User login
FDA advisors recommend nintedanib for SSc interstitial lung disease
The Food and Drug Administration Arthritis Advisory Committee recommended approval of nintedanib for the treatment of interstitial lung disease in patients with systemic sclerosis by a 10-7 vote on July 25, 2019. If the FDA acts in accord with the panel’s recommendation, it would make nintedanib (Ofev) the first drug to receive marketing approval for this indication.
Nintedanib has had FDA approval for treating idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis since 2014, and the manufacturer, Boehringer Ingelheim, designed the current pivotal trial with 576 patients to broaden the indication to patients with a different but similar fibrotic lung disease, interstitial lung disease (ILD), that is a common and eventually lethal complication of systemic sclerosis. The results of the pivotal study, the SENSCIS (Safety and Efficacy of Nintedanib in Systemic Sclerosis) trial, recently appeared in print and showed that patients randomized to receive 150 mg of nintedanib orally twice daily had an average 41-mL cut in the rate of loss of forced vital capacity (FVC) during 52 weeks on treatment, compared with those randomized to placebo. This was a 44% relative reduction in rate of FVC loss that was statistically significant for the study’s primary endpoint (N Engl J Med. 2019 June 27;380[26]:2518-28).
Votes in favor of FDA approval for many on the panel seemed to stem from a combination of the fact that nintedanib met the pivotal trial’s primary endpoint; which had been developed in consultation with the FDA, as well as the absence of any new safety signals when compared with prior experience using the drug; the lack of any treatment specifically recognized as beneficial to systemic sclerosis patients who develop the terminal complication of ILD; and the challenge of running a second trial in an orphan disease with an estimated U.S. prevalence of no more than 100,000 patients. Several committee members who voted in favor of nintedanib’s approval also voiced concern that the case in favor of its benefit/risk balance was not open and shut.
“I have a fair amount of apprehension,” admitted the committee’s chair, Daniel H. Solomon, MD, a rheumatologist and professor of medicine at Harvard Medical School, Boston. “I support the needs of patients, but we don’t want to give them false hope. We need to be able to say who will benefit, and the single study [SENSCIS] results don’t tell us how to use the drug. I want to understand which patient subgroups benefit.” He suggested that the FDA mandate further data collection through postmarketing studies.
Comments from panel members who voted against recommending approval generally focused on what was generally agreed to be a very modest treatment effect with a 41-mL average difference in FVC decline that has marginal clinical meaningfulness. Although the SENSCIS results met the study’s primary endpoint it was neutral for all prespecified secondary endpoints, including a measure of quality of life, although many on the panel agreed that a good measure of quality of life in the target patient population is lacking. Some sensitivity analyses run by FDA staffers also failed to confirm the primary result. Fewer questions arose about safety, although some panelists expressed concern about gastrointestinal effects, especially diarrhea, that seemed to link with treatment, as well as a signal for an increased incidence of pneumonia among patients on nintedanib. The data also showed a possible signal of reduced efficacy among patients who also received treatment with the immunosuppressive agent mycophenolate mofetil, often used off label to treat systemic sclerosis patients with ILD. However, a statistician involved in the discussion warned against overinterpreting this or other subgroup analyses.
Dr. Solomon has received research support from AbbVie, Amgen, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Genentech, Janssen, and Pfizer.
The Food and Drug Administration Arthritis Advisory Committee recommended approval of nintedanib for the treatment of interstitial lung disease in patients with systemic sclerosis by a 10-7 vote on July 25, 2019. If the FDA acts in accord with the panel’s recommendation, it would make nintedanib (Ofev) the first drug to receive marketing approval for this indication.
Nintedanib has had FDA approval for treating idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis since 2014, and the manufacturer, Boehringer Ingelheim, designed the current pivotal trial with 576 patients to broaden the indication to patients with a different but similar fibrotic lung disease, interstitial lung disease (ILD), that is a common and eventually lethal complication of systemic sclerosis. The results of the pivotal study, the SENSCIS (Safety and Efficacy of Nintedanib in Systemic Sclerosis) trial, recently appeared in print and showed that patients randomized to receive 150 mg of nintedanib orally twice daily had an average 41-mL cut in the rate of loss of forced vital capacity (FVC) during 52 weeks on treatment, compared with those randomized to placebo. This was a 44% relative reduction in rate of FVC loss that was statistically significant for the study’s primary endpoint (N Engl J Med. 2019 June 27;380[26]:2518-28).
Votes in favor of FDA approval for many on the panel seemed to stem from a combination of the fact that nintedanib met the pivotal trial’s primary endpoint; which had been developed in consultation with the FDA, as well as the absence of any new safety signals when compared with prior experience using the drug; the lack of any treatment specifically recognized as beneficial to systemic sclerosis patients who develop the terminal complication of ILD; and the challenge of running a second trial in an orphan disease with an estimated U.S. prevalence of no more than 100,000 patients. Several committee members who voted in favor of nintedanib’s approval also voiced concern that the case in favor of its benefit/risk balance was not open and shut.
“I have a fair amount of apprehension,” admitted the committee’s chair, Daniel H. Solomon, MD, a rheumatologist and professor of medicine at Harvard Medical School, Boston. “I support the needs of patients, but we don’t want to give them false hope. We need to be able to say who will benefit, and the single study [SENSCIS] results don’t tell us how to use the drug. I want to understand which patient subgroups benefit.” He suggested that the FDA mandate further data collection through postmarketing studies.
Comments from panel members who voted against recommending approval generally focused on what was generally agreed to be a very modest treatment effect with a 41-mL average difference in FVC decline that has marginal clinical meaningfulness. Although the SENSCIS results met the study’s primary endpoint it was neutral for all prespecified secondary endpoints, including a measure of quality of life, although many on the panel agreed that a good measure of quality of life in the target patient population is lacking. Some sensitivity analyses run by FDA staffers also failed to confirm the primary result. Fewer questions arose about safety, although some panelists expressed concern about gastrointestinal effects, especially diarrhea, that seemed to link with treatment, as well as a signal for an increased incidence of pneumonia among patients on nintedanib. The data also showed a possible signal of reduced efficacy among patients who also received treatment with the immunosuppressive agent mycophenolate mofetil, often used off label to treat systemic sclerosis patients with ILD. However, a statistician involved in the discussion warned against overinterpreting this or other subgroup analyses.
Dr. Solomon has received research support from AbbVie, Amgen, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Genentech, Janssen, and Pfizer.
The Food and Drug Administration Arthritis Advisory Committee recommended approval of nintedanib for the treatment of interstitial lung disease in patients with systemic sclerosis by a 10-7 vote on July 25, 2019. If the FDA acts in accord with the panel’s recommendation, it would make nintedanib (Ofev) the first drug to receive marketing approval for this indication.
Nintedanib has had FDA approval for treating idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis since 2014, and the manufacturer, Boehringer Ingelheim, designed the current pivotal trial with 576 patients to broaden the indication to patients with a different but similar fibrotic lung disease, interstitial lung disease (ILD), that is a common and eventually lethal complication of systemic sclerosis. The results of the pivotal study, the SENSCIS (Safety and Efficacy of Nintedanib in Systemic Sclerosis) trial, recently appeared in print and showed that patients randomized to receive 150 mg of nintedanib orally twice daily had an average 41-mL cut in the rate of loss of forced vital capacity (FVC) during 52 weeks on treatment, compared with those randomized to placebo. This was a 44% relative reduction in rate of FVC loss that was statistically significant for the study’s primary endpoint (N Engl J Med. 2019 June 27;380[26]:2518-28).
Votes in favor of FDA approval for many on the panel seemed to stem from a combination of the fact that nintedanib met the pivotal trial’s primary endpoint; which had been developed in consultation with the FDA, as well as the absence of any new safety signals when compared with prior experience using the drug; the lack of any treatment specifically recognized as beneficial to systemic sclerosis patients who develop the terminal complication of ILD; and the challenge of running a second trial in an orphan disease with an estimated U.S. prevalence of no more than 100,000 patients. Several committee members who voted in favor of nintedanib’s approval also voiced concern that the case in favor of its benefit/risk balance was not open and shut.
“I have a fair amount of apprehension,” admitted the committee’s chair, Daniel H. Solomon, MD, a rheumatologist and professor of medicine at Harvard Medical School, Boston. “I support the needs of patients, but we don’t want to give them false hope. We need to be able to say who will benefit, and the single study [SENSCIS] results don’t tell us how to use the drug. I want to understand which patient subgroups benefit.” He suggested that the FDA mandate further data collection through postmarketing studies.
Comments from panel members who voted against recommending approval generally focused on what was generally agreed to be a very modest treatment effect with a 41-mL average difference in FVC decline that has marginal clinical meaningfulness. Although the SENSCIS results met the study’s primary endpoint it was neutral for all prespecified secondary endpoints, including a measure of quality of life, although many on the panel agreed that a good measure of quality of life in the target patient population is lacking. Some sensitivity analyses run by FDA staffers also failed to confirm the primary result. Fewer questions arose about safety, although some panelists expressed concern about gastrointestinal effects, especially diarrhea, that seemed to link with treatment, as well as a signal for an increased incidence of pneumonia among patients on nintedanib. The data also showed a possible signal of reduced efficacy among patients who also received treatment with the immunosuppressive agent mycophenolate mofetil, often used off label to treat systemic sclerosis patients with ILD. However, a statistician involved in the discussion warned against overinterpreting this or other subgroup analyses.
Dr. Solomon has received research support from AbbVie, Amgen, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Genentech, Janssen, and Pfizer.
NIH launches 5-year, $10 million study on acute flaccid myelitis
Researchers at the University of Alabama at Birmingham will lead a 5-year, federally-funded study of acute flaccid myelitis (AFM) – a rare pediatric neurologic disease.
The National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases (NIAID) awarded the $10 million grant to primary investigator David Kimberlin, MD, a UAB professor of pediatrics. Carlos Pardo-Villamizar, MD, professor of neurology and pathology at Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore, is the co-principal investigator.
The university will organize and implement the international, multisite study. Its primary goal is to examine the incidence and distribution of AFM, and its pathogenesis and progression. Enrollment is expected to commence next fall. Investigators will enroll children with symptoms of AFM and follow them for 1 year. Household contacts of the subjects will serve as comparators.
In addition to collecting data about risk factors and disease progression, the researchers will collect clinical specimens, including blood and cerebrospinal fluid. More details about the design and study sites will be released then, according to a press statement issued by NIAID.
AFM targets spinal nerves and often develops after a mild respiratory illness. The disease mounted a global epidemic comeback in 2014, primarily affecting children; it has occurred concurrently with enterovirus outbreaks.
“Growing epidemiological evidence suggests that enterovirus-D68 [EV-D68] could play a role,” the statement noted. “Most people who become infected with EV-D68 are asymptomatic or experience mild, cold-like symptoms. Researchers and physicians are working to understand if there is a connection between these viral outbreaks and AFM, and if so, why some children but not others experience this sudden muscle weakness and paralysis.”
The study will draw on the expertise of the AFM Task Force, established last fall. The group comprises physicians, scientists, and public health experts from diverse disciplines and institutions who will assist in the ongoing investigation.
The AFM natural history study is funded under contract HHSN272201600018C.
Researchers at the University of Alabama at Birmingham will lead a 5-year, federally-funded study of acute flaccid myelitis (AFM) – a rare pediatric neurologic disease.
The National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases (NIAID) awarded the $10 million grant to primary investigator David Kimberlin, MD, a UAB professor of pediatrics. Carlos Pardo-Villamizar, MD, professor of neurology and pathology at Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore, is the co-principal investigator.
The university will organize and implement the international, multisite study. Its primary goal is to examine the incidence and distribution of AFM, and its pathogenesis and progression. Enrollment is expected to commence next fall. Investigators will enroll children with symptoms of AFM and follow them for 1 year. Household contacts of the subjects will serve as comparators.
In addition to collecting data about risk factors and disease progression, the researchers will collect clinical specimens, including blood and cerebrospinal fluid. More details about the design and study sites will be released then, according to a press statement issued by NIAID.
AFM targets spinal nerves and often develops after a mild respiratory illness. The disease mounted a global epidemic comeback in 2014, primarily affecting children; it has occurred concurrently with enterovirus outbreaks.
“Growing epidemiological evidence suggests that enterovirus-D68 [EV-D68] could play a role,” the statement noted. “Most people who become infected with EV-D68 are asymptomatic or experience mild, cold-like symptoms. Researchers and physicians are working to understand if there is a connection between these viral outbreaks and AFM, and if so, why some children but not others experience this sudden muscle weakness and paralysis.”
The study will draw on the expertise of the AFM Task Force, established last fall. The group comprises physicians, scientists, and public health experts from diverse disciplines and institutions who will assist in the ongoing investigation.
The AFM natural history study is funded under contract HHSN272201600018C.
Researchers at the University of Alabama at Birmingham will lead a 5-year, federally-funded study of acute flaccid myelitis (AFM) – a rare pediatric neurologic disease.
The National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases (NIAID) awarded the $10 million grant to primary investigator David Kimberlin, MD, a UAB professor of pediatrics. Carlos Pardo-Villamizar, MD, professor of neurology and pathology at Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore, is the co-principal investigator.
The university will organize and implement the international, multisite study. Its primary goal is to examine the incidence and distribution of AFM, and its pathogenesis and progression. Enrollment is expected to commence next fall. Investigators will enroll children with symptoms of AFM and follow them for 1 year. Household contacts of the subjects will serve as comparators.
In addition to collecting data about risk factors and disease progression, the researchers will collect clinical specimens, including blood and cerebrospinal fluid. More details about the design and study sites will be released then, according to a press statement issued by NIAID.
