User login
EMERGENCY MEDICINE is a practical, peer-reviewed monthly publication and Web site that meets the educational needs of emergency clinicians and urgent care clinicians for their practice.
Recall widens for diabetes drug metformin
The recall of extended-release metformin continues this month as 76 more lots have been flagged for a possible cancer-causing ingredient.
The Food and Drug Administration announced the latest recall, involving Marksans Pharma Limited and Sun Pharmaceutical Industries products, on Oct. 5. It involves the 500-mg and 700-mg tablets. More than 175 different drug combinations have been recalled since late May.
Consumers can see all the recalled metformin products at this FDA website. The agency says that immediate-release metformin does not appear to have the same contamination problem.
The FDA has been investigating the presence of nitrosamines, known to be possible carcinogens, in the popular diabetes medications since December, when they were first discovered in drugs in other countries. The agency said this month they still do not know the source of nitrosamines in the medications.
The investigation and subsequent recalls follow similar ones for contamination of popular heartburn and blood pressure drugs also for nitrosamines, such as N-Nitrosodimethylamine (NDMA).
The FDA says patients taking metformin products that have been recalled should continue taking the medication until a doctor or pharmacist gives them a replacement or a different treatment option. It could be dangerous for patients with type 2 diabetes to stop taking the medication without first talking to their doctor.
The agency has asked drug manufacturers to test products before batches are released into the market. The companies must tell the FDA if any product shows levels of nitrosamines above the acceptable limit.
The risk from nitrosamines is not clear. The FDA says they may increase the risk of cancer in people who are exposed to high levels over a long period of time, “but we do not anticipate that shorter-term exposure at levels above the acceptable intake limit would lead to an increase in the risk of cancer.”
This article first appeared on WebMD.com.
The recall of extended-release metformin continues this month as 76 more lots have been flagged for a possible cancer-causing ingredient.
The Food and Drug Administration announced the latest recall, involving Marksans Pharma Limited and Sun Pharmaceutical Industries products, on Oct. 5. It involves the 500-mg and 700-mg tablets. More than 175 different drug combinations have been recalled since late May.
Consumers can see all the recalled metformin products at this FDA website. The agency says that immediate-release metformin does not appear to have the same contamination problem.
The FDA has been investigating the presence of nitrosamines, known to be possible carcinogens, in the popular diabetes medications since December, when they were first discovered in drugs in other countries. The agency said this month they still do not know the source of nitrosamines in the medications.
The investigation and subsequent recalls follow similar ones for contamination of popular heartburn and blood pressure drugs also for nitrosamines, such as N-Nitrosodimethylamine (NDMA).
The FDA says patients taking metformin products that have been recalled should continue taking the medication until a doctor or pharmacist gives them a replacement or a different treatment option. It could be dangerous for patients with type 2 diabetes to stop taking the medication without first talking to their doctor.
The agency has asked drug manufacturers to test products before batches are released into the market. The companies must tell the FDA if any product shows levels of nitrosamines above the acceptable limit.
The risk from nitrosamines is not clear. The FDA says they may increase the risk of cancer in people who are exposed to high levels over a long period of time, “but we do not anticipate that shorter-term exposure at levels above the acceptable intake limit would lead to an increase in the risk of cancer.”
This article first appeared on WebMD.com.
The recall of extended-release metformin continues this month as 76 more lots have been flagged for a possible cancer-causing ingredient.
The Food and Drug Administration announced the latest recall, involving Marksans Pharma Limited and Sun Pharmaceutical Industries products, on Oct. 5. It involves the 500-mg and 700-mg tablets. More than 175 different drug combinations have been recalled since late May.
Consumers can see all the recalled metformin products at this FDA website. The agency says that immediate-release metformin does not appear to have the same contamination problem.
The FDA has been investigating the presence of nitrosamines, known to be possible carcinogens, in the popular diabetes medications since December, when they were first discovered in drugs in other countries. The agency said this month they still do not know the source of nitrosamines in the medications.
The investigation and subsequent recalls follow similar ones for contamination of popular heartburn and blood pressure drugs also for nitrosamines, such as N-Nitrosodimethylamine (NDMA).
The FDA says patients taking metformin products that have been recalled should continue taking the medication until a doctor or pharmacist gives them a replacement or a different treatment option. It could be dangerous for patients with type 2 diabetes to stop taking the medication without first talking to their doctor.
The agency has asked drug manufacturers to test products before batches are released into the market. The companies must tell the FDA if any product shows levels of nitrosamines above the acceptable limit.
The risk from nitrosamines is not clear. The FDA says they may increase the risk of cancer in people who are exposed to high levels over a long period of time, “but we do not anticipate that shorter-term exposure at levels above the acceptable intake limit would lead to an increase in the risk of cancer.”
This article first appeared on WebMD.com.
NACMI: Clear benefit with PCI in STEMI COVID-19 patients
Patients with COVID-19 who present with ST-segment elevation MI (STEMI) represent a unique, high-risk population with greater risks for in-hospital death and stroke, according to initial results from the North American COVID-19 ST-Segment Elevation Myocardial Infarction Registry (NACMI).
Although COVID-19–confirmed patients were less likely to undergo angiography than patients under investigation (PUI) for COVID-19 or historical STEMI activation controls, 71% underwent primary percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI).
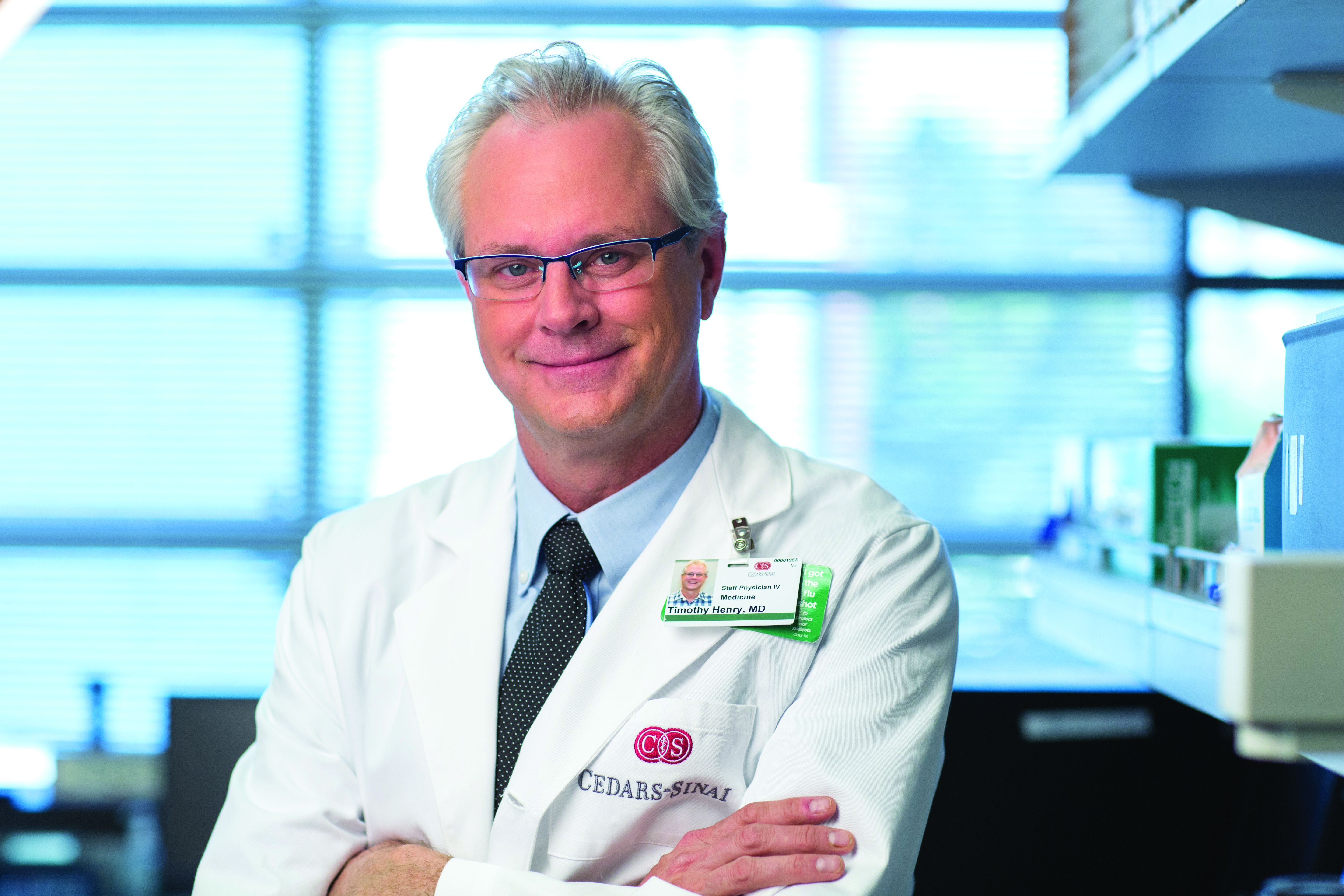
“Primary PCI is preferable and feasible in COVID-19–positive patients, with door-to-balloon times similar to PUI or COVID-negative patients, and that supports the updated COVID-specific STEMI guidelines,” study cochair Timothy D. Henry, MD, said in a late-breaking clinical science session at TCT 2020, the Transcatheter Cardiovascular Therapeutics virtual annual meeting.
The multisociety COVID-specific guidelines were initially issued in April, endorsing PCI as the standard of care and allowing for consideration of fibrinolysis-based therapy at non-PCI capable hospitals.
Five previous publications on a total of 174 COVID-19 patients with ST-elevation have shown there are more frequent in-hospital STEMI presentations, more cases without a clear culprit lesion, more thrombotic lesions and microthrombi, and higher mortality, ranging from 12% to 72%. Still, there has been considerable controversy over exactly what to do when COVID-19 patients with ST elevation reach the cath lab, he said at the meeting sponsored by the Cardiovascular Research Foundation.
NACMI represents the largest experience with ST-elevation patients and is a unique collaboration between the Society for Cardiovascular Angiography and Interventions, Canadian Association of Interventional Cardiology, American College of Cardiology, and Midwest STEMI Consortium, noted Dr. Henry, who is medical director of the Lindner Center for Research and Education at the Christ Hospital, Cincinnati.
The registry enrolled any COVID-19–positive patient or person under investigation older than 18 years with ST-segment elevation or new-onset left bundle branch block on electrocardiogram with a clinical correlate of myocardial ischemia such as chest pain, dyspnea, cardiac arrest, shock, or mechanical ventilation. There were no exclusion criteria.
Data from 171 patients with confirmed COVID-19 and 423 PUI from 64 sites were then propensity-matched to a control population from the Midwest STEMI Consortium, a prospective, multicenter registry of consecutive STEMI patients.
The three groups were similar in sex and age but there was a striking difference in race, with 27% of African American and 24% of Hispanic patients COVID-confirmed, compared with 11% and 6% in the PUI group and 4% and 1% in the control group. Likewise, there was a significant increase in diabetes (44% vs. 33% vs. 20%), which has been reported previously with influenza.
COVID-19–positive patients, as compared with PUI and controls, were significantly more likely to present with cardiogenic shock before PCI (20% vs. 14% vs. 5%), but not cardiac arrest (12% vs. 17% vs. 11%), and to have lower left ventricular ejection fractions (45% vs. 45% vs. 50%).
They also presented with more atypical symptoms than PUI patients, particularly infiltrates on chest x-ray (49% vs. 17%) and dyspnea (58% vs. 38%). Data were not available for these outcomes among historic controls.
Importantly, 21% of the COVID-19 patients did not undergo angiography, compared with 5% of PUI patients and 0% of controls (P < .001), “which is much higher than we would expect or have suspected,” Dr. Henry said. Thrombolytic use was very uncommon in those undergoing angiography, likely as a result of the guidelines.
Very surprisingly, there were no differences in door-to-balloon times between the COVID-positive, PUI, and control groups despite the ongoing pandemic (80 min vs. 78 min vs. 86 min).
But there was clear worsening in in-hospital mortality in COVID-19–positive patients (32% vs. 12% and 6%; P < .001), as well as in-hospital stroke (3.4% vs. 2% vs. 0.6%) that reached statistical significance only when compared with historical controls (P = .039). Total length of stay was twice as long in COVID-confirmed patients as in both PUI and controls (6 days vs. 3 days; P < .001).
Following the formal presentation, invited discussant Philippe Gabriel Steg, MD, Imperial College London, said the researchers have provided a great service in reporting the data so quickly but noted that an ongoing French registry of events before, during, and after the first COVID-19 wave has not seen an increased death rate.
“Can you tease out whether the increased death rate is related to cardiovascular deaths or to COVID-related pneumonias, shocks, ARDSs [acute respiratory distress syndromes], and so on and so forth? Because our impression – and that’s what we’ve published in Lancet Public Health – is that the cardiovascular morality rate doesn’t seem that affected by COVID.”
Dr. Henry replied that these are early data but “I will tell you that patients who did get PCI had a mortality rate that was only around 12% or 13%, and the patients who did not undergo angiography or were treated with medical therapy had higher mortality. Now, of course, that’s selected and we need to do a much better matching and look at that, but that’s our goal and we will have that information,” he said.
During a press briefing on the study, discussant Renu Virmani, MD, president and founder of CVPath Institute, noted that, in their analysis of 40 autopsy cases from Bergamot, Italy, small intramyocardial microthrombi were seen in nine patients, whereas epicardial microthrombi were seen in only three or four.
“Some of the cases are being taken as being related to coronary disease but may be more thrombotic than anything else,” she said. “I think there’s a combination, and that’s why the outcomes are so poor. You didn’t show us TIMI flow but that’s something to think about: Was TIMI flow different in the patients who died because you have very high mortality? I think we need to get to the bottom of what is the underlying cause of that thrombosis.”
Future topics of interest include ethnic and regional/country differences; time-to-treatment including chest pain onset-to-arrival; transfer, in-hospital, and no-culprit patients; changes over time during the pandemic; and eventually 1-year outcomes, Dr. Henry said.
Press briefing moderator Ajay Kirtane, MD, director of the cardiac catheterization labs at NewYork-Presbyterian/Columbia University Irving, New York, remarked that “a lot of times people will pooh-pooh observational data, but this is exactly the type of data that we need to try to be able to gather information about what our practices are, how they fit. And I think many of us around the world will see these data, and it will echo their own experience.”
The study was funded by the Society for Cardiovascular Angiography and Interventions and the Canadian Association of Interventional Cardiology. Dr. Henry has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
Patients with COVID-19 who present with ST-segment elevation MI (STEMI) represent a unique, high-risk population with greater risks for in-hospital death and stroke, according to initial results from the North American COVID-19 ST-Segment Elevation Myocardial Infarction Registry (NACMI).
Although COVID-19–confirmed patients were less likely to undergo angiography than patients under investigation (PUI) for COVID-19 or historical STEMI activation controls, 71% underwent primary percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI).
“Primary PCI is preferable and feasible in COVID-19–positive patients, with door-to-balloon times similar to PUI or COVID-negative patients, and that supports the updated COVID-specific STEMI guidelines,” study cochair Timothy D. Henry, MD, said in a late-breaking clinical science session at TCT 2020, the Transcatheter Cardiovascular Therapeutics virtual annual meeting.
The multisociety COVID-specific guidelines were initially issued in April, endorsing PCI as the standard of care and allowing for consideration of fibrinolysis-based therapy at non-PCI capable hospitals.
Five previous publications on a total of 174 COVID-19 patients with ST-elevation have shown there are more frequent in-hospital STEMI presentations, more cases without a clear culprit lesion, more thrombotic lesions and microthrombi, and higher mortality, ranging from 12% to 72%. Still, there has been considerable controversy over exactly what to do when COVID-19 patients with ST elevation reach the cath lab, he said at the meeting sponsored by the Cardiovascular Research Foundation.
NACMI represents the largest experience with ST-elevation patients and is a unique collaboration between the Society for Cardiovascular Angiography and Interventions, Canadian Association of Interventional Cardiology, American College of Cardiology, and Midwest STEMI Consortium, noted Dr. Henry, who is medical director of the Lindner Center for Research and Education at the Christ Hospital, Cincinnati.
The registry enrolled any COVID-19–positive patient or person under investigation older than 18 years with ST-segment elevation or new-onset left bundle branch block on electrocardiogram with a clinical correlate of myocardial ischemia such as chest pain, dyspnea, cardiac arrest, shock, or mechanical ventilation. There were no exclusion criteria.
Data from 171 patients with confirmed COVID-19 and 423 PUI from 64 sites were then propensity-matched to a control population from the Midwest STEMI Consortium, a prospective, multicenter registry of consecutive STEMI patients.
The three groups were similar in sex and age but there was a striking difference in race, with 27% of African American and 24% of Hispanic patients COVID-confirmed, compared with 11% and 6% in the PUI group and 4% and 1% in the control group. Likewise, there was a significant increase in diabetes (44% vs. 33% vs. 20%), which has been reported previously with influenza.
COVID-19–positive patients, as compared with PUI and controls, were significantly more likely to present with cardiogenic shock before PCI (20% vs. 14% vs. 5%), but not cardiac arrest (12% vs. 17% vs. 11%), and to have lower left ventricular ejection fractions (45% vs. 45% vs. 50%).
They also presented with more atypical symptoms than PUI patients, particularly infiltrates on chest x-ray (49% vs. 17%) and dyspnea (58% vs. 38%). Data were not available for these outcomes among historic controls.
Importantly, 21% of the COVID-19 patients did not undergo angiography, compared with 5% of PUI patients and 0% of controls (P < .001), “which is much higher than we would expect or have suspected,” Dr. Henry said. Thrombolytic use was very uncommon in those undergoing angiography, likely as a result of the guidelines.
Very surprisingly, there were no differences in door-to-balloon times between the COVID-positive, PUI, and control groups despite the ongoing pandemic (80 min vs. 78 min vs. 86 min).
But there was clear worsening in in-hospital mortality in COVID-19–positive patients (32% vs. 12% and 6%; P < .001), as well as in-hospital stroke (3.4% vs. 2% vs. 0.6%) that reached statistical significance only when compared with historical controls (P = .039). Total length of stay was twice as long in COVID-confirmed patients as in both PUI and controls (6 days vs. 3 days; P < .001).
Following the formal presentation, invited discussant Philippe Gabriel Steg, MD, Imperial College London, said the researchers have provided a great service in reporting the data so quickly but noted that an ongoing French registry of events before, during, and after the first COVID-19 wave has not seen an increased death rate.
“Can you tease out whether the increased death rate is related to cardiovascular deaths or to COVID-related pneumonias, shocks, ARDSs [acute respiratory distress syndromes], and so on and so forth? Because our impression – and that’s what we’ve published in Lancet Public Health – is that the cardiovascular morality rate doesn’t seem that affected by COVID.”
Dr. Henry replied that these are early data but “I will tell you that patients who did get PCI had a mortality rate that was only around 12% or 13%, and the patients who did not undergo angiography or were treated with medical therapy had higher mortality. Now, of course, that’s selected and we need to do a much better matching and look at that, but that’s our goal and we will have that information,” he said.
