User login
Concurrent Romiplostim With FOLFIRINOX for Secondary Prevention of Thrombocytopenia in a Patient With Myelodysplastic Syndrome and Pancreatic Adenocarcinoma
Inroduction
Romiplostim is an agonist of the thrombopoietin receptor that stimulates platelet production. Several studies have evaluated the role of romiplostim in the prevention of chemotherapy-induced thrombocytopenia (CIT). Romiplostim may reduce dose reductions, treatment delays, bleeding events, and transfusions.
Less is known about treatment of CIT in patients with pre-existing thrombocytopenia (TCP), such as those with myelodysplastic syndrome (MDS). Here we present a case of a patient with TCP secondary to MDS who was given romiplostim during the treatment of pancreatic adenocarcinoma with FOLFIRINOX.
Case Report
The patient is a 76-year-old male with history of chronic TCP (baseline platelets 50-90 K/μL) presumed secondary to myelodysplastic syndrome, although a bone marrow biopsy was inconclusive. He had not had any major bleeding events or transfusions, aside from one unit of platelets given after a cervical spine fusion.
He was later diagnosed with borderline-resectable pancreatic adenocarcinoma, Stage IbT2N0. Plan made to administer neoadjuvant FOLFIRNOX chemotherapy, followed by Whipple.
The patient was started on romiplostim with a dose range of 1-10 mcg/kg weekly to maintain platelets between 60-200. We initially planned to give all 12 cycles neoadjuvantly but found that we could not maintain a platelet count over 50 K/μL despite maximal uptitration of romiplostim so the Whipple was performed after Cycle 9. Three additional cycles were given post-operatively. There were no dose-reductions, although oxaliplatin was held after cycle 9 due to neuropathy. He developed a jejunal bleed post-Whipple that required embolization but did not require transfusion.
Summary
This was a case in which romiplostim was successfully used during FOLFIRINOX to support platelets in a patient with baseline TCP from MDS. Despite a jejunal bleed after Whipple, the patient tolerated the treatment well and was able to complete all 12 cycles of peri-operative FOLFIRINOX. This approach may be beneficial in other patients with pre-existing TCP receiving chemotherapy.
Inroduction
Romiplostim is an agonist of the thrombopoietin receptor that stimulates platelet production. Several studies have evaluated the role of romiplostim in the prevention of chemotherapy-induced thrombocytopenia (CIT). Romiplostim may reduce dose reductions, treatment delays, bleeding events, and transfusions.
Less is known about treatment of CIT in patients with pre-existing thrombocytopenia (TCP), such as those with myelodysplastic syndrome (MDS). Here we present a case of a patient with TCP secondary to MDS who was given romiplostim during the treatment of pancreatic adenocarcinoma with FOLFIRINOX.
Case Report
The patient is a 76-year-old male with history of chronic TCP (baseline platelets 50-90 K/μL) presumed secondary to myelodysplastic syndrome, although a bone marrow biopsy was inconclusive. He had not had any major bleeding events or transfusions, aside from one unit of platelets given after a cervical spine fusion.
He was later diagnosed with borderline-resectable pancreatic adenocarcinoma, Stage IbT2N0. Plan made to administer neoadjuvant FOLFIRNOX chemotherapy, followed by Whipple.
The patient was started on romiplostim with a dose range of 1-10 mcg/kg weekly to maintain platelets between 60-200. We initially planned to give all 12 cycles neoadjuvantly but found that we could not maintain a platelet count over 50 K/μL despite maximal uptitration of romiplostim so the Whipple was performed after Cycle 9. Three additional cycles were given post-operatively. There were no dose-reductions, although oxaliplatin was held after cycle 9 due to neuropathy. He developed a jejunal bleed post-Whipple that required embolization but did not require transfusion.
Summary
This was a case in which romiplostim was successfully used during FOLFIRINOX to support platelets in a patient with baseline TCP from MDS. Despite a jejunal bleed after Whipple, the patient tolerated the treatment well and was able to complete all 12 cycles of peri-operative FOLFIRINOX. This approach may be beneficial in other patients with pre-existing TCP receiving chemotherapy.
Inroduction
Romiplostim is an agonist of the thrombopoietin receptor that stimulates platelet production. Several studies have evaluated the role of romiplostim in the prevention of chemotherapy-induced thrombocytopenia (CIT). Romiplostim may reduce dose reductions, treatment delays, bleeding events, and transfusions.
Less is known about treatment of CIT in patients with pre-existing thrombocytopenia (TCP), such as those with myelodysplastic syndrome (MDS). Here we present a case of a patient with TCP secondary to MDS who was given romiplostim during the treatment of pancreatic adenocarcinoma with FOLFIRINOX.
Case Report
The patient is a 76-year-old male with history of chronic TCP (baseline platelets 50-90 K/μL) presumed secondary to myelodysplastic syndrome, although a bone marrow biopsy was inconclusive. He had not had any major bleeding events or transfusions, aside from one unit of platelets given after a cervical spine fusion.
He was later diagnosed with borderline-resectable pancreatic adenocarcinoma, Stage IbT2N0. Plan made to administer neoadjuvant FOLFIRNOX chemotherapy, followed by Whipple.
The patient was started on romiplostim with a dose range of 1-10 mcg/kg weekly to maintain platelets between 60-200. We initially planned to give all 12 cycles neoadjuvantly but found that we could not maintain a platelet count over 50 K/μL despite maximal uptitration of romiplostim so the Whipple was performed after Cycle 9. Three additional cycles were given post-operatively. There were no dose-reductions, although oxaliplatin was held after cycle 9 due to neuropathy. He developed a jejunal bleed post-Whipple that required embolization but did not require transfusion.
Summary
This was a case in which romiplostim was successfully used during FOLFIRINOX to support platelets in a patient with baseline TCP from MDS. Despite a jejunal bleed after Whipple, the patient tolerated the treatment well and was able to complete all 12 cycles of peri-operative FOLFIRINOX. This approach may be beneficial in other patients with pre-existing TCP receiving chemotherapy.
Date with adult model leads to testicular cancer diagnosis
For 7 years, Belle Grace had been working with children and adults diagnosed with autism. But during the COVID-19 pandemic, like many other people, she began to look for alternative streams of revenue.
In May 2020, Ms. Grace created a profile on the adult content subscription site OnlyFans.
“I was taking some time off of work and found myself on OnlyFans as a bit of a side hustle,” said Ms. Grace. “It wasn’t until I started earning five times more than my standard wage that I decided to go full-time and make that career change.”
She soon built up a regular clientele, hosting intimate video chats.
While video chatting with one of her loyal subscribers, Ms. Grace noticed something different about his testicles. Hesitantly, she mentioned that one testicle was a lot larger than the other – a change she hadn’t noticed before during their 2 years of interacting.
Ms. Grace says she was nervous about bringing up the subject with her subscriber. She suggested that he should see a doctor to have his testicles checked out, but her client didn’t go right away.
Ms. Grace says he waited a couple of months to go in for a check-up because he was slightly embarrassed. When he finally went to the doctor, he was given a diagnosis of testicular cancer.
Although Ms. Grace says that the conversation with her subscriber was a bit awkward, she’s happy she gathered the courage to bring it to his attention.
Testicular cancer is relatively rare, but it usually has a good prognosis – the survival rate is about 95%, according to Alexander Kutikov, MD, professor of surgical oncology at Fox Chase Cancer Center in Philadelphia.
Dr. Kutikov emphasized that men shouldn’t wait if they notice any changes in their genitals. The quicker they go see a doctor, the better the outcome is likely to be if it does turn out to be something serious.
For testicular cancer, “the treatment can be much more simple if it’s caught early – avoiding chemotherapy and avoiding major surgery,” Dr. Kutikov said.
“But even testicular cancers that present after they have spread can be cured. So a delay is suboptimal, but it’s not as devastating as some other cancers,” he added.
Most men who are diagnosed with testicular cancer present after noticing changes in the scrotum where one testicle feels and looks different from the other, Dr. Kutikov commented. In addition, there is usually a very firm mass or nodule that can be felt under the skin.
“Another common symptom is back pain, because testicular cancer can go to the lymph nodes in the back as well,” he said.
Dr. Kutikov says it all comes down to being aware of your body and noticing any major changes.
Ms. Grace suggests that sexual intimacy offers an opportunity for noting physical changes, “because you and your sexual partner are able to see each other’s bodies in the most intimate [manner].”
“People should be telling their partners if they notice any changes,” she says, for example, on their skin, such as sores or rashes, or lumps under the skin. “Even a change in a mole could be essential for your partner’s health,” she said.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
For 7 years, Belle Grace had been working with children and adults diagnosed with autism. But during the COVID-19 pandemic, like many other people, she began to look for alternative streams of revenue.
In May 2020, Ms. Grace created a profile on the adult content subscription site OnlyFans.
“I was taking some time off of work and found myself on OnlyFans as a bit of a side hustle,” said Ms. Grace. “It wasn’t until I started earning five times more than my standard wage that I decided to go full-time and make that career change.”
She soon built up a regular clientele, hosting intimate video chats.
While video chatting with one of her loyal subscribers, Ms. Grace noticed something different about his testicles. Hesitantly, she mentioned that one testicle was a lot larger than the other – a change she hadn’t noticed before during their 2 years of interacting.
Ms. Grace says she was nervous about bringing up the subject with her subscriber. She suggested that he should see a doctor to have his testicles checked out, but her client didn’t go right away.
Ms. Grace says he waited a couple of months to go in for a check-up because he was slightly embarrassed. When he finally went to the doctor, he was given a diagnosis of testicular cancer.
Although Ms. Grace says that the conversation with her subscriber was a bit awkward, she’s happy she gathered the courage to bring it to his attention.
Testicular cancer is relatively rare, but it usually has a good prognosis – the survival rate is about 95%, according to Alexander Kutikov, MD, professor of surgical oncology at Fox Chase Cancer Center in Philadelphia.
Dr. Kutikov emphasized that men shouldn’t wait if they notice any changes in their genitals. The quicker they go see a doctor, the better the outcome is likely to be if it does turn out to be something serious.
For testicular cancer, “the treatment can be much more simple if it’s caught early – avoiding chemotherapy and avoiding major surgery,” Dr. Kutikov said.
“But even testicular cancers that present after they have spread can be cured. So a delay is suboptimal, but it’s not as devastating as some other cancers,” he added.
Most men who are diagnosed with testicular cancer present after noticing changes in the scrotum where one testicle feels and looks different from the other, Dr. Kutikov commented. In addition, there is usually a very firm mass or nodule that can be felt under the skin.
“Another common symptom is back pain, because testicular cancer can go to the lymph nodes in the back as well,” he said.
Dr. Kutikov says it all comes down to being aware of your body and noticing any major changes.
Ms. Grace suggests that sexual intimacy offers an opportunity for noting physical changes, “because you and your sexual partner are able to see each other’s bodies in the most intimate [manner].”
“People should be telling their partners if they notice any changes,” she says, for example, on their skin, such as sores or rashes, or lumps under the skin. “Even a change in a mole could be essential for your partner’s health,” she said.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
For 7 years, Belle Grace had been working with children and adults diagnosed with autism. But during the COVID-19 pandemic, like many other people, she began to look for alternative streams of revenue.
In May 2020, Ms. Grace created a profile on the adult content subscription site OnlyFans.
“I was taking some time off of work and found myself on OnlyFans as a bit of a side hustle,” said Ms. Grace. “It wasn’t until I started earning five times more than my standard wage that I decided to go full-time and make that career change.”
She soon built up a regular clientele, hosting intimate video chats.
While video chatting with one of her loyal subscribers, Ms. Grace noticed something different about his testicles. Hesitantly, she mentioned that one testicle was a lot larger than the other – a change she hadn’t noticed before during their 2 years of interacting.
Ms. Grace says she was nervous about bringing up the subject with her subscriber. She suggested that he should see a doctor to have his testicles checked out, but her client didn’t go right away.
Ms. Grace says he waited a couple of months to go in for a check-up because he was slightly embarrassed. When he finally went to the doctor, he was given a diagnosis of testicular cancer.
Although Ms. Grace says that the conversation with her subscriber was a bit awkward, she’s happy she gathered the courage to bring it to his attention.
Testicular cancer is relatively rare, but it usually has a good prognosis – the survival rate is about 95%, according to Alexander Kutikov, MD, professor of surgical oncology at Fox Chase Cancer Center in Philadelphia.
Dr. Kutikov emphasized that men shouldn’t wait if they notice any changes in their genitals. The quicker they go see a doctor, the better the outcome is likely to be if it does turn out to be something serious.
For testicular cancer, “the treatment can be much more simple if it’s caught early – avoiding chemotherapy and avoiding major surgery,” Dr. Kutikov said.
“But even testicular cancers that present after they have spread can be cured. So a delay is suboptimal, but it’s not as devastating as some other cancers,” he added.
Most men who are diagnosed with testicular cancer present after noticing changes in the scrotum where one testicle feels and looks different from the other, Dr. Kutikov commented. In addition, there is usually a very firm mass or nodule that can be felt under the skin.
“Another common symptom is back pain, because testicular cancer can go to the lymph nodes in the back as well,” he said.
Dr. Kutikov says it all comes down to being aware of your body and noticing any major changes.
Ms. Grace suggests that sexual intimacy offers an opportunity for noting physical changes, “because you and your sexual partner are able to see each other’s bodies in the most intimate [manner].”
“People should be telling their partners if they notice any changes,” she says, for example, on their skin, such as sores or rashes, or lumps under the skin. “Even a change in a mole could be essential for your partner’s health,” she said.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The ‘great dynamism’ of radiation oncology
The field of radiation oncology has rapidly evolved in recent years, thanks in large part to findings from randomized clinical trials (RCTs) that have helped shift therapeutic standards, a review of the literature shows.
Highlights from this research reveal how high-tech radiotherapy, such as hypofractionation and stereotactic body radiotherapy, has improved care for many patients, how personalized radiotherapy using image-based guidance has helped tailor treatments, and how endpoints that focus on quality of life and patient satisfaction are emerging.
For instance, Charles B. Simone II, MD, FACRO, who was not involved in the current work, pointed to “a proliferation of trials assessing hypofractionation in the curative setting and stereotactic body radiation therapy in the curative and poly- and oligometastatic settings that have allowed for increased patient convenience and dose intensification, respectively.”
Dr. Simone, chief medical officer, New York Proton Center, Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center, also noted that the first personalized radiotherapy trials using imaging and biological markers have “the profound potential to individualize treatment and improve patient outcomes.”
The review was published in the European Journal of Cancer.
An evolving field
Given the fast-changing landscape for cancer therapeutics and a deluge of research studies, the authors wanted to understand the most notable advances established in recent trials as well as caveats to some approaches and emerging areas to watch.
In the review, Sophie Espenel, MD, from the department of radiation oncology, Gustave Roussy Cancer Campus, Villejuif, France, and colleagues identified 1,347 radiotherapy RCTs that were conducted from January 2018 to December 2021. Of these, the authors selected 110 large phase 2 or 3 RCTs that contained data showing practice-changing or emerging concepts.
Overall, the studies showed “great dynamism” in radiation oncology research and covered a wide range of radiotherapy practices, according to Dr. Espenel and coauthors.
A central area of research has focused on radioimmunotherapy, an approach that aims to enhance the antitumor immune response. One RCT in the preoperative setting showed, for instance, that concurrent stereotactic body radiotherapy delivered at 24 Gy over eight fractions, along with the anti–PD-L1 agent durvalumab, increased major pathologic complete response rates almost eightfold in comparison with durvalumab alone for patients with early-stage lung cancer (53.3% vs. 6.7%).
Although promising, not all trials that evaluated a concurrent chemoradiotherapy-immunotherapy strategy showed positive results. One RCT of locally advanced head and neck squamous cell carcinoma, for instance, found that median progression-free survival was not reached when adding the anti–PD-L1 avelumab to chemoradiotherapy. In addition, trials in the metastatic setting have shown conflicting results, the authors note.
Another topic of interest is that of newer radiosensitizers. A trial that evaluated high-risk locoregionally advanced head and neck squamous cell carcinoma highlighted the efficacy of xevinapant, a pro-apoptotic agent that inhibits apoptosis proteins. Xevinapant was used for the first time in conjunction with a standard high-dose cisplatin chemoradiotherapy. In this study, locoregional control at 18 months was achieved for 54% of patients who received xevinapant vs. 33% of those who received standard care. The toxicity profiles were similar.
The use of high-tech radiotherapy is gaining ground. It allows patients to receive more targeted treatments at lower doses and in shorter time frames. One trial found, for instance, that a more hypofractionated adjuvant whole breast approach, using 26 Gy in five fractions over a week, is as effective and safe as 40 Gy in 15 fractions over 3 weeks. The researchers found that there was no difference in the incidence of locoregional relapses, disease-free survival, and overall survival between the regimens.
Dr. Simone also noted that advanced treatment modalities, such as intensity-modulated radiotherapy, stereotactic radiosurgery, and proton therapy, have the potential to improve patient-reported adverse events and clinical outcomes. “I have seen this both in my clinical practice and in several recent publications,” he says.
Personalization of radiotherapy is also an emerging area that may allow for more tailored treatments with improved outcomes. The authors highlighted a study that found that PMSA PET-CT was better than conventional CT for accurately staging prostate cancer. This approach was also less expensive and led to less radiation exposure.
On the basis of this research, “PMSA PET-CT has since become the [standard of care] for prostate cancer staging,” the authors explain.
Dr. Espenel and colleagues note that as patients survive longer, quality of life and patient satisfaction are increasingly becoming endpoints in RCTs. Experts are focusing more attention on sequelae of treatments and advances in technology that can spare critical organs from radiation and reduce overall treatment time.
Shared decision-making is becoming increasingly possible in many cases as well. For example, with some clinical trials that involved different treatment modalities, outcomes were equivalent, but toxicity profiles differed, allowing patients to choose therapeutic options tailored to their preferences.
Overall, these data demonstrate “a great dynamism of radiation oncology research in most primary tumor types,” the researchers write.
The study received no outside financial support. The authors have disclosed no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Simone is chair of the American Society for Radiation Oncology Lung Resource Panel and the American Society for Radiation Oncology Veteran Affairs Radiation Oncology Quality Surveillance Blue Ribbon Lung Panel and has received honorarium from Varian Medical Systems.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The field of radiation oncology has rapidly evolved in recent years, thanks in large part to findings from randomized clinical trials (RCTs) that have helped shift therapeutic standards, a review of the literature shows.