AFM targets spinal nerves and often develops after a mild respiratory illness. The disease mounted a global epidemic comeback in 2014, primarily affecting children; it has occurred concurrently with enterovirus outbreaks.
“Growing epidemiological evidence suggests that enterovirus-D68 [EV-D68] could play a role,” the statement noted. “Most people who become infected with EV-D68 are asymptomatic or experience mild, cold-like symptoms. Researchers and physicians are working to understand if there is a connection between these viral outbreaks and AFM, and if so, why some children but not others experience this sudden muscle weakness and paralysis.”
The study will draw on the expertise of the AFM Task Force, established last fall. The group comprises physicians, scientists, and public health experts from diverse disciplines and institutions who will assist in the ongoing investigation.
The AFM natural history study is funded under contract HHSN272201600018C.
FDA approves Otezla for treatment of Behçet’s-associated oral ulcers
The Food and Drug Administration has expanded the indication for apremilast (Otezla) to include the treatment of oral ulcers associated with Behçet’s disease in adults, according to an announcement from the manufacturer, Celgene.
FDA approval was based on results of the randomized, placebo-controlled, double-blind, phase 3 RELIEF trial, in which 207 patients with Behçet’s disease with active ulcers underwent treatment for 12 weeks with 30 mg apremilast or placebo. When measured on a visual analog scale, the reduction in pain from oral ulcers after 12 weeks in patients receiving apremilast was 42.7 points, compared with 18.7 points in the placebo group. Just over 50% of apremilast patients achieved complete response by week 12, compared with 22.3% in the placebo group.
The most common adverse events associated with apremilast during RELIEF were diarrhea, nausea, headache, and upper respiratory infection. This was consistent with apremilast’s known safety profile.
Apremilast is also indicated for treatment of patients with moderate to severe plaque psoriasis who are candidates for phototherapy or systemic therapy, and for patients with active psoriatic arthritis.
“Oral ulcers are a recurring and debilitating manifestation that affects nearly everyone living with Behçet’s disease and have an important negative impact on the quality of life for these patients. In the clinical trial, Otezla demonstrated improvements in measures of oral ulcers at week 12. Otezla has the potential to be a needed treatment option for U.S. patients and their physicians, who previously had limited options available,” Yusuf Yazici, MD, clinical associate professor in the department of medicine at New York University, said in the announcement.
The Food and Drug Administration has expanded the indication for apremilast (Otezla) to include the treatment of oral ulcers associated with Behçet’s disease in adults, according to an announcement from the manufacturer, Celgene.
FDA approval was based on results of the randomized, placebo-controlled, double-blind, phase 3 RELIEF trial, in which 207 patients with Behçet’s disease with active ulcers underwent treatment for 12 weeks with 30 mg apremilast or placebo. When measured on a visual analog scale, the reduction in pain from oral ulcers after 12 weeks in patients receiving apremilast was 42.7 points, compared with 18.7 points in the placebo group. Just over 50% of apremilast patients achieved complete response by week 12, compared with 22.3% in the placebo group.
The most common adverse events associated with apremilast during RELIEF were diarrhea, nausea, headache, and upper respiratory infection. This was consistent with apremilast’s known safety profile.
Apremilast is also indicated for treatment of patients with moderate to severe plaque psoriasis who are candidates for phototherapy or systemic therapy, and for patients with active psoriatic arthritis.
“Oral ulcers are a recurring and debilitating manifestation that affects nearly everyone living with Behçet’s disease and have an important negative impact on the quality of life for these patients. In the clinical trial, Otezla demonstrated improvements in measures of oral ulcers at week 12. Otezla has the potential to be a needed treatment option for U.S. patients and their physicians, who previously had limited options available,” Yusuf Yazici, MD, clinical associate professor in the department of medicine at New York University, said in the announcement.
The Food and Drug Administration has expanded the indication for apremilast (Otezla) to include the treatment of oral ulcers associated with Behçet’s disease in adults, according to an announcement from the manufacturer, Celgene.
FDA approval was based on results of the randomized, placebo-controlled, double-blind, phase 3 RELIEF trial, in which 207 patients with Behçet’s disease with active ulcers underwent treatment for 12 weeks with 30 mg apremilast or placebo. When measured on a visual analog scale, the reduction in pain from oral ulcers after 12 weeks in patients receiving apremilast was 42.7 points, compared with 18.7 points in the placebo group. Just over 50% of apremilast patients achieved complete response by week 12, compared with 22.3% in the placebo group.
The most common adverse events associated with apremilast during RELIEF were diarrhea, nausea, headache, and upper respiratory infection. This was consistent with apremilast’s known safety profile.
Apremilast is also indicated for treatment of patients with moderate to severe plaque psoriasis who are candidates for phototherapy or systemic therapy, and for patients with active psoriatic arthritis.
“Oral ulcers are a recurring and debilitating manifestation that affects nearly everyone living with Behçet’s disease and have an important negative impact on the quality of life for these patients. In the clinical trial, Otezla demonstrated improvements in measures of oral ulcers at week 12. Otezla has the potential to be a needed treatment option for U.S. patients and their physicians, who previously had limited options available,” Yusuf Yazici, MD, clinical associate professor in the department of medicine at New York University, said in the announcement.
Study refines ALS risk among first-degree relatives of patients with disease
, according to a recent Irish population–based study.
Among first-degree relatives of individuals with ALS whose genetic status was unknown, the lifetime risk of developing ALS was 1.4%, compared with 0.3% in the general population (P less than .001).
Overall, lifetime heritability for the 1,117 patients in the heritability study cohort was 52.3% (95% confidence interval, 42.9%-61.7%). The highest heritability was seen in mother-daughter dyads; here, the concordance rate for ALS was 2.6% and the heritability estimate was 66.2% (95% CI, 58.5%-73.9%), “pointing to a previously unrecognized sex-mediated association with disease heritability,” Marie Ryan, MD, and coauthors at Trinity College Dublin wrote in JAMA Neurology.
For the purposes of this study, heritability was defined as “the proportion of variance in liability that is attributable to additive genetic factors,” explained the investigators. Their model was applied to 1,123 Irish patients with incident ALS over a 10-year study period, drawing on a national database. Complete medical histories were available for both parents of every individual in the cohort, and the investigators identified 32 parent-offspring dyads with ALS.
In their assessment of “liability” for ALS, Dr. Ryan and colleagues accounted for age-specific and sex-specific ALS incidence rates, using a well-delineated United States reference population. They also took into account competing mortality risks that might intervene before an individual developed ALS.
Although mother-daughter dyads yielded the highest heritability estimates, heritability was also elevated among father-son dyads, at 50.1% (95% CI, 42.0%-59.4%). Opposite-sex dyads (mother-son and father-daughter) yielded similar, and lower, heritability estimates of 34%-38%. Dr. Ryan and coinvestigators acknowledged that female sex hormones might play a role in mediating risk for ALS, but the contribution and mechanism are currently unknown.
The investigators identified 674 patients in the cohort who had been tested for C9orf72; large repeat expansions in the GGGGCC segment of this gene are known to cause ALS. In all, 69 patients were C9orf72 positive, and 14 of these individuals (20.3%) reported that one parent had ALS. Among the entire cohort, 23 of the 32 patients with parents who also had ALS had C9orf72 testing, and 14 of 23 (60.9%) were positive. This discrepancy, wrote Dr. Ryan and coauthors, suggests that “genetic anticipation or pleiotropic effects may have masked the clinical phenotype in their parents.”
Parents were a mean 69.6 years old at the time of diagnosis, and offspring were a mean 52.0 years old; 56% of patients in the study cohort were male.
“[I]n our study, ALS heritability was assessed for the first time in a population in whom genetic mutations have been excluded,” wrote Dr. Ryan and coinvestigators. “We have found that, in the absence of known ALS-associated genetic mutations in the proband, first-degree relatives of individuals with ALS remain at increased risk of developing ALS compared with the general population.”
Dr. Ryan and one coauthor reported receiving funding from Science Foundation Ireland, and one coauthor reported receiving book royalties from Taylor & Francis, and fees from Cytokinetics and Wave Pharmaceuticals. The study was funded by Science Foundation Ireland and the Motor Neurone Disease Association.
SOURCE: Ryan M et al. JAMA Neurol. 2019 Jul 22. doi: 10.1001/jamaneurol.2019.2044.
, according to a recent Irish population–based study.
Among first-degree relatives of individuals with ALS whose genetic status was unknown, the lifetime risk of developing ALS was 1.4%, compared with 0.3% in the general population (P less than .001).
Overall, lifetime heritability for the 1,117 patients in the heritability study cohort was 52.3% (95% confidence interval, 42.9%-61.7%). The highest heritability was seen in mother-daughter dyads; here, the concordance rate for ALS was 2.6% and the heritability estimate was 66.2% (95% CI, 58.5%-73.9%), “pointing to a previously unrecognized sex-mediated association with disease heritability,” Marie Ryan, MD, and coauthors at Trinity College Dublin wrote in JAMA Neurology.
For the purposes of this study, heritability was defined as “the proportion of variance in liability that is attributable to additive genetic factors,” explained the investigators. Their model was applied to 1,123 Irish patients with incident ALS over a 10-year study period, drawing on a national database. Complete medical histories were available for both parents of every individual in the cohort, and the investigators identified 32 parent-offspring dyads with ALS.
In their assessment of “liability” for ALS, Dr. Ryan and colleagues accounted for age-specific and sex-specific ALS incidence rates, using a well-delineated United States reference population. They also took into account competing mortality risks that might intervene before an individual developed ALS.
Although mother-daughter dyads yielded the highest heritability estimates, heritability was also elevated among father-son dyads, at 50.1% (95% CI, 42.0%-59.4%). Opposite-sex dyads (mother-son and father-daughter) yielded similar, and lower, heritability estimates of 34%-38%. Dr. Ryan and coinvestigators acknowledged that female sex hormones might play a role in mediating risk for ALS, but the contribution and mechanism are currently unknown.
The investigators identified 674 patients in the cohort who had been tested for C9orf72; large repeat expansions in the GGGGCC segment of this gene are known to cause ALS. In all, 69 patients were C9orf72 positive, and 14 of these individuals (20.3%) reported that one parent had ALS. Among the entire cohort, 23 of the 32 patients with parents who also had ALS had C9orf72 testing, and 14 of 23 (60.9%) were positive. This discrepancy, wrote Dr. Ryan and coauthors, suggests that “genetic anticipation or pleiotropic effects may have masked the clinical phenotype in their parents.”
Parents were a mean 69.6 years old at the time of diagnosis, and offspring were a mean 52.0 years old; 56% of patients in the study cohort were male.
“[I]n our study, ALS heritability was assessed for the first time in a population in whom genetic mutations have been excluded,” wrote Dr. Ryan and coinvestigators. “We have found that, in the absence of known ALS-associated genetic mutations in the proband, first-degree relatives of individuals with ALS remain at increased risk of developing ALS compared with the general population.”
Dr. Ryan and one coauthor reported receiving funding from Science Foundation Ireland, and one coauthor reported receiving book royalties from Taylor & Francis, and fees from Cytokinetics and Wave Pharmaceuticals. The study was funded by Science Foundation Ireland and the Motor Neurone Disease Association.
SOURCE: Ryan M et al. JAMA Neurol. 2019 Jul 22. doi: 10.1001/jamaneurol.2019.2044.
, according to a recent Irish population–based study.
Among first-degree relatives of individuals with ALS whose genetic status was unknown, the lifetime risk of developing ALS was 1.4%, compared with 0.3% in the general population (P less than .001).
Overall, lifetime heritability for the 1,117 patients in the heritability study cohort was 52.3% (95% confidence interval, 42.9%-61.7%). The highest heritability was seen in mother-daughter dyads; here, the concordance rate for ALS was 2.6% and the heritability estimate was 66.2% (95% CI, 58.5%-73.9%), “pointing to a previously unrecognized sex-mediated association with disease heritability,” Marie Ryan, MD, and coauthors at Trinity College Dublin wrote in JAMA Neurology.
For the purposes of this study, heritability was defined as “the proportion of variance in liability that is attributable to additive genetic factors,” explained the investigators. Their model was applied to 1,123 Irish patients with incident ALS over a 10-year study period, drawing on a national database. Complete medical histories were available for both parents of every individual in the cohort, and the investigators identified 32 parent-offspring dyads with ALS.
In their assessment of “liability” for ALS, Dr. Ryan and colleagues accounted for age-specific and sex-specific ALS incidence rates, using a well-delineated United States reference population. They also took into account competing mortality risks that might intervene before an individual developed ALS.
Although mother-daughter dyads yielded the highest heritability estimates, heritability was also elevated among father-son dyads, at 50.1% (95% CI, 42.0%-59.4%). Opposite-sex dyads (mother-son and father-daughter) yielded similar, and lower, heritability estimates of 34%-38%. Dr. Ryan and coinvestigators acknowledged that female sex hormones might play a role in mediating risk for ALS, but the contribution and mechanism are currently unknown.
The investigators identified 674 patients in the cohort who had been tested for C9orf72; large repeat expansions in the GGGGCC segment of this gene are known to cause ALS. In all, 69 patients were C9orf72 positive, and 14 of these individuals (20.3%) reported that one parent had ALS. Among the entire cohort, 23 of the 32 patients with parents who also had ALS had C9orf72 testing, and 14 of 23 (60.9%) were positive. This discrepancy, wrote Dr. Ryan and coauthors, suggests that “genetic anticipation or pleiotropic effects may have masked the clinical phenotype in their parents.”
Parents were a mean 69.6 years old at the time of diagnosis, and offspring were a mean 52.0 years old; 56% of patients in the study cohort were male.
