User login
Bringing you the latest news, research and reviews, exclusive interviews, podcasts, quizzes, and more.
div[contains(@class, 'header__large-screen')]
div[contains(@class, 'read-next-article')]
div[contains(@class, 'main-prefix')]
div[contains(@class, 'nav-primary')]
nav[contains(@class, 'nav-primary')]
section[contains(@class, 'footer-nav-section-wrapper')]
footer[@id='footer']
section[contains(@class, 'nav-hidden')]
div[contains(@class, 'ce-card-content')]
nav[contains(@class, 'nav-ce-stack')]
div[contains(@class, 'view-medstat-quiz-listing-panes')]
div[contains(@class, 'pane-article-sidebar-latest-news')]
The right indoor relative humidity could ward off COVID
The “sweet spot” associated with reduced COVID-19 cases and deaths is 40%-60% indoor relative humidity, an MIT news release said. People who maintained indoor relative humidity outside those parameters had higher rates of catching COVID-19.
Most people are comfortable with 30%-50% relative humidity, researchers said. An airplane cabin has about 20% relative humidity.
Relative humidity is the amount of moisture in the air, compared with the total moisture the air can hold at a given temperature before saturating and forming condensation.
The study was published in The Journal of the Royal Society Interface. Researchers examined COVID-19 data and meteorological measurements from 121 countries from January 2020 through August 2020, before vaccines became available to the public.
“When outdoor temperatures were below the typical human comfort range, they assumed indoor spaces were heated to reach that comfort range. Based on the added heating, they calculated the associated drop in indoor relative humidity,” the MIT news release said.
The research teams found that when a region reported a rise in COVID-19 cases and deaths, the region’s estimated indoor relative humidity was either lower than 40% or higher than 60%, the release said.
“There’s potentially a protective effect of this intermediate indoor relative humidity,” said Connor Verheyen, the lead author and a PhD student in medical engineering and medical physics in the Harvard-MIT Program in Health Sciences and Technology.
Widespread use of the 40%-60% indoor humidity range could reduce the need for lockdowns and other widespread restrictions, the study concluded.
“Unlike measures that depend on individual compliance (for example, masking or hand-washing), indoor RH optimization would achieve high compliance because all occupants of a common indoor space would be exposed to similar ambient conditions,” the study said. “Compared to the long timelines and high costs of vaccine production and distribution, humidity control systems could potentially be implemented more quickly and cheaply in certain indoor settings.”
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
The “sweet spot” associated with reduced COVID-19 cases and deaths is 40%-60% indoor relative humidity, an MIT news release said. People who maintained indoor relative humidity outside those parameters had higher rates of catching COVID-19.
Most people are comfortable with 30%-50% relative humidity, researchers said. An airplane cabin has about 20% relative humidity.
Relative humidity is the amount of moisture in the air, compared with the total moisture the air can hold at a given temperature before saturating and forming condensation.
The study was published in The Journal of the Royal Society Interface. Researchers examined COVID-19 data and meteorological measurements from 121 countries from January 2020 through August 2020, before vaccines became available to the public.
“When outdoor temperatures were below the typical human comfort range, they assumed indoor spaces were heated to reach that comfort range. Based on the added heating, they calculated the associated drop in indoor relative humidity,” the MIT news release said.
The research teams found that when a region reported a rise in COVID-19 cases and deaths, the region’s estimated indoor relative humidity was either lower than 40% or higher than 60%, the release said.
“There’s potentially a protective effect of this intermediate indoor relative humidity,” said Connor Verheyen, the lead author and a PhD student in medical engineering and medical physics in the Harvard-MIT Program in Health Sciences and Technology.
Widespread use of the 40%-60% indoor humidity range could reduce the need for lockdowns and other widespread restrictions, the study concluded.
“Unlike measures that depend on individual compliance (for example, masking or hand-washing), indoor RH optimization would achieve high compliance because all occupants of a common indoor space would be exposed to similar ambient conditions,” the study said. “Compared to the long timelines and high costs of vaccine production and distribution, humidity control systems could potentially be implemented more quickly and cheaply in certain indoor settings.”
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
The “sweet spot” associated with reduced COVID-19 cases and deaths is 40%-60% indoor relative humidity, an MIT news release said. People who maintained indoor relative humidity outside those parameters had higher rates of catching COVID-19.
Most people are comfortable with 30%-50% relative humidity, researchers said. An airplane cabin has about 20% relative humidity.
Relative humidity is the amount of moisture in the air, compared with the total moisture the air can hold at a given temperature before saturating and forming condensation.
The study was published in The Journal of the Royal Society Interface. Researchers examined COVID-19 data and meteorological measurements from 121 countries from January 2020 through August 2020, before vaccines became available to the public.
“When outdoor temperatures were below the typical human comfort range, they assumed indoor spaces were heated to reach that comfort range. Based on the added heating, they calculated the associated drop in indoor relative humidity,” the MIT news release said.
The research teams found that when a region reported a rise in COVID-19 cases and deaths, the region’s estimated indoor relative humidity was either lower than 40% or higher than 60%, the release said.
“There’s potentially a protective effect of this intermediate indoor relative humidity,” said Connor Verheyen, the lead author and a PhD student in medical engineering and medical physics in the Harvard-MIT Program in Health Sciences and Technology.
Widespread use of the 40%-60% indoor humidity range could reduce the need for lockdowns and other widespread restrictions, the study concluded.
“Unlike measures that depend on individual compliance (for example, masking or hand-washing), indoor RH optimization would achieve high compliance because all occupants of a common indoor space would be exposed to similar ambient conditions,” the study said. “Compared to the long timelines and high costs of vaccine production and distribution, humidity control systems could potentially be implemented more quickly and cheaply in certain indoor settings.”
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
FROM THE JOURNAL OF THE ROYAL SOCIETY INTERFACE
HDL cholesterol not linked to CHD risk in Blacks: REGARDS
High-density lipoprotein cholesterol may not be as effective a biomarker of cardiovascular disease risk as once thought, particularly in Black adults, according to results from a large biracial cohort study that also raised questions about the validity of high HDL cholesterol as a potentially protective factor in White and Black adults alike.
“I think this opens the door to suggest that every biomarker we use might have a race-specific association with disease outcome,” Nathalie Pamir, PhD, an associate professor at Oregon Health & Science University in Portland, said in an interview. “So, something as basic as HDL cholesterol – we’ve known about it since 1970 – has a race signature.”
Dr. Pamir and colleagues reported their findings from the REGARDS (Reasons for Geographic and Racial Differences in Stroke) cohort study that recruited 30,239 Black and White individuals aged 45 years and older from the contiguous United States from 2003 to 2007.
The study found that LDL cholesterol “modestly” predicted coronary heart disease (CHD) risk in Black and White adults. However, low HDL cholesterol, while associated with an increased risk in White patients (hazard ratio, 1.22; 95% confidence interval, 1.05-1.43), did not have a similar association in Blacks (HR, 0.94; 95% CI: 0.78-1.14). And high HDL cholesterol wasn’t found to be predictive in either group (HR, 0.96; 95% CI, 0.79-1.16 for White participants: HR, 0.91; 95% CI, 0.74-1.12 for Black participants).
Among 23,901 study participants who were CHD-risk free over a 10-year follow-up, 664 and 951 CHD events occurred in Black and White participants, respectively. The study cohort was 57.8% White and 58.4% women, with a mean age of 65 years.
The study noted that LDL cholesterol and triglycerides conferred similar risks for CHD in both White and Black participants.
Acknowledging that this study focused on Blacks, Dr. Pamir added that “we need to know about Asian Americans; we need to know about Hispanic Americans.”
Change of approach to lipid management called for
Dr. Pamir noted that the current understanding about HDL cholesterol and CHD risk comes from the Framingham heart study in the 1970s, whose population was 100% White.
Care algorithms derived from the Framingham study as well as the Multi-Ethnic Study of Atherosclerosis incorporate that association between HDL cholesterol and CHD risk, she noted, but these findings from REGARDS should change how cardiologists approach lipid management in Black and White patients.
“The conversation would go something like: High HDL cholesterol levels put you in a higher risk [bracket] but HDL cholesterol levels are not something we treat; we have no drugs for that,” Dr. Pamir said.
“The conversation would continue along the lines that: ‘You need to do more exercise, you need to change your diet, incorporate healthy fats, walnuts, and omega 3s.’
“But what might the conversation be for Black patients? ‘We don’t see the association that we see for White patients. Do adopt the good habits to exercise and dietary changes, but don’t get too worried about it.’ ”
The study report raises “caution” about using the Framingham, MESA, and other algorithms for evaluating CHD risk. Dr. Pamir explained what that means. “We might be underestimating risk, because what our study showed was that, when we looked at clinically high HDL cholesterol, about 60 mg/dL, it has no benefit for White and Black patients.”
She added, “So that pat on the back we get for patients that have high HDL-C levels? Maybe that pat on the back shouldn’t be there.”
In an invited commentary, Keith C. Ferdinand, MD, of Tulane University in New Orleans, wrote that using HDL cholesterol in risk calculations could inaccurately assess atherosclerotic cardiovascular risk in Black adults “and become a barrier to optimal care.”
In an interview, he said the REGARDS findings call for consideration of other biomarkers for evaluating CHD risk and point to the importance of socioeconomic factors in health outcomes.
“Physicians and other clinicians need to recognize the powerful impact of the social determinants of health and to also recognize the limits of HDL itself as either protective if it’s high or a definitive predictor of risk if it’s low, and focus on some more modern approaches, including coronary artery calcium scoring.”
He also said risk evaluation should include lipoprotein(a), which, he noted in the editorial, the European Atherosclerosis Society recommends measuring. “One of the reasons it’s underutilized is that we really don’t have a specific treatment for it,” he said of Lp(a) in the United States.
In his editorial comment, Dr. Ferdinand called for future research aimed at eliminating health disparities. “Regardless of the development of better tools for the assessment of risk, newer drugs to treat CVD, the use of coronary artery calcium, if we don’t apply evidence-based medicine equally across the population based on race, ethnicity, sex, gender, socioeconomic status, or geography, then the disparities are going to persist,” he said.
The National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke and the National Institute on Aging provided funding for the study. Dr. Pamir has no relevant relationships to disclose. Dr. Ferdinand disclosed relationships with Boehringer Ingelheim, Novartis, Janssen, and Lilly.
High-density lipoprotein cholesterol may not be as effective a biomarker of cardiovascular disease risk as once thought, particularly in Black adults, according to results from a large biracial cohort study that also raised questions about the validity of high HDL cholesterol as a potentially protective factor in White and Black adults alike.
“I think this opens the door to suggest that every biomarker we use might have a race-specific association with disease outcome,” Nathalie Pamir, PhD, an associate professor at Oregon Health & Science University in Portland, said in an interview. “So, something as basic as HDL cholesterol – we’ve known about it since 1970 – has a race signature.”
Dr. Pamir and colleagues reported their findings from the REGARDS (Reasons for Geographic and Racial Differences in Stroke) cohort study that recruited 30,239 Black and White individuals aged 45 years and older from the contiguous United States from 2003 to 2007.
The study found that LDL cholesterol “modestly” predicted coronary heart disease (CHD) risk in Black and White adults. However, low HDL cholesterol, while associated with an increased risk in White patients (hazard ratio, 1.22; 95% confidence interval, 1.05-1.43), did not have a similar association in Blacks (HR, 0.94; 95% CI: 0.78-1.14). And high HDL cholesterol wasn’t found to be predictive in either group (HR, 0.96; 95% CI, 0.79-1.16 for White participants: HR, 0.91; 95% CI, 0.74-1.12 for Black participants).
Among 23,901 study participants who were CHD-risk free over a 10-year follow-up, 664 and 951 CHD events occurred in Black and White participants, respectively. The study cohort was 57.8% White and 58.4% women, with a mean age of 65 years.
The study noted that LDL cholesterol and triglycerides conferred similar risks for CHD in both White and Black participants.
Acknowledging that this study focused on Blacks, Dr. Pamir added that “we need to know about Asian Americans; we need to know about Hispanic Americans.”
Change of approach to lipid management called for
Dr. Pamir noted that the current understanding about HDL cholesterol and CHD risk comes from the Framingham heart study in the 1970s, whose population was 100% White.
Care algorithms derived from the Framingham study as well as the Multi-Ethnic Study of Atherosclerosis incorporate that association between HDL cholesterol and CHD risk, she noted, but these findings from REGARDS should change how cardiologists approach lipid management in Black and White patients.
“The conversation would go something like: High HDL cholesterol levels put you in a higher risk [bracket] but HDL cholesterol levels are not something we treat; we have no drugs for that,” Dr. Pamir said.
“The conversation would continue along the lines that: ‘You need to do more exercise, you need to change your diet, incorporate healthy fats, walnuts, and omega 3s.’
“But what might the conversation be for Black patients? ‘We don’t see the association that we see for White patients. Do adopt the good habits to exercise and dietary changes, but don’t get too worried about it.’ ”
The study report raises “caution” about using the Framingham, MESA, and other algorithms for evaluating CHD risk. Dr. Pamir explained what that means. “We might be underestimating risk, because what our study showed was that, when we looked at clinically high HDL cholesterol, about 60 mg/dL, it has no benefit for White and Black patients.”
She added, “So that pat on the back we get for patients that have high HDL-C levels? Maybe that pat on the back shouldn’t be there.”
In an invited commentary, Keith C. Ferdinand, MD, of Tulane University in New Orleans, wrote that using HDL cholesterol in risk calculations could inaccurately assess atherosclerotic cardiovascular risk in Black adults “and become a barrier to optimal care.”
In an interview, he said the REGARDS findings call for consideration of other biomarkers for evaluating CHD risk and point to the importance of socioeconomic factors in health outcomes.
“Physicians and other clinicians need to recognize the powerful impact of the social determinants of health and to also recognize the limits of HDL itself as either protective if it’s high or a definitive predictor of risk if it’s low, and focus on some more modern approaches, including coronary artery calcium scoring.”
He also said risk evaluation should include lipoprotein(a), which, he noted in the editorial, the European Atherosclerosis Society recommends measuring. “One of the reasons it’s underutilized is that we really don’t have a specific treatment for it,” he said of Lp(a) in the United States.
In his editorial comment, Dr. Ferdinand called for future research aimed at eliminating health disparities. “Regardless of the development of better tools for the assessment of risk, newer drugs to treat CVD, the use of coronary artery calcium, if we don’t apply evidence-based medicine equally across the population based on race, ethnicity, sex, gender, socioeconomic status, or geography, then the disparities are going to persist,” he said.
The National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke and the National Institute on Aging provided funding for the study. Dr. Pamir has no relevant relationships to disclose. Dr. Ferdinand disclosed relationships with Boehringer Ingelheim, Novartis, Janssen, and Lilly.
High-density lipoprotein cholesterol may not be as effective a biomarker of cardiovascular disease risk as once thought, particularly in Black adults, according to results from a large biracial cohort study that also raised questions about the validity of high HDL cholesterol as a potentially protective factor in White and Black adults alike.
“I think this opens the door to suggest that every biomarker we use might have a race-specific association with disease outcome,” Nathalie Pamir, PhD, an associate professor at Oregon Health & Science University in Portland, said in an interview. “So, something as basic as HDL cholesterol – we’ve known about it since 1970 – has a race signature.”
Dr. Pamir and colleagues reported their findings from the REGARDS (Reasons for Geographic and Racial Differences in Stroke) cohort study that recruited 30,239 Black and White individuals aged 45 years and older from the contiguous United States from 2003 to 2007.
The study found that LDL cholesterol “modestly” predicted coronary heart disease (CHD) risk in Black and White adults. However, low HDL cholesterol, while associated with an increased risk in White patients (hazard ratio, 1.22; 95% confidence interval, 1.05-1.43), did not have a similar association in Blacks (HR, 0.94; 95% CI: 0.78-1.14). And high HDL cholesterol wasn’t found to be predictive in either group (HR, 0.96; 95% CI, 0.79-1.16 for White participants: HR, 0.91; 95% CI, 0.74-1.12 for Black participants).
Among 23,901 study participants who were CHD-risk free over a 10-year follow-up, 664 and 951 CHD events occurred in Black and White participants, respectively. The study cohort was 57.8% White and 58.4% women, with a mean age of 65 years.
The study noted that LDL cholesterol and triglycerides conferred similar risks for CHD in both White and Black participants.
Acknowledging that this study focused on Blacks, Dr. Pamir added that “we need to know about Asian Americans; we need to know about Hispanic Americans.”
Change of approach to lipid management called for
Dr. Pamir noted that the current understanding about HDL cholesterol and CHD risk comes from the Framingham heart study in the 1970s, whose population was 100% White.
Care algorithms derived from the Framingham study as well as the Multi-Ethnic Study of Atherosclerosis incorporate that association between HDL cholesterol and CHD risk, she noted, but these findings from REGARDS should change how cardiologists approach lipid management in Black and White patients.
“The conversation would go something like: High HDL cholesterol levels put you in a higher risk [bracket] but HDL cholesterol levels are not something we treat; we have no drugs for that,” Dr. Pamir said.
“The conversation would continue along the lines that: ‘You need to do more exercise, you need to change your diet, incorporate healthy fats, walnuts, and omega 3s.’
“But what might the conversation be for Black patients? ‘We don’t see the association that we see for White patients. Do adopt the good habits to exercise and dietary changes, but don’t get too worried about it.’ ”
The study report raises “caution” about using the Framingham, MESA, and other algorithms for evaluating CHD risk. Dr. Pamir explained what that means. “We might be underestimating risk, because what our study showed was that, when we looked at clinically high HDL cholesterol, about 60 mg/dL, it has no benefit for White and Black patients.”
She added, “So that pat on the back we get for patients that have high HDL-C levels? Maybe that pat on the back shouldn’t be there.”
In an invited commentary, Keith C. Ferdinand, MD, of Tulane University in New Orleans, wrote that using HDL cholesterol in risk calculations could inaccurately assess atherosclerotic cardiovascular risk in Black adults “and become a barrier to optimal care.”
