User login
Clinical Psychiatry News is the online destination and multimedia properties of Clinica Psychiatry News, the independent news publication for psychiatrists. Since 1971, Clinical Psychiatry News has been the leading source of news and commentary about clinical developments in psychiatry as well as health care policy and regulations that affect the physician's practice.
Dear Drupal User: You're seeing this because you're logged in to Drupal, and not redirected to MDedge.com/psychiatry.
Depression
adolescent depression
adolescent major depressive disorder
adolescent schizophrenia
adolescent with major depressive disorder
animals
autism
baby
brexpiprazole
child
child bipolar
child depression
child schizophrenia
children with bipolar disorder
children with depression
children with major depressive disorder
compulsive behaviors
cure
elderly bipolar
elderly depression
elderly major depressive disorder
elderly schizophrenia
elderly with dementia
first break
first episode
gambling
gaming
geriatric depression
geriatric major depressive disorder
geriatric schizophrenia
infant
ketamine
kid
major depressive disorder
major depressive disorder in adolescents
major depressive disorder in children
parenting
pediatric
pediatric bipolar
pediatric depression
pediatric major depressive disorder
pediatric schizophrenia
pregnancy
pregnant
rexulti
skin care
suicide
teen
wine
section[contains(@class, 'nav-hidden')]
footer[@id='footer']
div[contains(@class, 'pane-pub-article-cpn')]
div[contains(@class, 'pane-pub-home-cpn')]
div[contains(@class, 'pane-pub-topic-cpn')]
div[contains(@class, 'panel-panel-inner')]
div[contains(@class, 'pane-node-field-article-topics')]
section[contains(@class, 'footer-nav-section-wrapper')]
Surprising link between herpes zoster and dementia
Herpes zoster does not appear to increase dementia risk – on the contrary, the viral infection may offer some protection, a large population-based study suggests.
“We were surprised by these results [and] the reasons for the decreased risk are unclear,” study author Sigrun Alba Johannesdottir Schmidt, MD, PhD, with Aarhus (Denmark) University Hospital, said in a news release.
The study was published online in Neurology.
Conflicting findings
Herpes zoster (HZ) is an acute, cutaneous viral infection caused by the reactivation of varicella-zoster virus (VZV). Previous population-based studies have reported both decreased and increased risks of dementia after having HZ.
It’s thought that HZ may contribute to the development of dementia through neuroinflammation, cerebral vasculopathy, or direct neural damage, but epidemiologic evidence is limited.
To investigate further, Dr. Schmidt and colleagues used Danish medical registries to identify 247,305 people who had visited a hospital for HZ or were prescribed antiviral medication for HZ over a 20-year period and matched them to 1,235,890 people who did not have HZ. For both cohorts, the median age was 64 years, and 61% were women.
Dementia was diagnosed in 9.7% of zoster patients and 10.3% of matched control persons during up to 21 years of follow-up.
Contrary to the researchers’ expectation, HZ was associated with a small (7%) decreased relative risk of all-cause dementia during follow-up (hazard ratio, 0.93; 95% confidence interval, 0.90-0.95).
There was no increased long-term risk of dementia in subgroup analyses, except possibly among those with HZ that involved the central nervous system (HR, 1.94; 95% CI, 0.78-4.80), which has been shown before.
However, the population attributable fraction of dementia caused by this rare complication is low (< 1%), suggesting that universal vaccination against VZV in the elderly has limited potential to reduce dementia risk, the investigators noted.
Nonetheless, Dr. Schmidt said shingles vaccination should be encouraged in older people because it can prevent complications from the disease.
The research team admitted that the slightly decreased long-term risk of dementia, including Alzheimer’s disease, was “unexpected.” The reasons for this decreased risk are unclear, they say, and could be explained by missed diagnoses of shingles in people with undiagnosed dementia.
They were not able to examine whether antiviral treatment modifies the association between HZ and dementia and said that this topic merits further research.
The study was supported by the Edel and Wilhelm Daubenmerkls Charitable Foundation. The authors disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Herpes zoster does not appear to increase dementia risk – on the contrary, the viral infection may offer some protection, a large population-based study suggests.
“We were surprised by these results [and] the reasons for the decreased risk are unclear,” study author Sigrun Alba Johannesdottir Schmidt, MD, PhD, with Aarhus (Denmark) University Hospital, said in a news release.
The study was published online in Neurology.
Conflicting findings
Herpes zoster (HZ) is an acute, cutaneous viral infection caused by the reactivation of varicella-zoster virus (VZV). Previous population-based studies have reported both decreased and increased risks of dementia after having HZ.
It’s thought that HZ may contribute to the development of dementia through neuroinflammation, cerebral vasculopathy, or direct neural damage, but epidemiologic evidence is limited.
To investigate further, Dr. Schmidt and colleagues used Danish medical registries to identify 247,305 people who had visited a hospital for HZ or were prescribed antiviral medication for HZ over a 20-year period and matched them to 1,235,890 people who did not have HZ. For both cohorts, the median age was 64 years, and 61% were women.
Dementia was diagnosed in 9.7% of zoster patients and 10.3% of matched control persons during up to 21 years of follow-up.
Contrary to the researchers’ expectation, HZ was associated with a small (7%) decreased relative risk of all-cause dementia during follow-up (hazard ratio, 0.93; 95% confidence interval, 0.90-0.95).
There was no increased long-term risk of dementia in subgroup analyses, except possibly among those with HZ that involved the central nervous system (HR, 1.94; 95% CI, 0.78-4.80), which has been shown before.
However, the population attributable fraction of dementia caused by this rare complication is low (< 1%), suggesting that universal vaccination against VZV in the elderly has limited potential to reduce dementia risk, the investigators noted.
Nonetheless, Dr. Schmidt said shingles vaccination should be encouraged in older people because it can prevent complications from the disease.
The research team admitted that the slightly decreased long-term risk of dementia, including Alzheimer’s disease, was “unexpected.” The reasons for this decreased risk are unclear, they say, and could be explained by missed diagnoses of shingles in people with undiagnosed dementia.
They were not able to examine whether antiviral treatment modifies the association between HZ and dementia and said that this topic merits further research.
The study was supported by the Edel and Wilhelm Daubenmerkls Charitable Foundation. The authors disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Herpes zoster does not appear to increase dementia risk – on the contrary, the viral infection may offer some protection, a large population-based study suggests.
“We were surprised by these results [and] the reasons for the decreased risk are unclear,” study author Sigrun Alba Johannesdottir Schmidt, MD, PhD, with Aarhus (Denmark) University Hospital, said in a news release.
The study was published online in Neurology.
Conflicting findings
Herpes zoster (HZ) is an acute, cutaneous viral infection caused by the reactivation of varicella-zoster virus (VZV). Previous population-based studies have reported both decreased and increased risks of dementia after having HZ.
It’s thought that HZ may contribute to the development of dementia through neuroinflammation, cerebral vasculopathy, or direct neural damage, but epidemiologic evidence is limited.
To investigate further, Dr. Schmidt and colleagues used Danish medical registries to identify 247,305 people who had visited a hospital for HZ or were prescribed antiviral medication for HZ over a 20-year period and matched them to 1,235,890 people who did not have HZ. For both cohorts, the median age was 64 years, and 61% were women.
Dementia was diagnosed in 9.7% of zoster patients and 10.3% of matched control persons during up to 21 years of follow-up.
Contrary to the researchers’ expectation, HZ was associated with a small (7%) decreased relative risk of all-cause dementia during follow-up (hazard ratio, 0.93; 95% confidence interval, 0.90-0.95).
There was no increased long-term risk of dementia in subgroup analyses, except possibly among those with HZ that involved the central nervous system (HR, 1.94; 95% CI, 0.78-4.80), which has been shown before.
However, the population attributable fraction of dementia caused by this rare complication is low (< 1%), suggesting that universal vaccination against VZV in the elderly has limited potential to reduce dementia risk, the investigators noted.
Nonetheless, Dr. Schmidt said shingles vaccination should be encouraged in older people because it can prevent complications from the disease.
The research team admitted that the slightly decreased long-term risk of dementia, including Alzheimer’s disease, was “unexpected.” The reasons for this decreased risk are unclear, they say, and could be explained by missed diagnoses of shingles in people with undiagnosed dementia.
They were not able to examine whether antiviral treatment modifies the association between HZ and dementia and said that this topic merits further research.
The study was supported by the Edel and Wilhelm Daubenmerkls Charitable Foundation. The authors disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Analysis shows predictive capabilities of sleep EEG
CHARLOTTE, N.C. – , a researcher reported at the annual meeting of the Associated Professional Sleep Societies. “Sleep EEGs contain decodable information about the risk of unfavorable outcomes,” said Haoqi Sun, PhD, an instructor of neurology at Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston, and lead study author. “The results suggest that it’s feasible to use sleep to identify people with high risk of unfavorable outcomes and it strengthens the concept of sleep as a window into brain and general health.”
The researchers performed a quantitative analysis of sleep data collected on 8,673 adults who had diagnostic sleep studies that included polysomnography (PSG). The analysis used ICD codes to consider these 11 health outcomes: dementia, mild cognitive impairment (MCI) or dementia, ischemic stroke, intracranial hemorrhage, atrial fibrillation, myocardial infarction, type 2 diabetes, hypertension, bipolar disorder, depression, and mortality.
Then, Dr. Sun explained, they extracted 86 spectral and time-domain features of REM and non-REM sleep from sleep EEG recordings, and analyzed that data by adjusting for eight covariates including age, sex, body mass index, and use of benzodiazepines, antidepressants, sedatives, antiseizure drugs, and stimulants.
Participants were partitioned into three sleep-quality groups: poor, average, and good. The outcome-wise mean prediction difference in 10-year cumulative incidence was 2.3% for the poor sleep group, 0.5% for the average sleep group, and 1.3% for the good sleep group.
The outcomes with the three greatest poor to average risk ratios were dementia (6.2; 95% confidence interval, 4.5-9.3), mortality (5.7; 95% CI, 5-7.5) and MCI or dementia (4; 95% CI, 3.2-4.9).
Ready for the clinic?
In an interview, Dr. Sun said the results demonstrated the potential of using EEG brain wave data to predict health outcomes on an individual basis, although he acknowledged that most of the 86 sleep features the researchers used are not readily available in the clinic.
He noted the spectral features used in the study can be captured through software compatible with PSG. “From there you can identify the various bands, the different frequency ranges, and then you can easily see within this range whether a person has a higher power or lower power,” he said. However, the spindle and slow-oscillation features that researchers used in the study are beyond the reach of most clinics.
Next steps
This research is in its early stage, Dr. Sun said, but at some point the data collected from sleep studies could be paired with machine learning to make the model workable for evaluating individual patients. “Our goal is to first make this individualized,” he said. “We want to minimize the noise in the recording and minimize the night-to-night variability in the findings. There is some clinical-informed approach and there is also some algorithm-informed approach where you can minimize the variation over time.”
The model also has the potential to predict outcomes, particularly with chronic diseases such as diabetes and dementia, well before a diagnosis is made, he said.
‘Fascinating’ and ‘provocative’
Donald Bliwise, PhD, professor of neurology at Emory Sleep Center in Atlanta, said the study was “fascinating; it’s provocative; it’s exciting and interesting,” but added, “Sleep is vital for health. That’s abundantly clear in a study like that, but trying to push it a little bit further with all of these 86 measurements of the EEG, I think it becomes complicated.”
The study methodology, particularly the use of cumulative incidence of various diseases, was laudable, he said, and the use of simpler EEG-measured sleep features, such as alpha band power, “make intuitive sense.”
But it’s less clear on how the more sophisticated features the study model used – for example, kurtosis of theta frequency or coupling between spindle and slow oscillation – rank on sleep quality, he said, adding that the researchers have most likely done that but couldn’t add that into the format of the presentation.
“Kurtosis of the theta frequency band we don’t get on everyone in the sleep lab,” Dr. Bliwise said. “We might be able to, but I don’t know how to quite plug that into a turnkey model.”
The clinical components of the study were conducted by M. Brandon Westover, MD, PhD, at Massachusetts General Hospital, and Robert J. Thomas, MD, at Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center, both in Boston. The study received support from the American Academy of Sleep Medicine Foundation. Dr. Sun has no relevant disclosures. Dr. Bliwise has no disclosures.
CHARLOTTE, N.C. – , a researcher reported at the annual meeting of the Associated Professional Sleep Societies. “Sleep EEGs contain decodable information about the risk of unfavorable outcomes,” said Haoqi Sun, PhD, an instructor of neurology at Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston, and lead study author. “The results suggest that it’s feasible to use sleep to identify people with high risk of unfavorable outcomes and it strengthens the concept of sleep as a window into brain and general health.”
The researchers performed a quantitative analysis of sleep data collected on 8,673 adults who had diagnostic sleep studies that included polysomnography (PSG). The analysis used ICD codes to consider these 11 health outcomes: dementia, mild cognitive impairment (MCI) or dementia, ischemic stroke, intracranial hemorrhage, atrial fibrillation, myocardial infarction, type 2 diabetes, hypertension, bipolar disorder, depression, and mortality.
Then, Dr. Sun explained, they extracted 86 spectral and time-domain features of REM and non-REM sleep from sleep EEG recordings, and analyzed that data by adjusting for eight covariates including age, sex, body mass index, and use of benzodiazepines, antidepressants, sedatives, antiseizure drugs, and stimulants.
Participants were partitioned into three sleep-quality groups: poor, average, and good. The outcome-wise mean prediction difference in 10-year cumulative incidence was 2.3% for the poor sleep group, 0.5% for the average sleep group, and 1.3% for the good sleep group.
The outcomes with the three greatest poor to average risk ratios were dementia (6.2; 95% confidence interval, 4.5-9.3), mortality (5.7; 95% CI, 5-7.5) and MCI or dementia (4; 95% CI, 3.2-4.9).
Ready for the clinic?
In an interview, Dr. Sun said the results demonstrated the potential of using EEG brain wave data to predict health outcomes on an individual basis, although he acknowledged that most of the 86 sleep features the researchers used are not readily available in the clinic.
He noted the spectral features used in the study can be captured through software compatible with PSG. “From there you can identify the various bands, the different frequency ranges, and then you can easily see within this range whether a person has a higher power or lower power,” he said. However, the spindle and slow-oscillation features that researchers used in the study are beyond the reach of most clinics.
Next steps
This research is in its early stage, Dr. Sun said, but at some point the data collected from sleep studies could be paired with machine learning to make the model workable for evaluating individual patients. “Our goal is to first make this individualized,” he said. “We want to minimize the noise in the recording and minimize the night-to-night variability in the findings. There is some clinical-informed approach and there is also some algorithm-informed approach where you can minimize the variation over time.”
The model also has the potential to predict outcomes, particularly with chronic diseases such as diabetes and dementia, well before a diagnosis is made, he said.
‘Fascinating’ and ‘provocative’
Donald Bliwise, PhD, professor of neurology at Emory Sleep Center in Atlanta, said the study was “fascinating; it’s provocative; it’s exciting and interesting,” but added, “Sleep is vital for health. That’s abundantly clear in a study like that, but trying to push it a little bit further with all of these 86 measurements of the EEG, I think it becomes complicated.”
The study methodology, particularly the use of cumulative incidence of various diseases, was laudable, he said, and the use of simpler EEG-measured sleep features, such as alpha band power, “make intuitive sense.”
But it’s less clear on how the more sophisticated features the study model used – for example, kurtosis of theta frequency or coupling between spindle and slow oscillation – rank on sleep quality, he said, adding that the researchers have most likely done that but couldn’t add that into the format of the presentation.
“Kurtosis of the theta frequency band we don’t get on everyone in the sleep lab,” Dr. Bliwise said. “We might be able to, but I don’t know how to quite plug that into a turnkey model.”
The clinical components of the study were conducted by M. Brandon Westover, MD, PhD, at Massachusetts General Hospital, and Robert J. Thomas, MD, at Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center, both in Boston. The study received support from the American Academy of Sleep Medicine Foundation. Dr. Sun has no relevant disclosures. Dr. Bliwise has no disclosures.
CHARLOTTE, N.C. – , a researcher reported at the annual meeting of the Associated Professional Sleep Societies. “Sleep EEGs contain decodable information about the risk of unfavorable outcomes,” said Haoqi Sun, PhD, an instructor of neurology at Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston, and lead study author. “The results suggest that it’s feasible to use sleep to identify people with high risk of unfavorable outcomes and it strengthens the concept of sleep as a window into brain and general health.”
The researchers performed a quantitative analysis of sleep data collected on 8,673 adults who had diagnostic sleep studies that included polysomnography (PSG). The analysis used ICD codes to consider these 11 health outcomes: dementia, mild cognitive impairment (MCI) or dementia, ischemic stroke, intracranial hemorrhage, atrial fibrillation, myocardial infarction, type 2 diabetes, hypertension, bipolar disorder, depression, and mortality.
Then, Dr. Sun explained, they extracted 86 spectral and time-domain features of REM and non-REM sleep from sleep EEG recordings, and analyzed that data by adjusting for eight covariates including age, sex, body mass index, and use of benzodiazepines, antidepressants, sedatives, antiseizure drugs, and stimulants.
Participants were partitioned into three sleep-quality groups: poor, average, and good. The outcome-wise mean prediction difference in 10-year cumulative incidence was 2.3% for the poor sleep group, 0.5% for the average sleep group, and 1.3% for the good sleep group.
The outcomes with the three greatest poor to average risk ratios were dementia (6.2; 95% confidence interval, 4.5-9.3), mortality (5.7; 95% CI, 5-7.5) and MCI or dementia (4; 95% CI, 3.2-4.9).
Ready for the clinic?
In an interview, Dr. Sun said the results demonstrated the potential of using EEG brain wave data to predict health outcomes on an individual basis, although he acknowledged that most of the 86 sleep features the researchers used are not readily available in the clinic.
He noted the spectral features used in the study can be captured through software compatible with PSG. “From there you can identify the various bands, the different frequency ranges, and then you can easily see within this range whether a person has a higher power or lower power,” he said. However, the spindle and slow-oscillation features that researchers used in the study are beyond the reach of most clinics.
