User login
Survey: Most physicians who treat STIs in their offices lack key injectable drugs
The majority of physicians surveyed who treat sexually transmitted infections (STIs) in their offices reported that they did not have on-site availability of the two primary injectable drugs for syphilis and gonorrhea, according to researchers from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
This lack of drug availability for immediate treatment is significant because STIs are on the rise in the United States. The numbers of reported cases of Neisseria gonorrhoeae and Treponema pallidum infections dramatically increased between 2013 and 2017, at 75% higher for gonorrhea and 153% higher for syphilis (primary and secondary), according to a research letter in the November issue of Emerging Infectious Diseases.
Optimal, same-day treatment of bacterial STIs with a highly effective regimen is critical for national STI control efforts and can help mitigate the development of drug resistance, the researchers stated. The recommended first-line treatment for uncomplicated gonorrhea is intramuscular ceftriaxone (250 mg), and for primary and secondary syphilis, it’s intramuscular penicillin G benzathine (2.5 million units), instead of using oral antimicrobial drug alternatives, which have been known to facilitate the development of drug resistance.
William S. Pearson, PhD, of the CDC and colleagues examined the on-site availability of the two injectable therapeutic agents among physicians who treated STIs in their office. They used the 2016 Physician Induction File of the National Ambulatory Medical Care Survey to assess the number of physicians who treat patients with STIs and had injectable antimicrobial drugs available on site. A total of 1,030 physicians (46.2% unweighted response rate), which represents an estimated 330,581 physicians in the United States, completed the Physician Induction File in 2016.
In this survey, physicians who reported evaluating or treating patients for STIs were asked which antimicrobial drugs they had available on site for same-day management of gonorrhea and syphilis, including intramuscular ceftriaxone and penicillin G benzathine at the recommended doses.
The researchers used this information to determine national estimates of reported on-site, same-day availability for these antimicrobial drugs and stratified results by patient-centered medical homes (PCMH) designation and U.S. region. They used multiple logistic regression models to determine if PCMH designation and region were predictive of on-site availability of the two medications.
An estimated 45.2% (149,483) of office-based physicians indicated that they evaluate patients for STIs in their offices. Of these, 77.9% reported not having penicillin G benzathine available on site, and 56.1% reported not having ceftriaxone.
Geographic differences in drug availability were not statistically significant. In addition, physicians in offices not designated PCMHs were more likely than those in offices designated as PCMHs to report lacking on-site availability of ceftriaxone (odds ratio, 2.03) and penicillin G benzathine (OR, 3.20).
“The costs of obtaining and carrying these medications, as well as issues of storage and shelf-life, should be explored to determine if these factors are barriers. In addition, the implications of prescribing alternative treatments or delaying care in situations when medications are not readily available on site should be further explored. Mitigating the lack of medication availability to treat these infections will help public health officials stop the rise in STI disease,” the researchers concluded.
The authors are all employees of the CDC and did not provide other disclosures.
SOURCE: Pearson WS et al. Emerg Infect Dis. 2019. doi: 10.3201/eid2511.190764.
The majority of physicians surveyed who treat sexually transmitted infections (STIs) in their offices reported that they did not have on-site availability of the two primary injectable drugs for syphilis and gonorrhea, according to researchers from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
This lack of drug availability for immediate treatment is significant because STIs are on the rise in the United States. The numbers of reported cases of Neisseria gonorrhoeae and Treponema pallidum infections dramatically increased between 2013 and 2017, at 75% higher for gonorrhea and 153% higher for syphilis (primary and secondary), according to a research letter in the November issue of Emerging Infectious Diseases.
Optimal, same-day treatment of bacterial STIs with a highly effective regimen is critical for national STI control efforts and can help mitigate the development of drug resistance, the researchers stated. The recommended first-line treatment for uncomplicated gonorrhea is intramuscular ceftriaxone (250 mg), and for primary and secondary syphilis, it’s intramuscular penicillin G benzathine (2.5 million units), instead of using oral antimicrobial drug alternatives, which have been known to facilitate the development of drug resistance.
William S. Pearson, PhD, of the CDC and colleagues examined the on-site availability of the two injectable therapeutic agents among physicians who treated STIs in their office. They used the 2016 Physician Induction File of the National Ambulatory Medical Care Survey to assess the number of physicians who treat patients with STIs and had injectable antimicrobial drugs available on site. A total of 1,030 physicians (46.2% unweighted response rate), which represents an estimated 330,581 physicians in the United States, completed the Physician Induction File in 2016.
In this survey, physicians who reported evaluating or treating patients for STIs were asked which antimicrobial drugs they had available on site for same-day management of gonorrhea and syphilis, including intramuscular ceftriaxone and penicillin G benzathine at the recommended doses.
The researchers used this information to determine national estimates of reported on-site, same-day availability for these antimicrobial drugs and stratified results by patient-centered medical homes (PCMH) designation and U.S. region. They used multiple logistic regression models to determine if PCMH designation and region were predictive of on-site availability of the two medications.
An estimated 45.2% (149,483) of office-based physicians indicated that they evaluate patients for STIs in their offices. Of these, 77.9% reported not having penicillin G benzathine available on site, and 56.1% reported not having ceftriaxone.
Geographic differences in drug availability were not statistically significant. In addition, physicians in offices not designated PCMHs were more likely than those in offices designated as PCMHs to report lacking on-site availability of ceftriaxone (odds ratio, 2.03) and penicillin G benzathine (OR, 3.20).
“The costs of obtaining and carrying these medications, as well as issues of storage and shelf-life, should be explored to determine if these factors are barriers. In addition, the implications of prescribing alternative treatments or delaying care in situations when medications are not readily available on site should be further explored. Mitigating the lack of medication availability to treat these infections will help public health officials stop the rise in STI disease,” the researchers concluded.
The authors are all employees of the CDC and did not provide other disclosures.
SOURCE: Pearson WS et al. Emerg Infect Dis. 2019. doi: 10.3201/eid2511.190764.
The majority of physicians surveyed who treat sexually transmitted infections (STIs) in their offices reported that they did not have on-site availability of the two primary injectable drugs for syphilis and gonorrhea, according to researchers from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
This lack of drug availability for immediate treatment is significant because STIs are on the rise in the United States. The numbers of reported cases of Neisseria gonorrhoeae and Treponema pallidum infections dramatically increased between 2013 and 2017, at 75% higher for gonorrhea and 153% higher for syphilis (primary and secondary), according to a research letter in the November issue of Emerging Infectious Diseases.
Optimal, same-day treatment of bacterial STIs with a highly effective regimen is critical for national STI control efforts and can help mitigate the development of drug resistance, the researchers stated. The recommended first-line treatment for uncomplicated gonorrhea is intramuscular ceftriaxone (250 mg), and for primary and secondary syphilis, it’s intramuscular penicillin G benzathine (2.5 million units), instead of using oral antimicrobial drug alternatives, which have been known to facilitate the development of drug resistance.
William S. Pearson, PhD, of the CDC and colleagues examined the on-site availability of the two injectable therapeutic agents among physicians who treated STIs in their office. They used the 2016 Physician Induction File of the National Ambulatory Medical Care Survey to assess the number of physicians who treat patients with STIs and had injectable antimicrobial drugs available on site. A total of 1,030 physicians (46.2% unweighted response rate), which represents an estimated 330,581 physicians in the United States, completed the Physician Induction File in 2016.
In this survey, physicians who reported evaluating or treating patients for STIs were asked which antimicrobial drugs they had available on site for same-day management of gonorrhea and syphilis, including intramuscular ceftriaxone and penicillin G benzathine at the recommended doses.
The researchers used this information to determine national estimates of reported on-site, same-day availability for these antimicrobial drugs and stratified results by patient-centered medical homes (PCMH) designation and U.S. region. They used multiple logistic regression models to determine if PCMH designation and region were predictive of on-site availability of the two medications.
An estimated 45.2% (149,483) of office-based physicians indicated that they evaluate patients for STIs in their offices. Of these, 77.9% reported not having penicillin G benzathine available on site, and 56.1% reported not having ceftriaxone.
Geographic differences in drug availability were not statistically significant. In addition, physicians in offices not designated PCMHs were more likely than those in offices designated as PCMHs to report lacking on-site availability of ceftriaxone (odds ratio, 2.03) and penicillin G benzathine (OR, 3.20).
“The costs of obtaining and carrying these medications, as well as issues of storage and shelf-life, should be explored to determine if these factors are barriers. In addition, the implications of prescribing alternative treatments or delaying care in situations when medications are not readily available on site should be further explored. Mitigating the lack of medication availability to treat these infections will help public health officials stop the rise in STI disease,” the researchers concluded.
The authors are all employees of the CDC and did not provide other disclosures.
SOURCE: Pearson WS et al. Emerg Infect Dis. 2019. doi: 10.3201/eid2511.190764.
FROM EMERGING INFECTIOUS DISEASES
Cell culture–based flu vaccine maintains immunogenicity
WASHINGTON – Influenza vaccines that substitute flu grown in cell-culture for the standard formulation of flu grown in eggs recently came onto the U.S. market, and new evidence confirmed that cell-grown flu works at least as well as its egg-grown counterpart for triggering immune responses.
Results from a randomized study with 148 evaluable subjects that directly compared the immune response of individuals aged 4-20 years old to the 2018-2019 commercial formulation of a mostly cell-based influenza vaccine with a commercially marketed, fully egg-based vaccine from the same vintage showed “no difference” between the two vaccines for inducing serologic titers on both the hemagluttination inhibition assay and by microneutralization, Richard K. Zimmerman, MD, said at an annual scientific meeting on infectious diseases.
The question addressed by the study was whether the primarily cell culture–grown vaccine would perform differently in children than a standard, egg-grown vaccine. “We thought that we might find something different, but we didn’t,” said Dr. Zimmerman, a professor of family medicine at the University of Pittsburgh who studies vaccines. The finding gave further support to using flu vaccines made without eggs because of their advantages over egg-based vaccines, he said in an interview.
Dr. Zimmerman cited two major, potential problems with egg-grown influenza vaccines. First, they require a big supply of eggs to manufacture, which can pose logistical challenges that are absent with cell culture–grown vaccine once the bioreactor capacity exists to produce the necessary amount of cells. This means that egg-free vaccine production can ramp up faster when a pandemic starts, he noted.
Second, over time, egg-grown vaccine strains of influenza have become increasingly adapted to grow in eggs with the result that “in some years the egg-grown virus is so different as to not work as well [Proc Natl Acad Sci. 2017 Nov;114[44]:12578-83]. With cell culture you bypass” issues of glycosylation mismatch or other antigenic problems caused by egg passage, he explained.
Dr. Zimmerman feels so strongly about the superiority of the cell-culture vaccine that “I am personally going to get a vaccine that’s not egg based,” and he advised the University of Pittsburgh Medical Center to focus its 2019-2020 flu vaccine purchase primarily on formulations made by cell culture. For the 2019-2020 season, that specifically is Flucelvax, an inactivated influenza vaccine licensed for people aged at least 4 years old, and Flublok, a recombinant flu vaccine also produced entirely in cell culture and licensed for people aged at least 18 years old. The 2019-2020 season is the first one during which the quadravalent Flucelvax vaccine has all four component strains (one H1N1, one H3N2, and two B strains) grown in cell culture.
The study run by Dr. Zimmerman and associates at the start of the 2018-2019 season used that season’s formulation of Flucelvax, which had only three of its four component strains grown in cell culture plus one strain (H1N1) grown in eggs. The Pittsburgh researchers randomized 168 individuals to receive the 2018-2019 Flucelvax vaccine or Fluzone, an entirely egg-made quadravelent vaccine, and they had analyzable results from 148 of the enrolled participants, more than 85% of whom were 9-20 years old. The study’s primary endpoint was the extent of seropositivity and seroconversion 28 days after immunization measured with both a hemagglutination inhibition assay and by a microneutralization assay. The results showed similar rates in the 75 children who received Flucelvax and the 73 who received Fluzone. For example, seropositivity against B Victoria lineage strains by the hemagglutination inhibition assay 28 days after vaccination was 76% in children who received Flucelvax, and it was 79% among those who got Fluzone, with a seroconversion rate of 34% in each of the two study subgroups.
“These findings do not say that egg-free is better, but it was certainly no worse. My guess is that in some years vaccines that are egg-free will make a big difference. In other years it may not. But you don’t know ahead of time,” Dr. Zimmerman said.
The study received no commercial funding but received free Fluzone vaccine from Sanofi Pasteur. Dr. Zimmerman had no disclosures.
WASHINGTON – Influenza vaccines that substitute flu grown in cell-culture for the standard formulation of flu grown in eggs recently came onto the U.S. market, and new evidence confirmed that cell-grown flu works at least as well as its egg-grown counterpart for triggering immune responses.
Results from a randomized study with 148 evaluable subjects that directly compared the immune response of individuals aged 4-20 years old to the 2018-2019 commercial formulation of a mostly cell-based influenza vaccine with a commercially marketed, fully egg-based vaccine from the same vintage showed “no difference” between the two vaccines for inducing serologic titers on both the hemagluttination inhibition assay and by microneutralization, Richard K. Zimmerman, MD, said at an annual scientific meeting on infectious diseases.
