User login
Abdominal Pain and Fever 48 Hours After Hysterosalpingography
A 37-year-old woman presented to the emergency department (ED) with 12 hours of fever and lower abdominal cramp pain. She had a history significant for hypothyroidism, infertility, and dysmenorrhea and had a hysterosalpingography (HSG) 48 hours prior for a comprehensive infertility workup.
On examination, the patient’s vital signs were a 94 bpm heart rate; 109/64 mm Hg blood pressure; 14 breaths per minute respiratory rate; 99% oxygen saturation on room air; and 101.2 °F temperature. The patient reported pain in the bilateral lower abdominal quadrants and no history of sexually transmitted infection, pelvic inflammatory disease, vaginal discharge or bleeding, dysuria, hematuria, melena, or bright red blood per rectum. A human chorionic gonadotropin urine test was negative on intake. The HSG 48 hours prior showed no concerning findings with normal uterine cavity and normal caliber fallopian tubes bilaterally.
On physical examination, the patient’s abdomen was nondistended, nonperitonitic, and without evidence of acute trauma or surgical scars. On palpation, the patient was tender in her suprapubic region and lower abdominal quadrants without evidence of guarding or rebound
The patient’s initial laboratory tests were as follows: white blood cells, 20.1 × 103/μL (reference range, 4-11 × 103/μL); hemoglobin, 12.1 g/dL (reference range, 12.1-15.1 g/dL); hematocrit, 37.1%, (reference range, 36%-48%); alanine aminotransferase, 84 U/L (reference range, 7-56 U/L); aspartate aminotransferase, 66 U/L (reference range, 8-33 U/L); and lipase, 25 U/L (5-60 U/L). Urinalysis was notable for only 5 red blood cells and negative for white blood cells, leukocyte esterase, and nitrites. The patient’s pain and fever were controlled with 1 g IV acetaminophen.
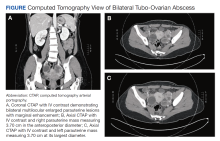
The patient’s fever, leukocytosis, and physical examination were concerning for possible intra-abdominal processes, so a
Discussion
The patient was diagnosed with bilateral tubo-ovarian abscess (TOA) likely secondary to her HSG procedure 48 hours before. TOA is a severe infectious, inflammatory condition involving a mass of the ovaries, fallopian tubes, or adjacent tissues of the upper female genital tract.1 Traditionally, TOAs are sequelae of undiagnosed or subclinical acute or chronic pelvic inflammatory disease (PID). This is known to occur via pathogen ascension from the lower to the upper female genital tract resulting in cervicitis, endometritis, salpingitis, oophoritis, and if left untreated, peritonitis.1 About 70,000 women are diagnosed with TOAs in the US every year. These patients require hospitalization as well as IV antibiotics for gold-standard treatment; however, some cases may require percutaneous drainage based on size, severity, and location.2
Diagnostic Considerations
Clinically, patients with TOAs present with fever, chills, lower abdominal pain, vaginal discharge with cervical motion tenderness, and an adnexal mass on examination.3 When a TOA is suspected, a urine human chorionic gonadotropin test and testing for C trachomatis and N gonorrhoeae are warranted. An ED workup often reveals leukocytosis, elevated C-reactive protein, and elevated erythrocyte sedimentation rate. Imaging is recommended once a TOA is suspected. Ultrasound is the gold-standard imaging modality and boasts a sensitivity of 93% and specificity of 98% for the detection of TOAs; however, CT has also been shown to be an effective diagnostic modality.4
Despite being common, TOAs are difficult to predict, detect, and diagnose; thus the clinician must often rely on thorough history taking and physical examination to raise suspicion.5 Although most frequently associated with sexual transmission, TOAs occur in not sexually active women in adolescence and adulthood. Specifically, TOAs also can present secondary to other intra-abdominal pathologies, such as appendicitis, diverticulitis, and pyelonephritis, as well as a complication of intrauterine procedures, such as an HSG, or less commonly, following intrauterine device (IUD) insertion.5-7
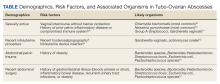
Given that sexually transmitted infections are the most common etiology of TOAs, C trachomatis and N gonorrhoeae are the most likely microorganisms to be isolated (Table).8-12 In not sexually active populations, Escherichia coli and Gardnerella vaginalis should be considered instead. Although rare, women with IUDs have been shown to have an increased incidence of PID/TOA secondary to Actinomyces israleii relative to women without IUDs.12 In patients with TOAs secondary to intraabdominal surgery, anaerobic bacteria, such as Bacterioides and Peptostreptococcus species in addition to Escherichia coli, are likely culprits.11
In patients after HSG, infectious complications are uncommon enough that the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists recommends against antibiotic prophylaxis unless there are risk factors of dilated fallopian tubes or a history of PID.13 Identifying a precise percentage of TOA as a complication of HSG is rather elusive in the literature, though, it is frequently noted that infection in general is uncommon, and the risk of developing PID is about 1.4% to 3.4%.14 However, in the retrospective study most often cited, all women who developed PID following HSG had evidence of dilated fallopian tubes. Given our patient had no history of PID or dilated fallopian tubes, her risk of developing infection (PID or postprocedural abscess) would be considered very low; therefore, the index of suspicion also was low.15
Following diagnosis, the patient was promptly admitted and treated with a course of IV ceftriaxone 1 g every 24 hours, IV doxycycline 100 mg every 12 hours, and a single dose of IV metronidazole 500 mg. Her leukocytosis, fever, and pain improved within 48 hours without the need for percutaneous drainage and the patient made a complete recovery.
Complications
TOAs can carry significant morbidity and mortality, and there are both acute and chronic complications associated. Even if properly treated, TOAs can rupture leading to severe illness, such as peritonitis and septic shock. This often requires surgical intervention and hemodynamic pressure support in the intensive care unit setting.16 One of the most feared long-term complications of TOAs is infertility secondary to structural abnormalities of the female reproductive tract.10 Adhesions, strictures, and scarring are associated with TOAs irrespective of medical or surgical management, and thus any women with a history of PID or TOA require advanced fertility workup if they are having difficulties with conception or implantation.17
Minimizing infectious transmission also is essential in the treatment of TOA/PID. All women who receive a diagnosis of PID or TOA should be evaluated for gonorrhea, chlamydia, HIV, and syphilis. Women should be instructed to abstain from sexual intercourse until therapy is complete, symptoms have resolved, and sex partners have been treated for potential chlamydial or gonococcal infections. All contraceptive methods can be continued during treatment.
Conclusions
This case presented several challenges as the bilateral TOAs developed postprocedure in a patient without risk factors. Furthermore, this case did not follow the classic presentation of ascending bacterial translocation to the ovaries over days to weeks. The diagnosis was complicated by a largely benign physical examination and a pelvic examination without evidence of abnormal vaginal discharge or cervicitis. The only indicators were fever, leukocytosis, and abdominal pain in the setting of a recent, uncomplicated HSG procedure. Vigilance is required to obtain the necessary history, and the differential of TOA must be broadened to include women without a history or symptoms of a sexually transmitted infection (contrary to the classic association). We aim to encourage heightened clinical suspicion for TOAs in patients who present with fever, leukocytosis, and abdominal pain after recent HSG or other intrauterine instrumentation procedures and therefore improve patient outcomes.
1. Gkrozou F, Tsonis O, Daniilidis A, Navrozoglou I, Paschopoulos M. Tubo-ovarian abscess: exploring optimal treatment options based on current evidence. J Endometr Pelvic Pain Disord. 2020;13(1):10-19. doi:10.1177/2284026520960649
2. Taylor KJ, Wasson JF, De Graaff C, Rosenfield AT, Andriole VT. Accuracy of grey-scale ultrasound diagnosis of abdominal and pelvic abscesses in 220 patients. Lancet. 1978;1(8055):83-84. doi:10.1016/s0140-6736(78)90016-8
3. Bridwell RE, Koyfman A, Long B. High risk and low prevalence diseases: tubo-ovarian abscess. Am J Emerg Med. 2022;57:70-75. doi:10.1016/j.ajem.2022.04.026
4. Lambert MJ, Villa M. Gynecologic ultrasound in emergency medicine. Emerg Med Clin North Am. 2004;22(3):683-696. doi:10.1016/j.emc.2004.04.016
5. Munro K, Gharaibeh A, Nagabushanam S, Martin C. Diagnosis and management of tubo-ovarian abscesses. Obstet Gynaecol. 2018;20(1):11-19. doi:10.1111/tog.12447
6. Fink D, Lim PPC, Desai A, Stephans AB, Wien MA. Recurrent tubo-ovarian abscess in a nonsexually active adolescent. Consultant. 2022;62(1):e26-e28. doi:10.25270/con.2021.04.00010
7. Hiller N, Fux T, Finkelstein A, Mezeh H, Simanovsky N. CT differentiation between tubo-ovarian and appendiceal origin of right lower quadrant abscess: CT, clinical, and laboratory correlation. Emerg Radiol. 2016;23:133-139. doi:10.1007/s10140-015-1372-z
8. Kairys N, Roepke C. Tubo-ovarian abscess. In: StatPearls. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; June 12, 2023.
9. Gao Y, Qu P, Zhou Y, Ding W. Risk factors for the development of tubo-ovarian abscesses in women with ovarian endometriosis: a retrospective matched case-control study. BMC Womens Health. 2021:21:43. doi:10.1186/s12905-021-01188-6
10. Curry A, Williams T, Penny ML. Pelvic inflammatory disease: diagnosis, management, and prevention. Am Fam Physician. 2019;100(6):357-364.
11. Landers DV, Sweet RL. Tubo-ovarian abscess: contemporary approach to management. Rev Infect Dis. 1983;5(5):876-884. doi:10.1093/clinids/5.5.876
12. Burkman R, Schlesselman S, McCaffrey L, Gupta PK, Spence M. The relationship of genital tract actinomycetes and the development of pelvic inflammatory disease. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1982;143(5):585-589. doi:10.1016/0002-9378(82)90552-x
13. Armstrong C. ACOG releases guidelines on antibiotic prophylaxis for gynecologic procedures. Am Fam Physician. 2007;75(7):1094-1096.
14. Pittaway DE, Winfield AC, Maxson W, Daniell J, Herbert C, Wentz AC. Prevention of acute pelvic inflammatory disease after hysterosalpingography: efficacy of doxycycline prophylaxis. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1983;147(6):623-626. doi:10.1016/0002-9378(83)90438-6
15. Committee on Practice Bulletins—Gynecology. Prevention of Infection After Gynecologic Procedures: ACOG Practice Bulletin, Number 195. Obstet Gynecol. 2018;131(6):e172-e189. doi:10.1097/AOG.0000000000002670
16. Tao X, Ge SQ, Chen L, Cai LS, Hwang MF, Wang CL. Relationships between female infertility and female genital infections and pelvic inflammatory disease: a population-based nested controlled study. Clinics (Sao Paulo). 2018;73:e364. Published 2018 Aug 9. doi:10.6061/clinics/2018/e364
17. Fouks Y, Azem F, Many A, Cohen Y, Levin I, Cohen A. Fertility outcomes in patients with tubo-ovarian abscesses after an oocyte retrieval: a longitudinal cohort analysis. Arch Gynecol Obstet. 2019;300(3):763-769. doi:10.1007/s00404-019-05230-9
A 37-year-old woman presented to the emergency department (ED) with 12 hours of fever and lower abdominal cramp pain. She had a history significant for hypothyroidism, infertility, and dysmenorrhea and had a hysterosalpingography (HSG) 48 hours prior for a comprehensive infertility workup.
On examination, the patient’s vital signs were a 94 bpm heart rate; 109/64 mm Hg blood pressure; 14 breaths per minute respiratory rate; 99% oxygen saturation on room air; and 101.2 °F temperature. The patient reported pain in the bilateral lower abdominal quadrants and no history of sexually transmitted infection, pelvic inflammatory disease, vaginal discharge or bleeding, dysuria, hematuria, melena, or bright red blood per rectum. A human chorionic gonadotropin urine test was negative on intake. The HSG 48 hours prior showed no concerning findings with normal uterine cavity and normal caliber fallopian tubes bilaterally.
On physical examination, the patient’s abdomen was nondistended, nonperitonitic, and without evidence of acute trauma or surgical scars. On palpation, the patient was tender in her suprapubic region and lower abdominal quadrants without evidence of guarding or rebound
The patient’s initial laboratory tests were as follows: white blood cells, 20.1 × 103/μL (reference range, 4-11 × 103/μL); hemoglobin, 12.1 g/dL (reference range, 12.1-15.1 g/dL); hematocrit, 37.1%, (reference range, 36%-48%); alanine aminotransferase, 84 U/L (reference range, 7-56 U/L); aspartate aminotransferase, 66 U/L (reference range, 8-33 U/L); and lipase, 25 U/L (5-60 U/L). Urinalysis was notable for only 5 red blood cells and negative for white blood cells, leukocyte esterase, and nitrites. The patient’s pain and fever were controlled with 1 g IV acetaminophen.
The patient’s fever, leukocytosis, and physical examination were concerning for possible intra-abdominal processes, so a
Discussion
The patient was diagnosed with bilateral tubo-ovarian abscess (TOA) likely secondary to her HSG procedure 48 hours before. TOA is a severe infectious, inflammatory condition involving a mass of the ovaries, fallopian tubes, or adjacent tissues of the upper female genital tract.1 Traditionally, TOAs are sequelae of undiagnosed or subclinical acute or chronic pelvic inflammatory disease (PID). This is known to occur via pathogen ascension from the lower to the upper female genital tract resulting in cervicitis, endometritis, salpingitis, oophoritis, and if left untreated, peritonitis.1 About 70,000 women are diagnosed with TOAs in the US every year. These patients require hospitalization as well as IV antibiotics for gold-standard treatment; however, some cases may require percutaneous drainage based on size, severity, and location.2
Diagnostic Considerations
Clinically, patients with TOAs present with fever, chills, lower abdominal pain, vaginal discharge with cervical motion tenderness, and an adnexal mass on examination.3 When a TOA is suspected, a urine human chorionic gonadotropin test and testing for C trachomatis and N gonorrhoeae are warranted. An ED workup often reveals leukocytosis, elevated C-reactive protein, and elevated erythrocyte sedimentation rate. Imaging is recommended once a TOA is suspected. Ultrasound is the gold-standard imaging modality and boasts a sensitivity of 93% and specificity of 98% for the detection of TOAs; however, CT has also been shown to be an effective diagnostic modality.4
Despite being common, TOAs are difficult to predict, detect, and diagnose; thus the clinician must often rely on thorough history taking and physical examination to raise suspicion.5 Although most frequently associated with sexual transmission, TOAs occur in not sexually active women in adolescence and adulthood. Specifically, TOAs also can present secondary to other intra-abdominal pathologies, such as appendicitis, diverticulitis, and pyelonephritis, as well as a complication of intrauterine procedures, such as an HSG, or less commonly, following intrauterine device (IUD) insertion.5-7
Given that sexually transmitted infections are the most common etiology of TOAs, C trachomatis and N gonorrhoeae are the most likely microorganisms to be isolated (Table).8-12 In not sexually active populations, Escherichia coli and Gardnerella vaginalis should be considered instead. Although rare, women with IUDs have been shown to have an increased incidence of PID/TOA secondary to Actinomyces israleii relative to women without IUDs.12 In patients with TOAs secondary to intraabdominal surgery, anaerobic bacteria, such as Bacterioides and Peptostreptococcus species in addition to Escherichia coli, are likely culprits.11
In patients after HSG, infectious complications are uncommon enough that the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists recommends against antibiotic prophylaxis unless there are risk factors of dilated fallopian tubes or a history of PID.13 Identifying a precise percentage of TOA as a complication of HSG is rather elusive in the literature, though, it is frequently noted that infection in general is uncommon, and the risk of developing PID is about 1.4% to 3.4%.14 However, in the retrospective study most often cited, all women who developed PID following HSG had evidence of dilated fallopian tubes. Given our patient had no history of PID or dilated fallopian tubes, her risk of developing infection (PID or postprocedural abscess) would be considered very low; therefore, the index of suspicion also was low.15
Following diagnosis, the patient was promptly admitted and treated with a course of IV ceftriaxone 1 g every 24 hours, IV doxycycline 100 mg every 12 hours, and a single dose of IV metronidazole 500 mg. Her leukocytosis, fever, and pain improved within 48 hours without the need for percutaneous drainage and the patient made a complete recovery.
Complications
TOAs can carry significant morbidity and mortality, and there are both acute and chronic complications associated. Even if properly treated, TOAs can rupture leading to severe illness, such as peritonitis and septic shock. This often requires surgical intervention and hemodynamic pressure support in the intensive care unit setting.16 One of the most feared long-term complications of TOAs is infertility secondary to structural abnormalities of the female reproductive tract.10 Adhesions, strictures, and scarring are associated with TOAs irrespective of medical or surgical management, and thus any women with a history of PID or TOA require advanced fertility workup if they are having difficulties with conception or implantation.17
Minimizing infectious transmission also is essential in the treatment of TOA/PID. All women who receive a diagnosis of PID or TOA should be evaluated for gonorrhea, chlamydia, HIV, and syphilis. Women should be instructed to abstain from sexual intercourse until therapy is complete, symptoms have resolved, and sex partners have been treated for potential chlamydial or gonococcal infections. All contraceptive methods can be continued during treatment.
Conclusions
This case presented several challenges as the bilateral TOAs developed postprocedure in a patient without risk factors. Furthermore, this case did not follow the classic presentation of ascending bacterial translocation to the ovaries over days to weeks. The diagnosis was complicated by a largely benign physical examination and a pelvic examination without evidence of abnormal vaginal discharge or cervicitis. The only indicators were fever, leukocytosis, and abdominal pain in the setting of a recent, uncomplicated HSG procedure. Vigilance is required to obtain the necessary history, and the differential of TOA must be broadened to include women without a history or symptoms of a sexually transmitted infection (contrary to the classic association). We aim to encourage heightened clinical suspicion for TOAs in patients who present with fever, leukocytosis, and abdominal pain after recent HSG or other intrauterine instrumentation procedures and therefore improve patient outcomes.
A 37-year-old woman presented to the emergency department (ED) with 12 hours of fever and lower abdominal cramp pain. She had a history significant for hypothyroidism, infertility, and dysmenorrhea and had a hysterosalpingography (HSG) 48 hours prior for a comprehensive infertility workup.
On examination, the patient’s vital signs were a 94 bpm heart rate; 109/64 mm Hg blood pressure; 14 breaths per minute respiratory rate; 99% oxygen saturation on room air; and 101.2 °F temperature. The patient reported pain in the bilateral lower abdominal quadrants and no history of sexually transmitted infection, pelvic inflammatory disease, vaginal discharge or bleeding, dysuria, hematuria, melena, or bright red blood per rectum. A human chorionic gonadotropin urine test was negative on intake. The HSG 48 hours prior showed no concerning findings with normal uterine cavity and normal caliber fallopian tubes bilaterally.
