User login
Official news magazine of the Society of Hospital Medicine
Copyright by Society of Hospital Medicine or related companies. All rights reserved. ISSN 1553-085X
nav[contains(@class, 'nav-ce-stack nav-ce-stack__large-screen')]
header[@id='header']
div[contains(@class, 'header__large-screen')]
div[contains(@class, 'read-next-article')]
div[contains(@class, 'main-prefix')]
div[contains(@class, 'nav-primary')]
nav[contains(@class, 'nav-primary')]
section[contains(@class, 'footer-nav-section-wrapper')]
footer[@id='footer']
section[contains(@class, 'nav-hidden')]
div[contains(@class, 'ce-card-content')]
nav[contains(@class, 'nav-ce-stack')]
div[contains(@class, 'view-medstat-quiz-listing-panes')]
div[contains(@class, 'pane-article-sidebar-latest-news')]
div[contains(@class, 'pane-pub-article-hospitalist')]


COVID-19: Are acute stroke patients avoiding emergency care?
(EDs).
Stroke specialists in New Orleans, Chicago, Seattle, and elsewhere told Medscape Medical News they are seeing a precipitous drop in the number of acute strokes at their institutions – and not just in the number of milder cases. Doctors on Twitter are sharing similar reports and are using social media to highlight this issue.
Gabriel Vidal, MD, a vascular and interventional neurologist at the Ochsner Medical Center, New Orleans, Louisiana, said there are “definitely” fewer patients with stroke and transient ischemic attack (TIA) seeking care at his facility and others throughout the New Orleans area, which has been hard hit by COVID-19.
“Even in Louisiana, we have a very large 53-hospital telestroke network, and the number of consults has diminished greatly,” Vidal added.
In Chicago, emergency medical service activations for patients with suspected strokes are down about 30%, Shyam Prabhakaran, MD, professor and chair of neurology at the University of Chicago Biological Sciences, Illinois, told Medscape Medical News.
“It appears to be that mild stroke and TIA patients may be more likely to stay at home and seek alternative care rather than come to the ED,” Prabhakaran said. However, “the severe strokes may be less affected and continue to come to emergency departments.”
“Getting the Word Out”
That may not be the whole story in Seattle, Washington, where a stroke specialist at Harborview Medical Center reported a drop in patients across the stroke-severity spectrum.
Some patients with milder strokes no longer come to Harborview for a comprehensive evaluation and workup, but that is only “a partial explanation,” said David Tirschwell, MD, medical director of comprehensive stroke care at the University of Washington (UW) Medicine Stroke Center at Harborview and a professor of neurology at UW.
“The thrombectomies are down also,” he added. “It’s hard to have great numbers in real time, but it’s probably safe to say it’s at least a 50% reduction in the number of admissions.”
As a stroke referral center, his institution is seeing fewer local cases and referrals from outside hospitals. “I think both of those sources for admissions of stroke cases are down,” Tirschwell said.
Recognizing the seriousness of forgoing essential care for acute stroke, neurologists, institutions, and medical groups are taking to social media to potentially save lives.
“Across our @FLStrokeReg we are seeing less patients with #stroke symptoms coming to our hospitals. We need to get the word out that our teams are working hard to safely provide care when needed during #COVID19,” tweeted Ralph Sacco, MD, chief and professor of neurology, University of Miami Miller School of Medicine in South Florida.
Although Florida Stroke Registry data are not publicly available, anecdotal reports suggest that stroke admissions are down among many hospitals, Sacco told Medscape Medical News.
Furthermore, this is not a phenomenon only in the United States. “This has also been reported in other nations hit by COVID-19,” he said.
China is a prime example. There, many stroke centers have shown reduced functioning “because of fear of in-hospital cross infection and lack of experienced stroke care experts,” Jing Zhao, MD, PhD, and colleagues write in an editorial published online March 31 in Stroke.
Preliminary data show that “thrombectomies in Shanghai decreased by 50% in the first month after the Spring Festival compared with the same period in 2019,” write the editorialists, who are from Kings College London and the University of Pennsylvania in Philadelphia.
“Although the control of the COVID-19 is very important, at the same time, the management of stroke must not be neglected,” they add.
“Over 9000 new stroke cases occur each day in China alone. It cannot be right that treatment for one potentially curable disease is euthanized at the expense of another.”
Fear Factor?
The reasons individuals who may have experienced a stroke are avoiding emergency care is unclear at the moment. “I’m not really sure anyone really understands why, quite honestly,” Tirschwell said.
Until survey data or other data emerge, many experts are assuming that fear of COVID-19 is trumping other medical concerns, including emergency treatment of stroke.
“We believe this could represent patients being fearful to come to medical facilities with stroke-like symptoms, given the COVID-19 pandemic,” said Sacco, who is also incoming editor-in-chief of Stroke.
The BBC has been getting the word out in the United Kingdom via social media, with a tweet to “Dial 999 for stroke emergencies despite coronavirus.”
The World Stroke Campaign is also using Twitter to emphasize the need for urgent stroke care when appropriate:
“Don’t let concerns about COVID19 prevent you from seeking emergency treatment for stroke. If you spot the signs of stroke act FAST. Get emergency medical assistance,” the group urged in a tweet.
Don’t Hesitate
The American Heart Association (AHA) has addressed this troubling trend as well.
“People with serious symptoms shouldn’t ignore them,” Sarah Perlman, MD, associate professor of emergency medicine at the University of Colorado School of Medicine, Denver, states in an article on the AHA website.
Perlman added that some individuals who have signs of stroke and heart disease may hesitate to seek care because of fear that they are adding to an overburdened healthcare staff and system. However, she dismissed those concerns outright.
“If you’re experiencing warning signs of a heart attack or stroke, call 911,” she said. “Clearly, if there’s an emergency, we are available and capable and eager to take care of you.”
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
(EDs).
Stroke specialists in New Orleans, Chicago, Seattle, and elsewhere told Medscape Medical News they are seeing a precipitous drop in the number of acute strokes at their institutions – and not just in the number of milder cases. Doctors on Twitter are sharing similar reports and are using social media to highlight this issue.
Gabriel Vidal, MD, a vascular and interventional neurologist at the Ochsner Medical Center, New Orleans, Louisiana, said there are “definitely” fewer patients with stroke and transient ischemic attack (TIA) seeking care at his facility and others throughout the New Orleans area, which has been hard hit by COVID-19.
“Even in Louisiana, we have a very large 53-hospital telestroke network, and the number of consults has diminished greatly,” Vidal added.
In Chicago, emergency medical service activations for patients with suspected strokes are down about 30%, Shyam Prabhakaran, MD, professor and chair of neurology at the University of Chicago Biological Sciences, Illinois, told Medscape Medical News.
“It appears to be that mild stroke and TIA patients may be more likely to stay at home and seek alternative care rather than come to the ED,” Prabhakaran said. However, “the severe strokes may be less affected and continue to come to emergency departments.”
“Getting the Word Out”
That may not be the whole story in Seattle, Washington, where a stroke specialist at Harborview Medical Center reported a drop in patients across the stroke-severity spectrum.
Some patients with milder strokes no longer come to Harborview for a comprehensive evaluation and workup, but that is only “a partial explanation,” said David Tirschwell, MD, medical director of comprehensive stroke care at the University of Washington (UW) Medicine Stroke Center at Harborview and a professor of neurology at UW.
“The thrombectomies are down also,” he added. “It’s hard to have great numbers in real time, but it’s probably safe to say it’s at least a 50% reduction in the number of admissions.”
As a stroke referral center, his institution is seeing fewer local cases and referrals from outside hospitals. “I think both of those sources for admissions of stroke cases are down,” Tirschwell said.
Recognizing the seriousness of forgoing essential care for acute stroke, neurologists, institutions, and medical groups are taking to social media to potentially save lives.
“Across our @FLStrokeReg we are seeing less patients with #stroke symptoms coming to our hospitals. We need to get the word out that our teams are working hard to safely provide care when needed during #COVID19,” tweeted Ralph Sacco, MD, chief and professor of neurology, University of Miami Miller School of Medicine in South Florida.
Although Florida Stroke Registry data are not publicly available, anecdotal reports suggest that stroke admissions are down among many hospitals, Sacco told Medscape Medical News.
Furthermore, this is not a phenomenon only in the United States. “This has also been reported in other nations hit by COVID-19,” he said.
China is a prime example. There, many stroke centers have shown reduced functioning “because of fear of in-hospital cross infection and lack of experienced stroke care experts,” Jing Zhao, MD, PhD, and colleagues write in an editorial published online March 31 in Stroke.
Preliminary data show that “thrombectomies in Shanghai decreased by 50% in the first month after the Spring Festival compared with the same period in 2019,” write the editorialists, who are from Kings College London and the University of Pennsylvania in Philadelphia.
“Although the control of the COVID-19 is very important, at the same time, the management of stroke must not be neglected,” they add.
“Over 9000 new stroke cases occur each day in China alone. It cannot be right that treatment for one potentially curable disease is euthanized at the expense of another.”
Fear Factor?
The reasons individuals who may have experienced a stroke are avoiding emergency care is unclear at the moment. “I’m not really sure anyone really understands why, quite honestly,” Tirschwell said.
Until survey data or other data emerge, many experts are assuming that fear of COVID-19 is trumping other medical concerns, including emergency treatment of stroke.
“We believe this could represent patients being fearful to come to medical facilities with stroke-like symptoms, given the COVID-19 pandemic,” said Sacco, who is also incoming editor-in-chief of Stroke.
The BBC has been getting the word out in the United Kingdom via social media, with a tweet to “Dial 999 for stroke emergencies despite coronavirus.”
The World Stroke Campaign is also using Twitter to emphasize the need for urgent stroke care when appropriate:
“Don’t let concerns about COVID19 prevent you from seeking emergency treatment for stroke. If you spot the signs of stroke act FAST. Get emergency medical assistance,” the group urged in a tweet.
Don’t Hesitate
The American Heart Association (AHA) has addressed this troubling trend as well.
“People with serious symptoms shouldn’t ignore them,” Sarah Perlman, MD, associate professor of emergency medicine at the University of Colorado School of Medicine, Denver, states in an article on the AHA website.
Perlman added that some individuals who have signs of stroke and heart disease may hesitate to seek care because of fear that they are adding to an overburdened healthcare staff and system. However, she dismissed those concerns outright.
“If you’re experiencing warning signs of a heart attack or stroke, call 911,” she said. “Clearly, if there’s an emergency, we are available and capable and eager to take care of you.”
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
(EDs).
Stroke specialists in New Orleans, Chicago, Seattle, and elsewhere told Medscape Medical News they are seeing a precipitous drop in the number of acute strokes at their institutions – and not just in the number of milder cases. Doctors on Twitter are sharing similar reports and are using social media to highlight this issue.
Gabriel Vidal, MD, a vascular and interventional neurologist at the Ochsner Medical Center, New Orleans, Louisiana, said there are “definitely” fewer patients with stroke and transient ischemic attack (TIA) seeking care at his facility and others throughout the New Orleans area, which has been hard hit by COVID-19.
“Even in Louisiana, we have a very large 53-hospital telestroke network, and the number of consults has diminished greatly,” Vidal added.
In Chicago, emergency medical service activations for patients with suspected strokes are down about 30%, Shyam Prabhakaran, MD, professor and chair of neurology at the University of Chicago Biological Sciences, Illinois, told Medscape Medical News.
“It appears to be that mild stroke and TIA patients may be more likely to stay at home and seek alternative care rather than come to the ED,” Prabhakaran said. However, “the severe strokes may be less affected and continue to come to emergency departments.”
“Getting the Word Out”
That may not be the whole story in Seattle, Washington, where a stroke specialist at Harborview Medical Center reported a drop in patients across the stroke-severity spectrum.
Some patients with milder strokes no longer come to Harborview for a comprehensive evaluation and workup, but that is only “a partial explanation,” said David Tirschwell, MD, medical director of comprehensive stroke care at the University of Washington (UW) Medicine Stroke Center at Harborview and a professor of neurology at UW.
“The thrombectomies are down also,” he added. “It’s hard to have great numbers in real time, but it’s probably safe to say it’s at least a 50% reduction in the number of admissions.”
As a stroke referral center, his institution is seeing fewer local cases and referrals from outside hospitals. “I think both of those sources for admissions of stroke cases are down,” Tirschwell said.
Recognizing the seriousness of forgoing essential care for acute stroke, neurologists, institutions, and medical groups are taking to social media to potentially save lives.
“Across our @FLStrokeReg we are seeing less patients with #stroke symptoms coming to our hospitals. We need to get the word out that our teams are working hard to safely provide care when needed during #COVID19,” tweeted Ralph Sacco, MD, chief and professor of neurology, University of Miami Miller School of Medicine in South Florida.
Although Florida Stroke Registry data are not publicly available, anecdotal reports suggest that stroke admissions are down among many hospitals, Sacco told Medscape Medical News.
Furthermore, this is not a phenomenon only in the United States. “This has also been reported in other nations hit by COVID-19,” he said.
