User login
Moving Beyond Traditional Methods for Treatment of Acne Keloidalis Nuchae
The Comparison
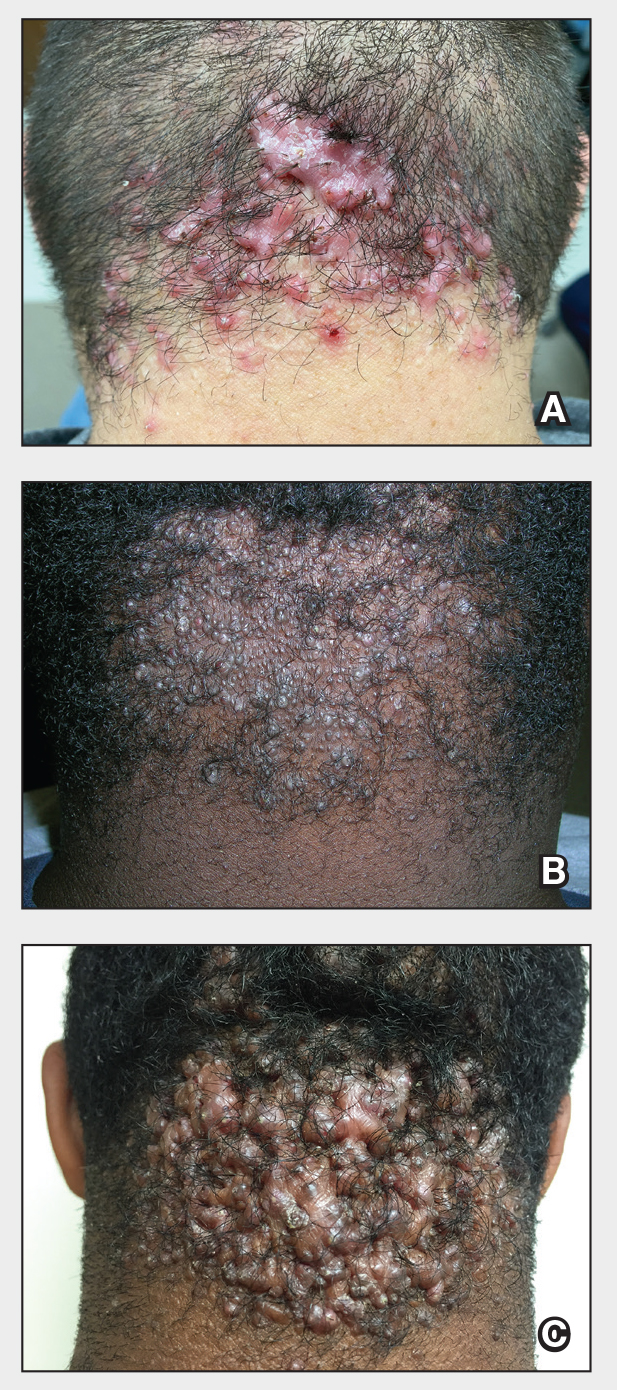
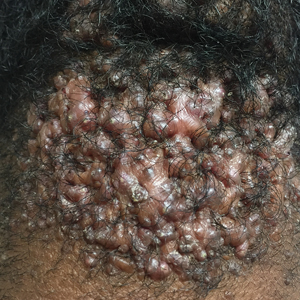
Acne keloidalis nuchae (AKN) is a chronic inflammatory condition commonly affecting the occipital scalp and posterior neck. It causes discrete or extensive fibrosing papules that may coalesce to form pronounced tumorlike masses1,2 with scarring alopecia (Figure, A–C).3 Pustules, hair tufts, secondary bacterial infections, abscesses, and sinus tracts also may occur.1 The pathogenesis of AKN has been characterized as varying stages of follicular inflammation at the infundibular and isthmus levels followed by fibrotic occlusion of the follicular lumen.4 Pruritus, pain, bleeding, oozing, and a feeling of scalp tightness may occur.1,5
Umar et al6 performed a retrospective review of 108 men with AKN—58% of African descent, 37% Hispanic, 3% Asian, and 2% Middle Eastern—and proposed a 3-tier classification system for AKN. Tier 1 focused on the distribution and sagittal spread of AKN lesions between the clinical demarcation lines of the occipital notch and posterior hairline. Tier 2 focused on the type of lesions present—discrete papules or nodules, coalescing/abutting lesions, plaques (raised, atrophic, or indurated), or dome-shaped tumoral masses. Tier 3 focused on the presence or absence of co-existing dissecting cellulitis or folliculitis decalvans.6
Epidemiology
Acne keloidalis nuchae primarily manifests in adolescent and adult men of African or Afro-Caribbean descent.7 Among African American men, the prevalence of AKN ranges from 0.5% to 13.6%.8 Similar ranges have been reported among Nigerian, South African, and West African men.1 Acne keloidalis nuchae also affects Asian and Hispanic men but rarely is seen in non-Hispanic White men or in women of any ethnicity.9,10 The male to female ratio is 20:1.1,11 Hair texture, hairstyling practices such as closely shaved or faded haircuts, and genetics likely contribute to development of AKN. Sports and occupations that require the use of headgear or a tight collar may increase the risk for AKN.12
Key clinical features in people with darker skin tones
- The lesions of AKN range in color from pink to dark brown or black. Postinflammatory hyperpigmentation or hyperchromia may be present around AKN lesions.
- Chronicity of AKN may lead to extended use of high-potency topical or intralesional corticosteroids, which causes transient or long-lasting hypopigmentation, especially in those with darker skin tones.
Worth noting
- Acne keloidalis nuchae can be disfiguring, which negatively impacts quality of life and self-esteem.12
- Some occupations (eg, military, police) have hair policies that may not be favorable to those with or at risk for AKN.
- Patients with AKN are 2 to 3 times more likely to present with metabolic syndrome, hypertension, type 2 diabetes mellitus, or obesity.13
Treatment
There are no treatments approved by the US Food and Drug Administration specifically for AKN. Treatment approaches are based on the pathophysiology, secondary impacts on the skin, and disease severity. Growing out the hair may prevent worsening and/or decrease the risk for new lesions.6
- Options include but are not limited to topical and systemic therapies (eg, topical corticosteroids, oral or topical antibiotics, isotretinoin, topical retinoids, imiquimod, pimecrolimus), light devices (eg, phototherapy, laser), ablative therapies (eg, laser, cryotherapy, radiotherapy), and surgery (eg, excision, follicular unit excision), often in combination.6,14,15
- Intralesional triamcinolone injections are considered standard of care. Adotama et al16 found that injecting triamcinolone into the deep dermis in the area of flat or papular AKN yielded better control of inflammation and decreased appearance of lesions compared with injecting individual lesions.
- For extensive AKN lesions that do not respond to less-invasive therapies, consider surgical techniques,6,17 such as follicular unit excision18 and more extensive surgical excisions building on approaches from pioneers Drs. John Kenney and Harold Pierce.19 An innovative surgical approach for removal of large AKNs is the bat excision technique—wound shape resembles a bat in a spread-eagled position—with secondary intention healing with or without debridement and/or tension sutures. The resulting linear scar acts as a new posterior hair line.20
Health disparity highlights
Access to a dermatologic or plastic surgeon with expertise in the surgical treatment of large AKNs may be challenging but is needed to reduce risk for recurrence and adverse events.
Close-cropped haircuts on the occipital scalp, which are particularly popular among men of African descent, increase the risk for AKN.5 Although this grooming style may be a personal preference, other hairstyles commonly worn by those with tightly coiled hair may be deemed “unprofessional” in society or the workplace,21 which leads to hairstyling practices that may increase the risk for AKN.
Acne keloidalis nuchae remains an understudied entity that adversely affects patients with skin of color.
- Ogunbiyi A. Acne keloidalis nuchae: prevalence, impact, and management challenges. Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol. 2016;9:483-489. doi:10.2147/CCID.S99225
- Al Aboud DM, Badri T. Acne keloidalis nuchae. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Updated July 31, 2023. Accessed August 2, 2024. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK459135/ 3.
- Sperling LC, Homoky C, Pratt L, et al. Acne keloidalis is a form of primary scarring alopecia. Arch Dermatol. 2000;136:479-484.
- Herzberg AJ, Dinehart SM, Kerns BJ, et al. Acne keloidalis: transverse microscopy, immunohistochemistry, and electron microscopy. Am J Dermatopathol. 1990;12:109-121. doi:10.1097/00000372-199004000-00001
- Saka B, Akakpo A-S, Téclessou JN, et al. Risk factors associated with acne keloidalis nuchae in black subjects: a case-control study. Ann Dermatol Venereol. 2020;147:350-354. doi:10.1016/j.annder.2020.01.007
- Umar S, Lee DJ, Lullo JJ. A retrospective cohort study and clinical classification system of acne keloidalis nuchae. J Clin Aesthet Dermatol. 2021;14:E61-E67.
- Reja M, Silverberg NB. Acne keloidalis nuchae. In: Silverberg NB, Durán-McKinster C, Tay YK, eds. Pediatric Skin of Color. Springer; 2015:141-145. doi:10.1007/978-1-4614-6654-3_16 8.
- Knable AL Jr, Hanke CW, Gonin R. Prevalence of acne keloidalis nuchae in football players. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1997;37:570-574. doi:10.1016/s0190-9622(97)70173-7
- Umar S, Ton D, Carter MJ, et al. Unveiling a shared precursor condition for acne keloidalis nuchae and primary cicatricial alopecias. Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol. 2023;16:2315-2327. doi:10.2147/CCID.S422310
- Na K, Oh SH, Kim SK. Acne keloidalis nuchae in Asian: a single institutional experience. PLoS One. 2017;12:e0189790. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0189790
- Ogunbiyi A, George A. Acne keloidalis in females: case report and review of literature. J Natl Med Assoc. 2005;97:736-738.
