User login
Electroacupuncture promising for depression-related insomnia
In a study of more than 200 adults with depression and comorbid insomnia, change from baseline to week 8 on the Pittsburgh Sleep Quality Index (PSQI) was 3 points greater in the group receiving EA versus a group receiving sham acupuncture (SA) plus standard care, and 5 points greater vs a control group receiving standard care only. The improvements were sustained during a 24-week postintervention follow-up.
The EA group also showed significant improvement in depression, insomnia, self-rated anxiety, and total sleep time – all of which were not found in the SA or control groups.
“Based on the results of our trial, we recommend patients with depression and insomnia seek the treatment of EA as an alternative and complementary therapy for better results,” study investigator Shifen Xu, PhD, Shanghai (China) Municipal Hospital of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Shanghai University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, told this news organization.
The findings were published online in JAMA Network Open.
Bidirectional relationship
“Sleep disturbance is the prominent symptom in patients with depression,” the investigators noted.
Depression and sleep issues have a bidirectional relationship, in that “poor sleep quality contributes to the development of depression, and having depression makes a person more likely to develop sleep issues,” they wrote.
Patients with co-occurring depression and sleep disorders are more difficult to treat and have a greater risk for relapse and recurrence of depression, they added.
Acupuncture may be an “effective drug-free approach to help treat mental illness and sleep disorders,” the researchers noted. A previous study suggested acupuncture may improve sleep efficacy and prolong total sleep in patients with primary insomnia.
“EA is the combination of traditional Chinese acupuncture with electric-impulse stimulation, and it can enhance the therapeutic effect of the acupoints throughout the needle retention time,” Dr. Xu said.
A previous pilot study of EA for depression-related insomnia showed significant improvements in sleep quality after EA treatment, but the sample size was small.
The current researchers, therefore, undertook the present study – with a larger sample size and comparison with SA and standard care. They divided 270 adults (mean age, 50.3 years; 71.9% women) at three tertiary hospitals in Shanghai into three groups, each consisting of 90 participants.
The EA plus standard care group and the SA plus standard care group received 30-minute treatments three times per week for 8 weeks. The control group received standard care only.
All participants had DSM-5–diagnosed depression; baseline PSQI scores greater than 7, with higher scores indicating worse sleep quality and a greater number or sleep disorders; and Hamilton Depression Rating Scales (HDRS-17) scores of 20-35, with higher scores indicating higher depression levels.
Patients with secondary depressive disorders caused by other conditions, medication, or psychotic disorders were excluded, as were patients with a history of alcohol abuse or drug dependence or those who had received acupuncture within the previous year.
Of the patients who completed the 8-week intervention, 83 were in the EA group, 81 in the SA group, and 83 in the control group. Almost all participants (91.5%) completed all outcome measurements by the end of the 24-week follow-up period (also known as week 32).
Calm mind, balanced mood
At the 8-week posttreatment assessment, which was the primary endpoint, the EA group had a mean reduction from baseline of 6.2 points (95% confidence interval, −6.9 to −5.6) in PSQI score.
There was a significant difference in PSQI score between the EA versus the SA group (−3.6 points; 95% CI, −4.4 to −2.8; P < .001) and vs the control group (−5.1 points; 95% CI, −6.0 to −4.2; P < .001).
The efficacy of EA in treating insomnia was sustained during the postintervention follow-up period when the EA group had a significantly greater reduction in PSQI score, compared with the SA group (−4.7; 95% CI, −5.4 to −3.9; P < .001) and the control group (−5.0; 95% CI, −5.8 to −4.1; P < .001).
Patients receiving EA also experienced significant (all P values < .001) improvement from baseline on secondary outcomes, including:
- Scores on the HDRS (−10.7; 95% CI, −11.8 to −9.7)
- Scores on the Insomnia Severity Index, (−7.6; 95% CI,−8.5 to −6.7)
- Scores on the Self-rated Anxiety Scale (−2.9; 95% CI, −4.1 to −1.7)
- Total sleep time, as recorded by sleep actigraphy (29.1 minutes; 95% CI, 21.5-36.7)
In addition, the EA group showed significant improvement in depression scores compared with the SA and control groups at both 8 and 32 weeks (all P values < .001).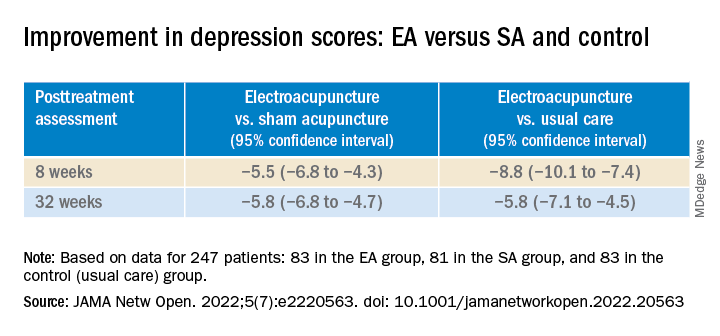
Participants in the EA group also had a 4.2% (95% CI, 2.6% - 5.8%) higher sleep efficiency score at week 8, compared with those in the SA group (P < .001).
In addition, they had lower scores on the Insomnia Severity Index and the Self-rated Anxiety Scale, and longer total sleep time, compared with the control group at week 8.
None of the participants reported any serious adverse events.
“Our findings constitute subjective and objective evidence of the efficacy and safety of EA with standard care in treating comorbid depression and insomnia compared with SA with standard care or standard care alone,” the investigators wrote.
“The acupoints we used in this trial mainly act on calming mind, relieving negative mood, and balancing the yin-yang,” Dr. Xu added.
Viable adjunctive treatment
Commenting on the study, Albert Yeung, MD, ScD, associate director of the Mass General Depression and Clinical Research Program and associate professor of psychiatry, Harvard Medical School, Boston, said that, with the evidence from this study, “acupuncture and/or electroacupuncture could be a viable adjunctive treatment for depressed patients who suffer from insomnia.”
Dr. Yeung, who was not involved with the study, is the coauthor of an accompanying editorial.
“More well-designed studies are warranted to provide evidence for integrating holistic treatment in medicine,” he said.
The study was funded by grants from the National Natural Science Foundation of China, and Shanghai Municipal Health. The investigators and Dr. Yeung reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
In a study of more than 200 adults with depression and comorbid insomnia, change from baseline to week 8 on the Pittsburgh Sleep Quality Index (PSQI) was 3 points greater in the group receiving EA versus a group receiving sham acupuncture (SA) plus standard care, and 5 points greater vs a control group receiving standard care only. The improvements were sustained during a 24-week postintervention follow-up.
The EA group also showed significant improvement in depression, insomnia, self-rated anxiety, and total sleep time – all of which were not found in the SA or control groups.
“Based on the results of our trial, we recommend patients with depression and insomnia seek the treatment of EA as an alternative and complementary therapy for better results,” study investigator Shifen Xu, PhD, Shanghai (China) Municipal Hospital of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Shanghai University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, told this news organization.
The findings were published online in JAMA Network Open.
Bidirectional relationship
“Sleep disturbance is the prominent symptom in patients with depression,” the investigators noted.
Depression and sleep issues have a bidirectional relationship, in that “poor sleep quality contributes to the development of depression, and having depression makes a person more likely to develop sleep issues,” they wrote.
Patients with co-occurring depression and sleep disorders are more difficult to treat and have a greater risk for relapse and recurrence of depression, they added.
Acupuncture may be an “effective drug-free approach to help treat mental illness and sleep disorders,” the researchers noted. A previous study suggested acupuncture may improve sleep efficacy and prolong total sleep in patients with primary insomnia.
“EA is the combination of traditional Chinese acupuncture with electric-impulse stimulation, and it can enhance the therapeutic effect of the acupoints throughout the needle retention time,” Dr. Xu said.
A previous pilot study of EA for depression-related insomnia showed significant improvements in sleep quality after EA treatment, but the sample size was small.
The current researchers, therefore, undertook the present study – with a larger sample size and comparison with SA and standard care. They divided 270 adults (mean age, 50.3 years; 71.9% women) at three tertiary hospitals in Shanghai into three groups, each consisting of 90 participants.
The EA plus standard care group and the SA plus standard care group received 30-minute treatments three times per week for 8 weeks. The control group received standard care only.
All participants had DSM-5–diagnosed depression; baseline PSQI scores greater than 7, with higher scores indicating worse sleep quality and a greater number or sleep disorders; and Hamilton Depression Rating Scales (HDRS-17) scores of 20-35, with higher scores indicating higher depression levels.
Patients with secondary depressive disorders caused by other conditions, medication, or psychotic disorders were excluded, as were patients with a history of alcohol abuse or drug dependence or those who had received acupuncture within the previous year.
Of the patients who completed the 8-week intervention, 83 were in the EA group, 81 in the SA group, and 83 in the control group. Almost all participants (91.5%) completed all outcome measurements by the end of the 24-week follow-up period (also known as week 32).
Calm mind, balanced mood
At the 8-week posttreatment assessment, which was the primary endpoint, the EA group had a mean reduction from baseline of 6.2 points (95% confidence interval, −6.9 to −5.6) in PSQI score.
There was a significant difference in PSQI score between the EA versus the SA group (−3.6 points; 95% CI, −4.4 to −2.8; P < .001) and vs the control group (−5.1 points; 95% CI, −6.0 to −4.2; P < .001).
The efficacy of EA in treating insomnia was sustained during the postintervention follow-up period when the EA group had a significantly greater reduction in PSQI score, compared with the SA group (−4.7; 95% CI, −5.4 to −3.9; P < .001) and the control group (−5.0; 95% CI, −5.8 to −4.1; P < .001).
Patients receiving EA also experienced significant (all P values < .001) improvement from baseline on secondary outcomes, including:
- Scores on the HDRS (−10.7; 95% CI, −11.8 to −9.7)
- Scores on the Insomnia Severity Index, (−7.6; 95% CI,−8.5 to −6.7)
- Scores on the Self-rated Anxiety Scale (−2.9; 95% CI, −4.1 to −1.7)
- Total sleep time, as recorded by sleep actigraphy (29.1 minutes; 95% CI, 21.5-36.7)
In addition, the EA group showed significant improvement in depression scores compared with the SA and control groups at both 8 and 32 weeks (all P values < .001).
Participants in the EA group also had a 4.2% (95% CI, 2.6% - 5.8%) higher sleep efficiency score at week 8, compared with those in the SA group (P < .001).
In addition, they had lower scores on the Insomnia Severity Index and the Self-rated Anxiety Scale, and longer total sleep time, compared with the control group at week 8.
None of the participants reported any serious adverse events.
“Our findings constitute subjective and objective evidence of the efficacy and safety of EA with standard care in treating comorbid depression and insomnia compared with SA with standard care or standard care alone,” the investigators wrote.
“The acupoints we used in this trial mainly act on calming mind, relieving negative mood, and balancing the yin-yang,” Dr. Xu added.
Viable adjunctive treatment
Commenting on the study, Albert Yeung, MD, ScD, associate director of the Mass General Depression and Clinical Research Program and associate professor of psychiatry, Harvard Medical School, Boston, said that, with the evidence from this study, “acupuncture and/or electroacupuncture could be a viable adjunctive treatment for depressed patients who suffer from insomnia.”
Dr. Yeung, who was not involved with the study, is the coauthor of an accompanying editorial.
“More well-designed studies are warranted to provide evidence for integrating holistic treatment in medicine,” he said.
The study was funded by grants from the National Natural Science Foundation of China, and Shanghai Municipal Health. The investigators and Dr. Yeung reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
In a study of more than 200 adults with depression and comorbid insomnia, change from baseline to week 8 on the Pittsburgh Sleep Quality Index (PSQI) was 3 points greater in the group receiving EA versus a group receiving sham acupuncture (SA) plus standard care, and 5 points greater vs a control group receiving standard care only. The improvements were sustained during a 24-week postintervention follow-up.
The EA group also showed significant improvement in depression, insomnia, self-rated anxiety, and total sleep time – all of which were not found in the SA or control groups.
“Based on the results of our trial, we recommend patients with depression and insomnia seek the treatment of EA as an alternative and complementary therapy for better results,” study investigator Shifen Xu, PhD, Shanghai (China) Municipal Hospital of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Shanghai University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, told this news organization.
The findings were published online in JAMA Network Open.
Bidirectional relationship
“Sleep disturbance is the prominent symptom in patients with depression,” the investigators noted.
Depression and sleep issues have a bidirectional relationship, in that “poor sleep quality contributes to the development of depression, and having depression makes a person more likely to develop sleep issues,” they wrote.
Patients with co-occurring depression and sleep disorders are more difficult to treat and have a greater risk for relapse and recurrence of depression, they added.
Acupuncture may be an “effective drug-free approach to help treat mental illness and sleep disorders,” the researchers noted. A previous study suggested acupuncture may improve sleep efficacy and prolong total sleep in patients with primary insomnia.
“EA is the combination of traditional Chinese acupuncture with electric-impulse stimulation, and it can enhance the therapeutic effect of the acupoints throughout the needle retention time,” Dr. Xu said.
A previous pilot study of EA for depression-related insomnia showed significant improvements in sleep quality after EA treatment, but the sample size was small.
The current researchers, therefore, undertook the present study – with a larger sample size and comparison with SA and standard care. They divided 270 adults (mean age, 50.3 years; 71.9% women) at three tertiary hospitals in Shanghai into three groups, each consisting of 90 participants.
The EA plus standard care group and the SA plus standard care group received 30-minute treatments three times per week for 8 weeks. The control group received standard care only.
All participants had DSM-5–diagnosed depression; baseline PSQI scores greater than 7, with higher scores indicating worse sleep quality and a greater number or sleep disorders; and Hamilton Depression Rating Scales (HDRS-17) scores of 20-35, with higher scores indicating higher depression levels.
Patients with secondary depressive disorders caused by other conditions, medication, or psychotic disorders were excluded, as were patients with a history of alcohol abuse or drug dependence or those who had received acupuncture within the previous year.
Of the patients who completed the 8-week intervention, 83 were in the EA group, 81 in the SA group, and 83 in the control group. Almost all participants (91.5%) completed all outcome measurements by the end of the 24-week follow-up period (also known as week 32).
Calm mind, balanced mood
At the 8-week posttreatment assessment, which was the primary endpoint, the EA group had a mean reduction from baseline of 6.2 points (95% confidence interval, −6.9 to −5.6) in PSQI score.
There was a significant difference in PSQI score between the EA versus the SA group (−3.6 points; 95% CI, −4.4 to −2.8; P < .001) and vs the control group (−5.1 points; 95% CI, −6.0 to −4.2; P < .001).
The efficacy of EA in treating insomnia was sustained during the postintervention follow-up period when the EA group had a significantly greater reduction in PSQI score, compared with the SA group (−4.7; 95% CI, −5.4 to −3.9; P < .001) and the control group (−5.0; 95% CI, −5.8 to −4.1; P < .001).
Patients receiving EA also experienced significant (all P values < .001) improvement from baseline on secondary outcomes, including:
- Scores on the HDRS (−10.7; 95% CI, −11.8 to −9.7)
- Scores on the Insomnia Severity Index, (−7.6; 95% CI,−8.5 to −6.7)
- Scores on the Self-rated Anxiety Scale (−2.9; 95% CI, −4.1 to −1.7)
- Total sleep time, as recorded by sleep actigraphy (29.1 minutes; 95% CI, 21.5-36.7)
In addition, the EA group showed significant improvement in depression scores compared with the SA and control groups at both 8 and 32 weeks (all P values < .001).
Participants in the EA group also had a 4.2% (95% CI, 2.6% - 5.8%) higher sleep efficiency score at week 8, compared with those in the SA group (P < .001).
In addition, they had lower scores on the Insomnia Severity Index and the Self-rated Anxiety Scale, and longer total sleep time, compared with the control group at week 8.
None of the participants reported any serious adverse events.
“Our findings constitute subjective and objective evidence of the efficacy and safety of EA with standard care in treating comorbid depression and insomnia compared with SA with standard care or standard care alone,” the investigators wrote.
“The acupoints we used in this trial mainly act on calming mind, relieving negative mood, and balancing the yin-yang,” Dr. Xu added.
Viable adjunctive treatment
Commenting on the study, Albert Yeung, MD, ScD, associate director of the Mass General Depression and Clinical Research Program and associate professor of psychiatry, Harvard Medical School, Boston, said that, with the evidence from this study, “acupuncture and/or electroacupuncture could be a viable adjunctive treatment for depressed patients who suffer from insomnia.”
Dr. Yeung, who was not involved with the study, is the coauthor of an accompanying editorial.
“More well-designed studies are warranted to provide evidence for integrating holistic treatment in medicine,” he said.
The study was funded by grants from the National Natural Science Foundation of China, and Shanghai Municipal Health. The investigators and Dr. Yeung reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM JAMA NETWORK OPEN
Red Flag: Suicide risk
How AI is helping prevent suicide in veterans

Medically reviewed by Jennifer Casarella, MD
Dan Miller has parked his Nissan Altima on the side of the road near a field outside Chicago and is holding a gun to his head.
Haunted for years by the compounded trauma of tours of duty in the Middle East and his work as a police officer in Chicago, at that moment, Dr. Miller saw no reason to live. And there were troubles at home with his wife and children, who had grown fearful of his behavior.
“My whole world was falling apart,” he says of that dark night in 2014. “It left a hole I didn’t know how to fill.”
He chose not to pull the trigger after a brochure on the passenger seat of his car gave him an unexpected perspective – and launched him on a path to help others in his situation.
Had Mr. Miller taken his life that night, he would have joined thousands of other veterans who died by suicide. About 17 U.S. veterans lose their lives this way each day, on average, according to the Department of Veterans Affairs. In 2019, the last year for which records are available, 6,261 veterans took their own lives – and the suicide rate for veterans was 52% higher than for nonveterans, the agency’s records show.
The problem has become so severe that
But that wasn’t available when Dan Miller’s life was unraveling.
In the years leading up to his near-suicide, his wife had pushed him to get help. “She said, ‘You’re not the same person you were when you left. The kids are scared of you. The pets are scared of you,” he recalls.
He resisted, even when his wife threatened divorce. Rising through the ranks of the Marines, Mr. Miller had become more emotionally isolated. He feared losing his job and the respect of others if he let anyone know what he was going through.
Finally, he gave the VHA a chance. He went in for an initial consultation in 2010 and didn’t find it helpful. He didn’t like being told what to do. So he stopped. He turned to obsessive exercise and excessive drinking.
That day in 2014, Mr. Miller’s wife told him she was taking the kids out for a playdate. After she left, he was served with divorce papers. Less than an hour later, he was parked in his car with his gun, ready to end his life.
But if it all had happened just a few years later, things might never have gotten to that point.
Scanning for suicide risk
In 2017, the VHA piloted its AI program, called REACH VET, that aims to help prevent veterans from dying by suicide.
Every month, a computer scans the electronic health records of all VHA patients who’ve had a health care visit for any reason in the last 2 years. It checks more than 140 variables and weights them to estimate someone’s overall suicide risk at that moment in time.
To build the risk algorithm, a computer combed through the medical records of 6,360 veterans confirmed to have died by suicide between 2009 and 2011. (The VHA continually updates the list of variables from the health records of VHA patients, including those who have died by suicide since then and others.)
Some variables are things you’d expect:
- A past suicide attempt.
- A diagnosis of depression or other mental illness.
- A diagnosis of a terminal illness.
Others are more surprising. For example, a diagnosis of arthritis or diabetes adds weight.
REACH VET flags the riskiest cases – the top 0.1% – for a mental health or primary care provider to review. They reach out to the patient to tell them how and why their record was flagged, discuss any recommended treatment changes, and ask them to come in for a visit.
“It’s an opportunity to talk about their risk factors, which is designed to lead to a conversation about safety planning,” says clinical psychologist Matthew Miller, PhD, national director of the U.S. Department of Veterans Affairs’ Suicide Prevention Program. He’s not related to Dan Miller.
Making a suicide safety plan
A safety plan is a document that outlines how a person can help prevent their own suicide in a crisis.
The plan may include:
- A list of personal triggers or warning signs.
- What’s helped them in the past.
- Names of people or organizations who can support them.
- Plans to remove means of suicide, such as guns, from their environment.
- Their reasons for living.
In people at risk for suicide, research shows that having a safety plan reduces suicidal thoughts and attempts, lowers rates of depression and hopelessness, and boosts veterans’ engagement with the health care system. It may also help people manage things that trigger their suicidal thoughts.
Getting the call
What if REACH VET had been around when Dan Miller was in crisis – and he’d gotten a call from the VHA?