China is a prime example. There, many stroke centers have shown reduced functioning “because of fear of in-hospital cross infection and lack of experienced stroke care experts,” Jing Zhao, MD, PhD, and colleagues write in an editorial published online March 31 in Stroke.
Preliminary data show that “thrombectomies in Shanghai decreased by 50% in the first month after the Spring Festival compared with the same period in 2019,” write the editorialists, who are from Kings College London and the University of Pennsylvania in Philadelphia.
“Although the control of the COVID-19 is very important, at the same time, the management of stroke must not be neglected,” they add.
“Over 9000 new stroke cases occur each day in China alone. It cannot be right that treatment for one potentially curable disease is euthanized at the expense of another.”
Fear Factor?
The reasons individuals who may have experienced a stroke are avoiding emergency care is unclear at the moment. “I’m not really sure anyone really understands why, quite honestly,” Tirschwell said.
Until survey data or other data emerge, many experts are assuming that fear of COVID-19 is trumping other medical concerns, including emergency treatment of stroke.
“We believe this could represent patients being fearful to come to medical facilities with stroke-like symptoms, given the COVID-19 pandemic,” said Sacco, who is also incoming editor-in-chief of Stroke.
The BBC has been getting the word out in the United Kingdom via social media, with a tweet to “Dial 999 for stroke emergencies despite coronavirus.”
The World Stroke Campaign is also using Twitter to emphasize the need for urgent stroke care when appropriate:
“Don’t let concerns about COVID19 prevent you from seeking emergency treatment for stroke. If you spot the signs of stroke act FAST. Get emergency medical assistance,” the group urged in a tweet.
Don’t Hesitate
The American Heart Association (AHA) has addressed this troubling trend as well.
“People with serious symptoms shouldn’t ignore them,” Sarah Perlman, MD, associate professor of emergency medicine at the University of Colorado School of Medicine, Denver, states in an article on the AHA website.
Perlman added that some individuals who have signs of stroke and heart disease may hesitate to seek care because of fear that they are adding to an overburdened healthcare staff and system. However, she dismissed those concerns outright.
“If you’re experiencing warning signs of a heart attack or stroke, call 911,” she said. “Clearly, if there’s an emergency, we are available and capable and eager to take care of you.”
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
COVID-19: Dramatic changes to telepsychiatry rules and regs
In the wake of the coronavirus pandemic,
Under the 1135 emergency waiver, Medicare has expanded telehealth services to include patients across the country – not just in rural areas or under other limited conditions, as was previously the case. In addition, there’s now a waiver to the Ryan Haight Act that allows the prescribing of controlled substances via telemedicine.
Peter Yellowlees, MD, from University of California, Davis, reported that outpatient service at his center was converted to an almost 100% telepsychiatry service from mid- to late March.
He and John Torous, MD, director of digital psychiatry at Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center, Boston, led a free webinar late last month sponsored by the Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration (SAMHSA).
During the hour-long event, they answered questions and offered tips on changes in licensure, patient safety, new prescribing rules, and equipment needed.
“Clinicians need to be aware of these changes so they can ensure they are reaching as many people as possible and taking advantage of the reduced barriers to offering safe and effective video visits,” Dr. Torous said in an interview.
‘This is huge’
The new 1135 waiver “basically says CMS will pay for any patient on Medicare who is seen by video by any provider who is correctly licensed in any state in this country,” Dr. Yellowlees told webinar attendees.
“You don’t need to be licensed in the state where the patient is if the patient is on Medicare. This opens up a huge number of patients we can now see on video,” he said. “And you can bill at normal Medicare rates for whatever you normally get for your in-person patients.”
Although this temporary rule only applies to Medicare and not to private insurers, or to patients on Medicaid, “these are really big changes. This is huge,” Dr. Torous said.
Previously, the “originating site” rule stated that, for the most part, clinicians had to be licensed in the state where the patient was located and not where the physician was stationed.
Asked about college students receiving mental health care who were in school in the psychiatrist’s area but are now back home in a state where the clinician doesn’t have a license, Dr. Yellowlees said that scenario could be a bit “tricky.”
“Most of those patients probably aren’t on Medicare. Legally, you [usually] can’t see them on video if they have private insurance or Medicaid. So, hopefully you can give them a 3-month supply of medication and then recommend they see a local provider,” he said.
Still, all states have their own rules, Dr. Yellowlees said. He and Dr. Torous noted that the Federation of State Medical Boards has a “very up-to-date” listing of policies at FSMB.org, all of which are organized by state. In addition, the American Psychiatric Association provides a telepsychiatry toolkit on its website.
Ryan Haight Act and prescribing
Physicians are now permitted to prescribe medication to patients assessed via telemedicine.
For those with substance use disorders, the U.S. Drug Enforcement Administration has announced a new waiver for the Ryan Haight Online Pharmacy Consumer Protection Act.
The waiver states that “practitioners in all areas of the United States may issue prescriptions for all schedule II-V controlled substances” – as long as it’s for a legitimate medical purpose; real-time, two-way interactive communication with patients has been used; and the clinician “is acting in accordance with applicable Federal and State laws.”
“It’s now possible to prescribe all the normal psychiatric drugs but also benzodiazepines, stimulants, and potentially narcotics over telepsychiatry,” even at a first visit via video, Dr. Yellowlees said.
However, he noted at this point the waiver is current for only 60 days. “This isn’t a permanent condition. It could be extended or even shortened at any given time.”
In addition, SAMHSA has relaxed some of its own regulations regarding telehealth and opioid treatment programs. An FAQ section on the organization’s website provides guidance for providing methadone and buprenorphine treatment.
“Some of the previous regulations will probably be put back in place later on, but the new changes are helpful now,” Dr. Yellowlees said.
Simple equipment needed
Regarding equipment, Dr. Yellowlees noted that the most important component is just a laptop, tablet, or smartphone – for the clinician and for the patient.
“You don’t need fancy new technology with a separate camera or microphone,” he said. However, it might be worth investing in a little better system down the line, he added.
Simple platforms that can be used to meet virtually with patients include FaceTime, Google Hangouts, and Skype.
Although some of these (such as FaceTime) are not HIPAA compliant, “that’s okay for now” under the new rules, Dr. Yellowlees said. While the health system/commercial version of Skype is compliant, the normal consumer-downloaded version is not, he noted.
“I would still strongly suggest using HIPAA-compliant video-conferencing programs in the long run,” he added.
Either way, it’s important for various safety practices to be put into place. For example, clinicians should be careful because the consumer version of Skype can show names of patients who were previously spoken with.
A business associate agreement (BAA) is something that HIPAA-compliant video systems will offer and which should be signed. It’s an agreement that “you’ll be, essentially, looking through a tunnel at the persona at the other end, and the company cannot get inside the tunnel and watch you while you’re having your interview,” said Dr. Yellowlees.
“There are multiple videoconferencing systems around that you can use,” he added. “The three major ones are from Zoom, Vidyo, and VSee, but there are probably 40 or 50 more.”
“There are a lot out there, and we’re certainly not endorsing any one of them,” Dr. Torous added.
When evaluating potential programs, Dr. Yellowlees suggested looking at Yelp-style reviews or telemedicine review sites, or talk with colleagues.
“Basically, you want systems that offer high-definition video quality and the ability to ‘lock’ and ‘unlock’ the rooms. And you want it to have an app so mobile devices can use it,” he said.
Phone vs. video
Some patients, especially older ones, may be resistant to the idea of video chats, preferring to talk via telephone instead.
“If you can use video, it’s better to do that if you can, especially when setting up the systems are relatively simple,” Dr. Yellowlees said, adding that it might just be an issue of patients needing help to get started.
However, “for some people, this is a barrier that we have to respect,” Dr. Torous said.
Either way, clinicians should check the American Medical Association’s website for information about coding for both video and phone visits.
Asked whether a clinician needs written consent from patients for conducting telepsychiatry visits, Dr. Yellowlees said it’s important to check state-by-state rules. For example, California allows a verbal consent.
In many cases, “simply jot down a note that consent was given and how” and write down the address where the patient is located at time of visit, such as for their home, he said.
If a patient wants to conduct a telehealth session while in their car, Dr. Yellowlees suggested getting the address of the parking lot. For safety, clinicians also are advised asking for the cell phone number of the patient as well as that of a loved one.
Vital signs
When it comes to checking vital signs, Dr. Yellowlees suggested asking patients to purchase an inexpensive blood pressure (BP) monitor, thermometer, etc, prior to an appointment.
“Ask them to do a BP test on video and show you the readings. For the AIMS [Abnormal Involuntary Movement Scale] test, or to check for tardive dyskinesia, instruct patients to come close to the camera to show movement.”
In addition, most psychiatric rating scales are available online, which patients can fill out before a telehealth visit. The Serious Mental Illness (SMI) Adviser mobile app also includes several of these scales, Dr. Torous noted.
Overall, “there have been dramatic changes in the rules and regulations governing [telepsychiatry] that, for the next 60 days, make it easier to offer telehealth to patients,” Dr. Torous said.
Therefore, all psychiatrists need to “get on board,” as soon as possible, Dr. Yellowlees added.
The webinar was funded in part by a grant from SAMHSA.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
In the wake of the coronavirus pandemic,
Under the 1135 emergency waiver, Medicare has expanded telehealth services to include patients across the country – not just in rural areas or under other limited conditions, as was previously the case. In addition, there’s now a waiver to the Ryan Haight Act that allows the prescribing of controlled substances via telemedicine.
Peter Yellowlees, MD, from University of California, Davis, reported that outpatient service at his center was converted to an almost 100% telepsychiatry service from mid- to late March.
He and John Torous, MD, director of digital psychiatry at Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center, Boston, led a free webinar late last month sponsored by the Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration (SAMHSA).
During the hour-long event, they answered questions and offered tips on changes in licensure, patient safety, new prescribing rules, and equipment needed.
“Clinicians need to be aware of these changes so they can ensure they are reaching as many people as possible and taking advantage of the reduced barriers to offering safe and effective video visits,” Dr. Torous said in an interview.
‘This is huge’
The new 1135 waiver “basically says CMS will pay for any patient on Medicare who is seen by video by any provider who is correctly licensed in any state in this country,” Dr. Yellowlees told webinar attendees.
“You don’t need to be licensed in the state where the patient is if the patient is on Medicare. This opens up a huge number of patients we can now see on video,” he said. “And you can bill at normal Medicare rates for whatever you normally get for your in-person patients.”
Although this temporary rule only applies to Medicare and not to private insurers, or to patients on Medicaid, “these are really big changes. This is huge,” Dr. Torous said.
Previously, the “originating site” rule stated that, for the most part, clinicians had to be licensed in the state where the patient was located and not where the physician was stationed.
Asked about college students receiving mental health care who were in school in the psychiatrist’s area but are now back home in a state where the clinician doesn’t have a license, Dr. Yellowlees said that scenario could be a bit “tricky.”
“Most of those patients probably aren’t on Medicare. Legally, you [usually] can’t see them on video if they have private insurance or Medicaid. So, hopefully you can give them a 3-month supply of medication and then recommend they see a local provider,” he said.
Still, all states have their own rules, Dr. Yellowlees said. He and Dr. Torous noted that the Federation of State Medical Boards has a “very up-to-date” listing of policies at FSMB.org, all of which are organized by state. In addition, the American Psychiatric Association provides a telepsychiatry toolkit on its website.
Ryan Haight Act and prescribing
Physicians are now permitted to prescribe medication to patients assessed via telemedicine.
For those with substance use disorders, the U.S. Drug Enforcement Administration has announced a new waiver for the Ryan Haight Online Pharmacy Consumer Protection Act.
The waiver states that “practitioners in all areas of the United States may issue prescriptions for all schedule II-V controlled substances” – as long as it’s for a legitimate medical purpose; real-time, two-way interactive communication with patients has been used; and the clinician “is acting in accordance with applicable Federal and State laws.”
“It’s now possible to prescribe all the normal psychiatric drugs but also benzodiazepines, stimulants, and potentially narcotics over telepsychiatry,” even at a first visit via video, Dr. Yellowlees said.
However, he noted at this point the waiver is current for only 60 days. “This isn’t a permanent condition. It could be extended or even shortened at any given time.”
In addition, SAMHSA has relaxed some of its own regulations regarding telehealth and opioid treatment programs. An FAQ section on the organization’s website provides guidance for providing methadone and buprenorphine treatment.
“Some of the previous regulations will probably be put back in place later on, but the new changes are helpful now,” Dr. Yellowlees said.
Simple equipment needed
Regarding equipment, Dr. Yellowlees noted that the most important component is just a laptop, tablet, or smartphone – for the clinician and for the patient.
“You don’t need fancy new technology with a separate camera or microphone,” he said. However, it might be worth investing in a little better system down the line, he added.
Simple platforms that can be used to meet virtually with patients include FaceTime, Google Hangouts, and Skype.
Although some of these (such as FaceTime) are not HIPAA compliant, “that’s okay for now” under the new rules, Dr. Yellowlees said. While the health system/commercial version of Skype is compliant, the normal consumer-downloaded version is not, he noted.
“I would still strongly suggest using HIPAA-compliant video-conferencing programs in the long run,” he added.
