User login
COVID-19 and the precipitous dismantlement of societal norms
As the life-altering coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic gradually ebbs, we are all its survivors. Now, we are experiencing COVID-19 fatigue, trying to emerge from its dense fog that pervaded every facet of our lives. We are fully cognizant that there will not be a return to the previous “normal.” The pernicious virus had a transformative effect that did not spare any component of our society. Full recovery will not be easy.
As the uncertainty lingers about another devastating return of the pandemic later this year, we can see the reverberation of this invisible assault on human existence. Although a relatively small fraction of the population lost their lives, the rest of us are valiantly trying to readjust to the multiple ways our world has changed. Consider the following abrupt and sweeping burdens inflicted by the pandemic within a few short weeks:
Mental health. The acute stress of thanatophobia generated a triad of anxiety, depression, and nosophobia on a large scale. The demand for psychiatric care rapidly escalated. Suicide rate increased not only because of the stress of being locked down at home (alien to most people’s lifestyle) but because of the coincidental timing of the pandemic during April and May, the peak time of year for suicide. Animal researchers use immobilization as a paradigm to stress a rat or mouse. Many humans immobilized during the pandemic have developed exquisite empathy towards those rodents! The impact on children may also have long-term effects because playing and socializing with friends is a vital part of their lives. Parents have noticed dysphoria and acting out among their children, and an intense compensatory preoccupation with video games and electronic communications with friends.
Physical health. Medical care focused heavily on COVID-19 victims, to the detriment of all other medical conditions. Non-COVID-19 hospital admissions plummeted, and all elective surgeries and procedures were put on hold, depriving many people of medical care they badly needed. Emergency department (ED) visits also declined dramatically, including the usual flow of heart attacks, stroke, pulmonary embolus, asthma attacks, etc. The minimization of driving greatly reduced the admission of accident victims to EDs. Colonoscopies, cardiac stents, hip replacements, MRIs, mammography, and other procedures that are vital to maintain health and quality of life were halted. Dentists shuttered their practices due to the high risk of infection from exposure to oral secretions and breathing. One can only imagine the suffering of having a toothache with no dental help available, and how that might lead to narcotic abuse.
Social health. The imperative of social distancing disrupted most ordinary human activities, such as dining out, sitting in an auditorium for Grand Rounds or a lecture, visiting friends at their homes, the cherished interactions between grandparents and grandchildren (the lack of which I painfully experienced), and even seeing each other’s smiles behind the ubiquitous masks. And forget about hugging or kissing. The aversion to being near anyone who is coughing or sneezing led to an adaptive social paranoia and the social shunning of anyone who appeared to have an upper respiratory infection, even if it was unrelated to COVID-19.
Redemption for the pharmaceutical industry. The deadly pandemic intensified the public’s awareness of the importance of developing treatments and vaccines for COVID-19. The often-demonized pharmaceutical companies, with their extensive R&D infrastructure, emerged as a major source of hope for discovering an effective treatment for the coronavirus infection, or—better still—one or more vaccines that will enable society to return to its normal functions. It was quite impressive how many pharmaceutical companies “came to the rescue” with clinical trials to repurpose existing medications or to develop new ones. It was very encouraging to see multiple vaccine candidates being developed and expedited for testing around the world. A process that usually takes years was reduced to a few months, thanks to the existing technical infrastructure and thousands of scientists who enable rapid drug development. It is possible that the public may gradually modify its perception of the pharmaceutical industry from a “corporate villain” to an “indispensable health industry” for urgent medical crises such as a pandemic, and also for hundreds of medical diseases that are still in need of safe, effective therapies.
Economic burden. The unimaginable nightmare scenario of a total shutdown of all businesses led to the unprecedented loss of millions of jobs and livelihoods, reflected in miles-long lines of families at food banks. Overnight, the government switched from worrying about its $20-trillion deficit to printing several more trillion dollars to rescue the economy from collapse. The huge magnitude of a trillion can be appreciated if one is aware that it takes roughly 32 years to count to 1 billion, and 32,000 years to count to 1 trillion. Stimulating the economy while the gross domestic product threatens to sink by terrifying percentages (20% to 30%) was urgently needed, even though it meant mortgaging the future, especially when interest rates, and servicing the debt, will inevitably rise from the current zero to much higher levels in the future. The collapse of the once-thriving airline industry (bookings were down an estimated 98%) is an example of why desperate measures were needed to salvage an economy paralyzed by a viral pandemic.
Continue to: Political repercussions
Political repercussions. In our already hyperpartisan country, the COVID-19 crisis created more fissures across party lines. The blame game escalated as each side tried to exploit the crisis for political gain during a presidential election year. None of the leaders, from mayors to governors to the president, had any notion of how to wisely manage an unforeseen catastrophic pandemic. Thus, a political cacophony has developed, further exacerbating the public’s anxiety and uncertainty, especially about how and when the pandemic will end.
Education disruption. Never before have all schools and colleges around the country abruptly closed and sent students of all ages to shelter at home. Massive havoc ensued, with a wholesale switch to solitary online learning, the loss of the unique school and college social experience in the classroom and on campus, and the loss of experiencing commencement to receive a diploma (an important milestone for every graduate). Even medical students were not allowed to complete their clinical rotations and were sent home to attend online classes. A complete paradigm shift emerged about entrance exams: the SAT and ACT were eliminated for college applicants, and the MCAT for medical school applicants. This was unthinkable before the pandemic descended upon us, but benchmarks suddenly evaporated to adjust to the new reality. Then there followed disastrous financial losses by institutions of higher learning as well as academic medical centers and teaching hospitals, all slashing their budgets, furloughing employees, cutting salaries, and eliminating programs. Even the “sacred” tenure of senior faculty became a casualty of the financial “exigency.” Children’s nutrition suffered, especially among those in lower socioeconomic groups for whom the main meal of the day was the school lunch, and was made worse by their parents’ loss of income. For millions of people, the emotional toll was inevitable following the draconian measure of closing all educational institutions to contain the spread of the pandemic.
Family burden. Sheltering at home might have been fun for a few days, but after many weeks, it festered into a major stress, especially for those living in a small house, condominium, or apartment. The resilience of many families was tested as the exercise of freedoms collided with the fear of getting infected. Families were deprived of celebrating birthdays, weddings, funerals, graduation parties, retirement parties, Mother’s Day, Father’s Day, and various religious holidays, including Easter, Passover, and Eid al-Fitr.
Sexual burden. Intimacy and sexual contact between consenting adults living apart were sacrificed on the altar of the pernicious viral pandemic. Mandatory social distancing of 6 feet or more to avoid each other’s droplets emanating from simple speech, not just sneezing or coughing, makes intimacy practically impossible. Thus, physical closeness became taboo, and avoiding another person’s saliva or body secretions became a must to avoid contracting the virus. Being single was quite a lonely experience during this pandemic!
Entertainment deprivation. Americans are known to thrive on an extensive diet of spectator sports. Going to football, basketball, baseball, or hockey games to root for one’s team is intrinsically American. The pursuit of happiness extends to attending concerts, movies, Broadway shows, theme parks, and cruises with thousands of others. The pandemic ripped all those pleasurable leisure activities from our daily lives, leaving a big hole in people’s lives at the precise time fun activities were needed as a useful diversion from the dismal stress of a pandemic. To make things worse, it is uncertain when (if ever) such group activities will be restored, especially if the pandemic returns with another wave. But optimists would hurry to remind us that the “Roaring 20s” blossomed in the decade following the 1918 Spanish Flu pandemic.
Continue to: Legal system
Legal system. Astounding changes were instigated by the pandemic, such as the release of thousands of inmates, including felons, to avoid the spread of the virus in crowded prisons. For us psychiatrists, the silver lining in that unexpected action is that many of those released were patients with mental illness who were incarcerated because of the lack of hospitals that would take them. The police started issuing citations instead of arresting and jailing violators. Enforcement of the law was welcome when it targeted those who gouged the public for personal profit during the scarcity of masks, sanitizers, or even toilet paper and soap.
Medical practice. In addition to delaying medical care for patients, the freeze on so-called elective surgeries or procedures (many of which were actually necessary) was financially ruinous for physicians. Another regrettable consequence of the pandemic is a drop in pediatric vaccinations because parents were reluctant to take their children to the pediatrician. On a more positive note, the massive switch to telehealth was advantageous for both patients and psychiatrists because this technology is well-suited for psychiatric care. Fortunately, regulations that hampered telepsychiatry practice were substantially loosened or eliminated, and even the usually sacrosanct HIPAA regulations were temporarily sidelined.
Medical research. Both human and animal research came to a screeching halt, and many research assistants were furloughed. Data collection was disrupted, and a generation of scientific and medical discoveries became a casualty of the pandemic.
Medical literature. It was stunning to see how quickly COVID-19 occupied most of the pages of prominent journals. The scholarly articles were frankly quite useful, covering topics ranging from risk factors to early symptoms to treatment and pathophysiology across multiple organs. As with other paradigm shifts, there was an accelerated publication push, sometimes with expedited peer reviews to inform health care workers and the public while the pandemic was still raging. However, a couple of very prominent journals had to retract flawed articles that were hastily published without the usual due diligence and rigorous peer review. The pandemic clearly disrupted the science publishing process.
Travel effects. The steep reduction of flights (by 98%) was financially catastrophic, not only for airline companies but to business travel across the country. However, fewer cars on the road resulted in fewer accidents and deaths, and also reduced pollution. Paradoxically, to prevent crowding in subways, trains, and buses, officials reversed their traditional instructions and advised the public to drive their own cars instead of using public transportation!
Continue to: Heroism of front-line medical personnel
Heroism of front-line medical personnel. Everyone saluted and prayed for the health care professionals working at the bedside of highly infectious patients who needed 24/7 intensive care. Many have died while carrying out the noble but hazardous medical duties. Those heroes deserve our lasting respect and admiration.
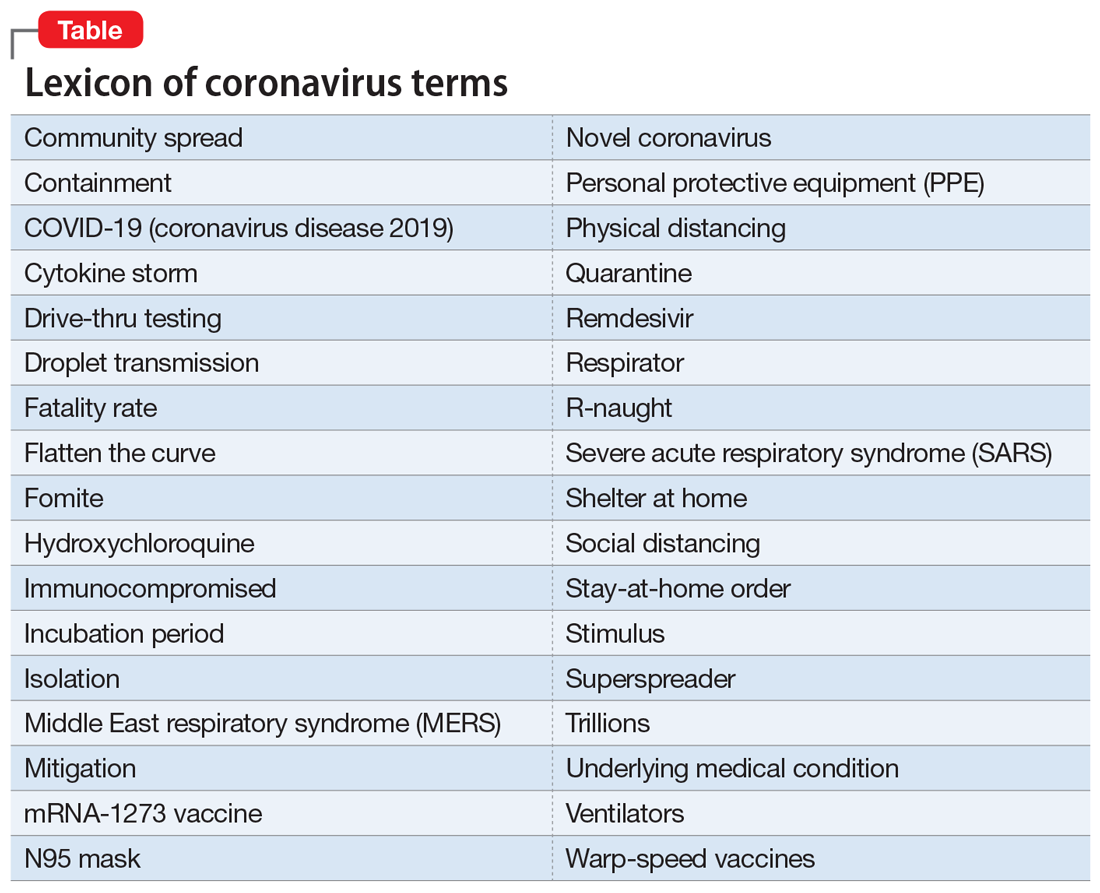
The COVID-19 pandemic insidiously permeated and altered every aspect of our complex society and revealed how fragile our “normal lifestyle” really is. It is possible that nothing will ever be the same again, and an uneasy sense of vulnerability will engulf us as we cautiously return to a “new normal.” Even our language has expanded with the lexicon of pandemic terminology (Table). We all pray and hope that this plague never returns. And let’s hope one or more vaccines are developed soon so we can manage future recurrences like the annual flu season. In the meantime, keep your masks and sanitizers close by…
Postscript: Shortly after I completed this editorial, the ongoing COVID-19 plague was overshadowed by the scourge of racism, with massive protests, at times laced by violence, triggered by the death of a black man in custody of the police, under condemnable circumstances. The COVID-19 pandemic and the necessary social distancing it requires were temporarily ignored during the ensuing protests. The combined effect of those overlapping scourges are jarring to the country’s psyche, complicating and perhaps sabotaging the social recovery from the pandemic.
As the life-altering coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic gradually ebbs, we are all its survivors. Now, we are experiencing COVID-19 fatigue, trying to emerge from its dense fog that pervaded every facet of our lives. We are fully cognizant that there will not be a return to the previous “normal.” The pernicious virus had a transformative effect that did not spare any component of our society. Full recovery will not be easy.
As the uncertainty lingers about another devastating return of the pandemic later this year, we can see the reverberation of this invisible assault on human existence. Although a relatively small fraction of the population lost their lives, the rest of us are valiantly trying to readjust to the multiple ways our world has changed. Consider the following abrupt and sweeping burdens inflicted by the pandemic within a few short weeks:
Mental health. The acute stress of thanatophobia generated a triad of anxiety, depression, and nosophobia on a large scale. The demand for psychiatric care rapidly escalated. Suicide rate increased not only because of the stress of being locked down at home (alien to most people’s lifestyle) but because of the coincidental timing of the pandemic during April and May, the peak time of year for suicide. Animal researchers use immobilization as a paradigm to stress a rat or mouse. Many humans immobilized during the pandemic have developed exquisite empathy towards those rodents! The impact on children may also have long-term effects because playing and socializing with friends is a vital part of their lives. Parents have noticed dysphoria and acting out among their children, and an intense compensatory preoccupation with video games and electronic communications with friends.
Physical health. Medical care focused heavily on COVID-19 victims, to the detriment of all other medical conditions. Non-COVID-19 hospital admissions plummeted, and all elective surgeries and procedures were put on hold, depriving many people of medical care they badly needed. Emergency department (ED) visits also declined dramatically, including the usual flow of heart attacks, stroke, pulmonary embolus, asthma attacks, etc. The minimization of driving greatly reduced the admission of accident victims to EDs. Colonoscopies, cardiac stents, hip replacements, MRIs, mammography, and other procedures that are vital to maintain health and quality of life were halted. Dentists shuttered their practices due to the high risk of infection from exposure to oral secretions and breathing. One can only imagine the suffering of having a toothache with no dental help available, and how that might lead to narcotic abuse.
Social health. The imperative of social distancing disrupted most ordinary human activities, such as dining out, sitting in an auditorium for Grand Rounds or a lecture, visiting friends at their homes, the cherished interactions between grandparents and grandchildren (the lack of which I painfully experienced), and even seeing each other’s smiles behind the ubiquitous masks. And forget about hugging or kissing. The aversion to being near anyone who is coughing or sneezing led to an adaptive social paranoia and the social shunning of anyone who appeared to have an upper respiratory infection, even if it was unrelated to COVID-19.
Redemption for the pharmaceutical industry. The deadly pandemic intensified the public’s awareness of the importance of developing treatments and vaccines for COVID-19. The often-demonized pharmaceutical companies, with their extensive R&D infrastructure, emerged as a major source of hope for discovering an effective treatment for the coronavirus infection, or—better still—one or more vaccines that will enable society to return to its normal functions. It was quite impressive how many pharmaceutical companies “came to the rescue” with clinical trials to repurpose existing medications or to develop new ones. It was very encouraging to see multiple vaccine candidates being developed and expedited for testing around the world. A process that usually takes years was reduced to a few months, thanks to the existing technical infrastructure and thousands of scientists who enable rapid drug development. It is possible that the public may gradually modify its perception of the pharmaceutical industry from a “corporate villain” to an “indispensable health industry” for urgent medical crises such as a pandemic, and also for hundreds of medical diseases that are still in need of safe, effective therapies.
Economic burden. The unimaginable nightmare scenario of a total shutdown of all businesses led to the unprecedented loss of millions of jobs and livelihoods, reflected in miles-long lines of families at food banks. Overnight, the government switched from worrying about its $20-trillion deficit to printing several more trillion dollars to rescue the economy from collapse. The huge magnitude of a trillion can be appreciated if one is aware that it takes roughly 32 years to count to 1 billion, and 32,000 years to count to 1 trillion. Stimulating the economy while the gross domestic product threatens to sink by terrifying percentages (20% to 30%) was urgently needed, even though it meant mortgaging the future, especially when interest rates, and servicing the debt, will inevitably rise from the current zero to much higher levels in the future. The collapse of the once-thriving airline industry (bookings were down an estimated 98%) is an example of why desperate measures were needed to salvage an economy paralyzed by a viral pandemic.
Continue to: Political repercussions
Political repercussions. In our already hyperpartisan country, the COVID-19 crisis created more fissures across party lines. The blame game escalated as each side tried to exploit the crisis for political gain during a presidential election year. None of the leaders, from mayors to governors to the president, had any notion of how to wisely manage an unforeseen catastrophic pandemic. Thus, a political cacophony has developed, further exacerbating the public’s anxiety and uncertainty, especially about how and when the pandemic will end.
Education disruption. Never before have all schools and colleges around the country abruptly closed and sent students of all ages to shelter at home. Massive havoc ensued, with a wholesale switch to solitary online learning, the loss of the unique school and college social experience in the classroom and on campus, and the loss of experiencing commencement to receive a diploma (an important milestone for every graduate). Even medical students were not allowed to complete their clinical rotations and were sent home to attend online classes. A complete paradigm shift emerged about entrance exams: the SAT and ACT were eliminated for college applicants, and the MCAT for medical school applicants. This was unthinkable before the pandemic descended upon us, but benchmarks suddenly evaporated to adjust to the new reality. Then there followed disastrous financial losses by institutions of higher learning as well as academic medical centers and teaching hospitals, all slashing their budgets, furloughing employees, cutting salaries, and eliminating programs. Even the “sacred” tenure of senior faculty became a casualty of the financial “exigency.” Children’s nutrition suffered, especially among those in lower socioeconomic groups for whom the main meal of the day was the school lunch, and was made worse by their parents’ loss of income. For millions of people, the emotional toll was inevitable following the draconian measure of closing all educational institutions to contain the spread of the pandemic.
Family burden. Sheltering at home might have been fun for a few days, but after many weeks, it festered into a major stress, especially for those living in a small house, condominium, or apartment. The resilience of many families was tested as the exercise of freedoms collided with the fear of getting infected. Families were deprived of celebrating birthdays, weddings, funerals, graduation parties, retirement parties, Mother’s Day, Father’s Day, and various religious holidays, including Easter, Passover, and Eid al-Fitr.
Sexual burden. Intimacy and sexual contact between consenting adults living apart were sacrificed on the altar of the pernicious viral pandemic. Mandatory social distancing of 6 feet or more to avoid each other’s droplets emanating from simple speech, not just sneezing or coughing, makes intimacy practically impossible. Thus, physical closeness became taboo, and avoiding another person’s saliva or body secretions became a must to avoid contracting the virus. Being single was quite a lonely experience during this pandemic!
Entertainment deprivation. Americans are known to thrive on an extensive diet of spectator sports. Going to football, basketball, baseball, or hockey games to root for one’s team is intrinsically American. The pursuit of happiness extends to attending concerts, movies, Broadway shows, theme parks, and cruises with thousands of others. The pandemic ripped all those pleasurable leisure activities from our daily lives, leaving a big hole in people’s lives at the precise time fun activities were needed as a useful diversion from the dismal stress of a pandemic. To make things worse, it is uncertain when (if ever) such group activities will be restored, especially if the pandemic returns with another wave. But optimists would hurry to remind us that the “Roaring 20s” blossomed in the decade following the 1918 Spanish Flu pandemic.
Continue to: Legal system
Legal system. Astounding changes were instigated by the pandemic, such as the release of thousands of inmates, including felons, to avoid the spread of the virus in crowded prisons. For us psychiatrists, the silver lining in that unexpected action is that many of those released were patients with mental illness who were incarcerated because of the lack of hospitals that would take them. The police started issuing citations instead of arresting and jailing violators. Enforcement of the law was welcome when it targeted those who gouged the public for personal profit during the scarcity of masks, sanitizers, or even toilet paper and soap.
Medical practice. In addition to delaying medical care for patients, the freeze on so-called elective surgeries or procedures (many of which were actually necessary) was financially ruinous for physicians. Another regrettable consequence of the pandemic is a drop in pediatric vaccinations because parents were reluctant to take their children to the pediatrician. On a more positive note, the massive switch to telehealth was advantageous for both patients and psychiatrists because this technology is well-suited for psychiatric care. Fortunately, regulations that hampered telepsychiatry practice were substantially loosened or eliminated, and even the usually sacrosanct HIPAA regulations were temporarily sidelined.
Medical research. Both human and animal research came to a screeching halt, and many research assistants were furloughed. Data collection was disrupted, and a generation of scientific and medical discoveries became a casualty of the pandemic.
Medical literature. It was stunning to see how quickly COVID-19 occupied most of the pages of prominent journals. The scholarly articles were frankly quite useful, covering topics ranging from risk factors to early symptoms to treatment and pathophysiology across multiple organs. As with other paradigm shifts, there was an accelerated publication push, sometimes with expedited peer reviews to inform health care workers and the public while the pandemic was still raging. However, a couple of very prominent journals had to retract flawed articles that were hastily published without the usual due diligence and rigorous peer review. The pandemic clearly disrupted the science publishing process.
Travel effects. The steep reduction of flights (by 98%) was financially catastrophic, not only for airline companies but to business travel across the country. However, fewer cars on the road resulted in fewer accidents and deaths, and also reduced pollution. Paradoxically, to prevent crowding in subways, trains, and buses, officials reversed their traditional instructions and advised the public to drive their own cars instead of using public transportation!
Continue to: Heroism of front-line medical personnel
Heroism of front-line medical personnel. Everyone saluted and prayed for the health care professionals working at the bedside of highly infectious patients who needed 24/7 intensive care. Many have died while carrying out the noble but hazardous medical duties. Those heroes deserve our lasting respect and admiration.
The COVID-19 pandemic insidiously permeated and altered every aspect of our complex society and revealed how fragile our “normal lifestyle” really is. It is possible that nothing will ever be the same again, and an uneasy sense of vulnerability will engulf us as we cautiously return to a “new normal.” Even our language has expanded with the lexicon of pandemic terminology (Table). We all pray and hope that this plague never returns. And let’s hope one or more vaccines are developed soon so we can manage future recurrences like the annual flu season. In the meantime, keep your masks and sanitizers close by…
Postscript: Shortly after I completed this editorial, the ongoing COVID-19 plague was overshadowed by the scourge of racism, with massive protests, at times laced by violence, triggered by the death of a black man in custody of the police, under condemnable circumstances. The COVID-19 pandemic and the necessary social distancing it requires were temporarily ignored during the ensuing protests. The combined effect of those overlapping scourges are jarring to the country’s psyche, complicating and perhaps sabotaging the social recovery from the pandemic.
As the life-altering coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic gradually ebbs, we are all its survivors. Now, we are experiencing COVID-19 fatigue, trying to emerge from its dense fog that pervaded every facet of our lives. We are fully cognizant that there will not be a return to the previous “normal.” The pernicious virus had a transformative effect that did not spare any component of our society. Full recovery will not be easy.
As the uncertainty lingers about another devastating return of the pandemic later this year, we can see the reverberation of this invisible assault on human existence. Although a relatively small fraction of the population lost their lives, the rest of us are valiantly trying to readjust to the multiple ways our world has changed. Consider the following abrupt and sweeping burdens inflicted by the pandemic within a few short weeks:
Mental health. The acute stress of thanatophobia generated a triad of anxiety, depression, and nosophobia on a large scale. The demand for psychiatric care rapidly escalated. Suicide rate increased not only because of the stress of being locked down at home (alien to most people’s lifestyle) but because of the coincidental timing of the pandemic during April and May, the peak time of year for suicide. Animal researchers use immobilization as a paradigm to stress a rat or mouse. Many humans immobilized during the pandemic have developed exquisite empathy towards those rodents! The impact on children may also have long-term effects because playing and socializing with friends is a vital part of their lives. Parents have noticed dysphoria and acting out among their children, and an intense compensatory preoccupation with video games and electronic communications with friends.
Physical health. Medical care focused heavily on COVID-19 victims, to the detriment of all other medical conditions. Non-COVID-19 hospital admissions plummeted, and all elective surgeries and procedures were put on hold, depriving many people of medical care they badly needed. Emergency department (ED) visits also declined dramatically, including the usual flow of heart attacks, stroke, pulmonary embolus, asthma attacks, etc. The minimization of driving greatly reduced the admission of accident victims to EDs. Colonoscopies, cardiac stents, hip replacements, MRIs, mammography, and other procedures that are vital to maintain health and quality of life were halted. Dentists shuttered their practices due to the high risk of infection from exposure to oral secretions and breathing. One can only imagine the suffering of having a toothache with no dental help available, and how that might lead to narcotic abuse.
Social health. The imperative of social distancing disrupted most ordinary human activities, such as dining out, sitting in an auditorium for Grand Rounds or a lecture, visiting friends at their homes, the cherished interactions between grandparents and grandchildren (the lack of which I painfully experienced), and even seeing each other’s smiles behind the ubiquitous masks. And forget about hugging or kissing. The aversion to being near anyone who is coughing or sneezing led to an adaptive social paranoia and the social shunning of anyone who appeared to have an upper respiratory infection, even if it was unrelated to COVID-19.
Redemption for the pharmaceutical industry. The deadly pandemic intensified the public’s awareness of the importance of developing treatments and vaccines for COVID-19. The often-demonized pharmaceutical companies, with their extensive R&D infrastructure, emerged as a major source of hope for discovering an effective treatment for the coronavirus infection, or—better still—one or more vaccines that will enable society to return to its normal functions. It was quite impressive how many pharmaceutical companies “came to the rescue” with clinical trials to repurpose existing medications or to develop new ones. It was very encouraging to see multiple vaccine candidates being developed and expedited for testing around the world. A process that usually takes years was reduced to a few months, thanks to the existing technical infrastructure and thousands of scientists who enable rapid drug development. It is possible that the public may gradually modify its perception of the pharmaceutical industry from a “corporate villain” to an “indispensable health industry” for urgent medical crises such as a pandemic, and also for hundreds of medical diseases that are still in need of safe, effective therapies.
Economic burden. The unimaginable nightmare scenario of a total shutdown of all businesses led to the unprecedented loss of millions of jobs and livelihoods, reflected in miles-long lines of families at food banks. Overnight, the government switched from worrying about its $20-trillion deficit to printing several more trillion dollars to rescue the economy from collapse. The huge magnitude of a trillion can be appreciated if one is aware that it takes roughly 32 years to count to 1 billion, and 32,000 years to count to 1 trillion. Stimulating the economy while the gross domestic product threatens to sink by terrifying percentages (20% to 30%) was urgently needed, even though it meant mortgaging the future, especially when interest rates, and servicing the debt, will inevitably rise from the current zero to much higher levels in the future. The collapse of the once-thriving airline industry (bookings were down an estimated 98%) is an example of why desperate measures were needed to salvage an economy paralyzed by a viral pandemic.
Continue to: Political repercussions
Political repercussions. In our already hyperpartisan country, the COVID-19 crisis created more fissures across party lines. The blame game escalated as each side tried to exploit the crisis for political gain during a presidential election year. None of the leaders, from mayors to governors to the president, had any notion of how to wisely manage an unforeseen catastrophic pandemic. Thus, a political cacophony has developed, further exacerbating the public’s anxiety and uncertainty, especially about how and when the pandemic will end.
Education disruption. Never before have all schools and colleges around the country abruptly closed and sent students of all ages to shelter at home. Massive havoc ensued, with a wholesale switch to solitary online learning, the loss of the unique school and college social experience in the classroom and on campus, and the loss of experiencing commencement to receive a diploma (an important milestone for every graduate). Even medical students were not allowed to complete their clinical rotations and were sent home to attend online classes. A complete paradigm shift emerged about entrance exams: the SAT and ACT were eliminated for college applicants, and the MCAT for medical school applicants. This was unthinkable before the pandemic descended upon us, but benchmarks suddenly evaporated to adjust to the new reality. Then there followed disastrous financial losses by institutions of higher learning as well as academic medical centers and teaching hospitals, all slashing their budgets, furloughing employees, cutting salaries, and eliminating programs. Even the “sacred” tenure of senior faculty became a casualty of the financial “exigency.” Children’s nutrition suffered, especially among those in lower socioeconomic groups for whom the main meal of the day was the school lunch, and was made worse by their parents’ loss of income. For millions of people, the emotional toll was inevitable following the draconian measure of closing all educational institutions to contain the spread of the pandemic.
Family burden. Sheltering at home might have been fun for a few days, but after many weeks, it festered into a major stress, especially for those living in a small house, condominium, or apartment. The resilience of many families was tested as the exercise of freedoms collided with the fear of getting infected. Families were deprived of celebrating birthdays, weddings, funerals, graduation parties, retirement parties, Mother’s Day, Father’s Day, and various religious holidays, including Easter, Passover, and Eid al-Fitr.
Sexual burden. Intimacy and sexual contact between consenting adults living apart were sacrificed on the altar of the pernicious viral pandemic. Mandatory social distancing of 6 feet or more to avoid each other’s droplets emanating from simple speech, not just sneezing or coughing, makes intimacy practically impossible. Thus, physical closeness became taboo, and avoiding another person’s saliva or body secretions became a must to avoid contracting the virus. Being single was quite a lonely experience during this pandemic!
Entertainment deprivation. Americans are known to thrive on an extensive diet of spectator sports. Going to football, basketball, baseball, or hockey games to root for one’s team is intrinsically American. The pursuit of happiness extends to attending concerts, movies, Broadway shows, theme parks, and cruises with thousands of others. The pandemic ripped all those pleasurable leisure activities from our daily lives, leaving a big hole in people’s lives at the precise time fun activities were needed as a useful diversion from the dismal stress of a pandemic. To make things worse, it is uncertain when (if ever) such group activities will be restored, especially if the pandemic returns with another wave. But optimists would hurry to remind us that the “Roaring 20s” blossomed in the decade following the 1918 Spanish Flu pandemic.
