User login
Bringing you the latest news, research and reviews, exclusive interviews, podcasts, quizzes, and more.
div[contains(@class, 'read-next-article')]
div[contains(@class, 'nav-primary')]
nav[contains(@class, 'nav-primary')]
section[contains(@class, 'footer-nav-section-wrapper')]
nav[contains(@class, 'nav-ce-stack nav-ce-stack__large-screen')]
header[@id='header']
div[contains(@class, 'header__large-screen')]
div[contains(@class, 'read-next-article')]
div[contains(@class, 'main-prefix')]
div[contains(@class, 'nav-primary')]
nav[contains(@class, 'nav-primary')]
section[contains(@class, 'footer-nav-section-wrapper')]
footer[@id='footer']
section[contains(@class, 'nav-hidden')]
div[contains(@class, 'ce-card-content')]
nav[contains(@class, 'nav-ce-stack')]
div[contains(@class, 'view-medstat-quiz-listing-panes')]
div[contains(@class, 'pane-article-sidebar-latest-news')]
‘Stop Teaching’ Children It’s Their Fault They’re Fat
The US Preventive Services Task Force (USPSTF) has published draft recommendations that 6-year-olds with obesity be lectured to about diet and exercise.
Never mind that there are no reproducible or scalable studies demonstrating durable and clinically meaningful benefits of this for adults let alone children. Never mind that children are not household decision-makers on matters of grocery shopping, cooking, or exercise. Never mind the corollary that many children so lectured who fail to see an impact on their weight will perceive that as their own personal failures. And of course, never mind that we’re privileged to be in an era with safe, effective, pharmacotherapeutic options for obesity. No. We must teach children it’s their fault if they’re fat. Because ultimately that’s what many of them will learn.
That’s not to say there’s no room for counseling. But with children as young as 6, that counseling should be delivered exclusively to their parents and caregivers. That counseling should focus as much if not more so on the impact of weight bias and the biological basis of obesity rather than diet and exercise, while explicitly teaching parents the means to discuss nutrition without risking their children feeling worse about themselves, increasing the risk for conflict over changes, or heightening their children’s chance of developing eating disorders or maladaptive relationships with food.
But back to the USPSTF’s actual recommendation for those 6 years old and up. They’re recommending “at least” 26 hours of lectures over a year-long interprofessional intervention. Putting aside the reality that this isn’t scalable time-wise or cost-wise to reach even a fraction of the roughly 15 million US children with obesity, there is also the issue of service provision. Because when it comes to obesity, if the intervention is purely educational, even if you want to believe there is a syllabus out there that would have a dramatic impact, its impact will vary wildly depending on the skill and approach of the service providers. This inconvenient truth is also the one that makes it impossible to meaningfully compare program outcomes even when they share the same content.
The USPSTF’s draft recommendations also explicitly avoid what the American Academy of Pediatrics has rightly embraced: the use where appropriate of medications or surgery. While opponents of the use of pharmacotherapy for childhood obesity tend to point to a lack of long-term data as rationale for its denial, something that the USPSTF has done, again, we have long-term data demonstrating a lack of scalable, clinically meaningful efficacy for service only based programs.
Childhood obesity is a flood and its ongoing current is relentless. Given its tremendous impact, especially at its extremes, on both physical and mental health, this is yet another example of systemic weight bias in action — it’s as if the USPSTF is recommending a swimming lesson–only approach while actively fearmongering, despite an absence of plausible mechanistic risk, about the long-term use of life jackets.
Dr. Freedhoff is associate professor, Department of Family Medicine, University of Ottawa; Medical Director, Bariatric Medical Institute, Ottawa, Ontario, Canada. Dr. Freedhoff has disclosed ties with Bariatric Medical Institute, Constant Health, and Novo Nordisk.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
The US Preventive Services Task Force (USPSTF) has published draft recommendations that 6-year-olds with obesity be lectured to about diet and exercise.
Never mind that there are no reproducible or scalable studies demonstrating durable and clinically meaningful benefits of this for adults let alone children. Never mind that children are not household decision-makers on matters of grocery shopping, cooking, or exercise. Never mind the corollary that many children so lectured who fail to see an impact on their weight will perceive that as their own personal failures. And of course, never mind that we’re privileged to be in an era with safe, effective, pharmacotherapeutic options for obesity. No. We must teach children it’s their fault if they’re fat. Because ultimately that’s what many of them will learn.
That’s not to say there’s no room for counseling. But with children as young as 6, that counseling should be delivered exclusively to their parents and caregivers. That counseling should focus as much if not more so on the impact of weight bias and the biological basis of obesity rather than diet and exercise, while explicitly teaching parents the means to discuss nutrition without risking their children feeling worse about themselves, increasing the risk for conflict over changes, or heightening their children’s chance of developing eating disorders or maladaptive relationships with food.
But back to the USPSTF’s actual recommendation for those 6 years old and up. They’re recommending “at least” 26 hours of lectures over a year-long interprofessional intervention. Putting aside the reality that this isn’t scalable time-wise or cost-wise to reach even a fraction of the roughly 15 million US children with obesity, there is also the issue of service provision. Because when it comes to obesity, if the intervention is purely educational, even if you want to believe there is a syllabus out there that would have a dramatic impact, its impact will vary wildly depending on the skill and approach of the service providers. This inconvenient truth is also the one that makes it impossible to meaningfully compare program outcomes even when they share the same content.
The USPSTF’s draft recommendations also explicitly avoid what the American Academy of Pediatrics has rightly embraced: the use where appropriate of medications or surgery. While opponents of the use of pharmacotherapy for childhood obesity tend to point to a lack of long-term data as rationale for its denial, something that the USPSTF has done, again, we have long-term data demonstrating a lack of scalable, clinically meaningful efficacy for service only based programs.
Childhood obesity is a flood and its ongoing current is relentless. Given its tremendous impact, especially at its extremes, on both physical and mental health, this is yet another example of systemic weight bias in action — it’s as if the USPSTF is recommending a swimming lesson–only approach while actively fearmongering, despite an absence of plausible mechanistic risk, about the long-term use of life jackets.
Dr. Freedhoff is associate professor, Department of Family Medicine, University of Ottawa; Medical Director, Bariatric Medical Institute, Ottawa, Ontario, Canada. Dr. Freedhoff has disclosed ties with Bariatric Medical Institute, Constant Health, and Novo Nordisk.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
The US Preventive Services Task Force (USPSTF) has published draft recommendations that 6-year-olds with obesity be lectured to about diet and exercise.
Never mind that there are no reproducible or scalable studies demonstrating durable and clinically meaningful benefits of this for adults let alone children. Never mind that children are not household decision-makers on matters of grocery shopping, cooking, or exercise. Never mind the corollary that many children so lectured who fail to see an impact on their weight will perceive that as their own personal failures. And of course, never mind that we’re privileged to be in an era with safe, effective, pharmacotherapeutic options for obesity. No. We must teach children it’s their fault if they’re fat. Because ultimately that’s what many of them will learn.
That’s not to say there’s no room for counseling. But with children as young as 6, that counseling should be delivered exclusively to their parents and caregivers. That counseling should focus as much if not more so on the impact of weight bias and the biological basis of obesity rather than diet and exercise, while explicitly teaching parents the means to discuss nutrition without risking their children feeling worse about themselves, increasing the risk for conflict over changes, or heightening their children’s chance of developing eating disorders or maladaptive relationships with food.
But back to the USPSTF’s actual recommendation for those 6 years old and up. They’re recommending “at least” 26 hours of lectures over a year-long interprofessional intervention. Putting aside the reality that this isn’t scalable time-wise or cost-wise to reach even a fraction of the roughly 15 million US children with obesity, there is also the issue of service provision. Because when it comes to obesity, if the intervention is purely educational, even if you want to believe there is a syllabus out there that would have a dramatic impact, its impact will vary wildly depending on the skill and approach of the service providers. This inconvenient truth is also the one that makes it impossible to meaningfully compare program outcomes even when they share the same content.
The USPSTF’s draft recommendations also explicitly avoid what the American Academy of Pediatrics has rightly embraced: the use where appropriate of medications or surgery. While opponents of the use of pharmacotherapy for childhood obesity tend to point to a lack of long-term data as rationale for its denial, something that the USPSTF has done, again, we have long-term data demonstrating a lack of scalable, clinically meaningful efficacy for service only based programs.
Childhood obesity is a flood and its ongoing current is relentless. Given its tremendous impact, especially at its extremes, on both physical and mental health, this is yet another example of systemic weight bias in action — it’s as if the USPSTF is recommending a swimming lesson–only approach while actively fearmongering, despite an absence of plausible mechanistic risk, about the long-term use of life jackets.
Dr. Freedhoff is associate professor, Department of Family Medicine, University of Ottawa; Medical Director, Bariatric Medical Institute, Ottawa, Ontario, Canada. Dr. Freedhoff has disclosed ties with Bariatric Medical Institute, Constant Health, and Novo Nordisk.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
EHR Tool Enhances Primary Aldosteronism Screening in Hypertensive Patients
Primary aldosteronism (PA) is a frequently overlooked yet common cause of secondary hypertension, presenting significant risk for cardiovascular morbidity and mortality.
But fewer than 4% of at-risk patients receive the recommended screening for PA, leaving a substantial gap in early detection and management, according to Adina F. Turcu, MD, MS, associate professor in endocrinology and internal medicine at University of Michigan Health in Ann Arbor.
In response to this clinical challenge, Dr. Turcu and her colleagues developed a best-practice advisory (BPA) to identify patients who were at risk for PA and embedded it into electronic health record at University of Michigan ambulatory clinics. Her team found that use of the tool led to increased rates of screening for PA, particularly among primary care physicians.
Over a 15-month period, Dr. Turcu and her colleagues tested the BPA through a quality improvement study, identifying 14,603 unique candidates for PA screening, with a mean age of 65.5 years and a diverse representation of ethnic backgrounds.
Notably, 48.1% of these candidates had treatment-resistant hypertension, 43.5% exhibited hypokalemia, 10.5% were younger than 35 years, and 3.1% had adrenal nodules. Of these candidates, 14.0% received orders for PA screening, with 70.5% completing the recommended screening within the system, and 17.4% receiving positive screening results.
The study, conducted over 6 months in 2023, targeted adults with hypertension and at least one of the following: Those who took four or more antihypertensive medications, exhibited hypokalemia, were younger than age 35 years, or had adrenal nodules. Patients previously tested for PA were excluded from the analysis.
The noninterruptive BPA was triggered during outpatient visits with clinicians who specialized in hypertension. The advisory would then offer an order set for PA screening and provide a link to interpretation guidance for results. Clinicians had the option to use, ignore, or decline the BPA.
“Although we were hoping for broader uptake of this EHR-embedded BPA, we were delighted to see an increase in PA screening rates to 14% of identified candidates as compared to an average of less than 3% in retrospective studies of similar populations, including in our own institution prior to implementing this BPA,” Dr. Turcu told this news organization.
Physician specialty played a crucial role in the utilization of the BPA. Internists and family medicine physicians accounted for the majority of screening orders, placing 40.0% and 28.1% of these, respectively. Family practitioners and internists predominantly used the embedded order set (80.3% and 68.9%, respectively).
“Hypertension often gets treated rather than screening for [causes of] secondary hypertension prior to treatment,” said Kaniksha Desai, MD, clinical associate professor and endocrinology quality director at Stanford University School of Medicine, Stanford, California, who was not involved in the research. But “primary hyperaldosteronism is a condition that can be treated surgically and has increased long term cardiovascular consequences if not identified. While guidelines recommend screening at-risk patients, this often can get lost in translation in clinical practice due to many factors, including time constraints and volume of patients.”
Patients who did vs did not undergo screening were more likely to be women, Black, and younger than age 35 years. Additionally, the likelihood of screening was higher among patients with obesity and dyslipidemia, whereas it was lower in those with chronic kidney disease and established cardiovascular complications.
According to Dr. Turcu, the findings from this study suggest that noninterruptive BPAs, especially when integrated into primary care workflows, hold promise as effective tools for PA screening.
When coupled with artificial intelligence to optimize detection yield, these refined BPAs could significantly contribute to personalized care for hypertension, the investigators said.
“Considering that in the United States almost one in two adults has hypertension, such automatized tools become instrumental to busy clinicians, particularly those in primary care,” Dr. Turcu said. “Our results indicate a promising opportunity to meaningfully improve PA awareness and enhance its diagnosis.”
Dr. Turcu reported receiving grants from the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute and Doris Duke Foundation, served as an investigator in a CinCor Pharma clinical trial, and received financial support to her institution during the conduct of the study. Dr. Desai reported no relevant financial disclosures.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Primary aldosteronism (PA) is a frequently overlooked yet common cause of secondary hypertension, presenting significant risk for cardiovascular morbidity and mortality.
But fewer than 4% of at-risk patients receive the recommended screening for PA, leaving a substantial gap in early detection and management, according to Adina F. Turcu, MD, MS, associate professor in endocrinology and internal medicine at University of Michigan Health in Ann Arbor.
In response to this clinical challenge, Dr. Turcu and her colleagues developed a best-practice advisory (BPA) to identify patients who were at risk for PA and embedded it into electronic health record at University of Michigan ambulatory clinics. Her team found that use of the tool led to increased rates of screening for PA, particularly among primary care physicians.
Over a 15-month period, Dr. Turcu and her colleagues tested the BPA through a quality improvement study, identifying 14,603 unique candidates for PA screening, with a mean age of 65.5 years and a diverse representation of ethnic backgrounds.
Notably, 48.1% of these candidates had treatment-resistant hypertension, 43.5% exhibited hypokalemia, 10.5% were younger than 35 years, and 3.1% had adrenal nodules. Of these candidates, 14.0% received orders for PA screening, with 70.5% completing the recommended screening within the system, and 17.4% receiving positive screening results.
The study, conducted over 6 months in 2023, targeted adults with hypertension and at least one of the following: Those who took four or more antihypertensive medications, exhibited hypokalemia, were younger than age 35 years, or had adrenal nodules. Patients previously tested for PA were excluded from the analysis.
The noninterruptive BPA was triggered during outpatient visits with clinicians who specialized in hypertension. The advisory would then offer an order set for PA screening and provide a link to interpretation guidance for results. Clinicians had the option to use, ignore, or decline the BPA.
“Although we were hoping for broader uptake of this EHR-embedded BPA, we were delighted to see an increase in PA screening rates to 14% of identified candidates as compared to an average of less than 3% in retrospective studies of similar populations, including in our own institution prior to implementing this BPA,” Dr. Turcu told this news organization.
Physician specialty played a crucial role in the utilization of the BPA. Internists and family medicine physicians accounted for the majority of screening orders, placing 40.0% and 28.1% of these, respectively. Family practitioners and internists predominantly used the embedded order set (80.3% and 68.9%, respectively).
“Hypertension often gets treated rather than screening for [causes of] secondary hypertension prior to treatment,” said Kaniksha Desai, MD, clinical associate professor and endocrinology quality director at Stanford University School of Medicine, Stanford, California, who was not involved in the research. But “primary hyperaldosteronism is a condition that can be treated surgically and has increased long term cardiovascular consequences if not identified. While guidelines recommend screening at-risk patients, this often can get lost in translation in clinical practice due to many factors, including time constraints and volume of patients.”
Patients who did vs did not undergo screening were more likely to be women, Black, and younger than age 35 years. Additionally, the likelihood of screening was higher among patients with obesity and dyslipidemia, whereas it was lower in those with chronic kidney disease and established cardiovascular complications.
According to Dr. Turcu, the findings from this study suggest that noninterruptive BPAs, especially when integrated into primary care workflows, hold promise as effective tools for PA screening.
When coupled with artificial intelligence to optimize detection yield, these refined BPAs could significantly contribute to personalized care for hypertension, the investigators said.
“Considering that in the United States almost one in two adults has hypertension, such automatized tools become instrumental to busy clinicians, particularly those in primary care,” Dr. Turcu said. “Our results indicate a promising opportunity to meaningfully improve PA awareness and enhance its diagnosis.”
Dr. Turcu reported receiving grants from the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute and Doris Duke Foundation, served as an investigator in a CinCor Pharma clinical trial, and received financial support to her institution during the conduct of the study. Dr. Desai reported no relevant financial disclosures.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Primary aldosteronism (PA) is a frequently overlooked yet common cause of secondary hypertension, presenting significant risk for cardiovascular morbidity and mortality.
But fewer than 4% of at-risk patients receive the recommended screening for PA, leaving a substantial gap in early detection and management, according to Adina F. Turcu, MD, MS, associate professor in endocrinology and internal medicine at University of Michigan Health in Ann Arbor.