During a press briefing on the study, discussant Renu Virmani, MD, president and founder of CVPath Institute, noted that, in their analysis of 40 autopsy cases from Bergamot, Italy, small intramyocardial microthrombi were seen in nine patients, whereas epicardial microthrombi were seen in only three or four.
“Some of the cases are being taken as being related to coronary disease but may be more thrombotic than anything else,” she said. “I think there’s a combination, and that’s why the outcomes are so poor. You didn’t show us TIMI flow but that’s something to think about: Was TIMI flow different in the patients who died because you have very high mortality? I think we need to get to the bottom of what is the underlying cause of that thrombosis.”
Future topics of interest include ethnic and regional/country differences; time-to-treatment including chest pain onset-to-arrival; transfer, in-hospital, and no-culprit patients; changes over time during the pandemic; and eventually 1-year outcomes, Dr. Henry said.
Press briefing moderator Ajay Kirtane, MD, director of the cardiac catheterization labs at NewYork-Presbyterian/Columbia University Irving, New York, remarked that “a lot of times people will pooh-pooh observational data, but this is exactly the type of data that we need to try to be able to gather information about what our practices are, how they fit. And I think many of us around the world will see these data, and it will echo their own experience.”
The study was funded by the Society for Cardiovascular Angiography and Interventions and the Canadian Association of Interventional Cardiology. Dr. Henry has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
Patients with COVID-19 who present with ST-segment elevation MI (STEMI) represent a unique, high-risk population with greater risks for in-hospital death and stroke, according to initial results from the North American COVID-19 ST-Segment Elevation Myocardial Infarction Registry (NACMI).
Although COVID-19–confirmed patients were less likely to undergo angiography than patients under investigation (PUI) for COVID-19 or historical STEMI activation controls, 71% underwent primary percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI).
“Primary PCI is preferable and feasible in COVID-19–positive patients, with door-to-balloon times similar to PUI or COVID-negative patients, and that supports the updated COVID-specific STEMI guidelines,” study cochair Timothy D. Henry, MD, said in a late-breaking clinical science session at TCT 2020, the Transcatheter Cardiovascular Therapeutics virtual annual meeting.
The multisociety COVID-specific guidelines were initially issued in April, endorsing PCI as the standard of care and allowing for consideration of fibrinolysis-based therapy at non-PCI capable hospitals.
Five previous publications on a total of 174 COVID-19 patients with ST-elevation have shown there are more frequent in-hospital STEMI presentations, more cases without a clear culprit lesion, more thrombotic lesions and microthrombi, and higher mortality, ranging from 12% to 72%. Still, there has been considerable controversy over exactly what to do when COVID-19 patients with ST elevation reach the cath lab, he said at the meeting sponsored by the Cardiovascular Research Foundation.
NACMI represents the largest experience with ST-elevation patients and is a unique collaboration between the Society for Cardiovascular Angiography and Interventions, Canadian Association of Interventional Cardiology, American College of Cardiology, and Midwest STEMI Consortium, noted Dr. Henry, who is medical director of the Lindner Center for Research and Education at the Christ Hospital, Cincinnati.
The registry enrolled any COVID-19–positive patient or person under investigation older than 18 years with ST-segment elevation or new-onset left bundle branch block on electrocardiogram with a clinical correlate of myocardial ischemia such as chest pain, dyspnea, cardiac arrest, shock, or mechanical ventilation. There were no exclusion criteria.
Data from 171 patients with confirmed COVID-19 and 423 PUI from 64 sites were then propensity-matched to a control population from the Midwest STEMI Consortium, a prospective, multicenter registry of consecutive STEMI patients.
The three groups were similar in sex and age but there was a striking difference in race, with 27% of African American and 24% of Hispanic patients COVID-confirmed, compared with 11% and 6% in the PUI group and 4% and 1% in the control group. Likewise, there was a significant increase in diabetes (44% vs. 33% vs. 20%), which has been reported previously with influenza.
COVID-19–positive patients, as compared with PUI and controls, were significantly more likely to present with cardiogenic shock before PCI (20% vs. 14% vs. 5%), but not cardiac arrest (12% vs. 17% vs. 11%), and to have lower left ventricular ejection fractions (45% vs. 45% vs. 50%).
They also presented with more atypical symptoms than PUI patients, particularly infiltrates on chest x-ray (49% vs. 17%) and dyspnea (58% vs. 38%). Data were not available for these outcomes among historic controls.
Importantly, 21% of the COVID-19 patients did not undergo angiography, compared with 5% of PUI patients and 0% of controls (P < .001), “which is much higher than we would expect or have suspected,” Dr. Henry said. Thrombolytic use was very uncommon in those undergoing angiography, likely as a result of the guidelines.
Very surprisingly, there were no differences in door-to-balloon times between the COVID-positive, PUI, and control groups despite the ongoing pandemic (80 min vs. 78 min vs. 86 min).
But there was clear worsening in in-hospital mortality in COVID-19–positive patients (32% vs. 12% and 6%; P < .001), as well as in-hospital stroke (3.4% vs. 2% vs. 0.6%) that reached statistical significance only when compared with historical controls (P = .039). Total length of stay was twice as long in COVID-confirmed patients as in both PUI and controls (6 days vs. 3 days; P < .001).
Following the formal presentation, invited discussant Philippe Gabriel Steg, MD, Imperial College London, said the researchers have provided a great service in reporting the data so quickly but noted that an ongoing French registry of events before, during, and after the first COVID-19 wave has not seen an increased death rate.
“Can you tease out whether the increased death rate is related to cardiovascular deaths or to COVID-related pneumonias, shocks, ARDSs [acute respiratory distress syndromes], and so on and so forth? Because our impression – and that’s what we’ve published in Lancet Public Health – is that the cardiovascular morality rate doesn’t seem that affected by COVID.”
Dr. Henry replied that these are early data but “I will tell you that patients who did get PCI had a mortality rate that was only around 12% or 13%, and the patients who did not undergo angiography or were treated with medical therapy had higher mortality. Now, of course, that’s selected and we need to do a much better matching and look at that, but that’s our goal and we will have that information,” he said.
During a press briefing on the study, discussant Renu Virmani, MD, president and founder of CVPath Institute, noted that, in their analysis of 40 autopsy cases from Bergamot, Italy, small intramyocardial microthrombi were seen in nine patients, whereas epicardial microthrombi were seen in only three or four.
“Some of the cases are being taken as being related to coronary disease but may be more thrombotic than anything else,” she said. “I think there’s a combination, and that’s why the outcomes are so poor. You didn’t show us TIMI flow but that’s something to think about: Was TIMI flow different in the patients who died because you have very high mortality? I think we need to get to the bottom of what is the underlying cause of that thrombosis.”
Future topics of interest include ethnic and regional/country differences; time-to-treatment including chest pain onset-to-arrival; transfer, in-hospital, and no-culprit patients; changes over time during the pandemic; and eventually 1-year outcomes, Dr. Henry said.
Press briefing moderator Ajay Kirtane, MD, director of the cardiac catheterization labs at NewYork-Presbyterian/Columbia University Irving, New York, remarked that “a lot of times people will pooh-pooh observational data, but this is exactly the type of data that we need to try to be able to gather information about what our practices are, how they fit. And I think many of us around the world will see these data, and it will echo their own experience.”
The study was funded by the Society for Cardiovascular Angiography and Interventions and the Canadian Association of Interventional Cardiology. Dr. Henry has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
Female cardiac advantage essentially lost after MI
Women are known to lag 5-10 years behind men in experiencing coronary heart disease (CHD), but new research suggests the gap narrows substantially following a myocardial infarction.
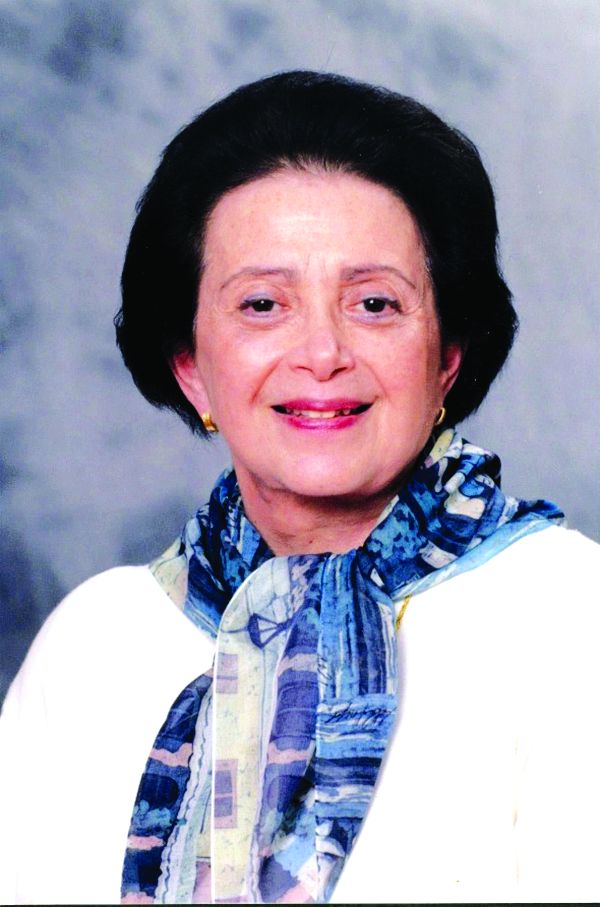
“Women lose a considerable portion, but not all, of their coronary and survival advantage – i.e., the lower event rates – after suffering a MI,” study author Sanne Peters, PhD, George Institute for Global Health, Imperial College London, said in an interview.
Previous studies of sex differences in event rates after a coronary event have produced mixed results and were primarily focused on mortality following MI. Importantly, the studies also lacked a control group without a history of CHD and, thus, were unable to provide a reference point for the disparity in event rates, she explained.
Using the MarketScan and Medicare databases, however, Dr. Peters and colleagues matched 339,890 U.S. adults hospitalized for an MI between January 2015 and December 2016 with 1,359,560 U.S. adults without a history of CHD.
Over a median 1.3 years follow-up, there were 12,518 MIs in the non-CHD group and 27,115 recurrent MIs in the MI group.
The age-standardized rate of MI per 1,000 person-years was 4.0 in women and 6.1 in men without a history of CHD, compared with 57.6 in women and 62.7 in men with a prior MI.
After multivariate adjustment, the women-to-men hazard ratio for MI was 0.64 (95% confidence interval, 0.62-0.67) in the non-CHD group and 0.94 (95% CI, 0.92-0.96) in the prior MI group, the authors reported Oct. 5 in the Journal of the American College of Cardiology
Additional results show the multivariate adjusted women-to-men hazard ratios for three other cardiovascular outcomes follow a similar pattern in the non-CHD and prior MI groups:
- CHD events: 0.53 (95% CI, 0.51-0.54) and 0.87 (95% CI, 0.85-0.89).
- Heart failure hospitalization: 0.93 (95% CI, 0.90-0.96) and 1.02 (95% CI, 1.00-1.04).
- All-cause mortality: 0.72 (95% CI, 0.71-0.73) and 0.90 (95% CI, 0.89-0.92).
“By including a control group of individuals without CHD, we demonstrated that the magnitude of the sex difference in cardiac event rates and survival is considerably smaller among those with prior MI than among those without a history of CHD,” Dr. Peters said.
Of note, the sex differences were consistent across age and race/ethnicity groups for all events, except for heart failure hospitalizations, where the adjusted hazard ratio for women vs. men age 80 years or older was 0.95 for those without a history of CHD (95% CI, 0.91-0.98) and 0.99 (95% CI, 0.96-1.02) for participants with a previous MI.
Dr. Peters said it’s not clear why the female advantage is attenuated post-MI but that one explanation is that women are less likely than men to receive guideline-recommended treatments and dosages or to adhere to prescribed therapies after MI hospitalization, which could put them at a higher risk of subsequent events and worse outcomes than men.
“Sex differences in pathophysiology of CHD and its complications may also explain, to some extent, why the rates of recurrent events are considerably more similar between the sexes than incident event rates,” she said. Compared with men, women have a higher incidence of MI with nonobstructive coronary artery disease and of heart failure with preserved ejection fraction, and evidence-based treatment options are more limited for both conditions.
“After people read this, I think the important thing to recognize is we need to push– as much as we can, with what meds we have, and what data we have – secondary prevention in these women,” Laxmi Mehta, MD, director of preventive cardiology and women’s cardiovascular health at Ohio State University, Columbus, said in an interview.
The lack of a female advantage post-MI should also elicit a “really meaningful conversation with our patients on shared decision-making of why they need to be on medications, remembering on our part to prescribe the medications, remembering to prescribe cardiac rehab, and also reminding our community we do need more data and need to investigate this further,” she said.
In an accompanying editorial, Nanette Wenger, MD, of Emory University, Atlanta, also points out that nonobstructive coronary disease is more common in women and, “yet, guideline-based therapies are those validated for obstructive coronary disease in a predominantly male population but, nonetheless, are applied for nonobstructive coronary disease.”
She advocates for aggressive evaluation and treatment for women with chest pain symptoms as well as early identification of women at risk for CHD, specifically those with metabolic syndrome, preeclampsia, hypertensive disorders of pregnancy, chronic inflammatory conditions, and high-risk race/ethnicity.
“Next, when coronary angiography is undertaken, particularly in younger women, an assiduous search for spontaneous coronary artery dissection and its appropriate management, as well as prompt and evidence-based interventions and medical therapies for an acute coronary event [are indicated],” Dr. Wenger wrote. “However, basic to improving outcomes for women is the elucidation of the optimal noninvasive techniques to identify microvascular disease, which could then enable delineation of appropriate preventive and therapeutic approaches.”
Dr. Peters is supported by a U.K. Medical Research Council Skills Development Fellowship. Dr. Mehta and Dr. Wenger disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
Women are known to lag 5-10 years behind men in experiencing coronary heart disease (CHD), but new research suggests the gap narrows substantially following a myocardial infarction.
“Women lose a considerable portion, but not all, of their coronary and survival advantage – i.e., the lower event rates – after suffering a MI,” study author Sanne Peters, PhD, George Institute for Global Health, Imperial College London, said in an interview.
Previous studies of sex differences in event rates after a coronary event have produced mixed results and were primarily focused on mortality following MI. Importantly, the studies also lacked a control group without a history of CHD and, thus, were unable to provide a reference point for the disparity in event rates, she explained.
Using the MarketScan and Medicare databases, however, Dr. Peters and colleagues matched 339,890 U.S. adults hospitalized for an MI between January 2015 and December 2016 with 1,359,560 U.S. adults without a history of CHD.
Over a median 1.3 years follow-up, there were 12,518 MIs in the non-CHD group and 27,115 recurrent MIs in the MI group.
The age-standardized rate of MI per 1,000 person-years was 4.0 in women and 6.1 in men without a history of CHD, compared with 57.6 in women and 62.7 in men with a prior MI.
After multivariate adjustment, the women-to-men hazard ratio for MI was 0.64 (95% confidence interval, 0.62-0.67) in the non-CHD group and 0.94 (95% CI, 0.92-0.96) in the prior MI group, the authors reported Oct. 5 in the Journal of the American College of Cardiology
Additional results show the multivariate adjusted women-to-men hazard ratios for three other cardiovascular outcomes follow a similar pattern in the non-CHD and prior MI groups:
- CHD events: 0.53 (95% CI, 0.51-0.54) and 0.87 (95% CI, 0.85-0.89).
- Heart failure hospitalization: 0.93 (95% CI, 0.90-0.96) and 1.02 (95% CI, 1.00-1.04).
- All-cause mortality: 0.72 (95% CI, 0.71-0.73) and 0.90 (95% CI, 0.89-0.92).
“By including a control group of individuals without CHD, we demonstrated that the magnitude of the sex difference in cardiac event rates and survival is considerably smaller among those with prior MI than among those without a history of CHD,” Dr. Peters said.
Of note, the sex differences were consistent across age and race/ethnicity groups for all events, except for heart failure hospitalizations, where the adjusted hazard ratio for women vs. men age 80 years or older was 0.95 for those without a history of CHD (95% CI, 0.91-0.98) and 0.99 (95% CI, 0.96-1.02) for participants with a previous MI.
Dr. Peters said it’s not clear why the female advantage is attenuated post-MI but that one explanation is that women are less likely than men to receive guideline-recommended treatments and dosages or to adhere to prescribed therapies after MI hospitalization, which could put them at a higher risk of subsequent events and worse outcomes than men.
“Sex differences in pathophysiology of CHD and its complications may also explain, to some extent, why the rates of recurrent events are considerably more similar between the sexes than incident event rates,” she said. Compared with men, women have a higher incidence of MI with nonobstructive coronary artery disease and of heart failure with preserved ejection fraction, and evidence-based treatment options are more limited for both conditions.
“After people read this, I think the important thing to recognize is we need to push– as much as we can, with what meds we have, and what data we have – secondary prevention in these women,” Laxmi Mehta, MD, director of preventive cardiology and women’s cardiovascular health at Ohio State University, Columbus, said in an interview.
The lack of a female advantage post-MI should also elicit a “really meaningful conversation with our patients on shared decision-making of why they need to be on medications, remembering on our part to prescribe the medications, remembering to prescribe cardiac rehab, and also reminding our community we do need more data and need to investigate this further,” she said.
In an accompanying editorial, Nanette Wenger, MD, of Emory University, Atlanta, also points out that nonobstructive coronary disease is more common in women and, “yet, guideline-based therapies are those validated for obstructive coronary disease in a predominantly male population but, nonetheless, are applied for nonobstructive coronary disease.”
She advocates for aggressive evaluation and treatment for women with chest pain symptoms as well as early identification of women at risk for CHD, specifically those with metabolic syndrome, preeclampsia, hypertensive disorders of pregnancy, chronic inflammatory conditions, and high-risk race/ethnicity.
“Next, when coronary angiography is undertaken, particularly in younger women, an assiduous search for spontaneous coronary artery dissection and its appropriate management, as well as prompt and evidence-based interventions and medical therapies for an acute coronary event [are indicated],” Dr. Wenger wrote. “However, basic to improving outcomes for women is the elucidation of the optimal noninvasive techniques to identify microvascular disease, which could then enable delineation of appropriate preventive and therapeutic approaches.”
Dr. Peters is supported by a U.K. Medical Research Council Skills Development Fellowship. Dr. Mehta and Dr. Wenger disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
Women are known to lag 5-10 years behind men in experiencing coronary heart disease (CHD), but new research suggests the gap narrows substantially following a myocardial infarction.
“Women lose a considerable portion, but not all, of their coronary and survival advantage – i.e., the lower event rates – after suffering a MI,” study author Sanne Peters, PhD, George Institute for Global Health, Imperial College London, said in an interview.
Previous studies of sex differences in event rates after a coronary event have produced mixed results and were primarily focused on mortality following MI. Importantly, the studies also lacked a control group without a history of CHD and, thus, were unable to provide a reference point for the disparity in event rates, she explained.
Using the MarketScan and Medicare databases, however, Dr. Peters and colleagues matched 339,890 U.S. adults hospitalized for an MI between January 2015 and December 2016 with 1,359,560 U.S. adults without a history of CHD.
