User login
One-week postsurgical interval for voiding trial increases pass rate
Women who underwent vaginal prolapse surgery and did not immediately have a successful voiding trial were seven times more likely to pass their second voiding trial if their follow-up was 7 days after surgery instead of 4 days, according to a study in the American Journal of Obstetrics and Gynecology.
“This information is useful for setting expectations and for counseling patients on when it might be best to repeat a voiding trial in those with transient incomplete bladder emptying on the day of surgery, especially for those who may not live close to their surgeon, or for those who have difficulty traveling to the office,” said Jeffrey S. Schachar, MD, of Wake Forest Baptist Health in Winston-Salem, N.C., and colleagues. “Despite a higher rate of initial unsuccessful office voiding trials, however, the early group did have significantly fewer days with an indwelling transurethral catheter, as well as total catheterization days,” including self-catheterization.
The researchers note that rates of temporary use of catheters after surgery vary widely, from 12% to 83%, likely because no consensus exists on how long to wait for voiding trials and what constitutes a successful trial.
“It is critical to identify patients with incomplete bladder emptying in order to prevent pain, myogenic and neurogenic damage, ureteral reflux and bladder overdistension that may further impair voiding function,” the authors wrote. “However, extending bladder drainage beyond the necessary recovery period may be associated with higher rates of urinary tract infection (UTI) and patient bother.”
To learn more about the best duration for postoperative catheter use, the researchers enrolled 102 patients before they underwent vaginal prolapse surgery at Wake Forest Baptist Health and Cleveland Clinic Florida from February 2017 to November 2019. The 29 patients with a successful voiding trial within 6 hours after surgery left the study, and 5 others were excluded for needing longer vaginal packing.
The voiding trial involved helping the patient stand to drain the bladder via the catheter, backfilling the bladder with 300 mL of saline solution through the catheter, removing the catheter to give women 1 hour to urinate, and then measuring the postvoid residual with a catheter or ultrasound. At least 100 mL postvoid residual was considered persistent incomplete bladder emptying.
The 60 remaining patients who did not pass the initial voiding trial and opted to remain in the study received a transurethral indwelling catheter and were randomly assigned to return for a second voiding trial either 2-4 days after surgery (depending on day of the week) or 7 days after surgery. The groups were demographically and clinically similar, with predominantly white postmenopausal, non-smoking women with stage II or III multicompartment pelvic organ prolapse.
Women without successful trials could continue with the transurethral catheter or give themselves intermittent catheterizations with a follow-up schedule determined by their surgeon. The researchers then tracked the women for 6 weeks to determine the rate of unsuccessful repeat voiding trials.
Among the women who returned 2-4 days post surgery, 23% had unsuccessful follow-up voiding trials, compared with 3% in the group returning 7 days after surgery (relative risk = 7; P = .02). The researchers calculated that one case of persistent postoperative incomplete bladder emptying was prevented for every five patients who used a catheter for 7 days after surgery.
Kevin A. Ault, MD, professor of obstetrics and gynecology at the University of Kansas Medical Center in Kansas City, said the study was well done, although the findings were unsurprising. He said the clinical implication is straightforward – to wait a week before doing a second voiding trial.
“I suspect these findings match the clinical experience of many surgeons. It is always good to see a well-done clinical trial on a topic,” Dr Ault said in an interview. “The most notable finding is how this impacts patient counseling. Gynecologists should tell their patients that it will take a week with a catheter when this problem arises.”
“The main limitation is whether this finding can be extrapolated to other gynecological surgeries, such as hysterectomy,” said Dr. Ault, who was not involved in the study. “Urinary retention is likely less common after that surgery, but it is still bothersome to patients.”
Dr. Schachar and associates also reported that patients in the earlier group “used significantly more morphine dose equivalents within 24 hours of the office voiding trial than the late-voiding trial group, which was expected given the proximity to surgery” (3 vs. 0.38; P = .005). However, new postoperative pain medication prescriptions and refills were similar in both groups.
Secondary endpoints included UTI rates, total days with a catheter, and patient experience of discomfort with the catheter. The two groups of women reported similar levels of catheter bother, but there was a nonsignificant difference in UTI rates: 23% in the earlier group, compared with 7% in the later group (P = .07).
The early-voiding trial group had an average 5 days with an indwelling transurethral catheter, compared with a significantly different 7 days in the later group (P = .0007). The early group also had fewer total days with an indwelling transurethral catheter and self-catheterization (6 days), compared with the late group (7 days; P = .0013). No patients had persistent incomplete bladder emptying after 17 days post surgery.
“Being able to adequately predict which patients are more likely to have unsuccessful postoperative voiding trials allows surgeons to better counsel their patients and may guide clinical decisions,” Dr. Schachar and associates said. They acknowledged, however, that their study’s biggest weakness is the small enrollment, which led to larger confidence intervals related to relative risk differences between the groups.
The study did not use external funding. Four of the investigators received grant, research funding, or honoraria from one or many medical device or pharmaceutical companies. The remaining researchers had no disclosures. Dr. Ault said he had no relevant financial disclosures.
SOURCE: Schachar JS et al. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2020 Jun. doi: 10.1016/j.ajog.2020.06.001.
Women who underwent vaginal prolapse surgery and did not immediately have a successful voiding trial were seven times more likely to pass their second voiding trial if their follow-up was 7 days after surgery instead of 4 days, according to a study in the American Journal of Obstetrics and Gynecology.
“This information is useful for setting expectations and for counseling patients on when it might be best to repeat a voiding trial in those with transient incomplete bladder emptying on the day of surgery, especially for those who may not live close to their surgeon, or for those who have difficulty traveling to the office,” said Jeffrey S. Schachar, MD, of Wake Forest Baptist Health in Winston-Salem, N.C., and colleagues. “Despite a higher rate of initial unsuccessful office voiding trials, however, the early group did have significantly fewer days with an indwelling transurethral catheter, as well as total catheterization days,” including self-catheterization.
The researchers note that rates of temporary use of catheters after surgery vary widely, from 12% to 83%, likely because no consensus exists on how long to wait for voiding trials and what constitutes a successful trial.
“It is critical to identify patients with incomplete bladder emptying in order to prevent pain, myogenic and neurogenic damage, ureteral reflux and bladder overdistension that may further impair voiding function,” the authors wrote. “However, extending bladder drainage beyond the necessary recovery period may be associated with higher rates of urinary tract infection (UTI) and patient bother.”
To learn more about the best duration for postoperative catheter use, the researchers enrolled 102 patients before they underwent vaginal prolapse surgery at Wake Forest Baptist Health and Cleveland Clinic Florida from February 2017 to November 2019. The 29 patients with a successful voiding trial within 6 hours after surgery left the study, and 5 others were excluded for needing longer vaginal packing.
The voiding trial involved helping the patient stand to drain the bladder via the catheter, backfilling the bladder with 300 mL of saline solution through the catheter, removing the catheter to give women 1 hour to urinate, and then measuring the postvoid residual with a catheter or ultrasound. At least 100 mL postvoid residual was considered persistent incomplete bladder emptying.
The 60 remaining patients who did not pass the initial voiding trial and opted to remain in the study received a transurethral indwelling catheter and were randomly assigned to return for a second voiding trial either 2-4 days after surgery (depending on day of the week) or 7 days after surgery. The groups were demographically and clinically similar, with predominantly white postmenopausal, non-smoking women with stage II or III multicompartment pelvic organ prolapse.
Women without successful trials could continue with the transurethral catheter or give themselves intermittent catheterizations with a follow-up schedule determined by their surgeon. The researchers then tracked the women for 6 weeks to determine the rate of unsuccessful repeat voiding trials.
Among the women who returned 2-4 days post surgery, 23% had unsuccessful follow-up voiding trials, compared with 3% in the group returning 7 days after surgery (relative risk = 7; P = .02). The researchers calculated that one case of persistent postoperative incomplete bladder emptying was prevented for every five patients who used a catheter for 7 days after surgery.
Kevin A. Ault, MD, professor of obstetrics and gynecology at the University of Kansas Medical Center in Kansas City, said the study was well done, although the findings were unsurprising. He said the clinical implication is straightforward – to wait a week before doing a second voiding trial.
“I suspect these findings match the clinical experience of many surgeons. It is always good to see a well-done clinical trial on a topic,” Dr Ault said in an interview. “The most notable finding is how this impacts patient counseling. Gynecologists should tell their patients that it will take a week with a catheter when this problem arises.”
“The main limitation is whether this finding can be extrapolated to other gynecological surgeries, such as hysterectomy,” said Dr. Ault, who was not involved in the study. “Urinary retention is likely less common after that surgery, but it is still bothersome to patients.”
Dr. Schachar and associates also reported that patients in the earlier group “used significantly more morphine dose equivalents within 24 hours of the office voiding trial than the late-voiding trial group, which was expected given the proximity to surgery” (3 vs. 0.38; P = .005). However, new postoperative pain medication prescriptions and refills were similar in both groups.
Secondary endpoints included UTI rates, total days with a catheter, and patient experience of discomfort with the catheter. The two groups of women reported similar levels of catheter bother, but there was a nonsignificant difference in UTI rates: 23% in the earlier group, compared with 7% in the later group (P = .07).
The early-voiding trial group had an average 5 days with an indwelling transurethral catheter, compared with a significantly different 7 days in the later group (P = .0007). The early group also had fewer total days with an indwelling transurethral catheter and self-catheterization (6 days), compared with the late group (7 days; P = .0013). No patients had persistent incomplete bladder emptying after 17 days post surgery.
“Being able to adequately predict which patients are more likely to have unsuccessful postoperative voiding trials allows surgeons to better counsel their patients and may guide clinical decisions,” Dr. Schachar and associates said. They acknowledged, however, that their study’s biggest weakness is the small enrollment, which led to larger confidence intervals related to relative risk differences between the groups.
The study did not use external funding. Four of the investigators received grant, research funding, or honoraria from one or many medical device or pharmaceutical companies. The remaining researchers had no disclosures. Dr. Ault said he had no relevant financial disclosures.
SOURCE: Schachar JS et al. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2020 Jun. doi: 10.1016/j.ajog.2020.06.001.
Women who underwent vaginal prolapse surgery and did not immediately have a successful voiding trial were seven times more likely to pass their second voiding trial if their follow-up was 7 days after surgery instead of 4 days, according to a study in the American Journal of Obstetrics and Gynecology.
“This information is useful for setting expectations and for counseling patients on when it might be best to repeat a voiding trial in those with transient incomplete bladder emptying on the day of surgery, especially for those who may not live close to their surgeon, or for those who have difficulty traveling to the office,” said Jeffrey S. Schachar, MD, of Wake Forest Baptist Health in Winston-Salem, N.C., and colleagues. “Despite a higher rate of initial unsuccessful office voiding trials, however, the early group did have significantly fewer days with an indwelling transurethral catheter, as well as total catheterization days,” including self-catheterization.
The researchers note that rates of temporary use of catheters after surgery vary widely, from 12% to 83%, likely because no consensus exists on how long to wait for voiding trials and what constitutes a successful trial.
“It is critical to identify patients with incomplete bladder emptying in order to prevent pain, myogenic and neurogenic damage, ureteral reflux and bladder overdistension that may further impair voiding function,” the authors wrote. “However, extending bladder drainage beyond the necessary recovery period may be associated with higher rates of urinary tract infection (UTI) and patient bother.”
To learn more about the best duration for postoperative catheter use, the researchers enrolled 102 patients before they underwent vaginal prolapse surgery at Wake Forest Baptist Health and Cleveland Clinic Florida from February 2017 to November 2019. The 29 patients with a successful voiding trial within 6 hours after surgery left the study, and 5 others were excluded for needing longer vaginal packing.
The voiding trial involved helping the patient stand to drain the bladder via the catheter, backfilling the bladder with 300 mL of saline solution through the catheter, removing the catheter to give women 1 hour to urinate, and then measuring the postvoid residual with a catheter or ultrasound. At least 100 mL postvoid residual was considered persistent incomplete bladder emptying.
The 60 remaining patients who did not pass the initial voiding trial and opted to remain in the study received a transurethral indwelling catheter and were randomly assigned to return for a second voiding trial either 2-4 days after surgery (depending on day of the week) or 7 days after surgery. The groups were demographically and clinically similar, with predominantly white postmenopausal, non-smoking women with stage II or III multicompartment pelvic organ prolapse.
Women without successful trials could continue with the transurethral catheter or give themselves intermittent catheterizations with a follow-up schedule determined by their surgeon. The researchers then tracked the women for 6 weeks to determine the rate of unsuccessful repeat voiding trials.
Among the women who returned 2-4 days post surgery, 23% had unsuccessful follow-up voiding trials, compared with 3% in the group returning 7 days after surgery (relative risk = 7; P = .02). The researchers calculated that one case of persistent postoperative incomplete bladder emptying was prevented for every five patients who used a catheter for 7 days after surgery.
Kevin A. Ault, MD, professor of obstetrics and gynecology at the University of Kansas Medical Center in Kansas City, said the study was well done, although the findings were unsurprising. He said the clinical implication is straightforward – to wait a week before doing a second voiding trial.
“I suspect these findings match the clinical experience of many surgeons. It is always good to see a well-done clinical trial on a topic,” Dr Ault said in an interview. “The most notable finding is how this impacts patient counseling. Gynecologists should tell their patients that it will take a week with a catheter when this problem arises.”
“The main limitation is whether this finding can be extrapolated to other gynecological surgeries, such as hysterectomy,” said Dr. Ault, who was not involved in the study. “Urinary retention is likely less common after that surgery, but it is still bothersome to patients.”
Dr. Schachar and associates also reported that patients in the earlier group “used significantly more morphine dose equivalents within 24 hours of the office voiding trial than the late-voiding trial group, which was expected given the proximity to surgery” (3 vs. 0.38; P = .005). However, new postoperative pain medication prescriptions and refills were similar in both groups.
Secondary endpoints included UTI rates, total days with a catheter, and patient experience of discomfort with the catheter. The two groups of women reported similar levels of catheter bother, but there was a nonsignificant difference in UTI rates: 23% in the earlier group, compared with 7% in the later group (P = .07).
The early-voiding trial group had an average 5 days with an indwelling transurethral catheter, compared with a significantly different 7 days in the later group (P = .0007). The early group also had fewer total days with an indwelling transurethral catheter and self-catheterization (6 days), compared with the late group (7 days; P = .0013). No patients had persistent incomplete bladder emptying after 17 days post surgery.
“Being able to adequately predict which patients are more likely to have unsuccessful postoperative voiding trials allows surgeons to better counsel their patients and may guide clinical decisions,” Dr. Schachar and associates said. They acknowledged, however, that their study’s biggest weakness is the small enrollment, which led to larger confidence intervals related to relative risk differences between the groups.
The study did not use external funding. Four of the investigators received grant, research funding, or honoraria from one or many medical device or pharmaceutical companies. The remaining researchers had no disclosures. Dr. Ault said he had no relevant financial disclosures.
SOURCE: Schachar JS et al. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2020 Jun. doi: 10.1016/j.ajog.2020.06.001.
FROM AMERICAN JOURNAL OF OBSTETRICS & GYNECOLOGY
What have we learned from COVID?
In 2015, I proposed virtual care for the division of adolescent medicine, to the administration of our Midwestern children and adolescent hospital; they gladly listened and accepted a copy of the resources I provided. Virtual care was acknowledged to be the future direction of our and other organizations.
Four years later, virtual visits were introduced in the pediatric urgent care, but with little usability as families were slow to adopt this new form of medicine. Fast forward to the COVID-19 crisis in March 2020, and virtual medicine was the only option to meet the needs of patients and to stop the economic consequences. Unfortunately, the expedited rollout at our and many other hospitals may have resulted in limited program development and a lack of shared best practices.
Since March 2020, both patients and medical providers have accepted virtual care, but we now have an opportunity to review some of the limitations to offering virtual care. Work in primary care centers may see limitations using virtual medicine to meet the needs of all patients. Take into consideration the ability to offer confidential care. Confidential care has been a challenge virtually. For example, while completing a virtual visit with a 19-year-old female, it was apparent she was not alone and when asked a benign question the commotion in the background told the real story. The young woman began to laugh and said, “That was my dad running out of the room.” Despite requesting that parents leave the call, they can be heard within earshot of the caller.
On a televisit, written words appear backwards on the video, requiring written questions to be mirror images. When asking questions meant to be confidential, we have used note cards with a question mark. Verbal directions asking the adolescent to give a thumbs up or down to answer the question are required to maintain privacy from others in the room. If the patient responds thumbs up, this leads to additional questions with note cards. Although not ideal, this process gets to the answers, and the adolescent can disclose confidential information without concern about being overheard. Child abuse and neglect professionals have found similar challenges talking to caregivers or children as they are uncertain if others in the home are out of the screen but listening to the questions or prompting responses.