Continue to: Legal system
Legal system. Astounding changes were instigated by the pandemic, such as the release of thousands of inmates, including felons, to avoid the spread of the virus in crowded prisons. For us psychiatrists, the silver lining in that unexpected action is that many of those released were patients with mental illness who were incarcerated because of the lack of hospitals that would take them. The police started issuing citations instead of arresting and jailing violators. Enforcement of the law was welcome when it targeted those who gouged the public for personal profit during the scarcity of masks, sanitizers, or even toilet paper and soap.
Medical practice. In addition to delaying medical care for patients, the freeze on so-called elective surgeries or procedures (many of which were actually necessary) was financially ruinous for physicians. Another regrettable consequence of the pandemic is a drop in pediatric vaccinations because parents were reluctant to take their children to the pediatrician. On a more positive note, the massive switch to telehealth was advantageous for both patients and psychiatrists because this technology is well-suited for psychiatric care. Fortunately, regulations that hampered telepsychiatry practice were substantially loosened or eliminated, and even the usually sacrosanct HIPAA regulations were temporarily sidelined.
Medical research. Both human and animal research came to a screeching halt, and many research assistants were furloughed. Data collection was disrupted, and a generation of scientific and medical discoveries became a casualty of the pandemic.
Medical literature. It was stunning to see how quickly COVID-19 occupied most of the pages of prominent journals. The scholarly articles were frankly quite useful, covering topics ranging from risk factors to early symptoms to treatment and pathophysiology across multiple organs. As with other paradigm shifts, there was an accelerated publication push, sometimes with expedited peer reviews to inform health care workers and the public while the pandemic was still raging. However, a couple of very prominent journals had to retract flawed articles that were hastily published without the usual due diligence and rigorous peer review. The pandemic clearly disrupted the science publishing process.
Travel effects. The steep reduction of flights (by 98%) was financially catastrophic, not only for airline companies but to business travel across the country. However, fewer cars on the road resulted in fewer accidents and deaths, and also reduced pollution. Paradoxically, to prevent crowding in subways, trains, and buses, officials reversed their traditional instructions and advised the public to drive their own cars instead of using public transportation!
Continue to: Heroism of front-line medical personnel
Heroism of front-line medical personnel. Everyone saluted and prayed for the health care professionals working at the bedside of highly infectious patients who needed 24/7 intensive care. Many have died while carrying out the noble but hazardous medical duties. Those heroes deserve our lasting respect and admiration.
The COVID-19 pandemic insidiously permeated and altered every aspect of our complex society and revealed how fragile our “normal lifestyle” really is. It is possible that nothing will ever be the same again, and an uneasy sense of vulnerability will engulf us as we cautiously return to a “new normal.” Even our language has expanded with the lexicon of pandemic terminology (Table). We all pray and hope that this plague never returns. And let’s hope one or more vaccines are developed soon so we can manage future recurrences like the annual flu season. In the meantime, keep your masks and sanitizers close by…
Postscript: Shortly after I completed this editorial, the ongoing COVID-19 plague was overshadowed by the scourge of racism, with massive protests, at times laced by violence, triggered by the death of a black man in custody of the police, under condemnable circumstances. The COVID-19 pandemic and the necessary social distancing it requires were temporarily ignored during the ensuing protests. The combined effect of those overlapping scourges are jarring to the country’s psyche, complicating and perhaps sabotaging the social recovery from the pandemic.
How to best use digital technology to help your patients
As psychiatrists, we are increasingly using digital technology, such as e-mail, video conferencing, social media, and text messaging, to communicate with and even treat our patients.1 The benefits of using digital technology for treating patients include, but are not limited to, enhancing access to psychiatric services that are unavailable due to a patient’s geographical location and/or physical disability; providing more cost‐effective delivery of services; and creating more ways for patients to communicate with their physicians.1 While there are benefits to using digital technology, there are also possible repercussions, such as breaches of confidentiality or boundary violations.2 Although there is no evidence-based guidance about how to best use digital technology in patient care,3 the following approaches can help you protect your patients and minimize your liability.
Assess competence. Determine how familiar and comfortable both you and your patient are with the specific software and/or devices you intend to use. Confirm that your patient can access the technology, and inform them of the benefits and risks of using digital technology in their care.1
Create a written policy about your use of digital technology, and review it with all patients to explain how it will be used in their treatment.1 This policy should include a back-up plan in the event of technology failures.1 It should clearly explain that the information gathered with this technology can become part of the patient’s medical record. It should also prohibit patients from using their devices to record other patients in the waiting room or other areas. Such a policy could enhance the protection of private information and help maintain clear boundaries.1 Review and update your policy as often as needed.
Obtain your patients’ written consent to use digital technology. If you want to post information about your patients on social media, obtain their written consent to do so, and mutually agree as to what information would be posted. This should not include their identity or confidential information.1
Do not accept friend requests or contact requests from current or former patients on any social networking platform. Do not follow your patients’ blogs, Twitter accounts, or any other accounts. Be aware that if you and your patients share the same “friend” network on social media, this may create boundary confusion, inappropriate dual relationships, and potential conflicts of interest.1 Keep personal and professional accounts separate to maintain appropriate boundaries and minimize compromising patient confidentiality. Do not post private information on professional practice accounts, and do not link/sync your personal accounts with professional accounts.
Do not store patient information on your personal electronic devices because these devices could be lost or hacked. Avoid contacting your patients via non-secured platforms because doing so could compromise patient confidentiality. Use encrypted software and firewalls for communicating with your patients and storing their information.1 Also, periodically assess your confidentiality policies and procedures to ensure compliance with appropriate statutes and laws.1
1. Reamer FG. Evolving standards of care in the age of cybertechnology. Behav Sci Law. 2018;36(2):257-269.
2. Ventola CL. Social media and health care professionals: benefits, risks, and best practices. P T. 2014;39(7):491-499, 520.
3. Logghe HJ, Boeck MA, Gusani NJ, et al. Best practices for surgeons’ social media use: statement of the Resident and Associate Society of the American College of Surgeons. J Am Coll Surg. 2018;226(3):317-327.
As psychiatrists, we are increasingly using digital technology, such as e-mail, video conferencing, social media, and text messaging, to communicate with and even treat our patients.1 The benefits of using digital technology for treating patients include, but are not limited to, enhancing access to psychiatric services that are unavailable due to a patient’s geographical location and/or physical disability; providing more cost‐effective delivery of services; and creating more ways for patients to communicate with their physicians.1 While there are benefits to using digital technology, there are also possible repercussions, such as breaches of confidentiality or boundary violations.2 Although there is no evidence-based guidance about how to best use digital technology in patient care,3 the following approaches can help you protect your patients and minimize your liability.
Assess competence. Determine how familiar and comfortable both you and your patient are with the specific software and/or devices you intend to use. Confirm that your patient can access the technology, and inform them of the benefits and risks of using digital technology in their care.1
Create a written policy about your use of digital technology, and review it with all patients to explain how it will be used in their treatment.1 This policy should include a back-up plan in the event of technology failures.1 It should clearly explain that the information gathered with this technology can become part of the patient’s medical record. It should also prohibit patients from using their devices to record other patients in the waiting room or other areas. Such a policy could enhance the protection of private information and help maintain clear boundaries.1 Review and update your policy as often as needed.
Obtain your patients’ written consent to use digital technology. If you want to post information about your patients on social media, obtain their written consent to do so, and mutually agree as to what information would be posted. This should not include their identity or confidential information.1
Do not accept friend requests or contact requests from current or former patients on any social networking platform. Do not follow your patients’ blogs, Twitter accounts, or any other accounts. Be aware that if you and your patients share the same “friend” network on social media, this may create boundary confusion, inappropriate dual relationships, and potential conflicts of interest.1 Keep personal and professional accounts separate to maintain appropriate boundaries and minimize compromising patient confidentiality. Do not post private information on professional practice accounts, and do not link/sync your personal accounts with professional accounts.
Do not store patient information on your personal electronic devices because these devices could be lost or hacked. Avoid contacting your patients via non-secured platforms because doing so could compromise patient confidentiality. Use encrypted software and firewalls for communicating with your patients and storing their information.1 Also, periodically assess your confidentiality policies and procedures to ensure compliance with appropriate statutes and laws.1
As psychiatrists, we are increasingly using digital technology, such as e-mail, video conferencing, social media, and text messaging, to communicate with and even treat our patients.1 The benefits of using digital technology for treating patients include, but are not limited to, enhancing access to psychiatric services that are unavailable due to a patient’s geographical location and/or physical disability; providing more cost‐effective delivery of services; and creating more ways for patients to communicate with their physicians.1 While there are benefits to using digital technology, there are also possible repercussions, such as breaches of confidentiality or boundary violations.2 Although there is no evidence-based guidance about how to best use digital technology in patient care,3 the following approaches can help you protect your patients and minimize your liability.
Assess competence. Determine how familiar and comfortable both you and your patient are with the specific software and/or devices you intend to use. Confirm that your patient can access the technology, and inform them of the benefits and risks of using digital technology in their care.1
Create a written policy about your use of digital technology, and review it with all patients to explain how it will be used in their treatment.1 This policy should include a back-up plan in the event of technology failures.1 It should clearly explain that the information gathered with this technology can become part of the patient’s medical record. It should also prohibit patients from using their devices to record other patients in the waiting room or other areas. Such a policy could enhance the protection of private information and help maintain clear boundaries.1 Review and update your policy as often as needed.
Obtain your patients’ written consent to use digital technology. If you want to post information about your patients on social media, obtain their written consent to do so, and mutually agree as to what information would be posted. This should not include their identity or confidential information.1
Do not accept friend requests or contact requests from current or former patients on any social networking platform. Do not follow your patients’ blogs, Twitter accounts, or any other accounts. Be aware that if you and your patients share the same “friend” network on social media, this may create boundary confusion, inappropriate dual relationships, and potential conflicts of interest.1 Keep personal and professional accounts separate to maintain appropriate boundaries and minimize compromising patient confidentiality. Do not post private information on professional practice accounts, and do not link/sync your personal accounts with professional accounts.
Do not store patient information on your personal electronic devices because these devices could be lost or hacked. Avoid contacting your patients via non-secured platforms because doing so could compromise patient confidentiality. Use encrypted software and firewalls for communicating with your patients and storing their information.1 Also, periodically assess your confidentiality policies and procedures to ensure compliance with appropriate statutes and laws.1
1. Reamer FG. Evolving standards of care in the age of cybertechnology. Behav Sci Law. 2018;36(2):257-269.
2. Ventola CL. Social media and health care professionals: benefits, risks, and best practices. P T. 2014;39(7):491-499, 520.
3. Logghe HJ, Boeck MA, Gusani NJ, et al. Best practices for surgeons’ social media use: statement of the Resident and Associate Society of the American College of Surgeons. J Am Coll Surg. 2018;226(3):317-327.
1. Reamer FG. Evolving standards of care in the age of cybertechnology. Behav Sci Law. 2018;36(2):257-269.
2. Ventola CL. Social media and health care professionals: benefits, risks, and best practices. P T. 2014;39(7):491-499, 520.
3. Logghe HJ, Boeck MA, Gusani NJ, et al. Best practices for surgeons’ social media use: statement of the Resident and Associate Society of the American College of Surgeons. J Am Coll Surg. 2018;226(3):317-327.
Two pandemics
This column is adapted from Dr. Eleryan’s speech at the George Washington University dermatology residency program’s virtual graduation ceremony on June 12.
I’ve been reflecting on my entire residency and the last 2 weeks have stood out the most. I have to admit that I’ve been angry, and so are numerous others who look like me. However, after conversations with a few important people in my life, I’ve realized that people care and are open to listening and changing if I give them the opportunity to see through my lens. I don’t want my legacy to be one of anger, but to be one of change, one of activism, one of heroism, and one of taking a stand in the midst of adversity.
So thank you to everyone who has played a part in my residency and is here to celebrate as I transition to the next step in my career.
But I must pause for a moment to say “I can’t breathe.” I can’t breathe because while I sit here in a place of honor for my accomplishments, I can’t forget that I’m standing in the gap for all of the black men and women who will never have the opportunity to experience a moment like this.
I can’t breathe because George Floyd, Breonna Taylor, Ahmaud Arbery, Tony McDade, Trayvon Martin, Philando Castile, Sandra Bland, Eric Garner, Tamir Rice, Mike Brown, Emmett Till, and so many others will never get to experience a celebratory occasion such as this because of their senseless executions as a likely result of racial bias.
As a black person in “the land of the free,” I have to live with the fact that my life may be taken for simply taking a stroll through a park, jogging through a neighborhood, driving down the street, walking back home from the store, or even sitting in my own home!
As a black physician, I must contend with the very notion that my privilege as a physician does not shield me from discrimination and bias. I recognize that my race walks into the room before I ever do. I know that many of my patients will question my abilities or my title – thinking I am the receptionist, food services worker, or even part of the janitorial staff – simply because of the color of my skin. And what’s even more disturbing is that some of my colleagues will confuse me with another black woman whom I look nothing like or challenge my intelligence and abilities and how I got my position.
All of this boils down to racism – pure and simple. Black people in this country don’t have the privilege of ignoring this truth. We know that this world is not colorblind; neither is anyone in it. We know that this is entrenched racism that for generations has created racial disparities in health care, education, housing, employment, and law enforcement. We weren’t born into a fragile or vulnerable state, yet we were born into a system of dis-enfranchisement, dis-investment, dis-crimination, dis-advantage, and dis-respect.
As physicians, we must recognize and acknowledge the lived experiences that walk through the door with our black patients. And we must understand that black patients walk around with the effects of trauma and toxic stress from just being black in America. That trauma and stress show up in very real ways that contribute to black people experiencing the brunt of chronic diseases and poorer health outcomes. There is no better example than the current COVID-19 pandemic. We are in the midst of a global pandemic from a virus that does not discriminate based on race, but black people are almost three times as likely to be hospitalized as are white people with COVID-19 . And why is that? Because of the “comorbidity” of racism that black people in this country live with. It is not a mere coincidence that the black population is overrepresented in essential jobs and black people are more likely to work in health care than are white people – all positions that increase the risk of infection and death from the virus. So, if we call COVID-19 a pandemic, racism most certainly has been a pandemic that this country has refused to acknowledge, treat, and vaccinate for centuries. We cannot ignore that both have tragically affected black people.
So as Pastor Reginald Sharpe Jr. in Chicago recently said, we’re dealing with two pandemics: One has no vaccination and one has no explanation; one can physiologically take your breath away because it affects the respiratory system, while the second can also take your breath away. Just ask Eric Garner and George Floyd.
As physicians, we must recognize that the mechanisms that tragically resulted in the deaths of George Floyd, Breonna Taylor, Ahmaud Arbery, and so many other black men and women are the same mechanisms that are harming and killing black people in our health care system. It’s not acceptable for institutions that built themselves on black and brown bodies to offer condolences, but to continue to do nothing about the racism that still runs rampant within. It’s not acceptable to do nothing. It’s important to note: Racist systems do not perpetuate themselves – the individuals operating within them do.
Martin Luther King Jr. once said, “He who passively accepts evil is as much involved in it as he who helps to perpetuate it. He who accepts evil without protesting against it is really cooperating with it.” Being well-intentioned, good-hearted, sad, or disheartened is not enough. We won’t be able to tear down the systems and institutions that have been a breeding ground for racism until outrage is met by action, not just from black people and people of color, but also by the white majority.
As physicians it’s time for us to look at how our health care institution – an institution instrumental in the victimization of black people – is affecting the health and well-being of our black patients. (For example, increased maternal mortality among black women.)
Are they being seen and heard? Are they receiving culturally relevant and sensitive care? Are their needs and concerns receiving the same amount of time and attention as other patients? It’s time to understand that, for many black patients, the health care system is another place of injustice that has not proved itself to be trustworthy or inclusive of black culture.
As physicians, we must affirm that the lives and health of black and brown people matter to us, that we see the racism they experience, and that we will use our platform as physicians to eliminate racism not just in the hospitals but in the world our patients live in.
So while I didn’t choose the body that I was born into, I fully embrace it and the challenges that come with it. I’m not here to make people feel comfortable, I’m here to continue the work of my ancestors, accomplish the dreams that they fought and lost their lives for, and most importantly, I’m here to continue the fight against the systems that work to prevent other marginalized persons from getting to where I am and even further.
The author James Baldwin once wrote, “Not everything that is faced can be changed, but nothing can be changed until it is faced.” So, I urge you to be loudly antiracist in every space that you hold. I urge you to educate yourselves about racism and white supremacy and privilege and how it permeates our health care system. I urge you to stand beside black people rather than in front of them. Use your privilege to amplify underheard voices and to challenge the biases of your peers, friends, and family members. Use your platform as physicians to advocate for a more just and equitable health care system.
So let me repeat ... we as physicians have the responsibility to eliminate racial bias in the practice of medicine and recognize racism as a threat to the health and well-being of black people and other people of color.
How do we do this? We are beyond lengthy dialogue and “Black History Month” talks. Now is the time for action. Taking action includes the following:
1. Medical academic institutions committing to having a diverse and inclusive faculty. We know it is critical and vital to the recruitment, success, and matriculation of medical students and residents of color to see faculty, particularly senior level faculty in their specialty, who look like them and can serve as mentors. Every year, these institutions need to set a goal that they will take additional steps to have at least one-third of their faculty be black and another third persons of color. In addition, senior faculty positions – those setting curricula, selecting incoming students and residents – must include at least one-third from underrepresented backgrounds (black, Hispanic, Native American/Indigenous).
2. Hospital administration has to resemble the communities in which the hospital serves. Unfortunately, all too often, we know this is not the case, and as a result, decisions that affect the care of black and brown people are often to their detriment because they perpetuate the racism within the existing system. In order to dismantle racism in the hospital system, hospital administrations must consist of diverse individuals. Therefore, hospitals need to commit to hiring and promoting black and brown staff to ensure one-third of its senior leaderships consists of individuals from underrepresented backgrounds.
3. Improving the pipeline that matriculates black and brown students into medical school and residency programs. Lack of access to mentors within the medical field, lack of funding for travel to/from interviews, and lack of knowledge of the overall application process are a few barriers faced by students of color seeking to enter into the medical field. In addition to current scholarship opportunities, medical schools need to allocate funds to connect underrepresented minority students with a range of lived experiences (not just those from impoverished backgrounds but also those from middle class backgrounds who face difficulty gaining acceptance into medical school and residency programs), such as connecting them with mentors by opening opportunities for them to shadow professionals at a conference, travel to residency interviews with most, if not all, expenses covered up front, and have access to local programs that expose them to physicians in several specialties.
These are just a few examples of the active steps we can take to dismantle racism and reconcile the effects of it in the medical field. So if I may borrow from other movements, “Time’s Up” for silence regarding the existence of racism and white supremacy, and now it’s time to truly show that “We are all in this together.”
It is not just my duty but yours also – to ensure that we never have to hear another black man, woman, or child say “I can’t breathe” at the hands of injustice.
Dr. Eleryan (@skinclusionMD) is a social justice activist and was co-chief resident in dermatology (2019-2020) at George Washington University, Washington, DC, and is an Alpha Omega Alpha inductee (2020). She will be a micrographic surgery and dermatologic oncology fellow at the University of California, Los Angeles, in July 2020.
This column is adapted from Dr. Eleryan’s speech at the George Washington University dermatology residency program’s virtual graduation ceremony on June 12.
I’ve been reflecting on my entire residency and the last 2 weeks have stood out the most. I have to admit that I’ve been angry, and so are numerous others who look like me. However, after conversations with a few important people in my life, I’ve realized that people care and are open to listening and changing if I give them the opportunity to see through my lens. I don’t want my legacy to be one of anger, but to be one of change, one of activism, one of heroism, and one of taking a stand in the midst of adversity.
So thank you to everyone who has played a part in my residency and is here to celebrate as I transition to the next step in my career.
But I must pause for a moment to say “I can’t breathe.” I can’t breathe because while I sit here in a place of honor for my accomplishments, I can’t forget that I’m standing in the gap for all of the black men and women who will never have the opportunity to experience a moment like this.
I can’t breathe because George Floyd, Breonna Taylor, Ahmaud Arbery, Tony McDade, Trayvon Martin, Philando Castile, Sandra Bland, Eric Garner, Tamir Rice, Mike Brown, Emmett Till, and so many others will never get to experience a celebratory occasion such as this because of their senseless executions as a likely result of racial bias.
As a black person in “the land of the free,” I have to live with the fact that my life may be taken for simply taking a stroll through a park, jogging through a neighborhood, driving down the street, walking back home from the store, or even sitting in my own home!
As a black physician, I must contend with the very notion that my privilege as a physician does not shield me from discrimination and bias. I recognize that my race walks into the room before I ever do. I know that many of my patients will question my abilities or my title – thinking I am the receptionist, food services worker, or even part of the janitorial staff – simply because of the color of my skin. And what’s even more disturbing is that some of my colleagues will confuse me with another black woman whom I look nothing like or challenge my intelligence and abilities and how I got my position.
All of this boils down to racism – pure and simple. Black people in this country don’t have the privilege of ignoring this truth. We know that this world is not colorblind; neither is anyone in it. We know that this is entrenched racism that for generations has created racial disparities in health care, education, housing, employment, and law enforcement. We weren’t born into a fragile or vulnerable state, yet we were born into a system of dis-enfranchisement, dis-investment, dis-crimination, dis-advantage, and dis-respect.
As physicians, we must recognize and acknowledge the lived experiences that walk through the door with our black patients. And we must understand that black patients walk around with the effects of trauma and toxic stress from just being black in America. That trauma and stress show up in very real ways that contribute to black people experiencing the brunt of chronic diseases and poorer health outcomes. There is no better example than the current COVID-19 pandemic. We are in the midst of a global pandemic from a virus that does not discriminate based on race, but black people are almost three times as likely to be hospitalized as are white people with COVID-19 . And why is that? Because of the “comorbidity” of racism that black people in this country live with. It is not a mere coincidence that the black population is overrepresented in essential jobs and black people are more likely to work in health care than are white people – all positions that increase the risk of infection and death from the virus. So, if we call COVID-19 a pandemic, racism most certainly has been a pandemic that this country has refused to acknowledge, treat, and vaccinate for centuries. We cannot ignore that both have tragically affected black people.
So as Pastor Reginald Sharpe Jr. in Chicago recently said, we’re dealing with two pandemics: One has no vaccination and one has no explanation; one can physiologically take your breath away because it affects the respiratory system, while the second can also take your breath away. Just ask Eric Garner and George Floyd.
As physicians, we must recognize that the mechanisms that tragically resulted in the deaths of George Floyd, Breonna Taylor, Ahmaud Arbery, and so many other black men and women are the same mechanisms that are harming and killing black people in our health care system. It’s not acceptable for institutions that built themselves on black and brown bodies to offer condolences, but to continue to do nothing about the racism that still runs rampant within. It’s not acceptable to do nothing. It’s important to note: Racist systems do not perpetuate themselves – the individuals operating within them do.
Martin Luther King Jr. once said, “He who passively accepts evil is as much involved in it as he who helps to perpetuate it. He who accepts evil without protesting against it is really cooperating with it.” Being well-intentioned, good-hearted, sad, or disheartened is not enough. We won’t be able to tear down the systems and institutions that have been a breeding ground for racism until outrage is met by action, not just from black people and people of color, but also by the white majority.
As physicians it’s time for us to look at how our health care institution – an institution instrumental in the victimization of black people – is affecting the health and well-being of our black patients. (For example, increased maternal mortality among black women.)
Are they being seen and heard? Are they receiving culturally relevant and sensitive care? Are their needs and concerns receiving the same amount of time and attention as other patients? It’s time to understand that, for many black patients, the health care system is another place of injustice that has not proved itself to be trustworthy or inclusive of black culture.
As physicians, we must affirm that the lives and health of black and brown people matter to us, that we see the racism they experience, and that we will use our platform as physicians to eliminate racism not just in the hospitals but in the world our patients live in.
So while I didn’t choose the body that I was born into, I fully embrace it and the challenges that come with it. I’m not here to make people feel comfortable, I’m here to continue the work of my ancestors, accomplish the dreams that they fought and lost their lives for, and most importantly, I’m here to continue the fight against the systems that work to prevent other marginalized persons from getting to where I am and even further.
The author James Baldwin once wrote, “Not everything that is faced can be changed, but nothing can be changed until it is faced.” So, I urge you to be loudly antiracist in every space that you hold. I urge you to educate yourselves about racism and white supremacy and privilege and how it permeates our health care system. I urge you to stand beside black people rather than in front of them. Use your privilege to amplify underheard voices and to challenge the biases of your peers, friends, and family members. Use your platform as physicians to advocate for a more just and equitable health care system.
So let me repeat ... we as physicians have the responsibility to eliminate racial bias in the practice of medicine and recognize racism as a threat to the health and well-being of black people and other people of color.
How do we do this? We are beyond lengthy dialogue and “Black History Month” talks. Now is the time for action. Taking action includes the following:
1. Medical academic institutions committing to having a diverse and inclusive faculty. We know it is critical and vital to the recruitment, success, and matriculation of medical students and residents of color to see faculty, particularly senior level faculty in their specialty, who look like them and can serve as mentors. Every year, these institutions need to set a goal that they will take additional steps to have at least one-third of their faculty be black and another third persons of color. In addition, senior faculty positions – those setting curricula, selecting incoming students and residents – must include at least one-third from underrepresented backgrounds (black, Hispanic, Native American/Indigenous).
2. Hospital administration has to resemble the communities in which the hospital serves. Unfortunately, all too often, we know this is not the case, and as a result, decisions that affect the care of black and brown people are often to their detriment because they perpetuate the racism within the existing system. In order to dismantle racism in the hospital system, hospital administrations must consist of diverse individuals. Therefore, hospitals need to commit to hiring and promoting black and brown staff to ensure one-third of its senior leaderships consists of individuals from underrepresented backgrounds.
3. Improving the pipeline that matriculates black and brown students into medical school and residency programs. Lack of access to mentors within the medical field, lack of funding for travel to/from interviews, and lack of knowledge of the overall application process are a few barriers faced by students of color seeking to enter into the medical field. In addition to current scholarship opportunities, medical schools need to allocate funds to connect underrepresented minority students with a range of lived experiences (not just those from impoverished backgrounds but also those from middle class backgrounds who face difficulty gaining acceptance into medical school and residency programs), such as connecting them with mentors by opening opportunities for them to shadow professionals at a conference, travel to residency interviews with most, if not all, expenses covered up front, and have access to local programs that expose them to physicians in several specialties.
These are just a few examples of the active steps we can take to dismantle racism and reconcile the effects of it in the medical field. So if I may borrow from other movements, “Time’s Up” for silence regarding the existence of racism and white supremacy, and now it’s time to truly show that “We are all in this together.”
It is not just my duty but yours also – to ensure that we never have to hear another black man, woman, or child say “I can’t breathe” at the hands of injustice.
Dr. Eleryan (@skinclusionMD) is a social justice activist and was co-chief resident in dermatology (2019-2020) at George Washington University, Washington, DC, and is an Alpha Omega Alpha inductee (2020). She will be a micrographic surgery and dermatologic oncology fellow at the University of California, Los Angeles, in July 2020.
This column is adapted from Dr. Eleryan’s speech at the George Washington University dermatology residency program’s virtual graduation ceremony on June 12.
I’ve been reflecting on my entire residency and the last 2 weeks have stood out the most. I have to admit that I’ve been angry, and so are numerous others who look like me. However, after conversations with a few important people in my life, I’ve realized that people care and are open to listening and changing if I give them the opportunity to see through my lens. I don’t want my legacy to be one of anger, but to be one of change, one of activism, one of heroism, and one of taking a stand in the midst of adversity.
So thank you to everyone who has played a part in my residency and is here to celebrate as I transition to the next step in my career.
But I must pause for a moment to say “I can’t breathe.” I can’t breathe because while I sit here in a place of honor for my accomplishments, I can’t forget that I’m standing in the gap for all of the black men and women who will never have the opportunity to experience a moment like this.
I can’t breathe because George Floyd, Breonna Taylor, Ahmaud Arbery, Tony McDade, Trayvon Martin, Philando Castile, Sandra Bland, Eric Garner, Tamir Rice, Mike Brown, Emmett Till, and so many others will never get to experience a celebratory occasion such as this because of their senseless executions as a likely result of racial bias.
As a black person in “the land of the free,” I have to live with the fact that my life may be taken for simply taking a stroll through a park, jogging through a neighborhood, driving down the street, walking back home from the store, or even sitting in my own home!
As a black physician, I must contend with the very notion that my privilege as a physician does not shield me from discrimination and bias. I recognize that my race walks into the room before I ever do. I know that many of my patients will question my abilities or my title – thinking I am the receptionist, food services worker, or even part of the janitorial staff – simply because of the color of my skin. And what’s even more disturbing is that some of my colleagues will confuse me with another black woman whom I look nothing like or challenge my intelligence and abilities and how I got my position.
All of this boils down to racism – pure and simple. Black people in this country don’t have the privilege of ignoring this truth. We know that this world is not colorblind; neither is anyone in it. We know that this is entrenched racism that for generations has created racial disparities in health care, education, housing, employment, and law enforcement. We weren’t born into a fragile or vulnerable state, yet we were born into a system of dis-enfranchisement, dis-investment, dis-crimination, dis-advantage, and dis-respect.
As physicians, we must recognize and acknowledge the lived experiences that walk through the door with our black patients. And we must understand that black patients walk around with the effects of trauma and toxic stress from just being black in America. That trauma and stress show up in very real ways that contribute to black people experiencing the brunt of chronic diseases and poorer health outcomes. There is no better example than the current COVID-19 pandemic. We are in the midst of a global pandemic from a virus that does not discriminate based on race, but black people are almost three times as likely to be hospitalized as are white people with COVID-19 . And why is that? Because of the “comorbidity” of racism that black people in this country live with. It is not a mere coincidence that the black population is overrepresented in essential jobs and black people are more likely to work in health care than are white people – all positions that increase the risk of infection and death from the virus. So, if we call COVID-19 a pandemic, racism most certainly has been a pandemic that this country has refused to acknowledge, treat, and vaccinate for centuries. We cannot ignore that both have tragically affected black people.
So as Pastor Reginald Sharpe Jr. in Chicago recently said, we’re dealing with two pandemics: One has no vaccination and one has no explanation; one can physiologically take your breath away because it affects the respiratory system, while the second can also take your breath away. Just ask Eric Garner and George Floyd.
As physicians, we must recognize that the mechanisms that tragically resulted in the deaths of George Floyd, Breonna Taylor, Ahmaud Arbery, and so many other black men and women are the same mechanisms that are harming and killing black people in our health care system. It’s not acceptable for institutions that built themselves on black and brown bodies to offer condolences, but to continue to do nothing about the racism that still runs rampant within. It’s not acceptable to do nothing. It’s important to note: Racist systems do not perpetuate themselves – the individuals operating within them do.
Martin Luther King Jr. once said, “He who passively accepts evil is as much involved in it as he who helps to perpetuate it. He who accepts evil without protesting against it is really cooperating with it.” Being well-intentioned, good-hearted, sad, or disheartened is not enough. We won’t be able to tear down the systems and institutions that have been a breeding ground for racism until outrage is met by action, not just from black people and people of color, but also by the white majority.
As physicians it’s time for us to look at how our health care institution – an institution instrumental in the victimization of black people – is affecting the health and well-being of our black patients. (For example, increased maternal mortality among black women.)
