User login
In Case You Missed It: COVID
New data on worldwide mental health impact of COVID-19
A new survey that assessed the mental health impact of COVID-19 across the globe shows high rates of trauma and clinical mood disorders related to the pandemic.
The survey, carried out by Sapien Labs, was conducted in eight English-speaking countries and included 49,000 adults. It showed that 57% of respondents experienced some COVID-19–related adversity or trauma.
Roughly one-quarter showed clinical signs of or were at risk for a mood disorder, and 40% described themselves as “succeeding or thriving.”
Those who reported the poorest mental health were young adults and individuals who experienced financial adversity or were unable to receive care for other medical conditions. Nonbinary gender and not getting enough sleep, exercise, or face-to-face socialization also increased the risk for poorer mental well-being.
“The data suggest that there will be long-term fallout from the pandemic on the mental health front,” Tara Thiagarajan, PhD, Sapien Labs founder and chief scientist, said in a press release.
Novel initiative
Dr. Thiagarajan said in an interview that she was running a company that provided microloans to 30,000 villages in India. The company included a research group the goal of which was to understand what predicts success in an individual and in a particular ecosystem, she said – “Why did some villages succeed and others didn’t?”
Dr. Thiagarajan and associates thought that “something big is happening in our life circumstances that causes changes in our brain and felt that we need to understand what they are and how they affect humanity. This was the impetus for founding Sapien Labs. “
The survey, which is part of the company’s Mental Health Million project, is an ongoing research initiative that makes data freely available to other researchers.
The investigators developed a “free and anonymous assessment tool,” the Mental Health Quotient (MHQ), which “encompasses a comprehensive view of our emotional, social, and cognitive function and capability,” said Dr. Thiagarajan.
The MHQ consists of 47 “elements of mental well-being.” Respondents’ MHQ scores ranged from –100 to +200. Negative scores indicate poorer mental well-being. Respondents were categorized as clinical, at risk, enduring, managing, succeeding, and thriving.
MHQ scores were computed for six “broad dimensions” of mental health: Core cognition, complex cognition, mood and outlook, drive and motivation, social self, and mind-body connection.
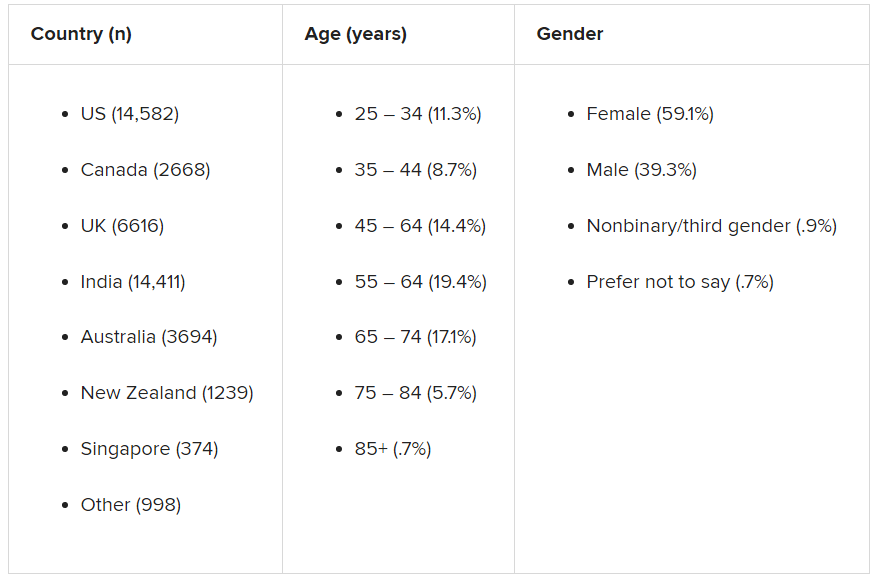
Participants were recruited through advertising on Google and Facebook in eight English-speaking countries – Canada, the United States, the United Kingdom, South Africa, Singapore, Australia, New Zealand, and India. The researchers collected demographic information, including age, education, and gender.
First step
The assessment was completed by 48,808 respondents between April 8 and Dec. 31, 2020.
A smaller sample of 2,000 people from the same countries who were polled by the investigators in 2019 was used as a comparator.
Taken together, the overall mental well-being score for 2020 was 8% lower than the score obtained in 2019 from the same countries, and the percentage of respondents who fell into the “clinical” category increased from 14% in 2009 to 26% in 2020.
Residents of Singapore had the highest MHQ score, followed by residents of the United States. At the other extreme, respondents from the United Kingdom and South Africa had the poorest MHQ scores.
“It is important to keep in mind that the English-speaking, Internet-enabled populace is not necessarily representative of each country as a whole,” the authors noted.
Youth hardest hit
whose average MHQ score was 29% lower than those aged at least 65 years.
Worldwide, 70% of respondents aged at least 65 years fell into the categories of “succeeding” or “thriving,” compared with just 17% of those aged 18-24 years.
“We saw a massive trend of diminishing mental well-being in younger individuals, suggesting that some societal force is at play that we need to get to the bottom of,” said Dr. Thiagarajan.
“Young people are still learning how to calibrate themselves in the world, and with age comes maturity, leading to a difference in emotional resilience,” she said.
Highest risk group
Mental well-being was poorest among nonbinary/third-gender respondents. Among those persons, more than 50% were classified as being at clinical risk, in comparison with males and females combined, and their MHQ scores were about 47 points lower.
Nonbinary individuals “are universally doing very poorly, relative to males or females,” said Dr. Thiagarajan. “This is a demographic at very high risk with a lot of suicidal thoughts.”
Respondents who had insufficient sleep, who lacked social interaction, and whose level of exercise was insufficient had lower MHQ scores of an “unexpected magnitude,” compared with their counterparts who had sufficient sleep, more social interaction, and more exercise (a discrepancy of 82, 66, and 46 points, respectively).
Only 3.9% of respondents reported having had COVID-19; 0.7% reported having had a severe case. Yet 57% of respondents reported that the pandemic had had negative consequences with regard to their health or their finances or social situation.
Those who were unable to get care for their other health conditions because of the pandemic (2% of all respondents) reported the worst mental well-being, followed by those who struggled for basic necessities (1.4%).
Reduced household income was associated with a 4% lower score but affected a higher percentage of people (17%). Social isolation was associated with a score of about 20 less. Higher rates of lifetime traumas and adversities were likewise associated with lower scores for mental well-being.
Creative, generous approach
Commenting on the survey results, Ken Duckworth, MD, clinical professor at Harvard Medical School, Boston, and chief medical officer of the National Alliance of Mental Illness, noted that the findings were similar to findings from studies in the United States, which showed disproportionately higher rates of mental health problems in younger individuals. Dr. Duckworth was not involved with the survey.
“The idea that this is an international phenomenon and the broad-stroke finding that younger people are suffering across nations is compelling and important for policymakers to look at,” he said.
Dr. Duckworth noted that although the findings are not “representative” of entire populations in a given country, the report is a “first step in a long journey.”
He described the report as “extremely brilliant, creative, and generous, allowing any academician to get access to the data.”
He saw it “less as a definitive report and more as a directionally informative survey that will yield great fruit over time.”
In a comment, Joshua Morganstein, MD, chair of the American Psychiatric Association’s Committee on the Psychiatric Dimensions of Disaster, said: “One of the important things a document like this highlights is the importance of understanding more where risk [for mental health disorders] is concentrated and what things have occurred or might occur that can buffer against that risk or protect us from it. We see that each nation has similar but also different challenges.”
Dr. Thiagarajan is the founder and chief scientist of Sapien Labs. Her coauthors are employees of Sapien Labs. Dr. Duckworth and Dr. Morganstein disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
A new survey that assessed the mental health impact of COVID-19 across the globe shows high rates of trauma and clinical mood disorders related to the pandemic.
The survey, carried out by Sapien Labs, was conducted in eight English-speaking countries and included 49,000 adults. It showed that 57% of respondents experienced some COVID-19–related adversity or trauma.
Roughly one-quarter showed clinical signs of or were at risk for a mood disorder, and 40% described themselves as “succeeding or thriving.”
Those who reported the poorest mental health were young adults and individuals who experienced financial adversity or were unable to receive care for other medical conditions. Nonbinary gender and not getting enough sleep, exercise, or face-to-face socialization also increased the risk for poorer mental well-being.
“The data suggest that there will be long-term fallout from the pandemic on the mental health front,” Tara Thiagarajan, PhD, Sapien Labs founder and chief scientist, said in a press release.
Novel initiative
Dr. Thiagarajan said in an interview that she was running a company that provided microloans to 30,000 villages in India. The company included a research group the goal of which was to understand what predicts success in an individual and in a particular ecosystem, she said – “Why did some villages succeed and others didn’t?”
Dr. Thiagarajan and associates thought that “something big is happening in our life circumstances that causes changes in our brain and felt that we need to understand what they are and how they affect humanity. This was the impetus for founding Sapien Labs. “
The survey, which is part of the company’s Mental Health Million project, is an ongoing research initiative that makes data freely available to other researchers.
The investigators developed a “free and anonymous assessment tool,” the Mental Health Quotient (MHQ), which “encompasses a comprehensive view of our emotional, social, and cognitive function and capability,” said Dr. Thiagarajan.
The MHQ consists of 47 “elements of mental well-being.” Respondents’ MHQ scores ranged from –100 to +200. Negative scores indicate poorer mental well-being. Respondents were categorized as clinical, at risk, enduring, managing, succeeding, and thriving.
MHQ scores were computed for six “broad dimensions” of mental health: Core cognition, complex cognition, mood and outlook, drive and motivation, social self, and mind-body connection.
Participants were recruited through advertising on Google and Facebook in eight English-speaking countries – Canada, the United States, the United Kingdom, South Africa, Singapore, Australia, New Zealand, and India. The researchers collected demographic information, including age, education, and gender.
First step
The assessment was completed by 48,808 respondents between April 8 and Dec. 31, 2020.

A smaller sample of 2,000 people from the same countries who were polled by the investigators in 2019 was used as a comparator.
Taken together, the overall mental well-being score for 2020 was 8% lower than the score obtained in 2019 from the same countries, and the percentage of respondents who fell into the “clinical” category increased from 14% in 2009 to 26% in 2020.
Residents of Singapore had the highest MHQ score, followed by residents of the United States. At the other extreme, respondents from the United Kingdom and South Africa had the poorest MHQ scores.
“It is important to keep in mind that the English-speaking, Internet-enabled populace is not necessarily representative of each country as a whole,” the authors noted.
Youth hardest hit
whose average MHQ score was 29% lower than those aged at least 65 years.
Worldwide, 70% of respondents aged at least 65 years fell into the categories of “succeeding” or “thriving,” compared with just 17% of those aged 18-24 years.
“We saw a massive trend of diminishing mental well-being in younger individuals, suggesting that some societal force is at play that we need to get to the bottom of,” said Dr. Thiagarajan.
“Young people are still learning how to calibrate themselves in the world, and with age comes maturity, leading to a difference in emotional resilience,” she said.
Highest risk group
Mental well-being was poorest among nonbinary/third-gender respondents. Among those persons, more than 50% were classified as being at clinical risk, in comparison with males and females combined, and their MHQ scores were about 47 points lower.
Nonbinary individuals “are universally doing very poorly, relative to males or females,” said Dr. Thiagarajan. “This is a demographic at very high risk with a lot of suicidal thoughts.”
Respondents who had insufficient sleep, who lacked social interaction, and whose level of exercise was insufficient had lower MHQ scores of an “unexpected magnitude,” compared with their counterparts who had sufficient sleep, more social interaction, and more exercise (a discrepancy of 82, 66, and 46 points, respectively).
Only 3.9% of respondents reported having had COVID-19; 0.7% reported having had a severe case. Yet 57% of respondents reported that the pandemic had had negative consequences with regard to their health or their finances or social situation.
Those who were unable to get care for their other health conditions because of the pandemic (2% of all respondents) reported the worst mental well-being, followed by those who struggled for basic necessities (1.4%).
Reduced household income was associated with a 4% lower score but affected a higher percentage of people (17%). Social isolation was associated with a score of about 20 less. Higher rates of lifetime traumas and adversities were likewise associated with lower scores for mental well-being.
Creative, generous approach
Commenting on the survey results, Ken Duckworth, MD, clinical professor at Harvard Medical School, Boston, and chief medical officer of the National Alliance of Mental Illness, noted that the findings were similar to findings from studies in the United States, which showed disproportionately higher rates of mental health problems in younger individuals. Dr. Duckworth was not involved with the survey.
“The idea that this is an international phenomenon and the broad-stroke finding that younger people are suffering across nations is compelling and important for policymakers to look at,” he said.
Dr. Duckworth noted that although the findings are not “representative” of entire populations in a given country, the report is a “first step in a long journey.”
He described the report as “extremely brilliant, creative, and generous, allowing any academician to get access to the data.”
He saw it “less as a definitive report and more as a directionally informative survey that will yield great fruit over time.”
In a comment, Joshua Morganstein, MD, chair of the American Psychiatric Association’s Committee on the Psychiatric Dimensions of Disaster, said: “One of the important things a document like this highlights is the importance of understanding more where risk [for mental health disorders] is concentrated and what things have occurred or might occur that can buffer against that risk or protect us from it. We see that each nation has similar but also different challenges.”
Dr. Thiagarajan is the founder and chief scientist of Sapien Labs. Her coauthors are employees of Sapien Labs. Dr. Duckworth and Dr. Morganstein disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
A new survey that assessed the mental health impact of COVID-19 across the globe shows high rates of trauma and clinical mood disorders related to the pandemic.
The survey, carried out by Sapien Labs, was conducted in eight English-speaking countries and included 49,000 adults. It showed that 57% of respondents experienced some COVID-19–related adversity or trauma.
Roughly one-quarter showed clinical signs of or were at risk for a mood disorder, and 40% described themselves as “succeeding or thriving.”
Those who reported the poorest mental health were young adults and individuals who experienced financial adversity or were unable to receive care for other medical conditions. Nonbinary gender and not getting enough sleep, exercise, or face-to-face socialization also increased the risk for poorer mental well-being.
“The data suggest that there will be long-term fallout from the pandemic on the mental health front,” Tara Thiagarajan, PhD, Sapien Labs founder and chief scientist, said in a press release.
Novel initiative
Dr. Thiagarajan said in an interview that she was running a company that provided microloans to 30,000 villages in India. The company included a research group the goal of which was to understand what predicts success in an individual and in a particular ecosystem, she said – “Why did some villages succeed and others didn’t?”
Dr. Thiagarajan and associates thought that “something big is happening in our life circumstances that causes changes in our brain and felt that we need to understand what they are and how they affect humanity. This was the impetus for founding Sapien Labs. “
The survey, which is part of the company’s Mental Health Million project, is an ongoing research initiative that makes data freely available to other researchers.
The investigators developed a “free and anonymous assessment tool,” the Mental Health Quotient (MHQ), which “encompasses a comprehensive view of our emotional, social, and cognitive function and capability,” said Dr. Thiagarajan.
The MHQ consists of 47 “elements of mental well-being.” Respondents’ MHQ scores ranged from –100 to +200. Negative scores indicate poorer mental well-being. Respondents were categorized as clinical, at risk, enduring, managing, succeeding, and thriving.
MHQ scores were computed for six “broad dimensions” of mental health: Core cognition, complex cognition, mood and outlook, drive and motivation, social self, and mind-body connection.
Participants were recruited through advertising on Google and Facebook in eight English-speaking countries – Canada, the United States, the United Kingdom, South Africa, Singapore, Australia, New Zealand, and India. The researchers collected demographic information, including age, education, and gender.
First step
The assessment was completed by 48,808 respondents between April 8 and Dec. 31, 2020.

A smaller sample of 2,000 people from the same countries who were polled by the investigators in 2019 was used as a comparator.
Taken together, the overall mental well-being score for 2020 was 8% lower than the score obtained in 2019 from the same countries, and the percentage of respondents who fell into the “clinical” category increased from 14% in 2009 to 26% in 2020.
