User login
When does acute pyelonephritis require imaging?
A previously healthy 44-year-old woman presents to the emergency department with 1 day of fever, flank pain, dysuria, and persistent nausea and vomiting. Her temperature is 38.7°C (101.7°F), heart rate 102 beats per minute, and blood pressure 120/70 mm Hg. She has costovertebral angle tenderness. Laboratory testing reveals mild leukocytosis and a normal serum creatinine level; urinalysis shows leukocytes, as well as leukocyte esterase and nitrites. She has no personal or family history of nephrolithiasis. Urine cultures are obtained, and she is started on intravenous antibiotics and intravenous hydration to treat pyelonephritis.
Is imaging indicated at this point? And if so, which study is recommended?
KEY FEATURES
Acute pyelonephritis, infection of the renal parenchyma and collecting system, most often results from an ascending infection of the lower urinary tract. It is estimated to account for 250,000 office visits and 200,000 hospital admissions each year in the United States.1
Lower urinary tract symptoms such as urinary frequency, urgency, and dysuria accompanied by fever, nausea, vomiting, and flank pain raise suspicion for acute pyelonephritis. Flank pain is a key, nearly universal feature of upper urinary tract infection in patients without diabetes, though it may be absent in up to 50% of patients with diabetes.2
Additional findings include costovertebral angle tenderness on physical examination and leukocytosis, pyuria, and bacteriuria on laboratory studies.
PREDICTING THE NEED FOR EARLY IMAGING
Though guidelines state that imaging is inappropriate in most patients with pyelonephritis,2–4 it is nevertheless often done for diagnosis or identification of complications, which have been reported in more than two-thirds of patients.2–4
Acute pyelonephritis is generally classified as complicated or uncomplicated, though different definitions exist with regard to these classifications. The American College of Radiology’s Appropriateness Criteria2 consider patients with diabetes, immune compromise, a history of urolithiasis, or anatomic abnormality to be at highest risk for complications, and therefore recommend early imaging to assess for hydronephrosis, pyonephrosis, emphysematous pyelonephritis, and intrinsic or perinephric abscess.2
A clinical rule for predicting the need for imaging in acute pyelonephritis was developed and validated in an emergency department population in the Netherlands.3 The study suggested that restricting early imaging to patients with a history of urolithiasis, a urine pH of 7.0 or higher, or renal insufficiency—defined as a glomerular filtration rate (GFR) of 40 mL/min/1.73m2 or lower as estimated by the Modification of Diet in Renal Disease formula—would provide a negative predictive value of 94% to 100% for detection of an urgent urologic disorder (pyonephrosis, renal abscess, or urolithiasis). This high negative predictive value highlights that an absence of these signs and symptoms can safely identify patients who do not need renal imaging.
The positive predictive value was less useful, as only 5% to 23% of patients who had at least 1 risk factor went on to have urgent urologic risk factors.3
Implementation of this prediction rule would have resulted in a relative reduction in imaging of 40% and an absolute reduction of 28%. Of note, use of reduced GFR in this prediction rule is not clearly validated for patients with chronic kidney disease, as the previous GFR for most patients in this study was unknown.3
Based on these data, initial imaging is recommended in patients with diabetes, immune compromise, a history of urolithiasis, anatomic abnormality, a urine pH 7.0 or higher, or a GFR 40 mL/min or lower in a patient with no history of significant renal dysfunction. Early imaging would also be reasonable in patients with a complex clinical presentation, early recurrence of symptoms after treatment, clinical decompensation, or critical illness.
TREATMENT FAILURE
In a retrospective review of 62 patients hospitalized for acute renal infection, Soulen et al5 found that the most reliable indicator of complicated acute pyelonephritis was the persistence of fever and leukocytosis at 72 hours. And another small prospective study of patients with uncomplicated pyelonephritis reported a time to defervescence of no more than 4 days.6
In accordance with the Appropriateness Criteria2 and based on the best available evidence, imaging is recommended in all patients who remain febrile or have persistent leukocytosis after 72 hours of antibiotic therapy. In such cases, there should be high suspicion for a complication requiring treatment.
OPTIONS FOR IMAGING
Computed tomography
Computed tomography (CT) of the abdomen and pelvis with contrast is considered the study of choice in complicated acute pyelonephritis. CT can detect focal parenchymal abnormalities, emphysematous changes, and anatomic anomalies, and can also define the extent of disease. It can also detect perinephric fluid collections and abscesses that necessitate a change in management.2,5
A retrospective study in 2017 found that contrast-enhanced CT done without the usual noncontrast and excretory phases had an accuracy of 90% to 92% for pyelonephritis and 96% to 99% for urolithiasis, suggesting that reduction in radiation exposure through use of only the contrast-enhanced phase of CT imaging may be reasonable.7
Magnetic resonance imaging
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is increasingly acknowledged as effective in the evaluation of renal pathology, including the diagnosis of pyelonephritis; but it lacks the level of evidence that CT provides for detecting renal abscesses, calculi, and emphysematous pyelonephritis.2,8,9
Though it is more costly and time-consuming than CT with contrast enhancement, MRI is nevertheless the imaging study of choice if iodinated contrast or ionizing radiation must be avoided.
MRI typically involves a precontrast phase and a gadolinium contrast-enhanced phase, though there are data to support diffusion-weighted MRI when exposure to gadolinium poses a risk to the patient, such as in pregnancy or renal impairment (particularly when the estimated GFR is < 30 mL/min/1.73 m2).10
Ultrasonography
Conventional ultrasonography is appealing due to its relatively low cost, its availability and portability, and the lack of radiation and contrast exposure. It is most helpful in detecting hydronephrosis and pyonephrosis rather than intrarenal or perinephric abscess.2,9
Color and power Doppler ultrasonography may improve testing characteristics but not to the level of CT; in one study, sensitivity for detection of pyelonephritis was 33.3% with ultrasonography vs 81.0% with CT.11
Recent studies of ultrasonography with contrast enhancement show promising results,2 and it may ultimately prove to have a similar efficacy with lower risk for patients, but this has not been validated in large studies, and its availability remains limited.
Ultrasonography should be considered for patients in whom obstruction (with resulting hydronephrosis or pyonephrosis) is a primary concern, particularly when contrast exposure or radiation is contraindicated and MRI is unavailable.2
Abdominal radiography
While emphysematous pyelonephritis or a large staghorn calculus may be seen on abdominal radiography, it is not recommended for the assessment of complications in acute pyelonephritis because it lacks sensitivity.2
RETURN TO THE CASE SCENARIO
The patient in our case scenario meets the clinical criteria for uncomplicated pyelonephritis and is therefore not a candidate for imaging. Intravenous antibiotics should be started and should lead to rapid improvement in her condition.
Acknowledgment: The authors would like to thank Dr. Lisa Blacklock for her review of the radiology section of this paper.
- Foxman B, Klemstine KL, Brown PD. Acute pyelonephritis in US hospitals in 1997: hospitalization and in-hospital mortality. Ann Epidemiol 2003; 13(2):144–150. pmid:12559674
- Expert Panel on Urologic Imaging: Nikolaidis P, Dogra VS, Goldfarb S, et al. ACR appropriateness criteria acute pyelonephritis. J Am Coll Radiol 2018; 15(11S):S232–S239. doi:10.1016/j.jacr.2018.09.011
- van Nieuwkoop C, Hoppe BP, Bonten TN, et al. Predicting the need for radiologic imaging in adults with febrile urinary tract infection. Clin Infect Dis 2010; 51(11):1266–1272. doi:10.1086/657071
- Kim Y, Seo MR, Kim SJ, et al. Usefulness of blood cultures and radiologic imaging studies in the management of patients with community-acquired acute pyelonephritis. Infect Chemother 2017; 49(1):22–30. doi:10.3947/ic.2017.49.1.22
- Soulen MC, Fishman EK, Goldman SM, Gatewood OM. Bacterial renal infection: role of CT. Radiology 1989; 171(3):703–707. doi:10.1148/radiology.171.3.2655002
- June CH, Browning MD, Smith LP, et al. Ultrasonography and computed tomography in severe urinary tract infection. Arch Intern Med 1985; 145(5):841–845. pmid:3888134
- Taniguchi LS, Torres US, Souza SM, Torres LR, D’Ippolito G. Are the unenhanced and excretory CT phases necessary for the evaluation of acute pyelonephritis? Acta Radiol 2017; 58(5):634–640. doi:10.1177/0284185116665424
- Rathod SB, Kumbhar SS, Nanivadekar A, Aman K. Role of diffusion-weighted MRI in acute pyelonephritis: a prospective study. Acta Radiol 2015; 56(2):244–249. doi:10.1177/0284185114520862
- Stunell H, Buckley O, Feeney J, Geoghegan T, Browne RF, Torreggiani WC. Imaging of acute pyelonephritis in the adult. Eur Radiol 2007; 17(7):1820–1828.
- American College of Radiology. ACR Manual on Contrast Media. www.acr.org/clinical-resources/contrast-manual. Accessed June 19, 2019.
- Yoo JM, Koh JS, Han CH, et al. Diagnosing acute pyelonephritis with CT, Tc-DMSA SPECT, and Doppler ultrasound: a comparative study. Korean J Urol 2010; 51(4):260–265. doi:10.4111/kju.2010.51.4.260
A previously healthy 44-year-old woman presents to the emergency department with 1 day of fever, flank pain, dysuria, and persistent nausea and vomiting. Her temperature is 38.7°C (101.7°F), heart rate 102 beats per minute, and blood pressure 120/70 mm Hg. She has costovertebral angle tenderness. Laboratory testing reveals mild leukocytosis and a normal serum creatinine level; urinalysis shows leukocytes, as well as leukocyte esterase and nitrites. She has no personal or family history of nephrolithiasis. Urine cultures are obtained, and she is started on intravenous antibiotics and intravenous hydration to treat pyelonephritis.
Is imaging indicated at this point? And if so, which study is recommended?
KEY FEATURES
Acute pyelonephritis, infection of the renal parenchyma and collecting system, most often results from an ascending infection of the lower urinary tract. It is estimated to account for 250,000 office visits and 200,000 hospital admissions each year in the United States.1
Lower urinary tract symptoms such as urinary frequency, urgency, and dysuria accompanied by fever, nausea, vomiting, and flank pain raise suspicion for acute pyelonephritis. Flank pain is a key, nearly universal feature of upper urinary tract infection in patients without diabetes, though it may be absent in up to 50% of patients with diabetes.2
Additional findings include costovertebral angle tenderness on physical examination and leukocytosis, pyuria, and bacteriuria on laboratory studies.
PREDICTING THE NEED FOR EARLY IMAGING
Though guidelines state that imaging is inappropriate in most patients with pyelonephritis,2–4 it is nevertheless often done for diagnosis or identification of complications, which have been reported in more than two-thirds of patients.2–4
Acute pyelonephritis is generally classified as complicated or uncomplicated, though different definitions exist with regard to these classifications. The American College of Radiology’s Appropriateness Criteria2 consider patients with diabetes, immune compromise, a history of urolithiasis, or anatomic abnormality to be at highest risk for complications, and therefore recommend early imaging to assess for hydronephrosis, pyonephrosis, emphysematous pyelonephritis, and intrinsic or perinephric abscess.2
A clinical rule for predicting the need for imaging in acute pyelonephritis was developed and validated in an emergency department population in the Netherlands.3 The study suggested that restricting early imaging to patients with a history of urolithiasis, a urine pH of 7.0 or higher, or renal insufficiency—defined as a glomerular filtration rate (GFR) of 40 mL/min/1.73m2 or lower as estimated by the Modification of Diet in Renal Disease formula—would provide a negative predictive value of 94% to 100% for detection of an urgent urologic disorder (pyonephrosis, renal abscess, or urolithiasis). This high negative predictive value highlights that an absence of these signs and symptoms can safely identify patients who do not need renal imaging.
The positive predictive value was less useful, as only 5% to 23% of patients who had at least 1 risk factor went on to have urgent urologic risk factors.3
Implementation of this prediction rule would have resulted in a relative reduction in imaging of 40% and an absolute reduction of 28%. Of note, use of reduced GFR in this prediction rule is not clearly validated for patients with chronic kidney disease, as the previous GFR for most patients in this study was unknown.3
Based on these data, initial imaging is recommended in patients with diabetes, immune compromise, a history of urolithiasis, anatomic abnormality, a urine pH 7.0 or higher, or a GFR 40 mL/min or lower in a patient with no history of significant renal dysfunction. Early imaging would also be reasonable in patients with a complex clinical presentation, early recurrence of symptoms after treatment, clinical decompensation, or critical illness.
TREATMENT FAILURE
In a retrospective review of 62 patients hospitalized for acute renal infection, Soulen et al5 found that the most reliable indicator of complicated acute pyelonephritis was the persistence of fever and leukocytosis at 72 hours. And another small prospective study of patients with uncomplicated pyelonephritis reported a time to defervescence of no more than 4 days.6
In accordance with the Appropriateness Criteria2 and based on the best available evidence, imaging is recommended in all patients who remain febrile or have persistent leukocytosis after 72 hours of antibiotic therapy. In such cases, there should be high suspicion for a complication requiring treatment.
OPTIONS FOR IMAGING
Computed tomography
Computed tomography (CT) of the abdomen and pelvis with contrast is considered the study of choice in complicated acute pyelonephritis. CT can detect focal parenchymal abnormalities, emphysematous changes, and anatomic anomalies, and can also define the extent of disease. It can also detect perinephric fluid collections and abscesses that necessitate a change in management.2,5
A retrospective study in 2017 found that contrast-enhanced CT done without the usual noncontrast and excretory phases had an accuracy of 90% to 92% for pyelonephritis and 96% to 99% for urolithiasis, suggesting that reduction in radiation exposure through use of only the contrast-enhanced phase of CT imaging may be reasonable.7
Magnetic resonance imaging
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is increasingly acknowledged as effective in the evaluation of renal pathology, including the diagnosis of pyelonephritis; but it lacks the level of evidence that CT provides for detecting renal abscesses, calculi, and emphysematous pyelonephritis.2,8,9
Though it is more costly and time-consuming than CT with contrast enhancement, MRI is nevertheless the imaging study of choice if iodinated contrast or ionizing radiation must be avoided.