In an interview, he said the REGARDS findings call for consideration of other biomarkers for evaluating CHD risk and point to the importance of socioeconomic factors in health outcomes.
“Physicians and other clinicians need to recognize the powerful impact of the social determinants of health and to also recognize the limits of HDL itself as either protective if it’s high or a definitive predictor of risk if it’s low, and focus on some more modern approaches, including coronary artery calcium scoring.”
He also said risk evaluation should include lipoprotein(a), which, he noted in the editorial, the European Atherosclerosis Society recommends measuring. “One of the reasons it’s underutilized is that we really don’t have a specific treatment for it,” he said of Lp(a) in the United States.
In his editorial comment, Dr. Ferdinand called for future research aimed at eliminating health disparities. “Regardless of the development of better tools for the assessment of risk, newer drugs to treat CVD, the use of coronary artery calcium, if we don’t apply evidence-based medicine equally across the population based on race, ethnicity, sex, gender, socioeconomic status, or geography, then the disparities are going to persist,” he said.
The National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke and the National Institute on Aging provided funding for the study. Dr. Pamir has no relevant relationships to disclose. Dr. Ferdinand disclosed relationships with Boehringer Ingelheim, Novartis, Janssen, and Lilly.
FROM JOURNAL OF THE AMERICAN COLLEGE OF CARDIOLOGY
Will ICER review aid bid for Medicare to pay for obesity drugs?
A report from a well-respected nonprofit group may bolster efforts to have Medicare, the largest U.S. purchaser of prescription drugs, cover obesity medicines, for which there has been accumulating evidence of significant benefit.
The Institute for Clinical and Economic Review (ICER) released a report last month on obesity medicines, based on extensive review of research done to date and input from clinicians, drug-makers, and members of the public.
Of the treatments reviewed, the ICER report gave the best ratings to two Novo Nordisk products, a B+ for semaglutide (Wegovy) and a B for liraglutide (Saxenda), while also making the case for price cuts. At an annual U.S. net price estimated at $13,618, semaglutide exceeds what ICER considers typical cost-effectiveness thresholds. ICER suggested a benchmark annual price range for semaglutide of between $7,500 and $9,800.
The ICER report also directs insurers in general to provide more generous coverage of obesity medicines, with a specific recommendation for the U.S. Congress to pass a pending bill known as the Treat and Reduce Obesity Act of 2021. The bill would undo a restriction on weight-loss drugs in the Medicare Part D plans, which covered about 49 million people last year. Sen. Tom Carper (D-Del.) and Sen. Bill Cassidy, MD, (R-La.) have repeatedly introduced versions of the bill since 2013.
“In both chambers of Congress and with bipartisan support, we’ve pushed to expand Medicare coverage of additional therapies and medications to treat obesity,” Sen. Cassidy said in an email. “This report confirms what we’ve worked on for nearly a decade – our legislation will help improve lives.”
The current House version of the bill has the backing of more than a third of the members of that chamber, with 113 Democratic and 40 Republican cosponsors. The Senate version has 22 sponsors.
Changing views
The ICER report comes amid a broader change in how clinicians view obesity.
The American Academy of Pediatrics is readying a new Clinical Practice Guideline for the Evaluation and Treatment of Pediatric Obesity that will mark a major shift in approach. Aaron S. Kelly, PhD, a professor of pediatrics at the University of Minnesota, Minneapolis, described it as a “sea change,” with obesity now seen as “a chronic, refractory, relapsing disease,” for which watchful waiting is no longer appropriate.
But the field of obesity treatment looked quite different in the early 2000s when Congress worked on a plan to add a pharmacy benefit to Medicare.
The deliberate omission of obesity medicine in the Medicare Part D benefit reflected both the state of science at the time and U.S. experience with a dangerous weight-loss drug combo in the late 1990s.
Initial expectations for weight-loss pills were high after the Food and Drug Administration cleared dexfenfluramine HCl (Redux) in 1996, which was part of the popular fen-phen combination. “Newly Approved Diet Drug Promises to Help Millions of Obese Americans – But Is No Magic Bullet,” read a headline about the Redux approval in The Washington Post
When work began in the 2000s to create a Medicare pharmacy benefit, lawmakers and congressional staff had a pool of about $400 billion available to establish what became the Part D program, Joel White, a former House staffer who helped draft the law, told this news organization in an email exchange.
Given the state of obesity research at the time, it seemed to make sense to exclude weight-loss medications, wrote Mr. White. Mr. White is now chief executive of the consulting firm Horizon, which has clients in the drug industry including the Pharmaceutical Research and Manufacturers of America.
“Now we know that obesity is a chronic disease of epidemic proportions. Decades of research have produced a series of advances in the way we understand and treat obesity. While scientists and many who work directly with those impacted by this epidemic understand how treatments have advanced, the law lags behind,” Mr. White said.
XXXCurrent payment policies for obesity treatments are based on “outdated information and ongoing misperception,” he noted. “While Part D has been a resounding success, our Medicare approach to obesity is not.”
“In addition, it makes no sense that Medicare covers the most drastic procedure (bariatric surgery) but not less-invasive, effective treatments,” he added. “We should have long ago lifted restrictions based on advances in science and medicine.”
Overcoming the stigma
Scott Kahan, MD, MPH, agreed and hopes that the new ICER report will help more patients secure needed medications, raising a “call to arms” about the need for better coverage of obesity drugs.
Dr. Kahan is director of the National Center for Weight and Wellness, a private clinic in Washington, and chair of the clinical committee for The Obesity Society. He also served as a member of a policy roundtable that ICER convened as part of research on the report on obesity drugs. Dr. Kahan, who also serves on the faculty at the Johns Hopkins Bloomberg School of Public Health, Baltimore, has received fees from drug makers such as Eli Lilly.
The ICER report may help what Dr. Kahan described as well-founded caution about obesity treatments in general.
“When it comes to weight loss, there are all of these magical treatments that are sold on social media and traditional media. There are a lot of bad actors in terms of people calling themselves experts and gurus and promising all kinds of crazy stuff,” said Dr. Kahan.
And there are long-standing stigmas about obesity, he stressed.
“That underlies a lot of the backward policies, including poor coverage for medications and the noncoverage by Medicare,” Dr. Kahan said. “There’s a societal ingrained set of beliefs and misperceptions and biases. That takes time to unwind, and I think we’re on the way, but we’re not quite there yet.”
Lifestyle changes not enough to tackle obesity
AHIP (formerly America’s Health Insurance Plans) told this news organization its members consider ICER reports when making decisions about which products to cover. “And health plans already cover obesity treatments that they consider medically necessary,” said David Allen, an AHIP spokesperson.
“It is important to note that every treatment does not work for every patient, and many patients experience adverse events and may discontinue treatment,” he added in an email. “Health insurance providers play an important role in helping [health care] providers and patients identify the treatment options that are most likely to be effective as well as affordable.”
Separately, the nonprofit watchdog group Public Citizen cautioned against liraglutide on its Worst Pills, Best Pills website. In its view, the drug is minimally effective and has many dangerous adverse effects, which are even more frequent with the higher-dose weight-loss version (a lower-dose version is approved for type 2 diabetes).
“There is currently no medication that can be used safely to achieve weight loss effortlessly and without dangerous adverse effects,” the group said. “Rather than focus on losing weight by turning to risky drugs, overweight and obese adults seeking to achieve better health should make reasonable and sustainable changes to their lifestyle, such as eating a healthy diet and getting regular exercise.”
Yet, many people find there is little help available for making lifestyle changes, and some patients and physicians say these modifications by themselves are not enough.
“The vast majority of people with obesity cannot achieve sustained weight loss through diet and exercise alone,” said David Rind, MD, chief medical officer of ICER, in an Oct. 20 statement. “As such, obesity, and its resulting physical health, mental health, and social burdens, is not a choice or failing, but a medical condition.”
The focus should now be on assuring that effective medications “are priced in alignment with their benefits so that they are accessible and affordable across U.S. society,” Dr. Rind urges.
‘My own demise with a fork and knife’
ICER sought public feedback on a draft version of the report before finalizing it.
In their comments on ICER’s work, several pharmaceutical researchers and Novo Nordisk questioned the calculations used in making judgments about the value of obesity drugs. In a statement, Novo Nordisk told this news organization that the company’s view is that ICER’s modeling “does not adequately address the real-world complexities of obesity, and consequently underestimates the health and societal impact medical treatments can have.”
Commenters also dug into aspects of ICER’s calculations, including ones that consider quality-adjusted life-years (QALYs). ICER describes QALY as an academic standard for measuring how well all different types of medical treatments can extend or improve patients’ lives. In an explainer on its website, ICER says this metric has served as a fundamental component of cost-effectiveness analyses in the United States and around the world for more than 30 years.
ICER and drug makers have been at odds for some time, with PhRMA having criticized the nonprofit group. A 2020 Reuters article detailed public relations strategies used by firms paid by drug makers to raise questions about ICER’s work. Critics accuse it of allying with insurers.
ICER’s list of its recent financial supporters includes Blue Cross Blue Shield of Massachusetts and the Kaiser Foundation Health Plan, but also many other groups, such as the U.S. Department of Veterans Affairs, the American Academy of Neurology, and the American College of Rheumatology.
The public comments on the ICER report also include one from an unidentified woman who wrote of her past struggles to lose weight.
She said her health plan wouldn’t cover behavioral programs or semaglutide as a weight-loss drug but did cover it eventually because of signs that she had developed insulin resistance. The patient said the drug worked for her, whereas other approaches to control weight had failed.
“To put it simply, I now experience hunger and satiety in a way that I can only assume people with normal metabolism do. I am 49 years old and approaching the age where serious comorbidities associated with obesity begin to manifest,” the patient wrote.
“I no longer worry about bringing about my own demise with a fork and knife because of misfiring hunger cues.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
A report from a well-respected nonprofit group may bolster efforts to have Medicare, the largest U.S. purchaser of prescription drugs, cover obesity medicines, for which there has been accumulating evidence of significant benefit.
The Institute for Clinical and Economic Review (ICER) released a report last month on obesity medicines, based on extensive review of research done to date and input from clinicians, drug-makers, and members of the public.
Of the treatments reviewed, the ICER report gave the best ratings to two Novo Nordisk products, a B+ for semaglutide (Wegovy) and a B for liraglutide (Saxenda), while also making the case for price cuts. At an annual U.S. net price estimated at $13,618, semaglutide exceeds what ICER considers typical cost-effectiveness thresholds. ICER suggested a benchmark annual price range for semaglutide of between $7,500 and $9,800.
The ICER report also directs insurers in general to provide more generous coverage of obesity medicines, with a specific recommendation for the U.S. Congress to pass a pending bill known as the Treat and Reduce Obesity Act of 2021. The bill would undo a restriction on weight-loss drugs in the Medicare Part D plans, which covered about 49 million people last year. Sen. Tom Carper (D-Del.) and Sen. Bill Cassidy, MD, (R-La.) have repeatedly introduced versions of the bill since 2013.
“In both chambers of Congress and with bipartisan support, we’ve pushed to expand Medicare coverage of additional therapies and medications to treat obesity,” Sen. Cassidy said in an email. “This report confirms what we’ve worked on for nearly a decade – our legislation will help improve lives.”
The current House version of the bill has the backing of more than a third of the members of that chamber, with 113 Democratic and 40 Republican cosponsors. The Senate version has 22 sponsors.
Changing views
The ICER report comes amid a broader change in how clinicians view obesity.
The American Academy of Pediatrics is readying a new Clinical Practice Guideline for the Evaluation and Treatment of Pediatric Obesity that will mark a major shift in approach. Aaron S. Kelly, PhD, a professor of pediatrics at the University of Minnesota, Minneapolis, described it as a “sea change,” with obesity now seen as “a chronic, refractory, relapsing disease,” for which watchful waiting is no longer appropriate.
But the field of obesity treatment looked quite different in the early 2000s when Congress worked on a plan to add a pharmacy benefit to Medicare.
The deliberate omission of obesity medicine in the Medicare Part D benefit reflected both the state of science at the time and U.S. experience with a dangerous weight-loss drug combo in the late 1990s.
Initial expectations for weight-loss pills were high after the Food and Drug Administration cleared dexfenfluramine HCl (Redux) in 1996, which was part of the popular fen-phen combination. “Newly Approved Diet Drug Promises to Help Millions of Obese Americans – But Is No Magic Bullet,” read a headline about the Redux approval in The Washington Post
When work began in the 2000s to create a Medicare pharmacy benefit, lawmakers and congressional staff had a pool of about $400 billion available to establish what became the Part D program, Joel White, a former House staffer who helped draft the law, told this news organization in an email exchange.
Given the state of obesity research at the time, it seemed to make sense to exclude weight-loss medications, wrote Mr. White. Mr. White is now chief executive of the consulting firm Horizon, which has clients in the drug industry including the Pharmaceutical Research and Manufacturers of America.
“Now we know that obesity is a chronic disease of epidemic proportions. Decades of research have produced a series of advances in the way we understand and treat obesity. While scientists and many who work directly with those impacted by this epidemic understand how treatments have advanced, the law lags behind,” Mr. White said.
XXXCurrent payment policies for obesity treatments are based on “outdated information and ongoing misperception,” he noted. “While Part D has been a resounding success, our Medicare approach to obesity is not.”
“In addition, it makes no sense that Medicare covers the most drastic procedure (bariatric surgery) but not less-invasive, effective treatments,” he added. “We should have long ago lifted restrictions based on advances in science and medicine.”
Overcoming the stigma
Scott Kahan, MD, MPH, agreed and hopes that the new ICER report will help more patients secure needed medications, raising a “call to arms” about the need for better coverage of obesity drugs.
Dr. Kahan is director of the National Center for Weight and Wellness, a private clinic in Washington, and chair of the clinical committee for The Obesity Society. He also served as a member of a policy roundtable that ICER convened as part of research on the report on obesity drugs. Dr. Kahan, who also serves on the faculty at the Johns Hopkins Bloomberg School of Public Health, Baltimore, has received fees from drug makers such as Eli Lilly.
The ICER report may help what Dr. Kahan described as well-founded caution about obesity treatments in general.
“When it comes to weight loss, there are all of these magical treatments that are sold on social media and traditional media. There are a lot of bad actors in terms of people calling themselves experts and gurus and promising all kinds of crazy stuff,” said Dr. Kahan.
And there are long-standing stigmas about obesity, he stressed.
“That underlies a lot of the backward policies, including poor coverage for medications and the noncoverage by Medicare,” Dr. Kahan said. “There’s a societal ingrained set of beliefs and misperceptions and biases. That takes time to unwind, and I think we’re on the way, but we’re not quite there yet.”
Lifestyle changes not enough to tackle obesity
AHIP (formerly America’s Health Insurance Plans) told this news organization its members consider ICER reports when making decisions about which products to cover. “And health plans already cover obesity treatments that they consider medically necessary,” said David Allen, an AHIP spokesperson.
“It is important to note that every treatment does not work for every patient, and many patients experience adverse events and may discontinue treatment,” he added in an email. “Health insurance providers play an important role in helping [health care] providers and patients identify the treatment options that are most likely to be effective as well as affordable.”
Separately, the nonprofit watchdog group Public Citizen cautioned against liraglutide on its Worst Pills, Best Pills website. In its view, the drug is minimally effective and has many dangerous adverse effects, which are even more frequent with the higher-dose weight-loss version (a lower-dose version is approved for type 2 diabetes).
“There is currently no medication that can be used safely to achieve weight loss effortlessly and without dangerous adverse effects,” the group said. “Rather than focus on losing weight by turning to risky drugs, overweight and obese adults seeking to achieve better health should make reasonable and sustainable changes to their lifestyle, such as eating a healthy diet and getting regular exercise.”
Yet, many people find there is little help available for making lifestyle changes, and some patients and physicians say these modifications by themselves are not enough.
“The vast majority of people with obesity cannot achieve sustained weight loss through diet and exercise alone,” said David Rind, MD, chief medical officer of ICER, in an Oct. 20 statement. “As such, obesity, and its resulting physical health, mental health, and social burdens, is not a choice or failing, but a medical condition.”
The focus should now be on assuring that effective medications “are priced in alignment with their benefits so that they are accessible and affordable across U.S. society,” Dr. Rind urges.
‘My own demise with a fork and knife’
ICER sought public feedback on a draft version of the report before finalizing it.
In their comments on ICER’s work, several pharmaceutical researchers and Novo Nordisk questioned the calculations used in making judgments about the value of obesity drugs. In a statement, Novo Nordisk told this news organization that the company’s view is that ICER’s modeling “does not adequately address the real-world complexities of obesity, and consequently underestimates the health and societal impact medical treatments can have.”
Commenters also dug into aspects of ICER’s calculations, including ones that consider quality-adjusted life-years (QALYs). ICER describes QALY as an academic standard for measuring how well all different types of medical treatments can extend or improve patients’ lives. In an explainer on its website, ICER says this metric has served as a fundamental component of cost-effectiveness analyses in the United States and around the world for more than 30 years.
ICER and drug makers have been at odds for some time, with PhRMA having criticized the nonprofit group. A 2020 Reuters article detailed public relations strategies used by firms paid by drug makers to raise questions about ICER’s work. Critics accuse it of allying with insurers.
ICER’s list of its recent financial supporters includes Blue Cross Blue Shield of Massachusetts and the Kaiser Foundation Health Plan, but also many other groups, such as the U.S. Department of Veterans Affairs, the American Academy of Neurology, and the American College of Rheumatology.
The public comments on the ICER report also include one from an unidentified woman who wrote of her past struggles to lose weight.
She said her health plan wouldn’t cover behavioral programs or semaglutide as a weight-loss drug but did cover it eventually because of signs that she had developed insulin resistance. The patient said the drug worked for her, whereas other approaches to control weight had failed.
“To put it simply, I now experience hunger and satiety in a way that I can only assume people with normal metabolism do. I am 49 years old and approaching the age where serious comorbidities associated with obesity begin to manifest,” the patient wrote.