Are they being seen and heard? Are they receiving culturally relevant and sensitive care? Are their needs and concerns receiving the same amount of time and attention as other patients? It’s time to understand that, for many black patients, the health care system is another place of injustice that has not proved itself to be trustworthy or inclusive of black culture.
As physicians, we must affirm that the lives and health of black and brown people matter to us, that we see the racism they experience, and that we will use our platform as physicians to eliminate racism not just in the hospitals but in the world our patients live in.
So while I didn’t choose the body that I was born into, I fully embrace it and the challenges that come with it. I’m not here to make people feel comfortable, I’m here to continue the work of my ancestors, accomplish the dreams that they fought and lost their lives for, and most importantly, I’m here to continue the fight against the systems that work to prevent other marginalized persons from getting to where I am and even further.
The author James Baldwin once wrote, “Not everything that is faced can be changed, but nothing can be changed until it is faced.” So, I urge you to be loudly antiracist in every space that you hold. I urge you to educate yourselves about racism and white supremacy and privilege and how it permeates our health care system. I urge you to stand beside black people rather than in front of them. Use your privilege to amplify underheard voices and to challenge the biases of your peers, friends, and family members. Use your platform as physicians to advocate for a more just and equitable health care system.
So let me repeat ... we as physicians have the responsibility to eliminate racial bias in the practice of medicine and recognize racism as a threat to the health and well-being of black people and other people of color.
How do we do this? We are beyond lengthy dialogue and “Black History Month” talks. Now is the time for action. Taking action includes the following:
1. Medical academic institutions committing to having a diverse and inclusive faculty. We know it is critical and vital to the recruitment, success, and matriculation of medical students and residents of color to see faculty, particularly senior level faculty in their specialty, who look like them and can serve as mentors. Every year, these institutions need to set a goal that they will take additional steps to have at least one-third of their faculty be black and another third persons of color. In addition, senior faculty positions – those setting curricula, selecting incoming students and residents – must include at least one-third from underrepresented backgrounds (black, Hispanic, Native American/Indigenous).
2. Hospital administration has to resemble the communities in which the hospital serves. Unfortunately, all too often, we know this is not the case, and as a result, decisions that affect the care of black and brown people are often to their detriment because they perpetuate the racism within the existing system. In order to dismantle racism in the hospital system, hospital administrations must consist of diverse individuals. Therefore, hospitals need to commit to hiring and promoting black and brown staff to ensure one-third of its senior leaderships consists of individuals from underrepresented backgrounds.
3. Improving the pipeline that matriculates black and brown students into medical school and residency programs. Lack of access to mentors within the medical field, lack of funding for travel to/from interviews, and lack of knowledge of the overall application process are a few barriers faced by students of color seeking to enter into the medical field. In addition to current scholarship opportunities, medical schools need to allocate funds to connect underrepresented minority students with a range of lived experiences (not just those from impoverished backgrounds but also those from middle class backgrounds who face difficulty gaining acceptance into medical school and residency programs), such as connecting them with mentors by opening opportunities for them to shadow professionals at a conference, travel to residency interviews with most, if not all, expenses covered up front, and have access to local programs that expose them to physicians in several specialties.
These are just a few examples of the active steps we can take to dismantle racism and reconcile the effects of it in the medical field. So if I may borrow from other movements, “Time’s Up” for silence regarding the existence of racism and white supremacy, and now it’s time to truly show that “We are all in this together.”
It is not just my duty but yours also – to ensure that we never have to hear another black man, woman, or child say “I can’t breathe” at the hands of injustice.
Dr. Eleryan (@skinclusionMD) is a social justice activist and was co-chief resident in dermatology (2019-2020) at George Washington University, Washington, DC, and is an Alpha Omega Alpha inductee (2020). She will be a micrographic surgery and dermatologic oncology fellow at the University of California, Los Angeles, in July 2020.
How racism contributes to the effects of SARS-CoV-2
It’s been about two months since I volunteered in a hospital in Brooklyn, working in an ICU taking care of patients with COVID-19.
Everyone seems to have forgotten the early days of the pandemic – the time when the ICUs were overrun, we were using FEMA ventilators, and endocrinologists and psychiatrists were acting as intensivists.
Even though things are opening up and people are taking summer vacations in a seemingly amnestic state, having witnessed multiple daily deaths remains a part of my daily consciousness. As I see the case numbers climbing juxtaposed against people being out and about without masks, my anxiety level is rising.
A virus doesn’t discriminate. It can fly through the air, landing on the next available surface. If that virus is SARS-CoV-2 and that surface is a human mucosal membrane, the virus makes itself at home. It orders furniture, buys a fancy mattress and a large high definition TV, hangs art on the walls, and settles in for the long haul. It’s not going anywhere anytime soon.
Even as an equal opportunity virus, what SARS-CoV-2 has done is to hold a mirror up to the healthcare system. It has shown us what was here all along. When people first started noticing that underrepresented minorities were more likely to contract the virus and get sick from it, I heard musings that this was likely because of their preexisting health conditions. For example, commentators on cable news were quick to point out that black people are more likely than other people to have hypertension or diabetes. So doesn’t that explain why they are more affected by this virus?
That certainly is part of the story, but it doesn’t entirely explain the discrepancies we’ve seen. For example, in New York 14% of the population is black, and 25% of those who had a COVID-related death were black patients. Similarly, 19% of the population is Hispanic or Latino, and they made up 26% of COVID-related deaths. On the other hand, 55% of the population in New York is white, and white people account for only 34% of COVID-related deaths.
Working in Brooklyn, I didn’t need to be a keen observer to notice that, out of our entire unit of about 20-25 patients, there was only one patient in a 2-week period who was neither black nor Hispanic.
As others have written, there are other factors at play. I’m not sure how many of those commentators back in March stopped to think about why black patients are more likely to have hypertension and diabetes, but the chronic stress of facing racism on a daily basis surely contributes. Beyond those medical problems, minorities are more likely to live in multigenerational housing, which means that it is harder for them to isolate from others. In addition, their living quarters tend to be further from health care centers and grocery stores, which makes it harder for them to access medical care and healthy food.
As if that weren’t enough to put their health at risk, people of color are also affected by environmental racism . Factories with toxic waste are more likely to be built in or near neighborhoods filled with people of color than in other communities. On top of that, black and Hispanic people are also more likely to be under- or uninsured, meaning they often delay seeking care in order to avoid astronomic healthcare costs.
Black and Hispanic people are also more likely than others to be working in the service industry or other essential services, which means they are less likely to be able to work from home. Consequently, they have to risk more exposures to other people and the virus than do those who have the privilege of working safely from home. They also are less likely to have available paid leave and, therefore, are more likely to work while sick.
With the deck completely stacked against them, underrepresented minorities also face systemic bias and racism when interacting with the health care system. Physicians mistakenly believe black patients experience less pain than other patients, according to some research. Black mothers have significantly worse health care outcomes than do their non-black counterparts, and the infant mortality rate for Black infants is much higher as well.
In my limited time in Brooklyn, taking care of almost exclusively black and Hispanic patients, I saw one physician assistant and one nurse who were black; one nurse practitioner was Hispanic. This mismatch is sadly common. Although 13% of the population of the United States is black, only 5% of physicians in the United States are black. Hispanic people, who make up 18% of the US population, are only 6% of physicians. This undoubtedly contributes to poorer outcomes for underrepresented minority patients who have a hard time finding physicians who look like them and understand them.
So while SARS-CoV-2 may not discriminate, the effects it has on patients depends on all of these other factors. If it flies through the air and lands on the mucosal tract of a person who works from home, has effective health insurance and a primary care physician, and lives in a community with no toxic exposures, that person may be more likely to kick it out before it has a chance to settle in. The reason we have such a huge disparity in outcomes related to COVID-19 by race is that a person meeting that description is less likely to be black or Hispanic. Race is not an independent risk factor; structural racism is.
When I drive by the mall that is now open or the restaurants that are now open with indoor dining, my heart rate quickens just a bit with anxiety. The pandemic fatigue people are experiencing is leading them to act in unsafe ways – gathering with more people, not wearing masks, not keeping a safe distance. I worry about everyone, sure, but I really worry about black and Hispanic people who are most vulnerable as a result of everyone else’s refusal to follow guidelines.
Dr. Salles is a bariatric surgeon and is currently a Scholar in Residence at Stanford (Calif.) University. Find her on Twitter @arghavan_salles.
It’s been about two months since I volunteered in a hospital in Brooklyn, working in an ICU taking care of patients with COVID-19.
Everyone seems to have forgotten the early days of the pandemic – the time when the ICUs were overrun, we were using FEMA ventilators, and endocrinologists and psychiatrists were acting as intensivists.
Even though things are opening up and people are taking summer vacations in a seemingly amnestic state, having witnessed multiple daily deaths remains a part of my daily consciousness. As I see the case numbers climbing juxtaposed against people being out and about without masks, my anxiety level is rising.
A virus doesn’t discriminate. It can fly through the air, landing on the next available surface. If that virus is SARS-CoV-2 and that surface is a human mucosal membrane, the virus makes itself at home. It orders furniture, buys a fancy mattress and a large high definition TV, hangs art on the walls, and settles in for the long haul. It’s not going anywhere anytime soon.
Even as an equal opportunity virus, what SARS-CoV-2 has done is to hold a mirror up to the healthcare system. It has shown us what was here all along. When people first started noticing that underrepresented minorities were more likely to contract the virus and get sick from it, I heard musings that this was likely because of their preexisting health conditions. For example, commentators on cable news were quick to point out that black people are more likely than other people to have hypertension or diabetes. So doesn’t that explain why they are more affected by this virus?
That certainly is part of the story, but it doesn’t entirely explain the discrepancies we’ve seen. For example, in New York 14% of the population is black, and 25% of those who had a COVID-related death were black patients. Similarly, 19% of the population is Hispanic or Latino, and they made up 26% of COVID-related deaths. On the other hand, 55% of the population in New York is white, and white people account for only 34% of COVID-related deaths.
Working in Brooklyn, I didn’t need to be a keen observer to notice that, out of our entire unit of about 20-25 patients, there was only one patient in a 2-week period who was neither black nor Hispanic.
As others have written, there are other factors at play. I’m not sure how many of those commentators back in March stopped to think about why black patients are more likely to have hypertension and diabetes, but the chronic stress of facing racism on a daily basis surely contributes. Beyond those medical problems, minorities are more likely to live in multigenerational housing, which means that it is harder for them to isolate from others. In addition, their living quarters tend to be further from health care centers and grocery stores, which makes it harder for them to access medical care and healthy food.
As if that weren’t enough to put their health at risk, people of color are also affected by environmental racism . Factories with toxic waste are more likely to be built in or near neighborhoods filled with people of color than in other communities. On top of that, black and Hispanic people are also more likely to be under- or uninsured, meaning they often delay seeking care in order to avoid astronomic healthcare costs.
Black and Hispanic people are also more likely than others to be working in the service industry or other essential services, which means they are less likely to be able to work from home. Consequently, they have to risk more exposures to other people and the virus than do those who have the privilege of working safely from home. They also are less likely to have available paid leave and, therefore, are more likely to work while sick.
With the deck completely stacked against them, underrepresented minorities also face systemic bias and racism when interacting with the health care system. Physicians mistakenly believe black patients experience less pain than other patients, according to some research. Black mothers have significantly worse health care outcomes than do their non-black counterparts, and the infant mortality rate for Black infants is much higher as well.
In my limited time in Brooklyn, taking care of almost exclusively black and Hispanic patients, I saw one physician assistant and one nurse who were black; one nurse practitioner was Hispanic. This mismatch is sadly common. Although 13% of the population of the United States is black, only 5% of physicians in the United States are black. Hispanic people, who make up 18% of the US population, are only 6% of physicians. This undoubtedly contributes to poorer outcomes for underrepresented minority patients who have a hard time finding physicians who look like them and understand them.
So while SARS-CoV-2 may not discriminate, the effects it has on patients depends on all of these other factors. If it flies through the air and lands on the mucosal tract of a person who works from home, has effective health insurance and a primary care physician, and lives in a community with no toxic exposures, that person may be more likely to kick it out before it has a chance to settle in. The reason we have such a huge disparity in outcomes related to COVID-19 by race is that a person meeting that description is less likely to be black or Hispanic. Race is not an independent risk factor; structural racism is.
When I drive by the mall that is now open or the restaurants that are now open with indoor dining, my heart rate quickens just a bit with anxiety. The pandemic fatigue people are experiencing is leading them to act in unsafe ways – gathering with more people, not wearing masks, not keeping a safe distance. I worry about everyone, sure, but I really worry about black and Hispanic people who are most vulnerable as a result of everyone else’s refusal to follow guidelines.
Dr. Salles is a bariatric surgeon and is currently a Scholar in Residence at Stanford (Calif.) University. Find her on Twitter @arghavan_salles.
It’s been about two months since I volunteered in a hospital in Brooklyn, working in an ICU taking care of patients with COVID-19.
Everyone seems to have forgotten the early days of the pandemic – the time when the ICUs were overrun, we were using FEMA ventilators, and endocrinologists and psychiatrists were acting as intensivists.
Even though things are opening up and people are taking summer vacations in a seemingly amnestic state, having witnessed multiple daily deaths remains a part of my daily consciousness. As I see the case numbers climbing juxtaposed against people being out and about without masks, my anxiety level is rising.
A virus doesn’t discriminate. It can fly through the air, landing on the next available surface. If that virus is SARS-CoV-2 and that surface is a human mucosal membrane, the virus makes itself at home. It orders furniture, buys a fancy mattress and a large high definition TV, hangs art on the walls, and settles in for the long haul. It’s not going anywhere anytime soon.
Even as an equal opportunity virus, what SARS-CoV-2 has done is to hold a mirror up to the healthcare system. It has shown us what was here all along. When people first started noticing that underrepresented minorities were more likely to contract the virus and get sick from it, I heard musings that this was likely because of their preexisting health conditions. For example, commentators on cable news were quick to point out that black people are more likely than other people to have hypertension or diabetes. So doesn’t that explain why they are more affected by this virus?
That certainly is part of the story, but it doesn’t entirely explain the discrepancies we’ve seen. For example, in New York 14% of the population is black, and 25% of those who had a COVID-related death were black patients. Similarly, 19% of the population is Hispanic or Latino, and they made up 26% of COVID-related deaths. On the other hand, 55% of the population in New York is white, and white people account for only 34% of COVID-related deaths.
Working in Brooklyn, I didn’t need to be a keen observer to notice that, out of our entire unit of about 20-25 patients, there was only one patient in a 2-week period who was neither black nor Hispanic.
As others have written, there are other factors at play. I’m not sure how many of those commentators back in March stopped to think about why black patients are more likely to have hypertension and diabetes, but the chronic stress of facing racism on a daily basis surely contributes. Beyond those medical problems, minorities are more likely to live in multigenerational housing, which means that it is harder for them to isolate from others. In addition, their living quarters tend to be further from health care centers and grocery stores, which makes it harder for them to access medical care and healthy food.
As if that weren’t enough to put their health at risk, people of color are also affected by environmental racism . Factories with toxic waste are more likely to be built in or near neighborhoods filled with people of color than in other communities. On top of that, black and Hispanic people are also more likely to be under- or uninsured, meaning they often delay seeking care in order to avoid astronomic healthcare costs.
Black and Hispanic people are also more likely than others to be working in the service industry or other essential services, which means they are less likely to be able to work from home. Consequently, they have to risk more exposures to other people and the virus than do those who have the privilege of working safely from home. They also are less likely to have available paid leave and, therefore, are more likely to work while sick.
With the deck completely stacked against them, underrepresented minorities also face systemic bias and racism when interacting with the health care system. Physicians mistakenly believe black patients experience less pain than other patients, according to some research. Black mothers have significantly worse health care outcomes than do their non-black counterparts, and the infant mortality rate for Black infants is much higher as well.
In my limited time in Brooklyn, taking care of almost exclusively black and Hispanic patients, I saw one physician assistant and one nurse who were black; one nurse practitioner was Hispanic. This mismatch is sadly common. Although 13% of the population of the United States is black, only 5% of physicians in the United States are black. Hispanic people, who make up 18% of the US population, are only 6% of physicians. This undoubtedly contributes to poorer outcomes for underrepresented minority patients who have a hard time finding physicians who look like them and understand them.
So while SARS-CoV-2 may not discriminate, the effects it has on patients depends on all of these other factors. If it flies through the air and lands on the mucosal tract of a person who works from home, has effective health insurance and a primary care physician, and lives in a community with no toxic exposures, that person may be more likely to kick it out before it has a chance to settle in. The reason we have such a huge disparity in outcomes related to COVID-19 by race is that a person meeting that description is less likely to be black or Hispanic. Race is not an independent risk factor; structural racism is.
When I drive by the mall that is now open or the restaurants that are now open with indoor dining, my heart rate quickens just a bit with anxiety. The pandemic fatigue people are experiencing is leading them to act in unsafe ways – gathering with more people, not wearing masks, not keeping a safe distance. I worry about everyone, sure, but I really worry about black and Hispanic people who are most vulnerable as a result of everyone else’s refusal to follow guidelines.
Dr. Salles is a bariatric surgeon and is currently a Scholar in Residence at Stanford (Calif.) University. Find her on Twitter @arghavan_salles.
Endothelial injury may play a major role in COVID-19–associated coagulopathy
A striking clinical feature of illness from SARS-CoV-2 is a marked increase in thrombotic and microvascular complications, or COVID-19–associated coagulopathy (CAC).
A new study suggests endothelial cell injury plays a major role in the pathogenesis of CAC, and blood levels of soluble thrombomodulin correlate with mortality.
George Goshua, MD, of Yale University, New Haven, Conn., presented this study as a late-breaking abstract at the virtual annual congress of the European Hematology Association.
Dr. Goshua cited past research showing CAC to be highly prevalent among hospitalized patients. Venous thromboembolism was found in 17% to 69% of patients, despite thromboprophylaxis.1-4 Arterial thrombosis has been seen in 3.6% to 4.0% of patients,1-3 and autopsy findings have shown microvascular thrombosis in as many as 87% of patients.5-7
For their study, Dr. Goshua and colleagues assessed endothelial cell damage, platelet activation, and hemostatic and fibrinolytic cascade effects of CAC.
The investigators measured markers of endothelial cell injury and platelet activation, plasminogen activation inhibitor 1 (PAI-1), and coagulation factors in stable and critically ill patients hospitalized with COVID-19. In addition, the team sought to identify biomarkers of mortality in hospitalized patients.
Dr. Goshua and colleagues studied 68 adults hospitalized for suspected COVID-19 – 48 in the ICU and 20 outside the ICU. Patients in the ICU received mechanical ventilation, while the non-ICU patients required supplemental oxygen (≤3 L/min per nasal cannula).
There were more men than women (69% vs. 31%) in the ICU population but not in the non-ICU population (40% vs. 60%). There were no statistically significant differences in age or comorbid conditions between the ICU and non-ICU patients.
Results and interpretation
Consistent with augmentation of the coagulation cascade – and as expected – D-dimer and thrombin-antithrombin levels were high in both the ICU and non-ICU populations, but levels were significantly higher (P < .001) among the ICU patients.
Endogenous anticoagulants (antithrombin and proteins C and S) and fibrinolytic enzymes (alpha 2-antiplasmin) were preserved, verifying that CAC is distinct from disseminated intravascular coagulation. Classic fibrinolysis did not occur, as PAI-1 was high in ICU and non-ICU patients, and lysis-30 was normal in nearly all ICU patients (96%).
Von Willebrand factor antigen and activity levels and factor VIII levels were markedly elevated in non-ICU and ICU patients, but they were significantly higher (P < .001) in the ICU cohort. This supports the hypothesis that endothelial cell damage and platelet activation play major roles in CAC.
Similarly, soluble P-selectin, which is shed from endothelial cells and platelets, was dramatically elevated in ICU patients in comparison with controls and non-ICU patients (P < .001 for both comparisons).
Levels of soluble thrombomodulin, which is released from endothelial cells, were not significantly different in ICU patients and controls. However, given thrombomodulin’s significant role in the coagulation cascade, Dr. Goshua and colleagues plotted receiver operating curves to see if soluble thrombomodulin levels were predictive of mortality.
The results showed that soluble thrombomodulin correlated with the probability of survival, both overall and in ICU patients. Soluble thrombomodulin levels greater than 3.26 ng/mL were associated with significantly worse survival in all patients (P = .0087) and ICU patients (P = .0309).
Influence on therapy
Laboratory perturbations were detected in both ICU and non-ICU patients, and otherwise healthy outpatients have exhibited potentially life-threatening CAC, according to Dr. Goshua.
These findings suggest the prothrombotic state occurs early in the pathogenesis of SARS-CoV-2 infection, is driven by platelet activation and endotheliopathy, and becomes more pronounced with worsening severity of infection.
The results of this study prompted a change in how Yale–New Haven Hospital manages COVID-19 patients. Patients without a clinical contraindication now receive aspirin at 81 mg daily in addition to the anticoagulation regimen typically used for all hospitalized COVID-19 patients.
Investigations regarding other medications that can influence platelet-endothelial cell interactions and modulate endothelial cell damage in CAC – such as dipyridamole, defibrotide, and eculizumab – are planned.
Challenges and unanswered questions
Virchow’s triad was described by the eminent German physician, Rudolf Virchow, MD, in the 19th century. It refers to the three broad categories of factors that can predispose patients to thrombosis — circulatory stasis, hypercoagulability, and endothelial injury.
Although all of these elements could be operative in CAC, the current study suggests platelet activation and endothelial cell injury in CAC may be of primary importance.
Because of the limited ability to test critically ill patients and concerns regarding exposure of additional hospital personnel to COVID-19 patients, the current report lacked clarity about the relationship of the detected laboratory abnormalities to confirmed thrombotic events.
It is unknown whether endothelial cells in different organs are damaged uniformly. It is also unclear if the laboratory abnormalities identified in this analysis can be used to monitor response to therapy, to guide follow-up management of discharged patients with CAC, or to identify infected outpatients who should receive prophylactic anticoagulation.
The mechanism by which SARS-CoV-2 injures endothelial cells is not explained by these data. Neutrophil defensins and other prothrombotic peptides or markers of inflammation could play key roles in pathogenesis, assessment of disease severity, or monitoring for therapeutic efficacy.
Today, we have more sophisticated diagnostic tools than Dr. Virchow had. We also have the ability to record and rapidly disseminate information globally. Still, with regard to the COVID-19 pandemic, clinicians face many of the same challenges that confronted Dr. Virchow in his era.
The analysis conducted by Dr. Goshua and colleagues goes a long way toward elucidating some of the mechanisms and therapeutic targets to meet these challenges.
Dr. Goshua disclosed no conflicts of interest.
Dr. Lyss was a community-based medical oncologist and clinical researcher for more than 35 years before his recent retirement. His clinical and research interests were focused on breast and lung cancers as well as expanding clinical trial access to medically underserved populations. He is based in St. Louis. He has no conflicts of interest.
SOURCE: Goshua G et al. EHA Congress. Abstract LB2605.
References
1. Klok FA et al. Confirmation of the high cumulative incidence of thrombotic complications in critically ill ICU patients with COVID-19: An updated analysis. Thromb Res. 2020;191:148-50. doi: 10.1016/j.thromres.2020.04.041.
2. Thomas W et al. Thrombotic complications of patients admitted to intensive care with COVID-19 at a teaching hospital in the United Kingdom. Thromb Res. 2020;191:76-7. doi: 10.1016/j.thromres.2020.04.028
3. Lodigiani C et al. Venous and arterial thromboembolic complications in COVID-19 patients admitted to an academic hospital in Milan, Italy. Thromb Res. 2020;191:9-14. doi: 10.1016/j.thromres.2020.04.024
4. Llitjos JF et al. High incidence of venous thromboembolic events in anticoagulated severe COVID-19 patients [published online ahead of print, 2020 Apr 22]. J Thromb Haemost. 2020;10.1111/jth.14869. doi: 10.1111/jth.14869
5. Carsana L et al. Pulmonary post-mortem findings in a large series of COVID-19 cases from Northern Italy. medRxiv 2020.04.19.20054262; doi: 10.1101/2020.04.19.20054262v1.
6. Menter T et al. Post-mortem examination of COVID19 patients reveals diffuse alveolar damage with severe capillary congestion and variegated findings of lungs and other organs suggesting vascular dysfunction [published online ahead of print, 2020 May 4]. Histopathology. 2020;10.1111/his.14134. doi: 10.1111/his.14134
7. Lax SF, et al. Pulmonary arterial thrombosis in COVID-19 with fatal outcome: Results from a prospective, single-center, clinicopathologic case series [published online ahead of print, 2020 May 14]. Ann Intern Med. 2020;M20-2566. doi: 10.7326/M20-2566.
A striking clinical feature of illness from SARS-CoV-2 is a marked increase in thrombotic and microvascular complications, or COVID-19–associated coagulopathy (CAC).
A new study suggests endothelial cell injury plays a major role in the pathogenesis of CAC, and blood levels of soluble thrombomodulin correlate with mortality.
George Goshua, MD, of Yale University, New Haven, Conn., presented this study as a late-breaking abstract at the virtual annual congress of the European Hematology Association.
Dr. Goshua cited past research showing CAC to be highly prevalent among hospitalized patients. Venous thromboembolism was found in 17% to 69% of patients, despite thromboprophylaxis.1-4 Arterial thrombosis has been seen in 3.6% to 4.0% of patients,1-3 and autopsy findings have shown microvascular thrombosis in as many as 87% of patients.5-7
For their study, Dr. Goshua and colleagues assessed endothelial cell damage, platelet activation, and hemostatic and fibrinolytic cascade effects of CAC.
The investigators measured markers of endothelial cell injury and platelet activation, plasminogen activation inhibitor 1 (PAI-1), and coagulation factors in stable and critically ill patients hospitalized with COVID-19. In addition, the team sought to identify biomarkers of mortality in hospitalized patients.
Dr. Goshua and colleagues studied 68 adults hospitalized for suspected COVID-19 – 48 in the ICU and 20 outside the ICU. Patients in the ICU received mechanical ventilation, while the non-ICU patients required supplemental oxygen (≤3 L/min per nasal cannula).
There were more men than women (69% vs. 31%) in the ICU population but not in the non-ICU population (40% vs. 60%). There were no statistically significant differences in age or comorbid conditions between the ICU and non-ICU patients.
Results and interpretation
Consistent with augmentation of the coagulation cascade – and as expected – D-dimer and thrombin-antithrombin levels were high in both the ICU and non-ICU populations, but levels were significantly higher (P < .001) among the ICU patients.
Endogenous anticoagulants (antithrombin and proteins C and S) and fibrinolytic enzymes (alpha 2-antiplasmin) were preserved, verifying that CAC is distinct from disseminated intravascular coagulation. Classic fibrinolysis did not occur, as PAI-1 was high in ICU and non-ICU patients, and lysis-30 was normal in nearly all ICU patients (96%).
Von Willebrand factor antigen and activity levels and factor VIII levels were markedly elevated in non-ICU and ICU patients, but they were significantly higher (P < .001) in the ICU cohort. This supports the hypothesis that endothelial cell damage and platelet activation play major roles in CAC.
Similarly, soluble P-selectin, which is shed from endothelial cells and platelets, was dramatically elevated in ICU patients in comparison with controls and non-ICU patients (P < .001 for both comparisons).
Levels of soluble thrombomodulin, which is released from endothelial cells, were not significantly different in ICU patients and controls. However, given thrombomodulin’s significant role in the coagulation cascade, Dr. Goshua and colleagues plotted receiver operating curves to see if soluble thrombomodulin levels were predictive of mortality.
The results showed that soluble thrombomodulin correlated with the probability of survival, both overall and in ICU patients. Soluble thrombomodulin levels greater than 3.26 ng/mL were associated with significantly worse survival in all patients (P = .0087) and ICU patients (P = .0309).
Influence on therapy
Laboratory perturbations were detected in both ICU and non-ICU patients, and otherwise healthy outpatients have exhibited potentially life-threatening CAC, according to Dr. Goshua.
These findings suggest the prothrombotic state occurs early in the pathogenesis of SARS-CoV-2 infection, is driven by platelet activation and endotheliopathy, and becomes more pronounced with worsening severity of infection.
The results of this study prompted a change in how Yale–New Haven Hospital manages COVID-19 patients. Patients without a clinical contraindication now receive aspirin at 81 mg daily in addition to the anticoagulation regimen typically used for all hospitalized COVID-19 patients.
Investigations regarding other medications that can influence platelet-endothelial cell interactions and modulate endothelial cell damage in CAC – such as dipyridamole, defibrotide, and eculizumab – are planned.
Challenges and unanswered questions
Virchow’s triad was described by the eminent German physician, Rudolf Virchow, MD, in the 19th century. It refers to the three broad categories of factors that can predispose patients to thrombosis — circulatory stasis, hypercoagulability, and endothelial injury.
Although all of these elements could be operative in CAC, the current study suggests platelet activation and endothelial cell injury in CAC may be of primary importance.
Because of the limited ability to test critically ill patients and concerns regarding exposure of additional hospital personnel to COVID-19 patients, the current report lacked clarity about the relationship of the detected laboratory abnormalities to confirmed thrombotic events.
It is unknown whether endothelial cells in different organs are damaged uniformly. It is also unclear if the laboratory abnormalities identified in this analysis can be used to monitor response to therapy, to guide follow-up management of discharged patients with CAC, or to identify infected outpatients who should receive prophylactic anticoagulation.
The mechanism by which SARS-CoV-2 injures endothelial cells is not explained by these data. Neutrophil defensins and other prothrombotic peptides or markers of inflammation could play key roles in pathogenesis, assessment of disease severity, or monitoring for therapeutic efficacy.
Today, we have more sophisticated diagnostic tools than Dr. Virchow had. We also have the ability to record and rapidly disseminate information globally. Still, with regard to the COVID-19 pandemic, clinicians face many of the same challenges that confronted Dr. Virchow in his era.
The analysis conducted by Dr. Goshua and colleagues goes a long way toward elucidating some of the mechanisms and therapeutic targets to meet these challenges.
Dr. Goshua disclosed no conflicts of interest.
Dr. Lyss was a community-based medical oncologist and clinical researcher for more than 35 years before his recent retirement. His clinical and research interests were focused on breast and lung cancers as well as expanding clinical trial access to medically underserved populations. He is based in St. Louis. He has no conflicts of interest.
SOURCE: Goshua G et al. EHA Congress. Abstract LB2605.
References
1. Klok FA et al. Confirmation of the high cumulative incidence of thrombotic complications in critically ill ICU patients with COVID-19: An updated analysis. Thromb Res. 2020;191:148-50. doi: 10.1016/j.thromres.2020.04.041.
2. Thomas W et al. Thrombotic complications of patients admitted to intensive care with COVID-19 at a teaching hospital in the United Kingdom. Thromb Res. 2020;191:76-7. doi: 10.1016/j.thromres.2020.04.028
3. Lodigiani C et al. Venous and arterial thromboembolic complications in COVID-19 patients admitted to an academic hospital in Milan, Italy. Thromb Res. 2020;191:9-14. doi: 10.1016/j.thromres.2020.04.024
4. Llitjos JF et al. High incidence of venous thromboembolic events in anticoagulated severe COVID-19 patients [published online ahead of print, 2020 Apr 22]. J Thromb Haemost. 2020;10.1111/jth.14869. doi: 10.1111/jth.14869
5. Carsana L et al. Pulmonary post-mortem findings in a large series of COVID-19 cases from Northern Italy. medRxiv 2020.04.19.20054262; doi: 10.1101/2020.04.19.20054262v1.
