User login
Aspirin exposure fails to reduce cardiovascular event risk
The benefits of aspirin use for the primary prevention of atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease (ASCVD) have been questioned in light of data showing neutral outcomes in low-risk patients and concerns about increased bleeding risk and mortality in healthy older adults, wrote Rita Del Pinto, MD, of University of L’Aquila (Italy) and colleagues in JAMA Network Open.
In the study, Dr. Del Pinto and colleagues conducted a post hoc analysis of data from more than 2,500 participants in SPRINT (Systolic Blood Pressure Intervention Trial), a multicenter, randomized trial conducted from 2010 to 2013.
The goal of SPRINT was to compare intensive and standard blood pressure–lowering strategies for hypertension patients. The primary outcome of the current study was risk of a first cardiovascular event, which included adjudicated myocardial infarction, non–myocardial infarction acute coronary syndrome, stroke, acute heart failure, and CVD death.“There has been considerable improvement in the management of cardiovascular risk factors since the first reports on aspirin use for cardiovascular prevention,” Dr. Del Pinto said in an interview.
“As for hypertension, not only have more effective antihypertensive medications become available, but also evidence has recently emerged in support of a downwards redefinition of blood pressure targets during treatment,” she said. “In this context, in an era when great attention is paid to the personalization of treatment, no specific studies had addressed the association of aspirin use as a primary prevention strategy in a cohort of relatively old, high-risk individuals with treated systolic blood pressure steadily below the recommended target,” she added.
The researchers assessed whether aspirin use in addition to standard blood pressure management (a target of less than 140 mm Hg) decreased risk and improved survival.
The study population included 2,664 adult patients; 29.3% were women, and 24.5% were aged 75 years and older. Half of the patients (1,332) received aspirin and 1,332 did not.
In a multivariate analysis, 42 cardiovascular events occurred in the aspirin group, compared with 20 events in those not exposed to aspirin (hazard ratio, 2.30). The findings were consistent in subgroup analyses of younger individuals, current and former smokers, and patients on statins.
An additional subgroup analysis of individuals randomized to standard care or intensive care in the SPRINT study showed no significant difference in primary outcome rates between individuals who received aspirin and those who did not. The rates for aspirin use vs. non–aspirin use were 5.85% vs. 3.60% in the standard treatment group and 4.66% vs. 2.56% in the intensive treatment group.
The study findings were limited by several factors, including the post hoc design, short follow-up period, and lack of data on the initiation of aspirin and bleeding events, the researchers wrote. However, the results suggest that modern management of hypertension may have redefined the potential benefits of aspirin in patients with hypertension, they concluded.
Findings confirm value of preventive care
“The study was conducted as a post-hoc analysis on an experimental cohort, which must be considered when interpreting the results,” Dr. Del Pinto said.
Despite the limitations, the study findings affirm that effective treatment of major cardiovascular risk factors, such as hypertension, with proven drugs is “a mainstay of the primary prevention of ASCVD,” she emphasized.
As for additional research, “Testing our findings in a dedicated setting with sufficiently long follow-up, where aspirin dose and indication, as well as any possible bleeding event, are reported could expand the clinical meaning of our observations,” said Dr. Del Pinto. “Also, the clinical impact of aspirin, even in combination with novel cardiovascular drugs such as direct oral anticoagulants, in populations exposed to combinations of risk factors, deserves further investigation.”
Data support shared decision-making
“While recent evidence has not shown a benefit of aspirin in the primary prevention of ASCVD in several populations, the subpopulation of patients with hypertension as an ASCVD risk factor is also of interest to the clinician,” Suman Pal, MD, of the University of New Mexico, Albuquerque, said in an interview. “The lack of benefit of aspirin in this study, despite its limitations, was surprising, and I would be eager to see how the role of aspirin in ASCVD prevention would continue to evolve in conjunction with improvement in other therapies for modification of risk factors.”
“The decision to continue aspirin in this subgroup of patients should warrant a discussion with patients and a reexamination of risks and benefits until further data are available,” Dr. Pal emphasized.
Larger studies with long-term follow-ups would be required to further clarify the role of aspirin in primary prevention of ASCVD in patients with hypertension without diabetes or chronic kidney disease, he added.
Data were supplied courtesy of BioLINCC. The study received no outside funding. The researchers and Dr. Pal had no financial conflicts to disclose.
The benefits of aspirin use for the primary prevention of atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease (ASCVD) have been questioned in light of data showing neutral outcomes in low-risk patients and concerns about increased bleeding risk and mortality in healthy older adults, wrote Rita Del Pinto, MD, of University of L’Aquila (Italy) and colleagues in JAMA Network Open.
In the study, Dr. Del Pinto and colleagues conducted a post hoc analysis of data from more than 2,500 participants in SPRINT (Systolic Blood Pressure Intervention Trial), a multicenter, randomized trial conducted from 2010 to 2013.
The goal of SPRINT was to compare intensive and standard blood pressure–lowering strategies for hypertension patients. The primary outcome of the current study was risk of a first cardiovascular event, which included adjudicated myocardial infarction, non–myocardial infarction acute coronary syndrome, stroke, acute heart failure, and CVD death.“There has been considerable improvement in the management of cardiovascular risk factors since the first reports on aspirin use for cardiovascular prevention,” Dr. Del Pinto said in an interview.
“As for hypertension, not only have more effective antihypertensive medications become available, but also evidence has recently emerged in support of a downwards redefinition of blood pressure targets during treatment,” she said. “In this context, in an era when great attention is paid to the personalization of treatment, no specific studies had addressed the association of aspirin use as a primary prevention strategy in a cohort of relatively old, high-risk individuals with treated systolic blood pressure steadily below the recommended target,” she added.
The researchers assessed whether aspirin use in addition to standard blood pressure management (a target of less than 140 mm Hg) decreased risk and improved survival.
The study population included 2,664 adult patients; 29.3% were women, and 24.5% were aged 75 years and older. Half of the patients (1,332) received aspirin and 1,332 did not.
In a multivariate analysis, 42 cardiovascular events occurred in the aspirin group, compared with 20 events in those not exposed to aspirin (hazard ratio, 2.30). The findings were consistent in subgroup analyses of younger individuals, current and former smokers, and patients on statins.
An additional subgroup analysis of individuals randomized to standard care or intensive care in the SPRINT study showed no significant difference in primary outcome rates between individuals who received aspirin and those who did not. The rates for aspirin use vs. non–aspirin use were 5.85% vs. 3.60% in the standard treatment group and 4.66% vs. 2.56% in the intensive treatment group.
The study findings were limited by several factors, including the post hoc design, short follow-up period, and lack of data on the initiation of aspirin and bleeding events, the researchers wrote. However, the results suggest that modern management of hypertension may have redefined the potential benefits of aspirin in patients with hypertension, they concluded.
Findings confirm value of preventive care
“The study was conducted as a post-hoc analysis on an experimental cohort, which must be considered when interpreting the results,” Dr. Del Pinto said.
Despite the limitations, the study findings affirm that effective treatment of major cardiovascular risk factors, such as hypertension, with proven drugs is “a mainstay of the primary prevention of ASCVD,” she emphasized.
As for additional research, “Testing our findings in a dedicated setting with sufficiently long follow-up, where aspirin dose and indication, as well as any possible bleeding event, are reported could expand the clinical meaning of our observations,” said Dr. Del Pinto. “Also, the clinical impact of aspirin, even in combination with novel cardiovascular drugs such as direct oral anticoagulants, in populations exposed to combinations of risk factors, deserves further investigation.”
Data support shared decision-making
“While recent evidence has not shown a benefit of aspirin in the primary prevention of ASCVD in several populations, the subpopulation of patients with hypertension as an ASCVD risk factor is also of interest to the clinician,” Suman Pal, MD, of the University of New Mexico, Albuquerque, said in an interview. “The lack of benefit of aspirin in this study, despite its limitations, was surprising, and I would be eager to see how the role of aspirin in ASCVD prevention would continue to evolve in conjunction with improvement in other therapies for modification of risk factors.”
“The decision to continue aspirin in this subgroup of patients should warrant a discussion with patients and a reexamination of risks and benefits until further data are available,” Dr. Pal emphasized.
Larger studies with long-term follow-ups would be required to further clarify the role of aspirin in primary prevention of ASCVD in patients with hypertension without diabetes or chronic kidney disease, he added.
Data were supplied courtesy of BioLINCC. The study received no outside funding. The researchers and Dr. Pal had no financial conflicts to disclose.
The benefits of aspirin use for the primary prevention of atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease (ASCVD) have been questioned in light of data showing neutral outcomes in low-risk patients and concerns about increased bleeding risk and mortality in healthy older adults, wrote Rita Del Pinto, MD, of University of L’Aquila (Italy) and colleagues in JAMA Network Open.
In the study, Dr. Del Pinto and colleagues conducted a post hoc analysis of data from more than 2,500 participants in SPRINT (Systolic Blood Pressure Intervention Trial), a multicenter, randomized trial conducted from 2010 to 2013.
The goal of SPRINT was to compare intensive and standard blood pressure–lowering strategies for hypertension patients. The primary outcome of the current study was risk of a first cardiovascular event, which included adjudicated myocardial infarction, non–myocardial infarction acute coronary syndrome, stroke, acute heart failure, and CVD death.“There has been considerable improvement in the management of cardiovascular risk factors since the first reports on aspirin use for cardiovascular prevention,” Dr. Del Pinto said in an interview.
“As for hypertension, not only have more effective antihypertensive medications become available, but also evidence has recently emerged in support of a downwards redefinition of blood pressure targets during treatment,” she said. “In this context, in an era when great attention is paid to the personalization of treatment, no specific studies had addressed the association of aspirin use as a primary prevention strategy in a cohort of relatively old, high-risk individuals with treated systolic blood pressure steadily below the recommended target,” she added.
The researchers assessed whether aspirin use in addition to standard blood pressure management (a target of less than 140 mm Hg) decreased risk and improved survival.
The study population included 2,664 adult patients; 29.3% were women, and 24.5% were aged 75 years and older. Half of the patients (1,332) received aspirin and 1,332 did not.
In a multivariate analysis, 42 cardiovascular events occurred in the aspirin group, compared with 20 events in those not exposed to aspirin (hazard ratio, 2.30). The findings were consistent in subgroup analyses of younger individuals, current and former smokers, and patients on statins.
An additional subgroup analysis of individuals randomized to standard care or intensive care in the SPRINT study showed no significant difference in primary outcome rates between individuals who received aspirin and those who did not. The rates for aspirin use vs. non–aspirin use were 5.85% vs. 3.60% in the standard treatment group and 4.66% vs. 2.56% in the intensive treatment group.
The study findings were limited by several factors, including the post hoc design, short follow-up period, and lack of data on the initiation of aspirin and bleeding events, the researchers wrote. However, the results suggest that modern management of hypertension may have redefined the potential benefits of aspirin in patients with hypertension, they concluded.
Findings confirm value of preventive care
“The study was conducted as a post-hoc analysis on an experimental cohort, which must be considered when interpreting the results,” Dr. Del Pinto said.
Despite the limitations, the study findings affirm that effective treatment of major cardiovascular risk factors, such as hypertension, with proven drugs is “a mainstay of the primary prevention of ASCVD,” she emphasized.
As for additional research, “Testing our findings in a dedicated setting with sufficiently long follow-up, where aspirin dose and indication, as well as any possible bleeding event, are reported could expand the clinical meaning of our observations,” said Dr. Del Pinto. “Also, the clinical impact of aspirin, even in combination with novel cardiovascular drugs such as direct oral anticoagulants, in populations exposed to combinations of risk factors, deserves further investigation.”
Data support shared decision-making
“While recent evidence has not shown a benefit of aspirin in the primary prevention of ASCVD in several populations, the subpopulation of patients with hypertension as an ASCVD risk factor is also of interest to the clinician,” Suman Pal, MD, of the University of New Mexico, Albuquerque, said in an interview. “The lack of benefit of aspirin in this study, despite its limitations, was surprising, and I would be eager to see how the role of aspirin in ASCVD prevention would continue to evolve in conjunction with improvement in other therapies for modification of risk factors.”
“The decision to continue aspirin in this subgroup of patients should warrant a discussion with patients and a reexamination of risks and benefits until further data are available,” Dr. Pal emphasized.
Larger studies with long-term follow-ups would be required to further clarify the role of aspirin in primary prevention of ASCVD in patients with hypertension without diabetes or chronic kidney disease, he added.
Data were supplied courtesy of BioLINCC. The study received no outside funding. The researchers and Dr. Pal had no financial conflicts to disclose.
FROM JAMA NETWORK OPEN
Combo of SGLT2 inhibitor + GLP-1 RA boosts diabetes survival
WASHINGTON – Patients with type 2 diabetes and established atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease treated with both an sodium-glucose transporter 2 inhibitor and a glucagonlike peptide–1 receptor agonist had a significant 80% cut in their rate of all-cause death during 1-year follow-up, compared with matched patients treated with an agent from either class alone in an observational, retrospective study of more than 15,000 people in the U.S. Veterans Affairs health system.
For the study’s primary endpoint, the combined rate of all-cause death, nonfatal MI, or nonfatal stroke, combined treatment with both an agent from the sodium-glucose transporter 2 (SGLT2) inhibitor class and from the glucagonlike peptide–1 receptor agonist (GLP-1 RA) class linked with a significant, roughly 50% cut in events during 1-year follow-up, compared with patients treated with an agent from just one of these two classes, Persio D. Lopez, MD, reported at the annual scientific sessions of the American College of Cardiology.
This improvement in the combined endpoint outcome resulted entirely from reduced all-cause mortality. Dual treatment showed no significant association with the incidence of nonfatal MIs or strokes, compared with monotherapy, with rates that were nearly identical regardless of whether patients took one of the agents or both, said Dr. Lopez, a cardiologist at Mount Sinai Morningside and the James J. Peters VA Medical Center, both in New York.
Combining classes for hard-to-control diabetes
“We’re not sure what drives combined use” of agents from both drug classes in these types of patients, admitted Dr. Lopez during his talk. “Our hypothesis is that dual treatment is used in patients with harder-to-control diabetes.”
Salim S. Virani, MD, PhD, who practices in the VA system but was not involved with the study, agreed that this is the likely explanation for most instances of high-risk VA patients with diabetes who receive agents from both classes.
“I have a few patients” on both classes, usually “patients with higher starting A1c levels who need greater glycemic control,” said Dr. Virani, professor of medicine at Baylor College of Medicine and a cardiologist at the Michael E. DeBakey VA Medical Center, both in Houston.
U.S. use of either drug class, let alone both, in patients with type 2 diabetes is still struggling to gain traction in U.S. practice and remains limited to a minority of these patients, a prescribing pattern reflected in recent VA data. Analysis of more than half a million patients in the VA system with type 2 diabetes and atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease (ASCVD) who received treatment at any of 130 VA medical centers throughout 2020 showed that 11% had received an SGLT2 inhibitor, and 8% a GLP-1 RA.
The most frequently used antidiabetes drug classes in these patients were insulin in 36%, biguanides in 47%, and sulfonylureas in 22%.
These data also showed a striking level of variability among the 130 VA centers, with some of the sites prescribing either an SGLT2 inhibitor or a GLP-1 RA to as few as about 3% each of these patients, while other centers had a roughly 10-fold higher prescription rate for each of about 25%-30% of their patients with type 2 diabetes and ASCVD.
Despite the overall modest level of use of both classes in these types of patients as recently as 2020, no barriers exist at the VA to prescribing an agent from one or both classes “if you provide a good reason” for a patient to receive the drugs, Dr. Virani said in an interview. He also predicted that use of both classes in these patients, including combination treatment, will likely soon expand.
‘A lot of interest’ in combining an SGLT2 inhibitor and a GLP-1 RA
“There will be a lot of interest in combing the two classes. It makes intuitive sense [to treat with both classes] because most patients with diabetes need more than one drug” for glycemic control, he noted. “Why not use two classes that each reduce a patient’s risk” for adverse outcomes involving ASCVD, heart failure, and renal dysfunction, added Dr. Virani.
The study run by Dr. Lopez and his associates used data collected in the National VA Database and included 121,156 patients with both type 2 diabetes and established ASCVD. Using propensity-score matching the researchers compiled three subgroups that each included 5,277 matched patients. One subgroup had patients prescribed an SGLT2 inhibitor, a second subgroup included patients on a GLP-1 RA, and a third subgroup had patients on agents from both classes. Patient matching relied on age, sex, left ventricular ejection fraction, hemoglobin A1c level, systolic blood pressure, and the presence of coronary artery disease or peripheral artery disease.
Patients included in the analysis averaged about 67 years of age; 97% were men, their average body mass index was about 34 kg/m2, their average A1c was about 7.9%, their average estimated glomerular filtration rate was about 55-66 mL/min per 1.73 m2, and their average left ventricular ejection fraction was about 55%. The database provided a median follow-up of 902 days (about 2.5 years). The prespecified primary endpoint focused on events that occurred during the first year of follow-up, but the investigators also ran a 3-year follow-up analysis on a post hoc basis.
The most common SGLT2 inhibitor received by these patients was empagliflozin (Jardiance), used on virtually everyone who received an agent from this class. In contrast, the GLP-1 RA drugs that patients received split more widely. The most prescribed agent was liraglutide (Victoza), followed by semaglutide (Ozempic), and dulaglutide (Trulicity), with fewer than 5% receiving exenatide (Bydureon, Byetta).
Regarding other treatments, about 97% of all patients received a statin, about 94% were on a renin-angiotensin system inhibitor, about 90% were on metformin, and roughly 75% were on insulin, aspirin, and a beta-blocker, with smaller numbers on other types of agents.
For the study’s primary endpoint, the 1-year incidence of combined ASCVD events including all-cause death, patients on agents from both classes had a significant 46% reduced rate compared with those on an SGLT2 inhibitor only, and a significant 49% reduced rate, compared with those on a GLP-1 RA only. These between-group separations broadened slightly during 3-year follow-up. Dr. Lopez did not report results of a direct comparison between patients on just an SGLT2 inhibitor and those on just a GLP-1 RA.
For the endpoint of all-cause death, those on combined treatment had a 1-year rate that was 83% below the rate among patients on only an SGLT2 inhibitor, and 81% below the rate among patients who received a GLP-1 RA but not the other class.
Dr. Lopez cautioned that selection bias could have influenced the outcomes of patients who received both classes rather than one or the other, and he also highlighted that the analysis relied on administrative data rather than information gleaned from more detailed medical records or prospectively collected findings and was limited by only including a very small number of women.
“Our results need to be validated in prospective studies,” he declared.
Dr. Lopez and Dr. Virani had no commercial disclosures.
WASHINGTON – Patients with type 2 diabetes and established atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease treated with both an sodium-glucose transporter 2 inhibitor and a glucagonlike peptide–1 receptor agonist had a significant 80% cut in their rate of all-cause death during 1-year follow-up, compared with matched patients treated with an agent from either class alone in an observational, retrospective study of more than 15,000 people in the U.S. Veterans Affairs health system.
For the study’s primary endpoint, the combined rate of all-cause death, nonfatal MI, or nonfatal stroke, combined treatment with both an agent from the sodium-glucose transporter 2 (SGLT2) inhibitor class and from the glucagonlike peptide–1 receptor agonist (GLP-1 RA) class linked with a significant, roughly 50% cut in events during 1-year follow-up, compared with patients treated with an agent from just one of these two classes, Persio D. Lopez, MD, reported at the annual scientific sessions of the American College of Cardiology.
This improvement in the combined endpoint outcome resulted entirely from reduced all-cause mortality. Dual treatment showed no significant association with the incidence of nonfatal MIs or strokes, compared with monotherapy, with rates that were nearly identical regardless of whether patients took one of the agents or both, said Dr. Lopez, a cardiologist at Mount Sinai Morningside and the James J. Peters VA Medical Center, both in New York.
Combining classes for hard-to-control diabetes
“We’re not sure what drives combined use” of agents from both drug classes in these types of patients, admitted Dr. Lopez during his talk. “Our hypothesis is that dual treatment is used in patients with harder-to-control diabetes.”
