User login
Intravenous immunoglobulin controls dermatomyositis in phase 3 trial
Nearly 50% achieve moderate improvement or better
The first multinational, phase 3, placebo-controlled trial conducted with intravenous immunoglobulin therapy (IVIg) for dermatomyositis has confirmed significant efficacy and acceptable safety, according to data presented at the opening plenary abstract session of the annual European Congress of Rheumatology.
At the week 16 evaluation of the trial, called ProDERM, the response rates were 78.7% and 43.8% (P = .0008) for active therapy and placebo, respectively, reported Rohit Aggarwal, MD, medical director of the Arthritis and Autoimmunity Center at the University of Pittsburgh.
ProDERM is a “much-awaited study,” according to session moderator Hendrik Schulze-Koops, MD, PhD, of the division of rheumatology and clinical immunology at Ludwig Maximilian University of Munich (Germany). He was not involved in the study.
“We all have been doing what we have been doing,” Dr. Schulze-Koops said, referring to the use of IVIg for the control of dermatomyositis, “but we had no evidence for support.”
This statement could apply not only to IVIg, which has long been listed among treatment options by the Myositis Association despite the absence of controlled studies, but also to most immunosuppressive therapies and other options used for this challenging disease.
The proprietary IVIg employed in this study, Octagam 10%, has been approved in the United States for the treatment of chronic immune thrombocytopenic purpura. Its manufacturer, Octagam, plans to file a supplemental new drug application with the Food and Drug Administration for the treatment of dermatomyositis. The agent is already approved for dermatomyositis by the European Medicines Agency, according to Dr. Aggarwal.
Multiple response criteria favor IVIg
In the trial, 95 patients with dermatomyositis were randomized to 2 g/kg of IVIg (Octagam 10%) or placebo administered every 4 weeks. In a subsequent open-label extension study in which patients on placebo were switched to active therapy, the same every-4-week treatment schedule was used. The patients’ mean age was 53; 75% were women, and 92% were White.
The primary endpoint was at least minimal improvement on 2016 ACR/EULAR (American College of Rheumatology/European Alliance of Associations for Rheumatology) myositis response criteria, defined as a 20-point or greater gain in the Total Improvement Score (TIS) and no clinical worsening at two consecutive visits. But IVIg also provided a large relative benefit over placebo using more rigorous definitions of improvement. For moderate improvement, defined as at least a 40-point TIS improvement, there was a 45.2% relative advantage for IVIg over placebo (68.1% vs. 22.9%; P < .0001). For major improvement, defined as at least a 60-point TIS improvement, the relative advantage was 23.6% (31.9% vs. 8.3%; P < .0062).
At 16 weeks, the mean TIS score was more than twice as high in those receiving IVIg than in those randomized to placebo (48.4 vs. 21.6). At that point, an open-label extension was initiated. Those in the IVIg group were permitted to remain on therapy for an additional 24 weeks if they had not worsened in the blinded phase.
The mean TIS score in the IVIg group continued to rise during the extension phase. By 12 weeks in this phase, it reached 54.0. Over the same period, mean TIS scores climbed steeply among the placebo-treated patients who had switched to active therapy, reaching 44.4.
At the end of 24 weeks of the extension trial, when patients initiated on IVIg had been on active therapy for 40 weeks, the mean TIS score advantage of starting on IVIg rather than placebo was relatively modest (55.4 vs. 51.1).
Benefit is significant for skin and muscle
Changes in the two major components of dermatomyositis were tracked individually. For skin symptoms, patients were evaluated with the Cutaneous Dermatomyositis Disease Areas and Severity Index (CDASI). For muscle involvement, symptoms were evaluated with the 8-item Manual Muscle Testing (MMT-8) tool.
“The effects of IVIg on the muscle and the skin were both highly statistically significant,” Dr. Aggarwal reported. He said the CDASI score was reduced by almost half at the end of 16 weeks among those treated with IVIg relative to those treated with placebo. Improvement in MMT-8 scores were also clinically as well as statistically significant.
The IVIg therapy was well tolerated. The most common adverse effects in this study, like those reported with IVIg when used to treat other diseases, were headache, pyrexia, and nausea, but Dr. Aggarwal reported that these were generally mild.
Serious adverse events, particularly thromboembolism, did occur over the course of the study, but the rate of events was only slightly higher in the group receiving active therapy (5.8% vs. 4.2%).
Patients who entered the study were permitted to remain on most immunosuppressive therapies, such as methotrexate, mycophenolate, tacrolimus, and glucocorticoids. Dr. Aggarwal said that the majority of patients were taking a glucocorticoid and at least one nonglucocorticoid immunosuppressant.
Effect on associated conditions is planned
The data from this trial have not yet been analyzed for the impact of IVIg on conditions that occur frequently in association with dermatomyositis, such as interstitial lung disease (ILD) and dysphagia, but Dr. Aggarwal reported that there are plans to do so. Although severe ILD was a trial exclusion, the presence of mild to moderate ILD and dysphagia were evaluated at baseline, so the impact of treatment can be assessed.
There are also plans to evaluate how the presence or absence of myositis-specific antibodies, which were also evaluated at baseline, affected response to IVIg.
Dr. Aggarwal has financial relationships with more than 15 pharmaceutical companies, including Octapharma, which provided financial support for this trial. Dr. Schulze-Koops reported no relevant potential conflicts of interest.
Nearly 50% achieve moderate improvement or better
Nearly 50% achieve moderate improvement or better
The first multinational, phase 3, placebo-controlled trial conducted with intravenous immunoglobulin therapy (IVIg) for dermatomyositis has confirmed significant efficacy and acceptable safety, according to data presented at the opening plenary abstract session of the annual European Congress of Rheumatology.
At the week 16 evaluation of the trial, called ProDERM, the response rates were 78.7% and 43.8% (P = .0008) for active therapy and placebo, respectively, reported Rohit Aggarwal, MD, medical director of the Arthritis and Autoimmunity Center at the University of Pittsburgh.
ProDERM is a “much-awaited study,” according to session moderator Hendrik Schulze-Koops, MD, PhD, of the division of rheumatology and clinical immunology at Ludwig Maximilian University of Munich (Germany). He was not involved in the study.
“We all have been doing what we have been doing,” Dr. Schulze-Koops said, referring to the use of IVIg for the control of dermatomyositis, “but we had no evidence for support.”
This statement could apply not only to IVIg, which has long been listed among treatment options by the Myositis Association despite the absence of controlled studies, but also to most immunosuppressive therapies and other options used for this challenging disease.
The proprietary IVIg employed in this study, Octagam 10%, has been approved in the United States for the treatment of chronic immune thrombocytopenic purpura. Its manufacturer, Octagam, plans to file a supplemental new drug application with the Food and Drug Administration for the treatment of dermatomyositis. The agent is already approved for dermatomyositis by the European Medicines Agency, according to Dr. Aggarwal.
Multiple response criteria favor IVIg
In the trial, 95 patients with dermatomyositis were randomized to 2 g/kg of IVIg (Octagam 10%) or placebo administered every 4 weeks. In a subsequent open-label extension study in which patients on placebo were switched to active therapy, the same every-4-week treatment schedule was used. The patients’ mean age was 53; 75% were women, and 92% were White.
The primary endpoint was at least minimal improvement on 2016 ACR/EULAR (American College of Rheumatology/European Alliance of Associations for Rheumatology) myositis response criteria, defined as a 20-point or greater gain in the Total Improvement Score (TIS) and no clinical worsening at two consecutive visits. But IVIg also provided a large relative benefit over placebo using more rigorous definitions of improvement. For moderate improvement, defined as at least a 40-point TIS improvement, there was a 45.2% relative advantage for IVIg over placebo (68.1% vs. 22.9%; P < .0001). For major improvement, defined as at least a 60-point TIS improvement, the relative advantage was 23.6% (31.9% vs. 8.3%; P < .0062).
At 16 weeks, the mean TIS score was more than twice as high in those receiving IVIg than in those randomized to placebo (48.4 vs. 21.6). At that point, an open-label extension was initiated. Those in the IVIg group were permitted to remain on therapy for an additional 24 weeks if they had not worsened in the blinded phase.
The mean TIS score in the IVIg group continued to rise during the extension phase. By 12 weeks in this phase, it reached 54.0. Over the same period, mean TIS scores climbed steeply among the placebo-treated patients who had switched to active therapy, reaching 44.4.
At the end of 24 weeks of the extension trial, when patients initiated on IVIg had been on active therapy for 40 weeks, the mean TIS score advantage of starting on IVIg rather than placebo was relatively modest (55.4 vs. 51.1).
Benefit is significant for skin and muscle
Changes in the two major components of dermatomyositis were tracked individually. For skin symptoms, patients were evaluated with the Cutaneous Dermatomyositis Disease Areas and Severity Index (CDASI). For muscle involvement, symptoms were evaluated with the 8-item Manual Muscle Testing (MMT-8) tool.
“The effects of IVIg on the muscle and the skin were both highly statistically significant,” Dr. Aggarwal reported. He said the CDASI score was reduced by almost half at the end of 16 weeks among those treated with IVIg relative to those treated with placebo. Improvement in MMT-8 scores were also clinically as well as statistically significant.
The IVIg therapy was well tolerated. The most common adverse effects in this study, like those reported with IVIg when used to treat other diseases, were headache, pyrexia, and nausea, but Dr. Aggarwal reported that these were generally mild.
Serious adverse events, particularly thromboembolism, did occur over the course of the study, but the rate of events was only slightly higher in the group receiving active therapy (5.8% vs. 4.2%).
Patients who entered the study were permitted to remain on most immunosuppressive therapies, such as methotrexate, mycophenolate, tacrolimus, and glucocorticoids. Dr. Aggarwal said that the majority of patients were taking a glucocorticoid and at least one nonglucocorticoid immunosuppressant.
Effect on associated conditions is planned
The data from this trial have not yet been analyzed for the impact of IVIg on conditions that occur frequently in association with dermatomyositis, such as interstitial lung disease (ILD) and dysphagia, but Dr. Aggarwal reported that there are plans to do so. Although severe ILD was a trial exclusion, the presence of mild to moderate ILD and dysphagia were evaluated at baseline, so the impact of treatment can be assessed.
There are also plans to evaluate how the presence or absence of myositis-specific antibodies, which were also evaluated at baseline, affected response to IVIg.
Dr. Aggarwal has financial relationships with more than 15 pharmaceutical companies, including Octapharma, which provided financial support for this trial. Dr. Schulze-Koops reported no relevant potential conflicts of interest.
The first multinational, phase 3, placebo-controlled trial conducted with intravenous immunoglobulin therapy (IVIg) for dermatomyositis has confirmed significant efficacy and acceptable safety, according to data presented at the opening plenary abstract session of the annual European Congress of Rheumatology.
At the week 16 evaluation of the trial, called ProDERM, the response rates were 78.7% and 43.8% (P = .0008) for active therapy and placebo, respectively, reported Rohit Aggarwal, MD, medical director of the Arthritis and Autoimmunity Center at the University of Pittsburgh.
ProDERM is a “much-awaited study,” according to session moderator Hendrik Schulze-Koops, MD, PhD, of the division of rheumatology and clinical immunology at Ludwig Maximilian University of Munich (Germany). He was not involved in the study.
“We all have been doing what we have been doing,” Dr. Schulze-Koops said, referring to the use of IVIg for the control of dermatomyositis, “but we had no evidence for support.”
This statement could apply not only to IVIg, which has long been listed among treatment options by the Myositis Association despite the absence of controlled studies, but also to most immunosuppressive therapies and other options used for this challenging disease.
The proprietary IVIg employed in this study, Octagam 10%, has been approved in the United States for the treatment of chronic immune thrombocytopenic purpura. Its manufacturer, Octagam, plans to file a supplemental new drug application with the Food and Drug Administration for the treatment of dermatomyositis. The agent is already approved for dermatomyositis by the European Medicines Agency, according to Dr. Aggarwal.
Multiple response criteria favor IVIg
In the trial, 95 patients with dermatomyositis were randomized to 2 g/kg of IVIg (Octagam 10%) or placebo administered every 4 weeks. In a subsequent open-label extension study in which patients on placebo were switched to active therapy, the same every-4-week treatment schedule was used. The patients’ mean age was 53; 75% were women, and 92% were White.
The primary endpoint was at least minimal improvement on 2016 ACR/EULAR (American College of Rheumatology/European Alliance of Associations for Rheumatology) myositis response criteria, defined as a 20-point or greater gain in the Total Improvement Score (TIS) and no clinical worsening at two consecutive visits. But IVIg also provided a large relative benefit over placebo using more rigorous definitions of improvement. For moderate improvement, defined as at least a 40-point TIS improvement, there was a 45.2% relative advantage for IVIg over placebo (68.1% vs. 22.9%; P < .0001). For major improvement, defined as at least a 60-point TIS improvement, the relative advantage was 23.6% (31.9% vs. 8.3%; P < .0062).
At 16 weeks, the mean TIS score was more than twice as high in those receiving IVIg than in those randomized to placebo (48.4 vs. 21.6). At that point, an open-label extension was initiated. Those in the IVIg group were permitted to remain on therapy for an additional 24 weeks if they had not worsened in the blinded phase.
The mean TIS score in the IVIg group continued to rise during the extension phase. By 12 weeks in this phase, it reached 54.0. Over the same period, mean TIS scores climbed steeply among the placebo-treated patients who had switched to active therapy, reaching 44.4.
At the end of 24 weeks of the extension trial, when patients initiated on IVIg had been on active therapy for 40 weeks, the mean TIS score advantage of starting on IVIg rather than placebo was relatively modest (55.4 vs. 51.1).
Benefit is significant for skin and muscle
Changes in the two major components of dermatomyositis were tracked individually. For skin symptoms, patients were evaluated with the Cutaneous Dermatomyositis Disease Areas and Severity Index (CDASI). For muscle involvement, symptoms were evaluated with the 8-item Manual Muscle Testing (MMT-8) tool.
“The effects of IVIg on the muscle and the skin were both highly statistically significant,” Dr. Aggarwal reported. He said the CDASI score was reduced by almost half at the end of 16 weeks among those treated with IVIg relative to those treated with placebo. Improvement in MMT-8 scores were also clinically as well as statistically significant.
The IVIg therapy was well tolerated. The most common adverse effects in this study, like those reported with IVIg when used to treat other diseases, were headache, pyrexia, and nausea, but Dr. Aggarwal reported that these were generally mild.
Serious adverse events, particularly thromboembolism, did occur over the course of the study, but the rate of events was only slightly higher in the group receiving active therapy (5.8% vs. 4.2%).
Patients who entered the study were permitted to remain on most immunosuppressive therapies, such as methotrexate, mycophenolate, tacrolimus, and glucocorticoids. Dr. Aggarwal said that the majority of patients were taking a glucocorticoid and at least one nonglucocorticoid immunosuppressant.
Effect on associated conditions is planned
The data from this trial have not yet been analyzed for the impact of IVIg on conditions that occur frequently in association with dermatomyositis, such as interstitial lung disease (ILD) and dysphagia, but Dr. Aggarwal reported that there are plans to do so. Although severe ILD was a trial exclusion, the presence of mild to moderate ILD and dysphagia were evaluated at baseline, so the impact of treatment can be assessed.
There are also plans to evaluate how the presence or absence of myositis-specific antibodies, which were also evaluated at baseline, affected response to IVIg.
Dr. Aggarwal has financial relationships with more than 15 pharmaceutical companies, including Octapharma, which provided financial support for this trial. Dr. Schulze-Koops reported no relevant potential conflicts of interest.
FROM THE EULAR 2021 CONGRESS
Ulcerative Heliotrope Rash in Antimelanoma Differentiation–Associated Gene 5 Dermatomyositis
Dermatomyositis (DM) is an autoimmune condition characterized by skin and muscle inflammation with an estimated incidence of 9 cases per 1 million people. The incidence of amyopathic DM, which includes antimelanoma differentiation–associated gene 5 (anti-MDA5) DM, is approximately 2 cases per 1 million people.1 Classic cutaneous manifestations of DM include a heliotrope rash, Gottron papules, and the shawl sign.
Case Reports
Patient 1
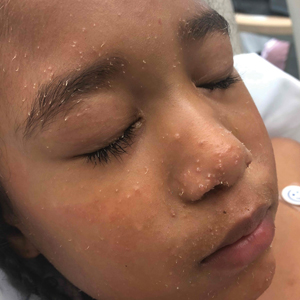
A woman in her 30s presented with diffuse arthralgias, bilateral eyelid edema, fatigue, and a progressive diffuse exanthem of 3 months’ duration. A review of systems was notable for the absence of myalgias. Physical examination revealed periorbital poikilodermatous patches with erythematous-to-violaceous plaques along the eyelid margins, violaceous papules on the dorsal knuckles, and edematous eroded plaques on the palmar fingertips. The patient was found to have a positive antinuclear antibody titer of 1:320 (reference range, <1:80) with a speckled pattern. A computed tomography (CT) scan of the chest showed patchy bilateral ground-glass opacities that were concerning for ILD. The cutaneous erosions, absence of myalgias, considerable proximal weakness, radiographic evidence of ILD, and positive antinuclear antibody test were clinically suggestive of anti-MDA5 DM. Further workup confirmed this diagnosis with positive reactivity to MDA5 by line immunoassay. The patient was treated with intravenous corticosteroids and was discharged after a 17-day hospitalization; however, she presented 2 months later to outpatient dermatology for progression of the cutaneous ulcerations, at which time an ulcerative heliotrope rash (Figure 1) was identified. Despite compliance with oral corticosteroids (1 mg/kg/d), she was hospitalized 1 month later for progressive respiratory insufficiency. A chest CT showed ground-glass linear opacities centrally located in all lobes of both lungs, consistent with rapidly progressive ILD. Over the course of her 5-day hospitalization, she was treated with corticosteroids, intravenous immunoglobulin (IVIG), and mycophenolate mofetil. The patient responded well to these therapies, leading to resolution of the respiratory symptoms, and she was discharged with plans to continue this regimen as an outpatient.
Patient 2
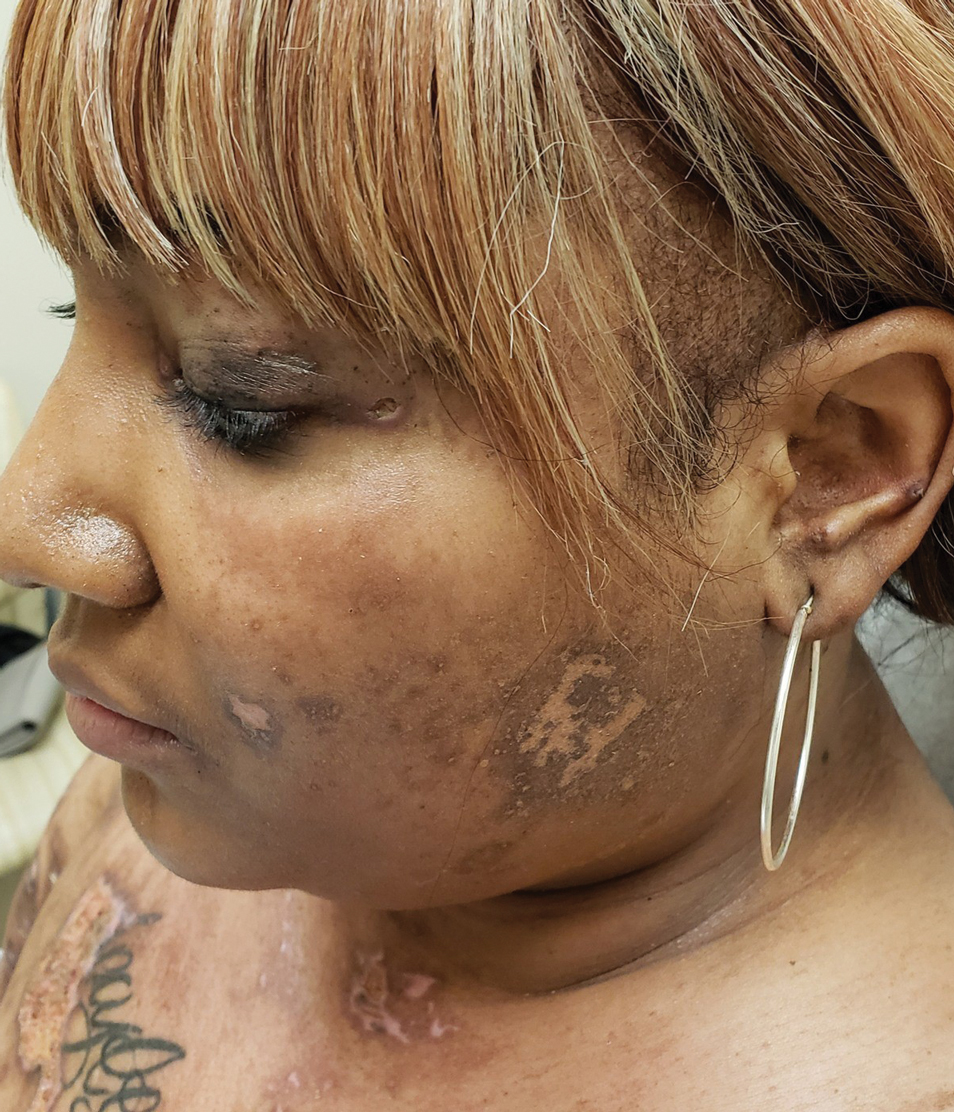
A woman in her late 30s with a history of known anti-MDA5 DM confirmed by line immunoassay 1 year prior presented to the emergency department with shortness of breath due to progressive ILD and a worsening exanthem. Dermatology was consulted to provide treatment recommendations. The treatment team was concerned for infection or anti-MDA5 DM disease progression. Physical examination revealed an ulcerative heliotrope rash (Figure 2) in addition to cutaneous findings classic for anti-MDA5 DM. Despite interventions, including high-dose corticosteroids, rituximab, IVIG, and plasma exchange, the ILD continued to progress, and the patient and her family elected to de-escalate aggressive medical care and pursue comfort care. The patient later died in in patient hospice.
Comment
Clinical Presentation of Anti-MDA5 DM
Dermatomyositis classically presents with cutaneous manifestations including a heliotropic erythematous rash and Gottron papules as well as accompanying muscle weakness.2 However, a subtype known as amyopathic DM, which includes anti-MDA5 DM, usually presents without muscle involvement.3 Clinical muscle weakness has been reported in cases of anti-MDA5 DM, though it is less likely in these patients.4 The characteristic cutaneous phenotype of
While a heliotrope rash is classic for DM, and ulcerations are a hallmark of the anti-MDA5 DM subtype, overlap of these cutaneous manifestations is not commonly reported. In both cases presented here, ulcerations of the lateral canthi were associated with progression of ILD.
Diagnosis of Anti-MDA5 DM
Anti-MDA5 DM is defined by the presence of the anti-MDA5 antibody in the serum, named for its reactivity against the RNA helicase encoded by MDA5, within the clinical context of cutaneous signs of DM as described above.12
As described by Rider et al,13 a thorough laboratory analysis, including complete blood cell count, serum electrolytes, calcium, magnesium, phosphorus, and thyroid-stimulating hormone, is necessary to rule out conditions with similar presentations. Additionally, serum analysis for elevated muscle enzymes (creatinine phosphokinase, aldolase, lactate dehydrogenase, alanine aminotransferase, and aspartate aminotransferase) is necessary to assess for subclinical muscle involvement. Serologic evidence of myositis usually denotes an alternative diagnosis.13 Antinuclear antibodies and myositis-specific antibody positivity are much less frequent in the anti-MDA5 DM subtype than in other forms of DM.6
Anti-MDA5 antibody titer, ferritin, and IL-18 can be trended and may be useful in the evaluation of the response to treatment and ILD status in patients with anti-MDA5 DM.14,15 Elevated alveolar-arterial gradient, serum ferritin, serum chitotriosidase, and serum chitinase-3-like protein 1 (YKL-40) have each been associated with poorer prognosis of anti-MDA5 DM. The aforementioned serologies therefore may be helpful in determination of risk stratification and treatment aggressiveness.16-19
Because of its strong association with RP-ILD, screening for pulmonary disease is necessary in all patients with confirmed or strongly suspected anti-MDA5 DM. Screening can be performed with pulmonary function testing; however, high-resolution chest CT is the gold standard for diagnosis of ILD.20
Finally, all patients with a new diagnosis of DM should be evaluated for underlying malignancy through cancer screenings, given the propensity for DM to present as a paraneoplastic process.21 However, reports have indicated that the anti-MDA5 DM subtype may have a reduced risk for or an inverse relationship with underlying malignancy.5
Treatment Options for Anti-MDA5 DM
Early and aggressive therapy should be considered in the treatment of anti-MDA5 DM because of its association with RP-ILD. No treatment protocol is well established; thus, an individualized therapeutic approach may be guided by symptom severity and the clinical, radiographic, or functional evidence of ILD.6 High-dose systemic corticosteroids are first line, either in combination with or as a bridge to corticosteroid-sparing agents for immunosuppression. Many steroid-sparing medications have been employed with varying success. Mycophenolate mofetil is a reasonable first-line corticosteroid-sparing immunosuppressant agent, given its added benefit of attenuating ILD progression.6 A combination of high-dose corticosteroids, cyclosporine, and cyclophosphamide is utilized by some initially in the treatment of anti-MDA5 with ILD.22,23 While others have used combinations of these immunomodulatory agents with mycophenolate mofetil, IVIG, rituximab, azathioprine, tofacitinib, and polymyxin B, direct hemoperfusion has been added, leading to successful remission.23-28
Conclusion
We present 2 patients with anti-MDA5 DM who demonstrated a rare cutaneous manifestation of an ulcerative heliotrope rash. In both cases, this cutaneous finding was associated with the development of RP-ILD. Because of the strong association with and rapid progression of ILD seen in anti-MDA5 DM, early identification and aggressive treatment of this subtype are imperative. The clinician should recognize nonacral locations of cutaneous ulcerations, including an ulcerated heliotrope rash, to optimize diagnosis and management.
- Bendewald MJ, Wetter DA, Li X, et al. Incidence of dermatomyositis and clinically amyopathic dermatomyositis: a population-based study in Olmsted County, Minnesota. Arch Dermatol. 2010;146:26-30. doi:10.1001/archdermatol.2009.328
- Bogdanov I, Kazandjieva J, Darlenski R, et al. Dermatomyositis: current concepts. Clin Dermatol. 2018;36:450-458. doi:10.1016/j.clindermatol.2018.04.003
- Caproni M, Cardinali C, Parodi A, et al. Amyopathic dermatomyositis: a review by the Italian Group of Immunodermatology. Arch Dermatol. 2002;138:23-27. doi:10.1001/archderm.138.1.23
- Li J, Liu Y, Li Y, et al. Associations between anti-melanoma differentiation-associated gene 5 antibody and demographics, clinical characteristics and laboratory results of patients with dermatomyositis: a systematic meta-analysis. J Dermatol. 2018;45:46-52. doi:10.1111/1346-8138.14092
- Fiorentino D, Chung L, Zwerner J, et al. The mucocutaneous and systemic phenotype of dermatomyositis patients with antibodies to MDA5 (CADM-140): a retrospective study. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2011;65:25-34. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2010.09.016
- Kurtzman DJB, Vleugels RA. Anti-melanoma differentiation–associated gene 5 (MDA5) dermatomyositis: a concise review with an emphasis on distinctive clinical features. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2018;78:776-785. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2017.12.010
- Narang NS, Casciola-Rosen L, Li S, et al. Cutaneous ulceration in dermatomyositis: association with anti-melanoma differentiation-associated gene 5 antibodies and interstitial lung disease: analysis of skin ulcers in dermatomyositis. Arthritis Care Res. 2015;67:667-672. doi:10.1002/acr.22498
- Charrow A, Vleugels RA. Cutaneous ulcerations in anti-MDA5 dermatomyositis. N Engl J Med. 2019;381:465. doi:10.1056/NEJMicm1816147
- Cao H, Xia Q, Pan M, et al. Gottron papules and Gottron sign with ulceration: a distinctive cutaneous feature in a subset of patients with classic dermatomyositis and clinically amyopathic dermatomyositis. J Rheumatol. 2016;43:1735-1742. doi:10.3899/jrheum.160024
- Moghadam-Kia S, Oddis CV, Sato S, et al. Antimelanoma differentiation-associated gene 5 antibody: expanding the clinical spectrum in North American patients with dermatomyositis. J Rheumatol. 2017;44:319-325. doi:10.3899/jrheum.160682
- Li L, Wang Q, Wen X, et al. Assessment of anti-MDA5 antibody as a diagnostic biomarker in patients with dermatomyositis-associated interstitial lung disease or rapidly progressive interstitial lung disease. Oncotarget. 2017;876129-76140. doi:10.18632/oncotarget.19050
- Sato S, Hoshino K, Satoh T, et al. RNA helicase encoded by melanoma differentiation-associated gene 5 is a major autoantigen in patients with clinically amyopathic dermatomyositis: association with rapidly progressive interstitial lung disease. Arthritis Rheum. 2009;60:2193-2200. doi:10.1002/art.24621
- Rider LG, Miller FW. Deciphering the clinical presentations, pathogenesis, and treatment of the idiopathic inflammatory myopathies. JAMA. 2011;305:183-190. doi:10.1001/jama.2010.1977
- Nishioka A, Tsunoda S, Abe T, et al. Serum neopterin as well as ferritin, soluble interleukin-2 receptor, KL-6 and anti-MDA5 antibody titer provide markers of the response to therapy in patients with interstitial lung disease complicating anti-MDA5 antibody-positive dermatomyositis. Mod Rheumatol. 2019;29:814-820. doi:10.1080/14397595.2018.1548918
- Gono T, Sato S, Kawaguchi Y, et al. Anti-MDA5 antibody, ferritin and IL-18 are useful for the evaluation of response to treatment in interstitial lung disease with anti-MDA5 antibody-positive dermatomyositis. Rheumatology. 2012;51:1563-1570. doi:10.1093/rheumatology/kes102
- Jiang L, Wang Y, Peng Q, et al. Serum YKL-40 level is associated with severity of interstitial lung disease and poor prognosis in dermatomyositis with anti-MDA5 antibody. Clin Rheumatol. 2019;38:1655-1663. doi:10.1007/s10067-019-04457-w
- Fujisawa T, Hozumi H, Yasui H, et al. Clinical significance of serum chitotriosidase level in anti-MDA5 antibody–positive dermatomyositis-associated interstitial lung disease. J Rheumatol. 2019;46:935-942. doi:10.3899/jrheum.180825
- Enomoto N, Oyama Y, Enomoto Y, et al. Prognostic evaluation of serum ferritin in acute exacerbation of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Clin Resp J. 2018;12:2378-2389. doi:10.1111/crj.12918
- Fujiki Y, Kotani T, Isoda K, et al. Evaluation of clinical prognostic factors for interstitial pneumonia in anti-MDA5 antibody-positive dermatomyositis patients. Mod Rheumatol. 2018;28:133-140. doi:10.1080/14397595.2017.1318468
- Raghu G, Remy-Jardin M, Myers JL, et al; American Thoracic Society, European Respiratory Society, Japanese Respiratory Society, and Latin American Thoracic Society. Diagnosis of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. an official ATS/ERS/JRS/ALAT clinical practice guideline. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2018;198:E44-E68. doi:10.1164/rccm.201807-1255ST
- Yang Z, Lin F, Qin B, et al. Polymyositis/dermatomyositis and malignancy risk: a metaanalysis study. J Rheumatol. 2015;42:282-291. doi:10.3899/jrheum.140566
- Hisanaga J, Kotani T, Fujiki Y, et al. Successful multi-target therapy including rituximab and mycophenolate mofetil in anti-melanoma differentiation-associated gene 5 antibody-positive rapidly progressive interstitial lung disease with clinically amyopathic dermatomyositis. Int J Rheumatic Dis. 2017;20:2182-2185. doi:10.1111/1756-185X.13136
- Kameda H, Nagasawa H, Ogawa H, et al. Combination therapy with corticosteroids, cyclosporin A, and intravenous pulse cyclophosphamide for acute/subacute interstitial pneumonia in patients with dermatomyositis. J Rheumatol. 2005;32:1719-1726.
- Endo Y, Koga T, Suzuki T, et al. Successful treatment of plasma exchange for rapidly progressive interstitial lung disease with anti–MDA5 antibody–positive dermatomyositis: a case report. Medicine. 2018;97:e0436. doi:10.1097/MD.0000000000010436
- So H, Wong VTL, Lao VWN, et al. Rituximab for refractory rapidly progressive interstitial lung disease related to anti-MDA5 antibody-positive amyopathic dermatomyositis. Clin Rheumatol. 2018;37:1983-1989. doi:10.1007/s10067-018-4122-2
- Kurasawa K, Arai S, Namiki Y, et al. Tofacitinib for refractory interstitial lung diseases in anti-melanoma differentiation-associated 5 gene antibody-positive dermatomyositis. Rheumatology. 2018;57:2114-2119. doi:10.1093/rheumatology/key188
- Nawata T, Kubo M, Okuda S, et al. Successful treatment with intravenous cyclophosphamide for anti-melanoma differentiation-associated gene 5 antibody-positive dermatomyositis associated with myelodysplastic syndrome. Scand J Rheumatol. 2017;46:496-498. doi:10.1080/03009742.2016.1253770
- Griger Z, Nagy-Vincze M, Dankó K. Pharmacological management of dermatomyositis. Exp Rev Clin Pharmacol. 2017;10:1109-1118. doi:10.1080/17512433.2017.1353910
Dermatomyositis (DM) is an autoimmune condition characterized by skin and muscle inflammation with an estimated incidence of 9 cases per 1 million people. The incidence of amyopathic DM, which includes antimelanoma differentiation–associated gene 5 (anti-MDA5) DM, is approximately 2 cases per 1 million people.1 Classic cutaneous manifestations of DM include a heliotrope rash, Gottron papules, and the shawl sign.
Case Reports
Patient 1
A woman in her 30s presented with diffuse arthralgias, bilateral eyelid edema, fatigue, and a progressive diffuse exanthem of 3 months’ duration. A review of systems was notable for the absence of myalgias. Physical examination revealed periorbital poikilodermatous patches with erythematous-to-violaceous plaques along the eyelid margins, violaceous papules on the dorsal knuckles, and edematous eroded plaques on the palmar fingertips. The patient was found to have a positive antinuclear antibody titer of 1:320 (reference range, <1:80) with a speckled pattern. A computed tomography (CT) scan of the chest showed patchy bilateral ground-glass opacities that were concerning for ILD. The cutaneous erosions, absence of myalgias, considerable proximal weakness, radiographic evidence of ILD, and positive antinuclear antibody test were clinically suggestive of anti-MDA5 DM. Further workup confirmed this diagnosis with positive reactivity to MDA5 by line immunoassay. The patient was treated with intravenous corticosteroids and was discharged after a 17-day hospitalization; however, she presented 2 months later to outpatient dermatology for progression of the cutaneous ulcerations, at which time an ulcerative heliotrope rash (Figure 1) was identified. Despite compliance with oral corticosteroids (1 mg/kg/d), she was hospitalized 1 month later for progressive respiratory insufficiency. A chest CT showed ground-glass linear opacities centrally located in all lobes of both lungs, consistent with rapidly progressive ILD. Over the course of her 5-day hospitalization, she was treated with corticosteroids, intravenous immunoglobulin (IVIG), and mycophenolate mofetil. The patient responded well to these therapies, leading to resolution of the respiratory symptoms, and she was discharged with plans to continue this regimen as an outpatient.

