User login
Flu vaccine cuts infection severity in kids and adults
WASHINGTON –
During recent U.S. flu seasons, children and adults who contracted influenza despite vaccination had significantly fewer severe infections and infection complications, compared with unimmunized people, according to two separate reports from CDC researchers presented at an annual scientific meeting on infectious diseases.
One of the reports tracked the impact of flu vaccine in children using data that the CDC collected at seven medical centers that participated in the agency’s New Vaccine Surveillance Network, which provided information on children aged 6 months to 17 years who were hospitalized for an acute respiratory illness, including more than 1,700 children during the 2016-2017 flu season and more than 1,900 during the 2017-2018 season. Roughly 10% of these children tested positive for influenza, and the subsequent analysis focused on these cases and compared incidence rates among children who had been vaccinated during the index season and those who had remained unvaccinated.
Combined data from both seasons showed that vaccinated children were 50% less likely to have been hospitalized for an acute influenza infection, compared with unvaccinated kids, a pattern consistently seen both in children aged 6 months to 8 years and in those aged 9-17 years. The pattern of vaccine effectiveness also held regardless of which flu strain caused the infections, reported Angela P. Campbell, MD, a CDC medical officer.
“We saw a nice benefit from vaccination, both in previously healthy children and in those with an underlying medical condition,” a finding that adds to existing evidence of vaccine effectiveness, Dr. Campbell said in a video interview. The results confirmed that flu vaccination does not just prevent infections but also cuts the rate of more severe infections that lead to hospitalization, she explained.
Another CDC study looked at data collected by the agency’s Influenza Hospitalization Surveillance Network from adults at least 18 years old who were hospitalized for a laboratory-confirmed influenza infection during five flu seasons, 2013-2014 through 2017-18. The data, which came from more than 250 acute-care hospitals in 13 states, included more than 43,000 people hospitalized for an identified influenza strain and with a known vaccination history who were not institutionalized and had not received any antiviral treatment.
After propensity-weighted adjustment to create better parity between the vaccinated and unvaccinated patients, the results showed that people 18-64 years old with vaccination had statistically significant decreases in mortality of a relative 36%, need for mechanical ventilation of 34%, pneumonia of 20%, and need for ICU admission of a relative 19%, as well as an 18% drop in average ICU length of stay, Shikha Garg, MD, said at the meeting. The propensity-weighted analysis of data from people at least 65 years old showed statistically significant relative reductions linked with vaccination: 46% reduction in the need for mechanical ventilation, 28% reduction in ICU admissions, and 9% reduction in hospitalized length of stay.
Further analysis of these outcomes by the strains that caused these influenza infections showed that the statistically significant benefits from vaccination were seen only in patients infected with an H1N1 strain. Statistically significant effects on these severe outcomes were not apparent among people infected with the H3N2 or B strains, said Dr. Garg, a medical epidemiologist at the CDC.
“All adults should receive an annual flu vaccination as it can improve outcomes among those who develop influenza despite vaccination,” she concluded.
Results from a third CDC study reported at the meeting examined the importance of two vaccine doses (administered at least 4 weeks apart) given to children aged 6 months to 8 years for the first season they receive flu vaccination, which is the immunization approach for flu recommended by the CDC. The findings from a total of more than 7,500 children immunized during the 2014-2018 seasons showed a clear increment in vaccine protection among kids who received two doses during their first season vaccinated, especially in children who were 2 years old or younger. In that age group, administration of two doses produced vaccine effectiveness of 53% versus a 23% vaccine effectiveness after a single vaccine dose, reported Jessie Chung, a CDC epidemiologist.
WASHINGTON –
During recent U.S. flu seasons, children and adults who contracted influenza despite vaccination had significantly fewer severe infections and infection complications, compared with unimmunized people, according to two separate reports from CDC researchers presented at an annual scientific meeting on infectious diseases.
One of the reports tracked the impact of flu vaccine in children using data that the CDC collected at seven medical centers that participated in the agency’s New Vaccine Surveillance Network, which provided information on children aged 6 months to 17 years who were hospitalized for an acute respiratory illness, including more than 1,700 children during the 2016-2017 flu season and more than 1,900 during the 2017-2018 season. Roughly 10% of these children tested positive for influenza, and the subsequent analysis focused on these cases and compared incidence rates among children who had been vaccinated during the index season and those who had remained unvaccinated.
Combined data from both seasons showed that vaccinated children were 50% less likely to have been hospitalized for an acute influenza infection, compared with unvaccinated kids, a pattern consistently seen both in children aged 6 months to 8 years and in those aged 9-17 years. The pattern of vaccine effectiveness also held regardless of which flu strain caused the infections, reported Angela P. Campbell, MD, a CDC medical officer.
“We saw a nice benefit from vaccination, both in previously healthy children and in those with an underlying medical condition,” a finding that adds to existing evidence of vaccine effectiveness, Dr. Campbell said in a video interview. The results confirmed that flu vaccination does not just prevent infections but also cuts the rate of more severe infections that lead to hospitalization, she explained.
Another CDC study looked at data collected by the agency’s Influenza Hospitalization Surveillance Network from adults at least 18 years old who were hospitalized for a laboratory-confirmed influenza infection during five flu seasons, 2013-2014 through 2017-18. The data, which came from more than 250 acute-care hospitals in 13 states, included more than 43,000 people hospitalized for an identified influenza strain and with a known vaccination history who were not institutionalized and had not received any antiviral treatment.
After propensity-weighted adjustment to create better parity between the vaccinated and unvaccinated patients, the results showed that people 18-64 years old with vaccination had statistically significant decreases in mortality of a relative 36%, need for mechanical ventilation of 34%, pneumonia of 20%, and need for ICU admission of a relative 19%, as well as an 18% drop in average ICU length of stay, Shikha Garg, MD, said at the meeting. The propensity-weighted analysis of data from people at least 65 years old showed statistically significant relative reductions linked with vaccination: 46% reduction in the need for mechanical ventilation, 28% reduction in ICU admissions, and 9% reduction in hospitalized length of stay.
Further analysis of these outcomes by the strains that caused these influenza infections showed that the statistically significant benefits from vaccination were seen only in patients infected with an H1N1 strain. Statistically significant effects on these severe outcomes were not apparent among people infected with the H3N2 or B strains, said Dr. Garg, a medical epidemiologist at the CDC.
“All adults should receive an annual flu vaccination as it can improve outcomes among those who develop influenza despite vaccination,” she concluded.
Results from a third CDC study reported at the meeting examined the importance of two vaccine doses (administered at least 4 weeks apart) given to children aged 6 months to 8 years for the first season they receive flu vaccination, which is the immunization approach for flu recommended by the CDC. The findings from a total of more than 7,500 children immunized during the 2014-2018 seasons showed a clear increment in vaccine protection among kids who received two doses during their first season vaccinated, especially in children who were 2 years old or younger. In that age group, administration of two doses produced vaccine effectiveness of 53% versus a 23% vaccine effectiveness after a single vaccine dose, reported Jessie Chung, a CDC epidemiologist.
WASHINGTON –
During recent U.S. flu seasons, children and adults who contracted influenza despite vaccination had significantly fewer severe infections and infection complications, compared with unimmunized people, according to two separate reports from CDC researchers presented at an annual scientific meeting on infectious diseases.
One of the reports tracked the impact of flu vaccine in children using data that the CDC collected at seven medical centers that participated in the agency’s New Vaccine Surveillance Network, which provided information on children aged 6 months to 17 years who were hospitalized for an acute respiratory illness, including more than 1,700 children during the 2016-2017 flu season and more than 1,900 during the 2017-2018 season. Roughly 10% of these children tested positive for influenza, and the subsequent analysis focused on these cases and compared incidence rates among children who had been vaccinated during the index season and those who had remained unvaccinated.
Combined data from both seasons showed that vaccinated children were 50% less likely to have been hospitalized for an acute influenza infection, compared with unvaccinated kids, a pattern consistently seen both in children aged 6 months to 8 years and in those aged 9-17 years. The pattern of vaccine effectiveness also held regardless of which flu strain caused the infections, reported Angela P. Campbell, MD, a CDC medical officer.
“We saw a nice benefit from vaccination, both in previously healthy children and in those with an underlying medical condition,” a finding that adds to existing evidence of vaccine effectiveness, Dr. Campbell said in a video interview. The results confirmed that flu vaccination does not just prevent infections but also cuts the rate of more severe infections that lead to hospitalization, she explained.
Another CDC study looked at data collected by the agency’s Influenza Hospitalization Surveillance Network from adults at least 18 years old who were hospitalized for a laboratory-confirmed influenza infection during five flu seasons, 2013-2014 through 2017-18. The data, which came from more than 250 acute-care hospitals in 13 states, included more than 43,000 people hospitalized for an identified influenza strain and with a known vaccination history who were not institutionalized and had not received any antiviral treatment.
After propensity-weighted adjustment to create better parity between the vaccinated and unvaccinated patients, the results showed that people 18-64 years old with vaccination had statistically significant decreases in mortality of a relative 36%, need for mechanical ventilation of 34%, pneumonia of 20%, and need for ICU admission of a relative 19%, as well as an 18% drop in average ICU length of stay, Shikha Garg, MD, said at the meeting. The propensity-weighted analysis of data from people at least 65 years old showed statistically significant relative reductions linked with vaccination: 46% reduction in the need for mechanical ventilation, 28% reduction in ICU admissions, and 9% reduction in hospitalized length of stay.
Further analysis of these outcomes by the strains that caused these influenza infections showed that the statistically significant benefits from vaccination were seen only in patients infected with an H1N1 strain. Statistically significant effects on these severe outcomes were not apparent among people infected with the H3N2 or B strains, said Dr. Garg, a medical epidemiologist at the CDC.
“All adults should receive an annual flu vaccination as it can improve outcomes among those who develop influenza despite vaccination,” she concluded.
Results from a third CDC study reported at the meeting examined the importance of two vaccine doses (administered at least 4 weeks apart) given to children aged 6 months to 8 years for the first season they receive flu vaccination, which is the immunization approach for flu recommended by the CDC. The findings from a total of more than 7,500 children immunized during the 2014-2018 seasons showed a clear increment in vaccine protection among kids who received two doses during their first season vaccinated, especially in children who were 2 years old or younger. In that age group, administration of two doses produced vaccine effectiveness of 53% versus a 23% vaccine effectiveness after a single vaccine dose, reported Jessie Chung, a CDC epidemiologist.
REPORTING FROM ID WEEK 2019
Stay Informed About Informed Consent
On May 24, 2011, a 53-year-old woman presented to a Wisconsin hospital emergency department (ED) with complaints of severe abdominal pain, a rapid heartbeat, and a fever of 101.3°F. During her 9-hour visit, she was treated by a PA and his supervising physician. She was seen by the physician for a total of 6 minutes; the rest of her care was provided by the PA. The patient was discharged around midnight with instructions to contact her gynecologist in the morning for management of uterine fibroids. At the time of discharge, her temperature was 102.9°F.
The following day, May 25, the patient collapsed in her home and was transported to another hospital. She was treated for septic shock from a group A streptococcus infection. Although the infection was halted, the patient sustained ischemic damage to her extremities and a month later required amputation of her 4 limbs.The plaintiff claimed that the supervising physician was negligent in failing to diagnose the strep A infection, which, left undetected, led to septic shock. She also alleged that the PA should have recognized the potential for her condition’s severity to quickly escalate. She maintained that the supervising physician should have been more involved in her case because of its complexity.
Plaintiff’s counsel also argued that the PA should have provided “alternative medical diagnoses,” which would have prompted consideration of other treatment options. The plaintiff contended that under Wisconsin’s informed consent law, both the PA and the physician failed to disclose enough information about her condition and failed to inform her of any choices for treatment.
The defense argued that the plaintiff received proper treatment based on the information available to the providers at the time.
VERDICT
The jury found for the plaintiff and apportioned 65% liability to the physician and 35% liability to the PA. A total of $25,342,096 was awarded to the plaintiff.
COMMENTARY
This is a huge verdict. Cases involving group A strep or necrotizing fasciitis frequently give rise to large medical malpractice verdicts, because everything about them is difficult to defend: Although there is typically trivial to no trauma involved, the wounds from these infections provide explicit images of damage, intraoperatively and postoperatively. Vasopressors required for hemodynamic support or sepsis itself frequently result in limb ischemia, gangrene, and amputation. In this case, the plaintiff, as a quadruple amputee, was a sympathetic and impressive courtroom presence—the personal toll was evident to anyone in the room.
Two providers—a PA and a physician—saw the patient. We are told only that she complained of severe abdominal pain, rapid heartbeat, and fever, which increased at some point during her ED stay. We aren’t given specifics on the rest of the patient’s vital signs or examination details. However, we can infer that the exam and lab findings were not impressive, because they weren’t mentioned in the case report. But as a result of the failure to catch the group A strep infection, the plaintiff suffered what one judge hearing the case described as a harrowing and unimaginable ordeal: the life-changing amputation of 4 limbs.1 While the jury did not find the PA or physician negligent, they still found the clinicians liable and awarded a staggering verdict.
Continue to: How could this happen?
How could this happen? The answer is the theory of recovery: The jury found that the physician and the PA failed to provide the patient with informed consent in the form of “alternative medical diagnoses.”2 The plaintiff’s attorney argued that the patient was never told a life-threatening bacterial infection was one possible diagnosis and claimed that if she had known, the patient would have pursued other treatment.
As in many malpractice cases, the plaintiff alleged failure to diagnose and failure to provide informed consent. Depending on state law, there are 3 standards for informed consent: subjective patient, reasonable patient, and reasonable physician.3 About half of the states have a physician-focused standard, while the other half have a patient-focused standard.3
Under the subjective patient standard, we would ask, “What would this patient need to know and understand to make an informed decision?”4 The subjective standard requires the clinician to essentially “get in the head” of a specific patient to determine what he or she would want to know when making a medical decision. This standard is problematic because it requires the clinician to have an intimate familiarity with the patient’s belief system and medical decision-making process—a daunting requirement for many clinicians, particularly in the absence of a longstanding clinician-patient relationship, as is the case in most emergency settings. Thankfully, the subjective patient standard is not followed by most states that have a patient-focused standard.