MRI typically involves a precontrast phase and a gadolinium contrast-enhanced phase, though there are data to support diffusion-weighted MRI when exposure to gadolinium poses a risk to the patient, such as in pregnancy or renal impairment (particularly when the estimated GFR is < 30 mL/min/1.73 m2).10
Ultrasonography
Conventional ultrasonography is appealing due to its relatively low cost, its availability and portability, and the lack of radiation and contrast exposure. It is most helpful in detecting hydronephrosis and pyonephrosis rather than intrarenal or perinephric abscess.2,9
Color and power Doppler ultrasonography may improve testing characteristics but not to the level of CT; in one study, sensitivity for detection of pyelonephritis was 33.3% with ultrasonography vs 81.0% with CT.11
Recent studies of ultrasonography with contrast enhancement show promising results,2 and it may ultimately prove to have a similar efficacy with lower risk for patients, but this has not been validated in large studies, and its availability remains limited.
Ultrasonography should be considered for patients in whom obstruction (with resulting hydronephrosis or pyonephrosis) is a primary concern, particularly when contrast exposure or radiation is contraindicated and MRI is unavailable.2
Abdominal radiography
While emphysematous pyelonephritis or a large staghorn calculus may be seen on abdominal radiography, it is not recommended for the assessment of complications in acute pyelonephritis because it lacks sensitivity.2
RETURN TO THE CASE SCENARIO
The patient in our case scenario meets the clinical criteria for uncomplicated pyelonephritis and is therefore not a candidate for imaging. Intravenous antibiotics should be started and should lead to rapid improvement in her condition.
Acknowledgment: The authors would like to thank Dr. Lisa Blacklock for her review of the radiology section of this paper.
A previously healthy 44-year-old woman presents to the emergency department with 1 day of fever, flank pain, dysuria, and persistent nausea and vomiting. Her temperature is 38.7°C (101.7°F), heart rate 102 beats per minute, and blood pressure 120/70 mm Hg. She has costovertebral angle tenderness. Laboratory testing reveals mild leukocytosis and a normal serum creatinine level; urinalysis shows leukocytes, as well as leukocyte esterase and nitrites. She has no personal or family history of nephrolithiasis. Urine cultures are obtained, and she is started on intravenous antibiotics and intravenous hydration to treat pyelonephritis.
Is imaging indicated at this point? And if so, which study is recommended?
KEY FEATURES
Acute pyelonephritis, infection of the renal parenchyma and collecting system, most often results from an ascending infection of the lower urinary tract. It is estimated to account for 250,000 office visits and 200,000 hospital admissions each year in the United States.1
Lower urinary tract symptoms such as urinary frequency, urgency, and dysuria accompanied by fever, nausea, vomiting, and flank pain raise suspicion for acute pyelonephritis. Flank pain is a key, nearly universal feature of upper urinary tract infection in patients without diabetes, though it may be absent in up to 50% of patients with diabetes.2
Additional findings include costovertebral angle tenderness on physical examination and leukocytosis, pyuria, and bacteriuria on laboratory studies.
PREDICTING THE NEED FOR EARLY IMAGING
Though guidelines state that imaging is inappropriate in most patients with pyelonephritis,2–4 it is nevertheless often done for diagnosis or identification of complications, which have been reported in more than two-thirds of patients.2–4
Acute pyelonephritis is generally classified as complicated or uncomplicated, though different definitions exist with regard to these classifications. The American College of Radiology’s Appropriateness Criteria2 consider patients with diabetes, immune compromise, a history of urolithiasis, or anatomic abnormality to be at highest risk for complications, and therefore recommend early imaging to assess for hydronephrosis, pyonephrosis, emphysematous pyelonephritis, and intrinsic or perinephric abscess.2
A clinical rule for predicting the need for imaging in acute pyelonephritis was developed and validated in an emergency department population in the Netherlands.3 The study suggested that restricting early imaging to patients with a history of urolithiasis, a urine pH of 7.0 or higher, or renal insufficiency—defined as a glomerular filtration rate (GFR) of 40 mL/min/1.73m2 or lower as estimated by the Modification of Diet in Renal Disease formula—would provide a negative predictive value of 94% to 100% for detection of an urgent urologic disorder (pyonephrosis, renal abscess, or urolithiasis). This high negative predictive value highlights that an absence of these signs and symptoms can safely identify patients who do not need renal imaging.
The positive predictive value was less useful, as only 5% to 23% of patients who had at least 1 risk factor went on to have urgent urologic risk factors.3
Implementation of this prediction rule would have resulted in a relative reduction in imaging of 40% and an absolute reduction of 28%. Of note, use of reduced GFR in this prediction rule is not clearly validated for patients with chronic kidney disease, as the previous GFR for most patients in this study was unknown.3
Based on these data, initial imaging is recommended in patients with diabetes, immune compromise, a history of urolithiasis, anatomic abnormality, a urine pH 7.0 or higher, or a GFR 40 mL/min or lower in a patient with no history of significant renal dysfunction. Early imaging would also be reasonable in patients with a complex clinical presentation, early recurrence of symptoms after treatment, clinical decompensation, or critical illness.
TREATMENT FAILURE
In a retrospective review of 62 patients hospitalized for acute renal infection, Soulen et al5 found that the most reliable indicator of complicated acute pyelonephritis was the persistence of fever and leukocytosis at 72 hours. And another small prospective study of patients with uncomplicated pyelonephritis reported a time to defervescence of no more than 4 days.6
In accordance with the Appropriateness Criteria2 and based on the best available evidence, imaging is recommended in all patients who remain febrile or have persistent leukocytosis after 72 hours of antibiotic therapy. In such cases, there should be high suspicion for a complication requiring treatment.
OPTIONS FOR IMAGING
Computed tomography
Computed tomography (CT) of the abdomen and pelvis with contrast is considered the study of choice in complicated acute pyelonephritis. CT can detect focal parenchymal abnormalities, emphysematous changes, and anatomic anomalies, and can also define the extent of disease. It can also detect perinephric fluid collections and abscesses that necessitate a change in management.2,5
A retrospective study in 2017 found that contrast-enhanced CT done without the usual noncontrast and excretory phases had an accuracy of 90% to 92% for pyelonephritis and 96% to 99% for urolithiasis, suggesting that reduction in radiation exposure through use of only the contrast-enhanced phase of CT imaging may be reasonable.7
Magnetic resonance imaging
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is increasingly acknowledged as effective in the evaluation of renal pathology, including the diagnosis of pyelonephritis; but it lacks the level of evidence that CT provides for detecting renal abscesses, calculi, and emphysematous pyelonephritis.2,8,9
Though it is more costly and time-consuming than CT with contrast enhancement, MRI is nevertheless the imaging study of choice if iodinated contrast or ionizing radiation must be avoided.
MRI typically involves a precontrast phase and a gadolinium contrast-enhanced phase, though there are data to support diffusion-weighted MRI when exposure to gadolinium poses a risk to the patient, such as in pregnancy or renal impairment (particularly when the estimated GFR is < 30 mL/min/1.73 m2).10
Ultrasonography
Conventional ultrasonography is appealing due to its relatively low cost, its availability and portability, and the lack of radiation and contrast exposure. It is most helpful in detecting hydronephrosis and pyonephrosis rather than intrarenal or perinephric abscess.2,9
Color and power Doppler ultrasonography may improve testing characteristics but not to the level of CT; in one study, sensitivity for detection of pyelonephritis was 33.3% with ultrasonography vs 81.0% with CT.11
Recent studies of ultrasonography with contrast enhancement show promising results,2 and it may ultimately prove to have a similar efficacy with lower risk for patients, but this has not been validated in large studies, and its availability remains limited.
Ultrasonography should be considered for patients in whom obstruction (with resulting hydronephrosis or pyonephrosis) is a primary concern, particularly when contrast exposure or radiation is contraindicated and MRI is unavailable.2
Abdominal radiography
While emphysematous pyelonephritis or a large staghorn calculus may be seen on abdominal radiography, it is not recommended for the assessment of complications in acute pyelonephritis because it lacks sensitivity.2
RETURN TO THE CASE SCENARIO
The patient in our case scenario meets the clinical criteria for uncomplicated pyelonephritis and is therefore not a candidate for imaging. Intravenous antibiotics should be started and should lead to rapid improvement in her condition.
Acknowledgment: The authors would like to thank Dr. Lisa Blacklock for her review of the radiology section of this paper.
- Foxman B, Klemstine KL, Brown PD. Acute pyelonephritis in US hospitals in 1997: hospitalization and in-hospital mortality. Ann Epidemiol 2003; 13(2):144–150. pmid:12559674
- Expert Panel on Urologic Imaging: Nikolaidis P, Dogra VS, Goldfarb S, et al. ACR appropriateness criteria acute pyelonephritis. J Am Coll Radiol 2018; 15(11S):S232–S239. doi:10.1016/j.jacr.2018.09.011
- van Nieuwkoop C, Hoppe BP, Bonten TN, et al. Predicting the need for radiologic imaging in adults with febrile urinary tract infection. Clin Infect Dis 2010; 51(11):1266–1272. doi:10.1086/657071
- Kim Y, Seo MR, Kim SJ, et al. Usefulness of blood cultures and radiologic imaging studies in the management of patients with community-acquired acute pyelonephritis. Infect Chemother 2017; 49(1):22–30. doi:10.3947/ic.2017.49.1.22
- Soulen MC, Fishman EK, Goldman SM, Gatewood OM. Bacterial renal infection: role of CT. Radiology 1989; 171(3):703–707. doi:10.1148/radiology.171.3.2655002
- June CH, Browning MD, Smith LP, et al. Ultrasonography and computed tomography in severe urinary tract infection. Arch Intern Med 1985; 145(5):841–845. pmid:3888134
- Taniguchi LS, Torres US, Souza SM, Torres LR, D’Ippolito G. Are the unenhanced and excretory CT phases necessary for the evaluation of acute pyelonephritis? Acta Radiol 2017; 58(5):634–640. doi:10.1177/0284185116665424
- Rathod SB, Kumbhar SS, Nanivadekar A, Aman K. Role of diffusion-weighted MRI in acute pyelonephritis: a prospective study. Acta Radiol 2015; 56(2):244–249. doi:10.1177/0284185114520862
- Stunell H, Buckley O, Feeney J, Geoghegan T, Browne RF, Torreggiani WC. Imaging of acute pyelonephritis in the adult. Eur Radiol 2007; 17(7):1820–1828.
- American College of Radiology. ACR Manual on Contrast Media. www.acr.org/clinical-resources/contrast-manual. Accessed June 19, 2019.
- Yoo JM, Koh JS, Han CH, et al. Diagnosing acute pyelonephritis with CT, Tc-DMSA SPECT, and Doppler ultrasound: a comparative study. Korean J Urol 2010; 51(4):260–265. doi:10.4111/kju.2010.51.4.260
- Foxman B, Klemstine KL, Brown PD. Acute pyelonephritis in US hospitals in 1997: hospitalization and in-hospital mortality. Ann Epidemiol 2003; 13(2):144–150. pmid:12559674
- Expert Panel on Urologic Imaging: Nikolaidis P, Dogra VS, Goldfarb S, et al. ACR appropriateness criteria acute pyelonephritis. J Am Coll Radiol 2018; 15(11S):S232–S239. doi:10.1016/j.jacr.2018.09.011
- van Nieuwkoop C, Hoppe BP, Bonten TN, et al. Predicting the need for radiologic imaging in adults with febrile urinary tract infection. Clin Infect Dis 2010; 51(11):1266–1272. doi:10.1086/657071
- Kim Y, Seo MR, Kim SJ, et al. Usefulness of blood cultures and radiologic imaging studies in the management of patients with community-acquired acute pyelonephritis. Infect Chemother 2017; 49(1):22–30. doi:10.3947/ic.2017.49.1.22
- Soulen MC, Fishman EK, Goldman SM, Gatewood OM. Bacterial renal infection: role of CT. Radiology 1989; 171(3):703–707. doi:10.1148/radiology.171.3.2655002
- June CH, Browning MD, Smith LP, et al. Ultrasonography and computed tomography in severe urinary tract infection. Arch Intern Med 1985; 145(5):841–845. pmid:3888134
- Taniguchi LS, Torres US, Souza SM, Torres LR, D’Ippolito G. Are the unenhanced and excretory CT phases necessary for the evaluation of acute pyelonephritis? Acta Radiol 2017; 58(5):634–640. doi:10.1177/0284185116665424
- Rathod SB, Kumbhar SS, Nanivadekar A, Aman K. Role of diffusion-weighted MRI in acute pyelonephritis: a prospective study. Acta Radiol 2015; 56(2):244–249. doi:10.1177/0284185114520862
- Stunell H, Buckley O, Feeney J, Geoghegan T, Browne RF, Torreggiani WC. Imaging of acute pyelonephritis in the adult. Eur Radiol 2007; 17(7):1820–1828.
- American College of Radiology. ACR Manual on Contrast Media. www.acr.org/clinical-resources/contrast-manual. Accessed June 19, 2019.
- Yoo JM, Koh JS, Han CH, et al. Diagnosing acute pyelonephritis with CT, Tc-DMSA SPECT, and Doppler ultrasound: a comparative study. Korean J Urol 2010; 51(4):260–265. doi:10.4111/kju.2010.51.4.260
Can unintended pregnancies be reduced by dispensing a year’s worth of hormonal contraception?
EVIDENCE SUMMARY
A 2013 systematic review studied the effect of dispensing a larger amount of pills on pregnancy rate, abortion rate, and overall cost to the health care system.1 Three of the 4 studies analyzed found lower rates of pregnancy and abortion, as well as lower cost despite increased pill wastage, in the groups that received more medication. The 1 study that didn’t show a significant difference between groups compared only short durations (1 vs 4 months).
The systematic review included a large retrospective cohort study from 2011 that examined public insurance data from more than 84,000 patients to compare pregnancy rates in women who were given a 1-year supply of oral contraceptives (12 or 13 packs) vs those given 1 or 3 packs at a time.2 The study found pregnancy rates of 2.9%, 3.3%, and 1.2% for 1, 3, and 12 or 13 months, respectively (P < .05; absolute risk reduction [ARR] = 1.7%; number needed to treat [NNT] = 59; relative risk reduction = 41%).
More pills lead to longer use of contraception
The systematic review also included a 2011 trial of 700 women starting oral contraceptives.3 It randomized them to receive a 7- or 3-month supply at their initial visit, then evaluated use of oral contraception at 6 months. All women were invited back for a 3-month follow-up visit, at which time the 3-month supply group would receive additional medication.
Fifty-one percent of the 7-month group were still using oral contraceptives at 6 months compared with 35% of the 3-month group (P < .001; NNT = 7). The contrast was starker for women younger than 18 years (49% vs 12%; NNT = 3). Notably, of the women who stopped using contraception, more in the 3-month group stopped because they ran out of medication (P = .02). Subjects in the 7-month group were more likely to have given birth and more likely to have 2 or more children.