Over a median 1.3 years follow-up, there were 12,518 MIs in the non-CHD group and 27,115 recurrent MIs in the MI group.
The age-standardized rate of MI per 1,000 person-years was 4.0 in women and 6.1 in men without a history of CHD, compared with 57.6 in women and 62.7 in men with a prior MI.
After multivariate adjustment, the women-to-men hazard ratio for MI was 0.64 (95% confidence interval, 0.62-0.67) in the non-CHD group and 0.94 (95% CI, 0.92-0.96) in the prior MI group, the authors reported Oct. 5 in the Journal of the American College of Cardiology
Additional results show the multivariate adjusted women-to-men hazard ratios for three other cardiovascular outcomes follow a similar pattern in the non-CHD and prior MI groups:
- CHD events: 0.53 (95% CI, 0.51-0.54) and 0.87 (95% CI, 0.85-0.89).
- Heart failure hospitalization: 0.93 (95% CI, 0.90-0.96) and 1.02 (95% CI, 1.00-1.04).
- All-cause mortality: 0.72 (95% CI, 0.71-0.73) and 0.90 (95% CI, 0.89-0.92).
“By including a control group of individuals without CHD, we demonstrated that the magnitude of the sex difference in cardiac event rates and survival is considerably smaller among those with prior MI than among those without a history of CHD,” Dr. Peters said.
Of note, the sex differences were consistent across age and race/ethnicity groups for all events, except for heart failure hospitalizations, where the adjusted hazard ratio for women vs. men age 80 years or older was 0.95 for those without a history of CHD (95% CI, 0.91-0.98) and 0.99 (95% CI, 0.96-1.02) for participants with a previous MI.
Dr. Peters said it’s not clear why the female advantage is attenuated post-MI but that one explanation is that women are less likely than men to receive guideline-recommended treatments and dosages or to adhere to prescribed therapies after MI hospitalization, which could put them at a higher risk of subsequent events and worse outcomes than men.
“Sex differences in pathophysiology of CHD and its complications may also explain, to some extent, why the rates of recurrent events are considerably more similar between the sexes than incident event rates,” she said. Compared with men, women have a higher incidence of MI with nonobstructive coronary artery disease and of heart failure with preserved ejection fraction, and evidence-based treatment options are more limited for both conditions.
“After people read this, I think the important thing to recognize is we need to push– as much as we can, with what meds we have, and what data we have – secondary prevention in these women,” Laxmi Mehta, MD, director of preventive cardiology and women’s cardiovascular health at Ohio State University, Columbus, said in an interview.
The lack of a female advantage post-MI should also elicit a “really meaningful conversation with our patients on shared decision-making of why they need to be on medications, remembering on our part to prescribe the medications, remembering to prescribe cardiac rehab, and also reminding our community we do need more data and need to investigate this further,” she said.
In an accompanying editorial, Nanette Wenger, MD, of Emory University, Atlanta, also points out that nonobstructive coronary disease is more common in women and, “yet, guideline-based therapies are those validated for obstructive coronary disease in a predominantly male population but, nonetheless, are applied for nonobstructive coronary disease.”
She advocates for aggressive evaluation and treatment for women with chest pain symptoms as well as early identification of women at risk for CHD, specifically those with metabolic syndrome, preeclampsia, hypertensive disorders of pregnancy, chronic inflammatory conditions, and high-risk race/ethnicity.
“Next, when coronary angiography is undertaken, particularly in younger women, an assiduous search for spontaneous coronary artery dissection and its appropriate management, as well as prompt and evidence-based interventions and medical therapies for an acute coronary event [are indicated],” Dr. Wenger wrote. “However, basic to improving outcomes for women is the elucidation of the optimal noninvasive techniques to identify microvascular disease, which could then enable delineation of appropriate preventive and therapeutic approaches.”
Dr. Peters is supported by a U.K. Medical Research Council Skills Development Fellowship. Dr. Mehta and Dr. Wenger disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
T2D treatments create tension between glycemic and cardiovascular goals
It was no surprise that updated guidelines recently published by the European Society of Cardiology for managing cardiovascular disease in patients with diabetes highlighted optimized treatment from a cardiovascular disease perspective, while a nearly concurrent update from two major diabetes societies saw the same issue from a more glycemic point of view.
This difference led to divergent approaches to managing hyperglycemia in patients with type 2 diabetes (T2D). The two diabetes societies that wrote one set of recommendations, the American Diabetes Association and the European Association for the Study of Diabetes, put metformin at the pinnacle of their drug hierarchy. Patients with T2D and established atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease (CVD), chronic kidney disease, or heart failure should all receive metformin first unless contraindicated or not tolerated, their updated consensus report said.
Once metformin is on board, a clinician can then add a second diabetes agent from among the two drug classes recently proven to also reduce cardiovascular and renal events, either the SGLT2 (sodium-glucose transporter 2) inhibitors, or GLP-1 (glucagonlike peptide–1) receptor agonists, they advised.
Cardiovascular disease focus represents a ‘major paradigm shift’
In contrast, the ESC guidelines called for upfront, systematic assessment of CVD risk in patients with T2D before treatment starts, and for patients in high- or very high–risk strata, the guidelines recommended starting the patient first on an SGLT2 inhibitor or a GLP-1 receptor agonist, and only adding metformin in patients who need additional glycemic control.
The guidelines also recommended starting treatment-naive patients with moderate CVD risk on metformin. For patients already on metformin, the new ESC guidelines called for adding an agent from at least one of these two drug classes with proven CVD benefits for those at high or very high CVD risk. The guidelines also note that the CVD benefits of the two newer drug classes differ and hence require further individualization depending on the risks faced by each patient, such as the risk for heart failure hospitalizations.
It’s an approach “driven by data from the cardiovascular outcome trials,” that showed several drugs from both the SGLT2 inhibitor and GLP-1 receptor agonist classes have substantial benefit for preventing cardiovascular events, renal events, hospitalizations for heart failure, and in some studies all-cause mortality, said Francesco Cosentino, MD, during a discussion of the guideline differences at the virtual annual meeting of the European Association for the Study of Diabetes.
The ESC approach also represents “a major paradigm shift,” a “change from a glucose-centric approach to an approach driven by cardiovascular disease events,” summed up Dr. Cosentino, professor of cardiology at the Karolinska Institute in Stockholm and chair of the task force that wrote the ESC’s 2019 updated guidelines. The ESC approach advocates initiating drugs for treating patients with T2D “based on cardiovascular disease risk classification,” he highlighted. Results from some SGLT2 inhibitor cardiovascular outcome trials showed that the CVD benefit was similar regardless of whether or not patients also received metformin.
ADA, EASD call for ‘a different emphasis’
“There is a different emphasis” in the statement issued by the diabetologists of the ADA and EASD, admitted Peter J. Grant, MD, a professor of diabetes and endocrinology at the University of Leeds (England) and cochair of the ESC guidelines task force. Dr. Grant represented the EASD on the task force, and the Association collaborated with the ESC in producing its guidelines.
“The ADA and EASD recommendations “look primarily at glucose control, with cardiovascular disease management as secondary.” In contrast, the ESC guidelines “are primarily cardiovascular disease risk guidelines, with a glucose interest,” Dr. Grant declared.
Despite his involvement in writing the ESC guidelines, Dr. Grant tilted toward the ADA/EASD statement as more globally relevant.
“There is much more to vasculopathy in diabetes than just macrovascular disease. Many patients with type 2 diabetes without macrovascular complications have microvascular disease,” including the potential for retinopathy, nephropathy, and neuropathy, he said. These complications can also have a strong impact on psychological well being and treatment satisfaction.
“It’s important that we’re not glucocentric any more, but it’s equally important that we treat glucose because it has such a benefit for microvascular disease.” Dr. Grant also cited metformin’s long history of safety and good tolerance, clinician comfort prescribing it, and its low price. Heavier reliance on SGLT2 inhibitors and GLP-1 receptor agonists will be expensive for the short term while the cost of these drugs remains high, which places a higher burden on “knowing we’re doing it right,” said Dr. Grant.
Dr. Cosentino pointed out that the higher cost of the drugs in the two classes shown to exert important cardiovascular and renal effects needs to be considered in a cost-effectiveness context, not just by cost alone.
‘Clinical inertia’ could be a danger
Dr. Cosentino played down a major disagreement between the two guidelines, suggesting that “focusing on the differences leads to clinical inertia” by the practicing community when they are unsure how to reconcile the two positions.
Dr. Grant agreed that adding a second drug to metformin right away made sense in at least selected patients. “Look at each patient and decide whether they need glycemic control. If so, and if they also have cardiovascular disease, use both drugs,” metformin, plus one agent from one of the two newer classes.
Something both experts agreed on is that it’s time to generally steer clear of sulfonylurea drugs. “We have evidence for harmful effects from sulfonylureas,” Dr. Cosentino said.
“I’d dump sulfonylureas,” was Dr. Grant’s assessment, but he added that they still have a role for patients who need additional glycemic control but can’t afford the newer drugs.
Dr. Cosentino has had financial relationships with Abbott, AstraZeneca, Boehringer Ingelheim, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Eli Lilly, Merck, Mundipharma, Novo Nordisk, and Pfizer, Dr. Grant has lectured on behalf of AstraZeneca, GlaxoSmithKline, Merck, Novo Nordisk, the Medicines Company, and Takeda, and he has been an adviser to Amgen, AstraZeneca, Novartis, Novo Nordisk, and Synexus.
It was no surprise that updated guidelines recently published by the European Society of Cardiology for managing cardiovascular disease in patients with diabetes highlighted optimized treatment from a cardiovascular disease perspective, while a nearly concurrent update from two major diabetes societies saw the same issue from a more glycemic point of view.
This difference led to divergent approaches to managing hyperglycemia in patients with type 2 diabetes (T2D). The two diabetes societies that wrote one set of recommendations, the American Diabetes Association and the European Association for the Study of Diabetes, put metformin at the pinnacle of their drug hierarchy. Patients with T2D and established atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease (CVD), chronic kidney disease, or heart failure should all receive metformin first unless contraindicated or not tolerated, their updated consensus report said.
Once metformin is on board, a clinician can then add a second diabetes agent from among the two drug classes recently proven to also reduce cardiovascular and renal events, either the SGLT2 (sodium-glucose transporter 2) inhibitors, or GLP-1 (glucagonlike peptide–1) receptor agonists, they advised.
Cardiovascular disease focus represents a ‘major paradigm shift’
In contrast, the ESC guidelines called for upfront, systematic assessment of CVD risk in patients with T2D before treatment starts, and for patients in high- or very high–risk strata, the guidelines recommended starting the patient first on an SGLT2 inhibitor or a GLP-1 receptor agonist, and only adding metformin in patients who need additional glycemic control.
The guidelines also recommended starting treatment-naive patients with moderate CVD risk on metformin. For patients already on metformin, the new ESC guidelines called for adding an agent from at least one of these two drug classes with proven CVD benefits for those at high or very high CVD risk. The guidelines also note that the CVD benefits of the two newer drug classes differ and hence require further individualization depending on the risks faced by each patient, such as the risk for heart failure hospitalizations.
It’s an approach “driven by data from the cardiovascular outcome trials,” that showed several drugs from both the SGLT2 inhibitor and GLP-1 receptor agonist classes have substantial benefit for preventing cardiovascular events, renal events, hospitalizations for heart failure, and in some studies all-cause mortality, said Francesco Cosentino, MD, during a discussion of the guideline differences at the virtual annual meeting of the European Association for the Study of Diabetes.
The ESC approach also represents “a major paradigm shift,” a “change from a glucose-centric approach to an approach driven by cardiovascular disease events,” summed up Dr. Cosentino, professor of cardiology at the Karolinska Institute in Stockholm and chair of the task force that wrote the ESC’s 2019 updated guidelines. The ESC approach advocates initiating drugs for treating patients with T2D “based on cardiovascular disease risk classification,” he highlighted. Results from some SGLT2 inhibitor cardiovascular outcome trials showed that the CVD benefit was similar regardless of whether or not patients also received metformin.
ADA, EASD call for ‘a different emphasis’
“There is a different emphasis” in the statement issued by the diabetologists of the ADA and EASD, admitted Peter J. Grant, MD, a professor of diabetes and endocrinology at the University of Leeds (England) and cochair of the ESC guidelines task force. Dr. Grant represented the EASD on the task force, and the Association collaborated with the ESC in producing its guidelines.
“The ADA and EASD recommendations “look primarily at glucose control, with cardiovascular disease management as secondary.” In contrast, the ESC guidelines “are primarily cardiovascular disease risk guidelines, with a glucose interest,” Dr. Grant declared.
Despite his involvement in writing the ESC guidelines, Dr. Grant tilted toward the ADA/EASD statement as more globally relevant.
“There is much more to vasculopathy in diabetes than just macrovascular disease. Many patients with type 2 diabetes without macrovascular complications have microvascular disease,” including the potential for retinopathy, nephropathy, and neuropathy, he said. These complications can also have a strong impact on psychological well being and treatment satisfaction.
“It’s important that we’re not glucocentric any more, but it’s equally important that we treat glucose because it has such a benefit for microvascular disease.” Dr. Grant also cited metformin’s long history of safety and good tolerance, clinician comfort prescribing it, and its low price. Heavier reliance on SGLT2 inhibitors and GLP-1 receptor agonists will be expensive for the short term while the cost of these drugs remains high, which places a higher burden on “knowing we’re doing it right,” said Dr. Grant.
Dr. Cosentino pointed out that the higher cost of the drugs in the two classes shown to exert important cardiovascular and renal effects needs to be considered in a cost-effectiveness context, not just by cost alone.
‘Clinical inertia’ could be a danger
Dr. Cosentino played down a major disagreement between the two guidelines, suggesting that “focusing on the differences leads to clinical inertia” by the practicing community when they are unsure how to reconcile the two positions.
Dr. Grant agreed that adding a second drug to metformin right away made sense in at least selected patients. “Look at each patient and decide whether they need glycemic control. If so, and if they also have cardiovascular disease, use both drugs,” metformin, plus one agent from one of the two newer classes.
Something both experts agreed on is that it’s time to generally steer clear of sulfonylurea drugs. “We have evidence for harmful effects from sulfonylureas,” Dr. Cosentino said.
“I’d dump sulfonylureas,” was Dr. Grant’s assessment, but he added that they still have a role for patients who need additional glycemic control but can’t afford the newer drugs.
Dr. Cosentino has had financial relationships with Abbott, AstraZeneca, Boehringer Ingelheim, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Eli Lilly, Merck, Mundipharma, Novo Nordisk, and Pfizer, Dr. Grant has lectured on behalf of AstraZeneca, GlaxoSmithKline, Merck, Novo Nordisk, the Medicines Company, and Takeda, and he has been an adviser to Amgen, AstraZeneca, Novartis, Novo Nordisk, and Synexus.
It was no surprise that updated guidelines recently published by the European Society of Cardiology for managing cardiovascular disease in patients with diabetes highlighted optimized treatment from a cardiovascular disease perspective, while a nearly concurrent update from two major diabetes societies saw the same issue from a more glycemic point of view.
This difference led to divergent approaches to managing hyperglycemia in patients with type 2 diabetes (T2D). The two diabetes societies that wrote one set of recommendations, the American Diabetes Association and the European Association for the Study of Diabetes, put metformin at the pinnacle of their drug hierarchy. Patients with T2D and established atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease (CVD), chronic kidney disease, or heart failure should all receive metformin first unless contraindicated or not tolerated, their updated consensus report said.
Once metformin is on board, a clinician can then add a second diabetes agent from among the two drug classes recently proven to also reduce cardiovascular and renal events, either the SGLT2 (sodium-glucose transporter 2) inhibitors, or GLP-1 (glucagonlike peptide–1) receptor agonists, they advised.
Cardiovascular disease focus represents a ‘major paradigm shift’
In contrast, the ESC guidelines called for upfront, systematic assessment of CVD risk in patients with T2D before treatment starts, and for patients in high- or very high–risk strata, the guidelines recommended starting the patient first on an SGLT2 inhibitor or a GLP-1 receptor agonist, and only adding metformin in patients who need additional glycemic control.
The guidelines also recommended starting treatment-naive patients with moderate CVD risk on metformin. For patients already on metformin, the new ESC guidelines called for adding an agent from at least one of these two drug classes with proven CVD benefits for those at high or very high CVD risk. The guidelines also note that the CVD benefits of the two newer drug classes differ and hence require further individualization depending on the risks faced by each patient, such as the risk for heart failure hospitalizations.
It’s an approach “driven by data from the cardiovascular outcome trials,” that showed several drugs from both the SGLT2 inhibitor and GLP-1 receptor agonist classes have substantial benefit for preventing cardiovascular events, renal events, hospitalizations for heart failure, and in some studies all-cause mortality, said Francesco Cosentino, MD, during a discussion of the guideline differences at the virtual annual meeting of the European Association for the Study of Diabetes.
The ESC approach also represents “a major paradigm shift,” a “change from a glucose-centric approach to an approach driven by cardiovascular disease events,” summed up Dr. Cosentino, professor of cardiology at the Karolinska Institute in Stockholm and chair of the task force that wrote the ESC’s 2019 updated guidelines. The ESC approach advocates initiating drugs for treating patients with T2D “based on cardiovascular disease risk classification,” he highlighted. Results from some SGLT2 inhibitor cardiovascular outcome trials showed that the CVD benefit was similar regardless of whether or not patients also received metformin.
ADA, EASD call for ‘a different emphasis’
“There is a different emphasis” in the statement issued by the diabetologists of the ADA and EASD, admitted Peter J. Grant, MD, a professor of diabetes and endocrinology at the University of Leeds (England) and cochair of the ESC guidelines task force. Dr. Grant represented the EASD on the task force, and the Association collaborated with the ESC in producing its guidelines.
“The ADA and EASD recommendations “look primarily at glucose control, with cardiovascular disease management as secondary.” In contrast, the ESC guidelines “are primarily cardiovascular disease risk guidelines, with a glucose interest,” Dr. Grant declared.
Despite his involvement in writing the ESC guidelines, Dr. Grant tilted toward the ADA/EASD statement as more globally relevant.
“There is much more to vasculopathy in diabetes than just macrovascular disease. Many patients with type 2 diabetes without macrovascular complications have microvascular disease,” including the potential for retinopathy, nephropathy, and neuropathy, he said. These complications can also have a strong impact on psychological well being and treatment satisfaction.
“It’s important that we’re not glucocentric any more, but it’s equally important that we treat glucose because it has such a benefit for microvascular disease.” Dr. Grant also cited metformin’s long history of safety and good tolerance, clinician comfort prescribing it, and its low price. Heavier reliance on SGLT2 inhibitors and GLP-1 receptor agonists will be expensive for the short term while the cost of these drugs remains high, which places a higher burden on “knowing we’re doing it right,” said Dr. Grant.
Dr. Cosentino pointed out that the higher cost of the drugs in the two classes shown to exert important cardiovascular and renal effects needs to be considered in a cost-effectiveness context, not just by cost alone.
‘Clinical inertia’ could be a danger
Dr. Cosentino played down a major disagreement between the two guidelines, suggesting that “focusing on the differences leads to clinical inertia” by the practicing community when they are unsure how to reconcile the two positions.