Under the objective reasonable patient standard, we would ask “What would the average patient need to know to be an informed participant in the decision?”4 One could argue that this standard more adequately allows the patient to be an active participant in shared decision-making. However, the drawback is that what is “reasonable” often falls on a spectrum, which would require the clinician to gauge the volume and type of information a patient cohort would want to have when making a medical decision. Under this standard, the plaintiff must prove that the clinician omitted information that a reasonable patient would want to know. Therefore, these standards are more friendly to the plaintiff, whereas the reasonable physician standard is more defendant friendly.
To meet the standard of care under a reasonable physician standard, information must be provided to the patient that a “reasonably prudent practitioner in the same field of practice or specialty” would provide to a patient.5 For a plaintiff to successfully sue under this standard, the plaintiff’s expert must testify that a reasonably prudent physician would have disclosed the omitted information.6 The reasonable physician standard is obviously better for malpractice defendants.
Continue to: While reasonable clinicians...
While reasonable clinicians can disagree (as can reasonable patients), clinicians are more likely to be closer in opinion. Clinicians are a smaller group whose opinions are underpinned by similar education, training, and experience. By contrast, among the general population, beliefs held by one hypothetical “reasonable person” are much less settled, and in some cases, wildly divergent from another’s. For example, vaccine skepticism would probably be considered unreasonable in the majority of jury pools but absolutely reasonable in some. The large size of the general population, coupled with opinions untethered to any definable discipline, make the reasonable patient standard hard to predict.
Additionally, the reasonable physician standard forces the plaintiff to prove his or her case by producing an expert witness (clinician) to specifically testify that the standard of care required the defendant clinician to disclose certain specific information, and that disclosure was lacking. That is an important requirement. Under patient-focused standards, the plaintiff doesn’t need a medical expert on this point and can simply argue to the jury that a reasonable patient would require an exhaustive discussion of each possibility in the differential diagnosis. Therefore, I would argue that the reasonable physician standard is more predictable and workable and should be followed.
At the time of this case, Wisconsin’s informed consent law was based on the reasonable patient standard. As a result of this case, Wisconsin lawmakers changed the law to a “reasonable physician standard,” which states “any physician who treats a patient shall inform the patient about the availability of reasonable alternate medical modes of treatment and about the benefits and risks of these treatments.”7 However, the law stipulates that this duty to inform does not require disclosure of (among others):
- Detailed technical information that in all probability a patient would not understand
- Risks apparent or known to the patient
- Extremely remote possibilities that might falsely or detrimentally alarm the patient
- Information about alternate medical modes of treatment for any condition the physician has not included in his or her diagnosis at the time the physician informs the patient.7
Finally, this case involved an extremely high verdict of more than $25 million. It may surprise you to learn that many states have caps for medical malpractice awards for noneconomic damages, such as pain and suffering. If you’re having a holiday dinner with friends or family members who are plaintiff’s attorneys and you’re itching for a good argument, skip current politics and go all-in: How about liability caps, Uncle Jim? Get ready for a lively debate.
Of the $25 million verdict, $16.5 million was awarded for pain and suffering—the jury was obviously shocked by the extent of the life-changing nature of the plaintiff’s injuries. At the time of this case, Wisconsin had a cap of $750,000 for noneconomic damages.8 However, plaintiffs may challenge state constitutionality of these caps when they feel they have the right case, which the plaintiff and her attorney felt they did. Two lower courts found the state cap unconstitutional and gave the plaintiff the full award. But the state Supreme Court later reversed that decision, upholding the cap.1 The court decided that the legislature had a rational basis for making the law and changes to it should occur through the legislature, not the courts. The dissenting justices argued that there was no rational basis for the $750,000 cap, because there was no evidence that clinicians would flee the state fearing malpractice liability, or practice more defensive medicine, or suffer runaway malpractice insurance premiums without the cap. As a result of this case, the cap was upheld, and there was a “lively debate” on this issue at the highest levels of government.
Continue to: IN SUM
IN SUM
Become familiar with your state’s informed consent laws. Involve patients in decision-making, and convey information related to reasonable treatment options and risks. Document all of these discussions. Lastly, state-level political discussions on issues of tort reform, caps, and malpractice matters are ongoing—so take n
1. Mayo v Wisconsin Injured Patients & Families Compensation Fund. WI 78 (2018).
2. Spivak C. Jury awards Milwaukee woman $25.3 million in medical malpractice case. Milwaukee Journal Sentinel. July 7, 2014.
3. Moore GP, Matlock AG, Kiley JL, et al. Emergency physicians: beware of the consent standard of care. Clin Pract Cases Emerg Med. 2018; 2(2):109-111.
4. Gossman W, Thornton I, Hipskind JE. Informed Consent. StatPearls. www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK430827/. Updated July 10, 2019. Accessed October 25, 2019.
5. King JS, Moulton BW. Rethinking informed consent: the case for shared medical decision-making. Am J Law Med. 2006;32:429-501.
6. Tashman v Gibbs, 556 SE 2d 772 (263 Va 2002).
7. Wis Stat subchapter 2, §448.30.
8. Wis Stat §893.55.
On May 24, 2011, a 53-year-old woman presented to a Wisconsin hospital emergency department (ED) with complaints of severe abdominal pain, a rapid heartbeat, and a fever of 101.3°F. During her 9-hour visit, she was treated by a PA and his supervising physician. She was seen by the physician for a total of 6 minutes; the rest of her care was provided by the PA. The patient was discharged around midnight with instructions to contact her gynecologist in the morning for management of uterine fibroids. At the time of discharge, her temperature was 102.9°F.
The following day, May 25, the patient collapsed in her home and was transported to another hospital. She was treated for septic shock from a group A streptococcus infection. Although the infection was halted, the patient sustained ischemic damage to her extremities and a month later required amputation of her 4 limbs.The plaintiff claimed that the supervising physician was negligent in failing to diagnose the strep A infection, which, left undetected, led to septic shock. She also alleged that the PA should have recognized the potential for her condition’s severity to quickly escalate. She maintained that the supervising physician should have been more involved in her case because of its complexity.
Plaintiff’s counsel also argued that the PA should have provided “alternative medical diagnoses,” which would have prompted consideration of other treatment options. The plaintiff contended that under Wisconsin’s informed consent law, both the PA and the physician failed to disclose enough information about her condition and failed to inform her of any choices for treatment.
The defense argued that the plaintiff received proper treatment based on the information available to the providers at the time.
VERDICT
The jury found for the plaintiff and apportioned 65% liability to the physician and 35% liability to the PA. A total of $25,342,096 was awarded to the plaintiff.
COMMENTARY
This is a huge verdict. Cases involving group A strep or necrotizing fasciitis frequently give rise to large medical malpractice verdicts, because everything about them is difficult to defend: Although there is typically trivial to no trauma involved, the wounds from these infections provide explicit images of damage, intraoperatively and postoperatively. Vasopressors required for hemodynamic support or sepsis itself frequently result in limb ischemia, gangrene, and amputation. In this case, the plaintiff, as a quadruple amputee, was a sympathetic and impressive courtroom presence—the personal toll was evident to anyone in the room.
Two providers—a PA and a physician—saw the patient. We are told only that she complained of severe abdominal pain, rapid heartbeat, and fever, which increased at some point during her ED stay. We aren’t given specifics on the rest of the patient’s vital signs or examination details. However, we can infer that the exam and lab findings were not impressive, because they weren’t mentioned in the case report. But as a result of the failure to catch the group A strep infection, the plaintiff suffered what one judge hearing the case described as a harrowing and unimaginable ordeal: the life-changing amputation of 4 limbs.1 While the jury did not find the PA or physician negligent, they still found the clinicians liable and awarded a staggering verdict.
Continue to: How could this happen?
How could this happen? The answer is the theory of recovery: The jury found that the physician and the PA failed to provide the patient with informed consent in the form of “alternative medical diagnoses.”2 The plaintiff’s attorney argued that the patient was never told a life-threatening bacterial infection was one possible diagnosis and claimed that if she had known, the patient would have pursued other treatment.
As in many malpractice cases, the plaintiff alleged failure to diagnose and failure to provide informed consent. Depending on state law, there are 3 standards for informed consent: subjective patient, reasonable patient, and reasonable physician.3 About half of the states have a physician-focused standard, while the other half have a patient-focused standard.3
Under the subjective patient standard, we would ask, “What would this patient need to know and understand to make an informed decision?”4 The subjective standard requires the clinician to essentially “get in the head” of a specific patient to determine what he or she would want to know when making a medical decision. This standard is problematic because it requires the clinician to have an intimate familiarity with the patient’s belief system and medical decision-making process—a daunting requirement for many clinicians, particularly in the absence of a longstanding clinician-patient relationship, as is the case in most emergency settings. Thankfully, the subjective patient standard is not followed by most states that have a patient-focused standard.
Under the objective reasonable patient standard, we would ask “What would the average patient need to know to be an informed participant in the decision?”4 One could argue that this standard more adequately allows the patient to be an active participant in shared decision-making. However, the drawback is that what is “reasonable” often falls on a spectrum, which would require the clinician to gauge the volume and type of information a patient cohort would want to have when making a medical decision. Under this standard, the plaintiff must prove that the clinician omitted information that a reasonable patient would want to know. Therefore, these standards are more friendly to the plaintiff, whereas the reasonable physician standard is more defendant friendly.
To meet the standard of care under a reasonable physician standard, information must be provided to the patient that a “reasonably prudent practitioner in the same field of practice or specialty” would provide to a patient.5 For a plaintiff to successfully sue under this standard, the plaintiff’s expert must testify that a reasonably prudent physician would have disclosed the omitted information.6 The reasonable physician standard is obviously better for malpractice defendants.
Continue to: While reasonable clinicians...
While reasonable clinicians can disagree (as can reasonable patients), clinicians are more likely to be closer in opinion. Clinicians are a smaller group whose opinions are underpinned by similar education, training, and experience. By contrast, among the general population, beliefs held by one hypothetical “reasonable person” are much less settled, and in some cases, wildly divergent from another’s. For example, vaccine skepticism would probably be considered unreasonable in the majority of jury pools but absolutely reasonable in some. The large size of the general population, coupled with opinions untethered to any definable discipline, make the reasonable patient standard hard to predict.
Additionally, the reasonable physician standard forces the plaintiff to prove his or her case by producing an expert witness (clinician) to specifically testify that the standard of care required the defendant clinician to disclose certain specific information, and that disclosure was lacking. That is an important requirement. Under patient-focused standards, the plaintiff doesn’t need a medical expert on this point and can simply argue to the jury that a reasonable patient would require an exhaustive discussion of each possibility in the differential diagnosis. Therefore, I would argue that the reasonable physician standard is more predictable and workable and should be followed.
At the time of this case, Wisconsin’s informed consent law was based on the reasonable patient standard. As a result of this case, Wisconsin lawmakers changed the law to a “reasonable physician standard,” which states “any physician who treats a patient shall inform the patient about the availability of reasonable alternate medical modes of treatment and about the benefits and risks of these treatments.”7 However, the law stipulates that this duty to inform does not require disclosure of (among others):
- Detailed technical information that in all probability a patient would not understand
- Risks apparent or known to the patient
- Extremely remote possibilities that might falsely or detrimentally alarm the patient
- Information about alternate medical modes of treatment for any condition the physician has not included in his or her diagnosis at the time the physician informs the patient.7
Finally, this case involved an extremely high verdict of more than $25 million. It may surprise you to learn that many states have caps for medical malpractice awards for noneconomic damages, such as pain and suffering. If you’re having a holiday dinner with friends or family members who are plaintiff’s attorneys and you’re itching for a good argument, skip current politics and go all-in: How about liability caps, Uncle Jim? Get ready for a lively debate.
Of the $25 million verdict, $16.5 million was awarded for pain and suffering—the jury was obviously shocked by the extent of the life-changing nature of the plaintiff’s injuries. At the time of this case, Wisconsin had a cap of $750,000 for noneconomic damages.8 However, plaintiffs may challenge state constitutionality of these caps when they feel they have the right case, which the plaintiff and her attorney felt they did. Two lower courts found the state cap unconstitutional and gave the plaintiff the full award. But the state Supreme Court later reversed that decision, upholding the cap.1 The court decided that the legislature had a rational basis for making the law and changes to it should occur through the legislature, not the courts. The dissenting justices argued that there was no rational basis for the $750,000 cap, because there was no evidence that clinicians would flee the state fearing malpractice liability, or practice more defensive medicine, or suffer runaway malpractice insurance premiums without the cap. As a result of this case, the cap was upheld, and there was a “lively debate” on this issue at the highest levels of government.
Continue to: IN SUM
IN SUM
Become familiar with your state’s informed consent laws. Involve patients in decision-making, and convey information related to reasonable treatment options and risks. Document all of these discussions. Lastly, state-level political discussions on issues of tort reform, caps, and malpractice matters are ongoing—so take n
On May 24, 2011, a 53-year-old woman presented to a Wisconsin hospital emergency department (ED) with complaints of severe abdominal pain, a rapid heartbeat, and a fever of 101.3°F. During her 9-hour visit, she was treated by a PA and his supervising physician. She was seen by the physician for a total of 6 minutes; the rest of her care was provided by the PA. The patient was discharged around midnight with instructions to contact her gynecologist in the morning for management of uterine fibroids. At the time of discharge, her temperature was 102.9°F.
The following day, May 25, the patient collapsed in her home and was transported to another hospital. She was treated for septic shock from a group A streptococcus infection. Although the infection was halted, the patient sustained ischemic damage to her extremities and a month later required amputation of her 4 limbs.The plaintiff claimed that the supervising physician was negligent in failing to diagnose the strep A infection, which, left undetected, led to septic shock. She also alleged that the PA should have recognized the potential for her condition’s severity to quickly escalate. She maintained that the supervising physician should have been more involved in her case because of its complexity.
