User login
Bringing you the latest news, research and reviews, exclusive interviews, podcasts, quizzes, and more.
Moderna announces first data showing efficacy of COVID-19 vaccine booster in development
among people already vaccinated for COVID-19, according to first results released May 5.
Furthermore, data from the company’s ongoing phase 2 study show the variant-specific booster, known as mRNA-1273.351, achieved higher antibody titers against the B.1.351 variant than did a booster with the original Moderna vaccine.
“We are encouraged by these new data, which reinforce our confidence that our booster strategy should be protective against these newly detected variants. The strong and rapid boost in titers to levels above primary vaccination also clearly demonstrates the ability of mRNA-1273 to induce immune memory,” Stéphane Bancel, chief executive officer of Moderna, said in a statement.
The phase 2 study researchers also are evaluating a multivariant booster that is a 50/50 mix of mRNA-1273.351 and mRNA-1273, the initial vaccine given Food and Drug Administration emergency use authorization, in a single vial.
Unlike the two-dose regimen with the original vaccine, the boosters are administered as a single dose immunization.
The trial participants received a booster 6-8 months after primary vaccination. Titers to the wild-type SARS-CoV-2 virus remained high and detectable in 37 out of 40 participants. However, prior to the booster, titers against the two variants of concern, B.1.351 and P.1, were lower, with about half of participants showing undetectable levels.
In contrast, 2 weeks after a booster with the original vaccine or the B.1.351 strain-specific product, pseudovirus neutralizing titers were boosted in all participants and all variants tested.
“Following [the] boost, geometric mean titers against the wild-type, B.1.351, and P.1 variants increased to levels similar to or higher than the previously reported peak titers against the ancestral (D614G) strain following primary vaccination,” the company stated.
Both mRNA-1273.351 and mRNA-1273 booster doses were generally well tolerated, the company reported. Safety and tolerability were generally comparable to those reported after the second dose of the original vaccine. Most adverse events were mild to moderate, with injection site pain most common in both groups. Participants also reported fatigue, headache, myalgia, and arthralgia.
The company plans to release data shortly on the booster efficacy at additional time points beyond 2 weeks for mRNA-1273.351, a lower-dose booster with mRNA-1272/351, as well as data on the multivariant mRNA vaccine booster.
In addition to the company’s phase 2 study, the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases is conducting a separate phase 1 study of mRNA-1273.351.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
among people already vaccinated for COVID-19, according to first results released May 5.
Furthermore, data from the company’s ongoing phase 2 study show the variant-specific booster, known as mRNA-1273.351, achieved higher antibody titers against the B.1.351 variant than did a booster with the original Moderna vaccine.
“We are encouraged by these new data, which reinforce our confidence that our booster strategy should be protective against these newly detected variants. The strong and rapid boost in titers to levels above primary vaccination also clearly demonstrates the ability of mRNA-1273 to induce immune memory,” Stéphane Bancel, chief executive officer of Moderna, said in a statement.
The phase 2 study researchers also are evaluating a multivariant booster that is a 50/50 mix of mRNA-1273.351 and mRNA-1273, the initial vaccine given Food and Drug Administration emergency use authorization, in a single vial.
Unlike the two-dose regimen with the original vaccine, the boosters are administered as a single dose immunization.
The trial participants received a booster 6-8 months after primary vaccination. Titers to the wild-type SARS-CoV-2 virus remained high and detectable in 37 out of 40 participants. However, prior to the booster, titers against the two variants of concern, B.1.351 and P.1, were lower, with about half of participants showing undetectable levels.
In contrast, 2 weeks after a booster with the original vaccine or the B.1.351 strain-specific product, pseudovirus neutralizing titers were boosted in all participants and all variants tested.
“Following [the] boost, geometric mean titers against the wild-type, B.1.351, and P.1 variants increased to levels similar to or higher than the previously reported peak titers against the ancestral (D614G) strain following primary vaccination,” the company stated.
Both mRNA-1273.351 and mRNA-1273 booster doses were generally well tolerated, the company reported. Safety and tolerability were generally comparable to those reported after the second dose of the original vaccine. Most adverse events were mild to moderate, with injection site pain most common in both groups. Participants also reported fatigue, headache, myalgia, and arthralgia.
The company plans to release data shortly on the booster efficacy at additional time points beyond 2 weeks for mRNA-1273.351, a lower-dose booster with mRNA-1272/351, as well as data on the multivariant mRNA vaccine booster.
In addition to the company’s phase 2 study, the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases is conducting a separate phase 1 study of mRNA-1273.351.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
among people already vaccinated for COVID-19, according to first results released May 5.
Furthermore, data from the company’s ongoing phase 2 study show the variant-specific booster, known as mRNA-1273.351, achieved higher antibody titers against the B.1.351 variant than did a booster with the original Moderna vaccine.
“We are encouraged by these new data, which reinforce our confidence that our booster strategy should be protective against these newly detected variants. The strong and rapid boost in titers to levels above primary vaccination also clearly demonstrates the ability of mRNA-1273 to induce immune memory,” Stéphane Bancel, chief executive officer of Moderna, said in a statement.
The phase 2 study researchers also are evaluating a multivariant booster that is a 50/50 mix of mRNA-1273.351 and mRNA-1273, the initial vaccine given Food and Drug Administration emergency use authorization, in a single vial.
Unlike the two-dose regimen with the original vaccine, the boosters are administered as a single dose immunization.
The trial participants received a booster 6-8 months after primary vaccination. Titers to the wild-type SARS-CoV-2 virus remained high and detectable in 37 out of 40 participants. However, prior to the booster, titers against the two variants of concern, B.1.351 and P.1, were lower, with about half of participants showing undetectable levels.
In contrast, 2 weeks after a booster with the original vaccine or the B.1.351 strain-specific product, pseudovirus neutralizing titers were boosted in all participants and all variants tested.
“Following [the] boost, geometric mean titers against the wild-type, B.1.351, and P.1 variants increased to levels similar to or higher than the previously reported peak titers against the ancestral (D614G) strain following primary vaccination,” the company stated.
Both mRNA-1273.351 and mRNA-1273 booster doses were generally well tolerated, the company reported. Safety and tolerability were generally comparable to those reported after the second dose of the original vaccine. Most adverse events were mild to moderate, with injection site pain most common in both groups. Participants also reported fatigue, headache, myalgia, and arthralgia.
The company plans to release data shortly on the booster efficacy at additional time points beyond 2 weeks for mRNA-1273.351, a lower-dose booster with mRNA-1272/351, as well as data on the multivariant mRNA vaccine booster.
In addition to the company’s phase 2 study, the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases is conducting a separate phase 1 study of mRNA-1273.351.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Study calls for sex-specific concussion management in adolescent soccer players
A large study of adolescent soccer players in Michigan revealed key differences in concussion injury metrics among males and females, underscoring a need to develop sex-specific approaches to managing injury in the sport.
Sport-related concussion (SRC) is a specific concern in young female athletes, study authors Abigail C. Bretzin, PhD, and colleagues noted in their paper, which appears in JAMA Network Open. Previous surveillance studies on SRC at the high school and college level have reported higher rates of injury risk and longer recovery outcomes in female soccer athletes. Taking a deeper dive into these trends, the investigators explored whether sex-associated differences existed in SRC, addressing the mechanics, management, and recovery from SRC.
“This is an area that is remarkably underresearched,” William Stewart, MBChB, PhD, the study’s corresponding author, said in an interview. Prior studies of males and females have shown that female axons are thinner, with fewer microtubules or internal scaffolding than male axons. This potentially increases risk of shear injury in females. Limited research has also cited differences in concussion risk across the menstrual cycle in female athletes.
Reporting system targets four injury areas
The investigators conducted a high school injury surveillance project in 43,741 male and 39,637 female soccer athletes participating in the Michigan High School Athletic Association (MHSAA) Head Injury Reporting System. The study included students from 9th to 12th grade, spanning from the beginning of academic year 2016-2017 to the end of academic year 2018-2019. Since 2015, the state has mandated high schools to submit data to MHSAA.
MHSAA captures data on four categories: person-to-person contact, person-to-object contact, person-to-playing surface contact, or uncertain about cause of the event. Study outcomes included details regarding injury mechanism, immediate management, and return-to-play time for each documented SRC.
Investigators reported notable differences among male and female players. Documented SRC risk was 1.88 times higher among adolescent girls than boys across all academic years (RR, 1.88; 95% CI, 1.69-2.09; P < .001). They also cited inconsistencies in distribution of injury mechanisms among the sexes. Females were most likely to suffer injury from equipment contact such as heading a ball (41.9%), whereas male players commonly sustained SRC from contact with another player (48.4%). The authors suggested that “female soccer athletes have lower neck strength and girth, compared with male athletes, with these variables inversely associated with linear and rotational head acceleration after soccer ball heading.”
Boys had greater odds of immediate removal from play and but also returned to the sport 2 days sooner than girls. “The possibility exists, therefore, that this longer recovery time might, in part, be reflective of our observed differences in immediate care, in particular removal from play,” the authors wrote. Immediate removal from play was also more common in cases where an athletic trainer played a part in evaluating players for SRC.
Eliminating the one-size-fits-all approach
Current concussion management is based on a “one-size-fits-all” model, said Dr. Stewart. Male and female athletes are treated following a common concussion management protocol, covering concussion detection through to rehabilitation. “This model of management is based on research that is almost exclusively in male athletes.”
What the study showed is this one-size-fits-all approach may be flawed, letting down female athletes. “We should be pursuing more research in sex differences in concussion and, importantly, putting these into practice in sex-specific concussion management protocols,” he suggested.
Future studies should also look at the effects of athletic trainer employment on SRC metrics. “Although this was a large, statewide epidemiological study of reported SRC in adolescent soccer athletes, inclusive of high schools with and without access to athletic trainers, the Head Injury Reporting System did not include information on the whether there were athletic trainer services available at each school, including specific athletic training services for soccer,” wrote the investigators, in citing the study’s limitations.
Girls report symptoms more often
“The researchers are to be commended for taking a prospective approach to address this common observation in high school sports,” said Keith J. Loud, MD, MSc, FAAP, a sports pediatrician at Children’s Hospital at Dartmouth-Hitchcock in Manchester, N.H. The results are “entirely believable,” said Dr. Loud, who was not affiliated with the study. “We have long postulated differences in neurophysiology, neck strength, style of play, and tendency to report as explanations for the observation that girls in high school soccer are diagnosed with more concussions than boys.”
The findings suggest that boys play more aggressively, but sustain fewer concussions, he added. Girls in the meantime, are more likely to speak up about their injury.
“Concussion diagnosis still relies to a large degree on the athlete to report symptoms, which is one of our hypotheses as to why girls seem to sustain more concussions – they report symptoms more often. That could also be why they have a prolonged recovery,” offered Dr. Loud. A main limitation of this study is it can’t overcome this reporting bias.
Dr. Loud was also concerned that girls were less likely to be removed from game play, even though they apparently sustained more concussions. “Perhaps that is because their injuries are less obvious on the field, and they are diagnosed when reported after the games.”
Dr. Stewart reported receiving grants from The Football Association and National Health Service Research Scotland during the study. He also served as a nonremunerated member of the Fédération Internationale de Football Association Independent Football Concussion Advisory Group and the Football Association Expert Panel on Concussion and Head Injury in Football. None of the other authors had disclosures.
A large study of adolescent soccer players in Michigan revealed key differences in concussion injury metrics among males and females, underscoring a need to develop sex-specific approaches to managing injury in the sport.
Sport-related concussion (SRC) is a specific concern in young female athletes, study authors Abigail C. Bretzin, PhD, and colleagues noted in their paper, which appears in JAMA Network Open. Previous surveillance studies on SRC at the high school and college level have reported higher rates of injury risk and longer recovery outcomes in female soccer athletes. Taking a deeper dive into these trends, the investigators explored whether sex-associated differences existed in SRC, addressing the mechanics, management, and recovery from SRC.
“This is an area that is remarkably underresearched,” William Stewart, MBChB, PhD, the study’s corresponding author, said in an interview. Prior studies of males and females have shown that female axons are thinner, with fewer microtubules or internal scaffolding than male axons. This potentially increases risk of shear injury in females. Limited research has also cited differences in concussion risk across the menstrual cycle in female athletes.
Reporting system targets four injury areas
The investigators conducted a high school injury surveillance project in 43,741 male and 39,637 female soccer athletes participating in the Michigan High School Athletic Association (MHSAA) Head Injury Reporting System. The study included students from 9th to 12th grade, spanning from the beginning of academic year 2016-2017 to the end of academic year 2018-2019. Since 2015, the state has mandated high schools to submit data to MHSAA.
MHSAA captures data on four categories: person-to-person contact, person-to-object contact, person-to-playing surface contact, or uncertain about cause of the event. Study outcomes included details regarding injury mechanism, immediate management, and return-to-play time for each documented SRC.
Investigators reported notable differences among male and female players. Documented SRC risk was 1.88 times higher among adolescent girls than boys across all academic years (RR, 1.88; 95% CI, 1.69-2.09; P < .001). They also cited inconsistencies in distribution of injury mechanisms among the sexes. Females were most likely to suffer injury from equipment contact such as heading a ball (41.9%), whereas male players commonly sustained SRC from contact with another player (48.4%). The authors suggested that “female soccer athletes have lower neck strength and girth, compared with male athletes, with these variables inversely associated with linear and rotational head acceleration after soccer ball heading.”
Boys had greater odds of immediate removal from play and but also returned to the sport 2 days sooner than girls. “The possibility exists, therefore, that this longer recovery time might, in part, be reflective of our observed differences in immediate care, in particular removal from play,” the authors wrote. Immediate removal from play was also more common in cases where an athletic trainer played a part in evaluating players for SRC.
Eliminating the one-size-fits-all approach
Current concussion management is based on a “one-size-fits-all” model, said Dr. Stewart. Male and female athletes are treated following a common concussion management protocol, covering concussion detection through to rehabilitation. “This model of management is based on research that is almost exclusively in male athletes.”
What the study showed is this one-size-fits-all approach may be flawed, letting down female athletes. “We should be pursuing more research in sex differences in concussion and, importantly, putting these into practice in sex-specific concussion management protocols,” he suggested.
Future studies should also look at the effects of athletic trainer employment on SRC metrics. “Although this was a large, statewide epidemiological study of reported SRC in adolescent soccer athletes, inclusive of high schools with and without access to athletic trainers, the Head Injury Reporting System did not include information on the whether there were athletic trainer services available at each school, including specific athletic training services for soccer,” wrote the investigators, in citing the study’s limitations.
Girls report symptoms more often
“The researchers are to be commended for taking a prospective approach to address this common observation in high school sports,” said Keith J. Loud, MD, MSc, FAAP, a sports pediatrician at Children’s Hospital at Dartmouth-Hitchcock in Manchester, N.H. The results are “entirely believable,” said Dr. Loud, who was not affiliated with the study. “We have long postulated differences in neurophysiology, neck strength, style of play, and tendency to report as explanations for the observation that girls in high school soccer are diagnosed with more concussions than boys.”
The findings suggest that boys play more aggressively, but sustain fewer concussions, he added. Girls in the meantime, are more likely to speak up about their injury.
“Concussion diagnosis still relies to a large degree on the athlete to report symptoms, which is one of our hypotheses as to why girls seem to sustain more concussions – they report symptoms more often. That could also be why they have a prolonged recovery,” offered Dr. Loud. A main limitation of this study is it can’t overcome this reporting bias.
Dr. Loud was also concerned that girls were less likely to be removed from game play, even though they apparently sustained more concussions. “Perhaps that is because their injuries are less obvious on the field, and they are diagnosed when reported after the games.”
Dr. Stewart reported receiving grants from The Football Association and National Health Service Research Scotland during the study. He also served as a nonremunerated member of the Fédération Internationale de Football Association Independent Football Concussion Advisory Group and the Football Association Expert Panel on Concussion and Head Injury in Football. None of the other authors had disclosures.
A large study of adolescent soccer players in Michigan revealed key differences in concussion injury metrics among males and females, underscoring a need to develop sex-specific approaches to managing injury in the sport.
Sport-related concussion (SRC) is a specific concern in young female athletes, study authors Abigail C. Bretzin, PhD, and colleagues noted in their paper, which appears in JAMA Network Open. Previous surveillance studies on SRC at the high school and college level have reported higher rates of injury risk and longer recovery outcomes in female soccer athletes. Taking a deeper dive into these trends, the investigators explored whether sex-associated differences existed in SRC, addressing the mechanics, management, and recovery from SRC.
“This is an area that is remarkably underresearched,” William Stewart, MBChB, PhD, the study’s corresponding author, said in an interview. Prior studies of males and females have shown that female axons are thinner, with fewer microtubules or internal scaffolding than male axons. This potentially increases risk of shear injury in females. Limited research has also cited differences in concussion risk across the menstrual cycle in female athletes.
Reporting system targets four injury areas
The investigators conducted a high school injury surveillance project in 43,741 male and 39,637 female soccer athletes participating in the Michigan High School Athletic Association (MHSAA) Head Injury Reporting System. The study included students from 9th to 12th grade, spanning from the beginning of academic year 2016-2017 to the end of academic year 2018-2019. Since 2015, the state has mandated high schools to submit data to MHSAA.
MHSAA captures data on four categories: person-to-person contact, person-to-object contact, person-to-playing surface contact, or uncertain about cause of the event. Study outcomes included details regarding injury mechanism, immediate management, and return-to-play time for each documented SRC.
Investigators reported notable differences among male and female players. Documented SRC risk was 1.88 times higher among adolescent girls than boys across all academic years (RR, 1.88; 95% CI, 1.69-2.09; P < .001). They also cited inconsistencies in distribution of injury mechanisms among the sexes. Females were most likely to suffer injury from equipment contact such as heading a ball (41.9%), whereas male players commonly sustained SRC from contact with another player (48.4%). The authors suggested that “female soccer athletes have lower neck strength and girth, compared with male athletes, with these variables inversely associated with linear and rotational head acceleration after soccer ball heading.”
Boys had greater odds of immediate removal from play and but also returned to the sport 2 days sooner than girls. “The possibility exists, therefore, that this longer recovery time might, in part, be reflective of our observed differences in immediate care, in particular removal from play,” the authors wrote. Immediate removal from play was also more common in cases where an athletic trainer played a part in evaluating players for SRC.
Eliminating the one-size-fits-all approach
Current concussion management is based on a “one-size-fits-all” model, said Dr. Stewart. Male and female athletes are treated following a common concussion management protocol, covering concussion detection through to rehabilitation. “This model of management is based on research that is almost exclusively in male athletes.”
What the study showed is this one-size-fits-all approach may be flawed, letting down female athletes. “We should be pursuing more research in sex differences in concussion and, importantly, putting these into practice in sex-specific concussion management protocols,” he suggested.
Future studies should also look at the effects of athletic trainer employment on SRC metrics. “Although this was a large, statewide epidemiological study of reported SRC in adolescent soccer athletes, inclusive of high schools with and without access to athletic trainers, the Head Injury Reporting System did not include information on the whether there were athletic trainer services available at each school, including specific athletic training services for soccer,” wrote the investigators, in citing the study’s limitations.
Girls report symptoms more often
“The researchers are to be commended for taking a prospective approach to address this common observation in high school sports,” said Keith J. Loud, MD, MSc, FAAP, a sports pediatrician at Children’s Hospital at Dartmouth-Hitchcock in Manchester, N.H. The results are “entirely believable,” said Dr. Loud, who was not affiliated with the study. “We have long postulated differences in neurophysiology, neck strength, style of play, and tendency to report as explanations for the observation that girls in high school soccer are diagnosed with more concussions than boys.”
The findings suggest that boys play more aggressively, but sustain fewer concussions, he added. Girls in the meantime, are more likely to speak up about their injury.
“Concussion diagnosis still relies to a large degree on the athlete to report symptoms, which is one of our hypotheses as to why girls seem to sustain more concussions – they report symptoms more often. That could also be why they have a prolonged recovery,” offered Dr. Loud. A main limitation of this study is it can’t overcome this reporting bias.
Dr. Loud was also concerned that girls were less likely to be removed from game play, even though they apparently sustained more concussions. “Perhaps that is because their injuries are less obvious on the field, and they are diagnosed when reported after the games.”
Dr. Stewart reported receiving grants from The Football Association and National Health Service Research Scotland during the study. He also served as a nonremunerated member of the Fédération Internationale de Football Association Independent Football Concussion Advisory Group and the Football Association Expert Panel on Concussion and Head Injury in Football. None of the other authors had disclosures.
FROM JAMA NETWORK OPEN
Starting April 5, patients can read your notes: 5 things to consider
Change in writing style is not mandated
The mandate, called “open notes” by many, is part of the 21st Century Cures Act, a wide-ranging piece of federal health care legislation. The previous deadline of Nov. 2, 2020, for enacting open notes was extended last year because of the exigencies of the COVID-19 pandemic.