Next steps
This research is in its early stage, Dr. Sun said, but at some point the data collected from sleep studies could be paired with machine learning to make the model workable for evaluating individual patients. “Our goal is to first make this individualized,” he said. “We want to minimize the noise in the recording and minimize the night-to-night variability in the findings. There is some clinical-informed approach and there is also some algorithm-informed approach where you can minimize the variation over time.”
The model also has the potential to predict outcomes, particularly with chronic diseases such as diabetes and dementia, well before a diagnosis is made, he said.
‘Fascinating’ and ‘provocative’
Donald Bliwise, PhD, professor of neurology at Emory Sleep Center in Atlanta, said the study was “fascinating; it’s provocative; it’s exciting and interesting,” but added, “Sleep is vital for health. That’s abundantly clear in a study like that, but trying to push it a little bit further with all of these 86 measurements of the EEG, I think it becomes complicated.”
The study methodology, particularly the use of cumulative incidence of various diseases, was laudable, he said, and the use of simpler EEG-measured sleep features, such as alpha band power, “make intuitive sense.”
But it’s less clear on how the more sophisticated features the study model used – for example, kurtosis of theta frequency or coupling between spindle and slow oscillation – rank on sleep quality, he said, adding that the researchers have most likely done that but couldn’t add that into the format of the presentation.
“Kurtosis of the theta frequency band we don’t get on everyone in the sleep lab,” Dr. Bliwise said. “We might be able to, but I don’t know how to quite plug that into a turnkey model.”
The clinical components of the study were conducted by M. Brandon Westover, MD, PhD, at Massachusetts General Hospital, and Robert J. Thomas, MD, at Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center, both in Boston. The study received support from the American Academy of Sleep Medicine Foundation. Dr. Sun has no relevant disclosures. Dr. Bliwise has no disclosures.
AT SLEEP 2022
‘My malpractice insurance doubled!’ Why, when fewer patients are suing?
Angela Intili, MD, an ob.gyn., was used to seeing her medical malpractice insurance premium rise slightly every couple of years. But she was shocked by the drastic rise she recently experienced.
In the last 2 years, Dr. Intili’s premiums shot from $60,000 to $130,000, she said.
“After 30 years of practice, this is the first time I’ve asked myself if I can even afford to continue practicing obstetrics and gynecology,” said Dr. Intili, 62, of Joliet, Ill. “It’s gotten very difficult to make ends meet as far as overhead because of the liability costs. I still love what I’m doing but I don’t know if I can afford to do it anymore.”
Even more frustrating for Dr. Intili was learning that claims in Illinois have sharply declined. From 2016 to 2020, tort filings in Illinois decreased by 43%, according to a state report.
“If claims are going down, I don’t understand why premium payments are going up,” she said.
Physicians across the country are experiencing a similar paradox. Claims are down, yet premiums are rising.
Medscape’s Malpractice Report 2021 found that 42% of primary care physicians were sued in 2020 through mid-2021, down from 52% in 2019. Fifty-six percent of specialists were sued in 2020 through mid-2021 compared with 62% in 2019, the report found. The pandemic was undoubtedly behind the decrease in suits, according to legal experts.
Yet, physicians paid higher premiums in 2021 and are on track for increases again in 2022, according to data and analysts.
According to Conning, direct premiums written for physicians increased 7.0% in 2021 (from $5.01 billion to $5.36 billion). Conning, an investment management firm that serves the insurance industry, analyzes annual financial reports filed by insurers to state insurance departments. The Medical Liability Monitor’s 2021 report found that premiums for internists, surgeons, and ob.gyns. in states without Patient Compensation Funds rose by an average of 2% in 2021.
The disparities raise questions about why physicians are paying higher premiums when having fewer claims is likely saving insurers’ money. Shouldn’t physicians’ rates reflect the reduction in claims?
Cases plummet during pandemic
During the pandemic, the volume of new medical malpractice claims dwindled to nearly nothing, said Michael Matray, editor of the Medical Liability Monitor, a national publication that analyzes medical liability insurance premiums.
“The court system closed for a while,” he said. “No elective procedures were being done in 2020 and the early parts of 2021. If you have no treatment, you have no malpractice, so of course, claims frequency tumbled down to a trickle.”
The number of large awards also decreased during the pandemic, noted Bill Burns, a director of insurance research at Conning.
“For claims that were already in the system, many of them could not be resolved because of the court closures, inability to take statements and depositions, etc.,” he said. “This resulted in a drop in verdicts.”
In 2021, there were 16 medical malpractice verdicts of $10 million or more in the United States, according to TransRe, an international reinsurance company that tracks large verdicts. In 2020, there were six verdicts of $10 million or more, TransRe research found. This is down from 52 verdicts of $10 million or more in 2019 and 46 verdicts of $10 million or more in 2018.
But although the pandemic lowered claims and decreased the number of payouts, one important aspect was untouched by the COVID era, said Richard E. Anderson, MD, chairman and CEO for The Doctors Company, a national medical liability insurer, and TDC Group.
“It’s a fair question: If claims are down, why are premiums continuing to go up?” Dr. Anderson said. “The answer is severity.”
High-dollar verdicts pave expensive path
The upward trend in severity has continued for about 6 years and has not slowed, Dr. Anderson said. Severity refers to high-dollar verdicts and settlements.
“We’re seeing record-high verdicts all over the country,” he said. “We used to have maps that showed the top 10 medical malpractice verdicts or awards, and they would be clustered where you’d expect them to be, New York, Florida, Illinois, and so forth. Now, if you look at those top 10 verdicts, they could be anywhere in the country.”
In Minnesota for instance, a jury awarded a record $111 million in damages to a college student in May after finding a hospital and an orthopedic surgeon negligent in treating his broken leg. In April, a Kansas City jury awarded a family $25 million after finding that an ob.gyn. and hospital failed to properly treat a mother in labor, causing brain damage to her infant.
Such record payouts factor into premium costs, said Ned Rand Jr., CEO for ProAssurance, a national medical liability insurer. Though only a minority of claims reach that level, when a high award occurs, it puts pressure on the ultimate cost to resolve claims, he said. The frequency of claims filed is also expected to soon rebound, he noted.
“As we price the product sitting here today, we have to factor both of those in,” Mr. Rand said. “That’s why we, as an industry, continue to see, by and large, rates going up. And we fell behind. Some of this severity, in particular, as an industry, we weren’t pricing fully for, so we’ve been playing catch-up.”
High-dollar awards – also called nuclear verdicts – set the arena for future settlements in similar cases, Dr. Anderson added.
“If it was an orthopedic case for instance, and there was a similar injury in another case, that’s the trial lawyers’ starting point for the award,” he said. “Now, they’re not going to get it, but it distorts the negotiations. As we have more and more nuclear verdicts, it becomes harder to settle claims for reasonable amounts.”
What does 2022 have in store?
Analysts say the backlog of malpractice claims in the court system could prove calamitous for premiums and the liability landscape.
Courts are slogging through the pileup caused by the pandemic, but it’s estimated that there is still about a one-third larger case backlog than normal, according to Mr. Matray.
Such delayed claims may end up costing more because of social inflation, said Mr. Burns.
“People look at the world differently than they did 2 years ago,” he said. “A jury may have awarded $5 million for a claim a few years ago. But then the pandemic hits, and we have the George Floyd incident, and we have people out of work and a shortage in baby formula. Yet, companies are still making a lot of money and many insurance companies are turning record profits. Today, that jury may look at a sympathetic malpractice victim and award $10 million for the same claim.”
Concerns also exist about a potential surge of new malpractice claims. Mr. Rand compares the possible wave to a large bubble.
“I liken it to a cartoon, when one character grabs the hose and a big bubble forms as the water builds up,” he said. “Then the character releases, and water comes flooding out. As an industry, we wait, wondering: Is there going to be this flood of claims as the court systems reopen and the statute of limitations approach around some of these claims? That’s an ongoing concern.”
As for impending premiums, physicians can expect rises in 2022 and again in 2023, according to Chris Wojciechowski, a partner at TigerRisk Partners, a reinsurance broker.
“In general, there is a lot of uncertainty around the state of the economy, the tort environment, litigation post COVID, and overall volatility across the capital markets,” he said. “Furthermore, thanks to social and financial inflation, the potential for very severe verdicts has increased dramatically, and as courthouses reopen, the trends are not looking favorable. While many of the physician carriers have strong balance sheets, they can’t lose money on an underwriting basis forever.”
For Dr. Intili, the Illinois ob.gyn., news of another impending increase in 2022 is distressing. She expects another 10%-20% rise in 2022, she said. If she were younger and earlier in her career, she might’ve considered moving, she said, but her family lives in Illinois and she cares for her older parents.
“I’m not ready to retire,” Dr. Intili said. “I’m looking into options, possibly becoming a hospitalist or doing locum tenens work. I’ve been a solo practitioner for 27 years and I love the autonomy. But these high premiums are making it almost impossible to continue.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Angela Intili, MD, an ob.gyn., was used to seeing her medical malpractice insurance premium rise slightly every couple of years. But she was shocked by the drastic rise she recently experienced.
In the last 2 years, Dr. Intili’s premiums shot from $60,000 to $130,000, she said.
“After 30 years of practice, this is the first time I’ve asked myself if I can even afford to continue practicing obstetrics and gynecology,” said Dr. Intili, 62, of Joliet, Ill. “It’s gotten very difficult to make ends meet as far as overhead because of the liability costs. I still love what I’m doing but I don’t know if I can afford to do it anymore.”
Even more frustrating for Dr. Intili was learning that claims in Illinois have sharply declined. From 2016 to 2020, tort filings in Illinois decreased by 43%, according to a state report.
“If claims are going down, I don’t understand why premium payments are going up,” she said.
Physicians across the country are experiencing a similar paradox. Claims are down, yet premiums are rising.
Medscape’s Malpractice Report 2021 found that 42% of primary care physicians were sued in 2020 through mid-2021, down from 52% in 2019. Fifty-six percent of specialists were sued in 2020 through mid-2021 compared with 62% in 2019, the report found. The pandemic was undoubtedly behind the decrease in suits, according to legal experts.
Yet, physicians paid higher premiums in 2021 and are on track for increases again in 2022, according to data and analysts.
According to Conning, direct premiums written for physicians increased 7.0% in 2021 (from $5.01 billion to $5.36 billion). Conning, an investment management firm that serves the insurance industry, analyzes annual financial reports filed by insurers to state insurance departments. The Medical Liability Monitor’s 2021 report found that premiums for internists, surgeons, and ob.gyns. in states without Patient Compensation Funds rose by an average of 2% in 2021.
The disparities raise questions about why physicians are paying higher premiums when having fewer claims is likely saving insurers’ money. Shouldn’t physicians’ rates reflect the reduction in claims?
Cases plummet during pandemic
During the pandemic, the volume of new medical malpractice claims dwindled to nearly nothing, said Michael Matray, editor of the Medical Liability Monitor, a national publication that analyzes medical liability insurance premiums.
“The court system closed for a while,” he said. “No elective procedures were being done in 2020 and the early parts of 2021. If you have no treatment, you have no malpractice, so of course, claims frequency tumbled down to a trickle.”
The number of large awards also decreased during the pandemic, noted Bill Burns, a director of insurance research at Conning.
“For claims that were already in the system, many of them could not be resolved because of the court closures, inability to take statements and depositions, etc.,” he said. “This resulted in a drop in verdicts.”
In 2021, there were 16 medical malpractice verdicts of $10 million or more in the United States, according to TransRe, an international reinsurance company that tracks large verdicts. In 2020, there were six verdicts of $10 million or more, TransRe research found. This is down from 52 verdicts of $10 million or more in 2019 and 46 verdicts of $10 million or more in 2018.
But although the pandemic lowered claims and decreased the number of payouts, one important aspect was untouched by the COVID era, said Richard E. Anderson, MD, chairman and CEO for The Doctors Company, a national medical liability insurer, and TDC Group.
“It’s a fair question: If claims are down, why are premiums continuing to go up?” Dr. Anderson said. “The answer is severity.”
High-dollar verdicts pave expensive path
The upward trend in severity has continued for about 6 years and has not slowed, Dr. Anderson said. Severity refers to high-dollar verdicts and settlements.
“We’re seeing record-high verdicts all over the country,” he said. “We used to have maps that showed the top 10 medical malpractice verdicts or awards, and they would be clustered where you’d expect them to be, New York, Florida, Illinois, and so forth. Now, if you look at those top 10 verdicts, they could be anywhere in the country.”
In Minnesota for instance, a jury awarded a record $111 million in damages to a college student in May after finding a hospital and an orthopedic surgeon negligent in treating his broken leg. In April, a Kansas City jury awarded a family $25 million after finding that an ob.gyn. and hospital failed to properly treat a mother in labor, causing brain damage to her infant.
Such record payouts factor into premium costs, said Ned Rand Jr., CEO for ProAssurance, a national medical liability insurer. Though only a minority of claims reach that level, when a high award occurs, it puts pressure on the ultimate cost to resolve claims, he said. The frequency of claims filed is also expected to soon rebound, he noted.
“As we price the product sitting here today, we have to factor both of those in,” Mr. Rand said. “That’s why we, as an industry, continue to see, by and large, rates going up. And we fell behind. Some of this severity, in particular, as an industry, we weren’t pricing fully for, so we’ve been playing catch-up.”
High-dollar awards – also called nuclear verdicts – set the arena for future settlements in similar cases, Dr. Anderson added.
“If it was an orthopedic case for instance, and there was a similar injury in another case, that’s the trial lawyers’ starting point for the award,” he said. “Now, they’re not going to get it, but it distorts the negotiations. As we have more and more nuclear verdicts, it becomes harder to settle claims for reasonable amounts.”
What does 2022 have in store?
Analysts say the backlog of malpractice claims in the court system could prove calamitous for premiums and the liability landscape.
Courts are slogging through the pileup caused by the pandemic, but it’s estimated that there is still about a one-third larger case backlog than normal, according to Mr. Matray.
Such delayed claims may end up costing more because of social inflation, said Mr. Burns.
“People look at the world differently than they did 2 years ago,” he said. “A jury may have awarded $5 million for a claim a few years ago. But then the pandemic hits, and we have the George Floyd incident, and we have people out of work and a shortage in baby formula. Yet, companies are still making a lot of money and many insurance companies are turning record profits. Today, that jury may look at a sympathetic malpractice victim and award $10 million for the same claim.”
Concerns also exist about a potential surge of new malpractice claims. Mr. Rand compares the possible wave to a large bubble.
“I liken it to a cartoon, when one character grabs the hose and a big bubble forms as the water builds up,” he said. “Then the character releases, and water comes flooding out. As an industry, we wait, wondering: Is there going to be this flood of claims as the court systems reopen and the statute of limitations approach around some of these claims? That’s an ongoing concern.”
As for impending premiums, physicians can expect rises in 2022 and again in 2023, according to Chris Wojciechowski, a partner at TigerRisk Partners, a reinsurance broker.
“In general, there is a lot of uncertainty around the state of the economy, the tort environment, litigation post COVID, and overall volatility across the capital markets,” he said. “Furthermore, thanks to social and financial inflation, the potential for very severe verdicts has increased dramatically, and as courthouses reopen, the trends are not looking favorable. While many of the physician carriers have strong balance sheets, they can’t lose money on an underwriting basis forever.”
For Dr. Intili, the Illinois ob.gyn., news of another impending increase in 2022 is distressing. She expects another 10%-20% rise in 2022, she said. If she were younger and earlier in her career, she might’ve considered moving, she said, but her family lives in Illinois and she cares for her older parents.
“I’m not ready to retire,” Dr. Intili said. “I’m looking into options, possibly becoming a hospitalist or doing locum tenens work. I’ve been a solo practitioner for 27 years and I love the autonomy. But these high premiums are making it almost impossible to continue.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Angela Intili, MD, an ob.gyn., was used to seeing her medical malpractice insurance premium rise slightly every couple of years. But she was shocked by the drastic rise she recently experienced.
In the last 2 years, Dr. Intili’s premiums shot from $60,000 to $130,000, she said.
“After 30 years of practice, this is the first time I’ve asked myself if I can even afford to continue practicing obstetrics and gynecology,” said Dr. Intili, 62, of Joliet, Ill. “It’s gotten very difficult to make ends meet as far as overhead because of the liability costs. I still love what I’m doing but I don’t know if I can afford to do it anymore.”
Even more frustrating for Dr. Intili was learning that claims in Illinois have sharply declined. From 2016 to 2020, tort filings in Illinois decreased by 43%, according to a state report.
“If claims are going down, I don’t understand why premium payments are going up,” she said.
Physicians across the country are experiencing a similar paradox. Claims are down, yet premiums are rising.
Medscape’s Malpractice Report 2021 found that 42% of primary care physicians were sued in 2020 through mid-2021, down from 52% in 2019. Fifty-six percent of specialists were sued in 2020 through mid-2021 compared with 62% in 2019, the report found. The pandemic was undoubtedly behind the decrease in suits, according to legal experts.
Yet, physicians paid higher premiums in 2021 and are on track for increases again in 2022, according to data and analysts.
According to Conning, direct premiums written for physicians increased 7.0% in 2021 (from $5.01 billion to $5.36 billion). Conning, an investment management firm that serves the insurance industry, analyzes annual financial reports filed by insurers to state insurance departments. The Medical Liability Monitor’s 2021 report found that premiums for internists, surgeons, and ob.gyns. in states without Patient Compensation Funds rose by an average of 2% in 2021.
The disparities raise questions about why physicians are paying higher premiums when having fewer claims is likely saving insurers’ money. Shouldn’t physicians’ rates reflect the reduction in claims?
Cases plummet during pandemic
During the pandemic, the volume of new medical malpractice claims dwindled to nearly nothing, said Michael Matray, editor of the Medical Liability Monitor, a national publication that analyzes medical liability insurance premiums.
“The court system closed for a while,” he said. “No elective procedures were being done in 2020 and the early parts of 2021. If you have no treatment, you have no malpractice, so of course, claims frequency tumbled down to a trickle.”