Patient 2
A woman in her late 30s with a history of known anti-MDA5 DM confirmed by line immunoassay 1 year prior presented to the emergency department with shortness of breath due to progressive ILD and a worsening exanthem. Dermatology was consulted to provide treatment recommendations. The treatment team was concerned for infection or anti-MDA5 DM disease progression. Physical examination revealed an ulcerative heliotrope rash (Figure 2) in addition to cutaneous findings classic for anti-MDA5 DM. Despite interventions, including high-dose corticosteroids, rituximab, IVIG, and plasma exchange, the ILD continued to progress, and the patient and her family elected to de-escalate aggressive medical care and pursue comfort care. The patient later died in in patient hospice.

Comment
Clinical Presentation of Anti-MDA5 DM
Dermatomyositis classically presents with cutaneous manifestations including a heliotropic erythematous rash and Gottron papules as well as accompanying muscle weakness.2 However, a subtype known as amyopathic DM, which includes anti-MDA5 DM, usually presents without muscle involvement.3 Clinical muscle weakness has been reported in cases of anti-MDA5 DM, though it is less likely in these patients.4 The characteristic cutaneous phenotype of
While a heliotrope rash is classic for DM, and ulcerations are a hallmark of the anti-MDA5 DM subtype, overlap of these cutaneous manifestations is not commonly reported. In both cases presented here, ulcerations of the lateral canthi were associated with progression of ILD.
Diagnosis of Anti-MDA5 DM
Anti-MDA5 DM is defined by the presence of the anti-MDA5 antibody in the serum, named for its reactivity against the RNA helicase encoded by MDA5, within the clinical context of cutaneous signs of DM as described above.12
As described by Rider et al,13 a thorough laboratory analysis, including complete blood cell count, serum electrolytes, calcium, magnesium, phosphorus, and thyroid-stimulating hormone, is necessary to rule out conditions with similar presentations. Additionally, serum analysis for elevated muscle enzymes (creatinine phosphokinase, aldolase, lactate dehydrogenase, alanine aminotransferase, and aspartate aminotransferase) is necessary to assess for subclinical muscle involvement. Serologic evidence of myositis usually denotes an alternative diagnosis.13 Antinuclear antibodies and myositis-specific antibody positivity are much less frequent in the anti-MDA5 DM subtype than in other forms of DM.6
Anti-MDA5 antibody titer, ferritin, and IL-18 can be trended and may be useful in the evaluation of the response to treatment and ILD status in patients with anti-MDA5 DM.14,15 Elevated alveolar-arterial gradient, serum ferritin, serum chitotriosidase, and serum chitinase-3-like protein 1 (YKL-40) have each been associated with poorer prognosis of anti-MDA5 DM. The aforementioned serologies therefore may be helpful in determination of risk stratification and treatment aggressiveness.16-19
Because of its strong association with RP-ILD, screening for pulmonary disease is necessary in all patients with confirmed or strongly suspected anti-MDA5 DM. Screening can be performed with pulmonary function testing; however, high-resolution chest CT is the gold standard for diagnosis of ILD.20
Finally, all patients with a new diagnosis of DM should be evaluated for underlying malignancy through cancer screenings, given the propensity for DM to present as a paraneoplastic process.21 However, reports have indicated that the anti-MDA5 DM subtype may have a reduced risk for or an inverse relationship with underlying malignancy.5
Treatment Options for Anti-MDA5 DM
Early and aggressive therapy should be considered in the treatment of anti-MDA5 DM because of its association with RP-ILD. No treatment protocol is well established; thus, an individualized therapeutic approach may be guided by symptom severity and the clinical, radiographic, or functional evidence of ILD.6 High-dose systemic corticosteroids are first line, either in combination with or as a bridge to corticosteroid-sparing agents for immunosuppression. Many steroid-sparing medications have been employed with varying success. Mycophenolate mofetil is a reasonable first-line corticosteroid-sparing immunosuppressant agent, given its added benefit of attenuating ILD progression.6 A combination of high-dose corticosteroids, cyclosporine, and cyclophosphamide is utilized by some initially in the treatment of anti-MDA5 with ILD.22,23 While others have used combinations of these immunomodulatory agents with mycophenolate mofetil, IVIG, rituximab, azathioprine, tofacitinib, and polymyxin B, direct hemoperfusion has been added, leading to successful remission.23-28
Conclusion
We present 2 patients with anti-MDA5 DM who demonstrated a rare cutaneous manifestation of an ulcerative heliotrope rash. In both cases, this cutaneous finding was associated with the development of RP-ILD. Because of the strong association with and rapid progression of ILD seen in anti-MDA5 DM, early identification and aggressive treatment of this subtype are imperative. The clinician should recognize nonacral locations of cutaneous ulcerations, including an ulcerated heliotrope rash, to optimize diagnosis and management.
Dermatomyositis (DM) is an autoimmune condition characterized by skin and muscle inflammation with an estimated incidence of 9 cases per 1 million people. The incidence of amyopathic DM, which includes antimelanoma differentiation–associated gene 5 (anti-MDA5) DM, is approximately 2 cases per 1 million people.1 Classic cutaneous manifestations of DM include a heliotrope rash, Gottron papules, and the shawl sign.
Case Reports
Patient 1
A woman in her 30s presented with diffuse arthralgias, bilateral eyelid edema, fatigue, and a progressive diffuse exanthem of 3 months’ duration. A review of systems was notable for the absence of myalgias. Physical examination revealed periorbital poikilodermatous patches with erythematous-to-violaceous plaques along the eyelid margins, violaceous papules on the dorsal knuckles, and edematous eroded plaques on the palmar fingertips. The patient was found to have a positive antinuclear antibody titer of 1:320 (reference range, <1:80) with a speckled pattern. A computed tomography (CT) scan of the chest showed patchy bilateral ground-glass opacities that were concerning for ILD. The cutaneous erosions, absence of myalgias, considerable proximal weakness, radiographic evidence of ILD, and positive antinuclear antibody test were clinically suggestive of anti-MDA5 DM. Further workup confirmed this diagnosis with positive reactivity to MDA5 by line immunoassay. The patient was treated with intravenous corticosteroids and was discharged after a 17-day hospitalization; however, she presented 2 months later to outpatient dermatology for progression of the cutaneous ulcerations, at which time an ulcerative heliotrope rash (Figure 1) was identified. Despite compliance with oral corticosteroids (1 mg/kg/d), she was hospitalized 1 month later for progressive respiratory insufficiency. A chest CT showed ground-glass linear opacities centrally located in all lobes of both lungs, consistent with rapidly progressive ILD. Over the course of her 5-day hospitalization, she was treated with corticosteroids, intravenous immunoglobulin (IVIG), and mycophenolate mofetil. The patient responded well to these therapies, leading to resolution of the respiratory symptoms, and she was discharged with plans to continue this regimen as an outpatient.

Patient 2
A woman in her late 30s with a history of known anti-MDA5 DM confirmed by line immunoassay 1 year prior presented to the emergency department with shortness of breath due to progressive ILD and a worsening exanthem. Dermatology was consulted to provide treatment recommendations. The treatment team was concerned for infection or anti-MDA5 DM disease progression. Physical examination revealed an ulcerative heliotrope rash (Figure 2) in addition to cutaneous findings classic for anti-MDA5 DM. Despite interventions, including high-dose corticosteroids, rituximab, IVIG, and plasma exchange, the ILD continued to progress, and the patient and her family elected to de-escalate aggressive medical care and pursue comfort care. The patient later died in in patient hospice.

Comment
Clinical Presentation of Anti-MDA5 DM
Dermatomyositis classically presents with cutaneous manifestations including a heliotropic erythematous rash and Gottron papules as well as accompanying muscle weakness.2 However, a subtype known as amyopathic DM, which includes anti-MDA5 DM, usually presents without muscle involvement.3 Clinical muscle weakness has been reported in cases of anti-MDA5 DM, though it is less likely in these patients.4 The characteristic cutaneous phenotype of
While a heliotrope rash is classic for DM, and ulcerations are a hallmark of the anti-MDA5 DM subtype, overlap of these cutaneous manifestations is not commonly reported. In both cases presented here, ulcerations of the lateral canthi were associated with progression of ILD.
Diagnosis of Anti-MDA5 DM
Anti-MDA5 DM is defined by the presence of the anti-MDA5 antibody in the serum, named for its reactivity against the RNA helicase encoded by MDA5, within the clinical context of cutaneous signs of DM as described above.12
As described by Rider et al,13 a thorough laboratory analysis, including complete blood cell count, serum electrolytes, calcium, magnesium, phosphorus, and thyroid-stimulating hormone, is necessary to rule out conditions with similar presentations. Additionally, serum analysis for elevated muscle enzymes (creatinine phosphokinase, aldolase, lactate dehydrogenase, alanine aminotransferase, and aspartate aminotransferase) is necessary to assess for subclinical muscle involvement. Serologic evidence of myositis usually denotes an alternative diagnosis.13 Antinuclear antibodies and myositis-specific antibody positivity are much less frequent in the anti-MDA5 DM subtype than in other forms of DM.6
Anti-MDA5 antibody titer, ferritin, and IL-18 can be trended and may be useful in the evaluation of the response to treatment and ILD status in patients with anti-MDA5 DM.14,15 Elevated alveolar-arterial gradient, serum ferritin, serum chitotriosidase, and serum chitinase-3-like protein 1 (YKL-40) have each been associated with poorer prognosis of anti-MDA5 DM. The aforementioned serologies therefore may be helpful in determination of risk stratification and treatment aggressiveness.16-19
Because of its strong association with RP-ILD, screening for pulmonary disease is necessary in all patients with confirmed or strongly suspected anti-MDA5 DM. Screening can be performed with pulmonary function testing; however, high-resolution chest CT is the gold standard for diagnosis of ILD.20
Finally, all patients with a new diagnosis of DM should be evaluated for underlying malignancy through cancer screenings, given the propensity for DM to present as a paraneoplastic process.21 However, reports have indicated that the anti-MDA5 DM subtype may have a reduced risk for or an inverse relationship with underlying malignancy.5
Treatment Options for Anti-MDA5 DM
Early and aggressive therapy should be considered in the treatment of anti-MDA5 DM because of its association with RP-ILD. No treatment protocol is well established; thus, an individualized therapeutic approach may be guided by symptom severity and the clinical, radiographic, or functional evidence of ILD.6 High-dose systemic corticosteroids are first line, either in combination with or as a bridge to corticosteroid-sparing agents for immunosuppression. Many steroid-sparing medications have been employed with varying success. Mycophenolate mofetil is a reasonable first-line corticosteroid-sparing immunosuppressant agent, given its added benefit of attenuating ILD progression.6 A combination of high-dose corticosteroids, cyclosporine, and cyclophosphamide is utilized by some initially in the treatment of anti-MDA5 with ILD.22,23 While others have used combinations of these immunomodulatory agents with mycophenolate mofetil, IVIG, rituximab, azathioprine, tofacitinib, and polymyxin B, direct hemoperfusion has been added, leading to successful remission.23-28
Conclusion
We present 2 patients with anti-MDA5 DM who demonstrated a rare cutaneous manifestation of an ulcerative heliotrope rash. In both cases, this cutaneous finding was associated with the development of RP-ILD. Because of the strong association with and rapid progression of ILD seen in anti-MDA5 DM, early identification and aggressive treatment of this subtype are imperative. The clinician should recognize nonacral locations of cutaneous ulcerations, including an ulcerated heliotrope rash, to optimize diagnosis and management.
- Bendewald MJ, Wetter DA, Li X, et al. Incidence of dermatomyositis and clinically amyopathic dermatomyositis: a population-based study in Olmsted County, Minnesota. Arch Dermatol. 2010;146:26-30. doi:10.1001/archdermatol.2009.328
- Bogdanov I, Kazandjieva J, Darlenski R, et al. Dermatomyositis: current concepts. Clin Dermatol. 2018;36:450-458. doi:10.1016/j.clindermatol.2018.04.003
- Caproni M, Cardinali C, Parodi A, et al. Amyopathic dermatomyositis: a review by the Italian Group of Immunodermatology. Arch Dermatol. 2002;138:23-27. doi:10.1001/archderm.138.1.23
- Li J, Liu Y, Li Y, et al. Associations between anti-melanoma differentiation-associated gene 5 antibody and demographics, clinical characteristics and laboratory results of patients with dermatomyositis: a systematic meta-analysis. J Dermatol. 2018;45:46-52. doi:10.1111/1346-8138.14092
- Fiorentino D, Chung L, Zwerner J, et al. The mucocutaneous and systemic phenotype of dermatomyositis patients with antibodies to MDA5 (CADM-140): a retrospective study. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2011;65:25-34. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2010.09.016
- Kurtzman DJB, Vleugels RA. Anti-melanoma differentiation–associated gene 5 (MDA5) dermatomyositis: a concise review with an emphasis on distinctive clinical features. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2018;78:776-785. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2017.12.010
- Narang NS, Casciola-Rosen L, Li S, et al. Cutaneous ulceration in dermatomyositis: association with anti-melanoma differentiation-associated gene 5 antibodies and interstitial lung disease: analysis of skin ulcers in dermatomyositis. Arthritis Care Res. 2015;67:667-672. doi:10.1002/acr.22498
- Charrow A, Vleugels RA. Cutaneous ulcerations in anti-MDA5 dermatomyositis. N Engl J Med. 2019;381:465. doi:10.1056/NEJMicm1816147
- Cao H, Xia Q, Pan M, et al. Gottron papules and Gottron sign with ulceration: a distinctive cutaneous feature in a subset of patients with classic dermatomyositis and clinically amyopathic dermatomyositis. J Rheumatol. 2016;43:1735-1742. doi:10.3899/jrheum.160024
- Moghadam-Kia S, Oddis CV, Sato S, et al. Antimelanoma differentiation-associated gene 5 antibody: expanding the clinical spectrum in North American patients with dermatomyositis. J Rheumatol. 2017;44:319-325. doi:10.3899/jrheum.160682
- Li L, Wang Q, Wen X, et al. Assessment of anti-MDA5 antibody as a diagnostic biomarker in patients with dermatomyositis-associated interstitial lung disease or rapidly progressive interstitial lung disease. Oncotarget. 2017;876129-76140. doi:10.18632/oncotarget.19050
- Sato S, Hoshino K, Satoh T, et al. RNA helicase encoded by melanoma differentiation-associated gene 5 is a major autoantigen in patients with clinically amyopathic dermatomyositis: association with rapidly progressive interstitial lung disease. Arthritis Rheum. 2009;60:2193-2200. doi:10.1002/art.24621
- Rider LG, Miller FW. Deciphering the clinical presentations, pathogenesis, and treatment of the idiopathic inflammatory myopathies. JAMA. 2011;305:183-190. doi:10.1001/jama.2010.1977
- Nishioka A, Tsunoda S, Abe T, et al. Serum neopterin as well as ferritin, soluble interleukin-2 receptor, KL-6 and anti-MDA5 antibody titer provide markers of the response to therapy in patients with interstitial lung disease complicating anti-MDA5 antibody-positive dermatomyositis. Mod Rheumatol. 2019;29:814-820. doi:10.1080/14397595.2018.1548918
- Gono T, Sato S, Kawaguchi Y, et al. Anti-MDA5 antibody, ferritin and IL-18 are useful for the evaluation of response to treatment in interstitial lung disease with anti-MDA5 antibody-positive dermatomyositis. Rheumatology. 2012;51:1563-1570. doi:10.1093/rheumatology/kes102
- Jiang L, Wang Y, Peng Q, et al. Serum YKL-40 level is associated with severity of interstitial lung disease and poor prognosis in dermatomyositis with anti-MDA5 antibody. Clin Rheumatol. 2019;38:1655-1663. doi:10.1007/s10067-019-04457-w
- Fujisawa T, Hozumi H, Yasui H, et al. Clinical significance of serum chitotriosidase level in anti-MDA5 antibody–positive dermatomyositis-associated interstitial lung disease. J Rheumatol. 2019;46:935-942. doi:10.3899/jrheum.180825
- Enomoto N, Oyama Y, Enomoto Y, et al. Prognostic evaluation of serum ferritin in acute exacerbation of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Clin Resp J. 2018;12:2378-2389. doi:10.1111/crj.12918
- Fujiki Y, Kotani T, Isoda K, et al. Evaluation of clinical prognostic factors for interstitial pneumonia in anti-MDA5 antibody-positive dermatomyositis patients. Mod Rheumatol. 2018;28:133-140. doi:10.1080/14397595.2017.1318468
- Raghu G, Remy-Jardin M, Myers JL, et al; American Thoracic Society, European Respiratory Society, Japanese Respiratory Society, and Latin American Thoracic Society. Diagnosis of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. an official ATS/ERS/JRS/ALAT clinical practice guideline. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2018;198:E44-E68. doi:10.1164/rccm.201807-1255ST
- Yang Z, Lin F, Qin B, et al. Polymyositis/dermatomyositis and malignancy risk: a metaanalysis study. J Rheumatol. 2015;42:282-291. doi:10.3899/jrheum.140566
- Hisanaga J, Kotani T, Fujiki Y, et al. Successful multi-target therapy including rituximab and mycophenolate mofetil in anti-melanoma differentiation-associated gene 5 antibody-positive rapidly progressive interstitial lung disease with clinically amyopathic dermatomyositis. Int J Rheumatic Dis. 2017;20:2182-2185. doi:10.1111/1756-185X.13136
- Kameda H, Nagasawa H, Ogawa H, et al. Combination therapy with corticosteroids, cyclosporin A, and intravenous pulse cyclophosphamide for acute/subacute interstitial pneumonia in patients with dermatomyositis. J Rheumatol. 2005;32:1719-1726.
- Endo Y, Koga T, Suzuki T, et al. Successful treatment of plasma exchange for rapidly progressive interstitial lung disease with anti–MDA5 antibody–positive dermatomyositis: a case report. Medicine. 2018;97:e0436. doi:10.1097/MD.0000000000010436
- So H, Wong VTL, Lao VWN, et al. Rituximab for refractory rapidly progressive interstitial lung disease related to anti-MDA5 antibody-positive amyopathic dermatomyositis. Clin Rheumatol. 2018;37:1983-1989. doi:10.1007/s10067-018-4122-2
- Kurasawa K, Arai S, Namiki Y, et al. Tofacitinib for refractory interstitial lung diseases in anti-melanoma differentiation-associated 5 gene antibody-positive dermatomyositis. Rheumatology. 2018;57:2114-2119. doi:10.1093/rheumatology/key188
- Nawata T, Kubo M, Okuda S, et al. Successful treatment with intravenous cyclophosphamide for anti-melanoma differentiation-associated gene 5 antibody-positive dermatomyositis associated with myelodysplastic syndrome. Scand J Rheumatol. 2017;46:496-498. doi:10.1080/03009742.2016.1253770
- Griger Z, Nagy-Vincze M, Dankó K. Pharmacological management of dermatomyositis. Exp Rev Clin Pharmacol. 2017;10:1109-1118. doi:10.1080/17512433.2017.1353910
- Bendewald MJ, Wetter DA, Li X, et al. Incidence of dermatomyositis and clinically amyopathic dermatomyositis: a population-based study in Olmsted County, Minnesota. Arch Dermatol. 2010;146:26-30. doi:10.1001/archdermatol.2009.328
- Bogdanov I, Kazandjieva J, Darlenski R, et al. Dermatomyositis: current concepts. Clin Dermatol. 2018;36:450-458. doi:10.1016/j.clindermatol.2018.04.003
- Caproni M, Cardinali C, Parodi A, et al. Amyopathic dermatomyositis: a review by the Italian Group of Immunodermatology. Arch Dermatol. 2002;138:23-27. doi:10.1001/archderm.138.1.23
- Li J, Liu Y, Li Y, et al. Associations between anti-melanoma differentiation-associated gene 5 antibody and demographics, clinical characteristics and laboratory results of patients with dermatomyositis: a systematic meta-analysis. J Dermatol. 2018;45:46-52. doi:10.1111/1346-8138.14092
- Fiorentino D, Chung L, Zwerner J, et al. The mucocutaneous and systemic phenotype of dermatomyositis patients with antibodies to MDA5 (CADM-140): a retrospective study. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2011;65:25-34. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2010.09.016
- Kurtzman DJB, Vleugels RA. Anti-melanoma differentiation–associated gene 5 (MDA5) dermatomyositis: a concise review with an emphasis on distinctive clinical features. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2018;78:776-785. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2017.12.010
- Narang NS, Casciola-Rosen L, Li S, et al. Cutaneous ulceration in dermatomyositis: association with anti-melanoma differentiation-associated gene 5 antibodies and interstitial lung disease: analysis of skin ulcers in dermatomyositis. Arthritis Care Res. 2015;67:667-672. doi:10.1002/acr.22498
- Charrow A, Vleugels RA. Cutaneous ulcerations in anti-MDA5 dermatomyositis. N Engl J Med. 2019;381:465. doi:10.1056/NEJMicm1816147
- Cao H, Xia Q, Pan M, et al. Gottron papules and Gottron sign with ulceration: a distinctive cutaneous feature in a subset of patients with classic dermatomyositis and clinically amyopathic dermatomyositis. J Rheumatol. 2016;43:1735-1742. doi:10.3899/jrheum.160024
- Moghadam-Kia S, Oddis CV, Sato S, et al. Antimelanoma differentiation-associated gene 5 antibody: expanding the clinical spectrum in North American patients with dermatomyositis. J Rheumatol. 2017;44:319-325. doi:10.3899/jrheum.160682
- Li L, Wang Q, Wen X, et al. Assessment of anti-MDA5 antibody as a diagnostic biomarker in patients with dermatomyositis-associated interstitial lung disease or rapidly progressive interstitial lung disease. Oncotarget. 2017;876129-76140. doi:10.18632/oncotarget.19050
- Sato S, Hoshino K, Satoh T, et al. RNA helicase encoded by melanoma differentiation-associated gene 5 is a major autoantigen in patients with clinically amyopathic dermatomyositis: association with rapidly progressive interstitial lung disease. Arthritis Rheum. 2009;60:2193-2200. doi:10.1002/art.24621
- Rider LG, Miller FW. Deciphering the clinical presentations, pathogenesis, and treatment of the idiopathic inflammatory myopathies. JAMA. 2011;305:183-190. doi:10.1001/jama.2010.1977
- Nishioka A, Tsunoda S, Abe T, et al. Serum neopterin as well as ferritin, soluble interleukin-2 receptor, KL-6 and anti-MDA5 antibody titer provide markers of the response to therapy in patients with interstitial lung disease complicating anti-MDA5 antibody-positive dermatomyositis. Mod Rheumatol. 2019;29:814-820. doi:10.1080/14397595.2018.1548918
- Gono T, Sato S, Kawaguchi Y, et al. Anti-MDA5 antibody, ferritin and IL-18 are useful for the evaluation of response to treatment in interstitial lung disease with anti-MDA5 antibody-positive dermatomyositis. Rheumatology. 2012;51:1563-1570. doi:10.1093/rheumatology/kes102
- Jiang L, Wang Y, Peng Q, et al. Serum YKL-40 level is associated with severity of interstitial lung disease and poor prognosis in dermatomyositis with anti-MDA5 antibody. Clin Rheumatol. 2019;38:1655-1663. doi:10.1007/s10067-019-04457-w
- Fujisawa T, Hozumi H, Yasui H, et al. Clinical significance of serum chitotriosidase level in anti-MDA5 antibody–positive dermatomyositis-associated interstitial lung disease. J Rheumatol. 2019;46:935-942. doi:10.3899/jrheum.180825
- Enomoto N, Oyama Y, Enomoto Y, et al. Prognostic evaluation of serum ferritin in acute exacerbation of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Clin Resp J. 2018;12:2378-2389. doi:10.1111/crj.12918
- Fujiki Y, Kotani T, Isoda K, et al. Evaluation of clinical prognostic factors for interstitial pneumonia in anti-MDA5 antibody-positive dermatomyositis patients. Mod Rheumatol. 2018;28:133-140. doi:10.1080/14397595.2017.1318468
- Raghu G, Remy-Jardin M, Myers JL, et al; American Thoracic Society, European Respiratory Society, Japanese Respiratory Society, and Latin American Thoracic Society. Diagnosis of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. an official ATS/ERS/JRS/ALAT clinical practice guideline. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2018;198:E44-E68. doi:10.1164/rccm.201807-1255ST
- Yang Z, Lin F, Qin B, et al. Polymyositis/dermatomyositis and malignancy risk: a metaanalysis study. J Rheumatol. 2015;42:282-291. doi:10.3899/jrheum.140566
- Hisanaga J, Kotani T, Fujiki Y, et al. Successful multi-target therapy including rituximab and mycophenolate mofetil in anti-melanoma differentiation-associated gene 5 antibody-positive rapidly progressive interstitial lung disease with clinically amyopathic dermatomyositis. Int J Rheumatic Dis. 2017;20:2182-2185. doi:10.1111/1756-185X.13136
- Kameda H, Nagasawa H, Ogawa H, et al. Combination therapy with corticosteroids, cyclosporin A, and intravenous pulse cyclophosphamide for acute/subacute interstitial pneumonia in patients with dermatomyositis. J Rheumatol. 2005;32:1719-1726.
- Endo Y, Koga T, Suzuki T, et al. Successful treatment of plasma exchange for rapidly progressive interstitial lung disease with anti–MDA5 antibody–positive dermatomyositis: a case report. Medicine. 2018;97:e0436. doi:10.1097/MD.0000000000010436
- So H, Wong VTL, Lao VWN, et al. Rituximab for refractory rapidly progressive interstitial lung disease related to anti-MDA5 antibody-positive amyopathic dermatomyositis. Clin Rheumatol. 2018;37:1983-1989. doi:10.1007/s10067-018-4122-2
- Kurasawa K, Arai S, Namiki Y, et al. Tofacitinib for refractory interstitial lung diseases in anti-melanoma differentiation-associated 5 gene antibody-positive dermatomyositis. Rheumatology. 2018;57:2114-2119. doi:10.1093/rheumatology/key188
- Nawata T, Kubo M, Okuda S, et al. Successful treatment with intravenous cyclophosphamide for anti-melanoma differentiation-associated gene 5 antibody-positive dermatomyositis associated with myelodysplastic syndrome. Scand J Rheumatol. 2017;46:496-498. doi:10.1080/03009742.2016.1253770
- Griger Z, Nagy-Vincze M, Dankó K. Pharmacological management of dermatomyositis. Exp Rev Clin Pharmacol. 2017;10:1109-1118. doi:10.1080/17512433.2017.1353910
Practice Points
- Antimelanoma differentiation–associated gene 5 dermatomyositis (anti-MDA5 DM) can present with an ulcerative heliotrope rash.
- Ulceration of the heliotrope rash in anti-MDA5 DM may indicate disease progression.
- Rapidly progressive interstitial lung disease is highly associated with anti-MDA5 DM.
Psoriatic Alopecia in a Patient With Crohn Disease: An Uncommon Manifestation of Tumor Necrosis Factor α Inhibitors
Tumor necrosis factor α (TNF-α) inhibitor–induced psoriasis is a known paradoxical adverse effect of this family of medications, which includes infliximab, adalimumab, etanercept, golimumab, and certolizumab. In the pediatric population, these therapies recently gained approval for nondermatologic conditions—meaning that this phenomenon is encountered more frequently.1 In a systematic review of TNF-α inhibitor–induced psoriasis, severe scalp involvement was associated with alopecia in 7.5% of cases.2 Onset of scalp psoriasis with alopecia in patients being treated with a TNF-α inhibitor should lead to consideration of this condition.
Psoriatic alopecia is an uncommon presentation of psoriasis. Although well described, alopecia as a clinical manifestation of scalp psoriasis is not a well-known concept among clinicians and has never been widely accepted. Adding to the diagnostic challenge is that psoriatic alopecia secondary to TNF-α inhibitor–induced psoriasis rarely has been reported in adults or children.3-5 Including our case, our review of the literature yielded 7 pediatric cases (≤18 years) of TNF-α inhibitor–induced psoriatic alopecia.6,7 A primary literature search of PubMed articles indexed for MEDLINE was conducted using the terms psoriatic alopecia, psoriasiform alopecia, TNF-α inhibitors, infliximab, adalimumab, etanercept, golimumab, and certolizumab.
We present the case of a pediatric patient with psoriatic alopecia secondary to treatment with adalimumab for Crohn disease (CD). We also provide a review of reported cases of psoriatic alopecia induced by a TNF-α inhibitor in the literature.
Case Report
A 12-year-old girl presented to our dermatology clinic with erythematous scaly plaques on the trunk, scalp, arms, and legs of 2 months’ duration. The lesions involved approximately 15% of the body surface area. The patient’s medical history was remarkable for CD diagnosed 4 years prior to presentation of the skin lesions. She had been treated for the past 2 years with adalimumab 40 mg once every 2 weeks and azathioprine 100 mg once daily. Because her CD was poorly controlled, the dosage of adalimumab was increased to 40 mg once weekly 6 months prior to the current presentation.
Our diagnosis was TNF-α inhibitor-induced psoriasis secondary to treatment with adalimumab.
The patient was treated with mometasone lotion 0.1% for the scalp lesions and triamcinolone cream 0.1% for the body lesions. Because of the extent of the psoriasis, we recommended changing adalimumab to ustekinumab, which is approved for CD in adults but is off label in children.
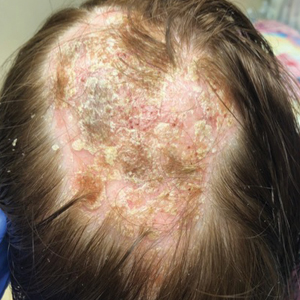
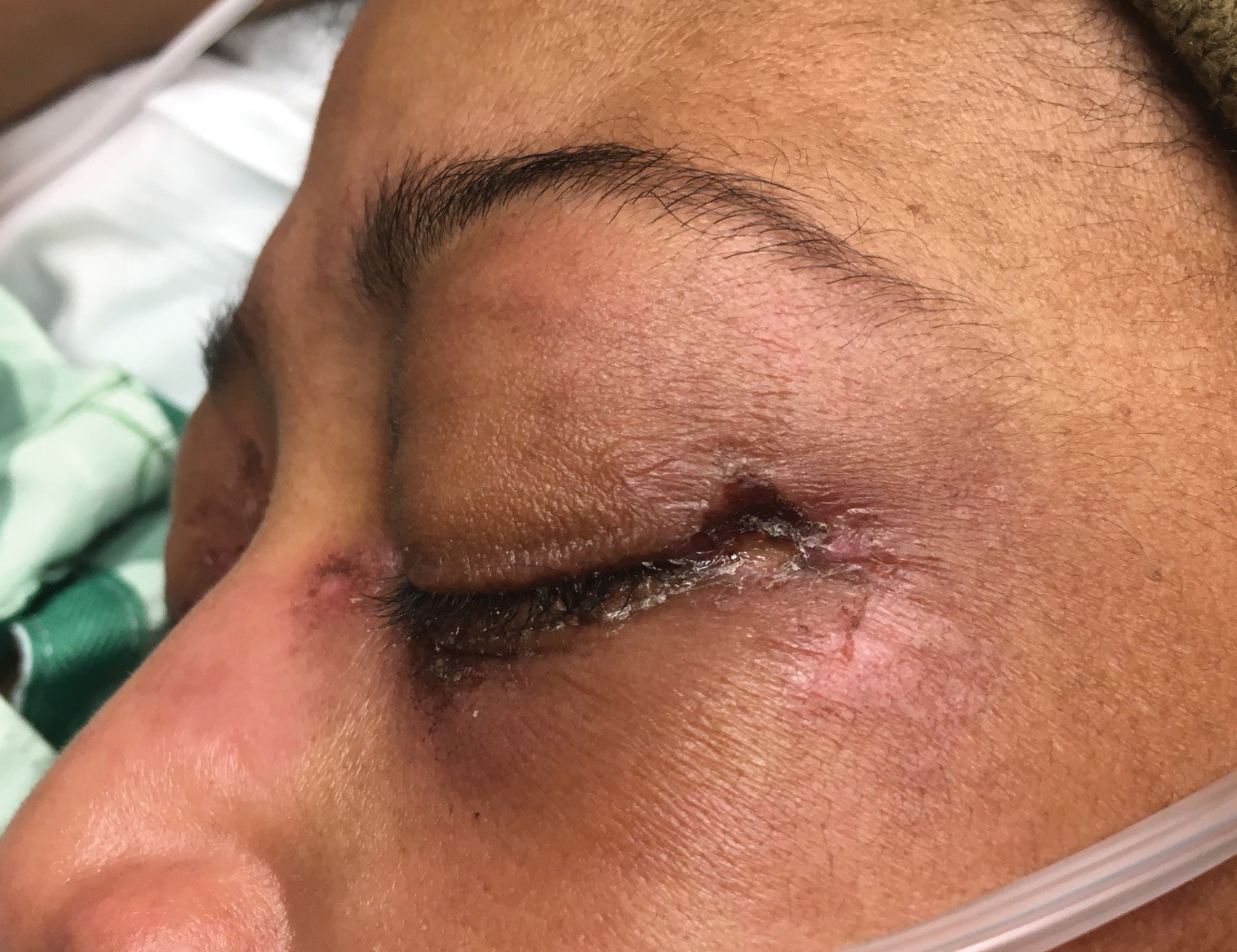
At 1-month follow-up, after receiving the induction dose of ustekinumab, the patient presented with partial improvement of the skin lesions but had developed a large, alopecic, erythematous plaque with thick yellowish scales on the scalp (Figure 1). She also had a positive hair pull test. The presumptive initial diagnosis of the alopecic scalp lesion was tinea capitis, for which multiple potassium hydroxide preparations of scales were performed, all yielding negative results. In addition, histopathologic examination with hematoxylin and eosin staining was performed (Figures 2A and 2B). Sterile tissue cultures for bacteria, fungi, and acid-fast bacilli were obtained and showed no growth. Periodic acid–Schiff staining was negative for fungal structures.
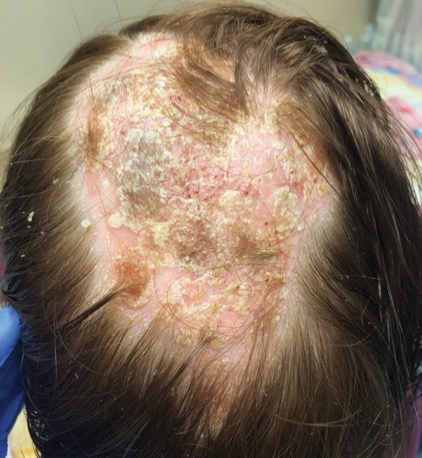
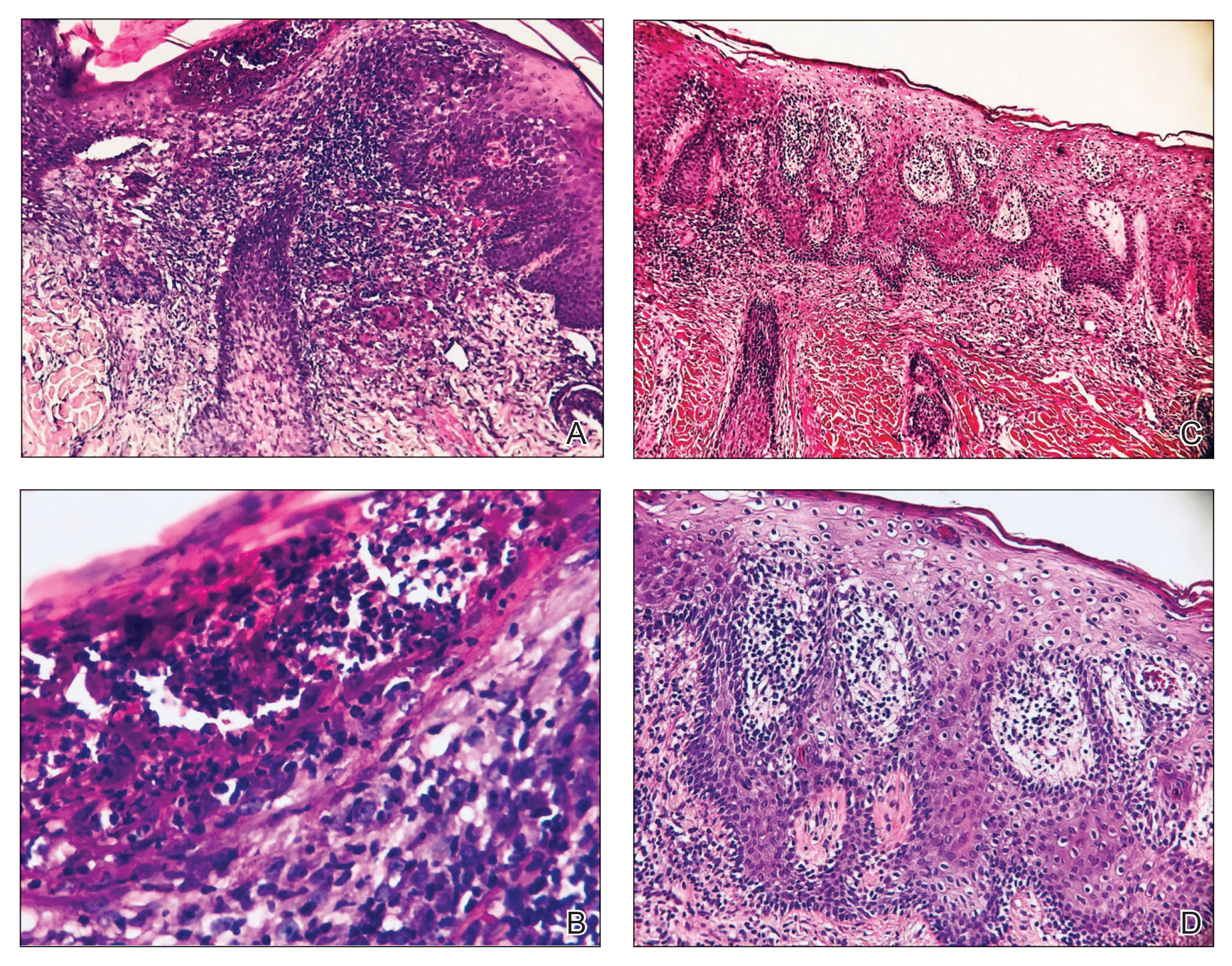
A second biopsy showed a psoriasiform pattern, parakeratosis, and hypogranulosis, highly suggestive of psoriasis (Figure 2C and 2D). Based on those findings, a diagnosis of psoriatic alopecia was made. The mometasone was switched to clobetasol lotion 0.05%. The patient continued treatment with ustekinumab. At 6-month follow-up, her CD was well controlled and she showed hair regrowth in previously alopecic areas (Figure 3).