Organizations must provide access via patient portals to the following types of notes: consultations, discharge summaries, histories, physical examination findings, imaging narratives, laboratory and pathology report narratives, and procedure and progress notes. Noncompliant organizations will eventually be subject to fines from the Department of Health & Human Services for “information blocking.”
This news organization reported on the mandate in 2020, and some readers said it was an unwelcome intrusion into practice. Since then, this news organization has run additional open notes stories about physician concerns, a perspective essay addressing those fears, and a reader poll about the phenomenon.
Now, as the legislation turns into a practical clinical matter, there are five key points clinicians should consider.
Clinicians don’t have to change writing style.
The new law mandates timely patient access to notes and test results, but it doesn’t require that clinicians alter their writing, said Scott MacDonald, MD, an internist and electronic health record medical director at University of California Davis Health in Sacramento.
“You don’t have to change your notes,” he said. However, patients are now part of the note audience and some health care systems are directing clinicians to make patient-friendly style changes.
Everyday experience should guide clinicians when writing notes, said one expert.
“When you’re not sure [of how to write a note], just mirror the way you would speak in the office – that’s going to get you right, including for mental health issues,” advised Leonor Fernandez, MD, an internist at Beth Deaconess Israel Medical Center, Boston, in her “take-away” comments in the online video, How to Write an Open Note.
According to a 2020 Medscape poll of 1,050 physicians, a majority (56%) anticipate that they will write notes differently, knowing that patients can read them via open notes. Nearly two-thirds (64%) believe that this new wrinkle in medical records will increase their workload. However, actual practice suggests that this is true for a minority of practitioners, according to the results from a recent study of more than 1,000 physicians in Boston, Seattle, and rural Pennsylvania, who already work in open notes settings. Only about one-third (37%) reported “spending more time on documentation.”
Note writing is going to change because of the addition of the patient reader, and something will be lost, argued Steven Reidbord, MD, a psychiatrist in private practice in San Francisco. By watering down the language for patients, “you are trading away the technical precision and other advantages of having a professional language,” commented Dr. Reidbord, who blogs for Psychology Today and has criticized the open notes movement in the past.
However, years of investigation from OpenNotes, the Boston-based advocacy and research organization, indicates that there are many gains with patient-accessible notes, including improved medical record accuracy, greater medication adherence, and potentially improved health care disparities among a range of patient types. In a 2019 study, researchers said that worry and confusion among note-reading patients are uncommon (5% and 3%, respectively), which addresses two criticisms voiced by multiple people last year.
Some clinical notes can be withheld.
The new rules from the federal government permit information blocking if there is clear evidence that doing so “will substantially reduce the risk of harm” to patients or to other third parties, Tom Delbanco, MD, and Charlotte Blease, PhD, of OpenNotes in Boston wrote in a commentary in February 2021.
There are also state-level laws that can supersede the new U.S. law and block access to notes, points out MacDonald. For example, California law dictates that providers cannot post cancer test results without talking with the patient first.
The OpenNotes organization also points out that, with regard to sensitive psychotherapy notes that are separated from the rest of a medical record, those notes “can be kept from patients without their permission, and such rules vary state by state.”
Some patients are more likely readers.
Some patients are more likely to peer into their files than others, said Liz Salmi, senior strategist at OpenNotes, who is also a brain cancer patient.
“Those patients who have more serious or chronic conditions ... are more likely to read their notes,” she said in an interview.
A new study of nearly 6,000 medical oncology patients at the University of Wisconsin confirmed that opinion. Patients with incurable metastatic disease were much more likely than those with early-stage, curable disease to read notes. Notably, younger patients were more likely than older ones to access notes, likely the result of generational tech savvy.
Despite the unpredictability of serious disease such as cancer, oncology patients find satisfaction in reading their notes, say experts. “We’ve overwhelmingly heard that patients like it,” Thomas LeBlanc, MD, medical oncologist at Duke University, Durham, N.C., where all patients already have access to clinicians’ notes, told this news organization in 2018.
You are part of the avant garde.
The United States and Scandinavian countries are the world leaders in implementing open notes in clinical practice, Dr. Blease said in an interview.
“It’s a phenomenal achievement” to have enacted open notes nationally, she said. For example, there are no open notes in Northern Ireland, Dr. Blease’s home country, or most of Europe.
In the United States, there are more than 200 medical organizations, including at least one in every state, that were voluntarily providing open notes before April 5, including interstate giants such as Banner Health and big-name medical centers such as Cleveland Clinic.
It may be hard for the United States to top Sweden’s embrace of the practice. The national open notes program now has 7.2 million patient accounts in a country of 10 million people, noted Maria Häggland, PhD, of Uppsala (Sweden) MedTech Science Innovation Center during a webinar last year.
The start day will come, and you may not notice.
“When April 5 happens, something brand new is going to happen symbolically,” Ms. Salmi said. Its importance is hard to measure.
“Patients say they trust their doctor more because they understand their thinking with open notes. How do you value that? We don’t have metrics for that,” she said.
Dr. MacDonald suggested that open notes are both new and not new. In the fall of 2020, he predicted that the launch day would come, and few clinicians would notice, in part because many patients already access truncated information via patient portals.
However, there are “sensitive issues,” such as with adolescents and reproductive health, where “we know that some parents have sign-in information for their teen’s portal,” he commented. With clinical notes now on full display, potential problems “may be out of our control.”
Still, the Sacramento-based physician and IT officer acknowledged that concerns about open notes may be a bit inflated. “I’ve been more worried about reassuring physicians that everything will be okay than what’s actually going to happen [as the law takes effect],” Dr. MacDonald said.
The OpenNotes organization is grant funded, and staff disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Change in writing style is not mandated
Change in writing style is not mandated
The mandate, called “open notes” by many, is part of the 21st Century Cures Act, a wide-ranging piece of federal health care legislation. The previous deadline of Nov. 2, 2020, for enacting open notes was extended last year because of the exigencies of the COVID-19 pandemic.
Organizations must provide access via patient portals to the following types of notes: consultations, discharge summaries, histories, physical examination findings, imaging narratives, laboratory and pathology report narratives, and procedure and progress notes. Noncompliant organizations will eventually be subject to fines from the Department of Health & Human Services for “information blocking.”
This news organization reported on the mandate in 2020, and some readers said it was an unwelcome intrusion into practice. Since then, this news organization has run additional open notes stories about physician concerns, a perspective essay addressing those fears, and a reader poll about the phenomenon.
Now, as the legislation turns into a practical clinical matter, there are five key points clinicians should consider.
Clinicians don’t have to change writing style.
The new law mandates timely patient access to notes and test results, but it doesn’t require that clinicians alter their writing, said Scott MacDonald, MD, an internist and electronic health record medical director at University of California Davis Health in Sacramento.
“You don’t have to change your notes,” he said. However, patients are now part of the note audience and some health care systems are directing clinicians to make patient-friendly style changes.
Everyday experience should guide clinicians when writing notes, said one expert.
“When you’re not sure [of how to write a note], just mirror the way you would speak in the office – that’s going to get you right, including for mental health issues,” advised Leonor Fernandez, MD, an internist at Beth Deaconess Israel Medical Center, Boston, in her “take-away” comments in the online video, How to Write an Open Note.
According to a 2020 Medscape poll of 1,050 physicians, a majority (56%) anticipate that they will write notes differently, knowing that patients can read them via open notes. Nearly two-thirds (64%) believe that this new wrinkle in medical records will increase their workload. However, actual practice suggests that this is true for a minority of practitioners, according to the results from a recent study of more than 1,000 physicians in Boston, Seattle, and rural Pennsylvania, who already work in open notes settings. Only about one-third (37%) reported “spending more time on documentation.”
Note writing is going to change because of the addition of the patient reader, and something will be lost, argued Steven Reidbord, MD, a psychiatrist in private practice in San Francisco. By watering down the language for patients, “you are trading away the technical precision and other advantages of having a professional language,” commented Dr. Reidbord, who blogs for Psychology Today and has criticized the open notes movement in the past.
However, years of investigation from OpenNotes, the Boston-based advocacy and research organization, indicates that there are many gains with patient-accessible notes, including improved medical record accuracy, greater medication adherence, and potentially improved health care disparities among a range of patient types. In a 2019 study, researchers said that worry and confusion among note-reading patients are uncommon (5% and 3%, respectively), which addresses two criticisms voiced by multiple people last year.
Some clinical notes can be withheld.
The new rules from the federal government permit information blocking if there is clear evidence that doing so “will substantially reduce the risk of harm” to patients or to other third parties, Tom Delbanco, MD, and Charlotte Blease, PhD, of OpenNotes in Boston wrote in a commentary in February 2021.
There are also state-level laws that can supersede the new U.S. law and block access to notes, points out MacDonald. For example, California law dictates that providers cannot post cancer test results without talking with the patient first.
The OpenNotes organization also points out that, with regard to sensitive psychotherapy notes that are separated from the rest of a medical record, those notes “can be kept from patients without their permission, and such rules vary state by state.”
Some patients are more likely readers.
Some patients are more likely to peer into their files than others, said Liz Salmi, senior strategist at OpenNotes, who is also a brain cancer patient.
“Those patients who have more serious or chronic conditions ... are more likely to read their notes,” she said in an interview.
A new study of nearly 6,000 medical oncology patients at the University of Wisconsin confirmed that opinion. Patients with incurable metastatic disease were much more likely than those with early-stage, curable disease to read notes. Notably, younger patients were more likely than older ones to access notes, likely the result of generational tech savvy.
Despite the unpredictability of serious disease such as cancer, oncology patients find satisfaction in reading their notes, say experts. “We’ve overwhelmingly heard that patients like it,” Thomas LeBlanc, MD, medical oncologist at Duke University, Durham, N.C., where all patients already have access to clinicians’ notes, told this news organization in 2018.
You are part of the avant garde.
The United States and Scandinavian countries are the world leaders in implementing open notes in clinical practice, Dr. Blease said in an interview.
“It’s a phenomenal achievement” to have enacted open notes nationally, she said. For example, there are no open notes in Northern Ireland, Dr. Blease’s home country, or most of Europe.
In the United States, there are more than 200 medical organizations, including at least one in every state, that were voluntarily providing open notes before April 5, including interstate giants such as Banner Health and big-name medical centers such as Cleveland Clinic.
It may be hard for the United States to top Sweden’s embrace of the practice. The national open notes program now has 7.2 million patient accounts in a country of 10 million people, noted Maria Häggland, PhD, of Uppsala (Sweden) MedTech Science Innovation Center during a webinar last year.
The start day will come, and you may not notice.
“When April 5 happens, something brand new is going to happen symbolically,” Ms. Salmi said. Its importance is hard to measure.
“Patients say they trust their doctor more because they understand their thinking with open notes. How do you value that? We don’t have metrics for that,” she said.
Dr. MacDonald suggested that open notes are both new and not new. In the fall of 2020, he predicted that the launch day would come, and few clinicians would notice, in part because many patients already access truncated information via patient portals.
However, there are “sensitive issues,” such as with adolescents and reproductive health, where “we know that some parents have sign-in information for their teen’s portal,” he commented. With clinical notes now on full display, potential problems “may be out of our control.”
Still, the Sacramento-based physician and IT officer acknowledged that concerns about open notes may be a bit inflated. “I’ve been more worried about reassuring physicians that everything will be okay than what’s actually going to happen [as the law takes effect],” Dr. MacDonald said.
The OpenNotes organization is grant funded, and staff disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The mandate, called “open notes” by many, is part of the 21st Century Cures Act, a wide-ranging piece of federal health care legislation. The previous deadline of Nov. 2, 2020, for enacting open notes was extended last year because of the exigencies of the COVID-19 pandemic.
Organizations must provide access via patient portals to the following types of notes: consultations, discharge summaries, histories, physical examination findings, imaging narratives, laboratory and pathology report narratives, and procedure and progress notes. Noncompliant organizations will eventually be subject to fines from the Department of Health & Human Services for “information blocking.”
This news organization reported on the mandate in 2020, and some readers said it was an unwelcome intrusion into practice. Since then, this news organization has run additional open notes stories about physician concerns, a perspective essay addressing those fears, and a reader poll about the phenomenon.
Now, as the legislation turns into a practical clinical matter, there are five key points clinicians should consider.
Clinicians don’t have to change writing style.
The new law mandates timely patient access to notes and test results, but it doesn’t require that clinicians alter their writing, said Scott MacDonald, MD, an internist and electronic health record medical director at University of California Davis Health in Sacramento.
“You don’t have to change your notes,” he said. However, patients are now part of the note audience and some health care systems are directing clinicians to make patient-friendly style changes.
Everyday experience should guide clinicians when writing notes, said one expert.
“When you’re not sure [of how to write a note], just mirror the way you would speak in the office – that’s going to get you right, including for mental health issues,” advised Leonor Fernandez, MD, an internist at Beth Deaconess Israel Medical Center, Boston, in her “take-away” comments in the online video, How to Write an Open Note.
According to a 2020 Medscape poll of 1,050 physicians, a majority (56%) anticipate that they will write notes differently, knowing that patients can read them via open notes. Nearly two-thirds (64%) believe that this new wrinkle in medical records will increase their workload. However, actual practice suggests that this is true for a minority of practitioners, according to the results from a recent study of more than 1,000 physicians in Boston, Seattle, and rural Pennsylvania, who already work in open notes settings. Only about one-third (37%) reported “spending more time on documentation.”
Note writing is going to change because of the addition of the patient reader, and something will be lost, argued Steven Reidbord, MD, a psychiatrist in private practice in San Francisco. By watering down the language for patients, “you are trading away the technical precision and other advantages of having a professional language,” commented Dr. Reidbord, who blogs for Psychology Today and has criticized the open notes movement in the past.
However, years of investigation from OpenNotes, the Boston-based advocacy and research organization, indicates that there are many gains with patient-accessible notes, including improved medical record accuracy, greater medication adherence, and potentially improved health care disparities among a range of patient types. In a 2019 study, researchers said that worry and confusion among note-reading patients are uncommon (5% and 3%, respectively), which addresses two criticisms voiced by multiple people last year.
Some clinical notes can be withheld.
The new rules from the federal government permit information blocking if there is clear evidence that doing so “will substantially reduce the risk of harm” to patients or to other third parties, Tom Delbanco, MD, and Charlotte Blease, PhD, of OpenNotes in Boston wrote in a commentary in February 2021.
There are also state-level laws that can supersede the new U.S. law and block access to notes, points out MacDonald. For example, California law dictates that providers cannot post cancer test results without talking with the patient first.
The OpenNotes organization also points out that, with regard to sensitive psychotherapy notes that are separated from the rest of a medical record, those notes “can be kept from patients without their permission, and such rules vary state by state.”
Some patients are more likely readers.
Some patients are more likely to peer into their files than others, said Liz Salmi, senior strategist at OpenNotes, who is also a brain cancer patient.
“Those patients who have more serious or chronic conditions ... are more likely to read their notes,” she said in an interview.
A new study of nearly 6,000 medical oncology patients at the University of Wisconsin confirmed that opinion. Patients with incurable metastatic disease were much more likely than those with early-stage, curable disease to read notes. Notably, younger patients were more likely than older ones to access notes, likely the result of generational tech savvy.
Despite the unpredictability of serious disease such as cancer, oncology patients find satisfaction in reading their notes, say experts. “We’ve overwhelmingly heard that patients like it,” Thomas LeBlanc, MD, medical oncologist at Duke University, Durham, N.C., where all patients already have access to clinicians’ notes, told this news organization in 2018.
You are part of the avant garde.
The United States and Scandinavian countries are the world leaders in implementing open notes in clinical practice, Dr. Blease said in an interview.
“It’s a phenomenal achievement” to have enacted open notes nationally, she said. For example, there are no open notes in Northern Ireland, Dr. Blease’s home country, or most of Europe.
In the United States, there are more than 200 medical organizations, including at least one in every state, that were voluntarily providing open notes before April 5, including interstate giants such as Banner Health and big-name medical centers such as Cleveland Clinic.
It may be hard for the United States to top Sweden’s embrace of the practice. The national open notes program now has 7.2 million patient accounts in a country of 10 million people, noted Maria Häggland, PhD, of Uppsala (Sweden) MedTech Science Innovation Center during a webinar last year.
The start day will come, and you may not notice.
“When April 5 happens, something brand new is going to happen symbolically,” Ms. Salmi said. Its importance is hard to measure.
“Patients say they trust their doctor more because they understand their thinking with open notes. How do you value that? We don’t have metrics for that,” she said.
Dr. MacDonald suggested that open notes are both new and not new. In the fall of 2020, he predicted that the launch day would come, and few clinicians would notice, in part because many patients already access truncated information via patient portals.
However, there are “sensitive issues,” such as with adolescents and reproductive health, where “we know that some parents have sign-in information for their teen’s portal,” he commented. With clinical notes now on full display, potential problems “may be out of our control.”
Still, the Sacramento-based physician and IT officer acknowledged that concerns about open notes may be a bit inflated. “I’ve been more worried about reassuring physicians that everything will be okay than what’s actually going to happen [as the law takes effect],” Dr. MacDonald said.
The OpenNotes organization is grant funded, and staff disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Prenatal dietary folate not enough to offset AEDs’ effect on kids’ cognition
New research underscores the importance of folic acid supplementation for pregnant women with epilepsy who are taking antiepileptic drugs (AEDs).
Dietary folate alone, even in the United States, where food is fortified with folic acid, is “not sufficient” to improve cognitive outcomes for children of women who take AEDs during pregnancy, the researchers report.
“We found that dietary folate was not related to outcomes,” study investigator Kimford Meador, MD, professor of neurology and neurologic sciences, Stanford (Calif.) University, told this news organization.
“Only when the mother was taking extra folate did we see an improvement in child outcomes,” he added.
The findings were published online Feb. 23 in Epilepsy and Behavior.
Cognitive boost
“Daily folate is recommended to women in the general populations to reduce congenital malformations,” Dr. Meador said. In addition, periconceptional use of folate has been shown in previous research to improve neurodevelopmental outcomes for children of mothers with epilepsy who are taking AEDs.
Whether folate-fortified food alone, without supplements, has any effect on cognitive outcomes in this population of children has not been examined previously.
To investigate, the researchers assessed 117 children from the Neurodevelopmental Effects of Antiepileptic Drugs (NEAD) study, a prospective, observational study of women with epilepsy who were taking one of four AEDs: carbamazepine, lamotrigine, phenytoin, or valproate.
Results showed that dietary folate from fortified food alone, without supplements, had no significant impact on IQ at age 6 years among children with prenatal exposure to AEDs.
In contrast, use of periconceptual folate supplements was significantly associated with a 10-point higher IQ at age 6 in the adjusted analyses (95% confidence interval, 5.2-15.0; P < .001).
These six other nutrients from food and supplements had no significant association with IQ at age 6 years: vitamins C, D, and E, omega-3, gamma tocopherol, and vitamin B12.
Optimal dose unclear
The findings indicate that folates, including natural folate and folic acid, in food do not have positive cognitive effects for children of women with epilepsy who take AEDs, the researchers write.
Dr. Meador noted that the optimal dose of folic acid supplementation to provide a cognitive benefit remains unclear.
The U.S. Centers for Disease Control recommends 0.4 mg/d for the general population of women of childbearing age. In Europe, the recommendation is 1 mg/d.
“Higher doses are recommended if there is a personal or family history of spina bifida in prior pregnancies, but there is some concern that very high doses of folate may be detrimental,” Dr. Meador said.
For women with epilepsy, he would recommend “at least 1 mg/d and not more than 4 mg/d.”
Proves a point?
Commenting on the study for this news organization, Derek Chong, MD, vice chair of neurology and director of epilepsy at Lenox Hill Hospital, New York, said the finding that folate fortification of food alone is not adequate for women with epilepsy is “not groundbreaking” but does prove something previously thought.
“Folic acid is important for all women, but it does seem like folic acid may be even more important in the epilepsy population,” said Dr. Chong, who was not involved with the research.
He cautioned that the current analysis included only four medications, three of which are not used very often anymore.
“Lamotrigine is probably the most commonly used one now. It’s unfortunate that this study did not include Keppra [levetiracetam], which probably is the number one medication that we use now,” Dr. Chong said.
The research was supported by the National Institutes of Health. Dr. Meador and Dr. Chong have reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
New research underscores the importance of folic acid supplementation for pregnant women with epilepsy who are taking antiepileptic drugs (AEDs).
Dietary folate alone, even in the United States, where food is fortified with folic acid, is “not sufficient” to improve cognitive outcomes for children of women who take AEDs during pregnancy, the researchers report.
“We found that dietary folate was not related to outcomes,” study investigator Kimford Meador, MD, professor of neurology and neurologic sciences, Stanford (Calif.) University, told this news organization.
“Only when the mother was taking extra folate did we see an improvement in child outcomes,” he added.