The number of large awards also decreased during the pandemic, noted Bill Burns, a director of insurance research at Conning.
“For claims that were already in the system, many of them could not be resolved because of the court closures, inability to take statements and depositions, etc.,” he said. “This resulted in a drop in verdicts.”
In 2021, there were 16 medical malpractice verdicts of $10 million or more in the United States, according to TransRe, an international reinsurance company that tracks large verdicts. In 2020, there were six verdicts of $10 million or more, TransRe research found. This is down from 52 verdicts of $10 million or more in 2019 and 46 verdicts of $10 million or more in 2018.
But although the pandemic lowered claims and decreased the number of payouts, one important aspect was untouched by the COVID era, said Richard E. Anderson, MD, chairman and CEO for The Doctors Company, a national medical liability insurer, and TDC Group.
“It’s a fair question: If claims are down, why are premiums continuing to go up?” Dr. Anderson said. “The answer is severity.”
High-dollar verdicts pave expensive path
The upward trend in severity has continued for about 6 years and has not slowed, Dr. Anderson said. Severity refers to high-dollar verdicts and settlements.
“We’re seeing record-high verdicts all over the country,” he said. “We used to have maps that showed the top 10 medical malpractice verdicts or awards, and they would be clustered where you’d expect them to be, New York, Florida, Illinois, and so forth. Now, if you look at those top 10 verdicts, they could be anywhere in the country.”
In Minnesota for instance, a jury awarded a record $111 million in damages to a college student in May after finding a hospital and an orthopedic surgeon negligent in treating his broken leg. In April, a Kansas City jury awarded a family $25 million after finding that an ob.gyn. and hospital failed to properly treat a mother in labor, causing brain damage to her infant.
Such record payouts factor into premium costs, said Ned Rand Jr., CEO for ProAssurance, a national medical liability insurer. Though only a minority of claims reach that level, when a high award occurs, it puts pressure on the ultimate cost to resolve claims, he said. The frequency of claims filed is also expected to soon rebound, he noted.
“As we price the product sitting here today, we have to factor both of those in,” Mr. Rand said. “That’s why we, as an industry, continue to see, by and large, rates going up. And we fell behind. Some of this severity, in particular, as an industry, we weren’t pricing fully for, so we’ve been playing catch-up.”
High-dollar awards – also called nuclear verdicts – set the arena for future settlements in similar cases, Dr. Anderson added.
“If it was an orthopedic case for instance, and there was a similar injury in another case, that’s the trial lawyers’ starting point for the award,” he said. “Now, they’re not going to get it, but it distorts the negotiations. As we have more and more nuclear verdicts, it becomes harder to settle claims for reasonable amounts.”
What does 2022 have in store?
Analysts say the backlog of malpractice claims in the court system could prove calamitous for premiums and the liability landscape.
Courts are slogging through the pileup caused by the pandemic, but it’s estimated that there is still about a one-third larger case backlog than normal, according to Mr. Matray.
Such delayed claims may end up costing more because of social inflation, said Mr. Burns.
“People look at the world differently than they did 2 years ago,” he said. “A jury may have awarded $5 million for a claim a few years ago. But then the pandemic hits, and we have the George Floyd incident, and we have people out of work and a shortage in baby formula. Yet, companies are still making a lot of money and many insurance companies are turning record profits. Today, that jury may look at a sympathetic malpractice victim and award $10 million for the same claim.”
Concerns also exist about a potential surge of new malpractice claims. Mr. Rand compares the possible wave to a large bubble.
“I liken it to a cartoon, when one character grabs the hose and a big bubble forms as the water builds up,” he said. “Then the character releases, and water comes flooding out. As an industry, we wait, wondering: Is there going to be this flood of claims as the court systems reopen and the statute of limitations approach around some of these claims? That’s an ongoing concern.”
As for impending premiums, physicians can expect rises in 2022 and again in 2023, according to Chris Wojciechowski, a partner at TigerRisk Partners, a reinsurance broker.
“In general, there is a lot of uncertainty around the state of the economy, the tort environment, litigation post COVID, and overall volatility across the capital markets,” he said. “Furthermore, thanks to social and financial inflation, the potential for very severe verdicts has increased dramatically, and as courthouses reopen, the trends are not looking favorable. While many of the physician carriers have strong balance sheets, they can’t lose money on an underwriting basis forever.”
For Dr. Intili, the Illinois ob.gyn., news of another impending increase in 2022 is distressing. She expects another 10%-20% rise in 2022, she said. If she were younger and earlier in her career, she might’ve considered moving, she said, but her family lives in Illinois and she cares for her older parents.
“I’m not ready to retire,” Dr. Intili said. “I’m looking into options, possibly becoming a hospitalist or doing locum tenens work. I’ve been a solo practitioner for 27 years and I love the autonomy. But these high premiums are making it almost impossible to continue.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Opioid use in the elderly a dementia risk factor?
in new findings that suggest exposure to these drugs may be another modifiable risk factor for dementia.
“Clinicians and others may want to consider that opioid exposure in those aged 75-80 increases dementia risk, and to balance the potential benefits of opioid use in old age with adverse side effects,” said Stephen Z. Levine, PhD, professor, department of community mental health, University of Haifa (Israel).
The study was published online in the American Journal of Geriatric Psychiatry.
Widespread use
Evidence points to a relatively high rate of opioid prescriptions among older adults. A Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report noted 19.2% of the U.S. adult population filled an opioid prescription in 2018, with the rate in those over 65 double that of adults aged 20-24 years (25% vs. 11.2%).
Disorders and illnesses for which opioids might be prescribed, including cancer and some pain conditions, “are far more prevalent in old age than at a younger age,” said Dr. Levine.
This high rate of opioid use underscores the need to consider the risks of opioid use in old age, said Dr. Levine. “Unfortunately, studies of the association between opioid use and dementia risk in old age are few, and their results are inconsistent.”
The study included 91,307 Israeli citizens aged 60 and over without dementia who were enrolled in the Meuhedet Healthcare Services, a nonprofit health maintenance organization (HMO) serving 14% of the country’s population. Meuhedet has maintained an up-to-date dementia registry since 2002.
The average age of the study sample was 68.29 years at the start of the study (in 2012).
In Israel, opioids are prescribed for a 30-day period. In this study, opioid exposure was defined as opioid medication fills covering 60 days (or two prescriptions) within a 120-day interval.
The primary outcome was incident dementia during follow-up from Jan. 1, 2013 to Oct. 30, 2017. The analysis controlled for a number of factors, including age, sex, smoking status, health conditions such as arthritis, depression, diabetes, osteoporosis, cognitive decline, vitamin deficiencies, cancer, cardiovascular conditions, and hospitalizations for falls.
Researchers also accounted for the competing risk of mortality.
During the study, 3.1% of subjects were exposed to opioids at a mean age of 73.94 years, and 5.8% of subjects developed dementia at an average age of 78.07 years.
Increased dementia risk
The risk of incident dementia was significantly increased in those exposed to opioids versus unexposed individuals in the 75- to 80-year age group (adjusted hazard ratio, 1.39; 95% confidence interval, 1.01-1.92; z statistic = 2.02; P < .05).
The authors noted the effect size for opioid exposure in this elderly age group is like other potentially modifiable risk factors for dementia, including body mass index and smoking.
The current study could not determine the biological explanation for the increased dementia risk among older opioid users. “Causal notions are challenging in observational studies and should be viewed with caution,” Dr. Levine noted.
However, a plausible mechanism highlighted in the literature is that opioids promote apoptosis of microglia and neurons that contribute to neurodegenerative diseases, he said.
The study included 14 sensitivity analyses, including those that looked at females, subjects older than 70, smokers, and groups with and without comorbid health conditions. The only sensitivity analysis that didn’t have similar findings to the primary analysis looked at dementia risk restricted to subjects without a vitamin deficiency.
“It’s reassuring that 13 or 14 sensitivity analyses found a significant association between opioid exposure and dementia risk,” said Dr. Levine.
Some prior studies did not show an association between opioid exposure and dementia risk. One possible reason for the discrepancy with the current findings is that the previous research didn’t account for age-specific opioid use effects, or the competing risk of mortality, said Dr. Levine.
Clinicians have a number of potential alternatives to opioids to treat various conditions including acetaminophen, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, amine reuptake inhibitors (ARIs), membrane stabilizers, muscle relaxants, topical capsaicin, botulinum toxin, cannabinoids, and steroids.
A limitation of the study was that it didn’t adjust for all possible comorbid health conditions, including vascular conditions, or for use of benzodiazepines, and surgical procedures.
In addition, since up to 50% of dementia cases are undetected, it’s possible some in the unexposed opioid group may actually have undiagnosed dementia, thereby reducing the effect sizes in the results.
Reverse causality is also a possibility as the neuropathological process associated with dementia could have started prior to opioid exposure. In addition, the results are limited to prolonged opioid exposure.
Interpret with caution
Commenting on the study, David Knopman, MD, a neurologist at Mayo Clinic in Rochester, Minn., whose research involves late-life cognitive disorders, was skeptical.
“On the face of it, the fact that an association was seen only in one narrow age range – 75+ to 80 years – ought to raise serious suspicion about the reliability and validity of the claim that opioid use is a risk factor for dementia, he said.
Although the researchers performed several sensitivity analyses, including accounting for mortality, “pharmacoepidemiological studies are terribly sensitive to residual biases” related to physician and patient choices related to medication use, added Dr. Knopman.
The claim that opioids are a dementia risk “should be viewed with great caution” and should not influence use of opioids where they’re truly indicated, he said.
“It would be a great pity if patients with pain requiring opioids avoid them because of fears about dementia based on the dubious relationship between age and opioid use.”
Dr. Levine and Dr. Knopman report no relevant financial disclosures.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
in new findings that suggest exposure to these drugs may be another modifiable risk factor for dementia.
“Clinicians and others may want to consider that opioid exposure in those aged 75-80 increases dementia risk, and to balance the potential benefits of opioid use in old age with adverse side effects,” said Stephen Z. Levine, PhD, professor, department of community mental health, University of Haifa (Israel).
The study was published online in the American Journal of Geriatric Psychiatry.
Widespread use
Evidence points to a relatively high rate of opioid prescriptions among older adults. A Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report noted 19.2% of the U.S. adult population filled an opioid prescription in 2018, with the rate in those over 65 double that of adults aged 20-24 years (25% vs. 11.2%).
Disorders and illnesses for which opioids might be prescribed, including cancer and some pain conditions, “are far more prevalent in old age than at a younger age,” said Dr. Levine.
This high rate of opioid use underscores the need to consider the risks of opioid use in old age, said Dr. Levine. “Unfortunately, studies of the association between opioid use and dementia risk in old age are few, and their results are inconsistent.”
The study included 91,307 Israeli citizens aged 60 and over without dementia who were enrolled in the Meuhedet Healthcare Services, a nonprofit health maintenance organization (HMO) serving 14% of the country’s population. Meuhedet has maintained an up-to-date dementia registry since 2002.
The average age of the study sample was 68.29 years at the start of the study (in 2012).
In Israel, opioids are prescribed for a 30-day period. In this study, opioid exposure was defined as opioid medication fills covering 60 days (or two prescriptions) within a 120-day interval.
The primary outcome was incident dementia during follow-up from Jan. 1, 2013 to Oct. 30, 2017. The analysis controlled for a number of factors, including age, sex, smoking status, health conditions such as arthritis, depression, diabetes, osteoporosis, cognitive decline, vitamin deficiencies, cancer, cardiovascular conditions, and hospitalizations for falls.
Researchers also accounted for the competing risk of mortality.
During the study, 3.1% of subjects were exposed to opioids at a mean age of 73.94 years, and 5.8% of subjects developed dementia at an average age of 78.07 years.
Increased dementia risk
The risk of incident dementia was significantly increased in those exposed to opioids versus unexposed individuals in the 75- to 80-year age group (adjusted hazard ratio, 1.39; 95% confidence interval, 1.01-1.92; z statistic = 2.02; P < .05).
The authors noted the effect size for opioid exposure in this elderly age group is like other potentially modifiable risk factors for dementia, including body mass index and smoking.
The current study could not determine the biological explanation for the increased dementia risk among older opioid users. “Causal notions are challenging in observational studies and should be viewed with caution,” Dr. Levine noted.
However, a plausible mechanism highlighted in the literature is that opioids promote apoptosis of microglia and neurons that contribute to neurodegenerative diseases, he said.
The study included 14 sensitivity analyses, including those that looked at females, subjects older than 70, smokers, and groups with and without comorbid health conditions. The only sensitivity analysis that didn’t have similar findings to the primary analysis looked at dementia risk restricted to subjects without a vitamin deficiency.
“It’s reassuring that 13 or 14 sensitivity analyses found a significant association between opioid exposure and dementia risk,” said Dr. Levine.
Some prior studies did not show an association between opioid exposure and dementia risk. One possible reason for the discrepancy with the current findings is that the previous research didn’t account for age-specific opioid use effects, or the competing risk of mortality, said Dr. Levine.
Clinicians have a number of potential alternatives to opioids to treat various conditions including acetaminophen, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, amine reuptake inhibitors (ARIs), membrane stabilizers, muscle relaxants, topical capsaicin, botulinum toxin, cannabinoids, and steroids.
A limitation of the study was that it didn’t adjust for all possible comorbid health conditions, including vascular conditions, or for use of benzodiazepines, and surgical procedures.
In addition, since up to 50% of dementia cases are undetected, it’s possible some in the unexposed opioid group may actually have undiagnosed dementia, thereby reducing the effect sizes in the results.
Reverse causality is also a possibility as the neuropathological process associated with dementia could have started prior to opioid exposure. In addition, the results are limited to prolonged opioid exposure.
Interpret with caution
Commenting on the study, David Knopman, MD, a neurologist at Mayo Clinic in Rochester, Minn., whose research involves late-life cognitive disorders, was skeptical.
“On the face of it, the fact that an association was seen only in one narrow age range – 75+ to 80 years – ought to raise serious suspicion about the reliability and validity of the claim that opioid use is a risk factor for dementia, he said.
Although the researchers performed several sensitivity analyses, including accounting for mortality, “pharmacoepidemiological studies are terribly sensitive to residual biases” related to physician and patient choices related to medication use, added Dr. Knopman.
The claim that opioids are a dementia risk “should be viewed with great caution” and should not influence use of opioids where they’re truly indicated, he said.
“It would be a great pity if patients with pain requiring opioids avoid them because of fears about dementia based on the dubious relationship between age and opioid use.”
Dr. Levine and Dr. Knopman report no relevant financial disclosures.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
in new findings that suggest exposure to these drugs may be another modifiable risk factor for dementia.
“Clinicians and others may want to consider that opioid exposure in those aged 75-80 increases dementia risk, and to balance the potential benefits of opioid use in old age with adverse side effects,” said Stephen Z. Levine, PhD, professor, department of community mental health, University of Haifa (Israel).
The study was published online in the American Journal of Geriatric Psychiatry.
Widespread use
Evidence points to a relatively high rate of opioid prescriptions among older adults. A Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report noted 19.2% of the U.S. adult population filled an opioid prescription in 2018, with the rate in those over 65 double that of adults aged 20-24 years (25% vs. 11.2%).
Disorders and illnesses for which opioids might be prescribed, including cancer and some pain conditions, “are far more prevalent in old age than at a younger age,” said Dr. Levine.
This high rate of opioid use underscores the need to consider the risks of opioid use in old age, said Dr. Levine. “Unfortunately, studies of the association between opioid use and dementia risk in old age are few, and their results are inconsistent.”
The study included 91,307 Israeli citizens aged 60 and over without dementia who were enrolled in the Meuhedet Healthcare Services, a nonprofit health maintenance organization (HMO) serving 14% of the country’s population. Meuhedet has maintained an up-to-date dementia registry since 2002.
The average age of the study sample was 68.29 years at the start of the study (in 2012).
In Israel, opioids are prescribed for a 30-day period. In this study, opioid exposure was defined as opioid medication fills covering 60 days (or two prescriptions) within a 120-day interval.
The primary outcome was incident dementia during follow-up from Jan. 1, 2013 to Oct. 30, 2017. The analysis controlled for a number of factors, including age, sex, smoking status, health conditions such as arthritis, depression, diabetes, osteoporosis, cognitive decline, vitamin deficiencies, cancer, cardiovascular conditions, and hospitalizations for falls.
Researchers also accounted for the competing risk of mortality.
During the study, 3.1% of subjects were exposed to opioids at a mean age of 73.94 years, and 5.8% of subjects developed dementia at an average age of 78.07 years.
Increased dementia risk
The risk of incident dementia was significantly increased in those exposed to opioids versus unexposed individuals in the 75- to 80-year age group (adjusted hazard ratio, 1.39; 95% confidence interval, 1.01-1.92; z statistic = 2.02; P < .05).
The authors noted the effect size for opioid exposure in this elderly age group is like other potentially modifiable risk factors for dementia, including body mass index and smoking.
The current study could not determine the biological explanation for the increased dementia risk among older opioid users. “Causal notions are challenging in observational studies and should be viewed with caution,” Dr. Levine noted.
However, a plausible mechanism highlighted in the literature is that opioids promote apoptosis of microglia and neurons that contribute to neurodegenerative diseases, he said.
The study included 14 sensitivity analyses, including those that looked at females, subjects older than 70, smokers, and groups with and without comorbid health conditions. The only sensitivity analysis that didn’t have similar findings to the primary analysis looked at dementia risk restricted to subjects without a vitamin deficiency.
“It’s reassuring that 13 or 14 sensitivity analyses found a significant association between opioid exposure and dementia risk,” said Dr. Levine.
Some prior studies did not show an association between opioid exposure and dementia risk. One possible reason for the discrepancy with the current findings is that the previous research didn’t account for age-specific opioid use effects, or the competing risk of mortality, said Dr. Levine.
Clinicians have a number of potential alternatives to opioids to treat various conditions including acetaminophen, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, amine reuptake inhibitors (ARIs), membrane stabilizers, muscle relaxants, topical capsaicin, botulinum toxin, cannabinoids, and steroids.