“[I]n our study, ALS heritability was assessed for the first time in a population in whom genetic mutations have been excluded,” wrote Dr. Ryan and coinvestigators. “We have found that, in the absence of known ALS-associated genetic mutations in the proband, first-degree relatives of individuals with ALS remain at increased risk of developing ALS compared with the general population.”
Dr. Ryan and one coauthor reported receiving funding from Science Foundation Ireland, and one coauthor reported receiving book royalties from Taylor & Francis, and fees from Cytokinetics and Wave Pharmaceuticals. The study was funded by Science Foundation Ireland and the Motor Neurone Disease Association.
SOURCE: Ryan M et al. JAMA Neurol. 2019 Jul 22. doi: 10.1001/jamaneurol.2019.2044.
FROM JAMA NEUROLOGY
A Unique Presentation of Lupus Erythematosus Tumidus in an Adolescent Boy
To the Editor:
Lupus erythematosus tumidus (LET) is a rarely diagnosed condition that was first described in 1909 by Hoffmann.1 Limited cases have been reported in the literature, with few documenting the disease in children.2 We report a unique clinical case of LET in a 14-year-old adolescent boy that was distributed solely on the hands. With slight heterogeneity in regards to clinical presentation and histopathology, there is a need for further exploration with regard to LET.
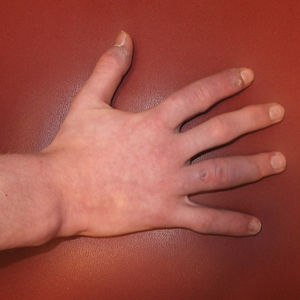
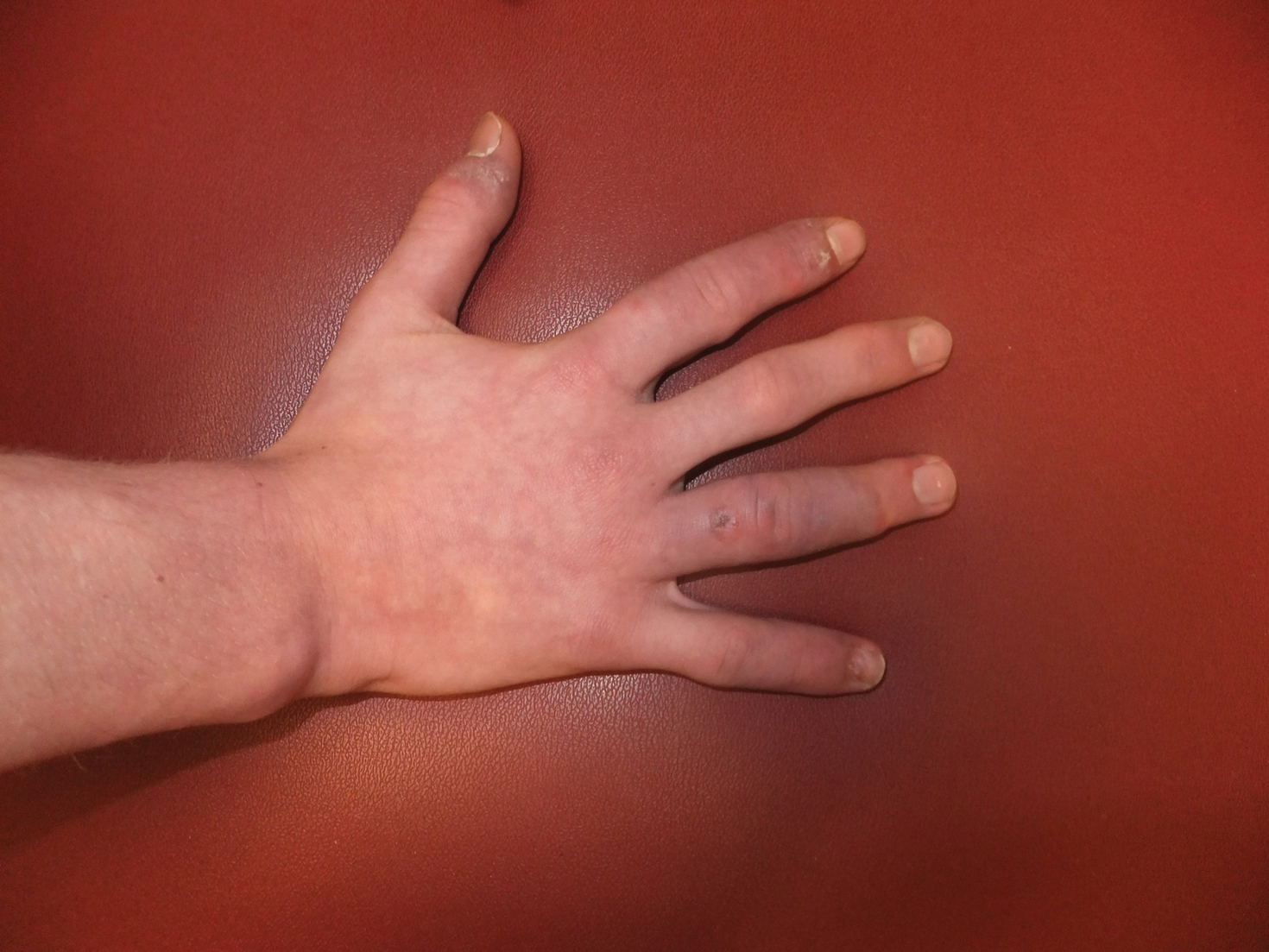
A 14-year-old adolescent boy presented to the dermatology clinic with progressive bilateral edema of 1 year’s duration with plaques and some scaling on the dorsal aspects of the digits and the nail bases predominantly on the right hand (Figure 1) and to a lesser extent on the left hand. The edema, erythema, and tenderness started in the right fifth digit; soon after the edema appeared, plaques began to form at the base of each nail bed, and the edema and erythema progressively spread to the other digits. He denied worsening of symptoms when exposed to cold temperatures. A complete review of systems was negative. The differential diagnoses included chilblain lupus erythematosus, perniosis, dermatomyositis, and polymorphous light eruption. A punch biopsy from the right fourth digit was performed.
The biopsy showed superficial and deep perivascular and periadnexal mononuclear inflammation with large amounts of interstitial mucin deposition (Figure 2). The epidermis exhibited a loose orthokeratotic scale with no signs of interface damage. A diagnosis of perniosis was entertained but was ruled out due to the lack of papillary dermal edema and large amounts of mucin. With the lack of interface change and large amounts of mucin, a diagnosis of LET was favored over chilblain lupus erythematosus, as the latter diagnosis typically demonstrates interface change. The patient was started on hydroxychloroquine 200 mg twice daily and a short course of prednisone, and improvement of the lesions/plaques was noted at follow-up 6 weeks later. Continued improvement was noted 2 years after the initial presentation. His condition recurred when the hydroxychloroquine dosage was reduced to 200 mg once daily after 1 year. The patient did not report any adverse sequelae to treatment.
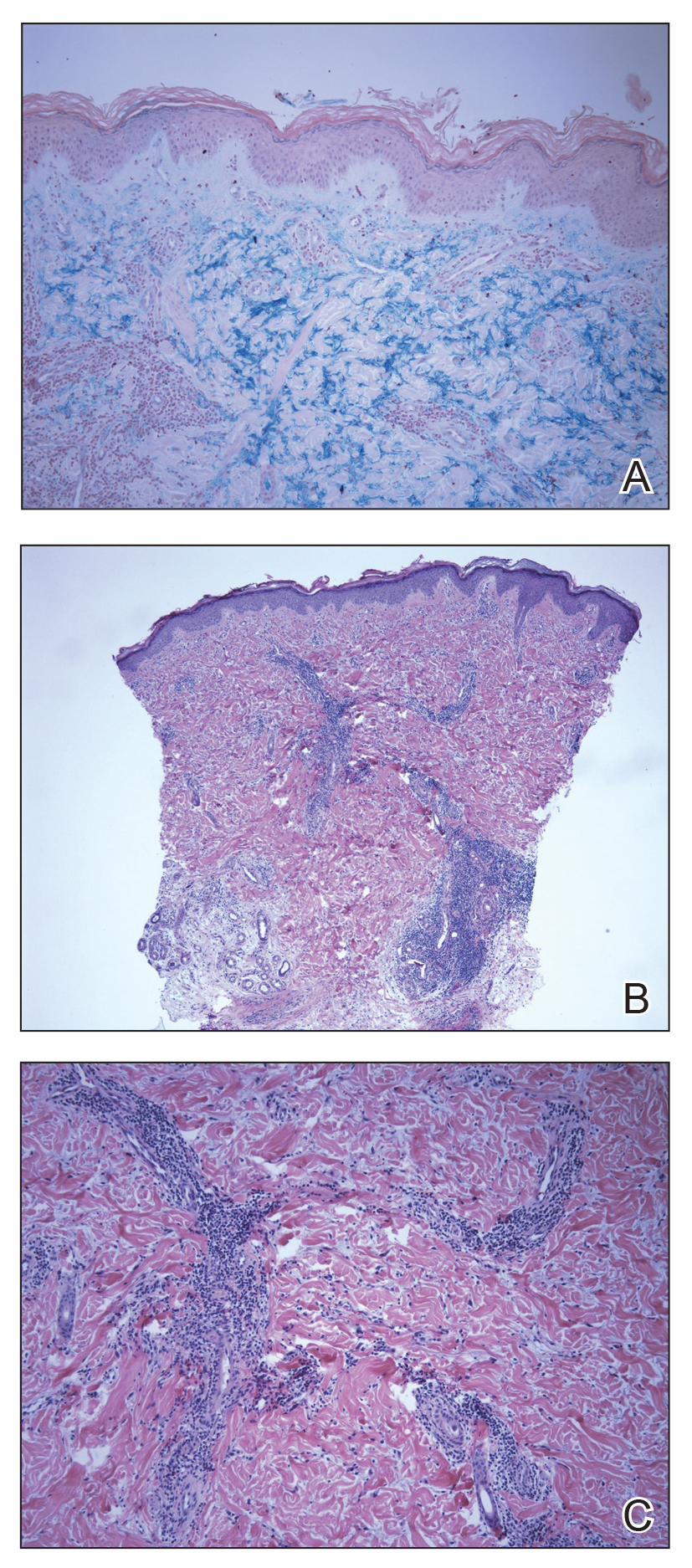
Histopathologic findings of superficial and deep perivascular and periadnexal lymphocytic infiltrates and interstitial dermal deposition of mucin in LET have remained consistent in the literature. Direct immunofluorescence has not revealed any complement or immunoglobulin deposition on the basement membrane.3,4 The epidermal characteristics are not as uniform, with the majority of cases in one review showing no epidermal changes and a minority showing minimal epidermal changes (eg, epidermal atrophy, hyperkeratosis, parakeratosis, acanthosis, spongiosis).5 When working up patients for LET, blood work usually is unremarkable, as LET rarely is associated with antinuclear antibodies or anti-Ro, anti-La, and anti-DNA antibodies.3,4 Lupus erythematosus tumidus generally is an independent process, but it has been reported to coexist with discoid lupus erythematosus and systemic lupus erythematosus in rare cases.6
The lesions of LET have been consistently described in the literature as photosensitive, erythematous, non-scarring, annular plaques and papules commonly occurring on the head/neck and other sun-exposed areas that do not cause hypopigmentation.3 Treatment of LET consists of systemic treatment with antimalarial drugs, sunscreens, and topical steroids for flares.
Lupus erythematosus tumidus is rare in children, with few case reports noted in the literature. Sonntag et al2 documented the disease in 3 children ranging from 3 to 8 years of age. Furthermore, Ruiz and Sanchez7 reported a case of LET in a 16-year-old adolescent girl. Our case is unique in that the lesions only occurred on the hands, whereas most case reports document distribution of the lesions on the head, neck, face, arms, back, and chest. Our patient’s age and the location of the lesions make it a unique clinical presentation of LET.
Reports in the literature show evidence of heterogeneity in the presentation, classification, and some of the histopathologic features of LET; however, there are minimal data on childhood LET. Further research and investigations are needed to more precisely define this condition.
Acknowledgment
The authors acknowledge Richard Schwartz, MD (Akron, Ohio), for reading the biopsy reports and assisting with photomicrographs.
- Hoffmann E. Demonstrationen: lupus erythematosus tumidus. Derm Zeitschr. 1909;16:159-160.
- Sonntag M, Lehmann P, Megahed M, et al. Lupus erythematosus tumidus in childhood. Dermatology. 2003;207:188-192.
- Schmitt V, Meuth AM, Amler S, et al. Lupus erythematosus tumidus is a separate subtype of cutaneous lupus erythematosus. Br J Dermatol. 2010;162:64-73.
- Vieira V, Del Pozo J, Yebra-Pimentel MT, et al. Lupus erythematosus tumidus: a series of 26 cases. Int J Dermatol. 2006;45:512-517.
- Kuhn A, Richter-Hintz D, Oslislo C, et al. Lupus erythematosus tumidus—a neglected subset of cutaneous lupus erythematosus: report of 40 cases. Arch Dermatol. 2000;136:1033-1041.
- Chen X, Wang S, Li L. A case report of lupus erythematosus tumidus converted from discoid lupus erythematosus. Medicine (Baltimore). 2018;97:e0375.
- Ruiz H, Sanchez J. Tumid lupus erythematosus. Am J Dermatopathol. 1999;21:356-360.