The question addressed by the study was whether the primarily cell culture–grown vaccine would perform differently in children than a standard, egg-grown vaccine. “We thought that we might find something different, but we didn’t,” said Dr. Zimmerman, a professor of family medicine at the University of Pittsburgh who studies vaccines. The finding gave further support to using flu vaccines made without eggs because of their advantages over egg-based vaccines, he said in an interview.
Dr. Zimmerman cited two major, potential problems with egg-grown influenza vaccines. First, they require a big supply of eggs to manufacture, which can pose logistical challenges that are absent with cell culture–grown vaccine once the bioreactor capacity exists to produce the necessary amount of cells. This means that egg-free vaccine production can ramp up faster when a pandemic starts, he noted.
Second, over time, egg-grown vaccine strains of influenza have become increasingly adapted to grow in eggs with the result that “in some years the egg-grown virus is so different as to not work as well [Proc Natl Acad Sci. 2017 Nov;114[44]:12578-83]. With cell culture you bypass” issues of glycosylation mismatch or other antigenic problems caused by egg passage, he explained.
Dr. Zimmerman feels so strongly about the superiority of the cell-culture vaccine that “I am personally going to get a vaccine that’s not egg based,” and he advised the University of Pittsburgh Medical Center to focus its 2019-2020 flu vaccine purchase primarily on formulations made by cell culture. For the 2019-2020 season, that specifically is Flucelvax, an inactivated influenza vaccine licensed for people aged at least 4 years old, and Flublok, a recombinant flu vaccine also produced entirely in cell culture and licensed for people aged at least 18 years old. The 2019-2020 season is the first one during which the quadravalent Flucelvax vaccine has all four component strains (one H1N1, one H3N2, and two B strains) grown in cell culture.
The study run by Dr. Zimmerman and associates at the start of the 2018-2019 season used that season’s formulation of Flucelvax, which had only three of its four component strains grown in cell culture plus one strain (H1N1) grown in eggs. The Pittsburgh researchers randomized 168 individuals to receive the 2018-2019 Flucelvax vaccine or Fluzone, an entirely egg-made quadravelent vaccine, and they had analyzable results from 148 of the enrolled participants, more than 85% of whom were 9-20 years old. The study’s primary endpoint was the extent of seropositivity and seroconversion 28 days after immunization measured with both a hemagglutination inhibition assay and by a microneutralization assay. The results showed similar rates in the 75 children who received Flucelvax and the 73 who received Fluzone. For example, seropositivity against B Victoria lineage strains by the hemagglutination inhibition assay 28 days after vaccination was 76% in children who received Flucelvax, and it was 79% among those who got Fluzone, with a seroconversion rate of 34% in each of the two study subgroups.
“These findings do not say that egg-free is better, but it was certainly no worse. My guess is that in some years vaccines that are egg-free will make a big difference. In other years it may not. But you don’t know ahead of time,” Dr. Zimmerman said.
The study received no commercial funding but received free Fluzone vaccine from Sanofi Pasteur. Dr. Zimmerman had no disclosures.
WASHINGTON – Influenza vaccines that substitute flu grown in cell-culture for the standard formulation of flu grown in eggs recently came onto the U.S. market, and new evidence confirmed that cell-grown flu works at least as well as its egg-grown counterpart for triggering immune responses.
Results from a randomized study with 148 evaluable subjects that directly compared the immune response of individuals aged 4-20 years old to the 2018-2019 commercial formulation of a mostly cell-based influenza vaccine with a commercially marketed, fully egg-based vaccine from the same vintage showed “no difference” between the two vaccines for inducing serologic titers on both the hemagluttination inhibition assay and by microneutralization, Richard K. Zimmerman, MD, said at an annual scientific meeting on infectious diseases.
The question addressed by the study was whether the primarily cell culture–grown vaccine would perform differently in children than a standard, egg-grown vaccine. “We thought that we might find something different, but we didn’t,” said Dr. Zimmerman, a professor of family medicine at the University of Pittsburgh who studies vaccines. The finding gave further support to using flu vaccines made without eggs because of their advantages over egg-based vaccines, he said in an interview.
Dr. Zimmerman cited two major, potential problems with egg-grown influenza vaccines. First, they require a big supply of eggs to manufacture, which can pose logistical challenges that are absent with cell culture–grown vaccine once the bioreactor capacity exists to produce the necessary amount of cells. This means that egg-free vaccine production can ramp up faster when a pandemic starts, he noted.
Second, over time, egg-grown vaccine strains of influenza have become increasingly adapted to grow in eggs with the result that “in some years the egg-grown virus is so different as to not work as well [Proc Natl Acad Sci. 2017 Nov;114[44]:12578-83]. With cell culture you bypass” issues of glycosylation mismatch or other antigenic problems caused by egg passage, he explained.
Dr. Zimmerman feels so strongly about the superiority of the cell-culture vaccine that “I am personally going to get a vaccine that’s not egg based,” and he advised the University of Pittsburgh Medical Center to focus its 2019-2020 flu vaccine purchase primarily on formulations made by cell culture. For the 2019-2020 season, that specifically is Flucelvax, an inactivated influenza vaccine licensed for people aged at least 4 years old, and Flublok, a recombinant flu vaccine also produced entirely in cell culture and licensed for people aged at least 18 years old. The 2019-2020 season is the first one during which the quadravalent Flucelvax vaccine has all four component strains (one H1N1, one H3N2, and two B strains) grown in cell culture.
The study run by Dr. Zimmerman and associates at the start of the 2018-2019 season used that season’s formulation of Flucelvax, which had only three of its four component strains grown in cell culture plus one strain (H1N1) grown in eggs. The Pittsburgh researchers randomized 168 individuals to receive the 2018-2019 Flucelvax vaccine or Fluzone, an entirely egg-made quadravelent vaccine, and they had analyzable results from 148 of the enrolled participants, more than 85% of whom were 9-20 years old. The study’s primary endpoint was the extent of seropositivity and seroconversion 28 days after immunization measured with both a hemagglutination inhibition assay and by a microneutralization assay. The results showed similar rates in the 75 children who received Flucelvax and the 73 who received Fluzone. For example, seropositivity against B Victoria lineage strains by the hemagglutination inhibition assay 28 days after vaccination was 76% in children who received Flucelvax, and it was 79% among those who got Fluzone, with a seroconversion rate of 34% in each of the two study subgroups.
“These findings do not say that egg-free is better, but it was certainly no worse. My guess is that in some years vaccines that are egg-free will make a big difference. In other years it may not. But you don’t know ahead of time,” Dr. Zimmerman said.
The study received no commercial funding but received free Fluzone vaccine from Sanofi Pasteur. Dr. Zimmerman had no disclosures.
REPORTING FROM ID WEEK 2019
Vaccination rates generally high in U.S. children in 2018
Vaccination rates among kindergartners during the 2018-2019 school year and children aged 24 months during 2016-2018 remained high, but several gaps in coverage remained, new research found.
The national vaccination rate for the almost 4 million kindergartners reported as enrolled in 2018-2019 was 94.9% for DTaP, 94.7% for 2 doses of MMR, and 94.8% for state-required doses of varicella. The MMR vaccination rate fell just short of the recommended 95% vaccination rate threshold, according to Ranee Seither, MPH, of the immunization services division at the National Center for Immunization and Respiratory Diseases (NCIRD), and associates.
By state, Mississippi had the highest vaccination rate, achieving at least 99.2% coverage for DTaP, MMR, and varicella. Colorado had the lowest vaccination rate for MMR and varicella at 87.4% and 86.5%, respectively; Idaho had the lowest DTaP vaccination rate at 88.8%.
A total of 20 states had at least 95% MMR coverage while 2 had under 90%, 21 states had at least 95% DTaP coverage with only Idaho having below 90%, and 20 states had at least 95% varicella coverage with 4 states having below 90%.
The investigators noted that, if all nonexempt kindergartners were vaccinated in accordance with local and state vaccination policies, nearly all states could achieve the 95% MMR vaccination threshold.
“Recent measles outbreaks in states with high overall MMR coverage, such as New York, highlight the need for assessing vaccination coverage at the local level. [The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention] encourage programs to use their local-level school assessment data to identify populations of undervaccinated students and to partner with schools and providers to reduce barriers to vaccination and improve coverage,” Dr. Seither and associates wrote.
In a study published in the same issue of the Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report, Holly A. Hill, MD, PhD, and associates from the immunization services division at NCIRD, found that, according to data collected from 25,059 participants in the National Immunization Survey–Child, national vaccination coverage in children aged 24 months was generally strong and stable.
The vaccines with coverage of at least 90% were poliovirus (92.7%), MMR (90.4%), hepatitis B (91%), and varicella (90%). Complete hepatitis A (74%), rotavirus (72.4%), influenza (53%), and combined seven-vaccine series (68.4%) rates were below 80%. Only 1.3% of children received no vaccinations.
In general, the highest rates of coverage were seen in children with private insurance, followed by those with other insurance, those with Medicaid, and finally those without insurance. Disparities also were seen depending on race/ethnicity, poverty level, and rural/urban location. Vaccination rates also varied by state; for example, 20 states had vaccination coverage for one dose of MMR below 90%, with 6 having coverage above 94% (Arkansas, Maine, Massachusetts, Mississippi, Rhode Island, Wisconsin).
“Improvements in childhood vaccination coverage will require that parents and other caregivers have access to vaccination providers and believe in the safety and effectiveness of vaccines. Increased opportunity for vaccination can be facilitated through expanded access to health insurance, greater promotion of available vaccines through the Vaccines for Children program, and solutions to logistical challenges such as transportation, child care, and time off from work. Providers can improve vaccination coverage overall and reduce disparities by administering all recommended vaccines during office visits,” Dr. Hill and associates wrote.
No conflicts of interest were reported by the investigators of either study.
SOURCES: Seither R et al. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep 2019;68:905-12; Hill HA et al. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep 2019;68:913-8.
Vaccination rates among kindergartners during the 2018-2019 school year and children aged 24 months during 2016-2018 remained high, but several gaps in coverage remained, new research found.
The national vaccination rate for the almost 4 million kindergartners reported as enrolled in 2018-2019 was 94.9% for DTaP, 94.7% for 2 doses of MMR, and 94.8% for state-required doses of varicella. The MMR vaccination rate fell just short of the recommended 95% vaccination rate threshold, according to Ranee Seither, MPH, of the immunization services division at the National Center for Immunization and Respiratory Diseases (NCIRD), and associates.
By state, Mississippi had the highest vaccination rate, achieving at least 99.2% coverage for DTaP, MMR, and varicella. Colorado had the lowest vaccination rate for MMR and varicella at 87.4% and 86.5%, respectively; Idaho had the lowest DTaP vaccination rate at 88.8%.
A total of 20 states had at least 95% MMR coverage while 2 had under 90%, 21 states had at least 95% DTaP coverage with only Idaho having below 90%, and 20 states had at least 95% varicella coverage with 4 states having below 90%.
The investigators noted that, if all nonexempt kindergartners were vaccinated in accordance with local and state vaccination policies, nearly all states could achieve the 95% MMR vaccination threshold.
“Recent measles outbreaks in states with high overall MMR coverage, such as New York, highlight the need for assessing vaccination coverage at the local level. [The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention] encourage programs to use their local-level school assessment data to identify populations of undervaccinated students and to partner with schools and providers to reduce barriers to vaccination and improve coverage,” Dr. Seither and associates wrote.
In a study published in the same issue of the Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report, Holly A. Hill, MD, PhD, and associates from the immunization services division at NCIRD, found that, according to data collected from 25,059 participants in the National Immunization Survey–Child, national vaccination coverage in children aged 24 months was generally strong and stable.
The vaccines with coverage of at least 90% were poliovirus (92.7%), MMR (90.4%), hepatitis B (91%), and varicella (90%). Complete hepatitis A (74%), rotavirus (72.4%), influenza (53%), and combined seven-vaccine series (68.4%) rates were below 80%. Only 1.3% of children received no vaccinations.
In general, the highest rates of coverage were seen in children with private insurance, followed by those with other insurance, those with Medicaid, and finally those without insurance. Disparities also were seen depending on race/ethnicity, poverty level, and rural/urban location. Vaccination rates also varied by state; for example, 20 states had vaccination coverage for one dose of MMR below 90%, with 6 having coverage above 94% (Arkansas, Maine, Massachusetts, Mississippi, Rhode Island, Wisconsin).
“Improvements in childhood vaccination coverage will require that parents and other caregivers have access to vaccination providers and believe in the safety and effectiveness of vaccines. Increased opportunity for vaccination can be facilitated through expanded access to health insurance, greater promotion of available vaccines through the Vaccines for Children program, and solutions to logistical challenges such as transportation, child care, and time off from work. Providers can improve vaccination coverage overall and reduce disparities by administering all recommended vaccines during office visits,” Dr. Hill and associates wrote.
No conflicts of interest were reported by the investigators of either study.
SOURCES: Seither R et al. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep 2019;68:905-12; Hill HA et al. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep 2019;68:913-8.
Vaccination rates among kindergartners during the 2018-2019 school year and children aged 24 months during 2016-2018 remained high, but several gaps in coverage remained, new research found.
The national vaccination rate for the almost 4 million kindergartners reported as enrolled in 2018-2019 was 94.9% for DTaP, 94.7% for 2 doses of MMR, and 94.8% for state-required doses of varicella. The MMR vaccination rate fell just short of the recommended 95% vaccination rate threshold, according to Ranee Seither, MPH, of the immunization services division at the National Center for Immunization and Respiratory Diseases (NCIRD), and associates.