Comment
Psoriatic alopecia induced by a TNF-α inhibitor was first reported in 2007 in a 30-year-old woman with ankylosing spondylitis who was being treated with adalimumab.8 She had erythematous, scaly, alopecic plaques on the scalp and palmoplantar pustulosis. Findings on skin biopsy were compatible with psoriasis. The patient’s severe scalp psoriasis failed to respond to topical steroid treatment and adalimumab cessation. The extensive hair loss responded to cyclosporine 3 mg/kg daily.8
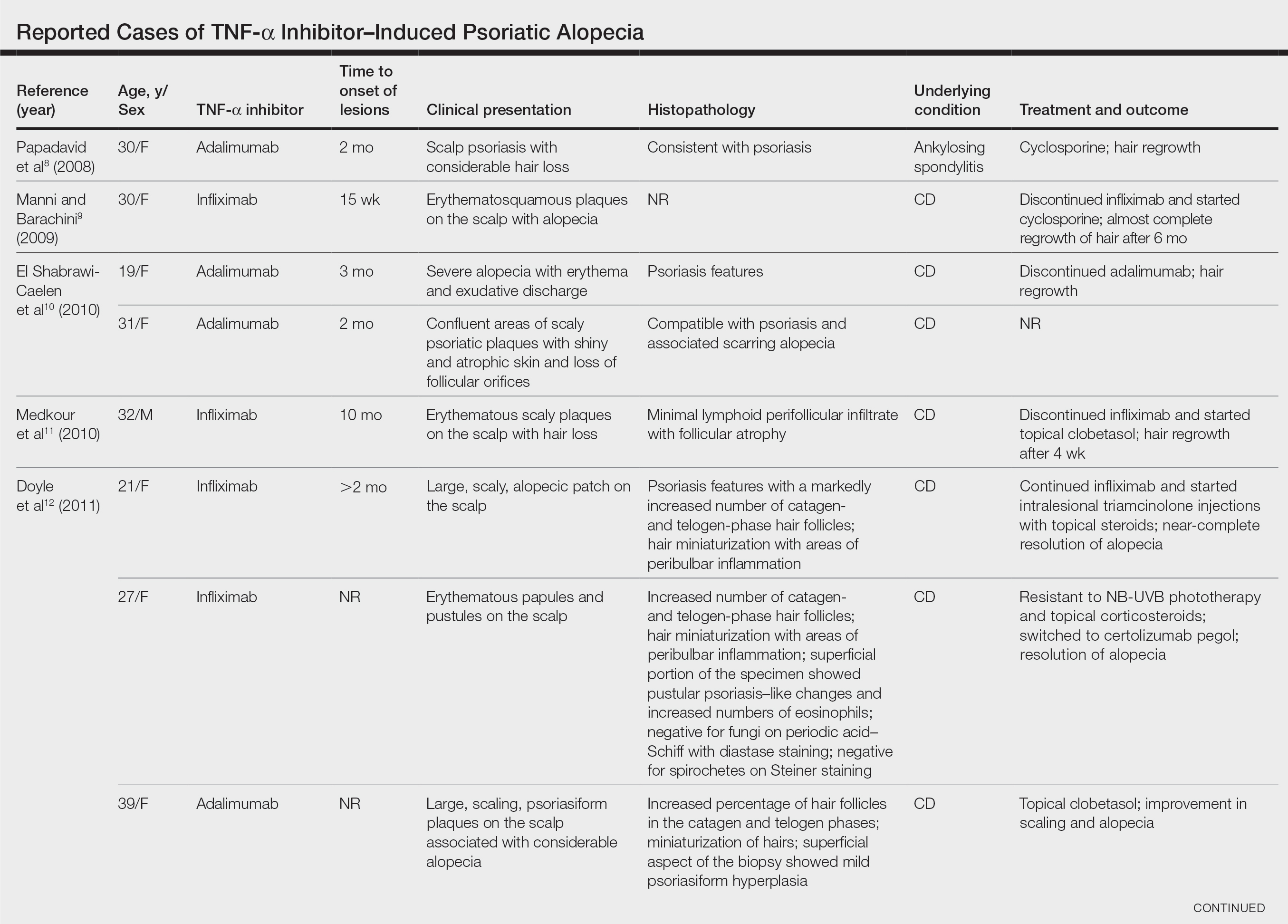
After conducting an extensive literature review, we found 26 cases of TNF-α–induced psoriatic alopecia, including the current case (Table).6-16 The mean age at diagnosis was 27.8 years (SD, 13.6 years; range, 7–60 years). The female-to-male ratio was 3.3:1. The most common underlying condition for which TNF-α inhibitors were prescribed was CD (77% [20/26]). Psoriatic alopecia most commonly was reported secondary to treatment with infliximab (54% [14/26]), followed by adalimumab (42% [11/26]). Golimumab was the causative drug in 1 (4%) case. We did not find reports of etanercept or certolizumab having induced this manifestation. The onset of the scalp lesions occurred 2 to 46 months after starting treatment with the causative medication.
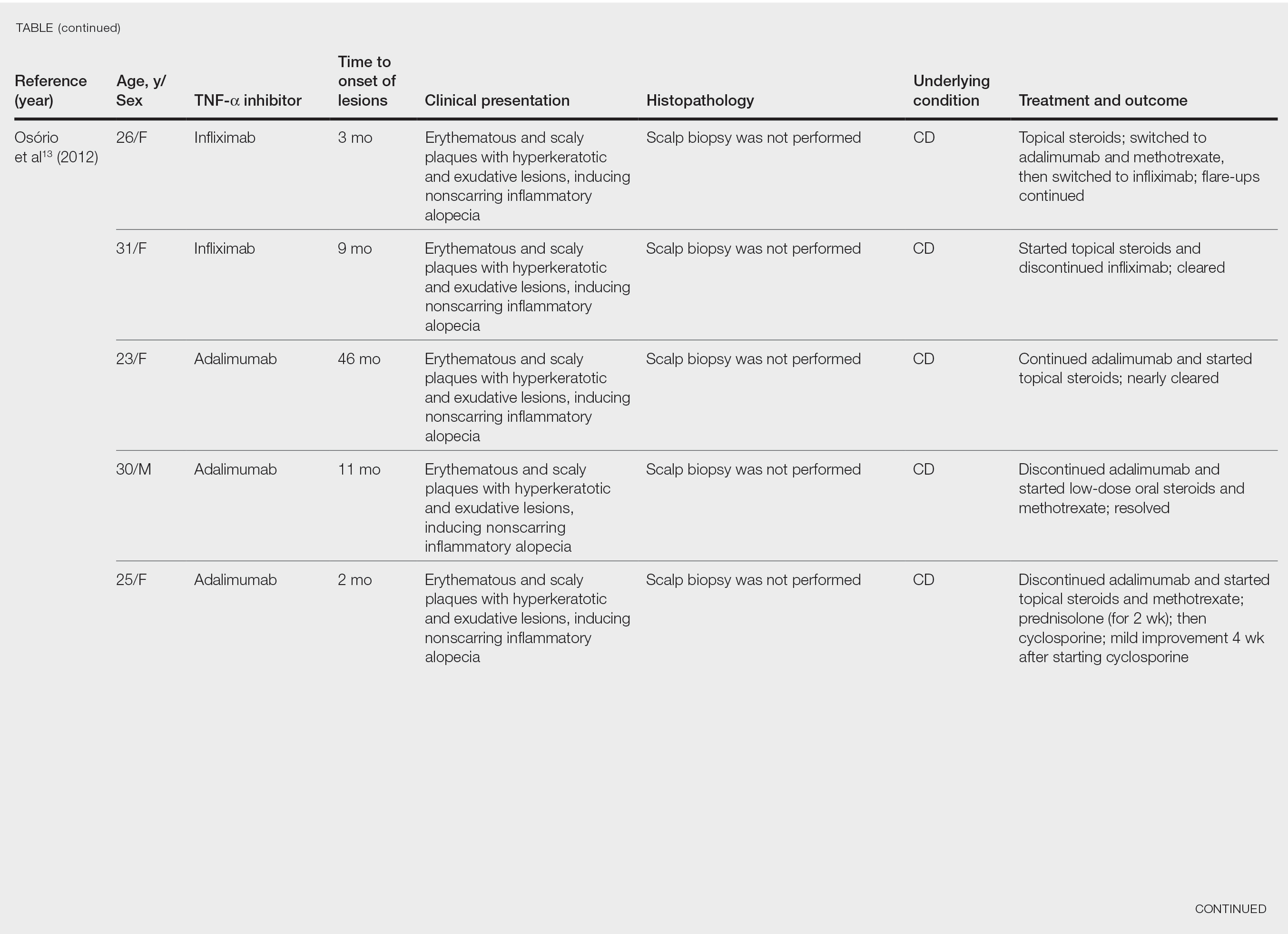
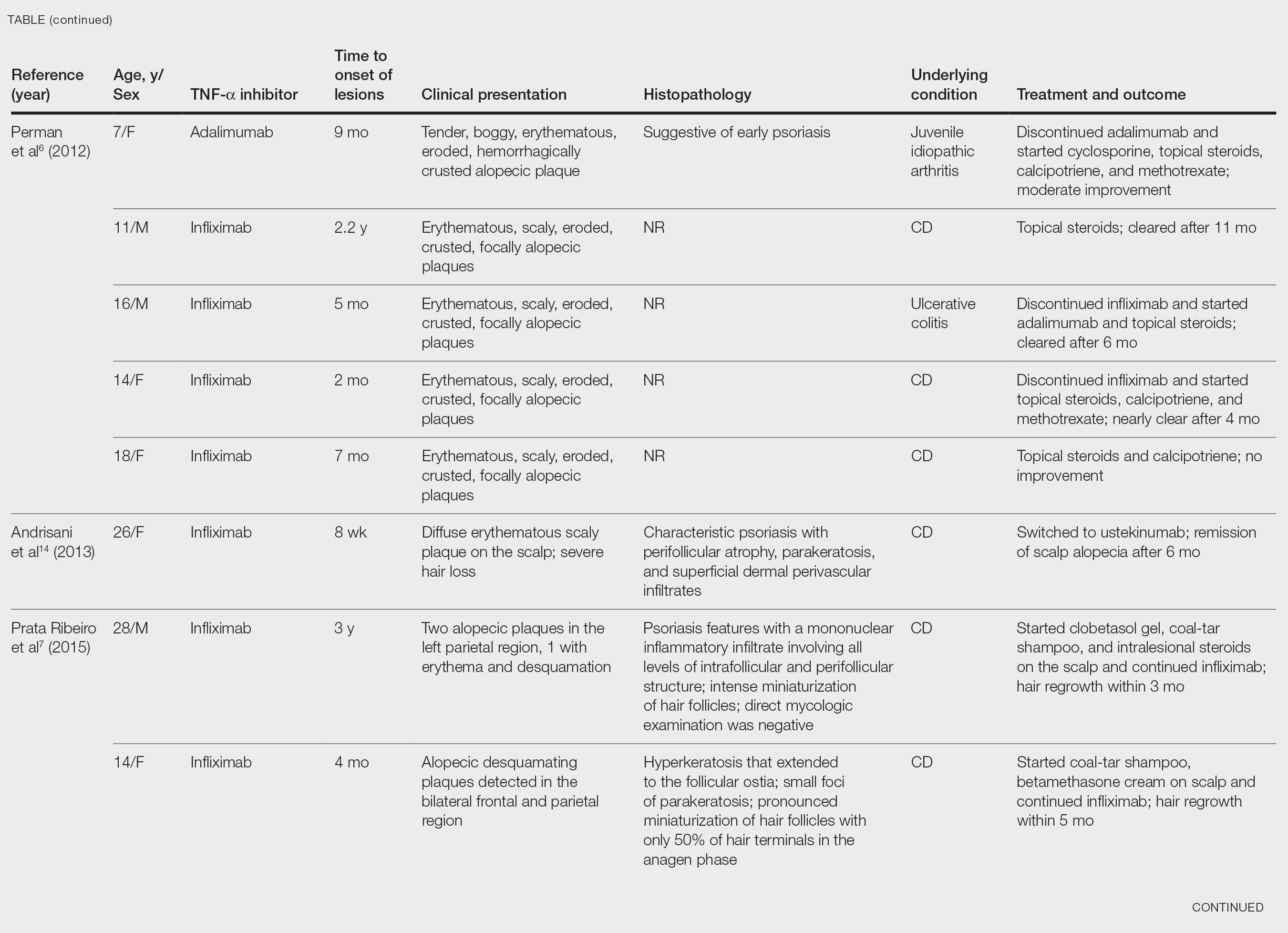
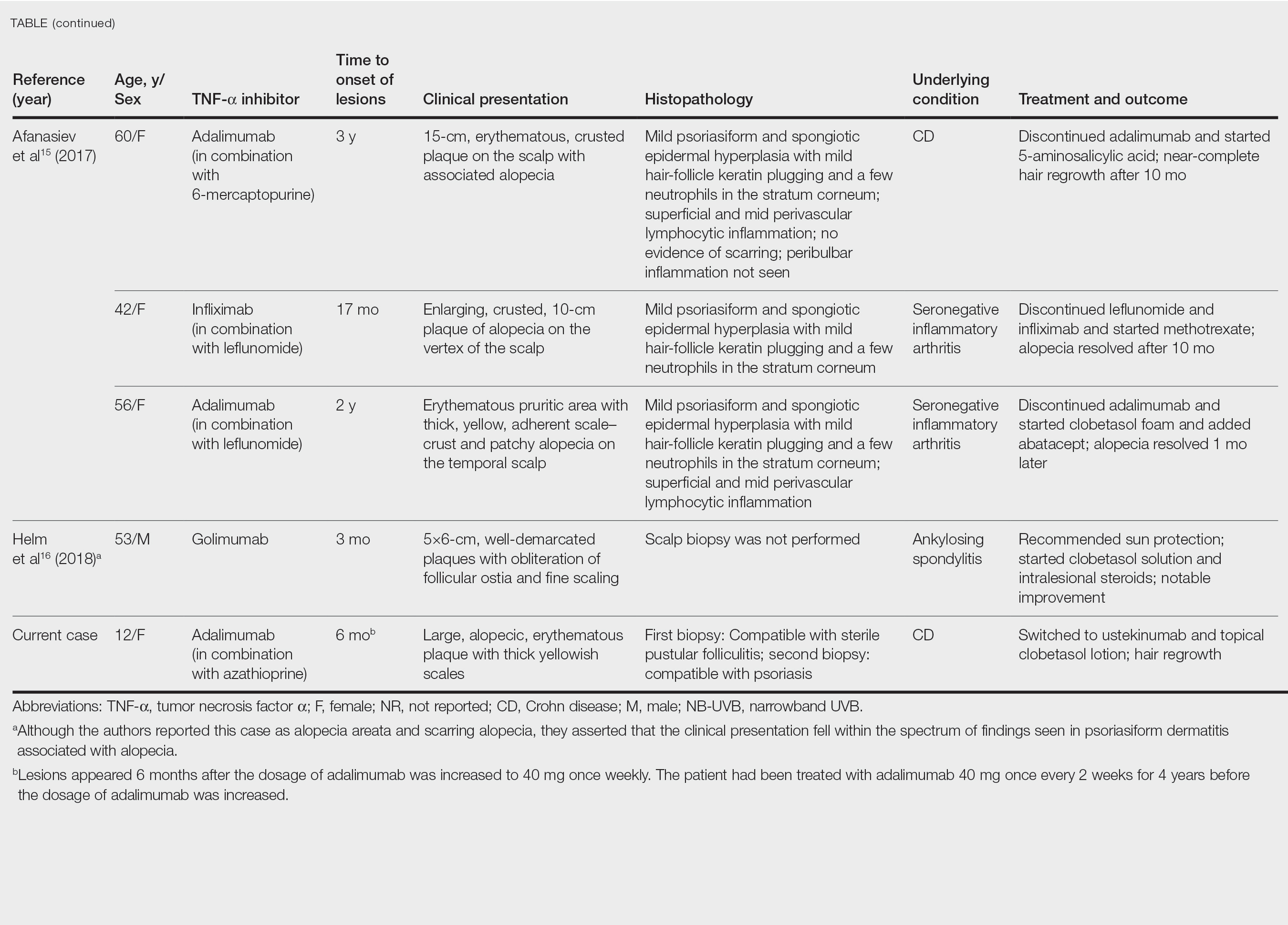
Laga et al17 reported that TNF-α inhibitor–induced psoriasis can have a variety of histopathologic findings, including typical findings of various stages of psoriasis, a lichenoid pattern mimicking remnants of lichen planus, and sterile pustular folliculitis. Our patient’s 2 scalp biopsies demonstrated results consistent with findings reported by Laga et al.17 In the first biopsy, findings were consistent with a dense neutrophilic infiltrate with negative sterile cultures and negative periodic acid–Schiff stain (sterile folliculitis), with crust and areas of parakeratosis. The second biopsy demonstrated psoriasiform hyperplasia, parakeratosis, and an absent granular layer, all typical features of psoriasis (Figure 2).
Including the current case, our review of the literature yielded 7 pediatric (ie, 0–18 years of age) cases of TNF-α inhibitor–induced psoriatic alopecia. Of the 6 previously reported pediatric cases, 5 occurred after administration of infliximab.6,7
Similar to our case, TNF-α inhibitor–induced psoriatic alopecia was reported in a 7-year-old girl who was treated with adalimumab for juvenile idiopathic arthritis.6 Nine months after starting treatment, that patient presented with a tender, erythematous, eroded, and crusted alopecic plaque along with scaly plaques on the scalp. Adalimumab was discontinued, and cyclosporine and topical steroids were started. Cyclosporine was then discontinued due to partial resolution of the psoriasis; the patient was started on abatacept, with persistence of the psoriasis and alopecia. The patient was then started on oral methotrexate 12.5 mg once weekly with moderate improvement and mild to moderate exacerbations.
Tumor necrosis factor α inhibitor–induced psoriasis may occur as a result of a cytokine imbalance. A TNF-α blockade leads to upregulation of interferon α (IFN-α) and TNF-α production by plasmacytoid dendritic cells (pDCs), usually in genetically susceptible people.6,7,9-15 The IFN-α induces maturation of myeloid dendritic cells (mDCs) responsible for increasing proinflammatory cytokines that contribute to psoriasis.11 Generation of TNF-α by pDCs leads to mature or activated dendritic cells derived from pDCs through autocrine TNF-α production and paracrine IFN-α production from immature mDCs.9 Once pDCs mature, they are incapable of producing IFN-α; TNF-α then inhibits IFN-α production by inducing pDC maturation.11 Overproduction of IFN-α during TNF-α inhibition induces expression of the chemokine receptor CXCR3 on T cells, which recruits T cells to the dermis. The T cells then produce TNF-α, causing psoriatic skin lesions.10,11,13,14
Although TNF-α inhibitor–induced psoriatic alopecia is uncommon, the condition should be considered in female patients with underlying proinflammatory disease—CD in particular. Perman et al6 reported 5 cases of psoriatic alopecia in which 3 patients initially were treated with griseofulvin because of suspected tinea capitis.
Conditions with similar clinical findings should be ruled out before making a diagnosis of TNF-α inhibitor–induced psoriatic alopecia. Although clinicopathologic correlation is essential for making the diagnosis, it is possible that the histologic findings will not be specific for psoriasis.17 It is important to be aware of this condition in patients being treated with a TNF-α inhibitor as early as 2 months to 4 years or longer after starting treatment.
Previously reported cases have demonstrated various treatment options that yielded improvement or resolution of TNF-α inhibitor–induced psoriatic alopecia. These include either continuation or discontinuation of the TNF-α inhibitor combined with topical or intralesional steroids, methotrexate, or cyclosporine. Another option is to switch the TNF-α inhibitor to another biologic. Outcomes vary from patient to patient, making the physician’s clinical judgment crucial in deciding which treatment route to take. Our patient showed notable improvement when she was switched from adalimumab to ustekinumab as well as the combination of ustekinumab and clobetasol lotion 0.05%.
Conclusion
We recommend an individualized approach that provides patients with the safest and least invasive treatment option for TNF-α inhibitor–induced psoriatic alopecia. In most reported cases, the problem resolved with treatment, thereby classifying this form of alopecia as noncicatricial alopecia.
- Horneff G, Seyger MMB, Arikan D, et al. Safety of adalimumab in pediatric patients with polyarticular juvenile idiopathic arthritis, enthesitis-related arthritis, psoriasis, and Crohn’s disease. J Pediatr. 2018;201:166-175.e3. doi:10.1016/j.jpeds.2018.05.042
- Brown G, Wang E, Leon A, et al. Tumor necrosis factor-α inhibitor-induced psoriasis: systematic review of clinical features, histopathological findings, and management experience. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2017;76:334-341. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2016.08.012
- George SMC, Taylor MR, Farrant PBJ. Psoriatic alopecia. Clin Exp Dermatol. 2015;40:717-721. doi:10.1111/ced.12715
- Shuster S. Psoriatic alopecia. Br J Dermatol. 1972;87:73-77. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2133.1972.tb05103.x
- Silva CY, Brown KL, Kurban AK, et al. Psoriatic alopecia—fact or fiction? a clinicohistopathologic reappraisal. Indian J Dermatol Venereol Leprol. 2012;78:611-619. doi:10.4103/0378-6323.100574
- Perman MJ, Lovell DJ, Denson LA, et al. Five cases of anti-tumor necrosis factor alpha-induced psoriasis presenting with severe scalp involvement in children. Pediatr Dermatol. 2012;29:454-459. doi:10.1111/j.1525-1470.2011.01521.x
- Prata Ribeiro LB, Gonçalves Rego JC, Duque Estrada B, et al. Alopecia secondary to anti-tumor necrosis factor-alpha therapy. An Bras Dermatol. 2015;90:232–235. doi:10.1590/abd1806-4841.20153084
- Papadavid E, Gazi S, Dalamaga M, et al. Palmoplantar and scalp psoriasis occurring during anti-tumour necrosis factor-alpha therapy: a case series of four patients and guidelines for management. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2008;22:380-382. doi:10.1111/j.1468-3083.2007.02335.x
- Manni E, Barachini P. Psoriasis induced by infliximab in a patient suffering from Crohn’s disease. Int J Immunopathol Pharmacol. 2009;22:841-844. doi:10.1177/039463200902200331
- El Shabrawi-Caelen L, La Placa M, Vincenzi C, et al. Adalimumab-induced psoriasis of the scalp with diffuse alopecia: a severe potentially irreversible cutaneous side effect of TNF-alpha blockers. Inflamm Bowel Dis. 2010;16:182-183. doi:10.1002/ibd.20954
- Medkour F, Babai S, Chanteloup E, et al. Development of diffuse psoriasis with alopecia during treatment of Crohn’s disease with infliximab. Gastroenterol Clin Biol. 2010;34:140-141. doi:10.1016/j.gcb.2009.10.021
- Doyle LA, Sperling LC, Baksh S, et al. Psoriatic alopecia/alopecia areata-like reactions secondary to anti-tumor necrosis factor-α therapy: a novel cause of noncicatricial alopecia. Am J Dermatopathol. 2011;33:161-166. doi:10.1097/DAD.0b013e3181ef7403
- Osório F, Magro F, Lisboa C, et al. Anti-TNF-alpha induced psoriasiform eruptions with severe scalp involvement and alopecia: report of five cases and review of the literature. Dermatology. 2012;225:163-167. doi:10.1159/000342503
- Andrisani G, Marzo M, Celleno L, et al. Development of psoriasis scalp with alopecia during treatment of Crohn’s disease with infliximab and rapid response to both diseases to ustekinumab. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2013;17:2831-2836.
- Afanasiev OK, Zhang CZ, Ruhoy SM. TNF-inhibitor associated psoriatic alopecia: diagnostic utility of sebaceous lobule atrophy. J Cutan Pathol. 2017;44:563-569. doi:10.1111/cup.12932
- Helm MM, Haddad S. Alopecia areata and scarring alopecia presenting during golimumab therapy for ankylosing spondylitis. N Am J Med Sci. 2018;11:22-24. doi:10.7156/najms.2018.110122
- Laga AC, Vleugels RA, Qureshi AA, et al. Histopathologic spectrum of psoriasiform skin reactions associated with tumor necrosis factor-a inhibitor therapy. a study of 16 biopsies. Am J Dermatopathol. 2010;32:568-573. doi:10.1097/DAD.0b013e3181cb3ff7
Tumor necrosis factor α (TNF-α) inhibitor–induced psoriasis is a known paradoxical adverse effect of this family of medications, which includes infliximab, adalimumab, etanercept, golimumab, and certolizumab. In the pediatric population, these therapies recently gained approval for nondermatologic conditions—meaning that this phenomenon is encountered more frequently.1 In a systematic review of TNF-α inhibitor–induced psoriasis, severe scalp involvement was associated with alopecia in 7.5% of cases.2 Onset of scalp psoriasis with alopecia in patients being treated with a TNF-α inhibitor should lead to consideration of this condition.
Psoriatic alopecia is an uncommon presentation of psoriasis. Although well described, alopecia as a clinical manifestation of scalp psoriasis is not a well-known concept among clinicians and has never been widely accepted. Adding to the diagnostic challenge is that psoriatic alopecia secondary to TNF-α inhibitor–induced psoriasis rarely has been reported in adults or children.3-5 Including our case, our review of the literature yielded 7 pediatric cases (≤18 years) of TNF-α inhibitor–induced psoriatic alopecia.6,7 A primary literature search of PubMed articles indexed for MEDLINE was conducted using the terms psoriatic alopecia, psoriasiform alopecia, TNF-α inhibitors, infliximab, adalimumab, etanercept, golimumab, and certolizumab.
We present the case of a pediatric patient with psoriatic alopecia secondary to treatment with adalimumab for Crohn disease (CD). We also provide a review of reported cases of psoriatic alopecia induced by a TNF-α inhibitor in the literature.
Case Report
A 12-year-old girl presented to our dermatology clinic with erythematous scaly plaques on the trunk, scalp, arms, and legs of 2 months’ duration. The lesions involved approximately 15% of the body surface area. The patient’s medical history was remarkable for CD diagnosed 4 years prior to presentation of the skin lesions. She had been treated for the past 2 years with adalimumab 40 mg once every 2 weeks and azathioprine 100 mg once daily. Because her CD was poorly controlled, the dosage of adalimumab was increased to 40 mg once weekly 6 months prior to the current presentation.
Our diagnosis was TNF-α inhibitor-induced psoriasis secondary to treatment with adalimumab.
The patient was treated with mometasone lotion 0.1% for the scalp lesions and triamcinolone cream 0.1% for the body lesions. Because of the extent of the psoriasis, we recommended changing adalimumab to ustekinumab, which is approved for CD in adults but is off label in children.
At 1-month follow-up, after receiving the induction dose of ustekinumab, the patient presented with partial improvement of the skin lesions but had developed a large, alopecic, erythematous plaque with thick yellowish scales on the scalp (Figure 1). She also had a positive hair pull test. The presumptive initial diagnosis of the alopecic scalp lesion was tinea capitis, for which multiple potassium hydroxide preparations of scales were performed, all yielding negative results. In addition, histopathologic examination with hematoxylin and eosin staining was performed (Figures 2A and 2B). Sterile tissue cultures for bacteria, fungi, and acid-fast bacilli were obtained and showed no growth. Periodic acid–Schiff staining was negative for fungal structures.