- Alexis A, Heath CR, Halder RM. Folliculitis keloidalis nuchae and pseudofolliculitis barbae: are prevention and effective treatment within reach? Dermatol Clin. 2014;32:183-191. doi:10.1016/j.det.2013.12.001
- Kridin K, Solomon A, Tzur-Bitan D, et al. Acne keloidalis nuchae and the metabolic syndrome: a population-based study. Am J Clin Dermatol. 2020;21:733-739. doi:10.1007/s40257-020-00541-z
- Smart K, Rodriguez I, Worswick S. Comorbidities and treatment options for acne keloidalis nuchae. Dermatol Ther. Published online May 25, 2024. doi:10.1155/2024/8336926
- Callender VD, Young CM, Haverstock CL, et al. An open label study of clobetasol propionate 0.05% and betamethasone valerate 0.12% foams in the treatment of mild to moderate acne keloidalis. Cutis. 2005;75:317-321.
- Adotama P, Grullon K, Ali S, et al. How we do it: our method for triamcinolone injections of acne keloidalis nuchae. Dermatol Surg. 2023;49:713-714. doi:10.1097/DSS.0000000000003803
- Beckett N, Lawson C, Cohen G. Electrosurgical excision of acne keloidalis nuchae with secondary intention healing. J Clin Aesthet Dermatol. 2011;4:36-39.
- Esmat SM, Abdel Hay RM, Abu Zeid OM, et al. The efficacy of laser-assisted hair removal in the treatment of acne keloidalis nuchae; a pilot study. Eur J Dermatol. 2012;22:645-650. doi:10.1684/ejd.2012.1830
- Dillard AD, Quarles FN. African-American pioneers in dermatology. In: Taylor SC, Kelly AP, Lim HW, et al, eds. Dermatology for Skin of Color. 2nd ed. McGraw-Hill Education; 2016:717-730.
- Umar S, David CV, Castillo JR, et al. Innovative surgical approaches and selection criteria of large acne keloidalis nuchae lesions. Plast Reconstr Surg Glob Open. 2019;7:E2215. doi:10.1097/GOX.0000000000002215
- Lee MS, Nambudiri VE. The CROWN act and dermatology: taking a stand against race-based hair discrimination. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2021;84:1181-1182. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2020.11.065
The Comparison

Acne keloidalis nuchae (AKN) is a chronic inflammatory condition commonly affecting the occipital scalp and posterior neck. It causes discrete or extensive fibrosing papules that may coalesce to form pronounced tumorlike masses1,2 with scarring alopecia (Figure, A–C).3 Pustules, hair tufts, secondary bacterial infections, abscesses, and sinus tracts also may occur.1 The pathogenesis of AKN has been characterized as varying stages of follicular inflammation at the infundibular and isthmus levels followed by fibrotic occlusion of the follicular lumen.4 Pruritus, pain, bleeding, oozing, and a feeling of scalp tightness may occur.1,5
Umar et al6 performed a retrospective review of 108 men with AKN—58% of African descent, 37% Hispanic, 3% Asian, and 2% Middle Eastern—and proposed a 3-tier classification system for AKN. Tier 1 focused on the distribution and sagittal spread of AKN lesions between the clinical demarcation lines of the occipital notch and posterior hairline. Tier 2 focused on the type of lesions present—discrete papules or nodules, coalescing/abutting lesions, plaques (raised, atrophic, or indurated), or dome-shaped tumoral masses. Tier 3 focused on the presence or absence of co-existing dissecting cellulitis or folliculitis decalvans.6
Epidemiology
Acne keloidalis nuchae primarily manifests in adolescent and adult men of African or Afro-Caribbean descent.7 Among African American men, the prevalence of AKN ranges from 0.5% to 13.6%.8 Similar ranges have been reported among Nigerian, South African, and West African men.1 Acne keloidalis nuchae also affects Asian and Hispanic men but rarely is seen in non-Hispanic White men or in women of any ethnicity.9,10 The male to female ratio is 20:1.1,11 Hair texture, hairstyling practices such as closely shaved or faded haircuts, and genetics likely contribute to development of AKN. Sports and occupations that require the use of headgear or a tight collar may increase the risk for AKN.12
Key clinical features in people with darker skin tones
- The lesions of AKN range in color from pink to dark brown or black. Postinflammatory hyperpigmentation or hyperchromia may be present around AKN lesions.
- Chronicity of AKN may lead to extended use of high-potency topical or intralesional corticosteroids, which causes transient or long-lasting hypopigmentation, especially in those with darker skin tones.
Worth noting
- Acne keloidalis nuchae can be disfiguring, which negatively impacts quality of life and self-esteem.12
- Some occupations (eg, military, police) have hair policies that may not be favorable to those with or at risk for AKN.
- Patients with AKN are 2 to 3 times more likely to present with metabolic syndrome, hypertension, type 2 diabetes mellitus, or obesity.13
Treatment
There are no treatments approved by the US Food and Drug Administration specifically for AKN. Treatment approaches are based on the pathophysiology, secondary impacts on the skin, and disease severity. Growing out the hair may prevent worsening and/or decrease the risk for new lesions.6
- Options include but are not limited to topical and systemic therapies (eg, topical corticosteroids, oral or topical antibiotics, isotretinoin, topical retinoids, imiquimod, pimecrolimus), light devices (eg, phototherapy, laser), ablative therapies (eg, laser, cryotherapy, radiotherapy), and surgery (eg, excision, follicular unit excision), often in combination.6,14,15
- Intralesional triamcinolone injections are considered standard of care. Adotama et al16 found that injecting triamcinolone into the deep dermis in the area of flat or papular AKN yielded better control of inflammation and decreased appearance of lesions compared with injecting individual lesions.
- For extensive AKN lesions that do not respond to less-invasive therapies, consider surgical techniques,6,17 such as follicular unit excision18 and more extensive surgical excisions building on approaches from pioneers Drs. John Kenney and Harold Pierce.19 An innovative surgical approach for removal of large AKNs is the bat excision technique—wound shape resembles a bat in a spread-eagled position—with secondary intention healing with or without debridement and/or tension sutures. The resulting linear scar acts as a new posterior hair line.20
Health disparity highlights
Access to a dermatologic or plastic surgeon with expertise in the surgical treatment of large AKNs may be challenging but is needed to reduce risk for recurrence and adverse events.
Close-cropped haircuts on the occipital scalp, which are particularly popular among men of African descent, increase the risk for AKN.5 Although this grooming style may be a personal preference, other hairstyles commonly worn by those with tightly coiled hair may be deemed “unprofessional” in society or the workplace,21 which leads to hairstyling practices that may increase the risk for AKN.
Acne keloidalis nuchae remains an understudied entity that adversely affects patients with skin of color.
The Comparison

Acne keloidalis nuchae (AKN) is a chronic inflammatory condition commonly affecting the occipital scalp and posterior neck. It causes discrete or extensive fibrosing papules that may coalesce to form pronounced tumorlike masses1,2 with scarring alopecia (Figure, A–C).3 Pustules, hair tufts, secondary bacterial infections, abscesses, and sinus tracts also may occur.1 The pathogenesis of AKN has been characterized as varying stages of follicular inflammation at the infundibular and isthmus levels followed by fibrotic occlusion of the follicular lumen.4 Pruritus, pain, bleeding, oozing, and a feeling of scalp tightness may occur.1,5
Umar et al6 performed a retrospective review of 108 men with AKN—58% of African descent, 37% Hispanic, 3% Asian, and 2% Middle Eastern—and proposed a 3-tier classification system for AKN. Tier 1 focused on the distribution and sagittal spread of AKN lesions between the clinical demarcation lines of the occipital notch and posterior hairline. Tier 2 focused on the type of lesions present—discrete papules or nodules, coalescing/abutting lesions, plaques (raised, atrophic, or indurated), or dome-shaped tumoral masses. Tier 3 focused on the presence or absence of co-existing dissecting cellulitis or folliculitis decalvans.6
Epidemiology
Acne keloidalis nuchae primarily manifests in adolescent and adult men of African or Afro-Caribbean descent.7 Among African American men, the prevalence of AKN ranges from 0.5% to 13.6%.8 Similar ranges have been reported among Nigerian, South African, and West African men.1 Acne keloidalis nuchae also affects Asian and Hispanic men but rarely is seen in non-Hispanic White men or in women of any ethnicity.9,10 The male to female ratio is 20:1.1,11 Hair texture, hairstyling practices such as closely shaved or faded haircuts, and genetics likely contribute to development of AKN. Sports and occupations that require the use of headgear or a tight collar may increase the risk for AKN.12
Key clinical features in people with darker skin tones
- The lesions of AKN range in color from pink to dark brown or black. Postinflammatory hyperpigmentation or hyperchromia may be present around AKN lesions.
- Chronicity of AKN may lead to extended use of high-potency topical or intralesional corticosteroids, which causes transient or long-lasting hypopigmentation, especially in those with darker skin tones.
Worth noting
- Acne keloidalis nuchae can be disfiguring, which negatively impacts quality of life and self-esteem.12
- Some occupations (eg, military, police) have hair policies that may not be favorable to those with or at risk for AKN.
- Patients with AKN are 2 to 3 times more likely to present with metabolic syndrome, hypertension, type 2 diabetes mellitus, or obesity.13
Treatment
There are no treatments approved by the US Food and Drug Administration specifically for AKN. Treatment approaches are based on the pathophysiology, secondary impacts on the skin, and disease severity. Growing out the hair may prevent worsening and/or decrease the risk for new lesions.6
- Options include but are not limited to topical and systemic therapies (eg, topical corticosteroids, oral or topical antibiotics, isotretinoin, topical retinoids, imiquimod, pimecrolimus), light devices (eg, phototherapy, laser), ablative therapies (eg, laser, cryotherapy, radiotherapy), and surgery (eg, excision, follicular unit excision), often in combination.6,14,15
- Intralesional triamcinolone injections are considered standard of care. Adotama et al16 found that injecting triamcinolone into the deep dermis in the area of flat or papular AKN yielded better control of inflammation and decreased appearance of lesions compared with injecting individual lesions.