Residents of Singapore had the highest MHQ score, followed by residents of the United States. At the other extreme, respondents from the United Kingdom and South Africa had the poorest MHQ scores.
“It is important to keep in mind that the English-speaking, Internet-enabled populace is not necessarily representative of each country as a whole,” the authors noted.
Youth hardest hit
whose average MHQ score was 29% lower than those aged at least 65 years.
Worldwide, 70% of respondents aged at least 65 years fell into the categories of “succeeding” or “thriving,” compared with just 17% of those aged 18-24 years.
“We saw a massive trend of diminishing mental well-being in younger individuals, suggesting that some societal force is at play that we need to get to the bottom of,” said Dr. Thiagarajan.
“Young people are still learning how to calibrate themselves in the world, and with age comes maturity, leading to a difference in emotional resilience,” she said.
Highest risk group
Mental well-being was poorest among nonbinary/third-gender respondents. Among those persons, more than 50% were classified as being at clinical risk, in comparison with males and females combined, and their MHQ scores were about 47 points lower.
Nonbinary individuals “are universally doing very poorly, relative to males or females,” said Dr. Thiagarajan. “This is a demographic at very high risk with a lot of suicidal thoughts.”
Respondents who had insufficient sleep, who lacked social interaction, and whose level of exercise was insufficient had lower MHQ scores of an “unexpected magnitude,” compared with their counterparts who had sufficient sleep, more social interaction, and more exercise (a discrepancy of 82, 66, and 46 points, respectively).
Only 3.9% of respondents reported having had COVID-19; 0.7% reported having had a severe case. Yet 57% of respondents reported that the pandemic had had negative consequences with regard to their health or their finances or social situation.
Those who were unable to get care for their other health conditions because of the pandemic (2% of all respondents) reported the worst mental well-being, followed by those who struggled for basic necessities (1.4%).
Reduced household income was associated with a 4% lower score but affected a higher percentage of people (17%). Social isolation was associated with a score of about 20 less. Higher rates of lifetime traumas and adversities were likewise associated with lower scores for mental well-being.
Creative, generous approach
Commenting on the survey results, Ken Duckworth, MD, clinical professor at Harvard Medical School, Boston, and chief medical officer of the National Alliance of Mental Illness, noted that the findings were similar to findings from studies in the United States, which showed disproportionately higher rates of mental health problems in younger individuals. Dr. Duckworth was not involved with the survey.
“The idea that this is an international phenomenon and the broad-stroke finding that younger people are suffering across nations is compelling and important for policymakers to look at,” he said.
Dr. Duckworth noted that although the findings are not “representative” of entire populations in a given country, the report is a “first step in a long journey.”
He described the report as “extremely brilliant, creative, and generous, allowing any academician to get access to the data.”
He saw it “less as a definitive report and more as a directionally informative survey that will yield great fruit over time.”
In a comment, Joshua Morganstein, MD, chair of the American Psychiatric Association’s Committee on the Psychiatric Dimensions of Disaster, said: “One of the important things a document like this highlights is the importance of understanding more where risk [for mental health disorders] is concentrated and what things have occurred or might occur that can buffer against that risk or protect us from it. We see that each nation has similar but also different challenges.”
Dr. Thiagarajan is the founder and chief scientist of Sapien Labs. Her coauthors are employees of Sapien Labs. Dr. Duckworth and Dr. Morganstein disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Tips to share with patients feeling vaccine FOMO
COVID-19 has filled our lives with so many challenges, and now we are faced with a new one. For some of our patients, getting a vaccine appointment feels a lot like winning the lottery.
At first, it might have been easy to be joyful for others’ good fortune, but after weeks and now months of seeing others get vaccinated, patience can wear thin. It also creates an imbalance when one member of a “bubble” is vaccinated and others aren’t. It can be painful to be the one who continues to miss out on activities as those around resume pleasures such as seeing friends, dining out, shopping, and traveling.
So many of our patients are feeling worn down from the chronic stress and are not in the best shape to deal with another issue: the fear of missing out. Yet,
Here are some tips to share with patients who are feeling vaccine envy.
- Acknowledge your feelings. Sure, you want to be happy for those getting vaccinated but it does hurt to be left behind. These feelings are real and deserve space. Share them with a trusted friend or therapist. It is indeed quite upsetting to have to wait. In the United States, we are used to having speedy access to medical care. It is unfortunate that so many have to wait for such an important intervention. You have a right to be upset.
- Express your concern to the family member or friend who is vaccinated. Discuss how it could affect your relationship and activities.
- Focus on what you can control. Double down on efforts to not catch or spread COVID. Vaccines are only one very modern way out of the pandemic. Stick to the basics so you feel a sense of control over your health destiny.
- Take advantage of the remaining days or weeks of quarantine. What did you want to accomplish during your time of limited activity? Did you always want to play the piano? These last slower days or weeks might be a great time to try (over Zoom of course). Have you put off cleaning your closet and organizing your drawers? There is nothing like a deadline to kick us into gear.
- Take your best guess for when you will be vaccinated and start to plan. Start to make those plans for late summer and fall.
- Keep things in perspective. We are ALL so fortunate that several vaccines were developed so quickly. Even if the wait is a few more weeks, an end is in sight. One year ago, we had no idea what lay ahead and the uncertainty caused so much anxiety. Now we can feel hopeful that more “normal days” will be returning soon in a predictable time frame.
- Focus on the herd. By now we know that “we are all in this together.” Although we aren’t leaving at the exact same time, mere months will separate us. The more our friends and family get vaccinated, the safer we all are.
Dr. Ritvo, a psychiatrist with more than 25 years’ experience, practices in Miami Beach. She is the author of “Bekindr – The Transformative Power of Kindness” (Hellertown, Pa.: Momosa Publishing, 2018).
COVID-19 has filled our lives with so many challenges, and now we are faced with a new one. For some of our patients, getting a vaccine appointment feels a lot like winning the lottery.
At first, it might have been easy to be joyful for others’ good fortune, but after weeks and now months of seeing others get vaccinated, patience can wear thin. It also creates an imbalance when one member of a “bubble” is vaccinated and others aren’t. It can be painful to be the one who continues to miss out on activities as those around resume pleasures such as seeing friends, dining out, shopping, and traveling.
So many of our patients are feeling worn down from the chronic stress and are not in the best shape to deal with another issue: the fear of missing out. Yet,
Here are some tips to share with patients who are feeling vaccine envy.
- Acknowledge your feelings. Sure, you want to be happy for those getting vaccinated but it does hurt to be left behind. These feelings are real and deserve space. Share them with a trusted friend or therapist. It is indeed quite upsetting to have to wait. In the United States, we are used to having speedy access to medical care. It is unfortunate that so many have to wait for such an important intervention. You have a right to be upset.
- Express your concern to the family member or friend who is vaccinated. Discuss how it could affect your relationship and activities.
- Focus on what you can control. Double down on efforts to not catch or spread COVID. Vaccines are only one very modern way out of the pandemic. Stick to the basics so you feel a sense of control over your health destiny.
- Take advantage of the remaining days or weeks of quarantine. What did you want to accomplish during your time of limited activity? Did you always want to play the piano? These last slower days or weeks might be a great time to try (over Zoom of course). Have you put off cleaning your closet and organizing your drawers? There is nothing like a deadline to kick us into gear.
- Take your best guess for when you will be vaccinated and start to plan. Start to make those plans for late summer and fall.
- Keep things in perspective. We are ALL so fortunate that several vaccines were developed so quickly. Even if the wait is a few more weeks, an end is in sight. One year ago, we had no idea what lay ahead and the uncertainty caused so much anxiety. Now we can feel hopeful that more “normal days” will be returning soon in a predictable time frame.
- Focus on the herd. By now we know that “we are all in this together.” Although we aren’t leaving at the exact same time, mere months will separate us. The more our friends and family get vaccinated, the safer we all are.
Dr. Ritvo, a psychiatrist with more than 25 years’ experience, practices in Miami Beach. She is the author of “Bekindr – The Transformative Power of Kindness” (Hellertown, Pa.: Momosa Publishing, 2018).
COVID-19 has filled our lives with so many challenges, and now we are faced with a new one. For some of our patients, getting a vaccine appointment feels a lot like winning the lottery.
At first, it might have been easy to be joyful for others’ good fortune, but after weeks and now months of seeing others get vaccinated, patience can wear thin. It also creates an imbalance when one member of a “bubble” is vaccinated and others aren’t. It can be painful to be the one who continues to miss out on activities as those around resume pleasures such as seeing friends, dining out, shopping, and traveling.
So many of our patients are feeling worn down from the chronic stress and are not in the best shape to deal with another issue: the fear of missing out. Yet,
Here are some tips to share with patients who are feeling vaccine envy.
- Acknowledge your feelings. Sure, you want to be happy for those getting vaccinated but it does hurt to be left behind. These feelings are real and deserve space. Share them with a trusted friend or therapist. It is indeed quite upsetting to have to wait. In the United States, we are used to having speedy access to medical care. It is unfortunate that so many have to wait for such an important intervention. You have a right to be upset.
- Express your concern to the family member or friend who is vaccinated. Discuss how it could affect your relationship and activities.
- Focus on what you can control. Double down on efforts to not catch or spread COVID. Vaccines are only one very modern way out of the pandemic. Stick to the basics so you feel a sense of control over your health destiny.
- Take advantage of the remaining days or weeks of quarantine. What did you want to accomplish during your time of limited activity? Did you always want to play the piano? These last slower days or weeks might be a great time to try (over Zoom of course). Have you put off cleaning your closet and organizing your drawers? There is nothing like a deadline to kick us into gear.
- Take your best guess for when you will be vaccinated and start to plan. Start to make those plans for late summer and fall.
- Keep things in perspective. We are ALL so fortunate that several vaccines were developed so quickly. Even if the wait is a few more weeks, an end is in sight. One year ago, we had no idea what lay ahead and the uncertainty caused so much anxiety. Now we can feel hopeful that more “normal days” will be returning soon in a predictable time frame.
- Focus on the herd. By now we know that “we are all in this together.” Although we aren’t leaving at the exact same time, mere months will separate us. The more our friends and family get vaccinated, the safer we all are.
Dr. Ritvo, a psychiatrist with more than 25 years’ experience, practices in Miami Beach. She is the author of “Bekindr – The Transformative Power of Kindness” (Hellertown, Pa.: Momosa Publishing, 2018).
‘Reassuring’ data on COVID-19 vaccines in pregnancy
Pregnant women can safely get vaccinated with the Pfizer-BioNTech and Moderna vaccines for COVID-19, surveillance data from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention suggest.
More than 30,000 women who received these vaccines have reported pregnancies through the CDC’s V-Safe voluntary reporting system, and their rates of complications are not significantly different from those of unvaccinated pregnant women, said Tom Shimabukuro, MD, MPH, MBA, deputy director of the CDC Immunization Safety Office.
“Overall, the data are reassuring with respect to vaccine safety in pregnant women,” he told this news organization.
Dr. Shimabukuro presented the data during a March 1 meeting of the Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices, a group of health experts selected by the Secretary of the U.S. Department of Health & Human Services.
The CDC has included pregnancy along with other underlying conditions that qualify people to be offered vaccines in the third priority tier (Phase 1c).
“There is evidence that pregnant women who get COVID-19 are at increased risk of severe illness and complications from severe illness,” Dr. Shimabukuro explained. “And there is also evidence that pregnant persons who get COVID-19 may be at increased risk for adverse pregnancy outcomes.”
The American College of Obstetrics and Gynecology recommends that “COVID-19 vaccines should not be withheld from pregnant individuals.”
By contrast, the World Health Organization recommends the vaccines only for those pregnant women who are “at high risk of exposure to SARS-CoV-2 (for example, health workers) or who have comorbidities which add to their risk of severe disease.”
Not enough information was available from the pivotal trials of the Moderna and Pfizer vaccines to assess risk in pregnant women, according to these manufacturers. Pfizer has announced a follow-up trial of its vaccine in healthy pregnant women.
Analyzing surveillance data
To better assess whether the Pfizer or Moderna vaccines cause problems in pregnancy or childbirth, Dr. Shimabukuro and colleagues analyzed data from V-Safe and the Vaccine Adverse Event Reporting System (VAERS).
The CDC encourages providers to inform people they vaccinate about the V-Safe program. Participants can voluntarily enter their data through a website, and may receive follow-up text messages and phone calls from the CDC asking for additional information at various times after vaccination. It is not a systematic survey, and the sample is not necessarily representative of everyone who gets the vaccine, Dr. Shimabukuro noted.
At the time of the study, V-Safe recorded 55,220,364 reports from people who received at least one dose of the Pfizer or Moderna vaccine through Feb. 16. These included 30,494 pregnancies, of which 16,039 were in women who received the Pfizer vaccine and 14,455 in women who received the Moderna vaccine.
Analyzing data collected through Jan. 13, 2021, the researchers found that both local and systemic reactions were similar between pregnant and nonpregnant women aged 16-54 years.
Most women reported pain, and some reported swelling, redness, and itching at the injection site. Of systemic reactions, fatigue was the most common, followed by headache, myalgia, chills, nausea, and fever. The systemic reactions were more common with the second Pfizer dose; fatigue affected a majority of both pregnant and nonpregnant women. Data on the second Moderna dose were not available.
The CDC enrolled 1,815 pregnant women for additional follow-up, among whom there were 275 completed pregnancies and 232 live births.
Rates of outcomes “of interest” were no higher among these women than in the general population. 
In contrast to V-Safe, data from VAERS, comanaged by the CDC and U.S. Food and Drug Administration, are from spontaneous reports of adverse events. The sources for those reports are varied. “That could be the health care provider,” Dr. Shimabukuro said. “That could be the patient themselves. It could be a caregiver for children.”
Just 154 VAERS reports through Feb. 16 concerned pregnant women, and of these, only 42 (27%) were for pregnancy-specific conditions, with the other 73% representing the types of adverse events reported for the general population of vaccinated people, such as headache and fatigue.
Of the 42 pregnancy-related events, there were 29 spontaneous abortions or miscarriages, with the remainder divided among 10 other pregnancy and neonatal conditions.
“When we looked at those outcomes and we compared the reporting rates, based on known background rates of these conditions, we did not see anything unexpected or concerning with respect to pregnancy or neonatal-specific conditions,” Dr. Shimabukuro said about the VAERS data.
The CDC did not collect data on fertility. “We’ve done a lot of work with other vaccines,” said Dr. Shimabukuro. “And just from a biological basis, we don’t have any evidence that vaccination, just in general, causes fertility problems.”
Also, Dr. Shimabukuro noted that the COVID-19 vaccine made by Janssen/Johnson & Johnson did not receive emergency authorization from the FDA in time to be included in the current report, but is being tracked for future reports.
Vaccination could benefit infants
In addition to the new safety data, experts continue to remind clinicians and the public that vaccination during pregnancy could benefit offspring. The unborn babies of pregnant women who receive the COVID-19 vaccine could be protected from the virus for the first several months of their lives, said White House COVID-19 czar Anthony Fauci, MD, at a briefing on March 10.
“We’ve seen this with many other vaccines,” Dr. Fauci said. “That’s a very good way you can get protection for the mother during pregnancy and also a transfer of protection for the infant, which will last a few months following the birth.”
Dr. Fauci also noted that the same vaccine platform used in Johnson & Johnson’s COVID-19 vaccine was successfully used for Ebola in pregnant women in Africa.
Dr. Shimabukuro has reported no relevant financial relationships.
Lindsay Kalter contributed to the reporting for this story.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Pregnant women can safely get vaccinated with the Pfizer-BioNTech and Moderna vaccines for COVID-19, surveillance data from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention suggest.
More than 30,000 women who received these vaccines have reported pregnancies through the CDC’s V-Safe voluntary reporting system, and their rates of complications are not significantly different from those of unvaccinated pregnant women, said Tom Shimabukuro, MD, MPH, MBA, deputy director of the CDC Immunization Safety Office.