Salim S. Virani, MD, PhD, who practices in the VA system but was not involved with the study, agreed that this is the likely explanation for most instances of high-risk VA patients with diabetes who receive agents from both classes.
“I have a few patients” on both classes, usually “patients with higher starting A1c levels who need greater glycemic control,” said Dr. Virani, professor of medicine at Baylor College of Medicine and a cardiologist at the Michael E. DeBakey VA Medical Center, both in Houston.
U.S. use of either drug class, let alone both, in patients with type 2 diabetes is still struggling to gain traction in U.S. practice and remains limited to a minority of these patients, a prescribing pattern reflected in recent VA data. Analysis of more than half a million patients in the VA system with type 2 diabetes and atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease (ASCVD) who received treatment at any of 130 VA medical centers throughout 2020 showed that 11% had received an SGLT2 inhibitor, and 8% a GLP-1 RA.
The most frequently used antidiabetes drug classes in these patients were insulin in 36%, biguanides in 47%, and sulfonylureas in 22%.
These data also showed a striking level of variability among the 130 VA centers, with some of the sites prescribing either an SGLT2 inhibitor or a GLP-1 RA to as few as about 3% each of these patients, while other centers had a roughly 10-fold higher prescription rate for each of about 25%-30% of their patients with type 2 diabetes and ASCVD.
Despite the overall modest level of use of both classes in these types of patients as recently as 2020, no barriers exist at the VA to prescribing an agent from one or both classes “if you provide a good reason” for a patient to receive the drugs, Dr. Virani said in an interview. He also predicted that use of both classes in these patients, including combination treatment, will likely soon expand.
‘A lot of interest’ in combining an SGLT2 inhibitor and a GLP-1 RA
“There will be a lot of interest in combing the two classes. It makes intuitive sense [to treat with both classes] because most patients with diabetes need more than one drug” for glycemic control, he noted. “Why not use two classes that each reduce a patient’s risk” for adverse outcomes involving ASCVD, heart failure, and renal dysfunction, added Dr. Virani.
The study run by Dr. Lopez and his associates used data collected in the National VA Database and included 121,156 patients with both type 2 diabetes and established ASCVD. Using propensity-score matching the researchers compiled three subgroups that each included 5,277 matched patients. One subgroup had patients prescribed an SGLT2 inhibitor, a second subgroup included patients on a GLP-1 RA, and a third subgroup had patients on agents from both classes. Patient matching relied on age, sex, left ventricular ejection fraction, hemoglobin A1c level, systolic blood pressure, and the presence of coronary artery disease or peripheral artery disease.
Patients included in the analysis averaged about 67 years of age; 97% were men, their average body mass index was about 34 kg/m2, their average A1c was about 7.9%, their average estimated glomerular filtration rate was about 55-66 mL/min per 1.73 m2, and their average left ventricular ejection fraction was about 55%. The database provided a median follow-up of 902 days (about 2.5 years). The prespecified primary endpoint focused on events that occurred during the first year of follow-up, but the investigators also ran a 3-year follow-up analysis on a post hoc basis.
The most common SGLT2 inhibitor received by these patients was empagliflozin (Jardiance), used on virtually everyone who received an agent from this class. In contrast, the GLP-1 RA drugs that patients received split more widely. The most prescribed agent was liraglutide (Victoza), followed by semaglutide (Ozempic), and dulaglutide (Trulicity), with fewer than 5% receiving exenatide (Bydureon, Byetta).
Regarding other treatments, about 97% of all patients received a statin, about 94% were on a renin-angiotensin system inhibitor, about 90% were on metformin, and roughly 75% were on insulin, aspirin, and a beta-blocker, with smaller numbers on other types of agents.
For the study’s primary endpoint, the 1-year incidence of combined ASCVD events including all-cause death, patients on agents from both classes had a significant 46% reduced rate compared with those on an SGLT2 inhibitor only, and a significant 49% reduced rate, compared with those on a GLP-1 RA only. These between-group separations broadened slightly during 3-year follow-up. Dr. Lopez did not report results of a direct comparison between patients on just an SGLT2 inhibitor and those on just a GLP-1 RA.
For the endpoint of all-cause death, those on combined treatment had a 1-year rate that was 83% below the rate among patients on only an SGLT2 inhibitor, and 81% below the rate among patients who received a GLP-1 RA but not the other class.
Dr. Lopez cautioned that selection bias could have influenced the outcomes of patients who received both classes rather than one or the other, and he also highlighted that the analysis relied on administrative data rather than information gleaned from more detailed medical records or prospectively collected findings and was limited by only including a very small number of women.
“Our results need to be validated in prospective studies,” he declared.
Dr. Lopez and Dr. Virani had no commercial disclosures.
WASHINGTON – Patients with type 2 diabetes and established atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease treated with both an sodium-glucose transporter 2 inhibitor and a glucagonlike peptide–1 receptor agonist had a significant 80% cut in their rate of all-cause death during 1-year follow-up, compared with matched patients treated with an agent from either class alone in an observational, retrospective study of more than 15,000 people in the U.S. Veterans Affairs health system.
For the study’s primary endpoint, the combined rate of all-cause death, nonfatal MI, or nonfatal stroke, combined treatment with both an agent from the sodium-glucose transporter 2 (SGLT2) inhibitor class and from the glucagonlike peptide–1 receptor agonist (GLP-1 RA) class linked with a significant, roughly 50% cut in events during 1-year follow-up, compared with patients treated with an agent from just one of these two classes, Persio D. Lopez, MD, reported at the annual scientific sessions of the American College of Cardiology.
This improvement in the combined endpoint outcome resulted entirely from reduced all-cause mortality. Dual treatment showed no significant association with the incidence of nonfatal MIs or strokes, compared with monotherapy, with rates that were nearly identical regardless of whether patients took one of the agents or both, said Dr. Lopez, a cardiologist at Mount Sinai Morningside and the James J. Peters VA Medical Center, both in New York.
Combining classes for hard-to-control diabetes
“We’re not sure what drives combined use” of agents from both drug classes in these types of patients, admitted Dr. Lopez during his talk. “Our hypothesis is that dual treatment is used in patients with harder-to-control diabetes.”
Salim S. Virani, MD, PhD, who practices in the VA system but was not involved with the study, agreed that this is the likely explanation for most instances of high-risk VA patients with diabetes who receive agents from both classes.
“I have a few patients” on both classes, usually “patients with higher starting A1c levels who need greater glycemic control,” said Dr. Virani, professor of medicine at Baylor College of Medicine and a cardiologist at the Michael E. DeBakey VA Medical Center, both in Houston.
U.S. use of either drug class, let alone both, in patients with type 2 diabetes is still struggling to gain traction in U.S. practice and remains limited to a minority of these patients, a prescribing pattern reflected in recent VA data. Analysis of more than half a million patients in the VA system with type 2 diabetes and atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease (ASCVD) who received treatment at any of 130 VA medical centers throughout 2020 showed that 11% had received an SGLT2 inhibitor, and 8% a GLP-1 RA.
The most frequently used antidiabetes drug classes in these patients were insulin in 36%, biguanides in 47%, and sulfonylureas in 22%.
These data also showed a striking level of variability among the 130 VA centers, with some of the sites prescribing either an SGLT2 inhibitor or a GLP-1 RA to as few as about 3% each of these patients, while other centers had a roughly 10-fold higher prescription rate for each of about 25%-30% of their patients with type 2 diabetes and ASCVD.
Despite the overall modest level of use of both classes in these types of patients as recently as 2020, no barriers exist at the VA to prescribing an agent from one or both classes “if you provide a good reason” for a patient to receive the drugs, Dr. Virani said in an interview. He also predicted that use of both classes in these patients, including combination treatment, will likely soon expand.
‘A lot of interest’ in combining an SGLT2 inhibitor and a GLP-1 RA
“There will be a lot of interest in combing the two classes. It makes intuitive sense [to treat with both classes] because most patients with diabetes need more than one drug” for glycemic control, he noted. “Why not use two classes that each reduce a patient’s risk” for adverse outcomes involving ASCVD, heart failure, and renal dysfunction, added Dr. Virani.
The study run by Dr. Lopez and his associates used data collected in the National VA Database and included 121,156 patients with both type 2 diabetes and established ASCVD. Using propensity-score matching the researchers compiled three subgroups that each included 5,277 matched patients. One subgroup had patients prescribed an SGLT2 inhibitor, a second subgroup included patients on a GLP-1 RA, and a third subgroup had patients on agents from both classes. Patient matching relied on age, sex, left ventricular ejection fraction, hemoglobin A1c level, systolic blood pressure, and the presence of coronary artery disease or peripheral artery disease.
Patients included in the analysis averaged about 67 years of age; 97% were men, their average body mass index was about 34 kg/m2, their average A1c was about 7.9%, their average estimated glomerular filtration rate was about 55-66 mL/min per 1.73 m2, and their average left ventricular ejection fraction was about 55%. The database provided a median follow-up of 902 days (about 2.5 years). The prespecified primary endpoint focused on events that occurred during the first year of follow-up, but the investigators also ran a 3-year follow-up analysis on a post hoc basis.
The most common SGLT2 inhibitor received by these patients was empagliflozin (Jardiance), used on virtually everyone who received an agent from this class. In contrast, the GLP-1 RA drugs that patients received split more widely. The most prescribed agent was liraglutide (Victoza), followed by semaglutide (Ozempic), and dulaglutide (Trulicity), with fewer than 5% receiving exenatide (Bydureon, Byetta).
Regarding other treatments, about 97% of all patients received a statin, about 94% were on a renin-angiotensin system inhibitor, about 90% were on metformin, and roughly 75% were on insulin, aspirin, and a beta-blocker, with smaller numbers on other types of agents.
For the study’s primary endpoint, the 1-year incidence of combined ASCVD events including all-cause death, patients on agents from both classes had a significant 46% reduced rate compared with those on an SGLT2 inhibitor only, and a significant 49% reduced rate, compared with those on a GLP-1 RA only. These between-group separations broadened slightly during 3-year follow-up. Dr. Lopez did not report results of a direct comparison between patients on just an SGLT2 inhibitor and those on just a GLP-1 RA.
For the endpoint of all-cause death, those on combined treatment had a 1-year rate that was 83% below the rate among patients on only an SGLT2 inhibitor, and 81% below the rate among patients who received a GLP-1 RA but not the other class.
Dr. Lopez cautioned that selection bias could have influenced the outcomes of patients who received both classes rather than one or the other, and he also highlighted that the analysis relied on administrative data rather than information gleaned from more detailed medical records or prospectively collected findings and was limited by only including a very small number of women.
“Our results need to be validated in prospective studies,” he declared.
Dr. Lopez and Dr. Virani had no commercial disclosures.
AT ACC 2022
FFR not better, just different from IVUS for revascularizing intermediate stenoses
In a head-to-head comparison of fractional flow reserve (FFR) and intravenous ultrasound (IVUS) for guiding revascularization during percutaneous intervention (PCI), outcomes were noninferior at 2 years, but the approaches appear to have different strengths, according to results of the FLAVOUR trial.
For the primary composite outcome of death from any cause, myocardial infarction, or revascularization at 24 months, the approaches performed comparatively, but there were substantial differences in the number of revascularization procedures performed, reported Bon-Kwon Koo, MD, at the annual scientific sessions of the American College of Cardiology.
At 24 months, 8.1% of the FFR group and 8.5% of the IVUS group had a primary event. The 0.4% difference was not significantly different and fulfilled the definition of noninferiority (P = .015). When the components of the primary endpoint were compared along with rates of stroke, the rates were also similar and not significantly different.
However, the proportion of patients who received a stent (44.4% vs. 65.3%), the total number of stents per patient (0.6 vs. 0.9), and the total stent length per patient (16.5 vs. 25.2) were significantly lower (all P < .001) in the FFR group.
FLAVOUR (Fractional Flow Reserve And IVUS for Clinical Outcomes in Patients With Intermediate Stenosis) confirmed the investigators’ hypothesis that an FFR-guided strategy for intermediate coronary stenosis is noninferior to IVUS for outcomes. In addition, patient-reported angina outcomes on the Seattle Angina Questionnaire were nearly identical across domains, including angina frequency, physical limitations, and treatment satisfaction.
FFR vs. IVUS differences revealed
However, the more important value of this study might its role in showing how the two approaches differ in ways unrelated to the primary outcome, according to Dr. Koo, chair of cardiology at Seoul (South Korea) National University Hospital, as well as several experts that commented on the results.
Most notably, the fact that FFR-guided PCI provides similar outcomes at 2 years even though it was associated with a substantially reduced rate of revascularizations is telling about its role relative to IVUS.
“These data confirm how a lot of us are already approaching this,” said an ACC-invited expert, Frederick G. Welt, MD, director of the cardiac catheterization at the University of Utah, Salt Lake City. “FFR should be used to decide who should get an intervention, and IVUS should be use to optimize the intervention.”
Dr. Koo explained that FFR is an invasive tool that provides a physiological assessment of the degree to which a stenosis is causing ischemia. IVUS is a tool that permits visualization and measurement of plaque severity and characteristics to better optimize PCI. They can both help guide PCI, but they are not necessarily competing strategies. Often, the information they provide is complementary.
In this multicenter trial conducted at 18 centers in Korea and China, 1,682 candidates with de novo stenoses of intermediate severity, defined as 40%-70%, were randomized to FFR- or IVUS-guided PCI. At 24 months, outcomes could be assessed in 832 of the FFR patients and 836 of the IVUS patients, which represented more than 99% of both groups.
In the study, the indications for stent placement were predefined for the FFR-guided and IVUS-guided approaches. The criteria to define optimal outcomes post PCI were also predefined. For FFR, this included a postprocedure value of at least 0.88. For IVUS, the definition of optimal outcome included a plaque burden of 55% or less at the stent edge and a minimal stent area of at least 5.5 mm2.
The primary outcome for those with optimal versus suboptimal FFR-guided PCI were similar at all time points. For those with an optimal post-PCI result, the event rate was only slightly higher for those with an optimal relative to a suboptimal result (12.3% vs. 11.8%).
Suboptimal IVUS differs from suboptimal FFR
In contrast, the event rates over the course of follow-up were consistently higher among those with a suboptimal relative to an optimal IVUS-guided PCI. At the end of 2 years, the numerically greater rate of events among those with a suboptimal IVUS-guided PCI was not significant (9.8% vs. 8.5%; P = .212), but the gap was larger than that seen with FFR-guided PCI.
FFR-guided and IVUS-guided PCI performed similarly for the primary outcome across numerous stratifications. These included age older or younger than 65 years, male or female sex, presence or absence of multivessel disease, and presence of diabetes. They were also similar for those with acute coronary syndrome (ACS) as an indication for PCI, which accounted for about 30% of patients, relative to those without ACS.
“I would say that at least some interventionalists in the U.S. would be uncomfortable using FFR in ACS patients,” said Dr. Welt, pointing out a potential difference between how these tools are used to guide PCI. Still, because “there are not a lot of data to compare these technologies,” he expressed appreciation for a study looking at these tools side-by-side.
A similar point was made by Ajay Kirtane, MD, director of Cardiac Catheterization Laboratories at New York–Presbyterian/Columbia University Irving Medical Center. With the slightly lower rates of primary events in those treated optimally according to IVUS relative to those treated optimally by FFR (8.5% vs. 12.3%), he suggested IVUS appears better for evaluating the physiology of the stenosis.
Dr. Kirtane pointed out that two-thirds of the lesions were left behind in those guided by FFR versus only about half of the lesions when PCI was guided by IVUS, yet outcomes were similar. He indicated that the data support current practice in which FFR is most commonly used to select PCI patients with intermediate disease for stent placement.
Dr. Koo has financial relationships with Abbott, Boston Scientific, and Philips Volcano. Dr. Welt has financial relationships with Medtronic and Xenter. Dr. Kirtane has financial relationships with Abbott, Amgen, Boston Scientific, Chiesi, Cardiovascular Systems Incorporate, Medtronic, Philips/Spectranetics, Recor Medical, and Regeneron. The study received a research grant from Boston Scientific.
In a head-to-head comparison of fractional flow reserve (FFR) and intravenous ultrasound (IVUS) for guiding revascularization during percutaneous intervention (PCI), outcomes were noninferior at 2 years, but the approaches appear to have different strengths, according to results of the FLAVOUR trial.
For the primary composite outcome of death from any cause, myocardial infarction, or revascularization at 24 months, the approaches performed comparatively, but there were substantial differences in the number of revascularization procedures performed, reported Bon-Kwon Koo, MD, at the annual scientific sessions of the American College of Cardiology.
At 24 months, 8.1% of the FFR group and 8.5% of the IVUS group had a primary event. The 0.4% difference was not significantly different and fulfilled the definition of noninferiority (P = .015). When the components of the primary endpoint were compared along with rates of stroke, the rates were also similar and not significantly different.
However, the proportion of patients who received a stent (44.4% vs. 65.3%), the total number of stents per patient (0.6 vs. 0.9), and the total stent length per patient (16.5 vs. 25.2) were significantly lower (all P < .001) in the FFR group.
FLAVOUR (Fractional Flow Reserve And IVUS for Clinical Outcomes in Patients With Intermediate Stenosis) confirmed the investigators’ hypothesis that an FFR-guided strategy for intermediate coronary stenosis is noninferior to IVUS for outcomes. In addition, patient-reported angina outcomes on the Seattle Angina Questionnaire were nearly identical across domains, including angina frequency, physical limitations, and treatment satisfaction.
FFR vs. IVUS differences revealed
However, the more important value of this study might its role in showing how the two approaches differ in ways unrelated to the primary outcome, according to Dr. Koo, chair of cardiology at Seoul (South Korea) National University Hospital, as well as several experts that commented on the results.
Most notably, the fact that FFR-guided PCI provides similar outcomes at 2 years even though it was associated with a substantially reduced rate of revascularizations is telling about its role relative to IVUS.
“These data confirm how a lot of us are already approaching this,” said an ACC-invited expert, Frederick G. Welt, MD, director of the cardiac catheterization at the University of Utah, Salt Lake City. “FFR should be used to decide who should get an intervention, and IVUS should be use to optimize the intervention.”
Dr. Koo explained that FFR is an invasive tool that provides a physiological assessment of the degree to which a stenosis is causing ischemia. IVUS is a tool that permits visualization and measurement of plaque severity and characteristics to better optimize PCI. They can both help guide PCI, but they are not necessarily competing strategies. Often, the information they provide is complementary.
In this multicenter trial conducted at 18 centers in Korea and China, 1,682 candidates with de novo stenoses of intermediate severity, defined as 40%-70%, were randomized to FFR- or IVUS-guided PCI. At 24 months, outcomes could be assessed in 832 of the FFR patients and 836 of the IVUS patients, which represented more than 99% of both groups.
In the study, the indications for stent placement were predefined for the FFR-guided and IVUS-guided approaches. The criteria to define optimal outcomes post PCI were also predefined. For FFR, this included a postprocedure value of at least 0.88. For IVUS, the definition of optimal outcome included a plaque burden of 55% or less at the stent edge and a minimal stent area of at least 5.5 mm2.
The primary outcome for those with optimal versus suboptimal FFR-guided PCI were similar at all time points. For those with an optimal post-PCI result, the event rate was only slightly higher for those with an optimal relative to a suboptimal result (12.3% vs. 11.8%).
Suboptimal IVUS differs from suboptimal FFR
In contrast, the event rates over the course of follow-up were consistently higher among those with a suboptimal relative to an optimal IVUS-guided PCI. At the end of 2 years, the numerically greater rate of events among those with a suboptimal IVUS-guided PCI was not significant (9.8% vs. 8.5%; P = .212), but the gap was larger than that seen with FFR-guided PCI.
FFR-guided and IVUS-guided PCI performed similarly for the primary outcome across numerous stratifications. These included age older or younger than 65 years, male or female sex, presence or absence of multivessel disease, and presence of diabetes. They were also similar for those with acute coronary syndrome (ACS) as an indication for PCI, which accounted for about 30% of patients, relative to those without ACS.