In response to this clinical challenge, Dr. Turcu and her colleagues developed a best-practice advisory (BPA) to identify patients who were at risk for PA and embedded it into electronic health record at University of Michigan ambulatory clinics. Her team found that use of the tool led to increased rates of screening for PA, particularly among primary care physicians.
Over a 15-month period, Dr. Turcu and her colleagues tested the BPA through a quality improvement study, identifying 14,603 unique candidates for PA screening, with a mean age of 65.5 years and a diverse representation of ethnic backgrounds.
Notably, 48.1% of these candidates had treatment-resistant hypertension, 43.5% exhibited hypokalemia, 10.5% were younger than 35 years, and 3.1% had adrenal nodules. Of these candidates, 14.0% received orders for PA screening, with 70.5% completing the recommended screening within the system, and 17.4% receiving positive screening results.
The study, conducted over 6 months in 2023, targeted adults with hypertension and at least one of the following: Those who took four or more antihypertensive medications, exhibited hypokalemia, were younger than age 35 years, or had adrenal nodules. Patients previously tested for PA were excluded from the analysis.
The noninterruptive BPA was triggered during outpatient visits with clinicians who specialized in hypertension. The advisory would then offer an order set for PA screening and provide a link to interpretation guidance for results. Clinicians had the option to use, ignore, or decline the BPA.
“Although we were hoping for broader uptake of this EHR-embedded BPA, we were delighted to see an increase in PA screening rates to 14% of identified candidates as compared to an average of less than 3% in retrospective studies of similar populations, including in our own institution prior to implementing this BPA,” Dr. Turcu told this news organization.
Physician specialty played a crucial role in the utilization of the BPA. Internists and family medicine physicians accounted for the majority of screening orders, placing 40.0% and 28.1% of these, respectively. Family practitioners and internists predominantly used the embedded order set (80.3% and 68.9%, respectively).
“Hypertension often gets treated rather than screening for [causes of] secondary hypertension prior to treatment,” said Kaniksha Desai, MD, clinical associate professor and endocrinology quality director at Stanford University School of Medicine, Stanford, California, who was not involved in the research. But “primary hyperaldosteronism is a condition that can be treated surgically and has increased long term cardiovascular consequences if not identified. While guidelines recommend screening at-risk patients, this often can get lost in translation in clinical practice due to many factors, including time constraints and volume of patients.”
Patients who did vs did not undergo screening were more likely to be women, Black, and younger than age 35 years. Additionally, the likelihood of screening was higher among patients with obesity and dyslipidemia, whereas it was lower in those with chronic kidney disease and established cardiovascular complications.
According to Dr. Turcu, the findings from this study suggest that noninterruptive BPAs, especially when integrated into primary care workflows, hold promise as effective tools for PA screening.
When coupled with artificial intelligence to optimize detection yield, these refined BPAs could significantly contribute to personalized care for hypertension, the investigators said.
“Considering that in the United States almost one in two adults has hypertension, such automatized tools become instrumental to busy clinicians, particularly those in primary care,” Dr. Turcu said. “Our results indicate a promising opportunity to meaningfully improve PA awareness and enhance its diagnosis.”
Dr. Turcu reported receiving grants from the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute and Doris Duke Foundation, served as an investigator in a CinCor Pharma clinical trial, and received financial support to her institution during the conduct of the study. Dr. Desai reported no relevant financial disclosures.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
A1c Helps Stratify Type 2 Diabetes Risk in Teens
A1c level strongly predicts the risk of developing type 2 diabetes among adolescents with overweight or obesity, new data suggested.
In a large California healthcare database over a 10-year period, the incidence of type 2 diabetes was relatively low overall among adolescents with overweight and obesity. However, the risk increased with baseline A1c levels above 6.0% as well as in those with more severe obesity, women, and Asian or Pacific Islanders.
The new findings were published online in JAMA Network Open by pediatric endocrinologist Francis M. Hoe, MD, of Kaiser Permanente Roseville Medical Center, Roseville, California, and colleagues.
Previous studies have examined the incidence of type 2 diabetes among all youth, regardless of weight class. This is one of the first large population studies to examine the incidence and risk for type 2 diabetes by incremental level of A1c in a racially and ethnically diverse group of youth with overweight and obesity, Dr. Hoe told this news organization in an interview.
“This study was only possible to do because Kaiser Permanente Northern California has nearly 1 million pediatric members. The biggest thing we learned is that risk for type 2 diabetes is low in overweight and obese youth, especially those with an HbA1c less than 5.9%,” he said.
Zeroing in on Those at Greatest Risk for Type 2 Diabetes
Currently, the American Diabetes Association (ADA) recommends screening for type 2 diabetes in adolescents with overweight (body mass index [BMI], 85th percentile or greater) or obesity (≥ 95th) who have at least one additional risk factor, including family history of type 2 diabetes and Native American, Black, or Hispanic ethnicity. About one in four US adolescents qualify by those criteria, the authors noted in the paper.
And, as for adults, ADA recommends subsequent annual diabetes screening in youth identified as having “prediabetes,” that is, a A1c level between 5.7% and 6.5%.
The new study confirmed that adolescents with A1c in the upper end of the prediabetes range were at a greater risk for type 2 diabetes. But those individuals were the minority. Adolescents with overweight/obesity who had baseline A1c levels in the lower end of the prediabetes range, 5.7%-5.8%, accounted for two thirds of those with prediabetes in the study population and had a very low incidence of type 2 diabetes compared with those with higher A1c levels.
“Specifically, we found an annual type 2 diabetes incidence of 0.2% for HbA1c of 5.7%-5.8%, which is much lower than adults. These adolescents will likely benefit from lifestyle intervention. But because their risk of developing type 2 diabetes is lower, they probably don’t need to be screened annually, as currently recommended by the ADA,” Dr. Hoe said.
Similarly, he added, “since obesity severity was associated with a higher risk for type 2 diabetes, increases in BMI percentile should also prompt consideration of repeat diabetes screening.”
Large Database Allows for Detailed Findings
The study population was 74,552 adolescents aged 10-17 years with overweight or obesity, of whom 49.4% were male, 64.6% were younger than 15 years, and 73.1% had obesity. Only 21.6% were White, while 43.6% were Hispanic, 11.1% Black, and 17.6% Asian or Pacific Islander.
Nearly a quarter, 22.9%, had baseline A1c in the prediabetes range of 5.7%-6.4%. Mean A1c rose with BMI category from overweight to moderate to severe obesity (P < .001 for each comparison). Baseline A1c was highest (5.53%) in Black adolescents and lowest in White teens (5.38%), also significant differences by group (P < .001).
Of the total 698 who developed diabetes during the follow-up, 89.7% were classified as having type 2 diabetes, with a median 3.8 years from baseline to diagnosis.
The overall incidence rate of type 2 diabetes during the follow-up was 2.1 per 1000 person-years. As the baseline A1c rose from less than 5.5% to 6.0%, from 6.1% to 6.2%, and from 6.3% to 6.4%, those incidence rates were 0.8, 8.1, 21.8, and 68.9 per 1000 person-years, respectively.
In a multivariate analysis, compared to baseline A1c below 5.5%, increased risk was ninefold for A1c 5.9%-6.0%, 23-fold for 6.1%-6.2%, and 72-fold for 6.3%-6.4%.
The incidence rates were higher in female than in male adolescents (2.4 vs 1.8 per 1000 person-years) and increased by BMI category from 0.6 to 1.3 to 4.3 for those with overweight, moderate obesity, and severe obesity, respectively.
Type 2 diabetes incidence per 1000 person-years also varied by race and ethnicity, ranging from 1.3 for White adolescents to 3.0 for Asian or Pacific Islanders.
“We plan on further exploring the effect of the weight and BMI change over time and how that may affect type 2 diabetes risk,” Dr. Hoe told this news organization.
This study was supported by a grant from the Kaiser Permanente Northern California Community Health program. Dr. Hoe and his coauthors had no further disclosures.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
A1c level strongly predicts the risk of developing type 2 diabetes among adolescents with overweight or obesity, new data suggested.
In a large California healthcare database over a 10-year period, the incidence of type 2 diabetes was relatively low overall among adolescents with overweight and obesity. However, the risk increased with baseline A1c levels above 6.0% as well as in those with more severe obesity, women, and Asian or Pacific Islanders.
The new findings were published online in JAMA Network Open by pediatric endocrinologist Francis M. Hoe, MD, of Kaiser Permanente Roseville Medical Center, Roseville, California, and colleagues.
Previous studies have examined the incidence of type 2 diabetes among all youth, regardless of weight class. This is one of the first large population studies to examine the incidence and risk for type 2 diabetes by incremental level of A1c in a racially and ethnically diverse group of youth with overweight and obesity, Dr. Hoe told this news organization in an interview.
“This study was only possible to do because Kaiser Permanente Northern California has nearly 1 million pediatric members. The biggest thing we learned is that risk for type 2 diabetes is low in overweight and obese youth, especially those with an HbA1c less than 5.9%,” he said.
Zeroing in on Those at Greatest Risk for Type 2 Diabetes
Currently, the American Diabetes Association (ADA) recommends screening for type 2 diabetes in adolescents with overweight (body mass index [BMI], 85th percentile or greater) or obesity (≥ 95th) who have at least one additional risk factor, including family history of type 2 diabetes and Native American, Black, or Hispanic ethnicity. About one in four US adolescents qualify by those criteria, the authors noted in the paper.
And, as for adults, ADA recommends subsequent annual diabetes screening in youth identified as having “prediabetes,” that is, a A1c level between 5.7% and 6.5%.
The new study confirmed that adolescents with A1c in the upper end of the prediabetes range were at a greater risk for type 2 diabetes. But those individuals were the minority. Adolescents with overweight/obesity who had baseline A1c levels in the lower end of the prediabetes range, 5.7%-5.8%, accounted for two thirds of those with prediabetes in the study population and had a very low incidence of type 2 diabetes compared with those with higher A1c levels.
“Specifically, we found an annual type 2 diabetes incidence of 0.2% for HbA1c of 5.7%-5.8%, which is much lower than adults. These adolescents will likely benefit from lifestyle intervention. But because their risk of developing type 2 diabetes is lower, they probably don’t need to be screened annually, as currently recommended by the ADA,” Dr. Hoe said.
Similarly, he added, “since obesity severity was associated with a higher risk for type 2 diabetes, increases in BMI percentile should also prompt consideration of repeat diabetes screening.”
Large Database Allows for Detailed Findings
The study population was 74,552 adolescents aged 10-17 years with overweight or obesity, of whom 49.4% were male, 64.6% were younger than 15 years, and 73.1% had obesity. Only 21.6% were White, while 43.6% were Hispanic, 11.1% Black, and 17.6% Asian or Pacific Islander.
Nearly a quarter, 22.9%, had baseline A1c in the prediabetes range of 5.7%-6.4%. Mean A1c rose with BMI category from overweight to moderate to severe obesity (P < .001 for each comparison). Baseline A1c was highest (5.53%) in Black adolescents and lowest in White teens (5.38%), also significant differences by group (P < .001).
Of the total 698 who developed diabetes during the follow-up, 89.7% were classified as having type 2 diabetes, with a median 3.8 years from baseline to diagnosis.
The overall incidence rate of type 2 diabetes during the follow-up was 2.1 per 1000 person-years. As the baseline A1c rose from less than 5.5% to 6.0%, from 6.1% to 6.2%, and from 6.3% to 6.4%, those incidence rates were 0.8, 8.1, 21.8, and 68.9 per 1000 person-years, respectively.
In a multivariate analysis, compared to baseline A1c below 5.5%, increased risk was ninefold for A1c 5.9%-6.0%, 23-fold for 6.1%-6.2%, and 72-fold for 6.3%-6.4%.
The incidence rates were higher in female than in male adolescents (2.4 vs 1.8 per 1000 person-years) and increased by BMI category from 0.6 to 1.3 to 4.3 for those with overweight, moderate obesity, and severe obesity, respectively.
Type 2 diabetes incidence per 1000 person-years also varied by race and ethnicity, ranging from 1.3 for White adolescents to 3.0 for Asian or Pacific Islanders.
“We plan on further exploring the effect of the weight and BMI change over time and how that may affect type 2 diabetes risk,” Dr. Hoe told this news organization.
This study was supported by a grant from the Kaiser Permanente Northern California Community Health program. Dr. Hoe and his coauthors had no further disclosures.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
A1c level strongly predicts the risk of developing type 2 diabetes among adolescents with overweight or obesity, new data suggested.
In a large California healthcare database over a 10-year period, the incidence of type 2 diabetes was relatively low overall among adolescents with overweight and obesity. However, the risk increased with baseline A1c levels above 6.0% as well as in those with more severe obesity, women, and Asian or Pacific Islanders.
The new findings were published online in JAMA Network Open by pediatric endocrinologist Francis M. Hoe, MD, of Kaiser Permanente Roseville Medical Center, Roseville, California, and colleagues.
Previous studies have examined the incidence of type 2 diabetes among all youth, regardless of weight class. This is one of the first large population studies to examine the incidence and risk for type 2 diabetes by incremental level of A1c in a racially and ethnically diverse group of youth with overweight and obesity, Dr. Hoe told this news organization in an interview.
“This study was only possible to do because Kaiser Permanente Northern California has nearly 1 million pediatric members. The biggest thing we learned is that risk for type 2 diabetes is low in overweight and obese youth, especially those with an HbA1c less than 5.9%,” he said.
Zeroing in on Those at Greatest Risk for Type 2 Diabetes
Currently, the American Diabetes Association (ADA) recommends screening for type 2 diabetes in adolescents with overweight (body mass index [BMI], 85th percentile or greater) or obesity (≥ 95th) who have at least one additional risk factor, including family history of type 2 diabetes and Native American, Black, or Hispanic ethnicity. About one in four US adolescents qualify by those criteria, the authors noted in the paper.
And, as for adults, ADA recommends subsequent annual diabetes screening in youth identified as having “prediabetes,” that is, a A1c level between 5.7% and 6.5%.
The new study confirmed that adolescents with A1c in the upper end of the prediabetes range were at a greater risk for type 2 diabetes. But those individuals were the minority. Adolescents with overweight/obesity who had baseline A1c levels in the lower end of the prediabetes range, 5.7%-5.8%, accounted for two thirds of those with prediabetes in the study population and had a very low incidence of type 2 diabetes compared with those with higher A1c levels.
“Specifically, we found an annual type 2 diabetes incidence of 0.2% for HbA1c of 5.7%-5.8%, which is much lower than adults. These adolescents will likely benefit from lifestyle intervention. But because their risk of developing type 2 diabetes is lower, they probably don’t need to be screened annually, as currently recommended by the ADA,” Dr. Hoe said.
Similarly, he added, “since obesity severity was associated with a higher risk for type 2 diabetes, increases in BMI percentile should also prompt consideration of repeat diabetes screening.”
Large Database Allows for Detailed Findings
The study population was 74,552 adolescents aged 10-17 years with overweight or obesity, of whom 49.4% were male, 64.6% were younger than 15 years, and 73.1% had obesity. Only 21.6% were White, while 43.6% were Hispanic, 11.1% Black, and 17.6% Asian or Pacific Islander.
Nearly a quarter, 22.9%, had baseline A1c in the prediabetes range of 5.7%-6.4%. Mean A1c rose with BMI category from overweight to moderate to severe obesity (P < .001 for each comparison). Baseline A1c was highest (5.53%) in Black adolescents and lowest in White teens (5.38%), also significant differences by group (P < .001).
Of the total 698 who developed diabetes during the follow-up, 89.7% were classified as having type 2 diabetes, with a median 3.8 years from baseline to diagnosis.
The overall incidence rate of type 2 diabetes during the follow-up was 2.1 per 1000 person-years. As the baseline A1c rose from less than 5.5% to 6.0%, from 6.1% to 6.2%, and from 6.3% to 6.4%, those incidence rates were 0.8, 8.1, 21.8, and 68.9 per 1000 person-years, respectively.
In a multivariate analysis, compared to baseline A1c below 5.5%, increased risk was ninefold for A1c 5.9%-6.0%, 23-fold for 6.1%-6.2%, and 72-fold for 6.3%-6.4%.
The incidence rates were higher in female than in male adolescents (2.4 vs 1.8 per 1000 person-years) and increased by BMI category from 0.6 to 1.3 to 4.3 for those with overweight, moderate obesity, and severe obesity, respectively.
Type 2 diabetes incidence per 1000 person-years also varied by race and ethnicity, ranging from 1.3 for White adolescents to 3.0 for Asian or Pacific Islanders.