“Overall, the data are reassuring with respect to vaccine safety in pregnant women,” he told this news organization.
Dr. Shimabukuro presented the data during a March 1 meeting of the Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices, a group of health experts selected by the Secretary of the U.S. Department of Health & Human Services.
The CDC has included pregnancy along with other underlying conditions that qualify people to be offered vaccines in the third priority tier (Phase 1c).
“There is evidence that pregnant women who get COVID-19 are at increased risk of severe illness and complications from severe illness,” Dr. Shimabukuro explained. “And there is also evidence that pregnant persons who get COVID-19 may be at increased risk for adverse pregnancy outcomes.”
The American College of Obstetrics and Gynecology recommends that “COVID-19 vaccines should not be withheld from pregnant individuals.”
By contrast, the World Health Organization recommends the vaccines only for those pregnant women who are “at high risk of exposure to SARS-CoV-2 (for example, health workers) or who have comorbidities which add to their risk of severe disease.”
Not enough information was available from the pivotal trials of the Moderna and Pfizer vaccines to assess risk in pregnant women, according to these manufacturers. Pfizer has announced a follow-up trial of its vaccine in healthy pregnant women.
Analyzing surveillance data
To better assess whether the Pfizer or Moderna vaccines cause problems in pregnancy or childbirth, Dr. Shimabukuro and colleagues analyzed data from V-Safe and the Vaccine Adverse Event Reporting System (VAERS).
The CDC encourages providers to inform people they vaccinate about the V-Safe program. Participants can voluntarily enter their data through a website, and may receive follow-up text messages and phone calls from the CDC asking for additional information at various times after vaccination. It is not a systematic survey, and the sample is not necessarily representative of everyone who gets the vaccine, Dr. Shimabukuro noted.
At the time of the study, V-Safe recorded 55,220,364 reports from people who received at least one dose of the Pfizer or Moderna vaccine through Feb. 16. These included 30,494 pregnancies, of which 16,039 were in women who received the Pfizer vaccine and 14,455 in women who received the Moderna vaccine.
Analyzing data collected through Jan. 13, 2021, the researchers found that both local and systemic reactions were similar between pregnant and nonpregnant women aged 16-54 years.
Most women reported pain, and some reported swelling, redness, and itching at the injection site. Of systemic reactions, fatigue was the most common, followed by headache, myalgia, chills, nausea, and fever. The systemic reactions were more common with the second Pfizer dose; fatigue affected a majority of both pregnant and nonpregnant women. Data on the second Moderna dose were not available.
The CDC enrolled 1,815 pregnant women for additional follow-up, among whom there were 275 completed pregnancies and 232 live births.
Rates of outcomes “of interest” were no higher among these women than in the general population. 
In contrast to V-Safe, data from VAERS, comanaged by the CDC and U.S. Food and Drug Administration, are from spontaneous reports of adverse events. The sources for those reports are varied. “That could be the health care provider,” Dr. Shimabukuro said. “That could be the patient themselves. It could be a caregiver for children.”
Just 154 VAERS reports through Feb. 16 concerned pregnant women, and of these, only 42 (27%) were for pregnancy-specific conditions, with the other 73% representing the types of adverse events reported for the general population of vaccinated people, such as headache and fatigue.
Of the 42 pregnancy-related events, there were 29 spontaneous abortions or miscarriages, with the remainder divided among 10 other pregnancy and neonatal conditions.
“When we looked at those outcomes and we compared the reporting rates, based on known background rates of these conditions, we did not see anything unexpected or concerning with respect to pregnancy or neonatal-specific conditions,” Dr. Shimabukuro said about the VAERS data.
The CDC did not collect data on fertility. “We’ve done a lot of work with other vaccines,” said Dr. Shimabukuro. “And just from a biological basis, we don’t have any evidence that vaccination, just in general, causes fertility problems.”
Also, Dr. Shimabukuro noted that the COVID-19 vaccine made by Janssen/Johnson & Johnson did not receive emergency authorization from the FDA in time to be included in the current report, but is being tracked for future reports.
Vaccination could benefit infants
In addition to the new safety data, experts continue to remind clinicians and the public that vaccination during pregnancy could benefit offspring. The unborn babies of pregnant women who receive the COVID-19 vaccine could be protected from the virus for the first several months of their lives, said White House COVID-19 czar Anthony Fauci, MD, at a briefing on March 10.
“We’ve seen this with many other vaccines,” Dr. Fauci said. “That’s a very good way you can get protection for the mother during pregnancy and also a transfer of protection for the infant, which will last a few months following the birth.”
Dr. Fauci also noted that the same vaccine platform used in Johnson & Johnson’s COVID-19 vaccine was successfully used for Ebola in pregnant women in Africa.
Dr. Shimabukuro has reported no relevant financial relationships.
Lindsay Kalter contributed to the reporting for this story.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Pregnant women can safely get vaccinated with the Pfizer-BioNTech and Moderna vaccines for COVID-19, surveillance data from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention suggest.
More than 30,000 women who received these vaccines have reported pregnancies through the CDC’s V-Safe voluntary reporting system, and their rates of complications are not significantly different from those of unvaccinated pregnant women, said Tom Shimabukuro, MD, MPH, MBA, deputy director of the CDC Immunization Safety Office.
“Overall, the data are reassuring with respect to vaccine safety in pregnant women,” he told this news organization.
Dr. Shimabukuro presented the data during a March 1 meeting of the Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices, a group of health experts selected by the Secretary of the U.S. Department of Health & Human Services.
The CDC has included pregnancy along with other underlying conditions that qualify people to be offered vaccines in the third priority tier (Phase 1c).
“There is evidence that pregnant women who get COVID-19 are at increased risk of severe illness and complications from severe illness,” Dr. Shimabukuro explained. “And there is also evidence that pregnant persons who get COVID-19 may be at increased risk for adverse pregnancy outcomes.”
The American College of Obstetrics and Gynecology recommends that “COVID-19 vaccines should not be withheld from pregnant individuals.”
By contrast, the World Health Organization recommends the vaccines only for those pregnant women who are “at high risk of exposure to SARS-CoV-2 (for example, health workers) or who have comorbidities which add to their risk of severe disease.”
Not enough information was available from the pivotal trials of the Moderna and Pfizer vaccines to assess risk in pregnant women, according to these manufacturers. Pfizer has announced a follow-up trial of its vaccine in healthy pregnant women.
Analyzing surveillance data
To better assess whether the Pfizer or Moderna vaccines cause problems in pregnancy or childbirth, Dr. Shimabukuro and colleagues analyzed data from V-Safe and the Vaccine Adverse Event Reporting System (VAERS).
The CDC encourages providers to inform people they vaccinate about the V-Safe program. Participants can voluntarily enter their data through a website, and may receive follow-up text messages and phone calls from the CDC asking for additional information at various times after vaccination. It is not a systematic survey, and the sample is not necessarily representative of everyone who gets the vaccine, Dr. Shimabukuro noted.
At the time of the study, V-Safe recorded 55,220,364 reports from people who received at least one dose of the Pfizer or Moderna vaccine through Feb. 16. These included 30,494 pregnancies, of which 16,039 were in women who received the Pfizer vaccine and 14,455 in women who received the Moderna vaccine.
Analyzing data collected through Jan. 13, 2021, the researchers found that both local and systemic reactions were similar between pregnant and nonpregnant women aged 16-54 years.
Most women reported pain, and some reported swelling, redness, and itching at the injection site. Of systemic reactions, fatigue was the most common, followed by headache, myalgia, chills, nausea, and fever. The systemic reactions were more common with the second Pfizer dose; fatigue affected a majority of both pregnant and nonpregnant women. Data on the second Moderna dose were not available.
The CDC enrolled 1,815 pregnant women for additional follow-up, among whom there were 275 completed pregnancies and 232 live births.
Rates of outcomes “of interest” were no higher among these women than in the general population. 
In contrast to V-Safe, data from VAERS, comanaged by the CDC and U.S. Food and Drug Administration, are from spontaneous reports of adverse events. The sources for those reports are varied. “That could be the health care provider,” Dr. Shimabukuro said. “That could be the patient themselves. It could be a caregiver for children.”
Just 154 VAERS reports through Feb. 16 concerned pregnant women, and of these, only 42 (27%) were for pregnancy-specific conditions, with the other 73% representing the types of adverse events reported for the general population of vaccinated people, such as headache and fatigue.
Of the 42 pregnancy-related events, there were 29 spontaneous abortions or miscarriages, with the remainder divided among 10 other pregnancy and neonatal conditions.
“When we looked at those outcomes and we compared the reporting rates, based on known background rates of these conditions, we did not see anything unexpected or concerning with respect to pregnancy or neonatal-specific conditions,” Dr. Shimabukuro said about the VAERS data.
The CDC did not collect data on fertility. “We’ve done a lot of work with other vaccines,” said Dr. Shimabukuro. “And just from a biological basis, we don’t have any evidence that vaccination, just in general, causes fertility problems.”
Also, Dr. Shimabukuro noted that the COVID-19 vaccine made by Janssen/Johnson & Johnson did not receive emergency authorization from the FDA in time to be included in the current report, but is being tracked for future reports.
Vaccination could benefit infants
In addition to the new safety data, experts continue to remind clinicians and the public that vaccination during pregnancy could benefit offspring. The unborn babies of pregnant women who receive the COVID-19 vaccine could be protected from the virus for the first several months of their lives, said White House COVID-19 czar Anthony Fauci, MD, at a briefing on March 10.
“We’ve seen this with many other vaccines,” Dr. Fauci said. “That’s a very good way you can get protection for the mother during pregnancy and also a transfer of protection for the infant, which will last a few months following the birth.”
Dr. Fauci also noted that the same vaccine platform used in Johnson & Johnson’s COVID-19 vaccine was successfully used for Ebola in pregnant women in Africa.
Dr. Shimabukuro has reported no relevant financial relationships.
Lindsay Kalter contributed to the reporting for this story.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
High obesity rates in Southern states magnify COVID threats
In January, as Mississippi health officials planned for their incoming shipments of COVID-19 vaccine, they assessed the state’s most vulnerable: health care workers, of course, and elderly people in nursing homes. But among those who needed urgent protection from the virus ripping across the Magnolia State were 1 million Mississippians with obesity.
Obesity and weight-related illnesses have been deadly liabilities in the COVID era. A report released this month by the World Obesity Federation found that increased body weight is the second-greatest predictor of COVID-related hospitalization and death across the globe, trailing only old age as a risk factor.
As a fixture of life in the American South – home to 9 of the nation’s 12 heaviest states – obesity is playing a role not only in COVID outcomes, but in the calculus of the vaccination rollout. Mississippi was one of the first states to add a body mass index of 30 or more (a rough gauge of obesity tied to height and weight) to the list of qualifying medical conditions for a shot. About 40% of the state’s adults meet that definition, according to federal health survey data, and combined with the risk group already eligible for vaccination – residents 65 and older – that means fully half of Mississippi’s adults are entitled to vie for a restricted allotment of shots.
At least 29 states have green-lighted obesity for inclusion in the first phases of the vaccine rollout, according to KFF – a vast widening of eligibility that has the potential to overwhelm government efforts and heighten competition for scarce doses.
“We have a lifesaving intervention, and we don’t have enough of it,” said Jen Kates, PhD, director of global health and HIV policy for Kaiser Family Foundation. “Hard choices are being made about who should go first, and there is no right answer.”
The sheer prevalence of obesity in the nation – two in three Americans exceed what is considered a healthy weight – was a public health concern well before the pandemic. But COVID-19 dramatically fast-tracked the discussion from warnings about the long-term damage excess fat tissue can pose to heart, lung and metabolic functions to far more immediate threats.
In the United Kingdom, for example, overweight COVID patients were 67% more likely to require intensive care, and obese patients three times likelier, according to the World Obesity Federation report. A Centers for Disease Control and Prevention study released Monday found a similar trend among U.S. patients and noted that the risk of COVID-related hospitalization, ventilation and death increased with patients’ obesity level.
The counties that hug the southern Mississippi River are home to some of the most concentrated pockets of extreme obesity in the United States. Coronavirus infections began surging in Southern states early last summer, and hospitalizations rose in step.
Deaths in rural stretches of Arkansas, Louisiana, Mississippi, and Tennessee have been overshadowed by the sheer number of deaths in metropolitan areas like New York, Los Angeles, and Essex County, N.J. But as a share of the population, the coronavirus has been similarly unsparing in many Southern communities. In sparsely populated Claiborne County, Miss., on the floodplains of the Mississippi River, 30 residents – about 1 in 300 – had died as of early March. In East Feliciana Parish, La., north of Baton Rouge, with 106 deaths, about 1 in 180 had died by then.
“It’s just math. If the population is more obese and obesity clearly contributes to worse outcomes, then neighborhoods, cities, states and countries that are more obese will have a greater toll from COVID,” said Dr. James de Lemos, MD, a professor of internal medicine at UT Southwestern Medical Center in Dallas who led a study of hospitalized COVID patients published in the medical journal Circulation.
And, because in the U.S. obesity rates tend to be relatively high among African Americans and Latinos who are poor, with diminished access to health care, “it’s a triple whammy,” Dr. de Lemos said. “All these things intersect.”
Poverty and limited access to medical care are common features in the South, where residents like Michelle Antonyshyn, a former registered nurse and mother of seven in Salem, Ark., say they are afraid of the virus. Ms. Antonyshyn, 49, has obesity and debilitating pain in her knees and back, though she does not have high blood pressure or diabetes, two underlying conditions that federal health officials have determined are added risk factors for severe cases of COVID-19.
Still, she said, she “was very concerned just knowing that being obese puts you more at risk for bad outcomes such as being on a ventilator and death.” As a precaution, Ms. Antonyshyn said, she and her large brood locked down early and stopped attending church services in person, watching online instead.
“It’s not the same as having fellowship, but the risk for me was enough,” said Ms. Antonyshyn.
Governors throughout the South seem to recognize that weight can contribute to COVID-19 complications and have pushed for vaccine eligibility rules that prioritize obesity. But on the ground, local health officials are girding for having to tell newly eligible people who qualify as obese that there aren’t enough shots to go around.
In Port Gibson, Miss., Mheja Williams, MD, medical director of the Claiborne County Family Health Center, has been receiving barely enough doses to inoculate the health workers and oldest seniors in her county of 9,600. One week in early February, she received 100 doses.
Obesity and extreme obesity are endemic in Claiborne County, and health officials say the “normalization” of obesity means people often don’t register their weight as a risk factor, whether for COVID or other health issues. The risks are exacerbated by a general flouting of pandemic etiquette: Dr. Williams said that middle-aged and younger residents are not especially vigilant about physical distancing and that mask use is rare.
The rise of obesity in the United States is well documented over the past half-century, as the nation turned from a diet of fruits, vegetables and limited meats to one laden with ultra-processed foods and rich with salt, fat, sugar, and flavorings, along with copious amounts of meat, fast food, and soda. The U.S. has generally led the global obesity race, setting records as even toddlers and young children grew implausibly, dangerously overweight.
Well before COVID, obesity was a leading cause of preventable death in the United States. The National Institutes of Health declared it a disease in 1998, one that fosters heart disease, stroke, type 2 diabetes, and breast, colon, and other cancers.
Researchers say it is no coincidence that nations like the United States, the United Kingdom, and Italy, with relatively high obesity rates, have proved particularly vulnerable to the novel coronavirus.
They believe the virus may exploit underlying metabolic and physiological impairments that often exist in concert with obesity. Extra fat can lead to a cascade of metabolic disruptions, chronic systemic inflammation, and hormonal dysregulation that may thwart the body’s response to infection.
Other respiratory viruses, like influenza and SARS, which appeared in China in 2002, rely on cholesterol to spread enveloped RNA virus to neighboring cells, and researchers have proposed that a similar mechanism may play a role in the spread of the novel coronavirus.