To the Editor:
Lupus erythematosus tumidus (LET) is a rarely diagnosed condition that was first described in 1909 by Hoffmann.1 Limited cases have been reported in the literature, with few documenting the disease in children.2 We report a unique clinical case of LET in a 14-year-old adolescent boy that was distributed solely on the hands. With slight heterogeneity in regards to clinical presentation and histopathology, there is a need for further exploration with regard to LET.
A 14-year-old adolescent boy presented to the dermatology clinic with progressive bilateral edema of 1 year’s duration with plaques and some scaling on the dorsal aspects of the digits and the nail bases predominantly on the right hand (Figure 1) and to a lesser extent on the left hand. The edema, erythema, and tenderness started in the right fifth digit; soon after the edema appeared, plaques began to form at the base of each nail bed, and the edema and erythema progressively spread to the other digits. He denied worsening of symptoms when exposed to cold temperatures. A complete review of systems was negative. The differential diagnoses included chilblain lupus erythematosus, perniosis, dermatomyositis, and polymorphous light eruption. A punch biopsy from the right fourth digit was performed.

The biopsy showed superficial and deep perivascular and periadnexal mononuclear inflammation with large amounts of interstitial mucin deposition (Figure 2). The epidermis exhibited a loose orthokeratotic scale with no signs of interface damage. A diagnosis of perniosis was entertained but was ruled out due to the lack of papillary dermal edema and large amounts of mucin. With the lack of interface change and large amounts of mucin, a diagnosis of LET was favored over chilblain lupus erythematosus, as the latter diagnosis typically demonstrates interface change. The patient was started on hydroxychloroquine 200 mg twice daily and a short course of prednisone, and improvement of the lesions/plaques was noted at follow-up 6 weeks later. Continued improvement was noted 2 years after the initial presentation. His condition recurred when the hydroxychloroquine dosage was reduced to 200 mg once daily after 1 year. The patient did not report any adverse sequelae to treatment.

Histopathologic findings of superficial and deep perivascular and periadnexal lymphocytic infiltrates and interstitial dermal deposition of mucin in LET have remained consistent in the literature. Direct immunofluorescence has not revealed any complement or immunoglobulin deposition on the basement membrane.3,4 The epidermal characteristics are not as uniform, with the majority of cases in one review showing no epidermal changes and a minority showing minimal epidermal changes (eg, epidermal atrophy, hyperkeratosis, parakeratosis, acanthosis, spongiosis).5 When working up patients for LET, blood work usually is unremarkable, as LET rarely is associated with antinuclear antibodies or anti-Ro, anti-La, and anti-DNA antibodies.3,4 Lupus erythematosus tumidus generally is an independent process, but it has been reported to coexist with discoid lupus erythematosus and systemic lupus erythematosus in rare cases.6
The lesions of LET have been consistently described in the literature as photosensitive, erythematous, non-scarring, annular plaques and papules commonly occurring on the head/neck and other sun-exposed areas that do not cause hypopigmentation.3 Treatment of LET consists of systemic treatment with antimalarial drugs, sunscreens, and topical steroids for flares.
Lupus erythematosus tumidus is rare in children, with few case reports noted in the literature. Sonntag et al2 documented the disease in 3 children ranging from 3 to 8 years of age. Furthermore, Ruiz and Sanchez7 reported a case of LET in a 16-year-old adolescent girl. Our case is unique in that the lesions only occurred on the hands, whereas most case reports document distribution of the lesions on the head, neck, face, arms, back, and chest. Our patient’s age and the location of the lesions make it a unique clinical presentation of LET.
Reports in the literature show evidence of heterogeneity in the presentation, classification, and some of the histopathologic features of LET; however, there are minimal data on childhood LET. Further research and investigations are needed to more precisely define this condition.
Acknowledgment
The authors acknowledge Richard Schwartz, MD (Akron, Ohio), for reading the biopsy reports and assisting with photomicrographs.
To the Editor:
Lupus erythematosus tumidus (LET) is a rarely diagnosed condition that was first described in 1909 by Hoffmann.1 Limited cases have been reported in the literature, with few documenting the disease in children.2 We report a unique clinical case of LET in a 14-year-old adolescent boy that was distributed solely on the hands. With slight heterogeneity in regards to clinical presentation and histopathology, there is a need for further exploration with regard to LET.
A 14-year-old adolescent boy presented to the dermatology clinic with progressive bilateral edema of 1 year’s duration with plaques and some scaling on the dorsal aspects of the digits and the nail bases predominantly on the right hand (Figure 1) and to a lesser extent on the left hand. The edema, erythema, and tenderness started in the right fifth digit; soon after the edema appeared, plaques began to form at the base of each nail bed, and the edema and erythema progressively spread to the other digits. He denied worsening of symptoms when exposed to cold temperatures. A complete review of systems was negative. The differential diagnoses included chilblain lupus erythematosus, perniosis, dermatomyositis, and polymorphous light eruption. A punch biopsy from the right fourth digit was performed.

The biopsy showed superficial and deep perivascular and periadnexal mononuclear inflammation with large amounts of interstitial mucin deposition (Figure 2). The epidermis exhibited a loose orthokeratotic scale with no signs of interface damage. A diagnosis of perniosis was entertained but was ruled out due to the lack of papillary dermal edema and large amounts of mucin. With the lack of interface change and large amounts of mucin, a diagnosis of LET was favored over chilblain lupus erythematosus, as the latter diagnosis typically demonstrates interface change. The patient was started on hydroxychloroquine 200 mg twice daily and a short course of prednisone, and improvement of the lesions/plaques was noted at follow-up 6 weeks later. Continued improvement was noted 2 years after the initial presentation. His condition recurred when the hydroxychloroquine dosage was reduced to 200 mg once daily after 1 year. The patient did not report any adverse sequelae to treatment.

Histopathologic findings of superficial and deep perivascular and periadnexal lymphocytic infiltrates and interstitial dermal deposition of mucin in LET have remained consistent in the literature. Direct immunofluorescence has not revealed any complement or immunoglobulin deposition on the basement membrane.3,4 The epidermal characteristics are not as uniform, with the majority of cases in one review showing no epidermal changes and a minority showing minimal epidermal changes (eg, epidermal atrophy, hyperkeratosis, parakeratosis, acanthosis, spongiosis).5 When working up patients for LET, blood work usually is unremarkable, as LET rarely is associated with antinuclear antibodies or anti-Ro, anti-La, and anti-DNA antibodies.3,4 Lupus erythematosus tumidus generally is an independent process, but it has been reported to coexist with discoid lupus erythematosus and systemic lupus erythematosus in rare cases.6
The lesions of LET have been consistently described in the literature as photosensitive, erythematous, non-scarring, annular plaques and papules commonly occurring on the head/neck and other sun-exposed areas that do not cause hypopigmentation.3 Treatment of LET consists of systemic treatment with antimalarial drugs, sunscreens, and topical steroids for flares.
Lupus erythematosus tumidus is rare in children, with few case reports noted in the literature. Sonntag et al2 documented the disease in 3 children ranging from 3 to 8 years of age. Furthermore, Ruiz and Sanchez7 reported a case of LET in a 16-year-old adolescent girl. Our case is unique in that the lesions only occurred on the hands, whereas most case reports document distribution of the lesions on the head, neck, face, arms, back, and chest. Our patient’s age and the location of the lesions make it a unique clinical presentation of LET.
Reports in the literature show evidence of heterogeneity in the presentation, classification, and some of the histopathologic features of LET; however, there are minimal data on childhood LET. Further research and investigations are needed to more precisely define this condition.
Acknowledgment
The authors acknowledge Richard Schwartz, MD (Akron, Ohio), for reading the biopsy reports and assisting with photomicrographs.
- Hoffmann E. Demonstrationen: lupus erythematosus tumidus. Derm Zeitschr. 1909;16:159-160.
- Sonntag M, Lehmann P, Megahed M, et al. Lupus erythematosus tumidus in childhood. Dermatology. 2003;207:188-192.
- Schmitt V, Meuth AM, Amler S, et al. Lupus erythematosus tumidus is a separate subtype of cutaneous lupus erythematosus. Br J Dermatol. 2010;162:64-73.
- Vieira V, Del Pozo J, Yebra-Pimentel MT, et al. Lupus erythematosus tumidus: a series of 26 cases. Int J Dermatol. 2006;45:512-517.
- Kuhn A, Richter-Hintz D, Oslislo C, et al. Lupus erythematosus tumidus—a neglected subset of cutaneous lupus erythematosus: report of 40 cases. Arch Dermatol. 2000;136:1033-1041.
- Chen X, Wang S, Li L. A case report of lupus erythematosus tumidus converted from discoid lupus erythematosus. Medicine (Baltimore). 2018;97:e0375.
- Ruiz H, Sanchez J. Tumid lupus erythematosus. Am J Dermatopathol. 1999;21:356-360.
- Hoffmann E. Demonstrationen: lupus erythematosus tumidus. Derm Zeitschr. 1909;16:159-160.
- Sonntag M, Lehmann P, Megahed M, et al. Lupus erythematosus tumidus in childhood. Dermatology. 2003;207:188-192.
- Schmitt V, Meuth AM, Amler S, et al. Lupus erythematosus tumidus is a separate subtype of cutaneous lupus erythematosus. Br J Dermatol. 2010;162:64-73.
- Vieira V, Del Pozo J, Yebra-Pimentel MT, et al. Lupus erythematosus tumidus: a series of 26 cases. Int J Dermatol. 2006;45:512-517.
- Kuhn A, Richter-Hintz D, Oslislo C, et al. Lupus erythematosus tumidus—a neglected subset of cutaneous lupus erythematosus: report of 40 cases. Arch Dermatol. 2000;136:1033-1041.
- Chen X, Wang S, Li L. A case report of lupus erythematosus tumidus converted from discoid lupus erythematosus. Medicine (Baltimore). 2018;97:e0375.
- Ruiz H, Sanchez J. Tumid lupus erythematosus. Am J Dermatopathol. 1999;21:356-360.
Practice Points
- Lupus erythematosus tumidus rarely occurs in the pediatric population.
- Lupus erythematosus tumidus is a unique subset of lupus associated with lack of interface change on histology and large amounts of mucin.
- Lesions typically present on the face and trunk but can very rarely present on the extremities and hands.
POEM outperforms pneumatic dilation in randomized achalasia trial
Peroral endoscopic myotomy (POEM) had a success rate exceeding 90%, versus just about 50% for standard balloon dilation in what investigators say is, to their knowledge, the first-ever randomized trial to evaluate POEM as a first-line modality for this esophageal motility disorder.
Reflux esophagitis was the major downside of POEM, according to investigators, who reported the complication in 41% of patients at a 2-year follow-up, as compared to just 7% of patients undergoing the standard balloon dilation.
Nevertheless, there were no serious adverse events among 63 POEM-treated patients, while one patient out of 63 undergoing pneumatic dilation had a perforation that required endoscopic closure and hospitalization, according to senior study author Albert J. Bredenoord, MD, PhD, of Amsterdam University Medical Center.
“These findings support consideration of POEM as an initial treatment option for patients with achalasia,” Dr. Bredenoord and coinvestigators said in a report on the study appearing in JAMA.
While endoscopic pneumatic dilation is the usual treatment for achalasia, POEM has become more commonly used following case series showing high rates of efficacy, according to the authors.
The POEM procedure also offers advantages over laparoscopic Heller myotomy, which is invasive and associated with severe complications, including a transmural perforation rate of 4%-10%, they said in their report.
Their randomized trial included 133 adults with newly diagnosed achalasia enrolled at one of six hospitals in Germany, Hong Kong, Italy, Netherlands, and the United States.
Patients were randomly assigned to undergo 1-2 pneumatic dilations performed by an endoscopist who had performed at least 20 such procedures in the past, or to a POEM procedure likewise performed by an expert who had already done more than 20 such procedures.
At baseline, patients’ Eckardt symptom scores ranged from 6 to 9 on a scale with 0 indicating the lowest severity, to 12 indicating the highest. The median Eckardt scores were 8 in the POEM group and 7 in the pneumatic dilation group.
Treatment success, defined as an Eckardt score under 3 and no severe complications or retreatment at 2 years, was achieved by 58 of 63 patients (92%) in the POEM group, compared with 34 of 63 patients (54%) in the pneumatic dilation group (P less than .001), investigators reported.
Reflux esophagitis was observed in 22 of 54 POEM-treated patients (41%) who underwent endoscopy at a 2-year evaluation, compared with only 2 of 29 patients (7%) who had received the balloon dilation procedure (P = .002). In line with that finding, both reflux symptoms and daily proton pump inhibitor use were more common in the POEM group, investigators said.
However, there were no differences between POEM and pneumatic dilation groups in quality of life and other secondary endpoints, including median barium column height and median integrated relaxation pressure, they reported.
Two serious adverse events related to treatment were seen, according to investigators, including one perforation requiring an endoscopic closure plus antibiotics and hospitalization for 13 days, and one hospital admission for a night because of severe chest pain with no signs of perforation.
“Although POEM is more invasive and requires more technical endoscopic skills, the risk of severe complications was not higher than with pneumatic dilation, especially when performed by experienced endoscopists,” Dr. Bredenoord and coauthors said in their report.
However, these results do not imply that the traditional dilation procedure should be abandoned, they said, as POEM is more invasive, more involved, and more likely to result in reflux esophagitis.
“It seems reasonable to offer both options to treatment-naive patients with achalasia and counsel them to select treatment based on the patient’s characteristics, personal preference, comorbidity, and disease subtype,” they said.
Funding for the study came from Fonds NutsOhra and the European Society of Gastrointestinal Endoscopy. Dr. Bredenoord reported disclosures related to Norgine, Laborie, Medtronic, Diversatek, Nutricia, Regeneron, Celgene, Bayer, and Dr. Falk Pharma.