Highlights from this research reveal how high-tech radiotherapy, such as hypofractionation and stereotactic body radiotherapy, has improved care for many patients, how personalized radiotherapy using image-based guidance has helped tailor treatments, and how endpoints that focus on quality of life and patient satisfaction are emerging.
For instance, Charles B. Simone II, MD, FACRO, who was not involved in the current work, pointed to “a proliferation of trials assessing hypofractionation in the curative setting and stereotactic body radiation therapy in the curative and poly- and oligometastatic settings that have allowed for increased patient convenience and dose intensification, respectively.”
Dr. Simone, chief medical officer, New York Proton Center, Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center, also noted that the first personalized radiotherapy trials using imaging and biological markers have “the profound potential to individualize treatment and improve patient outcomes.”
The review was published in the European Journal of Cancer.
An evolving field
Given the fast-changing landscape for cancer therapeutics and a deluge of research studies, the authors wanted to understand the most notable advances established in recent trials as well as caveats to some approaches and emerging areas to watch.
In the review, Sophie Espenel, MD, from the department of radiation oncology, Gustave Roussy Cancer Campus, Villejuif, France, and colleagues identified 1,347 radiotherapy RCTs that were conducted from January 2018 to December 2021. Of these, the authors selected 110 large phase 2 or 3 RCTs that contained data showing practice-changing or emerging concepts.
Overall, the studies showed “great dynamism” in radiation oncology research and covered a wide range of radiotherapy practices, according to Dr. Espenel and coauthors.
A central area of research has focused on radioimmunotherapy, an approach that aims to enhance the antitumor immune response. One RCT in the preoperative setting showed, for instance, that concurrent stereotactic body radiotherapy delivered at 24 Gy over eight fractions, along with the anti–PD-L1 agent durvalumab, increased major pathologic complete response rates almost eightfold in comparison with durvalumab alone for patients with early-stage lung cancer (53.3% vs. 6.7%).
Although promising, not all trials that evaluated a concurrent chemoradiotherapy-immunotherapy strategy showed positive results. One RCT of locally advanced head and neck squamous cell carcinoma, for instance, found that median progression-free survival was not reached when adding the anti–PD-L1 avelumab to chemoradiotherapy. In addition, trials in the metastatic setting have shown conflicting results, the authors note.
Another topic of interest is that of newer radiosensitizers. A trial that evaluated high-risk locoregionally advanced head and neck squamous cell carcinoma highlighted the efficacy of xevinapant, a pro-apoptotic agent that inhibits apoptosis proteins. Xevinapant was used for the first time in conjunction with a standard high-dose cisplatin chemoradiotherapy. In this study, locoregional control at 18 months was achieved for 54% of patients who received xevinapant vs. 33% of those who received standard care. The toxicity profiles were similar.
The use of high-tech radiotherapy is gaining ground. It allows patients to receive more targeted treatments at lower doses and in shorter time frames. One trial found, for instance, that a more hypofractionated adjuvant whole breast approach, using 26 Gy in five fractions over a week, is as effective and safe as 40 Gy in 15 fractions over 3 weeks. The researchers found that there was no difference in the incidence of locoregional relapses, disease-free survival, and overall survival between the regimens.
Dr. Simone also noted that advanced treatment modalities, such as intensity-modulated radiotherapy, stereotactic radiosurgery, and proton therapy, have the potential to improve patient-reported adverse events and clinical outcomes. “I have seen this both in my clinical practice and in several recent publications,” he says.
Personalization of radiotherapy is also an emerging area that may allow for more tailored treatments with improved outcomes. The authors highlighted a study that found that PMSA PET-CT was better than conventional CT for accurately staging prostate cancer. This approach was also less expensive and led to less radiation exposure.
On the basis of this research, “PMSA PET-CT has since become the [standard of care] for prostate cancer staging,” the authors explain.
Dr. Espenel and colleagues note that as patients survive longer, quality of life and patient satisfaction are increasingly becoming endpoints in RCTs. Experts are focusing more attention on sequelae of treatments and advances in technology that can spare critical organs from radiation and reduce overall treatment time.
Shared decision-making is becoming increasingly possible in many cases as well. For example, with some clinical trials that involved different treatment modalities, outcomes were equivalent, but toxicity profiles differed, allowing patients to choose therapeutic options tailored to their preferences.
Overall, these data demonstrate “a great dynamism of radiation oncology research in most primary tumor types,” the researchers write.
The study received no outside financial support. The authors have disclosed no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Simone is chair of the American Society for Radiation Oncology Lung Resource Panel and the American Society for Radiation Oncology Veteran Affairs Radiation Oncology Quality Surveillance Blue Ribbon Lung Panel and has received honorarium from Varian Medical Systems.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The field of radiation oncology has rapidly evolved in recent years, thanks in large part to findings from randomized clinical trials (RCTs) that have helped shift therapeutic standards, a review of the literature shows.
Highlights from this research reveal how high-tech radiotherapy, such as hypofractionation and stereotactic body radiotherapy, has improved care for many patients, how personalized radiotherapy using image-based guidance has helped tailor treatments, and how endpoints that focus on quality of life and patient satisfaction are emerging.
For instance, Charles B. Simone II, MD, FACRO, who was not involved in the current work, pointed to “a proliferation of trials assessing hypofractionation in the curative setting and stereotactic body radiation therapy in the curative and poly- and oligometastatic settings that have allowed for increased patient convenience and dose intensification, respectively.”
Dr. Simone, chief medical officer, New York Proton Center, Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center, also noted that the first personalized radiotherapy trials using imaging and biological markers have “the profound potential to individualize treatment and improve patient outcomes.”
The review was published in the European Journal of Cancer.
An evolving field
Given the fast-changing landscape for cancer therapeutics and a deluge of research studies, the authors wanted to understand the most notable advances established in recent trials as well as caveats to some approaches and emerging areas to watch.
In the review, Sophie Espenel, MD, from the department of radiation oncology, Gustave Roussy Cancer Campus, Villejuif, France, and colleagues identified 1,347 radiotherapy RCTs that were conducted from January 2018 to December 2021. Of these, the authors selected 110 large phase 2 or 3 RCTs that contained data showing practice-changing or emerging concepts.
Overall, the studies showed “great dynamism” in radiation oncology research and covered a wide range of radiotherapy practices, according to Dr. Espenel and coauthors.
A central area of research has focused on radioimmunotherapy, an approach that aims to enhance the antitumor immune response. One RCT in the preoperative setting showed, for instance, that concurrent stereotactic body radiotherapy delivered at 24 Gy over eight fractions, along with the anti–PD-L1 agent durvalumab, increased major pathologic complete response rates almost eightfold in comparison with durvalumab alone for patients with early-stage lung cancer (53.3% vs. 6.7%).
Although promising, not all trials that evaluated a concurrent chemoradiotherapy-immunotherapy strategy showed positive results. One RCT of locally advanced head and neck squamous cell carcinoma, for instance, found that median progression-free survival was not reached when adding the anti–PD-L1 avelumab to chemoradiotherapy. In addition, trials in the metastatic setting have shown conflicting results, the authors note.
Another topic of interest is that of newer radiosensitizers. A trial that evaluated high-risk locoregionally advanced head and neck squamous cell carcinoma highlighted the efficacy of xevinapant, a pro-apoptotic agent that inhibits apoptosis proteins. Xevinapant was used for the first time in conjunction with a standard high-dose cisplatin chemoradiotherapy. In this study, locoregional control at 18 months was achieved for 54% of patients who received xevinapant vs. 33% of those who received standard care. The toxicity profiles were similar.
The use of high-tech radiotherapy is gaining ground. It allows patients to receive more targeted treatments at lower doses and in shorter time frames. One trial found, for instance, that a more hypofractionated adjuvant whole breast approach, using 26 Gy in five fractions over a week, is as effective and safe as 40 Gy in 15 fractions over 3 weeks. The researchers found that there was no difference in the incidence of locoregional relapses, disease-free survival, and overall survival between the regimens.
Dr. Simone also noted that advanced treatment modalities, such as intensity-modulated radiotherapy, stereotactic radiosurgery, and proton therapy, have the potential to improve patient-reported adverse events and clinical outcomes. “I have seen this both in my clinical practice and in several recent publications,” he says.
Personalization of radiotherapy is also an emerging area that may allow for more tailored treatments with improved outcomes. The authors highlighted a study that found that PMSA PET-CT was better than conventional CT for accurately staging prostate cancer. This approach was also less expensive and led to less radiation exposure.
On the basis of this research, “PMSA PET-CT has since become the [standard of care] for prostate cancer staging,” the authors explain.
Dr. Espenel and colleagues note that as patients survive longer, quality of life and patient satisfaction are increasingly becoming endpoints in RCTs. Experts are focusing more attention on sequelae of treatments and advances in technology that can spare critical organs from radiation and reduce overall treatment time.
Shared decision-making is becoming increasingly possible in many cases as well. For example, with some clinical trials that involved different treatment modalities, outcomes were equivalent, but toxicity profiles differed, allowing patients to choose therapeutic options tailored to their preferences.
Overall, these data demonstrate “a great dynamism of radiation oncology research in most primary tumor types,” the researchers write.
The study received no outside financial support. The authors have disclosed no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Simone is chair of the American Society for Radiation Oncology Lung Resource Panel and the American Society for Radiation Oncology Veteran Affairs Radiation Oncology Quality Surveillance Blue Ribbon Lung Panel and has received honorarium from Varian Medical Systems.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM THE EUROPEAN JOURNAL OF CANCER
Annual PSA screening important for Black men
, new data suggest.
The data come from a review of 45,834 veterans (aged 55-69 years) who had been diagnosed with prostate cancer. About one-third of these men self-identified as non-Hispanic Black, and the rest were White.
During the study period (2004-2017), 2,465 men (5.4%) died of the disease.
The review found that annual prostate-specific antigen (PSA) screening significantly reduced the risk of dying from prostate cancer among Black men but not White men.
The study was published online in JAMA Oncology.
“These results may be biologically plausible because a shorter screening interval may be valuable for detecting aggressive disease, which is more common in Black men,” say investigators, led by University of California, San Diego, radiation oncology resident Michael Sherer, MD.
“Given that Black men are younger at diagnosis and have worse prostate cancer survival compared with White men,” more intensive screening recommendations “may benefit Black patients,” they write.
The study “conclusions are reasonable,” said Christopher Wallis, MD, PhD, a urologic oncologist at Mount Sinai Hospital in Toronto, when asked for comment.
Annual screening may well have “a greater potential to benefit” Black men, he said. “While we would ideally see randomized data supporting this, those data are unlikely to ever be forthcoming. Thus, this study provides a strong rationale to support the recommendations from many guideline panels (including those from the American Urological Association) that Black men, in the context of shared decision-making, may benefit more from PSA-based prostate cancer screening than the population at large,” he added.
Overall, the findings could help inform screening discussions with Black men, the investigators comments. In its most recent guidance, the U.S. Preventive Services Task Force recommends shared decision-making regarding PSA screening for men aged 55-69 years.
Similar screening frequency
For their study, the team reviewed Veterans Health Administration data to assess PSA screening patterns – which they categorized as no screening, less than annual screening, or annual screening – in the 5 years leading up to diagnosis.
They then correlated screening behaviors with the subsequent risk of dying from prostate cancer.
Overall, the reduction in risk of prostate cancer–specific mortality (PCSM) associated with screening was similar among Black men (subdistribution hazard ratio, 0.56; P = .001) and White men (sHR, 0.58; P = .001).
However, on multivariable regression, annual screening, in comparison with some screening, was associated with a significant reduction in the risk of dying from prostate cancer only among Black men (sHR, 0.65; P = .02), not among White men (sHR, 0.91; P = .35).
The cumulative incidence of PCSM among Black men was 4.7% with annual screening but 7.3% with only some screening.
Among White men, the cumulative incidence of PCSM with annual screening was 5.9% vs. 6.9% with less than annual screening.
Screening frequency was similar between Black men and White men. Black men were younger on average (61.8 vs. 63.1 years) and had slightly higher PSA levels at diagnosis but were not more likely to have regional or metastatic disease.
No funding was reported for this study. The investigators have disclosed no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Wallis has received personal fees from Janssen Canada.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
, new data suggest.
The data come from a review of 45,834 veterans (aged 55-69 years) who had been diagnosed with prostate cancer. About one-third of these men self-identified as non-Hispanic Black, and the rest were White.
During the study period (2004-2017), 2,465 men (5.4%) died of the disease.
The review found that annual prostate-specific antigen (PSA) screening significantly reduced the risk of dying from prostate cancer among Black men but not White men.
The study was published online in JAMA Oncology.
“These results may be biologically plausible because a shorter screening interval may be valuable for detecting aggressive disease, which is more common in Black men,” say investigators, led by University of California, San Diego, radiation oncology resident Michael Sherer, MD.
“Given that Black men are younger at diagnosis and have worse prostate cancer survival compared with White men,” more intensive screening recommendations “may benefit Black patients,” they write.
The study “conclusions are reasonable,” said Christopher Wallis, MD, PhD, a urologic oncologist at Mount Sinai Hospital in Toronto, when asked for comment.
Annual screening may well have “a greater potential to benefit” Black men, he said. “While we would ideally see randomized data supporting this, those data are unlikely to ever be forthcoming. Thus, this study provides a strong rationale to support the recommendations from many guideline panels (including those from the American Urological Association) that Black men, in the context of shared decision-making, may benefit more from PSA-based prostate cancer screening than the population at large,” he added.
Overall, the findings could help inform screening discussions with Black men, the investigators comments. In its most recent guidance, the U.S. Preventive Services Task Force recommends shared decision-making regarding PSA screening for men aged 55-69 years.
Similar screening frequency
For their study, the team reviewed Veterans Health Administration data to assess PSA screening patterns – which they categorized as no screening, less than annual screening, or annual screening – in the 5 years leading up to diagnosis.
They then correlated screening behaviors with the subsequent risk of dying from prostate cancer.
Overall, the reduction in risk of prostate cancer–specific mortality (PCSM) associated with screening was similar among Black men (subdistribution hazard ratio, 0.56; P = .001) and White men (sHR, 0.58; P = .001).
However, on multivariable regression, annual screening, in comparison with some screening, was associated with a significant reduction in the risk of dying from prostate cancer only among Black men (sHR, 0.65; P = .02), not among White men (sHR, 0.91; P = .35).
The cumulative incidence of PCSM among Black men was 4.7% with annual screening but 7.3% with only some screening.
Among White men, the cumulative incidence of PCSM with annual screening was 5.9% vs. 6.9% with less than annual screening.
Screening frequency was similar between Black men and White men. Black men were younger on average (61.8 vs. 63.1 years) and had slightly higher PSA levels at diagnosis but were not more likely to have regional or metastatic disease.
No funding was reported for this study. The investigators have disclosed no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Wallis has received personal fees from Janssen Canada.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
, new data suggest.
The data come from a review of 45,834 veterans (aged 55-69 years) who had been diagnosed with prostate cancer. About one-third of these men self-identified as non-Hispanic Black, and the rest were White.
During the study period (2004-2017), 2,465 men (5.4%) died of the disease.
The review found that annual prostate-specific antigen (PSA) screening significantly reduced the risk of dying from prostate cancer among Black men but not White men.
The study was published online in JAMA Oncology.
“These results may be biologically plausible because a shorter screening interval may be valuable for detecting aggressive disease, which is more common in Black men,” say investigators, led by University of California, San Diego, radiation oncology resident Michael Sherer, MD.
“Given that Black men are younger at diagnosis and have worse prostate cancer survival compared with White men,” more intensive screening recommendations “may benefit Black patients,” they write.
The study “conclusions are reasonable,” said Christopher Wallis, MD, PhD, a urologic oncologist at Mount Sinai Hospital in Toronto, when asked for comment.
Annual screening may well have “a greater potential to benefit” Black men, he said. “While we would ideally see randomized data supporting this, those data are unlikely to ever be forthcoming. Thus, this study provides a strong rationale to support the recommendations from many guideline panels (including those from the American Urological Association) that Black men, in the context of shared decision-making, may benefit more from PSA-based prostate cancer screening than the population at large,” he added.
Overall, the findings could help inform screening discussions with Black men, the investigators comments. In its most recent guidance, the U.S. Preventive Services Task Force recommends shared decision-making regarding PSA screening for men aged 55-69 years.
Similar screening frequency
For their study, the team reviewed Veterans Health Administration data to assess PSA screening patterns – which they categorized as no screening, less than annual screening, or annual screening – in the 5 years leading up to diagnosis.
They then correlated screening behaviors with the subsequent risk of dying from prostate cancer.
Overall, the reduction in risk of prostate cancer–specific mortality (PCSM) associated with screening was similar among Black men (subdistribution hazard ratio, 0.56; P = .001) and White men (sHR, 0.58; P = .001).
However, on multivariable regression, annual screening, in comparison with some screening, was associated with a significant reduction in the risk of dying from prostate cancer only among Black men (sHR, 0.65; P = .02), not among White men (sHR, 0.91; P = .35).
The cumulative incidence of PCSM among Black men was 4.7% with annual screening but 7.3% with only some screening.
Among White men, the cumulative incidence of PCSM with annual screening was 5.9% vs. 6.9% with less than annual screening.
Screening frequency was similar between Black men and White men. Black men were younger on average (61.8 vs. 63.1 years) and had slightly higher PSA levels at diagnosis but were not more likely to have regional or metastatic disease.
No funding was reported for this study. The investigators have disclosed no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Wallis has received personal fees from Janssen Canada.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM JAMA ONCOLOGY
Getting cancer research on track again may require a ‘behemoth’ effort
In 2016, as vice president, Joe Biden launched the Cancer Moonshot program just 1 year after his son Beau died from glioblastoma multiforme. His objective, he said, was to “cure” cancer, but to get close to that goal, to get cancer research just back up to pre-COVID-19 pandemic levels.
There has been a significant decrease in the launch of new clinical trials for cancer and biologic therapies since 2020. “That can affect every aspect of our research operation. It really affected our capacity to continue to move forward at a fast pace. It will require a behemoth effort to get back to pre-COVID times,” said Tanios S. Bekaii-Saab, MD, leader of the gastrointestinal cancer program at Mayo Clinic in Phoenix.
Congress passed the 21st Century Cures Act in 2016 authorizing $1.8 billion for Cancer Moonshot over 7 years. More recently, the program received $194 million from the $6.9 billion National Cancer Institute budget in FY 2022.
Joseph Alvarnas, MD, a hematologist oncologist and vice president of government affairs at City of Hope, Duarte, Calif., sees the Moonshot budget as a potential shortcoming.