There are also practical problems for coronavirus patients with obesity admitted to the hospital. They can be more difficult to intubate because of excess central weight pressing down on the diaphragm, making breathing with infected lungs even more difficult.
Physicians who specialize in treating patients with obesity say public health officials need to be more forthright and urgent in their messaging, telegraphing the risks of this COVID era.
“It should be explicit and direct,” said Fatima Stanford, MD, an obesity medicine specialist at Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston, and a Harvard Medical School instructor.
Dr. Stanford denounces the fat-shaming and bullying that people with obesity often experience. But telling patients – and the public – that obesity increases the risk of hospitalization and death is crucial, she said.
“I don’t think it’s stigmatizing,” she said. “If you tell them in that way, it’s not to scare you, it’s just giving information. Sometimes people are just unaware.”
KHN (Kaiser Health News) is a national newsroom that produces in-depth journalism about health issues. Together with Policy Analysis and Polling, KHN is one of the three major operating programs at KFF (Kaiser Family Foundation). KFF is an endowed nonprofit organization providing information on health issues to the nation.
In January, as Mississippi health officials planned for their incoming shipments of COVID-19 vaccine, they assessed the state’s most vulnerable: health care workers, of course, and elderly people in nursing homes. But among those who needed urgent protection from the virus ripping across the Magnolia State were 1 million Mississippians with obesity.
Obesity and weight-related illnesses have been deadly liabilities in the COVID era. A report released this month by the World Obesity Federation found that increased body weight is the second-greatest predictor of COVID-related hospitalization and death across the globe, trailing only old age as a risk factor.
As a fixture of life in the American South – home to 9 of the nation’s 12 heaviest states – obesity is playing a role not only in COVID outcomes, but in the calculus of the vaccination rollout. Mississippi was one of the first states to add a body mass index of 30 or more (a rough gauge of obesity tied to height and weight) to the list of qualifying medical conditions for a shot. About 40% of the state’s adults meet that definition, according to federal health survey data, and combined with the risk group already eligible for vaccination – residents 65 and older – that means fully half of Mississippi’s adults are entitled to vie for a restricted allotment of shots.
At least 29 states have green-lighted obesity for inclusion in the first phases of the vaccine rollout, according to KFF – a vast widening of eligibility that has the potential to overwhelm government efforts and heighten competition for scarce doses.
“We have a lifesaving intervention, and we don’t have enough of it,” said Jen Kates, PhD, director of global health and HIV policy for Kaiser Family Foundation. “Hard choices are being made about who should go first, and there is no right answer.”
The sheer prevalence of obesity in the nation – two in three Americans exceed what is considered a healthy weight – was a public health concern well before the pandemic. But COVID-19 dramatically fast-tracked the discussion from warnings about the long-term damage excess fat tissue can pose to heart, lung and metabolic functions to far more immediate threats.
In the United Kingdom, for example, overweight COVID patients were 67% more likely to require intensive care, and obese patients three times likelier, according to the World Obesity Federation report. A Centers for Disease Control and Prevention study released Monday found a similar trend among U.S. patients and noted that the risk of COVID-related hospitalization, ventilation and death increased with patients’ obesity level.
The counties that hug the southern Mississippi River are home to some of the most concentrated pockets of extreme obesity in the United States. Coronavirus infections began surging in Southern states early last summer, and hospitalizations rose in step.
Deaths in rural stretches of Arkansas, Louisiana, Mississippi, and Tennessee have been overshadowed by the sheer number of deaths in metropolitan areas like New York, Los Angeles, and Essex County, N.J. But as a share of the population, the coronavirus has been similarly unsparing in many Southern communities. In sparsely populated Claiborne County, Miss., on the floodplains of the Mississippi River, 30 residents – about 1 in 300 – had died as of early March. In East Feliciana Parish, La., north of Baton Rouge, with 106 deaths, about 1 in 180 had died by then.
“It’s just math. If the population is more obese and obesity clearly contributes to worse outcomes, then neighborhoods, cities, states and countries that are more obese will have a greater toll from COVID,” said Dr. James de Lemos, MD, a professor of internal medicine at UT Southwestern Medical Center in Dallas who led a study of hospitalized COVID patients published in the medical journal Circulation.
And, because in the U.S. obesity rates tend to be relatively high among African Americans and Latinos who are poor, with diminished access to health care, “it’s a triple whammy,” Dr. de Lemos said. “All these things intersect.”
Poverty and limited access to medical care are common features in the South, where residents like Michelle Antonyshyn, a former registered nurse and mother of seven in Salem, Ark., say they are afraid of the virus. Ms. Antonyshyn, 49, has obesity and debilitating pain in her knees and back, though she does not have high blood pressure or diabetes, two underlying conditions that federal health officials have determined are added risk factors for severe cases of COVID-19.
Still, she said, she “was very concerned just knowing that being obese puts you more at risk for bad outcomes such as being on a ventilator and death.” As a precaution, Ms. Antonyshyn said, she and her large brood locked down early and stopped attending church services in person, watching online instead.
“It’s not the same as having fellowship, but the risk for me was enough,” said Ms. Antonyshyn.
Governors throughout the South seem to recognize that weight can contribute to COVID-19 complications and have pushed for vaccine eligibility rules that prioritize obesity. But on the ground, local health officials are girding for having to tell newly eligible people who qualify as obese that there aren’t enough shots to go around.
In Port Gibson, Miss., Mheja Williams, MD, medical director of the Claiborne County Family Health Center, has been receiving barely enough doses to inoculate the health workers and oldest seniors in her county of 9,600. One week in early February, she received 100 doses.
Obesity and extreme obesity are endemic in Claiborne County, and health officials say the “normalization” of obesity means people often don’t register their weight as a risk factor, whether for COVID or other health issues. The risks are exacerbated by a general flouting of pandemic etiquette: Dr. Williams said that middle-aged and younger residents are not especially vigilant about physical distancing and that mask use is rare.
The rise of obesity in the United States is well documented over the past half-century, as the nation turned from a diet of fruits, vegetables and limited meats to one laden with ultra-processed foods and rich with salt, fat, sugar, and flavorings, along with copious amounts of meat, fast food, and soda. The U.S. has generally led the global obesity race, setting records as even toddlers and young children grew implausibly, dangerously overweight.
Well before COVID, obesity was a leading cause of preventable death in the United States. The National Institutes of Health declared it a disease in 1998, one that fosters heart disease, stroke, type 2 diabetes, and breast, colon, and other cancers.
Researchers say it is no coincidence that nations like the United States, the United Kingdom, and Italy, with relatively high obesity rates, have proved particularly vulnerable to the novel coronavirus.
They believe the virus may exploit underlying metabolic and physiological impairments that often exist in concert with obesity. Extra fat can lead to a cascade of metabolic disruptions, chronic systemic inflammation, and hormonal dysregulation that may thwart the body’s response to infection.
Other respiratory viruses, like influenza and SARS, which appeared in China in 2002, rely on cholesterol to spread enveloped RNA virus to neighboring cells, and researchers have proposed that a similar mechanism may play a role in the spread of the novel coronavirus.
There are also practical problems for coronavirus patients with obesity admitted to the hospital. They can be more difficult to intubate because of excess central weight pressing down on the diaphragm, making breathing with infected lungs even more difficult.
Physicians who specialize in treating patients with obesity say public health officials need to be more forthright and urgent in their messaging, telegraphing the risks of this COVID era.
“It should be explicit and direct,” said Fatima Stanford, MD, an obesity medicine specialist at Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston, and a Harvard Medical School instructor.
Dr. Stanford denounces the fat-shaming and bullying that people with obesity often experience. But telling patients – and the public – that obesity increases the risk of hospitalization and death is crucial, she said.
“I don’t think it’s stigmatizing,” she said. “If you tell them in that way, it’s not to scare you, it’s just giving information. Sometimes people are just unaware.”
KHN (Kaiser Health News) is a national newsroom that produces in-depth journalism about health issues. Together with Policy Analysis and Polling, KHN is one of the three major operating programs at KFF (Kaiser Family Foundation). KFF is an endowed nonprofit organization providing information on health issues to the nation.
In January, as Mississippi health officials planned for their incoming shipments of COVID-19 vaccine, they assessed the state’s most vulnerable: health care workers, of course, and elderly people in nursing homes. But among those who needed urgent protection from the virus ripping across the Magnolia State were 1 million Mississippians with obesity.
Obesity and weight-related illnesses have been deadly liabilities in the COVID era. A report released this month by the World Obesity Federation found that increased body weight is the second-greatest predictor of COVID-related hospitalization and death across the globe, trailing only old age as a risk factor.
As a fixture of life in the American South – home to 9 of the nation’s 12 heaviest states – obesity is playing a role not only in COVID outcomes, but in the calculus of the vaccination rollout. Mississippi was one of the first states to add a body mass index of 30 or more (a rough gauge of obesity tied to height and weight) to the list of qualifying medical conditions for a shot. About 40% of the state’s adults meet that definition, according to federal health survey data, and combined with the risk group already eligible for vaccination – residents 65 and older – that means fully half of Mississippi’s adults are entitled to vie for a restricted allotment of shots.
At least 29 states have green-lighted obesity for inclusion in the first phases of the vaccine rollout, according to KFF – a vast widening of eligibility that has the potential to overwhelm government efforts and heighten competition for scarce doses.
“We have a lifesaving intervention, and we don’t have enough of it,” said Jen Kates, PhD, director of global health and HIV policy for Kaiser Family Foundation. “Hard choices are being made about who should go first, and there is no right answer.”
The sheer prevalence of obesity in the nation – two in three Americans exceed what is considered a healthy weight – was a public health concern well before the pandemic. But COVID-19 dramatically fast-tracked the discussion from warnings about the long-term damage excess fat tissue can pose to heart, lung and metabolic functions to far more immediate threats.
In the United Kingdom, for example, overweight COVID patients were 67% more likely to require intensive care, and obese patients three times likelier, according to the World Obesity Federation report. A Centers for Disease Control and Prevention study released Monday found a similar trend among U.S. patients and noted that the risk of COVID-related hospitalization, ventilation and death increased with patients’ obesity level.
The counties that hug the southern Mississippi River are home to some of the most concentrated pockets of extreme obesity in the United States. Coronavirus infections began surging in Southern states early last summer, and hospitalizations rose in step.
Deaths in rural stretches of Arkansas, Louisiana, Mississippi, and Tennessee have been overshadowed by the sheer number of deaths in metropolitan areas like New York, Los Angeles, and Essex County, N.J. But as a share of the population, the coronavirus has been similarly unsparing in many Southern communities. In sparsely populated Claiborne County, Miss., on the floodplains of the Mississippi River, 30 residents – about 1 in 300 – had died as of early March. In East Feliciana Parish, La., north of Baton Rouge, with 106 deaths, about 1 in 180 had died by then.
“It’s just math. If the population is more obese and obesity clearly contributes to worse outcomes, then neighborhoods, cities, states and countries that are more obese will have a greater toll from COVID,” said Dr. James de Lemos, MD, a professor of internal medicine at UT Southwestern Medical Center in Dallas who led a study of hospitalized COVID patients published in the medical journal Circulation.
And, because in the U.S. obesity rates tend to be relatively high among African Americans and Latinos who are poor, with diminished access to health care, “it’s a triple whammy,” Dr. de Lemos said. “All these things intersect.”
Poverty and limited access to medical care are common features in the South, where residents like Michelle Antonyshyn, a former registered nurse and mother of seven in Salem, Ark., say they are afraid of the virus. Ms. Antonyshyn, 49, has obesity and debilitating pain in her knees and back, though she does not have high blood pressure or diabetes, two underlying conditions that federal health officials have determined are added risk factors for severe cases of COVID-19.
Still, she said, she “was very concerned just knowing that being obese puts you more at risk for bad outcomes such as being on a ventilator and death.” As a precaution, Ms. Antonyshyn said, she and her large brood locked down early and stopped attending church services in person, watching online instead.
“It’s not the same as having fellowship, but the risk for me was enough,” said Ms. Antonyshyn.
Governors throughout the South seem to recognize that weight can contribute to COVID-19 complications and have pushed for vaccine eligibility rules that prioritize obesity. But on the ground, local health officials are girding for having to tell newly eligible people who qualify as obese that there aren’t enough shots to go around.
In Port Gibson, Miss., Mheja Williams, MD, medical director of the Claiborne County Family Health Center, has been receiving barely enough doses to inoculate the health workers and oldest seniors in her county of 9,600. One week in early February, she received 100 doses.
Obesity and extreme obesity are endemic in Claiborne County, and health officials say the “normalization” of obesity means people often don’t register their weight as a risk factor, whether for COVID or other health issues. The risks are exacerbated by a general flouting of pandemic etiquette: Dr. Williams said that middle-aged and younger residents are not especially vigilant about physical distancing and that mask use is rare.
The rise of obesity in the United States is well documented over the past half-century, as the nation turned from a diet of fruits, vegetables and limited meats to one laden with ultra-processed foods and rich with salt, fat, sugar, and flavorings, along with copious amounts of meat, fast food, and soda. The U.S. has generally led the global obesity race, setting records as even toddlers and young children grew implausibly, dangerously overweight.
Well before COVID, obesity was a leading cause of preventable death in the United States. The National Institutes of Health declared it a disease in 1998, one that fosters heart disease, stroke, type 2 diabetes, and breast, colon, and other cancers.
Researchers say it is no coincidence that nations like the United States, the United Kingdom, and Italy, with relatively high obesity rates, have proved particularly vulnerable to the novel coronavirus.
They believe the virus may exploit underlying metabolic and physiological impairments that often exist in concert with obesity. Extra fat can lead to a cascade of metabolic disruptions, chronic systemic inflammation, and hormonal dysregulation that may thwart the body’s response to infection.
Other respiratory viruses, like influenza and SARS, which appeared in China in 2002, rely on cholesterol to spread enveloped RNA virus to neighboring cells, and researchers have proposed that a similar mechanism may play a role in the spread of the novel coronavirus.
There are also practical problems for coronavirus patients with obesity admitted to the hospital. They can be more difficult to intubate because of excess central weight pressing down on the diaphragm, making breathing with infected lungs even more difficult.
Physicians who specialize in treating patients with obesity say public health officials need to be more forthright and urgent in their messaging, telegraphing the risks of this COVID era.
“It should be explicit and direct,” said Fatima Stanford, MD, an obesity medicine specialist at Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston, and a Harvard Medical School instructor.
Dr. Stanford denounces the fat-shaming and bullying that people with obesity often experience. But telling patients – and the public – that obesity increases the risk of hospitalization and death is crucial, she said.
“I don’t think it’s stigmatizing,” she said. “If you tell them in that way, it’s not to scare you, it’s just giving information. Sometimes people are just unaware.”
KHN (Kaiser Health News) is a national newsroom that produces in-depth journalism about health issues. Together with Policy Analysis and Polling, KHN is one of the three major operating programs at KFF (Kaiser Family Foundation). KFF is an endowed nonprofit organization providing information on health issues to the nation.
COVID-19 virus reinfections rare; riskiest after age 65
When researchers analyzed test results of 4 million people in Denmark, they found that less than 1% of those who tested positive experienced reinfection.
Initial infection was associated with about 80% protection overall against getting SARS-CoV-2 again. However, among those older than 65, the protection plummeted to 47%.
“Not everybody is protected against reinfection after a first infection. Older people are at higher risk of catching it again,” co–lead author Daniela Michlmayr, PhD, said in an interview. “Our findings emphasize the importance of policies to protect the elderly and of adhering to infection control measures and restrictions, even if previously infected with COVID-19.”
Verifying the need for vaccination
“The findings also highlight the need to vaccinate people who had COVID-19 before, as natural immunity to infection – especially among the elderly 65 and older – cannot be relied upon,” added Dr. Michlmayr, a researcher in the department of bacteria, parasites, and fungi at the Staten Serums Institut, Copenhagen.
The population-based observational study was published online March 17 in The Lancet.