“I would say that at least some interventionalists in the U.S. would be uncomfortable using FFR in ACS patients,” said Dr. Welt, pointing out a potential difference between how these tools are used to guide PCI. Still, because “there are not a lot of data to compare these technologies,” he expressed appreciation for a study looking at these tools side-by-side.
A similar point was made by Ajay Kirtane, MD, director of Cardiac Catheterization Laboratories at New York–Presbyterian/Columbia University Irving Medical Center. With the slightly lower rates of primary events in those treated optimally according to IVUS relative to those treated optimally by FFR (8.5% vs. 12.3%), he suggested IVUS appears better for evaluating the physiology of the stenosis.
Dr. Kirtane pointed out that two-thirds of the lesions were left behind in those guided by FFR versus only about half of the lesions when PCI was guided by IVUS, yet outcomes were similar. He indicated that the data support current practice in which FFR is most commonly used to select PCI patients with intermediate disease for stent placement.
Dr. Koo has financial relationships with Abbott, Boston Scientific, and Philips Volcano. Dr. Welt has financial relationships with Medtronic and Xenter. Dr. Kirtane has financial relationships with Abbott, Amgen, Boston Scientific, Chiesi, Cardiovascular Systems Incorporate, Medtronic, Philips/Spectranetics, Recor Medical, and Regeneron. The study received a research grant from Boston Scientific.
In a head-to-head comparison of fractional flow reserve (FFR) and intravenous ultrasound (IVUS) for guiding revascularization during percutaneous intervention (PCI), outcomes were noninferior at 2 years, but the approaches appear to have different strengths, according to results of the FLAVOUR trial.
For the primary composite outcome of death from any cause, myocardial infarction, or revascularization at 24 months, the approaches performed comparatively, but there were substantial differences in the number of revascularization procedures performed, reported Bon-Kwon Koo, MD, at the annual scientific sessions of the American College of Cardiology.
At 24 months, 8.1% of the FFR group and 8.5% of the IVUS group had a primary event. The 0.4% difference was not significantly different and fulfilled the definition of noninferiority (P = .015). When the components of the primary endpoint were compared along with rates of stroke, the rates were also similar and not significantly different.
However, the proportion of patients who received a stent (44.4% vs. 65.3%), the total number of stents per patient (0.6 vs. 0.9), and the total stent length per patient (16.5 vs. 25.2) were significantly lower (all P < .001) in the FFR group.
FLAVOUR (Fractional Flow Reserve And IVUS for Clinical Outcomes in Patients With Intermediate Stenosis) confirmed the investigators’ hypothesis that an FFR-guided strategy for intermediate coronary stenosis is noninferior to IVUS for outcomes. In addition, patient-reported angina outcomes on the Seattle Angina Questionnaire were nearly identical across domains, including angina frequency, physical limitations, and treatment satisfaction.
FFR vs. IVUS differences revealed
However, the more important value of this study might its role in showing how the two approaches differ in ways unrelated to the primary outcome, according to Dr. Koo, chair of cardiology at Seoul (South Korea) National University Hospital, as well as several experts that commented on the results.
Most notably, the fact that FFR-guided PCI provides similar outcomes at 2 years even though it was associated with a substantially reduced rate of revascularizations is telling about its role relative to IVUS.
“These data confirm how a lot of us are already approaching this,” said an ACC-invited expert, Frederick G. Welt, MD, director of the cardiac catheterization at the University of Utah, Salt Lake City. “FFR should be used to decide who should get an intervention, and IVUS should be use to optimize the intervention.”
Dr. Koo explained that FFR is an invasive tool that provides a physiological assessment of the degree to which a stenosis is causing ischemia. IVUS is a tool that permits visualization and measurement of plaque severity and characteristics to better optimize PCI. They can both help guide PCI, but they are not necessarily competing strategies. Often, the information they provide is complementary.
In this multicenter trial conducted at 18 centers in Korea and China, 1,682 candidates with de novo stenoses of intermediate severity, defined as 40%-70%, were randomized to FFR- or IVUS-guided PCI. At 24 months, outcomes could be assessed in 832 of the FFR patients and 836 of the IVUS patients, which represented more than 99% of both groups.
In the study, the indications for stent placement were predefined for the FFR-guided and IVUS-guided approaches. The criteria to define optimal outcomes post PCI were also predefined. For FFR, this included a postprocedure value of at least 0.88. For IVUS, the definition of optimal outcome included a plaque burden of 55% or less at the stent edge and a minimal stent area of at least 5.5 mm2.
The primary outcome for those with optimal versus suboptimal FFR-guided PCI were similar at all time points. For those with an optimal post-PCI result, the event rate was only slightly higher for those with an optimal relative to a suboptimal result (12.3% vs. 11.8%).
Suboptimal IVUS differs from suboptimal FFR
In contrast, the event rates over the course of follow-up were consistently higher among those with a suboptimal relative to an optimal IVUS-guided PCI. At the end of 2 years, the numerically greater rate of events among those with a suboptimal IVUS-guided PCI was not significant (9.8% vs. 8.5%; P = .212), but the gap was larger than that seen with FFR-guided PCI.
FFR-guided and IVUS-guided PCI performed similarly for the primary outcome across numerous stratifications. These included age older or younger than 65 years, male or female sex, presence or absence of multivessel disease, and presence of diabetes. They were also similar for those with acute coronary syndrome (ACS) as an indication for PCI, which accounted for about 30% of patients, relative to those without ACS.
“I would say that at least some interventionalists in the U.S. would be uncomfortable using FFR in ACS patients,” said Dr. Welt, pointing out a potential difference between how these tools are used to guide PCI. Still, because “there are not a lot of data to compare these technologies,” he expressed appreciation for a study looking at these tools side-by-side.
A similar point was made by Ajay Kirtane, MD, director of Cardiac Catheterization Laboratories at New York–Presbyterian/Columbia University Irving Medical Center. With the slightly lower rates of primary events in those treated optimally according to IVUS relative to those treated optimally by FFR (8.5% vs. 12.3%), he suggested IVUS appears better for evaluating the physiology of the stenosis.
Dr. Kirtane pointed out that two-thirds of the lesions were left behind in those guided by FFR versus only about half of the lesions when PCI was guided by IVUS, yet outcomes were similar. He indicated that the data support current practice in which FFR is most commonly used to select PCI patients with intermediate disease for stent placement.
Dr. Koo has financial relationships with Abbott, Boston Scientific, and Philips Volcano. Dr. Welt has financial relationships with Medtronic and Xenter. Dr. Kirtane has financial relationships with Abbott, Amgen, Boston Scientific, Chiesi, Cardiovascular Systems Incorporate, Medtronic, Philips/Spectranetics, Recor Medical, and Regeneron. The study received a research grant from Boston Scientific.
FROM ACC 2022
AHA statement addresses CVD risk in NAFLD
At least one in four adults worldwide is thought to have nonalcoholic fatty liver disease, a major risk factor for cardiovascular disease (CVD), which is the leading cause of death in NAFLD, but the condition is widely underdiagnosed, according to a new American Heart Association scientific statement on NAFLD and cardiovascular risks.
The statement, published in Arteriosclerosis, Thrombosis, and Vascular Biology, aims to increase awareness of NAFLD among cardiologists and other clinicians treating vulnerable patients. It pulls together the existing evidence for using imaging to diagnose NAFLD as well as the role of current and emerging treatments for managing the disease.
“NAFLD is common, but most patients are undiagnosed,” statement writing committee chair P. Barton Duell, MD, said in an interview. “The identification of normal liver enzyme levels does not exclude the diagnosis of NAFLD. Early diagnosis and treatment are necessary to improve the health of patients with established NAFLD, as well as preventing the development of NAFLD in patients who are at risk for the condition.”
Dr. Duell is a professor at the Knight Cardiovascular Institute and division of endocrinology, diabetes and clinical nutrition at Oregon Health & Science University, Portland.
This is the AHA’s first scientific statement on NAFLD. In 2021, the association issued a statement on obesity and CVD). Also in 2021, a multiorganization group headed by the American Gastroenterological Association published a “Call to Action” on nonalcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH) , a form of NAFLD that’s characterized by inflammation and scarring of the liver, and typically requires a liver biopsy for diagnosis.
Key take-homes
The AHA statement on NAFLD is sweeping. Among its key take-home messages:
- Calling into question the effectiveness of AST and ALT testing for diagnosing NAFLD and NASH.
- Providing context to the role of insulin resistance – either with or without diabetes – as well as obesity (particularly visceral adiposity), metabolic syndrome, and dyslipidemia in NAFLD.
- Advocating for lifestyle interventions – diet, exercise, weight loss and alcohol avoidance – as the key therapeutic intervention for NAFLD.
- Asserting that glucagonlike peptide–1 receptor agonists may modestly improve NAFLD.
The statement also tackles the differences in terminology different organizations use to describe NAFLD. “The terminology section is important to ensure everyone is using the right terminology in assessing patients, as well as choosing appropriate treatment interventions,” Dr. Duell said.
The statement also explores genetic factors that can predispose people to NAFLD, Dr. Duell pointed out, and it goes into detail about strategies for screening NAFLD and NASH. “It is not possible to diagnose NAFLD without understanding the pros and cons of various screening modalities, as well as the lack of sensitivity of some tests for detection of NAFLD We hope this information will increase success in screening for and early identification of NAFLD.”
Dr. Duell explained the rationale for issuing the statement. “Rates of NAFLD are increasing worldwide in association with rising rates of elevated body mass index and the metabolic syndrome, but the condition is commonly undiagnosed,” he said. “This allows patients to experience progression of disease, leading to hepatic and cardiovascular complications.”
Avoiding NAFLD risk factors along with early diagnosis and treatment “may have the potential to mitigate long-term complications from NAFLD,” Dr. Duell said.
“This is one of first times where we really look at cardiovascular risks associated with NAFLD and pinpoint the risk factors, the imaging tools that can be used for diagnosing fatty liver disease, and ultimately what potential treatments we can consider,” Tiffany M. Powell-Wiley, MD, MPH, author of the AHA statement on obesity and CV risk, said in an interview.
“NAFLD has not been at the forefront of cardiologists’ minds, but this statement highlights the importance of liver fat as a fat depot,” said Dr. Powell-Wiley, chief of the Social Determinants of Obesity and Cardiovascular Risk Laboratory at the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute in Bethesda, Md.
“It does provide greater clarity for us as cardiologists, especially when thinking about what is required for diagnosis and ultimately how this relates to cardiovascular disease for people with fatty liver disease,” she said.
Dr. Duell and Dr. Powell-Wiley have no relevant relationships to disclose.
At least one in four adults worldwide is thought to have nonalcoholic fatty liver disease, a major risk factor for cardiovascular disease (CVD), which is the leading cause of death in NAFLD, but the condition is widely underdiagnosed, according to a new American Heart Association scientific statement on NAFLD and cardiovascular risks.
The statement, published in Arteriosclerosis, Thrombosis, and Vascular Biology, aims to increase awareness of NAFLD among cardiologists and other clinicians treating vulnerable patients. It pulls together the existing evidence for using imaging to diagnose NAFLD as well as the role of current and emerging treatments for managing the disease.
“NAFLD is common, but most patients are undiagnosed,” statement writing committee chair P. Barton Duell, MD, said in an interview. “The identification of normal liver enzyme levels does not exclude the diagnosis of NAFLD. Early diagnosis and treatment are necessary to improve the health of patients with established NAFLD, as well as preventing the development of NAFLD in patients who are at risk for the condition.”
Dr. Duell is a professor at the Knight Cardiovascular Institute and division of endocrinology, diabetes and clinical nutrition at Oregon Health & Science University, Portland.
This is the AHA’s first scientific statement on NAFLD. In 2021, the association issued a statement on obesity and CVD). Also in 2021, a multiorganization group headed by the American Gastroenterological Association published a “Call to Action” on nonalcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH) , a form of NAFLD that’s characterized by inflammation and scarring of the liver, and typically requires a liver biopsy for diagnosis.
Key take-homes
The AHA statement on NAFLD is sweeping. Among its key take-home messages:
- Calling into question the effectiveness of AST and ALT testing for diagnosing NAFLD and NASH.
- Providing context to the role of insulin resistance – either with or without diabetes – as well as obesity (particularly visceral adiposity), metabolic syndrome, and dyslipidemia in NAFLD.
- Advocating for lifestyle interventions – diet, exercise, weight loss and alcohol avoidance – as the key therapeutic intervention for NAFLD.
- Asserting that glucagonlike peptide–1 receptor agonists may modestly improve NAFLD.
The statement also tackles the differences in terminology different organizations use to describe NAFLD. “The terminology section is important to ensure everyone is using the right terminology in assessing patients, as well as choosing appropriate treatment interventions,” Dr. Duell said.
The statement also explores genetic factors that can predispose people to NAFLD, Dr. Duell pointed out, and it goes into detail about strategies for screening NAFLD and NASH. “It is not possible to diagnose NAFLD without understanding the pros and cons of various screening modalities, as well as the lack of sensitivity of some tests for detection of NAFLD We hope this information will increase success in screening for and early identification of NAFLD.”
Dr. Duell explained the rationale for issuing the statement. “Rates of NAFLD are increasing worldwide in association with rising rates of elevated body mass index and the metabolic syndrome, but the condition is commonly undiagnosed,” he said. “This allows patients to experience progression of disease, leading to hepatic and cardiovascular complications.”
Avoiding NAFLD risk factors along with early diagnosis and treatment “may have the potential to mitigate long-term complications from NAFLD,” Dr. Duell said.
“This is one of first times where we really look at cardiovascular risks associated with NAFLD and pinpoint the risk factors, the imaging tools that can be used for diagnosing fatty liver disease, and ultimately what potential treatments we can consider,” Tiffany M. Powell-Wiley, MD, MPH, author of the AHA statement on obesity and CV risk, said in an interview.
“NAFLD has not been at the forefront of cardiologists’ minds, but this statement highlights the importance of liver fat as a fat depot,” said Dr. Powell-Wiley, chief of the Social Determinants of Obesity and Cardiovascular Risk Laboratory at the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute in Bethesda, Md.
“It does provide greater clarity for us as cardiologists, especially when thinking about what is required for diagnosis and ultimately how this relates to cardiovascular disease for people with fatty liver disease,” she said.
Dr. Duell and Dr. Powell-Wiley have no relevant relationships to disclose.
At least one in four adults worldwide is thought to have nonalcoholic fatty liver disease, a major risk factor for cardiovascular disease (CVD), which is the leading cause of death in NAFLD, but the condition is widely underdiagnosed, according to a new American Heart Association scientific statement on NAFLD and cardiovascular risks.
The statement, published in Arteriosclerosis, Thrombosis, and Vascular Biology, aims to increase awareness of NAFLD among cardiologists and other clinicians treating vulnerable patients. It pulls together the existing evidence for using imaging to diagnose NAFLD as well as the role of current and emerging treatments for managing the disease.
“NAFLD is common, but most patients are undiagnosed,” statement writing committee chair P. Barton Duell, MD, said in an interview. “The identification of normal liver enzyme levels does not exclude the diagnosis of NAFLD. Early diagnosis and treatment are necessary to improve the health of patients with established NAFLD, as well as preventing the development of NAFLD in patients who are at risk for the condition.”
Dr. Duell is a professor at the Knight Cardiovascular Institute and division of endocrinology, diabetes and clinical nutrition at Oregon Health & Science University, Portland.
This is the AHA’s first scientific statement on NAFLD. In 2021, the association issued a statement on obesity and CVD). Also in 2021, a multiorganization group headed by the American Gastroenterological Association published a “Call to Action” on nonalcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH) , a form of NAFLD that’s characterized by inflammation and scarring of the liver, and typically requires a liver biopsy for diagnosis.
Key take-homes
The AHA statement on NAFLD is sweeping. Among its key take-home messages:
- Calling into question the effectiveness of AST and ALT testing for diagnosing NAFLD and NASH.
- Providing context to the role of insulin resistance – either with or without diabetes – as well as obesity (particularly visceral adiposity), metabolic syndrome, and dyslipidemia in NAFLD.
- Advocating for lifestyle interventions – diet, exercise, weight loss and alcohol avoidance – as the key therapeutic intervention for NAFLD.
- Asserting that glucagonlike peptide–1 receptor agonists may modestly improve NAFLD.
The statement also tackles the differences in terminology different organizations use to describe NAFLD. “The terminology section is important to ensure everyone is using the right terminology in assessing patients, as well as choosing appropriate treatment interventions,” Dr. Duell said.
The statement also explores genetic factors that can predispose people to NAFLD, Dr. Duell pointed out, and it goes into detail about strategies for screening NAFLD and NASH. “It is not possible to diagnose NAFLD without understanding the pros and cons of various screening modalities, as well as the lack of sensitivity of some tests for detection of NAFLD We hope this information will increase success in screening for and early identification of NAFLD.”
Dr. Duell explained the rationale for issuing the statement. “Rates of NAFLD are increasing worldwide in association with rising rates of elevated body mass index and the metabolic syndrome, but the condition is commonly undiagnosed,” he said. “This allows patients to experience progression of disease, leading to hepatic and cardiovascular complications.”
Avoiding NAFLD risk factors along with early diagnosis and treatment “may have the potential to mitigate long-term complications from NAFLD,” Dr. Duell said.
“This is one of first times where we really look at cardiovascular risks associated with NAFLD and pinpoint the risk factors, the imaging tools that can be used for diagnosing fatty liver disease, and ultimately what potential treatments we can consider,” Tiffany M. Powell-Wiley, MD, MPH, author of the AHA statement on obesity and CV risk, said in an interview.
“NAFLD has not been at the forefront of cardiologists’ minds, but this statement highlights the importance of liver fat as a fat depot,” said Dr. Powell-Wiley, chief of the Social Determinants of Obesity and Cardiovascular Risk Laboratory at the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute in Bethesda, Md.
“It does provide greater clarity for us as cardiologists, especially when thinking about what is required for diagnosis and ultimately how this relates to cardiovascular disease for people with fatty liver disease,” she said.
Dr. Duell and Dr. Powell-Wiley have no relevant relationships to disclose.
FROM ARTERIOSCLEROSIS, THROMBOSIS, AND VASCULAR BIOLOGY
Erectile dysfunction drugs linked to ocular conditions
, researchers say.
Patients in an insurance database who were prescribed sildenafil (Viagra), tadalafil (Cialis), vardenafil (Levitra), or avanafil (Stendra) were almost twice as likely as were patients not prescribed the drugs to have ischemic optic neuropathy, retinal vascular occlusion, or serous retinal detachment.
In 2020, physicians wrote about 20 million monthly prescriptions for PDE5Is in the United States alone, said Mahyar Etminan, PharmD, associate professor of ophthalmology at the University of British Columbia, Vancouver.
“We don’t want to alarm people taking them, but generally speaking, if they experience visual problems or changes in vision, then these drugs may be the culprits, and they should check it out,” he said in an interview.
The study was published in JAMA Ophthalmology.
Previous reports, including postmarketing studies by the drug makers, have documented ocular events. The monographs for sildenafil, tadalafil, vardenafil, and avanafil warn users about ischemic optic neuropathy, the researchers found.
The monographs for sildenafil, tadalafil, and vardenafil list retinal vascular occlusion as a potential adverse event but do not quantify the risk. None of the drug monographs mention serous retinal detachment.
Previous research has associated PDE5Is with compromised perfusion of the optic nerve. Some researchers have speculated that the choroid blood vessels can undergo smooth muscle relaxation through a cyclic guanosine monophosphate pathway that can lead to choroidal congestion.
To get a better handle on the ocular risks of PDE51s, Dr. Etminan and his colleagues analyzed health insurance claim records from the PharMetrics Plus database of 213,033 men who had not experienced any of the three ocular conditions in the year before they became regular users of the medications.
They identified 1,146 patients who had been diagnosed with at least one of the three conditions.
The overall number of conditions diagnosed was small relative to the size of the population, 15.5 cases per 10,000 person-years. “So that’s still relatively rare, but the problem is that these are very heavily used medications,” Dr. Etminan said.
For each man diagnosed with one of the ocular conditions, the researchers matched four control persons who were the same age and could be followed for the same length of time. There was a total of 4,584 control persons.