Plaintiff’s counsel also argued that the PA should have provided “alternative medical diagnoses,” which would have prompted consideration of other treatment options. The plaintiff contended that under Wisconsin’s informed consent law, both the PA and the physician failed to disclose enough information about her condition and failed to inform her of any choices for treatment.
The defense argued that the plaintiff received proper treatment based on the information available to the providers at the time.
VERDICT
The jury found for the plaintiff and apportioned 65% liability to the physician and 35% liability to the PA. A total of $25,342,096 was awarded to the plaintiff.
COMMENTARY
This is a huge verdict. Cases involving group A strep or necrotizing fasciitis frequently give rise to large medical malpractice verdicts, because everything about them is difficult to defend: Although there is typically trivial to no trauma involved, the wounds from these infections provide explicit images of damage, intraoperatively and postoperatively. Vasopressors required for hemodynamic support or sepsis itself frequently result in limb ischemia, gangrene, and amputation. In this case, the plaintiff, as a quadruple amputee, was a sympathetic and impressive courtroom presence—the personal toll was evident to anyone in the room.
Two providers—a PA and a physician—saw the patient. We are told only that she complained of severe abdominal pain, rapid heartbeat, and fever, which increased at some point during her ED stay. We aren’t given specifics on the rest of the patient’s vital signs or examination details. However, we can infer that the exam and lab findings were not impressive, because they weren’t mentioned in the case report. But as a result of the failure to catch the group A strep infection, the plaintiff suffered what one judge hearing the case described as a harrowing and unimaginable ordeal: the life-changing amputation of 4 limbs.1 While the jury did not find the PA or physician negligent, they still found the clinicians liable and awarded a staggering verdict.
Continue to: How could this happen?
How could this happen? The answer is the theory of recovery: The jury found that the physician and the PA failed to provide the patient with informed consent in the form of “alternative medical diagnoses.”2 The plaintiff’s attorney argued that the patient was never told a life-threatening bacterial infection was one possible diagnosis and claimed that if she had known, the patient would have pursued other treatment.
As in many malpractice cases, the plaintiff alleged failure to diagnose and failure to provide informed consent. Depending on state law, there are 3 standards for informed consent: subjective patient, reasonable patient, and reasonable physician.3 About half of the states have a physician-focused standard, while the other half have a patient-focused standard.3
Under the subjective patient standard, we would ask, “What would this patient need to know and understand to make an informed decision?”4 The subjective standard requires the clinician to essentially “get in the head” of a specific patient to determine what he or she would want to know when making a medical decision. This standard is problematic because it requires the clinician to have an intimate familiarity with the patient’s belief system and medical decision-making process—a daunting requirement for many clinicians, particularly in the absence of a longstanding clinician-patient relationship, as is the case in most emergency settings. Thankfully, the subjective patient standard is not followed by most states that have a patient-focused standard.
Under the objective reasonable patient standard, we would ask “What would the average patient need to know to be an informed participant in the decision?”4 One could argue that this standard more adequately allows the patient to be an active participant in shared decision-making. However, the drawback is that what is “reasonable” often falls on a spectrum, which would require the clinician to gauge the volume and type of information a patient cohort would want to have when making a medical decision. Under this standard, the plaintiff must prove that the clinician omitted information that a reasonable patient would want to know. Therefore, these standards are more friendly to the plaintiff, whereas the reasonable physician standard is more defendant friendly.
To meet the standard of care under a reasonable physician standard, information must be provided to the patient that a “reasonably prudent practitioner in the same field of practice or specialty” would provide to a patient.5 For a plaintiff to successfully sue under this standard, the plaintiff’s expert must testify that a reasonably prudent physician would have disclosed the omitted information.6 The reasonable physician standard is obviously better for malpractice defendants.
Continue to: While reasonable clinicians...
While reasonable clinicians can disagree (as can reasonable patients), clinicians are more likely to be closer in opinion. Clinicians are a smaller group whose opinions are underpinned by similar education, training, and experience. By contrast, among the general population, beliefs held by one hypothetical “reasonable person” are much less settled, and in some cases, wildly divergent from another’s. For example, vaccine skepticism would probably be considered unreasonable in the majority of jury pools but absolutely reasonable in some. The large size of the general population, coupled with opinions untethered to any definable discipline, make the reasonable patient standard hard to predict.
Additionally, the reasonable physician standard forces the plaintiff to prove his or her case by producing an expert witness (clinician) to specifically testify that the standard of care required the defendant clinician to disclose certain specific information, and that disclosure was lacking. That is an important requirement. Under patient-focused standards, the plaintiff doesn’t need a medical expert on this point and can simply argue to the jury that a reasonable patient would require an exhaustive discussion of each possibility in the differential diagnosis. Therefore, I would argue that the reasonable physician standard is more predictable and workable and should be followed.
At the time of this case, Wisconsin’s informed consent law was based on the reasonable patient standard. As a result of this case, Wisconsin lawmakers changed the law to a “reasonable physician standard,” which states “any physician who treats a patient shall inform the patient about the availability of reasonable alternate medical modes of treatment and about the benefits and risks of these treatments.”7 However, the law stipulates that this duty to inform does not require disclosure of (among others):
- Detailed technical information that in all probability a patient would not understand
- Risks apparent or known to the patient
- Extremely remote possibilities that might falsely or detrimentally alarm the patient
- Information about alternate medical modes of treatment for any condition the physician has not included in his or her diagnosis at the time the physician informs the patient.7
Finally, this case involved an extremely high verdict of more than $25 million. It may surprise you to learn that many states have caps for medical malpractice awards for noneconomic damages, such as pain and suffering. If you’re having a holiday dinner with friends or family members who are plaintiff’s attorneys and you’re itching for a good argument, skip current politics and go all-in: How about liability caps, Uncle Jim? Get ready for a lively debate.
Of the $25 million verdict, $16.5 million was awarded for pain and suffering—the jury was obviously shocked by the extent of the life-changing nature of the plaintiff’s injuries. At the time of this case, Wisconsin had a cap of $750,000 for noneconomic damages.8 However, plaintiffs may challenge state constitutionality of these caps when they feel they have the right case, which the plaintiff and her attorney felt they did. Two lower courts found the state cap unconstitutional and gave the plaintiff the full award. But the state Supreme Court later reversed that decision, upholding the cap.1 The court decided that the legislature had a rational basis for making the law and changes to it should occur through the legislature, not the courts. The dissenting justices argued that there was no rational basis for the $750,000 cap, because there was no evidence that clinicians would flee the state fearing malpractice liability, or practice more defensive medicine, or suffer runaway malpractice insurance premiums without the cap. As a result of this case, the cap was upheld, and there was a “lively debate” on this issue at the highest levels of government.
Continue to: IN SUM
IN SUM
Become familiar with your state’s informed consent laws. Involve patients in decision-making, and convey information related to reasonable treatment options and risks. Document all of these discussions. Lastly, state-level political discussions on issues of tort reform, caps, and malpractice matters are ongoing—so take n
1. Mayo v Wisconsin Injured Patients & Families Compensation Fund. WI 78 (2018).
2. Spivak C. Jury awards Milwaukee woman $25.3 million in medical malpractice case. Milwaukee Journal Sentinel. July 7, 2014.
3. Moore GP, Matlock AG, Kiley JL, et al. Emergency physicians: beware of the consent standard of care. Clin Pract Cases Emerg Med. 2018; 2(2):109-111.
4. Gossman W, Thornton I, Hipskind JE. Informed Consent. StatPearls. www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK430827/. Updated July 10, 2019. Accessed October 25, 2019.
5. King JS, Moulton BW. Rethinking informed consent: the case for shared medical decision-making. Am J Law Med. 2006;32:429-501.
6. Tashman v Gibbs, 556 SE 2d 772 (263 Va 2002).
7. Wis Stat subchapter 2, §448.30.
8. Wis Stat §893.55.
1. Mayo v Wisconsin Injured Patients & Families Compensation Fund. WI 78 (2018).
2. Spivak C. Jury awards Milwaukee woman $25.3 million in medical malpractice case. Milwaukee Journal Sentinel. July 7, 2014.
3. Moore GP, Matlock AG, Kiley JL, et al. Emergency physicians: beware of the consent standard of care. Clin Pract Cases Emerg Med. 2018; 2(2):109-111.
4. Gossman W, Thornton I, Hipskind JE. Informed Consent. StatPearls. www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK430827/. Updated July 10, 2019. Accessed October 25, 2019.
5. King JS, Moulton BW. Rethinking informed consent: the case for shared medical decision-making. Am J Law Med. 2006;32:429-501.
6. Tashman v Gibbs, 556 SE 2d 772 (263 Va 2002).
7. Wis Stat subchapter 2, §448.30.
8. Wis Stat §893.55.
No infection increase seen with biologics in older psoriasis patients
MADRID – Psoriasis patients aged 65 years and older are at more than twice the risk of serious bacterial and opportunistic infections, compared with younger patients, but that risk is not further elevated by being on biologic agents, Joseph F. Merola, MD, reported at the annual congress of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology.
He presented a large, The study implications, he said, are clear: When moderate to severe psoriasis warrants consideration of highly effective biologic therapies, that therapeutic option shouldn’t be taken off the table on the basis of a mistaken belief that biologics pose a greater infection risk just because the affected patient is over age 65 years.
“We really think that older patients should be offered treatments at the same level of disease control as all the rest of our psoriasis patients, in the context of shared decision making,” said Dr. Merola, a dermatologist and rheumatologist who is the director of the Center for Skin and Related Musculoskeletal Diseases at Brigham and Women’s Hospital, Boston.
The study utilized longitudinal claims data from a very large U.S. database covering the years 2003-2017. Among the 185 million covered lives were 1.1 million individuals with psoriasis, including 150,000 aged 65 years or older. After excluding older psoriasis patients with comorbid cancer or autoimmune disease, the investigators were left with 11,218 older psoriasis patients initiating systemic therapy for the first time and therefore eligible for propensity score matching using a highly accurate proprietary platform. The final study population consisted of 2,795 older psoriasis patients newly initiating biologic therapy, 2,795 others newly initiating nonbiologic systemic agents, and 2,529 seniors starting phototherapy. The matching was based upon factors including age, sex, prior infections, comorbid psoriatic arthritis, diabetes, and obesity.
The primary study endpoint was the rate of serious bacterial or opportunistic infections requiring hospitalization during the first 6 months of treatment. The bottom line: The rates were closely similar across all three groups, with the most common serious infections being pneumonia and cellulitis.
In contrast, among a population of 115,047 senior psoriasis patients who never used systemic therapy, the risk of serious infection was 12.2 events per 1,000 patients over 6 months, compared with 5.3 events in 120,174 matched controls without psoriasis. That translates to a 2.24-fold increased risk.
One audience member commented that a limitation of the study was that all biologics were lumped together. He would expect that the tumor necrosis factor inhibitors, for example, would be associated with a significantly higher serious infection risk than biologics with other targets.
Dr. Merola conceded the point, adding that the investigators are trying to reanalyze the data in a more granular way to address that shortcoming. Other study limitations included an inability to access the specific doses of systemic treatments used or to stratify patients by disease severity.
Another audience member noted that dermatologists often reassure surgeons that there’s no increased risk of infection associated with psoriasis when in fact there is increased risk in older psoriasis patients, according to these new data.
“We’re not trying to send a message to surgeons to withhold a knee transplant because of a psoriasis plaque over the knee,” Dr. Merola replied. “I think we’ve all been there; we’ve all fought that battle.” Based on the data, he said, he would advise that “our patients who need to be on systemics should remain appropriately on systemics as we see fit.”
The study was entirely funded by Brigham and Women’s Hospital. Dr. Merola reported serving as a consultant to and/or recipient of research grants from nearly two dozen pharmaceutical companies.
MADRID – Psoriasis patients aged 65 years and older are at more than twice the risk of serious bacterial and opportunistic infections, compared with younger patients, but that risk is not further elevated by being on biologic agents, Joseph F. Merola, MD, reported at the annual congress of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology.
He presented a large, The study implications, he said, are clear: When moderate to severe psoriasis warrants consideration of highly effective biologic therapies, that therapeutic option shouldn’t be taken off the table on the basis of a mistaken belief that biologics pose a greater infection risk just because the affected patient is over age 65 years.
“We really think that older patients should be offered treatments at the same level of disease control as all the rest of our psoriasis patients, in the context of shared decision making,” said Dr. Merola, a dermatologist and rheumatologist who is the director of the Center for Skin and Related Musculoskeletal Diseases at Brigham and Women’s Hospital, Boston.
The study utilized longitudinal claims data from a very large U.S. database covering the years 2003-2017. Among the 185 million covered lives were 1.1 million individuals with psoriasis, including 150,000 aged 65 years or older. After excluding older psoriasis patients with comorbid cancer or autoimmune disease, the investigators were left with 11,218 older psoriasis patients initiating systemic therapy for the first time and therefore eligible for propensity score matching using a highly accurate proprietary platform. The final study population consisted of 2,795 older psoriasis patients newly initiating biologic therapy, 2,795 others newly initiating nonbiologic systemic agents, and 2,529 seniors starting phototherapy. The matching was based upon factors including age, sex, prior infections, comorbid psoriatic arthritis, diabetes, and obesity.
The primary study endpoint was the rate of serious bacterial or opportunistic infections requiring hospitalization during the first 6 months of treatment. The bottom line: The rates were closely similar across all three groups, with the most common serious infections being pneumonia and cellulitis.
In contrast, among a population of 115,047 senior psoriasis patients who never used systemic therapy, the risk of serious infection was 12.2 events per 1,000 patients over 6 months, compared with 5.3 events in 120,174 matched controls without psoriasis. That translates to a 2.24-fold increased risk.
One audience member commented that a limitation of the study was that all biologics were lumped together. He would expect that the tumor necrosis factor inhibitors, for example, would be associated with a significantly higher serious infection risk than biologics with other targets.
Dr. Merola conceded the point, adding that the investigators are trying to reanalyze the data in a more granular way to address that shortcoming. Other study limitations included an inability to access the specific doses of systemic treatments used or to stratify patients by disease severity.