A 2017 case study examined proposed legislation in California that required health plans to cover a 12-month supply of combined hormonal contraceptives.4 The California Health Benefits Review Program surveyed health insurers and reviewed contraception usage patterns. They found that, if the legislation passed, the state could expect a 30% reduction in unintended pregnancy (ARR = 2%; NNT = 50), resulting in 6000 fewer live births and 7000 fewer abortions per year.
RECOMMENDATIONS
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC)’s Selected Practice Recommendations for Contraceptive Use recommend prescribing or providing as much as a 1-year supply of combined hormonal contraceptives at the initial visit and each return visit.5
The American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists (ACOG) supports over-the-counter access to oral contraceptives, effectively allowing an unlimited supply.6
EDITOR’S TAKEAWAY
Adequate evidence of benefits and strong support from the CDC and ACOG should encourage us to offer 1-year supplies of combined oral contraceptives. Even though the higher-quality studies reviewed also showed a cost savings, up-front patient expense may remain a challenge.
1. Steenland MW, Rodriguez MI, Marchbanks PA, et al. How does the number of oral contraceptive pill packs dispensed or prescribed affect continuation and other measures of consistent and correct use? A systematic review. Contraception. 2013;87:605-610.
2. Foster DG, Hulett D, Bradsberry M, et al. Number of oral contraceptive pill packages dispensed and subsequent unintended pregnancies. Obstet Gynecol. 2011;117:566-572.
3. White KO, Westhoff C. The effect of pack supply on oral contraceptive pill continuation: a randomized controlled trial. Obstet Gynecol. 2011;118:615-622.
4. McMenamin SB, Charles SA, Tabatabaeepour N, et al. Implications of dispensing self-administered hormonal contraceptives in a 1-year supply: a California case study. Contraception. 2017;95:449-451.
5. Curtis KM, Jatlaoui TC, Tepper NK, et al. U.S. Selected Practice Recommendations for Contraceptive Use, 2016. MMWR Recomm Rep. 2016;65:1-66.
6. Committee on Gynecologic Practice, American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists. Committee Opinion No. 544: Over-the-counter access to oral contraceptives. Obstet Gynecol. 2012;120:1527-1531.
EVIDENCE SUMMARY
A 2013 systematic review studied the effect of dispensing a larger amount of pills on pregnancy rate, abortion rate, and overall cost to the health care system.1 Three of the 4 studies analyzed found lower rates of pregnancy and abortion, as well as lower cost despite increased pill wastage, in the groups that received more medication. The 1 study that didn’t show a significant difference between groups compared only short durations (1 vs 4 months).
The systematic review included a large retrospective cohort study from 2011 that examined public insurance data from more than 84,000 patients to compare pregnancy rates in women who were given a 1-year supply of oral contraceptives (12 or 13 packs) vs those given 1 or 3 packs at a time.2 The study found pregnancy rates of 2.9%, 3.3%, and 1.2% for 1, 3, and 12 or 13 months, respectively (P < .05; absolute risk reduction [ARR] = 1.7%; number needed to treat [NNT] = 59; relative risk reduction = 41%).
More pills lead to longer use of contraception
The systematic review also included a 2011 trial of 700 women starting oral contraceptives.3 It randomized them to receive a 7- or 3-month supply at their initial visit, then evaluated use of oral contraception at 6 months. All women were invited back for a 3-month follow-up visit, at which time the 3-month supply group would receive additional medication.
Fifty-one percent of the 7-month group were still using oral contraceptives at 6 months compared with 35% of the 3-month group (P < .001; NNT = 7). The contrast was starker for women younger than 18 years (49% vs 12%; NNT = 3). Notably, of the women who stopped using contraception, more in the 3-month group stopped because they ran out of medication (P = .02). Subjects in the 7-month group were more likely to have given birth and more likely to have 2 or more children.
A 2017 case study examined proposed legislation in California that required health plans to cover a 12-month supply of combined hormonal contraceptives.4 The California Health Benefits Review Program surveyed health insurers and reviewed contraception usage patterns. They found that, if the legislation passed, the state could expect a 30% reduction in unintended pregnancy (ARR = 2%; NNT = 50), resulting in 6000 fewer live births and 7000 fewer abortions per year.
RECOMMENDATIONS
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC)’s Selected Practice Recommendations for Contraceptive Use recommend prescribing or providing as much as a 1-year supply of combined hormonal contraceptives at the initial visit and each return visit.5
The American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists (ACOG) supports over-the-counter access to oral contraceptives, effectively allowing an unlimited supply.6
EDITOR’S TAKEAWAY
Adequate evidence of benefits and strong support from the CDC and ACOG should encourage us to offer 1-year supplies of combined oral contraceptives. Even though the higher-quality studies reviewed also showed a cost savings, up-front patient expense may remain a challenge.
EVIDENCE SUMMARY
A 2013 systematic review studied the effect of dispensing a larger amount of pills on pregnancy rate, abortion rate, and overall cost to the health care system.1 Three of the 4 studies analyzed found lower rates of pregnancy and abortion, as well as lower cost despite increased pill wastage, in the groups that received more medication. The 1 study that didn’t show a significant difference between groups compared only short durations (1 vs 4 months).
The systematic review included a large retrospective cohort study from 2011 that examined public insurance data from more than 84,000 patients to compare pregnancy rates in women who were given a 1-year supply of oral contraceptives (12 or 13 packs) vs those given 1 or 3 packs at a time.2 The study found pregnancy rates of 2.9%, 3.3%, and 1.2% for 1, 3, and 12 or 13 months, respectively (P < .05; absolute risk reduction [ARR] = 1.7%; number needed to treat [NNT] = 59; relative risk reduction = 41%).
More pills lead to longer use of contraception
The systematic review also included a 2011 trial of 700 women starting oral contraceptives.3 It randomized them to receive a 7- or 3-month supply at their initial visit, then evaluated use of oral contraception at 6 months. All women were invited back for a 3-month follow-up visit, at which time the 3-month supply group would receive additional medication.
Fifty-one percent of the 7-month group were still using oral contraceptives at 6 months compared with 35% of the 3-month group (P < .001; NNT = 7). The contrast was starker for women younger than 18 years (49% vs 12%; NNT = 3). Notably, of the women who stopped using contraception, more in the 3-month group stopped because they ran out of medication (P = .02). Subjects in the 7-month group were more likely to have given birth and more likely to have 2 or more children.
A 2017 case study examined proposed legislation in California that required health plans to cover a 12-month supply of combined hormonal contraceptives.4 The California Health Benefits Review Program surveyed health insurers and reviewed contraception usage patterns. They found that, if the legislation passed, the state could expect a 30% reduction in unintended pregnancy (ARR = 2%; NNT = 50), resulting in 6000 fewer live births and 7000 fewer abortions per year.
RECOMMENDATIONS
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC)’s Selected Practice Recommendations for Contraceptive Use recommend prescribing or providing as much as a 1-year supply of combined hormonal contraceptives at the initial visit and each return visit.5
The American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists (ACOG) supports over-the-counter access to oral contraceptives, effectively allowing an unlimited supply.6
EDITOR’S TAKEAWAY
Adequate evidence of benefits and strong support from the CDC and ACOG should encourage us to offer 1-year supplies of combined oral contraceptives. Even though the higher-quality studies reviewed also showed a cost savings, up-front patient expense may remain a challenge.
1. Steenland MW, Rodriguez MI, Marchbanks PA, et al. How does the number of oral contraceptive pill packs dispensed or prescribed affect continuation and other measures of consistent and correct use? A systematic review. Contraception. 2013;87:605-610.
2. Foster DG, Hulett D, Bradsberry M, et al. Number of oral contraceptive pill packages dispensed and subsequent unintended pregnancies. Obstet Gynecol. 2011;117:566-572.
3. White KO, Westhoff C. The effect of pack supply on oral contraceptive pill continuation: a randomized controlled trial. Obstet Gynecol. 2011;118:615-622.
4. McMenamin SB, Charles SA, Tabatabaeepour N, et al. Implications of dispensing self-administered hormonal contraceptives in a 1-year supply: a California case study. Contraception. 2017;95:449-451.
5. Curtis KM, Jatlaoui TC, Tepper NK, et al. U.S. Selected Practice Recommendations for Contraceptive Use, 2016. MMWR Recomm Rep. 2016;65:1-66.
6. Committee on Gynecologic Practice, American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists. Committee Opinion No. 544: Over-the-counter access to oral contraceptives. Obstet Gynecol. 2012;120:1527-1531.
1. Steenland MW, Rodriguez MI, Marchbanks PA, et al. How does the number of oral contraceptive pill packs dispensed or prescribed affect continuation and other measures of consistent and correct use? A systematic review. Contraception. 2013;87:605-610.
2. Foster DG, Hulett D, Bradsberry M, et al. Number of oral contraceptive pill packages dispensed and subsequent unintended pregnancies. Obstet Gynecol. 2011;117:566-572.
3. White KO, Westhoff C. The effect of pack supply on oral contraceptive pill continuation: a randomized controlled trial. Obstet Gynecol. 2011;118:615-622.
4. McMenamin SB, Charles SA, Tabatabaeepour N, et al. Implications of dispensing self-administered hormonal contraceptives in a 1-year supply: a California case study. Contraception. 2017;95:449-451.
5. Curtis KM, Jatlaoui TC, Tepper NK, et al. U.S. Selected Practice Recommendations for Contraceptive Use, 2016. MMWR Recomm Rep. 2016;65:1-66.
6. Committee on Gynecologic Practice, American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists. Committee Opinion No. 544: Over-the-counter access to oral contraceptives. Obstet Gynecol. 2012;120:1527-1531.
EVIDENCE-BASED ANSWER:
Probably, although studies that looked directly at this outcome are limited. A systematic review showed that women who received a larger number of pills at one time were more likely to continue using combined hormonal contraception 7 to 15 months later (strength of recommendation [SOR]: A, consistent evidence from 2 cohort studies and 1 randomized, controlled trial), which might be extrapolated to indicate lower unintended pregnancy rates.
One of the large retrospective cohort studies included in the review demonstrated a significantly lower rate of pregnancy among women who received 12 or 13 packs of oral contraceptives at an office visit compared with 1 or 3 packs (SOR: B, large retrospective cohort study).
Placental bacteria not linked to adverse pregnancy outcomes
such as preeclampsia or spontaneous preterm birth, a study has found.
Dr. Marcus C. de Goffau, of Wellcome Sanger Institute, Cambridge, England, and coauthors wrote that placental dysfunction is linked to a number of common adverse pregnancy outcomes, but in many cases the cause of that dysfunction is unknown.
“Several studies have used sequencing-based methods for bacterial detection (metagenomics and 16S rRNA gene amplicon sequencing), and have concluded that the placenta is physiologically colonized by a diverse population of bacteria (the ‘placental microbiome’) and that the nature of this colonization may differ between healthy and complicated pregnancies,” they wrote.
In a paper published in the July 31 edition of Nature (doi: 10.1038/s41586-019-1451-5), researchers reported the outcomes of a study involving two cohorts. The first included 80 babies delivered by prelabor caesarean section, of whom 20 were small for gestational age, 20 were delivered to mothers with preeclampsia, and 40 were matched controls. The second cohort comprised 100 patients with preeclampsia, 100 small-for-gestational-age infants, 100 preterm births, and 198 matched controls, with two controls having been used twice.
The bacterial content of the placentas was analyzed via deep metagenomic sequencing of total DNA and 16S rRNA gene amplicon sequencing in cohort 1, and 16S rRNA gene amplicon from two different kits for cohort 2’s samples. In the first cohort, samples were also spiked with Salmonella bongori as a positive control.
For cohort 1, researchers were able to detect the S. bongori in all samples, but all other bacterial signals showed clear links to different batches, which the authors said showed they were the result of contamination. This was further supported by the discovery that the Escherichia coli signal seen in a number of batches was all from the same bacterial strain.
In the second cohort, researchers found Bradyrhizobium in nearly all samples, and Burkholderia – which has been thought to play a role in preterm birth – in some samples.
However in the case of the Burkholderia, significant variation between different runs of tests was found, and both Bradyrhizobium and Burkholderia were also found in negative controls.
Researchers also saw a high prevalence of four “ecologically unexpected” bacterial groups but were able to show that these were likely contaminants from a reagent used to wash the placental samples.
The study found that vaginal organisms such as lactobacilli and vaginosis-associated bacteria were more abundant in the second cohort, where babies were delivered by a mix of vaginal, intrapartum and prelabor caesarean section, compared with the first cohort, who were all prelabor caesarean section deliveries.
The only organism that met all the criteria for a genuine placenta-associated bacterial signal was Streptococcus agalactiae, but the authors found no association between it and pregnancy outcomes.
However, they did sound a warning that the perinatal transmission of S. agalactiae from the mother’s genital tract to the neonate could be a cause of fatal sepsis in the infant.
“Further studies will be required to determine the association between the presence of the organism in the placenta and fetal or neonatal disease,” they wrote.
The researchers also found significant associations between the delivery-associated vaginal bacteria Lactobacillus iners and preeclampsia, and between Streptococcus anginosus and the Ureaplasma genus – both of which are associated with vaginosis – and preterm birth.
“We conclude that bacterial placental infection is not a major cause of placentally related complications of human pregnancy and that the human placenta does not have a resident microbiome,” the authors wrote. “Although we see no evidence of a placental microbiome, the frequency of detection of vaginal bacteria in the placenta increased after intrapartum [cesarean] section, suggesting ascending or haematogenous spread.”
The Medical Research Council and the National Institute for Health Research Cambridge Biomedical Research Centre supported the study. Five authors declared grants and support from private industry outside the submitted work.
SOURCE: de Goffau M et al. Nature. 2019 Jul 31. doi: 10.1038/s41586-019-1451-5.
such as preeclampsia or spontaneous preterm birth, a study has found.
Dr. Marcus C. de Goffau, of Wellcome Sanger Institute, Cambridge, England, and coauthors wrote that placental dysfunction is linked to a number of common adverse pregnancy outcomes, but in many cases the cause of that dysfunction is unknown.
“Several studies have used sequencing-based methods for bacterial detection (metagenomics and 16S rRNA gene amplicon sequencing), and have concluded that the placenta is physiologically colonized by a diverse population of bacteria (the ‘placental microbiome’) and that the nature of this colonization may differ between healthy and complicated pregnancies,” they wrote.
In a paper published in the July 31 edition of Nature (doi: 10.1038/s41586-019-1451-5), researchers reported the outcomes of a study involving two cohorts. The first included 80 babies delivered by prelabor caesarean section, of whom 20 were small for gestational age, 20 were delivered to mothers with preeclampsia, and 40 were matched controls. The second cohort comprised 100 patients with preeclampsia, 100 small-for-gestational-age infants, 100 preterm births, and 198 matched controls, with two controls having been used twice.