A second biopsy showed a psoriasiform pattern, parakeratosis, and hypogranulosis, highly suggestive of psoriasis (Figure 2C and 2D). Based on those findings, a diagnosis of psoriatic alopecia was made. The mometasone was switched to clobetasol lotion 0.05%. The patient continued treatment with ustekinumab. At 6-month follow-up, her CD was well controlled and she showed hair regrowth in previously alopecic areas (Figure 3).

Comment
Psoriatic alopecia induced by a TNF-α inhibitor was first reported in 2007 in a 30-year-old woman with ankylosing spondylitis who was being treated with adalimumab.8 She had erythematous, scaly, alopecic plaques on the scalp and palmoplantar pustulosis. Findings on skin biopsy were compatible with psoriasis. The patient’s severe scalp psoriasis failed to respond to topical steroid treatment and adalimumab cessation. The extensive hair loss responded to cyclosporine 3 mg/kg daily.8
After conducting an extensive literature review, we found 26 cases of TNF-α–induced psoriatic alopecia, including the current case (Table).6-16 The mean age at diagnosis was 27.8 years (SD, 13.6 years; range, 7–60 years). The female-to-male ratio was 3.3:1. The most common underlying condition for which TNF-α inhibitors were prescribed was CD (77% [20/26]). Psoriatic alopecia most commonly was reported secondary to treatment with infliximab (54% [14/26]), followed by adalimumab (42% [11/26]). Golimumab was the causative drug in 1 (4%) case. We did not find reports of etanercept or certolizumab having induced this manifestation. The onset of the scalp lesions occurred 2 to 46 months after starting treatment with the causative medication.




Laga et al17 reported that TNF-α inhibitor–induced psoriasis can have a variety of histopathologic findings, including typical findings of various stages of psoriasis, a lichenoid pattern mimicking remnants of lichen planus, and sterile pustular folliculitis. Our patient’s 2 scalp biopsies demonstrated results consistent with findings reported by Laga et al.17 In the first biopsy, findings were consistent with a dense neutrophilic infiltrate with negative sterile cultures and negative periodic acid–Schiff stain (sterile folliculitis), with crust and areas of parakeratosis. The second biopsy demonstrated psoriasiform hyperplasia, parakeratosis, and an absent granular layer, all typical features of psoriasis (Figure 2).
Including the current case, our review of the literature yielded 7 pediatric (ie, 0–18 years of age) cases of TNF-α inhibitor–induced psoriatic alopecia. Of the 6 previously reported pediatric cases, 5 occurred after administration of infliximab.6,7
Similar to our case, TNF-α inhibitor–induced psoriatic alopecia was reported in a 7-year-old girl who was treated with adalimumab for juvenile idiopathic arthritis.6 Nine months after starting treatment, that patient presented with a tender, erythematous, eroded, and crusted alopecic plaque along with scaly plaques on the scalp. Adalimumab was discontinued, and cyclosporine and topical steroids were started. Cyclosporine was then discontinued due to partial resolution of the psoriasis; the patient was started on abatacept, with persistence of the psoriasis and alopecia. The patient was then started on oral methotrexate 12.5 mg once weekly with moderate improvement and mild to moderate exacerbations.
Tumor necrosis factor α inhibitor–induced psoriasis may occur as a result of a cytokine imbalance. A TNF-α blockade leads to upregulation of interferon α (IFN-α) and TNF-α production by plasmacytoid dendritic cells (pDCs), usually in genetically susceptible people.6,7,9-15 The IFN-α induces maturation of myeloid dendritic cells (mDCs) responsible for increasing proinflammatory cytokines that contribute to psoriasis.11 Generation of TNF-α by pDCs leads to mature or activated dendritic cells derived from pDCs through autocrine TNF-α production and paracrine IFN-α production from immature mDCs.9 Once pDCs mature, they are incapable of producing IFN-α; TNF-α then inhibits IFN-α production by inducing pDC maturation.11 Overproduction of IFN-α during TNF-α inhibition induces expression of the chemokine receptor CXCR3 on T cells, which recruits T cells to the dermis. The T cells then produce TNF-α, causing psoriatic skin lesions.10,11,13,14
Although TNF-α inhibitor–induced psoriatic alopecia is uncommon, the condition should be considered in female patients with underlying proinflammatory disease—CD in particular. Perman et al6 reported 5 cases of psoriatic alopecia in which 3 patients initially were treated with griseofulvin because of suspected tinea capitis.
Conditions with similar clinical findings should be ruled out before making a diagnosis of TNF-α inhibitor–induced psoriatic alopecia. Although clinicopathologic correlation is essential for making the diagnosis, it is possible that the histologic findings will not be specific for psoriasis.17 It is important to be aware of this condition in patients being treated with a TNF-α inhibitor as early as 2 months to 4 years or longer after starting treatment.
Previously reported cases have demonstrated various treatment options that yielded improvement or resolution of TNF-α inhibitor–induced psoriatic alopecia. These include either continuation or discontinuation of the TNF-α inhibitor combined with topical or intralesional steroids, methotrexate, or cyclosporine. Another option is to switch the TNF-α inhibitor to another biologic. Outcomes vary from patient to patient, making the physician’s clinical judgment crucial in deciding which treatment route to take. Our patient showed notable improvement when she was switched from adalimumab to ustekinumab as well as the combination of ustekinumab and clobetasol lotion 0.05%.
Conclusion
We recommend an individualized approach that provides patients with the safest and least invasive treatment option for TNF-α inhibitor–induced psoriatic alopecia. In most reported cases, the problem resolved with treatment, thereby classifying this form of alopecia as noncicatricial alopecia.
Tumor necrosis factor α (TNF-α) inhibitor–induced psoriasis is a known paradoxical adverse effect of this family of medications, which includes infliximab, adalimumab, etanercept, golimumab, and certolizumab. In the pediatric population, these therapies recently gained approval for nondermatologic conditions—meaning that this phenomenon is encountered more frequently.1 In a systematic review of TNF-α inhibitor–induced psoriasis, severe scalp involvement was associated with alopecia in 7.5% of cases.2 Onset of scalp psoriasis with alopecia in patients being treated with a TNF-α inhibitor should lead to consideration of this condition.
Psoriatic alopecia is an uncommon presentation of psoriasis. Although well described, alopecia as a clinical manifestation of scalp psoriasis is not a well-known concept among clinicians and has never been widely accepted. Adding to the diagnostic challenge is that psoriatic alopecia secondary to TNF-α inhibitor–induced psoriasis rarely has been reported in adults or children.3-5 Including our case, our review of the literature yielded 7 pediatric cases (≤18 years) of TNF-α inhibitor–induced psoriatic alopecia.6,7 A primary literature search of PubMed articles indexed for MEDLINE was conducted using the terms psoriatic alopecia, psoriasiform alopecia, TNF-α inhibitors, infliximab, adalimumab, etanercept, golimumab, and certolizumab.
We present the case of a pediatric patient with psoriatic alopecia secondary to treatment with adalimumab for Crohn disease (CD). We also provide a review of reported cases of psoriatic alopecia induced by a TNF-α inhibitor in the literature.
Case Report
A 12-year-old girl presented to our dermatology clinic with erythematous scaly plaques on the trunk, scalp, arms, and legs of 2 months’ duration. The lesions involved approximately 15% of the body surface area. The patient’s medical history was remarkable for CD diagnosed 4 years prior to presentation of the skin lesions. She had been treated for the past 2 years with adalimumab 40 mg once every 2 weeks and azathioprine 100 mg once daily. Because her CD was poorly controlled, the dosage of adalimumab was increased to 40 mg once weekly 6 months prior to the current presentation.
Our diagnosis was TNF-α inhibitor-induced psoriasis secondary to treatment with adalimumab.
The patient was treated with mometasone lotion 0.1% for the scalp lesions and triamcinolone cream 0.1% for the body lesions. Because of the extent of the psoriasis, we recommended changing adalimumab to ustekinumab, which is approved for CD in adults but is off label in children.
At 1-month follow-up, after receiving the induction dose of ustekinumab, the patient presented with partial improvement of the skin lesions but had developed a large, alopecic, erythematous plaque with thick yellowish scales on the scalp (Figure 1). She also had a positive hair pull test. The presumptive initial diagnosis of the alopecic scalp lesion was tinea capitis, for which multiple potassium hydroxide preparations of scales were performed, all yielding negative results. In addition, histopathologic examination with hematoxylin and eosin staining was performed (Figures 2A and 2B). Sterile tissue cultures for bacteria, fungi, and acid-fast bacilli were obtained and showed no growth. Periodic acid–Schiff staining was negative for fungal structures.


A second biopsy showed a psoriasiform pattern, parakeratosis, and hypogranulosis, highly suggestive of psoriasis (Figure 2C and 2D). Based on those findings, a diagnosis of psoriatic alopecia was made. The mometasone was switched to clobetasol lotion 0.05%. The patient continued treatment with ustekinumab. At 6-month follow-up, her CD was well controlled and she showed hair regrowth in previously alopecic areas (Figure 3).

Comment
Psoriatic alopecia induced by a TNF-α inhibitor was first reported in 2007 in a 30-year-old woman with ankylosing spondylitis who was being treated with adalimumab.8 She had erythematous, scaly, alopecic plaques on the scalp and palmoplantar pustulosis. Findings on skin biopsy were compatible with psoriasis. The patient’s severe scalp psoriasis failed to respond to topical steroid treatment and adalimumab cessation. The extensive hair loss responded to cyclosporine 3 mg/kg daily.8
After conducting an extensive literature review, we found 26 cases of TNF-α–induced psoriatic alopecia, including the current case (Table).6-16 The mean age at diagnosis was 27.8 years (SD, 13.6 years; range, 7–60 years). The female-to-male ratio was 3.3:1. The most common underlying condition for which TNF-α inhibitors were prescribed was CD (77% [20/26]). Psoriatic alopecia most commonly was reported secondary to treatment with infliximab (54% [14/26]), followed by adalimumab (42% [11/26]). Golimumab was the causative drug in 1 (4%) case. We did not find reports of etanercept or certolizumab having induced this manifestation. The onset of the scalp lesions occurred 2 to 46 months after starting treatment with the causative medication.