- For extensive AKN lesions that do not respond to less-invasive therapies, consider surgical techniques,6,17 such as follicular unit excision18 and more extensive surgical excisions building on approaches from pioneers Drs. John Kenney and Harold Pierce.19 An innovative surgical approach for removal of large AKNs is the bat excision technique—wound shape resembles a bat in a spread-eagled position—with secondary intention healing with or without debridement and/or tension sutures. The resulting linear scar acts as a new posterior hair line.20
Health disparity highlights
Access to a dermatologic or plastic surgeon with expertise in the surgical treatment of large AKNs may be challenging but is needed to reduce risk for recurrence and adverse events.
Close-cropped haircuts on the occipital scalp, which are particularly popular among men of African descent, increase the risk for AKN.5 Although this grooming style may be a personal preference, other hairstyles commonly worn by those with tightly coiled hair may be deemed “unprofessional” in society or the workplace,21 which leads to hairstyling practices that may increase the risk for AKN.
Acne keloidalis nuchae remains an understudied entity that adversely affects patients with skin of color.
- Ogunbiyi A. Acne keloidalis nuchae: prevalence, impact, and management challenges. Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol. 2016;9:483-489. doi:10.2147/CCID.S99225
- Al Aboud DM, Badri T. Acne keloidalis nuchae. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Updated July 31, 2023. Accessed August 2, 2024. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK459135/ 3.
- Sperling LC, Homoky C, Pratt L, et al. Acne keloidalis is a form of primary scarring alopecia. Arch Dermatol. 2000;136:479-484.
- Herzberg AJ, Dinehart SM, Kerns BJ, et al. Acne keloidalis: transverse microscopy, immunohistochemistry, and electron microscopy. Am J Dermatopathol. 1990;12:109-121. doi:10.1097/00000372-199004000-00001
- Saka B, Akakpo A-S, Téclessou JN, et al. Risk factors associated with acne keloidalis nuchae in black subjects: a case-control study. Ann Dermatol Venereol. 2020;147:350-354. doi:10.1016/j.annder.2020.01.007
- Umar S, Lee DJ, Lullo JJ. A retrospective cohort study and clinical classification system of acne keloidalis nuchae. J Clin Aesthet Dermatol. 2021;14:E61-E67.
- Reja M, Silverberg NB. Acne keloidalis nuchae. In: Silverberg NB, Durán-McKinster C, Tay YK, eds. Pediatric Skin of Color. Springer; 2015:141-145. doi:10.1007/978-1-4614-6654-3_16 8.
- Knable AL Jr, Hanke CW, Gonin R. Prevalence of acne keloidalis nuchae in football players. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1997;37:570-574. doi:10.1016/s0190-9622(97)70173-7
- Umar S, Ton D, Carter MJ, et al. Unveiling a shared precursor condition for acne keloidalis nuchae and primary cicatricial alopecias. Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol. 2023;16:2315-2327. doi:10.2147/CCID.S422310
- Na K, Oh SH, Kim SK. Acne keloidalis nuchae in Asian: a single institutional experience. PLoS One. 2017;12:e0189790. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0189790
- Ogunbiyi A, George A. Acne keloidalis in females: case report and review of literature. J Natl Med Assoc. 2005;97:736-738.
- Alexis A, Heath CR, Halder RM. Folliculitis keloidalis nuchae and pseudofolliculitis barbae: are prevention and effective treatment within reach? Dermatol Clin. 2014;32:183-191. doi:10.1016/j.det.2013.12.001
- Kridin K, Solomon A, Tzur-Bitan D, et al. Acne keloidalis nuchae and the metabolic syndrome: a population-based study. Am J Clin Dermatol. 2020;21:733-739. doi:10.1007/s40257-020-00541-z
- Smart K, Rodriguez I, Worswick S. Comorbidities and treatment options for acne keloidalis nuchae. Dermatol Ther. Published online May 25, 2024. doi:10.1155/2024/8336926
- Callender VD, Young CM, Haverstock CL, et al. An open label study of clobetasol propionate 0.05% and betamethasone valerate 0.12% foams in the treatment of mild to moderate acne keloidalis. Cutis. 2005;75:317-321.
- Adotama P, Grullon K, Ali S, et al. How we do it: our method for triamcinolone injections of acne keloidalis nuchae. Dermatol Surg. 2023;49:713-714. doi:10.1097/DSS.0000000000003803
- Beckett N, Lawson C, Cohen G. Electrosurgical excision of acne keloidalis nuchae with secondary intention healing. J Clin Aesthet Dermatol. 2011;4:36-39.
- Esmat SM, Abdel Hay RM, Abu Zeid OM, et al. The efficacy of laser-assisted hair removal in the treatment of acne keloidalis nuchae; a pilot study. Eur J Dermatol. 2012;22:645-650. doi:10.1684/ejd.2012.1830
- Dillard AD, Quarles FN. African-American pioneers in dermatology. In: Taylor SC, Kelly AP, Lim HW, et al, eds. Dermatology for Skin of Color. 2nd ed. McGraw-Hill Education; 2016:717-730.
- Umar S, David CV, Castillo JR, et al. Innovative surgical approaches and selection criteria of large acne keloidalis nuchae lesions. Plast Reconstr Surg Glob Open. 2019;7:E2215. doi:10.1097/GOX.0000000000002215
- Lee MS, Nambudiri VE. The CROWN act and dermatology: taking a stand against race-based hair discrimination. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2021;84:1181-1182. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2020.11.065
- Ogunbiyi A. Acne keloidalis nuchae: prevalence, impact, and management challenges. Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol. 2016;9:483-489. doi:10.2147/CCID.S99225
- Al Aboud DM, Badri T. Acne keloidalis nuchae. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Updated July 31, 2023. Accessed August 2, 2024. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK459135/ 3.
- Sperling LC, Homoky C, Pratt L, et al. Acne keloidalis is a form of primary scarring alopecia. Arch Dermatol. 2000;136:479-484.
- Herzberg AJ, Dinehart SM, Kerns BJ, et al. Acne keloidalis: transverse microscopy, immunohistochemistry, and electron microscopy. Am J Dermatopathol. 1990;12:109-121. doi:10.1097/00000372-199004000-00001
- Saka B, Akakpo A-S, Téclessou JN, et al. Risk factors associated with acne keloidalis nuchae in black subjects: a case-control study. Ann Dermatol Venereol. 2020;147:350-354. doi:10.1016/j.annder.2020.01.007
- Umar S, Lee DJ, Lullo JJ. A retrospective cohort study and clinical classification system of acne keloidalis nuchae. J Clin Aesthet Dermatol. 2021;14:E61-E67.
- Reja M, Silverberg NB. Acne keloidalis nuchae. In: Silverberg NB, Durán-McKinster C, Tay YK, eds. Pediatric Skin of Color. Springer; 2015:141-145. doi:10.1007/978-1-4614-6654-3_16 8.
- Knable AL Jr, Hanke CW, Gonin R. Prevalence of acne keloidalis nuchae in football players. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1997;37:570-574. doi:10.1016/s0190-9622(97)70173-7
- Umar S, Ton D, Carter MJ, et al. Unveiling a shared precursor condition for acne keloidalis nuchae and primary cicatricial alopecias. Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol. 2023;16:2315-2327. doi:10.2147/CCID.S422310
- Na K, Oh SH, Kim SK. Acne keloidalis nuchae in Asian: a single institutional experience. PLoS One. 2017;12:e0189790. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0189790
- Ogunbiyi A, George A. Acne keloidalis in females: case report and review of literature. J Natl Med Assoc. 2005;97:736-738.
- Alexis A, Heath CR, Halder RM. Folliculitis keloidalis nuchae and pseudofolliculitis barbae: are prevention and effective treatment within reach? Dermatol Clin. 2014;32:183-191. doi:10.1016/j.det.2013.12.001
- Kridin K, Solomon A, Tzur-Bitan D, et al. Acne keloidalis nuchae and the metabolic syndrome: a population-based study. Am J Clin Dermatol. 2020;21:733-739. doi:10.1007/s40257-020-00541-z
- Smart K, Rodriguez I, Worswick S. Comorbidities and treatment options for acne keloidalis nuchae. Dermatol Ther. Published online May 25, 2024. doi:10.1155/2024/8336926
- Callender VD, Young CM, Haverstock CL, et al. An open label study of clobetasol propionate 0.05% and betamethasone valerate 0.12% foams in the treatment of mild to moderate acne keloidalis. Cutis. 2005;75:317-321.
- Adotama P, Grullon K, Ali S, et al. How we do it: our method for triamcinolone injections of acne keloidalis nuchae. Dermatol Surg. 2023;49:713-714. doi:10.1097/DSS.0000000000003803
- Beckett N, Lawson C, Cohen G. Electrosurgical excision of acne keloidalis nuchae with secondary intention healing. J Clin Aesthet Dermatol. 2011;4:36-39.
- Esmat SM, Abdel Hay RM, Abu Zeid OM, et al. The efficacy of laser-assisted hair removal in the treatment of acne keloidalis nuchae; a pilot study. Eur J Dermatol. 2012;22:645-650. doi:10.1684/ejd.2012.1830
- Dillard AD, Quarles FN. African-American pioneers in dermatology. In: Taylor SC, Kelly AP, Lim HW, et al, eds. Dermatology for Skin of Color. 2nd ed. McGraw-Hill Education; 2016:717-730.