“I no longer worry about bringing about my own demise with a fork and knife because of misfiring hunger cues.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
A report from a well-respected nonprofit group may bolster efforts to have Medicare, the largest U.S. purchaser of prescription drugs, cover obesity medicines, for which there has been accumulating evidence of significant benefit.
The Institute for Clinical and Economic Review (ICER) released a report last month on obesity medicines, based on extensive review of research done to date and input from clinicians, drug-makers, and members of the public.
Of the treatments reviewed, the ICER report gave the best ratings to two Novo Nordisk products, a B+ for semaglutide (Wegovy) and a B for liraglutide (Saxenda), while also making the case for price cuts. At an annual U.S. net price estimated at $13,618, semaglutide exceeds what ICER considers typical cost-effectiveness thresholds. ICER suggested a benchmark annual price range for semaglutide of between $7,500 and $9,800.
The ICER report also directs insurers in general to provide more generous coverage of obesity medicines, with a specific recommendation for the U.S. Congress to pass a pending bill known as the Treat and Reduce Obesity Act of 2021. The bill would undo a restriction on weight-loss drugs in the Medicare Part D plans, which covered about 49 million people last year. Sen. Tom Carper (D-Del.) and Sen. Bill Cassidy, MD, (R-La.) have repeatedly introduced versions of the bill since 2013.
“In both chambers of Congress and with bipartisan support, we’ve pushed to expand Medicare coverage of additional therapies and medications to treat obesity,” Sen. Cassidy said in an email. “This report confirms what we’ve worked on for nearly a decade – our legislation will help improve lives.”
The current House version of the bill has the backing of more than a third of the members of that chamber, with 113 Democratic and 40 Republican cosponsors. The Senate version has 22 sponsors.
Changing views
The ICER report comes amid a broader change in how clinicians view obesity.
The American Academy of Pediatrics is readying a new Clinical Practice Guideline for the Evaluation and Treatment of Pediatric Obesity that will mark a major shift in approach. Aaron S. Kelly, PhD, a professor of pediatrics at the University of Minnesota, Minneapolis, described it as a “sea change,” with obesity now seen as “a chronic, refractory, relapsing disease,” for which watchful waiting is no longer appropriate.
But the field of obesity treatment looked quite different in the early 2000s when Congress worked on a plan to add a pharmacy benefit to Medicare.
The deliberate omission of obesity medicine in the Medicare Part D benefit reflected both the state of science at the time and U.S. experience with a dangerous weight-loss drug combo in the late 1990s.
Initial expectations for weight-loss pills were high after the Food and Drug Administration cleared dexfenfluramine HCl (Redux) in 1996, which was part of the popular fen-phen combination. “Newly Approved Diet Drug Promises to Help Millions of Obese Americans – But Is No Magic Bullet,” read a headline about the Redux approval in The Washington Post
When work began in the 2000s to create a Medicare pharmacy benefit, lawmakers and congressional staff had a pool of about $400 billion available to establish what became the Part D program, Joel White, a former House staffer who helped draft the law, told this news organization in an email exchange.
Given the state of obesity research at the time, it seemed to make sense to exclude weight-loss medications, wrote Mr. White. Mr. White is now chief executive of the consulting firm Horizon, which has clients in the drug industry including the Pharmaceutical Research and Manufacturers of America.
“Now we know that obesity is a chronic disease of epidemic proportions. Decades of research have produced a series of advances in the way we understand and treat obesity. While scientists and many who work directly with those impacted by this epidemic understand how treatments have advanced, the law lags behind,” Mr. White said.
XXXCurrent payment policies for obesity treatments are based on “outdated information and ongoing misperception,” he noted. “While Part D has been a resounding success, our Medicare approach to obesity is not.”
“In addition, it makes no sense that Medicare covers the most drastic procedure (bariatric surgery) but not less-invasive, effective treatments,” he added. “We should have long ago lifted restrictions based on advances in science and medicine.”
Overcoming the stigma
Scott Kahan, MD, MPH, agreed and hopes that the new ICER report will help more patients secure needed medications, raising a “call to arms” about the need for better coverage of obesity drugs.
Dr. Kahan is director of the National Center for Weight and Wellness, a private clinic in Washington, and chair of the clinical committee for The Obesity Society. He also served as a member of a policy roundtable that ICER convened as part of research on the report on obesity drugs. Dr. Kahan, who also serves on the faculty at the Johns Hopkins Bloomberg School of Public Health, Baltimore, has received fees from drug makers such as Eli Lilly.
The ICER report may help what Dr. Kahan described as well-founded caution about obesity treatments in general.
“When it comes to weight loss, there are all of these magical treatments that are sold on social media and traditional media. There are a lot of bad actors in terms of people calling themselves experts and gurus and promising all kinds of crazy stuff,” said Dr. Kahan.
And there are long-standing stigmas about obesity, he stressed.
“That underlies a lot of the backward policies, including poor coverage for medications and the noncoverage by Medicare,” Dr. Kahan said. “There’s a societal ingrained set of beliefs and misperceptions and biases. That takes time to unwind, and I think we’re on the way, but we’re not quite there yet.”
Lifestyle changes not enough to tackle obesity
AHIP (formerly America’s Health Insurance Plans) told this news organization its members consider ICER reports when making decisions about which products to cover. “And health plans already cover obesity treatments that they consider medically necessary,” said David Allen, an AHIP spokesperson.
“It is important to note that every treatment does not work for every patient, and many patients experience adverse events and may discontinue treatment,” he added in an email. “Health insurance providers play an important role in helping [health care] providers and patients identify the treatment options that are most likely to be effective as well as affordable.”
Separately, the nonprofit watchdog group Public Citizen cautioned against liraglutide on its Worst Pills, Best Pills website. In its view, the drug is minimally effective and has many dangerous adverse effects, which are even more frequent with the higher-dose weight-loss version (a lower-dose version is approved for type 2 diabetes).
“There is currently no medication that can be used safely to achieve weight loss effortlessly and without dangerous adverse effects,” the group said. “Rather than focus on losing weight by turning to risky drugs, overweight and obese adults seeking to achieve better health should make reasonable and sustainable changes to their lifestyle, such as eating a healthy diet and getting regular exercise.”
Yet, many people find there is little help available for making lifestyle changes, and some patients and physicians say these modifications by themselves are not enough.
“The vast majority of people with obesity cannot achieve sustained weight loss through diet and exercise alone,” said David Rind, MD, chief medical officer of ICER, in an Oct. 20 statement. “As such, obesity, and its resulting physical health, mental health, and social burdens, is not a choice or failing, but a medical condition.”
The focus should now be on assuring that effective medications “are priced in alignment with their benefits so that they are accessible and affordable across U.S. society,” Dr. Rind urges.
‘My own demise with a fork and knife’
ICER sought public feedback on a draft version of the report before finalizing it.
In their comments on ICER’s work, several pharmaceutical researchers and Novo Nordisk questioned the calculations used in making judgments about the value of obesity drugs. In a statement, Novo Nordisk told this news organization that the company’s view is that ICER’s modeling “does not adequately address the real-world complexities of obesity, and consequently underestimates the health and societal impact medical treatments can have.”
Commenters also dug into aspects of ICER’s calculations, including ones that consider quality-adjusted life-years (QALYs). ICER describes QALY as an academic standard for measuring how well all different types of medical treatments can extend or improve patients’ lives. In an explainer on its website, ICER says this metric has served as a fundamental component of cost-effectiveness analyses in the United States and around the world for more than 30 years.
ICER and drug makers have been at odds for some time, with PhRMA having criticized the nonprofit group. A 2020 Reuters article detailed public relations strategies used by firms paid by drug makers to raise questions about ICER’s work. Critics accuse it of allying with insurers.
ICER’s list of its recent financial supporters includes Blue Cross Blue Shield of Massachusetts and the Kaiser Foundation Health Plan, but also many other groups, such as the U.S. Department of Veterans Affairs, the American Academy of Neurology, and the American College of Rheumatology.
The public comments on the ICER report also include one from an unidentified woman who wrote of her past struggles to lose weight.
She said her health plan wouldn’t cover behavioral programs or semaglutide as a weight-loss drug but did cover it eventually because of signs that she had developed insulin resistance. The patient said the drug worked for her, whereas other approaches to control weight had failed.
“To put it simply, I now experience hunger and satiety in a way that I can only assume people with normal metabolism do. I am 49 years old and approaching the age where serious comorbidities associated with obesity begin to manifest,” the patient wrote.
“I no longer worry about bringing about my own demise with a fork and knife because of misfiring hunger cues.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Nurse practitioner fined $20k for advertising herself as ‘Doctor Sarah’
Last month, the San Luis Obispo County, California, District Attorney Dan Dow filed a complaint against Sarah Erny, RN, NP, citing unfair business practices and unprofessional conduct.
According to court documents, California’s Medical Practice Act does not permit individuals to refer to themselves as “doctor, physician, or any other terms or letters indicating or implying that he or she is a physician and surgeon ... without having ... a certificate as a physician and surgeon.”
Individuals who misrepresent themselves are subject to misdemeanor charges and civil penalties.
In addition to the fine, Ms. Erny agreed to refrain from referring to herself as a doctor in her practice and on social media. She has already deleted her Twitter account.
The case underscores tensions between physicians fighting to preserve their scope of practice and the allied professionals that U.S. lawmakers increasingly see as a less expensive way to improve access to health care.
The American Medical Association and specialty groups strongly oppose a new bill, the Improving Care and Access to Nurses Act, that would expand the scope of practice for nurse practitioners and physician assistants.
Court records show that Ms. Erny earned a doctor of nursing practice (DNP) degree from Vanderbilt University, Nashville, Tenn., and that she met the state requirements to obtain licensure as a registered nurse and nurse practitioner. In 2018, she opened a practice in Arroyo Grande, California, called Holistic Women’s Healing, where she provided medical services and drug supplements to patients.
She also entered a collaborative agreement with ob.gyn. Anika Moore, MD, for approximately 3 years. Dr. Moore’s medical practice was in another county and state, and the physician returned every 2 to 3 months to review a portion of Ms. Erny’s patient files.
Ms. Erny and Dr. Moore terminated the collaborative agreement in March, according to court documents.
However, Mr. Dow alleged that Ms. Erny regularly referred to herself as “Dr. Sarah” or “Dr. Sarah Erny” in her online advertising and social media accounts. Her patients “were so proud of her” that they called her doctor, and her supervising physician instructed staff to do the same.
Mr. Dow said Ms. Erny did not clearly advise the public that she was not a medical doctor and failed to identify her supervising physician. “Simply put, there is a great need for health care providers to state their level of training and licensing clearly and honestly in all of their advertising and marketing materials,” he said in a press release.
In California, nurse practitioners who have been certified by the Board of Registered Nursing may use the following titles: Advanced Practice Registered Nurse; Certified Nurse Practitioner; APRN-CNP; RN and NP; or a combination of other letters or words to identify specialization, such as adult nurse practitioner, pediatric nurse practitioner, obstetrical-gynecological nurse practitioner, and family nurse practitioner.
As educational requirements shift for advanced practice clinicians, similar cases will likely emerge, said Grant Martsolf, PhD, MPH, RN, FAAN, professor at the University of Pittsburgh School of Nursing.
“Scope of practice is governed by states, [so they] will have to figure [it] out as more professional disciplines move to clinical doctorates as the entry to practice. Pharma, [physical therapy], and [occupational therapy] have already done this, and advanced practice nursing is on its way. [Certified registered nurse anesthetists] are already required to get a DNP to sit for certification,” he said.
More guidance is needed, especially when considering other professions like dentists, clinical psychologists, and individuals with clinical or research doctorates who often call themselves doctors, Dr. Martsolf said.
“It seems that the honorific of ‘Dr.’ emerges from the degree, not from being a physician or surgeon,” he said.
Beyond the false advertising, Mr. Dow alleged that Ms. Erny did not file a fictitious business name statement for 2020 and 2021 – a requirement under the California Business and Professions Code to identify who is operating the business.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Last month, the San Luis Obispo County, California, District Attorney Dan Dow filed a complaint against Sarah Erny, RN, NP, citing unfair business practices and unprofessional conduct.
According to court documents, California’s Medical Practice Act does not permit individuals to refer to themselves as “doctor, physician, or any other terms or letters indicating or implying that he or she is a physician and surgeon ... without having ... a certificate as a physician and surgeon.”
Individuals who misrepresent themselves are subject to misdemeanor charges and civil penalties.
In addition to the fine, Ms. Erny agreed to refrain from referring to herself as a doctor in her practice and on social media. She has already deleted her Twitter account.
The case underscores tensions between physicians fighting to preserve their scope of practice and the allied professionals that U.S. lawmakers increasingly see as a less expensive way to improve access to health care.
The American Medical Association and specialty groups strongly oppose a new bill, the Improving Care and Access to Nurses Act, that would expand the scope of practice for nurse practitioners and physician assistants.
Court records show that Ms. Erny earned a doctor of nursing practice (DNP) degree from Vanderbilt University, Nashville, Tenn., and that she met the state requirements to obtain licensure as a registered nurse and nurse practitioner. In 2018, she opened a practice in Arroyo Grande, California, called Holistic Women’s Healing, where she provided medical services and drug supplements to patients.
She also entered a collaborative agreement with ob.gyn. Anika Moore, MD, for approximately 3 years. Dr. Moore’s medical practice was in another county and state, and the physician returned every 2 to 3 months to review a portion of Ms. Erny’s patient files.
Ms. Erny and Dr. Moore terminated the collaborative agreement in March, according to court documents.
However, Mr. Dow alleged that Ms. Erny regularly referred to herself as “Dr. Sarah” or “Dr. Sarah Erny” in her online advertising and social media accounts. Her patients “were so proud of her” that they called her doctor, and her supervising physician instructed staff to do the same.
Mr. Dow said Ms. Erny did not clearly advise the public that she was not a medical doctor and failed to identify her supervising physician. “Simply put, there is a great need for health care providers to state their level of training and licensing clearly and honestly in all of their advertising and marketing materials,” he said in a press release.
In California, nurse practitioners who have been certified by the Board of Registered Nursing may use the following titles: Advanced Practice Registered Nurse; Certified Nurse Practitioner; APRN-CNP; RN and NP; or a combination of other letters or words to identify specialization, such as adult nurse practitioner, pediatric nurse practitioner, obstetrical-gynecological nurse practitioner, and family nurse practitioner.
As educational requirements shift for advanced practice clinicians, similar cases will likely emerge, said Grant Martsolf, PhD, MPH, RN, FAAN, professor at the University of Pittsburgh School of Nursing.
“Scope of practice is governed by states, [so they] will have to figure [it] out as more professional disciplines move to clinical doctorates as the entry to practice. Pharma, [physical therapy], and [occupational therapy] have already done this, and advanced practice nursing is on its way. [Certified registered nurse anesthetists] are already required to get a DNP to sit for certification,” he said.
More guidance is needed, especially when considering other professions like dentists, clinical psychologists, and individuals with clinical or research doctorates who often call themselves doctors, Dr. Martsolf said.
“It seems that the honorific of ‘Dr.’ emerges from the degree, not from being a physician or surgeon,” he said.
Beyond the false advertising, Mr. Dow alleged that Ms. Erny did not file a fictitious business name statement for 2020 and 2021 – a requirement under the California Business and Professions Code to identify who is operating the business.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Last month, the San Luis Obispo County, California, District Attorney Dan Dow filed a complaint against Sarah Erny, RN, NP, citing unfair business practices and unprofessional conduct.
According to court documents, California’s Medical Practice Act does not permit individuals to refer to themselves as “doctor, physician, or any other terms or letters indicating or implying that he or she is a physician and surgeon ... without having ... a certificate as a physician and surgeon.”
Individuals who misrepresent themselves are subject to misdemeanor charges and civil penalties.
In addition to the fine, Ms. Erny agreed to refrain from referring to herself as a doctor in her practice and on social media. She has already deleted her Twitter account.
The case underscores tensions between physicians fighting to preserve their scope of practice and the allied professionals that U.S. lawmakers increasingly see as a less expensive way to improve access to health care.
The American Medical Association and specialty groups strongly oppose a new bill, the Improving Care and Access to Nurses Act, that would expand the scope of practice for nurse practitioners and physician assistants.
Court records show that Ms. Erny earned a doctor of nursing practice (DNP) degree from Vanderbilt University, Nashville, Tenn., and that she met the state requirements to obtain licensure as a registered nurse and nurse practitioner. In 2018, she opened a practice in Arroyo Grande, California, called Holistic Women’s Healing, where she provided medical services and drug supplements to patients.
She also entered a collaborative agreement with ob.gyn. Anika Moore, MD, for approximately 3 years. Dr. Moore’s medical practice was in another county and state, and the physician returned every 2 to 3 months to review a portion of Ms. Erny’s patient files.
Ms. Erny and Dr. Moore terminated the collaborative agreement in March, according to court documents.
However, Mr. Dow alleged that Ms. Erny regularly referred to herself as “Dr. Sarah” or “Dr. Sarah Erny” in her online advertising and social media accounts. Her patients “were so proud of her” that they called her doctor, and her supervising physician instructed staff to do the same.
Mr. Dow said Ms. Erny did not clearly advise the public that she was not a medical doctor and failed to identify her supervising physician. “Simply put, there is a great need for health care providers to state their level of training and licensing clearly and honestly in all of their advertising and marketing materials,” he said in a press release.
In California, nurse practitioners who have been certified by the Board of Registered Nursing may use the following titles: Advanced Practice Registered Nurse; Certified Nurse Practitioner; APRN-CNP; RN and NP; or a combination of other letters or words to identify specialization, such as adult nurse practitioner, pediatric nurse practitioner, obstetrical-gynecological nurse practitioner, and family nurse practitioner.
As educational requirements shift for advanced practice clinicians, similar cases will likely emerge, said Grant Martsolf, PhD, MPH, RN, FAAN, professor at the University of Pittsburgh School of Nursing.
“Scope of practice is governed by states, [so they] will have to figure [it] out as more professional disciplines move to clinical doctorates as the entry to practice. Pharma, [physical therapy], and [occupational therapy] have already done this, and advanced practice nursing is on its way. [Certified registered nurse anesthetists] are already required to get a DNP to sit for certification,” he said.
