User login
Small study finds high dose vitamin D relieved toxic erythema of chemotherapy
seen on an inpatient dermatology consultative service.
Currently, chemotherapy cessation, delay, or dose modification are the “only reliable methods of resolving TEC,” and supportive agents such as topical corticosteroids, topical keratolytics, and pain control are associated with variable and “relatively slow improvement involving 2 to 4 weeks of recovery after chemotherapy interruption,” Cuong V. Nguyen, MD, of the department of dermatology at Northwestern University, Chicago, and colleagues, wrote in a research letter.
Onset of TEC in the six patients occurred a mean of 8.5 days after chemotherapy. Vitamin D – 50,000 IU for one patient and 100,000 IU for the others – was administered a mean of 4.3 days from rash onset and again in 7 days. Triamcinolone, 0.1%, or clobetasol, 0.05%, ointments were also prescribed.
All patients experienced symptomatic improvement in pain, pruritus, or swelling within a day of the first vitamin D treatment, and improvement in redness within 1 to 4 days, the authors said. The second treatment was administered for residual symptoms.
Adam Friedman, MD, professor and chair of dermatology and director of the supportive oncodermatology clinic at George Washington University, Washington, said that supporting patients through the “expected, disabling and often treatment-limiting side effects of oncologic therapies” is an area that is “in its infancy” and is characterized by limited evidence-based approaches.
“Creativity is therefore a must,” he said, commenting on the research letter. “Practice starts with anecdote, and this is certainly an exciting finding ... I look forward to trialing this with our patients at GW.”
Five of the six patients had a hematologic condition that required induction chemotherapy before hematopoietic stem cell transplant, and one was receiving regorafenib for treatment of glioblastoma multiforme. Diagnosis of TEC was established by clinical presentation, and five of the six patients underwent a biopsy. Biopsy findings were consistent with a TEC diagnosis in three patients, and showed nonspecific perivascular dermatitis in two, the investigators reported.
Further research is needed to determine optimal dosing, “delineate safety concerns and potential role in cancer treatment, and establish whether a durable response in patients with continuous chemotherapy, such as in an outpatient setting, is possible,” they said.
Dr. Nguyen and his coauthors reported no conflict of interest disclosures.
seen on an inpatient dermatology consultative service.
Currently, chemotherapy cessation, delay, or dose modification are the “only reliable methods of resolving TEC,” and supportive agents such as topical corticosteroids, topical keratolytics, and pain control are associated with variable and “relatively slow improvement involving 2 to 4 weeks of recovery after chemotherapy interruption,” Cuong V. Nguyen, MD, of the department of dermatology at Northwestern University, Chicago, and colleagues, wrote in a research letter.
Onset of TEC in the six patients occurred a mean of 8.5 days after chemotherapy. Vitamin D – 50,000 IU for one patient and 100,000 IU for the others – was administered a mean of 4.3 days from rash onset and again in 7 days. Triamcinolone, 0.1%, or clobetasol, 0.05%, ointments were also prescribed.
All patients experienced symptomatic improvement in pain, pruritus, or swelling within a day of the first vitamin D treatment, and improvement in redness within 1 to 4 days, the authors said. The second treatment was administered for residual symptoms.
Adam Friedman, MD, professor and chair of dermatology and director of the supportive oncodermatology clinic at George Washington University, Washington, said that supporting patients through the “expected, disabling and often treatment-limiting side effects of oncologic therapies” is an area that is “in its infancy” and is characterized by limited evidence-based approaches.
“Creativity is therefore a must,” he said, commenting on the research letter. “Practice starts with anecdote, and this is certainly an exciting finding ... I look forward to trialing this with our patients at GW.”
Five of the six patients had a hematologic condition that required induction chemotherapy before hematopoietic stem cell transplant, and one was receiving regorafenib for treatment of glioblastoma multiforme. Diagnosis of TEC was established by clinical presentation, and five of the six patients underwent a biopsy. Biopsy findings were consistent with a TEC diagnosis in three patients, and showed nonspecific perivascular dermatitis in two, the investigators reported.
Further research is needed to determine optimal dosing, “delineate safety concerns and potential role in cancer treatment, and establish whether a durable response in patients with continuous chemotherapy, such as in an outpatient setting, is possible,” they said.
Dr. Nguyen and his coauthors reported no conflict of interest disclosures.
seen on an inpatient dermatology consultative service.
Currently, chemotherapy cessation, delay, or dose modification are the “only reliable methods of resolving TEC,” and supportive agents such as topical corticosteroids, topical keratolytics, and pain control are associated with variable and “relatively slow improvement involving 2 to 4 weeks of recovery after chemotherapy interruption,” Cuong V. Nguyen, MD, of the department of dermatology at Northwestern University, Chicago, and colleagues, wrote in a research letter.
Onset of TEC in the six patients occurred a mean of 8.5 days after chemotherapy. Vitamin D – 50,000 IU for one patient and 100,000 IU for the others – was administered a mean of 4.3 days from rash onset and again in 7 days. Triamcinolone, 0.1%, or clobetasol, 0.05%, ointments were also prescribed.
All patients experienced symptomatic improvement in pain, pruritus, or swelling within a day of the first vitamin D treatment, and improvement in redness within 1 to 4 days, the authors said. The second treatment was administered for residual symptoms.
Adam Friedman, MD, professor and chair of dermatology and director of the supportive oncodermatology clinic at George Washington University, Washington, said that supporting patients through the “expected, disabling and often treatment-limiting side effects of oncologic therapies” is an area that is “in its infancy” and is characterized by limited evidence-based approaches.
“Creativity is therefore a must,” he said, commenting on the research letter. “Practice starts with anecdote, and this is certainly an exciting finding ... I look forward to trialing this with our patients at GW.”
Five of the six patients had a hematologic condition that required induction chemotherapy before hematopoietic stem cell transplant, and one was receiving regorafenib for treatment of glioblastoma multiforme. Diagnosis of TEC was established by clinical presentation, and five of the six patients underwent a biopsy. Biopsy findings were consistent with a TEC diagnosis in three patients, and showed nonspecific perivascular dermatitis in two, the investigators reported.
Further research is needed to determine optimal dosing, “delineate safety concerns and potential role in cancer treatment, and establish whether a durable response in patients with continuous chemotherapy, such as in an outpatient setting, is possible,” they said.
Dr. Nguyen and his coauthors reported no conflict of interest disclosures.
FROM JAMA DERMATOLOGY
New PDT therapy for CTCL to be reviewed by FDA
based on phase 3 findings published in JAMA Dermatology.
The treatment employs an ointment formulation of synthetic hypericin (HyBryte), a photosensitizer, that is preferentially absorbed into malignant cells and activated with visible light – rather than ultraviolet light – approximately 24 hours later. Investigators saw significant clinical responses in both patch and plaque type lesions and across races during the 24-week placebo-controlled, double-blinded, phase 3, randomized clinical trial.
“Traditional phototherapy, ultraviolet B phototherapy, has a limited depth of penetration, so patients with thicker plaque lesions don’t respond as well ... and UVB phototherapy typically is less effective in penetrating pigmented skin,” Ellen J. Kim, MD, lead author of the FLASH phase 3 trial, said in an interview.
Visible light in the yellow-red spectrum (500-650 nm) “penetrates deeper into the skin” and is nonmutagenic in vitro, so “theoretically it should have a much more favorable long-term safety profile,” said Dr. Kim, a dermatologist at the University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia.
Currently, she said, the risk of secondary malignancies inherent with UV PDT, including melanoma, is a deterrent for some patients, especially “patients with really fair skin and a history of skin cancer.”
Hypericin PDT also seems well suited for use with an at-home light unit. “In our field, it’s not about which therapy is [universally] better or best, but a matter of what works best for each patient at that moment in time, depending on the side-effect profile and other issues such as access,” Dr. Kim said. “It will be great to have another option for an incurable disease that requires chronic management.”
Mycosis fungoides (MF)/CTCL is considered an orphan disease, and the treatment has received orphan drug and fast track designations from the FDA, and orphan designation from the European Medicines Agency, according to a press release from its developer, Soligenix. The company is anticipating potential approval in the second half of 2023 and is targeting early 2024 for a U.S. launch, the statement said.
Phase 3 results
The pivotal trial involved 169 patients at 39 academic and community-based U.S. medical centers and consisted of several 6-week cycles of twice-weekly treatment punctuated by 2-week breaks. In cycle 1, patients were randomized 2:1 to receive hypericin or placebo treatment of three index lesions. Cycle 2 involved the crossover of placebo patients to active treatment of index lesions, and cycle 3 (optional) involved open-label treatment of all desired lesions (index and nonindex).
The trial defined the primary endpoint in phase 1 as 50% or greater improvement in the modified Composite Assessment of Index Lesion Severity score – a tool that’s endorsed by U.S. and international MF/CTCL specialty group consensus guidelines. For cycles 2 and 3, open-label response rates were secondary endpoints. Responses were assessed after 2-week rest periods to allow for treatment-induced skin reactions to subside.
After one cycle of treatment, topical hypericin PDT was more effective than placebo (an index lesion response rate of 16% vs. 4%; P =.04). The index lesion response rate with treatment increased to 40% after two cycles and 49% after three cycles. All were statistically significant changes.
Response rates were similar in patch and plaque-type lesions and regardless of age, sex, race, stage IA versus IB, time since diagnosis, and number of prior therapies. Adverse events were primarily mild application-site skin reactions. No serious drug-related adverse events occurred, Dr. Kim said, and “we had a low drop-out rate overall.”
Into the real world
The 24-week phase 3 trial duration is short, considering that “typically, phototherapy takes between 4 to 24 months [to achieve] full responses in CTCL,” Dr. Kim said in the interview.
So with real-world application, she said, “we’ll want to see where the overall response peaks with longer treatment, what the effects are of continuous treatment without any built-in breaks, and whether we will indeed see less skin cancer development in patients who are at higher risk of developing skin cancers from light treatment.”
Such questions will be explored as part of a new 4-year, 50-patient, open-label, multicenter study with the primary aim of investigating home-based hypericin PDT therapy in a supervised setting, said Dr. Kim, principal investigator of this study. Patients who are doing well after 6 weeks of twice-weekly therapy will be given at-home light units to continue therapy and achieve 1 year of treatment with no breaks. They will be monitored with video-based telemedicine.
“Long term, having a home unit should really improve patient access and compliance and hopefully effectiveness,” Dr. Kim said. Based on the phase 3 experience, “we think that continuous treatment will be well tolerated and that we may see greater responses.”
On Dec. 19, Soligenix announced that enrollment had begun in a phase 2a study of synthetic hypericin for treating patients with mild to moderate psoriasis.
Dr. Kim reported to JAMA Dermatology grants from Innate Pharma and Galderma; consulting/advisory fees from Almirall, Galderma, and Helsinn; and honoraria from Ology and UptoDate.
based on phase 3 findings published in JAMA Dermatology.
The treatment employs an ointment formulation of synthetic hypericin (HyBryte), a photosensitizer, that is preferentially absorbed into malignant cells and activated with visible light – rather than ultraviolet light – approximately 24 hours later. Investigators saw significant clinical responses in both patch and plaque type lesions and across races during the 24-week placebo-controlled, double-blinded, phase 3, randomized clinical trial.
“Traditional phototherapy, ultraviolet B phototherapy, has a limited depth of penetration, so patients with thicker plaque lesions don’t respond as well ... and UVB phototherapy typically is less effective in penetrating pigmented skin,” Ellen J. Kim, MD, lead author of the FLASH phase 3 trial, said in an interview.
Visible light in the yellow-red spectrum (500-650 nm) “penetrates deeper into the skin” and is nonmutagenic in vitro, so “theoretically it should have a much more favorable long-term safety profile,” said Dr. Kim, a dermatologist at the University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia.
Currently, she said, the risk of secondary malignancies inherent with UV PDT, including melanoma, is a deterrent for some patients, especially “patients with really fair skin and a history of skin cancer.”
Hypericin PDT also seems well suited for use with an at-home light unit. “In our field, it’s not about which therapy is [universally] better or best, but a matter of what works best for each patient at that moment in time, depending on the side-effect profile and other issues such as access,” Dr. Kim said. “It will be great to have another option for an incurable disease that requires chronic management.”
Mycosis fungoides (MF)/CTCL is considered an orphan disease, and the treatment has received orphan drug and fast track designations from the FDA, and orphan designation from the European Medicines Agency, according to a press release from its developer, Soligenix. The company is anticipating potential approval in the second half of 2023 and is targeting early 2024 for a U.S. launch, the statement said.
Phase 3 results
The pivotal trial involved 169 patients at 39 academic and community-based U.S. medical centers and consisted of several 6-week cycles of twice-weekly treatment punctuated by 2-week breaks. In cycle 1, patients were randomized 2:1 to receive hypericin or placebo treatment of three index lesions. Cycle 2 involved the crossover of placebo patients to active treatment of index lesions, and cycle 3 (optional) involved open-label treatment of all desired lesions (index and nonindex).
The trial defined the primary endpoint in phase 1 as 50% or greater improvement in the modified Composite Assessment of Index Lesion Severity score – a tool that’s endorsed by U.S. and international MF/CTCL specialty group consensus guidelines. For cycles 2 and 3, open-label response rates were secondary endpoints. Responses were assessed after 2-week rest periods to allow for treatment-induced skin reactions to subside.
After one cycle of treatment, topical hypericin PDT was more effective than placebo (an index lesion response rate of 16% vs. 4%; P =.04). The index lesion response rate with treatment increased to 40% after two cycles and 49% after three cycles. All were statistically significant changes.
Response rates were similar in patch and plaque-type lesions and regardless of age, sex, race, stage IA versus IB, time since diagnosis, and number of prior therapies. Adverse events were primarily mild application-site skin reactions. No serious drug-related adverse events occurred, Dr. Kim said, and “we had a low drop-out rate overall.”
Into the real world
The 24-week phase 3 trial duration is short, considering that “typically, phototherapy takes between 4 to 24 months [to achieve] full responses in CTCL,” Dr. Kim said in the interview.
So with real-world application, she said, “we’ll want to see where the overall response peaks with longer treatment, what the effects are of continuous treatment without any built-in breaks, and whether we will indeed see less skin cancer development in patients who are at higher risk of developing skin cancers from light treatment.”
Such questions will be explored as part of a new 4-year, 50-patient, open-label, multicenter study with the primary aim of investigating home-based hypericin PDT therapy in a supervised setting, said Dr. Kim, principal investigator of this study. Patients who are doing well after 6 weeks of twice-weekly therapy will be given at-home light units to continue therapy and achieve 1 year of treatment with no breaks. They will be monitored with video-based telemedicine.
“Long term, having a home unit should really improve patient access and compliance and hopefully effectiveness,” Dr. Kim said. Based on the phase 3 experience, “we think that continuous treatment will be well tolerated and that we may see greater responses.”
On Dec. 19, Soligenix announced that enrollment had begun in a phase 2a study of synthetic hypericin for treating patients with mild to moderate psoriasis.
Dr. Kim reported to JAMA Dermatology grants from Innate Pharma and Galderma; consulting/advisory fees from Almirall, Galderma, and Helsinn; and honoraria from Ology and UptoDate.
based on phase 3 findings published in JAMA Dermatology.
The treatment employs an ointment formulation of synthetic hypericin (HyBryte), a photosensitizer, that is preferentially absorbed into malignant cells and activated with visible light – rather than ultraviolet light – approximately 24 hours later. Investigators saw significant clinical responses in both patch and plaque type lesions and across races during the 24-week placebo-controlled, double-blinded, phase 3, randomized clinical trial.
“Traditional phototherapy, ultraviolet B phototherapy, has a limited depth of penetration, so patients with thicker plaque lesions don’t respond as well ... and UVB phototherapy typically is less effective in penetrating pigmented skin,” Ellen J. Kim, MD, lead author of the FLASH phase 3 trial, said in an interview.
Visible light in the yellow-red spectrum (500-650 nm) “penetrates deeper into the skin” and is nonmutagenic in vitro, so “theoretically it should have a much more favorable long-term safety profile,” said Dr. Kim, a dermatologist at the University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia.