“The priorities are well founded and based on what we would think are the most important things to cover, but, if we’re going to achieve these extraordinarily ambitious goals of halving cancer mortality and serving communities more equitably, it’s going to need more funding positioned at making these things real,” he said.
Moonshot is being positioned as an opportunity to double down on efforts started in 2016, but treating cancer is complex and goes well beyond funding new research.
“We know that we have amazing research and progress around innovations that will drive us toward the goal of reducing the death rate from cancer. But we also know that we have tools that aren’t reaching all parts of the country, so we have a great opportunity to make sure that we’re doing all we can to prevent, detect and treat cancer,” Dr. Carnival said.
Can cancer be cured?
The Biden administration relaunched Moonshot in 2022 with newly defined goals: Cut the rate of cancer-related deaths in half within 25 years; improve the experience of people with cancer, cancer survivors, and their families; and “end cancer as we know it,” President Biden said in a press conference in February.
Cancer is the second leading cause of death in the United States after heart disease, but it may indeed be possible to cut the total number of cancer-related deaths in half over the next 25 years.
“As a hematologist who’s been involved in both research and clinical care, I think it’s important to realize this is actually doable. Between 1990 and 2020 cancer mortality rates decreased by 31%, and in the last American Cancer Society’s annual report, mortality rates dropped by the largest percentages for 2 consecutive years in a row. The question shifts now from ‘Is this possible? to ‘How do we ensure that it’s possible?’ The spirit of Cancer Moonshot 2.0 is identifying the multiple paths to move this effort forward,” Dr. Alvarnas said.
But without a significant infusion of cash for research, it’s doubtful cancer-related deaths will drop by 50% over the next 25 years.
“There are a lot of big and lofty goals in Cancer Moonshot, and the words ‘ending cancer,’ well those are big words,” Dr. Bekaii-Saab said. “The reality is how do we measure in 25 years the impact of this today? I think it will require significantly more funding over the next few years to achieve the goals set by the Moonshot. Otherwise it will be a 7-year done deal that will accrue a lot of great numbers but won’t make a dent in those goals for the next 25 years. To stop it at some point and not invest more into it, we will probably lose most of the benefit.”
Closing the loop on data sharing
Moonshot has been instrumental in fostering research collaborations by encouraging data sharing among scientists.
“It also brought together a new way for the National Cancer Institute and Department of Energy to drive progress on some of the big data initiatives. The initial Cancer Moonshot infused a sense of urgency and hope into this effort,” said Danielle Carnival, PhD, coordinator of Cancer Moonshot.
Between 2017 and 2022, Cancer Moonshot created more than 70 consortiums or programs, and funded about 240 research projects. Its fundamental goals of improving data sharing and encouraging collaboration are very important, Dr. Bekaii-Saab said.
“Because, historically, what happens with cancer is that researchers compete for resources...and they become very protective of their data. Sharing gets more difficult, collaborations become more onerous, and it becomes counterproductive,” he said.
Dr. Bekaii-Saab highlighted two networks created specifically for data sharing. They include the Human Tumor Atlas for cellular, morphological, and molecular tumor data, and PDXNet, a patient derived xenograft research network.
A shift in funding priorities?
Cancer funding has been stagnant for years. When adjusted for growth, it hasn’t had a significant infusion of funding since at least 2003—at least in relative terms, Dr. Bekaii-Saab said. “This affects a lot of the things we do, including NCI-funded clinical trials. It pushes us to work with the private sector, which is not necessarily a detriment, but it doesn’t advance the academic mission at the same level. So, overall, I wouldn’t call it tragic, but I do think we’re falling behind,” he said.
“I think when we do the process for the budget for FY24 and after we’ve had time to really explore the best ideas and build the foundation for some of these new aspects of the Cancer Moonshot, we hope to have something more concrete going toward these efforts,” Dr. Carnival said.
But in addition to funding, Dr. Alvarnas says, it is equally important to address gaps in care. Not all patients have access to existing cancer treatments.
“The great challenge to us in the 2020s is not only about developing new and more effective technologies, but also in doing a better job of getting existing life-saving treatments into the hands of underserved populations. One of the really positive challenges set forth by the Biden administration is the idea that financing care equity is as important, if not more so, than advancing technologies. If there’s been stagnation, it’s because from a government and resourcing point of view, that priority has been ineffectively supported financially.”
The pandemic stymies cancer research
The pandemic has had a significant impact on cancer research. As in other fields, it disrupted ongoing research, but it may have also contributed to the loss of employees who resigned in what’s been called the “Great Resignation.” “A lot of employees just decided to change jobs in the middle of the pandemic, which led to a cancer research staffing crisis,” Dr. Bekaii-Saab said.
“We all recognized that turning so much of the attention of the entire biomedical research engine and health system to the COVID-19 pandemic would have an impact across cancer research, screenings and care,” Dr. Carnival said. “There is work to do to get us back to whole, but from a research perspective, we’ve seen a reorientation of the trial networks we were using for COVID-19 research, back to their initial purpose. Some of those are cancer and oncology networks, so we’re excited about that and fully believe that we can catch up.”
But then there’s also the impact the pandemic has had on cancer patients who delayed their care at the primary level. This, Dr. Bekaii-Saab fears, will lead to more patients presenting with more advanced disease in years to come. “One of the biggest problems was that a lot of patients delayed their care at the primary level. My biggest concern is that in the years to come we will see a lot more patients presenting with more advanced cancer.”
In 2016, as vice president, Joe Biden launched the Cancer Moonshot program just 1 year after his son Beau died from glioblastoma multiforme. His objective, he said, was to “cure” cancer, but to get close to that goal, to get cancer research just back up to pre-COVID-19 pandemic levels.
There has been a significant decrease in the launch of new clinical trials for cancer and biologic therapies since 2020. “That can affect every aspect of our research operation. It really affected our capacity to continue to move forward at a fast pace. It will require a behemoth effort to get back to pre-COVID times,” said Tanios S. Bekaii-Saab, MD, leader of the gastrointestinal cancer program at Mayo Clinic in Phoenix.
Congress passed the 21st Century Cures Act in 2016 authorizing $1.8 billion for Cancer Moonshot over 7 years. More recently, the program received $194 million from the $6.9 billion National Cancer Institute budget in FY 2022.
Joseph Alvarnas, MD, a hematologist oncologist and vice president of government affairs at City of Hope, Duarte, Calif., sees the Moonshot budget as a potential shortcoming.
“The priorities are well founded and based on what we would think are the most important things to cover, but, if we’re going to achieve these extraordinarily ambitious goals of halving cancer mortality and serving communities more equitably, it’s going to need more funding positioned at making these things real,” he said.
Moonshot is being positioned as an opportunity to double down on efforts started in 2016, but treating cancer is complex and goes well beyond funding new research.
“We know that we have amazing research and progress around innovations that will drive us toward the goal of reducing the death rate from cancer. But we also know that we have tools that aren’t reaching all parts of the country, so we have a great opportunity to make sure that we’re doing all we can to prevent, detect and treat cancer,” Dr. Carnival said.
Can cancer be cured?
The Biden administration relaunched Moonshot in 2022 with newly defined goals: Cut the rate of cancer-related deaths in half within 25 years; improve the experience of people with cancer, cancer survivors, and their families; and “end cancer as we know it,” President Biden said in a press conference in February.
Cancer is the second leading cause of death in the United States after heart disease, but it may indeed be possible to cut the total number of cancer-related deaths in half over the next 25 years.
“As a hematologist who’s been involved in both research and clinical care, I think it’s important to realize this is actually doable. Between 1990 and 2020 cancer mortality rates decreased by 31%, and in the last American Cancer Society’s annual report, mortality rates dropped by the largest percentages for 2 consecutive years in a row. The question shifts now from ‘Is this possible? to ‘How do we ensure that it’s possible?’ The spirit of Cancer Moonshot 2.0 is identifying the multiple paths to move this effort forward,” Dr. Alvarnas said.
But without a significant infusion of cash for research, it’s doubtful cancer-related deaths will drop by 50% over the next 25 years.
“There are a lot of big and lofty goals in Cancer Moonshot, and the words ‘ending cancer,’ well those are big words,” Dr. Bekaii-Saab said. “The reality is how do we measure in 25 years the impact of this today? I think it will require significantly more funding over the next few years to achieve the goals set by the Moonshot. Otherwise it will be a 7-year done deal that will accrue a lot of great numbers but won’t make a dent in those goals for the next 25 years. To stop it at some point and not invest more into it, we will probably lose most of the benefit.”
Closing the loop on data sharing
Moonshot has been instrumental in fostering research collaborations by encouraging data sharing among scientists.
“It also brought together a new way for the National Cancer Institute and Department of Energy to drive progress on some of the big data initiatives. The initial Cancer Moonshot infused a sense of urgency and hope into this effort,” said Danielle Carnival, PhD, coordinator of Cancer Moonshot.
Between 2017 and 2022, Cancer Moonshot created more than 70 consortiums or programs, and funded about 240 research projects. Its fundamental goals of improving data sharing and encouraging collaboration are very important, Dr. Bekaii-Saab said.
“Because, historically, what happens with cancer is that researchers compete for resources...and they become very protective of their data. Sharing gets more difficult, collaborations become more onerous, and it becomes counterproductive,” he said.
Dr. Bekaii-Saab highlighted two networks created specifically for data sharing. They include the Human Tumor Atlas for cellular, morphological, and molecular tumor data, and PDXNet, a patient derived xenograft research network.
A shift in funding priorities?
Cancer funding has been stagnant for years. When adjusted for growth, it hasn’t had a significant infusion of funding since at least 2003—at least in relative terms, Dr. Bekaii-Saab said. “This affects a lot of the things we do, including NCI-funded clinical trials. It pushes us to work with the private sector, which is not necessarily a detriment, but it doesn’t advance the academic mission at the same level. So, overall, I wouldn’t call it tragic, but I do think we’re falling behind,” he said.
“I think when we do the process for the budget for FY24 and after we’ve had time to really explore the best ideas and build the foundation for some of these new aspects of the Cancer Moonshot, we hope to have something more concrete going toward these efforts,” Dr. Carnival said.
But in addition to funding, Dr. Alvarnas says, it is equally important to address gaps in care. Not all patients have access to existing cancer treatments.
“The great challenge to us in the 2020s is not only about developing new and more effective technologies, but also in doing a better job of getting existing life-saving treatments into the hands of underserved populations. One of the really positive challenges set forth by the Biden administration is the idea that financing care equity is as important, if not more so, than advancing technologies. If there’s been stagnation, it’s because from a government and resourcing point of view, that priority has been ineffectively supported financially.”
The pandemic stymies cancer research
The pandemic has had a significant impact on cancer research. As in other fields, it disrupted ongoing research, but it may have also contributed to the loss of employees who resigned in what’s been called the “Great Resignation.” “A lot of employees just decided to change jobs in the middle of the pandemic, which led to a cancer research staffing crisis,” Dr. Bekaii-Saab said.
“We all recognized that turning so much of the attention of the entire biomedical research engine and health system to the COVID-19 pandemic would have an impact across cancer research, screenings and care,” Dr. Carnival said. “There is work to do to get us back to whole, but from a research perspective, we’ve seen a reorientation of the trial networks we were using for COVID-19 research, back to their initial purpose. Some of those are cancer and oncology networks, so we’re excited about that and fully believe that we can catch up.”
But then there’s also the impact the pandemic has had on cancer patients who delayed their care at the primary level. This, Dr. Bekaii-Saab fears, will lead to more patients presenting with more advanced disease in years to come. “One of the biggest problems was that a lot of patients delayed their care at the primary level. My biggest concern is that in the years to come we will see a lot more patients presenting with more advanced cancer.”
In 2016, as vice president, Joe Biden launched the Cancer Moonshot program just 1 year after his son Beau died from glioblastoma multiforme. His objective, he said, was to “cure” cancer, but to get close to that goal, to get cancer research just back up to pre-COVID-19 pandemic levels.
There has been a significant decrease in the launch of new clinical trials for cancer and biologic therapies since 2020. “That can affect every aspect of our research operation. It really affected our capacity to continue to move forward at a fast pace. It will require a behemoth effort to get back to pre-COVID times,” said Tanios S. Bekaii-Saab, MD, leader of the gastrointestinal cancer program at Mayo Clinic in Phoenix.
Congress passed the 21st Century Cures Act in 2016 authorizing $1.8 billion for Cancer Moonshot over 7 years. More recently, the program received $194 million from the $6.9 billion National Cancer Institute budget in FY 2022.
Joseph Alvarnas, MD, a hematologist oncologist and vice president of government affairs at City of Hope, Duarte, Calif., sees the Moonshot budget as a potential shortcoming.
“The priorities are well founded and based on what we would think are the most important things to cover, but, if we’re going to achieve these extraordinarily ambitious goals of halving cancer mortality and serving communities more equitably, it’s going to need more funding positioned at making these things real,” he said.
Moonshot is being positioned as an opportunity to double down on efforts started in 2016, but treating cancer is complex and goes well beyond funding new research.
“We know that we have amazing research and progress around innovations that will drive us toward the goal of reducing the death rate from cancer. But we also know that we have tools that aren’t reaching all parts of the country, so we have a great opportunity to make sure that we’re doing all we can to prevent, detect and treat cancer,” Dr. Carnival said.
Can cancer be cured?
The Biden administration relaunched Moonshot in 2022 with newly defined goals: Cut the rate of cancer-related deaths in half within 25 years; improve the experience of people with cancer, cancer survivors, and their families; and “end cancer as we know it,” President Biden said in a press conference in February.
Cancer is the second leading cause of death in the United States after heart disease, but it may indeed be possible to cut the total number of cancer-related deaths in half over the next 25 years.
“As a hematologist who’s been involved in both research and clinical care, I think it’s important to realize this is actually doable. Between 1990 and 2020 cancer mortality rates decreased by 31%, and in the last American Cancer Society’s annual report, mortality rates dropped by the largest percentages for 2 consecutive years in a row. The question shifts now from ‘Is this possible? to ‘How do we ensure that it’s possible?’ The spirit of Cancer Moonshot 2.0 is identifying the multiple paths to move this effort forward,” Dr. Alvarnas said.
But without a significant infusion of cash for research, it’s doubtful cancer-related deaths will drop by 50% over the next 25 years.
“There are a lot of big and lofty goals in Cancer Moonshot, and the words ‘ending cancer,’ well those are big words,” Dr. Bekaii-Saab said. “The reality is how do we measure in 25 years the impact of this today? I think it will require significantly more funding over the next few years to achieve the goals set by the Moonshot. Otherwise it will be a 7-year done deal that will accrue a lot of great numbers but won’t make a dent in those goals for the next 25 years. To stop it at some point and not invest more into it, we will probably lose most of the benefit.”
Closing the loop on data sharing
Moonshot has been instrumental in fostering research collaborations by encouraging data sharing among scientists.
“It also brought together a new way for the National Cancer Institute and Department of Energy to drive progress on some of the big data initiatives. The initial Cancer Moonshot infused a sense of urgency and hope into this effort,” said Danielle Carnival, PhD, coordinator of Cancer Moonshot.
Between 2017 and 2022, Cancer Moonshot created more than 70 consortiums or programs, and funded about 240 research projects. Its fundamental goals of improving data sharing and encouraging collaboration are very important, Dr. Bekaii-Saab said.
“Because, historically, what happens with cancer is that researchers compete for resources...and they become very protective of their data. Sharing gets more difficult, collaborations become more onerous, and it becomes counterproductive,” he said.
Dr. Bekaii-Saab highlighted two networks created specifically for data sharing. They include the Human Tumor Atlas for cellular, morphological, and molecular tumor data, and PDXNet, a patient derived xenograft research network.
A shift in funding priorities?
Cancer funding has been stagnant for years. When adjusted for growth, it hasn’t had a significant infusion of funding since at least 2003—at least in relative terms, Dr. Bekaii-Saab said. “This affects a lot of the things we do, including NCI-funded clinical trials. It pushes us to work with the private sector, which is not necessarily a detriment, but it doesn’t advance the academic mission at the same level. So, overall, I wouldn’t call it tragic, but I do think we’re falling behind,” he said.
“I think when we do the process for the budget for FY24 and after we’ve had time to really explore the best ideas and build the foundation for some of these new aspects of the Cancer Moonshot, we hope to have something more concrete going toward these efforts,” Dr. Carnival said.
But in addition to funding, Dr. Alvarnas says, it is equally important to address gaps in care. Not all patients have access to existing cancer treatments.
“The great challenge to us in the 2020s is not only about developing new and more effective technologies, but also in doing a better job of getting existing life-saving treatments into the hands of underserved populations. One of the really positive challenges set forth by the Biden administration is the idea that financing care equity is as important, if not more so, than advancing technologies. If there’s been stagnation, it’s because from a government and resourcing point of view, that priority has been ineffectively supported financially.”
The pandemic stymies cancer research
The pandemic has had a significant impact on cancer research. As in other fields, it disrupted ongoing research, but it may have also contributed to the loss of employees who resigned in what’s been called the “Great Resignation.” “A lot of employees just decided to change jobs in the middle of the pandemic, which led to a cancer research staffing crisis,” Dr. Bekaii-Saab said.
“We all recognized that turning so much of the attention of the entire biomedical research engine and health system to the COVID-19 pandemic would have an impact across cancer research, screenings and care,” Dr. Carnival said. “There is work to do to get us back to whole, but from a research perspective, we’ve seen a reorientation of the trial networks we were using for COVID-19 research, back to their initial purpose. Some of those are cancer and oncology networks, so we’re excited about that and fully believe that we can catch up.”
But then there’s also the impact the pandemic has had on cancer patients who delayed their care at the primary level. This, Dr. Bekaii-Saab fears, will lead to more patients presenting with more advanced disease in years to come. “One of the biggest problems was that a lot of patients delayed their care at the primary level. My biggest concern is that in the years to come we will see a lot more patients presenting with more advanced cancer.”
The Effect of Race on Outcomes in Veterans With Hepatocellular Carcinoma at a Single Center
Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is the sixth most common and third most deadly malignancy worldwide, carrying a mean survival rate without treatment of 6 to 20 months depending on stage.1 Fifty-seven percent of patients with liver cancer are diagnosed with regional or distant metastatic disease that carries 5-year relative survival rates of 10.7% and 3.1%, respectively.2 HCC arises most commonly from liver cirrhosis due to chronic hepatocyte injury, which may be mediated by viral hepatitis, alcoholism, and metabolic disease. Other less common causes include autoimmune disease, exposure to environmental hazards, and certain genetic diseases, such as α-1 antitrypsin deficiency and Wilson disease.