Either way, it’s important for various safety practices to be put into place. For example, clinicians should be careful because the consumer version of Skype can show names of patients who were previously spoken with.
A business associate agreement (BAA) is something that HIPAA-compliant video systems will offer and which should be signed. It’s an agreement that “you’ll be, essentially, looking through a tunnel at the persona at the other end, and the company cannot get inside the tunnel and watch you while you’re having your interview,” said Dr. Yellowlees.
“There are multiple videoconferencing systems around that you can use,” he added. “The three major ones are from Zoom, Vidyo, and VSee, but there are probably 40 or 50 more.”
“There are a lot out there, and we’re certainly not endorsing any one of them,” Dr. Torous added.
When evaluating potential programs, Dr. Yellowlees suggested looking at Yelp-style reviews or telemedicine review sites, or talk with colleagues.
“Basically, you want systems that offer high-definition video quality and the ability to ‘lock’ and ‘unlock’ the rooms. And you want it to have an app so mobile devices can use it,” he said.
Phone vs. video
Some patients, especially older ones, may be resistant to the idea of video chats, preferring to talk via telephone instead.
“If you can use video, it’s better to do that if you can, especially when setting up the systems are relatively simple,” Dr. Yellowlees said, adding that it might just be an issue of patients needing help to get started.
However, “for some people, this is a barrier that we have to respect,” Dr. Torous said.
Either way, clinicians should check the American Medical Association’s website for information about coding for both video and phone visits.
Asked whether a clinician needs written consent from patients for conducting telepsychiatry visits, Dr. Yellowlees said it’s important to check state-by-state rules. For example, California allows a verbal consent.
In many cases, “simply jot down a note that consent was given and how” and write down the address where the patient is located at time of visit, such as for their home, he said.
If a patient wants to conduct a telehealth session while in their car, Dr. Yellowlees suggested getting the address of the parking lot. For safety, clinicians also are advised asking for the cell phone number of the patient as well as that of a loved one.
Vital signs
When it comes to checking vital signs, Dr. Yellowlees suggested asking patients to purchase an inexpensive blood pressure (BP) monitor, thermometer, etc, prior to an appointment.
“Ask them to do a BP test on video and show you the readings. For the AIMS [Abnormal Involuntary Movement Scale] test, or to check for tardive dyskinesia, instruct patients to come close to the camera to show movement.”
In addition, most psychiatric rating scales are available online, which patients can fill out before a telehealth visit. The Serious Mental Illness (SMI) Adviser mobile app also includes several of these scales, Dr. Torous noted.
Overall, “there have been dramatic changes in the rules and regulations governing [telepsychiatry] that, for the next 60 days, make it easier to offer telehealth to patients,” Dr. Torous said.
Therefore, all psychiatrists need to “get on board,” as soon as possible, Dr. Yellowlees added.
The webinar was funded in part by a grant from SAMHSA.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
In the wake of the coronavirus pandemic,
Under the 1135 emergency waiver, Medicare has expanded telehealth services to include patients across the country – not just in rural areas or under other limited conditions, as was previously the case. In addition, there’s now a waiver to the Ryan Haight Act that allows the prescribing of controlled substances via telemedicine.
Peter Yellowlees, MD, from University of California, Davis, reported that outpatient service at his center was converted to an almost 100% telepsychiatry service from mid- to late March.
He and John Torous, MD, director of digital psychiatry at Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center, Boston, led a free webinar late last month sponsored by the Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration (SAMHSA).
During the hour-long event, they answered questions and offered tips on changes in licensure, patient safety, new prescribing rules, and equipment needed.
“Clinicians need to be aware of these changes so they can ensure they are reaching as many people as possible and taking advantage of the reduced barriers to offering safe and effective video visits,” Dr. Torous said in an interview.
‘This is huge’
The new 1135 waiver “basically says CMS will pay for any patient on Medicare who is seen by video by any provider who is correctly licensed in any state in this country,” Dr. Yellowlees told webinar attendees.
“You don’t need to be licensed in the state where the patient is if the patient is on Medicare. This opens up a huge number of patients we can now see on video,” he said. “And you can bill at normal Medicare rates for whatever you normally get for your in-person patients.”
Although this temporary rule only applies to Medicare and not to private insurers, or to patients on Medicaid, “these are really big changes. This is huge,” Dr. Torous said.
Previously, the “originating site” rule stated that, for the most part, clinicians had to be licensed in the state where the patient was located and not where the physician was stationed.
Asked about college students receiving mental health care who were in school in the psychiatrist’s area but are now back home in a state where the clinician doesn’t have a license, Dr. Yellowlees said that scenario could be a bit “tricky.”
“Most of those patients probably aren’t on Medicare. Legally, you [usually] can’t see them on video if they have private insurance or Medicaid. So, hopefully you can give them a 3-month supply of medication and then recommend they see a local provider,” he said.
Still, all states have their own rules, Dr. Yellowlees said. He and Dr. Torous noted that the Federation of State Medical Boards has a “very up-to-date” listing of policies at FSMB.org, all of which are organized by state. In addition, the American Psychiatric Association provides a telepsychiatry toolkit on its website.
Ryan Haight Act and prescribing
Physicians are now permitted to prescribe medication to patients assessed via telemedicine.
For those with substance use disorders, the U.S. Drug Enforcement Administration has announced a new waiver for the Ryan Haight Online Pharmacy Consumer Protection Act.
The waiver states that “practitioners in all areas of the United States may issue prescriptions for all schedule II-V controlled substances” – as long as it’s for a legitimate medical purpose; real-time, two-way interactive communication with patients has been used; and the clinician “is acting in accordance with applicable Federal and State laws.”
“It’s now possible to prescribe all the normal psychiatric drugs but also benzodiazepines, stimulants, and potentially narcotics over telepsychiatry,” even at a first visit via video, Dr. Yellowlees said.
However, he noted at this point the waiver is current for only 60 days. “This isn’t a permanent condition. It could be extended or even shortened at any given time.”
In addition, SAMHSA has relaxed some of its own regulations regarding telehealth and opioid treatment programs. An FAQ section on the organization’s website provides guidance for providing methadone and buprenorphine treatment.
“Some of the previous regulations will probably be put back in place later on, but the new changes are helpful now,” Dr. Yellowlees said.
Simple equipment needed
Regarding equipment, Dr. Yellowlees noted that the most important component is just a laptop, tablet, or smartphone – for the clinician and for the patient.
“You don’t need fancy new technology with a separate camera or microphone,” he said. However, it might be worth investing in a little better system down the line, he added.
Simple platforms that can be used to meet virtually with patients include FaceTime, Google Hangouts, and Skype.
Although some of these (such as FaceTime) are not HIPAA compliant, “that’s okay for now” under the new rules, Dr. Yellowlees said. While the health system/commercial version of Skype is compliant, the normal consumer-downloaded version is not, he noted.
“I would still strongly suggest using HIPAA-compliant video-conferencing programs in the long run,” he added.
Either way, it’s important for various safety practices to be put into place. For example, clinicians should be careful because the consumer version of Skype can show names of patients who were previously spoken with.
A business associate agreement (BAA) is something that HIPAA-compliant video systems will offer and which should be signed. It’s an agreement that “you’ll be, essentially, looking through a tunnel at the persona at the other end, and the company cannot get inside the tunnel and watch you while you’re having your interview,” said Dr. Yellowlees.
“There are multiple videoconferencing systems around that you can use,” he added. “The three major ones are from Zoom, Vidyo, and VSee, but there are probably 40 or 50 more.”
“There are a lot out there, and we’re certainly not endorsing any one of them,” Dr. Torous added.
When evaluating potential programs, Dr. Yellowlees suggested looking at Yelp-style reviews or telemedicine review sites, or talk with colleagues.
“Basically, you want systems that offer high-definition video quality and the ability to ‘lock’ and ‘unlock’ the rooms. And you want it to have an app so mobile devices can use it,” he said.
Phone vs. video
Some patients, especially older ones, may be resistant to the idea of video chats, preferring to talk via telephone instead.
“If you can use video, it’s better to do that if you can, especially when setting up the systems are relatively simple,” Dr. Yellowlees said, adding that it might just be an issue of patients needing help to get started.
However, “for some people, this is a barrier that we have to respect,” Dr. Torous said.
Either way, clinicians should check the American Medical Association’s website for information about coding for both video and phone visits.
Asked whether a clinician needs written consent from patients for conducting telepsychiatry visits, Dr. Yellowlees said it’s important to check state-by-state rules. For example, California allows a verbal consent.
In many cases, “simply jot down a note that consent was given and how” and write down the address where the patient is located at time of visit, such as for their home, he said.
If a patient wants to conduct a telehealth session while in their car, Dr. Yellowlees suggested getting the address of the parking lot. For safety, clinicians also are advised asking for the cell phone number of the patient as well as that of a loved one.
Vital signs
When it comes to checking vital signs, Dr. Yellowlees suggested asking patients to purchase an inexpensive blood pressure (BP) monitor, thermometer, etc, prior to an appointment.
“Ask them to do a BP test on video and show you the readings. For the AIMS [Abnormal Involuntary Movement Scale] test, or to check for tardive dyskinesia, instruct patients to come close to the camera to show movement.”
In addition, most psychiatric rating scales are available online, which patients can fill out before a telehealth visit. The Serious Mental Illness (SMI) Adviser mobile app also includes several of these scales, Dr. Torous noted.
Overall, “there have been dramatic changes in the rules and regulations governing [telepsychiatry] that, for the next 60 days, make it easier to offer telehealth to patients,” Dr. Torous said.
Therefore, all psychiatrists need to “get on board,” as soon as possible, Dr. Yellowlees added.
The webinar was funded in part by a grant from SAMHSA.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
Comorbidities the rule in New York’s COVID-19 deaths
In New York state, just over 86% of reported COVID-19 deaths involved at least one comorbidity, according to the state’s department of health.
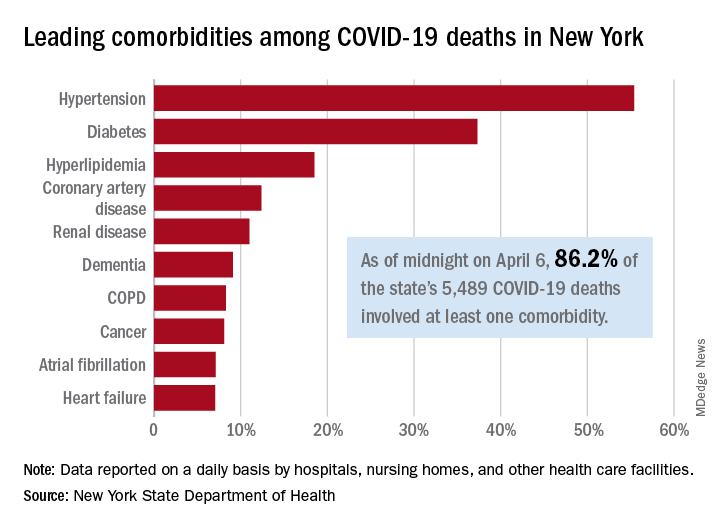
As of midnight on April 6, there had been 5,489 fatalities caused by COVID-19 in the state, of which 86.2% (4,732) had at least one underlying condition, the New York State Department of Health reported April 7 on its COVID-19 tracker.
The leading comorbidity, seen in 55.4% of all deaths, was hypertension. In comparison, a recent estimate from the U.S. Department of Health & Human Services put the prevalence of high blood pressure at about 45% in the overall adult population.
In New York, the rest of the 10 most common comorbidities in COVID-19 fatalities were diabetes (37.3%), hyperlipidemia (18.5%), coronary artery disease (12.4%), renal disease (11.0%), dementia (9.1%), chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (8.3%), cancer (8.1%), atrial fibrillation (7.1%), and heart failure (7.1%), the NYSDOH said.
Other data on the tracker site show that 63% of all deaths involved a patient who was aged 70 years or older and that 61% of COVID-19 patients who have died in New York were male and 38.8% were female (sex unknown for 0.2%). Among all individuals who have tested positive, 54.8% were male and 44.6% were female (sex unknown for 0.6%).
As of the end of day on April 6, a total of 340,058 persons had been tested in the state and 40.8% (138,863) were positive for the SARS-CoV-2 virus. By county, the highest positive rates are in New York City: Queens at 57.4%, Brooklyn at 52.4%, and the Bronx at 52.3%, according to the NYSDOH.
In New York state, just over 86% of reported COVID-19 deaths involved at least one comorbidity, according to the state’s department of health.

As of midnight on April 6, there had been 5,489 fatalities caused by COVID-19 in the state, of which 86.2% (4,732) had at least one underlying condition, the New York State Department of Health reported April 7 on its COVID-19 tracker.
The leading comorbidity, seen in 55.4% of all deaths, was hypertension. In comparison, a recent estimate from the U.S. Department of Health & Human Services put the prevalence of high blood pressure at about 45% in the overall adult population.