By state, Mississippi had the highest vaccination rate, achieving at least 99.2% coverage for DTaP, MMR, and varicella. Colorado had the lowest vaccination rate for MMR and varicella at 87.4% and 86.5%, respectively; Idaho had the lowest DTaP vaccination rate at 88.8%.
A total of 20 states had at least 95% MMR coverage while 2 had under 90%, 21 states had at least 95% DTaP coverage with only Idaho having below 90%, and 20 states had at least 95% varicella coverage with 4 states having below 90%.
The investigators noted that, if all nonexempt kindergartners were vaccinated in accordance with local and state vaccination policies, nearly all states could achieve the 95% MMR vaccination threshold.
“Recent measles outbreaks in states with high overall MMR coverage, such as New York, highlight the need for assessing vaccination coverage at the local level. [The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention] encourage programs to use their local-level school assessment data to identify populations of undervaccinated students and to partner with schools and providers to reduce barriers to vaccination and improve coverage,” Dr. Seither and associates wrote.
In a study published in the same issue of the Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report, Holly A. Hill, MD, PhD, and associates from the immunization services division at NCIRD, found that, according to data collected from 25,059 participants in the National Immunization Survey–Child, national vaccination coverage in children aged 24 months was generally strong and stable.
The vaccines with coverage of at least 90% were poliovirus (92.7%), MMR (90.4%), hepatitis B (91%), and varicella (90%). Complete hepatitis A (74%), rotavirus (72.4%), influenza (53%), and combined seven-vaccine series (68.4%) rates were below 80%. Only 1.3% of children received no vaccinations.
In general, the highest rates of coverage were seen in children with private insurance, followed by those with other insurance, those with Medicaid, and finally those without insurance. Disparities also were seen depending on race/ethnicity, poverty level, and rural/urban location. Vaccination rates also varied by state; for example, 20 states had vaccination coverage for one dose of MMR below 90%, with 6 having coverage above 94% (Arkansas, Maine, Massachusetts, Mississippi, Rhode Island, Wisconsin).
“Improvements in childhood vaccination coverage will require that parents and other caregivers have access to vaccination providers and believe in the safety and effectiveness of vaccines. Increased opportunity for vaccination can be facilitated through expanded access to health insurance, greater promotion of available vaccines through the Vaccines for Children program, and solutions to logistical challenges such as transportation, child care, and time off from work. Providers can improve vaccination coverage overall and reduce disparities by administering all recommended vaccines during office visits,” Dr. Hill and associates wrote.
No conflicts of interest were reported by the investigators of either study.
SOURCES: Seither R et al. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep 2019;68:905-12; Hill HA et al. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep 2019;68:913-8.
FROM THE MMWR
In utero Zika exposure can have delayed consequences
WASHINGTON – Evidence continues to mount that infants born to moms infected with Zika virus during pregnancy can have neurodevelopmental abnormalities as they age even if they showed no defects at birth, based on follow-up of 890 Colombian children tracked by epidemiologists from the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
Among the 890 neonates born to mothers apparently infected with Zika during pregnancy and followed for up to 2 years, 40 of the 852 (5%) without a detectable birth defect at delivery went on to show some type of neurodevelopmental sequelae during up to 24 months of age, Margaret Honein, PhD, said at an annual scientific meeting on infectious diseases.
In addition, among the children without birth defects at delivery who received follow-up examinations out to about 2 years, the incidence of “alerts” for possible neurodevelopmental issues was 15%-20% for each of the four domains studied (gross motor, fine motor, hearing and language, and personal and social functions), said Dr. Honein, an epidemiologist and chief of the birth defects branch of the CDC. In contrast, 17 of the 38 children (45%) followed who had identifiable birth defects at delivery also showed neurodevelopmental abnormalities when reexamined as long as 2 years after birth. These possible neurodevelopmental abnormalities, designated as alerts, were identified in comparison with a contemporaneous cohort of children born to uninfected mothers in the same regions of Colombia and assessed by the CDC researchers.
This cohort of children born to mothers who became infected with Zika virus during the 2016 Colombian epidemic will not undergo any planned, additional follow-up beyond the initial 2 years, Dr. Honein noted.
The findings she reported were consistent with observations from a much smaller cohort of 70 infants born to Colombian mothers infected with Zika virus while pregnant who had a normal head circumference and a normal clinical examination at delivery. When assessed once or twice 4-18 months after birth, these 70 infants showed an overall greater than one standard deviation (z-score) drop in their scores on the Warner Initial Developmental Evaluation of Adaptive and Functional Skills (WIDEA) metric by 12 months after birth and continuing out to 18 months, said Sarah B. Mulkey, MD, a fetal-neonatal neurologist at Children’s National Health System in Washington. These deficits were especially pronounced in the mobility and social cognition domains of the four-domain WIDEA metric. The social cognition domain is an important predictor of later problems with executive function and other neurologic disorders, Dr. Mulkey said while reporting her findings in a separate talk at the meeting. She acknowledged that the analysis was flawed by comparing the WIDEA outcomes of the Zika virus–exposed children to healthy children from either inner-city Chicago or Canada. Dr. Mulkey said that she and her associates plan to characterize a population of Zika virus–unexposed children in Colombia to use for future comparisons.
The study reported by Dr. Honein involved an enhanced surveillance program launched by the CDC in 2016 in three regions of Colombia and included 1,190 pregnancies accompanied by Zika symptoms in the mother and with a reported pregnancy outcome, including 1,185 live births. Nearly half of the Zika infections occurred during the first trimester, and 34% occurred during the second trimester. However, fewer than a third of the pregnant women underwent some type of laboratory testing to confirm their infection, either by serology or by a DNA-based assay, and of these 28% had a positive finding. Dr. Honein cautioned that many of the specimens that tested negative for Zika virus may have been false negatives.
The birth defects identified among the infants born from an apparently affected pregnancy included brain abnormalities, eye anomalies, and microcephaly, with 5% of the 1,185 live births showing one or more of these outcomes. The neurodevelopmental deficits identified during follow-up of 890 of the children out to 2 years included seizures; abnormalities of tone, movement, or swallowing; and impairments of vision or hearing.
WASHINGTON – Evidence continues to mount that infants born to moms infected with Zika virus during pregnancy can have neurodevelopmental abnormalities as they age even if they showed no defects at birth, based on follow-up of 890 Colombian children tracked by epidemiologists from the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
Among the 890 neonates born to mothers apparently infected with Zika during pregnancy and followed for up to 2 years, 40 of the 852 (5%) without a detectable birth defect at delivery went on to show some type of neurodevelopmental sequelae during up to 24 months of age, Margaret Honein, PhD, said at an annual scientific meeting on infectious diseases.
In addition, among the children without birth defects at delivery who received follow-up examinations out to about 2 years, the incidence of “alerts” for possible neurodevelopmental issues was 15%-20% for each of the four domains studied (gross motor, fine motor, hearing and language, and personal and social functions), said Dr. Honein, an epidemiologist and chief of the birth defects branch of the CDC. In contrast, 17 of the 38 children (45%) followed who had identifiable birth defects at delivery also showed neurodevelopmental abnormalities when reexamined as long as 2 years after birth. These possible neurodevelopmental abnormalities, designated as alerts, were identified in comparison with a contemporaneous cohort of children born to uninfected mothers in the same regions of Colombia and assessed by the CDC researchers.
This cohort of children born to mothers who became infected with Zika virus during the 2016 Colombian epidemic will not undergo any planned, additional follow-up beyond the initial 2 years, Dr. Honein noted.
The findings she reported were consistent with observations from a much smaller cohort of 70 infants born to Colombian mothers infected with Zika virus while pregnant who had a normal head circumference and a normal clinical examination at delivery. When assessed once or twice 4-18 months after birth, these 70 infants showed an overall greater than one standard deviation (z-score) drop in their scores on the Warner Initial Developmental Evaluation of Adaptive and Functional Skills (WIDEA) metric by 12 months after birth and continuing out to 18 months, said Sarah B. Mulkey, MD, a fetal-neonatal neurologist at Children’s National Health System in Washington. These deficits were especially pronounced in the mobility and social cognition domains of the four-domain WIDEA metric. The social cognition domain is an important predictor of later problems with executive function and other neurologic disorders, Dr. Mulkey said while reporting her findings in a separate talk at the meeting. She acknowledged that the analysis was flawed by comparing the WIDEA outcomes of the Zika virus–exposed children to healthy children from either inner-city Chicago or Canada. Dr. Mulkey said that she and her associates plan to characterize a population of Zika virus–unexposed children in Colombia to use for future comparisons.
The study reported by Dr. Honein involved an enhanced surveillance program launched by the CDC in 2016 in three regions of Colombia and included 1,190 pregnancies accompanied by Zika symptoms in the mother and with a reported pregnancy outcome, including 1,185 live births. Nearly half of the Zika infections occurred during the first trimester, and 34% occurred during the second trimester. However, fewer than a third of the pregnant women underwent some type of laboratory testing to confirm their infection, either by serology or by a DNA-based assay, and of these 28% had a positive finding. Dr. Honein cautioned that many of the specimens that tested negative for Zika virus may have been false negatives.
The birth defects identified among the infants born from an apparently affected pregnancy included brain abnormalities, eye anomalies, and microcephaly, with 5% of the 1,185 live births showing one or more of these outcomes. The neurodevelopmental deficits identified during follow-up of 890 of the children out to 2 years included seizures; abnormalities of tone, movement, or swallowing; and impairments of vision or hearing.
WASHINGTON – Evidence continues to mount that infants born to moms infected with Zika virus during pregnancy can have neurodevelopmental abnormalities as they age even if they showed no defects at birth, based on follow-up of 890 Colombian children tracked by epidemiologists from the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
Among the 890 neonates born to mothers apparently infected with Zika during pregnancy and followed for up to 2 years, 40 of the 852 (5%) without a detectable birth defect at delivery went on to show some type of neurodevelopmental sequelae during up to 24 months of age, Margaret Honein, PhD, said at an annual scientific meeting on infectious diseases.
In addition, among the children without birth defects at delivery who received follow-up examinations out to about 2 years, the incidence of “alerts” for possible neurodevelopmental issues was 15%-20% for each of the four domains studied (gross motor, fine motor, hearing and language, and personal and social functions), said Dr. Honein, an epidemiologist and chief of the birth defects branch of the CDC. In contrast, 17 of the 38 children (45%) followed who had identifiable birth defects at delivery also showed neurodevelopmental abnormalities when reexamined as long as 2 years after birth. These possible neurodevelopmental abnormalities, designated as alerts, were identified in comparison with a contemporaneous cohort of children born to uninfected mothers in the same regions of Colombia and assessed by the CDC researchers.
This cohort of children born to mothers who became infected with Zika virus during the 2016 Colombian epidemic will not undergo any planned, additional follow-up beyond the initial 2 years, Dr. Honein noted.
The findings she reported were consistent with observations from a much smaller cohort of 70 infants born to Colombian mothers infected with Zika virus while pregnant who had a normal head circumference and a normal clinical examination at delivery. When assessed once or twice 4-18 months after birth, these 70 infants showed an overall greater than one standard deviation (z-score) drop in their scores on the Warner Initial Developmental Evaluation of Adaptive and Functional Skills (WIDEA) metric by 12 months after birth and continuing out to 18 months, said Sarah B. Mulkey, MD, a fetal-neonatal neurologist at Children’s National Health System in Washington. These deficits were especially pronounced in the mobility and social cognition domains of the four-domain WIDEA metric. The social cognition domain is an important predictor of later problems with executive function and other neurologic disorders, Dr. Mulkey said while reporting her findings in a separate talk at the meeting. She acknowledged that the analysis was flawed by comparing the WIDEA outcomes of the Zika virus–exposed children to healthy children from either inner-city Chicago or Canada. Dr. Mulkey said that she and her associates plan to characterize a population of Zika virus–unexposed children in Colombia to use for future comparisons.
The study reported by Dr. Honein involved an enhanced surveillance program launched by the CDC in 2016 in three regions of Colombia and included 1,190 pregnancies accompanied by Zika symptoms in the mother and with a reported pregnancy outcome, including 1,185 live births. Nearly half of the Zika infections occurred during the first trimester, and 34% occurred during the second trimester. However, fewer than a third of the pregnant women underwent some type of laboratory testing to confirm their infection, either by serology or by a DNA-based assay, and of these 28% had a positive finding. Dr. Honein cautioned that many of the specimens that tested negative for Zika virus may have been false negatives.
The birth defects identified among the infants born from an apparently affected pregnancy included brain abnormalities, eye anomalies, and microcephaly, with 5% of the 1,185 live births showing one or more of these outcomes. The neurodevelopmental deficits identified during follow-up of 890 of the children out to 2 years included seizures; abnormalities of tone, movement, or swallowing; and impairments of vision or hearing.
REPORTING FROM ID WEEK 2019
PJP prophylaxis may be unnecessary for CLL patients on BTK inhibitors
EDINBURGH – Routine empiric prophylaxis against pneumocystis jiroveci pneumonia (PJP) may be unwarranted in chronic lymphocytic leukemia patients initiating Bruton tyrosine kinase (BTK) inhibitor therapy, a retrospective chart review suggests.