The researchers compared regular users of PDE5Is (those who had received at least one prescription for a PDE5I every 3 months in the year before the ocular diagnosis) with nonusers (those who had not received a PDE5I prescription during that time).
Patients with the ocular conditions were more likely than were those in the control group to have hypertension, diabetes, cardiovascular disease, or sleep apnea. After controlling for these covariates, the researchers found that the users were overall 85% more likely to be diagnosed with one or more of them (incidence rate ratio [IRR], 1.85).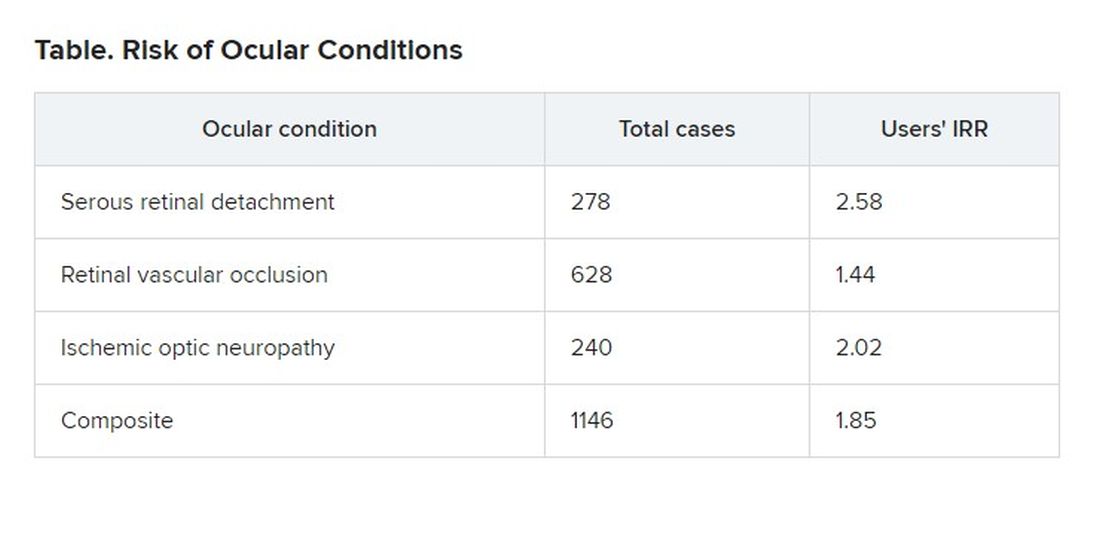
The researchers also found that the risk was even greater for those patients who were given five or more prescriptions of PDE5Is, compared to those given fewer than five prescriptions, suggesting a dose response.
On the basis of these findings, Dr. Etminan thinks drug companies should add warnings about serous retinal detachment and retinal vascular occlusion to the drug monographs.
Asked to comment, Pfizer, which developed Viagra, referred questions to its spinoff company, Viatris, which did not respond. Eli Lilly, which makes Cialis, also did not respond to a request for comment. Vivus, which makes Stendra, could not be reached by press time.
Bayer, which makes Levitra, declined to provide anyone who could answer questions, but it provided a statement noting that the occurrence of ocular adverse events is already known among PDE5I users and that retinal vascular occlusion and ischemic optic neuropathy are mentioned in the product information.
“For example, non-arteritic anterior ischemic optic neuropathy (NAION) is a very rare condition which occurs with an overall higher risk in the population usually suffering from erectile dysfunction (ED) – that is, elderly men with concomitant diseases such as diabetes, dyslipidemia, and hypertension – compared to the general population,” the statement said.
Because of the retrospective nature of the analysis, Dr. Etminan acknowledged that researchers could not prove that the increased risk of ocular disease was associated with use of the drugs rather than some underlying condition. But in addition to adjusting for known risk factors, they also separately analyzed men without hypertension, diabetes, or coronary artery disease and still found that the risk of the ocular conditions was roughly double for men with PDE5I prescriptions.
Howard Pomeranz, MD, PhD, professor of ophthalmology at Northwell Health in Great Neck, N.Y., who was not involved in this study, said its findings confirmed similar research that he conducted on ischemic optic neuropathy.
He told this news organization that people taking PDE5Is should weigh the risk against the benefit, but added that the calculation might be different for people who use them to treat pulmonary hypertension rather than erectile dysfunction.
Although people taking the drugs should discuss any changes in their vision with their practitioners, he said they should not be concerned about a “bluish type of tint to the vision that may occur transiently for anywhere from a few minutes up to 40 or 45 minutes.”
Drug companies and regulators should consider changing the monographs in light of this new evidence, Dr. Pomeranz said. “Perhaps this data might drive the warning to be perhaps a little bit stronger, now that there’s more data to suggest maybe a bit of a stronger association and not just some chance association between using these drugs and these visual events.”
The study was funded by the University of British Columbia. Dr. Etminan and Dr. Pomeranz have disclosed no relevant financial interests.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com
, researchers say.
Patients in an insurance database who were prescribed sildenafil (Viagra), tadalafil (Cialis), vardenafil (Levitra), or avanafil (Stendra) were almost twice as likely as were patients not prescribed the drugs to have ischemic optic neuropathy, retinal vascular occlusion, or serous retinal detachment.
In 2020, physicians wrote about 20 million monthly prescriptions for PDE5Is in the United States alone, said Mahyar Etminan, PharmD, associate professor of ophthalmology at the University of British Columbia, Vancouver.
“We don’t want to alarm people taking them, but generally speaking, if they experience visual problems or changes in vision, then these drugs may be the culprits, and they should check it out,” he said in an interview.
The study was published in JAMA Ophthalmology.
Previous reports, including postmarketing studies by the drug makers, have documented ocular events. The monographs for sildenafil, tadalafil, vardenafil, and avanafil warn users about ischemic optic neuropathy, the researchers found.
The monographs for sildenafil, tadalafil, and vardenafil list retinal vascular occlusion as a potential adverse event but do not quantify the risk. None of the drug monographs mention serous retinal detachment.
Previous research has associated PDE5Is with compromised perfusion of the optic nerve. Some researchers have speculated that the choroid blood vessels can undergo smooth muscle relaxation through a cyclic guanosine monophosphate pathway that can lead to choroidal congestion.
To get a better handle on the ocular risks of PDE51s, Dr. Etminan and his colleagues analyzed health insurance claim records from the PharMetrics Plus database of 213,033 men who had not experienced any of the three ocular conditions in the year before they became regular users of the medications.
They identified 1,146 patients who had been diagnosed with at least one of the three conditions.
The overall number of conditions diagnosed was small relative to the size of the population, 15.5 cases per 10,000 person-years. “So that’s still relatively rare, but the problem is that these are very heavily used medications,” Dr. Etminan said.
For each man diagnosed with one of the ocular conditions, the researchers matched four control persons who were the same age and could be followed for the same length of time. There was a total of 4,584 control persons.
The researchers compared regular users of PDE5Is (those who had received at least one prescription for a PDE5I every 3 months in the year before the ocular diagnosis) with nonusers (those who had not received a PDE5I prescription during that time).
Patients with the ocular conditions were more likely than were those in the control group to have hypertension, diabetes, cardiovascular disease, or sleep apnea. After controlling for these covariates, the researchers found that the users were overall 85% more likely to be diagnosed with one or more of them (incidence rate ratio [IRR], 1.85).
The researchers also found that the risk was even greater for those patients who were given five or more prescriptions of PDE5Is, compared to those given fewer than five prescriptions, suggesting a dose response.
On the basis of these findings, Dr. Etminan thinks drug companies should add warnings about serous retinal detachment and retinal vascular occlusion to the drug monographs.
Asked to comment, Pfizer, which developed Viagra, referred questions to its spinoff company, Viatris, which did not respond. Eli Lilly, which makes Cialis, also did not respond to a request for comment. Vivus, which makes Stendra, could not be reached by press time.
Bayer, which makes Levitra, declined to provide anyone who could answer questions, but it provided a statement noting that the occurrence of ocular adverse events is already known among PDE5I users and that retinal vascular occlusion and ischemic optic neuropathy are mentioned in the product information.
“For example, non-arteritic anterior ischemic optic neuropathy (NAION) is a very rare condition which occurs with an overall higher risk in the population usually suffering from erectile dysfunction (ED) – that is, elderly men with concomitant diseases such as diabetes, dyslipidemia, and hypertension – compared to the general population,” the statement said.
Because of the retrospective nature of the analysis, Dr. Etminan acknowledged that researchers could not prove that the increased risk of ocular disease was associated with use of the drugs rather than some underlying condition. But in addition to adjusting for known risk factors, they also separately analyzed men without hypertension, diabetes, or coronary artery disease and still found that the risk of the ocular conditions was roughly double for men with PDE5I prescriptions.
Howard Pomeranz, MD, PhD, professor of ophthalmology at Northwell Health in Great Neck, N.Y., who was not involved in this study, said its findings confirmed similar research that he conducted on ischemic optic neuropathy.
He told this news organization that people taking PDE5Is should weigh the risk against the benefit, but added that the calculation might be different for people who use them to treat pulmonary hypertension rather than erectile dysfunction.
Although people taking the drugs should discuss any changes in their vision with their practitioners, he said they should not be concerned about a “bluish type of tint to the vision that may occur transiently for anywhere from a few minutes up to 40 or 45 minutes.”
Drug companies and regulators should consider changing the monographs in light of this new evidence, Dr. Pomeranz said. “Perhaps this data might drive the warning to be perhaps a little bit stronger, now that there’s more data to suggest maybe a bit of a stronger association and not just some chance association between using these drugs and these visual events.”
The study was funded by the University of British Columbia. Dr. Etminan and Dr. Pomeranz have disclosed no relevant financial interests.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com
, researchers say.
Patients in an insurance database who were prescribed sildenafil (Viagra), tadalafil (Cialis), vardenafil (Levitra), or avanafil (Stendra) were almost twice as likely as were patients not prescribed the drugs to have ischemic optic neuropathy, retinal vascular occlusion, or serous retinal detachment.
In 2020, physicians wrote about 20 million monthly prescriptions for PDE5Is in the United States alone, said Mahyar Etminan, PharmD, associate professor of ophthalmology at the University of British Columbia, Vancouver.
“We don’t want to alarm people taking them, but generally speaking, if they experience visual problems or changes in vision, then these drugs may be the culprits, and they should check it out,” he said in an interview.
The study was published in JAMA Ophthalmology.
Previous reports, including postmarketing studies by the drug makers, have documented ocular events. The monographs for sildenafil, tadalafil, vardenafil, and avanafil warn users about ischemic optic neuropathy, the researchers found.
The monographs for sildenafil, tadalafil, and vardenafil list retinal vascular occlusion as a potential adverse event but do not quantify the risk. None of the drug monographs mention serous retinal detachment.
Previous research has associated PDE5Is with compromised perfusion of the optic nerve. Some researchers have speculated that the choroid blood vessels can undergo smooth muscle relaxation through a cyclic guanosine monophosphate pathway that can lead to choroidal congestion.
To get a better handle on the ocular risks of PDE51s, Dr. Etminan and his colleagues analyzed health insurance claim records from the PharMetrics Plus database of 213,033 men who had not experienced any of the three ocular conditions in the year before they became regular users of the medications.
They identified 1,146 patients who had been diagnosed with at least one of the three conditions.
The overall number of conditions diagnosed was small relative to the size of the population, 15.5 cases per 10,000 person-years. “So that’s still relatively rare, but the problem is that these are very heavily used medications,” Dr. Etminan said.
For each man diagnosed with one of the ocular conditions, the researchers matched four control persons who were the same age and could be followed for the same length of time. There was a total of 4,584 control persons.
The researchers compared regular users of PDE5Is (those who had received at least one prescription for a PDE5I every 3 months in the year before the ocular diagnosis) with nonusers (those who had not received a PDE5I prescription during that time).
Patients with the ocular conditions were more likely than were those in the control group to have hypertension, diabetes, cardiovascular disease, or sleep apnea. After controlling for these covariates, the researchers found that the users were overall 85% more likely to be diagnosed with one or more of them (incidence rate ratio [IRR], 1.85).
The researchers also found that the risk was even greater for those patients who were given five or more prescriptions of PDE5Is, compared to those given fewer than five prescriptions, suggesting a dose response.
On the basis of these findings, Dr. Etminan thinks drug companies should add warnings about serous retinal detachment and retinal vascular occlusion to the drug monographs.
Asked to comment, Pfizer, which developed Viagra, referred questions to its spinoff company, Viatris, which did not respond. Eli Lilly, which makes Cialis, also did not respond to a request for comment. Vivus, which makes Stendra, could not be reached by press time.
Bayer, which makes Levitra, declined to provide anyone who could answer questions, but it provided a statement noting that the occurrence of ocular adverse events is already known among PDE5I users and that retinal vascular occlusion and ischemic optic neuropathy are mentioned in the product information.
“For example, non-arteritic anterior ischemic optic neuropathy (NAION) is a very rare condition which occurs with an overall higher risk in the population usually suffering from erectile dysfunction (ED) – that is, elderly men with concomitant diseases such as diabetes, dyslipidemia, and hypertension – compared to the general population,” the statement said.
Because of the retrospective nature of the analysis, Dr. Etminan acknowledged that researchers could not prove that the increased risk of ocular disease was associated with use of the drugs rather than some underlying condition. But in addition to adjusting for known risk factors, they also separately analyzed men without hypertension, diabetes, or coronary artery disease and still found that the risk of the ocular conditions was roughly double for men with PDE5I prescriptions.
Howard Pomeranz, MD, PhD, professor of ophthalmology at Northwell Health in Great Neck, N.Y., who was not involved in this study, said its findings confirmed similar research that he conducted on ischemic optic neuropathy.
He told this news organization that people taking PDE5Is should weigh the risk against the benefit, but added that the calculation might be different for people who use them to treat pulmonary hypertension rather than erectile dysfunction.
Although people taking the drugs should discuss any changes in their vision with their practitioners, he said they should not be concerned about a “bluish type of tint to the vision that may occur transiently for anywhere from a few minutes up to 40 or 45 minutes.”
Drug companies and regulators should consider changing the monographs in light of this new evidence, Dr. Pomeranz said. “Perhaps this data might drive the warning to be perhaps a little bit stronger, now that there’s more data to suggest maybe a bit of a stronger association and not just some chance association between using these drugs and these visual events.”
The study was funded by the University of British Columbia. Dr. Etminan and Dr. Pomeranz have disclosed no relevant financial interests.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com
Study: Physical fitness in children linked with concentration, quality of life
The findings of the German study involving more than 6,500 kids emphasize the importance of cardiorespiratory health in childhood, and support physical fitness initiatives in schools, according to lead author Katharina Köble, MSc, of the Technical University of Munich (Germany), and colleagues.
“Recent studies show that only a few children meet the recommendations of physical activity,” the investigators wrote in Journal of Clinical Medicine.
While the health benefits of physical activity are clearly documented, Ms. Köble and colleagues noted that typical measures of activity, such as accelerometers or self-reported questionnaires, are suboptimal research tools.
“Physical fitness is a more objective parameter to quantify when evaluating health promotion,” the investigators wrote. “Furthermore, cardiorespiratory fitness as part of physical fitness is more strongly related to risk factors of cardiovascular disease than physical activity.”
According to the investigators, physical fitness has also been linked with better concentration and HRQOL, but never in the same population of children.
The new study aimed to address this knowledge gap by assessing 6,533 healthy children aged 6-10 years, approximately half boys and half girls. Associations between physical fitness, concentration, and HRQOL were evaluated using multiple linear regression analysis in participants aged 9-10 years.
Physical fitness was measured using a series of challenges, including curl-ups (pull-ups with palms facing body), push-ups, standing long jump, handgrip strength measurement, and Progressive Aerobic Cardiovascular Endurance Run (PACER). Performing the multistage shuttle run, PACER, “requires participants to maintain the pace set by an audio signal, which progressively increases the intensity every minute.” Results of the PACER test were used to estimate VO2max.
Concentration was measured using the d2-R test, “a paper-pencil cancellation test, where subjects have to cross out all ‘d’ letters with two dashes under a time limit.”
HRQOL was evaluated with the KINDL questionnaire, which covers emotional well-being, physical well-being, everyday functioning (school), friends, family, and self-esteem.
Analysis showed that physical fitness improved with age (P < .001), except for VO2max in girls (P = .129). Concentration also improved with age (P < .001), while HRQOL did not (P = .179).
Among children aged 9-10 years, VO2max scores were strongly associated with both HRQOL (P < .001) and concentration (P < .001).
“VO2max was found to be one of the main factors influencing concentration levels and HRQOL dimensions in primary school children,” the investigators wrote. “Physical fitness, especially cardiorespiratory performance, should therefore be promoted more specifically in school settings to support the promotion of an overall healthy lifestyle in children and adolescents.”
Findings are having a real-word impact, according to researcher
In an interview, Ms. Köble noted that the findings are already having a real-world impact.
“We continued data assessment in the long-term and specifically adapted prevention programs in school to the needs of the school children we identified in our study,” she said. “Schools are partially offering specific movement and nutrition classes now.”
In addition, Ms. Köble and colleagues plan on educating teachers about the “urgent need for sufficient physical activity.”
“Academic performance should be considered as an additional health factor in future studies, as well as screen time and eating patterns, as all those variables showed interactions with physical fitness and concentration. In a subanalysis, we showed that children with better physical fitness and concentration values were those who usually went to higher education secondary schools,” they wrote.
VO2max did not correlate with BMI
Gregory Weaver, MD, a pediatrician at Cleveland Clinic Children’s, voiced some concerns about the reliability of the findings. He noted that VO2max did not correlate with body mass index or other measures of physical fitness, and that using the PACER test to estimate VO2max may have skewed the association between physical fitness and concentration.
“It is quite conceivable that children who can maintain the focus to perform maximally on this test will also do well on other tests of attention/concentration,” Dr. Weaver said. “Most children I know would have a very difficult time performing a physical fitness test which requires them to match a recorded pace that slowly increases overtime. I’m not an expert in the area, but it is my understanding that usually VO2max tests involve a treadmill which allows investigators to have complete control over pace.”
Dr. Weaver concluded that more work is needed to determine if physical fitness interventions can have a positive impact on HRQOL and concentration.
“I think the authors of this study attempted to ask an important question about the possible association between physical fitness and concentration among school aged children,” Dr. Weaver said in an interview. “But what is even more vital are studies demonstrating that a change in modifiable health factors like nutrition, physical fitness, or the built environment can improve quality of life. I was hoping the authors would show that an improvement in VO2max over time resulted in an improvement in concentration. Frustratingly, that is not what this article demonstrates.”
The investigators and Dr. Weaver reported no conflicts of interest.
The findings of the German study involving more than 6,500 kids emphasize the importance of cardiorespiratory health in childhood, and support physical fitness initiatives in schools, according to lead author Katharina Köble, MSc, of the Technical University of Munich (Germany), and colleagues.
“Recent studies show that only a few children meet the recommendations of physical activity,” the investigators wrote in Journal of Clinical Medicine.
While the health benefits of physical activity are clearly documented, Ms. Köble and colleagues noted that typical measures of activity, such as accelerometers or self-reported questionnaires, are suboptimal research tools.
“Physical fitness is a more objective parameter to quantify when evaluating health promotion,” the investigators wrote. “Furthermore, cardiorespiratory fitness as part of physical fitness is more strongly related to risk factors of cardiovascular disease than physical activity.”
According to the investigators, physical fitness has also been linked with better concentration and HRQOL, but never in the same population of children.
The new study aimed to address this knowledge gap by assessing 6,533 healthy children aged 6-10 years, approximately half boys and half girls. Associations between physical fitness, concentration, and HRQOL were evaluated using multiple linear regression analysis in participants aged 9-10 years.
Physical fitness was measured using a series of challenges, including curl-ups (pull-ups with palms facing body), push-ups, standing long jump, handgrip strength measurement, and Progressive Aerobic Cardiovascular Endurance Run (PACER). Performing the multistage shuttle run, PACER, “requires participants to maintain the pace set by an audio signal, which progressively increases the intensity every minute.” Results of the PACER test were used to estimate VO2max.