On physical examination, the patient’s abdomen was nondistended, nonperitonitic, and without evidence of acute trauma or surgical scars. On palpation, the patient was tender in her suprapubic region and lower abdominal quadrants without evidence of guarding or rebound
The patient’s initial laboratory tests were as follows: white blood cells, 20.1 × 103/μL (reference range, 4-11 × 103/μL); hemoglobin, 12.1 g/dL (reference range, 12.1-15.1 g/dL); hematocrit, 37.1%, (reference range, 36%-48%); alanine aminotransferase, 84 U/L (reference range, 7-56 U/L); aspartate aminotransferase, 66 U/L (reference range, 8-33 U/L); and lipase, 25 U/L (5-60 U/L). Urinalysis was notable for only 5 red blood cells and negative for white blood cells, leukocyte esterase, and nitrites. The patient’s pain and fever were controlled with 1 g IV acetaminophen.
The patient’s fever, leukocytosis, and physical examination were concerning for possible intra-abdominal processes, so a
Discussion
The patient was diagnosed with bilateral tubo-ovarian abscess (TOA) likely secondary to her HSG procedure 48 hours before. TOA is a severe infectious, inflammatory condition involving a mass of the ovaries, fallopian tubes, or adjacent tissues of the upper female genital tract.1 Traditionally, TOAs are sequelae of undiagnosed or subclinical acute or chronic pelvic inflammatory disease (PID). This is known to occur via pathogen ascension from the lower to the upper female genital tract resulting in cervicitis, endometritis, salpingitis, oophoritis, and if left untreated, peritonitis.1 About 70,000 women are diagnosed with TOAs in the US every year. These patients require hospitalization as well as IV antibiotics for gold-standard treatment; however, some cases may require percutaneous drainage based on size, severity, and location.2
Diagnostic Considerations
Clinically, patients with TOAs present with fever, chills, lower abdominal pain, vaginal discharge with cervical motion tenderness, and an adnexal mass on examination.3 When a TOA is suspected, a urine human chorionic gonadotropin test and testing for C trachomatis and N gonorrhoeae are warranted. An ED workup often reveals leukocytosis, elevated C-reactive protein, and elevated erythrocyte sedimentation rate. Imaging is recommended once a TOA is suspected. Ultrasound is the gold-standard imaging modality and boasts a sensitivity of 93% and specificity of 98% for the detection of TOAs; however, CT has also been shown to be an effective diagnostic modality.4
Despite being common, TOAs are difficult to predict, detect, and diagnose; thus the clinician must often rely on thorough history taking and physical examination to raise suspicion.5 Although most frequently associated with sexual transmission, TOAs occur in not sexually active women in adolescence and adulthood. Specifically, TOAs also can present secondary to other intra-abdominal pathologies, such as appendicitis, diverticulitis, and pyelonephritis, as well as a complication of intrauterine procedures, such as an HSG, or less commonly, following intrauterine device (IUD) insertion.5-7
Given that sexually transmitted infections are the most common etiology of TOAs, C trachomatis and N gonorrhoeae are the most likely microorganisms to be isolated (Table).8-12 In not sexually active populations, Escherichia coli and Gardnerella vaginalis should be considered instead. Although rare, women with IUDs have been shown to have an increased incidence of PID/TOA secondary to Actinomyces israleii relative to women without IUDs.12 In patients with TOAs secondary to intraabdominal surgery, anaerobic bacteria, such as Bacterioides and Peptostreptococcus species in addition to Escherichia coli, are likely culprits.11
In patients after HSG, infectious complications are uncommon enough that the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists recommends against antibiotic prophylaxis unless there are risk factors of dilated fallopian tubes or a history of PID.13 Identifying a precise percentage of TOA as a complication of HSG is rather elusive in the literature, though, it is frequently noted that infection in general is uncommon, and the risk of developing PID is about 1.4% to 3.4%.14 However, in the retrospective study most often cited, all women who developed PID following HSG had evidence of dilated fallopian tubes. Given our patient had no history of PID or dilated fallopian tubes, her risk of developing infection (PID or postprocedural abscess) would be considered very low; therefore, the index of suspicion also was low.15
Following diagnosis, the patient was promptly admitted and treated with a course of IV ceftriaxone 1 g every 24 hours, IV doxycycline 100 mg every 12 hours, and a single dose of IV metronidazole 500 mg. Her leukocytosis, fever, and pain improved within 48 hours without the need for percutaneous drainage and the patient made a complete recovery.
Complications
TOAs can carry significant morbidity and mortality, and there are both acute and chronic complications associated. Even if properly treated, TOAs can rupture leading to severe illness, such as peritonitis and septic shock. This often requires surgical intervention and hemodynamic pressure support in the intensive care unit setting.16 One of the most feared long-term complications of TOAs is infertility secondary to structural abnormalities of the female reproductive tract.10 Adhesions, strictures, and scarring are associated with TOAs irrespective of medical or surgical management, and thus any women with a history of PID or TOA require advanced fertility workup if they are having difficulties with conception or implantation.17
Minimizing infectious transmission also is essential in the treatment of TOA/PID. All women who receive a diagnosis of PID or TOA should be evaluated for gonorrhea, chlamydia, HIV, and syphilis. Women should be instructed to abstain from sexual intercourse until therapy is complete, symptoms have resolved, and sex partners have been treated for potential chlamydial or gonococcal infections. All contraceptive methods can be continued during treatment.
Conclusions
This case presented several challenges as the bilateral TOAs developed postprocedure in a patient without risk factors. Furthermore, this case did not follow the classic presentation of ascending bacterial translocation to the ovaries over days to weeks. The diagnosis was complicated by a largely benign physical examination and a pelvic examination without evidence of abnormal vaginal discharge or cervicitis. The only indicators were fever, leukocytosis, and abdominal pain in the setting of a recent, uncomplicated HSG procedure. Vigilance is required to obtain the necessary history, and the differential of TOA must be broadened to include women without a history or symptoms of a sexually transmitted infection (contrary to the classic association). We aim to encourage heightened clinical suspicion for TOAs in patients who present with fever, leukocytosis, and abdominal pain after recent HSG or other intrauterine instrumentation procedures and therefore improve patient outcomes.
1. Gkrozou F, Tsonis O, Daniilidis A, Navrozoglou I, Paschopoulos M. Tubo-ovarian abscess: exploring optimal treatment options based on current evidence. J Endometr Pelvic Pain Disord. 2020;13(1):10-19. doi:10.1177/2284026520960649
2. Taylor KJ, Wasson JF, De Graaff C, Rosenfield AT, Andriole VT. Accuracy of grey-scale ultrasound diagnosis of abdominal and pelvic abscesses in 220 patients. Lancet. 1978;1(8055):83-84. doi:10.1016/s0140-6736(78)90016-8
3. Bridwell RE, Koyfman A, Long B. High risk and low prevalence diseases: tubo-ovarian abscess. Am J Emerg Med. 2022;57:70-75. doi:10.1016/j.ajem.2022.04.026
4. Lambert MJ, Villa M. Gynecologic ultrasound in emergency medicine. Emerg Med Clin North Am. 2004;22(3):683-696. doi:10.1016/j.emc.2004.04.016
5. Munro K, Gharaibeh A, Nagabushanam S, Martin C. Diagnosis and management of tubo-ovarian abscesses. Obstet Gynaecol. 2018;20(1):11-19. doi:10.1111/tog.12447
6. Fink D, Lim PPC, Desai A, Stephans AB, Wien MA. Recurrent tubo-ovarian abscess in a nonsexually active adolescent. Consultant. 2022;62(1):e26-e28. doi:10.25270/con.2021.04.00010
7. Hiller N, Fux T, Finkelstein A, Mezeh H, Simanovsky N. CT differentiation between tubo-ovarian and appendiceal origin of right lower quadrant abscess: CT, clinical, and laboratory correlation. Emerg Radiol. 2016;23:133-139. doi:10.1007/s10140-015-1372-z
8. Kairys N, Roepke C. Tubo-ovarian abscess. In: StatPearls. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; June 12, 2023.
9. Gao Y, Qu P, Zhou Y, Ding W. Risk factors for the development of tubo-ovarian abscesses in women with ovarian endometriosis: a retrospective matched case-control study. BMC Womens Health. 2021:21:43. doi:10.1186/s12905-021-01188-6
10. Curry A, Williams T, Penny ML. Pelvic inflammatory disease: diagnosis, management, and prevention. Am Fam Physician. 2019;100(6):357-364.
11. Landers DV, Sweet RL. Tubo-ovarian abscess: contemporary approach to management. Rev Infect Dis. 1983;5(5):876-884. doi:10.1093/clinids/5.5.876
12. Burkman R, Schlesselman S, McCaffrey L, Gupta PK, Spence M. The relationship of genital tract actinomycetes and the development of pelvic inflammatory disease. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1982;143(5):585-589. doi:10.1016/0002-9378(82)90552-x
13. Armstrong C. ACOG releases guidelines on antibiotic prophylaxis for gynecologic procedures. Am Fam Physician. 2007;75(7):1094-1096.
14. Pittaway DE, Winfield AC, Maxson W, Daniell J, Herbert C, Wentz AC. Prevention of acute pelvic inflammatory disease after hysterosalpingography: efficacy of doxycycline prophylaxis. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1983;147(6):623-626. doi:10.1016/0002-9378(83)90438-6
15. Committee on Practice Bulletins—Gynecology. Prevention of Infection After Gynecologic Procedures: ACOG Practice Bulletin, Number 195. Obstet Gynecol. 2018;131(6):e172-e189. doi:10.1097/AOG.0000000000002670
16. Tao X, Ge SQ, Chen L, Cai LS, Hwang MF, Wang CL. Relationships between female infertility and female genital infections and pelvic inflammatory disease: a population-based nested controlled study. Clinics (Sao Paulo). 2018;73:e364. Published 2018 Aug 9. doi:10.6061/clinics/2018/e364
17. Fouks Y, Azem F, Many A, Cohen Y, Levin I, Cohen A. Fertility outcomes in patients with tubo-ovarian abscesses after an oocyte retrieval: a longitudinal cohort analysis. Arch Gynecol Obstet. 2019;300(3):763-769. doi:10.1007/s00404-019-05230-9
1. Gkrozou F, Tsonis O, Daniilidis A, Navrozoglou I, Paschopoulos M. Tubo-ovarian abscess: exploring optimal treatment options based on current evidence. J Endometr Pelvic Pain Disord. 2020;13(1):10-19. doi:10.1177/2284026520960649
2. Taylor KJ, Wasson JF, De Graaff C, Rosenfield AT, Andriole VT. Accuracy of grey-scale ultrasound diagnosis of abdominal and pelvic abscesses in 220 patients. Lancet. 1978;1(8055):83-84. doi:10.1016/s0140-6736(78)90016-8
3. Bridwell RE, Koyfman A, Long B. High risk and low prevalence diseases: tubo-ovarian abscess. Am J Emerg Med. 2022;57:70-75. doi:10.1016/j.ajem.2022.04.026
4. Lambert MJ, Villa M. Gynecologic ultrasound in emergency medicine. Emerg Med Clin North Am. 2004;22(3):683-696. doi:10.1016/j.emc.2004.04.016
5. Munro K, Gharaibeh A, Nagabushanam S, Martin C. Diagnosis and management of tubo-ovarian abscesses. Obstet Gynaecol. 2018;20(1):11-19. doi:10.1111/tog.12447
6. Fink D, Lim PPC, Desai A, Stephans AB, Wien MA. Recurrent tubo-ovarian abscess in a nonsexually active adolescent. Consultant. 2022;62(1):e26-e28. doi:10.25270/con.2021.04.00010
7. Hiller N, Fux T, Finkelstein A, Mezeh H, Simanovsky N. CT differentiation between tubo-ovarian and appendiceal origin of right lower quadrant abscess: CT, clinical, and laboratory correlation. Emerg Radiol. 2016;23:133-139. doi:10.1007/s10140-015-1372-z
8. Kairys N, Roepke C. Tubo-ovarian abscess. In: StatPearls. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; June 12, 2023.
9. Gao Y, Qu P, Zhou Y, Ding W. Risk factors for the development of tubo-ovarian abscesses in women with ovarian endometriosis: a retrospective matched case-control study. BMC Womens Health. 2021:21:43. doi:10.1186/s12905-021-01188-6
10. Curry A, Williams T, Penny ML. Pelvic inflammatory disease: diagnosis, management, and prevention. Am Fam Physician. 2019;100(6):357-364.
11. Landers DV, Sweet RL. Tubo-ovarian abscess: contemporary approach to management. Rev Infect Dis. 1983;5(5):876-884. doi:10.1093/clinids/5.5.876
12. Burkman R, Schlesselman S, McCaffrey L, Gupta PK, Spence M. The relationship of genital tract actinomycetes and the development of pelvic inflammatory disease. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1982;143(5):585-589. doi:10.1016/0002-9378(82)90552-x
13. Armstrong C. ACOG releases guidelines on antibiotic prophylaxis for gynecologic procedures. Am Fam Physician. 2007;75(7):1094-1096.
14. Pittaway DE, Winfield AC, Maxson W, Daniell J, Herbert C, Wentz AC. Prevention of acute pelvic inflammatory disease after hysterosalpingography: efficacy of doxycycline prophylaxis. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1983;147(6):623-626. doi:10.1016/0002-9378(83)90438-6
15. Committee on Practice Bulletins—Gynecology. Prevention of Infection After Gynecologic Procedures: ACOG Practice Bulletin, Number 195. Obstet Gynecol. 2018;131(6):e172-e189. doi:10.1097/AOG.0000000000002670
16. Tao X, Ge SQ, Chen L, Cai LS, Hwang MF, Wang CL. Relationships between female infertility and female genital infections and pelvic inflammatory disease: a population-based nested controlled study. Clinics (Sao Paulo). 2018;73:e364. Published 2018 Aug 9. doi:10.6061/clinics/2018/e364
17. Fouks Y, Azem F, Many A, Cohen Y, Levin I, Cohen A. Fertility outcomes in patients with tubo-ovarian abscesses after an oocyte retrieval: a longitudinal cohort analysis. Arch Gynecol Obstet. 2019;300(3):763-769. doi:10.1007/s00404-019-05230-9
Why aren’t doctors managing pain during gynecologic procedures?
During a fellowship rotation in gynecology, Rebekah D. Fenton, MD, asked the attending physicians what pain management options they could offer patients for insertion of an intrauterine device (IUD). Their answer surprised her: None.
The research on the effectiveness of pain management techniques during the procedure were not strong enough to warrant providing potential relief.
But Dr. Fenton knew the attending physician was wrong: She’d received the drug lidocaine during a recent visit to her own ob.gyn. to get an IUD placed. The local anesthetic enabled her to avoid the experiences of many patients who often withstand debilitating cramping and pain during insertion, side effects that can last for hours after the procedure has ended.
By not teaching her how to administer pain treatment options such as lidocaine gel or injection, “they made the decision for me, whether I could give patients this option,” said Dr. Fenton, now an adolescent medicine specialist at Alivio Medical Center in Chicago.
As a result, patients undergoing IUD placements, biopsies, hysteroscopies, and pelvic exams are often subject to pain that could be mitigated.
Some research suggests simple numbing agents, including lidocaine, may induce less pain without the need for full anesthesia. But clinicians don’t always present these options.
During gynecologic procedures, the amount of pain a patient can expect is often downplayed by clinicians. Because every patient experiences the sensation differently, discussing options for pain management and the range of possible pain is paramount in building patient-clinician trust, and ultimately providing the best care for patients in the long run, according to Megan Wasson, DO, chair of the department of medical and surgical gynecology at Mayo Clinic Arizona in Phoenix.
“It comes down to shared decision-making so the patient is aware of the pain that should be expected and what avenue they want to go down,” Dr. Wasson said. “It’s not a one-size-fits-all.”
Lack of uniform protocols
The American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists (ACOG) has clear guidelines for pain management during pregnancy and delivery but not for many routine gynecologic procedures. Some experts say not offering options for pain management based on lack of efficacy evidence can undermine a patient’s experience.
ACOG does have recommendations for reducing dilation pain during a hysteroscopy, including providing intravaginal misoprostol and estrogen. The organization also recommends performing a vaginoscopy instead if possible because the procedure is typically less painful than is a hysteroscopy.
For an IUD placement, ACOG states that the procedure “may cause temporary discomfort” and recommends that patients take over-the-counter pain relief before a procedure. The most recent clinical bulletin on the topic, published in 2016, states routine misoprostol is not recommended for IUD placement, although it may be considered with difficult insertions for management of pain.
A clinical inquiry published in 2020 outlined the efficacy of several pain options that practitioners can weigh with patients. The inquiry cited a 2019 meta-analysis of 38 studies that found lidocaine-prilocaine cream to be the most effective option for pain management during IUD placement, reducing insertion pain by nearly 30%. The inquiry concluded that a combination of 600 mcg of misoprostol and 4% lidocaine gel may be effective, while lower dosages of both drugs were not effective. A 2018 clinical trial cited in the analysis found that though a 20-cc 1% lidocaine paracervical block on its own did not reduce pain, the block mixed with sodium bicarbonate reduced pain during IUD insertion by 22%.
Some doctors make the decision to not use lidocaine without offering it to patients first, according to Dr. Fenton. Instead, clinicians should discuss any potential drawbacks, such as pain from administering the numbing agent with a needle or the procedure taking extra time while the patient waits for the lidocaine to kick in.
“That always felt unfair, to make that decision for [the patient],” Dr. Fenton said.
Often clinicians won’t know how a patient will respond to a procedure: A 2014 secondary analysis of a clinical trial compared how patients rated their pain after an IUD procedure to the amount of pain physicians perceived the procedure to cause. They found that the average pain scores patients reported were nearly twice as high as clinician expectations were.
ACOG’s guideline states that the evidence backing paracervical blocks and lidocaine to IUD insertion pain is controversial. The American College of Physicians also cites “low-quality evidence” to support patient reports of pain and discomfort during pelvic exams. Some studies have found up to 60% of women report these negative experiences.
The varying evidence highlights the need for a personalized approach – one that includes patients – to pain management for routine gynecological procedures.
“Usually patients are pretty good predictors,” said Lisa Bayer, MD, MPH, associate professor of obstetrics and gynecology at Oregon Health & Science University in Portland. “They can anticipate what different things are going to feel like based on previous experiences.”
Making patients part of the discussion
Clinicians should have open discussions with patients about their past experiences and current anxieties about a gynecologic procedure, according to Dr. Bayer.
“Part of it is just creating a really safe environment of trust as a medical provider,” she said.
A study published in 2016 of more than 800 patients undergoing oocyte retrieval, which has clear protocols for pain management, found that previous negative gynecologic experiences were significantly correlated to greater amounts of pain reported during the procedure.
If pain isn’t properly managed, patients may avoid care in the future, putting them at risk for unplanned pregnancies, skipped cancer screenings, and complications from undiagnosed conditions and infections, Dr. Bayer added. Clinician offices will not always have access to all pain management options, so making referrals to another physician who has access to the appropriate technique may be the best thing for the patient, Dr. Bayer said.