“It absolutely, positively would have helped because one of the biggest things on that day when I got served was feeling completely alone and that I had no one to turn to,” Mr. Miller says. He’s now a speaker for the Wounded Warrior Project, a nonprofit that serves veterans and active-duty service people.
Vets’ reactions to the unexpected VHA phone call, psychologist Dr. Miller says, “run the gamut from ‘Thank you for contacting me. Let’s talk,’ to ‘What are you talking about? Leave me alone!’ ”
Nothing stops all suicides. But REACH VET is having an impact. In a clinical trial, vets contacted through REACH VET had more doctor visits, were more likely to have a written suicide prevention safety plan, and had fewer hospital admissions for mental health, ER visits, and suicide attempts.
An assist from AI
Even simple outreach can make a big difference. And there’s research to prove it.
One study included 4,730 veterans recently discharged from psychiatric care at the VHA, a group considered at high risk for suicide.
Half of them got 13 caring emails from hospital staff in the weeks after leaving the hospital. The emails mentioned personal things the patient had shared, like a love of hiking, and wished them well. The other veterans got routine follow-up but no emails.
Two years later, those who got the caring emails were less likely to have died by suicide than the other vets. The study was published in 2014 in Contemporary Clinical Trials.
Researchers have done studies like this many times: with handwritten notes from the primary care doctor, postcards from the ER, and so forth. The results never vary: The notes reduce suicide risk.
“If we could use AI to identify people to receive notes or phone calls, it would be a very effective and inexpensive way to guide follow-up care,” says Rebecca Bernert, PhD, director and founder of the Suicide Prevention Research Laboratory at Stanford (Calif.) University.
AI doesn’t replace clinical judgment.
“AI can capture data that we miss due to the limits of our humanity,” psychologist Dr. Miller says. “There’s suicide prevention processes founded on big data and AI, and there are processes founded in clinical intuition and acumen.”
AI is only as good as the data it’s based on. If that data lacks diversity, it may miss things. And variables that apply to veterans may differ in civilians.
Stopping suicidal thoughts
Google is putting AI to work against suicide, too. Its MUM (Multitask Unified Model) technology seeks to understand the intent behind what we google.
MUM powers Google Search. It can often tell the difference between a search for information about suicide for someone writing a research paper on the topic and a search for information on how or where to carry out a suicide.
When Google Search detects that someone in the United States might be in crisis and at risk of suicide, the first search results that person gets are the number for the National Suicide Prevention Lifeline and other resources for people in crisis.
Google Home Assistant works in the same way. When a user makes a query that signals a suicide-related crisis, the gadget serves up resources that offer help.
MUM is working to understand the nuances of crisis language in 75 languages so that Google Search can provide people in crisis with hotlines or other resources in many countries.
“We want to find partners that are accessible to users in terms of hours of operation. We have a strong preference for finding partners that promise confidentiality and privacy to the extent that those are permitted [in that country],” says Anne Merritt, MD, a product manager at Google Search.
Other companies are working on apps that use AI to spot suicide risk in other ways, including voice technology that may notice subtle changes in the voice of someone who’s depressed and may be thinking of suicide. Those are still in development but show promise. Keep in mind that apps do not require government approval, so if you try one, be sure to let your health care provider know.
Changing the channel
Seeing a hotline number on your phone or computer screen can help, Dan Miller says. “If I happened to be online, searching maybe for a bridge to jump off of ... and suddenly that pops up on the screen, it’s like it changes the channel.”
It may not work for everyone, he says, but that search result could interrupt someone’s suicidal train of thought.
That’s crucial, psychologist Dr. Miller says, because most suicide attempts escalate from first thought to potentially fatal action in just 1 hour. That’s how fast it happened for Dan Miller in 2014.
“When you’re able to put time and space between the suicidal thought and the access to the method to act on that thought, you save lives,” Dr. Bernert says.
Making a different choice
An interruption in Mr. Miller’s thinking is what had saved his life.
Holding the gun to his head, Mr. Miller looked over at the passenger seat at a brochure from Wounded Warrior Project, which he had just learned about. Mr. Miller noticed a photo of a man in a wheelchair, a veteran like him, who had no legs. He thought that the man looked worse off than him but hadn’t given up.
Mr. Miller put down his gun and decided to get help.
Recovering from a near suicide attempt, he says, is a journey. It doesn’t happen overnight. Now, 8 years later, Mr. Miller is planning a brief break from the speaker circuit. He plans to spend 2 weeks in an outpatient counseling program for posttraumatic stress disorder and traumatic brain injury.
“Telling my story to strangers – part of it is healing me in a way, but I’m learning that repeating the story over and over again is also keeping me from letting it go. And I’m still healing.”
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
How AI is helping prevent suicide in veterans
How AI is helping prevent suicide in veterans

Medically reviewed by Jennifer Casarella, MD
Dan Miller has parked his Nissan Altima on the side of the road near a field outside Chicago and is holding a gun to his head.
Haunted for years by the compounded trauma of tours of duty in the Middle East and his work as a police officer in Chicago, at that moment, Dr. Miller saw no reason to live. And there were troubles at home with his wife and children, who had grown fearful of his behavior.
“My whole world was falling apart,” he says of that dark night in 2014. “It left a hole I didn’t know how to fill.”
He chose not to pull the trigger after a brochure on the passenger seat of his car gave him an unexpected perspective – and launched him on a path to help others in his situation.
Had Mr. Miller taken his life that night, he would have joined thousands of other veterans who died by suicide. About 17 U.S. veterans lose their lives this way each day, on average, according to the Department of Veterans Affairs. In 2019, the last year for which records are available, 6,261 veterans took their own lives – and the suicide rate for veterans was 52% higher than for nonveterans, the agency’s records show.
The problem has become so severe that
But that wasn’t available when Dan Miller’s life was unraveling.
In the years leading up to his near-suicide, his wife had pushed him to get help. “She said, ‘You’re not the same person you were when you left. The kids are scared of you. The pets are scared of you,” he recalls.
He resisted, even when his wife threatened divorce. Rising through the ranks of the Marines, Mr. Miller had become more emotionally isolated. He feared losing his job and the respect of others if he let anyone know what he was going through.
Finally, he gave the VHA a chance. He went in for an initial consultation in 2010 and didn’t find it helpful. He didn’t like being told what to do. So he stopped. He turned to obsessive exercise and excessive drinking.
That day in 2014, Mr. Miller’s wife told him she was taking the kids out for a playdate. After she left, he was served with divorce papers. Less than an hour later, he was parked in his car with his gun, ready to end his life.
But if it all had happened just a few years later, things might never have gotten to that point.
Scanning for suicide risk
In 2017, the VHA piloted its AI program, called REACH VET, that aims to help prevent veterans from dying by suicide.
Every month, a computer scans the electronic health records of all VHA patients who’ve had a health care visit for any reason in the last 2 years. It checks more than 140 variables and weights them to estimate someone’s overall suicide risk at that moment in time.
To build the risk algorithm, a computer combed through the medical records of 6,360 veterans confirmed to have died by suicide between 2009 and 2011. (The VHA continually updates the list of variables from the health records of VHA patients, including those who have died by suicide since then and others.)
Some variables are things you’d expect:
- A past suicide attempt.
- A diagnosis of depression or other mental illness.
- A diagnosis of a terminal illness.
Others are more surprising. For example, a diagnosis of arthritis or diabetes adds weight.
REACH VET flags the riskiest cases – the top 0.1% – for a mental health or primary care provider to review. They reach out to the patient to tell them how and why their record was flagged, discuss any recommended treatment changes, and ask them to come in for a visit.
“It’s an opportunity to talk about their risk factors, which is designed to lead to a conversation about safety planning,” says clinical psychologist Matthew Miller, PhD, national director of the U.S. Department of Veterans Affairs’ Suicide Prevention Program. He’s not related to Dan Miller.
Making a suicide safety plan
A safety plan is a document that outlines how a person can help prevent their own suicide in a crisis.
The plan may include:
- A list of personal triggers or warning signs.
- What’s helped them in the past.
- Names of people or organizations who can support them.
- Plans to remove means of suicide, such as guns, from their environment.
- Their reasons for living.
In people at risk for suicide, research shows that having a safety plan reduces suicidal thoughts and attempts, lowers rates of depression and hopelessness, and boosts veterans’ engagement with the health care system. It may also help people manage things that trigger their suicidal thoughts.
Getting the call
What if REACH VET had been around when Dan Miller was in crisis – and he’d gotten a call from the VHA?
“It absolutely, positively would have helped because one of the biggest things on that day when I got served was feeling completely alone and that I had no one to turn to,” Mr. Miller says. He’s now a speaker for the Wounded Warrior Project, a nonprofit that serves veterans and active-duty service people.
Vets’ reactions to the unexpected VHA phone call, psychologist Dr. Miller says, “run the gamut from ‘Thank you for contacting me. Let’s talk,’ to ‘What are you talking about? Leave me alone!’ ”
Nothing stops all suicides. But REACH VET is having an impact. In a clinical trial, vets contacted through REACH VET had more doctor visits, were more likely to have a written suicide prevention safety plan, and had fewer hospital admissions for mental health, ER visits, and suicide attempts.
An assist from AI
Even simple outreach can make a big difference. And there’s research to prove it.
One study included 4,730 veterans recently discharged from psychiatric care at the VHA, a group considered at high risk for suicide.
Half of them got 13 caring emails from hospital staff in the weeks after leaving the hospital. The emails mentioned personal things the patient had shared, like a love of hiking, and wished them well. The other veterans got routine follow-up but no emails.
Two years later, those who got the caring emails were less likely to have died by suicide than the other vets. The study was published in 2014 in Contemporary Clinical Trials.
Researchers have done studies like this many times: with handwritten notes from the primary care doctor, postcards from the ER, and so forth. The results never vary: The notes reduce suicide risk.
“If we could use AI to identify people to receive notes or phone calls, it would be a very effective and inexpensive way to guide follow-up care,” says Rebecca Bernert, PhD, director and founder of the Suicide Prevention Research Laboratory at Stanford (Calif.) University.
AI doesn’t replace clinical judgment.
“AI can capture data that we miss due to the limits of our humanity,” psychologist Dr. Miller says. “There’s suicide prevention processes founded on big data and AI, and there are processes founded in clinical intuition and acumen.”
AI is only as good as the data it’s based on. If that data lacks diversity, it may miss things. And variables that apply to veterans may differ in civilians.
Stopping suicidal thoughts
Google is putting AI to work against suicide, too. Its MUM (Multitask Unified Model) technology seeks to understand the intent behind what we google.
MUM powers Google Search. It can often tell the difference between a search for information about suicide for someone writing a research paper on the topic and a search for information on how or where to carry out a suicide.
When Google Search detects that someone in the United States might be in crisis and at risk of suicide, the first search results that person gets are the number for the National Suicide Prevention Lifeline and other resources for people in crisis.
Google Home Assistant works in the same way. When a user makes a query that signals a suicide-related crisis, the gadget serves up resources that offer help.
MUM is working to understand the nuances of crisis language in 75 languages so that Google Search can provide people in crisis with hotlines or other resources in many countries.
“We want to find partners that are accessible to users in terms of hours of operation. We have a strong preference for finding partners that promise confidentiality and privacy to the extent that those are permitted [in that country],” says Anne Merritt, MD, a product manager at Google Search.
Other companies are working on apps that use AI to spot suicide risk in other ways, including voice technology that may notice subtle changes in the voice of someone who’s depressed and may be thinking of suicide. Those are still in development but show promise. Keep in mind that apps do not require government approval, so if you try one, be sure to let your health care provider know.
Changing the channel
Seeing a hotline number on your phone or computer screen can help, Dan Miller says. “If I happened to be online, searching maybe for a bridge to jump off of ... and suddenly that pops up on the screen, it’s like it changes the channel.”
It may not work for everyone, he says, but that search result could interrupt someone’s suicidal train of thought.
That’s crucial, psychologist Dr. Miller says, because most suicide attempts escalate from first thought to potentially fatal action in just 1 hour. That’s how fast it happened for Dan Miller in 2014.
“When you’re able to put time and space between the suicidal thought and the access to the method to act on that thought, you save lives,” Dr. Bernert says.
Making a different choice
An interruption in Mr. Miller’s thinking is what had saved his life.
Holding the gun to his head, Mr. Miller looked over at the passenger seat at a brochure from Wounded Warrior Project, which he had just learned about. Mr. Miller noticed a photo of a man in a wheelchair, a veteran like him, who had no legs. He thought that the man looked worse off than him but hadn’t given up.
Mr. Miller put down his gun and decided to get help.
Recovering from a near suicide attempt, he says, is a journey. It doesn’t happen overnight. Now, 8 years later, Mr. Miller is planning a brief break from the speaker circuit. He plans to spend 2 weeks in an outpatient counseling program for posttraumatic stress disorder and traumatic brain injury.
“Telling my story to strangers – part of it is healing me in a way, but I’m learning that repeating the story over and over again is also keeping me from letting it go. And I’m still healing.”
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.

Medically reviewed by Jennifer Casarella, MD
Dan Miller has parked his Nissan Altima on the side of the road near a field outside Chicago and is holding a gun to his head.
Haunted for years by the compounded trauma of tours of duty in the Middle East and his work as a police officer in Chicago, at that moment, Dr. Miller saw no reason to live. And there were troubles at home with his wife and children, who had grown fearful of his behavior.
“My whole world was falling apart,” he says of that dark night in 2014. “It left a hole I didn’t know how to fill.”
He chose not to pull the trigger after a brochure on the passenger seat of his car gave him an unexpected perspective – and launched him on a path to help others in his situation.
Had Mr. Miller taken his life that night, he would have joined thousands of other veterans who died by suicide. About 17 U.S. veterans lose their lives this way each day, on average, according to the Department of Veterans Affairs. In 2019, the last year for which records are available, 6,261 veterans took their own lives – and the suicide rate for veterans was 52% higher than for nonveterans, the agency’s records show.
The problem has become so severe that
But that wasn’t available when Dan Miller’s life was unraveling.
In the years leading up to his near-suicide, his wife had pushed him to get help. “She said, ‘You’re not the same person you were when you left. The kids are scared of you. The pets are scared of you,” he recalls.
He resisted, even when his wife threatened divorce. Rising through the ranks of the Marines, Mr. Miller had become more emotionally isolated. He feared losing his job and the respect of others if he let anyone know what he was going through.
Finally, he gave the VHA a chance. He went in for an initial consultation in 2010 and didn’t find it helpful. He didn’t like being told what to do. So he stopped. He turned to obsessive exercise and excessive drinking.
That day in 2014, Mr. Miller’s wife told him she was taking the kids out for a playdate. After she left, he was served with divorce papers. Less than an hour later, he was parked in his car with his gun, ready to end his life.
But if it all had happened just a few years later, things might never have gotten to that point.
Scanning for suicide risk
In 2017, the VHA piloted its AI program, called REACH VET, that aims to help prevent veterans from dying by suicide.
Every month, a computer scans the electronic health records of all VHA patients who’ve had a health care visit for any reason in the last 2 years. It checks more than 140 variables and weights them to estimate someone’s overall suicide risk at that moment in time.
To build the risk algorithm, a computer combed through the medical records of 6,360 veterans confirmed to have died by suicide between 2009 and 2011. (The VHA continually updates the list of variables from the health records of VHA patients, including those who have died by suicide since then and others.)
Some variables are things you’d expect:
- A past suicide attempt.
- A diagnosis of depression or other mental illness.
- A diagnosis of a terminal illness.
Others are more surprising. For example, a diagnosis of arthritis or diabetes adds weight.
REACH VET flags the riskiest cases – the top 0.1% – for a mental health or primary care provider to review. They reach out to the patient to tell them how and why their record was flagged, discuss any recommended treatment changes, and ask them to come in for a visit.
“It’s an opportunity to talk about their risk factors, which is designed to lead to a conversation about safety planning,” says clinical psychologist Matthew Miller, PhD, national director of the U.S. Department of Veterans Affairs’ Suicide Prevention Program. He’s not related to Dan Miller.
Making a suicide safety plan
A safety plan is a document that outlines how a person can help prevent their own suicide in a crisis.
The plan may include:
- A list of personal triggers or warning signs.
- What’s helped them in the past.
- Names of people or organizations who can support them.
- Plans to remove means of suicide, such as guns, from their environment.
- Their reasons for living.
In people at risk for suicide, research shows that having a safety plan reduces suicidal thoughts and attempts, lowers rates of depression and hopelessness, and boosts veterans’ engagement with the health care system. It may also help people manage things that trigger their suicidal thoughts.
Getting the call
What if REACH VET had been around when Dan Miller was in crisis – and he’d gotten a call from the VHA?
“It absolutely, positively would have helped because one of the biggest things on that day when I got served was feeling completely alone and that I had no one to turn to,” Mr. Miller says. He’s now a speaker for the Wounded Warrior Project, a nonprofit that serves veterans and active-duty service people.
Vets’ reactions to the unexpected VHA phone call, psychologist Dr. Miller says, “run the gamut from ‘Thank you for contacting me. Let’s talk,’ to ‘What are you talking about? Leave me alone!’ ”
Nothing stops all suicides. But REACH VET is having an impact. In a clinical trial, vets contacted through REACH VET had more doctor visits, were more likely to have a written suicide prevention safety plan, and had fewer hospital admissions for mental health, ER visits, and suicide attempts.
An assist from AI
Even simple outreach can make a big difference. And there’s research to prove it.
One study included 4,730 veterans recently discharged from psychiatric care at the VHA, a group considered at high risk for suicide.
Half of them got 13 caring emails from hospital staff in the weeks after leaving the hospital. The emails mentioned personal things the patient had shared, like a love of hiking, and wished them well. The other veterans got routine follow-up but no emails.
Two years later, those who got the caring emails were less likely to have died by suicide than the other vets. The study was published in 2014 in Contemporary Clinical Trials.
Researchers have done studies like this many times: with handwritten notes from the primary care doctor, postcards from the ER, and so forth. The results never vary: The notes reduce suicide risk.
“If we could use AI to identify people to receive notes or phone calls, it would be a very effective and inexpensive way to guide follow-up care,” says Rebecca Bernert, PhD, director and founder of the Suicide Prevention Research Laboratory at Stanford (Calif.) University.
AI doesn’t replace clinical judgment.
“AI can capture data that we miss due to the limits of our humanity,” psychologist Dr. Miller says. “There’s suicide prevention processes founded on big data and AI, and there are processes founded in clinical intuition and acumen.”
AI is only as good as the data it’s based on. If that data lacks diversity, it may miss things. And variables that apply to veterans may differ in civilians.
Stopping suicidal thoughts
Google is putting AI to work against suicide, too. Its MUM (Multitask Unified Model) technology seeks to understand the intent behind what we google.
MUM powers Google Search. It can often tell the difference between a search for information about suicide for someone writing a research paper on the topic and a search for information on how or where to carry out a suicide.
When Google Search detects that someone in the United States might be in crisis and at risk of suicide, the first search results that person gets are the number for the National Suicide Prevention Lifeline and other resources for people in crisis.
Google Home Assistant works in the same way. When a user makes a query that signals a suicide-related crisis, the gadget serves up resources that offer help.
MUM is working to understand the nuances of crisis language in 75 languages so that Google Search can provide people in crisis with hotlines or other resources in many countries.
“We want to find partners that are accessible to users in terms of hours of operation. We have a strong preference for finding partners that promise confidentiality and privacy to the extent that those are permitted [in that country],” says Anne Merritt, MD, a product manager at Google Search.
Other companies are working on apps that use AI to spot suicide risk in other ways, including voice technology that may notice subtle changes in the voice of someone who’s depressed and may be thinking of suicide. Those are still in development but show promise. Keep in mind that apps do not require government approval, so if you try one, be sure to let your health care provider know.
Changing the channel
Seeing a hotline number on your phone or computer screen can help, Dan Miller says. “If I happened to be online, searching maybe for a bridge to jump off of ... and suddenly that pops up on the screen, it’s like it changes the channel.”
It may not work for everyone, he says, but that search result could interrupt someone’s suicidal train of thought.
That’s crucial, psychologist Dr. Miller says, because most suicide attempts escalate from first thought to potentially fatal action in just 1 hour. That’s how fast it happened for Dan Miller in 2014.
“When you’re able to put time and space between the suicidal thought and the access to the method to act on that thought, you save lives,” Dr. Bernert says.
Making a different choice
An interruption in Mr. Miller’s thinking is what had saved his life.
Holding the gun to his head, Mr. Miller looked over at the passenger seat at a brochure from Wounded Warrior Project, which he had just learned about. Mr. Miller noticed a photo of a man in a wheelchair, a veteran like him, who had no legs. He thought that the man looked worse off than him but hadn’t given up.
Mr. Miller put down his gun and decided to get help.