The bacterial content of the placentas was analyzed via deep metagenomic sequencing of total DNA and 16S rRNA gene amplicon sequencing in cohort 1, and 16S rRNA gene amplicon from two different kits for cohort 2’s samples. In the first cohort, samples were also spiked with Salmonella bongori as a positive control.
For cohort 1, researchers were able to detect the S. bongori in all samples, but all other bacterial signals showed clear links to different batches, which the authors said showed they were the result of contamination. This was further supported by the discovery that the Escherichia coli signal seen in a number of batches was all from the same bacterial strain.
In the second cohort, researchers found Bradyrhizobium in nearly all samples, and Burkholderia – which has been thought to play a role in preterm birth – in some samples.
However in the case of the Burkholderia, significant variation between different runs of tests was found, and both Bradyrhizobium and Burkholderia were also found in negative controls.
Researchers also saw a high prevalence of four “ecologically unexpected” bacterial groups but were able to show that these were likely contaminants from a reagent used to wash the placental samples.
The study found that vaginal organisms such as lactobacilli and vaginosis-associated bacteria were more abundant in the second cohort, where babies were delivered by a mix of vaginal, intrapartum and prelabor caesarean section, compared with the first cohort, who were all prelabor caesarean section deliveries.
The only organism that met all the criteria for a genuine placenta-associated bacterial signal was Streptococcus agalactiae, but the authors found no association between it and pregnancy outcomes.
However, they did sound a warning that the perinatal transmission of S. agalactiae from the mother’s genital tract to the neonate could be a cause of fatal sepsis in the infant.
“Further studies will be required to determine the association between the presence of the organism in the placenta and fetal or neonatal disease,” they wrote.
The researchers also found significant associations between the delivery-associated vaginal bacteria Lactobacillus iners and preeclampsia, and between Streptococcus anginosus and the Ureaplasma genus – both of which are associated with vaginosis – and preterm birth.
“We conclude that bacterial placental infection is not a major cause of placentally related complications of human pregnancy and that the human placenta does not have a resident microbiome,” the authors wrote. “Although we see no evidence of a placental microbiome, the frequency of detection of vaginal bacteria in the placenta increased after intrapartum [cesarean] section, suggesting ascending or haematogenous spread.”
The Medical Research Council and the National Institute for Health Research Cambridge Biomedical Research Centre supported the study. Five authors declared grants and support from private industry outside the submitted work.
SOURCE: de Goffau M et al. Nature. 2019 Jul 31. doi: 10.1038/s41586-019-1451-5.
such as preeclampsia or spontaneous preterm birth, a study has found.
Dr. Marcus C. de Goffau, of Wellcome Sanger Institute, Cambridge, England, and coauthors wrote that placental dysfunction is linked to a number of common adverse pregnancy outcomes, but in many cases the cause of that dysfunction is unknown.
“Several studies have used sequencing-based methods for bacterial detection (metagenomics and 16S rRNA gene amplicon sequencing), and have concluded that the placenta is physiologically colonized by a diverse population of bacteria (the ‘placental microbiome’) and that the nature of this colonization may differ between healthy and complicated pregnancies,” they wrote.
In a paper published in the July 31 edition of Nature (doi: 10.1038/s41586-019-1451-5), researchers reported the outcomes of a study involving two cohorts. The first included 80 babies delivered by prelabor caesarean section, of whom 20 were small for gestational age, 20 were delivered to mothers with preeclampsia, and 40 were matched controls. The second cohort comprised 100 patients with preeclampsia, 100 small-for-gestational-age infants, 100 preterm births, and 198 matched controls, with two controls having been used twice.
The bacterial content of the placentas was analyzed via deep metagenomic sequencing of total DNA and 16S rRNA gene amplicon sequencing in cohort 1, and 16S rRNA gene amplicon from two different kits for cohort 2’s samples. In the first cohort, samples were also spiked with Salmonella bongori as a positive control.
For cohort 1, researchers were able to detect the S. bongori in all samples, but all other bacterial signals showed clear links to different batches, which the authors said showed they were the result of contamination. This was further supported by the discovery that the Escherichia coli signal seen in a number of batches was all from the same bacterial strain.
In the second cohort, researchers found Bradyrhizobium in nearly all samples, and Burkholderia – which has been thought to play a role in preterm birth – in some samples.
However in the case of the Burkholderia, significant variation between different runs of tests was found, and both Bradyrhizobium and Burkholderia were also found in negative controls.
Researchers also saw a high prevalence of four “ecologically unexpected” bacterial groups but were able to show that these were likely contaminants from a reagent used to wash the placental samples.
The study found that vaginal organisms such as lactobacilli and vaginosis-associated bacteria were more abundant in the second cohort, where babies were delivered by a mix of vaginal, intrapartum and prelabor caesarean section, compared with the first cohort, who were all prelabor caesarean section deliveries.
The only organism that met all the criteria for a genuine placenta-associated bacterial signal was Streptococcus agalactiae, but the authors found no association between it and pregnancy outcomes.
However, they did sound a warning that the perinatal transmission of S. agalactiae from the mother’s genital tract to the neonate could be a cause of fatal sepsis in the infant.
“Further studies will be required to determine the association between the presence of the organism in the placenta and fetal or neonatal disease,” they wrote.
The researchers also found significant associations between the delivery-associated vaginal bacteria Lactobacillus iners and preeclampsia, and between Streptococcus anginosus and the Ureaplasma genus – both of which are associated with vaginosis – and preterm birth.
“We conclude that bacterial placental infection is not a major cause of placentally related complications of human pregnancy and that the human placenta does not have a resident microbiome,” the authors wrote. “Although we see no evidence of a placental microbiome, the frequency of detection of vaginal bacteria in the placenta increased after intrapartum [cesarean] section, suggesting ascending or haematogenous spread.”
The Medical Research Council and the National Institute for Health Research Cambridge Biomedical Research Centre supported the study. Five authors declared grants and support from private industry outside the submitted work.
SOURCE: de Goffau M et al. Nature. 2019 Jul 31. doi: 10.1038/s41586-019-1451-5.
FROM NATURE
Key clinical point: Researchers found no evidence of a placental biome or a link between placental bacterial contamination and adverse pregnancy outcomes.
Major finding: No bacterial contamination of the placenta was associated with adverse pregnancy outcomes such as preeclampsia.
Study details: Cohort study of more than 500 placental samples.
Disclosures: The Medical Research Council and the National Institute for Health Research Cambridge Biomedical Research Centre supported the study. Five authors declared grants and support from private industry outside the submitted work.
Source: de Goffau M et al. Nature. 2019 Jul 31. doi: 10.1038/s41586-019-1451-5.
Don’t Mix Off-label Use With Off-the-rack Pills
A pregnant woman in Wisconsin received prenatal care from a family practitioner. The patient had hypertension, so at about 38 weeks’ gestation, the decision was made to induce labor.
On May 15, 2012, the family practitioner used misoprostol to induce labor. The patient received 100 mcg vaginally at 12:24
At 1:28
Variable late decelerations occurred at 11:36
Although the family practitioner was present at the bedside at 12:40
The on-call physician accomplished a vacuum delivery at 1:30
The child now has severe cerebral palsy, with gross motor involvement in the arms and legs. He can communicate through augmentative communication devices but cannot actually speak. He will require full-time care for the rest of his life.
Continue to: The defense took the position...
The defense took the position that while the dosage of misoprostol was excessive, the drug was no longer active in the mother’s body, based on its half-life, when the fetal distress occurred.
VERDICT
Four days before trial, the case was settled for $9 million.
COMMENTARY
I suspect many of you have made a pot roast—and at least some of you have used the simple, tried-and-true method of putting the meat into the slow cooker with a packet of onion soup mix. It makes a tasty dinner with minimal effort. But onion soup packets are for making onion soup—not seasoning pot roast. Guess what? You just used that soup mix off-label!
As clinicians, we all use medications for clinical indications that haven’t been specifically authorized by the FDA—and we shouldn’t stop. Off-label prescribing is legal, common, and often supported by the standard of care.
But there is a risk: The pill or tablet prepared by the manufacturer is generally aimed at the intended on-label use, not off-label uses. In this case, misoprostol (brand name, Cytotec) is approved by the FDA for prevention and treatment of gastrointestinal ulcers and peptic ulcer disease. The package insert describes dosing as follows:
The recommended adult oral dose of Cytotec for reducing the risk of NSAID-induced gastric ulcers is 200 mcg four times daily with food. If this dose cannot be tolerated, a dose of 100 mcg can be used.1
Continue to: We should not be shocked...
We should not be shocked, then, that Cytotec is supplied as 100- and 200-mcg round white tablets. However, it is frequently used off label for cervical ripening during labor at a dose of “25 mcg inserted into the posterior vaginal fornix.”2
This brings us to the malpractice trap. While off-label use may be appropriate, off-label uses may not neatly “fit” with the substance prepared by the manufacturer. To be properly administered for cervical ripening, the available tablet of misoprostol must be cut with a pill cutter or razor prior to administration.3 Furthermore, dosage is more accurate if the tablet fragments are individually weighed after cutting.3
In this case, the discrepancy between the pill prepared by the manufacturer (100 mcg) and the dosage needed (25 mcg) appears to have caught the defendant family practitioner off guard. So the take-home message is: Use medications as supported by the standard of care—but when using a drug off label, do not assume the product supplied by the manufacturer is appropriate for use as is.
Another interesting aspect of this case is the defense strategy. Most clinicians are aware that the tort of negligence involves (1) duty, (2) breach, (3) causation, and (4) harm. However, it is more logically consistent to think of the elements in this way: (1) duty, (2) breach, (3) harm, and if harm has occurred, (4) examine causation (ie, the logical connection between breach and harm).
In malpractice cases, attorneys frequently focus on one of these specific elements. In this case, the physician’s duty of care and the harm stemming from cerebral palsy are clearly established. Thus, breach and causation take center stage.
Continue to: The defense lawyers...
The defense lawyers acknowledged there was a breach, noting the dosage was “excessive.” However, they argued that this error didn’t matter because the drug was no longer active in the patient’s body. In other words, there was no causal connection between the inappropriately high dose and the resultant uterine tachysystole and fetal distress. This is a difficult road for several reasons.
First, the chief danger of using misoprostol is uterine hyperstimulation and fetal distress. The defense would have to argue the hyperstimulation and fetal distress were coincidental and unrelated to the misoprostol—which carries a black box warning for these very adverse effects. The plaintiff’s attorney is sure to make a big deal out of the black box warning in front of the jury—noting any reasonable clinician practicing obstetrics should be aware of the risks that come with misoprostol’s use. You can almost hear the argument in summation: “It is so important, they drew a warning box around it.”
Furthermore, making the argument that the misoprostol was not in the mother’s system at the time the fetal distress started would entail dueling expert testimony about pharmacokinetics and bioavailability—concepts that are difficult for lay jurors to understand. Misoprostol has a half-life of about 20 to 40 min when administered orally and about 60 min when administered vaginally.4 We know the mother received the overdose of misoprostol at 12:24
The plaintiff’s team might counter with an expert’s explanation that misoprostol’s bioavailability is increased 2- to 3-fold with vaginal versus oral administration. It would also be observed that compared with oral administration, vaginal administration of misoprostol is associated with a slower increase in plasma concentrations but longer elevations (peaking about 1-2 hours after vaginal administration).5
At best, the defense expert would be able to argue that the serum level likely peaked 1 to 2 hours after administration (1:24-2:24
Continue to: Most jurors would...
Most jurors would take a skeptical view of the defendant’s argument that the negative outcome in this case was coincidental. Some might even be angered by it. This realization likely prompted the defense to settle this case for $9 million.
IN SUMMARY
Onion soup mix makes great soup, but it’s an even better seasoning for pot roast. Similarly, there are pharmacologic agents that are effective for conditions for which they are not formally indicated. Do not withhold judicious off-label use of medications when appropriate. However, be aware that off-label uses may require extra attention, and dosing and administration may not be consistent with the product you have on hand. Don’t hesitate to seek guidance from pharmacy colleagues when you have questions—they are an underutilized resource and are generally happy to share their expertise.
1. Cytotec [package insert]. New York, NY: Pfizer Inc; 2009.
2. Misoprostol: dosing considerations. PDR: Prescribers’ Digital Reference. www.pdr.net/drug-summary/Cytotec-misoprostol-1044#8. Accessed July 29, 2019.
3. Williams MC, Tsibris JC, Davis G, et al. Dose variation that is associated with approximated one-quarter tablet doses of misoprostol. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2002;187(3):615-619.
4. Yount SM, Lassiter N. The pharmacology of prostaglandins for induction of labor. J Midwifery Womens Health. 2013;58(2):133-144; quiz 238-239.
5. Danielsson KG, Marions L, Rodriguez A, et al. Comparison between oral and vaginal administration of misoprostol on uterine contractility. Obstet Gynecol. 1999;93(2):275-280.
A pregnant woman in Wisconsin received prenatal care from a family practitioner. The patient had hypertension, so at about 38 weeks’ gestation, the decision was made to induce labor.
On May 15, 2012, the family practitioner used misoprostol to induce labor. The patient received 100 mcg vaginally at 12:24
At 1:28
Variable late decelerations occurred at 11:36
Although the family practitioner was present at the bedside at 12:40
The on-call physician accomplished a vacuum delivery at 1:30
The child now has severe cerebral palsy, with gross motor involvement in the arms and legs. He can communicate through augmentative communication devices but cannot actually speak. He will require full-time care for the rest of his life.
Continue to: The defense took the position...
The defense took the position that while the dosage of misoprostol was excessive, the drug was no longer active in the mother’s body, based on its half-life, when the fetal distress occurred.
VERDICT
Four days before trial, the case was settled for $9 million.
COMMENTARY
I suspect many of you have made a pot roast—and at least some of you have used the simple, tried-and-true method of putting the meat into the slow cooker with a packet of onion soup mix. It makes a tasty dinner with minimal effort. But onion soup packets are for making onion soup—not seasoning pot roast. Guess what? You just used that soup mix off-label!
As clinicians, we all use medications for clinical indications that haven’t been specifically authorized by the FDA—and we shouldn’t stop. Off-label prescribing is legal, common, and often supported by the standard of care.
But there is a risk: The pill or tablet prepared by the manufacturer is generally aimed at the intended on-label use, not off-label uses. In this case, misoprostol (brand name, Cytotec) is approved by the FDA for prevention and treatment of gastrointestinal ulcers and peptic ulcer disease. The package insert describes dosing as follows:
The recommended adult oral dose of Cytotec for reducing the risk of NSAID-induced gastric ulcers is 200 mcg four times daily with food. If this dose cannot be tolerated, a dose of 100 mcg can be used.1
Continue to: We should not be shocked...