“We plan on further exploring the effect of the weight and BMI change over time and how that may affect type 2 diabetes risk,” Dr. Hoe told this news organization.
This study was supported by a grant from the Kaiser Permanente Northern California Community Health program. Dr. Hoe and his coauthors had no further disclosures.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM JAMA NETWORK OPEN
Why Is Kidney Disease So Often Missed?
Nearly 37 million Americans, or 15%, have chronic kidney disease (CKD), but 9 in 10 adults with the condition are not aware of their diagnosis. A recent study from Stanford University found that
What should primary care providers be doing differently?
The current standard of care is to screen people with underlying conditions that put them at higher risk of developing CKD, most commonly diabetes and hypertension. That’s why the American Diabetes Association recommends annual screening for CKD in patients with type 1 diabetes as well as those with type 2 diabetes.
And the American Heart Association (AHA) released an advisory last year that defined cardiovascular-kidney-metabolic (CKM) syndrome, a constellation of conditions that often occur together: obesity, diabetes, CKD, and cardiovascular disease. They propose a staged approach to identifying and monitoring CKM throughout the lifespan, which includes regular monitoring of the urine albumin-creatinine ratio in patients who have developed diabetes, hypertension, metabolic syndrome, or any signs of kidney disease.
But despite recognition from the subspecialty professional societies of the importance of screening persons with risk factors — additional conditions are obesity and family history of CKD — real-world implementation lags.
Sylvia Rosas, MD, is a nephrologist and associate professor of medicine at Harvard University in Cambridge, Massachusetts, who also serves as president of the National Kidney Foundation. In an interview with this news organization, she cited several alarming facts about the state of CKD screening in the United States.
“Of people with diabetes who have insurance, only 40% get both the glomerular filtration rate (GFR) and the albumin performed, and for those who have hypertension, only 10%,” Dr. Rosas said. She is referring to a urine spot test that measures the amount of albumin in the urine, which is then paired with a serum measurement of creatinine to estimate the glomerular filtration rate. Both tests are needed to detect the asymptomatic stages of CKD, because the presence of albumin in the urine usually precedes drops in the GFR, which indicates more serious disease.
Dr. Rosas said she is frustrated by the low rate of testing compared with other commonly recommended preventive screenings, given the low cost and simplicity of assessment. Serum creatinine often is obtained as part of a routine chemistry panel, and the albumin test requires a single spot urine test. Yet, in 2018, 61% of US adults aged 50-75 years had received a colonoscopy in the past 10 years. Compared with the high price and inconvenience of undergoing colonoscopy, Dr. Rosas has trouble believing that “we cannot get more than 40% of people [with diabetes] to pee in a cup.”
But the biggest issue is that if people with risk factors don’t get screened before they develop symptoms of CKD, it is often too late to avoid dialysis or the need for transplantation.
The early warning symptoms are few, according to Nisha Bansal, MD, a professor in the department of nephrology at the University of Washington in Seattle. “New hypertension is a really important early sign,” Dr. Bansal said. “We know kidney disease almost certainly causes hypertension, so I would definitely think about screening for kidney disease.” Other findings on exam are the appearance of new edema or signs of fluid retention in the hands or around the eyes, along with findings in the urine of albumin, protein, or blood.
But most patients don’t have any symptoms in the early stages, and they can be nonspecific. “It is fatigue and some nausea,” Dr. Rosas said. “It’s only way at the end that you start vomiting, get itchy, or have hiccups.” Data from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention have shown that over one third of patients at high risk for kidney failure are unaware of their disease. According to Dr. Rosas, these are patients who often receive the diagnosis of CKD and start dialysis the same day.
Why Not Screen Everyone?
For many conditions, like HIV or different types of cancer, the US Preventive Services Task Force (USPSTF) recommends broad screening of asymptomatic individuals so that early treatment can improve outcomes.
But when the USPSTF considered the question in 2012 of whether adults should be screened for CKD regardless of symptoms, it found little evidence that early detection could change the course of their illness. At that time, the standard of care for treating early stages of CKD generally focused on treating the comorbid conditions, such as diabetes, hypertension, and cardiovascular disease.
But the equation has changed with the availability of new drugs to treat CKD, such as sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 (SGLT2) inhibitors and mineralocorticoid receptor antagonists (MRAs).
“I consider these blockbuster drugs,” Dr. Bansal said. “For the first time in decades, we’re showing that this class of medications, the SGLT2 inhibitors, substantially reduce risk of loss of kidney function.”
Expressed in the lumen of the proximal renal tubules, SGLT2 reabsorbs filtered glucose from the tubular lumen. Inhibition of SGLT2 promotes urinary glucose excretion and reduces sodium reabsorption, increasing delivery of sodium to the distal tubule. The first SGLT2 inhibitor, canagliflozin, was approved in 2013 for use as an antihyperglycemic agent but subsequently was shown to have serendipitous benefits for the heart and kidneys.
Clinical trials have documented reductions in the risk for cardiovascular events in patients with type 2 diabetes, as well as decreases in the risk for progression to end-stage renal disease, cardiovascular mortality, and hospitalization for heart failure. Updated international guidelines from 2022 recommend treating all patients with type 2 diabetes and CKD with an estimated GFR ≥ 20 mL/min/1.73 m2 with an SGLT2 inhibitor.
But several trials of SGLT2 inhibitors also demonstrated benefits in reducing the risk for cardiovascular-related death or hospitalization for heart failure, even in patients without diabetes. Although initial approval from the US Food and Drug Administration was limited to patients with diabetes and heart failure, the agency has recently expanded its indications to include adults with CKD who do not have diabetes.
Dr. Bansal said she was happy to see this widening of the indications, which makes more patients eligible to receive SGLT2 inhibitors. “I really think this early CKD group is a great group to consider for those medications,” she said.
Dr. Bansal also pointed out that MRAs are another class of drugs with an interesting history. Earlier steroidal MRAs were found to have anti-inflammatory and antifibrotic properties, and in 1960 spironolactone was approved for use as a diuretic for the management of edema, primary aldosteronism, and hypertension. But even as their use in cardiology rose, MRAs had less utility for CKD, given adverse events such as hyperkalemia and hormonal effects like gynecomastia.
But the latest generation of nonsteroidal MRAs (nsMRAs) has higher selectivity for the mineralocorticoid receptor than sex-steroid hormone receptors, reducing androgenic side effects and preventing elevated potassium. Finerenone, the only nsMRA approved in the United States, has been shown in clinical trials to reduce the incidence of cardiovascular events (death from cardiovascular causes, nonfatal myocardial infarction, nonfatal stroke, or hospitalization for heart failure) and CKD outcomes, including kidney failure, decrease in estimated GFR, or death from renal causes.
EPIC Changes Coming?
In light of treatment advances that offer hope of preventing progression of CKD in patients identified early, both the National Kidney Foundation and the American Kidney Fund lobbied the USPSTF in 2022 to conduct a fresh review of recent data to evaluate the need for updated screening recommendations.
The task force completed development of a research plan and collection of public comments in early 2023 and is now reviewing evidence before developing a draft recommendation.
A team of health policy researchers from Stanford is hoping that some of their recently published work will attract the panel’s attention. The first study, published in 2022, evaluated the cost-effectiveness of dapagliflozin, an SGLT2 inhibitor that has been shown to reduce mortality by 48% in CKD patients without diabetes.
The Stanford team found that adding dapagliflozin to standard care for these patients improved life expectancy by 2 years and reduced the percentage of those who needed dialysis or kidney transplant from 17% to 11%.
More recently, Marika Cusick, a doctoral candidate in health policy at the Stanford School of Medicine in Stanford, California, served as first author of an evaluation of the cost-effectiveness of screening asymptomatic adults. “We assessed screening for albuminuria in conjunction with conventional CKD therapy in addition to this new SGLT2 inhibitor class of drugs,” she said. They projected how this might change CKD progression in US adults who are aged 35 or older compared with standard therapy alone.
The findings were favorable. “A one-time screening would result in a reduction of 398,000 cases of kidney replacement therapy [defined as needing either dialysis or renal transplant] among 158 million US adults who are currently aged 35-75 years,” Ms. Cusick told this news organization.
In terms of quality-adjusted life years (QALYs), a one-time screening at age 55 years yielded an incremental cost-effectiveness ratio of $86,300 per QALY. Screening every 10 years between the ages of 35 and 75 years cost less than $100,000 per QALY gained.
According to Doug Owens, MD, professor and chair of the department of health policy at Stanford School of Medicine, “There’s a societal decision about how much are we willing to pay for additional length and quality of life. And this fits within what is generally considered reasonable for the US.”
For example, in the United States, screening for breast cancer among women aged 40-64 years costs $51,000 per QALY, whereas screening for lung cancer using USPSTF guidelines ranges from $72,639 to $156,774 per QALY.
A former member of the USPSTF, Owens predicted that the current review process would take at least another year. Meanwhile, he and Ms. Cusick are hoping that their work influences the USPSTF to recommend screening asymptomatic adults. “Increasing the awareness of these drugs and their effectiveness is a crucial first step,” he said.
Although adherence to current recommendations for screening of people at risk is poor, Dr. Rosas suggested that the USPSTF guidelines would be more influential in changing practice among primary care physicians than subspecialty guidelines would.
“When you have a recommendation like that, they’re putting it in the electronic health record,” she said. By adding best practice alerts to their electronic health record systems, health systems can make it easier for primary care doctors to check all the boxes.
In line with the AHA’s holistic approach towards managing cardiovascular illnesses, CKD, and metabolic disease, Dr. Bansal suggested an additional strategy: “I think we’re moving toward more interdisciplinary care models, where primary care doctors, nephrologist, cardiologists, and endocrinologists — all of us — should be working together in a collaborative care model, to help break down some of these barriers in terms of screening as well as implementation of these therapies.”
Dr. Bansal, Ms. Cusick, and Dr. Owens reported no financial conflicts of interest. Dr. Rosas receives funding from AstraZeneca and Bayer for serving on advisory boards and clinical research funding, as well as funding from the National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases for clinical trials.
Dr. Thomas is a pediatrician and epidemiologist living in Portland, Oregon.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Nearly 37 million Americans, or 15%, have chronic kidney disease (CKD), but 9 in 10 adults with the condition are not aware of their diagnosis. A recent study from Stanford University found that
What should primary care providers be doing differently?
The current standard of care is to screen people with underlying conditions that put them at higher risk of developing CKD, most commonly diabetes and hypertension. That’s why the American Diabetes Association recommends annual screening for CKD in patients with type 1 diabetes as well as those with type 2 diabetes.
And the American Heart Association (AHA) released an advisory last year that defined cardiovascular-kidney-metabolic (CKM) syndrome, a constellation of conditions that often occur together: obesity, diabetes, CKD, and cardiovascular disease. They propose a staged approach to identifying and monitoring CKM throughout the lifespan, which includes regular monitoring of the urine albumin-creatinine ratio in patients who have developed diabetes, hypertension, metabolic syndrome, or any signs of kidney disease.
But despite recognition from the subspecialty professional societies of the importance of screening persons with risk factors — additional conditions are obesity and family history of CKD — real-world implementation lags.
Sylvia Rosas, MD, is a nephrologist and associate professor of medicine at Harvard University in Cambridge, Massachusetts, who also serves as president of the National Kidney Foundation. In an interview with this news organization, she cited several alarming facts about the state of CKD screening in the United States.
“Of people with diabetes who have insurance, only 40% get both the glomerular filtration rate (GFR) and the albumin performed, and for those who have hypertension, only 10%,” Dr. Rosas said. She is referring to a urine spot test that measures the amount of albumin in the urine, which is then paired with a serum measurement of creatinine to estimate the glomerular filtration rate. Both tests are needed to detect the asymptomatic stages of CKD, because the presence of albumin in the urine usually precedes drops in the GFR, which indicates more serious disease.
Dr. Rosas said she is frustrated by the low rate of testing compared with other commonly recommended preventive screenings, given the low cost and simplicity of assessment. Serum creatinine often is obtained as part of a routine chemistry panel, and the albumin test requires a single spot urine test. Yet, in 2018, 61% of US adults aged 50-75 years had received a colonoscopy in the past 10 years. Compared with the high price and inconvenience of undergoing colonoscopy, Dr. Rosas has trouble believing that “we cannot get more than 40% of people [with diabetes] to pee in a cup.”
But the biggest issue is that if people with risk factors don’t get screened before they develop symptoms of CKD, it is often too late to avoid dialysis or the need for transplantation.
The early warning symptoms are few, according to Nisha Bansal, MD, a professor in the department of nephrology at the University of Washington in Seattle. “New hypertension is a really important early sign,” Dr. Bansal said. “We know kidney disease almost certainly causes hypertension, so I would definitely think about screening for kidney disease.” Other findings on exam are the appearance of new edema or signs of fluid retention in the hands or around the eyes, along with findings in the urine of albumin, protein, or blood.
But most patients don’t have any symptoms in the early stages, and they can be nonspecific. “It is fatigue and some nausea,” Dr. Rosas said. “It’s only way at the end that you start vomiting, get itchy, or have hiccups.” Data from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention have shown that over one third of patients at high risk for kidney failure are unaware of their disease. According to Dr. Rosas, these are patients who often receive the diagnosis of CKD and start dialysis the same day.
Why Not Screen Everyone?
For many conditions, like HIV or different types of cancer, the US Preventive Services Task Force (USPSTF) recommends broad screening of asymptomatic individuals so that early treatment can improve outcomes.
But when the USPSTF considered the question in 2012 of whether adults should be screened for CKD regardless of symptoms, it found little evidence that early detection could change the course of their illness. At that time, the standard of care for treating early stages of CKD generally focused on treating the comorbid conditions, such as diabetes, hypertension, and cardiovascular disease.
But the equation has changed with the availability of new drugs to treat CKD, such as sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 (SGLT2) inhibitors and mineralocorticoid receptor antagonists (MRAs).
“I consider these blockbuster drugs,” Dr. Bansal said. “For the first time in decades, we’re showing that this class of medications, the SGLT2 inhibitors, substantially reduce risk of loss of kidney function.”
Expressed in the lumen of the proximal renal tubules, SGLT2 reabsorbs filtered glucose from the tubular lumen. Inhibition of SGLT2 promotes urinary glucose excretion and reduces sodium reabsorption, increasing delivery of sodium to the distal tubule. The first SGLT2 inhibitor, canagliflozin, was approved in 2013 for use as an antihyperglycemic agent but subsequently was shown to have serendipitous benefits for the heart and kidneys.
Clinical trials have documented reductions in the risk for cardiovascular events in patients with type 2 diabetes, as well as decreases in the risk for progression to end-stage renal disease, cardiovascular mortality, and hospitalization for heart failure. Updated international guidelines from 2022 recommend treating all patients with type 2 diabetes and CKD with an estimated GFR ≥ 20 mL/min/1.73 m2 with an SGLT2 inhibitor.
But several trials of SGLT2 inhibitors also demonstrated benefits in reducing the risk for cardiovascular-related death or hospitalization for heart failure, even in patients without diabetes. Although initial approval from the US Food and Drug Administration was limited to patients with diabetes and heart failure, the agency has recently expanded its indications to include adults with CKD who do not have diabetes.
Dr. Bansal said she was happy to see this widening of the indications, which makes more patients eligible to receive SGLT2 inhibitors. “I really think this early CKD group is a great group to consider for those medications,” she said.
Dr. Bansal also pointed out that MRAs are another class of drugs with an interesting history. Earlier steroidal MRAs were found to have anti-inflammatory and antifibrotic properties, and in 1960 spironolactone was approved for use as a diuretic for the management of edema, primary aldosteronism, and hypertension. But even as their use in cardiology rose, MRAs had less utility for CKD, given adverse events such as hyperkalemia and hormonal effects like gynecomastia.
But the latest generation of nonsteroidal MRAs (nsMRAs) has higher selectivity for the mineralocorticoid receptor than sex-steroid hormone receptors, reducing androgenic side effects and preventing elevated potassium. Finerenone, the only nsMRA approved in the United States, has been shown in clinical trials to reduce the incidence of cardiovascular events (death from cardiovascular causes, nonfatal myocardial infarction, nonfatal stroke, or hospitalization for heart failure) and CKD outcomes, including kidney failure, decrease in estimated GFR, or death from renal causes.
EPIC Changes Coming?
In light of treatment advances that offer hope of preventing progression of CKD in patients identified early, both the National Kidney Foundation and the American Kidney Fund lobbied the USPSTF in 2022 to conduct a fresh review of recent data to evaluate the need for updated screening recommendations.
The task force completed development of a research plan and collection of public comments in early 2023 and is now reviewing evidence before developing a draft recommendation.
