User login
FDA to allow alternative respiratory devices to treat COVID-19
“Whenever possible, health care facilities should use FDA-cleared conventional/standard full-featured ventilators when necessary to support patients with respiratory failure, or a device subject to an Emergency Use Authorization (EUA), if any,” FDA stated in a guidance document issued March 22.
“However, to help ensure the availability of the greatest possible number of devices for this purpose, ... FDA does not intend to object to limited modifications to indications, claims, functionality, or to the hardware, software, or materials of FDA-cleared devices used to support patients with respiratory failure or respiratory insufficiency, without prior submission of a premarket notification” for the duration of the declared national emergency related to the COVID-19 pandemic.
FDA Commissioner Stephen Hahn, MD, said in a statement that the agency is doing everything it can to support patients, health care professionals, and others during this pandemic.
“One of the most impactful steps we can take is to help with access and availability to life-saving medical treatments,” he said. “Our policy issued today demonstrates our ability to react and adapt quickly during this pandemic and help very ill patients access the lifesaving ventilator support they need. To do that, we are providing maximum regulatory flexibility to facilitate an increase in ventilator inventory, while still providing crucial FDA oversight. We believe this action will immediately increase ventilator availability.”
The document identified examples of where modifications would not create undue risk, including the use of powered emergency ventilators and anesthesia gas machines for patients needing mechanical ventilation; the use of ventilators outside of their cleared environment; the use of devices used to treat patients with sleep apnea, such as CPAPs and BiPAPs, to treat respiratory insufficiency when appropriate design mitigations are in place to minimize aerosolization; and the use of oxygen concentrators for primary supply when medically necessary and clinically appropriate.
The agency also is allowing for changes to the hardware, software, and materials to FDA-cleared ventilators and anesthesia gas machines, such as modifications to motors, batteries, or other electrical components; material changes to components in the gas pathways or with other patient tissue contact; the introduction of filtration to minimize aerosolization; and other hardware and software modifications.
FDA is also allowing for products to be used past their indicated shelf life.
“Whenever possible, health care facilities should use FDA-cleared conventional/standard full-featured ventilators when necessary to support patients with respiratory failure, or a device subject to an Emergency Use Authorization (EUA), if any,” FDA stated in a guidance document issued March 22.
“However, to help ensure the availability of the greatest possible number of devices for this purpose, ... FDA does not intend to object to limited modifications to indications, claims, functionality, or to the hardware, software, or materials of FDA-cleared devices used to support patients with respiratory failure or respiratory insufficiency, without prior submission of a premarket notification” for the duration of the declared national emergency related to the COVID-19 pandemic.
FDA Commissioner Stephen Hahn, MD, said in a statement that the agency is doing everything it can to support patients, health care professionals, and others during this pandemic.
“One of the most impactful steps we can take is to help with access and availability to life-saving medical treatments,” he said. “Our policy issued today demonstrates our ability to react and adapt quickly during this pandemic and help very ill patients access the lifesaving ventilator support they need. To do that, we are providing maximum regulatory flexibility to facilitate an increase in ventilator inventory, while still providing crucial FDA oversight. We believe this action will immediately increase ventilator availability.”
The document identified examples of where modifications would not create undue risk, including the use of powered emergency ventilators and anesthesia gas machines for patients needing mechanical ventilation; the use of ventilators outside of their cleared environment; the use of devices used to treat patients with sleep apnea, such as CPAPs and BiPAPs, to treat respiratory insufficiency when appropriate design mitigations are in place to minimize aerosolization; and the use of oxygen concentrators for primary supply when medically necessary and clinically appropriate.
The agency also is allowing for changes to the hardware, software, and materials to FDA-cleared ventilators and anesthesia gas machines, such as modifications to motors, batteries, or other electrical components; material changes to components in the gas pathways or with other patient tissue contact; the introduction of filtration to minimize aerosolization; and other hardware and software modifications.
FDA is also allowing for products to be used past their indicated shelf life.
“Whenever possible, health care facilities should use FDA-cleared conventional/standard full-featured ventilators when necessary to support patients with respiratory failure, or a device subject to an Emergency Use Authorization (EUA), if any,” FDA stated in a guidance document issued March 22.
“However, to help ensure the availability of the greatest possible number of devices for this purpose, ... FDA does not intend to object to limited modifications to indications, claims, functionality, or to the hardware, software, or materials of FDA-cleared devices used to support patients with respiratory failure or respiratory insufficiency, without prior submission of a premarket notification” for the duration of the declared national emergency related to the COVID-19 pandemic.
FDA Commissioner Stephen Hahn, MD, said in a statement that the agency is doing everything it can to support patients, health care professionals, and others during this pandemic.
“One of the most impactful steps we can take is to help with access and availability to life-saving medical treatments,” he said. “Our policy issued today demonstrates our ability to react and adapt quickly during this pandemic and help very ill patients access the lifesaving ventilator support they need. To do that, we are providing maximum regulatory flexibility to facilitate an increase in ventilator inventory, while still providing crucial FDA oversight. We believe this action will immediately increase ventilator availability.”
The document identified examples of where modifications would not create undue risk, including the use of powered emergency ventilators and anesthesia gas machines for patients needing mechanical ventilation; the use of ventilators outside of their cleared environment; the use of devices used to treat patients with sleep apnea, such as CPAPs and BiPAPs, to treat respiratory insufficiency when appropriate design mitigations are in place to minimize aerosolization; and the use of oxygen concentrators for primary supply when medically necessary and clinically appropriate.
The agency also is allowing for changes to the hardware, software, and materials to FDA-cleared ventilators and anesthesia gas machines, such as modifications to motors, batteries, or other electrical components; material changes to components in the gas pathways or with other patient tissue contact; the introduction of filtration to minimize aerosolization; and other hardware and software modifications.
FDA is also allowing for products to be used past their indicated shelf life.
Tribes Outperform Federal Government in COVID-19 Response
Several days ago, Rodney Bordeaux, president of the Rosebud Sioux Tribe in South Dakota, sent a strongly worded SOS to the directors of the World Health Organization and the Pan American Health Organization about COVID-19, saying, “We have approximately 30,000 tribal members living in south central South Dakota with access to fewer than 200 beds within our reservation.”
Not only were beds woefully inadequate to the needs of potential COVID-19 victims, but tests to find out who might need the beds also were lacking. “We believe that some kits have been sent to the states,” Bordeaux wrote, “but it is the states that have been determining who gets a test and who does not.”
In Michigan, Aaron Payment, chair of the Sault Ste. Marie Tribe of Chippewa Indians, told the Native America Calling radio show, “We’re the largest tribe east of the Mississippi, and we have two test kits.”
The “chronically underfunded” Indian Health Service (IHS) was underprepared for handling virus response, Melissa Riley, PhD, executive director of Indigenous Women Rising, charged in a March 24 opinion piece in Rewire News. “If IHS can barely keep up with broken bones and preventive care,” she wrote, “what makes our people across the country think IHS can handle the outbreak of COVID-19?”
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) does not break down data on cases according to race or ethnicity, but according to the IHS website, 42 people in the agency’s jurisdiction had tested positive for COVID-19 as of Mar. 24. Of those, 29 were in Navajo Country. By the evening of that day, according to Native News Online, the number of Navajos testing positive had risen to 49. Given the often-invisible spread of the virus, many more are likely to be infected.
The IHS website directs visitors to visit CDC pages for more information. However, these pages do not provide information “in a culturally literate and responsive manner,” Riley says, that explain ways to stay indoors, nor do they offer contacts for indigenous people—despite the fact, she adds, that on the West Coast they were among the first to contract the virus and to reach out with questions.
For its part, the IHS has said it “continues to work closely with our tribal partners to coordinate a comprehensive public health response to COVID-19,” holding weekly conference calls with tribal and urban Indian health organization leaders to “provide updates, answer questions, and hear concerns.” It also is in constant contact with the White House and the CDC, IHS says. IHS facilities “generally” have access to testing for individuals who may have COVID-19, the website says: However, “there are nationwide shortages of materials that may temporarily affect the availability of COVID-19 testing at a particular location.” Tribes, the website recommends, should first follow their usual process for ordering supplies. If they can’t access supplies, they should contact their IHS Area Office, which can access supplies through the IH National Supply Service Center.
Bordeaux, Payment, and Riley are not alone in their criticisms and concerns. Native Americans and Alaska Natives were hit disproportionately during the 2009 H1N1 influenza pandemic: The death rate was 4 times higher than in all other racial and ethnic groups combined. The NIH says AI/ANs are particularly vulnerable to epidemic infections, due to poverty, underlying chronic illnesses (including asthma), and delayed access to care.
Tribes began taking steps early on to protect their members, even before the federal and state governments began requiring such measures. Lummi Nation leaders, in the Pacific Northwest, for instance, began preparing when the virus first appeared in Wuhan in late 2019, according to an article in The Guardian, and declared a state of emergency on March 3—10 days before President Trump did.
The tribe has been “beefing up” emergency plans, reorganizing services, and gathering medical supplies. It also approved $1 million for emergency response, including repurposing a community fitness center into a field hospital. “We quickly recognized the need to make sacrifices for the greater good, in order to protect our people and the wider community,” Dr. Dakotah Lane, medical director of the tribal health service, said in the Guardian interview.
On March 17, the Navajo Nation shut down its 4 casinos after an Arizona tribe member was diagnosed with the virus. President Jonathan Nez says the tribe stands to lose $3 million to $5 million in revenue. But “[t]he health and well-being of our Navajo people is of utmost importance and not just profit,” Nez said in a Navajo Times interview.
In the meantime, bending to pressure from Rep. Deb Haaland (D-NM) and “a handful” of other lawmakers, according to an article in The Guardian, Congress designated $40 million for tribal health and Urban Indian Health organizations as part of the emergency federal relief legislation.
While the states received the emergency funds immediately, the CDC disburses the money to tribes, who have yet to receive any. Haaland, the first Native American woman elected to Congress, says the tribes needed the money “yesterday.”
Several days ago, Rodney Bordeaux, president of the Rosebud Sioux Tribe in South Dakota, sent a strongly worded SOS to the directors of the World Health Organization and the Pan American Health Organization about COVID-19, saying, “We have approximately 30,000 tribal members living in south central South Dakota with access to fewer than 200 beds within our reservation.”
Not only were beds woefully inadequate to the needs of potential COVID-19 victims, but tests to find out who might need the beds also were lacking. “We believe that some kits have been sent to the states,” Bordeaux wrote, “but it is the states that have been determining who gets a test and who does not.”
In Michigan, Aaron Payment, chair of the Sault Ste. Marie Tribe of Chippewa Indians, told the Native America Calling radio show, “We’re the largest tribe east of the Mississippi, and we have two test kits.”
The “chronically underfunded” Indian Health Service (IHS) was underprepared for handling virus response, Melissa Riley, PhD, executive director of Indigenous Women Rising, charged in a March 24 opinion piece in Rewire News. “If IHS can barely keep up with broken bones and preventive care,” she wrote, “what makes our people across the country think IHS can handle the outbreak of COVID-19?”
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) does not break down data on cases according to race or ethnicity, but according to the IHS website, 42 people in the agency’s jurisdiction had tested positive for COVID-19 as of Mar. 24. Of those, 29 were in Navajo Country. By the evening of that day, according to Native News Online, the number of Navajos testing positive had risen to 49. Given the often-invisible spread of the virus, many more are likely to be infected.
The IHS website directs visitors to visit CDC pages for more information. However, these pages do not provide information “in a culturally literate and responsive manner,” Riley says, that explain ways to stay indoors, nor do they offer contacts for indigenous people—despite the fact, she adds, that on the West Coast they were among the first to contract the virus and to reach out with questions.
For its part, the IHS has said it “continues to work closely with our tribal partners to coordinate a comprehensive public health response to COVID-19,” holding weekly conference calls with tribal and urban Indian health organization leaders to “provide updates, answer questions, and hear concerns.” It also is in constant contact with the White House and the CDC, IHS says. IHS facilities “generally” have access to testing for individuals who may have COVID-19, the website says: However, “there are nationwide shortages of materials that may temporarily affect the availability of COVID-19 testing at a particular location.” Tribes, the website recommends, should first follow their usual process for ordering supplies. If they can’t access supplies, they should contact their IHS Area Office, which can access supplies through the IH National Supply Service Center.
Bordeaux, Payment, and Riley are not alone in their criticisms and concerns. Native Americans and Alaska Natives were hit disproportionately during the 2009 H1N1 influenza pandemic: The death rate was 4 times higher than in all other racial and ethnic groups combined. The NIH says AI/ANs are particularly vulnerable to epidemic infections, due to poverty, underlying chronic illnesses (including asthma), and delayed access to care.
Tribes began taking steps early on to protect their members, even before the federal and state governments began requiring such measures. Lummi Nation leaders, in the Pacific Northwest, for instance, began preparing when the virus first appeared in Wuhan in late 2019, according to an article in The Guardian, and declared a state of emergency on March 3—10 days before President Trump did.
The tribe has been “beefing up” emergency plans, reorganizing services, and gathering medical supplies. It also approved $1 million for emergency response, including repurposing a community fitness center into a field hospital. “We quickly recognized the need to make sacrifices for the greater good, in order to protect our people and the wider community,” Dr. Dakotah Lane, medical director of the tribal health service, said in the Guardian interview.
On March 17, the Navajo Nation shut down its 4 casinos after an Arizona tribe member was diagnosed with the virus. President Jonathan Nez says the tribe stands to lose $3 million to $5 million in revenue. But “[t]he health and well-being of our Navajo people is of utmost importance and not just profit,” Nez said in a Navajo Times interview.
In the meantime, bending to pressure from Rep. Deb Haaland (D-NM) and “a handful” of other lawmakers, according to an article in The Guardian, Congress designated $40 million for tribal health and Urban Indian Health organizations as part of the emergency federal relief legislation.
While the states received the emergency funds immediately, the CDC disburses the money to tribes, who have yet to receive any. Haaland, the first Native American woman elected to Congress, says the tribes needed the money “yesterday.”
Several days ago, Rodney Bordeaux, president of the Rosebud Sioux Tribe in South Dakota, sent a strongly worded SOS to the directors of the World Health Organization and the Pan American Health Organization about COVID-19, saying, “We have approximately 30,000 tribal members living in south central South Dakota with access to fewer than 200 beds within our reservation.”
Not only were beds woefully inadequate to the needs of potential COVID-19 victims, but tests to find out who might need the beds also were lacking. “We believe that some kits have been sent to the states,” Bordeaux wrote, “but it is the states that have been determining who gets a test and who does not.”
In Michigan, Aaron Payment, chair of the Sault Ste. Marie Tribe of Chippewa Indians, told the Native America Calling radio show, “We’re the largest tribe east of the Mississippi, and we have two test kits.”
The “chronically underfunded” Indian Health Service (IHS) was underprepared for handling virus response, Melissa Riley, PhD, executive director of Indigenous Women Rising, charged in a March 24 opinion piece in Rewire News. “If IHS can barely keep up with broken bones and preventive care,” she wrote, “what makes our people across the country think IHS can handle the outbreak of COVID-19?”
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) does not break down data on cases according to race or ethnicity, but according to the IHS website, 42 people in the agency’s jurisdiction had tested positive for COVID-19 as of Mar. 24. Of those, 29 were in Navajo Country. By the evening of that day, according to Native News Online, the number of Navajos testing positive had risen to 49. Given the often-invisible spread of the virus, many more are likely to be infected.
The IHS website directs visitors to visit CDC pages for more information. However, these pages do not provide information “in a culturally literate and responsive manner,” Riley says, that explain ways to stay indoors, nor do they offer contacts for indigenous people—despite the fact, she adds, that on the West Coast they were among the first to contract the virus and to reach out with questions.
For its part, the IHS has said it “continues to work closely with our tribal partners to coordinate a comprehensive public health response to COVID-19,” holding weekly conference calls with tribal and urban Indian health organization leaders to “provide updates, answer questions, and hear concerns.” It also is in constant contact with the White House and the CDC, IHS says. IHS facilities “generally” have access to testing for individuals who may have COVID-19, the website says: However, “there are nationwide shortages of materials that may temporarily affect the availability of COVID-19 testing at a particular location.” Tribes, the website recommends, should first follow their usual process for ordering supplies. If they can’t access supplies, they should contact their IHS Area Office, which can access supplies through the IH National Supply Service Center.
Bordeaux, Payment, and Riley are not alone in their criticisms and concerns. Native Americans and Alaska Natives were hit disproportionately during the 2009 H1N1 influenza pandemic: The death rate was 4 times higher than in all other racial and ethnic groups combined. The NIH says AI/ANs are particularly vulnerable to epidemic infections, due to poverty, underlying chronic illnesses (including asthma), and delayed access to care.
Tribes began taking steps early on to protect their members, even before the federal and state governments began requiring such measures. Lummi Nation leaders, in the Pacific Northwest, for instance, began preparing when the virus first appeared in Wuhan in late 2019, according to an article in The Guardian, and declared a state of emergency on March 3—10 days before President Trump did.
The tribe has been “beefing up” emergency plans, reorganizing services, and gathering medical supplies. It also approved $1 million for emergency response, including repurposing a community fitness center into a field hospital. “We quickly recognized the need to make sacrifices for the greater good, in order to protect our people and the wider community,” Dr. Dakotah Lane, medical director of the tribal health service, said in the Guardian interview.
On March 17, the Navajo Nation shut down its 4 casinos after an Arizona tribe member was diagnosed with the virus. President Jonathan Nez says the tribe stands to lose $3 million to $5 million in revenue. But “[t]he health and well-being of our Navajo people is of utmost importance and not just profit,” Nez said in a Navajo Times interview.
In the meantime, bending to pressure from Rep. Deb Haaland (D-NM) and “a handful” of other lawmakers, according to an article in The Guardian, Congress designated $40 million for tribal health and Urban Indian Health organizations as part of the emergency federal relief legislation.
While the states received the emergency funds immediately, the CDC disburses the money to tribes, who have yet to receive any. Haaland, the first Native American woman elected to Congress, says the tribes needed the money “yesterday.”
Three COVID-19 rapid diagnostic tests get FDA thumbs-up
The first authorization, announced by the agency on March 21, was for the Xpert Xpress SARS-CoV-2 test, a rapid molecular diagnostic test for qualitative detection of SARS-CoV-2, the virus causing COVID-19.
The test, manufactured by Cepheid, has a detection time of 45 minutes and has been designed to operate on any of the company’s more than 23,000 automated GeneXpert Systems worldwide, according to a statement from the company.
The agency said in its EUA approval document the test is for a “qualitative detection of nucleic acid from the SARS-CoV-2 in nasopharyngeal swab and/or nasal wash/aspirate specimens collected from patients who are suspected of having COVID-19 infection.” Positive results are indicative of an infection but do not rule out other potential infections, it noted.