SOURCE: Ponds FA et al. JAMA. 2019;322(2):134-44. doi: 10.1001/jama.2019.8859.
Peroral endoscopic myotomy (POEM) had a success rate exceeding 90%, versus just about 50% for standard balloon dilation in what investigators say is, to their knowledge, the first-ever randomized trial to evaluate POEM as a first-line modality for this esophageal motility disorder.
Reflux esophagitis was the major downside of POEM, according to investigators, who reported the complication in 41% of patients at a 2-year follow-up, as compared to just 7% of patients undergoing the standard balloon dilation.
Nevertheless, there were no serious adverse events among 63 POEM-treated patients, while one patient out of 63 undergoing pneumatic dilation had a perforation that required endoscopic closure and hospitalization, according to senior study author Albert J. Bredenoord, MD, PhD, of Amsterdam University Medical Center.
“These findings support consideration of POEM as an initial treatment option for patients with achalasia,” Dr. Bredenoord and coinvestigators said in a report on the study appearing in JAMA.
While endoscopic pneumatic dilation is the usual treatment for achalasia, POEM has become more commonly used following case series showing high rates of efficacy, according to the authors.
The POEM procedure also offers advantages over laparoscopic Heller myotomy, which is invasive and associated with severe complications, including a transmural perforation rate of 4%-10%, they said in their report.
Their randomized trial included 133 adults with newly diagnosed achalasia enrolled at one of six hospitals in Germany, Hong Kong, Italy, Netherlands, and the United States.
Patients were randomly assigned to undergo 1-2 pneumatic dilations performed by an endoscopist who had performed at least 20 such procedures in the past, or to a POEM procedure likewise performed by an expert who had already done more than 20 such procedures.
At baseline, patients’ Eckardt symptom scores ranged from 6 to 9 on a scale with 0 indicating the lowest severity, to 12 indicating the highest. The median Eckardt scores were 8 in the POEM group and 7 in the pneumatic dilation group.
Treatment success, defined as an Eckardt score under 3 and no severe complications or retreatment at 2 years, was achieved by 58 of 63 patients (92%) in the POEM group, compared with 34 of 63 patients (54%) in the pneumatic dilation group (P less than .001), investigators reported.
Reflux esophagitis was observed in 22 of 54 POEM-treated patients (41%) who underwent endoscopy at a 2-year evaluation, compared with only 2 of 29 patients (7%) who had received the balloon dilation procedure (P = .002). In line with that finding, both reflux symptoms and daily proton pump inhibitor use were more common in the POEM group, investigators said.
However, there were no differences between POEM and pneumatic dilation groups in quality of life and other secondary endpoints, including median barium column height and median integrated relaxation pressure, they reported.
Two serious adverse events related to treatment were seen, according to investigators, including one perforation requiring an endoscopic closure plus antibiotics and hospitalization for 13 days, and one hospital admission for a night because of severe chest pain with no signs of perforation.
“Although POEM is more invasive and requires more technical endoscopic skills, the risk of severe complications was not higher than with pneumatic dilation, especially when performed by experienced endoscopists,” Dr. Bredenoord and coauthors said in their report.
However, these results do not imply that the traditional dilation procedure should be abandoned, they said, as POEM is more invasive, more involved, and more likely to result in reflux esophagitis.
“It seems reasonable to offer both options to treatment-naive patients with achalasia and counsel them to select treatment based on the patient’s characteristics, personal preference, comorbidity, and disease subtype,” they said.
Funding for the study came from Fonds NutsOhra and the European Society of Gastrointestinal Endoscopy. Dr. Bredenoord reported disclosures related to Norgine, Laborie, Medtronic, Diversatek, Nutricia, Regeneron, Celgene, Bayer, and Dr. Falk Pharma.
SOURCE: Ponds FA et al. JAMA. 2019;322(2):134-44. doi: 10.1001/jama.2019.8859.
Peroral endoscopic myotomy (POEM) had a success rate exceeding 90%, versus just about 50% for standard balloon dilation in what investigators say is, to their knowledge, the first-ever randomized trial to evaluate POEM as a first-line modality for this esophageal motility disorder.
Reflux esophagitis was the major downside of POEM, according to investigators, who reported the complication in 41% of patients at a 2-year follow-up, as compared to just 7% of patients undergoing the standard balloon dilation.
Nevertheless, there were no serious adverse events among 63 POEM-treated patients, while one patient out of 63 undergoing pneumatic dilation had a perforation that required endoscopic closure and hospitalization, according to senior study author Albert J. Bredenoord, MD, PhD, of Amsterdam University Medical Center.
“These findings support consideration of POEM as an initial treatment option for patients with achalasia,” Dr. Bredenoord and coinvestigators said in a report on the study appearing in JAMA.
While endoscopic pneumatic dilation is the usual treatment for achalasia, POEM has become more commonly used following case series showing high rates of efficacy, according to the authors.
The POEM procedure also offers advantages over laparoscopic Heller myotomy, which is invasive and associated with severe complications, including a transmural perforation rate of 4%-10%, they said in their report.
Their randomized trial included 133 adults with newly diagnosed achalasia enrolled at one of six hospitals in Germany, Hong Kong, Italy, Netherlands, and the United States.
Patients were randomly assigned to undergo 1-2 pneumatic dilations performed by an endoscopist who had performed at least 20 such procedures in the past, or to a POEM procedure likewise performed by an expert who had already done more than 20 such procedures.
At baseline, patients’ Eckardt symptom scores ranged from 6 to 9 on a scale with 0 indicating the lowest severity, to 12 indicating the highest. The median Eckardt scores were 8 in the POEM group and 7 in the pneumatic dilation group.
Treatment success, defined as an Eckardt score under 3 and no severe complications or retreatment at 2 years, was achieved by 58 of 63 patients (92%) in the POEM group, compared with 34 of 63 patients (54%) in the pneumatic dilation group (P less than .001), investigators reported.
Reflux esophagitis was observed in 22 of 54 POEM-treated patients (41%) who underwent endoscopy at a 2-year evaluation, compared with only 2 of 29 patients (7%) who had received the balloon dilation procedure (P = .002). In line with that finding, both reflux symptoms and daily proton pump inhibitor use were more common in the POEM group, investigators said.
However, there were no differences between POEM and pneumatic dilation groups in quality of life and other secondary endpoints, including median barium column height and median integrated relaxation pressure, they reported.
Two serious adverse events related to treatment were seen, according to investigators, including one perforation requiring an endoscopic closure plus antibiotics and hospitalization for 13 days, and one hospital admission for a night because of severe chest pain with no signs of perforation.
“Although POEM is more invasive and requires more technical endoscopic skills, the risk of severe complications was not higher than with pneumatic dilation, especially when performed by experienced endoscopists,” Dr. Bredenoord and coauthors said in their report.
However, these results do not imply that the traditional dilation procedure should be abandoned, they said, as POEM is more invasive, more involved, and more likely to result in reflux esophagitis.
“It seems reasonable to offer both options to treatment-naive patients with achalasia and counsel them to select treatment based on the patient’s characteristics, personal preference, comorbidity, and disease subtype,” they said.
Funding for the study came from Fonds NutsOhra and the European Society of Gastrointestinal Endoscopy. Dr. Bredenoord reported disclosures related to Norgine, Laborie, Medtronic, Diversatek, Nutricia, Regeneron, Celgene, Bayer, and Dr. Falk Pharma.
SOURCE: Ponds FA et al. JAMA. 2019;322(2):134-44. doi: 10.1001/jama.2019.8859.
FROM JAMA
CDC Advisory: Acute Flaccid Myelitis
Late summer is the season to be especially alert for possible cases of acute flaccid myelitis (AFM), the CDC says.
Since 2014, when the CDC began tracking AFM, 570 cases, mostly in children, have been reported. Outbreaks have followed a pattern: every 2 years, spiking between August and October. Nearly all states and DC have reported cases. The largest outbreak, 233 cases, was in 2018. Theoretically, 2019 would be an off year, but too little is known about AFM to say outbreaks are unlikely.
AFM starts with symptoms similar to those of a viral infection but can progress rapidly to limb weakness, then respiratory failure. Most patients are previously healthy children, average age 5 years old, who had respiratory symptoms or fever consistent with a viral infection less than a week before they experienced sudden weakness in their arms or legs. On average, the CDC receives reports of suspected AFM cases 18 days after the patient develops limb weakness.
The CDC believes viruses play a role, but which ones is still unclear. Symptoms have been found to develop after poliovirus, West Nile virus, and adenovirus infections. In an analysis of confirmed cases from 2018, CDC researchers detected enteroviruses and rhinoviruses in nearly half of stool and respiratory specimens. However, of 74 cases with a cerebral spinal fluid specimen, only 2 were positive for enteroviruses. All specimens tested negative for poliovirus.
But even when it is associated with a viral infection, it is not known how the infection triggered the AFM, or why it triggers AFM in some people and not others. AFM is rare—affecting ≤ 2 children per million in the US every year. Viral infections from enteroviruses are common, especially in children—and especially in the late summer/early autumn months. It is not known why a small number of people develop AFM while most others recover.
AFM can be difficult to diagnose because the symptoms are similar to those of neurologic diseases, such as Guillain-Barré syndrome. As of yet, no laboratory test is available; diagnosis is done through physical examination and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) scans of the spinal cord.
There also are no proven ways to treat or prevent AFM. That is why timing is so key. The CDC says as soon as AFM is suspected, collect cerebral spinal fluid, serum, stool, and nasopharyngeal swabs. If an MRI shows a spinal lesion with some gray matter involvement, alert the health department and send specimens and medical records. Refer to specialists, monitor the patient for worsening symptoms, hospitalize if indicated, and begin treatment and rehabilitation.
In short: no specific etiology, no specific way to diagnose, and no specific treatment exist for AFM. Treatments, including immunoglobulin, corticosteroids, and antivirals have been tried, but no clear evidence exists that any have affected recovery. Other treatment is supportive, with physical and occupational therapy.
The length of recovery time varies. Some people make a full recovery, most have continued muscle weakness even after a year.
The CDC is researching possible risk factors, conducting advanced laboratory testing and research to determine how viral infections may lead to AFM, and tracking long-term patient outcomes.
Clinicians can contact neurologists who specialize in AFM through the AFM Physician Consult and Support Portal: https://myelitis.org/living-with-myelitis/resources/afm-physician-support-portal/.
Late summer is the season to be especially alert for possible cases of acute flaccid myelitis (AFM), the CDC says.
Since 2014, when the CDC began tracking AFM, 570 cases, mostly in children, have been reported. Outbreaks have followed a pattern: every 2 years, spiking between August and October. Nearly all states and DC have reported cases. The largest outbreak, 233 cases, was in 2018. Theoretically, 2019 would be an off year, but too little is known about AFM to say outbreaks are unlikely.
AFM starts with symptoms similar to those of a viral infection but can progress rapidly to limb weakness, then respiratory failure. Most patients are previously healthy children, average age 5 years old, who had respiratory symptoms or fever consistent with a viral infection less than a week before they experienced sudden weakness in their arms or legs. On average, the CDC receives reports of suspected AFM cases 18 days after the patient develops limb weakness.
The CDC believes viruses play a role, but which ones is still unclear. Symptoms have been found to develop after poliovirus, West Nile virus, and adenovirus infections. In an analysis of confirmed cases from 2018, CDC researchers detected enteroviruses and rhinoviruses in nearly half of stool and respiratory specimens. However, of 74 cases with a cerebral spinal fluid specimen, only 2 were positive for enteroviruses. All specimens tested negative for poliovirus.
But even when it is associated with a viral infection, it is not known how the infection triggered the AFM, or why it triggers AFM in some people and not others. AFM is rare—affecting ≤ 2 children per million in the US every year. Viral infections from enteroviruses are common, especially in children—and especially in the late summer/early autumn months. It is not known why a small number of people develop AFM while most others recover.
AFM can be difficult to diagnose because the symptoms are similar to those of neurologic diseases, such as Guillain-Barré syndrome. As of yet, no laboratory test is available; diagnosis is done through physical examination and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) scans of the spinal cord.
There also are no proven ways to treat or prevent AFM. That is why timing is so key. The CDC says as soon as AFM is suspected, collect cerebral spinal fluid, serum, stool, and nasopharyngeal swabs. If an MRI shows a spinal lesion with some gray matter involvement, alert the health department and send specimens and medical records. Refer to specialists, monitor the patient for worsening symptoms, hospitalize if indicated, and begin treatment and rehabilitation.
In short: no specific etiology, no specific way to diagnose, and no specific treatment exist for AFM. Treatments, including immunoglobulin, corticosteroids, and antivirals have been tried, but no clear evidence exists that any have affected recovery. Other treatment is supportive, with physical and occupational therapy.
The length of recovery time varies. Some people make a full recovery, most have continued muscle weakness even after a year.
The CDC is researching possible risk factors, conducting advanced laboratory testing and research to determine how viral infections may lead to AFM, and tracking long-term patient outcomes.
Clinicians can contact neurologists who specialize in AFM through the AFM Physician Consult and Support Portal: https://myelitis.org/living-with-myelitis/resources/afm-physician-support-portal/.
Late summer is the season to be especially alert for possible cases of acute flaccid myelitis (AFM), the CDC says.
Since 2014, when the CDC began tracking AFM, 570 cases, mostly in children, have been reported. Outbreaks have followed a pattern: every 2 years, spiking between August and October. Nearly all states and DC have reported cases. The largest outbreak, 233 cases, was in 2018. Theoretically, 2019 would be an off year, but too little is known about AFM to say outbreaks are unlikely.