More guidance is needed, especially when considering other professions like dentists, clinical psychologists, and individuals with clinical or research doctorates who often call themselves doctors, Dr. Martsolf said.
“It seems that the honorific of ‘Dr.’ emerges from the degree, not from being a physician or surgeon,” he said.
Beyond the false advertising, Mr. Dow alleged that Ms. Erny did not file a fictitious business name statement for 2020 and 2021 – a requirement under the California Business and Professions Code to identify who is operating the business.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Patients trying to lose weight overestimate their diet quality
Only 28% of the participants had good agreement – defined as a difference of 6 points or less – between their perceived diet quality and its actual quality based on Healthy Eating Index–2015 (HEI) scores at the end of the 12-month intervention.
Even fewer – only 13% – had good agreement with their perceived and actual improvement in diet quality.
Jessica Cheng, PhD, Harvard School of Public Health, Boston, presented the findings in an oral session at the American Heart Association scientific sessions.
The study suggests that “patients can benefit from concrete advice on aspects of their diet that could most benefit by being changed,” Dr. Cheng said in an interview.
“But once they know what to change, they may need additional advice on how to make and sustain those changes. Providers may direct their patients to resources such as dietitians, medically tailored meals, MyPlate, healthy recipes, etc.,” she advised.
“The findings are not surprising given that dietary recalls are subject to recall bias and depend on the person’s baseline nutrition knowledge or literacy,” Deepika Laddu, PhD, who was not involved with this research, said in an interview.
Misperception of diet intake is common in individuals with overweight or obesity, and one 90-minute session with a dietitian is not enough, according to Dr. Laddu, assistant professor at the University of Illinois at Chicago.
“The Dietary Guidelines for Americans does a really nice job at presenting all of the options,” she said. However, “understanding what a healthy diet pattern is, or how to adopt it, is confusing, due to a lot of ‘noise’, that is, the mixed messaging and unproven health claims, which add to inadequacies in health or nutrition literacy.”
“It is important to recognize that changing dietary practices is behaviorally challenging and complex,” she emphasized.
People who are interested in making dietary changes need to have ongoing conversations with a qualified health care professional, which most often starts with their primary care clinician.
“Given the well-known time constraints during a typical clinical visit, beyond that initial conversation, it is absolutely critical that patients be referred to qualified healthcare professionals such as a registered dietitian, nurse practitioner, health coach/educator or diabetes educator, etc, for ongoing support.”
These providers can assess the patient’s initial diet, perceptions of a healthy diet, and diet goals, and address any gaps in health literacy, to enable the patient to develop long-lasting, realistic, and healthy eating behaviors.
Perceived vs. actual diet quality
Healthy eating is essential for heart and general health and longevity, but it is unclear if people who make lifestyle (diet and physical activity) changes to lose weight have an accurate perception of diet quality.
The researchers analyzed data from the SMARTER trial of 502 adults aged 35-58 living in the greater Pittsburgh area who were trying to lose weight.
Participants received a 90-minute weight loss counseling session addressing behavioral strategies and establishing dietary and physical activity goals. They all received instructions on how to monitor their diet, physical activity, and weight daily, using a smartphone app, a wristband tracker (Fitbit Charge 2), and a smart wireless scale. Half of the participants also received real-time personalized feedback on those behaviors, up to three times a day, via the study app.
The participants replied to two 24-hour dietary recall questionnaires at study entry and two questionnaires at 12 months.
Researchers analyzed data from the 116 participants who provided information about diet quality. At 1 year, they were asked to rate their diet quality, but also rate their diet quality 12 months earlier at baseline, on a scale of 0-100, where 100 is best.
The average weight loss at 12 months was similar in the groups with and without feedback from the app (roughly 3.2% of baseline weight), so the two study arms were combined. The participants had a mean age of 52 years; 80% were women and 87% were White. They had an average body mass index of 33 kg/m2.
Based on the information from the food recall questionnaires, the researchers calculated the patients’ HEI scores at the start and end of the study. The HEI score is a measure of how well a person’s diet adheres to the 2015-2020 Dietary Guidelines for Americans. It is based on an adequate consumption of nine types of foods – total fruits, whole fruits, total vegetables, greens and beans, total protein foods, seafood, and plant proteins (up to 5 points each), and whole grains, dairy, and fatty acids (up to 10 points each) – and reduced consumption of four dietary components – refined grains, sodium, added sugars, and saturated fats (up to 10 points each).
The healthiest diet has an HEI score of 100, and the Healthy People 2020 goal was an HEI score of 74, Dr. Cheng noted.
At 12 months, on average, the participants rated their diet quality at 70.5 points, whereas the researchers calculated that their average HEI score was only 56.
Participants thought they had improved their diet quality by about 20 points, Dr. Cheng reported. “However, the HEI would suggest they’ve improved it by 1.5 points, which is not a lot out of 100.”
“Future studies should examine the effects of helping people close the gap between their perceptions and objective diet quality measurements,” Dr. Cheng said in a press release from the AHA.
The study was funded by the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute, a division of the National Institutes of Health. Dr. Cheng and Dr. Laddu reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Only 28% of the participants had good agreement – defined as a difference of 6 points or less – between their perceived diet quality and its actual quality based on Healthy Eating Index–2015 (HEI) scores at the end of the 12-month intervention.
Even fewer – only 13% – had good agreement with their perceived and actual improvement in diet quality.
Jessica Cheng, PhD, Harvard School of Public Health, Boston, presented the findings in an oral session at the American Heart Association scientific sessions.
The study suggests that “patients can benefit from concrete advice on aspects of their diet that could most benefit by being changed,” Dr. Cheng said in an interview.
“But once they know what to change, they may need additional advice on how to make and sustain those changes. Providers may direct their patients to resources such as dietitians, medically tailored meals, MyPlate, healthy recipes, etc.,” she advised.
“The findings are not surprising given that dietary recalls are subject to recall bias and depend on the person’s baseline nutrition knowledge or literacy,” Deepika Laddu, PhD, who was not involved with this research, said in an interview.
Misperception of diet intake is common in individuals with overweight or obesity, and one 90-minute session with a dietitian is not enough, according to Dr. Laddu, assistant professor at the University of Illinois at Chicago.
“The Dietary Guidelines for Americans does a really nice job at presenting all of the options,” she said. However, “understanding what a healthy diet pattern is, or how to adopt it, is confusing, due to a lot of ‘noise’, that is, the mixed messaging and unproven health claims, which add to inadequacies in health or nutrition literacy.”
“It is important to recognize that changing dietary practices is behaviorally challenging and complex,” she emphasized.
People who are interested in making dietary changes need to have ongoing conversations with a qualified health care professional, which most often starts with their primary care clinician.
“Given the well-known time constraints during a typical clinical visit, beyond that initial conversation, it is absolutely critical that patients be referred to qualified healthcare professionals such as a registered dietitian, nurse practitioner, health coach/educator or diabetes educator, etc, for ongoing support.”
These providers can assess the patient’s initial diet, perceptions of a healthy diet, and diet goals, and address any gaps in health literacy, to enable the patient to develop long-lasting, realistic, and healthy eating behaviors.
Perceived vs. actual diet quality
Healthy eating is essential for heart and general health and longevity, but it is unclear if people who make lifestyle (diet and physical activity) changes to lose weight have an accurate perception of diet quality.
The researchers analyzed data from the SMARTER trial of 502 adults aged 35-58 living in the greater Pittsburgh area who were trying to lose weight.
Participants received a 90-minute weight loss counseling session addressing behavioral strategies and establishing dietary and physical activity goals. They all received instructions on how to monitor their diet, physical activity, and weight daily, using a smartphone app, a wristband tracker (Fitbit Charge 2), and a smart wireless scale. Half of the participants also received real-time personalized feedback on those behaviors, up to three times a day, via the study app.
The participants replied to two 24-hour dietary recall questionnaires at study entry and two questionnaires at 12 months.
Researchers analyzed data from the 116 participants who provided information about diet quality. At 1 year, they were asked to rate their diet quality, but also rate their diet quality 12 months earlier at baseline, on a scale of 0-100, where 100 is best.
The average weight loss at 12 months was similar in the groups with and without feedback from the app (roughly 3.2% of baseline weight), so the two study arms were combined. The participants had a mean age of 52 years; 80% were women and 87% were White. They had an average body mass index of 33 kg/m2.
Based on the information from the food recall questionnaires, the researchers calculated the patients’ HEI scores at the start and end of the study. The HEI score is a measure of how well a person’s diet adheres to the 2015-2020 Dietary Guidelines for Americans. It is based on an adequate consumption of nine types of foods – total fruits, whole fruits, total vegetables, greens and beans, total protein foods, seafood, and plant proteins (up to 5 points each), and whole grains, dairy, and fatty acids (up to 10 points each) – and reduced consumption of four dietary components – refined grains, sodium, added sugars, and saturated fats (up to 10 points each).
The healthiest diet has an HEI score of 100, and the Healthy People 2020 goal was an HEI score of 74, Dr. Cheng noted.
At 12 months, on average, the participants rated their diet quality at 70.5 points, whereas the researchers calculated that their average HEI score was only 56.
Participants thought they had improved their diet quality by about 20 points, Dr. Cheng reported. “However, the HEI would suggest they’ve improved it by 1.5 points, which is not a lot out of 100.”
“Future studies should examine the effects of helping people close the gap between their perceptions and objective diet quality measurements,” Dr. Cheng said in a press release from the AHA.
The study was funded by the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute, a division of the National Institutes of Health. Dr. Cheng and Dr. Laddu reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Only 28% of the participants had good agreement – defined as a difference of 6 points or less – between their perceived diet quality and its actual quality based on Healthy Eating Index–2015 (HEI) scores at the end of the 12-month intervention.
Even fewer – only 13% – had good agreement with their perceived and actual improvement in diet quality.
Jessica Cheng, PhD, Harvard School of Public Health, Boston, presented the findings in an oral session at the American Heart Association scientific sessions.
The study suggests that “patients can benefit from concrete advice on aspects of their diet that could most benefit by being changed,” Dr. Cheng said in an interview.
“But once they know what to change, they may need additional advice on how to make and sustain those changes. Providers may direct their patients to resources such as dietitians, medically tailored meals, MyPlate, healthy recipes, etc.,” she advised.
“The findings are not surprising given that dietary recalls are subject to recall bias and depend on the person’s baseline nutrition knowledge or literacy,” Deepika Laddu, PhD, who was not involved with this research, said in an interview.
Misperception of diet intake is common in individuals with overweight or obesity, and one 90-minute session with a dietitian is not enough, according to Dr. Laddu, assistant professor at the University of Illinois at Chicago.
“The Dietary Guidelines for Americans does a really nice job at presenting all of the options,” she said. However, “understanding what a healthy diet pattern is, or how to adopt it, is confusing, due to a lot of ‘noise’, that is, the mixed messaging and unproven health claims, which add to inadequacies in health or nutrition literacy.”
“It is important to recognize that changing dietary practices is behaviorally challenging and complex,” she emphasized.
People who are interested in making dietary changes need to have ongoing conversations with a qualified health care professional, which most often starts with their primary care clinician.
“Given the well-known time constraints during a typical clinical visit, beyond that initial conversation, it is absolutely critical that patients be referred to qualified healthcare professionals such as a registered dietitian, nurse practitioner, health coach/educator or diabetes educator, etc, for ongoing support.”
These providers can assess the patient’s initial diet, perceptions of a healthy diet, and diet goals, and address any gaps in health literacy, to enable the patient to develop long-lasting, realistic, and healthy eating behaviors.
Perceived vs. actual diet quality
Healthy eating is essential for heart and general health and longevity, but it is unclear if people who make lifestyle (diet and physical activity) changes to lose weight have an accurate perception of diet quality.
The researchers analyzed data from the SMARTER trial of 502 adults aged 35-58 living in the greater Pittsburgh area who were trying to lose weight.
Participants received a 90-minute weight loss counseling session addressing behavioral strategies and establishing dietary and physical activity goals. They all received instructions on how to monitor their diet, physical activity, and weight daily, using a smartphone app, a wristband tracker (Fitbit Charge 2), and a smart wireless scale. Half of the participants also received real-time personalized feedback on those behaviors, up to three times a day, via the study app.
The participants replied to two 24-hour dietary recall questionnaires at study entry and two questionnaires at 12 months.
Researchers analyzed data from the 116 participants who provided information about diet quality. At 1 year, they were asked to rate their diet quality, but also rate their diet quality 12 months earlier at baseline, on a scale of 0-100, where 100 is best.
The average weight loss at 12 months was similar in the groups with and without feedback from the app (roughly 3.2% of baseline weight), so the two study arms were combined. The participants had a mean age of 52 years; 80% were women and 87% were White. They had an average body mass index of 33 kg/m2.
Based on the information from the food recall questionnaires, the researchers calculated the patients’ HEI scores at the start and end of the study. The HEI score is a measure of how well a person’s diet adheres to the 2015-2020 Dietary Guidelines for Americans. It is based on an adequate consumption of nine types of foods – total fruits, whole fruits, total vegetables, greens and beans, total protein foods, seafood, and plant proteins (up to 5 points each), and whole grains, dairy, and fatty acids (up to 10 points each) – and reduced consumption of four dietary components – refined grains, sodium, added sugars, and saturated fats (up to 10 points each).
The healthiest diet has an HEI score of 100, and the Healthy People 2020 goal was an HEI score of 74, Dr. Cheng noted.
At 12 months, on average, the participants rated their diet quality at 70.5 points, whereas the researchers calculated that their average HEI score was only 56.
Participants thought they had improved their diet quality by about 20 points, Dr. Cheng reported. “However, the HEI would suggest they’ve improved it by 1.5 points, which is not a lot out of 100.”
“Future studies should examine the effects of helping people close the gap between their perceptions and objective diet quality measurements,” Dr. Cheng said in a press release from the AHA.
The study was funded by the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute, a division of the National Institutes of Health. Dr. Cheng and Dr. Laddu reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM AHA 2022
Mortality after acute stroke worsened by accompanying acute AFib
The study covered in this summary was published on ResearchSquare.com as a preprint and has not yet been peer-reviewed.
Key takeaway
Why this matters
- A comprehensive understanding of the relationship between acute AF and risk for acute ischemic stroke and prognosis will help improve management and treatment of patients with acute ischemic stroke.
Study design
- The retrospective study included patients with acute ischemic stroke within the prior 24 hours; 12-lead electrocardiogram in the emergency department; and hospitalization and treatment at the hospital stroke center.
- The cohort of 706 patients admitted to a single center in Shanghai, China, from December 2019 to December 2021, included 142 with episodes of acute AF and 564 without such episodes.
- Patients with acute ischemic stroke and acute AF – including AF of new onset, paroxysmal, persistent, or permanent with symptoms such as palpitations or dizziness attributed to rapid ventricular rates – were identified.
- Neurological deficits were assessed using the 7-day National Institutes of Health Stroke Scale/Score (NIHSS). Patients with a 7-day NIHSS score of at least 16 were considered to have moderate to severe stroke.
- Associations between acute AF onset and the severity of early neurological deficits were assessed and related to all-cause mortality within 30 days of the stroke.
Key results
- Patients with acute AF were older than those without acute AF (80.3 years vs. 71.0 years; P < .001).
- Baseline NIHSS scores averaged 16.09 for the stroke patients with acute AF and 8.65 for those without acute AF (P < .001).
- Significantly more patients with acute AF than without acute AF had a 7-day NIHSS score of at least 16 (45.1% vs. 14.4%; P < .001).
- More patients with than without acute AF underwent transcatheter thrombectomy (44.4% vs. 24.5%; P < .001) or received thrombolytic therapy (31.6% vs. 19.7%; P = .005).
- Patients aged 73 years or older showed baseline NIHSS score and acute AF as independent risk factors for early neurological deficits in stroke patients admitted to the emergency department.
- Mortality at 30 days was significantly higher in patients with acute AF than in those without acute AF (30.3% vs. 10.1%; P < .001).
- Baseline NIHSS had an adjusted odds ratio for 30-day mortality of 1.18 (95% confidence interval, 1.15-1.22; P < .001).
- Other independent predictors included acute AF (1.87 [95% CI, 1.09-3.19; P = .022]) and age 73 or older (2.00 [95% CI, 1.18-3.37; P = .01]).
Limitations
- The study was retrospective and didn’t have access to some potentially relevant data, such as duration of AF.
- The single-center study with limited generalizability does not necessarily represent the broad population of stroke patients in China or elsewhere.
Disclosures
- This study was supported by the Cardiovascular Multidisciplinary Integrated Research Fund and Construction of Shanghai Municipal Health Commission.
- The authors report no relevant financial relationships.
This is a summary of a preprint research study, “Acute Atrial Fibrillation During Onset of Stroke Indicates Higher Probability of Post-Stroke Death Outcomes,” written by Yongxia Li, from the Shanghai Sixth People’s Hospital, and colleagues, on ResearchSquare.com. This study has not yet been peer reviewed. The full text of the study can be found on ResearchSquare.com.A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The study covered in this summary was published on ResearchSquare.com as a preprint and has not yet been peer-reviewed.
Key takeaway
Why this matters
- A comprehensive understanding of the relationship between acute AF and risk for acute ischemic stroke and prognosis will help improve management and treatment of patients with acute ischemic stroke.
Study design
- The retrospective study included patients with acute ischemic stroke within the prior 24 hours; 12-lead electrocardiogram in the emergency department; and hospitalization and treatment at the hospital stroke center.
- The cohort of 706 patients admitted to a single center in Shanghai, China, from December 2019 to December 2021, included 142 with episodes of acute AF and 564 without such episodes.
- Patients with acute ischemic stroke and acute AF – including AF of new onset, paroxysmal, persistent, or permanent with symptoms such as palpitations or dizziness attributed to rapid ventricular rates – were identified.
- Neurological deficits were assessed using the 7-day National Institutes of Health Stroke Scale/Score (NIHSS). Patients with a 7-day NIHSS score of at least 16 were considered to have moderate to severe stroke.
