User login
Not Keeping Up With the Joneses
Dr. Jones and Dr. Joans are neurologists in town. I don’t know either one particularly well.
I don’t know their backstory, either, but they seem to have some intense competition going on.
Technically all of us neuros in the area compete with each other, but it’s pretty friendly. There are plenty of patients, and we all get along on the occasions we run into each other at the hospital or Costco or a meeting. Occasionally we call to bounce a case off each other. None of us advertise.
But Jones and Joans have kicked it up a notch. One got an EEG machine, the other got an EEG machine. A few weeks later one got a balance testing gadget, then the other got the same thing. One invested in all kinds of fancy devices to detect concussions, and shortly afterward so did the other one. Within a few months each bought their own Doppler equipment and hired an ultrasound tech. One took out a glossy ad in a local magazine, the next month so had the other. Both point out that they’ve been named on different “best doctor” lists. I assume it’s only a matter of time before each invests in their own MRI.
This kind of thing requires a lot of money to support, so both have jumped into the world of medical liens and hired NPs and PAs to increase patient volume.
I’m sure they both make more money than I ever will, and they can have it.
I don’t need that kind of complexity in my life. I have my own EMG/NCV machine, and beyond that I send all the testing (and complicated EMG/NCVs) to other facilities. I don’t want to figure out how to make payments on all those new gadgets, or hire staff to run them, or learn all the new codes I’d need (I do all my own coding, anyway), or decide if the advertising will pay for itself, or deal with liens.
I’m not even sure I want to be that busy. Obviously, I don’t want to be empty, but I also like having some degree of sanity. Time to review tests, type up notes, return calls ... all the things you have to do on the fly between patients, because if you don’t get them done at the office then you have to do them when you get home. Believe me, I already have enough going on there.
I have no desire to advertise that I’m the best neurologist in town (though I believe I’m the best in my building, since there isn’t another one) or to be the busiest, or to be involved in a game of one-upmanship with the nice group down the street.
If Drs. Jones and Joans want to do that, fine. More power to them.
For me, I’ve chosen simplicity in my practice, and prefer it.
I’m willing to trade that for money.
Dr. Block has a solo neurology practice in Scottsdale, Arizona.
Dr. Jones and Dr. Joans are neurologists in town. I don’t know either one particularly well.
I don’t know their backstory, either, but they seem to have some intense competition going on.
Technically all of us neuros in the area compete with each other, but it’s pretty friendly. There are plenty of patients, and we all get along on the occasions we run into each other at the hospital or Costco or a meeting. Occasionally we call to bounce a case off each other. None of us advertise.
But Jones and Joans have kicked it up a notch. One got an EEG machine, the other got an EEG machine. A few weeks later one got a balance testing gadget, then the other got the same thing. One invested in all kinds of fancy devices to detect concussions, and shortly afterward so did the other one. Within a few months each bought their own Doppler equipment and hired an ultrasound tech. One took out a glossy ad in a local magazine, the next month so had the other. Both point out that they’ve been named on different “best doctor” lists. I assume it’s only a matter of time before each invests in their own MRI.
This kind of thing requires a lot of money to support, so both have jumped into the world of medical liens and hired NPs and PAs to increase patient volume.
I’m sure they both make more money than I ever will, and they can have it.
I don’t need that kind of complexity in my life. I have my own EMG/NCV machine, and beyond that I send all the testing (and complicated EMG/NCVs) to other facilities. I don’t want to figure out how to make payments on all those new gadgets, or hire staff to run them, or learn all the new codes I’d need (I do all my own coding, anyway), or decide if the advertising will pay for itself, or deal with liens.
I’m not even sure I want to be that busy. Obviously, I don’t want to be empty, but I also like having some degree of sanity. Time to review tests, type up notes, return calls ... all the things you have to do on the fly between patients, because if you don’t get them done at the office then you have to do them when you get home. Believe me, I already have enough going on there.
I have no desire to advertise that I’m the best neurologist in town (though I believe I’m the best in my building, since there isn’t another one) or to be the busiest, or to be involved in a game of one-upmanship with the nice group down the street.
If Drs. Jones and Joans want to do that, fine. More power to them.
For me, I’ve chosen simplicity in my practice, and prefer it.
I’m willing to trade that for money.
Dr. Block has a solo neurology practice in Scottsdale, Arizona.
Dr. Jones and Dr. Joans are neurologists in town. I don’t know either one particularly well.
I don’t know their backstory, either, but they seem to have some intense competition going on.
Technically all of us neuros in the area compete with each other, but it’s pretty friendly. There are plenty of patients, and we all get along on the occasions we run into each other at the hospital or Costco or a meeting. Occasionally we call to bounce a case off each other. None of us advertise.
But Jones and Joans have kicked it up a notch. One got an EEG machine, the other got an EEG machine. A few weeks later one got a balance testing gadget, then the other got the same thing. One invested in all kinds of fancy devices to detect concussions, and shortly afterward so did the other one. Within a few months each bought their own Doppler equipment and hired an ultrasound tech. One took out a glossy ad in a local magazine, the next month so had the other. Both point out that they’ve been named on different “best doctor” lists. I assume it’s only a matter of time before each invests in their own MRI.
This kind of thing requires a lot of money to support, so both have jumped into the world of medical liens and hired NPs and PAs to increase patient volume.
I’m sure they both make more money than I ever will, and they can have it.
I don’t need that kind of complexity in my life. I have my own EMG/NCV machine, and beyond that I send all the testing (and complicated EMG/NCVs) to other facilities. I don’t want to figure out how to make payments on all those new gadgets, or hire staff to run them, or learn all the new codes I’d need (I do all my own coding, anyway), or decide if the advertising will pay for itself, or deal with liens.
I’m not even sure I want to be that busy. Obviously, I don’t want to be empty, but I also like having some degree of sanity. Time to review tests, type up notes, return calls ... all the things you have to do on the fly between patients, because if you don’t get them done at the office then you have to do them when you get home. Believe me, I already have enough going on there.
I have no desire to advertise that I’m the best neurologist in town (though I believe I’m the best in my building, since there isn’t another one) or to be the busiest, or to be involved in a game of one-upmanship with the nice group down the street.
If Drs. Jones and Joans want to do that, fine. More power to them.
For me, I’ve chosen simplicity in my practice, and prefer it.
I’m willing to trade that for money.
Dr. Block has a solo neurology practice in Scottsdale, Arizona.
Once-Weekly Insulin: A Game-Changer for Primary Care
Presented at the European Association for the Study of Diabetes (EASD) 2024 congress in Madrid, the QWINT-2 study established that. Study participants were, however, receiving noninsulin glucose-lowering agents, including glucagon-like peptide 1 (GLP-1) receptor agonists.
Slightly higher rates of mild to moderate hypoglycemia were noted with efsitora compared with degludec, but no significant differences in severe hypoglycemia were observed. Nor was there any difference in weight gain between groups, and adverse events were balanced between study arms.
This study positions insulin efsitora alongside once-weekly insulin icodec as a novel long-acting insulin therapy. In the ONWARDS 3 trial, icodec was noninferior to once-daily degludec, in terms of A1c reduction. It also had an adverse effect profile like that of efsitora with respect to hypoglycemia and weight change.
So, what are the implications of a once-weekly insulin for primary care?
“Game-changer” is an overused term, but from the perspective of primary care, it applies to once-weekly insulin.
I initiate basal insulin much less frequently these days, given the multitude of noninsulin options now available to me in primary care, particularly the GLP-1 receptor agonists and the dual GLP-1/glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide receptor agonists. The American Diabetes Association/EASD 2022 consensus report also reminds me that GLP-1 receptor agonists should be considered in all individuals with T2D before insulin, unless they are contraindicated. GLP-1 receptor agonists are insulin-sparing agents with a lower injection burden and a lower risk for hypoglycemia. They also promote significant weight loss compared with basal insulin.
But progressive beta-cell decline and insulin deficiency are among the key pathophysiologic abnormalities in T2D. Eventually, many patients with T2D, despite lifestyle interventions and medication adherence, do require insulin.
Understandably, many of my patients have reservations about commencing insulin. Significant stigma about starting insulin persists, because others often perceive insulin use as a failure to manage T2D. Patients frequently fear injections, and many are worried about how insulin therapy, specifically the risk for hypoglycemia, will affect their daily activities such as driving.
Clinicians often experience therapeutic inertia, hesitating to escalate therapy to insulin because of a lack of confidence and competence, which often results from inadequate education. Lengthy referral-to-treatment waiting times are common in the United Kingdom, and there is concern about the workload implications associated with insulin initiation.
Workload is a particular concern for my community nursing colleagues, who must visit some of my more frail and functionally dependent patients daily to administer their insulin.
In addition, the delivery of high-quality diabetes care in nursing homes, particularly for patients requiring insulin, has been a perennial challenge in the UK, again because of a lack of confidence and competence due to an absence of education for nursing and ancillary staff.
Moreover, it is not appropriate to switch many of these frail patients to noninsulin therapies because of their insulinopenia, as well as the significant weight (and sometimes muscle) loss associated with GLP-1 receptor agonists. Also, sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitors are associated with a risk for volume depletion and diabetic ketoacidosis.
I believe that the availability of a once-weekly insulin will help overcome many of the above barriers.
From a patient’s viewpoint, simplification of insulin therapy with once-weekly insulin will substantially reduce the number of injections required (from 365 to 52 over 1 year). This change will improve compliance and concordance even in patients with injection anxiety. These results will hopefully translate into improved glycemic control and a lower risk for the complications of T2D. Real-world evidence for these outcomes is not yet available, however. Also, the reduced amount of insulin consumables that once-weekly dosing requires will also help improve the environmental footprint of insulin therapy.
From a clinician’s viewpoint, once-weekly insulin may seem less daunting and could reduce therapeutic inertia, thus facilitating earlier initiation of insulin therapy and reducing the risk for complications of T2D. Although education remains pivotal, this ease of dosing may be more acceptable to many clinicians because it has less of an effect on workload. This dosing could even save time because it requires less intensive follow-up than daily basal insulin does.
My community nurse colleagues were ecstatic when I mentioned that once-weekly basal insulin was on the horizon. This formulation could reduce the number of weekly home visits from 7 to just 1, thus freeing up considerable healthcare resources. And if once-weekly insulin is coupled with continuous glucose monitoring, then remote review of glucose data can further streamline and optimize the management of T2D in frail older patients. I am sure that my nursing-home colleagues will be equally enthusiastic about simplifying insulin regimens and monitoring.
Finally, an unanswered question is how I manage “sick days” for patients on weekly insulin dosing. Of course, the golden rule of never stopping insulin during intercurrent illness must be followed, but is any dose titration required for once-weekly insulin? I suspect not, but do I need to consider adding a once-daily basal insulin or rapid-acting insulin to mitigate the glucose counterregulatory hormone response during acute illness? Initially, I will be asking specialist diabetes teams for further advice on managing sick days.
In conclusion, once-weekly dosing of insulin is a game-changer for primary care and could finally be the driver to quash therapeutic inertia and address common patient barriers when escalation to insulin is required.
Dr. Fernando, general practitioner partner, North Berwick Health Centre, North Berwick, Scotland, disclosed ties with Amarin, Amgen, AstraZeneca, Bayer, Boehringer Ingelheim, Dexcom, Daiichi Sankyo, Lilly, Menarini, Novartis, Novo Nordisk, Roche Diagnostics, Embecta, Roche Diabetes Care, and Sanofi.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Presented at the European Association for the Study of Diabetes (EASD) 2024 congress in Madrid, the QWINT-2 study established that. Study participants were, however, receiving noninsulin glucose-lowering agents, including glucagon-like peptide 1 (GLP-1) receptor agonists.
Slightly higher rates of mild to moderate hypoglycemia were noted with efsitora compared with degludec, but no significant differences in severe hypoglycemia were observed. Nor was there any difference in weight gain between groups, and adverse events were balanced between study arms.
This study positions insulin efsitora alongside once-weekly insulin icodec as a novel long-acting insulin therapy. In the ONWARDS 3 trial, icodec was noninferior to once-daily degludec, in terms of A1c reduction. It also had an adverse effect profile like that of efsitora with respect to hypoglycemia and weight change.
So, what are the implications of a once-weekly insulin for primary care?
“Game-changer” is an overused term, but from the perspective of primary care, it applies to once-weekly insulin.
I initiate basal insulin much less frequently these days, given the multitude of noninsulin options now available to me in primary care, particularly the GLP-1 receptor agonists and the dual GLP-1/glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide receptor agonists. The American Diabetes Association/EASD 2022 consensus report also reminds me that GLP-1 receptor agonists should be considered in all individuals with T2D before insulin, unless they are contraindicated. GLP-1 receptor agonists are insulin-sparing agents with a lower injection burden and a lower risk for hypoglycemia. They also promote significant weight loss compared with basal insulin.
But progressive beta-cell decline and insulin deficiency are among the key pathophysiologic abnormalities in T2D. Eventually, many patients with T2D, despite lifestyle interventions and medication adherence, do require insulin.
Understandably, many of my patients have reservations about commencing insulin. Significant stigma about starting insulin persists, because others often perceive insulin use as a failure to manage T2D. Patients frequently fear injections, and many are worried about how insulin therapy, specifically the risk for hypoglycemia, will affect their daily activities such as driving.
Clinicians often experience therapeutic inertia, hesitating to escalate therapy to insulin because of a lack of confidence and competence, which often results from inadequate education. Lengthy referral-to-treatment waiting times are common in the United Kingdom, and there is concern about the workload implications associated with insulin initiation.
Workload is a particular concern for my community nursing colleagues, who must visit some of my more frail and functionally dependent patients daily to administer their insulin.
In addition, the delivery of high-quality diabetes care in nursing homes, particularly for patients requiring insulin, has been a perennial challenge in the UK, again because of a lack of confidence and competence due to an absence of education for nursing and ancillary staff.
Moreover, it is not appropriate to switch many of these frail patients to noninsulin therapies because of their insulinopenia, as well as the significant weight (and sometimes muscle) loss associated with GLP-1 receptor agonists. Also, sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitors are associated with a risk for volume depletion and diabetic ketoacidosis.
I believe that the availability of a once-weekly insulin will help overcome many of the above barriers.
From a patient’s viewpoint, simplification of insulin therapy with once-weekly insulin will substantially reduce the number of injections required (from 365 to 52 over 1 year). This change will improve compliance and concordance even in patients with injection anxiety. These results will hopefully translate into improved glycemic control and a lower risk for the complications of T2D. Real-world evidence for these outcomes is not yet available, however. Also, the reduced amount of insulin consumables that once-weekly dosing requires will also help improve the environmental footprint of insulin therapy.
From a clinician’s viewpoint, once-weekly insulin may seem less daunting and could reduce therapeutic inertia, thus facilitating earlier initiation of insulin therapy and reducing the risk for complications of T2D. Although education remains pivotal, this ease of dosing may be more acceptable to many clinicians because it has less of an effect on workload. This dosing could even save time because it requires less intensive follow-up than daily basal insulin does.
My community nurse colleagues were ecstatic when I mentioned that once-weekly basal insulin was on the horizon. This formulation could reduce the number of weekly home visits from 7 to just 1, thus freeing up considerable healthcare resources. And if once-weekly insulin is coupled with continuous glucose monitoring, then remote review of glucose data can further streamline and optimize the management of T2D in frail older patients. I am sure that my nursing-home colleagues will be equally enthusiastic about simplifying insulin regimens and monitoring.
Finally, an unanswered question is how I manage “sick days” for patients on weekly insulin dosing. Of course, the golden rule of never stopping insulin during intercurrent illness must be followed, but is any dose titration required for once-weekly insulin? I suspect not, but do I need to consider adding a once-daily basal insulin or rapid-acting insulin to mitigate the glucose counterregulatory hormone response during acute illness? Initially, I will be asking specialist diabetes teams for further advice on managing sick days.
In conclusion, once-weekly dosing of insulin is a game-changer for primary care and could finally be the driver to quash therapeutic inertia and address common patient barriers when escalation to insulin is required.
