User login
AD severity linked to S. aureus clonal complex types
A new study offers insight into the over time.
The research “suggests that different CC types might harbor different virulence factors and that the patient’s immune system needs to adjust to this,” concluded the authors of the study, published in the British Journal of Dermatology.
There is a strong association between disease severity and colonization with S. aureus in patients with AD, and as many as 90% are colonized with the microbe but, the authors pointed out, it’s not entirely clear how S. aureus affects the development of AD.
They added that there’s been little research into the possible effects of changes in S. aureus clonal types over time. Still, “new studies indicate that specific clonal types could be linked to specific host phenotypes, illustrating that host-microbe interactions might be important for colonization of AD skin,” they said.
The authors, led by Maja-Lisa Clausen, MD, of the department of dermatology at the University of Copenhagen, tracked 63 adult patients with AD at Denmark’s Bispebjerg Hospital from 2013-2015 to a 2016-2017 follow-up period. Their mean age was 36 years.
They analyzed bacterial swabs taken from the nose, lesional skin, and nonlesional skin. Of the 63 participants, 47 (75%) were colonized with S. aureus in at least one location when the study began, and 27 of those (57%) were still colonized at follow-up. Of the 16 patients not colonized at baseline, 7 patients (44%) had become colonized by follow-up.
Of the 27 patients who were colonized at both time points, 14 (52%) had no change in CC type.
Those who were colonized at follow-up in at least one of the three sites sampled had more severe disease, with a mean SCORAD – or disease severity score – of 37, compared with those who were not colonized at that time, with a mean SCORAD of 28 (P = .067).
There was a much bigger gap in mean SCORAD score between the 14 patients who had the same CC type at both baseline and follow-up (a mean score of 30), compared with the 11 patients with different CC types at follow-up (a mean score of 47), a statistically significant difference (P = .03). Mean severity scores went up in those who changed CC types and down in those whose CC types remained the same.
The findings “illustrate that colonization changes over time, and also probably reflect the relapsing course of this disease, as colonization likely occurs in relation to worsening of the eczema,” the study authors wrote. They cautioned that “other factors should be taken into considerations as these are known to influence AD severity, including change in treatment regimens, climate, or other disease.”
Novo Nordisk Foundation funded the study. No relevant disclosures were reported.
SOURCE: Clausen, ML et al. Br J Dermatol. 2018 Aug 2. doi: 10.1111/bjd.17033.
A new study offers insight into the over time.
The research “suggests that different CC types might harbor different virulence factors and that the patient’s immune system needs to adjust to this,” concluded the authors of the study, published in the British Journal of Dermatology.
There is a strong association between disease severity and colonization with S. aureus in patients with AD, and as many as 90% are colonized with the microbe but, the authors pointed out, it’s not entirely clear how S. aureus affects the development of AD.
They added that there’s been little research into the possible effects of changes in S. aureus clonal types over time. Still, “new studies indicate that specific clonal types could be linked to specific host phenotypes, illustrating that host-microbe interactions might be important for colonization of AD skin,” they said.
The authors, led by Maja-Lisa Clausen, MD, of the department of dermatology at the University of Copenhagen, tracked 63 adult patients with AD at Denmark’s Bispebjerg Hospital from 2013-2015 to a 2016-2017 follow-up period. Their mean age was 36 years.
They analyzed bacterial swabs taken from the nose, lesional skin, and nonlesional skin. Of the 63 participants, 47 (75%) were colonized with S. aureus in at least one location when the study began, and 27 of those (57%) were still colonized at follow-up. Of the 16 patients not colonized at baseline, 7 patients (44%) had become colonized by follow-up.
Of the 27 patients who were colonized at both time points, 14 (52%) had no change in CC type.
Those who were colonized at follow-up in at least one of the three sites sampled had more severe disease, with a mean SCORAD – or disease severity score – of 37, compared with those who were not colonized at that time, with a mean SCORAD of 28 (P = .067).
There was a much bigger gap in mean SCORAD score between the 14 patients who had the same CC type at both baseline and follow-up (a mean score of 30), compared with the 11 patients with different CC types at follow-up (a mean score of 47), a statistically significant difference (P = .03). Mean severity scores went up in those who changed CC types and down in those whose CC types remained the same.
The findings “illustrate that colonization changes over time, and also probably reflect the relapsing course of this disease, as colonization likely occurs in relation to worsening of the eczema,” the study authors wrote. They cautioned that “other factors should be taken into considerations as these are known to influence AD severity, including change in treatment regimens, climate, or other disease.”
Novo Nordisk Foundation funded the study. No relevant disclosures were reported.
SOURCE: Clausen, ML et al. Br J Dermatol. 2018 Aug 2. doi: 10.1111/bjd.17033.
A new study offers insight into the over time.
The research “suggests that different CC types might harbor different virulence factors and that the patient’s immune system needs to adjust to this,” concluded the authors of the study, published in the British Journal of Dermatology.
There is a strong association between disease severity and colonization with S. aureus in patients with AD, and as many as 90% are colonized with the microbe but, the authors pointed out, it’s not entirely clear how S. aureus affects the development of AD.
They added that there’s been little research into the possible effects of changes in S. aureus clonal types over time. Still, “new studies indicate that specific clonal types could be linked to specific host phenotypes, illustrating that host-microbe interactions might be important for colonization of AD skin,” they said.
The authors, led by Maja-Lisa Clausen, MD, of the department of dermatology at the University of Copenhagen, tracked 63 adult patients with AD at Denmark’s Bispebjerg Hospital from 2013-2015 to a 2016-2017 follow-up period. Their mean age was 36 years.
They analyzed bacterial swabs taken from the nose, lesional skin, and nonlesional skin. Of the 63 participants, 47 (75%) were colonized with S. aureus in at least one location when the study began, and 27 of those (57%) were still colonized at follow-up. Of the 16 patients not colonized at baseline, 7 patients (44%) had become colonized by follow-up.
Of the 27 patients who were colonized at both time points, 14 (52%) had no change in CC type.
Those who were colonized at follow-up in at least one of the three sites sampled had more severe disease, with a mean SCORAD – or disease severity score – of 37, compared with those who were not colonized at that time, with a mean SCORAD of 28 (P = .067).
There was a much bigger gap in mean SCORAD score between the 14 patients who had the same CC type at both baseline and follow-up (a mean score of 30), compared with the 11 patients with different CC types at follow-up (a mean score of 47), a statistically significant difference (P = .03). Mean severity scores went up in those who changed CC types and down in those whose CC types remained the same.
The findings “illustrate that colonization changes over time, and also probably reflect the relapsing course of this disease, as colonization likely occurs in relation to worsening of the eczema,” the study authors wrote. They cautioned that “other factors should be taken into considerations as these are known to influence AD severity, including change in treatment regimens, climate, or other disease.”
Novo Nordisk Foundation funded the study. No relevant disclosures were reported.
SOURCE: Clausen, ML et al. Br J Dermatol. 2018 Aug 2. doi: 10.1111/bjd.17033.
FROM BRITISH JOURNAL OF DERMATOLOGY
Key clinical point: Changes in skin colonization of Staphylococcus aureus clonal complex (CC) types in patients with atopic dermatitis (AD) over time may be related to relapses.
Major finding: Mean SCORAD among the 14 participants with the same CC type at baseline and follow-up was 30, vs. 47 in the 11 patients with different CC types at follow-up (P = .03).
Study details: The study of 63 adults with AD compared the association of disease severity and colonization with S. aureus, and changes in S. aureus clonal complex types over time.
Disclosures: Novo Nordisk Foundation funded the study. No relevant disclosures were reported.
Source: Clausen ML et al. Br J Dermatol. 2018 Aug 2. doi: 10.1111/bjd.17033.
Infliximab biosimilar only moderately less expensive in Medicare Part D
The infliximab-dyyb biosimilar was only moderately less expensive than the originator infliximab product Remicade in the United States in 2017 under Medicare Part D, an analysis shows.
Infliximab-dyyb (Inflectra) cost 18% less than infliximab, with an annual cost exceeding $14,000 in an analysis published online Sept. 4 in JAMA by Jinoos Yazdany, MD, of the division of rheumatology at the University of California, San Francisco, and her coauthors.
However, “without biosimilar gap discounts in 2017, beneficiaries would have paid more than $5,100 for infliximab-dyyb, or nearly $1,700 more in projected out-of-pocket costs than infliximab,” Dr. Yazdany and her coauthors wrote.
Biologics represent only 2% of U.S. prescriptions but made up 38% of drug spending in 2015 and accounted for 70% of growth in drug spending from 2010 to 2015, according to Dr. Yazdany and her colleagues.
Biologics for rheumatoid arthritis (RA) cost more than $14,000 per year, and in 2015, 3 were among the top 15 drugs in terms of Medicare expenditures, they added.
While biosimilars are supposed to increase competition and lower prices, it’s an open question whether they actually reduce out-of-pocket expenditures for the 43 million individuals with drug benefits under Medicare Part D.
That uncertainty is due in part to the complex cost-sharing design of Part D, which includes an initial deductible, a coverage phase, a coverage gap, and catastrophic coverage.
In 2017, the plan included an initial $400 deductible, followed by the coverage phase, in which the patient paid 25% of drug costs. In the coverage gap, which started at $3,700 in total drug costs, the patient’s share of drug costs increased to 40% for biologics, and 51% for biosimilars. In the catastrophic coverage phase, triggered when out-of-pocket costs exceeded $4,950, the patient was responsible for 5% of drug costs.
“Currently, beneficiaries receive a 50% manufacturer discount during the gap for brand-name drugs and biologics, but not for biosimilars,” Dr. Yazdany and her coauthors said in the report.
To evaluate cost-sharing for infliximab-dyyb, which in 2016 became the first available RA biosimilar, the authors analyzed data for all Part D plans in the June 2017 Medicare Prescription Drug Plan Formulary, Pharmacy Network, and Pricing Information Files.
Out of 2,547 plans, only 10% covered the biosimilar, while 96% covered infliximab, the authors found.
The mean total cost of infliximab-dyyb was “modestly lower,” they reported. Eight-week prescription costs were $2,185 for infliximab-dyyb versus $2,667 for infliximab, while annual costs were $14,202 for the biosimilar and $17,335 for infliximab.
However, all plans required coinsurance cost-sharing for the biosimilar, they said. The mean coinsurance rate was 26.6% of the total drug cost for the biosimilar and 28.4% for infliximab.
For beneficiaries, projected annual out-of-pocket costs without the gap discount were $5,118 for infliximab-dyyb and $3,432 for infliximab, the researchers said.
Biosimilar gap discounts are set to start in 2019, according to the authors. However, they said those discounts may not substantially reduce out-of-pocket costs for Part D beneficiaries because of the high price of infliximab-dyyb and a coinsurance cost-sharing rate similar to that of infliximab.
“Further policies are needed to address affordability and access to specialty drugs,” Dr. Yazdany and her coauthors concluded.
The study was funded in part by grants from the Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality, the Robert L. Kroc Endowed Chair in Rheumatic and Connective Tissue Diseases, and other sources. Dr. Yazdany reported receiving an independent investigator award from Pfizer. Her coauthors reported no conflict of interest disclosures.
The infliximab-dyyb biosimilar was only moderately less expensive than the originator infliximab product Remicade in the United States in 2017 under Medicare Part D, an analysis shows.
Infliximab-dyyb (Inflectra) cost 18% less than infliximab, with an annual cost exceeding $14,000 in an analysis published online Sept. 4 in JAMA by Jinoos Yazdany, MD, of the division of rheumatology at the University of California, San Francisco, and her coauthors.
However, “without biosimilar gap discounts in 2017, beneficiaries would have paid more than $5,100 for infliximab-dyyb, or nearly $1,700 more in projected out-of-pocket costs than infliximab,” Dr. Yazdany and her coauthors wrote.
Biologics represent only 2% of U.S. prescriptions but made up 38% of drug spending in 2015 and accounted for 70% of growth in drug spending from 2010 to 2015, according to Dr. Yazdany and her colleagues.
Biologics for rheumatoid arthritis (RA) cost more than $14,000 per year, and in 2015, 3 were among the top 15 drugs in terms of Medicare expenditures, they added.
While biosimilars are supposed to increase competition and lower prices, it’s an open question whether they actually reduce out-of-pocket expenditures for the 43 million individuals with drug benefits under Medicare Part D.
That uncertainty is due in part to the complex cost-sharing design of Part D, which includes an initial deductible, a coverage phase, a coverage gap, and catastrophic coverage.
In 2017, the plan included an initial $400 deductible, followed by the coverage phase, in which the patient paid 25% of drug costs. In the coverage gap, which started at $3,700 in total drug costs, the patient’s share of drug costs increased to 40% for biologics, and 51% for biosimilars. In the catastrophic coverage phase, triggered when out-of-pocket costs exceeded $4,950, the patient was responsible for 5% of drug costs.
“Currently, beneficiaries receive a 50% manufacturer discount during the gap for brand-name drugs and biologics, but not for biosimilars,” Dr. Yazdany and her coauthors said in the report.
To evaluate cost-sharing for infliximab-dyyb, which in 2016 became the first available RA biosimilar, the authors analyzed data for all Part D plans in the June 2017 Medicare Prescription Drug Plan Formulary, Pharmacy Network, and Pricing Information Files.
Out of 2,547 plans, only 10% covered the biosimilar, while 96% covered infliximab, the authors found.
The mean total cost of infliximab-dyyb was “modestly lower,” they reported. Eight-week prescription costs were $2,185 for infliximab-dyyb versus $2,667 for infliximab, while annual costs were $14,202 for the biosimilar and $17,335 for infliximab.
However, all plans required coinsurance cost-sharing for the biosimilar, they said. The mean coinsurance rate was 26.6% of the total drug cost for the biosimilar and 28.4% for infliximab.
For beneficiaries, projected annual out-of-pocket costs without the gap discount were $5,118 for infliximab-dyyb and $3,432 for infliximab, the researchers said.
Biosimilar gap discounts are set to start in 2019, according to the authors. However, they said those discounts may not substantially reduce out-of-pocket costs for Part D beneficiaries because of the high price of infliximab-dyyb and a coinsurance cost-sharing rate similar to that of infliximab.
“Further policies are needed to address affordability and access to specialty drugs,” Dr. Yazdany and her coauthors concluded.
The study was funded in part by grants from the Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality, the Robert L. Kroc Endowed Chair in Rheumatic and Connective Tissue Diseases, and other sources. Dr. Yazdany reported receiving an independent investigator award from Pfizer. Her coauthors reported no conflict of interest disclosures.
The infliximab-dyyb biosimilar was only moderately less expensive than the originator infliximab product Remicade in the United States in 2017 under Medicare Part D, an analysis shows.
Infliximab-dyyb (Inflectra) cost 18% less than infliximab, with an annual cost exceeding $14,000 in an analysis published online Sept. 4 in JAMA by Jinoos Yazdany, MD, of the division of rheumatology at the University of California, San Francisco, and her coauthors.
However, “without biosimilar gap discounts in 2017, beneficiaries would have paid more than $5,100 for infliximab-dyyb, or nearly $1,700 more in projected out-of-pocket costs than infliximab,” Dr. Yazdany and her coauthors wrote.