Among 212 patients with chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) who were treated with ibrutinib or acalabrutinib either as monotherapy or as part of a combination regimen for at least 30 days between Jan. 1, 2010, and Feb. 1, 2019, at Dana-Farber Cancer Institute and Brigham and Women’s Hospital in Boston, 125 (59%) received PJP prophylaxis, including either trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole (74%) or atovaquone (26%), Christine Ryan, MD, reported at the International Workshop on CLL.
Two PJP cases occurred in the 120 patients on single-agent ibrutinib, including one in a previously untreated patient and one in a patient with relapsed/refractory CLL. Neither patient had received PJP prophylaxis, said Dr. Ryan, a senior resident at Brigham and Women’s Hospital.
No PJP cases occurred in the 21 patients who received acalabrutinib monotherapy or in the 14 patients who received acalabrutinib combination therapy, and 1 occurred in a trial cohort of 57 patients receiving frontline ibrutinib plus fludarabine-based chemotherapy (FCR). The latter had been prescribed PJP prophylaxis, but “unfortunately self-discontinued the prophylaxis” 2 months prior to the infection, Dr. Ryan said.
“The overall prevalence of PJP in patients not on prophylaxis was 3.4%, there were no cases of PJP in patients on prophylaxis, and the incidence rate in patients not on prophylaxis was 1.9 per 100 person-years, with a number needed to treat to prevent 1 case of PJP calculated to be 42 patients,” she said.
In addition to PJP, three cases of proven or probable invasive fungal infections (IFI) occurred, including one case of pulmonary histoplasmosis in the ibrutinib plus FCR trial cohort and two cases of aspergillosis, including a pulmonary case and a brain abscess, in an ibrutinib plus umbralisib trial cohort.
“The overall prevalence of aspergillosis or histoplasmosis in our entire cohort was 1.4%, and notably there were no cases of IFI in the single-agent therapy cohort, but the prevalence in the ibrutinib-combination therapy patients was 4.2%,” Dr. Ryan said.
Patients included in the review were adults with a median age of 64.8 years, and 64% were men. The median duration of BTK inhibitor therapy was 23.2 months.
“We know that CLL patients treated with fludarabine have an increased risk of PJP,” she said. “As such, it is routinely recommended that patients receiving fludarabine-containing chemotherapy regimens are prescribed PJP prophylaxis.”
Additionally, the increasing use of oral BTK inhibitors has raised concerns about the potential risk of PJP or other IFIs in patients on those agents, Dr. Ryan explained, noting that existing case reports and case series looking at PJP have shown varying prevalence rates, and little is known about the effects of prophylaxis.
“At present, there are no international guidelines regarding the use of antimicrobial prophylaxis in CLL patients treated with BTK inhibitors, and prophylaxis practices vary widely across countries and institutions,” she said.
The findings of the current study demonstrate that such variation exists “even within our own institution,” Dr. Ryan added.
The findings also show an overall low PJP prevalence of 3.4% in patients not receiving prophylaxis, which falls below the “commonly accepted threshold of 5%, above which routine prophylaxis becomes recommended,” she said.
“Overall, our data suggest that routine PJP or IFI prophylaxis in patients receiving BTK inhibitors may not be needed, but this is definitely an area that requires further study, ideally with a prospective trial with a larger sample size and multiple institutions, to support the development of consensus guidelines on this issue,” she said.
Dr. Ryan reported having no financial disclosures.
EDINBURGH – Routine empiric prophylaxis against pneumocystis jiroveci pneumonia (PJP) may be unwarranted in chronic lymphocytic leukemia patients initiating Bruton tyrosine kinase (BTK) inhibitor therapy, a retrospective chart review suggests.
Among 212 patients with chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) who were treated with ibrutinib or acalabrutinib either as monotherapy or as part of a combination regimen for at least 30 days between Jan. 1, 2010, and Feb. 1, 2019, at Dana-Farber Cancer Institute and Brigham and Women’s Hospital in Boston, 125 (59%) received PJP prophylaxis, including either trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole (74%) or atovaquone (26%), Christine Ryan, MD, reported at the International Workshop on CLL.
Two PJP cases occurred in the 120 patients on single-agent ibrutinib, including one in a previously untreated patient and one in a patient with relapsed/refractory CLL. Neither patient had received PJP prophylaxis, said Dr. Ryan, a senior resident at Brigham and Women’s Hospital.
No PJP cases occurred in the 21 patients who received acalabrutinib monotherapy or in the 14 patients who received acalabrutinib combination therapy, and 1 occurred in a trial cohort of 57 patients receiving frontline ibrutinib plus fludarabine-based chemotherapy (FCR). The latter had been prescribed PJP prophylaxis, but “unfortunately self-discontinued the prophylaxis” 2 months prior to the infection, Dr. Ryan said.
“The overall prevalence of PJP in patients not on prophylaxis was 3.4%, there were no cases of PJP in patients on prophylaxis, and the incidence rate in patients not on prophylaxis was 1.9 per 100 person-years, with a number needed to treat to prevent 1 case of PJP calculated to be 42 patients,” she said.
In addition to PJP, three cases of proven or probable invasive fungal infections (IFI) occurred, including one case of pulmonary histoplasmosis in the ibrutinib plus FCR trial cohort and two cases of aspergillosis, including a pulmonary case and a brain abscess, in an ibrutinib plus umbralisib trial cohort.
“The overall prevalence of aspergillosis or histoplasmosis in our entire cohort was 1.4%, and notably there were no cases of IFI in the single-agent therapy cohort, but the prevalence in the ibrutinib-combination therapy patients was 4.2%,” Dr. Ryan said.
Patients included in the review were adults with a median age of 64.8 years, and 64% were men. The median duration of BTK inhibitor therapy was 23.2 months.
“We know that CLL patients treated with fludarabine have an increased risk of PJP,” she said. “As such, it is routinely recommended that patients receiving fludarabine-containing chemotherapy regimens are prescribed PJP prophylaxis.”
Additionally, the increasing use of oral BTK inhibitors has raised concerns about the potential risk of PJP or other IFIs in patients on those agents, Dr. Ryan explained, noting that existing case reports and case series looking at PJP have shown varying prevalence rates, and little is known about the effects of prophylaxis.
“At present, there are no international guidelines regarding the use of antimicrobial prophylaxis in CLL patients treated with BTK inhibitors, and prophylaxis practices vary widely across countries and institutions,” she said.
The findings of the current study demonstrate that such variation exists “even within our own institution,” Dr. Ryan added.
The findings also show an overall low PJP prevalence of 3.4% in patients not receiving prophylaxis, which falls below the “commonly accepted threshold of 5%, above which routine prophylaxis becomes recommended,” she said.
“Overall, our data suggest that routine PJP or IFI prophylaxis in patients receiving BTK inhibitors may not be needed, but this is definitely an area that requires further study, ideally with a prospective trial with a larger sample size and multiple institutions, to support the development of consensus guidelines on this issue,” she said.
Dr. Ryan reported having no financial disclosures.
EDINBURGH – Routine empiric prophylaxis against pneumocystis jiroveci pneumonia (PJP) may be unwarranted in chronic lymphocytic leukemia patients initiating Bruton tyrosine kinase (BTK) inhibitor therapy, a retrospective chart review suggests.
Among 212 patients with chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) who were treated with ibrutinib or acalabrutinib either as monotherapy or as part of a combination regimen for at least 30 days between Jan. 1, 2010, and Feb. 1, 2019, at Dana-Farber Cancer Institute and Brigham and Women’s Hospital in Boston, 125 (59%) received PJP prophylaxis, including either trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole (74%) or atovaquone (26%), Christine Ryan, MD, reported at the International Workshop on CLL.
Two PJP cases occurred in the 120 patients on single-agent ibrutinib, including one in a previously untreated patient and one in a patient with relapsed/refractory CLL. Neither patient had received PJP prophylaxis, said Dr. Ryan, a senior resident at Brigham and Women’s Hospital.
No PJP cases occurred in the 21 patients who received acalabrutinib monotherapy or in the 14 patients who received acalabrutinib combination therapy, and 1 occurred in a trial cohort of 57 patients receiving frontline ibrutinib plus fludarabine-based chemotherapy (FCR). The latter had been prescribed PJP prophylaxis, but “unfortunately self-discontinued the prophylaxis” 2 months prior to the infection, Dr. Ryan said.
“The overall prevalence of PJP in patients not on prophylaxis was 3.4%, there were no cases of PJP in patients on prophylaxis, and the incidence rate in patients not on prophylaxis was 1.9 per 100 person-years, with a number needed to treat to prevent 1 case of PJP calculated to be 42 patients,” she said.
In addition to PJP, three cases of proven or probable invasive fungal infections (IFI) occurred, including one case of pulmonary histoplasmosis in the ibrutinib plus FCR trial cohort and two cases of aspergillosis, including a pulmonary case and a brain abscess, in an ibrutinib plus umbralisib trial cohort.
“The overall prevalence of aspergillosis or histoplasmosis in our entire cohort was 1.4%, and notably there were no cases of IFI in the single-agent therapy cohort, but the prevalence in the ibrutinib-combination therapy patients was 4.2%,” Dr. Ryan said.
Patients included in the review were adults with a median age of 64.8 years, and 64% were men. The median duration of BTK inhibitor therapy was 23.2 months.
“We know that CLL patients treated with fludarabine have an increased risk of PJP,” she said. “As such, it is routinely recommended that patients receiving fludarabine-containing chemotherapy regimens are prescribed PJP prophylaxis.”
Additionally, the increasing use of oral BTK inhibitors has raised concerns about the potential risk of PJP or other IFIs in patients on those agents, Dr. Ryan explained, noting that existing case reports and case series looking at PJP have shown varying prevalence rates, and little is known about the effects of prophylaxis.
“At present, there are no international guidelines regarding the use of antimicrobial prophylaxis in CLL patients treated with BTK inhibitors, and prophylaxis practices vary widely across countries and institutions,” she said.
The findings of the current study demonstrate that such variation exists “even within our own institution,” Dr. Ryan added.
The findings also show an overall low PJP prevalence of 3.4% in patients not receiving prophylaxis, which falls below the “commonly accepted threshold of 5%, above which routine prophylaxis becomes recommended,” she said.
“Overall, our data suggest that routine PJP or IFI prophylaxis in patients receiving BTK inhibitors may not be needed, but this is definitely an area that requires further study, ideally with a prospective trial with a larger sample size and multiple institutions, to support the development of consensus guidelines on this issue,” she said.
Dr. Ryan reported having no financial disclosures.
REPORTING FROM IWCLL 2019
Valacyclovir safely cut vertical CMV transmission
WASHINGTON – Daily treatment with valacyclovir for at least 6 weeks safely cut the cytomegalovirus (CMV) vertical transmission rate from mothers to fetuses in women with a primary CMV infection during the three weeks before conception through their first trimester. That finding emerged from a randomized, controlled, single-center Israeli study with 92 women.
The rate of congenital fetal infection with CMV was 11% among neonates born to 45 women treated with 8 g/day of valacyclovir, compared with a 30% rate among the infants born to 47 women who received placebo, a statistically significant difference, Keren Shahar-Nissan, MD, said at an annual scientific meeting on infectious diseases. The results also showed that the valacyclovir regimen was well tolerated, with no increase compared with placebo in adverse events and with no need for dosage adjustment regardless of a 16 pill/day regimen to deliver the 8 g/day of valacyclovir or placebo that participants received.
Dr. Shahar-Nissan said that she and her associates felt comfortable administering this amount of valacyclovir to pregnant woman given previous reports of the safety of this dosage for both women and their fetuses. These reports included 20 pregnant women safely treated for 7 weeks with 8 g/day during the late second or early third trimester (BJOG. 2007 Sept;114[9]:1113-21); more than 600 women in a Danish nationwide study treated with any dosage of valacyclovir during preconception, the first trimester, or the second or third trimesters with a prevalence of births defects not significantly different from unexposed pregnancies (JAMA. 2010 Aug 25;304[8]:859-66); and a prospective, open-label study of 8 g/day valacyclovir to treat 43 women carrying CMV-infected fetuses starting at a median 26 weeks gestation and continuing through delivery (Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2016 Oct;215[4]:462.e1-462.e10).
The study she ran enrolled women seen at Helen Schneider Hospital for Women in Petah Tikva, Israel, during November 2015-October 2018 who had a serologically-proven primary CMV infection that began at any time from 3 weeks before conception through the first trimester, excluding patients with renal dysfunction, liver disease, bone-marrow suppression, or acyclovir sensitivity. Screening for active CMV infection is common among newly-pregnant Israeli women, usually at the time of their first obstetrical consultation for a suspected pregnancy, noted Dr. Shahar-Nissan, a pediatrician at Schneider Children’s Medical Center of Israel in Petah Tikva. About a quarter of the enrolled women became infected during the 3 weeks prior to conception, and nearly two-thirds became infected during the first 8 weeks of pregnancy.
The valacyclovir intervention appeared to be effective specifically for preventing vertical transmission of infection acquired early during pregnancy. In this subgroup the transmission rate was 11% with valacyclovir treatment and 48% on placebo. Valacyclovir seemed to have no effect on vertical transmission of infections that began before conception, likely because treatment began too late to prevent transmission.
“I think this study is enough” to convince the U.S. Food and Drug Administration to add this treatment indication to the labeling of valacyclovir, a drug that has been available in generic formulations for many years, Dr. Shahar-Nissan said in an interview. Before approaching the FDA, her first goal is publishing the findings, she added.