Downplaying the experience
Informing a patient that she will feel only a little discomfort during a procedure – when a clinician doesn’t know how exactly the patient will react – can also result in distrust.
When a clinician says, “ ’It’s only going to be a little cramp, it’s only going to be a little pinch,’ we know extreme pain is a possibility, we’ve seen it,” Dr. Fenton said. “But if we choose to disregard that [possibility], it feels invalidating for patients.”
Failing to fully explain the possible pain scale can also directly interfere with the procedure at hand.
“My first concern is if they aren’t anticipating the amount of pain they are going to experience, they may move; For biopsies and IUD insertions, we need them to be still,” Dr. Wasson said. “If they are unable to tolerate the procedure, we’ve put them through pain and not been able to accomplish the primary goal.”
Managing both pain and what patients can expect is even more crucial for adolescent and teenage patients who are often having their first gynecologic experience.
“We’re framing what these experiences look like,” Dr. Fenton said. “That means there are opportunities for creating a space that builds trust and security for the patients moving forward.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
During a fellowship rotation in gynecology, Rebekah D. Fenton, MD, asked the attending physicians what pain management options they could offer patients for insertion of an intrauterine device (IUD). Their answer surprised her: None.
The research on the effectiveness of pain management techniques during the procedure were not strong enough to warrant providing potential relief.
But Dr. Fenton knew the attending physician was wrong: She’d received the drug lidocaine during a recent visit to her own ob.gyn. to get an IUD placed. The local anesthetic enabled her to avoid the experiences of many patients who often withstand debilitating cramping and pain during insertion, side effects that can last for hours after the procedure has ended.
By not teaching her how to administer pain treatment options such as lidocaine gel or injection, “they made the decision for me, whether I could give patients this option,” said Dr. Fenton, now an adolescent medicine specialist at Alivio Medical Center in Chicago.
As a result, patients undergoing IUD placements, biopsies, hysteroscopies, and pelvic exams are often subject to pain that could be mitigated.
Some research suggests simple numbing agents, including lidocaine, may induce less pain without the need for full anesthesia. But clinicians don’t always present these options.
During gynecologic procedures, the amount of pain a patient can expect is often downplayed by clinicians. Because every patient experiences the sensation differently, discussing options for pain management and the range of possible pain is paramount in building patient-clinician trust, and ultimately providing the best care for patients in the long run, according to Megan Wasson, DO, chair of the department of medical and surgical gynecology at Mayo Clinic Arizona in Phoenix.
“It comes down to shared decision-making so the patient is aware of the pain that should be expected and what avenue they want to go down,” Dr. Wasson said. “It’s not a one-size-fits-all.”
Lack of uniform protocols
The American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists (ACOG) has clear guidelines for pain management during pregnancy and delivery but not for many routine gynecologic procedures. Some experts say not offering options for pain management based on lack of efficacy evidence can undermine a patient’s experience.
ACOG does have recommendations for reducing dilation pain during a hysteroscopy, including providing intravaginal misoprostol and estrogen. The organization also recommends performing a vaginoscopy instead if possible because the procedure is typically less painful than is a hysteroscopy.
For an IUD placement, ACOG states that the procedure “may cause temporary discomfort” and recommends that patients take over-the-counter pain relief before a procedure. The most recent clinical bulletin on the topic, published in 2016, states routine misoprostol is not recommended for IUD placement, although it may be considered with difficult insertions for management of pain.
A clinical inquiry published in 2020 outlined the efficacy of several pain options that practitioners can weigh with patients. The inquiry cited a 2019 meta-analysis of 38 studies that found lidocaine-prilocaine cream to be the most effective option for pain management during IUD placement, reducing insertion pain by nearly 30%. The inquiry concluded that a combination of 600 mcg of misoprostol and 4% lidocaine gel may be effective, while lower dosages of both drugs were not effective. A 2018 clinical trial cited in the analysis found that though a 20-cc 1% lidocaine paracervical block on its own did not reduce pain, the block mixed with sodium bicarbonate reduced pain during IUD insertion by 22%.
Some doctors make the decision to not use lidocaine without offering it to patients first, according to Dr. Fenton. Instead, clinicians should discuss any potential drawbacks, such as pain from administering the numbing agent with a needle or the procedure taking extra time while the patient waits for the lidocaine to kick in.
“That always felt unfair, to make that decision for [the patient],” Dr. Fenton said.
Often clinicians won’t know how a patient will respond to a procedure: A 2014 secondary analysis of a clinical trial compared how patients rated their pain after an IUD procedure to the amount of pain physicians perceived the procedure to cause. They found that the average pain scores patients reported were nearly twice as high as clinician expectations were.
ACOG’s guideline states that the evidence backing paracervical blocks and lidocaine to IUD insertion pain is controversial. The American College of Physicians also cites “low-quality evidence” to support patient reports of pain and discomfort during pelvic exams. Some studies have found up to 60% of women report these negative experiences.
The varying evidence highlights the need for a personalized approach – one that includes patients – to pain management for routine gynecological procedures.
“Usually patients are pretty good predictors,” said Lisa Bayer, MD, MPH, associate professor of obstetrics and gynecology at Oregon Health & Science University in Portland. “They can anticipate what different things are going to feel like based on previous experiences.”
Making patients part of the discussion
Clinicians should have open discussions with patients about their past experiences and current anxieties about a gynecologic procedure, according to Dr. Bayer.
“Part of it is just creating a really safe environment of trust as a medical provider,” she said.
A study published in 2016 of more than 800 patients undergoing oocyte retrieval, which has clear protocols for pain management, found that previous negative gynecologic experiences were significantly correlated to greater amounts of pain reported during the procedure.
If pain isn’t properly managed, patients may avoid care in the future, putting them at risk for unplanned pregnancies, skipped cancer screenings, and complications from undiagnosed conditions and infections, Dr. Bayer added. Clinician offices will not always have access to all pain management options, so making referrals to another physician who has access to the appropriate technique may be the best thing for the patient, Dr. Bayer said.
Downplaying the experience
Informing a patient that she will feel only a little discomfort during a procedure – when a clinician doesn’t know how exactly the patient will react – can also result in distrust.
When a clinician says, “ ’It’s only going to be a little cramp, it’s only going to be a little pinch,’ we know extreme pain is a possibility, we’ve seen it,” Dr. Fenton said. “But if we choose to disregard that [possibility], it feels invalidating for patients.”
Failing to fully explain the possible pain scale can also directly interfere with the procedure at hand.
“My first concern is if they aren’t anticipating the amount of pain they are going to experience, they may move; For biopsies and IUD insertions, we need them to be still,” Dr. Wasson said. “If they are unable to tolerate the procedure, we’ve put them through pain and not been able to accomplish the primary goal.”
Managing both pain and what patients can expect is even more crucial for adolescent and teenage patients who are often having their first gynecologic experience.
“We’re framing what these experiences look like,” Dr. Fenton said. “That means there are opportunities for creating a space that builds trust and security for the patients moving forward.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
During a fellowship rotation in gynecology, Rebekah D. Fenton, MD, asked the attending physicians what pain management options they could offer patients for insertion of an intrauterine device (IUD). Their answer surprised her: None.
The research on the effectiveness of pain management techniques during the procedure were not strong enough to warrant providing potential relief.
But Dr. Fenton knew the attending physician was wrong: She’d received the drug lidocaine during a recent visit to her own ob.gyn. to get an IUD placed. The local anesthetic enabled her to avoid the experiences of many patients who often withstand debilitating cramping and pain during insertion, side effects that can last for hours after the procedure has ended.
By not teaching her how to administer pain treatment options such as lidocaine gel or injection, “they made the decision for me, whether I could give patients this option,” said Dr. Fenton, now an adolescent medicine specialist at Alivio Medical Center in Chicago.
As a result, patients undergoing IUD placements, biopsies, hysteroscopies, and pelvic exams are often subject to pain that could be mitigated.
Some research suggests simple numbing agents, including lidocaine, may induce less pain without the need for full anesthesia. But clinicians don’t always present these options.
During gynecologic procedures, the amount of pain a patient can expect is often downplayed by clinicians. Because every patient experiences the sensation differently, discussing options for pain management and the range of possible pain is paramount in building patient-clinician trust, and ultimately providing the best care for patients in the long run, according to Megan Wasson, DO, chair of the department of medical and surgical gynecology at Mayo Clinic Arizona in Phoenix.
“It comes down to shared decision-making so the patient is aware of the pain that should be expected and what avenue they want to go down,” Dr. Wasson said. “It’s not a one-size-fits-all.”
Lack of uniform protocols
The American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists (ACOG) has clear guidelines for pain management during pregnancy and delivery but not for many routine gynecologic procedures. Some experts say not offering options for pain management based on lack of efficacy evidence can undermine a patient’s experience.
ACOG does have recommendations for reducing dilation pain during a hysteroscopy, including providing intravaginal misoprostol and estrogen. The organization also recommends performing a vaginoscopy instead if possible because the procedure is typically less painful than is a hysteroscopy.
For an IUD placement, ACOG states that the procedure “may cause temporary discomfort” and recommends that patients take over-the-counter pain relief before a procedure. The most recent clinical bulletin on the topic, published in 2016, states routine misoprostol is not recommended for IUD placement, although it may be considered with difficult insertions for management of pain.
A clinical inquiry published in 2020 outlined the efficacy of several pain options that practitioners can weigh with patients. The inquiry cited a 2019 meta-analysis of 38 studies that found lidocaine-prilocaine cream to be the most effective option for pain management during IUD placement, reducing insertion pain by nearly 30%. The inquiry concluded that a combination of 600 mcg of misoprostol and 4% lidocaine gel may be effective, while lower dosages of both drugs were not effective. A 2018 clinical trial cited in the analysis found that though a 20-cc 1% lidocaine paracervical block on its own did not reduce pain, the block mixed with sodium bicarbonate reduced pain during IUD insertion by 22%.
Some doctors make the decision to not use lidocaine without offering it to patients first, according to Dr. Fenton. Instead, clinicians should discuss any potential drawbacks, such as pain from administering the numbing agent with a needle or the procedure taking extra time while the patient waits for the lidocaine to kick in.
“That always felt unfair, to make that decision for [the patient],” Dr. Fenton said.
Often clinicians won’t know how a patient will respond to a procedure: A 2014 secondary analysis of a clinical trial compared how patients rated their pain after an IUD procedure to the amount of pain physicians perceived the procedure to cause. They found that the average pain scores patients reported were nearly twice as high as clinician expectations were.
ACOG’s guideline states that the evidence backing paracervical blocks and lidocaine to IUD insertion pain is controversial. The American College of Physicians also cites “low-quality evidence” to support patient reports of pain and discomfort during pelvic exams. Some studies have found up to 60% of women report these negative experiences.
The varying evidence highlights the need for a personalized approach – one that includes patients – to pain management for routine gynecological procedures.
“Usually patients are pretty good predictors,” said Lisa Bayer, MD, MPH, associate professor of obstetrics and gynecology at Oregon Health & Science University in Portland. “They can anticipate what different things are going to feel like based on previous experiences.”
Making patients part of the discussion
Clinicians should have open discussions with patients about their past experiences and current anxieties about a gynecologic procedure, according to Dr. Bayer.
“Part of it is just creating a really safe environment of trust as a medical provider,” she said.
A study published in 2016 of more than 800 patients undergoing oocyte retrieval, which has clear protocols for pain management, found that previous negative gynecologic experiences were significantly correlated to greater amounts of pain reported during the procedure.
If pain isn’t properly managed, patients may avoid care in the future, putting them at risk for unplanned pregnancies, skipped cancer screenings, and complications from undiagnosed conditions and infections, Dr. Bayer added. Clinician offices will not always have access to all pain management options, so making referrals to another physician who has access to the appropriate technique may be the best thing for the patient, Dr. Bayer said.
Downplaying the experience
Informing a patient that she will feel only a little discomfort during a procedure – when a clinician doesn’t know how exactly the patient will react – can also result in distrust.
When a clinician says, “ ’It’s only going to be a little cramp, it’s only going to be a little pinch,’ we know extreme pain is a possibility, we’ve seen it,” Dr. Fenton said. “But if we choose to disregard that [possibility], it feels invalidating for patients.”
Failing to fully explain the possible pain scale can also directly interfere with the procedure at hand.
“My first concern is if they aren’t anticipating the amount of pain they are going to experience, they may move; For biopsies and IUD insertions, we need them to be still,” Dr. Wasson said. “If they are unable to tolerate the procedure, we’ve put them through pain and not been able to accomplish the primary goal.”
Managing both pain and what patients can expect is even more crucial for adolescent and teenage patients who are often having their first gynecologic experience.
“We’re framing what these experiences look like,” Dr. Fenton said. “That means there are opportunities for creating a space that builds trust and security for the patients moving forward.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Perinatal depression rarely stands alone
Mental health conditions are the leading cause of pregnancy-related death in Illinois (40%) and across the United States (21%).1,2 Funding bodies, such as the Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality3 and the Health Resources and Service Administration,4 have spotlights on improving screening and access to care for depression and substance use disorders (SUDs). However, the needs of individuals with multiple mental health conditions still often go unrecognized and unaddressed in perinatal health settings.
The U.S. Preventive Services Task Force recommends that all adults be screened for depression, alcohol use, and drug use, and will be recommending screening for anxiety.5,6 The American College of Obstetrics and Gynecology recommends screening for perinatal mental health conditions including depression, anxiety, bipolar disorder, acute postpartum psychosis, and suicidality; however, despite these recommendations, screening and treatment for comorbid mental health disorders during pregnancy and the postpartum is not standard practice.7
Addressing perinatal mental health is critical because untreated mental health conditions during the perinatal period can cause long-term adverse psychiatric and medical outcomes for the birthing person, the baby, and the family.8 This commentary highlights the importance of recognizing and screening for perinatal mental health comorbidities, improving referral rates for mental health treatment, and raising awareness of the importance of addressing rural perinatal mental health.
Perinatal mental health comorbidities
Major depressive disorder is the most common mental health condition during the perinatal period9 and is often comorbid.10-12 In “Perinatal mental health in low-income urban and rural patients: The importance of screening for comorbidities,” Craemer et al.13 reported that nearly half of the perinatal patients who screened positive for MDD also screened positive for at least one other mental health condition, among them general anxiety disorder (GAD), SUD, posttraumatic stress disorder (PTSD), and suicidality.
Many (9%) of the perinatal patients with MDD had a severe comorbidity profile characterized by four diagnoses – MDD, GAD, SUD, and PTSD. In routine medical care these comorbidities often go undetected even though the risk to mothers and babies increases with more severe mental health symptoms.8
The high frequency of perinatal mental health comorbidities Craemer et al.13 found demonstrates a compelling need for comorbid mental health screening during the perinatal period, particularly for low-income Black, Hispanic, and rural birthing persons. Positive screens for perinatal mental health disorders may reflect the onset of these disorders in pregnancy or the postpartum, or preexisting disorders that have gone undetected or untreated before pregnancy.
For many patients, the perinatal period is the first time they are screened for any mental health disorder; typically, they are screened solely for depression. Screening alone can have a positive impact on perinatal mental health. In fact, the USPSTF found that programs to screen perinatal patients, with or without treatment-related support, resulted in a 2%-9% absolute reduction in depression prevalence.14 However, screening for MDD is too infrequent for many reasons, including the logistics of integrating screening into the clinic workflow and limited provider availability, time, and training in mental health.
We recommend screening perinatal patients for mental health comorbidities. This recommendation may seem impractical given the lack of screening tools for comorbid mental health conditions; however, the Computerized Adaptive Test for Mental Health (CAT-MH), the validated tool15-17 used in this study, is an ideal option. CAT-MH is uniquely capable of screening for MDD, GAD, PTSD, SUD, and suicidality in one platform and is routinely used in diverse settings including the Veterans Administration,18 foster care,19 and universities.20 The main limitation of this more comprehensive screening is that it takes about 10 minutes per patient. However, CAT-MH is self-administered and can be done in the waiting room or on a mobile device prior to a clinic visit.
CAT-MH can also be easily integrated into clinical workflow when added to the Electronic Medical Record21, and is a more comprehensive tool than existing perinatal depression tools such as the Perinatal Health Questionaire-9 (PHQ-9) and Edinburgh Perinatal Depression Scale (EPDS).22 Another limitation is cost – currently $5.00 per assessment – however, this is less than routine blood work.23 If CAT-MH is not an option, we recommend a stepped approach of screening for GAD when perinatal patients screen positive for MDD, as this is the most common comorbidity profile. The GAD-7 is a free and widely available tool.24
Barriers to care
In Craemer et al,13 nearly two-thirds (64.9%) of perinatal patients with a positive screen did not receive a referral to follow-up care or a medication prescription. These low referral rates may reflect a variety of widely recognized barriers to care, including lack of referral options, provider and/or patient reluctance to pursue referrals, barriers to insurance coverage, or inadequate behavioral health infrastructure to ensure referral and diagnostic follow-up.
Further, rural residing perinatal patients are an underserved population that need more resources and screening. Despite an on-site behavioral specialist at the rural clinic, Craemer et al13 found a stark disparity in referral rates: referrals to treatment for a positive diagnosis was over two times less at the rural clinic (23.9%), compared with the urban clinics (51.6%). The most common treatment offered at the rural clinic was a prescription for medication (17.4%), while referral to follow-up care was the most common at the urban clinics (35.5%). Rural areas not only have a shortage of health care providers, but community members seeking mental health care often encounter greater stigma, compared with urban residents.25,26
These data highlight an unmet need for referrals to treatment for patients in rural communities, particularly in Illinois where the pregnancy-related mortality ratio attributable to mental health conditions is three times greater in rural areas, compared with those residing in urban Cook County (Chicago).2 Increasing access and availability to mental health treatment and prevention resources in Illinois, especially in rural areas, is an opportunity to prevent pregnancy-related mortality attributable to mental health conditions.
Overall, there is a critical need for screening for perinatal mental health comorbidities, increased attention to low rates of referral to mental health treatment, and investing in rural perinatal mental health. Addressing perinatal mental health disorders is key to decreasing the burden of maternal mortality, particularly in Illinois.
Ms. Craemer and Ms. Sayah are senior research specialists at the Center for Research on Women & Gender, University of Illinois at Chicago. Dr. Duffecy is a professor of clinical psychiatry at the University of Illinois at Chicago. Dr. Geller is a professor of obstetrics & gynecology and director of the Center for Research on Women & Gender, University of Illinois at Chicago. Dr. Maki is a professor of psychiatry, psychology, and obstetrics & gynecology at the University of Illinois at Chicago.
References
1. Trost S et al. Pregnancy-related deaths: Data from maternal mortality review committees in 36 states, 2017-2019. Atlanta: Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, U.S. Department of Health & Human Services, 2022.