“The findings make sense, as patients who are immunocompromised or of advanced age may not mount an immune response that is as long-lasting,” David Hirschwerk, MD, said in an interview. “It does underscore the importance of vaccination for people of more advanced age, even if they previously were infected with COVID.
“For those who were infected last spring and have not yet been vaccinated, this helps to support the value of still pursuing the vaccine,” added Dr. Hirschwerk, an infectious disease specialist at Northwell Health in Manhasset, N.Y.
Evidence on reinfection risk was limited prior to this study. “Little is known about protection against SARS-CoV-2 repeat infections, but two studies in the UK have found that immunity could last at least 5 to 6 months after infection,” the authors noted.
Along with co–lead author Christian Holm Hansen, PhD, Dr. Michlmayr and colleagues found that 2.11% of 525,339 individuals tested positive for SARS-CoV-2 during the first surge in Denmark from March to May 2020. Within this group, 0.65% tested positive during a second surge from September to December.
By the end of 2020, more than 10 million people had undergone free polymerase chain reaction testing by the Danish government or through the national TestDenmark program.
“My overall take is that it is great to have such a big dataset looking at this question,” E. John Wherry, PhD, said in an interview. The findings support “what we’ve seen in previous, smaller studies.”
Natural protection against reinfection of approximately 80% “is not as good as the vaccines, but not bad,” added Dr. Wherry, director of the Institute for Immunology at the University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia.
Age alters immunity?
“Our finding that older people were more likely than younger people to test positive again if they had already tested positive could be explained by natural age-related changes in the immune system of older adults, also referred to as immune senescence,” the authors noted.
The investigators found no significant differences in reinfection rates between women and men.
As with the previous research, this study also indicates that an initial bout with SARS-CoV-2 infection appears to confer protection for at least 6 months. The researchers found no significant differences between people who were followed for 3-6 months and those followed for 7 months or longer.
Variants not included
To account for possible bias among people who got tested repeatedly, Dr. Michlmayr and colleagues performed a sensitivity analysis in a subgroup. They assessed reinfection rates among people who underwent testing frequently and routinely – nurses, doctors, social workers, and health care assistants – and found that 1.2% tested positive a second time during the second surge.
A limitation of the study was the inability to correlate symptoms with risk for reinfection. Also, the researchers did not account for SARS-CoV-2 variants, noting that “during the study period, such variants were not yet established in Denmark; although into 2021 this pattern is changing.”
Asked to speculate whether the results would be different had the study accounted for variants, Dr. Hirschwerk said, “It depends upon the variant, but certainly for the B.1.351 variant, there already has been data clearly demonstrating risk of reinfection with SARS-CoV-2 despite prior infection with the original strain of virus.”
The emergence of SARS-CoV-2 variants of concern that could escape natural and vaccine-related immunity “complicates matters further,” Rosemary J. Boyton, MBBS, and Daniel M. Altmann, PhD, both of Imperial College London, wrote in an accompanying comment in The Lancet.
“Emerging variants of concern might shift immunity below a protective margin, prompting the need for updated vaccines. Interestingly, vaccine responses even after single dose are substantially enhanced in individuals with a history of infection with SARS-CoV-2,” they added.
The current study confirms that “the hope of protective immunity through natural infections might not be within our reach, and a global vaccination program with high efficacy vaccines is the enduring solution,” Dr. Boyton and Dr. Altmann noted.
Cause for alarm?
Despite evidence that reinfection is relatively rare, “many will find the data reported by Hansen and colleagues about protection through natural infection relatively alarming,” Dr. Boyton and Dr. Altmann wrote in their commentary. The 80% protection rate from reinfection in general and the 47% rate among people aged 65 and older “are more concerning figures than offered by previous studies.”
Vaccines appear to provide better quality, quantity, and durability of protection against repeated infection – measured in terms of neutralizing antibodies and T cells – compared with previous infection with SARS-CoV-2, Dr. Boyton and Dr. Altmann wrote.
More research needed
The duration of natural protection against reinfection remains an unanswered question, the researchers noted, “because too little time has elapsed since the beginning of the pandemic.”
Future prospective and longitudinal cohort studies coupled with molecular surveillance are needed to characterize antibody titers and waning of protection against repeat infections, the authors noted. Furthermore, more answers are needed regarding how some virus variants might contribute to reinfection risk.
No funding for the study has been reported. Dr. Michlmayr, Dr. Hirschwerk, Dr. Wherry, Dr. Boyton, and Dr. Altmann have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
When researchers analyzed test results of 4 million people in Denmark, they found that less than 1% of those who tested positive experienced reinfection.
Initial infection was associated with about 80% protection overall against getting SARS-CoV-2 again. However, among those older than 65, the protection plummeted to 47%.
“Not everybody is protected against reinfection after a first infection. Older people are at higher risk of catching it again,” co–lead author Daniela Michlmayr, PhD, said in an interview. “Our findings emphasize the importance of policies to protect the elderly and of adhering to infection control measures and restrictions, even if previously infected with COVID-19.”
Verifying the need for vaccination
“The findings also highlight the need to vaccinate people who had COVID-19 before, as natural immunity to infection – especially among the elderly 65 and older – cannot be relied upon,” added Dr. Michlmayr, a researcher in the department of bacteria, parasites, and fungi at the Staten Serums Institut, Copenhagen.
The population-based observational study was published online March 17 in The Lancet.
“The findings make sense, as patients who are immunocompromised or of advanced age may not mount an immune response that is as long-lasting,” David Hirschwerk, MD, said in an interview. “It does underscore the importance of vaccination for people of more advanced age, even if they previously were infected with COVID.
“For those who were infected last spring and have not yet been vaccinated, this helps to support the value of still pursuing the vaccine,” added Dr. Hirschwerk, an infectious disease specialist at Northwell Health in Manhasset, N.Y.
Evidence on reinfection risk was limited prior to this study. “Little is known about protection against SARS-CoV-2 repeat infections, but two studies in the UK have found that immunity could last at least 5 to 6 months after infection,” the authors noted.
Along with co–lead author Christian Holm Hansen, PhD, Dr. Michlmayr and colleagues found that 2.11% of 525,339 individuals tested positive for SARS-CoV-2 during the first surge in Denmark from March to May 2020. Within this group, 0.65% tested positive during a second surge from September to December.
By the end of 2020, more than 10 million people had undergone free polymerase chain reaction testing by the Danish government or through the national TestDenmark program.
“My overall take is that it is great to have such a big dataset looking at this question,” E. John Wherry, PhD, said in an interview. The findings support “what we’ve seen in previous, smaller studies.”
Natural protection against reinfection of approximately 80% “is not as good as the vaccines, but not bad,” added Dr. Wherry, director of the Institute for Immunology at the University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia.
Age alters immunity?
“Our finding that older people were more likely than younger people to test positive again if they had already tested positive could be explained by natural age-related changes in the immune system of older adults, also referred to as immune senescence,” the authors noted.
The investigators found no significant differences in reinfection rates between women and men.
As with the previous research, this study also indicates that an initial bout with SARS-CoV-2 infection appears to confer protection for at least 6 months. The researchers found no significant differences between people who were followed for 3-6 months and those followed for 7 months or longer.
Variants not included
To account for possible bias among people who got tested repeatedly, Dr. Michlmayr and colleagues performed a sensitivity analysis in a subgroup. They assessed reinfection rates among people who underwent testing frequently and routinely – nurses, doctors, social workers, and health care assistants – and found that 1.2% tested positive a second time during the second surge.
A limitation of the study was the inability to correlate symptoms with risk for reinfection. Also, the researchers did not account for SARS-CoV-2 variants, noting that “during the study period, such variants were not yet established in Denmark; although into 2021 this pattern is changing.”
Asked to speculate whether the results would be different had the study accounted for variants, Dr. Hirschwerk said, “It depends upon the variant, but certainly for the B.1.351 variant, there already has been data clearly demonstrating risk of reinfection with SARS-CoV-2 despite prior infection with the original strain of virus.”
The emergence of SARS-CoV-2 variants of concern that could escape natural and vaccine-related immunity “complicates matters further,” Rosemary J. Boyton, MBBS, and Daniel M. Altmann, PhD, both of Imperial College London, wrote in an accompanying comment in The Lancet.
“Emerging variants of concern might shift immunity below a protective margin, prompting the need for updated vaccines. Interestingly, vaccine responses even after single dose are substantially enhanced in individuals with a history of infection with SARS-CoV-2,” they added.
The current study confirms that “the hope of protective immunity through natural infections might not be within our reach, and a global vaccination program with high efficacy vaccines is the enduring solution,” Dr. Boyton and Dr. Altmann noted.
Cause for alarm?
Despite evidence that reinfection is relatively rare, “many will find the data reported by Hansen and colleagues about protection through natural infection relatively alarming,” Dr. Boyton and Dr. Altmann wrote in their commentary. The 80% protection rate from reinfection in general and the 47% rate among people aged 65 and older “are more concerning figures than offered by previous studies.”
Vaccines appear to provide better quality, quantity, and durability of protection against repeated infection – measured in terms of neutralizing antibodies and T cells – compared with previous infection with SARS-CoV-2, Dr. Boyton and Dr. Altmann wrote.
More research needed
The duration of natural protection against reinfection remains an unanswered question, the researchers noted, “because too little time has elapsed since the beginning of the pandemic.”
Future prospective and longitudinal cohort studies coupled with molecular surveillance are needed to characterize antibody titers and waning of protection against repeat infections, the authors noted. Furthermore, more answers are needed regarding how some virus variants might contribute to reinfection risk.
No funding for the study has been reported. Dr. Michlmayr, Dr. Hirschwerk, Dr. Wherry, Dr. Boyton, and Dr. Altmann have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
When researchers analyzed test results of 4 million people in Denmark, they found that less than 1% of those who tested positive experienced reinfection.
Initial infection was associated with about 80% protection overall against getting SARS-CoV-2 again. However, among those older than 65, the protection plummeted to 47%.
“Not everybody is protected against reinfection after a first infection. Older people are at higher risk of catching it again,” co–lead author Daniela Michlmayr, PhD, said in an interview. “Our findings emphasize the importance of policies to protect the elderly and of adhering to infection control measures and restrictions, even if previously infected with COVID-19.”
Verifying the need for vaccination
“The findings also highlight the need to vaccinate people who had COVID-19 before, as natural immunity to infection – especially among the elderly 65 and older – cannot be relied upon,” added Dr. Michlmayr, a researcher in the department of bacteria, parasites, and fungi at the Staten Serums Institut, Copenhagen.
The population-based observational study was published online March 17 in The Lancet.
“The findings make sense, as patients who are immunocompromised or of advanced age may not mount an immune response that is as long-lasting,” David Hirschwerk, MD, said in an interview. “It does underscore the importance of vaccination for people of more advanced age, even if they previously were infected with COVID.
“For those who were infected last spring and have not yet been vaccinated, this helps to support the value of still pursuing the vaccine,” added Dr. Hirschwerk, an infectious disease specialist at Northwell Health in Manhasset, N.Y.
Evidence on reinfection risk was limited prior to this study. “Little is known about protection against SARS-CoV-2 repeat infections, but two studies in the UK have found that immunity could last at least 5 to 6 months after infection,” the authors noted.
Along with co–lead author Christian Holm Hansen, PhD, Dr. Michlmayr and colleagues found that 2.11% of 525,339 individuals tested positive for SARS-CoV-2 during the first surge in Denmark from March to May 2020. Within this group, 0.65% tested positive during a second surge from September to December.
By the end of 2020, more than 10 million people had undergone free polymerase chain reaction testing by the Danish government or through the national TestDenmark program.
“My overall take is that it is great to have such a big dataset looking at this question,” E. John Wherry, PhD, said in an interview. The findings support “what we’ve seen in previous, smaller studies.”
Natural protection against reinfection of approximately 80% “is not as good as the vaccines, but not bad,” added Dr. Wherry, director of the Institute for Immunology at the University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia.
Age alters immunity?
“Our finding that older people were more likely than younger people to test positive again if they had already tested positive could be explained by natural age-related changes in the immune system of older adults, also referred to as immune senescence,” the authors noted.
The investigators found no significant differences in reinfection rates between women and men.
As with the previous research, this study also indicates that an initial bout with SARS-CoV-2 infection appears to confer protection for at least 6 months. The researchers found no significant differences between people who were followed for 3-6 months and those followed for 7 months or longer.
Variants not included
To account for possible bias among people who got tested repeatedly, Dr. Michlmayr and colleagues performed a sensitivity analysis in a subgroup. They assessed reinfection rates among people who underwent testing frequently and routinely – nurses, doctors, social workers, and health care assistants – and found that 1.2% tested positive a second time during the second surge.
A limitation of the study was the inability to correlate symptoms with risk for reinfection. Also, the researchers did not account for SARS-CoV-2 variants, noting that “during the study period, such variants were not yet established in Denmark; although into 2021 this pattern is changing.”
Asked to speculate whether the results would be different had the study accounted for variants, Dr. Hirschwerk said, “It depends upon the variant, but certainly for the B.1.351 variant, there already has been data clearly demonstrating risk of reinfection with SARS-CoV-2 despite prior infection with the original strain of virus.”
The emergence of SARS-CoV-2 variants of concern that could escape natural and vaccine-related immunity “complicates matters further,” Rosemary J. Boyton, MBBS, and Daniel M. Altmann, PhD, both of Imperial College London, wrote in an accompanying comment in The Lancet.
“Emerging variants of concern might shift immunity below a protective margin, prompting the need for updated vaccines. Interestingly, vaccine responses even after single dose are substantially enhanced in individuals with a history of infection with SARS-CoV-2,” they added.
The current study confirms that “the hope of protective immunity through natural infections might not be within our reach, and a global vaccination program with high efficacy vaccines is the enduring solution,” Dr. Boyton and Dr. Altmann noted.
Cause for alarm?
Despite evidence that reinfection is relatively rare, “many will find the data reported by Hansen and colleagues about protection through natural infection relatively alarming,” Dr. Boyton and Dr. Altmann wrote in their commentary. The 80% protection rate from reinfection in general and the 47% rate among people aged 65 and older “are more concerning figures than offered by previous studies.”
Vaccines appear to provide better quality, quantity, and durability of protection against repeated infection – measured in terms of neutralizing antibodies and T cells – compared with previous infection with SARS-CoV-2, Dr. Boyton and Dr. Altmann wrote.
More research needed
The duration of natural protection against reinfection remains an unanswered question, the researchers noted, “because too little time has elapsed since the beginning of the pandemic.”
Future prospective and longitudinal cohort studies coupled with molecular surveillance are needed to characterize antibody titers and waning of protection against repeat infections, the authors noted. Furthermore, more answers are needed regarding how some virus variants might contribute to reinfection risk.
No funding for the study has been reported. Dr. Michlmayr, Dr. Hirschwerk, Dr. Wherry, Dr. Boyton, and Dr. Altmann have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Baby born to partially vaccinated mom has COVID-19 antibodies
A baby girl who was born 3 weeks after her mom got the first dose of the Moderna COVID-19 vaccine has antibodies against the coronavirus, according to a preprint paper published on the medRxiv server Feb. 5. The paper hasn’t yet been peer reviewed.
The mom, a health care worker in Florida, developed COVID-19 antibodies after she received the shot. Testing showed that the antibodies passed through the placenta to the baby.
“Maternal vaccination for influenza and TDaP have been well studied in terms of safety and efficacy for protection of the newborn by placental passage of antibodies,” Paul Gilbert, MD, and Chad Rudnick, MD, pediatricians and researchers at Florida Atlantic University, wrote in the paper.
Previous research has indicated that moms who have recovered from COVID-19 can deliver babies with antibodies, according to Insider, but this may be the first report that shows how vaccination during pregnancy can provide antibodies as well.
Dr. Gilbert and Dr. Rudnick said they were fortunate to connect with the mom in Boca Raton. She hadn’t contracted COVID-19 and was able to get the vaccine at the end of her pregnancy in January. When the baby was born, they were able to test the cord blood to look for antibodies specifically from the vaccine.