Another audience member noted that dermatologists often reassure surgeons that there’s no increased risk of infection associated with psoriasis when in fact there is increased risk in older psoriasis patients, according to these new data.
“We’re not trying to send a message to surgeons to withhold a knee transplant because of a psoriasis plaque over the knee,” Dr. Merola replied. “I think we’ve all been there; we’ve all fought that battle.” Based on the data, he said, he would advise that “our patients who need to be on systemics should remain appropriately on systemics as we see fit.”
The study was entirely funded by Brigham and Women’s Hospital. Dr. Merola reported serving as a consultant to and/or recipient of research grants from nearly two dozen pharmaceutical companies.
MADRID – Psoriasis patients aged 65 years and older are at more than twice the risk of serious bacterial and opportunistic infections, compared with younger patients, but that risk is not further elevated by being on biologic agents, Joseph F. Merola, MD, reported at the annual congress of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology.
He presented a large, The study implications, he said, are clear: When moderate to severe psoriasis warrants consideration of highly effective biologic therapies, that therapeutic option shouldn’t be taken off the table on the basis of a mistaken belief that biologics pose a greater infection risk just because the affected patient is over age 65 years.
“We really think that older patients should be offered treatments at the same level of disease control as all the rest of our psoriasis patients, in the context of shared decision making,” said Dr. Merola, a dermatologist and rheumatologist who is the director of the Center for Skin and Related Musculoskeletal Diseases at Brigham and Women’s Hospital, Boston.
The study utilized longitudinal claims data from a very large U.S. database covering the years 2003-2017. Among the 185 million covered lives were 1.1 million individuals with psoriasis, including 150,000 aged 65 years or older. After excluding older psoriasis patients with comorbid cancer or autoimmune disease, the investigators were left with 11,218 older psoriasis patients initiating systemic therapy for the first time and therefore eligible for propensity score matching using a highly accurate proprietary platform. The final study population consisted of 2,795 older psoriasis patients newly initiating biologic therapy, 2,795 others newly initiating nonbiologic systemic agents, and 2,529 seniors starting phototherapy. The matching was based upon factors including age, sex, prior infections, comorbid psoriatic arthritis, diabetes, and obesity.
The primary study endpoint was the rate of serious bacterial or opportunistic infections requiring hospitalization during the first 6 months of treatment. The bottom line: The rates were closely similar across all three groups, with the most common serious infections being pneumonia and cellulitis.
In contrast, among a population of 115,047 senior psoriasis patients who never used systemic therapy, the risk of serious infection was 12.2 events per 1,000 patients over 6 months, compared with 5.3 events in 120,174 matched controls without psoriasis. That translates to a 2.24-fold increased risk.
One audience member commented that a limitation of the study was that all biologics were lumped together. He would expect that the tumor necrosis factor inhibitors, for example, would be associated with a significantly higher serious infection risk than biologics with other targets.
Dr. Merola conceded the point, adding that the investigators are trying to reanalyze the data in a more granular way to address that shortcoming. Other study limitations included an inability to access the specific doses of systemic treatments used or to stratify patients by disease severity.
Another audience member noted that dermatologists often reassure surgeons that there’s no increased risk of infection associated with psoriasis when in fact there is increased risk in older psoriasis patients, according to these new data.
“We’re not trying to send a message to surgeons to withhold a knee transplant because of a psoriasis plaque over the knee,” Dr. Merola replied. “I think we’ve all been there; we’ve all fought that battle.” Based on the data, he said, he would advise that “our patients who need to be on systemics should remain appropriately on systemics as we see fit.”
The study was entirely funded by Brigham and Women’s Hospital. Dr. Merola reported serving as a consultant to and/or recipient of research grants from nearly two dozen pharmaceutical companies.
REPORTING FROM EADV 2019
Birth year linked to influenza-subtype susceptibility
WASHINGTON – People may differ in their susceptibility to different influenza subtypes based in part on the year when they were born and the flu strains that circulated during their birth year, according to infection patterns during a recent U.S. flu season.
“Our findings may indicate protection against H1 [influenza] viruses in age groups with early exposure to H1N1pdm09 during the 2009 pandemic or to older, antigenically similar H1N1 viruses,” Shikha Garg, MD, said at an annual scientific meeting on infectious diseases. If results from further studies confirm this relationship it could have implications for flu vaccine effectiveness in various age groups and influence the composition of flu vaccines based on the ages of the people who will receive them, said Dr. Garg, a medical epidemiologist with the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention in Atlanta.
The analysis she reported using data collected by the CDC’s Influenza Hospitalization Surveillance Network on 18,699 people hospitalized for influenza infection during the 2018-2019 season, Oct. 1, 2018–April 30, 2019. The database provides a representative sampling of patients hospitalized for influenza at more than 250 acute care hospitals in 13 states. During the season studied, both the H1N1 and H3N2 subtypes circulated and caused similar cumulative rates of infections, with H1N1 causing about 32 confirmed cases per 100,000 people and H3N2 causing about 29 cases/100,000.
But a more granular analysis that divided the hospitalized patients by their birth year showed an excess of H1N1 infections in two demographic slices: those born during 2010-2019 (corresponding to children 0-9 years old), in whom H1N1 accounted for roughly 60% of cases; and also in those born during 1948-1995 (people aged 24-70 years old) in whom H1N1 caused roughly 70% or more of all infections in some for some birth-year groups in this demographic range. In contrast, infection with the circulating H3N2 strain in the 2018-2019 season dominated among those born during 1996-2009 (people aged 10-23), as well as in those born in 1947 or earlier (those who were at least 71 years old). Some age groups within those born in 1996-2009 had H3N2 infection rates that made up 70% or more of all flu infections, and among nonagenarians well over three-quarters of flu infection were by the H3N2 subtype.
Dr. Garg also showed a similar pattern of predominant flu subtype by age using U.S. influenza hospitalization data for the 2017-2018 season, as well as for all types of 2018-2019 U.S. influenza infections that underwent strain typing including outpatients as well as in patients. All of these findings support the hypothesis and extend the data published earlier this year by Dr. Garg and several of her CDC colleagues that described a pattern of “antigen imprinting” that appeared caused by influenza exposure during the first year of life (J Infect Dis. 2019 Sep 1;220[5]:820-9). However, more data are needed to better assess time trends for children who were first exposed to H1N1 influenza during the 2009 pandemic, Dr. Garg said.
[email protected]
SOURCE: Garg S. ID Week 2019, Abstract LB19.
WASHINGTON – People may differ in their susceptibility to different influenza subtypes based in part on the year when they were born and the flu strains that circulated during their birth year, according to infection patterns during a recent U.S. flu season.
“Our findings may indicate protection against H1 [influenza] viruses in age groups with early exposure to H1N1pdm09 during the 2009 pandemic or to older, antigenically similar H1N1 viruses,” Shikha Garg, MD, said at an annual scientific meeting on infectious diseases. If results from further studies confirm this relationship it could have implications for flu vaccine effectiveness in various age groups and influence the composition of flu vaccines based on the ages of the people who will receive them, said Dr. Garg, a medical epidemiologist with the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention in Atlanta.
The analysis she reported using data collected by the CDC’s Influenza Hospitalization Surveillance Network on 18,699 people hospitalized for influenza infection during the 2018-2019 season, Oct. 1, 2018–April 30, 2019. The database provides a representative sampling of patients hospitalized for influenza at more than 250 acute care hospitals in 13 states. During the season studied, both the H1N1 and H3N2 subtypes circulated and caused similar cumulative rates of infections, with H1N1 causing about 32 confirmed cases per 100,000 people and H3N2 causing about 29 cases/100,000.
But a more granular analysis that divided the hospitalized patients by their birth year showed an excess of H1N1 infections in two demographic slices: those born during 2010-2019 (corresponding to children 0-9 years old), in whom H1N1 accounted for roughly 60% of cases; and also in those born during 1948-1995 (people aged 24-70 years old) in whom H1N1 caused roughly 70% or more of all infections in some for some birth-year groups in this demographic range. In contrast, infection with the circulating H3N2 strain in the 2018-2019 season dominated among those born during 1996-2009 (people aged 10-23), as well as in those born in 1947 or earlier (those who were at least 71 years old). Some age groups within those born in 1996-2009 had H3N2 infection rates that made up 70% or more of all flu infections, and among nonagenarians well over three-quarters of flu infection were by the H3N2 subtype.
Dr. Garg also showed a similar pattern of predominant flu subtype by age using U.S. influenza hospitalization data for the 2017-2018 season, as well as for all types of 2018-2019 U.S. influenza infections that underwent strain typing including outpatients as well as in patients. All of these findings support the hypothesis and extend the data published earlier this year by Dr. Garg and several of her CDC colleagues that described a pattern of “antigen imprinting” that appeared caused by influenza exposure during the first year of life (J Infect Dis. 2019 Sep 1;220[5]:820-9). However, more data are needed to better assess time trends for children who were first exposed to H1N1 influenza during the 2009 pandemic, Dr. Garg said.
[email protected]
SOURCE: Garg S. ID Week 2019, Abstract LB19.
WASHINGTON – People may differ in their susceptibility to different influenza subtypes based in part on the year when they were born and the flu strains that circulated during their birth year, according to infection patterns during a recent U.S. flu season.
“Our findings may indicate protection against H1 [influenza] viruses in age groups with early exposure to H1N1pdm09 during the 2009 pandemic or to older, antigenically similar H1N1 viruses,” Shikha Garg, MD, said at an annual scientific meeting on infectious diseases. If results from further studies confirm this relationship it could have implications for flu vaccine effectiveness in various age groups and influence the composition of flu vaccines based on the ages of the people who will receive them, said Dr. Garg, a medical epidemiologist with the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention in Atlanta.
The analysis she reported using data collected by the CDC’s Influenza Hospitalization Surveillance Network on 18,699 people hospitalized for influenza infection during the 2018-2019 season, Oct. 1, 2018–April 30, 2019. The database provides a representative sampling of patients hospitalized for influenza at more than 250 acute care hospitals in 13 states. During the season studied, both the H1N1 and H3N2 subtypes circulated and caused similar cumulative rates of infections, with H1N1 causing about 32 confirmed cases per 100,000 people and H3N2 causing about 29 cases/100,000.
But a more granular analysis that divided the hospitalized patients by their birth year showed an excess of H1N1 infections in two demographic slices: those born during 2010-2019 (corresponding to children 0-9 years old), in whom H1N1 accounted for roughly 60% of cases; and also in those born during 1948-1995 (people aged 24-70 years old) in whom H1N1 caused roughly 70% or more of all infections in some for some birth-year groups in this demographic range. In contrast, infection with the circulating H3N2 strain in the 2018-2019 season dominated among those born during 1996-2009 (people aged 10-23), as well as in those born in 1947 or earlier (those who were at least 71 years old). Some age groups within those born in 1996-2009 had H3N2 infection rates that made up 70% or more of all flu infections, and among nonagenarians well over three-quarters of flu infection were by the H3N2 subtype.
Dr. Garg also showed a similar pattern of predominant flu subtype by age using U.S. influenza hospitalization data for the 2017-2018 season, as well as for all types of 2018-2019 U.S. influenza infections that underwent strain typing including outpatients as well as in patients. All of these findings support the hypothesis and extend the data published earlier this year by Dr. Garg and several of her CDC colleagues that described a pattern of “antigen imprinting” that appeared caused by influenza exposure during the first year of life (J Infect Dis. 2019 Sep 1;220[5]:820-9). However, more data are needed to better assess time trends for children who were first exposed to H1N1 influenza during the 2009 pandemic, Dr. Garg said.
[email protected]
SOURCE: Garg S. ID Week 2019, Abstract LB19.
REPORTING FROM ID WEEK 2019
NIH seeks gene-based cures for HIV, sickle cell disease
The National Institutes of Health and the Bill & Melinda Gates Foundation have announced that they plan to invest $100 million each over the next 4 years to develop affordable, gene-based cures for sickle cell disease (SCD) and HIV.
The initiative follows an announcement from President Trump that set a goal of ending the HIV epidemic in the United States in the next 10 years, seeking to reduce the number of diagnoses by 90% by 2030. The Trump administration has also identified SCD as an “intractable health challenge with the potential for dramatic advances in the coming years,” the NIH said in a statement.
Gene-based therapy has become a reality in recent years thanks to dramatic advances, but the cost is prohibitive in many parts of the world. “The collaboration between the NIH and the Gates Foundation sets out a bold goal of advancing safe, effective, and durable gene-based cures to clinical trials in the United States and relevant countries in sub-Saharan Africa within the next 7-10 years. The ultimate goal is to scale and implement these treatments globally in areas hardest hit by these diseases,” the NIH said.
Both diseases are a significant burden on low- and middle-income countries, as 95% of the 38 million people living with HIV globally are in the developing world, with 67% living in sub-Saharan Africa; about half of the HIV-infected population receives no treatment for the disease. An estimated 15 million children will be born with SCD over the next 30 years, with three-quarters of those births occurring in sub-Saharan Africa. About 50%-90% of children born with SCD will die before age 5 years.
The collaboration will focus on coordination in two areas: identifying potential candidate cures for SCD and HIV for preclinical and clinical evaluation, and defining long-term opportunities to work together and with African partners on advancing promising candidates to late-phase clinical trials, with funding to be determined as candidates progress.
“In recent years, gene-based treatments have been groundbreaking for rare genetic disorders and infectious diseases. While these treatments are exciting, people in low- and middle-income countries do not have access to these breakthroughs. By working with the NIH and scientists across Africa, we aim to ensure these approaches will improve the lives of those most in need and bring the incredible promise of gene-based treatments to the world of public health,” said Trevor Mundel, MD, PhD, president of the global health program at the Bill & Melinda Gates Foundation.
The National Institutes of Health and the Bill & Melinda Gates Foundation have announced that they plan to invest $100 million each over the next 4 years to develop affordable, gene-based cures for sickle cell disease (SCD) and HIV.