Biologics represent only 2% of U.S. prescriptions but made up 38% of drug spending in 2015 and accounted for 70% of growth in drug spending from 2010 to 2015, according to Dr. Yazdany and her colleagues.
Biologics for rheumatoid arthritis (RA) cost more than $14,000 per year, and in 2015, 3 were among the top 15 drugs in terms of Medicare expenditures, they added.
While biosimilars are supposed to increase competition and lower prices, it’s an open question whether they actually reduce out-of-pocket expenditures for the 43 million individuals with drug benefits under Medicare Part D.
That uncertainty is due in part to the complex cost-sharing design of Part D, which includes an initial deductible, a coverage phase, a coverage gap, and catastrophic coverage.
In 2017, the plan included an initial $400 deductible, followed by the coverage phase, in which the patient paid 25% of drug costs. In the coverage gap, which started at $3,700 in total drug costs, the patient’s share of drug costs increased to 40% for biologics, and 51% for biosimilars. In the catastrophic coverage phase, triggered when out-of-pocket costs exceeded $4,950, the patient was responsible for 5% of drug costs.
“Currently, beneficiaries receive a 50% manufacturer discount during the gap for brand-name drugs and biologics, but not for biosimilars,” Dr. Yazdany and her coauthors said in the report.
To evaluate cost-sharing for infliximab-dyyb, which in 2016 became the first available RA biosimilar, the authors analyzed data for all Part D plans in the June 2017 Medicare Prescription Drug Plan Formulary, Pharmacy Network, and Pricing Information Files.
Out of 2,547 plans, only 10% covered the biosimilar, while 96% covered infliximab, the authors found.
The mean total cost of infliximab-dyyb was “modestly lower,” they reported. Eight-week prescription costs were $2,185 for infliximab-dyyb versus $2,667 for infliximab, while annual costs were $14,202 for the biosimilar and $17,335 for infliximab.
However, all plans required coinsurance cost-sharing for the biosimilar, they said. The mean coinsurance rate was 26.6% of the total drug cost for the biosimilar and 28.4% for infliximab.
For beneficiaries, projected annual out-of-pocket costs without the gap discount were $5,118 for infliximab-dyyb and $3,432 for infliximab, the researchers said.
Biosimilar gap discounts are set to start in 2019, according to the authors. However, they said those discounts may not substantially reduce out-of-pocket costs for Part D beneficiaries because of the high price of infliximab-dyyb and a coinsurance cost-sharing rate similar to that of infliximab.
“Further policies are needed to address affordability and access to specialty drugs,” Dr. Yazdany and her coauthors concluded.
The study was funded in part by grants from the Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality, the Robert L. Kroc Endowed Chair in Rheumatic and Connective Tissue Diseases, and other sources. Dr. Yazdany reported receiving an independent investigator award from Pfizer. Her coauthors reported no conflict of interest disclosures.
FROM JAMA
Key clinical point:
Major finding: Infliximab-dyyb was 18% less costly than infliximab, with an annual cost exceeding $14,000.
Study details: Analysis of data for 2,547 Part D plans in the June 2017 Medicare Prescription Drug Plan Formulary, Pharmacy Network, and Pricing Information Files.
Disclosures: The study was funded in part by grants from the Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality, the Robert L. Kroc Endowed Chair in Rheumatic and Connective Tissue Diseases, and other sources. One author reported receiving an independent investigator award from Pfizer.
Source: Yazdany J et al. JAMA. 2018;320(9):931-3.
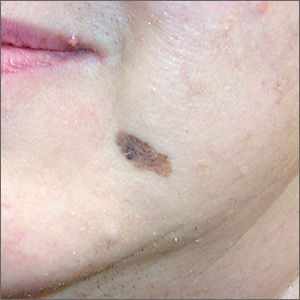
Growing spot on face
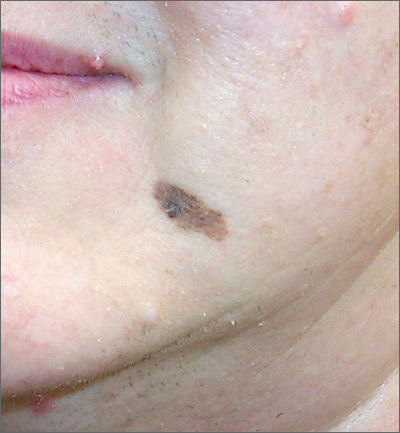
The FP suspected melanoma and recommended immediate biopsy. The patient consented, and the physician performed a broad shave biopsy that included most of the pigmented lesion. Pathology revealed a lentigo maligna melanoma with a Breslow depth of 0.3 mm.
Lentigo maligna melanoma occurs in 4% to 15% of cutaneous melanomas. It’s similar to the superficial spreading type and appears as a flat (or mildly elevated) mottled tan, brown, or dark-brown discoloration. This type of melanoma is found most often in the elderly and arises on chronically sun-exposed, damaged skin on the face, ears, arms, and upper trunk. The average age of onset is 65 years and it grows slowly over 5 to 20 years.
When melanoma is suspected, it’s best to provide a specimen with adequate depth and breadth. Unfortunately, choosing the darkest and most raised area does not guarantee the correct diagnosis in a partial biopsy.
In cases of suspected lentigo maligna melanoma on the face, a broad shave provides a better sample than a punch biopsy. The broad shave biopsy (also known as saucerization) is best performed with a razor blade. (See the Watch & Learn video on “Shave biopsy.”)
In this case, the relatively small size of the lesion and the high risk for melanoma would make an elliptical excisional biopsy a good alternative. The saucerization has the advantage of being quick and easy to perform so that it can be done on the day that the melanoma is suspected.
This patient was referred for Mohs surgery for complete excision and repair. A sentinel lymph node biopsy was not indicated, and the prognosis for this stage Ia melanoma was relatively good.
Photos and text for Photo Rounds Friday courtesy of Richard P. Usatine, MD. This case was adapted from: Mayeaux, EJ, Usatine, R. Lentigo maligna. In: Usatine R, Smith M, Mayeaux EJ, et al. Color Atlas of Family Medicine. 2nd ed. New York, NY: McGraw-Hill; 2013:981-984.
To learn more about the Color Atlas of Family Medicine, see: www.amazon.com/Color-Family-Medicine-Richard-Usatine/dp/0071769641/.
You can now get the second edition of the Color Atlas of Family Medicine as an app by clicking on this link: usatinemedia.com.

The FP suspected melanoma and recommended immediate biopsy. The patient consented, and the physician performed a broad shave biopsy that included most of the pigmented lesion. Pathology revealed a lentigo maligna melanoma with a Breslow depth of 0.3 mm.
Lentigo maligna melanoma occurs in 4% to 15% of cutaneous melanomas. It’s similar to the superficial spreading type and appears as a flat (or mildly elevated) mottled tan, brown, or dark-brown discoloration. This type of melanoma is found most often in the elderly and arises on chronically sun-exposed, damaged skin on the face, ears, arms, and upper trunk. The average age of onset is 65 years and it grows slowly over 5 to 20 years.
When melanoma is suspected, it’s best to provide a specimen with adequate depth and breadth. Unfortunately, choosing the darkest and most raised area does not guarantee the correct diagnosis in a partial biopsy.
In cases of suspected lentigo maligna melanoma on the face, a broad shave provides a better sample than a punch biopsy. The broad shave biopsy (also known as saucerization) is best performed with a razor blade. (See the Watch & Learn video on “Shave biopsy.”)
In this case, the relatively small size of the lesion and the high risk for melanoma would make an elliptical excisional biopsy a good alternative. The saucerization has the advantage of being quick and easy to perform so that it can be done on the day that the melanoma is suspected.
This patient was referred for Mohs surgery for complete excision and repair. A sentinel lymph node biopsy was not indicated, and the prognosis for this stage Ia melanoma was relatively good.
Photos and text for Photo Rounds Friday courtesy of Richard P. Usatine, MD. This case was adapted from: Mayeaux, EJ, Usatine, R. Lentigo maligna. In: Usatine R, Smith M, Mayeaux EJ, et al. Color Atlas of Family Medicine. 2nd ed. New York, NY: McGraw-Hill; 2013:981-984.
To learn more about the Color Atlas of Family Medicine, see: www.amazon.com/Color-Family-Medicine-Richard-Usatine/dp/0071769641/.
You can now get the second edition of the Color Atlas of Family Medicine as an app by clicking on this link: usatinemedia.com.

The FP suspected melanoma and recommended immediate biopsy. The patient consented, and the physician performed a broad shave biopsy that included most of the pigmented lesion. Pathology revealed a lentigo maligna melanoma with a Breslow depth of 0.3 mm.
Lentigo maligna melanoma occurs in 4% to 15% of cutaneous melanomas. It’s similar to the superficial spreading type and appears as a flat (or mildly elevated) mottled tan, brown, or dark-brown discoloration. This type of melanoma is found most often in the elderly and arises on chronically sun-exposed, damaged skin on the face, ears, arms, and upper trunk. The average age of onset is 65 years and it grows slowly over 5 to 20 years.
When melanoma is suspected, it’s best to provide a specimen with adequate depth and breadth. Unfortunately, choosing the darkest and most raised area does not guarantee the correct diagnosis in a partial biopsy.
In cases of suspected lentigo maligna melanoma on the face, a broad shave provides a better sample than a punch biopsy. The broad shave biopsy (also known as saucerization) is best performed with a razor blade. (See the Watch & Learn video on “Shave biopsy.”)
In this case, the relatively small size of the lesion and the high risk for melanoma would make an elliptical excisional biopsy a good alternative. The saucerization has the advantage of being quick and easy to perform so that it can be done on the day that the melanoma is suspected.
This patient was referred for Mohs surgery for complete excision and repair. A sentinel lymph node biopsy was not indicated, and the prognosis for this stage Ia melanoma was relatively good.
Photos and text for Photo Rounds Friday courtesy of Richard P. Usatine, MD. This case was adapted from: Mayeaux, EJ, Usatine, R. Lentigo maligna. In: Usatine R, Smith M, Mayeaux EJ, et al. Color Atlas of Family Medicine. 2nd ed. New York, NY: McGraw-Hill; 2013:981-984.
To learn more about the Color Atlas of Family Medicine, see: www.amazon.com/Color-Family-Medicine-Richard-Usatine/dp/0071769641/.
You can now get the second edition of the Color Atlas of Family Medicine as an app by clicking on this link: usatinemedia.com.
Woman, 18, With Sore Throat, Fever, and Painful Rash
IN THIS ARTICLE
- Diagnosis
- Management
- Outcome for the case patient
An 18-year-old woman presents to urgent care with a one-day history of sudden-onset sore throat, chills, malaise, and fever (102.5°F). On physical examination, the tonsils and pharynx are erythematous, and anterior cervical lymph nodes are tender on palpation. A rapid strep test is negative. The patient is instructed to use throat lozenges and take ibuprofen (400 mg every 8 h) as needed for pain.
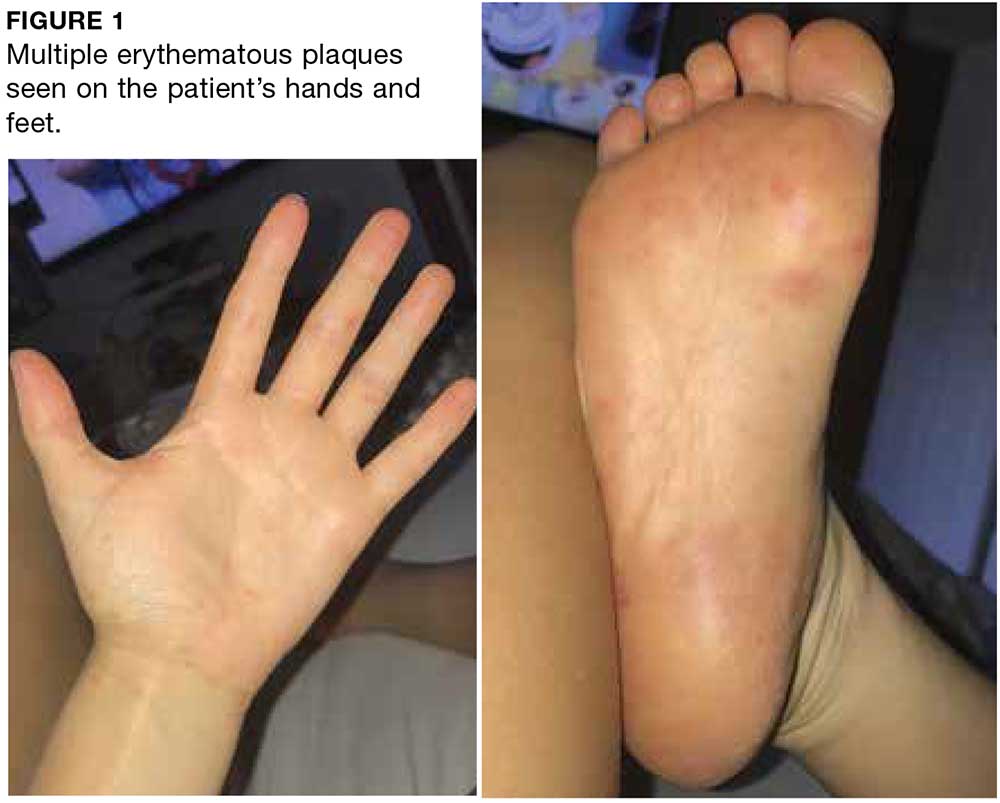
On day 2, the patient’s fever resolves, but a painful rash develops on her palms and soles. Clinical examination reveals multiple erythematous plaques on the hands and feet (see Figure 1). The patient is diagnosed with hand-foot-and-mouth disease (HFMD).
DISCUSSION
HFMD is caused by enteroviruses, most commonly coxsackievirus A16 (CV-A16) or enterovirus 71 (EV71).1 However, a newly recognized strain, CV-A6, has caused worldwide outbreaks of HFMD in both children and adults. Although less common than CV-A16 or EV71, CV-A6 is associated with a more severe disease course.1 The CV-A6 strain was first identified in Finland in 2008 during a major outbreak of HFMD; it reached the United States in 2011.2,3 Accurate statistics on the prevalence of CV-A6 in the US are difficult to obtain because HFMD is not a reportable condition.
Clinical presentation
HFMD typically manifests with painful oral lesions, with or without a macular, maculopapular, or vesicular exanthema. If a fever is present, it is usually below 101°F. The oral lesions are typically benign and manifest as erythematous macules that progress to vesicles with an erythematous halo. These lesions tend to be painful and may interfere with eating or drinking. Signs and symptoms associated with the more virulent form, CV-A6, may include
- Higher fever
- Wider distribution of lesions
- More extensive skin involvement
- Longer duration
- Palmar and plantar desquamation
- Nail dystrophy.4,5
Laboratory diagnosis
Most symptomatic enterovirus infections are diagnosed based on clinical findings alone, reducing the need for laboratory testing. Laboratory confirmation may be warranted for more severe infections and during outbreaks. Molecular methods, such as reverse transcriptase polymerase chain reaction, are typically used for identifying enteroviruses, as they are rapid, sensitive, and widely available in hospital and commercial laboratories.6 Viral culture methods are labor-intensive, expensive, and reserved for typing the isolate. Serology is not useful in the diagnosis of acute infection.