“We were very excited to see, once the test result came back, that the antibodies from the mom’s vaccine did in fact pass through the placenta to the newborn,” Dr. Rudnick told WPTV, an NBC affiliate in West Palm Beach.
“We knew that we were going to be potentially one of the first in the world to report it, and that opportunity probably only comes once in a career,” Dr. Gilbert told WPTV.
In the preprint, Dr. Gilbert and Dr. Rudnick said a “vigorous, healthy, full-term” baby was born, and the mom received the second dose of the Moderna vaccine during the postpartum period. The newborn received a normal “well-infant” evaluation and was breastfeeding.
The two doctors called for a “significant and urgent need” to research the safety and efficacy of COVID-19 vaccines during pregnancy. They also encouraged other researchers to create pregnancy and breastfeeding registries to study COVID-19 vaccines in pregnant and breastfeeding moms and newborns.
Dr. Gilbert and Dr. Rudnick are now preparing their research for publication and hope future studies will investigate the amount and length of antibody response in newborns.
“Total antibody measurements may be used to determine how long protection is expected, which may help to determine when the best time would be to begin vaccination,” they wrote.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
A baby girl who was born 3 weeks after her mom got the first dose of the Moderna COVID-19 vaccine has antibodies against the coronavirus, according to a preprint paper published on the medRxiv server Feb. 5. The paper hasn’t yet been peer reviewed.
The mom, a health care worker in Florida, developed COVID-19 antibodies after she received the shot. Testing showed that the antibodies passed through the placenta to the baby.
“Maternal vaccination for influenza and TDaP have been well studied in terms of safety and efficacy for protection of the newborn by placental passage of antibodies,” Paul Gilbert, MD, and Chad Rudnick, MD, pediatricians and researchers at Florida Atlantic University, wrote in the paper.
Previous research has indicated that moms who have recovered from COVID-19 can deliver babies with antibodies, according to Insider, but this may be the first report that shows how vaccination during pregnancy can provide antibodies as well.
Dr. Gilbert and Dr. Rudnick said they were fortunate to connect with the mom in Boca Raton. She hadn’t contracted COVID-19 and was able to get the vaccine at the end of her pregnancy in January. When the baby was born, they were able to test the cord blood to look for antibodies specifically from the vaccine.
“We were very excited to see, once the test result came back, that the antibodies from the mom’s vaccine did in fact pass through the placenta to the newborn,” Dr. Rudnick told WPTV, an NBC affiliate in West Palm Beach.
“We knew that we were going to be potentially one of the first in the world to report it, and that opportunity probably only comes once in a career,” Dr. Gilbert told WPTV.
In the preprint, Dr. Gilbert and Dr. Rudnick said a “vigorous, healthy, full-term” baby was born, and the mom received the second dose of the Moderna vaccine during the postpartum period. The newborn received a normal “well-infant” evaluation and was breastfeeding.
The two doctors called for a “significant and urgent need” to research the safety and efficacy of COVID-19 vaccines during pregnancy. They also encouraged other researchers to create pregnancy and breastfeeding registries to study COVID-19 vaccines in pregnant and breastfeeding moms and newborns.
Dr. Gilbert and Dr. Rudnick are now preparing their research for publication and hope future studies will investigate the amount and length of antibody response in newborns.
“Total antibody measurements may be used to determine how long protection is expected, which may help to determine when the best time would be to begin vaccination,” they wrote.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
A baby girl who was born 3 weeks after her mom got the first dose of the Moderna COVID-19 vaccine has antibodies against the coronavirus, according to a preprint paper published on the medRxiv server Feb. 5. The paper hasn’t yet been peer reviewed.
The mom, a health care worker in Florida, developed COVID-19 antibodies after she received the shot. Testing showed that the antibodies passed through the placenta to the baby.
“Maternal vaccination for influenza and TDaP have been well studied in terms of safety and efficacy for protection of the newborn by placental passage of antibodies,” Paul Gilbert, MD, and Chad Rudnick, MD, pediatricians and researchers at Florida Atlantic University, wrote in the paper.
Previous research has indicated that moms who have recovered from COVID-19 can deliver babies with antibodies, according to Insider, but this may be the first report that shows how vaccination during pregnancy can provide antibodies as well.
Dr. Gilbert and Dr. Rudnick said they were fortunate to connect with the mom in Boca Raton. She hadn’t contracted COVID-19 and was able to get the vaccine at the end of her pregnancy in January. When the baby was born, they were able to test the cord blood to look for antibodies specifically from the vaccine.
“We were very excited to see, once the test result came back, that the antibodies from the mom’s vaccine did in fact pass through the placenta to the newborn,” Dr. Rudnick told WPTV, an NBC affiliate in West Palm Beach.
“We knew that we were going to be potentially one of the first in the world to report it, and that opportunity probably only comes once in a career,” Dr. Gilbert told WPTV.
In the preprint, Dr. Gilbert and Dr. Rudnick said a “vigorous, healthy, full-term” baby was born, and the mom received the second dose of the Moderna vaccine during the postpartum period. The newborn received a normal “well-infant” evaluation and was breastfeeding.
The two doctors called for a “significant and urgent need” to research the safety and efficacy of COVID-19 vaccines during pregnancy. They also encouraged other researchers to create pregnancy and breastfeeding registries to study COVID-19 vaccines in pregnant and breastfeeding moms and newborns.
Dr. Gilbert and Dr. Rudnick are now preparing their research for publication and hope future studies will investigate the amount and length of antibody response in newborns.
“Total antibody measurements may be used to determine how long protection is expected, which may help to determine when the best time would be to begin vaccination,” they wrote.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
New guidelines dispel myths about COVID-19 treatment
Recommendations, as well as conspiracy theories about COVID-19, have changed at distressing rates over the past year. No disease has ever been more politicized, or more polarizing.
Experts, as well as the least educated, take a stand on what they believe is the most important way to prevent and treat this virus.
Just recently, a study was published revealing that ivermectin is not effective as a COVID-19 treatment while people continue to claim it works. It has never been more important for doctors, and especially family physicians, to have accurate and updated guidelines.
The NIH and CDC have been publishing recommendations and guidelines for the prevention and treatment of COVID-19 since the start of the pandemic. Like any new disease, these have been changing to keep up as new knowledge related to the disease becomes available.
NIH updates treatment guidelines
A recent update to the NIH COVID-19 treatment guidelines was published on March 5, 2021. While the complete guidelines are quite extensive, spanning over 200 pages, it’s most important to understand the most recent updates in them.
Since preventative medicine is an integral part of primary care, it is important to note that no medications have been advised to prevent infection with COVID-19. In fact, taking drugs for pre-exposure prophylaxis (PrEp) is not recommended even in the highest-risk patients, such as health care workers.
In the updated guidelines, tocilizumab in a single IV dose of 8 mg/kg up to a maximum of 800 mg can be given only in combination with dexamethasone (or equivalent corticosteroid) in certain hospitalized patients exhibiting rapid respiratory decompensation. These patients include recently hospitalized patients who have been admitted to the ICU within the previous 24 hours and now require mechanical ventilation or high-flow oxygen via nasal cannula. Those not in the ICU who require rapidly increasing oxygen levels and have significantly increased levels of inflammatory markers should also receive this therapy. In the new guidance, the NIH recommends treating other hospitalized patients who require oxygen with remdesivir, remdesivir + dexamethasone, or dexamethasone alone.
In outpatients, those who have mild to moderate infection and are at increased risk of developing severe disease and/or hospitalization can be treated with bamlanivimab 700 mg + etesevimab 1,400 mg. This should be started as soon as possible after a confirmed diagnosis and within 10 days of symptom onset, according to the NIH recommendations. There is no evidence to support its use in patients hospitalized because of infection. However, it can be used in patients hospitalized for other reasons who have mild to moderate infection, but should be reserved – because of limited supply – for those with the highest risk of complications.
Hydroxychloroquine and casirivimab + imdevimab
One medication that has been touted in the media as a tool to treat COVID-19 has been hydroxychloroquine. Past guidelines recommended against this medication as a treatment because it lacked efficacy and posed risks for no therapeutic benefit. The most recent guidelines also recommend against the use of hydroxychloroquine for pre- and postexposure prophylaxis.
Casirivimab + imdevimab has been another talked about therapy. However, current guidelines recommend against its use in hospitalized patients. In addition, it is advised that hospitalized patients be enrolled in a clinical trial to receive it.
Since the pandemic began, the world has seen more than 120 million infections and more than 2 million deaths. Family physicians have a vital role to play as we are often the first ones patients turn to for treatment and advice. It is imperative we stay current with the guidelines and follow the most recent updates as research data are published.
Dr. Girgis practices family medicine in South River, N.J., and is a clinical assistant professor of family medicine at Robert Wood Johnson Medical School, New Brunswick, N.J. You can contact her at [email protected].
Recommendations, as well as conspiracy theories about COVID-19, have changed at distressing rates over the past year. No disease has ever been more politicized, or more polarizing.
Experts, as well as the least educated, take a stand on what they believe is the most important way to prevent and treat this virus.
Just recently, a study was published revealing that ivermectin is not effective as a COVID-19 treatment while people continue to claim it works. It has never been more important for doctors, and especially family physicians, to have accurate and updated guidelines.
The NIH and CDC have been publishing recommendations and guidelines for the prevention and treatment of COVID-19 since the start of the pandemic. Like any new disease, these have been changing to keep up as new knowledge related to the disease becomes available.
NIH updates treatment guidelines
A recent update to the NIH COVID-19 treatment guidelines was published on March 5, 2021. While the complete guidelines are quite extensive, spanning over 200 pages, it’s most important to understand the most recent updates in them.
Since preventative medicine is an integral part of primary care, it is important to note that no medications have been advised to prevent infection with COVID-19. In fact, taking drugs for pre-exposure prophylaxis (PrEp) is not recommended even in the highest-risk patients, such as health care workers.
In the updated guidelines, tocilizumab in a single IV dose of 8 mg/kg up to a maximum of 800 mg can be given only in combination with dexamethasone (or equivalent corticosteroid) in certain hospitalized patients exhibiting rapid respiratory decompensation. These patients include recently hospitalized patients who have been admitted to the ICU within the previous 24 hours and now require mechanical ventilation or high-flow oxygen via nasal cannula. Those not in the ICU who require rapidly increasing oxygen levels and have significantly increased levels of inflammatory markers should also receive this therapy. In the new guidance, the NIH recommends treating other hospitalized patients who require oxygen with remdesivir, remdesivir + dexamethasone, or dexamethasone alone.
In outpatients, those who have mild to moderate infection and are at increased risk of developing severe disease and/or hospitalization can be treated with bamlanivimab 700 mg + etesevimab 1,400 mg. This should be started as soon as possible after a confirmed diagnosis and within 10 days of symptom onset, according to the NIH recommendations. There is no evidence to support its use in patients hospitalized because of infection. However, it can be used in patients hospitalized for other reasons who have mild to moderate infection, but should be reserved – because of limited supply – for those with the highest risk of complications.
Hydroxychloroquine and casirivimab + imdevimab
One medication that has been touted in the media as a tool to treat COVID-19 has been hydroxychloroquine. Past guidelines recommended against this medication as a treatment because it lacked efficacy and posed risks for no therapeutic benefit. The most recent guidelines also recommend against the use of hydroxychloroquine for pre- and postexposure prophylaxis.
Casirivimab + imdevimab has been another talked about therapy. However, current guidelines recommend against its use in hospitalized patients. In addition, it is advised that hospitalized patients be enrolled in a clinical trial to receive it.
Since the pandemic began, the world has seen more than 120 million infections and more than 2 million deaths. Family physicians have a vital role to play as we are often the first ones patients turn to for treatment and advice. It is imperative we stay current with the guidelines and follow the most recent updates as research data are published.
Dr. Girgis practices family medicine in South River, N.J., and is a clinical assistant professor of family medicine at Robert Wood Johnson Medical School, New Brunswick, N.J. You can contact her at [email protected].
Recommendations, as well as conspiracy theories about COVID-19, have changed at distressing rates over the past year. No disease has ever been more politicized, or more polarizing.
Experts, as well as the least educated, take a stand on what they believe is the most important way to prevent and treat this virus.
Just recently, a study was published revealing that ivermectin is not effective as a COVID-19 treatment while people continue to claim it works. It has never been more important for doctors, and especially family physicians, to have accurate and updated guidelines.
The NIH and CDC have been publishing recommendations and guidelines for the prevention and treatment of COVID-19 since the start of the pandemic. Like any new disease, these have been changing to keep up as new knowledge related to the disease becomes available.
NIH updates treatment guidelines
A recent update to the NIH COVID-19 treatment guidelines was published on March 5, 2021. While the complete guidelines are quite extensive, spanning over 200 pages, it’s most important to understand the most recent updates in them.
Since preventative medicine is an integral part of primary care, it is important to note that no medications have been advised to prevent infection with COVID-19. In fact, taking drugs for pre-exposure prophylaxis (PrEp) is not recommended even in the highest-risk patients, such as health care workers.
In the updated guidelines, tocilizumab in a single IV dose of 8 mg/kg up to a maximum of 800 mg can be given only in combination with dexamethasone (or equivalent corticosteroid) in certain hospitalized patients exhibiting rapid respiratory decompensation. These patients include recently hospitalized patients who have been admitted to the ICU within the previous 24 hours and now require mechanical ventilation or high-flow oxygen via nasal cannula. Those not in the ICU who require rapidly increasing oxygen levels and have significantly increased levels of inflammatory markers should also receive this therapy. In the new guidance, the NIH recommends treating other hospitalized patients who require oxygen with remdesivir, remdesivir + dexamethasone, or dexamethasone alone.
In outpatients, those who have mild to moderate infection and are at increased risk of developing severe disease and/or hospitalization can be treated with bamlanivimab 700 mg + etesevimab 1,400 mg. This should be started as soon as possible after a confirmed diagnosis and within 10 days of symptom onset, according to the NIH recommendations. There is no evidence to support its use in patients hospitalized because of infection. However, it can be used in patients hospitalized for other reasons who have mild to moderate infection, but should be reserved – because of limited supply – for those with the highest risk of complications.
Hydroxychloroquine and casirivimab + imdevimab
One medication that has been touted in the media as a tool to treat COVID-19 has been hydroxychloroquine. Past guidelines recommended against this medication as a treatment because it lacked efficacy and posed risks for no therapeutic benefit. The most recent guidelines also recommend against the use of hydroxychloroquine for pre- and postexposure prophylaxis.
Casirivimab + imdevimab has been another talked about therapy. However, current guidelines recommend against its use in hospitalized patients. In addition, it is advised that hospitalized patients be enrolled in a clinical trial to receive it.
Since the pandemic began, the world has seen more than 120 million infections and more than 2 million deaths. Family physicians have a vital role to play as we are often the first ones patients turn to for treatment and advice. It is imperative we stay current with the guidelines and follow the most recent updates as research data are published.
Dr. Girgis practices family medicine in South River, N.J., and is a clinical assistant professor of family medicine at Robert Wood Johnson Medical School, New Brunswick, N.J. You can contact her at [email protected].
Let’s not criticize off-label prescribing
The public health crisis sparked by COVID-19 has engendered much debate in the realm where politics, journalism, law, and medicine meet.
Doctors have used the media to name other doctors as sources of harmful misinformation, in some cases going so far as to invoke medical practice board oversight as a potential intervention when doctors make public statements deemed too far out of bounds scientifically. Over the past year, some physicians have been harshly criticized for speaking about off-label prescribing, a widely accepted part of everyday medical practice.
The science and ethics of off-label prescribing have not changed; what has changed is the quality of dialogue around it. As psychiatrists, it does not fall within our scope of practice to offer definitive public opinions on the treatment of COVID-19, nor is that our purpose here. However, we can speak to a process that damages patients and doctors alike by undermining trust. All of this heat around bad medical information, in our opinion, amounts to using the methods of other fields to evaluate science and clinical practice. A remedy, then, to improve the quality of public medical intelligence would be to clarify the rules of scientific debate and to once again clearly state that off-label prescribing is part and parcel of the good practice of clinical medicine.