Dr. Grant agreed that adding a second drug to metformin right away made sense in at least selected patients. “Look at each patient and decide whether they need glycemic control. If so, and if they also have cardiovascular disease, use both drugs,” metformin, plus one agent from one of the two newer classes.
Something both experts agreed on is that it’s time to generally steer clear of sulfonylurea drugs. “We have evidence for harmful effects from sulfonylureas,” Dr. Cosentino said.
“I’d dump sulfonylureas,” was Dr. Grant’s assessment, but he added that they still have a role for patients who need additional glycemic control but can’t afford the newer drugs.
Dr. Cosentino has had financial relationships with Abbott, AstraZeneca, Boehringer Ingelheim, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Eli Lilly, Merck, Mundipharma, Novo Nordisk, and Pfizer, Dr. Grant has lectured on behalf of AstraZeneca, GlaxoSmithKline, Merck, Novo Nordisk, the Medicines Company, and Takeda, and he has been an adviser to Amgen, AstraZeneca, Novartis, Novo Nordisk, and Synexus.
FROM EASD 2020
AHA issues new scientific statement on heart health for LGBTQ adults
Cardiovascular health should be routinely assessed and addressed in LGBTQ adults, the American Heart Association concluded in a new scientific statement.
“Among the most important takeaways from this scientific statement is the need for health care providers in clinical settings to routinely assess sexual orientation and gender identity,” Billy A. Caceres, PhD, RN, chair of the statement writing group, said in an interview.
“This will help health care providers engage LGBTQ patients in discussions about their heart health that account for the unique experiences of this population,” said Dr. Caceres, assistant professor at Columbia University, New York.
The statement was published online Oct. 8 in Circulation.
‘Invisible’ population
There are roughly 11 million LGBTQ adults in the United States, yet they are often “invisible in health care settings and cardiovascular research,” Dr. Caceres noted. The AHA scientific statement is the first from a national organization in the United States to comprehensively summarize the evidence on cardiovascular (CV) research in LGBTQ adults.
There is mounting evidence that LGBTQ adults experience worse CV health relative to their cisgender heterosexual peers. Disparities in CV health may be driven by unique psychosocial stressors in the LGBTQ individuals such as family rejection and anxiety of concealment of their sexual orientation or gender identity.
While there is limited information on the CV health of LGBTQ people, the writing group said providers should be aware of the following:
- LGBTQ adults are more likely to use tobacco than their cisgender heterosexual peers.
- Transgender adults may be less physically active than their cisgender counterparts. Gender-affirming care might play a role in promoting physical activity among transgender people.
- Transgender women may be at increased risk for heart disease because of behavioral and clinical factors (such as the use of gender-affirming hormones like estrogen).
- Transgender women and nonbinary persons are more likely to binge drink.
- Lesbian and bisexual women have a higher prevalence of obesity than heterosexual women do.
“We need to better understand how to support LGBTQ adults in optimizing their CV health. To do this, we will need rigorous research that examines potential explanations for the CV health disparities that have been observed in LGBTQ adults,” Dr. Caceres said.
He noted that research is also needed within the LGBTQ population among groups that might be at greater risk for heart disease, including racial- and ethnic-minority and low-income LGBTQ adults.
“Researchers should also design and test evidence-based interventions to promote the heart health of LGBTQ adults. This is an area that is greatly lacking within CV health research,” said Dr. Caceres.
Discrimination in health care
Discrimination against LGBTQ adults in health care settings also remains a problem, the authors noted.
The writing group cites data showing that nearly 56% of sexual-minority and 70% of gender-minority adults report having experienced some form of discrimination from clinicians, including the use of harsh/abusive language.
“Perhaps most alarming,” roughly 8% of sexual-minority and 25% of transgender individuals have been denied health care by clinicians, they noted.
“LGBTQ individuals are delaying primary care and preventative visits because there is a great fear of being treated differently. Being treated differently often means receiving inadequate or inferior care because of sexual orientation or gender identity,” Dr. Caceres said in a news release.
The writing group calls for greater emphasis on LGBTQ health issues in the education of all health care providers. Dr. Caceres said it’s “paramount to include content about LGBTQ health in clinical training and licensure requirements in order to address these cardiovascular health disparities.”
Traditionally, there has been very little LGBTQ-related content in health care professional education training. A 2018 online survey of students at 10 medical schools found that approximately 80% of students did not feel competent to provide care for transgender patients.
But that may soon change. In September 2020, the Accreditation Review Commission on Education for the Physician Assistant began requiring LGBTQ curricular content, the writing group notes.
The AHA scientific statement on LGBTQ was developed by the writing group on behalf of the AHA Council on Cardiovascular and Stroke Nursing, the Council on Hypertension, the Council on Lifestyle and Cardiometabolic Health, the Council on Peripheral Vascular Disease, and the Stroke Council.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
Cardiovascular health should be routinely assessed and addressed in LGBTQ adults, the American Heart Association concluded in a new scientific statement.
“Among the most important takeaways from this scientific statement is the need for health care providers in clinical settings to routinely assess sexual orientation and gender identity,” Billy A. Caceres, PhD, RN, chair of the statement writing group, said in an interview.
“This will help health care providers engage LGBTQ patients in discussions about their heart health that account for the unique experiences of this population,” said Dr. Caceres, assistant professor at Columbia University, New York.
The statement was published online Oct. 8 in Circulation.
‘Invisible’ population
There are roughly 11 million LGBTQ adults in the United States, yet they are often “invisible in health care settings and cardiovascular research,” Dr. Caceres noted. The AHA scientific statement is the first from a national organization in the United States to comprehensively summarize the evidence on cardiovascular (CV) research in LGBTQ adults.
There is mounting evidence that LGBTQ adults experience worse CV health relative to their cisgender heterosexual peers. Disparities in CV health may be driven by unique psychosocial stressors in the LGBTQ individuals such as family rejection and anxiety of concealment of their sexual orientation or gender identity.
While there is limited information on the CV health of LGBTQ people, the writing group said providers should be aware of the following:
- LGBTQ adults are more likely to use tobacco than their cisgender heterosexual peers.
- Transgender adults may be less physically active than their cisgender counterparts. Gender-affirming care might play a role in promoting physical activity among transgender people.
- Transgender women may be at increased risk for heart disease because of behavioral and clinical factors (such as the use of gender-affirming hormones like estrogen).
- Transgender women and nonbinary persons are more likely to binge drink.
- Lesbian and bisexual women have a higher prevalence of obesity than heterosexual women do.
“We need to better understand how to support LGBTQ adults in optimizing their CV health. To do this, we will need rigorous research that examines potential explanations for the CV health disparities that have been observed in LGBTQ adults,” Dr. Caceres said.
He noted that research is also needed within the LGBTQ population among groups that might be at greater risk for heart disease, including racial- and ethnic-minority and low-income LGBTQ adults.
“Researchers should also design and test evidence-based interventions to promote the heart health of LGBTQ adults. This is an area that is greatly lacking within CV health research,” said Dr. Caceres.
Discrimination in health care
Discrimination against LGBTQ adults in health care settings also remains a problem, the authors noted.
The writing group cites data showing that nearly 56% of sexual-minority and 70% of gender-minority adults report having experienced some form of discrimination from clinicians, including the use of harsh/abusive language.
“Perhaps most alarming,” roughly 8% of sexual-minority and 25% of transgender individuals have been denied health care by clinicians, they noted.
“LGBTQ individuals are delaying primary care and preventative visits because there is a great fear of being treated differently. Being treated differently often means receiving inadequate or inferior care because of sexual orientation or gender identity,” Dr. Caceres said in a news release.
The writing group calls for greater emphasis on LGBTQ health issues in the education of all health care providers. Dr. Caceres said it’s “paramount to include content about LGBTQ health in clinical training and licensure requirements in order to address these cardiovascular health disparities.”
Traditionally, there has been very little LGBTQ-related content in health care professional education training. A 2018 online survey of students at 10 medical schools found that approximately 80% of students did not feel competent to provide care for transgender patients.
But that may soon change. In September 2020, the Accreditation Review Commission on Education for the Physician Assistant began requiring LGBTQ curricular content, the writing group notes.
The AHA scientific statement on LGBTQ was developed by the writing group on behalf of the AHA Council on Cardiovascular and Stroke Nursing, the Council on Hypertension, the Council on Lifestyle and Cardiometabolic Health, the Council on Peripheral Vascular Disease, and the Stroke Council.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
Cardiovascular health should be routinely assessed and addressed in LGBTQ adults, the American Heart Association concluded in a new scientific statement.
“Among the most important takeaways from this scientific statement is the need for health care providers in clinical settings to routinely assess sexual orientation and gender identity,” Billy A. Caceres, PhD, RN, chair of the statement writing group, said in an interview.
“This will help health care providers engage LGBTQ patients in discussions about their heart health that account for the unique experiences of this population,” said Dr. Caceres, assistant professor at Columbia University, New York.
The statement was published online Oct. 8 in Circulation.
‘Invisible’ population
There are roughly 11 million LGBTQ adults in the United States, yet they are often “invisible in health care settings and cardiovascular research,” Dr. Caceres noted. The AHA scientific statement is the first from a national organization in the United States to comprehensively summarize the evidence on cardiovascular (CV) research in LGBTQ adults.
There is mounting evidence that LGBTQ adults experience worse CV health relative to their cisgender heterosexual peers. Disparities in CV health may be driven by unique psychosocial stressors in the LGBTQ individuals such as family rejection and anxiety of concealment of their sexual orientation or gender identity.
While there is limited information on the CV health of LGBTQ people, the writing group said providers should be aware of the following:
- LGBTQ adults are more likely to use tobacco than their cisgender heterosexual peers.
- Transgender adults may be less physically active than their cisgender counterparts. Gender-affirming care might play a role in promoting physical activity among transgender people.
- Transgender women may be at increased risk for heart disease because of behavioral and clinical factors (such as the use of gender-affirming hormones like estrogen).
- Transgender women and nonbinary persons are more likely to binge drink.
- Lesbian and bisexual women have a higher prevalence of obesity than heterosexual women do.
“We need to better understand how to support LGBTQ adults in optimizing their CV health. To do this, we will need rigorous research that examines potential explanations for the CV health disparities that have been observed in LGBTQ adults,” Dr. Caceres said.
He noted that research is also needed within the LGBTQ population among groups that might be at greater risk for heart disease, including racial- and ethnic-minority and low-income LGBTQ adults.
“Researchers should also design and test evidence-based interventions to promote the heart health of LGBTQ adults. This is an area that is greatly lacking within CV health research,” said Dr. Caceres.
Discrimination in health care
Discrimination against LGBTQ adults in health care settings also remains a problem, the authors noted.
The writing group cites data showing that nearly 56% of sexual-minority and 70% of gender-minority adults report having experienced some form of discrimination from clinicians, including the use of harsh/abusive language.
“Perhaps most alarming,” roughly 8% of sexual-minority and 25% of transgender individuals have been denied health care by clinicians, they noted.
“LGBTQ individuals are delaying primary care and preventative visits because there is a great fear of being treated differently. Being treated differently often means receiving inadequate or inferior care because of sexual orientation or gender identity,” Dr. Caceres said in a news release.
The writing group calls for greater emphasis on LGBTQ health issues in the education of all health care providers. Dr. Caceres said it’s “paramount to include content about LGBTQ health in clinical training and licensure requirements in order to address these cardiovascular health disparities.”
Traditionally, there has been very little LGBTQ-related content in health care professional education training. A 2018 online survey of students at 10 medical schools found that approximately 80% of students did not feel competent to provide care for transgender patients.
But that may soon change. In September 2020, the Accreditation Review Commission on Education for the Physician Assistant began requiring LGBTQ curricular content, the writing group notes.
The AHA scientific statement on LGBTQ was developed by the writing group on behalf of the AHA Council on Cardiovascular and Stroke Nursing, the Council on Hypertension, the Council on Lifestyle and Cardiometabolic Health, the Council on Peripheral Vascular Disease, and the Stroke Council.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
Empagliflozin cut PA pressures in heart failure patients
Elevated pulmonary artery diastolic pressure is “perhaps the best predictor of bad outcomes in patients with heart failure, including hospitalization and death,” and new evidence clearly showed that the sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 (SGLT2) inhibitor empagliflozin cuts this metric in patients by a clinically significant amount, Mikhail Kosiborod, MD, said at the virtual annual scientific meeting of the Heart Failure Society of America.
The evidence he collected from a total of 65 heart failure patients with either reduced or preserved ejection fraction is the first documentation from a randomized, controlled study to show a direct effect by a SGLT2 inhibitor on pulmonary artery (PA) pressures.
Other key findings were that the drop in PA diastolic pressure with empagliflozin treatment compared with placebo became discernible early (within the first 4 weeks on treatment), that the pressure-lowering effect steadily grew over time, and that it showed no link to the intensity of loop diuretic treatment, which held steady during 12 weeks on treatment and 13 weeks of overall monitoring.
The study’s primary endpoint was the change from baseline in PA diastolic pressure after 12 weeks on treatment. The 31 patients who completed the full 12-week course had an average drop in their PA diastolic pressure of about 1.5 mm Hg, compared with 28 patients who completed 12 weeks on placebo. Average PA diastolic pressure at baseline was about 21 mm Hg in both treatment arms, and on treatment this fell by more than 0.5 mm Hg among those who received empagliflozin and rose by close to 1 mm Hg among control patients.
“There appears to be a direct effect of empagliflozin on pulmonary artery pressure that’s not been previously demonstrated” by an SGLT2 inhibitor, Dr. Kosiborod said. “I think this is one mechanism of action” for this drug class. “If you control pulmonary artery filling pressures you can prevent hospitalizations and deaths.”
Small reductions matter
“Small pressure differences are particularly important for pulmonary hypertension,” commented Lynne W. Stevenson, MD, professor of medicine at Vanderbilt University Medical Center in Nashville, Tenn., and the report’s designated discussant.
“In the Vanderbilt heart failure database, patients with a pulmonary artery mean pressure of 20-24 mm Hg had 30% higher mortality than patients with lower pressures,” Dr. Stevenson noted. “This has led to a new definition of pulmonary hypertension, a mean pulmonary artery pressure above at or above 20 mm Hg.”
In Dr. Kosiborod’s study, patients began with an average PA mean pressure of about 30 mm Hg, and empagliflozin treatment led to a reduction in this metric with about the same magnitude as its effect on PA diastolic pressure. Empagliflozin also produced a similar reduction in average PA systolic pressure.
A study built on ambulatory PA monitoring
The results “also provide more proof for the concept of ambulatory hemodynamic monitoring” in patients with heart failure to monitor their status, she added. The study enrolled only patients who had already received a CardioMEMS implant as part of their routine care. This device allows for frequent, noninvasive monitoring of PA pressures. Researchers collected PA pressure data from patients twice daily for the entire 13-week study.
The EMBRACE HF (Empagliflozin Impact on Hemodynamics in Patients With Heart Failure) study enrolled patients with established heart failure, a CardioMEMS implant, and New York Heart Association class II-IV symptoms at any of eight U.S. centers. Patients averaged about 65 years old, and slightly more than half had class III disease, which denotes marked limitation of physical activity.
Despite the brief treatment period, patients who received empagliflozin showed other evidence of benefit including a trend toward improved quality of life scores, reduced levels of two different forms of brain natriuretic peptide, and significant weight loss, compared with controls, that averaged 2.4 kg.
The mechanism by which empagliflozin and other drugs in its class might lower PA filling pressures is unclear, but Dr. Kosiborod stressed that the consistent level of loop diuretic use during the study seems to rule out a diuretic effect from the SGLT2 inhibitor as having a role. A pulmonary vasculature effect is “much more likely,” perhaps mediated through modified endothelial function and vasodilation, he suggested.
EMBRACE HF was funded by Boehringer Ingelheim, the company that markets empagliflozin (Jardiance) along with Eli Lilly. Dr. Kosiborod has received research support and honoraria from Boehringer Ingelheim, and he has received honoraria from several other companies. Dr. Stevenson had no disclosures.
Elevated pulmonary artery diastolic pressure is “perhaps the best predictor of bad outcomes in patients with heart failure, including hospitalization and death,” and new evidence clearly showed that the sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 (SGLT2) inhibitor empagliflozin cuts this metric in patients by a clinically significant amount, Mikhail Kosiborod, MD, said at the virtual annual scientific meeting of the Heart Failure Society of America.
The evidence he collected from a total of 65 heart failure patients with either reduced or preserved ejection fraction is the first documentation from a randomized, controlled study to show a direct effect by a SGLT2 inhibitor on pulmonary artery (PA) pressures.
Other key findings were that the drop in PA diastolic pressure with empagliflozin treatment compared with placebo became discernible early (within the first 4 weeks on treatment), that the pressure-lowering effect steadily grew over time, and that it showed no link to the intensity of loop diuretic treatment, which held steady during 12 weeks on treatment and 13 weeks of overall monitoring.
The study’s primary endpoint was the change from baseline in PA diastolic pressure after 12 weeks on treatment. The 31 patients who completed the full 12-week course had an average drop in their PA diastolic pressure of about 1.5 mm Hg, compared with 28 patients who completed 12 weeks on placebo. Average PA diastolic pressure at baseline was about 21 mm Hg in both treatment arms, and on treatment this fell by more than 0.5 mm Hg among those who received empagliflozin and rose by close to 1 mm Hg among control patients.
“There appears to be a direct effect of empagliflozin on pulmonary artery pressure that’s not been previously demonstrated” by an SGLT2 inhibitor, Dr. Kosiborod said. “I think this is one mechanism of action” for this drug class. “If you control pulmonary artery filling pressures you can prevent hospitalizations and deaths.”
Small reductions matter
“Small pressure differences are particularly important for pulmonary hypertension,” commented Lynne W. Stevenson, MD, professor of medicine at Vanderbilt University Medical Center in Nashville, Tenn., and the report’s designated discussant.
“In the Vanderbilt heart failure database, patients with a pulmonary artery mean pressure of 20-24 mm Hg had 30% higher mortality than patients with lower pressures,” Dr. Stevenson noted. “This has led to a new definition of pulmonary hypertension, a mean pulmonary artery pressure above at or above 20 mm Hg.”
In Dr. Kosiborod’s study, patients began with an average PA mean pressure of about 30 mm Hg, and empagliflozin treatment led to a reduction in this metric with about the same magnitude as its effect on PA diastolic pressure. Empagliflozin also produced a similar reduction in average PA systolic pressure.
A study built on ambulatory PA monitoring
The results “also provide more proof for the concept of ambulatory hemodynamic monitoring” in patients with heart failure to monitor their status, she added. The study enrolled only patients who had already received a CardioMEMS implant as part of their routine care. This device allows for frequent, noninvasive monitoring of PA pressures. Researchers collected PA pressure data from patients twice daily for the entire 13-week study.
The EMBRACE HF (Empagliflozin Impact on Hemodynamics in Patients With Heart Failure) study enrolled patients with established heart failure, a CardioMEMS implant, and New York Heart Association class II-IV symptoms at any of eight U.S. centers. Patients averaged about 65 years old, and slightly more than half had class III disease, which denotes marked limitation of physical activity.