Recovering from a near suicide attempt, he says, is a journey. It doesn’t happen overnight. Now, 8 years later, Mr. Miller is planning a brief break from the speaker circuit. He plans to spend 2 weeks in an outpatient counseling program for posttraumatic stress disorder and traumatic brain injury.
“Telling my story to strangers – part of it is healing me in a way, but I’m learning that repeating the story over and over again is also keeping me from letting it go. And I’m still healing.”
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
Antidepressants may curb opioid overdose
Investigators analyzed insurance claims for more than 200,000 adults with a history of depression. Of these, 8,200 experienced adverse events (AEs) during the year after initiation of opioid therapy.
However, the risk for an AE such as overdose and other forms of self-harm was reduced among patients who had been treated with antidepressants for at least 6 weeks.
The take-home message is that clinicians and health systems need to be more aware that individuals in pain are more likely to be depressed and at higher risk for AEs – so the depression should be treated “more liberally,” corresponding author Bradley Stein, MD, PhD, a practicing psychiatrist in Pittsburgh and director of the Rand Corporation Opioid Policy Center, told this news organization.
“If you are treating someone with pain, particularly chronic pain, it’s critically important to better assess their depression and not to attribute depressive symptoms only to pain,” Dr. Stein said.
The findings were published online in Psychiatric Services.
Promising approach?
Opioid treatment for pain “complicates the interactions among pain, depression, and self-harm,” the investigators write. Individuals with depression receiving long-term opioid therapy are two to three times more likely to misuse opioids, compared with individuals who do not have depression.
Although comorbid depression “substantially increases overdose and suicide risk, it remains underdiagnosed and undertreated among individuals with chronic pain,” the researchers note. They add that increasing access to depression treatment may be a “potentially promising approach to preventing overdoses and suicide” in these patients.
“We know that individuals using opioids who have a history of depression are more likely to have negative outcomes, such as overdoses and self-harm events,” Dr. Stein said. “We wanted to see whether antidepressants, which would treat depression in these individuals, would help with that.”
The researchers assessed a database of commercial insurance claims of adults with a history of depression who received opioids between 2007 and 2017 (n = 283,374). The data included 336,599 opioid treatment episodes.
To be included in the study, patients had to have been diagnosed with depression before they filled their first opioid prescription.
The “outcome of interest” was time from the beginning of an opioid episode until an adverse event, such as opioid poisoning, overdose of nonopioid controlled or illicit substances, or self-harm unrelated to overdose.
Participants were followed from the onset of the opioid episode until an AE occurred, loss to follow-up, or week 52, whichever came first.
The “key independent variable” was filling an antidepressant prescription. The patient’s sex and age were considered to be independent variables as well.
Teasing out antidepressant effect
Of participants with a history of depression treatment, 8,203 experienced at least one AE during the 12 months after treatment initiation (n = 47,486 AEs). Approximately half (50.8%) filled an antidepressant prescription at least once during the 12 months after the opioid episode began.
AEs were more likely among men than among women. The highest risk was in patients aged 18-24 years.
After adjusting for age and sex, participants who had received antidepressants had a greater risk for all adverse outcomes during the first 6 weeks of antidepressant treatment. However, those who had received antidepressants for 6 weeks or longer were at reduced risk for all adverse outcomes.

“We took advantage of the fact that, for most people, antidepressants take a while to work and aren’t immediately effective, so we were able to use that difference in our research,” Dr. Stein said.
“We wouldn’t expect to see an immediate effect of antidepressants, so the difference between what we saw immediately after the person had started treatment and the time it took for the antidepressant to be effective enabled us to tease out the effect of the antidepressant,” he added.
Consider CBT?
Andrew Saxon, MD, professor, department of psychiatry and behavioral sciences, University of Washington School of Medicine, Seattle, said clinicians “tend to think categorically and give people diagnoses that are clear-cut.” But neurobiologically, “it may be hard to distinguish where chronic pain ends and depression begins, or whether there’s some commonality.”
For patients with chronic pain and those taking opioids, “we need to be very attuned to the possibility or likelihood that they have major depression and other psychiatric diagnoses, like PTSD and anxiety disorders, which are very common,” said Dr. Saxon, who is also the director of the Center of Excellence in Substance Abuse Treatment and Education at the VA Puget Sound Health Care System. He was not involved with the current research.
He noted that treating those disorders “is a very important component of managing chronic pain.” However, “patients just starting antidepressants need to be carefully monitored when they’re getting stabilized on their antidepressants because they can have side effects, particularly early on, that can destabilize them.”
Dr. Saxon added that beyond pharmacotherapy, cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) for pain might be an even better intervention for addressing both pain and depression.
Also commenting for this article, Brian Hurley, MD, an addiction medicine specialist and the medical director of the Division of Substance Abuse Prevention and Control for the Los Angeles County Department of Public Health, said: “In the context of the largest wave of overdose mortality in U.S. history, we know comparatively little about the impact of mental health interventions that mitigate overdose risks.”
This study “contributes important new information that treating depression with antidepressant medications reduces overdose and self-harm risks for people who are prescribed opioids,” said Dr. Hurley, who is also the president-elect of the American Society of Addiction Medicine.
It also “underscores the general importance of integrated mental health and substance use disorder treatment in both primary care and in mental health settings,” added Dr. Hurley, who was not involved with the study.
The study was funded by the National Institute on Drug Abuse. The investigators and commenters reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Investigators analyzed insurance claims for more than 200,000 adults with a history of depression. Of these, 8,200 experienced adverse events (AEs) during the year after initiation of opioid therapy.
However, the risk for an AE such as overdose and other forms of self-harm was reduced among patients who had been treated with antidepressants for at least 6 weeks.
The take-home message is that clinicians and health systems need to be more aware that individuals in pain are more likely to be depressed and at higher risk for AEs – so the depression should be treated “more liberally,” corresponding author Bradley Stein, MD, PhD, a practicing psychiatrist in Pittsburgh and director of the Rand Corporation Opioid Policy Center, told this news organization.
“If you are treating someone with pain, particularly chronic pain, it’s critically important to better assess their depression and not to attribute depressive symptoms only to pain,” Dr. Stein said.
The findings were published online in Psychiatric Services.
Promising approach?
Opioid treatment for pain “complicates the interactions among pain, depression, and self-harm,” the investigators write. Individuals with depression receiving long-term opioid therapy are two to three times more likely to misuse opioids, compared with individuals who do not have depression.
Although comorbid depression “substantially increases overdose and suicide risk, it remains underdiagnosed and undertreated among individuals with chronic pain,” the researchers note. They add that increasing access to depression treatment may be a “potentially promising approach to preventing overdoses and suicide” in these patients.
“We know that individuals using opioids who have a history of depression are more likely to have negative outcomes, such as overdoses and self-harm events,” Dr. Stein said. “We wanted to see whether antidepressants, which would treat depression in these individuals, would help with that.”
The researchers assessed a database of commercial insurance claims of adults with a history of depression who received opioids between 2007 and 2017 (n = 283,374). The data included 336,599 opioid treatment episodes.
To be included in the study, patients had to have been diagnosed with depression before they filled their first opioid prescription.
The “outcome of interest” was time from the beginning of an opioid episode until an adverse event, such as opioid poisoning, overdose of nonopioid controlled or illicit substances, or self-harm unrelated to overdose.
Participants were followed from the onset of the opioid episode until an AE occurred, loss to follow-up, or week 52, whichever came first.
The “key independent variable” was filling an antidepressant prescription. The patient’s sex and age were considered to be independent variables as well.
Teasing out antidepressant effect
Of participants with a history of depression treatment, 8,203 experienced at least one AE during the 12 months after treatment initiation (n = 47,486 AEs). Approximately half (50.8%) filled an antidepressant prescription at least once during the 12 months after the opioid episode began.
AEs were more likely among men than among women. The highest risk was in patients aged 18-24 years.
After adjusting for age and sex, participants who had received antidepressants had a greater risk for all adverse outcomes during the first 6 weeks of antidepressant treatment. However, those who had received antidepressants for 6 weeks or longer were at reduced risk for all adverse outcomes.

“We took advantage of the fact that, for most people, antidepressants take a while to work and aren’t immediately effective, so we were able to use that difference in our research,” Dr. Stein said.
“We wouldn’t expect to see an immediate effect of antidepressants, so the difference between what we saw immediately after the person had started treatment and the time it took for the antidepressant to be effective enabled us to tease out the effect of the antidepressant,” he added.
Consider CBT?
Andrew Saxon, MD, professor, department of psychiatry and behavioral sciences, University of Washington School of Medicine, Seattle, said clinicians “tend to think categorically and give people diagnoses that are clear-cut.” But neurobiologically, “it may be hard to distinguish where chronic pain ends and depression begins, or whether there’s some commonality.”
For patients with chronic pain and those taking opioids, “we need to be very attuned to the possibility or likelihood that they have major depression and other psychiatric diagnoses, like PTSD and anxiety disorders, which are very common,” said Dr. Saxon, who is also the director of the Center of Excellence in Substance Abuse Treatment and Education at the VA Puget Sound Health Care System. He was not involved with the current research.
He noted that treating those disorders “is a very important component of managing chronic pain.” However, “patients just starting antidepressants need to be carefully monitored when they’re getting stabilized on their antidepressants because they can have side effects, particularly early on, that can destabilize them.”
Dr. Saxon added that beyond pharmacotherapy, cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) for pain might be an even better intervention for addressing both pain and depression.
Also commenting for this article, Brian Hurley, MD, an addiction medicine specialist and the medical director of the Division of Substance Abuse Prevention and Control for the Los Angeles County Department of Public Health, said: “In the context of the largest wave of overdose mortality in U.S. history, we know comparatively little about the impact of mental health interventions that mitigate overdose risks.”
This study “contributes important new information that treating depression with antidepressant medications reduces overdose and self-harm risks for people who are prescribed opioids,” said Dr. Hurley, who is also the president-elect of the American Society of Addiction Medicine.
It also “underscores the general importance of integrated mental health and substance use disorder treatment in both primary care and in mental health settings,” added Dr. Hurley, who was not involved with the study.
The study was funded by the National Institute on Drug Abuse. The investigators and commenters reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Investigators analyzed insurance claims for more than 200,000 adults with a history of depression. Of these, 8,200 experienced adverse events (AEs) during the year after initiation of opioid therapy.
However, the risk for an AE such as overdose and other forms of self-harm was reduced among patients who had been treated with antidepressants for at least 6 weeks.
The take-home message is that clinicians and health systems need to be more aware that individuals in pain are more likely to be depressed and at higher risk for AEs – so the depression should be treated “more liberally,” corresponding author Bradley Stein, MD, PhD, a practicing psychiatrist in Pittsburgh and director of the Rand Corporation Opioid Policy Center, told this news organization.
“If you are treating someone with pain, particularly chronic pain, it’s critically important to better assess their depression and not to attribute depressive symptoms only to pain,” Dr. Stein said.
The findings were published online in Psychiatric Services.
Promising approach?
Opioid treatment for pain “complicates the interactions among pain, depression, and self-harm,” the investigators write. Individuals with depression receiving long-term opioid therapy are two to three times more likely to misuse opioids, compared with individuals who do not have depression.
Although comorbid depression “substantially increases overdose and suicide risk, it remains underdiagnosed and undertreated among individuals with chronic pain,” the researchers note. They add that increasing access to depression treatment may be a “potentially promising approach to preventing overdoses and suicide” in these patients.
“We know that individuals using opioids who have a history of depression are more likely to have negative outcomes, such as overdoses and self-harm events,” Dr. Stein said. “We wanted to see whether antidepressants, which would treat depression in these individuals, would help with that.”
The researchers assessed a database of commercial insurance claims of adults with a history of depression who received opioids between 2007 and 2017 (n = 283,374). The data included 336,599 opioid treatment episodes.
To be included in the study, patients had to have been diagnosed with depression before they filled their first opioid prescription.
The “outcome of interest” was time from the beginning of an opioid episode until an adverse event, such as opioid poisoning, overdose of nonopioid controlled or illicit substances, or self-harm unrelated to overdose.
Participants were followed from the onset of the opioid episode until an AE occurred, loss to follow-up, or week 52, whichever came first.
The “key independent variable” was filling an antidepressant prescription. The patient’s sex and age were considered to be independent variables as well.
Teasing out antidepressant effect
Of participants with a history of depression treatment, 8,203 experienced at least one AE during the 12 months after treatment initiation (n = 47,486 AEs). Approximately half (50.8%) filled an antidepressant prescription at least once during the 12 months after the opioid episode began.
AEs were more likely among men than among women. The highest risk was in patients aged 18-24 years.
After adjusting for age and sex, participants who had received antidepressants had a greater risk for all adverse outcomes during the first 6 weeks of antidepressant treatment. However, those who had received antidepressants for 6 weeks or longer were at reduced risk for all adverse outcomes.

“We took advantage of the fact that, for most people, antidepressants take a while to work and aren’t immediately effective, so we were able to use that difference in our research,” Dr. Stein said.
“We wouldn’t expect to see an immediate effect of antidepressants, so the difference between what we saw immediately after the person had started treatment and the time it took for the antidepressant to be effective enabled us to tease out the effect of the antidepressant,” he added.
Consider CBT?
Andrew Saxon, MD, professor, department of psychiatry and behavioral sciences, University of Washington School of Medicine, Seattle, said clinicians “tend to think categorically and give people diagnoses that are clear-cut.” But neurobiologically, “it may be hard to distinguish where chronic pain ends and depression begins, or whether there’s some commonality.”
For patients with chronic pain and those taking opioids, “we need to be very attuned to the possibility or likelihood that they have major depression and other psychiatric diagnoses, like PTSD and anxiety disorders, which are very common,” said Dr. Saxon, who is also the director of the Center of Excellence in Substance Abuse Treatment and Education at the VA Puget Sound Health Care System. He was not involved with the current research.
He noted that treating those disorders “is a very important component of managing chronic pain.” However, “patients just starting antidepressants need to be carefully monitored when they’re getting stabilized on their antidepressants because they can have side effects, particularly early on, that can destabilize them.”
Dr. Saxon added that beyond pharmacotherapy, cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) for pain might be an even better intervention for addressing both pain and depression.
Also commenting for this article, Brian Hurley, MD, an addiction medicine specialist and the medical director of the Division of Substance Abuse Prevention and Control for the Los Angeles County Department of Public Health, said: “In the context of the largest wave of overdose mortality in U.S. history, we know comparatively little about the impact of mental health interventions that mitigate overdose risks.”
This study “contributes important new information that treating depression with antidepressant medications reduces overdose and self-harm risks for people who are prescribed opioids,” said Dr. Hurley, who is also the president-elect of the American Society of Addiction Medicine.
It also “underscores the general importance of integrated mental health and substance use disorder treatment in both primary care and in mental health settings,” added Dr. Hurley, who was not involved with the study.
The study was funded by the National Institute on Drug Abuse. The investigators and commenters reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM PSYCHIATRIC SERVICES
Inflammatory profiles impact major depressive disorder
Early onset of disease in patients with major depressive disorder may be linked to a specific inflammatory profile, based on data from 234 individuals.
Major depressive disorder (MDD) remains common, and evidence suggests that it is increasing among younger individuals, but data on early-onset MDD in adults are limited, Ana Paula Anzolin, a graduate student at the Universidade Federal do Rio Grande do Sul, Porto Alegre, Brazil, and colleagues wrote.
Although previous studies have shown abnormal cytokine production in patients with MDD, the impact of inflammation on MDD and disease onset and progression remains unclear, they said.
In a study published in Psychiatry Research, the authors identified outpatients aged 18-85 years with confirmed MDD and scores of at least 8 on the HAM-D scale who were undergoing treatment at a single center. Early onset was defined as a diagnosis of MDD before age 30 years (99 patients) and late onset was defined as a diagnosis at age 30 years and older (135 patients). The researchers measured levels of interleukin-6, IL-1 beta, IL-10, and tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNF-alpha).
Overall, the level of cytokine profiles in early- versus late-onset disease was significantly higher for IL-1B and TNF-alpha (P < .001 for both). The significant difference between early- and late-onset disease remained regardless of comorbidity with autoimmune diseases, the researchers noted.
IL-6 levels were higher in the early-onset group and IL-10 levels were higher in the late-onset group, but these differences were not significant.
the researchers wrote.
The results also support findings from previous studies that suggest a divergence between early- and late adult–onset depression, they said. More research on early-onset MDD in adults is needed, as these patients tend to have more severe symptoms, more medical and psychiatric comorbidities, and an increased risk of depressive episodes and suicide attempts.
The study findings were limited by several factors including the lack of a control group, the retrospective assessment of disease onset, and the limited cytokines studied, which do not reflect changes in the entire immune network response, the researchers noted.
However, the study is the first known to examine the association of serum cytokines and early- and late-onset MDD in adults, and the results support the use of IL-1B and TNF-alpha as potential treatment targets in the development of new therapies for MDD, they concluded.
The study was supported by the Fundo de Incentivo à Pesquisa – Hospital de Clínicas de Porto Alegre, the Conselho Nacional de Desenvolvimento Científico e Tecnológico, and the Coordenação de Aperfeiçoamento de Pessoal de Nível Superior. The researchers had no financial conflicts to disclose.
Early onset of disease in patients with major depressive disorder may be linked to a specific inflammatory profile, based on data from 234 individuals.
Major depressive disorder (MDD) remains common, and evidence suggests that it is increasing among younger individuals, but data on early-onset MDD in adults are limited, Ana Paula Anzolin, a graduate student at the Universidade Federal do Rio Grande do Sul, Porto Alegre, Brazil, and colleagues wrote.
Although previous studies have shown abnormal cytokine production in patients with MDD, the impact of inflammation on MDD and disease onset and progression remains unclear, they said.
In a study published in Psychiatry Research, the authors identified outpatients aged 18-85 years with confirmed MDD and scores of at least 8 on the HAM-D scale who were undergoing treatment at a single center. Early onset was defined as a diagnosis of MDD before age 30 years (99 patients) and late onset was defined as a diagnosis at age 30 years and older (135 patients). The researchers measured levels of interleukin-6, IL-1 beta, IL-10, and tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNF-alpha).
Overall, the level of cytokine profiles in early- versus late-onset disease was significantly higher for IL-1B and TNF-alpha (P < .001 for both). The significant difference between early- and late-onset disease remained regardless of comorbidity with autoimmune diseases, the researchers noted.
IL-6 levels were higher in the early-onset group and IL-10 levels were higher in the late-onset group, but these differences were not significant.
the researchers wrote.
The results also support findings from previous studies that suggest a divergence between early- and late adult–onset depression, they said. More research on early-onset MDD in adults is needed, as these patients tend to have more severe symptoms, more medical and psychiatric comorbidities, and an increased risk of depressive episodes and suicide attempts.
The study findings were limited by several factors including the lack of a control group, the retrospective assessment of disease onset, and the limited cytokines studied, which do not reflect changes in the entire immune network response, the researchers noted.
However, the study is the first known to examine the association of serum cytokines and early- and late-onset MDD in adults, and the results support the use of IL-1B and TNF-alpha as potential treatment targets in the development of new therapies for MDD, they concluded.
The study was supported by the Fundo de Incentivo à Pesquisa – Hospital de Clínicas de Porto Alegre, the Conselho Nacional de Desenvolvimento Científico e Tecnológico, and the Coordenação de Aperfeiçoamento de Pessoal de Nível Superior. The researchers had no financial conflicts to disclose.
Early onset of disease in patients with major depressive disorder may be linked to a specific inflammatory profile, based on data from 234 individuals.
Major depressive disorder (MDD) remains common, and evidence suggests that it is increasing among younger individuals, but data on early-onset MDD in adults are limited, Ana Paula Anzolin, a graduate student at the Universidade Federal do Rio Grande do Sul, Porto Alegre, Brazil, and colleagues wrote.
Although previous studies have shown abnormal cytokine production in patients with MDD, the impact of inflammation on MDD and disease onset and progression remains unclear, they said.
In a study published in Psychiatry Research, the authors identified outpatients aged 18-85 years with confirmed MDD and scores of at least 8 on the HAM-D scale who were undergoing treatment at a single center. Early onset was defined as a diagnosis of MDD before age 30 years (99 patients) and late onset was defined as a diagnosis at age 30 years and older (135 patients). The researchers measured levels of interleukin-6, IL-1 beta, IL-10, and tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNF-alpha).
Overall, the level of cytokine profiles in early- versus late-onset disease was significantly higher for IL-1B and TNF-alpha (P < .001 for both). The significant difference between early- and late-onset disease remained regardless of comorbidity with autoimmune diseases, the researchers noted.
