follow, which would be a major breakthrough.
The off-label use of baricitinib—alone or in combination with phototherapy—appears to be promising in studies with a small sample size (an important limitation). The results of clinical trials will help us elucidate the efficacy and safety of baricitinib for vitiligo treatment, which could be a subject of debate. Recently, the FDA issued a warning due to findings showing that the use of tofacitinib has been associated with an increased risk of serious heart-related events, such heart attack, stroke, cancer, blood clots, and death.14 In response, the FDA issued warnings for 2 other JAK inhibitors—baricitinib and upadacitinib. Unlike tofacitinib, baricitinib and upadacitinib have not been studied in large safety clinical trials, and as a result, their risks have not been adequately evaluated. However, due to the shared mechanisms of action of these drugs, the FDA believes that these medications may pose similar risks as those observed in the tofacitinib safety trial.14
Disadvantages of JAK inhibitors include the high cost, immune-related side effects, potential cardiovascular adverse effects, and limited availability worldwide. If current and future clinical trials obtain objective evidence with a large sample size that yields positive outcomes with tolerable or acceptable side effects, and if the drug is affordable for hospitals and patients, the use of oral or topical baricitinib will be embraced and may be approved for vitiligo.
- Berger BJ, Rudolph RI, Leyden JJ. Letter: transient acantholytic dermatosis. Arch Dermatol. 1974;109:913. doi:10.1001/archderm.1974.01630060081033
- Hu Z, Wang T. Beyond skin white spots: vitiligo and associated comorbidities. Front Med (Lausanne). 2023;10:1072837. doi:10.3389/fmed.2023.1072837
- Rzepecki AK, McLellan BN, Elbuluk N. Beyond traditional treatment: the importance of psychosocial therapy in vitiligo. J Drugs Dermatol. 2018;17:688-691.
- Topical ruxolitinib evaluation in vitiligo study 1 (TRuE-V1). ClinicalTrials.gov identifier: NCT04052425. Updated September 21, 2022. Accessed August 16, 2024. https://clinicaltrials.gov/study/NCT04052425
- US Food and Drug Administration. FDA approves topical treatment addressing repigmentation in vitiligo in patients aged 12 and older. July 19, 2022. Accessed August 16, 2024. https://www.fda.gov/drugs/news-events-human-drugs/fda-approves-topical-treatment-addressing-repigmentation-vitiligo-patients-aged-12-and-older
- Harris JE, Harris TH, Weninger W, et al. A mouse model of vitiligo with focused epidermal depigmentation requires IFN-γ for autoreactive CD8+ T-cell accumulation in the skin. J Invest Dermatol. 2012;132:1869-1876. doi:10.1038/jid.2011.463
- Garcia-Melendo C, Cubiró X, Puig L. Janus kinase inhibitors in dermatology: part 1—general considerations and applications in vitiligo and alopecia areata. Actas Dermosifiliogr. 2021;112:503-515. doi:10.1016/j.ad.2020.12.003
- Mumford BP, Gibson A, Chong AH. Repigmentation of vitiligo with oral baricitinib. Australas J Dermatol. 2020;61:374-376. doi:10.1111/ajd.13348
- Dong J, Huang X, Ma LP, et al. Baricitinib is effective in treating progressing vitiligo in vivo and in vitro. Dose Response. 2022;20:15593258221105370. doi:10.1177/15593258221105370
- Li X, Sun Y, Du J, et al. Excellent repigmentation of generalized vitiligo with oral baricitinib combined with NB-UVB phototherapy. Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol. 2023;16:635-638. doi:10.2147/CCID.S396430
- Liu LY, Strassner JP, Refat MA, et al. Repigmentation in vitiligo using the Janus kinase inhibitor tofacitinib may require concomitant light exposure. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2017;77:675-682.e1. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2017.05.043
- Evaluation safety, efficacy baricitinib plus excimer light versus excimer light alone in non segmental vitiligo. ClinicalTrials.gov identifier: NCT05950542. Updated July 18, 2023. Accessed August 16, 2024. https://clinicaltrials.gov/study/NCT05950542
- Evaluation of effect and tolerance of the association of baricitinib and phototherapy versus phototherapy in adults with progressive vitiligo (BARVIT). ClinicalTrials.gov identifier: NCT04822584. Updated June 13, 2023. Accessed August 16, 2024. https://clinicaltrials.gov/study/NCT04822584
- US Food and Drug Administration. FDA requires warnings about increased risk of serious heart-related events, cancer, blood clots, and death for JAK inhibitors that treat certain chronic inflammatory conditions. December 7, 2021. Accessed August 16, 2024. https://www.fda.gov/drugs/drug-safety-and-availability/fda-requires-warnings-about-increased-risk-serious-heart-related-events-cancer-blood-clots-and-death
- Berger BJ, Rudolph RI, Leyden JJ. Letter: transient acantholytic dermatosis. Arch Dermatol. 1974;109:913. doi:10.1001/archderm.1974.01630060081033
- Hu Z, Wang T. Beyond skin white spots: vitiligo and associated comorbidities. Front Med (Lausanne). 2023;10:1072837. doi:10.3389/fmed.2023.1072837
- Rzepecki AK, McLellan BN, Elbuluk N. Beyond traditional treatment: the importance of psychosocial therapy in vitiligo. J Drugs Dermatol. 2018;17:688-691.