In New York, the rest of the 10 most common comorbidities in COVID-19 fatalities were diabetes (37.3%), hyperlipidemia (18.5%), coronary artery disease (12.4%), renal disease (11.0%), dementia (9.1%), chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (8.3%), cancer (8.1%), atrial fibrillation (7.1%), and heart failure (7.1%), the NYSDOH said.
Other data on the tracker site show that 63% of all deaths involved a patient who was aged 70 years or older and that 61% of COVID-19 patients who have died in New York were male and 38.8% were female (sex unknown for 0.2%). Among all individuals who have tested positive, 54.8% were male and 44.6% were female (sex unknown for 0.6%).
As of the end of day on April 6, a total of 340,058 persons had been tested in the state and 40.8% (138,863) were positive for the SARS-CoV-2 virus. By county, the highest positive rates are in New York City: Queens at 57.4%, Brooklyn at 52.4%, and the Bronx at 52.3%, according to the NYSDOH.
In New York state, just over 86% of reported COVID-19 deaths involved at least one comorbidity, according to the state’s department of health.

As of midnight on April 6, there had been 5,489 fatalities caused by COVID-19 in the state, of which 86.2% (4,732) had at least one underlying condition, the New York State Department of Health reported April 7 on its COVID-19 tracker.
The leading comorbidity, seen in 55.4% of all deaths, was hypertension. In comparison, a recent estimate from the U.S. Department of Health & Human Services put the prevalence of high blood pressure at about 45% in the overall adult population.
In New York, the rest of the 10 most common comorbidities in COVID-19 fatalities were diabetes (37.3%), hyperlipidemia (18.5%), coronary artery disease (12.4%), renal disease (11.0%), dementia (9.1%), chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (8.3%), cancer (8.1%), atrial fibrillation (7.1%), and heart failure (7.1%), the NYSDOH said.
Other data on the tracker site show that 63% of all deaths involved a patient who was aged 70 years or older and that 61% of COVID-19 patients who have died in New York were male and 38.8% were female (sex unknown for 0.2%). Among all individuals who have tested positive, 54.8% were male and 44.6% were female (sex unknown for 0.6%).
As of the end of day on April 6, a total of 340,058 persons had been tested in the state and 40.8% (138,863) were positive for the SARS-CoV-2 virus. By county, the highest positive rates are in New York City: Queens at 57.4%, Brooklyn at 52.4%, and the Bronx at 52.3%, according to the NYSDOH.
SARS-CoV-2 escapes cotton, surgical masks of infected
June 9, 2020 — Editor’s note: The study on which this news story is based has been retracted by the journal. The retraction notice can be found here.
according to Seongman Bae, MD, of the University of Ulsan College of Medicine in Seoul, South Korea, and associates.
The report was published in Annals of Internal Medicine.
Because the COVID-19 pandemic has caused a shortage of N95 and surgical masks, cotton masks have gained interest as a substitute, as surgical masks have been shown to effectively filter influenza virus, the researchers wrote. However, the size of and concentrations of SARS-CoV-2 in aerosols generated during coughing are unknown.
To compare the effectiveness of cotton and surgical masks, a group of patients infected with SARS-CoV-2 coughed into petri dishes while wearing no mask, a surgical mask, and a cotton mask. The mask surfaces were swabbed afterward to assess viral positivity on the mask itself.
The median nasopharyngeal and saliva viral load was 5.66 log copies/mL and 4.00 log copies/mL, respectively. The median viral loads after coughing was 2.56 log copies/mL without a mask, 2.42 log copies/mL with a surgical mask, and 1.85 log copies/mL with a cotton mask. All outer surfaces of the mask were positive for SARS-CoV-2, while most inner surfaces were negative.
The investigators acknowledged that the test did not include N95 masks and does not reflect the actual infection transmission, and that they didn’t know whether cotton or surgical masks shorten the travel distance of droplets while coughing.
“Further study is needed to recommend whether face masks decrease transmission of virus from asymptomatic individuals or those with suspected COVID-19 who are not coughing,” they added.
The study was funded by a grant from the government-wide R&D Fund Project for Infectious Disease Research. The investigators reported that they had no conflicts of interest.
SOURCE: Bae S et al. Ann Intern Med. 2020 Apr 6. doi: 10.7326/M20-1342.
Correction, 4/9/20: The headline of an earlier version of this article misstated a finding of this study. Whether cotton and surgical masks can block transmission was not investigated.
June 9, 2020 — Editor’s note: The study on which this news story is based has been retracted by the journal. The retraction notice can be found here.
according to Seongman Bae, MD, of the University of Ulsan College of Medicine in Seoul, South Korea, and associates.
The report was published in Annals of Internal Medicine.
Because the COVID-19 pandemic has caused a shortage of N95 and surgical masks, cotton masks have gained interest as a substitute, as surgical masks have been shown to effectively filter influenza virus, the researchers wrote. However, the size of and concentrations of SARS-CoV-2 in aerosols generated during coughing are unknown.
To compare the effectiveness of cotton and surgical masks, a group of patients infected with SARS-CoV-2 coughed into petri dishes while wearing no mask, a surgical mask, and a cotton mask. The mask surfaces were swabbed afterward to assess viral positivity on the mask itself.
The median nasopharyngeal and saliva viral load was 5.66 log copies/mL and 4.00 log copies/mL, respectively. The median viral loads after coughing was 2.56 log copies/mL without a mask, 2.42 log copies/mL with a surgical mask, and 1.85 log copies/mL with a cotton mask. All outer surfaces of the mask were positive for SARS-CoV-2, while most inner surfaces were negative.
The investigators acknowledged that the test did not include N95 masks and does not reflect the actual infection transmission, and that they didn’t know whether cotton or surgical masks shorten the travel distance of droplets while coughing.
“Further study is needed to recommend whether face masks decrease transmission of virus from asymptomatic individuals or those with suspected COVID-19 who are not coughing,” they added.
The study was funded by a grant from the government-wide R&D Fund Project for Infectious Disease Research. The investigators reported that they had no conflicts of interest.
SOURCE: Bae S et al. Ann Intern Med. 2020 Apr 6. doi: 10.7326/M20-1342.
Correction, 4/9/20: The headline of an earlier version of this article misstated a finding of this study. Whether cotton and surgical masks can block transmission was not investigated.
June 9, 2020 — Editor’s note: The study on which this news story is based has been retracted by the journal. The retraction notice can be found here.
according to Seongman Bae, MD, of the University of Ulsan College of Medicine in Seoul, South Korea, and associates.
The report was published in Annals of Internal Medicine.
Because the COVID-19 pandemic has caused a shortage of N95 and surgical masks, cotton masks have gained interest as a substitute, as surgical masks have been shown to effectively filter influenza virus, the researchers wrote. However, the size of and concentrations of SARS-CoV-2 in aerosols generated during coughing are unknown.
To compare the effectiveness of cotton and surgical masks, a group of patients infected with SARS-CoV-2 coughed into petri dishes while wearing no mask, a surgical mask, and a cotton mask. The mask surfaces were swabbed afterward to assess viral positivity on the mask itself.
The median nasopharyngeal and saliva viral load was 5.66 log copies/mL and 4.00 log copies/mL, respectively. The median viral loads after coughing was 2.56 log copies/mL without a mask, 2.42 log copies/mL with a surgical mask, and 1.85 log copies/mL with a cotton mask. All outer surfaces of the mask were positive for SARS-CoV-2, while most inner surfaces were negative.
The investigators acknowledged that the test did not include N95 masks and does not reflect the actual infection transmission, and that they didn’t know whether cotton or surgical masks shorten the travel distance of droplets while coughing.
“Further study is needed to recommend whether face masks decrease transmission of virus from asymptomatic individuals or those with suspected COVID-19 who are not coughing,” they added.
The study was funded by a grant from the government-wide R&D Fund Project for Infectious Disease Research. The investigators reported that they had no conflicts of interest.
SOURCE: Bae S et al. Ann Intern Med. 2020 Apr 6. doi: 10.7326/M20-1342.
Correction, 4/9/20: The headline of an earlier version of this article misstated a finding of this study. Whether cotton and surgical masks can block transmission was not investigated.
FROM ANNALS OF INTERNAL MEDICINE
Treatment for RA, SpA may not affect COVID-19 severity
Patients being treated for RA or spondyloarthritis who develop symptoms of COVID-19 do not appear to be at higher risk of respiratory or life-threatening complications, results from a new study in Italy suggest.
Such patients, the study authors wrote, do not need to be taken off their immunosuppressive medications if they develop COVID-19 symptoms.
In a letter published in Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases, Sara Monti, MD, and colleagues in the rheumatology department of the Fondazione IRCCS Policlinico in San Matteo, Italy, described results from an observational cohort of 320 patients (68% women; mean age, 55 years) with RA or spondyloarthritis from a single outpatient clinic. The vast majority of subjects (92%) were taking biologic disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (bDMARD), including tumor necrosis factor inhibitors, while the rest were taking targeted synthetic DMARDs (tsDMARD).
Four patients in the cohort developed laboratory-confirmed COVID-19; another four developed symptoms highly suggestive of the disease but did not receive confirmatory testing, and five had contact with a confirmed COVID-19 case but did not develop symptoms of COVID-19.
Among the eight confirmed and suspected COVID-19 patients, only one was hospitalized. All temporarily withdrew bDMARD or tsDMARD treatment at symptom onset.
“To date, there have been no significant relapses of the rheumatic disease,” Dr. Monti and colleagues reported. “None of the patients with a confirmed diagnosis of COVID-19 or with a highly suggestive clinical picture developed severe respiratory complications or died. Only one patient, aged 65, required admission to hospital and low-flow oxygen supplementation for a few days.”
The findings “do not allow any conclusions on the incidence rate of SARS-CoV-2 infection in patients with rheumatic diseases, nor on the overall outcome of immunocompromised patients affected by COVID-19,” the investigators cautioned, adding that such patients should receive careful attention and follow-up. “However, our preliminary experience shows that patients with chronic arthritis treated with bDMARDs or tsDMARDs do not seem to be at increased risk of respiratory or life-threatening complications from SARS-CoV-2, compared with the general population.”
Dr. Monti and colleagues noted that, during previous outbreaks of other coronaviruses, no increased mortality was reported for people taking immunosuppressive drugs for a range of conditions, including autoimmune diseases.
“These data can support rheumatologists [in] avoiding the unjustifiable preventive withdrawal of DMARDs, which could lead to an increased risk of relapses and morbidity from the chronic rheumatological condition,” the researchers concluded.
Dr. Monti and colleagues reported no outside funding or financial conflicts of interest.
SOURCE: Monti S et al. Ann Rheum Dis. 2020 April 2. doi: 10.1136/annrheumdis-2020-217424.
Patients being treated for RA or spondyloarthritis who develop symptoms of COVID-19 do not appear to be at higher risk of respiratory or life-threatening complications, results from a new study in Italy suggest.
Such patients, the study authors wrote, do not need to be taken off their immunosuppressive medications if they develop COVID-19 symptoms.
In a letter published in Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases, Sara Monti, MD, and colleagues in the rheumatology department of the Fondazione IRCCS Policlinico in San Matteo, Italy, described results from an observational cohort of 320 patients (68% women; mean age, 55 years) with RA or spondyloarthritis from a single outpatient clinic. The vast majority of subjects (92%) were taking biologic disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (bDMARD), including tumor necrosis factor inhibitors, while the rest were taking targeted synthetic DMARDs (tsDMARD).
Four patients in the cohort developed laboratory-confirmed COVID-19; another four developed symptoms highly suggestive of the disease but did not receive confirmatory testing, and five had contact with a confirmed COVID-19 case but did not develop symptoms of COVID-19.
Among the eight confirmed and suspected COVID-19 patients, only one was hospitalized. All temporarily withdrew bDMARD or tsDMARD treatment at symptom onset.
“To date, there have been no significant relapses of the rheumatic disease,” Dr. Monti and colleagues reported. “None of the patients with a confirmed diagnosis of COVID-19 or with a highly suggestive clinical picture developed severe respiratory complications or died. Only one patient, aged 65, required admission to hospital and low-flow oxygen supplementation for a few days.”
The findings “do not allow any conclusions on the incidence rate of SARS-CoV-2 infection in patients with rheumatic diseases, nor on the overall outcome of immunocompromised patients affected by COVID-19,” the investigators cautioned, adding that such patients should receive careful attention and follow-up. “However, our preliminary experience shows that patients with chronic arthritis treated with bDMARDs or tsDMARDs do not seem to be at increased risk of respiratory or life-threatening complications from SARS-CoV-2, compared with the general population.”
Dr. Monti and colleagues noted that, during previous outbreaks of other coronaviruses, no increased mortality was reported for people taking immunosuppressive drugs for a range of conditions, including autoimmune diseases.
“These data can support rheumatologists [in] avoiding the unjustifiable preventive withdrawal of DMARDs, which could lead to an increased risk of relapses and morbidity from the chronic rheumatological condition,” the researchers concluded.
Dr. Monti and colleagues reported no outside funding or financial conflicts of interest.
SOURCE: Monti S et al. Ann Rheum Dis. 2020 April 2. doi: 10.1136/annrheumdis-2020-217424.