2. Illinois Department of Public Health. Illinois maternal morbidity and mortality report 2016-2017. 2021.
3. AHRQ. Funding opportunities to address opioid and other substance use disorders. Updated 2023.
4. HRSA. Screening and treatment for maternal mental health and substance use disorders.
5. U.S. Preventive Services Task Force. Recommendations for primary care practice. Accessed May 26, 2023.
6. U.S. Preventive Services Task Force. Draft recommendation statement: Anxiety in adults: Screening. 2022.
7. ACOG. Screening and diagnosis of mental health conditions during pregnancy and postpartum. Clinical Practice Guideline. Number 4. 2023 June.
8. Meltzer-Brody S and Stuebe A. The long-term psychiatric and medical prognosis of perinatal mental illness. Best Pract Res Clin Obstet Gynaecol. 2014 Jan. doi: 10.1016/j.bpobgyn.2013.08.009.
9. Van Niel MS and Payne JL. Perinatal depression: A review. Cleve Clin J Med. 2020 May. doi: 10.3949/ccjm.87a.19054.
10. Wisner KL et al. Onset timing, thoughts of self-harm, and diagnoses in postpartum women with screen-positive depression findings. 2013 May. doi: 10.1001/jamapsychiatry.2013.87.
11. Falah-Hassani K et al. The prevalence of antenatal and postnatal co-morbid anxiety and depression: A meta-analysis. Psychol Med. 2017 Sep. doi: 10.1017/S0033291717000617.
12. Pentecost R et al. Scoping review of the associations between perinatal substance use and perinatal depression and anxiety. J Obstet Gynecol Neonatal Nurs. 2021 Jul. doi: 10.1016/j.jogn.2021.02.008.
13. Craemer KA et al. Perinatal mental health in low-income urban and rural patients: The importance of screening for comorbidities. Gen Hosp Psychiatry. 2023 Jul-Aug. doi: 10.1016/j.genhosppsych.2023.05.007.
14. O’Connor E et al. Primary care screening for and treatment of depression in pregnant and postpartum women: Evidence report and systematic review for the U.S. Preventive Services Task Force. JAMA. 2016 Jan 26. doi: 10.1001/jama.2015.18948.
15. Kozhimannil KB et al. Racial and ethnic disparities in postpartum depression care among low-income women. Psychiatr Serv. 2011 Jun. doi: 10.1176/ps.62.6.pss6206_0619.
16. Wenzel ES et al. Depression and anxiety symptoms across pregnancy and the postpartum in low-income Black and Latina women. Arch Womens Ment Health. 2021 Dec. doi: 10.1007/s00737-021-01139-y.
17. Gibbons RD et al. Development of a computerized adaptive substance use disorder scale for screening and measurement: The CAT‐SUD. Addiction. 2020 Jul. doi: 10.1111/add.14938.
18. Brenner LA et al. Validation of a computerized adaptive test suicide scale (CAT-SS) among united states military veterans. PloS One. 2022 Jan 21. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0261920.
19. The Center for State Child Welfare Data. Using technology to diagnose and report on behavioral health challenges facing foster youth. 2018.
20. Kim JJ et al. The experience of depression, anxiety, and mania among perinatal women. Arch Womens Ment Health. 2016 Oct. doi: 10.1007/s00737-016-0632-6.
21. Tepper MC et al. Toward population health: Using a learning behavioral health system and measurement-based care to improve access, care, outcomes, and disparities. Community Ment Health J. 2022 Nov. doi: 10.1007/s10597-022-00957-3.
22. Wenzel E et al. Using computerised adaptive tests to screen for perinatal depression in underserved women of colour. Evid Based Ment Health. 2022 Feb. doi: 10.1136/ebmental-2021-300262.
23. Sanger-Katz M. They want it to be secret: How a common blood test can cost $11 or almost $1,000. New York Times. 2019 Apr 19.
24. Spitzer RL et al. A brief measure for assessing generalized anxiety disorder: The GAD-7. Arch Intern Med. 2006 May 22. doi: 10.1001/archinte.166.10.1092.
25. Mollard E et al. An integrative review of postpartum depression in rural US communities. Arch Psychiatr Nurs. 2016 Jun. doi: 10.1016/j.apnu.2015.12.003.
26. Anglim AJ and Radke SM. Rural maternal health care outcomes, drivers, and patient perspectives. Clin Obstet Gynecol. 2022 Dec 1. doi: 10.1097/GRF.0000000000000753.
Mental health conditions are the leading cause of pregnancy-related death in Illinois (40%) and across the United States (21%).1,2 Funding bodies, such as the Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality3 and the Health Resources and Service Administration,4 have spotlights on improving screening and access to care for depression and substance use disorders (SUDs). However, the needs of individuals with multiple mental health conditions still often go unrecognized and unaddressed in perinatal health settings.
The U.S. Preventive Services Task Force recommends that all adults be screened for depression, alcohol use, and drug use, and will be recommending screening for anxiety.5,6 The American College of Obstetrics and Gynecology recommends screening for perinatal mental health conditions including depression, anxiety, bipolar disorder, acute postpartum psychosis, and suicidality; however, despite these recommendations, screening and treatment for comorbid mental health disorders during pregnancy and the postpartum is not standard practice.7
Addressing perinatal mental health is critical because untreated mental health conditions during the perinatal period can cause long-term adverse psychiatric and medical outcomes for the birthing person, the baby, and the family.8 This commentary highlights the importance of recognizing and screening for perinatal mental health comorbidities, improving referral rates for mental health treatment, and raising awareness of the importance of addressing rural perinatal mental health.
Perinatal mental health comorbidities
Major depressive disorder is the most common mental health condition during the perinatal period9 and is often comorbid.10-12 In “Perinatal mental health in low-income urban and rural patients: The importance of screening for comorbidities,” Craemer et al.13 reported that nearly half of the perinatal patients who screened positive for MDD also screened positive for at least one other mental health condition, among them general anxiety disorder (GAD), SUD, posttraumatic stress disorder (PTSD), and suicidality.
Many (9%) of the perinatal patients with MDD had a severe comorbidity profile characterized by four diagnoses – MDD, GAD, SUD, and PTSD. In routine medical care these comorbidities often go undetected even though the risk to mothers and babies increases with more severe mental health symptoms.8
The high frequency of perinatal mental health comorbidities Craemer et al.13 found demonstrates a compelling need for comorbid mental health screening during the perinatal period, particularly for low-income Black, Hispanic, and rural birthing persons. Positive screens for perinatal mental health disorders may reflect the onset of these disorders in pregnancy or the postpartum, or preexisting disorders that have gone undetected or untreated before pregnancy.
For many patients, the perinatal period is the first time they are screened for any mental health disorder; typically, they are screened solely for depression. Screening alone can have a positive impact on perinatal mental health. In fact, the USPSTF found that programs to screen perinatal patients, with or without treatment-related support, resulted in a 2%-9% absolute reduction in depression prevalence.14 However, screening for MDD is too infrequent for many reasons, including the logistics of integrating screening into the clinic workflow and limited provider availability, time, and training in mental health.
We recommend screening perinatal patients for mental health comorbidities. This recommendation may seem impractical given the lack of screening tools for comorbid mental health conditions; however, the Computerized Adaptive Test for Mental Health (CAT-MH), the validated tool15-17 used in this study, is an ideal option. CAT-MH is uniquely capable of screening for MDD, GAD, PTSD, SUD, and suicidality in one platform and is routinely used in diverse settings including the Veterans Administration,18 foster care,19 and universities.20 The main limitation of this more comprehensive screening is that it takes about 10 minutes per patient. However, CAT-MH is self-administered and can be done in the waiting room or on a mobile device prior to a clinic visit.
CAT-MH can also be easily integrated into clinical workflow when added to the Electronic Medical Record21, and is a more comprehensive tool than existing perinatal depression tools such as the Perinatal Health Questionaire-9 (PHQ-9) and Edinburgh Perinatal Depression Scale (EPDS).22 Another limitation is cost – currently $5.00 per assessment – however, this is less than routine blood work.23 If CAT-MH is not an option, we recommend a stepped approach of screening for GAD when perinatal patients screen positive for MDD, as this is the most common comorbidity profile. The GAD-7 is a free and widely available tool.24
Barriers to care
In Craemer et al,13 nearly two-thirds (64.9%) of perinatal patients with a positive screen did not receive a referral to follow-up care or a medication prescription. These low referral rates may reflect a variety of widely recognized barriers to care, including lack of referral options, provider and/or patient reluctance to pursue referrals, barriers to insurance coverage, or inadequate behavioral health infrastructure to ensure referral and diagnostic follow-up.
Further, rural residing perinatal patients are an underserved population that need more resources and screening. Despite an on-site behavioral specialist at the rural clinic, Craemer et al13 found a stark disparity in referral rates: referrals to treatment for a positive diagnosis was over two times less at the rural clinic (23.9%), compared with the urban clinics (51.6%). The most common treatment offered at the rural clinic was a prescription for medication (17.4%), while referral to follow-up care was the most common at the urban clinics (35.5%). Rural areas not only have a shortage of health care providers, but community members seeking mental health care often encounter greater stigma, compared with urban residents.25,26
These data highlight an unmet need for referrals to treatment for patients in rural communities, particularly in Illinois where the pregnancy-related mortality ratio attributable to mental health conditions is three times greater in rural areas, compared with those residing in urban Cook County (Chicago).2 Increasing access and availability to mental health treatment and prevention resources in Illinois, especially in rural areas, is an opportunity to prevent pregnancy-related mortality attributable to mental health conditions.
Overall, there is a critical need for screening for perinatal mental health comorbidities, increased attention to low rates of referral to mental health treatment, and investing in rural perinatal mental health. Addressing perinatal mental health disorders is key to decreasing the burden of maternal mortality, particularly in Illinois.
Ms. Craemer and Ms. Sayah are senior research specialists at the Center for Research on Women & Gender, University of Illinois at Chicago. Dr. Duffecy is a professor of clinical psychiatry at the University of Illinois at Chicago. Dr. Geller is a professor of obstetrics & gynecology and director of the Center for Research on Women & Gender, University of Illinois at Chicago. Dr. Maki is a professor of psychiatry, psychology, and obstetrics & gynecology at the University of Illinois at Chicago.
References
1. Trost S et al. Pregnancy-related deaths: Data from maternal mortality review committees in 36 states, 2017-2019. Atlanta: Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, U.S. Department of Health & Human Services, 2022.
2. Illinois Department of Public Health. Illinois maternal morbidity and mortality report 2016-2017. 2021.
3. AHRQ. Funding opportunities to address opioid and other substance use disorders. Updated 2023.
4. HRSA. Screening and treatment for maternal mental health and substance use disorders.
5. U.S. Preventive Services Task Force. Recommendations for primary care practice. Accessed May 26, 2023.
6. U.S. Preventive Services Task Force. Draft recommendation statement: Anxiety in adults: Screening. 2022.
7. ACOG. Screening and diagnosis of mental health conditions during pregnancy and postpartum. Clinical Practice Guideline. Number 4. 2023 June.
8. Meltzer-Brody S and Stuebe A. The long-term psychiatric and medical prognosis of perinatal mental illness. Best Pract Res Clin Obstet Gynaecol. 2014 Jan. doi: 10.1016/j.bpobgyn.2013.08.009.
9. Van Niel MS and Payne JL. Perinatal depression: A review. Cleve Clin J Med. 2020 May. doi: 10.3949/ccjm.87a.19054.
10. Wisner KL et al. Onset timing, thoughts of self-harm, and diagnoses in postpartum women with screen-positive depression findings. 2013 May. doi: 10.1001/jamapsychiatry.2013.87.
11. Falah-Hassani K et al. The prevalence of antenatal and postnatal co-morbid anxiety and depression: A meta-analysis. Psychol Med. 2017 Sep. doi: 10.1017/S0033291717000617.
12. Pentecost R et al. Scoping review of the associations between perinatal substance use and perinatal depression and anxiety. J Obstet Gynecol Neonatal Nurs. 2021 Jul. doi: 10.1016/j.jogn.2021.02.008.
13. Craemer KA et al. Perinatal mental health in low-income urban and rural patients: The importance of screening for comorbidities. Gen Hosp Psychiatry. 2023 Jul-Aug. doi: 10.1016/j.genhosppsych.2023.05.007.
14. O’Connor E et al. Primary care screening for and treatment of depression in pregnant and postpartum women: Evidence report and systematic review for the U.S. Preventive Services Task Force. JAMA. 2016 Jan 26. doi: 10.1001/jama.2015.18948.
15. Kozhimannil KB et al. Racial and ethnic disparities in postpartum depression care among low-income women. Psychiatr Serv. 2011 Jun. doi: 10.1176/ps.62.6.pss6206_0619.
16. Wenzel ES et al. Depression and anxiety symptoms across pregnancy and the postpartum in low-income Black and Latina women. Arch Womens Ment Health. 2021 Dec. doi: 10.1007/s00737-021-01139-y.
17. Gibbons RD et al. Development of a computerized adaptive substance use disorder scale for screening and measurement: The CAT‐SUD. Addiction. 2020 Jul. doi: 10.1111/add.14938.
18. Brenner LA et al. Validation of a computerized adaptive test suicide scale (CAT-SS) among united states military veterans. PloS One. 2022 Jan 21. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0261920.
19. The Center for State Child Welfare Data. Using technology to diagnose and report on behavioral health challenges facing foster youth. 2018.
20. Kim JJ et al. The experience of depression, anxiety, and mania among perinatal women. Arch Womens Ment Health. 2016 Oct. doi: 10.1007/s00737-016-0632-6.
21. Tepper MC et al. Toward population health: Using a learning behavioral health system and measurement-based care to improve access, care, outcomes, and disparities. Community Ment Health J. 2022 Nov. doi: 10.1007/s10597-022-00957-3.
22. Wenzel E et al. Using computerised adaptive tests to screen for perinatal depression in underserved women of colour. Evid Based Ment Health. 2022 Feb. doi: 10.1136/ebmental-2021-300262.
23. Sanger-Katz M. They want it to be secret: How a common blood test can cost $11 or almost $1,000. New York Times. 2019 Apr 19.
24. Spitzer RL et al. A brief measure for assessing generalized anxiety disorder: The GAD-7. Arch Intern Med. 2006 May 22. doi: 10.1001/archinte.166.10.1092.
25. Mollard E et al. An integrative review of postpartum depression in rural US communities. Arch Psychiatr Nurs. 2016 Jun. doi: 10.1016/j.apnu.2015.12.003.
26. Anglim AJ and Radke SM. Rural maternal health care outcomes, drivers, and patient perspectives. Clin Obstet Gynecol. 2022 Dec 1. doi: 10.1097/GRF.0000000000000753.
Mental health conditions are the leading cause of pregnancy-related death in Illinois (40%) and across the United States (21%).1,2 Funding bodies, such as the Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality3 and the Health Resources and Service Administration,4 have spotlights on improving screening and access to care for depression and substance use disorders (SUDs). However, the needs of individuals with multiple mental health conditions still often go unrecognized and unaddressed in perinatal health settings.
The U.S. Preventive Services Task Force recommends that all adults be screened for depression, alcohol use, and drug use, and will be recommending screening for anxiety.5,6 The American College of Obstetrics and Gynecology recommends screening for perinatal mental health conditions including depression, anxiety, bipolar disorder, acute postpartum psychosis, and suicidality; however, despite these recommendations, screening and treatment for comorbid mental health disorders during pregnancy and the postpartum is not standard practice.7
Addressing perinatal mental health is critical because untreated mental health conditions during the perinatal period can cause long-term adverse psychiatric and medical outcomes for the birthing person, the baby, and the family.8 This commentary highlights the importance of recognizing and screening for perinatal mental health comorbidities, improving referral rates for mental health treatment, and raising awareness of the importance of addressing rural perinatal mental health.
Perinatal mental health comorbidities
Major depressive disorder is the most common mental health condition during the perinatal period9 and is often comorbid.10-12 In “Perinatal mental health in low-income urban and rural patients: The importance of screening for comorbidities,” Craemer et al.13 reported that nearly half of the perinatal patients who screened positive for MDD also screened positive for at least one other mental health condition, among them general anxiety disorder (GAD), SUD, posttraumatic stress disorder (PTSD), and suicidality.
Many (9%) of the perinatal patients with MDD had a severe comorbidity profile characterized by four diagnoses – MDD, GAD, SUD, and PTSD. In routine medical care these comorbidities often go undetected even though the risk to mothers and babies increases with more severe mental health symptoms.8
The high frequency of perinatal mental health comorbidities Craemer et al.13 found demonstrates a compelling need for comorbid mental health screening during the perinatal period, particularly for low-income Black, Hispanic, and rural birthing persons. Positive screens for perinatal mental health disorders may reflect the onset of these disorders in pregnancy or the postpartum, or preexisting disorders that have gone undetected or untreated before pregnancy.
For many patients, the perinatal period is the first time they are screened for any mental health disorder; typically, they are screened solely for depression. Screening alone can have a positive impact on perinatal mental health. In fact, the USPSTF found that programs to screen perinatal patients, with or without treatment-related support, resulted in a 2%-9% absolute reduction in depression prevalence.14 However, screening for MDD is too infrequent for many reasons, including the logistics of integrating screening into the clinic workflow and limited provider availability, time, and training in mental health.
We recommend screening perinatal patients for mental health comorbidities. This recommendation may seem impractical given the lack of screening tools for comorbid mental health conditions; however, the Computerized Adaptive Test for Mental Health (CAT-MH), the validated tool15-17 used in this study, is an ideal option. CAT-MH is uniquely capable of screening for MDD, GAD, PTSD, SUD, and suicidality in one platform and is routinely used in diverse settings including the Veterans Administration,18 foster care,19 and universities.20 The main limitation of this more comprehensive screening is that it takes about 10 minutes per patient. However, CAT-MH is self-administered and can be done in the waiting room or on a mobile device prior to a clinic visit.
CAT-MH can also be easily integrated into clinical workflow when added to the Electronic Medical Record21, and is a more comprehensive tool than existing perinatal depression tools such as the Perinatal Health Questionaire-9 (PHQ-9) and Edinburgh Perinatal Depression Scale (EPDS).22 Another limitation is cost – currently $5.00 per assessment – however, this is less than routine blood work.23 If CAT-MH is not an option, we recommend a stepped approach of screening for GAD when perinatal patients screen positive for MDD, as this is the most common comorbidity profile. The GAD-7 is a free and widely available tool.24
Barriers to care
In Craemer et al,13 nearly two-thirds (64.9%) of perinatal patients with a positive screen did not receive a referral to follow-up care or a medication prescription. These low referral rates may reflect a variety of widely recognized barriers to care, including lack of referral options, provider and/or patient reluctance to pursue referrals, barriers to insurance coverage, or inadequate behavioral health infrastructure to ensure referral and diagnostic follow-up.