[email protected]
On Twitter @mitchelzoler
This small Israeli study is very important. The powerful finding of the study was buttressed by its placebo-controlled design and by its follow-up. The findings need replication in a larger study, but despite the small size of the current study the findings are noteworthy because of the desperate need for a safe and effective intervention to reduce the risk for maternal-fetal transmission of cytomegalovirus (CMV) when a woman has a first infection just before conception or early during pregnancy. Several years ago, the Institute of Medicine made prevention of prenatal CMV transmission (by vaccination) a major health priority based on the high estimated burden of congenital CMV infection, Addressing this still unmet need remains an important goal given the substantial disability that congenital CMV causes for thousands of infants born each year.
Janet A. Englund, MD, is a professor of pediatric infectious diseases at the University of Washington in Seattle and at Seattle Children’s Hospital. She had no relevant disclosures. She made these comments in an interview.
This small Israeli study is very important. The powerful finding of the study was buttressed by its placebo-controlled design and by its follow-up. The findings need replication in a larger study, but despite the small size of the current study the findings are noteworthy because of the desperate need for a safe and effective intervention to reduce the risk for maternal-fetal transmission of cytomegalovirus (CMV) when a woman has a first infection just before conception or early during pregnancy. Several years ago, the Institute of Medicine made prevention of prenatal CMV transmission (by vaccination) a major health priority based on the high estimated burden of congenital CMV infection, Addressing this still unmet need remains an important goal given the substantial disability that congenital CMV causes for thousands of infants born each year.
Janet A. Englund, MD, is a professor of pediatric infectious diseases at the University of Washington in Seattle and at Seattle Children’s Hospital. She had no relevant disclosures. She made these comments in an interview.
This small Israeli study is very important. The powerful finding of the study was buttressed by its placebo-controlled design and by its follow-up. The findings need replication in a larger study, but despite the small size of the current study the findings are noteworthy because of the desperate need for a safe and effective intervention to reduce the risk for maternal-fetal transmission of cytomegalovirus (CMV) when a woman has a first infection just before conception or early during pregnancy. Several years ago, the Institute of Medicine made prevention of prenatal CMV transmission (by vaccination) a major health priority based on the high estimated burden of congenital CMV infection, Addressing this still unmet need remains an important goal given the substantial disability that congenital CMV causes for thousands of infants born each year.
Janet A. Englund, MD, is a professor of pediatric infectious diseases at the University of Washington in Seattle and at Seattle Children’s Hospital. She had no relevant disclosures. She made these comments in an interview.
WASHINGTON – Daily treatment with valacyclovir for at least 6 weeks safely cut the cytomegalovirus (CMV) vertical transmission rate from mothers to fetuses in women with a primary CMV infection during the three weeks before conception through their first trimester. That finding emerged from a randomized, controlled, single-center Israeli study with 92 women.
The rate of congenital fetal infection with CMV was 11% among neonates born to 45 women treated with 8 g/day of valacyclovir, compared with a 30% rate among the infants born to 47 women who received placebo, a statistically significant difference, Keren Shahar-Nissan, MD, said at an annual scientific meeting on infectious diseases. The results also showed that the valacyclovir regimen was well tolerated, with no increase compared with placebo in adverse events and with no need for dosage adjustment regardless of a 16 pill/day regimen to deliver the 8 g/day of valacyclovir or placebo that participants received.
Dr. Shahar-Nissan said that she and her associates felt comfortable administering this amount of valacyclovir to pregnant woman given previous reports of the safety of this dosage for both women and their fetuses. These reports included 20 pregnant women safely treated for 7 weeks with 8 g/day during the late second or early third trimester (BJOG. 2007 Sept;114[9]:1113-21); more than 600 women in a Danish nationwide study treated with any dosage of valacyclovir during preconception, the first trimester, or the second or third trimesters with a prevalence of births defects not significantly different from unexposed pregnancies (JAMA. 2010 Aug 25;304[8]:859-66); and a prospective, open-label study of 8 g/day valacyclovir to treat 43 women carrying CMV-infected fetuses starting at a median 26 weeks gestation and continuing through delivery (Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2016 Oct;215[4]:462.e1-462.e10).
The study she ran enrolled women seen at Helen Schneider Hospital for Women in Petah Tikva, Israel, during November 2015-October 2018 who had a serologically-proven primary CMV infection that began at any time from 3 weeks before conception through the first trimester, excluding patients with renal dysfunction, liver disease, bone-marrow suppression, or acyclovir sensitivity. Screening for active CMV infection is common among newly-pregnant Israeli women, usually at the time of their first obstetrical consultation for a suspected pregnancy, noted Dr. Shahar-Nissan, a pediatrician at Schneider Children’s Medical Center of Israel in Petah Tikva. About a quarter of the enrolled women became infected during the 3 weeks prior to conception, and nearly two-thirds became infected during the first 8 weeks of pregnancy.
The valacyclovir intervention appeared to be effective specifically for preventing vertical transmission of infection acquired early during pregnancy. In this subgroup the transmission rate was 11% with valacyclovir treatment and 48% on placebo. Valacyclovir seemed to have no effect on vertical transmission of infections that began before conception, likely because treatment began too late to prevent transmission.
“I think this study is enough” to convince the U.S. Food and Drug Administration to add this treatment indication to the labeling of valacyclovir, a drug that has been available in generic formulations for many years, Dr. Shahar-Nissan said in an interview. Before approaching the FDA, her first goal is publishing the findings, she added.
[email protected]
On Twitter @mitchelzoler
WASHINGTON – Daily treatment with valacyclovir for at least 6 weeks safely cut the cytomegalovirus (CMV) vertical transmission rate from mothers to fetuses in women with a primary CMV infection during the three weeks before conception through their first trimester. That finding emerged from a randomized, controlled, single-center Israeli study with 92 women.
The rate of congenital fetal infection with CMV was 11% among neonates born to 45 women treated with 8 g/day of valacyclovir, compared with a 30% rate among the infants born to 47 women who received placebo, a statistically significant difference, Keren Shahar-Nissan, MD, said at an annual scientific meeting on infectious diseases. The results also showed that the valacyclovir regimen was well tolerated, with no increase compared with placebo in adverse events and with no need for dosage adjustment regardless of a 16 pill/day regimen to deliver the 8 g/day of valacyclovir or placebo that participants received.
Dr. Shahar-Nissan said that she and her associates felt comfortable administering this amount of valacyclovir to pregnant woman given previous reports of the safety of this dosage for both women and their fetuses. These reports included 20 pregnant women safely treated for 7 weeks with 8 g/day during the late second or early third trimester (BJOG. 2007 Sept;114[9]:1113-21); more than 600 women in a Danish nationwide study treated with any dosage of valacyclovir during preconception, the first trimester, or the second or third trimesters with a prevalence of births defects not significantly different from unexposed pregnancies (JAMA. 2010 Aug 25;304[8]:859-66); and a prospective, open-label study of 8 g/day valacyclovir to treat 43 women carrying CMV-infected fetuses starting at a median 26 weeks gestation and continuing through delivery (Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2016 Oct;215[4]:462.e1-462.e10).
The study she ran enrolled women seen at Helen Schneider Hospital for Women in Petah Tikva, Israel, during November 2015-October 2018 who had a serologically-proven primary CMV infection that began at any time from 3 weeks before conception through the first trimester, excluding patients with renal dysfunction, liver disease, bone-marrow suppression, or acyclovir sensitivity. Screening for active CMV infection is common among newly-pregnant Israeli women, usually at the time of their first obstetrical consultation for a suspected pregnancy, noted Dr. Shahar-Nissan, a pediatrician at Schneider Children’s Medical Center of Israel in Petah Tikva. About a quarter of the enrolled women became infected during the 3 weeks prior to conception, and nearly two-thirds became infected during the first 8 weeks of pregnancy.
The valacyclovir intervention appeared to be effective specifically for preventing vertical transmission of infection acquired early during pregnancy. In this subgroup the transmission rate was 11% with valacyclovir treatment and 48% on placebo. Valacyclovir seemed to have no effect on vertical transmission of infections that began before conception, likely because treatment began too late to prevent transmission.
“I think this study is enough” to convince the U.S. Food and Drug Administration to add this treatment indication to the labeling of valacyclovir, a drug that has been available in generic formulations for many years, Dr. Shahar-Nissan said in an interview. Before approaching the FDA, her first goal is publishing the findings, she added.
[email protected]
On Twitter @mitchelzoler
REPORTING FROM ID WEEK 2019
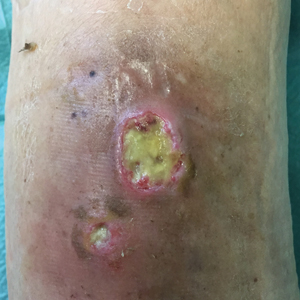
Short-term statin use linked to risk of skin and soft tissue infections
according to a sequence symmetry analysis of prescription claims over a 10-year period reported in the British Journal of Clinical Pharmacology.
In the study, statin use for as little as 91 days was linked with elevated risks of SSTIs and diabetes. However, the increased risk of infection was seen in individuals who did and did not develop diabetes, wrote Humphrey Ko, of the school of pharmacy and biomedical sciences, Curtin University, Perth, Australia, and colleagues.
The current literature on the impact of statins on SSTIs is conflicted, they noted. Previous research shows that statins “may reduce the risk of community-acquired [Staphylococcus aureus] bacteremia and exert antibacterial effects against S. aureus,” and therefore may have potential for reducing SSTI risk “or evolve into promising novel treatments for SSTIs,” the researchers said; they noted, however, that other data show that statins may induce new-onset diabetes.
They examined prescription claims (for statins, antidiabetic medications, and antistaphylococcal antibiotics) from 2001 to 2011 from the Australian Department of Veterans’ Affairs that included more than 228,000 veterans, war widows, and widowers. Prescriptions for antistaphylococcal antibiotics were used as a marker of SSTIs.
Overall, statins were significantly associated with an increased risk of SSTIs at 91 days (adjusted sequence ratio, 1.40). The risk of SSTIs from statin use was similar at 182 (ASR, 1.41) and 365 days (ASR, 1.40). In this case, the ASRs represent the incidence rate ratios of prescribing antibiotics in statin-exposed versus statin-nonexposed person-time.
Statins were associated with a significantly increased risk of new onset diabetes, but the SSTI risk was not significantly different between statin users with and without diabetes. Statin users who did not have diabetes had significant SSTI risks at 91, 182, and 365 days (ASR, 1.39, 1.41, and 1.37, respectively) and statin users with diabetes had similarly significant risks of SSTIs (ASR,1.43, 1.42, and 1.49, respectively).
In addition, socioeconomic status appeared to have no significant effect on the relationship between statin use, SSTIs, and diabetes, the researchers noted.
The findings were limited by several factors including the inability to account for patient compliance in taking the medications, a lack of dosage data to determine the impact of dosage on outcomes, and potential confounding by the presence of diabetes, they said. However, the results suggest that “it would seem prudent for clinicians to monitor blood glucose levels of statin users who are predisposed to diabetes, and be mindful of possible increased SSTI risks in such patients,” they concluded. Statins, they added, “may increase SSTI risk via direct or indirect mechanisms.”
More clinical trials are needed to confirm the mechanisms, and “to ascertain the effect of statins on gut dysbiosis, impaired bile acid metabolism, vitamin D levels, and cholesterol inhibition on skin function,” they wrote.
The study was supported in part by the Australian Government Research Training Program Scholarship, the Curtin Health Innovation Research Institute Biosciences Research Precinct Core Facility, and the School of Pharmacy and Biomedical Sciences (Curtin University). The researchers had no financial conflicts to disclose.
SOURCE: Ko H et al. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 2019 Oct 9. doi: 10.1111/bcp.14077.
according to a sequence symmetry analysis of prescription claims over a 10-year period reported in the British Journal of Clinical Pharmacology.
In the study, statin use for as little as 91 days was linked with elevated risks of SSTIs and diabetes. However, the increased risk of infection was seen in individuals who did and did not develop diabetes, wrote Humphrey Ko, of the school of pharmacy and biomedical sciences, Curtin University, Perth, Australia, and colleagues.
The current literature on the impact of statins on SSTIs is conflicted, they noted. Previous research shows that statins “may reduce the risk of community-acquired [Staphylococcus aureus] bacteremia and exert antibacterial effects against S. aureus,” and therefore may have potential for reducing SSTI risk “or evolve into promising novel treatments for SSTIs,” the researchers said; they noted, however, that other data show that statins may induce new-onset diabetes.
They examined prescription claims (for statins, antidiabetic medications, and antistaphylococcal antibiotics) from 2001 to 2011 from the Australian Department of Veterans’ Affairs that included more than 228,000 veterans, war widows, and widowers. Prescriptions for antistaphylococcal antibiotics were used as a marker of SSTIs.
Overall, statins were significantly associated with an increased risk of SSTIs at 91 days (adjusted sequence ratio, 1.40). The risk of SSTIs from statin use was similar at 182 (ASR, 1.41) and 365 days (ASR, 1.40). In this case, the ASRs represent the incidence rate ratios of prescribing antibiotics in statin-exposed versus statin-nonexposed person-time.