The company plans to roll out the test by March 30, according to the FDA.
Cepheid said in a statement that it has almost 5,000 GeneXpert systems in the United States that are capable of point-of-care testing and ready for use in hospitals. “Our automated systems do not require users to have specialty training to perform testing – they are capable of running 24/7, with many systems already doing so today,” Warren Kocmond, the company’s president, said in the statement.
FDA Commissioner Stephen Hahn, MD said in a statement that the authorization marked “an important step in expanding the availability of testing and, importantly, rapid results. Point-of-care testing means that results are delivered to the patient in the patient-care settings, like hospitals, urgent care centers, and emergency rooms, instead of samples being sent to a laboratory. With today’s authorization, there is now an option for testing at the point of care, which enables patient access to more immediate results.”
On March 23, the agency issued an emergency use authorization to bioMerieux subsidiary BioFire Defense LLC for its BIOFIRE COVID-19 test, which detects SARS-CoV-2 from a nasopharyngeal swab in about 45 minutes.
The test was developed with funding from the U.S. Department of Defense.
“Positive results are indicative of the presence of SARS-CoV-2 RNA; clinical correlation with patient history and other diagnostic information is necessary to determine patient infection status,” the agency said in its approval document. It again noted that positive results did not rule out bacterial infection or coinfection with other viruses.
Also on March 23, the agency issued an EUA to Mesa Biotech for its Accula SARS-CoV-2 test, which gives COVID-19 diagnostic results in 30 minutes.
The test is indicated for “qualitative, visual detection of nucleic acid from the SARS-CoV-2 in throat swab and nasal swab specimens combined, collected from patients suspected of COVID-19 by their health care provider,” according to the FDA approval document. “The SARS-CoV-2 nucleic acid is generally detectable in throat and nasal swab specimens during the acute phase of infection. Positive results are indicative of the presence of SARS-CoV-2 nucleic acid; clinical correlation with patient history and other diagnostic information is necessary to determine patient infection status. Positive results do not rule out bacterial infection or coinfection with other viruses.”
Mesa Biotech said in a statement that the test is designed for point-of-care use, including at temporary screening facilities, physician office labs, urgent care, and long-term nursing facilities.
“Our test will provide a highly accessible means for health care professionals to access laboratory quality results close in their office to aid in the decision to isolate, treat, or dismiss potential carriers of the virus,” Hong Cai, the CEO and cofounder of Mesa Biotech, said in a statement. “The potential to reduce the growing strain on our nation’s hospitals is tremendous.”
In separate letters to the three companies notifying them of the authorizations, the FDA said the emergency use of the products met the criteria for issuances of authorization because the SARS-CoV-2 can cause a serious or life-threatening disease or condition; it was “reasonable to believe
that [the] product may be effective in diagnosing COVID-19; and there is no “adequate, approved, and available alternative” to the emergency use of the three products.
The first authorization, announced by the agency on March 21, was for the Xpert Xpress SARS-CoV-2 test, a rapid molecular diagnostic test for qualitative detection of SARS-CoV-2, the virus causing COVID-19.
The test, manufactured by Cepheid, has a detection time of 45 minutes and has been designed to operate on any of the company’s more than 23,000 automated GeneXpert Systems worldwide, according to a statement from the company.
The agency said in its EUA approval document the test is for a “qualitative detection of nucleic acid from the SARS-CoV-2 in nasopharyngeal swab and/or nasal wash/aspirate specimens collected from patients who are suspected of having COVID-19 infection.” Positive results are indicative of an infection but do not rule out other potential infections, it noted.
The company plans to roll out the test by March 30, according to the FDA.
Cepheid said in a statement that it has almost 5,000 GeneXpert systems in the United States that are capable of point-of-care testing and ready for use in hospitals. “Our automated systems do not require users to have specialty training to perform testing – they are capable of running 24/7, with many systems already doing so today,” Warren Kocmond, the company’s president, said in the statement.
FDA Commissioner Stephen Hahn, MD said in a statement that the authorization marked “an important step in expanding the availability of testing and, importantly, rapid results. Point-of-care testing means that results are delivered to the patient in the patient-care settings, like hospitals, urgent care centers, and emergency rooms, instead of samples being sent to a laboratory. With today’s authorization, there is now an option for testing at the point of care, which enables patient access to more immediate results.”
On March 23, the agency issued an emergency use authorization to bioMerieux subsidiary BioFire Defense LLC for its BIOFIRE COVID-19 test, which detects SARS-CoV-2 from a nasopharyngeal swab in about 45 minutes.
The test was developed with funding from the U.S. Department of Defense.
“Positive results are indicative of the presence of SARS-CoV-2 RNA; clinical correlation with patient history and other diagnostic information is necessary to determine patient infection status,” the agency said in its approval document. It again noted that positive results did not rule out bacterial infection or coinfection with other viruses.
Also on March 23, the agency issued an EUA to Mesa Biotech for its Accula SARS-CoV-2 test, which gives COVID-19 diagnostic results in 30 minutes.
The test is indicated for “qualitative, visual detection of nucleic acid from the SARS-CoV-2 in throat swab and nasal swab specimens combined, collected from patients suspected of COVID-19 by their health care provider,” according to the FDA approval document. “The SARS-CoV-2 nucleic acid is generally detectable in throat and nasal swab specimens during the acute phase of infection. Positive results are indicative of the presence of SARS-CoV-2 nucleic acid; clinical correlation with patient history and other diagnostic information is necessary to determine patient infection status. Positive results do not rule out bacterial infection or coinfection with other viruses.”
Mesa Biotech said in a statement that the test is designed for point-of-care use, including at temporary screening facilities, physician office labs, urgent care, and long-term nursing facilities.
“Our test will provide a highly accessible means for health care professionals to access laboratory quality results close in their office to aid in the decision to isolate, treat, or dismiss potential carriers of the virus,” Hong Cai, the CEO and cofounder of Mesa Biotech, said in a statement. “The potential to reduce the growing strain on our nation’s hospitals is tremendous.”
In separate letters to the three companies notifying them of the authorizations, the FDA said the emergency use of the products met the criteria for issuances of authorization because the SARS-CoV-2 can cause a serious or life-threatening disease or condition; it was “reasonable to believe
that [the] product may be effective in diagnosing COVID-19; and there is no “adequate, approved, and available alternative” to the emergency use of the three products.
The first authorization, announced by the agency on March 21, was for the Xpert Xpress SARS-CoV-2 test, a rapid molecular diagnostic test for qualitative detection of SARS-CoV-2, the virus causing COVID-19.
The test, manufactured by Cepheid, has a detection time of 45 minutes and has been designed to operate on any of the company’s more than 23,000 automated GeneXpert Systems worldwide, according to a statement from the company.
The agency said in its EUA approval document the test is for a “qualitative detection of nucleic acid from the SARS-CoV-2 in nasopharyngeal swab and/or nasal wash/aspirate specimens collected from patients who are suspected of having COVID-19 infection.” Positive results are indicative of an infection but do not rule out other potential infections, it noted.
The company plans to roll out the test by March 30, according to the FDA.
Cepheid said in a statement that it has almost 5,000 GeneXpert systems in the United States that are capable of point-of-care testing and ready for use in hospitals. “Our automated systems do not require users to have specialty training to perform testing – they are capable of running 24/7, with many systems already doing so today,” Warren Kocmond, the company’s president, said in the statement.
FDA Commissioner Stephen Hahn, MD said in a statement that the authorization marked “an important step in expanding the availability of testing and, importantly, rapid results. Point-of-care testing means that results are delivered to the patient in the patient-care settings, like hospitals, urgent care centers, and emergency rooms, instead of samples being sent to a laboratory. With today’s authorization, there is now an option for testing at the point of care, which enables patient access to more immediate results.”
On March 23, the agency issued an emergency use authorization to bioMerieux subsidiary BioFire Defense LLC for its BIOFIRE COVID-19 test, which detects SARS-CoV-2 from a nasopharyngeal swab in about 45 minutes.
The test was developed with funding from the U.S. Department of Defense.
“Positive results are indicative of the presence of SARS-CoV-2 RNA; clinical correlation with patient history and other diagnostic information is necessary to determine patient infection status,” the agency said in its approval document. It again noted that positive results did not rule out bacterial infection or coinfection with other viruses.
Also on March 23, the agency issued an EUA to Mesa Biotech for its Accula SARS-CoV-2 test, which gives COVID-19 diagnostic results in 30 minutes.
The test is indicated for “qualitative, visual detection of nucleic acid from the SARS-CoV-2 in throat swab and nasal swab specimens combined, collected from patients suspected of COVID-19 by their health care provider,” according to the FDA approval document. “The SARS-CoV-2 nucleic acid is generally detectable in throat and nasal swab specimens during the acute phase of infection. Positive results are indicative of the presence of SARS-CoV-2 nucleic acid; clinical correlation with patient history and other diagnostic information is necessary to determine patient infection status. Positive results do not rule out bacterial infection or coinfection with other viruses.”
Mesa Biotech said in a statement that the test is designed for point-of-care use, including at temporary screening facilities, physician office labs, urgent care, and long-term nursing facilities.
“Our test will provide a highly accessible means for health care professionals to access laboratory quality results close in their office to aid in the decision to isolate, treat, or dismiss potential carriers of the virus,” Hong Cai, the CEO and cofounder of Mesa Biotech, said in a statement. “The potential to reduce the growing strain on our nation’s hospitals is tremendous.”
In separate letters to the three companies notifying them of the authorizations, the FDA said the emergency use of the products met the criteria for issuances of authorization because the SARS-CoV-2 can cause a serious or life-threatening disease or condition; it was “reasonable to believe
that [the] product may be effective in diagnosing COVID-19; and there is no “adequate, approved, and available alternative” to the emergency use of the three products.
COVID-19 prompts ‘lifesaving’ policy change for opioid addiction
In the face of the US COVID-19 pandemic, the US Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration (SAMHSA) has announced policy changes to allow some patients in opioid treatment programs (OTP) to take home their medication.
According to the agency, states may request “blanket exceptions” for all stable patients in an OTP to receive a 28-day supply of take-home doses of medications such as methadone and buprenorphine, which are used to treat opioid use disorder (OUD).
States may request up to 14 days of take-home medication for patients who are less stable but who can, in the judgment of OTP clinicians, safely handle this level of take-home medication.
“SAMHSA recognizes the evolving issues surrounding COVID-19 and the emerging needs OTPs continue to face,” the agency writes in its updated guidance.
“SAMHSA affirms its commitment to supporting OTPs in any way possible during this time. As such, we are expanding our previous guidance to provide increased flexibility,” the agency said.
A ‘Lifesaving’ Decision
Commenting on the SAMHSA policy change, Richard Saitz, MD, professor and chair of the department of community health sciences, Boston University School of Public Health, said, the policy “is not only a good idea, it is critical and lifesaving.”
“This approach had to be done now. With the reduction in face-to-face visits, patients with opioid use disorder need a way to access treatment. If they cannot get opioid agonists, they would withdraw and return to illicit opioid use and high overdose risk and it would be cruel,” said Saitz.
“It is possible that there will be some diversion and some risk of overdose or misuse, but even for less stable patients the benefit likely far outweighs the risk,” he told Medscape Medical News.
Saitz believes policy changes like this should have been made before a crisis.
“Honestly, this is perhaps a silver lining of the crisis” and could lead to permanent change in how OUD is treated in the US, he said.
“Just like we are learning what can be done without a medical in-person visit, we will learn that it is perfectly fine to treat patients with addiction more like we treat patients with other chronic diseases who take medication that has risks and benefits,” Saitz said.
in cases when a patient is quarantined because of coronavirus.
Typically, only licensed practitioners can dispense or administer OUD medications to patients, but during the COVID-19 crisis, treatment program staff members, law enforcement officers, and national guard personnel will be allowed to deliver OUD medications to an approved “lockbox” at the patient’s doorstep. The change applies only while the coronavirus public health emergency lasts.
“This is also an excellent idea,” Saitz said.
ASAM Also Responds
In addition, the American Society of Addiction Medicine (ASAM) released a focused update to its National Practice Guideline for the Treatment of Opioid Use Disorder (NPG).
The update is “especially critical in the context of the ongoing COVID-19 emergency, which threatens to curtail patient access to evidence-based treatment,” the organization said in a news release. The new document updates the 2015 NPG. It includes 13 new recommendations and major revisions to 35 existing recommendations.
One new recommendation states that comprehensive assessment of a patient is critical for treatment planning, but completing all assessments should not delay or preclude initiating pharmacotherapy for OUD. Another new recommendation states that there is no recommended time limit for pharmacotherapy.
ASAM continues to recommend that patients’ psychosocial needs be assessed and psychosocial treatment offered. However, if patients can’t access psychosocial treatment because they are in isolation or have other risk factors that preclude external interactions, clinicians should not delay initiation of medication for the treatment of addiction.
Expanding the use of telemedicine might also be appropriate for many patients, ASAM announced.
They note that the NPG is the first to address in a single document all medications currently approved by the US Food and Drug Administration to treat OUD and opioid withdrawal, including all available buprenorphine formulations.
“All of the updated recommendations are designed to both improve the quality and consistency of care and reduce barriers to access to care for Americans living with OUD. The updated recommendations aim to support initiation of buprenorphine treatment in the emergency department and other urgent care settings,” the society said in the release.
“In addition, [the recommendations] provide greater flexibility on dosing during the initiation of buprenorphine treatment and for initiation of buprenorphine at home (which is also an important change in the midst of the COVID-19 crisis).”
The full document is available online.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
In the face of the US COVID-19 pandemic, the US Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration (SAMHSA) has announced policy changes to allow some patients in opioid treatment programs (OTP) to take home their medication.
According to the agency, states may request “blanket exceptions” for all stable patients in an OTP to receive a 28-day supply of take-home doses of medications such as methadone and buprenorphine, which are used to treat opioid use disorder (OUD).
States may request up to 14 days of take-home medication for patients who are less stable but who can, in the judgment of OTP clinicians, safely handle this level of take-home medication.
“SAMHSA recognizes the evolving issues surrounding COVID-19 and the emerging needs OTPs continue to face,” the agency writes in its updated guidance.
“SAMHSA affirms its commitment to supporting OTPs in any way possible during this time. As such, we are expanding our previous guidance to provide increased flexibility,” the agency said.
A ‘Lifesaving’ Decision
Commenting on the SAMHSA policy change, Richard Saitz, MD, professor and chair of the department of community health sciences, Boston University School of Public Health, said, the policy “is not only a good idea, it is critical and lifesaving.”
“This approach had to be done now. With the reduction in face-to-face visits, patients with opioid use disorder need a way to access treatment. If they cannot get opioid agonists, they would withdraw and return to illicit opioid use and high overdose risk and it would be cruel,” said Saitz.
“It is possible that there will be some diversion and some risk of overdose or misuse, but even for less stable patients the benefit likely far outweighs the risk,” he told Medscape Medical News.
Saitz believes policy changes like this should have been made before a crisis.
“Honestly, this is perhaps a silver lining of the crisis” and could lead to permanent change in how OUD is treated in the US, he said.
“Just like we are learning what can be done without a medical in-person visit, we will learn that it is perfectly fine to treat patients with addiction more like we treat patients with other chronic diseases who take medication that has risks and benefits,” Saitz said.
in cases when a patient is quarantined because of coronavirus.
Typically, only licensed practitioners can dispense or administer OUD medications to patients, but during the COVID-19 crisis, treatment program staff members, law enforcement officers, and national guard personnel will be allowed to deliver OUD medications to an approved “lockbox” at the patient’s doorstep. The change applies only while the coronavirus public health emergency lasts.
“This is also an excellent idea,” Saitz said.
ASAM Also Responds
In addition, the American Society of Addiction Medicine (ASAM) released a focused update to its National Practice Guideline for the Treatment of Opioid Use Disorder (NPG).
The update is “especially critical in the context of the ongoing COVID-19 emergency, which threatens to curtail patient access to evidence-based treatment,” the organization said in a news release. The new document updates the 2015 NPG. It includes 13 new recommendations and major revisions to 35 existing recommendations.
One new recommendation states that comprehensive assessment of a patient is critical for treatment planning, but completing all assessments should not delay or preclude initiating pharmacotherapy for OUD. Another new recommendation states that there is no recommended time limit for pharmacotherapy.
ASAM continues to recommend that patients’ psychosocial needs be assessed and psychosocial treatment offered. However, if patients can’t access psychosocial treatment because they are in isolation or have other risk factors that preclude external interactions, clinicians should not delay initiation of medication for the treatment of addiction.
Expanding the use of telemedicine might also be appropriate for many patients, ASAM announced.
They note that the NPG is the first to address in a single document all medications currently approved by the US Food and Drug Administration to treat OUD and opioid withdrawal, including all available buprenorphine formulations.
“All of the updated recommendations are designed to both improve the quality and consistency of care and reduce barriers to access to care for Americans living with OUD. The updated recommendations aim to support initiation of buprenorphine treatment in the emergency department and other urgent care settings,” the society said in the release.
“In addition, [the recommendations] provide greater flexibility on dosing during the initiation of buprenorphine treatment and for initiation of buprenorphine at home (which is also an important change in the midst of the COVID-19 crisis).”
The full document is available online.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
In the face of the US COVID-19 pandemic, the US Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration (SAMHSA) has announced policy changes to allow some patients in opioid treatment programs (OTP) to take home their medication.
According to the agency, states may request “blanket exceptions” for all stable patients in an OTP to receive a 28-day supply of take-home doses of medications such as methadone and buprenorphine, which are used to treat opioid use disorder (OUD).
States may request up to 14 days of take-home medication for patients who are less stable but who can, in the judgment of OTP clinicians, safely handle this level of take-home medication.
“SAMHSA recognizes the evolving issues surrounding COVID-19 and the emerging needs OTPs continue to face,” the agency writes in its updated guidance.
“SAMHSA affirms its commitment to supporting OTPs in any way possible during this time. As such, we are expanding our previous guidance to provide increased flexibility,” the agency said.
A ‘Lifesaving’ Decision
Commenting on the SAMHSA policy change, Richard Saitz, MD, professor and chair of the department of community health sciences, Boston University School of Public Health, said, the policy “is not only a good idea, it is critical and lifesaving.”
“This approach had to be done now. With the reduction in face-to-face visits, patients with opioid use disorder need a way to access treatment. If they cannot get opioid agonists, they would withdraw and return to illicit opioid use and high overdose risk and it would be cruel,” said Saitz.
“It is possible that there will be some diversion and some risk of overdose or misuse, but even for less stable patients the benefit likely far outweighs the risk,” he told Medscape Medical News.