AFM starts with symptoms similar to those of a viral infection but can progress rapidly to limb weakness, then respiratory failure. Most patients are previously healthy children, average age 5 years old, who had respiratory symptoms or fever consistent with a viral infection less than a week before they experienced sudden weakness in their arms or legs. On average, the CDC receives reports of suspected AFM cases 18 days after the patient develops limb weakness.
The CDC believes viruses play a role, but which ones is still unclear. Symptoms have been found to develop after poliovirus, West Nile virus, and adenovirus infections. In an analysis of confirmed cases from 2018, CDC researchers detected enteroviruses and rhinoviruses in nearly half of stool and respiratory specimens. However, of 74 cases with a cerebral spinal fluid specimen, only 2 were positive for enteroviruses. All specimens tested negative for poliovirus.
But even when it is associated with a viral infection, it is not known how the infection triggered the AFM, or why it triggers AFM in some people and not others. AFM is rare—affecting ≤ 2 children per million in the US every year. Viral infections from enteroviruses are common, especially in children—and especially in the late summer/early autumn months. It is not known why a small number of people develop AFM while most others recover.
AFM can be difficult to diagnose because the symptoms are similar to those of neurologic diseases, such as Guillain-Barré syndrome. As of yet, no laboratory test is available; diagnosis is done through physical examination and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) scans of the spinal cord.
There also are no proven ways to treat or prevent AFM. That is why timing is so key. The CDC says as soon as AFM is suspected, collect cerebral spinal fluid, serum, stool, and nasopharyngeal swabs. If an MRI shows a spinal lesion with some gray matter involvement, alert the health department and send specimens and medical records. Refer to specialists, monitor the patient for worsening symptoms, hospitalize if indicated, and begin treatment and rehabilitation.
In short: no specific etiology, no specific way to diagnose, and no specific treatment exist for AFM. Treatments, including immunoglobulin, corticosteroids, and antivirals have been tried, but no clear evidence exists that any have affected recovery. Other treatment is supportive, with physical and occupational therapy.
The length of recovery time varies. Some people make a full recovery, most have continued muscle weakness even after a year.
The CDC is researching possible risk factors, conducting advanced laboratory testing and research to determine how viral infections may lead to AFM, and tracking long-term patient outcomes.
Clinicians can contact neurologists who specialize in AFM through the AFM Physician Consult and Support Portal: https://myelitis.org/living-with-myelitis/resources/afm-physician-support-portal/.
Ebola outbreak: WHO/OCHA call for more aid, better security
The continuing outbreak of Ebola in the Democratic Republic of the Congo (DRC) was the subject of a special United Nations high-level event organized by the World Health Organization (WHO) and the United Nations Office for the Coordination of Humanitarian Affairs (OCHA). It was comoderated by Tedros Adhanom Ghebreyesus, Director-General of the World Health Organization, and Mark Lowcock, the UN Under-Secretary-General for Humanitarian Affairs and Emergency Relief Coordinator.

The DRC Ebola outbreak has drawn continuing concern and was highlighted by an even greater feeling of urgency as “on the eve of the conference,” according to one speaker.
That same infected individual – a priest arriving by bus to the city from an affected area – died of the disease the day after the conference concluded, according to the DRC authorities.
In his opening remarks, Mr. Lowcock stressed the importance of coordinating international efforts with the on-the-ground responses being carried out under the direction of Oly Ilunga Kalenga, MD, the DRC’s Minister of Public Health, who was also present and spoke at the meeting. Dr. Kalenga resigned his post on July 22, 2019.*
Mr. Lowcock stressed three points in particular that make for unique changes to the current response, compared with the earlier outbreak of 2014-2016.
First, in the previous outbreak in West Africa, “we didn’t have the vaccine and we didn’t have some of the successful treatments” that are currently available. Furthermore, more than 160,000 people have now been vaccinated and “the vaccine has a high degree of effectiveness.” This is an asset compared to the previous situation, he stated.
In his second point, he warned that the outbreak in the DRC “is taking place in an insecure and complex area with multiple armed groups present and large-scale preexisting humanitarian needs. Special interests distort the context. A history of disaffection with national authorities and foreigners generates distrust and makes the response more complicated. And one manifestation of that is attacks against health facilities and health care workers.” He added that “two more of our colleagues, trying to be part of the solution,” were killed in the past few days before the meeting. “Therefore, security for the response is of absolutely paramount importance, and we are trying to strengthen the way the UN family supports the government’s own security.”
The third major difference from the West Africa outbreak, Mr. Lowcock pointed out, was the issue of money. There was more than $2 billion in international support available for that earlier response. However, “what we have available for us in the DRC is just a small fraction of that. Donors released funds early on ... but much more is needed.” He warned that the cost of reaching zero cases must not be underestimated, and that the fourth strategic response plan for this outbreak, currently under development, “will be budgeted at a much higher level than the previous three plans, and that’s because it’s our assessment that we need a bigger, more comprehensive response if we’re to get to zero cases than we’ve had hitherto.”
In fact, he said, “unless there is a big scale up in the response, we’re unlikely to get to zero cases.”
The meeting also featured speakers outlining more local aspects of the response and discussing how international workers were coordinating more and more with local authorities and health practitioners in order to deliver health care on the ground while attempting to avoid the distrust created in the past, while still ensuring security for foreign personnel.
Commenting on the issue of security, Rory Stewart, the United Kingdom’s Secretary of State for International Development, described how a major DRC Ebola treatment center was attacked and burned by military insurgents, but is now rebuilt. He said that, while there have been some improvements and reasons to be hopeful, “this isn’t a moment for complacency; [the situation] is literally on the knife-edge.” He added: “If you go into that treatment center now, you will see that, although there are very good medical procedures, there are really, really worrying security procedures. The entire protection for the medical staff consists of a small square of sandbags about the height of this table [he raised his hand just above the standard conference table he was sitting at], behind which the doctors and nurses are supposed to hide if armed men get into the compound.”
In his presentation, David Gressly, the UN Emergency Ebola Response Coordinator (speaking by video from the DRC), stressed the need to cooperate with local authorities and to build local trust, stating that “the UN is putting together a tight, disciplined, coordinated system for rapid response and operational adjustments so that we can shift from chasing the disease to getting ahead of it. We need to quickly detect cases ... that have moved into areas of risk to stop the transmission early.”
Matshidiso Moeti, MD, WHO Regional Director for Africa, added in her presentation: “We’ve identified nine high-risk countries. Among those, Burundi, South Sudan, and Uganda face the highest risk and require our concerted and continued efforts.” She said that more than 10,000 health care workers in areas of high risk have so far been vaccinated against the disease.
In his concluding statement, Dr. Kalenga described the current state of affairs in his country with a modicum of hope. “A community that has been told it has a case of Ebola is a community that is traumatized by the very announcement of this epidemic. With time, the community has learned to face up to this epidemic differently. In some villages we are given a very different welcome than before. ... The villagers ask: ‘What should we do to make sure the Ebola case is the only one? The first and the last one?’ Throughout this epidemic, we have seen the people become more aware, and a certain acceptance of the very difficult and lethal diagnosis. ... So we have seen that work in the community has been maturing and bearing fruit.”
However, he pointed out, “there is a whole debate around the area of vaccinations, and we do need to close down this debate. At this point in time, we have a vaccine that is highly effective, a vaccine that is accepted by the population, after whole periods of mistrust. So we’ve come to a point in time when the population is accepting a vaccine, a vaccine that works, so we decided to no longer open the debate on vaccines and vaccination. ....We don’t want contradictory messages going out here, we don’t want different schemes going out. ...We have an effective weapon, we have an effective molecule. Let’s focus on that. Let’s all go in the same direction,” he concluded.
On July 11, an announcement by DRC officials stated that Merck’s rVSV-ZEBOV would be the only vaccine that will be used during the current Ebola outbreak in North Kivu and Ituri provinces, and that no other clinical vaccine trials to be allowed in the country so as not to confuse the population.
In that same announcement, the DRC reported that, since the beginning of the epidemic, the cumulative number of Ebola cases was 2,451, of which 2,357 were confirmed and 94 probable. There were 1,647 deaths (1,553 confirmed and 94 probable) and 683 people who survived. An additional 364 suspected cases were under investigation.
*Updated Aug. 1, 2019.
SOURCE: United Nations WHO/OCHA Webcast and Media Stakeout. July 15, 2019.
The continuing outbreak of Ebola in the Democratic Republic of the Congo (DRC) was the subject of a special United Nations high-level event organized by the World Health Organization (WHO) and the United Nations Office for the Coordination of Humanitarian Affairs (OCHA). It was comoderated by Tedros Adhanom Ghebreyesus, Director-General of the World Health Organization, and Mark Lowcock, the UN Under-Secretary-General for Humanitarian Affairs and Emergency Relief Coordinator.

The DRC Ebola outbreak has drawn continuing concern and was highlighted by an even greater feeling of urgency as “on the eve of the conference,” according to one speaker.
That same infected individual – a priest arriving by bus to the city from an affected area – died of the disease the day after the conference concluded, according to the DRC authorities.
In his opening remarks, Mr. Lowcock stressed the importance of coordinating international efforts with the on-the-ground responses being carried out under the direction of Oly Ilunga Kalenga, MD, the DRC’s Minister of Public Health, who was also present and spoke at the meeting. Dr. Kalenga resigned his post on July 22, 2019.*
Mr. Lowcock stressed three points in particular that make for unique changes to the current response, compared with the earlier outbreak of 2014-2016.
First, in the previous outbreak in West Africa, “we didn’t have the vaccine and we didn’t have some of the successful treatments” that are currently available. Furthermore, more than 160,000 people have now been vaccinated and “the vaccine has a high degree of effectiveness.” This is an asset compared to the previous situation, he stated.
In his second point, he warned that the outbreak in the DRC “is taking place in an insecure and complex area with multiple armed groups present and large-scale preexisting humanitarian needs. Special interests distort the context. A history of disaffection with national authorities and foreigners generates distrust and makes the response more complicated. And one manifestation of that is attacks against health facilities and health care workers.” He added that “two more of our colleagues, trying to be part of the solution,” were killed in the past few days before the meeting. “Therefore, security for the response is of absolutely paramount importance, and we are trying to strengthen the way the UN family supports the government’s own security.”
The third major difference from the West Africa outbreak, Mr. Lowcock pointed out, was the issue of money. There was more than $2 billion in international support available for that earlier response. However, “what we have available for us in the DRC is just a small fraction of that. Donors released funds early on ... but much more is needed.” He warned that the cost of reaching zero cases must not be underestimated, and that the fourth strategic response plan for this outbreak, currently under development, “will be budgeted at a much higher level than the previous three plans, and that’s because it’s our assessment that we need a bigger, more comprehensive response if we’re to get to zero cases than we’ve had hitherto.”
In fact, he said, “unless there is a big scale up in the response, we’re unlikely to get to zero cases.”
The meeting also featured speakers outlining more local aspects of the response and discussing how international workers were coordinating more and more with local authorities and health practitioners in order to deliver health care on the ground while attempting to avoid the distrust created in the past, while still ensuring security for foreign personnel.
Commenting on the issue of security, Rory Stewart, the United Kingdom’s Secretary of State for International Development, described how a major DRC Ebola treatment center was attacked and burned by military insurgents, but is now rebuilt. He said that, while there have been some improvements and reasons to be hopeful, “this isn’t a moment for complacency; [the situation] is literally on the knife-edge.” He added: “If you go into that treatment center now, you will see that, although there are very good medical procedures, there are really, really worrying security procedures. The entire protection for the medical staff consists of a small square of sandbags about the height of this table [he raised his hand just above the standard conference table he was sitting at], behind which the doctors and nurses are supposed to hide if armed men get into the compound.”
In his presentation, David Gressly, the UN Emergency Ebola Response Coordinator (speaking by video from the DRC), stressed the need to cooperate with local authorities and to build local trust, stating that “the UN is putting together a tight, disciplined, coordinated system for rapid response and operational adjustments so that we can shift from chasing the disease to getting ahead of it. We need to quickly detect cases ... that have moved into areas of risk to stop the transmission early.”
Matshidiso Moeti, MD, WHO Regional Director for Africa, added in her presentation: “We’ve identified nine high-risk countries. Among those, Burundi, South Sudan, and Uganda face the highest risk and require our concerted and continued efforts.” She said that more than 10,000 health care workers in areas of high risk have so far been vaccinated against the disease.
In his concluding statement, Dr. Kalenga described the current state of affairs in his country with a modicum of hope. “A community that has been told it has a case of Ebola is a community that is traumatized by the very announcement of this epidemic. With time, the community has learned to face up to this epidemic differently. In some villages we are given a very different welcome than before. ... The villagers ask: ‘What should we do to make sure the Ebola case is the only one? The first and the last one?’ Throughout this epidemic, we have seen the people become more aware, and a certain acceptance of the very difficult and lethal diagnosis. ... So we have seen that work in the community has been maturing and bearing fruit.”
However, he pointed out, “there is a whole debate around the area of vaccinations, and we do need to close down this debate. At this point in time, we have a vaccine that is highly effective, a vaccine that is accepted by the population, after whole periods of mistrust. So we’ve come to a point in time when the population is accepting a vaccine, a vaccine that works, so we decided to no longer open the debate on vaccines and vaccination. ....We don’t want contradictory messages going out here, we don’t want different schemes going out. ...We have an effective weapon, we have an effective molecule. Let’s focus on that. Let’s all go in the same direction,” he concluded.
On July 11, an announcement by DRC officials stated that Merck’s rVSV-ZEBOV would be the only vaccine that will be used during the current Ebola outbreak in North Kivu and Ituri provinces, and that no other clinical vaccine trials to be allowed in the country so as not to confuse the population.