A limitation of the study was that it didn’t adjust for all possible comorbid health conditions, including vascular conditions, or for use of benzodiazepines, and surgical procedures.
In addition, since up to 50% of dementia cases are undetected, it’s possible some in the unexposed opioid group may actually have undiagnosed dementia, thereby reducing the effect sizes in the results.
Reverse causality is also a possibility as the neuropathological process associated with dementia could have started prior to opioid exposure. In addition, the results are limited to prolonged opioid exposure.
Interpret with caution
Commenting on the study, David Knopman, MD, a neurologist at Mayo Clinic in Rochester, Minn., whose research involves late-life cognitive disorders, was skeptical.
“On the face of it, the fact that an association was seen only in one narrow age range – 75+ to 80 years – ought to raise serious suspicion about the reliability and validity of the claim that opioid use is a risk factor for dementia, he said.
Although the researchers performed several sensitivity analyses, including accounting for mortality, “pharmacoepidemiological studies are terribly sensitive to residual biases” related to physician and patient choices related to medication use, added Dr. Knopman.
The claim that opioids are a dementia risk “should be viewed with great caution” and should not influence use of opioids where they’re truly indicated, he said.
“It would be a great pity if patients with pain requiring opioids avoid them because of fears about dementia based on the dubious relationship between age and opioid use.”
Dr. Levine and Dr. Knopman report no relevant financial disclosures.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM AMERICAN JOURNAL OF GERIATRIC PSYCHIATRY
Asian American teens have highest rate of suicidal ideation
NEW ORLEANS – In an unexpected finding, researchers discovered that According to a weighted analysis, 24% of Asian Americans reported thinking about or planning suicide vs. 22% of Whites and Blacks and 20% of Hispanics (P < .01).
“We were shocked,” said study lead author Esha Hansoti, MD, who conducted the research at UT Southwestern Medical Center, Dallas, and is now a psychiatry resident at Zucker Hillside Hospital Northwell/Hofstra in Glen Oaks, NY. The findings were released at the annual meeting of the American Psychiatric Association.
Dr. Hansoti and colleagues launched the analysis in light of sparse research into Asian American mental health, she said. Even within this population, she said, mental illness “tends to be overlooked” and discussion of the topic may be considered taboo.
For the new study, researchers analyzed the 2019 Youth Risk Behavior Survey, conducted biennially by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, which had more than 13,000 participants in grades 9-12.
A weighted bivariate analysis of 618 Asian American adolescents – adjusted for age, sex, and depressive symptoms – found no statistically significant impact on suicidal ideation by gender, age, substance use, sexual/physical dating violence, or fluency in English.
However, several groups had a statistically significant higher risk, including victims of forced sexual intercourse and those who were threatened or bullied at school.
Those who didn’t get mostly A grades were also at high risk: Adolescents with mostly Ds and Fs were more likely to have acknowledged suicidal ideation than those with mostly As (adjusted odds ratio [AOR] = 3.2).
Gays and lesbians (AOR = 7.9 vs. heterosexuals), and bisexuals (AOR = 5.2 vs. heterosexuals) also showed sharply higher rates of suicidal ideation.
It’s not clear why Asian American adolescents may be at higher risk of suicidal ideation. The survey was completed prior to the COVID-19 pandemic, which spawned bigotry against people of Asian descent and an ongoing outbreak of high-profile violence against Asian Americans across the country.
Dr. Hansoti noted that Asian Americans face the pressures to live up to the standards of being a “model minority.” In addition, “very few Asian American adolescents are taken to a therapist, and few mental health providers are Asian Americans.”
She urged fellow psychiatrists “to remember that our perceptions of Asian Americans might hinder some of the diagnoses we could be making. Be thoughtful about how their ethnicity and race affects their presentation and their own perception of their illness.”
She added that Asian Americans may experience mental illness and anxiety “more somatically and physically than emotionally.”
In an interview, Anne Saw, PhD, associate professor of clinical-community psychology at DePaul University, Chicago, said the findings are “helpful for corroborating other studies identifying risk factors of suicidal ideation among Asian American adolescents. Since this research utilizes the Youth Risk Behavior Survey, these findings can be compared with risk factors of suicidal ideation among adolescents from other racial/ethnic backgrounds to pinpoint general as well as specific risk factors, thus informing how we can tailor interventions for specific groups.”
According to Dr. Saw, while it’s clear that suicide is a leading cause of death among Asian American adolescents, it’s still unknown which specific subgroups other than girls and LGBTIA+ individuals are especially vulnerable and which culturally tailored interventions are most effective for decreasing suicide risk.
“Psychiatrists should understand that risk and protective factors for suicidal behavior in Asian American adolescents are multifaceted and require careful attention and intervention across different environments,” she said.
No funding and no disclosures were reported.
NEW ORLEANS – In an unexpected finding, researchers discovered that According to a weighted analysis, 24% of Asian Americans reported thinking about or planning suicide vs. 22% of Whites and Blacks and 20% of Hispanics (P < .01).
“We were shocked,” said study lead author Esha Hansoti, MD, who conducted the research at UT Southwestern Medical Center, Dallas, and is now a psychiatry resident at Zucker Hillside Hospital Northwell/Hofstra in Glen Oaks, NY. The findings were released at the annual meeting of the American Psychiatric Association.
Dr. Hansoti and colleagues launched the analysis in light of sparse research into Asian American mental health, she said. Even within this population, she said, mental illness “tends to be overlooked” and discussion of the topic may be considered taboo.
For the new study, researchers analyzed the 2019 Youth Risk Behavior Survey, conducted biennially by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, which had more than 13,000 participants in grades 9-12.
A weighted bivariate analysis of 618 Asian American adolescents – adjusted for age, sex, and depressive symptoms – found no statistically significant impact on suicidal ideation by gender, age, substance use, sexual/physical dating violence, or fluency in English.
However, several groups had a statistically significant higher risk, including victims of forced sexual intercourse and those who were threatened or bullied at school.
Those who didn’t get mostly A grades were also at high risk: Adolescents with mostly Ds and Fs were more likely to have acknowledged suicidal ideation than those with mostly As (adjusted odds ratio [AOR] = 3.2).
Gays and lesbians (AOR = 7.9 vs. heterosexuals), and bisexuals (AOR = 5.2 vs. heterosexuals) also showed sharply higher rates of suicidal ideation.
It’s not clear why Asian American adolescents may be at higher risk of suicidal ideation. The survey was completed prior to the COVID-19 pandemic, which spawned bigotry against people of Asian descent and an ongoing outbreak of high-profile violence against Asian Americans across the country.
Dr. Hansoti noted that Asian Americans face the pressures to live up to the standards of being a “model minority.” In addition, “very few Asian American adolescents are taken to a therapist, and few mental health providers are Asian Americans.”
She urged fellow psychiatrists “to remember that our perceptions of Asian Americans might hinder some of the diagnoses we could be making. Be thoughtful about how their ethnicity and race affects their presentation and their own perception of their illness.”
She added that Asian Americans may experience mental illness and anxiety “more somatically and physically than emotionally.”
In an interview, Anne Saw, PhD, associate professor of clinical-community psychology at DePaul University, Chicago, said the findings are “helpful for corroborating other studies identifying risk factors of suicidal ideation among Asian American adolescents. Since this research utilizes the Youth Risk Behavior Survey, these findings can be compared with risk factors of suicidal ideation among adolescents from other racial/ethnic backgrounds to pinpoint general as well as specific risk factors, thus informing how we can tailor interventions for specific groups.”
According to Dr. Saw, while it’s clear that suicide is a leading cause of death among Asian American adolescents, it’s still unknown which specific subgroups other than girls and LGBTIA+ individuals are especially vulnerable and which culturally tailored interventions are most effective for decreasing suicide risk.
“Psychiatrists should understand that risk and protective factors for suicidal behavior in Asian American adolescents are multifaceted and require careful attention and intervention across different environments,” she said.
No funding and no disclosures were reported.
NEW ORLEANS – In an unexpected finding, researchers discovered that According to a weighted analysis, 24% of Asian Americans reported thinking about or planning suicide vs. 22% of Whites and Blacks and 20% of Hispanics (P < .01).
“We were shocked,” said study lead author Esha Hansoti, MD, who conducted the research at UT Southwestern Medical Center, Dallas, and is now a psychiatry resident at Zucker Hillside Hospital Northwell/Hofstra in Glen Oaks, NY. The findings were released at the annual meeting of the American Psychiatric Association.
Dr. Hansoti and colleagues launched the analysis in light of sparse research into Asian American mental health, she said. Even within this population, she said, mental illness “tends to be overlooked” and discussion of the topic may be considered taboo.
For the new study, researchers analyzed the 2019 Youth Risk Behavior Survey, conducted biennially by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, which had more than 13,000 participants in grades 9-12.
A weighted bivariate analysis of 618 Asian American adolescents – adjusted for age, sex, and depressive symptoms – found no statistically significant impact on suicidal ideation by gender, age, substance use, sexual/physical dating violence, or fluency in English.
However, several groups had a statistically significant higher risk, including victims of forced sexual intercourse and those who were threatened or bullied at school.
Those who didn’t get mostly A grades were also at high risk: Adolescents with mostly Ds and Fs were more likely to have acknowledged suicidal ideation than those with mostly As (adjusted odds ratio [AOR] = 3.2).
Gays and lesbians (AOR = 7.9 vs. heterosexuals), and bisexuals (AOR = 5.2 vs. heterosexuals) also showed sharply higher rates of suicidal ideation.
It’s not clear why Asian American adolescents may be at higher risk of suicidal ideation. The survey was completed prior to the COVID-19 pandemic, which spawned bigotry against people of Asian descent and an ongoing outbreak of high-profile violence against Asian Americans across the country.
Dr. Hansoti noted that Asian Americans face the pressures to live up to the standards of being a “model minority.” In addition, “very few Asian American adolescents are taken to a therapist, and few mental health providers are Asian Americans.”
She urged fellow psychiatrists “to remember that our perceptions of Asian Americans might hinder some of the diagnoses we could be making. Be thoughtful about how their ethnicity and race affects their presentation and their own perception of their illness.”
She added that Asian Americans may experience mental illness and anxiety “more somatically and physically than emotionally.”
In an interview, Anne Saw, PhD, associate professor of clinical-community psychology at DePaul University, Chicago, said the findings are “helpful for corroborating other studies identifying risk factors of suicidal ideation among Asian American adolescents. Since this research utilizes the Youth Risk Behavior Survey, these findings can be compared with risk factors of suicidal ideation among adolescents from other racial/ethnic backgrounds to pinpoint general as well as specific risk factors, thus informing how we can tailor interventions for specific groups.”
According to Dr. Saw, while it’s clear that suicide is a leading cause of death among Asian American adolescents, it’s still unknown which specific subgroups other than girls and LGBTIA+ individuals are especially vulnerable and which culturally tailored interventions are most effective for decreasing suicide risk.
“Psychiatrists should understand that risk and protective factors for suicidal behavior in Asian American adolescents are multifaceted and require careful attention and intervention across different environments,” she said.
No funding and no disclosures were reported.
AT APA 2022
Youth with bipolar disorder at high risk of eating disorders
Investigators studied close to 200 youth with BD and found that more than 25% had a lifetime ED, which included anorexia nervosa (AN), bulimia nervosa (BN), and an ED not otherwise specified (NOS).
Those with comorbid EDs were more likely to be female and to have BD-II subtype. Their presentations were also more complicated and included a history of suicidality, additional psychiatric conditions, smoking, and a history of sexual abuse, as well as more severe depression and emotional instability.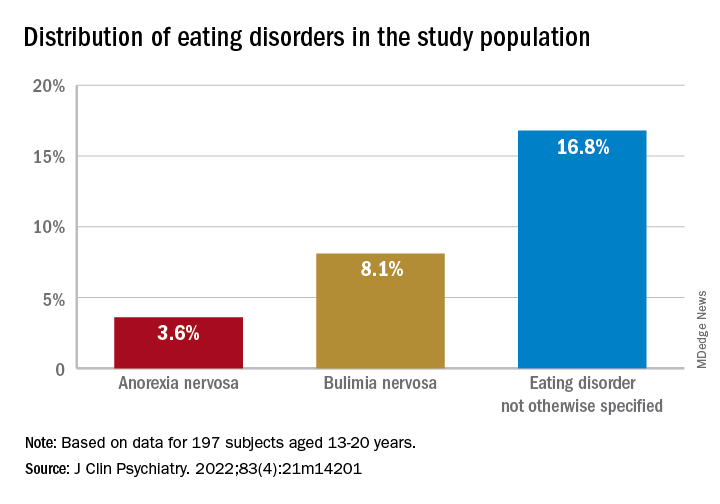
“We think the take-home message is that, in addition to other more recognized psychiatric comorbidities, youth with BD are also vulnerable to developing EDs. Thus, clinicians should be routinely monitoring for eating, appetite, and body image disturbances when working with this population,” lead author Diana Khoubaeva, research analyst at the Centre for Youth Bipolar Disorder, Centre for Addiction and Mental Health, Toronto, and senior author Benjamin Goldstein, MD, PhD, director of the Centre for Youth Bipolar Disorder, wrote in an e-mail to this news organization.
“Given the more complicated clinical picture of youth with co-occurring BD and EDs, this combination warrants careful attention,” the investigators note.
The study was published online May 11 in the Journal of Clinical Psychiatry.
Lack of research
“From the existing literature, we learned that EDs are not uncommon in individuals with BD, and that they are often associated with a more severe clinical profile,” say the researchers. “However, the majority of these studies have been limited to adult samples, and there was a real scarcity of studies that examined this co-occurrence in youth.”
This is “surprising” because EDs often have their onset in adolescence, so the researchers decided to explore the issue in their “fairly large sample of youth with BD.”
To investigate the issue, the researchers studied 197 youth (aged 13-20 years) with a diagnosis of BD (BD-I, BD-II, or BD-NOS) who were recruited between 2009 and 2017 (mean [standard deviation] age, 16.69 [1.50] years; 67.5% female).
ED diagnoses included both current and lifetime AN, BN, and ED-NOS. The researchers used the Kiddie Schedule for Affective Disorders and Schizophrenia for School Age Children, Present and Lifetime Version (K-SADS-PL) to determine the diagnosis of BD.
They also collected information about comorbid psychiatric disorders, as well as substance use disorders and cigarette smoking. The Life Problems Inventory (LPI) was used to identify dimensional borderline personality traits.
Information about physical and sexual abuse, suicidal ideation, nonsuicidal self-injury (NSSI), and affect regulation were obtained from other measurement tools. Participants’ height and weight were measured to calculate body mass index.
Neurobiological and environmental factors
Of the total sample, 24.84% had received a diagnosis of ED in their lifetime.
Moreover, 28.9% had a lifetime history of binge eating. Of these, 17.7% also had been diagnosed with an ED.
Participants with BD-II were significantly more likely than those with BD-I to report both current and lifetime BN. There were no significant differences by BD subtype in AN, ED-NOS, or binge eating.
Higher correlates of clinical characteristics, psychiatric morbidity, treatment history, and dimensional traits in those with vs. those without an ED are detailed in the accompanying table.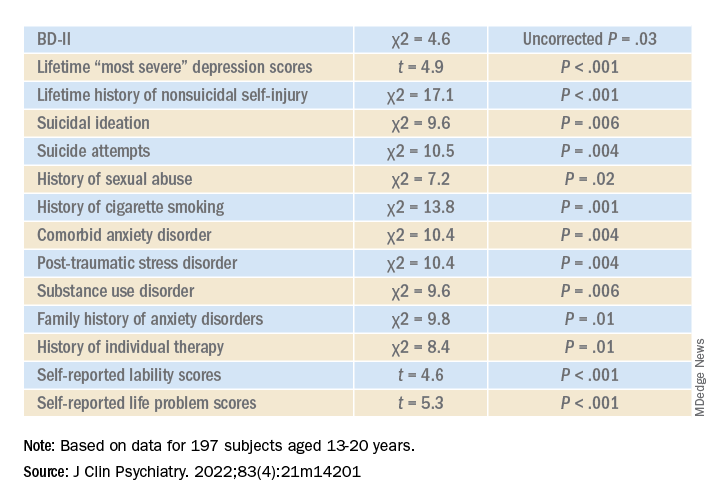
The ED group scored significantly higher on all LPI scores, including impulsivity, emotional dysregulation, identity confusion, and interpersonal problems, compared to those without an ED. They also were less likely to report lifetime lithium use (chi2 = 7.9, P = .01).
Multivariate analysis revealed that lifetime EDs were significantly associated with female sex, history of cigarette smoking, history of individual therapy, family history of anxiety, and LPI total score and were negatively associated with BD-I subtype.
“The comorbidity [between EDs and BD] could be driven by both neurobiological and environmental factors,” Dr. Khoubaeva and Dr. Goldstein noted. EDs and BD “are both illnesses that are fundamentally linked with dysfunction in reward systems – that is, there are imbalances in terms of too much or too little reward seeking.”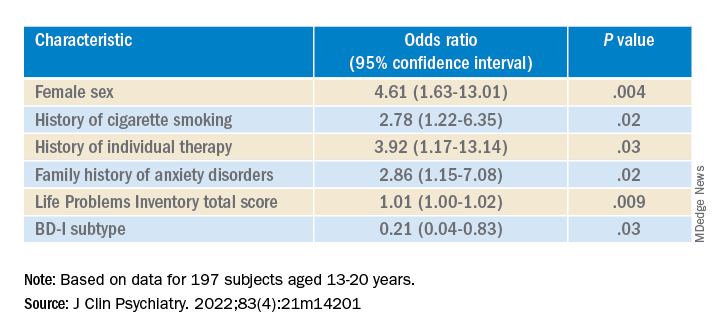
They added that individuals affected by these conditions have “ongoing challenges with instability of emotions and ability to manage emotions; and eating too much or too little can be a manifestation of coping with emotions.”
In addition, medications commonly used to treat BD “are known to have side effects such as weight/appetite/metabolic changes, which may make it harder to regulate eating, and which may exacerbate preexisting body image challenges.”