- Topical ruxolitinib evaluation in vitiligo study 1 (TRuE-V1). ClinicalTrials.gov identifier: NCT04052425. Updated September 21, 2022. Accessed August 16, 2024. https://clinicaltrials.gov/study/NCT04052425
- US Food and Drug Administration. FDA approves topical treatment addressing repigmentation in vitiligo in patients aged 12 and older. July 19, 2022. Accessed August 16, 2024. https://www.fda.gov/drugs/news-events-human-drugs/fda-approves-topical-treatment-addressing-repigmentation-vitiligo-patients-aged-12-and-older
- Harris JE, Harris TH, Weninger W, et al. A mouse model of vitiligo with focused epidermal depigmentation requires IFN-γ for autoreactive CD8+ T-cell accumulation in the skin. J Invest Dermatol. 2012;132:1869-1876. doi:10.1038/jid.2011.463
- Garcia-Melendo C, Cubiró X, Puig L. Janus kinase inhibitors in dermatology: part 1—general considerations and applications in vitiligo and alopecia areata. Actas Dermosifiliogr. 2021;112:503-515. doi:10.1016/j.ad.2020.12.003
- Mumford BP, Gibson A, Chong AH. Repigmentation of vitiligo with oral baricitinib. Australas J Dermatol. 2020;61:374-376. doi:10.1111/ajd.13348
- Dong J, Huang X, Ma LP, et al. Baricitinib is effective in treating progressing vitiligo in vivo and in vitro. Dose Response. 2022;20:15593258221105370. doi:10.1177/15593258221105370
- Li X, Sun Y, Du J, et al. Excellent repigmentation of generalized vitiligo with oral baricitinib combined with NB-UVB phototherapy. Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol. 2023;16:635-638. doi:10.2147/CCID.S396430
- Liu LY, Strassner JP, Refat MA, et al. Repigmentation in vitiligo using the Janus kinase inhibitor tofacitinib may require concomitant light exposure. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2017;77:675-682.e1. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2017.05.043
- Evaluation safety, efficacy baricitinib plus excimer light versus excimer light alone in non segmental vitiligo. ClinicalTrials.gov identifier: NCT05950542. Updated July 18, 2023. Accessed August 16, 2024. https://clinicaltrials.gov/study/NCT05950542
- Evaluation of effect and tolerance of the association of baricitinib and phototherapy versus phototherapy in adults with progressive vitiligo (BARVIT). ClinicalTrials.gov identifier: NCT04822584. Updated June 13, 2023. Accessed August 16, 2024. https://clinicaltrials.gov/study/NCT04822584
- US Food and Drug Administration. FDA requires warnings about increased risk of serious heart-related events, cancer, blood clots, and death for JAK inhibitors that treat certain chronic inflammatory conditions. December 7, 2021. Accessed August 16, 2024. https://www.fda.gov/drugs/drug-safety-and-availability/fda-requires-warnings-about-increased-risk-serious-heart-related-events-cancer-blood-clots-and-death