We should not be shocked, then, that Cytotec is supplied as 100- and 200-mcg round white tablets. However, it is frequently used off label for cervical ripening during labor at a dose of “25 mcg inserted into the posterior vaginal fornix.”2
This brings us to the malpractice trap. While off-label use may be appropriate, off-label uses may not neatly “fit” with the substance prepared by the manufacturer. To be properly administered for cervical ripening, the available tablet of misoprostol must be cut with a pill cutter or razor prior to administration.3 Furthermore, dosage is more accurate if the tablet fragments are individually weighed after cutting.3
In this case, the discrepancy between the pill prepared by the manufacturer (100 mcg) and the dosage needed (25 mcg) appears to have caught the defendant family practitioner off guard. So the take-home message is: Use medications as supported by the standard of care—but when using a drug off label, do not assume the product supplied by the manufacturer is appropriate for use as is.
Another interesting aspect of this case is the defense strategy. Most clinicians are aware that the tort of negligence involves (1) duty, (2) breach, (3) causation, and (4) harm. However, it is more logically consistent to think of the elements in this way: (1) duty, (2) breach, (3) harm, and if harm has occurred, (4) examine causation (ie, the logical connection between breach and harm).
In malpractice cases, attorneys frequently focus on one of these specific elements. In this case, the physician’s duty of care and the harm stemming from cerebral palsy are clearly established. Thus, breach and causation take center stage.
Continue to: The defense lawyers...
The defense lawyers acknowledged there was a breach, noting the dosage was “excessive.” However, they argued that this error didn’t matter because the drug was no longer active in the patient’s body. In other words, there was no causal connection between the inappropriately high dose and the resultant uterine tachysystole and fetal distress. This is a difficult road for several reasons.
First, the chief danger of using misoprostol is uterine hyperstimulation and fetal distress. The defense would have to argue the hyperstimulation and fetal distress were coincidental and unrelated to the misoprostol—which carries a black box warning for these very adverse effects. The plaintiff’s attorney is sure to make a big deal out of the black box warning in front of the jury—noting any reasonable clinician practicing obstetrics should be aware of the risks that come with misoprostol’s use. You can almost hear the argument in summation: “It is so important, they drew a warning box around it.”
Furthermore, making the argument that the misoprostol was not in the mother’s system at the time the fetal distress started would entail dueling expert testimony about pharmacokinetics and bioavailability—concepts that are difficult for lay jurors to understand. Misoprostol has a half-life of about 20 to 40 min when administered orally and about 60 min when administered vaginally.4 We know the mother received the overdose of misoprostol at 12:24
The plaintiff’s team might counter with an expert’s explanation that misoprostol’s bioavailability is increased 2- to 3-fold with vaginal versus oral administration. It would also be observed that compared with oral administration, vaginal administration of misoprostol is associated with a slower increase in plasma concentrations but longer elevations (peaking about 1-2 hours after vaginal administration).5
At best, the defense expert would be able to argue that the serum level likely peaked 1 to 2 hours after administration (1:24-2:24
Continue to: Most jurors would...
Most jurors would take a skeptical view of the defendant’s argument that the negative outcome in this case was coincidental. Some might even be angered by it. This realization likely prompted the defense to settle this case for $9 million.
IN SUMMARY
Onion soup mix makes great soup, but it’s an even better seasoning for pot roast. Similarly, there are pharmacologic agents that are effective for conditions for which they are not formally indicated. Do not withhold judicious off-label use of medications when appropriate. However, be aware that off-label uses may require extra attention, and dosing and administration may not be consistent with the product you have on hand. Don’t hesitate to seek guidance from pharmacy colleagues when you have questions—they are an underutilized resource and are generally happy to share their expertise.
A pregnant woman in Wisconsin received prenatal care from a family practitioner. The patient had hypertension, so at about 38 weeks’ gestation, the decision was made to induce labor.
On May 15, 2012, the family practitioner used misoprostol to induce labor. The patient received 100 mcg vaginally at 12:24
At 1:28
Variable late decelerations occurred at 11:36
Although the family practitioner was present at the bedside at 12:40
The on-call physician accomplished a vacuum delivery at 1:30
The child now has severe cerebral palsy, with gross motor involvement in the arms and legs. He can communicate through augmentative communication devices but cannot actually speak. He will require full-time care for the rest of his life.
Continue to: The defense took the position...
The defense took the position that while the dosage of misoprostol was excessive, the drug was no longer active in the mother’s body, based on its half-life, when the fetal distress occurred.
VERDICT
Four days before trial, the case was settled for $9 million.
COMMENTARY
I suspect many of you have made a pot roast—and at least some of you have used the simple, tried-and-true method of putting the meat into the slow cooker with a packet of onion soup mix. It makes a tasty dinner with minimal effort. But onion soup packets are for making onion soup—not seasoning pot roast. Guess what? You just used that soup mix off-label!
As clinicians, we all use medications for clinical indications that haven’t been specifically authorized by the FDA—and we shouldn’t stop. Off-label prescribing is legal, common, and often supported by the standard of care.
But there is a risk: The pill or tablet prepared by the manufacturer is generally aimed at the intended on-label use, not off-label uses. In this case, misoprostol (brand name, Cytotec) is approved by the FDA for prevention and treatment of gastrointestinal ulcers and peptic ulcer disease. The package insert describes dosing as follows:
The recommended adult oral dose of Cytotec for reducing the risk of NSAID-induced gastric ulcers is 200 mcg four times daily with food. If this dose cannot be tolerated, a dose of 100 mcg can be used.1
Continue to: We should not be shocked...
We should not be shocked, then, that Cytotec is supplied as 100- and 200-mcg round white tablets. However, it is frequently used off label for cervical ripening during labor at a dose of “25 mcg inserted into the posterior vaginal fornix.”2
This brings us to the malpractice trap. While off-label use may be appropriate, off-label uses may not neatly “fit” with the substance prepared by the manufacturer. To be properly administered for cervical ripening, the available tablet of misoprostol must be cut with a pill cutter or razor prior to administration.3 Furthermore, dosage is more accurate if the tablet fragments are individually weighed after cutting.3
In this case, the discrepancy between the pill prepared by the manufacturer (100 mcg) and the dosage needed (25 mcg) appears to have caught the defendant family practitioner off guard. So the take-home message is: Use medications as supported by the standard of care—but when using a drug off label, do not assume the product supplied by the manufacturer is appropriate for use as is.
Another interesting aspect of this case is the defense strategy. Most clinicians are aware that the tort of negligence involves (1) duty, (2) breach, (3) causation, and (4) harm. However, it is more logically consistent to think of the elements in this way: (1) duty, (2) breach, (3) harm, and if harm has occurred, (4) examine causation (ie, the logical connection between breach and harm).
In malpractice cases, attorneys frequently focus on one of these specific elements. In this case, the physician’s duty of care and the harm stemming from cerebral palsy are clearly established. Thus, breach and causation take center stage.
Continue to: The defense lawyers...
The defense lawyers acknowledged there was a breach, noting the dosage was “excessive.” However, they argued that this error didn’t matter because the drug was no longer active in the patient’s body. In other words, there was no causal connection between the inappropriately high dose and the resultant uterine tachysystole and fetal distress. This is a difficult road for several reasons.
First, the chief danger of using misoprostol is uterine hyperstimulation and fetal distress. The defense would have to argue the hyperstimulation and fetal distress were coincidental and unrelated to the misoprostol—which carries a black box warning for these very adverse effects. The plaintiff’s attorney is sure to make a big deal out of the black box warning in front of the jury—noting any reasonable clinician practicing obstetrics should be aware of the risks that come with misoprostol’s use. You can almost hear the argument in summation: “It is so important, they drew a warning box around it.”
Furthermore, making the argument that the misoprostol was not in the mother’s system at the time the fetal distress started would entail dueling expert testimony about pharmacokinetics and bioavailability—concepts that are difficult for lay jurors to understand. Misoprostol has a half-life of about 20 to 40 min when administered orally and about 60 min when administered vaginally.4 We know the mother received the overdose of misoprostol at 12:24
The plaintiff’s team might counter with an expert’s explanation that misoprostol’s bioavailability is increased 2- to 3-fold with vaginal versus oral administration. It would also be observed that compared with oral administration, vaginal administration of misoprostol is associated with a slower increase in plasma concentrations but longer elevations (peaking about 1-2 hours after vaginal administration).5
At best, the defense expert would be able to argue that the serum level likely peaked 1 to 2 hours after administration (1:24-2:24
Continue to: Most jurors would...
Most jurors would take a skeptical view of the defendant’s argument that the negative outcome in this case was coincidental. Some might even be angered by it. This realization likely prompted the defense to settle this case for $9 million.
IN SUMMARY
Onion soup mix makes great soup, but it’s an even better seasoning for pot roast. Similarly, there are pharmacologic agents that are effective for conditions for which they are not formally indicated. Do not withhold judicious off-label use of medications when appropriate. However, be aware that off-label uses may require extra attention, and dosing and administration may not be consistent with the product you have on hand. Don’t hesitate to seek guidance from pharmacy colleagues when you have questions—they are an underutilized resource and are generally happy to share their expertise.
1. Cytotec [package insert]. New York, NY: Pfizer Inc; 2009.
2. Misoprostol: dosing considerations. PDR: Prescribers’ Digital Reference. www.pdr.net/drug-summary/Cytotec-misoprostol-1044#8. Accessed July 29, 2019.
3. Williams MC, Tsibris JC, Davis G, et al. Dose variation that is associated with approximated one-quarter tablet doses of misoprostol. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2002;187(3):615-619.
4. Yount SM, Lassiter N. The pharmacology of prostaglandins for induction of labor. J Midwifery Womens Health. 2013;58(2):133-144; quiz 238-239.
5. Danielsson KG, Marions L, Rodriguez A, et al. Comparison between oral and vaginal administration of misoprostol on uterine contractility. Obstet Gynecol. 1999;93(2):275-280.
1. Cytotec [package insert]. New York, NY: Pfizer Inc; 2009.
2. Misoprostol: dosing considerations. PDR: Prescribers’ Digital Reference. www.pdr.net/drug-summary/Cytotec-misoprostol-1044#8. Accessed July 29, 2019.
3. Williams MC, Tsibris JC, Davis G, et al. Dose variation that is associated with approximated one-quarter tablet doses of misoprostol. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2002;187(3):615-619.
4. Yount SM, Lassiter N. The pharmacology of prostaglandins for induction of labor. J Midwifery Womens Health. 2013;58(2):133-144; quiz 238-239.
5. Danielsson KG, Marions L, Rodriguez A, et al. Comparison between oral and vaginal administration of misoprostol on uterine contractility. Obstet Gynecol. 1999;93(2):275-280.
U.S. fertility rate, teen births are on the decline
The general fertility rate in the United States decreased 2% between 2017 and 2018, according to a report from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
Fertility rates, defined as births per 1,000 women aged 15-44 years, declined for all racial/ethnic groups studied.
Teen birth rates, or births among girls aged 15-19 years, declined from 2017 to 2018 as well.
These data come from the National Vital Statistics System’s Natality Data File, which includes information from birth certificates for all births in the United States.
The data show a decline in the general fertility rate from 60.3 per 1,000 women in 2017 to 59.1 per 1,000 women in 2018, a significant decrease (P less than .05).
Fertility rates declined across the three largest racial/ethnic groups studied, decreasing:
- 3% in Hispanic women, from 67.6 to 65.9 per 1,000.
- 2% in non-Hispanic black women, from 63.1 to 62.0 per 1,000.
- 2% in non-Hispanic white women, from 57.2 to 56.3 per 1,000.
Similarly, teen birth rates declined 7% from 2017 to 2018, decreasing from 18.8 to 17.4 births per 1,000 girls aged 15-19 years (P less than .05). Rates decreased:
- 8% in Hispanic teens, from 28.9 to 26.7 per 1,000.
- 4% in non-Hispanic black teens, from 27.5 to 26.3 per 1,000.
- 8% in non-Hispanic white teens, from 13.2 to 12.1 per 1,000.
The data also show an increase in the rate of vaginal births after previous cesarean (VBAC) delivery. The percentage of VBAC deliveries increased from 12.8% in 2017 to 13.3% in 2018 (P less than .05).
VBAC delivery rates increased across all racial/ethnic groups studied, although the increase among non-Hispanic back women was not significant.
Finally, the report shows an increase in preterm and early term births from 2017 to 2018. Preterm deliveries (less than 37 weeks of gestation) increased from 9.93% to 10.02%, and early term deliveries (37-38 weeks) increased from 26.00% to 26.53% (P less than .05).
At the same time, full-term births (39-40 weeks) decreased from 57.49% to 57.24%, and late- and post-term births (41 weeks or more) decreased from 6.58 % to 6.20% (P less than .05). These findings were consistent across the racial/ethnic groups studied.
SOURCE: Martin JA et al. NCHS Data Brief. 2019 July; no 346.
The general fertility rate in the United States decreased 2% between 2017 and 2018, according to a report from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
Fertility rates, defined as births per 1,000 women aged 15-44 years, declined for all racial/ethnic groups studied.
Teen birth rates, or births among girls aged 15-19 years, declined from 2017 to 2018 as well.
These data come from the National Vital Statistics System’s Natality Data File, which includes information from birth certificates for all births in the United States.
The data show a decline in the general fertility rate from 60.3 per 1,000 women in 2017 to 59.1 per 1,000 women in 2018, a significant decrease (P less than .05).
Fertility rates declined across the three largest racial/ethnic groups studied, decreasing:
- 3% in Hispanic women, from 67.6 to 65.9 per 1,000.
- 2% in non-Hispanic black women, from 63.1 to 62.0 per 1,000.
- 2% in non-Hispanic white women, from 57.2 to 56.3 per 1,000.
Similarly, teen birth rates declined 7% from 2017 to 2018, decreasing from 18.8 to 17.4 births per 1,000 girls aged 15-19 years (P less than .05). Rates decreased:
- 8% in Hispanic teens, from 28.9 to 26.7 per 1,000.
- 4% in non-Hispanic black teens, from 27.5 to 26.3 per 1,000.
- 8% in non-Hispanic white teens, from 13.2 to 12.1 per 1,000.
The data also show an increase in the rate of vaginal births after previous cesarean (VBAC) delivery. The percentage of VBAC deliveries increased from 12.8% in 2017 to 13.3% in 2018 (P less than .05).
VBAC delivery rates increased across all racial/ethnic groups studied, although the increase among non-Hispanic back women was not significant.
Finally, the report shows an increase in preterm and early term births from 2017 to 2018. Preterm deliveries (less than 37 weeks of gestation) increased from 9.93% to 10.02%, and early term deliveries (37-38 weeks) increased from 26.00% to 26.53% (P less than .05).