Continue to: Differential diagnosis
Differential diagnosis
The differential diagnosis of HFMD includes conditions with oral lesions and maculopapular, vesicular lesions involving the palms and/or soles, as well as erythroderma.
Oral lesions. Aphthous ulcers are shallow, painful oral lesions not accompanied by skin rashes. Herpes gingivostomatitis, caused by herpes simplex virus (HSV), is often preceded by a prodrome of fever. The associated lesions manifest as vesicular clusters on a red base that evolve into large, painful ulcers. HSV mouth lesions can populate the gingivae, pharynx, hard palate, lips, and perioral skin. Skin lesions may occur unilaterally.
Rashes involving palms and soles. A number of conditions manifest with skin lesions similar to those of HFMD. An autoeczematization reaction consisting of a pruritic, papulovesicular eruption secondary to dermatophyte infection (eg, tinea pedis, tinea manuum, tinea cruris, tinea corporis, tinea capitis) should be ruled out. This type of reaction is thought to be a delayed hypersensitivity response to fungal antigens. Pruritus and the absence of mouth sores distinguishes this reaction from HFMD.7
Secondary syphilis can manifest with a short-lived macular rash involving the palm and soles, as well as oral mucous patches and generalized lymphadenopathy. Syphilis testing, including rapid plasma reagin or Venereal Disease Research Laboratory test with fluorescent treponemal antibody absorption, can rule out this diagnosis.
Erythema multiforme, which is more common in young adults, is characterized by target lesions on the palms and soles and erosions and/or bullae in the mouth and mucous membranes. It is usually preceded by a trigger, such as HSV infection.
Continue to: Erythroderma
Erythroderma. In addition to a rash, erythema multiforme can cause desquamation later in the disease course. Toxic shock syndrome (TSS), a life-threatening condition caused by Streptococcus or Staphylococcus, has an abrupt onset that is associated with high fever and hypotension. TSS causes a sunburn-like rash on the palms and soles that desquamates weeks after onset. Scarlet fever, caused by group A Streptococcus, can cause an erythematous rash with desquamation in children and adolescents. Scalded skin syndrome is a desquamative condition caused by Staphylococcus that occurs primarily in infants and young children.
Management
There is no specific antiviral treatment for HFMD, and thus management is mainly supportive. Fever and pain can be managed with ibuprofen or acetaminophen. Children who are unable to maintain oral hydration may require hospitalization for IV fluids.
Prevention of HFMD requires strict hand hygiene—washing with soap and water—as well as thoroughly cleaning and disinfecting surfaces that come in contact with infected oral secretions or feces.8
OUTCOME FOR THE CASE PATIENT
The patient was discharged and instructed to take ibuprofen as needed.
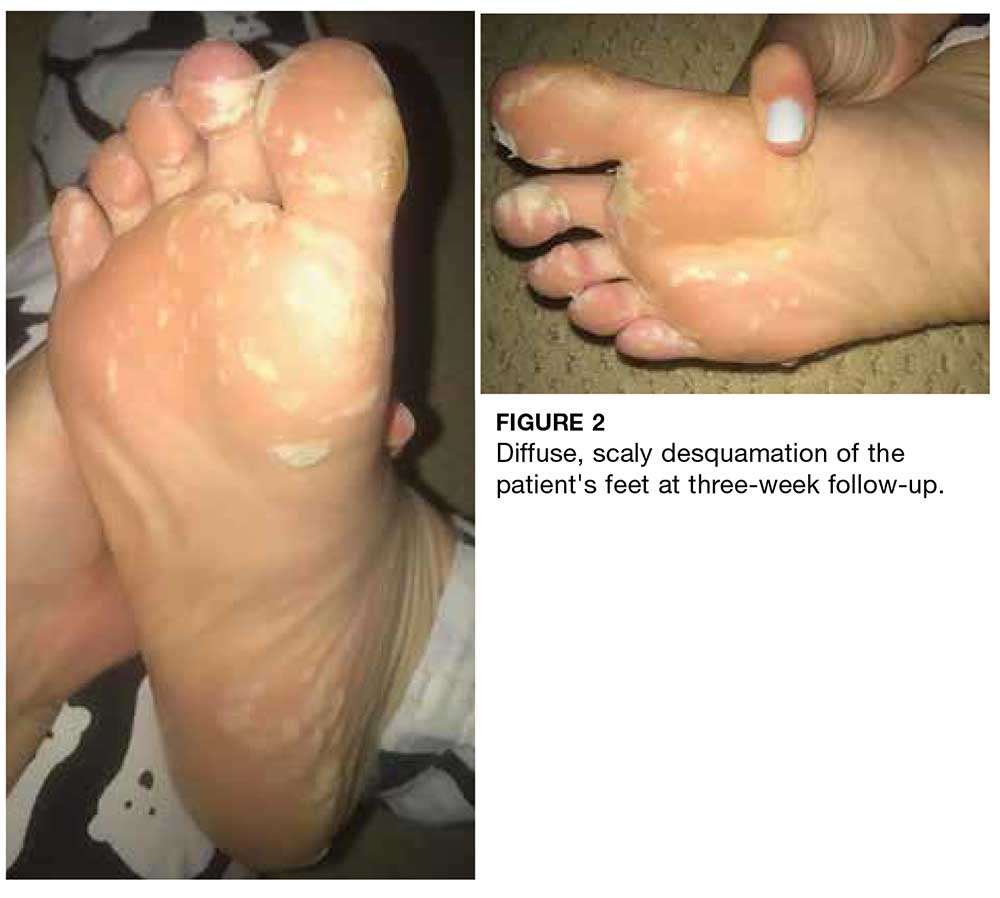
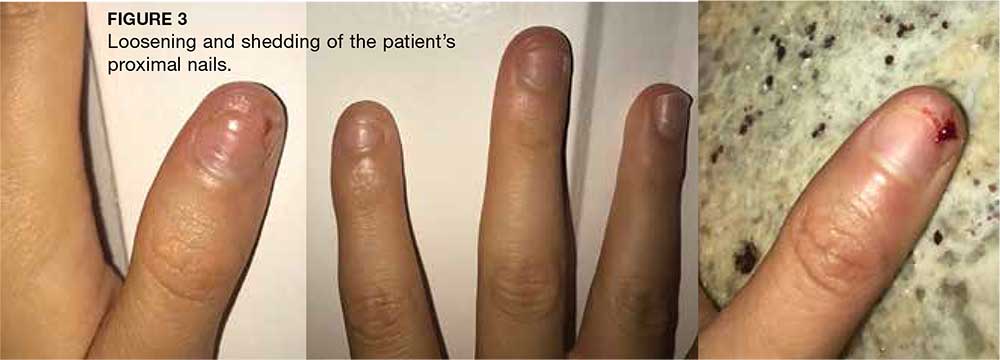
About three weeks later, the patient’s palms and soles began to peel. Clinical examination at follow-up revealed painful, diffuse, scaly desquamation of the hands and feet (see Figure 2). The patient also experienced loosening and shedding of the proximal nails (see Figure 3). She was diagnosed with postviral shedding.
Continue to: About eight weeks after the desquamatory rash manifested...
About eight weeks after the desquamatory rash manifested, complete resolution was seen. The patient experienced continued onychom
CONCLUSION
Clinicians should be mindful of the increasing incidence of HFMD in the adult population, since it may mimic other disease states. The extent and chronicity of this patient’s clinical manifestations were unusual and may have been caused by CV-A6.
1. Ben-Chetrit E, Wiener-Well Y, Shulman LM, et al. Coxsackievirus A6-related hand foot and mouth disease: skin manifestations in a cluster of adult patients. J Clin Virol. 2014;59(3):201-203.
2. Blomqvist S, Klemola P, Kajalainen S, et al. Co-circulation of coxsackie viruses A6 and A10 in hand, foot, mouth disease outbreak in Finland. J Clin Virol. 2010;48(1):49-54.
3. Downing C, Ramirez-Fort MK, Doan HQ, et al. Coxsackievirus A6 associated hand, foot and mouth disease in adults: clinical presentation and review of the literature. J Clin Virol. 2014;60(4):381-386.
4. Lott JP, Liu K, Landry ML, et al. Atypical hand-foot-and-mouth disease associated with coxsackievirus A6 infection. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2013;69(5):736-741.
5. Feder HM Jr, Bennett N, Modlin JF. Atypical hand, foot, and mouth disease: a vesiculobullous eruption caused by Coxsackie virus A6. Lancet Infect Dis. 2014;14(1):83-86.
6. Pozo F, Casas I, Tenorio A, et al. Evaluation of a commercially available reverse transcription-PCR assay for diagnosis of enteroviral infection in archival and prospectively collected cerebrospinal fluid specimens. J Clin Microbiol. 1998;36(6):1741-1745.
7. Cheng N, Rucker Wright D, Cohen BA. Dermatophytid in tinea capitis: rarely reported common phenomenon with clinical implications. Pediatrics. 2011;128(2):e453-e457.
8. Ruan F, Yang T, Ma H, et al. Risk factors for hand, foot, and mouth disease and herpangina and the preventive effect of hand-washing. Pediatrics. 2011;127(4):e898- e904.
IN THIS ARTICLE
- Diagnosis
- Management
- Outcome for the case patient
An 18-year-old woman presents to urgent care with a one-day history of sudden-onset sore throat, chills, malaise, and fever (102.5°F). On physical examination, the tonsils and pharynx are erythematous, and anterior cervical lymph nodes are tender on palpation. A rapid strep test is negative. The patient is instructed to use throat lozenges and take ibuprofen (400 mg every 8 h) as needed for pain.
On day 2, the patient’s fever resolves, but a painful rash develops on her palms and soles. Clinical examination reveals multiple erythematous plaques on the hands and feet (see Figure 1). The patient is diagnosed with hand-foot-and-mouth disease (HFMD).

DISCUSSION
HFMD is caused by enteroviruses, most commonly coxsackievirus A16 (CV-A16) or enterovirus 71 (EV71).1 However, a newly recognized strain, CV-A6, has caused worldwide outbreaks of HFMD in both children and adults. Although less common than CV-A16 or EV71, CV-A6 is associated with a more severe disease course.1 The CV-A6 strain was first identified in Finland in 2008 during a major outbreak of HFMD; it reached the United States in 2011.2,3 Accurate statistics on the prevalence of CV-A6 in the US are difficult to obtain because HFMD is not a reportable condition.
Clinical presentation
HFMD typically manifests with painful oral lesions, with or without a macular, maculopapular, or vesicular exanthema. If a fever is present, it is usually below 101°F. The oral lesions are typically benign and manifest as erythematous macules that progress to vesicles with an erythematous halo. These lesions tend to be painful and may interfere with eating or drinking. Signs and symptoms associated with the more virulent form, CV-A6, may include
- Higher fever
- Wider distribution of lesions
- More extensive skin involvement
- Longer duration
- Palmar and plantar desquamation
- Nail dystrophy.4,5
Laboratory diagnosis
Most symptomatic enterovirus infections are diagnosed based on clinical findings alone, reducing the need for laboratory testing. Laboratory confirmation may be warranted for more severe infections and during outbreaks. Molecular methods, such as reverse transcriptase polymerase chain reaction, are typically used for identifying enteroviruses, as they are rapid, sensitive, and widely available in hospital and commercial laboratories.6 Viral culture methods are labor-intensive, expensive, and reserved for typing the isolate. Serology is not useful in the diagnosis of acute infection.
Continue to: Differential diagnosis
Differential diagnosis
The differential diagnosis of HFMD includes conditions with oral lesions and maculopapular, vesicular lesions involving the palms and/or soles, as well as erythroderma.
Oral lesions. Aphthous ulcers are shallow, painful oral lesions not accompanied by skin rashes. Herpes gingivostomatitis, caused by herpes simplex virus (HSV), is often preceded by a prodrome of fever. The associated lesions manifest as vesicular clusters on a red base that evolve into large, painful ulcers. HSV mouth lesions can populate the gingivae, pharynx, hard palate, lips, and perioral skin. Skin lesions may occur unilaterally.
Rashes involving palms and soles. A number of conditions manifest with skin lesions similar to those of HFMD. An autoeczematization reaction consisting of a pruritic, papulovesicular eruption secondary to dermatophyte infection (eg, tinea pedis, tinea manuum, tinea cruris, tinea corporis, tinea capitis) should be ruled out. This type of reaction is thought to be a delayed hypersensitivity response to fungal antigens. Pruritus and the absence of mouth sores distinguishes this reaction from HFMD.7
Secondary syphilis can manifest with a short-lived macular rash involving the palm and soles, as well as oral mucous patches and generalized lymphadenopathy. Syphilis testing, including rapid plasma reagin or Venereal Disease Research Laboratory test with fluorescent treponemal antibody absorption, can rule out this diagnosis.
Erythema multiforme, which is more common in young adults, is characterized by target lesions on the palms and soles and erosions and/or bullae in the mouth and mucous membranes. It is usually preceded by a trigger, such as HSV infection.
Continue to: Erythroderma
Erythroderma. In addition to a rash, erythema multiforme can cause desquamation later in the disease course. Toxic shock syndrome (TSS), a life-threatening condition caused by Streptococcus or Staphylococcus, has an abrupt onset that is associated with high fever and hypotension. TSS causes a sunburn-like rash on the palms and soles that desquamates weeks after onset. Scarlet fever, caused by group A Streptococcus, can cause an erythematous rash with desquamation in children and adolescents. Scalded skin syndrome is a desquamative condition caused by Staphylococcus that occurs primarily in infants and young children.
Management
There is no specific antiviral treatment for HFMD, and thus management is mainly supportive. Fever and pain can be managed with ibuprofen or acetaminophen. Children who are unable to maintain oral hydration may require hospitalization for IV fluids.
Prevention of HFMD requires strict hand hygiene—washing with soap and water—as well as thoroughly cleaning and disinfecting surfaces that come in contact with infected oral secretions or feces.8
OUTCOME FOR THE CASE PATIENT
The patient was discharged and instructed to take ibuprofen as needed.

About three weeks later, the patient’s palms and soles began to peel. Clinical examination at follow-up revealed painful, diffuse, scaly desquamation of the hands and feet (see Figure 2). The patient also experienced loosening and shedding of the proximal nails (see Figure 3). She was diagnosed with postviral shedding.

Continue to: About eight weeks after the desquamatory rash manifested...
About eight weeks after the desquamatory rash manifested, complete resolution was seen. The patient experienced continued onychom
CONCLUSION
Clinicians should be mindful of the increasing incidence of HFMD in the adult population, since it may mimic other disease states. The extent and chronicity of this patient’s clinical manifestations were unusual and may have been caused by CV-A6.
IN THIS ARTICLE
- Diagnosis
- Management
- Outcome for the case patient
An 18-year-old woman presents to urgent care with a one-day history of sudden-onset sore throat, chills, malaise, and fever (102.5°F). On physical examination, the tonsils and pharynx are erythematous, and anterior cervical lymph nodes are tender on palpation. A rapid strep test is negative. The patient is instructed to use throat lozenges and take ibuprofen (400 mg every 8 h) as needed for pain.
On day 2, the patient’s fever resolves, but a painful rash develops on her palms and soles. Clinical examination reveals multiple erythematous plaques on the hands and feet (see Figure 1). The patient is diagnosed with hand-foot-and-mouth disease (HFMD).