Dr. Fernando, general practitioner partner, North Berwick Health Centre, North Berwick, Scotland, disclosed ties with Amarin, Amgen, AstraZeneca, Bayer, Boehringer Ingelheim, Dexcom, Daiichi Sankyo, Lilly, Menarini, Novartis, Novo Nordisk, Roche Diagnostics, Embecta, Roche Diabetes Care, and Sanofi.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Presented at the European Association for the Study of Diabetes (EASD) 2024 congress in Madrid, the QWINT-2 study established that. Study participants were, however, receiving noninsulin glucose-lowering agents, including glucagon-like peptide 1 (GLP-1) receptor agonists.
Slightly higher rates of mild to moderate hypoglycemia were noted with efsitora compared with degludec, but no significant differences in severe hypoglycemia were observed. Nor was there any difference in weight gain between groups, and adverse events were balanced between study arms.
This study positions insulin efsitora alongside once-weekly insulin icodec as a novel long-acting insulin therapy. In the ONWARDS 3 trial, icodec was noninferior to once-daily degludec, in terms of A1c reduction. It also had an adverse effect profile like that of efsitora with respect to hypoglycemia and weight change.
So, what are the implications of a once-weekly insulin for primary care?
“Game-changer” is an overused term, but from the perspective of primary care, it applies to once-weekly insulin.
I initiate basal insulin much less frequently these days, given the multitude of noninsulin options now available to me in primary care, particularly the GLP-1 receptor agonists and the dual GLP-1/glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide receptor agonists. The American Diabetes Association/EASD 2022 consensus report also reminds me that GLP-1 receptor agonists should be considered in all individuals with T2D before insulin, unless they are contraindicated. GLP-1 receptor agonists are insulin-sparing agents with a lower injection burden and a lower risk for hypoglycemia. They also promote significant weight loss compared with basal insulin.
But progressive beta-cell decline and insulin deficiency are among the key pathophysiologic abnormalities in T2D. Eventually, many patients with T2D, despite lifestyle interventions and medication adherence, do require insulin.
Understandably, many of my patients have reservations about commencing insulin. Significant stigma about starting insulin persists, because others often perceive insulin use as a failure to manage T2D. Patients frequently fear injections, and many are worried about how insulin therapy, specifically the risk for hypoglycemia, will affect their daily activities such as driving.
Clinicians often experience therapeutic inertia, hesitating to escalate therapy to insulin because of a lack of confidence and competence, which often results from inadequate education. Lengthy referral-to-treatment waiting times are common in the United Kingdom, and there is concern about the workload implications associated with insulin initiation.
Workload is a particular concern for my community nursing colleagues, who must visit some of my more frail and functionally dependent patients daily to administer their insulin.
In addition, the delivery of high-quality diabetes care in nursing homes, particularly for patients requiring insulin, has been a perennial challenge in the UK, again because of a lack of confidence and competence due to an absence of education for nursing and ancillary staff.
Moreover, it is not appropriate to switch many of these frail patients to noninsulin therapies because of their insulinopenia, as well as the significant weight (and sometimes muscle) loss associated with GLP-1 receptor agonists. Also, sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitors are associated with a risk for volume depletion and diabetic ketoacidosis.
I believe that the availability of a once-weekly insulin will help overcome many of the above barriers.
From a patient’s viewpoint, simplification of insulin therapy with once-weekly insulin will substantially reduce the number of injections required (from 365 to 52 over 1 year). This change will improve compliance and concordance even in patients with injection anxiety. These results will hopefully translate into improved glycemic control and a lower risk for the complications of T2D. Real-world evidence for these outcomes is not yet available, however. Also, the reduced amount of insulin consumables that once-weekly dosing requires will also help improve the environmental footprint of insulin therapy.
From a clinician’s viewpoint, once-weekly insulin may seem less daunting and could reduce therapeutic inertia, thus facilitating earlier initiation of insulin therapy and reducing the risk for complications of T2D. Although education remains pivotal, this ease of dosing may be more acceptable to many clinicians because it has less of an effect on workload. This dosing could even save time because it requires less intensive follow-up than daily basal insulin does.
My community nurse colleagues were ecstatic when I mentioned that once-weekly basal insulin was on the horizon. This formulation could reduce the number of weekly home visits from 7 to just 1, thus freeing up considerable healthcare resources. And if once-weekly insulin is coupled with continuous glucose monitoring, then remote review of glucose data can further streamline and optimize the management of T2D in frail older patients. I am sure that my nursing-home colleagues will be equally enthusiastic about simplifying insulin regimens and monitoring.
Finally, an unanswered question is how I manage “sick days” for patients on weekly insulin dosing. Of course, the golden rule of never stopping insulin during intercurrent illness must be followed, but is any dose titration required for once-weekly insulin? I suspect not, but do I need to consider adding a once-daily basal insulin or rapid-acting insulin to mitigate the glucose counterregulatory hormone response during acute illness? Initially, I will be asking specialist diabetes teams for further advice on managing sick days.
In conclusion, once-weekly dosing of insulin is a game-changer for primary care and could finally be the driver to quash therapeutic inertia and address common patient barriers when escalation to insulin is required.
Dr. Fernando, general practitioner partner, North Berwick Health Centre, North Berwick, Scotland, disclosed ties with Amarin, Amgen, AstraZeneca, Bayer, Boehringer Ingelheim, Dexcom, Daiichi Sankyo, Lilly, Menarini, Novartis, Novo Nordisk, Roche Diagnostics, Embecta, Roche Diabetes Care, and Sanofi.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Treating Family: Ethicist Discusses Whether It’s Appropriate
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
There’s a very interesting story in the medical press. A few years ago, a plastic surgeon named Edmond Cabbabe was preparing to do a follow-up cosmetic procedure on his wife at Mercy Hospital South, which is a big hospital in the St. Louis, Missouri, area.
He put her on the operating schedule, and he had done that when he had performed the original operation on her. On the day of the surgery, he got a call from the hospital saying the procedure was canceled. They said that the hospital’s policy, maybe a new one, would not allow doctors to operate on family members.
This physician was a past president of the Missouri State Medical Association. I think he was also on the board or president of the American Medical Association (AMA) Foundation. This was a physician not only in a skilled area where he felt confident he could take care of his wife, but also someone who was prominent in medical politics and medical policy.
The AMA forever has had a policy that says don’t treat relatives. This physician basically said, I think that policy is too restrictive, too cautious, and it doesn’t make much sense to continue to say that you can’t treat family and friends.
By implication, he was saying, I know exactly what I’m doing in my field and I know exactly what I’m doing with her procedure. I should have a right to perform it. I think I do a great job and I’d be best for her.
If you look at medical boards, every once in a while in some state, someone is brought up on a charge of doing different things with family members and saying that they’re going to get censured. They don’t usually lose their license, but they get a reprimand or get told that is just not ethical to do.
I think, in the long run, the policy about not treating your family and friends makes sense. The problem is, as is well known from the social sciences and psychology, people get biased when they deal with those they care about, love, and hold close to them.
It’s hard for the doctor to be objective when dealing with people that they really like or love. It’s also difficult for patients because they may not want to bring up something or they are uncomfortable talking with a doctor who’s a family member or close friend. They may not want to complain. They may be a little bit embarrassed about things. It just adds an emotional edge, I think, that’s difficult.
All that said, do I know doctors who regularly prescribe, say, an ointment for something that’s itchy or some kind of a pill when allergy season breaks out? I do. Do I think they’re acting in a horribly unethical manner? I don’t.
You need some judgment here. There are absolutely minor things where objectivity, fear, and anxiety are not in play. You’re going to be able to prescribe the routine thing for the routine itch without worrying too much about whether it’s a stranger, a friend, or your daughter.
What sorts of things am I really talking about when I say that minor variability ought to be allowed? It’s one thing when someone has poison ivy and they’re going to need some kind of standard medicine to treat it. A very different area that’s much more dangerous, and one I would avoid, is in the mental health field, and for that matter, the pain field.
It’s tempting to say: “Oh, my relative is just having a bad time. I’ll give her a little bit of antidepressant medicine,” or “They seem to be having pain after an operation or something, and I’m going to give them a little bit of pain meds just to get them through.”
Those areas are flying red flags. It’s easy to abuse and easy for someone to become a user and manipulate a friend or a doctor who’s a relative into getting things that another doctor wouldn’t be giving. I think that’s the space where you’ve got to exercise extreme caution.
Time and again, when those people get called up in front of the boards for treating relatives, it’s in those spaces of mental health, anxiety, and pain control. Again, when you know that there’s a likelihood of abuse, I think that’s the place where the line has to hold. Don’t treat the relative. Don’t treat the friend.
At the end of the day, I wouldn’t change the AMA policy. I think we should keep it in place and morally try to discourage doctors from caring for those they’re close to or they have emotional ties to.
At the same time, as with all ethical situations, there has to be a little bit of wiggle room for those super-minor cases where it just makes sense to say: “You don’t have to go find somebody else to do this. I can prescribe this ointment or this minor thing for you. No one’s objectivity is going to be soured, and you’re not going to feel in any way at risk because I’m going to prescribe this for you.”
Common sense ought to prevail. The default position is don’t do it; however, maybe with a tiny bit of space for what’s minor, what’s routine, and what really does just save people some inconvenience, there I might just give a little.
Dr. Caplan, Director, Division of Medical Ethics, New York University Langone Medical Center, New York City, has disclosed relationships with Johnson & Johnson’s Panel for Compassionate Drug Use and Medscape.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
There’s a very interesting story in the medical press. A few years ago, a plastic surgeon named Edmond Cabbabe was preparing to do a follow-up cosmetic procedure on his wife at Mercy Hospital South, which is a big hospital in the St. Louis, Missouri, area.
He put her on the operating schedule, and he had done that when he had performed the original operation on her. On the day of the surgery, he got a call from the hospital saying the procedure was canceled. They said that the hospital’s policy, maybe a new one, would not allow doctors to operate on family members.
This physician was a past president of the Missouri State Medical Association. I think he was also on the board or president of the American Medical Association (AMA) Foundation. This was a physician not only in a skilled area where he felt confident he could take care of his wife, but also someone who was prominent in medical politics and medical policy.
The AMA forever has had a policy that says don’t treat relatives. This physician basically said, I think that policy is too restrictive, too cautious, and it doesn’t make much sense to continue to say that you can’t treat family and friends.
By implication, he was saying, I know exactly what I’m doing in my field and I know exactly what I’m doing with her procedure. I should have a right to perform it. I think I do a great job and I’d be best for her.
If you look at medical boards, every once in a while in some state, someone is brought up on a charge of doing different things with family members and saying that they’re going to get censured. They don’t usually lose their license, but they get a reprimand or get told that is just not ethical to do.
I think, in the long run, the policy about not treating your family and friends makes sense. The problem is, as is well known from the social sciences and psychology, people get biased when they deal with those they care about, love, and hold close to them.
It’s hard for the doctor to be objective when dealing with people that they really like or love. It’s also difficult for patients because they may not want to bring up something or they are uncomfortable talking with a doctor who’s a family member or close friend. They may not want to complain. They may be a little bit embarrassed about things. It just adds an emotional edge, I think, that’s difficult.
All that said, do I know doctors who regularly prescribe, say, an ointment for something that’s itchy or some kind of a pill when allergy season breaks out? I do. Do I think they’re acting in a horribly unethical manner? I don’t.
You need some judgment here. There are absolutely minor things where objectivity, fear, and anxiety are not in play. You’re going to be able to prescribe the routine thing for the routine itch without worrying too much about whether it’s a stranger, a friend, or your daughter.
What sorts of things am I really talking about when I say that minor variability ought to be allowed? It’s one thing when someone has poison ivy and they’re going to need some kind of standard medicine to treat it. A very different area that’s much more dangerous, and one I would avoid, is in the mental health field, and for that matter, the pain field.
It’s tempting to say: “Oh, my relative is just having a bad time. I’ll give her a little bit of antidepressant medicine,” or “They seem to be having pain after an operation or something, and I’m going to give them a little bit of pain meds just to get them through.”
Those areas are flying red flags. It’s easy to abuse and easy for someone to become a user and manipulate a friend or a doctor who’s a relative into getting things that another doctor wouldn’t be giving. I think that’s the space where you’ve got to exercise extreme caution.
Time and again, when those people get called up in front of the boards for treating relatives, it’s in those spaces of mental health, anxiety, and pain control. Again, when you know that there’s a likelihood of abuse, I think that’s the place where the line has to hold. Don’t treat the relative. Don’t treat the friend.
At the end of the day, I wouldn’t change the AMA policy. I think we should keep it in place and morally try to discourage doctors from caring for those they’re close to or they have emotional ties to.
At the same time, as with all ethical situations, there has to be a little bit of wiggle room for those super-minor cases where it just makes sense to say: “You don’t have to go find somebody else to do this. I can prescribe this ointment or this minor thing for you. No one’s objectivity is going to be soured, and you’re not going to feel in any way at risk because I’m going to prescribe this for you.”
Common sense ought to prevail. The default position is don’t do it; however, maybe with a tiny bit of space for what’s minor, what’s routine, and what really does just save people some inconvenience, there I might just give a little.
Dr. Caplan, Director, Division of Medical Ethics, New York University Langone Medical Center, New York City, has disclosed relationships with Johnson & Johnson’s Panel for Compassionate Drug Use and Medscape.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
There’s a very interesting story in the medical press. A few years ago, a plastic surgeon named Edmond Cabbabe was preparing to do a follow-up cosmetic procedure on his wife at Mercy Hospital South, which is a big hospital in the St. Louis, Missouri, area.
He put her on the operating schedule, and he had done that when he had performed the original operation on her. On the day of the surgery, he got a call from the hospital saying the procedure was canceled. They said that the hospital’s policy, maybe a new one, would not allow doctors to operate on family members.
This physician was a past president of the Missouri State Medical Association. I think he was also on the board or president of the American Medical Association (AMA) Foundation. This was a physician not only in a skilled area where he felt confident he could take care of his wife, but also someone who was prominent in medical politics and medical policy.
The AMA forever has had a policy that says don’t treat relatives. This physician basically said, I think that policy is too restrictive, too cautious, and it doesn’t make much sense to continue to say that you can’t treat family and friends.
By implication, he was saying, I know exactly what I’m doing in my field and I know exactly what I’m doing with her procedure. I should have a right to perform it. I think I do a great job and I’d be best for her.
If you look at medical boards, every once in a while in some state, someone is brought up on a charge of doing different things with family members and saying that they’re going to get censured. They don’t usually lose their license, but they get a reprimand or get told that is just not ethical to do.
I think, in the long run, the policy about not treating your family and friends makes sense. The problem is, as is well known from the social sciences and psychology, people get biased when they deal with those they care about, love, and hold close to them.
It’s hard for the doctor to be objective when dealing with people that they really like or love. It’s also difficult for patients because they may not want to bring up something or they are uncomfortable talking with a doctor who’s a family member or close friend. They may not want to complain. They may be a little bit embarrassed about things. It just adds an emotional edge, I think, that’s difficult.
All that said, do I know doctors who regularly prescribe, say, an ointment for something that’s itchy or some kind of a pill when allergy season breaks out? I do. Do I think they’re acting in a horribly unethical manner? I don’t.
You need some judgment here. There are absolutely minor things where objectivity, fear, and anxiety are not in play. You’re going to be able to prescribe the routine thing for the routine itch without worrying too much about whether it’s a stranger, a friend, or your daughter.
What sorts of things am I really talking about when I say that minor variability ought to be allowed? It’s one thing when someone has poison ivy and they’re going to need some kind of standard medicine to treat it. A very different area that’s much more dangerous, and one I would avoid, is in the mental health field, and for that matter, the pain field.
It’s tempting to say: “Oh, my relative is just having a bad time. I’ll give her a little bit of antidepressant medicine,” or “They seem to be having pain after an operation or something, and I’m going to give them a little bit of pain meds just to get them through.”
Those areas are flying red flags. It’s easy to abuse and easy for someone to become a user and manipulate a friend or a doctor who’s a relative into getting things that another doctor wouldn’t be giving. I think that’s the space where you’ve got to exercise extreme caution.
Time and again, when those people get called up in front of the boards for treating relatives, it’s in those spaces of mental health, anxiety, and pain control. Again, when you know that there’s a likelihood of abuse, I think that’s the place where the line has to hold. Don’t treat the relative. Don’t treat the friend.
At the end of the day, I wouldn’t change the AMA policy. I think we should keep it in place and morally try to discourage doctors from caring for those they’re close to or they have emotional ties to.