Currently, she said, the risk of secondary malignancies inherent with UV PDT, including melanoma, is a deterrent for some patients, especially “patients with really fair skin and a history of skin cancer.”
Hypericin PDT also seems well suited for use with an at-home light unit. “In our field, it’s not about which therapy is [universally] better or best, but a matter of what works best for each patient at that moment in time, depending on the side-effect profile and other issues such as access,” Dr. Kim said. “It will be great to have another option for an incurable disease that requires chronic management.”
Mycosis fungoides (MF)/CTCL is considered an orphan disease, and the treatment has received orphan drug and fast track designations from the FDA, and orphan designation from the European Medicines Agency, according to a press release from its developer, Soligenix. The company is anticipating potential approval in the second half of 2023 and is targeting early 2024 for a U.S. launch, the statement said.
Phase 3 results
The pivotal trial involved 169 patients at 39 academic and community-based U.S. medical centers and consisted of several 6-week cycles of twice-weekly treatment punctuated by 2-week breaks. In cycle 1, patients were randomized 2:1 to receive hypericin or placebo treatment of three index lesions. Cycle 2 involved the crossover of placebo patients to active treatment of index lesions, and cycle 3 (optional) involved open-label treatment of all desired lesions (index and nonindex).
The trial defined the primary endpoint in phase 1 as 50% or greater improvement in the modified Composite Assessment of Index Lesion Severity score – a tool that’s endorsed by U.S. and international MF/CTCL specialty group consensus guidelines. For cycles 2 and 3, open-label response rates were secondary endpoints. Responses were assessed after 2-week rest periods to allow for treatment-induced skin reactions to subside.
After one cycle of treatment, topical hypericin PDT was more effective than placebo (an index lesion response rate of 16% vs. 4%; P =.04). The index lesion response rate with treatment increased to 40% after two cycles and 49% after three cycles. All were statistically significant changes.
Response rates were similar in patch and plaque-type lesions and regardless of age, sex, race, stage IA versus IB, time since diagnosis, and number of prior therapies. Adverse events were primarily mild application-site skin reactions. No serious drug-related adverse events occurred, Dr. Kim said, and “we had a low drop-out rate overall.”
Into the real world
The 24-week phase 3 trial duration is short, considering that “typically, phototherapy takes between 4 to 24 months [to achieve] full responses in CTCL,” Dr. Kim said in the interview.
So with real-world application, she said, “we’ll want to see where the overall response peaks with longer treatment, what the effects are of continuous treatment without any built-in breaks, and whether we will indeed see less skin cancer development in patients who are at higher risk of developing skin cancers from light treatment.”
Such questions will be explored as part of a new 4-year, 50-patient, open-label, multicenter study with the primary aim of investigating home-based hypericin PDT therapy in a supervised setting, said Dr. Kim, principal investigator of this study. Patients who are doing well after 6 weeks of twice-weekly therapy will be given at-home light units to continue therapy and achieve 1 year of treatment with no breaks. They will be monitored with video-based telemedicine.
“Long term, having a home unit should really improve patient access and compliance and hopefully effectiveness,” Dr. Kim said. Based on the phase 3 experience, “we think that continuous treatment will be well tolerated and that we may see greater responses.”
On Dec. 19, Soligenix announced that enrollment had begun in a phase 2a study of synthetic hypericin for treating patients with mild to moderate psoriasis.
Dr. Kim reported to JAMA Dermatology grants from Innate Pharma and Galderma; consulting/advisory fees from Almirall, Galderma, and Helsinn; and honoraria from Ology and UptoDate.
Have you heard of VEXAS syndrome?
Its name is an acronym: Vacuoles, E1 enzyme, X-linked, Autoinflammatory, Somatic. The prevalence of this syndrome is unknown, but it is not so rare. As it is an X-linked disease, men are predominantly affected.
First identification
The NIH team screened the exomes and genomes of 2,560 individuals. Of this group, 1,477 had been referred because of undiagnosed recurrent fevers, systemic inflammation, or both, and 1,083 were affected by atypical, unclassified disorders. The researchers identified 25 men with a somatic mutation in the ubiquitin-like modifier activating enzyme 1 (UBA1) gene, which is involved in the protein ubiquitylation system. This posttranslational modification has a pleiotropic function that likely explains the clinical heterogeneity seen in VEXAS patients: regulation of protein turnover, especially those involved in the cell cycle, cell death, and signal transduction. Ubiquitylation is also involved in nonproteolytic functions, such as assembly of multiprotein complexes, intracellular signaling, inflammatory signaling, and DNA repair.
Clinical presentation
The clinicobiological presentation of VEXAS syndrome is very heterogeneous. Typically, patients present with a systemic inflammatory disease with unexplained episodes of fever, involvement of the lungs, skin, blood vessels, and joints. Molecular diagnosis is made by the sequencing of UBA1.
Most patients present with the characteristic clinical signs of other inflammatory diseases, such as polyarteritis nodosa and recurrent polychondritis. But VEXAS patients are at high risk of developing hematologic conditions. Indeed, the following were seen among the 25 participants in the NIH study: macrocytic anemia (96%), venous thromboembolism (44%), myelodysplastic syndrome (24%), and multiple myeloma or monoclonal gammopathy of undetermined significance (20%).
In VEXAS patients, levels of serum inflammatory markers are increased. These markers include tumor necrosis factor, interleukin-8, interleukin-6, interferon-inducible protein-10, interferon-gamma, C-reactive protein. In addition, there is aberrant activation of innate immune-signaling pathways.
In a large-scale analysis of a multicenter case series of 116 French patients, researchers found that VEXAS syndrome primarily affected men. The disease was progressive, and onset occurred after age 50 years. These patients can be divided into three phenotypically distinct clusters on the basis of integration of clinical and biological data. In the 58 cases in which myelodysplastic syndrome was present, the mortality rates were higher. The researchers also reported that the UBA1 p.Met41L mutation was associated with a better prognosis.
Treatment data
VEXAS syndrome resists the classical therapeutic arsenal. Patients require high-dose glucocorticoids, and prognosis appears to be poor. The available treatment data are retrospective. Of the 25 participants in the NIH study, 40% died within 5 years from disease-related causes or complications related to treatment. Among the promising therapeutic avenues is the use of inhibitors of the Janus kinase pathway.
This article was translated from Univadis France. A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Its name is an acronym: Vacuoles, E1 enzyme, X-linked, Autoinflammatory, Somatic. The prevalence of this syndrome is unknown, but it is not so rare. As it is an X-linked disease, men are predominantly affected.
First identification
The NIH team screened the exomes and genomes of 2,560 individuals. Of this group, 1,477 had been referred because of undiagnosed recurrent fevers, systemic inflammation, or both, and 1,083 were affected by atypical, unclassified disorders. The researchers identified 25 men with a somatic mutation in the ubiquitin-like modifier activating enzyme 1 (UBA1) gene, which is involved in the protein ubiquitylation system. This posttranslational modification has a pleiotropic function that likely explains the clinical heterogeneity seen in VEXAS patients: regulation of protein turnover, especially those involved in the cell cycle, cell death, and signal transduction. Ubiquitylation is also involved in nonproteolytic functions, such as assembly of multiprotein complexes, intracellular signaling, inflammatory signaling, and DNA repair.
Clinical presentation
The clinicobiological presentation of VEXAS syndrome is very heterogeneous. Typically, patients present with a systemic inflammatory disease with unexplained episodes of fever, involvement of the lungs, skin, blood vessels, and joints. Molecular diagnosis is made by the sequencing of UBA1.
Most patients present with the characteristic clinical signs of other inflammatory diseases, such as polyarteritis nodosa and recurrent polychondritis. But VEXAS patients are at high risk of developing hematologic conditions. Indeed, the following were seen among the 25 participants in the NIH study: macrocytic anemia (96%), venous thromboembolism (44%), myelodysplastic syndrome (24%), and multiple myeloma or monoclonal gammopathy of undetermined significance (20%).
In VEXAS patients, levels of serum inflammatory markers are increased. These markers include tumor necrosis factor, interleukin-8, interleukin-6, interferon-inducible protein-10, interferon-gamma, C-reactive protein. In addition, there is aberrant activation of innate immune-signaling pathways.
In a large-scale analysis of a multicenter case series of 116 French patients, researchers found that VEXAS syndrome primarily affected men. The disease was progressive, and onset occurred after age 50 years. These patients can be divided into three phenotypically distinct clusters on the basis of integration of clinical and biological data. In the 58 cases in which myelodysplastic syndrome was present, the mortality rates were higher. The researchers also reported that the UBA1 p.Met41L mutation was associated with a better prognosis.
Treatment data
VEXAS syndrome resists the classical therapeutic arsenal. Patients require high-dose glucocorticoids, and prognosis appears to be poor. The available treatment data are retrospective. Of the 25 participants in the NIH study, 40% died within 5 years from disease-related causes or complications related to treatment. Among the promising therapeutic avenues is the use of inhibitors of the Janus kinase pathway.
This article was translated from Univadis France. A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Its name is an acronym: Vacuoles, E1 enzyme, X-linked, Autoinflammatory, Somatic. The prevalence of this syndrome is unknown, but it is not so rare. As it is an X-linked disease, men are predominantly affected.
First identification
The NIH team screened the exomes and genomes of 2,560 individuals. Of this group, 1,477 had been referred because of undiagnosed recurrent fevers, systemic inflammation, or both, and 1,083 were affected by atypical, unclassified disorders. The researchers identified 25 men with a somatic mutation in the ubiquitin-like modifier activating enzyme 1 (UBA1) gene, which is involved in the protein ubiquitylation system. This posttranslational modification has a pleiotropic function that likely explains the clinical heterogeneity seen in VEXAS patients: regulation of protein turnover, especially those involved in the cell cycle, cell death, and signal transduction. Ubiquitylation is also involved in nonproteolytic functions, such as assembly of multiprotein complexes, intracellular signaling, inflammatory signaling, and DNA repair.
Clinical presentation
The clinicobiological presentation of VEXAS syndrome is very heterogeneous. Typically, patients present with a systemic inflammatory disease with unexplained episodes of fever, involvement of the lungs, skin, blood vessels, and joints. Molecular diagnosis is made by the sequencing of UBA1.
Most patients present with the characteristic clinical signs of other inflammatory diseases, such as polyarteritis nodosa and recurrent polychondritis. But VEXAS patients are at high risk of developing hematologic conditions. Indeed, the following were seen among the 25 participants in the NIH study: macrocytic anemia (96%), venous thromboembolism (44%), myelodysplastic syndrome (24%), and multiple myeloma or monoclonal gammopathy of undetermined significance (20%).
In VEXAS patients, levels of serum inflammatory markers are increased. These markers include tumor necrosis factor, interleukin-8, interleukin-6, interferon-inducible protein-10, interferon-gamma, C-reactive protein. In addition, there is aberrant activation of innate immune-signaling pathways.
In a large-scale analysis of a multicenter case series of 116 French patients, researchers found that VEXAS syndrome primarily affected men. The disease was progressive, and onset occurred after age 50 years. These patients can be divided into three phenotypically distinct clusters on the basis of integration of clinical and biological data. In the 58 cases in which myelodysplastic syndrome was present, the mortality rates were higher. The researchers also reported that the UBA1 p.Met41L mutation was associated with a better prognosis.
Treatment data
VEXAS syndrome resists the classical therapeutic arsenal. Patients require high-dose glucocorticoids, and prognosis appears to be poor. The available treatment data are retrospective. Of the 25 participants in the NIH study, 40% died within 5 years from disease-related causes or complications related to treatment. Among the promising therapeutic avenues is the use of inhibitors of the Janus kinase pathway.
This article was translated from Univadis France. A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Applications for laser-assisted drug delivery on the horizon, expert says
For those who view fractional ablative laser–assisted drug delivery as a pie-in-the-sky procedure that will take years to work its way into routine clinical practice, think again.
According to Merete Haedersdal, MD, PhD, DMSc, .
“The groundwork has been established over a decade with more than 100 publications available on PubMed,” Dr. Haedersdal, professor of dermatology at the University of Copenhagen, said during a virtual course on laser and aesthetic skin therapy. “There is no doubt that by drilling tiny little holes or channels with ablative fractional lasers, we enhance drug delivery to the skin, and we also empower different topical treatment regimens. Also, laser-assisted drug delivery holds the potential to bring new innovations into established medicine.”
Many studies have demonstrated that clinicians can enhance drug uptake into the skin with the fractional 10,600 nm CO2 laser, the fractional 2,940 nm erbium:YAG laser, and the 1,927 nm thulium laser, but proper tuning of the devices is key. The lower the density, the better, Dr. Haedersdal said.
“Typically, we use 5% density or 5% coverage, sometimes 10%-15%, but don’t go higher in order to avoid the risk of having a systemic uptake,” she said during the meeting, which was sponsored by Harvard Medical School, Massachusetts General Hospital, and the Wellman Center for Photomedicine. “Also, the pulse energy for channel depth needs to be tailored to the specific dermatologic disease being treated,” she said, noting that for melasma, for example, “very low pulse energies” would be used, but they would be higher for treating thicker lesions, such as a hypertrophic scar.
Treatment with ablative fractional lasers enhances drug accumulation in the skin of any drug or substance applied to the skin, and clinical indications are expanding rapidly. Established indications include combining ablative fractional lasers and photodynamic therapy (PDT) for AKs and combining ablative fractional lasers and triamcinolone or 5-FU for scars. “Although we have a good body of evidence, particularly for AKs, it’s still an off-label use,” she emphasized.
Evolving indications include concomitant use of ablative fractional laser and vitamins and cosmeceuticals for rejuvenation; lidocaine for local anesthetics; tranexamic acid and hydroquinone for melasma; antifungals for onychomycosis; Botox for hyperhidrosis; minoxidil for alopecia; and betamethasone for vitiligo. A promising treatment for skin cancer “on the horizon,” she said, is the “combination of ablative fractional laser with PD1 inhibitors and chemotherapy.”
Data on AKs
Evidence supporting laser-assisted drug delivery for AKs comes from more than 10 randomized, controlled trials in the dermatology literature involving 400-plus immunocompetent and immunosuppressed patients. These trials have found ablative fractional laser–assisted PDT to be significantly more efficacious than PDT alone up to 12 months postoperatively and to foster lower rates of AK recurrence.
In a meta-analysis and systematic review, German researchers concluded that PDT combined with ablative laser treatment for AKs is more efficient but not more painful than either therapy alone. They recommended the combined regimen for patients with severe photodamage, field cancerization, and multiple AKs.
In 2020, an international consensus panel of experts, including Dr. Haedersdal, published recommendations regarding laser treatment of traumatic scars and contractures. The panel members determined that laser-assisted delivery of corticosteroids and antimetabolites was recommended for hypertrophic scars and cited triamcinolone acetonide suspension (TAC) as the most common corticosteroid used in combination with ablative fractional lasers. “It can be applied in concentrations of 40 mg/mL or less depending on the degree of hypertrophy,” they wrote.
In addition, they stated that 5-FU solution is “most commonly applied in a concentration of 50 mg/mL alone, or mixed with TAC in ratios of 9:1 or 3:1.”
According to the best available evidence, the clinical approach for hypertrophic scars supports combination treatment with ablative fractional laser and triamcinolone acetonide either alone or in combination with 5-FU. For atrophic scars, laser-assisted delivery of poly-L-lactic acid has been shown to be efficient. “Both of these treatments improve texture and thickness but also dyschromia and scar functionality,” said Dr. Haedersdal, who is also a visiting scientist at the Wellman Center for Photomedicine, Boston.
Commenting on patient safety with laser-assisted drug delivery, “the combination of lasers and topicals can be a powerful cocktail,” she said. “You can expect intensified local skin reactions. When treating larger areas, consider the risk of systemic absorption and the risk of potential toxicity. There is also the potential for infection with pathogens such as Staphylococcus aureus. The take-home message here is that you should only use the type and amount of drug no higher than administered during intradermal injection.”