The researchers recommend implementing trauma-informed care, assessing and addressing suicidality and self-injury, and prioritizing therapies that target emotional dysregulation, such as dialectical behavioral therapy.
‘Clarion call’
Commenting on the study, Roger McIntyre, MD, professor of psychiatry and pharmacology, University of Toronto, and head of the Mood Disorders Psychopharmacology Unit, said the study is “the first of its kind to comprehensively characterize the prevalence of ED in youth living with BD.
“It could be hypothesized that EDs have overlapping domain disturbances of cognitive dysfunction, such as executive function and impulse control, as well as cognitive reward processes,” said Dr. McIntyre, who is the chairman and executive director of the Brain and Cognitive Discover Foundation, Toronto, and was not involved with the study.
“The data are a clarion call for clinicians to routinely screen for EDs in youth with BD and, when present, to be aware of the greater complexity, severity, and risk in this patient subpopulation. The higher prevalence of ED in youth with BD-II is an additional reminder of the severity, morbidity, and complexity of BD-II,” Dr. McIntyre said.
The study received no direct funding. It was supported by philanthropic donations to the Centre for Youth Bipolar Disorder and the CAMH Discovery Fund. Dr. Goldstein reports grant support from Brain Canada, Canadian Institutes of Health Research, Heart and Stroke Foundation, National Institute of Mental Health, and the departments of psychiatry at the University of Toronto and Sunnybrook Health Sciences Centre. He also acknowledges his position as RBC investments chair in Children›s Mental Health and Developmental Psychopathology at CAMH, a joint Hospital-University chair among the University of Toronto, CAMH, and the CAMH Foundation. Ms. Khoubaeva reports no relevant financial relationships. The other authors’ disclosures are listed in the original article. Dr. McIntyre has received research grant support from CIHR/GACD/National Natural Science Foundation of China (NSFC); speaker/consultation fees from Lundbeck, Janssen, Alkermes, Neumora Therapeutics, Mitsubishi Tanabe, Purdue, Pfizer, Otsuka, Takeda, Neurocrine, Sunovion, Bausch Health, Axsome, Novo Nordisk, Kris, Sanofi, Eisai, Intra-Cellular, NewBridge Pharmaceuticals, Abbvie, and Atai Life Sciences. Dr. McIntyre is a CEO of Braxia Scientific.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Investigators studied close to 200 youth with BD and found that more than 25% had a lifetime ED, which included anorexia nervosa (AN), bulimia nervosa (BN), and an ED not otherwise specified (NOS).
Those with comorbid EDs were more likely to be female and to have BD-II subtype. Their presentations were also more complicated and included a history of suicidality, additional psychiatric conditions, smoking, and a history of sexual abuse, as well as more severe depression and emotional instability.
“We think the take-home message is that, in addition to other more recognized psychiatric comorbidities, youth with BD are also vulnerable to developing EDs. Thus, clinicians should be routinely monitoring for eating, appetite, and body image disturbances when working with this population,” lead author Diana Khoubaeva, research analyst at the Centre for Youth Bipolar Disorder, Centre for Addiction and Mental Health, Toronto, and senior author Benjamin Goldstein, MD, PhD, director of the Centre for Youth Bipolar Disorder, wrote in an e-mail to this news organization.
“Given the more complicated clinical picture of youth with co-occurring BD and EDs, this combination warrants careful attention,” the investigators note.
The study was published online May 11 in the Journal of Clinical Psychiatry.
Lack of research
“From the existing literature, we learned that EDs are not uncommon in individuals with BD, and that they are often associated with a more severe clinical profile,” say the researchers. “However, the majority of these studies have been limited to adult samples, and there was a real scarcity of studies that examined this co-occurrence in youth.”
This is “surprising” because EDs often have their onset in adolescence, so the researchers decided to explore the issue in their “fairly large sample of youth with BD.”
To investigate the issue, the researchers studied 197 youth (aged 13-20 years) with a diagnosis of BD (BD-I, BD-II, or BD-NOS) who were recruited between 2009 and 2017 (mean [standard deviation] age, 16.69 [1.50] years; 67.5% female).
ED diagnoses included both current and lifetime AN, BN, and ED-NOS. The researchers used the Kiddie Schedule for Affective Disorders and Schizophrenia for School Age Children, Present and Lifetime Version (K-SADS-PL) to determine the diagnosis of BD.
They also collected information about comorbid psychiatric disorders, as well as substance use disorders and cigarette smoking. The Life Problems Inventory (LPI) was used to identify dimensional borderline personality traits.
Information about physical and sexual abuse, suicidal ideation, nonsuicidal self-injury (NSSI), and affect regulation were obtained from other measurement tools. Participants’ height and weight were measured to calculate body mass index.
Neurobiological and environmental factors
Of the total sample, 24.84% had received a diagnosis of ED in their lifetime.
Moreover, 28.9% had a lifetime history of binge eating. Of these, 17.7% also had been diagnosed with an ED.
Participants with BD-II were significantly more likely than those with BD-I to report both current and lifetime BN. There were no significant differences by BD subtype in AN, ED-NOS, or binge eating.
Higher correlates of clinical characteristics, psychiatric morbidity, treatment history, and dimensional traits in those with vs. those without an ED are detailed in the accompanying table.
The ED group scored significantly higher on all LPI scores, including impulsivity, emotional dysregulation, identity confusion, and interpersonal problems, compared to those without an ED. They also were less likely to report lifetime lithium use (chi2 = 7.9, P = .01).
Multivariate analysis revealed that lifetime EDs were significantly associated with female sex, history of cigarette smoking, history of individual therapy, family history of anxiety, and LPI total score and were negatively associated with BD-I subtype.
“The comorbidity [between EDs and BD] could be driven by both neurobiological and environmental factors,” Dr. Khoubaeva and Dr. Goldstein noted. EDs and BD “are both illnesses that are fundamentally linked with dysfunction in reward systems – that is, there are imbalances in terms of too much or too little reward seeking.”
They added that individuals affected by these conditions have “ongoing challenges with instability of emotions and ability to manage emotions; and eating too much or too little can be a manifestation of coping with emotions.”
In addition, medications commonly used to treat BD “are known to have side effects such as weight/appetite/metabolic changes, which may make it harder to regulate eating, and which may exacerbate preexisting body image challenges.”
The researchers recommend implementing trauma-informed care, assessing and addressing suicidality and self-injury, and prioritizing therapies that target emotional dysregulation, such as dialectical behavioral therapy.
‘Clarion call’
Commenting on the study, Roger McIntyre, MD, professor of psychiatry and pharmacology, University of Toronto, and head of the Mood Disorders Psychopharmacology Unit, said the study is “the first of its kind to comprehensively characterize the prevalence of ED in youth living with BD.
“It could be hypothesized that EDs have overlapping domain disturbances of cognitive dysfunction, such as executive function and impulse control, as well as cognitive reward processes,” said Dr. McIntyre, who is the chairman and executive director of the Brain and Cognitive Discover Foundation, Toronto, and was not involved with the study.
“The data are a clarion call for clinicians to routinely screen for EDs in youth with BD and, when present, to be aware of the greater complexity, severity, and risk in this patient subpopulation. The higher prevalence of ED in youth with BD-II is an additional reminder of the severity, morbidity, and complexity of BD-II,” Dr. McIntyre said.
The study received no direct funding. It was supported by philanthropic donations to the Centre for Youth Bipolar Disorder and the CAMH Discovery Fund. Dr. Goldstein reports grant support from Brain Canada, Canadian Institutes of Health Research, Heart and Stroke Foundation, National Institute of Mental Health, and the departments of psychiatry at the University of Toronto and Sunnybrook Health Sciences Centre. He also acknowledges his position as RBC investments chair in Children›s Mental Health and Developmental Psychopathology at CAMH, a joint Hospital-University chair among the University of Toronto, CAMH, and the CAMH Foundation. Ms. Khoubaeva reports no relevant financial relationships. The other authors’ disclosures are listed in the original article. Dr. McIntyre has received research grant support from CIHR/GACD/National Natural Science Foundation of China (NSFC); speaker/consultation fees from Lundbeck, Janssen, Alkermes, Neumora Therapeutics, Mitsubishi Tanabe, Purdue, Pfizer, Otsuka, Takeda, Neurocrine, Sunovion, Bausch Health, Axsome, Novo Nordisk, Kris, Sanofi, Eisai, Intra-Cellular, NewBridge Pharmaceuticals, Abbvie, and Atai Life Sciences. Dr. McIntyre is a CEO of Braxia Scientific.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Investigators studied close to 200 youth with BD and found that more than 25% had a lifetime ED, which included anorexia nervosa (AN), bulimia nervosa (BN), and an ED not otherwise specified (NOS).
Those with comorbid EDs were more likely to be female and to have BD-II subtype. Their presentations were also more complicated and included a history of suicidality, additional psychiatric conditions, smoking, and a history of sexual abuse, as well as more severe depression and emotional instability.
“We think the take-home message is that, in addition to other more recognized psychiatric comorbidities, youth with BD are also vulnerable to developing EDs. Thus, clinicians should be routinely monitoring for eating, appetite, and body image disturbances when working with this population,” lead author Diana Khoubaeva, research analyst at the Centre for Youth Bipolar Disorder, Centre for Addiction and Mental Health, Toronto, and senior author Benjamin Goldstein, MD, PhD, director of the Centre for Youth Bipolar Disorder, wrote in an e-mail to this news organization.
“Given the more complicated clinical picture of youth with co-occurring BD and EDs, this combination warrants careful attention,” the investigators note.
The study was published online May 11 in the Journal of Clinical Psychiatry.
Lack of research
“From the existing literature, we learned that EDs are not uncommon in individuals with BD, and that they are often associated with a more severe clinical profile,” say the researchers. “However, the majority of these studies have been limited to adult samples, and there was a real scarcity of studies that examined this co-occurrence in youth.”
This is “surprising” because EDs often have their onset in adolescence, so the researchers decided to explore the issue in their “fairly large sample of youth with BD.”
To investigate the issue, the researchers studied 197 youth (aged 13-20 years) with a diagnosis of BD (BD-I, BD-II, or BD-NOS) who were recruited between 2009 and 2017 (mean [standard deviation] age, 16.69 [1.50] years; 67.5% female).
ED diagnoses included both current and lifetime AN, BN, and ED-NOS. The researchers used the Kiddie Schedule for Affective Disorders and Schizophrenia for School Age Children, Present and Lifetime Version (K-SADS-PL) to determine the diagnosis of BD.
They also collected information about comorbid psychiatric disorders, as well as substance use disorders and cigarette smoking. The Life Problems Inventory (LPI) was used to identify dimensional borderline personality traits.
Information about physical and sexual abuse, suicidal ideation, nonsuicidal self-injury (NSSI), and affect regulation were obtained from other measurement tools. Participants’ height and weight were measured to calculate body mass index.
Neurobiological and environmental factors
Of the total sample, 24.84% had received a diagnosis of ED in their lifetime.
Moreover, 28.9% had a lifetime history of binge eating. Of these, 17.7% also had been diagnosed with an ED.
Participants with BD-II were significantly more likely than those with BD-I to report both current and lifetime BN. There were no significant differences by BD subtype in AN, ED-NOS, or binge eating.
Higher correlates of clinical characteristics, psychiatric morbidity, treatment history, and dimensional traits in those with vs. those without an ED are detailed in the accompanying table.
The ED group scored significantly higher on all LPI scores, including impulsivity, emotional dysregulation, identity confusion, and interpersonal problems, compared to those without an ED. They also were less likely to report lifetime lithium use (chi2 = 7.9, P = .01).
Multivariate analysis revealed that lifetime EDs were significantly associated with female sex, history of cigarette smoking, history of individual therapy, family history of anxiety, and LPI total score and were negatively associated with BD-I subtype.
“The comorbidity [between EDs and BD] could be driven by both neurobiological and environmental factors,” Dr. Khoubaeva and Dr. Goldstein noted. EDs and BD “are both illnesses that are fundamentally linked with dysfunction in reward systems – that is, there are imbalances in terms of too much or too little reward seeking.”
They added that individuals affected by these conditions have “ongoing challenges with instability of emotions and ability to manage emotions; and eating too much or too little can be a manifestation of coping with emotions.”
In addition, medications commonly used to treat BD “are known to have side effects such as weight/appetite/metabolic changes, which may make it harder to regulate eating, and which may exacerbate preexisting body image challenges.”
The researchers recommend implementing trauma-informed care, assessing and addressing suicidality and self-injury, and prioritizing therapies that target emotional dysregulation, such as dialectical behavioral therapy.
‘Clarion call’
Commenting on the study, Roger McIntyre, MD, professor of psychiatry and pharmacology, University of Toronto, and head of the Mood Disorders Psychopharmacology Unit, said the study is “the first of its kind to comprehensively characterize the prevalence of ED in youth living with BD.
“It could be hypothesized that EDs have overlapping domain disturbances of cognitive dysfunction, such as executive function and impulse control, as well as cognitive reward processes,” said Dr. McIntyre, who is the chairman and executive director of the Brain and Cognitive Discover Foundation, Toronto, and was not involved with the study.
“The data are a clarion call for clinicians to routinely screen for EDs in youth with BD and, when present, to be aware of the greater complexity, severity, and risk in this patient subpopulation. The higher prevalence of ED in youth with BD-II is an additional reminder of the severity, morbidity, and complexity of BD-II,” Dr. McIntyre said.
The study received no direct funding. It was supported by philanthropic donations to the Centre for Youth Bipolar Disorder and the CAMH Discovery Fund. Dr. Goldstein reports grant support from Brain Canada, Canadian Institutes of Health Research, Heart and Stroke Foundation, National Institute of Mental Health, and the departments of psychiatry at the University of Toronto and Sunnybrook Health Sciences Centre. He also acknowledges his position as RBC investments chair in Children›s Mental Health and Developmental Psychopathology at CAMH, a joint Hospital-University chair among the University of Toronto, CAMH, and the CAMH Foundation. Ms. Khoubaeva reports no relevant financial relationships. The other authors’ disclosures are listed in the original article. Dr. McIntyre has received research grant support from CIHR/GACD/National Natural Science Foundation of China (NSFC); speaker/consultation fees from Lundbeck, Janssen, Alkermes, Neumora Therapeutics, Mitsubishi Tanabe, Purdue, Pfizer, Otsuka, Takeda, Neurocrine, Sunovion, Bausch Health, Axsome, Novo Nordisk, Kris, Sanofi, Eisai, Intra-Cellular, NewBridge Pharmaceuticals, Abbvie, and Atai Life Sciences. Dr. McIntyre is a CEO of Braxia Scientific.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM THE JOURNAL OF CLINICAL PSYCHIATRY
Genetic testing for best antidepressant accurate, cost effective
new research suggests.
CYP2D6 and CYP2C19, from the cytochrome P450 family, are involved in the metabolism and elimination of various molecules, including medications. Variants in the genes encoding these enzymes affect the speed at which drugs are metabolized, altering their pharmacokinetic profiles.
The researchers studied 125 patients with MDD and used CYP2D6 and CYP2C19 genotyping to determine the presence of actionable phenotypes in line with Food and Drug Administration labeling.
They found that, in many cases, pharmacogenetic testing could have predicted poor response to the initial treatment selection and could have helped guide subsequent choices to improve outcomes.
In addition, a pharmacoeconomic evaluation that combined direct and indirect costs resulting from MDD with the prevalence of CYP2D6 and CYP2C19 phenotypes showed that testing for functional variants in both genes would be cost effective at a national level.
Had psychiatrists who treated patients in the study known about their metabolizing profiles, it “might have contributed to switches in medication” and could have reduced “delays in response,” said lead researcher Alessio Squassina, PhD, associate professor of pharmacology at the University of Cagliari (Italy).
The findings were presented at the European Psychiatric Association 2022 Congress.
Highly variable response rates
Dr. Squassina noted that the response to antidepressants is a “highly variable trait,” and while it is known that genetics play a role, their contribution is “still not completely understood.”
He explained that the use of pharmacogenetics, which leverages genetic information to guide treatment decision-making, has increased significantly.
While regulatory bodies, including the FDA, have been “very active” in defining strict criteria for interpreting the information from pharmacogenetic tests, there remains some “discrepancy” in their clinical utility.
Dr. Squassina said the FDA provides guidance on use of genetic testing on the labels of 34 psychiatric medications. Of these, 79% relate to CYP2D6, 12% relate to CYP2C19, and 9% relate to other genes.
These labels provide guidance on when genetic testing is recommended or required, as well as potentially clinically actionable gene-drug associations in patients with certain functional alleles.
However, Dr. Squassina noted that the distribution of such alleles is not the same across Europe, so it’s possible that a psychiatrist in Italy may be less likely to treat a patient with a phenotype affecting response to treatment or risk of adverse events than one in Norway or Sweden.
For the study, the investigators examined the frequency of CYP2D6 and CYP2C19 phenotypes in psychiatric patients in Sardinia and their relationship with pharmacologic treatment and cost-effectiveness.
They set out to recruit 200 patients with MDD who had a documented 5-year medical and treatment history, including alterations in treatment, adverse events, hospitalizations, suicide, and symptom scores, as well as sociodemographic variables.
An interim analysis of the first 125 patients recruited to the study showed that the most common CYP2D6 phenotype was normal metabolizers (NM), at 60.5%, followed by intermediate metabolizers (IM), at 28.2%, ultrarapid metabolizers (UR), at 8.9%, and poor metabolizers (PM), at 2.4%.
For CYP2C19, the most common phenotype was NM (49%), followed by IM (29.0%), UR (25.0%), and PM (4.0%). While there were differences in the overall European averages, they were not significant.
To highlight the potential impact that pharmacogenetic testing could have had on patient care and outcome, Dr. Squassina highlighted two cases.
The first concerned a patient with a CYP2D6 IM and CYP2C19 UR phenotype, who did not respond to escitalopram. The FDA drug label indicates this phenotype is actionable and recommends an alternative drug.
The patient was subsequently switched to venlafaxine. The FDA drug label on venlafaxine notes that patients with this phenotype are likely to have a suboptimal response to this drug, and again, this patient did not respond to treatment.