- Associations between acute AF onset and the severity of early neurological deficits were assessed and related to all-cause mortality within 30 days of the stroke.
Key results
- Patients with acute AF were older than those without acute AF (80.3 years vs. 71.0 years; P < .001).
- Baseline NIHSS scores averaged 16.09 for the stroke patients with acute AF and 8.65 for those without acute AF (P < .001).
- Significantly more patients with acute AF than without acute AF had a 7-day NIHSS score of at least 16 (45.1% vs. 14.4%; P < .001).
- More patients with than without acute AF underwent transcatheter thrombectomy (44.4% vs. 24.5%; P < .001) or received thrombolytic therapy (31.6% vs. 19.7%; P = .005).
- Patients aged 73 years or older showed baseline NIHSS score and acute AF as independent risk factors for early neurological deficits in stroke patients admitted to the emergency department.
- Mortality at 30 days was significantly higher in patients with acute AF than in those without acute AF (30.3% vs. 10.1%; P < .001).
- Baseline NIHSS had an adjusted odds ratio for 30-day mortality of 1.18 (95% confidence interval, 1.15-1.22; P < .001).
- Other independent predictors included acute AF (1.87 [95% CI, 1.09-3.19; P = .022]) and age 73 or older (2.00 [95% CI, 1.18-3.37; P = .01]).
Limitations
- The study was retrospective and didn’t have access to some potentially relevant data, such as duration of AF.
- The single-center study with limited generalizability does not necessarily represent the broad population of stroke patients in China or elsewhere.
Disclosures
- This study was supported by the Cardiovascular Multidisciplinary Integrated Research Fund and Construction of Shanghai Municipal Health Commission.
- The authors report no relevant financial relationships.
This is a summary of a preprint research study, “Acute Atrial Fibrillation During Onset of Stroke Indicates Higher Probability of Post-Stroke Death Outcomes,” written by Yongxia Li, from the Shanghai Sixth People’s Hospital, and colleagues, on ResearchSquare.com. This study has not yet been peer reviewed. The full text of the study can be found on ResearchSquare.com.A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The study covered in this summary was published on ResearchSquare.com as a preprint and has not yet been peer-reviewed.
Key takeaway
Why this matters
- A comprehensive understanding of the relationship between acute AF and risk for acute ischemic stroke and prognosis will help improve management and treatment of patients with acute ischemic stroke.
Study design
- The retrospective study included patients with acute ischemic stroke within the prior 24 hours; 12-lead electrocardiogram in the emergency department; and hospitalization and treatment at the hospital stroke center.
- The cohort of 706 patients admitted to a single center in Shanghai, China, from December 2019 to December 2021, included 142 with episodes of acute AF and 564 without such episodes.
- Patients with acute ischemic stroke and acute AF – including AF of new onset, paroxysmal, persistent, or permanent with symptoms such as palpitations or dizziness attributed to rapid ventricular rates – were identified.
- Neurological deficits were assessed using the 7-day National Institutes of Health Stroke Scale/Score (NIHSS). Patients with a 7-day NIHSS score of at least 16 were considered to have moderate to severe stroke.
- Associations between acute AF onset and the severity of early neurological deficits were assessed and related to all-cause mortality within 30 days of the stroke.
Key results
- Patients with acute AF were older than those without acute AF (80.3 years vs. 71.0 years; P < .001).
- Baseline NIHSS scores averaged 16.09 for the stroke patients with acute AF and 8.65 for those without acute AF (P < .001).
- Significantly more patients with acute AF than without acute AF had a 7-day NIHSS score of at least 16 (45.1% vs. 14.4%; P < .001).
- More patients with than without acute AF underwent transcatheter thrombectomy (44.4% vs. 24.5%; P < .001) or received thrombolytic therapy (31.6% vs. 19.7%; P = .005).
- Patients aged 73 years or older showed baseline NIHSS score and acute AF as independent risk factors for early neurological deficits in stroke patients admitted to the emergency department.
- Mortality at 30 days was significantly higher in patients with acute AF than in those without acute AF (30.3% vs. 10.1%; P < .001).
- Baseline NIHSS had an adjusted odds ratio for 30-day mortality of 1.18 (95% confidence interval, 1.15-1.22; P < .001).
- Other independent predictors included acute AF (1.87 [95% CI, 1.09-3.19; P = .022]) and age 73 or older (2.00 [95% CI, 1.18-3.37; P = .01]).
Limitations
- The study was retrospective and didn’t have access to some potentially relevant data, such as duration of AF.
- The single-center study with limited generalizability does not necessarily represent the broad population of stroke patients in China or elsewhere.
Disclosures
- This study was supported by the Cardiovascular Multidisciplinary Integrated Research Fund and Construction of Shanghai Municipal Health Commission.
- The authors report no relevant financial relationships.
This is a summary of a preprint research study, “Acute Atrial Fibrillation During Onset of Stroke Indicates Higher Probability of Post-Stroke Death Outcomes,” written by Yongxia Li, from the Shanghai Sixth People’s Hospital, and colleagues, on ResearchSquare.com. This study has not yet been peer reviewed. The full text of the study can be found on ResearchSquare.com.A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Major life stressors ‘strongly predictive’ of long COVID symptoms
new research suggests.
Major life stressors in the year after hospital discharge for COVID-19 are “strongly predictive of a lot of the important outcomes that people may face after COVID,” lead investigator Jennifer A. Frontera, MD, a professor in the department of neurology at New York University Langone Health, said in an interview.
These outcomes include depression, brain fog, fatigue, trouble sleeping, and other long COVID symptoms.
The findings were published online in the Journal of the Neurological Sciences.
Major stressful events common
Dr. Frontera and the NYU Neurology COVID-19 study team evaluated 451 adults who survived a COVID hospital stay. Of these, 383 completed a 6-month follow-up, 242 completed a 12-month follow-up, and 174 completed follow-up at both time points.
Within 1 year of discharge, 77 (17%) patients died and 51% suffered a major stressful life event.
In multivariable analyses, major life stressors – including financial insecurity, food insecurity, death of a close contact, and new disability – were strong independent predictors of disability, trouble with activities of daily living, depression, fatigue, sleep problems, and prolonged post-acute COVID symptoms. The adjusted odds ratios for these outcomes ranged from 2.5 to 20.8.
The research also confirmed the contribution of traditional risk factors for long COVID symptoms, as shown in past studies. These include older age, poor pre-COVID functional status, and more severe initial COVID-19 infection.
Long-term sequelae of COVID are increasingly recognized as major public health issues.
It has been estimated that roughly 16 million U.S. adults aged 18-65 years ave long COVID, with the often debilitating symptoms keeping up to 4 million out of work.
Holistic approach
Dr. Frontera said it’s important to realize that “sleep, fatigue, anxiety, depression, even cognition are so interwoven with each other that anything that impacts any one of them could have repercussions on the other.”
She added that it “certainly makes sense that there is an interplay or even a bidirectional relationship between the stressors that people face and how well they can recover after COVID.”
Therapies that lessen the trauma of the most stress-inducing life events need to be a central part of treatment for long COVID, with more research needed to validate the best approaches, Dr. Frontera said.
She also noted that social services or case management resources may be able to help address at least some of the stressors that individuals are under – and it is important to refer them to these resources. Referral to mental health services is also important.
“I think it’s really important to take a holistic approach and try to deal with whatever the problem may be,” said Dr. Frontera.
“I’m a neurologist, but as part of my evaluation, I really need to address if there are life stressors or mental health issues that may be impacting this person’s function,” she added.
The study had no commercial funding. The investigators reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
new research suggests.
Major life stressors in the year after hospital discharge for COVID-19 are “strongly predictive of a lot of the important outcomes that people may face after COVID,” lead investigator Jennifer A. Frontera, MD, a professor in the department of neurology at New York University Langone Health, said in an interview.
These outcomes include depression, brain fog, fatigue, trouble sleeping, and other long COVID symptoms.
The findings were published online in the Journal of the Neurological Sciences.
Major stressful events common
Dr. Frontera and the NYU Neurology COVID-19 study team evaluated 451 adults who survived a COVID hospital stay. Of these, 383 completed a 6-month follow-up, 242 completed a 12-month follow-up, and 174 completed follow-up at both time points.
Within 1 year of discharge, 77 (17%) patients died and 51% suffered a major stressful life event.
In multivariable analyses, major life stressors – including financial insecurity, food insecurity, death of a close contact, and new disability – were strong independent predictors of disability, trouble with activities of daily living, depression, fatigue, sleep problems, and prolonged post-acute COVID symptoms. The adjusted odds ratios for these outcomes ranged from 2.5 to 20.8.
The research also confirmed the contribution of traditional risk factors for long COVID symptoms, as shown in past studies. These include older age, poor pre-COVID functional status, and more severe initial COVID-19 infection.
Long-term sequelae of COVID are increasingly recognized as major public health issues.
It has been estimated that roughly 16 million U.S. adults aged 18-65 years ave long COVID, with the often debilitating symptoms keeping up to 4 million out of work.
Holistic approach
Dr. Frontera said it’s important to realize that “sleep, fatigue, anxiety, depression, even cognition are so interwoven with each other that anything that impacts any one of them could have repercussions on the other.”
She added that it “certainly makes sense that there is an interplay or even a bidirectional relationship between the stressors that people face and how well they can recover after COVID.”
Therapies that lessen the trauma of the most stress-inducing life events need to be a central part of treatment for long COVID, with more research needed to validate the best approaches, Dr. Frontera said.
She also noted that social services or case management resources may be able to help address at least some of the stressors that individuals are under – and it is important to refer them to these resources. Referral to mental health services is also important.
“I think it’s really important to take a holistic approach and try to deal with whatever the problem may be,” said Dr. Frontera.
“I’m a neurologist, but as part of my evaluation, I really need to address if there are life stressors or mental health issues that may be impacting this person’s function,” she added.
The study had no commercial funding. The investigators reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
new research suggests.
Major life stressors in the year after hospital discharge for COVID-19 are “strongly predictive of a lot of the important outcomes that people may face after COVID,” lead investigator Jennifer A. Frontera, MD, a professor in the department of neurology at New York University Langone Health, said in an interview.
These outcomes include depression, brain fog, fatigue, trouble sleeping, and other long COVID symptoms.
The findings were published online in the Journal of the Neurological Sciences.
Major stressful events common
Dr. Frontera and the NYU Neurology COVID-19 study team evaluated 451 adults who survived a COVID hospital stay. Of these, 383 completed a 6-month follow-up, 242 completed a 12-month follow-up, and 174 completed follow-up at both time points.
Within 1 year of discharge, 77 (17%) patients died and 51% suffered a major stressful life event.
In multivariable analyses, major life stressors – including financial insecurity, food insecurity, death of a close contact, and new disability – were strong independent predictors of disability, trouble with activities of daily living, depression, fatigue, sleep problems, and prolonged post-acute COVID symptoms. The adjusted odds ratios for these outcomes ranged from 2.5 to 20.8.
The research also confirmed the contribution of traditional risk factors for long COVID symptoms, as shown in past studies. These include older age, poor pre-COVID functional status, and more severe initial COVID-19 infection.
Long-term sequelae of COVID are increasingly recognized as major public health issues.
It has been estimated that roughly 16 million U.S. adults aged 18-65 years ave long COVID, with the often debilitating symptoms keeping up to 4 million out of work.
Holistic approach
Dr. Frontera said it’s important to realize that “sleep, fatigue, anxiety, depression, even cognition are so interwoven with each other that anything that impacts any one of them could have repercussions on the other.”
She added that it “certainly makes sense that there is an interplay or even a bidirectional relationship between the stressors that people face and how well they can recover after COVID.”
Therapies that lessen the trauma of the most stress-inducing life events need to be a central part of treatment for long COVID, with more research needed to validate the best approaches, Dr. Frontera said.
She also noted that social services or case management resources may be able to help address at least some of the stressors that individuals are under – and it is important to refer them to these resources. Referral to mental health services is also important.
“I think it’s really important to take a holistic approach and try to deal with whatever the problem may be,” said Dr. Frontera.
“I’m a neurologist, but as part of my evaluation, I really need to address if there are life stressors or mental health issues that may be impacting this person’s function,” she added.
The study had no commercial funding. The investigators reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM THE JOURNAL OF THE NEUROLOGICAL SCIENCES
Why your professional persona may be considered unprofessional
On one of the first days of medical school, Adaira Landry, MD, applied her favorite dark shade of lipstick and headed to her orientation. She was eager to learn about program expectations and connect with fellow aspiring physicians. But when Dr. Landry got there, one of her brand-new peers turned to her and asked, “Why do you wear your lipstick like an angry Black woman?”
“Imagine hearing that,” Dr. Landry, now an emergency medical physician in Boston, says. “It was so hurtful.”
So, what is a “standard-issue doctor” expected to look like? Physicians manage their appearances in myriad ways: through clothes, accessories, hair style, makeup; through a social media presence or lack thereof; in the rhythms and nuances of their interactions with patients and colleagues. These things add up to a professional “persona” – the Latin word for “mask,” or the face on display for the world to see.
While the health care field itself is diversifying, its guidelines for professionalism appear slower to change, often excluding or frowning upon expressions of individual personality or identity.
“Medicine is run primarily by men. It’s an objective truth,” Dr. Landry says. “Currently and historically, the standard of professionalism, especially in the physical sense, was set by them. As we increase diversity and welcome people bringing their authentic self to work, the prior definitions of professionalism are obviously in need of change.”
Split social media personalities
In August 2020, the Journal of Vascular Surgery published a study on the “prevalence of unprofessional social media content among young vascular surgeons.” The content that was deemed “unprofessional” included opinions on political issues like abortion and gun control. Photos of physicians holding alcoholic drinks or wearing “inappropriate/offensive attire,” including underwear, “provocative Halloween costumes,” and “bikinis/swimwear” were also censured. Six men and one woman worked on the study, and three of the male researchers took on the task of seeking out the “unprofessional” photos on social media. The resulting paper was reviewed by an all-male editorial board.
The study sparked immediate backlash and prompted hundreds of health care professionals to post photos of themselves in bathing suits with the hashtag “#medbikini.” The journal then retracted the study and issued an apology on Twitter, recognizing “errors in the design of the study with regards to conscious and unconscious bias.”
The researchers’ original definition of professionalism suggests that physicians should manage their personae even outside of work hours. “I think medicine in general is a very conservative and hierarchical field of study and of work, to say the least,” says Sarah Fraser, MD, a family medicine physician in Nova Scotia, Canada. “There’s this view that we have to have completely separate personal and professional lives, like church and state.”
The #medbikini controversy inspired Dr. Fraser to write an op-ed for the British Medical Journal blog about the flaws of requiring physicians to keep their personal and professional selves separate. The piece referenced Robert Louis Stevenson’s 1886 Gothic novella “The Strange Case of Dr. Jekyll and Mr. Hyde,” in which the respected scientist Dr. Jekyll creates an alter ego so he can express his evil urges without experiencing guilt, punishment, or loss of livelihood. Dr. Fraser likened this story to the pressure physicians feel to shrink or split themselves to squeeze into a narrow definition of professionalism.
But Dr. Landry points out that some elements of expression seen as unprofessional cannot be entirely separated from a physician’s fundamental identity. “For Black women, our daily behaviors and forms of expression that are deemed ‘unprofessional’ are much more subtle than being able to wear a bikini on social media,” she says. “The way we wear our hair, the tone of our voice, the color of our lipstick, the way we wear scrub caps are parts of us that are called into question.”
Keeping up appearances
The stereotype of what a doctor should look like starts to shape physicians’ professional personae in medical school. When Jennifer Caputo-Seidler, MD, started medical school in 2008, the dress code requirements for male students were simple: pants, a button-down shirt, a tie. But then there were the rules for women: Hair should be tied back. Minimal makeup. No flashy jewelry. Nothing without sleeves. Neutral colors. High necklines. Low hemlines. “The message I got was that we need to dress like the men in order to be taken seriously and to be seen as professional,” says Dr. Caputo-Seidler, now an assistant professor of medicine at the University of South Florida, Tampa, “and so that’s what I did.”
A 2018 analysis of 78 “draw-a-scientist” studies found that children have overwhelmingly associated scientific fields with men for the last 50 years. Overall, children drew 73% of scientists as men. The drawings grew more gender diverse over time, but even as more women entered scientific fields, both boys and girls continued to draw significantly more male than female scientists.
Not everyone at Dr. Caputo-Seidler’s medical school adhered to the environment’s gendered expectations. One resident she worked with often wore voluminous hairstyles, lipstick, and high heels. Dr. Caputo-Seidler overheard her peers as they gossiped behind the resident’s back, ridiculing the way she looked.
“She was good at her job,” Dr. Caputo-Seidler says. “She knew her patients. She had things down. She was, by all measures, very competent. But when people saw her dressing outside the norm and being forward with her femininity, there was definitely a lot of chatter about it.”
While expectations for a conservative appearance may disproportionately affect women, and particularly women of color, they also affect men who deviate from the norm. “As an LGBTQ+ person working as a ‘professional,’ I have countless stories and moments where I had my professionalism questioned,” Blair Peters, MD, a plastic surgeon and assistant professor at Oregon Health & Science University, Portland, wrote on Twitter. “Why is it ‘unprofessional’ to have colored hair? Why is it ‘unprofessional’ to have a visible tattoo? Why is it ‘unprofessional’ to wear bright colors and patterns?”
Dr. Fraser remembers a fellow medical student who had full-sleeve tattoos on both of his arms. A preceptor made a comment about it to Dr. Fraser, and then instructed the student to cover up his tattoos. “I think that there are scenarios when having tattoos or having different-colored hair or expressing your individual personality could help you even better bond with your patients,” Dr. Fraser says, “especially if you’re, for example, working with youth.”
Unmasking health care
Beyond the facets of dress codes and social media posts, the issue of professional personae speaks to the deeper issue of inclusion in medicine. As the field grows increasingly diverse, health care institutions and those they serve may need to expand their definitions of professionalism to include more truthful expressions of who contemporary health care professionals are as people.