Dr. Haedersdal disclosed that she has received equipment from Cherry Imaging, Cynosure-Hologic, MiraDry, and PerfAction Technologies. She has also received research grants from Leo Pharma, Lutronic, Mirai Medical, Novoxel, and Venus Concept.
For those who view fractional ablative laser–assisted drug delivery as a pie-in-the-sky procedure that will take years to work its way into routine clinical practice, think again.
According to Merete Haedersdal, MD, PhD, DMSc, .
“The groundwork has been established over a decade with more than 100 publications available on PubMed,” Dr. Haedersdal, professor of dermatology at the University of Copenhagen, said during a virtual course on laser and aesthetic skin therapy. “There is no doubt that by drilling tiny little holes or channels with ablative fractional lasers, we enhance drug delivery to the skin, and we also empower different topical treatment regimens. Also, laser-assisted drug delivery holds the potential to bring new innovations into established medicine.”
Many studies have demonstrated that clinicians can enhance drug uptake into the skin with the fractional 10,600 nm CO2 laser, the fractional 2,940 nm erbium:YAG laser, and the 1,927 nm thulium laser, but proper tuning of the devices is key. The lower the density, the better, Dr. Haedersdal said.
“Typically, we use 5% density or 5% coverage, sometimes 10%-15%, but don’t go higher in order to avoid the risk of having a systemic uptake,” she said during the meeting, which was sponsored by Harvard Medical School, Massachusetts General Hospital, and the Wellman Center for Photomedicine. “Also, the pulse energy for channel depth needs to be tailored to the specific dermatologic disease being treated,” she said, noting that for melasma, for example, “very low pulse energies” would be used, but they would be higher for treating thicker lesions, such as a hypertrophic scar.
Treatment with ablative fractional lasers enhances drug accumulation in the skin of any drug or substance applied to the skin, and clinical indications are expanding rapidly. Established indications include combining ablative fractional lasers and photodynamic therapy (PDT) for AKs and combining ablative fractional lasers and triamcinolone or 5-FU for scars. “Although we have a good body of evidence, particularly for AKs, it’s still an off-label use,” she emphasized.
Evolving indications include concomitant use of ablative fractional laser and vitamins and cosmeceuticals for rejuvenation; lidocaine for local anesthetics; tranexamic acid and hydroquinone for melasma; antifungals for onychomycosis; Botox for hyperhidrosis; minoxidil for alopecia; and betamethasone for vitiligo. A promising treatment for skin cancer “on the horizon,” she said, is the “combination of ablative fractional laser with PD1 inhibitors and chemotherapy.”
Data on AKs
Evidence supporting laser-assisted drug delivery for AKs comes from more than 10 randomized, controlled trials in the dermatology literature involving 400-plus immunocompetent and immunosuppressed patients. These trials have found ablative fractional laser–assisted PDT to be significantly more efficacious than PDT alone up to 12 months postoperatively and to foster lower rates of AK recurrence.
In a meta-analysis and systematic review, German researchers concluded that PDT combined with ablative laser treatment for AKs is more efficient but not more painful than either therapy alone. They recommended the combined regimen for patients with severe photodamage, field cancerization, and multiple AKs.
In 2020, an international consensus panel of experts, including Dr. Haedersdal, published recommendations regarding laser treatment of traumatic scars and contractures. The panel members determined that laser-assisted delivery of corticosteroids and antimetabolites was recommended for hypertrophic scars and cited triamcinolone acetonide suspension (TAC) as the most common corticosteroid used in combination with ablative fractional lasers. “It can be applied in concentrations of 40 mg/mL or less depending on the degree of hypertrophy,” they wrote.
In addition, they stated that 5-FU solution is “most commonly applied in a concentration of 50 mg/mL alone, or mixed with TAC in ratios of 9:1 or 3:1.”
According to the best available evidence, the clinical approach for hypertrophic scars supports combination treatment with ablative fractional laser and triamcinolone acetonide either alone or in combination with 5-FU. For atrophic scars, laser-assisted delivery of poly-L-lactic acid has been shown to be efficient. “Both of these treatments improve texture and thickness but also dyschromia and scar functionality,” said Dr. Haedersdal, who is also a visiting scientist at the Wellman Center for Photomedicine, Boston.
Commenting on patient safety with laser-assisted drug delivery, “the combination of lasers and topicals can be a powerful cocktail,” she said. “You can expect intensified local skin reactions. When treating larger areas, consider the risk of systemic absorption and the risk of potential toxicity. There is also the potential for infection with pathogens such as Staphylococcus aureus. The take-home message here is that you should only use the type and amount of drug no higher than administered during intradermal injection.”
Dr. Haedersdal disclosed that she has received equipment from Cherry Imaging, Cynosure-Hologic, MiraDry, and PerfAction Technologies. She has also received research grants from Leo Pharma, Lutronic, Mirai Medical, Novoxel, and Venus Concept.
For those who view fractional ablative laser–assisted drug delivery as a pie-in-the-sky procedure that will take years to work its way into routine clinical practice, think again.
According to Merete Haedersdal, MD, PhD, DMSc, .
“The groundwork has been established over a decade with more than 100 publications available on PubMed,” Dr. Haedersdal, professor of dermatology at the University of Copenhagen, said during a virtual course on laser and aesthetic skin therapy. “There is no doubt that by drilling tiny little holes or channels with ablative fractional lasers, we enhance drug delivery to the skin, and we also empower different topical treatment regimens. Also, laser-assisted drug delivery holds the potential to bring new innovations into established medicine.”
Many studies have demonstrated that clinicians can enhance drug uptake into the skin with the fractional 10,600 nm CO2 laser, the fractional 2,940 nm erbium:YAG laser, and the 1,927 nm thulium laser, but proper tuning of the devices is key. The lower the density, the better, Dr. Haedersdal said.
“Typically, we use 5% density or 5% coverage, sometimes 10%-15%, but don’t go higher in order to avoid the risk of having a systemic uptake,” she said during the meeting, which was sponsored by Harvard Medical School, Massachusetts General Hospital, and the Wellman Center for Photomedicine. “Also, the pulse energy for channel depth needs to be tailored to the specific dermatologic disease being treated,” she said, noting that for melasma, for example, “very low pulse energies” would be used, but they would be higher for treating thicker lesions, such as a hypertrophic scar.
Treatment with ablative fractional lasers enhances drug accumulation in the skin of any drug or substance applied to the skin, and clinical indications are expanding rapidly. Established indications include combining ablative fractional lasers and photodynamic therapy (PDT) for AKs and combining ablative fractional lasers and triamcinolone or 5-FU for scars. “Although we have a good body of evidence, particularly for AKs, it’s still an off-label use,” she emphasized.
Evolving indications include concomitant use of ablative fractional laser and vitamins and cosmeceuticals for rejuvenation; lidocaine for local anesthetics; tranexamic acid and hydroquinone for melasma; antifungals for onychomycosis; Botox for hyperhidrosis; minoxidil for alopecia; and betamethasone for vitiligo. A promising treatment for skin cancer “on the horizon,” she said, is the “combination of ablative fractional laser with PD1 inhibitors and chemotherapy.”
Data on AKs
Evidence supporting laser-assisted drug delivery for AKs comes from more than 10 randomized, controlled trials in the dermatology literature involving 400-plus immunocompetent and immunosuppressed patients. These trials have found ablative fractional laser–assisted PDT to be significantly more efficacious than PDT alone up to 12 months postoperatively and to foster lower rates of AK recurrence.
In a meta-analysis and systematic review, German researchers concluded that PDT combined with ablative laser treatment for AKs is more efficient but not more painful than either therapy alone. They recommended the combined regimen for patients with severe photodamage, field cancerization, and multiple AKs.
In 2020, an international consensus panel of experts, including Dr. Haedersdal, published recommendations regarding laser treatment of traumatic scars and contractures. The panel members determined that laser-assisted delivery of corticosteroids and antimetabolites was recommended for hypertrophic scars and cited triamcinolone acetonide suspension (TAC) as the most common corticosteroid used in combination with ablative fractional lasers. “It can be applied in concentrations of 40 mg/mL or less depending on the degree of hypertrophy,” they wrote.
In addition, they stated that 5-FU solution is “most commonly applied in a concentration of 50 mg/mL alone, or mixed with TAC in ratios of 9:1 or 3:1.”
According to the best available evidence, the clinical approach for hypertrophic scars supports combination treatment with ablative fractional laser and triamcinolone acetonide either alone or in combination with 5-FU. For atrophic scars, laser-assisted delivery of poly-L-lactic acid has been shown to be efficient. “Both of these treatments improve texture and thickness but also dyschromia and scar functionality,” said Dr. Haedersdal, who is also a visiting scientist at the Wellman Center for Photomedicine, Boston.
Commenting on patient safety with laser-assisted drug delivery, “the combination of lasers and topicals can be a powerful cocktail,” she said. “You can expect intensified local skin reactions. When treating larger areas, consider the risk of systemic absorption and the risk of potential toxicity. There is also the potential for infection with pathogens such as Staphylococcus aureus. The take-home message here is that you should only use the type and amount of drug no higher than administered during intradermal injection.”
Dr. Haedersdal disclosed that she has received equipment from Cherry Imaging, Cynosure-Hologic, MiraDry, and PerfAction Technologies. She has also received research grants from Leo Pharma, Lutronic, Mirai Medical, Novoxel, and Venus Concept.
FROM A LASER & AESTHETIC SKIN THERAPY COURSE
Consider quality of life, comorbidities in hidradenitis suppurativa
LAS VEGAS – , Robert G. Micheletti, MD, said in a presentation at MedscapeLive’s annual Las Vegas Dermatology Seminar.
For patients with HS, “the quality-of-life impact is profound, greater than any other systematically studied dermatologic condition,” said Dr. Micheletti, associate professor of dermatology at the Hospital of the University of Pennsylavnia, and chief of hospital dermatology, and chief of dermatology at Pennsylvania Hospital, Philadelphia.
Two key aspects of quality of life that affect HS patients are sexual health and overall pain, he said. The female-to-male ratio of HS is approximately 3:1, and data show that approximately 40% of female HS patients experience fertility issues and have unaddressed questions about HS and pregnancy, said Dr. Micheletti. Additionally, data from a systematic review showed that 50%-60% of patients with HS reported sexual dysfunction. Impaired sexual function is also associated with both overall impaired quality of life ratings and the presence of mood disorders, he noted.
Pain also has a significant impact on quality of life for HS patients. When these patients present in an emergency department, 70% report severe pain, and approximately 60% receive opioids, said Dr. Micheletti.
Data from a 2021 study showed that HS patients are significantly more likely to receive opioids compared with controls, and also more likely to be diagnosed with opioid use disorder than controls, especially if they are seen by nondermatologists, he noted.
For acute pain, Dr. Micheletti recommended starting with acetaminophen 500 mg every 4 to 6 hours as needed, and topical nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs). “It still makes sense to do topical care,” said Dr. Micheletti, but he added that he also prescribes medications for anxiety for these patients.
Patients with increased pain severity or refractory disease may benefit from systemic NSAIDs, or intralesional triamcinolone, he noted. Incision and draining of abscesses may provide temporary symptomatic relief, but keep in mind that lesions will recur, he noted.
For the most severe cases, Dr. Micheletti advised adding tramadol as a first-line opioid, or another short-acting opioid for breakthrough pain.
To manage patients with HS who have chronic pain, Dr. Micheletti recommended starting with HS disease–directed therapy, but also screening for pain severity and psychological comorbidities.
His strategies in these cases include nonpharmacological pain management in the form of physical therapy, wound care, and behavioral health. His algorithm for nociceptive pain is NSAIDs with or without acetaminophen; duloxetine or nortriptyline are other options. For neuropathic pain, gabapentin and/or duloxetine are top choices, but pregabalin, venlafaxine, and nortriptyline are on the list as well.
Topical NSAIDs or topical lidocaine may serve as add-ons to systemic therapy in more severe cases, or as first-line therapy for milder chronic pain, Dr. Micheletti noted. Patients who have failed treatment with at least two pharmacologic agents, suffer medically refractory HS with debilitating pain, or use opioids on an ongoing basis should be referred to a pain management specialist, he said.
Don’t forget lifestyle
Although data on the impact of diet on patients with HS are limited, “we know anecdotally that dairy and refined carbohydrates are associated with exacerbations,” said Dr. Micheletti.
In addition, many patients use complementary medicine “and they aren’t always telling us,” he emphasized. Smoking is prevalent among patients with HS, and is a risk factor for the disease in general, and for more severe and refractory disease, he added. Consequently, screening for tobacco smoking is recommended for patients with HS not only because of the impact on disease, but because it is a potentially modifiable cardiovascular risk factor, he explained.
Consider comorbidities
Cardiovascular disease is among several comorbidities associated with HS, said Dr. Micheletti. HS foundations in the United States and Canada recently published evidence-based recommendations for comorbidity screening. The recommendations included screening for 19 specific comorbidities: acne, dissecting cellulitis, pilonidal disease, pyoderma gangrenosum, depression, anxiety, suicide, smoking, substance abuse, polycystic ovary syndrome, obesity, dyslipidemia, diabetes mellitus, metabolic syndrome, hypertension, cardiovascular disease, inflammatory bowel disease, spondyloarthritis, and sexual dysfunction.
Dr. Micheletti highlighted cardiovascular comorbidities, and noted the association between HS and modifiable cardiovascular risk factors: smoking, obesity, diabetes mellitus, and dyslipidemia. “HS is also independently associated with cardiovascular disease leading to myocardial infarction, stroke, cardiovascular-associated death, and all-cause mortality compared to controls,” he said. Studies show an incidence rate ratio of 1.53 for major adverse cardiovascular events in patients with HS compared with controls, with the highest relative risk among those aged 18-29 years, he added.
Medical management
Depending on the patient, medical management of HS may involve antibiotics, hormonal agents, and biologics, said Dr. Micheletti. Some of the most commonly used antibiotic regimens for HS are those recommended in treatment guidelines, including doxycycline and a clindamycin/rifampin combination, he said. However, the use of trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole or ciprofloxacin has been associated with increased antibiotic resistance and is not supported by available evidence, he noted.
Hormonal therapies may help some women with HS, said Dr. Micheletti. Options include spironolactone, metformin, or estrogen-containing hormonal contraceptives, he said.
When it comes to biologics, only 33% of HS patients meet criteria for their use (Hurley stage II or III, moderate or severe HS), he noted. However, research suggests “a huge gap” in the use of anti-TNF therapy even among patients for whom it is recommended, he said.
Of the TNF-alpha inhibitors, data on adalimumab, which is FDA-approved for HS, are the most recent. Adalimumab “is our gold standard biologic and our gateway biologic, for HS at this time,” Dr. Micheletti said.
However, those who respond to adalimumab “can continue to do better, but they can wax and wane and flare,” he cautioned. Infliximab, while not approved for HS, has been studied in patients with HS and is prescribed by some providers. Although no comparative studies have been done for infliximab versus adalimumab, “anecdotally, response to infliximab tends to be better, and it is the most effective biologic in common use for severe HS,” he noted.
Dr. Micheletti’s top treatment recommendations for using biologics start with considering biosimilars. Most patients on biosimilars do fine, but some patients who previously responded to infliximab will unpredictably lose efficacy or have reactions when switched to a biosimilar, he said.
Patients on biologics also may experience waning efficacy in the wake of an immune response stimulated by foreign antibodies, said Dr. Micheletti. “Anti-drug antibody formation is more likely to occur when treatment is interrupted,” he noted. Minimize the risk of antibody formation by paying attention to adherence issues and dosing frequency, he advised.
If patients fail both adalimumab and infliximab, Dr. Micheletti tells them not to lose hope, and that treatment is a trial-and-error process that may involve more than one therapy. Other biologics in active use for HS include ustekinumab, anakinra, secukinumab, brodalumab, golimumab, and JAK inhibitors, any of which might be effective in any given patient, he said.