In that same announcement, the DRC reported that, since the beginning of the epidemic, the cumulative number of Ebola cases was 2,451, of which 2,357 were confirmed and 94 probable. There were 1,647 deaths (1,553 confirmed and 94 probable) and 683 people who survived. An additional 364 suspected cases were under investigation.
*Updated Aug. 1, 2019.
SOURCE: United Nations WHO/OCHA Webcast and Media Stakeout. July 15, 2019.
The continuing outbreak of Ebola in the Democratic Republic of the Congo (DRC) was the subject of a special United Nations high-level event organized by the World Health Organization (WHO) and the United Nations Office for the Coordination of Humanitarian Affairs (OCHA). It was comoderated by Tedros Adhanom Ghebreyesus, Director-General of the World Health Organization, and Mark Lowcock, the UN Under-Secretary-General for Humanitarian Affairs and Emergency Relief Coordinator.

The DRC Ebola outbreak has drawn continuing concern and was highlighted by an even greater feeling of urgency as “on the eve of the conference,” according to one speaker.
That same infected individual – a priest arriving by bus to the city from an affected area – died of the disease the day after the conference concluded, according to the DRC authorities.
In his opening remarks, Mr. Lowcock stressed the importance of coordinating international efforts with the on-the-ground responses being carried out under the direction of Oly Ilunga Kalenga, MD, the DRC’s Minister of Public Health, who was also present and spoke at the meeting. Dr. Kalenga resigned his post on July 22, 2019.*
Mr. Lowcock stressed three points in particular that make for unique changes to the current response, compared with the earlier outbreak of 2014-2016.
First, in the previous outbreak in West Africa, “we didn’t have the vaccine and we didn’t have some of the successful treatments” that are currently available. Furthermore, more than 160,000 people have now been vaccinated and “the vaccine has a high degree of effectiveness.” This is an asset compared to the previous situation, he stated.
In his second point, he warned that the outbreak in the DRC “is taking place in an insecure and complex area with multiple armed groups present and large-scale preexisting humanitarian needs. Special interests distort the context. A history of disaffection with national authorities and foreigners generates distrust and makes the response more complicated. And one manifestation of that is attacks against health facilities and health care workers.” He added that “two more of our colleagues, trying to be part of the solution,” were killed in the past few days before the meeting. “Therefore, security for the response is of absolutely paramount importance, and we are trying to strengthen the way the UN family supports the government’s own security.”
The third major difference from the West Africa outbreak, Mr. Lowcock pointed out, was the issue of money. There was more than $2 billion in international support available for that earlier response. However, “what we have available for us in the DRC is just a small fraction of that. Donors released funds early on ... but much more is needed.” He warned that the cost of reaching zero cases must not be underestimated, and that the fourth strategic response plan for this outbreak, currently under development, “will be budgeted at a much higher level than the previous three plans, and that’s because it’s our assessment that we need a bigger, more comprehensive response if we’re to get to zero cases than we’ve had hitherto.”
In fact, he said, “unless there is a big scale up in the response, we’re unlikely to get to zero cases.”
The meeting also featured speakers outlining more local aspects of the response and discussing how international workers were coordinating more and more with local authorities and health practitioners in order to deliver health care on the ground while attempting to avoid the distrust created in the past, while still ensuring security for foreign personnel.
Commenting on the issue of security, Rory Stewart, the United Kingdom’s Secretary of State for International Development, described how a major DRC Ebola treatment center was attacked and burned by military insurgents, but is now rebuilt. He said that, while there have been some improvements and reasons to be hopeful, “this isn’t a moment for complacency; [the situation] is literally on the knife-edge.” He added: “If you go into that treatment center now, you will see that, although there are very good medical procedures, there are really, really worrying security procedures. The entire protection for the medical staff consists of a small square of sandbags about the height of this table [he raised his hand just above the standard conference table he was sitting at], behind which the doctors and nurses are supposed to hide if armed men get into the compound.”
In his presentation, David Gressly, the UN Emergency Ebola Response Coordinator (speaking by video from the DRC), stressed the need to cooperate with local authorities and to build local trust, stating that “the UN is putting together a tight, disciplined, coordinated system for rapid response and operational adjustments so that we can shift from chasing the disease to getting ahead of it. We need to quickly detect cases ... that have moved into areas of risk to stop the transmission early.”
Matshidiso Moeti, MD, WHO Regional Director for Africa, added in her presentation: “We’ve identified nine high-risk countries. Among those, Burundi, South Sudan, and Uganda face the highest risk and require our concerted and continued efforts.” She said that more than 10,000 health care workers in areas of high risk have so far been vaccinated against the disease.
In his concluding statement, Dr. Kalenga described the current state of affairs in his country with a modicum of hope. “A community that has been told it has a case of Ebola is a community that is traumatized by the very announcement of this epidemic. With time, the community has learned to face up to this epidemic differently. In some villages we are given a very different welcome than before. ... The villagers ask: ‘What should we do to make sure the Ebola case is the only one? The first and the last one?’ Throughout this epidemic, we have seen the people become more aware, and a certain acceptance of the very difficult and lethal diagnosis. ... So we have seen that work in the community has been maturing and bearing fruit.”
However, he pointed out, “there is a whole debate around the area of vaccinations, and we do need to close down this debate. At this point in time, we have a vaccine that is highly effective, a vaccine that is accepted by the population, after whole periods of mistrust. So we’ve come to a point in time when the population is accepting a vaccine, a vaccine that works, so we decided to no longer open the debate on vaccines and vaccination. ....We don’t want contradictory messages going out here, we don’t want different schemes going out. ...We have an effective weapon, we have an effective molecule. Let’s focus on that. Let’s all go in the same direction,” he concluded.
On July 11, an announcement by DRC officials stated that Merck’s rVSV-ZEBOV would be the only vaccine that will be used during the current Ebola outbreak in North Kivu and Ituri provinces, and that no other clinical vaccine trials to be allowed in the country so as not to confuse the population.
In that same announcement, the DRC reported that, since the beginning of the epidemic, the cumulative number of Ebola cases was 2,451, of which 2,357 were confirmed and 94 probable. There were 1,647 deaths (1,553 confirmed and 94 probable) and 683 people who survived. An additional 364 suspected cases were under investigation.
*Updated Aug. 1, 2019.
SOURCE: United Nations WHO/OCHA Webcast and Media Stakeout. July 15, 2019.
REPORTING FROM A UN MEETING LIVE WEBCAST
Ibrutinib tops chlorambucil against CLL
AMSTERDAM – After 5 years, a large majority of patients with chronic lymphocytic leukemia treated with front-line ibrutinib (Imbruvica) have not experienced disease progression, and the median progression-free survival has still not been reached, long-term follow-up from the RESONATE-2 shows.
The 5-year estimated progression-free survival (PFS) rates were 70% for patients who had been randomized to receive ibrutinib monotherapy, compared with 12% for patients randomized to chlorambucil, reported Alessandra Tedeschi, MD, from Azienda Ospedaliera Niguarda Ca’ Granda in Milan.
Ibrutinib was also associated with a halving of risk for death, compared with chlorambucil, she said at the annual congress of the European Hematology Association.
“Importantly, the rate of progression during ibrutinib treatment was very low; only 8 – that is, 6% of patients” – experienced disease progression while receiving ibrutinib, she noted.
In the RESONATE-2 (PCYC-1115) trial, investigators enrolled 269 adults aged 65 years and older with previously untreated CLL/small lymphocytic lymphoma (SLL). Patients at the younger end of the age range (65-69 years) had to have comorbidities that would have made them ineligible for the FCR chemotherapy regimen (fludarabine, cyclophosphamide, and rituximab). Additionally, patients with the deleterious 17p deletion were excluded.
Patients were stratified by performance status and Rai stage and then randomized to receive either ibrutinib 420 mg once daily until disease progression or unacceptable toxicity (136 patients) or chlorambucil 0.5 mg/kg to a maximum of 0.8 mg/kg for up to 12 cycles (133 patients). The trial also had an extension study for patients who had disease progression as confirmed by an independent review committee or who had completed the RESONATE-2 trial. Of the 133 patients in the chlorambucil arm, 76 (57% of the intention-to-treat population) were crossed over to ibrutinib following disease progression.
The median duration of ibrutinib treatment was 57.1 months, with 73% of patients being on it for more than 3 years, 65% for more than 4 years, and 27% for more than 5 years. As of the data cutoff, 79 patients (58%) were continuing with ibrutinib on study.
At 5 years, 70% of ibrutinib-treated patients and 12% of chlorambucil-treated patients were estimated to be progression-free and alive (hazard ratio for PFS with ibrutinib 0.146 (95% confidence interval, 0.10-0.22). The benefit of ibrutinib was consistent for patients with high-risk genomic features, including the 11q deletion and unmutated immunoglobulin heavy-chain variable genes.
Estimated 5-year overall survival was also better with ibrutinib, at 83% vs. 68% (hazard ratio, 0.45; 95% CI, 0.266-0.761).
The most common grade 3 or greater adverse events occurring with ibrutinib were neutropenia (13%), pneumonia (12%), hypertension (8%), anemia (7%), hyponatremia (6%), atrial fibrillation (5%), and cataract (5%). The rates of most adverse events decreased over time, and dose reductions because of adverse events also diminished over time, from 5% of patients in the first year down to zero in years 4 through 5.
Patients responded to subsequent CLL therapies following ibrutinib discontinuation, including chemoimmunotherapy and other kinase inhibitors, Dr. Tedeschi said.
The trial was sponsored by Pharmacyclics with collaboration from Janssen Research & Development. Dr. Tedeschi reported advisory board activities with Janssen, AbbVie, and BeiGene.
SOURCE: Tedeschi A et al. EHA Congress, Abstract S107.
AMSTERDAM – After 5 years, a large majority of patients with chronic lymphocytic leukemia treated with front-line ibrutinib (Imbruvica) have not experienced disease progression, and the median progression-free survival has still not been reached, long-term follow-up from the RESONATE-2 shows.
The 5-year estimated progression-free survival (PFS) rates were 70% for patients who had been randomized to receive ibrutinib monotherapy, compared with 12% for patients randomized to chlorambucil, reported Alessandra Tedeschi, MD, from Azienda Ospedaliera Niguarda Ca’ Granda in Milan.
Ibrutinib was also associated with a halving of risk for death, compared with chlorambucil, she said at the annual congress of the European Hematology Association.
“Importantly, the rate of progression during ibrutinib treatment was very low; only 8 – that is, 6% of patients” – experienced disease progression while receiving ibrutinib, she noted.
In the RESONATE-2 (PCYC-1115) trial, investigators enrolled 269 adults aged 65 years and older with previously untreated CLL/small lymphocytic lymphoma (SLL). Patients at the younger end of the age range (65-69 years) had to have comorbidities that would have made them ineligible for the FCR chemotherapy regimen (fludarabine, cyclophosphamide, and rituximab). Additionally, patients with the deleterious 17p deletion were excluded.
Patients were stratified by performance status and Rai stage and then randomized to receive either ibrutinib 420 mg once daily until disease progression or unacceptable toxicity (136 patients) or chlorambucil 0.5 mg/kg to a maximum of 0.8 mg/kg for up to 12 cycles (133 patients). The trial also had an extension study for patients who had disease progression as confirmed by an independent review committee or who had completed the RESONATE-2 trial. Of the 133 patients in the chlorambucil arm, 76 (57% of the intention-to-treat population) were crossed over to ibrutinib following disease progression.
The median duration of ibrutinib treatment was 57.1 months, with 73% of patients being on it for more than 3 years, 65% for more than 4 years, and 27% for more than 5 years. As of the data cutoff, 79 patients (58%) were continuing with ibrutinib on study.
At 5 years, 70% of ibrutinib-treated patients and 12% of chlorambucil-treated patients were estimated to be progression-free and alive (hazard ratio for PFS with ibrutinib 0.146 (95% confidence interval, 0.10-0.22). The benefit of ibrutinib was consistent for patients with high-risk genomic features, including the 11q deletion and unmutated immunoglobulin heavy-chain variable genes.
Estimated 5-year overall survival was also better with ibrutinib, at 83% vs. 68% (hazard ratio, 0.45; 95% CI, 0.266-0.761).
The most common grade 3 or greater adverse events occurring with ibrutinib were neutropenia (13%), pneumonia (12%), hypertension (8%), anemia (7%), hyponatremia (6%), atrial fibrillation (5%), and cataract (5%). The rates of most adverse events decreased over time, and dose reductions because of adverse events also diminished over time, from 5% of patients in the first year down to zero in years 4 through 5.
Patients responded to subsequent CLL therapies following ibrutinib discontinuation, including chemoimmunotherapy and other kinase inhibitors, Dr. Tedeschi said.
The trial was sponsored by Pharmacyclics with collaboration from Janssen Research & Development. Dr. Tedeschi reported advisory board activities with Janssen, AbbVie, and BeiGene.
SOURCE: Tedeschi A et al. EHA Congress, Abstract S107.
AMSTERDAM – After 5 years, a large majority of patients with chronic lymphocytic leukemia treated with front-line ibrutinib (Imbruvica) have not experienced disease progression, and the median progression-free survival has still not been reached, long-term follow-up from the RESONATE-2 shows.
The 5-year estimated progression-free survival (PFS) rates were 70% for patients who had been randomized to receive ibrutinib monotherapy, compared with 12% for patients randomized to chlorambucil, reported Alessandra Tedeschi, MD, from Azienda Ospedaliera Niguarda Ca’ Granda in Milan.