Patients being treated for RA or spondyloarthritis who develop symptoms of COVID-19 do not appear to be at higher risk of respiratory or life-threatening complications, results from a new study in Italy suggest.
Such patients, the study authors wrote, do not need to be taken off their immunosuppressive medications if they develop COVID-19 symptoms.
In a letter published in Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases, Sara Monti, MD, and colleagues in the rheumatology department of the Fondazione IRCCS Policlinico in San Matteo, Italy, described results from an observational cohort of 320 patients (68% women; mean age, 55 years) with RA or spondyloarthritis from a single outpatient clinic. The vast majority of subjects (92%) were taking biologic disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (bDMARD), including tumor necrosis factor inhibitors, while the rest were taking targeted synthetic DMARDs (tsDMARD).
Four patients in the cohort developed laboratory-confirmed COVID-19; another four developed symptoms highly suggestive of the disease but did not receive confirmatory testing, and five had contact with a confirmed COVID-19 case but did not develop symptoms of COVID-19.
Among the eight confirmed and suspected COVID-19 patients, only one was hospitalized. All temporarily withdrew bDMARD or tsDMARD treatment at symptom onset.
“To date, there have been no significant relapses of the rheumatic disease,” Dr. Monti and colleagues reported. “None of the patients with a confirmed diagnosis of COVID-19 or with a highly suggestive clinical picture developed severe respiratory complications or died. Only one patient, aged 65, required admission to hospital and low-flow oxygen supplementation for a few days.”
The findings “do not allow any conclusions on the incidence rate of SARS-CoV-2 infection in patients with rheumatic diseases, nor on the overall outcome of immunocompromised patients affected by COVID-19,” the investigators cautioned, adding that such patients should receive careful attention and follow-up. “However, our preliminary experience shows that patients with chronic arthritis treated with bDMARDs or tsDMARDs do not seem to be at increased risk of respiratory or life-threatening complications from SARS-CoV-2, compared with the general population.”
Dr. Monti and colleagues noted that, during previous outbreaks of other coronaviruses, no increased mortality was reported for people taking immunosuppressive drugs for a range of conditions, including autoimmune diseases.
“These data can support rheumatologists [in] avoiding the unjustifiable preventive withdrawal of DMARDs, which could lead to an increased risk of relapses and morbidity from the chronic rheumatological condition,” the researchers concluded.
Dr. Monti and colleagues reported no outside funding or financial conflicts of interest.
SOURCE: Monti S et al. Ann Rheum Dis. 2020 April 2. doi: 10.1136/annrheumdis-2020-217424.
FROM ANNALS OF THE RHEUMATIC DISEASES
‘The kids will be all right,’ won’t they?
Pediatric patients and COVID-19
The coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic affects us in many ways. Pediatric patients, interestingly, are largely unaffected clinically by this disease. Less than 1% of documented infections occur in children under 10 years old, according to a review of over 72,000 cases from China.1 In that review, most children were asymptomatic or had mild illness, only three required intensive care, and only one death had been reported as of March 10, 2020. This is in stark contrast to the shocking morbidity and mortality statistics we are becoming all too familiar with on the adult side.
From a social standpoint, however, our pediatric patients’ lives have been turned upside down. Their schedules and routines upended, their education and friendships interrupted, and many are likely experiencing real anxiety and fear.2 For countless children, school is a major source of social, emotional, and nutritional support that has been cut off. Some will lose parents, grandparents, or other loved ones to this disease. Parents will lose jobs and will be unable to afford necessities. Pediatric patients will experience delays of procedures or treatments because of the pandemic. Some have projected that rates of child abuse will increase as has been reported during natural disasters.3
Pediatricians around the country are coming together to tackle these issues in creative ways, including the rapid expansion of virtual/telehealth programs. The school systems are developing strategies to deliver online content, and even food, to their students’ homes. Hopefully these tactics will mitigate some of the potential effects on the mental and physical well-being of these patients.
How about my kids? Will they be all right? I am lucky that my husband and I will have jobs throughout this ordeal. Unfortunately, given my role as a hospitalist and my husband’s as a pulmonary/critical care physician, these same jobs that will keep our kids nourished and supported pose the greatest threat to them. As health care workers, we are worried about protecting our families, which may include vulnerable members. The Spanish health ministry announced that medical professionals account for approximately one in eight documented COVID-19 infections in Spain.4 With inadequate supplies of personal protective equipment (PPE) in our own nation, we are concerned that our statistics could be similar.
There are multiple strategies to protect ourselves and our families during this difficult time. First, appropriate PPE is essential and integrity with the process must be maintained always. Hospital leaders can protect us by tirelessly working to acquire PPE. In Grand Rapids, Mich., our health system has partnered with multiple local manufacturing companies, including Steelcase, who are producing PPE for our workforce.5 Leaders can diligently update their system’s PPE recommendations to be in line with the latest CDC recommendations and disseminate the information regularly. Hospitalists should frequently check with their Infection Prevention department to make sure they understand if there have been any changes to the recommendations. Innovative solutions for sterilization of PPE, stethoscopes, badges and other equipment, such as with the use of UV boxes or hydrogen peroxide vapor,6 should be explored to minimize contamination. Hospitalists should bring a set of clothes and shoes to change into upon arrival to work and to change out of prior to leaving the hospital.
We must also keep our heads strong. Currently the anxiety amongst physicians is palpable but there is solidarity. Hospital leaders must ensure that hospitalists have easy access to free mental health resources, such as virtual counseling. Wellness teams must rise to the occasion with innovative tactics to support us. For example, Spectrum Health’s wellness team is sponsoring a blog where physicians can discuss COVID-19–related challenges openly. Hospitalist leaders should ensure that there is a structure for debriefing after critical incidents, which are sure to increase in frequency. Email lists and discussion boards sponsored by professional society also provide a collaborative venue for some of these discussions. We must take advantage of these resources and communicate with each other.
For me, in the end it comes back to the kids. My kids and most pediatric patients are not likely to be hospitalized from COVID-19, but they are also not immune to the toll that fighting this pandemic will take on our families. We took an oath to protect our patients, but what do we owe to our own children? At a minimum we can optimize how we protect ourselves every day, both physically and mentally. As we come together as a strong community to fight this pandemic, in addition to saving lives, we are working to ensure that, in the end, the kids will be all right.
Dr. Hadley is chief of pediatric hospital medicine at Spectrum Health/Helen DeVos Children’s Hospital in Grand Rapids, Mich., and clinical assistant professor at Michigan State University, East Lansing.
References
1. Wu Z, McGoogan JM. Characteristics of and important lessons from the coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) outbreak in China: Summary of a report of 72 314 cases from the Chinese Center for Disease Control and Prevention. JAMA. 2020 Feb 24. doi: 10.1001/jama.2020.2648.
2. Hagan JF Jr; American Academy of Pediatrics Committee on Psychosocial Aspects of Child and Family Health; Task Force on Terrorism. Psychosocial implications of disaster or terrorism on children: A guide for the pediatrician. Pediatrics. 2005;116(3):787-795.
3. Gearhart S et al. The impact of natural disasters on domestic violence: An analysis of reports of simple assault in Florida (1997-2007). Violence Gend. 2018 Jun. doi: 10.1089/vio.2017.0077.
4. Minder R, Peltier E. Virus knocks thousands of health workers out of action in Europe. The New York Times. March 24, 2020.
5. McVicar B. West Michigan businesses hustle to produce medical supplies amid coronavirus pandemic. MLive. March 25, 2020.
6. Kenney PA et al. Hydrogen Peroxide Vapor sterilization of N95 respirators for reuse. medRxiv preprint. 2020 Mar. doi: 10.1101/2020.03.24.20041087.
Pediatric patients and COVID-19
Pediatric patients and COVID-19
The coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic affects us in many ways. Pediatric patients, interestingly, are largely unaffected clinically by this disease. Less than 1% of documented infections occur in children under 10 years old, according to a review of over 72,000 cases from China.1 In that review, most children were asymptomatic or had mild illness, only three required intensive care, and only one death had been reported as of March 10, 2020. This is in stark contrast to the shocking morbidity and mortality statistics we are becoming all too familiar with on the adult side.
From a social standpoint, however, our pediatric patients’ lives have been turned upside down. Their schedules and routines upended, their education and friendships interrupted, and many are likely experiencing real anxiety and fear.2 For countless children, school is a major source of social, emotional, and nutritional support that has been cut off. Some will lose parents, grandparents, or other loved ones to this disease. Parents will lose jobs and will be unable to afford necessities. Pediatric patients will experience delays of procedures or treatments because of the pandemic. Some have projected that rates of child abuse will increase as has been reported during natural disasters.3
Pediatricians around the country are coming together to tackle these issues in creative ways, including the rapid expansion of virtual/telehealth programs. The school systems are developing strategies to deliver online content, and even food, to their students’ homes. Hopefully these tactics will mitigate some of the potential effects on the mental and physical well-being of these patients.
How about my kids? Will they be all right? I am lucky that my husband and I will have jobs throughout this ordeal. Unfortunately, given my role as a hospitalist and my husband’s as a pulmonary/critical care physician, these same jobs that will keep our kids nourished and supported pose the greatest threat to them. As health care workers, we are worried about protecting our families, which may include vulnerable members. The Spanish health ministry announced that medical professionals account for approximately one in eight documented COVID-19 infections in Spain.4 With inadequate supplies of personal protective equipment (PPE) in our own nation, we are concerned that our statistics could be similar.
There are multiple strategies to protect ourselves and our families during this difficult time. First, appropriate PPE is essential and integrity with the process must be maintained always. Hospital leaders can protect us by tirelessly working to acquire PPE. In Grand Rapids, Mich., our health system has partnered with multiple local manufacturing companies, including Steelcase, who are producing PPE for our workforce.5 Leaders can diligently update their system’s PPE recommendations to be in line with the latest CDC recommendations and disseminate the information regularly. Hospitalists should frequently check with their Infection Prevention department to make sure they understand if there have been any changes to the recommendations. Innovative solutions for sterilization of PPE, stethoscopes, badges and other equipment, such as with the use of UV boxes or hydrogen peroxide vapor,6 should be explored to minimize contamination. Hospitalists should bring a set of clothes and shoes to change into upon arrival to work and to change out of prior to leaving the hospital.
We must also keep our heads strong. Currently the anxiety amongst physicians is palpable but there is solidarity. Hospital leaders must ensure that hospitalists have easy access to free mental health resources, such as virtual counseling. Wellness teams must rise to the occasion with innovative tactics to support us. For example, Spectrum Health’s wellness team is sponsoring a blog where physicians can discuss COVID-19–related challenges openly. Hospitalist leaders should ensure that there is a structure for debriefing after critical incidents, which are sure to increase in frequency. Email lists and discussion boards sponsored by professional society also provide a collaborative venue for some of these discussions. We must take advantage of these resources and communicate with each other.
For me, in the end it comes back to the kids. My kids and most pediatric patients are not likely to be hospitalized from COVID-19, but they are also not immune to the toll that fighting this pandemic will take on our families. We took an oath to protect our patients, but what do we owe to our own children? At a minimum we can optimize how we protect ourselves every day, both physically and mentally. As we come together as a strong community to fight this pandemic, in addition to saving lives, we are working to ensure that, in the end, the kids will be all right.
Dr. Hadley is chief of pediatric hospital medicine at Spectrum Health/Helen DeVos Children’s Hospital in Grand Rapids, Mich., and clinical assistant professor at Michigan State University, East Lansing.
References
1. Wu Z, McGoogan JM. Characteristics of and important lessons from the coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) outbreak in China: Summary of a report of 72 314 cases from the Chinese Center for Disease Control and Prevention. JAMA. 2020 Feb 24. doi: 10.1001/jama.2020.2648.
2. Hagan JF Jr; American Academy of Pediatrics Committee on Psychosocial Aspects of Child and Family Health; Task Force on Terrorism. Psychosocial implications of disaster or terrorism on children: A guide for the pediatrician. Pediatrics. 2005;116(3):787-795.
3. Gearhart S et al. The impact of natural disasters on domestic violence: An analysis of reports of simple assault in Florida (1997-2007). Violence Gend. 2018 Jun. doi: 10.1089/vio.2017.0077.
4. Minder R, Peltier E. Virus knocks thousands of health workers out of action in Europe. The New York Times. March 24, 2020.
5. McVicar B. West Michigan businesses hustle to produce medical supplies amid coronavirus pandemic. MLive. March 25, 2020.
6. Kenney PA et al. Hydrogen Peroxide Vapor sterilization of N95 respirators for reuse. medRxiv preprint. 2020 Mar. doi: 10.1101/2020.03.24.20041087.
The coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic affects us in many ways. Pediatric patients, interestingly, are largely unaffected clinically by this disease. Less than 1% of documented infections occur in children under 10 years old, according to a review of over 72,000 cases from China.1 In that review, most children were asymptomatic or had mild illness, only three required intensive care, and only one death had been reported as of March 10, 2020. This is in stark contrast to the shocking morbidity and mortality statistics we are becoming all too familiar with on the adult side.