6. Menter T et al. Post-mortem examination of COVID19 patients reveals diffuse alveolar damage with severe capillary congestion and variegated findings of lungs and other organs suggesting vascular dysfunction [published online ahead of print, 2020 May 4]. Histopathology. 2020;10.1111/his.14134. doi: 10.1111/his.14134
7. Lax SF, et al. Pulmonary arterial thrombosis in COVID-19 with fatal outcome: Results from a prospective, single-center, clinicopathologic case series [published online ahead of print, 2020 May 14]. Ann Intern Med. 2020;M20-2566. doi: 10.7326/M20-2566.
A striking clinical feature of illness from SARS-CoV-2 is a marked increase in thrombotic and microvascular complications, or COVID-19–associated coagulopathy (CAC).
A new study suggests endothelial cell injury plays a major role in the pathogenesis of CAC, and blood levels of soluble thrombomodulin correlate with mortality.
George Goshua, MD, of Yale University, New Haven, Conn., presented this study as a late-breaking abstract at the virtual annual congress of the European Hematology Association.
Dr. Goshua cited past research showing CAC to be highly prevalent among hospitalized patients. Venous thromboembolism was found in 17% to 69% of patients, despite thromboprophylaxis.1-4 Arterial thrombosis has been seen in 3.6% to 4.0% of patients,1-3 and autopsy findings have shown microvascular thrombosis in as many as 87% of patients.5-7
For their study, Dr. Goshua and colleagues assessed endothelial cell damage, platelet activation, and hemostatic and fibrinolytic cascade effects of CAC.
The investigators measured markers of endothelial cell injury and platelet activation, plasminogen activation inhibitor 1 (PAI-1), and coagulation factors in stable and critically ill patients hospitalized with COVID-19. In addition, the team sought to identify biomarkers of mortality in hospitalized patients.
Dr. Goshua and colleagues studied 68 adults hospitalized for suspected COVID-19 – 48 in the ICU and 20 outside the ICU. Patients in the ICU received mechanical ventilation, while the non-ICU patients required supplemental oxygen (≤3 L/min per nasal cannula).
There were more men than women (69% vs. 31%) in the ICU population but not in the non-ICU population (40% vs. 60%). There were no statistically significant differences in age or comorbid conditions between the ICU and non-ICU patients.
Results and interpretation
Consistent with augmentation of the coagulation cascade – and as expected – D-dimer and thrombin-antithrombin levels were high in both the ICU and non-ICU populations, but levels were significantly higher (P < .001) among the ICU patients.
Endogenous anticoagulants (antithrombin and proteins C and S) and fibrinolytic enzymes (alpha 2-antiplasmin) were preserved, verifying that CAC is distinct from disseminated intravascular coagulation. Classic fibrinolysis did not occur, as PAI-1 was high in ICU and non-ICU patients, and lysis-30 was normal in nearly all ICU patients (96%).
Von Willebrand factor antigen and activity levels and factor VIII levels were markedly elevated in non-ICU and ICU patients, but they were significantly higher (P < .001) in the ICU cohort. This supports the hypothesis that endothelial cell damage and platelet activation play major roles in CAC.
Similarly, soluble P-selectin, which is shed from endothelial cells and platelets, was dramatically elevated in ICU patients in comparison with controls and non-ICU patients (P < .001 for both comparisons).
Levels of soluble thrombomodulin, which is released from endothelial cells, were not significantly different in ICU patients and controls. However, given thrombomodulin’s significant role in the coagulation cascade, Dr. Goshua and colleagues plotted receiver operating curves to see if soluble thrombomodulin levels were predictive of mortality.
The results showed that soluble thrombomodulin correlated with the probability of survival, both overall and in ICU patients. Soluble thrombomodulin levels greater than 3.26 ng/mL were associated with significantly worse survival in all patients (P = .0087) and ICU patients (P = .0309).
Influence on therapy
Laboratory perturbations were detected in both ICU and non-ICU patients, and otherwise healthy outpatients have exhibited potentially life-threatening CAC, according to Dr. Goshua.
These findings suggest the prothrombotic state occurs early in the pathogenesis of SARS-CoV-2 infection, is driven by platelet activation and endotheliopathy, and becomes more pronounced with worsening severity of infection.
The results of this study prompted a change in how Yale–New Haven Hospital manages COVID-19 patients. Patients without a clinical contraindication now receive aspirin at 81 mg daily in addition to the anticoagulation regimen typically used for all hospitalized COVID-19 patients.
Investigations regarding other medications that can influence platelet-endothelial cell interactions and modulate endothelial cell damage in CAC – such as dipyridamole, defibrotide, and eculizumab – are planned.
Challenges and unanswered questions
Virchow’s triad was described by the eminent German physician, Rudolf Virchow, MD, in the 19th century. It refers to the three broad categories of factors that can predispose patients to thrombosis — circulatory stasis, hypercoagulability, and endothelial injury.
Although all of these elements could be operative in CAC, the current study suggests platelet activation and endothelial cell injury in CAC may be of primary importance.
Because of the limited ability to test critically ill patients and concerns regarding exposure of additional hospital personnel to COVID-19 patients, the current report lacked clarity about the relationship of the detected laboratory abnormalities to confirmed thrombotic events.
It is unknown whether endothelial cells in different organs are damaged uniformly. It is also unclear if the laboratory abnormalities identified in this analysis can be used to monitor response to therapy, to guide follow-up management of discharged patients with CAC, or to identify infected outpatients who should receive prophylactic anticoagulation.
The mechanism by which SARS-CoV-2 injures endothelial cells is not explained by these data. Neutrophil defensins and other prothrombotic peptides or markers of inflammation could play key roles in pathogenesis, assessment of disease severity, or monitoring for therapeutic efficacy.
Today, we have more sophisticated diagnostic tools than Dr. Virchow had. We also have the ability to record and rapidly disseminate information globally. Still, with regard to the COVID-19 pandemic, clinicians face many of the same challenges that confronted Dr. Virchow in his era.
The analysis conducted by Dr. Goshua and colleagues goes a long way toward elucidating some of the mechanisms and therapeutic targets to meet these challenges.
Dr. Goshua disclosed no conflicts of interest.
Dr. Lyss was a community-based medical oncologist and clinical researcher for more than 35 years before his recent retirement. His clinical and research interests were focused on breast and lung cancers as well as expanding clinical trial access to medically underserved populations. He is based in St. Louis. He has no conflicts of interest.
SOURCE: Goshua G et al. EHA Congress. Abstract LB2605.
References
1. Klok FA et al. Confirmation of the high cumulative incidence of thrombotic complications in critically ill ICU patients with COVID-19: An updated analysis. Thromb Res. 2020;191:148-50. doi: 10.1016/j.thromres.2020.04.041.
2. Thomas W et al. Thrombotic complications of patients admitted to intensive care with COVID-19 at a teaching hospital in the United Kingdom. Thromb Res. 2020;191:76-7. doi: 10.1016/j.thromres.2020.04.028
3. Lodigiani C et al. Venous and arterial thromboembolic complications in COVID-19 patients admitted to an academic hospital in Milan, Italy. Thromb Res. 2020;191:9-14. doi: 10.1016/j.thromres.2020.04.024
4. Llitjos JF et al. High incidence of venous thromboembolic events in anticoagulated severe COVID-19 patients [published online ahead of print, 2020 Apr 22]. J Thromb Haemost. 2020;10.1111/jth.14869. doi: 10.1111/jth.14869
5. Carsana L et al. Pulmonary post-mortem findings in a large series of COVID-19 cases from Northern Italy. medRxiv 2020.04.19.20054262; doi: 10.1101/2020.04.19.20054262v1.
6. Menter T et al. Post-mortem examination of COVID19 patients reveals diffuse alveolar damage with severe capillary congestion and variegated findings of lungs and other organs suggesting vascular dysfunction [published online ahead of print, 2020 May 4]. Histopathology. 2020;10.1111/his.14134. doi: 10.1111/his.14134
7. Lax SF, et al. Pulmonary arterial thrombosis in COVID-19 with fatal outcome: Results from a prospective, single-center, clinicopathologic case series [published online ahead of print, 2020 May 14]. Ann Intern Med. 2020;M20-2566. doi: 10.7326/M20-2566.
FROM EHA CONGRESS
Will primary care physicians be COVID-19’s next victims?
In a recently published editorial, Tom Frieden, MD, MPH, former head of the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, argued that primary care is in deep trouble, its long-standing financial problems exacerbated by the fallout from the COVID-19 pandemic. Those arguments resonated with Kenny Lin, MD, MPH, a family physician, professor at Georgetown University School of Medicine, and a regular contributor to Medscape. He spoke with Dr. Frieden about his concerns.
Dr. Lin: Why did you feel that it was important to write this piece focused on primary care?
Dr. Frieden: I’m glad you asked that question. Given all that is going on, one might ask, what is the importance of primary care? We’ve got this epidemic going on that requires public health and hospital systems. Why voice concern about primary care now?
It’s really striking to see that the number of visits has plummeted. Because of our payment structure, that means incomes have plummeted. We’re hearing about doctors’ offices getting boarded up and shuttering. As I write in the piece, it’s one thing for a theater or a restaurant or another important community entity to shut because of economic downturn, and these are real losses, but to lose their only primary care practice or one of the few in an area really is a matter of life and death for many communities.
Dr. Lin: I agree. In my own practice we haven’t had to furlough anyone, but we’ve put people on forced paid time off. We’ve been reallocating physicians to other parts of our health system. It is definitely a concern. A solo practitioner or someone in a rural practice would most likely be even much more heavily hit. You’ve argued that the neglect of our public health system on a national level has led to many preventable deaths from COVID-19. Do you feel that something similar has happened in primary care? How could a stronger, better-funded primary care infrastructure better prepare us for the next pandemic?
Dr. Frieden: All over the world, we see an overemphasis on hospital care and an underemphasis on primary care, outpatient care, family medicine. As a result, we pay more. We have larger risks, and we don’t prevent diseases that we could prevent. It’s fundamentally about the economic incentives of our health care system. Of course, that often reflects the political reality of different profit centers and cost centers of care. That won’t change with tweaking around the edges. It will only change if we change the way we pay for health care. Money talks. We need to start paying at least part of what we pay based on health outcomes.
Many years ago a colleague and I wrote an article, “Health Care as If Health Mattered.” If you step back and look at how we pay for health care, very little, if any, of our payment structure is based on how much health the care system delivers. Part of that can be addressed by going to capitated models, which I think do better. But you have also got to put into those capitated systems some quality and outcome measures that are both valid and not too burdensome to report on. That’s not easy. We could talk a lot about some of the information systems and payment systems, but I think the bottom line is that we need to be able to deal not only with health emergencies, but also with preventive care, care of chronic diseases, and behavioral health care in ways that maximize health.
One of the ways to do that is simple, monthly, capitated payments along with what I call a registry-based outcomes system.
I’m a tuberculosis specialist by training. In tuberculosis there really is a great information system. We track every single patient who has been diagnosed, and we hold every clinician accountable for whether or not they’ve successfully treated that patient. An optimal health care system should do the same with treatment of hypertension, diabetes, seizure disorder, and other common conditions in which treatment makes a really big difference. Preventive care, especially vaccine delivery, is another example.
I understand that physicians will point out that patients may not come in for that care, or they’re hard to deal with, or they refuse recommended treatment. We don’t expect 100%. But we should expect that, if we’re paying for health care, we should get health.
To do that, I think we need much more support for primary care, both in terms of the absolute amount of dollars going in and the administrative support. Some of our systems are so complicated that you can’t manage them without a billing department. How does a one- or two-physician practice deal with systems that will take dozens of hours a week to manage? You have to deal with the administrative complexity, the structure of the incentives, and the structure of care.
I think these are all things that we have to address. But for a minute, let’s helicopter up and look at the big picture. Without additional help from Congress, tens of thousands of primary care physicians could go out of business in the coming weeks. This is a crisis, and this will be very hard to rebuild. We don’t have a strong, resilient primary care infrastructure today, and if we’re not careful it’ll be even weaker as we try to rebuild.
It has been encouraging to see some of the care innovations that have occurred in response to the pandemic. I’m particularly encouraged by the widespread interest in and support for telemedicine. Telemedicine is a very important way of making care safer, more accessible, less expensive, more efficient. There have been a lot of restrictions on it, not just in the United States but globally, for many years. It’s really interesting to see those restrictions rapidly change. I give credit to the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services for quick changes in this area.
Now, telemedicine isn’t a cure-all. There are lots of things you can’t do from a distance. It’s a pale reflection of reality, compared with an in-person first visit with a patient. But it’s a whole lot better than nothing. If we look at some of the best health systems in the United States, they’ve gone to as much as 80% of clinical visits done by telemedicine. I don’t think we’re going to go back. Even if COVID is no longer the threat that it is today, if you can do things more quickly, more efficiently, and more conveniently for both patients and doctors, do them. Obviously, it won’t be all visits, but it could be a large proportion of visits and an important part of strengthening our primary care system.
My initiative, Resolve to Save Lives, which is part of the global health organization Vital Strategies, has done work in the area of public health around the world. I am really struck by how weak primary care systems are in so many countries. Strong primary care systems are the exception rather than the rule, but they’re also a best buy in health care. They’re crucially important, and they’re going to work differently in different countries, in different states, in different communities. We need to do a better job of supporting primary care, building primary care, and paying for primary care.
Dr. Lin: You’ve identified two needs. The immediate need is that primary care practices need revenue now to not have to close in the immediate aftermath or the ongoing COVID epidemic, but also there’s the long term, the percentage of health care dollars that are going to primary care in the long term. You pointed out in your article that currently 5% or less of health care spending is in primary care, which is a lot less percentage-wise than in many other countries. I think the question always comes up is that we want to increase that share, but the money has to come from somewhere. Where is that extra money going to come from? Dr. Frieden: I’m not an expert in health care finance, but one thing I’ve learned over the years is that one person’s waste, fraud, and abuse is somebody else’s profit center. It’s not going to be easy. On the one hand, we do need to think about more efficient ways to organize primary care; on the other hand, we have to figure out a way to internalize some of the savings. If you give good primary care and, therefore, someone doesn’t get hospitalized, you can actually lose money in the current system, whereas you’re saving the system a lot of money by preventing that hospitalization.
I think our health system does have significant inefficiencies in terms of the number of tests and interventions that are done that are really not proven to help patients. It has been demonstrated for decades now that the usual economic incentives don’t operate in health care. In health care, supply often generates demand. The number of gallbladder operations is proportional not to population but to the number of gallbladder surgeons. That’s a problem, and it’s a problem that we’re going to have to assess. “Gatekeeper” is an unpleasant word, but if a primary care practitioner could be the advocate for patients so that we’re not pushing for patients to get more care or to get less care but to get the right care, we have the potential to reduce costs while improving quality.
Dr. Lin: You accurately point out that the fee-for-service payment system has been the major culprit in the declining revenues of primary care practices since the start of the pandemic. But for the majority of primary care physicians, including myself, fee-for-service is all that we’ve ever known. Do you think that primary care is ready for such an abrupt financing change, particularly in a very short period of time?Dr. Frieden: You’re certainly accurate in saying that nothing about health care finance is easy. Trying to address these problems at the national or state level has been extremely difficult. I think that the pilot programs in Medicare are very important. Medicaid is a particular challenge because it’s a state-based program and many of the costs are driven by nursing home and long-term care. When you take those costs out, the actual funding per patient or per provider is quite low in most places.
It’s hard enough to reorganize if you’ve got ample resources, but to reorganize when they are insufficient is particularly hard. I would say only that there are no quick and simple answers to this question, but there is a widespread understanding that what we’re doing now doesn’t make sense. We pay top dollar and we get – despite fantastic doctors and fantastic hospitals – lousy outcomes. I’m a public health physician. I’m an internal medicine and infectious disease specialist. Fundamentally, I look at the data. If you think of our health care system as a patient, the patient is not doing well. We’re not functional to the degree we need to be, particularly when you think of what an enormous outlier our per capita expenditures are [compared with other developed countries] – almost twice the average upper-income country and 25% more than any other upper-income country.
Now, anyone who tells you that change is going to be pain-free is not leveling with you. In addition to things like telemedicine, we have to make much more use of team-based care and task sharing. There are lots of things that doctors are doing these days that they really shouldn’t.
Dr. Lin: In your recent op-ed, you noted the pivot to telehealth that primary care practices have made very quickly in response to the pandemic. That certainly was the experience for my practice. But what are some other strategies that you think are important to support the goal of better care delivery in our primary care practices?Dr. Frieden: Another really important innovation is team-based care. There are lots of things that doctors are doing today that nurses, nurse practitioners, physician assistants, and community health workers can do better and for less money. Frankly, I think that should increase the job satisfaction of physicians, to be doing work that is specific to the physician, requiring either more patient interaction or advanced reasoning or experience.
In my own field of tuberculosis control, I learned how to treat tuberculosis because the nurse at the TB clinic kept correcting me because that’s all she did. She did tuberculosis care, so she had seen everything. Even though I’d finished an infectious disease fellowship and internal medicine residency, the public health nurse knew TB a whole lot better than I did.
Similarly, as we work on hypertension control, you can protocolize most of this care and do a much better job. That’s been proven for more than 40 years, and yet we still don’t do it.
One of the big parts of being able to do more with the same or fewer resources is going to be more team-based care. That’s really a task-sharing approach. I think of that as a triple win: You get better care for lower costs with more employment. What’s not to like?
Dr. Lin: I’m hopeful, as you are, that many of these innovations that have been made by necessity will persist beyond the duration of COVID-19. As you said, the health care system has been really difficult to change, and it often takes something like this to galvanize enough consensus that things need to change.
Dr. Frieden: I think the bottom line here is that we should pay our primary health care providers to keep us healthy and ensure that we have a payment system that lets them do that without risking bankruptcy. That’s not too much to ask of our system. It’s important for our health. It’s important for our economy. It’s important for our communities.
Dr. Lin teaches family medicine, preventive medicine, and health policy at Georgetown University School of Medicine. He is deputy editor of the journal American Family Physician. Follow him on Twitter. He has served as a director, officer, partner, employee, adviser, consultant, or trustee for MedStar Georgetown University Hospital and received income in an amount equal to or greater than $250 from UpToDate, Wiley-Blackwell, and American Academy of Family Physicians.
Dr. Frieden is a physician with advanced training in internal medicine, infectious disease, public health, and epidemiology. He has served as director of the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention and as commissioner of the New York City Health Department. Currently he is president and CEO of Resolve to Save Lives. Follow him on Twitter. Thomas R. Frieden, MD, MPH, has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
In a recently published editorial, Tom Frieden, MD, MPH, former head of the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, argued that primary care is in deep trouble, its long-standing financial problems exacerbated by the fallout from the COVID-19 pandemic. Those arguments resonated with Kenny Lin, MD, MPH, a family physician, professor at Georgetown University School of Medicine, and a regular contributor to Medscape. He spoke with Dr. Frieden about his concerns.
Dr. Lin: Why did you feel that it was important to write this piece focused on primary care?
Dr. Frieden: I’m glad you asked that question. Given all that is going on, one might ask, what is the importance of primary care? We’ve got this epidemic going on that requires public health and hospital systems. Why voice concern about primary care now?
It’s really striking to see that the number of visits has plummeted. Because of our payment structure, that means incomes have plummeted. We’re hearing about doctors’ offices getting boarded up and shuttering. As I write in the piece, it’s one thing for a theater or a restaurant or another important community entity to shut because of economic downturn, and these are real losses, but to lose their only primary care practice or one of the few in an area really is a matter of life and death for many communities.
Dr. Lin: I agree. In my own practice we haven’t had to furlough anyone, but we’ve put people on forced paid time off. We’ve been reallocating physicians to other parts of our health system. It is definitely a concern. A solo practitioner or someone in a rural practice would most likely be even much more heavily hit. You’ve argued that the neglect of our public health system on a national level has led to many preventable deaths from COVID-19. Do you feel that something similar has happened in primary care? How could a stronger, better-funded primary care infrastructure better prepare us for the next pandemic?
Dr. Frieden: All over the world, we see an overemphasis on hospital care and an underemphasis on primary care, outpatient care, family medicine. As a result, we pay more. We have larger risks, and we don’t prevent diseases that we could prevent. It’s fundamentally about the economic incentives of our health care system. Of course, that often reflects the political reality of different profit centers and cost centers of care. That won’t change with tweaking around the edges. It will only change if we change the way we pay for health care. Money talks. We need to start paying at least part of what we pay based on health outcomes.
Many years ago a colleague and I wrote an article, “Health Care as If Health Mattered.” If you step back and look at how we pay for health care, very little, if any, of our payment structure is based on how much health the care system delivers. Part of that can be addressed by going to capitated models, which I think do better. But you have also got to put into those capitated systems some quality and outcome measures that are both valid and not too burdensome to report on. That’s not easy. We could talk a lot about some of the information systems and payment systems, but I think the bottom line is that we need to be able to deal not only with health emergencies, but also with preventive care, care of chronic diseases, and behavioral health care in ways that maximize health.
One of the ways to do that is simple, monthly, capitated payments along with what I call a registry-based outcomes system.
I’m a tuberculosis specialist by training. In tuberculosis there really is a great information system. We track every single patient who has been diagnosed, and we hold every clinician accountable for whether or not they’ve successfully treated that patient. An optimal health care system should do the same with treatment of hypertension, diabetes, seizure disorder, and other common conditions in which treatment makes a really big difference. Preventive care, especially vaccine delivery, is another example.
I understand that physicians will point out that patients may not come in for that care, or they’re hard to deal with, or they refuse recommended treatment. We don’t expect 100%. But we should expect that, if we’re paying for health care, we should get health.
To do that, I think we need much more support for primary care, both in terms of the absolute amount of dollars going in and the administrative support. Some of our systems are so complicated that you can’t manage them without a billing department. How does a one- or two-physician practice deal with systems that will take dozens of hours a week to manage? You have to deal with the administrative complexity, the structure of the incentives, and the structure of care.
I think these are all things that we have to address. But for a minute, let’s helicopter up and look at the big picture. Without additional help from Congress, tens of thousands of primary care physicians could go out of business in the coming weeks. This is a crisis, and this will be very hard to rebuild. We don’t have a strong, resilient primary care infrastructure today, and if we’re not careful it’ll be even weaker as we try to rebuild.
It has been encouraging to see some of the care innovations that have occurred in response to the pandemic. I’m particularly encouraged by the widespread interest in and support for telemedicine. Telemedicine is a very important way of making care safer, more accessible, less expensive, more efficient. There have been a lot of restrictions on it, not just in the United States but globally, for many years. It’s really interesting to see those restrictions rapidly change. I give credit to the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services for quick changes in this area.
Now, telemedicine isn’t a cure-all. There are lots of things you can’t do from a distance. It’s a pale reflection of reality, compared with an in-person first visit with a patient. But it’s a whole lot better than nothing. If we look at some of the best health systems in the United States, they’ve gone to as much as 80% of clinical visits done by telemedicine. I don’t think we’re going to go back. Even if COVID is no longer the threat that it is today, if you can do things more quickly, more efficiently, and more conveniently for both patients and doctors, do them. Obviously, it won’t be all visits, but it could be a large proportion of visits and an important part of strengthening our primary care system.
My initiative, Resolve to Save Lives, which is part of the global health organization Vital Strategies, has done work in the area of public health around the world. I am really struck by how weak primary care systems are in so many countries. Strong primary care systems are the exception rather than the rule, but they’re also a best buy in health care. They’re crucially important, and they’re going to work differently in different countries, in different states, in different communities. We need to do a better job of supporting primary care, building primary care, and paying for primary care.
Dr. Lin: You’ve identified two needs. The immediate need is that primary care practices need revenue now to not have to close in the immediate aftermath or the ongoing COVID epidemic, but also there’s the long term, the percentage of health care dollars that are going to primary care in the long term. You pointed out in your article that currently 5% or less of health care spending is in primary care, which is a lot less percentage-wise than in many other countries. I think the question always comes up is that we want to increase that share, but the money has to come from somewhere. Where is that extra money going to come from? Dr. Frieden: I’m not an expert in health care finance, but one thing I’ve learned over the years is that one person’s waste, fraud, and abuse is somebody else’s profit center. It’s not going to be easy. On the one hand, we do need to think about more efficient ways to organize primary care; on the other hand, we have to figure out a way to internalize some of the savings. If you give good primary care and, therefore, someone doesn’t get hospitalized, you can actually lose money in the current system, whereas you’re saving the system a lot of money by preventing that hospitalization.
I think our health system does have significant inefficiencies in terms of the number of tests and interventions that are done that are really not proven to help patients. It has been demonstrated for decades now that the usual economic incentives don’t operate in health care. In health care, supply often generates demand. The number of gallbladder operations is proportional not to population but to the number of gallbladder surgeons. That’s a problem, and it’s a problem that we’re going to have to assess. “Gatekeeper” is an unpleasant word, but if a primary care practitioner could be the advocate for patients so that we’re not pushing for patients to get more care or to get less care but to get the right care, we have the potential to reduce costs while improving quality.
Dr. Lin: You accurately point out that the fee-for-service payment system has been the major culprit in the declining revenues of primary care practices since the start of the pandemic. But for the majority of primary care physicians, including myself, fee-for-service is all that we’ve ever known. Do you think that primary care is ready for such an abrupt financing change, particularly in a very short period of time?Dr. Frieden: You’re certainly accurate in saying that nothing about health care finance is easy. Trying to address these problems at the national or state level has been extremely difficult. I think that the pilot programs in Medicare are very important. Medicaid is a particular challenge because it’s a state-based program and many of the costs are driven by nursing home and long-term care. When you take those costs out, the actual funding per patient or per provider is quite low in most places.
It’s hard enough to reorganize if you’ve got ample resources, but to reorganize when they are insufficient is particularly hard. I would say only that there are no quick and simple answers to this question, but there is a widespread understanding that what we’re doing now doesn’t make sense. We pay top dollar and we get – despite fantastic doctors and fantastic hospitals – lousy outcomes. I’m a public health physician. I’m an internal medicine and infectious disease specialist. Fundamentally, I look at the data. If you think of our health care system as a patient, the patient is not doing well. We’re not functional to the degree we need to be, particularly when you think of what an enormous outlier our per capita expenditures are [compared with other developed countries] – almost twice the average upper-income country and 25% more than any other upper-income country.
Now, anyone who tells you that change is going to be pain-free is not leveling with you. In addition to things like telemedicine, we have to make much more use of team-based care and task sharing. There are lots of things that doctors are doing these days that they really shouldn’t.
Dr. Lin: In your recent op-ed, you noted the pivot to telehealth that primary care practices have made very quickly in response to the pandemic. That certainly was the experience for my practice. But what are some other strategies that you think are important to support the goal of better care delivery in our primary care practices?Dr. Frieden: Another really important innovation is team-based care. There are lots of things that doctors are doing today that nurses, nurse practitioners, physician assistants, and community health workers can do better and for less money. Frankly, I think that should increase the job satisfaction of physicians, to be doing work that is specific to the physician, requiring either more patient interaction or advanced reasoning or experience.
In my own field of tuberculosis control, I learned how to treat tuberculosis because the nurse at the TB clinic kept correcting me because that’s all she did. She did tuberculosis care, so she had seen everything. Even though I’d finished an infectious disease fellowship and internal medicine residency, the public health nurse knew TB a whole lot better than I did.
Similarly, as we work on hypertension control, you can protocolize most of this care and do a much better job. That’s been proven for more than 40 years, and yet we still don’t do it.
One of the big parts of being able to do more with the same or fewer resources is going to be more team-based care. That’s really a task-sharing approach. I think of that as a triple win: You get better care for lower costs with more employment. What’s not to like?
Dr. Lin: I’m hopeful, as you are, that many of these innovations that have been made by necessity will persist beyond the duration of COVID-19. As you said, the health care system has been really difficult to change, and it often takes something like this to galvanize enough consensus that things need to change.
Dr. Frieden: I think the bottom line here is that we should pay our primary health care providers to keep us healthy and ensure that we have a payment system that lets them do that without risking bankruptcy. That’s not too much to ask of our system. It’s important for our health. It’s important for our economy. It’s important for our communities.
Dr. Lin teaches family medicine, preventive medicine, and health policy at Georgetown University School of Medicine. He is deputy editor of the journal American Family Physician. Follow him on Twitter. He has served as a director, officer, partner, employee, adviser, consultant, or trustee for MedStar Georgetown University Hospital and received income in an amount equal to or greater than $250 from UpToDate, Wiley-Blackwell, and American Academy of Family Physicians.
Dr. Frieden is a physician with advanced training in internal medicine, infectious disease, public health, and epidemiology. He has served as director of the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention and as commissioner of the New York City Health Department. Currently he is president and CEO of Resolve to Save Lives. Follow him on Twitter. Thomas R. Frieden, MD, MPH, has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
In a recently published editorial, Tom Frieden, MD, MPH, former head of the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, argued that primary care is in deep trouble, its long-standing financial problems exacerbated by the fallout from the COVID-19 pandemic. Those arguments resonated with Kenny Lin, MD, MPH, a family physician, professor at Georgetown University School of Medicine, and a regular contributor to Medscape. He spoke with Dr. Frieden about his concerns.
Dr. Lin: Why did you feel that it was important to write this piece focused on primary care?
Dr. Frieden: I’m glad you asked that question. Given all that is going on, one might ask, what is the importance of primary care? We’ve got this epidemic going on that requires public health and hospital systems. Why voice concern about primary care now?
It’s really striking to see that the number of visits has plummeted. Because of our payment structure, that means incomes have plummeted. We’re hearing about doctors’ offices getting boarded up and shuttering. As I write in the piece, it’s one thing for a theater or a restaurant or another important community entity to shut because of economic downturn, and these are real losses, but to lose their only primary care practice or one of the few in an area really is a matter of life and death for many communities.
Dr. Lin: I agree. In my own practice we haven’t had to furlough anyone, but we’ve put people on forced paid time off. We’ve been reallocating physicians to other parts of our health system. It is definitely a concern. A solo practitioner or someone in a rural practice would most likely be even much more heavily hit. You’ve argued that the neglect of our public health system on a national level has led to many preventable deaths from COVID-19. Do you feel that something similar has happened in primary care? How could a stronger, better-funded primary care infrastructure better prepare us for the next pandemic?
Dr. Frieden: All over the world, we see an overemphasis on hospital care and an underemphasis on primary care, outpatient care, family medicine. As a result, we pay more. We have larger risks, and we don’t prevent diseases that we could prevent. It’s fundamentally about the economic incentives of our health care system. Of course, that often reflects the political reality of different profit centers and cost centers of care. That won’t change with tweaking around the edges. It will only change if we change the way we pay for health care. Money talks. We need to start paying at least part of what we pay based on health outcomes.
Many years ago a colleague and I wrote an article, “Health Care as If Health Mattered.” If you step back and look at how we pay for health care, very little, if any, of our payment structure is based on how much health the care system delivers. Part of that can be addressed by going to capitated models, which I think do better. But you have also got to put into those capitated systems some quality and outcome measures that are both valid and not too burdensome to report on. That’s not easy. We could talk a lot about some of the information systems and payment systems, but I think the bottom line is that we need to be able to deal not only with health emergencies, but also with preventive care, care of chronic diseases, and behavioral health care in ways that maximize health.
One of the ways to do that is simple, monthly, capitated payments along with what I call a registry-based outcomes system.