Despite the brief treatment period, patients who received empagliflozin showed other evidence of benefit including a trend toward improved quality of life scores, reduced levels of two different forms of brain natriuretic peptide, and significant weight loss, compared with controls, that averaged 2.4 kg.
The mechanism by which empagliflozin and other drugs in its class might lower PA filling pressures is unclear, but Dr. Kosiborod stressed that the consistent level of loop diuretic use during the study seems to rule out a diuretic effect from the SGLT2 inhibitor as having a role. A pulmonary vasculature effect is “much more likely,” perhaps mediated through modified endothelial function and vasodilation, he suggested.
EMBRACE HF was funded by Boehringer Ingelheim, the company that markets empagliflozin (Jardiance) along with Eli Lilly. Dr. Kosiborod has received research support and honoraria from Boehringer Ingelheim, and he has received honoraria from several other companies. Dr. Stevenson had no disclosures.
Elevated pulmonary artery diastolic pressure is “perhaps the best predictor of bad outcomes in patients with heart failure, including hospitalization and death,” and new evidence clearly showed that the sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 (SGLT2) inhibitor empagliflozin cuts this metric in patients by a clinically significant amount, Mikhail Kosiborod, MD, said at the virtual annual scientific meeting of the Heart Failure Society of America.
The evidence he collected from a total of 65 heart failure patients with either reduced or preserved ejection fraction is the first documentation from a randomized, controlled study to show a direct effect by a SGLT2 inhibitor on pulmonary artery (PA) pressures.
Other key findings were that the drop in PA diastolic pressure with empagliflozin treatment compared with placebo became discernible early (within the first 4 weeks on treatment), that the pressure-lowering effect steadily grew over time, and that it showed no link to the intensity of loop diuretic treatment, which held steady during 12 weeks on treatment and 13 weeks of overall monitoring.
The study’s primary endpoint was the change from baseline in PA diastolic pressure after 12 weeks on treatment. The 31 patients who completed the full 12-week course had an average drop in their PA diastolic pressure of about 1.5 mm Hg, compared with 28 patients who completed 12 weeks on placebo. Average PA diastolic pressure at baseline was about 21 mm Hg in both treatment arms, and on treatment this fell by more than 0.5 mm Hg among those who received empagliflozin and rose by close to 1 mm Hg among control patients.
“There appears to be a direct effect of empagliflozin on pulmonary artery pressure that’s not been previously demonstrated” by an SGLT2 inhibitor, Dr. Kosiborod said. “I think this is one mechanism of action” for this drug class. “If you control pulmonary artery filling pressures you can prevent hospitalizations and deaths.”
Small reductions matter
“Small pressure differences are particularly important for pulmonary hypertension,” commented Lynne W. Stevenson, MD, professor of medicine at Vanderbilt University Medical Center in Nashville, Tenn., and the report’s designated discussant.
“In the Vanderbilt heart failure database, patients with a pulmonary artery mean pressure of 20-24 mm Hg had 30% higher mortality than patients with lower pressures,” Dr. Stevenson noted. “This has led to a new definition of pulmonary hypertension, a mean pulmonary artery pressure above at or above 20 mm Hg.”
In Dr. Kosiborod’s study, patients began with an average PA mean pressure of about 30 mm Hg, and empagliflozin treatment led to a reduction in this metric with about the same magnitude as its effect on PA diastolic pressure. Empagliflozin also produced a similar reduction in average PA systolic pressure.
A study built on ambulatory PA monitoring
The results “also provide more proof for the concept of ambulatory hemodynamic monitoring” in patients with heart failure to monitor their status, she added. The study enrolled only patients who had already received a CardioMEMS implant as part of their routine care. This device allows for frequent, noninvasive monitoring of PA pressures. Researchers collected PA pressure data from patients twice daily for the entire 13-week study.
The EMBRACE HF (Empagliflozin Impact on Hemodynamics in Patients With Heart Failure) study enrolled patients with established heart failure, a CardioMEMS implant, and New York Heart Association class II-IV symptoms at any of eight U.S. centers. Patients averaged about 65 years old, and slightly more than half had class III disease, which denotes marked limitation of physical activity.
Despite the brief treatment period, patients who received empagliflozin showed other evidence of benefit including a trend toward improved quality of life scores, reduced levels of two different forms of brain natriuretic peptide, and significant weight loss, compared with controls, that averaged 2.4 kg.
The mechanism by which empagliflozin and other drugs in its class might lower PA filling pressures is unclear, but Dr. Kosiborod stressed that the consistent level of loop diuretic use during the study seems to rule out a diuretic effect from the SGLT2 inhibitor as having a role. A pulmonary vasculature effect is “much more likely,” perhaps mediated through modified endothelial function and vasodilation, he suggested.
EMBRACE HF was funded by Boehringer Ingelheim, the company that markets empagliflozin (Jardiance) along with Eli Lilly. Dr. Kosiborod has received research support and honoraria from Boehringer Ingelheim, and he has received honoraria from several other companies. Dr. Stevenson had no disclosures.
FROM HFSA 2020
The socioeconomic revolving door of 30-day heart failure readmissions
Patients receiving even top-notch hospital care for heart failure (HF) are, once discharged to home, at higher short-term risk of another HF hospitalization if home is in a socioeconomically deprived neighborhood. That helps explain why Blacks in the United States have a much higher 30-day HF readmission risk than Whites, a disparity that only worsens with the level of neighborhood deprivation, a new analysis suggests.
Some systemic and entrenched socioeconomic inequities that health care providers have little sway over, and which disproportionately affect Black individuals, are independent and robust predictors of worsened HF outcomes, Alanna A. Morris, MD, MSc, Emory University, Atlanta, said during her presentation at the virtual annual scientific meeting of the Heart Failure Society of America.
In a retrospective cohort study, Blacks had a 45% higher risk of 30-day readmission than Whites (P < .001) independent of cardiovascular risk factors, clinical history, comorbidities, type and location of hospital, and type of third-party payer coverage. The analysis included more than 30,000 patients with at least one HF hospitalization at centers in a major metropolitan health system.
The racial disparity widened with worsening socioeconomic deprivation of patients’ residential neighborhoods, that is, with rising quartiles of neighborhood scores on the Social Deprivation Index (SDI).
The SDI, based on U.S. census data, incorporates seven socioeconomic criteria, including household income, education level, employment, and prevalence of rented housing and households that are without a car, single parent, or overcrowded.
There was a 4–percentage point gap in adjusted 30-day readmission rate between Blacks and Whites in the lowest quartile that widened to more than 8 points by the third quartile; the disparity in both the second and fourth quartiles was the same, at about 5.5 percentage points.
A remaining question, Dr. Morris said in an interview, is why the outcomes disparity between Blacks and Whites peaks in the third SDI quartile but drops a bit in the fourth quartile representing the most severe neighborhood deprivation.
“Our hypothesis is that when you look at patients who are the poorest, who live in the most deprived neighborhoods, race may be less of a factor,” she said. Socioeconomic deprivation may have similar consequences for everyone “regardless of race, ethnicity, gender, or other demographic characteristics if you live in a neighborhood that’s highly deprived.”
Based on the current study, “it does appear that increased heart failure incident rates are related to living in deprived neighborhoods, and it raises important clinical and public health concerns that must be addressed,” Keith C. Ferdinand, MD, Tulane University, New Orleans, said as invited discussant after the presentation from Dr. Morris.
“These findings could serve as an aid to policy makers, going forward, in terms of allocating resources for primary health care,” he said. “And it’s important looking at these data and other [data] that we target heart failure patients who reside in deprived neighborhoods before, during, and [after] hospitalization.”
Dr. Morris agreed that policy makers are in a better position to attack the racial disparity in HF readmission rates identified in the study. “This is not a problem that can be fixed within the health care system.”
If the reported interpretation is correct, it could add a twist to the public health care debate in the United States, observed session moderator Mandeep R. Mehra, MD, Brigham and Woman’s Hospital in Boston.
That debate, he noted, has often focused on insurability, access to coverage, and the merits or shortcomings of a single-payer system. Yet the study suggests outcomes disparities stemming from neighborhood deprivation will not be corrected by improved access to health insurance, a conclusion he finds “startling,” Dr. Mehra said in an interview.
Some proposed explanations for the disparities by race blame unequal access to health care and or variable health insurance coverage, Dr. Morris observed in an interview. But “that may not fully explain the increased risk that we see.”
Black patients followed at Emory University’s advanced HF clinic still have a higher risk of rehospitalization than Whites. “These are patients who have insurance, who are followed by advanced heart failure providers, who are on equal amounts of guideline-recommended medical therapy – and you still see about a 50% higher risk of rehospitalization,” Dr. Morris said, citing data that isn’t part of the current analysis.
“We can say that these patients are certainly able to access care, because they are able to access our emergency room and be taken care of within the hospital setting,” he said. The study controlled for whether health coverage was by private insurance, Medicare, or Medicaid.
Instead, the current analysis points to socioeconomic and environmental factors as a major source of the disparity in 30-day readmissions, Dr. Morris said.
“When patients are discharged from our healthcare systems, they still go back into environments where they don’t have the same resources as patients who live in higher-SDI neighborhoods,” she explained.
For example, “we tell them to eat low-sodium [foods], exercise, eat fresh fruits and vegetables, take their medicines, but the reality is that certain neighborhoods within the United States – and this is much more true for Blacks – make it very difficult to follow those self-care recommendations.”
The analysis included 16,147 Black patients and 14,483 White patients hospitalized with HF within the Emory Healthcare system at least once from 2010-2018, Dr. Morris reported. Compared with Whites, Blacks were younger (63.5 vs 69.1 years) and less likely to be 65 or older (48.9% vs. 66.5%); more likely to be women (53.5% vs. 42.2%), more likely to reside in deprived census tracts and to have diabetes, hypertension, or chronic kidney disease; and had higher comorbidity scores.
In all, 20.6% of Black and 13.5% of White patients were readmitted for HF within 30 days of discharge, for an unadjusted risk ratio of 1.52 (95% CI, 1.44-1.61).
The RR hardly budged, 1.45 (95% CI, 1.37-1.54, P < .001), after adjustment for age, sex, type of insurance, type of HF, vital signs and laboratory values, medical history (diabetes, hypertension, atrial fibrillation, coronary disease, chronic kidney disease, and chronic pulmonary disease), Charlson Comorbidity Index, discharging medical specialty, and hospital location.
The excess in 30-day HF readmissions for Black, compared with White patients climbed from the first to the third neighborhood SDI quartile, the disparity peaking at 8.2 absolute percentage points.
A major criticism of the Hospital Readmissions Reduction Program component of the Affordable Care Act, Dr. Morris said in a Q&A discussion after her presentation, is that it can hold hospitals “responsible for structural inequalities that exist beyond the health care system,” including neighborhood deprivation.
“But public policy makers have to realize that there are certain patients we take care of who don’t have the resources to carry out the therapeutic lifestyle changes that will allow them to live healthy.”
The HRRP’s 30-day HF readmission metric that steers reimbursement “is penalizing health care systems across the United States” with its premise that hospital performance can be measured by 30-day HF readmission rates, Dr. Morris said in an interview.
“The reality is that some of these patients are going to a postdischarge environment that is inherently high risk, and that many of them are going to come back to us within 30 days,” she said. “We would like to make sure that we don’t put excess penalties on health care systems that take care of disproportionate numbers of African Americans in neighborhoods that have fewer resources.”
Dr. Morris and Dr. Ferdinand have disclosed no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Mehra discloses consulting or serving on an advisory board for Abbott, Medtronic, Janssen, Leviticus, NupulseCV, FineHeart, Portola, Bayer, the Baim Institute for Clinical Research, and Mesoblast.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
Patients receiving even top-notch hospital care for heart failure (HF) are, once discharged to home, at higher short-term risk of another HF hospitalization if home is in a socioeconomically deprived neighborhood. That helps explain why Blacks in the United States have a much higher 30-day HF readmission risk than Whites, a disparity that only worsens with the level of neighborhood deprivation, a new analysis suggests.
Some systemic and entrenched socioeconomic inequities that health care providers have little sway over, and which disproportionately affect Black individuals, are independent and robust predictors of worsened HF outcomes, Alanna A. Morris, MD, MSc, Emory University, Atlanta, said during her presentation at the virtual annual scientific meeting of the Heart Failure Society of America.
In a retrospective cohort study, Blacks had a 45% higher risk of 30-day readmission than Whites (P < .001) independent of cardiovascular risk factors, clinical history, comorbidities, type and location of hospital, and type of third-party payer coverage. The analysis included more than 30,000 patients with at least one HF hospitalization at centers in a major metropolitan health system.
The racial disparity widened with worsening socioeconomic deprivation of patients’ residential neighborhoods, that is, with rising quartiles of neighborhood scores on the Social Deprivation Index (SDI).
The SDI, based on U.S. census data, incorporates seven socioeconomic criteria, including household income, education level, employment, and prevalence of rented housing and households that are without a car, single parent, or overcrowded.
There was a 4–percentage point gap in adjusted 30-day readmission rate between Blacks and Whites in the lowest quartile that widened to more than 8 points by the third quartile; the disparity in both the second and fourth quartiles was the same, at about 5.5 percentage points.
A remaining question, Dr. Morris said in an interview, is why the outcomes disparity between Blacks and Whites peaks in the third SDI quartile but drops a bit in the fourth quartile representing the most severe neighborhood deprivation.
“Our hypothesis is that when you look at patients who are the poorest, who live in the most deprived neighborhoods, race may be less of a factor,” she said. Socioeconomic deprivation may have similar consequences for everyone “regardless of race, ethnicity, gender, or other demographic characteristics if you live in a neighborhood that’s highly deprived.”
Based on the current study, “it does appear that increased heart failure incident rates are related to living in deprived neighborhoods, and it raises important clinical and public health concerns that must be addressed,” Keith C. Ferdinand, MD, Tulane University, New Orleans, said as invited discussant after the presentation from Dr. Morris.
“These findings could serve as an aid to policy makers, going forward, in terms of allocating resources for primary health care,” he said. “And it’s important looking at these data and other [data] that we target heart failure patients who reside in deprived neighborhoods before, during, and [after] hospitalization.”
Dr. Morris agreed that policy makers are in a better position to attack the racial disparity in HF readmission rates identified in the study. “This is not a problem that can be fixed within the health care system.”
If the reported interpretation is correct, it could add a twist to the public health care debate in the United States, observed session moderator Mandeep R. Mehra, MD, Brigham and Woman’s Hospital in Boston.
That debate, he noted, has often focused on insurability, access to coverage, and the merits or shortcomings of a single-payer system. Yet the study suggests outcomes disparities stemming from neighborhood deprivation will not be corrected by improved access to health insurance, a conclusion he finds “startling,” Dr. Mehra said in an interview.
Some proposed explanations for the disparities by race blame unequal access to health care and or variable health insurance coverage, Dr. Morris observed in an interview. But “that may not fully explain the increased risk that we see.”
Black patients followed at Emory University’s advanced HF clinic still have a higher risk of rehospitalization than Whites. “These are patients who have insurance, who are followed by advanced heart failure providers, who are on equal amounts of guideline-recommended medical therapy – and you still see about a 50% higher risk of rehospitalization,” Dr. Morris said, citing data that isn’t part of the current analysis.
“We can say that these patients are certainly able to access care, because they are able to access our emergency room and be taken care of within the hospital setting,” he said. The study controlled for whether health coverage was by private insurance, Medicare, or Medicaid.
Instead, the current analysis points to socioeconomic and environmental factors as a major source of the disparity in 30-day readmissions, Dr. Morris said.
“When patients are discharged from our healthcare systems, they still go back into environments where they don’t have the same resources as patients who live in higher-SDI neighborhoods,” she explained.
For example, “we tell them to eat low-sodium [foods], exercise, eat fresh fruits and vegetables, take their medicines, but the reality is that certain neighborhoods within the United States – and this is much more true for Blacks – make it very difficult to follow those self-care recommendations.”
The analysis included 16,147 Black patients and 14,483 White patients hospitalized with HF within the Emory Healthcare system at least once from 2010-2018, Dr. Morris reported. Compared with Whites, Blacks were younger (63.5 vs 69.1 years) and less likely to be 65 or older (48.9% vs. 66.5%); more likely to be women (53.5% vs. 42.2%), more likely to reside in deprived census tracts and to have diabetes, hypertension, or chronic kidney disease; and had higher comorbidity scores.
In all, 20.6% of Black and 13.5% of White patients were readmitted for HF within 30 days of discharge, for an unadjusted risk ratio of 1.52 (95% CI, 1.44-1.61).
The RR hardly budged, 1.45 (95% CI, 1.37-1.54, P < .001), after adjustment for age, sex, type of insurance, type of HF, vital signs and laboratory values, medical history (diabetes, hypertension, atrial fibrillation, coronary disease, chronic kidney disease, and chronic pulmonary disease), Charlson Comorbidity Index, discharging medical specialty, and hospital location.
The excess in 30-day HF readmissions for Black, compared with White patients climbed from the first to the third neighborhood SDI quartile, the disparity peaking at 8.2 absolute percentage points.
A major criticism of the Hospital Readmissions Reduction Program component of the Affordable Care Act, Dr. Morris said in a Q&A discussion after her presentation, is that it can hold hospitals “responsible for structural inequalities that exist beyond the health care system,” including neighborhood deprivation.
“But public policy makers have to realize that there are certain patients we take care of who don’t have the resources to carry out the therapeutic lifestyle changes that will allow them to live healthy.”
The HRRP’s 30-day HF readmission metric that steers reimbursement “is penalizing health care systems across the United States” with its premise that hospital performance can be measured by 30-day HF readmission rates, Dr. Morris said in an interview.
“The reality is that some of these patients are going to a postdischarge environment that is inherently high risk, and that many of them are going to come back to us within 30 days,” she said. “We would like to make sure that we don’t put excess penalties on health care systems that take care of disproportionate numbers of African Americans in neighborhoods that have fewer resources.”
Dr. Morris and Dr. Ferdinand have disclosed no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Mehra discloses consulting or serving on an advisory board for Abbott, Medtronic, Janssen, Leviticus, NupulseCV, FineHeart, Portola, Bayer, the Baim Institute for Clinical Research, and Mesoblast.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
Patients receiving even top-notch hospital care for heart failure (HF) are, once discharged to home, at higher short-term risk of another HF hospitalization if home is in a socioeconomically deprived neighborhood. That helps explain why Blacks in the United States have a much higher 30-day HF readmission risk than Whites, a disparity that only worsens with the level of neighborhood deprivation, a new analysis suggests.
Some systemic and entrenched socioeconomic inequities that health care providers have little sway over, and which disproportionately affect Black individuals, are independent and robust predictors of worsened HF outcomes, Alanna A. Morris, MD, MSc, Emory University, Atlanta, said during her presentation at the virtual annual scientific meeting of the Heart Failure Society of America.
In a retrospective cohort study, Blacks had a 45% higher risk of 30-day readmission than Whites (P < .001) independent of cardiovascular risk factors, clinical history, comorbidities, type and location of hospital, and type of third-party payer coverage. The analysis included more than 30,000 patients with at least one HF hospitalization at centers in a major metropolitan health system.