Further, rural residing perinatal patients are an underserved population that need more resources and screening. Despite an on-site behavioral specialist at the rural clinic, Craemer et al13 found a stark disparity in referral rates: referrals to treatment for a positive diagnosis was over two times less at the rural clinic (23.9%), compared with the urban clinics (51.6%). The most common treatment offered at the rural clinic was a prescription for medication (17.4%), while referral to follow-up care was the most common at the urban clinics (35.5%). Rural areas not only have a shortage of health care providers, but community members seeking mental health care often encounter greater stigma, compared with urban residents.25,26
These data highlight an unmet need for referrals to treatment for patients in rural communities, particularly in Illinois where the pregnancy-related mortality ratio attributable to mental health conditions is three times greater in rural areas, compared with those residing in urban Cook County (Chicago).2 Increasing access and availability to mental health treatment and prevention resources in Illinois, especially in rural areas, is an opportunity to prevent pregnancy-related mortality attributable to mental health conditions.
Overall, there is a critical need for screening for perinatal mental health comorbidities, increased attention to low rates of referral to mental health treatment, and investing in rural perinatal mental health. Addressing perinatal mental health disorders is key to decreasing the burden of maternal mortality, particularly in Illinois.
Ms. Craemer and Ms. Sayah are senior research specialists at the Center for Research on Women & Gender, University of Illinois at Chicago. Dr. Duffecy is a professor of clinical psychiatry at the University of Illinois at Chicago. Dr. Geller is a professor of obstetrics & gynecology and director of the Center for Research on Women & Gender, University of Illinois at Chicago. Dr. Maki is a professor of psychiatry, psychology, and obstetrics & gynecology at the University of Illinois at Chicago.
References
1. Trost S et al. Pregnancy-related deaths: Data from maternal mortality review committees in 36 states, 2017-2019. Atlanta: Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, U.S. Department of Health & Human Services, 2022.
2. Illinois Department of Public Health. Illinois maternal morbidity and mortality report 2016-2017. 2021.
3. AHRQ. Funding opportunities to address opioid and other substance use disorders. Updated 2023.
4. HRSA. Screening and treatment for maternal mental health and substance use disorders.
5. U.S. Preventive Services Task Force. Recommendations for primary care practice. Accessed May 26, 2023.
6. U.S. Preventive Services Task Force. Draft recommendation statement: Anxiety in adults: Screening. 2022.
7. ACOG. Screening and diagnosis of mental health conditions during pregnancy and postpartum. Clinical Practice Guideline. Number 4. 2023 June.
8. Meltzer-Brody S and Stuebe A. The long-term psychiatric and medical prognosis of perinatal mental illness. Best Pract Res Clin Obstet Gynaecol. 2014 Jan. doi: 10.1016/j.bpobgyn.2013.08.009.
9. Van Niel MS and Payne JL. Perinatal depression: A review. Cleve Clin J Med. 2020 May. doi: 10.3949/ccjm.87a.19054.
10. Wisner KL et al. Onset timing, thoughts of self-harm, and diagnoses in postpartum women with screen-positive depression findings. 2013 May. doi: 10.1001/jamapsychiatry.2013.87.
11. Falah-Hassani K et al. The prevalence of antenatal and postnatal co-morbid anxiety and depression: A meta-analysis. Psychol Med. 2017 Sep. doi: 10.1017/S0033291717000617.
12. Pentecost R et al. Scoping review of the associations between perinatal substance use and perinatal depression and anxiety. J Obstet Gynecol Neonatal Nurs. 2021 Jul. doi: 10.1016/j.jogn.2021.02.008.
13. Craemer KA et al. Perinatal mental health in low-income urban and rural patients: The importance of screening for comorbidities. Gen Hosp Psychiatry. 2023 Jul-Aug. doi: 10.1016/j.genhosppsych.2023.05.007.
14. O’Connor E et al. Primary care screening for and treatment of depression in pregnant and postpartum women: Evidence report and systematic review for the U.S. Preventive Services Task Force. JAMA. 2016 Jan 26. doi: 10.1001/jama.2015.18948.
15. Kozhimannil KB et al. Racial and ethnic disparities in postpartum depression care among low-income women. Psychiatr Serv. 2011 Jun. doi: 10.1176/ps.62.6.pss6206_0619.
16. Wenzel ES et al. Depression and anxiety symptoms across pregnancy and the postpartum in low-income Black and Latina women. Arch Womens Ment Health. 2021 Dec. doi: 10.1007/s00737-021-01139-y.
17. Gibbons RD et al. Development of a computerized adaptive substance use disorder scale for screening and measurement: The CAT‐SUD. Addiction. 2020 Jul. doi: 10.1111/add.14938.
18. Brenner LA et al. Validation of a computerized adaptive test suicide scale (CAT-SS) among united states military veterans. PloS One. 2022 Jan 21. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0261920.
19. The Center for State Child Welfare Data. Using technology to diagnose and report on behavioral health challenges facing foster youth. 2018.
20. Kim JJ et al. The experience of depression, anxiety, and mania among perinatal women. Arch Womens Ment Health. 2016 Oct. doi: 10.1007/s00737-016-0632-6.
21. Tepper MC et al. Toward population health: Using a learning behavioral health system and measurement-based care to improve access, care, outcomes, and disparities. Community Ment Health J. 2022 Nov. doi: 10.1007/s10597-022-00957-3.
22. Wenzel E et al. Using computerised adaptive tests to screen for perinatal depression in underserved women of colour. Evid Based Ment Health. 2022 Feb. doi: 10.1136/ebmental-2021-300262.
23. Sanger-Katz M. They want it to be secret: How a common blood test can cost $11 or almost $1,000. New York Times. 2019 Apr 19.
24. Spitzer RL et al. A brief measure for assessing generalized anxiety disorder: The GAD-7. Arch Intern Med. 2006 May 22. doi: 10.1001/archinte.166.10.1092.
25. Mollard E et al. An integrative review of postpartum depression in rural US communities. Arch Psychiatr Nurs. 2016 Jun. doi: 10.1016/j.apnu.2015.12.003.
26. Anglim AJ and Radke SM. Rural maternal health care outcomes, drivers, and patient perspectives. Clin Obstet Gynecol. 2022 Dec 1. doi: 10.1097/GRF.0000000000000753.
No more hot flashes? AI device could stop menopause symptom
Vasomotor symptoms the sudden rises in body temperature that affect about 75% of menopausal women, have drawn interest after the approval of a new oral drug and research linking hot flashes to Alzheimer’s, heart disease, and stroke.
Now entering the discussion are researchers from the University of Massachusetts, Amherst, and Embr Labs (a Massachusetts Institute of Technology spinoff) who say they’ve developed a machine-learning algorithm that can predict a hot flash.
The device, which sells for $299, is already touted as a way to manage menopausal hot flashes.
But once the algorithm is added, the device will be able to “continuously monitor physiological signals – skin temperature, body temperature, sweating, activity level, or heart rate – and identify early indicators that a hot flash is building,” said Michael Busa, PhD, director of the Center for Human Health and Performance at UMass Amherst, who led the team that developed the algorithm.
That data would be sent to a computing platform in the cloud, where the algorithm can flag signs of an impending hot flash, Dr. Busa said. The device would automatically prompt cooling in less than a second, which could effectively stop the hot flash in its tracks or at least help to take the edge off.
Exploring cooling therapy for hot flashes
“There is always tremendous interest in anything that is nonhormonal and effective in treatment of hot flashes,” said Karen Adams, MD, an ob.gyn. and director of the menopause and healthy aging program at Stanford (Calif.) University. (Dr. Adams was not involved in developing this technology.)
Hormone therapy is the primary treatment, easing hot flashes in 3-4 weeks, Dr. Adams said. “But some women do not want to take estrogen, or should not due to medical contraindications.”
Hormone therapy is generally not recommended for people with a history of breast cancer, blood clots, or diseases of their heart or blood vessels. Recent research presented at the annual meeting of the Menopause Society found that hormone therapy may not work as well in women with obesity.
For nonhormonal treatments, the Food and Drug Administration cleared the oral med fezolinetant (Veozah) in May. Antidepressant medications can also be used as a first-line treatment in those who can’t take estrogen. Another oral drug, elinzanetant, is in late-stage clinical trials.
But there has been little clinical investigation – only two small studies, Dr. Adams said – examining cooling therapy as a treatment for hot flashes. That’s something the makers of this device hope to change.
“Despite the fact that seeking cooling relief is a woman’s immediate natural response to the onset of a hot flash, there is limited work done to understand the benefits of this natural therapy,” said Matthew Smith, PhD, chief technology officer at Embr Labs. “This is in part because the technology didn’t exist to deliver cooling in an immediate, reproducible manner.”
The algorithm’s performance has been benchmarked using data from women having hot flashes, Dr. Smith said. Results have been submitted for publication.
The Embr Wave has been shown to help menopausal women with hot flashes sleep better. It has also been tested as a therapy for hot flashes related to cancer treatment.
But to truly evaluate the device as a treatment for hot flashes, it should be tested in randomized trials including a “sham treatment arm” – where some people get the real treatment while others get the sham treatment, Dr. Adams said.
“Device studies tend to have high placebo response rates that can only be truly evaluated when there is a sham treatment in the study,” she said. “If such a device were shown to be safe and effective, we would absolutely recommend it. But we’re a long way from that.”
A version of this article appeared on WebMD.com.
Vasomotor symptoms the sudden rises in body temperature that affect about 75% of menopausal women, have drawn interest after the approval of a new oral drug and research linking hot flashes to Alzheimer’s, heart disease, and stroke.
Now entering the discussion are researchers from the University of Massachusetts, Amherst, and Embr Labs (a Massachusetts Institute of Technology spinoff) who say they’ve developed a machine-learning algorithm that can predict a hot flash.
The device, which sells for $299, is already touted as a way to manage menopausal hot flashes.
But once the algorithm is added, the device will be able to “continuously monitor physiological signals – skin temperature, body temperature, sweating, activity level, or heart rate – and identify early indicators that a hot flash is building,” said Michael Busa, PhD, director of the Center for Human Health and Performance at UMass Amherst, who led the team that developed the algorithm.
That data would be sent to a computing platform in the cloud, where the algorithm can flag signs of an impending hot flash, Dr. Busa said. The device would automatically prompt cooling in less than a second, which could effectively stop the hot flash in its tracks or at least help to take the edge off.
Exploring cooling therapy for hot flashes
“There is always tremendous interest in anything that is nonhormonal and effective in treatment of hot flashes,” said Karen Adams, MD, an ob.gyn. and director of the menopause and healthy aging program at Stanford (Calif.) University. (Dr. Adams was not involved in developing this technology.)
Hormone therapy is the primary treatment, easing hot flashes in 3-4 weeks, Dr. Adams said. “But some women do not want to take estrogen, or should not due to medical contraindications.”
Hormone therapy is generally not recommended for people with a history of breast cancer, blood clots, or diseases of their heart or blood vessels. Recent research presented at the annual meeting of the Menopause Society found that hormone therapy may not work as well in women with obesity.
For nonhormonal treatments, the Food and Drug Administration cleared the oral med fezolinetant (Veozah) in May. Antidepressant medications can also be used as a first-line treatment in those who can’t take estrogen. Another oral drug, elinzanetant, is in late-stage clinical trials.
But there has been little clinical investigation – only two small studies, Dr. Adams said – examining cooling therapy as a treatment for hot flashes. That’s something the makers of this device hope to change.
“Despite the fact that seeking cooling relief is a woman’s immediate natural response to the onset of a hot flash, there is limited work done to understand the benefits of this natural therapy,” said Matthew Smith, PhD, chief technology officer at Embr Labs. “This is in part because the technology didn’t exist to deliver cooling in an immediate, reproducible manner.”
The algorithm’s performance has been benchmarked using data from women having hot flashes, Dr. Smith said. Results have been submitted for publication.
The Embr Wave has been shown to help menopausal women with hot flashes sleep better. It has also been tested as a therapy for hot flashes related to cancer treatment.
But to truly evaluate the device as a treatment for hot flashes, it should be tested in randomized trials including a “sham treatment arm” – where some people get the real treatment while others get the sham treatment, Dr. Adams said.
“Device studies tend to have high placebo response rates that can only be truly evaluated when there is a sham treatment in the study,” she said. “If such a device were shown to be safe and effective, we would absolutely recommend it. But we’re a long way from that.”
A version of this article appeared on WebMD.com.
Vasomotor symptoms the sudden rises in body temperature that affect about 75% of menopausal women, have drawn interest after the approval of a new oral drug and research linking hot flashes to Alzheimer’s, heart disease, and stroke.
Now entering the discussion are researchers from the University of Massachusetts, Amherst, and Embr Labs (a Massachusetts Institute of Technology spinoff) who say they’ve developed a machine-learning algorithm that can predict a hot flash.
The device, which sells for $299, is already touted as a way to manage menopausal hot flashes.
But once the algorithm is added, the device will be able to “continuously monitor physiological signals – skin temperature, body temperature, sweating, activity level, or heart rate – and identify early indicators that a hot flash is building,” said Michael Busa, PhD, director of the Center for Human Health and Performance at UMass Amherst, who led the team that developed the algorithm.
That data would be sent to a computing platform in the cloud, where the algorithm can flag signs of an impending hot flash, Dr. Busa said. The device would automatically prompt cooling in less than a second, which could effectively stop the hot flash in its tracks or at least help to take the edge off.
Exploring cooling therapy for hot flashes
“There is always tremendous interest in anything that is nonhormonal and effective in treatment of hot flashes,” said Karen Adams, MD, an ob.gyn. and director of the menopause and healthy aging program at Stanford (Calif.) University. (Dr. Adams was not involved in developing this technology.)
Hormone therapy is the primary treatment, easing hot flashes in 3-4 weeks, Dr. Adams said. “But some women do not want to take estrogen, or should not due to medical contraindications.”
Hormone therapy is generally not recommended for people with a history of breast cancer, blood clots, or diseases of their heart or blood vessels. Recent research presented at the annual meeting of the Menopause Society found that hormone therapy may not work as well in women with obesity.
For nonhormonal treatments, the Food and Drug Administration cleared the oral med fezolinetant (Veozah) in May. Antidepressant medications can also be used as a first-line treatment in those who can’t take estrogen. Another oral drug, elinzanetant, is in late-stage clinical trials.
But there has been little clinical investigation – only two small studies, Dr. Adams said – examining cooling therapy as a treatment for hot flashes. That’s something the makers of this device hope to change.
“Despite the fact that seeking cooling relief is a woman’s immediate natural response to the onset of a hot flash, there is limited work done to understand the benefits of this natural therapy,” said Matthew Smith, PhD, chief technology officer at Embr Labs. “This is in part because the technology didn’t exist to deliver cooling in an immediate, reproducible manner.”
The algorithm’s performance has been benchmarked using data from women having hot flashes, Dr. Smith said. Results have been submitted for publication.
The Embr Wave has been shown to help menopausal women with hot flashes sleep better. It has also been tested as a therapy for hot flashes related to cancer treatment.
But to truly evaluate the device as a treatment for hot flashes, it should be tested in randomized trials including a “sham treatment arm” – where some people get the real treatment while others get the sham treatment, Dr. Adams said.
“Device studies tend to have high placebo response rates that can only be truly evaluated when there is a sham treatment in the study,” she said. “If such a device were shown to be safe and effective, we would absolutely recommend it. But we’re a long way from that.”
A version of this article appeared on WebMD.com.
Air pollution tied to postpartum depression
TOPLINE:
METHODOLOGY:
- Researchers analyzed data on 340,679 women who had singleton live births at Kaiser Permanente Southern California facilities between 2008 and 2016.
- Ambient air pollution exposures were assessed based on maternal residential addresses using monthly averages of particulate matter ≤ 2.5 mcm (PM2.5), PM ≤ 10 mcm (PM10), nitrogen dioxide, and ozone from Environmental Protection Agency monitoring stations.
- Constituents of PM2.5 (sulfate, nitrate, ammonium, organic matter, and black carbon) were obtained from models based on satellite, ground-based monitor, and chemical transport modeling data.
- Women with an Edinburgh Postnatal Depression Scale score of at least 10 during the first 6 months postpartum were referred for further assessment, including diagnosis and treatment.
TAKEAWAY:
- A total of 25,674 women had PPD (7.5%).
- Positive associations were observed between PPD ozone (adjusted odds ratio, 1.09), PM10 (aOR, 1.02), and PM2.5 (aOR, 1.02), with no statistically significant association with nitrogen dioxide.
- Among PM2.5 constituents, black carbon had the strongest association with PPD (OR 1.04).
- Overall, a higher risk of PPD was associated with ozone exposure during the entire pregnancy and postpartum periods and with PM exposure during the late pregnancy and postpartum periods.
IN PRACTICE:
“These findings suggest that long-term antepartum and postpartum air pollution exposure is a potentially modifiable environmental risk factor for PPD and an important public health issue to address for improved maternal mental health,” the authors wrote.
SOURCE:
The study, with first author Yi Sun, PhD, Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences and Peking Medical College, Beijing, was published online in JAMA Network Open.
LIMITATIONS:
Postpartum exposures were estimated using only maternal address at delivery, which may have led to exposure misclassification. Potential exposure misclassifications may also exist since indoor and personal exposure levels could not be estimated. Although several covariates were adjusted for, some residual or unmeasured covariates were inevitable due to data unavailability, such as psychiatric history, adverse life events, and marital status, which may affect mental health.
DISCLOSURES:
This study was supported by a grant from the National Institute of Environmental Health Sciences. The authors report no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
METHODOLOGY:
- Researchers analyzed data on 340,679 women who had singleton live births at Kaiser Permanente Southern California facilities between 2008 and 2016.
- Ambient air pollution exposures were assessed based on maternal residential addresses using monthly averages of particulate matter ≤ 2.5 mcm (PM2.5), PM ≤ 10 mcm (PM10), nitrogen dioxide, and ozone from Environmental Protection Agency monitoring stations.
- Constituents of PM2.5 (sulfate, nitrate, ammonium, organic matter, and black carbon) were obtained from models based on satellite, ground-based monitor, and chemical transport modeling data.
- Women with an Edinburgh Postnatal Depression Scale score of at least 10 during the first 6 months postpartum were referred for further assessment, including diagnosis and treatment.
TAKEAWAY:
- A total of 25,674 women had PPD (7.5%).
- Positive associations were observed between PPD ozone (adjusted odds ratio, 1.09), PM10 (aOR, 1.02), and PM2.5 (aOR, 1.02), with no statistically significant association with nitrogen dioxide.
- Among PM2.5 constituents, black carbon had the strongest association with PPD (OR 1.04).
- Overall, a higher risk of PPD was associated with ozone exposure during the entire pregnancy and postpartum periods and with PM exposure during the late pregnancy and postpartum periods.
IN PRACTICE:
“These findings suggest that long-term antepartum and postpartum air pollution exposure is a potentially modifiable environmental risk factor for PPD and an important public health issue to address for improved maternal mental health,” the authors wrote.
SOURCE:
The study, with first author Yi Sun, PhD, Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences and Peking Medical College, Beijing, was published online in JAMA Network Open.