Another patient with a CYP2D6 NM and CYP2C19 IM phenotype was also prescribed escitalopram. The FDA label on this drug notes that patients with this phenotype can try venlafaxine but may not respond. Indeed, this patient did not respond and was switched to venlafaxine and started responding.
“The psychiatrists [in these cases] may made have made different [drug] choices if they had known the genotypes in advance,” Dr. Squassina said.
Cost effective?
To determine the cost-effectiveness of screening for CYP2D6 and CYP2C19 phenotypes in patients with MDD, the researchers used real-world data to develop a Markov model with a hypothetical cohort of 2000 MDD patients, half of whom underwent pharmacogenetic testing, to determine the potential impact on outcomes over an 18-week period.
The model included the cost of medications and hospitalization, psychiatric counseling, loss of productivity, and the estimated probability of response and adverse events, adjusted for the patient’s likelihood of having a particular metabolizing phenotype.
Results showed that, for CYP2C19, compared to no testing, pharmacogenetic testing would be cost-effective at an incremental cost-effective ratio (ICER) of €60,000 ($64,000 USD) per quality-adjusted life-year (QALY).
This, Squassina said, is “below the willingness to pay threshold” for health authorities in developed countries.
For CYP2D6, pharmacogenetic testing would become cost-effective at an ICER of approximately €47,000 ($40,000 USD) per QALY.
The team plans to complete recruitment and perform a “detailed evaluation of all the variables, especially those relating to the medication history and changes in dosage, and adverse drug reactions.” The researchers would also like to study genetic phenotypes for other metabolizing enzymes and repeat the pharmacoeconomic analysis with the complete dataset.
A glimpse into the future
Approached for comment, Alessandro Serretti, MD, PhD, department of biomedical and neuromotor sciences, University of Bologna (Italy), who was not involved in the study, said the findings show there is a “small but evident benefit” from CYP profiling, “which makes sense.”
He added that in the Netherlands and other European countries, efforts are already underway to record the CYP status of patients at a national level. “Sooner or later, all Western countries will implement it as a routine,” he said in an interview.
He explained that, when such testing is widely available, electronic health record data will allow physicians to immediately select the optimal antidepressant for an individual patient. This will end the current trial-and-error process that leads to delayed treatment and will help avoid serious consequences, such as suicide.
While reducing a single patient’s treatment by a few weeks with the most appropriate antidepressant choice does not make a large difference in the cost per episode, at a population level, it has the potential to make a significant difference.
Dr. Serretti does not envisage genotyping all 333 million Europeans for the CYP phenotype at this point but imagines that in the future, individuals will undergo whole-genome sequencing to determine risks for cancer, dementia, and heart disease, at which point they will also undergo CYP functional allele profiling, and all these data will be recorded on individuals’ EHR.
“So, every doctor, a psychiatrist or cardiologist, can see everything, whenever they need it,” he said.
The study was funded by Fondazione di Sardegna and Regione Autonoma della Sardegna. The authors disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
new research suggests.
CYP2D6 and CYP2C19, from the cytochrome P450 family, are involved in the metabolism and elimination of various molecules, including medications. Variants in the genes encoding these enzymes affect the speed at which drugs are metabolized, altering their pharmacokinetic profiles.
The researchers studied 125 patients with MDD and used CYP2D6 and CYP2C19 genotyping to determine the presence of actionable phenotypes in line with Food and Drug Administration labeling.
They found that, in many cases, pharmacogenetic testing could have predicted poor response to the initial treatment selection and could have helped guide subsequent choices to improve outcomes.
In addition, a pharmacoeconomic evaluation that combined direct and indirect costs resulting from MDD with the prevalence of CYP2D6 and CYP2C19 phenotypes showed that testing for functional variants in both genes would be cost effective at a national level.
Had psychiatrists who treated patients in the study known about their metabolizing profiles, it “might have contributed to switches in medication” and could have reduced “delays in response,” said lead researcher Alessio Squassina, PhD, associate professor of pharmacology at the University of Cagliari (Italy).
The findings were presented at the European Psychiatric Association 2022 Congress.
Highly variable response rates
Dr. Squassina noted that the response to antidepressants is a “highly variable trait,” and while it is known that genetics play a role, their contribution is “still not completely understood.”
He explained that the use of pharmacogenetics, which leverages genetic information to guide treatment decision-making, has increased significantly.
While regulatory bodies, including the FDA, have been “very active” in defining strict criteria for interpreting the information from pharmacogenetic tests, there remains some “discrepancy” in their clinical utility.
Dr. Squassina said the FDA provides guidance on use of genetic testing on the labels of 34 psychiatric medications. Of these, 79% relate to CYP2D6, 12% relate to CYP2C19, and 9% relate to other genes.
These labels provide guidance on when genetic testing is recommended or required, as well as potentially clinically actionable gene-drug associations in patients with certain functional alleles.
However, Dr. Squassina noted that the distribution of such alleles is not the same across Europe, so it’s possible that a psychiatrist in Italy may be less likely to treat a patient with a phenotype affecting response to treatment or risk of adverse events than one in Norway or Sweden.
For the study, the investigators examined the frequency of CYP2D6 and CYP2C19 phenotypes in psychiatric patients in Sardinia and their relationship with pharmacologic treatment and cost-effectiveness.
They set out to recruit 200 patients with MDD who had a documented 5-year medical and treatment history, including alterations in treatment, adverse events, hospitalizations, suicide, and symptom scores, as well as sociodemographic variables.
An interim analysis of the first 125 patients recruited to the study showed that the most common CYP2D6 phenotype was normal metabolizers (NM), at 60.5%, followed by intermediate metabolizers (IM), at 28.2%, ultrarapid metabolizers (UR), at 8.9%, and poor metabolizers (PM), at 2.4%.
For CYP2C19, the most common phenotype was NM (49%), followed by IM (29.0%), UR (25.0%), and PM (4.0%). While there were differences in the overall European averages, they were not significant.
To highlight the potential impact that pharmacogenetic testing could have had on patient care and outcome, Dr. Squassina highlighted two cases.
The first concerned a patient with a CYP2D6 IM and CYP2C19 UR phenotype, who did not respond to escitalopram. The FDA drug label indicates this phenotype is actionable and recommends an alternative drug.
The patient was subsequently switched to venlafaxine. The FDA drug label on venlafaxine notes that patients with this phenotype are likely to have a suboptimal response to this drug, and again, this patient did not respond to treatment.
Another patient with a CYP2D6 NM and CYP2C19 IM phenotype was also prescribed escitalopram. The FDA label on this drug notes that patients with this phenotype can try venlafaxine but may not respond. Indeed, this patient did not respond and was switched to venlafaxine and started responding.
“The psychiatrists [in these cases] may made have made different [drug] choices if they had known the genotypes in advance,” Dr. Squassina said.
Cost effective?
To determine the cost-effectiveness of screening for CYP2D6 and CYP2C19 phenotypes in patients with MDD, the researchers used real-world data to develop a Markov model with a hypothetical cohort of 2000 MDD patients, half of whom underwent pharmacogenetic testing, to determine the potential impact on outcomes over an 18-week period.
The model included the cost of medications and hospitalization, psychiatric counseling, loss of productivity, and the estimated probability of response and adverse events, adjusted for the patient’s likelihood of having a particular metabolizing phenotype.
Results showed that, for CYP2C19, compared to no testing, pharmacogenetic testing would be cost-effective at an incremental cost-effective ratio (ICER) of €60,000 ($64,000 USD) per quality-adjusted life-year (QALY).
This, Squassina said, is “below the willingness to pay threshold” for health authorities in developed countries.
For CYP2D6, pharmacogenetic testing would become cost-effective at an ICER of approximately €47,000 ($40,000 USD) per QALY.
The team plans to complete recruitment and perform a “detailed evaluation of all the variables, especially those relating to the medication history and changes in dosage, and adverse drug reactions.” The researchers would also like to study genetic phenotypes for other metabolizing enzymes and repeat the pharmacoeconomic analysis with the complete dataset.
A glimpse into the future
Approached for comment, Alessandro Serretti, MD, PhD, department of biomedical and neuromotor sciences, University of Bologna (Italy), who was not involved in the study, said the findings show there is a “small but evident benefit” from CYP profiling, “which makes sense.”
He added that in the Netherlands and other European countries, efforts are already underway to record the CYP status of patients at a national level. “Sooner or later, all Western countries will implement it as a routine,” he said in an interview.
He explained that, when such testing is widely available, electronic health record data will allow physicians to immediately select the optimal antidepressant for an individual patient. This will end the current trial-and-error process that leads to delayed treatment and will help avoid serious consequences, such as suicide.
While reducing a single patient’s treatment by a few weeks with the most appropriate antidepressant choice does not make a large difference in the cost per episode, at a population level, it has the potential to make a significant difference.
Dr. Serretti does not envisage genotyping all 333 million Europeans for the CYP phenotype at this point but imagines that in the future, individuals will undergo whole-genome sequencing to determine risks for cancer, dementia, and heart disease, at which point they will also undergo CYP functional allele profiling, and all these data will be recorded on individuals’ EHR.
“So, every doctor, a psychiatrist or cardiologist, can see everything, whenever they need it,” he said.
The study was funded by Fondazione di Sardegna and Regione Autonoma della Sardegna. The authors disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
new research suggests.
CYP2D6 and CYP2C19, from the cytochrome P450 family, are involved in the metabolism and elimination of various molecules, including medications. Variants in the genes encoding these enzymes affect the speed at which drugs are metabolized, altering their pharmacokinetic profiles.
The researchers studied 125 patients with MDD and used CYP2D6 and CYP2C19 genotyping to determine the presence of actionable phenotypes in line with Food and Drug Administration labeling.
They found that, in many cases, pharmacogenetic testing could have predicted poor response to the initial treatment selection and could have helped guide subsequent choices to improve outcomes.
In addition, a pharmacoeconomic evaluation that combined direct and indirect costs resulting from MDD with the prevalence of CYP2D6 and CYP2C19 phenotypes showed that testing for functional variants in both genes would be cost effective at a national level.
Had psychiatrists who treated patients in the study known about their metabolizing profiles, it “might have contributed to switches in medication” and could have reduced “delays in response,” said lead researcher Alessio Squassina, PhD, associate professor of pharmacology at the University of Cagliari (Italy).
The findings were presented at the European Psychiatric Association 2022 Congress.
Highly variable response rates
Dr. Squassina noted that the response to antidepressants is a “highly variable trait,” and while it is known that genetics play a role, their contribution is “still not completely understood.”
He explained that the use of pharmacogenetics, which leverages genetic information to guide treatment decision-making, has increased significantly.
While regulatory bodies, including the FDA, have been “very active” in defining strict criteria for interpreting the information from pharmacogenetic tests, there remains some “discrepancy” in their clinical utility.
Dr. Squassina said the FDA provides guidance on use of genetic testing on the labels of 34 psychiatric medications. Of these, 79% relate to CYP2D6, 12% relate to CYP2C19, and 9% relate to other genes.
These labels provide guidance on when genetic testing is recommended or required, as well as potentially clinically actionable gene-drug associations in patients with certain functional alleles.
However, Dr. Squassina noted that the distribution of such alleles is not the same across Europe, so it’s possible that a psychiatrist in Italy may be less likely to treat a patient with a phenotype affecting response to treatment or risk of adverse events than one in Norway or Sweden.
For the study, the investigators examined the frequency of CYP2D6 and CYP2C19 phenotypes in psychiatric patients in Sardinia and their relationship with pharmacologic treatment and cost-effectiveness.
They set out to recruit 200 patients with MDD who had a documented 5-year medical and treatment history, including alterations in treatment, adverse events, hospitalizations, suicide, and symptom scores, as well as sociodemographic variables.
An interim analysis of the first 125 patients recruited to the study showed that the most common CYP2D6 phenotype was normal metabolizers (NM), at 60.5%, followed by intermediate metabolizers (IM), at 28.2%, ultrarapid metabolizers (UR), at 8.9%, and poor metabolizers (PM), at 2.4%.
For CYP2C19, the most common phenotype was NM (49%), followed by IM (29.0%), UR (25.0%), and PM (4.0%). While there were differences in the overall European averages, they were not significant.
To highlight the potential impact that pharmacogenetic testing could have had on patient care and outcome, Dr. Squassina highlighted two cases.
The first concerned a patient with a CYP2D6 IM and CYP2C19 UR phenotype, who did not respond to escitalopram. The FDA drug label indicates this phenotype is actionable and recommends an alternative drug.
The patient was subsequently switched to venlafaxine. The FDA drug label on venlafaxine notes that patients with this phenotype are likely to have a suboptimal response to this drug, and again, this patient did not respond to treatment.
Another patient with a CYP2D6 NM and CYP2C19 IM phenotype was also prescribed escitalopram. The FDA label on this drug notes that patients with this phenotype can try venlafaxine but may not respond. Indeed, this patient did not respond and was switched to venlafaxine and started responding.
“The psychiatrists [in these cases] may made have made different [drug] choices if they had known the genotypes in advance,” Dr. Squassina said.
Cost effective?
To determine the cost-effectiveness of screening for CYP2D6 and CYP2C19 phenotypes in patients with MDD, the researchers used real-world data to develop a Markov model with a hypothetical cohort of 2000 MDD patients, half of whom underwent pharmacogenetic testing, to determine the potential impact on outcomes over an 18-week period.
The model included the cost of medications and hospitalization, psychiatric counseling, loss of productivity, and the estimated probability of response and adverse events, adjusted for the patient’s likelihood of having a particular metabolizing phenotype.
Results showed that, for CYP2C19, compared to no testing, pharmacogenetic testing would be cost-effective at an incremental cost-effective ratio (ICER) of €60,000 ($64,000 USD) per quality-adjusted life-year (QALY).
This, Squassina said, is “below the willingness to pay threshold” for health authorities in developed countries.
For CYP2D6, pharmacogenetic testing would become cost-effective at an ICER of approximately €47,000 ($40,000 USD) per QALY.
The team plans to complete recruitment and perform a “detailed evaluation of all the variables, especially those relating to the medication history and changes in dosage, and adverse drug reactions.” The researchers would also like to study genetic phenotypes for other metabolizing enzymes and repeat the pharmacoeconomic analysis with the complete dataset.
A glimpse into the future
Approached for comment, Alessandro Serretti, MD, PhD, department of biomedical and neuromotor sciences, University of Bologna (Italy), who was not involved in the study, said the findings show there is a “small but evident benefit” from CYP profiling, “which makes sense.”
He added that in the Netherlands and other European countries, efforts are already underway to record the CYP status of patients at a national level. “Sooner or later, all Western countries will implement it as a routine,” he said in an interview.
He explained that, when such testing is widely available, electronic health record data will allow physicians to immediately select the optimal antidepressant for an individual patient. This will end the current trial-and-error process that leads to delayed treatment and will help avoid serious consequences, such as suicide.
While reducing a single patient’s treatment by a few weeks with the most appropriate antidepressant choice does not make a large difference in the cost per episode, at a population level, it has the potential to make a significant difference.
Dr. Serretti does not envisage genotyping all 333 million Europeans for the CYP phenotype at this point but imagines that in the future, individuals will undergo whole-genome sequencing to determine risks for cancer, dementia, and heart disease, at which point they will also undergo CYP functional allele profiling, and all these data will be recorded on individuals’ EHR.
“So, every doctor, a psychiatrist or cardiologist, can see everything, whenever they need it,” he said.
The study was funded by Fondazione di Sardegna and Regione Autonoma della Sardegna. The authors disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM EPA 2022
Alcohol, degraded sleep related in young adults
CHARLOTTE, N.C. – Sleep and alcohol consumption in young adults seems to follow a “vicious cycle,” as one observer called it. and those who went to bed earlier and slept longer tended to drink less the next day, a study of drinking and sleeping habits in 21- to 29-year-olds found.
“Sleep is a potential factor that we could intervene on to really identify how to improve drinking behaviors among young adults,” David Reichenberger, a graduate student at Penn State University, University Park, said in an interview after he presented his findings at the annual meeting of the Associated Professional Sleep Societies.
This is one of the few studies of alcohol consumption and sleep patterns that used an objective measure of alcohol consumption, Mr. Reichenberger said. The study evaluated sleep and alcohol consumption patterns in 222 regularly drinking young adults over 6 consecutive days. Study participants completed morning smartphone-based questionnaires, reporting their previous night’s bedtime, sleep duration, sleep quality, and number of drinks consumed. They also wore an alcohol monitor that continuously measured their transdermal alcohol consumption (TAC).
The study analyzed the data using two sets of multilevel models: A linear model that looked at how each drinking predictor was associated with each sleep variable and a Poisson model to determine how sleep predicted next-day alcohol use.
“We found that higher average peak TAC – that is, how intoxicated they got – was associated with a 19-minute later bedtime among young adults,” Mr. Reichenberger said. “Later bedtimes were then associated with a 26% greater TAC among those adults” (P < .02).
Patterns of alcohol consumption and sleep
On days when participants recorded a higher peak TAC, bedtime was delayed, sleep duration was shorter, and subjective sleep quality was worse, he said. However, none of the sleep variables predicted next-day peak TAC.
“We found an association between the duration of the drinking episode and later bedtimes among young adults,” he added. “And on days when the drinking episodes were longer, subsequent sleep was delayed and sleep quality was worse. But we also found that after nights when they had a later bedtime, next-day drinking episodes were about 7% longer.”
Conversely, young adults who had earlier bedtimes and longer sleep durations tended to consume fewer drinks and they achieved lower intoxication levels the next day, Mr. Reichenberger said.
Between-person results showed that young adults who tended to go to bed later drank on average 24% more the next day (P < .01). Also, each extra hour of sleep was associated with a 14% decrease in drinking the next day (P < .03).
Participants who drank more went to bed on average 12-19 minutes later (P < .01) and slept 5 fewer minutes (P < .01). Within-person results showed that on nights when participants drank more than usual they went to bed 8-13 minutes later (P < .01), slept 2-4 fewer minutes (P < .03), and had worse sleep quality (P < .01).