Surgical solutions
For HS patients with chronic, recurring inflammation and drainage associated with a sinus tract, surgical deroofing may the best treatment option, Dr. Micheletti said. “Deroofing involves the use of a probe to trace the extent of the subcutaneous tract, followed by incision and removal of the tract ‘roof,’ ’’ he explained. The deroofing procedure involves local anesthesia and has a low morbidity rate, as well as a low recurrence rate and high levels of patient satisfaction, he said.
“The acute role for surgery is to remove active foci of inflammation and relieve pain,” which is achieved more effectively with deroofing, said Dr. Micheletti. By contrast, incision and drainage is associated with an almost 100% recurrence rate, he added.
When planning elective surgery for HS, Dr. Micheletti noted that holding infliximab for less than 4 weeks does not affect postoperative infection rates in patients with rheumatoid arthritis, and a recent randomized, controlled trial showed that adalimumab can be continued safely through HS surgeries.
In fact, “continuing TNF inhibitors through elective surgery does not increase infection risk and results in better disease control,” and dermatologists should work with surgery to balance infection and disease flare concerns in HS patients, he said.
Dr. Micheletti disclosed serving as a consultant or advisor for Adaptimmune and Vertex, and research funding from Amgen and Cabaletta Bio. MedscapeLive and this news organization are owned by the same parent company.
LAS VEGAS – , Robert G. Micheletti, MD, said in a presentation at MedscapeLive’s annual Las Vegas Dermatology Seminar.
For patients with HS, “the quality-of-life impact is profound, greater than any other systematically studied dermatologic condition,” said Dr. Micheletti, associate professor of dermatology at the Hospital of the University of Pennsylavnia, and chief of hospital dermatology, and chief of dermatology at Pennsylvania Hospital, Philadelphia.
Two key aspects of quality of life that affect HS patients are sexual health and overall pain, he said. The female-to-male ratio of HS is approximately 3:1, and data show that approximately 40% of female HS patients experience fertility issues and have unaddressed questions about HS and pregnancy, said Dr. Micheletti. Additionally, data from a systematic review showed that 50%-60% of patients with HS reported sexual dysfunction. Impaired sexual function is also associated with both overall impaired quality of life ratings and the presence of mood disorders, he noted.
Pain also has a significant impact on quality of life for HS patients. When these patients present in an emergency department, 70% report severe pain, and approximately 60% receive opioids, said Dr. Micheletti.
Data from a 2021 study showed that HS patients are significantly more likely to receive opioids compared with controls, and also more likely to be diagnosed with opioid use disorder than controls, especially if they are seen by nondermatologists, he noted.
For acute pain, Dr. Micheletti recommended starting with acetaminophen 500 mg every 4 to 6 hours as needed, and topical nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs). “It still makes sense to do topical care,” said Dr. Micheletti, but he added that he also prescribes medications for anxiety for these patients.
Patients with increased pain severity or refractory disease may benefit from systemic NSAIDs, or intralesional triamcinolone, he noted. Incision and draining of abscesses may provide temporary symptomatic relief, but keep in mind that lesions will recur, he noted.
For the most severe cases, Dr. Micheletti advised adding tramadol as a first-line opioid, or another short-acting opioid for breakthrough pain.
To manage patients with HS who have chronic pain, Dr. Micheletti recommended starting with HS disease–directed therapy, but also screening for pain severity and psychological comorbidities.
His strategies in these cases include nonpharmacological pain management in the form of physical therapy, wound care, and behavioral health. His algorithm for nociceptive pain is NSAIDs with or without acetaminophen; duloxetine or nortriptyline are other options. For neuropathic pain, gabapentin and/or duloxetine are top choices, but pregabalin, venlafaxine, and nortriptyline are on the list as well.
Topical NSAIDs or topical lidocaine may serve as add-ons to systemic therapy in more severe cases, or as first-line therapy for milder chronic pain, Dr. Micheletti noted. Patients who have failed treatment with at least two pharmacologic agents, suffer medically refractory HS with debilitating pain, or use opioids on an ongoing basis should be referred to a pain management specialist, he said.
Don’t forget lifestyle
Although data on the impact of diet on patients with HS are limited, “we know anecdotally that dairy and refined carbohydrates are associated with exacerbations,” said Dr. Micheletti.
In addition, many patients use complementary medicine “and they aren’t always telling us,” he emphasized. Smoking is prevalent among patients with HS, and is a risk factor for the disease in general, and for more severe and refractory disease, he added. Consequently, screening for tobacco smoking is recommended for patients with HS not only because of the impact on disease, but because it is a potentially modifiable cardiovascular risk factor, he explained.
Consider comorbidities
Cardiovascular disease is among several comorbidities associated with HS, said Dr. Micheletti. HS foundations in the United States and Canada recently published evidence-based recommendations for comorbidity screening. The recommendations included screening for 19 specific comorbidities: acne, dissecting cellulitis, pilonidal disease, pyoderma gangrenosum, depression, anxiety, suicide, smoking, substance abuse, polycystic ovary syndrome, obesity, dyslipidemia, diabetes mellitus, metabolic syndrome, hypertension, cardiovascular disease, inflammatory bowel disease, spondyloarthritis, and sexual dysfunction.
Dr. Micheletti highlighted cardiovascular comorbidities, and noted the association between HS and modifiable cardiovascular risk factors: smoking, obesity, diabetes mellitus, and dyslipidemia. “HS is also independently associated with cardiovascular disease leading to myocardial infarction, stroke, cardiovascular-associated death, and all-cause mortality compared to controls,” he said. Studies show an incidence rate ratio of 1.53 for major adverse cardiovascular events in patients with HS compared with controls, with the highest relative risk among those aged 18-29 years, he added.
Medical management
Depending on the patient, medical management of HS may involve antibiotics, hormonal agents, and biologics, said Dr. Micheletti. Some of the most commonly used antibiotic regimens for HS are those recommended in treatment guidelines, including doxycycline and a clindamycin/rifampin combination, he said. However, the use of trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole or ciprofloxacin has been associated with increased antibiotic resistance and is not supported by available evidence, he noted.
Hormonal therapies may help some women with HS, said Dr. Micheletti. Options include spironolactone, metformin, or estrogen-containing hormonal contraceptives, he said.
When it comes to biologics, only 33% of HS patients meet criteria for their use (Hurley stage II or III, moderate or severe HS), he noted. However, research suggests “a huge gap” in the use of anti-TNF therapy even among patients for whom it is recommended, he said.
Of the TNF-alpha inhibitors, data on adalimumab, which is FDA-approved for HS, are the most recent. Adalimumab “is our gold standard biologic and our gateway biologic, for HS at this time,” Dr. Micheletti said.
However, those who respond to adalimumab “can continue to do better, but they can wax and wane and flare,” he cautioned. Infliximab, while not approved for HS, has been studied in patients with HS and is prescribed by some providers. Although no comparative studies have been done for infliximab versus adalimumab, “anecdotally, response to infliximab tends to be better, and it is the most effective biologic in common use for severe HS,” he noted.
Dr. Micheletti’s top treatment recommendations for using biologics start with considering biosimilars. Most patients on biosimilars do fine, but some patients who previously responded to infliximab will unpredictably lose efficacy or have reactions when switched to a biosimilar, he said.
Patients on biologics also may experience waning efficacy in the wake of an immune response stimulated by foreign antibodies, said Dr. Micheletti. “Anti-drug antibody formation is more likely to occur when treatment is interrupted,” he noted. Minimize the risk of antibody formation by paying attention to adherence issues and dosing frequency, he advised.
If patients fail both adalimumab and infliximab, Dr. Micheletti tells them not to lose hope, and that treatment is a trial-and-error process that may involve more than one therapy. Other biologics in active use for HS include ustekinumab, anakinra, secukinumab, brodalumab, golimumab, and JAK inhibitors, any of which might be effective in any given patient, he said.
Surgical solutions
For HS patients with chronic, recurring inflammation and drainage associated with a sinus tract, surgical deroofing may the best treatment option, Dr. Micheletti said. “Deroofing involves the use of a probe to trace the extent of the subcutaneous tract, followed by incision and removal of the tract ‘roof,’ ’’ he explained. The deroofing procedure involves local anesthesia and has a low morbidity rate, as well as a low recurrence rate and high levels of patient satisfaction, he said.
“The acute role for surgery is to remove active foci of inflammation and relieve pain,” which is achieved more effectively with deroofing, said Dr. Micheletti. By contrast, incision and drainage is associated with an almost 100% recurrence rate, he added.
When planning elective surgery for HS, Dr. Micheletti noted that holding infliximab for less than 4 weeks does not affect postoperative infection rates in patients with rheumatoid arthritis, and a recent randomized, controlled trial showed that adalimumab can be continued safely through HS surgeries.
In fact, “continuing TNF inhibitors through elective surgery does not increase infection risk and results in better disease control,” and dermatologists should work with surgery to balance infection and disease flare concerns in HS patients, he said.
Dr. Micheletti disclosed serving as a consultant or advisor for Adaptimmune and Vertex, and research funding from Amgen and Cabaletta Bio. MedscapeLive and this news organization are owned by the same parent company.
LAS VEGAS – , Robert G. Micheletti, MD, said in a presentation at MedscapeLive’s annual Las Vegas Dermatology Seminar.
For patients with HS, “the quality-of-life impact is profound, greater than any other systematically studied dermatologic condition,” said Dr. Micheletti, associate professor of dermatology at the Hospital of the University of Pennsylavnia, and chief of hospital dermatology, and chief of dermatology at Pennsylvania Hospital, Philadelphia.
Two key aspects of quality of life that affect HS patients are sexual health and overall pain, he said. The female-to-male ratio of HS is approximately 3:1, and data show that approximately 40% of female HS patients experience fertility issues and have unaddressed questions about HS and pregnancy, said Dr. Micheletti. Additionally, data from a systematic review showed that 50%-60% of patients with HS reported sexual dysfunction. Impaired sexual function is also associated with both overall impaired quality of life ratings and the presence of mood disorders, he noted.
Pain also has a significant impact on quality of life for HS patients. When these patients present in an emergency department, 70% report severe pain, and approximately 60% receive opioids, said Dr. Micheletti.
Data from a 2021 study showed that HS patients are significantly more likely to receive opioids compared with controls, and also more likely to be diagnosed with opioid use disorder than controls, especially if they are seen by nondermatologists, he noted.
For acute pain, Dr. Micheletti recommended starting with acetaminophen 500 mg every 4 to 6 hours as needed, and topical nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs). “It still makes sense to do topical care,” said Dr. Micheletti, but he added that he also prescribes medications for anxiety for these patients.
Patients with increased pain severity or refractory disease may benefit from systemic NSAIDs, or intralesional triamcinolone, he noted. Incision and draining of abscesses may provide temporary symptomatic relief, but keep in mind that lesions will recur, he noted.
For the most severe cases, Dr. Micheletti advised adding tramadol as a first-line opioid, or another short-acting opioid for breakthrough pain.
To manage patients with HS who have chronic pain, Dr. Micheletti recommended starting with HS disease–directed therapy, but also screening for pain severity and psychological comorbidities.
His strategies in these cases include nonpharmacological pain management in the form of physical therapy, wound care, and behavioral health. His algorithm for nociceptive pain is NSAIDs with or without acetaminophen; duloxetine or nortriptyline are other options. For neuropathic pain, gabapentin and/or duloxetine are top choices, but pregabalin, venlafaxine, and nortriptyline are on the list as well.
Topical NSAIDs or topical lidocaine may serve as add-ons to systemic therapy in more severe cases, or as first-line therapy for milder chronic pain, Dr. Micheletti noted. Patients who have failed treatment with at least two pharmacologic agents, suffer medically refractory HS with debilitating pain, or use opioids on an ongoing basis should be referred to a pain management specialist, he said.
Don’t forget lifestyle
Although data on the impact of diet on patients with HS are limited, “we know anecdotally that dairy and refined carbohydrates are associated with exacerbations,” said Dr. Micheletti.
In addition, many patients use complementary medicine “and they aren’t always telling us,” he emphasized. Smoking is prevalent among patients with HS, and is a risk factor for the disease in general, and for more severe and refractory disease, he added. Consequently, screening for tobacco smoking is recommended for patients with HS not only because of the impact on disease, but because it is a potentially modifiable cardiovascular risk factor, he explained.
Consider comorbidities
Cardiovascular disease is among several comorbidities associated with HS, said Dr. Micheletti. HS foundations in the United States and Canada recently published evidence-based recommendations for comorbidity screening. The recommendations included screening for 19 specific comorbidities: acne, dissecting cellulitis, pilonidal disease, pyoderma gangrenosum, depression, anxiety, suicide, smoking, substance abuse, polycystic ovary syndrome, obesity, dyslipidemia, diabetes mellitus, metabolic syndrome, hypertension, cardiovascular disease, inflammatory bowel disease, spondyloarthritis, and sexual dysfunction.
Dr. Micheletti highlighted cardiovascular comorbidities, and noted the association between HS and modifiable cardiovascular risk factors: smoking, obesity, diabetes mellitus, and dyslipidemia. “HS is also independently associated with cardiovascular disease leading to myocardial infarction, stroke, cardiovascular-associated death, and all-cause mortality compared to controls,” he said. Studies show an incidence rate ratio of 1.53 for major adverse cardiovascular events in patients with HS compared with controls, with the highest relative risk among those aged 18-29 years, he added.
Medical management
Depending on the patient, medical management of HS may involve antibiotics, hormonal agents, and biologics, said Dr. Micheletti. Some of the most commonly used antibiotic regimens for HS are those recommended in treatment guidelines, including doxycycline and a clindamycin/rifampin combination, he said. However, the use of trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole or ciprofloxacin has been associated with increased antibiotic resistance and is not supported by available evidence, he noted.
Hormonal therapies may help some women with HS, said Dr. Micheletti. Options include spironolactone, metformin, or estrogen-containing hormonal contraceptives, he said.
When it comes to biologics, only 33% of HS patients meet criteria for their use (Hurley stage II or III, moderate or severe HS), he noted. However, research suggests “a huge gap” in the use of anti-TNF therapy even among patients for whom it is recommended, he said.
Of the TNF-alpha inhibitors, data on adalimumab, which is FDA-approved for HS, are the most recent. Adalimumab “is our gold standard biologic and our gateway biologic, for HS at this time,” Dr. Micheletti said.
However, those who respond to adalimumab “can continue to do better, but they can wax and wane and flare,” he cautioned. Infliximab, while not approved for HS, has been studied in patients with HS and is prescribed by some providers. Although no comparative studies have been done for infliximab versus adalimumab, “anecdotally, response to infliximab tends to be better, and it is the most effective biologic in common use for severe HS,” he noted.
Dr. Micheletti’s top treatment recommendations for using biologics start with considering biosimilars. Most patients on biosimilars do fine, but some patients who previously responded to infliximab will unpredictably lose efficacy or have reactions when switched to a biosimilar, he said.
Patients on biologics also may experience waning efficacy in the wake of an immune response stimulated by foreign antibodies, said Dr. Micheletti. “Anti-drug antibody formation is more likely to occur when treatment is interrupted,” he noted. Minimize the risk of antibody formation by paying attention to adherence issues and dosing frequency, he advised.
If patients fail both adalimumab and infliximab, Dr. Micheletti tells them not to lose hope, and that treatment is a trial-and-error process that may involve more than one therapy. Other biologics in active use for HS include ustekinumab, anakinra, secukinumab, brodalumab, golimumab, and JAK inhibitors, any of which might be effective in any given patient, he said.
Surgical solutions
For HS patients with chronic, recurring inflammation and drainage associated with a sinus tract, surgical deroofing may the best treatment option, Dr. Micheletti said. “Deroofing involves the use of a probe to trace the extent of the subcutaneous tract, followed by incision and removal of the tract ‘roof,’ ’’ he explained. The deroofing procedure involves local anesthesia and has a low morbidity rate, as well as a low recurrence rate and high levels of patient satisfaction, he said.
“The acute role for surgery is to remove active foci of inflammation and relieve pain,” which is achieved more effectively with deroofing, said Dr. Micheletti. By contrast, incision and drainage is associated with an almost 100% recurrence rate, he added.