LIMITATIONS:
Postpartum exposures were estimated using only maternal address at delivery, which may have led to exposure misclassification. Potential exposure misclassifications may also exist since indoor and personal exposure levels could not be estimated. Although several covariates were adjusted for, some residual or unmeasured covariates were inevitable due to data unavailability, such as psychiatric history, adverse life events, and marital status, which may affect mental health.
DISCLOSURES:
This study was supported by a grant from the National Institute of Environmental Health Sciences. The authors report no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
METHODOLOGY:
- Researchers analyzed data on 340,679 women who had singleton live births at Kaiser Permanente Southern California facilities between 2008 and 2016.
- Ambient air pollution exposures were assessed based on maternal residential addresses using monthly averages of particulate matter ≤ 2.5 mcm (PM2.5), PM ≤ 10 mcm (PM10), nitrogen dioxide, and ozone from Environmental Protection Agency monitoring stations.
- Constituents of PM2.5 (sulfate, nitrate, ammonium, organic matter, and black carbon) were obtained from models based on satellite, ground-based monitor, and chemical transport modeling data.
- Women with an Edinburgh Postnatal Depression Scale score of at least 10 during the first 6 months postpartum were referred for further assessment, including diagnosis and treatment.
TAKEAWAY:
- A total of 25,674 women had PPD (7.5%).
- Positive associations were observed between PPD ozone (adjusted odds ratio, 1.09), PM10 (aOR, 1.02), and PM2.5 (aOR, 1.02), with no statistically significant association with nitrogen dioxide.
- Among PM2.5 constituents, black carbon had the strongest association with PPD (OR 1.04).
- Overall, a higher risk of PPD was associated with ozone exposure during the entire pregnancy and postpartum periods and with PM exposure during the late pregnancy and postpartum periods.
IN PRACTICE:
“These findings suggest that long-term antepartum and postpartum air pollution exposure is a potentially modifiable environmental risk factor for PPD and an important public health issue to address for improved maternal mental health,” the authors wrote.
SOURCE:
The study, with first author Yi Sun, PhD, Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences and Peking Medical College, Beijing, was published online in JAMA Network Open.
LIMITATIONS:
Postpartum exposures were estimated using only maternal address at delivery, which may have led to exposure misclassification. Potential exposure misclassifications may also exist since indoor and personal exposure levels could not be estimated. Although several covariates were adjusted for, some residual or unmeasured covariates were inevitable due to data unavailability, such as psychiatric history, adverse life events, and marital status, which may affect mental health.
DISCLOSURES:
This study was supported by a grant from the National Institute of Environmental Health Sciences. The authors report no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM JAMA NETWORK OPEN
GI symptoms during menopause deserve attention
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
Welcome back to another GI Common Concerns.
Today, I want to highlight some information about menopause.
Approximately 1.5 million women in the United States per year enter into menopause. Hysterectomy is also one of the most common surgeries for women worldwide, with an estimated 20%-40% undergoing this procedure by the age of 60.
Therefore, whether it’s because of biologic onset with age or surgical induction, menopause is a very common condition, and it’s important that we understand its symptoms and the latest information around it.
Impact on GI motility
One of the clearest functional symptoms to be aware of with menopause relates to alterations in hormonal balance. This has an impact on gastrointestinal (GI) motility by increasing abdominal muscle stimulation related to different patterns of secretion and can result in a number of symptomatic changes.
One such change that can occur is food intolerance. It is believed that menopause-associated food intolerance has multiple possible causes and may be related more to alterations to the microbiome, which can be contributed to by diet, activity, sleep cycle, and other factors.
When food intolerances are triggered in the perimenopausal or menopausal patient, it may lead you to recommend the well-established FODMAP diet, which is known to reduce symptoms. But the answer for every patient is not simply placing them on a FODMAP diet and telling them they have irritable bowel syndrome.
Other approaches can be considered for addressing food intolerance in these patients. The data are quite strong that adjunctive use of a dietitian is tremendously helpful in this particular population.
When it comes to menopausal patients, however, we need to consider other changes in their activity or adverse contributors to their mental health, such as stress or anxiety. These all contribute to more of a multifactorial composite in this population, for which irritable bowel syndrome serves as a similar example.
This means that we may need to expand our horizons rather than to focus on solely on antispasmodic or diet-related interventions.
Instead, we can start to consider more of a multidimensional treatment approach consisting of education, relaxation, cognitive-behavioral therapy, and physical activity. Certainly, there are now behavioral interventions using Internet-based digital formats to increase the acceptability and sustainability among patients.
Choosing such a multidisciplinary approach can be quite helpful.
The metabolic consequences of altering hormonal balance
Recent data from a rat model study investigated the metabolic impact of changing hormonal balance.
Investigators looked at ovariectomized rats and found that there was a biologic change in the diversity of the general GI biome. There were also noteworthy associations with weight fluctuations and dramatic changes in the spatial memory and cognitive performance characteristics of these rats, which was subsequently improved by supplemental estrogen.
This indicates that we may be able to remediate these effects with the similar use of supplemental hormone replacement treatments.
Another recent study looked at nonalcoholic fatty liver disease, which is very common in the general population and has a > 20% worldwide prevalence in postmenopausal women. Albeit small in numbers, this was a very interesting study.
Investigators looked at the delivery method for menopausal hormone therapy, which was transdermal for 75 patients and oral for 293 patients. Then, they looked at ultrasound definition of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease after 1 year as the endpoint. They found an approximate 7% reduction in the patients who received the transdermal administration compared with a 4% increase in the patients who received it orally.
Again, we have to remember this is a relatively small study, but the results indicate that the route of estrogen administration may be an important consideration in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease.
Sleep disturbances: fragmentation, duration, and quality
Sleep is something that’s near and dear to my heart and is the focus of a lot of our research.
Sleep disturbances are really part and parcel of menopause and are observed with hormonal imbalances and temperature intolerances. Disturbances such as sleep fragmentation, shorter sleep duration, and poorer sleep quality have a dramatic effect not only on the biome but also on sensory thresholds.
Therefore, as we start to look at mitigating strategies here, we need to focus on sleep and ask the right questions.
In my own practice, I try not to just ask, “How did you sleep last night?” That’s because sleep can be somewhat amnestic. You may have a cognitive awakening or a noncognitive awakening but still have experienced fragmentation.
As a result, my focus is on next-day function. I ask my patients, “When you get up in the morning, are you refreshed? Do you have the ability to perform daytime activities? Do you experience early fatigue or cognitive changes that occur?”
These questions can provide good insights into the sleep efficiency of the previous night.
The effect of the microbiome on osteoporosis
One final topic I found very interesting pertains to the effects of menopause on osteoporosis.
We certainly know that postmenopausal women have a very high prevalence of osteopenia, and that osteoporosis is a progression of that, as well as that increased bone-related disease affects fractures and related morbidity and mortality.
However, there’s accumulating evidence on the osteoporotic effects of biomarker changes in menopause, which shows that the biome regulates the pathophysiologic process of at least a large degree of osteoporosis.
This starts to make sense when you look at the pro-inflammatory factors that increase with changes in biome diversity, in particular tumor necrosis factor alpha (which is something we also see in inflammatory bowel disease), interleukin-1, and increased activated osteoclasts.
Therefore, when it comes to decreasing bone loss among patients who are perimenopausal or postmenopausal, we don’t yet have a clear answer. Hormone therapy, diet, activity, vitamin D supplementation, and other things may positively change the biome. They are worthy topics for patients to bring up with their ob.gyns. or primary care doctors.
Although it may be a little bit outside the scope of gastroenterology, in my opinion there are a number of new findings relating to menopause that we as a field need to be more proactive in addressing.
Ask the right questions when these people come in to you, irrespective of why they’re there. Start to ask about the quality of their sleep. What are their other functional symptoms? What are their other potential osteoporosis-related risks?
We must do a better job about individualizing care. Rather than treating patients as disease states, we must start to do specific patient-focused care.
I hope this gives you some provocative thoughts when you have your next session with a patient in the perimenopausal or menopausal state. There are lots of things that we continue to learn.
Dr. Johnson is professor of medicine and chief of gastroenterology at Eastern Virginia Medical School in Norfolk, Va., and a past president of the American College of Gastroenterology. He serves as an adviser to ISOThrive and Johnson & Johnson.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
Welcome back to another GI Common Concerns.
Today, I want to highlight some information about menopause.
Approximately 1.5 million women in the United States per year enter into menopause. Hysterectomy is also one of the most common surgeries for women worldwide, with an estimated 20%-40% undergoing this procedure by the age of 60.
Therefore, whether it’s because of biologic onset with age or surgical induction, menopause is a very common condition, and it’s important that we understand its symptoms and the latest information around it.
Impact on GI motility
One of the clearest functional symptoms to be aware of with menopause relates to alterations in hormonal balance. This has an impact on gastrointestinal (GI) motility by increasing abdominal muscle stimulation related to different patterns of secretion and can result in a number of symptomatic changes.
One such change that can occur is food intolerance. It is believed that menopause-associated food intolerance has multiple possible causes and may be related more to alterations to the microbiome, which can be contributed to by diet, activity, sleep cycle, and other factors.
When food intolerances are triggered in the perimenopausal or menopausal patient, it may lead you to recommend the well-established FODMAP diet, which is known to reduce symptoms. But the answer for every patient is not simply placing them on a FODMAP diet and telling them they have irritable bowel syndrome.
Other approaches can be considered for addressing food intolerance in these patients. The data are quite strong that adjunctive use of a dietitian is tremendously helpful in this particular population.
When it comes to menopausal patients, however, we need to consider other changes in their activity or adverse contributors to their mental health, such as stress or anxiety. These all contribute to more of a multifactorial composite in this population, for which irritable bowel syndrome serves as a similar example.
This means that we may need to expand our horizons rather than to focus on solely on antispasmodic or diet-related interventions.
Instead, we can start to consider more of a multidimensional treatment approach consisting of education, relaxation, cognitive-behavioral therapy, and physical activity. Certainly, there are now behavioral interventions using Internet-based digital formats to increase the acceptability and sustainability among patients.
Choosing such a multidisciplinary approach can be quite helpful.
The metabolic consequences of altering hormonal balance
Recent data from a rat model study investigated the metabolic impact of changing hormonal balance.
Investigators looked at ovariectomized rats and found that there was a biologic change in the diversity of the general GI biome. There were also noteworthy associations with weight fluctuations and dramatic changes in the spatial memory and cognitive performance characteristics of these rats, which was subsequently improved by supplemental estrogen.
This indicates that we may be able to remediate these effects with the similar use of supplemental hormone replacement treatments.
Another recent study looked at nonalcoholic fatty liver disease, which is very common in the general population and has a > 20% worldwide prevalence in postmenopausal women. Albeit small in numbers, this was a very interesting study.
Investigators looked at the delivery method for menopausal hormone therapy, which was transdermal for 75 patients and oral for 293 patients. Then, they looked at ultrasound definition of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease after 1 year as the endpoint. They found an approximate 7% reduction in the patients who received the transdermal administration compared with a 4% increase in the patients who received it orally.
Again, we have to remember this is a relatively small study, but the results indicate that the route of estrogen administration may be an important consideration in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease.
Sleep disturbances: fragmentation, duration, and quality
Sleep is something that’s near and dear to my heart and is the focus of a lot of our research.
Sleep disturbances are really part and parcel of menopause and are observed with hormonal imbalances and temperature intolerances. Disturbances such as sleep fragmentation, shorter sleep duration, and poorer sleep quality have a dramatic effect not only on the biome but also on sensory thresholds.
Therefore, as we start to look at mitigating strategies here, we need to focus on sleep and ask the right questions.
In my own practice, I try not to just ask, “How did you sleep last night?” That’s because sleep can be somewhat amnestic. You may have a cognitive awakening or a noncognitive awakening but still have experienced fragmentation.
As a result, my focus is on next-day function. I ask my patients, “When you get up in the morning, are you refreshed? Do you have the ability to perform daytime activities? Do you experience early fatigue or cognitive changes that occur?”
These questions can provide good insights into the sleep efficiency of the previous night.
The effect of the microbiome on osteoporosis
One final topic I found very interesting pertains to the effects of menopause on osteoporosis.
We certainly know that postmenopausal women have a very high prevalence of osteopenia, and that osteoporosis is a progression of that, as well as that increased bone-related disease affects fractures and related morbidity and mortality.
However, there’s accumulating evidence on the osteoporotic effects of biomarker changes in menopause, which shows that the biome regulates the pathophysiologic process of at least a large degree of osteoporosis.
This starts to make sense when you look at the pro-inflammatory factors that increase with changes in biome diversity, in particular tumor necrosis factor alpha (which is something we also see in inflammatory bowel disease), interleukin-1, and increased activated osteoclasts.
Therefore, when it comes to decreasing bone loss among patients who are perimenopausal or postmenopausal, we don’t yet have a clear answer. Hormone therapy, diet, activity, vitamin D supplementation, and other things may positively change the biome. They are worthy topics for patients to bring up with their ob.gyns. or primary care doctors.
Although it may be a little bit outside the scope of gastroenterology, in my opinion there are a number of new findings relating to menopause that we as a field need to be more proactive in addressing.
Ask the right questions when these people come in to you, irrespective of why they’re there. Start to ask about the quality of their sleep. What are their other functional symptoms? What are their other potential osteoporosis-related risks?
We must do a better job about individualizing care. Rather than treating patients as disease states, we must start to do specific patient-focused care.
I hope this gives you some provocative thoughts when you have your next session with a patient in the perimenopausal or menopausal state. There are lots of things that we continue to learn.
Dr. Johnson is professor of medicine and chief of gastroenterology at Eastern Virginia Medical School in Norfolk, Va., and a past president of the American College of Gastroenterology. He serves as an adviser to ISOThrive and Johnson & Johnson.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
Welcome back to another GI Common Concerns.
Today, I want to highlight some information about menopause.
Approximately 1.5 million women in the United States per year enter into menopause. Hysterectomy is also one of the most common surgeries for women worldwide, with an estimated 20%-40% undergoing this procedure by the age of 60.
Therefore, whether it’s because of biologic onset with age or surgical induction, menopause is a very common condition, and it’s important that we understand its symptoms and the latest information around it.
Impact on GI motility
One of the clearest functional symptoms to be aware of with menopause relates to alterations in hormonal balance. This has an impact on gastrointestinal (GI) motility by increasing abdominal muscle stimulation related to different patterns of secretion and can result in a number of symptomatic changes.
One such change that can occur is food intolerance. It is believed that menopause-associated food intolerance has multiple possible causes and may be related more to alterations to the microbiome, which can be contributed to by diet, activity, sleep cycle, and other factors.
When food intolerances are triggered in the perimenopausal or menopausal patient, it may lead you to recommend the well-established FODMAP diet, which is known to reduce symptoms. But the answer for every patient is not simply placing them on a FODMAP diet and telling them they have irritable bowel syndrome.
Other approaches can be considered for addressing food intolerance in these patients. The data are quite strong that adjunctive use of a dietitian is tremendously helpful in this particular population.
When it comes to menopausal patients, however, we need to consider other changes in their activity or adverse contributors to their mental health, such as stress or anxiety. These all contribute to more of a multifactorial composite in this population, for which irritable bowel syndrome serves as a similar example.
This means that we may need to expand our horizons rather than to focus on solely on antispasmodic or diet-related interventions.
Instead, we can start to consider more of a multidimensional treatment approach consisting of education, relaxation, cognitive-behavioral therapy, and physical activity. Certainly, there are now behavioral interventions using Internet-based digital formats to increase the acceptability and sustainability among patients.
Choosing such a multidisciplinary approach can be quite helpful.
The metabolic consequences of altering hormonal balance
Recent data from a rat model study investigated the metabolic impact of changing hormonal balance.
Investigators looked at ovariectomized rats and found that there was a biologic change in the diversity of the general GI biome. There were also noteworthy associations with weight fluctuations and dramatic changes in the spatial memory and cognitive performance characteristics of these rats, which was subsequently improved by supplemental estrogen.
This indicates that we may be able to remediate these effects with the similar use of supplemental hormone replacement treatments.
Another recent study looked at nonalcoholic fatty liver disease, which is very common in the general population and has a > 20% worldwide prevalence in postmenopausal women. Albeit small in numbers, this was a very interesting study.
Investigators looked at the delivery method for menopausal hormone therapy, which was transdermal for 75 patients and oral for 293 patients. Then, they looked at ultrasound definition of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease after 1 year as the endpoint. They found an approximate 7% reduction in the patients who received the transdermal administration compared with a 4% increase in the patients who received it orally.
Again, we have to remember this is a relatively small study, but the results indicate that the route of estrogen administration may be an important consideration in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease.
Sleep disturbances: fragmentation, duration, and quality
Sleep is something that’s near and dear to my heart and is the focus of a lot of our research.
Sleep disturbances are really part and parcel of menopause and are observed with hormonal imbalances and temperature intolerances. Disturbances such as sleep fragmentation, shorter sleep duration, and poorer sleep quality have a dramatic effect not only on the biome but also on sensory thresholds.
Therefore, as we start to look at mitigating strategies here, we need to focus on sleep and ask the right questions.
In my own practice, I try not to just ask, “How did you sleep last night?” That’s because sleep can be somewhat amnestic. You may have a cognitive awakening or a noncognitive awakening but still have experienced fragmentation.
As a result, my focus is on next-day function. I ask my patients, “When you get up in the morning, are you refreshed? Do you have the ability to perform daytime activities? Do you experience early fatigue or cognitive changes that occur?”
These questions can provide good insights into the sleep efficiency of the previous night.
The effect of the microbiome on osteoporosis
One final topic I found very interesting pertains to the effects of menopause on osteoporosis.
We certainly know that postmenopausal women have a very high prevalence of osteopenia, and that osteoporosis is a progression of that, as well as that increased bone-related disease affects fractures and related morbidity and mortality.
However, there’s accumulating evidence on the osteoporotic effects of biomarker changes in menopause, which shows that the biome regulates the pathophysiologic process of at least a large degree of osteoporosis.
This starts to make sense when you look at the pro-inflammatory factors that increase with changes in biome diversity, in particular tumor necrosis factor alpha (which is something we also see in inflammatory bowel disease), interleukin-1, and increased activated osteoclasts.
Therefore, when it comes to decreasing bone loss among patients who are perimenopausal or postmenopausal, we don’t yet have a clear answer. Hormone therapy, diet, activity, vitamin D supplementation, and other things may positively change the biome. They are worthy topics for patients to bring up with their ob.gyns. or primary care doctors.
Although it may be a little bit outside the scope of gastroenterology, in my opinion there are a number of new findings relating to menopause that we as a field need to be more proactive in addressing.
Ask the right questions when these people come in to you, irrespective of why they’re there. Start to ask about the quality of their sleep. What are their other functional symptoms? What are their other potential osteoporosis-related risks?
We must do a better job about individualizing care. Rather than treating patients as disease states, we must start to do specific patient-focused care.
I hope this gives you some provocative thoughts when you have your next session with a patient in the perimenopausal or menopausal state. There are lots of things that we continue to learn.