Obtaining vitals may be restricted and picking up hypertension or changes in weight has been limited to face to face visits. To continue to provide virtual care will require screening stations. I foresee a kiosk at the grocery or drugstore with a computer and the ability to obtain vitals or portions of an exam such as heart and lung evaluations. Patients could go at their convenience and the results could be sent to their providers. Technology already exists to use a cell phone to take photos of a toddler’s sore ear drum, and to obtain basic pulse oximetry and ECG, but these have a cost and may be available only to those able to afford these tools.
Billing issues have developed when patients go to a lab on the same day as a virtual visit. Completing a virtual visit for a sore throat thought to be streptococcal pharyngitis should not be finalized without access to a streptococcal throat swab. Until families have home kits to evaluate for strep throat, the families must bring the patient to a clinic or lab to obtain a pharyngeal culture. Furthermore, insurance reimbursement standards will need to be set for ongoing virtual health to become a sustainable option.
Workflows have been disrupted by balancing face to face visits with virtual visits. Unless the virtual visit has been set up for the medical team to access immediately, there are delays accessing the virtual platform, resulting in unnecessary gaps in care. Arranging schedules to separate face to face visits from virtual visits offers more efficiency. Creating a block of virtual visits separated from face-to-face visits or assigning providers to virtual-only schedules may be the best option for an efficient clinic flow. Telemedicine visit templates may need to be created as virtual visits become standard practice.
At present, virtual visits can only be offered to English-speaking patients. The inability to offer translators limits access to a small number of patients. Given COVID-19’s impact on the underserved communities, having a safe resource to reach these patients has been limited, leaving face-to-face visits as their only option. Requiring a face-to-face visit during peak illness has placed patients at risk. They have refused health care as opposed to exposure to the illness in health care settings.
We have innovative opportunities to create a new health care system. Despite the initial struggles with the adoption of virtual care, patients and providers have begun embracing the technology. Best practices and shared resources will be required to have a successful system before brick and mortar organizations can be reduced or insurance companies create their own health care systems which can branch across state lines.
Ms. Thew is the medical director of the department of adolescent medicine at Children’s Wisconsin in Milwaukee. She said she had no relevant financial disclosures. Email her at [email protected].
The article was updated 7/17/2020.
In 2015, I proposed virtual care for the division of adolescent medicine, to the administration of our Midwestern children and adolescent hospital; they gladly listened and accepted a copy of the resources I provided. Virtual care was acknowledged to be the future direction of our and other organizations.
Four years later, virtual visits were introduced in the pediatric urgent care, but with little usability as families were slow to adopt this new form of medicine. Fast forward to the COVID-19 crisis in March 2020, and virtual medicine was the only option to meet the needs of patients and to stop the economic consequences. Unfortunately, the expedited rollout at our and many other hospitals may have resulted in limited program development and a lack of shared best practices.
Since March 2020, both patients and medical providers have accepted virtual care, but we now have an opportunity to review some of the limitations to offering virtual care. Work in primary care centers may see limitations using virtual medicine to meet the needs of all patients. Take into consideration the ability to offer confidential care. Confidential care has been a challenge virtually. For example, while completing a virtual visit with a 19-year-old female, it was apparent she was not alone and when asked a benign question the commotion in the background told the real story. The young woman began to laugh and said, “That was my dad running out of the room.” Despite requesting that parents leave the call, they can be heard within earshot of the caller.
On a televisit, written words appear backwards on the video, requiring written questions to be mirror images. When asking questions meant to be confidential, we have used note cards with a question mark. Verbal directions asking the adolescent to give a thumbs up or down to answer the question are required to maintain privacy from others in the room. If the patient responds thumbs up, this leads to additional questions with note cards. Although not ideal, this process gets to the answers, and the adolescent can disclose confidential information without concern about being overheard. Child abuse and neglect professionals have found similar challenges talking to caregivers or children as they are uncertain if others in the home are out of the screen but listening to the questions or prompting responses.
Obtaining vitals may be restricted and picking up hypertension or changes in weight has been limited to face to face visits. To continue to provide virtual care will require screening stations. I foresee a kiosk at the grocery or drugstore with a computer and the ability to obtain vitals or portions of an exam such as heart and lung evaluations. Patients could go at their convenience and the results could be sent to their providers. Technology already exists to use a cell phone to take photos of a toddler’s sore ear drum, and to obtain basic pulse oximetry and ECG, but these have a cost and may be available only to those able to afford these tools.
Billing issues have developed when patients go to a lab on the same day as a virtual visit. Completing a virtual visit for a sore throat thought to be streptococcal pharyngitis should not be finalized without access to a streptococcal throat swab. Until families have home kits to evaluate for strep throat, the families must bring the patient to a clinic or lab to obtain a pharyngeal culture. Furthermore, insurance reimbursement standards will need to be set for ongoing virtual health to become a sustainable option.
Workflows have been disrupted by balancing face to face visits with virtual visits. Unless the virtual visit has been set up for the medical team to access immediately, there are delays accessing the virtual platform, resulting in unnecessary gaps in care. Arranging schedules to separate face to face visits from virtual visits offers more efficiency. Creating a block of virtual visits separated from face-to-face visits or assigning providers to virtual-only schedules may be the best option for an efficient clinic flow. Telemedicine visit templates may need to be created as virtual visits become standard practice.
At present, virtual visits can only be offered to English-speaking patients. The inability to offer translators limits access to a small number of patients. Given COVID-19’s impact on the underserved communities, having a safe resource to reach these patients has been limited, leaving face-to-face visits as their only option. Requiring a face-to-face visit during peak illness has placed patients at risk. They have refused health care as opposed to exposure to the illness in health care settings.
We have innovative opportunities to create a new health care system. Despite the initial struggles with the adoption of virtual care, patients and providers have begun embracing the technology. Best practices and shared resources will be required to have a successful system before brick and mortar organizations can be reduced or insurance companies create their own health care systems which can branch across state lines.
Ms. Thew is the medical director of the department of adolescent medicine at Children’s Wisconsin in Milwaukee. She said she had no relevant financial disclosures. Email her at [email protected].
The article was updated 7/17/2020.
In 2015, I proposed virtual care for the division of adolescent medicine, to the administration of our Midwestern children and adolescent hospital; they gladly listened and accepted a copy of the resources I provided. Virtual care was acknowledged to be the future direction of our and other organizations.
Four years later, virtual visits were introduced in the pediatric urgent care, but with little usability as families were slow to adopt this new form of medicine. Fast forward to the COVID-19 crisis in March 2020, and virtual medicine was the only option to meet the needs of patients and to stop the economic consequences. Unfortunately, the expedited rollout at our and many other hospitals may have resulted in limited program development and a lack of shared best practices.
Since March 2020, both patients and medical providers have accepted virtual care, but we now have an opportunity to review some of the limitations to offering virtual care. Work in primary care centers may see limitations using virtual medicine to meet the needs of all patients. Take into consideration the ability to offer confidential care. Confidential care has been a challenge virtually. For example, while completing a virtual visit with a 19-year-old female, it was apparent she was not alone and when asked a benign question the commotion in the background told the real story. The young woman began to laugh and said, “That was my dad running out of the room.” Despite requesting that parents leave the call, they can be heard within earshot of the caller.
On a televisit, written words appear backwards on the video, requiring written questions to be mirror images. When asking questions meant to be confidential, we have used note cards with a question mark. Verbal directions asking the adolescent to give a thumbs up or down to answer the question are required to maintain privacy from others in the room. If the patient responds thumbs up, this leads to additional questions with note cards. Although not ideal, this process gets to the answers, and the adolescent can disclose confidential information without concern about being overheard. Child abuse and neglect professionals have found similar challenges talking to caregivers or children as they are uncertain if others in the home are out of the screen but listening to the questions or prompting responses.
Obtaining vitals may be restricted and picking up hypertension or changes in weight has been limited to face to face visits. To continue to provide virtual care will require screening stations. I foresee a kiosk at the grocery or drugstore with a computer and the ability to obtain vitals or portions of an exam such as heart and lung evaluations. Patients could go at their convenience and the results could be sent to their providers. Technology already exists to use a cell phone to take photos of a toddler’s sore ear drum, and to obtain basic pulse oximetry and ECG, but these have a cost and may be available only to those able to afford these tools.
Billing issues have developed when patients go to a lab on the same day as a virtual visit. Completing a virtual visit for a sore throat thought to be streptococcal pharyngitis should not be finalized without access to a streptococcal throat swab. Until families have home kits to evaluate for strep throat, the families must bring the patient to a clinic or lab to obtain a pharyngeal culture. Furthermore, insurance reimbursement standards will need to be set for ongoing virtual health to become a sustainable option.
Workflows have been disrupted by balancing face to face visits with virtual visits. Unless the virtual visit has been set up for the medical team to access immediately, there are delays accessing the virtual platform, resulting in unnecessary gaps in care. Arranging schedules to separate face to face visits from virtual visits offers more efficiency. Creating a block of virtual visits separated from face-to-face visits or assigning providers to virtual-only schedules may be the best option for an efficient clinic flow. Telemedicine visit templates may need to be created as virtual visits become standard practice.
At present, virtual visits can only be offered to English-speaking patients. The inability to offer translators limits access to a small number of patients. Given COVID-19’s impact on the underserved communities, having a safe resource to reach these patients has been limited, leaving face-to-face visits as their only option. Requiring a face-to-face visit during peak illness has placed patients at risk. They have refused health care as opposed to exposure to the illness in health care settings.
We have innovative opportunities to create a new health care system. Despite the initial struggles with the adoption of virtual care, patients and providers have begun embracing the technology. Best practices and shared resources will be required to have a successful system before brick and mortar organizations can be reduced or insurance companies create their own health care systems which can branch across state lines.
Ms. Thew is the medical director of the department of adolescent medicine at Children’s Wisconsin in Milwaukee. She said she had no relevant financial disclosures. Email her at [email protected].
The article was updated 7/17/2020.
Provide support in uncertain times
A sense of safety and stability, both emotional and physical, is crucial in promoting the healthy development of youth. Between the global pandemic, need for social distancing, economic downturn, and increased awareness of racial disparities, for many this sense of stability has been rattled.
School closures have led to a loss of social interaction, challenges to continued academic growth, and, for some students, lack of access to nutrition and increased food insecurity. For students with learning or mental health challenges, closures may have eliminated or significantly reduced desperately needed supports received in school.1 While these trying circumstances have been difficult for many, the transition back to school in the fall also may be challenging because of the uncertainty about what this will look like and possible change in routine. Some students or their families may have anxiety about returning, either because of a history of adverse experiences at school such as bullying, or because of fears about exposure for themselves or others to severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2).
The past several months also brought about greater awareness of systemic racial disparities, whether as reflected in health care, education, or the criminal justice system. According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention data, Latinx and African-American individuals in the United States have had a threefold greater chance of contracting SARS-CoV-2 and have a twofold greater risk of death, compared with white people in the same communities.2 Other social determinants of health – economic stability, education, social factors such as incarceration and discrimination, and neighborhood factors including access to healthy food – play a role in this vulnerability.
The pandemic has resulted in a need for social distancing, and as a result, isolation. Children and teens exposed to the news may have anxiety about what they see or hear. Additional pressures in the family can include economic uncertainty, loss of employment for the primary wage earner of the household, or stress related to family members being first responders.
Any one of these factors is a potentially significant stressor, so how do we best support youth to help them survive and hopefully thrive during this time?
- It is important to establish a sense of routine; this can help create a sense of stability and safety. Recognizing that circumstances are not the same as they were 5 or 6 months ago, encouraging structure should not come at the cost of preserving connection.
- Note positive behavior and choices made by children and make sure they know it was observed.
- Many children have experienced increased screen time with the lack of structure of the traditional school day or summer camp and extracurricular activities. Limiting screen time and being mindful of its potential impact on mood is prudent.
- Self-care for parents and guardians is important. This time is stressful for the adults of the household, let alone children who are learning self-regulation skills.
- Listen to children’s or teens’ concerns and share information in developmentally appropriate ways. It is okay to not have all of the answers.
- Balance fostering a sense of gratitude with not invalidating a child’s or teen’s experience. Showing empathy during this time is vital. While there may be other soccer seasons, it is normal to experience grief about the loss of experiences during this time.
- Parents and guardians know their children best, so it is prudent for them to be mindful of concerning changes such as an increase in sadness, anxiety, or irritability that negatively impacts daily functioning such as sleeping, eating, or relationships with family and friends.
- Promote social interactions with appropriate safeguards in place. Unfortunately, the number of SARS-CoV-2 infections is increasing in multiple states, and there is the potential to return to some of the previous restrictions. However, encouraging social interaction while following local guidelines and with cautions such as limiting the number of people present, meeting outside, or considering interacting with others who are similarly social distancing can help foster social connection and development.
- Maintain connection digitally when in-person contact is not an option.3 Social groups, places of worship, and other activities have been agile in developing virtual communities. Communication by voice and/or video is thought to be more powerful than by written communication (text, email) alone.4 However, it is important to consider those who may have limited to no access to electronic methods.
- Encourage open communication with children about diversity and bias, and consider how our interactions with others may affect our children’s perspectives.5
- As providers, it is crucial that we address structural and institutional systems that negatively impact the health, safety, and access to care including our Black, indigenous, and people of color (BIPOC) and lesbian, gay, bisexual, transgender/transsexual, queer/questioning, intersex, and allied/asexual/aromantic/agender (LGBTQIA) patients.
Dr. Strange is an assistant professor in the department of psychiatry at the University of Vermont Medical Center and University of Vermont Robert Larner College of Medicine, both in Burlington. She works with children and adolescents. Dr. Strange has no relevant financial disclosures. Email her at [email protected].
Online resources for parents and families
- Child Mind Institute: Coping With the Coronavirus Crisis: Supporting Your Kids.
- American Psychological Association: Talking with children about discrimination.
- Common Sense Media: Help with determining appropriateness of media for children.
Hotlines
- National Suicide Prevention Hotline: 1-800-273-8255
- GLBT National Hotline: 888-843-4564
- The California Peer-Run Warm Line: 1-855-845-7415
- Trevor Project: 866-488-7386 or text TREVOR to 1-202-304-1200
- Trans Lifeline: 877-565-8860
- Crisis Text Line: Text HOME to 741741
References
1. JAMA Pediatr. 2020 Apr 14. doi: 10.1001/jamapediatrics.2020.1456.
2. CDC: COVID-19 in Racial and Ethnic Minority Groups.
3. JAMA. 2020 Mar 23. doi: 10.1001/jama.2020.4469.
4. JAMA Intern Med. 2020 Apr 10. doi: 10.1001/jamainternmed.2020.1562.
5. American Psychological Association: Talking with children about discrimination.
A sense of safety and stability, both emotional and physical, is crucial in promoting the healthy development of youth. Between the global pandemic, need for social distancing, economic downturn, and increased awareness of racial disparities, for many this sense of stability has been rattled.
School closures have led to a loss of social interaction, challenges to continued academic growth, and, for some students, lack of access to nutrition and increased food insecurity. For students with learning or mental health challenges, closures may have eliminated or significantly reduced desperately needed supports received in school.1 While these trying circumstances have been difficult for many, the transition back to school in the fall also may be challenging because of the uncertainty about what this will look like and possible change in routine. Some students or their families may have anxiety about returning, either because of a history of adverse experiences at school such as bullying, or because of fears about exposure for themselves or others to severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2).
The past several months also brought about greater awareness of systemic racial disparities, whether as reflected in health care, education, or the criminal justice system. According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention data, Latinx and African-American individuals in the United States have had a threefold greater chance of contracting SARS-CoV-2 and have a twofold greater risk of death, compared with white people in the same communities.2 Other social determinants of health – economic stability, education, social factors such as incarceration and discrimination, and neighborhood factors including access to healthy food – play a role in this vulnerability.
The pandemic has resulted in a need for social distancing, and as a result, isolation. Children and teens exposed to the news may have anxiety about what they see or hear. Additional pressures in the family can include economic uncertainty, loss of employment for the primary wage earner of the household, or stress related to family members being first responders.
Any one of these factors is a potentially significant stressor, so how do we best support youth to help them survive and hopefully thrive during this time?
- It is important to establish a sense of routine; this can help create a sense of stability and safety. Recognizing that circumstances are not the same as they were 5 or 6 months ago, encouraging structure should not come at the cost of preserving connection.
- Note positive behavior and choices made by children and make sure they know it was observed.
- Many children have experienced increased screen time with the lack of structure of the traditional school day or summer camp and extracurricular activities. Limiting screen time and being mindful of its potential impact on mood is prudent.
- Self-care for parents and guardians is important. This time is stressful for the adults of the household, let alone children who are learning self-regulation skills.
- Listen to children’s or teens’ concerns and share information in developmentally appropriate ways. It is okay to not have all of the answers.
- Balance fostering a sense of gratitude with not invalidating a child’s or teen’s experience. Showing empathy during this time is vital. While there may be other soccer seasons, it is normal to experience grief about the loss of experiences during this time.