From a social standpoint, however, our pediatric patients’ lives have been turned upside down. Their schedules and routines upended, their education and friendships interrupted, and many are likely experiencing real anxiety and fear.2 For countless children, school is a major source of social, emotional, and nutritional support that has been cut off. Some will lose parents, grandparents, or other loved ones to this disease. Parents will lose jobs and will be unable to afford necessities. Pediatric patients will experience delays of procedures or treatments because of the pandemic. Some have projected that rates of child abuse will increase as has been reported during natural disasters.3
Pediatricians around the country are coming together to tackle these issues in creative ways, including the rapid expansion of virtual/telehealth programs. The school systems are developing strategies to deliver online content, and even food, to their students’ homes. Hopefully these tactics will mitigate some of the potential effects on the mental and physical well-being of these patients.
How about my kids? Will they be all right? I am lucky that my husband and I will have jobs throughout this ordeal. Unfortunately, given my role as a hospitalist and my husband’s as a pulmonary/critical care physician, these same jobs that will keep our kids nourished and supported pose the greatest threat to them. As health care workers, we are worried about protecting our families, which may include vulnerable members. The Spanish health ministry announced that medical professionals account for approximately one in eight documented COVID-19 infections in Spain.4 With inadequate supplies of personal protective equipment (PPE) in our own nation, we are concerned that our statistics could be similar.
There are multiple strategies to protect ourselves and our families during this difficult time. First, appropriate PPE is essential and integrity with the process must be maintained always. Hospital leaders can protect us by tirelessly working to acquire PPE. In Grand Rapids, Mich., our health system has partnered with multiple local manufacturing companies, including Steelcase, who are producing PPE for our workforce.5 Leaders can diligently update their system’s PPE recommendations to be in line with the latest CDC recommendations and disseminate the information regularly. Hospitalists should frequently check with their Infection Prevention department to make sure they understand if there have been any changes to the recommendations. Innovative solutions for sterilization of PPE, stethoscopes, badges and other equipment, such as with the use of UV boxes or hydrogen peroxide vapor,6 should be explored to minimize contamination. Hospitalists should bring a set of clothes and shoes to change into upon arrival to work and to change out of prior to leaving the hospital.
We must also keep our heads strong. Currently the anxiety amongst physicians is palpable but there is solidarity. Hospital leaders must ensure that hospitalists have easy access to free mental health resources, such as virtual counseling. Wellness teams must rise to the occasion with innovative tactics to support us. For example, Spectrum Health’s wellness team is sponsoring a blog where physicians can discuss COVID-19–related challenges openly. Hospitalist leaders should ensure that there is a structure for debriefing after critical incidents, which are sure to increase in frequency. Email lists and discussion boards sponsored by professional society also provide a collaborative venue for some of these discussions. We must take advantage of these resources and communicate with each other.
For me, in the end it comes back to the kids. My kids and most pediatric patients are not likely to be hospitalized from COVID-19, but they are also not immune to the toll that fighting this pandemic will take on our families. We took an oath to protect our patients, but what do we owe to our own children? At a minimum we can optimize how we protect ourselves every day, both physically and mentally. As we come together as a strong community to fight this pandemic, in addition to saving lives, we are working to ensure that, in the end, the kids will be all right.
Dr. Hadley is chief of pediatric hospital medicine at Spectrum Health/Helen DeVos Children’s Hospital in Grand Rapids, Mich., and clinical assistant professor at Michigan State University, East Lansing.
References
1. Wu Z, McGoogan JM. Characteristics of and important lessons from the coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) outbreak in China: Summary of a report of 72 314 cases from the Chinese Center for Disease Control and Prevention. JAMA. 2020 Feb 24. doi: 10.1001/jama.2020.2648.
2. Hagan JF Jr; American Academy of Pediatrics Committee on Psychosocial Aspects of Child and Family Health; Task Force on Terrorism. Psychosocial implications of disaster or terrorism on children: A guide for the pediatrician. Pediatrics. 2005;116(3):787-795.
3. Gearhart S et al. The impact of natural disasters on domestic violence: An analysis of reports of simple assault in Florida (1997-2007). Violence Gend. 2018 Jun. doi: 10.1089/vio.2017.0077.
4. Minder R, Peltier E. Virus knocks thousands of health workers out of action in Europe. The New York Times. March 24, 2020.
5. McVicar B. West Michigan businesses hustle to produce medical supplies amid coronavirus pandemic. MLive. March 25, 2020.
6. Kenney PA et al. Hydrogen Peroxide Vapor sterilization of N95 respirators for reuse. medRxiv preprint. 2020 Mar. doi: 10.1101/2020.03.24.20041087.
COVID-19 linked to multiple cardiovascular presentations
It’s becoming clear that COVID-19 infection can involve the cardiovascular system in many different ways, and this has “evolving” potential implications for treatment, say a team of cardiologists on the frontlines of the COVID-19 battle in New York City.
In an article published online April 3 in Circulation, Justin Fried, MD, Division of Cardiology, Columbia University, New York City, and colleagues present four case studies of COVID-19 patients with various cardiovascular presentations.
Case 1 is a 64-year-old woman whose predominant symptoms on admission were cardiac in nature, including chest pain and ST elevation, but without fever, cough, or other symptoms suggestive of COVID-19.
“In patients presenting with what appears to be a typical cardiac syndrome, COVID-19 infection should be in the differential during the current pandemic, even in the absence of fever or cough,” the clinicians advise.
Case 2 is a 38-year-old man with cardiogenic shock and acute respiratory distress with profound hypoxia who was rescued with veno-arterial-venous extracorporeal membrane oxygenation (VV ECMO).
The initial presentation of this patient was more characteristic of severe COVID-19 disease, and cardiac involvement only became apparent after the initiation of ECMO, Fried and colleagues report.
Based on this case, they advise a “low threshold” to assess for cardiogenic shock in patients with acute systolic heart failure related to COVID-19. If inotropic support fails in these patients, intra-aortic balloon pump should be considered first for mechanical circulatory support because it requires the least maintenance from medical support staff.
In addition, in their experience, when a patient on VV ECMO develops superimposed cardiogenic shock, adding an arterial conduit at a relatively low blood flow rate may provide the necessary circulatory support without inducing left ventricular distension, they note.
“Our experience confirms that rescue of patients even with profound cardiogenic or mixed shock may be possible with temporary hemodynamic support at centers with availability of such devices,” Fried and colleagues report.
Case 3 is a 64-year-old woman with underlying cardiac disease who developed profound decompensation with COVID-19 infection.
This case demonstrates that the infection can cause decompensation of underlying heart failure and may lead to mixed shock, the clinicians say.
“Invasive hemodynamic monitoring, if feasible, may be helpful to manage the cardiac component of shock in such cases. Medications that prolong the QT interval are being considered for COVID-19 patients and may require closer monitoring in patients with underlying structural heart disease,” they note.
Case 4 is a 51-year-old man who underwent a heart transplant in 2007 and a kidney transplant in 2010. He had COVID-19 symptoms akin to those seen in nonimmunosuppressed patients with COVID-19.
The COVID-19 pandemic presents a “unique challenge” for solid organ transplant recipients, with only “limited” data on how to adjust immunosuppression during COVID-19 infection, Fried and colleagues say.
The pandemic also creates a challenge for the management of heart failure patients on the heart transplant wait list; the risks of delaying a transplant need to be balanced against the risks of donor infection and uncertainty regarding the impact of post-transplant immunosuppression protocols, they note.
As reported by Medscape Medical News, the American Heart Association has developed a COVID-19 patient registry to collect data on cardiovascular conditions and outcomes related to COVID-19 infection.
To participate in the registry, contact [email protected].
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
It’s becoming clear that COVID-19 infection can involve the cardiovascular system in many different ways, and this has “evolving” potential implications for treatment, say a team of cardiologists on the frontlines of the COVID-19 battle in New York City.
In an article published online April 3 in Circulation, Justin Fried, MD, Division of Cardiology, Columbia University, New York City, and colleagues present four case studies of COVID-19 patients with various cardiovascular presentations.
Case 1 is a 64-year-old woman whose predominant symptoms on admission were cardiac in nature, including chest pain and ST elevation, but without fever, cough, or other symptoms suggestive of COVID-19.
“In patients presenting with what appears to be a typical cardiac syndrome, COVID-19 infection should be in the differential during the current pandemic, even in the absence of fever or cough,” the clinicians advise.
Case 2 is a 38-year-old man with cardiogenic shock and acute respiratory distress with profound hypoxia who was rescued with veno-arterial-venous extracorporeal membrane oxygenation (VV ECMO).
The initial presentation of this patient was more characteristic of severe COVID-19 disease, and cardiac involvement only became apparent after the initiation of ECMO, Fried and colleagues report.
Based on this case, they advise a “low threshold” to assess for cardiogenic shock in patients with acute systolic heart failure related to COVID-19. If inotropic support fails in these patients, intra-aortic balloon pump should be considered first for mechanical circulatory support because it requires the least maintenance from medical support staff.
In addition, in their experience, when a patient on VV ECMO develops superimposed cardiogenic shock, adding an arterial conduit at a relatively low blood flow rate may provide the necessary circulatory support without inducing left ventricular distension, they note.
“Our experience confirms that rescue of patients even with profound cardiogenic or mixed shock may be possible with temporary hemodynamic support at centers with availability of such devices,” Fried and colleagues report.
Case 3 is a 64-year-old woman with underlying cardiac disease who developed profound decompensation with COVID-19 infection.
This case demonstrates that the infection can cause decompensation of underlying heart failure and may lead to mixed shock, the clinicians say.
“Invasive hemodynamic monitoring, if feasible, may be helpful to manage the cardiac component of shock in such cases. Medications that prolong the QT interval are being considered for COVID-19 patients and may require closer monitoring in patients with underlying structural heart disease,” they note.
Case 4 is a 51-year-old man who underwent a heart transplant in 2007 and a kidney transplant in 2010. He had COVID-19 symptoms akin to those seen in nonimmunosuppressed patients with COVID-19.
The COVID-19 pandemic presents a “unique challenge” for solid organ transplant recipients, with only “limited” data on how to adjust immunosuppression during COVID-19 infection, Fried and colleagues say.
The pandemic also creates a challenge for the management of heart failure patients on the heart transplant wait list; the risks of delaying a transplant need to be balanced against the risks of donor infection and uncertainty regarding the impact of post-transplant immunosuppression protocols, they note.
As reported by Medscape Medical News, the American Heart Association has developed a COVID-19 patient registry to collect data on cardiovascular conditions and outcomes related to COVID-19 infection.
To participate in the registry, contact [email protected].
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
It’s becoming clear that COVID-19 infection can involve the cardiovascular system in many different ways, and this has “evolving” potential implications for treatment, say a team of cardiologists on the frontlines of the COVID-19 battle in New York City.
In an article published online April 3 in Circulation, Justin Fried, MD, Division of Cardiology, Columbia University, New York City, and colleagues present four case studies of COVID-19 patients with various cardiovascular presentations.
Case 1 is a 64-year-old woman whose predominant symptoms on admission were cardiac in nature, including chest pain and ST elevation, but without fever, cough, or other symptoms suggestive of COVID-19.
“In patients presenting with what appears to be a typical cardiac syndrome, COVID-19 infection should be in the differential during the current pandemic, even in the absence of fever or cough,” the clinicians advise.
Case 2 is a 38-year-old man with cardiogenic shock and acute respiratory distress with profound hypoxia who was rescued with veno-arterial-venous extracorporeal membrane oxygenation (VV ECMO).
The initial presentation of this patient was more characteristic of severe COVID-19 disease, and cardiac involvement only became apparent after the initiation of ECMO, Fried and colleagues report.
Based on this case, they advise a “low threshold” to assess for cardiogenic shock in patients with acute systolic heart failure related to COVID-19. If inotropic support fails in these patients, intra-aortic balloon pump should be considered first for mechanical circulatory support because it requires the least maintenance from medical support staff.
In addition, in their experience, when a patient on VV ECMO develops superimposed cardiogenic shock, adding an arterial conduit at a relatively low blood flow rate may provide the necessary circulatory support without inducing left ventricular distension, they note.
“Our experience confirms that rescue of patients even with profound cardiogenic or mixed shock may be possible with temporary hemodynamic support at centers with availability of such devices,” Fried and colleagues report.
Case 3 is a 64-year-old woman with underlying cardiac disease who developed profound decompensation with COVID-19 infection.
This case demonstrates that the infection can cause decompensation of underlying heart failure and may lead to mixed shock, the clinicians say.
“Invasive hemodynamic monitoring, if feasible, may be helpful to manage the cardiac component of shock in such cases. Medications that prolong the QT interval are being considered for COVID-19 patients and may require closer monitoring in patients with underlying structural heart disease,” they note.
Case 4 is a 51-year-old man who underwent a heart transplant in 2007 and a kidney transplant in 2010. He had COVID-19 symptoms akin to those seen in nonimmunosuppressed patients with COVID-19.
The COVID-19 pandemic presents a “unique challenge” for solid organ transplant recipients, with only “limited” data on how to adjust immunosuppression during COVID-19 infection, Fried and colleagues say.