Dr. Johnson is professor of medicine and chief of gastroenterology at Eastern Virginia Medical School in Norfolk, Va., and a past president of the American College of Gastroenterology. He serves as an adviser to ISOThrive and Johnson & Johnson.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Postmenopausal testosterone for low libido only, doctors say
Your patients may see ads claiming that testosterone replacement therapy (TRT) offers postmenopausal women health benefits beyond restored sex drive: that TRT can improve their mood, energy, and thinking and give them stronger bones and bigger muscles.
How accurate are these claims? According to six experts who talked with this news organization, not very.
“Right now in this country and around the world, testosterone’s only use in postmenopausal women is for libido,” said Adrian Sandra Dobs, MD, MHS, professor of medicine and director of the Johns Hopkins Clinical Research Network at Johns Hopkins Medicine, Baltimore.
“Treating postmenopausal women with testosterone is a rarity. Some physicians and some wellness centers make their money out of prescribing estrogen and testosterone to women in patches, gels, creams, capsules, pellets, and other forms. she added by phone.
“One has to be very careful about using testosterone in women,” Dr. Dobs cautioned. “There’s a lot of hype out there.”
Low testosterone in women has not been well studied, and no testosterone treatments for this condition have been approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration. Providers need to adjust male treatment data to their female patients, who require significantly lower doses than males. Contraindications and long-term side effects are poorly understood, said Mary Rosser, MD, PhD, assistant professor of women’s health and director of integrated women’s health at Columbia University Irving Medical Center, New York.
“Despite this preponderance of scientific evidence and recommendations, the myths about testosterone die hard, including that it improves women’s muscle function, endurance, and well-being,” Dr. Rosser said.
“Websites that use compounded products or pellets are not FDA-regulated; therefore, they have no responsibility to prove their claims. They can entice women into using this stuff with all kinds of promises about ‘hormone balancing’ and other meaningless terms. The Endocrine Society statement reviewed the clinical studies on testosterone for various indications surrounding physical endurance, well-being, and mental health – and the studies do not support its use,” Dr. Rosser added.
According to the Australasian Menopause Society, women’s blood testosterone levels tend to peak in their 20s, slowly decline to around 25% of peak levels at menopause, then rise again in later years.
Susan Davis, PhD, and her colleagues at Monash University, Melbourne, found in a study that TRT in postmenopausal women may improve sexual well-being and that side effects include acne and increased hair growth. But they found no benefits for cognition, bone mineral density, body composition, muscle strength, or psychological well-being, and they note that more data are needed on long-term safety.
Postmenopausal testosterone recommended for libido only
“Hypoactive sexual desire disorder (HSDD) is really the only indication for postmenopausal testosterone use,” Nanette F. Santoro, MD, professor and chair of obstetrics and gynecology at the University of Colorado School of Medicine, Aurora, noted by email. “In clinical studies using androgen gel containing testosterone, testosterone treatment has resulted in a mean of one more satisfying sexual encounter per month. Consensus statements issued by the Endocrine Society, The International Menopause Society, and the North American Menopause Society have come to similar conclusions: The only indication for androgen therapy for women is HSDD,” added Santoro, an author of the Endocrine Society statement.
“Sexual health and the sense of well-being are very much related,” Sandra Ann Carson, MD, professor of obstetrics and gynecology at Yale Medicine, New Haven, Conn., said by phone. “So we give testosterone to increase sexual desire. Testosterone is not a treatment for decreased sense of well-being alone. Women who lose their sense of well-being due to depression or other factors need to have a mental health evaluation, not testosterone.”
“Because no female product is presently approved by a national regulatory body, male formulations can be judiciously used in female doses and blood testosterone concentrations must be monitored regularly,” Dr. Rosser said. “The recommendation is for considering use of compounded testosterone for hypoactive sexual desire only; it is against use for overall health and wellness.”
“The real mischief occurs when women are exposed to doses that are supraphysiologic,” Dr. Rosser cautioned. “At high doses that approach and sometimes exceed men’s levels of testosterone, women can have deepening of the voice, adverse changes in cholesterol, and even breast atrophy. This can occur with bioidentical compounded testosterone and with testosterone pellets. The National Academies of Science, Engineering, and Medicine recommend unequivocally that such preparations not be used.”
Not all postmenopausal women should take TRT, said Meredith McClure, MD, assistant professor in the department of obstetrics and gynecology of UT Southwestern Medical School, Dallas, because it has only been shown in trials to help with HSDD.
She advised clinicians to avoid prescribing testosterone to patients who “can’t take estrogen, including if [they] have hormone-sensitive cancer, blood clot risk, liver disease, heart attack, stroke, or undiagnosed genital bleeding.”
TRT for non-libido issues may sometimes be appropriate
“Perhaps women with hip fracture or cancer cachexia could benefit from testosterone to build muscle mass,” said Dr. Dobbs, who is involved in an ongoing study of testosterone treatment in women with hip fracture. “But as yet, we have no proof that testosterone helps.”
In rare cases, Stanley G. Korenman, MD, a reproductive endocrinologist and associate dean for ethics at UCLA Health, treats postmenopausal patients with TRT for reasons other than low libido. “I have a very specialized practice in reproductive endocrinology and internal medicine and am one of very few people in the country who do this kind of management,” he said in an interview. “If my postmenopausal patients have low testosterone and lack energy, I’m willing to give them low doses. If they feel more energetic, we continue, but if they don’t, we stop. I don’t think there’s any risk whatsoever at the low level I prescribe.
“I prescribe standard gel that comes in a squirt bottle, and I suggest they take half a squirt every other day – about one-eighth of a male dose – on the sole of the foot, where hair does not grow.
“I would not prescribe testosterone for bone health. We have bisphosphonates and other much better treatments for that. And I would not prescribe it to someone who is seriously emotionally disturbed or seriously depressed. This is not a treatment for depression.”
“Postmenopausal testosterone is not ‘the latest greatest thing,’ but being very low risk, it’s worth trying once in a while, in the appropriate patient, at the right dose,” Dr. Korenman advised. He cautioned people to “avoid the longevity salespeople who sell all sorts of things in all sorts of doses to try to keep us alive forever.”
All contributors report no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Your patients may see ads claiming that testosterone replacement therapy (TRT) offers postmenopausal women health benefits beyond restored sex drive: that TRT can improve their mood, energy, and thinking and give them stronger bones and bigger muscles.
How accurate are these claims? According to six experts who talked with this news organization, not very.
“Right now in this country and around the world, testosterone’s only use in postmenopausal women is for libido,” said Adrian Sandra Dobs, MD, MHS, professor of medicine and director of the Johns Hopkins Clinical Research Network at Johns Hopkins Medicine, Baltimore.
“Treating postmenopausal women with testosterone is a rarity. Some physicians and some wellness centers make their money out of prescribing estrogen and testosterone to women in patches, gels, creams, capsules, pellets, and other forms. she added by phone.
“One has to be very careful about using testosterone in women,” Dr. Dobs cautioned. “There’s a lot of hype out there.”
Low testosterone in women has not been well studied, and no testosterone treatments for this condition have been approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration. Providers need to adjust male treatment data to their female patients, who require significantly lower doses than males. Contraindications and long-term side effects are poorly understood, said Mary Rosser, MD, PhD, assistant professor of women’s health and director of integrated women’s health at Columbia University Irving Medical Center, New York.
“Despite this preponderance of scientific evidence and recommendations, the myths about testosterone die hard, including that it improves women’s muscle function, endurance, and well-being,” Dr. Rosser said.
“Websites that use compounded products or pellets are not FDA-regulated; therefore, they have no responsibility to prove their claims. They can entice women into using this stuff with all kinds of promises about ‘hormone balancing’ and other meaningless terms. The Endocrine Society statement reviewed the clinical studies on testosterone for various indications surrounding physical endurance, well-being, and mental health – and the studies do not support its use,” Dr. Rosser added.
According to the Australasian Menopause Society, women’s blood testosterone levels tend to peak in their 20s, slowly decline to around 25% of peak levels at menopause, then rise again in later years.
Susan Davis, PhD, and her colleagues at Monash University, Melbourne, found in a study that TRT in postmenopausal women may improve sexual well-being and that side effects include acne and increased hair growth. But they found no benefits for cognition, bone mineral density, body composition, muscle strength, or psychological well-being, and they note that more data are needed on long-term safety.
Postmenopausal testosterone recommended for libido only
“Hypoactive sexual desire disorder (HSDD) is really the only indication for postmenopausal testosterone use,” Nanette F. Santoro, MD, professor and chair of obstetrics and gynecology at the University of Colorado School of Medicine, Aurora, noted by email. “In clinical studies using androgen gel containing testosterone, testosterone treatment has resulted in a mean of one more satisfying sexual encounter per month. Consensus statements issued by the Endocrine Society, The International Menopause Society, and the North American Menopause Society have come to similar conclusions: The only indication for androgen therapy for women is HSDD,” added Santoro, an author of the Endocrine Society statement.
“Sexual health and the sense of well-being are very much related,” Sandra Ann Carson, MD, professor of obstetrics and gynecology at Yale Medicine, New Haven, Conn., said by phone. “So we give testosterone to increase sexual desire. Testosterone is not a treatment for decreased sense of well-being alone. Women who lose their sense of well-being due to depression or other factors need to have a mental health evaluation, not testosterone.”
“Because no female product is presently approved by a national regulatory body, male formulations can be judiciously used in female doses and blood testosterone concentrations must be monitored regularly,” Dr. Rosser said. “The recommendation is for considering use of compounded testosterone for hypoactive sexual desire only; it is against use for overall health and wellness.”
“The real mischief occurs when women are exposed to doses that are supraphysiologic,” Dr. Rosser cautioned. “At high doses that approach and sometimes exceed men’s levels of testosterone, women can have deepening of the voice, adverse changes in cholesterol, and even breast atrophy. This can occur with bioidentical compounded testosterone and with testosterone pellets. The National Academies of Science, Engineering, and Medicine recommend unequivocally that such preparations not be used.”
Not all postmenopausal women should take TRT, said Meredith McClure, MD, assistant professor in the department of obstetrics and gynecology of UT Southwestern Medical School, Dallas, because it has only been shown in trials to help with HSDD.
She advised clinicians to avoid prescribing testosterone to patients who “can’t take estrogen, including if [they] have hormone-sensitive cancer, blood clot risk, liver disease, heart attack, stroke, or undiagnosed genital bleeding.”
TRT for non-libido issues may sometimes be appropriate
“Perhaps women with hip fracture or cancer cachexia could benefit from testosterone to build muscle mass,” said Dr. Dobbs, who is involved in an ongoing study of testosterone treatment in women with hip fracture. “But as yet, we have no proof that testosterone helps.”
In rare cases, Stanley G. Korenman, MD, a reproductive endocrinologist and associate dean for ethics at UCLA Health, treats postmenopausal patients with TRT for reasons other than low libido. “I have a very specialized practice in reproductive endocrinology and internal medicine and am one of very few people in the country who do this kind of management,” he said in an interview. “If my postmenopausal patients have low testosterone and lack energy, I’m willing to give them low doses. If they feel more energetic, we continue, but if they don’t, we stop. I don’t think there’s any risk whatsoever at the low level I prescribe.
“I prescribe standard gel that comes in a squirt bottle, and I suggest they take half a squirt every other day – about one-eighth of a male dose – on the sole of the foot, where hair does not grow.
“I would not prescribe testosterone for bone health. We have bisphosphonates and other much better treatments for that. And I would not prescribe it to someone who is seriously emotionally disturbed or seriously depressed. This is not a treatment for depression.”
“Postmenopausal testosterone is not ‘the latest greatest thing,’ but being very low risk, it’s worth trying once in a while, in the appropriate patient, at the right dose,” Dr. Korenman advised. He cautioned people to “avoid the longevity salespeople who sell all sorts of things in all sorts of doses to try to keep us alive forever.”
All contributors report no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Your patients may see ads claiming that testosterone replacement therapy (TRT) offers postmenopausal women health benefits beyond restored sex drive: that TRT can improve their mood, energy, and thinking and give them stronger bones and bigger muscles.
How accurate are these claims? According to six experts who talked with this news organization, not very.
“Right now in this country and around the world, testosterone’s only use in postmenopausal women is for libido,” said Adrian Sandra Dobs, MD, MHS, professor of medicine and director of the Johns Hopkins Clinical Research Network at Johns Hopkins Medicine, Baltimore.
“Treating postmenopausal women with testosterone is a rarity. Some physicians and some wellness centers make their money out of prescribing estrogen and testosterone to women in patches, gels, creams, capsules, pellets, and other forms. she added by phone.
“One has to be very careful about using testosterone in women,” Dr. Dobs cautioned. “There’s a lot of hype out there.”
Low testosterone in women has not been well studied, and no testosterone treatments for this condition have been approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration. Providers need to adjust male treatment data to their female patients, who require significantly lower doses than males. Contraindications and long-term side effects are poorly understood, said Mary Rosser, MD, PhD, assistant professor of women’s health and director of integrated women’s health at Columbia University Irving Medical Center, New York.
“Despite this preponderance of scientific evidence and recommendations, the myths about testosterone die hard, including that it improves women’s muscle function, endurance, and well-being,” Dr. Rosser said.
“Websites that use compounded products or pellets are not FDA-regulated; therefore, they have no responsibility to prove their claims. They can entice women into using this stuff with all kinds of promises about ‘hormone balancing’ and other meaningless terms. The Endocrine Society statement reviewed the clinical studies on testosterone for various indications surrounding physical endurance, well-being, and mental health – and the studies do not support its use,” Dr. Rosser added.
According to the Australasian Menopause Society, women’s blood testosterone levels tend to peak in their 20s, slowly decline to around 25% of peak levels at menopause, then rise again in later years.
Susan Davis, PhD, and her colleagues at Monash University, Melbourne, found in a study that TRT in postmenopausal women may improve sexual well-being and that side effects include acne and increased hair growth. But they found no benefits for cognition, bone mineral density, body composition, muscle strength, or psychological well-being, and they note that more data are needed on long-term safety.
Postmenopausal testosterone recommended for libido only
“Hypoactive sexual desire disorder (HSDD) is really the only indication for postmenopausal testosterone use,” Nanette F. Santoro, MD, professor and chair of obstetrics and gynecology at the University of Colorado School of Medicine, Aurora, noted by email. “In clinical studies using androgen gel containing testosterone, testosterone treatment has resulted in a mean of one more satisfying sexual encounter per month. Consensus statements issued by the Endocrine Society, The International Menopause Society, and the North American Menopause Society have come to similar conclusions: The only indication for androgen therapy for women is HSDD,” added Santoro, an author of the Endocrine Society statement.
“Sexual health and the sense of well-being are very much related,” Sandra Ann Carson, MD, professor of obstetrics and gynecology at Yale Medicine, New Haven, Conn., said by phone. “So we give testosterone to increase sexual desire. Testosterone is not a treatment for decreased sense of well-being alone. Women who lose their sense of well-being due to depression or other factors need to have a mental health evaluation, not testosterone.”
“Because no female product is presently approved by a national regulatory body, male formulations can be judiciously used in female doses and blood testosterone concentrations must be monitored regularly,” Dr. Rosser said. “The recommendation is for considering use of compounded testosterone for hypoactive sexual desire only; it is against use for overall health and wellness.”
“The real mischief occurs when women are exposed to doses that are supraphysiologic,” Dr. Rosser cautioned. “At high doses that approach and sometimes exceed men’s levels of testosterone, women can have deepening of the voice, adverse changes in cholesterol, and even breast atrophy. This can occur with bioidentical compounded testosterone and with testosterone pellets. The National Academies of Science, Engineering, and Medicine recommend unequivocally that such preparations not be used.”
Not all postmenopausal women should take TRT, said Meredith McClure, MD, assistant professor in the department of obstetrics and gynecology of UT Southwestern Medical School, Dallas, because it has only been shown in trials to help with HSDD.
She advised clinicians to avoid prescribing testosterone to patients who “can’t take estrogen, including if [they] have hormone-sensitive cancer, blood clot risk, liver disease, heart attack, stroke, or undiagnosed genital bleeding.”
TRT for non-libido issues may sometimes be appropriate
“Perhaps women with hip fracture or cancer cachexia could benefit from testosterone to build muscle mass,” said Dr. Dobbs, who is involved in an ongoing study of testosterone treatment in women with hip fracture. “But as yet, we have no proof that testosterone helps.”
In rare cases, Stanley G. Korenman, MD, a reproductive endocrinologist and associate dean for ethics at UCLA Health, treats postmenopausal patients with TRT for reasons other than low libido. “I have a very specialized practice in reproductive endocrinology and internal medicine and am one of very few people in the country who do this kind of management,” he said in an interview. “If my postmenopausal patients have low testosterone and lack energy, I’m willing to give them low doses. If they feel more energetic, we continue, but if they don’t, we stop. I don’t think there’s any risk whatsoever at the low level I prescribe.
“I prescribe standard gel that comes in a squirt bottle, and I suggest they take half a squirt every other day – about one-eighth of a male dose – on the sole of the foot, where hair does not grow.
“I would not prescribe testosterone for bone health. We have bisphosphonates and other much better treatments for that. And I would not prescribe it to someone who is seriously emotionally disturbed or seriously depressed. This is not a treatment for depression.”
“Postmenopausal testosterone is not ‘the latest greatest thing,’ but being very low risk, it’s worth trying once in a while, in the appropriate patient, at the right dose,” Dr. Korenman advised. He cautioned people to “avoid the longevity salespeople who sell all sorts of things in all sorts of doses to try to keep us alive forever.”
All contributors report no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Obesity boosts gestational diabetes risk in women with PCOS
In a population-based cohort study that included more than 1.2 million hospital live births, PCOS was associated with a 5% increase in risk for gestational diabetes. Almost 90% of this association was mediated by obesity.
“Women with PCOS are at higher risk, but it’s only 5% higher than the general population. However, that risk rises substantially with obesity,” senior author Maria P. Velez, MD, PhD, clinician-scientist and associate professor of obstetrics and gynecology at Queen’s University, Kingston, Ont., said in an interview. “Our study highlights the need for counseling our patients about the importance of weight optimization, ideally starting with lifestyle changes like diet and exercise.”The findings were published in the Journal of Obstetrics and Gynaecology Canada.
Major mediator
The estimated prevalence of PCOS is 8%-13%, and affected patients often present with anovulation, hyperandrogenism, obesity, metabolic syndrome, and infertility. Prepregnancy insulin resistance is common among women with PCOS and may play a major part in the pathogenesis of gestational diabetes. In addition, PCOS is often accompanied by excess weight gain; about 60% of women with PCOS are overweight or obese.
Previous research has shown that PCOS is a risk factor for gestational diabetes independent of obesity, while other research has shown that obesity has an important effect on this risk.
For the current study, the researchers used causal mediation analysis to elucidate more clearly the effect of obesity on the development of gestational diabetes among patients with PCOS. No previous study has used causal mediation analysis to examine this relationship.