Saitz believes policy changes like this should have been made before a crisis.
“Honestly, this is perhaps a silver lining of the crisis” and could lead to permanent change in how OUD is treated in the US, he said.
“Just like we are learning what can be done without a medical in-person visit, we will learn that it is perfectly fine to treat patients with addiction more like we treat patients with other chronic diseases who take medication that has risks and benefits,” Saitz said.
in cases when a patient is quarantined because of coronavirus.
Typically, only licensed practitioners can dispense or administer OUD medications to patients, but during the COVID-19 crisis, treatment program staff members, law enforcement officers, and national guard personnel will be allowed to deliver OUD medications to an approved “lockbox” at the patient’s doorstep. The change applies only while the coronavirus public health emergency lasts.
“This is also an excellent idea,” Saitz said.
ASAM Also Responds
In addition, the American Society of Addiction Medicine (ASAM) released a focused update to its National Practice Guideline for the Treatment of Opioid Use Disorder (NPG).
The update is “especially critical in the context of the ongoing COVID-19 emergency, which threatens to curtail patient access to evidence-based treatment,” the organization said in a news release. The new document updates the 2015 NPG. It includes 13 new recommendations and major revisions to 35 existing recommendations.
One new recommendation states that comprehensive assessment of a patient is critical for treatment planning, but completing all assessments should not delay or preclude initiating pharmacotherapy for OUD. Another new recommendation states that there is no recommended time limit for pharmacotherapy.
ASAM continues to recommend that patients’ psychosocial needs be assessed and psychosocial treatment offered. However, if patients can’t access psychosocial treatment because they are in isolation or have other risk factors that preclude external interactions, clinicians should not delay initiation of medication for the treatment of addiction.
Expanding the use of telemedicine might also be appropriate for many patients, ASAM announced.
They note that the NPG is the first to address in a single document all medications currently approved by the US Food and Drug Administration to treat OUD and opioid withdrawal, including all available buprenorphine formulations.
“All of the updated recommendations are designed to both improve the quality and consistency of care and reduce barriers to access to care for Americans living with OUD. The updated recommendations aim to support initiation of buprenorphine treatment in the emergency department and other urgent care settings,” the society said in the release.
“In addition, [the recommendations] provide greater flexibility on dosing during the initiation of buprenorphine treatment and for initiation of buprenorphine at home (which is also an important change in the midst of the COVID-19 crisis).”
The full document is available online.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Clinicians petition government for national quarantine
Clinicians across the United States are petitioning the federal government to follow the lead of South Korea, China, and other nations by imposing an immediate nationwide quarantine to slow the inevitable spread of COVID-19. Without federal action, the creators say, their lives and the lives of their colleagues, patients, and families are being put at increased risk.
In addition to the quarantine, the petition, posted on the website Change.org, calls on U.S. leaders to institute emergency production and distribution of personal protective equipment for healthcare workers and to rapidly increase access to testing.
The petition – which garnered more than 40,000 signatures in just 12 hours and as of this writing was approaching 94,000 – was started by an apolitical Facebook group to focus attention on what members see as the most critical issues for clinicians: slowing the spread of the virus through a coast-to-coast quarantine, protection of medical personnel with adequate supplies of essential equipment, and widespread testing.
“We started this group last Friday out of the realization that clinicians needed information about the outbreak and weren’t getting it,” said coadministrator Jessica McIntyre, MD, a pediatric hospitalist at Elliot Hospital in Manchester, N.H.
“We wanted to get ahead of it and connect with people before we were in the trenches experiencing it and to see what other programs were doing. From a local perspective, it has been really hard to see what people are doing in other states, especially when the protocols in our own states are changing every single day as we collect more information,” she said in an interview.
The Horse Has Bolted
A family medicine physician in Illinois helped launch the Facebook group. She asked that her name not be used but said in an interview that earlier actions may have prevented or at least delayed the need for the more draconian measures that her group is recommending.
“Clearly South Korea is one of the superstars as far as response has gone, but the concern we have in the United States is that we’re well beyond that point – we needed to be testing people over a month ago, in the hope of preventing a quarantine,” she said in an interview.
According to National Public Radio, as of March 13, South Korea had conducted 3,600 tests per million population, compared with five per million in the United States.
“I think the most concerning part is to see where Italy is now and where we are in comparison. Our ICUs have not yet overflowed, but I think we’re definitely looking at that in the next few weeks – hopefully longer, but I suspect that it will happen shortly,” she continued.
She cited work by Harvard University biostatistician Xihong Lin, PhD, that shows that when health authorities in Wuhan, China – widely cited as the epicenter of the global pandemic – cordoned off the city, the infection rate dropped from one person infecting 3.8 others to one infecting 1.25, thereby significantly slowing the rate of transmission.
“This is absolutely what we need to be doing,” she said.
Real News
Within 3 days of its creation, the online group had accrued more than 80,000 members with advanced medical training, including MDs, DOs, physician assistants, nurse practitioners, and certified registered nurse anesthetists.
“A lot of us were already very busy with our day-to-day work outside of COVID-19, and I think a lot of us felt unsure about where to get the best information,” said coadministrator David Janssen, MD, a family medicine physician in group practice in Sioux Center, Iowa,
“If you turn on the TV, there’s a lot of politicizing of the issue, and there’s a lot of good information, but also a lot of bad information. When health care providers talk to other health care providers, that’s often how we get our information and how we learn,” he said in an interview.
The COVID-19 U.S. Physicians/APP Facebook group includes 20 volunteer moderators who handle hundreds of posts per hour from persons seeking information on the novel coronavirus, what to tell patients, and how to protect themselves.
“It’s been wonderful to see how providers have been helping other providers sort through issues. Teaching hospitals have their hands on the latest research, but a lot of people like myself are at small community hospitals, critical-access hospitals, where we may have a lot of questions but don’t necessarily have the answers readily available to us,” Dr. Janssen said.
Dr. Janssen said that his community of about 8,000 residents initially had only four COVID-19 testing kits, or one for every 2,000 people. The situation has since improved, and more tests are now available, he added.
Dr. McIntyre, Dr. Janssen, and the Illinois family physician have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Clinicians across the United States are petitioning the federal government to follow the lead of South Korea, China, and other nations by imposing an immediate nationwide quarantine to slow the inevitable spread of COVID-19. Without federal action, the creators say, their lives and the lives of their colleagues, patients, and families are being put at increased risk.
In addition to the quarantine, the petition, posted on the website Change.org, calls on U.S. leaders to institute emergency production and distribution of personal protective equipment for healthcare workers and to rapidly increase access to testing.
The petition – which garnered more than 40,000 signatures in just 12 hours and as of this writing was approaching 94,000 – was started by an apolitical Facebook group to focus attention on what members see as the most critical issues for clinicians: slowing the spread of the virus through a coast-to-coast quarantine, protection of medical personnel with adequate supplies of essential equipment, and widespread testing.
“We started this group last Friday out of the realization that clinicians needed information about the outbreak and weren’t getting it,” said coadministrator Jessica McIntyre, MD, a pediatric hospitalist at Elliot Hospital in Manchester, N.H.
“We wanted to get ahead of it and connect with people before we were in the trenches experiencing it and to see what other programs were doing. From a local perspective, it has been really hard to see what people are doing in other states, especially when the protocols in our own states are changing every single day as we collect more information,” she said in an interview.
The Horse Has Bolted
A family medicine physician in Illinois helped launch the Facebook group. She asked that her name not be used but said in an interview that earlier actions may have prevented or at least delayed the need for the more draconian measures that her group is recommending.
“Clearly South Korea is one of the superstars as far as response has gone, but the concern we have in the United States is that we’re well beyond that point – we needed to be testing people over a month ago, in the hope of preventing a quarantine,” she said in an interview.
According to National Public Radio, as of March 13, South Korea had conducted 3,600 tests per million population, compared with five per million in the United States.
“I think the most concerning part is to see where Italy is now and where we are in comparison. Our ICUs have not yet overflowed, but I think we’re definitely looking at that in the next few weeks – hopefully longer, but I suspect that it will happen shortly,” she continued.
She cited work by Harvard University biostatistician Xihong Lin, PhD, that shows that when health authorities in Wuhan, China – widely cited as the epicenter of the global pandemic – cordoned off the city, the infection rate dropped from one person infecting 3.8 others to one infecting 1.25, thereby significantly slowing the rate of transmission.
“This is absolutely what we need to be doing,” she said.
Real News
Within 3 days of its creation, the online group had accrued more than 80,000 members with advanced medical training, including MDs, DOs, physician assistants, nurse practitioners, and certified registered nurse anesthetists.
“A lot of us were already very busy with our day-to-day work outside of COVID-19, and I think a lot of us felt unsure about where to get the best information,” said coadministrator David Janssen, MD, a family medicine physician in group practice in Sioux Center, Iowa,
“If you turn on the TV, there’s a lot of politicizing of the issue, and there’s a lot of good information, but also a lot of bad information. When health care providers talk to other health care providers, that’s often how we get our information and how we learn,” he said in an interview.
The COVID-19 U.S. Physicians/APP Facebook group includes 20 volunteer moderators who handle hundreds of posts per hour from persons seeking information on the novel coronavirus, what to tell patients, and how to protect themselves.
“It’s been wonderful to see how providers have been helping other providers sort through issues. Teaching hospitals have their hands on the latest research, but a lot of people like myself are at small community hospitals, critical-access hospitals, where we may have a lot of questions but don’t necessarily have the answers readily available to us,” Dr. Janssen said.
Dr. Janssen said that his community of about 8,000 residents initially had only four COVID-19 testing kits, or one for every 2,000 people. The situation has since improved, and more tests are now available, he added.
Dr. McIntyre, Dr. Janssen, and the Illinois family physician have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Clinicians across the United States are petitioning the federal government to follow the lead of South Korea, China, and other nations by imposing an immediate nationwide quarantine to slow the inevitable spread of COVID-19. Without federal action, the creators say, their lives and the lives of their colleagues, patients, and families are being put at increased risk.
In addition to the quarantine, the petition, posted on the website Change.org, calls on U.S. leaders to institute emergency production and distribution of personal protective equipment for healthcare workers and to rapidly increase access to testing.
The petition – which garnered more than 40,000 signatures in just 12 hours and as of this writing was approaching 94,000 – was started by an apolitical Facebook group to focus attention on what members see as the most critical issues for clinicians: slowing the spread of the virus through a coast-to-coast quarantine, protection of medical personnel with adequate supplies of essential equipment, and widespread testing.
“We started this group last Friday out of the realization that clinicians needed information about the outbreak and weren’t getting it,” said coadministrator Jessica McIntyre, MD, a pediatric hospitalist at Elliot Hospital in Manchester, N.H.
“We wanted to get ahead of it and connect with people before we were in the trenches experiencing it and to see what other programs were doing. From a local perspective, it has been really hard to see what people are doing in other states, especially when the protocols in our own states are changing every single day as we collect more information,” she said in an interview.
The Horse Has Bolted
A family medicine physician in Illinois helped launch the Facebook group. She asked that her name not be used but said in an interview that earlier actions may have prevented or at least delayed the need for the more draconian measures that her group is recommending.
“Clearly South Korea is one of the superstars as far as response has gone, but the concern we have in the United States is that we’re well beyond that point – we needed to be testing people over a month ago, in the hope of preventing a quarantine,” she said in an interview.
According to National Public Radio, as of March 13, South Korea had conducted 3,600 tests per million population, compared with five per million in the United States.
“I think the most concerning part is to see where Italy is now and where we are in comparison. Our ICUs have not yet overflowed, but I think we’re definitely looking at that in the next few weeks – hopefully longer, but I suspect that it will happen shortly,” she continued.
She cited work by Harvard University biostatistician Xihong Lin, PhD, that shows that when health authorities in Wuhan, China – widely cited as the epicenter of the global pandemic – cordoned off the city, the infection rate dropped from one person infecting 3.8 others to one infecting 1.25, thereby significantly slowing the rate of transmission.
“This is absolutely what we need to be doing,” she said.
Real News
Within 3 days of its creation, the online group had accrued more than 80,000 members with advanced medical training, including MDs, DOs, physician assistants, nurse practitioners, and certified registered nurse anesthetists.
“A lot of us were already very busy with our day-to-day work outside of COVID-19, and I think a lot of us felt unsure about where to get the best information,” said coadministrator David Janssen, MD, a family medicine physician in group practice in Sioux Center, Iowa,
“If you turn on the TV, there’s a lot of politicizing of the issue, and there’s a lot of good information, but also a lot of bad information. When health care providers talk to other health care providers, that’s often how we get our information and how we learn,” he said in an interview.
The COVID-19 U.S. Physicians/APP Facebook group includes 20 volunteer moderators who handle hundreds of posts per hour from persons seeking information on the novel coronavirus, what to tell patients, and how to protect themselves.
“It’s been wonderful to see how providers have been helping other providers sort through issues. Teaching hospitals have their hands on the latest research, but a lot of people like myself are at small community hospitals, critical-access hospitals, where we may have a lot of questions but don’t necessarily have the answers readily available to us,” Dr. Janssen said.
Dr. Janssen said that his community of about 8,000 residents initially had only four COVID-19 testing kits, or one for every 2,000 people. The situation has since improved, and more tests are now available, he added.
Dr. McIntyre, Dr. Janssen, and the Illinois family physician have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The apology in medicine—yes, no, or maybe?
This is the third and final article in a series focusing on malpractice, liability, and reform. In the first article, we looked at the background on malpractice and reasons malpractice rates have been so high—including large verdicts and lawsuit-prone physicians. In the second article we considered recent experience and developments in malpractice exposure, who is sued and why. Finally, in this third article, we focus on apologies, apology laws, and liability.
“I’m sorry”
In childhood we are all taught the basic courtesies: “please” and “thank you,” and “I’m sorry,” when harm has occurred. Should we as adult health care providers fear the consequences of apologizing? Apologies are a way for clinicians to express empathy; they also serve as a tool to reduce medical malpractice claims.1

Apologies, ethics, and care
The American Medical Association takes the position that a physician has an ethical duty to disclose a harmful error to a patient.2,3 Indeed this approach has been an impetus for states to enact apology laws, which we discuss below. As pointed out in this 2013 article title, “Dealing with a medical mistake: Should physicians apologize to patients?”,4 the legal benefits of any apology are an issue. It is a controversial area in medicine still today, including in obstetrics and gynecology.
“Ethical codes for both M.D.s and D.O.s suggest providers should display honesty and empathy following adverse events and errors.”1,3,5 In addition, the American Medical Association states, “a physician should at all times deal honestly and openly with patients.”2 Concerns about liability that may result from truthful disclosure should not affect the physician’s honesty (TABLE). Increasingly, the law has sided with that principle through apology laws.

Some patients sue to get answers to the “What happened?” and “Why did it happen?” questions.6 They also sometimes are motivated by a desire to help ensure that the same injury does not happen to others. Silence on the part of the clinician may be seen as a lack of sympathy or remorse and patients may fear that other patients will be harmed.1
The relationship between physician and patient involves vulnerability and requires trust. When an injury occurs, the relationship can be injured as well. Barriers to apology in part reflect “the culture of medicine” as well as the “inherent psychological difficulties in facing one’s mistakes and apologizing for them.” However, apology by the provider may result in “effective resolution of disputes related to medical error.”7
The patient’s perspective is critical to this type of outcome, of course. A study from the United Kingdom noted that one-third of patients who experience a medical error have a desire to receive an apology or explanation. Furthermore, patients need assurance that a plan of action to prevent such a future occurrence is in place.8 Surveys reflect that patients desire, or even expect, the physician to acknowledge an error.9 We will see that there is evidence that some kinds of apologies tend to diminish blame and make the injured patient less likely to pursue litigation.10 For instance, Dahan and colleagues completed a study that highlights the “act of apology,” which can be seen as a “language art.”11 Medical schools have recognized the importance of the apology and now incorporate training focused on error disclosure and provision of apologies into the curriculum.12
Continue to: Legal issues and medical apologies...
Legal issues and medical apologies
From a legal standpoint, traditionally, an apology from a physician to a patient could be used against a physician in a medical liability (malpractice) case as proof of negligence.
Statements of interest. Such out-of-court statements ordinarily would be “hearsay” and excluded from evidence; there is, however, an exception to this hearsay rule that allows “confessions” or “statements against interest” to be admissible against the party making the statement. The theory is that when a statement is harmful to the person making it, the person likely thought that it was true, and the statement should be admissible at trial. We do not generally go around confessing to things that are not true. Following an auto crash, if one driver jumps out of the car saying, “I am so sorry I hit you. I was using my cell phone and did not see you stop,” the statement is against the interest of the driver and could be used in court.
As a matter of general legal principle, the same issue can arise in medical practice. Suppose a physician says, “I am so sorry for your injury. We made a mistake in interpreting the data from the monitors.” That sounds a lot like not just an apology but a statement against interest. Malpractice cases generally are based on the claim that a “doctor failed to do what a reasonable provider in the same specialty would have done in a similar situation.”13 An apology may be little more than general sympathy (“I’m sorry to tell you that we have not cured the infection. Unfortunately, that will mean more time in the hospital.”), but it can include a confession of error (“I’m sorry we got the x-ray backward and removed the wrong kidney.”). In the latter kind of apology, courts traditionally have found a “statement against interest.”
The legal consequence of a statement against interest is that the statement may be admitted in court. Such statements do not automatically establish negligence, but they can be powerful evidence when presented to a jury.
Courts have struggled with medical apologies. General sympathy or feelings of regret or compassion do not generally rise to the level of an admission that the physician did not use reasonable care under the circumstances and ordinarily are not admissible. (For further details, we refer you to the case of Cobbs v. Grant.14 Even if a physician said to the patient that he “blamed himself for [the patient] being back in the hospital for a second time,…the statement signifies compassion, or at most, a feeling of remorse, for plaintiff’s ordeal.”) On the other hand, in cases in which a physician in an apology referred to a “careless” mistake or even a “negligent” mistake, courts have allowed it admitted at trial as a statement against interest. (A 1946 case, Woronka v. Sewall, is an example.15 In that case, the physician said to the patient, “My God, what a mess…she had a very hard delivery, and it was a burning shame to get [an injury] on top of it, and it was because of negligence when they were upstairs.”) Some of these cases come down to the provider’s use of a single word: fault, careless, or negligence.
The ambiguity over the legal place of medical apologies in medicine led attorneys to urge medical providers to avoid statements that might even remotely be taken as statements against interest, including real apologies. The confusion over the admissibility of medical apologies led state legislatures to adopt apology laws. These laws essentially limit what statements against interest may be introduced in professional liability cases when a provider has issued a responsibility or apologized.