The pandemic also creates a challenge for the management of heart failure patients on the heart transplant wait list; the risks of delaying a transplant need to be balanced against the risks of donor infection and uncertainty regarding the impact of post-transplant immunosuppression protocols, they note.
As reported by Medscape Medical News, the American Heart Association has developed a COVID-19 patient registry to collect data on cardiovascular conditions and outcomes related to COVID-19 infection.
To participate in the registry, contact [email protected].
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Tips for self-care during the COVID-19 crisis
I think it’s fair to say, none of us have seen anything like this before. Yet here we are, and we must lead. We are many weeks into the COVID-19 crisis. We moved our offices home and tried not to miss a beat. Our patients need us more than ever – and in different ways.
Lest we become like the shoemaker’s daughter who has no shoes, let’s make sure we take care of ourselves. The shock waves from this pandemic are going to be massive and long lasting. I am already witnessing massive psychological growth on the part of my patients, and I hope, myself and my family. We must be strong as individuals and as a group of professionals.
Now more than ever, we need to set boundaries. So many are suffering. We must take stock of our own lives. Many of us are extremely fortunate. We have homes, families, and plenty of food. We are doctors performing essential services, and we can do so without risking our lives.
The priority is to make sure you are safe, and keeping your family and loved ones safe. As physicians, we have learned to distance ourselves from illness, but the coronavirus has affected us in disproportionate numbers.
To be physically and mentally strong, we must get enough sleep. This is exhausting for some and energizing for others. It is definitely a marathon not a sprint, so pace yourself. Eat well. This is no time for empty calories, and that goes for alcohol as well.
Create new routines. Exercise at the same time each day or perhaps twice a day. Try to be productive during certain hours, and relax at other times. Eat at similar times each day. We must strive to quickly create a “new normal” as we spend our days at home.
Find safe alternatives to your usual workout routine. Use YouTube and Instagram to help you find ways to stay fit in your own home. Ask friends for tips and consider sharing workout time with them via Zoom or FaceTime. New options are coming on line daily.
Make sure you are getting enough information to stay safe, and follow the advice of experts. Then turn off the news. I offer the same advice for financial worries. Try not to stress too much about finances right now. Most of us are feeling the pain of lost income and lost savings. Many of us have spouses or partners who suddenly found themselves out of work. Most likely, we will have ample ability to recover financially as we move forward and find ourselves with more work than ever.
Meditate. This may be advice you have been telling your patients for years but never found the time to try yourself. You can begin very simply with an app called Headspace or Calm. Google “5-minute meditation” on YouTube or find a meditation of any length you desire. If not now, when?
Reach out to one another. We can all use a caring word, or some humor or advice about how to move our practices online.
You may find your concentration is decreased, so be realistic in your expectations of yourself. I am finding shorter sessions more often are providing more comfort to some patients. Other patients are digging deeper than ever emotionally, and the work is becoming more rewarding.
Make sure you take a break to engage in positive activities. Read a book. Listen to soft music. Dim the lights. Watch the sunset, or be in nature if you can do so safely. Watch a TedTalk. Brush up on a foreign language. Take a deep breath. Journal. Puzzles, games, cooking, magazines, and humor all provide much needed respite from the stress. If you are lucky enough to be with family, try to take advantage of this unique time.
Try to avoid or minimize conflict with others. We need one another now more than ever. If you lose your cool, forgive yourself and make amends.
Even in these most challenging times, we must focus on what we are grateful for. Express gratitude to those around you as it will lift their mood as well. I know I am extremely grateful to be able to continue meaningful work when so many are unable to do so.
The next waves of this virus will be hitting our specialty directly so be strong and be prepared. It is an honor to serve, and we must rise to the occasion.
Dr. Ritvo, a psychiatrist with more than 25 years’ experience, practices in Miami Beach, Fla. She is the author of “Bekindr – The Transformative Power of Kindness” (Hellertown, Pa.: Momosa Publishing, 2018), and is the founder of the Bekindr Global Initiative, a movement aimed at cultivating kindness in the world. Dr. Ritvo also is the cofounder of the Bold Beauty Project, a nonprofit group that pairs women with disabilities with photographers who create art exhibitions to raise awareness.
I think it’s fair to say, none of us have seen anything like this before. Yet here we are, and we must lead. We are many weeks into the COVID-19 crisis. We moved our offices home and tried not to miss a beat. Our patients need us more than ever – and in different ways.
Lest we become like the shoemaker’s daughter who has no shoes, let’s make sure we take care of ourselves. The shock waves from this pandemic are going to be massive and long lasting. I am already witnessing massive psychological growth on the part of my patients, and I hope, myself and my family. We must be strong as individuals and as a group of professionals.
Now more than ever, we need to set boundaries. So many are suffering. We must take stock of our own lives. Many of us are extremely fortunate. We have homes, families, and plenty of food. We are doctors performing essential services, and we can do so without risking our lives.
The priority is to make sure you are safe, and keeping your family and loved ones safe. As physicians, we have learned to distance ourselves from illness, but the coronavirus has affected us in disproportionate numbers.
To be physically and mentally strong, we must get enough sleep. This is exhausting for some and energizing for others. It is definitely a marathon not a sprint, so pace yourself. Eat well. This is no time for empty calories, and that goes for alcohol as well.
Create new routines. Exercise at the same time each day or perhaps twice a day. Try to be productive during certain hours, and relax at other times. Eat at similar times each day. We must strive to quickly create a “new normal” as we spend our days at home.
Find safe alternatives to your usual workout routine. Use YouTube and Instagram to help you find ways to stay fit in your own home. Ask friends for tips and consider sharing workout time with them via Zoom or FaceTime. New options are coming on line daily.
Make sure you are getting enough information to stay safe, and follow the advice of experts. Then turn off the news. I offer the same advice for financial worries. Try not to stress too much about finances right now. Most of us are feeling the pain of lost income and lost savings. Many of us have spouses or partners who suddenly found themselves out of work. Most likely, we will have ample ability to recover financially as we move forward and find ourselves with more work than ever.
Meditate. This may be advice you have been telling your patients for years but never found the time to try yourself. You can begin very simply with an app called Headspace or Calm. Google “5-minute meditation” on YouTube or find a meditation of any length you desire. If not now, when?
Reach out to one another. We can all use a caring word, or some humor or advice about how to move our practices online.
You may find your concentration is decreased, so be realistic in your expectations of yourself. I am finding shorter sessions more often are providing more comfort to some patients. Other patients are digging deeper than ever emotionally, and the work is becoming more rewarding.
Make sure you take a break to engage in positive activities. Read a book. Listen to soft music. Dim the lights. Watch the sunset, or be in nature if you can do so safely. Watch a TedTalk. Brush up on a foreign language. Take a deep breath. Journal. Puzzles, games, cooking, magazines, and humor all provide much needed respite from the stress. If you are lucky enough to be with family, try to take advantage of this unique time.
Try to avoid or minimize conflict with others. We need one another now more than ever. If you lose your cool, forgive yourself and make amends.
Even in these most challenging times, we must focus on what we are grateful for. Express gratitude to those around you as it will lift their mood as well. I know I am extremely grateful to be able to continue meaningful work when so many are unable to do so.
The next waves of this virus will be hitting our specialty directly so be strong and be prepared. It is an honor to serve, and we must rise to the occasion.
Dr. Ritvo, a psychiatrist with more than 25 years’ experience, practices in Miami Beach, Fla. She is the author of “Bekindr – The Transformative Power of Kindness” (Hellertown, Pa.: Momosa Publishing, 2018), and is the founder of the Bekindr Global Initiative, a movement aimed at cultivating kindness in the world. Dr. Ritvo also is the cofounder of the Bold Beauty Project, a nonprofit group that pairs women with disabilities with photographers who create art exhibitions to raise awareness.
I think it’s fair to say, none of us have seen anything like this before. Yet here we are, and we must lead. We are many weeks into the COVID-19 crisis. We moved our offices home and tried not to miss a beat. Our patients need us more than ever – and in different ways.
Lest we become like the shoemaker’s daughter who has no shoes, let’s make sure we take care of ourselves. The shock waves from this pandemic are going to be massive and long lasting. I am already witnessing massive psychological growth on the part of my patients, and I hope, myself and my family. We must be strong as individuals and as a group of professionals.
Now more than ever, we need to set boundaries. So many are suffering. We must take stock of our own lives. Many of us are extremely fortunate. We have homes, families, and plenty of food. We are doctors performing essential services, and we can do so without risking our lives.
The priority is to make sure you are safe, and keeping your family and loved ones safe. As physicians, we have learned to distance ourselves from illness, but the coronavirus has affected us in disproportionate numbers.
To be physically and mentally strong, we must get enough sleep. This is exhausting for some and energizing for others. It is definitely a marathon not a sprint, so pace yourself. Eat well. This is no time for empty calories, and that goes for alcohol as well.
Create new routines. Exercise at the same time each day or perhaps twice a day. Try to be productive during certain hours, and relax at other times. Eat at similar times each day. We must strive to quickly create a “new normal” as we spend our days at home.
Find safe alternatives to your usual workout routine. Use YouTube and Instagram to help you find ways to stay fit in your own home. Ask friends for tips and consider sharing workout time with them via Zoom or FaceTime. New options are coming on line daily.
Make sure you are getting enough information to stay safe, and follow the advice of experts. Then turn off the news. I offer the same advice for financial worries. Try not to stress too much about finances right now. Most of us are feeling the pain of lost income and lost savings. Many of us have spouses or partners who suddenly found themselves out of work. Most likely, we will have ample ability to recover financially as we move forward and find ourselves with more work than ever.
Meditate. This may be advice you have been telling your patients for years but never found the time to try yourself. You can begin very simply with an app called Headspace or Calm. Google “5-minute meditation” on YouTube or find a meditation of any length you desire. If not now, when?
Reach out to one another. We can all use a caring word, or some humor or advice about how to move our practices online.
You may find your concentration is decreased, so be realistic in your expectations of yourself. I am finding shorter sessions more often are providing more comfort to some patients. Other patients are digging deeper than ever emotionally, and the work is becoming more rewarding.
Make sure you take a break to engage in positive activities. Read a book. Listen to soft music. Dim the lights. Watch the sunset, or be in nature if you can do so safely. Watch a TedTalk. Brush up on a foreign language. Take a deep breath. Journal. Puzzles, games, cooking, magazines, and humor all provide much needed respite from the stress. If you are lucky enough to be with family, try to take advantage of this unique time.
Try to avoid or minimize conflict with others. We need one another now more than ever. If you lose your cool, forgive yourself and make amends.
Even in these most challenging times, we must focus on what we are grateful for. Express gratitude to those around you as it will lift their mood as well. I know I am extremely grateful to be able to continue meaningful work when so many are unable to do so.
The next waves of this virus will be hitting our specialty directly so be strong and be prepared. It is an honor to serve, and we must rise to the occasion.
Dr. Ritvo, a psychiatrist with more than 25 years’ experience, practices in Miami Beach, Fla. She is the author of “Bekindr – The Transformative Power of Kindness” (Hellertown, Pa.: Momosa Publishing, 2018), and is the founder of the Bekindr Global Initiative, a movement aimed at cultivating kindness in the world. Dr. Ritvo also is the cofounder of the Bold Beauty Project, a nonprofit group that pairs women with disabilities with photographers who create art exhibitions to raise awareness.
AMA president calls for greater reliance on science in COVID-19 fight
The president of the American Medical Association is calling on politicians and the media to rely on science and evidence to help the public through the COVID-19 pandemic.
“We live in a time when misinformation, falsehoods, and outright lies spread like viruses online, through social media and even, at times, in the media at large,” Patrice A. Harris, MD, said during an April 7 address. “We have witnessed a concerning shift over the last several decades where policy decisions seem to be driven by ideology and politics instead of facts and evidence. The result is a growing mistrust in American institutions, in science, and in the counsel of leading experts whose lives are dedicated to the pursuit of evidence and reason.”
To that end, she called on everyone – from politicians to the general public – to trust the scientific evidence.
Dr. Harris noted that the scientific data on COVID-19 have already yielded important lessons about who is more likely to be affected and how easily the virus can spread. The data also point to the effectiveness of stay-at-home and shelter-in-place orders. “This is our best chance to slow the spread of the virus,” she said, adding that the enhanced emphasis on hand washing and other hygiene practices “may seem ‘simplistic,’ but they are, in fact, based in science and evidence.”
And, as the pandemic continues, Dr. Harris said that now is the time to rely on science. She said the AMA “calls on all elected officials to affirm science, evidence, and fact in their words and actions,” and she urged that the government’s scientific institutions be led by experts who are “protected from political influence.”
It is incumbent upon everyone to actively work to contain and stop the spread of misinformation related to COVID-19, she said. “We must ensure the war is against the virus and not against science,” Dr. Harris said.
The president of the American Medical Association is calling on politicians and the media to rely on science and evidence to help the public through the COVID-19 pandemic.