Statins were associated with a significantly increased risk of new onset diabetes, but the SSTI risk was not significantly different between statin users with and without diabetes. Statin users who did not have diabetes had significant SSTI risks at 91, 182, and 365 days (ASR, 1.39, 1.41, and 1.37, respectively) and statin users with diabetes had similarly significant risks of SSTIs (ASR,1.43, 1.42, and 1.49, respectively).
In addition, socioeconomic status appeared to have no significant effect on the relationship between statin use, SSTIs, and diabetes, the researchers noted.
The findings were limited by several factors including the inability to account for patient compliance in taking the medications, a lack of dosage data to determine the impact of dosage on outcomes, and potential confounding by the presence of diabetes, they said. However, the results suggest that “it would seem prudent for clinicians to monitor blood glucose levels of statin users who are predisposed to diabetes, and be mindful of possible increased SSTI risks in such patients,” they concluded. Statins, they added, “may increase SSTI risk via direct or indirect mechanisms.”
More clinical trials are needed to confirm the mechanisms, and “to ascertain the effect of statins on gut dysbiosis, impaired bile acid metabolism, vitamin D levels, and cholesterol inhibition on skin function,” they wrote.
The study was supported in part by the Australian Government Research Training Program Scholarship, the Curtin Health Innovation Research Institute Biosciences Research Precinct Core Facility, and the School of Pharmacy and Biomedical Sciences (Curtin University). The researchers had no financial conflicts to disclose.
SOURCE: Ko H et al. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 2019 Oct 9. doi: 10.1111/bcp.14077.
according to a sequence symmetry analysis of prescription claims over a 10-year period reported in the British Journal of Clinical Pharmacology.
In the study, statin use for as little as 91 days was linked with elevated risks of SSTIs and diabetes. However, the increased risk of infection was seen in individuals who did and did not develop diabetes, wrote Humphrey Ko, of the school of pharmacy and biomedical sciences, Curtin University, Perth, Australia, and colleagues.
The current literature on the impact of statins on SSTIs is conflicted, they noted. Previous research shows that statins “may reduce the risk of community-acquired [Staphylococcus aureus] bacteremia and exert antibacterial effects against S. aureus,” and therefore may have potential for reducing SSTI risk “or evolve into promising novel treatments for SSTIs,” the researchers said; they noted, however, that other data show that statins may induce new-onset diabetes.
They examined prescription claims (for statins, antidiabetic medications, and antistaphylococcal antibiotics) from 2001 to 2011 from the Australian Department of Veterans’ Affairs that included more than 228,000 veterans, war widows, and widowers. Prescriptions for antistaphylococcal antibiotics were used as a marker of SSTIs.
Overall, statins were significantly associated with an increased risk of SSTIs at 91 days (adjusted sequence ratio, 1.40). The risk of SSTIs from statin use was similar at 182 (ASR, 1.41) and 365 days (ASR, 1.40). In this case, the ASRs represent the incidence rate ratios of prescribing antibiotics in statin-exposed versus statin-nonexposed person-time.
Statins were associated with a significantly increased risk of new onset diabetes, but the SSTI risk was not significantly different between statin users with and without diabetes. Statin users who did not have diabetes had significant SSTI risks at 91, 182, and 365 days (ASR, 1.39, 1.41, and 1.37, respectively) and statin users with diabetes had similarly significant risks of SSTIs (ASR,1.43, 1.42, and 1.49, respectively).
In addition, socioeconomic status appeared to have no significant effect on the relationship between statin use, SSTIs, and diabetes, the researchers noted.
The findings were limited by several factors including the inability to account for patient compliance in taking the medications, a lack of dosage data to determine the impact of dosage on outcomes, and potential confounding by the presence of diabetes, they said. However, the results suggest that “it would seem prudent for clinicians to monitor blood glucose levels of statin users who are predisposed to diabetes, and be mindful of possible increased SSTI risks in such patients,” they concluded. Statins, they added, “may increase SSTI risk via direct or indirect mechanisms.”
More clinical trials are needed to confirm the mechanisms, and “to ascertain the effect of statins on gut dysbiosis, impaired bile acid metabolism, vitamin D levels, and cholesterol inhibition on skin function,” they wrote.
The study was supported in part by the Australian Government Research Training Program Scholarship, the Curtin Health Innovation Research Institute Biosciences Research Precinct Core Facility, and the School of Pharmacy and Biomedical Sciences (Curtin University). The researchers had no financial conflicts to disclose.
SOURCE: Ko H et al. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 2019 Oct 9. doi: 10.1111/bcp.14077.
FROM THE BRITISH JOURNAL OF CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
Painless Round Ulcers on the Leg
The Diagnosis: Cutaneous Tuberculosis
The patient's medical history was notable for bone tuberculosis (TB) treated in childhood. Skin biopsy revealed neutrophilic infiltrates with necrosis without granulomas. A real-time polymerase chain reaction test detected Mycobacterium tuberculosis complex in the skin fragment, which was confirmed by culture of the biopsy specimen using a liquid growth medium that grew M tuberculosis. Tuberculotic foci were not present on the lungs, gastrointestinal tract, kidneys, and bones by radiologic, microbiologic, and ultrasonographic investigations. The patient was started on 4 antituberculotic drugs--isoniazid 300 mg, rifampicin 600 mg, ethambutol 1200 mg, pyrazinamide 1500 mg--once daily for 2 months followed by isoniazid 300 mg and rifampicin 600 mg once daily for another 4 months with resolution of the skin lesions.
Cutaneous TB is an infectious disease caused by M tuberculosis and accounts for only 1.5% of extrapulmonary TB cases.1,2 Similar to other forms of TB, a resurgence of cutaneous TB has been noted in parts of the world where human immunodeficiency virus infection is prevalent and remains to be one of the most elusive and more difficult diseases to diagnose.3 Thought to be a predominantly occupational disease, it is being encountered more frequently in healthy individuals where the source of infection remains unidentified in most cases.4 The clinical types depend on the method of infection, virulence of the bacillus, immune status of the host, and presence or absence of host sensitization to M tuberculosis.2 The route of infection is used to classify cutaneous mycobacteriosis.5 Inoculation from an exogenous source can produce TB verrucosa cutis in individuals who have previously been sensitized to M tuberculosis or tuberculous chancre in individuals without prior exposure to the bacterium.4 Cutaneous TB resulting from direct spread to the skin from an underlying contiguous structure in most cases spreads from lymph nodes and bone (scrofuloderma). Immunosuppressed patients with advanced TB of the lung, gastrointestinal tract, or the genitourinary tract may present with periorificial TB.4 Dissemination to the skin caused by hematogenous spread can occur in the form of lupus vulgaris, miliary TB, or metastatic tuberculous abscesses (gummas).4,5 A fourth category--cutaneous TB from paradoxical expansion--also was proposed. Paradoxical expansion is defined as the transient expansion of a preexisting lesion or the appearance of new lesions during appropriate anti-TB therapy.5
Although histopathology and protein chain reaction tests are useful, the gold standard for diagnosis is still the isolation of M tuberculosis on culture.3,6 Treatment regimens of cutaneous TB are similar to those of pulmonary TB, with a 4-agent regimen given for 2 months followed by a 2-drug regimen for the next 4 months.1,7 The differential diagnosis of leg ulcers includes stasis ulcer, necrobiotic xanthogranuloma, pyoderma gangrenosum, and squamous cell carcinoma, among others. Cutaneous biopsy, microbiological culture, and a high degree of suspicion are fundamental for the final diagnosis. Cutaneous TB should be suspected in immunocompetent as well as in immunosuppressed patients who present with ulcerated lesions that do not respond to antibacterial treatment.
- Karoney MJ, Kaumbuki EK, Koech MK, et al. Primary cutaneous tuberculosis in a 27-year-old medical intern from needle-stick injury: a case report. Clin Case Rep. 2015;3:39-42.
- Spelta K, Diniz LM. Cutaneous tuberculosis: a 26-year retrospective study in an endemic area of tuberculosis, Vitória, Espírito Santo, Brazil. Rev Inst Med Trop Sao Paulo. 2016;58:49.
- Sahin N, Aydin NE, Senol M, et al. Longstanding skin ulcers due to Mycobacterium tuberculosis in a healthy man. Trop Biomed. 2010;27:120-124.
- Semaan R, Traboulsi R, Kanj S. Primary Mycobacterium tuberculosis complex cutaneous infection: report of two cases and literature review. Int J Infect Dis. 2008;12:472-477.
- Ram R, Uppin S, Swarnalatha G, et al. Isolated skin ulcers due to Mycobacterium tuberculosis in a renal allograft recipient. Nat Clin Pract Nephrol. 2007;3:688-693.
- Bravo FG, Gotuzzo E. Cutaneous tuberculosis. Clin Dermatol. 2007;25:173-180.
- Handog EB, Gabriel TG, Pineda RT. Management of cutaneous tuberculosis. Dermatol Ther. 2008;21:154-161.
The Diagnosis: Cutaneous Tuberculosis
The patient's medical history was notable for bone tuberculosis (TB) treated in childhood. Skin biopsy revealed neutrophilic infiltrates with necrosis without granulomas. A real-time polymerase chain reaction test detected Mycobacterium tuberculosis complex in the skin fragment, which was confirmed by culture of the biopsy specimen using a liquid growth medium that grew M tuberculosis. Tuberculotic foci were not present on the lungs, gastrointestinal tract, kidneys, and bones by radiologic, microbiologic, and ultrasonographic investigations. The patient was started on 4 antituberculotic drugs--isoniazid 300 mg, rifampicin 600 mg, ethambutol 1200 mg, pyrazinamide 1500 mg--once daily for 2 months followed by isoniazid 300 mg and rifampicin 600 mg once daily for another 4 months with resolution of the skin lesions.
Cutaneous TB is an infectious disease caused by M tuberculosis and accounts for only 1.5% of extrapulmonary TB cases.1,2 Similar to other forms of TB, a resurgence of cutaneous TB has been noted in parts of the world where human immunodeficiency virus infection is prevalent and remains to be one of the most elusive and more difficult diseases to diagnose.3 Thought to be a predominantly occupational disease, it is being encountered more frequently in healthy individuals where the source of infection remains unidentified in most cases.4 The clinical types depend on the method of infection, virulence of the bacillus, immune status of the host, and presence or absence of host sensitization to M tuberculosis.2 The route of infection is used to classify cutaneous mycobacteriosis.5 Inoculation from an exogenous source can produce TB verrucosa cutis in individuals who have previously been sensitized to M tuberculosis or tuberculous chancre in individuals without prior exposure to the bacterium.4 Cutaneous TB resulting from direct spread to the skin from an underlying contiguous structure in most cases spreads from lymph nodes and bone (scrofuloderma). Immunosuppressed patients with advanced TB of the lung, gastrointestinal tract, or the genitourinary tract may present with periorificial TB.4 Dissemination to the skin caused by hematogenous spread can occur in the form of lupus vulgaris, miliary TB, or metastatic tuberculous abscesses (gummas).4,5 A fourth category--cutaneous TB from paradoxical expansion--also was proposed. Paradoxical expansion is defined as the transient expansion of a preexisting lesion or the appearance of new lesions during appropriate anti-TB therapy.5
Although histopathology and protein chain reaction tests are useful, the gold standard for diagnosis is still the isolation of M tuberculosis on culture.3,6 Treatment regimens of cutaneous TB are similar to those of pulmonary TB, with a 4-agent regimen given for 2 months followed by a 2-drug regimen for the next 4 months.1,7 The differential diagnosis of leg ulcers includes stasis ulcer, necrobiotic xanthogranuloma, pyoderma gangrenosum, and squamous cell carcinoma, among others. Cutaneous biopsy, microbiological culture, and a high degree of suspicion are fundamental for the final diagnosis. Cutaneous TB should be suspected in immunocompetent as well as in immunosuppressed patients who present with ulcerated lesions that do not respond to antibacterial treatment.
The Diagnosis: Cutaneous Tuberculosis
The patient's medical history was notable for bone tuberculosis (TB) treated in childhood. Skin biopsy revealed neutrophilic infiltrates with necrosis without granulomas. A real-time polymerase chain reaction test detected Mycobacterium tuberculosis complex in the skin fragment, which was confirmed by culture of the biopsy specimen using a liquid growth medium that grew M tuberculosis. Tuberculotic foci were not present on the lungs, gastrointestinal tract, kidneys, and bones by radiologic, microbiologic, and ultrasonographic investigations. The patient was started on 4 antituberculotic drugs--isoniazid 300 mg, rifampicin 600 mg, ethambutol 1200 mg, pyrazinamide 1500 mg--once daily for 2 months followed by isoniazid 300 mg and rifampicin 600 mg once daily for another 4 months with resolution of the skin lesions.