- Parents and guardians know their children best, so it is prudent for them to be mindful of concerning changes such as an increase in sadness, anxiety, or irritability that negatively impacts daily functioning such as sleeping, eating, or relationships with family and friends.
- Promote social interactions with appropriate safeguards in place. Unfortunately, the number of SARS-CoV-2 infections is increasing in multiple states, and there is the potential to return to some of the previous restrictions. However, encouraging social interaction while following local guidelines and with cautions such as limiting the number of people present, meeting outside, or considering interacting with others who are similarly social distancing can help foster social connection and development.
- Maintain connection digitally when in-person contact is not an option.3 Social groups, places of worship, and other activities have been agile in developing virtual communities. Communication by voice and/or video is thought to be more powerful than by written communication (text, email) alone.4 However, it is important to consider those who may have limited to no access to electronic methods.
- Encourage open communication with children about diversity and bias, and consider how our interactions with others may affect our children’s perspectives.5
- As providers, it is crucial that we address structural and institutional systems that negatively impact the health, safety, and access to care including our Black, indigenous, and people of color (BIPOC) and lesbian, gay, bisexual, transgender/transsexual, queer/questioning, intersex, and allied/asexual/aromantic/agender (LGBTQIA) patients.
Dr. Strange is an assistant professor in the department of psychiatry at the University of Vermont Medical Center and University of Vermont Robert Larner College of Medicine, both in Burlington. She works with children and adolescents. Dr. Strange has no relevant financial disclosures. Email her at [email protected].
Online resources for parents and families
- Child Mind Institute: Coping With the Coronavirus Crisis: Supporting Your Kids.
- American Psychological Association: Talking with children about discrimination.
- Common Sense Media: Help with determining appropriateness of media for children.
Hotlines
- National Suicide Prevention Hotline: 1-800-273-8255
- GLBT National Hotline: 888-843-4564
- The California Peer-Run Warm Line: 1-855-845-7415
- Trevor Project: 866-488-7386 or text TREVOR to 1-202-304-1200
- Trans Lifeline: 877-565-8860
- Crisis Text Line: Text HOME to 741741
References
1. JAMA Pediatr. 2020 Apr 14. doi: 10.1001/jamapediatrics.2020.1456.
2. CDC: COVID-19 in Racial and Ethnic Minority Groups.
3. JAMA. 2020 Mar 23. doi: 10.1001/jama.2020.4469.
4. JAMA Intern Med. 2020 Apr 10. doi: 10.1001/jamainternmed.2020.1562.
5. American Psychological Association: Talking with children about discrimination.
A sense of safety and stability, both emotional and physical, is crucial in promoting the healthy development of youth. Between the global pandemic, need for social distancing, economic downturn, and increased awareness of racial disparities, for many this sense of stability has been rattled.
School closures have led to a loss of social interaction, challenges to continued academic growth, and, for some students, lack of access to nutrition and increased food insecurity. For students with learning or mental health challenges, closures may have eliminated or significantly reduced desperately needed supports received in school.1 While these trying circumstances have been difficult for many, the transition back to school in the fall also may be challenging because of the uncertainty about what this will look like and possible change in routine. Some students or their families may have anxiety about returning, either because of a history of adverse experiences at school such as bullying, or because of fears about exposure for themselves or others to severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2).
The past several months also brought about greater awareness of systemic racial disparities, whether as reflected in health care, education, or the criminal justice system. According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention data, Latinx and African-American individuals in the United States have had a threefold greater chance of contracting SARS-CoV-2 and have a twofold greater risk of death, compared with white people in the same communities.2 Other social determinants of health – economic stability, education, social factors such as incarceration and discrimination, and neighborhood factors including access to healthy food – play a role in this vulnerability.
The pandemic has resulted in a need for social distancing, and as a result, isolation. Children and teens exposed to the news may have anxiety about what they see or hear. Additional pressures in the family can include economic uncertainty, loss of employment for the primary wage earner of the household, or stress related to family members being first responders.
Any one of these factors is a potentially significant stressor, so how do we best support youth to help them survive and hopefully thrive during this time?
- It is important to establish a sense of routine; this can help create a sense of stability and safety. Recognizing that circumstances are not the same as they were 5 or 6 months ago, encouraging structure should not come at the cost of preserving connection.
- Note positive behavior and choices made by children and make sure they know it was observed.
- Many children have experienced increased screen time with the lack of structure of the traditional school day or summer camp and extracurricular activities. Limiting screen time and being mindful of its potential impact on mood is prudent.
- Self-care for parents and guardians is important. This time is stressful for the adults of the household, let alone children who are learning self-regulation skills.
- Listen to children’s or teens’ concerns and share information in developmentally appropriate ways. It is okay to not have all of the answers.
- Balance fostering a sense of gratitude with not invalidating a child’s or teen’s experience. Showing empathy during this time is vital. While there may be other soccer seasons, it is normal to experience grief about the loss of experiences during this time.
- Parents and guardians know their children best, so it is prudent for them to be mindful of concerning changes such as an increase in sadness, anxiety, or irritability that negatively impacts daily functioning such as sleeping, eating, or relationships with family and friends.
- Promote social interactions with appropriate safeguards in place. Unfortunately, the number of SARS-CoV-2 infections is increasing in multiple states, and there is the potential to return to some of the previous restrictions. However, encouraging social interaction while following local guidelines and with cautions such as limiting the number of people present, meeting outside, or considering interacting with others who are similarly social distancing can help foster social connection and development.
- Maintain connection digitally when in-person contact is not an option.3 Social groups, places of worship, and other activities have been agile in developing virtual communities. Communication by voice and/or video is thought to be more powerful than by written communication (text, email) alone.4 However, it is important to consider those who may have limited to no access to electronic methods.
- Encourage open communication with children about diversity and bias, and consider how our interactions with others may affect our children’s perspectives.5
- As providers, it is crucial that we address structural and institutional systems that negatively impact the health, safety, and access to care including our Black, indigenous, and people of color (BIPOC) and lesbian, gay, bisexual, transgender/transsexual, queer/questioning, intersex, and allied/asexual/aromantic/agender (LGBTQIA) patients.
Dr. Strange is an assistant professor in the department of psychiatry at the University of Vermont Medical Center and University of Vermont Robert Larner College of Medicine, both in Burlington. She works with children and adolescents. Dr. Strange has no relevant financial disclosures. Email her at [email protected].
Online resources for parents and families
- Child Mind Institute: Coping With the Coronavirus Crisis: Supporting Your Kids.
- American Psychological Association: Talking with children about discrimination.
- Common Sense Media: Help with determining appropriateness of media for children.
Hotlines
- National Suicide Prevention Hotline: 1-800-273-8255
- GLBT National Hotline: 888-843-4564
- The California Peer-Run Warm Line: 1-855-845-7415
- Trevor Project: 866-488-7386 or text TREVOR to 1-202-304-1200
- Trans Lifeline: 877-565-8860
- Crisis Text Line: Text HOME to 741741
References
1. JAMA Pediatr. 2020 Apr 14. doi: 10.1001/jamapediatrics.2020.1456.
2. CDC: COVID-19 in Racial and Ethnic Minority Groups.
3. JAMA. 2020 Mar 23. doi: 10.1001/jama.2020.4469.
4. JAMA Intern Med. 2020 Apr 10. doi: 10.1001/jamainternmed.2020.1562.
5. American Psychological Association: Talking with children about discrimination.
COVID-19: A primary care perspective
With the COVID-19 pandemic, we are experiencing a once-in-a-100-year event. Dr. Steven A. Schulz, who is serving children on the front line in upstate New York, and I outline some of the challenges primary care pediatricians have been facing and solutions that have succeeded.
Reduction in direct patient care and its consequences
Because of the unknowns of COVID-19, many parents have not wanted to bring their children to a medical office because of fear of contracting SARS-CoV-2. At the same time, pediatricians have restricted in-person visits to prevent spread of SARS-CoV-2 and to help flatten the curve of infection. Use of pediatric medical professional services, compared with last year, dropped by 52% in March 2020 and by 58% in April, according to FAIR Health, a nonprofit organization that manages a database of 31 million claims. This is resulting in decreased immunization rates, which increases concern for secondary spikes of other preventable illnesses; for example, data from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention showed that, from mid-March to mid-April 2020, physicians in the Vaccines for Children program ordered 2.5 million fewer doses of vaccines and 250,000 fewer doses of measles-containing vaccines, compared with the same period in 2019. Fewer children are being seen for well visits, which means opportunities are lost for adequate monitoring of growth, development, physical wellness, and social determinants of health.
This is occurring at a time when families have been experiencing increased stress in terms of finances, social isolation, finding adequate child care, and serving as parent, teacher, and breadwinner. An increase in injuries is occurring because of inadequate parental supervision because many parents have been distracted while working from home. An increase in cases of severe abuse is occurring because schools, child care providers, physicians, and other mandated reporters in the community have decreased interaction with children. Children’s Hospital Colorado in Colorado Springs saw a 118% increase in the number of trauma cases in its ED between January and April 2020. Some of these were accidental injuries caused by falls or bicycle accidents, but there was a 200% increase in nonaccidental trauma, which was associated with a steep fall in calls to the state’s child abuse hotline. Academic gains are being lost, and there has been worry for a prolonged “summer slide” risk, especially for children living in poverty and children with developmental disabilities.
The COVID-19 pandemic also is affecting physicians and staff. As frontline personnel, we are at risk to contract the virus, and news media reminds us of severe illness and deaths among health care workers. The pandemic is affecting financial viability; estimated revenue of pediatric offices fell by 45% in March 2020 and 48% in April, compared with the previous year, according to FAIR Health. Nurses and staff have been furloughed. Practices have had to apply for grants and Paycheck Protection Program funds while extending credit lines.
Limited testing capability for SARS-CoV-2
Testing for SARS-CoV-2 has been variably available. There have been problems with false positive and especially false negative results (BMJ. 2020 May 12. doi: 10.1136/bmj.m1808).The best specimen collection method has yet to be determined. Blood testing for antibody has been touted, but it remains unclear if there is clinical benefit because a positive result offers no guarantee of immunity, and immunity may quickly wane. Perhaps widespread primary care office–based testing will be in place by the fall, with hope for future reliable point of care results.
Evolving knowledge regarding SARS-CoV-2 and MIS-C
It initially was thought that children were relatively spared from serious illness caused by COVID-19. Then reports of cases of newly identified multisystem inflammatory syndrome of children occurred. It has been unclear how children contribute to the spread of COVID-19 illness, although emerging evidence indicates it is lower than adult transmission. What will happen when children return to school and daycare in the fall?
The challenges have led to creative solutions for how to deliver care.
Adapting to telehealth to provide care
At least for the short term, HIPAA regulations have been relaxed to allow for video visits using platforms such as FaceTime, Skype, Zoom, Doximity, and Doxy.me. Some of these platforms are HIPAA compliant and will be long-term solutions; however, electronic medical record portals allowing for video visits are the more secure option, according to HIPAA.
It has been a learning experience to see what can be accomplished with a video visit. Taking a history and visual examination of injuries and rashes has been possible. Addressing mental health concerns through the video exchange generally has been effective.
However, video visits change the provider-patient interpersonal dynamic and offer only visual exam capabilities, compared with an in-person visit. We cannot look in ears, palpate a liver and spleen, touch and examine a joint or bone, or feel a rash. Video visits also are dependent on the quality of patient Internet access, sufficient data plans, and mutual capabilities to address the inevitable technological glitches on the provider’s end as well. Expanding information technology infrastructure ability and added licensure costs have occurred. Practices and health systems have been working with insurance companies to ensure telephone and video visits are reimbursed on a comparable level to in-office visits.
A new type of office visit and developing appropriate safety plans
Patients must be universally screened prior to arrival during appointment scheduling for well and illness visits. Patients aged older than 2 years and caregivers must wear masks on entering the facility. In many practices, patients are scheduled during specific sick or well visit time slots throughout the day. Waiting rooms chairs need to be spaced for 6-foot social distancing, and cars in the parking lot often serve as waiting rooms until staff can meet patients at the door and take them to the exam room. Alternate entrances, car-side exams, and drive-by and/or tent testing facilities often have become part of the new normal everyday practice. Creating virtual visit time blocks in provider’s schedules has allowed for decreased office congestion. Patients often are checked out from their room, as opposed to waiting in a line at a check out desk. Nurse triage protocols also have been adapted and enhanced to meet needs and concerns.
With the need for summer physicals and many regions opening up, a gradual return toward baseline has been evolving, although some of the twists of a “new normal” will stay in place. The new normal has been for providers and staff to wear surgical masks and face shields; sometimes N95 masks, gloves, and gowns have been needed. Cleaning rooms and equipment between patient visits has become a major, new time-consuming task. Acquiring and maintaining adequate supplies has been a challenge.
Summary
The American Academy of Pediatrics, CDC, and state and local health departments have been providing informative and regular updates, webinars, and best practices guidelines. Pediatricians, community organizations, schools, and mental health professionals have been collaborating, overcoming hurdles, and working together to help mitigate the effects of the pandemic on children, their families, and our communities. Continued education, cooperation, and adaptation will be needed in the months ahead. If there is a silver lining to this pandemic experience, it may be that families have grown closer together as they sheltered in place (and we have grown closer to our own families as well). One day perhaps a child who lived through this pandemic might be asked what it was like, and their recollection might be that it was a wonderful time because their parents stayed home all the time, took care of them, taught them their school work, and took lots of long family walks.
Dr. Schulz is pediatric medical director, Rochester (N.Y.) Regional Health. Dr. Pichichero is a specialist in pediatric infectious diseases and director of the Research Institute at Rochester (N.Y.) General Hospital. Dr. Schulz and Dr. Pichichero said they have no relevant financial disclosures. Email them at [email protected].
This article was updated 7/16/2020.
With the COVID-19 pandemic, we are experiencing a once-in-a-100-year event. Dr. Steven A. Schulz, who is serving children on the front line in upstate New York, and I outline some of the challenges primary care pediatricians have been facing and solutions that have succeeded.
Reduction in direct patient care and its consequences
Because of the unknowns of COVID-19, many parents have not wanted to bring their children to a medical office because of fear of contracting SARS-CoV-2. At the same time, pediatricians have restricted in-person visits to prevent spread of SARS-CoV-2 and to help flatten the curve of infection. Use of pediatric medical professional services, compared with last year, dropped by 52% in March 2020 and by 58% in April, according to FAIR Health, a nonprofit organization that manages a database of 31 million claims. This is resulting in decreased immunization rates, which increases concern for secondary spikes of other preventable illnesses; for example, data from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention showed that, from mid-March to mid-April 2020, physicians in the Vaccines for Children program ordered 2.5 million fewer doses of vaccines and 250,000 fewer doses of measles-containing vaccines, compared with the same period in 2019. Fewer children are being seen for well visits, which means opportunities are lost for adequate monitoring of growth, development, physical wellness, and social determinants of health.
This is occurring at a time when families have been experiencing increased stress in terms of finances, social isolation, finding adequate child care, and serving as parent, teacher, and breadwinner. An increase in injuries is occurring because of inadequate parental supervision because many parents have been distracted while working from home. An increase in cases of severe abuse is occurring because schools, child care providers, physicians, and other mandated reporters in the community have decreased interaction with children. Children’s Hospital Colorado in Colorado Springs saw a 118% increase in the number of trauma cases in its ED between January and April 2020. Some of these were accidental injuries caused by falls or bicycle accidents, but there was a 200% increase in nonaccidental trauma, which was associated with a steep fall in calls to the state’s child abuse hotline. Academic gains are being lost, and there has been worry for a prolonged “summer slide” risk, especially for children living in poverty and children with developmental disabilities.
The COVID-19 pandemic also is affecting physicians and staff. As frontline personnel, we are at risk to contract the virus, and news media reminds us of severe illness and deaths among health care workers. The pandemic is affecting financial viability; estimated revenue of pediatric offices fell by 45% in March 2020 and 48% in April, compared with the previous year, according to FAIR Health. Nurses and staff have been furloughed. Practices have had to apply for grants and Paycheck Protection Program funds while extending credit lines.
Limited testing capability for SARS-CoV-2
Testing for SARS-CoV-2 has been variably available. There have been problems with false positive and especially false negative results (BMJ. 2020 May 12. doi: 10.1136/bmj.m1808).The best specimen collection method has yet to be determined. Blood testing for antibody has been touted, but it remains unclear if there is clinical benefit because a positive result offers no guarantee of immunity, and immunity may quickly wane. Perhaps widespread primary care office–based testing will be in place by the fall, with hope for future reliable point of care results.
Evolving knowledge regarding SARS-CoV-2 and MIS-C
It initially was thought that children were relatively spared from serious illness caused by COVID-19. Then reports of cases of newly identified multisystem inflammatory syndrome of children occurred. It has been unclear how children contribute to the spread of COVID-19 illness, although emerging evidence indicates it is lower than adult transmission. What will happen when children return to school and daycare in the fall?