At the same time, as with all ethical situations, there has to be a little bit of wiggle room for those super-minor cases where it just makes sense to say: “You don’t have to go find somebody else to do this. I can prescribe this ointment or this minor thing for you. No one’s objectivity is going to be soured, and you’re not going to feel in any way at risk because I’m going to prescribe this for you.”
Common sense ought to prevail. The default position is don’t do it; however, maybe with a tiny bit of space for what’s minor, what’s routine, and what really does just save people some inconvenience, there I might just give a little.
Dr. Caplan, Director, Division of Medical Ethics, New York University Langone Medical Center, New York City, has disclosed relationships with Johnson & Johnson’s Panel for Compassionate Drug Use and Medscape.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Should There Be a Mandatory Retirement Age for Physicians?
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
I’d like to pose a question: When should doctors retire? When, as practicing physicians or surgeons, do we become too old to deliver competent service?
You will be amazed to hear, those of you who have listened to my videos before — and although it is a matter of public knowledge — that I’m 68. I know it’s impossible to imagine, due to this youthful appearance, visage, and so on, but I am. I’ve been a cancer doctor for 40 years; therefore, I need to think a little about retirement.
There are two elements of this for me. I’m a university professor, and in Oxford we did vote, as a democracy of scholars, to have a mandatory retirement age around 68. This is so that we can bring new blood forward so that we can create the space to promote new professors, to bring youngsters in to make new ideas, and to get rid of us fusty old lot.
The other argument would be, of course, that we are wise, we’re experienced, we are world-weary, and we’re successful — otherwise, we wouldn’t have lasted as academics as long. Nevertheless, we voted to do that.
It’s possible to have a discussion with the university to extend this, and for those of us who are clinical academics, I have an honorary appointment as a consultant cancer physician in the hospital and my university professorial appointment, too.
I can extend it probably until I’m about 70. It feels like a nice, round number at which to retire — somewhat arbitrarily, one would admit. But does that feel right?
In the United States, more than 25% of the physician workforce is over the age of 65. There are many studies showing that there is a 20% cognitive decline for most individuals between the ages of 45 and 65.
Are we as capable as an elderly workforce as once we were? Clearly, it’s hardly individualistic. It depends on each of our own health status, where we started from, and so on, but are there any general rules that we can apply? I think these are starting to creep in around the sense of revalidation.
In the United Kingdom, we have a General Medical Council (GMC). I need to have a license to practice from the GMC and a sense of fitness to practice. I have annual appraisals within the hospital system, in which I explore delivery of care, how I’m doing as a mentor, am I reaching the milestones I’ve set in terms of academic achievements, and so on.
This is a peer-to-peer process. We have senior physicians — people like myself — who act as appraisers to support our colleagues and to maintain that sense of fitness to practice. Every 5 years, I’m revalidated by the GMC. They take account of the annual appraisals and a report made by the senior physician within my hospital network who’s a so-called designated person.
These two elements come together with patient feedback, with 360-degree feedback from colleagues, and so on. This is quite a firmly regulated system that I think works. Our mandatory retirement age of 65 has gone. That was phased out by the government. In fact, our NHS is making an effort to retain older elders in the workforce.
They see the benefits of mentorship, experience, leadership, and networks. At a time when the majority of NHS are actively seeking to retire when 65, the NHS is trying to retain and pull back those of us who have been around for that wee bit longer and who still feel committed to doing it.
I’d be really interested to see what you think. There’s variation from country to country. I know that, in Australia, they’re talking about annual appraisals of doctors over the age of 70. I’d be very interested to hear what you think is likely to happen in the United States.
I think our system works pretty well, as long as you’re within the NHS and hospital system. If you wanted to still practice, but practice privately, you would still have to find somebody who’d be prepared to conduct appraisals and so on outside of the NHS. It’s an interesting area.
For myself, I still feel competent. Patients seem to like me. That’s an objective assessment by this 360-degree thing in which patients reflected very positively, indeed, in my approach to the delivery of the care and so on, as did colleagues. I’m still publishing, I go to meetings, I cheer things, bits and bobs. I’d say I’m a wee bit unusual in terms of still having a strong academic profile in doing stuff.
It’s an interesting question. Richard Doll, one of the world’s great epidemiologists who, of course, was the dominant discoverer of the link between smoking and lung cancer, was attending seminars, sitting in the front row, and coming into university 3 days a week at age 90, continuing to be contributory with his extraordinarily sharp intellect and vast, vast experience.
When I think of experience, all young cancer doctors are now immunologists. When I was a young doctor, I was a clinical pharmacologist. There are many lessons and tricks that I learned which I do need to pass on to the younger generation of today. What do you think? Should there be a mandatory retirement age? How do we best measure, assess, and revalidate elderly physicians and surgeons? How can we continue to contribute to those who choose to do so? For the time being, as always, thanks for listening.
Dr. Kerr is professor, Nuffield Department of Clinical Laboratory Science, University of Oxford, and professor of cancer medicine, Oxford Cancer Centre, Oxford, United Kingdom. He has disclosed ties with Celleron Therapeutics, Oxford Cancer Biomarkers (Board of Directors); Afrox (charity; Trustee); GlaxoSmithKline and Bayer HealthCare Pharmaceuticals (Consultant), Genomic Health; Merck Serono, and Roche.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
I’d like to pose a question: When should doctors retire? When, as practicing physicians or surgeons, do we become too old to deliver competent service?
You will be amazed to hear, those of you who have listened to my videos before — and although it is a matter of public knowledge — that I’m 68. I know it’s impossible to imagine, due to this youthful appearance, visage, and so on, but I am. I’ve been a cancer doctor for 40 years; therefore, I need to think a little about retirement.
There are two elements of this for me. I’m a university professor, and in Oxford we did vote, as a democracy of scholars, to have a mandatory retirement age around 68. This is so that we can bring new blood forward so that we can create the space to promote new professors, to bring youngsters in to make new ideas, and to get rid of us fusty old lot.
The other argument would be, of course, that we are wise, we’re experienced, we are world-weary, and we’re successful — otherwise, we wouldn’t have lasted as academics as long. Nevertheless, we voted to do that.
It’s possible to have a discussion with the university to extend this, and for those of us who are clinical academics, I have an honorary appointment as a consultant cancer physician in the hospital and my university professorial appointment, too.
I can extend it probably until I’m about 70. It feels like a nice, round number at which to retire — somewhat arbitrarily, one would admit. But does that feel right?
In the United States, more than 25% of the physician workforce is over the age of 65. There are many studies showing that there is a 20% cognitive decline for most individuals between the ages of 45 and 65.
Are we as capable as an elderly workforce as once we were? Clearly, it’s hardly individualistic. It depends on each of our own health status, where we started from, and so on, but are there any general rules that we can apply? I think these are starting to creep in around the sense of revalidation.
In the United Kingdom, we have a General Medical Council (GMC). I need to have a license to practice from the GMC and a sense of fitness to practice. I have annual appraisals within the hospital system, in which I explore delivery of care, how I’m doing as a mentor, am I reaching the milestones I’ve set in terms of academic achievements, and so on.
This is a peer-to-peer process. We have senior physicians — people like myself — who act as appraisers to support our colleagues and to maintain that sense of fitness to practice. Every 5 years, I’m revalidated by the GMC. They take account of the annual appraisals and a report made by the senior physician within my hospital network who’s a so-called designated person.
These two elements come together with patient feedback, with 360-degree feedback from colleagues, and so on. This is quite a firmly regulated system that I think works. Our mandatory retirement age of 65 has gone. That was phased out by the government. In fact, our NHS is making an effort to retain older elders in the workforce.
They see the benefits of mentorship, experience, leadership, and networks. At a time when the majority of NHS are actively seeking to retire when 65, the NHS is trying to retain and pull back those of us who have been around for that wee bit longer and who still feel committed to doing it.
I’d be really interested to see what you think. There’s variation from country to country. I know that, in Australia, they’re talking about annual appraisals of doctors over the age of 70. I’d be very interested to hear what you think is likely to happen in the United States.
I think our system works pretty well, as long as you’re within the NHS and hospital system. If you wanted to still practice, but practice privately, you would still have to find somebody who’d be prepared to conduct appraisals and so on outside of the NHS. It’s an interesting area.
For myself, I still feel competent. Patients seem to like me. That’s an objective assessment by this 360-degree thing in which patients reflected very positively, indeed, in my approach to the delivery of the care and so on, as did colleagues. I’m still publishing, I go to meetings, I cheer things, bits and bobs. I’d say I’m a wee bit unusual in terms of still having a strong academic profile in doing stuff.
It’s an interesting question. Richard Doll, one of the world’s great epidemiologists who, of course, was the dominant discoverer of the link between smoking and lung cancer, was attending seminars, sitting in the front row, and coming into university 3 days a week at age 90, continuing to be contributory with his extraordinarily sharp intellect and vast, vast experience.
When I think of experience, all young cancer doctors are now immunologists. When I was a young doctor, I was a clinical pharmacologist. There are many lessons and tricks that I learned which I do need to pass on to the younger generation of today. What do you think? Should there be a mandatory retirement age? How do we best measure, assess, and revalidate elderly physicians and surgeons? How can we continue to contribute to those who choose to do so? For the time being, as always, thanks for listening.
Dr. Kerr is professor, Nuffield Department of Clinical Laboratory Science, University of Oxford, and professor of cancer medicine, Oxford Cancer Centre, Oxford, United Kingdom. He has disclosed ties with Celleron Therapeutics, Oxford Cancer Biomarkers (Board of Directors); Afrox (charity; Trustee); GlaxoSmithKline and Bayer HealthCare Pharmaceuticals (Consultant), Genomic Health; Merck Serono, and Roche.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
I’d like to pose a question: When should doctors retire? When, as practicing physicians or surgeons, do we become too old to deliver competent service?
You will be amazed to hear, those of you who have listened to my videos before — and although it is a matter of public knowledge — that I’m 68. I know it’s impossible to imagine, due to this youthful appearance, visage, and so on, but I am. I’ve been a cancer doctor for 40 years; therefore, I need to think a little about retirement.
There are two elements of this for me. I’m a university professor, and in Oxford we did vote, as a democracy of scholars, to have a mandatory retirement age around 68. This is so that we can bring new blood forward so that we can create the space to promote new professors, to bring youngsters in to make new ideas, and to get rid of us fusty old lot.
The other argument would be, of course, that we are wise, we’re experienced, we are world-weary, and we’re successful — otherwise, we wouldn’t have lasted as academics as long. Nevertheless, we voted to do that.
It’s possible to have a discussion with the university to extend this, and for those of us who are clinical academics, I have an honorary appointment as a consultant cancer physician in the hospital and my university professorial appointment, too.
I can extend it probably until I’m about 70. It feels like a nice, round number at which to retire — somewhat arbitrarily, one would admit. But does that feel right?
In the United States, more than 25% of the physician workforce is over the age of 65. There are many studies showing that there is a 20% cognitive decline for most individuals between the ages of 45 and 65.
Are we as capable as an elderly workforce as once we were? Clearly, it’s hardly individualistic. It depends on each of our own health status, where we started from, and so on, but are there any general rules that we can apply? I think these are starting to creep in around the sense of revalidation.
In the United Kingdom, we have a General Medical Council (GMC). I need to have a license to practice from the GMC and a sense of fitness to practice. I have annual appraisals within the hospital system, in which I explore delivery of care, how I’m doing as a mentor, am I reaching the milestones I’ve set in terms of academic achievements, and so on.
This is a peer-to-peer process. We have senior physicians — people like myself — who act as appraisers to support our colleagues and to maintain that sense of fitness to practice. Every 5 years, I’m revalidated by the GMC. They take account of the annual appraisals and a report made by the senior physician within my hospital network who’s a so-called designated person.
These two elements come together with patient feedback, with 360-degree feedback from colleagues, and so on. This is quite a firmly regulated system that I think works. Our mandatory retirement age of 65 has gone. That was phased out by the government. In fact, our NHS is making an effort to retain older elders in the workforce.
They see the benefits of mentorship, experience, leadership, and networks. At a time when the majority of NHS are actively seeking to retire when 65, the NHS is trying to retain and pull back those of us who have been around for that wee bit longer and who still feel committed to doing it.
I’d be really interested to see what you think. There’s variation from country to country. I know that, in Australia, they’re talking about annual appraisals of doctors over the age of 70. I’d be very interested to hear what you think is likely to happen in the United States.
I think our system works pretty well, as long as you’re within the NHS and hospital system. If you wanted to still practice, but practice privately, you would still have to find somebody who’d be prepared to conduct appraisals and so on outside of the NHS. It’s an interesting area.
For myself, I still feel competent. Patients seem to like me. That’s an objective assessment by this 360-degree thing in which patients reflected very positively, indeed, in my approach to the delivery of the care and so on, as did colleagues. I’m still publishing, I go to meetings, I cheer things, bits and bobs. I’d say I’m a wee bit unusual in terms of still having a strong academic profile in doing stuff.
It’s an interesting question. Richard Doll, one of the world’s great epidemiologists who, of course, was the dominant discoverer of the link between smoking and lung cancer, was attending seminars, sitting in the front row, and coming into university 3 days a week at age 90, continuing to be contributory with his extraordinarily sharp intellect and vast, vast experience.
When I think of experience, all young cancer doctors are now immunologists. When I was a young doctor, I was a clinical pharmacologist. There are many lessons and tricks that I learned which I do need to pass on to the younger generation of today. What do you think? Should there be a mandatory retirement age? How do we best measure, assess, and revalidate elderly physicians and surgeons? How can we continue to contribute to those who choose to do so? For the time being, as always, thanks for listening.
Dr. Kerr is professor, Nuffield Department of Clinical Laboratory Science, University of Oxford, and professor of cancer medicine, Oxford Cancer Centre, Oxford, United Kingdom. He has disclosed ties with Celleron Therapeutics, Oxford Cancer Biomarkers (Board of Directors); Afrox (charity; Trustee); GlaxoSmithKline and Bayer HealthCare Pharmaceuticals (Consultant), Genomic Health; Merck Serono, and Roche.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Hidden in Plain Sight: The Growing Epidemic of Ultraprocessed Food Addiction
Yet, even as this evidence mounted, these food items have become increasingly prominent in diets globally.
Now, recent studies are unlocking why cutting back on ultraprocessed foods can be so challenging. In their ability to fuel intense cravings, loss of control, and even withdrawal symptoms, ultraprocessed foods appear as capable of triggering addiction as traditional culprits like tobacco and alcohol.
This has driven efforts to better understand the addictive nature of these foods and identify strategies for combating it.
The Key Role of the Food Industry
Some foods are more likely to trigger addictions than others. For instance, in our studies, participants frequently mention chocolate, pizza, French fries, potato chips, and soda as some of the most addictive foods. What these foods all share is an ability to deliver high doses of refined carbohydrates, fat, or salt at levels exceeding those found in natural foods (eg, fruits, vegetables, beans).
Furthermore, ultraprocessed foods are industrially mass-produced in a process that relies on the heavy use of flavor enhancers and additives, as well as preservatives and packaging that make them shelf-stable. This has flooded our food supply with cheap, accessible, hyperrewarding foods that our brains are not well equipped to resist.
To add to these already substantial effects, the food industry often employs strategies reminiscent of Big Tobacco. They engineer foods to hit our “bliss points,” maximizing craving and fostering brand loyalty from a young age. This product engineering, coupled with aggressive marketing, makes these foods both attractive and seemingly ubiquitous.
How Many People Are Affected?
Addiction to ultraprocessed food is more common than you might think. According to the Yale Food Addiction Scale — a tool that uses the same criteria for diagnosing substance use disorders to assess ultraprocessed food addiction (UPFA) — about 14% of adults and 12% of children show clinically significant signs of addiction to such foods. This is quite similar to addiction rates among adults for legal substances like alcohol and tobacco.
Research has shown that behaviors and brain mechanisms contributing to addictive disorders, such as cravings and impulsivity, also apply to UPFA.
Many more people outside of those who meet the criteria for UPFA are influenced by their addictive properties. Picture a teenager craving a sugary drink after school, a child needing the morning cereal fix, or adults reaching for candy and fast food; these scenarios illustrate how addictive ultraprocessed foods permeate our daily lives.