Cutaneous TB is an infectious disease caused by M tuberculosis and accounts for only 1.5% of extrapulmonary TB cases.1,2 Similar to other forms of TB, a resurgence of cutaneous TB has been noted in parts of the world where human immunodeficiency virus infection is prevalent and remains to be one of the most elusive and more difficult diseases to diagnose.3 Thought to be a predominantly occupational disease, it is being encountered more frequently in healthy individuals where the source of infection remains unidentified in most cases.4 The clinical types depend on the method of infection, virulence of the bacillus, immune status of the host, and presence or absence of host sensitization to M tuberculosis.2 The route of infection is used to classify cutaneous mycobacteriosis.5 Inoculation from an exogenous source can produce TB verrucosa cutis in individuals who have previously been sensitized to M tuberculosis or tuberculous chancre in individuals without prior exposure to the bacterium.4 Cutaneous TB resulting from direct spread to the skin from an underlying contiguous structure in most cases spreads from lymph nodes and bone (scrofuloderma). Immunosuppressed patients with advanced TB of the lung, gastrointestinal tract, or the genitourinary tract may present with periorificial TB.4 Dissemination to the skin caused by hematogenous spread can occur in the form of lupus vulgaris, miliary TB, or metastatic tuberculous abscesses (gummas).4,5 A fourth category--cutaneous TB from paradoxical expansion--also was proposed. Paradoxical expansion is defined as the transient expansion of a preexisting lesion or the appearance of new lesions during appropriate anti-TB therapy.5
Although histopathology and protein chain reaction tests are useful, the gold standard for diagnosis is still the isolation of M tuberculosis on culture.3,6 Treatment regimens of cutaneous TB are similar to those of pulmonary TB, with a 4-agent regimen given for 2 months followed by a 2-drug regimen for the next 4 months.1,7 The differential diagnosis of leg ulcers includes stasis ulcer, necrobiotic xanthogranuloma, pyoderma gangrenosum, and squamous cell carcinoma, among others. Cutaneous biopsy, microbiological culture, and a high degree of suspicion are fundamental for the final diagnosis. Cutaneous TB should be suspected in immunocompetent as well as in immunosuppressed patients who present with ulcerated lesions that do not respond to antibacterial treatment.
- Karoney MJ, Kaumbuki EK, Koech MK, et al. Primary cutaneous tuberculosis in a 27-year-old medical intern from needle-stick injury: a case report. Clin Case Rep. 2015;3:39-42.
- Spelta K, Diniz LM. Cutaneous tuberculosis: a 26-year retrospective study in an endemic area of tuberculosis, Vitória, Espírito Santo, Brazil. Rev Inst Med Trop Sao Paulo. 2016;58:49.
- Sahin N, Aydin NE, Senol M, et al. Longstanding skin ulcers due to Mycobacterium tuberculosis in a healthy man. Trop Biomed. 2010;27:120-124.
- Semaan R, Traboulsi R, Kanj S. Primary Mycobacterium tuberculosis complex cutaneous infection: report of two cases and literature review. Int J Infect Dis. 2008;12:472-477.
- Ram R, Uppin S, Swarnalatha G, et al. Isolated skin ulcers due to Mycobacterium tuberculosis in a renal allograft recipient. Nat Clin Pract Nephrol. 2007;3:688-693.
- Bravo FG, Gotuzzo E. Cutaneous tuberculosis. Clin Dermatol. 2007;25:173-180.
- Handog EB, Gabriel TG, Pineda RT. Management of cutaneous tuberculosis. Dermatol Ther. 2008;21:154-161.
- Karoney MJ, Kaumbuki EK, Koech MK, et al. Primary cutaneous tuberculosis in a 27-year-old medical intern from needle-stick injury: a case report. Clin Case Rep. 2015;3:39-42.
- Spelta K, Diniz LM. Cutaneous tuberculosis: a 26-year retrospective study in an endemic area of tuberculosis, Vitória, Espírito Santo, Brazil. Rev Inst Med Trop Sao Paulo. 2016;58:49.
- Sahin N, Aydin NE, Senol M, et al. Longstanding skin ulcers due to Mycobacterium tuberculosis in a healthy man. Trop Biomed. 2010;27:120-124.
- Semaan R, Traboulsi R, Kanj S. Primary Mycobacterium tuberculosis complex cutaneous infection: report of two cases and literature review. Int J Infect Dis. 2008;12:472-477.
- Ram R, Uppin S, Swarnalatha G, et al. Isolated skin ulcers due to Mycobacterium tuberculosis in a renal allograft recipient. Nat Clin Pract Nephrol. 2007;3:688-693.
- Bravo FG, Gotuzzo E. Cutaneous tuberculosis. Clin Dermatol. 2007;25:173-180.
- Handog EB, Gabriel TG, Pineda RT. Management of cutaneous tuberculosis. Dermatol Ther. 2008;21:154-161.
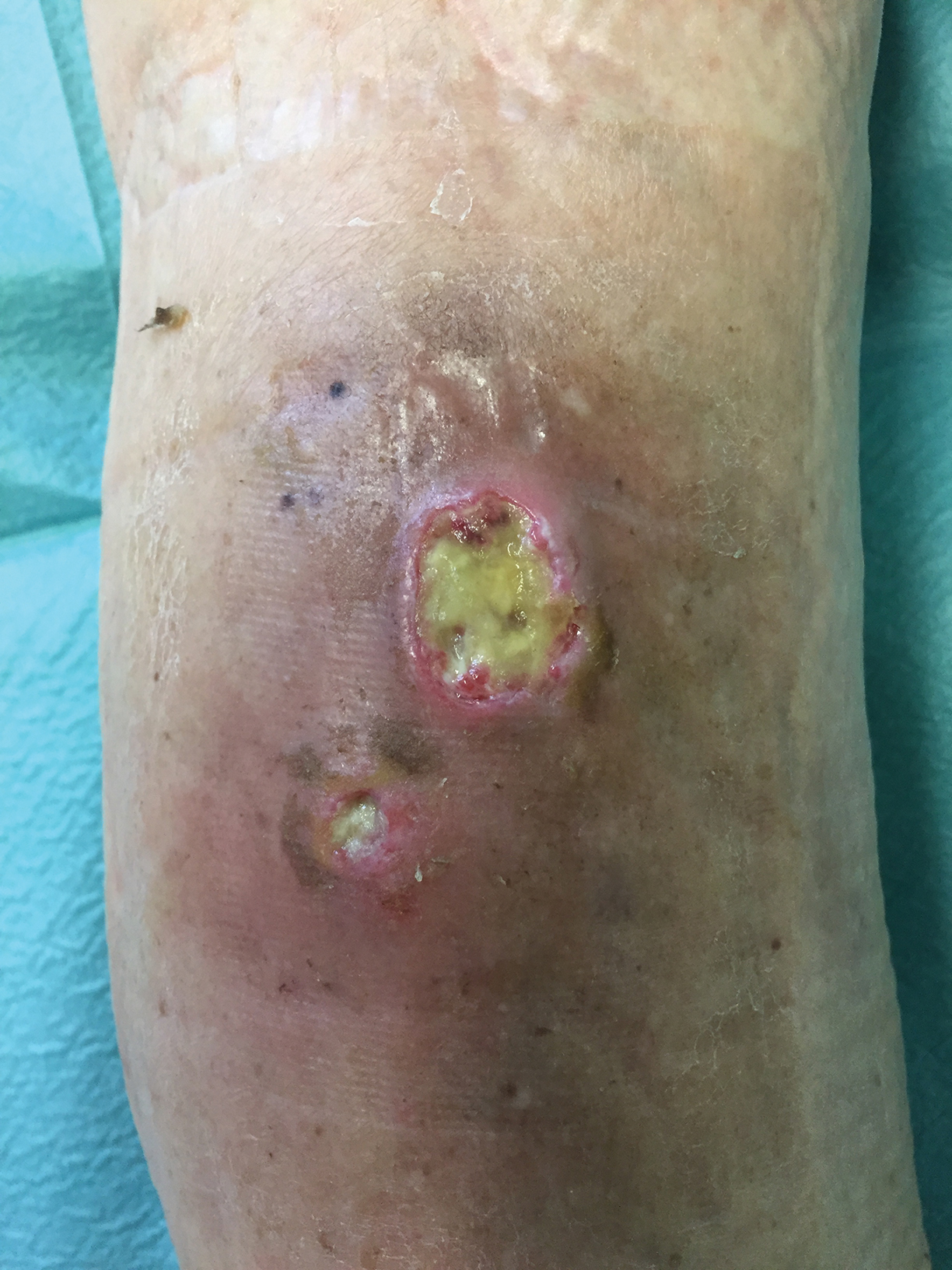
A 78-year-old man was referred to our clinic for evaluation of 2 painless round ulcers with an undermined edge and purulent discharge on the left posterior leg of 2 months' duration. The ulcers had appeared following a presumed trauma. He had received repeated courses of oral antibiotics and antifungals without improvement. No regional lymphadenopathy could be detected. Biochemical analyses were within reference range. Human immunodeficiency virus 1 and 2, hepatitis B and C antibodies, and a VDRL test were all negative.
Influenza: U.S. activity was low this summer
Influenza activity in the United States was typically low over the summer months, with influenza A(H3N2) viruses predominating, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
From May 19 to Sept. 28, 2019, weekly flu activity – measured by the percentage of outpatient visits to health care professionals for influenza-like illness (ILI) – was below the national baseline of 2.2%, ranging from 0.7% to 1.4%. Since mid-August, however, when the rate was last 0.7%, it has been climbing slowly but steadily and was up to 1.3% for the week ending Sept. 28, CDC data show.
The various public health laboratories of the U.S. Influenza Surveillance System tested over 7,600 respiratory samples from May 19 to Sept. 28, and 22.7% were positive for influenza viruses, Scott Epperson, DVM, and associates at the CDC’s influenza division said Oct. 10 in the MMWR.
Of the 1,737 samples found to be positive, 69.8% were influenza A and 30.2% were influenza B. The subtype split among specimens positive for Influenza A was 71.9% A(H3N2) and 28.1% A(H1N1)pdm09, while the samples positive for influenza B went 93.9% B/Victoria and 6.1% B/Yamagata, they reported.
Over the same time period in the Southern Hemisphere, “seasonal influenza viruses circulated widely, with influenza A(H3) predominating in many regions; however, influenza A(H1N1)pdm09 and influenza B viruses were predominant in some countries,” the CDC investigators noted.
They also reported the World Health Organization recommendations for the Southern Hemisphere’s 2020 flu vaccines. Components of the egg-based trivalent vaccine are an A/Brisbane/02/2018(H1N1)pdm09-like virus, an A/South Australia/34/2019(H3N2)-like virus, and a B/Washington/02/2019-like virus(B/Victoria lineage). The recommended quadrivalent vaccine adds a B/Phuket/3073/2013-like virus(B/Yamagata lineage), they wrote.
“It is too early in the season to know which viruses will circulate in the United States later this fall and winter or how severe the season might be; however, regardless of what is circulating, the best protection against influenza is an influenza vaccination,” Dr. Epperson and associates wrote.
SOURCE: Epperson S et al. MMWR. 2019 Oct 11;68(40):880-4.
Influenza activity in the United States was typically low over the summer months, with influenza A(H3N2) viruses predominating, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.

From May 19 to Sept. 28, 2019, weekly flu activity – measured by the percentage of outpatient visits to health care professionals for influenza-like illness (ILI) – was below the national baseline of 2.2%, ranging from 0.7% to 1.4%. Since mid-August, however, when the rate was last 0.7%, it has been climbing slowly but steadily and was up to 1.3% for the week ending Sept. 28, CDC data show.
The various public health laboratories of the U.S. Influenza Surveillance System tested over 7,600 respiratory samples from May 19 to Sept. 28, and 22.7% were positive for influenza viruses, Scott Epperson, DVM, and associates at the CDC’s influenza division said Oct. 10 in the MMWR.
Of the 1,737 samples found to be positive, 69.8% were influenza A and 30.2% were influenza B. The subtype split among specimens positive for Influenza A was 71.9% A(H3N2) and 28.1% A(H1N1)pdm09, while the samples positive for influenza B went 93.9% B/Victoria and 6.1% B/Yamagata, they reported.
Over the same time period in the Southern Hemisphere, “seasonal influenza viruses circulated widely, with influenza A(H3) predominating in many regions; however, influenza A(H1N1)pdm09 and influenza B viruses were predominant in some countries,” the CDC investigators noted.
They also reported the World Health Organization recommendations for the Southern Hemisphere’s 2020 flu vaccines. Components of the egg-based trivalent vaccine are an A/Brisbane/02/2018(H1N1)pdm09-like virus, an A/South Australia/34/2019(H3N2)-like virus, and a B/Washington/02/2019-like virus(B/Victoria lineage). The recommended quadrivalent vaccine adds a B/Phuket/3073/2013-like virus(B/Yamagata lineage), they wrote.
“It is too early in the season to know which viruses will circulate in the United States later this fall and winter or how severe the season might be; however, regardless of what is circulating, the best protection against influenza is an influenza vaccination,” Dr. Epperson and associates wrote.
SOURCE: Epperson S et al. MMWR. 2019 Oct 11;68(40):880-4.
Influenza activity in the United States was typically low over the summer months, with influenza A(H3N2) viruses predominating, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.

From May 19 to Sept. 28, 2019, weekly flu activity – measured by the percentage of outpatient visits to health care professionals for influenza-like illness (ILI) – was below the national baseline of 2.2%, ranging from 0.7% to 1.4%. Since mid-August, however, when the rate was last 0.7%, it has been climbing slowly but steadily and was up to 1.3% for the week ending Sept. 28, CDC data show.
The various public health laboratories of the U.S. Influenza Surveillance System tested over 7,600 respiratory samples from May 19 to Sept. 28, and 22.7% were positive for influenza viruses, Scott Epperson, DVM, and associates at the CDC’s influenza division said Oct. 10 in the MMWR.