The findings were published online Feb. 23 in Epilepsy and Behavior.
Cognitive boost
“Daily folate is recommended to women in the general populations to reduce congenital malformations,” Dr. Meador said. In addition, periconceptional use of folate has been shown in previous research to improve neurodevelopmental outcomes for children of mothers with epilepsy who are taking AEDs.
Whether folate-fortified food alone, without supplements, has any effect on cognitive outcomes in this population of children has not been examined previously.
To investigate, the researchers assessed 117 children from the Neurodevelopmental Effects of Antiepileptic Drugs (NEAD) study, a prospective, observational study of women with epilepsy who were taking one of four AEDs: carbamazepine, lamotrigine, phenytoin, or valproate.
Results showed that dietary folate from fortified food alone, without supplements, had no significant impact on IQ at age 6 years among children with prenatal exposure to AEDs.
In contrast, use of periconceptual folate supplements was significantly associated with a 10-point higher IQ at age 6 in the adjusted analyses (95% confidence interval, 5.2-15.0; P < .001).
These six other nutrients from food and supplements had no significant association with IQ at age 6 years: vitamins C, D, and E, omega-3, gamma tocopherol, and vitamin B12.
Optimal dose unclear
The findings indicate that folates, including natural folate and folic acid, in food do not have positive cognitive effects for children of women with epilepsy who take AEDs, the researchers write.
Dr. Meador noted that the optimal dose of folic acid supplementation to provide a cognitive benefit remains unclear.
The U.S. Centers for Disease Control recommends 0.4 mg/d for the general population of women of childbearing age. In Europe, the recommendation is 1 mg/d.
“Higher doses are recommended if there is a personal or family history of spina bifida in prior pregnancies, but there is some concern that very high doses of folate may be detrimental,” Dr. Meador said.
For women with epilepsy, he would recommend “at least 1 mg/d and not more than 4 mg/d.”
Proves a point?
Commenting on the study for this news organization, Derek Chong, MD, vice chair of neurology and director of epilepsy at Lenox Hill Hospital, New York, said the finding that folate fortification of food alone is not adequate for women with epilepsy is “not groundbreaking” but does prove something previously thought.
“Folic acid is important for all women, but it does seem like folic acid may be even more important in the epilepsy population,” said Dr. Chong, who was not involved with the research.
He cautioned that the current analysis included only four medications, three of which are not used very often anymore.
“Lamotrigine is probably the most commonly used one now. It’s unfortunate that this study did not include Keppra [levetiracetam], which probably is the number one medication that we use now,” Dr. Chong said.
The research was supported by the National Institutes of Health. Dr. Meador and Dr. Chong have reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
New research underscores the importance of folic acid supplementation for pregnant women with epilepsy who are taking antiepileptic drugs (AEDs).
Dietary folate alone, even in the United States, where food is fortified with folic acid, is “not sufficient” to improve cognitive outcomes for children of women who take AEDs during pregnancy, the researchers report.
“We found that dietary folate was not related to outcomes,” study investigator Kimford Meador, MD, professor of neurology and neurologic sciences, Stanford (Calif.) University, told this news organization.
“Only when the mother was taking extra folate did we see an improvement in child outcomes,” he added.
The findings were published online Feb. 23 in Epilepsy and Behavior.
Cognitive boost
“Daily folate is recommended to women in the general populations to reduce congenital malformations,” Dr. Meador said. In addition, periconceptional use of folate has been shown in previous research to improve neurodevelopmental outcomes for children of mothers with epilepsy who are taking AEDs.
Whether folate-fortified food alone, without supplements, has any effect on cognitive outcomes in this population of children has not been examined previously.
To investigate, the researchers assessed 117 children from the Neurodevelopmental Effects of Antiepileptic Drugs (NEAD) study, a prospective, observational study of women with epilepsy who were taking one of four AEDs: carbamazepine, lamotrigine, phenytoin, or valproate.
Results showed that dietary folate from fortified food alone, without supplements, had no significant impact on IQ at age 6 years among children with prenatal exposure to AEDs.
In contrast, use of periconceptual folate supplements was significantly associated with a 10-point higher IQ at age 6 in the adjusted analyses (95% confidence interval, 5.2-15.0; P < .001).
These six other nutrients from food and supplements had no significant association with IQ at age 6 years: vitamins C, D, and E, omega-3, gamma tocopherol, and vitamin B12.
Optimal dose unclear
The findings indicate that folates, including natural folate and folic acid, in food do not have positive cognitive effects for children of women with epilepsy who take AEDs, the researchers write.
Dr. Meador noted that the optimal dose of folic acid supplementation to provide a cognitive benefit remains unclear.
The U.S. Centers for Disease Control recommends 0.4 mg/d for the general population of women of childbearing age. In Europe, the recommendation is 1 mg/d.
“Higher doses are recommended if there is a personal or family history of spina bifida in prior pregnancies, but there is some concern that very high doses of folate may be detrimental,” Dr. Meador said.
For women with epilepsy, he would recommend “at least 1 mg/d and not more than 4 mg/d.”
Proves a point?
Commenting on the study for this news organization, Derek Chong, MD, vice chair of neurology and director of epilepsy at Lenox Hill Hospital, New York, said the finding that folate fortification of food alone is not adequate for women with epilepsy is “not groundbreaking” but does prove something previously thought.
“Folic acid is important for all women, but it does seem like folic acid may be even more important in the epilepsy population,” said Dr. Chong, who was not involved with the research.
He cautioned that the current analysis included only four medications, three of which are not used very often anymore.
“Lamotrigine is probably the most commonly used one now. It’s unfortunate that this study did not include Keppra [levetiracetam], which probably is the number one medication that we use now,” Dr. Chong said.
The research was supported by the National Institutes of Health. Dr. Meador and Dr. Chong have reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
JAMA podcast on racism in medicine faces backlash
Published on Feb. 23, the episode is hosted on JAMA’s learning platform for doctors and is available for continuing medical education credits.
“No physician is racist, so how can there be structural racism in health care? An explanation of the idea by doctors for doctors in this user-friendly podcast,” JAMA wrote in a Twitter post to promote the episode. That tweet has since been deleted.
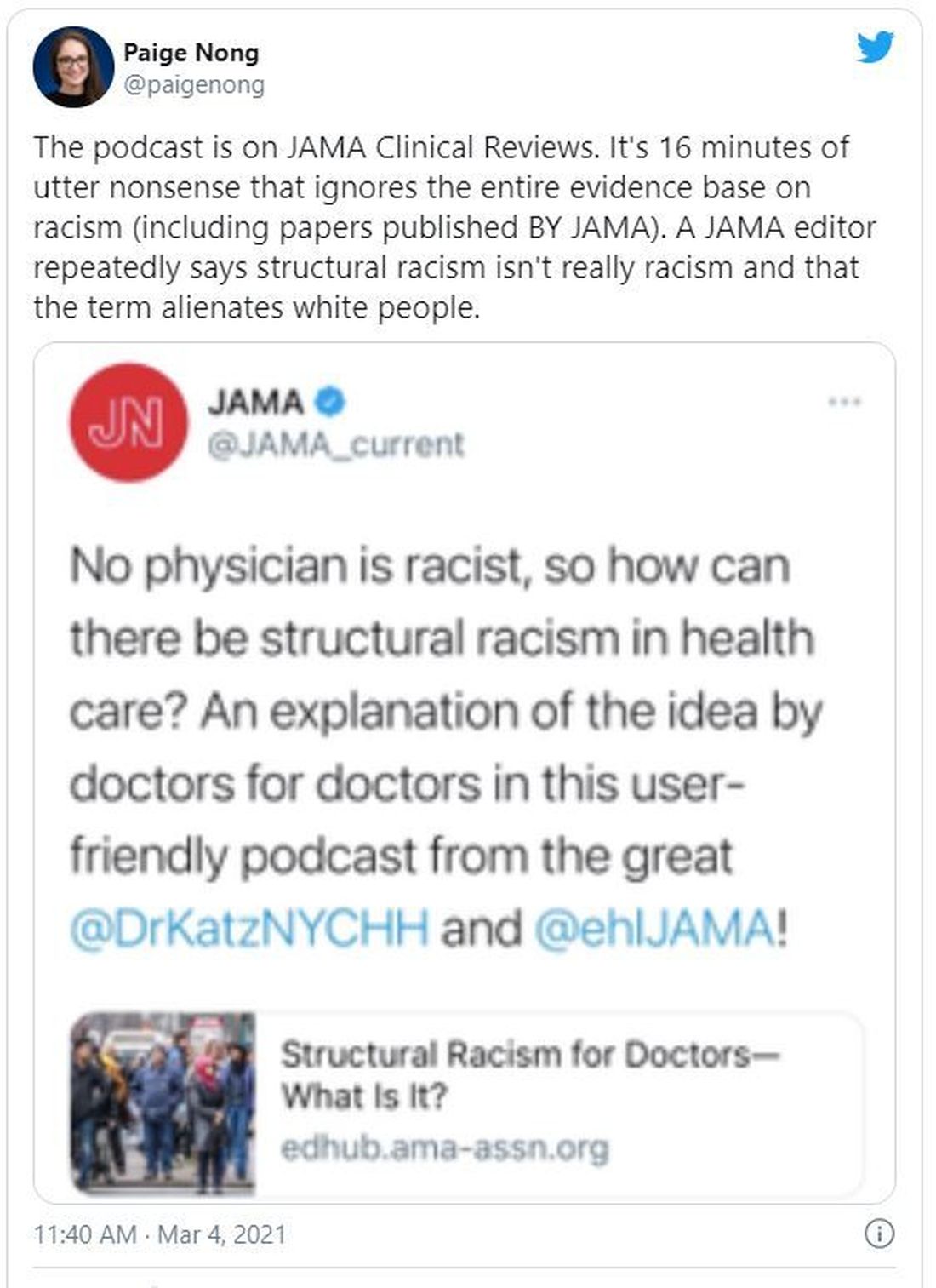
The episode features host Ed Livingston, MD, deputy editor for clinical reviews and education at JAMA, and guest Mitchell Katz, MD, president and CEO for NYC Health + Hospitals and deputy editor for JAMA Internal Medicine. Dr. Livingston approaches the episode as “structural racism for skeptics,” and Dr. Katz tries to explain how structural racism deepens health disparities and what health systems can do about it.
“Many physicians are skeptical of structural racism, the idea that economic, educational, and other societal systems preferentially disadvantage Black Americans and other communities of color,” the episode description says.
In the podcast, Dr. Livingston and Dr. Katz speak about health care disparities and racial inequality. Dr. Livingston, who says he “didn’t understand the concept” going into the episode, suggests that racism was made illegal in the 1960s and that the discussion of “structural racism” should shift away from the term “racism” and focus on socioeconomic status instead.
“What you’re talking about isn’t so much racism ... it isn’t their race, it isn’t their color, it’s their socioeconomic status,” Dr. Livingston says. “Is that a fair statement?”
But Dr. Katz says that “acknowledging structural racism can be helpful to us. Structural racism refers to a system in which policies or practices or how we look at people perpetuates racial inequality.”
Dr. Katz points to the creation of a hospital in San Francisco in the 1880s to treat patients of Chinese ethnicity separately. Outside of health care, he talks about environmental racism between neighborhoods with inequalities in hospitals, schools, and social services.
“All of those things have an impact on that minority person,” Dr. Katz says. “The big thing we can all do is move away from trying to interrogate each other’s opinions and move to a place where we are looking at the policies of our institutions and making sure that they promote equality.”
Dr. Livingston concludes the episode by reemphasizing that “racism” should be taken out of the conversation and it should instead focus on the “structural” aspect of socioeconomics.
“Minorities ... aren’t [in those neighborhoods] because they’re not allowed to buy houses or they can’t get a job because they’re Black or Hispanic. That would be illegal,” Dr. Livingston says. “But disproportionality does exist.”
Efforts to reach Dr. Livingston were unsuccessful. Dr. Katz distanced himself from Dr. Livingston in a statement released on March 4.
“Systemic and interpersonal racism both still exist in our country — they must be rooted out. I do not share the JAMA host’s belief of doing away with the word ‘racism’ will help us be more successful in ending inequities that exists across racial and ethnic lines,” Dr. Katz said. “Further, I believe that we will only produce an equitable society when social and political structures do not continue to produce and perpetuate disparate results based on social race and ethnicity.”
Dr. Katz reiterated that both interpersonal and structural racism continue to exist in the United States, “and it is woefully naive to say that no physician is a racist just because the Civil Rights Act of 1964 forbade it.”
He also recommended JAMA use this controversy “as a learning opportunity for continued dialogue and create another podcast series as an open conversation that invites diverse experts in the field to have an open discussion about structural racism in healthcare.”
The podcast and JAMA’s tweet promoting it were widely criticized on Twitter. In interviews with WebMD, many doctors expressed disbelief that such a respected journal would lend its name to this podcast episode.
B. Bobby Chiong, MD, a radiologist in New York, said although JAMA’s effort to engage with its audience about racism is laudable, it missed the mark.
“I think the backlash comes from how they tried to make a podcast about the subject and somehow made themselves an example of unconscious bias and unfamiliarity with just how embedded in our system is structural racism,” he said.
Perhaps the podcast’s worst offense was its failure to address the painful history of racial bias in this country that still permeates the medical community, says Tamara Saint-Surin, MD, assistant professor at the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill.
“For physicians in leadership to have the belief that structural racism does not exist in medicine, they don’t really appreciate what affects their patients and what their patients were dealing with,” Dr. Saint-Surin said in an interview. “It was a very harmful podcast and goes to show we still have so much work to do.”
Along with a flawed premise, she says, the podcast was not nearly long enough to address such a nuanced issue. And Dr. Livingston focused on interpersonal racism rather than structural racism, she said, failing to address widespread problems such as higher rates of asthma among Black populations living in areas with poor air quality.
The number of Black doctors remains low and the lack of representation adds to an environment already rife with racism, according to many medical professionals.
Shirlene Obuobi, MD, an internal medicine doctor in Chicago, said JAMA failed to live up to its own standards by publishing material that lacked research and expertise.
“I can’t submit a clinical trial to JAMA without them combing through methods with a fine-tooth comb,” Dr. Obuobi said. “They didn’t uphold the standards they normally apply to anyone else.”
Both the editor of JAMA and the head of the American Medical Association issued statements criticizing the episode and the tweet that promoted it.
JAMA Editor-in-Chief Howard Bauchner, MD, said, “The language of the tweet, and some portions of the podcast, do not reflect my commitment as editorial leader of JAMA and JAMA Network to call out and discuss the adverse effects of injustice, inequity, and racism in society and medicine as JAMA has done for many years.” He said JAMA will schedule a future podcast to address the concerns raised about the recent episode.
AMA CEO James L. Madara, MD, said, “The AMA’s House of Delegates passed policy stating that racism is structural, systemic, cultural, and interpersonal, and we are deeply disturbed – and angered – by a recent JAMA podcast that questioned the existence of structural racism and the affiliated tweet that promoted the podcast and stated ‘no physician is racist, so how can there be structural racism in health care?’ ”
He continued: “JAMA has editorial independence from AMA, but this tweet and podcast are inconsistent with the policies and views of AMA, and I’m concerned about and acknowledge the harms they have caused. Structural racism in health care and our society exists, and it is incumbent on all of us to fix it.”
This article was updated 3/5/21.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
Published on Feb. 23, the episode is hosted on JAMA’s learning platform for doctors and is available for continuing medical education credits.
“No physician is racist, so how can there be structural racism in health care? An explanation of the idea by doctors for doctors in this user-friendly podcast,” JAMA wrote in a Twitter post to promote the episode. That tweet has since been deleted.

The episode features host Ed Livingston, MD, deputy editor for clinical reviews and education at JAMA, and guest Mitchell Katz, MD, president and CEO for NYC Health + Hospitals and deputy editor for JAMA Internal Medicine. Dr. Livingston approaches the episode as “structural racism for skeptics,” and Dr. Katz tries to explain how structural racism deepens health disparities and what health systems can do about it.
“Many physicians are skeptical of structural racism, the idea that economic, educational, and other societal systems preferentially disadvantage Black Americans and other communities of color,” the episode description says.
In the podcast, Dr. Livingston and Dr. Katz speak about health care disparities and racial inequality. Dr. Livingston, who says he “didn’t understand the concept” going into the episode, suggests that racism was made illegal in the 1960s and that the discussion of “structural racism” should shift away from the term “racism” and focus on socioeconomic status instead.
“What you’re talking about isn’t so much racism ... it isn’t their race, it isn’t their color, it’s their socioeconomic status,” Dr. Livingston says. “Is that a fair statement?”
But Dr. Katz says that “acknowledging structural racism can be helpful to us. Structural racism refers to a system in which policies or practices or how we look at people perpetuates racial inequality.”
Dr. Katz points to the creation of a hospital in San Francisco in the 1880s to treat patients of Chinese ethnicity separately. Outside of health care, he talks about environmental racism between neighborhoods with inequalities in hospitals, schools, and social services.
“All of those things have an impact on that minority person,” Dr. Katz says. “The big thing we can all do is move away from trying to interrogate each other’s opinions and move to a place where we are looking at the policies of our institutions and making sure that they promote equality.”
Dr. Livingston concludes the episode by reemphasizing that “racism” should be taken out of the conversation and it should instead focus on the “structural” aspect of socioeconomics.
“Minorities ... aren’t [in those neighborhoods] because they’re not allowed to buy houses or they can’t get a job because they’re Black or Hispanic. That would be illegal,” Dr. Livingston says. “But disproportionality does exist.”
Efforts to reach Dr. Livingston were unsuccessful. Dr. Katz distanced himself from Dr. Livingston in a statement released on March 4.
“Systemic and interpersonal racism both still exist in our country — they must be rooted out. I do not share the JAMA host’s belief of doing away with the word ‘racism’ will help us be more successful in ending inequities that exists across racial and ethnic lines,” Dr. Katz said. “Further, I believe that we will only produce an equitable society when social and political structures do not continue to produce and perpetuate disparate results based on social race and ethnicity.”
Dr. Katz reiterated that both interpersonal and structural racism continue to exist in the United States, “and it is woefully naive to say that no physician is a racist just because the Civil Rights Act of 1964 forbade it.”
He also recommended JAMA use this controversy “as a learning opportunity for continued dialogue and create another podcast series as an open conversation that invites diverse experts in the field to have an open discussion about structural racism in healthcare.”
The podcast and JAMA’s tweet promoting it were widely criticized on Twitter. In interviews with WebMD, many doctors expressed disbelief that such a respected journal would lend its name to this podcast episode.
B. Bobby Chiong, MD, a radiologist in New York, said although JAMA’s effort to engage with its audience about racism is laudable, it missed the mark.
“I think the backlash comes from how they tried to make a podcast about the subject and somehow made themselves an example of unconscious bias and unfamiliarity with just how embedded in our system is structural racism,” he said.
Perhaps the podcast’s worst offense was its failure to address the painful history of racial bias in this country that still permeates the medical community, says Tamara Saint-Surin, MD, assistant professor at the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill.
“For physicians in leadership to have the belief that structural racism does not exist in medicine, they don’t really appreciate what affects their patients and what their patients were dealing with,” Dr. Saint-Surin said in an interview. “It was a very harmful podcast and goes to show we still have so much work to do.”
Along with a flawed premise, she says, the podcast was not nearly long enough to address such a nuanced issue. And Dr. Livingston focused on interpersonal racism rather than structural racism, she said, failing to address widespread problems such as higher rates of asthma among Black populations living in areas with poor air quality.
The number of Black doctors remains low and the lack of representation adds to an environment already rife with racism, according to many medical professionals.
Shirlene Obuobi, MD, an internal medicine doctor in Chicago, said JAMA failed to live up to its own standards by publishing material that lacked research and expertise.
“I can’t submit a clinical trial to JAMA without them combing through methods with a fine-tooth comb,” Dr. Obuobi said. “They didn’t uphold the standards they normally apply to anyone else.”
Both the editor of JAMA and the head of the American Medical Association issued statements criticizing the episode and the tweet that promoted it.
JAMA Editor-in-Chief Howard Bauchner, MD, said, “The language of the tweet, and some portions of the podcast, do not reflect my commitment as editorial leader of JAMA and JAMA Network to call out and discuss the adverse effects of injustice, inequity, and racism in society and medicine as JAMA has done for many years.” He said JAMA will schedule a future podcast to address the concerns raised about the recent episode.
AMA CEO James L. Madara, MD, said, “The AMA’s House of Delegates passed policy stating that racism is structural, systemic, cultural, and interpersonal, and we are deeply disturbed – and angered – by a recent JAMA podcast that questioned the existence of structural racism and the affiliated tweet that promoted the podcast and stated ‘no physician is racist, so how can there be structural racism in health care?’ ”
He continued: “JAMA has editorial independence from AMA, but this tweet and podcast are inconsistent with the policies and views of AMA, and I’m concerned about and acknowledge the harms they have caused. Structural racism in health care and our society exists, and it is incumbent on all of us to fix it.”