The initiative follows an announcement from President Trump that set a goal of ending the HIV epidemic in the United States in the next 10 years, seeking to reduce the number of diagnoses by 90% by 2030. The Trump administration has also identified SCD as an “intractable health challenge with the potential for dramatic advances in the coming years,” the NIH said in a statement.
Gene-based therapy has become a reality in recent years thanks to dramatic advances, but the cost is prohibitive in many parts of the world. “The collaboration between the NIH and the Gates Foundation sets out a bold goal of advancing safe, effective, and durable gene-based cures to clinical trials in the United States and relevant countries in sub-Saharan Africa within the next 7-10 years. The ultimate goal is to scale and implement these treatments globally in areas hardest hit by these diseases,” the NIH said.
Both diseases are a significant burden on low- and middle-income countries, as 95% of the 38 million people living with HIV globally are in the developing world, with 67% living in sub-Saharan Africa; about half of the HIV-infected population receives no treatment for the disease. An estimated 15 million children will be born with SCD over the next 30 years, with three-quarters of those births occurring in sub-Saharan Africa. About 50%-90% of children born with SCD will die before age 5 years.
The collaboration will focus on coordination in two areas: identifying potential candidate cures for SCD and HIV for preclinical and clinical evaluation, and defining long-term opportunities to work together and with African partners on advancing promising candidates to late-phase clinical trials, with funding to be determined as candidates progress.
“In recent years, gene-based treatments have been groundbreaking for rare genetic disorders and infectious diseases. While these treatments are exciting, people in low- and middle-income countries do not have access to these breakthroughs. By working with the NIH and scientists across Africa, we aim to ensure these approaches will improve the lives of those most in need and bring the incredible promise of gene-based treatments to the world of public health,” said Trevor Mundel, MD, PhD, president of the global health program at the Bill & Melinda Gates Foundation.
The National Institutes of Health and the Bill & Melinda Gates Foundation have announced that they plan to invest $100 million each over the next 4 years to develop affordable, gene-based cures for sickle cell disease (SCD) and HIV.
The initiative follows an announcement from President Trump that set a goal of ending the HIV epidemic in the United States in the next 10 years, seeking to reduce the number of diagnoses by 90% by 2030. The Trump administration has also identified SCD as an “intractable health challenge with the potential for dramatic advances in the coming years,” the NIH said in a statement.
Gene-based therapy has become a reality in recent years thanks to dramatic advances, but the cost is prohibitive in many parts of the world. “The collaboration between the NIH and the Gates Foundation sets out a bold goal of advancing safe, effective, and durable gene-based cures to clinical trials in the United States and relevant countries in sub-Saharan Africa within the next 7-10 years. The ultimate goal is to scale and implement these treatments globally in areas hardest hit by these diseases,” the NIH said.
Both diseases are a significant burden on low- and middle-income countries, as 95% of the 38 million people living with HIV globally are in the developing world, with 67% living in sub-Saharan Africa; about half of the HIV-infected population receives no treatment for the disease. An estimated 15 million children will be born with SCD over the next 30 years, with three-quarters of those births occurring in sub-Saharan Africa. About 50%-90% of children born with SCD will die before age 5 years.
The collaboration will focus on coordination in two areas: identifying potential candidate cures for SCD and HIV for preclinical and clinical evaluation, and defining long-term opportunities to work together and with African partners on advancing promising candidates to late-phase clinical trials, with funding to be determined as candidates progress.
“In recent years, gene-based treatments have been groundbreaking for rare genetic disorders and infectious diseases. While these treatments are exciting, people in low- and middle-income countries do not have access to these breakthroughs. By working with the NIH and scientists across Africa, we aim to ensure these approaches will improve the lives of those most in need and bring the incredible promise of gene-based treatments to the world of public health,” said Trevor Mundel, MD, PhD, president of the global health program at the Bill & Melinda Gates Foundation.
Secondary Syphilis Mimicking Molluscum Contagiosum in the Beard Area of an AIDS Patient
To the Editor:
A 46-year-old man with a history of AIDS (viral load, 28,186 copies/mL; CD4 count, 22 cells/μL) presented with a 40-lb weight loss over the last 6 months as well as dysphagia and a new-onset pruritic facial eruption of 1 week’s duration. The facial lesions quickly spread to involve the beard area and the upper neck. His medical history was notable for nicotine dependence, seborrheic dermatitis, molluscum contagiosum (MC), treated neurosyphilis and latent tuberculosis, hypertension, a liver mass suspected to be a hemangioma, and erythrocytosis. He was diagnosed with human immunodeficiency virus infection 19 years prior to presentation and was not compliant with the prescribed highly active antiretroviral therapy.
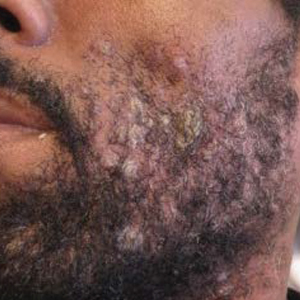
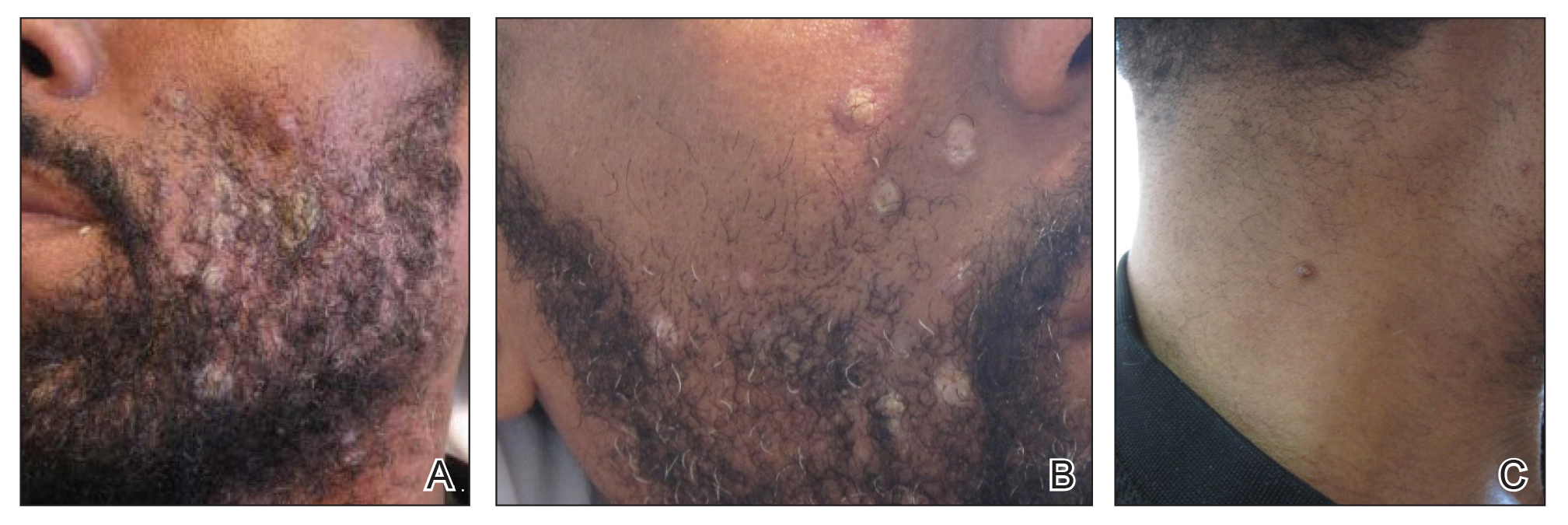
Skin examination revealed multiple discrete and coalescing, 2- to 12-mm, nonumbilicated, hyperkeratotic papules and nodules localized to the left and right beard areas (Figure 1A). A few discrete, 2- to 5-mm, umbilicated papules were noted in the right beard area (Figure 1B), as well as on the right side of the neck (Figure 1C), buttocks, and legs. Mild erythema with yellow-white scale was present in the alar creases. Examination of the oropharyngeal mucosa revealed multiple thick white plaques that were easily scraped off with a tongue depressor. Examination of the palms, soles, and anogenital areas was normal.
A punch biopsy of a nonumbilicated hyperkeratotic papule from the left beard area demonstrated spongiosis; neutrophilic microabscess formation; plasma cells; and a superficial and deep perivascular, predominantly lymphohistiocytic infiltrate (Figure 2A). Spirochete immunohistochemical staining of tissue highlighted abundant organisms in the dermoepidermal junction and vascular endothelial cells (Figure 2B). Other tissue stains for bacteria, including acid-fast bacilli, and fungi were negative. Bacterial culture of tissue from the lesion in the left beard area grew Staphylococcus aureus. Results of acid-fast and fungal cultures of tissue were negative. Shave biopsy of the umbilicated papule on the right side of the neck demonstrated classic invagination of the epidermis into the dermis and intracytoplasmic viral inclusions consistent with MC (Figure 2C). Spirochete immunohistochemical staining of the same tissue sample was negative (Figure 2D).
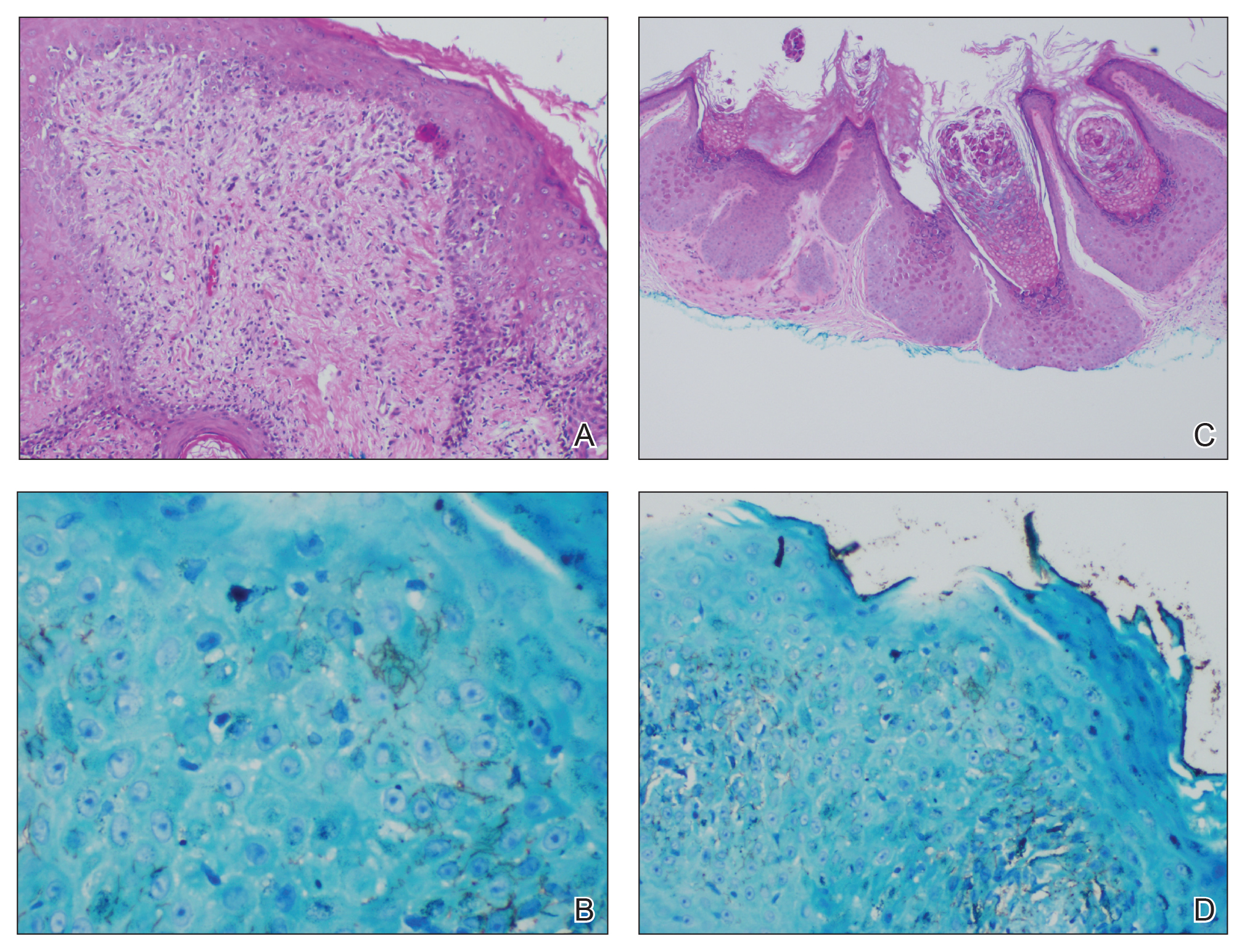
Serum rapid plasma reagin was reactive with a titer of 1:128 compared to the last known reactive rapid plasma reagin titer of 1:1 five years prior to presentation. A fluorescent treponemal antibody absorption test and VDRL test of cerebrospinal fluid was nonreactive. Fungal, bacterial, and acid-fast cultures of cerebral spinal fluid and a cryptococcal antigen test were negative. Serum cryptococcal antigen and coccidioides complement fixation tests were negative. Cytomegalovirus plasma polymerase chain reaction and urine histoplasma antigen testing were negative. Computed tomography of the chest revealed a new 1.9×1.6×2.1-cm3 cavitary lesion with distal tree-in-bud opacities in the lingula of the left lung. Acid-fast blood culture was negative, and acid-fast sputum culture was positive for Mycobacterium kansasii.
The cutaneous pathology findings and serologic findings confirmed the diagnoses of cutaneous secondary syphilis (SS) in the beard area and MC on the right side of the neck. Clinical diagnoses of seborrheic dermatitis of the alar creases and esophageal candidiasis also were made. The patient was treated with intramuscular penicillin G 2.4 million U once weekly for 3 weeks. The lesions confined to the beard area rapidly resolved within 7 days after the first dose of antibiotics, which further supported the diagnosis of localized cutaneous SS. Fluconazole 100 mg once daily was prescribed for the esophageal candidiasis, and he also was started on a regimen of rifampin 600 mg once daily, isoniazid 300 mg once daily, ethambutol 1200 mg once daily, and pyrazinamide 1500 mg once daily.