Multiple staging systems for HCC exist that incorporate some variation of the following features: size and invasion of the tumor, distant metastases, and liver function. Stage-directed treatments for HCC include ablation, embolization, resection, transplant, and systemic therapy, such as tyrosine kinase inhibitors, immunotherapies, and monoclonal antibodies. In addition to tumor/node/metastasis (TNM) staging, α-fetoprotein (AFP) is a diagnostic marker with prognostic value in HCC with higher levels correlating to higher tumor burden and a worse prognosis. With treatment, the 5-year survival rate for early stage HCC ranges from 60% to 80% but decreases significantly with higher stages.1 HCC screening in at-risk populations has accounted for > 40% of diagnoses since the practice became widely adopted, and earlier recognition has led to an improvement in survival even when adjusting for lead time bias.3
Systemic therapy for advanced disease continues to improve. Sorafenib remained the standard first-line systemic therapy since it was introduced in 2008.4 First-line therapy improved with immunotherapies. The phase 3 IMBrave150 trial comparing atezolizumab plus bevacizumab to sorafenib showed a median overall survival (OS) > 19 months with 7.7% of patients achieving a complete response.5 HIMALAYA, another phase 3 trial set for publication later this year, also reported promising results when a priming dose of the CTLA-4 inhibitor tremelimumab followed by durvalumab was compared with sorafenib.6
There has been a rise in incidence of HCC in the United States across all races and ethnicities, though Black, Hispanic, and Asian patients remain disproportionately affected. Subsequently, identifying causative biologic, socioeconomic, and cultural factors, as well as implicit bias in health care continues to be a topic of great interest.7-9 Using Surveillance, Epidemiology, and End Results (SEER) data, a number of large studies have found that Black patients with HCC were more likely to present with an advanced stage, less likely to receive curative intent treatment, and had significantly reduced survival compared with that of White patients.1,7-9 An analysis of 1117 patients by Rich and colleagues noted a 34% increased risk of death for Black patients with HCC compared with that of White patients, and other studies have shown about a 50% reduction in rate of liver transplantation for Black patients.10-12 Our study aimed to investigate potential disparities in incidence, etiology, AFP level at diagnosis, and outcomes of HCC in Black and White veterans managed at the Memphis Veterans Affairs Medical Center (VAMC) in Tennessee.
Methods
A single center retrospective chart review was conducted at the Memphis VAMC using the Computerized Patient Record System (CPRS) and the International Statistical Classification of Diseases, Tenth Revision (ICD-10) code C22.0 for HCC. Initial results were manually refined by prespecified criteria. Patients were included if they were diagnosed with HCC and received HCC treatment at the Memphis VAMC. Patients were excluded if HCC was not diagnosed histologically or clinically by imaging characteristics and AFP level, if the patient’s primary treatment was not provided at the Memphis VAMC, if they were lost to follow-up, or if race was not specified as either Black or White.
The following patient variables were examined: age, sex, comorbidities (alcohol or substance use disorder, cirrhosis, HIV), tumor stage, AFP, method of diagnosis, first-line treatments, systemic treatment, surgical options offered, and mortality. Staging was based on the American Joint Committee on Cancer TNM staging for HCC.13 Surgical options were recorded as resection or transplant. Patients who were offered treatment but lost to follow-up were excluded from the analysis.
Data Analysis
Our primary endpoint was identifying differences in OS among Memphis VAMC patients with HCC related to race. Kaplan-Meier analysis was used to investigate differences in OS and cumulative hazard ratio (HR) for death. Cox regression multivariate analysis further evaluated discrepancies among investigated patient variables, including age, race, alcohol, tobacco, or illicit drug use, HIV coinfection, and cirrhosis. Treatment factors were further defined by first-line treatment, systemic therapy, surgical resection, and transplant. χ2 analysis was used to investigate differences in treatment modalities.
Results
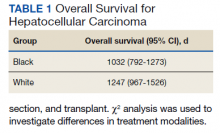
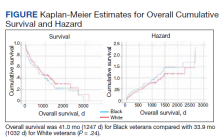
We identified 227 veterans, 95 Black and 132 White, between 2009 and 2021 meeting criteria for primary HCC treated at the Memphis VAMC. This study did not show a significant difference in OS between White and Black veterans (P = .24). Kaplan-Meier assessment showed OS was 1247 days (41 months) for Black veterans compared with 1032 days (34 months) for White veterans (Figure; Table 1).
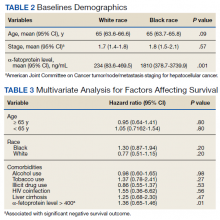
Additionally, no significant difference was found between veterans for age or stage at diagnosis when stratified by race. The mean age of diagnosis for both groups was 65 years (P = .09). The mean TNM staging was 1.7 for White veterans vs 1.8 for Black veterans (P = .57). There was a significant increase in the AFP level at diagnosis for Black veterans (P = .001) (Table 2).
The most common initial treatment for both groups was transarterial chemoembolization and radiofrequency ablation with 68% of White and 64% of Black veterans receiving this therapy. There was no significant difference between who received systemic therapy.
However, we found significant differences by race for some forms of treatment. In our analysis, significant differences existed between those who did not receive any form of treatment as well as who received surgical resection and transplant. Among Black veterans, 11.6% received no treatment vs 6.1% for White veterans (P = .001). Only 2.1% of Black veterans underwent surgical resection vs 8.3% of White veterans (P = .046). Similarly, 13 (9.8%) White veterans vs 3 (3.2%) Black veterans received orthotopic liver transplantation (P = .052) in our cohort (eAppendix available at doi:10.12788/fp.0304). We found no differences in patient characteristics affecting OS, including alcohol use, tobacco use, illicit drug use, HIV coinfection, or liver cirrhosis (Table 3).
Discussion
In this retrospective analysis, Black veterans with HCC did not experience a statistically significant decrease in OS compared with that of White veterans despite some differences in therapy offered. Other studies have found that surgery was less frequently recommended to Black patients across multiple cancer types, and in most cases this carried a negative impact on OS.8,10,11,14,15 A number of other studies have demonstrated a greater percentage of Black patients receiving no treatment, although these studies are often based on SEER data, which captures only cancer-directed surgery and no other methods of treatment. Inequities in patient factors like insurance and socioeconomic status as well as willingness to receive certain treatments are often cited as major influences in health care disparities, but systemic and clinician factors like hospital volume, clinician expertise, specialist availability, and implicit racial bias all affect outcomes.16 One benefit of our study was that CPRS provided a centralized recording of all treatments received. Interestingly, the treatment discrepancy in our study was not attributable to a statistically significant difference in tumor stage at presentation. There should be no misconception that US Department of Veterans Affairs patients are less affected by socioeconomic inequities, though still this suggests clinician and systemic factors were significant drivers behind our findings.
This study did not intend to determine differences in incidence of HCC by race, although many studies have shown an age-adjusted incidence of HCC among Black and Hispanic patients up to twice that of White patients.1,8-10 Notably, the rate of orthotopic liver transplantation in this study was low regardless of race compared with that of other larger studies of patients with HCC.12,15 Discrepancies in HCC care among White and Black patients have been suggested to stem from a variety of influences, including access to early diagnosis and treatment of hepatitis C virus, comorbid conditions, as well as complex socioeconomic factors. It also has been shown that oncologists’ implicit racial bias has a negative impact on patients’ perceived quality of communication, their confidence in the recommended treatment, and the understood difficulty of the treatment by the patient and should be considered as a contributor to health disparities.17,18
Studies evaluating survival in HCC using SEER data generally stratify disease by localized, regional, or distant metastasis. For our study, TNM staging provided a more accurate assessment of the disease and reduced the chances that broader staging definitions could obscure differences in treatment choices. Future studies could be improved by stratifying patients by variables impacting treatment choice, such as Child-Pugh score or Barcelona Clinic Liver Cancer staging. Our study demonstrated a statistically significant difference in AFP level between White and Black veterans. This has been observed in prior studies as well, and while no specific cause has been identified, it suggests differences in tumor biologic features across different races. In addition, we found that an elevated AFP level at the time of diagnosis (defined as > 400) correlates with a worsened OS (HR, 1.36; P = .01).
Limitations
This study has several limitations, notably the number of veterans eligible for analysis at a single institution. A larger cohort would be needed to evaluate for statistically significant differences in outcomes by race. Additionally, our study did not account for therapy that was offered to but not pursued by the patient, and this would be useful to determine whether patient or practitioner factors were the more significant influence on the type of therapy received.
Conclusions
This study demonstrated a statistically significant difference in the rate of resection and liver transplantation between White and Black veterans at a single institution, although no difference in OS was observed. This discrepancy was not explained by differences in tumor staging. Additional, larger studies will be useful in clarifying the biologic, cultural, and socioeconomic drivers in HCC treatment and mortality.
Acknowledgments
The authors thank Lorri Reaves, Memphis Veterans Affairs Medical Center, Department of Hepatology.
1. Altekruse SF, McGlynn KA, Reichman ME. Hepatocellular carcinoma incidence, mortality, and survival trends in the United States from 1975 to 2005. J Clin Oncol. 2009;27(9):1485-1491. doi:10.1200/JCO.2008.20.7753
2. Howlader N, Noone AM, Krapcho M, et al (eds). SEER Cancer Statistics Review, 1975-2012, National Cancer Institute. Accessed July 8, 2022. https://seer.cancer.gov/archive/csr/1975_2012/results_merged/sect_14_liver_bile.pdf#page=8
3. Singal AG, Mittal S, Yerokun OA, et al. Hepatocellular carcinoma screening associated with early tumor detection and improved survival among patients with cirrhosis in the US. Am J Med. 2017;130(9):1099-1106.e1. doi:10.1016/j.amjmed.2017.01.021
4. Llovet JM, Ricci S, Mazzaferro V, et al. Sorafenib in advanced hepatocellular carcinoma. N Engl J Med. 2008;359(4):378-390. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa0708857
5. Finn RS, Qin S, Ikeda M, et al. Atezolizumab plus bevacizumab in unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma. N Engl J Med. 2020;382(20):1894-1905. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa1915745
6. Abou-Alfa GK, Chan SL, Kudo M, et al. Phase 3 randomized, open-label, multicenter study of tremelimumab (T) and durvalumab (D) as first-line therapy in patients (pts) with unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma (uHCC): HIMALAYA. J Clin Oncol. 2022;40(suppl 4):379. doi:10.1200/JCO.2022.40.4_suppl.379
7. Franco RA, Fan Y, Jarosek S, Bae S, Galbraith J. Racial and geographic disparities in hepatocellular carcinoma outcomes. Am J Prev Med. 2018;55(5)(suppl 1):S40-S48. doi:10.1016/j.amepre.2018.05.030
8. Ha J, Yan M, Aguilar M, et al. Race/ethnicity-specific disparities in hepatocellular carcinoma stage at diagnosis and its impact on receipt of curative therapies. J Clin Gastroenterol. 2016;50(5):423-430. doi:10.1097/MCG.0000000000000448
9. Wong R, Corley DA. Racial and ethnic variations in hepatocellular carcinoma incidence within the United States. Am J Med. 2008;121(6):525-531. doi:10.1016/j.amjmed.2008.03.005
10. Rich NE, Hester C, Odewole M, et al. Racial and ethnic differences in presentation and outcomes of hepatocellular carcinoma. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2019;17(3):551-559.e1. doi:10.1016/j.cgh.2018.05.039
11. Peters NA, Javed AA, He J, Wolfgang CL, Weiss MJ. Association of socioeconomics, surgical therapy, and survival of early stage hepatocellular carcinoma. J Surg Res. 2017;210:253-260. doi:10.1016/j.jss.2016.11.042
12. Wong RJ, Devaki P, Nguyen L, Cheung R, Nguyen MH. Ethnic disparities and liver transplantation rates in hepatocellular carcinoma patients in the recent era: results from the Surveillance, Epidemiology, and End Results registry. Liver Transpl. 2014;20(5):528-535. doi:10.1002/lt.23820
13. Minagawa M, Ikai I, Matsuyama Y, Yamaoka Y, Makuuchi M. Staging of hepatocellular carcinoma: assessment of the Japanese TNM and AJCC/UICC TNM systems in a cohort of 13,772 patients in Japan. Ann Surg. 2007;245(6):909-922. doi:10.1097/01.sla.0000254368.65878.da.
14. Harrison LE, Reichman T, Koneru B, et al. Racial discrepancies in the outcome of patients with hepatocellular carcinoma. Arch Surg. 2004;139(9):992-996. doi:10.1001/archsurg.139.9.992
15. Sloane D, Chen H, Howell C. Racial disparity in primary hepatocellular carcinoma: tumor stage at presentation, surgical treatment and survival. J Natl Med Assoc. 2006;98(12):1934-1939.
16. Haider AH, Scott VK, Rehman KA, et al. Racial disparities in surgical care and outcomes in the United States: a comprehensive review of patient, provider, and systemic factors. J Am Coll Surg. 2013;216(3):482-92.e12. doi:10.1016/j.jamcollsurg.2012.11.014
17. Cooper LA, Roter DL, Carson KA, et al. The associations of clinicians’ implicit attitudes about race with medical visit communication and patient ratings of interpersonal care. Am J Public Health. 2012;102(5):979-987. doi:10.2105/AJPH.2011.300558
18. Penner LA, Dovidio JF, Gonzalez R, et al. The effects of oncologist implicit racial bias in racially discordant oncology interactions. J Clin Oncol. 2016;34(24):2874-2880. doi:10.1200/JCO.2015.66.3658
Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is the sixth most common and third most deadly malignancy worldwide, carrying a mean survival rate without treatment of 6 to 20 months depending on stage.1 Fifty-seven percent of patients with liver cancer are diagnosed with regional or distant metastatic disease that carries 5-year relative survival rates of 10.7% and 3.1%, respectively.2 HCC arises most commonly from liver cirrhosis due to chronic hepatocyte injury, which may be mediated by viral hepatitis, alcoholism, and metabolic disease. Other less common causes include autoimmune disease, exposure to environmental hazards, and certain genetic diseases, such as α-1 antitrypsin deficiency and Wilson disease.
Multiple staging systems for HCC exist that incorporate some variation of the following features: size and invasion of the tumor, distant metastases, and liver function. Stage-directed treatments for HCC include ablation, embolization, resection, transplant, and systemic therapy, such as tyrosine kinase inhibitors, immunotherapies, and monoclonal antibodies. In addition to tumor/node/metastasis (TNM) staging, α-fetoprotein (AFP) is a diagnostic marker with prognostic value in HCC with higher levels correlating to higher tumor burden and a worse prognosis. With treatment, the 5-year survival rate for early stage HCC ranges from 60% to 80% but decreases significantly with higher stages.1 HCC screening in at-risk populations has accounted for > 40% of diagnoses since the practice became widely adopted, and earlier recognition has led to an improvement in survival even when adjusting for lead time bias.3
Systemic therapy for advanced disease continues to improve. Sorafenib remained the standard first-line systemic therapy since it was introduced in 2008.4 First-line therapy improved with immunotherapies. The phase 3 IMBrave150 trial comparing atezolizumab plus bevacizumab to sorafenib showed a median overall survival (OS) > 19 months with 7.7% of patients achieving a complete response.5 HIMALAYA, another phase 3 trial set for publication later this year, also reported promising results when a priming dose of the CTLA-4 inhibitor tremelimumab followed by durvalumab was compared with sorafenib.6
There has been a rise in incidence of HCC in the United States across all races and ethnicities, though Black, Hispanic, and Asian patients remain disproportionately affected. Subsequently, identifying causative biologic, socioeconomic, and cultural factors, as well as implicit bias in health care continues to be a topic of great interest.7-9 Using Surveillance, Epidemiology, and End Results (SEER) data, a number of large studies have found that Black patients with HCC were more likely to present with an advanced stage, less likely to receive curative intent treatment, and had significantly reduced survival compared with that of White patients.1,7-9 An analysis of 1117 patients by Rich and colleagues noted a 34% increased risk of death for Black patients with HCC compared with that of White patients, and other studies have shown about a 50% reduction in rate of liver transplantation for Black patients.10-12 Our study aimed to investigate potential disparities in incidence, etiology, AFP level at diagnosis, and outcomes of HCC in Black and White veterans managed at the Memphis Veterans Affairs Medical Center (VAMC) in Tennessee.
Methods
A single center retrospective chart review was conducted at the Memphis VAMC using the Computerized Patient Record System (CPRS) and the International Statistical Classification of Diseases, Tenth Revision (ICD-10) code C22.0 for HCC. Initial results were manually refined by prespecified criteria. Patients were included if they were diagnosed with HCC and received HCC treatment at the Memphis VAMC. Patients were excluded if HCC was not diagnosed histologically or clinically by imaging characteristics and AFP level, if the patient’s primary treatment was not provided at the Memphis VAMC, if they were lost to follow-up, or if race was not specified as either Black or White.
The following patient variables were examined: age, sex, comorbidities (alcohol or substance use disorder, cirrhosis, HIV), tumor stage, AFP, method of diagnosis, first-line treatments, systemic treatment, surgical options offered, and mortality. Staging was based on the American Joint Committee on Cancer TNM staging for HCC.13 Surgical options were recorded as resection or transplant. Patients who were offered treatment but lost to follow-up were excluded from the analysis.
Data Analysis
Our primary endpoint was identifying differences in OS among Memphis VAMC patients with HCC related to race. Kaplan-Meier analysis was used to investigate differences in OS and cumulative hazard ratio (HR) for death. Cox regression multivariate analysis further evaluated discrepancies among investigated patient variables, including age, race, alcohol, tobacco, or illicit drug use, HIV coinfection, and cirrhosis. Treatment factors were further defined by first-line treatment, systemic therapy, surgical resection, and transplant. χ2 analysis was used to investigate differences in treatment modalities.
Results
We identified 227 veterans, 95 Black and 132 White, between 2009 and 2021 meeting criteria for primary HCC treated at the Memphis VAMC. This study did not show a significant difference in OS between White and Black veterans (P = .24). Kaplan-Meier assessment showed OS was 1247 days (41 months) for Black veterans compared with 1032 days (34 months) for White veterans (Figure; Table 1).
Additionally, no significant difference was found between veterans for age or stage at diagnosis when stratified by race. The mean age of diagnosis for both groups was 65 years (P = .09). The mean TNM staging was 1.7 for White veterans vs 1.8 for Black veterans (P = .57). There was a significant increase in the AFP level at diagnosis for Black veterans (P = .001) (Table 2).