This article was updated 3/5/21.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
Published on Feb. 23, the episode is hosted on JAMA’s learning platform for doctors and is available for continuing medical education credits.
“No physician is racist, so how can there be structural racism in health care? An explanation of the idea by doctors for doctors in this user-friendly podcast,” JAMA wrote in a Twitter post to promote the episode. That tweet has since been deleted.

The episode features host Ed Livingston, MD, deputy editor for clinical reviews and education at JAMA, and guest Mitchell Katz, MD, president and CEO for NYC Health + Hospitals and deputy editor for JAMA Internal Medicine. Dr. Livingston approaches the episode as “structural racism for skeptics,” and Dr. Katz tries to explain how structural racism deepens health disparities and what health systems can do about it.
“Many physicians are skeptical of structural racism, the idea that economic, educational, and other societal systems preferentially disadvantage Black Americans and other communities of color,” the episode description says.
In the podcast, Dr. Livingston and Dr. Katz speak about health care disparities and racial inequality. Dr. Livingston, who says he “didn’t understand the concept” going into the episode, suggests that racism was made illegal in the 1960s and that the discussion of “structural racism” should shift away from the term “racism” and focus on socioeconomic status instead.
“What you’re talking about isn’t so much racism ... it isn’t their race, it isn’t their color, it’s their socioeconomic status,” Dr. Livingston says. “Is that a fair statement?”
But Dr. Katz says that “acknowledging structural racism can be helpful to us. Structural racism refers to a system in which policies or practices or how we look at people perpetuates racial inequality.”
Dr. Katz points to the creation of a hospital in San Francisco in the 1880s to treat patients of Chinese ethnicity separately. Outside of health care, he talks about environmental racism between neighborhoods with inequalities in hospitals, schools, and social services.
“All of those things have an impact on that minority person,” Dr. Katz says. “The big thing we can all do is move away from trying to interrogate each other’s opinions and move to a place where we are looking at the policies of our institutions and making sure that they promote equality.”
Dr. Livingston concludes the episode by reemphasizing that “racism” should be taken out of the conversation and it should instead focus on the “structural” aspect of socioeconomics.
“Minorities ... aren’t [in those neighborhoods] because they’re not allowed to buy houses or they can’t get a job because they’re Black or Hispanic. That would be illegal,” Dr. Livingston says. “But disproportionality does exist.”
Efforts to reach Dr. Livingston were unsuccessful. Dr. Katz distanced himself from Dr. Livingston in a statement released on March 4.
“Systemic and interpersonal racism both still exist in our country — they must be rooted out. I do not share the JAMA host’s belief of doing away with the word ‘racism’ will help us be more successful in ending inequities that exists across racial and ethnic lines,” Dr. Katz said. “Further, I believe that we will only produce an equitable society when social and political structures do not continue to produce and perpetuate disparate results based on social race and ethnicity.”
Dr. Katz reiterated that both interpersonal and structural racism continue to exist in the United States, “and it is woefully naive to say that no physician is a racist just because the Civil Rights Act of 1964 forbade it.”
He also recommended JAMA use this controversy “as a learning opportunity for continued dialogue and create another podcast series as an open conversation that invites diverse experts in the field to have an open discussion about structural racism in healthcare.”
The podcast and JAMA’s tweet promoting it were widely criticized on Twitter. In interviews with WebMD, many doctors expressed disbelief that such a respected journal would lend its name to this podcast episode.
B. Bobby Chiong, MD, a radiologist in New York, said although JAMA’s effort to engage with its audience about racism is laudable, it missed the mark.
“I think the backlash comes from how they tried to make a podcast about the subject and somehow made themselves an example of unconscious bias and unfamiliarity with just how embedded in our system is structural racism,” he said.
Perhaps the podcast’s worst offense was its failure to address the painful history of racial bias in this country that still permeates the medical community, says Tamara Saint-Surin, MD, assistant professor at the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill.
“For physicians in leadership to have the belief that structural racism does not exist in medicine, they don’t really appreciate what affects their patients and what their patients were dealing with,” Dr. Saint-Surin said in an interview. “It was a very harmful podcast and goes to show we still have so much work to do.”
Along with a flawed premise, she says, the podcast was not nearly long enough to address such a nuanced issue. And Dr. Livingston focused on interpersonal racism rather than structural racism, she said, failing to address widespread problems such as higher rates of asthma among Black populations living in areas with poor air quality.
The number of Black doctors remains low and the lack of representation adds to an environment already rife with racism, according to many medical professionals.
Shirlene Obuobi, MD, an internal medicine doctor in Chicago, said JAMA failed to live up to its own standards by publishing material that lacked research and expertise.
“I can’t submit a clinical trial to JAMA without them combing through methods with a fine-tooth comb,” Dr. Obuobi said. “They didn’t uphold the standards they normally apply to anyone else.”
Both the editor of JAMA and the head of the American Medical Association issued statements criticizing the episode and the tweet that promoted it.
JAMA Editor-in-Chief Howard Bauchner, MD, said, “The language of the tweet, and some portions of the podcast, do not reflect my commitment as editorial leader of JAMA and JAMA Network to call out and discuss the adverse effects of injustice, inequity, and racism in society and medicine as JAMA has done for many years.” He said JAMA will schedule a future podcast to address the concerns raised about the recent episode.
AMA CEO James L. Madara, MD, said, “The AMA’s House of Delegates passed policy stating that racism is structural, systemic, cultural, and interpersonal, and we are deeply disturbed – and angered – by a recent JAMA podcast that questioned the existence of structural racism and the affiliated tweet that promoted the podcast and stated ‘no physician is racist, so how can there be structural racism in health care?’ ”
He continued: “JAMA has editorial independence from AMA, but this tweet and podcast are inconsistent with the policies and views of AMA, and I’m concerned about and acknowledge the harms they have caused. Structural racism in health care and our society exists, and it is incumbent on all of us to fix it.”
This article was updated 3/5/21.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
Study: Central sleep apnea is common in ticagrelor users post ACS
The prevalence of asymptomatic central sleep apnea after acute coronary syndrome is high and may be associated with the use of ticagrelor, a new study finds.
Prior studies have suggested that ticagrelor is associated with an increased likelihood of central sleep apnea. The drug’s label notes that two respiratory conditions – central sleep apnea and Cheyne-Stokes respiration – are adverse reactions that were identified after the drug’s approval in the United States in 2011. “Because these reactions are reported voluntarily from a population of an unknown size, it is not always possible to reliably estimate their frequency or establish a causal relationship to drug exposure,” the label says.
Among 80 patients receiving ticagrelor, 24 had central sleep apnea hypopnea syndrome (CSAHS), whereas of 41 patients not taking ticagrelor, 3 had this condition (30% vs. 7.3%, P = .004), in the new study published online Jan. 20, 2021, in Sleep Medicine. A multivariable analysis included in the paper found that age and ticagrelor administration were the only two factors associated with the occurrence of CSAHS.
Findings are ‘striking’
The different rates of central sleep apnea in the study are striking, but it is not clear that asymptomatic central sleep apnea in patients taking ticagrelor is a concern, Ofer Jacobowitz, MD, PhD, associate professor of otolaryngology at Hofstra University, Hempstead, N.Y, said in an interview.
“Whether this particular drug-induced central sleep apnea is consequential” is an open question, noted Dr. Jacobowitz. “There is no evidence that shows that this is definitely harmful.”
“The different types of central sleep apnea are caused by different mechanisms and this one, we don’t know,” Dr. Jacobwitz added.
Study author continues to prescribe ticagrelor
One of the study authors, Philippe Meurin, MD, said that he continues to prescribe ticagrelor every day and that the side effect is not necessarily important.
It is possible that central sleep apnea may resolve, although further studies would need to examine central sleep apnea over time to establish the duration of the condition, he added. Nevertheless, awareness of the association could have implications for clinical practice, Dr. Meurin said.
Central sleep apnea is rare, and if doctors detect it during a sleep study, they may perform extensive tests to assess for possible neurologic diseases, for example, when the cause may be attributed to the medication, he said. In addition, if a patient who is taking ticagrelor has dyspnea, the presence of central sleep apnea may suggest that dyspnea could be related to the drug, although this possibility needs further study, he noted.
Study included patients with ACS history, but no heart failure
Dr. Meurin, of Centre de Réadaptation Cardiaque de La Brie, Les Grands Prés, Villeneuve-Saint-Denis, France, and colleagues included in their study patients between 1 week and 1 year after acute coronary syndrome who did not have heart failure or a history of sleep apnea.
After an overnight sleep study, they classified patients as normal, as having CSAHS (i.e., an apnea-hypopnea index of 15 or greater, mostly with central sleep apneas), or as having obstructive sleep apnea hypopnea syndrome (OSAHS; i.e., an apnea-hypopnea index of 15 or greater, mostly with obstructive sleep apneas).
The prospective study included 121 consecutive patients between January 2018 and March 2020. Patients had a mean age of 56.8, and 88% were men.
Switching to another P2Y12 inhibitor ‘does not seem appropriate’
“CSAHS could be promoted by the use of ticagrelor, a relatively new drug that modifies the apneic threshold,” the study authors wrote. “Regarding underlying mechanisms, the most probable explanation seems to be increased chemosensitivity to hypercapnia by a direct P2Y12 inhibitory effect on the central nervous system.”
Doctors should not overestimate the severity of the adverse reaction or consider it the same way they do OSASH, they added.
Among patients with acute coronary syndrome in the PLATO study, ticagrelor, compared with clopidogrel, “significantly reduced the rate of death from vascular causes, myocardial infarction, or stroke,” Dr. Meurin and colleagues said. “Because in this study more than 9,000 patients received ticagrelor for 12 months, CSAHS (even if it seems frequent in our study) did not seem to impair the good efficacy/tolerance balance of the drug. Therefore, in asymptomatic CSAHS patients, switching from ticagrelor to another P2Y12 inhibitor does not seem appropriate.”
A recent analysis of data from randomized, controlled trials with ticagrelor did not find excess cases of sleep apnea with the drug. But an asymptomatic adverse event such as central sleep apnea “cannot emerge from a post hoc analysis,” Dr. Meurin and colleagues said.
The analysis of randomized trial data was conducted by Marc S. Sabatine, MD, MPH, chairman of the Thrombolysis in Myocardial Infarction (TIMI) Study Group at Brigham and Women’s Hospital, and coauthors. It was published in JACC: Cardiovascular Interventions in April 2020.
They “used the gold standard for medical evidence (randomized, placebo-controlled trials) and found 158 cases of sleep apnea reported, with absolutely no difference between ticagrelor and placebo,” Dr. Sabatine said in an interview. Their analysis examined clinically overt apnea, he noted.
“It is quite clear that when looking at large numbers in placebo-controlled trials, there is no excess,” Dr. Sabatine said. “Meurin et al. are examining a different outcome: the results of a lab test in what may be entirely asymptomatic patients.”
A randomized trial could confirm the association, he said.
“The association may be real, but also may be play of chance or confounded,” said Dr. Sabatine. “To convince the medical community, the next step would be for the investigators to do a randomized trial and test whether ticagrelor increases the risk of central sleep apnea.”
Dr. Meurin and the study coauthors had no disclosures. The analysis of randomized, controlled trial data by Dr. Sabatine and colleagues was funded by AstraZeneca, which distributes ticagrelor under the trade name Brilinta. Dr. Sabatine has been a consultant for AstraZeneca and received research grants through Brigham and Women’s Hospital from AstraZeneca. He has consulted for and received grants through the hospital from other companies as well. Dr. Jacobowitz had no relevant disclosures.
[email protected]
The prevalence of asymptomatic central sleep apnea after acute coronary syndrome is high and may be associated with the use of ticagrelor, a new study finds.
Prior studies have suggested that ticagrelor is associated with an increased likelihood of central sleep apnea. The drug’s label notes that two respiratory conditions – central sleep apnea and Cheyne-Stokes respiration – are adverse reactions that were identified after the drug’s approval in the United States in 2011. “Because these reactions are reported voluntarily from a population of an unknown size, it is not always possible to reliably estimate their frequency or establish a causal relationship to drug exposure,” the label says.
Among 80 patients receiving ticagrelor, 24 had central sleep apnea hypopnea syndrome (CSAHS), whereas of 41 patients not taking ticagrelor, 3 had this condition (30% vs. 7.3%, P = .004), in the new study published online Jan. 20, 2021, in Sleep Medicine. A multivariable analysis included in the paper found that age and ticagrelor administration were the only two factors associated with the occurrence of CSAHS.
Findings are ‘striking’
The different rates of central sleep apnea in the study are striking, but it is not clear that asymptomatic central sleep apnea in patients taking ticagrelor is a concern, Ofer Jacobowitz, MD, PhD, associate professor of otolaryngology at Hofstra University, Hempstead, N.Y, said in an interview.
“Whether this particular drug-induced central sleep apnea is consequential” is an open question, noted Dr. Jacobowitz. “There is no evidence that shows that this is definitely harmful.”
“The different types of central sleep apnea are caused by different mechanisms and this one, we don’t know,” Dr. Jacobwitz added.
Study author continues to prescribe ticagrelor
One of the study authors, Philippe Meurin, MD, said that he continues to prescribe ticagrelor every day and that the side effect is not necessarily important.
It is possible that central sleep apnea may resolve, although further studies would need to examine central sleep apnea over time to establish the duration of the condition, he added. Nevertheless, awareness of the association could have implications for clinical practice, Dr. Meurin said.
Central sleep apnea is rare, and if doctors detect it during a sleep study, they may perform extensive tests to assess for possible neurologic diseases, for example, when the cause may be attributed to the medication, he said. In addition, if a patient who is taking ticagrelor has dyspnea, the presence of central sleep apnea may suggest that dyspnea could be related to the drug, although this possibility needs further study, he noted.
Study included patients with ACS history, but no heart failure
Dr. Meurin, of Centre de Réadaptation Cardiaque de La Brie, Les Grands Prés, Villeneuve-Saint-Denis, France, and colleagues included in their study patients between 1 week and 1 year after acute coronary syndrome who did not have heart failure or a history of sleep apnea.
After an overnight sleep study, they classified patients as normal, as having CSAHS (i.e., an apnea-hypopnea index of 15 or greater, mostly with central sleep apneas), or as having obstructive sleep apnea hypopnea syndrome (OSAHS; i.e., an apnea-hypopnea index of 15 or greater, mostly with obstructive sleep apneas).
The prospective study included 121 consecutive patients between January 2018 and March 2020. Patients had a mean age of 56.8, and 88% were men.
Switching to another P2Y12 inhibitor ‘does not seem appropriate’
“CSAHS could be promoted by the use of ticagrelor, a relatively new drug that modifies the apneic threshold,” the study authors wrote. “Regarding underlying mechanisms, the most probable explanation seems to be increased chemosensitivity to hypercapnia by a direct P2Y12 inhibitory effect on the central nervous system.”
Doctors should not overestimate the severity of the adverse reaction or consider it the same way they do OSASH, they added.
Among patients with acute coronary syndrome in the PLATO study, ticagrelor, compared with clopidogrel, “significantly reduced the rate of death from vascular causes, myocardial infarction, or stroke,” Dr. Meurin and colleagues said. “Because in this study more than 9,000 patients received ticagrelor for 12 months, CSAHS (even if it seems frequent in our study) did not seem to impair the good efficacy/tolerance balance of the drug. Therefore, in asymptomatic CSAHS patients, switching from ticagrelor to another P2Y12 inhibitor does not seem appropriate.”
A recent analysis of data from randomized, controlled trials with ticagrelor did not find excess cases of sleep apnea with the drug. But an asymptomatic adverse event such as central sleep apnea “cannot emerge from a post hoc analysis,” Dr. Meurin and colleagues said.
The analysis of randomized trial data was conducted by Marc S. Sabatine, MD, MPH, chairman of the Thrombolysis in Myocardial Infarction (TIMI) Study Group at Brigham and Women’s Hospital, and coauthors. It was published in JACC: Cardiovascular Interventions in April 2020.
They “used the gold standard for medical evidence (randomized, placebo-controlled trials) and found 158 cases of sleep apnea reported, with absolutely no difference between ticagrelor and placebo,” Dr. Sabatine said in an interview. Their analysis examined clinically overt apnea, he noted.
“It is quite clear that when looking at large numbers in placebo-controlled trials, there is no excess,” Dr. Sabatine said. “Meurin et al. are examining a different outcome: the results of a lab test in what may be entirely asymptomatic patients.”
A randomized trial could confirm the association, he said.
“The association may be real, but also may be play of chance or confounded,” said Dr. Sabatine. “To convince the medical community, the next step would be for the investigators to do a randomized trial and test whether ticagrelor increases the risk of central sleep apnea.”
Dr. Meurin and the study coauthors had no disclosures. The analysis of randomized, controlled trial data by Dr. Sabatine and colleagues was funded by AstraZeneca, which distributes ticagrelor under the trade name Brilinta. Dr. Sabatine has been a consultant for AstraZeneca and received research grants through Brigham and Women’s Hospital from AstraZeneca. He has consulted for and received grants through the hospital from other companies as well. Dr. Jacobowitz had no relevant disclosures.
[email protected]
The prevalence of asymptomatic central sleep apnea after acute coronary syndrome is high and may be associated with the use of ticagrelor, a new study finds.
Prior studies have suggested that ticagrelor is associated with an increased likelihood of central sleep apnea. The drug’s label notes that two respiratory conditions – central sleep apnea and Cheyne-Stokes respiration – are adverse reactions that were identified after the drug’s approval in the United States in 2011. “Because these reactions are reported voluntarily from a population of an unknown size, it is not always possible to reliably estimate their frequency or establish a causal relationship to drug exposure,” the label says.
Among 80 patients receiving ticagrelor, 24 had central sleep apnea hypopnea syndrome (CSAHS), whereas of 41 patients not taking ticagrelor, 3 had this condition (30% vs. 7.3%, P = .004), in the new study published online Jan. 20, 2021, in Sleep Medicine. A multivariable analysis included in the paper found that age and ticagrelor administration were the only two factors associated with the occurrence of CSAHS.
Findings are ‘striking’
The different rates of central sleep apnea in the study are striking, but it is not clear that asymptomatic central sleep apnea in patients taking ticagrelor is a concern, Ofer Jacobowitz, MD, PhD, associate professor of otolaryngology at Hofstra University, Hempstead, N.Y, said in an interview.
“Whether this particular drug-induced central sleep apnea is consequential” is an open question, noted Dr. Jacobowitz. “There is no evidence that shows that this is definitely harmful.”
“The different types of central sleep apnea are caused by different mechanisms and this one, we don’t know,” Dr. Jacobwitz added.
Study author continues to prescribe ticagrelor
One of the study authors, Philippe Meurin, MD, said that he continues to prescribe ticagrelor every day and that the side effect is not necessarily important.
It is possible that central sleep apnea may resolve, although further studies would need to examine central sleep apnea over time to establish the duration of the condition, he added. Nevertheless, awareness of the association could have implications for clinical practice, Dr. Meurin said.
Central sleep apnea is rare, and if doctors detect it during a sleep study, they may perform extensive tests to assess for possible neurologic diseases, for example, when the cause may be attributed to the medication, he said. In addition, if a patient who is taking ticagrelor has dyspnea, the presence of central sleep apnea may suggest that dyspnea could be related to the drug, although this possibility needs further study, he noted.
Study included patients with ACS history, but no heart failure
Dr. Meurin, of Centre de Réadaptation Cardiaque de La Brie, Les Grands Prés, Villeneuve-Saint-Denis, France, and colleagues included in their study patients between 1 week and 1 year after acute coronary syndrome who did not have heart failure or a history of sleep apnea.
After an overnight sleep study, they classified patients as normal, as having CSAHS (i.e., an apnea-hypopnea index of 15 or greater, mostly with central sleep apneas), or as having obstructive sleep apnea hypopnea syndrome (OSAHS; i.e., an apnea-hypopnea index of 15 or greater, mostly with obstructive sleep apneas).
The prospective study included 121 consecutive patients between January 2018 and March 2020. Patients had a mean age of 56.8, and 88% were men.
Switching to another P2Y12 inhibitor ‘does not seem appropriate’
“CSAHS could be promoted by the use of ticagrelor, a relatively new drug that modifies the apneic threshold,” the study authors wrote. “Regarding underlying mechanisms, the most probable explanation seems to be increased chemosensitivity to hypercapnia by a direct P2Y12 inhibitory effect on the central nervous system.”
Doctors should not overestimate the severity of the adverse reaction or consider it the same way they do OSASH, they added.