The racial disparity widened with worsening socioeconomic deprivation of patients’ residential neighborhoods, that is, with rising quartiles of neighborhood scores on the Social Deprivation Index (SDI).
The SDI, based on U.S. census data, incorporates seven socioeconomic criteria, including household income, education level, employment, and prevalence of rented housing and households that are without a car, single parent, or overcrowded.
There was a 4–percentage point gap in adjusted 30-day readmission rate between Blacks and Whites in the lowest quartile that widened to more than 8 points by the third quartile; the disparity in both the second and fourth quartiles was the same, at about 5.5 percentage points.
A remaining question, Dr. Morris said in an interview, is why the outcomes disparity between Blacks and Whites peaks in the third SDI quartile but drops a bit in the fourth quartile representing the most severe neighborhood deprivation.
“Our hypothesis is that when you look at patients who are the poorest, who live in the most deprived neighborhoods, race may be less of a factor,” she said. Socioeconomic deprivation may have similar consequences for everyone “regardless of race, ethnicity, gender, or other demographic characteristics if you live in a neighborhood that’s highly deprived.”
Based on the current study, “it does appear that increased heart failure incident rates are related to living in deprived neighborhoods, and it raises important clinical and public health concerns that must be addressed,” Keith C. Ferdinand, MD, Tulane University, New Orleans, said as invited discussant after the presentation from Dr. Morris.
“These findings could serve as an aid to policy makers, going forward, in terms of allocating resources for primary health care,” he said. “And it’s important looking at these data and other [data] that we target heart failure patients who reside in deprived neighborhoods before, during, and [after] hospitalization.”
Dr. Morris agreed that policy makers are in a better position to attack the racial disparity in HF readmission rates identified in the study. “This is not a problem that can be fixed within the health care system.”
If the reported interpretation is correct, it could add a twist to the public health care debate in the United States, observed session moderator Mandeep R. Mehra, MD, Brigham and Woman’s Hospital in Boston.
That debate, he noted, has often focused on insurability, access to coverage, and the merits or shortcomings of a single-payer system. Yet the study suggests outcomes disparities stemming from neighborhood deprivation will not be corrected by improved access to health insurance, a conclusion he finds “startling,” Dr. Mehra said in an interview.
Some proposed explanations for the disparities by race blame unequal access to health care and or variable health insurance coverage, Dr. Morris observed in an interview. But “that may not fully explain the increased risk that we see.”
Black patients followed at Emory University’s advanced HF clinic still have a higher risk of rehospitalization than Whites. “These are patients who have insurance, who are followed by advanced heart failure providers, who are on equal amounts of guideline-recommended medical therapy – and you still see about a 50% higher risk of rehospitalization,” Dr. Morris said, citing data that isn’t part of the current analysis.
“We can say that these patients are certainly able to access care, because they are able to access our emergency room and be taken care of within the hospital setting,” he said. The study controlled for whether health coverage was by private insurance, Medicare, or Medicaid.
Instead, the current analysis points to socioeconomic and environmental factors as a major source of the disparity in 30-day readmissions, Dr. Morris said.
“When patients are discharged from our healthcare systems, they still go back into environments where they don’t have the same resources as patients who live in higher-SDI neighborhoods,” she explained.
For example, “we tell them to eat low-sodium [foods], exercise, eat fresh fruits and vegetables, take their medicines, but the reality is that certain neighborhoods within the United States – and this is much more true for Blacks – make it very difficult to follow those self-care recommendations.”
The analysis included 16,147 Black patients and 14,483 White patients hospitalized with HF within the Emory Healthcare system at least once from 2010-2018, Dr. Morris reported. Compared with Whites, Blacks were younger (63.5 vs 69.1 years) and less likely to be 65 or older (48.9% vs. 66.5%); more likely to be women (53.5% vs. 42.2%), more likely to reside in deprived census tracts and to have diabetes, hypertension, or chronic kidney disease; and had higher comorbidity scores.
In all, 20.6% of Black and 13.5% of White patients were readmitted for HF within 30 days of discharge, for an unadjusted risk ratio of 1.52 (95% CI, 1.44-1.61).
The RR hardly budged, 1.45 (95% CI, 1.37-1.54, P < .001), after adjustment for age, sex, type of insurance, type of HF, vital signs and laboratory values, medical history (diabetes, hypertension, atrial fibrillation, coronary disease, chronic kidney disease, and chronic pulmonary disease), Charlson Comorbidity Index, discharging medical specialty, and hospital location.
The excess in 30-day HF readmissions for Black, compared with White patients climbed from the first to the third neighborhood SDI quartile, the disparity peaking at 8.2 absolute percentage points.
A major criticism of the Hospital Readmissions Reduction Program component of the Affordable Care Act, Dr. Morris said in a Q&A discussion after her presentation, is that it can hold hospitals “responsible for structural inequalities that exist beyond the health care system,” including neighborhood deprivation.
“But public policy makers have to realize that there are certain patients we take care of who don’t have the resources to carry out the therapeutic lifestyle changes that will allow them to live healthy.”
The HRRP’s 30-day HF readmission metric that steers reimbursement “is penalizing health care systems across the United States” with its premise that hospital performance can be measured by 30-day HF readmission rates, Dr. Morris said in an interview.
“The reality is that some of these patients are going to a postdischarge environment that is inherently high risk, and that many of them are going to come back to us within 30 days,” she said. “We would like to make sure that we don’t put excess penalties on health care systems that take care of disproportionate numbers of African Americans in neighborhoods that have fewer resources.”
Dr. Morris and Dr. Ferdinand have disclosed no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Mehra discloses consulting or serving on an advisory board for Abbott, Medtronic, Janssen, Leviticus, NupulseCV, FineHeart, Portola, Bayer, the Baim Institute for Clinical Research, and Mesoblast.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
Surgeon general pushes for improved hypertension control
Roughly half of American adults have hypertension, and about 71% of these cases are uncontrolled, according to data from the American Heart Association.
If left uncontrolled, hypertension can increase risk for conditions including heart disease, stroke, kidney disease, pregnancy complications, and cognitive decline, surgeon general Vice Adm. Jerome M. Adams, MD, said in a teleconference on Oct. 7. Hispanic and Black individuals are disproportionately affected, he added.
“We cannot wait to deal with this epidemic of uncontrolled high blood pressure,” even in the midst of the ongoing COVID-19 pandemic, said Dr. Adams. “We know what works” to help control hypertension, he added, citing his own use of a blood pressure monitoring device at home.
The Department of Health & Human Services has issued a Call to Action to Control Hypertension based on the latest science and research.
Dr. Adams outlined three goals to improve hypertension control, starting with making it a national priority. The Call to Action supports increasing awareness of the health risks associated with hypertension, recognizing the economic impact, overcoming barriers to controlling hypertension, and promoting health equity.
“In 2020, disparities in the burden of disease – especially among minority populations – have been recognized during the COVID-19 pandemic. A growing body of evidence has shown that people with underlying health conditions, including cardiovascular disease, are at increased risk of worse outcomes related to COVID-19 infection,” according to the Call to Action.
A second goal is to build and sustain communities that support individuals in taking responsibility for their health and blood pressure control, Dr. Adams said. He cited the need to create places for safe physical activity, access to healthy food, and opportunities to connect to resources to support lifestyle changes.
Finally, clinicians should continue to use standardized treatment approaches and promote team-based care to maximize outcomes for patients, Dr. Adams said.
Success starts with making hypertension control a priority across the leadership team, regardless of the size, location, or demographic population at a health care setting, he said. Dr. Adams cited the Million Hearts 2022 program, an ongoing initiative to prevent 1 million heart attacks in the United States over 5 years, as a way that HHS is recognizing and rewarding success stories in hypertension control from across the country.
Empowering patients and equipping them to take charge of their hypertension essential to reducing the epidemic of high blood pressure, especially during the ongoing pandemic, Dr. Adams said. His message to clinicians to extend to patients is that it is safe to visit their doctors. Hospitals have worked to create a safe environment, however, patients can and should monitor their blood pressure regularly at home, using a self-measured blood pressure monitoring (SMBP) device, which may be covered by some insurers.
“I would encourage people to know their numbers,” and that 130/80 mm Hg is considered high and a risk factor for poor health outcomes, Dr. Adams said. Clinicians also should continue to support patients in lifestyle changes such as healthy eating and exercising regularly to help control high blood pressure.
The AHA expressed support for the surgeon general’s Call to Action. “Today’s call to action references updated hypertension guidelines the AHA and the American College of Cardiology issued in 2017 that apply the latest science to help clinicians work with patients to control their blood pressure,” the AHA said in a statement. The AHA also called on the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services and other insurance providers “to include coverage of SMBP devices for treatment and management of hypertension.”
The Call to Action was accompanied by a Viewpoint from Dr. Adams and Janet S. Wright, MD, also of the HHS, published in JAMA. Dr. Adams and Dr. Wright emphasized that the timing of the Call to Action recognizes that many of the same social factors that support or impede successful high blood pressure control are factors in worse outcomes from COVID-19 infections as well.
“When coupled with widespread implementation of best practices in clinical settings and empowering individuals to actively manage their blood pressure, acknowledging and addressing a community’s social conditions may generate sustained improvements in control of both hypertension and COVID-19,” they said.
Read and download the full Call to Action here, and read the Executive Summary at hhs.gov.
Roughly half of American adults have hypertension, and about 71% of these cases are uncontrolled, according to data from the American Heart Association.
If left uncontrolled, hypertension can increase risk for conditions including heart disease, stroke, kidney disease, pregnancy complications, and cognitive decline, surgeon general Vice Adm. Jerome M. Adams, MD, said in a teleconference on Oct. 7. Hispanic and Black individuals are disproportionately affected, he added.
“We cannot wait to deal with this epidemic of uncontrolled high blood pressure,” even in the midst of the ongoing COVID-19 pandemic, said Dr. Adams. “We know what works” to help control hypertension, he added, citing his own use of a blood pressure monitoring device at home.
The Department of Health & Human Services has issued a Call to Action to Control Hypertension based on the latest science and research.
Dr. Adams outlined three goals to improve hypertension control, starting with making it a national priority. The Call to Action supports increasing awareness of the health risks associated with hypertension, recognizing the economic impact, overcoming barriers to controlling hypertension, and promoting health equity.
“In 2020, disparities in the burden of disease – especially among minority populations – have been recognized during the COVID-19 pandemic. A growing body of evidence has shown that people with underlying health conditions, including cardiovascular disease, are at increased risk of worse outcomes related to COVID-19 infection,” according to the Call to Action.
A second goal is to build and sustain communities that support individuals in taking responsibility for their health and blood pressure control, Dr. Adams said. He cited the need to create places for safe physical activity, access to healthy food, and opportunities to connect to resources to support lifestyle changes.
Finally, clinicians should continue to use standardized treatment approaches and promote team-based care to maximize outcomes for patients, Dr. Adams said.
Success starts with making hypertension control a priority across the leadership team, regardless of the size, location, or demographic population at a health care setting, he said. Dr. Adams cited the Million Hearts 2022 program, an ongoing initiative to prevent 1 million heart attacks in the United States over 5 years, as a way that HHS is recognizing and rewarding success stories in hypertension control from across the country.
Empowering patients and equipping them to take charge of their hypertension essential to reducing the epidemic of high blood pressure, especially during the ongoing pandemic, Dr. Adams said. His message to clinicians to extend to patients is that it is safe to visit their doctors. Hospitals have worked to create a safe environment, however, patients can and should monitor their blood pressure regularly at home, using a self-measured blood pressure monitoring (SMBP) device, which may be covered by some insurers.
“I would encourage people to know their numbers,” and that 130/80 mm Hg is considered high and a risk factor for poor health outcomes, Dr. Adams said. Clinicians also should continue to support patients in lifestyle changes such as healthy eating and exercising regularly to help control high blood pressure.
The AHA expressed support for the surgeon general’s Call to Action. “Today’s call to action references updated hypertension guidelines the AHA and the American College of Cardiology issued in 2017 that apply the latest science to help clinicians work with patients to control their blood pressure,” the AHA said in a statement. The AHA also called on the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services and other insurance providers “to include coverage of SMBP devices for treatment and management of hypertension.”
The Call to Action was accompanied by a Viewpoint from Dr. Adams and Janet S. Wright, MD, also of the HHS, published in JAMA. Dr. Adams and Dr. Wright emphasized that the timing of the Call to Action recognizes that many of the same social factors that support or impede successful high blood pressure control are factors in worse outcomes from COVID-19 infections as well.
“When coupled with widespread implementation of best practices in clinical settings and empowering individuals to actively manage their blood pressure, acknowledging and addressing a community’s social conditions may generate sustained improvements in control of both hypertension and COVID-19,” they said.
Read and download the full Call to Action here, and read the Executive Summary at hhs.gov.
Roughly half of American adults have hypertension, and about 71% of these cases are uncontrolled, according to data from the American Heart Association.
If left uncontrolled, hypertension can increase risk for conditions including heart disease, stroke, kidney disease, pregnancy complications, and cognitive decline, surgeon general Vice Adm. Jerome M. Adams, MD, said in a teleconference on Oct. 7. Hispanic and Black individuals are disproportionately affected, he added.
“We cannot wait to deal with this epidemic of uncontrolled high blood pressure,” even in the midst of the ongoing COVID-19 pandemic, said Dr. Adams. “We know what works” to help control hypertension, he added, citing his own use of a blood pressure monitoring device at home.
The Department of Health & Human Services has issued a Call to Action to Control Hypertension based on the latest science and research.
Dr. Adams outlined three goals to improve hypertension control, starting with making it a national priority. The Call to Action supports increasing awareness of the health risks associated with hypertension, recognizing the economic impact, overcoming barriers to controlling hypertension, and promoting health equity.
“In 2020, disparities in the burden of disease – especially among minority populations – have been recognized during the COVID-19 pandemic. A growing body of evidence has shown that people with underlying health conditions, including cardiovascular disease, are at increased risk of worse outcomes related to COVID-19 infection,” according to the Call to Action.
A second goal is to build and sustain communities that support individuals in taking responsibility for their health and blood pressure control, Dr. Adams said. He cited the need to create places for safe physical activity, access to healthy food, and opportunities to connect to resources to support lifestyle changes.
Finally, clinicians should continue to use standardized treatment approaches and promote team-based care to maximize outcomes for patients, Dr. Adams said.
Success starts with making hypertension control a priority across the leadership team, regardless of the size, location, or demographic population at a health care setting, he said. Dr. Adams cited the Million Hearts 2022 program, an ongoing initiative to prevent 1 million heart attacks in the United States over 5 years, as a way that HHS is recognizing and rewarding success stories in hypertension control from across the country.
Empowering patients and equipping them to take charge of their hypertension essential to reducing the epidemic of high blood pressure, especially during the ongoing pandemic, Dr. Adams said. His message to clinicians to extend to patients is that it is safe to visit their doctors. Hospitals have worked to create a safe environment, however, patients can and should monitor their blood pressure regularly at home, using a self-measured blood pressure monitoring (SMBP) device, which may be covered by some insurers.
“I would encourage people to know their numbers,” and that 130/80 mm Hg is considered high and a risk factor for poor health outcomes, Dr. Adams said. Clinicians also should continue to support patients in lifestyle changes such as healthy eating and exercising regularly to help control high blood pressure.
The AHA expressed support for the surgeon general’s Call to Action. “Today’s call to action references updated hypertension guidelines the AHA and the American College of Cardiology issued in 2017 that apply the latest science to help clinicians work with patients to control their blood pressure,” the AHA said in a statement. The AHA also called on the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services and other insurance providers “to include coverage of SMBP devices for treatment and management of hypertension.”
The Call to Action was accompanied by a Viewpoint from Dr. Adams and Janet S. Wright, MD, also of the HHS, published in JAMA. Dr. Adams and Dr. Wright emphasized that the timing of the Call to Action recognizes that many of the same social factors that support or impede successful high blood pressure control are factors in worse outcomes from COVID-19 infections as well.
“When coupled with widespread implementation of best practices in clinical settings and empowering individuals to actively manage their blood pressure, acknowledging and addressing a community’s social conditions may generate sustained improvements in control of both hypertension and COVID-19,” they said.
Read and download the full Call to Action here, and read the Executive Summary at hhs.gov.
MI recurrences drop, but women underestimate disease risk
The number of heart attack survivors in the United States who experienced repeat attacks within a year decreased between 2008 and 2017, especially among women, yet women’s awareness of their risk of death from heart disease also decreased, according to data from a pair of studies published in Circulation.
Recurrent MI rates drop, but not enough
Although the overall morbidity and mortality from coronary heart disease (CHD) in the United States has been on the decline for decades, CHD remains the leading cause of death and disability in both sexes, wrote Sanne A.E. Peters, PhD, of Imperial College London, and colleagues.
To better assess the rates of recurrent CHD by sex, the researchers reviewed data from 770,408 women and 700,477 men younger than 65 years with commercial health insurance or aged 66 years and older with Medicare who were hospitalized for myocardial infarction between 2008 and 2017. The patients were followed for 1 year for recurrent MIs, recurrent CHD events, heart failure hospitalization, and all-cause mortality.
In the study of recurrent heart disease, the rate of recurrent heart attacks per 1,000 person-years declined from 89.2 to 72.3 in women and from 94.2 to 81.3 in men. In addition, the rate of recurrent heart disease events (defined as either an MI or an artery-opening procedure), dropped per 1,000 person-years from 166.3 to 133.3 in women and from 198.1 to 176.8 in men. The reduction was significantly greater among women compared with men (P < .001 for both recurrent MIs and recurrent CHD events) and the differences by sex were consistent throughout the study period.
However, no significant difference occurred in recurrent MI rates among younger women (aged 21-54 years), or men aged 55-79 years, the researchers noted.
Heart failure rates per 1,000 person-years decreased from 177.4 to 158.1 in women and from 162.9 to 156.1 in men during the study period, and all-cause mortality decreased per 1,000 person-years from 403.2 to 389.5 for women and from 436.1 to 417.9 in men.
Potential contributing factors to the reductions in rates of recurrent events after a heart attack may include improved acute cardiac procedures, in-hospital therapy, and secondary prevention, the researchers noted. In addition, “changes in the type and definition of MI may also have contributed to the decline in recurrent events,” they said. “Also, the introduction and increasing sensitivity of cardiac biomarkers assays, especially cardiac troponin, may have contributed to an increased detection of less severe MIs over time, which, in turn, could have resulted in artifactual reductions in the consequences of MI,” they said.
The study findings were limited by several factors including the use of claims data, lack of information on the severity of heart attacks, and inability to analyze population subgroups, but the results were strengthened by the use of a large, multicultural database.
Despite the decline seen in this study, overall rates of recurrent MI, recurrent CHD events, heart failure hospitalization, and mortality remain high, the researchers said, and the results “highlight the need for interventions to ensure men and women receive guideline recommended treatment to lower the risk for recurrent MI, recurrent CHD, heart failure, and mortality after hospital discharge for MI,” they concluded.
Many women don’t recognize heart disease risk
Although women showed a greater reduction in recurrent MI and recurrent CHD events compared with men, the awareness of heart disease as the No. 1 killer of women has declined, according to a special report from the American Heart Association.