- Umar S, David CV, Castillo JR, et al. Innovative surgical approaches and selection criteria of large acne keloidalis nuchae lesions. Plast Reconstr Surg Glob Open. 2019;7:E2215. doi:10.1097/GOX.0000000000002215
- Lee MS, Nambudiri VE. The CROWN act and dermatology: taking a stand against race-based hair discrimination. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2021;84:1181-1182. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2020.11.065
Benefits of High-Dose Vitamin D in Managing Cutaneous Adverse Events Induced by Chemotherapy and Radiation Therapy
Vitamin D (VD) regulates keratinocyte proliferation and differentiation, modulates inflammatory pathways, and protects against cellular damage in the skin. 1 In the setting of tissue injury and acute skin inflammation, active vitamin D—1,25(OH) 2 D—suppresses signaling from pro-inflammatory chemokines and cytokines such as IFN- γ and IL-17. 2,3 This suppression reduces proliferation of helper T cells (T H 1, T H 17) and B cells, decreasing tissue damage from reactive oxygen species release while enhancing secretion of the anti-inflammatory cytokine IL-10 by antigen-presenting cells. 2-4
Suboptimal VD levels have been associated with numerous health consequences including malignancy, prompting interest in VD supplementation for improving cancer-related outcomes.5 Beyond disease prognosis, high-dose VD supplementation has been suggested as a potential therapy for adverse events (AEs) related to cancer treatments. In one study, mice that received oral vitamin D3 supplementation of 11,500 IU/kg daily had fewer doxorubicin-induced cardiotoxic effects on ejection fraction (P<.0001) and stroke volume (P<.01) than mice that received VD supplementation of 1500 IU/kg daily.6
In this review, we examine the impact of chemoradiation on 25(OH)D levels—which more accurately reflects VD stores than 1,25(OH)2D levels—and the impact of suboptimal VD on cutaneous toxicities related to chemoradiation. To define the suboptimal VD threshold, we used the Endocrine Society’s clinical practice guidelines, which characterize suboptimal 25(OH)D levels as insufficiency (21–29 ng/mL [52.5–72.5 nmol/L]) or deficiency (<20 ng/mL [50 nmol/L])7; deficiency can be further categorized as severe deficiency (<12 ng/mL [30 nmol/L]).8 This review also evaluates the evidence for vitamin D3 supplementation to alleviate the cutaneous AEs of chemotherapy and radiation treatments.
Effects of Chemotherapy on Vitamin D Levels
A high prevalence of VD deficiency is seen in various cancers. In a retrospective review of 25(OH)D levels in 2098 adults with solid tumors of any stage (6% had metastatic disease [n=124]), suboptimal levels were found in 69% of patients with breast cancer (n=617), 75% with colorectal cancer (n=84), 72% with gynecologic cancer (n=65), 79% with kidney and bladder cancer (n=145), 83% with pancreatic and upper gastrointestinal tract cancer (n=178), 73% with lung cancer (n=73), 69% with prostate cancer (n=225), 61% with skin cancer (n=399), and 63% with thyroid cancer (n=172).5 Suboptimal VD also has been found in hematologic malignancies. In a prospective cohort study, mean serum 25(OH)D levels in 23 patients with recently diagnosed acute myeloid leukemia demonstrated VD deficiency (mean [SD], 18.6 [6.6] nmol/L).9 Given that many patients already exhibit a baseline VD deficiency at cancer diagnosis, it is important to understand the relationship between VD and cancer treatment modalities.5
In the United States, breast and colorectal cancers were estimated to be the first and fourth most common cancers, with 313,510 and 152,810 predicted new cases in 2024, respectively.10 This review will focus on breast and colorectal cancer when describing VD variation associated with chemotherapy exposure due to their high prevalence.
Effects of Chemotherapy on Vitamin D Levels in Breast Cancer—Breast cancer studies have shown suboptimal VD levels in 76% of females 75 years or younger with any T1, T2, or T3; N0 or N1; and M0 breast cancer, in which 38.5% (n=197) had insufficient and 37.5% (n=192) had deficient 25(OH)D levels.11 In a study of female patients with primary breast cancer (stage I, II, or III and T1 with high Ki67 expression [≥30%], T2, or T3), VD deficiency was seen in 60% of patients not receiving VD supplementation.12,13 A systematic review that included 7 studies of different types of breast cancer suggested that circulating 25(OH)D may be associated with improved prognosis.14 Thus, studies have investigated risk factors associated with poor or worsening VD status in individuals with breast cancer, including exposure to chemotherapy and/or radiation treatment.12,15-18
A prospective cohort study assessed 25(OH)D levels in 95 patients with any breast cancer (stages I, II, IIIA, IIIB) before and after initiating chemotherapy with docetaxel, doxorubicin, epirubicin, 5-fluorouracil, or cyclophosphamide, compared with a group of 52 females without cancer.17 In the breast cancer group, approximately 80% (76/95) had suboptimal and 50% (47/95) had deficient VD levels before chemotherapy initiation (mean [SD], 54.1 [22.8] nmol/L). In the comparison group, 60% (31/52) had suboptimal and 30% (15/52) had deficient VD at baseline (mean [SD], 66.1 [23.5] nmol/L), which was higher than the breast cancer group (P=.03). A subgroup analysis excluded participants who started, stopped, or lacked data on dietary supplements containing VD (n=39); in the remaining 56 participants, a significant decrease in 25(OH)D levels was observed shortly after finishing chemotherapy compared with the prechemotherapy baseline value (mean, −7.9 nmol/L; P=.004). Notably, 6 months after chemotherapy completion, 25(OH)D levels increased (mean, +12.8 nmol/L; P<.001). Vitamin D levels remained stable in the comparison group (P=.987).17
Consistent with these findings, a cross-sectional study assessing VD status in 394 female patients with primary breast cancer (stage I, II, or III and T1 with high Ki67 expression [≥30%], T2, or T3), found that a history of chemotherapy was associated with increased odds of 25(OH)D levels less than 20 ng/mL compared with breast cancer patients with no prior chemotherapy (odds ratio, 1.86; 95% CI, 1.03-3.38).12 Although the study data included chemotherapy history, no information was provided on specific chemotherapy agents or regimens used in this cohort, limiting the ability to detect the drugs most often implicated.
Both studies indicated a complex interplay between chemotherapy and VD levels in breast cancer patients. Although Kok et al17 suggested a transient decrease in VD levels during chemotherapy with a subsequent recovery after cessation, Fassio et al12 highlighted the increased odds of VD deficiency associated with chemotherapy. Ultimately, larger randomized controlled trials are needed to better understand the relationship between chemotherapy and VD status in breast cancer patients.
Effects of Chemotherapy on Vitamin D Levels in Colorectal Cancer—Similar to patterns seen in breast cancer, a systematic review with 6 studies of different types of colorectal cancer suggested that circulating 25(OH)D levels may be associated with prognosis.14 Studies also have investigated the relationship between colorectal chemotherapy regimens and VD status.15,16,18,19
A retrospective study assessed 25(OH)D levels in 315 patients with any colorectal cancer (stage I–IV).15 Patients were included in the analysis if they received less than 400 IU daily of VD supplementation at baseline. For the whole study sample, the mean (SD) VD level was 23.7 (13.71) ng/mL. Patients who had not received chemotherapy within 3 months of the VD level assessment were categorized as the no chemotherapy group, and the others were designated as the chemotherapy group; the latter group was exposed to various chemotherapy regimens, including combinations of irinotecan, oxaliplatin, 5-fluorouracil, leucovorin, bevacizumab, or cetuximab. Multivariate analysis showed that the chemotherapy group was 3.7 times more likely to have very low VD levels (≤15 ng/mL) compared with those in the no chemotherapy group (P<.0001).15
A separate cross-sectional study examined serum 25(OH)D concentrations in 1201 patients with any newly diagnosed colorectal carcinoma (stage I–III); 91% of cases were adenocarcinoma.18 In a multivariate analysis, chemotherapy plus surgery was associated with lower VD levels than surgery alone 6 months after diagnosis (mean, −8.74 nmol/L; 95% CI, −11.30 to −6.18 nmol/L), specifically decreasing by a mean of 6.7 nmol/L (95% CI, −9.8 to −3.8 nmol/L) after adjusting for demographic and lifestyle factors.18 However, a prospective cohort study demonstrated different findings.19 Comparing 58 patients with newly diagnosed colorectal adenocarcinoma (stages I–IV) who underwent chemotherapy and 36 patients who did not receive chemotherapy, there was no significant change in 25(OH)D levels from the time of diagnosis to 6 months later. Median VD levels decreased by 0.7 ng/mL in those who received chemotherapy, while a minimal (and not significant) increase of 1.6 ng/mL was observed in those without chemotherapy intervention (P=.26). Notably, supplementation was not restricted in this cohort, which may have resulted in higher VD levels in those taking supplements.19
Since time of year and geographic location can influence VD levels, one prospective cohort study controlled for differential sun exposure due to these factors in their analysis.16 Assessment of 25(OH)D levels was completed in 81 chemotherapy-naïve cancer patients immediately before beginning chemotherapy as well as 6 and 12 weeks into treatment. More than 8 primary cancer types were represented in this study, with breast (34% [29/81]) and colorectal (14% [12/81]) cancer being the most common, but the cancer stages of the participants were not detailed. Vitamin D levels decreased after commencing chemotherapy, with the largest drop occurring 6 weeks into treatment. From the 6- to 12-week end points, VD increased but remained below the original baseline level (baseline: mean [SD], 49.2 [22.3] nmol/L; 6 weeks: mean [SD], 40.9 [19.0] nmol/L; 12 weeks: mean [SD], 45.9 [19.7] nmol/L; P=.05).16
Although focused on breast and colorectal cancers, these studies suggest that various chemotherapy regimens may confer a higher risk for VD deficiency compared with VD status at diagnosis and/or prior to chemotherapy treatment. However, most of these studies only discussed stage-based differences, excluding analysis of the variety of cancer subtypes that comprise breast and colorectal malignancies, which may limit our ability to extrapolate from these data. Ultimately, larger randomized controlled trials are needed to better understand the relationship between chemotherapy and VD status across various primary cancer types.
Effects of Radiation Therapy on Vitamin D Levels
Unlike chemotherapy, studies on the association between radiation therapy and VD levels are minimal, with most reports in the literature discussing the use of VD to potentiate the effects of radiation therapy. In one cross-sectional analysis of 1201 patients with newly diagnosed stage I, II, or III colorectal cancer of any type (94% were adenocarcinoma), radiation plus surgery was associated with slightly lower 25(OH)D levels than surgery alone for tumor treatment 6 months after diagnosis (mean, −3.17; 95% CI, −6.07 to −0.28 nmol/L). However, after adjustment for demographic and lifestyle factors, this decrease in VD levels attributable to radiotherapy was not statistically significant compared with the surgery-only cohort (mean, −1.78; 95% CI, −5.07 to 1.52 nmol/L).18
Similarly, a cross-sectional study assessing VD status in 394 female patients with primary breast cancer (stage I, II, or III and T1 with high Ki67 expression [≥30%], T2, or T3), found that a history of radiotherapy was not associated with a difference in serum 25(OH)D levels compared with those with breast cancer without prior radiotherapy (odds ratio, 0.90; 95% CI, 0.52-1.54).12 From the limited existing literature specifically addressing variations of VD levels with radiation, radiation therapy does not appear to significantly impact VD levels.