I’m a tuberculosis specialist by training. In tuberculosis there really is a great information system. We track every single patient who has been diagnosed, and we hold every clinician accountable for whether or not they’ve successfully treated that patient. An optimal health care system should do the same with treatment of hypertension, diabetes, seizure disorder, and other common conditions in which treatment makes a really big difference. Preventive care, especially vaccine delivery, is another example.
I understand that physicians will point out that patients may not come in for that care, or they’re hard to deal with, or they refuse recommended treatment. We don’t expect 100%. But we should expect that, if we’re paying for health care, we should get health.
To do that, I think we need much more support for primary care, both in terms of the absolute amount of dollars going in and the administrative support. Some of our systems are so complicated that you can’t manage them without a billing department. How does a one- or two-physician practice deal with systems that will take dozens of hours a week to manage? You have to deal with the administrative complexity, the structure of the incentives, and the structure of care.
I think these are all things that we have to address. But for a minute, let’s helicopter up and look at the big picture. Without additional help from Congress, tens of thousands of primary care physicians could go out of business in the coming weeks. This is a crisis, and this will be very hard to rebuild. We don’t have a strong, resilient primary care infrastructure today, and if we’re not careful it’ll be even weaker as we try to rebuild.
It has been encouraging to see some of the care innovations that have occurred in response to the pandemic. I’m particularly encouraged by the widespread interest in and support for telemedicine. Telemedicine is a very important way of making care safer, more accessible, less expensive, more efficient. There have been a lot of restrictions on it, not just in the United States but globally, for many years. It’s really interesting to see those restrictions rapidly change. I give credit to the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services for quick changes in this area.
Now, telemedicine isn’t a cure-all. There are lots of things you can’t do from a distance. It’s a pale reflection of reality, compared with an in-person first visit with a patient. But it’s a whole lot better than nothing. If we look at some of the best health systems in the United States, they’ve gone to as much as 80% of clinical visits done by telemedicine. I don’t think we’re going to go back. Even if COVID is no longer the threat that it is today, if you can do things more quickly, more efficiently, and more conveniently for both patients and doctors, do them. Obviously, it won’t be all visits, but it could be a large proportion of visits and an important part of strengthening our primary care system.
My initiative, Resolve to Save Lives, which is part of the global health organization Vital Strategies, has done work in the area of public health around the world. I am really struck by how weak primary care systems are in so many countries. Strong primary care systems are the exception rather than the rule, but they’re also a best buy in health care. They’re crucially important, and they’re going to work differently in different countries, in different states, in different communities. We need to do a better job of supporting primary care, building primary care, and paying for primary care.
Dr. Lin: You’ve identified two needs. The immediate need is that primary care practices need revenue now to not have to close in the immediate aftermath or the ongoing COVID epidemic, but also there’s the long term, the percentage of health care dollars that are going to primary care in the long term. You pointed out in your article that currently 5% or less of health care spending is in primary care, which is a lot less percentage-wise than in many other countries. I think the question always comes up is that we want to increase that share, but the money has to come from somewhere. Where is that extra money going to come from? Dr. Frieden: I’m not an expert in health care finance, but one thing I’ve learned over the years is that one person’s waste, fraud, and abuse is somebody else’s profit center. It’s not going to be easy. On the one hand, we do need to think about more efficient ways to organize primary care; on the other hand, we have to figure out a way to internalize some of the savings. If you give good primary care and, therefore, someone doesn’t get hospitalized, you can actually lose money in the current system, whereas you’re saving the system a lot of money by preventing that hospitalization.
I think our health system does have significant inefficiencies in terms of the number of tests and interventions that are done that are really not proven to help patients. It has been demonstrated for decades now that the usual economic incentives don’t operate in health care. In health care, supply often generates demand. The number of gallbladder operations is proportional not to population but to the number of gallbladder surgeons. That’s a problem, and it’s a problem that we’re going to have to assess. “Gatekeeper” is an unpleasant word, but if a primary care practitioner could be the advocate for patients so that we’re not pushing for patients to get more care or to get less care but to get the right care, we have the potential to reduce costs while improving quality.
Dr. Lin: You accurately point out that the fee-for-service payment system has been the major culprit in the declining revenues of primary care practices since the start of the pandemic. But for the majority of primary care physicians, including myself, fee-for-service is all that we’ve ever known. Do you think that primary care is ready for such an abrupt financing change, particularly in a very short period of time?Dr. Frieden: You’re certainly accurate in saying that nothing about health care finance is easy. Trying to address these problems at the national or state level has been extremely difficult. I think that the pilot programs in Medicare are very important. Medicaid is a particular challenge because it’s a state-based program and many of the costs are driven by nursing home and long-term care. When you take those costs out, the actual funding per patient or per provider is quite low in most places.
It’s hard enough to reorganize if you’ve got ample resources, but to reorganize when they are insufficient is particularly hard. I would say only that there are no quick and simple answers to this question, but there is a widespread understanding that what we’re doing now doesn’t make sense. We pay top dollar and we get – despite fantastic doctors and fantastic hospitals – lousy outcomes. I’m a public health physician. I’m an internal medicine and infectious disease specialist. Fundamentally, I look at the data. If you think of our health care system as a patient, the patient is not doing well. We’re not functional to the degree we need to be, particularly when you think of what an enormous outlier our per capita expenditures are [compared with other developed countries] – almost twice the average upper-income country and 25% more than any other upper-income country.
Now, anyone who tells you that change is going to be pain-free is not leveling with you. In addition to things like telemedicine, we have to make much more use of team-based care and task sharing. There are lots of things that doctors are doing these days that they really shouldn’t.
Dr. Lin: In your recent op-ed, you noted the pivot to telehealth that primary care practices have made very quickly in response to the pandemic. That certainly was the experience for my practice. But what are some other strategies that you think are important to support the goal of better care delivery in our primary care practices?Dr. Frieden: Another really important innovation is team-based care. There are lots of things that doctors are doing today that nurses, nurse practitioners, physician assistants, and community health workers can do better and for less money. Frankly, I think that should increase the job satisfaction of physicians, to be doing work that is specific to the physician, requiring either more patient interaction or advanced reasoning or experience.
In my own field of tuberculosis control, I learned how to treat tuberculosis because the nurse at the TB clinic kept correcting me because that’s all she did. She did tuberculosis care, so she had seen everything. Even though I’d finished an infectious disease fellowship and internal medicine residency, the public health nurse knew TB a whole lot better than I did.
Similarly, as we work on hypertension control, you can protocolize most of this care and do a much better job. That’s been proven for more than 40 years, and yet we still don’t do it.
One of the big parts of being able to do more with the same or fewer resources is going to be more team-based care. That’s really a task-sharing approach. I think of that as a triple win: You get better care for lower costs with more employment. What’s not to like?
Dr. Lin: I’m hopeful, as you are, that many of these innovations that have been made by necessity will persist beyond the duration of COVID-19. As you said, the health care system has been really difficult to change, and it often takes something like this to galvanize enough consensus that things need to change.
Dr. Frieden: I think the bottom line here is that we should pay our primary health care providers to keep us healthy and ensure that we have a payment system that lets them do that without risking bankruptcy. That’s not too much to ask of our system. It’s important for our health. It’s important for our economy. It’s important for our communities.
Dr. Lin teaches family medicine, preventive medicine, and health policy at Georgetown University School of Medicine. He is deputy editor of the journal American Family Physician. Follow him on Twitter. He has served as a director, officer, partner, employee, adviser, consultant, or trustee for MedStar Georgetown University Hospital and received income in an amount equal to or greater than $250 from UpToDate, Wiley-Blackwell, and American Academy of Family Physicians.
Dr. Frieden is a physician with advanced training in internal medicine, infectious disease, public health, and epidemiology. He has served as director of the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention and as commissioner of the New York City Health Department. Currently he is president and CEO of Resolve to Save Lives. Follow him on Twitter. Thomas R. Frieden, MD, MPH, has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
How can we better engage black men as patients?
I’m a black man, husband, father, son, brother, and a board-certified psychiatrist, child and adolescent psychiatry fellow, and addiction medicine fellow. I write this article as the latter, a colleague, from the former’s perspective, which you would not need to verify via Google, social media, or a badge upon meeting me.
July is Minority Mental Health Awareness Month, established to bring awareness to the unique struggles that marginalized groups face concerning mental illness in the United States.
Given the events of the last few months, including a global pandemic and videotaped killings of Ahmaud Arbery and George Floyd, two unarmed black men, America’s structural racism and inequality are being challenged in historic ways. Black people are suffering. In fact, I was not surprised to learn1 that some black families with sons have expanded the “talk” – which traditionally has focused on dealing with police officers – to include vigilantes.
Because of my extensive work with and treatment of men of color, I would like to answer a key question: “How do psychiatrists and other mental health clinicians better engage men of color? Before the “how,” let’s review the state of black men’s mental health.
According to Healthy People 2020, mental disorders are the leading cause of disability in the United States.2 Among those with diagnosable mental disorders, black people are more likely than are their white counterparts to experience severe symptoms and protracted diseases. Roughly 7% of black men meet the criteria for a lifetime prevalence of major depressive disorder.3 Applying that figure to recent national population estimates means that there are 1.4 million black men currently suffering from major depression. Suicide has been on a continued uptrend among black male youth for more than 2 decades. Moreover, given the high rates of stigma and unmet need in this population, it is likely that these figures are even more dire.
Compared with other groups, black men in the United States face a disproportionate burden of preventable morbidity and mortality rates. Of all the health concerns faced by black men, mental health challenges may be among the most stigmatized.4 Evidence suggests that black men have more adverse life experiences than do men of other racial/ethnic groups, and consequently, experience poorer mental health.5 Black men experience high rates of poverty, unemployment, and underemployment, and are incarcerated at much higher rates than those of men of other racial/ethnic groups.6 It is notable that black male youth are often perceived as older by law enforcement, beginning as early as 10 years old, often resulting in negative interactions.7
Despite those challenges, black men are often expected to project strength, they are expected to minimize displays of emotion when off the field or court (i.e., “Just shut up and dribble”), and they are expected to be true versions of folk hero John Henry. This caricature of black males is used at times to validate shootings of unarmed black males (adults and youth).
Black men’s mental health should be a priority for those in the mental health field. This is particularly the case light of our field’s historical involvement in and promotion of stereotyped clinical descriptions of black men and contributing to health disparities that persist. Black men are nearly six times as likely to be diagnosed with schizophrenia as are white men. To read about holdovers from the days of targeted advertising against black protesters of the 1960s and 1970s, check out “The Protest Psychosis” (Beacon Press, 2010) by psychiatrist and anthropologist Jonathan Metzl, MD, PhD. If you go further back in psychiatric history, the late 1800s, you can learn about the devious diagnosis of drapetomania attributed to enslaved people who were seeking freedom.
Those on the front lines providing mental health services should understand black men’s mental health from an ecological perspective. Beyond the emotional burden that mental illness imposes on the individual, there are more considerable interpersonal and societal implications for the state of black men’s mental health. As such, in our full capacity like other men, black men play an essential role within families, churches, neighborhoods, and organizations.
Given our brief review, we can reconsider our question, “How do psychiatrists and mental health clinicians better engage men of color?”
I will suggest a few fundamental principles that honestly can be applied to any patient but should be strongly considered with your black male patients – given they are likely not accustomed to engaging with the health care system, let alone with a mental health clinician:
1. Create a comfortable environment. Because of stigma, persistent myths, and lack of normalcy with talking to a mental health professional, many patients, including black men, do not have a framework for a psychiatric/psychological evaluation or treatment. It would be essential to set the frame of your encounter. Evidence suggests this can improve engagement and follow-up care among black men.8 In addition, keep in mind that “fictive kin”9 tend to play a major role in the transmission of culture, health promotion, and decision-making in the black community. This helps explain why barbershop initiatives10 are effective. If clinicians are able to allow black male patients to feel comfortable, the clinician, too, might become part of that fictive community and enhance the patient-provider relationship.
2. Allow for storytelling. In the age of the checklist, it can be relatively easy to lose sight that our patients, including black men, have their own narratives. Evidence suggests that physicians interrupt patients early and often. Challenge yourself to allow the patient to tell his story. In consideration of an initial evaluation, it may help to begin by first gathering sociodemographic information (i.e. housing, education, employment, family, etc.); doing so will allow the patient time to get comfortable before you assess possible psychiatric symptoms.
3. Confidentiality assurance. Many black men have a distrust for the health care profession; as such, it is vital that clinicians emphasize that their patients’ information and history will be used only to help the patient. It will be important to inform black male patients of their rights, because often in the greater society, their rights seem to be negated.
4. Be aware of nonverbal language. Given black men’s stereotyped roles in society and recognition that they are regularly perceived as threats, many black men have become adept at reading nonverbal cues (i.e., purse clutched, side comment, etc.). In doing so, clinicians must be attuned to their own nonverbal language. For example, a glance at one’s watch might be interpreted as you’re not listening. It would be better to be upfront and candid by saying something like, “I need to check the time,” rather than attempting to be stealth. Being transparent in that way will let the patient know that you will be upfront with him.
5. Be respectful. During an encounter, and in particular when discussing treatment plans, clinicians must allow the patient space to process and be involved in his care. Allowing the patient time to think through how he would want to proceed provides him a sense of personal agency and lets him know that he is capable of improving his mental wellness.
Black male patients need to feel comfortable, safe, able to trust the clinician. They must feel listened to, understood, and respected. This information might help some clinicians better understand what needs to happen between a black male patient and a nonblack clinician so the patient can feel good about his mental health engagement. To some, these recommendations might seem obvious or too simple, yet if we consider the countless reports of poor patient treatment engagement, adherence, and retention, we cannot deny the need for change. Having black male patients disclose important information during encounters could prevent poor clinical interactions that leave them feeling uncomfortable, uncertain, skeptical, disrespected, and further cynical about mental health care.
Dr. Simon practices at Boston Children’s Hospital. He has no disclosures.
References
1. Bunn C. After Arbery shooting, black parents are rethinking “the talk” to explain white vigilantes. NBC News. 2020 May 19.
2. U.S. Department of Health and Human Services. Office of Disease Prevention and Promotion. Healthy People 2020.
3. Ward E and Mangesha M. Am J Orthopsychiatry. 2013 Apr-Jul;83(2 0 3):386-97.
4. Holden KB et al. J Mens health. 2012 Jun 1;9(2):63-9.
5. Brown TH et al. Fam Community Health. 2015 Oct-Dec;38(4):307-18.
6. Jäggi et al. Soc Ment Health. 2016 Nov;6(3):187-296.
7. Goff PA et al. J Pers Soc Psychol. 2014;106(4):526-45.
8. Alsan M et al. National Bureau of Economic Research. NBER Working Paper No. 24787. 2018 Jun. Revised 2019 Aug.
9. Spruill IJ. J Nat Black Nurses Assoc. 2014 Dec;25(2):23-30.
10. Graham LF et al. Am J Mens Health. 2018 Sep;12(5):1307-16.
I’m a black man, husband, father, son, brother, and a board-certified psychiatrist, child and adolescent psychiatry fellow, and addiction medicine fellow. I write this article as the latter, a colleague, from the former’s perspective, which you would not need to verify via Google, social media, or a badge upon meeting me.
July is Minority Mental Health Awareness Month, established to bring awareness to the unique struggles that marginalized groups face concerning mental illness in the United States.
Given the events of the last few months, including a global pandemic and videotaped killings of Ahmaud Arbery and George Floyd, two unarmed black men, America’s structural racism and inequality are being challenged in historic ways. Black people are suffering. In fact, I was not surprised to learn1 that some black families with sons have expanded the “talk” – which traditionally has focused on dealing with police officers – to include vigilantes.
Because of my extensive work with and treatment of men of color, I would like to answer a key question: “How do psychiatrists and other mental health clinicians better engage men of color? Before the “how,” let’s review the state of black men’s mental health.
According to Healthy People 2020, mental disorders are the leading cause of disability in the United States.2 Among those with diagnosable mental disorders, black people are more likely than are their white counterparts to experience severe symptoms and protracted diseases. Roughly 7% of black men meet the criteria for a lifetime prevalence of major depressive disorder.3 Applying that figure to recent national population estimates means that there are 1.4 million black men currently suffering from major depression. Suicide has been on a continued uptrend among black male youth for more than 2 decades. Moreover, given the high rates of stigma and unmet need in this population, it is likely that these figures are even more dire.
Compared with other groups, black men in the United States face a disproportionate burden of preventable morbidity and mortality rates. Of all the health concerns faced by black men, mental health challenges may be among the most stigmatized.4 Evidence suggests that black men have more adverse life experiences than do men of other racial/ethnic groups, and consequently, experience poorer mental health.5 Black men experience high rates of poverty, unemployment, and underemployment, and are incarcerated at much higher rates than those of men of other racial/ethnic groups.6 It is notable that black male youth are often perceived as older by law enforcement, beginning as early as 10 years old, often resulting in negative interactions.7
Despite those challenges, black men are often expected to project strength, they are expected to minimize displays of emotion when off the field or court (i.e., “Just shut up and dribble”), and they are expected to be true versions of folk hero John Henry. This caricature of black males is used at times to validate shootings of unarmed black males (adults and youth).
Black men’s mental health should be a priority for those in the mental health field. This is particularly the case light of our field’s historical involvement in and promotion of stereotyped clinical descriptions of black men and contributing to health disparities that persist. Black men are nearly six times as likely to be diagnosed with schizophrenia as are white men. To read about holdovers from the days of targeted advertising against black protesters of the 1960s and 1970s, check out “The Protest Psychosis” (Beacon Press, 2010) by psychiatrist and anthropologist Jonathan Metzl, MD, PhD. If you go further back in psychiatric history, the late 1800s, you can learn about the devious diagnosis of drapetomania attributed to enslaved people who were seeking freedom.
Those on the front lines providing mental health services should understand black men’s mental health from an ecological perspective. Beyond the emotional burden that mental illness imposes on the individual, there are more considerable interpersonal and societal implications for the state of black men’s mental health. As such, in our full capacity like other men, black men play an essential role within families, churches, neighborhoods, and organizations.
Given our brief review, we can reconsider our question, “How do psychiatrists and mental health clinicians better engage men of color?”
I will suggest a few fundamental principles that honestly can be applied to any patient but should be strongly considered with your black male patients – given they are likely not accustomed to engaging with the health care system, let alone with a mental health clinician:
1. Create a comfortable environment. Because of stigma, persistent myths, and lack of normalcy with talking to a mental health professional, many patients, including black men, do not have a framework for a psychiatric/psychological evaluation or treatment. It would be essential to set the frame of your encounter. Evidence suggests this can improve engagement and follow-up care among black men.8 In addition, keep in mind that “fictive kin”9 tend to play a major role in the transmission of culture, health promotion, and decision-making in the black community. This helps explain why barbershop initiatives10 are effective. If clinicians are able to allow black male patients to feel comfortable, the clinician, too, might become part of that fictive community and enhance the patient-provider relationship.
2. Allow for storytelling. In the age of the checklist, it can be relatively easy to lose sight that our patients, including black men, have their own narratives. Evidence suggests that physicians interrupt patients early and often. Challenge yourself to allow the patient to tell his story. In consideration of an initial evaluation, it may help to begin by first gathering sociodemographic information (i.e. housing, education, employment, family, etc.); doing so will allow the patient time to get comfortable before you assess possible psychiatric symptoms.
3. Confidentiality assurance. Many black men have a distrust for the health care profession; as such, it is vital that clinicians emphasize that their patients’ information and history will be used only to help the patient. It will be important to inform black male patients of their rights, because often in the greater society, their rights seem to be negated.
4. Be aware of nonverbal language. Given black men’s stereotyped roles in society and recognition that they are regularly perceived as threats, many black men have become adept at reading nonverbal cues (i.e., purse clutched, side comment, etc.). In doing so, clinicians must be attuned to their own nonverbal language. For example, a glance at one’s watch might be interpreted as you’re not listening. It would be better to be upfront and candid by saying something like, “I need to check the time,” rather than attempting to be stealth. Being transparent in that way will let the patient know that you will be upfront with him.
5. Be respectful. During an encounter, and in particular when discussing treatment plans, clinicians must allow the patient space to process and be involved in his care. Allowing the patient time to think through how he would want to proceed provides him a sense of personal agency and lets him know that he is capable of improving his mental wellness.
Black male patients need to feel comfortable, safe, able to trust the clinician. They must feel listened to, understood, and respected. This information might help some clinicians better understand what needs to happen between a black male patient and a nonblack clinician so the patient can feel good about his mental health engagement. To some, these recommendations might seem obvious or too simple, yet if we consider the countless reports of poor patient treatment engagement, adherence, and retention, we cannot deny the need for change. Having black male patients disclose important information during encounters could prevent poor clinical interactions that leave them feeling uncomfortable, uncertain, skeptical, disrespected, and further cynical about mental health care.
Dr. Simon practices at Boston Children’s Hospital. He has no disclosures.
References
1. Bunn C. After Arbery shooting, black parents are rethinking “the talk” to explain white vigilantes. NBC News. 2020 May 19.
2. U.S. Department of Health and Human Services. Office of Disease Prevention and Promotion. Healthy People 2020.
3. Ward E and Mangesha M. Am J Orthopsychiatry. 2013 Apr-Jul;83(2 0 3):386-97.
4. Holden KB et al. J Mens health. 2012 Jun 1;9(2):63-9.
5. Brown TH et al. Fam Community Health. 2015 Oct-Dec;38(4):307-18.
6. Jäggi et al. Soc Ment Health. 2016 Nov;6(3):187-296.
7. Goff PA et al. J Pers Soc Psychol. 2014;106(4):526-45.
8. Alsan M et al. National Bureau of Economic Research. NBER Working Paper No. 24787. 2018 Jun. Revised 2019 Aug.
9. Spruill IJ. J Nat Black Nurses Assoc. 2014 Dec;25(2):23-30.
10. Graham LF et al. Am J Mens Health. 2018 Sep;12(5):1307-16.
I’m a black man, husband, father, son, brother, and a board-certified psychiatrist, child and adolescent psychiatry fellow, and addiction medicine fellow. I write this article as the latter, a colleague, from the former’s perspective, which you would not need to verify via Google, social media, or a badge upon meeting me.
July is Minority Mental Health Awareness Month, established to bring awareness to the unique struggles that marginalized groups face concerning mental illness in the United States.
Given the events of the last few months, including a global pandemic and videotaped killings of Ahmaud Arbery and George Floyd, two unarmed black men, America’s structural racism and inequality are being challenged in historic ways. Black people are suffering. In fact, I was not surprised to learn1 that some black families with sons have expanded the “talk” – which traditionally has focused on dealing with police officers – to include vigilantes.
Because of my extensive work with and treatment of men of color, I would like to answer a key question: “How do psychiatrists and other mental health clinicians better engage men of color? Before the “how,” let’s review the state of black men’s mental health.
According to Healthy People 2020, mental disorders are the leading cause of disability in the United States.2 Among those with diagnosable mental disorders, black people are more likely than are their white counterparts to experience severe symptoms and protracted diseases. Roughly 7% of black men meet the criteria for a lifetime prevalence of major depressive disorder.3 Applying that figure to recent national population estimates means that there are 1.4 million black men currently suffering from major depression. Suicide has been on a continued uptrend among black male youth for more than 2 decades. Moreover, given the high rates of stigma and unmet need in this population, it is likely that these figures are even more dire.
Compared with other groups, black men in the United States face a disproportionate burden of preventable morbidity and mortality rates. Of all the health concerns faced by black men, mental health challenges may be among the most stigmatized.4 Evidence suggests that black men have more adverse life experiences than do men of other racial/ethnic groups, and consequently, experience poorer mental health.5 Black men experience high rates of poverty, unemployment, and underemployment, and are incarcerated at much higher rates than those of men of other racial/ethnic groups.6 It is notable that black male youth are often perceived as older by law enforcement, beginning as early as 10 years old, often resulting in negative interactions.7
Despite those challenges, black men are often expected to project strength, they are expected to minimize displays of emotion when off the field or court (i.e., “Just shut up and dribble”), and they are expected to be true versions of folk hero John Henry. This caricature of black males is used at times to validate shootings of unarmed black males (adults and youth).
Black men’s mental health should be a priority for those in the mental health field. This is particularly the case light of our field’s historical involvement in and promotion of stereotyped clinical descriptions of black men and contributing to health disparities that persist. Black men are nearly six times as likely to be diagnosed with schizophrenia as are white men. To read about holdovers from the days of targeted advertising against black protesters of the 1960s and 1970s, check out “The Protest Psychosis” (Beacon Press, 2010) by psychiatrist and anthropologist Jonathan Metzl, MD, PhD. If you go further back in psychiatric history, the late 1800s, you can learn about the devious diagnosis of drapetomania attributed to enslaved people who were seeking freedom.
Those on the front lines providing mental health services should understand black men’s mental health from an ecological perspective. Beyond the emotional burden that mental illness imposes on the individual, there are more considerable interpersonal and societal implications for the state of black men’s mental health. As such, in our full capacity like other men, black men play an essential role within families, churches, neighborhoods, and organizations.
Given our brief review, we can reconsider our question, “How do psychiatrists and mental health clinicians better engage men of color?”
I will suggest a few fundamental principles that honestly can be applied to any patient but should be strongly considered with your black male patients – given they are likely not accustomed to engaging with the health care system, let alone with a mental health clinician:
1. Create a comfortable environment. Because of stigma, persistent myths, and lack of normalcy with talking to a mental health professional, many patients, including black men, do not have a framework for a psychiatric/psychological evaluation or treatment. It would be essential to set the frame of your encounter. Evidence suggests this can improve engagement and follow-up care among black men.8 In addition, keep in mind that “fictive kin”9 tend to play a major role in the transmission of culture, health promotion, and decision-making in the black community. This helps explain why barbershop initiatives10 are effective. If clinicians are able to allow black male patients to feel comfortable, the clinician, too, might become part of that fictive community and enhance the patient-provider relationship.
2. Allow for storytelling. In the age of the checklist, it can be relatively easy to lose sight that our patients, including black men, have their own narratives. Evidence suggests that physicians interrupt patients early and often. Challenge yourself to allow the patient to tell his story. In consideration of an initial evaluation, it may help to begin by first gathering sociodemographic information (i.e. housing, education, employment, family, etc.); doing so will allow the patient time to get comfortable before you assess possible psychiatric symptoms.
3. Confidentiality assurance. Many black men have a distrust for the health care profession; as such, it is vital that clinicians emphasize that their patients’ information and history will be used only to help the patient. It will be important to inform black male patients of their rights, because often in the greater society, their rights seem to be negated.
4. Be aware of nonverbal language. Given black men’s stereotyped roles in society and recognition that they are regularly perceived as threats, many black men have become adept at reading nonverbal cues (i.e., purse clutched, side comment, etc.). In doing so, clinicians must be attuned to their own nonverbal language. For example, a glance at one’s watch might be interpreted as you’re not listening. It would be better to be upfront and candid by saying something like, “I need to check the time,” rather than attempting to be stealth. Being transparent in that way will let the patient know that you will be upfront with him.
5. Be respectful. During an encounter, and in particular when discussing treatment plans, clinicians must allow the patient space to process and be involved in his care. Allowing the patient time to think through how he would want to proceed provides him a sense of personal agency and lets him know that he is capable of improving his mental wellness.
Black male patients need to feel comfortable, safe, able to trust the clinician. They must feel listened to, understood, and respected. This information might help some clinicians better understand what needs to happen between a black male patient and a nonblack clinician so the patient can feel good about his mental health engagement. To some, these recommendations might seem obvious or too simple, yet if we consider the countless reports of poor patient treatment engagement, adherence, and retention, we cannot deny the need for change. Having black male patients disclose important information during encounters could prevent poor clinical interactions that leave them feeling uncomfortable, uncertain, skeptical, disrespected, and further cynical about mental health care.
Dr. Simon practices at Boston Children’s Hospital. He has no disclosures.
References
1. Bunn C. After Arbery shooting, black parents are rethinking “the talk” to explain white vigilantes. NBC News. 2020 May 19.
2. U.S. Department of Health and Human Services. Office of Disease Prevention and Promotion. Healthy People 2020.
3. Ward E and Mangesha M. Am J Orthopsychiatry. 2013 Apr-Jul;83(2 0 3):386-97.
4. Holden KB et al. J Mens health. 2012 Jun 1;9(2):63-9.
5. Brown TH et al. Fam Community Health. 2015 Oct-Dec;38(4):307-18.
6. Jäggi et al. Soc Ment Health. 2016 Nov;6(3):187-296.
7. Goff PA et al. J Pers Soc Psychol. 2014;106(4):526-45.
8. Alsan M et al. National Bureau of Economic Research. NBER Working Paper No. 24787. 2018 Jun. Revised 2019 Aug.
9. Spruill IJ. J Nat Black Nurses Assoc. 2014 Dec;25(2):23-30.
10. Graham LF et al. Am J Mens Health. 2018 Sep;12(5):1307-16.
The merger of personal and professional: A psychologist’s experience with the effects of COVID-19
The concepts of days, weeks, and months have all but lost their meaning during the times of coronavirus. This became all too clear when I found myself weeks into June before realizing that we were in the second half of 2020. The world has been in the grips of COVID-19 (the disease caused by SARS-CoV-2) for over half a year, and the end is still not in sight. Even more chilling is the fact that the virus’s effects will continue to be felt by humanity for years to come.
By now, most of us have been affected by COVID-19, whether directly or indirectly. Consequently, we’ve seen that the psychological toll the pandemic takes is as wide ranging as the disease caused by the novel coronavirus itself. Confusion, denial, fear, anxiety, depression/sadness, and emotional dysregulation have become all too common an experience. Many mental health experts have even likened our psychological response to COVID-19 to that of trauma survivors.
In early 2020, triggered by two separate but related threats. In addition to concerns regarding COVID-19, we also began to experience fear for our physical safety as anti-Chinese sentiment began to rise across the country and the world. Discrimination and acts of violence toward Chinese people worldwide began to spread almost as rapidly as the virus itself. Anxiety and fear became a common daily experience of countless people, myself included.
In late March, amid coping with existing stressors, my situation became significantly worse when my brother, a New York City firefighter, contracted COVID-19 while working on the front lines. Shortly thereafter, my parents, both aged 60 years and older, with whom my brother shares a home, contracted the virus as well. My anxiety triggers related to the spread of the virus and xenophobia suddenly became a distant memory. I now found myself grappling with the much greater fear of losing my entire family.
At the time, the availability of testing was very limited, even for those working on the front lines. Although not without a short delay, my brother was able to access testing through Fire Department of New York connections. After about 3 weeks in self-isolation at home and with the use of over the counter pain relievers, he made a full recovery and returned to work. My parents, on the other hand, were placed at the end of a weeks-long line for testing, during which time their conditions deteriorated. Nine days following the onset of my mother’s symptoms, her condition had gotten so bad, she required hospitalization. Six days later, my father followed suit.
Being in the epicenter of the COVID-19 outbreak, New York hospitals were severely overwhelmed. Upon admission, my mother was held in the ED and other temporary open spaces in the hospital for nearly 24 hours because there was a lack of available patient rooms. During this time, she was packed into small spaces with dozens of other patients afflicted with the same disease. Four days later, she was transferred to a different hospital 10 miles away to make room for new patients. Decisions needed to be made rapidly and often with limited communication, which made for a roller coaster of emotions that would not relent.