From a public health standpoint, this comes at a significant cost. Even experiencing one or two symptoms of UPFA, such as intense cravings or a feeling of loss of control over intake, can lead to consuming too many calories, sugar, fat, and sodium in a way that puts health at risk.
Clinical Implications
Numerous studies have found that individuals who exhibit UPFA have more severe mental and physical health challenges. For example, UPFA is associated with higher rates of diet-related diseases (like type 2 diabetes), greater overall mental health issues, and generally poorer outcomes in weight loss treatments.
Despite the growing understanding of UPFA’s relevance in clinical settings, research is still limited on how to best treat, manage, or prevent it. Most of the existing work has focused on investigating whether UPFA is indeed a real condition, with efforts to create clinical guidelines only just beginning.
Of note, UPFA isn’t officially recognized as a diagnosis — yet. If it were, it could spark much more research into how to handle it clinically.
There is some debate about whether we really need this new diagnosis, given that eating disorders are already recognized. However, the statistics tell a different story: Around 14% of people might have UPFA compared with about 1% for binge-type eating disorders. This suggests that many individuals with problematic eating habits are currently flying under the radar with our existing diagnostic categories.
What’s even more concerning is that these individuals often suffer significant problems and exhibit distinct brain differences, even if they do not neatly fit into an existing eating disorder diagnosis. Officially recognizing UPFA could open up new avenues for support and lead to better treatments aimed at reducing compulsive eating patterns.
Treatment Options
Treatment options for UPFA are still being explored. Initial evidence suggests that medications used for treating substance addiction, such as naltrexone and bupropion, might help with highly processed food addiction as well. Newer drugs, like glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists, which appear to curb food cravings and manage addictive behaviors, also look promising.
Psychosocial approaches can also be used to address UPFA. Strategies include:
- Helping individuals become more aware of their triggers for addictive patterns of intake. This often involves identifying certain types of food (eg, potato chips, candy), specific places or times of day (eg, sitting on the couch at night while watching TV), and particular emotional states (eg, anger, loneliness, boredom, sadness). Increasing awareness of personal triggers can help people minimize their exposure to these and develop coping strategies when they do arise.
- Many people use ultraprocessed foods to cope with challenging emotions. Helping individuals develop healthier strategies to regulate their emotions can be key. This may include seeking out social support, journaling, going for a walk, or practicing mindfulness.
- UPFA can be associated with erratic and inconsistent eating patterns. Stabilizing eating habits by consuming regular meals composed of more minimally processed foods (eg, vegetables, fruits, high-quality protein, beans) can help heal the body and reduce vulnerability to ultraprocessed food triggers.
- Many people with UPFA have other existing mental health conditions, including mood disorders, anxiety, substance use disorders, or trauma-related disorders. Addressing these co-occurring mental health conditions can help reduce reliance on ultraprocessed foods.
Public-policy interventions may also help safeguard vulnerable populations from developing UPFA. For instance, support exists for policies to protect children from cigarette marketing and to put clear addiction warning labels on cigarette packages. A similar approach could be applied to reduce the harms associated with ultraprocessed foods, particularly for children.
Combating this growing problem requires treating ultraprocessed foods like other addictive substances. By identifying the threat posed by these common food items, we can not only help patients with UPFA, but also potentially stave off the development of several diet-related conditions.
Dr. Gearhardt, professor of psychology, University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Yet, even as this evidence mounted, these food items have become increasingly prominent in diets globally.
Now, recent studies are unlocking why cutting back on ultraprocessed foods can be so challenging. In their ability to fuel intense cravings, loss of control, and even withdrawal symptoms, ultraprocessed foods appear as capable of triggering addiction as traditional culprits like tobacco and alcohol.
This has driven efforts to better understand the addictive nature of these foods and identify strategies for combating it.
The Key Role of the Food Industry
Some foods are more likely to trigger addictions than others. For instance, in our studies, participants frequently mention chocolate, pizza, French fries, potato chips, and soda as some of the most addictive foods. What these foods all share is an ability to deliver high doses of refined carbohydrates, fat, or salt at levels exceeding those found in natural foods (eg, fruits, vegetables, beans).
Furthermore, ultraprocessed foods are industrially mass-produced in a process that relies on the heavy use of flavor enhancers and additives, as well as preservatives and packaging that make them shelf-stable. This has flooded our food supply with cheap, accessible, hyperrewarding foods that our brains are not well equipped to resist.
To add to these already substantial effects, the food industry often employs strategies reminiscent of Big Tobacco. They engineer foods to hit our “bliss points,” maximizing craving and fostering brand loyalty from a young age. This product engineering, coupled with aggressive marketing, makes these foods both attractive and seemingly ubiquitous.
How Many People Are Affected?
Addiction to ultraprocessed food is more common than you might think. According to the Yale Food Addiction Scale — a tool that uses the same criteria for diagnosing substance use disorders to assess ultraprocessed food addiction (UPFA) — about 14% of adults and 12% of children show clinically significant signs of addiction to such foods. This is quite similar to addiction rates among adults for legal substances like alcohol and tobacco.
Research has shown that behaviors and brain mechanisms contributing to addictive disorders, such as cravings and impulsivity, also apply to UPFA.
Many more people outside of those who meet the criteria for UPFA are influenced by their addictive properties. Picture a teenager craving a sugary drink after school, a child needing the morning cereal fix, or adults reaching for candy and fast food; these scenarios illustrate how addictive ultraprocessed foods permeate our daily lives.
From a public health standpoint, this comes at a significant cost. Even experiencing one or two symptoms of UPFA, such as intense cravings or a feeling of loss of control over intake, can lead to consuming too many calories, sugar, fat, and sodium in a way that puts health at risk.
Clinical Implications
Numerous studies have found that individuals who exhibit UPFA have more severe mental and physical health challenges. For example, UPFA is associated with higher rates of diet-related diseases (like type 2 diabetes), greater overall mental health issues, and generally poorer outcomes in weight loss treatments.
Despite the growing understanding of UPFA’s relevance in clinical settings, research is still limited on how to best treat, manage, or prevent it. Most of the existing work has focused on investigating whether UPFA is indeed a real condition, with efforts to create clinical guidelines only just beginning.
Of note, UPFA isn’t officially recognized as a diagnosis — yet. If it were, it could spark much more research into how to handle it clinically.
There is some debate about whether we really need this new diagnosis, given that eating disorders are already recognized. However, the statistics tell a different story: Around 14% of people might have UPFA compared with about 1% for binge-type eating disorders. This suggests that many individuals with problematic eating habits are currently flying under the radar with our existing diagnostic categories.
What’s even more concerning is that these individuals often suffer significant problems and exhibit distinct brain differences, even if they do not neatly fit into an existing eating disorder diagnosis. Officially recognizing UPFA could open up new avenues for support and lead to better treatments aimed at reducing compulsive eating patterns.
Treatment Options
Treatment options for UPFA are still being explored. Initial evidence suggests that medications used for treating substance addiction, such as naltrexone and bupropion, might help with highly processed food addiction as well. Newer drugs, like glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists, which appear to curb food cravings and manage addictive behaviors, also look promising.
Psychosocial approaches can also be used to address UPFA. Strategies include:
- Helping individuals become more aware of their triggers for addictive patterns of intake. This often involves identifying certain types of food (eg, potato chips, candy), specific places or times of day (eg, sitting on the couch at night while watching TV), and particular emotional states (eg, anger, loneliness, boredom, sadness). Increasing awareness of personal triggers can help people minimize their exposure to these and develop coping strategies when they do arise.
- Many people use ultraprocessed foods to cope with challenging emotions. Helping individuals develop healthier strategies to regulate their emotions can be key. This may include seeking out social support, journaling, going for a walk, or practicing mindfulness.
- UPFA can be associated with erratic and inconsistent eating patterns. Stabilizing eating habits by consuming regular meals composed of more minimally processed foods (eg, vegetables, fruits, high-quality protein, beans) can help heal the body and reduce vulnerability to ultraprocessed food triggers.
- Many people with UPFA have other existing mental health conditions, including mood disorders, anxiety, substance use disorders, or trauma-related disorders. Addressing these co-occurring mental health conditions can help reduce reliance on ultraprocessed foods.
Public-policy interventions may also help safeguard vulnerable populations from developing UPFA. For instance, support exists for policies to protect children from cigarette marketing and to put clear addiction warning labels on cigarette packages. A similar approach could be applied to reduce the harms associated with ultraprocessed foods, particularly for children.
Combating this growing problem requires treating ultraprocessed foods like other addictive substances. By identifying the threat posed by these common food items, we can not only help patients with UPFA, but also potentially stave off the development of several diet-related conditions.
Dr. Gearhardt, professor of psychology, University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Yet, even as this evidence mounted, these food items have become increasingly prominent in diets globally.
Now, recent studies are unlocking why cutting back on ultraprocessed foods can be so challenging. In their ability to fuel intense cravings, loss of control, and even withdrawal symptoms, ultraprocessed foods appear as capable of triggering addiction as traditional culprits like tobacco and alcohol.
This has driven efforts to better understand the addictive nature of these foods and identify strategies for combating it.
The Key Role of the Food Industry
Some foods are more likely to trigger addictions than others. For instance, in our studies, participants frequently mention chocolate, pizza, French fries, potato chips, and soda as some of the most addictive foods. What these foods all share is an ability to deliver high doses of refined carbohydrates, fat, or salt at levels exceeding those found in natural foods (eg, fruits, vegetables, beans).
Furthermore, ultraprocessed foods are industrially mass-produced in a process that relies on the heavy use of flavor enhancers and additives, as well as preservatives and packaging that make them shelf-stable. This has flooded our food supply with cheap, accessible, hyperrewarding foods that our brains are not well equipped to resist.
To add to these already substantial effects, the food industry often employs strategies reminiscent of Big Tobacco. They engineer foods to hit our “bliss points,” maximizing craving and fostering brand loyalty from a young age. This product engineering, coupled with aggressive marketing, makes these foods both attractive and seemingly ubiquitous.
How Many People Are Affected?
Addiction to ultraprocessed food is more common than you might think. According to the Yale Food Addiction Scale — a tool that uses the same criteria for diagnosing substance use disorders to assess ultraprocessed food addiction (UPFA) — about 14% of adults and 12% of children show clinically significant signs of addiction to such foods. This is quite similar to addiction rates among adults for legal substances like alcohol and tobacco.
Research has shown that behaviors and brain mechanisms contributing to addictive disorders, such as cravings and impulsivity, also apply to UPFA.
Many more people outside of those who meet the criteria for UPFA are influenced by their addictive properties. Picture a teenager craving a sugary drink after school, a child needing the morning cereal fix, or adults reaching for candy and fast food; these scenarios illustrate how addictive ultraprocessed foods permeate our daily lives.
From a public health standpoint, this comes at a significant cost. Even experiencing one or two symptoms of UPFA, such as intense cravings or a feeling of loss of control over intake, can lead to consuming too many calories, sugar, fat, and sodium in a way that puts health at risk.
Clinical Implications
Numerous studies have found that individuals who exhibit UPFA have more severe mental and physical health challenges. For example, UPFA is associated with higher rates of diet-related diseases (like type 2 diabetes), greater overall mental health issues, and generally poorer outcomes in weight loss treatments.
Despite the growing understanding of UPFA’s relevance in clinical settings, research is still limited on how to best treat, manage, or prevent it. Most of the existing work has focused on investigating whether UPFA is indeed a real condition, with efforts to create clinical guidelines only just beginning.
Of note, UPFA isn’t officially recognized as a diagnosis — yet. If it were, it could spark much more research into how to handle it clinically.
There is some debate about whether we really need this new diagnosis, given that eating disorders are already recognized. However, the statistics tell a different story: Around 14% of people might have UPFA compared with about 1% for binge-type eating disorders. This suggests that many individuals with problematic eating habits are currently flying under the radar with our existing diagnostic categories.
What’s even more concerning is that these individuals often suffer significant problems and exhibit distinct brain differences, even if they do not neatly fit into an existing eating disorder diagnosis. Officially recognizing UPFA could open up new avenues for support and lead to better treatments aimed at reducing compulsive eating patterns.
Treatment Options
Treatment options for UPFA are still being explored. Initial evidence suggests that medications used for treating substance addiction, such as naltrexone and bupropion, might help with highly processed food addiction as well. Newer drugs, like glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists, which appear to curb food cravings and manage addictive behaviors, also look promising.
Psychosocial approaches can also be used to address UPFA. Strategies include:
- Helping individuals become more aware of their triggers for addictive patterns of intake. This often involves identifying certain types of food (eg, potato chips, candy), specific places or times of day (eg, sitting on the couch at night while watching TV), and particular emotional states (eg, anger, loneliness, boredom, sadness). Increasing awareness of personal triggers can help people minimize their exposure to these and develop coping strategies when they do arise.
- Many people use ultraprocessed foods to cope with challenging emotions. Helping individuals develop healthier strategies to regulate their emotions can be key. This may include seeking out social support, journaling, going for a walk, or practicing mindfulness.
- UPFA can be associated with erratic and inconsistent eating patterns. Stabilizing eating habits by consuming regular meals composed of more minimally processed foods (eg, vegetables, fruits, high-quality protein, beans) can help heal the body and reduce vulnerability to ultraprocessed food triggers.
- Many people with UPFA have other existing mental health conditions, including mood disorders, anxiety, substance use disorders, or trauma-related disorders. Addressing these co-occurring mental health conditions can help reduce reliance on ultraprocessed foods.
Public-policy interventions may also help safeguard vulnerable populations from developing UPFA. For instance, support exists for policies to protect children from cigarette marketing and to put clear addiction warning labels on cigarette packages. A similar approach could be applied to reduce the harms associated with ultraprocessed foods, particularly for children.
Combating this growing problem requires treating ultraprocessed foods like other addictive substances. By identifying the threat posed by these common food items, we can not only help patients with UPFA, but also potentially stave off the development of several diet-related conditions.
Dr. Gearhardt, professor of psychology, University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
‘Reform School’ for Pharmacy Benefit Managers: How Might Legislation Help Patients?
The term “reform school” is a bit outdated. It used to refer to institutions where young offenders were sent instead of prison. Some argue that pharmacy benefit managers (PBMs) should bypass reform school and go straight to prison. “PBM reform” has become a ubiquitous term, encompassing any legislative or regulatory efforts aimed at curbing PBMs’ bad behavior. When discussing PBM reform, it’s crucial to understand the various segments of the healthcare system affected by PBMs. This complexity often makes it challenging to determine what these reform packages would actually achieve and who they would benefit.
Pharmacists have long been vocal critics of PBMs, and while their issues are extremely important, it is essential to remember that the ultimate victims of PBM misconduct, in terms of access to care, are patients. At some point, we will all be patients, making this issue universally relevant. It has been quite challenging to follow federal legislation on this topic as these packages attempt to address a number of bad behaviors by PBMs affecting a variety of victims. This discussion will examine those reforms that would directly improve patient’s access to available and affordable medications.
Policy Categories of PBM Reform
There are five policy categories of PBM reform legislation overall, including three that have the greatest potential to directly address patient needs. The first is patient access to medications (utilization management, copay assistance, prior authorization, etc.), followed by delinking drug list prices from PBM income and pass-through of price concessions from the manufacturer. The remaining two categories involve transparency and pharmacy-facing reform, both of which are very important. However, this discussion will revolve around the first three categories. It should be noted that many of the legislation packages addressing the categories of patient access, delinking, and pass-through also include transparency issues, particularly as they relate to pharmacy-facing issues.
Patient Access to Medications — Step Therapy Legislation
One of the major obstacles to patient access to medications is the use of PBM utilization management tools such as step therapy (“fail first”), prior authorizations, nonmedical switching, and formulary exclusions. These tools dictate when patients can obtain necessary medications and for how long patients who are stable on their current treatments can remain on them.
While many states have enacted step therapy reforms to prevent stable patients from being whip-sawed between medications that maximize PBM profits (often labeled as “savings”), these state protections apply only to state-regulated health plans. These include fully insured health plans and those offered through the Affordable Care Act’s Health Insurance Marketplace. It also includes state employees, state corrections, and, in some cases, state labor unions. State legislation does not extend to patients covered by employer self-insured health plans, called ERISA plans for the federal law that governs employee benefit plans, the Employee Retirement Income Security Act. These ERISA plans include nearly 35 million people nationwide.