The challenges have led to creative solutions for how to deliver care.
Adapting to telehealth to provide care
At least for the short term, HIPAA regulations have been relaxed to allow for video visits using platforms such as FaceTime, Skype, Zoom, Doximity, and Doxy.me. Some of these platforms are HIPAA compliant and will be long-term solutions; however, electronic medical record portals allowing for video visits are the more secure option, according to HIPAA.
It has been a learning experience to see what can be accomplished with a video visit. Taking a history and visual examination of injuries and rashes has been possible. Addressing mental health concerns through the video exchange generally has been effective.
However, video visits change the provider-patient interpersonal dynamic and offer only visual exam capabilities, compared with an in-person visit. We cannot look in ears, palpate a liver and spleen, touch and examine a joint or bone, or feel a rash. Video visits also are dependent on the quality of patient Internet access, sufficient data plans, and mutual capabilities to address the inevitable technological glitches on the provider’s end as well. Expanding information technology infrastructure ability and added licensure costs have occurred. Practices and health systems have been working with insurance companies to ensure telephone and video visits are reimbursed on a comparable level to in-office visits.
A new type of office visit and developing appropriate safety plans
Patients must be universally screened prior to arrival during appointment scheduling for well and illness visits. Patients aged older than 2 years and caregivers must wear masks on entering the facility. In many practices, patients are scheduled during specific sick or well visit time slots throughout the day. Waiting rooms chairs need to be spaced for 6-foot social distancing, and cars in the parking lot often serve as waiting rooms until staff can meet patients at the door and take them to the exam room. Alternate entrances, car-side exams, and drive-by and/or tent testing facilities often have become part of the new normal everyday practice. Creating virtual visit time blocks in provider’s schedules has allowed for decreased office congestion. Patients often are checked out from their room, as opposed to waiting in a line at a check out desk. Nurse triage protocols also have been adapted and enhanced to meet needs and concerns.
With the need for summer physicals and many regions opening up, a gradual return toward baseline has been evolving, although some of the twists of a “new normal” will stay in place. The new normal has been for providers and staff to wear surgical masks and face shields; sometimes N95 masks, gloves, and gowns have been needed. Cleaning rooms and equipment between patient visits has become a major, new time-consuming task. Acquiring and maintaining adequate supplies has been a challenge.
Summary
The American Academy of Pediatrics, CDC, and state and local health departments have been providing informative and regular updates, webinars, and best practices guidelines. Pediatricians, community organizations, schools, and mental health professionals have been collaborating, overcoming hurdles, and working together to help mitigate the effects of the pandemic on children, their families, and our communities. Continued education, cooperation, and adaptation will be needed in the months ahead. If there is a silver lining to this pandemic experience, it may be that families have grown closer together as they sheltered in place (and we have grown closer to our own families as well). One day perhaps a child who lived through this pandemic might be asked what it was like, and their recollection might be that it was a wonderful time because their parents stayed home all the time, took care of them, taught them their school work, and took lots of long family walks.
Dr. Schulz is pediatric medical director, Rochester (N.Y.) Regional Health. Dr. Pichichero is a specialist in pediatric infectious diseases and director of the Research Institute at Rochester (N.Y.) General Hospital. Dr. Schulz and Dr. Pichichero said they have no relevant financial disclosures. Email them at [email protected].
This article was updated 7/16/2020.
With the COVID-19 pandemic, we are experiencing a once-in-a-100-year event. Dr. Steven A. Schulz, who is serving children on the front line in upstate New York, and I outline some of the challenges primary care pediatricians have been facing and solutions that have succeeded.
Reduction in direct patient care and its consequences
Because of the unknowns of COVID-19, many parents have not wanted to bring their children to a medical office because of fear of contracting SARS-CoV-2. At the same time, pediatricians have restricted in-person visits to prevent spread of SARS-CoV-2 and to help flatten the curve of infection. Use of pediatric medical professional services, compared with last year, dropped by 52% in March 2020 and by 58% in April, according to FAIR Health, a nonprofit organization that manages a database of 31 million claims. This is resulting in decreased immunization rates, which increases concern for secondary spikes of other preventable illnesses; for example, data from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention showed that, from mid-March to mid-April 2020, physicians in the Vaccines for Children program ordered 2.5 million fewer doses of vaccines and 250,000 fewer doses of measles-containing vaccines, compared with the same period in 2019. Fewer children are being seen for well visits, which means opportunities are lost for adequate monitoring of growth, development, physical wellness, and social determinants of health.
This is occurring at a time when families have been experiencing increased stress in terms of finances, social isolation, finding adequate child care, and serving as parent, teacher, and breadwinner. An increase in injuries is occurring because of inadequate parental supervision because many parents have been distracted while working from home. An increase in cases of severe abuse is occurring because schools, child care providers, physicians, and other mandated reporters in the community have decreased interaction with children. Children’s Hospital Colorado in Colorado Springs saw a 118% increase in the number of trauma cases in its ED between January and April 2020. Some of these were accidental injuries caused by falls or bicycle accidents, but there was a 200% increase in nonaccidental trauma, which was associated with a steep fall in calls to the state’s child abuse hotline. Academic gains are being lost, and there has been worry for a prolonged “summer slide” risk, especially for children living in poverty and children with developmental disabilities.
The COVID-19 pandemic also is affecting physicians and staff. As frontline personnel, we are at risk to contract the virus, and news media reminds us of severe illness and deaths among health care workers. The pandemic is affecting financial viability; estimated revenue of pediatric offices fell by 45% in March 2020 and 48% in April, compared with the previous year, according to FAIR Health. Nurses and staff have been furloughed. Practices have had to apply for grants and Paycheck Protection Program funds while extending credit lines.
Limited testing capability for SARS-CoV-2
Testing for SARS-CoV-2 has been variably available. There have been problems with false positive and especially false negative results (BMJ. 2020 May 12. doi: 10.1136/bmj.m1808).The best specimen collection method has yet to be determined. Blood testing for antibody has been touted, but it remains unclear if there is clinical benefit because a positive result offers no guarantee of immunity, and immunity may quickly wane. Perhaps widespread primary care office–based testing will be in place by the fall, with hope for future reliable point of care results.
Evolving knowledge regarding SARS-CoV-2 and MIS-C
It initially was thought that children were relatively spared from serious illness caused by COVID-19. Then reports of cases of newly identified multisystem inflammatory syndrome of children occurred. It has been unclear how children contribute to the spread of COVID-19 illness, although emerging evidence indicates it is lower than adult transmission. What will happen when children return to school and daycare in the fall?
The challenges have led to creative solutions for how to deliver care.
Adapting to telehealth to provide care
At least for the short term, HIPAA regulations have been relaxed to allow for video visits using platforms such as FaceTime, Skype, Zoom, Doximity, and Doxy.me. Some of these platforms are HIPAA compliant and will be long-term solutions; however, electronic medical record portals allowing for video visits are the more secure option, according to HIPAA.
It has been a learning experience to see what can be accomplished with a video visit. Taking a history and visual examination of injuries and rashes has been possible. Addressing mental health concerns through the video exchange generally has been effective.
However, video visits change the provider-patient interpersonal dynamic and offer only visual exam capabilities, compared with an in-person visit. We cannot look in ears, palpate a liver and spleen, touch and examine a joint or bone, or feel a rash. Video visits also are dependent on the quality of patient Internet access, sufficient data plans, and mutual capabilities to address the inevitable technological glitches on the provider’s end as well. Expanding information technology infrastructure ability and added licensure costs have occurred. Practices and health systems have been working with insurance companies to ensure telephone and video visits are reimbursed on a comparable level to in-office visits.
A new type of office visit and developing appropriate safety plans
Patients must be universally screened prior to arrival during appointment scheduling for well and illness visits. Patients aged older than 2 years and caregivers must wear masks on entering the facility. In many practices, patients are scheduled during specific sick or well visit time slots throughout the day. Waiting rooms chairs need to be spaced for 6-foot social distancing, and cars in the parking lot often serve as waiting rooms until staff can meet patients at the door and take them to the exam room. Alternate entrances, car-side exams, and drive-by and/or tent testing facilities often have become part of the new normal everyday practice. Creating virtual visit time blocks in provider’s schedules has allowed for decreased office congestion. Patients often are checked out from their room, as opposed to waiting in a line at a check out desk. Nurse triage protocols also have been adapted and enhanced to meet needs and concerns.
With the need for summer physicals and many regions opening up, a gradual return toward baseline has been evolving, although some of the twists of a “new normal” will stay in place. The new normal has been for providers and staff to wear surgical masks and face shields; sometimes N95 masks, gloves, and gowns have been needed. Cleaning rooms and equipment between patient visits has become a major, new time-consuming task. Acquiring and maintaining adequate supplies has been a challenge.
Summary
The American Academy of Pediatrics, CDC, and state and local health departments have been providing informative and regular updates, webinars, and best practices guidelines. Pediatricians, community organizations, schools, and mental health professionals have been collaborating, overcoming hurdles, and working together to help mitigate the effects of the pandemic on children, their families, and our communities. Continued education, cooperation, and adaptation will be needed in the months ahead. If there is a silver lining to this pandemic experience, it may be that families have grown closer together as they sheltered in place (and we have grown closer to our own families as well). One day perhaps a child who lived through this pandemic might be asked what it was like, and their recollection might be that it was a wonderful time because their parents stayed home all the time, took care of them, taught them their school work, and took lots of long family walks.
Dr. Schulz is pediatric medical director, Rochester (N.Y.) Regional Health. Dr. Pichichero is a specialist in pediatric infectious diseases and director of the Research Institute at Rochester (N.Y.) General Hospital. Dr. Schulz and Dr. Pichichero said they have no relevant financial disclosures. Email them at [email protected].
This article was updated 7/16/2020.
The public’s trust in science
Having been a bench research scientist 30 years ago, I am flabbergasted at what is and is not currently possible. In a few weeks, scientists sequenced a novel coronavirus and used the genetic sequence to select candidate molecules for a vaccine. But we still can’t reliably say how much protection a cloth mask provides. Worse yet, even if/when we could reliably quantify contagion, it isn’t clear that the public will believe us anyhow.
The good news is that the public worldwide did believe scientists about the threat of a pandemic and the need to flatten the curve. Saving lives has not been about the strength of an antibiotic or the skill in managing a ventilator, but the credibility of medical scientists. The degree of acceptance was variable and subject to a variety of delays caused by regional politicians, but The bad news is that the public’s trust in that scientific advice has waned, the willingness to accept onerous restrictions has fatigued, and the cooperation for maintaining these social changes is evaporating.
I will leave pontificating about the spread of COVID-19 to other experts in other forums. My focus is on the public’s trust in the professionalism of physicians, nurses, medical scientists, and the health care industry as a whole. That trust has been our most valuable tool in fighting the pandemic so far. There have been situations in which weaknesses in modern science have let society down during the pandemic of the century. In my February 2020 column, at the beginning of the outbreak, a month before it was declared a pandemic, when its magnitude was still unclear, I emphasized the importance of having a trusted scientific spokesperson providing timely, accurate information to the public. That, obviously, did not happen in the United States and the degree of the ensuing disaster is still to be revealed.
Scientists have made some wrong decisions about this novel threat. The advice on masks is an illustrative example. For many years, infection control nurses have insisted that medical students wear a mask to protect themselves, even if they were observing rounds from just inside the doorway of a room of a baby with bronchiolitis. The landfills are full of briefly worn surgical masks. Now the story goes: Surgical masks don’t protect staff; they protect others. Changes like that contribute to a credibility gap.
For 3 months, there was conflicting advice about the appropriateness of masks. In early March 2020, some health care workers were disciplined for wearing personal masks. Now, most scientists recommend the public use masks to reduce contagion. Significant subgroups in the U.S. population have refused, mostly to signal their contrarian politics. In June there was an anecdote of a success story from the Show Me state of Missouri, where a mask is credited for preventing an outbreak from a sick hair stylist.
It is hard to find something more reliable than an anecdote. On June 1, a meta-analysis funded by the World Health Organization was published online by Lancet. It supports the idea that masks are beneficial. It is mostly forest plots, so you can try to interpret it yourself. There were 172 observational studies in the systematic review, and the meta-analysis contains 44 relevant comparative studies and 0 randomized controlled trials. Most of those forest plots have an I2 of 75% or worse, which to me indicates that they are not much more reliable than a good anecdote. My primary conclusion was that modern academic science, in an era with a shortage of toilet paper, should convert to printing on soft tissue paper.
It is important to note that the guesstimated overall benefit of cloth masks was a relative risk of 0.30. That benefit is easily nullified if the false security of a mask causes people to congregate together in groups three times larger or for three times more minutes. N95 masks were more effective.
A different article was published in PNAS on June 11. Its senior author was awarded the Nobel Prize in Chemistry in 1995. That article touted the benefits of masks. The article is facing heavy criticism for flaws in methodology and flaws in the peer review process. A long list of signatories have joined a letter asking for the article’s retraction.
This article, when combined with the two instances of prominent articles being retracted in the prior month by the New England Journal of Medicine and The Lancet, is accumulating evidence the peer review system is not working as intended.
There are many heroes in this pandemic, from the frontline health care workers in hotspots to the grocery workers and cleaning staff. There is hope, indeed some faith, that medical scientists in the foreseeable future will provide treatments and a vaccine for this viral plague. This month, the credibility of scientists again plays a major role as communities respond to outbreaks related to reopening the economy. Let’s celebrate the victories, resolve to fix the impure system, and restore a high level of public trust in science. Lives depend on it.
Dr. Powell is a pediatric hospitalist and clinical ethics consultant living in St. Louis. He has no relevant financial disclosures. Email him at [email protected].
Having been a bench research scientist 30 years ago, I am flabbergasted at what is and is not currently possible. In a few weeks, scientists sequenced a novel coronavirus and used the genetic sequence to select candidate molecules for a vaccine. But we still can’t reliably say how much protection a cloth mask provides. Worse yet, even if/when we could reliably quantify contagion, it isn’t clear that the public will believe us anyhow.
The good news is that the public worldwide did believe scientists about the threat of a pandemic and the need to flatten the curve. Saving lives has not been about the strength of an antibiotic or the skill in managing a ventilator, but the credibility of medical scientists. The degree of acceptance was variable and subject to a variety of delays caused by regional politicians, but The bad news is that the public’s trust in that scientific advice has waned, the willingness to accept onerous restrictions has fatigued, and the cooperation for maintaining these social changes is evaporating.
I will leave pontificating about the spread of COVID-19 to other experts in other forums. My focus is on the public’s trust in the professionalism of physicians, nurses, medical scientists, and the health care industry as a whole. That trust has been our most valuable tool in fighting the pandemic so far. There have been situations in which weaknesses in modern science have let society down during the pandemic of the century. In my February 2020 column, at the beginning of the outbreak, a month before it was declared a pandemic, when its magnitude was still unclear, I emphasized the importance of having a trusted scientific spokesperson providing timely, accurate information to the public. That, obviously, did not happen in the United States and the degree of the ensuing disaster is still to be revealed.
Scientists have made some wrong decisions about this novel threat. The advice on masks is an illustrative example. For many years, infection control nurses have insisted that medical students wear a mask to protect themselves, even if they were observing rounds from just inside the doorway of a room of a baby with bronchiolitis. The landfills are full of briefly worn surgical masks. Now the story goes: Surgical masks don’t protect staff; they protect others. Changes like that contribute to a credibility gap.
For 3 months, there was conflicting advice about the appropriateness of masks. In early March 2020, some health care workers were disciplined for wearing personal masks. Now, most scientists recommend the public use masks to reduce contagion. Significant subgroups in the U.S. population have refused, mostly to signal their contrarian politics. In June there was an anecdote of a success story from the Show Me state of Missouri, where a mask is credited for preventing an outbreak from a sick hair stylist.
It is hard to find something more reliable than an anecdote. On June 1, a meta-analysis funded by the World Health Organization was published online by Lancet. It supports the idea that masks are beneficial. It is mostly forest plots, so you can try to interpret it yourself. There were 172 observational studies in the systematic review, and the meta-analysis contains 44 relevant comparative studies and 0 randomized controlled trials. Most of those forest plots have an I2 of 75% or worse, which to me indicates that they are not much more reliable than a good anecdote. My primary conclusion was that modern academic science, in an era with a shortage of toilet paper, should convert to printing on soft tissue paper.
It is important to note that the guesstimated overall benefit of cloth masks was a relative risk of 0.30. That benefit is easily nullified if the false security of a mask causes people to congregate together in groups three times larger or for three times more minutes. N95 masks were more effective.
A different article was published in PNAS on June 11. Its senior author was awarded the Nobel Prize in Chemistry in 1995. That article touted the benefits of masks. The article is facing heavy criticism for flaws in methodology and flaws in the peer review process. A long list of signatories have joined a letter asking for the article’s retraction.