Laga et al17 reported that TNF-α inhibitor–induced psoriasis can have a variety of histopathologic findings, including typical findings of various stages of psoriasis, a lichenoid pattern mimicking remnants of lichen planus, and sterile pustular folliculitis. Our patient’s 2 scalp biopsies demonstrated results consistent with findings reported by Laga et al.17 In the first biopsy, findings were consistent with a dense neutrophilic infiltrate with negative sterile cultures and negative periodic acid–Schiff stain (sterile folliculitis), with crust and areas of parakeratosis. The second biopsy demonstrated psoriasiform hyperplasia, parakeratosis, and an absent granular layer, all typical features of psoriasis (Figure 2).
Including the current case, our review of the literature yielded 7 pediatric (ie, 0–18 years of age) cases of TNF-α inhibitor–induced psoriatic alopecia. Of the 6 previously reported pediatric cases, 5 occurred after administration of infliximab.6,7
Similar to our case, TNF-α inhibitor–induced psoriatic alopecia was reported in a 7-year-old girl who was treated with adalimumab for juvenile idiopathic arthritis.6 Nine months after starting treatment, that patient presented with a tender, erythematous, eroded, and crusted alopecic plaque along with scaly plaques on the scalp. Adalimumab was discontinued, and cyclosporine and topical steroids were started. Cyclosporine was then discontinued due to partial resolution of the psoriasis; the patient was started on abatacept, with persistence of the psoriasis and alopecia. The patient was then started on oral methotrexate 12.5 mg once weekly with moderate improvement and mild to moderate exacerbations.
Tumor necrosis factor α inhibitor–induced psoriasis may occur as a result of a cytokine imbalance. A TNF-α blockade leads to upregulation of interferon α (IFN-α) and TNF-α production by plasmacytoid dendritic cells (pDCs), usually in genetically susceptible people.6,7,9-15 The IFN-α induces maturation of myeloid dendritic cells (mDCs) responsible for increasing proinflammatory cytokines that contribute to psoriasis.11 Generation of TNF-α by pDCs leads to mature or activated dendritic cells derived from pDCs through autocrine TNF-α production and paracrine IFN-α production from immature mDCs.9 Once pDCs mature, they are incapable of producing IFN-α; TNF-α then inhibits IFN-α production by inducing pDC maturation.11 Overproduction of IFN-α during TNF-α inhibition induces expression of the chemokine receptor CXCR3 on T cells, which recruits T cells to the dermis. The T cells then produce TNF-α, causing psoriatic skin lesions.10,11,13,14
Although TNF-α inhibitor–induced psoriatic alopecia is uncommon, the condition should be considered in female patients with underlying proinflammatory disease—CD in particular. Perman et al6 reported 5 cases of psoriatic alopecia in which 3 patients initially were treated with griseofulvin because of suspected tinea capitis.
Conditions with similar clinical findings should be ruled out before making a diagnosis of TNF-α inhibitor–induced psoriatic alopecia. Although clinicopathologic correlation is essential for making the diagnosis, it is possible that the histologic findings will not be specific for psoriasis.17 It is important to be aware of this condition in patients being treated with a TNF-α inhibitor as early as 2 months to 4 years or longer after starting treatment.
Previously reported cases have demonstrated various treatment options that yielded improvement or resolution of TNF-α inhibitor–induced psoriatic alopecia. These include either continuation or discontinuation of the TNF-α inhibitor combined with topical or intralesional steroids, methotrexate, or cyclosporine. Another option is to switch the TNF-α inhibitor to another biologic. Outcomes vary from patient to patient, making the physician’s clinical judgment crucial in deciding which treatment route to take. Our patient showed notable improvement when she was switched from adalimumab to ustekinumab as well as the combination of ustekinumab and clobetasol lotion 0.05%.
Conclusion
We recommend an individualized approach that provides patients with the safest and least invasive treatment option for TNF-α inhibitor–induced psoriatic alopecia. In most reported cases, the problem resolved with treatment, thereby classifying this form of alopecia as noncicatricial alopecia.
- Horneff G, Seyger MMB, Arikan D, et al. Safety of adalimumab in pediatric patients with polyarticular juvenile idiopathic arthritis, enthesitis-related arthritis, psoriasis, and Crohn’s disease. J Pediatr. 2018;201:166-175.e3. doi:10.1016/j.jpeds.2018.05.042
- Brown G, Wang E, Leon A, et al. Tumor necrosis factor-α inhibitor-induced psoriasis: systematic review of clinical features, histopathological findings, and management experience. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2017;76:334-341. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2016.08.012
- George SMC, Taylor MR, Farrant PBJ. Psoriatic alopecia. Clin Exp Dermatol. 2015;40:717-721. doi:10.1111/ced.12715
- Shuster S. Psoriatic alopecia. Br J Dermatol. 1972;87:73-77. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2133.1972.tb05103.x
- Silva CY, Brown KL, Kurban AK, et al. Psoriatic alopecia—fact or fiction? a clinicohistopathologic reappraisal. Indian J Dermatol Venereol Leprol. 2012;78:611-619. doi:10.4103/0378-6323.100574
- Perman MJ, Lovell DJ, Denson LA, et al. Five cases of anti-tumor necrosis factor alpha-induced psoriasis presenting with severe scalp involvement in children. Pediatr Dermatol. 2012;29:454-459. doi:10.1111/j.1525-1470.2011.01521.x
- Prata Ribeiro LB, Gonçalves Rego JC, Duque Estrada B, et al. Alopecia secondary to anti-tumor necrosis factor-alpha therapy. An Bras Dermatol. 2015;90:232–235. doi:10.1590/abd1806-4841.20153084
- Papadavid E, Gazi S, Dalamaga M, et al. Palmoplantar and scalp psoriasis occurring during anti-tumour necrosis factor-alpha therapy: a case series of four patients and guidelines for management. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2008;22:380-382. doi:10.1111/j.1468-3083.2007.02335.x
- Manni E, Barachini P. Psoriasis induced by infliximab in a patient suffering from Crohn’s disease. Int J Immunopathol Pharmacol. 2009;22:841-844. doi:10.1177/039463200902200331
- El Shabrawi-Caelen L, La Placa M, Vincenzi C, et al. Adalimumab-induced psoriasis of the scalp with diffuse alopecia: a severe potentially irreversible cutaneous side effect of TNF-alpha blockers. Inflamm Bowel Dis. 2010;16:182-183. doi:10.1002/ibd.20954
- Medkour F, Babai S, Chanteloup E, et al. Development of diffuse psoriasis with alopecia during treatment of Crohn’s disease with infliximab. Gastroenterol Clin Biol. 2010;34:140-141. doi:10.1016/j.gcb.2009.10.021
- Doyle LA, Sperling LC, Baksh S, et al. Psoriatic alopecia/alopecia areata-like reactions secondary to anti-tumor necrosis factor-α therapy: a novel cause of noncicatricial alopecia. Am J Dermatopathol. 2011;33:161-166. doi:10.1097/DAD.0b013e3181ef7403
- Osório F, Magro F, Lisboa C, et al. Anti-TNF-alpha induced psoriasiform eruptions with severe scalp involvement and alopecia: report of five cases and review of the literature. Dermatology. 2012;225:163-167. doi:10.1159/000342503
- Andrisani G, Marzo M, Celleno L, et al. Development of psoriasis scalp with alopecia during treatment of Crohn’s disease with infliximab and rapid response to both diseases to ustekinumab. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2013;17:2831-2836.
- Afanasiev OK, Zhang CZ, Ruhoy SM. TNF-inhibitor associated psoriatic alopecia: diagnostic utility of sebaceous lobule atrophy. J Cutan Pathol. 2017;44:563-569. doi:10.1111/cup.12932
- Helm MM, Haddad S. Alopecia areata and scarring alopecia presenting during golimumab therapy for ankylosing spondylitis. N Am J Med Sci. 2018;11:22-24. doi:10.7156/najms.2018.110122
- Laga AC, Vleugels RA, Qureshi AA, et al. Histopathologic spectrum of psoriasiform skin reactions associated with tumor necrosis factor-a inhibitor therapy. a study of 16 biopsies. Am J Dermatopathol. 2010;32:568-573. doi:10.1097/DAD.0b013e3181cb3ff7
- Horneff G, Seyger MMB, Arikan D, et al. Safety of adalimumab in pediatric patients with polyarticular juvenile idiopathic arthritis, enthesitis-related arthritis, psoriasis, and Crohn’s disease. J Pediatr. 2018;201:166-175.e3. doi:10.1016/j.jpeds.2018.05.042
- Brown G, Wang E, Leon A, et al. Tumor necrosis factor-α inhibitor-induced psoriasis: systematic review of clinical features, histopathological findings, and management experience. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2017;76:334-341. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2016.08.012
- George SMC, Taylor MR, Farrant PBJ. Psoriatic alopecia. Clin Exp Dermatol. 2015;40:717-721. doi:10.1111/ced.12715
- Shuster S. Psoriatic alopecia. Br J Dermatol. 1972;87:73-77. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2133.1972.tb05103.x
- Silva CY, Brown KL, Kurban AK, et al. Psoriatic alopecia—fact or fiction? a clinicohistopathologic reappraisal. Indian J Dermatol Venereol Leprol. 2012;78:611-619. doi:10.4103/0378-6323.100574
- Perman MJ, Lovell DJ, Denson LA, et al. Five cases of anti-tumor necrosis factor alpha-induced psoriasis presenting with severe scalp involvement in children. Pediatr Dermatol. 2012;29:454-459. doi:10.1111/j.1525-1470.2011.01521.x
- Prata Ribeiro LB, Gonçalves Rego JC, Duque Estrada B, et al. Alopecia secondary to anti-tumor necrosis factor-alpha therapy. An Bras Dermatol. 2015;90:232–235. doi:10.1590/abd1806-4841.20153084
- Papadavid E, Gazi S, Dalamaga M, et al. Palmoplantar and scalp psoriasis occurring during anti-tumour necrosis factor-alpha therapy: a case series of four patients and guidelines for management. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2008;22:380-382. doi:10.1111/j.1468-3083.2007.02335.x
- Manni E, Barachini P. Psoriasis induced by infliximab in a patient suffering from Crohn’s disease. Int J Immunopathol Pharmacol. 2009;22:841-844. doi:10.1177/039463200902200331
- El Shabrawi-Caelen L, La Placa M, Vincenzi C, et al. Adalimumab-induced psoriasis of the scalp with diffuse alopecia: a severe potentially irreversible cutaneous side effect of TNF-alpha blockers. Inflamm Bowel Dis. 2010;16:182-183. doi:10.1002/ibd.20954
- Medkour F, Babai S, Chanteloup E, et al. Development of diffuse psoriasis with alopecia during treatment of Crohn’s disease with infliximab. Gastroenterol Clin Biol. 2010;34:140-141. doi:10.1016/j.gcb.2009.10.021
- Doyle LA, Sperling LC, Baksh S, et al. Psoriatic alopecia/alopecia areata-like reactions secondary to anti-tumor necrosis factor-α therapy: a novel cause of noncicatricial alopecia. Am J Dermatopathol. 2011;33:161-166. doi:10.1097/DAD.0b013e3181ef7403
- Osório F, Magro F, Lisboa C, et al. Anti-TNF-alpha induced psoriasiform eruptions with severe scalp involvement and alopecia: report of five cases and review of the literature. Dermatology. 2012;225:163-167. doi:10.1159/000342503
- Andrisani G, Marzo M, Celleno L, et al. Development of psoriasis scalp with alopecia during treatment of Crohn’s disease with infliximab and rapid response to both diseases to ustekinumab. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2013;17:2831-2836.
- Afanasiev OK, Zhang CZ, Ruhoy SM. TNF-inhibitor associated psoriatic alopecia: diagnostic utility of sebaceous lobule atrophy. J Cutan Pathol. 2017;44:563-569. doi:10.1111/cup.12932
- Helm MM, Haddad S. Alopecia areata and scarring alopecia presenting during golimumab therapy for ankylosing spondylitis. N Am J Med Sci. 2018;11:22-24. doi:10.7156/najms.2018.110122
- Laga AC, Vleugels RA, Qureshi AA, et al. Histopathologic spectrum of psoriasiform skin reactions associated with tumor necrosis factor-a inhibitor therapy. a study of 16 biopsies. Am J Dermatopathol. 2010;32:568-573. doi:10.1097/DAD.0b013e3181cb3ff7
Practice Points
- Psoriatic alopecia is a rare nonscarring alopecia that can present as a complication of treatment with tumor necrosis factor α inhibitors.
- This finding commonly is seen in females undergoing treatment with infliximab or adalimumab, usually for Crohn disease.
- Histopathologic findings can show a psoriasiform-pattern, neutrophil-rich, inflammatory infiltrate involving hair follicles or a lichenoid pattern.
FDA panel narrowly backs avacopan approval
A panel of federal advisers on May 6 lent support to the ChemoCentryx bid for approval of avacopan for a rare and serious autoimmune condition. But they also flagged concerns about both the evidence supporting claims of a benefit for this experimental drug and its safety.
At a meeting of the Food and Drug Administration’s Arthritis Advisory Committee, panelists voted 10-8 on a question of whether the risk-benefit profile of avacopan is adequate to support approval.
ChemoCentryx is seeking approval of avacopan for antineutrophil cytoplasmic autoantibody (ANCA)–associated vasculitis in the subtypes of granulomatosis with polyangiitis (GPA) and microscopic polyangiitis (MPA).
Regardless of their vote on this approval question, the panelists shared an interest in avacopan’s potential to reduce glucocorticoid use among some patients with ANCA-associated vasculitis, also called AAV. Mara L. Becker, MD, MSCE, the chair of the FDA’s panel, was among the panelists who said they reluctantly voted no.
“It pains me because I really want more steroid-sparing” medicines, said Dr. Becker of Duke University, Durham, N.C., who cited a need to gather more data on avacopan.
Margrit Wiesendanger, MD, PhD, of the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York, who was among the panelists voting yes, spoke of a need for caution if the FDA approves avacopan.
“Judicious use of this new medication will be warranted and perhaps additional guidance could be given to rheumatologists to help them decide for whom this medication is best,” she said.
Panelists had spoken earlier of avacopan as a possible alternative medicine for people with AAV who have conditions that make glucocorticoids riskier for them, such as those who have diabetes.
Close votes on safety profile, efficacy
The panel also voted 10-8 on a question about whether the safety profile of avacopan is adequate to support approval of avacopan for the treatment of adult patients with AAV.
In addition, the panel voted 9-9 on a question about whether efficacy data support approval of avacopan for the treatment of adult patients with AAV.
The FDA considers the recommendations of its advisory panels, but is not bound by them.
The FDA staff clearly expressed the view that ChemoCentryx fell short with the evidence presented for avacopan approval. Shares of San Carlos, Calif.–based ChemoCentryx dropped sharply from a May 3 closing price of $48.82 to a May 4 closing price of $26.63 after the FDA released the staff’s review of avacopan.
In a briefing prepared for the meeting, FDA staff detailed concerns about the evidence ChemoCentryx is using to seek approval. While acknowledging a need for new treatments for AAV as a rare condition, FDA staff honed in on what they described flaws in the testing of this experimental medicine, which is a small-molecule antagonist of the receptor of C5a, an end product of the complement cascade that acts as a potent neutrophil chemoattractant and agonist.
The FDA usually requires two phase 3 studies for approval of a new medicine but will do so with a single trial in cases of exceptional need, the agency staff said. But in these cases, the bar rises for the evidence provided from that single trial.
Difficulties in interpretation of complex study design
In the case of avacopan, though, the data from the key avacopan trial, Study CL010_168, known as ADVOCATE, there were substantial uncertainties around the phase 3 study design and results, raising questions about the adequacy of this single trial to inform the benefit-risk assessment.
In the briefing document, the FDA staff noted that it had “communicated many of the concerns” about ChemoCentryx’s research earlier to the company.
“Complexities of the study design, as detailed in the briefing document, raise questions about the interpretability of the data to define a clinically meaningful benefit of avacopan and its role in the management of AAV,” the FDA staff wrote.
“We acknowledge that AAV is a rare and serious disease associated with high morbidity and increased mortality. It is also a disease with high unmet need for new therapies. However, FDA wants to ensure that new products have a defined context of use, i.e., how a product would be used, and a favorable benefit-risk assessment for patients,” the staff added.
In addition, there were differences in the assessments performed by investigators and the adjudication committee, most frequently related to the attribution of persistent vasculitis, the FDA staff noted.
Statistical analyses of the primary endpoint using investigators’ estimates “resulted in more conservative estimates of treatment effect, e.g., statistical significance for superiority would no longer be demonstrated,” the FDA staff noted. “While the prespecified analysis used the Adjudicator assessments, the assessment based on the Investigators, experienced in management of vasculitis, may better reflect real-world use.”
Imbalances in use of glucocorticoids and maintenance therapy
Also among the complications in assessing the ADVOCATE trial data were the glucocorticoids taken by patients in the study, the FDA staff said.
In the avacopan arm of the trial, 86% of patients received non–study-supplied glucocorticoids. In addition, more avacopan‐treated patients experienced adverse events and serious adverse events within the hepatobiliary system leading to discontinuation.
Subgroups given different treatments represented another challenge in interpreting ADVOCATE results for the FDA staff.
At week 26, the proportion of patients in disease remission in the avacopan group (72.3%) was noninferior to the prednisone group (70.1%), the FDA staff said in the briefing document.
But at week 52, a disparity was observed between subgroups that had received rituximab and cyclophosphamide (intravenous and oral) induction treatment. The estimated risk difference for disease remission at week 52 was 15.0% (95% CI, 2.2%-27.7%) in the subgroup receiving induction with rituximab and 3.3% (95% CI, –14.8% to 21.4%) in the cyclophosphamide plus maintenance azathioprine subgroup, the agency’s staff said.
“Based on the data, there is no evidence of clinically meaningful treatment effect in the cyclophosphamide induction subgroup,” the FDA staff wrote. “Further, the treatment comparison in the complementary rituximab induction subgroup may not be considered meaningful because these patients did not receive maintenance therapy, i.e., due to undertreating of patients, the effect observed in the rituximab subgroup may not represent a clinically meaningful treatment effect, compared to standard of care.”
Rachel L. Glaser, MD, clinical team leader in FDA’s division of rheumatology and transplant medicine, reiterated these concerns to the advisory committee at the May 6 meeting.
“Throughout the development program, FDA advised the applicant that a noninferiority comparison would not be sufficient to show that avacopan can replaced glucocorticoids as it would be difficult to establish whether avacopan is effective or whether an effect was due to the rituximab or cyclophosphamide administered to both treatment arms,” she said.
In its briefing for the meeting, ChemoCentryx noted the limits of treatments now available for AAV. It also emphasized the toll of the condition, ranging from skin manifestations to glomerulonephritis to life-threatening pulmonary hemorrhage. If untreated, 80% of patients with GPA or MPA die within 2 years of disease onset, ChemoCentryx said in its briefing materials for the meeting.
The side effects of glucocorticoids were well known to the FDA panelists and the ChemoCentryx presenters. Witnesses at an open public hearing told their own stories of depression, anxiety, and irritability caused by these medicines.
During the ChemoCentryx presentation, a presenter for the company, Peter Merkel, MD, MPH, of the University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, said avacopan would provide patients with AAV with an alternative allowing them “to go on a much lower glucocorticoids regimen.”
A similar view was presented in a February 2021 editorial in the New England Journal of Medicine, titled “Avacopan – Time to Replace Glucocorticoids?” Written by Kenneth J. Warrington, MD, of the Mayo Clinic, Rochester, Minn., the opinion article called the ADVOCATE trial “a milestone in the treatment of ANCA-associated vasculitis; complement inhibition with avacopan has glucocorticoid-sparing effects and results in superior disease control.”
Dr. Warrington reported no conflicts in connection with his editorial nor payments from ChemoCentryx. He did report grants from other firms such as Eli Lilly.
Julia Lewis, MD, of Vanderbilt University, Nashville, Tenn., was among the more skeptical members of the FDA panel. She was among the “nays” in all three voting questions put to the panel. Still, she said there were signs of “clinically meaningful benefit” in the data presented, but noted that the nonstudy use of glucocorticoids made it difficult to interpret the ADVOCATE results.
Dr. Lewis noted that the FDA usually requires two studies for a drug approval, particularly with a compound not yet cleared for any use. While ANCA-associated vasculitis is rare, it would be possible to recruit patients for another trial of avacopan, adding to the results reported already for avacopan from ADVOCATE, she said.
“Were there to be another study, this would certainly be a supportive study and maybe qualify as two studies,” she said.
A panel of federal advisers on May 6 lent support to the ChemoCentryx bid for approval of avacopan for a rare and serious autoimmune condition. But they also flagged concerns about both the evidence supporting claims of a benefit for this experimental drug and its safety.
At a meeting of the Food and Drug Administration’s Arthritis Advisory Committee, panelists voted 10-8 on a question of whether the risk-benefit profile of avacopan is adequate to support approval.
ChemoCentryx is seeking approval of avacopan for antineutrophil cytoplasmic autoantibody (ANCA)–associated vasculitis in the subtypes of granulomatosis with polyangiitis (GPA) and microscopic polyangiitis (MPA).
Regardless of their vote on this approval question, the panelists shared an interest in avacopan’s potential to reduce glucocorticoid use among some patients with ANCA-associated vasculitis, also called AAV. Mara L. Becker, MD, MSCE, the chair of the FDA’s panel, was among the panelists who said they reluctantly voted no.
“It pains me because I really want more steroid-sparing” medicines, said Dr. Becker of Duke University, Durham, N.C., who cited a need to gather more data on avacopan.
Margrit Wiesendanger, MD, PhD, of the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York, who was among the panelists voting yes, spoke of a need for caution if the FDA approves avacopan.
“Judicious use of this new medication will be warranted and perhaps additional guidance could be given to rheumatologists to help them decide for whom this medication is best,” she said.
Panelists had spoken earlier of avacopan as a possible alternative medicine for people with AAV who have conditions that make glucocorticoids riskier for them, such as those who have diabetes.
Close votes on safety profile, efficacy
The panel also voted 10-8 on a question about whether the safety profile of avacopan is adequate to support approval of avacopan for the treatment of adult patients with AAV.
In addition, the panel voted 9-9 on a question about whether efficacy data support approval of avacopan for the treatment of adult patients with AAV.
The FDA considers the recommendations of its advisory panels, but is not bound by them.
The FDA staff clearly expressed the view that ChemoCentryx fell short with the evidence presented for avacopan approval. Shares of San Carlos, Calif.–based ChemoCentryx dropped sharply from a May 3 closing price of $48.82 to a May 4 closing price of $26.63 after the FDA released the staff’s review of avacopan.
In a briefing prepared for the meeting, FDA staff detailed concerns about the evidence ChemoCentryx is using to seek approval. While acknowledging a need for new treatments for AAV as a rare condition, FDA staff honed in on what they described flaws in the testing of this experimental medicine, which is a small-molecule antagonist of the receptor of C5a, an end product of the complement cascade that acts as a potent neutrophil chemoattractant and agonist.
The FDA usually requires two phase 3 studies for approval of a new medicine but will do so with a single trial in cases of exceptional need, the agency staff said. But in these cases, the bar rises for the evidence provided from that single trial.
Difficulties in interpretation of complex study design
In the case of avacopan, though, the data from the key avacopan trial, Study CL010_168, known as ADVOCATE, there were substantial uncertainties around the phase 3 study design and results, raising questions about the adequacy of this single trial to inform the benefit-risk assessment.
In the briefing document, the FDA staff noted that it had “communicated many of the concerns” about ChemoCentryx’s research earlier to the company.
“Complexities of the study design, as detailed in the briefing document, raise questions about the interpretability of the data to define a clinically meaningful benefit of avacopan and its role in the management of AAV,” the FDA staff wrote.
“We acknowledge that AAV is a rare and serious disease associated with high morbidity and increased mortality. It is also a disease with high unmet need for new therapies. However, FDA wants to ensure that new products have a defined context of use, i.e., how a product would be used, and a favorable benefit-risk assessment for patients,” the staff added.
In addition, there were differences in the assessments performed by investigators and the adjudication committee, most frequently related to the attribution of persistent vasculitis, the FDA staff noted.
Statistical analyses of the primary endpoint using investigators’ estimates “resulted in more conservative estimates of treatment effect, e.g., statistical significance for superiority would no longer be demonstrated,” the FDA staff noted. “While the prespecified analysis used the Adjudicator assessments, the assessment based on the Investigators, experienced in management of vasculitis, may better reflect real-world use.”
Imbalances in use of glucocorticoids and maintenance therapy
Also among the complications in assessing the ADVOCATE trial data were the glucocorticoids taken by patients in the study, the FDA staff said.
In the avacopan arm of the trial, 86% of patients received non–study-supplied glucocorticoids. In addition, more avacopan‐treated patients experienced adverse events and serious adverse events within the hepatobiliary system leading to discontinuation.
Subgroups given different treatments represented another challenge in interpreting ADVOCATE results for the FDA staff.
At week 26, the proportion of patients in disease remission in the avacopan group (72.3%) was noninferior to the prednisone group (70.1%), the FDA staff said in the briefing document.
But at week 52, a disparity was observed between subgroups that had received rituximab and cyclophosphamide (intravenous and oral) induction treatment. The estimated risk difference for disease remission at week 52 was 15.0% (95% CI, 2.2%-27.7%) in the subgroup receiving induction with rituximab and 3.3% (95% CI, –14.8% to 21.4%) in the cyclophosphamide plus maintenance azathioprine subgroup, the agency’s staff said.
“Based on the data, there is no evidence of clinically meaningful treatment effect in the cyclophosphamide induction subgroup,” the FDA staff wrote. “Further, the treatment comparison in the complementary rituximab induction subgroup may not be considered meaningful because these patients did not receive maintenance therapy, i.e., due to undertreating of patients, the effect observed in the rituximab subgroup may not represent a clinically meaningful treatment effect, compared to standard of care.”
Rachel L. Glaser, MD, clinical team leader in FDA’s division of rheumatology and transplant medicine, reiterated these concerns to the advisory committee at the May 6 meeting.
“Throughout the development program, FDA advised the applicant that a noninferiority comparison would not be sufficient to show that avacopan can replaced glucocorticoids as it would be difficult to establish whether avacopan is effective or whether an effect was due to the rituximab or cyclophosphamide administered to both treatment arms,” she said.
In its briefing for the meeting, ChemoCentryx noted the limits of treatments now available for AAV. It also emphasized the toll of the condition, ranging from skin manifestations to glomerulonephritis to life-threatening pulmonary hemorrhage. If untreated, 80% of patients with GPA or MPA die within 2 years of disease onset, ChemoCentryx said in its briefing materials for the meeting.
The side effects of glucocorticoids were well known to the FDA panelists and the ChemoCentryx presenters. Witnesses at an open public hearing told their own stories of depression, anxiety, and irritability caused by these medicines.
During the ChemoCentryx presentation, a presenter for the company, Peter Merkel, MD, MPH, of the University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, said avacopan would provide patients with AAV with an alternative allowing them “to go on a much lower glucocorticoids regimen.”
A similar view was presented in a February 2021 editorial in the New England Journal of Medicine, titled “Avacopan – Time to Replace Glucocorticoids?” Written by Kenneth J. Warrington, MD, of the Mayo Clinic, Rochester, Minn., the opinion article called the ADVOCATE trial “a milestone in the treatment of ANCA-associated vasculitis; complement inhibition with avacopan has glucocorticoid-sparing effects and results in superior disease control.”
Dr. Warrington reported no conflicts in connection with his editorial nor payments from ChemoCentryx. He did report grants from other firms such as Eli Lilly.
Julia Lewis, MD, of Vanderbilt University, Nashville, Tenn., was among the more skeptical members of the FDA panel. She was among the “nays” in all three voting questions put to the panel. Still, she said there were signs of “clinically meaningful benefit” in the data presented, but noted that the nonstudy use of glucocorticoids made it difficult to interpret the ADVOCATE results.
Dr. Lewis noted that the FDA usually requires two studies for a drug approval, particularly with a compound not yet cleared for any use. While ANCA-associated vasculitis is rare, it would be possible to recruit patients for another trial of avacopan, adding to the results reported already for avacopan from ADVOCATE, she said.
“Were there to be another study, this would certainly be a supportive study and maybe qualify as two studies,” she said.
A panel of federal advisers on May 6 lent support to the ChemoCentryx bid for approval of avacopan for a rare and serious autoimmune condition. But they also flagged concerns about both the evidence supporting claims of a benefit for this experimental drug and its safety.
At a meeting of the Food and Drug Administration’s Arthritis Advisory Committee, panelists voted 10-8 on a question of whether the risk-benefit profile of avacopan is adequate to support approval.
ChemoCentryx is seeking approval of avacopan for antineutrophil cytoplasmic autoantibody (ANCA)–associated vasculitis in the subtypes of granulomatosis with polyangiitis (GPA) and microscopic polyangiitis (MPA).
Regardless of their vote on this approval question, the panelists shared an interest in avacopan’s potential to reduce glucocorticoid use among some patients with ANCA-associated vasculitis, also called AAV. Mara L. Becker, MD, MSCE, the chair of the FDA’s panel, was among the panelists who said they reluctantly voted no.
“It pains me because I really want more steroid-sparing” medicines, said Dr. Becker of Duke University, Durham, N.C., who cited a need to gather more data on avacopan.
Margrit Wiesendanger, MD, PhD, of the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York, who was among the panelists voting yes, spoke of a need for caution if the FDA approves avacopan.
“Judicious use of this new medication will be warranted and perhaps additional guidance could be given to rheumatologists to help them decide for whom this medication is best,” she said.
Panelists had spoken earlier of avacopan as a possible alternative medicine for people with AAV who have conditions that make glucocorticoids riskier for them, such as those who have diabetes.
Close votes on safety profile, efficacy
The panel also voted 10-8 on a question about whether the safety profile of avacopan is adequate to support approval of avacopan for the treatment of adult patients with AAV.
In addition, the panel voted 9-9 on a question about whether efficacy data support approval of avacopan for the treatment of adult patients with AAV.
The FDA considers the recommendations of its advisory panels, but is not bound by them.
The FDA staff clearly expressed the view that ChemoCentryx fell short with the evidence presented for avacopan approval. Shares of San Carlos, Calif.–based ChemoCentryx dropped sharply from a May 3 closing price of $48.82 to a May 4 closing price of $26.63 after the FDA released the staff’s review of avacopan.
In a briefing prepared for the meeting, FDA staff detailed concerns about the evidence ChemoCentryx is using to seek approval. While acknowledging a need for new treatments for AAV as a rare condition, FDA staff honed in on what they described flaws in the testing of this experimental medicine, which is a small-molecule antagonist of the receptor of C5a, an end product of the complement cascade that acts as a potent neutrophil chemoattractant and agonist.
The FDA usually requires two phase 3 studies for approval of a new medicine but will do so with a single trial in cases of exceptional need, the agency staff said. But in these cases, the bar rises for the evidence provided from that single trial.
Difficulties in interpretation of complex study design
In the case of avacopan, though, the data from the key avacopan trial, Study CL010_168, known as ADVOCATE, there were substantial uncertainties around the phase 3 study design and results, raising questions about the adequacy of this single trial to inform the benefit-risk assessment.
In the briefing document, the FDA staff noted that it had “communicated many of the concerns” about ChemoCentryx’s research earlier to the company.
“Complexities of the study design, as detailed in the briefing document, raise questions about the interpretability of the data to define a clinically meaningful benefit of avacopan and its role in the management of AAV,” the FDA staff wrote.
“We acknowledge that AAV is a rare and serious disease associated with high morbidity and increased mortality. It is also a disease with high unmet need for new therapies. However, FDA wants to ensure that new products have a defined context of use, i.e., how a product would be used, and a favorable benefit-risk assessment for patients,” the staff added.
In addition, there were differences in the assessments performed by investigators and the adjudication committee, most frequently related to the attribution of persistent vasculitis, the FDA staff noted.
Statistical analyses of the primary endpoint using investigators’ estimates “resulted in more conservative estimates of treatment effect, e.g., statistical significance for superiority would no longer be demonstrated,” the FDA staff noted. “While the prespecified analysis used the Adjudicator assessments, the assessment based on the Investigators, experienced in management of vasculitis, may better reflect real-world use.”
Imbalances in use of glucocorticoids and maintenance therapy
Also among the complications in assessing the ADVOCATE trial data were the glucocorticoids taken by patients in the study, the FDA staff said.
In the avacopan arm of the trial, 86% of patients received non–study-supplied glucocorticoids. In addition, more avacopan‐treated patients experienced adverse events and serious adverse events within the hepatobiliary system leading to discontinuation.
Subgroups given different treatments represented another challenge in interpreting ADVOCATE results for the FDA staff.
At week 26, the proportion of patients in disease remission in the avacopan group (72.3%) was noninferior to the prednisone group (70.1%), the FDA staff said in the briefing document.
But at week 52, a disparity was observed between subgroups that had received rituximab and cyclophosphamide (intravenous and oral) induction treatment. The estimated risk difference for disease remission at week 52 was 15.0% (95% CI, 2.2%-27.7%) in the subgroup receiving induction with rituximab and 3.3% (95% CI, –14.8% to 21.4%) in the cyclophosphamide plus maintenance azathioprine subgroup, the agency’s staff said.
“Based on the data, there is no evidence of clinically meaningful treatment effect in the cyclophosphamide induction subgroup,” the FDA staff wrote. “Further, the treatment comparison in the complementary rituximab induction subgroup may not be considered meaningful because these patients did not receive maintenance therapy, i.e., due to undertreating of patients, the effect observed in the rituximab subgroup may not represent a clinically meaningful treatment effect, compared to standard of care.”
Rachel L. Glaser, MD, clinical team leader in FDA’s division of rheumatology and transplant medicine, reiterated these concerns to the advisory committee at the May 6 meeting.
“Throughout the development program, FDA advised the applicant that a noninferiority comparison would not be sufficient to show that avacopan can replaced glucocorticoids as it would be difficult to establish whether avacopan is effective or whether an effect was due to the rituximab or cyclophosphamide administered to both treatment arms,” she said.
In its briefing for the meeting, ChemoCentryx noted the limits of treatments now available for AAV. It also emphasized the toll of the condition, ranging from skin manifestations to glomerulonephritis to life-threatening pulmonary hemorrhage. If untreated, 80% of patients with GPA or MPA die within 2 years of disease onset, ChemoCentryx said in its briefing materials for the meeting.
The side effects of glucocorticoids were well known to the FDA panelists and the ChemoCentryx presenters. Witnesses at an open public hearing told their own stories of depression, anxiety, and irritability caused by these medicines.
During the ChemoCentryx presentation, a presenter for the company, Peter Merkel, MD, MPH, of the University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, said avacopan would provide patients with AAV with an alternative allowing them “to go on a much lower glucocorticoids regimen.”
A similar view was presented in a February 2021 editorial in the New England Journal of Medicine, titled “Avacopan – Time to Replace Glucocorticoids?” Written by Kenneth J. Warrington, MD, of the Mayo Clinic, Rochester, Minn., the opinion article called the ADVOCATE trial “a milestone in the treatment of ANCA-associated vasculitis; complement inhibition with avacopan has glucocorticoid-sparing effects and results in superior disease control.”
Dr. Warrington reported no conflicts in connection with his editorial nor payments from ChemoCentryx. He did report grants from other firms such as Eli Lilly.
Julia Lewis, MD, of Vanderbilt University, Nashville, Tenn., was among the more skeptical members of the FDA panel. She was among the “nays” in all three voting questions put to the panel. Still, she said there were signs of “clinically meaningful benefit” in the data presented, but noted that the nonstudy use of glucocorticoids made it difficult to interpret the ADVOCATE results.
Dr. Lewis noted that the FDA usually requires two studies for a drug approval, particularly with a compound not yet cleared for any use. While ANCA-associated vasculitis is rare, it would be possible to recruit patients for another trial of avacopan, adding to the results reported already for avacopan from ADVOCATE, she said.
“Were there to be another study, this would certainly be a supportive study and maybe qualify as two studies,” she said.
Black patients with cutaneous sarcoidosis may have more systemic and CV disease
according to a retrospective chart review of patients seen at Massachusetts General Hospital and Brigham and Women’s Hospital, both in Boston.
Black patients were also significantly more likely to have two or more organs involved and have higher rates of cardiac involvement, the latter of which is associated with worse prognosis. “Our data suggest there may be substantial variations in organ involvement between racial groups of patients presenting with cutaneous sarcoidosis,” said medical student Kylee Kus, a medical student at Oakland University, Auburn Hills, Mich., who presented the findings with Bina Kassamali, a medical student at Harvard University, Boston, at the annual Skin of Color Society scientific symposium.
Sotonye Imadojemu, MD, MBE; Avery LeChance, MD, MPH; and Ruth Anne Vleugels, MD, MPH, MBA; of Brigham and Women’s Hospital, are cosenior authors of the abstract.
The researchers identified 111 patients who were diagnosed with cutaneous sarcoidosis over a 20-year period (January 2000–December 2019), 50 of whom presented without established extracutaneous disease. They examined the charts of these 50 patients for whether subsequent work-up revealed systemic disease.
Of the 50 patients, 9 were Black. Seven of these nine patients (77.8%), were found to have systemic involvement, compared with 14 of 41 (46.3%) non-Black patients – a 31.5% higher probability (P < .05). One-third of the nine Black patients were found to have disease in one organ, and 44.4% in two or more organs. In non-Black patients, these rates were 12.2% and 34.1%, respectively.
Cardiovascular involvement was not found in any of the non-Black patients who had extracutaneous disease, but was found in 29% of the Black patients with extracutaneous disease, a statistically significant difference.
Black patients are known to be at higher risk for sarcoidosis than non-Black patients, and because “there is an association between cardiac sarcoid involvement and poor prognosis largely due to manifestations such as heart block, arrhythmias, and heart failure ... the study helps demonstrate how this organ involvement can disproportionately affect the Black population,” Ms. Kassamali said in an interview after the meeting.
A separate, recently published analysis of data from the same patient population examined the work-ups that patients received after a dermatologist’s diagnosis of sarcoidosis and found that patients with no previous systemic work-up were subsequently assessed for cardiac involvement in only 58.3% of cases. Assessment for pulmonary and ocular disease was completed more than 90% of the time.
“Crucial testing for cardiac involvement fell short,” Dr. Imadojemu, of the department of dermatology, Brigham and Women’s Hospital, and coinvestigators wrote in the research letter.
“Because the cutaneous manifestations of sarcoidosis often present at disease onset, dermatologists may be the first physicians to diagnose a patient with sarcoidosis,” they wrote. “As such, dermatologists are often responsible for initiating the appropriate evaluation of patients with sarcoidosis.”
Pulmonary involvement occurs in nearly all cases of sarcoidosis, while ocular and cardiac disease develop in approximately 25% and 10% of patients, respectively. Cardiac sarcoidosis is usually asymptomatic and accounts for 13%-25% of sarcoidosis-related deaths in the United States, they wrote.
An electrocardiogram is the appropriate initial screening tool and “is warranted in all patients with sarcoidosis,” they advised.
according to a retrospective chart review of patients seen at Massachusetts General Hospital and Brigham and Women’s Hospital, both in Boston.
Black patients were also significantly more likely to have two or more organs involved and have higher rates of cardiac involvement, the latter of which is associated with worse prognosis. “Our data suggest there may be substantial variations in organ involvement between racial groups of patients presenting with cutaneous sarcoidosis,” said medical student Kylee Kus, a medical student at Oakland University, Auburn Hills, Mich., who presented the findings with Bina Kassamali, a medical student at Harvard University, Boston, at the annual Skin of Color Society scientific symposium.
Sotonye Imadojemu, MD, MBE; Avery LeChance, MD, MPH; and Ruth Anne Vleugels, MD, MPH, MBA; of Brigham and Women’s Hospital, are cosenior authors of the abstract.
The researchers identified 111 patients who were diagnosed with cutaneous sarcoidosis over a 20-year period (January 2000–December 2019), 50 of whom presented without established extracutaneous disease. They examined the charts of these 50 patients for whether subsequent work-up revealed systemic disease.
Of the 50 patients, 9 were Black. Seven of these nine patients (77.8%), were found to have systemic involvement, compared with 14 of 41 (46.3%) non-Black patients – a 31.5% higher probability (P < .05). One-third of the nine Black patients were found to have disease in one organ, and 44.4% in two or more organs. In non-Black patients, these rates were 12.2% and 34.1%, respectively.
Cardiovascular involvement was not found in any of the non-Black patients who had extracutaneous disease, but was found in 29% of the Black patients with extracutaneous disease, a statistically significant difference.
Black patients are known to be at higher risk for sarcoidosis than non-Black patients, and because “there is an association between cardiac sarcoid involvement and poor prognosis largely due to manifestations such as heart block, arrhythmias, and heart failure ... the study helps demonstrate how this organ involvement can disproportionately affect the Black population,” Ms. Kassamali said in an interview after the meeting.
A separate, recently published analysis of data from the same patient population examined the work-ups that patients received after a dermatologist’s diagnosis of sarcoidosis and found that patients with no previous systemic work-up were subsequently assessed for cardiac involvement in only 58.3% of cases. Assessment for pulmonary and ocular disease was completed more than 90% of the time.
“Crucial testing for cardiac involvement fell short,” Dr. Imadojemu, of the department of dermatology, Brigham and Women’s Hospital, and coinvestigators wrote in the research letter.
“Because the cutaneous manifestations of sarcoidosis often present at disease onset, dermatologists may be the first physicians to diagnose a patient with sarcoidosis,” they wrote. “As such, dermatologists are often responsible for initiating the appropriate evaluation of patients with sarcoidosis.”
Pulmonary involvement occurs in nearly all cases of sarcoidosis, while ocular and cardiac disease develop in approximately 25% and 10% of patients, respectively. Cardiac sarcoidosis is usually asymptomatic and accounts for 13%-25% of sarcoidosis-related deaths in the United States, they wrote.
An electrocardiogram is the appropriate initial screening tool and “is warranted in all patients with sarcoidosis,” they advised.
according to a retrospective chart review of patients seen at Massachusetts General Hospital and Brigham and Women’s Hospital, both in Boston.
Black patients were also significantly more likely to have two or more organs involved and have higher rates of cardiac involvement, the latter of which is associated with worse prognosis. “Our data suggest there may be substantial variations in organ involvement between racial groups of patients presenting with cutaneous sarcoidosis,” said medical student Kylee Kus, a medical student at Oakland University, Auburn Hills, Mich., who presented the findings with Bina Kassamali, a medical student at Harvard University, Boston, at the annual Skin of Color Society scientific symposium.
Sotonye Imadojemu, MD, MBE; Avery LeChance, MD, MPH; and Ruth Anne Vleugels, MD, MPH, MBA; of Brigham and Women’s Hospital, are cosenior authors of the abstract.
The researchers identified 111 patients who were diagnosed with cutaneous sarcoidosis over a 20-year period (January 2000–December 2019), 50 of whom presented without established extracutaneous disease. They examined the charts of these 50 patients for whether subsequent work-up revealed systemic disease.
Of the 50 patients, 9 were Black. Seven of these nine patients (77.8%), were found to have systemic involvement, compared with 14 of 41 (46.3%) non-Black patients – a 31.5% higher probability (P < .05). One-third of the nine Black patients were found to have disease in one organ, and 44.4% in two or more organs. In non-Black patients, these rates were 12.2% and 34.1%, respectively.
Cardiovascular involvement was not found in any of the non-Black patients who had extracutaneous disease, but was found in 29% of the Black patients with extracutaneous disease, a statistically significant difference.
Black patients are known to be at higher risk for sarcoidosis than non-Black patients, and because “there is an association between cardiac sarcoid involvement and poor prognosis largely due to manifestations such as heart block, arrhythmias, and heart failure ... the study helps demonstrate how this organ involvement can disproportionately affect the Black population,” Ms. Kassamali said in an interview after the meeting.
A separate, recently published analysis of data from the same patient population examined the work-ups that patients received after a dermatologist’s diagnosis of sarcoidosis and found that patients with no previous systemic work-up were subsequently assessed for cardiac involvement in only 58.3% of cases. Assessment for pulmonary and ocular disease was completed more than 90% of the time.
“Crucial testing for cardiac involvement fell short,” Dr. Imadojemu, of the department of dermatology, Brigham and Women’s Hospital, and coinvestigators wrote in the research letter.
“Because the cutaneous manifestations of sarcoidosis often present at disease onset, dermatologists may be the first physicians to diagnose a patient with sarcoidosis,” they wrote. “As such, dermatologists are often responsible for initiating the appropriate evaluation of patients with sarcoidosis.”
Pulmonary involvement occurs in nearly all cases of sarcoidosis, while ocular and cardiac disease develop in approximately 25% and 10% of patients, respectively. Cardiac sarcoidosis is usually asymptomatic and accounts for 13%-25% of sarcoidosis-related deaths in the United States, they wrote.
An electrocardiogram is the appropriate initial screening tool and “is warranted in all patients with sarcoidosis,” they advised.
FROM SOC SOCIETY 2021
Squamous Cell Carcinoma in Hidradenitis Suppurativa Lesions Following Tumor Necrosis Factor α Inhibitors
To the Editor:
Hidradenitis suppurativa (HS) is a chronic inflammatory skin condition with high morbidity rates. Symptoms typically develop between puberty and the third decade of life, affecting twice as many females as males, with an overall disease prevalence of 1% to 4%.1 The pathogenesis is theorized to be related to an immune response to follicular occlusion and rupture in genetically susceptible individuals.
Among the complications associated with HS, the development of cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma (SCC) is 4.6-times more likely within HS lesions than in normal skin and typically is seen in the setting of long-standing disease, particularly in men with HS lesions located on the buttocks and genital region for more than 20 years.2 In 2015, the tumor necrosis factor (TNF) inhibitor adalimumab was approved by the US Food and Drug Administration for the treatment of HS. Tumor necrosis factor α inhibitors have been associated with an increased risk for skin cancer in other clinical settings.3,4 We present a case of locally advanced SCC that developed in a patient with HS who was treated with adalimumab and infliximab (both TNF-α inhibitors), ultimately leading to the patient’s death.
A 59-year-old man who smoked with a 40-year history of severe HS, who previously was lost to follow-up, presented to our dermatology clinic with lesions on the buttocks. Physical examination demonstrated confluent, indurated, boggy plaques; scattered sinus tracts with purulent drainage; scattered cystlike nodules; and tenderness to palpation consistent with Hurley stage III disease (Figure 1A). No involvement of the axillae or groin was noted. He was started on doxycycline and a prednisone taper with minimal improvement and subsequently was switched to adalimumab 3 months later. Adalimumab provided little relief and was discontinued; therapy was transitioned to infliximab 3 months later.
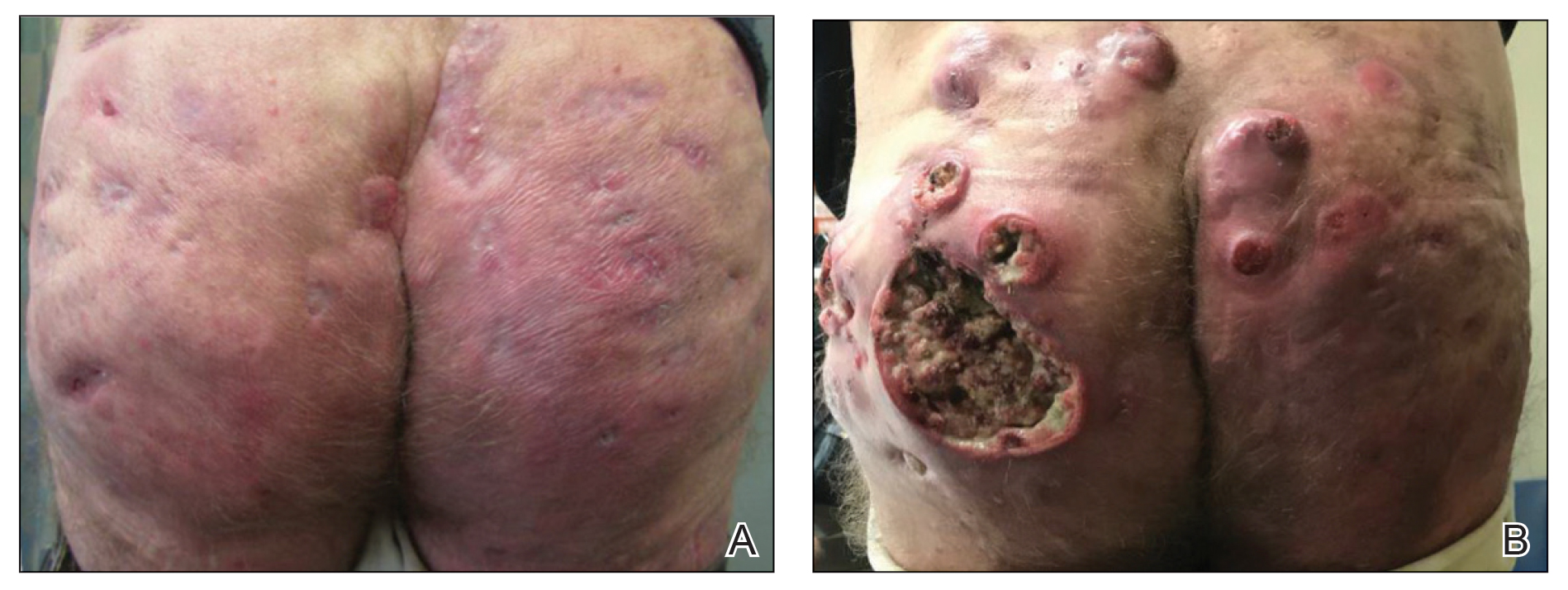
The patient returned to our clinic 3 months later with a severe flare and intractable pain after 4 infusions of infliximab. Physical examination showed a 7×5-cm deep malodorous ulcer with fibrinous exudate on the left buttock, several 2- to 3-cm shallow ulcers draining yellow exudate, and numerous fluctuant subcutaneous nodules on a background of scarring and sinus tracts. He was started again on doxycycline and a prednisone taper. At follow-up 2 weeks later, the largest ulcer had increased to 8 cm, and more indurated and tender subcutaneous nodules and scattered ulcerations developed (Figure 1B). Two punch biopsies of the left buttock revealed an invasive keratinizing carcinoma with no connection to the epidermis, consistent with SCC (Figure 2). Human papillomavirus (HPV) test results with probes for 37 HPV types—13 that were high risk (HPV-16, −18, −31, −33, −35, −39, −45, −51, −52, −56, −58, −59, −68)—were negative. Computerized tomography demonstrated diffuse thickening of the skin on the buttocks, inguinal adenopathy suspicious for nodal metastases, and no evidence of distant metastatic disease. Given the extent of the disease, surgical treatment was not an option, and he began receiving palliative radiotherapy. However, his health declined, and he developed aspiration pneumonia and hypotension requiring pressor support. He was transitioned to hospice care and died 3 months after presentation.
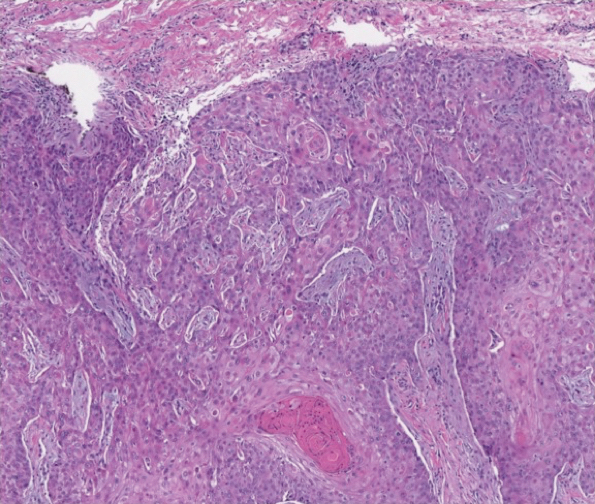
Tumor necrosis factor α antagonist treatment is being increasingly used to control HS but also may increase the risk for SCC development. We performed a search of PubMed articles indexed for MEDLINE as well as Web of Science using the terms hidradenitis suppurativa or acne inversa and one of the following—tumor necrosis factor inhibitor, infliximab, adalimumab, or etanercept—and squamous cell carcinoma or Marjolin ulcer. Seven cases of SCC arising in an HS patient treated with a TNF-α inhibitor have been reported (Table).5-10 Four cases were associated with infliximab use, 2 with adalimumab, and our case occurred after both adalimumab and infliximab treatment. All individuals were men with severe, long-standing disease of the anogenital region. In addition to smoking, HPV-16 positivity also has been reported as a risk factor for developing SCC in the setting of HS.11 In our patient, however, HPV testing did not cover all HPV strains, but several high-risk strains, including HPV-16, were negative.
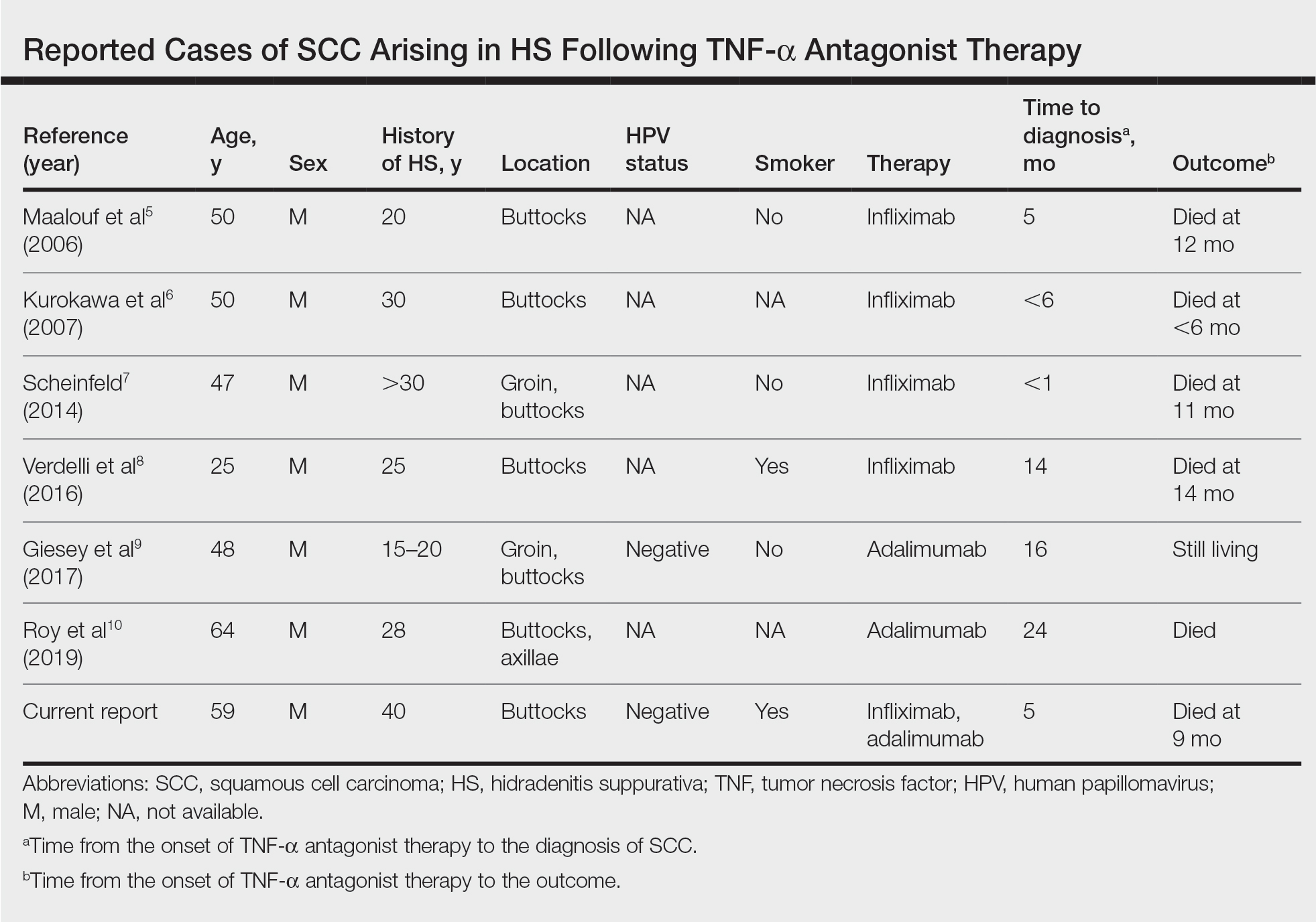
Hidradenitis suppurativa is caused by an immune response to ruptured follicles and TNF-α antagonists are useful in suppressing this response; however, immunosuppression can lead to an increased susceptibility to malignancy, especially in SCC. It is unclear whether the use of infliximab or adalimumab is causal, additive, or a confounder in the development of SCC in patients with severe HS. It is possible that these agents increase the rapidity of the development of SCC in already-susceptible patients. Although TNF-α antagonists can be an effective therapeutic option for patients with moderate to severe HS, the potential risk for contributing to skin cancer development should raise provider suspicion in high-risk patients. Given the findings in this report, it may be suitable for providers to consider a biopsy prior to initiating TNF-α therapy in men older than 20 years with moderate to severe HS of the groin or buttocks, in addition to more frequent monitoring and a lower threshold to biopsy lesions with rapid growth or ulceration.
- Alikhan A, Lynch PJ, Eisen DB. Hidradenitis suppurativa: a comprehensive review. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2009;60:539-561; quiz 562-533.
- Lapins J, Ye W, Nyren O, et al. Incidence of cancer among patients with hidradenitis suppurativa. Arch Dermatol. 2001;137:730-734.
- Askling J, Fahrbach K, Nordstrom B, et al. Cancer risk with tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNF) inhibitors: meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials of adalimumab, etanercept, and infliximab using patient level data. Pharmacoepidemiol Drug Saf. 2011;20:119-130.
- Mariette X, Matucci-Cerinic M, Pavelka K, et al. Malignancies associated with tumour necrosis factor inhibitors in registries and prospective observational studies: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Ann Rheum Dis. 2011;70:1895-1904.
- Maalouf E, Faye O, Poli F, et al. Fatal epidermoid carcinoma in hidradenitis suppurativa following treatment with infliximab. Ann Dermatol Venereol. 2006;133(5 pt 1):473-474.
- Kurokawa I, Nishimura K, Yamanaka K, et al. Cytokeratin expression in squamous cell carcinoma arising from hidradenitis suppurativa (acne inversa). J Cutan Pathol. 2007;34:675-678.
- Scheinfeld N. A case of a patient with stage III familial hidradenitis suppurativa treated with 3 courses of infliximab and died of metastatic squamous cell carcinoma. Dermatol Online J. 2014;20(3).
- Verdelli A, Antiga E, Bonciani D, et al. A fatal case of hidradenitis suppurativa associated with sepsis and squamous cell carcinoma. Int J Dermatol. 2016;55:E52-E53.
- Giesey R, Delost GR, Honaker J, et al. Metastatic squamous cell carcinoma in a patient treated with adalimumab for hidradenitis suppurativa. JAAD Case Rep. 2017;3:489-491.
- Roy C, Roy S, Ghazawi F, et al. Cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma arising in hidradenitis suppurativa: a case report. SAGE Open Med Case Rep. 2019;7:2050313X19847359.
- Lavogiez C, Delaporte E, Darras-Vercambre S, et al. Clinicopathological study of 13 cases of squamous cell carcinoma complicating hidradenitis suppurativa. Dermatology. 2010;220:147-153.
To the Editor:
Hidradenitis suppurativa (HS) is a chronic inflammatory skin condition with high morbidity rates. Symptoms typically develop between puberty and the third decade of life, affecting twice as many females as males, with an overall disease prevalence of 1% to 4%.1 The pathogenesis is theorized to be related to an immune response to follicular occlusion and rupture in genetically susceptible individuals.
Among the complications associated with HS, the development of cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma (SCC) is 4.6-times more likely within HS lesions than in normal skin and typically is seen in the setting of long-standing disease, particularly in men with HS lesions located on the buttocks and genital region for more than 20 years.2 In 2015, the tumor necrosis factor (TNF) inhibitor adalimumab was approved by the US Food and Drug Administration for the treatment of HS. Tumor necrosis factor α inhibitors have been associated with an increased risk for skin cancer in other clinical settings.3,4 We present a case of locally advanced SCC that developed in a patient with HS who was treated with adalimumab and infliximab (both TNF-α inhibitors), ultimately leading to the patient’s death.
A 59-year-old man who smoked with a 40-year history of severe HS, who previously was lost to follow-up, presented to our dermatology clinic with lesions on the buttocks. Physical examination demonstrated confluent, indurated, boggy plaques; scattered sinus tracts with purulent drainage; scattered cystlike nodules; and tenderness to palpation consistent with Hurley stage III disease (Figure 1A). No involvement of the axillae or groin was noted. He was started on doxycycline and a prednisone taper with minimal improvement and subsequently was switched to adalimumab 3 months later. Adalimumab provided little relief and was discontinued; therapy was transitioned to infliximab 3 months later.