Among patients with acute coronary syndrome in the PLATO study, ticagrelor, compared with clopidogrel, “significantly reduced the rate of death from vascular causes, myocardial infarction, or stroke,” Dr. Meurin and colleagues said. “Because in this study more than 9,000 patients received ticagrelor for 12 months, CSAHS (even if it seems frequent in our study) did not seem to impair the good efficacy/tolerance balance of the drug. Therefore, in asymptomatic CSAHS patients, switching from ticagrelor to another P2Y12 inhibitor does not seem appropriate.”
A recent analysis of data from randomized, controlled trials with ticagrelor did not find excess cases of sleep apnea with the drug. But an asymptomatic adverse event such as central sleep apnea “cannot emerge from a post hoc analysis,” Dr. Meurin and colleagues said.
The analysis of randomized trial data was conducted by Marc S. Sabatine, MD, MPH, chairman of the Thrombolysis in Myocardial Infarction (TIMI) Study Group at Brigham and Women’s Hospital, and coauthors. It was published in JACC: Cardiovascular Interventions in April 2020.
They “used the gold standard for medical evidence (randomized, placebo-controlled trials) and found 158 cases of sleep apnea reported, with absolutely no difference between ticagrelor and placebo,” Dr. Sabatine said in an interview. Their analysis examined clinically overt apnea, he noted.
“It is quite clear that when looking at large numbers in placebo-controlled trials, there is no excess,” Dr. Sabatine said. “Meurin et al. are examining a different outcome: the results of a lab test in what may be entirely asymptomatic patients.”
A randomized trial could confirm the association, he said.
“The association may be real, but also may be play of chance or confounded,” said Dr. Sabatine. “To convince the medical community, the next step would be for the investigators to do a randomized trial and test whether ticagrelor increases the risk of central sleep apnea.”
Dr. Meurin and the study coauthors had no disclosures. The analysis of randomized, controlled trial data by Dr. Sabatine and colleagues was funded by AstraZeneca, which distributes ticagrelor under the trade name Brilinta. Dr. Sabatine has been a consultant for AstraZeneca and received research grants through Brigham and Women’s Hospital from AstraZeneca. He has consulted for and received grants through the hospital from other companies as well. Dr. Jacobowitz had no relevant disclosures.
[email protected]
FROM SLEEP MEDICINE
Strep A and tic worsening: Final word?
Exposure to Group A streptococcus (GAS) does not appear to worsen symptoms of Tourette syndrome and other chronic tic disorders (CTDs) in children and adolescents, new research suggests.
Investigators studied over 700 children and teenagers with CTDs, one-third of whom also had attention deficit hyperactivity disorder and one-third who had obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD).
The youngsters were followed for an average of 16 months and evaluated at 4-month intervals to see if they were infected with GAS. Tic severity was monitored through telephone interviews, in-person visits, and parental reports.
A little less than half the children experienced worsening of tics during the study period, but the researchers found no association between these exacerbations and GAS exposure.
There was also no link between GAS and worsening OCD. However, researchers did find an association between GAS exposure and an increase in hyperactivity and impulsivity in patients with ADHD.
“This study does not support GAS exposures as contributing factors for tic exacerbations in children with CTD,” the authors note.
“Specific work-up or active management of GAS infections is unlikely to help modifying the course of tics in CTD and is therefore not recommended,” they conclude.
The study was published online in Neurology.
‘Intense debate’
The association between GAS and CTD stems from the description of Pediatric Autoimmune Neuropsychiatric Disorders Associated with Streptococcal infection (PANDAS) – a condition that is now incorporated in the pediatric acute neuropsychiatric syndromes (PANS), the authors note. Tics constitute an “accompanying feature” of this condition.
However, neither population-based nor longitudinal clinical studies “could definitely establish if tic exacerbations in CTD are associated with GAS infections,” they note.
“The link between streptococcus and tics in children is still a matter of intense debate,” said study author Davide Martino, MD, PhD, director of the Movement Disorders Program at the University of Calgary (Alta.), in a press release.
“We wanted to look at that question, as well as a possible link between strep and behavioral symptoms like obsessive-compulsive disorder and attention deficit hyperactivity disorder,” he said.
The researchers followed 715 children with CTD (mean age 10.7 years, 76.8% male) who were drawn from 16 specialist clinics in nine countries. Almost all (90.8%) had a diagnosis of Tourette syndrome (TS); 31.7% had OCD, and 36.1% had ADHD.
Participants received a throat swab at baseline, and of these, 8.4% tested positive for GAS.
Participants were evaluated over a 16- to 18-month period, consisting of:
- Face-to-face interviews and collection of throat swabs and serum at 4-month intervals.
- Telephone interviews at 4-month intervals, which took place at 2 months between study visit.
- Weekly diaries: Parents were asked to indicate any worsening of tics and focus on detecting the earliest possible tic exacerbation.
Beyond the regularly scheduled visits, parents were instructed to report, by phone or email, any noticeable increase in tic severity and then attend an in-person visit.
Tic exacerbations were defined as an increase of greater than or equal to 6 points on the Yale Global Tic Severity Scale-Total Tic Severity Score (YGTSS-TTS), compared with the previous assessment.
OCD and ADHD symptoms were assessed according to the Yale-Brown Obsessive-Compulsive Scale and the parent-reported Swanson, Nolan, and Pelham-IV (SNAP-IV) questionnaire.
The researchers divided GAS exposures into four categories: new definite exposure; new possible exposure; ongoing definite exposure; and ongoing possible exposure.
Unlikely trigger
During the follow-up period, 43.1% (n = 308) of participants experienced tic exacerbations. Of these, 218 participants experienced one exacerbation, while 90 participants experienced two, three, or four exacerbations.
The researchers did not find a significant association between GAS exposure status and tic exacerbation.
Participants who did develop a GAS-associated exacerbation (n = 49) were younger at study exit (9.63 vs. 11.4 years, P < .0001) and were more likely to be male (46/49 vs. 210/259, Fisher’s = .035), compared with participants who developed a non-GAS-associated tic exacerbation (n = 259).
Additional analyses were adjusted for sex, age at onset, exposure to psychotropic medications, exposures to antibiotics, geographical regions, and number of visits in the time interval of interest. These analyses continued to yield no significant association between new or ongoing concurrent GAS exposure episodes and tic exacerbation events.
Of the children in the study, 103 had a positive throat swab, indicating a new definite GAS exposure, whereas 46 had a positive throat swab indicating an ongoing definite exposure (n = 149 visits). Of these visits, only 20 corresponded to tic exacerbations.
There was also no association between GAS exposure and OCD symptom severity. However, it was associated with longitudinal changes (between 17% and 21%, depending on GAS exposure definition) in the severity of hyperactivity-impulsivity symptoms in children with ADHD.
“It is known that immune activation may concur with tic severity in youth with CTDs and that psychosocial stress levels may predict short-term future tic severity in these patients,” the authors write.
“Our findings suggest that GAS is unlikely to be the main trigger for immune activation in these patients,” they add.
Brick or cornerstone?
Commenting on the study for this news organization, Margo Thienemann, MD, clinical professor of psychiatry, Stanford (Calif.) University, said that in the clinic population they treat, GAS, other pathogens, and other stresses can “each be associated with PANS symptom exacerbations.”
However, these “would not be likely to cause PANS symptoms exacerbations in the vast majority of individuals, only individuals with genetic backgrounds and immunologic dysfunctions creating susceptibility,” said Dr. Thienemann, who also directs the Pediatric Acute-Onset Neuropsychiatric Syndrome (PANS) Clinic at Stanford Children’s Health. She was not involved with the study.
In an accompanying editorial, Andrea Cavanna, MD, PhD, honorary reader in neuropsychiatry, Birmingham (England) Medical School and Keith Coffman, MD, director, Tourette Syndrome Center of Excellence, Children’s Mercy Hospital, Kansas City, Mo., suggest that perhaps the “interaction of psychosocial stress and GAS infections contributes more to tic exacerbation than psychosocial stress alone.”
“Time will tell whether this study stands as another brick – a cornerstone? – in the wall that separates streptococcus from tics,” they write.
The study was supported by the European Union’s Seventh Framework Program. Dr. Martino has received honoraria for lecturing from the Movement Disorders Society, Tourette Syndrome Association of America, and Dystonia Medical Research Foundation Canada; research funding support from Dystonia Medical Research Foundation Canada, the University of Calgary (Alta.), the Michael P. Smith Family, the Owerko Foundation, Ipsen Corporate, the Parkinson Association of Alberta, and the Canadian Institutes for Health Research; and royalties from Springer-Verlag. The other authors’ disclosures are listed in the original article. Dr. Cavanna, Dr. Coffman, and Dr. Thienemann have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Exposure to Group A streptococcus (GAS) does not appear to worsen symptoms of Tourette syndrome and other chronic tic disorders (CTDs) in children and adolescents, new research suggests.
Investigators studied over 700 children and teenagers with CTDs, one-third of whom also had attention deficit hyperactivity disorder and one-third who had obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD).
The youngsters were followed for an average of 16 months and evaluated at 4-month intervals to see if they were infected with GAS. Tic severity was monitored through telephone interviews, in-person visits, and parental reports.
A little less than half the children experienced worsening of tics during the study period, but the researchers found no association between these exacerbations and GAS exposure.
There was also no link between GAS and worsening OCD. However, researchers did find an association between GAS exposure and an increase in hyperactivity and impulsivity in patients with ADHD.
“This study does not support GAS exposures as contributing factors for tic exacerbations in children with CTD,” the authors note.
“Specific work-up or active management of GAS infections is unlikely to help modifying the course of tics in CTD and is therefore not recommended,” they conclude.
The study was published online in Neurology.
‘Intense debate’
The association between GAS and CTD stems from the description of Pediatric Autoimmune Neuropsychiatric Disorders Associated with Streptococcal infection (PANDAS) – a condition that is now incorporated in the pediatric acute neuropsychiatric syndromes (PANS), the authors note. Tics constitute an “accompanying feature” of this condition.
However, neither population-based nor longitudinal clinical studies “could definitely establish if tic exacerbations in CTD are associated with GAS infections,” they note.
“The link between streptococcus and tics in children is still a matter of intense debate,” said study author Davide Martino, MD, PhD, director of the Movement Disorders Program at the University of Calgary (Alta.), in a press release.
“We wanted to look at that question, as well as a possible link between strep and behavioral symptoms like obsessive-compulsive disorder and attention deficit hyperactivity disorder,” he said.
The researchers followed 715 children with CTD (mean age 10.7 years, 76.8% male) who were drawn from 16 specialist clinics in nine countries. Almost all (90.8%) had a diagnosis of Tourette syndrome (TS); 31.7% had OCD, and 36.1% had ADHD.
Participants received a throat swab at baseline, and of these, 8.4% tested positive for GAS.
Participants were evaluated over a 16- to 18-month period, consisting of:
- Face-to-face interviews and collection of throat swabs and serum at 4-month intervals.
- Telephone interviews at 4-month intervals, which took place at 2 months between study visit.
- Weekly diaries: Parents were asked to indicate any worsening of tics and focus on detecting the earliest possible tic exacerbation.
Beyond the regularly scheduled visits, parents were instructed to report, by phone or email, any noticeable increase in tic severity and then attend an in-person visit.
Tic exacerbations were defined as an increase of greater than or equal to 6 points on the Yale Global Tic Severity Scale-Total Tic Severity Score (YGTSS-TTS), compared with the previous assessment.
OCD and ADHD symptoms were assessed according to the Yale-Brown Obsessive-Compulsive Scale and the parent-reported Swanson, Nolan, and Pelham-IV (SNAP-IV) questionnaire.
The researchers divided GAS exposures into four categories: new definite exposure; new possible exposure; ongoing definite exposure; and ongoing possible exposure.
Unlikely trigger
During the follow-up period, 43.1% (n = 308) of participants experienced tic exacerbations. Of these, 218 participants experienced one exacerbation, while 90 participants experienced two, three, or four exacerbations.
The researchers did not find a significant association between GAS exposure status and tic exacerbation.
Participants who did develop a GAS-associated exacerbation (n = 49) were younger at study exit (9.63 vs. 11.4 years, P < .0001) and were more likely to be male (46/49 vs. 210/259, Fisher’s = .035), compared with participants who developed a non-GAS-associated tic exacerbation (n = 259).
Additional analyses were adjusted for sex, age at onset, exposure to psychotropic medications, exposures to antibiotics, geographical regions, and number of visits in the time interval of interest. These analyses continued to yield no significant association between new or ongoing concurrent GAS exposure episodes and tic exacerbation events.
Of the children in the study, 103 had a positive throat swab, indicating a new definite GAS exposure, whereas 46 had a positive throat swab indicating an ongoing definite exposure (n = 149 visits). Of these visits, only 20 corresponded to tic exacerbations.
There was also no association between GAS exposure and OCD symptom severity. However, it was associated with longitudinal changes (between 17% and 21%, depending on GAS exposure definition) in the severity of hyperactivity-impulsivity symptoms in children with ADHD.
“It is known that immune activation may concur with tic severity in youth with CTDs and that psychosocial stress levels may predict short-term future tic severity in these patients,” the authors write.
“Our findings suggest that GAS is unlikely to be the main trigger for immune activation in these patients,” they add.
Brick or cornerstone?
Commenting on the study for this news organization, Margo Thienemann, MD, clinical professor of psychiatry, Stanford (Calif.) University, said that in the clinic population they treat, GAS, other pathogens, and other stresses can “each be associated with PANS symptom exacerbations.”
However, these “would not be likely to cause PANS symptoms exacerbations in the vast majority of individuals, only individuals with genetic backgrounds and immunologic dysfunctions creating susceptibility,” said Dr. Thienemann, who also directs the Pediatric Acute-Onset Neuropsychiatric Syndrome (PANS) Clinic at Stanford Children’s Health. She was not involved with the study.
In an accompanying editorial, Andrea Cavanna, MD, PhD, honorary reader in neuropsychiatry, Birmingham (England) Medical School and Keith Coffman, MD, director, Tourette Syndrome Center of Excellence, Children’s Mercy Hospital, Kansas City, Mo., suggest that perhaps the “interaction of psychosocial stress and GAS infections contributes more to tic exacerbation than psychosocial stress alone.”
“Time will tell whether this study stands as another brick – a cornerstone? – in the wall that separates streptococcus from tics,” they write.
The study was supported by the European Union’s Seventh Framework Program. Dr. Martino has received honoraria for lecturing from the Movement Disorders Society, Tourette Syndrome Association of America, and Dystonia Medical Research Foundation Canada; research funding support from Dystonia Medical Research Foundation Canada, the University of Calgary (Alta.), the Michael P. Smith Family, the Owerko Foundation, Ipsen Corporate, the Parkinson Association of Alberta, and the Canadian Institutes for Health Research; and royalties from Springer-Verlag. The other authors’ disclosures are listed in the original article. Dr. Cavanna, Dr. Coffman, and Dr. Thienemann have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Exposure to Group A streptococcus (GAS) does not appear to worsen symptoms of Tourette syndrome and other chronic tic disorders (CTDs) in children and adolescents, new research suggests.
Investigators studied over 700 children and teenagers with CTDs, one-third of whom also had attention deficit hyperactivity disorder and one-third who had obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD).
The youngsters were followed for an average of 16 months and evaluated at 4-month intervals to see if they were infected with GAS. Tic severity was monitored through telephone interviews, in-person visits, and parental reports.
A little less than half the children experienced worsening of tics during the study period, but the researchers found no association between these exacerbations and GAS exposure.
There was also no link between GAS and worsening OCD. However, researchers did find an association between GAS exposure and an increase in hyperactivity and impulsivity in patients with ADHD.
“This study does not support GAS exposures as contributing factors for tic exacerbations in children with CTD,” the authors note.
“Specific work-up or active management of GAS infections is unlikely to help modifying the course of tics in CTD and is therefore not recommended,” they conclude.
The study was published online in Neurology.
‘Intense debate’
The association between GAS and CTD stems from the description of Pediatric Autoimmune Neuropsychiatric Disorders Associated with Streptococcal infection (PANDAS) – a condition that is now incorporated in the pediatric acute neuropsychiatric syndromes (PANS), the authors note. Tics constitute an “accompanying feature” of this condition.
However, neither population-based nor longitudinal clinical studies “could definitely establish if tic exacerbations in CTD are associated with GAS infections,” they note.
“The link between streptococcus and tics in children is still a matter of intense debate,” said study author Davide Martino, MD, PhD, director of the Movement Disorders Program at the University of Calgary (Alta.), in a press release.
“We wanted to look at that question, as well as a possible link between strep and behavioral symptoms like obsessive-compulsive disorder and attention deficit hyperactivity disorder,” he said.
The researchers followed 715 children with CTD (mean age 10.7 years, 76.8% male) who were drawn from 16 specialist clinics in nine countries. Almost all (90.8%) had a diagnosis of Tourette syndrome (TS); 31.7% had OCD, and 36.1% had ADHD.
Participants received a throat swab at baseline, and of these, 8.4% tested positive for GAS.
Participants were evaluated over a 16- to 18-month period, consisting of:
- Face-to-face interviews and collection of throat swabs and serum at 4-month intervals.
- Telephone interviews at 4-month intervals, which took place at 2 months between study visit.
- Weekly diaries: Parents were asked to indicate any worsening of tics and focus on detecting the earliest possible tic exacerbation.
Beyond the regularly scheduled visits, parents were instructed to report, by phone or email, any noticeable increase in tic severity and then attend an in-person visit.
Tic exacerbations were defined as an increase of greater than or equal to 6 points on the Yale Global Tic Severity Scale-Total Tic Severity Score (YGTSS-TTS), compared with the previous assessment.
OCD and ADHD symptoms were assessed according to the Yale-Brown Obsessive-Compulsive Scale and the parent-reported Swanson, Nolan, and Pelham-IV (SNAP-IV) questionnaire.
The researchers divided GAS exposures into four categories: new definite exposure; new possible exposure; ongoing definite exposure; and ongoing possible exposure.
Unlikely trigger
During the follow-up period, 43.1% (n = 308) of participants experienced tic exacerbations. Of these, 218 participants experienced one exacerbation, while 90 participants experienced two, three, or four exacerbations.
The researchers did not find a significant association between GAS exposure status and tic exacerbation.
Participants who did develop a GAS-associated exacerbation (n = 49) were younger at study exit (9.63 vs. 11.4 years, P < .0001) and were more likely to be male (46/49 vs. 210/259, Fisher’s = .035), compared with participants who developed a non-GAS-associated tic exacerbation (n = 259).
Additional analyses were adjusted for sex, age at onset, exposure to psychotropic medications, exposures to antibiotics, geographical regions, and number of visits in the time interval of interest. These analyses continued to yield no significant association between new or ongoing concurrent GAS exposure episodes and tic exacerbation events.
Of the children in the study, 103 had a positive throat swab, indicating a new definite GAS exposure, whereas 46 had a positive throat swab indicating an ongoing definite exposure (n = 149 visits). Of these visits, only 20 corresponded to tic exacerbations.
There was also no association between GAS exposure and OCD symptom severity. However, it was associated with longitudinal changes (between 17% and 21%, depending on GAS exposure definition) in the severity of hyperactivity-impulsivity symptoms in children with ADHD.
“It is known that immune activation may concur with tic severity in youth with CTDs and that psychosocial stress levels may predict short-term future tic severity in these patients,” the authors write.
“Our findings suggest that GAS is unlikely to be the main trigger for immune activation in these patients,” they add.
Brick or cornerstone?
Commenting on the study for this news organization, Margo Thienemann, MD, clinical professor of psychiatry, Stanford (Calif.) University, said that in the clinic population they treat, GAS, other pathogens, and other stresses can “each be associated with PANS symptom exacerbations.”
However, these “would not be likely to cause PANS symptoms exacerbations in the vast majority of individuals, only individuals with genetic backgrounds and immunologic dysfunctions creating susceptibility,” said Dr. Thienemann, who also directs the Pediatric Acute-Onset Neuropsychiatric Syndrome (PANS) Clinic at Stanford Children’s Health. She was not involved with the study.
In an accompanying editorial, Andrea Cavanna, MD, PhD, honorary reader in neuropsychiatry, Birmingham (England) Medical School and Keith Coffman, MD, director, Tourette Syndrome Center of Excellence, Children’s Mercy Hospital, Kansas City, Mo., suggest that perhaps the “interaction of psychosocial stress and GAS infections contributes more to tic exacerbation than psychosocial stress alone.”
“Time will tell whether this study stands as another brick – a cornerstone? – in the wall that separates streptococcus from tics,” they write.
The study was supported by the European Union’s Seventh Framework Program. Dr. Martino has received honoraria for lecturing from the Movement Disorders Society, Tourette Syndrome Association of America, and Dystonia Medical Research Foundation Canada; research funding support from Dystonia Medical Research Foundation Canada, the University of Calgary (Alta.), the Michael P. Smith Family, the Owerko Foundation, Ipsen Corporate, the Parkinson Association of Alberta, and the Canadian Institutes for Health Research; and royalties from Springer-Verlag. The other authors’ disclosures are listed in the original article. Dr. Cavanna, Dr. Coffman, and Dr. Thienemann have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Biggest challenges practices faced from COVID last year: MGMA
according to a December 2020 report from the Medical Group Management Association.