Concentration was measured using the d2-R test, “a paper-pencil cancellation test, where subjects have to cross out all ‘d’ letters with two dashes under a time limit.”
HRQOL was evaluated with the KINDL questionnaire, which covers emotional well-being, physical well-being, everyday functioning (school), friends, family, and self-esteem.
Analysis showed that physical fitness improved with age (P < .001), except for VO2max in girls (P = .129). Concentration also improved with age (P < .001), while HRQOL did not (P = .179).
Among children aged 9-10 years, VO2max scores were strongly associated with both HRQOL (P < .001) and concentration (P < .001).
“VO2max was found to be one of the main factors influencing concentration levels and HRQOL dimensions in primary school children,” the investigators wrote. “Physical fitness, especially cardiorespiratory performance, should therefore be promoted more specifically in school settings to support the promotion of an overall healthy lifestyle in children and adolescents.”
Findings are having a real-word impact, according to researcher
In an interview, Ms. Köble noted that the findings are already having a real-world impact.
“We continued data assessment in the long-term and specifically adapted prevention programs in school to the needs of the school children we identified in our study,” she said. “Schools are partially offering specific movement and nutrition classes now.”
In addition, Ms. Köble and colleagues plan on educating teachers about the “urgent need for sufficient physical activity.”
“Academic performance should be considered as an additional health factor in future studies, as well as screen time and eating patterns, as all those variables showed interactions with physical fitness and concentration. In a subanalysis, we showed that children with better physical fitness and concentration values were those who usually went to higher education secondary schools,” they wrote.
VO2max did not correlate with BMI
Gregory Weaver, MD, a pediatrician at Cleveland Clinic Children’s, voiced some concerns about the reliability of the findings. He noted that VO2max did not correlate with body mass index or other measures of physical fitness, and that using the PACER test to estimate VO2max may have skewed the association between physical fitness and concentration.
“It is quite conceivable that children who can maintain the focus to perform maximally on this test will also do well on other tests of attention/concentration,” Dr. Weaver said. “Most children I know would have a very difficult time performing a physical fitness test which requires them to match a recorded pace that slowly increases overtime. I’m not an expert in the area, but it is my understanding that usually VO2max tests involve a treadmill which allows investigators to have complete control over pace.”
Dr. Weaver concluded that more work is needed to determine if physical fitness interventions can have a positive impact on HRQOL and concentration.
“I think the authors of this study attempted to ask an important question about the possible association between physical fitness and concentration among school aged children,” Dr. Weaver said in an interview. “But what is even more vital are studies demonstrating that a change in modifiable health factors like nutrition, physical fitness, or the built environment can improve quality of life. I was hoping the authors would show that an improvement in VO2max over time resulted in an improvement in concentration. Frustratingly, that is not what this article demonstrates.”
The investigators and Dr. Weaver reported no conflicts of interest.
The findings of the German study involving more than 6,500 kids emphasize the importance of cardiorespiratory health in childhood, and support physical fitness initiatives in schools, according to lead author Katharina Köble, MSc, of the Technical University of Munich (Germany), and colleagues.
“Recent studies show that only a few children meet the recommendations of physical activity,” the investigators wrote in Journal of Clinical Medicine.
While the health benefits of physical activity are clearly documented, Ms. Köble and colleagues noted that typical measures of activity, such as accelerometers or self-reported questionnaires, are suboptimal research tools.
“Physical fitness is a more objective parameter to quantify when evaluating health promotion,” the investigators wrote. “Furthermore, cardiorespiratory fitness as part of physical fitness is more strongly related to risk factors of cardiovascular disease than physical activity.”
According to the investigators, physical fitness has also been linked with better concentration and HRQOL, but never in the same population of children.
The new study aimed to address this knowledge gap by assessing 6,533 healthy children aged 6-10 years, approximately half boys and half girls. Associations between physical fitness, concentration, and HRQOL were evaluated using multiple linear regression analysis in participants aged 9-10 years.
Physical fitness was measured using a series of challenges, including curl-ups (pull-ups with palms facing body), push-ups, standing long jump, handgrip strength measurement, and Progressive Aerobic Cardiovascular Endurance Run (PACER). Performing the multistage shuttle run, PACER, “requires participants to maintain the pace set by an audio signal, which progressively increases the intensity every minute.” Results of the PACER test were used to estimate VO2max.
Concentration was measured using the d2-R test, “a paper-pencil cancellation test, where subjects have to cross out all ‘d’ letters with two dashes under a time limit.”
HRQOL was evaluated with the KINDL questionnaire, which covers emotional well-being, physical well-being, everyday functioning (school), friends, family, and self-esteem.
Analysis showed that physical fitness improved with age (P < .001), except for VO2max in girls (P = .129). Concentration also improved with age (P < .001), while HRQOL did not (P = .179).
Among children aged 9-10 years, VO2max scores were strongly associated with both HRQOL (P < .001) and concentration (P < .001).
“VO2max was found to be one of the main factors influencing concentration levels and HRQOL dimensions in primary school children,” the investigators wrote. “Physical fitness, especially cardiorespiratory performance, should therefore be promoted more specifically in school settings to support the promotion of an overall healthy lifestyle in children and adolescents.”
Findings are having a real-word impact, according to researcher
In an interview, Ms. Köble noted that the findings are already having a real-world impact.
“We continued data assessment in the long-term and specifically adapted prevention programs in school to the needs of the school children we identified in our study,” she said. “Schools are partially offering specific movement and nutrition classes now.”
In addition, Ms. Köble and colleagues plan on educating teachers about the “urgent need for sufficient physical activity.”
“Academic performance should be considered as an additional health factor in future studies, as well as screen time and eating patterns, as all those variables showed interactions with physical fitness and concentration. In a subanalysis, we showed that children with better physical fitness and concentration values were those who usually went to higher education secondary schools,” they wrote.
VO2max did not correlate with BMI
Gregory Weaver, MD, a pediatrician at Cleveland Clinic Children’s, voiced some concerns about the reliability of the findings. He noted that VO2max did not correlate with body mass index or other measures of physical fitness, and that using the PACER test to estimate VO2max may have skewed the association between physical fitness and concentration.
“It is quite conceivable that children who can maintain the focus to perform maximally on this test will also do well on other tests of attention/concentration,” Dr. Weaver said. “Most children I know would have a very difficult time performing a physical fitness test which requires them to match a recorded pace that slowly increases overtime. I’m not an expert in the area, but it is my understanding that usually VO2max tests involve a treadmill which allows investigators to have complete control over pace.”
Dr. Weaver concluded that more work is needed to determine if physical fitness interventions can have a positive impact on HRQOL and concentration.
“I think the authors of this study attempted to ask an important question about the possible association between physical fitness and concentration among school aged children,” Dr. Weaver said in an interview. “But what is even more vital are studies demonstrating that a change in modifiable health factors like nutrition, physical fitness, or the built environment can improve quality of life. I was hoping the authors would show that an improvement in VO2max over time resulted in an improvement in concentration. Frustratingly, that is not what this article demonstrates.”
The investigators and Dr. Weaver reported no conflicts of interest.
FROM THE JOURNAL OF CLINICAL MEDICINE
Novel tool could calculate CVD risk in T2DM
A genetic risk score based on blood pressure has been shown to potentially help determine the increased risk for heart attack or stroke in people with type 2 diabetes, suggesting that glucose control alone won’t be enough to control a person’s genetic risk for other cardiometabolic diseases.
The study analyzed genetic data from 6,335 participants, characterized as a high-risk multiethnic type 2 diabetes population, in the Action to Control Cardiovascular Risk in Diabetes study (ACCORD). Investigators developed a multivariable-adjustable model that found that, with each degree increase in the genetic score, the risk of cardiovascular disease (CVD) events increased 12%. However, the study found no relationship between glycemic control therapy and BP genetic risk score in CVD risk (P < .10).
Researchers at the University of Alabama at Birmingham reported on the risk score in a research letter
“This study highlights that commonly occurring changes in our DNA that cumulatively contribute to a higher risk of BP and hypertension can predispose T2DM [type 2 diabetes mellitus] patients to a higher risk of CVD events,” lead author Pankaj Arora, MD, said in a comment. The genetic risk score used in the study was effective at identifying CVD risks among the study participants even after accounting for conventional CV risk factors, added Dr. Arora, who’s director of the cardiovascular clinical and translational research and cardiovascular genetics clinic programs at UAB. “We recognize that cardiometabolic diseases travel together. Simply controlling the blood glucose level in isolation without considering an individual’s genetic risk for other cardiometabolic diseases may not yield a reduction of CVD risk in T2DM.”
The study used a map of more than 1,000 common genetic variants known to affect BP and compared that with the DNA of study participants to determine their genetic risks. Dr. Arora and colleagues wrote that the “results invigorate the potential implications” of using a BP polygenic risk score to address CVD risks through early intervention with lifestyle modifications such as diet, exercise, smoking cessation, weight management, and BP control in people with high genetic risk.
Gene profiles like the model the UAB researchers developed are still far away from the clinic, Dr. Arora said. “While such gene profiles are being used regularly in cancer management, these gene profiles are not easily available for cardiologists and endocrinologists to order.” He noted that the cardiogenomics clinic at UAB is one of the few centers that provide this kind of gene profiling in the United States. “Studies like this are bringing gene profiling closer to the doorstep of all cardiology and endocrinology clinics.”
The next step for the research is to expand the genetic variants used in the profiles. “We are now trying to develop a gene profile that encompasses more than 1 million common genetic variations and will be more informative,” Dr. Arora said. He added that few randomized clinical trials have shown using a BP genetic risk score in the clinic would improve outcomes of people with T2DM.
Kiran Musunuru, MD, PhD, MPH, director of the genetic and epigenetic origins of disease program at the University of Pennsylvania’s cardiovascular program in Philadelphia, provided context on what the study adds to the understanding of CVD risk in people with T2DM. “We know that patients with type 2 diabetes are at increased risk of cardiovascular disease, some of which is due to coexisting risk factors like abnormal lipids and hypertension,” he said in a comment. “This study shows that genetic predisposition to high blood pressure is one of the drivers of risk in these patients.” Dr. Musunuru is also chair of the writing group for the American Heart Association scientific statement on the use of genetics and genomics in clinical care.
However, he noted that collecting that kind of genetic data is challenging because few companies offer the tests and few centers do routine genetic testing. “As more studies like this one demonstrate the potential benefits of genetic testing, we can expect to see broader adoption by clinicians,” Dr. Musunuru said.
Dr. Arora receives funding from the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute and the Doris Duke Charitable Foundation. The ACCORD study received funding from Abbott Laboratories, Amylin Pharmaceutical, AstraZeneca, Bayer, Closer Healthcare, GlaxoSmithKline Pharmaceuticals, King Pharmaceuticals, Merck, Novartis, Novo Nordisk, Omron Healthcare, Sanofi-Aventis US, and Schering-Plough. Dr. Musunuru has no relevant relationships to disclose.
A genetic risk score based on blood pressure has been shown to potentially help determine the increased risk for heart attack or stroke in people with type 2 diabetes, suggesting that glucose control alone won’t be enough to control a person’s genetic risk for other cardiometabolic diseases.
The study analyzed genetic data from 6,335 participants, characterized as a high-risk multiethnic type 2 diabetes population, in the Action to Control Cardiovascular Risk in Diabetes study (ACCORD). Investigators developed a multivariable-adjustable model that found that, with each degree increase in the genetic score, the risk of cardiovascular disease (CVD) events increased 12%. However, the study found no relationship between glycemic control therapy and BP genetic risk score in CVD risk (P < .10).
Researchers at the University of Alabama at Birmingham reported on the risk score in a research letter
“This study highlights that commonly occurring changes in our DNA that cumulatively contribute to a higher risk of BP and hypertension can predispose T2DM [type 2 diabetes mellitus] patients to a higher risk of CVD events,” lead author Pankaj Arora, MD, said in a comment. The genetic risk score used in the study was effective at identifying CVD risks among the study participants even after accounting for conventional CV risk factors, added Dr. Arora, who’s director of the cardiovascular clinical and translational research and cardiovascular genetics clinic programs at UAB. “We recognize that cardiometabolic diseases travel together. Simply controlling the blood glucose level in isolation without considering an individual’s genetic risk for other cardiometabolic diseases may not yield a reduction of CVD risk in T2DM.”
The study used a map of more than 1,000 common genetic variants known to affect BP and compared that with the DNA of study participants to determine their genetic risks. Dr. Arora and colleagues wrote that the “results invigorate the potential implications” of using a BP polygenic risk score to address CVD risks through early intervention with lifestyle modifications such as diet, exercise, smoking cessation, weight management, and BP control in people with high genetic risk.
Gene profiles like the model the UAB researchers developed are still far away from the clinic, Dr. Arora said. “While such gene profiles are being used regularly in cancer management, these gene profiles are not easily available for cardiologists and endocrinologists to order.” He noted that the cardiogenomics clinic at UAB is one of the few centers that provide this kind of gene profiling in the United States. “Studies like this are bringing gene profiling closer to the doorstep of all cardiology and endocrinology clinics.”
The next step for the research is to expand the genetic variants used in the profiles. “We are now trying to develop a gene profile that encompasses more than 1 million common genetic variations and will be more informative,” Dr. Arora said. He added that few randomized clinical trials have shown using a BP genetic risk score in the clinic would improve outcomes of people with T2DM.
Kiran Musunuru, MD, PhD, MPH, director of the genetic and epigenetic origins of disease program at the University of Pennsylvania’s cardiovascular program in Philadelphia, provided context on what the study adds to the understanding of CVD risk in people with T2DM. “We know that patients with type 2 diabetes are at increased risk of cardiovascular disease, some of which is due to coexisting risk factors like abnormal lipids and hypertension,” he said in a comment. “This study shows that genetic predisposition to high blood pressure is one of the drivers of risk in these patients.” Dr. Musunuru is also chair of the writing group for the American Heart Association scientific statement on the use of genetics and genomics in clinical care.
However, he noted that collecting that kind of genetic data is challenging because few companies offer the tests and few centers do routine genetic testing. “As more studies like this one demonstrate the potential benefits of genetic testing, we can expect to see broader adoption by clinicians,” Dr. Musunuru said.
Dr. Arora receives funding from the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute and the Doris Duke Charitable Foundation. The ACCORD study received funding from Abbott Laboratories, Amylin Pharmaceutical, AstraZeneca, Bayer, Closer Healthcare, GlaxoSmithKline Pharmaceuticals, King Pharmaceuticals, Merck, Novartis, Novo Nordisk, Omron Healthcare, Sanofi-Aventis US, and Schering-Plough. Dr. Musunuru has no relevant relationships to disclose.
A genetic risk score based on blood pressure has been shown to potentially help determine the increased risk for heart attack or stroke in people with type 2 diabetes, suggesting that glucose control alone won’t be enough to control a person’s genetic risk for other cardiometabolic diseases.
The study analyzed genetic data from 6,335 participants, characterized as a high-risk multiethnic type 2 diabetes population, in the Action to Control Cardiovascular Risk in Diabetes study (ACCORD). Investigators developed a multivariable-adjustable model that found that, with each degree increase in the genetic score, the risk of cardiovascular disease (CVD) events increased 12%. However, the study found no relationship between glycemic control therapy and BP genetic risk score in CVD risk (P < .10).
Researchers at the University of Alabama at Birmingham reported on the risk score in a research letter
“This study highlights that commonly occurring changes in our DNA that cumulatively contribute to a higher risk of BP and hypertension can predispose T2DM [type 2 diabetes mellitus] patients to a higher risk of CVD events,” lead author Pankaj Arora, MD, said in a comment. The genetic risk score used in the study was effective at identifying CVD risks among the study participants even after accounting for conventional CV risk factors, added Dr. Arora, who’s director of the cardiovascular clinical and translational research and cardiovascular genetics clinic programs at UAB. “We recognize that cardiometabolic diseases travel together. Simply controlling the blood glucose level in isolation without considering an individual’s genetic risk for other cardiometabolic diseases may not yield a reduction of CVD risk in T2DM.”
The study used a map of more than 1,000 common genetic variants known to affect BP and compared that with the DNA of study participants to determine their genetic risks. Dr. Arora and colleagues wrote that the “results invigorate the potential implications” of using a BP polygenic risk score to address CVD risks through early intervention with lifestyle modifications such as diet, exercise, smoking cessation, weight management, and BP control in people with high genetic risk.
Gene profiles like the model the UAB researchers developed are still far away from the clinic, Dr. Arora said. “While such gene profiles are being used regularly in cancer management, these gene profiles are not easily available for cardiologists and endocrinologists to order.” He noted that the cardiogenomics clinic at UAB is one of the few centers that provide this kind of gene profiling in the United States. “Studies like this are bringing gene profiling closer to the doorstep of all cardiology and endocrinology clinics.”
The next step for the research is to expand the genetic variants used in the profiles. “We are now trying to develop a gene profile that encompasses more than 1 million common genetic variations and will be more informative,” Dr. Arora said. He added that few randomized clinical trials have shown using a BP genetic risk score in the clinic would improve outcomes of people with T2DM.
Kiran Musunuru, MD, PhD, MPH, director of the genetic and epigenetic origins of disease program at the University of Pennsylvania’s cardiovascular program in Philadelphia, provided context on what the study adds to the understanding of CVD risk in people with T2DM. “We know that patients with type 2 diabetes are at increased risk of cardiovascular disease, some of which is due to coexisting risk factors like abnormal lipids and hypertension,” he said in a comment. “This study shows that genetic predisposition to high blood pressure is one of the drivers of risk in these patients.” Dr. Musunuru is also chair of the writing group for the American Heart Association scientific statement on the use of genetics and genomics in clinical care.
However, he noted that collecting that kind of genetic data is challenging because few companies offer the tests and few centers do routine genetic testing. “As more studies like this one demonstrate the potential benefits of genetic testing, we can expect to see broader adoption by clinicians,” Dr. Musunuru said.
Dr. Arora receives funding from the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute and the Doris Duke Charitable Foundation. The ACCORD study received funding from Abbott Laboratories, Amylin Pharmaceutical, AstraZeneca, Bayer, Closer Healthcare, GlaxoSmithKline Pharmaceuticals, King Pharmaceuticals, Merck, Novartis, Novo Nordisk, Omron Healthcare, Sanofi-Aventis US, and Schering-Plough. Dr. Musunuru has no relevant relationships to disclose.
FROM HYPERTENSION
Early PCSK9 inhibition in AMI yields plaque regression
When the PCSK9 inhibitor alirocumab is added to high-intensity statins soon after an acute myocardial infarction (AMI), the reduction in atheroma volume is doubled at 12 months, compared with placebo, while other key signs of plaque stabilization, such as fibrous cap thickness, are also significantly and substantially improved, according to the results of the PACMAN-AMI trial.
The study is consistent with other PCSK9 inhibitor trials, supporting the concept that “we should be seeking very low levels of LDL-C in high-risk patients,” reported Lorenz Räber, MD, PhD, of Bern (Switz.) University Hospital, at the annual scientific sessions of the American College of Cardiology.
The low LCL-C target, the data from PACMAN-AMI suggest, is below 50 mg/dL, but even lower is better. When displayed graphically, the improvements in remodeling characteristics “get very steep” as levels descend below a 50 mg/dL threshold, Dr. Räber reported. This was true regardless of study arm.
In PACMAN-AMI, 300 AMI patients (with either ST-elevation or non-ST-elevaion) were randomized to 150 mg alirocumab or placebo administered by subcutaneous injection within 24 hours after an urgent percutaneous intervention (PCI) and stent placement. All patients received their assigned therapy on top of a high-intensity statin in the form of 20 mg of rosuvastatin daily.
Primary outcome was atheroma volume
The primary endpoint was atheroma volume as determined by intravenous ultrasound (IVUS), but the secondary endpoints of maximum lipid core burden, as determined by near infrared spectroscopy (NIRS), and fibrous cap thickness, as determined by optical coherence tomography (OCT), were also adequately powered, according to Dr. Räber.