DISCUSSION
HFMD is caused by enteroviruses, most commonly coxsackievirus A16 (CV-A16) or enterovirus 71 (EV71).1 However, a newly recognized strain, CV-A6, has caused worldwide outbreaks of HFMD in both children and adults. Although less common than CV-A16 or EV71, CV-A6 is associated with a more severe disease course.1 The CV-A6 strain was first identified in Finland in 2008 during a major outbreak of HFMD; it reached the United States in 2011.2,3 Accurate statistics on the prevalence of CV-A6 in the US are difficult to obtain because HFMD is not a reportable condition.
Clinical presentation
HFMD typically manifests with painful oral lesions, with or without a macular, maculopapular, or vesicular exanthema. If a fever is present, it is usually below 101°F. The oral lesions are typically benign and manifest as erythematous macules that progress to vesicles with an erythematous halo. These lesions tend to be painful and may interfere with eating or drinking. Signs and symptoms associated with the more virulent form, CV-A6, may include
- Higher fever
- Wider distribution of lesions
- More extensive skin involvement
- Longer duration
- Palmar and plantar desquamation
- Nail dystrophy.4,5
Laboratory diagnosis
Most symptomatic enterovirus infections are diagnosed based on clinical findings alone, reducing the need for laboratory testing. Laboratory confirmation may be warranted for more severe infections and during outbreaks. Molecular methods, such as reverse transcriptase polymerase chain reaction, are typically used for identifying enteroviruses, as they are rapid, sensitive, and widely available in hospital and commercial laboratories.6 Viral culture methods are labor-intensive, expensive, and reserved for typing the isolate. Serology is not useful in the diagnosis of acute infection.
Continue to: Differential diagnosis
Differential diagnosis
The differential diagnosis of HFMD includes conditions with oral lesions and maculopapular, vesicular lesions involving the palms and/or soles, as well as erythroderma.
Oral lesions. Aphthous ulcers are shallow, painful oral lesions not accompanied by skin rashes. Herpes gingivostomatitis, caused by herpes simplex virus (HSV), is often preceded by a prodrome of fever. The associated lesions manifest as vesicular clusters on a red base that evolve into large, painful ulcers. HSV mouth lesions can populate the gingivae, pharynx, hard palate, lips, and perioral skin. Skin lesions may occur unilaterally.
Rashes involving palms and soles. A number of conditions manifest with skin lesions similar to those of HFMD. An autoeczematization reaction consisting of a pruritic, papulovesicular eruption secondary to dermatophyte infection (eg, tinea pedis, tinea manuum, tinea cruris, tinea corporis, tinea capitis) should be ruled out. This type of reaction is thought to be a delayed hypersensitivity response to fungal antigens. Pruritus and the absence of mouth sores distinguishes this reaction from HFMD.7
Secondary syphilis can manifest with a short-lived macular rash involving the palm and soles, as well as oral mucous patches and generalized lymphadenopathy. Syphilis testing, including rapid plasma reagin or Venereal Disease Research Laboratory test with fluorescent treponemal antibody absorption, can rule out this diagnosis.
Erythema multiforme, which is more common in young adults, is characterized by target lesions on the palms and soles and erosions and/or bullae in the mouth and mucous membranes. It is usually preceded by a trigger, such as HSV infection.
Continue to: Erythroderma
Erythroderma. In addition to a rash, erythema multiforme can cause desquamation later in the disease course. Toxic shock syndrome (TSS), a life-threatening condition caused by Streptococcus or Staphylococcus, has an abrupt onset that is associated with high fever and hypotension. TSS causes a sunburn-like rash on the palms and soles that desquamates weeks after onset. Scarlet fever, caused by group A Streptococcus, can cause an erythematous rash with desquamation in children and adolescents. Scalded skin syndrome is a desquamative condition caused by Staphylococcus that occurs primarily in infants and young children.
Management
There is no specific antiviral treatment for HFMD, and thus management is mainly supportive. Fever and pain can be managed with ibuprofen or acetaminophen. Children who are unable to maintain oral hydration may require hospitalization for IV fluids.
Prevention of HFMD requires strict hand hygiene—washing with soap and water—as well as thoroughly cleaning and disinfecting surfaces that come in contact with infected oral secretions or feces.8
OUTCOME FOR THE CASE PATIENT
The patient was discharged and instructed to take ibuprofen as needed.

About three weeks later, the patient’s palms and soles began to peel. Clinical examination at follow-up revealed painful, diffuse, scaly desquamation of the hands and feet (see Figure 2). The patient also experienced loosening and shedding of the proximal nails (see Figure 3). She was diagnosed with postviral shedding.

Continue to: About eight weeks after the desquamatory rash manifested...
About eight weeks after the desquamatory rash manifested, complete resolution was seen. The patient experienced continued onychom
CONCLUSION
Clinicians should be mindful of the increasing incidence of HFMD in the adult population, since it may mimic other disease states. The extent and chronicity of this patient’s clinical manifestations were unusual and may have been caused by CV-A6.
1. Ben-Chetrit E, Wiener-Well Y, Shulman LM, et al. Coxsackievirus A6-related hand foot and mouth disease: skin manifestations in a cluster of adult patients. J Clin Virol. 2014;59(3):201-203.
2. Blomqvist S, Klemola P, Kajalainen S, et al. Co-circulation of coxsackie viruses A6 and A10 in hand, foot, mouth disease outbreak in Finland. J Clin Virol. 2010;48(1):49-54.
3. Downing C, Ramirez-Fort MK, Doan HQ, et al. Coxsackievirus A6 associated hand, foot and mouth disease in adults: clinical presentation and review of the literature. J Clin Virol. 2014;60(4):381-386.
4. Lott JP, Liu K, Landry ML, et al. Atypical hand-foot-and-mouth disease associated with coxsackievirus A6 infection. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2013;69(5):736-741.
5. Feder HM Jr, Bennett N, Modlin JF. Atypical hand, foot, and mouth disease: a vesiculobullous eruption caused by Coxsackie virus A6. Lancet Infect Dis. 2014;14(1):83-86.
6. Pozo F, Casas I, Tenorio A, et al. Evaluation of a commercially available reverse transcription-PCR assay for diagnosis of enteroviral infection in archival and prospectively collected cerebrospinal fluid specimens. J Clin Microbiol. 1998;36(6):1741-1745.
7. Cheng N, Rucker Wright D, Cohen BA. Dermatophytid in tinea capitis: rarely reported common phenomenon with clinical implications. Pediatrics. 2011;128(2):e453-e457.
8. Ruan F, Yang T, Ma H, et al. Risk factors for hand, foot, and mouth disease and herpangina and the preventive effect of hand-washing. Pediatrics. 2011;127(4):e898- e904.
1. Ben-Chetrit E, Wiener-Well Y, Shulman LM, et al. Coxsackievirus A6-related hand foot and mouth disease: skin manifestations in a cluster of adult patients. J Clin Virol. 2014;59(3):201-203.
2. Blomqvist S, Klemola P, Kajalainen S, et al. Co-circulation of coxsackie viruses A6 and A10 in hand, foot, mouth disease outbreak in Finland. J Clin Virol. 2010;48(1):49-54.
3. Downing C, Ramirez-Fort MK, Doan HQ, et al. Coxsackievirus A6 associated hand, foot and mouth disease in adults: clinical presentation and review of the literature. J Clin Virol. 2014;60(4):381-386.
4. Lott JP, Liu K, Landry ML, et al. Atypical hand-foot-and-mouth disease associated with coxsackievirus A6 infection. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2013;69(5):736-741.
5. Feder HM Jr, Bennett N, Modlin JF. Atypical hand, foot, and mouth disease: a vesiculobullous eruption caused by Coxsackie virus A6. Lancet Infect Dis. 2014;14(1):83-86.
6. Pozo F, Casas I, Tenorio A, et al. Evaluation of a commercially available reverse transcription-PCR assay for diagnosis of enteroviral infection in archival and prospectively collected cerebrospinal fluid specimens. J Clin Microbiol. 1998;36(6):1741-1745.
7. Cheng N, Rucker Wright D, Cohen BA. Dermatophytid in tinea capitis: rarely reported common phenomenon with clinical implications. Pediatrics. 2011;128(2):e453-e457.
8. Ruan F, Yang T, Ma H, et al. Risk factors for hand, foot, and mouth disease and herpangina and the preventive effect of hand-washing. Pediatrics. 2011;127(4):e898- e904.
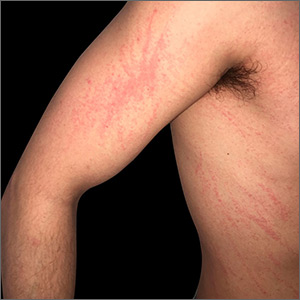
Linear streaks on trunk, extremities
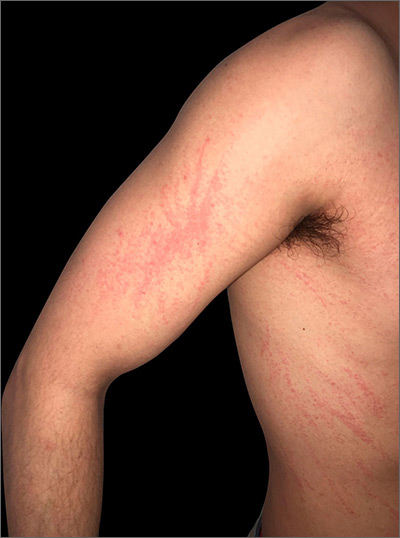
Based on the clinical findings, the patient was diagnosed with flagellate shiitake mushroom dermatitis. (Subsequent treponemal and nontreponemal tests were negative for syphilis.)
Shiitake dermatitis is a rare disease that appears in susceptible patients after the consumption of large amounts of raw or undercooked shiitake mushrooms. The eruption is believed to be attributable to either a toxic or hypersensitivity reaction to lentinan, a polysaccharide component found within the mushroom cell wall.1 Shiitake dermatitis is self-limiting and treatment focuses on symptomatic management.
Early recognition and proper counseling should ensure symptomatic relief and prevent future episodes. In addition, anyone preparing shiitake mushrooms should make sure that they are fully cooked before serving or eating them.2
In the case described here, the patient was advised to avoid eating undercooked shiitake mushrooms in the future and he was prescribed topical steroids (mometasone furoate 0.1% cream). The eruption resolved 2 weeks later.
References
1. Nguyen AH, Gonzaga MI, Lim VM, et al. Clinical features of shiitake dermatitis: a systematic review. Int J Dermatol. 2017;56:610-616.
2. Stephany MP, Chung S, Handler MZ, et al. Shiitake mushroom dermatitis: a review. Am J Clin Dermatol. 2016;17:485-489.

Based on the clinical findings, the patient was diagnosed with flagellate shiitake mushroom dermatitis. (Subsequent treponemal and nontreponemal tests were negative for syphilis.)
Shiitake dermatitis is a rare disease that appears in susceptible patients after the consumption of large amounts of raw or undercooked shiitake mushrooms. The eruption is believed to be attributable to either a toxic or hypersensitivity reaction to lentinan, a polysaccharide component found within the mushroom cell wall.1 Shiitake dermatitis is self-limiting and treatment focuses on symptomatic management.
Early recognition and proper counseling should ensure symptomatic relief and prevent future episodes. In addition, anyone preparing shiitake mushrooms should make sure that they are fully cooked before serving or eating them.2
In the case described here, the patient was advised to avoid eating undercooked shiitake mushrooms in the future and he was prescribed topical steroids (mometasone furoate 0.1% cream). The eruption resolved 2 weeks later.
References
1. Nguyen AH, Gonzaga MI, Lim VM, et al. Clinical features of shiitake dermatitis: a systematic review. Int J Dermatol. 2017;56:610-616.
2. Stephany MP, Chung S, Handler MZ, et al. Shiitake mushroom dermatitis: a review. Am J Clin Dermatol. 2016;17:485-489.

Based on the clinical findings, the patient was diagnosed with flagellate shiitake mushroom dermatitis. (Subsequent treponemal and nontreponemal tests were negative for syphilis.)
Shiitake dermatitis is a rare disease that appears in susceptible patients after the consumption of large amounts of raw or undercooked shiitake mushrooms. The eruption is believed to be attributable to either a toxic or hypersensitivity reaction to lentinan, a polysaccharide component found within the mushroom cell wall.1 Shiitake dermatitis is self-limiting and treatment focuses on symptomatic management.
Early recognition and proper counseling should ensure symptomatic relief and prevent future episodes. In addition, anyone preparing shiitake mushrooms should make sure that they are fully cooked before serving or eating them.2
In the case described here, the patient was advised to avoid eating undercooked shiitake mushrooms in the future and he was prescribed topical steroids (mometasone furoate 0.1% cream). The eruption resolved 2 weeks later.
References
1. Nguyen AH, Gonzaga MI, Lim VM, et al. Clinical features of shiitake dermatitis: a systematic review. Int J Dermatol. 2017;56:610-616.
2. Stephany MP, Chung S, Handler MZ, et al. Shiitake mushroom dermatitis: a review. Am J Clin Dermatol. 2016;17:485-489.
Orodental issues often associated with facial port-wine stains
LAKE TAHOE, CALIF. – Several years ago, David H. Darrow, MD, DDS, began to notice a pattern in the conversation threads on websites dedicated to support for parents of children with facial port-wine stains (PWS).
, and that the alveolar ridge was lower on the side of the face that harbored the lesion. “Most importantly, parents were concerned that dentists were not touching their children because they were concerned about bleeding,” Dr. Darrow said at the annual meeting of the Society for Pediatric Dermatology. A search in the medical literature for port-wine stains and oral cavity changes, did not turn up much except for a few articles on bleeding. “One said that port-wine stains or capillary malformations rarely present major problems for the oral and maxillofacial surgeon. The other said that periodontal probing should not be done, as even gentle probing can result in uncontrolled bleeding,” he noted.
This prompted Dr. Darrow, who directs the Center for Hemangiomas and Vascular Birthmarks at the Eastern Virginia Medical School, Norfolk, and coinvestigators, Megan B. Dowling, MD, and Yueqin Zhao, PhD, to characterize manifestations of PWS in the oral cavity via an anonymous paired survey of volunteers with facial PWS and their dentists who were recruited from birthmarks.com and 10 collaborating physician practices (J Am Acad Dermatol 2012;67:687-93). Volunteers ranged in age from 1 to 62 years; mean age was 29 years. A total of 30 patients participated, and most (67%) were female.
The five most common oral manifestations reported by the patients were lip hyperplasia (53%), stained gingiva (47%), malocclusion (30%), bleeding gingiva (27%), and spacing between teeth (23%). Only 3% reported bleeding from dental procedures. When the researchers evaluated the orodental findings in the paired patient-physician responses, “most of the time there was good agreement between the patient and the dentist,” Dr. Darrow said. “The only one that fell out of agreement was lip hyperplasia. That’s probably because most dentists look right past the lips and into the oral cavity.”
When the researchers examined patients who had stained gingiva versus those who did not, they found that early-stage lesions demonstrated a reddish blush of the oral mucosa and gingiva, while late-stage lesions demonstrated increased blush of the oral tissues, as well as hyperplasia of the soft tissue or bone in the affected area. “Based on our review of the literature, bleeding of gums is rarely prolonged and dental procedures are safe,” Dr. Darrow said.