The report was assembled from the results of weekly Stat polls by MGMA, which consists of 15,000 group practices representing more than 350,000 physicians. During the course of the year, more than 4,800 practice leaders were surveyed, but the individual polls had far fewer respondents.
The 2020 data represents snapshots from different points in the developing public health crisis. Still, much of what practices experienced earlier in the pandemic continues to apply, and it’s likely to persist this year as long as the coronavirus spreads and its toll deepens.
One top-line conclusion of the report: the economic pain felt by practices has resulted in layoffs, furloughs, and/or reduced compensation for providers and staff.
In the May 19 weekly survey, 82% of respondents said some or all of their providers’ compensation had been affected by the crisis. About 62% said every provider had been affected. Provider compensation was cut in several ways, including reduced hours and salaries, reduced or eliminated bonuses, and lower allowances for continuing medical education.
About 61% of health care leaders said in the June 26 poll that their own compensation had decreased.
In the following week’s survey, one in three managers said their organization had reduced staff compensation. Nearly all of the respondents in this category predicted the salary reductions would be temporary.
As of March 17, early in the pandemic, 40% of health care leaders said they were experiencing staff shortages. An April 21 poll found that 53% of health care leaders were taking steps to address their providers’ and staffers’ mental health.
“The mental and emotional toll on everyone continues to be a concern, as public health authorities continue to report alarming numbers of new [COVID-19] cases, hospitalizations, and deaths,” MGMA commented.
Telehealth and remote monitoring
Nearly all of the health care leaders surveyed on March 31 reported that their practices had expanded telehealth access because of COVID-19. The percentage of patient visits handled remotely had dropped substantially by the fall, according to a Harvard University/Commonwealth Fund/Phreesia survey. Still, it remains significantly higher than it was before the pandemic.
“At the end of 2020, telemedicine continues to play a vital role in everyday practice operations and long-term planning,” the MGMA report said. One indication of this, the association said, is that health care leaders are recognizing new best practices in specialty telemedicine, such as pediatrics and ob.gyn.
According to an April 28 poll, the top three coding/billing challenges for telehealth and telephone visits amid COVID-19 were inconsistent payer rules, pay parity and accuracy, and documentation of virtual visits.
While the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services has loosened its regulations to allow reimbursement of telehealth in all locations and at the same level as in-person visits, most of those changes will not last beyond the public health crisis without new legislation.
More health care leaders are considering the use of remote patient monitoring, MGMA said, but only 21% of practices offered such services as of Sept. 15. The report drew a connection between these plans and the current challenge of deferred care.
In the July 21 poll, 87% of health care leaders reported that safety concerns were the top reason that patients deferred care amid COVID-19. The MGMA report quoted JaeLynn Williams, CEO of Air Methods, which provides helicopter ambulance services, as saying that many people are staying home even when they face life-threatening conditions such as chest pain, drug symptoms, inflamed appendix, and gallbladder pain.
Operational issues
Overall, MGMA said, practices that have taken a financial risk have done better during the pandemic than fee-for-service practices because their monthly capitation revenue has continued unabated. In contrast, “most groups’ struggles to sustain visits and procedures meant less revenue and lower compensation,” the report said.
In the August 18 survey, one in three health care leaders reported their practices were changing their operational metrics and how often they looked at those measures because of the pandemic. “Practice managers are asking for dashboard data in weeks instead of months to measure the drop in charges and forecast the resulting change in collections,” MGMA noted. “The type of data practice managers are asking for has also changed.”
Among the new metrics that practices are interested in, according to an MGMA article, are measures that track telehealth visits, the productivity of staff working at home, and the number of ancillary services and procedures that new patients might need based on historical data.
Nearly all health care leaders surveyed on Aug. 11 said the cost of obtaining personal protective equipment had increased during 2020. MGMA said it expects this situation to worsen if the pandemic lasts through the summer of 2021.
While everyone is talking about the botched launch of the COVID-19 vaccination campaign, there were also problems with flu vaccination in 2020. In the Sept. 25 poll, 34% of health care leaders reported their practices were experiencing delays in getting the flu vaccine.
Looking ahead
Looking further ahead, the report recommended that practices make plans to boost staff morale by restoring bonuses.
In addition, MGMA suggested that physician groups reassess their space needs. “The equation is simple – fewer nonclinical staff members at your facility means you should repurpose that office space or consider finding a better fit for your new real estate needs in 2021.”
Finally, MGMA noted that the practices expanding rather than contracting their business are those increasing their value-based revenues by taking on more risk. For those groups, “growing the patient panel can help [them] seek better rates in contract negotiations.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
according to a December 2020 report from the Medical Group Management Association.
The report was assembled from the results of weekly Stat polls by MGMA, which consists of 15,000 group practices representing more than 350,000 physicians. During the course of the year, more than 4,800 practice leaders were surveyed, but the individual polls had far fewer respondents.
The 2020 data represents snapshots from different points in the developing public health crisis. Still, much of what practices experienced earlier in the pandemic continues to apply, and it’s likely to persist this year as long as the coronavirus spreads and its toll deepens.
One top-line conclusion of the report: the economic pain felt by practices has resulted in layoffs, furloughs, and/or reduced compensation for providers and staff.
In the May 19 weekly survey, 82% of respondents said some or all of their providers’ compensation had been affected by the crisis. About 62% said every provider had been affected. Provider compensation was cut in several ways, including reduced hours and salaries, reduced or eliminated bonuses, and lower allowances for continuing medical education.
About 61% of health care leaders said in the June 26 poll that their own compensation had decreased.
In the following week’s survey, one in three managers said their organization had reduced staff compensation. Nearly all of the respondents in this category predicted the salary reductions would be temporary.
As of March 17, early in the pandemic, 40% of health care leaders said they were experiencing staff shortages. An April 21 poll found that 53% of health care leaders were taking steps to address their providers’ and staffers’ mental health.
“The mental and emotional toll on everyone continues to be a concern, as public health authorities continue to report alarming numbers of new [COVID-19] cases, hospitalizations, and deaths,” MGMA commented.
Telehealth and remote monitoring
Nearly all of the health care leaders surveyed on March 31 reported that their practices had expanded telehealth access because of COVID-19. The percentage of patient visits handled remotely had dropped substantially by the fall, according to a Harvard University/Commonwealth Fund/Phreesia survey. Still, it remains significantly higher than it was before the pandemic.
“At the end of 2020, telemedicine continues to play a vital role in everyday practice operations and long-term planning,” the MGMA report said. One indication of this, the association said, is that health care leaders are recognizing new best practices in specialty telemedicine, such as pediatrics and ob.gyn.
According to an April 28 poll, the top three coding/billing challenges for telehealth and telephone visits amid COVID-19 were inconsistent payer rules, pay parity and accuracy, and documentation of virtual visits.
While the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services has loosened its regulations to allow reimbursement of telehealth in all locations and at the same level as in-person visits, most of those changes will not last beyond the public health crisis without new legislation.
More health care leaders are considering the use of remote patient monitoring, MGMA said, but only 21% of practices offered such services as of Sept. 15. The report drew a connection between these plans and the current challenge of deferred care.
In the July 21 poll, 87% of health care leaders reported that safety concerns were the top reason that patients deferred care amid COVID-19. The MGMA report quoted JaeLynn Williams, CEO of Air Methods, which provides helicopter ambulance services, as saying that many people are staying home even when they face life-threatening conditions such as chest pain, drug symptoms, inflamed appendix, and gallbladder pain.
Operational issues
Overall, MGMA said, practices that have taken a financial risk have done better during the pandemic than fee-for-service practices because their monthly capitation revenue has continued unabated. In contrast, “most groups’ struggles to sustain visits and procedures meant less revenue and lower compensation,” the report said.
In the August 18 survey, one in three health care leaders reported their practices were changing their operational metrics and how often they looked at those measures because of the pandemic. “Practice managers are asking for dashboard data in weeks instead of months to measure the drop in charges and forecast the resulting change in collections,” MGMA noted. “The type of data practice managers are asking for has also changed.”
Among the new metrics that practices are interested in, according to an MGMA article, are measures that track telehealth visits, the productivity of staff working at home, and the number of ancillary services and procedures that new patients might need based on historical data.
Nearly all health care leaders surveyed on Aug. 11 said the cost of obtaining personal protective equipment had increased during 2020. MGMA said it expects this situation to worsen if the pandemic lasts through the summer of 2021.
While everyone is talking about the botched launch of the COVID-19 vaccination campaign, there were also problems with flu vaccination in 2020. In the Sept. 25 poll, 34% of health care leaders reported their practices were experiencing delays in getting the flu vaccine.
Looking ahead
Looking further ahead, the report recommended that practices make plans to boost staff morale by restoring bonuses.
In addition, MGMA suggested that physician groups reassess their space needs. “The equation is simple – fewer nonclinical staff members at your facility means you should repurpose that office space or consider finding a better fit for your new real estate needs in 2021.”
Finally, MGMA noted that the practices expanding rather than contracting their business are those increasing their value-based revenues by taking on more risk. For those groups, “growing the patient panel can help [them] seek better rates in contract negotiations.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
according to a December 2020 report from the Medical Group Management Association.
The report was assembled from the results of weekly Stat polls by MGMA, which consists of 15,000 group practices representing more than 350,000 physicians. During the course of the year, more than 4,800 practice leaders were surveyed, but the individual polls had far fewer respondents.
The 2020 data represents snapshots from different points in the developing public health crisis. Still, much of what practices experienced earlier in the pandemic continues to apply, and it’s likely to persist this year as long as the coronavirus spreads and its toll deepens.
One top-line conclusion of the report: the economic pain felt by practices has resulted in layoffs, furloughs, and/or reduced compensation for providers and staff.
In the May 19 weekly survey, 82% of respondents said some or all of their providers’ compensation had been affected by the crisis. About 62% said every provider had been affected. Provider compensation was cut in several ways, including reduced hours and salaries, reduced or eliminated bonuses, and lower allowances for continuing medical education.
About 61% of health care leaders said in the June 26 poll that their own compensation had decreased.
In the following week’s survey, one in three managers said their organization had reduced staff compensation. Nearly all of the respondents in this category predicted the salary reductions would be temporary.
As of March 17, early in the pandemic, 40% of health care leaders said they were experiencing staff shortages. An April 21 poll found that 53% of health care leaders were taking steps to address their providers’ and staffers’ mental health.
“The mental and emotional toll on everyone continues to be a concern, as public health authorities continue to report alarming numbers of new [COVID-19] cases, hospitalizations, and deaths,” MGMA commented.
Telehealth and remote monitoring
Nearly all of the health care leaders surveyed on March 31 reported that their practices had expanded telehealth access because of COVID-19. The percentage of patient visits handled remotely had dropped substantially by the fall, according to a Harvard University/Commonwealth Fund/Phreesia survey. Still, it remains significantly higher than it was before the pandemic.
“At the end of 2020, telemedicine continues to play a vital role in everyday practice operations and long-term planning,” the MGMA report said. One indication of this, the association said, is that health care leaders are recognizing new best practices in specialty telemedicine, such as pediatrics and ob.gyn.
According to an April 28 poll, the top three coding/billing challenges for telehealth and telephone visits amid COVID-19 were inconsistent payer rules, pay parity and accuracy, and documentation of virtual visits.
While the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services has loosened its regulations to allow reimbursement of telehealth in all locations and at the same level as in-person visits, most of those changes will not last beyond the public health crisis without new legislation.
More health care leaders are considering the use of remote patient monitoring, MGMA said, but only 21% of practices offered such services as of Sept. 15. The report drew a connection between these plans and the current challenge of deferred care.
In the July 21 poll, 87% of health care leaders reported that safety concerns were the top reason that patients deferred care amid COVID-19. The MGMA report quoted JaeLynn Williams, CEO of Air Methods, which provides helicopter ambulance services, as saying that many people are staying home even when they face life-threatening conditions such as chest pain, drug symptoms, inflamed appendix, and gallbladder pain.
Operational issues
Overall, MGMA said, practices that have taken a financial risk have done better during the pandemic than fee-for-service practices because their monthly capitation revenue has continued unabated. In contrast, “most groups’ struggles to sustain visits and procedures meant less revenue and lower compensation,” the report said.
In the August 18 survey, one in three health care leaders reported their practices were changing their operational metrics and how often they looked at those measures because of the pandemic. “Practice managers are asking for dashboard data in weeks instead of months to measure the drop in charges and forecast the resulting change in collections,” MGMA noted. “The type of data practice managers are asking for has also changed.”
Among the new metrics that practices are interested in, according to an MGMA article, are measures that track telehealth visits, the productivity of staff working at home, and the number of ancillary services and procedures that new patients might need based on historical data.
Nearly all health care leaders surveyed on Aug. 11 said the cost of obtaining personal protective equipment had increased during 2020. MGMA said it expects this situation to worsen if the pandemic lasts through the summer of 2021.
While everyone is talking about the botched launch of the COVID-19 vaccination campaign, there were also problems with flu vaccination in 2020. In the Sept. 25 poll, 34% of health care leaders reported their practices were experiencing delays in getting the flu vaccine.
Looking ahead
Looking further ahead, the report recommended that practices make plans to boost staff morale by restoring bonuses.
In addition, MGMA suggested that physician groups reassess their space needs. “The equation is simple – fewer nonclinical staff members at your facility means you should repurpose that office space or consider finding a better fit for your new real estate needs in 2021.”
Finally, MGMA noted that the practices expanding rather than contracting their business are those increasing their value-based revenues by taking on more risk. For those groups, “growing the patient panel can help [them] seek better rates in contract negotiations.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Medicaid to cover routine costs for patients in trials
A boost for patients with cancer and other serious illnesses.
Congress has ordered the holdouts among U.S. states to have their Medicaid programs cover expenses related to participation in certain clinical trials, a move that was hailed by the American Society of Clinical Oncology and other groups as a boost to trials as well as to patients with serious illness who have lower incomes.
A massive wrap-up spending/COVID-19 relief bill that was signed into law Dec. 27 carried with it a mandate on Medicaid. States are ordered to put in place Medicaid payment policies for routine items and services, such as the cost of physician visits or laboratory tests, that are provided in connection with participation in clinical trials for serious and life-threatening conditions. The law includes a January 2022 target date for this coverage through Medicaid.
Medicare and other large insurers already pick up the tab for these kinds of expenses, leaving Medicaid as an outlier, ASCO noted in a press statement. ASCO and other cancer groups have for years pressed Medicaid to cover routine expenses for people participating in clinical trials. Already, 15 states, including California, require their Medicaid programs to cover these expenses, according to ASCO.
“We believe that the trials can bring extra benefits to patients,” said Monica M. Bertagnolli, MD, of Dana-Farber Cancer Institute, Boston. Dr. Bertagnolli has worked for years to secure Medicaid coverage for expenses connected to clinical trials.
Although Medicaid covers costs of standard care for cancer patients, people enrolled in the program may have concerns about participating in clinical studies, said Dr. Bertagnolli, chair of the Association for Clinical Oncology, which was established by ASCO to promote wider access to cancer care. Having extra medical expenses may be more than these patients can tolerate.
“Many of them just say, ‘I can’t take that financial risk, so I’ll just stay with standard of care,’ “ Dr. Bertagnolli said in an interview.
Equity issues
Medicaid has expanded greatly, owing to financial aid provided to states through the Affordable Care Act of 2010.
To date, 38 of 50 U.S. states have accepted federal aid to lift income limits for Medicaid eligibility, according to a tally kept by the nonprofit Kaiser Family Foundation. This Medicaid expansion has given more of the nation’s working poor access to health.care, including cancer treatment. Between 2013 and January 2020, enrollment in Medicaid in expansion states increased by about 12.4 million, according to the Medicaid and CHIP Payment and Access Commission.
Medicaid is the nation’s dominant health insurer. Enrollment has been around 70 million in recent months.
That tops the 61 million enrolled in Medicare, the federal program for people aged 65 and older and those with disabilities. (There’s some overlap between Medicare and Medicaid. About 12.8 million persons were dually eligible for these programs in 2018.) UnitedHealth, a giant private insurer, has about 43 million domestic customers.
Medicaid also serves many of the groups of people for which researchers have been seeking to increase participation in clinical trials. ASCO’s Association for Clinical Oncology and dozens of its partners raised this point in a letter to congressional leaders on Feb. 15, 2020.
“Lack of participation in clinical trials from the Medicaid population means these patients are being excluded from potentially life-saving trials and are not reflected in the outcome of the clinical research,” the groups wrote. “Increased access to clinical trial participation for Medicaid enrollees helps ensure medical research results more accurately capture and reflect the populations of this country.”
The ACA’s Medicaid expansion is working to address some of the racial gaps in insurance coverage, according to a January 2020 report from the nonprofit Commonwealth Fund.
Black and Hispanic adults are almost twice as likely as are White adults to have incomes that are less than 200% of the federal poverty level, according to the Commonwealth Fund report. The report also said that people in these groups reported significantly higher rates of cost-related problems in receiving care before the Medicaid expansion began in 2014.
The uninsured rate for Black adults dropped from 24.4% in 2013 to 14.4% in 2018; the rate for Hispanic adults fell from 40.2% to 24.9%, according to the Commonwealth Fund report.
There are concerns, though, about attempts by some governors to impose onerous restrictions on adults enrolled in Medicaid, Dr. Bertagnolli said. She was president of ASCO in 2018 when the group called on the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services to reject state requests to create restrictions that could hinder people’s access to cancer screening or care.
The Trump administration encouraged governors to adopt work requirements. As a result, a dozen states approved these policies, according to a November report from the nonprofit Center on Budget and Policy Priorities. The efforts were blocked by courts.
Data from the limited period of implementation in Arkansas, Michigan, and New Hampshire provide evidence that these kinds of requirements don’t work as intended, according to the CBPP report.
“In all three states, evidence suggests that people who were working and people with serious health needs who should have been eligible for exemptions lost coverage or were at risk of losing coverage due to red tape,” CBPP analysts Jennifer Wagner and Jessica Schubel wrote in their report.
In 2019, The New England Journal of Medicine published an article about the early stages of the Arkansas experiment with Medicaid work rules. Almost 17,000 adults lost their health care coverage in the initial months of implementation, but there appeared to be no significant difference in employment, Benjamin Sommers, MD, PhD, of the Harvard School of Public Health, Boston, and colleagues wrote in their article.
For many people in Arkansas, coverage was lost because of difficulties in reporting compliance with the Medicaid work rule, not because of the employment mandate itself, according to the authors. More than 95% of persons who were targeted by Arkansas’ Medicaid work policy already met its requirements or should have been exempt, they wrote.
Democrats have tended to oppose efforts to attach work requirements, which can include volunteer activities or career training, to Medicaid. Dr. Bertagnolli said there is a need to guard against any future bid to add work requirements to the program.
Extra bureaucratic hurdles may pose an especially tough burden on working adults enrolled in Medicaid, she said.
People who qualify for the program may already be worried about their finances while juggling continued demands of child care and employment, she said. They don’t need to be put at risk of losing access to medical care over administrative rules while undergoing cancer treatment, she said.
“We have to take care of people who are sick. That’s just the way it is,” Dr. Bertagnolli said.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
A boost for patients with cancer and other serious illnesses.
A boost for patients with cancer and other serious illnesses.
Congress has ordered the holdouts among U.S. states to have their Medicaid programs cover expenses related to participation in certain clinical trials, a move that was hailed by the American Society of Clinical Oncology and other groups as a boost to trials as well as to patients with serious illness who have lower incomes.
A massive wrap-up spending/COVID-19 relief bill that was signed into law Dec. 27 carried with it a mandate on Medicaid. States are ordered to put in place Medicaid payment policies for routine items and services, such as the cost of physician visits or laboratory tests, that are provided in connection with participation in clinical trials for serious and life-threatening conditions. The law includes a January 2022 target date for this coverage through Medicaid.
Medicare and other large insurers already pick up the tab for these kinds of expenses, leaving Medicaid as an outlier, ASCO noted in a press statement. ASCO and other cancer groups have for years pressed Medicaid to cover routine expenses for people participating in clinical trials. Already, 15 states, including California, require their Medicaid programs to cover these expenses, according to ASCO.
“We believe that the trials can bring extra benefits to patients,” said Monica M. Bertagnolli, MD, of Dana-Farber Cancer Institute, Boston. Dr. Bertagnolli has worked for years to secure Medicaid coverage for expenses connected to clinical trials.
Although Medicaid covers costs of standard care for cancer patients, people enrolled in the program may have concerns about participating in clinical studies, said Dr. Bertagnolli, chair of the Association for Clinical Oncology, which was established by ASCO to promote wider access to cancer care. Having extra medical expenses may be more than these patients can tolerate.