Syphilis is well known as the great masquerader due to its many possible manifestations. Many patients present with typical palmar and plantar dermatoses.1 Other documented SS presentations include eruptions ranging from a few to diffusely disseminated maculopapular lesions with or without scale on the trunk and upper extremities; pustular and nodular lesions of the face; alopecia; grayish white patches on the oral mucosa; and ulcerative, psoriasiform, follicular, and lichenoid lesions.2 Cutaneous SS has not been commonly reported in a localized distribution to the beard area with a clinical appearance mimicking hyperkeratotic MC lesions.3 Secondary syphilis is not known to spread through autoinoculation, presumably from shaving (as in our case), as might occur with other cutaneous infectious processes such as MC, verruca vulgaris, S aureus, and dermatophytosis in the beard area.
The differential diagnosis for hyperkeratotic papules and nodules localized to the beard area in human immunodeficiency virus–infected males includes MC, verruca vulgaris, chronic verrucous varicella-zoster virus, crusted scabies, tuberculosis verrucosa cutis, hypertrophic lichen planus, and disseminated deep fungal infections including cryptococcosis and coccidioidomycosis. In the setting of immunosuppression, the diagnosis of hyperkeratotic MC was favored in our patient given the co-location of classic umbilicated MC lesions with the hyperkeratotic papules and nodules. It is common to see MC autoinoculated in the beard area in men from shaving, as well as for MC to present in an atypical manner, particularly as hyperkeratotic lesions, in patients with AIDS.4 The predominant localized beard distribution and lack of other mucocutaneous manifestations of SS at presentation supported a clinical diagnosis of hyperkeratotic MC in our patient.
Unique presentations of SS have been documented, including nodular lesions of the face, but they typically have been accompanied by other stigmata of SS such as the classic palmoplantar or truncal maculopapular rash.3 One notable difference in our case was the localized beard distribution of the syphilitic cutaneous lesions in a man with AIDS. Our case reinforces the importance of cutaneous biopsies in immunocompromised patients. It is known that SS spreads hematogenously; however, in our case it was suspected that the new lesions may have spread locally through autoinoculation via beard hair removal, as the hyperkeratotic lesions were limited to the beard area. Koebnerization secondary to trauma induced by beard hair removal was considered in this case; however, koebnerization is known to occur in noninfectious dermatologic conditions, such as psoriasis, lichen planus, lichen nitidus, and vitiligo, but not in infections such as syphilis. Our case is pivotal in raising the question of whether SS can be autoinoculated in the beard area.
- Baughn RE, Musher DM. Secondary syphilitic lesions. Clin Microbiol Rev. 2005;18:205-216.
- Dourmishev LA, Dourmishev AL. Syphilis: uncommon presentations in adults. Clin Dermatol. 2005;23:555-564.
- Cohen SE, Klausner JD, Engelman J, et al. Syphilis in the modern era: an update for physicians. Infect Dis Clin North Am. 2013;27:705-722.
- Filo-Rogulska M, Pindycka-Plaszcznska M, Januszewski K, et al. Disseminated atypical molluscum contagiosum as a presenting symptom of HIV infection. Postepy Dermatol Alergol. 2013;30:56-58.
To the Editor:
A 46-year-old man with a history of AIDS (viral load, 28,186 copies/mL; CD4 count, 22 cells/μL) presented with a 40-lb weight loss over the last 6 months as well as dysphagia and a new-onset pruritic facial eruption of 1 week’s duration. The facial lesions quickly spread to involve the beard area and the upper neck. His medical history was notable for nicotine dependence, seborrheic dermatitis, molluscum contagiosum (MC), treated neurosyphilis and latent tuberculosis, hypertension, a liver mass suspected to be a hemangioma, and erythrocytosis. He was diagnosed with human immunodeficiency virus infection 19 years prior to presentation and was not compliant with the prescribed highly active antiretroviral therapy.
Skin examination revealed multiple discrete and coalescing, 2- to 12-mm, nonumbilicated, hyperkeratotic papules and nodules localized to the left and right beard areas (Figure 1A). A few discrete, 2- to 5-mm, umbilicated papules were noted in the right beard area (Figure 1B), as well as on the right side of the neck (Figure 1C), buttocks, and legs. Mild erythema with yellow-white scale was present in the alar creases. Examination of the oropharyngeal mucosa revealed multiple thick white plaques that were easily scraped off with a tongue depressor. Examination of the palms, soles, and anogenital areas was normal.

A punch biopsy of a nonumbilicated hyperkeratotic papule from the left beard area demonstrated spongiosis; neutrophilic microabscess formation; plasma cells; and a superficial and deep perivascular, predominantly lymphohistiocytic infiltrate (Figure 2A). Spirochete immunohistochemical staining of tissue highlighted abundant organisms in the dermoepidermal junction and vascular endothelial cells (Figure 2B). Other tissue stains for bacteria, including acid-fast bacilli, and fungi were negative. Bacterial culture of tissue from the lesion in the left beard area grew Staphylococcus aureus. Results of acid-fast and fungal cultures of tissue were negative. Shave biopsy of the umbilicated papule on the right side of the neck demonstrated classic invagination of the epidermis into the dermis and intracytoplasmic viral inclusions consistent with MC (Figure 2C). Spirochete immunohistochemical staining of the same tissue sample was negative (Figure 2D).

Serum rapid plasma reagin was reactive with a titer of 1:128 compared to the last known reactive rapid plasma reagin titer of 1:1 five years prior to presentation. A fluorescent treponemal antibody absorption test and VDRL test of cerebrospinal fluid was nonreactive. Fungal, bacterial, and acid-fast cultures of cerebral spinal fluid and a cryptococcal antigen test were negative. Serum cryptococcal antigen and coccidioides complement fixation tests were negative. Cytomegalovirus plasma polymerase chain reaction and urine histoplasma antigen testing were negative. Computed tomography of the chest revealed a new 1.9×1.6×2.1-cm3 cavitary lesion with distal tree-in-bud opacities in the lingula of the left lung. Acid-fast blood culture was negative, and acid-fast sputum culture was positive for Mycobacterium kansasii.
The cutaneous pathology findings and serologic findings confirmed the diagnoses of cutaneous secondary syphilis (SS) in the beard area and MC on the right side of the neck. Clinical diagnoses of seborrheic dermatitis of the alar creases and esophageal candidiasis also were made. The patient was treated with intramuscular penicillin G 2.4 million U once weekly for 3 weeks. The lesions confined to the beard area rapidly resolved within 7 days after the first dose of antibiotics, which further supported the diagnosis of localized cutaneous SS. Fluconazole 100 mg once daily was prescribed for the esophageal candidiasis, and he also was started on a regimen of rifampin 600 mg once daily, isoniazid 300 mg once daily, ethambutol 1200 mg once daily, and pyrazinamide 1500 mg once daily.
Syphilis is well known as the great masquerader due to its many possible manifestations. Many patients present with typical palmar and plantar dermatoses.1 Other documented SS presentations include eruptions ranging from a few to diffusely disseminated maculopapular lesions with or without scale on the trunk and upper extremities; pustular and nodular lesions of the face; alopecia; grayish white patches on the oral mucosa; and ulcerative, psoriasiform, follicular, and lichenoid lesions.2 Cutaneous SS has not been commonly reported in a localized distribution to the beard area with a clinical appearance mimicking hyperkeratotic MC lesions.3 Secondary syphilis is not known to spread through autoinoculation, presumably from shaving (as in our case), as might occur with other cutaneous infectious processes such as MC, verruca vulgaris, S aureus, and dermatophytosis in the beard area.
The differential diagnosis for hyperkeratotic papules and nodules localized to the beard area in human immunodeficiency virus–infected males includes MC, verruca vulgaris, chronic verrucous varicella-zoster virus, crusted scabies, tuberculosis verrucosa cutis, hypertrophic lichen planus, and disseminated deep fungal infections including cryptococcosis and coccidioidomycosis. In the setting of immunosuppression, the diagnosis of hyperkeratotic MC was favored in our patient given the co-location of classic umbilicated MC lesions with the hyperkeratotic papules and nodules. It is common to see MC autoinoculated in the beard area in men from shaving, as well as for MC to present in an atypical manner, particularly as hyperkeratotic lesions, in patients with AIDS.4 The predominant localized beard distribution and lack of other mucocutaneous manifestations of SS at presentation supported a clinical diagnosis of hyperkeratotic MC in our patient.
Unique presentations of SS have been documented, including nodular lesions of the face, but they typically have been accompanied by other stigmata of SS such as the classic palmoplantar or truncal maculopapular rash.3 One notable difference in our case was the localized beard distribution of the syphilitic cutaneous lesions in a man with AIDS. Our case reinforces the importance of cutaneous biopsies in immunocompromised patients. It is known that SS spreads hematogenously; however, in our case it was suspected that the new lesions may have spread locally through autoinoculation via beard hair removal, as the hyperkeratotic lesions were limited to the beard area. Koebnerization secondary to trauma induced by beard hair removal was considered in this case; however, koebnerization is known to occur in noninfectious dermatologic conditions, such as psoriasis, lichen planus, lichen nitidus, and vitiligo, but not in infections such as syphilis. Our case is pivotal in raising the question of whether SS can be autoinoculated in the beard area.
To the Editor:
A 46-year-old man with a history of AIDS (viral load, 28,186 copies/mL; CD4 count, 22 cells/μL) presented with a 40-lb weight loss over the last 6 months as well as dysphagia and a new-onset pruritic facial eruption of 1 week’s duration. The facial lesions quickly spread to involve the beard area and the upper neck. His medical history was notable for nicotine dependence, seborrheic dermatitis, molluscum contagiosum (MC), treated neurosyphilis and latent tuberculosis, hypertension, a liver mass suspected to be a hemangioma, and erythrocytosis. He was diagnosed with human immunodeficiency virus infection 19 years prior to presentation and was not compliant with the prescribed highly active antiretroviral therapy.
Skin examination revealed multiple discrete and coalescing, 2- to 12-mm, nonumbilicated, hyperkeratotic papules and nodules localized to the left and right beard areas (Figure 1A). A few discrete, 2- to 5-mm, umbilicated papules were noted in the right beard area (Figure 1B), as well as on the right side of the neck (Figure 1C), buttocks, and legs. Mild erythema with yellow-white scale was present in the alar creases. Examination of the oropharyngeal mucosa revealed multiple thick white plaques that were easily scraped off with a tongue depressor. Examination of the palms, soles, and anogenital areas was normal.

A punch biopsy of a nonumbilicated hyperkeratotic papule from the left beard area demonstrated spongiosis; neutrophilic microabscess formation; plasma cells; and a superficial and deep perivascular, predominantly lymphohistiocytic infiltrate (Figure 2A). Spirochete immunohistochemical staining of tissue highlighted abundant organisms in the dermoepidermal junction and vascular endothelial cells (Figure 2B). Other tissue stains for bacteria, including acid-fast bacilli, and fungi were negative. Bacterial culture of tissue from the lesion in the left beard area grew Staphylococcus aureus. Results of acid-fast and fungal cultures of tissue were negative. Shave biopsy of the umbilicated papule on the right side of the neck demonstrated classic invagination of the epidermis into the dermis and intracytoplasmic viral inclusions consistent with MC (Figure 2C). Spirochete immunohistochemical staining of the same tissue sample was negative (Figure 2D).

Serum rapid plasma reagin was reactive with a titer of 1:128 compared to the last known reactive rapid plasma reagin titer of 1:1 five years prior to presentation. A fluorescent treponemal antibody absorption test and VDRL test of cerebrospinal fluid was nonreactive. Fungal, bacterial, and acid-fast cultures of cerebral spinal fluid and a cryptococcal antigen test were negative. Serum cryptococcal antigen and coccidioides complement fixation tests were negative. Cytomegalovirus plasma polymerase chain reaction and urine histoplasma antigen testing were negative. Computed tomography of the chest revealed a new 1.9×1.6×2.1-cm3 cavitary lesion with distal tree-in-bud opacities in the lingula of the left lung. Acid-fast blood culture was negative, and acid-fast sputum culture was positive for Mycobacterium kansasii.
The cutaneous pathology findings and serologic findings confirmed the diagnoses of cutaneous secondary syphilis (SS) in the beard area and MC on the right side of the neck. Clinical diagnoses of seborrheic dermatitis of the alar creases and esophageal candidiasis also were made. The patient was treated with intramuscular penicillin G 2.4 million U once weekly for 3 weeks. The lesions confined to the beard area rapidly resolved within 7 days after the first dose of antibiotics, which further supported the diagnosis of localized cutaneous SS. Fluconazole 100 mg once daily was prescribed for the esophageal candidiasis, and he also was started on a regimen of rifampin 600 mg once daily, isoniazid 300 mg once daily, ethambutol 1200 mg once daily, and pyrazinamide 1500 mg once daily.
Syphilis is well known as the great masquerader due to its many possible manifestations. Many patients present with typical palmar and plantar dermatoses.1 Other documented SS presentations include eruptions ranging from a few to diffusely disseminated maculopapular lesions with or without scale on the trunk and upper extremities; pustular and nodular lesions of the face; alopecia; grayish white patches on the oral mucosa; and ulcerative, psoriasiform, follicular, and lichenoid lesions.2 Cutaneous SS has not been commonly reported in a localized distribution to the beard area with a clinical appearance mimicking hyperkeratotic MC lesions.3 Secondary syphilis is not known to spread through autoinoculation, presumably from shaving (as in our case), as might occur with other cutaneous infectious processes such as MC, verruca vulgaris, S aureus, and dermatophytosis in the beard area.
The differential diagnosis for hyperkeratotic papules and nodules localized to the beard area in human immunodeficiency virus–infected males includes MC, verruca vulgaris, chronic verrucous varicella-zoster virus, crusted scabies, tuberculosis verrucosa cutis, hypertrophic lichen planus, and disseminated deep fungal infections including cryptococcosis and coccidioidomycosis. In the setting of immunosuppression, the diagnosis of hyperkeratotic MC was favored in our patient given the co-location of classic umbilicated MC lesions with the hyperkeratotic papules and nodules. It is common to see MC autoinoculated in the beard area in men from shaving, as well as for MC to present in an atypical manner, particularly as hyperkeratotic lesions, in patients with AIDS.4 The predominant localized beard distribution and lack of other mucocutaneous manifestations of SS at presentation supported a clinical diagnosis of hyperkeratotic MC in our patient.