Continue to: Apology statutes...
Apology statutes
Massachusetts was the first state to enact an apology law—in 1986.1 As of 2019, a clear majority of states have some form of apology statute. “Apology laws are gaining traction,” was the first sentence in a 2012 review on the subject by Saitta and colleagues.3 Only a few (5 states) have “strong” statutes that have broad protection for statements of fault, error, and negligence, as well as sympathy. The other 33 states have statutes that only protect against statements of sympathy.4,16 FIGURE 1 is a US map showing the apology laws by state.1
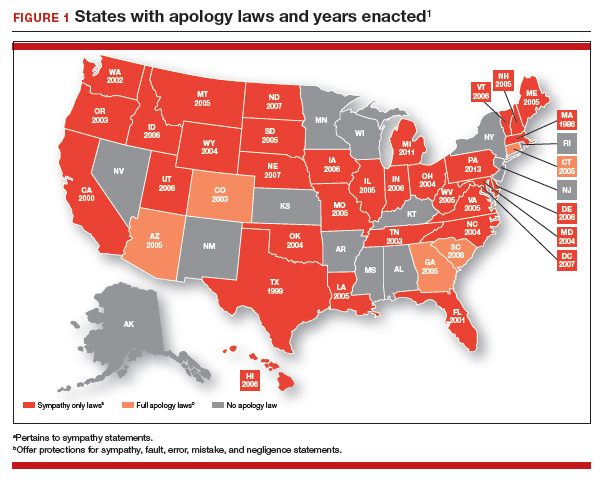
Do apology statutes and apologies reduce liability?
The positive aspects of apology include personal, psychological, and emotional benefits to both the one apologizing and the one receiving the apology. It also may have financial benefits to health care providers.4 The assumption has been, and there has been some evidence for the proposition, that apologies reduce the possibility of malpractice claims. That is one of the reasons that institutions may have formal apology policies. Indeed, there is evidence that apologies reduce financial awards to patients, as manifest in the states of Pennsylvania and Kentucky.4 Apologies appear to reduce patient anger and can open the door to better communication with the provider. There is evidence that some kinds of apologies tend to diminish blame and make the injured patient less likely to pursue litigation.10 The conclusion from these studies might be that honest and open communication serves to decrease the incidence of medical malpractice lawsuit initiation and that honesty is the best policy.
It is important to note the difference, however, between apologies (or institutional apology policies) and apology laws. There is some evidence that apology and institutional apology policies may reduce malpractice claims or losses.17,18 On the other hand, the studies of apology laws have not found that these laws have much impact on malpractice rates. An especially good and thorough study of the effect of apology laws nationwide, using insurance claims data, essentially found little net effect of the apology laws.19,20 One other study could find no evidence that apology statutes reduce defensive medicine (so no reduction in provider concerns over liability).21
It should be noted that most studies on medical apology and its effects on malpractice claims generally have looked at the narrow or limited apology statutes (that do not cover expressions of fault or negligence). Few states have the broader statutes, and it is possible that those broader statutes would be more effective in reducing liability. Removing the disincentives to medical apologies is a good thing, but in and of itself it is probably not a liability game changer.
Continue to: Institutional policy and apology...
Institutional policy and apology
Some institutions have established an “inclusion of apology” strategy for medical errors. These policies appear to have a meaningful effect on reducing medical malpractice costs. These programs commonly include a proactive investigation, disclosure of error, and apologies. Such policies have been studied at the University of Michigan and the Veterans Affairs (VA) Hospital in Lexington, Kentucky. The University of Michigan program resulted in a 60% reduction in compensation costs for medical errors.22 It also cut litigation costs by half.23 The review of the Kentucky VA program also was positive.17 FIGURE 2 illustrates the key features of the Michigan program.24
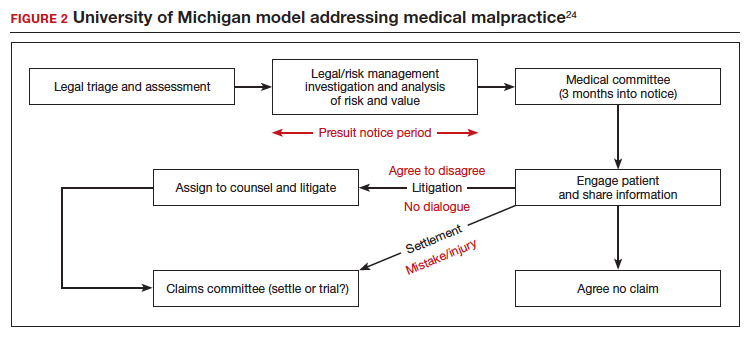
Conclusions: Effective apologies
Our conclusions, first, are that apologies are important from all perspectives: ethical, medical, and legal. On the other hand, all of the attention given in recent years to apology statutes may have been misplaced, at least if they were intended to be malpractice reform.17
Institutional apology and response programs are likely successful because they are thoughtfully put together, generally based on the best understanding of how injured patients respond to apologies and what it takes to be sincere, and communicate that sincerity, in the apology. What is an effective apology?, “The acceptance of responsibility for having caused harm.” It may, for example, mean accepting some financial responsibility for the harm. It is also important that the apology is conveyed in such a way that it includes an element of self-critical expression.25 Although there are many formulations of the elements of an effective apology, one example is, “(1) acknowledging and accepting responsibility for the offense; (2) expressing remorse with forbearance, sincerity, and honesty; (3) explaining the understanding of the offense; and (4) willingness to make reparations.”26
At the other extreme is a medical professional, after a bad event, trying to engage in a half-hearted, awkward, or insincere apology on an ad hoc and poorly planned basis. Worse still, “when victims perceive apologies to be insincere and designed simply to cool them off, they react with more rather than less indignation.”27 Of course, the “forced apology” may be the worst of all. An instance of this was addressed in a New Zealand study in which providers were “forced” to provide a written apology to a couple (Mr. and Mrs. B) and a separate written apology to Baby B when there was failure to discuss vitamin K administration during the antenatal period when it was indicated.28 Rather than emphasizing required apology in such a case, which can seem hollow and disingenuous, emphasis was placed on the apology providing a “positive-physiological” effect for those harmed, and on strategies that “nurture the development of the moral maturity required for authentic apology.”
The great advantage of institutional or practice-wide policies is that they can be developed in the calm of planning, with good foresight and careful consideration. This is much different from having to come up with some approach in the heat of something having gone wrong. Ultimately, however, apologies are not about liability. They are about caring for, respecting, and communicating with those who are harmed. Apologizing is often the right and professional thing to do.
- Afrassiab Z. Why mediation & “sorry” make sense: apology statutes as a catalyst for change in medical malpractice. J Dispute Resolutions. 2019.
- AMA Council on Ethical and Judicial Affairs. AMA code of medical ethics’ opinions on patient safety. Virtual Mentor. 2011;13:626-628.
- Saitta N, Hodge SD. Efficacy of a physician’s words of empathy: an overview of state apology laws. J Am Osteopath Assn. 2012;112:302-306.
- Dealing with a medical mistake: Should physicians apologize to patients? Med Economics. November 10, 2013.
- AOA code of ethics. American Osteopathic Association website. http://www.osteopathic.org/inside-aoa/about /leadershipPages/aos-code-of-ethics.aspx. Accessed January 15, 2020.
- You had me at “I’m sorry”: the impact of physicians’ apologies on medical malpractice litigation. Natl Law Review. November 6, 2018. https://www.natlawreview.com /article/you-had-me-i-m-sorry-impact-physicians-apologiesmedical-malpractice-litigation. Accessed February 6, 2020.
- Robbennolt JK. Apologies and medical error. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2009;467:376-382.
- Bismark MM. The power of apology. N Z Med J. 2009;122:96-106.
- Witman AB, Park DM, Hardin SB. How do patients want physicians to handle mistakes? A survey of internal medicine patients in an academic setting. Arch Intern Med. 1996;156:2565-2569.
- Lawthers AG, Localio AR, Laird NM, et al. Physicians’ perceptions of the risk of being sued. J Health Polit Policy Law. 1992;17:463-482.
- Dahan S, Ducard D, Caeymaex L. Apology in cases of medical error disclosure: thoughts based on a preliminary study. PLoS One. 2017;12:e0181854.
- Halbach JL, Sullivan LL. Teaching medical students about medical errors and patient safety: evaluation of a required curriculum. Acad Med. 2005;80:600-606.
- Nussbaum L. Trial and error: legislating ADR for medical malpractice reform. 2017. Scholarly Works. https://scholars .law.unlv.edu/facpub/1011. Accessed February 7, 2020.
- Cobbs v. Grant, 8 Cal. 3d 229, 104 Cal. Rptr. 505, 502 P.2d 1 (1972).
- Woronka v. Sewall, 320 Mass. 362, 69 N.E.2d 581 (1946).
- Wei M. Doctors, apologies and the law: an analysis and critique of apology law. J Health Law. 2007;40:107-159.
- Kraman SS, Hamm G. Risk management: extreme honesty may be the best policy. Ann Intern Med. 1999;131:963-967.
- Liebman CB, Hyman CS. Medical error disclosure, mediation skills, and malpractice litigation: a demonstration project in Pennsylvania. 2005. https://perma.cc/7257-99GU. Accessed February 7, 2020.
- McMichael BJ, Van Horn RL, Viscusi WK. “Sorry” is never enough: how state apology laws fail to reduce medical malpractice liability risk. Stanford Law Rev. 2019;71:341-409.
- Ho B, Liu E. What’s an apology worth? Decomposing the effect of apologies on medical malpractice payments using state apology laws. J Empirical Legal Studies. 2011;8:179-199.
- McMichael BJ. The failure of sorry: an empirical evaluation of apology laws, health care, and medical malpractice. Lewis & Clark Law Rev. 2017. https://law.lclark.edu/live/files/27734- lcb224article3mcmichaelpdf. Accessed February 7, 2020.
- Kachalia A, Kaufman SR, Boothman R, et al. Liability claims and costs before and after implementation of a medical error disclosure program. Ann Intern Med. 2010;153:213-221.
- Boothman RC, Blackwell AC, Campbell DA Jr, et al. A better approach to medical malpractice claims? The University of Michigan experience. J Health Life Sci Law. 2009;2:125-159.
- The Michigan model: Medical malpractice and patient safety at Michigan Medicine. University of Michigan website. https:// www.uofmhealth.org/michigan-model-medical-malpracticeand-patient-safety-umhs#summary. Accessed February 7, 2020.
- Mastroianni AC, Mello MM, Sommer S, et al. The flaws in state ‘apology’ and ‘disclosure’ laws dilute their intended impact on malpractice suits. Health Aff (Millwood). 2010;29:1611-1619.
- Davis ER. I’m sorry I’m scared of litigation: evaluating the effectiveness of apology laws. Forum: Tennessee Student Legal J. 2016;3. https://trace.tennessee.edu/forum/vol3/iss1/4/. Accessed February 7, 2020.
- Miller DT. Disrespect and the experience of injustice. Annu Rev Psychol. 2001;52:527-553.
- McLennan S, Walker S, Rich LE. Should health care providers be forced to apologise after things go wrong? J Bioeth Inq. 2014;11:431-435
This is the third and final article in a series focusing on malpractice, liability, and reform. In the first article, we looked at the background on malpractice and reasons malpractice rates have been so high—including large verdicts and lawsuit-prone physicians. In the second article we considered recent experience and developments in malpractice exposure, who is sued and why. Finally, in this third article, we focus on apologies, apology laws, and liability.
“I’m sorry”
In childhood we are all taught the basic courtesies: “please” and “thank you,” and “I’m sorry,” when harm has occurred. Should we as adult health care providers fear the consequences of apologizing? Apologies are a way for clinicians to express empathy; they also serve as a tool to reduce medical malpractice claims.1

Apologies, ethics, and care
The American Medical Association takes the position that a physician has an ethical duty to disclose a harmful error to a patient.2,3 Indeed this approach has been an impetus for states to enact apology laws, which we discuss below. As pointed out in this 2013 article title, “Dealing with a medical mistake: Should physicians apologize to patients?”,4 the legal benefits of any apology are an issue. It is a controversial area in medicine still today, including in obstetrics and gynecology.
“Ethical codes for both M.D.s and D.O.s suggest providers should display honesty and empathy following adverse events and errors.”1,3,5 In addition, the American Medical Association states, “a physician should at all times deal honestly and openly with patients.”2 Concerns about liability that may result from truthful disclosure should not affect the physician’s honesty (TABLE). Increasingly, the law has sided with that principle through apology laws.

Some patients sue to get answers to the “What happened?” and “Why did it happen?” questions.6 They also sometimes are motivated by a desire to help ensure that the same injury does not happen to others. Silence on the part of the clinician may be seen as a lack of sympathy or remorse and patients may fear that other patients will be harmed.1
The relationship between physician and patient involves vulnerability and requires trust. When an injury occurs, the relationship can be injured as well. Barriers to apology in part reflect “the culture of medicine” as well as the “inherent psychological difficulties in facing one’s mistakes and apologizing for them.” However, apology by the provider may result in “effective resolution of disputes related to medical error.”7
The patient’s perspective is critical to this type of outcome, of course. A study from the United Kingdom noted that one-third of patients who experience a medical error have a desire to receive an apology or explanation. Furthermore, patients need assurance that a plan of action to prevent such a future occurrence is in place.8 Surveys reflect that patients desire, or even expect, the physician to acknowledge an error.9 We will see that there is evidence that some kinds of apologies tend to diminish blame and make the injured patient less likely to pursue litigation.10 For instance, Dahan and colleagues completed a study that highlights the “act of apology,” which can be seen as a “language art.”11 Medical schools have recognized the importance of the apology and now incorporate training focused on error disclosure and provision of apologies into the curriculum.12
Continue to: Legal issues and medical apologies...
Legal issues and medical apologies
From a legal standpoint, traditionally, an apology from a physician to a patient could be used against a physician in a medical liability (malpractice) case as proof of negligence.
Statements of interest. Such out-of-court statements ordinarily would be “hearsay” and excluded from evidence; there is, however, an exception to this hearsay rule that allows “confessions” or “statements against interest” to be admissible against the party making the statement. The theory is that when a statement is harmful to the person making it, the person likely thought that it was true, and the statement should be admissible at trial. We do not generally go around confessing to things that are not true. Following an auto crash, if one driver jumps out of the car saying, “I am so sorry I hit you. I was using my cell phone and did not see you stop,” the statement is against the interest of the driver and could be used in court.
As a matter of general legal principle, the same issue can arise in medical practice. Suppose a physician says, “I am so sorry for your injury. We made a mistake in interpreting the data from the monitors.” That sounds a lot like not just an apology but a statement against interest. Malpractice cases generally are based on the claim that a “doctor failed to do what a reasonable provider in the same specialty would have done in a similar situation.”13 An apology may be little more than general sympathy (“I’m sorry to tell you that we have not cured the infection. Unfortunately, that will mean more time in the hospital.”), but it can include a confession of error (“I’m sorry we got the x-ray backward and removed the wrong kidney.”). In the latter kind of apology, courts traditionally have found a “statement against interest.”
The legal consequence of a statement against interest is that the statement may be admitted in court. Such statements do not automatically establish negligence, but they can be powerful evidence when presented to a jury.
Courts have struggled with medical apologies. General sympathy or feelings of regret or compassion do not generally rise to the level of an admission that the physician did not use reasonable care under the circumstances and ordinarily are not admissible. (For further details, we refer you to the case of Cobbs v. Grant.14 Even if a physician said to the patient that he “blamed himself for [the patient] being back in the hospital for a second time,…the statement signifies compassion, or at most, a feeling of remorse, for plaintiff’s ordeal.”) On the other hand, in cases in which a physician in an apology referred to a “careless” mistake or even a “negligent” mistake, courts have allowed it admitted at trial as a statement against interest. (A 1946 case, Woronka v. Sewall, is an example.15 In that case, the physician said to the patient, “My God, what a mess…she had a very hard delivery, and it was a burning shame to get [an injury] on top of it, and it was because of negligence when they were upstairs.”) Some of these cases come down to the provider’s use of a single word: fault, careless, or negligence.
The ambiguity over the legal place of medical apologies in medicine led attorneys to urge medical providers to avoid statements that might even remotely be taken as statements against interest, including real apologies. The confusion over the admissibility of medical apologies led state legislatures to adopt apology laws. These laws essentially limit what statements against interest may be introduced in professional liability cases when a provider has issued a responsibility or apologized.
Continue to: Apology statutes...
Apology statutes
Massachusetts was the first state to enact an apology law—in 1986.1 As of 2019, a clear majority of states have some form of apology statute. “Apology laws are gaining traction,” was the first sentence in a 2012 review on the subject by Saitta and colleagues.3 Only a few (5 states) have “strong” statutes that have broad protection for statements of fault, error, and negligence, as well as sympathy. The other 33 states have statutes that only protect against statements of sympathy.4,16 FIGURE 1 is a US map showing the apology laws by state.1

Do apology statutes and apologies reduce liability?
The positive aspects of apology include personal, psychological, and emotional benefits to both the one apologizing and the one receiving the apology. It also may have financial benefits to health care providers.4 The assumption has been, and there has been some evidence for the proposition, that apologies reduce the possibility of malpractice claims. That is one of the reasons that institutions may have formal apology policies. Indeed, there is evidence that apologies reduce financial awards to patients, as manifest in the states of Pennsylvania and Kentucky.4 Apologies appear to reduce patient anger and can open the door to better communication with the provider. There is evidence that some kinds of apologies tend to diminish blame and make the injured patient less likely to pursue litigation.10 The conclusion from these studies might be that honest and open communication serves to decrease the incidence of medical malpractice lawsuit initiation and that honesty is the best policy.
It is important to note the difference, however, between apologies (or institutional apology policies) and apology laws. There is some evidence that apology and institutional apology policies may reduce malpractice claims or losses.17,18 On the other hand, the studies of apology laws have not found that these laws have much impact on malpractice rates. An especially good and thorough study of the effect of apology laws nationwide, using insurance claims data, essentially found little net effect of the apology laws.19,20 One other study could find no evidence that apology statutes reduce defensive medicine (so no reduction in provider concerns over liability).21
It should be noted that most studies on medical apology and its effects on malpractice claims generally have looked at the narrow or limited apology statutes (that do not cover expressions of fault or negligence). Few states have the broader statutes, and it is possible that those broader statutes would be more effective in reducing liability. Removing the disincentives to medical apologies is a good thing, but in and of itself it is probably not a liability game changer.
Continue to: Institutional policy and apology...