Based on survey data from 2009, 65% of women were aware that heart disease was their leading cause of death (LCOD); by 2019 the number dropped to 44%. The 10-year decline occurred across all races and ethnicities, as well as ages, with the exception of women aged 65 years and older.
The American Heart Association has conducted national surveys since 1997 to monitor awareness of cardiovascular disease among U.S. women. Data from earlier surveys showed increased awareness of heart disease as LCOD and increased awareness of heart attack symptoms between 1997 and 2012, wrote Mary Cushman, MD, of the University of Vermont, Burlington, chair of the writing group for the statement, and colleagues.
However, overall awareness and knowledge of heart disease among women remains poor, they wrote.
“Awareness programs designed to educate the public about CVD among women in the United States include Go Red for Women by the American Heart Association; The Heart Truth by the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute; and Make the Call, Don’t Miss a Beat by the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services,” the researchers noted. To determine the change in awareness of heart disease as the LCOD among women, the researchers conducted a multivariate analysis of 1,158 women who completed the 2009 survey and 1,345 who completed the 2019 survey. The average age was 50 years; roughly 70% of the participants in the 2009 survey and 62% in the 2019 survey were non-Hispanic White.
The greatest declines in awareness of heart disease as LCOD occurred among Hispanics and non-Hispanic Blacks and among all respondents aged 25-34 years.
Awareness of heart disease as LCOD was 30% lower among women with high blood pressure compared with women overall, the researchers noted.
“In both surveys, higher educational attainment was strongly related to awareness that heart disease is the LCOD,” the researchers said. However, the results highlight the need for renewed efforts to educate younger women, Hispanic women, and non-Hispanic Black women, they emphasized. Unpublished data from the AHA survey showed that “younger women were less likely to report leading a heart-healthy lifestyle and were more likely to identify multiple barriers to leading a heart-healthy lifestyle, including lack of time, stress, and lack of confidence,” they wrote.
In addition, awareness of heart attack warning signs declined overall and within each ethnic group between 2009 and 2019.
The survey results were limited by several factors including the use of an online-only model that might limit generalizability to populations without online access, and was conducted only in English, the researchers wrote.
Heart disease needs new PR plan
The study of heart disease risk awareness among women was an important update to understand how well the message about women’s risk is getting out, said Martha Gulati, MD, president-elect of the American Society of Preventive Cardiology, in an interview.
The issue remains that heart disease is the No. 1 killer of women, and the decrease in awareness “means we need to amplify our message,” she said.
“I also question whether the symbol of the red dress [for women’s heart disease] is working, and it seems that now is the time to change this symbol,” she emphasized. “I wear a red dress pin on my lab coat and every day someone asks what it means, and no one recognizes it,” she said. “I think ‘Go Red for Women’ is great and part of our outward campaign, but our symbol needs to change to increase the connection and awareness in women,” she said.
What might be a better symbol? Simply, a heart, said Dr. Gulati. But “we need to study whatever is next to really connect with women and make them understand their risk for heart disease,” she added.
“Additionally, we really need to get to minority women,” she said. “We are lagging there, and the survey was conducted in English so it missed many people,” she noted.
Dr. Gulati said she was shocked at how much awareness of heart disease risk has fallen among women, even in those with risk factors such as hypertension, who were 30% less likely to be aware that heart disease remains their leading cause of death. “Younger women as well as very unaware; what this means to me is that our public education efforts need to be amplified,” Dr. Gulati said.
Barriers to educating women about heart disease risk include language and access to affordable screening, Dr. Gulati emphasized. “We need to ensure screening for heart disease is always included as a covered cost for a preventive service,” she said.
“Research needs to be done to identify what works toward educating women about cardiac risk. We need to identify a marketing tool to increase awareness in women. It might be something different for one race versus another,” Dr. Gulati said. “Our messaging needs to improve, but how we improve it needs more than just health care professionals,” she said.
Focus on prevention to reduce MI recurrence
“The study regarding recurrent events after MI is important because we really don’t know much about recurrent coronary heart disease after a MI over time,” said Dr. Gulati. These data can be helpful in managing surviving patients and understanding future risk, she said. “But I was surprised to see fewer recurrent events in women, as women still have more heart failure than men even if it has declined with time,” she noted.
Dr. Gulati questioned several aspects of the study and highlighted some of the limitations. “These are claims data, so do they accurately reflect the U.S. population?” she asked. “Remember, this is a study of people who survived a heart attack; those who didn’t survive aren’t included, and that group is more likely to be women, especially women younger than 55 years,” she said.
In addition, Dr. Gulati noted the lack of data on type of heart attack and on treatment adherence or referral to cardiac rehab, as well as lack of data on long-term medication adherence or follow-up care.
Prevention is the key take-home message from both studies, “whether we are talking primary prevention for the heart disease awareness study or secondary prevention for the recurrent heart attack study,” Dr. Gulati said.
The recurrent heart disease study was supported in part by Amgen and the University of Alabama at Birmingham. Lead author Dr. Peters disclosed support from a UK Medical Research Council Skills Development Fellowship with no financial conflicts. Dr. Cushman had no financial conflicts to disclose; several coauthors on the writing committee disclosed relationships with companies including Amarin and Boehringer Ingelheim. Dr. Gulati had no financial conflicts to disclose.
SOURCE: Peters SAE et al. Circulation. 2020 Sep 21. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.120.047065; Cushman M et al. Circulation. 2020 Sep 21. doi: 10.1161/CIR.0000000000000907.
The number of heart attack survivors in the United States who experienced repeat attacks within a year decreased between 2008 and 2017, especially among women, yet women’s awareness of their risk of death from heart disease also decreased, according to data from a pair of studies published in Circulation.
Recurrent MI rates drop, but not enough
Although the overall morbidity and mortality from coronary heart disease (CHD) in the United States has been on the decline for decades, CHD remains the leading cause of death and disability in both sexes, wrote Sanne A.E. Peters, PhD, of Imperial College London, and colleagues.
To better assess the rates of recurrent CHD by sex, the researchers reviewed data from 770,408 women and 700,477 men younger than 65 years with commercial health insurance or aged 66 years and older with Medicare who were hospitalized for myocardial infarction between 2008 and 2017. The patients were followed for 1 year for recurrent MIs, recurrent CHD events, heart failure hospitalization, and all-cause mortality.
In the study of recurrent heart disease, the rate of recurrent heart attacks per 1,000 person-years declined from 89.2 to 72.3 in women and from 94.2 to 81.3 in men. In addition, the rate of recurrent heart disease events (defined as either an MI or an artery-opening procedure), dropped per 1,000 person-years from 166.3 to 133.3 in women and from 198.1 to 176.8 in men. The reduction was significantly greater among women compared with men (P < .001 for both recurrent MIs and recurrent CHD events) and the differences by sex were consistent throughout the study period.
However, no significant difference occurred in recurrent MI rates among younger women (aged 21-54 years), or men aged 55-79 years, the researchers noted.
Heart failure rates per 1,000 person-years decreased from 177.4 to 158.1 in women and from 162.9 to 156.1 in men during the study period, and all-cause mortality decreased per 1,000 person-years from 403.2 to 389.5 for women and from 436.1 to 417.9 in men.
Potential contributing factors to the reductions in rates of recurrent events after a heart attack may include improved acute cardiac procedures, in-hospital therapy, and secondary prevention, the researchers noted. In addition, “changes in the type and definition of MI may also have contributed to the decline in recurrent events,” they said. “Also, the introduction and increasing sensitivity of cardiac biomarkers assays, especially cardiac troponin, may have contributed to an increased detection of less severe MIs over time, which, in turn, could have resulted in artifactual reductions in the consequences of MI,” they said.
The study findings were limited by several factors including the use of claims data, lack of information on the severity of heart attacks, and inability to analyze population subgroups, but the results were strengthened by the use of a large, multicultural database.
Despite the decline seen in this study, overall rates of recurrent MI, recurrent CHD events, heart failure hospitalization, and mortality remain high, the researchers said, and the results “highlight the need for interventions to ensure men and women receive guideline recommended treatment to lower the risk for recurrent MI, recurrent CHD, heart failure, and mortality after hospital discharge for MI,” they concluded.
Many women don’t recognize heart disease risk
Although women showed a greater reduction in recurrent MI and recurrent CHD events compared with men, the awareness of heart disease as the No. 1 killer of women has declined, according to a special report from the American Heart Association.
Based on survey data from 2009, 65% of women were aware that heart disease was their leading cause of death (LCOD); by 2019 the number dropped to 44%. The 10-year decline occurred across all races and ethnicities, as well as ages, with the exception of women aged 65 years and older.
The American Heart Association has conducted national surveys since 1997 to monitor awareness of cardiovascular disease among U.S. women. Data from earlier surveys showed increased awareness of heart disease as LCOD and increased awareness of heart attack symptoms between 1997 and 2012, wrote Mary Cushman, MD, of the University of Vermont, Burlington, chair of the writing group for the statement, and colleagues.
However, overall awareness and knowledge of heart disease among women remains poor, they wrote.
“Awareness programs designed to educate the public about CVD among women in the United States include Go Red for Women by the American Heart Association; The Heart Truth by the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute; and Make the Call, Don’t Miss a Beat by the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services,” the researchers noted. To determine the change in awareness of heart disease as the LCOD among women, the researchers conducted a multivariate analysis of 1,158 women who completed the 2009 survey and 1,345 who completed the 2019 survey. The average age was 50 years; roughly 70% of the participants in the 2009 survey and 62% in the 2019 survey were non-Hispanic White.
The greatest declines in awareness of heart disease as LCOD occurred among Hispanics and non-Hispanic Blacks and among all respondents aged 25-34 years.
Awareness of heart disease as LCOD was 30% lower among women with high blood pressure compared with women overall, the researchers noted.
“In both surveys, higher educational attainment was strongly related to awareness that heart disease is the LCOD,” the researchers said. However, the results highlight the need for renewed efforts to educate younger women, Hispanic women, and non-Hispanic Black women, they emphasized. Unpublished data from the AHA survey showed that “younger women were less likely to report leading a heart-healthy lifestyle and were more likely to identify multiple barriers to leading a heart-healthy lifestyle, including lack of time, stress, and lack of confidence,” they wrote.
In addition, awareness of heart attack warning signs declined overall and within each ethnic group between 2009 and 2019.
The survey results were limited by several factors including the use of an online-only model that might limit generalizability to populations without online access, and was conducted only in English, the researchers wrote.
Heart disease needs new PR plan
The study of heart disease risk awareness among women was an important update to understand how well the message about women’s risk is getting out, said Martha Gulati, MD, president-elect of the American Society of Preventive Cardiology, in an interview.
The issue remains that heart disease is the No. 1 killer of women, and the decrease in awareness “means we need to amplify our message,” she said.
“I also question whether the symbol of the red dress [for women’s heart disease] is working, and it seems that now is the time to change this symbol,” she emphasized. “I wear a red dress pin on my lab coat and every day someone asks what it means, and no one recognizes it,” she said. “I think ‘Go Red for Women’ is great and part of our outward campaign, but our symbol needs to change to increase the connection and awareness in women,” she said.
What might be a better symbol? Simply, a heart, said Dr. Gulati. But “we need to study whatever is next to really connect with women and make them understand their risk for heart disease,” she added.
“Additionally, we really need to get to minority women,” she said. “We are lagging there, and the survey was conducted in English so it missed many people,” she noted.
Dr. Gulati said she was shocked at how much awareness of heart disease risk has fallen among women, even in those with risk factors such as hypertension, who were 30% less likely to be aware that heart disease remains their leading cause of death. “Younger women as well as very unaware; what this means to me is that our public education efforts need to be amplified,” Dr. Gulati said.
Barriers to educating women about heart disease risk include language and access to affordable screening, Dr. Gulati emphasized. “We need to ensure screening for heart disease is always included as a covered cost for a preventive service,” she said.
“Research needs to be done to identify what works toward educating women about cardiac risk. We need to identify a marketing tool to increase awareness in women. It might be something different for one race versus another,” Dr. Gulati said. “Our messaging needs to improve, but how we improve it needs more than just health care professionals,” she said.
Focus on prevention to reduce MI recurrence
“The study regarding recurrent events after MI is important because we really don’t know much about recurrent coronary heart disease after a MI over time,” said Dr. Gulati. These data can be helpful in managing surviving patients and understanding future risk, she said. “But I was surprised to see fewer recurrent events in women, as women still have more heart failure than men even if it has declined with time,” she noted.
Dr. Gulati questioned several aspects of the study and highlighted some of the limitations. “These are claims data, so do they accurately reflect the U.S. population?” she asked. “Remember, this is a study of people who survived a heart attack; those who didn’t survive aren’t included, and that group is more likely to be women, especially women younger than 55 years,” she said.
In addition, Dr. Gulati noted the lack of data on type of heart attack and on treatment adherence or referral to cardiac rehab, as well as lack of data on long-term medication adherence or follow-up care.
Prevention is the key take-home message from both studies, “whether we are talking primary prevention for the heart disease awareness study or secondary prevention for the recurrent heart attack study,” Dr. Gulati said.
The recurrent heart disease study was supported in part by Amgen and the University of Alabama at Birmingham. Lead author Dr. Peters disclosed support from a UK Medical Research Council Skills Development Fellowship with no financial conflicts. Dr. Cushman had no financial conflicts to disclose; several coauthors on the writing committee disclosed relationships with companies including Amarin and Boehringer Ingelheim. Dr. Gulati had no financial conflicts to disclose.
SOURCE: Peters SAE et al. Circulation. 2020 Sep 21. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.120.047065; Cushman M et al. Circulation. 2020 Sep 21. doi: 10.1161/CIR.0000000000000907.
The number of heart attack survivors in the United States who experienced repeat attacks within a year decreased between 2008 and 2017, especially among women, yet women’s awareness of their risk of death from heart disease also decreased, according to data from a pair of studies published in Circulation.
Recurrent MI rates drop, but not enough
Although the overall morbidity and mortality from coronary heart disease (CHD) in the United States has been on the decline for decades, CHD remains the leading cause of death and disability in both sexes, wrote Sanne A.E. Peters, PhD, of Imperial College London, and colleagues.
To better assess the rates of recurrent CHD by sex, the researchers reviewed data from 770,408 women and 700,477 men younger than 65 years with commercial health insurance or aged 66 years and older with Medicare who were hospitalized for myocardial infarction between 2008 and 2017. The patients were followed for 1 year for recurrent MIs, recurrent CHD events, heart failure hospitalization, and all-cause mortality.
In the study of recurrent heart disease, the rate of recurrent heart attacks per 1,000 person-years declined from 89.2 to 72.3 in women and from 94.2 to 81.3 in men. In addition, the rate of recurrent heart disease events (defined as either an MI or an artery-opening procedure), dropped per 1,000 person-years from 166.3 to 133.3 in women and from 198.1 to 176.8 in men. The reduction was significantly greater among women compared with men (P < .001 for both recurrent MIs and recurrent CHD events) and the differences by sex were consistent throughout the study period.
However, no significant difference occurred in recurrent MI rates among younger women (aged 21-54 years), or men aged 55-79 years, the researchers noted.
Heart failure rates per 1,000 person-years decreased from 177.4 to 158.1 in women and from 162.9 to 156.1 in men during the study period, and all-cause mortality decreased per 1,000 person-years from 403.2 to 389.5 for women and from 436.1 to 417.9 in men.
Potential contributing factors to the reductions in rates of recurrent events after a heart attack may include improved acute cardiac procedures, in-hospital therapy, and secondary prevention, the researchers noted. In addition, “changes in the type and definition of MI may also have contributed to the decline in recurrent events,” they said. “Also, the introduction and increasing sensitivity of cardiac biomarkers assays, especially cardiac troponin, may have contributed to an increased detection of less severe MIs over time, which, in turn, could have resulted in artifactual reductions in the consequences of MI,” they said.
The study findings were limited by several factors including the use of claims data, lack of information on the severity of heart attacks, and inability to analyze population subgroups, but the results were strengthened by the use of a large, multicultural database.
Despite the decline seen in this study, overall rates of recurrent MI, recurrent CHD events, heart failure hospitalization, and mortality remain high, the researchers said, and the results “highlight the need for interventions to ensure men and women receive guideline recommended treatment to lower the risk for recurrent MI, recurrent CHD, heart failure, and mortality after hospital discharge for MI,” they concluded.
Many women don’t recognize heart disease risk
Although women showed a greater reduction in recurrent MI and recurrent CHD events compared with men, the awareness of heart disease as the No. 1 killer of women has declined, according to a special report from the American Heart Association.
Based on survey data from 2009, 65% of women were aware that heart disease was their leading cause of death (LCOD); by 2019 the number dropped to 44%. The 10-year decline occurred across all races and ethnicities, as well as ages, with the exception of women aged 65 years and older.
The American Heart Association has conducted national surveys since 1997 to monitor awareness of cardiovascular disease among U.S. women. Data from earlier surveys showed increased awareness of heart disease as LCOD and increased awareness of heart attack symptoms between 1997 and 2012, wrote Mary Cushman, MD, of the University of Vermont, Burlington, chair of the writing group for the statement, and colleagues.
However, overall awareness and knowledge of heart disease among women remains poor, they wrote.
“Awareness programs designed to educate the public about CVD among women in the United States include Go Red for Women by the American Heart Association; The Heart Truth by the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute; and Make the Call, Don’t Miss a Beat by the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services,” the researchers noted. To determine the change in awareness of heart disease as the LCOD among women, the researchers conducted a multivariate analysis of 1,158 women who completed the 2009 survey and 1,345 who completed the 2019 survey. The average age was 50 years; roughly 70% of the participants in the 2009 survey and 62% in the 2019 survey were non-Hispanic White.
The greatest declines in awareness of heart disease as LCOD occurred among Hispanics and non-Hispanic Blacks and among all respondents aged 25-34 years.
Awareness of heart disease as LCOD was 30% lower among women with high blood pressure compared with women overall, the researchers noted.
“In both surveys, higher educational attainment was strongly related to awareness that heart disease is the LCOD,” the researchers said. However, the results highlight the need for renewed efforts to educate younger women, Hispanic women, and non-Hispanic Black women, they emphasized. Unpublished data from the AHA survey showed that “younger women were less likely to report leading a heart-healthy lifestyle and were more likely to identify multiple barriers to leading a heart-healthy lifestyle, including lack of time, stress, and lack of confidence,” they wrote.
In addition, awareness of heart attack warning signs declined overall and within each ethnic group between 2009 and 2019.
The survey results were limited by several factors including the use of an online-only model that might limit generalizability to populations without online access, and was conducted only in English, the researchers wrote.
Heart disease needs new PR plan
The study of heart disease risk awareness among women was an important update to understand how well the message about women’s risk is getting out, said Martha Gulati, MD, president-elect of the American Society of Preventive Cardiology, in an interview.
The issue remains that heart disease is the No. 1 killer of women, and the decrease in awareness “means we need to amplify our message,” she said.