The findings are important, he continued, because capillary malformations of the oral cavity may result in periodontal disease associated with gingival overgrowth. The depth of the gingival pocket should be no more than 2-3 mm. “When you have areas of inflammation and deep-pocket formation, plaque and bacteria slowly erode the connection between the tooth and the soft tissue,” he explained. “At some point, that pocket becomes so deep that it reaches down into the bone in which the tooth is anchored. As that bone is eroded, the teeth loosen and begin to fall out. The goals of therapy are prevention of periodontal disease with meticulous oral hygiene.”
Soft tissue hyperplasia may be exacerbated by medications such as calcium channel blockers, cyclosporine, and phenytoin and phenobarbital, which are sometimes used by patients with Sturge-Weber syndrome, he said.
Dr. Darrow reported having no financial disclosures.
LAKE TAHOE, CALIF. – Several years ago, David H. Darrow, MD, DDS, began to notice a pattern in the conversation threads on websites dedicated to support for parents of children with facial port-wine stains (PWS).
, and that the alveolar ridge was lower on the side of the face that harbored the lesion. “Most importantly, parents were concerned that dentists were not touching their children because they were concerned about bleeding,” Dr. Darrow said at the annual meeting of the Society for Pediatric Dermatology. A search in the medical literature for port-wine stains and oral cavity changes, did not turn up much except for a few articles on bleeding. “One said that port-wine stains or capillary malformations rarely present major problems for the oral and maxillofacial surgeon. The other said that periodontal probing should not be done, as even gentle probing can result in uncontrolled bleeding,” he noted.
This prompted Dr. Darrow, who directs the Center for Hemangiomas and Vascular Birthmarks at the Eastern Virginia Medical School, Norfolk, and coinvestigators, Megan B. Dowling, MD, and Yueqin Zhao, PhD, to characterize manifestations of PWS in the oral cavity via an anonymous paired survey of volunteers with facial PWS and their dentists who were recruited from birthmarks.com and 10 collaborating physician practices (J Am Acad Dermatol 2012;67:687-93). Volunteers ranged in age from 1 to 62 years; mean age was 29 years. A total of 30 patients participated, and most (67%) were female.
The five most common oral manifestations reported by the patients were lip hyperplasia (53%), stained gingiva (47%), malocclusion (30%), bleeding gingiva (27%), and spacing between teeth (23%). Only 3% reported bleeding from dental procedures. When the researchers evaluated the orodental findings in the paired patient-physician responses, “most of the time there was good agreement between the patient and the dentist,” Dr. Darrow said. “The only one that fell out of agreement was lip hyperplasia. That’s probably because most dentists look right past the lips and into the oral cavity.”
When the researchers examined patients who had stained gingiva versus those who did not, they found that early-stage lesions demonstrated a reddish blush of the oral mucosa and gingiva, while late-stage lesions demonstrated increased blush of the oral tissues, as well as hyperplasia of the soft tissue or bone in the affected area. “Based on our review of the literature, bleeding of gums is rarely prolonged and dental procedures are safe,” Dr. Darrow said.
The findings are important, he continued, because capillary malformations of the oral cavity may result in periodontal disease associated with gingival overgrowth. The depth of the gingival pocket should be no more than 2-3 mm. “When you have areas of inflammation and deep-pocket formation, plaque and bacteria slowly erode the connection between the tooth and the soft tissue,” he explained. “At some point, that pocket becomes so deep that it reaches down into the bone in which the tooth is anchored. As that bone is eroded, the teeth loosen and begin to fall out. The goals of therapy are prevention of periodontal disease with meticulous oral hygiene.”
Soft tissue hyperplasia may be exacerbated by medications such as calcium channel blockers, cyclosporine, and phenytoin and phenobarbital, which are sometimes used by patients with Sturge-Weber syndrome, he said.
Dr. Darrow reported having no financial disclosures.
LAKE TAHOE, CALIF. – Several years ago, David H. Darrow, MD, DDS, began to notice a pattern in the conversation threads on websites dedicated to support for parents of children with facial port-wine stains (PWS).
, and that the alveolar ridge was lower on the side of the face that harbored the lesion. “Most importantly, parents were concerned that dentists were not touching their children because they were concerned about bleeding,” Dr. Darrow said at the annual meeting of the Society for Pediatric Dermatology. A search in the medical literature for port-wine stains and oral cavity changes, did not turn up much except for a few articles on bleeding. “One said that port-wine stains or capillary malformations rarely present major problems for the oral and maxillofacial surgeon. The other said that periodontal probing should not be done, as even gentle probing can result in uncontrolled bleeding,” he noted.
This prompted Dr. Darrow, who directs the Center for Hemangiomas and Vascular Birthmarks at the Eastern Virginia Medical School, Norfolk, and coinvestigators, Megan B. Dowling, MD, and Yueqin Zhao, PhD, to characterize manifestations of PWS in the oral cavity via an anonymous paired survey of volunteers with facial PWS and their dentists who were recruited from birthmarks.com and 10 collaborating physician practices (J Am Acad Dermatol 2012;67:687-93). Volunteers ranged in age from 1 to 62 years; mean age was 29 years. A total of 30 patients participated, and most (67%) were female.
The five most common oral manifestations reported by the patients were lip hyperplasia (53%), stained gingiva (47%), malocclusion (30%), bleeding gingiva (27%), and spacing between teeth (23%). Only 3% reported bleeding from dental procedures. When the researchers evaluated the orodental findings in the paired patient-physician responses, “most of the time there was good agreement between the patient and the dentist,” Dr. Darrow said. “The only one that fell out of agreement was lip hyperplasia. That’s probably because most dentists look right past the lips and into the oral cavity.”
When the researchers examined patients who had stained gingiva versus those who did not, they found that early-stage lesions demonstrated a reddish blush of the oral mucosa and gingiva, while late-stage lesions demonstrated increased blush of the oral tissues, as well as hyperplasia of the soft tissue or bone in the affected area. “Based on our review of the literature, bleeding of gums is rarely prolonged and dental procedures are safe,” Dr. Darrow said.
The findings are important, he continued, because capillary malformations of the oral cavity may result in periodontal disease associated with gingival overgrowth. The depth of the gingival pocket should be no more than 2-3 mm. “When you have areas of inflammation and deep-pocket formation, plaque and bacteria slowly erode the connection between the tooth and the soft tissue,” he explained. “At some point, that pocket becomes so deep that it reaches down into the bone in which the tooth is anchored. As that bone is eroded, the teeth loosen and begin to fall out. The goals of therapy are prevention of periodontal disease with meticulous oral hygiene.”
Soft tissue hyperplasia may be exacerbated by medications such as calcium channel blockers, cyclosporine, and phenytoin and phenobarbital, which are sometimes used by patients with Sturge-Weber syndrome, he said.
Dr. Darrow reported having no financial disclosures.
REPORTING FROM SPD 2018
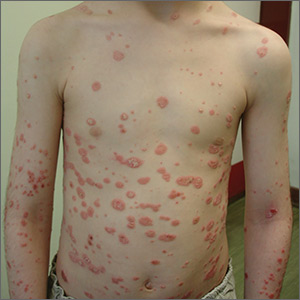
Rapid-onset rash in child
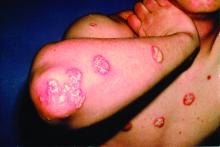
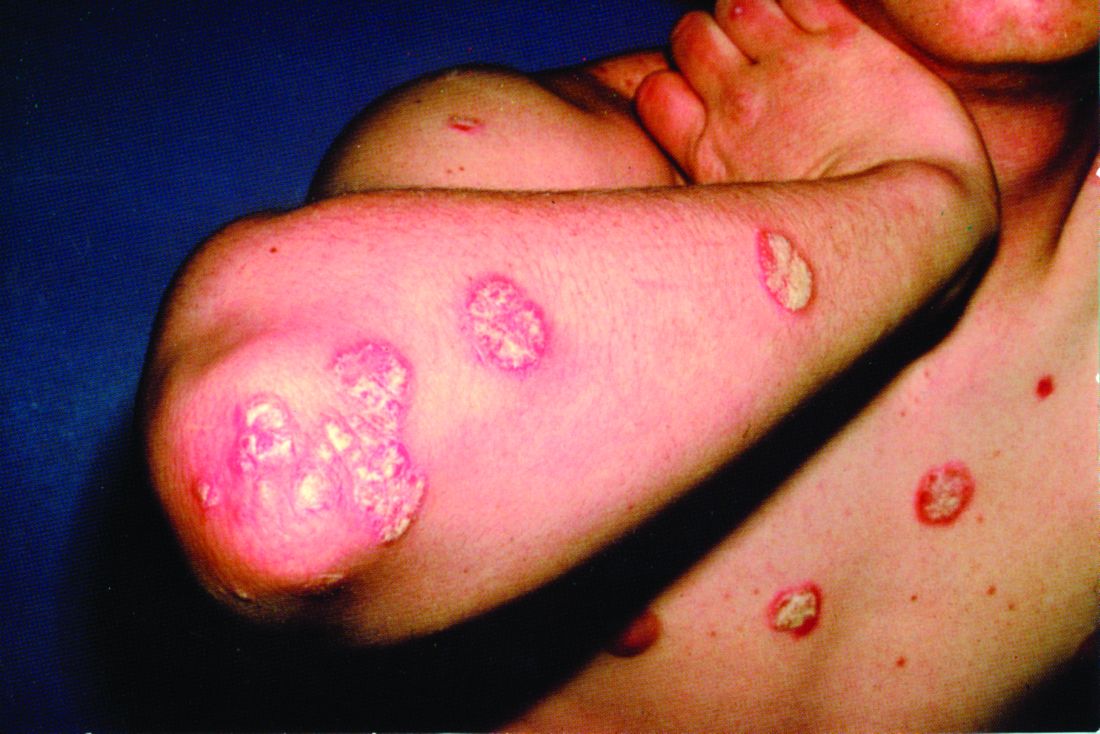
A 7-year-old boy was brought to his family physician for evaluation of a mildly pruritic spreading rash. Ten days earlier, the skin eruption had appeared, and he was given a diagnosis of streptococcal pharyngitis, which was confirmed by a throat swab and a positive antistreptolysin O titer. The child had no personal or family history of skin disorders, including eczema or psoriasis. He hadn’t used any topical agents or new medications recently, nor had he been exposed to triggering plants, animals, or chemicals. There was no history of trauma, friction, or rubbing in the area.
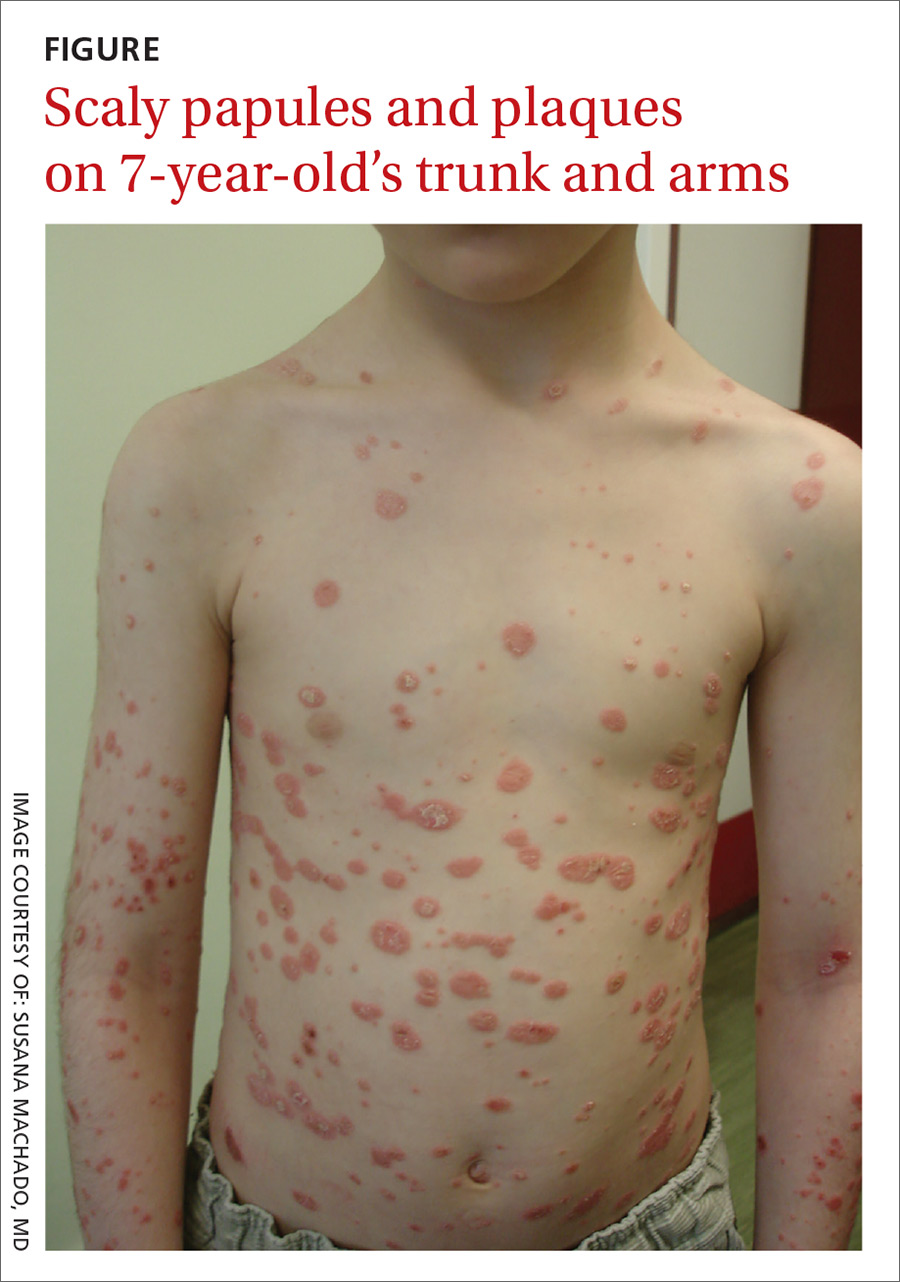
Physical examination revealed multiple erythematous, scaly papules and plaques of varying size on the patient’s trunk, arms, and legs (FIGURE). His palms and soles were spared.
WHAT IS YOUR DIAGNOSIS?
HOW WOULD YOU TREAT THIS PATIENT?
Diagnosis: Guttate psoriasis
A diagnosis of guttate psoriasis was made based on the physical exam findings and the preceding group A beta-hemolytic streptococcal infection.
This condition affects approximately 2% of all patients with psoriasis; it is characterized by the acute onset of multiple erythematosquamous papules and small plaques that look like droplets (“gutta”).1 It tends to affect children and young adults and typically occurs following an acute infection (eg, streptococcal pharyngitis).2,3 In this case, a rapid strep test and throat culture positive for group A Streptococcus supported the diagnosis.
Although this particular phenotype of psoriasis is usually associated with streptococcal infection and mainly occurs in patients with the HLA-Cw6+ allele, the specific immunologic response that causes these skin lesions is poorly understood.4 Antigenic similarities between streptococcal proteins and keratinocyte antigens might explain why the condition is triggered by streptococcal infections.5
Pityriasis rosea and tinea corporis are part of the differential
The differential includes skin conditions such as pityriasis rosea, tinea corporis, varicella, and insect bites.