Institutional policy and apology
Some institutions have established an “inclusion of apology” strategy for medical errors. These policies appear to have a meaningful effect on reducing medical malpractice costs. These programs commonly include a proactive investigation, disclosure of error, and apologies. Such policies have been studied at the University of Michigan and the Veterans Affairs (VA) Hospital in Lexington, Kentucky. The University of Michigan program resulted in a 60% reduction in compensation costs for medical errors.22 It also cut litigation costs by half.23 The review of the Kentucky VA program also was positive.17 FIGURE 2 illustrates the key features of the Michigan program.24

Conclusions: Effective apologies
Our conclusions, first, are that apologies are important from all perspectives: ethical, medical, and legal. On the other hand, all of the attention given in recent years to apology statutes may have been misplaced, at least if they were intended to be malpractice reform.17
Institutional apology and response programs are likely successful because they are thoughtfully put together, generally based on the best understanding of how injured patients respond to apologies and what it takes to be sincere, and communicate that sincerity, in the apology. What is an effective apology?, “The acceptance of responsibility for having caused harm.” It may, for example, mean accepting some financial responsibility for the harm. It is also important that the apology is conveyed in such a way that it includes an element of self-critical expression.25 Although there are many formulations of the elements of an effective apology, one example is, “(1) acknowledging and accepting responsibility for the offense; (2) expressing remorse with forbearance, sincerity, and honesty; (3) explaining the understanding of the offense; and (4) willingness to make reparations.”26
At the other extreme is a medical professional, after a bad event, trying to engage in a half-hearted, awkward, or insincere apology on an ad hoc and poorly planned basis. Worse still, “when victims perceive apologies to be insincere and designed simply to cool them off, they react with more rather than less indignation.”27 Of course, the “forced apology” may be the worst of all. An instance of this was addressed in a New Zealand study in which providers were “forced” to provide a written apology to a couple (Mr. and Mrs. B) and a separate written apology to Baby B when there was failure to discuss vitamin K administration during the antenatal period when it was indicated.28 Rather than emphasizing required apology in such a case, which can seem hollow and disingenuous, emphasis was placed on the apology providing a “positive-physiological” effect for those harmed, and on strategies that “nurture the development of the moral maturity required for authentic apology.”
The great advantage of institutional or practice-wide policies is that they can be developed in the calm of planning, with good foresight and careful consideration. This is much different from having to come up with some approach in the heat of something having gone wrong. Ultimately, however, apologies are not about liability. They are about caring for, respecting, and communicating with those who are harmed. Apologizing is often the right and professional thing to do.
This is the third and final article in a series focusing on malpractice, liability, and reform. In the first article, we looked at the background on malpractice and reasons malpractice rates have been so high—including large verdicts and lawsuit-prone physicians. In the second article we considered recent experience and developments in malpractice exposure, who is sued and why. Finally, in this third article, we focus on apologies, apology laws, and liability.
“I’m sorry”
In childhood we are all taught the basic courtesies: “please” and “thank you,” and “I’m sorry,” when harm has occurred. Should we as adult health care providers fear the consequences of apologizing? Apologies are a way for clinicians to express empathy; they also serve as a tool to reduce medical malpractice claims.1

Apologies, ethics, and care
The American Medical Association takes the position that a physician has an ethical duty to disclose a harmful error to a patient.2,3 Indeed this approach has been an impetus for states to enact apology laws, which we discuss below. As pointed out in this 2013 article title, “Dealing with a medical mistake: Should physicians apologize to patients?”,4 the legal benefits of any apology are an issue. It is a controversial area in medicine still today, including in obstetrics and gynecology.
“Ethical codes for both M.D.s and D.O.s suggest providers should display honesty and empathy following adverse events and errors.”1,3,5 In addition, the American Medical Association states, “a physician should at all times deal honestly and openly with patients.”2 Concerns about liability that may result from truthful disclosure should not affect the physician’s honesty (TABLE). Increasingly, the law has sided with that principle through apology laws.

Some patients sue to get answers to the “What happened?” and “Why did it happen?” questions.6 They also sometimes are motivated by a desire to help ensure that the same injury does not happen to others. Silence on the part of the clinician may be seen as a lack of sympathy or remorse and patients may fear that other patients will be harmed.1
The relationship between physician and patient involves vulnerability and requires trust. When an injury occurs, the relationship can be injured as well. Barriers to apology in part reflect “the culture of medicine” as well as the “inherent psychological difficulties in facing one’s mistakes and apologizing for them.” However, apology by the provider may result in “effective resolution of disputes related to medical error.”7
The patient’s perspective is critical to this type of outcome, of course. A study from the United Kingdom noted that one-third of patients who experience a medical error have a desire to receive an apology or explanation. Furthermore, patients need assurance that a plan of action to prevent such a future occurrence is in place.8 Surveys reflect that patients desire, or even expect, the physician to acknowledge an error.9 We will see that there is evidence that some kinds of apologies tend to diminish blame and make the injured patient less likely to pursue litigation.10 For instance, Dahan and colleagues completed a study that highlights the “act of apology,” which can be seen as a “language art.”11 Medical schools have recognized the importance of the apology and now incorporate training focused on error disclosure and provision of apologies into the curriculum.12
Continue to: Legal issues and medical apologies...
Legal issues and medical apologies
From a legal standpoint, traditionally, an apology from a physician to a patient could be used against a physician in a medical liability (malpractice) case as proof of negligence.
Statements of interest. Such out-of-court statements ordinarily would be “hearsay” and excluded from evidence; there is, however, an exception to this hearsay rule that allows “confessions” or “statements against interest” to be admissible against the party making the statement. The theory is that when a statement is harmful to the person making it, the person likely thought that it was true, and the statement should be admissible at trial. We do not generally go around confessing to things that are not true. Following an auto crash, if one driver jumps out of the car saying, “I am so sorry I hit you. I was using my cell phone and did not see you stop,” the statement is against the interest of the driver and could be used in court.
As a matter of general legal principle, the same issue can arise in medical practice. Suppose a physician says, “I am so sorry for your injury. We made a mistake in interpreting the data from the monitors.” That sounds a lot like not just an apology but a statement against interest. Malpractice cases generally are based on the claim that a “doctor failed to do what a reasonable provider in the same specialty would have done in a similar situation.”13 An apology may be little more than general sympathy (“I’m sorry to tell you that we have not cured the infection. Unfortunately, that will mean more time in the hospital.”), but it can include a confession of error (“I’m sorry we got the x-ray backward and removed the wrong kidney.”). In the latter kind of apology, courts traditionally have found a “statement against interest.”
The legal consequence of a statement against interest is that the statement may be admitted in court. Such statements do not automatically establish negligence, but they can be powerful evidence when presented to a jury.
Courts have struggled with medical apologies. General sympathy or feelings of regret or compassion do not generally rise to the level of an admission that the physician did not use reasonable care under the circumstances and ordinarily are not admissible. (For further details, we refer you to the case of Cobbs v. Grant.14 Even if a physician said to the patient that he “blamed himself for [the patient] being back in the hospital for a second time,…the statement signifies compassion, or at most, a feeling of remorse, for plaintiff’s ordeal.”) On the other hand, in cases in which a physician in an apology referred to a “careless” mistake or even a “negligent” mistake, courts have allowed it admitted at trial as a statement against interest. (A 1946 case, Woronka v. Sewall, is an example.15 In that case, the physician said to the patient, “My God, what a mess…she had a very hard delivery, and it was a burning shame to get [an injury] on top of it, and it was because of negligence when they were upstairs.”) Some of these cases come down to the provider’s use of a single word: fault, careless, or negligence.
The ambiguity over the legal place of medical apologies in medicine led attorneys to urge medical providers to avoid statements that might even remotely be taken as statements against interest, including real apologies. The confusion over the admissibility of medical apologies led state legislatures to adopt apology laws. These laws essentially limit what statements against interest may be introduced in professional liability cases when a provider has issued a responsibility or apologized.
Continue to: Apology statutes...
Apology statutes
Massachusetts was the first state to enact an apology law—in 1986.1 As of 2019, a clear majority of states have some form of apology statute. “Apology laws are gaining traction,” was the first sentence in a 2012 review on the subject by Saitta and colleagues.3 Only a few (5 states) have “strong” statutes that have broad protection for statements of fault, error, and negligence, as well as sympathy. The other 33 states have statutes that only protect against statements of sympathy.4,16 FIGURE 1 is a US map showing the apology laws by state.1

Do apology statutes and apologies reduce liability?
The positive aspects of apology include personal, psychological, and emotional benefits to both the one apologizing and the one receiving the apology. It also may have financial benefits to health care providers.4 The assumption has been, and there has been some evidence for the proposition, that apologies reduce the possibility of malpractice claims. That is one of the reasons that institutions may have formal apology policies. Indeed, there is evidence that apologies reduce financial awards to patients, as manifest in the states of Pennsylvania and Kentucky.4 Apologies appear to reduce patient anger and can open the door to better communication with the provider. There is evidence that some kinds of apologies tend to diminish blame and make the injured patient less likely to pursue litigation.10 The conclusion from these studies might be that honest and open communication serves to decrease the incidence of medical malpractice lawsuit initiation and that honesty is the best policy.
It is important to note the difference, however, between apologies (or institutional apology policies) and apology laws. There is some evidence that apology and institutional apology policies may reduce malpractice claims or losses.17,18 On the other hand, the studies of apology laws have not found that these laws have much impact on malpractice rates. An especially good and thorough study of the effect of apology laws nationwide, using insurance claims data, essentially found little net effect of the apology laws.19,20 One other study could find no evidence that apology statutes reduce defensive medicine (so no reduction in provider concerns over liability).21
It should be noted that most studies on medical apology and its effects on malpractice claims generally have looked at the narrow or limited apology statutes (that do not cover expressions of fault or negligence). Few states have the broader statutes, and it is possible that those broader statutes would be more effective in reducing liability. Removing the disincentives to medical apologies is a good thing, but in and of itself it is probably not a liability game changer.
Continue to: Institutional policy and apology...
Institutional policy and apology
Some institutions have established an “inclusion of apology” strategy for medical errors. These policies appear to have a meaningful effect on reducing medical malpractice costs. These programs commonly include a proactive investigation, disclosure of error, and apologies. Such policies have been studied at the University of Michigan and the Veterans Affairs (VA) Hospital in Lexington, Kentucky. The University of Michigan program resulted in a 60% reduction in compensation costs for medical errors.22 It also cut litigation costs by half.23 The review of the Kentucky VA program also was positive.17 FIGURE 2 illustrates the key features of the Michigan program.24

Conclusions: Effective apologies
Our conclusions, first, are that apologies are important from all perspectives: ethical, medical, and legal. On the other hand, all of the attention given in recent years to apology statutes may have been misplaced, at least if they were intended to be malpractice reform.17
Institutional apology and response programs are likely successful because they are thoughtfully put together, generally based on the best understanding of how injured patients respond to apologies and what it takes to be sincere, and communicate that sincerity, in the apology. What is an effective apology?, “The acceptance of responsibility for having caused harm.” It may, for example, mean accepting some financial responsibility for the harm. It is also important that the apology is conveyed in such a way that it includes an element of self-critical expression.25 Although there are many formulations of the elements of an effective apology, one example is, “(1) acknowledging and accepting responsibility for the offense; (2) expressing remorse with forbearance, sincerity, and honesty; (3) explaining the understanding of the offense; and (4) willingness to make reparations.”26
At the other extreme is a medical professional, after a bad event, trying to engage in a half-hearted, awkward, or insincere apology on an ad hoc and poorly planned basis. Worse still, “when victims perceive apologies to be insincere and designed simply to cool them off, they react with more rather than less indignation.”27 Of course, the “forced apology” may be the worst of all. An instance of this was addressed in a New Zealand study in which providers were “forced” to provide a written apology to a couple (Mr. and Mrs. B) and a separate written apology to Baby B when there was failure to discuss vitamin K administration during the antenatal period when it was indicated.28 Rather than emphasizing required apology in such a case, which can seem hollow and disingenuous, emphasis was placed on the apology providing a “positive-physiological” effect for those harmed, and on strategies that “nurture the development of the moral maturity required for authentic apology.”
The great advantage of institutional or practice-wide policies is that they can be developed in the calm of planning, with good foresight and careful consideration. This is much different from having to come up with some approach in the heat of something having gone wrong. Ultimately, however, apologies are not about liability. They are about caring for, respecting, and communicating with those who are harmed. Apologizing is often the right and professional thing to do.
- Afrassiab Z. Why mediation & “sorry” make sense: apology statutes as a catalyst for change in medical malpractice. J Dispute Resolutions. 2019.
- AMA Council on Ethical and Judicial Affairs. AMA code of medical ethics’ opinions on patient safety. Virtual Mentor. 2011;13:626-628.
- Saitta N, Hodge SD. Efficacy of a physician’s words of empathy: an overview of state apology laws. J Am Osteopath Assn. 2012;112:302-306.
- Dealing with a medical mistake: Should physicians apologize to patients? Med Economics. November 10, 2013.
- AOA code of ethics. American Osteopathic Association website. http://www.osteopathic.org/inside-aoa/about /leadershipPages/aos-code-of-ethics.aspx. Accessed January 15, 2020.
- You had me at “I’m sorry”: the impact of physicians’ apologies on medical malpractice litigation. Natl Law Review. November 6, 2018. https://www.natlawreview.com /article/you-had-me-i-m-sorry-impact-physicians-apologiesmedical-malpractice-litigation. Accessed February 6, 2020.
- Robbennolt JK. Apologies and medical error. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2009;467:376-382.
- Bismark MM. The power of apology. N Z Med J. 2009;122:96-106.
- Witman AB, Park DM, Hardin SB. How do patients want physicians to handle mistakes? A survey of internal medicine patients in an academic setting. Arch Intern Med. 1996;156:2565-2569.
- Lawthers AG, Localio AR, Laird NM, et al. Physicians’ perceptions of the risk of being sued. J Health Polit Policy Law. 1992;17:463-482.
- Dahan S, Ducard D, Caeymaex L. Apology in cases of medical error disclosure: thoughts based on a preliminary study. PLoS One. 2017;12:e0181854.
- Halbach JL, Sullivan LL. Teaching medical students about medical errors and patient safety: evaluation of a required curriculum. Acad Med. 2005;80:600-606.
- Nussbaum L. Trial and error: legislating ADR for medical malpractice reform. 2017. Scholarly Works. https://scholars .law.unlv.edu/facpub/1011. Accessed February 7, 2020.
- Cobbs v. Grant, 8 Cal. 3d 229, 104 Cal. Rptr. 505, 502 P.2d 1 (1972).
- Woronka v. Sewall, 320 Mass. 362, 69 N.E.2d 581 (1946).
- Wei M. Doctors, apologies and the law: an analysis and critique of apology law. J Health Law. 2007;40:107-159.
- Kraman SS, Hamm G. Risk management: extreme honesty may be the best policy. Ann Intern Med. 1999;131:963-967.
- Liebman CB, Hyman CS. Medical error disclosure, mediation skills, and malpractice litigation: a demonstration project in Pennsylvania. 2005. https://perma.cc/7257-99GU. Accessed February 7, 2020.
- McMichael BJ, Van Horn RL, Viscusi WK. “Sorry” is never enough: how state apology laws fail to reduce medical malpractice liability risk. Stanford Law Rev. 2019;71:341-409.
- Ho B, Liu E. What’s an apology worth? Decomposing the effect of apologies on medical malpractice payments using state apology laws. J Empirical Legal Studies. 2011;8:179-199.
- McMichael BJ. The failure of sorry: an empirical evaluation of apology laws, health care, and medical malpractice. Lewis & Clark Law Rev. 2017. https://law.lclark.edu/live/files/27734- lcb224article3mcmichaelpdf. Accessed February 7, 2020.
- Kachalia A, Kaufman SR, Boothman R, et al. Liability claims and costs before and after implementation of a medical error disclosure program. Ann Intern Med. 2010;153:213-221.
- Boothman RC, Blackwell AC, Campbell DA Jr, et al. A better approach to medical malpractice claims? The University of Michigan experience. J Health Life Sci Law. 2009;2:125-159.
- The Michigan model: Medical malpractice and patient safety at Michigan Medicine. University of Michigan website. https:// www.uofmhealth.org/michigan-model-medical-malpracticeand-patient-safety-umhs#summary. Accessed February 7, 2020.
- Mastroianni AC, Mello MM, Sommer S, et al. The flaws in state ‘apology’ and ‘disclosure’ laws dilute their intended impact on malpractice suits. Health Aff (Millwood). 2010;29:1611-1619.
- Davis ER. I’m sorry I’m scared of litigation: evaluating the effectiveness of apology laws. Forum: Tennessee Student Legal J. 2016;3. https://trace.tennessee.edu/forum/vol3/iss1/4/. Accessed February 7, 2020.
- Miller DT. Disrespect and the experience of injustice. Annu Rev Psychol. 2001;52:527-553.
- McLennan S, Walker S, Rich LE. Should health care providers be forced to apologise after things go wrong? J Bioeth Inq. 2014;11:431-435
- Afrassiab Z. Why mediation & “sorry” make sense: apology statutes as a catalyst for change in medical malpractice. J Dispute Resolutions. 2019.
- AMA Council on Ethical and Judicial Affairs. AMA code of medical ethics’ opinions on patient safety. Virtual Mentor. 2011;13:626-628.
- Saitta N, Hodge SD. Efficacy of a physician’s words of empathy: an overview of state apology laws. J Am Osteopath Assn. 2012;112:302-306.
- Dealing with a medical mistake: Should physicians apologize to patients? Med Economics. November 10, 2013.
- AOA code of ethics. American Osteopathic Association website. http://www.osteopathic.org/inside-aoa/about /leadershipPages/aos-code-of-ethics.aspx. Accessed January 15, 2020.
- You had me at “I’m sorry”: the impact of physicians’ apologies on medical malpractice litigation. Natl Law Review. November 6, 2018. https://www.natlawreview.com /article/you-had-me-i-m-sorry-impact-physicians-apologiesmedical-malpractice-litigation. Accessed February 6, 2020.
- Robbennolt JK. Apologies and medical error. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2009;467:376-382.
- Bismark MM. The power of apology. N Z Med J. 2009;122:96-106.
- Witman AB, Park DM, Hardin SB. How do patients want physicians to handle mistakes? A survey of internal medicine patients in an academic setting. Arch Intern Med. 1996;156:2565-2569.
- Lawthers AG, Localio AR, Laird NM, et al. Physicians’ perceptions of the risk of being sued. J Health Polit Policy Law. 1992;17:463-482.
- Dahan S, Ducard D, Caeymaex L. Apology in cases of medical error disclosure: thoughts based on a preliminary study. PLoS One. 2017;12:e0181854.