Confusion. One of the few things we know with certainty about coronavirus is how much we don’t know. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention data indicate that older adults with underlying health conditions have worse outcomes. Yet my mother, who is younger and in better physical health than my father, became much sicker in a drastically shorter period of time. Furthermore, my parents’ symptoms were completely inconsistent with one another’s. Based on their symptoms alone, it appeared as though they were suffering with different conditions entirely. My mother experienced body aches and gastrointestinal symptoms, whereas my father developed the typical cough and fever associated with COVID-19. In addition to confusion regarding their symptoms and, therefore, in determining the best at-home supportive care prior to their hospitalizations, the lack of available testing made the very question of whether they even had COVID-19 an uncertainty.
Denial. When my family members first became symptomatic, I found myself in a state of denial not unlike that of individuals experiencing grief. I frequently engaged in both internal and external dialogues in which I would attempt to convince myself of the reasons why my family did not have COVID-19.
“My brother wears PPE while at work.”
“My father’s cough was mild.”
“My mother does not have a cough or a fever.”
Despite knowing better, I was initially unable to accept that everyone in my family had contracted a disease that had already claimed the lives of tens of thousands globally.
Fear. In order to prevent the spread of infection, many hospitals made changes to their visitor policies, placing greater restrictions on who can come and go. This has meant hospital patients who have died from COVID-19 complications have done so separated from their loved ones. After transporting my mother to the hospital ED, I was politely but firmly asked to leave per the new visitor policy. I felt as though there were cinder blocks attached to my feet as I reluctantly walked away, not knowing if it would be the last time I would see her. I experienced a fear and sadness so intense, it continues to elicit an emotional response today as I think back on that moment.
Anxiety. The difference between fear and anxiety is fear is an emotional response to a known threat or danger, and anxiety is a response to an unknown threat or danger. The days that followed my parents’ hospitalizations were riddled with anxiety that would come in waves. How were they doing? Could they breathe? Do the overwhelmed hospital staff have time to take care of them? What can I do to help? Is there anything I can do to help? The worrisome thoughts and unanswerable questions were incessant and seemed unresponsive to my efforts to quell them.
Sadness. To feel sadness is to be human. In my work as a psychologist, I emphasize the value in experiencing this emotion when therapeutically beneficial. This technique is used as part of acceptance and commitment therapy (ACT), which emphasizes the value of being present or in touch with one’s thoughts and emotions, instead of working to eliminate them. During these scary times, I leaned into this notion more than ever. I gave myself permission to not feel okay, to cry more than I had in a long time, and to be unapologetically sad. I flip-flopped between states of near-despair and hopeful, with the switch usually following a call from a member of the hospital care team with updates on my parents’ conditions.
My parents’ road to recovery extended far beyond their discharge from the hospital and was not without incident, but with support and appropriate follow-up care, they have since made full recoveries from COVID-19. Although the relief and happiness this brings me is immeasurable, the experience has left a lasting impression on me as both a person and a psychologist. Speaking as a person, I cannot overstate the value of relying on one’s social support network while coping with stressors related to COVID-19. Whether you are directly or indirectly affected by the disease, the emotional effects can feel equally intense. As in times of happiness and celebration, times of sadness can and should be shared by those who are equipped to provide support. This can be tricky in an era during which isolation is prescribed for our safety, but we have more options today for connecting virtually with others than ever before, including video conferencing, email, and that old friend, the telephone. Furthermore, identify and assert your boundaries. Sometimes, saying no to others is the best way to say yes to yourself. Certain work, chores, and social obligations that can wait, should wait.
As a psychologist, my experience has given me a renewed appreciation for the power of the therapeutic use of self in psychotherapy. The factor with the greatest effects on psychotherapy outcomes is the quality of the therapeutic alliance, a concept introduced by Sigmund Freud in 1912. I believe a therapist’s willingness to show that we, too, experience life’s ups and downs strengthens our ability to demonstrate empathy and further promote a sense of alliance. Therapists are not immune to the effects of COVID-19, and to acknowledge this fact allows us to relate to our patients on a basic human level, which is more important now than ever.
Dr. Tseng, a licensed clinical psychologist, is in private practice in New York. She disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
The concepts of days, weeks, and months have all but lost their meaning during the times of coronavirus. This became all too clear when I found myself weeks into June before realizing that we were in the second half of 2020. The world has been in the grips of COVID-19 (the disease caused by SARS-CoV-2) for over half a year, and the end is still not in sight. Even more chilling is the fact that the virus’s effects will continue to be felt by humanity for years to come.
By now, most of us have been affected by COVID-19, whether directly or indirectly. Consequently, we’ve seen that the psychological toll the pandemic takes is as wide ranging as the disease caused by the novel coronavirus itself. Confusion, denial, fear, anxiety, depression/sadness, and emotional dysregulation have become all too common an experience. Many mental health experts have even likened our psychological response to COVID-19 to that of trauma survivors.
In early 2020, triggered by two separate but related threats. In addition to concerns regarding COVID-19, we also began to experience fear for our physical safety as anti-Chinese sentiment began to rise across the country and the world. Discrimination and acts of violence toward Chinese people worldwide began to spread almost as rapidly as the virus itself. Anxiety and fear became a common daily experience of countless people, myself included.
In late March, amid coping with existing stressors, my situation became significantly worse when my brother, a New York City firefighter, contracted COVID-19 while working on the front lines. Shortly thereafter, my parents, both aged 60 years and older, with whom my brother shares a home, contracted the virus as well. My anxiety triggers related to the spread of the virus and xenophobia suddenly became a distant memory. I now found myself grappling with the much greater fear of losing my entire family.
At the time, the availability of testing was very limited, even for those working on the front lines. Although not without a short delay, my brother was able to access testing through Fire Department of New York connections. After about 3 weeks in self-isolation at home and with the use of over the counter pain relievers, he made a full recovery and returned to work. My parents, on the other hand, were placed at the end of a weeks-long line for testing, during which time their conditions deteriorated. Nine days following the onset of my mother’s symptoms, her condition had gotten so bad, she required hospitalization. Six days later, my father followed suit.
Being in the epicenter of the COVID-19 outbreak, New York hospitals were severely overwhelmed. Upon admission, my mother was held in the ED and other temporary open spaces in the hospital for nearly 24 hours because there was a lack of available patient rooms. During this time, she was packed into small spaces with dozens of other patients afflicted with the same disease. Four days later, she was transferred to a different hospital 10 miles away to make room for new patients. Decisions needed to be made rapidly and often with limited communication, which made for a roller coaster of emotions that would not relent.
Confusion. One of the few things we know with certainty about coronavirus is how much we don’t know. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention data indicate that older adults with underlying health conditions have worse outcomes. Yet my mother, who is younger and in better physical health than my father, became much sicker in a drastically shorter period of time. Furthermore, my parents’ symptoms were completely inconsistent with one another’s. Based on their symptoms alone, it appeared as though they were suffering with different conditions entirely. My mother experienced body aches and gastrointestinal symptoms, whereas my father developed the typical cough and fever associated with COVID-19. In addition to confusion regarding their symptoms and, therefore, in determining the best at-home supportive care prior to their hospitalizations, the lack of available testing made the very question of whether they even had COVID-19 an uncertainty.
Denial. When my family members first became symptomatic, I found myself in a state of denial not unlike that of individuals experiencing grief. I frequently engaged in both internal and external dialogues in which I would attempt to convince myself of the reasons why my family did not have COVID-19.
“My brother wears PPE while at work.”
“My father’s cough was mild.”
“My mother does not have a cough or a fever.”
Despite knowing better, I was initially unable to accept that everyone in my family had contracted a disease that had already claimed the lives of tens of thousands globally.
Fear. In order to prevent the spread of infection, many hospitals made changes to their visitor policies, placing greater restrictions on who can come and go. This has meant hospital patients who have died from COVID-19 complications have done so separated from their loved ones. After transporting my mother to the hospital ED, I was politely but firmly asked to leave per the new visitor policy. I felt as though there were cinder blocks attached to my feet as I reluctantly walked away, not knowing if it would be the last time I would see her. I experienced a fear and sadness so intense, it continues to elicit an emotional response today as I think back on that moment.
Anxiety. The difference between fear and anxiety is fear is an emotional response to a known threat or danger, and anxiety is a response to an unknown threat or danger. The days that followed my parents’ hospitalizations were riddled with anxiety that would come in waves. How were they doing? Could they breathe? Do the overwhelmed hospital staff have time to take care of them? What can I do to help? Is there anything I can do to help? The worrisome thoughts and unanswerable questions were incessant and seemed unresponsive to my efforts to quell them.
Sadness. To feel sadness is to be human. In my work as a psychologist, I emphasize the value in experiencing this emotion when therapeutically beneficial. This technique is used as part of acceptance and commitment therapy (ACT), which emphasizes the value of being present or in touch with one’s thoughts and emotions, instead of working to eliminate them. During these scary times, I leaned into this notion more than ever. I gave myself permission to not feel okay, to cry more than I had in a long time, and to be unapologetically sad. I flip-flopped between states of near-despair and hopeful, with the switch usually following a call from a member of the hospital care team with updates on my parents’ conditions.
My parents’ road to recovery extended far beyond their discharge from the hospital and was not without incident, but with support and appropriate follow-up care, they have since made full recoveries from COVID-19. Although the relief and happiness this brings me is immeasurable, the experience has left a lasting impression on me as both a person and a psychologist. Speaking as a person, I cannot overstate the value of relying on one’s social support network while coping with stressors related to COVID-19. Whether you are directly or indirectly affected by the disease, the emotional effects can feel equally intense. As in times of happiness and celebration, times of sadness can and should be shared by those who are equipped to provide support. This can be tricky in an era during which isolation is prescribed for our safety, but we have more options today for connecting virtually with others than ever before, including video conferencing, email, and that old friend, the telephone. Furthermore, identify and assert your boundaries. Sometimes, saying no to others is the best way to say yes to yourself. Certain work, chores, and social obligations that can wait, should wait.
As a psychologist, my experience has given me a renewed appreciation for the power of the therapeutic use of self in psychotherapy. The factor with the greatest effects on psychotherapy outcomes is the quality of the therapeutic alliance, a concept introduced by Sigmund Freud in 1912. I believe a therapist’s willingness to show that we, too, experience life’s ups and downs strengthens our ability to demonstrate empathy and further promote a sense of alliance. Therapists are not immune to the effects of COVID-19, and to acknowledge this fact allows us to relate to our patients on a basic human level, which is more important now than ever.
Dr. Tseng, a licensed clinical psychologist, is in private practice in New York. She disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
The concepts of days, weeks, and months have all but lost their meaning during the times of coronavirus. This became all too clear when I found myself weeks into June before realizing that we were in the second half of 2020. The world has been in the grips of COVID-19 (the disease caused by SARS-CoV-2) for over half a year, and the end is still not in sight. Even more chilling is the fact that the virus’s effects will continue to be felt by humanity for years to come.
By now, most of us have been affected by COVID-19, whether directly or indirectly. Consequently, we’ve seen that the psychological toll the pandemic takes is as wide ranging as the disease caused by the novel coronavirus itself. Confusion, denial, fear, anxiety, depression/sadness, and emotional dysregulation have become all too common an experience. Many mental health experts have even likened our psychological response to COVID-19 to that of trauma survivors.
In early 2020, triggered by two separate but related threats. In addition to concerns regarding COVID-19, we also began to experience fear for our physical safety as anti-Chinese sentiment began to rise across the country and the world. Discrimination and acts of violence toward Chinese people worldwide began to spread almost as rapidly as the virus itself. Anxiety and fear became a common daily experience of countless people, myself included.
In late March, amid coping with existing stressors, my situation became significantly worse when my brother, a New York City firefighter, contracted COVID-19 while working on the front lines. Shortly thereafter, my parents, both aged 60 years and older, with whom my brother shares a home, contracted the virus as well. My anxiety triggers related to the spread of the virus and xenophobia suddenly became a distant memory. I now found myself grappling with the much greater fear of losing my entire family.
At the time, the availability of testing was very limited, even for those working on the front lines. Although not without a short delay, my brother was able to access testing through Fire Department of New York connections. After about 3 weeks in self-isolation at home and with the use of over the counter pain relievers, he made a full recovery and returned to work. My parents, on the other hand, were placed at the end of a weeks-long line for testing, during which time their conditions deteriorated. Nine days following the onset of my mother’s symptoms, her condition had gotten so bad, she required hospitalization. Six days later, my father followed suit.
Being in the epicenter of the COVID-19 outbreak, New York hospitals were severely overwhelmed. Upon admission, my mother was held in the ED and other temporary open spaces in the hospital for nearly 24 hours because there was a lack of available patient rooms. During this time, she was packed into small spaces with dozens of other patients afflicted with the same disease. Four days later, she was transferred to a different hospital 10 miles away to make room for new patients. Decisions needed to be made rapidly and often with limited communication, which made for a roller coaster of emotions that would not relent.
Confusion. One of the few things we know with certainty about coronavirus is how much we don’t know. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention data indicate that older adults with underlying health conditions have worse outcomes. Yet my mother, who is younger and in better physical health than my father, became much sicker in a drastically shorter period of time. Furthermore, my parents’ symptoms were completely inconsistent with one another’s. Based on their symptoms alone, it appeared as though they were suffering with different conditions entirely. My mother experienced body aches and gastrointestinal symptoms, whereas my father developed the typical cough and fever associated with COVID-19. In addition to confusion regarding their symptoms and, therefore, in determining the best at-home supportive care prior to their hospitalizations, the lack of available testing made the very question of whether they even had COVID-19 an uncertainty.
Denial. When my family members first became symptomatic, I found myself in a state of denial not unlike that of individuals experiencing grief. I frequently engaged in both internal and external dialogues in which I would attempt to convince myself of the reasons why my family did not have COVID-19.
“My brother wears PPE while at work.”
“My father’s cough was mild.”
“My mother does not have a cough or a fever.”
Despite knowing better, I was initially unable to accept that everyone in my family had contracted a disease that had already claimed the lives of tens of thousands globally.
Fear. In order to prevent the spread of infection, many hospitals made changes to their visitor policies, placing greater restrictions on who can come and go. This has meant hospital patients who have died from COVID-19 complications have done so separated from their loved ones. After transporting my mother to the hospital ED, I was politely but firmly asked to leave per the new visitor policy. I felt as though there were cinder blocks attached to my feet as I reluctantly walked away, not knowing if it would be the last time I would see her. I experienced a fear and sadness so intense, it continues to elicit an emotional response today as I think back on that moment.
Anxiety. The difference between fear and anxiety is fear is an emotional response to a known threat or danger, and anxiety is a response to an unknown threat or danger. The days that followed my parents’ hospitalizations were riddled with anxiety that would come in waves. How were they doing? Could they breathe? Do the overwhelmed hospital staff have time to take care of them? What can I do to help? Is there anything I can do to help? The worrisome thoughts and unanswerable questions were incessant and seemed unresponsive to my efforts to quell them.
Sadness. To feel sadness is to be human. In my work as a psychologist, I emphasize the value in experiencing this emotion when therapeutically beneficial. This technique is used as part of acceptance and commitment therapy (ACT), which emphasizes the value of being present or in touch with one’s thoughts and emotions, instead of working to eliminate them. During these scary times, I leaned into this notion more than ever. I gave myself permission to not feel okay, to cry more than I had in a long time, and to be unapologetically sad. I flip-flopped between states of near-despair and hopeful, with the switch usually following a call from a member of the hospital care team with updates on my parents’ conditions.
My parents’ road to recovery extended far beyond their discharge from the hospital and was not without incident, but with support and appropriate follow-up care, they have since made full recoveries from COVID-19. Although the relief and happiness this brings me is immeasurable, the experience has left a lasting impression on me as both a person and a psychologist. Speaking as a person, I cannot overstate the value of relying on one’s social support network while coping with stressors related to COVID-19. Whether you are directly or indirectly affected by the disease, the emotional effects can feel equally intense. As in times of happiness and celebration, times of sadness can and should be shared by those who are equipped to provide support. This can be tricky in an era during which isolation is prescribed for our safety, but we have more options today for connecting virtually with others than ever before, including video conferencing, email, and that old friend, the telephone. Furthermore, identify and assert your boundaries. Sometimes, saying no to others is the best way to say yes to yourself. Certain work, chores, and social obligations that can wait, should wait.
As a psychologist, my experience has given me a renewed appreciation for the power of the therapeutic use of self in psychotherapy. The factor with the greatest effects on psychotherapy outcomes is the quality of the therapeutic alliance, a concept introduced by Sigmund Freud in 1912. I believe a therapist’s willingness to show that we, too, experience life’s ups and downs strengthens our ability to demonstrate empathy and further promote a sense of alliance. Therapists are not immune to the effects of COVID-19, and to acknowledge this fact allows us to relate to our patients on a basic human level, which is more important now than ever.
Dr. Tseng, a licensed clinical psychologist, is in private practice in New York. She disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
George Floyd, race, and psychiatry: How to talk to patients
Editor’s Note: This transcript from the June 5 special episode of the Psychcast has been edited for clarity.
Nick Andrews: This is the Psychcast, the official podcast of MDedge Psychiatry. I am the voice of the MDedge podcasts, Nick Andrews. We are bringing this special edition of the Psychcast from MDedge in response to all of the unrest, peaceful or otherwise, in the United States in the aftermath of the shocking murder of George Floyd in late May of 2020.
Dr. Lorenzo Norris agreed to have this “after hours” discussion, believing the most appropriate response would be for us to have a real conversation about it. So welcome aboard.
Lorenzo Norris, MD: I’m happy to be here, Nick, and I’m so pleased to be talking with our guest, Dr. Brandon Newsome, a young black male psychiatrist. Dr. Newsome, sir, tell us a little about yourself and where you’re coming from.
Brandon Newsome, MD: I’m a 4th-year psychiatry resident at Boston Medical Center, so I’m about to graduate and to become a first-year fellow, as of July, at Children’s National Medical Center in Washington, D.C. I was born and raised in the South so I can talk about those experiences, and now I’ve been in the Northeast for the past 4 years.
Dr. Norris: Let’s get right into it. This is a time in our country that we’ve not seen – I shouldn’t say we, because depending on where you live in America, you have seen this and you’ve seen this multiple times.
I see a lot of myself in Dr. Newsome right now, and I am struggling with this: I’m talking to you about the same stuff I was talking about when I was a 4th-year resident. I’m talking to you about the same stuff I was talking about when I was a college student. I’m still talking about the same stuff I was talking about when I was a medical student. I’m still talking about the same things that were the impetus for the hip-hop generation regarding police brutality and violence.
We are still talking about the use of lethal force and abuse of power, particularly by police or law enforcement officers, and how that is perpetrated against African American men in particular, and the unfortunate and tragic murder of Mr. George Floyd. Dr. Newsome, tell me how you’re thinking about this. Before we even get into how our patients or our colleagues are doing, how are you doing with this?
Dr. Newsome: It’s been difficult. Like you, I’ve heard this story time and time again. I was just on a panel, having a conversation about race and policing, and I realized we had the same conversation during my first or second year of residency because there had been another death. But even though all of these unfortunate deaths are triggering us, this one is a little different for me for a few reasons. As you know, this is happening with the backdrop of the COVID-19 crisis and we’re already seeing so many people, especially from black and brown communities, dying from that.
And then I’m witnessing what happened, watching that video and thinking about all the interventions we’ve already tried. We tried body cameras, and the dude was wearing a body camera. We tried to get our police officers to be engaged, to try to check their roles, but people were there, witnessing everything, and nothing happened. An upstander was there, a white upstander, a firefighter who was telling them to check his pulse. Still nothing happened; it didn’t stop them.
I believe the backdrop of the COVID-19 crisis makes it a whole lot more painful for me and many others. I am part of a black physician email group and it’s been triggering for all of us because we all imagine that this could be me one day, especially when you think about the Amy Coopers of the world, among other things.
Dr. Norris: I completely agree. We’re dealing with loss of life due to a virus, including, [personally speaking] that of my departed grandmother Why am I bringing this up? I bring it up because, regardless of one’s socioeconomic strata or title or whatnot, particularly in the black community, this is the kind of mess we’re dealing with. We’re dealing with the stress of COVID-19 that is disproportionately affecting African Americans. We’re dealing with social isolation, we’re dealing with the economic recession and the collapse that everyone else is dealing with, and on top of that we are now dealing with another murder. But this particular murder resonates very differently because, as you said, it seemed like every single thing that could have been done was done.
You will read reports that Mr. Floyd was resisting arrest. But you look at this video; this is not a man resisting arrest. This is a man trying to say, please, you are killing me. These are other people saying the same thing. These are police officers not acting right. This is so many different things going on, and when you hear this and look at this video, you can come to no other conclusion than it is murder.
As psychiatrists, we frequently have to restrain people, and it is always understood that restraint can turn into assault extremely quickly. But in this particular case, there was no thought or concern about this man’s life or his health. There are many good police officers that do think of that, and so this was shocking. It was jarring. It was another thing piled on an already taxed black America. I was talking with my black male colleagues about this, and I think a lot of people don’t actually realize that, while there are black male psychiatrists, there are only a few of us.
Dr. Newsome: True that.
Dr. Norris: There are only so many black male physicians, period, and black male psychiatrists in particular. At different points in time we are called on to take leadership roles, and to talk, to speak on things and be a voice. Well, I have to tell you, after a while, this is pretty goddamn tiring for us to contain our disappointment, our anger, and our rage and still stay hopeful, optimistic, and still be a voice for those who are not able to speak.
Dr. Newsome: I agree that sometimes it can be tiring to have to take leadership roles and continue to talk about all these things, but I also feel that, at least for me, it gives me some sort of route to address the angst and do something with it. I believe all of us are just figuring out how to deal with these feelings that we shouldn’t have to feel because of a murder that was televised.
Dr. Norris: Thank you. For a murder that was televised; that was tweeted; that was broadbanded; that was streamed.
Now we’ve laid the framework, in terms of what we’re feeling. Let’s move on to why you and I are in this profession, and that’s our patients. What are you seeing on the front lines? What are you seeing with our patients?
Dr. Newsome: I was speaking with one of my black male patients, and he was fearful. He had been perfectly fine, even in the COVID crisis, he was doing well. But when you get this milieu of police violence, now he’s feeling this intense fear. Should I be walking alone at night? What happens if I am the one who is at the wrong place at the wrong time?
I also find that some of my nonminority patients sometimes find difficulty making sense of it. Minority individuals already know these things are happening. But some of the nonminorities are wondering how or why would something like this happen in America? This is just how America is for the black folks.
Dr. Norris: Could you elaborate on that? I always found that to be a very interesting dynamic for those who are not minorities or people of color. I will have folks in a psychotherapy session who are just bewildered by events like this. It is not the America they think they know – they are shocked that this is actually what’s going on.
Dr. Newsome: It’s all about experiences. If you didn’t grow up around a lot of minorities, you haven’t necessarily had these conversations. Even speaking for myself, sometimes I don’t want to discuss these things; you never know what you’re going to get. You might find an ally, or you might find someone who isn’t at all supportive. I think the surprise is from lack of exposure. If you don’t have to live through racism, you can most certainly have blinders on and not notice.
Dr. Norris: Can you comment on the fear you’re seeing in some folks? Can it get to the point of reactivating PTSD?
Dr. Newsome: I notice it more with black individuals, a fear that they might be the ones who may die; or with black mothers, wondering, what about my child? Is this what they are going to have to live with for the rest of their lives? Older people would say that we fought already and it’s still going on. What are the fruits of the labor we put in?
Dr. Norris: I agree with you completely. What are the fruits? You’re going to see those strong reactions. You’re going to see fear, you’re going to see anger, and you’re also going to see guilt that they could not stop this. I’m speaking particularly about some of my nonminority patients. It goes along with that confusion. This manifests in a desperate need to do something.
But here’s the problem: You don’t really know what to do because no one is educated on it. And as you said before, race is a very polarized subject. No one even likes to talk about racism because it’s so, oh my goodness. We’ve run away from it so much to the point that we can’t deal with it. We all have to start to own that. You can’t just stay siloed, because eventually, it’s going to come back and affect you.
I could easily be Mr. Floyd, but at the same time, due to my station and things of that nature, I have a certain level of privilege and autonomy. There could be a tendency to put your head under the sand, you know, look at how far we’ve come, Barack Obama. But you’ve got to say, no, we still have enormous amounts of work to do.
We’ve been talking about the patients. What have you noticed in your colleagues and how they’ve been feeling about this?
Dr. Newsome: Again, I see them feeling saddened by the events. One of the other things I’ve noticed is that some people are in environments where they have program directors and chairs who will directly condemn certain behaviors and say, “This is racist, this shouldn’t happen.” But then there are other programs that have been more silent. I’ve had people say that this is the first time that they have felt isolated in a long while.
We all participate in these physician WhatsApp groups, and according to some of the comments, people are realizing that these folks that they were just on the front lines with, fighting COVID, are perhaps not the allies that they originally thought they were, based on the things these people are saying.
Dr. Norris: Wow. It’s good that we’re talking about this from the viewpoint of two different generations. You’ve got the WhatsApp group and Google Hangouts and all that kind of good stuff, and I’m still with pagers and such. That’s interesting – the reality that folks you thought were your allies turn out not to be, because you’re bringing up difficult conversations that we don’t normally talk about.
I have noticed that some people around me have been silent because they don’t know what to say. They’re so concerned that I’m going to be offended or they’re going to hurt me or say the wrong thing, so they stay quiet. As I reflect now, this is the wrong thing to do. Own your concern. I’ve been in two large meetings now, and I’ve had multiple people whom I consider friends say, I wanted to email or text you right then and ask you how you’re doing, but I didn’t because I didn’t know what to say. I have entered meetings recently, and the meeting felt tense, and I’m thinking, what’s going on? And now I realize they did not know what to say or how to approach it.
That’s been a very interesting dynamic and tells us where we are with this. Today, for example, I was pleased to have the support of my dean’s group. I felt I had to speak out, I just had to straight out tell them. Do you want to know what I’m feeling? I’m feeling rage. I’m feeling rage. And you all have to understand that, because I have to speak for those who aren’t necessarily going to be able to express themselves. More importantly, I have to speak for myself and I’m feeling rage.
How our colleagues are processing this and how they’re thinking about this runs the gamut. But I think about people not necessarily knowing what to say or how to approach it. I absolutely agree that with the leadership, you’re going to get many different responses, and sometimes you’re left to wonder, do I have to watch what I say? But I’m definitely supported at my institution.
What else are you seeing out there in terms of your colleagues or how people think about it?
Dr. Newsome: This also spurs some folks to activism. Some have been participating in protests. There will be White Coats for Black Lives protests, among other things. So it’s spurred folks to action, and it’s also spurred folks to try to be part of a community. Of course, with the whole COVID crisis, we can’t necessarily come together, so we’ve been doing Zoom gatherings more than anything else. But it has encouraged folks to want to do that more, too, because they want to check in on their brother or their sister to make sure they are doing well, and also to be able to express what’s going on with them in a community where they know they can get validation.
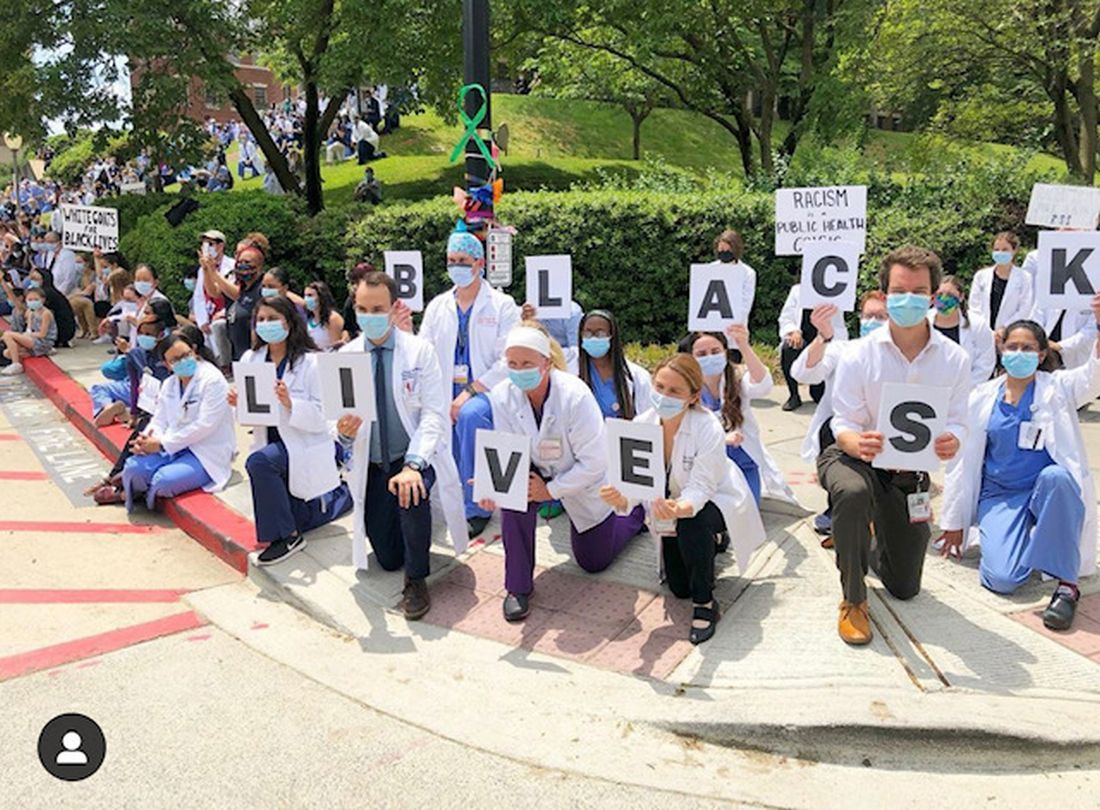

Dr. Norris: I’m going to push you a bit because I detect in your tone something similar to what I’m feeling. I just got the email, the White Coats For Black Lives email. But I think your feeling is similar to mine – I’ve done this before. I’ve done White Coats for Black Lives. You all may have protested. But this display in Washington, D.C., of the use of military and law enforcement to clear a public square of peaceful protesters is above and beyond the pale of anything I’ve ever seen in my life. We have to label that for the danger it is, for the threat to everything this country and the people that bled for this country stand for.
So while I’m going to participate in White Coats for Black Lives and many other things, I am looking for what is actually going to move the needle. I think the protests are great, but at this point in time I want institutions, I want money, I want lawyers, I want a systematic approach.
Dr. Newsome: I most certainly agree. Of course, the protests are really important, but depending on where you are, you have a different lens. As physicians, especially as black physicians, since there are so few of us, we have a unique opportunity to leverage that, whether that means communicating through op-eds or calling your senators and talking with them to try to move things forward.
Physicians are mobilizing. In the last few days, a physician created a Zoom event and hundreds of physicians joined to try to figure out how we can structurally fix this problem. So I most certainly believe that in this effort to address racism, we physicians will need to lend our voices and our privilege to move the needle as best we can.
Dr. Norris: Some of our colleagues in Black Psychiatrists of America have put out a press release on racism in which they propose some actions that should be taken immediately. I think this is a useful thing to talk about.
The first action: “Declare racism a public health problem and establish national goals for addressing this as a health equity issue. Give priority to addressing the issues of health care disparities, including the mental health needs of historically marginalized communities across the U.S.”
What do you think about that?
Dr. Newsome: Those are two extremely important steps. The question is: How do you make that happen?
Dr. Norris: You’re reading my mind. I love that our colleagues put that out there, but that was my next question.