“I also question whether the symbol of the red dress [for women’s heart disease] is working, and it seems that now is the time to change this symbol,” she emphasized. “I wear a red dress pin on my lab coat and every day someone asks what it means, and no one recognizes it,” she said. “I think ‘Go Red for Women’ is great and part of our outward campaign, but our symbol needs to change to increase the connection and awareness in women,” she said.
What might be a better symbol? Simply, a heart, said Dr. Gulati. But “we need to study whatever is next to really connect with women and make them understand their risk for heart disease,” she added.
“Additionally, we really need to get to minority women,” she said. “We are lagging there, and the survey was conducted in English so it missed many people,” she noted.
Dr. Gulati said she was shocked at how much awareness of heart disease risk has fallen among women, even in those with risk factors such as hypertension, who were 30% less likely to be aware that heart disease remains their leading cause of death. “Younger women as well as very unaware; what this means to me is that our public education efforts need to be amplified,” Dr. Gulati said.
Barriers to educating women about heart disease risk include language and access to affordable screening, Dr. Gulati emphasized. “We need to ensure screening for heart disease is always included as a covered cost for a preventive service,” she said.
“Research needs to be done to identify what works toward educating women about cardiac risk. We need to identify a marketing tool to increase awareness in women. It might be something different for one race versus another,” Dr. Gulati said. “Our messaging needs to improve, but how we improve it needs more than just health care professionals,” she said.
Focus on prevention to reduce MI recurrence
“The study regarding recurrent events after MI is important because we really don’t know much about recurrent coronary heart disease after a MI over time,” said Dr. Gulati. These data can be helpful in managing surviving patients and understanding future risk, she said. “But I was surprised to see fewer recurrent events in women, as women still have more heart failure than men even if it has declined with time,” she noted.
Dr. Gulati questioned several aspects of the study and highlighted some of the limitations. “These are claims data, so do they accurately reflect the U.S. population?” she asked. “Remember, this is a study of people who survived a heart attack; those who didn’t survive aren’t included, and that group is more likely to be women, especially women younger than 55 years,” she said.
In addition, Dr. Gulati noted the lack of data on type of heart attack and on treatment adherence or referral to cardiac rehab, as well as lack of data on long-term medication adherence or follow-up care.
Prevention is the key take-home message from both studies, “whether we are talking primary prevention for the heart disease awareness study or secondary prevention for the recurrent heart attack study,” Dr. Gulati said.
The recurrent heart disease study was supported in part by Amgen and the University of Alabama at Birmingham. Lead author Dr. Peters disclosed support from a UK Medical Research Council Skills Development Fellowship with no financial conflicts. Dr. Cushman had no financial conflicts to disclose; several coauthors on the writing committee disclosed relationships with companies including Amarin and Boehringer Ingelheim. Dr. Gulati had no financial conflicts to disclose.
SOURCE: Peters SAE et al. Circulation. 2020 Sep 21. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.120.047065; Cushman M et al. Circulation. 2020 Sep 21. doi: 10.1161/CIR.0000000000000907.
FROM CIRCULATION
Psychosocial resilience associated with better cardiovascular health in Blacks
Resilience might deserve targeting
Increased psychosocial resilience, which captures a sense of purpose, optimism, and life-coping strategies, correlates with improved cardiovascular (CV) health in Black Americans, according to a study that might hold a key for identifying new strategies for CV disease prevention.
“Our findings highlight the importance of individual psychosocial factors that promote cardiovascular health among Black adults, traditionally considered to be a high-risk population,” according to a team of authors collaborating on a study produced by the Morehouse-Emory Cardiovascular Center for Health Equity in Atlanta.
Studies associating psychosocial resilience with improved health outcomes have been published before. In a 12-study review of this concept, it was emphasized that resilience is a dynamic process, not a personality trait, and has shown promise as a target of efforts to relieve the burden of disease (Johnston MC et al. Psychosomatics 2015;56:168-80).
In this study, which received partial support from the American Heart Association, psychosocial resilience was evaluated at both the individual level and at the community level among 389 Black adults living in Atlanta. The senior author was Tené T. Lewis, PhD, of the department of epidemiology at Emory’s Rollins School of Public Health (Circ Cardiovasc Qual Outcomes 2020 Oct 7;13:3006638).
Psychosocial resilience was calculated across the domains of environmental mastery, purpose of life, optimism, coping, and lack of depression with standardized tests, such as the Life Orientation Test-Revised questionnaire for optimism and the Ryff Scales of Psychological Well-Being for the domains of environmental mastery and purpose of life. A composite score for psychosocial resilience was reached by calculating the median score across the measured domains.
Patients with high psychosocial resilience, defined as a composite score above the median, or low resilience, defined as a lower score, were then compared for CV health based on the AHA’s Life’s Simple 7 (LS7) score.
LS7 scores incorporate measures for exercise, diet, smoking history, blood pressure, glucose, cholesterol, and body mass index. Composite LS7 scores range from 0 to 14. Prior work cited by the authors have associated each 1-unit increase in LS7 score with a 13% lower risk of CVD.
As a continuous variable for CV risk at the individual level, each higher standard-deviation increment in the composite psychosocial resilience score was associated with a highly significant 0.42-point increase in LS7 score (P < .001) for study participants. In other words, increasing resilience predicted lower CV risk scores.
Resilience was also calculated at the community level by looking at census tract-level rates of CV mortality and morbidity relative to socioeconomic status. Again, high CV resilience, defined as scores above the median, were compared with lower scores across neighborhoods with similar median household income. As a continuous variable in this analysis, each higher standard-deviation increment in the resilience score was associated with a 0.27-point increase in LS7 score (P = .01).
After adjustment for sociodemographic factors, the association between psychosocial resilience and CV health remained significant for both the individual and community calculations, according to the authors. When examined jointly, high individual psychosocial resilience remained independently associated with improved CV health, but living in a high-resilience neighborhood was not an independent predictor.
When evaluated individually, each of the domains in the psychosocial resistance score were positively correlated with higher LS7 scores, meaning lower CV risk. The strongest associations on a statistical level were low depressive symptoms (P = .001), environmental mastery (P = .006), and purpose in life (P = .009).
The impact of high psychosocial resistance scores was greatest in Black adults living in low-resilience neighborhoods. Among these subjects, high resilience was associated with a nearly 1-point increase in LS7 score relative to low resilience (8.38 vs. 7.42). This was unexpected, but it “is consistent with some broader conceptual literature that posits that individual psychosocial resilience matters more under conditions of adversity,” the authors reported.
Understanding disparities is key
Black race has repeatedly been associated with an increased risk of CV events, but this study is valuable for providing a fresh perspective on the potential reasons, according to the authors of an accompanying editorial, Amber E. Johnson, MD, and Jared Magnani, MD, who are both affiliated with the division of cardiology at the University of Pittsburgh (Circ Cardiovasc Qual Outcomes 2020 Oct 7. doi: 10.1161/CIRCOUTCOMES.120.007357.
“Clinicians increasingly recognize that race-based disparities do not stem inherently from race; instead, the disparities stem from the underlying social determinations of health,” they wrote, citing such variables as unequal access to pay and acceptable living conditions “and the structural racism that perpetuates them.”
They agreed with the authors that promotion of psychosocial resilience among Black people living in communities with poor CV health has the potential to improve CV outcomes, but they warned that this is complex. Although they contend that resilience techniques can be taught, they cautioned there might be limitations if the underlying factors associated with poor psychosocial resilience remain unchanged.
“Thus, the superficial application of positive psychology strategies is likely insufficient to bring parity to CV health outcomes,” they wrote, concluding that strategies to promote health equity would negate the need for interventions to bolster resilience.
Studies that focus on Black adults and cardiovascular health, including this investigation into the role of psychosocial factors “are much needed and very welcome,” said Harlan M. Krumholz, MD, a cardiologist and professor in the Institute for Social and Policy Studies at Yale University, New Haven, Conn.
He sees a broad array of potential directions of research.
“The study opens many questions about whether the resilience can be strengthened by interventions; whether addressing structural racism could reduce the need for such resilience, and whether this association is specific to Black adults in an urban center or is generally present in other settings and in other populations,” Dr. Krumholz said.
An effort is now needed to determine “whether this is a marker or a mediator of cardiovascular health,” he added.
In either case, resilience is a potentially important factor for understanding racial disparities in CV-disease prevalence and outcomes, according to the authors of the accompanying editorial and Dr. Krumholz.
SOURCE: Kim JH et al. Circ Cardiovasc Qual Outcomes. 2020 Oct 7;13:e006638.
Resilience might deserve targeting
Resilience might deserve targeting
Increased psychosocial resilience, which captures a sense of purpose, optimism, and life-coping strategies, correlates with improved cardiovascular (CV) health in Black Americans, according to a study that might hold a key for identifying new strategies for CV disease prevention.
“Our findings highlight the importance of individual psychosocial factors that promote cardiovascular health among Black adults, traditionally considered to be a high-risk population,” according to a team of authors collaborating on a study produced by the Morehouse-Emory Cardiovascular Center for Health Equity in Atlanta.
Studies associating psychosocial resilience with improved health outcomes have been published before. In a 12-study review of this concept, it was emphasized that resilience is a dynamic process, not a personality trait, and has shown promise as a target of efforts to relieve the burden of disease (Johnston MC et al. Psychosomatics 2015;56:168-80).
In this study, which received partial support from the American Heart Association, psychosocial resilience was evaluated at both the individual level and at the community level among 389 Black adults living in Atlanta. The senior author was Tené T. Lewis, PhD, of the department of epidemiology at Emory’s Rollins School of Public Health (Circ Cardiovasc Qual Outcomes 2020 Oct 7;13:3006638).
Psychosocial resilience was calculated across the domains of environmental mastery, purpose of life, optimism, coping, and lack of depression with standardized tests, such as the Life Orientation Test-Revised questionnaire for optimism and the Ryff Scales of Psychological Well-Being for the domains of environmental mastery and purpose of life. A composite score for psychosocial resilience was reached by calculating the median score across the measured domains.
Patients with high psychosocial resilience, defined as a composite score above the median, or low resilience, defined as a lower score, were then compared for CV health based on the AHA’s Life’s Simple 7 (LS7) score.
LS7 scores incorporate measures for exercise, diet, smoking history, blood pressure, glucose, cholesterol, and body mass index. Composite LS7 scores range from 0 to 14. Prior work cited by the authors have associated each 1-unit increase in LS7 score with a 13% lower risk of CVD.
As a continuous variable for CV risk at the individual level, each higher standard-deviation increment in the composite psychosocial resilience score was associated with a highly significant 0.42-point increase in LS7 score (P < .001) for study participants. In other words, increasing resilience predicted lower CV risk scores.
Resilience was also calculated at the community level by looking at census tract-level rates of CV mortality and morbidity relative to socioeconomic status. Again, high CV resilience, defined as scores above the median, were compared with lower scores across neighborhoods with similar median household income. As a continuous variable in this analysis, each higher standard-deviation increment in the resilience score was associated with a 0.27-point increase in LS7 score (P = .01).
After adjustment for sociodemographic factors, the association between psychosocial resilience and CV health remained significant for both the individual and community calculations, according to the authors. When examined jointly, high individual psychosocial resilience remained independently associated with improved CV health, but living in a high-resilience neighborhood was not an independent predictor.
When evaluated individually, each of the domains in the psychosocial resistance score were positively correlated with higher LS7 scores, meaning lower CV risk. The strongest associations on a statistical level were low depressive symptoms (P = .001), environmental mastery (P = .006), and purpose in life (P = .009).
The impact of high psychosocial resistance scores was greatest in Black adults living in low-resilience neighborhoods. Among these subjects, high resilience was associated with a nearly 1-point increase in LS7 score relative to low resilience (8.38 vs. 7.42). This was unexpected, but it “is consistent with some broader conceptual literature that posits that individual psychosocial resilience matters more under conditions of adversity,” the authors reported.
Understanding disparities is key
Black race has repeatedly been associated with an increased risk of CV events, but this study is valuable for providing a fresh perspective on the potential reasons, according to the authors of an accompanying editorial, Amber E. Johnson, MD, and Jared Magnani, MD, who are both affiliated with the division of cardiology at the University of Pittsburgh (Circ Cardiovasc Qual Outcomes 2020 Oct 7. doi: 10.1161/CIRCOUTCOMES.120.007357.
“Clinicians increasingly recognize that race-based disparities do not stem inherently from race; instead, the disparities stem from the underlying social determinations of health,” they wrote, citing such variables as unequal access to pay and acceptable living conditions “and the structural racism that perpetuates them.”
They agreed with the authors that promotion of psychosocial resilience among Black people living in communities with poor CV health has the potential to improve CV outcomes, but they warned that this is complex. Although they contend that resilience techniques can be taught, they cautioned there might be limitations if the underlying factors associated with poor psychosocial resilience remain unchanged.
“Thus, the superficial application of positive psychology strategies is likely insufficient to bring parity to CV health outcomes,” they wrote, concluding that strategies to promote health equity would negate the need for interventions to bolster resilience.
Studies that focus on Black adults and cardiovascular health, including this investigation into the role of psychosocial factors “are much needed and very welcome,” said Harlan M. Krumholz, MD, a cardiologist and professor in the Institute for Social and Policy Studies at Yale University, New Haven, Conn.
He sees a broad array of potential directions of research.
“The study opens many questions about whether the resilience can be strengthened by interventions; whether addressing structural racism could reduce the need for such resilience, and whether this association is specific to Black adults in an urban center or is generally present in other settings and in other populations,” Dr. Krumholz said.
An effort is now needed to determine “whether this is a marker or a mediator of cardiovascular health,” he added.
In either case, resilience is a potentially important factor for understanding racial disparities in CV-disease prevalence and outcomes, according to the authors of the accompanying editorial and Dr. Krumholz.
SOURCE: Kim JH et al. Circ Cardiovasc Qual Outcomes. 2020 Oct 7;13:e006638.
Increased psychosocial resilience, which captures a sense of purpose, optimism, and life-coping strategies, correlates with improved cardiovascular (CV) health in Black Americans, according to a study that might hold a key for identifying new strategies for CV disease prevention.
“Our findings highlight the importance of individual psychosocial factors that promote cardiovascular health among Black adults, traditionally considered to be a high-risk population,” according to a team of authors collaborating on a study produced by the Morehouse-Emory Cardiovascular Center for Health Equity in Atlanta.
Studies associating psychosocial resilience with improved health outcomes have been published before. In a 12-study review of this concept, it was emphasized that resilience is a dynamic process, not a personality trait, and has shown promise as a target of efforts to relieve the burden of disease (Johnston MC et al. Psychosomatics 2015;56:168-80).
In this study, which received partial support from the American Heart Association, psychosocial resilience was evaluated at both the individual level and at the community level among 389 Black adults living in Atlanta. The senior author was Tené T. Lewis, PhD, of the department of epidemiology at Emory’s Rollins School of Public Health (Circ Cardiovasc Qual Outcomes 2020 Oct 7;13:3006638).
Psychosocial resilience was calculated across the domains of environmental mastery, purpose of life, optimism, coping, and lack of depression with standardized tests, such as the Life Orientation Test-Revised questionnaire for optimism and the Ryff Scales of Psychological Well-Being for the domains of environmental mastery and purpose of life. A composite score for psychosocial resilience was reached by calculating the median score across the measured domains.
Patients with high psychosocial resilience, defined as a composite score above the median, or low resilience, defined as a lower score, were then compared for CV health based on the AHA’s Life’s Simple 7 (LS7) score.
LS7 scores incorporate measures for exercise, diet, smoking history, blood pressure, glucose, cholesterol, and body mass index. Composite LS7 scores range from 0 to 14. Prior work cited by the authors have associated each 1-unit increase in LS7 score with a 13% lower risk of CVD.
As a continuous variable for CV risk at the individual level, each higher standard-deviation increment in the composite psychosocial resilience score was associated with a highly significant 0.42-point increase in LS7 score (P < .001) for study participants. In other words, increasing resilience predicted lower CV risk scores.
Resilience was also calculated at the community level by looking at census tract-level rates of CV mortality and morbidity relative to socioeconomic status. Again, high CV resilience, defined as scores above the median, were compared with lower scores across neighborhoods with similar median household income. As a continuous variable in this analysis, each higher standard-deviation increment in the resilience score was associated with a 0.27-point increase in LS7 score (P = .01).
After adjustment for sociodemographic factors, the association between psychosocial resilience and CV health remained significant for both the individual and community calculations, according to the authors. When examined jointly, high individual psychosocial resilience remained independently associated with improved CV health, but living in a high-resilience neighborhood was not an independent predictor.
When evaluated individually, each of the domains in the psychosocial resistance score were positively correlated with higher LS7 scores, meaning lower CV risk. The strongest associations on a statistical level were low depressive symptoms (P = .001), environmental mastery (P = .006), and purpose in life (P = .009).
The impact of high psychosocial resistance scores was greatest in Black adults living in low-resilience neighborhoods. Among these subjects, high resilience was associated with a nearly 1-point increase in LS7 score relative to low resilience (8.38 vs. 7.42). This was unexpected, but it “is consistent with some broader conceptual literature that posits that individual psychosocial resilience matters more under conditions of adversity,” the authors reported.
Understanding disparities is key
Black race has repeatedly been associated with an increased risk of CV events, but this study is valuable for providing a fresh perspective on the potential reasons, according to the authors of an accompanying editorial, Amber E. Johnson, MD, and Jared Magnani, MD, who are both affiliated with the division of cardiology at the University of Pittsburgh (Circ Cardiovasc Qual Outcomes 2020 Oct 7. doi: 10.1161/CIRCOUTCOMES.120.007357.
“Clinicians increasingly recognize that race-based disparities do not stem inherently from race; instead, the disparities stem from the underlying social determinations of health,” they wrote, citing such variables as unequal access to pay and acceptable living conditions “and the structural racism that perpetuates them.”
They agreed with the authors that promotion of psychosocial resilience among Black people living in communities with poor CV health has the potential to improve CV outcomes, but they warned that this is complex. Although they contend that resilience techniques can be taught, they cautioned there might be limitations if the underlying factors associated with poor psychosocial resilience remain unchanged.
“Thus, the superficial application of positive psychology strategies is likely insufficient to bring parity to CV health outcomes,” they wrote, concluding that strategies to promote health equity would negate the need for interventions to bolster resilience.
Studies that focus on Black adults and cardiovascular health, including this investigation into the role of psychosocial factors “are much needed and very welcome,” said Harlan M. Krumholz, MD, a cardiologist and professor in the Institute for Social and Policy Studies at Yale University, New Haven, Conn.
He sees a broad array of potential directions of research.
“The study opens many questions about whether the resilience can be strengthened by interventions; whether addressing structural racism could reduce the need for such resilience, and whether this association is specific to Black adults in an urban center or is generally present in other settings and in other populations,” Dr. Krumholz said.
An effort is now needed to determine “whether this is a marker or a mediator of cardiovascular health,” he added.
In either case, resilience is a potentially important factor for understanding racial disparities in CV-disease prevalence and outcomes, according to the authors of the accompanying editorial and Dr. Krumholz.
SOURCE: Kim JH et al. Circ Cardiovasc Qual Outcomes. 2020 Oct 7;13:e006638.
FROM CIRCULATION: CARDIOVASCULAR QUALITY AND OUTCOMES