- Halbach JL, Sullivan LL. Teaching medical students about medical errors and patient safety: evaluation of a required curriculum. Acad Med. 2005;80:600-606.
- Nussbaum L. Trial and error: legislating ADR for medical malpractice reform. 2017. Scholarly Works. https://scholars .law.unlv.edu/facpub/1011. Accessed February 7, 2020.
- Cobbs v. Grant, 8 Cal. 3d 229, 104 Cal. Rptr. 505, 502 P.2d 1 (1972).
- Woronka v. Sewall, 320 Mass. 362, 69 N.E.2d 581 (1946).
- Wei M. Doctors, apologies and the law: an analysis and critique of apology law. J Health Law. 2007;40:107-159.
- Kraman SS, Hamm G. Risk management: extreme honesty may be the best policy. Ann Intern Med. 1999;131:963-967.
- Liebman CB, Hyman CS. Medical error disclosure, mediation skills, and malpractice litigation: a demonstration project in Pennsylvania. 2005. https://perma.cc/7257-99GU. Accessed February 7, 2020.
- McMichael BJ, Van Horn RL, Viscusi WK. “Sorry” is never enough: how state apology laws fail to reduce medical malpractice liability risk. Stanford Law Rev. 2019;71:341-409.
- Ho B, Liu E. What’s an apology worth? Decomposing the effect of apologies on medical malpractice payments using state apology laws. J Empirical Legal Studies. 2011;8:179-199.
- McMichael BJ. The failure of sorry: an empirical evaluation of apology laws, health care, and medical malpractice. Lewis & Clark Law Rev. 2017. https://law.lclark.edu/live/files/27734- lcb224article3mcmichaelpdf. Accessed February 7, 2020.
- Kachalia A, Kaufman SR, Boothman R, et al. Liability claims and costs before and after implementation of a medical error disclosure program. Ann Intern Med. 2010;153:213-221.
- Boothman RC, Blackwell AC, Campbell DA Jr, et al. A better approach to medical malpractice claims? The University of Michigan experience. J Health Life Sci Law. 2009;2:125-159.
- The Michigan model: Medical malpractice and patient safety at Michigan Medicine. University of Michigan website. https:// www.uofmhealth.org/michigan-model-medical-malpracticeand-patient-safety-umhs#summary. Accessed February 7, 2020.
- Mastroianni AC, Mello MM, Sommer S, et al. The flaws in state ‘apology’ and ‘disclosure’ laws dilute their intended impact on malpractice suits. Health Aff (Millwood). 2010;29:1611-1619.
- Davis ER. I’m sorry I’m scared of litigation: evaluating the effectiveness of apology laws. Forum: Tennessee Student Legal J. 2016;3. https://trace.tennessee.edu/forum/vol3/iss1/4/. Accessed February 7, 2020.
- Miller DT. Disrespect and the experience of injustice. Annu Rev Psychol. 2001;52:527-553.
- McLennan S, Walker S, Rich LE. Should health care providers be forced to apologise after things go wrong? J Bioeth Inq. 2014;11:431-435
To Prevent Pernicious Political Activities: The Hatch Act and Government Ethics
The impeachment trial has concluded. By the time you read this editorial, Super Tuesday will be over. Then there will be the political party conventions, and finally the general election. Politics is everywhere and will be for the rest of 2020. As a preventive ethics measure, the legal arms of almost every federal agency will be sending cautionary e-mails to employees to remind us that any political activity undertaken must comply with the Hatch Act. Many of you who have worked in federal health care for some years may have heard a fellow employee say, “be careful you don’t violate the Hatch Act.”
Most readers probably had not heard of the statute before entering federal service. And you may have had an experience similar to mine in my early federal career when through osmosis I absorbed my peers fear and trembling when the Hatch Act was mentioned. This was the situation even though you were not at all sure you understood what the lawyers were warning you not to do. In my decades in federal service, I have heard that the Hatch Act dictates everything from you cannot vote to you can run for political office.
All this makes the timing right to review a piece of legislation that governs the political actions of every federal health and administrative professional. The Hatch Act sets apart federal employees from many, if not most, of our civilian counterparts, who, depending on your perspective, have more freedom to express their political views or are not held to such a high standard of ethical conduct.
In legalese, the Hatch Act is Political Activity Authorized; Prohibitions, 5 USC §7323 (1939). The title of this editorial, “To Prevent Pernicious Political Activities” is the formal title of the Hatch Act enacted at a time when government legislation was written in more ornamental rhetoric than the staid language of the current bureaucratic style. The alliterative title phrase of the act is an apt, if dated, encapsulation of the legislative intention of the act, which in modern parlance:
The law’s purpose is to ensure that federal programs are administered in a nonpartisan fashion, to protect federal employees from political coercion in the workplace, and to ensure that federal employees are advanced based on merit and not based on political affiliation. 2
For all its poetic turn of phrase, the title is historically accurate. The Hatch Act was passed in response to rampant partisan activity in public office. It was a key part of an effort to professionalize civil service, and as an essential aspect of that process, to protect federal employees from widespread political influence. The ethical principle behind the legislation is the one that still stands as the ideal for federal practitioners: to serve the people and act for the good of the public and republic.
The Hatch Act was intended to prevent unscrupulous politicians from intimidating federal employees and usurping the machinery of major government agencies to achieve their political ambitions. Imagine if your supervisor was running for office or supporting a particular candidate and ordered you to put a campaign sign in your yard, attend a political rally, and wear a campaign button on your lapel or you would be fired. All that and far worse happened in the good old USA before the Hatch Act.3
The Office of Special Counsel (OSC) is the authoritative guardian of the Hatch Act providing opinions on whether an activity is permitted under the act; investigating compliance with the provisions of the act; taking disciplinary action against the employee for serious violations; and prosecuting those violations before the Merit Systems Protection Board. Now I understand why the incantation “Hatch Act” casts a chill on our civil service souls. While there have been recent allegations against a high-profile political appointee, federal practitioners are not immune to prosecution.4 In 2017, Federal Times reported that the OSC sought disciplinary action against a VA physician for 15 violations of the Hatch Act after he ran for a state Senate seat in 2014.5
Fortunately, the OSC has produced a handy list of “Though Shalt Nots” and “You Cans” as a guide to the Hatch Act.6 Only the highpoints are mentioned here:
- Thou shalt not be a candidate for nomination or election to a partisan public office;
- Thou shalt not use a position of official public authority to influence or interfere with the result of an election;
- Thou shalt not solicit or host, accept, or receive a donation or contribution to a partisan political party, candidate, or group; and
- Thou shalt not engage in political activity on behalf of a partisan political party, candidate, or group while on duty, in a federal space, wearing a federal uniform, or driving a federal vehicle.
Covered under these daunting prohibitions is ordinary American politicking like hosting fundraisers or inviting your coworkers to a political rally, distributing campaign materials, and wearing a T-shirt with your favorite candidates smiling face at work. The new hotbed of concern for the Hatch Act is, you guessed it, social media—you cannot use your blog, Facebook, Instagram, or e-mail account to comment pro or con for a partisan candidate, party, office, or group.6
You may be asking at this point whether you can even watch the political debates? Yes, that is allowed under the Hatch Act along with running for nonpartisan election and participating in nonpartisan campaigns; voting, and registering others to vote; you can contribute money to political campaigns, parties, or partisan groups; attend political rallies, meetings and fundraisers; and even join a political party. Of course these activities must be on your own time and dime, not that of your federal employer. All of these “You Cans” enable a federal employee to engage in the bare minimum of democracy: voting in elections, but opponents argue they bar the civil servant from fully participating in the complex richness of the American political process.7
Nonetheless, since its inception the Hatch Act has been a matter of fierce debate among federal employees and other advocates of civil liberties. Those who feel it should be relaxed contend that the modern merit-based system of government service has rendered the provisions of the Hatch Act unnecessary, even obsolete. In addition, unlike in 1939, critics of the act claim there are now formidable whistleblower protections for employees who experience political coercion. Over the years there have been several efforts to weaken the conflict of interest safeguards that the act contains, leading many commentators to think that some of the amendments and reforms have blurred the tight boundaries between the professional and the political. Others such as the government unions and the American Civil Liberties Union (ACLU) believe that the tight line drawn between public and private binds the liberty of civil servants.8 Those who defend the Hatch Act believe that the wall it erects between professional and personal in the realm of political activities for federal employees must remain high and strong to protect the integrity of the administrative branch and the public trust.9
So, as political advertisements dominate television programming and the texts never stop asking for campaign donations, you can cast your own vote for or against the Hatch Act. As for me and my house, we will follow President Jefferson in preferring to be the property of the people rather than be indebted to the powerful. You need never encounter a true conflict of interest if you have no false conflict of obligation: history teaches us that serving 2 masters usually turns out badly for the slave. Many of you will completely disagree with my stance, holding that your constitutional rights as a citizen are being curtailed, if not outright denied, simply because you choose to serve your country. Our ability to freely hold and express our differences of opinions about the Hatch Act and so much else is what keeps democracy alive.
1. Rayner BL. Life of Thomas Jefferson With Selections From the Most Valuable Portions of his Voluminous and Unrivalled Private Correspondence. Boston, MA: Lilly, Wait, Colman, and Holden; 1834:356.
2. US Office of Special Counsel. Hatch Act overview. https://osc.gov/Services/Pages/HatchAct.aspx. Accessed February 24, 2020.
3. Brown AJ. Public employee participation: Hatch Acts in the federal and state governments. Public Integrity. 2000;2(2):105-120.
4. Phillips A. What is the Hatch Act, and why did Kellyanne Conway get accused of violating it so egregiously? Washington Post. June 13, 2019. https://www.washingtonpost.com/politics/2019/06/13/what-is-hatch-act-why-did-kellyanne-conway-get-accused-violating-it-so-egregiously. Accessed February 24, 2020.
5. Bur J. Special counsel: VA doctor violated Hatch Act while campaigning. https://www.federaltimes.com/federal-oversight/watchdogs/2017/11/22/special-counsel-va-doctor-violated-hatch-act-while-campaigning. Published November 22, 2017. Accessed February 24, 2020.
6. US Office of Special Counsel. A guide to the Hatch Act for the federal employee. https://osc.gov/Documents/Outreach%20and%20Training/Handouts/A%20Guide%20to%20the%20Hatch%20Act%20for%20Federal%20Employees.pdf. Published September 2014. Accessed February 24, 2020.
7. Brown C, Maskell J. Hatch Act restrictions on federal employee’s political activities in the digital age. https://fas.org/sgp/crs/misc/R44469.pdf. Published April 13, 2016. Accessed February 24, 2020.
8. Thurber KT Jr. Revising the Hatch Act: a practitioner’s perspective. Public Manag. 1993;22(1):43.
9. Pearson WM, Castle DS. Expanding the opportunity for partisan activity among government employees: potential effects of federal executive’s political involvement. Int J Public Adm. 2007;16(4):511-525.
The impeachment trial has concluded. By the time you read this editorial, Super Tuesday will be over. Then there will be the political party conventions, and finally the general election. Politics is everywhere and will be for the rest of 2020. As a preventive ethics measure, the legal arms of almost every federal agency will be sending cautionary e-mails to employees to remind us that any political activity undertaken must comply with the Hatch Act. Many of you who have worked in federal health care for some years may have heard a fellow employee say, “be careful you don’t violate the Hatch Act.”
Most readers probably had not heard of the statute before entering federal service. And you may have had an experience similar to mine in my early federal career when through osmosis I absorbed my peers fear and trembling when the Hatch Act was mentioned. This was the situation even though you were not at all sure you understood what the lawyers were warning you not to do. In my decades in federal service, I have heard that the Hatch Act dictates everything from you cannot vote to you can run for political office.
All this makes the timing right to review a piece of legislation that governs the political actions of every federal health and administrative professional. The Hatch Act sets apart federal employees from many, if not most, of our civilian counterparts, who, depending on your perspective, have more freedom to express their political views or are not held to such a high standard of ethical conduct.
In legalese, the Hatch Act is Political Activity Authorized; Prohibitions, 5 USC §7323 (1939). The title of this editorial, “To Prevent Pernicious Political Activities” is the formal title of the Hatch Act enacted at a time when government legislation was written in more ornamental rhetoric than the staid language of the current bureaucratic style. The alliterative title phrase of the act is an apt, if dated, encapsulation of the legislative intention of the act, which in modern parlance:
The law’s purpose is to ensure that federal programs are administered in a nonpartisan fashion, to protect federal employees from political coercion in the workplace, and to ensure that federal employees are advanced based on merit and not based on political affiliation. 2
For all its poetic turn of phrase, the title is historically accurate. The Hatch Act was passed in response to rampant partisan activity in public office. It was a key part of an effort to professionalize civil service, and as an essential aspect of that process, to protect federal employees from widespread political influence. The ethical principle behind the legislation is the one that still stands as the ideal for federal practitioners: to serve the people and act for the good of the public and republic.
The Hatch Act was intended to prevent unscrupulous politicians from intimidating federal employees and usurping the machinery of major government agencies to achieve their political ambitions. Imagine if your supervisor was running for office or supporting a particular candidate and ordered you to put a campaign sign in your yard, attend a political rally, and wear a campaign button on your lapel or you would be fired. All that and far worse happened in the good old USA before the Hatch Act.3
The Office of Special Counsel (OSC) is the authoritative guardian of the Hatch Act providing opinions on whether an activity is permitted under the act; investigating compliance with the provisions of the act; taking disciplinary action against the employee for serious violations; and prosecuting those violations before the Merit Systems Protection Board. Now I understand why the incantation “Hatch Act” casts a chill on our civil service souls. While there have been recent allegations against a high-profile political appointee, federal practitioners are not immune to prosecution.4 In 2017, Federal Times reported that the OSC sought disciplinary action against a VA physician for 15 violations of the Hatch Act after he ran for a state Senate seat in 2014.5
Fortunately, the OSC has produced a handy list of “Though Shalt Nots” and “You Cans” as a guide to the Hatch Act.6 Only the highpoints are mentioned here:
- Thou shalt not be a candidate for nomination or election to a partisan public office;
- Thou shalt not use a position of official public authority to influence or interfere with the result of an election;
- Thou shalt not solicit or host, accept, or receive a donation or contribution to a partisan political party, candidate, or group; and
- Thou shalt not engage in political activity on behalf of a partisan political party, candidate, or group while on duty, in a federal space, wearing a federal uniform, or driving a federal vehicle.
Covered under these daunting prohibitions is ordinary American politicking like hosting fundraisers or inviting your coworkers to a political rally, distributing campaign materials, and wearing a T-shirt with your favorite candidates smiling face at work. The new hotbed of concern for the Hatch Act is, you guessed it, social media—you cannot use your blog, Facebook, Instagram, or e-mail account to comment pro or con for a partisan candidate, party, office, or group.6
You may be asking at this point whether you can even watch the political debates? Yes, that is allowed under the Hatch Act along with running for nonpartisan election and participating in nonpartisan campaigns; voting, and registering others to vote; you can contribute money to political campaigns, parties, or partisan groups; attend political rallies, meetings and fundraisers; and even join a political party. Of course these activities must be on your own time and dime, not that of your federal employer. All of these “You Cans” enable a federal employee to engage in the bare minimum of democracy: voting in elections, but opponents argue they bar the civil servant from fully participating in the complex richness of the American political process.7
Nonetheless, since its inception the Hatch Act has been a matter of fierce debate among federal employees and other advocates of civil liberties. Those who feel it should be relaxed contend that the modern merit-based system of government service has rendered the provisions of the Hatch Act unnecessary, even obsolete. In addition, unlike in 1939, critics of the act claim there are now formidable whistleblower protections for employees who experience political coercion. Over the years there have been several efforts to weaken the conflict of interest safeguards that the act contains, leading many commentators to think that some of the amendments and reforms have blurred the tight boundaries between the professional and the political. Others such as the government unions and the American Civil Liberties Union (ACLU) believe that the tight line drawn between public and private binds the liberty of civil servants.8 Those who defend the Hatch Act believe that the wall it erects between professional and personal in the realm of political activities for federal employees must remain high and strong to protect the integrity of the administrative branch and the public trust.9
So, as political advertisements dominate television programming and the texts never stop asking for campaign donations, you can cast your own vote for or against the Hatch Act. As for me and my house, we will follow President Jefferson in preferring to be the property of the people rather than be indebted to the powerful. You need never encounter a true conflict of interest if you have no false conflict of obligation: history teaches us that serving 2 masters usually turns out badly for the slave. Many of you will completely disagree with my stance, holding that your constitutional rights as a citizen are being curtailed, if not outright denied, simply because you choose to serve your country. Our ability to freely hold and express our differences of opinions about the Hatch Act and so much else is what keeps democracy alive.
The impeachment trial has concluded. By the time you read this editorial, Super Tuesday will be over. Then there will be the political party conventions, and finally the general election. Politics is everywhere and will be for the rest of 2020. As a preventive ethics measure, the legal arms of almost every federal agency will be sending cautionary e-mails to employees to remind us that any political activity undertaken must comply with the Hatch Act. Many of you who have worked in federal health care for some years may have heard a fellow employee say, “be careful you don’t violate the Hatch Act.”
Most readers probably had not heard of the statute before entering federal service. And you may have had an experience similar to mine in my early federal career when through osmosis I absorbed my peers fear and trembling when the Hatch Act was mentioned. This was the situation even though you were not at all sure you understood what the lawyers were warning you not to do. In my decades in federal service, I have heard that the Hatch Act dictates everything from you cannot vote to you can run for political office.
All this makes the timing right to review a piece of legislation that governs the political actions of every federal health and administrative professional. The Hatch Act sets apart federal employees from many, if not most, of our civilian counterparts, who, depending on your perspective, have more freedom to express their political views or are not held to such a high standard of ethical conduct.
In legalese, the Hatch Act is Political Activity Authorized; Prohibitions, 5 USC §7323 (1939). The title of this editorial, “To Prevent Pernicious Political Activities” is the formal title of the Hatch Act enacted at a time when government legislation was written in more ornamental rhetoric than the staid language of the current bureaucratic style. The alliterative title phrase of the act is an apt, if dated, encapsulation of the legislative intention of the act, which in modern parlance:
The law’s purpose is to ensure that federal programs are administered in a nonpartisan fashion, to protect federal employees from political coercion in the workplace, and to ensure that federal employees are advanced based on merit and not based on political affiliation. 2
For all its poetic turn of phrase, the title is historically accurate. The Hatch Act was passed in response to rampant partisan activity in public office. It was a key part of an effort to professionalize civil service, and as an essential aspect of that process, to protect federal employees from widespread political influence. The ethical principle behind the legislation is the one that still stands as the ideal for federal practitioners: to serve the people and act for the good of the public and republic.