The most common initial treatment for both groups was transarterial chemoembolization and radiofrequency ablation with 68% of White and 64% of Black veterans receiving this therapy. There was no significant difference between who received systemic therapy.
However, we found significant differences by race for some forms of treatment. In our analysis, significant differences existed between those who did not receive any form of treatment as well as who received surgical resection and transplant. Among Black veterans, 11.6% received no treatment vs 6.1% for White veterans (P = .001). Only 2.1% of Black veterans underwent surgical resection vs 8.3% of White veterans (P = .046). Similarly, 13 (9.8%) White veterans vs 3 (3.2%) Black veterans received orthotopic liver transplantation (P = .052) in our cohort (eAppendix available at doi:10.12788/fp.0304). We found no differences in patient characteristics affecting OS, including alcohol use, tobacco use, illicit drug use, HIV coinfection, or liver cirrhosis (Table 3).
Discussion
In this retrospective analysis, Black veterans with HCC did not experience a statistically significant decrease in OS compared with that of White veterans despite some differences in therapy offered. Other studies have found that surgery was less frequently recommended to Black patients across multiple cancer types, and in most cases this carried a negative impact on OS.8,10,11,14,15 A number of other studies have demonstrated a greater percentage of Black patients receiving no treatment, although these studies are often based on SEER data, which captures only cancer-directed surgery and no other methods of treatment. Inequities in patient factors like insurance and socioeconomic status as well as willingness to receive certain treatments are often cited as major influences in health care disparities, but systemic and clinician factors like hospital volume, clinician expertise, specialist availability, and implicit racial bias all affect outcomes.16 One benefit of our study was that CPRS provided a centralized recording of all treatments received. Interestingly, the treatment discrepancy in our study was not attributable to a statistically significant difference in tumor stage at presentation. There should be no misconception that US Department of Veterans Affairs patients are less affected by socioeconomic inequities, though still this suggests clinician and systemic factors were significant drivers behind our findings.
This study did not intend to determine differences in incidence of HCC by race, although many studies have shown an age-adjusted incidence of HCC among Black and Hispanic patients up to twice that of White patients.1,8-10 Notably, the rate of orthotopic liver transplantation in this study was low regardless of race compared with that of other larger studies of patients with HCC.12,15 Discrepancies in HCC care among White and Black patients have been suggested to stem from a variety of influences, including access to early diagnosis and treatment of hepatitis C virus, comorbid conditions, as well as complex socioeconomic factors. It also has been shown that oncologists’ implicit racial bias has a negative impact on patients’ perceived quality of communication, their confidence in the recommended treatment, and the understood difficulty of the treatment by the patient and should be considered as a contributor to health disparities.17,18
Studies evaluating survival in HCC using SEER data generally stratify disease by localized, regional, or distant metastasis. For our study, TNM staging provided a more accurate assessment of the disease and reduced the chances that broader staging definitions could obscure differences in treatment choices. Future studies could be improved by stratifying patients by variables impacting treatment choice, such as Child-Pugh score or Barcelona Clinic Liver Cancer staging. Our study demonstrated a statistically significant difference in AFP level between White and Black veterans. This has been observed in prior studies as well, and while no specific cause has been identified, it suggests differences in tumor biologic features across different races. In addition, we found that an elevated AFP level at the time of diagnosis (defined as > 400) correlates with a worsened OS (HR, 1.36; P = .01).
Limitations
This study has several limitations, notably the number of veterans eligible for analysis at a single institution. A larger cohort would be needed to evaluate for statistically significant differences in outcomes by race. Additionally, our study did not account for therapy that was offered to but not pursued by the patient, and this would be useful to determine whether patient or practitioner factors were the more significant influence on the type of therapy received.
Conclusions
This study demonstrated a statistically significant difference in the rate of resection and liver transplantation between White and Black veterans at a single institution, although no difference in OS was observed. This discrepancy was not explained by differences in tumor staging. Additional, larger studies will be useful in clarifying the biologic, cultural, and socioeconomic drivers in HCC treatment and mortality.
Acknowledgments
The authors thank Lorri Reaves, Memphis Veterans Affairs Medical Center, Department of Hepatology.
Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is the sixth most common and third most deadly malignancy worldwide, carrying a mean survival rate without treatment of 6 to 20 months depending on stage.1 Fifty-seven percent of patients with liver cancer are diagnosed with regional or distant metastatic disease that carries 5-year relative survival rates of 10.7% and 3.1%, respectively.2 HCC arises most commonly from liver cirrhosis due to chronic hepatocyte injury, which may be mediated by viral hepatitis, alcoholism, and metabolic disease. Other less common causes include autoimmune disease, exposure to environmental hazards, and certain genetic diseases, such as α-1 antitrypsin deficiency and Wilson disease.
Multiple staging systems for HCC exist that incorporate some variation of the following features: size and invasion of the tumor, distant metastases, and liver function. Stage-directed treatments for HCC include ablation, embolization, resection, transplant, and systemic therapy, such as tyrosine kinase inhibitors, immunotherapies, and monoclonal antibodies. In addition to tumor/node/metastasis (TNM) staging, α-fetoprotein (AFP) is a diagnostic marker with prognostic value in HCC with higher levels correlating to higher tumor burden and a worse prognosis. With treatment, the 5-year survival rate for early stage HCC ranges from 60% to 80% but decreases significantly with higher stages.1 HCC screening in at-risk populations has accounted for > 40% of diagnoses since the practice became widely adopted, and earlier recognition has led to an improvement in survival even when adjusting for lead time bias.3
Systemic therapy for advanced disease continues to improve. Sorafenib remained the standard first-line systemic therapy since it was introduced in 2008.4 First-line therapy improved with immunotherapies. The phase 3 IMBrave150 trial comparing atezolizumab plus bevacizumab to sorafenib showed a median overall survival (OS) > 19 months with 7.7% of patients achieving a complete response.5 HIMALAYA, another phase 3 trial set for publication later this year, also reported promising results when a priming dose of the CTLA-4 inhibitor tremelimumab followed by durvalumab was compared with sorafenib.6
There has been a rise in incidence of HCC in the United States across all races and ethnicities, though Black, Hispanic, and Asian patients remain disproportionately affected. Subsequently, identifying causative biologic, socioeconomic, and cultural factors, as well as implicit bias in health care continues to be a topic of great interest.7-9 Using Surveillance, Epidemiology, and End Results (SEER) data, a number of large studies have found that Black patients with HCC were more likely to present with an advanced stage, less likely to receive curative intent treatment, and had significantly reduced survival compared with that of White patients.1,7-9 An analysis of 1117 patients by Rich and colleagues noted a 34% increased risk of death for Black patients with HCC compared with that of White patients, and other studies have shown about a 50% reduction in rate of liver transplantation for Black patients.10-12 Our study aimed to investigate potential disparities in incidence, etiology, AFP level at diagnosis, and outcomes of HCC in Black and White veterans managed at the Memphis Veterans Affairs Medical Center (VAMC) in Tennessee.
Methods
A single center retrospective chart review was conducted at the Memphis VAMC using the Computerized Patient Record System (CPRS) and the International Statistical Classification of Diseases, Tenth Revision (ICD-10) code C22.0 for HCC. Initial results were manually refined by prespecified criteria. Patients were included if they were diagnosed with HCC and received HCC treatment at the Memphis VAMC. Patients were excluded if HCC was not diagnosed histologically or clinically by imaging characteristics and AFP level, if the patient’s primary treatment was not provided at the Memphis VAMC, if they were lost to follow-up, or if race was not specified as either Black or White.
The following patient variables were examined: age, sex, comorbidities (alcohol or substance use disorder, cirrhosis, HIV), tumor stage, AFP, method of diagnosis, first-line treatments, systemic treatment, surgical options offered, and mortality. Staging was based on the American Joint Committee on Cancer TNM staging for HCC.13 Surgical options were recorded as resection or transplant. Patients who were offered treatment but lost to follow-up were excluded from the analysis.
Data Analysis
Our primary endpoint was identifying differences in OS among Memphis VAMC patients with HCC related to race. Kaplan-Meier analysis was used to investigate differences in OS and cumulative hazard ratio (HR) for death. Cox regression multivariate analysis further evaluated discrepancies among investigated patient variables, including age, race, alcohol, tobacco, or illicit drug use, HIV coinfection, and cirrhosis. Treatment factors were further defined by first-line treatment, systemic therapy, surgical resection, and transplant. χ2 analysis was used to investigate differences in treatment modalities.
Results
We identified 227 veterans, 95 Black and 132 White, between 2009 and 2021 meeting criteria for primary HCC treated at the Memphis VAMC. This study did not show a significant difference in OS between White and Black veterans (P = .24). Kaplan-Meier assessment showed OS was 1247 days (41 months) for Black veterans compared with 1032 days (34 months) for White veterans (Figure; Table 1).
Additionally, no significant difference was found between veterans for age or stage at diagnosis when stratified by race. The mean age of diagnosis for both groups was 65 years (P = .09). The mean TNM staging was 1.7 for White veterans vs 1.8 for Black veterans (P = .57). There was a significant increase in the AFP level at diagnosis for Black veterans (P = .001) (Table 2).
The most common initial treatment for both groups was transarterial chemoembolization and radiofrequency ablation with 68% of White and 64% of Black veterans receiving this therapy. There was no significant difference between who received systemic therapy.
However, we found significant differences by race for some forms of treatment. In our analysis, significant differences existed between those who did not receive any form of treatment as well as who received surgical resection and transplant. Among Black veterans, 11.6% received no treatment vs 6.1% for White veterans (P = .001). Only 2.1% of Black veterans underwent surgical resection vs 8.3% of White veterans (P = .046). Similarly, 13 (9.8%) White veterans vs 3 (3.2%) Black veterans received orthotopic liver transplantation (P = .052) in our cohort (eAppendix available at doi:10.12788/fp.0304). We found no differences in patient characteristics affecting OS, including alcohol use, tobacco use, illicit drug use, HIV coinfection, or liver cirrhosis (Table 3).
Discussion
In this retrospective analysis, Black veterans with HCC did not experience a statistically significant decrease in OS compared with that of White veterans despite some differences in therapy offered. Other studies have found that surgery was less frequently recommended to Black patients across multiple cancer types, and in most cases this carried a negative impact on OS.8,10,11,14,15 A number of other studies have demonstrated a greater percentage of Black patients receiving no treatment, although these studies are often based on SEER data, which captures only cancer-directed surgery and no other methods of treatment. Inequities in patient factors like insurance and socioeconomic status as well as willingness to receive certain treatments are often cited as major influences in health care disparities, but systemic and clinician factors like hospital volume, clinician expertise, specialist availability, and implicit racial bias all affect outcomes.16 One benefit of our study was that CPRS provided a centralized recording of all treatments received. Interestingly, the treatment discrepancy in our study was not attributable to a statistically significant difference in tumor stage at presentation. There should be no misconception that US Department of Veterans Affairs patients are less affected by socioeconomic inequities, though still this suggests clinician and systemic factors were significant drivers behind our findings.
This study did not intend to determine differences in incidence of HCC by race, although many studies have shown an age-adjusted incidence of HCC among Black and Hispanic patients up to twice that of White patients.1,8-10 Notably, the rate of orthotopic liver transplantation in this study was low regardless of race compared with that of other larger studies of patients with HCC.12,15 Discrepancies in HCC care among White and Black patients have been suggested to stem from a variety of influences, including access to early diagnosis and treatment of hepatitis C virus, comorbid conditions, as well as complex socioeconomic factors. It also has been shown that oncologists’ implicit racial bias has a negative impact on patients’ perceived quality of communication, their confidence in the recommended treatment, and the understood difficulty of the treatment by the patient and should be considered as a contributor to health disparities.17,18
Studies evaluating survival in HCC using SEER data generally stratify disease by localized, regional, or distant metastasis. For our study, TNM staging provided a more accurate assessment of the disease and reduced the chances that broader staging definitions could obscure differences in treatment choices. Future studies could be improved by stratifying patients by variables impacting treatment choice, such as Child-Pugh score or Barcelona Clinic Liver Cancer staging. Our study demonstrated a statistically significant difference in AFP level between White and Black veterans. This has been observed in prior studies as well, and while no specific cause has been identified, it suggests differences in tumor biologic features across different races. In addition, we found that an elevated AFP level at the time of diagnosis (defined as > 400) correlates with a worsened OS (HR, 1.36; P = .01).
Limitations
This study has several limitations, notably the number of veterans eligible for analysis at a single institution. A larger cohort would be needed to evaluate for statistically significant differences in outcomes by race. Additionally, our study did not account for therapy that was offered to but not pursued by the patient, and this would be useful to determine whether patient or practitioner factors were the more significant influence on the type of therapy received.
Conclusions
This study demonstrated a statistically significant difference in the rate of resection and liver transplantation between White and Black veterans at a single institution, although no difference in OS was observed. This discrepancy was not explained by differences in tumor staging. Additional, larger studies will be useful in clarifying the biologic, cultural, and socioeconomic drivers in HCC treatment and mortality.
Acknowledgments
The authors thank Lorri Reaves, Memphis Veterans Affairs Medical Center, Department of Hepatology.
1. Altekruse SF, McGlynn KA, Reichman ME. Hepatocellular carcinoma incidence, mortality, and survival trends in the United States from 1975 to 2005. J Clin Oncol. 2009;27(9):1485-1491. doi:10.1200/JCO.2008.20.7753
2. Howlader N, Noone AM, Krapcho M, et al (eds). SEER Cancer Statistics Review, 1975-2012, National Cancer Institute. Accessed July 8, 2022. https://seer.cancer.gov/archive/csr/1975_2012/results_merged/sect_14_liver_bile.pdf#page=8
3. Singal AG, Mittal S, Yerokun OA, et al. Hepatocellular carcinoma screening associated with early tumor detection and improved survival among patients with cirrhosis in the US. Am J Med. 2017;130(9):1099-1106.e1. doi:10.1016/j.amjmed.2017.01.021
4. Llovet JM, Ricci S, Mazzaferro V, et al. Sorafenib in advanced hepatocellular carcinoma. N Engl J Med. 2008;359(4):378-390. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa0708857
5. Finn RS, Qin S, Ikeda M, et al. Atezolizumab plus bevacizumab in unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma. N Engl J Med. 2020;382(20):1894-1905. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa1915745
6. Abou-Alfa GK, Chan SL, Kudo M, et al. Phase 3 randomized, open-label, multicenter study of tremelimumab (T) and durvalumab (D) as first-line therapy in patients (pts) with unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma (uHCC): HIMALAYA. J Clin Oncol. 2022;40(suppl 4):379. doi:10.1200/JCO.2022.40.4_suppl.379
7. Franco RA, Fan Y, Jarosek S, Bae S, Galbraith J. Racial and geographic disparities in hepatocellular carcinoma outcomes. Am J Prev Med. 2018;55(5)(suppl 1):S40-S48. doi:10.1016/j.amepre.2018.05.030
8. Ha J, Yan M, Aguilar M, et al. Race/ethnicity-specific disparities in hepatocellular carcinoma stage at diagnosis and its impact on receipt of curative therapies. J Clin Gastroenterol. 2016;50(5):423-430. doi:10.1097/MCG.0000000000000448
9. Wong R, Corley DA. Racial and ethnic variations in hepatocellular carcinoma incidence within the United States. Am J Med. 2008;121(6):525-531. doi:10.1016/j.amjmed.2008.03.005
10. Rich NE, Hester C, Odewole M, et al. Racial and ethnic differences in presentation and outcomes of hepatocellular carcinoma. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2019;17(3):551-559.e1. doi:10.1016/j.cgh.2018.05.039
11. Peters NA, Javed AA, He J, Wolfgang CL, Weiss MJ. Association of socioeconomics, surgical therapy, and survival of early stage hepatocellular carcinoma. J Surg Res. 2017;210:253-260. doi:10.1016/j.jss.2016.11.042
12. Wong RJ, Devaki P, Nguyen L, Cheung R, Nguyen MH. Ethnic disparities and liver transplantation rates in hepatocellular carcinoma patients in the recent era: results from the Surveillance, Epidemiology, and End Results registry. Liver Transpl. 2014;20(5):528-535. doi:10.1002/lt.23820
13. Minagawa M, Ikai I, Matsuyama Y, Yamaoka Y, Makuuchi M. Staging of hepatocellular carcinoma: assessment of the Japanese TNM and AJCC/UICC TNM systems in a cohort of 13,772 patients in Japan. Ann Surg. 2007;245(6):909-922. doi:10.1097/01.sla.0000254368.65878.da.
14. Harrison LE, Reichman T, Koneru B, et al. Racial discrepancies in the outcome of patients with hepatocellular carcinoma. Arch Surg. 2004;139(9):992-996. doi:10.1001/archsurg.139.9.992
15. Sloane D, Chen H, Howell C. Racial disparity in primary hepatocellular carcinoma: tumor stage at presentation, surgical treatment and survival. J Natl Med Assoc. 2006;98(12):1934-1939.