Mr. Reichenberger acknowledged one limitation of the study: Measuring sleep and alcohol consumption patterns over 6 days might not be long enough. Future studies should address that.
A ‘vicious cycle’
Hans P.A. Van Dongen, PhD, director of the Sleep and Performance Research Center at Washington State University, Spokane, said in an interview that the findings imply a “vicious cycle” between sleep and alcohol consumption. “You create a problem and then it perpetuates itself or reinforces itself.”
In older adults, alcohol tends to act as a “sleep aid,” Dr. Van Dongen noted. “Then it disrupts their sleep later on and then the next night they need to use the sleep aid again because they had a really poor night and they’re tired and they want to fall asleep.”
He added: “I think what is new here is that’s not very likely the mechanism that they’re using alcohol as a sleep aid in younger adults that we see in older adults, so I think there is a new element to it. Now does anybody know how that works exactly? No, that’s the next thing.”
The Penn State study identifies “a signal there that needs to be followed up on,” Dr. Van Dongen said. “There’s something nature’s trying to tell us but it’s not exactly clear what it’s trying to tell us.”
The National Institute on Drug Abuse provided funding for the study. Mr. Reichenberger has no relevant disclosures. Dr. Van Dongen has no disclosures to report.
CHARLOTTE, N.C. – Sleep and alcohol consumption in young adults seems to follow a “vicious cycle,” as one observer called it. and those who went to bed earlier and slept longer tended to drink less the next day, a study of drinking and sleeping habits in 21- to 29-year-olds found.
“Sleep is a potential factor that we could intervene on to really identify how to improve drinking behaviors among young adults,” David Reichenberger, a graduate student at Penn State University, University Park, said in an interview after he presented his findings at the annual meeting of the Associated Professional Sleep Societies.
This is one of the few studies of alcohol consumption and sleep patterns that used an objective measure of alcohol consumption, Mr. Reichenberger said. The study evaluated sleep and alcohol consumption patterns in 222 regularly drinking young adults over 6 consecutive days. Study participants completed morning smartphone-based questionnaires, reporting their previous night’s bedtime, sleep duration, sleep quality, and number of drinks consumed. They also wore an alcohol monitor that continuously measured their transdermal alcohol consumption (TAC).
The study analyzed the data using two sets of multilevel models: A linear model that looked at how each drinking predictor was associated with each sleep variable and a Poisson model to determine how sleep predicted next-day alcohol use.
“We found that higher average peak TAC – that is, how intoxicated they got – was associated with a 19-minute later bedtime among young adults,” Mr. Reichenberger said. “Later bedtimes were then associated with a 26% greater TAC among those adults” (P < .02).
Patterns of alcohol consumption and sleep
On days when participants recorded a higher peak TAC, bedtime was delayed, sleep duration was shorter, and subjective sleep quality was worse, he said. However, none of the sleep variables predicted next-day peak TAC.
“We found an association between the duration of the drinking episode and later bedtimes among young adults,” he added. “And on days when the drinking episodes were longer, subsequent sleep was delayed and sleep quality was worse. But we also found that after nights when they had a later bedtime, next-day drinking episodes were about 7% longer.”
Conversely, young adults who had earlier bedtimes and longer sleep durations tended to consume fewer drinks and they achieved lower intoxication levels the next day, Mr. Reichenberger said.
Between-person results showed that young adults who tended to go to bed later drank on average 24% more the next day (P < .01). Also, each extra hour of sleep was associated with a 14% decrease in drinking the next day (P < .03).
Participants who drank more went to bed on average 12-19 minutes later (P < .01) and slept 5 fewer minutes (P < .01). Within-person results showed that on nights when participants drank more than usual they went to bed 8-13 minutes later (P < .01), slept 2-4 fewer minutes (P < .03), and had worse sleep quality (P < .01).
Mr. Reichenberger acknowledged one limitation of the study: Measuring sleep and alcohol consumption patterns over 6 days might not be long enough. Future studies should address that.
A ‘vicious cycle’
Hans P.A. Van Dongen, PhD, director of the Sleep and Performance Research Center at Washington State University, Spokane, said in an interview that the findings imply a “vicious cycle” between sleep and alcohol consumption. “You create a problem and then it perpetuates itself or reinforces itself.”
In older adults, alcohol tends to act as a “sleep aid,” Dr. Van Dongen noted. “Then it disrupts their sleep later on and then the next night they need to use the sleep aid again because they had a really poor night and they’re tired and they want to fall asleep.”
He added: “I think what is new here is that’s not very likely the mechanism that they’re using alcohol as a sleep aid in younger adults that we see in older adults, so I think there is a new element to it. Now does anybody know how that works exactly? No, that’s the next thing.”
The Penn State study identifies “a signal there that needs to be followed up on,” Dr. Van Dongen said. “There’s something nature’s trying to tell us but it’s not exactly clear what it’s trying to tell us.”
The National Institute on Drug Abuse provided funding for the study. Mr. Reichenberger has no relevant disclosures. Dr. Van Dongen has no disclosures to report.
CHARLOTTE, N.C. – Sleep and alcohol consumption in young adults seems to follow a “vicious cycle,” as one observer called it. and those who went to bed earlier and slept longer tended to drink less the next day, a study of drinking and sleeping habits in 21- to 29-year-olds found.
“Sleep is a potential factor that we could intervene on to really identify how to improve drinking behaviors among young adults,” David Reichenberger, a graduate student at Penn State University, University Park, said in an interview after he presented his findings at the annual meeting of the Associated Professional Sleep Societies.
This is one of the few studies of alcohol consumption and sleep patterns that used an objective measure of alcohol consumption, Mr. Reichenberger said. The study evaluated sleep and alcohol consumption patterns in 222 regularly drinking young adults over 6 consecutive days. Study participants completed morning smartphone-based questionnaires, reporting their previous night’s bedtime, sleep duration, sleep quality, and number of drinks consumed. They also wore an alcohol monitor that continuously measured their transdermal alcohol consumption (TAC).
The study analyzed the data using two sets of multilevel models: A linear model that looked at how each drinking predictor was associated with each sleep variable and a Poisson model to determine how sleep predicted next-day alcohol use.
“We found that higher average peak TAC – that is, how intoxicated they got – was associated with a 19-minute later bedtime among young adults,” Mr. Reichenberger said. “Later bedtimes were then associated with a 26% greater TAC among those adults” (P < .02).
Patterns of alcohol consumption and sleep
On days when participants recorded a higher peak TAC, bedtime was delayed, sleep duration was shorter, and subjective sleep quality was worse, he said. However, none of the sleep variables predicted next-day peak TAC.
“We found an association between the duration of the drinking episode and later bedtimes among young adults,” he added. “And on days when the drinking episodes were longer, subsequent sleep was delayed and sleep quality was worse. But we also found that after nights when they had a later bedtime, next-day drinking episodes were about 7% longer.”
Conversely, young adults who had earlier bedtimes and longer sleep durations tended to consume fewer drinks and they achieved lower intoxication levels the next day, Mr. Reichenberger said.
Between-person results showed that young adults who tended to go to bed later drank on average 24% more the next day (P < .01). Also, each extra hour of sleep was associated with a 14% decrease in drinking the next day (P < .03).
Participants who drank more went to bed on average 12-19 minutes later (P < .01) and slept 5 fewer minutes (P < .01). Within-person results showed that on nights when participants drank more than usual they went to bed 8-13 minutes later (P < .01), slept 2-4 fewer minutes (P < .03), and had worse sleep quality (P < .01).
Mr. Reichenberger acknowledged one limitation of the study: Measuring sleep and alcohol consumption patterns over 6 days might not be long enough. Future studies should address that.
A ‘vicious cycle’
Hans P.A. Van Dongen, PhD, director of the Sleep and Performance Research Center at Washington State University, Spokane, said in an interview that the findings imply a “vicious cycle” between sleep and alcohol consumption. “You create a problem and then it perpetuates itself or reinforces itself.”
In older adults, alcohol tends to act as a “sleep aid,” Dr. Van Dongen noted. “Then it disrupts their sleep later on and then the next night they need to use the sleep aid again because they had a really poor night and they’re tired and they want to fall asleep.”
He added: “I think what is new here is that’s not very likely the mechanism that they’re using alcohol as a sleep aid in younger adults that we see in older adults, so I think there is a new element to it. Now does anybody know how that works exactly? No, that’s the next thing.”
The Penn State study identifies “a signal there that needs to be followed up on,” Dr. Van Dongen said. “There’s something nature’s trying to tell us but it’s not exactly clear what it’s trying to tell us.”
The National Institute on Drug Abuse provided funding for the study. Mr. Reichenberger has no relevant disclosures. Dr. Van Dongen has no disclosures to report.
At SLEEP 2022
Parkinson’s disease could be hiding behind those nightmares
Living the dream, diagnosing the nightmare
Does a bad dream mean you should be consulting your doctor about an impending neurologic disease? Maybe.
New research published in eClinicalMedicine suggests that, for some people, bad dreams and nightmares have been associated with developing Parkinson’s disease later in life. Dr. Abidemi I. Otaiku of the University of Birmingham (England) analyzed data from a cohort study involving 3,818 older men, of whom 2.3% were diagnosed with Parkinson’s during the 12 years of follow-up.
Dr. Otaiku found those with frequent nightmares – at least once per week – were twice as likely to develop Parkinson’s than were those without, with most of the diagnoses coming in the first 5 years.
Although more research needs to be done, “identifying the significance of bad dreams and nightmares could indicate that individuals who experience changes to their dreams in older age – without any obvious trigger – should seek medical advice,” he said in a Eurekalert statement.
Dr. Otaiku pointed out that studying dreams can tell us a lot about how our brains work and are structured. By using electroencephalography, Dr. Otaiku plans to look into the biological reasons for why we dream the way we do.
So could it be that those killer clowns are actually giving you a heads up on your health?
Maybe next time try a paper route
There’s just no winning with teenagers sometimes. You tell them to go outside, they’ll sit in the dark playing video games all night. You tell them to get better grades, they’ll skip school. You tell them to get a hobby, they’ll scam the German government for millions of euros.
The COVID-19 pandemic has been tricky for governments to manage. Massive amounts of infrastructure needed to be set up, and that means corners got cut. Germany was no exception in this regard; the government entrusted the Kassenärztlichen Vereinigung, a doctor’s association, with overseeing COVID testing and payment at private test centers. To make things a bit easier, all they required private test centers to provide to receive reimbursement was an invoice.
This is where our 17-year-old from Freiburg comes in. In a spark of entrepreneurial genius, he decided to falsify documents and create an entirely fictional COVID test center. The KV approved it, and between March and July of 2021, he sent in thousands of fake invoices. Over that 4-month period, he submitted 500,000 invoices and received 5.7 million euros as compensation. That’s a few thousand tests per day, which was absolutely absurd, but he avoided scrutiny for months.
In the end, it wasn’t even the KV that noticed the fraud, but the bank. A bank employee noticed millions flowing into the account of a teenager and suspected money laundering, alerting the government. Fortunately for our young friend, since he was under 18 when he hatched his scheme, he was tried as a minor, avoiding jail time. His ill-gotten gains were confiscated, he has to pay a relatively minimal fine, and he will be on probation for 1 year. And presumably, he’ll be on the receiving end of the grounding of a lifetime.
You look like I need more sleep
Like most people, not getting our beauty sleep can make us look tired and feel less attractive, but a new study from Sweden shows that the sleep deprived also are more likely to find others less attractive. That’s probably not a good finding for singles who often go out trying to meet someone after a long day of work.
For the study, 45 young men and women were required to spend one night with no sleep and then another night with the possibility of 8 hours of sleep. The following mornings, eye-tracking technology was used as they looked at images of happy, angry, fearful, and neutral faces. The subjects then rated the faces for attractiveness, trustworthiness, and healthiness.
“The finding that sleep-deprived subjects in our experiment rated angry faces as less trustworthy and healthy-looking and neutral and fearful faces as less attractive indicates that sleep loss is associated with more negative social impressions of others,” senior author Christian Benedict of Uppsala University said in a statement.
When we are sleep deprived, the researchers added, we might not stop to really look at someone else, which has a negative impact on how we perceive people because we are not focusing on what their facial expressions are really telling us.
We already knew that not sleeping well has many negative effects on us, but now – thank you very much, science – we have something else to think about. Better hope your crush at work gets enough sleep so you’ll be accurately noticed.
The expanding-hole illusion of science
Time for a LOTME-style reality check: I think, therefore I am.
So far, so good. Next step: I think, therefore I am. I think.
Works for us. Now for the biggie: I think I am seeing the black hole in the middle of this image expanding.
Does that work for you? Do you perceive the black hole as expanding? If you do, then you fit in with the 86% of subjects in a recent study who perceived the same thing.
Lead author Bruno Laeng of the University of Oslo explained the effect in a statement from Frontiers Science News. “The circular smear or shadow gradient of the central black hole evokes a marked impression of optic flow, as if the observer were heading forward into a hole or tunnel. ... The pupil reacts to how we perceive light – even if this ‘light’ is imaginary like in the illusion – and not just to the amount of light energy that actually enters the eye.”
The illusion is so good at deceiving the brain “that it even prompts a dilation reflex of the pupils to let in more light, just as would happen if we were really moving into a dark area,” the investigators said.
Of the 50 men and women who had their eye movements measured while looking at the illusion, only 14% didn’t perceive the illusion when the hole was black. When the hole was a color, that figure went up to 20%. There also was a strong dilation reflex with black holes, but colored holes caused the subjects’ pupils to constrict, they noted.
Dr. Laeng and his associates can’t explain why some people don’t see the movement, but they did offer this: “Pupils’ dilation or contraction reflex is not a closed-loop mechanism, like a photocell opening a door, impervious to any other information than the actual amount of light stimulating the photoreceptor. Rather, the eye adjusts to perceived and even imagined light, not simply to physical energy.”
And now, back to our reality check: We think we perceive the light of a cheeseburger, therefore it’s time for lunch.
Living the dream, diagnosing the nightmare
Does a bad dream mean you should be consulting your doctor about an impending neurologic disease? Maybe.
New research published in eClinicalMedicine suggests that, for some people, bad dreams and nightmares have been associated with developing Parkinson’s disease later in life. Dr. Abidemi I. Otaiku of the University of Birmingham (England) analyzed data from a cohort study involving 3,818 older men, of whom 2.3% were diagnosed with Parkinson’s during the 12 years of follow-up.
Dr. Otaiku found those with frequent nightmares – at least once per week – were twice as likely to develop Parkinson’s than were those without, with most of the diagnoses coming in the first 5 years.
Although more research needs to be done, “identifying the significance of bad dreams and nightmares could indicate that individuals who experience changes to their dreams in older age – without any obvious trigger – should seek medical advice,” he said in a Eurekalert statement.
Dr. Otaiku pointed out that studying dreams can tell us a lot about how our brains work and are structured. By using electroencephalography, Dr. Otaiku plans to look into the biological reasons for why we dream the way we do.
So could it be that those killer clowns are actually giving you a heads up on your health?
Maybe next time try a paper route
There’s just no winning with teenagers sometimes. You tell them to go outside, they’ll sit in the dark playing video games all night. You tell them to get better grades, they’ll skip school. You tell them to get a hobby, they’ll scam the German government for millions of euros.
The COVID-19 pandemic has been tricky for governments to manage. Massive amounts of infrastructure needed to be set up, and that means corners got cut. Germany was no exception in this regard; the government entrusted the Kassenärztlichen Vereinigung, a doctor’s association, with overseeing COVID testing and payment at private test centers. To make things a bit easier, all they required private test centers to provide to receive reimbursement was an invoice.
This is where our 17-year-old from Freiburg comes in. In a spark of entrepreneurial genius, he decided to falsify documents and create an entirely fictional COVID test center. The KV approved it, and between March and July of 2021, he sent in thousands of fake invoices. Over that 4-month period, he submitted 500,000 invoices and received 5.7 million euros as compensation. That’s a few thousand tests per day, which was absolutely absurd, but he avoided scrutiny for months.
In the end, it wasn’t even the KV that noticed the fraud, but the bank. A bank employee noticed millions flowing into the account of a teenager and suspected money laundering, alerting the government. Fortunately for our young friend, since he was under 18 when he hatched his scheme, he was tried as a minor, avoiding jail time. His ill-gotten gains were confiscated, he has to pay a relatively minimal fine, and he will be on probation for 1 year. And presumably, he’ll be on the receiving end of the grounding of a lifetime.
You look like I need more sleep
Like most people, not getting our beauty sleep can make us look tired and feel less attractive, but a new study from Sweden shows that the sleep deprived also are more likely to find others less attractive. That’s probably not a good finding for singles who often go out trying to meet someone after a long day of work.
For the study, 45 young men and women were required to spend one night with no sleep and then another night with the possibility of 8 hours of sleep. The following mornings, eye-tracking technology was used as they looked at images of happy, angry, fearful, and neutral faces. The subjects then rated the faces for attractiveness, trustworthiness, and healthiness.
“The finding that sleep-deprived subjects in our experiment rated angry faces as less trustworthy and healthy-looking and neutral and fearful faces as less attractive indicates that sleep loss is associated with more negative social impressions of others,” senior author Christian Benedict of Uppsala University said in a statement.
When we are sleep deprived, the researchers added, we might not stop to really look at someone else, which has a negative impact on how we perceive people because we are not focusing on what their facial expressions are really telling us.
We already knew that not sleeping well has many negative effects on us, but now – thank you very much, science – we have something else to think about. Better hope your crush at work gets enough sleep so you’ll be accurately noticed.
The expanding-hole illusion of science
Time for a LOTME-style reality check: I think, therefore I am.
So far, so good. Next step: I think, therefore I am. I think.
Works for us. Now for the biggie: I think I am seeing the black hole in the middle of this image expanding.
Does that work for you? Do you perceive the black hole as expanding? If you do, then you fit in with the 86% of subjects in a recent study who perceived the same thing.