Physicians who work in the field of professional discipline have thought about the limits of propriety in making charges of impropriety. We (R.S.E. and R.S.K.) asked the American Psychiatric Association’s Ethics Committee to expand upon its existing commentary on innovative practice and making allegations of professional misconduct. We used the committee’s answers to our questions as the basis for the arguments we are making in this piece.
The APA’s Ethics Committee uses clear-cut benchmarks to define innovative medical care: “The standards of care ... evolve with evidence from research and observations of practice. Among the expected supports for innovative practice are scientific testing, peer-reviewed publication, replication, and broad or widespread acceptance within a relevant scientific or professional community.” When it comes to off-label prescribing for any medical condition, it is easy enough to ascertain whether clinical reports have appeared in peer-reviewed journals.
Two of the biggest blockbusters in psychiatry, chlorpromazine and lithium, began as drugs used for other conditions almost since the inception of our field. In other words, the use of these drugs for mental illness began, in today’s jargon, as off-label. We practitioners of psychiatry live in the land of off-label prescribing and have always comfortably done so. In fact, almost all of medicine does. The key in today’s world of best-practice medicine is obtaining a truly informed consent.
For COVID-19, our incredible psychotropic molecules may once again be doing some trail-blazing off-label work. Late last year, Eric J. Lenze, MD, professor of psychiatry and director of the Healthy Mind Lab at Washington University in St. Louis, reported in a preliminary study of adult outpatients with symptomatic COVID-19 that those treated with fluvoxamine “had a lower likelihood of clinical deterioration over 15 days,” compared with those on placebo (JAMA. 2020;324[22]:2292-300). We were heartened to see Dr. Lenze discuss his work on a recent “60 Minutes” segment. David Seftel, MD, MBA, a clinician who administered fluvoxamine as early treatment for a COVID-19 outbreak that occurred in a community of racetrack employees and their families in the San Francisco Bay Area, also was featured. Rather than waiting for the results of large clinical trials, Dr. Lenze and Dr. Seftel proceeded, based on reports published in peer-reviewed journals, to treat patients whose lives were at risk.
If we find ourselves strongly disagreeing about the science of off-label prescribing, the proper response is to critique methodologies, not the character or competence of colleagues. The APA Ethics Committee discourages use of the media as a forum for making allegations of incompetent or unethical practice: “Judgments regarding violations of established norms of ethical or professional conduct should be made not by individuals but by bodies authorized to take evidence and make informed decisions.”
At least one state legislature is taking action to protect patients’ access to the doctors they trust. In Arizona, SB 1416 passed in the Senate and is now working its way through the House. This bill would prohibit medical boards from disciplining doctors for speaking out about or prescribing off-label drugs when a reasonable basis for use exists.
Psychological research on the “backfire effect” suggests that heavy-handed campaigns to enforce medical consensus will only harden minds in ways that neither advance science nor improve the quality of clinical decision-making.
Medical disciplinary boards and the news media were neither designed nor are they equipped to adjudicate scientific debates. Science is never settled: Hypothesis and theory are always open to testing and revision as new evidence emerges. There is a place in medicine for formal disciplinary processes, as well-delineated by professional bodies such as the APA Ethics Committee. Another important part of protecting the public is to support an environment of scientific inquiry in which diversity of opinion is welcomed. As physicians, we translate science into excellent clinical care every day in our practices, and we advance science by sharing what we learn through friendly collegial communication and collaboration.
Dr. Emmons is part-time clinical associate professor in the department of psychiatry at the University of Vermont, Burlington, and is a past chair of the Ethics Committee for the Vermont District Branch of the American Psychiatric Association. He is in private practice in Moretown, Vt., and disclosed no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Kohanski is in private practice in Dayton, N.J., and is a diplomate of the American Board of Psychiatry & Neurology. She also is the host and author of Clinical Correlation, a series of the Psychcast. Dr. Kohanski disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
The public health crisis sparked by COVID-19 has engendered much debate in the realm where politics, journalism, law, and medicine meet.
Doctors have used the media to name other doctors as sources of harmful misinformation, in some cases going so far as to invoke medical practice board oversight as a potential intervention when doctors make public statements deemed too far out of bounds scientifically. Over the past year, some physicians have been harshly criticized for speaking about off-label prescribing, a widely accepted part of everyday medical practice.
The science and ethics of off-label prescribing have not changed; what has changed is the quality of dialogue around it. As psychiatrists, it does not fall within our scope of practice to offer definitive public opinions on the treatment of COVID-19, nor is that our purpose here. However, we can speak to a process that damages patients and doctors alike by undermining trust. All of this heat around bad medical information, in our opinion, amounts to using the methods of other fields to evaluate science and clinical practice. A remedy, then, to improve the quality of public medical intelligence would be to clarify the rules of scientific debate and to once again clearly state that off-label prescribing is part and parcel of the good practice of clinical medicine.
Physicians who work in the field of professional discipline have thought about the limits of propriety in making charges of impropriety. We (R.S.E. and R.S.K.) asked the American Psychiatric Association’s Ethics Committee to expand upon its existing commentary on innovative practice and making allegations of professional misconduct. We used the committee’s answers to our questions as the basis for the arguments we are making in this piece.
The APA’s Ethics Committee uses clear-cut benchmarks to define innovative medical care: “The standards of care ... evolve with evidence from research and observations of practice. Among the expected supports for innovative practice are scientific testing, peer-reviewed publication, replication, and broad or widespread acceptance within a relevant scientific or professional community.” When it comes to off-label prescribing for any medical condition, it is easy enough to ascertain whether clinical reports have appeared in peer-reviewed journals.
Two of the biggest blockbusters in psychiatry, chlorpromazine and lithium, began as drugs used for other conditions almost since the inception of our field. In other words, the use of these drugs for mental illness began, in today’s jargon, as off-label. We practitioners of psychiatry live in the land of off-label prescribing and have always comfortably done so. In fact, almost all of medicine does. The key in today’s world of best-practice medicine is obtaining a truly informed consent.
For COVID-19, our incredible psychotropic molecules may once again be doing some trail-blazing off-label work. Late last year, Eric J. Lenze, MD, professor of psychiatry and director of the Healthy Mind Lab at Washington University in St. Louis, reported in a preliminary study of adult outpatients with symptomatic COVID-19 that those treated with fluvoxamine “had a lower likelihood of clinical deterioration over 15 days,” compared with those on placebo (JAMA. 2020;324[22]:2292-300). We were heartened to see Dr. Lenze discuss his work on a recent “60 Minutes” segment. David Seftel, MD, MBA, a clinician who administered fluvoxamine as early treatment for a COVID-19 outbreak that occurred in a community of racetrack employees and their families in the San Francisco Bay Area, also was featured. Rather than waiting for the results of large clinical trials, Dr. Lenze and Dr. Seftel proceeded, based on reports published in peer-reviewed journals, to treat patients whose lives were at risk.
If we find ourselves strongly disagreeing about the science of off-label prescribing, the proper response is to critique methodologies, not the character or competence of colleagues. The APA Ethics Committee discourages use of the media as a forum for making allegations of incompetent or unethical practice: “Judgments regarding violations of established norms of ethical or professional conduct should be made not by individuals but by bodies authorized to take evidence and make informed decisions.”
At least one state legislature is taking action to protect patients’ access to the doctors they trust. In Arizona, SB 1416 passed in the Senate and is now working its way through the House. This bill would prohibit medical boards from disciplining doctors for speaking out about or prescribing off-label drugs when a reasonable basis for use exists.
Psychological research on the “backfire effect” suggests that heavy-handed campaigns to enforce medical consensus will only harden minds in ways that neither advance science nor improve the quality of clinical decision-making.
Medical disciplinary boards and the news media were neither designed nor are they equipped to adjudicate scientific debates. Science is never settled: Hypothesis and theory are always open to testing and revision as new evidence emerges. There is a place in medicine for formal disciplinary processes, as well-delineated by professional bodies such as the APA Ethics Committee. Another important part of protecting the public is to support an environment of scientific inquiry in which diversity of opinion is welcomed. As physicians, we translate science into excellent clinical care every day in our practices, and we advance science by sharing what we learn through friendly collegial communication and collaboration.
Dr. Emmons is part-time clinical associate professor in the department of psychiatry at the University of Vermont, Burlington, and is a past chair of the Ethics Committee for the Vermont District Branch of the American Psychiatric Association. He is in private practice in Moretown, Vt., and disclosed no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Kohanski is in private practice in Dayton, N.J., and is a diplomate of the American Board of Psychiatry & Neurology. She also is the host and author of Clinical Correlation, a series of the Psychcast. Dr. Kohanski disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
The public health crisis sparked by COVID-19 has engendered much debate in the realm where politics, journalism, law, and medicine meet.
Doctors have used the media to name other doctors as sources of harmful misinformation, in some cases going so far as to invoke medical practice board oversight as a potential intervention when doctors make public statements deemed too far out of bounds scientifically. Over the past year, some physicians have been harshly criticized for speaking about off-label prescribing, a widely accepted part of everyday medical practice.
The science and ethics of off-label prescribing have not changed; what has changed is the quality of dialogue around it. As psychiatrists, it does not fall within our scope of practice to offer definitive public opinions on the treatment of COVID-19, nor is that our purpose here. However, we can speak to a process that damages patients and doctors alike by undermining trust. All of this heat around bad medical information, in our opinion, amounts to using the methods of other fields to evaluate science and clinical practice. A remedy, then, to improve the quality of public medical intelligence would be to clarify the rules of scientific debate and to once again clearly state that off-label prescribing is part and parcel of the good practice of clinical medicine.
Physicians who work in the field of professional discipline have thought about the limits of propriety in making charges of impropriety. We (R.S.E. and R.S.K.) asked the American Psychiatric Association’s Ethics Committee to expand upon its existing commentary on innovative practice and making allegations of professional misconduct. We used the committee’s answers to our questions as the basis for the arguments we are making in this piece.
The APA’s Ethics Committee uses clear-cut benchmarks to define innovative medical care: “The standards of care ... evolve with evidence from research and observations of practice. Among the expected supports for innovative practice are scientific testing, peer-reviewed publication, replication, and broad or widespread acceptance within a relevant scientific or professional community.” When it comes to off-label prescribing for any medical condition, it is easy enough to ascertain whether clinical reports have appeared in peer-reviewed journals.
Two of the biggest blockbusters in psychiatry, chlorpromazine and lithium, began as drugs used for other conditions almost since the inception of our field. In other words, the use of these drugs for mental illness began, in today’s jargon, as off-label. We practitioners of psychiatry live in the land of off-label prescribing and have always comfortably done so. In fact, almost all of medicine does. The key in today’s world of best-practice medicine is obtaining a truly informed consent.
For COVID-19, our incredible psychotropic molecules may once again be doing some trail-blazing off-label work. Late last year, Eric J. Lenze, MD, professor of psychiatry and director of the Healthy Mind Lab at Washington University in St. Louis, reported in a preliminary study of adult outpatients with symptomatic COVID-19 that those treated with fluvoxamine “had a lower likelihood of clinical deterioration over 15 days,” compared with those on placebo (JAMA. 2020;324[22]:2292-300). We were heartened to see Dr. Lenze discuss his work on a recent “60 Minutes” segment. David Seftel, MD, MBA, a clinician who administered fluvoxamine as early treatment for a COVID-19 outbreak that occurred in a community of racetrack employees and their families in the San Francisco Bay Area, also was featured. Rather than waiting for the results of large clinical trials, Dr. Lenze and Dr. Seftel proceeded, based on reports published in peer-reviewed journals, to treat patients whose lives were at risk.
If we find ourselves strongly disagreeing about the science of off-label prescribing, the proper response is to critique methodologies, not the character or competence of colleagues. The APA Ethics Committee discourages use of the media as a forum for making allegations of incompetent or unethical practice: “Judgments regarding violations of established norms of ethical or professional conduct should be made not by individuals but by bodies authorized to take evidence and make informed decisions.”
At least one state legislature is taking action to protect patients’ access to the doctors they trust. In Arizona, SB 1416 passed in the Senate and is now working its way through the House. This bill would prohibit medical boards from disciplining doctors for speaking out about or prescribing off-label drugs when a reasonable basis for use exists.
Psychological research on the “backfire effect” suggests that heavy-handed campaigns to enforce medical consensus will only harden minds in ways that neither advance science nor improve the quality of clinical decision-making.
Medical disciplinary boards and the news media were neither designed nor are they equipped to adjudicate scientific debates. Science is never settled: Hypothesis and theory are always open to testing and revision as new evidence emerges. There is a place in medicine for formal disciplinary processes, as well-delineated by professional bodies such as the APA Ethics Committee. Another important part of protecting the public is to support an environment of scientific inquiry in which diversity of opinion is welcomed. As physicians, we translate science into excellent clinical care every day in our practices, and we advance science by sharing what we learn through friendly collegial communication and collaboration.
Dr. Emmons is part-time clinical associate professor in the department of psychiatry at the University of Vermont, Burlington, and is a past chair of the Ethics Committee for the Vermont District Branch of the American Psychiatric Association. He is in private practice in Moretown, Vt., and disclosed no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Kohanski is in private practice in Dayton, N.J., and is a diplomate of the American Board of Psychiatry & Neurology. She also is the host and author of Clinical Correlation, a series of the Psychcast. Dr. Kohanski disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
Updated recommendations released on COVID-19 and pediatric ALL
The main threat to the vast majority of children with acute lymphoblastic leukemia still remains the ALL itself, according to updated recommendations released by the Leukemia Committee of the French Society for the Fight Against Cancers and Leukemias in Children and Adolescents (SFCE).
“The situation of the current COVID-19 pandemic is continuously evolving. We thus have taken the more recent knowledge into account to update the previous recommendations from the Leukemia Committee,” Jérémie Rouger-Gaudichon, MD, of Pediatric Hemato-Immuno-Oncology Unit, Centre Hospitalier Universitaire, Caen (France), and colleagues wrote on behalf of the SFCE.
The updated recommendations are based on data collected in a real-time prospective survey among the 30 SFCE centers since April 2020. As of December 2020, 127 cases of COVID-19 were reported, most of them being enrolled in the PEDONCOVID study (NCT04433871) according to the report. Of these, eight patients required hospitalization in intensive care unit and one patient with relapsed acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL) died from ARDS with multiorgan failure. This confirms earlier reports that SARS-CoV-2 infection can be severe in some children with cancer and/or having hematopoietic stem cell transplant (HSCT), according to the report, which was published online in Bulletin du Cancer.
Recommendations
General recommendations were provided in the report, including the following:
- Test for SARS-CoV-2 (preferably by PCR or at least by immunological tests, on nasopharyngeal swab) before starting intensive induction chemotherapy or other intensive phase of treatment, for ALL patients, with or without symptoms.
- Delay systemic treatment if possible (e.g., absence of major hyperleukocytosis) in positive patients. During later phases, if patients test positive, tests should be repeated over time until negativity, especially before the beginning of an intensive course.
- Isolate any COVID-19–negative child or adolescent to allow treatment to continue (facial mask, social distancing, barrier measures, no contact with individuals suspected of COVID-19 or COVID-19–positive), in particular for patients to be allografted.
- Limit visitation to parents and potentially siblings in patients slated for HSCT and follow all necessary sanitary procedures for those visits.
The report provides a lengthy discussion of more detailed recommendations, including the following for first-line treatment of ALL:
- For patients with high-risk ALL, an individualized decision regarding transplantation and its timing should weigh the risks of transplantation in an epidemic context of COVID-19 against the risk linked to ALL.
- Minimizing hospital visits by the use of home blood tests and partial use of telemedicine may be considered.
- A physical examination should be performed regularly to avoid any delay in the diagnosis of treatment complications or relapse and preventative measures for SARS-CoV-2 should be applied in the home.