This article, when combined with the two instances of prominent articles being retracted in the prior month by the New England Journal of Medicine and The Lancet, is accumulating evidence the peer review system is not working as intended.
There are many heroes in this pandemic, from the frontline health care workers in hotspots to the grocery workers and cleaning staff. There is hope, indeed some faith, that medical scientists in the foreseeable future will provide treatments and a vaccine for this viral plague. This month, the credibility of scientists again plays a major role as communities respond to outbreaks related to reopening the economy. Let’s celebrate the victories, resolve to fix the impure system, and restore a high level of public trust in science. Lives depend on it.
Dr. Powell is a pediatric hospitalist and clinical ethics consultant living in St. Louis. He has no relevant financial disclosures. Email him at [email protected].
Having been a bench research scientist 30 years ago, I am flabbergasted at what is and is not currently possible. In a few weeks, scientists sequenced a novel coronavirus and used the genetic sequence to select candidate molecules for a vaccine. But we still can’t reliably say how much protection a cloth mask provides. Worse yet, even if/when we could reliably quantify contagion, it isn’t clear that the public will believe us anyhow.
The good news is that the public worldwide did believe scientists about the threat of a pandemic and the need to flatten the curve. Saving lives has not been about the strength of an antibiotic or the skill in managing a ventilator, but the credibility of medical scientists. The degree of acceptance was variable and subject to a variety of delays caused by regional politicians, but The bad news is that the public’s trust in that scientific advice has waned, the willingness to accept onerous restrictions has fatigued, and the cooperation for maintaining these social changes is evaporating.
I will leave pontificating about the spread of COVID-19 to other experts in other forums. My focus is on the public’s trust in the professionalism of physicians, nurses, medical scientists, and the health care industry as a whole. That trust has been our most valuable tool in fighting the pandemic so far. There have been situations in which weaknesses in modern science have let society down during the pandemic of the century. In my February 2020 column, at the beginning of the outbreak, a month before it was declared a pandemic, when its magnitude was still unclear, I emphasized the importance of having a trusted scientific spokesperson providing timely, accurate information to the public. That, obviously, did not happen in the United States and the degree of the ensuing disaster is still to be revealed.
Scientists have made some wrong decisions about this novel threat. The advice on masks is an illustrative example. For many years, infection control nurses have insisted that medical students wear a mask to protect themselves, even if they were observing rounds from just inside the doorway of a room of a baby with bronchiolitis. The landfills are full of briefly worn surgical masks. Now the story goes: Surgical masks don’t protect staff; they protect others. Changes like that contribute to a credibility gap.
For 3 months, there was conflicting advice about the appropriateness of masks. In early March 2020, some health care workers were disciplined for wearing personal masks. Now, most scientists recommend the public use masks to reduce contagion. Significant subgroups in the U.S. population have refused, mostly to signal their contrarian politics. In June there was an anecdote of a success story from the Show Me state of Missouri, where a mask is credited for preventing an outbreak from a sick hair stylist.
It is hard to find something more reliable than an anecdote. On June 1, a meta-analysis funded by the World Health Organization was published online by Lancet. It supports the idea that masks are beneficial. It is mostly forest plots, so you can try to interpret it yourself. There were 172 observational studies in the systematic review, and the meta-analysis contains 44 relevant comparative studies and 0 randomized controlled trials. Most of those forest plots have an I2 of 75% or worse, which to me indicates that they are not much more reliable than a good anecdote. My primary conclusion was that modern academic science, in an era with a shortage of toilet paper, should convert to printing on soft tissue paper.
It is important to note that the guesstimated overall benefit of cloth masks was a relative risk of 0.30. That benefit is easily nullified if the false security of a mask causes people to congregate together in groups three times larger or for three times more minutes. N95 masks were more effective.
A different article was published in PNAS on June 11. Its senior author was awarded the Nobel Prize in Chemistry in 1995. That article touted the benefits of masks. The article is facing heavy criticism for flaws in methodology and flaws in the peer review process. A long list of signatories have joined a letter asking for the article’s retraction.
This article, when combined with the two instances of prominent articles being retracted in the prior month by the New England Journal of Medicine and The Lancet, is accumulating evidence the peer review system is not working as intended.
There are many heroes in this pandemic, from the frontline health care workers in hotspots to the grocery workers and cleaning staff. There is hope, indeed some faith, that medical scientists in the foreseeable future will provide treatments and a vaccine for this viral plague. This month, the credibility of scientists again plays a major role as communities respond to outbreaks related to reopening the economy. Let’s celebrate the victories, resolve to fix the impure system, and restore a high level of public trust in science. Lives depend on it.
Dr. Powell is a pediatric hospitalist and clinical ethics consultant living in St. Louis. He has no relevant financial disclosures. Email him at [email protected].
Children rarely transmit SARS-CoV-2 within households
“Unlike with other viral respiratory infections, children do not seem to be a major vector of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) transmission, with most pediatric cases described inside familial clusters and no documentation of child-to-child or child-to-adult transmission,” said Klara M. Posfay-Barbe, MD, of the University of Geneva, Switzerland, and colleagues.
In a study published in Pediatrics, the researchers analyzed data from all COVID-19 patients younger than 16 years who were identified between March 10, 2020, and April 10, 2020, through a hospital surveillance network. Parents and household contacts were called for contact tracing.
In 31 of 39 (79%) households, at least one adult family member had a suspected or confirmed SARS-CoV-2 infection before onset of symptoms in the child. These findings support data from previous studies suggesting that children mainly become infected from adult family members rather than transmitting the virus to them, the researchers said
In only 3 of 39 (8%) households was the study child the first to develop symptoms. “Surprisingly, in 33% of households, symptomatic HHCs [household contacts] tested negative despite belonging to a familial cluster with confirmed SARS-CoV-2 cases, suggesting an underreporting of cases,” Dr. Posfay-Barbe and associates noted.
The findings were limited by several factors including potential underreporting of cases because those with mild or atypical presentations may not have sought medical care, and the inability to confirm child-to-adult transmission. The results were strengthened by the extensive contact tracing and very few individuals lost to follow-up, they said; however, more diagnostic screening and contact tracing are needed to improve understanding of household transmission of SARS-CoV-2, they concluded.
Resolving the issue of how much children contribute to transmission of SARS-CoV-2 is essential to making informed decisions about public health, including how to structure schools and child-care facility reopening, Benjamin Lee, MD, and William V. Raszka Jr., MD, both of the University of Vermont, Burlington, said in an accompanying editorial (Pediatrics. 2020 Jul 10. doi: 10.1542/peds/2020-004879).
The data in the current study support other studies of transmission among household contacts in China suggesting that, in most cases of childhood infections, “the child was not the source of infection and that children most frequently acquire COVID-19 from adults, rather than transmitting it to them,” they wrote.
In addition, the limited data on transmission of SARS-CoV-2 by children outside of the household show few cases of secondary infection from children identified with SARS-CoV-2 in school settings in studies from France and Australia, Dr. Lee and Dr. Raszka noted.
the editorialists wrote. “This would be another manner by which SARS-CoV2 differs drastically from influenza, for which school-based transmission is well recognized as a significant driver of epidemic disease and forms the basis for most evidence regarding school closures as public health strategy.”
“Therefore, serious consideration should be paid toward strategies that allow schools to remain open, even during periods of COVID-19 spread,” the editorialists concluded. “In doing so, we could minimize the potentially profound adverse social, developmental, and health costs that our children will continue to suffer until an effective treatment or vaccine can be developed and distributed or, failing that, until we reach herd immunity,” Dr. Lee and Dr. Raszka emphasized.
The study received no outside funding. The researchers and editorialists had no financial conflicts to disclose.
SOURCE: Posfay-Barbe KM et al. Pediatrics. 2020 Jul 10. doi: 10.1542/peds.2020-1576.
“Unlike with other viral respiratory infections, children do not seem to be a major vector of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) transmission, with most pediatric cases described inside familial clusters and no documentation of child-to-child or child-to-adult transmission,” said Klara M. Posfay-Barbe, MD, of the University of Geneva, Switzerland, and colleagues.
In a study published in Pediatrics, the researchers analyzed data from all COVID-19 patients younger than 16 years who were identified between March 10, 2020, and April 10, 2020, through a hospital surveillance network. Parents and household contacts were called for contact tracing.
In 31 of 39 (79%) households, at least one adult family member had a suspected or confirmed SARS-CoV-2 infection before onset of symptoms in the child. These findings support data from previous studies suggesting that children mainly become infected from adult family members rather than transmitting the virus to them, the researchers said
In only 3 of 39 (8%) households was the study child the first to develop symptoms. “Surprisingly, in 33% of households, symptomatic HHCs [household contacts] tested negative despite belonging to a familial cluster with confirmed SARS-CoV-2 cases, suggesting an underreporting of cases,” Dr. Posfay-Barbe and associates noted.
The findings were limited by several factors including potential underreporting of cases because those with mild or atypical presentations may not have sought medical care, and the inability to confirm child-to-adult transmission. The results were strengthened by the extensive contact tracing and very few individuals lost to follow-up, they said; however, more diagnostic screening and contact tracing are needed to improve understanding of household transmission of SARS-CoV-2, they concluded.
Resolving the issue of how much children contribute to transmission of SARS-CoV-2 is essential to making informed decisions about public health, including how to structure schools and child-care facility reopening, Benjamin Lee, MD, and William V. Raszka Jr., MD, both of the University of Vermont, Burlington, said in an accompanying editorial (Pediatrics. 2020 Jul 10. doi: 10.1542/peds/2020-004879).
The data in the current study support other studies of transmission among household contacts in China suggesting that, in most cases of childhood infections, “the child was not the source of infection and that children most frequently acquire COVID-19 from adults, rather than transmitting it to them,” they wrote.
In addition, the limited data on transmission of SARS-CoV-2 by children outside of the household show few cases of secondary infection from children identified with SARS-CoV-2 in school settings in studies from France and Australia, Dr. Lee and Dr. Raszka noted.
the editorialists wrote. “This would be another manner by which SARS-CoV2 differs drastically from influenza, for which school-based transmission is well recognized as a significant driver of epidemic disease and forms the basis for most evidence regarding school closures as public health strategy.”
“Therefore, serious consideration should be paid toward strategies that allow schools to remain open, even during periods of COVID-19 spread,” the editorialists concluded. “In doing so, we could minimize the potentially profound adverse social, developmental, and health costs that our children will continue to suffer until an effective treatment or vaccine can be developed and distributed or, failing that, until we reach herd immunity,” Dr. Lee and Dr. Raszka emphasized.
The study received no outside funding. The researchers and editorialists had no financial conflicts to disclose.
SOURCE: Posfay-Barbe KM et al. Pediatrics. 2020 Jul 10. doi: 10.1542/peds.2020-1576.
“Unlike with other viral respiratory infections, children do not seem to be a major vector of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) transmission, with most pediatric cases described inside familial clusters and no documentation of child-to-child or child-to-adult transmission,” said Klara M. Posfay-Barbe, MD, of the University of Geneva, Switzerland, and colleagues.
In a study published in Pediatrics, the researchers analyzed data from all COVID-19 patients younger than 16 years who were identified between March 10, 2020, and April 10, 2020, through a hospital surveillance network. Parents and household contacts were called for contact tracing.
In 31 of 39 (79%) households, at least one adult family member had a suspected or confirmed SARS-CoV-2 infection before onset of symptoms in the child. These findings support data from previous studies suggesting that children mainly become infected from adult family members rather than transmitting the virus to them, the researchers said
In only 3 of 39 (8%) households was the study child the first to develop symptoms. “Surprisingly, in 33% of households, symptomatic HHCs [household contacts] tested negative despite belonging to a familial cluster with confirmed SARS-CoV-2 cases, suggesting an underreporting of cases,” Dr. Posfay-Barbe and associates noted.
The findings were limited by several factors including potential underreporting of cases because those with mild or atypical presentations may not have sought medical care, and the inability to confirm child-to-adult transmission. The results were strengthened by the extensive contact tracing and very few individuals lost to follow-up, they said; however, more diagnostic screening and contact tracing are needed to improve understanding of household transmission of SARS-CoV-2, they concluded.
Resolving the issue of how much children contribute to transmission of SARS-CoV-2 is essential to making informed decisions about public health, including how to structure schools and child-care facility reopening, Benjamin Lee, MD, and William V. Raszka Jr., MD, both of the University of Vermont, Burlington, said in an accompanying editorial (Pediatrics. 2020 Jul 10. doi: 10.1542/peds/2020-004879).
The data in the current study support other studies of transmission among household contacts in China suggesting that, in most cases of childhood infections, “the child was not the source of infection and that children most frequently acquire COVID-19 from adults, rather than transmitting it to them,” they wrote.
In addition, the limited data on transmission of SARS-CoV-2 by children outside of the household show few cases of secondary infection from children identified with SARS-CoV-2 in school settings in studies from France and Australia, Dr. Lee and Dr. Raszka noted.
the editorialists wrote. “This would be another manner by which SARS-CoV2 differs drastically from influenza, for which school-based transmission is well recognized as a significant driver of epidemic disease and forms the basis for most evidence regarding school closures as public health strategy.”
“Therefore, serious consideration should be paid toward strategies that allow schools to remain open, even during periods of COVID-19 spread,” the editorialists concluded. “In doing so, we could minimize the potentially profound adverse social, developmental, and health costs that our children will continue to suffer until an effective treatment or vaccine can be developed and distributed or, failing that, until we reach herd immunity,” Dr. Lee and Dr. Raszka emphasized.
The study received no outside funding. The researchers and editorialists had no financial conflicts to disclose.
SOURCE: Posfay-Barbe KM et al. Pediatrics. 2020 Jul 10. doi: 10.1542/peds.2020-1576.
FROM PEDIATRICS
Risky business: Longer-course prophylactic perioperative antimicrobials
Background: National guidelines recommend that surgical prophylactic antimicrobials be initiated within 1 hour prior to incision and discontinued 24 hours postoperatively. However, the risks and benefits of longer duration of antimicrobials are uncertain.
Study design: Retrospective cohort study.
Setting: Veterans Affairs hospitals.
Synopsis: After stratification by type of surgery and adjustment for covariates, antibiotic prophylaxis greater than 24 hours was not associated with lower SSI risk.
However, the odds of postoperative AKI increased with each additional day of prophylaxis (adjusted odds ratios, 1.82; 95% confidence interval,1.54-2.16 and aOR, 1.79; 95% CI, 1.27-2.53) with longer than 72 hours prophylaxis for cardiac and noncardiac surgery, respectively). Similarly, C. difficile infections increased with each additional day beyond 24 hours (aOR, 3.65; 95% CI, 2.40-5.55 with more than 72 hours of use).
Bottom line: Each day of perioperative antimicrobial prophylaxis beyond 24 hours increases the risk for postoperative AKI or C. difficile infection without reducing the risk of surgical site infection.
Citation: Branch-Elliman W et al. Association of duration and type of surgical prophylaxis with antimicrobial-associated adverse events. JAMA Surg. 2019 Apr 24. doi: 10.1001/jamasurg.2019.0569.
Dr. Miller is a hospitalist at the University of Colorado at Denver, Aurora.
Background: National guidelines recommend that surgical prophylactic antimicrobials be initiated within 1 hour prior to incision and discontinued 24 hours postoperatively. However, the risks and benefits of longer duration of antimicrobials are uncertain.
Study design: Retrospective cohort study.
Setting: Veterans Affairs hospitals.
Synopsis: After stratification by type of surgery and adjustment for covariates, antibiotic prophylaxis greater than 24 hours was not associated with lower SSI risk.
However, the odds of postoperative AKI increased with each additional day of prophylaxis (adjusted odds ratios, 1.82; 95% confidence interval,1.54-2.16 and aOR, 1.79; 95% CI, 1.27-2.53) with longer than 72 hours prophylaxis for cardiac and noncardiac surgery, respectively). Similarly, C. difficile infections increased with each additional day beyond 24 hours (aOR, 3.65; 95% CI, 2.40-5.55 with more than 72 hours of use).
Bottom line: Each day of perioperative antimicrobial prophylaxis beyond 24 hours increases the risk for postoperative AKI or C. difficile infection without reducing the risk of surgical site infection.
Citation: Branch-Elliman W et al. Association of duration and type of surgical prophylaxis with antimicrobial-associated adverse events. JAMA Surg. 2019 Apr 24. doi: 10.1001/jamasurg.2019.0569.
Dr. Miller is a hospitalist at the University of Colorado at Denver, Aurora.
Background: National guidelines recommend that surgical prophylactic antimicrobials be initiated within 1 hour prior to incision and discontinued 24 hours postoperatively. However, the risks and benefits of longer duration of antimicrobials are uncertain.
Study design: Retrospective cohort study.
Setting: Veterans Affairs hospitals.