Vitamin D Levels and the Severity of Chemotherapy- or Radiation Therapy–Induced AEs
A prospective cohort of 241 patients did not find an increase in the incidence or severity of chemotherapy-induced cutaneous toxicities in those with suboptimal 1,25(OH)2D3 levels (≤75 nmol/L).20 Eight different primary cancer types were represented, including breast and colorectal cancer; the tumor stages of the participants were not detailed. Forty-one patients had normal 1,25(OH)2D3 levels, while the remaining 200 had suboptimal levels. There was no significant association between serum VD levels and the following dermatologic toxicities: desquamation (P=.26), xerosis (P=.15), mucositis (P=.30), or painful rash (P=.87). Surprisingly, nail changes and hand-foot reactions occurred with greater frequency in patients with normal VD levels (P=.01 and P=.03, respectively).20 Hand-foot reaction is part of the toxic erythema of chemotherapy (TEC) spectrum, which is comprised of a range of cytotoxic skin injuries that typically manifest within 2 to 3 weeks of exposure to the offending chemotherapeutic agents, often characterized by erythema, pain, swelling, and blistering, particularly in intertriginous and acral areas.21-23 Recovery from TEC generally takes at least 2 to 4 weeks and may necessitate cessation of the offending chemotherapeutic agent.21,24 Notably, this study measured 1,25(OH)2D3 levels instead of 25(OH)D levels, which may not reliably indicate body stores of VD.7,20 These results underscore the complex nature between chemotherapy and VD; however, VD levels alone do not appear to be a sufficient biomarker for predicting chemotherapy-associated cutaneous AEs.
Interestingly, radiation therapy–induced AEs may be associated with VD levels. A prospective cohort study of 98 patients with prostate, bladder, or gynecologic cancers (tumor stages were not detailed) undergoing pelvic radiotherapy found that females and males with 25(OH)D levels below a threshold of 35 and 40 nmol/L, respectively, were more likely to experience higher Radiation Therapy Oncology Group (RTOG) grade acute proctitis compared with those with VD above these thresholds.25 Specifically, VD below these thresholds was associated with increased odds of RTOG grade 2 or higher radiation-induced proctitis (OR, 3.07; 95% CI, 1.27-7.50 [P=.013]). Additionally, a weak correlation was noted between VD below these thresholds and the RTOG grade, with a Spearman correlation value of −0.189 (P=.031).25
One prospective cohort study included 28 patients with any cancer of the oral cavity, oropharynx, hypopharynx, or larynx stages II, III, or IVA; 93% (26/28) were stage III or IVA.26 The 20 (71%) patients with suboptimal 25(OH)D levels (≤75 nmol/L) experienced a higher prevalence of grade II radiation dermatitis compared with the 8 (29%) patients with optimal VD levels (χ22 =5.973; P=.0505). This pattern persisted with the severity of mucositis; patients from the suboptimal VD group presented with higher rates of grades II and III mucositis compared with the VD optimal group (χ22 =13.627; P=.0011).26 Recognizing the small cohort evaluated in the study, we highlight the importance of further studies to clarify these associations.
Chemotherapy-Induced Cutaneous Events Treated with High-Dose Vitamin D
Chemotherapeutic agents are known to induce cellular damage, resulting in a range of cutaneous AEs that can invoke discontinuation of otherwise effective chemotherapeutic interventions.27,28 Recent research has explored the potential of high-dose vitamin D3 as a therapeutic agent to mitigate cutaneous reactions.29,30
A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial investigated the use of a single high dose of oral 25(OH)D to treat topical nitrogen mustard (NM)–induced rash.29 To characterize baseline inflammatory responses from NM injury without intervention, clinical measures, serum studies, and tissue analyses from skin biopsies were performed on 28 healthy adults after exposure to topical NM—a chemotherapeutic agent classified as a DNA alkylator. Two weeks later, participants were exposed to topical NM a second time and were split into 2 groups: 14 patients received a single 200,000-IU dose of oral 25(OH)D while the other 14 participants were given a placebo. Using the inflammatory markers induced from baseline exposure to NM alone, posttreatment analysis revealed that the punch biopsies from
Although Ernst et al29 did not observe any clinically significant improvements with VD treatment, a case series of 6 patients with either glioblastoma multiforme, acute myeloid leukemia, or aplastic anemia did demonstrate clinical improvement of TEC after receiving high-dose vitamin D3.30 The mean time to onset of TEC was noted at 8.5 days following administration of the inciting chemotherapeutic agent, which included combinations of anthracycline, antimetabolite, kinase inhibitor, B-cell lymphoma 2 inhibitor, purine analogue, and alkylating agents. A combination of clinical and histologic findings was used to diagnose TEC. Baseline 25(OH)D levels were not established prior to treatment. The treatment regimen for 1 patient included 2 doses of 50,000 IU of VD spaced 1 week apart, totaling 100,000 IU, while the remaining 5 patients received a total of 200,000 IU, also split into 2 doses given 1 week apart. All patients received their first dose of VD within a week of the cutaneous eruption. Following the initial VD dose, there was a notable improvement in pain, pruritus, or swelling by the next day. Reduction in erythema also was observed within 1 to 4 days.30
No AEs associated with VD supplementation were reported, suggesting a potential beneficial role of high-dose VD in accelerating recovery from chemotherapy-induced rashes without evident safety concerns.
Radiation Therapy–Induced Cutaneous Events Treated with High-Dose Vitamin D
Radiation dermatitis is a common and often severe complication of radiation therapy that affects more than 90% of patients undergoing treatment, with half of these individuals experiencing grade 2 toxicity, according to the National Cancer Institute’s Common Terminology Criteria for Adverse Events.31,32 Radiation damage to basal keratinocytes and hair follicle stem cells disrupts the renewal of the skin’s outer layer, while a surge of free radicals causes irreversible DNA damage.33 Symptoms of radiation dermatitis can vary from mild pink erythema to tissue ulceration and necrosis, typically within 1 to 4 weeks of radiation exposure.34 The resulting dermatitis can take 2 to 4 weeks to heal, notably impacting patient quality of life and often necessitating modifications or interruptions in cancer therapy.33
Prior studies have demonstrated the use of high-dose VD to improve the healing of UV-irradiated skin. A randomized controlled trial investigated high-dose vitamin D3 to treat experimentally induced sunburn in 20 healthy adults. Compared with those who received a placebo, participants receiving the oral dose of 200,000 IU of vitamin D3 demonstrated suppression of the pro-inflammatory mediators tumor necrosis factor α (P=.04) and inducible nitric oxide synthase (P=.02), while expression of tissue repair enhancer arginase 1 was increased (P<.005).35 The mechanism of this enhanced tissue repair was investigated using a mouse model, in which intraperitoneal 25(OH)D was administered following severe UV-induced skin injury. On immunofluorescence microscopy, mice treated with VD showed enhanced autophagy within the macrophages infiltrating UV-irradiated skin.36 The use of high-dose VD to treat UV-irradiated skin in these studies established a precedent for using VD to heal cutaneous injury caused by ionizing radiation therapy.
Some studies have focused on the role of VD for treating acute radiation dermatitis. A study of 23 patients with ductal carcinoma in situ or localized invasive ductal carcinoma breast cancer compared the effectiveness of topical calcipotriol to that of a standard hydrating ointment.37 Participants were randomized to 1 of 2 treatments before starting adjuvant radiotherapy to evaluate their potential in preventing radiation dermatitis. In 87% (20/23) of these patients, no difference in skin reaction was observed between the 2 treatments, suggesting that topical VD application may not offer any advantage over the standard hydrating ointment for the prevention of radiation dermatitis.37
Benefits of high-dose oral VD for treating radiation dermatitis also have been reported. Nguyen et al38 documented 3 cases in which patients with neuroendocrine carcinoma of the pancreas, tonsillar carcinoma, and breast cancer received 200,000 IU of oral ergocalciferol distributed over 2 doses given 7 days apart for radiation dermatitis. These patients experienced substantial improvements in pain, swelling, and redness within a week of the initial dose. Additionally, a case of radiation recall dermatitis, which occurred a week after vinorelbine chemotherapy, was treated with 2 doses totaling 100,000 IU of oral ergocalciferol. This patient also had improvement in pain and swelling but continued to have tumor-related induration and ulceration.39
Although topical VD did not show significant benefits over standard treatments for radiation dermatitis, high-dose oral VD appears promising in improving patient outcomes of pain and swelling more rapidly than current practices. Further research is needed to confirm these findings and establish standardized treatment protocols.
Final Thoughts
Suboptimal VD levels are prevalent in numerous cancer types. Chemotherapy often is associated with acute, potentially transient worsening of VD status in patients with breast and colorectal cancer. Although 25(OH)D levels have not corresponded with increased frequency of chemotherapy-related dermatologic AEs, suboptimal 25(OH)D levels appear to be associated with increased severity of radiation-induced mucositis and dermatitis.20,25,26 The use of high-dose VD as a therapeutic agent shows promise in mitigating chemotherapy-induced and radiation therapy–induced rashes in multiple cancer types with reduction of inflammatory markers and a durable anti-inflammatory impact. Although the mechanisms of cellular injury vary among chemotherapeutic agents, the anti-inflammatory and tissue repair properties of VD may make it an effective treatment for chemotherapy-induced cutaneous damage regardless of injury mechanism.2-4,35 However, reports of clinical improvement vary, and further objective studies to classify optimal dosing, administration, and outcome measures are needed. The absence of reported AEs associated with high-dose VD supplementation is encouraging, but selection of a safe and optimal dosing regimen can only occur with dedicated clinical trials.