At the same time, full-term births (39-40 weeks) decreased from 57.49% to 57.24%, and late- and post-term births (41 weeks or more) decreased from 6.58 % to 6.20% (P less than .05). These findings were consistent across the racial/ethnic groups studied.
SOURCE: Martin JA et al. NCHS Data Brief. 2019 July; no 346.
The general fertility rate in the United States decreased 2% between 2017 and 2018, according to a report from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
Fertility rates, defined as births per 1,000 women aged 15-44 years, declined for all racial/ethnic groups studied.
Teen birth rates, or births among girls aged 15-19 years, declined from 2017 to 2018 as well.
These data come from the National Vital Statistics System’s Natality Data File, which includes information from birth certificates for all births in the United States.
The data show a decline in the general fertility rate from 60.3 per 1,000 women in 2017 to 59.1 per 1,000 women in 2018, a significant decrease (P less than .05).
Fertility rates declined across the three largest racial/ethnic groups studied, decreasing:
- 3% in Hispanic women, from 67.6 to 65.9 per 1,000.
- 2% in non-Hispanic black women, from 63.1 to 62.0 per 1,000.
- 2% in non-Hispanic white women, from 57.2 to 56.3 per 1,000.
Similarly, teen birth rates declined 7% from 2017 to 2018, decreasing from 18.8 to 17.4 births per 1,000 girls aged 15-19 years (P less than .05). Rates decreased:
- 8% in Hispanic teens, from 28.9 to 26.7 per 1,000.
- 4% in non-Hispanic black teens, from 27.5 to 26.3 per 1,000.
- 8% in non-Hispanic white teens, from 13.2 to 12.1 per 1,000.
The data also show an increase in the rate of vaginal births after previous cesarean (VBAC) delivery. The percentage of VBAC deliveries increased from 12.8% in 2017 to 13.3% in 2018 (P less than .05).
VBAC delivery rates increased across all racial/ethnic groups studied, although the increase among non-Hispanic back women was not significant.
Finally, the report shows an increase in preterm and early term births from 2017 to 2018. Preterm deliveries (less than 37 weeks of gestation) increased from 9.93% to 10.02%, and early term deliveries (37-38 weeks) increased from 26.00% to 26.53% (P less than .05).
At the same time, full-term births (39-40 weeks) decreased from 57.49% to 57.24%, and late- and post-term births (41 weeks or more) decreased from 6.58 % to 6.20% (P less than .05). These findings were consistent across the racial/ethnic groups studied.
SOURCE: Martin JA et al. NCHS Data Brief. 2019 July; no 346.
Postpartum care: State scorecard for Medicaid enrollees
Timely postpartum care for Medicaid enrollees varies considerably, ranging from 17% to 74% among the states, according to the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services.
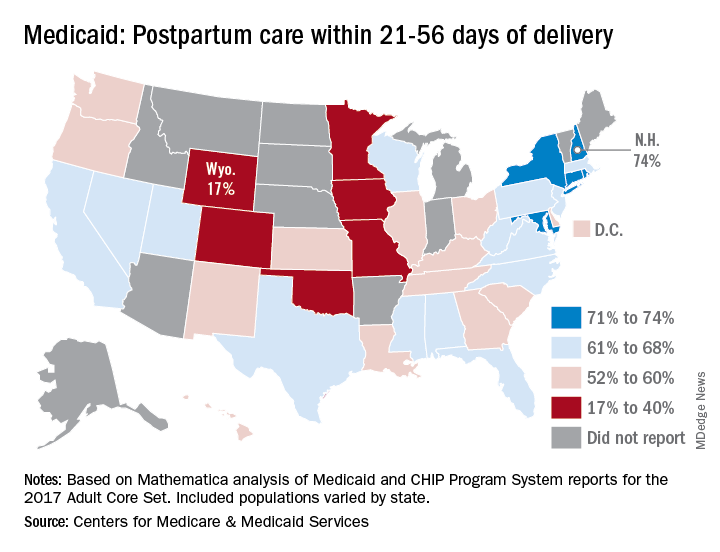
A national median of 60% of women saw a health care provider within 21-56 days of their delivery, CMS reported in its Medicaid and Children’s Health Insurance Program Scorecard.
“Medicaid is the largest payer for maternity care in the United States. The program has an important role to play in improving maternal and perinatal health outcomes,” the CMS noted.
New Hampshire’s rate of 74% was the highest of any state, just edging out Maryland and Rhode Island, each at 73%. The only other states over 70% were Connecticut and New York, which both reported rates of 71%, scorecard data show.
In Wyoming, the state with the lowest rate, 17% of Medicaid enrollees received timely postpartum care. The other four states with rates below 40% were Oklahoma (22%), Colorado (35%), Iowa (37%), and Missouri (38%), the CMS said after a recent refresh of data in the scorecard.
“The included populations … can vary by state. For example, some states report data on certain populations such as those covered under managed care but not those covered under fee for service. This variation in data and calculation methods can affect measure performance and comparisons between states,” the CMS said.
The scorecard is based on Mathematica analysis of Medicaid and CHIP Program System reports for the 2017 Adult Core Set, and the measurement period was Nov. 6, 2015, to Nov. 5, 2016. Twelve states did not report data on postpartum care to the CMS.
“More and more states are voluntarily reporting their health outcomes in the scorecard, and the new data is leading us into an era of increased transparency and accountability, so that together we can improve the quality of care we give to the vulnerable Americans that depend on this vital program,” CMS Administrator Seema Verma said in a written statement.
Timely postpartum care for Medicaid enrollees varies considerably, ranging from 17% to 74% among the states, according to the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services.

A national median of 60% of women saw a health care provider within 21-56 days of their delivery, CMS reported in its Medicaid and Children’s Health Insurance Program Scorecard.
“Medicaid is the largest payer for maternity care in the United States. The program has an important role to play in improving maternal and perinatal health outcomes,” the CMS noted.
New Hampshire’s rate of 74% was the highest of any state, just edging out Maryland and Rhode Island, each at 73%. The only other states over 70% were Connecticut and New York, which both reported rates of 71%, scorecard data show.
In Wyoming, the state with the lowest rate, 17% of Medicaid enrollees received timely postpartum care. The other four states with rates below 40% were Oklahoma (22%), Colorado (35%), Iowa (37%), and Missouri (38%), the CMS said after a recent refresh of data in the scorecard.
“The included populations … can vary by state. For example, some states report data on certain populations such as those covered under managed care but not those covered under fee for service. This variation in data and calculation methods can affect measure performance and comparisons between states,” the CMS said.
The scorecard is based on Mathematica analysis of Medicaid and CHIP Program System reports for the 2017 Adult Core Set, and the measurement period was Nov. 6, 2015, to Nov. 5, 2016. Twelve states did not report data on postpartum care to the CMS.
“More and more states are voluntarily reporting their health outcomes in the scorecard, and the new data is leading us into an era of increased transparency and accountability, so that together we can improve the quality of care we give to the vulnerable Americans that depend on this vital program,” CMS Administrator Seema Verma said in a written statement.
Timely postpartum care for Medicaid enrollees varies considerably, ranging from 17% to 74% among the states, according to the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services.

A national median of 60% of women saw a health care provider within 21-56 days of their delivery, CMS reported in its Medicaid and Children’s Health Insurance Program Scorecard.
“Medicaid is the largest payer for maternity care in the United States. The program has an important role to play in improving maternal and perinatal health outcomes,” the CMS noted.
New Hampshire’s rate of 74% was the highest of any state, just edging out Maryland and Rhode Island, each at 73%. The only other states over 70% were Connecticut and New York, which both reported rates of 71%, scorecard data show.
In Wyoming, the state with the lowest rate, 17% of Medicaid enrollees received timely postpartum care. The other four states with rates below 40% were Oklahoma (22%), Colorado (35%), Iowa (37%), and Missouri (38%), the CMS said after a recent refresh of data in the scorecard.
“The included populations … can vary by state. For example, some states report data on certain populations such as those covered under managed care but not those covered under fee for service. This variation in data and calculation methods can affect measure performance and comparisons between states,” the CMS said.
The scorecard is based on Mathematica analysis of Medicaid and CHIP Program System reports for the 2017 Adult Core Set, and the measurement period was Nov. 6, 2015, to Nov. 5, 2016. Twelve states did not report data on postpartum care to the CMS.
“More and more states are voluntarily reporting their health outcomes in the scorecard, and the new data is leading us into an era of increased transparency and accountability, so that together we can improve the quality of care we give to the vulnerable Americans that depend on this vital program,” CMS Administrator Seema Verma said in a written statement.
Depression, anxiety among elderly breast cancer survivors linked to increased opioid use, death
Mental health comorbidities increase the rates of opioid use and mortality among breast cancer survivors on endocrine therapy, based on a retrospective study of more than 10,000 patients in a Medicare-linked database.
Screen for mental health conditions in the early stages of cancer care and lean toward opioid alternatives for pain management, advised lead author Raj Desai, MS, of the University of Florida, Gainesville, and colleagues.
“The complex relationship among breast cancer, mental health problems, and the use of opioids is not well understood, despite the high prevalence of mental health comorbidities like depression and anxiety in breast cancer survivors, and the high rate of opioid use in those on AET [adjuvant endocrine therapy],” the investigators wrote in the Journal of Oncology Practice.
“Therefore, this study aimed to determine whether breast cancer survivors with varying levels of mental health comorbidities, such as depression and anxiety, are more likely to use opioids for AET-related pain,” they added.
The study involved 10,452 breast cancer survivors who first filled an AET prescription from 2006 to 2012 and had follow-up records available for at least 2 years. All patients had a diagnosis of incident, primary, hormone receptor–positive, stage I-III breast cancer. Data were drawn from the Surveillance, Epidemiology, and End Results–Medicare linked database. Records were evaluated for diagnoses of mental health conditions such as depression and anxiety, opioid use, and survival.
Analysis showed that the most common mental health conditions were depression and anxiety, diagnosed in 554 and 246 women, respectively. Patients with mental health comorbidities were compared with patients who did not have such problems, using both unmatched and matched cohorts. While unmatched comparison for opioid use was not statistically significant, matched comparison showed that survivors with mental health comorbidities were 33% more likely to use opioids than those without mental health comorbidities (95% confidence interval, 1.06-1.68). Similarly, greater adjusted probabilities of opioid use were reported in the mental health comorbidity cohort (72.5% vs. 66.9%; P = .01).
Concerning survival, unmatched comparison revealed a 44% higher risk of death among women with depression and a 32% increase associated with anxiety. Matched comparison showed an even higher increased risk of mortality among women with any mental health comorbidity (49%; P less than .05).
The investigators concluded that opioid use among breast cancer survivors with mental health comorbidities “remains a significant problem.”
“A need exists for collaborative care in the management of mental health comorbidities in women with breast cancer, which could improve symptoms, adherence to treatment, and recovery from these mental conditions,” the investigators wrote. “Mental health treatments also are recommended to be offered in primary care, which not only would be convenient for patients, but also would reduce the stigma associated with treatments for mental health comorbidities and improve the patient-provider relationship.”
The investigators reported financial relationships with Merck.
SOURCE: Desai R et al. J Oncol Pract. 2019 Jul 19. doi: 10.1200/JOP.18.00781.
Mental health comorbidities increase the rates of opioid use and mortality among breast cancer survivors on endocrine therapy, based on a retrospective study of more than 10,000 patients in a Medicare-linked database.
Screen for mental health conditions in the early stages of cancer care and lean toward opioid alternatives for pain management, advised lead author Raj Desai, MS, of the University of Florida, Gainesville, and colleagues.
“The complex relationship among breast cancer, mental health problems, and the use of opioids is not well understood, despite the high prevalence of mental health comorbidities like depression and anxiety in breast cancer survivors, and the high rate of opioid use in those on AET [adjuvant endocrine therapy],” the investigators wrote in the Journal of Oncology Practice.
“Therefore, this study aimed to determine whether breast cancer survivors with varying levels of mental health comorbidities, such as depression and anxiety, are more likely to use opioids for AET-related pain,” they added.
The study involved 10,452 breast cancer survivors who first filled an AET prescription from 2006 to 2012 and had follow-up records available for at least 2 years. All patients had a diagnosis of incident, primary, hormone receptor–positive, stage I-III breast cancer. Data were drawn from the Surveillance, Epidemiology, and End Results–Medicare linked database. Records were evaluated for diagnoses of mental health conditions such as depression and anxiety, opioid use, and survival.
Analysis showed that the most common mental health conditions were depression and anxiety, diagnosed in 554 and 246 women, respectively. Patients with mental health comorbidities were compared with patients who did not have such problems, using both unmatched and matched cohorts. While unmatched comparison for opioid use was not statistically significant, matched comparison showed that survivors with mental health comorbidities were 33% more likely to use opioids than those without mental health comorbidities (95% confidence interval, 1.06-1.68). Similarly, greater adjusted probabilities of opioid use were reported in the mental health comorbidity cohort (72.5% vs. 66.9%; P = .01).
Concerning survival, unmatched comparison revealed a 44% higher risk of death among women with depression and a 32% increase associated with anxiety. Matched comparison showed an even higher increased risk of mortality among women with any mental health comorbidity (49%; P less than .05).
The investigators concluded that opioid use among breast cancer survivors with mental health comorbidities “remains a significant problem.”
“A need exists for collaborative care in the management of mental health comorbidities in women with breast cancer, which could improve symptoms, adherence to treatment, and recovery from these mental conditions,” the investigators wrote. “Mental health treatments also are recommended to be offered in primary care, which not only would be convenient for patients, but also would reduce the stigma associated with treatments for mental health comorbidities and improve the patient-provider relationship.”
The investigators reported financial relationships with Merck.
SOURCE: Desai R et al. J Oncol Pract. 2019 Jul 19. doi: 10.1200/JOP.18.00781.
Mental health comorbidities increase the rates of opioid use and mortality among breast cancer survivors on endocrine therapy, based on a retrospective study of more than 10,000 patients in a Medicare-linked database.
Screen for mental health conditions in the early stages of cancer care and lean toward opioid alternatives for pain management, advised lead author Raj Desai, MS, of the University of Florida, Gainesville, and colleagues.
“The complex relationship among breast cancer, mental health problems, and the use of opioids is not well understood, despite the high prevalence of mental health comorbidities like depression and anxiety in breast cancer survivors, and the high rate of opioid use in those on AET [adjuvant endocrine therapy],” the investigators wrote in the Journal of Oncology Practice.
“Therefore, this study aimed to determine whether breast cancer survivors with varying levels of mental health comorbidities, such as depression and anxiety, are more likely to use opioids for AET-related pain,” they added.