Synopsis: After stratification by type of surgery and adjustment for covariates, antibiotic prophylaxis greater than 24 hours was not associated with lower SSI risk.
However, the odds of postoperative AKI increased with each additional day of prophylaxis (adjusted odds ratios, 1.82; 95% confidence interval,1.54-2.16 and aOR, 1.79; 95% CI, 1.27-2.53) with longer than 72 hours prophylaxis for cardiac and noncardiac surgery, respectively). Similarly, C. difficile infections increased with each additional day beyond 24 hours (aOR, 3.65; 95% CI, 2.40-5.55 with more than 72 hours of use).
Bottom line: Each day of perioperative antimicrobial prophylaxis beyond 24 hours increases the risk for postoperative AKI or C. difficile infection without reducing the risk of surgical site infection.
Citation: Branch-Elliman W et al. Association of duration and type of surgical prophylaxis with antimicrobial-associated adverse events. JAMA Surg. 2019 Apr 24. doi: 10.1001/jamasurg.2019.0569.
Dr. Miller is a hospitalist at the University of Colorado at Denver, Aurora.
How effective is elagolix treatment in women with fibroids and HMB?
Simon JA, Al-Hendy A, Archer DF, et al. Elagolix treatment for up to 12 months in women with heavy menstrual bleeding and uterine leiomyomas. Obstet Gynecol. 2020;135:1313-1326.
Expert Commentary
Uterine fibroids are common (occurring in up to 80% of reproductive-age women),1,2 and often associated with heavy menstrual bleeding (HMB). There are surgical and medical options, but typically medical options are used for short periods of time. Elagolix with hormonal add-back therapy was recently approved (May 29, 2020) by the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) for treatment of HMB in women with uterine fibroids for up to 24 months.
Elagolix is an oral, nonpeptide gonadotropin-releasing hormone antagonist that results in a dose-dependent reduction of gonadotropins and ovarian sex hormones. There are now 2 approved products containing elagolix, with different indications:
- Orilissa. Elagolix was approved in 2018 by the FDA for moderate to severe pain associated with endometriosis. For that indication there are 2 dose options of elagolix (150 mg for up to 2 years and 200 mg for up to 6 months) and there is no hormonal add-back therapy.
- Oriahnn. Elagolix and hormonal add-back therapy was approved in 2020 for HMB associated with uterine fibroids for up to 24 months. The total daily dose of elagolix is 600 mg (elagolix 300 mg in the morning with estradiol 1 mg/norethindrone acetate 0.5 mg and then in the evening elagolix 300 mg and no hormonal add-back).
This new class of drug, GnRH antagonist, is an important one for women’s health, and emerging science will continue to expand its potential uses, such as in reproductive health, as well as long-term efficacy and safety. The difference in daily dose of elagolix for endometriosis (150 mg for 24 months) compared with HMB associated with fibroids (600 mg for 24 months) is why the hormonal add-back therapy is important and allows for protection of bone density.
This is an important manuscript because it highlights a medical option for women with HMB associated with fibroids, which can be used for a long period of time. Further, the improvement in bleeding is both impressive and maintained in the extension study. Approximately 90% of women show improvement in their menstrual bleeding associated with fibroids.
The question of what to do after 24 months of therapy with elagolix and hormonal add-back therapy is an important one, but providers should recognize that the limiting factor with this elagolix and hormonal add-back therapy is bone mineral density (BMD). We will only learn more and more moving forward if this is a clinically meaningful reason for stopping treatment at 24 months. The FDA takes a strict view of safety, and providers must weigh this with the benefit of therapy.
One other highlight between the 2 approved medications is that Orilissa does not have a black box warning, given that there is no hormonal add-back therapy. Oriahnn does have a warning, regarding thromboembolic disorders and vascular events:
- Estrogen and progestin combinations, including Oriahnn, increase the risk of thrombotic or thromboembolic disorders, especially in women at increased risk for these events.
- Oriahnn is contraindicated in women with current or a history of thrombotic or thromboembolic disorders and in women at increased risk for these events, including women over 35 years of age who smoke or women with uncontrolled hypertension.
Continue to: Details about the study...
Details about the study
The study by Simon et al is an extension study (UF-EXTEND), in that women could participate if they had completed 1 of the 2 pivotal studies on elagolix. The pivotal studies (Elaris UF1 and UF2) were both randomized, double-blinded, placebo-controlled studies with up to 6 months of therapy; for UF-EXTEND, however, participants were randomly assigned to either combined elagolix and hormone replacement therapy or elagolix alone for an additional 6 months of therapy. Although it was known that all participants would receive elagolix in UF-EXTEND, those who received hormonal add-back therapy were blinded. All women were then followed up for an additional 12 months after treatment ended.
The efficacy of elagolix was measured by the objective alkaline hematin method for menstrual blood loss with the a priori coprimary endpoints. The elagolix and hormonal add-back therapy group showed objective improvement in menstrual blood loss at 12 months in 87.9% of women in the extension study (89.4% in the elagolix alone group). This compares with 72.2% improvement at 6 months of treatment in the UF1 and UF2 studies for those taking elagolix and hormonal add-back therapy. These findings illustrate maintenance of the efficacy seen within the 6-month pivotal studies using elagolix over an extended amount of time.
The safety of elagolix also was demonstrated in UF-EXTEND. The 3 most common adverse events were similar to those found in Elaris UF1 and UF2 and included hot flushes, headache, and nausea. In the elagolix and hormonal add-back therapy group during the extension study, the percentage with hot flushes was 7%, headache 6%, and nausea 4%. These are small percentages, which is encouraging for providers and women with HMB associated with fibroids.
Effects on bone density
Bone density was evaluated at baseline in the UF1 and UF2 studies, through treatment, and then 12 months after the extended treatment was stopped. The hormonal add-back therapy of estradiol 1 mg/norethindrone acetate 0.5 mg significantly protected bone density. Some women did not have a decrease in bone density, but for those who did the average was less than 5% for the lumbar spine. The lumbar spine is considered the most reactive, so this illustrates the safety that combined therapy offers women with HMB and fibroids.
The lumbar spine is considered the most reactive, so this site is often used as the main focus with BMD studies. As Simon et al show, the lumbar spine mean BMD percent change from baseline for the elagolix with add-back therapy was -1.5% (95% confidence interval [CI], -1.9 to -1.0) in women who received up to 12 months of treatment at month 6 in the extension study. After stopping elagolix with add-back therapy, at 6 months the elagolix with add-back therapy had a Z-score of -0.6% (95% CI, -1.1 to -0.1). This shows a trend toward baseline, or a recovery within a short time from stopping medication.
Continue to: Study strengths and limitations...
Study strengths and limitations
Strengths of this study include its overall design; efficacy endpoints, which were all established a priori; the fact that measurement of menstrual blood loss was done with the objective alkaline hematin method; and the statistical analysis, which is thorough and well presented. This extension study allowed further evaluation of efficacy and safety for elagolix. Although the authors point out that there may be some selection bias in an extension study, the fact that so many women elected to continue into the extended study is a positive reflection of the treatment.
As providers learn of new therapies for management of HMB associated with fibroids, it is important to consider who will benefit the most. In my opinion, any woman with heavy periods associated with fibroids could be a candidate for elagolix with add-back therapy. This treatment is highly effective, well tolerated, and safe. My approach to management includes educating a woman on all potential therapies and this new option of elagolix and add-back therapy is an important one. The decision for an individual woman on how to manage heavy periods associated with fibroids should consider her contraceptive needs, medical issues, and the risk and benefit of individual therapies. ●
Elagolix and hormonal add-back therapy offer a long-term medical option for women with HMB associated with fibroids that is both effective and safe.
ANDREA S. LUKES, MD, MHSc
- Stewart EA, Nicholson WK, Bradley L, et al. The burden of uterine fibroids for African-American women: results of a national survey. J Women’s Health. 2013;22:807-816.
- Baird DD, Dunson DB, Hill MC, et al. High cumulative incidence of uterine leiomyoma in black and white women: ultrasound evidence. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2003;188:100-107.
Simon JA, Al-Hendy A, Archer DF, et al. Elagolix treatment for up to 12 months in women with heavy menstrual bleeding and uterine leiomyomas. Obstet Gynecol. 2020;135:1313-1326.
Expert Commentary
Uterine fibroids are common (occurring in up to 80% of reproductive-age women),1,2 and often associated with heavy menstrual bleeding (HMB). There are surgical and medical options, but typically medical options are used for short periods of time. Elagolix with hormonal add-back therapy was recently approved (May 29, 2020) by the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) for treatment of HMB in women with uterine fibroids for up to 24 months.
Elagolix is an oral, nonpeptide gonadotropin-releasing hormone antagonist that results in a dose-dependent reduction of gonadotropins and ovarian sex hormones. There are now 2 approved products containing elagolix, with different indications:
- Orilissa. Elagolix was approved in 2018 by the FDA for moderate to severe pain associated with endometriosis. For that indication there are 2 dose options of elagolix (150 mg for up to 2 years and 200 mg for up to 6 months) and there is no hormonal add-back therapy.
- Oriahnn. Elagolix and hormonal add-back therapy was approved in 2020 for HMB associated with uterine fibroids for up to 24 months. The total daily dose of elagolix is 600 mg (elagolix 300 mg in the morning with estradiol 1 mg/norethindrone acetate 0.5 mg and then in the evening elagolix 300 mg and no hormonal add-back).
This new class of drug, GnRH antagonist, is an important one for women’s health, and emerging science will continue to expand its potential uses, such as in reproductive health, as well as long-term efficacy and safety. The difference in daily dose of elagolix for endometriosis (150 mg for 24 months) compared with HMB associated with fibroids (600 mg for 24 months) is why the hormonal add-back therapy is important and allows for protection of bone density.
This is an important manuscript because it highlights a medical option for women with HMB associated with fibroids, which can be used for a long period of time. Further, the improvement in bleeding is both impressive and maintained in the extension study. Approximately 90% of women show improvement in their menstrual bleeding associated with fibroids.
The question of what to do after 24 months of therapy with elagolix and hormonal add-back therapy is an important one, but providers should recognize that the limiting factor with this elagolix and hormonal add-back therapy is bone mineral density (BMD). We will only learn more and more moving forward if this is a clinically meaningful reason for stopping treatment at 24 months. The FDA takes a strict view of safety, and providers must weigh this with the benefit of therapy.
One other highlight between the 2 approved medications is that Orilissa does not have a black box warning, given that there is no hormonal add-back therapy. Oriahnn does have a warning, regarding thromboembolic disorders and vascular events:
- Estrogen and progestin combinations, including Oriahnn, increase the risk of thrombotic or thromboembolic disorders, especially in women at increased risk for these events.
- Oriahnn is contraindicated in women with current or a history of thrombotic or thromboembolic disorders and in women at increased risk for these events, including women over 35 years of age who smoke or women with uncontrolled hypertension.
Continue to: Details about the study...
Details about the study
The study by Simon et al is an extension study (UF-EXTEND), in that women could participate if they had completed 1 of the 2 pivotal studies on elagolix. The pivotal studies (Elaris UF1 and UF2) were both randomized, double-blinded, placebo-controlled studies with up to 6 months of therapy; for UF-EXTEND, however, participants were randomly assigned to either combined elagolix and hormone replacement therapy or elagolix alone for an additional 6 months of therapy. Although it was known that all participants would receive elagolix in UF-EXTEND, those who received hormonal add-back therapy were blinded. All women were then followed up for an additional 12 months after treatment ended.
The efficacy of elagolix was measured by the objective alkaline hematin method for menstrual blood loss with the a priori coprimary endpoints. The elagolix and hormonal add-back therapy group showed objective improvement in menstrual blood loss at 12 months in 87.9% of women in the extension study (89.4% in the elagolix alone group). This compares with 72.2% improvement at 6 months of treatment in the UF1 and UF2 studies for those taking elagolix and hormonal add-back therapy. These findings illustrate maintenance of the efficacy seen within the 6-month pivotal studies using elagolix over an extended amount of time.
The safety of elagolix also was demonstrated in UF-EXTEND. The 3 most common adverse events were similar to those found in Elaris UF1 and UF2 and included hot flushes, headache, and nausea. In the elagolix and hormonal add-back therapy group during the extension study, the percentage with hot flushes was 7%, headache 6%, and nausea 4%. These are small percentages, which is encouraging for providers and women with HMB associated with fibroids.
Effects on bone density
Bone density was evaluated at baseline in the UF1 and UF2 studies, through treatment, and then 12 months after the extended treatment was stopped. The hormonal add-back therapy of estradiol 1 mg/norethindrone acetate 0.5 mg significantly protected bone density. Some women did not have a decrease in bone density, but for those who did the average was less than 5% for the lumbar spine. The lumbar spine is considered the most reactive, so this illustrates the safety that combined therapy offers women with HMB and fibroids.
The lumbar spine is considered the most reactive, so this site is often used as the main focus with BMD studies. As Simon et al show, the lumbar spine mean BMD percent change from baseline for the elagolix with add-back therapy was -1.5% (95% confidence interval [CI], -1.9 to -1.0) in women who received up to 12 months of treatment at month 6 in the extension study. After stopping elagolix with add-back therapy, at 6 months the elagolix with add-back therapy had a Z-score of -0.6% (95% CI, -1.1 to -0.1). This shows a trend toward baseline, or a recovery within a short time from stopping medication.
Continue to: Study strengths and limitations...
Study strengths and limitations
Strengths of this study include its overall design; efficacy endpoints, which were all established a priori; the fact that measurement of menstrual blood loss was done with the objective alkaline hematin method; and the statistical analysis, which is thorough and well presented. This extension study allowed further evaluation of efficacy and safety for elagolix. Although the authors point out that there may be some selection bias in an extension study, the fact that so many women elected to continue into the extended study is a positive reflection of the treatment.
As providers learn of new therapies for management of HMB associated with fibroids, it is important to consider who will benefit the most. In my opinion, any woman with heavy periods associated with fibroids could be a candidate for elagolix with add-back therapy. This treatment is highly effective, well tolerated, and safe. My approach to management includes educating a woman on all potential therapies and this new option of elagolix and add-back therapy is an important one. The decision for an individual woman on how to manage heavy periods associated with fibroids should consider her contraceptive needs, medical issues, and the risk and benefit of individual therapies. ●
Elagolix and hormonal add-back therapy offer a long-term medical option for women with HMB associated with fibroids that is both effective and safe.
ANDREA S. LUKES, MD, MHSc
Simon JA, Al-Hendy A, Archer DF, et al. Elagolix treatment for up to 12 months in women with heavy menstrual bleeding and uterine leiomyomas. Obstet Gynecol. 2020;135:1313-1326.
Expert Commentary
Uterine fibroids are common (occurring in up to 80% of reproductive-age women),1,2 and often associated with heavy menstrual bleeding (HMB). There are surgical and medical options, but typically medical options are used for short periods of time. Elagolix with hormonal add-back therapy was recently approved (May 29, 2020) by the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) for treatment of HMB in women with uterine fibroids for up to 24 months.
Elagolix is an oral, nonpeptide gonadotropin-releasing hormone antagonist that results in a dose-dependent reduction of gonadotropins and ovarian sex hormones. There are now 2 approved products containing elagolix, with different indications:
- Orilissa. Elagolix was approved in 2018 by the FDA for moderate to severe pain associated with endometriosis. For that indication there are 2 dose options of elagolix (150 mg for up to 2 years and 200 mg for up to 6 months) and there is no hormonal add-back therapy.
- Oriahnn. Elagolix and hormonal add-back therapy was approved in 2020 for HMB associated with uterine fibroids for up to 24 months. The total daily dose of elagolix is 600 mg (elagolix 300 mg in the morning with estradiol 1 mg/norethindrone acetate 0.5 mg and then in the evening elagolix 300 mg and no hormonal add-back).
This new class of drug, GnRH antagonist, is an important one for women’s health, and emerging science will continue to expand its potential uses, such as in reproductive health, as well as long-term efficacy and safety. The difference in daily dose of elagolix for endometriosis (150 mg for 24 months) compared with HMB associated with fibroids (600 mg for 24 months) is why the hormonal add-back therapy is important and allows for protection of bone density.
This is an important manuscript because it highlights a medical option for women with HMB associated with fibroids, which can be used for a long period of time. Further, the improvement in bleeding is both impressive and maintained in the extension study. Approximately 90% of women show improvement in their menstrual bleeding associated with fibroids.
The question of what to do after 24 months of therapy with elagolix and hormonal add-back therapy is an important one, but providers should recognize that the limiting factor with this elagolix and hormonal add-back therapy is bone mineral density (BMD). We will only learn more and more moving forward if this is a clinically meaningful reason for stopping treatment at 24 months. The FDA takes a strict view of safety, and providers must weigh this with the benefit of therapy.
One other highlight between the 2 approved medications is that Orilissa does not have a black box warning, given that there is no hormonal add-back therapy. Oriahnn does have a warning, regarding thromboembolic disorders and vascular events:
- Estrogen and progestin combinations, including Oriahnn, increase the risk of thrombotic or thromboembolic disorders, especially in women at increased risk for these events.