Pityriasis rosea can manifest as a papulosquamous eruption, but it has an inward-facing scale, called a collarette. The “Christmas tree” pattern on the back that is preceded by a solitary 2- to 10-cm oval, pink, scaly herald patch (in 17%-50% of cases) is key to the diagnosis.6 (For more information, see “Rash on trunk and upper arms.”)
Continue to: Tinea corporis...
Tinea corporis is a dermatophyte infection that causes flat, red, scaly lesions that progress into annular lesions with central clearing or brown discoloration. The plaques can range from a few centimeters to several inches in size, but are always characterized by the slowly advancing border.6
Varicella also affects the trunk and extremities, but a key clinical finding is crops of characteristic lesions, including papules, vesicles, pustules, and crusted lesions in different stages that manifest simultaneously.6
Insect bites usually appear as urticarial papules and plaques associated with outdoor exposure. The lesions are distributed where insects are likely to bite.6
Treat the infection, control the psoriasis
The first-line treatment for streptococcal infection is amoxicillin (50 mg/kg/d [maximum: 1000 mg/d] orally for 10 d) or penicillin G benzathine (for children < 60 lb, 6 × 105 units intramuscularly; children ≥ 60 lb, 1.2 × 106 units intramuscularly).7 For the psoriasis lesions, treatment options include topical glucocorticosteroids, vitamin D derivatives, or combinations of both.5 In most cases, guttate psoriasis completely resolves. However, one-third of children with guttate psoriasis go on to develop plaque psoriasis later in life.8
Our patient was treated with penicillin G benzathine (1.2 × 106 units intramuscularly) and a calcipotriol/betamethasone combination gel. The streptococcal infection and skin lesions completely resolved. No adverse events were reported, and no relapse was observed after 3 months.
CORRESPONDENCE
Rita Matos, MD, Rua Actor Mário Viegas SN Rio Tinto, Portugal; [email protected]
1. Maciejewska-Radomska A, Szczerkowska-Dobosz A, Rebała K, et al. Frequency of streptococcal upper respiratory tract infections and HLA-Cw*06 allele in 70 patients with guttate psoriasis from northern Poland. Postepy Dermatol Alergol. 2015;32:455-458.
2. Garritsen FM, Kraag DE, de Graaf M. Guttate psoriasis triggered by perianal streptococcal infection. Clin Exp Dermatol. 2017;42:536-538.
3. Pfingstler LF, Maroon M, Mowad C. Guttate psoriasis outcomes. Cutis. 2016;97:140-144.
4. Ruiz-Romeu E, Ferran M, Sagristà M, et al. Streptococcus pyogenes-induced cutaneous lymphocyte antigen-positive T cell-dependent epidermal cell activation triggers TH17 responses in patients with guttate psoriasis. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2016;138:491-499.
5. Boehncke WH, Schön MP. Psoriasis. Lancet. 2015;386:983-994.
6. Ely JW, Seabury Stone M. The generalized rash: part I. Differential diagnosis. Am Fam Physician. 2010;81:726-734.
7. Kalra MG, Higgins KE, Perez ED. Common questions about streptococcal pharyngitis. Am Fam Physician. 2016;94:24-31.
8. Martin BA, Chalmers RJ, Telfer NR. How great is the risk of further psoriasis following a single episode of acute guttate psoriasis? Arch Dermatol. 1996;132: 717-718.
A 7-year-old boy was brought to his family physician for evaluation of a mildly pruritic spreading rash. Ten days earlier, the skin eruption had appeared, and he was given a diagnosis of streptococcal pharyngitis, which was confirmed by a throat swab and a positive antistreptolysin O titer. The child had no personal or family history of skin disorders, including eczema or psoriasis. He hadn’t used any topical agents or new medications recently, nor had he been exposed to triggering plants, animals, or chemicals. There was no history of trauma, friction, or rubbing in the area.
Physical examination revealed multiple erythematous, scaly papules and plaques of varying size on the patient’s trunk, arms, and legs (FIGURE). His palms and soles were spared.

WHAT IS YOUR DIAGNOSIS?
HOW WOULD YOU TREAT THIS PATIENT?
Diagnosis: Guttate psoriasis
A diagnosis of guttate psoriasis was made based on the physical exam findings and the preceding group A beta-hemolytic streptococcal infection.
This condition affects approximately 2% of all patients with psoriasis; it is characterized by the acute onset of multiple erythematosquamous papules and small plaques that look like droplets (“gutta”).1 It tends to affect children and young adults and typically occurs following an acute infection (eg, streptococcal pharyngitis).2,3 In this case, a rapid strep test and throat culture positive for group A Streptococcus supported the diagnosis.
Although this particular phenotype of psoriasis is usually associated with streptococcal infection and mainly occurs in patients with the HLA-Cw6+ allele, the specific immunologic response that causes these skin lesions is poorly understood.4 Antigenic similarities between streptococcal proteins and keratinocyte antigens might explain why the condition is triggered by streptococcal infections.5
Pityriasis rosea and tinea corporis are part of the differential
The differential includes skin conditions such as pityriasis rosea, tinea corporis, varicella, and insect bites.
Pityriasis rosea can manifest as a papulosquamous eruption, but it has an inward-facing scale, called a collarette. The “Christmas tree” pattern on the back that is preceded by a solitary 2- to 10-cm oval, pink, scaly herald patch (in 17%-50% of cases) is key to the diagnosis.6 (For more information, see “Rash on trunk and upper arms.”)
Continue to: Tinea corporis...
Tinea corporis is a dermatophyte infection that causes flat, red, scaly lesions that progress into annular lesions with central clearing or brown discoloration. The plaques can range from a few centimeters to several inches in size, but are always characterized by the slowly advancing border.6
Varicella also affects the trunk and extremities, but a key clinical finding is crops of characteristic lesions, including papules, vesicles, pustules, and crusted lesions in different stages that manifest simultaneously.6
Insect bites usually appear as urticarial papules and plaques associated with outdoor exposure. The lesions are distributed where insects are likely to bite.6
Treat the infection, control the psoriasis
The first-line treatment for streptococcal infection is amoxicillin (50 mg/kg/d [maximum: 1000 mg/d] orally for 10 d) or penicillin G benzathine (for children < 60 lb, 6 × 105 units intramuscularly; children ≥ 60 lb, 1.2 × 106 units intramuscularly).7 For the psoriasis lesions, treatment options include topical glucocorticosteroids, vitamin D derivatives, or combinations of both.5 In most cases, guttate psoriasis completely resolves. However, one-third of children with guttate psoriasis go on to develop plaque psoriasis later in life.8
Our patient was treated with penicillin G benzathine (1.2 × 106 units intramuscularly) and a calcipotriol/betamethasone combination gel. The streptococcal infection and skin lesions completely resolved. No adverse events were reported, and no relapse was observed after 3 months.
CORRESPONDENCE
Rita Matos, MD, Rua Actor Mário Viegas SN Rio Tinto, Portugal; [email protected]
A 7-year-old boy was brought to his family physician for evaluation of a mildly pruritic spreading rash. Ten days earlier, the skin eruption had appeared, and he was given a diagnosis of streptococcal pharyngitis, which was confirmed by a throat swab and a positive antistreptolysin O titer. The child had no personal or family history of skin disorders, including eczema or psoriasis. He hadn’t used any topical agents or new medications recently, nor had he been exposed to triggering plants, animals, or chemicals. There was no history of trauma, friction, or rubbing in the area.
Physical examination revealed multiple erythematous, scaly papules and plaques of varying size on the patient’s trunk, arms, and legs (FIGURE). His palms and soles were spared.

WHAT IS YOUR DIAGNOSIS?
HOW WOULD YOU TREAT THIS PATIENT?
Diagnosis: Guttate psoriasis
A diagnosis of guttate psoriasis was made based on the physical exam findings and the preceding group A beta-hemolytic streptococcal infection.
This condition affects approximately 2% of all patients with psoriasis; it is characterized by the acute onset of multiple erythematosquamous papules and small plaques that look like droplets (“gutta”).1 It tends to affect children and young adults and typically occurs following an acute infection (eg, streptococcal pharyngitis).2,3 In this case, a rapid strep test and throat culture positive for group A Streptococcus supported the diagnosis.
Although this particular phenotype of psoriasis is usually associated with streptococcal infection and mainly occurs in patients with the HLA-Cw6+ allele, the specific immunologic response that causes these skin lesions is poorly understood.4 Antigenic similarities between streptococcal proteins and keratinocyte antigens might explain why the condition is triggered by streptococcal infections.5
Pityriasis rosea and tinea corporis are part of the differential
The differential includes skin conditions such as pityriasis rosea, tinea corporis, varicella, and insect bites.
Pityriasis rosea can manifest as a papulosquamous eruption, but it has an inward-facing scale, called a collarette. The “Christmas tree” pattern on the back that is preceded by a solitary 2- to 10-cm oval, pink, scaly herald patch (in 17%-50% of cases) is key to the diagnosis.6 (For more information, see “Rash on trunk and upper arms.”)
Continue to: Tinea corporis...
Tinea corporis is a dermatophyte infection that causes flat, red, scaly lesions that progress into annular lesions with central clearing or brown discoloration. The plaques can range from a few centimeters to several inches in size, but are always characterized by the slowly advancing border.6
Varicella also affects the trunk and extremities, but a key clinical finding is crops of characteristic lesions, including papules, vesicles, pustules, and crusted lesions in different stages that manifest simultaneously.6
Insect bites usually appear as urticarial papules and plaques associated with outdoor exposure. The lesions are distributed where insects are likely to bite.6
Treat the infection, control the psoriasis
The first-line treatment for streptococcal infection is amoxicillin (50 mg/kg/d [maximum: 1000 mg/d] orally for 10 d) or penicillin G benzathine (for children < 60 lb, 6 × 105 units intramuscularly; children ≥ 60 lb, 1.2 × 106 units intramuscularly).7 For the psoriasis lesions, treatment options include topical glucocorticosteroids, vitamin D derivatives, or combinations of both.5 In most cases, guttate psoriasis completely resolves. However, one-third of children with guttate psoriasis go on to develop plaque psoriasis later in life.8
Our patient was treated with penicillin G benzathine (1.2 × 106 units intramuscularly) and a calcipotriol/betamethasone combination gel. The streptococcal infection and skin lesions completely resolved. No adverse events were reported, and no relapse was observed after 3 months.
CORRESPONDENCE
Rita Matos, MD, Rua Actor Mário Viegas SN Rio Tinto, Portugal; [email protected]
1. Maciejewska-Radomska A, Szczerkowska-Dobosz A, Rebała K, et al. Frequency of streptococcal upper respiratory tract infections and HLA-Cw*06 allele in 70 patients with guttate psoriasis from northern Poland. Postepy Dermatol Alergol. 2015;32:455-458.
2. Garritsen FM, Kraag DE, de Graaf M. Guttate psoriasis triggered by perianal streptococcal infection. Clin Exp Dermatol. 2017;42:536-538.
3. Pfingstler LF, Maroon M, Mowad C. Guttate psoriasis outcomes. Cutis. 2016;97:140-144.
4. Ruiz-Romeu E, Ferran M, Sagristà M, et al. Streptococcus pyogenes-induced cutaneous lymphocyte antigen-positive T cell-dependent epidermal cell activation triggers TH17 responses in patients with guttate psoriasis. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2016;138:491-499.
5. Boehncke WH, Schön MP. Psoriasis. Lancet. 2015;386:983-994.
6. Ely JW, Seabury Stone M. The generalized rash: part I. Differential diagnosis. Am Fam Physician. 2010;81:726-734.
7. Kalra MG, Higgins KE, Perez ED. Common questions about streptococcal pharyngitis. Am Fam Physician. 2016;94:24-31.
8. Martin BA, Chalmers RJ, Telfer NR. How great is the risk of further psoriasis following a single episode of acute guttate psoriasis? Arch Dermatol. 1996;132: 717-718.
1. Maciejewska-Radomska A, Szczerkowska-Dobosz A, Rebała K, et al. Frequency of streptococcal upper respiratory tract infections and HLA-Cw*06 allele in 70 patients with guttate psoriasis from northern Poland. Postepy Dermatol Alergol. 2015;32:455-458.
2. Garritsen FM, Kraag DE, de Graaf M. Guttate psoriasis triggered by perianal streptococcal infection. Clin Exp Dermatol. 2017;42:536-538.
3. Pfingstler LF, Maroon M, Mowad C. Guttate psoriasis outcomes. Cutis. 2016;97:140-144.
4. Ruiz-Romeu E, Ferran M, Sagristà M, et al. Streptococcus pyogenes-induced cutaneous lymphocyte antigen-positive T cell-dependent epidermal cell activation triggers TH17 responses in patients with guttate psoriasis. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2016;138:491-499.
5. Boehncke WH, Schön MP. Psoriasis. Lancet. 2015;386:983-994.
6. Ely JW, Seabury Stone M. The generalized rash: part I. Differential diagnosis. Am Fam Physician. 2010;81:726-734.
7. Kalra MG, Higgins KE, Perez ED. Common questions about streptococcal pharyngitis. Am Fam Physician. 2016;94:24-31.
8. Martin BA, Chalmers RJ, Telfer NR. How great is the risk of further psoriasis following a single episode of acute guttate psoriasis? Arch Dermatol. 1996;132: 717-718.
Bone biopsy in suspected osteomyelitis: Culture and histology matter
Diabetic foot ulcers and infections can lead to osteomyelitis, a potentially devastating infection in the bone.
How much of a difference can osteomyelitis make to a patient’s prognosis? A 2014 commentary by Benjamin A. Lipsky, MD, a prominent expert in problems associated with diabetic patients’ feet who’s with the University of Washington, Seattle, hints at the potential toll: “Overall, about 20% of patients with a diabetic foot infection (and over 60% of those with severe infections) have underlying osteomyelitis, which dramatically increases the risk of lower-extremity amputation” (Diabetes Care. 2014 Mar;37[3]:593-5).
Diagnosis of osteomyelitis, which relies on a bone biopsy, is clearly important. But there’s a big gap in diagnostic findings depending on whether doctors request culture or histology results, according to a new study released at the 2018 scientific meeting of the American Diabetes Association (Diabetes. 2018 Jul. doi: 10.2337/db18-110-OR).
In an interview, lead author and podiatrist Peter A. Crisologo, DPM, of University of Texas Southwestern Medical Center, Dallas, explained the study findings and offered guidance for requesting bone biopsies in possible cases of osteomyelitis.
Q: What makes diagnosis and treatment of osteomyelitis unique?
A: In the foot, there’s not a lot of soft tissue between the outside world and your bone. If the wounds on the feet go deep enough, they can spread a bacterial infection to the bone. This changes how foot infections are treated.
If you have a skin infection, it requires 11-12 days of antibiotics. Things start ramping up once you start getting into the bone. You’re talking potential surgery and 6 weeks of antibiotics through IV treatments. This is why it’s really important that you get your diagnosis right.
A lot of people say “I’m going to do the safe thing” and treat a bone infection with an extended course of antibiotics.
That’s not necessarily safe. If you’re overdiagnosing – for example, you identify bacteria that’s just a contaminant – you could put a patient through 6 weeks of IV treatment along with the risks of a PICC (peripherally inserted central catheter ) line infection, complications from IV placement, and complications from the antibiotic.