Dr. Fraser suggests that the benefits of physicians embracing self-expression – rather than assimilating to an outdated model of professionalism – extend beyond the individual.
“Whether it comes to what you choose to wear to the clinic on a day-to-day basis, or what you choose to share on a social media account, as long as it’s not harming others, then I think that it’s a positive thing to be able to be yourself and express yourself,” she says. “I feel like doctors are expected to have a different personality when we’re at the clinic, and usually it’s more conservative or objective or aloof. But I think that by being open about who we are, we’ll actually help build a trusting relationship with both patients and society.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
On one of the first days of medical school, Adaira Landry, MD, applied her favorite dark shade of lipstick and headed to her orientation. She was eager to learn about program expectations and connect with fellow aspiring physicians. But when Dr. Landry got there, one of her brand-new peers turned to her and asked, “Why do you wear your lipstick like an angry Black woman?”
“Imagine hearing that,” Dr. Landry, now an emergency medical physician in Boston, says. “It was so hurtful.”
So, what is a “standard-issue doctor” expected to look like? Physicians manage their appearances in myriad ways: through clothes, accessories, hair style, makeup; through a social media presence or lack thereof; in the rhythms and nuances of their interactions with patients and colleagues. These things add up to a professional “persona” – the Latin word for “mask,” or the face on display for the world to see.
While the health care field itself is diversifying, its guidelines for professionalism appear slower to change, often excluding or frowning upon expressions of individual personality or identity.
“Medicine is run primarily by men. It’s an objective truth,” Dr. Landry says. “Currently and historically, the standard of professionalism, especially in the physical sense, was set by them. As we increase diversity and welcome people bringing their authentic self to work, the prior definitions of professionalism are obviously in need of change.”
Split social media personalities
In August 2020, the Journal of Vascular Surgery published a study on the “prevalence of unprofessional social media content among young vascular surgeons.” The content that was deemed “unprofessional” included opinions on political issues like abortion and gun control. Photos of physicians holding alcoholic drinks or wearing “inappropriate/offensive attire,” including underwear, “provocative Halloween costumes,” and “bikinis/swimwear” were also censured. Six men and one woman worked on the study, and three of the male researchers took on the task of seeking out the “unprofessional” photos on social media. The resulting paper was reviewed by an all-male editorial board.
The study sparked immediate backlash and prompted hundreds of health care professionals to post photos of themselves in bathing suits with the hashtag “#medbikini.” The journal then retracted the study and issued an apology on Twitter, recognizing “errors in the design of the study with regards to conscious and unconscious bias.”
The researchers’ original definition of professionalism suggests that physicians should manage their personae even outside of work hours. “I think medicine in general is a very conservative and hierarchical field of study and of work, to say the least,” says Sarah Fraser, MD, a family medicine physician in Nova Scotia, Canada. “There’s this view that we have to have completely separate personal and professional lives, like church and state.”
The #medbikini controversy inspired Dr. Fraser to write an op-ed for the British Medical Journal blog about the flaws of requiring physicians to keep their personal and professional selves separate. The piece referenced Robert Louis Stevenson’s 1886 Gothic novella “The Strange Case of Dr. Jekyll and Mr. Hyde,” in which the respected scientist Dr. Jekyll creates an alter ego so he can express his evil urges without experiencing guilt, punishment, or loss of livelihood. Dr. Fraser likened this story to the pressure physicians feel to shrink or split themselves to squeeze into a narrow definition of professionalism.
But Dr. Landry points out that some elements of expression seen as unprofessional cannot be entirely separated from a physician’s fundamental identity. “For Black women, our daily behaviors and forms of expression that are deemed ‘unprofessional’ are much more subtle than being able to wear a bikini on social media,” she says. “The way we wear our hair, the tone of our voice, the color of our lipstick, the way we wear scrub caps are parts of us that are called into question.”
Keeping up appearances
The stereotype of what a doctor should look like starts to shape physicians’ professional personae in medical school. When Jennifer Caputo-Seidler, MD, started medical school in 2008, the dress code requirements for male students were simple: pants, a button-down shirt, a tie. But then there were the rules for women: Hair should be tied back. Minimal makeup. No flashy jewelry. Nothing without sleeves. Neutral colors. High necklines. Low hemlines. “The message I got was that we need to dress like the men in order to be taken seriously and to be seen as professional,” says Dr. Caputo-Seidler, now an assistant professor of medicine at the University of South Florida, Tampa, “and so that’s what I did.”
A 2018 analysis of 78 “draw-a-scientist” studies found that children have overwhelmingly associated scientific fields with men for the last 50 years. Overall, children drew 73% of scientists as men. The drawings grew more gender diverse over time, but even as more women entered scientific fields, both boys and girls continued to draw significantly more male than female scientists.
Not everyone at Dr. Caputo-Seidler’s medical school adhered to the environment’s gendered expectations. One resident she worked with often wore voluminous hairstyles, lipstick, and high heels. Dr. Caputo-Seidler overheard her peers as they gossiped behind the resident’s back, ridiculing the way she looked.
“She was good at her job,” Dr. Caputo-Seidler says. “She knew her patients. She had things down. She was, by all measures, very competent. But when people saw her dressing outside the norm and being forward with her femininity, there was definitely a lot of chatter about it.”
While expectations for a conservative appearance may disproportionately affect women, and particularly women of color, they also affect men who deviate from the norm. “As an LGBTQ+ person working as a ‘professional,’ I have countless stories and moments where I had my professionalism questioned,” Blair Peters, MD, a plastic surgeon and assistant professor at Oregon Health & Science University, Portland, wrote on Twitter. “Why is it ‘unprofessional’ to have colored hair? Why is it ‘unprofessional’ to have a visible tattoo? Why is it ‘unprofessional’ to wear bright colors and patterns?”
Dr. Fraser remembers a fellow medical student who had full-sleeve tattoos on both of his arms. A preceptor made a comment about it to Dr. Fraser, and then instructed the student to cover up his tattoos. “I think that there are scenarios when having tattoos or having different-colored hair or expressing your individual personality could help you even better bond with your patients,” Dr. Fraser says, “especially if you’re, for example, working with youth.”
Unmasking health care
Beyond the facets of dress codes and social media posts, the issue of professional personae speaks to the deeper issue of inclusion in medicine. As the field grows increasingly diverse, health care institutions and those they serve may need to expand their definitions of professionalism to include more truthful expressions of who contemporary health care professionals are as people.
Dr. Fraser suggests that the benefits of physicians embracing self-expression – rather than assimilating to an outdated model of professionalism – extend beyond the individual.
“Whether it comes to what you choose to wear to the clinic on a day-to-day basis, or what you choose to share on a social media account, as long as it’s not harming others, then I think that it’s a positive thing to be able to be yourself and express yourself,” she says. “I feel like doctors are expected to have a different personality when we’re at the clinic, and usually it’s more conservative or objective or aloof. But I think that by being open about who we are, we’ll actually help build a trusting relationship with both patients and society.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
On one of the first days of medical school, Adaira Landry, MD, applied her favorite dark shade of lipstick and headed to her orientation. She was eager to learn about program expectations and connect with fellow aspiring physicians. But when Dr. Landry got there, one of her brand-new peers turned to her and asked, “Why do you wear your lipstick like an angry Black woman?”
“Imagine hearing that,” Dr. Landry, now an emergency medical physician in Boston, says. “It was so hurtful.”
So, what is a “standard-issue doctor” expected to look like? Physicians manage their appearances in myriad ways: through clothes, accessories, hair style, makeup; through a social media presence or lack thereof; in the rhythms and nuances of their interactions with patients and colleagues. These things add up to a professional “persona” – the Latin word for “mask,” or the face on display for the world to see.
While the health care field itself is diversifying, its guidelines for professionalism appear slower to change, often excluding or frowning upon expressions of individual personality or identity.
“Medicine is run primarily by men. It’s an objective truth,” Dr. Landry says. “Currently and historically, the standard of professionalism, especially in the physical sense, was set by them. As we increase diversity and welcome people bringing their authentic self to work, the prior definitions of professionalism are obviously in need of change.”
Split social media personalities
In August 2020, the Journal of Vascular Surgery published a study on the “prevalence of unprofessional social media content among young vascular surgeons.” The content that was deemed “unprofessional” included opinions on political issues like abortion and gun control. Photos of physicians holding alcoholic drinks or wearing “inappropriate/offensive attire,” including underwear, “provocative Halloween costumes,” and “bikinis/swimwear” were also censured. Six men and one woman worked on the study, and three of the male researchers took on the task of seeking out the “unprofessional” photos on social media. The resulting paper was reviewed by an all-male editorial board.
The study sparked immediate backlash and prompted hundreds of health care professionals to post photos of themselves in bathing suits with the hashtag “#medbikini.” The journal then retracted the study and issued an apology on Twitter, recognizing “errors in the design of the study with regards to conscious and unconscious bias.”
The researchers’ original definition of professionalism suggests that physicians should manage their personae even outside of work hours. “I think medicine in general is a very conservative and hierarchical field of study and of work, to say the least,” says Sarah Fraser, MD, a family medicine physician in Nova Scotia, Canada. “There’s this view that we have to have completely separate personal and professional lives, like church and state.”
The #medbikini controversy inspired Dr. Fraser to write an op-ed for the British Medical Journal blog about the flaws of requiring physicians to keep their personal and professional selves separate. The piece referenced Robert Louis Stevenson’s 1886 Gothic novella “The Strange Case of Dr. Jekyll and Mr. Hyde,” in which the respected scientist Dr. Jekyll creates an alter ego so he can express his evil urges without experiencing guilt, punishment, or loss of livelihood. Dr. Fraser likened this story to the pressure physicians feel to shrink or split themselves to squeeze into a narrow definition of professionalism.
But Dr. Landry points out that some elements of expression seen as unprofessional cannot be entirely separated from a physician’s fundamental identity. “For Black women, our daily behaviors and forms of expression that are deemed ‘unprofessional’ are much more subtle than being able to wear a bikini on social media,” she says. “The way we wear our hair, the tone of our voice, the color of our lipstick, the way we wear scrub caps are parts of us that are called into question.”
Keeping up appearances
The stereotype of what a doctor should look like starts to shape physicians’ professional personae in medical school. When Jennifer Caputo-Seidler, MD, started medical school in 2008, the dress code requirements for male students were simple: pants, a button-down shirt, a tie. But then there were the rules for women: Hair should be tied back. Minimal makeup. No flashy jewelry. Nothing without sleeves. Neutral colors. High necklines. Low hemlines. “The message I got was that we need to dress like the men in order to be taken seriously and to be seen as professional,” says Dr. Caputo-Seidler, now an assistant professor of medicine at the University of South Florida, Tampa, “and so that’s what I did.”
A 2018 analysis of 78 “draw-a-scientist” studies found that children have overwhelmingly associated scientific fields with men for the last 50 years. Overall, children drew 73% of scientists as men. The drawings grew more gender diverse over time, but even as more women entered scientific fields, both boys and girls continued to draw significantly more male than female scientists.
Not everyone at Dr. Caputo-Seidler’s medical school adhered to the environment’s gendered expectations. One resident she worked with often wore voluminous hairstyles, lipstick, and high heels. Dr. Caputo-Seidler overheard her peers as they gossiped behind the resident’s back, ridiculing the way she looked.
“She was good at her job,” Dr. Caputo-Seidler says. “She knew her patients. She had things down. She was, by all measures, very competent. But when people saw her dressing outside the norm and being forward with her femininity, there was definitely a lot of chatter about it.”
While expectations for a conservative appearance may disproportionately affect women, and particularly women of color, they also affect men who deviate from the norm. “As an LGBTQ+ person working as a ‘professional,’ I have countless stories and moments where I had my professionalism questioned,” Blair Peters, MD, a plastic surgeon and assistant professor at Oregon Health & Science University, Portland, wrote on Twitter. “Why is it ‘unprofessional’ to have colored hair? Why is it ‘unprofessional’ to have a visible tattoo? Why is it ‘unprofessional’ to wear bright colors and patterns?”
Dr. Fraser remembers a fellow medical student who had full-sleeve tattoos on both of his arms. A preceptor made a comment about it to Dr. Fraser, and then instructed the student to cover up his tattoos. “I think that there are scenarios when having tattoos or having different-colored hair or expressing your individual personality could help you even better bond with your patients,” Dr. Fraser says, “especially if you’re, for example, working with youth.”
Unmasking health care
Beyond the facets of dress codes and social media posts, the issue of professional personae speaks to the deeper issue of inclusion in medicine. As the field grows increasingly diverse, health care institutions and those they serve may need to expand their definitions of professionalism to include more truthful expressions of who contemporary health care professionals are as people.
Dr. Fraser suggests that the benefits of physicians embracing self-expression – rather than assimilating to an outdated model of professionalism – extend beyond the individual.
“Whether it comes to what you choose to wear to the clinic on a day-to-day basis, or what you choose to share on a social media account, as long as it’s not harming others, then I think that it’s a positive thing to be able to be yourself and express yourself,” she says. “I feel like doctors are expected to have a different personality when we’re at the clinic, and usually it’s more conservative or objective or aloof. But I think that by being open about who we are, we’ll actually help build a trusting relationship with both patients and society.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
IRONMAN galvanizes case for IV iron repletion in heart failure
CHICAGO – Another major study appears to back the use of intravenous iron repletion in patients with heart failure (HF) and iron deficiency, strengthening largely consistent evidence, researchers say, that the treatment may improve symptoms and prevent some HF-related hospital admissions.
To be sure, the IRONMAN trial, which compared intravenous iron versus usual care in such patients – most with reduced ejection fraction and not hospitalized – failed to show a benefit for its primary endpoint. The 18% reduction in risk for HF hospitalization or cardiovascular (CV) death seen in the trial, however encouraging, can only be called a trend (P = .07).
But the intervention showed signs of benefit for some secondary endpoints, including quality of life scores, and hinted at such an effect on HF hospitalization. Risk for the latter endpoint dropped 20% (P = .085) over a median follow-up of 2.7 years.
The findings “build upon the other data we have that correcting iron deficiency can help improve well-being, and particularly reduce the risk of hospitalization, in a broad range of [HF] patients,” said Paul Kalra, MD, of the University of Glasgow and Portsmouth (England) Hospitals University NHS Trust.
The tested regimen “was well tolerated with no safety concerns” and offers “reassurance about the long-term safety” of the intravenous iron it used, ferric derisomaltose (MonoFerric), in patients with HF, Dr. Kalra said at a media briefing on the trial.
The remarks preceded his formal presentation of IRONMAN at the American Heart Association scientific sessions. Dr. Kalra is also lead author on the trial’s publication in The Lancet.
IRONMAN strengthens the base of evidence supporting intravenous iron in HF with iron deficiency, especially chronic HF in outpatients, Dr. Kalra and others said. It also supports efficacy for a form of intravenous iron not previously tested in a major HF trial.
Still, “the totality of data are now supporting intravenous iron per se,” regardless of the iron agent used, said Dr. Kalra. But ferric derisomaltose may have dosing advantages, he observed, “and we’ve now got these long-term safety data.”
The strongest prior support for intravenous iron in HF came from hospitalized patients who received it as ferric carboxymaltose (Ferinject) and were followed only 12 months. That was in the AFFIRM-AHF trial, published 2 years ago, which also missed its primary endpoint – the same one used in IRONMAN. Some outcomes in the two trials were similar.
The risk for HF hospitalization or CV death for intravenous iron therapy, compared with usual care, in AFFIRM-AHF fell 21% (P = .059), missing significance but apparently driven by a 26% drop in risk for HF readmissions (P = .013). But neither that trial nor IRONMAN suggested a benefit for CV mortality on its own.
The COVID effect
In IRONMAN, Dr. Kalra said, usual care could include oral iron supplementation, which 17% of patients in the control group received. That could potentially have kept the intravenous iron group from making a better showing for the primary endpoint, he proposed.
And some iron doses and other treatments were missed by a substantial number of patients in both groups who entered the trial after the United Kingdom’s national lockdown in response to the COVID-19 pandemic, he observed. “Patients were not able to come into hospitals for research visits, or in fact when they were able, may not have wanted to.”
So, the group conducted a “prespecified” sensitivity analysis that excluded the 9% of patients enrolled by the end of March 2020, about the time of the first lockdown, and followed the remainder for another 6 months.
In that analysis, risk for HF hospitalization or CV death declined 24% in the intravenous iron group, a marginal but significant result (P = .047) that was dominated by an improvement in HF hospitalizations.
Effects on guidelines
The intravenous iron recommendations in the European HF guidelines refer only to ferric carboxymaltose without mentioning other forms, such as ferric derisomaltose, “but this is now a class effect given the similarities between AFFIRM-AHF and IRONMAN,” said Gregory D. Lewis, MD, Mass General Brigham, Boston, invited discussant for Dr. Kalra’s presentation at the AHA session.
“In the United States, we relegate IV iron to improvement in functional capacity as a comorbidity of heart failure. Perhaps this role will expand,” added Dr. Lewis, who is medical director of his center’s heart transplant program.
He also wondered aloud whether the purported clinical benefits of intravenous iron in HF patients with iron deficiency, not as yet supported by a significant primary-endpoint showing in one of the major trials, currently justify expansion of its use in practice.
“With the benefits of IV iron on exercise capacity and quality of life, and the safety of administering high doses of IV iron,” potentially reducing HF polypharmacy, he noted, “should we be considering IV iron more commonly for utilization in our patients even if we find that heart failure hospitalizations and mortality are only modestly improved?”
IRONMAN “asked whether there’s benefit to IV iron in the longer term,” Kiran Musunuru, MD, PhD, MPH, University of Pennsylvania,Philadelphia, observed at the media briefing. As the trial was reported, “that does in fact, seem to be the case,” said Dr. Musunuru, who was not involved in IRONMAN.
Therefore, he said, “this study reinforces the message that we should be routinely monitoring our heart failure patients for iron deficiency and supplementing them as needed.”
A commentary linked to the IRONMAN publication agreed. The trial “increases the evidence base for the treatment of iron deficiency with intravenous iron supplementation,” wrote the editorialists, led by Theresa A. McDonagh, MD, King’s College Hospital and School of Cardiovascular Sciences, London.