The Hatch Act was intended to prevent unscrupulous politicians from intimidating federal employees and usurping the machinery of major government agencies to achieve their political ambitions. Imagine if your supervisor was running for office or supporting a particular candidate and ordered you to put a campaign sign in your yard, attend a political rally, and wear a campaign button on your lapel or you would be fired. All that and far worse happened in the good old USA before the Hatch Act.3
The Office of Special Counsel (OSC) is the authoritative guardian of the Hatch Act providing opinions on whether an activity is permitted under the act; investigating compliance with the provisions of the act; taking disciplinary action against the employee for serious violations; and prosecuting those violations before the Merit Systems Protection Board. Now I understand why the incantation “Hatch Act” casts a chill on our civil service souls. While there have been recent allegations against a high-profile political appointee, federal practitioners are not immune to prosecution.4 In 2017, Federal Times reported that the OSC sought disciplinary action against a VA physician for 15 violations of the Hatch Act after he ran for a state Senate seat in 2014.5
Fortunately, the OSC has produced a handy list of “Though Shalt Nots” and “You Cans” as a guide to the Hatch Act.6 Only the highpoints are mentioned here:
- Thou shalt not be a candidate for nomination or election to a partisan public office;
- Thou shalt not use a position of official public authority to influence or interfere with the result of an election;
- Thou shalt not solicit or host, accept, or receive a donation or contribution to a partisan political party, candidate, or group; and
- Thou shalt not engage in political activity on behalf of a partisan political party, candidate, or group while on duty, in a federal space, wearing a federal uniform, or driving a federal vehicle.
Covered under these daunting prohibitions is ordinary American politicking like hosting fundraisers or inviting your coworkers to a political rally, distributing campaign materials, and wearing a T-shirt with your favorite candidates smiling face at work. The new hotbed of concern for the Hatch Act is, you guessed it, social media—you cannot use your blog, Facebook, Instagram, or e-mail account to comment pro or con for a partisan candidate, party, office, or group.6
You may be asking at this point whether you can even watch the political debates? Yes, that is allowed under the Hatch Act along with running for nonpartisan election and participating in nonpartisan campaigns; voting, and registering others to vote; you can contribute money to political campaigns, parties, or partisan groups; attend political rallies, meetings and fundraisers; and even join a political party. Of course these activities must be on your own time and dime, not that of your federal employer. All of these “You Cans” enable a federal employee to engage in the bare minimum of democracy: voting in elections, but opponents argue they bar the civil servant from fully participating in the complex richness of the American political process.7
Nonetheless, since its inception the Hatch Act has been a matter of fierce debate among federal employees and other advocates of civil liberties. Those who feel it should be relaxed contend that the modern merit-based system of government service has rendered the provisions of the Hatch Act unnecessary, even obsolete. In addition, unlike in 1939, critics of the act claim there are now formidable whistleblower protections for employees who experience political coercion. Over the years there have been several efforts to weaken the conflict of interest safeguards that the act contains, leading many commentators to think that some of the amendments and reforms have blurred the tight boundaries between the professional and the political. Others such as the government unions and the American Civil Liberties Union (ACLU) believe that the tight line drawn between public and private binds the liberty of civil servants.8 Those who defend the Hatch Act believe that the wall it erects between professional and personal in the realm of political activities for federal employees must remain high and strong to protect the integrity of the administrative branch and the public trust.9
So, as political advertisements dominate television programming and the texts never stop asking for campaign donations, you can cast your own vote for or against the Hatch Act. As for me and my house, we will follow President Jefferson in preferring to be the property of the people rather than be indebted to the powerful. You need never encounter a true conflict of interest if you have no false conflict of obligation: history teaches us that serving 2 masters usually turns out badly for the slave. Many of you will completely disagree with my stance, holding that your constitutional rights as a citizen are being curtailed, if not outright denied, simply because you choose to serve your country. Our ability to freely hold and express our differences of opinions about the Hatch Act and so much else is what keeps democracy alive.
1. Rayner BL. Life of Thomas Jefferson With Selections From the Most Valuable Portions of his Voluminous and Unrivalled Private Correspondence. Boston, MA: Lilly, Wait, Colman, and Holden; 1834:356.
2. US Office of Special Counsel. Hatch Act overview. https://osc.gov/Services/Pages/HatchAct.aspx. Accessed February 24, 2020.
3. Brown AJ. Public employee participation: Hatch Acts in the federal and state governments. Public Integrity. 2000;2(2):105-120.
4. Phillips A. What is the Hatch Act, and why did Kellyanne Conway get accused of violating it so egregiously? Washington Post. June 13, 2019. https://www.washingtonpost.com/politics/2019/06/13/what-is-hatch-act-why-did-kellyanne-conway-get-accused-violating-it-so-egregiously. Accessed February 24, 2020.
5. Bur J. Special counsel: VA doctor violated Hatch Act while campaigning. https://www.federaltimes.com/federal-oversight/watchdogs/2017/11/22/special-counsel-va-doctor-violated-hatch-act-while-campaigning. Published November 22, 2017. Accessed February 24, 2020.
6. US Office of Special Counsel. A guide to the Hatch Act for the federal employee. https://osc.gov/Documents/Outreach%20and%20Training/Handouts/A%20Guide%20to%20the%20Hatch%20Act%20for%20Federal%20Employees.pdf. Published September 2014. Accessed February 24, 2020.
7. Brown C, Maskell J. Hatch Act restrictions on federal employee’s political activities in the digital age. https://fas.org/sgp/crs/misc/R44469.pdf. Published April 13, 2016. Accessed February 24, 2020.
8. Thurber KT Jr. Revising the Hatch Act: a practitioner’s perspective. Public Manag. 1993;22(1):43.
9. Pearson WM, Castle DS. Expanding the opportunity for partisan activity among government employees: potential effects of federal executive’s political involvement. Int J Public Adm. 2007;16(4):511-525.
1. Rayner BL. Life of Thomas Jefferson With Selections From the Most Valuable Portions of his Voluminous and Unrivalled Private Correspondence. Boston, MA: Lilly, Wait, Colman, and Holden; 1834:356.
2. US Office of Special Counsel. Hatch Act overview. https://osc.gov/Services/Pages/HatchAct.aspx. Accessed February 24, 2020.
3. Brown AJ. Public employee participation: Hatch Acts in the federal and state governments. Public Integrity. 2000;2(2):105-120.
4. Phillips A. What is the Hatch Act, and why did Kellyanne Conway get accused of violating it so egregiously? Washington Post. June 13, 2019. https://www.washingtonpost.com/politics/2019/06/13/what-is-hatch-act-why-did-kellyanne-conway-get-accused-violating-it-so-egregiously. Accessed February 24, 2020.
5. Bur J. Special counsel: VA doctor violated Hatch Act while campaigning. https://www.federaltimes.com/federal-oversight/watchdogs/2017/11/22/special-counsel-va-doctor-violated-hatch-act-while-campaigning. Published November 22, 2017. Accessed February 24, 2020.
6. US Office of Special Counsel. A guide to the Hatch Act for the federal employee. https://osc.gov/Documents/Outreach%20and%20Training/Handouts/A%20Guide%20to%20the%20Hatch%20Act%20for%20Federal%20Employees.pdf. Published September 2014. Accessed February 24, 2020.
7. Brown C, Maskell J. Hatch Act restrictions on federal employee’s political activities in the digital age. https://fas.org/sgp/crs/misc/R44469.pdf. Published April 13, 2016. Accessed February 24, 2020.
8. Thurber KT Jr. Revising the Hatch Act: a practitioner’s perspective. Public Manag. 1993;22(1):43.
9. Pearson WM, Castle DS. Expanding the opportunity for partisan activity among government employees: potential effects of federal executive’s political involvement. Int J Public Adm. 2007;16(4):511-525.
DoD ‘Taking all Necessary Precautions’ Against COVID-19
In late February, a soldier stationed at Camp Carroll near Daegu, South Korea, was the first military member to test positive for the coronavirus (COVID-19). Before being diagnosed, he visited other areas, including Camp Walker in Daegu, according to a statement released by US Forces Korea. More than 75,000 troops are stationed in countries with virus outbreaks, including Japan, Italy, and Bahrain.
Military research laboratories are working “feverishly around the horn” to come up with a vaccine, Joint Chiefs of Staff Chairman Gen. Mark A. Milley said in a March 2, 2020, news conference. At the same conference, Defense Secretary Mark T. Esper, MD, said US Department of Defense (DoD) civilian and military leadership are working together to prepare for short-and long-term scenarios.
The US Northern Command is the “global integrator,” Esper said, with the DoD communicating regularly with operational commanders to assess how the virus might impact exercises and ongoing operations around the world. For example, a command post exercise in South Korea has been postponed; Exercise Cobra Gold in Thailand is continuing.
Commanders are taking all necessary precautions because the virus is unique to every situation and every location, Esper said: “We’re relying on them to make good judgments.”
He emphasized that commanders at all levels have the authority and guidance they need to operate. In a late February video teleconference, Esper had told commanders deployed overseas that he wanted them to give him a heads-up before making decisions related to protecting their troops, according to The New York Times.
The New York Times article cited an exchange in which Gen. Robert Abrams, commander of American forces in South Korea, where > 4,000 coronavirus cases have been confirmed, discussed his options to protect American military personnel against the virus. Esper said he wanted advance notice, according to an official briefed on the call and quoted in the Times article. Gen. Abrams said although he would try to give Sec. Esper advance warning, he might have to make urgent health decisions before receiving final approval from Washington.
In a statement responding to the Times article, Jonathan Hoffman, Assistant to the Secretary of Defense for Public Affairs, said the Secretary of Defense has given the Global Combatant Commanders the “clear and unequivocal authority” to take any and all actions necessary to ensure the health and safety of US service members, civilian DoD personnel, families, and dependents.
In the video teleconference, Hoffman said, Secretary Espers “directed commanders to take all force health protection measures, and to notify their chain of command when actions are taken so that DoD leadership can inform the interagency—including US Department of Health and Human Services, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), the Department of Homeland Security, the State Department, and the White House—and the American people.” Esper “explicitly did not direct them to ‘clear’ their force health decisions in advance,” Hoffman said. “[T]hat is a dangerous and inaccurate mischaracterization.”
In January, the Office of the Under Secretary of Defense released a memorandum on force health protection guidance for the coronavirus outbreak. The DoD, it says, will follow the CDC guidance and will “closely coordinate with interagency partners to ensure accurate and timely information is available.”
“An informed, common-sense approach minimizes the chances of getting sick,” military health officials say. But, “due to the dynamic nature of this outbreak,” people should frequently check the CDC website for additional updates. Related Military Health System information and links to the CDC are available at https://www.health.mil/News/In-the-Spotlight/Coronavirus.
The CDC provides a summary of its latest recommendations and DoD health care providers can access COVID-19–specific guidance, including information on evaluating “persons under investigation,” at https://www.cdc.gov/coronavirus/2019-nCoV/clinical-criteria.html.
Sec. Esper, in the Monday news conference, said, “My number-one priority remains to protect our forces and their families; second is to safeguard our mission capabilities and third [is] to support the interagency whole-of-government’s approach. We will continue to take all necessary precautions to ensure that our people are safe and able to continue their very important mission.”
In late February, a soldier stationed at Camp Carroll near Daegu, South Korea, was the first military member to test positive for the coronavirus (COVID-19). Before being diagnosed, he visited other areas, including Camp Walker in Daegu, according to a statement released by US Forces Korea. More than 75,000 troops are stationed in countries with virus outbreaks, including Japan, Italy, and Bahrain.
Military research laboratories are working “feverishly around the horn” to come up with a vaccine, Joint Chiefs of Staff Chairman Gen. Mark A. Milley said in a March 2, 2020, news conference. At the same conference, Defense Secretary Mark T. Esper, MD, said US Department of Defense (DoD) civilian and military leadership are working together to prepare for short-and long-term scenarios.
The US Northern Command is the “global integrator,” Esper said, with the DoD communicating regularly with operational commanders to assess how the virus might impact exercises and ongoing operations around the world. For example, a command post exercise in South Korea has been postponed; Exercise Cobra Gold in Thailand is continuing.
Commanders are taking all necessary precautions because the virus is unique to every situation and every location, Esper said: “We’re relying on them to make good judgments.”
He emphasized that commanders at all levels have the authority and guidance they need to operate. In a late February video teleconference, Esper had told commanders deployed overseas that he wanted them to give him a heads-up before making decisions related to protecting their troops, according to The New York Times.
The New York Times article cited an exchange in which Gen. Robert Abrams, commander of American forces in South Korea, where > 4,000 coronavirus cases have been confirmed, discussed his options to protect American military personnel against the virus. Esper said he wanted advance notice, according to an official briefed on the call and quoted in the Times article. Gen. Abrams said although he would try to give Sec. Esper advance warning, he might have to make urgent health decisions before receiving final approval from Washington.
In a statement responding to the Times article, Jonathan Hoffman, Assistant to the Secretary of Defense for Public Affairs, said the Secretary of Defense has given the Global Combatant Commanders the “clear and unequivocal authority” to take any and all actions necessary to ensure the health and safety of US service members, civilian DoD personnel, families, and dependents.
In the video teleconference, Hoffman said, Secretary Espers “directed commanders to take all force health protection measures, and to notify their chain of command when actions are taken so that DoD leadership can inform the interagency—including US Department of Health and Human Services, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), the Department of Homeland Security, the State Department, and the White House—and the American people.” Esper “explicitly did not direct them to ‘clear’ their force health decisions in advance,” Hoffman said. “[T]hat is a dangerous and inaccurate mischaracterization.”
In January, the Office of the Under Secretary of Defense released a memorandum on force health protection guidance for the coronavirus outbreak. The DoD, it says, will follow the CDC guidance and will “closely coordinate with interagency partners to ensure accurate and timely information is available.”
“An informed, common-sense approach minimizes the chances of getting sick,” military health officials say. But, “due to the dynamic nature of this outbreak,” people should frequently check the CDC website for additional updates. Related Military Health System information and links to the CDC are available at https://www.health.mil/News/In-the-Spotlight/Coronavirus.
The CDC provides a summary of its latest recommendations and DoD health care providers can access COVID-19–specific guidance, including information on evaluating “persons under investigation,” at https://www.cdc.gov/coronavirus/2019-nCoV/clinical-criteria.html.
Sec. Esper, in the Monday news conference, said, “My number-one priority remains to protect our forces and their families; second is to safeguard our mission capabilities and third [is] to support the interagency whole-of-government’s approach. We will continue to take all necessary precautions to ensure that our people are safe and able to continue their very important mission.”
In late February, a soldier stationed at Camp Carroll near Daegu, South Korea, was the first military member to test positive for the coronavirus (COVID-19). Before being diagnosed, he visited other areas, including Camp Walker in Daegu, according to a statement released by US Forces Korea. More than 75,000 troops are stationed in countries with virus outbreaks, including Japan, Italy, and Bahrain.
Military research laboratories are working “feverishly around the horn” to come up with a vaccine, Joint Chiefs of Staff Chairman Gen. Mark A. Milley said in a March 2, 2020, news conference. At the same conference, Defense Secretary Mark T. Esper, MD, said US Department of Defense (DoD) civilian and military leadership are working together to prepare for short-and long-term scenarios.
The US Northern Command is the “global integrator,” Esper said, with the DoD communicating regularly with operational commanders to assess how the virus might impact exercises and ongoing operations around the world. For example, a command post exercise in South Korea has been postponed; Exercise Cobra Gold in Thailand is continuing.
Commanders are taking all necessary precautions because the virus is unique to every situation and every location, Esper said: “We’re relying on them to make good judgments.”
He emphasized that commanders at all levels have the authority and guidance they need to operate. In a late February video teleconference, Esper had told commanders deployed overseas that he wanted them to give him a heads-up before making decisions related to protecting their troops, according to The New York Times.
The New York Times article cited an exchange in which Gen. Robert Abrams, commander of American forces in South Korea, where > 4,000 coronavirus cases have been confirmed, discussed his options to protect American military personnel against the virus. Esper said he wanted advance notice, according to an official briefed on the call and quoted in the Times article. Gen. Abrams said although he would try to give Sec. Esper advance warning, he might have to make urgent health decisions before receiving final approval from Washington.
In a statement responding to the Times article, Jonathan Hoffman, Assistant to the Secretary of Defense for Public Affairs, said the Secretary of Defense has given the Global Combatant Commanders the “clear and unequivocal authority” to take any and all actions necessary to ensure the health and safety of US service members, civilian DoD personnel, families, and dependents.
In the video teleconference, Hoffman said, Secretary Espers “directed commanders to take all force health protection measures, and to notify their chain of command when actions are taken so that DoD leadership can inform the interagency—including US Department of Health and Human Services, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), the Department of Homeland Security, the State Department, and the White House—and the American people.” Esper “explicitly did not direct them to ‘clear’ their force health decisions in advance,” Hoffman said. “[T]hat is a dangerous and inaccurate mischaracterization.”
In January, the Office of the Under Secretary of Defense released a memorandum on force health protection guidance for the coronavirus outbreak. The DoD, it says, will follow the CDC guidance and will “closely coordinate with interagency partners to ensure accurate and timely information is available.”
“An informed, common-sense approach minimizes the chances of getting sick,” military health officials say. But, “due to the dynamic nature of this outbreak,” people should frequently check the CDC website for additional updates. Related Military Health System information and links to the CDC are available at https://www.health.mil/News/In-the-Spotlight/Coronavirus.
The CDC provides a summary of its latest recommendations and DoD health care providers can access COVID-19–specific guidance, including information on evaluating “persons under investigation,” at https://www.cdc.gov/coronavirus/2019-nCoV/clinical-criteria.html.
Sec. Esper, in the Monday news conference, said, “My number-one priority remains to protect our forces and their families; second is to safeguard our mission capabilities and third [is] to support the interagency whole-of-government’s approach. We will continue to take all necessary precautions to ensure that our people are safe and able to continue their very important mission.”
FDA moves to expand coronavirus testing capacity; CDC clarifies testing criteria
The White House Coronavirus Task Force appeared at a press briefing March 2 to provide updates about testing strategies and public health coordination to address the current outbreak of the coronavirus COVID-19. Speaking at the briefing, led by Vice President Mike Pence, Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) director Robert Redfield, MD, said, “Working with our public health partners we continue to be able to identify new community cases and use our public health efforts to aggressively confirm, isolate, and do contact tracking.” Calling state, local, tribal, and territorial public health departments “the backbone of the public health system in our country,” Dr. Redfield noted that he expected many more confirmed COVID-19 cases to emerge.
At least some of the expected increase in confirmed cases of COVID-19 will occur because of expanded testing capacity, noted several of the task force members. On Feb. 29, the Food and Drug Administration issued a the virus that is causing the current outbreak of COVID-19.