A team of health policy researchers from Stanford is hoping that some of their recently published work will attract the panel’s attention. The first study, published in 2022, evaluated the cost-effectiveness of dapagliflozin, an SGLT2 inhibitor that has been shown to reduce mortality by 48% in CKD patients without diabetes.
The Stanford team found that adding dapagliflozin to standard care for these patients improved life expectancy by 2 years and reduced the percentage of those who needed dialysis or kidney transplant from 17% to 11%.
More recently, Marika Cusick, a doctoral candidate in health policy at the Stanford School of Medicine in Stanford, California, served as first author of an evaluation of the cost-effectiveness of screening asymptomatic adults. “We assessed screening for albuminuria in conjunction with conventional CKD therapy in addition to this new SGLT2 inhibitor class of drugs,” she said. They projected how this might change CKD progression in US adults who are aged 35 or older compared with standard therapy alone.
The findings were favorable. “A one-time screening would result in a reduction of 398,000 cases of kidney replacement therapy [defined as needing either dialysis or renal transplant] among 158 million US adults who are currently aged 35-75 years,” Ms. Cusick told this news organization.
In terms of quality-adjusted life years (QALYs), a one-time screening at age 55 years yielded an incremental cost-effectiveness ratio of $86,300 per QALY. Screening every 10 years between the ages of 35 and 75 years cost less than $100,000 per QALY gained.
According to Doug Owens, MD, professor and chair of the department of health policy at Stanford School of Medicine, “There’s a societal decision about how much are we willing to pay for additional length and quality of life. And this fits within what is generally considered reasonable for the US.”
For example, in the United States, screening for breast cancer among women aged 40-64 years costs $51,000 per QALY, whereas screening for lung cancer using USPSTF guidelines ranges from $72,639 to $156,774 per QALY.
A former member of the USPSTF, Owens predicted that the current review process would take at least another year. Meanwhile, he and Ms. Cusick are hoping that their work influences the USPSTF to recommend screening asymptomatic adults. “Increasing the awareness of these drugs and their effectiveness is a crucial first step,” he said.
Although adherence to current recommendations for screening of people at risk is poor, Dr. Rosas suggested that the USPSTF guidelines would be more influential in changing practice among primary care physicians than subspecialty guidelines would.
“When you have a recommendation like that, they’re putting it in the electronic health record,” she said. By adding best practice alerts to their electronic health record systems, health systems can make it easier for primary care doctors to check all the boxes.
In line with the AHA’s holistic approach towards managing cardiovascular illnesses, CKD, and metabolic disease, Dr. Bansal suggested an additional strategy: “I think we’re moving toward more interdisciplinary care models, where primary care doctors, nephrologist, cardiologists, and endocrinologists — all of us — should be working together in a collaborative care model, to help break down some of these barriers in terms of screening as well as implementation of these therapies.”
Dr. Bansal, Ms. Cusick, and Dr. Owens reported no financial conflicts of interest. Dr. Rosas receives funding from AstraZeneca and Bayer for serving on advisory boards and clinical research funding, as well as funding from the National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases for clinical trials.
Dr. Thomas is a pediatrician and epidemiologist living in Portland, Oregon.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Nearly 37 million Americans, or 15%, have chronic kidney disease (CKD), but 9 in 10 adults with the condition are not aware of their diagnosis. A recent study from Stanford University found that
What should primary care providers be doing differently?
The current standard of care is to screen people with underlying conditions that put them at higher risk of developing CKD, most commonly diabetes and hypertension. That’s why the American Diabetes Association recommends annual screening for CKD in patients with type 1 diabetes as well as those with type 2 diabetes.
And the American Heart Association (AHA) released an advisory last year that defined cardiovascular-kidney-metabolic (CKM) syndrome, a constellation of conditions that often occur together: obesity, diabetes, CKD, and cardiovascular disease. They propose a staged approach to identifying and monitoring CKM throughout the lifespan, which includes regular monitoring of the urine albumin-creatinine ratio in patients who have developed diabetes, hypertension, metabolic syndrome, or any signs of kidney disease.
But despite recognition from the subspecialty professional societies of the importance of screening persons with risk factors — additional conditions are obesity and family history of CKD — real-world implementation lags.
Sylvia Rosas, MD, is a nephrologist and associate professor of medicine at Harvard University in Cambridge, Massachusetts, who also serves as president of the National Kidney Foundation. In an interview with this news organization, she cited several alarming facts about the state of CKD screening in the United States.
“Of people with diabetes who have insurance, only 40% get both the glomerular filtration rate (GFR) and the albumin performed, and for those who have hypertension, only 10%,” Dr. Rosas said. She is referring to a urine spot test that measures the amount of albumin in the urine, which is then paired with a serum measurement of creatinine to estimate the glomerular filtration rate. Both tests are needed to detect the asymptomatic stages of CKD, because the presence of albumin in the urine usually precedes drops in the GFR, which indicates more serious disease.
Dr. Rosas said she is frustrated by the low rate of testing compared with other commonly recommended preventive screenings, given the low cost and simplicity of assessment. Serum creatinine often is obtained as part of a routine chemistry panel, and the albumin test requires a single spot urine test. Yet, in 2018, 61% of US adults aged 50-75 years had received a colonoscopy in the past 10 years. Compared with the high price and inconvenience of undergoing colonoscopy, Dr. Rosas has trouble believing that “we cannot get more than 40% of people [with diabetes] to pee in a cup.”
But the biggest issue is that if people with risk factors don’t get screened before they develop symptoms of CKD, it is often too late to avoid dialysis or the need for transplantation.
The early warning symptoms are few, according to Nisha Bansal, MD, a professor in the department of nephrology at the University of Washington in Seattle. “New hypertension is a really important early sign,” Dr. Bansal said. “We know kidney disease almost certainly causes hypertension, so I would definitely think about screening for kidney disease.” Other findings on exam are the appearance of new edema or signs of fluid retention in the hands or around the eyes, along with findings in the urine of albumin, protein, or blood.
But most patients don’t have any symptoms in the early stages, and they can be nonspecific. “It is fatigue and some nausea,” Dr. Rosas said. “It’s only way at the end that you start vomiting, get itchy, or have hiccups.” Data from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention have shown that over one third of patients at high risk for kidney failure are unaware of their disease. According to Dr. Rosas, these are patients who often receive the diagnosis of CKD and start dialysis the same day.
Why Not Screen Everyone?
For many conditions, like HIV or different types of cancer, the US Preventive Services Task Force (USPSTF) recommends broad screening of asymptomatic individuals so that early treatment can improve outcomes.
But when the USPSTF considered the question in 2012 of whether adults should be screened for CKD regardless of symptoms, it found little evidence that early detection could change the course of their illness. At that time, the standard of care for treating early stages of CKD generally focused on treating the comorbid conditions, such as diabetes, hypertension, and cardiovascular disease.
But the equation has changed with the availability of new drugs to treat CKD, such as sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 (SGLT2) inhibitors and mineralocorticoid receptor antagonists (MRAs).
“I consider these blockbuster drugs,” Dr. Bansal said. “For the first time in decades, we’re showing that this class of medications, the SGLT2 inhibitors, substantially reduce risk of loss of kidney function.”
Expressed in the lumen of the proximal renal tubules, SGLT2 reabsorbs filtered glucose from the tubular lumen. Inhibition of SGLT2 promotes urinary glucose excretion and reduces sodium reabsorption, increasing delivery of sodium to the distal tubule. The first SGLT2 inhibitor, canagliflozin, was approved in 2013 for use as an antihyperglycemic agent but subsequently was shown to have serendipitous benefits for the heart and kidneys.
Clinical trials have documented reductions in the risk for cardiovascular events in patients with type 2 diabetes, as well as decreases in the risk for progression to end-stage renal disease, cardiovascular mortality, and hospitalization for heart failure. Updated international guidelines from 2022 recommend treating all patients with type 2 diabetes and CKD with an estimated GFR ≥ 20 mL/min/1.73 m2 with an SGLT2 inhibitor.
But several trials of SGLT2 inhibitors also demonstrated benefits in reducing the risk for cardiovascular-related death or hospitalization for heart failure, even in patients without diabetes. Although initial approval from the US Food and Drug Administration was limited to patients with diabetes and heart failure, the agency has recently expanded its indications to include adults with CKD who do not have diabetes.
Dr. Bansal said she was happy to see this widening of the indications, which makes more patients eligible to receive SGLT2 inhibitors. “I really think this early CKD group is a great group to consider for those medications,” she said.
Dr. Bansal also pointed out that MRAs are another class of drugs with an interesting history. Earlier steroidal MRAs were found to have anti-inflammatory and antifibrotic properties, and in 1960 spironolactone was approved for use as a diuretic for the management of edema, primary aldosteronism, and hypertension. But even as their use in cardiology rose, MRAs had less utility for CKD, given adverse events such as hyperkalemia and hormonal effects like gynecomastia.
But the latest generation of nonsteroidal MRAs (nsMRAs) has higher selectivity for the mineralocorticoid receptor than sex-steroid hormone receptors, reducing androgenic side effects and preventing elevated potassium. Finerenone, the only nsMRA approved in the United States, has been shown in clinical trials to reduce the incidence of cardiovascular events (death from cardiovascular causes, nonfatal myocardial infarction, nonfatal stroke, or hospitalization for heart failure) and CKD outcomes, including kidney failure, decrease in estimated GFR, or death from renal causes.
EPIC Changes Coming?
In light of treatment advances that offer hope of preventing progression of CKD in patients identified early, both the National Kidney Foundation and the American Kidney Fund lobbied the USPSTF in 2022 to conduct a fresh review of recent data to evaluate the need for updated screening recommendations.
The task force completed development of a research plan and collection of public comments in early 2023 and is now reviewing evidence before developing a draft recommendation.
A team of health policy researchers from Stanford is hoping that some of their recently published work will attract the panel’s attention. The first study, published in 2022, evaluated the cost-effectiveness of dapagliflozin, an SGLT2 inhibitor that has been shown to reduce mortality by 48% in CKD patients without diabetes.
The Stanford team found that adding dapagliflozin to standard care for these patients improved life expectancy by 2 years and reduced the percentage of those who needed dialysis or kidney transplant from 17% to 11%.
More recently, Marika Cusick, a doctoral candidate in health policy at the Stanford School of Medicine in Stanford, California, served as first author of an evaluation of the cost-effectiveness of screening asymptomatic adults. “We assessed screening for albuminuria in conjunction with conventional CKD therapy in addition to this new SGLT2 inhibitor class of drugs,” she said. They projected how this might change CKD progression in US adults who are aged 35 or older compared with standard therapy alone.
The findings were favorable. “A one-time screening would result in a reduction of 398,000 cases of kidney replacement therapy [defined as needing either dialysis or renal transplant] among 158 million US adults who are currently aged 35-75 years,” Ms. Cusick told this news organization.
In terms of quality-adjusted life years (QALYs), a one-time screening at age 55 years yielded an incremental cost-effectiveness ratio of $86,300 per QALY. Screening every 10 years between the ages of 35 and 75 years cost less than $100,000 per QALY gained.
According to Doug Owens, MD, professor and chair of the department of health policy at Stanford School of Medicine, “There’s a societal decision about how much are we willing to pay for additional length and quality of life. And this fits within what is generally considered reasonable for the US.”
For example, in the United States, screening for breast cancer among women aged 40-64 years costs $51,000 per QALY, whereas screening for lung cancer using USPSTF guidelines ranges from $72,639 to $156,774 per QALY.
A former member of the USPSTF, Owens predicted that the current review process would take at least another year. Meanwhile, he and Ms. Cusick are hoping that their work influences the USPSTF to recommend screening asymptomatic adults. “Increasing the awareness of these drugs and their effectiveness is a crucial first step,” he said.
Although adherence to current recommendations for screening of people at risk is poor, Dr. Rosas suggested that the USPSTF guidelines would be more influential in changing practice among primary care physicians than subspecialty guidelines would.
“When you have a recommendation like that, they’re putting it in the electronic health record,” she said. By adding best practice alerts to their electronic health record systems, health systems can make it easier for primary care doctors to check all the boxes.
In line with the AHA’s holistic approach towards managing cardiovascular illnesses, CKD, and metabolic disease, Dr. Bansal suggested an additional strategy: “I think we’re moving toward more interdisciplinary care models, where primary care doctors, nephrologist, cardiologists, and endocrinologists — all of us — should be working together in a collaborative care model, to help break down some of these barriers in terms of screening as well as implementation of these therapies.”
Dr. Bansal, Ms. Cusick, and Dr. Owens reported no financial conflicts of interest. Dr. Rosas receives funding from AstraZeneca and Bayer for serving on advisory boards and clinical research funding, as well as funding from the National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases for clinical trials.
Dr. Thomas is a pediatrician and epidemiologist living in Portland, Oregon.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Tips and Techniques to Boost Colonoscopy Quality
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
When it comes to the use of colonoscopy to reduce the risk for cancer, quality is key.
There are a number of performance improvements we can make in our practices so that we can do better. This is evident in several recently published studies and a recent review article on the topic, which I’d like to profile for you; many of these key quality indicators you can implement now.
Even though it may take more time before they’re supported in the guidelines, you’ll see that the evidence behind these is extraordinarily strong.
Increasing the Adenoma Detection Rate
Certainly, we all do what we can to increase the adenoma detection rate (ADR).
However, at the moment, the nationally recommended benchmark is to achieve an ADR of 25%, which is inordinately low. The ADR rate reported in the GIQuIC registry data is closer to 39%, and in high-level detectors, it’s actually in the greater-than-50% range.
There’s no question that we can do more, and there are a number of ways to do that.
First, This may actually decrease your withdrawal time because you don’t spend so much time trying to face these folds.
In considering tools to aid ADR, don’t forget electronic chromoendoscopy (eg, narrow-band imaging).
There are a number of new artificial intelligence options out there as well, which have been reported to increase the ADR by approximately 10%. Of importance, this improvement even occurs among expert endoscopists.
There’s also important emerging data about ADR in fecal immunochemical test (FIT)–positive patients. FIT-positive status increases the ADR threshold by 15%-20%. This places you in an ADR range of approximately 50%, which is really the norm when screening patients that present for colonoscopy because of FIT positivity.
Adenoma Per Colonoscopy: A Possible ADR Substitute
Growing evidence supports the use of adenoma per colonoscopy (APC) as a substitute to ADR. This would allow you to record every adenoma and attribute it to that index colonoscopy.
A high-quality paper showed that the APC value should be around 0.6 to achieve the current ADR minimum threshold of 25%. Having the APC < 0.6 seems to be associated with an increased risk for residual polyp. Sessile serrated lesions also increased the hazard ratio for interval colorectal cancer. This was evaluated recently with data from the New Hampshire Colonoscopy Registry, which Dr Joseph Anderson has led for so long. They showed that 21% of endoscopists had an ADR of 25% or greater but still had APCs < 0.6.
Therefore, when it comes to remedial corrective work, doctors need to be reevaluated, retrained, and educated in the ways that they can incorporate this. The APC in high-level detectors is > 1.0.
APC may be something you want to consider using internally. It does require that you place each polyp into an individual jar, which can increase incremental cost. Nonetheless, there is clear evidence that APC positively changes outcomes.
Including Sessile Serrated Lesions in ADR Detectors
Unfortunately, some of the high-level ADR detectors aren’t so “high level” when it comes to detecting sessile serrated lesions. It’s not quite as concordant as we had previously thought.
Nonetheless, there are many adjunctive things you can do with sessile serrated lesions, including narrow-band imaging and chromoendoscopy.
When it comes to establishing a discriminant, the numbers should be 5%-6% if we’re going to set a quality ratio and an index. However, this is somewhat dependent on your pathologist because they have to read these correctly. Lesions that are ≥ 6 mm above the sigmoid colon and anything in the right colon should be evaluated really closely as a sessile serrated lesion.
I’ve had indications where the pathologist says the lesion is hyperplastic, to which I say, “I’m going to follow as a sessile serrated lesion.” This is because it’s apparent to me in the endoscopic appearance and the narrow-band imaging appearance that it was characteristic of sessile serrated lesions.
Best Practices in Bowel Preparations
The US Multi-Society Task Force recommends that adequate bowel preparation should occur in 85% or more of outpatients, and for the European Society for Gastrointestinal Endoscopy, it’s 90% or more.
I’ll pass along a tip I use in my patients undergoing bowel preparation: I make them aware that during this process, they want to see a clear, yellow, urine-like color to their stool. Otherwise, many patients will think if they’ve had some diarrhea, they don’t need to finish prep. Setting that expectation for them upfront is really important.