The study involved 10,452 breast cancer survivors who first filled an AET prescription from 2006 to 2012 and had follow-up records available for at least 2 years. All patients had a diagnosis of incident, primary, hormone receptor–positive, stage I-III breast cancer. Data were drawn from the Surveillance, Epidemiology, and End Results–Medicare linked database. Records were evaluated for diagnoses of mental health conditions such as depression and anxiety, opioid use, and survival.
Analysis showed that the most common mental health conditions were depression and anxiety, diagnosed in 554 and 246 women, respectively. Patients with mental health comorbidities were compared with patients who did not have such problems, using both unmatched and matched cohorts. While unmatched comparison for opioid use was not statistically significant, matched comparison showed that survivors with mental health comorbidities were 33% more likely to use opioids than those without mental health comorbidities (95% confidence interval, 1.06-1.68). Similarly, greater adjusted probabilities of opioid use were reported in the mental health comorbidity cohort (72.5% vs. 66.9%; P = .01).
Concerning survival, unmatched comparison revealed a 44% higher risk of death among women with depression and a 32% increase associated with anxiety. Matched comparison showed an even higher increased risk of mortality among women with any mental health comorbidity (49%; P less than .05).
The investigators concluded that opioid use among breast cancer survivors with mental health comorbidities “remains a significant problem.”
“A need exists for collaborative care in the management of mental health comorbidities in women with breast cancer, which could improve symptoms, adherence to treatment, and recovery from these mental conditions,” the investigators wrote. “Mental health treatments also are recommended to be offered in primary care, which not only would be convenient for patients, but also would reduce the stigma associated with treatments for mental health comorbidities and improve the patient-provider relationship.”
The investigators reported financial relationships with Merck.
SOURCE: Desai R et al. J Oncol Pract. 2019 Jul 19. doi: 10.1200/JOP.18.00781.
FROM THE JOURNAL OF ONCOLOGY PRACTICE
Lymphoma risk prompts FDA recall of Allergan’s textured breast implants
The Food and Drug Administration requested on July 24 that Allergan pull six brands of textured breast implants and breast expanders from the U.S. market, an action the agency took because of new data that substantially increased the number of women who developed a rare cancer – anaplastic large-cell lymphoma – in association with receiving these textured breast devices.
This is the first product recall the FDA has made to address the issue of breast implant–associated anaplastic large-cell lymphoma (BIA-ALCL), a complication that first came to national attention with a 2011 FDA report that had tallied 60 identified BIA-ALCL cases worldwide. By the end of September 2018, the number of reported worldwide BIA-ALCL cases had jumped to 457 cases reported to the agency via medical device reporting. In July 2019, the FDA cited a total of 573 unique, global case reports for BIA-ALCL sent to the agency through July 6, including 33 episodes that led to death.
It was inclusion of these additional 116 cases since September 2018 and 24 additional deaths that led FDA researchers to conclude that “the risk of BIA-ALCL with Allergan BIOCELL textured implants is approximately six-times the risk of BIA-ALCL with textured implants from other manufacturers marketing in the U.S.,” according to a statement from the agency.
The FDA is not recommending that patients who received one of the six products covered by the recall have the material removed if symptoms have not appeared because of the potential risk from explantation.
The agency also stressed that its investigation of the risk posed by placement of other brands of textured breast implants is ongoing and that overall less than 5% of all breast implants performed in current U.S. practice involve the macrotextured implants of the type specified in the Allergan recall.
This U.S. recall follows similar actions taken in France (and the rest of the European Union), Canada, and Australia, and it contrasts with the agency’s prior decision in May 2019 not to start a recall or ban of textured implants following a advisory committee meeting that discussed BIA-ALCL.
The six products that Allergan agreed to recall from marketing at the FDA’s request are four textured breast implants (Natrelle Saline-Filled Breast Implants, Natrelle Silicone-Filled Breast Implants, Natrelle Inspira Silicone-Filled breast Implants, and Natrelle 410 Highly Cohesive Anatomically Shaped Silicone-Filled Breast Implants) and two tissue expanders used prior to a breast implant (Natrelle 133 Plus Tissue Expander and the Natrelle 133 Tissue Expander with Suture Tabs).
FDA officials said they are considering recommendations for changes to the labeling of breast implant products, including a possible boxed warning and beefed up patient information.
“The recall of these textured implants is a big deal in protecting women from the potential risks of developing, and dying from, this rare type of aggressive lymphoma,” Joshua Brody, MD, a medical oncologist and director of the lymphoma immunotherapy program at Mount Sinai Medical Center in New York said in a statement. “While case reports have suggested a potential link between some types of breast implants and this disease – anaplastic lymphoma – for over 20 years, it has taken time to gain sufficient evidence to suggest, and understand, the causality. Some types of implants induce inflammation, which can both increase the chance of developing cancer, and also help to ‘hide’ developing cancers from the immune system. By preventing further use of these implants, the FDA is helping women to protect themselves from the medically serious and emotionally exhausting effects of these risks.”
Dr. Brody reported having no relevant disclosures.
The Food and Drug Administration requested on July 24 that Allergan pull six brands of textured breast implants and breast expanders from the U.S. market, an action the agency took because of new data that substantially increased the number of women who developed a rare cancer – anaplastic large-cell lymphoma – in association with receiving these textured breast devices.
This is the first product recall the FDA has made to address the issue of breast implant–associated anaplastic large-cell lymphoma (BIA-ALCL), a complication that first came to national attention with a 2011 FDA report that had tallied 60 identified BIA-ALCL cases worldwide. By the end of September 2018, the number of reported worldwide BIA-ALCL cases had jumped to 457 cases reported to the agency via medical device reporting. In July 2019, the FDA cited a total of 573 unique, global case reports for BIA-ALCL sent to the agency through July 6, including 33 episodes that led to death.
It was inclusion of these additional 116 cases since September 2018 and 24 additional deaths that led FDA researchers to conclude that “the risk of BIA-ALCL with Allergan BIOCELL textured implants is approximately six-times the risk of BIA-ALCL with textured implants from other manufacturers marketing in the U.S.,” according to a statement from the agency.
The FDA is not recommending that patients who received one of the six products covered by the recall have the material removed if symptoms have not appeared because of the potential risk from explantation.
The agency also stressed that its investigation of the risk posed by placement of other brands of textured breast implants is ongoing and that overall less than 5% of all breast implants performed in current U.S. practice involve the macrotextured implants of the type specified in the Allergan recall.
This U.S. recall follows similar actions taken in France (and the rest of the European Union), Canada, and Australia, and it contrasts with the agency’s prior decision in May 2019 not to start a recall or ban of textured implants following a advisory committee meeting that discussed BIA-ALCL.
The six products that Allergan agreed to recall from marketing at the FDA’s request are four textured breast implants (Natrelle Saline-Filled Breast Implants, Natrelle Silicone-Filled Breast Implants, Natrelle Inspira Silicone-Filled breast Implants, and Natrelle 410 Highly Cohesive Anatomically Shaped Silicone-Filled Breast Implants) and two tissue expanders used prior to a breast implant (Natrelle 133 Plus Tissue Expander and the Natrelle 133 Tissue Expander with Suture Tabs).
FDA officials said they are considering recommendations for changes to the labeling of breast implant products, including a possible boxed warning and beefed up patient information.
“The recall of these textured implants is a big deal in protecting women from the potential risks of developing, and dying from, this rare type of aggressive lymphoma,” Joshua Brody, MD, a medical oncologist and director of the lymphoma immunotherapy program at Mount Sinai Medical Center in New York said in a statement. “While case reports have suggested a potential link between some types of breast implants and this disease – anaplastic lymphoma – for over 20 years, it has taken time to gain sufficient evidence to suggest, and understand, the causality. Some types of implants induce inflammation, which can both increase the chance of developing cancer, and also help to ‘hide’ developing cancers from the immune system. By preventing further use of these implants, the FDA is helping women to protect themselves from the medically serious and emotionally exhausting effects of these risks.”
Dr. Brody reported having no relevant disclosures.
The Food and Drug Administration requested on July 24 that Allergan pull six brands of textured breast implants and breast expanders from the U.S. market, an action the agency took because of new data that substantially increased the number of women who developed a rare cancer – anaplastic large-cell lymphoma – in association with receiving these textured breast devices.
This is the first product recall the FDA has made to address the issue of breast implant–associated anaplastic large-cell lymphoma (BIA-ALCL), a complication that first came to national attention with a 2011 FDA report that had tallied 60 identified BIA-ALCL cases worldwide. By the end of September 2018, the number of reported worldwide BIA-ALCL cases had jumped to 457 cases reported to the agency via medical device reporting. In July 2019, the FDA cited a total of 573 unique, global case reports for BIA-ALCL sent to the agency through July 6, including 33 episodes that led to death.
It was inclusion of these additional 116 cases since September 2018 and 24 additional deaths that led FDA researchers to conclude that “the risk of BIA-ALCL with Allergan BIOCELL textured implants is approximately six-times the risk of BIA-ALCL with textured implants from other manufacturers marketing in the U.S.,” according to a statement from the agency.
The FDA is not recommending that patients who received one of the six products covered by the recall have the material removed if symptoms have not appeared because of the potential risk from explantation.
The agency also stressed that its investigation of the risk posed by placement of other brands of textured breast implants is ongoing and that overall less than 5% of all breast implants performed in current U.S. practice involve the macrotextured implants of the type specified in the Allergan recall.
This U.S. recall follows similar actions taken in France (and the rest of the European Union), Canada, and Australia, and it contrasts with the agency’s prior decision in May 2019 not to start a recall or ban of textured implants following a advisory committee meeting that discussed BIA-ALCL.
The six products that Allergan agreed to recall from marketing at the FDA’s request are four textured breast implants (Natrelle Saline-Filled Breast Implants, Natrelle Silicone-Filled Breast Implants, Natrelle Inspira Silicone-Filled breast Implants, and Natrelle 410 Highly Cohesive Anatomically Shaped Silicone-Filled Breast Implants) and two tissue expanders used prior to a breast implant (Natrelle 133 Plus Tissue Expander and the Natrelle 133 Tissue Expander with Suture Tabs).
FDA officials said they are considering recommendations for changes to the labeling of breast implant products, including a possible boxed warning and beefed up patient information.
“The recall of these textured implants is a big deal in protecting women from the potential risks of developing, and dying from, this rare type of aggressive lymphoma,” Joshua Brody, MD, a medical oncologist and director of the lymphoma immunotherapy program at Mount Sinai Medical Center in New York said in a statement. “While case reports have suggested a potential link between some types of breast implants and this disease – anaplastic lymphoma – for over 20 years, it has taken time to gain sufficient evidence to suggest, and understand, the causality. Some types of implants induce inflammation, which can both increase the chance of developing cancer, and also help to ‘hide’ developing cancers from the immune system. By preventing further use of these implants, the FDA is helping women to protect themselves from the medically serious and emotionally exhausting effects of these risks.”
Dr. Brody reported having no relevant disclosures.
Sexual Dysfunction in MS
A 37-year-old woman presents to her primary care clinic with a chief complaint of depression. She was diagnosed with relapsing multiple sclerosis (MS) at age 29 and is currently taking an injectable preventive therapy. Over the past 6 months, she has had increased marital strain secondary to losing her job because “I couldn’t mentally keep up with the work anymore.” This has caused financial difficulties for her family. In addition, she tires easily and has been napping in the afternoon. She and her husband are experiencing intimacy difficulties, and she confirms problems with vaginal dryness and a general loss of her sexual drive.
Sexual dysfunction in MS is common, affecting 40% to 80% of women and 50% to 90% of men with MS. It is an “invisible” symptom, similar to fatigue, cognitive dysfunction, and pain.1-3
There are three ways that MS patients can be affected by sexual dysfunction, and they are categorized as primary, secondary, and tertiary. Primary sexual dysfunction results from demyelination/axonal destruction of the central nervous system, which potentially leads to altered genital sensation or paresthesia. Secondary sexual dysfunction stems from nonsexual MS symptoms, such as fatigue, spasticity, tremor, impairments in concentration/attention, and iatrogenic causes (eg, adverse effects of medication). Tertiary sexual dysfunction involves the psychosocial/cultural aspects of the disease that can impact a patient’s sexual drive.
SYMPTOMS
Like many other symptoms associated with MS, the symptoms of sexual dysfunction are highly variable. In women, the most common complaints are fatigue, decrease in genital sensation (27%-47%), decrease in libido (31%-74%) and vaginal lubrication (36%-48%), and difficulty with orgasm.4 In men with MS, in addition to erectile problems, surveys have identified decreased genital sensation, fatigue (75%), difficulty with ejaculation (18%-50%), decreased interest or arousal (39%), and anorgasmia (37%) as fairly common complaints.2
TREATMENT
Managing sexual dysfunction in a patient with MS is dependent on the underlying problem. Some examples include
- For many patients, their disease causes significant anxiety and worry about current and potentially future disability—which can make intimacy more difficult. Sometimes, referral to a mental health professional may be required to help the patient
with individual and/or couples counseling to further elucidate underlying intimacy issues. - For patients experiencing MS-associated fatigue, suggest planning for sexual activity in the morning, since fatigue is known to worsen throughout the day.
- For those who qualify for antidepressant medications, remember that some (eg, selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors) can further decrease libido and therefore should be avoided if possible.
- For women who have difficulty with lubrication, a nonpetroleum-based lubricant may reduce vaginal dryness, while use of a vibrator may assist with genital stimulation.
- For men who cannot maintain erection, phosphodiesterase inhibitor drugs (eg, sildenafil) can be helpful; other options include alprostadil urethral suppositories and intracavernous injections.
The patient is screened for depression using the Patient Health Questionnaire, which yields a score of 17 (moderately severe). You discuss the need for active treatment with her, and she agrees to start an antidepressant medication. Bupropion is chosen, given its effectiveness and lack of adverse effects (including sexual dysfunction). The patient also is encouraged to use nonpetroleum-based lubricants. Finally, a referral is made for couples counseling, and a 6-week follow-up appointment is scheduled.
CONCLUSION
Sexual dysfunction in MS is quite common in both women and men, and the related symptoms are often multifactorial. Strategies to address sexual dysfunction in MS require a tailored approach. Fortunately, any treatments for sexual dysfunction initiated by the patient’s primary care provider will not have an adverse effect on the patient’s outcome with MS. For more complicated cases of MS-associated sexual dysfunction, urology referral is recommended.
1. Foley FW, Sander A. Sexuality, multiple sclerosis and women. Mult Scler Manage. 1997;4:1-9.
2. Calabro RS, De Luca R, Conti-Nibali V, et al. Sexual dysfunction in male patients with multiple sclerosis: a need for counseling! Int J Neurosci. 2014;124(8):547-557.