IL-6 levels were higher in the early-onset group and IL-10 levels were higher in the late-onset group, but these differences were not significant.
the researchers wrote.
The results also support findings from previous studies that suggest a divergence between early- and late adult–onset depression, they said. More research on early-onset MDD in adults is needed, as these patients tend to have more severe symptoms, more medical and psychiatric comorbidities, and an increased risk of depressive episodes and suicide attempts.
The study findings were limited by several factors including the lack of a control group, the retrospective assessment of disease onset, and the limited cytokines studied, which do not reflect changes in the entire immune network response, the researchers noted.
However, the study is the first known to examine the association of serum cytokines and early- and late-onset MDD in adults, and the results support the use of IL-1B and TNF-alpha as potential treatment targets in the development of new therapies for MDD, they concluded.
The study was supported by the Fundo de Incentivo à Pesquisa – Hospital de Clínicas de Porto Alegre, the Conselho Nacional de Desenvolvimento Científico e Tecnológico, and the Coordenação de Aperfeiçoamento de Pessoal de Nível Superior. The researchers had no financial conflicts to disclose.
FROM PSYCHIATRY RESEARCH
The heartache of bereavement can be fatal in heart failure
that points to the need for greater integration of psychosocial risk factors in the treatment of HF.
The adjusted relative risk of dying was nearly 30% higher among bereaved patients with HF (1.29; 95% confidence interval, 1.27-1.30) and slightly higher for those grieving the loss of more than one family member (RR, 1.35).
The highest risk was in the first week after the loss (RR, 1.78) but persisted after 5 years of follow-up (RR, 1.30).
“Heart failure is a very difficult condition and has a very poor prognosis comparable to many, many cancers,” senior author Krisztina László, PhD, Karolinska Institutet, Stockholm, said in an interview. “So it’s important for us to be aware of these increased risks and to understand them better.”
The early risk for death could be related to stress-induced cardiomyopathy, or Takotsubo syndrome, as well as activation of the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis, the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system, and sympathetic nervous system, she explained. Higher long-term risks may reflect chronic stress, leading to poorly managed disease and an unhealthy lifestyle.
“If we understand better the underlying mechanisms maybe we can give more specific advice,” Dr. László said. “At this stage, I think having an awareness of the risk and trying to follow patients or at least not let them fall out of usual care, asking questions, trying to understand what their needs are, maybe that is what we can do well.”
A recent position paper by the European Association of Preventive Cardiology pointed out that psychosocial risk factors, like depression and social isolation, can exacerbate heart failure and calls for better integration of psychosocial factors in the treatment of patients with chronic HF.
“We don’t do a very good job of it, but I think they are very important,” observed Stuart D. Russell, MD, a professor of medicine who specializes in advanced HF at Duke University, Durham, N.C., and was not involved in the study.
“When we hear about a spouse dying, we might call and give condolences, but it’s probably a group of patients that for the next 6 months or so we need to watch more closely and see if there are things we can impact both medically as well as socially to perhaps prevent some of this increase in mortality,” he told this news organization.
Although several studies have linked bereavement with adverse health outcomes, this is just one of two studies to look specifically at its role in HF prognosis, Dr. László noted. A 2013 study of 66,000 male veterans reported that widowers had nearly a 38% higher all-cause mortality risk than did married veterans.
The present study extends those findings to 490,527 patients in the Swedish Heart Failure Registry between 2000 and 2018 and/or in the Swedish Patient Register with a primary diagnosis of HF between 1987 and 2018. During a mean follow-up of 3.7 years, 12% of participants had a family member die, and 383,674 participants died.
Results showed the HF mortality risk increased 10% after the death of a child, 20% with the death of a spouse/partner, 13% with a sibling’s death, and 5% with the death of a grandchild.
No increased risk was seen after the death of a parent, which is likely owed to a median patient age of about 75 years and “is in line with our expectations of the life cycle,” Dr. László said.
An association between bereavement and mortality risk was observed in cases of loss caused by cardiovascular disease (RR, 1.34) and other natural causes (RR, 1.27) but also in cases of unnatural deaths, such as suicide (RR, 1.13).
The overall findings were similar regardless of left ventricular ejection fraction and New York Heart Association functional class and were not affected by sex or country of birth.
Dr. Russell agreed that the death of a parent would be expected among these older patients with HF but said that “if the mechanism of this truly is kind of this increased stress hormones and Takotsubo-type mechanism, you’d think it would be worse if it was your kid that died. That shocked me a bit.”
The strong association between mortality and the loss of a spouse or partner was not surprising, given that they’re an important source of mutual social support, he added.
“If it’s a 75-year-old whose spouse dies, we need to make sure that we have the children’s phone number or other people that we can reach out to and say: ‘Can you check on them?’ ” he said. “And we need to make sure that somebody else is coming in with them because I would guess that probably at least half of what patients hear in a clinic visit goes in one ear and out the other and it’s going to make that much better. So we need to find who that new support person is for the patient.”
Asked whether there are efforts underway to incorporate psychosocial factors into current U.S. guidelines, Dr. Russell replied, “certainly within heart failure, I don’t think we’re really discussing it and, that may be the best part of this paper. It really makes us think about a different way of approaching these older patients.”
Dr. László said that future studies are needed to investigate whether less severe sources of stress may also contribute to poor HF prognosis.
“In our population, 12% of patients were affected, which is quite high, but there are patients with heart failure who experience on a daily basis other sources of stress, which are less severe but chronic and affect large numbers,” she said. “This may also have important public health implications and will be an important next step.”
The authors noted that they were unable to eliminate residual confounding by genetic factors or unmeasured socioeconomic-, lifestyle-, or health-related factors shared by family members. Other limitations are limited power to detect a modest effect in some of the subanalyses and that the findings may be generalizable only to countries with social and cultural contexts and health-related factors similar to those of Sweden.
The study was supported by grants from the Swedish Council for Working Life and Social Research, the Karolinska Institutet’s Research Foundation, and the China Scholarship Council. Dr. László is also supported by a grant from the Heart and Lung Foundation. All other authors and Dr. Russell reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
that points to the need for greater integration of psychosocial risk factors in the treatment of HF.
The adjusted relative risk of dying was nearly 30% higher among bereaved patients with HF (1.29; 95% confidence interval, 1.27-1.30) and slightly higher for those grieving the loss of more than one family member (RR, 1.35).
The highest risk was in the first week after the loss (RR, 1.78) but persisted after 5 years of follow-up (RR, 1.30).
“Heart failure is a very difficult condition and has a very poor prognosis comparable to many, many cancers,” senior author Krisztina László, PhD, Karolinska Institutet, Stockholm, said in an interview. “So it’s important for us to be aware of these increased risks and to understand them better.”
The early risk for death could be related to stress-induced cardiomyopathy, or Takotsubo syndrome, as well as activation of the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis, the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system, and sympathetic nervous system, she explained. Higher long-term risks may reflect chronic stress, leading to poorly managed disease and an unhealthy lifestyle.
“If we understand better the underlying mechanisms maybe we can give more specific advice,” Dr. László said. “At this stage, I think having an awareness of the risk and trying to follow patients or at least not let them fall out of usual care, asking questions, trying to understand what their needs are, maybe that is what we can do well.”
A recent position paper by the European Association of Preventive Cardiology pointed out that psychosocial risk factors, like depression and social isolation, can exacerbate heart failure and calls for better integration of psychosocial factors in the treatment of patients with chronic HF.
“We don’t do a very good job of it, but I think they are very important,” observed Stuart D. Russell, MD, a professor of medicine who specializes in advanced HF at Duke University, Durham, N.C., and was not involved in the study.
“When we hear about a spouse dying, we might call and give condolences, but it’s probably a group of patients that for the next 6 months or so we need to watch more closely and see if there are things we can impact both medically as well as socially to perhaps prevent some of this increase in mortality,” he told this news organization.
Although several studies have linked bereavement with adverse health outcomes, this is just one of two studies to look specifically at its role in HF prognosis, Dr. László noted. A 2013 study of 66,000 male veterans reported that widowers had nearly a 38% higher all-cause mortality risk than did married veterans.
The present study extends those findings to 490,527 patients in the Swedish Heart Failure Registry between 2000 and 2018 and/or in the Swedish Patient Register with a primary diagnosis of HF between 1987 and 2018. During a mean follow-up of 3.7 years, 12% of participants had a family member die, and 383,674 participants died.
Results showed the HF mortality risk increased 10% after the death of a child, 20% with the death of a spouse/partner, 13% with a sibling’s death, and 5% with the death of a grandchild.
No increased risk was seen after the death of a parent, which is likely owed to a median patient age of about 75 years and “is in line with our expectations of the life cycle,” Dr. László said.
An association between bereavement and mortality risk was observed in cases of loss caused by cardiovascular disease (RR, 1.34) and other natural causes (RR, 1.27) but also in cases of unnatural deaths, such as suicide (RR, 1.13).
The overall findings were similar regardless of left ventricular ejection fraction and New York Heart Association functional class and were not affected by sex or country of birth.
Dr. Russell agreed that the death of a parent would be expected among these older patients with HF but said that “if the mechanism of this truly is kind of this increased stress hormones and Takotsubo-type mechanism, you’d think it would be worse if it was your kid that died. That shocked me a bit.”
The strong association between mortality and the loss of a spouse or partner was not surprising, given that they’re an important source of mutual social support, he added.
“If it’s a 75-year-old whose spouse dies, we need to make sure that we have the children’s phone number or other people that we can reach out to and say: ‘Can you check on them?’ ” he said. “And we need to make sure that somebody else is coming in with them because I would guess that probably at least half of what patients hear in a clinic visit goes in one ear and out the other and it’s going to make that much better. So we need to find who that new support person is for the patient.”
Asked whether there are efforts underway to incorporate psychosocial factors into current U.S. guidelines, Dr. Russell replied, “certainly within heart failure, I don’t think we’re really discussing it and, that may be the best part of this paper. It really makes us think about a different way of approaching these older patients.”
Dr. László said that future studies are needed to investigate whether less severe sources of stress may also contribute to poor HF prognosis.
“In our population, 12% of patients were affected, which is quite high, but there are patients with heart failure who experience on a daily basis other sources of stress, which are less severe but chronic and affect large numbers,” she said. “This may also have important public health implications and will be an important next step.”
The authors noted that they were unable to eliminate residual confounding by genetic factors or unmeasured socioeconomic-, lifestyle-, or health-related factors shared by family members. Other limitations are limited power to detect a modest effect in some of the subanalyses and that the findings may be generalizable only to countries with social and cultural contexts and health-related factors similar to those of Sweden.
The study was supported by grants from the Swedish Council for Working Life and Social Research, the Karolinska Institutet’s Research Foundation, and the China Scholarship Council. Dr. László is also supported by a grant from the Heart and Lung Foundation. All other authors and Dr. Russell reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
that points to the need for greater integration of psychosocial risk factors in the treatment of HF.
The adjusted relative risk of dying was nearly 30% higher among bereaved patients with HF (1.29; 95% confidence interval, 1.27-1.30) and slightly higher for those grieving the loss of more than one family member (RR, 1.35).
The highest risk was in the first week after the loss (RR, 1.78) but persisted after 5 years of follow-up (RR, 1.30).
“Heart failure is a very difficult condition and has a very poor prognosis comparable to many, many cancers,” senior author Krisztina László, PhD, Karolinska Institutet, Stockholm, said in an interview. “So it’s important for us to be aware of these increased risks and to understand them better.”
The early risk for death could be related to stress-induced cardiomyopathy, or Takotsubo syndrome, as well as activation of the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis, the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system, and sympathetic nervous system, she explained. Higher long-term risks may reflect chronic stress, leading to poorly managed disease and an unhealthy lifestyle.
“If we understand better the underlying mechanisms maybe we can give more specific advice,” Dr. László said. “At this stage, I think having an awareness of the risk and trying to follow patients or at least not let them fall out of usual care, asking questions, trying to understand what their needs are, maybe that is what we can do well.”
A recent position paper by the European Association of Preventive Cardiology pointed out that psychosocial risk factors, like depression and social isolation, can exacerbate heart failure and calls for better integration of psychosocial factors in the treatment of patients with chronic HF.
“We don’t do a very good job of it, but I think they are very important,” observed Stuart D. Russell, MD, a professor of medicine who specializes in advanced HF at Duke University, Durham, N.C., and was not involved in the study.
“When we hear about a spouse dying, we might call and give condolences, but it’s probably a group of patients that for the next 6 months or so we need to watch more closely and see if there are things we can impact both medically as well as socially to perhaps prevent some of this increase in mortality,” he told this news organization.
Although several studies have linked bereavement with adverse health outcomes, this is just one of two studies to look specifically at its role in HF prognosis, Dr. László noted. A 2013 study of 66,000 male veterans reported that widowers had nearly a 38% higher all-cause mortality risk than did married veterans.
The present study extends those findings to 490,527 patients in the Swedish Heart Failure Registry between 2000 and 2018 and/or in the Swedish Patient Register with a primary diagnosis of HF between 1987 and 2018. During a mean follow-up of 3.7 years, 12% of participants had a family member die, and 383,674 participants died.
Results showed the HF mortality risk increased 10% after the death of a child, 20% with the death of a spouse/partner, 13% with a sibling’s death, and 5% with the death of a grandchild.
No increased risk was seen after the death of a parent, which is likely owed to a median patient age of about 75 years and “is in line with our expectations of the life cycle,” Dr. László said.
An association between bereavement and mortality risk was observed in cases of loss caused by cardiovascular disease (RR, 1.34) and other natural causes (RR, 1.27) but also in cases of unnatural deaths, such as suicide (RR, 1.13).
The overall findings were similar regardless of left ventricular ejection fraction and New York Heart Association functional class and were not affected by sex or country of birth.
Dr. Russell agreed that the death of a parent would be expected among these older patients with HF but said that “if the mechanism of this truly is kind of this increased stress hormones and Takotsubo-type mechanism, you’d think it would be worse if it was your kid that died. That shocked me a bit.”
The strong association between mortality and the loss of a spouse or partner was not surprising, given that they’re an important source of mutual social support, he added.
“If it’s a 75-year-old whose spouse dies, we need to make sure that we have the children’s phone number or other people that we can reach out to and say: ‘Can you check on them?’ ” he said. “And we need to make sure that somebody else is coming in with them because I would guess that probably at least half of what patients hear in a clinic visit goes in one ear and out the other and it’s going to make that much better. So we need to find who that new support person is for the patient.”
Asked whether there are efforts underway to incorporate psychosocial factors into current U.S. guidelines, Dr. Russell replied, “certainly within heart failure, I don’t think we’re really discussing it and, that may be the best part of this paper. It really makes us think about a different way of approaching these older patients.”
Dr. László said that future studies are needed to investigate whether less severe sources of stress may also contribute to poor HF prognosis.
“In our population, 12% of patients were affected, which is quite high, but there are patients with heart failure who experience on a daily basis other sources of stress, which are less severe but chronic and affect large numbers,” she said. “This may also have important public health implications and will be an important next step.”
The authors noted that they were unable to eliminate residual confounding by genetic factors or unmeasured socioeconomic-, lifestyle-, or health-related factors shared by family members. Other limitations are limited power to detect a modest effect in some of the subanalyses and that the findings may be generalizable only to countries with social and cultural contexts and health-related factors similar to those of Sweden.
The study was supported by grants from the Swedish Council for Working Life and Social Research, the Karolinska Institutet’s Research Foundation, and the China Scholarship Council. Dr. László is also supported by a grant from the Heart and Lung Foundation. All other authors and Dr. Russell reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM JACC: HEART FAILURE
Depression screens do not reduce suicidal acts in teens: Study
Screening adolescents for signs of depression does not reduce their emergency department visits, hospitalizations, or treatment for suicidal behaviors, according to research published in Preventive Medicine. Adolescents who underwent a depression screening were just as likely to need these services as those who did not.
In 2016, the U.S. Preventive Services Task Force recommended that adolescents aged 12-18 years be screened for major depressive disorder, provided that effective treatment options and follow-up strategies are in place.
“The main goal of depression screening is really to reduce adverse psychiatric outcomes. But I think a collateral hope is that, in reducing these adverse psychiatric outcomes, you would also reduce avoidable health services use,” such as ED visits or hospitalizations, said Kira Riehm, PhD, a postdoctoral fellow in epidemiology at Columbia University, New York, who led the research. Dr. Riehm designed the new study, which was part of her doctoral work at Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore, to test this premise.
Dr. Riehm and colleagues compared 14,433 adolescents aged 12-18 years who were screened for depression at least once during a wellness visit from 2014 to 2017 to 43,299 adolescents who were not screened for depression during such visits. Depression screenings were interspersed among a total of 281,463 adolescent wellness visits from 2014 to 2017, which represented 5% of all visits.
The researchers used diagnostic codes from a database of insurance claims to determine who had undergone depression screening. They then compared use of ED services, inpatient hospitalizations, and the number of treatments for suicidal behaviors between the two groups for the 2 years following the wellness visit.
The average age of the adolescents who underwent screening was 13-14 years, as was the average age of adolescents who were not screened. Both groups were evenly matched with respect to being male or female.
The researchers estimated that a high majority of adolescents in the sample were White (83%). Black persons represented 7% of the sample; Hispanic/Latino, 5%; and Asian, 3%. Insurance claims don’t always include racial and ethnicity data, Dr. Riehm said, so her group statistically imputed these proportions. The claims data also do not include details about which type of screening tool was used or the results of the screening, such as whether a teen exhibited mild or severe depression.
Adolescents in both groups were just as likely to go to the ED for any reason, be admitted to the hospital for any reason, or undergo treatment for suicidal behaviors. The researchers observed a slight association between being screened for depression and going to the ED specifically for a mental health reason (relative risk, 1.16; 95% confidence interval, 1.00-1.33). The sex of the adolescents had no bearing on whether they used these services.
“I think people think of [depression screening] as one event. But in reality, screening is a series of different events that all have to be happening in order for a screening program to work,” Dr. Riehm told this news organization.
These events could include ensuring that adolescents who exhibit signs of depression receive a proper assessment, receive medications if needed, and have access to psychotherapists who can help them. Without these supports in place, she said, a one-off depression screening may have limited benefit.
“There’s a lot of places where people could drop out of that care continuum,” Dr. Riehm said.
“One-time screening may not be enough,” said Trân Đoàn, PhD, MPH, a postdoctoral researcher in the University of Pittsburgh department of pediatrics.
Dr. Đoàn, who was not involved in the research, noted that the American Academy of Pediatrics recommends annual screening of all adolescents for depressive symptoms. Given that only 5% of the visits in this sample included any kind of depression screening, Dr. Đoàn said, some pediatric practices may not have felt they had the resources to adequately address positive screenings for depression.
Both Dr. Riehm and Dr. Đoàn are focusing on the link between depression screening and health outcomes. In her own doctoral work at the University of Michigan, Dr. Đoàn modeled the effects of universal annual depression screening in primary care settings on the health status of people aged 12-22 years. She is currently preparing this work for publication.
“I did find that, over the long term, there is improvement in health outcomes if we were to screen on an annual basis,” provided improved screening is coupled with comprehensive treatment plans, Dr. Đoàn said. The model’s health outcomes measures included an increase in life expectancy as well as a greater proportion of depression-free days among adolescents who receive appropriate treatment.
Dr. Riehm and Dr. Đoàn disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Screening adolescents for signs of depression does not reduce their emergency department visits, hospitalizations, or treatment for suicidal behaviors, according to research published in Preventive Medicine. Adolescents who underwent a depression screening were just as likely to need these services as those who did not.
In 2016, the U.S. Preventive Services Task Force recommended that adolescents aged 12-18 years be screened for major depressive disorder, provided that effective treatment options and follow-up strategies are in place.
“The main goal of depression screening is really to reduce adverse psychiatric outcomes. But I think a collateral hope is that, in reducing these adverse psychiatric outcomes, you would also reduce avoidable health services use,” such as ED visits or hospitalizations, said Kira Riehm, PhD, a postdoctoral fellow in epidemiology at Columbia University, New York, who led the research. Dr. Riehm designed the new study, which was part of her doctoral work at Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore, to test this premise.
Dr. Riehm and colleagues compared 14,433 adolescents aged 12-18 years who were screened for depression at least once during a wellness visit from 2014 to 2017 to 43,299 adolescents who were not screened for depression during such visits. Depression screenings were interspersed among a total of 281,463 adolescent wellness visits from 2014 to 2017, which represented 5% of all visits.
The researchers used diagnostic codes from a database of insurance claims to determine who had undergone depression screening. They then compared use of ED services, inpatient hospitalizations, and the number of treatments for suicidal behaviors between the two groups for the 2 years following the wellness visit.