This is where the Safe Step Act (S.652/H.R.2630) becomes crucial, as it allows employees to request exceptions to harmful fail-first protocols. The bill has gained significant momentum, having been reported out of the Senate HELP Committee and discussed in House markups. The Safe Step Act would mandate that an exception to a step therapy protocol must be granted if:
- The required treatment has been ineffective
- The treatment is expected to be ineffective, and delaying effective treatment would lead to irreversible consequences
- The treatment will cause or is likely to cause an adverse reaction
- The treatment is expected to prevent the individual from performing daily activities or occupational responsibilities
- The individual is stable on their current prescription drugs
- There are other circumstances as determined by the Employee Benefits Security Administration
This legislation is vital for ensuring that patients have timely access to the medications they need without unnecessary delays or disruptions.
Patient Access to Medications — Prior Authorizations
Another significant issue affecting patient access to medications is prior authorizations (PAs). According to an American Medical Association survey, nearly one in four physicians (24%) report that a PA has led to a serious adverse event for a patient in their care. In rheumatology, PAs often result in delays in care (even for those initially approved) and a significant increase in steroid usage. In particular, PAs in Medicare Advantage (MA) plans are harmful to Medicare beneficiaries.
The Improving Seniors’ Timely Access to Care Act (H.R.8702 / S.4532) aims to reform PAs used in MA plans, making the process more efficient and transparent to improve access to care for seniors. Unfortunately, it does not cover Part D drugs and may only cover Part B drugs depending on the MA plan’s benefit package. Here are the key provisions of the act:
- Electronic PA: Implementing real-time decisions for routinely approved items and services.
- Transparency: Requiring annual publication of PA information, such as the percentage of requests approved and the average response time.
- Quality and Timeliness Standards: The Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS) will set standards for the quality and timeliness of PA determinations.
- Streamlining Approvals: Simplifying the approval process and reducing the time allowed for health plans to consider PA requests.
This bill passed the House in September 2022 but stalled in the Senate because of an unfavorable Congressional Budget Office score. CMS has since finalized portions of this bill via regulation, zeroing out the CBO score and increasing the chances of its passage.
Delinking Drug Prices from PBM Income and Pass-Through of Price Concessions
Affordability is a crucial aspect of accessibility, especially when it comes to medications. Over the years, we’ve learned that PBMs often favor placing the highest list price drugs on formularies because the rebates and various fees they receive from manufacturers are based on a percentage of the list price. In other words, the higher the medication’s price, the more money the PBM makes.
This practice is evident in both commercial and government formularies, where brand-name drugs are often preferred, while lower-priced generics are either excluded or placed on higher tiers. As a result, while major PBMs benefit from these rebates and fees, patients continue to pay their cost share based on the list price of the medication.
To improve the affordability of medications, a key aspect of PBM reform should be to disincentivize PBMs from selecting higher-priced medications and/or require the pass-through of manufacturer price concessions to patients.
Several major PBM reform bills are currently being considered that address either the delinking of price concessions from the list price of the drug or some form of pass-through of these concessions. These reforms are essential to ensure that patients can access affordable medications without being burdened by inflated costs.
The legislation includes the Pharmacy Benefit Manager Reform Act (S.1339); the Modernizing & Ensuring PBM Accountability Act (S.2973); the Better Mental Health Care, Lower Cost Drugs, and Extenders Act (S.3430); the Protecting Patients Against PBM Abuses Act (H.R. 2880); the DRUG Act (S.2474 / H.R.6283); and the Share the Savings with Seniors Act (S.2474 / H.R.5376).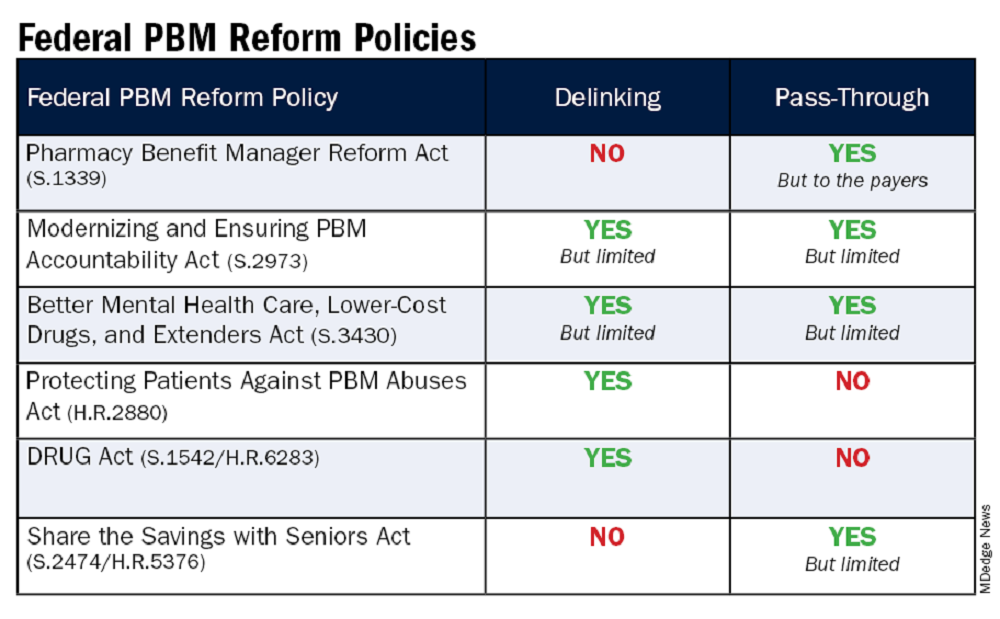
As with all legislation, there are limitations and compromises in each of these. However, these bills are a good first step in addressing PBM remuneration (rebates and fees) based on the list price of the drug and/or passing through to the patient the benefit of manufacturer price concessions. By focusing on key areas like utilization management, delinking drug prices from PBM income, and allowing patients to directly benefit from manufacturer price concessions, we can work toward a more equitable and efficient healthcare system. Reigning in PBM bad behavior is a challenge, but the potential benefits for patient care and access make it a crucial fight worth pursuing.
Please help in efforts to improve patients’ access to available and affordable medications by contacting your representatives in Congress to impart to them the importance of passing legislation. The CSRO’s legislative map tool can help to inform you of the latest information on these and other bills and assist you in engaging with your representatives on them.
Dr. Feldman is a rheumatologist in private practice with The Rheumatology Group in New Orleans. She is the CSRO’s vice president of Advocacy and Government Affairs and its immediate past president, as well as past chair of the Alliance for Safe Biologic Medicines and a past member of the American College of Rheumatology insurance subcommittee. She has no relevant conflicts of interest to disclose. You can reach her at [email protected].
The term “reform school” is a bit outdated. It used to refer to institutions where young offenders were sent instead of prison. Some argue that pharmacy benefit managers (PBMs) should bypass reform school and go straight to prison. “PBM reform” has become a ubiquitous term, encompassing any legislative or regulatory efforts aimed at curbing PBMs’ bad behavior. When discussing PBM reform, it’s crucial to understand the various segments of the healthcare system affected by PBMs. This complexity often makes it challenging to determine what these reform packages would actually achieve and who they would benefit.
Pharmacists have long been vocal critics of PBMs, and while their issues are extremely important, it is essential to remember that the ultimate victims of PBM misconduct, in terms of access to care, are patients. At some point, we will all be patients, making this issue universally relevant. It has been quite challenging to follow federal legislation on this topic as these packages attempt to address a number of bad behaviors by PBMs affecting a variety of victims. This discussion will examine those reforms that would directly improve patient’s access to available and affordable medications.
Policy Categories of PBM Reform
There are five policy categories of PBM reform legislation overall, including three that have the greatest potential to directly address patient needs. The first is patient access to medications (utilization management, copay assistance, prior authorization, etc.), followed by delinking drug list prices from PBM income and pass-through of price concessions from the manufacturer. The remaining two categories involve transparency and pharmacy-facing reform, both of which are very important. However, this discussion will revolve around the first three categories. It should be noted that many of the legislation packages addressing the categories of patient access, delinking, and pass-through also include transparency issues, particularly as they relate to pharmacy-facing issues.
Patient Access to Medications — Step Therapy Legislation
One of the major obstacles to patient access to medications is the use of PBM utilization management tools such as step therapy (“fail first”), prior authorizations, nonmedical switching, and formulary exclusions. These tools dictate when patients can obtain necessary medications and for how long patients who are stable on their current treatments can remain on them.
While many states have enacted step therapy reforms to prevent stable patients from being whip-sawed between medications that maximize PBM profits (often labeled as “savings”), these state protections apply only to state-regulated health plans. These include fully insured health plans and those offered through the Affordable Care Act’s Health Insurance Marketplace. It also includes state employees, state corrections, and, in some cases, state labor unions. State legislation does not extend to patients covered by employer self-insured health plans, called ERISA plans for the federal law that governs employee benefit plans, the Employee Retirement Income Security Act. These ERISA plans include nearly 35 million people nationwide.
This is where the Safe Step Act (S.652/H.R.2630) becomes crucial, as it allows employees to request exceptions to harmful fail-first protocols. The bill has gained significant momentum, having been reported out of the Senate HELP Committee and discussed in House markups. The Safe Step Act would mandate that an exception to a step therapy protocol must be granted if:
- The required treatment has been ineffective
- The treatment is expected to be ineffective, and delaying effective treatment would lead to irreversible consequences
- The treatment will cause or is likely to cause an adverse reaction
- The treatment is expected to prevent the individual from performing daily activities or occupational responsibilities
- The individual is stable on their current prescription drugs
- There are other circumstances as determined by the Employee Benefits Security Administration
This legislation is vital for ensuring that patients have timely access to the medications they need without unnecessary delays or disruptions.
Patient Access to Medications — Prior Authorizations
Another significant issue affecting patient access to medications is prior authorizations (PAs). According to an American Medical Association survey, nearly one in four physicians (24%) report that a PA has led to a serious adverse event for a patient in their care. In rheumatology, PAs often result in delays in care (even for those initially approved) and a significant increase in steroid usage. In particular, PAs in Medicare Advantage (MA) plans are harmful to Medicare beneficiaries.
The Improving Seniors’ Timely Access to Care Act (H.R.8702 / S.4532) aims to reform PAs used in MA plans, making the process more efficient and transparent to improve access to care for seniors. Unfortunately, it does not cover Part D drugs and may only cover Part B drugs depending on the MA plan’s benefit package. Here are the key provisions of the act:
- Electronic PA: Implementing real-time decisions for routinely approved items and services.
- Transparency: Requiring annual publication of PA information, such as the percentage of requests approved and the average response time.
- Quality and Timeliness Standards: The Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS) will set standards for the quality and timeliness of PA determinations.
- Streamlining Approvals: Simplifying the approval process and reducing the time allowed for health plans to consider PA requests.
This bill passed the House in September 2022 but stalled in the Senate because of an unfavorable Congressional Budget Office score. CMS has since finalized portions of this bill via regulation, zeroing out the CBO score and increasing the chances of its passage.
Delinking Drug Prices from PBM Income and Pass-Through of Price Concessions
Affordability is a crucial aspect of accessibility, especially when it comes to medications. Over the years, we’ve learned that PBMs often favor placing the highest list price drugs on formularies because the rebates and various fees they receive from manufacturers are based on a percentage of the list price. In other words, the higher the medication’s price, the more money the PBM makes.
This practice is evident in both commercial and government formularies, where brand-name drugs are often preferred, while lower-priced generics are either excluded or placed on higher tiers. As a result, while major PBMs benefit from these rebates and fees, patients continue to pay their cost share based on the list price of the medication.
To improve the affordability of medications, a key aspect of PBM reform should be to disincentivize PBMs from selecting higher-priced medications and/or require the pass-through of manufacturer price concessions to patients.
Several major PBM reform bills are currently being considered that address either the delinking of price concessions from the list price of the drug or some form of pass-through of these concessions. These reforms are essential to ensure that patients can access affordable medications without being burdened by inflated costs.
The legislation includes the Pharmacy Benefit Manager Reform Act (S.1339); the Modernizing & Ensuring PBM Accountability Act (S.2973); the Better Mental Health Care, Lower Cost Drugs, and Extenders Act (S.3430); the Protecting Patients Against PBM Abuses Act (H.R. 2880); the DRUG Act (S.2474 / H.R.6283); and the Share the Savings with Seniors Act (S.2474 / H.R.5376).
As with all legislation, there are limitations and compromises in each of these. However, these bills are a good first step in addressing PBM remuneration (rebates and fees) based on the list price of the drug and/or passing through to the patient the benefit of manufacturer price concessions. By focusing on key areas like utilization management, delinking drug prices from PBM income, and allowing patients to directly benefit from manufacturer price concessions, we can work toward a more equitable and efficient healthcare system. Reigning in PBM bad behavior is a challenge, but the potential benefits for patient care and access make it a crucial fight worth pursuing.
Please help in efforts to improve patients’ access to available and affordable medications by contacting your representatives in Congress to impart to them the importance of passing legislation. The CSRO’s legislative map tool can help to inform you of the latest information on these and other bills and assist you in engaging with your representatives on them.
Dr. Feldman is a rheumatologist in private practice with The Rheumatology Group in New Orleans. She is the CSRO’s vice president of Advocacy and Government Affairs and its immediate past president, as well as past chair of the Alliance for Safe Biologic Medicines and a past member of the American College of Rheumatology insurance subcommittee. She has no relevant conflicts of interest to disclose. You can reach her at [email protected].
The term “reform school” is a bit outdated. It used to refer to institutions where young offenders were sent instead of prison. Some argue that pharmacy benefit managers (PBMs) should bypass reform school and go straight to prison. “PBM reform” has become a ubiquitous term, encompassing any legislative or regulatory efforts aimed at curbing PBMs’ bad behavior. When discussing PBM reform, it’s crucial to understand the various segments of the healthcare system affected by PBMs. This complexity often makes it challenging to determine what these reform packages would actually achieve and who they would benefit.
Pharmacists have long been vocal critics of PBMs, and while their issues are extremely important, it is essential to remember that the ultimate victims of PBM misconduct, in terms of access to care, are patients. At some point, we will all be patients, making this issue universally relevant. It has been quite challenging to follow federal legislation on this topic as these packages attempt to address a number of bad behaviors by PBMs affecting a variety of victims. This discussion will examine those reforms that would directly improve patient’s access to available and affordable medications.
Policy Categories of PBM Reform
There are five policy categories of PBM reform legislation overall, including three that have the greatest potential to directly address patient needs. The first is patient access to medications (utilization management, copay assistance, prior authorization, etc.), followed by delinking drug list prices from PBM income and pass-through of price concessions from the manufacturer. The remaining two categories involve transparency and pharmacy-facing reform, both of which are very important. However, this discussion will revolve around the first three categories. It should be noted that many of the legislation packages addressing the categories of patient access, delinking, and pass-through also include transparency issues, particularly as they relate to pharmacy-facing issues.
Patient Access to Medications — Step Therapy Legislation
One of the major obstacles to patient access to medications is the use of PBM utilization management tools such as step therapy (“fail first”), prior authorizations, nonmedical switching, and formulary exclusions. These tools dictate when patients can obtain necessary medications and for how long patients who are stable on their current treatments can remain on them.
While many states have enacted step therapy reforms to prevent stable patients from being whip-sawed between medications that maximize PBM profits (often labeled as “savings”), these state protections apply only to state-regulated health plans. These include fully insured health plans and those offered through the Affordable Care Act’s Health Insurance Marketplace. It also includes state employees, state corrections, and, in some cases, state labor unions. State legislation does not extend to patients covered by employer self-insured health plans, called ERISA plans for the federal law that governs employee benefit plans, the Employee Retirement Income Security Act. These ERISA plans include nearly 35 million people nationwide.
This is where the Safe Step Act (S.652/H.R.2630) becomes crucial, as it allows employees to request exceptions to harmful fail-first protocols. The bill has gained significant momentum, having been reported out of the Senate HELP Committee and discussed in House markups. The Safe Step Act would mandate that an exception to a step therapy protocol must be granted if:
- The required treatment has been ineffective
- The treatment is expected to be ineffective, and delaying effective treatment would lead to irreversible consequences
- The treatment will cause or is likely to cause an adverse reaction
- The treatment is expected to prevent the individual from performing daily activities or occupational responsibilities
- The individual is stable on their current prescription drugs
- There are other circumstances as determined by the Employee Benefits Security Administration
This legislation is vital for ensuring that patients have timely access to the medications they need without unnecessary delays or disruptions.