The nurses also should be aware of this because if there’s a murky brown effluent upon presentation for the colonoscopy, there’s a greater than 50% chance that they’re going to have had an inadequate preparation. In such cases, you would want to preempt the colonoscopy and perhaps send them out for a re-prep that day or bring them back for a rescheduled appointment.
Resection Considerations
There is substantial variation when it comes to lesion resection, which makes it an important quality indicator on which to focus: High-level detectors aren’t always high-level resectors.
There are two validated instruments that you can use to gauge the adequacy of resection. Those aren’t really ready for prime time in every practice, though they may be seen in fellowship programs.
The idea here is that you want to get a ≥ 2 mm margin for cold snare polypectomy in lesions 1-10 mm in size. This has been a challenge, as findings indicate we don’t do this that well.
Joseph Anderson and colleagues recently published a study using a 2-mm resection margin. They reported that this was only possible in approximately 28% of polyps. For a 1-mm margin, the rate was 84%.
We simply need to set clearer margins when setting our snare. Make sure you’re close enough to the polyp, push down on the snare, and get a good margin of tissue.
When the sample contracts are placed into the formalin, it’s not quite so simple to define the margin at the time of the surgical resection. This often requires an audit evaluation by the pathologist.
There are two other considerations regarding resection.
The first is about the referral for surgery. Referral should not occur for any benign lesions ascribed by your endoscopic advanced imaging techniques and classifications that are not thought to have intramucosal carcinoma. These should be referred to an expert endoscopic evaluation. If you can’t do it, then somebody else should. And you shouldn’t attempt it unless you can get it totally because resection of partially resected lesions is much more complicated. The European Society of Gastrointestinal Endoscopy says this applies to any benign lesion of any size, which I think really is the emerging standard of care. You should consider and offer that to the patient. It may require a referral for outside of your institution.
The second additional consideration is around the minimization of cold forceps for removal of polyps. The US Multi-Society Task Force says cold forceps shouldn’t be used for any lesions > 2 mm, whereas for the European Society of Gastrointestinal Endoscopy, it is > 3 mm. However, it’s still done very commonly in clinical practice. Nibbling the polyp is not an option. Cold snare is actually quicker, more effective, has better outcomes, and is something that you can bill for when you look at the coding.
In summary, there are a lot of things that we can do now to improve colonoscopy. Quality indicators continue to emerge with a compelling, excellent evidence base that strongly supports their use. Given that, I think most of these are actionable now, and it’s not necessary to wait for the guidelines to begin using them. I’d therefore challenge all of us to incorporate them in our continual efforts to do better.
Dr. Johnson is professor of medicine and chief of gastroenterology at Eastern Virginia Medical School in Norfolk, and a past president of the American College of Gastroenterology. His primary focus is the clinical practice of gastroenterology. He has published extensively in the internal medicine/gastroenterology literature, with principal research interests in esophageal and colon disease, and more recently in sleep and microbiome effects on gastrointestinal health and disease. He has disclosed ties with ISOTHRIVE and Johnson & Johnson.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
When it comes to the use of colonoscopy to reduce the risk for cancer, quality is key.
There are a number of performance improvements we can make in our practices so that we can do better. This is evident in several recently published studies and a recent review article on the topic, which I’d like to profile for you; many of these key quality indicators you can implement now.
Even though it may take more time before they’re supported in the guidelines, you’ll see that the evidence behind these is extraordinarily strong.
Increasing the Adenoma Detection Rate
Certainly, we all do what we can to increase the adenoma detection rate (ADR).
However, at the moment, the nationally recommended benchmark is to achieve an ADR of 25%, which is inordinately low. The ADR rate reported in the GIQuIC registry data is closer to 39%, and in high-level detectors, it’s actually in the greater-than-50% range.
There’s no question that we can do more, and there are a number of ways to do that.
First, This may actually decrease your withdrawal time because you don’t spend so much time trying to face these folds.
In considering tools to aid ADR, don’t forget electronic chromoendoscopy (eg, narrow-band imaging).
There are a number of new artificial intelligence options out there as well, which have been reported to increase the ADR by approximately 10%. Of importance, this improvement even occurs among expert endoscopists.
There’s also important emerging data about ADR in fecal immunochemical test (FIT)–positive patients. FIT-positive status increases the ADR threshold by 15%-20%. This places you in an ADR range of approximately 50%, which is really the norm when screening patients that present for colonoscopy because of FIT positivity.
Adenoma Per Colonoscopy: A Possible ADR Substitute
Growing evidence supports the use of adenoma per colonoscopy (APC) as a substitute to ADR. This would allow you to record every adenoma and attribute it to that index colonoscopy.
A high-quality paper showed that the APC value should be around 0.6 to achieve the current ADR minimum threshold of 25%. Having the APC < 0.6 seems to be associated with an increased risk for residual polyp. Sessile serrated lesions also increased the hazard ratio for interval colorectal cancer. This was evaluated recently with data from the New Hampshire Colonoscopy Registry, which Dr Joseph Anderson has led for so long. They showed that 21% of endoscopists had an ADR of 25% or greater but still had APCs < 0.6.
Therefore, when it comes to remedial corrective work, doctors need to be reevaluated, retrained, and educated in the ways that they can incorporate this. The APC in high-level detectors is > 1.0.
APC may be something you want to consider using internally. It does require that you place each polyp into an individual jar, which can increase incremental cost. Nonetheless, there is clear evidence that APC positively changes outcomes.
Including Sessile Serrated Lesions in ADR Detectors
Unfortunately, some of the high-level ADR detectors aren’t so “high level” when it comes to detecting sessile serrated lesions. It’s not quite as concordant as we had previously thought.
Nonetheless, there are many adjunctive things you can do with sessile serrated lesions, including narrow-band imaging and chromoendoscopy.
When it comes to establishing a discriminant, the numbers should be 5%-6% if we’re going to set a quality ratio and an index. However, this is somewhat dependent on your pathologist because they have to read these correctly. Lesions that are ≥ 6 mm above the sigmoid colon and anything in the right colon should be evaluated really closely as a sessile serrated lesion.
I’ve had indications where the pathologist says the lesion is hyperplastic, to which I say, “I’m going to follow as a sessile serrated lesion.” This is because it’s apparent to me in the endoscopic appearance and the narrow-band imaging appearance that it was characteristic of sessile serrated lesions.
Best Practices in Bowel Preparations
The US Multi-Society Task Force recommends that adequate bowel preparation should occur in 85% or more of outpatients, and for the European Society for Gastrointestinal Endoscopy, it’s 90% or more.
I’ll pass along a tip I use in my patients undergoing bowel preparation: I make them aware that during this process, they want to see a clear, yellow, urine-like color to their stool. Otherwise, many patients will think if they’ve had some diarrhea, they don’t need to finish prep. Setting that expectation for them upfront is really important.
The nurses also should be aware of this because if there’s a murky brown effluent upon presentation for the colonoscopy, there’s a greater than 50% chance that they’re going to have had an inadequate preparation. In such cases, you would want to preempt the colonoscopy and perhaps send them out for a re-prep that day or bring them back for a rescheduled appointment.
Resection Considerations
There is substantial variation when it comes to lesion resection, which makes it an important quality indicator on which to focus: High-level detectors aren’t always high-level resectors.
There are two validated instruments that you can use to gauge the adequacy of resection. Those aren’t really ready for prime time in every practice, though they may be seen in fellowship programs.
The idea here is that you want to get a ≥ 2 mm margin for cold snare polypectomy in lesions 1-10 mm in size. This has been a challenge, as findings indicate we don’t do this that well.
Joseph Anderson and colleagues recently published a study using a 2-mm resection margin. They reported that this was only possible in approximately 28% of polyps. For a 1-mm margin, the rate was 84%.
We simply need to set clearer margins when setting our snare. Make sure you’re close enough to the polyp, push down on the snare, and get a good margin of tissue.
When the sample contracts are placed into the formalin, it’s not quite so simple to define the margin at the time of the surgical resection. This often requires an audit evaluation by the pathologist.
There are two other considerations regarding resection.
The first is about the referral for surgery. Referral should not occur for any benign lesions ascribed by your endoscopic advanced imaging techniques and classifications that are not thought to have intramucosal carcinoma. These should be referred to an expert endoscopic evaluation. If you can’t do it, then somebody else should. And you shouldn’t attempt it unless you can get it totally because resection of partially resected lesions is much more complicated. The European Society of Gastrointestinal Endoscopy says this applies to any benign lesion of any size, which I think really is the emerging standard of care. You should consider and offer that to the patient. It may require a referral for outside of your institution.
The second additional consideration is around the minimization of cold forceps for removal of polyps. The US Multi-Society Task Force says cold forceps shouldn’t be used for any lesions > 2 mm, whereas for the European Society of Gastrointestinal Endoscopy, it is > 3 mm. However, it’s still done very commonly in clinical practice. Nibbling the polyp is not an option. Cold snare is actually quicker, more effective, has better outcomes, and is something that you can bill for when you look at the coding.
In summary, there are a lot of things that we can do now to improve colonoscopy. Quality indicators continue to emerge with a compelling, excellent evidence base that strongly supports their use. Given that, I think most of these are actionable now, and it’s not necessary to wait for the guidelines to begin using them. I’d therefore challenge all of us to incorporate them in our continual efforts to do better.
Dr. Johnson is professor of medicine and chief of gastroenterology at Eastern Virginia Medical School in Norfolk, and a past president of the American College of Gastroenterology. His primary focus is the clinical practice of gastroenterology. He has published extensively in the internal medicine/gastroenterology literature, with principal research interests in esophageal and colon disease, and more recently in sleep and microbiome effects on gastrointestinal health and disease. He has disclosed ties with ISOTHRIVE and Johnson & Johnson.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
When it comes to the use of colonoscopy to reduce the risk for cancer, quality is key.
There are a number of performance improvements we can make in our practices so that we can do better. This is evident in several recently published studies and a recent review article on the topic, which I’d like to profile for you; many of these key quality indicators you can implement now.
Even though it may take more time before they’re supported in the guidelines, you’ll see that the evidence behind these is extraordinarily strong.
Increasing the Adenoma Detection Rate
Certainly, we all do what we can to increase the adenoma detection rate (ADR).
However, at the moment, the nationally recommended benchmark is to achieve an ADR of 25%, which is inordinately low. The ADR rate reported in the GIQuIC registry data is closer to 39%, and in high-level detectors, it’s actually in the greater-than-50% range.
There’s no question that we can do more, and there are a number of ways to do that.
First, This may actually decrease your withdrawal time because you don’t spend so much time trying to face these folds.
In considering tools to aid ADR, don’t forget electronic chromoendoscopy (eg, narrow-band imaging).
There are a number of new artificial intelligence options out there as well, which have been reported to increase the ADR by approximately 10%. Of importance, this improvement even occurs among expert endoscopists.
There’s also important emerging data about ADR in fecal immunochemical test (FIT)–positive patients. FIT-positive status increases the ADR threshold by 15%-20%. This places you in an ADR range of approximately 50%, which is really the norm when screening patients that present for colonoscopy because of FIT positivity.
Adenoma Per Colonoscopy: A Possible ADR Substitute
Growing evidence supports the use of adenoma per colonoscopy (APC) as a substitute to ADR. This would allow you to record every adenoma and attribute it to that index colonoscopy.
A high-quality paper showed that the APC value should be around 0.6 to achieve the current ADR minimum threshold of 25%. Having the APC < 0.6 seems to be associated with an increased risk for residual polyp. Sessile serrated lesions also increased the hazard ratio for interval colorectal cancer. This was evaluated recently with data from the New Hampshire Colonoscopy Registry, which Dr Joseph Anderson has led for so long. They showed that 21% of endoscopists had an ADR of 25% or greater but still had APCs < 0.6.
Therefore, when it comes to remedial corrective work, doctors need to be reevaluated, retrained, and educated in the ways that they can incorporate this. The APC in high-level detectors is > 1.0.
APC may be something you want to consider using internally. It does require that you place each polyp into an individual jar, which can increase incremental cost. Nonetheless, there is clear evidence that APC positively changes outcomes.
Including Sessile Serrated Lesions in ADR Detectors
Unfortunately, some of the high-level ADR detectors aren’t so “high level” when it comes to detecting sessile serrated lesions. It’s not quite as concordant as we had previously thought.
Nonetheless, there are many adjunctive things you can do with sessile serrated lesions, including narrow-band imaging and chromoendoscopy.
When it comes to establishing a discriminant, the numbers should be 5%-6% if we’re going to set a quality ratio and an index. However, this is somewhat dependent on your pathologist because they have to read these correctly. Lesions that are ≥ 6 mm above the sigmoid colon and anything in the right colon should be evaluated really closely as a sessile serrated lesion.
I’ve had indications where the pathologist says the lesion is hyperplastic, to which I say, “I’m going to follow as a sessile serrated lesion.” This is because it’s apparent to me in the endoscopic appearance and the narrow-band imaging appearance that it was characteristic of sessile serrated lesions.
Best Practices in Bowel Preparations
The US Multi-Society Task Force recommends that adequate bowel preparation should occur in 85% or more of outpatients, and for the European Society for Gastrointestinal Endoscopy, it’s 90% or more.
I’ll pass along a tip I use in my patients undergoing bowel preparation: I make them aware that during this process, they want to see a clear, yellow, urine-like color to their stool. Otherwise, many patients will think if they’ve had some diarrhea, they don’t need to finish prep. Setting that expectation for them upfront is really important.
The nurses also should be aware of this because if there’s a murky brown effluent upon presentation for the colonoscopy, there’s a greater than 50% chance that they’re going to have had an inadequate preparation. In such cases, you would want to preempt the colonoscopy and perhaps send them out for a re-prep that day or bring them back for a rescheduled appointment.
Resection Considerations
There is substantial variation when it comes to lesion resection, which makes it an important quality indicator on which to focus: High-level detectors aren’t always high-level resectors.
There are two validated instruments that you can use to gauge the adequacy of resection. Those aren’t really ready for prime time in every practice, though they may be seen in fellowship programs.
The idea here is that you want to get a ≥ 2 mm margin for cold snare polypectomy in lesions 1-10 mm in size. This has been a challenge, as findings indicate we don’t do this that well.
Joseph Anderson and colleagues recently published a study using a 2-mm resection margin. They reported that this was only possible in approximately 28% of polyps. For a 1-mm margin, the rate was 84%.
We simply need to set clearer margins when setting our snare. Make sure you’re close enough to the polyp, push down on the snare, and get a good margin of tissue.
When the sample contracts are placed into the formalin, it’s not quite so simple to define the margin at the time of the surgical resection. This often requires an audit evaluation by the pathologist.
There are two other considerations regarding resection.
The first is about the referral for surgery. Referral should not occur for any benign lesions ascribed by your endoscopic advanced imaging techniques and classifications that are not thought to have intramucosal carcinoma. These should be referred to an expert endoscopic evaluation. If you can’t do it, then somebody else should. And you shouldn’t attempt it unless you can get it totally because resection of partially resected lesions is much more complicated. The European Society of Gastrointestinal Endoscopy says this applies to any benign lesion of any size, which I think really is the emerging standard of care. You should consider and offer that to the patient. It may require a referral for outside of your institution.
The second additional consideration is around the minimization of cold forceps for removal of polyps. The US Multi-Society Task Force says cold forceps shouldn’t be used for any lesions > 2 mm, whereas for the European Society of Gastrointestinal Endoscopy, it is > 3 mm. However, it’s still done very commonly in clinical practice. Nibbling the polyp is not an option. Cold snare is actually quicker, more effective, has better outcomes, and is something that you can bill for when you look at the coding.
In summary, there are a lot of things that we can do now to improve colonoscopy. Quality indicators continue to emerge with a compelling, excellent evidence base that strongly supports their use. Given that, I think most of these are actionable now, and it’s not necessary to wait for the guidelines to begin using them. I’d therefore challenge all of us to incorporate them in our continual efforts to do better.
Dr. Johnson is professor of medicine and chief of gastroenterology at Eastern Virginia Medical School in Norfolk, and a past president of the American College of Gastroenterology. His primary focus is the clinical practice of gastroenterology. He has published extensively in the internal medicine/gastroenterology literature, with principal research interests in esophageal and colon disease, and more recently in sleep and microbiome effects on gastrointestinal health and disease. He has disclosed ties with ISOTHRIVE and Johnson & Johnson.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Continued Caution Needed Combining Nitrates With ED Drugs
New research supports continued caution in prescribing a phosphodiesterase-5 inhibitor (PDE5i) to treat erectile dysfunction (ED) in men with heart disease using nitrate medications.