Dr. Newsome: There is going to be a town hall about this and I’m hoping that we can plan how we envision this happening. I can imagine that 20 or 30 years ago there was also a fear in society that there would be episodes of police brutality. I can imagine that there were similar ideals and hopes. But I think we need to put all of our minds together and ask: How are we going to accomplish this? Is this going to be something we’re going to put our money into? Is this going to be something we’re going to get senators and legislatures onboard with to make policy?
Dr. Norris: Let me read off some of the other action points they put out. There are six of them.
“Establish a governmental multidisciplinary and ethnically diverse commission with representatives from the major health care professional associations in medicine, nursing, psychiatry, public health, psychology, social work, etc., and the faith-based community to provide recommendations to Congress regarding policies on how to best improve the health and well-being of our nation’s black citizens.”
That’s a very solid overall recommendation. My question is, doesn’t that, in some way, shape, or form already exist? Could we not put up policy statements from all of these folks regarding racism and things of that nature? I agree with what they’re saying, but part of me wonders why certain things in the current system aren’t working. That becomes the question. Are we not integrated enough? Do we not have enough cross talk? Do we not have enough money behind it? So I agree with that goal, but I would be curious if that doesn’t already exist. What are your thoughts about that, Dr. Newsome?
Dr. Newsome: I would imagine that the National Institute on Minority Mental Health and Health Disparities would have something similar. I believe one of the things you mentioned is really important. In addition to making these recommendations, we need to be looking at where these leaks are occurring that keep them from working. What is the current structure and why is it the way it is with regard to the governance?
Dr. Norris: Here is another of their action statements: “Declare ‘civic mental health’ a national priority and incorporate it into the educational curriculum from K through college, as well as in the training of local, state, and national officials, law enforcement, and the criminal justice system.”
Let me be clear, I like every single one of these action statements. I encourage everyone to participate in dialogue and discussion. You may agree with some of these, and some of them you may not, but if there is one you agree with, that you really are motivated about, that’s one that you need to explore and dig into a bit more, because it’s too big for us to handle on our own, just like racism and equality.
I’m going to tell you, I like this statement. I do like this. Obviously these are broad points, but I do like the idea of training law enforcement officers about “civic mental health.” For example, Dr. Michael Compton, who has done a lot of great work in the area of mental health and prevention, has worked with police officers to help them interact with those with mental health conditions by modulating their own emotional response. I’m very interested in these types of recommendations that particularly target law enforcement officers, and helping with that ”emotional quotient.” I’m interested in seeing how far that can spread in the country. What do you think, Dr. Newsome?
Dr. Newsome: Educating police officers about how to interact would be quite important. I believe the National Alliance on Mental Illness does some of that work, partnering with law enforcement agencies, talking about mental health and cues to look at. There also are some programs where people ride along with mental health clinicians and police officers, which I find to be really helpful. But clearly, what’s going on right now isn’t working. So I would be open to any reasonable idea.
Dr. Norris: Here’s one last action point: “Establish police community review boards with power to take action in areas of police misconduct pending formal review by the appropriate authorities. This will offer a level of empowerment when communities feel they have a voice that can be heard.”
This is where I want my focus to be, as I move forward to try to do something sustainable. To deal with police brutality and abuse of power in general, but specifically as it relates to African American men and the lethal use of force. We need to work on policies that will enable African American men to make it to court, so that every encounter with a police officer is not literally viewed as a potentially lethal encounter.
A lot of people aren’t going to like me saying that, but it’s the absolute truth. You have to think like that, as an African American male, regardless of your station, regardless of where you live, this is the reality. There are many, many good police officers out there. I have a few friends who are law enforcement officers. I work with security at the George Washington Hospital constantly. But that still does not change the fact that if I get pulled over at a traffic stop, I know precisely certain things I need to do and not do, or the encounter could end badly. By that I mean loss of life.
So I encourage anything where we can start to take a systematic look at law enforcement and empower communities to look at who is doing it right and who is doing it wrong. Information is coming out now about the man who murdered Mr. Floyd, and this was not the first time he was involved in misconduct. There were red flags; we have to start to confront this. We have to learn from every single one of these situations and grow because another one is going to happen next week, it’s just whether or not you hear about it. That’s the reality of the state of America. You may not like to hear it, but that’s just a fact.
To hear the entire conversation, go to mdedge.com/podcasts or listen wherever you find your podcasts.
Editor’s Note: This transcript from the June 5 special episode of the Psychcast has been edited for clarity.
Nick Andrews: This is the Psychcast, the official podcast of MDedge Psychiatry. I am the voice of the MDedge podcasts, Nick Andrews. We are bringing this special edition of the Psychcast from MDedge in response to all of the unrest, peaceful or otherwise, in the United States in the aftermath of the shocking murder of George Floyd in late May of 2020.
Dr. Lorenzo Norris agreed to have this “after hours” discussion, believing the most appropriate response would be for us to have a real conversation about it. So welcome aboard.
Lorenzo Norris, MD: I’m happy to be here, Nick, and I’m so pleased to be talking with our guest, Dr. Brandon Newsome, a young black male psychiatrist. Dr. Newsome, sir, tell us a little about yourself and where you’re coming from.
Brandon Newsome, MD: I’m a 4th-year psychiatry resident at Boston Medical Center, so I’m about to graduate and to become a first-year fellow, as of July, at Children’s National Medical Center in Washington, D.C. I was born and raised in the South so I can talk about those experiences, and now I’ve been in the Northeast for the past 4 years.
Dr. Norris: Let’s get right into it. This is a time in our country that we’ve not seen – I shouldn’t say we, because depending on where you live in America, you have seen this and you’ve seen this multiple times.
I see a lot of myself in Dr. Newsome right now, and I am struggling with this: I’m talking to you about the same stuff I was talking about when I was a 4th-year resident. I’m talking to you about the same stuff I was talking about when I was a college student. I’m still talking about the same stuff I was talking about when I was a medical student. I’m still talking about the same things that were the impetus for the hip-hop generation regarding police brutality and violence.
We are still talking about the use of lethal force and abuse of power, particularly by police or law enforcement officers, and how that is perpetrated against African American men in particular, and the unfortunate and tragic murder of Mr. George Floyd. Dr. Newsome, tell me how you’re thinking about this. Before we even get into how our patients or our colleagues are doing, how are you doing with this?
Dr. Newsome: It’s been difficult. Like you, I’ve heard this story time and time again. I was just on a panel, having a conversation about race and policing, and I realized we had the same conversation during my first or second year of residency because there had been another death. But even though all of these unfortunate deaths are triggering us, this one is a little different for me for a few reasons. As you know, this is happening with the backdrop of the COVID-19 crisis and we’re already seeing so many people, especially from black and brown communities, dying from that.
And then I’m witnessing what happened, watching that video and thinking about all the interventions we’ve already tried. We tried body cameras, and the dude was wearing a body camera. We tried to get our police officers to be engaged, to try to check their roles, but people were there, witnessing everything, and nothing happened. An upstander was there, a white upstander, a firefighter who was telling them to check his pulse. Still nothing happened; it didn’t stop them.
I believe the backdrop of the COVID-19 crisis makes it a whole lot more painful for me and many others. I am part of a black physician email group and it’s been triggering for all of us because we all imagine that this could be me one day, especially when you think about the Amy Coopers of the world, among other things.
Dr. Norris: I completely agree. We’re dealing with loss of life due to a virus, including, [personally speaking] that of my departed grandmother Why am I bringing this up? I bring it up because, regardless of one’s socioeconomic strata or title or whatnot, particularly in the black community, this is the kind of mess we’re dealing with. We’re dealing with the stress of COVID-19 that is disproportionately affecting African Americans. We’re dealing with social isolation, we’re dealing with the economic recession and the collapse that everyone else is dealing with, and on top of that we are now dealing with another murder. But this particular murder resonates very differently because, as you said, it seemed like every single thing that could have been done was done.
You will read reports that Mr. Floyd was resisting arrest. But you look at this video; this is not a man resisting arrest. This is a man trying to say, please, you are killing me. These are other people saying the same thing. These are police officers not acting right. This is so many different things going on, and when you hear this and look at this video, you can come to no other conclusion than it is murder.
As psychiatrists, we frequently have to restrain people, and it is always understood that restraint can turn into assault extremely quickly. But in this particular case, there was no thought or concern about this man’s life or his health. There are many good police officers that do think of that, and so this was shocking. It was jarring. It was another thing piled on an already taxed black America. I was talking with my black male colleagues about this, and I think a lot of people don’t actually realize that, while there are black male psychiatrists, there are only a few of us.
Dr. Newsome: True that.
Dr. Norris: There are only so many black male physicians, period, and black male psychiatrists in particular. At different points in time we are called on to take leadership roles, and to talk, to speak on things and be a voice. Well, I have to tell you, after a while, this is pretty goddamn tiring for us to contain our disappointment, our anger, and our rage and still stay hopeful, optimistic, and still be a voice for those who are not able to speak.
Dr. Newsome: I agree that sometimes it can be tiring to have to take leadership roles and continue to talk about all these things, but I also feel that, at least for me, it gives me some sort of route to address the angst and do something with it. I believe all of us are just figuring out how to deal with these feelings that we shouldn’t have to feel because of a murder that was televised.
Dr. Norris: Thank you. For a murder that was televised; that was tweeted; that was broadbanded; that was streamed.
Now we’ve laid the framework, in terms of what we’re feeling. Let’s move on to why you and I are in this profession, and that’s our patients. What are you seeing on the front lines? What are you seeing with our patients?
Dr. Newsome: I was speaking with one of my black male patients, and he was fearful. He had been perfectly fine, even in the COVID crisis, he was doing well. But when you get this milieu of police violence, now he’s feeling this intense fear. Should I be walking alone at night? What happens if I am the one who is at the wrong place at the wrong time?
I also find that some of my nonminority patients sometimes find difficulty making sense of it. Minority individuals already know these things are happening. But some of the nonminorities are wondering how or why would something like this happen in America? This is just how America is for the black folks.
Dr. Norris: Could you elaborate on that? I always found that to be a very interesting dynamic for those who are not minorities or people of color. I will have folks in a psychotherapy session who are just bewildered by events like this. It is not the America they think they know – they are shocked that this is actually what’s going on.
Dr. Newsome: It’s all about experiences. If you didn’t grow up around a lot of minorities, you haven’t necessarily had these conversations. Even speaking for myself, sometimes I don’t want to discuss these things; you never know what you’re going to get. You might find an ally, or you might find someone who isn’t at all supportive. I think the surprise is from lack of exposure. If you don’t have to live through racism, you can most certainly have blinders on and not notice.
Dr. Norris: Can you comment on the fear you’re seeing in some folks? Can it get to the point of reactivating PTSD?
Dr. Newsome: I notice it more with black individuals, a fear that they might be the ones who may die; or with black mothers, wondering, what about my child? Is this what they are going to have to live with for the rest of their lives? Older people would say that we fought already and it’s still going on. What are the fruits of the labor we put in?
Dr. Norris: I agree with you completely. What are the fruits? You’re going to see those strong reactions. You’re going to see fear, you’re going to see anger, and you’re also going to see guilt that they could not stop this. I’m speaking particularly about some of my nonminority patients. It goes along with that confusion. This manifests in a desperate need to do something.
But here’s the problem: You don’t really know what to do because no one is educated on it. And as you said before, race is a very polarized subject. No one even likes to talk about racism because it’s so, oh my goodness. We’ve run away from it so much to the point that we can’t deal with it. We all have to start to own that. You can’t just stay siloed, because eventually, it’s going to come back and affect you.
I could easily be Mr. Floyd, but at the same time, due to my station and things of that nature, I have a certain level of privilege and autonomy. There could be a tendency to put your head under the sand, you know, look at how far we’ve come, Barack Obama. But you’ve got to say, no, we still have enormous amounts of work to do.
We’ve been talking about the patients. What have you noticed in your colleagues and how they’ve been feeling about this?
Dr. Newsome: Again, I see them feeling saddened by the events. One of the other things I’ve noticed is that some people are in environments where they have program directors and chairs who will directly condemn certain behaviors and say, “This is racist, this shouldn’t happen.” But then there are other programs that have been more silent. I’ve had people say that this is the first time that they have felt isolated in a long while.
We all participate in these physician WhatsApp groups, and according to some of the comments, people are realizing that these folks that they were just on the front lines with, fighting COVID, are perhaps not the allies that they originally thought they were, based on the things these people are saying.
Dr. Norris: Wow. It’s good that we’re talking about this from the viewpoint of two different generations. You’ve got the WhatsApp group and Google Hangouts and all that kind of good stuff, and I’m still with pagers and such. That’s interesting – the reality that folks you thought were your allies turn out not to be, because you’re bringing up difficult conversations that we don’t normally talk about.
I have noticed that some people around me have been silent because they don’t know what to say. They’re so concerned that I’m going to be offended or they’re going to hurt me or say the wrong thing, so they stay quiet. As I reflect now, this is the wrong thing to do. Own your concern. I’ve been in two large meetings now, and I’ve had multiple people whom I consider friends say, I wanted to email or text you right then and ask you how you’re doing, but I didn’t because I didn’t know what to say. I have entered meetings recently, and the meeting felt tense, and I’m thinking, what’s going on? And now I realize they did not know what to say or how to approach it.
That’s been a very interesting dynamic and tells us where we are with this. Today, for example, I was pleased to have the support of my dean’s group. I felt I had to speak out, I just had to straight out tell them. Do you want to know what I’m feeling? I’m feeling rage. I’m feeling rage. And you all have to understand that, because I have to speak for those who aren’t necessarily going to be able to express themselves. More importantly, I have to speak for myself and I’m feeling rage.
How our colleagues are processing this and how they’re thinking about this runs the gamut. But I think about people not necessarily knowing what to say or how to approach it. I absolutely agree that with the leadership, you’re going to get many different responses, and sometimes you’re left to wonder, do I have to watch what I say? But I’m definitely supported at my institution.
What else are you seeing out there in terms of your colleagues or how people think about it?
Dr. Newsome: This also spurs some folks to activism. Some have been participating in protests. There will be White Coats for Black Lives protests, among other things. So it’s spurred folks to action, and it’s also spurred folks to try to be part of a community. Of course, with the whole COVID crisis, we can’t necessarily come together, so we’ve been doing Zoom gatherings more than anything else. But it has encouraged folks to want to do that more, too, because they want to check in on their brother or their sister to make sure they are doing well, and also to be able to express what’s going on with them in a community where they know they can get validation.

Dr. Norris: I’m going to push you a bit because I detect in your tone something similar to what I’m feeling. I just got the email, the White Coats For Black Lives email. But I think your feeling is similar to mine – I’ve done this before. I’ve done White Coats for Black Lives. You all may have protested. But this display in Washington, D.C., of the use of military and law enforcement to clear a public square of peaceful protesters is above and beyond the pale of anything I’ve ever seen in my life. We have to label that for the danger it is, for the threat to everything this country and the people that bled for this country stand for.
So while I’m going to participate in White Coats for Black Lives and many other things, I am looking for what is actually going to move the needle. I think the protests are great, but at this point in time I want institutions, I want money, I want lawyers, I want a systematic approach.
Dr. Newsome: I most certainly agree. Of course, the protests are really important, but depending on where you are, you have a different lens. As physicians, especially as black physicians, since there are so few of us, we have a unique opportunity to leverage that, whether that means communicating through op-eds or calling your senators and talking with them to try to move things forward.
Physicians are mobilizing. In the last few days, a physician created a Zoom event and hundreds of physicians joined to try to figure out how we can structurally fix this problem. So I most certainly believe that in this effort to address racism, we physicians will need to lend our voices and our privilege to move the needle as best we can.
Dr. Norris: Some of our colleagues in Black Psychiatrists of America have put out a press release on racism in which they propose some actions that should be taken immediately. I think this is a useful thing to talk about.
The first action: “Declare racism a public health problem and establish national goals for addressing this as a health equity issue. Give priority to addressing the issues of health care disparities, including the mental health needs of historically marginalized communities across the U.S.”
What do you think about that?
Dr. Newsome: Those are two extremely important steps. The question is: How do you make that happen?
Dr. Norris: You’re reading my mind. I love that our colleagues put that out there, but that was my next question.
Dr. Newsome: There is going to be a town hall about this and I’m hoping that we can plan how we envision this happening. I can imagine that 20 or 30 years ago there was also a fear in society that there would be episodes of police brutality. I can imagine that there were similar ideals and hopes. But I think we need to put all of our minds together and ask: How are we going to accomplish this? Is this going to be something we’re going to put our money into? Is this going to be something we’re going to get senators and legislatures onboard with to make policy?
Dr. Norris: Let me read off some of the other action points they put out. There are six of them.
“Establish a governmental multidisciplinary and ethnically diverse commission with representatives from the major health care professional associations in medicine, nursing, psychiatry, public health, psychology, social work, etc., and the faith-based community to provide recommendations to Congress regarding policies on how to best improve the health and well-being of our nation’s black citizens.”
That’s a very solid overall recommendation. My question is, doesn’t that, in some way, shape, or form already exist? Could we not put up policy statements from all of these folks regarding racism and things of that nature? I agree with what they’re saying, but part of me wonders why certain things in the current system aren’t working. That becomes the question. Are we not integrated enough? Do we not have enough cross talk? Do we not have enough money behind it? So I agree with that goal, but I would be curious if that doesn’t already exist. What are your thoughts about that, Dr. Newsome?
Dr. Newsome: I would imagine that the National Institute on Minority Mental Health and Health Disparities would have something similar. I believe one of the things you mentioned is really important. In addition to making these recommendations, we need to be looking at where these leaks are occurring that keep them from working. What is the current structure and why is it the way it is with regard to the governance?
Dr. Norris: Here is another of their action statements: “Declare ‘civic mental health’ a national priority and incorporate it into the educational curriculum from K through college, as well as in the training of local, state, and national officials, law enforcement, and the criminal justice system.”
Let me be clear, I like every single one of these action statements. I encourage everyone to participate in dialogue and discussion. You may agree with some of these, and some of them you may not, but if there is one you agree with, that you really are motivated about, that’s one that you need to explore and dig into a bit more, because it’s too big for us to handle on our own, just like racism and equality.
I’m going to tell you, I like this statement. I do like this. Obviously these are broad points, but I do like the idea of training law enforcement officers about “civic mental health.” For example, Dr. Michael Compton, who has done a lot of great work in the area of mental health and prevention, has worked with police officers to help them interact with those with mental health conditions by modulating their own emotional response. I’m very interested in these types of recommendations that particularly target law enforcement officers, and helping with that ”emotional quotient.” I’m interested in seeing how far that can spread in the country. What do you think, Dr. Newsome?
Dr. Newsome: Educating police officers about how to interact would be quite important. I believe the National Alliance on Mental Illness does some of that work, partnering with law enforcement agencies, talking about mental health and cues to look at. There also are some programs where people ride along with mental health clinicians and police officers, which I find to be really helpful. But clearly, what’s going on right now isn’t working. So I would be open to any reasonable idea.
Dr. Norris: Here’s one last action point: “Establish police community review boards with power to take action in areas of police misconduct pending formal review by the appropriate authorities. This will offer a level of empowerment when communities feel they have a voice that can be heard.”
This is where I want my focus to be, as I move forward to try to do something sustainable. To deal with police brutality and abuse of power in general, but specifically as it relates to African American men and the lethal use of force. We need to work on policies that will enable African American men to make it to court, so that every encounter with a police officer is not literally viewed as a potentially lethal encounter.
A lot of people aren’t going to like me saying that, but it’s the absolute truth. You have to think like that, as an African American male, regardless of your station, regardless of where you live, this is the reality. There are many, many good police officers out there. I have a few friends who are law enforcement officers. I work with security at the George Washington Hospital constantly. But that still does not change the fact that if I get pulled over at a traffic stop, I know precisely certain things I need to do and not do, or the encounter could end badly. By that I mean loss of life.
So I encourage anything where we can start to take a systematic look at law enforcement and empower communities to look at who is doing it right and who is doing it wrong. Information is coming out now about the man who murdered Mr. Floyd, and this was not the first time he was involved in misconduct. There were red flags; we have to start to confront this. We have to learn from every single one of these situations and grow because another one is going to happen next week, it’s just whether or not you hear about it. That’s the reality of the state of America. You may not like to hear it, but that’s just a fact.
To hear the entire conversation, go to mdedge.com/podcasts or listen wherever you find your podcasts.
Editor’s Note: This transcript from the June 5 special episode of the Psychcast has been edited for clarity.
Nick Andrews: This is the Psychcast, the official podcast of MDedge Psychiatry. I am the voice of the MDedge podcasts, Nick Andrews. We are bringing this special edition of the Psychcast from MDedge in response to all of the unrest, peaceful or otherwise, in the United States in the aftermath of the shocking murder of George Floyd in late May of 2020.
Dr. Lorenzo Norris agreed to have this “after hours” discussion, believing the most appropriate response would be for us to have a real conversation about it. So welcome aboard.
Lorenzo Norris, MD: I’m happy to be here, Nick, and I’m so pleased to be talking with our guest, Dr. Brandon Newsome, a young black male psychiatrist. Dr. Newsome, sir, tell us a little about yourself and where you’re coming from.
Brandon Newsome, MD: I’m a 4th-year psychiatry resident at Boston Medical Center, so I’m about to graduate and to become a first-year fellow, as of July, at Children’s National Medical Center in Washington, D.C. I was born and raised in the South so I can talk about those experiences, and now I’ve been in the Northeast for the past 4 years.
Dr. Norris: Let’s get right into it. This is a time in our country that we’ve not seen – I shouldn’t say we, because depending on where you live in America, you have seen this and you’ve seen this multiple times.
I see a lot of myself in Dr. Newsome right now, and I am struggling with this: I’m talking to you about the same stuff I was talking about when I was a 4th-year resident. I’m talking to you about the same stuff I was talking about when I was a college student. I’m still talking about the same stuff I was talking about when I was a medical student. I’m still talking about the same things that were the impetus for the hip-hop generation regarding police brutality and violence.
We are still talking about the use of lethal force and abuse of power, particularly by police or law enforcement officers, and how that is perpetrated against African American men in particular, and the unfortunate and tragic murder of Mr. George Floyd. Dr. Newsome, tell me how you’re thinking about this. Before we even get into how our patients or our colleagues are doing, how are you doing with this?
Dr. Newsome: It’s been difficult. Like you, I’ve heard this story time and time again. I was just on a panel, having a conversation about race and policing, and I realized we had the same conversation during my first or second year of residency because there had been another death. But even though all of these unfortunate deaths are triggering us, this one is a little different for me for a few reasons. As you know, this is happening with the backdrop of the COVID-19 crisis and we’re already seeing so many people, especially from black and brown communities, dying from that.
And then I’m witnessing what happened, watching that video and thinking about all the interventions we’ve already tried. We tried body cameras, and the dude was wearing a body camera. We tried to get our police officers to be engaged, to try to check their roles, but people were there, witnessing everything, and nothing happened. An upstander was there, a white upstander, a firefighter who was telling them to check his pulse. Still nothing happened; it didn’t stop them.
I believe the backdrop of the COVID-19 crisis makes it a whole lot more painful for me and many others. I am part of a black physician email group and it’s been triggering for all of us because we all imagine that this could be me one day, especially when you think about the Amy Coopers of the world, among other things.
Dr. Norris: I completely agree. We’re dealing with loss of life due to a virus, including, [personally speaking] that of my departed grandmother Why am I bringing this up? I bring it up because, regardless of one’s socioeconomic strata or title or whatnot, particularly in the black community, this is the kind of mess we’re dealing with. We’re dealing with the stress of COVID-19 that is disproportionately affecting African Americans. We’re dealing with social isolation, we’re dealing with the economic recession and the collapse that everyone else is dealing with, and on top of that we are now dealing with another murder. But this particular murder resonates very differently because, as you said, it seemed like every single thing that could have been done was done.
You will read reports that Mr. Floyd was resisting arrest. But you look at this video; this is not a man resisting arrest. This is a man trying to say, please, you are killing me. These are other people saying the same thing. These are police officers not acting right. This is so many different things going on, and when you hear this and look at this video, you can come to no other conclusion than it is murder.
As psychiatrists, we frequently have to restrain people, and it is always understood that restraint can turn into assault extremely quickly. But in this particular case, there was no thought or concern about this man’s life or his health. There are many good police officers that do think of that, and so this was shocking. It was jarring. It was another thing piled on an already taxed black America. I was talking with my black male colleagues about this, and I think a lot of people don’t actually realize that, while there are black male psychiatrists, there are only a few of us.
Dr. Newsome: True that.
Dr. Norris: There are only so many black male physicians, period, and black male psychiatrists in particular. At different points in time we are called on to take leadership roles, and to talk, to speak on things and be a voice. Well, I have to tell you, after a while, this is pretty goddamn tiring for us to contain our disappointment, our anger, and our rage and still stay hopeful, optimistic, and still be a voice for those who are not able to speak.
Dr. Newsome: I agree that sometimes it can be tiring to have to take leadership roles and continue to talk about all these things, but I also feel that, at least for me, it gives me some sort of route to address the angst and do something with it. I believe all of us are just figuring out how to deal with these feelings that we shouldn’t have to feel because of a murder that was televised.
Dr. Norris: Thank you. For a murder that was televised; that was tweeted; that was broadbanded; that was streamed.
Now we’ve laid the framework, in terms of what we’re feeling. Let’s move on to why you and I are in this profession, and that’s our patients. What are you seeing on the front lines? What are you seeing with our patients?
Dr. Newsome: I was speaking with one of my black male patients, and he was fearful. He had been perfectly fine, even in the COVID crisis, he was doing well. But when you get this milieu of police violence, now he’s feeling this intense fear. Should I be walking alone at night? What happens if I am the one who is at the wrong place at the wrong time?
I also find that some of my nonminority patients sometimes find difficulty making sense of it. Minority individuals already know these things are happening. But some of the nonminorities are wondering how or why would something like this happen in America? This is just how America is for the black folks.
Dr. Norris: Could you elaborate on that? I always found that to be a very interesting dynamic for those who are not minorities or people of color. I will have folks in a psychotherapy session who are just bewildered by events like this. It is not the America they think they know – they are shocked that this is actually what’s going on.
Dr. Newsome: It’s all about experiences. If you didn’t grow up around a lot of minorities, you haven’t necessarily had these conversations. Even speaking for myself, sometimes I don’t want to discuss these things; you never know what you’re going to get. You might find an ally, or you might find someone who isn’t at all supportive. I think the surprise is from lack of exposure. If you don’t have to live through racism, you can most certainly have blinders on and not notice.
Dr. Norris: Can you comment on the fear you’re seeing in some folks? Can it get to the point of reactivating PTSD?
Dr. Newsome: I notice it more with black individuals, a fear that they might be the ones who may die; or with black mothers, wondering, what about my child? Is this what they are going to have to live with for the rest of their lives? Older people would say that we fought already and it’s still going on. What are the fruits of the labor we put in?
Dr. Norris: I agree with you completely. What are the fruits? You’re going to see those strong reactions. You’re going to see fear, you’re going to see anger, and you’re also going to see guilt that they could not stop this. I’m speaking particularly about some of my nonminority patients. It goes along with that confusion. This manifests in a desperate need to do something.
But here’s the problem: You don’t really know what to do because no one is educated on it. And as you said before, race is a very polarized subject. No one even likes to talk about racism because it’s so, oh my goodness. We’ve run away from it so much to the point that we can’t deal with it. We all have to start to own that. You can’t just stay siloed, because eventually, it’s going to come back and affect you.
I could easily be Mr. Floyd, but at the same time, due to my station and things of that nature, I have a certain level of privilege and autonomy. There could be a tendency to put your head under the sand, you know, look at how far we’ve come, Barack Obama. But you’ve got to say, no, we still have enormous amounts of work to do.
We’ve been talking about the patients. What have you noticed in your colleagues and how they’ve been feeling about this?
Dr. Newsome: Again, I see them feeling saddened by the events. One of the other things I’ve noticed is that some people are in environments where they have program directors and chairs who will directly condemn certain behaviors and say, “This is racist, this shouldn’t happen.” But then there are other programs that have been more silent. I’ve had people say that this is the first time that they have felt isolated in a long while.
We all participate in these physician WhatsApp groups, and according to some of the comments, people are realizing that these folks that they were just on the front lines with, fighting COVID, are perhaps not the allies that they originally thought they were, based on the things these people are saying.
Dr. Norris: Wow. It’s good that we’re talking about this from the viewpoint of two different generations. You’ve got the WhatsApp group and Google Hangouts and all that kind of good stuff, and I’m still with pagers and such. That’s interesting – the reality that folks you thought were your allies turn out not to be, because you’re bringing up difficult conversations that we don’t normally talk about.
I have noticed that some people around me have been silent because they don’t know what to say. They’re so concerned that I’m going to be offended or they’re going to hurt me or say the wrong thing, so they stay quiet. As I reflect now, this is the wrong thing to do. Own your concern. I’ve been in two large meetings now, and I’ve had multiple people whom I consider friends say, I wanted to email or text you right then and ask you how you’re doing, but I didn’t because I didn’t know what to say. I have entered meetings recently, and the meeting felt tense, and I’m thinking, what’s going on? And now I realize they did not know what to say or how to approach it.
That’s been a very interesting dynamic and tells us where we are with this. Today, for example, I was pleased to have the support of my dean’s group. I felt I had to speak out, I just had to straight out tell them. Do you want to know what I’m feeling? I’m feeling rage. I’m feeling rage. And you all have to understand that, because I have to speak for those who aren’t necessarily going to be able to express themselves. More importantly, I have to speak for myself and I’m feeling rage.
How our colleagues are processing this and how they’re thinking about this runs the gamut. But I think about people not necessarily knowing what to say or how to approach it. I absolutely agree that with the leadership, you’re going to get many different responses, and sometimes you’re left to wonder, do I have to watch what I say? But I’m definitely supported at my institution.
What else are you seeing out there in terms of your colleagues or how people think about it?
Dr. Newsome: This also spurs some folks to activism. Some have been participating in protests. There will be White Coats for Black Lives protests, among other things. So it’s spurred folks to action, and it’s also spurred folks to try to be part of a community. Of course, with the whole COVID crisis, we can’t necessarily come together, so we’ve been doing Zoom gatherings more than anything else. But it has encouraged folks to want to do that more, too, because they want to check in on their brother or their sister to make sure they are doing well, and also to be able to express what’s going on with them in a community where they know they can get validation.

Dr. Norris: I’m going to push you a bit because I detect in your tone something similar to what I’m feeling. I just got the email, the White Coats For Black Lives email. But I think your feeling is similar to mine – I’ve done this before. I’ve done White Coats for Black Lives. You all may have protested. But this display in Washington, D.C., of the use of military and law enforcement to clear a public square of peaceful protesters is above and beyond the pale of anything I’ve ever seen in my life. We have to label that for the danger it is, for the threat to everything this country and the people that bled for this country stand for.
So while I’m going to participate in White Coats for Black Lives and many other things, I am looking for what is actually going to move the needle. I think the protests are great, but at this point in time I want institutions, I want money, I want lawyers, I want a systematic approach.
Dr. Newsome: I most certainly agree. Of course, the protests are really important, but depending on where you are, you have a different lens. As physicians, especially as black physicians, since there are so few of us, we have a unique opportunity to leverage that, whether that means communicating through op-eds or calling your senators and talking with them to try to move things forward.
Physicians are mobilizing. In the last few days, a physician created a Zoom event and hundreds of physicians joined to try to figure out how we can structurally fix this problem. So I most certainly believe that in this effort to address racism, we physicians will need to lend our voices and our privilege to move the needle as best we can.