The average age of the adolescents who underwent screening was 13-14 years, as was the average age of adolescents who were not screened. Both groups were evenly matched with respect to being male or female.
The researchers estimated that a high majority of adolescents in the sample were White (83%). Black persons represented 7% of the sample; Hispanic/Latino, 5%; and Asian, 3%. Insurance claims don’t always include racial and ethnicity data, Dr. Riehm said, so her group statistically imputed these proportions. The claims data also do not include details about which type of screening tool was used or the results of the screening, such as whether a teen exhibited mild or severe depression.
Adolescents in both groups were just as likely to go to the ED for any reason, be admitted to the hospital for any reason, or undergo treatment for suicidal behaviors. The researchers observed a slight association between being screened for depression and going to the ED specifically for a mental health reason (relative risk, 1.16; 95% confidence interval, 1.00-1.33). The sex of the adolescents had no bearing on whether they used these services.
“I think people think of [depression screening] as one event. But in reality, screening is a series of different events that all have to be happening in order for a screening program to work,” Dr. Riehm told this news organization.
These events could include ensuring that adolescents who exhibit signs of depression receive a proper assessment, receive medications if needed, and have access to psychotherapists who can help them. Without these supports in place, she said, a one-off depression screening may have limited benefit.
“There’s a lot of places where people could drop out of that care continuum,” Dr. Riehm said.
“One-time screening may not be enough,” said Trân Đoàn, PhD, MPH, a postdoctoral researcher in the University of Pittsburgh department of pediatrics.
Dr. Đoàn, who was not involved in the research, noted that the American Academy of Pediatrics recommends annual screening of all adolescents for depressive symptoms. Given that only 5% of the visits in this sample included any kind of depression screening, Dr. Đoàn said, some pediatric practices may not have felt they had the resources to adequately address positive screenings for depression.
Both Dr. Riehm and Dr. Đoàn are focusing on the link between depression screening and health outcomes. In her own doctoral work at the University of Michigan, Dr. Đoàn modeled the effects of universal annual depression screening in primary care settings on the health status of people aged 12-22 years. She is currently preparing this work for publication.
“I did find that, over the long term, there is improvement in health outcomes if we were to screen on an annual basis,” provided improved screening is coupled with comprehensive treatment plans, Dr. Đoàn said. The model’s health outcomes measures included an increase in life expectancy as well as a greater proportion of depression-free days among adolescents who receive appropriate treatment.
Dr. Riehm and Dr. Đoàn disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Screening adolescents for signs of depression does not reduce their emergency department visits, hospitalizations, or treatment for suicidal behaviors, according to research published in Preventive Medicine. Adolescents who underwent a depression screening were just as likely to need these services as those who did not.
In 2016, the U.S. Preventive Services Task Force recommended that adolescents aged 12-18 years be screened for major depressive disorder, provided that effective treatment options and follow-up strategies are in place.
“The main goal of depression screening is really to reduce adverse psychiatric outcomes. But I think a collateral hope is that, in reducing these adverse psychiatric outcomes, you would also reduce avoidable health services use,” such as ED visits or hospitalizations, said Kira Riehm, PhD, a postdoctoral fellow in epidemiology at Columbia University, New York, who led the research. Dr. Riehm designed the new study, which was part of her doctoral work at Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore, to test this premise.
Dr. Riehm and colleagues compared 14,433 adolescents aged 12-18 years who were screened for depression at least once during a wellness visit from 2014 to 2017 to 43,299 adolescents who were not screened for depression during such visits. Depression screenings were interspersed among a total of 281,463 adolescent wellness visits from 2014 to 2017, which represented 5% of all visits.
The researchers used diagnostic codes from a database of insurance claims to determine who had undergone depression screening. They then compared use of ED services, inpatient hospitalizations, and the number of treatments for suicidal behaviors between the two groups for the 2 years following the wellness visit.
The average age of the adolescents who underwent screening was 13-14 years, as was the average age of adolescents who were not screened. Both groups were evenly matched with respect to being male or female.
The researchers estimated that a high majority of adolescents in the sample were White (83%). Black persons represented 7% of the sample; Hispanic/Latino, 5%; and Asian, 3%. Insurance claims don’t always include racial and ethnicity data, Dr. Riehm said, so her group statistically imputed these proportions. The claims data also do not include details about which type of screening tool was used or the results of the screening, such as whether a teen exhibited mild or severe depression.
Adolescents in both groups were just as likely to go to the ED for any reason, be admitted to the hospital for any reason, or undergo treatment for suicidal behaviors. The researchers observed a slight association between being screened for depression and going to the ED specifically for a mental health reason (relative risk, 1.16; 95% confidence interval, 1.00-1.33). The sex of the adolescents had no bearing on whether they used these services.
“I think people think of [depression screening] as one event. But in reality, screening is a series of different events that all have to be happening in order for a screening program to work,” Dr. Riehm told this news organization.
These events could include ensuring that adolescents who exhibit signs of depression receive a proper assessment, receive medications if needed, and have access to psychotherapists who can help them. Without these supports in place, she said, a one-off depression screening may have limited benefit.
“There’s a lot of places where people could drop out of that care continuum,” Dr. Riehm said.
“One-time screening may not be enough,” said Trân Đoàn, PhD, MPH, a postdoctoral researcher in the University of Pittsburgh department of pediatrics.
Dr. Đoàn, who was not involved in the research, noted that the American Academy of Pediatrics recommends annual screening of all adolescents for depressive symptoms. Given that only 5% of the visits in this sample included any kind of depression screening, Dr. Đoàn said, some pediatric practices may not have felt they had the resources to adequately address positive screenings for depression.
Both Dr. Riehm and Dr. Đoàn are focusing on the link between depression screening and health outcomes. In her own doctoral work at the University of Michigan, Dr. Đoàn modeled the effects of universal annual depression screening in primary care settings on the health status of people aged 12-22 years. She is currently preparing this work for publication.
“I did find that, over the long term, there is improvement in health outcomes if we were to screen on an annual basis,” provided improved screening is coupled with comprehensive treatment plans, Dr. Đoàn said. The model’s health outcomes measures included an increase in life expectancy as well as a greater proportion of depression-free days among adolescents who receive appropriate treatment.
Dr. Riehm and Dr. Đoàn disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM PREVENTIVE MEDICINE
Are social networks threatening adolescents’ mental health?
When it comes to the link between mental health and social networks, be careful of jumping to conclusions. This warning came from Margot Morgiève, PhD, sociology researcher at the French National Institute of Health and Medical Research and the Center for Research in Medicine, Science, Health, Mental Health, and Society (Inserm-Cermes 3). She delivered her remarks at the opening session of the Pediatric Societies Congress organized by the French Society of Pediatrics, based on an increasing amount of scientific literature on the subject.
In 2021, 4.2 billion people, or more than half the world’s population, used social networks, and 80.3% of French citizens had a social network account.
‘Facebook depression’
Between those who condemn social networks for causing problems in adolescents and those who, in contrast, view it as a lifeline, what do we really know about their impact on the mental health of young people?
Although several studies have found a significant association between the heavy use of social networks and anxiety, depressive symptoms, and stress, there have also been reports of decreased life satisfaction, as well as reduced general well-being and self-esteem.
“Due to an increased [concurrence] between mood disorders or depression and the use of social networks, researchers wanted to establish a new disorder: ‘Facebook Depression,’ ” commented Dr. Morgiève, who is also a clinical psychologist and coordinator of the chat and social network unit for the French national suicide prevention hotline 3114.
“But they quickly realized that it would be wrong to recognize it as a characterized disorder, because it would appear that the harmful effects of social networks on mental health are not linked to the social network itself, but rather to problematic social network use.”
Teens’ fantasy life
There are three major categories of problematic social network use, the first being social comparison. This refers to the spontaneous tendency of social beings to compare themselves to individuals who appear to be more attractive than them.
This is nothing new, but it is exacerbated on social networks. Users emphasize the positive aspects of their life and present themselves as balanced, popular, and satisfied.
However, this leads to strong normative constraints, which result in a negative self-assessment, thereby lowering self-esteem and promoting the emergence of depressive symptoms. “Thus, it isn’t the social network that creates depression, but rather the phenomenon of comparison, which it pushes to the extreme,” said Dr. Morgiève.
The second problem associated with social networks is their propensity to promote addictive behavior through [observational learning], which can give rise to compulsive and uncontrolled behavior, as illustrated by “FOMO,” or fear of missing out.
Hence the idea of defining a specific entity called “social network addiction,” which was also quickly abandoned. It is the very features of social networks that generate this fear and thus this tendency, just like news feeds (constant updating of a personalized news list).
“Substitutive” use is the third major category. This is when time spent in the online environment replaces that spent offline. Excessive users report a feeling of loneliness and an awareness of a lack of intimate connections.
Language of distress
Initial studies using artificial intelligence and machine learning tend to show that a digital language of distress exists. Authors noticed that themes associated with self-loathing, loneliness, suicide, death, and self-harm correlated with users who exhibited the highest levels of depression.
The very structure of the language (more words, more use of “I,” more references to death, and fewer verbs) correlated with users in distress.
According to the authors, the typical social network practice of vaguebooking – writing a post that may incite worry, such as “better days are coming” – is a significant predictive factor of suicidal ideation. A visual language of distress also reportedly exists – for example, the use of darker shades, like the black-and-white inkwell filter with no enhancements in Instagram.
Internet risks and dangers
Digital environments entail many risks and dangers. Suicide pacts and online suicides (like the suicide of a young girl on Periscope in 2016) remain rare but go viral. The same is true of challenges. In 2015, the Blue Whale Challenge consisted of a list of 50 challenges ranging from the benign to the dramatic, with the final challenge being to “hang yourself.”
Its huge media coverage might well have added to its viral success had the social networks not quickly reacted in a positive manner.
Trolling, for its part, consists of posting provocative content with the intent of either sparking conflict or causing distress.
Cyberbullying, the most common online risk adolescents face, is the repeated spreading of false, embarrassing, or hostile information.
A growing danger is sexting (sending, receiving, or passing on sexually explicit photographs, messages, or images). The serious potential consequences of sexting include revenge porn or cyber rape, which is defined as the distribution of illicit content without consent, the practice of which has been linked to depression and involvement in risky behavior.
The risk of suicide exposure should no longer be overlooked, in view of the hypothesis that some online content relating to suicide may produce a suggestive effect with respect to the idea or the method of suicide, as well as precipitating suicide attempts.
“People who post suicidal comments are in communities that are closely connected by bonds of affiliation (memberships, friendships) and activities (retweets, likes, comments),” explained Dr. Morgiève.
But in these communities, emotionally charged information that spreads rapidly and repetitively could promote corumination, hence the concept of “suicidocosme [suicide world]», developed in 2017 by Charles-Edouard Notredame, MD, of the child and adolescent psychiatry department at Lille (France) University Hospital. This, in turn, can produce and increase the suicide contagion based on the Werther effect model.
Just one of many examples is Marilyn Monroe’s suicide in 1962, which increased the suicide rate by 40% in Los Angeles. The Werther effect is especially significant because two biases are present: the prestige bias (identification with the person one admires) and similarity bias (identification with the person who resembles me).
Similarity bias is the most decisive in adolescence. It should be noted that the positive counterpart to the Werther effect is the Papageno effect. The Belgian singer-songwriter Stromae’s TV appearances earlier this year, in which he spoke about his suicidal ideations, enabling young people to recognize their suffering and seek help, is an example of the Papageno effect.
Support on social networks?
Social networks can increase connectedness, for example, the feeling of being connected to something meaningful outside oneself. Connectedness promotes psychological well-being and quality of life.
The very characteristics of social networks can enhance elements of connectedness, both objectively by increasing users’ social sphere, and subjectively by reinforcing the feeling of social belonging and subjective well-being.
Taking Facebook and its “anniversary” feature as an example, it has been shown that the greater the number of Facebook friends, the more individuals saw themselves as being connected to a community.
“Millennials, or people born between the beginning of the 1980s and the end of the 1990s, are thus more likely to take advantage of the digital social environment to establish a new relationship with psychological suffering and its attempts to ease it,” said Dr. Morgiève.
They are also more likely to naturally turn to the digital space to look for help. More and more of them are searching the Internet for information on mental health and sharing experiences to get support.”
An example is the It Gets Better Project, which is a good illustration of the structure of online peer communities, with stories from LGBTQ+ individuals who describe how they succeeded in coping with adversity during their adolescence. In this way, social media seems to help identify peers and positive resources that are usually unavailable outside of the digital space. As a result, thanks to normative models on extremely strong social networks that are easy to conform to, these online peer-support communities have the potential to facilitate social interactions and reinforce a feeling both of hope and of belonging to a group.”
Promoting access to care
In Dr. Morgiève’s opinion, “access to care, particularly in the area of adolescent mental health, is extremely critical, given the lack of support precisely when they need it the most, as [evidenced] by the number of suicide attempts.
“There are two types of barriers to seeking help which can explain this. The first is structural barriers: help is too expensive or too far away or the wait is too long. The second refers to personal barriers, including denying the need for help, which may involve a self-sufficiency bias, the feeling that one cannot be helped, refusal to bother close friends and family, fear of being stigmatized, and a feeling of shame.”
These types of barriers are particularly difficult to overcome because the beliefs regarding care and caregivers are limiting (doubts about caregiver confidentiality, reliability, and competence). This is observed especially in adolescents because of the desire for emancipation and development of identity. So [the help relationship] may be experienced as subordination or alienation.
On a positive note, it is the very properties of social networks that will enable these obstacles to seeking help to be overcome. The fact that they are available everywhere makes up for young people’s lack of mobility and regional disparities. In addition, it ensures discretion and freedom of use, while reducing inhibitions.
The fact that social networks are free of charge overcomes structural obstacles, such as financial and organizational costs, as well as personal obstacles, thereby facilitating engagement and lessening the motivational cost. The dissociative pseudonymity or anonymity reduces the feeling of vulnerability associated with revealing oneself, as well as fears of a breach of confidentiality.
Dr. Morgiève summed it up by saying: “While offline life is silent because young people don’t talk about their suicidal ideations, online life truly removes inhibitions about speaking, relationships, and sharing experiences. Thus, the internet offers adolescents new opportunities to express themselves, which they’re not doing in real life.”
Professionals go digital
France records one suicide every hour (8,885 deaths a year) and one suicide attempt every 4 minutes. Since the 1950s, government-funded telehealth prevention and assistance programs, such as S.O.S. Amitié, Suicide Écoute, SOS Suicide Phénix, etc., have been developed. Their values and principles are anonymity, nondirectivity, nonjudgment, and neutrality. In addition to these nonprofit offerings, a professional teleprevention program, the confidential suicide prevention hotline 3114 – with professionals who are available to listen 24 hours a day, 7 days a week – was launched by the Ministry of Health and Prevention in October 2021.
Its values and principles include confidentiality, proactivity, concern, and caring for others. To date, 13 of 17 centers have opened. In the space of 6 months, they have received 50,000 calls, with an average of 400-500 calls a day. The dedicated chat application was codesigned with users (suicide attempters). And now social networks are joining in. For example, the hotline number 3114 appears whenever a TikTok user types the word “suicide.”
Dr. Morgiève said she has no conflicts of interest regarding the subject presented.
This article was translated from the Medscape French edition. A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
When it comes to the link between mental health and social networks, be careful of jumping to conclusions. This warning came from Margot Morgiève, PhD, sociology researcher at the French National Institute of Health and Medical Research and the Center for Research in Medicine, Science, Health, Mental Health, and Society (Inserm-Cermes 3). She delivered her remarks at the opening session of the Pediatric Societies Congress organized by the French Society of Pediatrics, based on an increasing amount of scientific literature on the subject.
In 2021, 4.2 billion people, or more than half the world’s population, used social networks, and 80.3% of French citizens had a social network account.
‘Facebook depression’
Between those who condemn social networks for causing problems in adolescents and those who, in contrast, view it as a lifeline, what do we really know about their impact on the mental health of young people?
Although several studies have found a significant association between the heavy use of social networks and anxiety, depressive symptoms, and stress, there have also been reports of decreased life satisfaction, as well as reduced general well-being and self-esteem.
“Due to an increased [concurrence] between mood disorders or depression and the use of social networks, researchers wanted to establish a new disorder: ‘Facebook Depression,’ ” commented Dr. Morgiève, who is also a clinical psychologist and coordinator of the chat and social network unit for the French national suicide prevention hotline 3114.
“But they quickly realized that it would be wrong to recognize it as a characterized disorder, because it would appear that the harmful effects of social networks on mental health are not linked to the social network itself, but rather to problematic social network use.”
Teens’ fantasy life
There are three major categories of problematic social network use, the first being social comparison. This refers to the spontaneous tendency of social beings to compare themselves to individuals who appear to be more attractive than them.
This is nothing new, but it is exacerbated on social networks. Users emphasize the positive aspects of their life and present themselves as balanced, popular, and satisfied.
However, this leads to strong normative constraints, which result in a negative self-assessment, thereby lowering self-esteem and promoting the emergence of depressive symptoms. “Thus, it isn’t the social network that creates depression, but rather the phenomenon of comparison, which it pushes to the extreme,” said Dr. Morgiève.
The second problem associated with social networks is their propensity to promote addictive behavior through [observational learning], which can give rise to compulsive and uncontrolled behavior, as illustrated by “FOMO,” or fear of missing out.
Hence the idea of defining a specific entity called “social network addiction,” which was also quickly abandoned. It is the very features of social networks that generate this fear and thus this tendency, just like news feeds (constant updating of a personalized news list).
“Substitutive” use is the third major category. This is when time spent in the online environment replaces that spent offline. Excessive users report a feeling of loneliness and an awareness of a lack of intimate connections.
Language of distress
Initial studies using artificial intelligence and machine learning tend to show that a digital language of distress exists. Authors noticed that themes associated with self-loathing, loneliness, suicide, death, and self-harm correlated with users who exhibited the highest levels of depression.
The very structure of the language (more words, more use of “I,” more references to death, and fewer verbs) correlated with users in distress.
According to the authors, the typical social network practice of vaguebooking – writing a post that may incite worry, such as “better days are coming” – is a significant predictive factor of suicidal ideation. A visual language of distress also reportedly exists – for example, the use of darker shades, like the black-and-white inkwell filter with no enhancements in Instagram.
Internet risks and dangers
Digital environments entail many risks and dangers. Suicide pacts and online suicides (like the suicide of a young girl on Periscope in 2016) remain rare but go viral. The same is true of challenges. In 2015, the Blue Whale Challenge consisted of a list of 50 challenges ranging from the benign to the dramatic, with the final challenge being to “hang yourself.”
Its huge media coverage might well have added to its viral success had the social networks not quickly reacted in a positive manner.
Trolling, for its part, consists of posting provocative content with the intent of either sparking conflict or causing distress.
Cyberbullying, the most common online risk adolescents face, is the repeated spreading of false, embarrassing, or hostile information.
A growing danger is sexting (sending, receiving, or passing on sexually explicit photographs, messages, or images). The serious potential consequences of sexting include revenge porn or cyber rape, which is defined as the distribution of illicit content without consent, the practice of which has been linked to depression and involvement in risky behavior.
The risk of suicide exposure should no longer be overlooked, in view of the hypothesis that some online content relating to suicide may produce a suggestive effect with respect to the idea or the method of suicide, as well as precipitating suicide attempts.
“People who post suicidal comments are in communities that are closely connected by bonds of affiliation (memberships, friendships) and activities (retweets, likes, comments),” explained Dr. Morgiève.
But in these communities, emotionally charged information that spreads rapidly and repetitively could promote corumination, hence the concept of “suicidocosme [suicide world]», developed in 2017 by Charles-Edouard Notredame, MD, of the child and adolescent psychiatry department at Lille (France) University Hospital. This, in turn, can produce and increase the suicide contagion based on the Werther effect model.
Just one of many examples is Marilyn Monroe’s suicide in 1962, which increased the suicide rate by 40% in Los Angeles. The Werther effect is especially significant because two biases are present: the prestige bias (identification with the person one admires) and similarity bias (identification with the person who resembles me).
Similarity bias is the most decisive in adolescence. It should be noted that the positive counterpart to the Werther effect is the Papageno effect. The Belgian singer-songwriter Stromae’s TV appearances earlier this year, in which he spoke about his suicidal ideations, enabling young people to recognize their suffering and seek help, is an example of the Papageno effect.
Support on social networks?
Social networks can increase connectedness, for example, the feeling of being connected to something meaningful outside oneself. Connectedness promotes psychological well-being and quality of life.
The very characteristics of social networks can enhance elements of connectedness, both objectively by increasing users’ social sphere, and subjectively by reinforcing the feeling of social belonging and subjective well-being.