- Oriahnn is contraindicated in women with current or a history of thrombotic or thromboembolic disorders and in women at increased risk for these events, including women over 35 years of age who smoke or women with uncontrolled hypertension.
Continue to: Details about the study...
Details about the study
The study by Simon et al is an extension study (UF-EXTEND), in that women could participate if they had completed 1 of the 2 pivotal studies on elagolix. The pivotal studies (Elaris UF1 and UF2) were both randomized, double-blinded, placebo-controlled studies with up to 6 months of therapy; for UF-EXTEND, however, participants were randomly assigned to either combined elagolix and hormone replacement therapy or elagolix alone for an additional 6 months of therapy. Although it was known that all participants would receive elagolix in UF-EXTEND, those who received hormonal add-back therapy were blinded. All women were then followed up for an additional 12 months after treatment ended.
The efficacy of elagolix was measured by the objective alkaline hematin method for menstrual blood loss with the a priori coprimary endpoints. The elagolix and hormonal add-back therapy group showed objective improvement in menstrual blood loss at 12 months in 87.9% of women in the extension study (89.4% in the elagolix alone group). This compares with 72.2% improvement at 6 months of treatment in the UF1 and UF2 studies for those taking elagolix and hormonal add-back therapy. These findings illustrate maintenance of the efficacy seen within the 6-month pivotal studies using elagolix over an extended amount of time.
The safety of elagolix also was demonstrated in UF-EXTEND. The 3 most common adverse events were similar to those found in Elaris UF1 and UF2 and included hot flushes, headache, and nausea. In the elagolix and hormonal add-back therapy group during the extension study, the percentage with hot flushes was 7%, headache 6%, and nausea 4%. These are small percentages, which is encouraging for providers and women with HMB associated with fibroids.
Effects on bone density
Bone density was evaluated at baseline in the UF1 and UF2 studies, through treatment, and then 12 months after the extended treatment was stopped. The hormonal add-back therapy of estradiol 1 mg/norethindrone acetate 0.5 mg significantly protected bone density. Some women did not have a decrease in bone density, but for those who did the average was less than 5% for the lumbar spine. The lumbar spine is considered the most reactive, so this illustrates the safety that combined therapy offers women with HMB and fibroids.
The lumbar spine is considered the most reactive, so this site is often used as the main focus with BMD studies. As Simon et al show, the lumbar spine mean BMD percent change from baseline for the elagolix with add-back therapy was -1.5% (95% confidence interval [CI], -1.9 to -1.0) in women who received up to 12 months of treatment at month 6 in the extension study. After stopping elagolix with add-back therapy, at 6 months the elagolix with add-back therapy had a Z-score of -0.6% (95% CI, -1.1 to -0.1). This shows a trend toward baseline, or a recovery within a short time from stopping medication.
Continue to: Study strengths and limitations...
Study strengths and limitations
Strengths of this study include its overall design; efficacy endpoints, which were all established a priori; the fact that measurement of menstrual blood loss was done with the objective alkaline hematin method; and the statistical analysis, which is thorough and well presented. This extension study allowed further evaluation of efficacy and safety for elagolix. Although the authors point out that there may be some selection bias in an extension study, the fact that so many women elected to continue into the extended study is a positive reflection of the treatment.
As providers learn of new therapies for management of HMB associated with fibroids, it is important to consider who will benefit the most. In my opinion, any woman with heavy periods associated with fibroids could be a candidate for elagolix with add-back therapy. This treatment is highly effective, well tolerated, and safe. My approach to management includes educating a woman on all potential therapies and this new option of elagolix and add-back therapy is an important one. The decision for an individual woman on how to manage heavy periods associated with fibroids should consider her contraceptive needs, medical issues, and the risk and benefit of individual therapies. ●
Elagolix and hormonal add-back therapy offer a long-term medical option for women with HMB associated with fibroids that is both effective and safe.
ANDREA S. LUKES, MD, MHSc
- Stewart EA, Nicholson WK, Bradley L, et al. The burden of uterine fibroids for African-American women: results of a national survey. J Women’s Health. 2013;22:807-816.
- Baird DD, Dunson DB, Hill MC, et al. High cumulative incidence of uterine leiomyoma in black and white women: ultrasound evidence. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2003;188:100-107.
- Stewart EA, Nicholson WK, Bradley L, et al. The burden of uterine fibroids for African-American women: results of a national survey. J Women’s Health. 2013;22:807-816.
- Baird DD, Dunson DB, Hill MC, et al. High cumulative incidence of uterine leiomyoma in black and white women: ultrasound evidence. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2003;188:100-107.
The Fetal Pillow: A new option for delivering the deeply impacted fetal head
Obstetricians know that a cesarean delivery (CD) for a woman with a prolonged second stage and a fetal head deeply impacted in the pelvis is challenging. In this situation, extensions of the uterine incision commonly occur, resulting in prolonged operative time and increased blood loss. Even more harrowing is the inability to deliver the fetal head, necessitating emergency assistance from other clinicians. In this situation, interventions that may be helpful include:
- extend or T the uterine incision
- enlist the aid of a clinician to push up on the fetal head with a vaginal hand (FIGURE 1)
- reverse breech extraction (FIGURE 2), and
- vaginal insertion of a Fetal Pillow prior to starting the delivery.
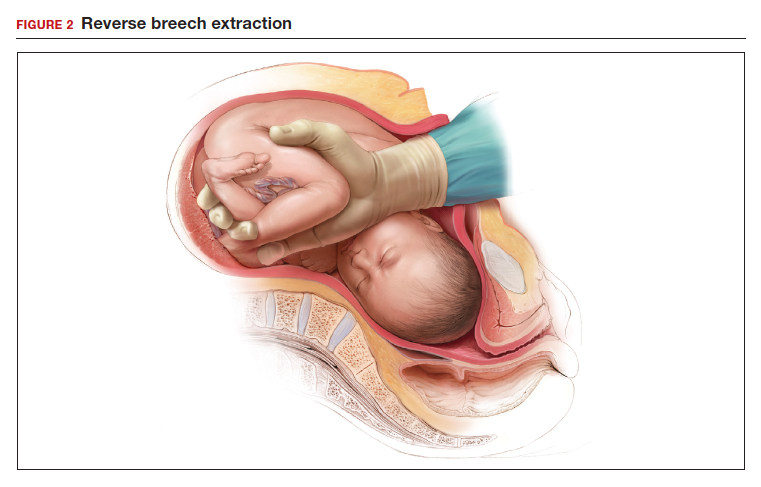
Evidence from clinical trials indicates that reverse breech extraction or insertion of a Fetal Pillow result in the best clinical outcomes.
Reverse breech extraction vs the push technique
Although the data are limited, most studies report that compared with pushing up with a vaginal hand (as shown in Figure 1), the reverse breech extraction technique (as shown in Figure 2) is associated with a reduction in extensions of the uterine incision, reduced blood loss, and reduced operative time.1 In a randomized trial, 108 women with obstructed labor undergoing CD in the second stage were randomly assigned to reverse breech extraction or pushing up with a vaginal hand.2 Following the uterine incision, the reverse breech extraction technique is performed by immediately reaching into the upper uterus and grasping the lower portion of the fetal leg and applying gentle traction on the leg until the second leg appeared. The lower legs are then pulled out of the uterus. Standard breech delivery maneuvers are used to deliver the shoulders and head. In the trial, compared with the push technique, reverse breech extraction was associated with fewer extensions of the uterine incision (30% vs 11%; P<.05), less blood loss (899 mL vs 1,257 mL; P<.001), and shorter operative time (56 min vs 89 min, P<.001). Fetal injury was similar with the push and breech extraction techniques (6% and 7%).
In another randomized trial, 192 women undergoing CD for obstructed labor were randomly assigned to reverse breech extraction or pushing the head up with a hand in the vagina.3 Compared with the vaginal push technique, reverse breech extraction was associated with fewer extensions of the uterine incision (19% vs 48%; P = .003), fewer cases of wound infection (2% vs 13%; P = .007), and fewer blood transfusions (2 vs 11; P = .012).
Additional options and adjuvants for facilitating delivery of a fetal head deeply impacted in the pelvis include: using a Coyne spoon, using nitroglycerine or terbutaline to relax the myometrium, breaking the vaginal suction on the fetal head before attempting delivery, keeping the wrist of the delivering hand as straight as possible to reduce uterine incision extensions, and incising the ring (if a Bandl’s ring is detected).
Continue to: The Fetal Pillow...
The Fetal Pillow
The Fetal Pillow (Safe Obstetric Systems, New York, New York) is a single-use fetal cephalic elevation device for managing the deeply impacted fetal head (FIGURE 3). The Fetal Pillow has a firm plastic base upon which is attached a soft silicon balloon. The Fetal Pillow is inserted into the vagina prior to initiating CD and the balloon is filled with 180 mL of saline, causing the fetal head to be pushed to a higher station (FIGURE 4). Use of the Fetal Pillow may be indicated prior to CD in the following situations:
- second stage labor with a deeply impacted head
- second stage labor and failed operative delivery
- occiput posterior position or deep transverse arrest
- absent progress in the first stage between 8 cm and 10 cm with a deeply impacted fetal head or excessive caput of the fetal head.
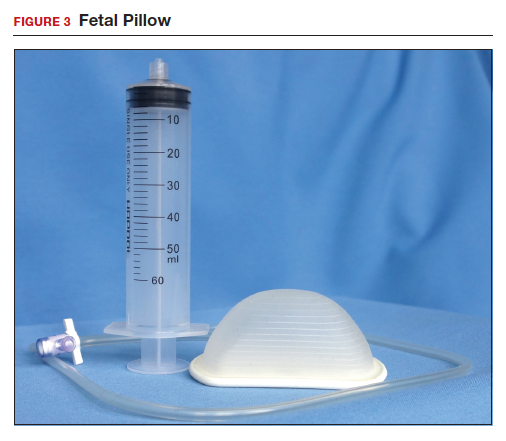
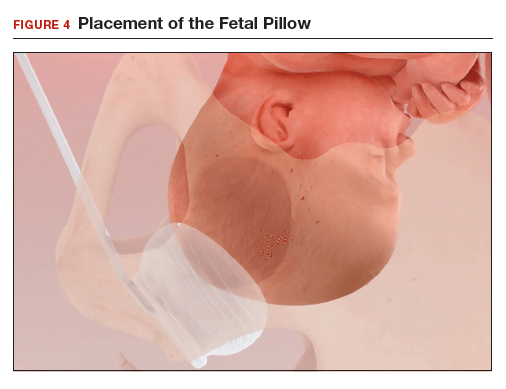
The Fetal Pillow is inserted after completing vaginal preparation for CD and before initiating skin preparation and abdominal draping. The steps for inserting the Fetal Pillow include:
- Use the 60 mL syringe to fully deflate the Fetal Pillow and leave the cock-stop open.
- Fold the Fetal Pillow by squeezing the firm plastic base, and with the patient’s legs in a frog-leg position, place the device in the vagina.
- Allow the firm plastic base to open to a flat position with the base against the posterior vaginal wall and the soft silicon balloon against the fetal head.
- Using pressure on the plastic base, gently push the Fetal Pillow posteriorly toward the sacrum of the mother.
- Use the 60 mL syringe to inflate the balloon with 180 mL of normal saline and close the valve.
- Straighten the patient’s legs and proceed with skin preparation and abdominal draping (FIGURE 4).
When the CD is completed, deflate the balloon by drawing out the saline with the 60 mL syringe and remove the device by hooking a finger around the firm plastic base. The Fetal Pillow is surprisingly easy to use.
Continue to: Effectiveness of the Fetal Pillow...
Effectiveness of the Fetal Pillow
In one randomized trial, 240 women undergoing CD were randomly allocated to a group in which the Fetal Pillow was placed in the vagina and inflated prior to the cesarean and a control group in which the Fetal Pillow was not used.
In another randomized trial, 60 nulliparous women undergoing CD in the second stage of labor had a Fetal Pillow inserted in the vagina and were randomly allocated to inflation of the pillow (Fetal Pillow group) or noninflation of the pillow (control group).5 In this study the mean length of the second stage was 4 hours. Compared with noninflation of the Fetal Pillow, use of the inflated Fetal Pillow was associated with a reduction in grade 3 extension of the uterine incision (extensions into the uterine artery, vagina, or bladder) (0% for inflation vs 13% for noninflation) and fewer difficult plus very difficult deliveries of the fetal head as reported by the surgeon (0% for inflation vs 37% for noninflation). There was no significant difference in blood loss between the two groups (800 mL vs 900 mL). These two randomized studies both reported that the use of the Fetal Pillow was associated with a reduction in grade 3 extensions of the uterine incision and a decrease in the difficulty of delivering the fetal head.
Consider trialing the Fetal Pillow
When a CD is performed after a prolonged second stage of labor, surgical complications are common, including extensions of the uterine incision and difficulty delivering the fetal head. When a grade 3 extension occurs—with tearing of a uterine artery, deep extension into the vagina, or damage to the bladder—the surgical repair can be extraordinarily challenging. Clinical trials report that both reverse breech extraction and the Fetal Pillow can facilitate CD in the setting of a prolonged second stage. For many obstetricians reverse breech extraction is a challenging obstetric maneuver. The insertion and inflation of a Fetal Pillow is a simple procedure. Obstetrician-gynecologists learn by doing. If you have never used the Fetal Pillow, I suggest you consider trialing it in your practice. ●
- Jeve YB, Navti OB, Konje JC. Comparison of techniques used to deliver a deeply impacted fetal head at full dilation: a systematic review and meta-analysis. BJOG. 2016;123:337-345.
- Fasubaa OB, Ezechi OC, Orji EO, et al. Delivery of the impacted head of the fetus at cesarean section after prolonged obstructed labor: a randomised comparative study of two methods. J Obstet Gynaecol. 2002;22:375-378.
- Nooh AM, Abdeldayem HM, Ben-Affan O. Reverse breech extraction versus the standard approach of pushing the impacted fetal head up through the vagina in caesarean section for obstructed labour: a randomised controlled trial. J Obstet Gynaecol. 2017;37:459-463.
- Seal SL, Dey A, Barman SC, et al. Randomized controlled trial of elevation of the fetal head with a fetal pillow during cesarean delivery at full cervical dilatation. Int J Gynaecol Obstet. 2016;133:178-182.
- Lassey SC, Little SE, Saadeh M,et al. Cephalic elevation device for second-stage cesarean delivery: a randomized controlled trial. Obstet Gynecol. 2020;135:879-884.
Obstetricians know that a cesarean delivery (CD) for a woman with a prolonged second stage and a fetal head deeply impacted in the pelvis is challenging. In this situation, extensions of the uterine incision commonly occur, resulting in prolonged operative time and increased blood loss. Even more harrowing is the inability to deliver the fetal head, necessitating emergency assistance from other clinicians. In this situation, interventions that may be helpful include:
- extend or T the uterine incision
- enlist the aid of a clinician to push up on the fetal head with a vaginal hand (FIGURE 1)
- reverse breech extraction (FIGURE 2), and
- vaginal insertion of a Fetal Pillow prior to starting the delivery.


Evidence from clinical trials indicates that reverse breech extraction or insertion of a Fetal Pillow result in the best clinical outcomes.
Reverse breech extraction vs the push technique
Although the data are limited, most studies report that compared with pushing up with a vaginal hand (as shown in Figure 1), the reverse breech extraction technique (as shown in Figure 2) is associated with a reduction in extensions of the uterine incision, reduced blood loss, and reduced operative time.1 In a randomized trial, 108 women with obstructed labor undergoing CD in the second stage were randomly assigned to reverse breech extraction or pushing up with a vaginal hand.2 Following the uterine incision, the reverse breech extraction technique is performed by immediately reaching into the upper uterus and grasping the lower portion of the fetal leg and applying gentle traction on the leg until the second leg appeared. The lower legs are then pulled out of the uterus. Standard breech delivery maneuvers are used to deliver the shoulders and head. In the trial, compared with the push technique, reverse breech extraction was associated with fewer extensions of the uterine incision (30% vs 11%; P<.05), less blood loss (899 mL vs 1,257 mL; P<.001), and shorter operative time (56 min vs 89 min, P<.001). Fetal injury was similar with the push and breech extraction techniques (6% and 7%).
In another randomized trial, 192 women undergoing CD for obstructed labor were randomly assigned to reverse breech extraction or pushing the head up with a hand in the vagina.3 Compared with the vaginal push technique, reverse breech extraction was associated with fewer extensions of the uterine incision (19% vs 48%; P = .003), fewer cases of wound infection (2% vs 13%; P = .007), and fewer blood transfusions (2 vs 11; P = .012).