The patient returned to our clinic 3 months later with a severe flare and intractable pain after 4 infusions of infliximab. Physical examination showed a 7×5-cm deep malodorous ulcer with fibrinous exudate on the left buttock, several 2- to 3-cm shallow ulcers draining yellow exudate, and numerous fluctuant subcutaneous nodules on a background of scarring and sinus tracts. He was started again on doxycycline and a prednisone taper. At follow-up 2 weeks later, the largest ulcer had increased to 8 cm, and more indurated and tender subcutaneous nodules and scattered ulcerations developed (Figure 1B). Two punch biopsies of the left buttock revealed an invasive keratinizing carcinoma with no connection to the epidermis, consistent with SCC (Figure 2). Human papillomavirus (HPV) test results with probes for 37 HPV types—13 that were high risk (HPV-16, −18, −31, −33, −35, −39, −45, −51, −52, −56, −58, −59, −68)—were negative. Computerized tomography demonstrated diffuse thickening of the skin on the buttocks, inguinal adenopathy suspicious for nodal metastases, and no evidence of distant metastatic disease. Given the extent of the disease, surgical treatment was not an option, and he began receiving palliative radiotherapy. However, his health declined, and he developed aspiration pneumonia and hypotension requiring pressor support. He was transitioned to hospice care and died 3 months after presentation.

Tumor necrosis factor α antagonist treatment is being increasingly used to control HS but also may increase the risk for SCC development. We performed a search of PubMed articles indexed for MEDLINE as well as Web of Science using the terms hidradenitis suppurativa or acne inversa and one of the following—tumor necrosis factor inhibitor, infliximab, adalimumab, or etanercept—and squamous cell carcinoma or Marjolin ulcer. Seven cases of SCC arising in an HS patient treated with a TNF-α inhibitor have been reported (Table).5-10 Four cases were associated with infliximab use, 2 with adalimumab, and our case occurred after both adalimumab and infliximab treatment. All individuals were men with severe, long-standing disease of the anogenital region. In addition to smoking, HPV-16 positivity also has been reported as a risk factor for developing SCC in the setting of HS.11 In our patient, however, HPV testing did not cover all HPV strains, but several high-risk strains, including HPV-16, were negative.

Hidradenitis suppurativa is caused by an immune response to ruptured follicles and TNF-α antagonists are useful in suppressing this response; however, immunosuppression can lead to an increased susceptibility to malignancy, especially in SCC. It is unclear whether the use of infliximab or adalimumab is causal, additive, or a confounder in the development of SCC in patients with severe HS. It is possible that these agents increase the rapidity of the development of SCC in already-susceptible patients. Although TNF-α antagonists can be an effective therapeutic option for patients with moderate to severe HS, the potential risk for contributing to skin cancer development should raise provider suspicion in high-risk patients. Given the findings in this report, it may be suitable for providers to consider a biopsy prior to initiating TNF-α therapy in men older than 20 years with moderate to severe HS of the groin or buttocks, in addition to more frequent monitoring and a lower threshold to biopsy lesions with rapid growth or ulceration.
To the Editor:
Hidradenitis suppurativa (HS) is a chronic inflammatory skin condition with high morbidity rates. Symptoms typically develop between puberty and the third decade of life, affecting twice as many females as males, with an overall disease prevalence of 1% to 4%.1 The pathogenesis is theorized to be related to an immune response to follicular occlusion and rupture in genetically susceptible individuals.
Among the complications associated with HS, the development of cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma (SCC) is 4.6-times more likely within HS lesions than in normal skin and typically is seen in the setting of long-standing disease, particularly in men with HS lesions located on the buttocks and genital region for more than 20 years.2 In 2015, the tumor necrosis factor (TNF) inhibitor adalimumab was approved by the US Food and Drug Administration for the treatment of HS. Tumor necrosis factor α inhibitors have been associated with an increased risk for skin cancer in other clinical settings.3,4 We present a case of locally advanced SCC that developed in a patient with HS who was treated with adalimumab and infliximab (both TNF-α inhibitors), ultimately leading to the patient’s death.
A 59-year-old man who smoked with a 40-year history of severe HS, who previously was lost to follow-up, presented to our dermatology clinic with lesions on the buttocks. Physical examination demonstrated confluent, indurated, boggy plaques; scattered sinus tracts with purulent drainage; scattered cystlike nodules; and tenderness to palpation consistent with Hurley stage III disease (Figure 1A). No involvement of the axillae or groin was noted. He was started on doxycycline and a prednisone taper with minimal improvement and subsequently was switched to adalimumab 3 months later. Adalimumab provided little relief and was discontinued; therapy was transitioned to infliximab 3 months later.

The patient returned to our clinic 3 months later with a severe flare and intractable pain after 4 infusions of infliximab. Physical examination showed a 7×5-cm deep malodorous ulcer with fibrinous exudate on the left buttock, several 2- to 3-cm shallow ulcers draining yellow exudate, and numerous fluctuant subcutaneous nodules on a background of scarring and sinus tracts. He was started again on doxycycline and a prednisone taper. At follow-up 2 weeks later, the largest ulcer had increased to 8 cm, and more indurated and tender subcutaneous nodules and scattered ulcerations developed (Figure 1B). Two punch biopsies of the left buttock revealed an invasive keratinizing carcinoma with no connection to the epidermis, consistent with SCC (Figure 2). Human papillomavirus (HPV) test results with probes for 37 HPV types—13 that were high risk (HPV-16, −18, −31, −33, −35, −39, −45, −51, −52, −56, −58, −59, −68)—were negative. Computerized tomography demonstrated diffuse thickening of the skin on the buttocks, inguinal adenopathy suspicious for nodal metastases, and no evidence of distant metastatic disease. Given the extent of the disease, surgical treatment was not an option, and he began receiving palliative radiotherapy. However, his health declined, and he developed aspiration pneumonia and hypotension requiring pressor support. He was transitioned to hospice care and died 3 months after presentation.

Tumor necrosis factor α antagonist treatment is being increasingly used to control HS but also may increase the risk for SCC development. We performed a search of PubMed articles indexed for MEDLINE as well as Web of Science using the terms hidradenitis suppurativa or acne inversa and one of the following—tumor necrosis factor inhibitor, infliximab, adalimumab, or etanercept—and squamous cell carcinoma or Marjolin ulcer. Seven cases of SCC arising in an HS patient treated with a TNF-α inhibitor have been reported (Table).5-10 Four cases were associated with infliximab use, 2 with adalimumab, and our case occurred after both adalimumab and infliximab treatment. All individuals were men with severe, long-standing disease of the anogenital region. In addition to smoking, HPV-16 positivity also has been reported as a risk factor for developing SCC in the setting of HS.11 In our patient, however, HPV testing did not cover all HPV strains, but several high-risk strains, including HPV-16, were negative.