Taking Facebook and its “anniversary” feature as an example, it has been shown that the greater the number of Facebook friends, the more individuals saw themselves as being connected to a community.
“Millennials, or people born between the beginning of the 1980s and the end of the 1990s, are thus more likely to take advantage of the digital social environment to establish a new relationship with psychological suffering and its attempts to ease it,” said Dr. Morgiève.
They are also more likely to naturally turn to the digital space to look for help. More and more of them are searching the Internet for information on mental health and sharing experiences to get support.”
An example is the It Gets Better Project, which is a good illustration of the structure of online peer communities, with stories from LGBTQ+ individuals who describe how they succeeded in coping with adversity during their adolescence. In this way, social media seems to help identify peers and positive resources that are usually unavailable outside of the digital space. As a result, thanks to normative models on extremely strong social networks that are easy to conform to, these online peer-support communities have the potential to facilitate social interactions and reinforce a feeling both of hope and of belonging to a group.”
Promoting access to care
In Dr. Morgiève’s opinion, “access to care, particularly in the area of adolescent mental health, is extremely critical, given the lack of support precisely when they need it the most, as [evidenced] by the number of suicide attempts.
“There are two types of barriers to seeking help which can explain this. The first is structural barriers: help is too expensive or too far away or the wait is too long. The second refers to personal barriers, including denying the need for help, which may involve a self-sufficiency bias, the feeling that one cannot be helped, refusal to bother close friends and family, fear of being stigmatized, and a feeling of shame.”
These types of barriers are particularly difficult to overcome because the beliefs regarding care and caregivers are limiting (doubts about caregiver confidentiality, reliability, and competence). This is observed especially in adolescents because of the desire for emancipation and development of identity. So [the help relationship] may be experienced as subordination or alienation.
On a positive note, it is the very properties of social networks that will enable these obstacles to seeking help to be overcome. The fact that they are available everywhere makes up for young people’s lack of mobility and regional disparities. In addition, it ensures discretion and freedom of use, while reducing inhibitions.
The fact that social networks are free of charge overcomes structural obstacles, such as financial and organizational costs, as well as personal obstacles, thereby facilitating engagement and lessening the motivational cost. The dissociative pseudonymity or anonymity reduces the feeling of vulnerability associated with revealing oneself, as well as fears of a breach of confidentiality.
Dr. Morgiève summed it up by saying: “While offline life is silent because young people don’t talk about their suicidal ideations, online life truly removes inhibitions about speaking, relationships, and sharing experiences. Thus, the internet offers adolescents new opportunities to express themselves, which they’re not doing in real life.”
Professionals go digital
France records one suicide every hour (8,885 deaths a year) and one suicide attempt every 4 minutes. Since the 1950s, government-funded telehealth prevention and assistance programs, such as S.O.S. Amitié, Suicide Écoute, SOS Suicide Phénix, etc., have been developed. Their values and principles are anonymity, nondirectivity, nonjudgment, and neutrality. In addition to these nonprofit offerings, a professional teleprevention program, the confidential suicide prevention hotline 3114 – with professionals who are available to listen 24 hours a day, 7 days a week – was launched by the Ministry of Health and Prevention in October 2021.
Its values and principles include confidentiality, proactivity, concern, and caring for others. To date, 13 of 17 centers have opened. In the space of 6 months, they have received 50,000 calls, with an average of 400-500 calls a day. The dedicated chat application was codesigned with users (suicide attempters). And now social networks are joining in. For example, the hotline number 3114 appears whenever a TikTok user types the word “suicide.”
Dr. Morgiève said she has no conflicts of interest regarding the subject presented.
This article was translated from the Medscape French edition. A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
When it comes to the link between mental health and social networks, be careful of jumping to conclusions. This warning came from Margot Morgiève, PhD, sociology researcher at the French National Institute of Health and Medical Research and the Center for Research in Medicine, Science, Health, Mental Health, and Society (Inserm-Cermes 3). She delivered her remarks at the opening session of the Pediatric Societies Congress organized by the French Society of Pediatrics, based on an increasing amount of scientific literature on the subject.
In 2021, 4.2 billion people, or more than half the world’s population, used social networks, and 80.3% of French citizens had a social network account.
‘Facebook depression’
Between those who condemn social networks for causing problems in adolescents and those who, in contrast, view it as a lifeline, what do we really know about their impact on the mental health of young people?
Although several studies have found a significant association between the heavy use of social networks and anxiety, depressive symptoms, and stress, there have also been reports of decreased life satisfaction, as well as reduced general well-being and self-esteem.
“Due to an increased [concurrence] between mood disorders or depression and the use of social networks, researchers wanted to establish a new disorder: ‘Facebook Depression,’ ” commented Dr. Morgiève, who is also a clinical psychologist and coordinator of the chat and social network unit for the French national suicide prevention hotline 3114.
“But they quickly realized that it would be wrong to recognize it as a characterized disorder, because it would appear that the harmful effects of social networks on mental health are not linked to the social network itself, but rather to problematic social network use.”
Teens’ fantasy life
There are three major categories of problematic social network use, the first being social comparison. This refers to the spontaneous tendency of social beings to compare themselves to individuals who appear to be more attractive than them.
This is nothing new, but it is exacerbated on social networks. Users emphasize the positive aspects of their life and present themselves as balanced, popular, and satisfied.
However, this leads to strong normative constraints, which result in a negative self-assessment, thereby lowering self-esteem and promoting the emergence of depressive symptoms. “Thus, it isn’t the social network that creates depression, but rather the phenomenon of comparison, which it pushes to the extreme,” said Dr. Morgiève.
The second problem associated with social networks is their propensity to promote addictive behavior through [observational learning], which can give rise to compulsive and uncontrolled behavior, as illustrated by “FOMO,” or fear of missing out.
Hence the idea of defining a specific entity called “social network addiction,” which was also quickly abandoned. It is the very features of social networks that generate this fear and thus this tendency, just like news feeds (constant updating of a personalized news list).
“Substitutive” use is the third major category. This is when time spent in the online environment replaces that spent offline. Excessive users report a feeling of loneliness and an awareness of a lack of intimate connections.
Language of distress
Initial studies using artificial intelligence and machine learning tend to show that a digital language of distress exists. Authors noticed that themes associated with self-loathing, loneliness, suicide, death, and self-harm correlated with users who exhibited the highest levels of depression.
The very structure of the language (more words, more use of “I,” more references to death, and fewer verbs) correlated with users in distress.
According to the authors, the typical social network practice of vaguebooking – writing a post that may incite worry, such as “better days are coming” – is a significant predictive factor of suicidal ideation. A visual language of distress also reportedly exists – for example, the use of darker shades, like the black-and-white inkwell filter with no enhancements in Instagram.
Internet risks and dangers
Digital environments entail many risks and dangers. Suicide pacts and online suicides (like the suicide of a young girl on Periscope in 2016) remain rare but go viral. The same is true of challenges. In 2015, the Blue Whale Challenge consisted of a list of 50 challenges ranging from the benign to the dramatic, with the final challenge being to “hang yourself.”
Its huge media coverage might well have added to its viral success had the social networks not quickly reacted in a positive manner.
Trolling, for its part, consists of posting provocative content with the intent of either sparking conflict or causing distress.
Cyberbullying, the most common online risk adolescents face, is the repeated spreading of false, embarrassing, or hostile information.
A growing danger is sexting (sending, receiving, or passing on sexually explicit photographs, messages, or images). The serious potential consequences of sexting include revenge porn or cyber rape, which is defined as the distribution of illicit content without consent, the practice of which has been linked to depression and involvement in risky behavior.
The risk of suicide exposure should no longer be overlooked, in view of the hypothesis that some online content relating to suicide may produce a suggestive effect with respect to the idea or the method of suicide, as well as precipitating suicide attempts.
“People who post suicidal comments are in communities that are closely connected by bonds of affiliation (memberships, friendships) and activities (retweets, likes, comments),” explained Dr. Morgiève.
But in these communities, emotionally charged information that spreads rapidly and repetitively could promote corumination, hence the concept of “suicidocosme [suicide world]», developed in 2017 by Charles-Edouard Notredame, MD, of the child and adolescent psychiatry department at Lille (France) University Hospital. This, in turn, can produce and increase the suicide contagion based on the Werther effect model.
Just one of many examples is Marilyn Monroe’s suicide in 1962, which increased the suicide rate by 40% in Los Angeles. The Werther effect is especially significant because two biases are present: the prestige bias (identification with the person one admires) and similarity bias (identification with the person who resembles me).
Similarity bias is the most decisive in adolescence. It should be noted that the positive counterpart to the Werther effect is the Papageno effect. The Belgian singer-songwriter Stromae’s TV appearances earlier this year, in which he spoke about his suicidal ideations, enabling young people to recognize their suffering and seek help, is an example of the Papageno effect.
Support on social networks?
Social networks can increase connectedness, for example, the feeling of being connected to something meaningful outside oneself. Connectedness promotes psychological well-being and quality of life.
The very characteristics of social networks can enhance elements of connectedness, both objectively by increasing users’ social sphere, and subjectively by reinforcing the feeling of social belonging and subjective well-being.
Taking Facebook and its “anniversary” feature as an example, it has been shown that the greater the number of Facebook friends, the more individuals saw themselves as being connected to a community.
“Millennials, or people born between the beginning of the 1980s and the end of the 1990s, are thus more likely to take advantage of the digital social environment to establish a new relationship with psychological suffering and its attempts to ease it,” said Dr. Morgiève.
They are also more likely to naturally turn to the digital space to look for help. More and more of them are searching the Internet for information on mental health and sharing experiences to get support.”
An example is the It Gets Better Project, which is a good illustration of the structure of online peer communities, with stories from LGBTQ+ individuals who describe how they succeeded in coping with adversity during their adolescence. In this way, social media seems to help identify peers and positive resources that are usually unavailable outside of the digital space. As a result, thanks to normative models on extremely strong social networks that are easy to conform to, these online peer-support communities have the potential to facilitate social interactions and reinforce a feeling both of hope and of belonging to a group.”
Promoting access to care
In Dr. Morgiève’s opinion, “access to care, particularly in the area of adolescent mental health, is extremely critical, given the lack of support precisely when they need it the most, as [evidenced] by the number of suicide attempts.
“There are two types of barriers to seeking help which can explain this. The first is structural barriers: help is too expensive or too far away or the wait is too long. The second refers to personal barriers, including denying the need for help, which may involve a self-sufficiency bias, the feeling that one cannot be helped, refusal to bother close friends and family, fear of being stigmatized, and a feeling of shame.”
These types of barriers are particularly difficult to overcome because the beliefs regarding care and caregivers are limiting (doubts about caregiver confidentiality, reliability, and competence). This is observed especially in adolescents because of the desire for emancipation and development of identity. So [the help relationship] may be experienced as subordination or alienation.
On a positive note, it is the very properties of social networks that will enable these obstacles to seeking help to be overcome. The fact that they are available everywhere makes up for young people’s lack of mobility and regional disparities. In addition, it ensures discretion and freedom of use, while reducing inhibitions.
The fact that social networks are free of charge overcomes structural obstacles, such as financial and organizational costs, as well as personal obstacles, thereby facilitating engagement and lessening the motivational cost. The dissociative pseudonymity or anonymity reduces the feeling of vulnerability associated with revealing oneself, as well as fears of a breach of confidentiality.
Dr. Morgiève summed it up by saying: “While offline life is silent because young people don’t talk about their suicidal ideations, online life truly removes inhibitions about speaking, relationships, and sharing experiences. Thus, the internet offers adolescents new opportunities to express themselves, which they’re not doing in real life.”
Professionals go digital
France records one suicide every hour (8,885 deaths a year) and one suicide attempt every 4 minutes. Since the 1950s, government-funded telehealth prevention and assistance programs, such as S.O.S. Amitié, Suicide Écoute, SOS Suicide Phénix, etc., have been developed. Their values and principles are anonymity, nondirectivity, nonjudgment, and neutrality. In addition to these nonprofit offerings, a professional teleprevention program, the confidential suicide prevention hotline 3114 – with professionals who are available to listen 24 hours a day, 7 days a week – was launched by the Ministry of Health and Prevention in October 2021.
Its values and principles include confidentiality, proactivity, concern, and caring for others. To date, 13 of 17 centers have opened. In the space of 6 months, they have received 50,000 calls, with an average of 400-500 calls a day. The dedicated chat application was codesigned with users (suicide attempters). And now social networks are joining in. For example, the hotline number 3114 appears whenever a TikTok user types the word “suicide.”
Dr. Morgiève said she has no conflicts of interest regarding the subject presented.
This article was translated from the Medscape French edition. A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The mother’s double jeopardy
Jamestown, Colo., is a small mountain town several miles up through Lefthand Canyon out of Boulder, in the Rocky Mountains. The canyon roads are steep, winding, and narrow, and peopled by brightly clad cyclists struggling up the hill and flying down faster than the cars. The road through Jamestown is dusty in the summer with brightly colored oil barrels strategically placed in the middle of the single road through town. Slashed across their sides: “SLOW DOWN! Watch out for our feral children!”
Wild child or hothouse child? What is the best choice? Women bear the brunt of this deciding, whether they are working outside of the home, or stay-at-home caregivers, or both. Women know they will be blamed if they get it wrong.
Society has exacted a tall order on women who choose to have children. Patriarchal norms ask (White) women who choose both to work and have children, if they are really a “stay-at-home” mother who must work, or a “working” mother who prefers work over their children. The underlying attitude can be read as: “Are you someone who prioritizes paid work over caregiving, or are you someone who prioritizes caregiving over work?” You may be seen as a bad mother if you prioritize work over the welfare of your child. If you prioritize your child over your work, then you are not a reliable, dedicated worker. The working mother can’t win.
Woman’s central question is what kind of mother should I be? Mothers struggle with this question all their lives; when their child has difficulties, society’s question is what did you do wrong with your child? Mothers internalize the standard of the “good mother” and are aware of each minor transgression that depicts them as the “bad mother.” It is hard to escape the impossible perfectionistic standard of the good mother. But perhaps it has come time to push back on the moral imbalance.
Internalized sexism
As women move out of the home into the workplace, the societal pressures to maintain the status quo bear down on women, trying to keep them in their place.
Social pressures employ subtle “technologies of the self,” so that women – as any oppressed group – learn to internalize these technologies, and monitor themselves.1 This is now widely accepted as internalized sexism, whereby women feel that they are not good enough, do not have the right qualifications, and are “less” than the dominant group (men). This phenomenon is also recognized when racial and ethnic biases are assimilated unconsciously, as internalized racism. Should we also have internalized “momism”?
Women are caught between trying to claim their individualism as well as feeling the responsibility to be the self-denying mother. Everyone has an opinion about the place of women. Conservative activist Phyllis Schlafly considered “women’s lib” to be un-American, citing women in the military and the establishment of federal day care centers as actions of a communist state. A similar ideology helped form the antifeminist organization Concerned Women for America, which self-reports that it is the largest American public policy women’s organization. Formed in opposition to the National Organization for Women, CWA is focused on maintaining the traditional family, as understood by (White) evangelical Christians.
An example similar to CWA is the Council of Biblical Manhood and Womanhood. It was established to help evangelical Christian churches defend themselves against an accommodation of secular feminism and also against evangelical feminism (which pushes for more equality in the church). It promotes complementarianism – the idea that masculinity and femininity are ordained by God and that men and women are created to complement each other.
At the other extreme, the most radical of feminists believe in the need to create a women-only society where women would be free from the patriarchy. Less angry but decidedly weirder are the feminists called “FEMEN” who once staged a protest at the Vatican where topless women feigned intercourse with crucifixes, chanting slogans against the pope and religion.
Most women tread a path between extremes, a path which is difficult and lonely. Without a firm ideology, this path is strewn with doubts and pitfalls. Some career-oriented women who have delayed motherhood, knowing that they will soon be biologically past their peak and possibly also without a partner, wonder if they should become single mothers using sperm donation. For many women, the workplace does not offer much help with maternity leave or childcare. Even when maternity leave is available, there is a still a lack of understanding about what is needed.
“Think of it as caregiver bias. If you just extend maternity leave, what is implied is that you’re still expecting me to be the primary source of care for my child, when in fact my partner wants to share the load and will need support to do so as well,” said Pamela Culpepper, an expert in corporate diversity and inclusion.2
Intensive mothering
When the glamor of the workplace wears off and/or when the misogyny and the harassment become too much, women who have the financial stability may decide to return to the role of the stay-at-home mother. Perhaps, in the home, she can feel fulfilled. Yet, young American urban and suburban mothers now parent under a new name – “intensive mothering.”
Conducting in-depth interviews of 38 women of diverse backgrounds in the United States, Sharon Hays found women describing their 2- to 4-year-old children as innocent and priceless, and believing that they – the mothers – should be primarily responsible for rearing their children, using “child-rearing methods that are child centered, expert guided, emotionally absorbing, labor intensive, and financially expensive.”3 Ms. Hays clarified four beliefs that were common to all the women in the study: mothers are more suitable caregivers than fathers; mothering should be child centered; parenting consists of a set of skills that need to be learned; and parenting is labor-intensive but an emotionally fulfilling activity.
Hays wondered if this type of mothering developed as the last defense against “the impoverishment of social ties, communal obligations and unremunerated commitments.”3 She suggested that women succumbing to social pressures to return to the home is yet another example of how society is set up to benefit men, capitalism, political leaders, and those who try to maintain a “traditional” form of family life.3 Ms. Hays concluded that the practice of intensive mothering is a class-based practice of privileged white women, entangled with capitalism in that the buying of “essential” baby products is equated with good mothering. She found this ideology to be oppressive of all women, regardless of their social class, ethnic background, household composition, and financial situation. Ms. Hays noted that many women experience guilt for not matching up to these ideals.
In “Dead End Feminism,” Elisabeth Badinter asks if the upheaval in the role of women has caused so much uncertainty that it is easier for women to regress to a time when they were in the home and knew themselves as mothers. They ask if this has been reinforced by the movement to embrace all things natural, eschewing the falseness of chemicals and other things that threaten Mother Earth.4
There is no escaping the power of the mother: she will continue to symbolize all that is good and bad as the embodiment of the Mother Archetype. All of this is the background against which you will see the new mother in the family. She will not articulate her dilemma, that is your role as the family psychiatrist.
Dr. Heru is professor of psychiatry at the University of Colorado at Denver, Aurora. She is editor of “Working With Families in Medical Settings: A Multidisciplinary Guide for Psychiatrists and Other Health Professionals” (New York: Routledge, 2013). She has no conflicts of interest to disclose. Contact Dr. Heru at [email protected].
References
1. Martin LH et al (eds.). Technologies of the Self: A Seminar with Michel Foucault. University of Massachusetts Press: Amherst, Mass.: University of Massachusetts Press, 2022.
2. How Pamela Culpepper Is Changing The Narrative Of Women In The Workplace. Huffpost. 2020 Mar 6. https://www.huffpost.com/entry/pamela-culpepper-diversity-inclusion-empowerment_n_5e56b6ffc5b62e9dc7dbc307.
3. Hays S. Cultural Contradictions of Motherhood. Yale University Press: New Haven, Conn.: Yale University Press, 1996.
4. Badinter E. (translated by Borossa J). Dead End Feminism. Malden, Mass.: Polity Press, 2006.
Jamestown, Colo., is a small mountain town several miles up through Lefthand Canyon out of Boulder, in the Rocky Mountains. The canyon roads are steep, winding, and narrow, and peopled by brightly clad cyclists struggling up the hill and flying down faster than the cars. The road through Jamestown is dusty in the summer with brightly colored oil barrels strategically placed in the middle of the single road through town. Slashed across their sides: “SLOW DOWN! Watch out for our feral children!”
Wild child or hothouse child? What is the best choice? Women bear the brunt of this deciding, whether they are working outside of the home, or stay-at-home caregivers, or both. Women know they will be blamed if they get it wrong.
Society has exacted a tall order on women who choose to have children. Patriarchal norms ask (White) women who choose both to work and have children, if they are really a “stay-at-home” mother who must work, or a “working” mother who prefers work over their children. The underlying attitude can be read as: “Are you someone who prioritizes paid work over caregiving, or are you someone who prioritizes caregiving over work?” You may be seen as a bad mother if you prioritize work over the welfare of your child. If you prioritize your child over your work, then you are not a reliable, dedicated worker. The working mother can’t win.
Woman’s central question is what kind of mother should I be? Mothers struggle with this question all their lives; when their child has difficulties, society’s question is what did you do wrong with your child? Mothers internalize the standard of the “good mother” and are aware of each minor transgression that depicts them as the “bad mother.” It is hard to escape the impossible perfectionistic standard of the good mother. But perhaps it has come time to push back on the moral imbalance.