“We live in a time when misinformation, falsehoods, and outright lies spread like viruses online, through social media and even, at times, in the media at large,” Patrice A. Harris, MD, said during an April 7 address. “We have witnessed a concerning shift over the last several decades where policy decisions seem to be driven by ideology and politics instead of facts and evidence. The result is a growing mistrust in American institutions, in science, and in the counsel of leading experts whose lives are dedicated to the pursuit of evidence and reason.”
To that end, she called on everyone – from politicians to the general public – to trust the scientific evidence.
Dr. Harris noted that the scientific data on COVID-19 have already yielded important lessons about who is more likely to be affected and how easily the virus can spread. The data also point to the effectiveness of stay-at-home and shelter-in-place orders. “This is our best chance to slow the spread of the virus,” she said, adding that the enhanced emphasis on hand washing and other hygiene practices “may seem ‘simplistic,’ but they are, in fact, based in science and evidence.”
And, as the pandemic continues, Dr. Harris said that now is the time to rely on science. She said the AMA “calls on all elected officials to affirm science, evidence, and fact in their words and actions,” and she urged that the government’s scientific institutions be led by experts who are “protected from political influence.”
It is incumbent upon everyone to actively work to contain and stop the spread of misinformation related to COVID-19, she said. “We must ensure the war is against the virus and not against science,” Dr. Harris said.
The president of the American Medical Association is calling on politicians and the media to rely on science and evidence to help the public through the COVID-19 pandemic.
“We live in a time when misinformation, falsehoods, and outright lies spread like viruses online, through social media and even, at times, in the media at large,” Patrice A. Harris, MD, said during an April 7 address. “We have witnessed a concerning shift over the last several decades where policy decisions seem to be driven by ideology and politics instead of facts and evidence. The result is a growing mistrust in American institutions, in science, and in the counsel of leading experts whose lives are dedicated to the pursuit of evidence and reason.”
To that end, she called on everyone – from politicians to the general public – to trust the scientific evidence.
Dr. Harris noted that the scientific data on COVID-19 have already yielded important lessons about who is more likely to be affected and how easily the virus can spread. The data also point to the effectiveness of stay-at-home and shelter-in-place orders. “This is our best chance to slow the spread of the virus,” she said, adding that the enhanced emphasis on hand washing and other hygiene practices “may seem ‘simplistic,’ but they are, in fact, based in science and evidence.”
And, as the pandemic continues, Dr. Harris said that now is the time to rely on science. She said the AMA “calls on all elected officials to affirm science, evidence, and fact in their words and actions,” and she urged that the government’s scientific institutions be led by experts who are “protected from political influence.”
It is incumbent upon everyone to actively work to contain and stop the spread of misinformation related to COVID-19, she said. “We must ensure the war is against the virus and not against science,” Dr. Harris said.
Nearly 24 tests for the novel coronavirus are available
according to the Infectious Diseases Society of America (IDSA).
“Based on what we know about influenza, it’s unlikely that all of these tests are going to perform exactly the same way,” said Angela M. Caliendo, MD, executive vice chair of the department of medicine at Brown University in Providence, R.I., at a press briefing. Although these tests are good, no test is perfect, she added.
The development and availability of testing has improved over time, but clinical laboratories still face challenges, said Kimberly E. Hanson, MD, associate professor of internal medicine at University of Utah, Salt Lake City. These challenges include shortages of devices for specimen collection, media, test tubes, and reagents. Although the goal is to test all symptomatic patients, these shortages require laboratories to prioritize health care workers and the sickest patients.
Tests are being approved through an abbreviated process
Two types of test, rapid tests and serology tests, are in use. Rapid tests use polymerase chain reactions to detect the virus in a clinical specimen. This type of testing is used to diagnose infection. Serology tests measure antibodies to the virus and are more appropriate for indicating whether a patient has been exposed to the virus.
The declaration of a national emergency enabled the FDA to activate its EUA policy, which allows for quicker approval of tests. Normally, a test must be assessed in the laboratory (such as with a mock specimen or an inactivated virus) and in a clinical study of patients. Under the EUA, clinical assessment is not required for the approval of a test. Consequently, the clinical performance of a test approved under EUA is unknown.
Collecting a specimen of good quality is critical to the quality of the test result, said Dr. Caliendo, the secretary of IDSA’s board of directors. Clinicians and investigators have used nasopharyngeal swabs, sputum, and specimens collected from deep within the lung. “We’re still collecting data to determine which is the best specimen type.” As coronavirus testing expands, particularly to drive-through testing sites, “we may be using people who are not as experienced, and so you might not get as high a quality specimen in that situation,” Dr. Caliendo added.
The timing of the test influences the quality of the result, as well, because the amount of virus is lower at the onset of symptoms than it is later. Another factor that affects the quality of the results is the test’s sensitivity.
The time to obtain results varies
The value of having several tests available is that it enables many patients to be tested simultaneously, said Dr. Hanson, a member of IDSA’s board of directors. It also helps to reduce potential problems with the supply of test kits. A test manufacturer, however, may supply parts of the test kit but not the whole kit. This requires the hospital or laboratory to obtain the remaining parts from other suppliers. Furthermore, test manufacturers may need to prioritize areas with high rates of infection or transmission when they ship their tests, which limits testing in other areas.
One reason for the lack of a national plan for testing is that the virus has affected different regions at different times, said Dr. Caliendo. Some tests are more difficult to perform than others, and not all laboratories are equally sophisticated, which can limit testing. It is necessary to test not only symptomatic patients who have been hospitalized, but also symptomatic patients in the community, said Dr. Caliendo. “Ideally, we’re going to need to couple acute diagnostics [testing while people are sick] with serologic testing. Serologic testing is going to be important for us to see who has been infected. That will give us an idea of who is left in our community who is at risk for developing infection.”
How quickly test results are available depends on the type of test and where it is administered. Recently established drive-through clinics can provide results in about 30 minutes. Tests performed in hospitals may take between 1 and 6 hours to yield results. “The issue is, do we have reagents that day?” said Dr. Caliendo. “We have to be careful whom we choose to test, and we screen that in the hospital so that we have enough tests to run as we need them.” But many locations have backlogs. “When you have a backlog of testing, you’re going to wait days, unfortunately, to get a result,” said Dr. Caliendo.
Dr. Caliendo and Dr. Hanson did not report disclosures for this briefing.
according to the Infectious Diseases Society of America (IDSA).
“Based on what we know about influenza, it’s unlikely that all of these tests are going to perform exactly the same way,” said Angela M. Caliendo, MD, executive vice chair of the department of medicine at Brown University in Providence, R.I., at a press briefing. Although these tests are good, no test is perfect, she added.
The development and availability of testing has improved over time, but clinical laboratories still face challenges, said Kimberly E. Hanson, MD, associate professor of internal medicine at University of Utah, Salt Lake City. These challenges include shortages of devices for specimen collection, media, test tubes, and reagents. Although the goal is to test all symptomatic patients, these shortages require laboratories to prioritize health care workers and the sickest patients.
Tests are being approved through an abbreviated process
Two types of test, rapid tests and serology tests, are in use. Rapid tests use polymerase chain reactions to detect the virus in a clinical specimen. This type of testing is used to diagnose infection. Serology tests measure antibodies to the virus and are more appropriate for indicating whether a patient has been exposed to the virus.
The declaration of a national emergency enabled the FDA to activate its EUA policy, which allows for quicker approval of tests. Normally, a test must be assessed in the laboratory (such as with a mock specimen or an inactivated virus) and in a clinical study of patients. Under the EUA, clinical assessment is not required for the approval of a test. Consequently, the clinical performance of a test approved under EUA is unknown.
Collecting a specimen of good quality is critical to the quality of the test result, said Dr. Caliendo, the secretary of IDSA’s board of directors. Clinicians and investigators have used nasopharyngeal swabs, sputum, and specimens collected from deep within the lung. “We’re still collecting data to determine which is the best specimen type.” As coronavirus testing expands, particularly to drive-through testing sites, “we may be using people who are not as experienced, and so you might not get as high a quality specimen in that situation,” Dr. Caliendo added.
The timing of the test influences the quality of the result, as well, because the amount of virus is lower at the onset of symptoms than it is later. Another factor that affects the quality of the results is the test’s sensitivity.
The time to obtain results varies
The value of having several tests available is that it enables many patients to be tested simultaneously, said Dr. Hanson, a member of IDSA’s board of directors. It also helps to reduce potential problems with the supply of test kits. A test manufacturer, however, may supply parts of the test kit but not the whole kit. This requires the hospital or laboratory to obtain the remaining parts from other suppliers. Furthermore, test manufacturers may need to prioritize areas with high rates of infection or transmission when they ship their tests, which limits testing in other areas.
One reason for the lack of a national plan for testing is that the virus has affected different regions at different times, said Dr. Caliendo. Some tests are more difficult to perform than others, and not all laboratories are equally sophisticated, which can limit testing. It is necessary to test not only symptomatic patients who have been hospitalized, but also symptomatic patients in the community, said Dr. Caliendo. “Ideally, we’re going to need to couple acute diagnostics [testing while people are sick] with serologic testing. Serologic testing is going to be important for us to see who has been infected. That will give us an idea of who is left in our community who is at risk for developing infection.”
How quickly test results are available depends on the type of test and where it is administered. Recently established drive-through clinics can provide results in about 30 minutes. Tests performed in hospitals may take between 1 and 6 hours to yield results. “The issue is, do we have reagents that day?” said Dr. Caliendo. “We have to be careful whom we choose to test, and we screen that in the hospital so that we have enough tests to run as we need them.” But many locations have backlogs. “When you have a backlog of testing, you’re going to wait days, unfortunately, to get a result,” said Dr. Caliendo.
Dr. Caliendo and Dr. Hanson did not report disclosures for this briefing.
according to the Infectious Diseases Society of America (IDSA).
“Based on what we know about influenza, it’s unlikely that all of these tests are going to perform exactly the same way,” said Angela M. Caliendo, MD, executive vice chair of the department of medicine at Brown University in Providence, R.I., at a press briefing. Although these tests are good, no test is perfect, she added.
The development and availability of testing has improved over time, but clinical laboratories still face challenges, said Kimberly E. Hanson, MD, associate professor of internal medicine at University of Utah, Salt Lake City. These challenges include shortages of devices for specimen collection, media, test tubes, and reagents. Although the goal is to test all symptomatic patients, these shortages require laboratories to prioritize health care workers and the sickest patients.
Tests are being approved through an abbreviated process
Two types of test, rapid tests and serology tests, are in use. Rapid tests use polymerase chain reactions to detect the virus in a clinical specimen. This type of testing is used to diagnose infection. Serology tests measure antibodies to the virus and are more appropriate for indicating whether a patient has been exposed to the virus.
The declaration of a national emergency enabled the FDA to activate its EUA policy, which allows for quicker approval of tests. Normally, a test must be assessed in the laboratory (such as with a mock specimen or an inactivated virus) and in a clinical study of patients. Under the EUA, clinical assessment is not required for the approval of a test. Consequently, the clinical performance of a test approved under EUA is unknown.
Collecting a specimen of good quality is critical to the quality of the test result, said Dr. Caliendo, the secretary of IDSA’s board of directors. Clinicians and investigators have used nasopharyngeal swabs, sputum, and specimens collected from deep within the lung. “We’re still collecting data to determine which is the best specimen type.” As coronavirus testing expands, particularly to drive-through testing sites, “we may be using people who are not as experienced, and so you might not get as high a quality specimen in that situation,” Dr. Caliendo added.
The timing of the test influences the quality of the result, as well, because the amount of virus is lower at the onset of symptoms than it is later. Another factor that affects the quality of the results is the test’s sensitivity.
The time to obtain results varies
The value of having several tests available is that it enables many patients to be tested simultaneously, said Dr. Hanson, a member of IDSA’s board of directors. It also helps to reduce potential problems with the supply of test kits. A test manufacturer, however, may supply parts of the test kit but not the whole kit. This requires the hospital or laboratory to obtain the remaining parts from other suppliers. Furthermore, test manufacturers may need to prioritize areas with high rates of infection or transmission when they ship their tests, which limits testing in other areas.
One reason for the lack of a national plan for testing is that the virus has affected different regions at different times, said Dr. Caliendo. Some tests are more difficult to perform than others, and not all laboratories are equally sophisticated, which can limit testing. It is necessary to test not only symptomatic patients who have been hospitalized, but also symptomatic patients in the community, said Dr. Caliendo. “Ideally, we’re going to need to couple acute diagnostics [testing while people are sick] with serologic testing. Serologic testing is going to be important for us to see who has been infected. That will give us an idea of who is left in our community who is at risk for developing infection.”
How quickly test results are available depends on the type of test and where it is administered. Recently established drive-through clinics can provide results in about 30 minutes. Tests performed in hospitals may take between 1 and 6 hours to yield results. “The issue is, do we have reagents that day?” said Dr. Caliendo. “We have to be careful whom we choose to test, and we screen that in the hospital so that we have enough tests to run as we need them.” But many locations have backlogs. “When you have a backlog of testing, you’re going to wait days, unfortunately, to get a result,” said Dr. Caliendo.
Dr. Caliendo and Dr. Hanson did not report disclosures for this briefing.