When planning elective surgery for HS, Dr. Micheletti noted that holding infliximab for less than 4 weeks does not affect postoperative infection rates in patients with rheumatoid arthritis, and a recent randomized, controlled trial showed that adalimumab can be continued safely through HS surgeries.
In fact, “continuing TNF inhibitors through elective surgery does not increase infection risk and results in better disease control,” and dermatologists should work with surgery to balance infection and disease flare concerns in HS patients, he said.
Dr. Micheletti disclosed serving as a consultant or advisor for Adaptimmune and Vertex, and research funding from Amgen and Cabaletta Bio. MedscapeLive and this news organization are owned by the same parent company.
AT INNOVATIONS IN DERMATOLOGY
Pandemic caused treatment delay for half of patients with CTCL, study finds
showed. However, among patients with CTCL diagnosed with COVID-19 during that time, no cases were acquired from outpatient visits.
“Delays in therapy for patients with cutaneous lymphomas should likely be avoided,” two of the study authors, Larisa J. Geskin, MD, of the department of dermatology at Columbia University Irving Medical Center, New York, and Bradley D. Kwinta, a medical student at Columbia University, told this news organization in a combined response via email.
“Continuing treatment and maintenance therapy appears critical to avoiding disease progression, highlighting the importance of maintenance therapy in CTCL,” they said. “These patients can be safely treated according to established treatment protocols while practicing physical distancing and using personal protective equipment without significantly increasing their risk of COVID-19 infection.”
The United States Cutaneous Lymphoma Consortium and the European Organization for Research and Treatment of Cancer developed emergency guidelines for the management of patients with cutaneous lymphomas during the pandemic to ensure patient safety, and the International Society for Cutaneous Lymphomas created an International Cutaneous Lymphomas Pandemic Section to collect data to assess the impact of these guidelines.
“Using this data, we can determine if these measures were effective in preventing COVID-19 infection, what the impact was of maintenance therapy, and how delays in treatment affected disease outcomes in CTCL patients,” the authors and their colleagues wrote in the study, which was published in the Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology.
They retrospectively analyzed data from the electronic medical records of 149 patients with CTCL who were being managed at one of nine international academic medical centers in seven countries from March to October 2020. Slightly more than half (56%) were male, 70% were White, 18% were Black, 52% had stage IA-IIA disease, and 19% acquired COVID-19 during the study period.
Of the 149 patients, 79 (53%) experienced a mean treatment delay of 3.2 months (range, 10 days to 10 months). After adjusting for age, race, biological sex, COVID-19 status, and disease stage, treatment delay was associated with a significant risk of disease relapse or progression across all stages (odds ratio, 5.00; P < .001). Specifically, for each additional month that a patient experienced treatment delay, the odds of disease progression increased by 37% (OR, 1.37; P < .001).
A total of 28 patients with CTCL (19%) were diagnosed with COVID-19, but none were acquired from outpatient office visits. Patients who contracted COVID-19 did not have a statistically significant increase in odds of disease progression, compared with COVID-negative patients (OR, 0.41; P = .07).
According to Dr. Geskin, who is also director of the Comprehensive Skin Cancer Center in the division of cutaneous oncology in the department of dermatology at Columbia, and Mr. Kwinta, no clinical trials exist to inform maintenance protocols in patients with cutaneous lymphomas. “There are also no randomized and controlled observational studies that demonstrate the impact that therapy delay may have on disease outcomes,” they said in the email. “In fact, the need for maintenance therapy for CTCL is often debated. Our findings demonstrate the importance of continuing treatment and the use of maintenance therapy in avoiding disease progression in these incurable lymphomas.”
They acknowledged certain limitations of the study, including its retrospective observational design. “Therefore, we cannot establish a definitive causal link between treatment delay and disease progression,” they said. “Our cohort of patients were on various and often multiple therapies, making it hard to extrapolate our data to discern which maintenance therapies were most effective in preventing disease progression.”
In addition, their data only includes patients from March to October 2020, “before the discovery of new variants and the development of COVID-19 vaccines,” they added. “Additional studies would be required to draw conclusions on how COVID-19 vaccines may affect patients with CTCL, including outcomes in the setting of new variants.”
The authors reported having no financial disclosures.
showed. However, among patients with CTCL diagnosed with COVID-19 during that time, no cases were acquired from outpatient visits.
“Delays in therapy for patients with cutaneous lymphomas should likely be avoided,” two of the study authors, Larisa J. Geskin, MD, of the department of dermatology at Columbia University Irving Medical Center, New York, and Bradley D. Kwinta, a medical student at Columbia University, told this news organization in a combined response via email.
“Continuing treatment and maintenance therapy appears critical to avoiding disease progression, highlighting the importance of maintenance therapy in CTCL,” they said. “These patients can be safely treated according to established treatment protocols while practicing physical distancing and using personal protective equipment without significantly increasing their risk of COVID-19 infection.”
The United States Cutaneous Lymphoma Consortium and the European Organization for Research and Treatment of Cancer developed emergency guidelines for the management of patients with cutaneous lymphomas during the pandemic to ensure patient safety, and the International Society for Cutaneous Lymphomas created an International Cutaneous Lymphomas Pandemic Section to collect data to assess the impact of these guidelines.
“Using this data, we can determine if these measures were effective in preventing COVID-19 infection, what the impact was of maintenance therapy, and how delays in treatment affected disease outcomes in CTCL patients,” the authors and their colleagues wrote in the study, which was published in the Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology.
They retrospectively analyzed data from the electronic medical records of 149 patients with CTCL who were being managed at one of nine international academic medical centers in seven countries from March to October 2020. Slightly more than half (56%) were male, 70% were White, 18% were Black, 52% had stage IA-IIA disease, and 19% acquired COVID-19 during the study period.
Of the 149 patients, 79 (53%) experienced a mean treatment delay of 3.2 months (range, 10 days to 10 months). After adjusting for age, race, biological sex, COVID-19 status, and disease stage, treatment delay was associated with a significant risk of disease relapse or progression across all stages (odds ratio, 5.00; P < .001). Specifically, for each additional month that a patient experienced treatment delay, the odds of disease progression increased by 37% (OR, 1.37; P < .001).
A total of 28 patients with CTCL (19%) were diagnosed with COVID-19, but none were acquired from outpatient office visits. Patients who contracted COVID-19 did not have a statistically significant increase in odds of disease progression, compared with COVID-negative patients (OR, 0.41; P = .07).
According to Dr. Geskin, who is also director of the Comprehensive Skin Cancer Center in the division of cutaneous oncology in the department of dermatology at Columbia, and Mr. Kwinta, no clinical trials exist to inform maintenance protocols in patients with cutaneous lymphomas. “There are also no randomized and controlled observational studies that demonstrate the impact that therapy delay may have on disease outcomes,” they said in the email. “In fact, the need for maintenance therapy for CTCL is often debated. Our findings demonstrate the importance of continuing treatment and the use of maintenance therapy in avoiding disease progression in these incurable lymphomas.”
They acknowledged certain limitations of the study, including its retrospective observational design. “Therefore, we cannot establish a definitive causal link between treatment delay and disease progression,” they said. “Our cohort of patients were on various and often multiple therapies, making it hard to extrapolate our data to discern which maintenance therapies were most effective in preventing disease progression.”
In addition, their data only includes patients from March to October 2020, “before the discovery of new variants and the development of COVID-19 vaccines,” they added. “Additional studies would be required to draw conclusions on how COVID-19 vaccines may affect patients with CTCL, including outcomes in the setting of new variants.”
The authors reported having no financial disclosures.
showed. However, among patients with CTCL diagnosed with COVID-19 during that time, no cases were acquired from outpatient visits.
“Delays in therapy for patients with cutaneous lymphomas should likely be avoided,” two of the study authors, Larisa J. Geskin, MD, of the department of dermatology at Columbia University Irving Medical Center, New York, and Bradley D. Kwinta, a medical student at Columbia University, told this news organization in a combined response via email.
“Continuing treatment and maintenance therapy appears critical to avoiding disease progression, highlighting the importance of maintenance therapy in CTCL,” they said. “These patients can be safely treated according to established treatment protocols while practicing physical distancing and using personal protective equipment without significantly increasing their risk of COVID-19 infection.”
The United States Cutaneous Lymphoma Consortium and the European Organization for Research and Treatment of Cancer developed emergency guidelines for the management of patients with cutaneous lymphomas during the pandemic to ensure patient safety, and the International Society for Cutaneous Lymphomas created an International Cutaneous Lymphomas Pandemic Section to collect data to assess the impact of these guidelines.
“Using this data, we can determine if these measures were effective in preventing COVID-19 infection, what the impact was of maintenance therapy, and how delays in treatment affected disease outcomes in CTCL patients,” the authors and their colleagues wrote in the study, which was published in the Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology.
They retrospectively analyzed data from the electronic medical records of 149 patients with CTCL who were being managed at one of nine international academic medical centers in seven countries from March to October 2020. Slightly more than half (56%) were male, 70% were White, 18% were Black, 52% had stage IA-IIA disease, and 19% acquired COVID-19 during the study period.
Of the 149 patients, 79 (53%) experienced a mean treatment delay of 3.2 months (range, 10 days to 10 months). After adjusting for age, race, biological sex, COVID-19 status, and disease stage, treatment delay was associated with a significant risk of disease relapse or progression across all stages (odds ratio, 5.00; P < .001). Specifically, for each additional month that a patient experienced treatment delay, the odds of disease progression increased by 37% (OR, 1.37; P < .001).
A total of 28 patients with CTCL (19%) were diagnosed with COVID-19, but none were acquired from outpatient office visits. Patients who contracted COVID-19 did not have a statistically significant increase in odds of disease progression, compared with COVID-negative patients (OR, 0.41; P = .07).
According to Dr. Geskin, who is also director of the Comprehensive Skin Cancer Center in the division of cutaneous oncology in the department of dermatology at Columbia, and Mr. Kwinta, no clinical trials exist to inform maintenance protocols in patients with cutaneous lymphomas. “There are also no randomized and controlled observational studies that demonstrate the impact that therapy delay may have on disease outcomes,” they said in the email. “In fact, the need for maintenance therapy for CTCL is often debated. Our findings demonstrate the importance of continuing treatment and the use of maintenance therapy in avoiding disease progression in these incurable lymphomas.”
They acknowledged certain limitations of the study, including its retrospective observational design. “Therefore, we cannot establish a definitive causal link between treatment delay and disease progression,” they said. “Our cohort of patients were on various and often multiple therapies, making it hard to extrapolate our data to discern which maintenance therapies were most effective in preventing disease progression.”
In addition, their data only includes patients from March to October 2020, “before the discovery of new variants and the development of COVID-19 vaccines,” they added. “Additional studies would be required to draw conclusions on how COVID-19 vaccines may affect patients with CTCL, including outcomes in the setting of new variants.”
The authors reported having no financial disclosures.
FROM THE JOURNAL OF THE AMERICAN ACADEMY OF DERMATOLOGY
HS treated in EDs not followed up in derm clinics, study finds
according to a study of a large national administrative data set.
“Patients with HS presenting to the ED for their disease exhibited high rates of ED return with low rates of dermatology follow-up after an initial ED visit,” lead study author Cynthia X. Wang, MD, MPHS, and colleagues in the division of dermatology and the Institute for Informatics, Washington University in St. Louis, wrote in JAMA Dermatology.
Patients who received opioid prescriptions and patients on Medicaid were more likely to return to the ED, they noted.
HS, a debilitating skin disease involving chronic follicular inflammation, frequently affects the axilla, anogenital, and inframammary areas, with painful nodules, abscesses, and sinus tracts that can form scars, the authors wrote. HS is linked with comorbidities including inflammatory bowel disease, obesity, diabetes, substance use, and psychiatric conditions, and is often misdiagnosed for an estimated 7-10 years.
In the retrospective cohort study, Dr. Wang and colleagues collected data from nationwide commercial and Medicaid databases. They included patients aged 18 to 64 years with two or more claims for HS and with at least one ED visit not resulting in admission for HS or a defined proxy (such as a related diagnosis of folliculitis, in a location typical for HS) between 2010 and 2019.
The median age of the 20,269 patients in the study was 32 years; most (82.9%) were female, and nearly 37% had commercial insurance and 63.2% had Medicaid. About half the patients on Medicaid were Black and 36.2% were White (race and ethnicity data were not available for commercially insured patients). In both insurance groups, the rates of comorbidities were high, including 22.5% with obesity and 11.9% with diabetes.
The researchers found that, at the index ED visit, 48.0% of patients had incision and drainage performed (51% among those with commercial insurance vs. 46.3% of those with Medicaid; P < .001); 72.6% of patients filled an oral antibiotic prescription within 7 days, with similar percentages in both insurance groups; and 48.9% filled an oral opioid medication prescription within 7 days (46.5% for commercial insurance vs. 50.3% for Medicaid; P < .001).
Regarding follow-up care, the investigators found that 17.2% of patients had at least one return ED visit for HS or proxy within 30 days (15.7% for commercial vs. 18.1% for Medicaid; P < .001), while 2.4% had a dermatology visit (5.3% for commercial vs. 0.7% for Medicaid; P < .001). In addition, 34% of patients had at least one return ED visit for HS or proxy within 180 days (27.2% for commercial insurance vs. 38% for Medicaid; P < .001), while 6.8% had a dermatology visit (14.1% for commercial vs. 2.5% for Medicaid; P < .001).
Patients with an opioid prescribed within 7 days of the ED visit were more likely to return to the ED, within 30 days (odds ratio, 1.67; 95% confidence interval, 1.54-1.80; P < .001), and within 180 days (OR, 1.48; 95% CI, 1.39-1.58; P < .001). But they were less likely to have dermatology follow-up within 30 days (OR, 0.78; 95% CI, 0.64-0.95; P = .01) and within 180 days (OR, 0.81; 95% CI, 0.71-0.91; P < .001).
Medicaid patients were more likely to return to the ED within 30 days (OR, 1.12; 95% CI, 1.03-1.22; P = .009) and within 180 days (OR, 1.48; 95% CI, 1.38-1.58; P < .001). But they were less likely to receive outpatient dermatology follow-up care within 30 days (OR, 0.12; 95% CI, 0.09-0.15; P < .001) and within 180 days (OR, 0.16; 95% CI, 0.14-0.18; P < .001).
“This study highlights potential areas of action to improve care for patients with HS,” the authors concluded, including cross-specialty education and interventions, and focus on patients most likely to return to the ED for care.
Findings are not surprising
Christopher Sayed, MD, professor of dermatology at the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill, said in an interview that the study results are expected. “Many patients have trouble establishing care with a dermatologist familiar with HS, so they seek more fragmented care at urgent cares and EDs,” he said.
“Some dermatologists are not familiar with HS or don’t accept insurance such as Medicaid,” Dr. Sayed added. “Many emergency room providers may not recognize that medical therapy for HS has evolved in a way that makes referral to a dermatologist more essential than ever. They may tell patients there is nothing else to do but return to the ED for the next flare. “Emergency medicine and dermatology training programs need to educate providers about appropriate long-term HS management.”
In an interview, Robert Glatter, MD, an emergency medicine physician at Lenox Hill Hospital in New York and assistant professor of emergency medicine at Hofstra University, Hempstead, N.Y., said that the study describes a reality he and his colleagues know too well.
“The study gives a true snapshot of the disarray and inequality that exists for patients disproportionately affected by HS. Those who are African American and low income suffer from lack of HS primary dermatologic care and follow-up at much higher rates than do other demographic groups,” he said.
Doctors would like to see the current situation change, Dr. Glatter noted. “It’s frustrating for emergency physicians and for dermatologists, who know that optimal follow-up care for this chronic and disabling disease should be with a dermatologist (and other surgical specialists if necessary).
“It’s a broken system. Patients can’t get appointments in nonacademic private settings because the bulk of dermatologists will not accept Medicaid. And many academic practices will not see these patients, either,” he commented. “We end up becoming a safety net of care.”
Replace the broken system with an integrated process
A solution to address the problem would be to set up follow-up dermatology appointments when patients arrive in EDs during and after normal business hours, Dr. Glatter suggested. “Developing a coordinated, structured, streamlined process requires buy-in from all stakeholders, including private dermatologists, academic dermatology clinics, and the government.”