- Bikle DD. Vitamin D and the skin: physiology and pathophysiology. Rev Endocr Metab Disord. 2012;13:3-19. doi:10.1007/s11154-011-9194-0
- Penna G, Adorini L. 1α,25-Dihydroxyvitamin D3 inhibits differentiation, maturation, activation, and survival of dendritic cells leading to impaired alloreactive T cell activation. J Immunol. 2000;164:2405-2411. doi:10.4049/jimmunol.164.5.2405
- Penna G, Amuchastegui S, Cossetti C, et al. Treatment of experimental autoimmune prostatitis in nonobese diabetic mice by the vitamin D receptor agonist elocalcitol. J Immunol. 2006;177:8504-8511. doi:10.4049/jimmunol.177.12.8504
- Heine G, Niesner U, Chang HD, et al. 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3 promotes IL-10 production in human B cells. Eur J Immunol. 2008;38:2210-2218. doi:10.1002/eji.200838216
- Hauser K, Walsh D, Shrotriya S, et al. Low 25-hydroxyvitamin D levels in people with a solid tumor cancer diagnosis: the tip of the iceberg? Support Care Cancer. 2014;22:1931-1939. doi:10.1007/s00520-014-2154-y
- Lee KJ, Wright G, Bryant H, et al. Cytoprotective effect of vitamin D on doxorubicin-induced cardiac toxicity in triple negative breast cancer. Int J Mol Sci. 2021;22:7439. doi:10.3390/ijms22147439
- Holick MF, Binkley NC, Bischoff-Ferrari HA, et al. Evaluation, treatment, and prevention of vitamin D deficiency: an Endocrine Society clinical practice guideline. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2011;96:1911-1930. doi:10.1210/jc.2011-0385
- Amrein K, Scherkl M, Hoffmann M, et al. Vitamin D deficiency 2.0: an update on the current status worldwide. Eur J Clin Nutr. 2020;74:1498-1513. doi:10.1038/s41430-020-0558-y
- Thomas X, Chelghoum Y, Fanari N, et al. Serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D levels are associated with prognosis in hematological malignancies. Hematology. 2011;16:278-283. doi:10.1179/102453311X13085644679908
- Siegel RL, Giaquinto AN, Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2024. CA Cancer J Clin. 2024;74:12-49. doi:10.3322/caac.21820
- Goodwin PJ, Ennis M, Pritchard KI, et al. Prognostic effects of 25-hydroxyvitamin D levels in early breast cancer. J Clin Oncol. 2009;27:3757-3763. doi:10.1200/JCO.2008.20.0725
- Fassio A, Porciello G, Carioli G, et al. Post-diagnosis serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D concentrations in women treated for breast cancer participating in a lifestyle trial in Italy. Reumatismo. 2024;76:21-34.
- Augustin LSA, Libra M, Crispo A, et al. Low glycemic index diet, exercise and vitamin D to reduce breast cancer recurrence (DEDiCa): design of a clinical trial. BMC Cancer. 2017;17:69. doi:10.1186/s12885-017-3064-4
- Toriola AT, Nguyen N, Scheitler-Ring K, et al. Circulating 25-hydroxyvitamin D levels and prognosis among cancer patients: a systematic review. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 2014;23:917-933. doi:10.1158/1055-9965.EPI-14-0053
- Fakih MG, Trump DL, Johnson CS, et al. Chemotherapy is linked to severe vitamin D deficiency in patients with colorectal cancer. Int J Colorectal Dis. 2009;24:219-224. doi:10.1007/s00384-008-0593-y
- Isenring EA, Teleni L, Woodman RJ, et al. Serum vitamin D decreases during chemotherapy: an Australian prospective cohort study. Asia Pac J Clin Nutr. 2018;27:962-967. doi:10.6133/apjcn.042018.01
- Kok DE, van den Berg MMGA, Posthuma L, et al. Changes in circulating levels of 25-hydroxyvitamin D3 in breast cancer patients receiving chemotherapy. Nutr Cancer. 2019;71:756-766. doi:10.1080/01635581.2018.1559938
- Wesselink E, Bours MJL, de Wilt JHW, et al. Chemotherapy and vitamin D supplement use are determinants of serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D levels during the first six months after colorectal cancer diagnosis. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 2020;199:105577. doi:10.1016/j.jsbmb.2020.105577
- Savoie MB, Paciorek A, Zhang L, et al. Vitamin D levels in patients with colorectal cancer before and after treatment initiation. J Gastrointest Cancer. 2019;50:769-779. doi:10.1007/s12029-018-0147-7
- Kitchen D, Hughes B, Gill I, et al. The relationship between vitamin D and chemotherapy-induced toxicity—a pilot study. Br J Cancer. 2012;107:158-160. doi:10.1038/bjc.2012.194
- Demircay Z, Gürbüz O, Alpdogan TB, et al. Chemotherapy-induced acral erythema in leukemic patients: a report of 15 cases. Int J Dermatol. 1997;36:593-598. doi:10.1046/j.1365-4362.1997.00040.x
- Valks R, Fraga J, Porras-Luque J, et al. Chemotherapy-induced eccrine squamous syringometaplasia. a distinctive eruption in patients receiving hematopoietic progenitor cells. Arch Dermatol. 1997;133;873-878. doi:10.1001/archderm.133.7.873
- Webber KA, Kos L, Holland KE, et al. Intertriginous eruption associated with chemotherapy in pediatric patients. Arch Dermatol. 2007;143:67-71. doi:10.1001/archderm.143.1.67
- Hunjan MK, Nowsheen S, Ramos-Rodriguez AJ, et al. Clinical and histopathological spectrum of toxic erythema of chemotherapy in patients who have undergone allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation. Hematol Oncol Stem Cell Ther. 2019;12:19-25. doi:10.1016/j.hemonc.2018.09.001
- Ghorbanzadeh-Moghaddam A, Gholamrezaei A, Hemati S. Vitamin D deficiency is associated with the severity of radiation-induced proctitis in cancer patients. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2015;92:613-618. doi:10.1016/j.ijrobp.2015.02.011
- Bhanu A, Waghmare CM, Jain VS, et al. Serum 25-hydroxy vitamin-D levels in head and neck cancer chemoradiation therapy: potential in cancer therapeutics. Indian J Cancer. Published online February 27, 2003. doi:10.4103/ijc.ijc_358_20
- Yang B, Xie X, Wu Z, et al. DNA damage-mediated cellular senescence promotes hand-foot syndrome that can be relieved by thymidine prodrug. Genes Dis. 2022;10:2557-2571. doi:10.1016/j.gendis.2022.10.004
- Lassere Y, Hoff P. Management of hand-foot syndrome in patients treated with capecitabine (Xeloda®). Eur J Oncol Nurs. 2004;8(suppl 1):S31-S40. doi:10.1016/j.ejon.2004.06.007
- Ernst MK, Evans ST, Techner JM, et al. Vitamin D3 and deconvoluting a rash. JCI Insight. 2023;8:E163789.
- Nguyen CV, Zheng L, Zhou XA, et al. High-dose vitamin d for the management of toxic erythema of chemotherapy in hospitalized patients. JAMA Dermatol. 2023;159:219-221. doi:10.1001/jamadermatol.2022.5397
- Fisher J, Scott C, Stevens R, et al. Randomized phase III study comparing best supportive care to biafine as a prophylactic agent for radiation-induced skin toxicity for women undergoing breast irradiation: Radiation Therapy Oncology Group (RTOG) 97-13. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2000;48:1307-1310. doi:10.1016/s0360-3016(00)00782-3
- Pignol JP, Olivotto I, Rakovitch E, et al. A multicenter randomized trial of breast intensity-modulated radiation therapy to reduce acute radiation dermatitis. J Clin Oncol. 2008;26:2085-2092. doi:10.1200/JCO.2007.15.2488
- Hymes SR, Strom EA, Fife C. Radiation dermatitis: clinical presentation, pathophysiology, and treatment 2006. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2006;54:28-46. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2005.08.054
- Ryan JL. Ionizing radiation: the good, the bad, and the ugly. J Invest Dermatol. 2012;132(3 pt 2):985-993. doi:10.1038/jid.2011.411
- Scott JF, Das LM, Ahsanuddin S, et al. Oral vitamin D rapidly attenuates inflammation from sunburn: an interventional study. J Invest Dermatol. 2017;137:2078-2086. doi:10.1016/j.jid.2017.04.040
- Das LM, Binko AM, Traylor ZP, et al. Vitamin D improves sunburns by increasing autophagy in M2 macrophages. Autophagy. 2019;15:813-826. doi:10.1080/15548627.2019.1569298
- Nasser NJ, Fenig S, Ravid A, et al. Vitamin D ointment for prevention of radiation dermatitis in breast cancer patients. NPJ Breast Cancer. 2017;3:10. doi:10.1038/s41523-017-0006-x
- Nguyen CV, Zheng L, Lu KQ. High-dose vitamin D for the management acute radiation dermatitis. JAAD Case Rep. 2023;39:47-50. doi:10.1016/j.jdcr.2023.07.001
- Nguyen CV, Lu KQ. Vitamin D3 and its potential to ameliorate chemical and radiation-induced skin injury during cancer therapy. Disaster Med Public Health Prep. 2024;18:E4. doi:10.1017/dmp.2023.211
Vitamin D (VD) regulates keratinocyte proliferation and differentiation, modulates inflammatory pathways, and protects against cellular damage in the skin. 1 In the setting of tissue injury and acute skin inflammation, active vitamin D—1,25(OH) 2 D—suppresses signaling from pro-inflammatory chemokines and cytokines such as IFN- γ and IL-17. 2,3 This suppression reduces proliferation of helper T cells (T H 1, T H 17) and B cells, decreasing tissue damage from reactive oxygen species release while enhancing secretion of the anti-inflammatory cytokine IL-10 by antigen-presenting cells. 2-4
Suboptimal VD levels have been associated with numerous health consequences including malignancy, prompting interest in VD supplementation for improving cancer-related outcomes.5 Beyond disease prognosis, high-dose VD supplementation has been suggested as a potential therapy for adverse events (AEs) related to cancer treatments. In one study, mice that received oral vitamin D3 supplementation of 11,500 IU/kg daily had fewer doxorubicin-induced cardiotoxic effects on ejection fraction (P<.0001) and stroke volume (P<.01) than mice that received VD supplementation of 1500 IU/kg daily.6
In this review, we examine the impact of chemoradiation on 25(OH)D levels—which more accurately reflects VD stores than 1,25(OH)2D levels—and the impact of suboptimal VD on cutaneous toxicities related to chemoradiation. To define the suboptimal VD threshold, we used the Endocrine Society’s clinical practice guidelines, which characterize suboptimal 25(OH)D levels as insufficiency (21–29 ng/mL [52.5–72.5 nmol/L]) or deficiency (<20 ng/mL [50 nmol/L])7; deficiency can be further categorized as severe deficiency (<12 ng/mL [30 nmol/L]).8 This review also evaluates the evidence for vitamin D3 supplementation to alleviate the cutaneous AEs of chemotherapy and radiation treatments.