Also, acute kidney injury develops in at least a third of the patients who undergo 6 weeks of antibiotics. That’s not to mention the cost of the visits and the labs you have to draw. But we don’t want to underdiagnose either. If osteomyelitis is underdiagnosed and then not treated, the infection can smolder and continue to progress and worsen.
Q: Your study looks at the bone biopsy. How does it fit into care of osteomyelitis in the diabetic foot?
A: A bone biopsy is the standard for diagnosis under the guidelines of the Infectious Diseases Society of America/International Working Group on the Diabetic Foot (Clin Infect Dis. 2012;54[12]:e132-73 ).
But beyond that, nobody says anything. Everyone has an operational definition of how a bone biopsy is interpreted, and there’s a need for a consensus on how a bone biopsy can be used to diagnose osteomyelitis.
You’ll get different percentages of your patients diagnosed with osteomyelitis. For example, someone may say the biopsy is only positive if the histology is positive, while another says the histology doesn’t matter if the culture is positive.
Q: Your study looks at histology and culture analyses. What do these reveal?
A: A traditional culture helps you identify the bacteria, as well as guide your treatment when it’s tested against antibiotics.
A traditional histology allows the pathologist to look under a microscope for signs of osteomyelitis: Do they see the right inflammatory cells, white cells, lymphocytes, combinations of cells? Does this look like an acute or chronic osteomyelitis?
Q: Why might it be wise to combine culture and histology analyses?
A: If you have bacteria that’s difficult to culture via traditional methods, it may be a bacteria that doesn’t grow well or easily. If you combine culture with histology, pathologists can look and say, “Your culture was negative but we see these other signs, so we feel this is osteomyelitis.”
Q: Your study examined 35 consecutive patients aged at least 21 years who had moderate or severe infections bone infections in the foot linked with type 1 diabetes (n = 4) or type 2 diabetes (n = 31).
The samples were analyzed via culture, histology, and culture/histology examinations. You also performed genetic sequencing (quantitative polymerase chain reaction targeting 16S rRNA). How does this test fit in to bone biopsies in the clinic?
A: That’s a newer method and not a standard of care treatment for the diabetic foot. This analysis looks at DNA that’s present, bypassing the analysis of difficult-to-grow bacteria.
Q: What did you discover?
A: In this study, histology had the lowest incidence of positively detecting osteomyelitis. (45.7%). The level increases when a culture is taken (68.6% vs. histology; P = .02).
Then it goes up when DNA is used because it’s catching everything (82.9%, P = .001 vs. histology and P = .31 vs. culture).
[The study also found that adding histology to culture or to genetic sequencing did not change positive findings.]
Q: Does the study suggest one approach is better than the others?
A: This paper doesn’t provide enough evidence to use one method over another. The main purpose was to raise the concern that diagnosis can change dramatically depending on how the gold standard of bone biopsy is interpreted.
Q: What were the pros and cons of the genetic sequencing approach?
A: When we use this approach, our positive diagnostic rate significantly increases. But there are also downsides. We don’t know whether the bacteria we see is alive or dead. We just know it was there. So are the patients truly positive? That’s a question we can’t answer.
Genetic sequencing also doesn’t tell us about susceptibilities to antibiotics.
Q: What is the take-home message here for physicians who may order bone biopsies?
A: The thing to do is request both traditional culture and traditional histology.
As far as DNA sequencing, that not something I’d recommend as a standard of care.
Q: Can you comment on cost and insurance coverage for these approaches?
A: As far as I know, genetic sequencing is not covered as it is not standard of care in the diabetic foot and is used mainly for research at this time.
Pathology and culture are standard of care when evaluating for osteomyelitis and should be a covered service. However, a patient should call their insurance company first prior to having the procedure done to see whether it is covered.
Q: What’s next for research in this area?
A: From here, the next step is bigger numbers: Increase the study size and look at this again. Also, we may be able to identify susceptibilities by identifying resistance within the DNA.
Dr. Crisologo and two other study authors report no relevant disclosures. One study author reported various disclosures including research support, consulting, and service on speakers' bureaus.
Diabetic foot ulcers and infections can lead to osteomyelitis, a potentially devastating infection in the bone.
How much of a difference can osteomyelitis make to a patient’s prognosis? A 2014 commentary by Benjamin A. Lipsky, MD, a prominent expert in problems associated with diabetic patients’ feet who’s with the University of Washington, Seattle, hints at the potential toll: “Overall, about 20% of patients with a diabetic foot infection (and over 60% of those with severe infections) have underlying osteomyelitis, which dramatically increases the risk of lower-extremity amputation” (Diabetes Care. 2014 Mar;37[3]:593-5).
Diagnosis of osteomyelitis, which relies on a bone biopsy, is clearly important. But there’s a big gap in diagnostic findings depending on whether doctors request culture or histology results, according to a new study released at the 2018 scientific meeting of the American Diabetes Association (Diabetes. 2018 Jul. doi: 10.2337/db18-110-OR).
In an interview, lead author and podiatrist Peter A. Crisologo, DPM, of University of Texas Southwestern Medical Center, Dallas, explained the study findings and offered guidance for requesting bone biopsies in possible cases of osteomyelitis.
Q: What makes diagnosis and treatment of osteomyelitis unique?
A: In the foot, there’s not a lot of soft tissue between the outside world and your bone. If the wounds on the feet go deep enough, they can spread a bacterial infection to the bone. This changes how foot infections are treated.
If you have a skin infection, it requires 11-12 days of antibiotics. Things start ramping up once you start getting into the bone. You’re talking potential surgery and 6 weeks of antibiotics through IV treatments. This is why it’s really important that you get your diagnosis right.
A lot of people say “I’m going to do the safe thing” and treat a bone infection with an extended course of antibiotics.
That’s not necessarily safe. If you’re overdiagnosing – for example, you identify bacteria that’s just a contaminant – you could put a patient through 6 weeks of IV treatment along with the risks of a PICC (peripherally inserted central catheter ) line infection, complications from IV placement, and complications from the antibiotic.
Also, acute kidney injury develops in at least a third of the patients who undergo 6 weeks of antibiotics. That’s not to mention the cost of the visits and the labs you have to draw. But we don’t want to underdiagnose either. If osteomyelitis is underdiagnosed and then not treated, the infection can smolder and continue to progress and worsen.
Q: Your study looks at the bone biopsy. How does it fit into care of osteomyelitis in the diabetic foot?
A: A bone biopsy is the standard for diagnosis under the guidelines of the Infectious Diseases Society of America/International Working Group on the Diabetic Foot (Clin Infect Dis. 2012;54[12]:e132-73 ).
But beyond that, nobody says anything. Everyone has an operational definition of how a bone biopsy is interpreted, and there’s a need for a consensus on how a bone biopsy can be used to diagnose osteomyelitis.
You’ll get different percentages of your patients diagnosed with osteomyelitis. For example, someone may say the biopsy is only positive if the histology is positive, while another says the histology doesn’t matter if the culture is positive.
Q: Your study looks at histology and culture analyses. What do these reveal?
A: A traditional culture helps you identify the bacteria, as well as guide your treatment when it’s tested against antibiotics.
A traditional histology allows the pathologist to look under a microscope for signs of osteomyelitis: Do they see the right inflammatory cells, white cells, lymphocytes, combinations of cells? Does this look like an acute or chronic osteomyelitis?
Q: Why might it be wise to combine culture and histology analyses?
A: If you have bacteria that’s difficult to culture via traditional methods, it may be a bacteria that doesn’t grow well or easily. If you combine culture with histology, pathologists can look and say, “Your culture was negative but we see these other signs, so we feel this is osteomyelitis.”
Q: Your study examined 35 consecutive patients aged at least 21 years who had moderate or severe infections bone infections in the foot linked with type 1 diabetes (n = 4) or type 2 diabetes (n = 31).
The samples were analyzed via culture, histology, and culture/histology examinations. You also performed genetic sequencing (quantitative polymerase chain reaction targeting 16S rRNA). How does this test fit in to bone biopsies in the clinic?
A: That’s a newer method and not a standard of care treatment for the diabetic foot. This analysis looks at DNA that’s present, bypassing the analysis of difficult-to-grow bacteria.
Q: What did you discover?
A: In this study, histology had the lowest incidence of positively detecting osteomyelitis. (45.7%). The level increases when a culture is taken (68.6% vs. histology; P = .02).
Then it goes up when DNA is used because it’s catching everything (82.9%, P = .001 vs. histology and P = .31 vs. culture).
[The study also found that adding histology to culture or to genetic sequencing did not change positive findings.]
Q: Does the study suggest one approach is better than the others?
A: This paper doesn’t provide enough evidence to use one method over another. The main purpose was to raise the concern that diagnosis can change dramatically depending on how the gold standard of bone biopsy is interpreted.
Q: What were the pros and cons of the genetic sequencing approach?
A: When we use this approach, our positive diagnostic rate significantly increases. But there are also downsides. We don’t know whether the bacteria we see is alive or dead. We just know it was there. So are the patients truly positive? That’s a question we can’t answer.
Genetic sequencing also doesn’t tell us about susceptibilities to antibiotics.
Q: What is the take-home message here for physicians who may order bone biopsies?
A: The thing to do is request both traditional culture and traditional histology.
As far as DNA sequencing, that not something I’d recommend as a standard of care.
Q: Can you comment on cost and insurance coverage for these approaches?
A: As far as I know, genetic sequencing is not covered as it is not standard of care in the diabetic foot and is used mainly for research at this time.
Pathology and culture are standard of care when evaluating for osteomyelitis and should be a covered service. However, a patient should call their insurance company first prior to having the procedure done to see whether it is covered.
Q: What’s next for research in this area?
A: From here, the next step is bigger numbers: Increase the study size and look at this again. Also, we may be able to identify susceptibilities by identifying resistance within the DNA.
Dr. Crisologo and two other study authors report no relevant disclosures. One study author reported various disclosures including research support, consulting, and service on speakers' bureaus.
Diabetic foot ulcers and infections can lead to osteomyelitis, a potentially devastating infection in the bone.
How much of a difference can osteomyelitis make to a patient’s prognosis? A 2014 commentary by Benjamin A. Lipsky, MD, a prominent expert in problems associated with diabetic patients’ feet who’s with the University of Washington, Seattle, hints at the potential toll: “Overall, about 20% of patients with a diabetic foot infection (and over 60% of those with severe infections) have underlying osteomyelitis, which dramatically increases the risk of lower-extremity amputation” (Diabetes Care. 2014 Mar;37[3]:593-5).
Diagnosis of osteomyelitis, which relies on a bone biopsy, is clearly important. But there’s a big gap in diagnostic findings depending on whether doctors request culture or histology results, according to a new study released at the 2018 scientific meeting of the American Diabetes Association (Diabetes. 2018 Jul. doi: 10.2337/db18-110-OR).
In an interview, lead author and podiatrist Peter A. Crisologo, DPM, of University of Texas Southwestern Medical Center, Dallas, explained the study findings and offered guidance for requesting bone biopsies in possible cases of osteomyelitis.
Q: What makes diagnosis and treatment of osteomyelitis unique?
A: In the foot, there’s not a lot of soft tissue between the outside world and your bone. If the wounds on the feet go deep enough, they can spread a bacterial infection to the bone. This changes how foot infections are treated.
If you have a skin infection, it requires 11-12 days of antibiotics. Things start ramping up once you start getting into the bone. You’re talking potential surgery and 6 weeks of antibiotics through IV treatments. This is why it’s really important that you get your diagnosis right.
A lot of people say “I’m going to do the safe thing” and treat a bone infection with an extended course of antibiotics.
That’s not necessarily safe. If you’re overdiagnosing – for example, you identify bacteria that’s just a contaminant – you could put a patient through 6 weeks of IV treatment along with the risks of a PICC (peripherally inserted central catheter ) line infection, complications from IV placement, and complications from the antibiotic.
Also, acute kidney injury develops in at least a third of the patients who undergo 6 weeks of antibiotics. That’s not to mention the cost of the visits and the labs you have to draw. But we don’t want to underdiagnose either. If osteomyelitis is underdiagnosed and then not treated, the infection can smolder and continue to progress and worsen.
Q: Your study looks at the bone biopsy. How does it fit into care of osteomyelitis in the diabetic foot?
A: A bone biopsy is the standard for diagnosis under the guidelines of the Infectious Diseases Society of America/International Working Group on the Diabetic Foot (Clin Infect Dis. 2012;54[12]:e132-73 ).
But beyond that, nobody says anything. Everyone has an operational definition of how a bone biopsy is interpreted, and there’s a need for a consensus on how a bone biopsy can be used to diagnose osteomyelitis.
You’ll get different percentages of your patients diagnosed with osteomyelitis. For example, someone may say the biopsy is only positive if the histology is positive, while another says the histology doesn’t matter if the culture is positive.
Q: Your study looks at histology and culture analyses. What do these reveal?
A: A traditional culture helps you identify the bacteria, as well as guide your treatment when it’s tested against antibiotics.
A traditional histology allows the pathologist to look under a microscope for signs of osteomyelitis: Do they see the right inflammatory cells, white cells, lymphocytes, combinations of cells? Does this look like an acute or chronic osteomyelitis?
Q: Why might it be wise to combine culture and histology analyses?
A: If you have bacteria that’s difficult to culture via traditional methods, it may be a bacteria that doesn’t grow well or easily. If you combine culture with histology, pathologists can look and say, “Your culture was negative but we see these other signs, so we feel this is osteomyelitis.”
Q: Your study examined 35 consecutive patients aged at least 21 years who had moderate or severe infections bone infections in the foot linked with type 1 diabetes (n = 4) or type 2 diabetes (n = 31).
The samples were analyzed via culture, histology, and culture/histology examinations. You also performed genetic sequencing (quantitative polymerase chain reaction targeting 16S rRNA). How does this test fit in to bone biopsies in the clinic?
A: That’s a newer method and not a standard of care treatment for the diabetic foot. This analysis looks at DNA that’s present, bypassing the analysis of difficult-to-grow bacteria.
Q: What did you discover?
A: In this study, histology had the lowest incidence of positively detecting osteomyelitis. (45.7%). The level increases when a culture is taken (68.6% vs. histology; P = .02).
Then it goes up when DNA is used because it’s catching everything (82.9%, P = .001 vs. histology and P = .31 vs. culture).
[The study also found that adding histology to culture or to genetic sequencing did not change positive findings.]
Q: Does the study suggest one approach is better than the others?
A: This paper doesn’t provide enough evidence to use one method over another. The main purpose was to raise the concern that diagnosis can change dramatically depending on how the gold standard of bone biopsy is interpreted.
Q: What were the pros and cons of the genetic sequencing approach?
A: When we use this approach, our positive diagnostic rate significantly increases. But there are also downsides. We don’t know whether the bacteria we see is alive or dead. We just know it was there. So are the patients truly positive? That’s a question we can’t answer.
Genetic sequencing also doesn’t tell us about susceptibilities to antibiotics.
Q: What is the take-home message here for physicians who may order bone biopsies?
A: The thing to do is request both traditional culture and traditional histology.
As far as DNA sequencing, that not something I’d recommend as a standard of care.
Q: Can you comment on cost and insurance coverage for these approaches?