In a large Swedish population study of men with stable coronary artery disease (CAD), the combined use of a PDE5i and nitrates was associated with a higher risk for cardiovascular (CV) morbidity and mortality.
“According to current recommendations, PDE5i are contraindicated in patients taking organic nitrates; however, in clinical practice, both are commonly prescribed, and concomitant use has increased,” first author Ylva Trolle Lagerros, MD, PhD, with Karolinska Institutet, Stockholm, Sweden, told this news organization.
and weigh the benefits of the medication against the possible increased risk for cardiovascular morbidity and mortality given by this combination,” Dr. Lagerros said.
The study was published online in the Journal of the American College of Cardiology (JACC).
The researchers used the Swedish Patient Register and the Prescribed Drug Register to assess the association between PDE5i treatment and CV outcomes in men with stable CAD treated with nitrate medication.
Among 55,777 men with a history of previous myocardial infarction (MI) or coronary revascularization who had filled at least two nitrate prescriptions (sublingual, oral, or both), 5710 also had at least two filled prescriptions of a PDE5i.
In multivariate-adjusted analysis, the combined use of PDE5i treatment with nitrates was associated with an increased relative risk for all studied outcomes, including all-cause mortality, CV and non-CV mortality, MI, heart failure, cardiac revascularization (hazard ratio), and major adverse cardiovascular events.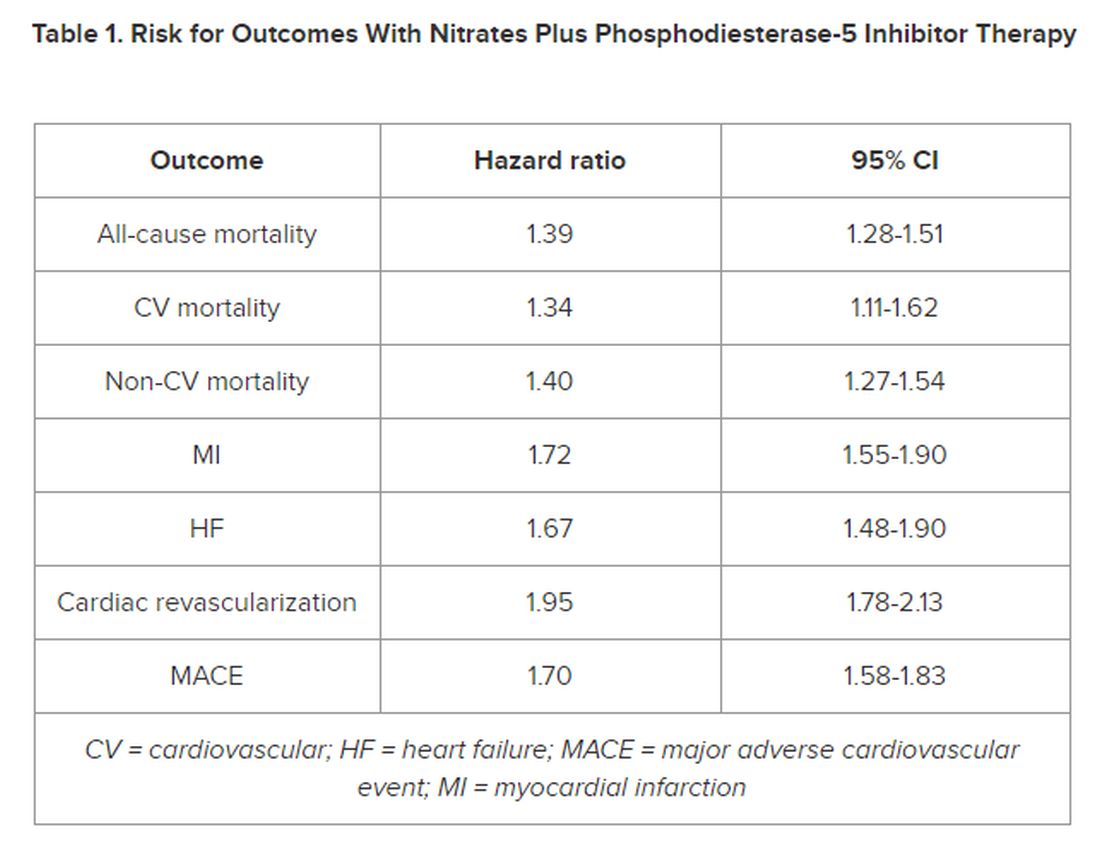
However, the number of events 28 days following a PDE5i prescription fill was “few, with lower incidence rates than in subjects taking nitrates only, indicating a low immediate risk for any event,” the authors noted in their article.
‘Common Bedfellows’
In a JACC editorial, Glenn N. Levine, MD, with Baylor College of Medicine, Houston, Texas, noted that, “ED and CAD are unfortunate, and all too common, bedfellows. But, as with most relationships, assuming proper precautions and care, they can coexist together for many years, perhaps even a lifetime.”
Dr. Levine noted that PDE5is are “reasonably safe” in most patients with stable CAD and only mild angina if not on chronic nitrate therapy. For those on chronic oral nitrate therapy, the use of PDE5is should continue to be regarded as “ill-advised at best and generally contraindicated.”
In some patients on oral nitrate therapy who want to use a PDE5i, particularly those who have undergone revascularization and have minimal or no angina, Dr. Levine said it may be reasonable to initiate a several-week trial of the nitrate therapy (or on a different class of antianginal therapy) and assess if the patient remains relatively angina-free.
In those patients with just rare exertional angina at generally higher levels of activity or those prescribed sublingual nitroglycerin “just in case,” it may be reasonable to prescribe PDE5i after a “clear and detailed” discussion with the patient of the risks for temporarily combining PDE5i and sublingual nitroglycerin.
Dr. Levine said these patients should be instructed not to take nitroglycerin within 24 hours of using a shorter-acting PDE5i and within 48 hours of using the longer-acting PDE5i tadalafil.
They should also be told to call 9-1-1 if angina develops during sexual intercourse and does not resolve upon cessation of such sexual activity, as well as to make medical personnel aware that they have recently used a PDE5i.
The study was funded by Region Stockholm, the Center for Innovative Medicine, and Karolinska Institutet. The researchers and editorial writer had declared no relevant conflicts of interest.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
New research supports continued caution in prescribing a phosphodiesterase-5 inhibitor (PDE5i) to treat erectile dysfunction (ED) in men with heart disease using nitrate medications.
In a large Swedish population study of men with stable coronary artery disease (CAD), the combined use of a PDE5i and nitrates was associated with a higher risk for cardiovascular (CV) morbidity and mortality.
“According to current recommendations, PDE5i are contraindicated in patients taking organic nitrates; however, in clinical practice, both are commonly prescribed, and concomitant use has increased,” first author Ylva Trolle Lagerros, MD, PhD, with Karolinska Institutet, Stockholm, Sweden, told this news organization.
and weigh the benefits of the medication against the possible increased risk for cardiovascular morbidity and mortality given by this combination,” Dr. Lagerros said.
The study was published online in the Journal of the American College of Cardiology (JACC).
The researchers used the Swedish Patient Register and the Prescribed Drug Register to assess the association between PDE5i treatment and CV outcomes in men with stable CAD treated with nitrate medication.
Among 55,777 men with a history of previous myocardial infarction (MI) or coronary revascularization who had filled at least two nitrate prescriptions (sublingual, oral, or both), 5710 also had at least two filled prescriptions of a PDE5i.
In multivariate-adjusted analysis, the combined use of PDE5i treatment with nitrates was associated with an increased relative risk for all studied outcomes, including all-cause mortality, CV and non-CV mortality, MI, heart failure, cardiac revascularization (hazard ratio), and major adverse cardiovascular events.
However, the number of events 28 days following a PDE5i prescription fill was “few, with lower incidence rates than in subjects taking nitrates only, indicating a low immediate risk for any event,” the authors noted in their article.
‘Common Bedfellows’
In a JACC editorial, Glenn N. Levine, MD, with Baylor College of Medicine, Houston, Texas, noted that, “ED and CAD are unfortunate, and all too common, bedfellows. But, as with most relationships, assuming proper precautions and care, they can coexist together for many years, perhaps even a lifetime.”
Dr. Levine noted that PDE5is are “reasonably safe” in most patients with stable CAD and only mild angina if not on chronic nitrate therapy. For those on chronic oral nitrate therapy, the use of PDE5is should continue to be regarded as “ill-advised at best and generally contraindicated.”
In some patients on oral nitrate therapy who want to use a PDE5i, particularly those who have undergone revascularization and have minimal or no angina, Dr. Levine said it may be reasonable to initiate a several-week trial of the nitrate therapy (or on a different class of antianginal therapy) and assess if the patient remains relatively angina-free.
In those patients with just rare exertional angina at generally higher levels of activity or those prescribed sublingual nitroglycerin “just in case,” it may be reasonable to prescribe PDE5i after a “clear and detailed” discussion with the patient of the risks for temporarily combining PDE5i and sublingual nitroglycerin.
Dr. Levine said these patients should be instructed not to take nitroglycerin within 24 hours of using a shorter-acting PDE5i and within 48 hours of using the longer-acting PDE5i tadalafil.
They should also be told to call 9-1-1 if angina develops during sexual intercourse and does not resolve upon cessation of such sexual activity, as well as to make medical personnel aware that they have recently used a PDE5i.
The study was funded by Region Stockholm, the Center for Innovative Medicine, and Karolinska Institutet. The researchers and editorial writer had declared no relevant conflicts of interest.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
New research supports continued caution in prescribing a phosphodiesterase-5 inhibitor (PDE5i) to treat erectile dysfunction (ED) in men with heart disease using nitrate medications.
In a large Swedish population study of men with stable coronary artery disease (CAD), the combined use of a PDE5i and nitrates was associated with a higher risk for cardiovascular (CV) morbidity and mortality.
“According to current recommendations, PDE5i are contraindicated in patients taking organic nitrates; however, in clinical practice, both are commonly prescribed, and concomitant use has increased,” first author Ylva Trolle Lagerros, MD, PhD, with Karolinska Institutet, Stockholm, Sweden, told this news organization.
and weigh the benefits of the medication against the possible increased risk for cardiovascular morbidity and mortality given by this combination,” Dr. Lagerros said.
The study was published online in the Journal of the American College of Cardiology (JACC).
The researchers used the Swedish Patient Register and the Prescribed Drug Register to assess the association between PDE5i treatment and CV outcomes in men with stable CAD treated with nitrate medication.
Among 55,777 men with a history of previous myocardial infarction (MI) or coronary revascularization who had filled at least two nitrate prescriptions (sublingual, oral, or both), 5710 also had at least two filled prescriptions of a PDE5i.
In multivariate-adjusted analysis, the combined use of PDE5i treatment with nitrates was associated with an increased relative risk for all studied outcomes, including all-cause mortality, CV and non-CV mortality, MI, heart failure, cardiac revascularization (hazard ratio), and major adverse cardiovascular events.
However, the number of events 28 days following a PDE5i prescription fill was “few, with lower incidence rates than in subjects taking nitrates only, indicating a low immediate risk for any event,” the authors noted in their article.
‘Common Bedfellows’
In a JACC editorial, Glenn N. Levine, MD, with Baylor College of Medicine, Houston, Texas, noted that, “ED and CAD are unfortunate, and all too common, bedfellows. But, as with most relationships, assuming proper precautions and care, they can coexist together for many years, perhaps even a lifetime.”
Dr. Levine noted that PDE5is are “reasonably safe” in most patients with stable CAD and only mild angina if not on chronic nitrate therapy. For those on chronic oral nitrate therapy, the use of PDE5is should continue to be regarded as “ill-advised at best and generally contraindicated.”
In some patients on oral nitrate therapy who want to use a PDE5i, particularly those who have undergone revascularization and have minimal or no angina, Dr. Levine said it may be reasonable to initiate a several-week trial of the nitrate therapy (or on a different class of antianginal therapy) and assess if the patient remains relatively angina-free.
In those patients with just rare exertional angina at generally higher levels of activity or those prescribed sublingual nitroglycerin “just in case,” it may be reasonable to prescribe PDE5i after a “clear and detailed” discussion with the patient of the risks for temporarily combining PDE5i and sublingual nitroglycerin.
Dr. Levine said these patients should be instructed not to take nitroglycerin within 24 hours of using a shorter-acting PDE5i and within 48 hours of using the longer-acting PDE5i tadalafil.
They should also be told to call 9-1-1 if angina develops during sexual intercourse and does not resolve upon cessation of such sexual activity, as well as to make medical personnel aware that they have recently used a PDE5i.
The study was funded by Region Stockholm, the Center for Innovative Medicine, and Karolinska Institutet. The researchers and editorial writer had declared no relevant conflicts of interest.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
FDA Clears AI-Powered Device for Noninvasive Skin Cancer Testing
The handheld wireless tool, which was developed by Miami-based DermaSensor Inc., operates on battery power, uses spectroscopy and algorithms to evaluate skin lesions for potential cancer in a matter of seconds, and is intended for use by primary care physicians. After the device completes the scan of a lesion, a result of “investigate further” (positive result) suggests further evaluation through a referral to a dermatologist, while “monitor” (negative result) suggests that there is no immediate need for a referral to a dermatologist.
In a pivotal trial of the device that evaluated 224 high risk lesions at 18 primary care study sites in the United States and 4 in Australia, the device had an overall sensitivity of 95.5% for detecting malignancy.
In a more recent validation study funded by DermaSensor, investigators tested 333 lesions at four U.S. dermatology offices and found that the overall device sensitivity was 97.04%, with subgroup sensitivity of 96.67% for melanoma, 97.22% for basal cell carcinoma, and 97.01% for squamous cell carcinoma. Overall specificity of the device was 26.22%.
The study authors, led by Tallahassee, Fla.–based dermatologist Armand B. Cognetta Jr., MD, concluded that DermaSensor’s rapid clinical analysis of lesions “allows for its easy integration into clinical practice infrastructures. Proper use of this device may aid in the reduction of morbidity and mortality associated with skin cancer through expedited and enhanced detection and intervention.”
According to marketing material from the DermaSensor website, the device’s AI algorithm was developed and validated with more than 20,000 scans, composed of more than 4,000 benign and malignant lesions. In a statement about the clearance, the FDA emphasized that the device “should not be used as the sole diagnostic criterion nor to confirm a diagnosis of skin cancer.” The agency is requiring that the manufacturer “conduct additional post-market clinical validation performance testing of the DermaSensor device in patients from demographic groups representative of the U.S. population, including populations who had limited representation of melanomas in the premarket studies, due to their having a relatively low incidence of the disease.”
According to a spokesperson for DermaSensor, pricing for the device is based on a subscription model: $199 per month for five patients or $399 per month for unlimited use. DermaSensor is currently commercially available in Europe and Australia.
Asked to comment, Vishal A. Patel, MD, director of cutaneous oncology at the George Washington Cancer Center, Washington, said that the FDA clearance of DermaSensor highlights the growing appreciation of AI-driven diagnostic support for primary care providers and dermatologists. "Skin cancers are a growing epidemic in the US and the ability to accurately identify potential suspicious lesions without immediately reaching for the scalpel is invaluable," Patel told this news organization. He was not involved with DermSensor studies.
"Furthermore, this tool can help address the shortage of dermatologists and long wait times by helping primary care providers accurately risk-stratify patients and identify those who need to be seen immediately for potential biopsy and expert care," he added. "However, just like with any new technology, we must use caution to not overutilize this tool," which he said, could "lead to overdiagnosis and overtreatment of early or innocuous lesions that are better managed with empiric field treatments."
Dr. Cognetta was a paid investigator for the study.
Dr. Patel disclosed that he is chief medical officer for Lazarus AI.
The handheld wireless tool, which was developed by Miami-based DermaSensor Inc., operates on battery power, uses spectroscopy and algorithms to evaluate skin lesions for potential cancer in a matter of seconds, and is intended for use by primary care physicians. After the device completes the scan of a lesion, a result of “investigate further” (positive result) suggests further evaluation through a referral to a dermatologist, while “monitor” (negative result) suggests that there is no immediate need for a referral to a dermatologist.
In a pivotal trial of the device that evaluated 224 high risk lesions at 18 primary care study sites in the United States and 4 in Australia, the device had an overall sensitivity of 95.5% for detecting malignancy.
In a more recent validation study funded by DermaSensor, investigators tested 333 lesions at four U.S. dermatology offices and found that the overall device sensitivity was 97.04%, with subgroup sensitivity of 96.67% for melanoma, 97.22% for basal cell carcinoma, and 97.01% for squamous cell carcinoma. Overall specificity of the device was 26.22%.