Patients with acute or chronic HF, iron deficiency, and reduced or mildly reduced ejection fractions “should be offered treatment with intravenous iron to reduce their risk of hospital admission for heart failure,” they concluded.
Mostly reduced-EF outpatients
The open-label, blinded-endpoint IRONMAN trial, conducted at 70 centers in the United Kingdom, entered adults with HF, ejection fractions 45% or lower within the previous 2 years, and iron deficiency defined as transferrin saturation less than 20% or serum ferritin levels below 100 mcg/L, the report states. They were either hospitalized for HF, had such a hospitalization within the past 6 months, or were outpatients with elevated natriuretic peptide levels; the third category accounted for two thirds of the trial population.
Of the 1,137 randomized patients, 569 were assigned to receive intravenous ferric derisomaltose at weight- and hemoglobin-adjusted dosages; 568 went to the usual-care group.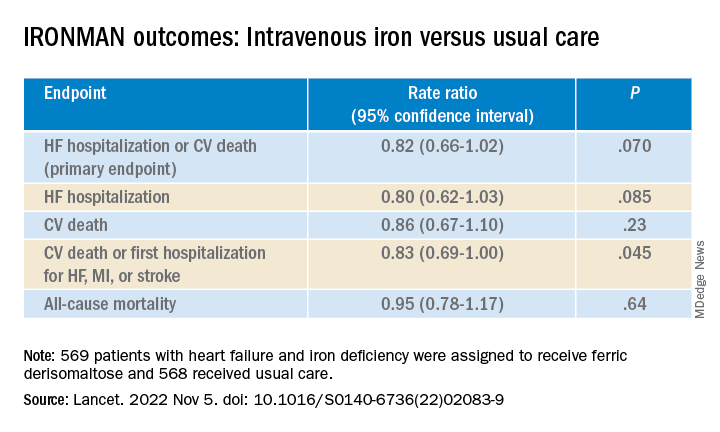
Those receiving intravenous iron visited the trial clinic 4 weeks later and then every 4 months. At those visits, they received a round of ferric derisomaltose if their ferritin levels were below 100 mcg/L, or 400 mcg/L or lower if transferrin saturation was below 25%, the published report states.
Mean scores on the Minnesota Living with Heart Failure Questionnaire improved by a marginally significant 3.33 points (P = .050) at 4 months in the intravenous iron group. The gain receded to a nonsignificant 2.57 points by 20 months (P = .23).
In COVID-related sensitivity analysis, the intravenous iron group showed a significant benefit for the primary endpoint and a trend for improved HF hospitalizations.
- HF hospitalization or CV death: RR, 0.76 (95% confidence interval, 0.58-1.00; P = .047)
- HF hospitalization: RR 0.76 (95% CI, 0.56-1.03; P = .077)
Fewer patients in the intravenous iron group experienced serious cardiac adverse events, 36% compared with 43% in for those on usual care, P = .016.
The recently updated European Society of Cardiology guidelines for HF made it a class 1 recommendation to assess iron status in every patient, Kalra observed. “It doesn›t specify how frequently, but I think we should be thinking about every 4-6 months.”
Dr. Kalra disclosed receiving research grants from Pharmacosmos; and consulting or lecturing for Amgen, AstraZeneca, Bayer, Boehringer Ingelheim, Novartis, Pfizer, Pharmacosmos, Servier, and Vifor Pharma. Dr. Musunuru disclosed significant ownership interest in Verve Therapeutics and Variant Bio. Dr. Lewis disclosed relationships with NXT, American Regent, and RIVUS; and receiving research grants from Cytokinetics and Amgen.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
CHICAGO – Another major study appears to back the use of intravenous iron repletion in patients with heart failure (HF) and iron deficiency, strengthening largely consistent evidence, researchers say, that the treatment may improve symptoms and prevent some HF-related hospital admissions.
To be sure, the IRONMAN trial, which compared intravenous iron versus usual care in such patients – most with reduced ejection fraction and not hospitalized – failed to show a benefit for its primary endpoint. The 18% reduction in risk for HF hospitalization or cardiovascular (CV) death seen in the trial, however encouraging, can only be called a trend (P = .07).
But the intervention showed signs of benefit for some secondary endpoints, including quality of life scores, and hinted at such an effect on HF hospitalization. Risk for the latter endpoint dropped 20% (P = .085) over a median follow-up of 2.7 years.
The findings “build upon the other data we have that correcting iron deficiency can help improve well-being, and particularly reduce the risk of hospitalization, in a broad range of [HF] patients,” said Paul Kalra, MD, of the University of Glasgow and Portsmouth (England) Hospitals University NHS Trust.
The tested regimen “was well tolerated with no safety concerns” and offers “reassurance about the long-term safety” of the intravenous iron it used, ferric derisomaltose (MonoFerric), in patients with HF, Dr. Kalra said at a media briefing on the trial.
The remarks preceded his formal presentation of IRONMAN at the American Heart Association scientific sessions. Dr. Kalra is also lead author on the trial’s publication in The Lancet.
IRONMAN strengthens the base of evidence supporting intravenous iron in HF with iron deficiency, especially chronic HF in outpatients, Dr. Kalra and others said. It also supports efficacy for a form of intravenous iron not previously tested in a major HF trial.
Still, “the totality of data are now supporting intravenous iron per se,” regardless of the iron agent used, said Dr. Kalra. But ferric derisomaltose may have dosing advantages, he observed, “and we’ve now got these long-term safety data.”
The strongest prior support for intravenous iron in HF came from hospitalized patients who received it as ferric carboxymaltose (Ferinject) and were followed only 12 months. That was in the AFFIRM-AHF trial, published 2 years ago, which also missed its primary endpoint – the same one used in IRONMAN. Some outcomes in the two trials were similar.
The risk for HF hospitalization or CV death for intravenous iron therapy, compared with usual care, in AFFIRM-AHF fell 21% (P = .059), missing significance but apparently driven by a 26% drop in risk for HF readmissions (P = .013). But neither that trial nor IRONMAN suggested a benefit for CV mortality on its own.
The COVID effect
In IRONMAN, Dr. Kalra said, usual care could include oral iron supplementation, which 17% of patients in the control group received. That could potentially have kept the intravenous iron group from making a better showing for the primary endpoint, he proposed.
And some iron doses and other treatments were missed by a substantial number of patients in both groups who entered the trial after the United Kingdom’s national lockdown in response to the COVID-19 pandemic, he observed. “Patients were not able to come into hospitals for research visits, or in fact when they were able, may not have wanted to.”
So, the group conducted a “prespecified” sensitivity analysis that excluded the 9% of patients enrolled by the end of March 2020, about the time of the first lockdown, and followed the remainder for another 6 months.
In that analysis, risk for HF hospitalization or CV death declined 24% in the intravenous iron group, a marginal but significant result (P = .047) that was dominated by an improvement in HF hospitalizations.
Effects on guidelines
The intravenous iron recommendations in the European HF guidelines refer only to ferric carboxymaltose without mentioning other forms, such as ferric derisomaltose, “but this is now a class effect given the similarities between AFFIRM-AHF and IRONMAN,” said Gregory D. Lewis, MD, Mass General Brigham, Boston, invited discussant for Dr. Kalra’s presentation at the AHA session.
“In the United States, we relegate IV iron to improvement in functional capacity as a comorbidity of heart failure. Perhaps this role will expand,” added Dr. Lewis, who is medical director of his center’s heart transplant program.
He also wondered aloud whether the purported clinical benefits of intravenous iron in HF patients with iron deficiency, not as yet supported by a significant primary-endpoint showing in one of the major trials, currently justify expansion of its use in practice.
“With the benefits of IV iron on exercise capacity and quality of life, and the safety of administering high doses of IV iron,” potentially reducing HF polypharmacy, he noted, “should we be considering IV iron more commonly for utilization in our patients even if we find that heart failure hospitalizations and mortality are only modestly improved?”
IRONMAN “asked whether there’s benefit to IV iron in the longer term,” Kiran Musunuru, MD, PhD, MPH, University of Pennsylvania,Philadelphia, observed at the media briefing. As the trial was reported, “that does in fact, seem to be the case,” said Dr. Musunuru, who was not involved in IRONMAN.
Therefore, he said, “this study reinforces the message that we should be routinely monitoring our heart failure patients for iron deficiency and supplementing them as needed.”
A commentary linked to the IRONMAN publication agreed. The trial “increases the evidence base for the treatment of iron deficiency with intravenous iron supplementation,” wrote the editorialists, led by Theresa A. McDonagh, MD, King’s College Hospital and School of Cardiovascular Sciences, London.
Patients with acute or chronic HF, iron deficiency, and reduced or mildly reduced ejection fractions “should be offered treatment with intravenous iron to reduce their risk of hospital admission for heart failure,” they concluded.
Mostly reduced-EF outpatients
The open-label, blinded-endpoint IRONMAN trial, conducted at 70 centers in the United Kingdom, entered adults with HF, ejection fractions 45% or lower within the previous 2 years, and iron deficiency defined as transferrin saturation less than 20% or serum ferritin levels below 100 mcg/L, the report states. They were either hospitalized for HF, had such a hospitalization within the past 6 months, or were outpatients with elevated natriuretic peptide levels; the third category accounted for two thirds of the trial population.
Of the 1,137 randomized patients, 569 were assigned to receive intravenous ferric derisomaltose at weight- and hemoglobin-adjusted dosages; 568 went to the usual-care group.
Those receiving intravenous iron visited the trial clinic 4 weeks later and then every 4 months. At those visits, they received a round of ferric derisomaltose if their ferritin levels were below 100 mcg/L, or 400 mcg/L or lower if transferrin saturation was below 25%, the published report states.
Mean scores on the Minnesota Living with Heart Failure Questionnaire improved by a marginally significant 3.33 points (P = .050) at 4 months in the intravenous iron group. The gain receded to a nonsignificant 2.57 points by 20 months (P = .23).
In COVID-related sensitivity analysis, the intravenous iron group showed a significant benefit for the primary endpoint and a trend for improved HF hospitalizations.
- HF hospitalization or CV death: RR, 0.76 (95% confidence interval, 0.58-1.00; P = .047)
- HF hospitalization: RR 0.76 (95% CI, 0.56-1.03; P = .077)
Fewer patients in the intravenous iron group experienced serious cardiac adverse events, 36% compared with 43% in for those on usual care, P = .016.
The recently updated European Society of Cardiology guidelines for HF made it a class 1 recommendation to assess iron status in every patient, Kalra observed. “It doesn›t specify how frequently, but I think we should be thinking about every 4-6 months.”
Dr. Kalra disclosed receiving research grants from Pharmacosmos; and consulting or lecturing for Amgen, AstraZeneca, Bayer, Boehringer Ingelheim, Novartis, Pfizer, Pharmacosmos, Servier, and Vifor Pharma. Dr. Musunuru disclosed significant ownership interest in Verve Therapeutics and Variant Bio. Dr. Lewis disclosed relationships with NXT, American Regent, and RIVUS; and receiving research grants from Cytokinetics and Amgen.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
CHICAGO – Another major study appears to back the use of intravenous iron repletion in patients with heart failure (HF) and iron deficiency, strengthening largely consistent evidence, researchers say, that the treatment may improve symptoms and prevent some HF-related hospital admissions.
To be sure, the IRONMAN trial, which compared intravenous iron versus usual care in such patients – most with reduced ejection fraction and not hospitalized – failed to show a benefit for its primary endpoint. The 18% reduction in risk for HF hospitalization or cardiovascular (CV) death seen in the trial, however encouraging, can only be called a trend (P = .07).
But the intervention showed signs of benefit for some secondary endpoints, including quality of life scores, and hinted at such an effect on HF hospitalization. Risk for the latter endpoint dropped 20% (P = .085) over a median follow-up of 2.7 years.
The findings “build upon the other data we have that correcting iron deficiency can help improve well-being, and particularly reduce the risk of hospitalization, in a broad range of [HF] patients,” said Paul Kalra, MD, of the University of Glasgow and Portsmouth (England) Hospitals University NHS Trust.
The tested regimen “was well tolerated with no safety concerns” and offers “reassurance about the long-term safety” of the intravenous iron it used, ferric derisomaltose (MonoFerric), in patients with HF, Dr. Kalra said at a media briefing on the trial.
The remarks preceded his formal presentation of IRONMAN at the American Heart Association scientific sessions. Dr. Kalra is also lead author on the trial’s publication in The Lancet.
IRONMAN strengthens the base of evidence supporting intravenous iron in HF with iron deficiency, especially chronic HF in outpatients, Dr. Kalra and others said. It also supports efficacy for a form of intravenous iron not previously tested in a major HF trial.
Still, “the totality of data are now supporting intravenous iron per se,” regardless of the iron agent used, said Dr. Kalra. But ferric derisomaltose may have dosing advantages, he observed, “and we’ve now got these long-term safety data.”
The strongest prior support for intravenous iron in HF came from hospitalized patients who received it as ferric carboxymaltose (Ferinject) and were followed only 12 months. That was in the AFFIRM-AHF trial, published 2 years ago, which also missed its primary endpoint – the same one used in IRONMAN. Some outcomes in the two trials were similar.
The risk for HF hospitalization or CV death for intravenous iron therapy, compared with usual care, in AFFIRM-AHF fell 21% (P = .059), missing significance but apparently driven by a 26% drop in risk for HF readmissions (P = .013). But neither that trial nor IRONMAN suggested a benefit for CV mortality on its own.
The COVID effect
In IRONMAN, Dr. Kalra said, usual care could include oral iron supplementation, which 17% of patients in the control group received. That could potentially have kept the intravenous iron group from making a better showing for the primary endpoint, he proposed.
And some iron doses and other treatments were missed by a substantial number of patients in both groups who entered the trial after the United Kingdom’s national lockdown in response to the COVID-19 pandemic, he observed. “Patients were not able to come into hospitals for research visits, or in fact when they were able, may not have wanted to.”
So, the group conducted a “prespecified” sensitivity analysis that excluded the 9% of patients enrolled by the end of March 2020, about the time of the first lockdown, and followed the remainder for another 6 months.
In that analysis, risk for HF hospitalization or CV death declined 24% in the intravenous iron group, a marginal but significant result (P = .047) that was dominated by an improvement in HF hospitalizations.
Effects on guidelines
The intravenous iron recommendations in the European HF guidelines refer only to ferric carboxymaltose without mentioning other forms, such as ferric derisomaltose, “but this is now a class effect given the similarities between AFFIRM-AHF and IRONMAN,” said Gregory D. Lewis, MD, Mass General Brigham, Boston, invited discussant for Dr. Kalra’s presentation at the AHA session.
“In the United States, we relegate IV iron to improvement in functional capacity as a comorbidity of heart failure. Perhaps this role will expand,” added Dr. Lewis, who is medical director of his center’s heart transplant program.
He also wondered aloud whether the purported clinical benefits of intravenous iron in HF patients with iron deficiency, not as yet supported by a significant primary-endpoint showing in one of the major trials, currently justify expansion of its use in practice.
“With the benefits of IV iron on exercise capacity and quality of life, and the safety of administering high doses of IV iron,” potentially reducing HF polypharmacy, he noted, “should we be considering IV iron more commonly for utilization in our patients even if we find that heart failure hospitalizations and mortality are only modestly improved?”
IRONMAN “asked whether there’s benefit to IV iron in the longer term,” Kiran Musunuru, MD, PhD, MPH, University of Pennsylvania,Philadelphia, observed at the media briefing. As the trial was reported, “that does in fact, seem to be the case,” said Dr. Musunuru, who was not involved in IRONMAN.
Therefore, he said, “this study reinforces the message that we should be routinely monitoring our heart failure patients for iron deficiency and supplementing them as needed.”
A commentary linked to the IRONMAN publication agreed. The trial “increases the evidence base for the treatment of iron deficiency with intravenous iron supplementation,” wrote the editorialists, led by Theresa A. McDonagh, MD, King’s College Hospital and School of Cardiovascular Sciences, London.
Patients with acute or chronic HF, iron deficiency, and reduced or mildly reduced ejection fractions “should be offered treatment with intravenous iron to reduce their risk of hospital admission for heart failure,” they concluded.
Mostly reduced-EF outpatients
The open-label, blinded-endpoint IRONMAN trial, conducted at 70 centers in the United Kingdom, entered adults with HF, ejection fractions 45% or lower within the previous 2 years, and iron deficiency defined as transferrin saturation less than 20% or serum ferritin levels below 100 mcg/L, the report states. They were either hospitalized for HF, had such a hospitalization within the past 6 months, or were outpatients with elevated natriuretic peptide levels; the third category accounted for two thirds of the trial population.
Of the 1,137 randomized patients, 569 were assigned to receive intravenous ferric derisomaltose at weight- and hemoglobin-adjusted dosages; 568 went to the usual-care group.
Those receiving intravenous iron visited the trial clinic 4 weeks later and then every 4 months. At those visits, they received a round of ferric derisomaltose if their ferritin levels were below 100 mcg/L, or 400 mcg/L or lower if transferrin saturation was below 25%, the published report states.
Mean scores on the Minnesota Living with Heart Failure Questionnaire improved by a marginally significant 3.33 points (P = .050) at 4 months in the intravenous iron group. The gain receded to a nonsignificant 2.57 points by 20 months (P = .23).
In COVID-related sensitivity analysis, the intravenous iron group showed a significant benefit for the primary endpoint and a trend for improved HF hospitalizations.
- HF hospitalization or CV death: RR, 0.76 (95% confidence interval, 0.58-1.00; P = .047)
- HF hospitalization: RR 0.76 (95% CI, 0.56-1.03; P = .077)
Fewer patients in the intravenous iron group experienced serious cardiac adverse events, 36% compared with 43% in for those on usual care, P = .016.
The recently updated European Society of Cardiology guidelines for HF made it a class 1 recommendation to assess iron status in every patient, Kalra observed. “It doesn›t specify how frequently, but I think we should be thinking about every 4-6 months.”