16. Haider AH, Scott VK, Rehman KA, et al. Racial disparities in surgical care and outcomes in the United States: a comprehensive review of patient, provider, and systemic factors. J Am Coll Surg. 2013;216(3):482-92.e12. doi:10.1016/j.jamcollsurg.2012.11.014
17. Cooper LA, Roter DL, Carson KA, et al. The associations of clinicians’ implicit attitudes about race with medical visit communication and patient ratings of interpersonal care. Am J Public Health. 2012;102(5):979-987. doi:10.2105/AJPH.2011.300558
18. Penner LA, Dovidio JF, Gonzalez R, et al. The effects of oncologist implicit racial bias in racially discordant oncology interactions. J Clin Oncol. 2016;34(24):2874-2880. doi:10.1200/JCO.2015.66.3658
1. Altekruse SF, McGlynn KA, Reichman ME. Hepatocellular carcinoma incidence, mortality, and survival trends in the United States from 1975 to 2005. J Clin Oncol. 2009;27(9):1485-1491. doi:10.1200/JCO.2008.20.7753
2. Howlader N, Noone AM, Krapcho M, et al (eds). SEER Cancer Statistics Review, 1975-2012, National Cancer Institute. Accessed July 8, 2022. https://seer.cancer.gov/archive/csr/1975_2012/results_merged/sect_14_liver_bile.pdf#page=8
3. Singal AG, Mittal S, Yerokun OA, et al. Hepatocellular carcinoma screening associated with early tumor detection and improved survival among patients with cirrhosis in the US. Am J Med. 2017;130(9):1099-1106.e1. doi:10.1016/j.amjmed.2017.01.021
4. Llovet JM, Ricci S, Mazzaferro V, et al. Sorafenib in advanced hepatocellular carcinoma. N Engl J Med. 2008;359(4):378-390. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa0708857
5. Finn RS, Qin S, Ikeda M, et al. Atezolizumab plus bevacizumab in unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma. N Engl J Med. 2020;382(20):1894-1905. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa1915745
6. Abou-Alfa GK, Chan SL, Kudo M, et al. Phase 3 randomized, open-label, multicenter study of tremelimumab (T) and durvalumab (D) as first-line therapy in patients (pts) with unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma (uHCC): HIMALAYA. J Clin Oncol. 2022;40(suppl 4):379. doi:10.1200/JCO.2022.40.4_suppl.379
7. Franco RA, Fan Y, Jarosek S, Bae S, Galbraith J. Racial and geographic disparities in hepatocellular carcinoma outcomes. Am J Prev Med. 2018;55(5)(suppl 1):S40-S48. doi:10.1016/j.amepre.2018.05.030
8. Ha J, Yan M, Aguilar M, et al. Race/ethnicity-specific disparities in hepatocellular carcinoma stage at diagnosis and its impact on receipt of curative therapies. J Clin Gastroenterol. 2016;50(5):423-430. doi:10.1097/MCG.0000000000000448
9. Wong R, Corley DA. Racial and ethnic variations in hepatocellular carcinoma incidence within the United States. Am J Med. 2008;121(6):525-531. doi:10.1016/j.amjmed.2008.03.005
10. Rich NE, Hester C, Odewole M, et al. Racial and ethnic differences in presentation and outcomes of hepatocellular carcinoma. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2019;17(3):551-559.e1. doi:10.1016/j.cgh.2018.05.039
11. Peters NA, Javed AA, He J, Wolfgang CL, Weiss MJ. Association of socioeconomics, surgical therapy, and survival of early stage hepatocellular carcinoma. J Surg Res. 2017;210:253-260. doi:10.1016/j.jss.2016.11.042
12. Wong RJ, Devaki P, Nguyen L, Cheung R, Nguyen MH. Ethnic disparities and liver transplantation rates in hepatocellular carcinoma patients in the recent era: results from the Surveillance, Epidemiology, and End Results registry. Liver Transpl. 2014;20(5):528-535. doi:10.1002/lt.23820
13. Minagawa M, Ikai I, Matsuyama Y, Yamaoka Y, Makuuchi M. Staging of hepatocellular carcinoma: assessment of the Japanese TNM and AJCC/UICC TNM systems in a cohort of 13,772 patients in Japan. Ann Surg. 2007;245(6):909-922. doi:10.1097/01.sla.0000254368.65878.da.
14. Harrison LE, Reichman T, Koneru B, et al. Racial discrepancies in the outcome of patients with hepatocellular carcinoma. Arch Surg. 2004;139(9):992-996. doi:10.1001/archsurg.139.9.992
15. Sloane D, Chen H, Howell C. Racial disparity in primary hepatocellular carcinoma: tumor stage at presentation, surgical treatment and survival. J Natl Med Assoc. 2006;98(12):1934-1939.
16. Haider AH, Scott VK, Rehman KA, et al. Racial disparities in surgical care and outcomes in the United States: a comprehensive review of patient, provider, and systemic factors. J Am Coll Surg. 2013;216(3):482-92.e12. doi:10.1016/j.jamcollsurg.2012.11.014
17. Cooper LA, Roter DL, Carson KA, et al. The associations of clinicians’ implicit attitudes about race with medical visit communication and patient ratings of interpersonal care. Am J Public Health. 2012;102(5):979-987. doi:10.2105/AJPH.2011.300558
18. Penner LA, Dovidio JF, Gonzalez R, et al. The effects of oncologist implicit racial bias in racially discordant oncology interactions. J Clin Oncol. 2016;34(24):2874-2880. doi:10.1200/JCO.2015.66.3658
‘Misleading’ focus on urinary symptoms preventing early prostate cancer diagnoses
Researchers from the University of Cambridge said there was “no evidence of a causal link between prostate cancer and either prostate size or troublesome male urinary symptoms” and called for early prostate cancer to be rebranded “as primarily an asymptomatic disease” to encourage more men to get tested earlier when the condition is more treatable.
The authors of the ‘Opinion’ article, published in the journal BMC Medicine, argued that persistence by health bodies in flagging prostate cancer as a symptomatic disease – frequently presenting with slow urinary flow, frequency, and nocturia – worked against efforts to reduce mortality rates, which had remained largely unaltered in the UK and many other countries over the past decade and largely driven by late detection.
Public advice by the NHS, for instance, acknowledges that prostate cancer may be symptomless for many years but lists ‘an increased need to pee,’ ‘straining while you pee,’ and ‘a feeling that your bladder has not fully emptied’ as the top three signs that should not be ignored.
Messaging gives men ‘a false sense of security’
No wonder, the authors argued, that lower urinary tract symptoms and prostate cancer risk had become “causally associated,” as reflected in a 2003 survey finding that 86% of the public thought that prostate cancer was accompanied by symptoms, while only 1% were aware that it could be asymptomatic.
Lead study author Vincent Gnanapragasam, PhD, professor of urology at the University of Cambridge and an honorary consultant urologist at Addenbrooke’s Hospital, maintained: “We urgently need to recognize that the information currently given to the public risks giving men a false sense of security if they don’t have any urinary symptoms. We need to emphasize that prostate cancer can be a silent or asymptomatic disease, particularly in its curable stages. Waiting out for urinary symptoms may mean missing opportunities to catch the disease when it’s treatable.”
Although prostate enlargement can cause the lower urinary tract problems mentioned in public health messaging, the researchers said this is rarely due to malignant prostate tumors, quoting some research suggesting that “mean prostate volume was lower in men found to have prostate cancer compared to those with benign biopsies.” The Prostate testing for cancer and Treatment (ProtecT) trial in the UK concluded there was “no association or a negative association with more severe symptoms and prostate cancer,” they said.
Screening program
The researchers said they were not advocating introducing an immediate screening program, and they acknowledged that updating advice to focus on the often symptomless nature of the disease could lead to an influx of men requesting a PSA test from their GPs. But concerns this could result in overinvestigation and overtreatment “which previously deterred greater promotion of PSA testing in men with no symptoms” had been lessened by today’s “image-based diagnostics and risk-adapted management strategies,” they said.
The authors hoped for an eventual “intelligent tiered screening program” for prostate cancer to be introduced. In the meantime, Dr. Gnanapragasam said, “We’re calling on organizations such as the NHS, as well as patient charities and the media, to review the current public messaging.”
Amy Rylance, head of improving care at Prostate Cancer UK said: “This study reinforces the fact that men shouldn’t wait for symptoms before they act. Early prostate cancer is often symptomless, which is why we urge men to be aware of their risk instead. This is particularly important for men over 50, Black men, and men with a family history of prostate cancer.
“We know that most people assume that they would have symptoms if they had prostate cancer, and that not having straightforward signs to look out for can cause anxiety or confusion. That’s why our risk checker is designed to help men understand their risk factors and what action they can take, regardless of symptoms.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.co.uk.
Researchers from the University of Cambridge said there was “no evidence of a causal link between prostate cancer and either prostate size or troublesome male urinary symptoms” and called for early prostate cancer to be rebranded “as primarily an asymptomatic disease” to encourage more men to get tested earlier when the condition is more treatable.
The authors of the ‘Opinion’ article, published in the journal BMC Medicine, argued that persistence by health bodies in flagging prostate cancer as a symptomatic disease – frequently presenting with slow urinary flow, frequency, and nocturia – worked against efforts to reduce mortality rates, which had remained largely unaltered in the UK and many other countries over the past decade and largely driven by late detection.
Public advice by the NHS, for instance, acknowledges that prostate cancer may be symptomless for many years but lists ‘an increased need to pee,’ ‘straining while you pee,’ and ‘a feeling that your bladder has not fully emptied’ as the top three signs that should not be ignored.
Messaging gives men ‘a false sense of security’
No wonder, the authors argued, that lower urinary tract symptoms and prostate cancer risk had become “causally associated,” as reflected in a 2003 survey finding that 86% of the public thought that prostate cancer was accompanied by symptoms, while only 1% were aware that it could be asymptomatic.
Lead study author Vincent Gnanapragasam, PhD, professor of urology at the University of Cambridge and an honorary consultant urologist at Addenbrooke’s Hospital, maintained: “We urgently need to recognize that the information currently given to the public risks giving men a false sense of security if they don’t have any urinary symptoms. We need to emphasize that prostate cancer can be a silent or asymptomatic disease, particularly in its curable stages. Waiting out for urinary symptoms may mean missing opportunities to catch the disease when it’s treatable.”
Although prostate enlargement can cause the lower urinary tract problems mentioned in public health messaging, the researchers said this is rarely due to malignant prostate tumors, quoting some research suggesting that “mean prostate volume was lower in men found to have prostate cancer compared to those with benign biopsies.” The Prostate testing for cancer and Treatment (ProtecT) trial in the UK concluded there was “no association or a negative association with more severe symptoms and prostate cancer,” they said.
Screening program
The researchers said they were not advocating introducing an immediate screening program, and they acknowledged that updating advice to focus on the often symptomless nature of the disease could lead to an influx of men requesting a PSA test from their GPs. But concerns this could result in overinvestigation and overtreatment “which previously deterred greater promotion of PSA testing in men with no symptoms” had been lessened by today’s “image-based diagnostics and risk-adapted management strategies,” they said.
The authors hoped for an eventual “intelligent tiered screening program” for prostate cancer to be introduced. In the meantime, Dr. Gnanapragasam said, “We’re calling on organizations such as the NHS, as well as patient charities and the media, to review the current public messaging.”
Amy Rylance, head of improving care at Prostate Cancer UK said: “This study reinforces the fact that men shouldn’t wait for symptoms before they act. Early prostate cancer is often symptomless, which is why we urge men to be aware of their risk instead. This is particularly important for men over 50, Black men, and men with a family history of prostate cancer.
“We know that most people assume that they would have symptoms if they had prostate cancer, and that not having straightforward signs to look out for can cause anxiety or confusion. That’s why our risk checker is designed to help men understand their risk factors and what action they can take, regardless of symptoms.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.co.uk.
Researchers from the University of Cambridge said there was “no evidence of a causal link between prostate cancer and either prostate size or troublesome male urinary symptoms” and called for early prostate cancer to be rebranded “as primarily an asymptomatic disease” to encourage more men to get tested earlier when the condition is more treatable.
The authors of the ‘Opinion’ article, published in the journal BMC Medicine, argued that persistence by health bodies in flagging prostate cancer as a symptomatic disease – frequently presenting with slow urinary flow, frequency, and nocturia – worked against efforts to reduce mortality rates, which had remained largely unaltered in the UK and many other countries over the past decade and largely driven by late detection.
Public advice by the NHS, for instance, acknowledges that prostate cancer may be symptomless for many years but lists ‘an increased need to pee,’ ‘straining while you pee,’ and ‘a feeling that your bladder has not fully emptied’ as the top three signs that should not be ignored.
Messaging gives men ‘a false sense of security’
No wonder, the authors argued, that lower urinary tract symptoms and prostate cancer risk had become “causally associated,” as reflected in a 2003 survey finding that 86% of the public thought that prostate cancer was accompanied by symptoms, while only 1% were aware that it could be asymptomatic.
Lead study author Vincent Gnanapragasam, PhD, professor of urology at the University of Cambridge and an honorary consultant urologist at Addenbrooke’s Hospital, maintained: “We urgently need to recognize that the information currently given to the public risks giving men a false sense of security if they don’t have any urinary symptoms. We need to emphasize that prostate cancer can be a silent or asymptomatic disease, particularly in its curable stages. Waiting out for urinary symptoms may mean missing opportunities to catch the disease when it’s treatable.”
Although prostate enlargement can cause the lower urinary tract problems mentioned in public health messaging, the researchers said this is rarely due to malignant prostate tumors, quoting some research suggesting that “mean prostate volume was lower in men found to have prostate cancer compared to those with benign biopsies.” The Prostate testing for cancer and Treatment (ProtecT) trial in the UK concluded there was “no association or a negative association with more severe symptoms and prostate cancer,” they said.
Screening program
The researchers said they were not advocating introducing an immediate screening program, and they acknowledged that updating advice to focus on the often symptomless nature of the disease could lead to an influx of men requesting a PSA test from their GPs. But concerns this could result in overinvestigation and overtreatment “which previously deterred greater promotion of PSA testing in men with no symptoms” had been lessened by today’s “image-based diagnostics and risk-adapted management strategies,” they said.
The authors hoped for an eventual “intelligent tiered screening program” for prostate cancer to be introduced. In the meantime, Dr. Gnanapragasam said, “We’re calling on organizations such as the NHS, as well as patient charities and the media, to review the current public messaging.”
Amy Rylance, head of improving care at Prostate Cancer UK said: “This study reinforces the fact that men shouldn’t wait for symptoms before they act. Early prostate cancer is often symptomless, which is why we urge men to be aware of their risk instead. This is particularly important for men over 50, Black men, and men with a family history of prostate cancer.
“We know that most people assume that they would have symptoms if they had prostate cancer, and that not having straightforward signs to look out for can cause anxiety or confusion. That’s why our risk checker is designed to help men understand their risk factors and what action they can take, regardless of symptoms.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.co.uk.
Blood test could provide insight into patients’ metastatic cancer
according to a new report.
The blood test focuses on circulating tumor DNA (ctDNA). By sequencing the complete genome of ctDNA, researchers can learn about the different metastases spread throughout the body.
“A key goal in cancer research is to better understand metastatic cancer in each affected person so we can select the best treatments and avoid giving toxic therapies to people who will not derive benefit,” senior author Alexander Wyatt, MD, DPhil, assistant professor of genitourinary cancer genomics at the University of British Columbia, Vancouver, and senior research scientist at the Vancouver Prostate Center, told this news organization.
“However, biopsies of metastatic cancer are rarely performed since they are invasive and have risks of complications,” he said. “In the past, this major barrier has prevented the widespread study of metastatic cancer and progress to better treatment of this lethal disease.”
The study was published in Nature.
Test methods
Blood-based biopsy technology, also known as “liquid biopsy,” has emerged as a tool for clinical cancer genotyping and longitudinal disease monitoring. Tests that use ctDNA have begun to influence the clinical management of people with cancer, the study authors wrote, though the full potential for understanding metastatic cancer biology hasn’t yet been unlocked.
Dr. Wyatt and colleagues analyzed serial plasma and synchronous metastases in patients with aggressive, treatment-resistant prostate cancer through deep whole-genome sequencing, which allows for a comprehensive assessment of every part of the genetic code within the cancer cells.
The researchers assessed all classes of genomic alterations and found that ctDNA contains multiple dominant populations, indicating that most people with metastatic cancer have different metastases spread around the body. They found that the whole-genome sequencing process provides a host of information about these different metastases.
The research team used newly developed computer programs to provide information about the genetic makeup of each cancer population, which can tell researchers about a person’s overall disease rather than about one metastatic tumor. In the future, this information could allow clinicians to make better decisions about managing a patient’s cancer.
The researchers studied multiple ctDNA samples collected over time to understand how a patient’s cancer evolved in response to treatment. They focused on inhibitors of the androgen receptor pathway. They found that current therapies for metastatic prostate cancer actively change the composition of cancer populations in the body and that treatment often selects for biologically aggressive cancer populations that underlie clinical resistance. This allowed them to pinpoint new genetic resistance mechanisms to the most common treatments for metastatic prostate cancer. The technique could be applied to other cancers as well.
The research team used nucleosome footprints in ctDNA to infer mRNA expression in metastases upon which biopsies were synchronously performed. They identified treatment-induced changes in androgen receptor transcription factor signaling activity. This means whole-genome sequencing of ctDNA can reveal the active processes occurring within cells, allowing clinicians to predict which treatments will be effective or ineffective in each patient.
“Our research significantly expands the breadth of cancer information that can be obtained from only a few drops of blood,” said Dr. Wyatt. “From a clinical perspective, this extra information can be used in new clinical trials that are testing strategies to direct cancer treatments only to those whose quality or whose length of life will be improved.”
Clinical trials
The study authors wrote that whole-genome ctDNA sequencing technology, which is minimally invasive, inexpensive, and scalable, is now being deployed in large clinical trials to help discover new treatment resistance mechanisms. These include precision oncology clinical trials that are being conducted with Canadian cancer patients at the Vancouver Prostate Centre and BC Cancer.
The technology can also be implemented in existing commercial ctDNA testing platforms, which means that patients could soon directly benefit from more comprehensive liquid biopsy testing. The research team has made the methods and computer code publicly and freely available so that the technology can be applied to other cancer types and clinical settings.
“Understanding how clonal evolution occurs and what drives it is one of the key questions that need to be addressed in almost all cancers, and this study provides that level of insight for advanced prostate cancer, as well as a model and tools for how to carry out this work,” Christopher Mueller, MD, PhD, a cancer biologist and geneticist at Queen’s Cancer Research Institute and a professor of biomedical and molecular sciences at Queen’s University, both in Kingston, Ont., said in an interview.
Dr. Mueller, who wasn’t involved with this study, has researched biomarkers and ctDNA as avenues for more precise management of advanced prostate cancer. He and his colleagues have developed blood tests for detecting and monitoring metastatic breast cancer, uveal melanoma, and prostate, pancreatic, and lung cancer.
“The expansion of treatment-resistant clones is how we lose almost all cancer patients, and they clearly demonstrate that in castrate-resistant prostate cancer, changes in the androgen receptor locus almost always drive this process,” Dr. Mueller said. “Understanding clonal evolution will allow us to design treatment strategies that overcome or limit their expansion, hopefully extending the lives of these patients.”
The study was funded by the Canadian Institutes of Health Research, the Canadian Cancer Society Research Institute, the Prostate Cancer Foundation, Prostate Cancer Canada, the Movember Foundation, the Jane and Aatos Erkko Foundation, the Academy of Finland Center of Excellence program, the Terry Fox New Frontiers Program, and the BC Cancer Foundation. Dr. Wyatt has served on advisory boards or has received honoraria from AstraZeneca, Astellas, Janssen, and Merck, and his research lab has a contract research agreement with ESSA Pharma. Dr. Mueller disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
according to a new report.
The blood test focuses on circulating tumor DNA (ctDNA). By sequencing the complete genome of ctDNA, researchers can learn about the different metastases spread throughout the body.