The study authors, led by Tallahassee, Fla.–based dermatologist Armand B. Cognetta Jr., MD, concluded that DermaSensor’s rapid clinical analysis of lesions “allows for its easy integration into clinical practice infrastructures. Proper use of this device may aid in the reduction of morbidity and mortality associated with skin cancer through expedited and enhanced detection and intervention.”
According to marketing material from the DermaSensor website, the device’s AI algorithm was developed and validated with more than 20,000 scans, composed of more than 4,000 benign and malignant lesions. In a statement about the clearance, the FDA emphasized that the device “should not be used as the sole diagnostic criterion nor to confirm a diagnosis of skin cancer.” The agency is requiring that the manufacturer “conduct additional post-market clinical validation performance testing of the DermaSensor device in patients from demographic groups representative of the U.S. population, including populations who had limited representation of melanomas in the premarket studies, due to their having a relatively low incidence of the disease.”
According to a spokesperson for DermaSensor, pricing for the device is based on a subscription model: $199 per month for five patients or $399 per month for unlimited use. DermaSensor is currently commercially available in Europe and Australia.
Asked to comment, Vishal A. Patel, MD, director of cutaneous oncology at the George Washington Cancer Center, Washington, said that the FDA clearance of DermaSensor highlights the growing appreciation of AI-driven diagnostic support for primary care providers and dermatologists. "Skin cancers are a growing epidemic in the US and the ability to accurately identify potential suspicious lesions without immediately reaching for the scalpel is invaluable," Patel told this news organization. He was not involved with DermSensor studies.
"Furthermore, this tool can help address the shortage of dermatologists and long wait times by helping primary care providers accurately risk-stratify patients and identify those who need to be seen immediately for potential biopsy and expert care," he added. "However, just like with any new technology, we must use caution to not overutilize this tool," which he said, could "lead to overdiagnosis and overtreatment of early or innocuous lesions that are better managed with empiric field treatments."
Dr. Cognetta was a paid investigator for the study.
Dr. Patel disclosed that he is chief medical officer for Lazarus AI.
The handheld wireless tool, which was developed by Miami-based DermaSensor Inc., operates on battery power, uses spectroscopy and algorithms to evaluate skin lesions for potential cancer in a matter of seconds, and is intended for use by primary care physicians. After the device completes the scan of a lesion, a result of “investigate further” (positive result) suggests further evaluation through a referral to a dermatologist, while “monitor” (negative result) suggests that there is no immediate need for a referral to a dermatologist.
In a pivotal trial of the device that evaluated 224 high risk lesions at 18 primary care study sites in the United States and 4 in Australia, the device had an overall sensitivity of 95.5% for detecting malignancy.
In a more recent validation study funded by DermaSensor, investigators tested 333 lesions at four U.S. dermatology offices and found that the overall device sensitivity was 97.04%, with subgroup sensitivity of 96.67% for melanoma, 97.22% for basal cell carcinoma, and 97.01% for squamous cell carcinoma. Overall specificity of the device was 26.22%.
The study authors, led by Tallahassee, Fla.–based dermatologist Armand B. Cognetta Jr., MD, concluded that DermaSensor’s rapid clinical analysis of lesions “allows for its easy integration into clinical practice infrastructures. Proper use of this device may aid in the reduction of morbidity and mortality associated with skin cancer through expedited and enhanced detection and intervention.”
According to marketing material from the DermaSensor website, the device’s AI algorithm was developed and validated with more than 20,000 scans, composed of more than 4,000 benign and malignant lesions. In a statement about the clearance, the FDA emphasized that the device “should not be used as the sole diagnostic criterion nor to confirm a diagnosis of skin cancer.” The agency is requiring that the manufacturer “conduct additional post-market clinical validation performance testing of the DermaSensor device in patients from demographic groups representative of the U.S. population, including populations who had limited representation of melanomas in the premarket studies, due to their having a relatively low incidence of the disease.”
According to a spokesperson for DermaSensor, pricing for the device is based on a subscription model: $199 per month for five patients or $399 per month for unlimited use. DermaSensor is currently commercially available in Europe and Australia.
Asked to comment, Vishal A. Patel, MD, director of cutaneous oncology at the George Washington Cancer Center, Washington, said that the FDA clearance of DermaSensor highlights the growing appreciation of AI-driven diagnostic support for primary care providers and dermatologists. "Skin cancers are a growing epidemic in the US and the ability to accurately identify potential suspicious lesions without immediately reaching for the scalpel is invaluable," Patel told this news organization. He was not involved with DermSensor studies.
"Furthermore, this tool can help address the shortage of dermatologists and long wait times by helping primary care providers accurately risk-stratify patients and identify those who need to be seen immediately for potential biopsy and expert care," he added. "However, just like with any new technology, we must use caution to not overutilize this tool," which he said, could "lead to overdiagnosis and overtreatment of early or innocuous lesions that are better managed with empiric field treatments."
Dr. Cognetta was a paid investigator for the study.
Dr. Patel disclosed that he is chief medical officer for Lazarus AI.
Direct Measurement of T3 Is Likely Vital, Say Researchers
To assess thyroid function, clinicians typically determine blood levels of thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) and thyroxine (T4) and do not directly measure triiodothyronine (T3).
However, linking socioeconomic forces, human biology, and aging,” researchers reported.
The study, with lead author Ralph I. Lawton, an MD-PhD student at Harvard Medical School, Boston, was published online on January 4, 2024, in Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences. In this national sample of healthy adults older than 20, free T3 was negatively related to household income. At age 40 and older, free T3 was significantly linked to being employed. Among adults from age 51 to 80, free T3 levels were inversely related to mortality.
“It is important to note that the more typically measured biomarkers for thyroid function (T4 and TSH) are poorly linked to free T3 levels,” Dr. Lawton and colleagues wrote.
The ratio of TSH:T4 explained only 1.7% of variation in T3 levels, they noted, which suggested that TSH and T4 may not be accurate surrogates of free T3. Thus, “direct measurement of free T3 is likely vital to properly stratify the effects of HPT-axis variation,” they maintained. “Improved methods for measurement [of T3] and further investigation of the role of free T3 in clinical conditions may be high yield,” according to the researchers.
Further studies of the relationship between the action of deiodinase in converting T4 to T3 and social forces and aging could elucidate critical biology. “New therapeutics targeting T3/T4 ratios,” they suggested, “may be more beneficial for a significant cohort of older individuals [with hypothyroidism] currently treated with levothyroxine [(LT4)].”
‘Cherry on Top’
“I think this is a really important paper,” thyroidology expert Antonio Bianco, MD, PhD, professor of medicine, The University of Chicago, who was not involved with this research, told this news organization.
His research group and others “have slowly been providing evidence of the relevance of measuring T3 levels,” he said. “This paper is sort of a cherry on top. It is really the most recent strong evidence that looking at T3 levels in plasma is really important. We need to do a better job at developing a much more precise assay for T3,” he said, “because now we know T3 is a very important parameter that endocrinologists should be looking for. We know that about 20 million Americans have hypothyroidism, and are being treated with T4 (levothyroxine),” Dr. Bianco continued.
“As endocrinologists, we believe that if you treat someone with levothyroxine, you normalize T3 levels. However, many times, with standard of care with levothyroxine, T3 levels are not normalized.”
Larger Variations in T3
Thyroid hormones (TSH, free T4, and free T3) influence many aspects of human physiology and behavior, but it is not known how variations in these levels in a population free of thyroid disease are associated with mortality and socioeconomic factors.
The researchers analyzed data from 7626 adults over age 20 up to age 80 who participated in the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey during 2007-2012 and had blood tests to determine TSH, free T4, and free T3 and were not being actively treated for thyroid conditions. Among the 3603 older adults (over age 50), there were 981 deaths up until the end of 2019. TSH levels were not linked to mortality, but increasing levels of free T3 and decreasing levels of free T4 were protective for mortality (hazard ratios, 0.88 and 1.26, respectively; P < .01).
There was a robust negative relationship between household income and employment and free T3 but no relationship between these factors and T4. There was a much larger variation across age in levels of free T3 than in levels of TSH or free T4. Free T4 and free T3 diverged at older ages, when free T4 increased and free T3 continually decreased.
Older adults with symptoms of hypothyroidism may have high free T4 levels despite low free T3, the researchers noted.
“In a nonclinical sample representative of the US population,” they summarized, “we find that free T3 is much more strongly related to all domains studied — age, sex, seasonality, household income, employment, and longevity — than the other molecules of the HPT axis.”
This work was supported by the Burroughs Wellcome Fund Career at Scientific Interface award, a Brain and Behavior Research Foundation young investigator award, the Howard Hughes Medical Institute, the National Institute of Aging, and the National Institute of General Medical Sciences. Dr. Bianco served as a consultant for AbbVie, Avion Pharmaceuticals, Synthonics, Synthion, and Thyron and recently published the book Rethinking Hypothyroidism: Why Treatment Must Change and What Patients Can Do.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
To assess thyroid function, clinicians typically determine blood levels of thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) and thyroxine (T4) and do not directly measure triiodothyronine (T3).
However, linking socioeconomic forces, human biology, and aging,” researchers reported.
The study, with lead author Ralph I. Lawton, an MD-PhD student at Harvard Medical School, Boston, was published online on January 4, 2024, in Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences. In this national sample of healthy adults older than 20, free T3 was negatively related to household income. At age 40 and older, free T3 was significantly linked to being employed. Among adults from age 51 to 80, free T3 levels were inversely related to mortality.
“It is important to note that the more typically measured biomarkers for thyroid function (T4 and TSH) are poorly linked to free T3 levels,” Dr. Lawton and colleagues wrote.
The ratio of TSH:T4 explained only 1.7% of variation in T3 levels, they noted, which suggested that TSH and T4 may not be accurate surrogates of free T3. Thus, “direct measurement of free T3 is likely vital to properly stratify the effects of HPT-axis variation,” they maintained. “Improved methods for measurement [of T3] and further investigation of the role of free T3 in clinical conditions may be high yield,” according to the researchers.
Further studies of the relationship between the action of deiodinase in converting T4 to T3 and social forces and aging could elucidate critical biology. “New therapeutics targeting T3/T4 ratios,” they suggested, “may be more beneficial for a significant cohort of older individuals [with hypothyroidism] currently treated with levothyroxine [(LT4)].”
‘Cherry on Top’
“I think this is a really important paper,” thyroidology expert Antonio Bianco, MD, PhD, professor of medicine, The University of Chicago, who was not involved with this research, told this news organization.
His research group and others “have slowly been providing evidence of the relevance of measuring T3 levels,” he said. “This paper is sort of a cherry on top. It is really the most recent strong evidence that looking at T3 levels in plasma is really important. We need to do a better job at developing a much more precise assay for T3,” he said, “because now we know T3 is a very important parameter that endocrinologists should be looking for. We know that about 20 million Americans have hypothyroidism, and are being treated with T4 (levothyroxine),” Dr. Bianco continued.
“As endocrinologists, we believe that if you treat someone with levothyroxine, you normalize T3 levels. However, many times, with standard of care with levothyroxine, T3 levels are not normalized.”
Larger Variations in T3
Thyroid hormones (TSH, free T4, and free T3) influence many aspects of human physiology and behavior, but it is not known how variations in these levels in a population free of thyroid disease are associated with mortality and socioeconomic factors.
The researchers analyzed data from 7626 adults over age 20 up to age 80 who participated in the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey during 2007-2012 and had blood tests to determine TSH, free T4, and free T3 and were not being actively treated for thyroid conditions. Among the 3603 older adults (over age 50), there were 981 deaths up until the end of 2019. TSH levels were not linked to mortality, but increasing levels of free T3 and decreasing levels of free T4 were protective for mortality (hazard ratios, 0.88 and 1.26, respectively; P < .01).
There was a robust negative relationship between household income and employment and free T3 but no relationship between these factors and T4. There was a much larger variation across age in levels of free T3 than in levels of TSH or free T4. Free T4 and free T3 diverged at older ages, when free T4 increased and free T3 continually decreased.
Older adults with symptoms of hypothyroidism may have high free T4 levels despite low free T3, the researchers noted.
“In a nonclinical sample representative of the US population,” they summarized, “we find that free T3 is much more strongly related to all domains studied — age, sex, seasonality, household income, employment, and longevity — than the other molecules of the HPT axis.”
This work was supported by the Burroughs Wellcome Fund Career at Scientific Interface award, a Brain and Behavior Research Foundation young investigator award, the Howard Hughes Medical Institute, the National Institute of Aging, and the National Institute of General Medical Sciences. Dr. Bianco served as a consultant for AbbVie, Avion Pharmaceuticals, Synthonics, Synthion, and Thyron and recently published the book Rethinking Hypothyroidism: Why Treatment Must Change and What Patients Can Do.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
To assess thyroid function, clinicians typically determine blood levels of thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) and thyroxine (T4) and do not directly measure triiodothyronine (T3).
However, linking socioeconomic forces, human biology, and aging,” researchers reported.
The study, with lead author Ralph I. Lawton, an MD-PhD student at Harvard Medical School, Boston, was published online on January 4, 2024, in Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences. In this national sample of healthy adults older than 20, free T3 was negatively related to household income. At age 40 and older, free T3 was significantly linked to being employed. Among adults from age 51 to 80, free T3 levels were inversely related to mortality.
“It is important to note that the more typically measured biomarkers for thyroid function (T4 and TSH) are poorly linked to free T3 levels,” Dr. Lawton and colleagues wrote.
The ratio of TSH:T4 explained only 1.7% of variation in T3 levels, they noted, which suggested that TSH and T4 may not be accurate surrogates of free T3. Thus, “direct measurement of free T3 is likely vital to properly stratify the effects of HPT-axis variation,” they maintained. “Improved methods for measurement [of T3] and further investigation of the role of free T3 in clinical conditions may be high yield,” according to the researchers.
Further studies of the relationship between the action of deiodinase in converting T4 to T3 and social forces and aging could elucidate critical biology. “New therapeutics targeting T3/T4 ratios,” they suggested, “may be more beneficial for a significant cohort of older individuals [with hypothyroidism] currently treated with levothyroxine [(LT4)].”
‘Cherry on Top’
“I think this is a really important paper,” thyroidology expert Antonio Bianco, MD, PhD, professor of medicine, The University of Chicago, who was not involved with this research, told this news organization.
His research group and others “have slowly been providing evidence of the relevance of measuring T3 levels,” he said. “This paper is sort of a cherry on top. It is really the most recent strong evidence that looking at T3 levels in plasma is really important. We need to do a better job at developing a much more precise assay for T3,” he said, “because now we know T3 is a very important parameter that endocrinologists should be looking for. We know that about 20 million Americans have hypothyroidism, and are being treated with T4 (levothyroxine),” Dr. Bianco continued.
“As endocrinologists, we believe that if you treat someone with levothyroxine, you normalize T3 levels. However, many times, with standard of care with levothyroxine, T3 levels are not normalized.”
Larger Variations in T3
Thyroid hormones (TSH, free T4, and free T3) influence many aspects of human physiology and behavior, but it is not known how variations in these levels in a population free of thyroid disease are associated with mortality and socioeconomic factors.
The researchers analyzed data from 7626 adults over age 20 up to age 80 who participated in the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey during 2007-2012 and had blood tests to determine TSH, free T4, and free T3 and were not being actively treated for thyroid conditions. Among the 3603 older adults (over age 50), there were 981 deaths up until the end of 2019. TSH levels were not linked to mortality, but increasing levels of free T3 and decreasing levels of free T4 were protective for mortality (hazard ratios, 0.88 and 1.26, respectively; P < .01).
There was a robust negative relationship between household income and employment and free T3 but no relationship between these factors and T4. There was a much larger variation across age in levels of free T3 than in levels of TSH or free T4. Free T4 and free T3 diverged at older ages, when free T4 increased and free T3 continually decreased.
Older adults with symptoms of hypothyroidism may have high free T4 levels despite low free T3, the researchers noted.
“In a nonclinical sample representative of the US population,” they summarized, “we find that free T3 is much more strongly related to all domains studied — age, sex, seasonality, household income, employment, and longevity — than the other molecules of the HPT axis.”
This work was supported by the Burroughs Wellcome Fund Career at Scientific Interface award, a Brain and Behavior Research Foundation young investigator award, the Howard Hughes Medical Institute, the National Institute of Aging, and the National Institute of General Medical Sciences. Dr. Bianco served as a consultant for AbbVie, Avion Pharmaceuticals, Synthonics, Synthion, and Thyron and recently published the book Rethinking Hypothyroidism: Why Treatment Must Change and What Patients Can Do.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Coming Soon: The First mRNA Vaccine for Melanoma?