Dr. Kalra disclosed receiving research grants from Pharmacosmos; and consulting or lecturing for Amgen, AstraZeneca, Bayer, Boehringer Ingelheim, Novartis, Pfizer, Pharmacosmos, Servier, and Vifor Pharma. Dr. Musunuru disclosed significant ownership interest in Verve Therapeutics and Variant Bio. Dr. Lewis disclosed relationships with NXT, American Regent, and RIVUS; and receiving research grants from Cytokinetics and Amgen.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
AT AHA 2022
Be aware, mindfulness training can lower systolic BP: MB-BP
CHICAGO – It’s been said that one can observe a lot just by watching. Turning such observation inward, new evidence suggests, might lead to blood pressure (BP) reductions that approach what’s possible from an antihypertensive agent.
Systolic BP fell over 6 months by almost 6 mm Hg, on average, in people with elevated BP who participated in an 8-week mindful awareness program as part of a randomized trial that included a usual-care control group.
The program taught established mindfulness-training techniques aimed at modifying behaviors regarding diet, exercise, and other controllable influences on the success of antihypertensive therapy.
Participants in the program, called Mindfulness-Based Blood Pressure Reduction (MB-BP), also the name of the single-center study, “showed potentially clinically relevant reductions in systolic blood pressure,” said principal investigator Eric B. Loucks, PhD, Brown University, Providence, R.I.
The phase 2 trial has some limitations, he observed, including on generalizability. For example, it entered about 200 mostly White, college-educated adults from one metropolitan area.
But if these findings are replicated in further studies, “preferably by other research groups, in a larger and broader population, and with longer follow-up,” Dr. Loucks said, the MB-BP intervention could become “an appealing approach to help control blood pressure.”
Dr. Loucks made the comments at a press conference prior to his formal presentation of MB-BP Nov. 6 at American Heart Association (AHA) Scientific Sessions 2022, held in Chicago and virtually.
Mindfulness-based interventions for elevated BP have not been widely studied, “so this is exactly what we need: a well-done trial with a control group to show that it actually works,” Amit Khera, MD, not connected with MB-BP, told this news organization.
The trial is “really important for proof of concept, but it had only 200 people. You need a larger one, and you need longer-term data,” agreed Dr. Khera, who directs the preventive cardiology program at the University of Texas Southwestern Medical Center, in Dallas. “Six months is good, but we want to see if it’s durable.”
Rhian M. Touyz, MBBCh, also not part of MB-BP, agreed that the nearly 6 mm Hg mean systolic BP reduction among program participants is clinically relevant. “I think in the context of global risk and reduction of target organ damage and cardiovascular events, it is significant in terms of events at a population level,” Dr. Touyz, McGill University Health Centre, Montreal, told this news organization.
Many patients on antihypertensive therapy that’s falling short resist the addition of another such agent, she observed, and instead might show further BP reduction from mindfulness training. The intervention probably also “would benefit health in general.” Mindfulness-based approaches could therefore be useful additions to treatment protocols for elevated BP, Dr. Touyz said.
How the training works
The MB-BP program used validated mindfulness-based stress-management techniques, adapted to address elevated BP, that included “personalized feedback and education about hypertension risk factors, mindful awareness training of participants’ relationships with hypertension risk factors, and support for behavior change,” Dr. Loucks and colleagues reported.
Participants were trained in mindfulness skills that included “self-awareness and emotion regulation,” Dr. Loucks said, which they then could apply to their “relationships with the things that we know influence blood pressure, like physical activity, diet, antihypertensive medication adherence, or alcohol consumption.”
One goal is to promote greater “attention control,” he said, “so that there’s some self-awareness that arises in terms of how we feel the next day, after a lot of alcohol consumption, for example, or lack of physical activity.” The process can provide insights that inspire patients to modify behaviors and risk factors that elevate BP, Dr. Loucks explained.
Effects on medication use
Systolic BP responses led some program participants to be managed on fewer or reduced dosages of antihypertensive meds, he told this news organization. Physicians seen outside of the trial could adjust their prescriptions, intensifying or pulling back on meds depending on their assessments of the patient. Any prescription changes would be documented by the researchers at the patient’s next class or trial-clinic visit.
The group that did the training, Dr. Loucks said, was 33% less likely to increase and 30% more likely to decrease their use of BP-lowering medications compared with the control group.
Elevated BP is so common and undertreated that “there is a need for every possible level of intervention, starting from the population level to the individual and everything else in between,” nephrologist Janani Rangaswami, MD, George Washington University, Washington, said at the press conference.
Therefore, “this mindfulness-based approach, in addition to standard of care with pharmacotherapy, is a really welcome addition to the hypertension literature,” said Dr. Rangaswami, who directs her center’s cardiorenal program. The systolic BP reduction seen in the intervention group, she agreed, was “clinically important and meaningful.”
Blinded assessments
The trial entered 201 patients with systolic and diastolic BP greater than 120 mm Hg and 80 mm Hg, respectively; 58.7% were women, 81% were White, and 73% were college-educated, Dr. Loucks reported.
The 100 assigned to the “enhanced usual care” control group received educational materials on controlling high BP. They and the 101 who followed the mindfulness-based program were given and trained on a home BP-monitoring device. They were then followed for the primary endpoint of change in systolic BP at 6 months.
Data management and outcomes assessments were conducted by trialists not involved in the training intervention who were blinded to randomization assignment.
In a prespecified unadjusted analysis by intention-to-treat, systolic BP in the intervention group dropped by a mean of 5.9 mm Hg (P < .001) compared with baseline and 4.5 mm Hg (P = .045), compared with the control group.
A post hoc analysis adjusted for sex and baseline BP showed an average 4.3 mm Hg reduction (P = .056) in those following the MB-BP program, compared with controls.
There were no observed significant effects on diastolic BP.
The study offered clues to how engagement in the MB-BP program might promote reductions in systolic BP, Dr. Loucks observed. For example, it may have led to increased activity levels, reduced sodium intake, and other dietary improvements.
Indeed, program participants averaged about 351 minutes less sedentary time (P = .02) and showed a 0.32-point improvement in Dietary Approaches to Stop Hypertension scores (P = .08), compared with the control group, Dr. Loucks reported. Other modifiable risk factors for elevated BP that could have responded to the mindfulness-based training, he proposed, include obesity, alcohol intake, and reaction to stress.
Dr. Loucks reports that he developed the MB-BP training and was a program instructor but did not receive related financial compensation; he had no other disclosures. Dr. Khera, Dr. Touyz, and Dr. Rangaswami had no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
CHICAGO – It’s been said that one can observe a lot just by watching. Turning such observation inward, new evidence suggests, might lead to blood pressure (BP) reductions that approach what’s possible from an antihypertensive agent.
Systolic BP fell over 6 months by almost 6 mm Hg, on average, in people with elevated BP who participated in an 8-week mindful awareness program as part of a randomized trial that included a usual-care control group.
The program taught established mindfulness-training techniques aimed at modifying behaviors regarding diet, exercise, and other controllable influences on the success of antihypertensive therapy.
Participants in the program, called Mindfulness-Based Blood Pressure Reduction (MB-BP), also the name of the single-center study, “showed potentially clinically relevant reductions in systolic blood pressure,” said principal investigator Eric B. Loucks, PhD, Brown University, Providence, R.I.
The phase 2 trial has some limitations, he observed, including on generalizability. For example, it entered about 200 mostly White, college-educated adults from one metropolitan area.
But if these findings are replicated in further studies, “preferably by other research groups, in a larger and broader population, and with longer follow-up,” Dr. Loucks said, the MB-BP intervention could become “an appealing approach to help control blood pressure.”
Dr. Loucks made the comments at a press conference prior to his formal presentation of MB-BP Nov. 6 at American Heart Association (AHA) Scientific Sessions 2022, held in Chicago and virtually.
Mindfulness-based interventions for elevated BP have not been widely studied, “so this is exactly what we need: a well-done trial with a control group to show that it actually works,” Amit Khera, MD, not connected with MB-BP, told this news organization.
The trial is “really important for proof of concept, but it had only 200 people. You need a larger one, and you need longer-term data,” agreed Dr. Khera, who directs the preventive cardiology program at the University of Texas Southwestern Medical Center, in Dallas. “Six months is good, but we want to see if it’s durable.”
Rhian M. Touyz, MBBCh, also not part of MB-BP, agreed that the nearly 6 mm Hg mean systolic BP reduction among program participants is clinically relevant. “I think in the context of global risk and reduction of target organ damage and cardiovascular events, it is significant in terms of events at a population level,” Dr. Touyz, McGill University Health Centre, Montreal, told this news organization.
Many patients on antihypertensive therapy that’s falling short resist the addition of another such agent, she observed, and instead might show further BP reduction from mindfulness training. The intervention probably also “would benefit health in general.” Mindfulness-based approaches could therefore be useful additions to treatment protocols for elevated BP, Dr. Touyz said.
How the training works
The MB-BP program used validated mindfulness-based stress-management techniques, adapted to address elevated BP, that included “personalized feedback and education about hypertension risk factors, mindful awareness training of participants’ relationships with hypertension risk factors, and support for behavior change,” Dr. Loucks and colleagues reported.
Participants were trained in mindfulness skills that included “self-awareness and emotion regulation,” Dr. Loucks said, which they then could apply to their “relationships with the things that we know influence blood pressure, like physical activity, diet, antihypertensive medication adherence, or alcohol consumption.”
One goal is to promote greater “attention control,” he said, “so that there’s some self-awareness that arises in terms of how we feel the next day, after a lot of alcohol consumption, for example, or lack of physical activity.” The process can provide insights that inspire patients to modify behaviors and risk factors that elevate BP, Dr. Loucks explained.
Effects on medication use
Systolic BP responses led some program participants to be managed on fewer or reduced dosages of antihypertensive meds, he told this news organization. Physicians seen outside of the trial could adjust their prescriptions, intensifying or pulling back on meds depending on their assessments of the patient. Any prescription changes would be documented by the researchers at the patient’s next class or trial-clinic visit.
The group that did the training, Dr. Loucks said, was 33% less likely to increase and 30% more likely to decrease their use of BP-lowering medications compared with the control group.
Elevated BP is so common and undertreated that “there is a need for every possible level of intervention, starting from the population level to the individual and everything else in between,” nephrologist Janani Rangaswami, MD, George Washington University, Washington, said at the press conference.
Therefore, “this mindfulness-based approach, in addition to standard of care with pharmacotherapy, is a really welcome addition to the hypertension literature,” said Dr. Rangaswami, who directs her center’s cardiorenal program. The systolic BP reduction seen in the intervention group, she agreed, was “clinically important and meaningful.”
Blinded assessments
The trial entered 201 patients with systolic and diastolic BP greater than 120 mm Hg and 80 mm Hg, respectively; 58.7% were women, 81% were White, and 73% were college-educated, Dr. Loucks reported.
The 100 assigned to the “enhanced usual care” control group received educational materials on controlling high BP. They and the 101 who followed the mindfulness-based program were given and trained on a home BP-monitoring device. They were then followed for the primary endpoint of change in systolic BP at 6 months.
Data management and outcomes assessments were conducted by trialists not involved in the training intervention who were blinded to randomization assignment.
In a prespecified unadjusted analysis by intention-to-treat, systolic BP in the intervention group dropped by a mean of 5.9 mm Hg (P < .001) compared with baseline and 4.5 mm Hg (P = .045), compared with the control group.
A post hoc analysis adjusted for sex and baseline BP showed an average 4.3 mm Hg reduction (P = .056) in those following the MB-BP program, compared with controls.
There were no observed significant effects on diastolic BP.
The study offered clues to how engagement in the MB-BP program might promote reductions in systolic BP, Dr. Loucks observed. For example, it may have led to increased activity levels, reduced sodium intake, and other dietary improvements.
Indeed, program participants averaged about 351 minutes less sedentary time (P = .02) and showed a 0.32-point improvement in Dietary Approaches to Stop Hypertension scores (P = .08), compared with the control group, Dr. Loucks reported. Other modifiable risk factors for elevated BP that could have responded to the mindfulness-based training, he proposed, include obesity, alcohol intake, and reaction to stress.
Dr. Loucks reports that he developed the MB-BP training and was a program instructor but did not receive related financial compensation; he had no other disclosures. Dr. Khera, Dr. Touyz, and Dr. Rangaswami had no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
CHICAGO – It’s been said that one can observe a lot just by watching. Turning such observation inward, new evidence suggests, might lead to blood pressure (BP) reductions that approach what’s possible from an antihypertensive agent.
Systolic BP fell over 6 months by almost 6 mm Hg, on average, in people with elevated BP who participated in an 8-week mindful awareness program as part of a randomized trial that included a usual-care control group.
The program taught established mindfulness-training techniques aimed at modifying behaviors regarding diet, exercise, and other controllable influences on the success of antihypertensive therapy.
Participants in the program, called Mindfulness-Based Blood Pressure Reduction (MB-BP), also the name of the single-center study, “showed potentially clinically relevant reductions in systolic blood pressure,” said principal investigator Eric B. Loucks, PhD, Brown University, Providence, R.I.
The phase 2 trial has some limitations, he observed, including on generalizability. For example, it entered about 200 mostly White, college-educated adults from one metropolitan area.
But if these findings are replicated in further studies, “preferably by other research groups, in a larger and broader population, and with longer follow-up,” Dr. Loucks said, the MB-BP intervention could become “an appealing approach to help control blood pressure.”
Dr. Loucks made the comments at a press conference prior to his formal presentation of MB-BP Nov. 6 at American Heart Association (AHA) Scientific Sessions 2022, held in Chicago and virtually.
Mindfulness-based interventions for elevated BP have not been widely studied, “so this is exactly what we need: a well-done trial with a control group to show that it actually works,” Amit Khera, MD, not connected with MB-BP, told this news organization.
The trial is “really important for proof of concept, but it had only 200 people. You need a larger one, and you need longer-term data,” agreed Dr. Khera, who directs the preventive cardiology program at the University of Texas Southwestern Medical Center, in Dallas. “Six months is good, but we want to see if it’s durable.”
Rhian M. Touyz, MBBCh, also not part of MB-BP, agreed that the nearly 6 mm Hg mean systolic BP reduction among program participants is clinically relevant. “I think in the context of global risk and reduction of target organ damage and cardiovascular events, it is significant in terms of events at a population level,” Dr. Touyz, McGill University Health Centre, Montreal, told this news organization.
Many patients on antihypertensive therapy that’s falling short resist the addition of another such agent, she observed, and instead might show further BP reduction from mindfulness training. The intervention probably also “would benefit health in general.” Mindfulness-based approaches could therefore be useful additions to treatment protocols for elevated BP, Dr. Touyz said.
How the training works
The MB-BP program used validated mindfulness-based stress-management techniques, adapted to address elevated BP, that included “personalized feedback and education about hypertension risk factors, mindful awareness training of participants’ relationships with hypertension risk factors, and support for behavior change,” Dr. Loucks and colleagues reported.
Participants were trained in mindfulness skills that included “self-awareness and emotion regulation,” Dr. Loucks said, which they then could apply to their “relationships with the things that we know influence blood pressure, like physical activity, diet, antihypertensive medication adherence, or alcohol consumption.”
One goal is to promote greater “attention control,” he said, “so that there’s some self-awareness that arises in terms of how we feel the next day, after a lot of alcohol consumption, for example, or lack of physical activity.” The process can provide insights that inspire patients to modify behaviors and risk factors that elevate BP, Dr. Loucks explained.
Effects on medication use
Systolic BP responses led some program participants to be managed on fewer or reduced dosages of antihypertensive meds, he told this news organization. Physicians seen outside of the trial could adjust their prescriptions, intensifying or pulling back on meds depending on their assessments of the patient. Any prescription changes would be documented by the researchers at the patient’s next class or trial-clinic visit.
The group that did the training, Dr. Loucks said, was 33% less likely to increase and 30% more likely to decrease their use of BP-lowering medications compared with the control group.
Elevated BP is so common and undertreated that “there is a need for every possible level of intervention, starting from the population level to the individual and everything else in between,” nephrologist Janani Rangaswami, MD, George Washington University, Washington, said at the press conference.
Therefore, “this mindfulness-based approach, in addition to standard of care with pharmacotherapy, is a really welcome addition to the hypertension literature,” said Dr. Rangaswami, who directs her center’s cardiorenal program. The systolic BP reduction seen in the intervention group, she agreed, was “clinically important and meaningful.”
Blinded assessments
The trial entered 201 patients with systolic and diastolic BP greater than 120 mm Hg and 80 mm Hg, respectively; 58.7% were women, 81% were White, and 73% were college-educated, Dr. Loucks reported.
The 100 assigned to the “enhanced usual care” control group received educational materials on controlling high BP. They and the 101 who followed the mindfulness-based program were given and trained on a home BP-monitoring device. They were then followed for the primary endpoint of change in systolic BP at 6 months.
Data management and outcomes assessments were conducted by trialists not involved in the training intervention who were blinded to randomization assignment.
In a prespecified unadjusted analysis by intention-to-treat, systolic BP in the intervention group dropped by a mean of 5.9 mm Hg (P < .001) compared with baseline and 4.5 mm Hg (P = .045), compared with the control group.
A post hoc analysis adjusted for sex and baseline BP showed an average 4.3 mm Hg reduction (P = .056) in those following the MB-BP program, compared with controls.
There were no observed significant effects on diastolic BP.
The study offered clues to how engagement in the MB-BP program might promote reductions in systolic BP, Dr. Loucks observed. For example, it may have led to increased activity levels, reduced sodium intake, and other dietary improvements.
Indeed, program participants averaged about 351 minutes less sedentary time (P = .02) and showed a 0.32-point improvement in Dietary Approaches to Stop Hypertension scores (P = .08), compared with the control group, Dr. Loucks reported. Other modifiable risk factors for elevated BP that could have responded to the mindfulness-based training, he proposed, include obesity, alcohol intake, and reaction to stress.
Dr. Loucks reports that he developed the MB-BP training and was a program instructor but did not receive related financial compensation; he had no other disclosures. Dr. Khera, Dr. Touyz, and Dr. Rangaswami had no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
AT AHA 2022