The imaging measures taken at baseline were repeated in exactly the same spot after 52 weeks on treatment.
For the primary outcome of atheroma volume, the mean 2.1% reduction among those randomized to alirocumab was more than double the 0.9% reduction in the placebo group (P = .001).
The mean reduction in lipid core volume based on a maximum lipid core burden index was also more than doubled (-79.42 vs. -37.60 maxLCBI4mm; P = .006). The increase in fibrous cap thickness was not quite twofold greater but very close (62.67 vs. 33.19 mcm; P = .001).
From baseline, the relative reductions in LDL-C, which were reached about 4 weeks after starting treatment and maintained over the course of the study, were greater in the group randomized to alirocumab (-84.8% vs. -50.7%). This was expected, but the more important finding was a near linear relationship between reductions of LDL-C and each of these endpoints regardless of treatment, fully explaining the advantage of alirocumab, according to Dr. Räber.
For the addition of alirocumab, “these findings indicate incremental coronary plaque regression, lipid core reduction, and plaque stabilization, and provide a mechanistic rationale in favor of early initiation of very intensive LDL-C lower in the setting of an acute MI,” he said.
The results of the PACMAN-AMI trial were published simultaneously at the time of the ACC presentation.
Results consistent with earlier trials
Alirocumab was well tolerated. Injection site reactions (6.1% vs. 3.3%) and general allergic reactions (3.4% vs. 0%) were more common on alirocumab, but there were no significant differences between the arms of this study for serious adverse events. There were slightly more neurocognitive events (2.0 vs. 0%) and abnormal alanine transferase levels (0.7% vs. 0%) in the alirocumab group.
The data are generally consistent with two previously published trials with another PCSK9 inhibitor, according to Dr. Räber. In the randomized GLAGOV trial published more than 5 years ago, evolocumab also produced about a 1% absolute reduction (P < .001) in plaque volume at the end of 78 weeks of follow-up relative to placebo.
However, that trial was limited to patients with coronary artery disease without a recent cardiovascular event. The more recent HUYGENS trial, which was presented virtually at the 2021 annual meeting of the European Society of Cardiology meeting and has not yet been published, looked at one of the endpoints also evaluated in PACMAN-AMI. In that study of 161 randomized NSTEMI patients, there was also about a doubling of fibrous cap thickness (42.7 vs. 21.5 mcm) for the PCSK9 inhibitor relative to placebo.
Clinical endpoints were not compared in either the PACMAN-AMI or HUYGENS trial.
PACMAN-AMI confirms plaque stabilization
Nevertheless, the message of plaque stabilization is important, according to Anthony N. DeMaria, MD, Founding Director of the Sulpizio Cardiovascular Center at the University of San Diego. Although he acknowledged that a 1% absolute reduction in mean plaque volume might “make you want to yawn,” he argued that this is a misreading of important changes observed in plaque physiology.
“What we have now is evidence that very low lipid levels result in plaque remodeling. The plaques might not get a whole lot smaller, but the changes are important,” he said, noting, for example, that a thicker fibrous cap and increased plaque stability “clearly plays a role in reducing risk of subsequent events.”
“You cannot help but be impressed by the relationship of lipid lowering and the favorable effect on remodeling,” he added.
The data associating PCSK9 inhibitors with protection from cardiovascular events is already extensive, according to Michael J. Blaha, MD, Director of Clinical Research for Ciccarone Center for Prevention of Cardiovascular Disease, Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore, but he called PACMAN-ACS “an extremely relevant study.”
“This provides more evidence of the mechanism of benefit, which I think is extremely important when talking to patients about the goals of therapy,” he said.
PACMAN-AMI provided a very simple take home message for Pamela B. Morris, MD, Director of Preventive Cardiology, Medical University of South Carolina, Charleston.
“This study shows that if you get LCL-C under 50 mg/dL regardless of treatment, there is a favorable remodeling effect,” Dr. Morris said. In AMI patients, the data confirm “go early and go low,” she added. “You should do whatever is necessary [go get to these lower targets].”
Dr. Räber has financial relationships with Abbott, Amgen, AstraZeneca, Boston Scientific, Biotronik, Canon, Heartflow, Medtronic, Occlutech, Regeneron, Sanofi, and Vifor. Dr. Blaha reports financial relationships with Akcea, Amgen, Bayer, Inozyme, Kaleido, Kowa, Medimmune, Novartis, Novo Nordisk, Regeneron, Roche, Sanofi, Siemens, and 89Bio. Dr. DeMaria reports no potential conflicts of interest. Dr. Morris reports a financial relationship with Amgen. The investigator-initiated trial received research grants from Infraredx, Regeneron, and Sanofi.
When the PCSK9 inhibitor alirocumab is added to high-intensity statins soon after an acute myocardial infarction (AMI), the reduction in atheroma volume is doubled at 12 months, compared with placebo, while other key signs of plaque stabilization, such as fibrous cap thickness, are also significantly and substantially improved, according to the results of the PACMAN-AMI trial.
The study is consistent with other PCSK9 inhibitor trials, supporting the concept that “we should be seeking very low levels of LDL-C in high-risk patients,” reported Lorenz Räber, MD, PhD, of Bern (Switz.) University Hospital, at the annual scientific sessions of the American College of Cardiology.
The low LCL-C target, the data from PACMAN-AMI suggest, is below 50 mg/dL, but even lower is better. When displayed graphically, the improvements in remodeling characteristics “get very steep” as levels descend below a 50 mg/dL threshold, Dr. Räber reported. This was true regardless of study arm.
In PACMAN-AMI, 300 AMI patients (with either ST-elevation or non-ST-elevaion) were randomized to 150 mg alirocumab or placebo administered by subcutaneous injection within 24 hours after an urgent percutaneous intervention (PCI) and stent placement. All patients received their assigned therapy on top of a high-intensity statin in the form of 20 mg of rosuvastatin daily.
Primary outcome was atheroma volume
The primary endpoint was atheroma volume as determined by intravenous ultrasound (IVUS), but the secondary endpoints of maximum lipid core burden, as determined by near infrared spectroscopy (NIRS), and fibrous cap thickness, as determined by optical coherence tomography (OCT), were also adequately powered, according to Dr. Räber.
The imaging measures taken at baseline were repeated in exactly the same spot after 52 weeks on treatment.
For the primary outcome of atheroma volume, the mean 2.1% reduction among those randomized to alirocumab was more than double the 0.9% reduction in the placebo group (P = .001).
The mean reduction in lipid core volume based on a maximum lipid core burden index was also more than doubled (-79.42 vs. -37.60 maxLCBI4mm; P = .006). The increase in fibrous cap thickness was not quite twofold greater but very close (62.67 vs. 33.19 mcm; P = .001).
From baseline, the relative reductions in LDL-C, which were reached about 4 weeks after starting treatment and maintained over the course of the study, were greater in the group randomized to alirocumab (-84.8% vs. -50.7%). This was expected, but the more important finding was a near linear relationship between reductions of LDL-C and each of these endpoints regardless of treatment, fully explaining the advantage of alirocumab, according to Dr. Räber.
For the addition of alirocumab, “these findings indicate incremental coronary plaque regression, lipid core reduction, and plaque stabilization, and provide a mechanistic rationale in favor of early initiation of very intensive LDL-C lower in the setting of an acute MI,” he said.
The results of the PACMAN-AMI trial were published simultaneously at the time of the ACC presentation.
Results consistent with earlier trials
Alirocumab was well tolerated. Injection site reactions (6.1% vs. 3.3%) and general allergic reactions (3.4% vs. 0%) were more common on alirocumab, but there were no significant differences between the arms of this study for serious adverse events. There were slightly more neurocognitive events (2.0 vs. 0%) and abnormal alanine transferase levels (0.7% vs. 0%) in the alirocumab group.
The data are generally consistent with two previously published trials with another PCSK9 inhibitor, according to Dr. Räber. In the randomized GLAGOV trial published more than 5 years ago, evolocumab also produced about a 1% absolute reduction (P < .001) in plaque volume at the end of 78 weeks of follow-up relative to placebo.
However, that trial was limited to patients with coronary artery disease without a recent cardiovascular event. The more recent HUYGENS trial, which was presented virtually at the 2021 annual meeting of the European Society of Cardiology meeting and has not yet been published, looked at one of the endpoints also evaluated in PACMAN-AMI. In that study of 161 randomized NSTEMI patients, there was also about a doubling of fibrous cap thickness (42.7 vs. 21.5 mcm) for the PCSK9 inhibitor relative to placebo.
Clinical endpoints were not compared in either the PACMAN-AMI or HUYGENS trial.
PACMAN-AMI confirms plaque stabilization
Nevertheless, the message of plaque stabilization is important, according to Anthony N. DeMaria, MD, Founding Director of the Sulpizio Cardiovascular Center at the University of San Diego. Although he acknowledged that a 1% absolute reduction in mean plaque volume might “make you want to yawn,” he argued that this is a misreading of important changes observed in plaque physiology.
“What we have now is evidence that very low lipid levels result in plaque remodeling. The plaques might not get a whole lot smaller, but the changes are important,” he said, noting, for example, that a thicker fibrous cap and increased plaque stability “clearly plays a role in reducing risk of subsequent events.”
“You cannot help but be impressed by the relationship of lipid lowering and the favorable effect on remodeling,” he added.
The data associating PCSK9 inhibitors with protection from cardiovascular events is already extensive, according to Michael J. Blaha, MD, Director of Clinical Research for Ciccarone Center for Prevention of Cardiovascular Disease, Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore, but he called PACMAN-ACS “an extremely relevant study.”
“This provides more evidence of the mechanism of benefit, which I think is extremely important when talking to patients about the goals of therapy,” he said.
PACMAN-AMI provided a very simple take home message for Pamela B. Morris, MD, Director of Preventive Cardiology, Medical University of South Carolina, Charleston.
“This study shows that if you get LCL-C under 50 mg/dL regardless of treatment, there is a favorable remodeling effect,” Dr. Morris said. In AMI patients, the data confirm “go early and go low,” she added. “You should do whatever is necessary [go get to these lower targets].”
Dr. Räber has financial relationships with Abbott, Amgen, AstraZeneca, Boston Scientific, Biotronik, Canon, Heartflow, Medtronic, Occlutech, Regeneron, Sanofi, and Vifor. Dr. Blaha reports financial relationships with Akcea, Amgen, Bayer, Inozyme, Kaleido, Kowa, Medimmune, Novartis, Novo Nordisk, Regeneron, Roche, Sanofi, Siemens, and 89Bio. Dr. DeMaria reports no potential conflicts of interest. Dr. Morris reports a financial relationship with Amgen. The investigator-initiated trial received research grants from Infraredx, Regeneron, and Sanofi.
When the PCSK9 inhibitor alirocumab is added to high-intensity statins soon after an acute myocardial infarction (AMI), the reduction in atheroma volume is doubled at 12 months, compared with placebo, while other key signs of plaque stabilization, such as fibrous cap thickness, are also significantly and substantially improved, according to the results of the PACMAN-AMI trial.
The study is consistent with other PCSK9 inhibitor trials, supporting the concept that “we should be seeking very low levels of LDL-C in high-risk patients,” reported Lorenz Räber, MD, PhD, of Bern (Switz.) University Hospital, at the annual scientific sessions of the American College of Cardiology.
The low LCL-C target, the data from PACMAN-AMI suggest, is below 50 mg/dL, but even lower is better. When displayed graphically, the improvements in remodeling characteristics “get very steep” as levels descend below a 50 mg/dL threshold, Dr. Räber reported. This was true regardless of study arm.
In PACMAN-AMI, 300 AMI patients (with either ST-elevation or non-ST-elevaion) were randomized to 150 mg alirocumab or placebo administered by subcutaneous injection within 24 hours after an urgent percutaneous intervention (PCI) and stent placement. All patients received their assigned therapy on top of a high-intensity statin in the form of 20 mg of rosuvastatin daily.
Primary outcome was atheroma volume
The primary endpoint was atheroma volume as determined by intravenous ultrasound (IVUS), but the secondary endpoints of maximum lipid core burden, as determined by near infrared spectroscopy (NIRS), and fibrous cap thickness, as determined by optical coherence tomography (OCT), were also adequately powered, according to Dr. Räber.
The imaging measures taken at baseline were repeated in exactly the same spot after 52 weeks on treatment.
For the primary outcome of atheroma volume, the mean 2.1% reduction among those randomized to alirocumab was more than double the 0.9% reduction in the placebo group (P = .001).
The mean reduction in lipid core volume based on a maximum lipid core burden index was also more than doubled (-79.42 vs. -37.60 maxLCBI4mm; P = .006). The increase in fibrous cap thickness was not quite twofold greater but very close (62.67 vs. 33.19 mcm; P = .001).
From baseline, the relative reductions in LDL-C, which were reached about 4 weeks after starting treatment and maintained over the course of the study, were greater in the group randomized to alirocumab (-84.8% vs. -50.7%). This was expected, but the more important finding was a near linear relationship between reductions of LDL-C and each of these endpoints regardless of treatment, fully explaining the advantage of alirocumab, according to Dr. Räber.
For the addition of alirocumab, “these findings indicate incremental coronary plaque regression, lipid core reduction, and plaque stabilization, and provide a mechanistic rationale in favor of early initiation of very intensive LDL-C lower in the setting of an acute MI,” he said.
The results of the PACMAN-AMI trial were published simultaneously at the time of the ACC presentation.
Results consistent with earlier trials
Alirocumab was well tolerated. Injection site reactions (6.1% vs. 3.3%) and general allergic reactions (3.4% vs. 0%) were more common on alirocumab, but there were no significant differences between the arms of this study for serious adverse events. There were slightly more neurocognitive events (2.0 vs. 0%) and abnormal alanine transferase levels (0.7% vs. 0%) in the alirocumab group.
The data are generally consistent with two previously published trials with another PCSK9 inhibitor, according to Dr. Räber. In the randomized GLAGOV trial published more than 5 years ago, evolocumab also produced about a 1% absolute reduction (P < .001) in plaque volume at the end of 78 weeks of follow-up relative to placebo.
However, that trial was limited to patients with coronary artery disease without a recent cardiovascular event. The more recent HUYGENS trial, which was presented virtually at the 2021 annual meeting of the European Society of Cardiology meeting and has not yet been published, looked at one of the endpoints also evaluated in PACMAN-AMI. In that study of 161 randomized NSTEMI patients, there was also about a doubling of fibrous cap thickness (42.7 vs. 21.5 mcm) for the PCSK9 inhibitor relative to placebo.
Clinical endpoints were not compared in either the PACMAN-AMI or HUYGENS trial.
PACMAN-AMI confirms plaque stabilization
Nevertheless, the message of plaque stabilization is important, according to Anthony N. DeMaria, MD, Founding Director of the Sulpizio Cardiovascular Center at the University of San Diego. Although he acknowledged that a 1% absolute reduction in mean plaque volume might “make you want to yawn,” he argued that this is a misreading of important changes observed in plaque physiology.
“What we have now is evidence that very low lipid levels result in plaque remodeling. The plaques might not get a whole lot smaller, but the changes are important,” he said, noting, for example, that a thicker fibrous cap and increased plaque stability “clearly plays a role in reducing risk of subsequent events.”
“You cannot help but be impressed by the relationship of lipid lowering and the favorable effect on remodeling,” he added.
The data associating PCSK9 inhibitors with protection from cardiovascular events is already extensive, according to Michael J. Blaha, MD, Director of Clinical Research for Ciccarone Center for Prevention of Cardiovascular Disease, Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore, but he called PACMAN-ACS “an extremely relevant study.”
“This provides more evidence of the mechanism of benefit, which I think is extremely important when talking to patients about the goals of therapy,” he said.
PACMAN-AMI provided a very simple take home message for Pamela B. Morris, MD, Director of Preventive Cardiology, Medical University of South Carolina, Charleston.
“This study shows that if you get LCL-C under 50 mg/dL regardless of treatment, there is a favorable remodeling effect,” Dr. Morris said. In AMI patients, the data confirm “go early and go low,” she added. “You should do whatever is necessary [go get to these lower targets].”
Dr. Räber has financial relationships with Abbott, Amgen, AstraZeneca, Boston Scientific, Biotronik, Canon, Heartflow, Medtronic, Occlutech, Regeneron, Sanofi, and Vifor. Dr. Blaha reports financial relationships with Akcea, Amgen, Bayer, Inozyme, Kaleido, Kowa, Medimmune, Novartis, Novo Nordisk, Regeneron, Roche, Sanofi, Siemens, and 89Bio. Dr. DeMaria reports no potential conflicts of interest. Dr. Morris reports a financial relationship with Amgen. The investigator-initiated trial received research grants from Infraredx, Regeneron, and Sanofi.
FROM ACC 2022
APOLLO: SLN360 clears first major hurdle, hammering Lp(a)
The short interfering RNA (siRNA) agent SLN360 was well tolerated and lowered lipoprotein(a) by up to 98% in volunteers without cardiovascular disease but with elevated Lp(a) in the small dose-ranging APOLLO trial.
Following a single subcutaneous dose of SLN360 (Silence Therapeutics), there was a dose-dependent reduction in Lp(a) plasma levels by a median of 46%, 86%, 96%, and 98% at about 45-60 days with 30-mg, 100-mg, 300-mg, and 600-mg doses, respectively.
Lp(a) levels at 150 days were 70% and 81% below baseline with the 300-and 600-mg doses.
In addition, for participants receiving the two highest doses, apolipoprotein B (apo B) was reduced was 21% and 24%, respectively, and LDL cholesterol (LDL-C), by 21% and 26%, respectively.
“The development of therapies targeting messenger RNA has made possible significant lowering of lipoprotein(a). Whether these reductions can impact on the incidence of ASCVD [atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease] or prevent progression of aortic stenosis remains to be determined but, we think, that optimism is warranted,” said principal investigator Steven E. Nissen, MD, Cleveland Clinic.
The results were presented in a late-breaking clinical trial session at the annual scientific sessions of the American College of Cardiology and published simultaneously in JAMA.
Elevated Lp(a) is a powerful genetic risk factor for ASCVD and aortic stenosis, which affects some 64 million Americans and 1.4 billion people globally. Although several experimental agents are under investigation, no currently approved drugs selectively lower Lp(a).
SLN360 is designed to lower Lp(a) production by using RNA interference to silence messenger RNA transcribed from the LPA gene in liver cells.
Testing vacuum
Dr. Nissen said in an interview that one of the big takeaways from the study is the need for greater testing of Lp(a). Automatic assays are available in almost every hospital, but two-unit systems (nmol/L and mg/dL) are used and thresholds for accelerated risk vary. The Cleveland Clinic currently tests all patients in its cardiac critical care unit and its prevention clinic.
“Someone comes in with an MI in their 40s and we measure it and it’s 100, 150 [mg/dL], clearly abnormal, and often these patients don’t have a lot of other risk factors,” Dr. Nissen said. “So the explanation very likely for their premature disease is this risk factor. We now have to educate everybody about the importance of getting it tested and finding out about it.”
During a media briefing, ACC 2022 program cochair Pamela B. Morris, MD, Medical University of South Carolina, Charleston, said testing for Lp(a) is not well reimbursed by insurance providers and that her patients will often cancel the test after learning it won’t be reimbursed because they don’t understand it.
“What Dr. Nissen is telling you: It should be measured in everyone at least once, we all believe that, but it hasn’t made it into the major guidelines,” she added. “I think what we’re going to have to do is have the guidelines mandate it and the insurers will follow.”
Guidelines currently list elevated Lp(a) as a “risk-enhancing factor,” which can help with at least recommending LDL-C treatment in patients with borderline risk and a sky-high Lp(a), noted Dr. Nissen. “But we need to go beyond that.”
Safety analyses
The first-in-human APOLLO trial evaluated 32 adults without known ASCVD and an Lp(a) concentration greater than 150 nmol/L (approximately 60 mg/dL) who received one of the four doses of SLN360 or placebo subcutaneously. Participants were monitored in a research unit for the first 24 hours and then followed periodically for up to 150 days. At baseline, their median Lp(a) level was 224 nmol/L, mean apo B level was 85 mg/dL, and mean LDL-C level was 108 mg/dL.