Having the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services study interventions for high utilizers of EDs for HS would also help with “the development of economic and logistical changes, including provider reimbursement and allocation of funds to address this ongoing disparity in care,” he added.
Ideally, larger health care systems could collaborate with academic and nonacademic dermatologists to design a referral network that cares for all uninsured or underinsured patients, he said. “Balancing patient care and improved outcomes – while working on a framework for reimbursement – would be in everyone’s best interest.”
The study was partially funded by a grant from the National Center for Advancing Translational Sciences of the National Institutes of Health. One author reported financial involvements with multiple pharmaceutical companies. Dr. Wang, the remaining coauthors, as well as Dr. Sayed and Dr. Glatter reported no conflicts of interest with the study. Dr. Glatter is an editor and columnist at Medscape.
according to a study of a large national administrative data set.
“Patients with HS presenting to the ED for their disease exhibited high rates of ED return with low rates of dermatology follow-up after an initial ED visit,” lead study author Cynthia X. Wang, MD, MPHS, and colleagues in the division of dermatology and the Institute for Informatics, Washington University in St. Louis, wrote in JAMA Dermatology.
Patients who received opioid prescriptions and patients on Medicaid were more likely to return to the ED, they noted.
HS, a debilitating skin disease involving chronic follicular inflammation, frequently affects the axilla, anogenital, and inframammary areas, with painful nodules, abscesses, and sinus tracts that can form scars, the authors wrote. HS is linked with comorbidities including inflammatory bowel disease, obesity, diabetes, substance use, and psychiatric conditions, and is often misdiagnosed for an estimated 7-10 years.
In the retrospective cohort study, Dr. Wang and colleagues collected data from nationwide commercial and Medicaid databases. They included patients aged 18 to 64 years with two or more claims for HS and with at least one ED visit not resulting in admission for HS or a defined proxy (such as a related diagnosis of folliculitis, in a location typical for HS) between 2010 and 2019.
The median age of the 20,269 patients in the study was 32 years; most (82.9%) were female, and nearly 37% had commercial insurance and 63.2% had Medicaid. About half the patients on Medicaid were Black and 36.2% were White (race and ethnicity data were not available for commercially insured patients). In both insurance groups, the rates of comorbidities were high, including 22.5% with obesity and 11.9% with diabetes.
The researchers found that, at the index ED visit, 48.0% of patients had incision and drainage performed (51% among those with commercial insurance vs. 46.3% of those with Medicaid; P < .001); 72.6% of patients filled an oral antibiotic prescription within 7 days, with similar percentages in both insurance groups; and 48.9% filled an oral opioid medication prescription within 7 days (46.5% for commercial insurance vs. 50.3% for Medicaid; P < .001).
Regarding follow-up care, the investigators found that 17.2% of patients had at least one return ED visit for HS or proxy within 30 days (15.7% for commercial vs. 18.1% for Medicaid; P < .001), while 2.4% had a dermatology visit (5.3% for commercial vs. 0.7% for Medicaid; P < .001). In addition, 34% of patients had at least one return ED visit for HS or proxy within 180 days (27.2% for commercial insurance vs. 38% for Medicaid; P < .001), while 6.8% had a dermatology visit (14.1% for commercial vs. 2.5% for Medicaid; P < .001).
Patients with an opioid prescribed within 7 days of the ED visit were more likely to return to the ED, within 30 days (odds ratio, 1.67; 95% confidence interval, 1.54-1.80; P < .001), and within 180 days (OR, 1.48; 95% CI, 1.39-1.58; P < .001). But they were less likely to have dermatology follow-up within 30 days (OR, 0.78; 95% CI, 0.64-0.95; P = .01) and within 180 days (OR, 0.81; 95% CI, 0.71-0.91; P < .001).
Medicaid patients were more likely to return to the ED within 30 days (OR, 1.12; 95% CI, 1.03-1.22; P = .009) and within 180 days (OR, 1.48; 95% CI, 1.38-1.58; P < .001). But they were less likely to receive outpatient dermatology follow-up care within 30 days (OR, 0.12; 95% CI, 0.09-0.15; P < .001) and within 180 days (OR, 0.16; 95% CI, 0.14-0.18; P < .001).
“This study highlights potential areas of action to improve care for patients with HS,” the authors concluded, including cross-specialty education and interventions, and focus on patients most likely to return to the ED for care.
Findings are not surprising
Christopher Sayed, MD, professor of dermatology at the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill, said in an interview that the study results are expected. “Many patients have trouble establishing care with a dermatologist familiar with HS, so they seek more fragmented care at urgent cares and EDs,” he said.
“Some dermatologists are not familiar with HS or don’t accept insurance such as Medicaid,” Dr. Sayed added. “Many emergency room providers may not recognize that medical therapy for HS has evolved in a way that makes referral to a dermatologist more essential than ever. They may tell patients there is nothing else to do but return to the ED for the next flare. “Emergency medicine and dermatology training programs need to educate providers about appropriate long-term HS management.”
In an interview, Robert Glatter, MD, an emergency medicine physician at Lenox Hill Hospital in New York and assistant professor of emergency medicine at Hofstra University, Hempstead, N.Y., said that the study describes a reality he and his colleagues know too well.
“The study gives a true snapshot of the disarray and inequality that exists for patients disproportionately affected by HS. Those who are African American and low income suffer from lack of HS primary dermatologic care and follow-up at much higher rates than do other demographic groups,” he said.
Doctors would like to see the current situation change, Dr. Glatter noted. “It’s frustrating for emergency physicians and for dermatologists, who know that optimal follow-up care for this chronic and disabling disease should be with a dermatologist (and other surgical specialists if necessary).
“It’s a broken system. Patients can’t get appointments in nonacademic private settings because the bulk of dermatologists will not accept Medicaid. And many academic practices will not see these patients, either,” he commented. “We end up becoming a safety net of care.”
Replace the broken system with an integrated process
A solution to address the problem would be to set up follow-up dermatology appointments when patients arrive in EDs during and after normal business hours, Dr. Glatter suggested. “Developing a coordinated, structured, streamlined process requires buy-in from all stakeholders, including private dermatologists, academic dermatology clinics, and the government.”
Having the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services study interventions for high utilizers of EDs for HS would also help with “the development of economic and logistical changes, including provider reimbursement and allocation of funds to address this ongoing disparity in care,” he added.
Ideally, larger health care systems could collaborate with academic and nonacademic dermatologists to design a referral network that cares for all uninsured or underinsured patients, he said. “Balancing patient care and improved outcomes – while working on a framework for reimbursement – would be in everyone’s best interest.”
The study was partially funded by a grant from the National Center for Advancing Translational Sciences of the National Institutes of Health. One author reported financial involvements with multiple pharmaceutical companies. Dr. Wang, the remaining coauthors, as well as Dr. Sayed and Dr. Glatter reported no conflicts of interest with the study. Dr. Glatter is an editor and columnist at Medscape.
according to a study of a large national administrative data set.
“Patients with HS presenting to the ED for their disease exhibited high rates of ED return with low rates of dermatology follow-up after an initial ED visit,” lead study author Cynthia X. Wang, MD, MPHS, and colleagues in the division of dermatology and the Institute for Informatics, Washington University in St. Louis, wrote in JAMA Dermatology.
Patients who received opioid prescriptions and patients on Medicaid were more likely to return to the ED, they noted.
HS, a debilitating skin disease involving chronic follicular inflammation, frequently affects the axilla, anogenital, and inframammary areas, with painful nodules, abscesses, and sinus tracts that can form scars, the authors wrote. HS is linked with comorbidities including inflammatory bowel disease, obesity, diabetes, substance use, and psychiatric conditions, and is often misdiagnosed for an estimated 7-10 years.
In the retrospective cohort study, Dr. Wang and colleagues collected data from nationwide commercial and Medicaid databases. They included patients aged 18 to 64 years with two or more claims for HS and with at least one ED visit not resulting in admission for HS or a defined proxy (such as a related diagnosis of folliculitis, in a location typical for HS) between 2010 and 2019.
The median age of the 20,269 patients in the study was 32 years; most (82.9%) were female, and nearly 37% had commercial insurance and 63.2% had Medicaid. About half the patients on Medicaid were Black and 36.2% were White (race and ethnicity data were not available for commercially insured patients). In both insurance groups, the rates of comorbidities were high, including 22.5% with obesity and 11.9% with diabetes.
The researchers found that, at the index ED visit, 48.0% of patients had incision and drainage performed (51% among those with commercial insurance vs. 46.3% of those with Medicaid; P < .001); 72.6% of patients filled an oral antibiotic prescription within 7 days, with similar percentages in both insurance groups; and 48.9% filled an oral opioid medication prescription within 7 days (46.5% for commercial insurance vs. 50.3% for Medicaid; P < .001).
Regarding follow-up care, the investigators found that 17.2% of patients had at least one return ED visit for HS or proxy within 30 days (15.7% for commercial vs. 18.1% for Medicaid; P < .001), while 2.4% had a dermatology visit (5.3% for commercial vs. 0.7% for Medicaid; P < .001). In addition, 34% of patients had at least one return ED visit for HS or proxy within 180 days (27.2% for commercial insurance vs. 38% for Medicaid; P < .001), while 6.8% had a dermatology visit (14.1% for commercial vs. 2.5% for Medicaid; P < .001).
Patients with an opioid prescribed within 7 days of the ED visit were more likely to return to the ED, within 30 days (odds ratio, 1.67; 95% confidence interval, 1.54-1.80; P < .001), and within 180 days (OR, 1.48; 95% CI, 1.39-1.58; P < .001). But they were less likely to have dermatology follow-up within 30 days (OR, 0.78; 95% CI, 0.64-0.95; P = .01) and within 180 days (OR, 0.81; 95% CI, 0.71-0.91; P < .001).
Medicaid patients were more likely to return to the ED within 30 days (OR, 1.12; 95% CI, 1.03-1.22; P = .009) and within 180 days (OR, 1.48; 95% CI, 1.38-1.58; P < .001). But they were less likely to receive outpatient dermatology follow-up care within 30 days (OR, 0.12; 95% CI, 0.09-0.15; P < .001) and within 180 days (OR, 0.16; 95% CI, 0.14-0.18; P < .001).
“This study highlights potential areas of action to improve care for patients with HS,” the authors concluded, including cross-specialty education and interventions, and focus on patients most likely to return to the ED for care.
Findings are not surprising
Christopher Sayed, MD, professor of dermatology at the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill, said in an interview that the study results are expected. “Many patients have trouble establishing care with a dermatologist familiar with HS, so they seek more fragmented care at urgent cares and EDs,” he said.
“Some dermatologists are not familiar with HS or don’t accept insurance such as Medicaid,” Dr. Sayed added. “Many emergency room providers may not recognize that medical therapy for HS has evolved in a way that makes referral to a dermatologist more essential than ever. They may tell patients there is nothing else to do but return to the ED for the next flare. “Emergency medicine and dermatology training programs need to educate providers about appropriate long-term HS management.”
In an interview, Robert Glatter, MD, an emergency medicine physician at Lenox Hill Hospital in New York and assistant professor of emergency medicine at Hofstra University, Hempstead, N.Y., said that the study describes a reality he and his colleagues know too well.
“The study gives a true snapshot of the disarray and inequality that exists for patients disproportionately affected by HS. Those who are African American and low income suffer from lack of HS primary dermatologic care and follow-up at much higher rates than do other demographic groups,” he said.
Doctors would like to see the current situation change, Dr. Glatter noted. “It’s frustrating for emergency physicians and for dermatologists, who know that optimal follow-up care for this chronic and disabling disease should be with a dermatologist (and other surgical specialists if necessary).
“It’s a broken system. Patients can’t get appointments in nonacademic private settings because the bulk of dermatologists will not accept Medicaid. And many academic practices will not see these patients, either,” he commented. “We end up becoming a safety net of care.”
Replace the broken system with an integrated process
A solution to address the problem would be to set up follow-up dermatology appointments when patients arrive in EDs during and after normal business hours, Dr. Glatter suggested. “Developing a coordinated, structured, streamlined process requires buy-in from all stakeholders, including private dermatologists, academic dermatology clinics, and the government.”
Having the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services study interventions for high utilizers of EDs for HS would also help with “the development of economic and logistical changes, including provider reimbursement and allocation of funds to address this ongoing disparity in care,” he added.
Ideally, larger health care systems could collaborate with academic and nonacademic dermatologists to design a referral network that cares for all uninsured or underinsured patients, he said. “Balancing patient care and improved outcomes – while working on a framework for reimbursement – would be in everyone’s best interest.”
The study was partially funded by a grant from the National Center for Advancing Translational Sciences of the National Institutes of Health. One author reported financial involvements with multiple pharmaceutical companies. Dr. Wang, the remaining coauthors, as well as Dr. Sayed and Dr. Glatter reported no conflicts of interest with the study. Dr. Glatter is an editor and columnist at Medscape.
FROM JAMA DERMATOLOGY
Applications for nano-pulse stimulation continue to evolve
During a virtual course on laser and aesthetic skin therapy, Yakir Levin, MD, PhD, likened nano-pulse stimulation to microneedling or radiofrequency microneedling “in that you have an array of microneedles that go into the skin,” he said. “However, it is actually completely different.”
The CellFX System uses nano-pulse stimulation to deliver ultrashort electrical energy pulses into the skin of target lesions via a console-based handheld applicator. In September 2022, the Food and Drug Administration cleared the CellFX system for treatment of sebaceous hyperplasia in patients with Fitzpatrick skin types I-II. This followed a general clearance of the device in 2021 for dermatologic procedures requiring ablation and resurfacing of the skin.
Pulses from the device deliver a “constant electrical potential gradient across cell membranes and organelle membranes, causing them to break down,” explained Dr. Levin, a dermatologist and physician scientist at Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston, where he practices cosmetic dermatology and conducts research on birthmarks in children. This creates pores in those membranes “and leads to a controlled form of cell death,” he said. “As a result, this treatment is limited to cells, so you can do it in the dermis without damaging the collagen network. It spares tissue that’s outside of the field, and it’s nonthermal.”
Images from electron microscopy have demonstrated swelling of the mitochondria and breakdown of nuclei within 2 hours of treatment in a rat study. “Within 1 day of treatment you have death of the cells and the beginning of involution of the lesion,” he said during the meeting, which was sponsored by Harvard Medical School, Massachusetts General Hospital, and the Wellman Center for Photomedicine. “This presents us with the opportunity to treat dermal lesions without causing damage to the epidermis or to the acellular portion of the dermis.”
In published studies, nano-pulse stimulation has been shown to be effective for treating sebaceous hyperplasia and warts. According to Dr. Levin, clinicians typically treat sebaceous hyperplasia with an radiofrequency microneedle or electrodesiccation, “where we shave off the top but do not try to hit the bottom because we don’t want to cause scarring of the dermis,” he said. “Using the nano-pulse stimulation technology, however, you end up with involution of the sebaceous lesion without damaging the surrounding dermis.”
In a prospective, randomized study, 72 individuals with sebaceous gland hyperplasia received nano-pulse stimulation to 222 lesions and they returned for three to four follow-up evaluations with photographs. At the final study visit, investigators rated 99.6% of the sebaceous gland lesions as clear or mostly clear, while 79% of the study participants said they were “satisfied” or “mostly satisfied” with the outcome.
At posttreatment day 60, 55% of the lesions were judged to have no hyperpigmentation and 31% exhibited mild posttreatment hyperpigmentation.
In a more recent study, researchers used the CellFX System to treat 195 cutaneous warts up to 10 mm wide in 62 individuals enrolled at one of five sites. They found that 75% of common warts, 73% of flat warts, and 44% of plantar warts were completely clear 60 days following the last nano-pulse stimulation treatment and did not recur within the 120-day observation period.
The most common reactions at the treatment sites were erythema (51%) and eschar formation (23%) on day 30.
According to Dr. Levin, promising future applications of nano-pulse stimulation include treatment of syringomas, dermatofibromas, and basal cell carcinomas.