Internalized sexism
As women move out of the home into the workplace, the societal pressures to maintain the status quo bear down on women, trying to keep them in their place.
Social pressures employ subtle “technologies of the self,” so that women – as any oppressed group – learn to internalize these technologies, and monitor themselves.1 This is now widely accepted as internalized sexism, whereby women feel that they are not good enough, do not have the right qualifications, and are “less” than the dominant group (men). This phenomenon is also recognized when racial and ethnic biases are assimilated unconsciously, as internalized racism. Should we also have internalized “momism”?
Women are caught between trying to claim their individualism as well as feeling the responsibility to be the self-denying mother. Everyone has an opinion about the place of women. Conservative activist Phyllis Schlafly considered “women’s lib” to be un-American, citing women in the military and the establishment of federal day care centers as actions of a communist state. A similar ideology helped form the antifeminist organization Concerned Women for America, which self-reports that it is the largest American public policy women’s organization. Formed in opposition to the National Organization for Women, CWA is focused on maintaining the traditional family, as understood by (White) evangelical Christians.
An example similar to CWA is the Council of Biblical Manhood and Womanhood. It was established to help evangelical Christian churches defend themselves against an accommodation of secular feminism and also against evangelical feminism (which pushes for more equality in the church). It promotes complementarianism – the idea that masculinity and femininity are ordained by God and that men and women are created to complement each other.
At the other extreme, the most radical of feminists believe in the need to create a women-only society where women would be free from the patriarchy. Less angry but decidedly weirder are the feminists called “FEMEN” who once staged a protest at the Vatican where topless women feigned intercourse with crucifixes, chanting slogans against the pope and religion.
Most women tread a path between extremes, a path which is difficult and lonely. Without a firm ideology, this path is strewn with doubts and pitfalls. Some career-oriented women who have delayed motherhood, knowing that they will soon be biologically past their peak and possibly also without a partner, wonder if they should become single mothers using sperm donation. For many women, the workplace does not offer much help with maternity leave or childcare. Even when maternity leave is available, there is a still a lack of understanding about what is needed.
“Think of it as caregiver bias. If you just extend maternity leave, what is implied is that you’re still expecting me to be the primary source of care for my child, when in fact my partner wants to share the load and will need support to do so as well,” said Pamela Culpepper, an expert in corporate diversity and inclusion.2
Intensive mothering
When the glamor of the workplace wears off and/or when the misogyny and the harassment become too much, women who have the financial stability may decide to return to the role of the stay-at-home mother. Perhaps, in the home, she can feel fulfilled. Yet, young American urban and suburban mothers now parent under a new name – “intensive mothering.”
Conducting in-depth interviews of 38 women of diverse backgrounds in the United States, Sharon Hays found women describing their 2- to 4-year-old children as innocent and priceless, and believing that they – the mothers – should be primarily responsible for rearing their children, using “child-rearing methods that are child centered, expert guided, emotionally absorbing, labor intensive, and financially expensive.”3 Ms. Hays clarified four beliefs that were common to all the women in the study: mothers are more suitable caregivers than fathers; mothering should be child centered; parenting consists of a set of skills that need to be learned; and parenting is labor-intensive but an emotionally fulfilling activity.
Hays wondered if this type of mothering developed as the last defense against “the impoverishment of social ties, communal obligations and unremunerated commitments.”3 She suggested that women succumbing to social pressures to return to the home is yet another example of how society is set up to benefit men, capitalism, political leaders, and those who try to maintain a “traditional” form of family life.3 Ms. Hays concluded that the practice of intensive mothering is a class-based practice of privileged white women, entangled with capitalism in that the buying of “essential” baby products is equated with good mothering. She found this ideology to be oppressive of all women, regardless of their social class, ethnic background, household composition, and financial situation. Ms. Hays noted that many women experience guilt for not matching up to these ideals.
In “Dead End Feminism,” Elisabeth Badinter asks if the upheaval in the role of women has caused so much uncertainty that it is easier for women to regress to a time when they were in the home and knew themselves as mothers. They ask if this has been reinforced by the movement to embrace all things natural, eschewing the falseness of chemicals and other things that threaten Mother Earth.4
There is no escaping the power of the mother: she will continue to symbolize all that is good and bad as the embodiment of the Mother Archetype. All of this is the background against which you will see the new mother in the family. She will not articulate her dilemma, that is your role as the family psychiatrist.
Dr. Heru is professor of psychiatry at the University of Colorado at Denver, Aurora. She is editor of “Working With Families in Medical Settings: A Multidisciplinary Guide for Psychiatrists and Other Health Professionals” (New York: Routledge, 2013). She has no conflicts of interest to disclose. Contact Dr. Heru at [email protected].
References
1. Martin LH et al (eds.). Technologies of the Self: A Seminar with Michel Foucault. University of Massachusetts Press: Amherst, Mass.: University of Massachusetts Press, 2022.
2. How Pamela Culpepper Is Changing The Narrative Of Women In The Workplace. Huffpost. 2020 Mar 6. https://www.huffpost.com/entry/pamela-culpepper-diversity-inclusion-empowerment_n_5e56b6ffc5b62e9dc7dbc307.
3. Hays S. Cultural Contradictions of Motherhood. Yale University Press: New Haven, Conn.: Yale University Press, 1996.
4. Badinter E. (translated by Borossa J). Dead End Feminism. Malden, Mass.: Polity Press, 2006.
Jamestown, Colo., is a small mountain town several miles up through Lefthand Canyon out of Boulder, in the Rocky Mountains. The canyon roads are steep, winding, and narrow, and peopled by brightly clad cyclists struggling up the hill and flying down faster than the cars. The road through Jamestown is dusty in the summer with brightly colored oil barrels strategically placed in the middle of the single road through town. Slashed across their sides: “SLOW DOWN! Watch out for our feral children!”
Wild child or hothouse child? What is the best choice? Women bear the brunt of this deciding, whether they are working outside of the home, or stay-at-home caregivers, or both. Women know they will be blamed if they get it wrong.
Society has exacted a tall order on women who choose to have children. Patriarchal norms ask (White) women who choose both to work and have children, if they are really a “stay-at-home” mother who must work, or a “working” mother who prefers work over their children. The underlying attitude can be read as: “Are you someone who prioritizes paid work over caregiving, or are you someone who prioritizes caregiving over work?” You may be seen as a bad mother if you prioritize work over the welfare of your child. If you prioritize your child over your work, then you are not a reliable, dedicated worker. The working mother can’t win.
Woman’s central question is what kind of mother should I be? Mothers struggle with this question all their lives; when their child has difficulties, society’s question is what did you do wrong with your child? Mothers internalize the standard of the “good mother” and are aware of each minor transgression that depicts them as the “bad mother.” It is hard to escape the impossible perfectionistic standard of the good mother. But perhaps it has come time to push back on the moral imbalance.
Internalized sexism
As women move out of the home into the workplace, the societal pressures to maintain the status quo bear down on women, trying to keep them in their place.
Social pressures employ subtle “technologies of the self,” so that women – as any oppressed group – learn to internalize these technologies, and monitor themselves.1 This is now widely accepted as internalized sexism, whereby women feel that they are not good enough, do not have the right qualifications, and are “less” than the dominant group (men). This phenomenon is also recognized when racial and ethnic biases are assimilated unconsciously, as internalized racism. Should we also have internalized “momism”?
Women are caught between trying to claim their individualism as well as feeling the responsibility to be the self-denying mother. Everyone has an opinion about the place of women. Conservative activist Phyllis Schlafly considered “women’s lib” to be un-American, citing women in the military and the establishment of federal day care centers as actions of a communist state. A similar ideology helped form the antifeminist organization Concerned Women for America, which self-reports that it is the largest American public policy women’s organization. Formed in opposition to the National Organization for Women, CWA is focused on maintaining the traditional family, as understood by (White) evangelical Christians.
An example similar to CWA is the Council of Biblical Manhood and Womanhood. It was established to help evangelical Christian churches defend themselves against an accommodation of secular feminism and also against evangelical feminism (which pushes for more equality in the church). It promotes complementarianism – the idea that masculinity and femininity are ordained by God and that men and women are created to complement each other.
At the other extreme, the most radical of feminists believe in the need to create a women-only society where women would be free from the patriarchy. Less angry but decidedly weirder are the feminists called “FEMEN” who once staged a protest at the Vatican where topless women feigned intercourse with crucifixes, chanting slogans against the pope and religion.
Most women tread a path between extremes, a path which is difficult and lonely. Without a firm ideology, this path is strewn with doubts and pitfalls. Some career-oriented women who have delayed motherhood, knowing that they will soon be biologically past their peak and possibly also without a partner, wonder if they should become single mothers using sperm donation. For many women, the workplace does not offer much help with maternity leave or childcare. Even when maternity leave is available, there is a still a lack of understanding about what is needed.
“Think of it as caregiver bias. If you just extend maternity leave, what is implied is that you’re still expecting me to be the primary source of care for my child, when in fact my partner wants to share the load and will need support to do so as well,” said Pamela Culpepper, an expert in corporate diversity and inclusion.2
Intensive mothering
When the glamor of the workplace wears off and/or when the misogyny and the harassment become too much, women who have the financial stability may decide to return to the role of the stay-at-home mother. Perhaps, in the home, she can feel fulfilled. Yet, young American urban and suburban mothers now parent under a new name – “intensive mothering.”
Conducting in-depth interviews of 38 women of diverse backgrounds in the United States, Sharon Hays found women describing their 2- to 4-year-old children as innocent and priceless, and believing that they – the mothers – should be primarily responsible for rearing their children, using “child-rearing methods that are child centered, expert guided, emotionally absorbing, labor intensive, and financially expensive.”3 Ms. Hays clarified four beliefs that were common to all the women in the study: mothers are more suitable caregivers than fathers; mothering should be child centered; parenting consists of a set of skills that need to be learned; and parenting is labor-intensive but an emotionally fulfilling activity.
Hays wondered if this type of mothering developed as the last defense against “the impoverishment of social ties, communal obligations and unremunerated commitments.”3 She suggested that women succumbing to social pressures to return to the home is yet another example of how society is set up to benefit men, capitalism, political leaders, and those who try to maintain a “traditional” form of family life.3 Ms. Hays concluded that the practice of intensive mothering is a class-based practice of privileged white women, entangled with capitalism in that the buying of “essential” baby products is equated with good mothering. She found this ideology to be oppressive of all women, regardless of their social class, ethnic background, household composition, and financial situation. Ms. Hays noted that many women experience guilt for not matching up to these ideals.
In “Dead End Feminism,” Elisabeth Badinter asks if the upheaval in the role of women has caused so much uncertainty that it is easier for women to regress to a time when they were in the home and knew themselves as mothers. They ask if this has been reinforced by the movement to embrace all things natural, eschewing the falseness of chemicals and other things that threaten Mother Earth.4
There is no escaping the power of the mother: she will continue to symbolize all that is good and bad as the embodiment of the Mother Archetype. All of this is the background against which you will see the new mother in the family. She will not articulate her dilemma, that is your role as the family psychiatrist.
Dr. Heru is professor of psychiatry at the University of Colorado at Denver, Aurora. She is editor of “Working With Families in Medical Settings: A Multidisciplinary Guide for Psychiatrists and Other Health Professionals” (New York: Routledge, 2013). She has no conflicts of interest to disclose. Contact Dr. Heru at [email protected].
References
1. Martin LH et al (eds.). Technologies of the Self: A Seminar with Michel Foucault. University of Massachusetts Press: Amherst, Mass.: University of Massachusetts Press, 2022.
2. How Pamela Culpepper Is Changing The Narrative Of Women In The Workplace. Huffpost. 2020 Mar 6. https://www.huffpost.com/entry/pamela-culpepper-diversity-inclusion-empowerment_n_5e56b6ffc5b62e9dc7dbc307.
3. Hays S. Cultural Contradictions of Motherhood. Yale University Press: New Haven, Conn.: Yale University Press, 1996.
4. Badinter E. (translated by Borossa J). Dead End Feminism. Malden, Mass.: Polity Press, 2006.
Termination of pregnancy for medical reasons: A mental health perspective
Termination of pregnancy for medical reasons (TFMR) occurs when a pregnancy is ended due to medical complications that threaten the health of a pregnant individual and/or fetus, or when a fetus has a poor prognosis or life-limiting diagnosis. It is distinct from the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists identification of all abortions as medically indicated. Common indications for TFMR include life-threatening pregnancy complications (eg, placental abruption, hyperemesis gravidarum, exacerbation of psychiatric illness), chromosomal abnormalities (eg, Trisomy 13, 18, and 21; Klinefelter syndrome), and fetal anomalies (eg, neural tube defects, cardiac defects, renal agenesis). In this article, we discuss the negative psychological outcomes of TFMR, and how to screen and intervene to best help women who experience TFMR.
Psychiatric sequelae of TFMR
Unlike abortions in general, negative psychological outcomes are common among women who experience TFMR.1 Nearly one-half of women develop symptoms of posttraumatic stress disorder (PTSD), and approximately one-fourth show signs of depression at 4 months after termination.2 Such symptoms usually improve with time but may return around trauma anniversaries (date of diagnosis or termination). Women with a history of trauma, a prior psychiatric diagnosis, and/or no living children are at greater risk. Self-blame, doubt, and high levels of distress are also risk factors.2-4 Protective factors include positive coping strategies (such as acceptance or reframing), higher perceived social support, and high self-efficacy.3,4
Screening: What to ask, and how
Use open-ended questions to ask about a patient’s obstetric history:
- Have you ever been pregnant?
- If you’re comfortable sharing, what were the outcomes of these pregnancies?
If a woman discloses that she has experienced a TFMR, screen for and normalize psychiatric outcomes by asking:
- Symptoms of grief, depression, and anxiety are common after TFMR. Have you experienced such symptoms?
- What impact has terminating your pregnancy for medical reasons had on your mental health?
Screening tools such as the General Self-Efficacy Scale can help assess predictive factors, while other scales can assess specific diagnoses (eg, Patient Health Questionaire-9 for depression, Impact of Event Scale-Revised and PTSD Checklist for DSM-5 for trauma-related symptoms, Traumatic Grief Inventory Self Report Version for pathological grief). The Edinburgh Postnatal Depression Scale can assess for depression, but if you use this instrument, exclude statements that reference a current pregnancy or recent delivery.
How to best help
Interventions should be specific and targeted. Thus, consider the individual nature of the experience and variation in attachment that can occur over time.5 OB-GYN and perinatal psychiatry clinicians can recommend local resources and support groups that specifically focus on TFMR, rather than on general pregnancy loss. Refer patients to therapists who specialize in pregnancy loss, reproductive trauma, and/or TFMR. Cognitive-behavioral therapy and acceptance and commitment therapy may be appropriate and effective.3 Online support groups (such as Termination of Pregnancy for Medical Reasons; www.facebook.com/groups/TFMRgroup/) can supplement or fill gaps in local resources. Suggest books that discuss TFMR, such
1. González-Ramos Z, Zuriguel-Pérez E, Albacar-Riobóo N, et al. The emotional responses of women when terminating a pregnancy for medical reasons: a scoping review. Midwifery. 2021;103:103095. doi:10.1016/j.midw.2021.103095
2. Korenromp MJ, Page-Christiaens GCML, van den Bout J, et al. Adjustment to termination of pregnancy for fetal anomaly: a longitudinal study in women at 4, 8, and 16 months. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2009;201(2):160.e1-7.
3. Lafarge C, Mitchell K, Fox P. Perinatal grief following a termination of pregnancy for foetal abnormality: the impact of coping strategies. Prenat Diagn. 2013;33(12):1173-1182.
4. Korenromp MJ, Christiaens GC, van den Bout J, et al. Long-term psychological consequences of pregnancy termination for fetal abnormality: a cross-sectional study. Prenat Diagn. 2005;25(3):253-260.
5. Lou S, Hvidtjørn D, Jørgensen ML, Vogel I. “I had to think: this is not a child.” A qualitative exploration of how women/couples articulate their relation to the fetus/child following termination of a wanted pregnancy due to Down syndrome. Sex Reprod Healthc. 2021;28:100606. doi: 10.1016/j.srhc.2021.100606
6. Brooks C (ed.). Our Heartbreaking Choices: Forty-Six Women Share Their Stories of Interrupting a Much-Wanted Pregnancy. iUniverse; 2008.
Termination of pregnancy for medical reasons (TFMR) occurs when a pregnancy is ended due to medical complications that threaten the health of a pregnant individual and/or fetus, or when a fetus has a poor prognosis or life-limiting diagnosis. It is distinct from the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists identification of all abortions as medically indicated. Common indications for TFMR include life-threatening pregnancy complications (eg, placental abruption, hyperemesis gravidarum, exacerbation of psychiatric illness), chromosomal abnormalities (eg, Trisomy 13, 18, and 21; Klinefelter syndrome), and fetal anomalies (eg, neural tube defects, cardiac defects, renal agenesis). In this article, we discuss the negative psychological outcomes of TFMR, and how to screen and intervene to best help women who experience TFMR.
Psychiatric sequelae of TFMR
Unlike abortions in general, negative psychological outcomes are common among women who experience TFMR.1 Nearly one-half of women develop symptoms of posttraumatic stress disorder (PTSD), and approximately one-fourth show signs of depression at 4 months after termination.2 Such symptoms usually improve with time but may return around trauma anniversaries (date of diagnosis or termination). Women with a history of trauma, a prior psychiatric diagnosis, and/or no living children are at greater risk. Self-blame, doubt, and high levels of distress are also risk factors.2-4 Protective factors include positive coping strategies (such as acceptance or reframing), higher perceived social support, and high self-efficacy.3,4
Screening: What to ask, and how
Use open-ended questions to ask about a patient’s obstetric history:
- Have you ever been pregnant?
- If you’re comfortable sharing, what were the outcomes of these pregnancies?
If a woman discloses that she has experienced a TFMR, screen for and normalize psychiatric outcomes by asking:
- Symptoms of grief, depression, and anxiety are common after TFMR. Have you experienced such symptoms?
- What impact has terminating your pregnancy for medical reasons had on your mental health?
Screening tools such as the General Self-Efficacy Scale can help assess predictive factors, while other scales can assess specific diagnoses (eg, Patient Health Questionaire-9 for depression, Impact of Event Scale-Revised and PTSD Checklist for DSM-5 for trauma-related symptoms, Traumatic Grief Inventory Self Report Version for pathological grief). The Edinburgh Postnatal Depression Scale can assess for depression, but if you use this instrument, exclude statements that reference a current pregnancy or recent delivery.
How to best help
Interventions should be specific and targeted. Thus, consider the individual nature of the experience and variation in attachment that can occur over time.5 OB-GYN and perinatal psychiatry clinicians can recommend local resources and support groups that specifically focus on TFMR, rather than on general pregnancy loss. Refer patients to therapists who specialize in pregnancy loss, reproductive trauma, and/or TFMR. Cognitive-behavioral therapy and acceptance and commitment therapy may be appropriate and effective.3 Online support groups (such as Termination of Pregnancy for Medical Reasons; www.facebook.com/groups/TFMRgroup/) can supplement or fill gaps in local resources. Suggest books that discuss TFMR, such
Termination of pregnancy for medical reasons (TFMR) occurs when a pregnancy is ended due to medical complications that threaten the health of a pregnant individual and/or fetus, or when a fetus has a poor prognosis or life-limiting diagnosis. It is distinct from the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists identification of all abortions as medically indicated. Common indications for TFMR include life-threatening pregnancy complications (eg, placental abruption, hyperemesis gravidarum, exacerbation of psychiatric illness), chromosomal abnormalities (eg, Trisomy 13, 18, and 21; Klinefelter syndrome), and fetal anomalies (eg, neural tube defects, cardiac defects, renal agenesis). In this article, we discuss the negative psychological outcomes of TFMR, and how to screen and intervene to best help women who experience TFMR.
Psychiatric sequelae of TFMR
Unlike abortions in general, negative psychological outcomes are common among women who experience TFMR.1 Nearly one-half of women develop symptoms of posttraumatic stress disorder (PTSD), and approximately one-fourth show signs of depression at 4 months after termination.2 Such symptoms usually improve with time but may return around trauma anniversaries (date of diagnosis or termination). Women with a history of trauma, a prior psychiatric diagnosis, and/or no living children are at greater risk. Self-blame, doubt, and high levels of distress are also risk factors.2-4 Protective factors include positive coping strategies (such as acceptance or reframing), higher perceived social support, and high self-efficacy.3,4
Screening: What to ask, and how
Use open-ended questions to ask about a patient’s obstetric history:
- Have you ever been pregnant?
- If you’re comfortable sharing, what were the outcomes of these pregnancies?