Unique presentations of SS have been documented, including nodular lesions of the face, but they typically have been accompanied by other stigmata of SS such as the classic palmoplantar or truncal maculopapular rash.3 One notable difference in our case was the localized beard distribution of the syphilitic cutaneous lesions in a man with AIDS. Our case reinforces the importance of cutaneous biopsies in immunocompromised patients. It is known that SS spreads hematogenously; however, in our case it was suspected that the new lesions may have spread locally through autoinoculation via beard hair removal, as the hyperkeratotic lesions were limited to the beard area. Koebnerization secondary to trauma induced by beard hair removal was considered in this case; however, koebnerization is known to occur in noninfectious dermatologic conditions, such as psoriasis, lichen planus, lichen nitidus, and vitiligo, but not in infections such as syphilis. Our case is pivotal in raising the question of whether SS can be autoinoculated in the beard area.
- Baughn RE, Musher DM. Secondary syphilitic lesions. Clin Microbiol Rev. 2005;18:205-216.
- Dourmishev LA, Dourmishev AL. Syphilis: uncommon presentations in adults. Clin Dermatol. 2005;23:555-564.
- Cohen SE, Klausner JD, Engelman J, et al. Syphilis in the modern era: an update for physicians. Infect Dis Clin North Am. 2013;27:705-722.
- Filo-Rogulska M, Pindycka-Plaszcznska M, Januszewski K, et al. Disseminated atypical molluscum contagiosum as a presenting symptom of HIV infection. Postepy Dermatol Alergol. 2013;30:56-58.
- Baughn RE, Musher DM. Secondary syphilitic lesions. Clin Microbiol Rev. 2005;18:205-216.
- Dourmishev LA, Dourmishev AL. Syphilis: uncommon presentations in adults. Clin Dermatol. 2005;23:555-564.
- Cohen SE, Klausner JD, Engelman J, et al. Syphilis in the modern era: an update for physicians. Infect Dis Clin North Am. 2013;27:705-722.
- Filo-Rogulska M, Pindycka-Plaszcznska M, Januszewski K, et al. Disseminated atypical molluscum contagiosum as a presenting symptom of HIV infection. Postepy Dermatol Alergol. 2013;30:56-58.
Practice Points
- Recognize typical and atypical presentations of secondary syphilis (SS).
- This case reinforces the importance of cutaneous biopsies in immunocompromised patients.
- Consider the possibility of autoinoculation in SS.
ACIP approves child and adolescent vaccination schedule for 2020
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention’s Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices voted unanimously to approve the child and adolescent immunization schedule for 2020.
by busy providers,” Candice Robinson, MD, MPH, of the CDC’s National Center for Immunization and Respiratory Diseases, said at the CDC’s October meeting of ACIP. Updates reflect changes in language in the adult vaccination schedule, notably the change in the definition of “contraindication.” The updated wording in the Notes substitutes “not recommended or contraindicated” instead of the word “contraindicated” only.
Another notable change was the addition of information on adolescent vaccination of children who received the meningococcal ACWY vaccine before 10 years of age. For “children in whom boosters are not recommended due to an ongoing or increased risk of meningococcal disease” (such as a healthy child traveling to an endemic area), they should receive MenACWY according to the recommended adolescent schedule. But those children for whom boosters are recommended because of increased disease risk from conditions including complement deficiency, HIV, or asplenia should “follow the booster schedule for persons at increased risk.”
Other changes include restructuring of the notes for the live attenuated influenza vaccine (LAIV) in special situations. The schedule now uses a bulleted list to show that LAIV should not be used in the following circumstances:
- Having history of severe allergic reaction to a previous vaccine or vaccine component.
- Using aspirin or a salicylate-containing medication.
- Being aged 2-4 years with a history of asthma or wheezing.
- Having immunocompromised conditions.
- Having anatomic or functional asplenia.
- Having cochlear implants.
- Experiencing cerebrospinal fluid–oropharyngeal communication.
- Having immunocompromised close contacts or caregivers.
- Being pregnant.
- Having received flu antivirals within the previous 48 hours.
In addition, language on shared clinical decision-making was added to the notes on the meningococcal B vaccine for adolescents and young adults aged 18-23 years not at increased risk. Based on shared clinical decision making, the recommendation is a “two-dose series of Bexsero at least 1 month apart” or “two-dose series of Trumenba at least 6 months apart; if dose two is administered earlier than 6 months, administer a third dose at least 4 months after dose two.”
Several vaccines’ Notes sections, including hepatitis B and meningococcal disease, added links to detailed recommendations in the corresponding issues of the CDC’s Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report, to allow clinicians easy access to additional information.
View the current Child & Adolescent Vaccination Schedule here.
The ACIP members had no financial conflicts to disclose.
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention’s Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices voted unanimously to approve the child and adolescent immunization schedule for 2020.
by busy providers,” Candice Robinson, MD, MPH, of the CDC’s National Center for Immunization and Respiratory Diseases, said at the CDC’s October meeting of ACIP. Updates reflect changes in language in the adult vaccination schedule, notably the change in the definition of “contraindication.” The updated wording in the Notes substitutes “not recommended or contraindicated” instead of the word “contraindicated” only.
Another notable change was the addition of information on adolescent vaccination of children who received the meningococcal ACWY vaccine before 10 years of age. For “children in whom boosters are not recommended due to an ongoing or increased risk of meningococcal disease” (such as a healthy child traveling to an endemic area), they should receive MenACWY according to the recommended adolescent schedule. But those children for whom boosters are recommended because of increased disease risk from conditions including complement deficiency, HIV, or asplenia should “follow the booster schedule for persons at increased risk.”
Other changes include restructuring of the notes for the live attenuated influenza vaccine (LAIV) in special situations. The schedule now uses a bulleted list to show that LAIV should not be used in the following circumstances:
- Having history of severe allergic reaction to a previous vaccine or vaccine component.
- Using aspirin or a salicylate-containing medication.
- Being aged 2-4 years with a history of asthma or wheezing.
- Having immunocompromised conditions.
- Having anatomic or functional asplenia.
- Having cochlear implants.
- Experiencing cerebrospinal fluid–oropharyngeal communication.
- Having immunocompromised close contacts or caregivers.
- Being pregnant.
- Having received flu antivirals within the previous 48 hours.
In addition, language on shared clinical decision-making was added to the notes on the meningococcal B vaccine for adolescents and young adults aged 18-23 years not at increased risk. Based on shared clinical decision making, the recommendation is a “two-dose series of Bexsero at least 1 month apart” or “two-dose series of Trumenba at least 6 months apart; if dose two is administered earlier than 6 months, administer a third dose at least 4 months after dose two.”
Several vaccines’ Notes sections, including hepatitis B and meningococcal disease, added links to detailed recommendations in the corresponding issues of the CDC’s Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report, to allow clinicians easy access to additional information.
View the current Child & Adolescent Vaccination Schedule here.
The ACIP members had no financial conflicts to disclose.
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention’s Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices voted unanimously to approve the child and adolescent immunization schedule for 2020.
by busy providers,” Candice Robinson, MD, MPH, of the CDC’s National Center for Immunization and Respiratory Diseases, said at the CDC’s October meeting of ACIP. Updates reflect changes in language in the adult vaccination schedule, notably the change in the definition of “contraindication.” The updated wording in the Notes substitutes “not recommended or contraindicated” instead of the word “contraindicated” only.
Another notable change was the addition of information on adolescent vaccination of children who received the meningococcal ACWY vaccine before 10 years of age. For “children in whom boosters are not recommended due to an ongoing or increased risk of meningococcal disease” (such as a healthy child traveling to an endemic area), they should receive MenACWY according to the recommended adolescent schedule. But those children for whom boosters are recommended because of increased disease risk from conditions including complement deficiency, HIV, or asplenia should “follow the booster schedule for persons at increased risk.”
Other changes include restructuring of the notes for the live attenuated influenza vaccine (LAIV) in special situations. The schedule now uses a bulleted list to show that LAIV should not be used in the following circumstances:
- Having history of severe allergic reaction to a previous vaccine or vaccine component.
- Using aspirin or a salicylate-containing medication.
- Being aged 2-4 years with a history of asthma or wheezing.
- Having immunocompromised conditions.
- Having anatomic or functional asplenia.
- Having cochlear implants.
- Experiencing cerebrospinal fluid–oropharyngeal communication.
- Having immunocompromised close contacts or caregivers.
- Being pregnant.
- Having received flu antivirals within the previous 48 hours.
In addition, language on shared clinical decision-making was added to the notes on the meningococcal B vaccine for adolescents and young adults aged 18-23 years not at increased risk. Based on shared clinical decision making, the recommendation is a “two-dose series of Bexsero at least 1 month apart” or “two-dose series of Trumenba at least 6 months apart; if dose two is administered earlier than 6 months, administer a third dose at least 4 months after dose two.”
Several vaccines’ Notes sections, including hepatitis B and meningococcal disease, added links to detailed recommendations in the corresponding issues of the CDC’s Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report, to allow clinicians easy access to additional information.
View the current Child & Adolescent Vaccination Schedule here.
The ACIP members had no financial conflicts to disclose.
FROM AN ACIP MEETING
ACIP approves 2020 adult vaccination schedule
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention’s Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices voted unanimously to approve the adult immunization schedule for 2020, although some fine-tuning may occur before publication.
“Some of the wordsmithing may be done later,” ACIP executive secretary Amanda Cohn, MD, said at the ACIP October meeting.
Key updates to the schedule included a change in wording for the definition of the red bars on the table to include “not recommended or contraindicated” instead of only the word “contraindicated.” Committee members were especially interested in changing this wording to guide clinicians in use of the live attenuated influenza vaccine because of its potential value in vaccinating health care personnel.
Other updates include language that vaccination of adolescents and young adults aged 16-23 years who are not at increased risk for meningococcal disease should be vaccinated as follows: “Based on shared clinical decision making, 2-dose series MenB-4C at least 1 month apart or 2-dose series MenB-FHbp at 0, 6 months.”
Similarly, clinical decision-making language was added to the notes for the pneumococcal polysaccharide vaccine (PPSV23) and the 13-valent pneumococcal conjugate vaccine (PCV13).
The routine vaccination calls for only one dose of PPSV23 given on or after the individual’s 65th birthday. Then, based on shared clinical decision making, a dose of PCV13 is recommended for immunocompetent individuals aged 65 years and older. The notes also state that, based on shared clinical decision making, PCV13 and PPSV23 should not be given in the same visit and, if both will be given, PCV13 should be first and should be given 1 year before PPSV23. In addition, “PPSV23 should be given at least 5 years after any previous PPSV23 dose.”
The schedule also adds shared clinical decision making to the notes on human papillomavirus vaccination for adults aged 27-45 years.
The committee members acknowledged the increasing complexity of the adult vaccination schedule, but several members agreed that it is accessible to many clinicians.
“We can’t let the perfect be the enemy of the good” said Jason Goldman, MD, liaison representing the American College of Physicians. “Those who want to learn the schedule will learn it; the health system will learn it,” even if not every specialist does.
The table “is something to draw you in,” said Sandra Fryhofer, MD, an internist who is liaison for the American Medical Association. The notes provide more details.
More specific information about contraindications for patients with cochlear implants, which also came up in the discussion, may be added to the schedule at a later date.
View the current adult vaccination schedule here.
The ACIP members had no financial conflicts to disclose.
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention’s Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices voted unanimously to approve the adult immunization schedule for 2020, although some fine-tuning may occur before publication.
“Some of the wordsmithing may be done later,” ACIP executive secretary Amanda Cohn, MD, said at the ACIP October meeting.
Key updates to the schedule included a change in wording for the definition of the red bars on the table to include “not recommended or contraindicated” instead of only the word “contraindicated.” Committee members were especially interested in changing this wording to guide clinicians in use of the live attenuated influenza vaccine because of its potential value in vaccinating health care personnel.
Other updates include language that vaccination of adolescents and young adults aged 16-23 years who are not at increased risk for meningococcal disease should be vaccinated as follows: “Based on shared clinical decision making, 2-dose series MenB-4C at least 1 month apart or 2-dose series MenB-FHbp at 0, 6 months.”
Similarly, clinical decision-making language was added to the notes for the pneumococcal polysaccharide vaccine (PPSV23) and the 13-valent pneumococcal conjugate vaccine (PCV13).
The routine vaccination calls for only one dose of PPSV23 given on or after the individual’s 65th birthday. Then, based on shared clinical decision making, a dose of PCV13 is recommended for immunocompetent individuals aged 65 years and older. The notes also state that, based on shared clinical decision making, PCV13 and PPSV23 should not be given in the same visit and, if both will be given, PCV13 should be first and should be given 1 year before PPSV23. In addition, “PPSV23 should be given at least 5 years after any previous PPSV23 dose.”
The schedule also adds shared clinical decision making to the notes on human papillomavirus vaccination for adults aged 27-45 years.
The committee members acknowledged the increasing complexity of the adult vaccination schedule, but several members agreed that it is accessible to many clinicians.
“We can’t let the perfect be the enemy of the good” said Jason Goldman, MD, liaison representing the American College of Physicians. “Those who want to learn the schedule will learn it; the health system will learn it,” even if not every specialist does.
The table “is something to draw you in,” said Sandra Fryhofer, MD, an internist who is liaison for the American Medical Association. The notes provide more details.
More specific information about contraindications for patients with cochlear implants, which also came up in the discussion, may be added to the schedule at a later date.
View the current adult vaccination schedule here.
The ACIP members had no financial conflicts to disclose.
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention’s Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices voted unanimously to approve the adult immunization schedule for 2020, although some fine-tuning may occur before publication.
“Some of the wordsmithing may be done later,” ACIP executive secretary Amanda Cohn, MD, said at the ACIP October meeting.