Additional options and adjuvants for facilitating delivery of a fetal head deeply impacted in the pelvis include: using a Coyne spoon, using nitroglycerine or terbutaline to relax the myometrium, breaking the vaginal suction on the fetal head before attempting delivery, keeping the wrist of the delivering hand as straight as possible to reduce uterine incision extensions, and incising the ring (if a Bandl’s ring is detected).
Continue to: The Fetal Pillow...
The Fetal Pillow
The Fetal Pillow (Safe Obstetric Systems, New York, New York) is a single-use fetal cephalic elevation device for managing the deeply impacted fetal head (FIGURE 3). The Fetal Pillow has a firm plastic base upon which is attached a soft silicon balloon. The Fetal Pillow is inserted into the vagina prior to initiating CD and the balloon is filled with 180 mL of saline, causing the fetal head to be pushed to a higher station (FIGURE 4). Use of the Fetal Pillow may be indicated prior to CD in the following situations:
- second stage labor with a deeply impacted head
- second stage labor and failed operative delivery
- occiput posterior position or deep transverse arrest
- absent progress in the first stage between 8 cm and 10 cm with a deeply impacted fetal head or excessive caput of the fetal head.


The Fetal Pillow is inserted after completing vaginal preparation for CD and before initiating skin preparation and abdominal draping. The steps for inserting the Fetal Pillow include:
- Use the 60 mL syringe to fully deflate the Fetal Pillow and leave the cock-stop open.
- Fold the Fetal Pillow by squeezing the firm plastic base, and with the patient’s legs in a frog-leg position, place the device in the vagina.
- Allow the firm plastic base to open to a flat position with the base against the posterior vaginal wall and the soft silicon balloon against the fetal head.
- Using pressure on the plastic base, gently push the Fetal Pillow posteriorly toward the sacrum of the mother.
- Use the 60 mL syringe to inflate the balloon with 180 mL of normal saline and close the valve.
- Straighten the patient’s legs and proceed with skin preparation and abdominal draping (FIGURE 4).
When the CD is completed, deflate the balloon by drawing out the saline with the 60 mL syringe and remove the device by hooking a finger around the firm plastic base. The Fetal Pillow is surprisingly easy to use.
Continue to: Effectiveness of the Fetal Pillow...
Effectiveness of the Fetal Pillow
In one randomized trial, 240 women undergoing CD were randomly allocated to a group in which the Fetal Pillow was placed in the vagina and inflated prior to the cesarean and a control group in which the Fetal Pillow was not used.
In another randomized trial, 60 nulliparous women undergoing CD in the second stage of labor had a Fetal Pillow inserted in the vagina and were randomly allocated to inflation of the pillow (Fetal Pillow group) or noninflation of the pillow (control group).5 In this study the mean length of the second stage was 4 hours. Compared with noninflation of the Fetal Pillow, use of the inflated Fetal Pillow was associated with a reduction in grade 3 extension of the uterine incision (extensions into the uterine artery, vagina, or bladder) (0% for inflation vs 13% for noninflation) and fewer difficult plus very difficult deliveries of the fetal head as reported by the surgeon (0% for inflation vs 37% for noninflation). There was no significant difference in blood loss between the two groups (800 mL vs 900 mL). These two randomized studies both reported that the use of the Fetal Pillow was associated with a reduction in grade 3 extensions of the uterine incision and a decrease in the difficulty of delivering the fetal head.
Consider trialing the Fetal Pillow
When a CD is performed after a prolonged second stage of labor, surgical complications are common, including extensions of the uterine incision and difficulty delivering the fetal head. When a grade 3 extension occurs—with tearing of a uterine artery, deep extension into the vagina, or damage to the bladder—the surgical repair can be extraordinarily challenging. Clinical trials report that both reverse breech extraction and the Fetal Pillow can facilitate CD in the setting of a prolonged second stage. For many obstetricians reverse breech extraction is a challenging obstetric maneuver. The insertion and inflation of a Fetal Pillow is a simple procedure. Obstetrician-gynecologists learn by doing. If you have never used the Fetal Pillow, I suggest you consider trialing it in your practice. ●
Obstetricians know that a cesarean delivery (CD) for a woman with a prolonged second stage and a fetal head deeply impacted in the pelvis is challenging. In this situation, extensions of the uterine incision commonly occur, resulting in prolonged operative time and increased blood loss. Even more harrowing is the inability to deliver the fetal head, necessitating emergency assistance from other clinicians. In this situation, interventions that may be helpful include:
- extend or T the uterine incision
- enlist the aid of a clinician to push up on the fetal head with a vaginal hand (FIGURE 1)
- reverse breech extraction (FIGURE 2), and
- vaginal insertion of a Fetal Pillow prior to starting the delivery.


Evidence from clinical trials indicates that reverse breech extraction or insertion of a Fetal Pillow result in the best clinical outcomes.
Reverse breech extraction vs the push technique
Although the data are limited, most studies report that compared with pushing up with a vaginal hand (as shown in Figure 1), the reverse breech extraction technique (as shown in Figure 2) is associated with a reduction in extensions of the uterine incision, reduced blood loss, and reduced operative time.1 In a randomized trial, 108 women with obstructed labor undergoing CD in the second stage were randomly assigned to reverse breech extraction or pushing up with a vaginal hand.2 Following the uterine incision, the reverse breech extraction technique is performed by immediately reaching into the upper uterus and grasping the lower portion of the fetal leg and applying gentle traction on the leg until the second leg appeared. The lower legs are then pulled out of the uterus. Standard breech delivery maneuvers are used to deliver the shoulders and head. In the trial, compared with the push technique, reverse breech extraction was associated with fewer extensions of the uterine incision (30% vs 11%; P<.05), less blood loss (899 mL vs 1,257 mL; P<.001), and shorter operative time (56 min vs 89 min, P<.001). Fetal injury was similar with the push and breech extraction techniques (6% and 7%).
In another randomized trial, 192 women undergoing CD for obstructed labor were randomly assigned to reverse breech extraction or pushing the head up with a hand in the vagina.3 Compared with the vaginal push technique, reverse breech extraction was associated with fewer extensions of the uterine incision (19% vs 48%; P = .003), fewer cases of wound infection (2% vs 13%; P = .007), and fewer blood transfusions (2 vs 11; P = .012).
Additional options and adjuvants for facilitating delivery of a fetal head deeply impacted in the pelvis include: using a Coyne spoon, using nitroglycerine or terbutaline to relax the myometrium, breaking the vaginal suction on the fetal head before attempting delivery, keeping the wrist of the delivering hand as straight as possible to reduce uterine incision extensions, and incising the ring (if a Bandl’s ring is detected).
Continue to: The Fetal Pillow...
The Fetal Pillow
The Fetal Pillow (Safe Obstetric Systems, New York, New York) is a single-use fetal cephalic elevation device for managing the deeply impacted fetal head (FIGURE 3). The Fetal Pillow has a firm plastic base upon which is attached a soft silicon balloon. The Fetal Pillow is inserted into the vagina prior to initiating CD and the balloon is filled with 180 mL of saline, causing the fetal head to be pushed to a higher station (FIGURE 4). Use of the Fetal Pillow may be indicated prior to CD in the following situations:
- second stage labor with a deeply impacted head
- second stage labor and failed operative delivery
- occiput posterior position or deep transverse arrest
- absent progress in the first stage between 8 cm and 10 cm with a deeply impacted fetal head or excessive caput of the fetal head.


The Fetal Pillow is inserted after completing vaginal preparation for CD and before initiating skin preparation and abdominal draping. The steps for inserting the Fetal Pillow include:
- Use the 60 mL syringe to fully deflate the Fetal Pillow and leave the cock-stop open.
- Fold the Fetal Pillow by squeezing the firm plastic base, and with the patient’s legs in a frog-leg position, place the device in the vagina.
- Allow the firm plastic base to open to a flat position with the base against the posterior vaginal wall and the soft silicon balloon against the fetal head.
- Using pressure on the plastic base, gently push the Fetal Pillow posteriorly toward the sacrum of the mother.
- Use the 60 mL syringe to inflate the balloon with 180 mL of normal saline and close the valve.
- Straighten the patient’s legs and proceed with skin preparation and abdominal draping (FIGURE 4).
When the CD is completed, deflate the balloon by drawing out the saline with the 60 mL syringe and remove the device by hooking a finger around the firm plastic base. The Fetal Pillow is surprisingly easy to use.
Continue to: Effectiveness of the Fetal Pillow...
Effectiveness of the Fetal Pillow
In one randomized trial, 240 women undergoing CD were randomly allocated to a group in which the Fetal Pillow was placed in the vagina and inflated prior to the cesarean and a control group in which the Fetal Pillow was not used.
In another randomized trial, 60 nulliparous women undergoing CD in the second stage of labor had a Fetal Pillow inserted in the vagina and were randomly allocated to inflation of the pillow (Fetal Pillow group) or noninflation of the pillow (control group).5 In this study the mean length of the second stage was 4 hours. Compared with noninflation of the Fetal Pillow, use of the inflated Fetal Pillow was associated with a reduction in grade 3 extension of the uterine incision (extensions into the uterine artery, vagina, or bladder) (0% for inflation vs 13% for noninflation) and fewer difficult plus very difficult deliveries of the fetal head as reported by the surgeon (0% for inflation vs 37% for noninflation). There was no significant difference in blood loss between the two groups (800 mL vs 900 mL). These two randomized studies both reported that the use of the Fetal Pillow was associated with a reduction in grade 3 extensions of the uterine incision and a decrease in the difficulty of delivering the fetal head.
Consider trialing the Fetal Pillow
When a CD is performed after a prolonged second stage of labor, surgical complications are common, including extensions of the uterine incision and difficulty delivering the fetal head. When a grade 3 extension occurs—with tearing of a uterine artery, deep extension into the vagina, or damage to the bladder—the surgical repair can be extraordinarily challenging. Clinical trials report that both reverse breech extraction and the Fetal Pillow can facilitate CD in the setting of a prolonged second stage. For many obstetricians reverse breech extraction is a challenging obstetric maneuver. The insertion and inflation of a Fetal Pillow is a simple procedure. Obstetrician-gynecologists learn by doing. If you have never used the Fetal Pillow, I suggest you consider trialing it in your practice. ●
- Jeve YB, Navti OB, Konje JC. Comparison of techniques used to deliver a deeply impacted fetal head at full dilation: a systematic review and meta-analysis. BJOG. 2016;123:337-345.
- Fasubaa OB, Ezechi OC, Orji EO, et al. Delivery of the impacted head of the fetus at cesarean section after prolonged obstructed labor: a randomised comparative study of two methods. J Obstet Gynaecol. 2002;22:375-378.
- Nooh AM, Abdeldayem HM, Ben-Affan O. Reverse breech extraction versus the standard approach of pushing the impacted fetal head up through the vagina in caesarean section for obstructed labour: a randomised controlled trial. J Obstet Gynaecol. 2017;37:459-463.
- Seal SL, Dey A, Barman SC, et al. Randomized controlled trial of elevation of the fetal head with a fetal pillow during cesarean delivery at full cervical dilatation. Int J Gynaecol Obstet. 2016;133:178-182.
- Lassey SC, Little SE, Saadeh M,et al. Cephalic elevation device for second-stage cesarean delivery: a randomized controlled trial. Obstet Gynecol. 2020;135:879-884.
- Jeve YB, Navti OB, Konje JC. Comparison of techniques used to deliver a deeply impacted fetal head at full dilation: a systematic review and meta-analysis. BJOG. 2016;123:337-345.
- Fasubaa OB, Ezechi OC, Orji EO, et al. Delivery of the impacted head of the fetus at cesarean section after prolonged obstructed labor: a randomised comparative study of two methods. J Obstet Gynaecol. 2002;22:375-378.
- Nooh AM, Abdeldayem HM, Ben-Affan O. Reverse breech extraction versus the standard approach of pushing the impacted fetal head up through the vagina in caesarean section for obstructed labour: a randomised controlled trial. J Obstet Gynaecol. 2017;37:459-463.
- Seal SL, Dey A, Barman SC, et al. Randomized controlled trial of elevation of the fetal head with a fetal pillow during cesarean delivery at full cervical dilatation. Int J Gynaecol Obstet. 2016;133:178-182.
- Lassey SC, Little SE, Saadeh M,et al. Cephalic elevation device for second-stage cesarean delivery: a randomized controlled trial. Obstet Gynecol. 2020;135:879-884.
Isthmocele repair: Simultaneous hysteroscopy and robotic-assisted laparoscopy

An isthmocele is a pouch-like anterior uterine wall defect at the site of a previous cesarean scar. The incidence is not well known, but it is estimated in the literature to be between 19% and 88%.1 Issues arising from an isthmocele may include abnormal uterine bleeding; abdominal pain; diminished fertility; ectopic pregnancy; or obstetric complications, such as uterine rupture. Repair of an isthmocele may be indicated for symptomatic relief and preservation of fertility. Multiple surgical approaches have been described in the literature, including laparoscopic, hysteroscopic, and vaginal approaches.
The objective of this video is to illustrate the use of robotic-assisted laparoscopy with simultaneous hysteroscopy as a feasible and safe approach for the repair of an isthmocele. Here we illustrate the key surgical steps of this approach, including:
- presurgical planning with magnetic resonance imaging
- diagnostic hysteroscopy for confirmation of isthmocele
- simultaneous laparoscopy for identification of borders
- strategic hysterotomy
- excision of scar tissue
- imbricated, tension-free closure.
We hope that you find this video useful to your clinical practice.
>> Dr. Arnold P. Advincula, and colleagues
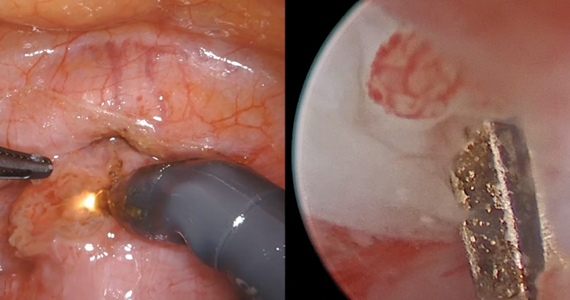
- Tower AM, Frishman GN. Cesarean scar defects: an underrecognized cause of abnormal uterine bleeding and other gynecologic complications. J Minim Invasive Gynecol. 2013;20:562-572. doi: 10.1016/j.jmig.2013.03.008.

An isthmocele is a pouch-like anterior uterine wall defect at the site of a previous cesarean scar. The incidence is not well known, but it is estimated in the literature to be between 19% and 88%.1 Issues arising from an isthmocele may include abnormal uterine bleeding; abdominal pain; diminished fertility; ectopic pregnancy; or obstetric complications, such as uterine rupture. Repair of an isthmocele may be indicated for symptomatic relief and preservation of fertility. Multiple surgical approaches have been described in the literature, including laparoscopic, hysteroscopic, and vaginal approaches.
The objective of this video is to illustrate the use of robotic-assisted laparoscopy with simultaneous hysteroscopy as a feasible and safe approach for the repair of an isthmocele. Here we illustrate the key surgical steps of this approach, including:
- presurgical planning with magnetic resonance imaging
- diagnostic hysteroscopy for confirmation of isthmocele
- simultaneous laparoscopy for identification of borders
- strategic hysterotomy
- excision of scar tissue
- imbricated, tension-free closure.
We hope that you find this video useful to your clinical practice.
>> Dr. Arnold P. Advincula, and colleagues


An isthmocele is a pouch-like anterior uterine wall defect at the site of a previous cesarean scar. The incidence is not well known, but it is estimated in the literature to be between 19% and 88%.1 Issues arising from an isthmocele may include abnormal uterine bleeding; abdominal pain; diminished fertility; ectopic pregnancy; or obstetric complications, such as uterine rupture. Repair of an isthmocele may be indicated for symptomatic relief and preservation of fertility. Multiple surgical approaches have been described in the literature, including laparoscopic, hysteroscopic, and vaginal approaches.
The objective of this video is to illustrate the use of robotic-assisted laparoscopy with simultaneous hysteroscopy as a feasible and safe approach for the repair of an isthmocele. Here we illustrate the key surgical steps of this approach, including:
- presurgical planning with magnetic resonance imaging
- diagnostic hysteroscopy for confirmation of isthmocele
- simultaneous laparoscopy for identification of borders
- strategic hysterotomy
- excision of scar tissue
- imbricated, tension-free closure.
We hope that you find this video useful to your clinical practice.
>> Dr. Arnold P. Advincula, and colleagues

- Tower AM, Frishman GN. Cesarean scar defects: an underrecognized cause of abnormal uterine bleeding and other gynecologic complications. J Minim Invasive Gynecol. 2013;20:562-572. doi: 10.1016/j.jmig.2013.03.008.
- Tower AM, Frishman GN. Cesarean scar defects: an underrecognized cause of abnormal uterine bleeding and other gynecologic complications. J Minim Invasive Gynecol. 2013;20:562-572. doi: 10.1016/j.jmig.2013.03.008.