Moderna and Merck have presented promising results from their phase 2b clinical trial that investigated a combination of a messenger RNA (mRNA) vaccine and a cancer drug for the treatment of melanoma.
Is mRNA set to shake up the world of cancer treatment? This is certainly what Moderna seems to think; the pharmaceutical company has published the results of a phase 2b trial combining its mRNA vaccine (mRNA-4157 [V940]) with Merck’s cancer drug KEYTRUDA. While these are not the final results but rather mid-term data from the 3-year follow-up, they are somewhat promising. The randomized KEYNOTE-942/mRNA-4157-P201 clinical trial involves patients with high-risk (stage III/IV) melanoma following complete resection.
Relapse Risk Halved
Treatment with mRNA-4157 (V940) in combination with pembrolizumab led to a clinically meaningful improvement in recurrence-free survival, reducing the risk for recurrence or death by 49%, compared with pembrolizumab alone. T, reducing the risk of developing distant metastasis or death by 62%. “The KEYNOTE-942/mRNA-4157-P201 study was the first demonstration of efficacy for an investigational mRNA cancer treatment in a randomized clinical trial and the first combination therapy to show a significant benefit over pembrolizumab alone in adjuvant melanoma,” said Kyle Holen, MD, Moderna’s senior vice president, after presenting these results.
Side Effects
The combined treatment also did not demonstrate more significant side effects than pembrolizumab alone. The number of patients reporting treatment-related adverse events of grade 3 or greater was similar between the arms (25% for mRNA-4157 [V940] with pembrolizumab vs 20% for KEYTRUDA alone). The most common adverse events of any grade attributed to mRNA-4157 (V940) were fatigue (60.6%), injection site pain (56.7%), and chills (49%). Based on data from the phase 2b KEYNOTE-942/mRNA-4157-P201 study, the US Food and Drug Administration and European Medicines Agency granted breakthrough therapy designation and recognition under the the Priority Medicines scheme, respectively, for mRNA-4157 (V940) in combination with KEYTRUDA for the adjuvant treatment of patients with high-risk melanoma.
Phase 3 Trial
In July, Moderna and Merck announced the launch of a phase 3 trial, assessing “mRNA-4157 [V940] in combination with pembrolizumab as adjuvant treatment in patients with high-risk resected melanoma [stages IIB-IV].” Stéphane Bancel, Moderna’s director general, believes that an mRNA vaccine for melanoma could be available in 2025.
Other Cancer Vaccines
Moderna is not the only laboratory to set its sights on developing a vaccine for cancer. In May, BioNTech, in partnership with Roche, proposed a phase 1 clinical trial of a vaccine targeting pancreatic cancer in Nature. In June, at the American Society of Clinical Oncology›s conference, Transgene presented its conclusions concerning its viral vector vaccines against ENT and papillomavirus-linked cancers. And in September, Ose Immunotherapeutics made headlines with its vaccine for advanced lung cancer.
This article was translated from Univadis France, which is part of the Medscape Professional Network.
Moderna and Merck have presented promising results from their phase 2b clinical trial that investigated a combination of a messenger RNA (mRNA) vaccine and a cancer drug for the treatment of melanoma.
Is mRNA set to shake up the world of cancer treatment? This is certainly what Moderna seems to think; the pharmaceutical company has published the results of a phase 2b trial combining its mRNA vaccine (mRNA-4157 [V940]) with Merck’s cancer drug KEYTRUDA. While these are not the final results but rather mid-term data from the 3-year follow-up, they are somewhat promising. The randomized KEYNOTE-942/mRNA-4157-P201 clinical trial involves patients with high-risk (stage III/IV) melanoma following complete resection.
Relapse Risk Halved
Treatment with mRNA-4157 (V940) in combination with pembrolizumab led to a clinically meaningful improvement in recurrence-free survival, reducing the risk for recurrence or death by 49%, compared with pembrolizumab alone. T, reducing the risk of developing distant metastasis or death by 62%. “The KEYNOTE-942/mRNA-4157-P201 study was the first demonstration of efficacy for an investigational mRNA cancer treatment in a randomized clinical trial and the first combination therapy to show a significant benefit over pembrolizumab alone in adjuvant melanoma,” said Kyle Holen, MD, Moderna’s senior vice president, after presenting these results.
Side Effects
The combined treatment also did not demonstrate more significant side effects than pembrolizumab alone. The number of patients reporting treatment-related adverse events of grade 3 or greater was similar between the arms (25% for mRNA-4157 [V940] with pembrolizumab vs 20% for KEYTRUDA alone). The most common adverse events of any grade attributed to mRNA-4157 (V940) were fatigue (60.6%), injection site pain (56.7%), and chills (49%). Based on data from the phase 2b KEYNOTE-942/mRNA-4157-P201 study, the US Food and Drug Administration and European Medicines Agency granted breakthrough therapy designation and recognition under the the Priority Medicines scheme, respectively, for mRNA-4157 (V940) in combination with KEYTRUDA for the adjuvant treatment of patients with high-risk melanoma.
Phase 3 Trial
In July, Moderna and Merck announced the launch of a phase 3 trial, assessing “mRNA-4157 [V940] in combination with pembrolizumab as adjuvant treatment in patients with high-risk resected melanoma [stages IIB-IV].” Stéphane Bancel, Moderna’s director general, believes that an mRNA vaccine for melanoma could be available in 2025.
Other Cancer Vaccines
Moderna is not the only laboratory to set its sights on developing a vaccine for cancer. In May, BioNTech, in partnership with Roche, proposed a phase 1 clinical trial of a vaccine targeting pancreatic cancer in Nature. In June, at the American Society of Clinical Oncology›s conference, Transgene presented its conclusions concerning its viral vector vaccines against ENT and papillomavirus-linked cancers. And in September, Ose Immunotherapeutics made headlines with its vaccine for advanced lung cancer.
This article was translated from Univadis France, which is part of the Medscape Professional Network.
Moderna and Merck have presented promising results from their phase 2b clinical trial that investigated a combination of a messenger RNA (mRNA) vaccine and a cancer drug for the treatment of melanoma.
Is mRNA set to shake up the world of cancer treatment? This is certainly what Moderna seems to think; the pharmaceutical company has published the results of a phase 2b trial combining its mRNA vaccine (mRNA-4157 [V940]) with Merck’s cancer drug KEYTRUDA. While these are not the final results but rather mid-term data from the 3-year follow-up, they are somewhat promising. The randomized KEYNOTE-942/mRNA-4157-P201 clinical trial involves patients with high-risk (stage III/IV) melanoma following complete resection.
Relapse Risk Halved
Treatment with mRNA-4157 (V940) in combination with pembrolizumab led to a clinically meaningful improvement in recurrence-free survival, reducing the risk for recurrence or death by 49%, compared with pembrolizumab alone. T, reducing the risk of developing distant metastasis or death by 62%. “The KEYNOTE-942/mRNA-4157-P201 study was the first demonstration of efficacy for an investigational mRNA cancer treatment in a randomized clinical trial and the first combination therapy to show a significant benefit over pembrolizumab alone in adjuvant melanoma,” said Kyle Holen, MD, Moderna’s senior vice president, after presenting these results.
Side Effects
The combined treatment also did not demonstrate more significant side effects than pembrolizumab alone. The number of patients reporting treatment-related adverse events of grade 3 or greater was similar between the arms (25% for mRNA-4157 [V940] with pembrolizumab vs 20% for KEYTRUDA alone). The most common adverse events of any grade attributed to mRNA-4157 (V940) were fatigue (60.6%), injection site pain (56.7%), and chills (49%). Based on data from the phase 2b KEYNOTE-942/mRNA-4157-P201 study, the US Food and Drug Administration and European Medicines Agency granted breakthrough therapy designation and recognition under the the Priority Medicines scheme, respectively, for mRNA-4157 (V940) in combination with KEYTRUDA for the adjuvant treatment of patients with high-risk melanoma.
Phase 3 Trial
In July, Moderna and Merck announced the launch of a phase 3 trial, assessing “mRNA-4157 [V940] in combination with pembrolizumab as adjuvant treatment in patients with high-risk resected melanoma [stages IIB-IV].” Stéphane Bancel, Moderna’s director general, believes that an mRNA vaccine for melanoma could be available in 2025.
Other Cancer Vaccines
Moderna is not the only laboratory to set its sights on developing a vaccine for cancer. In May, BioNTech, in partnership with Roche, proposed a phase 1 clinical trial of a vaccine targeting pancreatic cancer in Nature. In June, at the American Society of Clinical Oncology›s conference, Transgene presented its conclusions concerning its viral vector vaccines against ENT and papillomavirus-linked cancers. And in September, Ose Immunotherapeutics made headlines with its vaccine for advanced lung cancer.
This article was translated from Univadis France, which is part of the Medscape Professional Network.
Efficacy of Topical Clascoterone for Acne Increased Over Time, Analysis Shows
TOPLINE:
METHODOLOGY:
- A 1% cream formulation of clascoterone, a topical androgen receptor inhibitor, is approved for the treatment of acne vulgaris in patients aged 12 years and older based on results from two identical phase 3 12-week trials, NCT02608450 and NCT02608476, and a long-term extension (LTE) study.
- The purpose of the current study was to evaluate the integrated efficacy of clascoterone cream 1% (Winlevi) in the intention-to-treat population of patients from all three trials.
- In the pivotal trials, investigators randomized patients with acne 1:1 to receive clascoterone cream 1% or vehicle twice daily for 12 weeks. Participants were eligible to enter the LTE study, in which patients applied clascoterone to the face, and if they wanted to, the trunk for up to 9 more months.
- To assess combined efficacy, researchers evaluated the proportion of patients who achieved an Investigator’s Global Assessment (IGA) of 0 or 1.
TAKEAWAY:
- Of the 1143 patients from the pivotal trials who completed 12 weeks of treatment, 576 were in the clascoterone group and 567 were in the vehicle group. Of the 600 patients who entered the LTE study, 311 were in the clascoterone group and 289 were in the vehicle group. Of these, 343 completed the LTE study.
- At week 12, the proportion of patients who achieved treatment success was higher in the clascoterone group than in the vehicle group (19.9% vs 7.7%, respectively; P < .0001).
- In the LTE study, the proportion of patients previously treated with clascoterone who achieved a facial IGA of 0/1 increased from 13.5% at extension day 0 to 29.9% at extension day 274, while the proportion of patients previously treated with vehicle and switched to clascoterone who achieved a facial IGA of 0/1 increased from 6.2% at extension day 0 to 30.4% at extension day 274.
- Similarly, the proportion of patients in the LTE study with a truncal IGA of 0/1 increased from 4.9% at extension day 0 to 31.7% on extension day 274.
IN PRACTICE:
“Clinicians may consider counseling patients that treatment persistence is required to maximize the efficacy of clascoterone treatment,” the authors concluded.
SOURCE:
Lawrence F. Eichenfield, MD, of the departments of dermatology and pediatrics at the University of California and Rady Children’s Hospital, San Diego, California, led the research. The study was published in the January 2024 issue of the Journal of Drugs in Dermatology.
LIMITATIONS:
There was a high patient discontinuation rate before and during the LET study. Also, no assessment was made as to how clascoterone affected patients’ quality of life.
DISCLOSURES:
Clascoterone manufacturer Cassiopea funded the studies. Dr. Eichenfield and fellow investigators Adelaide A. Hebert, MD, and Linda Stein Gold, MD, received compensation from Cassiopea as advisers and disclosed ties to many other pharmaceutical companies.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
METHODOLOGY:
- A 1% cream formulation of clascoterone, a topical androgen receptor inhibitor, is approved for the treatment of acne vulgaris in patients aged 12 years and older based on results from two identical phase 3 12-week trials, NCT02608450 and NCT02608476, and a long-term extension (LTE) study.
- The purpose of the current study was to evaluate the integrated efficacy of clascoterone cream 1% (Winlevi) in the intention-to-treat population of patients from all three trials.
- In the pivotal trials, investigators randomized patients with acne 1:1 to receive clascoterone cream 1% or vehicle twice daily for 12 weeks. Participants were eligible to enter the LTE study, in which patients applied clascoterone to the face, and if they wanted to, the trunk for up to 9 more months.
- To assess combined efficacy, researchers evaluated the proportion of patients who achieved an Investigator’s Global Assessment (IGA) of 0 or 1.
TAKEAWAY:
- Of the 1143 patients from the pivotal trials who completed 12 weeks of treatment, 576 were in the clascoterone group and 567 were in the vehicle group. Of the 600 patients who entered the LTE study, 311 were in the clascoterone group and 289 were in the vehicle group. Of these, 343 completed the LTE study.
- At week 12, the proportion of patients who achieved treatment success was higher in the clascoterone group than in the vehicle group (19.9% vs 7.7%, respectively; P < .0001).
- In the LTE study, the proportion of patients previously treated with clascoterone who achieved a facial IGA of 0/1 increased from 13.5% at extension day 0 to 29.9% at extension day 274, while the proportion of patients previously treated with vehicle and switched to clascoterone who achieved a facial IGA of 0/1 increased from 6.2% at extension day 0 to 30.4% at extension day 274.
- Similarly, the proportion of patients in the LTE study with a truncal IGA of 0/1 increased from 4.9% at extension day 0 to 31.7% on extension day 274.
IN PRACTICE:
“Clinicians may consider counseling patients that treatment persistence is required to maximize the efficacy of clascoterone treatment,” the authors concluded.
SOURCE:
Lawrence F. Eichenfield, MD, of the departments of dermatology and pediatrics at the University of California and Rady Children’s Hospital, San Diego, California, led the research. The study was published in the January 2024 issue of the Journal of Drugs in Dermatology.
LIMITATIONS:
There was a high patient discontinuation rate before and during the LET study. Also, no assessment was made as to how clascoterone affected patients’ quality of life.
DISCLOSURES:
Clascoterone manufacturer Cassiopea funded the studies. Dr. Eichenfield and fellow investigators Adelaide A. Hebert, MD, and Linda Stein Gold, MD, received compensation from Cassiopea as advisers and disclosed ties to many other pharmaceutical companies.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
METHODOLOGY:
- A 1% cream formulation of clascoterone, a topical androgen receptor inhibitor, is approved for the treatment of acne vulgaris in patients aged 12 years and older based on results from two identical phase 3 12-week trials, NCT02608450 and NCT02608476, and a long-term extension (LTE) study.
- The purpose of the current study was to evaluate the integrated efficacy of clascoterone cream 1% (Winlevi) in the intention-to-treat population of patients from all three trials.
- In the pivotal trials, investigators randomized patients with acne 1:1 to receive clascoterone cream 1% or vehicle twice daily for 12 weeks. Participants were eligible to enter the LTE study, in which patients applied clascoterone to the face, and if they wanted to, the trunk for up to 9 more months.
- To assess combined efficacy, researchers evaluated the proportion of patients who achieved an Investigator’s Global Assessment (IGA) of 0 or 1.
TAKEAWAY:
- Of the 1143 patients from the pivotal trials who completed 12 weeks of treatment, 576 were in the clascoterone group and 567 were in the vehicle group. Of the 600 patients who entered the LTE study, 311 were in the clascoterone group and 289 were in the vehicle group. Of these, 343 completed the LTE study.
- At week 12, the proportion of patients who achieved treatment success was higher in the clascoterone group than in the vehicle group (19.9% vs 7.7%, respectively; P < .0001).
- In the LTE study, the proportion of patients previously treated with clascoterone who achieved a facial IGA of 0/1 increased from 13.5% at extension day 0 to 29.9% at extension day 274, while the proportion of patients previously treated with vehicle and switched to clascoterone who achieved a facial IGA of 0/1 increased from 6.2% at extension day 0 to 30.4% at extension day 274.
- Similarly, the proportion of patients in the LTE study with a truncal IGA of 0/1 increased from 4.9% at extension day 0 to 31.7% on extension day 274.
IN PRACTICE:
“Clinicians may consider counseling patients that treatment persistence is required to maximize the efficacy of clascoterone treatment,” the authors concluded.
SOURCE:
Lawrence F. Eichenfield, MD, of the departments of dermatology and pediatrics at the University of California and Rady Children’s Hospital, San Diego, California, led the research. The study was published in the January 2024 issue of the Journal of Drugs in Dermatology.
LIMITATIONS:
There was a high patient discontinuation rate before and during the LET study. Also, no assessment was made as to how clascoterone affected patients’ quality of life.
DISCLOSURES:
Clascoterone manufacturer Cassiopea funded the studies. Dr. Eichenfield and fellow investigators Adelaide A. Hebert, MD, and Linda Stein Gold, MD, received compensation from Cassiopea as advisers and disclosed ties to many other pharmaceutical companies.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.