A: As far as I know, genetic sequencing is not covered as it is not standard of care in the diabetic foot and is used mainly for research at this time.
Pathology and culture are standard of care when evaluating for osteomyelitis and should be a covered service. However, a patient should call their insurance company first prior to having the procedure done to see whether it is covered.
Q: What’s next for research in this area?
A: From here, the next step is bigger numbers: Increase the study size and look at this again. Also, we may be able to identify susceptibilities by identifying resistance within the DNA.
Dr. Crisologo and two other study authors report no relevant disclosures. One study author reported various disclosures including research support, consulting, and service on speakers' bureaus.
EXPERT ANALYSIS FROM ADA 2018
Risankizumab proves more effective in psoriasis than ustekinumab
, according to results of a pair of head-to-head trials published in the Lancet.
The replicate phase 3, randomized, double-blind, placebo- and active comparator–controlled trials, UltIMMa-1 (NCT02684370) and UltIMMa-2 (NCT02684375) altogether randomized 997 patients to risankizumab, ustekinumab, or placebo. The coprimary endpoints were the proportions of patients achieving 90% reduction in Psoriasis Area and Severity Index (PASI 90) at 16 weeks and a static Physician Global Assessment (sPGA) score of 0 or 1, and the 15 ranked secondary endpoints included proportions of those achieving PASI 100 or sPGA 0, both of which demonstrate total clearance of psoriasis, as well as measures of quality of life improvement.
Compared with those receiving either ustekinumab or placebo, a significantly higher proportion of patients receiving risankizumab achieved the coprimary endpoints, and all secondary endpoints were met. In UltIMMA-1, 75.3% of risankizumab patients achieved PASI 90, compared with 4.9% of placebo patients and 42% of ustekinumab patients (P less than .0001 when comparing it with both placebo and ustekinumab); sPGA of 0 or 1 was achieved by 87.8% of risankizumab patients and only 7.8% of placebo patients and 63% of ustekinumab patients (P less than .0001 when comparing it with both placebo and ustekinumab). Results were similar in UltIMMA-2: 74.8% of risankizumab patients achieved PASI 90, and 83.7% of them achieved sPGA 0 or 1 (P less than .0001 when comparing them with placebo and ustekinumab). According to results of the secondary endpoints, both studies also showed greater rates of clearance and improvements in quality of life among patients receiving risankizumab than among those receiving either placebo or ustekinumab.
The safety profiles across treatment groups were similar in both studies, with the most common adverse events including upper respiratory tract infection, headache, and diarrhea.
Risankizumab is a humanized IgG1 monoclonal antibody that targets the p19 subunit of only interleukin-23, unlike the studies’ active comparator, ustekinumab, which targets both interleukin-23 and interleukin-12. “Selectively blocking interleukin 23 with a p19 inhibitor appears to be one of the best ways to treat psoriasis,” commented Abigail Cline, MD, and Steven R. Feldman, MD, PhD, both of Wake Forest University, Winston-Salem, N.C., in an accompanying editorial (Lancet. 2018 Aug 7;392:616-71.).
The authors of the study reported relationships with various industry entities, including AbbVie, which sponsored the studies and developed risankizumab, and Boehringer Ingelheim, which collaborated in the studies. The authors of the editorial also disclosed relationships with entities, including AbbVie.
SOURCE: Gordon KB et al. Lancet. 2018 Aug 7;392:650-61.
, according to results of a pair of head-to-head trials published in the Lancet.
The replicate phase 3, randomized, double-blind, placebo- and active comparator–controlled trials, UltIMMa-1 (NCT02684370) and UltIMMa-2 (NCT02684375) altogether randomized 997 patients to risankizumab, ustekinumab, or placebo. The coprimary endpoints were the proportions of patients achieving 90% reduction in Psoriasis Area and Severity Index (PASI 90) at 16 weeks and a static Physician Global Assessment (sPGA) score of 0 or 1, and the 15 ranked secondary endpoints included proportions of those achieving PASI 100 or sPGA 0, both of which demonstrate total clearance of psoriasis, as well as measures of quality of life improvement.
Compared with those receiving either ustekinumab or placebo, a significantly higher proportion of patients receiving risankizumab achieved the coprimary endpoints, and all secondary endpoints were met. In UltIMMA-1, 75.3% of risankizumab patients achieved PASI 90, compared with 4.9% of placebo patients and 42% of ustekinumab patients (P less than .0001 when comparing it with both placebo and ustekinumab); sPGA of 0 or 1 was achieved by 87.8% of risankizumab patients and only 7.8% of placebo patients and 63% of ustekinumab patients (P less than .0001 when comparing it with both placebo and ustekinumab). Results were similar in UltIMMA-2: 74.8% of risankizumab patients achieved PASI 90, and 83.7% of them achieved sPGA 0 or 1 (P less than .0001 when comparing them with placebo and ustekinumab). According to results of the secondary endpoints, both studies also showed greater rates of clearance and improvements in quality of life among patients receiving risankizumab than among those receiving either placebo or ustekinumab.
The safety profiles across treatment groups were similar in both studies, with the most common adverse events including upper respiratory tract infection, headache, and diarrhea.
Risankizumab is a humanized IgG1 monoclonal antibody that targets the p19 subunit of only interleukin-23, unlike the studies’ active comparator, ustekinumab, which targets both interleukin-23 and interleukin-12. “Selectively blocking interleukin 23 with a p19 inhibitor appears to be one of the best ways to treat psoriasis,” commented Abigail Cline, MD, and Steven R. Feldman, MD, PhD, both of Wake Forest University, Winston-Salem, N.C., in an accompanying editorial (Lancet. 2018 Aug 7;392:616-71.).
The authors of the study reported relationships with various industry entities, including AbbVie, which sponsored the studies and developed risankizumab, and Boehringer Ingelheim, which collaborated in the studies. The authors of the editorial also disclosed relationships with entities, including AbbVie.
SOURCE: Gordon KB et al. Lancet. 2018 Aug 7;392:650-61.
, according to results of a pair of head-to-head trials published in the Lancet.
The replicate phase 3, randomized, double-blind, placebo- and active comparator–controlled trials, UltIMMa-1 (NCT02684370) and UltIMMa-2 (NCT02684375) altogether randomized 997 patients to risankizumab, ustekinumab, or placebo. The coprimary endpoints were the proportions of patients achieving 90% reduction in Psoriasis Area and Severity Index (PASI 90) at 16 weeks and a static Physician Global Assessment (sPGA) score of 0 or 1, and the 15 ranked secondary endpoints included proportions of those achieving PASI 100 or sPGA 0, both of which demonstrate total clearance of psoriasis, as well as measures of quality of life improvement.
Compared with those receiving either ustekinumab or placebo, a significantly higher proportion of patients receiving risankizumab achieved the coprimary endpoints, and all secondary endpoints were met. In UltIMMA-1, 75.3% of risankizumab patients achieved PASI 90, compared with 4.9% of placebo patients and 42% of ustekinumab patients (P less than .0001 when comparing it with both placebo and ustekinumab); sPGA of 0 or 1 was achieved by 87.8% of risankizumab patients and only 7.8% of placebo patients and 63% of ustekinumab patients (P less than .0001 when comparing it with both placebo and ustekinumab). Results were similar in UltIMMA-2: 74.8% of risankizumab patients achieved PASI 90, and 83.7% of them achieved sPGA 0 or 1 (P less than .0001 when comparing them with placebo and ustekinumab). According to results of the secondary endpoints, both studies also showed greater rates of clearance and improvements in quality of life among patients receiving risankizumab than among those receiving either placebo or ustekinumab.
The safety profiles across treatment groups were similar in both studies, with the most common adverse events including upper respiratory tract infection, headache, and diarrhea.
Risankizumab is a humanized IgG1 monoclonal antibody that targets the p19 subunit of only interleukin-23, unlike the studies’ active comparator, ustekinumab, which targets both interleukin-23 and interleukin-12. “Selectively blocking interleukin 23 with a p19 inhibitor appears to be one of the best ways to treat psoriasis,” commented Abigail Cline, MD, and Steven R. Feldman, MD, PhD, both of Wake Forest University, Winston-Salem, N.C., in an accompanying editorial (Lancet. 2018 Aug 7;392:616-71.).
The authors of the study reported relationships with various industry entities, including AbbVie, which sponsored the studies and developed risankizumab, and Boehringer Ingelheim, which collaborated in the studies. The authors of the editorial also disclosed relationships with entities, including AbbVie.
SOURCE: Gordon KB et al. Lancet. 2018 Aug 7;392:650-61.
FROM THE LANCET
Itraconazole for BCC: Does it work?
CHICAGO – Justin J. Leitenberger, MD, declared at the annual meeting of the American College of Mohs Surgery.
The oral antifungal inhibits the hedgehog signaling pathway, a key driver of BCC. And while itraconazole is not as potent an inhibitor of hedgehog pathway expression as, say vismodegib (Erivedge), the antifungal acts at a separate site on the pathway, making it an attractive candidate for combination therapy, explained Dr. Leitenberger of Oregon Health & Science University, Portland.
Dermatologists at Stanford University have led the way in exploring oral itraconazole as a treatment for BCC. Among a series of 29 patients with one or more large but nonadvanced BCCs, 19 were treated using oral itraconazole at 200 mg b.i.d. for 1 month or 100 mg b.i.d. for an average of 2.3 months. Hedgehog pathway expression was reduced by 65% in the itraconazole-treated patients, as compared with the 90% reduction which is achieved with vismodegib.
Of more direct clinical relevance, however, itraconazole also reduced tumor area by 24%. Four of eight patients with 57 tumors achieved a partial response, and the other four had stable disease (J Clin Oncol. 2014 Mar 10;32[8]:745-51).
The Stanford group has also shown that combination therapy with oral itraconazole and intravenous arsenic trioxide reduces hedgehog pathway expression by 75%, up by an absolute 10% from itraconazole alone. The two agents inhibit the pathway at different sites.
Five patients with metastatic BCC who relapsed after treatment with vismodegib received intravenous arsenic trioxide for the first 5 days of every month, followed by oral itraconazole at 200 mg b.i.d. on days 6-28. Three patients completed three such cycles, while two discontinued early because of progressive disease or adverse events including a grade 3 infection and grade 2 transaminitis. All three patients who completed three treatment cycles achieved stable disease. The Stanford investigators speculated that concurrent continuous dosing might be required to obtain tumor shrinkage (JAMA Dermatol. 2016 Apr;152[4]:452-6).
Lots more work remains to be done in order to optimize combination therapy utilizing oral itraconazole for advanced BCC. Different dosing regimens and combinations of hedgehog pathway inhibitors need to be studied. Another important question is how effective itraconazole-based combinations will be in vismodegib-naive as compared with vismodegib-resistant patients, Dr. Leitenberger observed.
He reported having no financial conflicts regarding his presentation.
CHICAGO – Justin J. Leitenberger, MD, declared at the annual meeting of the American College of Mohs Surgery.
The oral antifungal inhibits the hedgehog signaling pathway, a key driver of BCC. And while itraconazole is not as potent an inhibitor of hedgehog pathway expression as, say vismodegib (Erivedge), the antifungal acts at a separate site on the pathway, making it an attractive candidate for combination therapy, explained Dr. Leitenberger of Oregon Health & Science University, Portland.
Dermatologists at Stanford University have led the way in exploring oral itraconazole as a treatment for BCC. Among a series of 29 patients with one or more large but nonadvanced BCCs, 19 were treated using oral itraconazole at 200 mg b.i.d. for 1 month or 100 mg b.i.d. for an average of 2.3 months. Hedgehog pathway expression was reduced by 65% in the itraconazole-treated patients, as compared with the 90% reduction which is achieved with vismodegib.
Of more direct clinical relevance, however, itraconazole also reduced tumor area by 24%. Four of eight patients with 57 tumors achieved a partial response, and the other four had stable disease (J Clin Oncol. 2014 Mar 10;32[8]:745-51).
The Stanford group has also shown that combination therapy with oral itraconazole and intravenous arsenic trioxide reduces hedgehog pathway expression by 75%, up by an absolute 10% from itraconazole alone. The two agents inhibit the pathway at different sites.
Five patients with metastatic BCC who relapsed after treatment with vismodegib received intravenous arsenic trioxide for the first 5 days of every month, followed by oral itraconazole at 200 mg b.i.d. on days 6-28. Three patients completed three such cycles, while two discontinued early because of progressive disease or adverse events including a grade 3 infection and grade 2 transaminitis. All three patients who completed three treatment cycles achieved stable disease. The Stanford investigators speculated that concurrent continuous dosing might be required to obtain tumor shrinkage (JAMA Dermatol. 2016 Apr;152[4]:452-6).
Lots more work remains to be done in order to optimize combination therapy utilizing oral itraconazole for advanced BCC. Different dosing regimens and combinations of hedgehog pathway inhibitors need to be studied. Another important question is how effective itraconazole-based combinations will be in vismodegib-naive as compared with vismodegib-resistant patients, Dr. Leitenberger observed.
He reported having no financial conflicts regarding his presentation.
CHICAGO – Justin J. Leitenberger, MD, declared at the annual meeting of the American College of Mohs Surgery.
The oral antifungal inhibits the hedgehog signaling pathway, a key driver of BCC. And while itraconazole is not as potent an inhibitor of hedgehog pathway expression as, say vismodegib (Erivedge), the antifungal acts at a separate site on the pathway, making it an attractive candidate for combination therapy, explained Dr. Leitenberger of Oregon Health & Science University, Portland.
Dermatologists at Stanford University have led the way in exploring oral itraconazole as a treatment for BCC. Among a series of 29 patients with one or more large but nonadvanced BCCs, 19 were treated using oral itraconazole at 200 mg b.i.d. for 1 month or 100 mg b.i.d. for an average of 2.3 months. Hedgehog pathway expression was reduced by 65% in the itraconazole-treated patients, as compared with the 90% reduction which is achieved with vismodegib.
Of more direct clinical relevance, however, itraconazole also reduced tumor area by 24%. Four of eight patients with 57 tumors achieved a partial response, and the other four had stable disease (J Clin Oncol. 2014 Mar 10;32[8]:745-51).
The Stanford group has also shown that combination therapy with oral itraconazole and intravenous arsenic trioxide reduces hedgehog pathway expression by 75%, up by an absolute 10% from itraconazole alone. The two agents inhibit the pathway at different sites.
Five patients with metastatic BCC who relapsed after treatment with vismodegib received intravenous arsenic trioxide for the first 5 days of every month, followed by oral itraconazole at 200 mg b.i.d. on days 6-28. Three patients completed three such cycles, while two discontinued early because of progressive disease or adverse events including a grade 3 infection and grade 2 transaminitis. All three patients who completed three treatment cycles achieved stable disease. The Stanford investigators speculated that concurrent continuous dosing might be required to obtain tumor shrinkage (JAMA Dermatol. 2016 Apr;152[4]:452-6).
Lots more work remains to be done in order to optimize combination therapy utilizing oral itraconazole for advanced BCC. Different dosing regimens and combinations of hedgehog pathway inhibitors need to be studied. Another important question is how effective itraconazole-based combinations will be in vismodegib-naive as compared with vismodegib-resistant patients, Dr. Leitenberger observed.
He reported having no financial conflicts regarding his presentation.
EXPERT ANALYSIS FROM THE ACMS ANNUAL MEETING