Patient Access to Medications — Prior Authorizations
Another significant issue affecting patient access to medications is prior authorizations (PAs). According to an American Medical Association survey, nearly one in four physicians (24%) report that a PA has led to a serious adverse event for a patient in their care. In rheumatology, PAs often result in delays in care (even for those initially approved) and a significant increase in steroid usage. In particular, PAs in Medicare Advantage (MA) plans are harmful to Medicare beneficiaries.
The Improving Seniors’ Timely Access to Care Act (H.R.8702 / S.4532) aims to reform PAs used in MA plans, making the process more efficient and transparent to improve access to care for seniors. Unfortunately, it does not cover Part D drugs and may only cover Part B drugs depending on the MA plan’s benefit package. Here are the key provisions of the act:
- Electronic PA: Implementing real-time decisions for routinely approved items and services.
- Transparency: Requiring annual publication of PA information, such as the percentage of requests approved and the average response time.
- Quality and Timeliness Standards: The Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS) will set standards for the quality and timeliness of PA determinations.
- Streamlining Approvals: Simplifying the approval process and reducing the time allowed for health plans to consider PA requests.
This bill passed the House in September 2022 but stalled in the Senate because of an unfavorable Congressional Budget Office score. CMS has since finalized portions of this bill via regulation, zeroing out the CBO score and increasing the chances of its passage.
Delinking Drug Prices from PBM Income and Pass-Through of Price Concessions
Affordability is a crucial aspect of accessibility, especially when it comes to medications. Over the years, we’ve learned that PBMs often favor placing the highest list price drugs on formularies because the rebates and various fees they receive from manufacturers are based on a percentage of the list price. In other words, the higher the medication’s price, the more money the PBM makes.
This practice is evident in both commercial and government formularies, where brand-name drugs are often preferred, while lower-priced generics are either excluded or placed on higher tiers. As a result, while major PBMs benefit from these rebates and fees, patients continue to pay their cost share based on the list price of the medication.
To improve the affordability of medications, a key aspect of PBM reform should be to disincentivize PBMs from selecting higher-priced medications and/or require the pass-through of manufacturer price concessions to patients.
Several major PBM reform bills are currently being considered that address either the delinking of price concessions from the list price of the drug or some form of pass-through of these concessions. These reforms are essential to ensure that patients can access affordable medications without being burdened by inflated costs.
The legislation includes the Pharmacy Benefit Manager Reform Act (S.1339); the Modernizing & Ensuring PBM Accountability Act (S.2973); the Better Mental Health Care, Lower Cost Drugs, and Extenders Act (S.3430); the Protecting Patients Against PBM Abuses Act (H.R. 2880); the DRUG Act (S.2474 / H.R.6283); and the Share the Savings with Seniors Act (S.2474 / H.R.5376).
As with all legislation, there are limitations and compromises in each of these. However, these bills are a good first step in addressing PBM remuneration (rebates and fees) based on the list price of the drug and/or passing through to the patient the benefit of manufacturer price concessions. By focusing on key areas like utilization management, delinking drug prices from PBM income, and allowing patients to directly benefit from manufacturer price concessions, we can work toward a more equitable and efficient healthcare system. Reigning in PBM bad behavior is a challenge, but the potential benefits for patient care and access make it a crucial fight worth pursuing.
Please help in efforts to improve patients’ access to available and affordable medications by contacting your representatives in Congress to impart to them the importance of passing legislation. The CSRO’s legislative map tool can help to inform you of the latest information on these and other bills and assist you in engaging with your representatives on them.
Dr. Feldman is a rheumatologist in private practice with The Rheumatology Group in New Orleans. She is the CSRO’s vice president of Advocacy and Government Affairs and its immediate past president, as well as past chair of the Alliance for Safe Biologic Medicines and a past member of the American College of Rheumatology insurance subcommittee. She has no relevant conflicts of interest to disclose. You can reach her at [email protected].
Playing the ‘Doctor’ Card: A Lesson in Three Hypotheticals
Scenario I. Let’s say you wake with a collection of symptoms. None of them is concerning, but the combination seems a bit unusual, or at least confusing. You would like to speak to your PCP, whom you have known for a long time, and ask for either reassurance or advice on whether you should make an appointment. However, your experience with the front office’s organization tells you that the quick 4-minute conversation you’re looking for is not going to happen easily.
You have that robotic phone message memorized. It begins suggesting that you think you have an emergency to call 911. Then it reminds you that if have a question about COVID to press “2,” which will take you to a recorded message and eventually link you to a triage nurse if the recording doesn’t answer your questions. If you need a prescription refill you should press “3.” If you are a doctor’s office and wish speak to the doctor press “4.” If you know you need an appointment press “5.” And finally if you have a question press “6” and leave a message and a nurse will get back to you before the end of the day.
The good news is that your PCP’s office is good to its word and will return your call the same day, but the bad news is that it is likely to be well into the afternoon. And, while you don’t consider your symptoms life-threatening, you don’t want getting an answer to be an exercise in schedule disruption.
You were a doctor before you retired and you still have an “office.” It’s really more of a combination den and studio. So, technically you are a doctor’s office wanting to speak to the doctor. And, you know that pressing “4” will get you the answer you are looking for in a matter of minutes.
Scenario II. Your spouse, or your aunt, or the elderly widow next door asks you to accompany her at an upcoming doctor’s visit because she had been having trouble understanding the physician’s plan regarding further diagnosis and possible treatment. She believes having you along as kind of an interpreter/advocate would be a big help. Do you agree and do you make any stipulations?
Scenario III. Your PCP has referred you to a specialist. You are filling out the previsit form(s). Do you list your occupation as “retired physician” or just “retired”? Or just leave it blank?
Whether you deserve it or not, graduating from medical school has conferred on you a specialness in the eyes of many people. It is assumed you are smarter than the average bear and in taking the Hippocratic oath you have joined an elite club. And, with that membership comes some special undefined privileges.
But with that specialness there are are some downsides. For example, in some states being a physician once allowed you to have a license plate with “MD” in the number sequence. Sometimes that helped you avoid the occasional parking ticket. That is until folks realized the “MD” made you a target for car thieves and drug seekers who mistakenly believe we all carry drugs in our glove compartments.
So what about that first scenario? Do you press “4” to jump yourself to the head of the queue and avoid the inconvenience of having to wait for a reasonably timely response from your PCP? After all, you are fellow physicians and you’ve known her for a decade or two. If you are retired is your time any more valuable than that of her other patients? If you are still in active practice you can argue that getting special attention will benefit your patients. But, if it’s a weekend and you are off it’s a bit harder to rationalize special treatment. Playing the doctor card in this situation is your own decision but you must be prepared to shoulder the perceptions by your PCP and her staff as well as your own sense of fairness.
The other two scenarios are much different. In neither are you risking the impression that you are asking for a favor. But, they each have their downsides. In the second scenario you are doing someone a favor to act as an interpreter. How could this have downside? Unfortunately, what happens too often in situations like this is that when the patient’s physician learns that you are a fellow physician, the rest of the visit becomes a dialogue in doctor-speak between the two physicians with the patient sitting by as an observer. In the end this discussion may benefit the patient by creating a treatment plan that the patient can understand either because they overheard it or more likely because you eventually explained it to them.
On the other the hand, this doctor-to-doctor chat has done nothing to build a doctor-patient relationship that had obviously been lacking something. In situations like this it is probably better to keep the doctor card up your sleeve to be played at the end of the visit or maybe not at all. Before agreeing to be an interpreter/advocate, ask the patient to avoid mentioning that you are a physician. Instead, ask that she introduce you as a friend or relative that she has asked to come along to serve as a memory bank. During the visit it may be helpful to occasionally interject and suggest that the patient ask a question that hasn’t been adequately addressed. While some physicians may be upset when they belatedly find you have not revealed up front that you are a physician, I find this a harmless omission that has the benefit of improving patient care.
The final scenario — in which you are the patient — is likely to occur more often as you get older. When filling out a previsit form, I often simply put retired or leave it blank. But, how I answer the question often seems to be irrelevant because I have learned that physicians and their staff read those boilerplate forms so cursorily that even when I report my status as “retired physician” everyone seems surprised if and when it later comes to light.
My rationale in keeping the doctor card close to my vest in these situations is that I want to be addressed without any assumptions regarding my medical knowledge, which in my situation is well over half a century old and spotty at best. I don’t want my physicians to say “I’m sure you understand.” Because I often don’t. I would like them to learn about who I am just as I hope they would other patients. I won’t be offended if they “talk down” to me. If this specialist is as good as I’ve heard she is, I want to hear her full performance, not one edited for fellow and former physicians.
It doesn’t arrive gold edged with a list of special privileges. If it comes with any extras, they are risks that must be avoided.
Dr. Wilkoff practiced primary care pediatrics in Brunswick, Maine, for nearly 40 years. He has authored several books on behavioral pediatrics, including “How to Say No to Your Toddler.” Other than a Littman stethoscope he accepted as a first-year medical student in 1966, Dr. Wilkoff reports having nothing to disclose. Email him at [email protected].
Scenario I. Let’s say you wake with a collection of symptoms. None of them is concerning, but the combination seems a bit unusual, or at least confusing. You would like to speak to your PCP, whom you have known for a long time, and ask for either reassurance or advice on whether you should make an appointment. However, your experience with the front office’s organization tells you that the quick 4-minute conversation you’re looking for is not going to happen easily.
You have that robotic phone message memorized. It begins suggesting that you think you have an emergency to call 911. Then it reminds you that if have a question about COVID to press “2,” which will take you to a recorded message and eventually link you to a triage nurse if the recording doesn’t answer your questions. If you need a prescription refill you should press “3.” If you are a doctor’s office and wish speak to the doctor press “4.” If you know you need an appointment press “5.” And finally if you have a question press “6” and leave a message and a nurse will get back to you before the end of the day.
The good news is that your PCP’s office is good to its word and will return your call the same day, but the bad news is that it is likely to be well into the afternoon. And, while you don’t consider your symptoms life-threatening, you don’t want getting an answer to be an exercise in schedule disruption.
You were a doctor before you retired and you still have an “office.” It’s really more of a combination den and studio. So, technically you are a doctor’s office wanting to speak to the doctor. And, you know that pressing “4” will get you the answer you are looking for in a matter of minutes.
Scenario II. Your spouse, or your aunt, or the elderly widow next door asks you to accompany her at an upcoming doctor’s visit because she had been having trouble understanding the physician’s plan regarding further diagnosis and possible treatment. She believes having you along as kind of an interpreter/advocate would be a big help. Do you agree and do you make any stipulations?
Scenario III. Your PCP has referred you to a specialist. You are filling out the previsit form(s). Do you list your occupation as “retired physician” or just “retired”? Or just leave it blank?
Whether you deserve it or not, graduating from medical school has conferred on you a specialness in the eyes of many people. It is assumed you are smarter than the average bear and in taking the Hippocratic oath you have joined an elite club. And, with that membership comes some special undefined privileges.
But with that specialness there are are some downsides. For example, in some states being a physician once allowed you to have a license plate with “MD” in the number sequence. Sometimes that helped you avoid the occasional parking ticket. That is until folks realized the “MD” made you a target for car thieves and drug seekers who mistakenly believe we all carry drugs in our glove compartments.
So what about that first scenario? Do you press “4” to jump yourself to the head of the queue and avoid the inconvenience of having to wait for a reasonably timely response from your PCP? After all, you are fellow physicians and you’ve known her for a decade or two. If you are retired is your time any more valuable than that of her other patients? If you are still in active practice you can argue that getting special attention will benefit your patients. But, if it’s a weekend and you are off it’s a bit harder to rationalize special treatment. Playing the doctor card in this situation is your own decision but you must be prepared to shoulder the perceptions by your PCP and her staff as well as your own sense of fairness.
The other two scenarios are much different. In neither are you risking the impression that you are asking for a favor. But, they each have their downsides. In the second scenario you are doing someone a favor to act as an interpreter. How could this have downside? Unfortunately, what happens too often in situations like this is that when the patient’s physician learns that you are a fellow physician, the rest of the visit becomes a dialogue in doctor-speak between the two physicians with the patient sitting by as an observer. In the end this discussion may benefit the patient by creating a treatment plan that the patient can understand either because they overheard it or more likely because you eventually explained it to them.
On the other the hand, this doctor-to-doctor chat has done nothing to build a doctor-patient relationship that had obviously been lacking something. In situations like this it is probably better to keep the doctor card up your sleeve to be played at the end of the visit or maybe not at all. Before agreeing to be an interpreter/advocate, ask the patient to avoid mentioning that you are a physician. Instead, ask that she introduce you as a friend or relative that she has asked to come along to serve as a memory bank. During the visit it may be helpful to occasionally interject and suggest that the patient ask a question that hasn’t been adequately addressed. While some physicians may be upset when they belatedly find you have not revealed up front that you are a physician, I find this a harmless omission that has the benefit of improving patient care.
The final scenario — in which you are the patient — is likely to occur more often as you get older. When filling out a previsit form, I often simply put retired or leave it blank. But, how I answer the question often seems to be irrelevant because I have learned that physicians and their staff read those boilerplate forms so cursorily that even when I report my status as “retired physician” everyone seems surprised if and when it later comes to light.
My rationale in keeping the doctor card close to my vest in these situations is that I want to be addressed without any assumptions regarding my medical knowledge, which in my situation is well over half a century old and spotty at best. I don’t want my physicians to say “I’m sure you understand.” Because I often don’t. I would like them to learn about who I am just as I hope they would other patients. I won’t be offended if they “talk down” to me. If this specialist is as good as I’ve heard she is, I want to hear her full performance, not one edited for fellow and former physicians.
It doesn’t arrive gold edged with a list of special privileges. If it comes with any extras, they are risks that must be avoided.
Dr. Wilkoff practiced primary care pediatrics in Brunswick, Maine, for nearly 40 years. He has authored several books on behavioral pediatrics, including “How to Say No to Your Toddler.” Other than a Littman stethoscope he accepted as a first-year medical student in 1966, Dr. Wilkoff reports having nothing to disclose. Email him at [email protected].
Scenario I. Let’s say you wake with a collection of symptoms. None of them is concerning, but the combination seems a bit unusual, or at least confusing. You would like to speak to your PCP, whom you have known for a long time, and ask for either reassurance or advice on whether you should make an appointment. However, your experience with the front office’s organization tells you that the quick 4-minute conversation you’re looking for is not going to happen easily.
You have that robotic phone message memorized. It begins suggesting that you think you have an emergency to call 911. Then it reminds you that if have a question about COVID to press “2,” which will take you to a recorded message and eventually link you to a triage nurse if the recording doesn’t answer your questions. If you need a prescription refill you should press “3.” If you are a doctor’s office and wish speak to the doctor press “4.” If you know you need an appointment press “5.” And finally if you have a question press “6” and leave a message and a nurse will get back to you before the end of the day.
The good news is that your PCP’s office is good to its word and will return your call the same day, but the bad news is that it is likely to be well into the afternoon. And, while you don’t consider your symptoms life-threatening, you don’t want getting an answer to be an exercise in schedule disruption.
You were a doctor before you retired and you still have an “office.” It’s really more of a combination den and studio. So, technically you are a doctor’s office wanting to speak to the doctor. And, you know that pressing “4” will get you the answer you are looking for in a matter of minutes.
Scenario II. Your spouse, or your aunt, or the elderly widow next door asks you to accompany her at an upcoming doctor’s visit because she had been having trouble understanding the physician’s plan regarding further diagnosis and possible treatment. She believes having you along as kind of an interpreter/advocate would be a big help. Do you agree and do you make any stipulations?
Scenario III. Your PCP has referred you to a specialist. You are filling out the previsit form(s). Do you list your occupation as “retired physician” or just “retired”? Or just leave it blank?
Whether you deserve it or not, graduating from medical school has conferred on you a specialness in the eyes of many people. It is assumed you are smarter than the average bear and in taking the Hippocratic oath you have joined an elite club. And, with that membership comes some special undefined privileges.