Lead author Bruno Laeng of the University of Oslo explained the effect in a statement from Frontiers Science News. “The circular smear or shadow gradient of the central black hole evokes a marked impression of optic flow, as if the observer were heading forward into a hole or tunnel. ... The pupil reacts to how we perceive light – even if this ‘light’ is imaginary like in the illusion – and not just to the amount of light energy that actually enters the eye.”
The illusion is so good at deceiving the brain “that it even prompts a dilation reflex of the pupils to let in more light, just as would happen if we were really moving into a dark area,” the investigators said.
Of the 50 men and women who had their eye movements measured while looking at the illusion, only 14% didn’t perceive the illusion when the hole was black. When the hole was a color, that figure went up to 20%. There also was a strong dilation reflex with black holes, but colored holes caused the subjects’ pupils to constrict, they noted.
Dr. Laeng and his associates can’t explain why some people don’t see the movement, but they did offer this: “Pupils’ dilation or contraction reflex is not a closed-loop mechanism, like a photocell opening a door, impervious to any other information than the actual amount of light stimulating the photoreceptor. Rather, the eye adjusts to perceived and even imagined light, not simply to physical energy.”
And now, back to our reality check: We think we perceive the light of a cheeseburger, therefore it’s time for lunch.
Living the dream, diagnosing the nightmare
Does a bad dream mean you should be consulting your doctor about an impending neurologic disease? Maybe.
New research published in eClinicalMedicine suggests that, for some people, bad dreams and nightmares have been associated with developing Parkinson’s disease later in life. Dr. Abidemi I. Otaiku of the University of Birmingham (England) analyzed data from a cohort study involving 3,818 older men, of whom 2.3% were diagnosed with Parkinson’s during the 12 years of follow-up.
Dr. Otaiku found those with frequent nightmares – at least once per week – were twice as likely to develop Parkinson’s than were those without, with most of the diagnoses coming in the first 5 years.
Although more research needs to be done, “identifying the significance of bad dreams and nightmares could indicate that individuals who experience changes to their dreams in older age – without any obvious trigger – should seek medical advice,” he said in a Eurekalert statement.
Dr. Otaiku pointed out that studying dreams can tell us a lot about how our brains work and are structured. By using electroencephalography, Dr. Otaiku plans to look into the biological reasons for why we dream the way we do.
So could it be that those killer clowns are actually giving you a heads up on your health?
Maybe next time try a paper route
There’s just no winning with teenagers sometimes. You tell them to go outside, they’ll sit in the dark playing video games all night. You tell them to get better grades, they’ll skip school. You tell them to get a hobby, they’ll scam the German government for millions of euros.
The COVID-19 pandemic has been tricky for governments to manage. Massive amounts of infrastructure needed to be set up, and that means corners got cut. Germany was no exception in this regard; the government entrusted the Kassenärztlichen Vereinigung, a doctor’s association, with overseeing COVID testing and payment at private test centers. To make things a bit easier, all they required private test centers to provide to receive reimbursement was an invoice.
This is where our 17-year-old from Freiburg comes in. In a spark of entrepreneurial genius, he decided to falsify documents and create an entirely fictional COVID test center. The KV approved it, and between March and July of 2021, he sent in thousands of fake invoices. Over that 4-month period, he submitted 500,000 invoices and received 5.7 million euros as compensation. That’s a few thousand tests per day, which was absolutely absurd, but he avoided scrutiny for months.
In the end, it wasn’t even the KV that noticed the fraud, but the bank. A bank employee noticed millions flowing into the account of a teenager and suspected money laundering, alerting the government. Fortunately for our young friend, since he was under 18 when he hatched his scheme, he was tried as a minor, avoiding jail time. His ill-gotten gains were confiscated, he has to pay a relatively minimal fine, and he will be on probation for 1 year. And presumably, he’ll be on the receiving end of the grounding of a lifetime.
You look like I need more sleep
Like most people, not getting our beauty sleep can make us look tired and feel less attractive, but a new study from Sweden shows that the sleep deprived also are more likely to find others less attractive. That’s probably not a good finding for singles who often go out trying to meet someone after a long day of work.
For the study, 45 young men and women were required to spend one night with no sleep and then another night with the possibility of 8 hours of sleep. The following mornings, eye-tracking technology was used as they looked at images of happy, angry, fearful, and neutral faces. The subjects then rated the faces for attractiveness, trustworthiness, and healthiness.
“The finding that sleep-deprived subjects in our experiment rated angry faces as less trustworthy and healthy-looking and neutral and fearful faces as less attractive indicates that sleep loss is associated with more negative social impressions of others,” senior author Christian Benedict of Uppsala University said in a statement.
When we are sleep deprived, the researchers added, we might not stop to really look at someone else, which has a negative impact on how we perceive people because we are not focusing on what their facial expressions are really telling us.
We already knew that not sleeping well has many negative effects on us, but now – thank you very much, science – we have something else to think about. Better hope your crush at work gets enough sleep so you’ll be accurately noticed.
The expanding-hole illusion of science
Time for a LOTME-style reality check: I think, therefore I am.
So far, so good. Next step: I think, therefore I am. I think.
Works for us. Now for the biggie: I think I am seeing the black hole in the middle of this image expanding.
Does that work for you? Do you perceive the black hole as expanding? If you do, then you fit in with the 86% of subjects in a recent study who perceived the same thing.
Lead author Bruno Laeng of the University of Oslo explained the effect in a statement from Frontiers Science News. “The circular smear or shadow gradient of the central black hole evokes a marked impression of optic flow, as if the observer were heading forward into a hole or tunnel. ... The pupil reacts to how we perceive light – even if this ‘light’ is imaginary like in the illusion – and not just to the amount of light energy that actually enters the eye.”
The illusion is so good at deceiving the brain “that it even prompts a dilation reflex of the pupils to let in more light, just as would happen if we were really moving into a dark area,” the investigators said.
Of the 50 men and women who had their eye movements measured while looking at the illusion, only 14% didn’t perceive the illusion when the hole was black. When the hole was a color, that figure went up to 20%. There also was a strong dilation reflex with black holes, but colored holes caused the subjects’ pupils to constrict, they noted.
Dr. Laeng and his associates can’t explain why some people don’t see the movement, but they did offer this: “Pupils’ dilation or contraction reflex is not a closed-loop mechanism, like a photocell opening a door, impervious to any other information than the actual amount of light stimulating the photoreceptor. Rather, the eye adjusts to perceived and even imagined light, not simply to physical energy.”
And now, back to our reality check: We think we perceive the light of a cheeseburger, therefore it’s time for lunch.
Schizophrenia patients in long-term facilities benefit from lower-dose antipsychotics
NEW ORLEANS –
“There is an argument by some experts in the field that state hospital populations represent a different set of patients who require higher antipsychotic dosages, with no alternative, but I don’t agree with that,” study lead author Mujeeb U. Shad, MD, GME-psychiatry program director and adjunct professor at the University of Nevada, Las Vegas, said in an interview.
In reducing doses, “patients appeared to blossom, becoming more active and less ‘zombie-like’; they started taking more interest in activities and their social [involvement] increased,” he said.
The study was among several presenting pros and cons of high antipsychotic doses at the 2022 annual meeting of the American Psychiatric Association.
Higher doses of antipsychotics are often relied upon when patients with acute psychosis fail to respond to standard treatment, however evidence supporting the approach is lacking.
And while some studies in fact show no benefit from the higher-dose maintenance therapy over conventional or even lower doses of antipsychotics, evidence regarding forensic patients hospitalized in long-term psychiatric facilities is also scant.
Meanwhile, the need to restore competency among those patients can be more pressing than normal.
“In a forensic population where executive cognitive function is one of the key elements to restore competency to stand trial, the continuation of high-dose therapy with excessive dopamine blockade may further compromise preexisting executive dysfunction to delay competency restoration,” Dr. Shad notes in the study.
The study describes a case series in which antipsychotic doses were lowered among 22 of Dr. Shad’s patients who had been determined to be incompetent to stand trial and referred to a state hospital to restore their competency.
With the objective of regaining the mental fitness to stand trial and being discharged from the facility, those on high doses of therapy, defined as a dose greater than 50% of the average package-insert dose, had their doses reduced to conventional dosages.
The approach led to as many as 68% of the patients being stabilized and discharged after having their competency restored, without symptom relapse, following an average antipsychotic dose reduction of 44%.
The average time to discharge following the dose reduction was just 2.3 months, after an average total hospitalization time of 11 months.
The shortest hospitalization durations (less than 7 months) were observed among those who did not receive changes in doses as they were already achieving efficacy with standard dosages.
Among two patients who were treated subtherapeutically, dose increases were required and they had the longest overall hospitalization (14.5 months)
Additional benefits of reduced dosages
Dr. Shad noted that, in addition to the earlier discharges, patients also had reductions in their polypharmacy, and in prolactin.
“We know that high prolactin level is such a huge problem, especially for female patients because it can cause osteoporosis, infertility, and abnormal menstruation, and the reductions in hyperprolactinemia can help reduce weight gain,” he said.
Dr. Shad added that he let some of those effects be his guide in making dose reductions.
“I was trying to gradually minimize the dose while monitoring the patients for relapse, and I used extrapyramidal symptoms and prolactin levels as my guide, looking for a sweet spot with the dosing,” he said.
“For example, if patients were taking an average of about 40-60 mg of a drug, I brought it down close to 20 mg, or close to the average package insert,” Dr. Shad said.
Key concerns among clinicians about reducing antipsychotic doses include the emergence of discontinuation or rebound symptoms, including psychosis, akathisia, or Parkinsonian symptoms, and studies, including a recent meta-analysis have supported those concerns, urging caution in reducing doses below standard levels.
However, Dr. Shad said his series suggests that reducing doses gradually while carefully monitoring extrapyramidal symptoms and prolactin levels may indeed pay off.
“They’re not the perfect guides, but they’re good guides, and with the right approach, [some] may be able to do this,” Dr. Shad said.
“However, the key to a successful dose reduction or discontinuation of an [antipsychotic medication] is to avoid abrupt discontinuation and follow a gradual dose reduction while monitoring symptoms and tolerability,” he said.
Commenting on the research, T. Scott Stroup, MD, a professor of psychiatry at Columbia University, New York, chimed in on the side of urging caution with higher doses and supporting possible benefits with the lower-dose approach.
“I agree that people who need antipsychotic medications should receive the lowest effective dose and that often this is identified by careful dose reduction,” he said in an interview.
Dr. Shad and Stroup had no disclosures to report.
NEW ORLEANS –
“There is an argument by some experts in the field that state hospital populations represent a different set of patients who require higher antipsychotic dosages, with no alternative, but I don’t agree with that,” study lead author Mujeeb U. Shad, MD, GME-psychiatry program director and adjunct professor at the University of Nevada, Las Vegas, said in an interview.
In reducing doses, “patients appeared to blossom, becoming more active and less ‘zombie-like’; they started taking more interest in activities and their social [involvement] increased,” he said.
The study was among several presenting pros and cons of high antipsychotic doses at the 2022 annual meeting of the American Psychiatric Association.
Higher doses of antipsychotics are often relied upon when patients with acute psychosis fail to respond to standard treatment, however evidence supporting the approach is lacking.
And while some studies in fact show no benefit from the higher-dose maintenance therapy over conventional or even lower doses of antipsychotics, evidence regarding forensic patients hospitalized in long-term psychiatric facilities is also scant.
Meanwhile, the need to restore competency among those patients can be more pressing than normal.
“In a forensic population where executive cognitive function is one of the key elements to restore competency to stand trial, the continuation of high-dose therapy with excessive dopamine blockade may further compromise preexisting executive dysfunction to delay competency restoration,” Dr. Shad notes in the study.
The study describes a case series in which antipsychotic doses were lowered among 22 of Dr. Shad’s patients who had been determined to be incompetent to stand trial and referred to a state hospital to restore their competency.
With the objective of regaining the mental fitness to stand trial and being discharged from the facility, those on high doses of therapy, defined as a dose greater than 50% of the average package-insert dose, had their doses reduced to conventional dosages.
The approach led to as many as 68% of the patients being stabilized and discharged after having their competency restored, without symptom relapse, following an average antipsychotic dose reduction of 44%.
The average time to discharge following the dose reduction was just 2.3 months, after an average total hospitalization time of 11 months.
The shortest hospitalization durations (less than 7 months) were observed among those who did not receive changes in doses as they were already achieving efficacy with standard dosages.
Among two patients who were treated subtherapeutically, dose increases were required and they had the longest overall hospitalization (14.5 months)
Additional benefits of reduced dosages
Dr. Shad noted that, in addition to the earlier discharges, patients also had reductions in their polypharmacy, and in prolactin.
“We know that high prolactin level is such a huge problem, especially for female patients because it can cause osteoporosis, infertility, and abnormal menstruation, and the reductions in hyperprolactinemia can help reduce weight gain,” he said.
Dr. Shad added that he let some of those effects be his guide in making dose reductions.
“I was trying to gradually minimize the dose while monitoring the patients for relapse, and I used extrapyramidal symptoms and prolactin levels as my guide, looking for a sweet spot with the dosing,” he said.
“For example, if patients were taking an average of about 40-60 mg of a drug, I brought it down close to 20 mg, or close to the average package insert,” Dr. Shad said.
Key concerns among clinicians about reducing antipsychotic doses include the emergence of discontinuation or rebound symptoms, including psychosis, akathisia, or Parkinsonian symptoms, and studies, including a recent meta-analysis have supported those concerns, urging caution in reducing doses below standard levels.
However, Dr. Shad said his series suggests that reducing doses gradually while carefully monitoring extrapyramidal symptoms and prolactin levels may indeed pay off.
“They’re not the perfect guides, but they’re good guides, and with the right approach, [some] may be able to do this,” Dr. Shad said.
“However, the key to a successful dose reduction or discontinuation of an [antipsychotic medication] is to avoid abrupt discontinuation and follow a gradual dose reduction while monitoring symptoms and tolerability,” he said.
Commenting on the research, T. Scott Stroup, MD, a professor of psychiatry at Columbia University, New York, chimed in on the side of urging caution with higher doses and supporting possible benefits with the lower-dose approach.
“I agree that people who need antipsychotic medications should receive the lowest effective dose and that often this is identified by careful dose reduction,” he said in an interview.
Dr. Shad and Stroup had no disclosures to report.
NEW ORLEANS –
“There is an argument by some experts in the field that state hospital populations represent a different set of patients who require higher antipsychotic dosages, with no alternative, but I don’t agree with that,” study lead author Mujeeb U. Shad, MD, GME-psychiatry program director and adjunct professor at the University of Nevada, Las Vegas, said in an interview.
In reducing doses, “patients appeared to blossom, becoming more active and less ‘zombie-like’; they started taking more interest in activities and their social [involvement] increased,” he said.
The study was among several presenting pros and cons of high antipsychotic doses at the 2022 annual meeting of the American Psychiatric Association.
Higher doses of antipsychotics are often relied upon when patients with acute psychosis fail to respond to standard treatment, however evidence supporting the approach is lacking.
And while some studies in fact show no benefit from the higher-dose maintenance therapy over conventional or even lower doses of antipsychotics, evidence regarding forensic patients hospitalized in long-term psychiatric facilities is also scant.
Meanwhile, the need to restore competency among those patients can be more pressing than normal.
“In a forensic population where executive cognitive function is one of the key elements to restore competency to stand trial, the continuation of high-dose therapy with excessive dopamine blockade may further compromise preexisting executive dysfunction to delay competency restoration,” Dr. Shad notes in the study.
The study describes a case series in which antipsychotic doses were lowered among 22 of Dr. Shad’s patients who had been determined to be incompetent to stand trial and referred to a state hospital to restore their competency.
With the objective of regaining the mental fitness to stand trial and being discharged from the facility, those on high doses of therapy, defined as a dose greater than 50% of the average package-insert dose, had their doses reduced to conventional dosages.
The approach led to as many as 68% of the patients being stabilized and discharged after having their competency restored, without symptom relapse, following an average antipsychotic dose reduction of 44%.
The average time to discharge following the dose reduction was just 2.3 months, after an average total hospitalization time of 11 months.
The shortest hospitalization durations (less than 7 months) were observed among those who did not receive changes in doses as they were already achieving efficacy with standard dosages.
Among two patients who were treated subtherapeutically, dose increases were required and they had the longest overall hospitalization (14.5 months)
Additional benefits of reduced dosages
Dr. Shad noted that, in addition to the earlier discharges, patients also had reductions in their polypharmacy, and in prolactin.
“We know that high prolactin level is such a huge problem, especially for female patients because it can cause osteoporosis, infertility, and abnormal menstruation, and the reductions in hyperprolactinemia can help reduce weight gain,” he said.
Dr. Shad added that he let some of those effects be his guide in making dose reductions.
“I was trying to gradually minimize the dose while monitoring the patients for relapse, and I used extrapyramidal symptoms and prolactin levels as my guide, looking for a sweet spot with the dosing,” he said.
“For example, if patients were taking an average of about 40-60 mg of a drug, I brought it down close to 20 mg, or close to the average package insert,” Dr. Shad said.
Key concerns among clinicians about reducing antipsychotic doses include the emergence of discontinuation or rebound symptoms, including psychosis, akathisia, or Parkinsonian symptoms, and studies, including a recent meta-analysis have supported those concerns, urging caution in reducing doses below standard levels.
However, Dr. Shad said his series suggests that reducing doses gradually while carefully monitoring extrapyramidal symptoms and prolactin levels may indeed pay off.
“They’re not the perfect guides, but they’re good guides, and with the right approach, [some] may be able to do this,” Dr. Shad said.
“However, the key to a successful dose reduction or discontinuation of an [antipsychotic medication] is to avoid abrupt discontinuation and follow a gradual dose reduction while monitoring symptoms and tolerability,” he said.
Commenting on the research, T. Scott Stroup, MD, a professor of psychiatry at Columbia University, New York, chimed in on the side of urging caution with higher doses and supporting possible benefits with the lower-dose approach.
“I agree that people who need antipsychotic medications should receive the lowest effective dose and that often this is identified by careful dose reduction,” he said in an interview.
Dr. Shad and Stroup had no disclosures to report.
FROM APA 2022