3. Gava G, Visconti M, Salvi F, et al. Prevalence and psychopathological determinants of sexual dysfunction and related distress in women with and without multiple sclerosis. J Sex Med. 2019;16(6):833-842.
4. Cordeau D, Courtois, F. Sexual disorders in women with MS: assessment and management. Ann Phys Rehabil Med. 2014; 57(5):337-47.
A 37-year-old woman presents to her primary care clinic with a chief complaint of depression. She was diagnosed with relapsing multiple sclerosis (MS) at age 29 and is currently taking an injectable preventive therapy. Over the past 6 months, she has had increased marital strain secondary to losing her job because “I couldn’t mentally keep up with the work anymore.” This has caused financial difficulties for her family. In addition, she tires easily and has been napping in the afternoon. She and her husband are experiencing intimacy difficulties, and she confirms problems with vaginal dryness and a general loss of her sexual drive.
Sexual dysfunction in MS is common, affecting 40% to 80% of women and 50% to 90% of men with MS. It is an “invisible” symptom, similar to fatigue, cognitive dysfunction, and pain.1-3
There are three ways that MS patients can be affected by sexual dysfunction, and they are categorized as primary, secondary, and tertiary. Primary sexual dysfunction results from demyelination/axonal destruction of the central nervous system, which potentially leads to altered genital sensation or paresthesia. Secondary sexual dysfunction stems from nonsexual MS symptoms, such as fatigue, spasticity, tremor, impairments in concentration/attention, and iatrogenic causes (eg, adverse effects of medication). Tertiary sexual dysfunction involves the psychosocial/cultural aspects of the disease that can impact a patient’s sexual drive.
SYMPTOMS
Like many other symptoms associated with MS, the symptoms of sexual dysfunction are highly variable. In women, the most common complaints are fatigue, decrease in genital sensation (27%-47%), decrease in libido (31%-74%) and vaginal lubrication (36%-48%), and difficulty with orgasm.4 In men with MS, in addition to erectile problems, surveys have identified decreased genital sensation, fatigue (75%), difficulty with ejaculation (18%-50%), decreased interest or arousal (39%), and anorgasmia (37%) as fairly common complaints.2
TREATMENT
Managing sexual dysfunction in a patient with MS is dependent on the underlying problem. Some examples include
- For many patients, their disease causes significant anxiety and worry about current and potentially future disability—which can make intimacy more difficult. Sometimes, referral to a mental health professional may be required to help the patient
with individual and/or couples counseling to further elucidate underlying intimacy issues. - For patients experiencing MS-associated fatigue, suggest planning for sexual activity in the morning, since fatigue is known to worsen throughout the day.
- For those who qualify for antidepressant medications, remember that some (eg, selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors) can further decrease libido and therefore should be avoided if possible.
- For women who have difficulty with lubrication, a nonpetroleum-based lubricant may reduce vaginal dryness, while use of a vibrator may assist with genital stimulation.
- For men who cannot maintain erection, phosphodiesterase inhibitor drugs (eg, sildenafil) can be helpful; other options include alprostadil urethral suppositories and intracavernous injections.
The patient is screened for depression using the Patient Health Questionnaire, which yields a score of 17 (moderately severe). You discuss the need for active treatment with her, and she agrees to start an antidepressant medication. Bupropion is chosen, given its effectiveness and lack of adverse effects (including sexual dysfunction). The patient also is encouraged to use nonpetroleum-based lubricants. Finally, a referral is made for couples counseling, and a 6-week follow-up appointment is scheduled.
CONCLUSION
Sexual dysfunction in MS is quite common in both women and men, and the related symptoms are often multifactorial. Strategies to address sexual dysfunction in MS require a tailored approach. Fortunately, any treatments for sexual dysfunction initiated by the patient’s primary care provider will not have an adverse effect on the patient’s outcome with MS. For more complicated cases of MS-associated sexual dysfunction, urology referral is recommended.
A 37-year-old woman presents to her primary care clinic with a chief complaint of depression. She was diagnosed with relapsing multiple sclerosis (MS) at age 29 and is currently taking an injectable preventive therapy. Over the past 6 months, she has had increased marital strain secondary to losing her job because “I couldn’t mentally keep up with the work anymore.” This has caused financial difficulties for her family. In addition, she tires easily and has been napping in the afternoon. She and her husband are experiencing intimacy difficulties, and she confirms problems with vaginal dryness and a general loss of her sexual drive.
Sexual dysfunction in MS is common, affecting 40% to 80% of women and 50% to 90% of men with MS. It is an “invisible” symptom, similar to fatigue, cognitive dysfunction, and pain.1-3
There are three ways that MS patients can be affected by sexual dysfunction, and they are categorized as primary, secondary, and tertiary. Primary sexual dysfunction results from demyelination/axonal destruction of the central nervous system, which potentially leads to altered genital sensation or paresthesia. Secondary sexual dysfunction stems from nonsexual MS symptoms, such as fatigue, spasticity, tremor, impairments in concentration/attention, and iatrogenic causes (eg, adverse effects of medication). Tertiary sexual dysfunction involves the psychosocial/cultural aspects of the disease that can impact a patient’s sexual drive.
SYMPTOMS
Like many other symptoms associated with MS, the symptoms of sexual dysfunction are highly variable. In women, the most common complaints are fatigue, decrease in genital sensation (27%-47%), decrease in libido (31%-74%) and vaginal lubrication (36%-48%), and difficulty with orgasm.4 In men with MS, in addition to erectile problems, surveys have identified decreased genital sensation, fatigue (75%), difficulty with ejaculation (18%-50%), decreased interest or arousal (39%), and anorgasmia (37%) as fairly common complaints.2
TREATMENT
Managing sexual dysfunction in a patient with MS is dependent on the underlying problem. Some examples include
- For many patients, their disease causes significant anxiety and worry about current and potentially future disability—which can make intimacy more difficult. Sometimes, referral to a mental health professional may be required to help the patient
with individual and/or couples counseling to further elucidate underlying intimacy issues. - For patients experiencing MS-associated fatigue, suggest planning for sexual activity in the morning, since fatigue is known to worsen throughout the day.
- For those who qualify for antidepressant medications, remember that some (eg, selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors) can further decrease libido and therefore should be avoided if possible.
- For women who have difficulty with lubrication, a nonpetroleum-based lubricant may reduce vaginal dryness, while use of a vibrator may assist with genital stimulation.
- For men who cannot maintain erection, phosphodiesterase inhibitor drugs (eg, sildenafil) can be helpful; other options include alprostadil urethral suppositories and intracavernous injections.
The patient is screened for depression using the Patient Health Questionnaire, which yields a score of 17 (moderately severe). You discuss the need for active treatment with her, and she agrees to start an antidepressant medication. Bupropion is chosen, given its effectiveness and lack of adverse effects (including sexual dysfunction). The patient also is encouraged to use nonpetroleum-based lubricants. Finally, a referral is made for couples counseling, and a 6-week follow-up appointment is scheduled.
CONCLUSION
Sexual dysfunction in MS is quite common in both women and men, and the related symptoms are often multifactorial. Strategies to address sexual dysfunction in MS require a tailored approach. Fortunately, any treatments for sexual dysfunction initiated by the patient’s primary care provider will not have an adverse effect on the patient’s outcome with MS. For more complicated cases of MS-associated sexual dysfunction, urology referral is recommended.
1. Foley FW, Sander A. Sexuality, multiple sclerosis and women. Mult Scler Manage. 1997;4:1-9.
2. Calabro RS, De Luca R, Conti-Nibali V, et al. Sexual dysfunction in male patients with multiple sclerosis: a need for counseling! Int J Neurosci. 2014;124(8):547-557.
3. Gava G, Visconti M, Salvi F, et al. Prevalence and psychopathological determinants of sexual dysfunction and related distress in women with and without multiple sclerosis. J Sex Med. 2019;16(6):833-842.
4. Cordeau D, Courtois, F. Sexual disorders in women with MS: assessment and management. Ann Phys Rehabil Med. 2014; 57(5):337-47.
1. Foley FW, Sander A. Sexuality, multiple sclerosis and women. Mult Scler Manage. 1997;4:1-9.
2. Calabro RS, De Luca R, Conti-Nibali V, et al. Sexual dysfunction in male patients with multiple sclerosis: a need for counseling! Int J Neurosci. 2014;124(8):547-557.
3. Gava G, Visconti M, Salvi F, et al. Prevalence and psychopathological determinants of sexual dysfunction and related distress in women with and without multiple sclerosis. J Sex Med. 2019;16(6):833-842.
4. Cordeau D, Courtois, F. Sexual disorders in women with MS: assessment and management. Ann Phys Rehabil Med. 2014; 57(5):337-47.
USPSTF updates, reaffirms recommendation for HBV screening in pregnant women
The according to task force member Douglas K. Owens, MD, of the Veterans Affairs Palo Alto (Calif.) Health Care System and other members of the task force.
The recommendation statement, published in JAMA, was based on an evidence report and systematic review also published in JAMA. In that review, two studies of fair quality were identified; one included 155,081 infants born to HBV-positive women identified for case management through the national Perinatal Hepatitis B Prevention Program from 1994 to 2008, and the other included 4,446 infants born in a large, regional health care organization in the United States between 1997 and 2010. In both, low rates of perinatal transmission were reported for those periods – between 0.5% and 1.9% – with the rate falling over time.
In the 2009 recommendation, the USPSTF found adequate evidence that serologic testing for hepatitis B surface antigen accurately identifies HBV infection, and that interventions were effective in preventing perinatal transmission. That recommendation has been reaffirmed in the current update, with HBV screening receiving a grade of A, which is the strongest the USPSTF offers.
In a related editorial, Neil S. Silverman, MD, of the Center for Fetal Medicine and Women’s Ultrasound in Los Angeles noted several improvements in maternal HBV therapy since the publication of the original 2009 recommendation, including maternal HBV-targeted antiviral therapy during pregnancy as an adjunct to neonatal immunoprophylaxis and the ability to refer women for chronic treatment of their HBV disease to prevent long-term infection complications. The task forces also noted that HBV screening of all pregnant women is mandated by law in 26 states.
One member of the task force reported receiving grants and/or personal fees from Healthwise, another member reported receiving personal fees from UpToDate; a third reported participating in the American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases’ Hepatitis B Guidance and Hepatitis B Systematic Review Group. The evidence and review study was funded by the Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality. Dr. Silverman reported no disclosures.
SOURCes: Owens DK et al. JAMA. 2019 Jul 23. doi: 10.1001/jama.2019.9365; Henderson JT et al. JAMA. 2019 Jul 23;32(4):360-2; Silverman NS. JAMA. 2019 Jul 23;32(4):312-14.
The according to task force member Douglas K. Owens, MD, of the Veterans Affairs Palo Alto (Calif.) Health Care System and other members of the task force.
The recommendation statement, published in JAMA, was based on an evidence report and systematic review also published in JAMA. In that review, two studies of fair quality were identified; one included 155,081 infants born to HBV-positive women identified for case management through the national Perinatal Hepatitis B Prevention Program from 1994 to 2008, and the other included 4,446 infants born in a large, regional health care organization in the United States between 1997 and 2010. In both, low rates of perinatal transmission were reported for those periods – between 0.5% and 1.9% – with the rate falling over time.
In the 2009 recommendation, the USPSTF found adequate evidence that serologic testing for hepatitis B surface antigen accurately identifies HBV infection, and that interventions were effective in preventing perinatal transmission. That recommendation has been reaffirmed in the current update, with HBV screening receiving a grade of A, which is the strongest the USPSTF offers.
In a related editorial, Neil S. Silverman, MD, of the Center for Fetal Medicine and Women’s Ultrasound in Los Angeles noted several improvements in maternal HBV therapy since the publication of the original 2009 recommendation, including maternal HBV-targeted antiviral therapy during pregnancy as an adjunct to neonatal immunoprophylaxis and the ability to refer women for chronic treatment of their HBV disease to prevent long-term infection complications. The task forces also noted that HBV screening of all pregnant women is mandated by law in 26 states.
One member of the task force reported receiving grants and/or personal fees from Healthwise, another member reported receiving personal fees from UpToDate; a third reported participating in the American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases’ Hepatitis B Guidance and Hepatitis B Systematic Review Group. The evidence and review study was funded by the Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality. Dr. Silverman reported no disclosures.
SOURCes: Owens DK et al. JAMA. 2019 Jul 23. doi: 10.1001/jama.2019.9365; Henderson JT et al. JAMA. 2019 Jul 23;32(4):360-2; Silverman NS. JAMA. 2019 Jul 23;32(4):312-14.
The according to task force member Douglas K. Owens, MD, of the Veterans Affairs Palo Alto (Calif.) Health Care System and other members of the task force.
The recommendation statement, published in JAMA, was based on an evidence report and systematic review also published in JAMA. In that review, two studies of fair quality were identified; one included 155,081 infants born to HBV-positive women identified for case management through the national Perinatal Hepatitis B Prevention Program from 1994 to 2008, and the other included 4,446 infants born in a large, regional health care organization in the United States between 1997 and 2010. In both, low rates of perinatal transmission were reported for those periods – between 0.5% and 1.9% – with the rate falling over time.
In the 2009 recommendation, the USPSTF found adequate evidence that serologic testing for hepatitis B surface antigen accurately identifies HBV infection, and that interventions were effective in preventing perinatal transmission. That recommendation has been reaffirmed in the current update, with HBV screening receiving a grade of A, which is the strongest the USPSTF offers.
In a related editorial, Neil S. Silverman, MD, of the Center for Fetal Medicine and Women’s Ultrasound in Los Angeles noted several improvements in maternal HBV therapy since the publication of the original 2009 recommendation, including maternal HBV-targeted antiviral therapy during pregnancy as an adjunct to neonatal immunoprophylaxis and the ability to refer women for chronic treatment of their HBV disease to prevent long-term infection complications. The task forces also noted that HBV screening of all pregnant women is mandated by law in 26 states.
One member of the task force reported receiving grants and/or personal fees from Healthwise, another member reported receiving personal fees from UpToDate; a third reported participating in the American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases’ Hepatitis B Guidance and Hepatitis B Systematic Review Group. The evidence and review study was funded by the Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality. Dr. Silverman reported no disclosures.
SOURCes: Owens DK et al. JAMA. 2019 Jul 23. doi: 10.1001/jama.2019.9365; Henderson JT et al. JAMA. 2019 Jul 23;32(4):360-2; Silverman NS. JAMA. 2019 Jul 23;32(4):312-14.
FROM JAMA