Treatment-emergent adverse events were generally mild, mostly grade 1 injection site reactions (83% at 30 mg, 100% at 100 mg, 67% at 300 mg, and 33% at 600 mg) and headache (33%, 17%, 0%, and 83%).
At the highest dose, C-reactive protein was increased in four patients and neutrophil counts in three. ALT and AST levels were elevated three times above the upper limit of normal in one patient at the lowest dose.
One participant in the lowest-dose group experienced two serious adverse events unrelated to SLN360 at day 45 after receiving a SARS-Co-V-2 vaccine.
Dr. Nissen noted that safety cannot be comprehensively assessed in a trial of this duration or size and that follow-up has been extended to 1 year in the two highest-dose groups.
Enrollment continues in the multiple-ascending dose portion of the study in patients with high Lp(a) and a history of stable ASCVD. A phase 2 study of SLN360 is also planned for the second half of 2022, pending regulatory discussions.
But will it reduce ASCVD events?
Study discussant Vera Bittner, MD, MSPH, University of Alabama at Birmingham, said that the development of Lp(a)-specific lowering agents has been a “holy grail” for years and congratulated the authors on a successful trial demonstrating very robust Lp(a) lowering.
She asked Dr. Nissen about the observation in proprotein convertase subtilisin/kexin type 9 inhibitor trials that absolute Lp(a) lowering is greater at higher baseline levels.
Dr. Nissen said this kind of analysis wasn’t possible because of the small sample size but “because these agents so effectively degrade messenger RNA, it’s very likely we will see robust suppression of plasma levels virtually regardless of the baseline level.”
Dr. Bittner also questioned if “LDL-C declined because of the cholesterol content in the lipoprotein(a) or is there some additional effect on LDL particles themselves?”
“It’s a really terrific question that will ultimately need to be answered,” Dr. Nissen replied. “There’s some controversy about the extent to which suppressing lipoprotein(a) will reduce LDL because the assays for LDL are measuring the LDL that’s in lipoprotein(a) and the LDL that is not. ... I think it’s probably a bystander effect, but it may also contribute to efficacy from a morbidity and mortality point of view, which is why we measured it.”
Dr. Bittner also called out the elevation in C-reactive protein and leukocytosis, which has not been seen in other siRNA studies. Dr. Nissen said the increases in C-reactive protein occurred in the first few days after administration and were gone after a week or so. “I don’t see it as a long-term limitation.”
In an accompanying editorial, Brian Ference, MD, MPhil, MSc, University of Cambridge (England), suggests that because circulating Lp(a) particles can progressively become trapped within the artery wall over time, it’s unlikely that lowering Lp(a) for only a few years starting later in life will eliminate the effect of lifelong exposure to Lp(a) and may only cut cardiovascular event risk by about 10%-15%.
He called for continued safety and efficacy evaluation of SLN360 and olpasiran, a similar siRNA agent in early development, and said further insights into whether large absolute reductions in Lp(a) can reduce the risk for major cardiovascular events will come from cardiovascular trials, such as the ongoing phase 3 Lp(a)HORIZON trial. It follows strong phase 2 results with the antisense agent AKCEA-APO(a)-LRx and has Dr. Nissen pulling double duty as study chair.
The study was funded by Silence Therapeutics. Dr. Nissen reported consulting for many pharmaceutical companies, which are directed to pay any renumeration directly to charity. Dr. Bittner reported consultant fees or honoraria from Pfizer; other from AstraZeneca, DalCor, Esperion, and Sanofi-Aventis; and research/research grants from Amgen and Novartis. Dr. Ference reported financial ties to Merck, Novartis, Amgen, Pfizer, Esperion Therapeutics, and numerous other companies.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The short interfering RNA (siRNA) agent SLN360 was well tolerated and lowered lipoprotein(a) by up to 98% in volunteers without cardiovascular disease but with elevated Lp(a) in the small dose-ranging APOLLO trial.
Following a single subcutaneous dose of SLN360 (Silence Therapeutics), there was a dose-dependent reduction in Lp(a) plasma levels by a median of 46%, 86%, 96%, and 98% at about 45-60 days with 30-mg, 100-mg, 300-mg, and 600-mg doses, respectively.
Lp(a) levels at 150 days were 70% and 81% below baseline with the 300-and 600-mg doses.
In addition, for participants receiving the two highest doses, apolipoprotein B (apo B) was reduced was 21% and 24%, respectively, and LDL cholesterol (LDL-C), by 21% and 26%, respectively.
“The development of therapies targeting messenger RNA has made possible significant lowering of lipoprotein(a). Whether these reductions can impact on the incidence of ASCVD [atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease] or prevent progression of aortic stenosis remains to be determined but, we think, that optimism is warranted,” said principal investigator Steven E. Nissen, MD, Cleveland Clinic.
The results were presented in a late-breaking clinical trial session at the annual scientific sessions of the American College of Cardiology and published simultaneously in JAMA.
Elevated Lp(a) is a powerful genetic risk factor for ASCVD and aortic stenosis, which affects some 64 million Americans and 1.4 billion people globally. Although several experimental agents are under investigation, no currently approved drugs selectively lower Lp(a).
SLN360 is designed to lower Lp(a) production by using RNA interference to silence messenger RNA transcribed from the LPA gene in liver cells.
Testing vacuum
Dr. Nissen said in an interview that one of the big takeaways from the study is the need for greater testing of Lp(a). Automatic assays are available in almost every hospital, but two-unit systems (nmol/L and mg/dL) are used and thresholds for accelerated risk vary. The Cleveland Clinic currently tests all patients in its cardiac critical care unit and its prevention clinic.
“Someone comes in with an MI in their 40s and we measure it and it’s 100, 150 [mg/dL], clearly abnormal, and often these patients don’t have a lot of other risk factors,” Dr. Nissen said. “So the explanation very likely for their premature disease is this risk factor. We now have to educate everybody about the importance of getting it tested and finding out about it.”
During a media briefing, ACC 2022 program cochair Pamela B. Morris, MD, Medical University of South Carolina, Charleston, said testing for Lp(a) is not well reimbursed by insurance providers and that her patients will often cancel the test after learning it won’t be reimbursed because they don’t understand it.
“What Dr. Nissen is telling you: It should be measured in everyone at least once, we all believe that, but it hasn’t made it into the major guidelines,” she added. “I think what we’re going to have to do is have the guidelines mandate it and the insurers will follow.”
Guidelines currently list elevated Lp(a) as a “risk-enhancing factor,” which can help with at least recommending LDL-C treatment in patients with borderline risk and a sky-high Lp(a), noted Dr. Nissen. “But we need to go beyond that.”
Safety analyses
The first-in-human APOLLO trial evaluated 32 adults without known ASCVD and an Lp(a) concentration greater than 150 nmol/L (approximately 60 mg/dL) who received one of the four doses of SLN360 or placebo subcutaneously. Participants were monitored in a research unit for the first 24 hours and then followed periodically for up to 150 days. At baseline, their median Lp(a) level was 224 nmol/L, mean apo B level was 85 mg/dL, and mean LDL-C level was 108 mg/dL.
Treatment-emergent adverse events were generally mild, mostly grade 1 injection site reactions (83% at 30 mg, 100% at 100 mg, 67% at 300 mg, and 33% at 600 mg) and headache (33%, 17%, 0%, and 83%).
At the highest dose, C-reactive protein was increased in four patients and neutrophil counts in three. ALT and AST levels were elevated three times above the upper limit of normal in one patient at the lowest dose.
One participant in the lowest-dose group experienced two serious adverse events unrelated to SLN360 at day 45 after receiving a SARS-Co-V-2 vaccine.
Dr. Nissen noted that safety cannot be comprehensively assessed in a trial of this duration or size and that follow-up has been extended to 1 year in the two highest-dose groups.
Enrollment continues in the multiple-ascending dose portion of the study in patients with high Lp(a) and a history of stable ASCVD. A phase 2 study of SLN360 is also planned for the second half of 2022, pending regulatory discussions.
But will it reduce ASCVD events?
Study discussant Vera Bittner, MD, MSPH, University of Alabama at Birmingham, said that the development of Lp(a)-specific lowering agents has been a “holy grail” for years and congratulated the authors on a successful trial demonstrating very robust Lp(a) lowering.
She asked Dr. Nissen about the observation in proprotein convertase subtilisin/kexin type 9 inhibitor trials that absolute Lp(a) lowering is greater at higher baseline levels.
Dr. Nissen said this kind of analysis wasn’t possible because of the small sample size but “because these agents so effectively degrade messenger RNA, it’s very likely we will see robust suppression of plasma levels virtually regardless of the baseline level.”
Dr. Bittner also questioned if “LDL-C declined because of the cholesterol content in the lipoprotein(a) or is there some additional effect on LDL particles themselves?”
“It’s a really terrific question that will ultimately need to be answered,” Dr. Nissen replied. “There’s some controversy about the extent to which suppressing lipoprotein(a) will reduce LDL because the assays for LDL are measuring the LDL that’s in lipoprotein(a) and the LDL that is not. ... I think it’s probably a bystander effect, but it may also contribute to efficacy from a morbidity and mortality point of view, which is why we measured it.”
Dr. Bittner also called out the elevation in C-reactive protein and leukocytosis, which has not been seen in other siRNA studies. Dr. Nissen said the increases in C-reactive protein occurred in the first few days after administration and were gone after a week or so. “I don’t see it as a long-term limitation.”
In an accompanying editorial, Brian Ference, MD, MPhil, MSc, University of Cambridge (England), suggests that because circulating Lp(a) particles can progressively become trapped within the artery wall over time, it’s unlikely that lowering Lp(a) for only a few years starting later in life will eliminate the effect of lifelong exposure to Lp(a) and may only cut cardiovascular event risk by about 10%-15%.
He called for continued safety and efficacy evaluation of SLN360 and olpasiran, a similar siRNA agent in early development, and said further insights into whether large absolute reductions in Lp(a) can reduce the risk for major cardiovascular events will come from cardiovascular trials, such as the ongoing phase 3 Lp(a)HORIZON trial. It follows strong phase 2 results with the antisense agent AKCEA-APO(a)-LRx and has Dr. Nissen pulling double duty as study chair.
The study was funded by Silence Therapeutics. Dr. Nissen reported consulting for many pharmaceutical companies, which are directed to pay any renumeration directly to charity. Dr. Bittner reported consultant fees or honoraria from Pfizer; other from AstraZeneca, DalCor, Esperion, and Sanofi-Aventis; and research/research grants from Amgen and Novartis. Dr. Ference reported financial ties to Merck, Novartis, Amgen, Pfizer, Esperion Therapeutics, and numerous other companies.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The short interfering RNA (siRNA) agent SLN360 was well tolerated and lowered lipoprotein(a) by up to 98% in volunteers without cardiovascular disease but with elevated Lp(a) in the small dose-ranging APOLLO trial.
Following a single subcutaneous dose of SLN360 (Silence Therapeutics), there was a dose-dependent reduction in Lp(a) plasma levels by a median of 46%, 86%, 96%, and 98% at about 45-60 days with 30-mg, 100-mg, 300-mg, and 600-mg doses, respectively.
Lp(a) levels at 150 days were 70% and 81% below baseline with the 300-and 600-mg doses.
In addition, for participants receiving the two highest doses, apolipoprotein B (apo B) was reduced was 21% and 24%, respectively, and LDL cholesterol (LDL-C), by 21% and 26%, respectively.
“The development of therapies targeting messenger RNA has made possible significant lowering of lipoprotein(a). Whether these reductions can impact on the incidence of ASCVD [atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease] or prevent progression of aortic stenosis remains to be determined but, we think, that optimism is warranted,” said principal investigator Steven E. Nissen, MD, Cleveland Clinic.
The results were presented in a late-breaking clinical trial session at the annual scientific sessions of the American College of Cardiology and published simultaneously in JAMA.
Elevated Lp(a) is a powerful genetic risk factor for ASCVD and aortic stenosis, which affects some 64 million Americans and 1.4 billion people globally. Although several experimental agents are under investigation, no currently approved drugs selectively lower Lp(a).
SLN360 is designed to lower Lp(a) production by using RNA interference to silence messenger RNA transcribed from the LPA gene in liver cells.
Testing vacuum
Dr. Nissen said in an interview that one of the big takeaways from the study is the need for greater testing of Lp(a). Automatic assays are available in almost every hospital, but two-unit systems (nmol/L and mg/dL) are used and thresholds for accelerated risk vary. The Cleveland Clinic currently tests all patients in its cardiac critical care unit and its prevention clinic.
“Someone comes in with an MI in their 40s and we measure it and it’s 100, 150 [mg/dL], clearly abnormal, and often these patients don’t have a lot of other risk factors,” Dr. Nissen said. “So the explanation very likely for their premature disease is this risk factor. We now have to educate everybody about the importance of getting it tested and finding out about it.”
During a media briefing, ACC 2022 program cochair Pamela B. Morris, MD, Medical University of South Carolina, Charleston, said testing for Lp(a) is not well reimbursed by insurance providers and that her patients will often cancel the test after learning it won’t be reimbursed because they don’t understand it.
“What Dr. Nissen is telling you: It should be measured in everyone at least once, we all believe that, but it hasn’t made it into the major guidelines,” she added. “I think what we’re going to have to do is have the guidelines mandate it and the insurers will follow.”
Guidelines currently list elevated Lp(a) as a “risk-enhancing factor,” which can help with at least recommending LDL-C treatment in patients with borderline risk and a sky-high Lp(a), noted Dr. Nissen. “But we need to go beyond that.”
Safety analyses
The first-in-human APOLLO trial evaluated 32 adults without known ASCVD and an Lp(a) concentration greater than 150 nmol/L (approximately 60 mg/dL) who received one of the four doses of SLN360 or placebo subcutaneously. Participants were monitored in a research unit for the first 24 hours and then followed periodically for up to 150 days. At baseline, their median Lp(a) level was 224 nmol/L, mean apo B level was 85 mg/dL, and mean LDL-C level was 108 mg/dL.
Treatment-emergent adverse events were generally mild, mostly grade 1 injection site reactions (83% at 30 mg, 100% at 100 mg, 67% at 300 mg, and 33% at 600 mg) and headache (33%, 17%, 0%, and 83%).
At the highest dose, C-reactive protein was increased in four patients and neutrophil counts in three. ALT and AST levels were elevated three times above the upper limit of normal in one patient at the lowest dose.
One participant in the lowest-dose group experienced two serious adverse events unrelated to SLN360 at day 45 after receiving a SARS-Co-V-2 vaccine.
Dr. Nissen noted that safety cannot be comprehensively assessed in a trial of this duration or size and that follow-up has been extended to 1 year in the two highest-dose groups.
Enrollment continues in the multiple-ascending dose portion of the study in patients with high Lp(a) and a history of stable ASCVD. A phase 2 study of SLN360 is also planned for the second half of 2022, pending regulatory discussions.
But will it reduce ASCVD events?
Study discussant Vera Bittner, MD, MSPH, University of Alabama at Birmingham, said that the development of Lp(a)-specific lowering agents has been a “holy grail” for years and congratulated the authors on a successful trial demonstrating very robust Lp(a) lowering.
She asked Dr. Nissen about the observation in proprotein convertase subtilisin/kexin type 9 inhibitor trials that absolute Lp(a) lowering is greater at higher baseline levels.
Dr. Nissen said this kind of analysis wasn’t possible because of the small sample size but “because these agents so effectively degrade messenger RNA, it’s very likely we will see robust suppression of plasma levels virtually regardless of the baseline level.”
Dr. Bittner also questioned if “LDL-C declined because of the cholesterol content in the lipoprotein(a) or is there some additional effect on LDL particles themselves?”
“It’s a really terrific question that will ultimately need to be answered,” Dr. Nissen replied. “There’s some controversy about the extent to which suppressing lipoprotein(a) will reduce LDL because the assays for LDL are measuring the LDL that’s in lipoprotein(a) and the LDL that is not. ... I think it’s probably a bystander effect, but it may also contribute to efficacy from a morbidity and mortality point of view, which is why we measured it.”
Dr. Bittner also called out the elevation in C-reactive protein and leukocytosis, which has not been seen in other siRNA studies. Dr. Nissen said the increases in C-reactive protein occurred in the first few days after administration and were gone after a week or so. “I don’t see it as a long-term limitation.”
In an accompanying editorial, Brian Ference, MD, MPhil, MSc, University of Cambridge (England), suggests that because circulating Lp(a) particles can progressively become trapped within the artery wall over time, it’s unlikely that lowering Lp(a) for only a few years starting later in life will eliminate the effect of lifelong exposure to Lp(a) and may only cut cardiovascular event risk by about 10%-15%.
He called for continued safety and efficacy evaluation of SLN360 and olpasiran, a similar siRNA agent in early development, and said further insights into whether large absolute reductions in Lp(a) can reduce the risk for major cardiovascular events will come from cardiovascular trials, such as the ongoing phase 3 Lp(a)HORIZON trial. It follows strong phase 2 results with the antisense agent AKCEA-APO(a)-LRx and has Dr. Nissen pulling double duty as study chair.
The study was funded by Silence Therapeutics. Dr. Nissen reported consulting for many pharmaceutical companies, which are directed to pay any renumeration directly to charity. Dr. Bittner reported consultant fees or honoraria from Pfizer; other from AstraZeneca, DalCor, Esperion, and Sanofi-Aventis; and research/research grants from Amgen and Novartis. Dr. Ference reported financial ties to Merck, Novartis, Amgen, Pfizer, Esperion Therapeutics, and numerous other companies.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM ACC 2022
Supermarket diet advice improves DASH adherence: SuperWIN
People who received personalized nutrition education in a series of sessions at their regular grocery store significantly improved adherence to a healthy diet, in a new “first-of-its-kind” study in which scientific researchers partnered with a large supermarket company.
In the SuperWIN study, participants were given individualized advice from supermarket-based dietitians using data on their own buying habits recorded on their supermarket loyalty cards. This was associated with an increased adherence to the DASH (Dietary Approaches to Stop Hypertension) diet, which emphasizes vegetables, fruits and whole grains while limiting foods that are high in saturated fat, sugar, and sodium and has been shown to lower blood pressure and LDL cholesterol.
One group of patients also received additional education about healthy eating and meal planning through online technologies, and this group showed even better adherence to the DASH diet.
The study was presented at the annual scientific sessions of the American College of Cardiology by Dylan Steen, MD, adjunct associate professor of medicine at the University of Cincinnati.
“The SuperWIN study provides evidence for the benefit of delivering healthy-eating interventions at modern supermarkets and retail-based clinics,” Dr. Steen said. “It demonstrates the efficacy of dietary interventions harnessing the physical environment of the supermarket, the retail-based dietitians working within the store, and the purchasing data captured on the store’s loyalty cards.”
The study was conducted in partnership with Kroger, the largest supermarket chain in the United States, which also operates a large chain of pharmacies and health clinics.
Dr. Steen said the study was addressing one of the biggest public health problems – unhealthy eating – with an innovative approach. “We need to think about how we can extend the reach of modern health care systems into communities and better deliver services right where people are; meet them where they live,” he said at an ACC press conference.
Commenting on the study at the press conference, Eileen Handberg, PhD, professor of medicine at University of Florida, Gainesville, and immediate past chair of the ACC Cardiovascular Care Team Council, said: “I am amazingly excited about this. There is so much potential here. We have never really taken advantage of the current explosion in retail-based health care before.”
Dr. Handberg suggested the study had major implications for the primary prevention of cardiovascular disease. “Little kids go shopping with their parents, so you have the ability here to change behavior from children on up if you can change the dynamic of the choices they make in the grocery store.”
In his presentation, Dr. Steen noted that, despite many longstanding guidelines on healthy eating, about 75% of Americans still have a poor-quality diet. This trial was conducted to see if a new approach could improve that situation. “If we change the environment in which we deliver dietary education, we can make a difference.”
The SuperWIN trial was conducted in 13 Kroger stores in Ohio and Kentucky. The study enrolled 267 people with at least one cardiovascular risk factor from a primary care network who regularly shopped at one of the study stores. All participants also had to be willing to follow the DASH diet, which was taught at each educational session in the trial.