If a woman discloses that she has experienced a TFMR, screen for and normalize psychiatric outcomes by asking:
- Symptoms of grief, depression, and anxiety are common after TFMR. Have you experienced such symptoms?
- What impact has terminating your pregnancy for medical reasons had on your mental health?
Screening tools such as the General Self-Efficacy Scale can help assess predictive factors, while other scales can assess specific diagnoses (eg, Patient Health Questionaire-9 for depression, Impact of Event Scale-Revised and PTSD Checklist for DSM-5 for trauma-related symptoms, Traumatic Grief Inventory Self Report Version for pathological grief). The Edinburgh Postnatal Depression Scale can assess for depression, but if you use this instrument, exclude statements that reference a current pregnancy or recent delivery.
How to best help
Interventions should be specific and targeted. Thus, consider the individual nature of the experience and variation in attachment that can occur over time.5 OB-GYN and perinatal psychiatry clinicians can recommend local resources and support groups that specifically focus on TFMR, rather than on general pregnancy loss. Refer patients to therapists who specialize in pregnancy loss, reproductive trauma, and/or TFMR. Cognitive-behavioral therapy and acceptance and commitment therapy may be appropriate and effective.3 Online support groups (such as Termination of Pregnancy for Medical Reasons; www.facebook.com/groups/TFMRgroup/) can supplement or fill gaps in local resources. Suggest books that discuss TFMR, such
1. González-Ramos Z, Zuriguel-Pérez E, Albacar-Riobóo N, et al. The emotional responses of women when terminating a pregnancy for medical reasons: a scoping review. Midwifery. 2021;103:103095. doi:10.1016/j.midw.2021.103095
2. Korenromp MJ, Page-Christiaens GCML, van den Bout J, et al. Adjustment to termination of pregnancy for fetal anomaly: a longitudinal study in women at 4, 8, and 16 months. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2009;201(2):160.e1-7.
3. Lafarge C, Mitchell K, Fox P. Perinatal grief following a termination of pregnancy for foetal abnormality: the impact of coping strategies. Prenat Diagn. 2013;33(12):1173-1182.
4. Korenromp MJ, Christiaens GC, van den Bout J, et al. Long-term psychological consequences of pregnancy termination for fetal abnormality: a cross-sectional study. Prenat Diagn. 2005;25(3):253-260.
5. Lou S, Hvidtjørn D, Jørgensen ML, Vogel I. “I had to think: this is not a child.” A qualitative exploration of how women/couples articulate their relation to the fetus/child following termination of a wanted pregnancy due to Down syndrome. Sex Reprod Healthc. 2021;28:100606. doi: 10.1016/j.srhc.2021.100606
6. Brooks C (ed.). Our Heartbreaking Choices: Forty-Six Women Share Their Stories of Interrupting a Much-Wanted Pregnancy. iUniverse; 2008.
1. González-Ramos Z, Zuriguel-Pérez E, Albacar-Riobóo N, et al. The emotional responses of women when terminating a pregnancy for medical reasons: a scoping review. Midwifery. 2021;103:103095. doi:10.1016/j.midw.2021.103095
2. Korenromp MJ, Page-Christiaens GCML, van den Bout J, et al. Adjustment to termination of pregnancy for fetal anomaly: a longitudinal study in women at 4, 8, and 16 months. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2009;201(2):160.e1-7.
3. Lafarge C, Mitchell K, Fox P. Perinatal grief following a termination of pregnancy for foetal abnormality: the impact of coping strategies. Prenat Diagn. 2013;33(12):1173-1182.
4. Korenromp MJ, Christiaens GC, van den Bout J, et al. Long-term psychological consequences of pregnancy termination for fetal abnormality: a cross-sectional study. Prenat Diagn. 2005;25(3):253-260.
5. Lou S, Hvidtjørn D, Jørgensen ML, Vogel I. “I had to think: this is not a child.” A qualitative exploration of how women/couples articulate their relation to the fetus/child following termination of a wanted pregnancy due to Down syndrome. Sex Reprod Healthc. 2021;28:100606. doi: 10.1016/j.srhc.2021.100606
6. Brooks C (ed.). Our Heartbreaking Choices: Forty-Six Women Share Their Stories of Interrupting a Much-Wanted Pregnancy. iUniverse; 2008.
Children with migraine at high risk of comorbid anxiety, depression
Children and adolescents with migraine are about twice as likely to have an anxiety or depressive disorder as those without migraine, results from a new review and meta-analysis suggest.
“This is compelling, high-level evidence showing there’s this established comorbidity between migraine and anxiety and depressive symptoms and disorders in this age group,” co-investigator Serena L. Orr, MD, a pediatric neurologist and headache specialist at Alberta Children’s Hospital and assistant professor in the department of pediatrics, University of Calgary (Alta.), told this news organization.
The results “should compel every clinician who is seeing a child or adolescent with migraine to screen for anxiety and depression and to manage that if it’s present. That should be the standard of care with this level of evidence,” Dr. Orr said.
The findings were presented at the American Headache Society (AHS) Annual Meeting 2022.
Incidence divergence
Previous studies have suggested that 10%-20% of children and adolescents will experience migraine at some point before adulthood, with the prevalence increasing after puberty.
While the female-to-male ratio is about 1:1 before puberty, there is a “big divergence in incidence curves” afterward – with the female-to-male ratio reaching 2-3:1 in adulthood, Dr. Orr noted. Experts believe hormones drive this divergence, she said, noting that male adults with migraine have lower testosterone levels than male adults without migraine.
Dr. Orr and her colleagues were keen to investigate the relationship between child migraine and anxiety symptoms and disorders, as well as between child migraine and depression symptoms and disorders. They searched the literature for related case-control, cross-sectional, and cohort studies with participants of ages up to 18 years.
The researchers selected 80 studies to include in the review. Most of the studies were carried out in the past 30 to 40 years and were in English and other languages. Both community-based and clinical studies were included.
Of the total, 73 studies reported on the association between the exposures and migraine, and 51 were amenable to quantitative pooling.
Results from a meta-analysis that included 16 studies that compared children and adolescents who had migraine with their healthy peers showed a significant association between migraine and anxiety symptoms (standardized mean difference, 1.13; 95% confidence interval, 0.64-1.63; P < .0001).
Compared with children who did not have migraine, those with migraine had almost twice the odds of an anxiety disorder in 15 studies (odds ratio, 1.93; 95% CI, 1.49-2.50; P < .0001).
In addition, there was an association between migraine and depressive symptoms in 17 relevant studies (SMD, 0.67; 95% CI, 0.46-0.87; P < .0001). Participants with versus without migraine also had higher odds of depressive disorders in 18 studies (OR, 2.01; 95% CI, 1.46-2.78; P < .0001).
Effect sizes were similar between community-based and clinic studies. Dr. Orr said it is important to note that the analysis wasn’t restricted to studies with “just kids with really high disease burden who are going to naturally be more predisposed to psychiatric comorbidity.”
‘Shocking’ lack of research
The researchers were also interested in determining whether having migraine along with anxiety or depression symptoms or disorders could affect headache-specific outcomes and whether such patients’ conditions would be more refractory to treatment. However, these outcomes were “all over the place” in the 18 relevant studies, Dr. Orr reported.
“Some looked at headache frequency, some at disability, some at school functioning; so, we were not able to put them into a meta-analysis,” she said.
Only two studies examined whether anxiety or depression earlier in childhood predisposes to subsequent migraine, so that issue is still unresolved, Dr. Orr added.
The investigators also assessed whether outcomes with migraine are similar to those with other headache types, such as tension-type headaches. “We did not find a difference at the symptom or disorder level, but there were fewer of those studies” – and these, too, were heterogeneous, said Dr. Orr.
The researchers did not find any studies of the association between migraine and trauma, which Dr. Orr said was “shocking.”
“In the broader pediatric chronic-pain literature, there’s research showing that having a trauma or stress-related disorder is associated with more chronic pain and worse chronic pain outcomes, but we could not find a study that specifically looked at that question in migraine,” she added.
Emerging evidence suggests there may be a bidirectional relationship between migraine and anxiety/depression, at least in adults. Dr. Orr said having these symptoms appears to raise the risk for migraine, but whether that’s environmental or driven by shared genetics isn’t clear.
Experiencing chronic pain may also predispose individuals to anxiety and depression, “but we need more studies on this.”
In addition to screening children with migraine for anxiety and depression, clinicians should advocate for better access to mental health resources for patients with these comorbidities, Dr. Orr noted.
She added that a limitation of the review was that 82.5% of the studies reported unadjusted associations and that 26.3% of the studies were of low quality.
High-level evidence
Sara Pavitt, MD, chief of the Pediatric Headache Program and assistant professor in the department of neurology, the University of Texas at Austin, said the investigators “should be applauded” for providing “high-level evidence” to better understand the relationship between migraine and anxiety and depression in pediatric patients.
Such information has been “lacking” for this patient population, said Dr. Pavitt, who was not involved with the research.
She noted that screening kids for mood disorders is challenging, given the relatively few pediatric mental health care providers. A referral for a psychiatric follow-up can mean a 9- to 12-month wait – or even longer for children who do not have insurance or use Medicare.
“Providers need to have more incentives to care for patients with Medicare or lack of insurance – these patients are often excluded from practices because reimbursement is so poor,” Dr. Pavitt said.
Additional pediatric studies are needed to understand how other mental health disorders, such as panic disorder, phobias, and posttraumatic stress disorder, may be related to migraine, she added.
The study received no outside funding. Dr. Orr has received grants from the Canadian Institutes of Health Research and royalties from Cambridge University Press for book publication, and she is on editorial boards of Headache, Neurology, and the American Migraine Foundation. Dr. Pavitt serves on an advisory board for Theranica, which produces a neuromodulation device for acute migraine treatment, although this is not directly relevant to this review.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Children and adolescents with migraine are about twice as likely to have an anxiety or depressive disorder as those without migraine, results from a new review and meta-analysis suggest.
“This is compelling, high-level evidence showing there’s this established comorbidity between migraine and anxiety and depressive symptoms and disorders in this age group,” co-investigator Serena L. Orr, MD, a pediatric neurologist and headache specialist at Alberta Children’s Hospital and assistant professor in the department of pediatrics, University of Calgary (Alta.), told this news organization.
The results “should compel every clinician who is seeing a child or adolescent with migraine to screen for anxiety and depression and to manage that if it’s present. That should be the standard of care with this level of evidence,” Dr. Orr said.
The findings were presented at the American Headache Society (AHS) Annual Meeting 2022.
Incidence divergence
Previous studies have suggested that 10%-20% of children and adolescents will experience migraine at some point before adulthood, with the prevalence increasing after puberty.
While the female-to-male ratio is about 1:1 before puberty, there is a “big divergence in incidence curves” afterward – with the female-to-male ratio reaching 2-3:1 in adulthood, Dr. Orr noted. Experts believe hormones drive this divergence, she said, noting that male adults with migraine have lower testosterone levels than male adults without migraine.
Dr. Orr and her colleagues were keen to investigate the relationship between child migraine and anxiety symptoms and disorders, as well as between child migraine and depression symptoms and disorders. They searched the literature for related case-control, cross-sectional, and cohort studies with participants of ages up to 18 years.
The researchers selected 80 studies to include in the review. Most of the studies were carried out in the past 30 to 40 years and were in English and other languages. Both community-based and clinical studies were included.
Of the total, 73 studies reported on the association between the exposures and migraine, and 51 were amenable to quantitative pooling.
Results from a meta-analysis that included 16 studies that compared children and adolescents who had migraine with their healthy peers showed a significant association between migraine and anxiety symptoms (standardized mean difference, 1.13; 95% confidence interval, 0.64-1.63; P < .0001).
Compared with children who did not have migraine, those with migraine had almost twice the odds of an anxiety disorder in 15 studies (odds ratio, 1.93; 95% CI, 1.49-2.50; P < .0001).
In addition, there was an association between migraine and depressive symptoms in 17 relevant studies (SMD, 0.67; 95% CI, 0.46-0.87; P < .0001). Participants with versus without migraine also had higher odds of depressive disorders in 18 studies (OR, 2.01; 95% CI, 1.46-2.78; P < .0001).
Effect sizes were similar between community-based and clinic studies. Dr. Orr said it is important to note that the analysis wasn’t restricted to studies with “just kids with really high disease burden who are going to naturally be more predisposed to psychiatric comorbidity.”
‘Shocking’ lack of research
The researchers were also interested in determining whether having migraine along with anxiety or depression symptoms or disorders could affect headache-specific outcomes and whether such patients’ conditions would be more refractory to treatment. However, these outcomes were “all over the place” in the 18 relevant studies, Dr. Orr reported.
“Some looked at headache frequency, some at disability, some at school functioning; so, we were not able to put them into a meta-analysis,” she said.
Only two studies examined whether anxiety or depression earlier in childhood predisposes to subsequent migraine, so that issue is still unresolved, Dr. Orr added.
The investigators also assessed whether outcomes with migraine are similar to those with other headache types, such as tension-type headaches. “We did not find a difference at the symptom or disorder level, but there were fewer of those studies” – and these, too, were heterogeneous, said Dr. Orr.
The researchers did not find any studies of the association between migraine and trauma, which Dr. Orr said was “shocking.”
“In the broader pediatric chronic-pain literature, there’s research showing that having a trauma or stress-related disorder is associated with more chronic pain and worse chronic pain outcomes, but we could not find a study that specifically looked at that question in migraine,” she added.
Emerging evidence suggests there may be a bidirectional relationship between migraine and anxiety/depression, at least in adults. Dr. Orr said having these symptoms appears to raise the risk for migraine, but whether that’s environmental or driven by shared genetics isn’t clear.
Experiencing chronic pain may also predispose individuals to anxiety and depression, “but we need more studies on this.”
In addition to screening children with migraine for anxiety and depression, clinicians should advocate for better access to mental health resources for patients with these comorbidities, Dr. Orr noted.
She added that a limitation of the review was that 82.5% of the studies reported unadjusted associations and that 26.3% of the studies were of low quality.
High-level evidence
Sara Pavitt, MD, chief of the Pediatric Headache Program and assistant professor in the department of neurology, the University of Texas at Austin, said the investigators “should be applauded” for providing “high-level evidence” to better understand the relationship between migraine and anxiety and depression in pediatric patients.
Such information has been “lacking” for this patient population, said Dr. Pavitt, who was not involved with the research.
She noted that screening kids for mood disorders is challenging, given the relatively few pediatric mental health care providers. A referral for a psychiatric follow-up can mean a 9- to 12-month wait – or even longer for children who do not have insurance or use Medicare.
“Providers need to have more incentives to care for patients with Medicare or lack of insurance – these patients are often excluded from practices because reimbursement is so poor,” Dr. Pavitt said.
Additional pediatric studies are needed to understand how other mental health disorders, such as panic disorder, phobias, and posttraumatic stress disorder, may be related to migraine, she added.
The study received no outside funding. Dr. Orr has received grants from the Canadian Institutes of Health Research and royalties from Cambridge University Press for book publication, and she is on editorial boards of Headache, Neurology, and the American Migraine Foundation. Dr. Pavitt serves on an advisory board for Theranica, which produces a neuromodulation device for acute migraine treatment, although this is not directly relevant to this review.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Children and adolescents with migraine are about twice as likely to have an anxiety or depressive disorder as those without migraine, results from a new review and meta-analysis suggest.
“This is compelling, high-level evidence showing there’s this established comorbidity between migraine and anxiety and depressive symptoms and disorders in this age group,” co-investigator Serena L. Orr, MD, a pediatric neurologist and headache specialist at Alberta Children’s Hospital and assistant professor in the department of pediatrics, University of Calgary (Alta.), told this news organization.
The results “should compel every clinician who is seeing a child or adolescent with migraine to screen for anxiety and depression and to manage that if it’s present. That should be the standard of care with this level of evidence,” Dr. Orr said.
The findings were presented at the American Headache Society (AHS) Annual Meeting 2022.
Incidence divergence
Previous studies have suggested that 10%-20% of children and adolescents will experience migraine at some point before adulthood, with the prevalence increasing after puberty.
While the female-to-male ratio is about 1:1 before puberty, there is a “big divergence in incidence curves” afterward – with the female-to-male ratio reaching 2-3:1 in adulthood, Dr. Orr noted. Experts believe hormones drive this divergence, she said, noting that male adults with migraine have lower testosterone levels than male adults without migraine.
Dr. Orr and her colleagues were keen to investigate the relationship between child migraine and anxiety symptoms and disorders, as well as between child migraine and depression symptoms and disorders. They searched the literature for related case-control, cross-sectional, and cohort studies with participants of ages up to 18 years.
The researchers selected 80 studies to include in the review. Most of the studies were carried out in the past 30 to 40 years and were in English and other languages. Both community-based and clinical studies were included.
Of the total, 73 studies reported on the association between the exposures and migraine, and 51 were amenable to quantitative pooling.
Results from a meta-analysis that included 16 studies that compared children and adolescents who had migraine with their healthy peers showed a significant association between migraine and anxiety symptoms (standardized mean difference, 1.13; 95% confidence interval, 0.64-1.63; P < .0001).
Compared with children who did not have migraine, those with migraine had almost twice the odds of an anxiety disorder in 15 studies (odds ratio, 1.93; 95% CI, 1.49-2.50; P < .0001).
In addition, there was an association between migraine and depressive symptoms in 17 relevant studies (SMD, 0.67; 95% CI, 0.46-0.87; P < .0001). Participants with versus without migraine also had higher odds of depressive disorders in 18 studies (OR, 2.01; 95% CI, 1.46-2.78; P < .0001).
Effect sizes were similar between community-based and clinic studies. Dr. Orr said it is important to note that the analysis wasn’t restricted to studies with “just kids with really high disease burden who are going to naturally be more predisposed to psychiatric comorbidity.”
‘Shocking’ lack of research
The researchers were also interested in determining whether having migraine along with anxiety or depression symptoms or disorders could affect headache-specific outcomes and whether such patients’ conditions would be more refractory to treatment. However, these outcomes were “all over the place” in the 18 relevant studies, Dr. Orr reported.
“Some looked at headache frequency, some at disability, some at school functioning; so, we were not able to put them into a meta-analysis,” she said.
Only two studies examined whether anxiety or depression earlier in childhood predisposes to subsequent migraine, so that issue is still unresolved, Dr. Orr added.
The investigators also assessed whether outcomes with migraine are similar to those with other headache types, such as tension-type headaches. “We did not find a difference at the symptom or disorder level, but there were fewer of those studies” – and these, too, were heterogeneous, said Dr. Orr.
The researchers did not find any studies of the association between migraine and trauma, which Dr. Orr said was “shocking.”
“In the broader pediatric chronic-pain literature, there’s research showing that having a trauma or stress-related disorder is associated with more chronic pain and worse chronic pain outcomes, but we could not find a study that specifically looked at that question in migraine,” she added.
Emerging evidence suggests there may be a bidirectional relationship between migraine and anxiety/depression, at least in adults. Dr. Orr said having these symptoms appears to raise the risk for migraine, but whether that’s environmental or driven by shared genetics isn’t clear.
Experiencing chronic pain may also predispose individuals to anxiety and depression, “but we need more studies on this.”
In addition to screening children with migraine for anxiety and depression, clinicians should advocate for better access to mental health resources for patients with these comorbidities, Dr. Orr noted.
She added that a limitation of the review was that 82.5% of the studies reported unadjusted associations and that 26.3% of the studies were of low quality.
High-level evidence
Sara Pavitt, MD, chief of the Pediatric Headache Program and assistant professor in the department of neurology, the University of Texas at Austin, said the investigators “should be applauded” for providing “high-level evidence” to better understand the relationship between migraine and anxiety and depression in pediatric patients.
Such information has been “lacking” for this patient population, said Dr. Pavitt, who was not involved with the research.
She noted that screening kids for mood disorders is challenging, given the relatively few pediatric mental health care providers. A referral for a psychiatric follow-up can mean a 9- to 12-month wait – or even longer for children who do not have insurance or use Medicare.
“Providers need to have more incentives to care for patients with Medicare or lack of insurance – these patients are often excluded from practices because reimbursement is so poor,” Dr. Pavitt said.
Additional pediatric studies are needed to understand how other mental health disorders, such as panic disorder, phobias, and posttraumatic stress disorder, may be related to migraine, she added.
The study received no outside funding. Dr. Orr has received grants from the Canadian Institutes of Health Research and royalties from Cambridge University Press for book publication, and she is on editorial boards of Headache, Neurology, and the American Migraine Foundation. Dr. Pavitt serves on an advisory board for Theranica, which produces a neuromodulation device for acute migraine treatment, although this is not directly relevant to this review.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.