Highly qualified laboratories, including both those run by public agencies and private labs, are now authorized to begin using their own validated test for the virus as long as they submit an Emergency Use Authorization (EUA) to the Food and Drug Administration within 15 days of notifying the agency of validation.
“To effectively respond to the COVID-19 outbreak, rapid detection of cases and contacts, appropriate clinical management and infection control, and implementation of community mitigation efforts are critical. This can best be achieved with wide availability of testing capabilities in health care settings, reference and commercial laboratories, and at the point of care,” the agency wrote in a press announcement of the expedited test expansion.
On Feb. 4, the Secretary of the Department of Health & Human Services declared a coronavirus public health emergency. The FDA was then authorized to allow individual laboratories with validated coronavirus tests to begin testing samples immediately. The goal is a more rapid and expanded testing capacity in the United States.
“The global emergence of COVID-19 is concerning, and we appreciate the efforts of the FDA to help bring more testing capability to the U.S.,” Nancy Messonnier, MD, director of the CDC’s National Center for Immunization and Respiratory Diseases (NCIRD), said in the press release.
The new guidance that permits the immediate use of clinical tests after individual development and validation, said the FDA, only applies to labs already certified to perform high complexity testing under Clinical Laboratory Improvement Amendments. Many governmental, academic, and private laboratories fall into this category, however.
“Under this policy, we expect certain laboratories who develop validated tests for coronavirus would begin using them right away prior to FDA review,” said Jeffrey Shuren, MD, JD, director of the FDA’s Center for Devices and Radiological Health. “We believe this action will support laboratories across the country working on this urgent public health situation,” he added in the press release.
“By the end of this week, close to a million tests will be available,” FDA Commissioner Stephen M. Hahn, MD, said during the March 2 briefing.*
Updated criteria
The CDC is maintaining updated criteria for the virus testing on its website. Testing criteria are based both on clinical features and epidemiologic risk.
Individuals with less severe clinical features – those who have either fever or signs and symptoms of lower respiratory disease such as cough or shortness of breath, but who don’t require hospitalization – should be tested if they have high epidemiologic risk. “High risk” is defined by the CDC as any individual, including health care workers, who has had close contact with a person with confirmed COVID-19 within the past 2 weeks. For health care workers, testing can be considered even if they have relatively mild respiratory symptoms or have had contact with a person who is suspected, but not yet confirmed, to have coronavirus.
In its testing guidance, the CDC recognizes that defining close contact is difficult. General guidelines are that individuals are considered to have been in close contact with a person who has COVID-19 if they were within about six feet of the person for a prolonged period, or cared for or have spent a prolonged amount of time in the same room or house as a person with confirmed COVID-19.
Individuals who have both fever and signs or symptoms of lower respiratory illness who require hospitalization should be tested if they have a history of travel from any affected geographic area within 14 days of the onset of their symptoms. The CDC now defines “affected geographic area” as any country or region that has at least a CDC Level 2 Travel Health Notice for COVID-19, so that the testing criteria themselves don’t need to be updated when new geographic areas are included in these alerts. As of March 3, China, Iran, Italy, Japan, and South Korea all have Level 2 or 3 travel alerts.
The CDC now recommends that any patient who has severe acute lower respiratory illness that requires hospitalization and doesn’t have an alternative diagnosis should be tested, even without any identified source of exposure.
“Despite seeing these new cases, the risk to the American people is low,” said the CDC’s Dr. Redfield. In response to a question from the press about how fast the coronavirus will spread across the United States, Dr. Redfield said, “From the beginning we’ve anticipated seeing community cases pop up.” He added that as these cases arise, testing and public health strategies will focus on unearthing linkages and contacts to learn how the virus is spreading. “We’ll use the public health strategies that we can to limit that transmission,” he said.
*An earlier version of this article misattributed this quote.
The White House Coronavirus Task Force appeared at a press briefing March 2 to provide updates about testing strategies and public health coordination to address the current outbreak of the coronavirus COVID-19. Speaking at the briefing, led by Vice President Mike Pence, Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) director Robert Redfield, MD, said, “Working with our public health partners we continue to be able to identify new community cases and use our public health efforts to aggressively confirm, isolate, and do contact tracking.” Calling state, local, tribal, and territorial public health departments “the backbone of the public health system in our country,” Dr. Redfield noted that he expected many more confirmed COVID-19 cases to emerge.
At least some of the expected increase in confirmed cases of COVID-19 will occur because of expanded testing capacity, noted several of the task force members. On Feb. 29, the Food and Drug Administration issued a the virus that is causing the current outbreak of COVID-19.
Highly qualified laboratories, including both those run by public agencies and private labs, are now authorized to begin using their own validated test for the virus as long as they submit an Emergency Use Authorization (EUA) to the Food and Drug Administration within 15 days of notifying the agency of validation.
“To effectively respond to the COVID-19 outbreak, rapid detection of cases and contacts, appropriate clinical management and infection control, and implementation of community mitigation efforts are critical. This can best be achieved with wide availability of testing capabilities in health care settings, reference and commercial laboratories, and at the point of care,” the agency wrote in a press announcement of the expedited test expansion.
On Feb. 4, the Secretary of the Department of Health & Human Services declared a coronavirus public health emergency. The FDA was then authorized to allow individual laboratories with validated coronavirus tests to begin testing samples immediately. The goal is a more rapid and expanded testing capacity in the United States.
“The global emergence of COVID-19 is concerning, and we appreciate the efforts of the FDA to help bring more testing capability to the U.S.,” Nancy Messonnier, MD, director of the CDC’s National Center for Immunization and Respiratory Diseases (NCIRD), said in the press release.
The new guidance that permits the immediate use of clinical tests after individual development and validation, said the FDA, only applies to labs already certified to perform high complexity testing under Clinical Laboratory Improvement Amendments. Many governmental, academic, and private laboratories fall into this category, however.
“Under this policy, we expect certain laboratories who develop validated tests for coronavirus would begin using them right away prior to FDA review,” said Jeffrey Shuren, MD, JD, director of the FDA’s Center for Devices and Radiological Health. “We believe this action will support laboratories across the country working on this urgent public health situation,” he added in the press release.
“By the end of this week, close to a million tests will be available,” FDA Commissioner Stephen M. Hahn, MD, said during the March 2 briefing.*
Updated criteria
The CDC is maintaining updated criteria for the virus testing on its website. Testing criteria are based both on clinical features and epidemiologic risk.
Individuals with less severe clinical features – those who have either fever or signs and symptoms of lower respiratory disease such as cough or shortness of breath, but who don’t require hospitalization – should be tested if they have high epidemiologic risk. “High risk” is defined by the CDC as any individual, including health care workers, who has had close contact with a person with confirmed COVID-19 within the past 2 weeks. For health care workers, testing can be considered even if they have relatively mild respiratory symptoms or have had contact with a person who is suspected, but not yet confirmed, to have coronavirus.
In its testing guidance, the CDC recognizes that defining close contact is difficult. General guidelines are that individuals are considered to have been in close contact with a person who has COVID-19 if they were within about six feet of the person for a prolonged period, or cared for or have spent a prolonged amount of time in the same room or house as a person with confirmed COVID-19.
Individuals who have both fever and signs or symptoms of lower respiratory illness who require hospitalization should be tested if they have a history of travel from any affected geographic area within 14 days of the onset of their symptoms. The CDC now defines “affected geographic area” as any country or region that has at least a CDC Level 2 Travel Health Notice for COVID-19, so that the testing criteria themselves don’t need to be updated when new geographic areas are included in these alerts. As of March 3, China, Iran, Italy, Japan, and South Korea all have Level 2 or 3 travel alerts.
The CDC now recommends that any patient who has severe acute lower respiratory illness that requires hospitalization and doesn’t have an alternative diagnosis should be tested, even without any identified source of exposure.
“Despite seeing these new cases, the risk to the American people is low,” said the CDC’s Dr. Redfield. In response to a question from the press about how fast the coronavirus will spread across the United States, Dr. Redfield said, “From the beginning we’ve anticipated seeing community cases pop up.” He added that as these cases arise, testing and public health strategies will focus on unearthing linkages and contacts to learn how the virus is spreading. “We’ll use the public health strategies that we can to limit that transmission,” he said.
*An earlier version of this article misattributed this quote.
The White House Coronavirus Task Force appeared at a press briefing March 2 to provide updates about testing strategies and public health coordination to address the current outbreak of the coronavirus COVID-19. Speaking at the briefing, led by Vice President Mike Pence, Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) director Robert Redfield, MD, said, “Working with our public health partners we continue to be able to identify new community cases and use our public health efforts to aggressively confirm, isolate, and do contact tracking.” Calling state, local, tribal, and territorial public health departments “the backbone of the public health system in our country,” Dr. Redfield noted that he expected many more confirmed COVID-19 cases to emerge.
At least some of the expected increase in confirmed cases of COVID-19 will occur because of expanded testing capacity, noted several of the task force members. On Feb. 29, the Food and Drug Administration issued a the virus that is causing the current outbreak of COVID-19.
Highly qualified laboratories, including both those run by public agencies and private labs, are now authorized to begin using their own validated test for the virus as long as they submit an Emergency Use Authorization (EUA) to the Food and Drug Administration within 15 days of notifying the agency of validation.
“To effectively respond to the COVID-19 outbreak, rapid detection of cases and contacts, appropriate clinical management and infection control, and implementation of community mitigation efforts are critical. This can best be achieved with wide availability of testing capabilities in health care settings, reference and commercial laboratories, and at the point of care,” the agency wrote in a press announcement of the expedited test expansion.
On Feb. 4, the Secretary of the Department of Health & Human Services declared a coronavirus public health emergency. The FDA was then authorized to allow individual laboratories with validated coronavirus tests to begin testing samples immediately. The goal is a more rapid and expanded testing capacity in the United States.
“The global emergence of COVID-19 is concerning, and we appreciate the efforts of the FDA to help bring more testing capability to the U.S.,” Nancy Messonnier, MD, director of the CDC’s National Center for Immunization and Respiratory Diseases (NCIRD), said in the press release.
The new guidance that permits the immediate use of clinical tests after individual development and validation, said the FDA, only applies to labs already certified to perform high complexity testing under Clinical Laboratory Improvement Amendments. Many governmental, academic, and private laboratories fall into this category, however.
“Under this policy, we expect certain laboratories who develop validated tests for coronavirus would begin using them right away prior to FDA review,” said Jeffrey Shuren, MD, JD, director of the FDA’s Center for Devices and Radiological Health. “We believe this action will support laboratories across the country working on this urgent public health situation,” he added in the press release.
“By the end of this week, close to a million tests will be available,” FDA Commissioner Stephen M. Hahn, MD, said during the March 2 briefing.*
Updated criteria
The CDC is maintaining updated criteria for the virus testing on its website. Testing criteria are based both on clinical features and epidemiologic risk.
Individuals with less severe clinical features – those who have either fever or signs and symptoms of lower respiratory disease such as cough or shortness of breath, but who don’t require hospitalization – should be tested if they have high epidemiologic risk. “High risk” is defined by the CDC as any individual, including health care workers, who has had close contact with a person with confirmed COVID-19 within the past 2 weeks. For health care workers, testing can be considered even if they have relatively mild respiratory symptoms or have had contact with a person who is suspected, but not yet confirmed, to have coronavirus.
In its testing guidance, the CDC recognizes that defining close contact is difficult. General guidelines are that individuals are considered to have been in close contact with a person who has COVID-19 if they were within about six feet of the person for a prolonged period, or cared for or have spent a prolonged amount of time in the same room or house as a person with confirmed COVID-19.
Individuals who have both fever and signs or symptoms of lower respiratory illness who require hospitalization should be tested if they have a history of travel from any affected geographic area within 14 days of the onset of their symptoms. The CDC now defines “affected geographic area” as any country or region that has at least a CDC Level 2 Travel Health Notice for COVID-19, so that the testing criteria themselves don’t need to be updated when new geographic areas are included in these alerts. As of March 3, China, Iran, Italy, Japan, and South Korea all have Level 2 or 3 travel alerts.
The CDC now recommends that any patient who has severe acute lower respiratory illness that requires hospitalization and doesn’t have an alternative diagnosis should be tested, even without any identified source of exposure.
“Despite seeing these new cases, the risk to the American people is low,” said the CDC’s Dr. Redfield. In response to a question from the press about how fast the coronavirus will spread across the United States, Dr. Redfield said, “From the beginning we’ve anticipated seeing community cases pop up.” He added that as these cases arise, testing and public health strategies will focus on unearthing linkages and contacts to learn how the virus is spreading. “We’ll use the public health strategies that we can to limit that transmission,” he said.
*An earlier version of this article misattributed this quote.
FROM A PRESS BRIEFING BY THE WHITE HOUSE CORONAVIRUS TASK FORCE
DoD and VA Release Updated List of Agent Orange Locations
The VA has released an updated list of locations outside of Vietnam where tactical herbicides have been used, tested, or stored by the US military. The list, which includes the “rainbow” herbicides (Agents Orange, Pink, Green, Purple, Blue, and White), comes from the DoD, after a “thorough review” of research, reports, and government publications in response to a November 2018 US Government Accountability Office (GAO) report.
The GAO made 6 recommendations, including that the DoD develop a process for updating the list, and that the DoD and the VA develop a process for coordinating the communication of the information. The DoD concurred with 4 recommendations.
The VA, responding to the GAO report, said it was “concerned that the report conflates the terms commercial herbicides with tactical herbicides, which are distinct from one another.” Certain testing and storage locations (eg, Kelly Air Force Base), it noted, are added to the list based on the presence of commercial herbicides or “mere components” of Agent Orange or other rainbow agents.
The distinction is important for veterans applying for disability benefits. The impetus for creating the list of testing and storage sites, the VA says, was to carry out the administration of providing disability benefits in accordance with the applicable Agent Orange statute and regulations. Exposure to tactical herbicides (herbicides intended for military operations in Vietnam) is required for the VA to grant benefits on a presumptive basis for Agent Orange conditions outside of Vietnam. Thus, the VA concludes in its response, unless the commercial herbicides were the “same composition, forms, and mixtures” as the estimated 20 million gallons of rainbow agents specifically produced for operations in Vietnam, the “discussion is misleading.”
The VA also did not concur with the recommendation that it take the lead on developing “clear and transparent criteria” for what constitutes a location to be included on the list.
The DoD and VA did agree with the recommendation that the DoD should be the lead agency for producing and updating the list, while the VA will be the lead agency in providing information to veterans. The list will be updated as verifiable information becomes available, said Defense Secretary Mark Esper.
The full list of locations is available at https://www.publichealth.va.gov/docs/agentorange/dod_herbicides_outside_vietnam.pdf.
The GAO report is available at https://www.gao.gov/assets/gao-19-24.pdf.
The VA has released an updated list of locations outside of Vietnam where tactical herbicides have been used, tested, or stored by the US military. The list, which includes the “rainbow” herbicides (Agents Orange, Pink, Green, Purple, Blue, and White), comes from the DoD, after a “thorough review” of research, reports, and government publications in response to a November 2018 US Government Accountability Office (GAO) report.
The GAO made 6 recommendations, including that the DoD develop a process for updating the list, and that the DoD and the VA develop a process for coordinating the communication of the information. The DoD concurred with 4 recommendations.
The VA, responding to the GAO report, said it was “concerned that the report conflates the terms commercial herbicides with tactical herbicides, which are distinct from one another.” Certain testing and storage locations (eg, Kelly Air Force Base), it noted, are added to the list based on the presence of commercial herbicides or “mere components” of Agent Orange or other rainbow agents.
The distinction is important for veterans applying for disability benefits. The impetus for creating the list of testing and storage sites, the VA says, was to carry out the administration of providing disability benefits in accordance with the applicable Agent Orange statute and regulations. Exposure to tactical herbicides (herbicides intended for military operations in Vietnam) is required for the VA to grant benefits on a presumptive basis for Agent Orange conditions outside of Vietnam. Thus, the VA concludes in its response, unless the commercial herbicides were the “same composition, forms, and mixtures” as the estimated 20 million gallons of rainbow agents specifically produced for operations in Vietnam, the “discussion is misleading.”
The VA also did not concur with the recommendation that it take the lead on developing “clear and transparent criteria” for what constitutes a location to be included on the list.
The DoD and VA did agree with the recommendation that the DoD should be the lead agency for producing and updating the list, while the VA will be the lead agency in providing information to veterans. The list will be updated as verifiable information becomes available, said Defense Secretary Mark Esper.
The full list of locations is available at https://www.publichealth.va.gov/docs/agentorange/dod_herbicides_outside_vietnam.pdf.
The GAO report is available at https://www.gao.gov/assets/gao-19-24.pdf.
The VA has released an updated list of locations outside of Vietnam where tactical herbicides have been used, tested, or stored by the US military. The list, which includes the “rainbow” herbicides (Agents Orange, Pink, Green, Purple, Blue, and White), comes from the DoD, after a “thorough review” of research, reports, and government publications in response to a November 2018 US Government Accountability Office (GAO) report.
The GAO made 6 recommendations, including that the DoD develop a process for updating the list, and that the DoD and the VA develop a process for coordinating the communication of the information. The DoD concurred with 4 recommendations.
The VA, responding to the GAO report, said it was “concerned that the report conflates the terms commercial herbicides with tactical herbicides, which are distinct from one another.” Certain testing and storage locations (eg, Kelly Air Force Base), it noted, are added to the list based on the presence of commercial herbicides or “mere components” of Agent Orange or other rainbow agents.
The distinction is important for veterans applying for disability benefits. The impetus for creating the list of testing and storage sites, the VA says, was to carry out the administration of providing disability benefits in accordance with the applicable Agent Orange statute and regulations. Exposure to tactical herbicides (herbicides intended for military operations in Vietnam) is required for the VA to grant benefits on a presumptive basis for Agent Orange conditions outside of Vietnam. Thus, the VA concludes in its response, unless the commercial herbicides were the “same composition, forms, and mixtures” as the estimated 20 million gallons of rainbow agents specifically produced for operations in Vietnam, the “discussion is misleading.”
The VA also did not concur with the recommendation that it take the lead on developing “clear and transparent criteria” for what constitutes a location to be included on the list.
The DoD and VA did agree with the recommendation that the DoD should be the lead agency for producing and updating the list, while the VA will be the lead agency in providing information to veterans. The list will be updated as verifiable information becomes available, said Defense Secretary Mark Esper.
The full list of locations is available at https://www.publichealth.va.gov/docs/agentorange/dod_herbicides_outside_vietnam.pdf.
The GAO report is available at https://www.gao.gov/assets/gao-19-24.pdf.