Dr. Levin reported financial interest in Accure Acne, Avava Medical, and Soltego. The CellFX system was developed and is marketed by Pulse Biosciences.
During a virtual course on laser and aesthetic skin therapy, Yakir Levin, MD, PhD, likened nano-pulse stimulation to microneedling or radiofrequency microneedling “in that you have an array of microneedles that go into the skin,” he said. “However, it is actually completely different.”
The CellFX System uses nano-pulse stimulation to deliver ultrashort electrical energy pulses into the skin of target lesions via a console-based handheld applicator. In September 2022, the Food and Drug Administration cleared the CellFX system for treatment of sebaceous hyperplasia in patients with Fitzpatrick skin types I-II. This followed a general clearance of the device in 2021 for dermatologic procedures requiring ablation and resurfacing of the skin.
Pulses from the device deliver a “constant electrical potential gradient across cell membranes and organelle membranes, causing them to break down,” explained Dr. Levin, a dermatologist and physician scientist at Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston, where he practices cosmetic dermatology and conducts research on birthmarks in children. This creates pores in those membranes “and leads to a controlled form of cell death,” he said. “As a result, this treatment is limited to cells, so you can do it in the dermis without damaging the collagen network. It spares tissue that’s outside of the field, and it’s nonthermal.”
Images from electron microscopy have demonstrated swelling of the mitochondria and breakdown of nuclei within 2 hours of treatment in a rat study. “Within 1 day of treatment you have death of the cells and the beginning of involution of the lesion,” he said during the meeting, which was sponsored by Harvard Medical School, Massachusetts General Hospital, and the Wellman Center for Photomedicine. “This presents us with the opportunity to treat dermal lesions without causing damage to the epidermis or to the acellular portion of the dermis.”
In published studies, nano-pulse stimulation has been shown to be effective for treating sebaceous hyperplasia and warts. According to Dr. Levin, clinicians typically treat sebaceous hyperplasia with an radiofrequency microneedle or electrodesiccation, “where we shave off the top but do not try to hit the bottom because we don’t want to cause scarring of the dermis,” he said. “Using the nano-pulse stimulation technology, however, you end up with involution of the sebaceous lesion without damaging the surrounding dermis.”
In a prospective, randomized study, 72 individuals with sebaceous gland hyperplasia received nano-pulse stimulation to 222 lesions and they returned for three to four follow-up evaluations with photographs. At the final study visit, investigators rated 99.6% of the sebaceous gland lesions as clear or mostly clear, while 79% of the study participants said they were “satisfied” or “mostly satisfied” with the outcome.
At posttreatment day 60, 55% of the lesions were judged to have no hyperpigmentation and 31% exhibited mild posttreatment hyperpigmentation.
In a more recent study, researchers used the CellFX System to treat 195 cutaneous warts up to 10 mm wide in 62 individuals enrolled at one of five sites. They found that 75% of common warts, 73% of flat warts, and 44% of plantar warts were completely clear 60 days following the last nano-pulse stimulation treatment and did not recur within the 120-day observation period.
The most common reactions at the treatment sites were erythema (51%) and eschar formation (23%) on day 30.
According to Dr. Levin, promising future applications of nano-pulse stimulation include treatment of syringomas, dermatofibromas, and basal cell carcinomas.
Dr. Levin reported financial interest in Accure Acne, Avava Medical, and Soltego. The CellFX system was developed and is marketed by Pulse Biosciences.
During a virtual course on laser and aesthetic skin therapy, Yakir Levin, MD, PhD, likened nano-pulse stimulation to microneedling or radiofrequency microneedling “in that you have an array of microneedles that go into the skin,” he said. “However, it is actually completely different.”
The CellFX System uses nano-pulse stimulation to deliver ultrashort electrical energy pulses into the skin of target lesions via a console-based handheld applicator. In September 2022, the Food and Drug Administration cleared the CellFX system for treatment of sebaceous hyperplasia in patients with Fitzpatrick skin types I-II. This followed a general clearance of the device in 2021 for dermatologic procedures requiring ablation and resurfacing of the skin.
Pulses from the device deliver a “constant electrical potential gradient across cell membranes and organelle membranes, causing them to break down,” explained Dr. Levin, a dermatologist and physician scientist at Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston, where he practices cosmetic dermatology and conducts research on birthmarks in children. This creates pores in those membranes “and leads to a controlled form of cell death,” he said. “As a result, this treatment is limited to cells, so you can do it in the dermis without damaging the collagen network. It spares tissue that’s outside of the field, and it’s nonthermal.”
Images from electron microscopy have demonstrated swelling of the mitochondria and breakdown of nuclei within 2 hours of treatment in a rat study. “Within 1 day of treatment you have death of the cells and the beginning of involution of the lesion,” he said during the meeting, which was sponsored by Harvard Medical School, Massachusetts General Hospital, and the Wellman Center for Photomedicine. “This presents us with the opportunity to treat dermal lesions without causing damage to the epidermis or to the acellular portion of the dermis.”
In published studies, nano-pulse stimulation has been shown to be effective for treating sebaceous hyperplasia and warts. According to Dr. Levin, clinicians typically treat sebaceous hyperplasia with an radiofrequency microneedle or electrodesiccation, “where we shave off the top but do not try to hit the bottom because we don’t want to cause scarring of the dermis,” he said. “Using the nano-pulse stimulation technology, however, you end up with involution of the sebaceous lesion without damaging the surrounding dermis.”
In a prospective, randomized study, 72 individuals with sebaceous gland hyperplasia received nano-pulse stimulation to 222 lesions and they returned for three to four follow-up evaluations with photographs. At the final study visit, investigators rated 99.6% of the sebaceous gland lesions as clear or mostly clear, while 79% of the study participants said they were “satisfied” or “mostly satisfied” with the outcome.
At posttreatment day 60, 55% of the lesions were judged to have no hyperpigmentation and 31% exhibited mild posttreatment hyperpigmentation.
In a more recent study, researchers used the CellFX System to treat 195 cutaneous warts up to 10 mm wide in 62 individuals enrolled at one of five sites. They found that 75% of common warts, 73% of flat warts, and 44% of plantar warts were completely clear 60 days following the last nano-pulse stimulation treatment and did not recur within the 120-day observation period.
The most common reactions at the treatment sites were erythema (51%) and eschar formation (23%) on day 30.
According to Dr. Levin, promising future applications of nano-pulse stimulation include treatment of syringomas, dermatofibromas, and basal cell carcinomas.
Dr. Levin reported financial interest in Accure Acne, Avava Medical, and Soltego. The CellFX system was developed and is marketed by Pulse Biosciences.
FROM A LASER & AESTHETIC SKIN THERAPY COURSE
Laser pioneer reflects on the future of robots in dermatology
In the opinion of R. Rox Anderson, MD, it’s only a matter of time before true robots make further inroads in dermatology.
“We humans just can’t do everything perfectly,” Dr. Anderson, a dermatologist who directs the Wellman Center for Photomedicine at Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston, said during a virtual course on laser and aesthetic skin therapy. “We have limited speed and special accuracy and are not good at repetitive tasks. We can’t see in the UV or infrared, and we’re qualitative, not quantitative. ... We’re good at high-level visual assessment.”
During a presentation at the meeting, which was sponsored by Harvard Medical School, Massachusetts General Hospital, and the Wellman Center, he distinguished between robotics and true robots. A prime example of robotics in medicine is the Da Vinci Surgical System in which a human user “is controlling every movement of this device with capabilities that humans don’t have, such as fine movement and high magnification of imaging,” said Dr. Anderson, who conceived and developed many of the nonscarring laser treatments now widely used in dermatology. “In the military, we have drone aircraft. The pilot is perhaps thousands of miles away; it’s still run by a human being in every way.”
By contrast, true robots are devices in which a human being programs the rules for action but the action itself is not exactly predictable. Artificial intelligence enables robots to perform certain tasks. “If you look at an Amazon warehouse, there’s barely anyone there; robots are packing and unpacking the shelves,” Dr. Anderson said.
Currently, he said, one true robot exists in dermatology: the Food and Drug Administration–cleared ARTAS Robotic Hair Restoration System, which precisely dissects follicular units from the donor area and eliminates the potential for human error. The device “extracts single follicular units from the occipital scalp and makes them available to the surgeon to do an artistic human job of implanting them in the frontal scalp,” Dr. Anderson said.
He predicts that a Mohs surgery robot with image-guided laser ablation would “launch a sea change in the whole field of surgical oncology, and I believe we are in a good position to do it. Everything for this is now sitting on the shelf and it’s unbelievable to me that a company hasn’t accomplished it yet.”
He would also like to see a true laser robot for surgery of tumors that would enable clinicians to download an app for their existing laser instead of having to buy a new device. Currently, “it takes about a half second to make a good optical coherence tomography image of basal cell carcinoma,” he said. “That image could be used for real-time robotic human control of, say, a laser to extirpate the tumor.”
Dr. Anderson’s “wish list” of applications for treatment with a robotic fractional laser includes those that target the sweat glands, sebaceous glands, nerves, inflammatory cells, white hair, blood vessels, lymphatics, hair, tumors, nevi, cysts, and surface contour. “It might be possible to have one software-programmable laser robot for many different applications in dermatology,” he added.
Dr. Anderson reported having received research funding and/or consulting fees from numerous device and pharmaceutical companies.
In the opinion of R. Rox Anderson, MD, it’s only a matter of time before true robots make further inroads in dermatology.
“We humans just can’t do everything perfectly,” Dr. Anderson, a dermatologist who directs the Wellman Center for Photomedicine at Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston, said during a virtual course on laser and aesthetic skin therapy. “We have limited speed and special accuracy and are not good at repetitive tasks. We can’t see in the UV or infrared, and we’re qualitative, not quantitative. ... We’re good at high-level visual assessment.”
During a presentation at the meeting, which was sponsored by Harvard Medical School, Massachusetts General Hospital, and the Wellman Center, he distinguished between robotics and true robots. A prime example of robotics in medicine is the Da Vinci Surgical System in which a human user “is controlling every movement of this device with capabilities that humans don’t have, such as fine movement and high magnification of imaging,” said Dr. Anderson, who conceived and developed many of the nonscarring laser treatments now widely used in dermatology. “In the military, we have drone aircraft. The pilot is perhaps thousands of miles away; it’s still run by a human being in every way.”
By contrast, true robots are devices in which a human being programs the rules for action but the action itself is not exactly predictable. Artificial intelligence enables robots to perform certain tasks. “If you look at an Amazon warehouse, there’s barely anyone there; robots are packing and unpacking the shelves,” Dr. Anderson said.
Currently, he said, one true robot exists in dermatology: the Food and Drug Administration–cleared ARTAS Robotic Hair Restoration System, which precisely dissects follicular units from the donor area and eliminates the potential for human error. The device “extracts single follicular units from the occipital scalp and makes them available to the surgeon to do an artistic human job of implanting them in the frontal scalp,” Dr. Anderson said.
He predicts that a Mohs surgery robot with image-guided laser ablation would “launch a sea change in the whole field of surgical oncology, and I believe we are in a good position to do it. Everything for this is now sitting on the shelf and it’s unbelievable to me that a company hasn’t accomplished it yet.”
He would also like to see a true laser robot for surgery of tumors that would enable clinicians to download an app for their existing laser instead of having to buy a new device. Currently, “it takes about a half second to make a good optical coherence tomography image of basal cell carcinoma,” he said. “That image could be used for real-time robotic human control of, say, a laser to extirpate the tumor.”
Dr. Anderson’s “wish list” of applications for treatment with a robotic fractional laser includes those that target the sweat glands, sebaceous glands, nerves, inflammatory cells, white hair, blood vessels, lymphatics, hair, tumors, nevi, cysts, and surface contour. “It might be possible to have one software-programmable laser robot for many different applications in dermatology,” he added.
Dr. Anderson reported having received research funding and/or consulting fees from numerous device and pharmaceutical companies.
In the opinion of R. Rox Anderson, MD, it’s only a matter of time before true robots make further inroads in dermatology.
“We humans just can’t do everything perfectly,” Dr. Anderson, a dermatologist who directs the Wellman Center for Photomedicine at Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston, said during a virtual course on laser and aesthetic skin therapy. “We have limited speed and special accuracy and are not good at repetitive tasks. We can’t see in the UV or infrared, and we’re qualitative, not quantitative. ... We’re good at high-level visual assessment.”
During a presentation at the meeting, which was sponsored by Harvard Medical School, Massachusetts General Hospital, and the Wellman Center, he distinguished between robotics and true robots. A prime example of robotics in medicine is the Da Vinci Surgical System in which a human user “is controlling every movement of this device with capabilities that humans don’t have, such as fine movement and high magnification of imaging,” said Dr. Anderson, who conceived and developed many of the nonscarring laser treatments now widely used in dermatology. “In the military, we have drone aircraft. The pilot is perhaps thousands of miles away; it’s still run by a human being in every way.”
By contrast, true robots are devices in which a human being programs the rules for action but the action itself is not exactly predictable. Artificial intelligence enables robots to perform certain tasks. “If you look at an Amazon warehouse, there’s barely anyone there; robots are packing and unpacking the shelves,” Dr. Anderson said.
Currently, he said, one true robot exists in dermatology: the Food and Drug Administration–cleared ARTAS Robotic Hair Restoration System, which precisely dissects follicular units from the donor area and eliminates the potential for human error. The device “extracts single follicular units from the occipital scalp and makes them available to the surgeon to do an artistic human job of implanting them in the frontal scalp,” Dr. Anderson said.
He predicts that a Mohs surgery robot with image-guided laser ablation would “launch a sea change in the whole field of surgical oncology, and I believe we are in a good position to do it. Everything for this is now sitting on the shelf and it’s unbelievable to me that a company hasn’t accomplished it yet.”
He would also like to see a true laser robot for surgery of tumors that would enable clinicians to download an app for their existing laser instead of having to buy a new device. Currently, “it takes about a half second to make a good optical coherence tomography image of basal cell carcinoma,” he said. “That image could be used for real-time robotic human control of, say, a laser to extirpate the tumor.”
Dr. Anderson’s “wish list” of applications for treatment with a robotic fractional laser includes those that target the sweat glands, sebaceous glands, nerves, inflammatory cells, white hair, blood vessels, lymphatics, hair, tumors, nevi, cysts, and surface contour. “It might be possible to have one software-programmable laser robot for many different applications in dermatology,” he added.
Dr. Anderson reported having received research funding and/or consulting fees from numerous device and pharmaceutical companies.
FROM A LASER & AESTHETIC SKIN THERAPY COURSE
Update on high-grade vulvar interepithelial neoplasia
Vulvar squamous cell carcinomas (VSCC) comprise approximately 90% of all vulvar malignancies. Unlike cervical SCC, which are predominantly human papilloma virus (HPV) positive, only a minority of VSCC are HPV positive – on the order of 15%-25% of cases. Most cases occur in the setting of lichen sclerosus and are HPV negative.
Lichen sclerosus is a chronic inflammatory dermatitis typically involving the anogenital area, which in some cases can become seriously distorted (e.g. atrophy of the labia minora, clitoral phimosis, and introital stenosis). Although most cases are diagnosed in postmenopausal women, LS can affect women of any age. The true prevalence of lichen sclerosus is unknown. Recent studies have shown a prevalence of 1 in 60; among older women, it can even be as high as 1 in 30. While lichen sclerosus is a pruriginous condition, it is often asymptomatic. It is not considered a premalignant condition. The diagnosis is clinical; however, suspicious lesions (erosions/ulcerations, hyperkeratosis, pigmented areas, ecchymosis, warty or papular lesions), particularly when recalcitrant to adequate first-line therapy, should be biopsied.
VSCC arises from precursor lesions or high-grade vulvar intraepithelial neoplasia (VIN). The 2015 International Society for the Study of Vulvovaginal Disease nomenclature classifies high-grade VIN into high-grade squamous intraepithelial lesion (HSIL) and differentiated VIN (dVIN). Most patients with high-grade VIN are diagnosed with HSIL or usual type VIN. A preponderance of these lesions (75%-85%) are HPV positive, predominantly HPV 16. Vulvar HSIL (vHSIL) lesions affect younger women. The lesions tend to be multifocal and extensive. On the other hand, dVIN typically affects older women and commonly develops as a solitary lesion. While dVIN accounts for only a small subset of patients with high-grade VIN, these lesions are HPV negative and associated with lichen sclerosus.