Ibrutinib was also associated with a halving of risk for death, compared with chlorambucil, she said at the annual congress of the European Hematology Association.
“Importantly, the rate of progression during ibrutinib treatment was very low; only 8 – that is, 6% of patients” – experienced disease progression while receiving ibrutinib, she noted.
In the RESONATE-2 (PCYC-1115) trial, investigators enrolled 269 adults aged 65 years and older with previously untreated CLL/small lymphocytic lymphoma (SLL). Patients at the younger end of the age range (65-69 years) had to have comorbidities that would have made them ineligible for the FCR chemotherapy regimen (fludarabine, cyclophosphamide, and rituximab). Additionally, patients with the deleterious 17p deletion were excluded.
Patients were stratified by performance status and Rai stage and then randomized to receive either ibrutinib 420 mg once daily until disease progression or unacceptable toxicity (136 patients) or chlorambucil 0.5 mg/kg to a maximum of 0.8 mg/kg for up to 12 cycles (133 patients). The trial also had an extension study for patients who had disease progression as confirmed by an independent review committee or who had completed the RESONATE-2 trial. Of the 133 patients in the chlorambucil arm, 76 (57% of the intention-to-treat population) were crossed over to ibrutinib following disease progression.
The median duration of ibrutinib treatment was 57.1 months, with 73% of patients being on it for more than 3 years, 65% for more than 4 years, and 27% for more than 5 years. As of the data cutoff, 79 patients (58%) were continuing with ibrutinib on study.
At 5 years, 70% of ibrutinib-treated patients and 12% of chlorambucil-treated patients were estimated to be progression-free and alive (hazard ratio for PFS with ibrutinib 0.146 (95% confidence interval, 0.10-0.22). The benefit of ibrutinib was consistent for patients with high-risk genomic features, including the 11q deletion and unmutated immunoglobulin heavy-chain variable genes.
Estimated 5-year overall survival was also better with ibrutinib, at 83% vs. 68% (hazard ratio, 0.45; 95% CI, 0.266-0.761).
The most common grade 3 or greater adverse events occurring with ibrutinib were neutropenia (13%), pneumonia (12%), hypertension (8%), anemia (7%), hyponatremia (6%), atrial fibrillation (5%), and cataract (5%). The rates of most adverse events decreased over time, and dose reductions because of adverse events also diminished over time, from 5% of patients in the first year down to zero in years 4 through 5.
Patients responded to subsequent CLL therapies following ibrutinib discontinuation, including chemoimmunotherapy and other kinase inhibitors, Dr. Tedeschi said.
The trial was sponsored by Pharmacyclics with collaboration from Janssen Research & Development. Dr. Tedeschi reported advisory board activities with Janssen, AbbVie, and BeiGene.
SOURCE: Tedeschi A et al. EHA Congress, Abstract S107.
REPORTING FROM EHA CONGRESS
CDC: Look for early symptoms of acute flaccid myelitis, report suspected cases
the CDC said in a telebriefing.
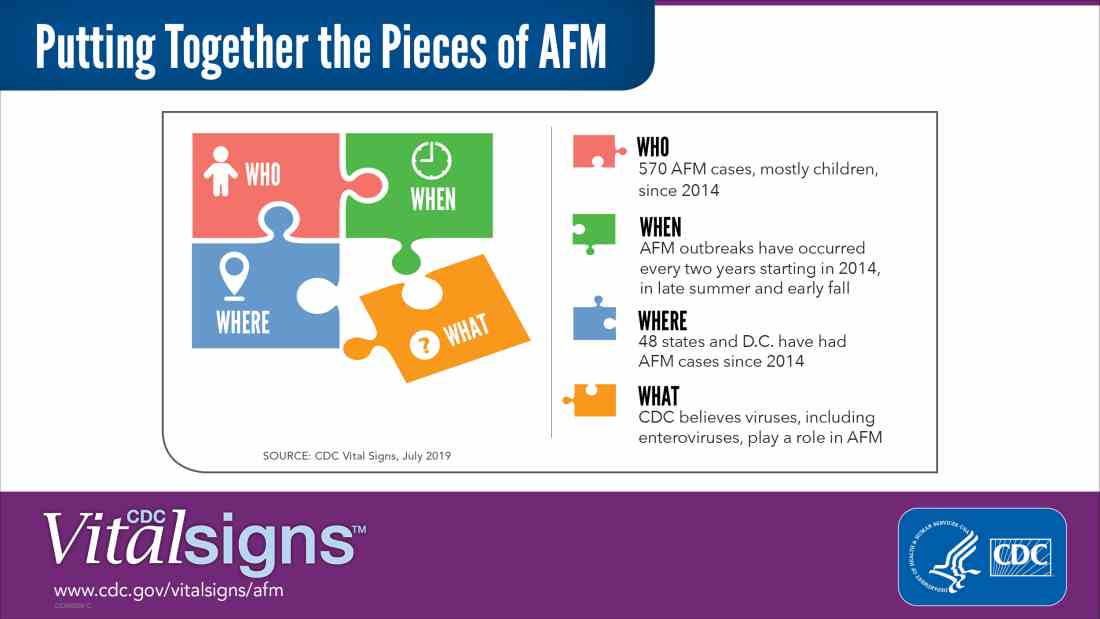
Acute flaccid myelitis (AFM) is defined as acute, flaccid muscle weakness that occurs less than 1 week after a fever or respiratory illness. Viruses, including enterovirus, are believed to play a role in AFM, but the cause still is unknown. The disease appears mostly in children, and the average age of a patient diagnosed with AFM is 5 years.
“Doctors and other clinicians in the United States play a critical role,” Anne Schuchat, MD, principal deputy director of the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, said in the telebriefing. “We ask for your help with early recognition of patients with AFM symptoms, prompt specimen collection for testing, and immediate reporting of suspected AFM cases to health departments.”
While there is no proven treatment for AFM, early diagnosis is critical to getting patients the best care possible, according to a Vital Signs report released today. This means that clinicians should not wait for the CDC’s case definition before diagnosis, the CDC said.
“When specimens are collected as soon as possible after symptom onset, we have a better chance of understanding the causes of AFM, these recurrent outbreaks, and developing a diagnostic test,” Dr. Schuchat said. “Rapid reporting also helps us to identify and respond to outbreaks early and alert other clinicians and the public.”
AFM appears to follow a seasonal and biennial pattern, with the number of cases increasing mainly in the late summer and early fall. As the season approaches where AFM cases increase, CDC is asking clinicians to look out for patients with suspected AFM so cases can be reported as early as possible.
Since the CDC began tracking AFM, the number of cases has risen every 2 years. In 2018, there were 233 cases in 41 states, the highest number of reported cases since the CDC began tracking AFM following an outbreak in 2014, according to a Vital Signs report. Overall, there have been 570 cases of AFM reported in 48 states and the District of Columbia since 2014.
There is yet to be a confirmatory test for AFM, but clinicians should obtain cerebrospinal fluid, serum, stool and nasopharyngeal swab from patients with suspected AFM as soon as possible, followed by an MRI. AFM has unique MRI features , such as gray matter involvement, that can help distinguish it from other diseases characterized by acute weakness.
In the Vital Signs report, which examined AFM in 2018, 92% of confirmed cases had respiratory symptoms or fever, and 42% of confirmed cases had upper limb involvement. The median time from limb weakness to hospitalization was 1 day, and time from weakness to MRI was 2 days. Cases were reported to the CDC a median of 18 days from onset of limb weakness, but time to reporting ranged between 18 days and 36 days, said Tom Clark, MD, MPH, deputy director of the division of viral diseases at CDC.
“This delay hampers our ability to understand the causes AFM,” he said. “We believe that recognizing AFM early is critical and can lead to better patient management.”
In lieu of a diagnostic test for AFM, clinicians should make management decisions through review of patient symptoms, exam findings, MRI, other test results, and in consulting with neurology experts. The Transverse Myelitis Association also has created a support portal for 24/7 physician consultation in AFM cases.
SOURCE: Lopez A et al. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2019;68:1-7 .
the CDC said in a telebriefing.

Acute flaccid myelitis (AFM) is defined as acute, flaccid muscle weakness that occurs less than 1 week after a fever or respiratory illness. Viruses, including enterovirus, are believed to play a role in AFM, but the cause still is unknown. The disease appears mostly in children, and the average age of a patient diagnosed with AFM is 5 years.
“Doctors and other clinicians in the United States play a critical role,” Anne Schuchat, MD, principal deputy director of the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, said in the telebriefing. “We ask for your help with early recognition of patients with AFM symptoms, prompt specimen collection for testing, and immediate reporting of suspected AFM cases to health departments.”
While there is no proven treatment for AFM, early diagnosis is critical to getting patients the best care possible, according to a Vital Signs report released today. This means that clinicians should not wait for the CDC’s case definition before diagnosis, the CDC said.
“When specimens are collected as soon as possible after symptom onset, we have a better chance of understanding the causes of AFM, these recurrent outbreaks, and developing a diagnostic test,” Dr. Schuchat said. “Rapid reporting also helps us to identify and respond to outbreaks early and alert other clinicians and the public.”
AFM appears to follow a seasonal and biennial pattern, with the number of cases increasing mainly in the late summer and early fall. As the season approaches where AFM cases increase, CDC is asking clinicians to look out for patients with suspected AFM so cases can be reported as early as possible.
Since the CDC began tracking AFM, the number of cases has risen every 2 years. In 2018, there were 233 cases in 41 states, the highest number of reported cases since the CDC began tracking AFM following an outbreak in 2014, according to a Vital Signs report. Overall, there have been 570 cases of AFM reported in 48 states and the District of Columbia since 2014.
There is yet to be a confirmatory test for AFM, but clinicians should obtain cerebrospinal fluid, serum, stool and nasopharyngeal swab from patients with suspected AFM as soon as possible, followed by an MRI. AFM has unique MRI features , such as gray matter involvement, that can help distinguish it from other diseases characterized by acute weakness.
In the Vital Signs report, which examined AFM in 2018, 92% of confirmed cases had respiratory symptoms or fever, and 42% of confirmed cases had upper limb involvement. The median time from limb weakness to hospitalization was 1 day, and time from weakness to MRI was 2 days. Cases were reported to the CDC a median of 18 days from onset of limb weakness, but time to reporting ranged between 18 days and 36 days, said Tom Clark, MD, MPH, deputy director of the division of viral diseases at CDC.
“This delay hampers our ability to understand the causes AFM,” he said. “We believe that recognizing AFM early is critical and can lead to better patient management.”
In lieu of a diagnostic test for AFM, clinicians should make management decisions through review of patient symptoms, exam findings, MRI, other test results, and in consulting with neurology experts. The Transverse Myelitis Association also has created a support portal for 24/7 physician consultation in AFM cases.
SOURCE: Lopez A et al. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2019;68:1-7 .
the CDC said in a telebriefing.

Acute flaccid myelitis (AFM) is defined as acute, flaccid muscle weakness that occurs less than 1 week after a fever or respiratory illness. Viruses, including enterovirus, are believed to play a role in AFM, but the cause still is unknown. The disease appears mostly in children, and the average age of a patient diagnosed with AFM is 5 years.
“Doctors and other clinicians in the United States play a critical role,” Anne Schuchat, MD, principal deputy director of the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, said in the telebriefing. “We ask for your help with early recognition of patients with AFM symptoms, prompt specimen collection for testing, and immediate reporting of suspected AFM cases to health departments.”
While there is no proven treatment for AFM, early diagnosis is critical to getting patients the best care possible, according to a Vital Signs report released today. This means that clinicians should not wait for the CDC’s case definition before diagnosis, the CDC said.
“When specimens are collected as soon as possible after symptom onset, we have a better chance of understanding the causes of AFM, these recurrent outbreaks, and developing a diagnostic test,” Dr. Schuchat said. “Rapid reporting also helps us to identify and respond to outbreaks early and alert other clinicians and the public.”
AFM appears to follow a seasonal and biennial pattern, with the number of cases increasing mainly in the late summer and early fall. As the season approaches where AFM cases increase, CDC is asking clinicians to look out for patients with suspected AFM so cases can be reported as early as possible.
Since the CDC began tracking AFM, the number of cases has risen every 2 years. In 2018, there were 233 cases in 41 states, the highest number of reported cases since the CDC began tracking AFM following an outbreak in 2014, according to a Vital Signs report. Overall, there have been 570 cases of AFM reported in 48 states and the District of Columbia since 2014.
There is yet to be a confirmatory test for AFM, but clinicians should obtain cerebrospinal fluid, serum, stool and nasopharyngeal swab from patients with suspected AFM as soon as possible, followed by an MRI. AFM has unique MRI features , such as gray matter involvement, that can help distinguish it from other diseases characterized by acute weakness.
In the Vital Signs report, which examined AFM in 2018, 92% of confirmed cases had respiratory symptoms or fever, and 42% of confirmed cases had upper limb involvement. The median time from limb weakness to hospitalization was 1 day, and time from weakness to MRI was 2 days. Cases were reported to the CDC a median of 18 days from onset of limb weakness, but time to reporting ranged between 18 days and 36 days, said Tom Clark, MD, MPH, deputy director of the division of viral diseases at CDC.
“This delay hampers our ability to understand the causes AFM,” he said. “We believe that recognizing AFM early is critical and can lead to better patient management.”
In lieu of a diagnostic test for AFM, clinicians should make management decisions through review of patient symptoms, exam findings, MRI, other test results, and in consulting with neurology experts. The Transverse Myelitis Association also has created a support portal for 24/7 physician consultation in AFM cases.
SOURCE: Lopez A et al. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2019;68:1-7 .
NEWS FROM THE FDA/CDC