Effects of Chemotherapy on Vitamin D Levels
A high prevalence of VD deficiency is seen in various cancers. In a retrospective review of 25(OH)D levels in 2098 adults with solid tumors of any stage (6% had metastatic disease [n=124]), suboptimal levels were found in 69% of patients with breast cancer (n=617), 75% with colorectal cancer (n=84), 72% with gynecologic cancer (n=65), 79% with kidney and bladder cancer (n=145), 83% with pancreatic and upper gastrointestinal tract cancer (n=178), 73% with lung cancer (n=73), 69% with prostate cancer (n=225), 61% with skin cancer (n=399), and 63% with thyroid cancer (n=172).5 Suboptimal VD also has been found in hematologic malignancies. In a prospective cohort study, mean serum 25(OH)D levels in 23 patients with recently diagnosed acute myeloid leukemia demonstrated VD deficiency (mean [SD], 18.6 [6.6] nmol/L).9 Given that many patients already exhibit a baseline VD deficiency at cancer diagnosis, it is important to understand the relationship between VD and cancer treatment modalities.5
In the United States, breast and colorectal cancers were estimated to be the first and fourth most common cancers, with 313,510 and 152,810 predicted new cases in 2024, respectively.10 This review will focus on breast and colorectal cancer when describing VD variation associated with chemotherapy exposure due to their high prevalence.
Effects of Chemotherapy on Vitamin D Levels in Breast Cancer—Breast cancer studies have shown suboptimal VD levels in 76% of females 75 years or younger with any T1, T2, or T3; N0 or N1; and M0 breast cancer, in which 38.5% (n=197) had insufficient and 37.5% (n=192) had deficient 25(OH)D levels.11 In a study of female patients with primary breast cancer (stage I, II, or III and T1 with high Ki67 expression [≥30%], T2, or T3), VD deficiency was seen in 60% of patients not receiving VD supplementation.12,13 A systematic review that included 7 studies of different types of breast cancer suggested that circulating 25(OH)D may be associated with improved prognosis.14 Thus, studies have investigated risk factors associated with poor or worsening VD status in individuals with breast cancer, including exposure to chemotherapy and/or radiation treatment.12,15-18
A prospective cohort study assessed 25(OH)D levels in 95 patients with any breast cancer (stages I, II, IIIA, IIIB) before and after initiating chemotherapy with docetaxel, doxorubicin, epirubicin, 5-fluorouracil, or cyclophosphamide, compared with a group of 52 females without cancer.17 In the breast cancer group, approximately 80% (76/95) had suboptimal and 50% (47/95) had deficient VD levels before chemotherapy initiation (mean [SD], 54.1 [22.8] nmol/L). In the comparison group, 60% (31/52) had suboptimal and 30% (15/52) had deficient VD at baseline (mean [SD], 66.1 [23.5] nmol/L), which was higher than the breast cancer group (P=.03). A subgroup analysis excluded participants who started, stopped, or lacked data on dietary supplements containing VD (n=39); in the remaining 56 participants, a significant decrease in 25(OH)D levels was observed shortly after finishing chemotherapy compared with the prechemotherapy baseline value (mean, −7.9 nmol/L; P=.004). Notably, 6 months after chemotherapy completion, 25(OH)D levels increased (mean, +12.8 nmol/L; P<.001). Vitamin D levels remained stable in the comparison group (P=.987).17
Consistent with these findings, a cross-sectional study assessing VD status in 394 female patients with primary breast cancer (stage I, II, or III and T1 with high Ki67 expression [≥30%], T2, or T3), found that a history of chemotherapy was associated with increased odds of 25(OH)D levels less than 20 ng/mL compared with breast cancer patients with no prior chemotherapy (odds ratio, 1.86; 95% CI, 1.03-3.38).12 Although the study data included chemotherapy history, no information was provided on specific chemotherapy agents or regimens used in this cohort, limiting the ability to detect the drugs most often implicated.
Both studies indicated a complex interplay between chemotherapy and VD levels in breast cancer patients. Although Kok et al17 suggested a transient decrease in VD levels during chemotherapy with a subsequent recovery after cessation, Fassio et al12 highlighted the increased odds of VD deficiency associated with chemotherapy. Ultimately, larger randomized controlled trials are needed to better understand the relationship between chemotherapy and VD status in breast cancer patients.
Effects of Chemotherapy on Vitamin D Levels in Colorectal Cancer—Similar to patterns seen in breast cancer, a systematic review with 6 studies of different types of colorectal cancer suggested that circulating 25(OH)D levels may be associated with prognosis.14 Studies also have investigated the relationship between colorectal chemotherapy regimens and VD status.15,16,18,19
A retrospective study assessed 25(OH)D levels in 315 patients with any colorectal cancer (stage I–IV).15 Patients were included in the analysis if they received less than 400 IU daily of VD supplementation at baseline. For the whole study sample, the mean (SD) VD level was 23.7 (13.71) ng/mL. Patients who had not received chemotherapy within 3 months of the VD level assessment were categorized as the no chemotherapy group, and the others were designated as the chemotherapy group; the latter group was exposed to various chemotherapy regimens, including combinations of irinotecan, oxaliplatin, 5-fluorouracil, leucovorin, bevacizumab, or cetuximab. Multivariate analysis showed that the chemotherapy group was 3.7 times more likely to have very low VD levels (≤15 ng/mL) compared with those in the no chemotherapy group (P<.0001).15
A separate cross-sectional study examined serum 25(OH)D concentrations in 1201 patients with any newly diagnosed colorectal carcinoma (stage I–III); 91% of cases were adenocarcinoma.18 In a multivariate analysis, chemotherapy plus surgery was associated with lower VD levels than surgery alone 6 months after diagnosis (mean, −8.74 nmol/L; 95% CI, −11.30 to −6.18 nmol/L), specifically decreasing by a mean of 6.7 nmol/L (95% CI, −9.8 to −3.8 nmol/L) after adjusting for demographic and lifestyle factors.18 However, a prospective cohort study demonstrated different findings.19 Comparing 58 patients with newly diagnosed colorectal adenocarcinoma (stages I–IV) who underwent chemotherapy and 36 patients who did not receive chemotherapy, there was no significant change in 25(OH)D levels from the time of diagnosis to 6 months later. Median VD levels decreased by 0.7 ng/mL in those who received chemotherapy, while a minimal (and not significant) increase of 1.6 ng/mL was observed in those without chemotherapy intervention (P=.26). Notably, supplementation was not restricted in this cohort, which may have resulted in higher VD levels in those taking supplements.19
Since time of year and geographic location can influence VD levels, one prospective cohort study controlled for differential sun exposure due to these factors in their analysis.16 Assessment of 25(OH)D levels was completed in 81 chemotherapy-naïve cancer patients immediately before beginning chemotherapy as well as 6 and 12 weeks into treatment. More than 8 primary cancer types were represented in this study, with breast (34% [29/81]) and colorectal (14% [12/81]) cancer being the most common, but the cancer stages of the participants were not detailed. Vitamin D levels decreased after commencing chemotherapy, with the largest drop occurring 6 weeks into treatment. From the 6- to 12-week end points, VD increased but remained below the original baseline level (baseline: mean [SD], 49.2 [22.3] nmol/L; 6 weeks: mean [SD], 40.9 [19.0] nmol/L; 12 weeks: mean [SD], 45.9 [19.7] nmol/L; P=.05).16
Although focused on breast and colorectal cancers, these studies suggest that various chemotherapy regimens may confer a higher risk for VD deficiency compared with VD status at diagnosis and/or prior to chemotherapy treatment. However, most of these studies only discussed stage-based differences, excluding analysis of the variety of cancer subtypes that comprise breast and colorectal malignancies, which may limit our ability to extrapolate from these data. Ultimately, larger randomized controlled trials are needed to better understand the relationship between chemotherapy and VD status across various primary cancer types.
Effects of Radiation Therapy on Vitamin D Levels
Unlike chemotherapy, studies on the association between radiation therapy and VD levels are minimal, with most reports in the literature discussing the use of VD to potentiate the effects of radiation therapy. In one cross-sectional analysis of 1201 patients with newly diagnosed stage I, II, or III colorectal cancer of any type (94% were adenocarcinoma), radiation plus surgery was associated with slightly lower 25(OH)D levels than surgery alone for tumor treatment 6 months after diagnosis (mean, −3.17; 95% CI, −6.07 to −0.28 nmol/L). However, after adjustment for demographic and lifestyle factors, this decrease in VD levels attributable to radiotherapy was not statistically significant compared with the surgery-only cohort (mean, −1.78; 95% CI, −5.07 to 1.52 nmol/L).18
Similarly, a cross-sectional study assessing VD status in 394 female patients with primary breast cancer (stage I, II, or III and T1 with high Ki67 expression [≥30%], T2, or T3), found that a history of radiotherapy was not associated with a difference in serum 25(OH)D levels compared with those with breast cancer without prior radiotherapy (odds ratio, 0.90; 95% CI, 0.52-1.54).12 From the limited existing literature specifically addressing variations of VD levels with radiation, radiation therapy does not appear to significantly impact VD levels.