But with that specialness there are are some downsides. For example, in some states being a physician once allowed you to have a license plate with “MD” in the number sequence. Sometimes that helped you avoid the occasional parking ticket. That is until folks realized the “MD” made you a target for car thieves and drug seekers who mistakenly believe we all carry drugs in our glove compartments.
So what about that first scenario? Do you press “4” to jump yourself to the head of the queue and avoid the inconvenience of having to wait for a reasonably timely response from your PCP? After all, you are fellow physicians and you’ve known her for a decade or two. If you are retired is your time any more valuable than that of her other patients? If you are still in active practice you can argue that getting special attention will benefit your patients. But, if it’s a weekend and you are off it’s a bit harder to rationalize special treatment. Playing the doctor card in this situation is your own decision but you must be prepared to shoulder the perceptions by your PCP and her staff as well as your own sense of fairness.
The other two scenarios are much different. In neither are you risking the impression that you are asking for a favor. But, they each have their downsides. In the second scenario you are doing someone a favor to act as an interpreter. How could this have downside? Unfortunately, what happens too often in situations like this is that when the patient’s physician learns that you are a fellow physician, the rest of the visit becomes a dialogue in doctor-speak between the two physicians with the patient sitting by as an observer. In the end this discussion may benefit the patient by creating a treatment plan that the patient can understand either because they overheard it or more likely because you eventually explained it to them.
On the other the hand, this doctor-to-doctor chat has done nothing to build a doctor-patient relationship that had obviously been lacking something. In situations like this it is probably better to keep the doctor card up your sleeve to be played at the end of the visit or maybe not at all. Before agreeing to be an interpreter/advocate, ask the patient to avoid mentioning that you are a physician. Instead, ask that she introduce you as a friend or relative that she has asked to come along to serve as a memory bank. During the visit it may be helpful to occasionally interject and suggest that the patient ask a question that hasn’t been adequately addressed. While some physicians may be upset when they belatedly find you have not revealed up front that you are a physician, I find this a harmless omission that has the benefit of improving patient care.
The final scenario — in which you are the patient — is likely to occur more often as you get older. When filling out a previsit form, I often simply put retired or leave it blank. But, how I answer the question often seems to be irrelevant because I have learned that physicians and their staff read those boilerplate forms so cursorily that even when I report my status as “retired physician” everyone seems surprised if and when it later comes to light.
My rationale in keeping the doctor card close to my vest in these situations is that I want to be addressed without any assumptions regarding my medical knowledge, which in my situation is well over half a century old and spotty at best. I don’t want my physicians to say “I’m sure you understand.” Because I often don’t. I would like them to learn about who I am just as I hope they would other patients. I won’t be offended if they “talk down” to me. If this specialist is as good as I’ve heard she is, I want to hear her full performance, not one edited for fellow and former physicians.
It doesn’t arrive gold edged with a list of special privileges. If it comes with any extras, they are risks that must be avoided.
Dr. Wilkoff practiced primary care pediatrics in Brunswick, Maine, for nearly 40 years. He has authored several books on behavioral pediatrics, including “How to Say No to Your Toddler.” Other than a Littman stethoscope he accepted as a first-year medical student in 1966, Dr. Wilkoff reports having nothing to disclose. Email him at [email protected].
The Small Business of Medicine
Black Friday is coming up. Although it seems (fortunately) to have lost some of its insanity since the pandemic, it’s still a huge shopping day for those who want to spend their day off in hand-to-hand combat at a Walmart. For me it’s a good day not to leave my house at all.
Following Black Friday we have Cyber Monday, where people go online to start buying stuff, presumably using business WiFi when they’re back at work. In spite of the apparent contradiction of having an online shopping day when people are at their jobs, it’s shamelessly promoted by the online retail giants.
Sandwiched between them is the quieter Small Business Saturday, started in 2010 by American Express and since gradually taking hold here and across the pond. The idea is to support the smaller local, perhaps family-owned, stores of varying kinds. Politicians love to talk about small businesses, calling them the backbone of the economy, promising to support them, etc.
I have no issue with that. I agree with it. I try to support my smaller, local places whenever I can. I’m glad AMEX started it, and that it’s taken off.
So why don’t we have a campaign to support small medical practices? Aren’t we small businesses, too? I’m the only doctor at my place, that’s about as small as you can get.
Like other small businesses, I don’t have the resources to advertise, aside from a simple website. At the same time I can’t drive too far without seeing a billboard, or hearing a radio ad, for one of the large local healthcare systems promising better convenience and care than that of their competitors.
I’m certainly not in a position to offer extended or weekend hours — I mean, I could, but I also have my own sanity to keep. But at the same time small practices may know their patients better than Huge Medicine Inc. We don’t have as many patients, and the staff turnover at small places is usually lower.
No one, though, is going to stand up for us, AMEX included (outside of cosmetic services, doctor visit charges are probably a tiny fraction of credit card company charges). Even our own organizations, like the AMA and others, won’t (at least not too much). They might pay lip service to us, but the reality is that most of their members work for large healthcare systems. Those groups probably make some big donations to them, too. So the last thing they want to do is tick them off.
I’m not against large groups. They have capabilities I don’t, like the ability to run research trials and have subspecialists. Even the best of us in solo practice needs someone better to refer to, such as an epileptologist, Parkinsonologist, neuromuscular disease-ologist, When I can’t help a patient any further those are the doctors I turn to, and, believe me, I appreciate them.
But
Dr. Block has a solo neurology practice in Scottsdale, Arizona.
Black Friday is coming up. Although it seems (fortunately) to have lost some of its insanity since the pandemic, it’s still a huge shopping day for those who want to spend their day off in hand-to-hand combat at a Walmart. For me it’s a good day not to leave my house at all.
Following Black Friday we have Cyber Monday, where people go online to start buying stuff, presumably using business WiFi when they’re back at work. In spite of the apparent contradiction of having an online shopping day when people are at their jobs, it’s shamelessly promoted by the online retail giants.
Sandwiched between them is the quieter Small Business Saturday, started in 2010 by American Express and since gradually taking hold here and across the pond. The idea is to support the smaller local, perhaps family-owned, stores of varying kinds. Politicians love to talk about small businesses, calling them the backbone of the economy, promising to support them, etc.
I have no issue with that. I agree with it. I try to support my smaller, local places whenever I can. I’m glad AMEX started it, and that it’s taken off.
So why don’t we have a campaign to support small medical practices? Aren’t we small businesses, too? I’m the only doctor at my place, that’s about as small as you can get.
Like other small businesses, I don’t have the resources to advertise, aside from a simple website. At the same time I can’t drive too far without seeing a billboard, or hearing a radio ad, for one of the large local healthcare systems promising better convenience and care than that of their competitors.
I’m certainly not in a position to offer extended or weekend hours — I mean, I could, but I also have my own sanity to keep. But at the same time small practices may know their patients better than Huge Medicine Inc. We don’t have as many patients, and the staff turnover at small places is usually lower.
No one, though, is going to stand up for us, AMEX included (outside of cosmetic services, doctor visit charges are probably a tiny fraction of credit card company charges). Even our own organizations, like the AMA and others, won’t (at least not too much). They might pay lip service to us, but the reality is that most of their members work for large healthcare systems. Those groups probably make some big donations to them, too. So the last thing they want to do is tick them off.
I’m not against large groups. They have capabilities I don’t, like the ability to run research trials and have subspecialists. Even the best of us in solo practice needs someone better to refer to, such as an epileptologist, Parkinsonologist, neuromuscular disease-ologist, When I can’t help a patient any further those are the doctors I turn to, and, believe me, I appreciate them.
But
Dr. Block has a solo neurology practice in Scottsdale, Arizona.
Black Friday is coming up. Although it seems (fortunately) to have lost some of its insanity since the pandemic, it’s still a huge shopping day for those who want to spend their day off in hand-to-hand combat at a Walmart. For me it’s a good day not to leave my house at all.
Following Black Friday we have Cyber Monday, where people go online to start buying stuff, presumably using business WiFi when they’re back at work. In spite of the apparent contradiction of having an online shopping day when people are at their jobs, it’s shamelessly promoted by the online retail giants.
Sandwiched between them is the quieter Small Business Saturday, started in 2010 by American Express and since gradually taking hold here and across the pond. The idea is to support the smaller local, perhaps family-owned, stores of varying kinds. Politicians love to talk about small businesses, calling them the backbone of the economy, promising to support them, etc.
I have no issue with that. I agree with it. I try to support my smaller, local places whenever I can. I’m glad AMEX started it, and that it’s taken off.
So why don’t we have a campaign to support small medical practices? Aren’t we small businesses, too? I’m the only doctor at my place, that’s about as small as you can get.
Like other small businesses, I don’t have the resources to advertise, aside from a simple website. At the same time I can’t drive too far without seeing a billboard, or hearing a radio ad, for one of the large local healthcare systems promising better convenience and care than that of their competitors.
I’m certainly not in a position to offer extended or weekend hours — I mean, I could, but I also have my own sanity to keep. But at the same time small practices may know their patients better than Huge Medicine Inc. We don’t have as many patients, and the staff turnover at small places is usually lower.
No one, though, is going to stand up for us, AMEX included (outside of cosmetic services, doctor visit charges are probably a tiny fraction of credit card company charges). Even our own organizations, like the AMA and others, won’t (at least not too much). They might pay lip service to us, but the reality is that most of their members work for large healthcare systems. Those groups probably make some big donations to them, too. So the last thing they want to do is tick them off.
I’m not against large groups. They have capabilities I don’t, like the ability to run research trials and have subspecialists. Even the best of us in solo practice needs someone better to refer to, such as an epileptologist, Parkinsonologist, neuromuscular disease-ologist, When I can’t help a patient any further those are the doctors I turn to, and, believe me, I appreciate them.
But
Dr. Block has a solo neurology practice in Scottsdale, Arizona.
Long COVID and Blame Hunting
I suspect that many of you have seen or read about a recent study regarding the “long COVID” enigma. The investigators surveyed the records of more than 4000 pediatric patients who had been infected and nearly 1400 who had not. The researchers then developed models in which 14 symptoms were more common in previous SARS-CoV2–infected individuals in all age groups, compared with the uninfected. There were four additional symptoms in children only and three additional symptoms in the adolescents.
Using these data, the investigators created research indices that “correlated with poor overall health and quality of life” and emphasized “neurocognitive, pain, and gastrointestinal symptoms in school-age children” and a “change or loss in smell or taste, pain, and fatigue/malaise-related symptoms in adolescents.”
So now thanks to these investigators we have research indices for characterizing PASC (post-acute sequelae of SARS-CoV-2, aka. long COVID). What should we to do with them? I’m not sure these results move us any further if our goal is finding something to help patients who believe, or have been told, that they have long COVID.
Even to a non-statistician like myself there appear to be some problems with this study. In an editorial accompanying this study, Suchitra Rao, MBBS, MSCS in the Department of Pediatrics, University of Colorado School of Medicine, Aurora, noted the study has the potential for ascertainment bias. For example, the researchers’ subject recruitment procedure resulted in a higher “proportion of neurocognitive/behavioral manifestations” may have skewed the results.
Also, some of the patient evaluations were not done at a consistent interval after the initial infection, which could result in recall bias. And, more importantly, because there were no baseline measurements to determine preinfection status, the investigators had no way of determining to what degree the patients’ underlying conditions may have reflected the quality of life scores.
Although I wouldn’t consider it a bias, I wonder if the investigators have a preconceived vision of what long COVID is going to look like once it is better understood. The fact that they undertook this project suggests that they believe the truth about the phenomenon will be discoverable using data based on collections of vague symptoms.
Or, do the researchers share my vision of long COVID that if it exists it will be something akin to the burst of Parkinson’s disease seen decades later in survivors of the 1918-1920 flu pandemic. Or, maybe it is something like post-polio syndrome, in which survivors in childhood develop atrophy and muscle weakness as they age. Do the researchers believe that COVID survivors are harboring some remnant of SARS-CoV-2 or its genome inside their bodies ticking like a time bomb ready to surface in the future? Think shingles.
I suspect that there are some folks who may or not share my ticking time bomb vision, but who, like me, wonder if there is really such a thing as long COVID – at least one in the form characterized by the work of these investigators. Unfortunately, the $1 billion the National Institutes of Health has invested in the Researching COVID to Enhance Recovery (RECOVER) initiative is not going to discover delayed sequelae until time is ready to tell us. What researchers are looking at now is a collection of patients, some who were not well to begin with but now describe a collection of vague symptoms, some of which are unique to COVID, but most are not. The loss of taste and smell being the one notable and important exception.
It is easy to understand why patients and their physicians would like to have a diagnosis like “long COVID” to at least validate their symptoms that up until now have eluded explanation or remedy. Not surprisingly, they may feel that, if researchers can’t find a cure, let’s at least have something we can lay the blame on.
A major flaw in this current attempt to characterize long COVID is the lack of a true control group. Yes, the subjects the researchers labeled as “uninfected” lived contemporaneously with the patients unfortunate enough to have acquired the virus. However, this illness was mysterious from its first appearance, continued to be more frightening as we struggled to learn more about it, and was clumsily managed in a way that turned our way of life upside down. This was particularly true for school-age children. It unmasked previously unsuspected underlying conditions and quickly acquired a poorly documented reputation for having a “long” variety.
Of course the “uninfected” also lived through these same tumultuous times. But knowing that you harbored, and may still harbor, this mysterious invader moves the infected and their families into a whole new level of concern and anxiety the rest of us who were more fortunate don’t share.
We must not ignore the fact that patients and their caregivers may receive some comfort when they have something to blame for their symptoms. However, we must shift our focus away from blame hunting, which up to this point has been fruitless. Instead, Each patient should be treated as an individual and not part of a group with similar symptoms cobbled together with data acquired under a cloud of bias.
Dr. Wilkoff practiced primary care pediatrics in Brunswick, Maine, for nearly 40 years. He has authored several books on behavioral pediatrics, including “How to Say No to Your Toddler.” Other than a Littman stethoscope he accepted as a first-year medical student in 1966, Dr. Wilkoff reports having nothing to disclose. Email him at [email protected].
I suspect that many of you have seen or read about a recent study regarding the “long COVID” enigma. The investigators surveyed the records of more than 4000 pediatric patients who had been infected and nearly 1400 who had not. The researchers then developed models in which 14 symptoms were more common in previous SARS-CoV2–infected individuals in all age groups, compared with the uninfected. There were four additional symptoms in children only and three additional symptoms in the adolescents.
Using these data, the investigators created research indices that “correlated with poor overall health and quality of life” and emphasized “neurocognitive, pain, and gastrointestinal symptoms in school-age children” and a “change or loss in smell or taste, pain, and fatigue/malaise-related symptoms in adolescents.”
So now thanks to these investigators we have research indices for characterizing PASC (post-acute sequelae of SARS-CoV-2, aka. long COVID). What should we to do with them? I’m not sure these results move us any further if our goal is finding something to help patients who believe, or have been told, that they have long COVID.
Even to a non-statistician like myself there appear to be some problems with this study. In an editorial accompanying this study, Suchitra Rao, MBBS, MSCS in the Department of Pediatrics, University of Colorado School of Medicine, Aurora, noted the study has the potential for ascertainment bias. For example, the researchers’ subject recruitment procedure resulted in a higher “proportion of neurocognitive/behavioral manifestations” may have skewed the results.
Also, some of the patient evaluations were not done at a consistent interval after the initial infection, which could result in recall bias. And, more importantly, because there were no baseline measurements to determine preinfection status, the investigators had no way of determining to what degree the patients’ underlying conditions may have reflected the quality of life scores.
Although I wouldn’t consider it a bias, I wonder if the investigators have a preconceived vision of what long COVID is going to look like once it is better understood. The fact that they undertook this project suggests that they believe the truth about the phenomenon will be discoverable using data based on collections of vague symptoms.
Or, do the researchers share my vision of long COVID that if it exists it will be something akin to the burst of Parkinson’s disease seen decades later in survivors of the 1918-1920 flu pandemic. Or, maybe it is something like post-polio syndrome, in which survivors in childhood develop atrophy and muscle weakness as they age. Do the researchers believe that COVID survivors are harboring some remnant of SARS-CoV-2 or its genome inside their bodies ticking like a time bomb ready to surface in the future? Think shingles.