Key updates to the schedule included a change in wording for the definition of the red bars on the table to include “not recommended or contraindicated” instead of only the word “contraindicated.” Committee members were especially interested in changing this wording to guide clinicians in use of the live attenuated influenza vaccine because of its potential value in vaccinating health care personnel.
Other updates include language that vaccination of adolescents and young adults aged 16-23 years who are not at increased risk for meningococcal disease should be vaccinated as follows: “Based on shared clinical decision making, 2-dose series MenB-4C at least 1 month apart or 2-dose series MenB-FHbp at 0, 6 months.”
Similarly, clinical decision-making language was added to the notes for the pneumococcal polysaccharide vaccine (PPSV23) and the 13-valent pneumococcal conjugate vaccine (PCV13).
The routine vaccination calls for only one dose of PPSV23 given on or after the individual’s 65th birthday. Then, based on shared clinical decision making, a dose of PCV13 is recommended for immunocompetent individuals aged 65 years and older. The notes also state that, based on shared clinical decision making, PCV13 and PPSV23 should not be given in the same visit and, if both will be given, PCV13 should be first and should be given 1 year before PPSV23. In addition, “PPSV23 should be given at least 5 years after any previous PPSV23 dose.”
The schedule also adds shared clinical decision making to the notes on human papillomavirus vaccination for adults aged 27-45 years.
The committee members acknowledged the increasing complexity of the adult vaccination schedule, but several members agreed that it is accessible to many clinicians.
“We can’t let the perfect be the enemy of the good” said Jason Goldman, MD, liaison representing the American College of Physicians. “Those who want to learn the schedule will learn it; the health system will learn it,” even if not every specialist does.
The table “is something to draw you in,” said Sandra Fryhofer, MD, an internist who is liaison for the American Medical Association. The notes provide more details.
More specific information about contraindications for patients with cochlear implants, which also came up in the discussion, may be added to the schedule at a later date.
View the current adult vaccination schedule here.
The ACIP members had no financial conflicts to disclose.
ACIP plans flu review for older adults
according to data presented at a meeting of the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention’s ACIP.
Lynette Brammer of the CDC’s National Center for Immunization and Respiratory Diseases (NCIRD) presented a surveillance update of the flu season in the United States so far. Overall, the influenza A(H3N2) viruses are predominant, although dominance varies in different regions of the country, and it is too soon to predict what strain will dominate later in the season.
“While two of the four vaccine components were updated for the Southern Hemisphere, the components selected for the 2019-2020 Northern Hemisphere vaccine, at this time, look appropriate for the season,” she said.
In other flu news, Lisa Groskopf, MD, of the NCIRD discussed the influenza work group’s plans for a meta-analysis to assess the relative benefit of different vaccines for older adults, in light of the growing variety of products available.
Currently, no preferential recommendations have been made for a specific vaccine for a particular age group. “There’s a dearth of data comparing these vaccines to one another,” said Dr. Groskopf. She added that, because vaccine effectiveness varies by season, the generalizability of effectiveness data is another challenge.
The work group’s systematic review and meta-analysis is designed to compare the high-dose inactivated influenza vaccine (HD-IIV), the adjuvanted inactivated influenza vaccine (aIIV), and the recombinant influenza vaccine (RIV). The study will include adults aged 65 years and older who receive trivalent or quadrivalent HD-IIV, aIIV, or RIV, compared with those who receive another influenza vaccine, a noninfluenza control vaccine, placebo, or no vaccine. The outcomes will include data on safety and effectiveness of the vaccines, Dr. Groskopf said.
In addition to safety and effectiveness, manufacturers such as Sanofi Pasteur continue to collect data on the success of available vaccines and develop new ones. Lee-Jah Chang, MD, of Sanofi Pasteur presented results of a noninferiority study of the company’s investigational high-dose quadrivalent influenza vaccine (QIV-HD; including two prevailing B viruses) versus the high-dose trivalent influenza vaccine (TID-HD). The study was conducted at 35 sites in the United States and included 2,670 adults aged 65 years and older.
Overall, the reactogenicity profile for patients given QIV-HD was similar to that of TID-HD, and approximately 5% of patients in the QIV group reported an immediate adverse event, Dr. Chang said. However, no related deaths or related adverse events of special interest occurred in any of the study groups.
Sanofi plans to pursue licensure of the QIV-HD vaccine, with a Center for Biologics Evaluation and Research action date of Nov. 4, 2019, said Dr. Chang. If the vaccine is licensed, it should be available for purchase by health care providers in the first quarter of 2020.
The ACIP members had no financial conflicts to disclose.
according to data presented at a meeting of the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention’s ACIP.
Lynette Brammer of the CDC’s National Center for Immunization and Respiratory Diseases (NCIRD) presented a surveillance update of the flu season in the United States so far. Overall, the influenza A(H3N2) viruses are predominant, although dominance varies in different regions of the country, and it is too soon to predict what strain will dominate later in the season.
“While two of the four vaccine components were updated for the Southern Hemisphere, the components selected for the 2019-2020 Northern Hemisphere vaccine, at this time, look appropriate for the season,” she said.
In other flu news, Lisa Groskopf, MD, of the NCIRD discussed the influenza work group’s plans for a meta-analysis to assess the relative benefit of different vaccines for older adults, in light of the growing variety of products available.
Currently, no preferential recommendations have been made for a specific vaccine for a particular age group. “There’s a dearth of data comparing these vaccines to one another,” said Dr. Groskopf. She added that, because vaccine effectiveness varies by season, the generalizability of effectiveness data is another challenge.
The work group’s systematic review and meta-analysis is designed to compare the high-dose inactivated influenza vaccine (HD-IIV), the adjuvanted inactivated influenza vaccine (aIIV), and the recombinant influenza vaccine (RIV). The study will include adults aged 65 years and older who receive trivalent or quadrivalent HD-IIV, aIIV, or RIV, compared with those who receive another influenza vaccine, a noninfluenza control vaccine, placebo, or no vaccine. The outcomes will include data on safety and effectiveness of the vaccines, Dr. Groskopf said.
In addition to safety and effectiveness, manufacturers such as Sanofi Pasteur continue to collect data on the success of available vaccines and develop new ones. Lee-Jah Chang, MD, of Sanofi Pasteur presented results of a noninferiority study of the company’s investigational high-dose quadrivalent influenza vaccine (QIV-HD; including two prevailing B viruses) versus the high-dose trivalent influenza vaccine (TID-HD). The study was conducted at 35 sites in the United States and included 2,670 adults aged 65 years and older.
Overall, the reactogenicity profile for patients given QIV-HD was similar to that of TID-HD, and approximately 5% of patients in the QIV group reported an immediate adverse event, Dr. Chang said. However, no related deaths or related adverse events of special interest occurred in any of the study groups.
Sanofi plans to pursue licensure of the QIV-HD vaccine, with a Center for Biologics Evaluation and Research action date of Nov. 4, 2019, said Dr. Chang. If the vaccine is licensed, it should be available for purchase by health care providers in the first quarter of 2020.
The ACIP members had no financial conflicts to disclose.
according to data presented at a meeting of the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention’s ACIP.
Lynette Brammer of the CDC’s National Center for Immunization and Respiratory Diseases (NCIRD) presented a surveillance update of the flu season in the United States so far. Overall, the influenza A(H3N2) viruses are predominant, although dominance varies in different regions of the country, and it is too soon to predict what strain will dominate later in the season.
“While two of the four vaccine components were updated for the Southern Hemisphere, the components selected for the 2019-2020 Northern Hemisphere vaccine, at this time, look appropriate for the season,” she said.
In other flu news, Lisa Groskopf, MD, of the NCIRD discussed the influenza work group’s plans for a meta-analysis to assess the relative benefit of different vaccines for older adults, in light of the growing variety of products available.
Currently, no preferential recommendations have been made for a specific vaccine for a particular age group. “There’s a dearth of data comparing these vaccines to one another,” said Dr. Groskopf. She added that, because vaccine effectiveness varies by season, the generalizability of effectiveness data is another challenge.
The work group’s systematic review and meta-analysis is designed to compare the high-dose inactivated influenza vaccine (HD-IIV), the adjuvanted inactivated influenza vaccine (aIIV), and the recombinant influenza vaccine (RIV). The study will include adults aged 65 years and older who receive trivalent or quadrivalent HD-IIV, aIIV, or RIV, compared with those who receive another influenza vaccine, a noninfluenza control vaccine, placebo, or no vaccine. The outcomes will include data on safety and effectiveness of the vaccines, Dr. Groskopf said.
In addition to safety and effectiveness, manufacturers such as Sanofi Pasteur continue to collect data on the success of available vaccines and develop new ones. Lee-Jah Chang, MD, of Sanofi Pasteur presented results of a noninferiority study of the company’s investigational high-dose quadrivalent influenza vaccine (QIV-HD; including two prevailing B viruses) versus the high-dose trivalent influenza vaccine (TID-HD). The study was conducted at 35 sites in the United States and included 2,670 adults aged 65 years and older.
Overall, the reactogenicity profile for patients given QIV-HD was similar to that of TID-HD, and approximately 5% of patients in the QIV group reported an immediate adverse event, Dr. Chang said. However, no related deaths or related adverse events of special interest occurred in any of the study groups.
Sanofi plans to pursue licensure of the QIV-HD vaccine, with a Center for Biologics Evaluation and Research action date of Nov. 4, 2019, said Dr. Chang. If the vaccine is licensed, it should be available for purchase by health care providers in the first quarter of 2020.
The ACIP members had no financial conflicts to disclose.
REPORTING FROM AN ACIP MEETING
ACIP recommends two options for pertussis vaccination
Either the Tdap or Td vaccine is an acceptable option for pertussis vaccination in most situations, recommended the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention’s Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices.
In a unanimous 14-0 vote at the October meeting, based on the immunization schedule for persons aged 7 years and older.
Safety data showed no differences in safety concerns between Tdap and Td, including data from pregnant women, said Fiona Havers, MD, of the CDC’s National Center for Immunization and Respiratory Diseases (NCIRD), Atlanta.
Several of the ACIP members noted that the revised language to include both Tdap and Td reflects the increased use of Tdap and allows for maximum flexibility in clinical settings.
The revised language advises that booster doses of “either Td or Tdap” every 10 years throughout life are recommended for continued protection against tetanus and diphtheria. In addition, either Td or Tdap should be used if a tetanus toxoid–containing vaccine is indicated for prophylaxis in nonpregnant individuals.
For catch-up recommendations, which also apply to pregnant women, the committee approved the following wording for a series of three doses for individuals aged 7-18 years and 19 years and older who have never been vaccinated, that “the preferred schedule is a dose of Tdap (preferably the first dose), followed by either Tdap or Td at least 4 weeks afterward and another dose of either Td or Tdap 6-12 months later.” Individuals in these same age groups who are not fully vaccinated should receive one dose of Tdap, and a dose of either Td or Tdap if additional doses are needed.
The committee also voted unanimously 14-0 to accept the updated wording for pertussis vaccination in the Vaccines for Children program.
The ACIP members had no financial conflicts to disclose.
Either the Tdap or Td vaccine is an acceptable option for pertussis vaccination in most situations, recommended the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention’s Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices.
In a unanimous 14-0 vote at the October meeting, based on the immunization schedule for persons aged 7 years and older.
Safety data showed no differences in safety concerns between Tdap and Td, including data from pregnant women, said Fiona Havers, MD, of the CDC’s National Center for Immunization and Respiratory Diseases (NCIRD), Atlanta.
Several of the ACIP members noted that the revised language to include both Tdap and Td reflects the increased use of Tdap and allows for maximum flexibility in clinical settings.
The revised language advises that booster doses of “either Td or Tdap” every 10 years throughout life are recommended for continued protection against tetanus and diphtheria. In addition, either Td or Tdap should be used if a tetanus toxoid–containing vaccine is indicated for prophylaxis in nonpregnant individuals.
For catch-up recommendations, which also apply to pregnant women, the committee approved the following wording for a series of three doses for individuals aged 7-18 years and 19 years and older who have never been vaccinated, that “the preferred schedule is a dose of Tdap (preferably the first dose), followed by either Tdap or Td at least 4 weeks afterward and another dose of either Td or Tdap 6-12 months later.” Individuals in these same age groups who are not fully vaccinated should receive one dose of Tdap, and a dose of either Td or Tdap if additional doses are needed.
The committee also voted unanimously 14-0 to accept the updated wording for pertussis vaccination in the Vaccines for Children program.
The ACIP members had no financial conflicts to disclose.
Either the Tdap or Td vaccine is an acceptable option for pertussis vaccination in most situations, recommended the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention’s Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices.
In a unanimous 14-0 vote at the October meeting, based on the immunization schedule for persons aged 7 years and older.
Safety data showed no differences in safety concerns between Tdap and Td, including data from pregnant women, said Fiona Havers, MD, of the CDC’s National Center for Immunization and Respiratory Diseases (NCIRD), Atlanta.
Several of the ACIP members noted that the revised language to include both Tdap and Td reflects the increased use of Tdap and allows for maximum flexibility in clinical settings.
The revised language advises that booster doses of “either Td or Tdap” every 10 years throughout life are recommended for continued protection against tetanus and diphtheria. In addition, either Td or Tdap should be used if a tetanus toxoid–containing vaccine is indicated for prophylaxis in nonpregnant individuals.
For catch-up recommendations, which also apply to pregnant women, the committee approved the following wording for a series of three doses for individuals aged 7-18 years and 19 years and older who have never been vaccinated, that “the preferred schedule is a dose of Tdap (preferably the first dose), followed by either Tdap or Td at least 4 weeks afterward and another dose of either Td or Tdap 6-12 months later.” Individuals in these same age groups who are not fully vaccinated should receive one dose of Tdap, and a dose of either Td or Tdap if additional doses are needed.
The committee also voted unanimously 14-0 to accept the updated wording for pertussis vaccination in the Vaccines for Children program.
The ACIP members had no financial conflicts to disclose.
FROM AN ACIP MEETING