Of the 1,737 samples found to be positive, 69.8% were influenza A and 30.2% were influenza B. The subtype split among specimens positive for Influenza A was 71.9% A(H3N2) and 28.1% A(H1N1)pdm09, while the samples positive for influenza B went 93.9% B/Victoria and 6.1% B/Yamagata, they reported.
Over the same time period in the Southern Hemisphere, “seasonal influenza viruses circulated widely, with influenza A(H3) predominating in many regions; however, influenza A(H1N1)pdm09 and influenza B viruses were predominant in some countries,” the CDC investigators noted.
They also reported the World Health Organization recommendations for the Southern Hemisphere’s 2020 flu vaccines. Components of the egg-based trivalent vaccine are an A/Brisbane/02/2018(H1N1)pdm09-like virus, an A/South Australia/34/2019(H3N2)-like virus, and a B/Washington/02/2019-like virus(B/Victoria lineage). The recommended quadrivalent vaccine adds a B/Phuket/3073/2013-like virus(B/Yamagata lineage), they wrote.
“It is too early in the season to know which viruses will circulate in the United States later this fall and winter or how severe the season might be; however, regardless of what is circulating, the best protection against influenza is an influenza vaccination,” Dr. Epperson and associates wrote.
SOURCE: Epperson S et al. MMWR. 2019 Oct 11;68(40):880-4.
FROM MMWR
Influenza vaccination modestly reduces risk of hospitalizations in patients with COPD
(COPD), according to data published in the Journal of Infectious Diseases.
“To the best of our knowledge, this is the first large, real-world population study to examine vaccine effectiveness in people with COPD using the test-negative design and influenza-specific study outcomes,” wrote Andrea S. Gershon, MD, of Sunnybrook Health Sciences Center in Toronto and colleagues. “These findings emphasize the need for more effective influenza vaccines for older COPD patients and other preventive strategies.”
A test-negative study design
Data suggest that 70% of COPD exacerbations are caused by infection, and influenza often is identified as the cause. Although all major COPD practice guidelines recommend seasonal influenza vaccination, the evidence indicating that vaccination reduces hospitalizations and death is limited. The inherent or corticosteroid-induced decrease in immune response to vaccination and respiratory infection among patients with COPD may reduce the effectiveness of influenza vaccination, wrote Dr. Gershon and colleagues.
The investigators used a test-negative design to evaluate how effectively influenza vaccination prevents laboratory-confirmed influenza–associated hospitalizations in community-dwelling older patients with COPD. They chose this design because it attenuates biases resulting from misclassification of infection and from differences in health care–seeking behavior between vaccinated and unvaccinated patients.
Dr. Gershon and colleagues examined health care administrative data and respiratory specimens collected from patients who had been tested for influenza during the 2010-2011 to 2015-2016 influenza seasons. Eligible patients were aged 66 years or older, had physician-diagnosed COPD, and had been tested for influenza within 3 days before and during an acute care hospitalization. The researchers determined influenza vaccination status using physician and pharmacist billing claims. They obtained demographic information through linkage with the provincial health insurance database. Multivariable logistic regression allowed Dr. Gershon and colleagues to estimate the adjusted odds ratio of influenza vaccination in people with laboratory-confirmed influenza, compared with those without.
Effectiveness did not vary by demographic factors
The investigators included 21,748 patients in their analysis. Of this population, 3,636 (16.7%) patients tested positive for influenza. Vaccinated patients were less likely than unvaccinated patients to test positive for influenza (15.3% vs. 18.6%). Vaccinated patients also were more likely to be older; live in an urban area; live in a higher income neighborhood; have had more outpatient visits with a physician in the previous year; have received a prescription for a COPD medication in the previous 6 months; have diabetes, asthma, or immunocompromising conditions; have a longer duration of COPD; and have had an outpatient COPD exacerbation in the previous year.
The overall unadjusted estimate of vaccine effectiveness against laboratory-confirmed influenza–associated hospitalizations was 21%. Multivariable adjustment yielded an effectiveness of 22%. When Dr. Gershon and colleagues corrected for misclassification of vaccination status among people with COPD, the effectiveness was estimated to be 43%. Vaccine effectiveness did not vary significantly according to influenza season, nor did it vary significantly by patient-specific factors such as age, sex, influenza subtype, codiagnosis of asthma, duration of COPD, previous outpatient COPD exacerbations, previous COPD hospitalization, previous receipt of inhaled corticosteroids, and previous pneumonia.
One limitation of the study was the possibility that COPD was misclassified because not all participants underwent pulmonary function testing. In addition, the estimates of vaccine effectiveness in the present study are specific to the outcome of influenza hospitalization and may not be generalizable to vaccine effectiveness estimates of outpatient outcomes, said the investigators. Finally, Dr. Gershon and colleagues could not identify the type of vaccine received.
“Given that a large pragmatic randomized controlled trial evaluating influenza vaccination would be unethical, this is likely the most robust estimate of vaccine effectiveness for hospitalizations in the COPD population to guide influenza vaccine recommendations for patients with COPD,” wrote Dr. Gershon and colleagues.
An Ontario Ministry of Health and Long-Term Care Health Systems Research Fund Capacity Grant and a Canadian Institutes of Health Research operating grant funded this research. One investigator received grants from the Canadian Institutes of Health Research during the study, and others received grants from pharmaceutical companies that were unrelated to this study.
SOURCE: Gershon AS et al. J Infect Dis. 2019 Sep 24. doi: 10.1093/infdis/jiz419.
(COPD), according to data published in the Journal of Infectious Diseases.
“To the best of our knowledge, this is the first large, real-world population study to examine vaccine effectiveness in people with COPD using the test-negative design and influenza-specific study outcomes,” wrote Andrea S. Gershon, MD, of Sunnybrook Health Sciences Center in Toronto and colleagues. “These findings emphasize the need for more effective influenza vaccines for older COPD patients and other preventive strategies.”
A test-negative study design
Data suggest that 70% of COPD exacerbations are caused by infection, and influenza often is identified as the cause. Although all major COPD practice guidelines recommend seasonal influenza vaccination, the evidence indicating that vaccination reduces hospitalizations and death is limited. The inherent or corticosteroid-induced decrease in immune response to vaccination and respiratory infection among patients with COPD may reduce the effectiveness of influenza vaccination, wrote Dr. Gershon and colleagues.
The investigators used a test-negative design to evaluate how effectively influenza vaccination prevents laboratory-confirmed influenza–associated hospitalizations in community-dwelling older patients with COPD. They chose this design because it attenuates biases resulting from misclassification of infection and from differences in health care–seeking behavior between vaccinated and unvaccinated patients.
Dr. Gershon and colleagues examined health care administrative data and respiratory specimens collected from patients who had been tested for influenza during the 2010-2011 to 2015-2016 influenza seasons. Eligible patients were aged 66 years or older, had physician-diagnosed COPD, and had been tested for influenza within 3 days before and during an acute care hospitalization. The researchers determined influenza vaccination status using physician and pharmacist billing claims. They obtained demographic information through linkage with the provincial health insurance database. Multivariable logistic regression allowed Dr. Gershon and colleagues to estimate the adjusted odds ratio of influenza vaccination in people with laboratory-confirmed influenza, compared with those without.
Effectiveness did not vary by demographic factors
The investigators included 21,748 patients in their analysis. Of this population, 3,636 (16.7%) patients tested positive for influenza. Vaccinated patients were less likely than unvaccinated patients to test positive for influenza (15.3% vs. 18.6%). Vaccinated patients also were more likely to be older; live in an urban area; live in a higher income neighborhood; have had more outpatient visits with a physician in the previous year; have received a prescription for a COPD medication in the previous 6 months; have diabetes, asthma, or immunocompromising conditions; have a longer duration of COPD; and have had an outpatient COPD exacerbation in the previous year.
The overall unadjusted estimate of vaccine effectiveness against laboratory-confirmed influenza–associated hospitalizations was 21%. Multivariable adjustment yielded an effectiveness of 22%. When Dr. Gershon and colleagues corrected for misclassification of vaccination status among people with COPD, the effectiveness was estimated to be 43%. Vaccine effectiveness did not vary significantly according to influenza season, nor did it vary significantly by patient-specific factors such as age, sex, influenza subtype, codiagnosis of asthma, duration of COPD, previous outpatient COPD exacerbations, previous COPD hospitalization, previous receipt of inhaled corticosteroids, and previous pneumonia.
One limitation of the study was the possibility that COPD was misclassified because not all participants underwent pulmonary function testing. In addition, the estimates of vaccine effectiveness in the present study are specific to the outcome of influenza hospitalization and may not be generalizable to vaccine effectiveness estimates of outpatient outcomes, said the investigators. Finally, Dr. Gershon and colleagues could not identify the type of vaccine received.
“Given that a large pragmatic randomized controlled trial evaluating influenza vaccination would be unethical, this is likely the most robust estimate of vaccine effectiveness for hospitalizations in the COPD population to guide influenza vaccine recommendations for patients with COPD,” wrote Dr. Gershon and colleagues.
An Ontario Ministry of Health and Long-Term Care Health Systems Research Fund Capacity Grant and a Canadian Institutes of Health Research operating grant funded this research. One investigator received grants from the Canadian Institutes of Health Research during the study, and others received grants from pharmaceutical companies that were unrelated to this study.
SOURCE: Gershon AS et al. J Infect Dis. 2019 Sep 24. doi: 10.1093/infdis/jiz419.
(COPD), according to data published in the Journal of Infectious Diseases.
“To the best of our knowledge, this is the first large, real-world population study to examine vaccine effectiveness in people with COPD using the test-negative design and influenza-specific study outcomes,” wrote Andrea S. Gershon, MD, of Sunnybrook Health Sciences Center in Toronto and colleagues. “These findings emphasize the need for more effective influenza vaccines for older COPD patients and other preventive strategies.”
A test-negative study design
Data suggest that 70% of COPD exacerbations are caused by infection, and influenza often is identified as the cause. Although all major COPD practice guidelines recommend seasonal influenza vaccination, the evidence indicating that vaccination reduces hospitalizations and death is limited. The inherent or corticosteroid-induced decrease in immune response to vaccination and respiratory infection among patients with COPD may reduce the effectiveness of influenza vaccination, wrote Dr. Gershon and colleagues.
The investigators used a test-negative design to evaluate how effectively influenza vaccination prevents laboratory-confirmed influenza–associated hospitalizations in community-dwelling older patients with COPD. They chose this design because it attenuates biases resulting from misclassification of infection and from differences in health care–seeking behavior between vaccinated and unvaccinated patients.
Dr. Gershon and colleagues examined health care administrative data and respiratory specimens collected from patients who had been tested for influenza during the 2010-2011 to 2015-2016 influenza seasons. Eligible patients were aged 66 years or older, had physician-diagnosed COPD, and had been tested for influenza within 3 days before and during an acute care hospitalization. The researchers determined influenza vaccination status using physician and pharmacist billing claims. They obtained demographic information through linkage with the provincial health insurance database. Multivariable logistic regression allowed Dr. Gershon and colleagues to estimate the adjusted odds ratio of influenza vaccination in people with laboratory-confirmed influenza, compared with those without.
Effectiveness did not vary by demographic factors
The investigators included 21,748 patients in their analysis. Of this population, 3,636 (16.7%) patients tested positive for influenza. Vaccinated patients were less likely than unvaccinated patients to test positive for influenza (15.3% vs. 18.6%). Vaccinated patients also were more likely to be older; live in an urban area; live in a higher income neighborhood; have had more outpatient visits with a physician in the previous year; have received a prescription for a COPD medication in the previous 6 months; have diabetes, asthma, or immunocompromising conditions; have a longer duration of COPD; and have had an outpatient COPD exacerbation in the previous year.
The overall unadjusted estimate of vaccine effectiveness against laboratory-confirmed influenza–associated hospitalizations was 21%. Multivariable adjustment yielded an effectiveness of 22%. When Dr. Gershon and colleagues corrected for misclassification of vaccination status among people with COPD, the effectiveness was estimated to be 43%. Vaccine effectiveness did not vary significantly according to influenza season, nor did it vary significantly by patient-specific factors such as age, sex, influenza subtype, codiagnosis of asthma, duration of COPD, previous outpatient COPD exacerbations, previous COPD hospitalization, previous receipt of inhaled corticosteroids, and previous pneumonia.
One limitation of the study was the possibility that COPD was misclassified because not all participants underwent pulmonary function testing. In addition, the estimates of vaccine effectiveness in the present study are specific to the outcome of influenza hospitalization and may not be generalizable to vaccine effectiveness estimates of outpatient outcomes, said the investigators. Finally, Dr. Gershon and colleagues could not identify the type of vaccine received.
“Given that a large pragmatic randomized controlled trial evaluating influenza vaccination would be unethical, this is likely the most robust estimate of vaccine effectiveness for hospitalizations in the COPD population to guide influenza vaccine recommendations for patients with COPD,” wrote Dr. Gershon and colleagues.
An Ontario Ministry of Health and Long-Term Care Health Systems Research Fund Capacity Grant and a Canadian Institutes of Health Research operating grant funded this research. One investigator received grants from the Canadian Institutes of Health Research during the study, and others received grants from pharmaceutical companies that were unrelated to this study.
SOURCE: Gershon AS et al. J Infect Dis. 2019 Sep 24. doi: 10.1093/infdis/jiz419.
FROM JOURNAL OF INFECTIOUS DISEASES