All participants received one “enhanced” medical nutrition therapy that was guided by the individual’s own dietary intake analytics.
They were then randomly assigned to one of three arms. The control group received no further education. The strategy 1 group received six additional teaching sessions in the supermarket aisles over a 3-month period. Each session was guided by updated individualized purchasing data provided to the dietitian and the participant.
The strategy 2 group received the same six additional teaching sessions as strategy 1, but they also had some additional teaching on healthy eating and meal planning from a variety of online shopping tools, and nutrition and health care apps.
“The supermarket analytics were automatically collected so the dietitians could tell what each person liked to eat, how much of each product they were buying and how much they were spending,” Dr. Steen explained.
COVID hit halfway through the trial, and 20 participants were withdrawn for their own safety as they could no longer visit the stores, but the trial continued with the rest of the participants with enhanced safety precautions. The overall analysis cohort was 247 participants.
The average age of the participants was mid-50s, around 70% were female, and most did not have a history of cardiovascular disease.
Eating habits were assessed by three 24-hour dietary recalls assessed at the start of the study and at 3 and 6 months. The DASH score, which is a measure of adherence to the DASH diet, was calculated from this information. The score can range from 0 to 90, with an increased score showing increased adherence.
In one analysis, the researchers compared the DASH scores from the two intervention groups together with the control group, and in a second analysis they compared the scores in the strategy 2 group with those in the strategy 1 group.
Before the pandemic there was “near 100%” attendance for the six visits over the 3-month study period, which Dr. Steen said he thought was “remarkable.” During the pandemic, attendance came down to around 80%.
Results showed that the DASH score increased in all three groups at 3 months, with stepwise increases corresponding to the intensity of the intervention. DASH scores increased by 5.8 points in the control group, by 8.6 points in the strategy 1 group, and by 12.4 points in the strategy 2 group.
DASH scores significantly differed between the two intervention groups and the control group (P = .02). “This shows that purchasing data–guided in-store tours do increase the efficacy of dietary education,” Dr. Steen said.
The difference in scores between the strategy 1 and strategy 2 groups was also significant (P = .01). “This shows online enhancements increase adherence to the DASH diet even further,” Dr. Steen commented
By 6 months, the scores had dropped off a little but were still increased from baseline: by 4.4 points in the control group, 6.6 points in the strategy 1 group, and 8.4 points in the strategy 2 group. “There was again a stepwise increase as the intervention intensified, but there was no longer a significant difference between the interventions and control,” Dr. Steen noted.
Secondary endpoints included blood pressure and body mass index. Systolic blood pressure decreased slightly in all three groups: by 2.8 mm Hg in the control group, 6.6 mm Hg in the strategy 1 group, and 5.7 mm Hg in the strategy 2 group. Body mass index was reduced by 0.2, 0.4 and 0.8, respectively, but the between-group differences were not significant.
Dr. Steen said this is the first study of its kind to date in which scientific researchers collaborated with a large supermarket chain. He explained they also involved a primary care network so that health care utilization information will be available.
“We can the integrate retail-based health care information with traditional health care information. And we can start to look at downstream health care utilization and cost outcomes as well, which will be important as we start to think how to evolve the health care system,” he commented. “The hope is that we can get more scientists working with more retailers to really drive the evidence to shape the evolution of our health care system.”
Challenges ahead
Dr. Handberg pointed out there would be challenges in reaching the underserved population who do not shop at the major supermarkets. “We need to figure out how to get partnerships across the whole spectrum of grocery stores.”
She also noted that 3 months (the duration of the study intervention) was not much time to change the eating habits of a family. “Interventions may have to be a bit more intensive to get the change in blood pressure and weight that we would want to see.”
Dr Handberg hoped the major grocery store companies will see the opportunities in this approach. “Changing behavior is very complicated, and the key will be how to make people stick with the changes. But grocery stores are smart. They have got us going to their pharmacies, so getting us to see a dietitian is not that much of a stretch.”
Moderator of the ACC late-breaker session at which the study was presented, Pamela Morris, MD, from the Medical University of South Carolina, Charleston, who is also ACC annual scientific session chair, asked whether the approach could be sustained.
“I am thinking back to the barber shop study of blood pressure treatment and to my knowledge those PharmDs are no longer in those barbershops, taking blood pressures, counseling patients, and prescribing antihypertensives. So is Kroger maintaining a long-term commitment to providing this education, or how can this be financed over the long term?” she asked.
Dr. Steen replied that he believed sustainability to be one of the key strengths of this model. “Retail-based health care is exploding in the U.S. The number of retail outlets offering a comprehensive list of services is going up all the time. These programs exist regardless of whether this trial was conducted or not.”
But Dr. Steen stressed that having an evidence base will be critically important.
“Validation is an enormous part of this evolution in retail-based health care – not only to figure out what works but also to engage payors and others in the process of supporting these interventions. I think the sustainability is there – it is sort of baked into the model – but research will be a huge part of cementing this in and helping us to understand what we should do.”
The study was funded by Kroger. Dr. Steen is a consultant for Sanofi and CEO and cofounder of High Enroll.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
People who received personalized nutrition education in a series of sessions at their regular grocery store significantly improved adherence to a healthy diet, in a new “first-of-its-kind” study in which scientific researchers partnered with a large supermarket company.
In the SuperWIN study, participants were given individualized advice from supermarket-based dietitians using data on their own buying habits recorded on their supermarket loyalty cards. This was associated with an increased adherence to the DASH (Dietary Approaches to Stop Hypertension) diet, which emphasizes vegetables, fruits and whole grains while limiting foods that are high in saturated fat, sugar, and sodium and has been shown to lower blood pressure and LDL cholesterol.
One group of patients also received additional education about healthy eating and meal planning through online technologies, and this group showed even better adherence to the DASH diet.
The study was presented at the annual scientific sessions of the American College of Cardiology by Dylan Steen, MD, adjunct associate professor of medicine at the University of Cincinnati.
“The SuperWIN study provides evidence for the benefit of delivering healthy-eating interventions at modern supermarkets and retail-based clinics,” Dr. Steen said. “It demonstrates the efficacy of dietary interventions harnessing the physical environment of the supermarket, the retail-based dietitians working within the store, and the purchasing data captured on the store’s loyalty cards.”
The study was conducted in partnership with Kroger, the largest supermarket chain in the United States, which also operates a large chain of pharmacies and health clinics.
Dr. Steen said the study was addressing one of the biggest public health problems – unhealthy eating – with an innovative approach. “We need to think about how we can extend the reach of modern health care systems into communities and better deliver services right where people are; meet them where they live,” he said at an ACC press conference.
Commenting on the study at the press conference, Eileen Handberg, PhD, professor of medicine at University of Florida, Gainesville, and immediate past chair of the ACC Cardiovascular Care Team Council, said: “I am amazingly excited about this. There is so much potential here. We have never really taken advantage of the current explosion in retail-based health care before.”
Dr. Handberg suggested the study had major implications for the primary prevention of cardiovascular disease. “Little kids go shopping with their parents, so you have the ability here to change behavior from children on up if you can change the dynamic of the choices they make in the grocery store.”
In his presentation, Dr. Steen noted that, despite many longstanding guidelines on healthy eating, about 75% of Americans still have a poor-quality diet. This trial was conducted to see if a new approach could improve that situation. “If we change the environment in which we deliver dietary education, we can make a difference.”
The SuperWIN trial was conducted in 13 Kroger stores in Ohio and Kentucky. The study enrolled 267 people with at least one cardiovascular risk factor from a primary care network who regularly shopped at one of the study stores. All participants also had to be willing to follow the DASH diet, which was taught at each educational session in the trial.
All participants received one “enhanced” medical nutrition therapy that was guided by the individual’s own dietary intake analytics.
They were then randomly assigned to one of three arms. The control group received no further education. The strategy 1 group received six additional teaching sessions in the supermarket aisles over a 3-month period. Each session was guided by updated individualized purchasing data provided to the dietitian and the participant.
The strategy 2 group received the same six additional teaching sessions as strategy 1, but they also had some additional teaching on healthy eating and meal planning from a variety of online shopping tools, and nutrition and health care apps.
“The supermarket analytics were automatically collected so the dietitians could tell what each person liked to eat, how much of each product they were buying and how much they were spending,” Dr. Steen explained.
COVID hit halfway through the trial, and 20 participants were withdrawn for their own safety as they could no longer visit the stores, but the trial continued with the rest of the participants with enhanced safety precautions. The overall analysis cohort was 247 participants.
The average age of the participants was mid-50s, around 70% were female, and most did not have a history of cardiovascular disease.
Eating habits were assessed by three 24-hour dietary recalls assessed at the start of the study and at 3 and 6 months. The DASH score, which is a measure of adherence to the DASH diet, was calculated from this information. The score can range from 0 to 90, with an increased score showing increased adherence.
In one analysis, the researchers compared the DASH scores from the two intervention groups together with the control group, and in a second analysis they compared the scores in the strategy 2 group with those in the strategy 1 group.
Before the pandemic there was “near 100%” attendance for the six visits over the 3-month study period, which Dr. Steen said he thought was “remarkable.” During the pandemic, attendance came down to around 80%.
Results showed that the DASH score increased in all three groups at 3 months, with stepwise increases corresponding to the intensity of the intervention. DASH scores increased by 5.8 points in the control group, by 8.6 points in the strategy 1 group, and by 12.4 points in the strategy 2 group.
DASH scores significantly differed between the two intervention groups and the control group (P = .02). “This shows that purchasing data–guided in-store tours do increase the efficacy of dietary education,” Dr. Steen said.
The difference in scores between the strategy 1 and strategy 2 groups was also significant (P = .01). “This shows online enhancements increase adherence to the DASH diet even further,” Dr. Steen commented
By 6 months, the scores had dropped off a little but were still increased from baseline: by 4.4 points in the control group, 6.6 points in the strategy 1 group, and 8.4 points in the strategy 2 group. “There was again a stepwise increase as the intervention intensified, but there was no longer a significant difference between the interventions and control,” Dr. Steen noted.
Secondary endpoints included blood pressure and body mass index. Systolic blood pressure decreased slightly in all three groups: by 2.8 mm Hg in the control group, 6.6 mm Hg in the strategy 1 group, and 5.7 mm Hg in the strategy 2 group. Body mass index was reduced by 0.2, 0.4 and 0.8, respectively, but the between-group differences were not significant.
Dr. Steen said this is the first study of its kind to date in which scientific researchers collaborated with a large supermarket chain. He explained they also involved a primary care network so that health care utilization information will be available.
“We can the integrate retail-based health care information with traditional health care information. And we can start to look at downstream health care utilization and cost outcomes as well, which will be important as we start to think how to evolve the health care system,” he commented. “The hope is that we can get more scientists working with more retailers to really drive the evidence to shape the evolution of our health care system.”
Challenges ahead
Dr. Handberg pointed out there would be challenges in reaching the underserved population who do not shop at the major supermarkets. “We need to figure out how to get partnerships across the whole spectrum of grocery stores.”
She also noted that 3 months (the duration of the study intervention) was not much time to change the eating habits of a family. “Interventions may have to be a bit more intensive to get the change in blood pressure and weight that we would want to see.”
Dr Handberg hoped the major grocery store companies will see the opportunities in this approach. “Changing behavior is very complicated, and the key will be how to make people stick with the changes. But grocery stores are smart. They have got us going to their pharmacies, so getting us to see a dietitian is not that much of a stretch.”
Moderator of the ACC late-breaker session at which the study was presented, Pamela Morris, MD, from the Medical University of South Carolina, Charleston, who is also ACC annual scientific session chair, asked whether the approach could be sustained.
“I am thinking back to the barber shop study of blood pressure treatment and to my knowledge those PharmDs are no longer in those barbershops, taking blood pressures, counseling patients, and prescribing antihypertensives. So is Kroger maintaining a long-term commitment to providing this education, or how can this be financed over the long term?” she asked.
Dr. Steen replied that he believed sustainability to be one of the key strengths of this model. “Retail-based health care is exploding in the U.S. The number of retail outlets offering a comprehensive list of services is going up all the time. These programs exist regardless of whether this trial was conducted or not.”
But Dr. Steen stressed that having an evidence base will be critically important.
“Validation is an enormous part of this evolution in retail-based health care – not only to figure out what works but also to engage payors and others in the process of supporting these interventions. I think the sustainability is there – it is sort of baked into the model – but research will be a huge part of cementing this in and helping us to understand what we should do.”
The study was funded by Kroger. Dr. Steen is a consultant for Sanofi and CEO and cofounder of High Enroll.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
People who received personalized nutrition education in a series of sessions at their regular grocery store significantly improved adherence to a healthy diet, in a new “first-of-its-kind” study in which scientific researchers partnered with a large supermarket company.
In the SuperWIN study, participants were given individualized advice from supermarket-based dietitians using data on their own buying habits recorded on their supermarket loyalty cards. This was associated with an increased adherence to the DASH (Dietary Approaches to Stop Hypertension) diet, which emphasizes vegetables, fruits and whole grains while limiting foods that are high in saturated fat, sugar, and sodium and has been shown to lower blood pressure and LDL cholesterol.
One group of patients also received additional education about healthy eating and meal planning through online technologies, and this group showed even better adherence to the DASH diet.
The study was presented at the annual scientific sessions of the American College of Cardiology by Dylan Steen, MD, adjunct associate professor of medicine at the University of Cincinnati.
“The SuperWIN study provides evidence for the benefit of delivering healthy-eating interventions at modern supermarkets and retail-based clinics,” Dr. Steen said. “It demonstrates the efficacy of dietary interventions harnessing the physical environment of the supermarket, the retail-based dietitians working within the store, and the purchasing data captured on the store’s loyalty cards.”
The study was conducted in partnership with Kroger, the largest supermarket chain in the United States, which also operates a large chain of pharmacies and health clinics.
Dr. Steen said the study was addressing one of the biggest public health problems – unhealthy eating – with an innovative approach. “We need to think about how we can extend the reach of modern health care systems into communities and better deliver services right where people are; meet them where they live,” he said at an ACC press conference.
Commenting on the study at the press conference, Eileen Handberg, PhD, professor of medicine at University of Florida, Gainesville, and immediate past chair of the ACC Cardiovascular Care Team Council, said: “I am amazingly excited about this. There is so much potential here. We have never really taken advantage of the current explosion in retail-based health care before.”
Dr. Handberg suggested the study had major implications for the primary prevention of cardiovascular disease. “Little kids go shopping with their parents, so you have the ability here to change behavior from children on up if you can change the dynamic of the choices they make in the grocery store.”
In his presentation, Dr. Steen noted that, despite many longstanding guidelines on healthy eating, about 75% of Americans still have a poor-quality diet. This trial was conducted to see if a new approach could improve that situation. “If we change the environment in which we deliver dietary education, we can make a difference.”
The SuperWIN trial was conducted in 13 Kroger stores in Ohio and Kentucky. The study enrolled 267 people with at least one cardiovascular risk factor from a primary care network who regularly shopped at one of the study stores. All participants also had to be willing to follow the DASH diet, which was taught at each educational session in the trial.
All participants received one “enhanced” medical nutrition therapy that was guided by the individual’s own dietary intake analytics.
They were then randomly assigned to one of three arms. The control group received no further education. The strategy 1 group received six additional teaching sessions in the supermarket aisles over a 3-month period. Each session was guided by updated individualized purchasing data provided to the dietitian and the participant.
The strategy 2 group received the same six additional teaching sessions as strategy 1, but they also had some additional teaching on healthy eating and meal planning from a variety of online shopping tools, and nutrition and health care apps.
“The supermarket analytics were automatically collected so the dietitians could tell what each person liked to eat, how much of each product they were buying and how much they were spending,” Dr. Steen explained.
COVID hit halfway through the trial, and 20 participants were withdrawn for their own safety as they could no longer visit the stores, but the trial continued with the rest of the participants with enhanced safety precautions. The overall analysis cohort was 247 participants.
The average age of the participants was mid-50s, around 70% were female, and most did not have a history of cardiovascular disease.
Eating habits were assessed by three 24-hour dietary recalls assessed at the start of the study and at 3 and 6 months. The DASH score, which is a measure of adherence to the DASH diet, was calculated from this information. The score can range from 0 to 90, with an increased score showing increased adherence.
In one analysis, the researchers compared the DASH scores from the two intervention groups together with the control group, and in a second analysis they compared the scores in the strategy 2 group with those in the strategy 1 group.
Before the pandemic there was “near 100%” attendance for the six visits over the 3-month study period, which Dr. Steen said he thought was “remarkable.” During the pandemic, attendance came down to around 80%.
Results showed that the DASH score increased in all three groups at 3 months, with stepwise increases corresponding to the intensity of the intervention. DASH scores increased by 5.8 points in the control group, by 8.6 points in the strategy 1 group, and by 12.4 points in the strategy 2 group.
DASH scores significantly differed between the two intervention groups and the control group (P = .02). “This shows that purchasing data–guided in-store tours do increase the efficacy of dietary education,” Dr. Steen said.
The difference in scores between the strategy 1 and strategy 2 groups was also significant (P = .01). “This shows online enhancements increase adherence to the DASH diet even further,” Dr. Steen commented
By 6 months, the scores had dropped off a little but were still increased from baseline: by 4.4 points in the control group, 6.6 points in the strategy 1 group, and 8.4 points in the strategy 2 group. “There was again a stepwise increase as the intervention intensified, but there was no longer a significant difference between the interventions and control,” Dr. Steen noted.
Secondary endpoints included blood pressure and body mass index. Systolic blood pressure decreased slightly in all three groups: by 2.8 mm Hg in the control group, 6.6 mm Hg in the strategy 1 group, and 5.7 mm Hg in the strategy 2 group. Body mass index was reduced by 0.2, 0.4 and 0.8, respectively, but the between-group differences were not significant.
Dr. Steen said this is the first study of its kind to date in which scientific researchers collaborated with a large supermarket chain. He explained they also involved a primary care network so that health care utilization information will be available.
“We can the integrate retail-based health care information with traditional health care information. And we can start to look at downstream health care utilization and cost outcomes as well, which will be important as we start to think how to evolve the health care system,” he commented. “The hope is that we can get more scientists working with more retailers to really drive the evidence to shape the evolution of our health care system.”
Challenges ahead
Dr. Handberg pointed out there would be challenges in reaching the underserved population who do not shop at the major supermarkets. “We need to figure out how to get partnerships across the whole spectrum of grocery stores.”
She also noted that 3 months (the duration of the study intervention) was not much time to change the eating habits of a family. “Interventions may have to be a bit more intensive to get the change in blood pressure and weight that we would want to see.”
Dr Handberg hoped the major grocery store companies will see the opportunities in this approach. “Changing behavior is very complicated, and the key will be how to make people stick with the changes. But grocery stores are smart. They have got us going to their pharmacies, so getting us to see a dietitian is not that much of a stretch.”
Moderator of the ACC late-breaker session at which the study was presented, Pamela Morris, MD, from the Medical University of South Carolina, Charleston, who is also ACC annual scientific session chair, asked whether the approach could be sustained.
“I am thinking back to the barber shop study of blood pressure treatment and to my knowledge those PharmDs are no longer in those barbershops, taking blood pressures, counseling patients, and prescribing antihypertensives. So is Kroger maintaining a long-term commitment to providing this education, or how can this be financed over the long term?” she asked.
Dr. Steen replied that he believed sustainability to be one of the key strengths of this model. “Retail-based health care is exploding in the U.S. The number of retail outlets offering a comprehensive list of services is going up all the time. These programs exist regardless of whether this trial was conducted or not.”
But Dr. Steen stressed that having an evidence base will be critically important.
“Validation is an enormous part of this evolution in retail-based health care – not only to figure out what works but also to engage payors and others in the process of supporting these interventions. I think the sustainability is there – it is sort of baked into the model – but research will be a huge part of cementing this in and helping us to understand what we should do.”
The study was funded by Kroger. Dr. Steen is a consultant for Sanofi and CEO and cofounder of High Enroll.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM ACC 2022