Dr. Norris: Some of our colleagues in Black Psychiatrists of America have put out a press release on racism in which they propose some actions that should be taken immediately. I think this is a useful thing to talk about.
The first action: “Declare racism a public health problem and establish national goals for addressing this as a health equity issue. Give priority to addressing the issues of health care disparities, including the mental health needs of historically marginalized communities across the U.S.”
What do you think about that?
Dr. Newsome: Those are two extremely important steps. The question is: How do you make that happen?
Dr. Norris: You’re reading my mind. I love that our colleagues put that out there, but that was my next question.
Dr. Newsome: There is going to be a town hall about this and I’m hoping that we can plan how we envision this happening. I can imagine that 20 or 30 years ago there was also a fear in society that there would be episodes of police brutality. I can imagine that there were similar ideals and hopes. But I think we need to put all of our minds together and ask: How are we going to accomplish this? Is this going to be something we’re going to put our money into? Is this going to be something we’re going to get senators and legislatures onboard with to make policy?
Dr. Norris: Let me read off some of the other action points they put out. There are six of them.
“Establish a governmental multidisciplinary and ethnically diverse commission with representatives from the major health care professional associations in medicine, nursing, psychiatry, public health, psychology, social work, etc., and the faith-based community to provide recommendations to Congress regarding policies on how to best improve the health and well-being of our nation’s black citizens.”
That’s a very solid overall recommendation. My question is, doesn’t that, in some way, shape, or form already exist? Could we not put up policy statements from all of these folks regarding racism and things of that nature? I agree with what they’re saying, but part of me wonders why certain things in the current system aren’t working. That becomes the question. Are we not integrated enough? Do we not have enough cross talk? Do we not have enough money behind it? So I agree with that goal, but I would be curious if that doesn’t already exist. What are your thoughts about that, Dr. Newsome?
Dr. Newsome: I would imagine that the National Institute on Minority Mental Health and Health Disparities would have something similar. I believe one of the things you mentioned is really important. In addition to making these recommendations, we need to be looking at where these leaks are occurring that keep them from working. What is the current structure and why is it the way it is with regard to the governance?
Dr. Norris: Here is another of their action statements: “Declare ‘civic mental health’ a national priority and incorporate it into the educational curriculum from K through college, as well as in the training of local, state, and national officials, law enforcement, and the criminal justice system.”
Let me be clear, I like every single one of these action statements. I encourage everyone to participate in dialogue and discussion. You may agree with some of these, and some of them you may not, but if there is one you agree with, that you really are motivated about, that’s one that you need to explore and dig into a bit more, because it’s too big for us to handle on our own, just like racism and equality.
I’m going to tell you, I like this statement. I do like this. Obviously these are broad points, but I do like the idea of training law enforcement officers about “civic mental health.” For example, Dr. Michael Compton, who has done a lot of great work in the area of mental health and prevention, has worked with police officers to help them interact with those with mental health conditions by modulating their own emotional response. I’m very interested in these types of recommendations that particularly target law enforcement officers, and helping with that ”emotional quotient.” I’m interested in seeing how far that can spread in the country. What do you think, Dr. Newsome?
Dr. Newsome: Educating police officers about how to interact would be quite important. I believe the National Alliance on Mental Illness does some of that work, partnering with law enforcement agencies, talking about mental health and cues to look at. There also are some programs where people ride along with mental health clinicians and police officers, which I find to be really helpful. But clearly, what’s going on right now isn’t working. So I would be open to any reasonable idea.
Dr. Norris: Here’s one last action point: “Establish police community review boards with power to take action in areas of police misconduct pending formal review by the appropriate authorities. This will offer a level of empowerment when communities feel they have a voice that can be heard.”
This is where I want my focus to be, as I move forward to try to do something sustainable. To deal with police brutality and abuse of power in general, but specifically as it relates to African American men and the lethal use of force. We need to work on policies that will enable African American men to make it to court, so that every encounter with a police officer is not literally viewed as a potentially lethal encounter.
A lot of people aren’t going to like me saying that, but it’s the absolute truth. You have to think like that, as an African American male, regardless of your station, regardless of where you live, this is the reality. There are many, many good police officers out there. I have a few friends who are law enforcement officers. I work with security at the George Washington Hospital constantly. But that still does not change the fact that if I get pulled over at a traffic stop, I know precisely certain things I need to do and not do, or the encounter could end badly. By that I mean loss of life.
So I encourage anything where we can start to take a systematic look at law enforcement and empower communities to look at who is doing it right and who is doing it wrong. Information is coming out now about the man who murdered Mr. Floyd, and this was not the first time he was involved in misconduct. There were red flags; we have to start to confront this. We have to learn from every single one of these situations and grow because another one is going to happen next week, it’s just whether or not you hear about it. That’s the reality of the state of America. You may not like to hear it, but that’s just a fact.
To hear the entire conversation, go to mdedge.com/podcasts or listen wherever you find your podcasts.
What COVID-19 has taught us about senior care
Across the globe, there are marked differences in how countries responded to the COVID-19 outbreak, with varying degrees of success in limiting the spread of the virus. Some countries learned important lessons from previous outbreaks, including SARS and MERS, and put policies in place that contributed to lower infection and death rates from COVID-19 in these countries. Others struggled to respond appropriately to the outbreak.
The United States and most of the world was not affected significantly by SARS and MERS. Hence there is a need for different perspectives and observations on lessons that can be learned from this outbreak to help develop effective strategies and policies for the future. It also makes sense to focus intently on the demographic most affected by COVID-19 – the elderly.
Medical care, for the most part, is governed by protocols that clearly detail processes to be followed for the prevention and treatment of disease. Caring for older patients requires going above and beyond the protocols. That is one of the lessons learned from the COVID-19 pandemic – a wake-up call for a more proactive approach for at-risk patients, in this case everyone over the age of 60 years.
In this context, it is important for medical outreach to continue with the senior population long after the pandemic has run its course. Many seniors, particularly those susceptible to other illnesses or exhibiting ongoing issues, would benefit from a consistent and preplanned pattern of contacts by medical professionals and agencies that work with the aging population. These proactive follow-ups can facilitate prevention and treatment and, at the same time, reduce costs that would otherwise increase when health care is reactive.
Lessons in infectious disease containment
As COVID-19 spread globally, there were contrasting responses from individual countries in their efforts to contain the disease. Unfortunately, Italy suffered from its decision to lock down only specific regions of the country initially. The leadership in Italy may have ignored the advice of medical experts and been caught off guard by the intensity of the spread of COVID-19. In fact, they might not have taken strict actions right away because they did not want their responses to be viewed as an overreaction to the disease.
The government decided to shut down areas where the infection rates were high (“red zones”) rather than implement restrictions nationally. This may have inadvertently increased the spread as Italians vacated those “red zones” for other areas of the country not yet affected by COVID-19. Italy’s decentralized health care system also played a part in the effects of the disease, with some regions demonstrating more success in slowing the reach of the disease. According to an article in the Harvard Business Review, the neighboring regions of Lombardy and Veneto applied similar approaches to social distancing and retail closures. Veneto was more proactive, and its response to the outbreak was multipronged, including putting a “strong emphasis on home diagnosis and care” and “specific efforts to monitor and protect health care and other essential workers.” These measures most likely contributed to a slowdown of the spread of the disease in Veneto’s health care facilities, which lessened the load on medical providers.1
Conversely, Taiwan implemented proactive measures swiftly after learning about COVID-19. Taiwan was impacted adversely by the SARS outbreak in 2003 and, afterward, revised their medical policies and procedures to respond quickly to future infectious disease crises. In the beginning, little was known about COVID-19 or how it spread. However, Taiwan’s swift public health response to COVID-19 included early travel restrictions, patient screening, and quarantining of symptomatic patients. The government emphasized education and created real-time digital updates and alerts sent to their citizens, as well as partnering with media to broadcast crucial proactive health information and quickly disproving false information related to COVID-19. They coordinated with organizations throughout the country to increase supplies of personal protective equipment (PPE).2
Although countries and even cities within a country differ in terms of population demographics, health resources, government policies, and cultural practices, initial success stories have some similarities, including the following:
- Early travel restrictions from countries with positive cases, with some circumstances requiring compulsory quarantine periods and testing before entry.
- Extensive testing and proactive tracing of symptomatic cases early. Contacts of people testing positive were also tested, irrespective of being symptomatic or asymptomatic. If testing kits were unavailable, the contacts were self-quarantined.
- Emphasis on avoiding overburdening hospitals by having the public health infrastructure to divert people exhibiting symptoms, including using public health hotlines to send patients to dedicated testing sites and drive-through testing, rather than have patients presenting to emergency rooms and hospitals. This approach protected medical staff from exposure and allowed the focus to remain on treating severe symptomatic patients.
The vastly different response to the COVID-19 outbreak in these two countries illuminates the need for better preparation in the United States. At the onset of this outbreak, emergency room medical professionals, hospitalists, and outpatient primary care providers did not know how to screen for or treat this virus. Additionally, there was limited information on the most effective contact protocols for medical professionals, patients, and visitors. Finally, the lack of PPE and COVID-19 test kits hindered the U.S. response. Once the country is on the road to recovery from COVID-19, it is imperative to set the groundwork to prepare for future outbreaks and create mechanisms to quickly identify vulnerable populations when outbreaks occur.
Senior care in future infectious disease outbreaks
How can medical providers translate lessons learned from this outbreak into improving the quality of care for seniors? The National Institute on Aging (NIA) maintains a website with information about healthy aging. Seniors and their caregivers can use this website to learn more about chronic diseases, lifestyle modifications, disease prevention, and mental health.
In times of a pandemic, this website provides consistent and accurate information and education. One recommendation for reaching the elderly population during future outbreaks is for NIA to develop and implement strategies to increase the use of the website, including adding more audio and visual interfaces and developing a mobile app. Other recommendations for improving the quality of care for seniors include the following:
1. Identify which populations may be most affected when future outbreaks occur.
2. Consider nontraditional platforms, including social media, for communicating with the general population and for medical providers worldwide to learn from each other about new diseases, including the signs, symptoms, and treatment plans. Some medical professionals created specific WhatsApp groups to communicate, and the World Health Organization sent updated information about COVID-19 to anyone who texted them via WhatsApp.3
3. Create a checklist of signs and symptoms related to current infectious diseases and assess every vulnerable patient.
4. Share these guidelines with medical facilities that treat these populations, such as senior care, assisted living and rehabilitation facilities, hospitals, and outpatient treatment centers. Teach the staff at these medical facilities how to screen patients for signs and symptoms of the disease.
5. Implement social isolation strategies, travel and visitor restrictions, and testing and screening as soon as possible at these medical facilities.
6. Recognize that these strategies may affect the psychological and emotional well-being of seniors, increasing their risk for depression and anxiety and negatively affecting their immunity and mental health. Additionally, the use of PPE, either by the medical providers or the patient, may cause anxiety in seniors and those with mild cognitive impairment.
7. Encourage these medical facilities to improve coping strategies with older patients, such as incorporating communication technology that helps seniors stay connected with their families, and participating in physical and mental exercise, as well as religious activities.
8. Ask these medical facilities to create isolation or quarantine rooms for infected seniors.
9. Work with family members to proactively report to medical professionals any symptoms noticed in their senior relatives. Educate seniors to report symptoms earlier.
10. Offer incentives for medical professionals to conduct on-site testing in primary care offices or senior care facilities instead of sending patients to hospital emergency rooms for evaluation. This will only be effective if there are enough test kits available.
11. Urge insurance companies and Medicare to allow additional medical visits for screening vulnerable populations. Encourage the use of telemedicine in place of in-office visits (preferably billed at the same rate as an in-office visit) where appropriate, especially with nonambulatory patients or those with transportation issues. Many insurance companies, including Medicare, approved COVID-19–related coverage of telemedicine in place of office visits to limit the spread of the disease.
12. Provide community health care and integration and better coordination of local, state, and national health care.
13. Hold regular epidemic and pandemic preparedness exercises in every hospital, nursing home, and assisted living facility.
Proactive health care outreach
It is easier to identify the signs and symptoms of already identified infectious diseases as opposed to a novel one like COVID-19. The United States faced a steep learning curve with COVID-19. Hospitalists and other medical professionals were not able to learn about COVID-19 in a journal. At first, they did not know how to screen patients coming into the ER, how to protect staff, or what the treatment plan was for this new disease. As a result, the medical system experienced disorder and confusion. Investing in community health care and better coordination of local, state, and national health care resources is a priority.
The senior citizen population appears to be most vulnerable to this virus and may be just as vulnerable in future outbreaks. Yet the insights gained from this pandemic can lead to a more comprehensive outreach to senior patients and increased screenings for comorbidities and future contagious diseases. An emphasis on proactive health care and outreach for seniors, with a focus on identifying and treating comorbid conditions, improves the medical care system overall and may prevent or slow future community outbreaks.
Dr. Kasarla is a hospitalist with APOGEE Physicians at Wise Surgical at Parkway in Fort Worth, Tex. He did his internal medicine residency at Mercy Hospital & Medical Center, Chicago. Readers can contact him at [email protected]. Dr. Devireddy is a family physician at Positive Health Medical Center, Kingston, Jamaica. Contact him at [email protected].
References
1. Pisano GP et al. Lessons from Italy’s response to coronavirus. Harvard Business Review. 2020 Mar 27. https://hbr.org/2020/03/lessons-from-italys-response-to-coronavirus.
2. Tu C. Lessons from Taiwan’s experience with COVID-19. New Atlanticist. 2020 Apr 7. https://atlanticcouncil.org/blogs/new-atlanticist/lessons-from-taiwans-experience-with-covid-19/.
3. Newman LH. WhatsApp is at the center of coronavirus response. WIRED. 2020 Mar 20. https://www.wired.com/story/whatsapp-coronavirus-who-information-app/.
Across the globe, there are marked differences in how countries responded to the COVID-19 outbreak, with varying degrees of success in limiting the spread of the virus. Some countries learned important lessons from previous outbreaks, including SARS and MERS, and put policies in place that contributed to lower infection and death rates from COVID-19 in these countries. Others struggled to respond appropriately to the outbreak.
The United States and most of the world was not affected significantly by SARS and MERS. Hence there is a need for different perspectives and observations on lessons that can be learned from this outbreak to help develop effective strategies and policies for the future. It also makes sense to focus intently on the demographic most affected by COVID-19 – the elderly.
Medical care, for the most part, is governed by protocols that clearly detail processes to be followed for the prevention and treatment of disease. Caring for older patients requires going above and beyond the protocols. That is one of the lessons learned from the COVID-19 pandemic – a wake-up call for a more proactive approach for at-risk patients, in this case everyone over the age of 60 years.
In this context, it is important for medical outreach to continue with the senior population long after the pandemic has run its course. Many seniors, particularly those susceptible to other illnesses or exhibiting ongoing issues, would benefit from a consistent and preplanned pattern of contacts by medical professionals and agencies that work with the aging population. These proactive follow-ups can facilitate prevention and treatment and, at the same time, reduce costs that would otherwise increase when health care is reactive.
Lessons in infectious disease containment
As COVID-19 spread globally, there were contrasting responses from individual countries in their efforts to contain the disease. Unfortunately, Italy suffered from its decision to lock down only specific regions of the country initially. The leadership in Italy may have ignored the advice of medical experts and been caught off guard by the intensity of the spread of COVID-19. In fact, they might not have taken strict actions right away because they did not want their responses to be viewed as an overreaction to the disease.
The government decided to shut down areas where the infection rates were high (“red zones”) rather than implement restrictions nationally. This may have inadvertently increased the spread as Italians vacated those “red zones” for other areas of the country not yet affected by COVID-19. Italy’s decentralized health care system also played a part in the effects of the disease, with some regions demonstrating more success in slowing the reach of the disease. According to an article in the Harvard Business Review, the neighboring regions of Lombardy and Veneto applied similar approaches to social distancing and retail closures. Veneto was more proactive, and its response to the outbreak was multipronged, including putting a “strong emphasis on home diagnosis and care” and “specific efforts to monitor and protect health care and other essential workers.” These measures most likely contributed to a slowdown of the spread of the disease in Veneto’s health care facilities, which lessened the load on medical providers.1
Conversely, Taiwan implemented proactive measures swiftly after learning about COVID-19. Taiwan was impacted adversely by the SARS outbreak in 2003 and, afterward, revised their medical policies and procedures to respond quickly to future infectious disease crises. In the beginning, little was known about COVID-19 or how it spread. However, Taiwan’s swift public health response to COVID-19 included early travel restrictions, patient screening, and quarantining of symptomatic patients. The government emphasized education and created real-time digital updates and alerts sent to their citizens, as well as partnering with media to broadcast crucial proactive health information and quickly disproving false information related to COVID-19. They coordinated with organizations throughout the country to increase supplies of personal protective equipment (PPE).2
Although countries and even cities within a country differ in terms of population demographics, health resources, government policies, and cultural practices, initial success stories have some similarities, including the following:
- Early travel restrictions from countries with positive cases, with some circumstances requiring compulsory quarantine periods and testing before entry.
- Extensive testing and proactive tracing of symptomatic cases early. Contacts of people testing positive were also tested, irrespective of being symptomatic or asymptomatic. If testing kits were unavailable, the contacts were self-quarantined.
- Emphasis on avoiding overburdening hospitals by having the public health infrastructure to divert people exhibiting symptoms, including using public health hotlines to send patients to dedicated testing sites and drive-through testing, rather than have patients presenting to emergency rooms and hospitals. This approach protected medical staff from exposure and allowed the focus to remain on treating severe symptomatic patients.
The vastly different response to the COVID-19 outbreak in these two countries illuminates the need for better preparation in the United States. At the onset of this outbreak, emergency room medical professionals, hospitalists, and outpatient primary care providers did not know how to screen for or treat this virus. Additionally, there was limited information on the most effective contact protocols for medical professionals, patients, and visitors. Finally, the lack of PPE and COVID-19 test kits hindered the U.S. response. Once the country is on the road to recovery from COVID-19, it is imperative to set the groundwork to prepare for future outbreaks and create mechanisms to quickly identify vulnerable populations when outbreaks occur.
Senior care in future infectious disease outbreaks
How can medical providers translate lessons learned from this outbreak into improving the quality of care for seniors? The National Institute on Aging (NIA) maintains a website with information about healthy aging. Seniors and their caregivers can use this website to learn more about chronic diseases, lifestyle modifications, disease prevention, and mental health.
In times of a pandemic, this website provides consistent and accurate information and education. One recommendation for reaching the elderly population during future outbreaks is for NIA to develop and implement strategies to increase the use of the website, including adding more audio and visual interfaces and developing a mobile app. Other recommendations for improving the quality of care for seniors include the following:
1. Identify which populations may be most affected when future outbreaks occur.
2. Consider nontraditional platforms, including social media, for communicating with the general population and for medical providers worldwide to learn from each other about new diseases, including the signs, symptoms, and treatment plans. Some medical professionals created specific WhatsApp groups to communicate, and the World Health Organization sent updated information about COVID-19 to anyone who texted them via WhatsApp.3
3. Create a checklist of signs and symptoms related to current infectious diseases and assess every vulnerable patient.
4. Share these guidelines with medical facilities that treat these populations, such as senior care, assisted living and rehabilitation facilities, hospitals, and outpatient treatment centers. Teach the staff at these medical facilities how to screen patients for signs and symptoms of the disease.
5. Implement social isolation strategies, travel and visitor restrictions, and testing and screening as soon as possible at these medical facilities.
6. Recognize that these strategies may affect the psychological and emotional well-being of seniors, increasing their risk for depression and anxiety and negatively affecting their immunity and mental health. Additionally, the use of PPE, either by the medical providers or the patient, may cause anxiety in seniors and those with mild cognitive impairment.
7. Encourage these medical facilities to improve coping strategies with older patients, such as incorporating communication technology that helps seniors stay connected with their families, and participating in physical and mental exercise, as well as religious activities.
8. Ask these medical facilities to create isolation or quarantine rooms for infected seniors.
9. Work with family members to proactively report to medical professionals any symptoms noticed in their senior relatives. Educate seniors to report symptoms earlier.
10. Offer incentives for medical professionals to conduct on-site testing in primary care offices or senior care facilities instead of sending patients to hospital emergency rooms for evaluation. This will only be effective if there are enough test kits available.
11. Urge insurance companies and Medicare to allow additional medical visits for screening vulnerable populations. Encourage the use of telemedicine in place of in-office visits (preferably billed at the same rate as an in-office visit) where appropriate, especially with nonambulatory patients or those with transportation issues. Many insurance companies, including Medicare, approved COVID-19–related coverage of telemedicine in place of office visits to limit the spread of the disease.
12. Provide community health care and integration and better coordination of local, state, and national health care.
13. Hold regular epidemic and pandemic preparedness exercises in every hospital, nursing home, and assisted living facility.
Proactive health care outreach
It is easier to identify the signs and symptoms of already identified infectious diseases as opposed to a novel one like COVID-19. The United States faced a steep learning curve with COVID-19. Hospitalists and other medical professionals were not able to learn about COVID-19 in a journal. At first, they did not know how to screen patients coming into the ER, how to protect staff, or what the treatment plan was for this new disease. As a result, the medical system experienced disorder and confusion. Investing in community health care and better coordination of local, state, and national health care resources is a priority.
The senior citizen population appears to be most vulnerable to this virus and may be just as vulnerable in future outbreaks. Yet the insights gained from this pandemic can lead to a more comprehensive outreach to senior patients and increased screenings for comorbidities and future contagious diseases. An emphasis on proactive health care and outreach for seniors, with a focus on identifying and treating comorbid conditions, improves the medical care system overall and may prevent or slow future community outbreaks.
Dr. Kasarla is a hospitalist with APOGEE Physicians at Wise Surgical at Parkway in Fort Worth, Tex. He did his internal medicine residency at Mercy Hospital & Medical Center, Chicago. Readers can contact him at [email protected]. Dr. Devireddy is a family physician at Positive Health Medical Center, Kingston, Jamaica. Contact him at [email protected].
References
1. Pisano GP et al. Lessons from Italy’s response to coronavirus. Harvard Business Review. 2020 Mar 27. https://hbr.org/2020/03/lessons-from-italys-response-to-coronavirus.
2. Tu C. Lessons from Taiwan’s experience with COVID-19. New Atlanticist. 2020 Apr 7. https://atlanticcouncil.org/blogs/new-atlanticist/lessons-from-taiwans-experience-with-covid-19/.
3. Newman LH. WhatsApp is at the center of coronavirus response. WIRED. 2020 Mar 20. https://www.wired.com/story/whatsapp-coronavirus-who-information-app/.
Across the globe, there are marked differences in how countries responded to the COVID-19 outbreak, with varying degrees of success in limiting the spread of the virus. Some countries learned important lessons from previous outbreaks, including SARS and MERS, and put policies in place that contributed to lower infection and death rates from COVID-19 in these countries. Others struggled to respond appropriately to the outbreak.
The United States and most of the world was not affected significantly by SARS and MERS. Hence there is a need for different perspectives and observations on lessons that can be learned from this outbreak to help develop effective strategies and policies for the future. It also makes sense to focus intently on the demographic most affected by COVID-19 – the elderly.
Medical care, for the most part, is governed by protocols that clearly detail processes to be followed for the prevention and treatment of disease. Caring for older patients requires going above and beyond the protocols. That is one of the lessons learned from the COVID-19 pandemic – a wake-up call for a more proactive approach for at-risk patients, in this case everyone over the age of 60 years.
In this context, it is important for medical outreach to continue with the senior population long after the pandemic has run its course. Many seniors, particularly those susceptible to other illnesses or exhibiting ongoing issues, would benefit from a consistent and preplanned pattern of contacts by medical professionals and agencies that work with the aging population. These proactive follow-ups can facilitate prevention and treatment and, at the same time, reduce costs that would otherwise increase when health care is reactive.
Lessons in infectious disease containment
As COVID-19 spread globally, there were contrasting responses from individual countries in their efforts to contain the disease. Unfortunately, Italy suffered from its decision to lock down only specific regions of the country initially. The leadership in Italy may have ignored the advice of medical experts and been caught off guard by the intensity of the spread of COVID-19. In fact, they might not have taken strict actions right away because they did not want their responses to be viewed as an overreaction to the disease.
The government decided to shut down areas where the infection rates were high (“red zones”) rather than implement restrictions nationally. This may have inadvertently increased the spread as Italians vacated those “red zones” for other areas of the country not yet affected by COVID-19. Italy’s decentralized health care system also played a part in the effects of the disease, with some regions demonstrating more success in slowing the reach of the disease. According to an article in the Harvard Business Review, the neighboring regions of Lombardy and Veneto applied similar approaches to social distancing and retail closures. Veneto was more proactive, and its response to the outbreak was multipronged, including putting a “strong emphasis on home diagnosis and care” and “specific efforts to monitor and protect health care and other essential workers.” These measures most likely contributed to a slowdown of the spread of the disease in Veneto’s health care facilities, which lessened the load on medical providers.1
Conversely, Taiwan implemented proactive measures swiftly after learning about COVID-19. Taiwan was impacted adversely by the SARS outbreak in 2003 and, afterward, revised their medical policies and procedures to respond quickly to future infectious disease crises. In the beginning, little was known about COVID-19 or how it spread. However, Taiwan’s swift public health response to COVID-19 included early travel restrictions, patient screening, and quarantining of symptomatic patients. The government emphasized education and created real-time digital updates and alerts sent to their citizens, as well as partnering with media to broadcast crucial proactive health information and quickly disproving false information related to COVID-19. They coordinated with organizations throughout the country to increase supplies of personal protective equipment (PPE).2
Although countries and even cities within a country differ in terms of population demographics, health resources, government policies, and cultural practices, initial success stories have some similarities, including the following:
- Early travel restrictions from countries with positive cases, with some circumstances requiring compulsory quarantine periods and testing before entry.
- Extensive testing and proactive tracing of symptomatic cases early. Contacts of people testing positive were also tested, irrespective of being symptomatic or asymptomatic. If testing kits were unavailable, the contacts were self-quarantined.
- Emphasis on avoiding overburdening hospitals by having the public health infrastructure to divert people exhibiting symptoms, including using public health hotlines to send patients to dedicated testing sites and drive-through testing, rather than have patients presenting to emergency rooms and hospitals. This approach protected medical staff from exposure and allowed the focus to remain on treating severe symptomatic patients.
The vastly different response to the COVID-19 outbreak in these two countries illuminates the need for better preparation in the United States. At the onset of this outbreak, emergency room medical professionals, hospitalists, and outpatient primary care providers did not know how to screen for or treat this virus. Additionally, there was limited information on the most effective contact protocols for medical professionals, patients, and visitors. Finally, the lack of PPE and COVID-19 test kits hindered the U.S. response. Once the country is on the road to recovery from COVID-19, it is imperative to set the groundwork to prepare for future outbreaks and create mechanisms to quickly identify vulnerable populations when outbreaks occur.
Senior care in future infectious disease outbreaks
How can medical providers translate lessons learned from this outbreak into improving the quality of care for seniors? The National Institute on Aging (NIA) maintains a website with information about healthy aging. Seniors and their caregivers can use this website to learn more about chronic diseases, lifestyle modifications, disease prevention, and mental health.
In times of a pandemic, this website provides consistent and accurate information and education. One recommendation for reaching the elderly population during future outbreaks is for NIA to develop and implement strategies to increase the use of the website, including adding more audio and visual interfaces and developing a mobile app. Other recommendations for improving the quality of care for seniors include the following:
1. Identify which populations may be most affected when future outbreaks occur.
2. Consider nontraditional platforms, including social media, for communicating with the general population and for medical providers worldwide to learn from each other about new diseases, including the signs, symptoms, and treatment plans. Some medical professionals created specific WhatsApp groups to communicate, and the World Health Organization sent updated information about COVID-19 to anyone who texted them via WhatsApp.3
3. Create a checklist of signs and symptoms related to current infectious diseases and assess every vulnerable patient.
4. Share these guidelines with medical facilities that treat these populations, such as senior care, assisted living and rehabilitation facilities, hospitals, and outpatient treatment centers. Teach the staff at these medical facilities how to screen patients for signs and symptoms of the disease.
5. Implement social isolation strategies, travel and visitor restrictions, and testing and screening as soon as possible at these medical facilities.
6. Recognize that these strategies may affect the psychological and emotional well-being of seniors, increasing their risk for depression and anxiety and negatively affecting their immunity and mental health. Additionally, the use of PPE, either by the medical providers or the patient, may cause anxiety in seniors and those with mild cognitive impairment.
7. Encourage these medical facilities to improve coping strategies with older patients, such as incorporating communication technology that helps seniors stay connected with their families, and participating in physical and mental exercise, as well as religious activities.
8. Ask these medical facilities to create isolation or quarantine rooms for infected seniors.
9. Work with family members to proactively report to medical professionals any symptoms noticed in their senior relatives. Educate seniors to report symptoms earlier.
10. Offer incentives for medical professionals to conduct on-site testing in primary care offices or senior care facilities instead of sending patients to hospital emergency rooms for evaluation. This will only be effective if there are enough test kits available.
11. Urge insurance companies and Medicare to allow additional medical visits for screening vulnerable populations. Encourage the use of telemedicine in place of in-office visits (preferably billed at the same rate as an in-office visit) where appropriate, especially with nonambulatory patients or those with transportation issues. Many insurance companies, including Medicare, approved COVID-19–related coverage of telemedicine in place of office visits to limit the spread of the disease.
12. Provide community health care and integration and better coordination of local, state, and national health care.
13. Hold regular epidemic and pandemic preparedness exercises in every hospital, nursing home, and assisted living facility.
Proactive health care outreach
It is easier to identify the signs and symptoms of already identified infectious diseases as opposed to a novel one like COVID-19. The United States faced a steep learning curve with COVID-19. Hospitalists and other medical professionals were not able to learn about COVID-19 in a journal. At first, they did not know how to screen patients coming into the ER, how to protect staff, or what the treatment plan was for this new disease. As a result, the medical system experienced disorder and confusion. Investing in community health care and better coordination of local, state, and national health care resources is a priority.
The senior citizen population appears to be most vulnerable to this virus and may be just as vulnerable in future outbreaks. Yet the insights gained from this pandemic can lead to a more comprehensive outreach to senior patients and increased screenings for comorbidities and future contagious diseases. An emphasis on proactive health care and outreach for seniors, with a focus on identifying and treating comorbid conditions, improves the medical care system overall and may prevent or slow future community outbreaks.
Dr. Kasarla is a hospitalist with APOGEE Physicians at Wise Surgical at Parkway in Fort Worth, Tex. He did his internal medicine residency at Mercy Hospital & Medical Center, Chicago. Readers can contact him at [email protected]. Dr. Devireddy is a family physician at Positive Health Medical Center, Kingston, Jamaica. Contact him at [email protected].
References
1. Pisano GP et al. Lessons from Italy’s response to coronavirus. Harvard Business Review. 2020 Mar 27. https://hbr.org/2020/03/lessons-from-italys-response-to-coronavirus.
2. Tu C. Lessons from Taiwan’s experience with COVID-19. New Atlanticist. 2020 Apr 7. https://atlanticcouncil.org/blogs/new-atlanticist/lessons-from-taiwans-experience-with-covid-19/.
3. Newman LH. WhatsApp is at the center of coronavirus response. WIRED. 2020 Mar 20. https://www.wired.com/story/whatsapp-coronavirus-who-information-app/.