“A key goal in cancer research is to better understand metastatic cancer in each affected person so we can select the best treatments and avoid giving toxic therapies to people who will not derive benefit,” senior author Alexander Wyatt, MD, DPhil, assistant professor of genitourinary cancer genomics at the University of British Columbia, Vancouver, and senior research scientist at the Vancouver Prostate Center, told this news organization.
“However, biopsies of metastatic cancer are rarely performed since they are invasive and have risks of complications,” he said. “In the past, this major barrier has prevented the widespread study of metastatic cancer and progress to better treatment of this lethal disease.”
The study was published in Nature.
Test methods
Blood-based biopsy technology, also known as “liquid biopsy,” has emerged as a tool for clinical cancer genotyping and longitudinal disease monitoring. Tests that use ctDNA have begun to influence the clinical management of people with cancer, the study authors wrote, though the full potential for understanding metastatic cancer biology hasn’t yet been unlocked.
Dr. Wyatt and colleagues analyzed serial plasma and synchronous metastases in patients with aggressive, treatment-resistant prostate cancer through deep whole-genome sequencing, which allows for a comprehensive assessment of every part of the genetic code within the cancer cells.
The researchers assessed all classes of genomic alterations and found that ctDNA contains multiple dominant populations, indicating that most people with metastatic cancer have different metastases spread around the body. They found that the whole-genome sequencing process provides a host of information about these different metastases.
The research team used newly developed computer programs to provide information about the genetic makeup of each cancer population, which can tell researchers about a person’s overall disease rather than about one metastatic tumor. In the future, this information could allow clinicians to make better decisions about managing a patient’s cancer.
The researchers studied multiple ctDNA samples collected over time to understand how a patient’s cancer evolved in response to treatment. They focused on inhibitors of the androgen receptor pathway. They found that current therapies for metastatic prostate cancer actively change the composition of cancer populations in the body and that treatment often selects for biologically aggressive cancer populations that underlie clinical resistance. This allowed them to pinpoint new genetic resistance mechanisms to the most common treatments for metastatic prostate cancer. The technique could be applied to other cancers as well.
The research team used nucleosome footprints in ctDNA to infer mRNA expression in metastases upon which biopsies were synchronously performed. They identified treatment-induced changes in androgen receptor transcription factor signaling activity. This means whole-genome sequencing of ctDNA can reveal the active processes occurring within cells, allowing clinicians to predict which treatments will be effective or ineffective in each patient.
“Our research significantly expands the breadth of cancer information that can be obtained from only a few drops of blood,” said Dr. Wyatt. “From a clinical perspective, this extra information can be used in new clinical trials that are testing strategies to direct cancer treatments only to those whose quality or whose length of life will be improved.”
Clinical trials
The study authors wrote that whole-genome ctDNA sequencing technology, which is minimally invasive, inexpensive, and scalable, is now being deployed in large clinical trials to help discover new treatment resistance mechanisms. These include precision oncology clinical trials that are being conducted with Canadian cancer patients at the Vancouver Prostate Centre and BC Cancer.
The technology can also be implemented in existing commercial ctDNA testing platforms, which means that patients could soon directly benefit from more comprehensive liquid biopsy testing. The research team has made the methods and computer code publicly and freely available so that the technology can be applied to other cancer types and clinical settings.
“Understanding how clonal evolution occurs and what drives it is one of the key questions that need to be addressed in almost all cancers, and this study provides that level of insight for advanced prostate cancer, as well as a model and tools for how to carry out this work,” Christopher Mueller, MD, PhD, a cancer biologist and geneticist at Queen’s Cancer Research Institute and a professor of biomedical and molecular sciences at Queen’s University, both in Kingston, Ont., said in an interview.
Dr. Mueller, who wasn’t involved with this study, has researched biomarkers and ctDNA as avenues for more precise management of advanced prostate cancer. He and his colleagues have developed blood tests for detecting and monitoring metastatic breast cancer, uveal melanoma, and prostate, pancreatic, and lung cancer.
“The expansion of treatment-resistant clones is how we lose almost all cancer patients, and they clearly demonstrate that in castrate-resistant prostate cancer, changes in the androgen receptor locus almost always drive this process,” Dr. Mueller said. “Understanding clonal evolution will allow us to design treatment strategies that overcome or limit their expansion, hopefully extending the lives of these patients.”
The study was funded by the Canadian Institutes of Health Research, the Canadian Cancer Society Research Institute, the Prostate Cancer Foundation, Prostate Cancer Canada, the Movember Foundation, the Jane and Aatos Erkko Foundation, the Academy of Finland Center of Excellence program, the Terry Fox New Frontiers Program, and the BC Cancer Foundation. Dr. Wyatt has served on advisory boards or has received honoraria from AstraZeneca, Astellas, Janssen, and Merck, and his research lab has a contract research agreement with ESSA Pharma. Dr. Mueller disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
according to a new report.
The blood test focuses on circulating tumor DNA (ctDNA). By sequencing the complete genome of ctDNA, researchers can learn about the different metastases spread throughout the body.
“A key goal in cancer research is to better understand metastatic cancer in each affected person so we can select the best treatments and avoid giving toxic therapies to people who will not derive benefit,” senior author Alexander Wyatt, MD, DPhil, assistant professor of genitourinary cancer genomics at the University of British Columbia, Vancouver, and senior research scientist at the Vancouver Prostate Center, told this news organization.
“However, biopsies of metastatic cancer are rarely performed since they are invasive and have risks of complications,” he said. “In the past, this major barrier has prevented the widespread study of metastatic cancer and progress to better treatment of this lethal disease.”
The study was published in Nature.
Test methods
Blood-based biopsy technology, also known as “liquid biopsy,” has emerged as a tool for clinical cancer genotyping and longitudinal disease monitoring. Tests that use ctDNA have begun to influence the clinical management of people with cancer, the study authors wrote, though the full potential for understanding metastatic cancer biology hasn’t yet been unlocked.
Dr. Wyatt and colleagues analyzed serial plasma and synchronous metastases in patients with aggressive, treatment-resistant prostate cancer through deep whole-genome sequencing, which allows for a comprehensive assessment of every part of the genetic code within the cancer cells.
The researchers assessed all classes of genomic alterations and found that ctDNA contains multiple dominant populations, indicating that most people with metastatic cancer have different metastases spread around the body. They found that the whole-genome sequencing process provides a host of information about these different metastases.
The research team used newly developed computer programs to provide information about the genetic makeup of each cancer population, which can tell researchers about a person’s overall disease rather than about one metastatic tumor. In the future, this information could allow clinicians to make better decisions about managing a patient’s cancer.
The researchers studied multiple ctDNA samples collected over time to understand how a patient’s cancer evolved in response to treatment. They focused on inhibitors of the androgen receptor pathway. They found that current therapies for metastatic prostate cancer actively change the composition of cancer populations in the body and that treatment often selects for biologically aggressive cancer populations that underlie clinical resistance. This allowed them to pinpoint new genetic resistance mechanisms to the most common treatments for metastatic prostate cancer. The technique could be applied to other cancers as well.
The research team used nucleosome footprints in ctDNA to infer mRNA expression in metastases upon which biopsies were synchronously performed. They identified treatment-induced changes in androgen receptor transcription factor signaling activity. This means whole-genome sequencing of ctDNA can reveal the active processes occurring within cells, allowing clinicians to predict which treatments will be effective or ineffective in each patient.
“Our research significantly expands the breadth of cancer information that can be obtained from only a few drops of blood,” said Dr. Wyatt. “From a clinical perspective, this extra information can be used in new clinical trials that are testing strategies to direct cancer treatments only to those whose quality or whose length of life will be improved.”
Clinical trials
The study authors wrote that whole-genome ctDNA sequencing technology, which is minimally invasive, inexpensive, and scalable, is now being deployed in large clinical trials to help discover new treatment resistance mechanisms. These include precision oncology clinical trials that are being conducted with Canadian cancer patients at the Vancouver Prostate Centre and BC Cancer.
The technology can also be implemented in existing commercial ctDNA testing platforms, which means that patients could soon directly benefit from more comprehensive liquid biopsy testing. The research team has made the methods and computer code publicly and freely available so that the technology can be applied to other cancer types and clinical settings.
“Understanding how clonal evolution occurs and what drives it is one of the key questions that need to be addressed in almost all cancers, and this study provides that level of insight for advanced prostate cancer, as well as a model and tools for how to carry out this work,” Christopher Mueller, MD, PhD, a cancer biologist and geneticist at Queen’s Cancer Research Institute and a professor of biomedical and molecular sciences at Queen’s University, both in Kingston, Ont., said in an interview.
Dr. Mueller, who wasn’t involved with this study, has researched biomarkers and ctDNA as avenues for more precise management of advanced prostate cancer. He and his colleagues have developed blood tests for detecting and monitoring metastatic breast cancer, uveal melanoma, and prostate, pancreatic, and lung cancer.
“The expansion of treatment-resistant clones is how we lose almost all cancer patients, and they clearly demonstrate that in castrate-resistant prostate cancer, changes in the androgen receptor locus almost always drive this process,” Dr. Mueller said. “Understanding clonal evolution will allow us to design treatment strategies that overcome or limit their expansion, hopefully extending the lives of these patients.”
The study was funded by the Canadian Institutes of Health Research, the Canadian Cancer Society Research Institute, the Prostate Cancer Foundation, Prostate Cancer Canada, the Movember Foundation, the Jane and Aatos Erkko Foundation, the Academy of Finland Center of Excellence program, the Terry Fox New Frontiers Program, and the BC Cancer Foundation. Dr. Wyatt has served on advisory boards or has received honoraria from AstraZeneca, Astellas, Janssen, and Merck, and his research lab has a contract research agreement with ESSA Pharma. Dr. Mueller disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM NATURE
Study confirms BRCA1 and BRCA2 linked to seven cancers
from prior analyses showing associations with breast, ovarian, prostate, and pancreatic cancers. The finding, published in JAMA Oncology suggests a possible broader clinical relevance for BRCA1 and BRCA2 genetic testing.
Pathogenic variants in BRCA1 were found to be associated with biliary tract cancer, in BRCA2 with esophageal cancer, and in BRCA1/2 with gastric cancer.
“The results suggest the range of cancer types associated with pathogenic variants in BRCA1 and BRCA2 is likely broader than that determined from previous analysis of largely European ancestry cohorts,” wrote authors who were led by Yukihide Momozawa, DVM, PhD, RIKEN Center for Integrative Medical Sciences, Japan.
“These risk association findings, together with our analysis of an association with family history of cancer and clinical phenotypes, are relevant for developing and adapting guidelines about genetic testing, treatment options, and treatability with PARP [poly adenosine diphosphate-ribose polymerase] inhibitors for each cancer type,” the authors wrote.
Dr. Momozawa and associates conducted a large-scale sequencing study across 14 common cancer types in 63,828 patients (mean age 64 years, 42% female) and 37,086 controls on data drawn from a Japanese nationwide biobank between April 2003 and March 2018. They estimated the risk of each cancer type and determined clinical characteristics associated with pathogenic variant carrier status, while also investigating the utility of family history in detecting patients with pathogenic variants.
Three hundred fifteen pathogenic variants were identified. An odds ratios of greater than 4.0 (with P < 1 × 10−4 as the threshold of significance) for the pathogenic variants were found for biliary tract cancer (OR, 17.4; 95% confidence interval, 5.8-51.9) in BRCA1, esophageal cancer (OR, 5.6; 95% CI, 2.9-11.0) in BRCA2, and gastric cancer (OR, 5.2; 95% CI, 2.6-10.5) in BRCA1, and (OR, 4.7; 95% CI, 3.1-7.1) in BRCA2. Two other cancer types were found to be associated with BRCA1, and four other cancer types with BRCA2. Enrichment of carrier patients was shown in biliary tract, female breast, ovarian, and prostate cancers in accordance with increased numbers of reported cancer types in relatives.
Male patients with breast cancer had a very high carrier frequency of pathogenic variants in BRCA2 (18.9%), but not BRCA1 (1.89%). Patients with ovarian cancer showed the next highest proportion (BRCA1, 4.86%; BRCA2, 3.42%). Frequency exceeding 1% was seen for several other cancer types (two cancer types for BRCA1, four cancer types for BRCA2). More than one cancer types was identified in 4,128 patients (6.3%). Carrier frequency of pathogenic variants in BRCA1 was 0.44% with one cancer type, 0.85% with two cancer types, and 0.69% with three cancer types. It was 0.97%, 1.40%, and 1.74%, respectively, in BRCA2.
“The results of this large-scale registry-based case-control study suggest that pathogenic variants in BRCA1 and BRCA2 were associated with the risk of seven cancer types. These results indicate broader clinical relevance of BRCA1 and BRCA2 genetic testing,” the authors wrote.
PARP inhibitors were developed based on the mechanism in BRCA1 and BRCA2 of homologous recombination repair defects associated with pathogenic variants. PARP inhibitors have been found to have therapeutic efficacy also in pathogenic variants found to be enriched in prostate and pancreatic cancers. While risk for additional cancer types (for example, biliary tract cancer, cervical cancer, colorectal cancer, endometrial cancer, esophageal cancer, and stomach cancer) has been reported after analyzing family members for the presence of pathogenic variants and performing case-control analyses, evidence for an association with these cancer types has not been considered sufficient for them to be adopted into clinical management guidelines, the authors wrote.
In an interview, Dr. Momozawa said that BRCA1 and BRCA2 genetic testing should be expanded in Japan. “But further studies are needed to reveal how much. If a clinical trial of a PARP inhibitor for these three cancer types reveals its clinical utility, the importance of this expansion will increase.”
Dr. Momozawa and associates state that while their selection of controls without a family history of cancer affects the generalizability of the study results, the estimated cumulative risks were comparable with those based on prospective cohorts, suggesting the study design did not greatly affect the results.
from prior analyses showing associations with breast, ovarian, prostate, and pancreatic cancers. The finding, published in JAMA Oncology suggests a possible broader clinical relevance for BRCA1 and BRCA2 genetic testing.
Pathogenic variants in BRCA1 were found to be associated with biliary tract cancer, in BRCA2 with esophageal cancer, and in BRCA1/2 with gastric cancer.
“The results suggest the range of cancer types associated with pathogenic variants in BRCA1 and BRCA2 is likely broader than that determined from previous analysis of largely European ancestry cohorts,” wrote authors who were led by Yukihide Momozawa, DVM, PhD, RIKEN Center for Integrative Medical Sciences, Japan.
“These risk association findings, together with our analysis of an association with family history of cancer and clinical phenotypes, are relevant for developing and adapting guidelines about genetic testing, treatment options, and treatability with PARP [poly adenosine diphosphate-ribose polymerase] inhibitors for each cancer type,” the authors wrote.
Dr. Momozawa and associates conducted a large-scale sequencing study across 14 common cancer types in 63,828 patients (mean age 64 years, 42% female) and 37,086 controls on data drawn from a Japanese nationwide biobank between April 2003 and March 2018. They estimated the risk of each cancer type and determined clinical characteristics associated with pathogenic variant carrier status, while also investigating the utility of family history in detecting patients with pathogenic variants.
Three hundred fifteen pathogenic variants were identified. An odds ratios of greater than 4.0 (with P < 1 × 10−4 as the threshold of significance) for the pathogenic variants were found for biliary tract cancer (OR, 17.4; 95% confidence interval, 5.8-51.9) in BRCA1, esophageal cancer (OR, 5.6; 95% CI, 2.9-11.0) in BRCA2, and gastric cancer (OR, 5.2; 95% CI, 2.6-10.5) in BRCA1, and (OR, 4.7; 95% CI, 3.1-7.1) in BRCA2. Two other cancer types were found to be associated with BRCA1, and four other cancer types with BRCA2. Enrichment of carrier patients was shown in biliary tract, female breast, ovarian, and prostate cancers in accordance with increased numbers of reported cancer types in relatives.
Male patients with breast cancer had a very high carrier frequency of pathogenic variants in BRCA2 (18.9%), but not BRCA1 (1.89%). Patients with ovarian cancer showed the next highest proportion (BRCA1, 4.86%; BRCA2, 3.42%). Frequency exceeding 1% was seen for several other cancer types (two cancer types for BRCA1, four cancer types for BRCA2). More than one cancer types was identified in 4,128 patients (6.3%). Carrier frequency of pathogenic variants in BRCA1 was 0.44% with one cancer type, 0.85% with two cancer types, and 0.69% with three cancer types. It was 0.97%, 1.40%, and 1.74%, respectively, in BRCA2.
“The results of this large-scale registry-based case-control study suggest that pathogenic variants in BRCA1 and BRCA2 were associated with the risk of seven cancer types. These results indicate broader clinical relevance of BRCA1 and BRCA2 genetic testing,” the authors wrote.
PARP inhibitors were developed based on the mechanism in BRCA1 and BRCA2 of homologous recombination repair defects associated with pathogenic variants. PARP inhibitors have been found to have therapeutic efficacy also in pathogenic variants found to be enriched in prostate and pancreatic cancers. While risk for additional cancer types (for example, biliary tract cancer, cervical cancer, colorectal cancer, endometrial cancer, esophageal cancer, and stomach cancer) has been reported after analyzing family members for the presence of pathogenic variants and performing case-control analyses, evidence for an association with these cancer types has not been considered sufficient for them to be adopted into clinical management guidelines, the authors wrote.
In an interview, Dr. Momozawa said that BRCA1 and BRCA2 genetic testing should be expanded in Japan. “But further studies are needed to reveal how much. If a clinical trial of a PARP inhibitor for these three cancer types reveals its clinical utility, the importance of this expansion will increase.”
Dr. Momozawa and associates state that while their selection of controls without a family history of cancer affects the generalizability of the study results, the estimated cumulative risks were comparable with those based on prospective cohorts, suggesting the study design did not greatly affect the results.
from prior analyses showing associations with breast, ovarian, prostate, and pancreatic cancers. The finding, published in JAMA Oncology suggests a possible broader clinical relevance for BRCA1 and BRCA2 genetic testing.
Pathogenic variants in BRCA1 were found to be associated with biliary tract cancer, in BRCA2 with esophageal cancer, and in BRCA1/2 with gastric cancer.
“The results suggest the range of cancer types associated with pathogenic variants in BRCA1 and BRCA2 is likely broader than that determined from previous analysis of largely European ancestry cohorts,” wrote authors who were led by Yukihide Momozawa, DVM, PhD, RIKEN Center for Integrative Medical Sciences, Japan.