“Many of them just say, ‘I can’t take that financial risk, so I’ll just stay with standard of care,’ “ Dr. Bertagnolli said in an interview.
Equity issues
Medicaid has expanded greatly, owing to financial aid provided to states through the Affordable Care Act of 2010.
To date, 38 of 50 U.S. states have accepted federal aid to lift income limits for Medicaid eligibility, according to a tally kept by the nonprofit Kaiser Family Foundation. This Medicaid expansion has given more of the nation’s working poor access to health.care, including cancer treatment. Between 2013 and January 2020, enrollment in Medicaid in expansion states increased by about 12.4 million, according to the Medicaid and CHIP Payment and Access Commission.
Medicaid is the nation’s dominant health insurer. Enrollment has been around 70 million in recent months.
That tops the 61 million enrolled in Medicare, the federal program for people aged 65 and older and those with disabilities. (There’s some overlap between Medicare and Medicaid. About 12.8 million persons were dually eligible for these programs in 2018.) UnitedHealth, a giant private insurer, has about 43 million domestic customers.
Medicaid also serves many of the groups of people for which researchers have been seeking to increase participation in clinical trials. ASCO’s Association for Clinical Oncology and dozens of its partners raised this point in a letter to congressional leaders on Feb. 15, 2020.
“Lack of participation in clinical trials from the Medicaid population means these patients are being excluded from potentially life-saving trials and are not reflected in the outcome of the clinical research,” the groups wrote. “Increased access to clinical trial participation for Medicaid enrollees helps ensure medical research results more accurately capture and reflect the populations of this country.”
The ACA’s Medicaid expansion is working to address some of the racial gaps in insurance coverage, according to a January 2020 report from the nonprofit Commonwealth Fund.
Black and Hispanic adults are almost twice as likely as are White adults to have incomes that are less than 200% of the federal poverty level, according to the Commonwealth Fund report. The report also said that people in these groups reported significantly higher rates of cost-related problems in receiving care before the Medicaid expansion began in 2014.
The uninsured rate for Black adults dropped from 24.4% in 2013 to 14.4% in 2018; the rate for Hispanic adults fell from 40.2% to 24.9%, according to the Commonwealth Fund report.
There are concerns, though, about attempts by some governors to impose onerous restrictions on adults enrolled in Medicaid, Dr. Bertagnolli said. She was president of ASCO in 2018 when the group called on the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services to reject state requests to create restrictions that could hinder people’s access to cancer screening or care.
The Trump administration encouraged governors to adopt work requirements. As a result, a dozen states approved these policies, according to a November report from the nonprofit Center on Budget and Policy Priorities. The efforts were blocked by courts.
Data from the limited period of implementation in Arkansas, Michigan, and New Hampshire provide evidence that these kinds of requirements don’t work as intended, according to the CBPP report.
“In all three states, evidence suggests that people who were working and people with serious health needs who should have been eligible for exemptions lost coverage or were at risk of losing coverage due to red tape,” CBPP analysts Jennifer Wagner and Jessica Schubel wrote in their report.
In 2019, The New England Journal of Medicine published an article about the early stages of the Arkansas experiment with Medicaid work rules. Almost 17,000 adults lost their health care coverage in the initial months of implementation, but there appeared to be no significant difference in employment, Benjamin Sommers, MD, PhD, of the Harvard School of Public Health, Boston, and colleagues wrote in their article.
For many people in Arkansas, coverage was lost because of difficulties in reporting compliance with the Medicaid work rule, not because of the employment mandate itself, according to the authors. More than 95% of persons who were targeted by Arkansas’ Medicaid work policy already met its requirements or should have been exempt, they wrote.
Democrats have tended to oppose efforts to attach work requirements, which can include volunteer activities or career training, to Medicaid. Dr. Bertagnolli said there is a need to guard against any future bid to add work requirements to the program.
Extra bureaucratic hurdles may pose an especially tough burden on working adults enrolled in Medicaid, she said.
People who qualify for the program may already be worried about their finances while juggling continued demands of child care and employment, she said. They don’t need to be put at risk of losing access to medical care over administrative rules while undergoing cancer treatment, she said.
“We have to take care of people who are sick. That’s just the way it is,” Dr. Bertagnolli said.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Congress has ordered the holdouts among U.S. states to have their Medicaid programs cover expenses related to participation in certain clinical trials, a move that was hailed by the American Society of Clinical Oncology and other groups as a boost to trials as well as to patients with serious illness who have lower incomes.
A massive wrap-up spending/COVID-19 relief bill that was signed into law Dec. 27 carried with it a mandate on Medicaid. States are ordered to put in place Medicaid payment policies for routine items and services, such as the cost of physician visits or laboratory tests, that are provided in connection with participation in clinical trials for serious and life-threatening conditions. The law includes a January 2022 target date for this coverage through Medicaid.
Medicare and other large insurers already pick up the tab for these kinds of expenses, leaving Medicaid as an outlier, ASCO noted in a press statement. ASCO and other cancer groups have for years pressed Medicaid to cover routine expenses for people participating in clinical trials. Already, 15 states, including California, require their Medicaid programs to cover these expenses, according to ASCO.
“We believe that the trials can bring extra benefits to patients,” said Monica M. Bertagnolli, MD, of Dana-Farber Cancer Institute, Boston. Dr. Bertagnolli has worked for years to secure Medicaid coverage for expenses connected to clinical trials.
Although Medicaid covers costs of standard care for cancer patients, people enrolled in the program may have concerns about participating in clinical studies, said Dr. Bertagnolli, chair of the Association for Clinical Oncology, which was established by ASCO to promote wider access to cancer care. Having extra medical expenses may be more than these patients can tolerate.
“Many of them just say, ‘I can’t take that financial risk, so I’ll just stay with standard of care,’ “ Dr. Bertagnolli said in an interview.
Equity issues
Medicaid has expanded greatly, owing to financial aid provided to states through the Affordable Care Act of 2010.
To date, 38 of 50 U.S. states have accepted federal aid to lift income limits for Medicaid eligibility, according to a tally kept by the nonprofit Kaiser Family Foundation. This Medicaid expansion has given more of the nation’s working poor access to health.care, including cancer treatment. Between 2013 and January 2020, enrollment in Medicaid in expansion states increased by about 12.4 million, according to the Medicaid and CHIP Payment and Access Commission.
Medicaid is the nation’s dominant health insurer. Enrollment has been around 70 million in recent months.
That tops the 61 million enrolled in Medicare, the federal program for people aged 65 and older and those with disabilities. (There’s some overlap between Medicare and Medicaid. About 12.8 million persons were dually eligible for these programs in 2018.) UnitedHealth, a giant private insurer, has about 43 million domestic customers.
Medicaid also serves many of the groups of people for which researchers have been seeking to increase participation in clinical trials. ASCO’s Association for Clinical Oncology and dozens of its partners raised this point in a letter to congressional leaders on Feb. 15, 2020.
“Lack of participation in clinical trials from the Medicaid population means these patients are being excluded from potentially life-saving trials and are not reflected in the outcome of the clinical research,” the groups wrote. “Increased access to clinical trial participation for Medicaid enrollees helps ensure medical research results more accurately capture and reflect the populations of this country.”
The ACA’s Medicaid expansion is working to address some of the racial gaps in insurance coverage, according to a January 2020 report from the nonprofit Commonwealth Fund.
Black and Hispanic adults are almost twice as likely as are White adults to have incomes that are less than 200% of the federal poverty level, according to the Commonwealth Fund report. The report also said that people in these groups reported significantly higher rates of cost-related problems in receiving care before the Medicaid expansion began in 2014.
The uninsured rate for Black adults dropped from 24.4% in 2013 to 14.4% in 2018; the rate for Hispanic adults fell from 40.2% to 24.9%, according to the Commonwealth Fund report.
There are concerns, though, about attempts by some governors to impose onerous restrictions on adults enrolled in Medicaid, Dr. Bertagnolli said. She was president of ASCO in 2018 when the group called on the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services to reject state requests to create restrictions that could hinder people’s access to cancer screening or care.
The Trump administration encouraged governors to adopt work requirements. As a result, a dozen states approved these policies, according to a November report from the nonprofit Center on Budget and Policy Priorities. The efforts were blocked by courts.
Data from the limited period of implementation in Arkansas, Michigan, and New Hampshire provide evidence that these kinds of requirements don’t work as intended, according to the CBPP report.
“In all three states, evidence suggests that people who were working and people with serious health needs who should have been eligible for exemptions lost coverage or were at risk of losing coverage due to red tape,” CBPP analysts Jennifer Wagner and Jessica Schubel wrote in their report.
In 2019, The New England Journal of Medicine published an article about the early stages of the Arkansas experiment with Medicaid work rules. Almost 17,000 adults lost their health care coverage in the initial months of implementation, but there appeared to be no significant difference in employment, Benjamin Sommers, MD, PhD, of the Harvard School of Public Health, Boston, and colleagues wrote in their article.
For many people in Arkansas, coverage was lost because of difficulties in reporting compliance with the Medicaid work rule, not because of the employment mandate itself, according to the authors. More than 95% of persons who were targeted by Arkansas’ Medicaid work policy already met its requirements or should have been exempt, they wrote.
Democrats have tended to oppose efforts to attach work requirements, which can include volunteer activities or career training, to Medicaid. Dr. Bertagnolli said there is a need to guard against any future bid to add work requirements to the program.
Extra bureaucratic hurdles may pose an especially tough burden on working adults enrolled in Medicaid, she said.
People who qualify for the program may already be worried about their finances while juggling continued demands of child care and employment, she said. They don’t need to be put at risk of losing access to medical care over administrative rules while undergoing cancer treatment, she said.
“We have to take care of people who are sick. That’s just the way it is,” Dr. Bertagnolli said.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Understanding messenger RNA and other SARS-CoV-2 vaccines
In mid-November, Pfizer/BioNTech were the first with surprising positive protection interim data for their coronavirus vaccine, BNT162b2. A week later, Moderna released interim efficacy results showing its coronavirus vaccine, mRNA-1273, also protected patients from developing SARS-CoV-2 infections. Both studies included mostly healthy adults. A diverse ethnic and racial vaccinated population was included. A reasonable number of persons aged over 65 years, and persons with stable compromising medical conditions were included. Adolescents aged 16 years and over were included. Younger adolescents have been vaccinated or such studies are in the planning or early implementation stage as 2020 came to a close.
These are new and revolutionary vaccines, although the ability to inject mRNA into animals dates back to 1990, technological advances today make it a reality.1 Traditional vaccines typically involve injection with antigens such as purified proteins or polysaccharides or inactivated/attenuated viruses. In the case of Pfizer’s and Moderna’s vaccines, the mRNA provides the genetic information to synthesize the spike protein that the SARS-CoV-2 virus uses to attach to and infect human cells. Each type of vaccine is packaged in proprietary lipid nanoparticles to protect the mRNA from rapid degradation, and the nanoparticles serve as an adjuvant to attract immune cells to the site of injection. (The properties of the respective lipid nanoparticle packaging may be the factor that impacts storage requirements discussed below.) When injected into muscle (myocyte), the lipid nanoparticles containing the mRNA inside are taken into muscle cells, where the cytoplasmic ribosomes detect and decode the mRNA resulting in the production of the spike protein antigen. It should be noted that the mRNA does not enter the nucleus, where the genetic information (DNA) of a cell is located, and can’t be reproduced or integrated into the DNA. The antigen is exported to the myocyte cell surface where the immune system’s antigen presenting cells detect the protein, ingest it, and take it to regional lymph nodes where interactions with T cells and B cells results in antibodies, T cell–mediated immunity, and generation of immune memory T cells and B cells. A particular subset of T cells – cytotoxic or killer T cells – destroy cells that have been infected by a pathogen. The SARS-CoV-2 mRNA vaccine from Pfizer was reported to induce powerful cytotoxic T-cell responses. Results for Moderna’s vaccine had not been reported at the time this column was prepared, but I anticipate the same positive results.
The revolutionary aspect of mRNA vaccines is the speed at which they can be designed and produced. This is why they lead the pack among the SARS-CoV-2 vaccine candidates and why the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases provided financial, technical, and/or clinical support. Indeed, once the amino acid sequence of a protein can be determined (a relatively easy task these days) it’s straightforward to synthesize mRNA in the lab – and it can be done incredibly fast. It is reported that the mRNA code for the vaccine by Moderna was made in 2 days and production development was completed in about 2 months.2
A 2007 World Health Organization report noted that infectious diseases are emerging at “the historically unprecedented rate of one per year.”3 Severe acute respiratory syndrome (SARS), Zika, Ebola, and avian and swine flu are recent examples. For most vaccines against emerging diseases, the challenge is about speed: developing and manufacturing a vaccine and getting it to persons who need it as quickly as possible. The current seasonal flu vaccine takes about 6 months to develop; it takes years for most of the traditional vaccines. That’s why once the infrastructure is in place, mRNA vaccines may prove to offer a big advantage as vaccines against emerging pathogens.
Early efficacy results have been surprising
Both vaccines were reported to produce about 95% efficacy in the final analysis. That was unexpectedly high because most vaccines for respiratory illness achieve efficacy of 60%-80%, e.g., flu vaccines. However, the efficacy rate may drop as time goes by because stimulation of short-term immunity would be in the earliest reported results.
Preventing SARS-CoV-2 cases is an important aspect of a coronavirus vaccine, but preventing severe illness is especially important considering that severe cases can result in prolonged intubation/artificial ventilation, prolonged disability and death. Pfizer/BioNTech had not released any data on the breakdown of severe cases as this column was finalized. In Moderna’s clinical trial, a secondary endpoint analyzed severe cases of COVID-19 and included 30 severe cases (as defined in the study protocol) in this analysis. All 30 cases occurred in the placebo group and none in the mRNA-1273–vaccinated group. In the Pfizer/BioNTech trial there were too few cases of severe illness to calculate efficacy.
Duration of immunity and need to revaccinate after initial primary vaccination are unknowns. Study of induction of B- and T-cell memory and levels of long-term protection have not been reported thus far.
Could mRNA COVID-19 vaccines be dangerous in the long term?
These will be the first-ever mRNA vaccines brought to market for humans. In order to receive Food and Drug Administration approval, the companies had to prove there were no immediate or short-term negative adverse effects from the vaccines. The companies reported that their independent data-monitoring committees hadn’t “reported any serious safety concerns.” However, fairly significant local reactions at the site of injection, fever, malaise, and fatigue occur with modest frequency following vaccinations with these products, reportedly in 10%-15% of vaccinees. Overall, the immediate reaction profile appears to be more severe than what occurs following seasonal influenza vaccination. When mass inoculations with these completely new and revolutionary vaccines begins, we will know virtually nothing about their long-term side effects. The possibility of systemic inflammatory responses that could lead to autoimmune conditions, persistence of the induced immunogen expression, development of autoreactive antibodies, and toxic effects of delivery components have been raised as theoretical concerns.4-6 None of these theoretical risks have been observed to date and postmarketing phase 4 safety monitoring studies are in place from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention and the companies that produce the vaccines. This is a risk public health authorities are willing to take because the risk to benefit calculation strongly favors taking theoretical risks, compared with clear benefits in preventing severe illnesses and death.
What about availability?
Pfizer/BioNTech expects to be able to produce up to 50 million vaccine doses in 2020 and up to 1.3 billion doses in 2021. Moderna expects to produce 20 million doses by the end of 2020, and 500 million to 1 billion doses in 2021. Storage requirements are inherent to the composition of the vaccines with their differing lipid nanoparticle delivery systems. Pfizer/BioNTech’s BNT162b2 has to be stored and transported at –80° C, which requires specialized freezers, which most doctors’ offices and pharmacies are unlikely to have on site, or dry ice containers. Once the vaccine is thawed, it can only remain in the refrigerator for 24 hours. Moderna’s mRNA-1273 will be much easier to distribute. The vaccine is stable in a standard freezer at –20° C for up to 6 months, in a refrigerator for up to 30 days within that 6-month shelf life, and at room temperature for up to 12 hours.
Timelines and testing other vaccines
Strong efficacy data from the two leading SARS-CoV-2 vaccines and emergency-use authorization Food and Drug Administration approval suggest the window for testing additional vaccine candidates in the United States could soon start to close. Of the more than 200 vaccines in development for SARS-CoV-2, at least 7 have a chance of gathering pivotal data before the front-runners become broadly available.
Testing diverse vaccine candidates, based on different technologies, is important for ensuring sufficient supply and could lead to products with tolerability and safety profiles that make them better suited, or more attractive, to subsets of the population. Different vaccine antigens and technologies also may yield different durations of protection, a question that will not be answered until long after the first products are on the market.
AstraZeneca enrolled about 23,000 subjects into its two phase 3 trials of AZD1222 (ChAdOx1 nCoV-19): a 40,000-subject U.S. trial and a 10,000-subject study in Brazil. AstraZeneca’s AZD1222, developed with the University of Oxford (England), uses a replication defective simian adenovirus vector called ChAdOx1.AZD1222 which encodes the SARS-CoV-2 spike protein. After injection, the viral vector delivers recombinant DNA that is decoded to mRNA, followed by mRNA decoding to become a protein. A serendipitous manufacturing error for the first 3,000 doses resulted in a half dose for those subjects before the error was discovered. Full doses were given to those subjects on second injections and those subjects showed 90% efficacy. Subjects who received 2 full doses showed 62% efficacy. A vaccine cannot be licensed based on 3,000 subjects so AstraZeneca has started a new phase 3 trial involving many more subjects to receive the combination lower dose followed by the full dose.
Johnson and Johnson (J&J) started its phase 3 trial evaluating a single dose of JNJ-78436735 in September. Phase 3 data may be reported by the end of2020. In November, J&J announced it was starting a second phase 3 trial to test two doses of the candidate. J&J’s JNJ-78436735 encodes the SARS-CoV-2 spike protein in an adenovirus serotype 26 (Ad26) vector, which is one of the two adenovirus vectors used in Sputnik V, the Russian vaccine reported to have 90% efficacy at an early interim analysis.
Sanofi and Novavax are both developing protein-based vaccines, a proven modality. Sanofi, in partnership with GlaxoSmithKline started a phase 1/2 clinical trial in the Fall 2020 with plans to commence a phase 3 trial in late December. Sanofi developed the protein ingredients and GlaxoSmithKline added one of their novel adjuvants. Novavax expects data from a U.K. phase 3 trial of NVX-CoV2373 in early 2021 and began a U.S. phase 3 study in late November. NVX-CoV2373 was created using Novavax’ recombinant nanoparticle technology to generate antigen derived from the coronavirus spike protein and contains Novavax’s patented saponin-based Matrix-M adjuvant.
Inovio Pharmaceuticals was gearing up to start a U.S. phase 2/3 trial of DNA vaccine INO-4800 by the end of 2020.
After Moderna and Pfizer-BioNTech, CureVac has the next most advanced mRNA vaccine. It was planned that a phase 2b/3 trial of CVnCoV would be conducted in Europe, Latin America, Africa, and Asia. Sanofi is also developing a mRNA vaccine as a second product in addition to its protein vaccine.
Vaxxinity planned to begin phase 3 testing of UB-612, a multitope peptide–based vaccine, in Brazil by the end of 2020.
However, emergency-use authorizations for the Pfizer and Moderna vaccines could hinder trial recruitment in at least two ways. Given the gravity of the pandemic, some stakeholders believe it would be ethical to unblind ongoing trials to give subjects the opportunity to switch to a vaccine proven to be effective. Even if unblinding doesn’t occur, as the two authorized vaccines start to become widely available, volunteering for clinical trials may become less attractive.
Dr. Pichichero is a specialist in pediatric infectious diseases, and director of the Research Institute at Rochester (N.Y.) General Hospital. He said he has no relevant financial disclosures. Email Dr. Pichichero at [email protected].
References
1. Wolff JA et al. Science. 1990 Mar 23. doi: 10.1126/science.1690918.
2. Jackson LA et al. N Engl J Med. 2020 Nov 12. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa2022483.
3. Prentice T and Reinders LT. The world health report 2007. (Geneva Switzerland: World Health Organization, 2007).
4. Peck KM and Lauring AS. J Virol. 2018. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01031-17.
5. Pepini T et al. J Immunol. 2017 May 15. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1601877.
6. Theofilopoulos AN et al. Annu Rev Immunol. 2005. doi: 10.1146/annurev.immunol.23.021704.115843.
In mid-November, Pfizer/BioNTech were the first with surprising positive protection interim data for their coronavirus vaccine, BNT162b2. A week later, Moderna released interim efficacy results showing its coronavirus vaccine, mRNA-1273, also protected patients from developing SARS-CoV-2 infections. Both studies included mostly healthy adults. A diverse ethnic and racial vaccinated population was included. A reasonable number of persons aged over 65 years, and persons with stable compromising medical conditions were included. Adolescents aged 16 years and over were included. Younger adolescents have been vaccinated or such studies are in the planning or early implementation stage as 2020 came to a close.