Using data from linked universal health databases in Ontario, the researchers analyzed data on 1,268,901 births between 2006 and 2018. Of these births, 386,748 were associated with maternal PCOS.
The rate of gestational diabetes was higher among women with PCOS (60.2 per 1000 births), compared with women without PCOS (48.6 per 1,000 births). The finding resulted in an adjusted relative risk of 1.05. Obesity mediated 89.7% of this association.
“We hope that these data will inform preconception counseling and gestational diabetes screening in pregnant women with PCOS,” said Dr. Velez. “We have the data now to counsel our patients on the importance of weight management before pregnancy. But we need more resources, such as specialized clinics, to help these patients cope with managing their weight. We can tell our patients to work on their weight management, but they need much more support from the health care system.”
Results ‘not surprising’
Commenting on the study, Francine Hippolyte, MD, vice chair of obstetrics and gynecology at Long Island Jewish Medical Center, Katz Women’s Hospital, New Hyde Park, N.Y., said that the results are “not at all surprising.” Dr. Hippolyte was not involved in the research.
“We do know that PCOS is and should be treated as a metabolic syndrome. It’s a lot more than just infertility or changes or abnormalities with one’s menstrual cycle. It impacts a woman’s risk for diabetes, prediabetes, and abnormal lipid profile, regardless of whether or not she is obese,” said Dr. Hippolyte.
She agrees with the need for specialized clinics to help such vulnerable patients manage their weight.
“It would be great if insurances would cover things like nutritional counseling or have nutritionists on their roster so that patients can easily access that service. Many patients want to do right, especially preconceptually, but it is difficult without having access to resources. Unfortunately, as clinicians, we’re not as well versed in nutrition as we would like to be or should be, so we need a multidisciplinary approach. We need nutrition and weight loss clinics and proper services to really help these patients.”
The study was supported by the Canadian Institute of Health Research and ICES. Dr. Velez and Dr. Hippolyte reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
In a population-based cohort study that included more than 1.2 million hospital live births, PCOS was associated with a 5% increase in risk for gestational diabetes. Almost 90% of this association was mediated by obesity.
“Women with PCOS are at higher risk, but it’s only 5% higher than the general population. However, that risk rises substantially with obesity,” senior author Maria P. Velez, MD, PhD, clinician-scientist and associate professor of obstetrics and gynecology at Queen’s University, Kingston, Ont., said in an interview. “Our study highlights the need for counseling our patients about the importance of weight optimization, ideally starting with lifestyle changes like diet and exercise.”The findings were published in the Journal of Obstetrics and Gynaecology Canada.
Major mediator
The estimated prevalence of PCOS is 8%-13%, and affected patients often present with anovulation, hyperandrogenism, obesity, metabolic syndrome, and infertility. Prepregnancy insulin resistance is common among women with PCOS and may play a major part in the pathogenesis of gestational diabetes. In addition, PCOS is often accompanied by excess weight gain; about 60% of women with PCOS are overweight or obese.
Previous research has shown that PCOS is a risk factor for gestational diabetes independent of obesity, while other research has shown that obesity has an important effect on this risk.
For the current study, the researchers used causal mediation analysis to elucidate more clearly the effect of obesity on the development of gestational diabetes among patients with PCOS. No previous study has used causal mediation analysis to examine this relationship.
Using data from linked universal health databases in Ontario, the researchers analyzed data on 1,268,901 births between 2006 and 2018. Of these births, 386,748 were associated with maternal PCOS.
The rate of gestational diabetes was higher among women with PCOS (60.2 per 1000 births), compared with women without PCOS (48.6 per 1,000 births). The finding resulted in an adjusted relative risk of 1.05. Obesity mediated 89.7% of this association.
“We hope that these data will inform preconception counseling and gestational diabetes screening in pregnant women with PCOS,” said Dr. Velez. “We have the data now to counsel our patients on the importance of weight management before pregnancy. But we need more resources, such as specialized clinics, to help these patients cope with managing their weight. We can tell our patients to work on their weight management, but they need much more support from the health care system.”
Results ‘not surprising’
Commenting on the study, Francine Hippolyte, MD, vice chair of obstetrics and gynecology at Long Island Jewish Medical Center, Katz Women’s Hospital, New Hyde Park, N.Y., said that the results are “not at all surprising.” Dr. Hippolyte was not involved in the research.
“We do know that PCOS is and should be treated as a metabolic syndrome. It’s a lot more than just infertility or changes or abnormalities with one’s menstrual cycle. It impacts a woman’s risk for diabetes, prediabetes, and abnormal lipid profile, regardless of whether or not she is obese,” said Dr. Hippolyte.
She agrees with the need for specialized clinics to help such vulnerable patients manage their weight.
“It would be great if insurances would cover things like nutritional counseling or have nutritionists on their roster so that patients can easily access that service. Many patients want to do right, especially preconceptually, but it is difficult without having access to resources. Unfortunately, as clinicians, we’re not as well versed in nutrition as we would like to be or should be, so we need a multidisciplinary approach. We need nutrition and weight loss clinics and proper services to really help these patients.”
The study was supported by the Canadian Institute of Health Research and ICES. Dr. Velez and Dr. Hippolyte reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
In a population-based cohort study that included more than 1.2 million hospital live births, PCOS was associated with a 5% increase in risk for gestational diabetes. Almost 90% of this association was mediated by obesity.
“Women with PCOS are at higher risk, but it’s only 5% higher than the general population. However, that risk rises substantially with obesity,” senior author Maria P. Velez, MD, PhD, clinician-scientist and associate professor of obstetrics and gynecology at Queen’s University, Kingston, Ont., said in an interview. “Our study highlights the need for counseling our patients about the importance of weight optimization, ideally starting with lifestyle changes like diet and exercise.”The findings were published in the Journal of Obstetrics and Gynaecology Canada.
Major mediator
The estimated prevalence of PCOS is 8%-13%, and affected patients often present with anovulation, hyperandrogenism, obesity, metabolic syndrome, and infertility. Prepregnancy insulin resistance is common among women with PCOS and may play a major part in the pathogenesis of gestational diabetes. In addition, PCOS is often accompanied by excess weight gain; about 60% of women with PCOS are overweight or obese.
Previous research has shown that PCOS is a risk factor for gestational diabetes independent of obesity, while other research has shown that obesity has an important effect on this risk.
For the current study, the researchers used causal mediation analysis to elucidate more clearly the effect of obesity on the development of gestational diabetes among patients with PCOS. No previous study has used causal mediation analysis to examine this relationship.
Using data from linked universal health databases in Ontario, the researchers analyzed data on 1,268,901 births between 2006 and 2018. Of these births, 386,748 were associated with maternal PCOS.
The rate of gestational diabetes was higher among women with PCOS (60.2 per 1000 births), compared with women without PCOS (48.6 per 1,000 births). The finding resulted in an adjusted relative risk of 1.05. Obesity mediated 89.7% of this association.
“We hope that these data will inform preconception counseling and gestational diabetes screening in pregnant women with PCOS,” said Dr. Velez. “We have the data now to counsel our patients on the importance of weight management before pregnancy. But we need more resources, such as specialized clinics, to help these patients cope with managing their weight. We can tell our patients to work on their weight management, but they need much more support from the health care system.”
Results ‘not surprising’
Commenting on the study, Francine Hippolyte, MD, vice chair of obstetrics and gynecology at Long Island Jewish Medical Center, Katz Women’s Hospital, New Hyde Park, N.Y., said that the results are “not at all surprising.” Dr. Hippolyte was not involved in the research.
“We do know that PCOS is and should be treated as a metabolic syndrome. It’s a lot more than just infertility or changes or abnormalities with one’s menstrual cycle. It impacts a woman’s risk for diabetes, prediabetes, and abnormal lipid profile, regardless of whether or not she is obese,” said Dr. Hippolyte.
She agrees with the need for specialized clinics to help such vulnerable patients manage their weight.
“It would be great if insurances would cover things like nutritional counseling or have nutritionists on their roster so that patients can easily access that service. Many patients want to do right, especially preconceptually, but it is difficult without having access to resources. Unfortunately, as clinicians, we’re not as well versed in nutrition as we would like to be or should be, so we need a multidisciplinary approach. We need nutrition and weight loss clinics and proper services to really help these patients.”
The study was supported by the Canadian Institute of Health Research and ICES. Dr. Velez and Dr. Hippolyte reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM JOURNAL OF OBSTETRICS AND GYNAECOLOGY CANADA
Lack of racial, ethnic diversity in cryopreserved donor sperm in the U.S.
, according to a study presented at the American Society for Reproductive Medicine’s 2023 meeting.
“This really highlights the need to identify barriers to increase recruitment of these donors so that we can support family-building for all populations,” said Lauren Gibbs, MD, a resident in the department of obstetrics and gynecology at the Morehouse School of Medicine in Atlanta.
Dr. Gibbs and her colleagues compared the racial and ethnic makeup of sperm donors from online and self-reported profiles at 14 of the largest donor banks in the United States for March and April of 2023. Historical data were pulled from two large, national banks. The investigators compared these data to census estimates from 2021 for men between the ages of 18 and 44 years.
Donors who identified as Hispanic (10.9%) or Black (3.3%) were significantly underrepresented as compared to the U.S. population, of which Hispanic men compose 22% and Black men make up 13.3%.
Asian donors were overrepresented, making up 21.9% of the donors but only 6.5% of the U.S. population. White donors were proportionately represented in relation to national demographics, making up 56.6% of the donors and representing 55% of the U.S. population, according to the researchers. None of the donors identified as Native/Hawaiian/Pacific Islander or American Indian/Alaskan Natives; these groups represent 0.22% and 0.79% of the U.S. population, respectively.
“Next steps will be figuring out why this is happening and how to address it,” said Valerie L Baker, MD, director in the division of reproductive endocrinology and infertility at Johns Hopkins Medicine in Lutherville, Md., who was not involved in the study.
The study sheds light on the need to identify and address the barriers that discourage potential donors from underrepresented groups from participating in sperm donation, according to Kimball Pomeroy, PhD, scientific director at the World Egg and Sperm Bank in Scottsdale, Ariz.
“Sometimes there are inhibitors of different ethnic groups to want to act as sperm or egg donors, so trying to understand if that’s the case is important; but I’m sure a lot of it is also related to access,” Dr. Pomeroy, who was not part of the study team, said in an interview.
Longitudinal data from the two national donor banks did not indicate any significant increase or decrease in donation trends across the 5-year period from 2018 to 2022, highlighting the persisting issue of representation disparities. Dr. Gibbs said strategies need to be developed to increase recruitment of donors from underrepresented groups. Increasing the diversity of the donor pool will ultimately support family-building options for all patients, according to Dr. Gibbs.
Funding for the study was provided by the EMD Serono REI Diversity Fellowship Grant. Dr. Gibbs reports no relevant financial relationships.
, according to a study presented at the American Society for Reproductive Medicine’s 2023 meeting.
“This really highlights the need to identify barriers to increase recruitment of these donors so that we can support family-building for all populations,” said Lauren Gibbs, MD, a resident in the department of obstetrics and gynecology at the Morehouse School of Medicine in Atlanta.
Dr. Gibbs and her colleagues compared the racial and ethnic makeup of sperm donors from online and self-reported profiles at 14 of the largest donor banks in the United States for March and April of 2023. Historical data were pulled from two large, national banks. The investigators compared these data to census estimates from 2021 for men between the ages of 18 and 44 years.
Donors who identified as Hispanic (10.9%) or Black (3.3%) were significantly underrepresented as compared to the U.S. population, of which Hispanic men compose 22% and Black men make up 13.3%.
Asian donors were overrepresented, making up 21.9% of the donors but only 6.5% of the U.S. population. White donors were proportionately represented in relation to national demographics, making up 56.6% of the donors and representing 55% of the U.S. population, according to the researchers. None of the donors identified as Native/Hawaiian/Pacific Islander or American Indian/Alaskan Natives; these groups represent 0.22% and 0.79% of the U.S. population, respectively.
“Next steps will be figuring out why this is happening and how to address it,” said Valerie L Baker, MD, director in the division of reproductive endocrinology and infertility at Johns Hopkins Medicine in Lutherville, Md., who was not involved in the study.
The study sheds light on the need to identify and address the barriers that discourage potential donors from underrepresented groups from participating in sperm donation, according to Kimball Pomeroy, PhD, scientific director at the World Egg and Sperm Bank in Scottsdale, Ariz.
“Sometimes there are inhibitors of different ethnic groups to want to act as sperm or egg donors, so trying to understand if that’s the case is important; but I’m sure a lot of it is also related to access,” Dr. Pomeroy, who was not part of the study team, said in an interview.
Longitudinal data from the two national donor banks did not indicate any significant increase or decrease in donation trends across the 5-year period from 2018 to 2022, highlighting the persisting issue of representation disparities. Dr. Gibbs said strategies need to be developed to increase recruitment of donors from underrepresented groups. Increasing the diversity of the donor pool will ultimately support family-building options for all patients, according to Dr. Gibbs.
Funding for the study was provided by the EMD Serono REI Diversity Fellowship Grant. Dr. Gibbs reports no relevant financial relationships.
, according to a study presented at the American Society for Reproductive Medicine’s 2023 meeting.
“This really highlights the need to identify barriers to increase recruitment of these donors so that we can support family-building for all populations,” said Lauren Gibbs, MD, a resident in the department of obstetrics and gynecology at the Morehouse School of Medicine in Atlanta.
Dr. Gibbs and her colleagues compared the racial and ethnic makeup of sperm donors from online and self-reported profiles at 14 of the largest donor banks in the United States for March and April of 2023. Historical data were pulled from two large, national banks. The investigators compared these data to census estimates from 2021 for men between the ages of 18 and 44 years.
Donors who identified as Hispanic (10.9%) or Black (3.3%) were significantly underrepresented as compared to the U.S. population, of which Hispanic men compose 22% and Black men make up 13.3%.
Asian donors were overrepresented, making up 21.9% of the donors but only 6.5% of the U.S. population. White donors were proportionately represented in relation to national demographics, making up 56.6% of the donors and representing 55% of the U.S. population, according to the researchers. None of the donors identified as Native/Hawaiian/Pacific Islander or American Indian/Alaskan Natives; these groups represent 0.22% and 0.79% of the U.S. population, respectively.
“Next steps will be figuring out why this is happening and how to address it,” said Valerie L Baker, MD, director in the division of reproductive endocrinology and infertility at Johns Hopkins Medicine in Lutherville, Md., who was not involved in the study.
The study sheds light on the need to identify and address the barriers that discourage potential donors from underrepresented groups from participating in sperm donation, according to Kimball Pomeroy, PhD, scientific director at the World Egg and Sperm Bank in Scottsdale, Ariz.
“Sometimes there are inhibitors of different ethnic groups to want to act as sperm or egg donors, so trying to understand if that’s the case is important; but I’m sure a lot of it is also related to access,” Dr. Pomeroy, who was not part of the study team, said in an interview.
Longitudinal data from the two national donor banks did not indicate any significant increase or decrease in donation trends across the 5-year period from 2018 to 2022, highlighting the persisting issue of representation disparities. Dr. Gibbs said strategies need to be developed to increase recruitment of donors from underrepresented groups. Increasing the diversity of the donor pool will ultimately support family-building options for all patients, according to Dr. Gibbs.
Funding for the study was provided by the EMD Serono REI Diversity Fellowship Grant. Dr. Gibbs reports no relevant financial relationships.
FROM ASRM 2023
Tech encourages HIV prevention among women
Access to technology, particularly cellphones, is tied to a higher awareness of pre-exposure prophylaxis (PrEP) in women, according to survey results presented at the Association of Nurses in AIDS Care 2023 Annual Meeting.
Those with limited access to technology, older women, and women who had been incarcerated were also less likely to be aware of their medication options.
Researchers collected responses from 206 women in New York and Philadelphia by computer survey. The women were HIV negative and eligible to receive medication but were not currently taking any.
Most participants were Black (61%) or Hispanic (24%), and the average age of participants was 39 years. Nearly 60% of the group reported they were not aware of PrEP.
Younger women, Hispanic women, women who had not been incarcerated, and women with access to technology were most likely to be aware that they could take medication to prevent HIV.
“Women who utilized their cell phones for activities such as texting, emailing, watching videos, playing games, downloading apps, and accessing social media were more likely to be aware of PrEP,” point out the researchers led by Su Kyung Kim, PhD, WHNP-BC, an assistant professor at Thomas Jefferson University, Philadelphia.
These findings could help direct efforts to increase awareness among women where uptake has remained low, the researchers report. “Mobile technologies, in particular, offer a nimble, customizable, and accessible way to reach this target population and increase awareness of PrEP.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Access to technology, particularly cellphones, is tied to a higher awareness of pre-exposure prophylaxis (PrEP) in women, according to survey results presented at the Association of Nurses in AIDS Care 2023 Annual Meeting.
Those with limited access to technology, older women, and women who had been incarcerated were also less likely to be aware of their medication options.
Researchers collected responses from 206 women in New York and Philadelphia by computer survey. The women were HIV negative and eligible to receive medication but were not currently taking any.
Most participants were Black (61%) or Hispanic (24%), and the average age of participants was 39 years. Nearly 60% of the group reported they were not aware of PrEP.
Younger women, Hispanic women, women who had not been incarcerated, and women with access to technology were most likely to be aware that they could take medication to prevent HIV.
“Women who utilized their cell phones for activities such as texting, emailing, watching videos, playing games, downloading apps, and accessing social media were more likely to be aware of PrEP,” point out the researchers led by Su Kyung Kim, PhD, WHNP-BC, an assistant professor at Thomas Jefferson University, Philadelphia.
These findings could help direct efforts to increase awareness among women where uptake has remained low, the researchers report. “Mobile technologies, in particular, offer a nimble, customizable, and accessible way to reach this target population and increase awareness of PrEP.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Access to technology, particularly cellphones, is tied to a higher awareness of pre-exposure prophylaxis (PrEP) in women, according to survey results presented at the Association of Nurses in AIDS Care 2023 Annual Meeting.
Those with limited access to technology, older women, and women who had been incarcerated were also less likely to be aware of their medication options.
Researchers collected responses from 206 women in New York and Philadelphia by computer survey. The women were HIV negative and eligible to receive medication but were not currently taking any.
Most participants were Black (61%) or Hispanic (24%), and the average age of participants was 39 years. Nearly 60% of the group reported they were not aware of PrEP.
Younger women, Hispanic women, women who had not been incarcerated, and women with access to technology were most likely to be aware that they could take medication to prevent HIV.
“Women who utilized their cell phones for activities such as texting, emailing, watching videos, playing games, downloading apps, and accessing social media were more likely to be aware of PrEP,” point out the researchers led by Su Kyung Kim, PhD, WHNP-BC, an assistant professor at Thomas Jefferson University, Philadelphia.
These findings could help direct efforts to increase awareness among women where uptake has remained low, the researchers report. “Mobile technologies, in particular, offer a nimble, customizable, and accessible way to reach this target population and increase awareness of PrEP.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.