Hidradenitis suppurativa is caused by an immune response to ruptured follicles and TNF-α antagonists are useful in suppressing this response; however, immunosuppression can lead to an increased susceptibility to malignancy, especially in SCC. It is unclear whether the use of infliximab or adalimumab is causal, additive, or a confounder in the development of SCC in patients with severe HS. It is possible that these agents increase the rapidity of the development of SCC in already-susceptible patients. Although TNF-α antagonists can be an effective therapeutic option for patients with moderate to severe HS, the potential risk for contributing to skin cancer development should raise provider suspicion in high-risk patients. Given the findings in this report, it may be suitable for providers to consider a biopsy prior to initiating TNF-α therapy in men older than 20 years with moderate to severe HS of the groin or buttocks, in addition to more frequent monitoring and a lower threshold to biopsy lesions with rapid growth or ulceration.
- Alikhan A, Lynch PJ, Eisen DB. Hidradenitis suppurativa: a comprehensive review. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2009;60:539-561; quiz 562-533.
- Lapins J, Ye W, Nyren O, et al. Incidence of cancer among patients with hidradenitis suppurativa. Arch Dermatol. 2001;137:730-734.
- Askling J, Fahrbach K, Nordstrom B, et al. Cancer risk with tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNF) inhibitors: meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials of adalimumab, etanercept, and infliximab using patient level data. Pharmacoepidemiol Drug Saf. 2011;20:119-130.
- Mariette X, Matucci-Cerinic M, Pavelka K, et al. Malignancies associated with tumour necrosis factor inhibitors in registries and prospective observational studies: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Ann Rheum Dis. 2011;70:1895-1904.
- Maalouf E, Faye O, Poli F, et al. Fatal epidermoid carcinoma in hidradenitis suppurativa following treatment with infliximab. Ann Dermatol Venereol. 2006;133(5 pt 1):473-474.
- Kurokawa I, Nishimura K, Yamanaka K, et al. Cytokeratin expression in squamous cell carcinoma arising from hidradenitis suppurativa (acne inversa). J Cutan Pathol. 2007;34:675-678.
- Scheinfeld N. A case of a patient with stage III familial hidradenitis suppurativa treated with 3 courses of infliximab and died of metastatic squamous cell carcinoma. Dermatol Online J. 2014;20(3).
- Verdelli A, Antiga E, Bonciani D, et al. A fatal case of hidradenitis suppurativa associated with sepsis and squamous cell carcinoma. Int J Dermatol. 2016;55:E52-E53.
- Giesey R, Delost GR, Honaker J, et al. Metastatic squamous cell carcinoma in a patient treated with adalimumab for hidradenitis suppurativa. JAAD Case Rep. 2017;3:489-491.
- Roy C, Roy S, Ghazawi F, et al. Cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma arising in hidradenitis suppurativa: a case report. SAGE Open Med Case Rep. 2019;7:2050313X19847359.
- Lavogiez C, Delaporte E, Darras-Vercambre S, et al. Clinicopathological study of 13 cases of squamous cell carcinoma complicating hidradenitis suppurativa. Dermatology. 2010;220:147-153.
- Alikhan A, Lynch PJ, Eisen DB. Hidradenitis suppurativa: a comprehensive review. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2009;60:539-561; quiz 562-533.
- Lapins J, Ye W, Nyren O, et al. Incidence of cancer among patients with hidradenitis suppurativa. Arch Dermatol. 2001;137:730-734.
- Askling J, Fahrbach K, Nordstrom B, et al. Cancer risk with tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNF) inhibitors: meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials of adalimumab, etanercept, and infliximab using patient level data. Pharmacoepidemiol Drug Saf. 2011;20:119-130.
- Mariette X, Matucci-Cerinic M, Pavelka K, et al. Malignancies associated with tumour necrosis factor inhibitors in registries and prospective observational studies: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Ann Rheum Dis. 2011;70:1895-1904.
- Maalouf E, Faye O, Poli F, et al. Fatal epidermoid carcinoma in hidradenitis suppurativa following treatment with infliximab. Ann Dermatol Venereol. 2006;133(5 pt 1):473-474.
- Kurokawa I, Nishimura K, Yamanaka K, et al. Cytokeratin expression in squamous cell carcinoma arising from hidradenitis suppurativa (acne inversa). J Cutan Pathol. 2007;34:675-678.
- Scheinfeld N. A case of a patient with stage III familial hidradenitis suppurativa treated with 3 courses of infliximab and died of metastatic squamous cell carcinoma. Dermatol Online J. 2014;20(3).
- Verdelli A, Antiga E, Bonciani D, et al. A fatal case of hidradenitis suppurativa associated with sepsis and squamous cell carcinoma. Int J Dermatol. 2016;55:E52-E53.
- Giesey R, Delost GR, Honaker J, et al. Metastatic squamous cell carcinoma in a patient treated with adalimumab for hidradenitis suppurativa. JAAD Case Rep. 2017;3:489-491.
- Roy C, Roy S, Ghazawi F, et al. Cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma arising in hidradenitis suppurativa: a case report. SAGE Open Med Case Rep. 2019;7:2050313X19847359.
- Lavogiez C, Delaporte E, Darras-Vercambre S, et al. Clinicopathological study of 13 cases of squamous cell carcinoma complicating hidradenitis suppurativa. Dermatology. 2010;220:147-153.
Practice Points
- Consider biopsy of representative lesions in men older than 20 years with moderate to severe disease of the groin and/or buttocks prior to initiation of tumor necrosis factor inhibitors.
- Consider more frequent clinical monitoring with a decrease in threshold to perform biopsy of any new or ulcerating lesions.
COVID-19’s impact on lupus inpatients examined in study
Severe COVID-19 infection was more likely in hospitalized patients with systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) who had comorbidities and risk factors associated with severe infection in the general population, notably older age, male gender, and hypertension, based on data from a nationwide epidemiologic study of inpatients in France.
“Recently, anti-interferon antibodies have been implicated in severe SARS-CoV-2 infection while it has been known for decades that patients with SLE may produce such autoantibodies,” but large-scale data on the risk of severe COVID-19 infection in SLE patients are limited, Arthur Mageau, MD, of Bichat–Claude Bernard Hospital in Paris, and colleagues wrote.
In a research letter published in Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases, the researchers used the French health care database Programme de Médicalisation des Systèmes d’Information to identify 11,055 adult SLE patients who had at least one hospital stay between March 1, 2020, and Oct.31, 2020. Of these, 1,411 (12.8%) also were diagnosed with COVID-19, and these patients had a total of 1,721 hospital stays.
Overall, in-hospital mortality was approximately four times higher among SLE patients with COVID-19 infection, compared with SLE patients without COVID-19 infection (9.5% vs. 2.4%, P < .001), and 293 (17%) of the COVID-19 hospital stays involved an intensive care unit. In the ICU, 78 (26.7%) of the COVID-19 patients required invasive ventilation, and 71 (24.7%) required noninvasive mechanical ventilation.
The SLE patients with COVID-19 who died were significantly more likely than the SLE patients with COVID-19 who recovered to be older and male, and to have conditions including chronic kidney disease, high blood pressure, chronic pulmonary disease, and a history of cardiovascular events or lupus nephritis. The study findings were limited by the focus on hospitalized patients only, so the results cannot be generalized to all lupus patients, the researchers said.
“Interestingly, while the overall mortality rate was lower in SLE/COVID-19–positive inpatients as compared with the total population admitted for SARS-CoV-2 infection in France during the same period (9.5% vs 15.7%, P < .0001), the mortality rate at a younger age tended to be higher in patients with SLE,” the researchers wrote, but the difference for these younger patients was not statistically significant. This disparity may be caused by the reduced need for immunosuppressive drugs in SLE patients as they age, and the observed increased mortality in younger SLE patients, compared with the general population, suggests that SLE may promote poor outcomes from COVID-19 infection.
Dr. Mageau received PhD fellowship support from the Agence Nationale pour la recherche. He and the other researchers had no financial conflicts to disclose. The study received no outside funding.
Severe COVID-19 infection was more likely in hospitalized patients with systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) who had comorbidities and risk factors associated with severe infection in the general population, notably older age, male gender, and hypertension, based on data from a nationwide epidemiologic study of inpatients in France.
“Recently, anti-interferon antibodies have been implicated in severe SARS-CoV-2 infection while it has been known for decades that patients with SLE may produce such autoantibodies,” but large-scale data on the risk of severe COVID-19 infection in SLE patients are limited, Arthur Mageau, MD, of Bichat–Claude Bernard Hospital in Paris, and colleagues wrote.
In a research letter published in Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases, the researchers used the French health care database Programme de Médicalisation des Systèmes d’Information to identify 11,055 adult SLE patients who had at least one hospital stay between March 1, 2020, and Oct.31, 2020. Of these, 1,411 (12.8%) also were diagnosed with COVID-19, and these patients had a total of 1,721 hospital stays.
Overall, in-hospital mortality was approximately four times higher among SLE patients with COVID-19 infection, compared with SLE patients without COVID-19 infection (9.5% vs. 2.4%, P < .001), and 293 (17%) of the COVID-19 hospital stays involved an intensive care unit. In the ICU, 78 (26.7%) of the COVID-19 patients required invasive ventilation, and 71 (24.7%) required noninvasive mechanical ventilation.
The SLE patients with COVID-19 who died were significantly more likely than the SLE patients with COVID-19 who recovered to be older and male, and to have conditions including chronic kidney disease, high blood pressure, chronic pulmonary disease, and a history of cardiovascular events or lupus nephritis. The study findings were limited by the focus on hospitalized patients only, so the results cannot be generalized to all lupus patients, the researchers said.
“Interestingly, while the overall mortality rate was lower in SLE/COVID-19–positive inpatients as compared with the total population admitted for SARS-CoV-2 infection in France during the same period (9.5% vs 15.7%, P < .0001), the mortality rate at a younger age tended to be higher in patients with SLE,” the researchers wrote, but the difference for these younger patients was not statistically significant. This disparity may be caused by the reduced need for immunosuppressive drugs in SLE patients as they age, and the observed increased mortality in younger SLE patients, compared with the general population, suggests that SLE may promote poor outcomes from COVID-19 infection.
Dr. Mageau received PhD fellowship support from the Agence Nationale pour la recherche. He and the other researchers had no financial conflicts to disclose. The study received no outside funding.
Severe COVID-19 infection was more likely in hospitalized patients with systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) who had comorbidities and risk factors associated with severe infection in the general population, notably older age, male gender, and hypertension, based on data from a nationwide epidemiologic study of inpatients in France.
“Recently, anti-interferon antibodies have been implicated in severe SARS-CoV-2 infection while it has been known for decades that patients with SLE may produce such autoantibodies,” but large-scale data on the risk of severe COVID-19 infection in SLE patients are limited, Arthur Mageau, MD, of Bichat–Claude Bernard Hospital in Paris, and colleagues wrote.
In a research letter published in Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases, the researchers used the French health care database Programme de Médicalisation des Systèmes d’Information to identify 11,055 adult SLE patients who had at least one hospital stay between March 1, 2020, and Oct.31, 2020. Of these, 1,411 (12.8%) also were diagnosed with COVID-19, and these patients had a total of 1,721 hospital stays.
Overall, in-hospital mortality was approximately four times higher among SLE patients with COVID-19 infection, compared with SLE patients without COVID-19 infection (9.5% vs. 2.4%, P < .001), and 293 (17%) of the COVID-19 hospital stays involved an intensive care unit. In the ICU, 78 (26.7%) of the COVID-19 patients required invasive ventilation, and 71 (24.7%) required noninvasive mechanical ventilation.
The SLE patients with COVID-19 who died were significantly more likely than the SLE patients with COVID-19 who recovered to be older and male, and to have conditions including chronic kidney disease, high blood pressure, chronic pulmonary disease, and a history of cardiovascular events or lupus nephritis. The study findings were limited by the focus on hospitalized patients only, so the results cannot be generalized to all lupus patients, the researchers said.
“Interestingly, while the overall mortality rate was lower in SLE/COVID-19–positive inpatients as compared with the total population admitted for SARS-CoV-2 infection in France during the same period (9.5% vs 15.7%, P < .0001), the mortality rate at a younger age tended to be higher in patients with SLE,” the researchers wrote, but the difference for these younger patients was not statistically significant. This disparity may be caused by the reduced need for immunosuppressive drugs in SLE patients as they age, and the observed increased mortality in younger SLE patients, compared with the general population, suggests that SLE may promote poor outcomes from COVID-19 infection.
Dr. Mageau received PhD fellowship support from the Agence Nationale pour la recherche. He and the other researchers had no financial conflicts to disclose. The study received no outside funding.
FROM ANNALS OF THE RHEUMATIC DISEASES
Candida Esophagitis Associated With Adalimumab for Hidradenitis Suppurativa
To the Editor:
Hidradenitis suppurativa (HS) is a chronic inflammatory disease characterized by the development of painful abscesses, fistulous tracts, and scars. It most commonly affects the apocrine gland–bearing areas of the body such as the axillary, inguinal, and anogenital regions. With a prevalence of approximately 1%, HS can lead to notable morbidity.1 The pathogenesis is thought to be due to occlusion of terminal hair follicles that subsequently stimulates release of proinflammatory cytokines from nearby keratinocytes. The mechanism of initial occlusion is not well understood but may be due to friction or trauma. An inflammatory mechanism of disease also has been hypothesized; however, the exact cytokine profile is not known. Treatment of HS consists of several different modalities, including oral retinoids, antibiotics, antiandrogenic therapy, and surgery.1,2 Adalimumab is a well-known biologic that has been approved by the US Food and Drug Administration for the treatment of HS.
Adalimumab is a human monoclonal antibody against tumor necrosis factor (TNF) α and is thought to improve HS by several mechanisms. Inhibition of TNF-α and other proinflammatory cytokines found in inflammatory lesions and apocrine glands directly decreases the severity of lesion size and the frequency of recurrence.3 Adalimumab also is thought to downregulate expression of keratin 6 and prevent the hyperkeratinization seen in HS.4 Additionally, TNF-α inhibition decreases production of IL-1, which has been shown to cause hypercornification of follicles and perpetuate HS pathogenesis.5
A 41-year-old woman with a history of endometriosis, adenomyosis, polycystic ovary syndrome, interstitial cystitis, asthma, fibromyalgia, depression, and Hashimoto thyroiditis presented to our dermatology clinic with active draining lesions and sinus tracts in the perivaginal area that were consistent with HS, which initially was treated with doxycycline 100 mg twice daily. She experienced minimal improvement of the HS lesions at 2-month follow-up.
Due to disease severity, adalimumab was started. The patient received a loading dose of 4 injections totaling 160 mg and 80 mg on day 15, followed by a maintenance dose of 40 mg/0.4 mL weekly. The patient reported substantial improvement of pain, and complete resolution of active lesions was noted on physical examination after 4 weeks of treatment with adalimumab.
Six weeks after adalimumab was started, the patient developed severe dysphagia. She was evaluated by a gastroenterologist and underwent endoscopy (Figure), which led to a diagnosis of esophageal candidiasis. Adalimumab was discontinued immediately thereafter. The patient started treatment with nystatin oral rinse 4 times daily and oral fluconazole 200 mg daily. The candidiasis resolved within 2 weeks; however, she experienced recurrence of HS with draining lesions in the perivaginal area approximately 8 weeks after discontinuation of adalimumab. The patient requested to restart adalimumab treatment despite the recent history of esophagitis. Adalimumab 40 mg/0.4 mL weekly was restarted along with oral fluconazole 200 mg twice weekly and nystatin oral rinse 4 times daily. This regimen resulted in complete resolution of HS symptoms within 6 weeks with no recurrence of esophageal candidiasis during 6 months of follow-up.
Although the side effect of Candida esophagitis associated with adalimumab treatment in our patient may be logical given the medication’s mechanism of action and side-effect profile, this case warrants additional attention. An increase in fungal infections occurs from treatment with adalimumab because TNF-α is involved in many immune regulatory steps that counteract infection. Candida typically activates the innate immune system through macrophages via pathogen-associated molecular pattern stimulation, subsequently stimulating the release of inflammatory cytokines such as TNF-α. The cellular immune system also is activated. Helper T cells (TH1) release TNF-α along with other proinflammatory cytokines to increase phagocytosis in polymorphonuclear cells and macrophages.6 Thus, inhibition of TNF-α compromises innate and cellular immunity, thereby increasing susceptibility to fungal organisms.
A PubMed search of articles indexed for MEDLINE using the terms Candida, candidiasis, esophageal, adalimumab, anti-TNF, and TNF revealed no reports of esophageal candidiasis in patients receiving adalimumab or any of the TNF inhibitors. Candida laryngitis was reported in a patient receiving adalimumab for treatment of rheumatoid arthritis.7 Other studies have demonstrated an incidence of mucocutaneous candidiasis, most notably oropharyngeal and vaginal candidiasis.8-10 One study found that anti-TNF medications were associated with an increased risk for candidiasis by a hazard ratio of 2.7 in patients with Crohn disease.8 Other studies have shown that the highest incidence of fungal infection is seen with the use of infliximab, while adalimumab is associated with lower rates of fungal infection.9,10 Although it is known that anti-TNF therapy predisposes patients to fungal infection, the dose of medication known to preclude the highest risk has not been studied. Furthermore, most studies assess rates of Candida infection in individuals receiving anti-TNF therapy in addition to several other immunosuppressant agents (ie, corticosteroids), which confounds the interpretation of results. Additional studies assessing rates of Candida and other opportunistic infections associated with use of adalimumab alone are needed to better guide clinical practices in dermatology.
Patients receiving adalimumab for dermatologic or other conditions should be closely monitored for opportunistic infections. Although immunomodulatory medications offer promising therapeutic benefits in patients with HS, larger studies regarding treatment with anti-TNF agents in HS are warranted to prevent complications from treatment and promote long-term efficacy and safety.
- Kurayev A, Ashkar H, Saraiya A, et al. Hidradenitis suppurativa: review of the pathogenesis and treatment. J Drugs Dermatol. 2016;15:1107-1022.
- Rambhatla PV, Lim HW, Hamzavi I. A systematic review of treatments for hidradenitis suppurativa. Arch Dermatol. 2012;148:439-446.
- van der Zee HH, de Ruiter L, van den Broecke DG, et al. Elevated levels of tumour necrosis factor (TNF)-alpha, interleukin (IL)-1beta and IL-10 in hidradenitis suppurativa skin: a rationale for targeting TNF-alpha and IL-1beta. Br J Dermatol. 2011;164:1292-1298.
- Shuja F, Chan CS, Rosen T. Biologic drugs for the treatment of hidradenitis suppurativa: an evidence-based review. Dermatol Clin. 2010;28:511-521, 523-514.
- Kutsch CL, Norris DA, Arend WP. Tumor necrosis factor-alpha induces interleukin-1 alpha and interleukin-1 receptor antagonist production by cultured human keratinocytes. J Invest Dermatol. 1993;101:79-85.
- Senet JM. Risk factors and physiopathology of candidiasis. Rev Iberoam Micol. 1997;14:6-13.
- Kobak S, Yilmaz H, Guclu O, et al. Severe candida laryngitis in a patient with rheumatoid arthritis treated with adalimumab. Eur J Rheumatol. 2014;1:167-169.
- Marehbian J, Arrighi HM, Hass S, et al. Adverse events associated with common therapy regimens for moderate-to-severe Crohn’s disease. Am J Gastroenterol. 2009;104:2524-2533.
- Tsiodras S, Samonis G, Boumpas DT, et al. Fungal infections complicating tumor necrosis factor alpha blockade therapy. Mayo Clin Proc. 2008;83:181-194.
- Aikawa NE, Rosa DT, Del Negro GM, et al. Systemic and localized infection by Candida species in patients with rheumatic diseases receiving anti-TNF therapy [in Portuguese]. Rev Bras Reumatol. doi:10.1016/j.rbr.2015.03.010
To the Editor:
Hidradenitis suppurativa (HS) is a chronic inflammatory disease characterized by the development of painful abscesses, fistulous tracts, and scars. It most commonly affects the apocrine gland–bearing areas of the body such as the axillary, inguinal, and anogenital regions. With a prevalence of approximately 1%, HS can lead to notable morbidity.1 The pathogenesis is thought to be due to occlusion of terminal hair follicles that subsequently stimulates release of proinflammatory cytokines from nearby keratinocytes. The mechanism of initial occlusion is not well understood but may be due to friction or trauma. An inflammatory mechanism of disease also has been hypothesized; however, the exact cytokine profile is not known. Treatment of HS consists of several different modalities, including oral retinoids, antibiotics, antiandrogenic therapy, and surgery.1,2 Adalimumab is a well-known biologic that has been approved by the US Food and Drug Administration for the treatment of HS.
Adalimumab is a human monoclonal antibody against tumor necrosis factor (TNF) α and is thought to improve HS by several mechanisms. Inhibition of TNF-α and other proinflammatory cytokines found in inflammatory lesions and apocrine glands directly decreases the severity of lesion size and the frequency of recurrence.3 Adalimumab also is thought to downregulate expression of keratin 6 and prevent the hyperkeratinization seen in HS.4 Additionally, TNF-α inhibition decreases production of IL-1, which has been shown to cause hypercornification of follicles and perpetuate HS pathogenesis.5
A 41-year-old woman with a history of endometriosis, adenomyosis, polycystic ovary syndrome, interstitial cystitis, asthma, fibromyalgia, depression, and Hashimoto thyroiditis presented to our dermatology clinic with active draining lesions and sinus tracts in the perivaginal area that were consistent with HS, which initially was treated with doxycycline 100 mg twice daily. She experienced minimal improvement of the HS lesions at 2-month follow-up.
Due to disease severity, adalimumab was started. The patient received a loading dose of 4 injections totaling 160 mg and 80 mg on day 15, followed by a maintenance dose of 40 mg/0.4 mL weekly. The patient reported substantial improvement of pain, and complete resolution of active lesions was noted on physical examination after 4 weeks of treatment with adalimumab.
Six weeks after adalimumab was started, the patient developed severe dysphagia. She was evaluated by a gastroenterologist and underwent endoscopy (Figure), which led to a diagnosis of esophageal candidiasis. Adalimumab was discontinued immediately thereafter. The patient started treatment with nystatin oral rinse 4 times daily and oral fluconazole 200 mg daily. The candidiasis resolved within 2 weeks; however, she experienced recurrence of HS with draining lesions in the perivaginal area approximately 8 weeks after discontinuation of adalimumab. The patient requested to restart adalimumab treatment despite the recent history of esophagitis. Adalimumab 40 mg/0.4 mL weekly was restarted along with oral fluconazole 200 mg twice weekly and nystatin oral rinse 4 times daily. This regimen resulted in complete resolution of HS symptoms within 6 weeks with no recurrence of esophageal candidiasis during 6 months of follow-up.

Although the side effect of Candida esophagitis associated with adalimumab treatment in our patient may be logical given the medication’s mechanism of action and side-effect profile, this case warrants additional attention. An increase in fungal infections occurs from treatment with adalimumab because TNF-α is involved in many immune regulatory steps that counteract infection. Candida typically activates the innate immune system through macrophages via pathogen-associated molecular pattern stimulation, subsequently stimulating the release of inflammatory cytokines such as TNF-α. The cellular immune system also is activated. Helper T cells (TH1) release TNF-α along with other proinflammatory cytokines to increase phagocytosis in polymorphonuclear cells and macrophages.6 Thus, inhibition of TNF-α compromises innate and cellular immunity, thereby increasing susceptibility to fungal organisms.
A PubMed search of articles indexed for MEDLINE using the terms Candida, candidiasis, esophageal, adalimumab, anti-TNF, and TNF revealed no reports of esophageal candidiasis in patients receiving adalimumab or any of the TNF inhibitors. Candida laryngitis was reported in a patient receiving adalimumab for treatment of rheumatoid arthritis.7 Other studies have demonstrated an incidence of mucocutaneous candidiasis, most notably oropharyngeal and vaginal candidiasis.8-10 One study found that anti-TNF medications were associated with an increased risk for candidiasis by a hazard ratio of 2.7 in patients with Crohn disease.8 Other studies have shown that the highest incidence of fungal infection is seen with the use of infliximab, while adalimumab is associated with lower rates of fungal infection.9,10 Although it is known that anti-TNF therapy predisposes patients to fungal infection, the dose of medication known to preclude the highest risk has not been studied. Furthermore, most studies assess rates of Candida infection in individuals receiving anti-TNF therapy in addition to several other immunosuppressant agents (ie, corticosteroids), which confounds the interpretation of results. Additional studies assessing rates of Candida and other opportunistic infections associated with use of adalimumab alone are needed to better guide clinical practices in dermatology.
Patients receiving adalimumab for dermatologic or other conditions should be closely monitored for opportunistic infections. Although immunomodulatory medications offer promising therapeutic benefits in patients with HS, larger studies regarding treatment with anti-TNF agents in HS are warranted to prevent complications from treatment and promote long-term efficacy and safety.
To the Editor:
Hidradenitis suppurativa (HS) is a chronic inflammatory disease characterized by the development of painful abscesses, fistulous tracts, and scars. It most commonly affects the apocrine gland–bearing areas of the body such as the axillary, inguinal, and anogenital regions. With a prevalence of approximately 1%, HS can lead to notable morbidity.1 The pathogenesis is thought to be due to occlusion of terminal hair follicles that subsequently stimulates release of proinflammatory cytokines from nearby keratinocytes. The mechanism of initial occlusion is not well understood but may be due to friction or trauma. An inflammatory mechanism of disease also has been hypothesized; however, the exact cytokine profile is not known. Treatment of HS consists of several different modalities, including oral retinoids, antibiotics, antiandrogenic therapy, and surgery.1,2 Adalimumab is a well-known biologic that has been approved by the US Food and Drug Administration for the treatment of HS.
Adalimumab is a human monoclonal antibody against tumor necrosis factor (TNF) α and is thought to improve HS by several mechanisms. Inhibition of TNF-α and other proinflammatory cytokines found in inflammatory lesions and apocrine glands directly decreases the severity of lesion size and the frequency of recurrence.3 Adalimumab also is thought to downregulate expression of keratin 6 and prevent the hyperkeratinization seen in HS.4 Additionally, TNF-α inhibition decreases production of IL-1, which has been shown to cause hypercornification of follicles and perpetuate HS pathogenesis.5
A 41-year-old woman with a history of endometriosis, adenomyosis, polycystic ovary syndrome, interstitial cystitis, asthma, fibromyalgia, depression, and Hashimoto thyroiditis presented to our dermatology clinic with active draining lesions and sinus tracts in the perivaginal area that were consistent with HS, which initially was treated with doxycycline 100 mg twice daily. She experienced minimal improvement of the HS lesions at 2-month follow-up.
Due to disease severity, adalimumab was started. The patient received a loading dose of 4 injections totaling 160 mg and 80 mg on day 15, followed by a maintenance dose of 40 mg/0.4 mL weekly. The patient reported substantial improvement of pain, and complete resolution of active lesions was noted on physical examination after 4 weeks of treatment with adalimumab.
Six weeks after adalimumab was started, the patient developed severe dysphagia. She was evaluated by a gastroenterologist and underwent endoscopy (Figure), which led to a diagnosis of esophageal candidiasis. Adalimumab was discontinued immediately thereafter. The patient started treatment with nystatin oral rinse 4 times daily and oral fluconazole 200 mg daily. The candidiasis resolved within 2 weeks; however, she experienced recurrence of HS with draining lesions in the perivaginal area approximately 8 weeks after discontinuation of adalimumab. The patient requested to restart adalimumab treatment despite the recent history of esophagitis. Adalimumab 40 mg/0.4 mL weekly was restarted along with oral fluconazole 200 mg twice weekly and nystatin oral rinse 4 times daily. This regimen resulted in complete resolution of HS symptoms within 6 weeks with no recurrence of esophageal candidiasis during 6 months of follow-up.