“These risk association findings, together with our analysis of an association with family history of cancer and clinical phenotypes, are relevant for developing and adapting guidelines about genetic testing, treatment options, and treatability with PARP [poly adenosine diphosphate-ribose polymerase] inhibitors for each cancer type,” the authors wrote.
Dr. Momozawa and associates conducted a large-scale sequencing study across 14 common cancer types in 63,828 patients (mean age 64 years, 42% female) and 37,086 controls on data drawn from a Japanese nationwide biobank between April 2003 and March 2018. They estimated the risk of each cancer type and determined clinical characteristics associated with pathogenic variant carrier status, while also investigating the utility of family history in detecting patients with pathogenic variants.
Three hundred fifteen pathogenic variants were identified. An odds ratios of greater than 4.0 (with P < 1 × 10−4 as the threshold of significance) for the pathogenic variants were found for biliary tract cancer (OR, 17.4; 95% confidence interval, 5.8-51.9) in BRCA1, esophageal cancer (OR, 5.6; 95% CI, 2.9-11.0) in BRCA2, and gastric cancer (OR, 5.2; 95% CI, 2.6-10.5) in BRCA1, and (OR, 4.7; 95% CI, 3.1-7.1) in BRCA2. Two other cancer types were found to be associated with BRCA1, and four other cancer types with BRCA2. Enrichment of carrier patients was shown in biliary tract, female breast, ovarian, and prostate cancers in accordance with increased numbers of reported cancer types in relatives.
Male patients with breast cancer had a very high carrier frequency of pathogenic variants in BRCA2 (18.9%), but not BRCA1 (1.89%). Patients with ovarian cancer showed the next highest proportion (BRCA1, 4.86%; BRCA2, 3.42%). Frequency exceeding 1% was seen for several other cancer types (two cancer types for BRCA1, four cancer types for BRCA2). More than one cancer types was identified in 4,128 patients (6.3%). Carrier frequency of pathogenic variants in BRCA1 was 0.44% with one cancer type, 0.85% with two cancer types, and 0.69% with three cancer types. It was 0.97%, 1.40%, and 1.74%, respectively, in BRCA2.
“The results of this large-scale registry-based case-control study suggest that pathogenic variants in BRCA1 and BRCA2 were associated with the risk of seven cancer types. These results indicate broader clinical relevance of BRCA1 and BRCA2 genetic testing,” the authors wrote.
PARP inhibitors were developed based on the mechanism in BRCA1 and BRCA2 of homologous recombination repair defects associated with pathogenic variants. PARP inhibitors have been found to have therapeutic efficacy also in pathogenic variants found to be enriched in prostate and pancreatic cancers. While risk for additional cancer types (for example, biliary tract cancer, cervical cancer, colorectal cancer, endometrial cancer, esophageal cancer, and stomach cancer) has been reported after analyzing family members for the presence of pathogenic variants and performing case-control analyses, evidence for an association with these cancer types has not been considered sufficient for them to be adopted into clinical management guidelines, the authors wrote.
In an interview, Dr. Momozawa said that BRCA1 and BRCA2 genetic testing should be expanded in Japan. “But further studies are needed to reveal how much. If a clinical trial of a PARP inhibitor for these three cancer types reveals its clinical utility, the importance of this expansion will increase.”
Dr. Momozawa and associates state that while their selection of controls without a family history of cancer affects the generalizability of the study results, the estimated cumulative risks were comparable with those based on prospective cohorts, suggesting the study design did not greatly affect the results.
FROM JAMA ONCOLOGY
Quality of life benefit exaggerated in some cancer studies
, according to a study published in JAMA Oncology.
The study found trials that failed to show improved quality of life often reported their quality of life outcomes more favorably. Non–immunotherapy-targeted drugs were found to lead to worse quality of life outcomes more often than did cytotoxic agents. And, while there is an association between quality of life benefit and overall survival, no such association was found with progression-free survival.
“In this study, we evaluated the outcomes of cancer drug trials with regard to patients’ quality of life and found that only a quarter of phase 3 cancer drug trials in the advanced-disease setting demonstrated improved quality of life,” wrote authors who were led by Bishal Gyawali, MD, PhD, of the Cancer Research Institute, Queen’s University, Kingston, Ont.
“Improved quality of life outcomes were associated with improved overall survival but not with improved progression-free survival. Importantly, almost half of the cancer drugs drug trials that showed improved progression-free survival showed no improved overall survival or quality of life (i.e., PFS-only benefit). Some reports included conclusions regarding quality of life (QOL) findings that were not directly supported by the trial data, particularly for inferior or non–statistically significant QOL outcomes, thereby framing the findings in a favorable light or downplaying detrimental effects of the study intervention on QOL. Furthermore, contrary to common perception, inferior QOL outcomes were more common with targeted drugs than cytotoxic drugs. Taken together, these findings have important policy implications,” the authors wrote.
These findings are based on the results of a cohort study of 45 phase 3 research clinical trials of 24,806 patients. Only a small percentage of patients showed QOL benefits. The study found that industry-funded clinical trial reports often framed QOL findings more favorably than was warranted by the data.
The study found improved QOL with experimental agents in 11 of 45 randomized controlled trials (24.4%). Studies that reported improved QOL were more likely to also show improved overall survival as compared with trials in which quality of life was not improved (7 of 11 [64%] versus 10 of 34 [29%] trials). For improved progression-free survival, however, there was no positive association (6 of 11 [55%] trials versus 17 of 34 [50%] trials without improved QOL). Among six trials reporting worsening QOL, three (50%) were trials of targeted drugs. Among 11 trials reporting improved QOL, 6 (55%) were trials of immunotherapy drugs. Among the 34 trials in which QOL was not improved compared with controls, the findings were framed favorably (versus neutrally or negatively) in the abstract or conclusions in 16 (47%), an observation that was statistically significantly associated with industry funding (chi-squared = 6.35; P = .01).
“It is important to clearly understand and communicate the effects of cancer drugs”
To fulfill the obligation to inform patients about proposed treatments, the authors wrote that it is important to clearly understand and communicate the effects of cancer drugs on patient quality of life alongside their effects on overall survival and intermediate end points such as progression-free survival. “Patients with advanced cancer expect treatment to help them live longer or have better lives,” the authors wrote. In that respect, in clinical trials of cancer medicines, overall survival and quality of life are the most important measures. Toxicity profiles and disease progression delays do not reliably predict quality of life, and studies have shown poor correlations between quality of life, overall survival, and progression-free survival. This raises the question of validity of progression-free survival as a surrogate endpoint. “Progression-free survival is meaningless without overall survival or quality of life gains,” Dr. Gyawali said in an interview.
Writing in The Lancet Oncology in March, Dr. Gyawali stated that, because progression free survival “does not directly measure how a patient feels or functions, or how long a patient lives, progression-free survival was not intended to inform clinical practice or establish whether a new therapy provides clinically meaningful benefits for patients. However, over the past 2 decades, it has become the most common primary endpoint in oncology clinical trials. We are deeply worried about how the term survival in this phrase can influence clinical practice and patient choices. We propose replacing the phrase progression-free survival with a less ambiguous term: progression-free interval.”
In JAMA Oncology, Dr. Gyawali aimed to elucidate relationships between QOL, overall survival, and progression-free survival, and to assess, as well, how QOL results are framed, especially in industry-sponsored research. When drug trials they analyzed showed no change in QOL but reported that QOL did not worsen or QOL was maintained rather than stating that QOL did not improve, or if there was downplaying of worse QOL outcomes, the study had favorable interpretation, Dr. Gyawali and associates wrote. The expectation of patients receiving cancer drugs would be improved QOL rather than “not worse” QOL, Dr. Gyawali said.
Regarding the finding that QOL outcomes were described as favorable in 47% of trials with unimproved QOL outcomes, Dr. Gyawali said, “the bias in reporting should be corrected by the reviewers and editors of journals. Also, quality of life reporting should be made mandatory. Without unbiased quality of life information, informed decision making on whether or not to use a certain drug is impossible. Patients and physicians need to know that information. Regulators can demand that this should be mandatory in all trials in noncurative settings.”
He remarked further on the worsening QOL in some targeted drug trials, “People tout chemo-free regimens as automatically having better quality of life, but that doesn’t seem to be the case. Targeted drugs can have a severe impact on quality of life, probably due to prolonged duration of side effects. Quality of life should be measured and reported for all drugs.”
Dr. Gyawali and associates noted the limitation in that several studies with negative QOL results are not published at all or are published after a considerable delay, so the present observations may understate the issues that have been raised.
Dr. Gyawali declared that he received no funding and disclosed no conflicts of interest for this study.
, according to a study published in JAMA Oncology.
The study found trials that failed to show improved quality of life often reported their quality of life outcomes more favorably. Non–immunotherapy-targeted drugs were found to lead to worse quality of life outcomes more often than did cytotoxic agents. And, while there is an association between quality of life benefit and overall survival, no such association was found with progression-free survival.
“In this study, we evaluated the outcomes of cancer drug trials with regard to patients’ quality of life and found that only a quarter of phase 3 cancer drug trials in the advanced-disease setting demonstrated improved quality of life,” wrote authors who were led by Bishal Gyawali, MD, PhD, of the Cancer Research Institute, Queen’s University, Kingston, Ont.
“Improved quality of life outcomes were associated with improved overall survival but not with improved progression-free survival. Importantly, almost half of the cancer drugs drug trials that showed improved progression-free survival showed no improved overall survival or quality of life (i.e., PFS-only benefit). Some reports included conclusions regarding quality of life (QOL) findings that were not directly supported by the trial data, particularly for inferior or non–statistically significant QOL outcomes, thereby framing the findings in a favorable light or downplaying detrimental effects of the study intervention on QOL. Furthermore, contrary to common perception, inferior QOL outcomes were more common with targeted drugs than cytotoxic drugs. Taken together, these findings have important policy implications,” the authors wrote.
These findings are based on the results of a cohort study of 45 phase 3 research clinical trials of 24,806 patients. Only a small percentage of patients showed QOL benefits. The study found that industry-funded clinical trial reports often framed QOL findings more favorably than was warranted by the data.
The study found improved QOL with experimental agents in 11 of 45 randomized controlled trials (24.4%). Studies that reported improved QOL were more likely to also show improved overall survival as compared with trials in which quality of life was not improved (7 of 11 [64%] versus 10 of 34 [29%] trials). For improved progression-free survival, however, there was no positive association (6 of 11 [55%] trials versus 17 of 34 [50%] trials without improved QOL). Among six trials reporting worsening QOL, three (50%) were trials of targeted drugs. Among 11 trials reporting improved QOL, 6 (55%) were trials of immunotherapy drugs. Among the 34 trials in which QOL was not improved compared with controls, the findings were framed favorably (versus neutrally or negatively) in the abstract or conclusions in 16 (47%), an observation that was statistically significantly associated with industry funding (chi-squared = 6.35; P = .01).
“It is important to clearly understand and communicate the effects of cancer drugs”
To fulfill the obligation to inform patients about proposed treatments, the authors wrote that it is important to clearly understand and communicate the effects of cancer drugs on patient quality of life alongside their effects on overall survival and intermediate end points such as progression-free survival. “Patients with advanced cancer expect treatment to help them live longer or have better lives,” the authors wrote. In that respect, in clinical trials of cancer medicines, overall survival and quality of life are the most important measures. Toxicity profiles and disease progression delays do not reliably predict quality of life, and studies have shown poor correlations between quality of life, overall survival, and progression-free survival. This raises the question of validity of progression-free survival as a surrogate endpoint. “Progression-free survival is meaningless without overall survival or quality of life gains,” Dr. Gyawali said in an interview.
Writing in The Lancet Oncology in March, Dr. Gyawali stated that, because progression free survival “does not directly measure how a patient feels or functions, or how long a patient lives, progression-free survival was not intended to inform clinical practice or establish whether a new therapy provides clinically meaningful benefits for patients. However, over the past 2 decades, it has become the most common primary endpoint in oncology clinical trials. We are deeply worried about how the term survival in this phrase can influence clinical practice and patient choices. We propose replacing the phrase progression-free survival with a less ambiguous term: progression-free interval.”
In JAMA Oncology, Dr. Gyawali aimed to elucidate relationships between QOL, overall survival, and progression-free survival, and to assess, as well, how QOL results are framed, especially in industry-sponsored research. When drug trials they analyzed showed no change in QOL but reported that QOL did not worsen or QOL was maintained rather than stating that QOL did not improve, or if there was downplaying of worse QOL outcomes, the study had favorable interpretation, Dr. Gyawali and associates wrote. The expectation of patients receiving cancer drugs would be improved QOL rather than “not worse” QOL, Dr. Gyawali said.
Regarding the finding that QOL outcomes were described as favorable in 47% of trials with unimproved QOL outcomes, Dr. Gyawali said, “the bias in reporting should be corrected by the reviewers and editors of journals. Also, quality of life reporting should be made mandatory. Without unbiased quality of life information, informed decision making on whether or not to use a certain drug is impossible. Patients and physicians need to know that information. Regulators can demand that this should be mandatory in all trials in noncurative settings.”
He remarked further on the worsening QOL in some targeted drug trials, “People tout chemo-free regimens as automatically having better quality of life, but that doesn’t seem to be the case. Targeted drugs can have a severe impact on quality of life, probably due to prolonged duration of side effects. Quality of life should be measured and reported for all drugs.”
Dr. Gyawali and associates noted the limitation in that several studies with negative QOL results are not published at all or are published after a considerable delay, so the present observations may understate the issues that have been raised.
Dr. Gyawali declared that he received no funding and disclosed no conflicts of interest for this study.
, according to a study published in JAMA Oncology.
The study found trials that failed to show improved quality of life often reported their quality of life outcomes more favorably. Non–immunotherapy-targeted drugs were found to lead to worse quality of life outcomes more often than did cytotoxic agents. And, while there is an association between quality of life benefit and overall survival, no such association was found with progression-free survival.
“In this study, we evaluated the outcomes of cancer drug trials with regard to patients’ quality of life and found that only a quarter of phase 3 cancer drug trials in the advanced-disease setting demonstrated improved quality of life,” wrote authors who were led by Bishal Gyawali, MD, PhD, of the Cancer Research Institute, Queen’s University, Kingston, Ont.
“Improved quality of life outcomes were associated with improved overall survival but not with improved progression-free survival. Importantly, almost half of the cancer drugs drug trials that showed improved progression-free survival showed no improved overall survival or quality of life (i.e., PFS-only benefit). Some reports included conclusions regarding quality of life (QOL) findings that were not directly supported by the trial data, particularly for inferior or non–statistically significant QOL outcomes, thereby framing the findings in a favorable light or downplaying detrimental effects of the study intervention on QOL. Furthermore, contrary to common perception, inferior QOL outcomes were more common with targeted drugs than cytotoxic drugs. Taken together, these findings have important policy implications,” the authors wrote.
These findings are based on the results of a cohort study of 45 phase 3 research clinical trials of 24,806 patients. Only a small percentage of patients showed QOL benefits. The study found that industry-funded clinical trial reports often framed QOL findings more favorably than was warranted by the data.
The study found improved QOL with experimental agents in 11 of 45 randomized controlled trials (24.4%). Studies that reported improved QOL were more likely to also show improved overall survival as compared with trials in which quality of life was not improved (7 of 11 [64%] versus 10 of 34 [29%] trials). For improved progression-free survival, however, there was no positive association (6 of 11 [55%] trials versus 17 of 34 [50%] trials without improved QOL). Among six trials reporting worsening QOL, three (50%) were trials of targeted drugs. Among 11 trials reporting improved QOL, 6 (55%) were trials of immunotherapy drugs. Among the 34 trials in which QOL was not improved compared with controls, the findings were framed favorably (versus neutrally or negatively) in the abstract or conclusions in 16 (47%), an observation that was statistically significantly associated with industry funding (chi-squared = 6.35; P = .01).
“It is important to clearly understand and communicate the effects of cancer drugs”
To fulfill the obligation to inform patients about proposed treatments, the authors wrote that it is important to clearly understand and communicate the effects of cancer drugs on patient quality of life alongside their effects on overall survival and intermediate end points such as progression-free survival. “Patients with advanced cancer expect treatment to help them live longer or have better lives,” the authors wrote. In that respect, in clinical trials of cancer medicines, overall survival and quality of life are the most important measures. Toxicity profiles and disease progression delays do not reliably predict quality of life, and studies have shown poor correlations between quality of life, overall survival, and progression-free survival. This raises the question of validity of progression-free survival as a surrogate endpoint. “Progression-free survival is meaningless without overall survival or quality of life gains,” Dr. Gyawali said in an interview.
Writing in The Lancet Oncology in March, Dr. Gyawali stated that, because progression free survival “does not directly measure how a patient feels or functions, or how long a patient lives, progression-free survival was not intended to inform clinical practice or establish whether a new therapy provides clinically meaningful benefits for patients. However, over the past 2 decades, it has become the most common primary endpoint in oncology clinical trials. We are deeply worried about how the term survival in this phrase can influence clinical practice and patient choices. We propose replacing the phrase progression-free survival with a less ambiguous term: progression-free interval.”
In JAMA Oncology, Dr. Gyawali aimed to elucidate relationships between QOL, overall survival, and progression-free survival, and to assess, as well, how QOL results are framed, especially in industry-sponsored research. When drug trials they analyzed showed no change in QOL but reported that QOL did not worsen or QOL was maintained rather than stating that QOL did not improve, or if there was downplaying of worse QOL outcomes, the study had favorable interpretation, Dr. Gyawali and associates wrote. The expectation of patients receiving cancer drugs would be improved QOL rather than “not worse” QOL, Dr. Gyawali said.
Regarding the finding that QOL outcomes were described as favorable in 47% of trials with unimproved QOL outcomes, Dr. Gyawali said, “the bias in reporting should be corrected by the reviewers and editors of journals. Also, quality of life reporting should be made mandatory. Without unbiased quality of life information, informed decision making on whether or not to use a certain drug is impossible. Patients and physicians need to know that information. Regulators can demand that this should be mandatory in all trials in noncurative settings.”
He remarked further on the worsening QOL in some targeted drug trials, “People tout chemo-free regimens as automatically having better quality of life, but that doesn’t seem to be the case. Targeted drugs can have a severe impact on quality of life, probably due to prolonged duration of side effects. Quality of life should be measured and reported for all drugs.”
Dr. Gyawali and associates noted the limitation in that several studies with negative QOL results are not published at all or are published after a considerable delay, so the present observations may understate the issues that have been raised.
Dr. Gyawali declared that he received no funding and disclosed no conflicts of interest for this study.
FROM JAMA ONCOLOGY