Both disease entities, vHSIL and dVIN, are increasing in incidence. There is a higher risk and shortened period of progression to cancer in patients with dVIN compared to HSIL. The cancer risk of vHSIL is relatively low. The 10-year cumulative VSCC risk reported in the literature is 10.3%; 9.7% for vHSIL and 50% for dVIN. Patients with vHSIL could benefit from less aggressive treatment modalities.
Patients present with a constellation of signs such as itching, pain, burning, bleeding, and discharge. Chronic symptoms portend HPV-independent lesions associated with lichen sclerosus while episodic signs are suggestive of HPV-positive lesions.
The recurrence risk of high-grade VIN is 46%-70%. Risk factors for recurrence include age greater than 50, immunosuppression, metasynchronous HSIL, and multifocal lesions. Recurrences occur in up to 50% of women who have undergone surgery. For those who undergo surgical treatment for high-grade VIN, recurrence is more common in the setting of positive margins, underlying lichen sclerosis, persistent HPV infection, and immunosuppression.
Management of high-grade VIN is determined by the lesion characteristics, patient characteristics, and medical expertise. Given the risk of progression of high-grade VIN to cancer and risk of underlying cancer, surgical therapy is typically recommended. The treatment of choice is surgical excision in cases of dVIN. Surgical treatments include CO2 laser ablation, wide local excision, and vulvectomy. Women who undergo surgical treatment for vHSIL have about a 50% chance of the condition recurring 1 year later, irrespective of whether treatment is by surgical excision or laser vaporization.
Since surgery can be associated with disfigurement and sexual dysfunction, alternatives to surgery should be considered in cases of vHSIL. The potential for effect on sexual function should be part of preoperative counseling and treatment. Women treated for VIN often experience increased inhibition of sexual excitement and increased inhibition of orgasm. One study found that in women undergoing vulvar excision for VIN, the impairment was found to be psychological in nature. Overall, the studies of sexual effect from treatment of VIN have found that women do not return to their pretreatment sexual function. However, the optimal management of vHSIL has not been determined. Nonsurgical options include topical therapies (imiquimod, 5-fluorouracil, cidofovir, and interferon) and nonpharmacologic treatments, such as photodynamic therapy.
Imiquimod, a topical immune modulator, is the most studied pharmacologic treatment of vHSIL. The drug induces secretion of cytokines, creating an immune response that clears the HPV infection. Imiquimod is safe and well tolerated. The clinical response rate varies between 35% and 81%. A recent study demonstrated the efficacy of imiquimod and the treatment was found to be noninferior to surgery. Adverse events differed, with local pain following surgical treatment and local pruritus and erythema associated with imiquimod use. Some patients did not respond to imiquimod; it was thought by the authors of the study that specific immunological factors affect the clinical response.
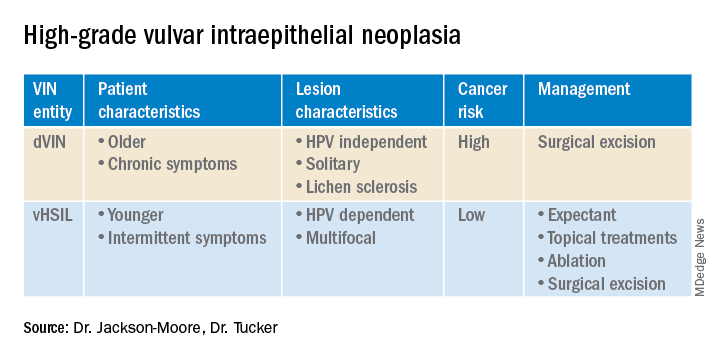
In conclusion, high-grade VIN is a heterogeneous disease made up of two distinct disease entities with rising incidence. In contrast to dVIN, the cancer risk is low for patients with vHSIL. Treatment should be driven by the clinical characteristics of the vulvar lesions, patients’ preferences, sexual activity, and compliance. Future directions include risk stratification of patients with vHSIL who are most likely to benefit from topical treatments, thus reducing overtreatment. Molecular biomarkers that could identify dVIN at an early stage are needed.
Dr. Jackson-Moore is associate professor in gynecologic oncology at the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill. Dr. Tucker is assistant professor of gynecologic oncology at the university.
References
Cendejas BR et al. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2015 Mar;212(3):291-7.
Lebreton M et al. J Gynecol Obstet Hum Reprod. 2020 Nov;49(9):101801.
Thuijs NB et al. Int J Cancer. 2021 Jan 1;148(1):90-8. doi: 10.1002/ijc.33198. .
Trutnovsky G et al. Lancet. 2022 May 7;399(10337):1790-8. Erratum in: Lancet. 2022 Oct 8;400(10359):1194.
Vulvar squamous cell carcinomas (VSCC) comprise approximately 90% of all vulvar malignancies. Unlike cervical SCC, which are predominantly human papilloma virus (HPV) positive, only a minority of VSCC are HPV positive – on the order of 15%-25% of cases. Most cases occur in the setting of lichen sclerosus and are HPV negative.
Lichen sclerosus is a chronic inflammatory dermatitis typically involving the anogenital area, which in some cases can become seriously distorted (e.g. atrophy of the labia minora, clitoral phimosis, and introital stenosis). Although most cases are diagnosed in postmenopausal women, LS can affect women of any age. The true prevalence of lichen sclerosus is unknown. Recent studies have shown a prevalence of 1 in 60; among older women, it can even be as high as 1 in 30. While lichen sclerosus is a pruriginous condition, it is often asymptomatic. It is not considered a premalignant condition. The diagnosis is clinical; however, suspicious lesions (erosions/ulcerations, hyperkeratosis, pigmented areas, ecchymosis, warty or papular lesions), particularly when recalcitrant to adequate first-line therapy, should be biopsied.
VSCC arises from precursor lesions or high-grade vulvar intraepithelial neoplasia (VIN). The 2015 International Society for the Study of Vulvovaginal Disease nomenclature classifies high-grade VIN into high-grade squamous intraepithelial lesion (HSIL) and differentiated VIN (dVIN). Most patients with high-grade VIN are diagnosed with HSIL or usual type VIN. A preponderance of these lesions (75%-85%) are HPV positive, predominantly HPV 16. Vulvar HSIL (vHSIL) lesions affect younger women. The lesions tend to be multifocal and extensive. On the other hand, dVIN typically affects older women and commonly develops as a solitary lesion. While dVIN accounts for only a small subset of patients with high-grade VIN, these lesions are HPV negative and associated with lichen sclerosus.
Both disease entities, vHSIL and dVIN, are increasing in incidence. There is a higher risk and shortened period of progression to cancer in patients with dVIN compared to HSIL. The cancer risk of vHSIL is relatively low. The 10-year cumulative VSCC risk reported in the literature is 10.3%; 9.7% for vHSIL and 50% for dVIN. Patients with vHSIL could benefit from less aggressive treatment modalities.
Patients present with a constellation of signs such as itching, pain, burning, bleeding, and discharge. Chronic symptoms portend HPV-independent lesions associated with lichen sclerosus while episodic signs are suggestive of HPV-positive lesions.
The recurrence risk of high-grade VIN is 46%-70%. Risk factors for recurrence include age greater than 50, immunosuppression, metasynchronous HSIL, and multifocal lesions. Recurrences occur in up to 50% of women who have undergone surgery. For those who undergo surgical treatment for high-grade VIN, recurrence is more common in the setting of positive margins, underlying lichen sclerosis, persistent HPV infection, and immunosuppression.
Management of high-grade VIN is determined by the lesion characteristics, patient characteristics, and medical expertise. Given the risk of progression of high-grade VIN to cancer and risk of underlying cancer, surgical therapy is typically recommended. The treatment of choice is surgical excision in cases of dVIN. Surgical treatments include CO2 laser ablation, wide local excision, and vulvectomy. Women who undergo surgical treatment for vHSIL have about a 50% chance of the condition recurring 1 year later, irrespective of whether treatment is by surgical excision or laser vaporization.
Since surgery can be associated with disfigurement and sexual dysfunction, alternatives to surgery should be considered in cases of vHSIL. The potential for effect on sexual function should be part of preoperative counseling and treatment. Women treated for VIN often experience increased inhibition of sexual excitement and increased inhibition of orgasm. One study found that in women undergoing vulvar excision for VIN, the impairment was found to be psychological in nature. Overall, the studies of sexual effect from treatment of VIN have found that women do not return to their pretreatment sexual function. However, the optimal management of vHSIL has not been determined. Nonsurgical options include topical therapies (imiquimod, 5-fluorouracil, cidofovir, and interferon) and nonpharmacologic treatments, such as photodynamic therapy.
Imiquimod, a topical immune modulator, is the most studied pharmacologic treatment of vHSIL. The drug induces secretion of cytokines, creating an immune response that clears the HPV infection. Imiquimod is safe and well tolerated. The clinical response rate varies between 35% and 81%. A recent study demonstrated the efficacy of imiquimod and the treatment was found to be noninferior to surgery. Adverse events differed, with local pain following surgical treatment and local pruritus and erythema associated with imiquimod use. Some patients did not respond to imiquimod; it was thought by the authors of the study that specific immunological factors affect the clinical response.

In conclusion, high-grade VIN is a heterogeneous disease made up of two distinct disease entities with rising incidence. In contrast to dVIN, the cancer risk is low for patients with vHSIL. Treatment should be driven by the clinical characteristics of the vulvar lesions, patients’ preferences, sexual activity, and compliance. Future directions include risk stratification of patients with vHSIL who are most likely to benefit from topical treatments, thus reducing overtreatment. Molecular biomarkers that could identify dVIN at an early stage are needed.
Dr. Jackson-Moore is associate professor in gynecologic oncology at the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill. Dr. Tucker is assistant professor of gynecologic oncology at the university.
References
Cendejas BR et al. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2015 Mar;212(3):291-7.
Lebreton M et al. J Gynecol Obstet Hum Reprod. 2020 Nov;49(9):101801.
Thuijs NB et al. Int J Cancer. 2021 Jan 1;148(1):90-8. doi: 10.1002/ijc.33198. .
Trutnovsky G et al. Lancet. 2022 May 7;399(10337):1790-8. Erratum in: Lancet. 2022 Oct 8;400(10359):1194.
Vulvar squamous cell carcinomas (VSCC) comprise approximately 90% of all vulvar malignancies. Unlike cervical SCC, which are predominantly human papilloma virus (HPV) positive, only a minority of VSCC are HPV positive – on the order of 15%-25% of cases. Most cases occur in the setting of lichen sclerosus and are HPV negative.
Lichen sclerosus is a chronic inflammatory dermatitis typically involving the anogenital area, which in some cases can become seriously distorted (e.g. atrophy of the labia minora, clitoral phimosis, and introital stenosis). Although most cases are diagnosed in postmenopausal women, LS can affect women of any age. The true prevalence of lichen sclerosus is unknown. Recent studies have shown a prevalence of 1 in 60; among older women, it can even be as high as 1 in 30. While lichen sclerosus is a pruriginous condition, it is often asymptomatic. It is not considered a premalignant condition. The diagnosis is clinical; however, suspicious lesions (erosions/ulcerations, hyperkeratosis, pigmented areas, ecchymosis, warty or papular lesions), particularly when recalcitrant to adequate first-line therapy, should be biopsied.
VSCC arises from precursor lesions or high-grade vulvar intraepithelial neoplasia (VIN). The 2015 International Society for the Study of Vulvovaginal Disease nomenclature classifies high-grade VIN into high-grade squamous intraepithelial lesion (HSIL) and differentiated VIN (dVIN). Most patients with high-grade VIN are diagnosed with HSIL or usual type VIN. A preponderance of these lesions (75%-85%) are HPV positive, predominantly HPV 16. Vulvar HSIL (vHSIL) lesions affect younger women. The lesions tend to be multifocal and extensive. On the other hand, dVIN typically affects older women and commonly develops as a solitary lesion. While dVIN accounts for only a small subset of patients with high-grade VIN, these lesions are HPV negative and associated with lichen sclerosus.
Both disease entities, vHSIL and dVIN, are increasing in incidence. There is a higher risk and shortened period of progression to cancer in patients with dVIN compared to HSIL. The cancer risk of vHSIL is relatively low. The 10-year cumulative VSCC risk reported in the literature is 10.3%; 9.7% for vHSIL and 50% for dVIN. Patients with vHSIL could benefit from less aggressive treatment modalities.
Patients present with a constellation of signs such as itching, pain, burning, bleeding, and discharge. Chronic symptoms portend HPV-independent lesions associated with lichen sclerosus while episodic signs are suggestive of HPV-positive lesions.
The recurrence risk of high-grade VIN is 46%-70%. Risk factors for recurrence include age greater than 50, immunosuppression, metasynchronous HSIL, and multifocal lesions. Recurrences occur in up to 50% of women who have undergone surgery. For those who undergo surgical treatment for high-grade VIN, recurrence is more common in the setting of positive margins, underlying lichen sclerosis, persistent HPV infection, and immunosuppression.
Management of high-grade VIN is determined by the lesion characteristics, patient characteristics, and medical expertise. Given the risk of progression of high-grade VIN to cancer and risk of underlying cancer, surgical therapy is typically recommended. The treatment of choice is surgical excision in cases of dVIN. Surgical treatments include CO2 laser ablation, wide local excision, and vulvectomy. Women who undergo surgical treatment for vHSIL have about a 50% chance of the condition recurring 1 year later, irrespective of whether treatment is by surgical excision or laser vaporization.
Since surgery can be associated with disfigurement and sexual dysfunction, alternatives to surgery should be considered in cases of vHSIL. The potential for effect on sexual function should be part of preoperative counseling and treatment. Women treated for VIN often experience increased inhibition of sexual excitement and increased inhibition of orgasm. One study found that in women undergoing vulvar excision for VIN, the impairment was found to be psychological in nature. Overall, the studies of sexual effect from treatment of VIN have found that women do not return to their pretreatment sexual function. However, the optimal management of vHSIL has not been determined. Nonsurgical options include topical therapies (imiquimod, 5-fluorouracil, cidofovir, and interferon) and nonpharmacologic treatments, such as photodynamic therapy.
Imiquimod, a topical immune modulator, is the most studied pharmacologic treatment of vHSIL. The drug induces secretion of cytokines, creating an immune response that clears the HPV infection. Imiquimod is safe and well tolerated. The clinical response rate varies between 35% and 81%. A recent study demonstrated the efficacy of imiquimod and the treatment was found to be noninferior to surgery. Adverse events differed, with local pain following surgical treatment and local pruritus and erythema associated with imiquimod use. Some patients did not respond to imiquimod; it was thought by the authors of the study that specific immunological factors affect the clinical response.

In conclusion, high-grade VIN is a heterogeneous disease made up of two distinct disease entities with rising incidence. In contrast to dVIN, the cancer risk is low for patients with vHSIL. Treatment should be driven by the clinical characteristics of the vulvar lesions, patients’ preferences, sexual activity, and compliance. Future directions include risk stratification of patients with vHSIL who are most likely to benefit from topical treatments, thus reducing overtreatment. Molecular biomarkers that could identify dVIN at an early stage are needed.
Dr. Jackson-Moore is associate professor in gynecologic oncology at the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill. Dr. Tucker is assistant professor of gynecologic oncology at the university.
References
Cendejas BR et al. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2015 Mar;212(3):291-7.
Lebreton M et al. J Gynecol Obstet Hum Reprod. 2020 Nov;49(9):101801.
Thuijs NB et al. Int J Cancer. 2021 Jan 1;148(1):90-8. doi: 10.1002/ijc.33198. .
Trutnovsky G et al. Lancet. 2022 May 7;399(10337):1790-8. Erratum in: Lancet. 2022 Oct 8;400(10359):1194.