I suspect that there are some folks who may or not share my ticking time bomb vision, but who, like me, wonder if there is really such a thing as long COVID – at least one in the form characterized by the work of these investigators. Unfortunately, the $1 billion the National Institutes of Health has invested in the Researching COVID to Enhance Recovery (RECOVER) initiative is not going to discover delayed sequelae until time is ready to tell us. What researchers are looking at now is a collection of patients, some who were not well to begin with but now describe a collection of vague symptoms, some of which are unique to COVID, but most are not. The loss of taste and smell being the one notable and important exception.
It is easy to understand why patients and their physicians would like to have a diagnosis like “long COVID” to at least validate their symptoms that up until now have eluded explanation or remedy. Not surprisingly, they may feel that, if researchers can’t find a cure, let’s at least have something we can lay the blame on.
A major flaw in this current attempt to characterize long COVID is the lack of a true control group. Yes, the subjects the researchers labeled as “uninfected” lived contemporaneously with the patients unfortunate enough to have acquired the virus. However, this illness was mysterious from its first appearance, continued to be more frightening as we struggled to learn more about it, and was clumsily managed in a way that turned our way of life upside down. This was particularly true for school-age children. It unmasked previously unsuspected underlying conditions and quickly acquired a poorly documented reputation for having a “long” variety.
Of course the “uninfected” also lived through these same tumultuous times. But knowing that you harbored, and may still harbor, this mysterious invader moves the infected and their families into a whole new level of concern and anxiety the rest of us who were more fortunate don’t share.
We must not ignore the fact that patients and their caregivers may receive some comfort when they have something to blame for their symptoms. However, we must shift our focus away from blame hunting, which up to this point has been fruitless. Instead, Each patient should be treated as an individual and not part of a group with similar symptoms cobbled together with data acquired under a cloud of bias.
Dr. Wilkoff practiced primary care pediatrics in Brunswick, Maine, for nearly 40 years. He has authored several books on behavioral pediatrics, including “How to Say No to Your Toddler.” Other than a Littman stethoscope he accepted as a first-year medical student in 1966, Dr. Wilkoff reports having nothing to disclose. Email him at [email protected].
I suspect that many of you have seen or read about a recent study regarding the “long COVID” enigma. The investigators surveyed the records of more than 4000 pediatric patients who had been infected and nearly 1400 who had not. The researchers then developed models in which 14 symptoms were more common in previous SARS-CoV2–infected individuals in all age groups, compared with the uninfected. There were four additional symptoms in children only and three additional symptoms in the adolescents.
Using these data, the investigators created research indices that “correlated with poor overall health and quality of life” and emphasized “neurocognitive, pain, and gastrointestinal symptoms in school-age children” and a “change or loss in smell or taste, pain, and fatigue/malaise-related symptoms in adolescents.”
So now thanks to these investigators we have research indices for characterizing PASC (post-acute sequelae of SARS-CoV-2, aka. long COVID). What should we to do with them? I’m not sure these results move us any further if our goal is finding something to help patients who believe, or have been told, that they have long COVID.
Even to a non-statistician like myself there appear to be some problems with this study. In an editorial accompanying this study, Suchitra Rao, MBBS, MSCS in the Department of Pediatrics, University of Colorado School of Medicine, Aurora, noted the study has the potential for ascertainment bias. For example, the researchers’ subject recruitment procedure resulted in a higher “proportion of neurocognitive/behavioral manifestations” may have skewed the results.
Also, some of the patient evaluations were not done at a consistent interval after the initial infection, which could result in recall bias. And, more importantly, because there were no baseline measurements to determine preinfection status, the investigators had no way of determining to what degree the patients’ underlying conditions may have reflected the quality of life scores.
Although I wouldn’t consider it a bias, I wonder if the investigators have a preconceived vision of what long COVID is going to look like once it is better understood. The fact that they undertook this project suggests that they believe the truth about the phenomenon will be discoverable using data based on collections of vague symptoms.
Or, do the researchers share my vision of long COVID that if it exists it will be something akin to the burst of Parkinson’s disease seen decades later in survivors of the 1918-1920 flu pandemic. Or, maybe it is something like post-polio syndrome, in which survivors in childhood develop atrophy and muscle weakness as they age. Do the researchers believe that COVID survivors are harboring some remnant of SARS-CoV-2 or its genome inside their bodies ticking like a time bomb ready to surface in the future? Think shingles.
I suspect that there are some folks who may or not share my ticking time bomb vision, but who, like me, wonder if there is really such a thing as long COVID – at least one in the form characterized by the work of these investigators. Unfortunately, the $1 billion the National Institutes of Health has invested in the Researching COVID to Enhance Recovery (RECOVER) initiative is not going to discover delayed sequelae until time is ready to tell us. What researchers are looking at now is a collection of patients, some who were not well to begin with but now describe a collection of vague symptoms, some of which are unique to COVID, but most are not. The loss of taste and smell being the one notable and important exception.
It is easy to understand why patients and their physicians would like to have a diagnosis like “long COVID” to at least validate their symptoms that up until now have eluded explanation or remedy. Not surprisingly, they may feel that, if researchers can’t find a cure, let’s at least have something we can lay the blame on.
A major flaw in this current attempt to characterize long COVID is the lack of a true control group. Yes, the subjects the researchers labeled as “uninfected” lived contemporaneously with the patients unfortunate enough to have acquired the virus. However, this illness was mysterious from its first appearance, continued to be more frightening as we struggled to learn more about it, and was clumsily managed in a way that turned our way of life upside down. This was particularly true for school-age children. It unmasked previously unsuspected underlying conditions and quickly acquired a poorly documented reputation for having a “long” variety.
Of course the “uninfected” also lived through these same tumultuous times. But knowing that you harbored, and may still harbor, this mysterious invader moves the infected and their families into a whole new level of concern and anxiety the rest of us who were more fortunate don’t share.
We must not ignore the fact that patients and their caregivers may receive some comfort when they have something to blame for their symptoms. However, we must shift our focus away from blame hunting, which up to this point has been fruitless. Instead, Each patient should be treated as an individual and not part of a group with similar symptoms cobbled together with data acquired under a cloud of bias.
Dr. Wilkoff practiced primary care pediatrics in Brunswick, Maine, for nearly 40 years. He has authored several books on behavioral pediatrics, including “How to Say No to Your Toddler.” Other than a Littman stethoscope he accepted as a first-year medical student in 1966, Dr. Wilkoff reports having nothing to disclose. Email him at [email protected].
Technoference
You see it all the time. It’s the family at the table next to you in the restaurant where the two teenage children are texting away on their phones. Or the playground, where a 3-year-old is playing with his toy truck and bulldozer in the sand and his father, immersed in his laptop, hasn’t said a word to his child.
It may trouble you when you witness social situations like that in which an electronic device is preventing or certainly interfering with interpersonal interactions. Or at least I hope it troubles you. Maybe it is so ubiquitous that you have come to accept it as the norm. It’s likely you may even be a participant. But, do you have a name for it?
It’s called “technoference,” a word coined by a doctoral student in human development and family studies at Penn State a decade ago “to describe the everyday intrusions and interruptions in couple interactions that take place due to technology devices and their always-on, ever-present nature.” Although, the original research that triggered the coinage was about couples, obviously the phenomenon occurs whenever people of any age are together in social situations.
While the word may not have crept into common parlance, we all know it when we see it. Technoference may not appear in the paper’s title, but it is a subject being investigated across a broad array of disciplines. One phone tracking study found that parents of young infants spend more than 5 hours each day on their smartphones. More than a quarter of that time the infant is engaged with the parent’s digital device. Technoference has been associated with decreased parent-child interaction during early childhood. It has been associated with more negative responses to children’s behavior, as well as an increased risk of child injury.
There are numerous studies suggesting an association between parental technoference and mental health difficulties in children. I have recently reviewed one of these studies that looks at the relationship of perceived parental technoference and the mental health of children entering adolescents. The authors collected longitudinal data of more than 1300 emerging adolescents, hoping to determine if the relationship between parental distraction and mental health was bidirectional. In other words, could a child’s mental health be contributing to his parents’ perceived distraction? Or was it primarily the parents’ technoference that was playing a role in the child’s mental health problems?
What investigators found was that higher levels of parental distraction were associated with higher levels of inattention and hyperactivity in the emerging adolescents, but not vice versa. On the other hand, higher levels of adolescent anxiety was associated with higher levels of perceived parental technoference, but not vice versa.
I know this sounds a bit confusing and a bit chicken-egg-chicken-eggish. The study was not designed to determine causation in these associations. However, the authors offer some possible scenarios that may provide a bit of clarity. It could be that parents who are concerned about their anxious child respond by retreating into the cyberspace to avoid tense situations or for support or information.
On the other hand, This explanation meshes with other studies demonstrating an association between parental distraction and aggression and attention problems in early childhood.
While one could spend more time imagining other factors that could be driving these bidirectional relationships, I’m not sure that it makes a heckuva lot of difference. Whether the child’s mental illness is the primary driver or the parent’s device-associated distraction is the dominant force isn’t the point. These are bidirectional relationships. If we are interested in pointing fingers, the common denominator is the device and our failure as a society to keep it in proper perspective. We all know that smartphones, tablets, and computers create an unhealthy distraction in personal relationships. The parents know and most of the children know. It’s time for us all to demonstrate some self-discipline. And that can begin for us as health care providers as we sit behind our computers spending more time looking at the screen than we do engaging the patient with our eyes.
Dr. Wilkoff practiced primary care pediatrics in Brunswick, Maine, for nearly 40 years. He has authored several books on behavioral pediatrics, including “How to Say No to Your Toddler.” Other than a Littman stethoscope he accepted as a first-year medical student in 1966, Dr. Wilkoff reports having nothing to disclose. Email him at [email protected].
You see it all the time. It’s the family at the table next to you in the restaurant where the two teenage children are texting away on their phones. Or the playground, where a 3-year-old is playing with his toy truck and bulldozer in the sand and his father, immersed in his laptop, hasn’t said a word to his child.
It may trouble you when you witness social situations like that in which an electronic device is preventing or certainly interfering with interpersonal interactions. Or at least I hope it troubles you. Maybe it is so ubiquitous that you have come to accept it as the norm. It’s likely you may even be a participant. But, do you have a name for it?
It’s called “technoference,” a word coined by a doctoral student in human development and family studies at Penn State a decade ago “to describe the everyday intrusions and interruptions in couple interactions that take place due to technology devices and their always-on, ever-present nature.” Although, the original research that triggered the coinage was about couples, obviously the phenomenon occurs whenever people of any age are together in social situations.
While the word may not have crept into common parlance, we all know it when we see it. Technoference may not appear in the paper’s title, but it is a subject being investigated across a broad array of disciplines. One phone tracking study found that parents of young infants spend more than 5 hours each day on their smartphones. More than a quarter of that time the infant is engaged with the parent’s digital device. Technoference has been associated with decreased parent-child interaction during early childhood. It has been associated with more negative responses to children’s behavior, as well as an increased risk of child injury.
There are numerous studies suggesting an association between parental technoference and mental health difficulties in children. I have recently reviewed one of these studies that looks at the relationship of perceived parental technoference and the mental health of children entering adolescents. The authors collected longitudinal data of more than 1300 emerging adolescents, hoping to determine if the relationship between parental distraction and mental health was bidirectional. In other words, could a child’s mental health be contributing to his parents’ perceived distraction? Or was it primarily the parents’ technoference that was playing a role in the child’s mental health problems?
What investigators found was that higher levels of parental distraction were associated with higher levels of inattention and hyperactivity in the emerging adolescents, but not vice versa. On the other hand, higher levels of adolescent anxiety was associated with higher levels of perceived parental technoference, but not vice versa.
I know this sounds a bit confusing and a bit chicken-egg-chicken-eggish. The study was not designed to determine causation in these associations. However, the authors offer some possible scenarios that may provide a bit of clarity. It could be that parents who are concerned about their anxious child respond by retreating into the cyberspace to avoid tense situations or for support or information.
On the other hand, This explanation meshes with other studies demonstrating an association between parental distraction and aggression and attention problems in early childhood.
While one could spend more time imagining other factors that could be driving these bidirectional relationships, I’m not sure that it makes a heckuva lot of difference. Whether the child’s mental illness is the primary driver or the parent’s device-associated distraction is the dominant force isn’t the point. These are bidirectional relationships. If we are interested in pointing fingers, the common denominator is the device and our failure as a society to keep it in proper perspective. We all know that smartphones, tablets, and computers create an unhealthy distraction in personal relationships. The parents know and most of the children know. It’s time for us all to demonstrate some self-discipline. And that can begin for us as health care providers as we sit behind our computers spending more time looking at the screen than we do engaging the patient with our eyes.
Dr. Wilkoff practiced primary care pediatrics in Brunswick, Maine, for nearly 40 years. He has authored several books on behavioral pediatrics, including “How to Say No to Your Toddler.” Other than a Littman stethoscope he accepted as a first-year medical student in 1966, Dr. Wilkoff reports having nothing to disclose. Email him at [email protected].
You see it all the time. It’s the family at the table next to you in the restaurant where the two teenage children are texting away on their phones. Or the playground, where a 3-year-old is playing with his toy truck and bulldozer in the sand and his father, immersed in his laptop, hasn’t said a word to his child.
It may trouble you when you witness social situations like that in which an electronic device is preventing or certainly interfering with interpersonal interactions. Or at least I hope it troubles you. Maybe it is so ubiquitous that you have come to accept it as the norm. It’s likely you may even be a participant. But, do you have a name for it?
It’s called “technoference,” a word coined by a doctoral student in human development and family studies at Penn State a decade ago “to describe the everyday intrusions and interruptions in couple interactions that take place due to technology devices and their always-on, ever-present nature.” Although, the original research that triggered the coinage was about couples, obviously the phenomenon occurs whenever people of any age are together in social situations.
While the word may not have crept into common parlance, we all know it when we see it. Technoference may not appear in the paper’s title, but it is a subject being investigated across a broad array of disciplines. One phone tracking study found that parents of young infants spend more than 5 hours each day on their smartphones. More than a quarter of that time the infant is engaged with the parent’s digital device. Technoference has been associated with decreased parent-child interaction during early childhood. It has been associated with more negative responses to children’s behavior, as well as an increased risk of child injury.
There are numerous studies suggesting an association between parental technoference and mental health difficulties in children. I have recently reviewed one of these studies that looks at the relationship of perceived parental technoference and the mental health of children entering adolescents. The authors collected longitudinal data of more than 1300 emerging adolescents, hoping to determine if the relationship between parental distraction and mental health was bidirectional. In other words, could a child’s mental health be contributing to his parents’ perceived distraction? Or was it primarily the parents’ technoference that was playing a role in the child’s mental health problems?
What investigators found was that higher levels of parental distraction were associated with higher levels of inattention and hyperactivity in the emerging adolescents, but not vice versa. On the other hand, higher levels of adolescent anxiety was associated with higher levels of perceived parental technoference, but not vice versa.
I know this sounds a bit confusing and a bit chicken-egg-chicken-eggish. The study was not designed to determine causation in these associations. However, the authors offer some possible scenarios that may provide a bit of clarity. It could be that parents who are concerned about their anxious child respond by retreating into the cyberspace to avoid tense situations or for support or information.
On the other hand, This explanation meshes with other studies demonstrating an association between parental distraction and aggression and attention problems in early childhood.
While one could spend more time imagining other factors that could be driving these bidirectional relationships, I’m not sure that it makes a heckuva lot of difference. Whether the child’s mental illness is the primary driver or the parent’s device-associated distraction is the dominant force isn’t the point. These are bidirectional relationships. If we are interested in pointing fingers, the common denominator is the device and our failure as a society to keep it in proper perspective. We all know that smartphones, tablets, and computers create an unhealthy distraction in personal relationships. The parents know and most of the children know. It’s time for us all to demonstrate some self-discipline. And that can begin for us as health care providers as we sit behind our computers spending more time looking at the screen than we do engaging the patient with our eyes.
Dr. Wilkoff practiced primary care pediatrics in Brunswick, Maine, for nearly 40 years. He has authored several books on behavioral pediatrics, including “How to Say No to Your Toddler.” Other than a Littman stethoscope he accepted as a first-year medical student in 1966, Dr. Wilkoff reports having nothing to disclose. Email him at [email protected].