Although the side effect of Candida esophagitis associated with adalimumab treatment in our patient may be logical given the medication’s mechanism of action and side-effect profile, this case warrants additional attention. An increase in fungal infections occurs from treatment with adalimumab because TNF-α is involved in many immune regulatory steps that counteract infection. Candida typically activates the innate immune system through macrophages via pathogen-associated molecular pattern stimulation, subsequently stimulating the release of inflammatory cytokines such as TNF-α. The cellular immune system also is activated. Helper T cells (TH1) release TNF-α along with other proinflammatory cytokines to increase phagocytosis in polymorphonuclear cells and macrophages.6 Thus, inhibition of TNF-α compromises innate and cellular immunity, thereby increasing susceptibility to fungal organisms.
A PubMed search of articles indexed for MEDLINE using the terms Candida, candidiasis, esophageal, adalimumab, anti-TNF, and TNF revealed no reports of esophageal candidiasis in patients receiving adalimumab or any of the TNF inhibitors. Candida laryngitis was reported in a patient receiving adalimumab for treatment of rheumatoid arthritis.7 Other studies have demonstrated an incidence of mucocutaneous candidiasis, most notably oropharyngeal and vaginal candidiasis.8-10 One study found that anti-TNF medications were associated with an increased risk for candidiasis by a hazard ratio of 2.7 in patients with Crohn disease.8 Other studies have shown that the highest incidence of fungal infection is seen with the use of infliximab, while adalimumab is associated with lower rates of fungal infection.9,10 Although it is known that anti-TNF therapy predisposes patients to fungal infection, the dose of medication known to preclude the highest risk has not been studied. Furthermore, most studies assess rates of Candida infection in individuals receiving anti-TNF therapy in addition to several other immunosuppressant agents (ie, corticosteroids), which confounds the interpretation of results. Additional studies assessing rates of Candida and other opportunistic infections associated with use of adalimumab alone are needed to better guide clinical practices in dermatology.
Patients receiving adalimumab for dermatologic or other conditions should be closely monitored for opportunistic infections. Although immunomodulatory medications offer promising therapeutic benefits in patients with HS, larger studies regarding treatment with anti-TNF agents in HS are warranted to prevent complications from treatment and promote long-term efficacy and safety.
- Kurayev A, Ashkar H, Saraiya A, et al. Hidradenitis suppurativa: review of the pathogenesis and treatment. J Drugs Dermatol. 2016;15:1107-1022.
- Rambhatla PV, Lim HW, Hamzavi I. A systematic review of treatments for hidradenitis suppurativa. Arch Dermatol. 2012;148:439-446.
- van der Zee HH, de Ruiter L, van den Broecke DG, et al. Elevated levels of tumour necrosis factor (TNF)-alpha, interleukin (IL)-1beta and IL-10 in hidradenitis suppurativa skin: a rationale for targeting TNF-alpha and IL-1beta. Br J Dermatol. 2011;164:1292-1298.
- Shuja F, Chan CS, Rosen T. Biologic drugs for the treatment of hidradenitis suppurativa: an evidence-based review. Dermatol Clin. 2010;28:511-521, 523-514.
- Kutsch CL, Norris DA, Arend WP. Tumor necrosis factor-alpha induces interleukin-1 alpha and interleukin-1 receptor antagonist production by cultured human keratinocytes. J Invest Dermatol. 1993;101:79-85.
- Senet JM. Risk factors and physiopathology of candidiasis. Rev Iberoam Micol. 1997;14:6-13.
- Kobak S, Yilmaz H, Guclu O, et al. Severe candida laryngitis in a patient with rheumatoid arthritis treated with adalimumab. Eur J Rheumatol. 2014;1:167-169.
- Marehbian J, Arrighi HM, Hass S, et al. Adverse events associated with common therapy regimens for moderate-to-severe Crohn’s disease. Am J Gastroenterol. 2009;104:2524-2533.
- Tsiodras S, Samonis G, Boumpas DT, et al. Fungal infections complicating tumor necrosis factor alpha blockade therapy. Mayo Clin Proc. 2008;83:181-194.
- Aikawa NE, Rosa DT, Del Negro GM, et al. Systemic and localized infection by Candida species in patients with rheumatic diseases receiving anti-TNF therapy [in Portuguese]. Rev Bras Reumatol. doi:10.1016/j.rbr.2015.03.010
- Kurayev A, Ashkar H, Saraiya A, et al. Hidradenitis suppurativa: review of the pathogenesis and treatment. J Drugs Dermatol. 2016;15:1107-1022.
- Rambhatla PV, Lim HW, Hamzavi I. A systematic review of treatments for hidradenitis suppurativa. Arch Dermatol. 2012;148:439-446.
- van der Zee HH, de Ruiter L, van den Broecke DG, et al. Elevated levels of tumour necrosis factor (TNF)-alpha, interleukin (IL)-1beta and IL-10 in hidradenitis suppurativa skin: a rationale for targeting TNF-alpha and IL-1beta. Br J Dermatol. 2011;164:1292-1298.
- Shuja F, Chan CS, Rosen T. Biologic drugs for the treatment of hidradenitis suppurativa: an evidence-based review. Dermatol Clin. 2010;28:511-521, 523-514.
- Kutsch CL, Norris DA, Arend WP. Tumor necrosis factor-alpha induces interleukin-1 alpha and interleukin-1 receptor antagonist production by cultured human keratinocytes. J Invest Dermatol. 1993;101:79-85.
- Senet JM. Risk factors and physiopathology of candidiasis. Rev Iberoam Micol. 1997;14:6-13.
- Kobak S, Yilmaz H, Guclu O, et al. Severe candida laryngitis in a patient with rheumatoid arthritis treated with adalimumab. Eur J Rheumatol. 2014;1:167-169.
- Marehbian J, Arrighi HM, Hass S, et al. Adverse events associated with common therapy regimens for moderate-to-severe Crohn’s disease. Am J Gastroenterol. 2009;104:2524-2533.
- Tsiodras S, Samonis G, Boumpas DT, et al. Fungal infections complicating tumor necrosis factor alpha blockade therapy. Mayo Clin Proc. 2008;83:181-194.
- Aikawa NE, Rosa DT, Del Negro GM, et al. Systemic and localized infection by Candida species in patients with rheumatic diseases receiving anti-TNF therapy [in Portuguese]. Rev Bras Reumatol. doi:10.1016/j.rbr.2015.03.010
Practice Points
- Adalimumab is an effective treatment for patients with hidradenitis suppurativa.
- There is risk for opportunistic infections with adalimumab, and patients should be monitored closely.
Nearly 20% of lupus patients have severe infection in first decade after diagnosis
People with systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) experienced significantly higher rates of first severe infections, a higher number of severe infections overall, and greater infection-related mortality, compared with controls, based on data from a population-based cohort study of more than 30,000 individuals.
Infections remain a leading cause of morbidity and early mortality in patients with SLE, wrote Kai Zhao, MSc, of Arthritis Research Canada, Richmond, and colleagues. However, “limitations from existing studies including selected samples, small sizes, and prevalent cohorts can negatively affect the accuracy of both the absolute and relative risk estimates of infections in SLE at the population level,” they said.
In a study published in Rheumatology, the researchers identified 5,169 people newly diagnosed with SLE between Jan. 1, 1997, and March 31, 2015, and matched them with 25,845 non-SLE controls using an administrative health database of all health care services funded in British Columbia during the time period. The investigators said the study is the first “to evaluate the risk of severe infections in a large population-based and incident SLE cohort.”
The average age of the patients was 46.9 at the time of their index SLE diagnosis, and 86% were women. The average follow-up period was approximately 10 years.
The primary outcome was the first severe infection after the onset of SLE that required hospitalization or occurred in the hospital setting. A total of 955 (18.5%) first severe infections occurred in the SLE group, compared with 1,988 (7.7%) in the controls, for incidence rates of 19.7 events per 1,000 person-years and 7.6 events per 1,000 person-years, respectively, yielding an 82% increased risk of severe infection for SLE patients after adjustment for confounding baseline factors.
Secondary outcomes of the total number of severe infections and infection-related mortality both showed significant increases in SLE patients, compared with controls. The total number of severe infections in the SLE and control groups was 1,898 and 3,114, respectively, with an adjusted risk ratio of 2.07.
As for mortality, a total of 539 deaths occurred in SLE patients during the study period, and 114 (21%) were related to severe infection. A total of 1,495 deaths occurred in the control group, including 269 (18%) related to severe infection. The adjusted hazard ratio was 1.61 after adjustment for confounding baseline variables.
The risks for first severe infection, total number of severe infections, and infection-related mortality were “independent of traditional risk factors for infection and the results remain robust in the presence of an unmeasured confounder (smoking) and competing risk of death,” the researchers said. Reasons for the increased risk are uncertain, but likely result from intrinsic factors such as immune system dysfunction and extrinsic factors such as the impact of immunosuppressive medications. “Future research can focus on quantifying the relative contributions of these intrinsic and extrinsic factors on the increased infection risk in SLE patients,” they added.
The study findings were limited by several factors linked to the observational design, including possible misdiagnosis of SLE and inaccurate measure of SLE onset, the researchers noted. In addition, no data were available for certain confounders such as smoking and nonhospitalized infections, they said.
However, the results were strengthened by the large size and general population and the use of sensitivity analyses, they noted. For SLE patients, “increased awareness of the risk of infections can identify their early signs and potentially prevent hospitalizations,” and clinicians can promote infection prevention strategies, including vaccinations when appropriate, they added.
Based on their findings, “we recommend a closer surveillance for severe infections in SLE patients and risk assessment for severe infections for SLE patients after diagnosis,” the researchers emphasized. “Further studies are warranted to further identify risk factors for infections in SLE patients to develop personalized treatment regimens and to select treatment in practice by synthesizing patient information,” they concluded.
The study was supported by the Canadian Institutes for Health Research. The researchers had no financial conflicts to disclose.
People with systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) experienced significantly higher rates of first severe infections, a higher number of severe infections overall, and greater infection-related mortality, compared with controls, based on data from a population-based cohort study of more than 30,000 individuals.
Infections remain a leading cause of morbidity and early mortality in patients with SLE, wrote Kai Zhao, MSc, of Arthritis Research Canada, Richmond, and colleagues. However, “limitations from existing studies including selected samples, small sizes, and prevalent cohorts can negatively affect the accuracy of both the absolute and relative risk estimates of infections in SLE at the population level,” they said.
In a study published in Rheumatology, the researchers identified 5,169 people newly diagnosed with SLE between Jan. 1, 1997, and March 31, 2015, and matched them with 25,845 non-SLE controls using an administrative health database of all health care services funded in British Columbia during the time period. The investigators said the study is the first “to evaluate the risk of severe infections in a large population-based and incident SLE cohort.”
The average age of the patients was 46.9 at the time of their index SLE diagnosis, and 86% were women. The average follow-up period was approximately 10 years.
The primary outcome was the first severe infection after the onset of SLE that required hospitalization or occurred in the hospital setting. A total of 955 (18.5%) first severe infections occurred in the SLE group, compared with 1,988 (7.7%) in the controls, for incidence rates of 19.7 events per 1,000 person-years and 7.6 events per 1,000 person-years, respectively, yielding an 82% increased risk of severe infection for SLE patients after adjustment for confounding baseline factors.
Secondary outcomes of the total number of severe infections and infection-related mortality both showed significant increases in SLE patients, compared with controls. The total number of severe infections in the SLE and control groups was 1,898 and 3,114, respectively, with an adjusted risk ratio of 2.07.
As for mortality, a total of 539 deaths occurred in SLE patients during the study period, and 114 (21%) were related to severe infection. A total of 1,495 deaths occurred in the control group, including 269 (18%) related to severe infection. The adjusted hazard ratio was 1.61 after adjustment for confounding baseline variables.
The risks for first severe infection, total number of severe infections, and infection-related mortality were “independent of traditional risk factors for infection and the results remain robust in the presence of an unmeasured confounder (smoking) and competing risk of death,” the researchers said. Reasons for the increased risk are uncertain, but likely result from intrinsic factors such as immune system dysfunction and extrinsic factors such as the impact of immunosuppressive medications. “Future research can focus on quantifying the relative contributions of these intrinsic and extrinsic factors on the increased infection risk in SLE patients,” they added.
The study findings were limited by several factors linked to the observational design, including possible misdiagnosis of SLE and inaccurate measure of SLE onset, the researchers noted. In addition, no data were available for certain confounders such as smoking and nonhospitalized infections, they said.
However, the results were strengthened by the large size and general population and the use of sensitivity analyses, they noted. For SLE patients, “increased awareness of the risk of infections can identify their early signs and potentially prevent hospitalizations,” and clinicians can promote infection prevention strategies, including vaccinations when appropriate, they added.
Based on their findings, “we recommend a closer surveillance for severe infections in SLE patients and risk assessment for severe infections for SLE patients after diagnosis,” the researchers emphasized. “Further studies are warranted to further identify risk factors for infections in SLE patients to develop personalized treatment regimens and to select treatment in practice by synthesizing patient information,” they concluded.
The study was supported by the Canadian Institutes for Health Research. The researchers had no financial conflicts to disclose.
People with systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) experienced significantly higher rates of first severe infections, a higher number of severe infections overall, and greater infection-related mortality, compared with controls, based on data from a population-based cohort study of more than 30,000 individuals.
Infections remain a leading cause of morbidity and early mortality in patients with SLE, wrote Kai Zhao, MSc, of Arthritis Research Canada, Richmond, and colleagues. However, “limitations from existing studies including selected samples, small sizes, and prevalent cohorts can negatively affect the accuracy of both the absolute and relative risk estimates of infections in SLE at the population level,” they said.
In a study published in Rheumatology, the researchers identified 5,169 people newly diagnosed with SLE between Jan. 1, 1997, and March 31, 2015, and matched them with 25,845 non-SLE controls using an administrative health database of all health care services funded in British Columbia during the time period. The investigators said the study is the first “to evaluate the risk of severe infections in a large population-based and incident SLE cohort.”
The average age of the patients was 46.9 at the time of their index SLE diagnosis, and 86% were women. The average follow-up period was approximately 10 years.
The primary outcome was the first severe infection after the onset of SLE that required hospitalization or occurred in the hospital setting. A total of 955 (18.5%) first severe infections occurred in the SLE group, compared with 1,988 (7.7%) in the controls, for incidence rates of 19.7 events per 1,000 person-years and 7.6 events per 1,000 person-years, respectively, yielding an 82% increased risk of severe infection for SLE patients after adjustment for confounding baseline factors.
Secondary outcomes of the total number of severe infections and infection-related mortality both showed significant increases in SLE patients, compared with controls. The total number of severe infections in the SLE and control groups was 1,898 and 3,114, respectively, with an adjusted risk ratio of 2.07.
As for mortality, a total of 539 deaths occurred in SLE patients during the study period, and 114 (21%) were related to severe infection. A total of 1,495 deaths occurred in the control group, including 269 (18%) related to severe infection. The adjusted hazard ratio was 1.61 after adjustment for confounding baseline variables.
The risks for first severe infection, total number of severe infections, and infection-related mortality were “independent of traditional risk factors for infection and the results remain robust in the presence of an unmeasured confounder (smoking) and competing risk of death,” the researchers said. Reasons for the increased risk are uncertain, but likely result from intrinsic factors such as immune system dysfunction and extrinsic factors such as the impact of immunosuppressive medications. “Future research can focus on quantifying the relative contributions of these intrinsic and extrinsic factors on the increased infection risk in SLE patients,” they added.
The study findings were limited by several factors linked to the observational design, including possible misdiagnosis of SLE and inaccurate measure of SLE onset, the researchers noted. In addition, no data were available for certain confounders such as smoking and nonhospitalized infections, they said.
However, the results were strengthened by the large size and general population and the use of sensitivity analyses, they noted. For SLE patients, “increased awareness of the risk of infections can identify their early signs and potentially prevent hospitalizations,” and clinicians can promote infection prevention strategies, including vaccinations when appropriate, they added.
Based on their findings, “we recommend a closer surveillance for severe infections in SLE patients and risk assessment for severe infections for SLE patients after diagnosis,” the researchers emphasized. “Further studies are warranted to further identify risk factors for infections in SLE patients to develop personalized treatment regimens and to select treatment in practice by synthesizing patient information,” they concluded.
The study was supported by the Canadian Institutes for Health Research. The researchers had no financial conflicts to disclose.
FROM RHEUMATOLOGY
Assessing Psychological Interventions for Hidradenitis Suppurativa as a First Step Toward Patient-Centered Practice
Hidradenitis suppurativa (HS)(also known as acne inversa) is a chronic, recurrent, and debilitating inflammatory dermatologic disease of the hair follicle. It usually presents after puberty, with painful, deep-seated, inflamed lesions in apocrine gland–bearing areas of the body, most commonly the axillae and inguinal and anogenital regions.1
Hidradenitis suppurativa patients have a high rate of psychologic and psychiatric comorbidities that often are interrelated and multidirectional. Approximately 1 in 4 adults with HS also experience depression (prevalence among all HS patients, 16.9%), and 1 in 5 experience anxiety (prevalence, 4.9%).2,3 Hidradenitis suppurativa has been associated with bipolar disorder, schizophrenia, and suicidality.2,4
These comorbidity factors have a remarkable impact on HS patients’ quality of life (QOL). Compared to other diseases, including psoriasis, stroke, and conditions that create candidacy for heart transplantation, HS was identified as the most impairing condition.5,6 It is estimated that more than 50% of HS patients experience a very or extremely large effect on their QOL, as measured by the dermatology life quality index.6
Pain, a major component of low QOL in HS patients, has an adverse impact on emotional health. Hidradenitis suppurativa causes body image dissatisfaction, leading to shame, embarrassment, lack of self-confidence, stigmatization, and social isolation.7-9 Furthermore, patients with HS have an increased risk for antidepressant drug use, completed suicide, and suicidal behavior compared to the general population.10
Focusing therapy on physical manifestations of HS only while ignoring the psychologic aspect could lead to a vicious cycle in which stress triggers flares, leading to worsening HS, leading to more stress, and so on.11 Therefore, psychological support for HS patients is critical, and we believe it should be an integral part of managing the disease.
There is no evidence to support effective therapeutic intervention for psychological aspects of HS. We conducted a PubMed search of articles indexed for MEDLINE using the term hidradenitis in combination with psychology, psychological, mindfulness, and cognitive behavioral therapy. No relevant articles were found. Most articles on HS focused on the low QOL associated with the disease and patient coping mechanisms. However, there are a number of psychological therapies to consider and evaluate for the management of HS.
Psychological Therapies to Consider in HS
Cognitive Behavioral Treatment
Cognitive behavioral treatment has been successfully used to manage skin diseases other than HS.12 Patients’ shame and stigmatization due to body dissatisfaction often cause social isolation, which might appear as social anxiety.9,13 Cognitive behavioral treatment, or compassion-focused therapy, could increase patients’ self-acceptance and reduce shameful feelings.13
Group Therapy
Alternatively, group therapy might be beneficial for HS patients. Research has shown that most HS patients know others affected by the same disease or attend an HS support group, and patients value the support of peers with the disease.13 Therefore, group therapy meetings with HS patients that are directed by a health care professional might reduce feelings of shame and stigmatization and increase feelings of social acceptance.
Mindfulness
Another approach for managing psychological aspects of skin diseases that might be useful in HS is mindfulness-based stress reduction (MBSR), developed by Kabat-Zinn and colleagues,14 which helps patients develop mindfulness through training in meditation. It is an intensive, structured, patient-centered approach that has been successfully used in a variety of settings.14,15
Current evidence supports the use of MBSR in the adjunct treatment of chronic pain, anxiety, and depression—symptoms that have a great impact on HS patients’ QOL.16 Furthermore, MBSR is offered in a group setting, which is potentially an opportunity for peer support and understanding; social support has been reported to be highly beneficial for HS patients.17
Can the Placebo Effect Aid in Managing HS?
A recent review that assessed the placebo effect in randomized clinical trials (RCTs) of treatments for cutaneous disease demonstrated that the placebo effect in HS therapy trials is higher than in RCTs of therapies for psoriasis and eczema. This finding highlights the importance of the physician-patient relationship when managing HS, which can result in greater treatment adherence and more patient education, empowerment, and encouragement toward beneficial lifestyle changes.18
Complementary psychological interventions for managing HS might maximize the placebo effect in clinical practice.18 The placebo effect in RCTs is higher for HS treatments than for psoriasis treatments, and if patients with psoriasis improved with psychological interventions,12 it would be reasonable to expect an improvement in QOL with psychological interventions for HS.
Final Thoughts
Although a number of studies have been published in the medical literature regarding psychological intervention in psoriasis management,12 we found no clinical studies assessing the psychological management of HS. We conclude that more research is necessary to develop psychological interventions targeting HS patients because a multidisciplinary and patient-centered approach is essential for the management of HS.
- Zouboulis CC, Desai N, Emtestam L, et al. European S1 guideline for the treatment of hidradenitis suppurativa/acne inversa. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2015;29:619-644.
- Patel KR, Lee HH, Rastogi S, et al. Association between hidradenitis suppurativa, depression, anxiety, and suicidality: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2020;83:737-744.
- Machado MO, Stergiopoulos V, Maes M, et al. Depression and anxiety in adults with hidradenitis suppurativa: a systematic review and meta-analysis. JAMA Dermatol. 2019;155:939-945.
- Huilaja L, Tiri H, Jokelainen J, et al. Patients with hidradenitis suppurativa have a high psychiatric disease burden: a Finnish nationwide registry study. J Invest Dermatol. 2018;138:46-51.
- Sampogna F, Fania L, Mazzanti C, et al. The broad-spectrum impact of hidradenitis suppurativa on quality of life: a comparison with psoriasis. Dermatology. 2019;235:308-314.
- von der Werth JM, Jemec GB. Morbidity in patients with hidradenitis suppurativa. Br J Dermatol. 2001;144:809-813.
- Esmann S, Jemec GBE. Psychosocial impact of hidradenitis suppurativa: a qualitative study. Acta Derm Venereol. 2011;91:328-332.
- Schneider-Burrus S, Jost A, Peters EMJ, et al. Association of hidradenitis suppurativa with body image. JAMA Dermatol. 2018;154:447-451.
- Koumaki D, Efthymiou O, Bozi E, et al. Perspectives on perceived stigma and self-stigma in patients with hidradenitis suppurativa. Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol. 2019;12:785-790.
- Thorlacius L, Cohen AD, Gislason GH, et al. Increased suicide risk in patients with hidradenitis suppurativa. J Invest Dermatol. 2018;138:52-57.
- Gill L, Williams M, Hamzavi I. Update on hidradenitis suppurativa: connecting the tracts. F1000Prime Rep. 2014;6:112.
- Qureshi AA, Awosika O, Baruffi F, et al. Psychological therapies in management of psoriatic skin disease: a systematic review. Am J Clin Dermatol. 2019;20:607-624.
- Keary E, Hevey D, Tobin AM. A qualitative analysis of psychological distress in hidradenitis suppurativa. Br J Dermatol. 2020;182:342-347.
- Kabat-Zinn J, Massion AO, Kristeller J, et al. Effectiveness of a meditation-based stress reduction program in the treatment of anxiety disorders. Am J Psychiatry. 1992;149:936-943.
- Evans S, Ferrando S, Findler M, et al. Mindfulness-based cognitive therapy for generalized anxiety disorder. J Anxiety Disord. 2008;22:716-721.
- Gotink RA, Chu P, Busschbach JJV, et al. Standardised mindfulness-based interventions in healthcare: an overview of systematic reviews and meta-analyses of RCTs. PLoS One. 2015;10:e0124344.
- Golbari NM, Porter ML, Kimball AM. Online communications among hidradenitis suppurativa patients reflect community needs. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2019;80:1760-1762.
- Ali AA, Seng EK, Alavi A, et al. Exploring changes in placebo treatment arms in hidradenitis suppurativa randomized clinical trials: a systematic review. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2020;82:45-53.
Hidradenitis suppurativa (HS)(also known as acne inversa) is a chronic, recurrent, and debilitating inflammatory dermatologic disease of the hair follicle. It usually presents after puberty, with painful, deep-seated, inflamed lesions in apocrine gland–bearing areas of the body, most commonly the axillae and inguinal and anogenital regions.1
Hidradenitis suppurativa patients have a high rate of psychologic and psychiatric comorbidities that often are interrelated and multidirectional. Approximately 1 in 4 adults with HS also experience depression (prevalence among all HS patients, 16.9%), and 1 in 5 experience anxiety (prevalence, 4.9%).2,3 Hidradenitis suppurativa has been associated with bipolar disorder, schizophrenia, and suicidality.2,4
These comorbidity factors have a remarkable impact on HS patients’ quality of life (QOL). Compared to other diseases, including psoriasis, stroke, and conditions that create candidacy for heart transplantation, HS was identified as the most impairing condition.5,6 It is estimated that more than 50% of HS patients experience a very or extremely large effect on their QOL, as measured by the dermatology life quality index.6
Pain, a major component of low QOL in HS patients, has an adverse impact on emotional health. Hidradenitis suppurativa causes body image dissatisfaction, leading to shame, embarrassment, lack of self-confidence, stigmatization, and social isolation.7-9 Furthermore, patients with HS have an increased risk for antidepressant drug use, completed suicide, and suicidal behavior compared to the general population.10
Focusing therapy on physical manifestations of HS only while ignoring the psychologic aspect could lead to a vicious cycle in which stress triggers flares, leading to worsening HS, leading to more stress, and so on.11 Therefore, psychological support for HS patients is critical, and we believe it should be an integral part of managing the disease.
There is no evidence to support effective therapeutic intervention for psychological aspects of HS. We conducted a PubMed search of articles indexed for MEDLINE using the term hidradenitis in combination with psychology, psychological, mindfulness, and cognitive behavioral therapy. No relevant articles were found. Most articles on HS focused on the low QOL associated with the disease and patient coping mechanisms. However, there are a number of psychological therapies to consider and evaluate for the management of HS.
Psychological Therapies to Consider in HS
Cognitive Behavioral Treatment
Cognitive behavioral treatment has been successfully used to manage skin diseases other than HS.12 Patients’ shame and stigmatization due to body dissatisfaction often cause social isolation, which might appear as social anxiety.9,13 Cognitive behavioral treatment, or compassion-focused therapy, could increase patients’ self-acceptance and reduce shameful feelings.13
Group Therapy
Alternatively, group therapy might be beneficial for HS patients. Research has shown that most HS patients know others affected by the same disease or attend an HS support group, and patients value the support of peers with the disease.13 Therefore, group therapy meetings with HS patients that are directed by a health care professional might reduce feelings of shame and stigmatization and increase feelings of social acceptance.
Mindfulness
Another approach for managing psychological aspects of skin diseases that might be useful in HS is mindfulness-based stress reduction (MBSR), developed by Kabat-Zinn and colleagues,14 which helps patients develop mindfulness through training in meditation. It is an intensive, structured, patient-centered approach that has been successfully used in a variety of settings.14,15
Current evidence supports the use of MBSR in the adjunct treatment of chronic pain, anxiety, and depression—symptoms that have a great impact on HS patients’ QOL.16 Furthermore, MBSR is offered in a group setting, which is potentially an opportunity for peer support and understanding; social support has been reported to be highly beneficial for HS patients.17
Can the Placebo Effect Aid in Managing HS?
A recent review that assessed the placebo effect in randomized clinical trials (RCTs) of treatments for cutaneous disease demonstrated that the placebo effect in HS therapy trials is higher than in RCTs of therapies for psoriasis and eczema. This finding highlights the importance of the physician-patient relationship when managing HS, which can result in greater treatment adherence and more patient education, empowerment, and encouragement toward beneficial lifestyle changes.18
Complementary psychological interventions for managing HS might maximize the placebo effect in clinical practice.18 The placebo effect in RCTs is higher for HS treatments than for psoriasis treatments, and if patients with psoriasis improved with psychological interventions,12 it would be reasonable to expect an improvement in QOL with psychological interventions for HS.
Final Thoughts
Although a number of studies have been published in the medical literature regarding psychological intervention in psoriasis management,12 we found no clinical studies assessing the psychological management of HS. We conclude that more research is necessary to develop psychological interventions targeting HS patients because a multidisciplinary and patient-centered approach is essential for the management of HS.
Hidradenitis suppurativa (HS)(also known as acne inversa) is a chronic, recurrent, and debilitating inflammatory dermatologic disease of the hair follicle. It usually presents after puberty, with painful, deep-seated, inflamed lesions in apocrine gland–bearing areas of the body, most commonly the axillae and inguinal and anogenital regions.1
Hidradenitis suppurativa patients have a high rate of psychologic and psychiatric comorbidities that often are interrelated and multidirectional. Approximately 1 in 4 adults with HS also experience depression (prevalence among all HS patients, 16.9%), and 1 in 5 experience anxiety (prevalence, 4.9%).2,3 Hidradenitis suppurativa has been associated with bipolar disorder, schizophrenia, and suicidality.2,4
These comorbidity factors have a remarkable impact on HS patients’ quality of life (QOL). Compared to other diseases, including psoriasis, stroke, and conditions that create candidacy for heart transplantation, HS was identified as the most impairing condition.5,6 It is estimated that more than 50% of HS patients experience a very or extremely large effect on their QOL, as measured by the dermatology life quality index.6
Pain, a major component of low QOL in HS patients, has an adverse impact on emotional health. Hidradenitis suppurativa causes body image dissatisfaction, leading to shame, embarrassment, lack of self-confidence, stigmatization, and social isolation.7-9 Furthermore, patients with HS have an increased risk for antidepressant drug use, completed suicide, and suicidal behavior compared to the general population.10
Focusing therapy on physical manifestations of HS only while ignoring the psychologic aspect could lead to a vicious cycle in which stress triggers flares, leading to worsening HS, leading to more stress, and so on.11 Therefore, psychological support for HS patients is critical, and we believe it should be an integral part of managing the disease.
There is no evidence to support effective therapeutic intervention for psychological aspects of HS. We conducted a PubMed search of articles indexed for MEDLINE using the term hidradenitis in combination with psychology, psychological, mindfulness, and cognitive behavioral therapy. No relevant articles were found. Most articles on HS focused on the low QOL associated with the disease and patient coping mechanisms. However, there are a number of psychological therapies to consider and evaluate for the management of HS.
Psychological Therapies to Consider in HS
Cognitive Behavioral Treatment
Cognitive behavioral treatment has been successfully used to manage skin diseases other than HS.12 Patients’ shame and stigmatization due to body dissatisfaction often cause social isolation, which might appear as social anxiety.9,13 Cognitive behavioral treatment, or compassion-focused therapy, could increase patients’ self-acceptance and reduce shameful feelings.13
Group Therapy
Alternatively, group therapy might be beneficial for HS patients. Research has shown that most HS patients know others affected by the same disease or attend an HS support group, and patients value the support of peers with the disease.13 Therefore, group therapy meetings with HS patients that are directed by a health care professional might reduce feelings of shame and stigmatization and increase feelings of social acceptance.
Mindfulness
Another approach for managing psychological aspects of skin diseases that might be useful in HS is mindfulness-based stress reduction (MBSR), developed by Kabat-Zinn and colleagues,14 which helps patients develop mindfulness through training in meditation. It is an intensive, structured, patient-centered approach that has been successfully used in a variety of settings.14,15
Current evidence supports the use of MBSR in the adjunct treatment of chronic pain, anxiety, and depression—symptoms that have a great impact on HS patients’ QOL.16 Furthermore, MBSR is offered in a group setting, which is potentially an opportunity for peer support and understanding; social support has been reported to be highly beneficial for HS patients.17
Can the Placebo Effect Aid in Managing HS?
A recent review that assessed the placebo effect in randomized clinical trials (RCTs) of treatments for cutaneous disease demonstrated that the placebo effect in HS therapy trials is higher than in RCTs of therapies for psoriasis and eczema. This finding highlights the importance of the physician-patient relationship when managing HS, which can result in greater treatment adherence and more patient education, empowerment, and encouragement toward beneficial lifestyle changes.18
Complementary psychological interventions for managing HS might maximize the placebo effect in clinical practice.18 The placebo effect in RCTs is higher for HS treatments than for psoriasis treatments, and if patients with psoriasis improved with psychological interventions,12 it would be reasonable to expect an improvement in QOL with psychological interventions for HS.
Final Thoughts
Although a number of studies have been published in the medical literature regarding psychological intervention in psoriasis management,12 we found no clinical studies assessing the psychological management of HS. We conclude that more research is necessary to develop psychological interventions targeting HS patients because a multidisciplinary and patient-centered approach is essential for the management of HS.
- Zouboulis CC, Desai N, Emtestam L, et al. European S1 guideline for the treatment of hidradenitis suppurativa/acne inversa. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2015;29:619-644.
- Patel KR, Lee HH, Rastogi S, et al. Association between hidradenitis suppurativa, depression, anxiety, and suicidality: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2020;83:737-744.
- Machado MO, Stergiopoulos V, Maes M, et al. Depression and anxiety in adults with hidradenitis suppurativa: a systematic review and meta-analysis. JAMA Dermatol. 2019;155:939-945.
- Huilaja L, Tiri H, Jokelainen J, et al. Patients with hidradenitis suppurativa have a high psychiatric disease burden: a Finnish nationwide registry study. J Invest Dermatol. 2018;138:46-51.
- Sampogna F, Fania L, Mazzanti C, et al. The broad-spectrum impact of hidradenitis suppurativa on quality of life: a comparison with psoriasis. Dermatology. 2019;235:308-314.
- von der Werth JM, Jemec GB. Morbidity in patients with hidradenitis suppurativa. Br J Dermatol. 2001;144:809-813.
- Esmann S, Jemec GBE. Psychosocial impact of hidradenitis suppurativa: a qualitative study. Acta Derm Venereol. 2011;91:328-332.
- Schneider-Burrus S, Jost A, Peters EMJ, et al. Association of hidradenitis suppurativa with body image. JAMA Dermatol. 2018;154:447-451.
- Koumaki D, Efthymiou O, Bozi E, et al. Perspectives on perceived stigma and self-stigma in patients with hidradenitis suppurativa. Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol. 2019;12:785-790.
- Thorlacius L, Cohen AD, Gislason GH, et al. Increased suicide risk in patients with hidradenitis suppurativa. J Invest Dermatol. 2018;138:52-57.
- Gill L, Williams M, Hamzavi I. Update on hidradenitis suppurativa: connecting the tracts. F1000Prime Rep. 2014;6:112.
- Qureshi AA, Awosika O, Baruffi F, et al. Psychological therapies in management of psoriatic skin disease: a systematic review. Am J Clin Dermatol. 2019;20:607-624.
- Keary E, Hevey D, Tobin AM. A qualitative analysis of psychological distress in hidradenitis suppurativa. Br J Dermatol. 2020;182:342-347.
- Kabat-Zinn J, Massion AO, Kristeller J, et al. Effectiveness of a meditation-based stress reduction program in the treatment of anxiety disorders. Am J Psychiatry. 1992;149:936-943.
- Evans S, Ferrando S, Findler M, et al. Mindfulness-based cognitive therapy for generalized anxiety disorder. J Anxiety Disord. 2008;22:716-721.
- Gotink RA, Chu P, Busschbach JJV, et al. Standardised mindfulness-based interventions in healthcare: an overview of systematic reviews and meta-analyses of RCTs. PLoS One. 2015;10:e0124344.
- Golbari NM, Porter ML, Kimball AM. Online communications among hidradenitis suppurativa patients reflect community needs. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2019;80:1760-1762.
- Ali AA, Seng EK, Alavi A, et al. Exploring changes in placebo treatment arms in hidradenitis suppurativa randomized clinical trials: a systematic review. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2020;82:45-53.
- Zouboulis CC, Desai N, Emtestam L, et al. European S1 guideline for the treatment of hidradenitis suppurativa/acne inversa. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2015;29:619-644.
- Patel KR, Lee HH, Rastogi S, et al. Association between hidradenitis suppurativa, depression, anxiety, and suicidality: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2020;83:737-744.
- Machado MO, Stergiopoulos V, Maes M, et al. Depression and anxiety in adults with hidradenitis suppurativa: a systematic review and meta-analysis. JAMA Dermatol. 2019;155:939-945.
- Huilaja L, Tiri H, Jokelainen J, et al. Patients with hidradenitis suppurativa have a high psychiatric disease burden: a Finnish nationwide registry study. J Invest Dermatol. 2018;138:46-51.
- Sampogna F, Fania L, Mazzanti C, et al. The broad-spectrum impact of hidradenitis suppurativa on quality of life: a comparison with psoriasis. Dermatology. 2019;235:308-314.
- von der Werth JM, Jemec GB. Morbidity in patients with hidradenitis suppurativa. Br J Dermatol. 2001;144:809-813.
- Esmann S, Jemec GBE. Psychosocial impact of hidradenitis suppurativa: a qualitative study. Acta Derm Venereol. 2011;91:328-332.
- Schneider-Burrus S, Jost A, Peters EMJ, et al. Association of hidradenitis suppurativa with body image. JAMA Dermatol. 2018;154:447-451.
- Koumaki D, Efthymiou O, Bozi E, et al. Perspectives on perceived stigma and self-stigma in patients with hidradenitis suppurativa. Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol. 2019;12:785-790.
- Thorlacius L, Cohen AD, Gislason GH, et al. Increased suicide risk in patients with hidradenitis suppurativa. J Invest Dermatol. 2018;138:52-57.
- Gill L, Williams M, Hamzavi I. Update on hidradenitis suppurativa: connecting the tracts. F1000Prime Rep. 2014;6:112.
- Qureshi AA, Awosika O, Baruffi F, et al. Psychological therapies in management of psoriatic skin disease: a systematic review. Am J Clin Dermatol. 2019;20:607-624.
- Keary E, Hevey D, Tobin AM. A qualitative analysis of psychological distress in hidradenitis suppurativa. Br J Dermatol. 2020;182:342-347.
- Kabat-Zinn J, Massion AO, Kristeller J, et al. Effectiveness of a meditation-based stress reduction program in the treatment of anxiety disorders. Am J Psychiatry. 1992;149:936-943.
- Evans S, Ferrando S, Findler M, et al. Mindfulness-based cognitive therapy for generalized anxiety disorder. J Anxiety Disord. 2008;22:716-721.
- Gotink RA, Chu P, Busschbach JJV, et al. Standardised mindfulness-based interventions in healthcare: an overview of systematic reviews and meta-analyses of RCTs. PLoS One. 2015;10:e0124344.
- Golbari NM, Porter ML, Kimball AM. Online communications among hidradenitis suppurativa patients reflect community needs. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2019;80:1760-1762.
- Ali AA, Seng EK, Alavi A, et al. Exploring changes in placebo treatment arms in hidradenitis suppurativa randomized clinical trials: a systematic review. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2020;82:45-53.
PRACTICE POINTS
- Although hidradenitis suppurativa (HS) has high rates of psychological comorbidities, management of the psychological aspects of the disease has not been studied extensively.
- Complementary psychological interventions should be evaluated for the management of HS.