Patients with relapsed ALL may be at more risk from the effects of COVID-19 disease, according to the others, so for ALL patients receiving second-line or more treatment the recommendations include the following:
- Testing must be performed before starting a chemotherapy block, and postponing chemotherapy in case of positive test should be discussed in accordance with each specific situation and benefits/risks ratio regarding the leukemia.
- First-relapse patients should follow the INTREALL treatment protocol as much as possible and those who reach appropriate complete remission should be considered promptly for allogeneic transplantation, despite the pandemic.
- Second relapse and refractory relapses require testing and negative results for inclusion in phase I-II trials being conducted by most if not all academic or industrial promoters.
- The indication for treatment with CAR-T cells must be weighed with the center that would perform the procedure to determine the feasibility of performing all necessary procedures including apheresis and manufacturing.
In the case of a SARS-CoV-2 infection diagnosis during the treatment of ALL, discussions should occur with regard to stopping and/or postponing all chemotherapies, according to the severity of the ALL, the stage of treatment and the severity of clinical and/or radiological signs. In addition, any specific anti-COVID-19 treatment must be discussed with the infectious diseases team, according to the report.
“Fortunately, SARS-CoV-2 infection appears nevertheless to be mild in most children with cancer/ALL. Thus, the main threat to the vast majority of children with ALL still remains the ALL itself. Long-term data including well-matched case-control studies will tell if treatment delays/modifications due to COVID-19 have impacted the outcome if children with ALL,” the authors stated. However, “despite extremely rapid advances obtained in less than one year, our knowledge of SARS-CoV-2 and its complications is still incomplete,” they concluded, adding that the recommendations will likely need to be updated within another few months.
The authors reported that they had no conflicts of interest.
The main threat to the vast majority of children with acute lymphoblastic leukemia still remains the ALL itself, according to updated recommendations released by the Leukemia Committee of the French Society for the Fight Against Cancers and Leukemias in Children and Adolescents (SFCE).
“The situation of the current COVID-19 pandemic is continuously evolving. We thus have taken the more recent knowledge into account to update the previous recommendations from the Leukemia Committee,” Jérémie Rouger-Gaudichon, MD, of Pediatric Hemato-Immuno-Oncology Unit, Centre Hospitalier Universitaire, Caen (France), and colleagues wrote on behalf of the SFCE.
The updated recommendations are based on data collected in a real-time prospective survey among the 30 SFCE centers since April 2020. As of December 2020, 127 cases of COVID-19 were reported, most of them being enrolled in the PEDONCOVID study (NCT04433871) according to the report. Of these, eight patients required hospitalization in intensive care unit and one patient with relapsed acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL) died from ARDS with multiorgan failure. This confirms earlier reports that SARS-CoV-2 infection can be severe in some children with cancer and/or having hematopoietic stem cell transplant (HSCT), according to the report, which was published online in Bulletin du Cancer.
Recommendations
General recommendations were provided in the report, including the following:
- Test for SARS-CoV-2 (preferably by PCR or at least by immunological tests, on nasopharyngeal swab) before starting intensive induction chemotherapy or other intensive phase of treatment, for ALL patients, with or without symptoms.
- Delay systemic treatment if possible (e.g., absence of major hyperleukocytosis) in positive patients. During later phases, if patients test positive, tests should be repeated over time until negativity, especially before the beginning of an intensive course.
- Isolate any COVID-19–negative child or adolescent to allow treatment to continue (facial mask, social distancing, barrier measures, no contact with individuals suspected of COVID-19 or COVID-19–positive), in particular for patients to be allografted.
- Limit visitation to parents and potentially siblings in patients slated for HSCT and follow all necessary sanitary procedures for those visits.
The report provides a lengthy discussion of more detailed recommendations, including the following for first-line treatment of ALL:
- For patients with high-risk ALL, an individualized decision regarding transplantation and its timing should weigh the risks of transplantation in an epidemic context of COVID-19 against the risk linked to ALL.
- Minimizing hospital visits by the use of home blood tests and partial use of telemedicine may be considered.
- A physical examination should be performed regularly to avoid any delay in the diagnosis of treatment complications or relapse and preventative measures for SARS-CoV-2 should be applied in the home.
Patients with relapsed ALL may be at more risk from the effects of COVID-19 disease, according to the others, so for ALL patients receiving second-line or more treatment the recommendations include the following:
- Testing must be performed before starting a chemotherapy block, and postponing chemotherapy in case of positive test should be discussed in accordance with each specific situation and benefits/risks ratio regarding the leukemia.
- First-relapse patients should follow the INTREALL treatment protocol as much as possible and those who reach appropriate complete remission should be considered promptly for allogeneic transplantation, despite the pandemic.
- Second relapse and refractory relapses require testing and negative results for inclusion in phase I-II trials being conducted by most if not all academic or industrial promoters.
- The indication for treatment with CAR-T cells must be weighed with the center that would perform the procedure to determine the feasibility of performing all necessary procedures including apheresis and manufacturing.
In the case of a SARS-CoV-2 infection diagnosis during the treatment of ALL, discussions should occur with regard to stopping and/or postponing all chemotherapies, according to the severity of the ALL, the stage of treatment and the severity of clinical and/or radiological signs. In addition, any specific anti-COVID-19 treatment must be discussed with the infectious diseases team, according to the report.
“Fortunately, SARS-CoV-2 infection appears nevertheless to be mild in most children with cancer/ALL. Thus, the main threat to the vast majority of children with ALL still remains the ALL itself. Long-term data including well-matched case-control studies will tell if treatment delays/modifications due to COVID-19 have impacted the outcome if children with ALL,” the authors stated. However, “despite extremely rapid advances obtained in less than one year, our knowledge of SARS-CoV-2 and its complications is still incomplete,” they concluded, adding that the recommendations will likely need to be updated within another few months.
The authors reported that they had no conflicts of interest.
The main threat to the vast majority of children with acute lymphoblastic leukemia still remains the ALL itself, according to updated recommendations released by the Leukemia Committee of the French Society for the Fight Against Cancers and Leukemias in Children and Adolescents (SFCE).
“The situation of the current COVID-19 pandemic is continuously evolving. We thus have taken the more recent knowledge into account to update the previous recommendations from the Leukemia Committee,” Jérémie Rouger-Gaudichon, MD, of Pediatric Hemato-Immuno-Oncology Unit, Centre Hospitalier Universitaire, Caen (France), and colleagues wrote on behalf of the SFCE.
The updated recommendations are based on data collected in a real-time prospective survey among the 30 SFCE centers since April 2020. As of December 2020, 127 cases of COVID-19 were reported, most of them being enrolled in the PEDONCOVID study (NCT04433871) according to the report. Of these, eight patients required hospitalization in intensive care unit and one patient with relapsed acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL) died from ARDS with multiorgan failure. This confirms earlier reports that SARS-CoV-2 infection can be severe in some children with cancer and/or having hematopoietic stem cell transplant (HSCT), according to the report, which was published online in Bulletin du Cancer.
Recommendations
General recommendations were provided in the report, including the following:
- Test for SARS-CoV-2 (preferably by PCR or at least by immunological tests, on nasopharyngeal swab) before starting intensive induction chemotherapy or other intensive phase of treatment, for ALL patients, with or without symptoms.
- Delay systemic treatment if possible (e.g., absence of major hyperleukocytosis) in positive patients. During later phases, if patients test positive, tests should be repeated over time until negativity, especially before the beginning of an intensive course.
- Isolate any COVID-19–negative child or adolescent to allow treatment to continue (facial mask, social distancing, barrier measures, no contact with individuals suspected of COVID-19 or COVID-19–positive), in particular for patients to be allografted.
- Limit visitation to parents and potentially siblings in patients slated for HSCT and follow all necessary sanitary procedures for those visits.
The report provides a lengthy discussion of more detailed recommendations, including the following for first-line treatment of ALL:
- For patients with high-risk ALL, an individualized decision regarding transplantation and its timing should weigh the risks of transplantation in an epidemic context of COVID-19 against the risk linked to ALL.
- Minimizing hospital visits by the use of home blood tests and partial use of telemedicine may be considered.
- A physical examination should be performed regularly to avoid any delay in the diagnosis of treatment complications or relapse and preventative measures for SARS-CoV-2 should be applied in the home.
Patients with relapsed ALL may be at more risk from the effects of COVID-19 disease, according to the others, so for ALL patients receiving second-line or more treatment the recommendations include the following:
- Testing must be performed before starting a chemotherapy block, and postponing chemotherapy in case of positive test should be discussed in accordance with each specific situation and benefits/risks ratio regarding the leukemia.
- First-relapse patients should follow the INTREALL treatment protocol as much as possible and those who reach appropriate complete remission should be considered promptly for allogeneic transplantation, despite the pandemic.
- Second relapse and refractory relapses require testing and negative results for inclusion in phase I-II trials being conducted by most if not all academic or industrial promoters.
- The indication for treatment with CAR-T cells must be weighed with the center that would perform the procedure to determine the feasibility of performing all necessary procedures including apheresis and manufacturing.
In the case of a SARS-CoV-2 infection diagnosis during the treatment of ALL, discussions should occur with regard to stopping and/or postponing all chemotherapies, according to the severity of the ALL, the stage of treatment and the severity of clinical and/or radiological signs. In addition, any specific anti-COVID-19 treatment must be discussed with the infectious diseases team, according to the report.
“Fortunately, SARS-CoV-2 infection appears nevertheless to be mild in most children with cancer/ALL. Thus, the main threat to the vast majority of children with ALL still remains the ALL itself. Long-term data including well-matched case-control studies will tell if treatment delays/modifications due to COVID-19 have impacted the outcome if children with ALL,” the authors stated. However, “despite extremely rapid advances obtained in less than one year, our knowledge of SARS-CoV-2 and its complications is still incomplete,” they concluded, adding that the recommendations will likely need to be updated within another few months.
The authors reported that they had no conflicts of interest.
FROM BULLETIN DU CANCER
Assessing Risk for Amputation Patients During a Pandemic
Risk assessment becomes more complex during a pandemic—but even more necessary. Researchers from Virginia Commonwealth University and Hunter Holmes McGuire Veterans Afffairs Medical Center who studied a population of veterans who underwent leg amputation found that “preoperative testing may not be a feasible and well-applied standard, making risk assessment in the setting of a pandemic even more crucial for surgeons undertaking lower extremity amputations in this high-risk population.”
In their study, the researchers found that a majority of the patients had one or more risk factor from the list published by the European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control (ECDC). What’s more, based on their data, the researchers say veteran amputees are at a much higher risk for complications and negative outcomes if infected with COVID-19, compared with the general population.
Of 50,083 veterans who needed nontraumatic lower extremity amputations between 1999 and 2018, 82% of those with above-knee amputations and 89% of those with below-knee amputations had at least one ECDC risk factor comorbidity. Hypertension and diabetes were the two most prevalent conditions in all cohorts, regardless of race.
Between 40% and 50% of the patients studied were current or past smokers, “well beyond the prevalence of smoking” in the general US population,” the researchers say. One quarter of the veterans were Black. That also is a greater proportion than the proportion of Black patients in the national male veteran population; race is an “especially concerning” potential COVID-19 progression factor, the researchers say.
A year after the COVID-19 pandemic began, the researchers examined the association of Risk Analysis Index scores with postoperative outcomes in 47,197 patients who underwent lower extremity amputation: 27,098 below the knee and 20,099 above the knee amputations.
Frailty was associated with increased rates of major cardiac, pulmonary, and renal complications, as well as sepsis, intubation greater than 48 hours, reintubation, and increased length of stay. Higher frailty scores were associated with up to triple the likelihood of a postoperative complication and up to 32 times likelihood of death within 30 days.
In a previous study, the researchers concluded that standardized frailty indicators might be particularly relevant in a pandemic that has a heavy impact in elderly patients with comorbidities. The risk factors for COVID-19, they note, are similar to many of the factors assessed in surgical frailty scores. Surgical frailty and its assessment, they add, have become “essential considerations” in perioperative management for aging patients.
Risk assessment becomes more complex during a pandemic—but even more necessary. Researchers from Virginia Commonwealth University and Hunter Holmes McGuire Veterans Afffairs Medical Center who studied a population of veterans who underwent leg amputation found that “preoperative testing may not be a feasible and well-applied standard, making risk assessment in the setting of a pandemic even more crucial for surgeons undertaking lower extremity amputations in this high-risk population.”
In their study, the researchers found that a majority of the patients had one or more risk factor from the list published by the European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control (ECDC). What’s more, based on their data, the researchers say veteran amputees are at a much higher risk for complications and negative outcomes if infected with COVID-19, compared with the general population.
Of 50,083 veterans who needed nontraumatic lower extremity amputations between 1999 and 2018, 82% of those with above-knee amputations and 89% of those with below-knee amputations had at least one ECDC risk factor comorbidity. Hypertension and diabetes were the two most prevalent conditions in all cohorts, regardless of race.
Between 40% and 50% of the patients studied were current or past smokers, “well beyond the prevalence of smoking” in the general US population,” the researchers say. One quarter of the veterans were Black. That also is a greater proportion than the proportion of Black patients in the national male veteran population; race is an “especially concerning” potential COVID-19 progression factor, the researchers say.
A year after the COVID-19 pandemic began, the researchers examined the association of Risk Analysis Index scores with postoperative outcomes in 47,197 patients who underwent lower extremity amputation: 27,098 below the knee and 20,099 above the knee amputations.
Frailty was associated with increased rates of major cardiac, pulmonary, and renal complications, as well as sepsis, intubation greater than 48 hours, reintubation, and increased length of stay. Higher frailty scores were associated with up to triple the likelihood of a postoperative complication and up to 32 times likelihood of death within 30 days.
In a previous study, the researchers concluded that standardized frailty indicators might be particularly relevant in a pandemic that has a heavy impact in elderly patients with comorbidities. The risk factors for COVID-19, they note, are similar to many of the factors assessed in surgical frailty scores. Surgical frailty and its assessment, they add, have become “essential considerations” in perioperative management for aging patients.
Risk assessment becomes more complex during a pandemic—but even more necessary. Researchers from Virginia Commonwealth University and Hunter Holmes McGuire Veterans Afffairs Medical Center who studied a population of veterans who underwent leg amputation found that “preoperative testing may not be a feasible and well-applied standard, making risk assessment in the setting of a pandemic even more crucial for surgeons undertaking lower extremity amputations in this high-risk population.”
In their study, the researchers found that a majority of the patients had one or more risk factor from the list published by the European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control (ECDC). What’s more, based on their data, the researchers say veteran amputees are at a much higher risk for complications and negative outcomes if infected with COVID-19, compared with the general population.
Of 50,083 veterans who needed nontraumatic lower extremity amputations between 1999 and 2018, 82% of those with above-knee amputations and 89% of those with below-knee amputations had at least one ECDC risk factor comorbidity. Hypertension and diabetes were the two most prevalent conditions in all cohorts, regardless of race.
Between 40% and 50% of the patients studied were current or past smokers, “well beyond the prevalence of smoking” in the general US population,” the researchers say. One quarter of the veterans were Black. That also is a greater proportion than the proportion of Black patients in the national male veteran population; race is an “especially concerning” potential COVID-19 progression factor, the researchers say.
A year after the COVID-19 pandemic began, the researchers examined the association of Risk Analysis Index scores with postoperative outcomes in 47,197 patients who underwent lower extremity amputation: 27,098 below the knee and 20,099 above the knee amputations.
Frailty was associated with increased rates of major cardiac, pulmonary, and renal complications, as well as sepsis, intubation greater than 48 hours, reintubation, and increased length of stay. Higher frailty scores were associated with up to triple the likelihood of a postoperative complication and up to 32 times likelihood of death within 30 days.
In a previous study, the researchers concluded that standardized frailty indicators might be particularly relevant in a pandemic that has a heavy impact in elderly patients with comorbidities. The risk factors for COVID-19, they note, are similar to many of the factors assessed in surgical frailty scores. Surgical frailty and its assessment, they add, have become “essential considerations” in perioperative management for aging patients.