These are new and revolutionary vaccines, although the ability to inject mRNA into animals dates back to 1990, technological advances today make it a reality.1 Traditional vaccines typically involve injection with antigens such as purified proteins or polysaccharides or inactivated/attenuated viruses. In the case of Pfizer’s and Moderna’s vaccines, the mRNA provides the genetic information to synthesize the spike protein that the SARS-CoV-2 virus uses to attach to and infect human cells. Each type of vaccine is packaged in proprietary lipid nanoparticles to protect the mRNA from rapid degradation, and the nanoparticles serve as an adjuvant to attract immune cells to the site of injection. (The properties of the respective lipid nanoparticle packaging may be the factor that impacts storage requirements discussed below.) When injected into muscle (myocyte), the lipid nanoparticles containing the mRNA inside are taken into muscle cells, where the cytoplasmic ribosomes detect and decode the mRNA resulting in the production of the spike protein antigen. It should be noted that the mRNA does not enter the nucleus, where the genetic information (DNA) of a cell is located, and can’t be reproduced or integrated into the DNA. The antigen is exported to the myocyte cell surface where the immune system’s antigen presenting cells detect the protein, ingest it, and take it to regional lymph nodes where interactions with T cells and B cells results in antibodies, T cell–mediated immunity, and generation of immune memory T cells and B cells. A particular subset of T cells – cytotoxic or killer T cells – destroy cells that have been infected by a pathogen. The SARS-CoV-2 mRNA vaccine from Pfizer was reported to induce powerful cytotoxic T-cell responses. Results for Moderna’s vaccine had not been reported at the time this column was prepared, but I anticipate the same positive results.
The revolutionary aspect of mRNA vaccines is the speed at which they can be designed and produced. This is why they lead the pack among the SARS-CoV-2 vaccine candidates and why the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases provided financial, technical, and/or clinical support. Indeed, once the amino acid sequence of a protein can be determined (a relatively easy task these days) it’s straightforward to synthesize mRNA in the lab – and it can be done incredibly fast. It is reported that the mRNA code for the vaccine by Moderna was made in 2 days and production development was completed in about 2 months.2
A 2007 World Health Organization report noted that infectious diseases are emerging at “the historically unprecedented rate of one per year.”3 Severe acute respiratory syndrome (SARS), Zika, Ebola, and avian and swine flu are recent examples. For most vaccines against emerging diseases, the challenge is about speed: developing and manufacturing a vaccine and getting it to persons who need it as quickly as possible. The current seasonal flu vaccine takes about 6 months to develop; it takes years for most of the traditional vaccines. That’s why once the infrastructure is in place, mRNA vaccines may prove to offer a big advantage as vaccines against emerging pathogens.
Early efficacy results have been surprising
Both vaccines were reported to produce about 95% efficacy in the final analysis. That was unexpectedly high because most vaccines for respiratory illness achieve efficacy of 60%-80%, e.g., flu vaccines. However, the efficacy rate may drop as time goes by because stimulation of short-term immunity would be in the earliest reported results.
Preventing SARS-CoV-2 cases is an important aspect of a coronavirus vaccine, but preventing severe illness is especially important considering that severe cases can result in prolonged intubation/artificial ventilation, prolonged disability and death. Pfizer/BioNTech had not released any data on the breakdown of severe cases as this column was finalized. In Moderna’s clinical trial, a secondary endpoint analyzed severe cases of COVID-19 and included 30 severe cases (as defined in the study protocol) in this analysis. All 30 cases occurred in the placebo group and none in the mRNA-1273–vaccinated group. In the Pfizer/BioNTech trial there were too few cases of severe illness to calculate efficacy.
Duration of immunity and need to revaccinate after initial primary vaccination are unknowns. Study of induction of B- and T-cell memory and levels of long-term protection have not been reported thus far.
Could mRNA COVID-19 vaccines be dangerous in the long term?
These will be the first-ever mRNA vaccines brought to market for humans. In order to receive Food and Drug Administration approval, the companies had to prove there were no immediate or short-term negative adverse effects from the vaccines. The companies reported that their independent data-monitoring committees hadn’t “reported any serious safety concerns.” However, fairly significant local reactions at the site of injection, fever, malaise, and fatigue occur with modest frequency following vaccinations with these products, reportedly in 10%-15% of vaccinees. Overall, the immediate reaction profile appears to be more severe than what occurs following seasonal influenza vaccination. When mass inoculations with these completely new and revolutionary vaccines begins, we will know virtually nothing about their long-term side effects. The possibility of systemic inflammatory responses that could lead to autoimmune conditions, persistence of the induced immunogen expression, development of autoreactive antibodies, and toxic effects of delivery components have been raised as theoretical concerns.4-6 None of these theoretical risks have been observed to date and postmarketing phase 4 safety monitoring studies are in place from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention and the companies that produce the vaccines. This is a risk public health authorities are willing to take because the risk to benefit calculation strongly favors taking theoretical risks, compared with clear benefits in preventing severe illnesses and death.
What about availability?
Pfizer/BioNTech expects to be able to produce up to 50 million vaccine doses in 2020 and up to 1.3 billion doses in 2021. Moderna expects to produce 20 million doses by the end of 2020, and 500 million to 1 billion doses in 2021. Storage requirements are inherent to the composition of the vaccines with their differing lipid nanoparticle delivery systems. Pfizer/BioNTech’s BNT162b2 has to be stored and transported at –80° C, which requires specialized freezers, which most doctors’ offices and pharmacies are unlikely to have on site, or dry ice containers. Once the vaccine is thawed, it can only remain in the refrigerator for 24 hours. Moderna’s mRNA-1273 will be much easier to distribute. The vaccine is stable in a standard freezer at –20° C for up to 6 months, in a refrigerator for up to 30 days within that 6-month shelf life, and at room temperature for up to 12 hours.
Timelines and testing other vaccines
Strong efficacy data from the two leading SARS-CoV-2 vaccines and emergency-use authorization Food and Drug Administration approval suggest the window for testing additional vaccine candidates in the United States could soon start to close. Of the more than 200 vaccines in development for SARS-CoV-2, at least 7 have a chance of gathering pivotal data before the front-runners become broadly available.
Testing diverse vaccine candidates, based on different technologies, is important for ensuring sufficient supply and could lead to products with tolerability and safety profiles that make them better suited, or more attractive, to subsets of the population. Different vaccine antigens and technologies also may yield different durations of protection, a question that will not be answered until long after the first products are on the market.
AstraZeneca enrolled about 23,000 subjects into its two phase 3 trials of AZD1222 (ChAdOx1 nCoV-19): a 40,000-subject U.S. trial and a 10,000-subject study in Brazil. AstraZeneca’s AZD1222, developed with the University of Oxford (England), uses a replication defective simian adenovirus vector called ChAdOx1.AZD1222 which encodes the SARS-CoV-2 spike protein. After injection, the viral vector delivers recombinant DNA that is decoded to mRNA, followed by mRNA decoding to become a protein. A serendipitous manufacturing error for the first 3,000 doses resulted in a half dose for those subjects before the error was discovered. Full doses were given to those subjects on second injections and those subjects showed 90% efficacy. Subjects who received 2 full doses showed 62% efficacy. A vaccine cannot be licensed based on 3,000 subjects so AstraZeneca has started a new phase 3 trial involving many more subjects to receive the combination lower dose followed by the full dose.
Johnson and Johnson (J&J) started its phase 3 trial evaluating a single dose of JNJ-78436735 in September. Phase 3 data may be reported by the end of2020. In November, J&J announced it was starting a second phase 3 trial to test two doses of the candidate. J&J’s JNJ-78436735 encodes the SARS-CoV-2 spike protein in an adenovirus serotype 26 (Ad26) vector, which is one of the two adenovirus vectors used in Sputnik V, the Russian vaccine reported to have 90% efficacy at an early interim analysis.
Sanofi and Novavax are both developing protein-based vaccines, a proven modality. Sanofi, in partnership with GlaxoSmithKline started a phase 1/2 clinical trial in the Fall 2020 with plans to commence a phase 3 trial in late December. Sanofi developed the protein ingredients and GlaxoSmithKline added one of their novel adjuvants. Novavax expects data from a U.K. phase 3 trial of NVX-CoV2373 in early 2021 and began a U.S. phase 3 study in late November. NVX-CoV2373 was created using Novavax’ recombinant nanoparticle technology to generate antigen derived from the coronavirus spike protein and contains Novavax’s patented saponin-based Matrix-M adjuvant.
Inovio Pharmaceuticals was gearing up to start a U.S. phase 2/3 trial of DNA vaccine INO-4800 by the end of 2020.
After Moderna and Pfizer-BioNTech, CureVac has the next most advanced mRNA vaccine. It was planned that a phase 2b/3 trial of CVnCoV would be conducted in Europe, Latin America, Africa, and Asia. Sanofi is also developing a mRNA vaccine as a second product in addition to its protein vaccine.
Vaxxinity planned to begin phase 3 testing of UB-612, a multitope peptide–based vaccine, in Brazil by the end of 2020.
However, emergency-use authorizations for the Pfizer and Moderna vaccines could hinder trial recruitment in at least two ways. Given the gravity of the pandemic, some stakeholders believe it would be ethical to unblind ongoing trials to give subjects the opportunity to switch to a vaccine proven to be effective. Even if unblinding doesn’t occur, as the two authorized vaccines start to become widely available, volunteering for clinical trials may become less attractive.
Dr. Pichichero is a specialist in pediatric infectious diseases, and director of the Research Institute at Rochester (N.Y.) General Hospital. He said he has no relevant financial disclosures. Email Dr. Pichichero at [email protected].
References
1. Wolff JA et al. Science. 1990 Mar 23. doi: 10.1126/science.1690918.
2. Jackson LA et al. N Engl J Med. 2020 Nov 12. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa2022483.
3. Prentice T and Reinders LT. The world health report 2007. (Geneva Switzerland: World Health Organization, 2007).
4. Peck KM and Lauring AS. J Virol. 2018. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01031-17.
5. Pepini T et al. J Immunol. 2017 May 15. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1601877.
6. Theofilopoulos AN et al. Annu Rev Immunol. 2005. doi: 10.1146/annurev.immunol.23.021704.115843.
In mid-November, Pfizer/BioNTech were the first with surprising positive protection interim data for their coronavirus vaccine, BNT162b2. A week later, Moderna released interim efficacy results showing its coronavirus vaccine, mRNA-1273, also protected patients from developing SARS-CoV-2 infections. Both studies included mostly healthy adults. A diverse ethnic and racial vaccinated population was included. A reasonable number of persons aged over 65 years, and persons with stable compromising medical conditions were included. Adolescents aged 16 years and over were included. Younger adolescents have been vaccinated or such studies are in the planning or early implementation stage as 2020 came to a close.

These are new and revolutionary vaccines, although the ability to inject mRNA into animals dates back to 1990, technological advances today make it a reality.1 Traditional vaccines typically involve injection with antigens such as purified proteins or polysaccharides or inactivated/attenuated viruses. In the case of Pfizer’s and Moderna’s vaccines, the mRNA provides the genetic information to synthesize the spike protein that the SARS-CoV-2 virus uses to attach to and infect human cells. Each type of vaccine is packaged in proprietary lipid nanoparticles to protect the mRNA from rapid degradation, and the nanoparticles serve as an adjuvant to attract immune cells to the site of injection. (The properties of the respective lipid nanoparticle packaging may be the factor that impacts storage requirements discussed below.) When injected into muscle (myocyte), the lipid nanoparticles containing the mRNA inside are taken into muscle cells, where the cytoplasmic ribosomes detect and decode the mRNA resulting in the production of the spike protein antigen. It should be noted that the mRNA does not enter the nucleus, where the genetic information (DNA) of a cell is located, and can’t be reproduced or integrated into the DNA. The antigen is exported to the myocyte cell surface where the immune system’s antigen presenting cells detect the protein, ingest it, and take it to regional lymph nodes where interactions with T cells and B cells results in antibodies, T cell–mediated immunity, and generation of immune memory T cells and B cells. A particular subset of T cells – cytotoxic or killer T cells – destroy cells that have been infected by a pathogen. The SARS-CoV-2 mRNA vaccine from Pfizer was reported to induce powerful cytotoxic T-cell responses. Results for Moderna’s vaccine had not been reported at the time this column was prepared, but I anticipate the same positive results.
The revolutionary aspect of mRNA vaccines is the speed at which they can be designed and produced. This is why they lead the pack among the SARS-CoV-2 vaccine candidates and why the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases provided financial, technical, and/or clinical support. Indeed, once the amino acid sequence of a protein can be determined (a relatively easy task these days) it’s straightforward to synthesize mRNA in the lab – and it can be done incredibly fast. It is reported that the mRNA code for the vaccine by Moderna was made in 2 days and production development was completed in about 2 months.2
A 2007 World Health Organization report noted that infectious diseases are emerging at “the historically unprecedented rate of one per year.”3 Severe acute respiratory syndrome (SARS), Zika, Ebola, and avian and swine flu are recent examples. For most vaccines against emerging diseases, the challenge is about speed: developing and manufacturing a vaccine and getting it to persons who need it as quickly as possible. The current seasonal flu vaccine takes about 6 months to develop; it takes years for most of the traditional vaccines. That’s why once the infrastructure is in place, mRNA vaccines may prove to offer a big advantage as vaccines against emerging pathogens.
Early efficacy results have been surprising
Both vaccines were reported to produce about 95% efficacy in the final analysis. That was unexpectedly high because most vaccines for respiratory illness achieve efficacy of 60%-80%, e.g., flu vaccines. However, the efficacy rate may drop as time goes by because stimulation of short-term immunity would be in the earliest reported results.
Preventing SARS-CoV-2 cases is an important aspect of a coronavirus vaccine, but preventing severe illness is especially important considering that severe cases can result in prolonged intubation/artificial ventilation, prolonged disability and death. Pfizer/BioNTech had not released any data on the breakdown of severe cases as this column was finalized. In Moderna’s clinical trial, a secondary endpoint analyzed severe cases of COVID-19 and included 30 severe cases (as defined in the study protocol) in this analysis. All 30 cases occurred in the placebo group and none in the mRNA-1273–vaccinated group. In the Pfizer/BioNTech trial there were too few cases of severe illness to calculate efficacy.
Duration of immunity and need to revaccinate after initial primary vaccination are unknowns. Study of induction of B- and T-cell memory and levels of long-term protection have not been reported thus far.
Could mRNA COVID-19 vaccines be dangerous in the long term?
These will be the first-ever mRNA vaccines brought to market for humans. In order to receive Food and Drug Administration approval, the companies had to prove there were no immediate or short-term negative adverse effects from the vaccines. The companies reported that their independent data-monitoring committees hadn’t “reported any serious safety concerns.” However, fairly significant local reactions at the site of injection, fever, malaise, and fatigue occur with modest frequency following vaccinations with these products, reportedly in 10%-15% of vaccinees. Overall, the immediate reaction profile appears to be more severe than what occurs following seasonal influenza vaccination. When mass inoculations with these completely new and revolutionary vaccines begins, we will know virtually nothing about their long-term side effects. The possibility of systemic inflammatory responses that could lead to autoimmune conditions, persistence of the induced immunogen expression, development of autoreactive antibodies, and toxic effects of delivery components have been raised as theoretical concerns.4-6 None of these theoretical risks have been observed to date and postmarketing phase 4 safety monitoring studies are in place from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention and the companies that produce the vaccines. This is a risk public health authorities are willing to take because the risk to benefit calculation strongly favors taking theoretical risks, compared with clear benefits in preventing severe illnesses and death.
What about availability?
Pfizer/BioNTech expects to be able to produce up to 50 million vaccine doses in 2020 and up to 1.3 billion doses in 2021. Moderna expects to produce 20 million doses by the end of 2020, and 500 million to 1 billion doses in 2021. Storage requirements are inherent to the composition of the vaccines with their differing lipid nanoparticle delivery systems. Pfizer/BioNTech’s BNT162b2 has to be stored and transported at –80° C, which requires specialized freezers, which most doctors’ offices and pharmacies are unlikely to have on site, or dry ice containers. Once the vaccine is thawed, it can only remain in the refrigerator for 24 hours. Moderna’s mRNA-1273 will be much easier to distribute. The vaccine is stable in a standard freezer at –20° C for up to 6 months, in a refrigerator for up to 30 days within that 6-month shelf life, and at room temperature for up to 12 hours.
Timelines and testing other vaccines
Strong efficacy data from the two leading SARS-CoV-2 vaccines and emergency-use authorization Food and Drug Administration approval suggest the window for testing additional vaccine candidates in the United States could soon start to close. Of the more than 200 vaccines in development for SARS-CoV-2, at least 7 have a chance of gathering pivotal data before the front-runners become broadly available.
Testing diverse vaccine candidates, based on different technologies, is important for ensuring sufficient supply and could lead to products with tolerability and safety profiles that make them better suited, or more attractive, to subsets of the population. Different vaccine antigens and technologies also may yield different durations of protection, a question that will not be answered until long after the first products are on the market.
AstraZeneca enrolled about 23,000 subjects into its two phase 3 trials of AZD1222 (ChAdOx1 nCoV-19): a 40,000-subject U.S. trial and a 10,000-subject study in Brazil. AstraZeneca’s AZD1222, developed with the University of Oxford (England), uses a replication defective simian adenovirus vector called ChAdOx1.AZD1222 which encodes the SARS-CoV-2 spike protein. After injection, the viral vector delivers recombinant DNA that is decoded to mRNA, followed by mRNA decoding to become a protein. A serendipitous manufacturing error for the first 3,000 doses resulted in a half dose for those subjects before the error was discovered. Full doses were given to those subjects on second injections and those subjects showed 90% efficacy. Subjects who received 2 full doses showed 62% efficacy. A vaccine cannot be licensed based on 3,000 subjects so AstraZeneca has started a new phase 3 trial involving many more subjects to receive the combination lower dose followed by the full dose.
Johnson and Johnson (J&J) started its phase 3 trial evaluating a single dose of JNJ-78436735 in September. Phase 3 data may be reported by the end of2020. In November, J&J announced it was starting a second phase 3 trial to test two doses of the candidate. J&J’s JNJ-78436735 encodes the SARS-CoV-2 spike protein in an adenovirus serotype 26 (Ad26) vector, which is one of the two adenovirus vectors used in Sputnik V, the Russian vaccine reported to have 90% efficacy at an early interim analysis.
Sanofi and Novavax are both developing protein-based vaccines, a proven modality. Sanofi, in partnership with GlaxoSmithKline started a phase 1/2 clinical trial in the Fall 2020 with plans to commence a phase 3 trial in late December. Sanofi developed the protein ingredients and GlaxoSmithKline added one of their novel adjuvants. Novavax expects data from a U.K. phase 3 trial of NVX-CoV2373 in early 2021 and began a U.S. phase 3 study in late November. NVX-CoV2373 was created using Novavax’ recombinant nanoparticle technology to generate antigen derived from the coronavirus spike protein and contains Novavax’s patented saponin-based Matrix-M adjuvant.
Inovio Pharmaceuticals was gearing up to start a U.S. phase 2/3 trial of DNA vaccine INO-4800 by the end of 2020.
After Moderna and Pfizer-BioNTech, CureVac has the next most advanced mRNA vaccine. It was planned that a phase 2b/3 trial of CVnCoV would be conducted in Europe, Latin America, Africa, and Asia. Sanofi is also developing a mRNA vaccine as a second product in addition to its protein vaccine.
Vaxxinity planned to begin phase 3 testing of UB-612, a multitope peptide–based vaccine, in Brazil by the end of 2020.
However, emergency-use authorizations for the Pfizer and Moderna vaccines could hinder trial recruitment in at least two ways. Given the gravity of the pandemic, some stakeholders believe it would be ethical to unblind ongoing trials to give subjects the opportunity to switch to a vaccine proven to be effective. Even if unblinding doesn’t occur, as the two authorized vaccines start to become widely available, volunteering for clinical trials may become less attractive.
Dr. Pichichero is a specialist in pediatric infectious diseases, and director of the Research Institute at Rochester (N.Y.) General Hospital. He said he has no relevant financial disclosures. Email Dr. Pichichero at [email protected].
References
1. Wolff JA et al. Science. 1990 Mar 23. doi: 10.1126/science.1690918.
2. Jackson LA et al. N Engl J Med. 2020 Nov 12. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa2022483.
3. Prentice T and Reinders LT. The world health report 2007. (Geneva Switzerland: World Health Organization, 2007).
4. Peck KM and Lauring AS. J Virol. 2018. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01031-17.
5. Pepini T et al. J Immunol. 2017 May 15. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1601877.
6. Theofilopoulos AN et al. Annu Rev Immunol. 2005. doi: 10.1146/annurev.immunol.23.021704.115843.