Vitamin D Levels and the Severity of Chemotherapy- or Radiation Therapy–Induced AEs
A prospective cohort of 241 patients did not find an increase in the incidence or severity of chemotherapy-induced cutaneous toxicities in those with suboptimal 1,25(OH)2D3 levels (≤75 nmol/L).20 Eight different primary cancer types were represented, including breast and colorectal cancer; the tumor stages of the participants were not detailed. Forty-one patients had normal 1,25(OH)2D3 levels, while the remaining 200 had suboptimal levels. There was no significant association between serum VD levels and the following dermatologic toxicities: desquamation (P=.26), xerosis (P=.15), mucositis (P=.30), or painful rash (P=.87). Surprisingly, nail changes and hand-foot reactions occurred with greater frequency in patients with normal VD levels (P=.01 and P=.03, respectively).20 Hand-foot reaction is part of the toxic erythema of chemotherapy (TEC) spectrum, which is comprised of a range of cytotoxic skin injuries that typically manifest within 2 to 3 weeks of exposure to the offending chemotherapeutic agents, often characterized by erythema, pain, swelling, and blistering, particularly in intertriginous and acral areas.21-23 Recovery from TEC generally takes at least 2 to 4 weeks and may necessitate cessation of the offending chemotherapeutic agent.21,24 Notably, this study measured 1,25(OH)2D3 levels instead of 25(OH)D levels, which may not reliably indicate body stores of VD.7,20 These results underscore the complex nature between chemotherapy and VD; however, VD levels alone do not appear to be a sufficient biomarker for predicting chemotherapy-associated cutaneous AEs.
Interestingly, radiation therapy–induced AEs may be associated with VD levels. A prospective cohort study of 98 patients with prostate, bladder, or gynecologic cancers (tumor stages were not detailed) undergoing pelvic radiotherapy found that females and males with 25(OH)D levels below a threshold of 35 and 40 nmol/L, respectively, were more likely to experience higher Radiation Therapy Oncology Group (RTOG) grade acute proctitis compared with those with VD above these thresholds.25 Specifically, VD below these thresholds was associated with increased odds of RTOG grade 2 or higher radiation-induced proctitis (OR, 3.07; 95% CI, 1.27-7.50 [P=.013]). Additionally, a weak correlation was noted between VD below these thresholds and the RTOG grade, with a Spearman correlation value of −0.189 (P=.031).25
One prospective cohort study included 28 patients with any cancer of the oral cavity, oropharynx, hypopharynx, or larynx stages II, III, or IVA; 93% (26/28) were stage III or IVA.26 The 20 (71%) patients with suboptimal 25(OH)D levels (≤75 nmol/L) experienced a higher prevalence of grade II radiation dermatitis compared with the 8 (29%) patients with optimal VD levels (χ22 =5.973; P=.0505). This pattern persisted with the severity of mucositis; patients from the suboptimal VD group presented with higher rates of grades II and III mucositis compared with the VD optimal group (χ22 =13.627; P=.0011).26 Recognizing the small cohort evaluated in the study, we highlight the importance of further studies to clarify these associations.
Chemotherapy-Induced Cutaneous Events Treated with High-Dose Vitamin D
Chemotherapeutic agents are known to induce cellular damage, resulting in a range of cutaneous AEs that can invoke discontinuation of otherwise effective chemotherapeutic interventions.27,28 Recent research has explored the potential of high-dose vitamin D3 as a therapeutic agent to mitigate cutaneous reactions.29,30
A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial investigated the use of a single high dose of oral 25(OH)D to treat topical nitrogen mustard (NM)–induced rash.29 To characterize baseline inflammatory responses from NM injury without intervention, clinical measures, serum studies, and tissue analyses from skin biopsies were performed on 28 healthy adults after exposure to topical NM—a chemotherapeutic agent classified as a DNA alkylator. Two weeks later, participants were exposed to topical NM a second time and were split into 2 groups: 14 patients received a single 200,000-IU dose of oral 25(OH)D while the other 14 participants were given a placebo. Using the inflammatory markers induced from baseline exposure to NM alone, posttreatment analysis revealed that the punch biopsies from
Although Ernst et al29 did not observe any clinically significant improvements with VD treatment, a case series of 6 patients with either glioblastoma multiforme, acute myeloid leukemia, or aplastic anemia did demonstrate clinical improvement of TEC after receiving high-dose vitamin D3.30 The mean time to onset of TEC was noted at 8.5 days following administration of the inciting chemotherapeutic agent, which included combinations of anthracycline, antimetabolite, kinase inhibitor, B-cell lymphoma 2 inhibitor, purine analogue, and alkylating agents. A combination of clinical and histologic findings was used to diagnose TEC. Baseline 25(OH)D levels were not established prior to treatment. The treatment regimen for 1 patient included 2 doses of 50,000 IU of VD spaced 1 week apart, totaling 100,000 IU, while the remaining 5 patients received a total of 200,000 IU, also split into 2 doses given 1 week apart. All patients received their first dose of VD within a week of the cutaneous eruption. Following the initial VD dose, there was a notable improvement in pain, pruritus, or swelling by the next day. Reduction in erythema also was observed within 1 to 4 days.30
No AEs associated with VD supplementation were reported, suggesting a potential beneficial role of high-dose VD in accelerating recovery from chemotherapy-induced rashes without evident safety concerns.
Radiation Therapy–Induced Cutaneous Events Treated with High-Dose Vitamin D
Radiation dermatitis is a common and often severe complication of radiation therapy that affects more than 90% of patients undergoing treatment, with half of these individuals experiencing grade 2 toxicity, according to the National Cancer Institute’s Common Terminology Criteria for Adverse Events.31,32 Radiation damage to basal keratinocytes and hair follicle stem cells disrupts the renewal of the skin’s outer layer, while a surge of free radicals causes irreversible DNA damage.33 Symptoms of radiation dermatitis can vary from mild pink erythema to tissue ulceration and necrosis, typically within 1 to 4 weeks of radiation exposure.34 The resulting dermatitis can take 2 to 4 weeks to heal, notably impacting patient quality of life and often necessitating modifications or interruptions in cancer therapy.33
Prior studies have demonstrated the use of high-dose VD to improve the healing of UV-irradiated skin. A randomized controlled trial investigated high-dose vitamin D3 to treat experimentally induced sunburn in 20 healthy adults. Compared with those who received a placebo, participants receiving the oral dose of 200,000 IU of vitamin D3 demonstrated suppression of the pro-inflammatory mediators tumor necrosis factor α (P=.04) and inducible nitric oxide synthase (P=.02), while expression of tissue repair enhancer arginase 1 was increased (P<.005).35 The mechanism of this enhanced tissue repair was investigated using a mouse model, in which intraperitoneal 25(OH)D was administered following severe UV-induced skin injury. On immunofluorescence microscopy, mice treated with VD showed enhanced autophagy within the macrophages infiltrating UV-irradiated skin.36 The use of high-dose VD to treat UV-irradiated skin in these studies established a precedent for using VD to heal cutaneous injury caused by ionizing radiation therapy.
Some studies have focused on the role of VD for treating acute radiation dermatitis. A study of 23 patients with ductal carcinoma in situ or localized invasive ductal carcinoma breast cancer compared the effectiveness of topical calcipotriol to that of a standard hydrating ointment.37 Participants were randomized to 1 of 2 treatments before starting adjuvant radiotherapy to evaluate their potential in preventing radiation dermatitis. In 87% (20/23) of these patients, no difference in skin reaction was observed between the 2 treatments, suggesting that topical VD application may not offer any advantage over the standard hydrating ointment for the prevention of radiation dermatitis.37
Benefits of high-dose oral VD for treating radiation dermatitis also have been reported. Nguyen et al38 documented 3 cases in which patients with neuroendocrine carcinoma of the pancreas, tonsillar carcinoma, and breast cancer received 200,000 IU of oral ergocalciferol distributed over 2 doses given 7 days apart for radiation dermatitis. These patients experienced substantial improvements in pain, swelling, and redness within a week of the initial dose. Additionally, a case of radiation recall dermatitis, which occurred a week after vinorelbine chemotherapy, was treated with 2 doses totaling 100,000 IU of oral ergocalciferol. This patient also had improvement in pain and swelling but continued to have tumor-related induration and ulceration.39
Although topical VD did not show significant benefits over standard treatments for radiation dermatitis, high-dose oral VD appears promising in improving patient outcomes of pain and swelling more rapidly than current practices. Further research is needed to confirm these findings and establish standardized treatment protocols.
Final Thoughts
Suboptimal VD levels are prevalent in numerous cancer types. Chemotherapy often is associated with acute, potentially transient worsening of VD status in patients with breast and colorectal cancer. Although 25(OH)D levels have not corresponded with increased frequency of chemotherapy-related dermatologic AEs, suboptimal 25(OH)D levels appear to be associated with increased severity of radiation-induced mucositis and dermatitis.20,25,26 The use of high-dose VD as a therapeutic agent shows promise in mitigating chemotherapy-induced and radiation therapy–induced rashes in multiple cancer types with reduction of inflammatory markers and a durable anti-inflammatory impact. Although the mechanisms of cellular injury vary among chemotherapeutic agents, the anti-inflammatory and tissue repair properties of VD may make it an effective treatment for chemotherapy-induced cutaneous damage regardless of injury mechanism.2-4,35 However, reports of clinical improvement vary, and further objective studies to classify optimal dosing, administration, and outcome measures are needed. The absence of reported AEs associated with high-dose VD supplementation is encouraging, but selection of a safe and optimal dosing regimen can only occur with dedicated clinical trials.
Vitamin D (VD) regulates keratinocyte proliferation and differentiation, modulates inflammatory pathways, and protects against cellular damage in the skin. 1 In the setting of tissue injury and acute skin inflammation, active vitamin D—1,25(OH) 2 D—suppresses signaling from pro-inflammatory chemokines and cytokines such as IFN- γ and IL-17. 2,3 This suppression reduces proliferation of helper T cells (T H 1, T H 17) and B cells, decreasing tissue damage from reactive oxygen species release while enhancing secretion of the anti-inflammatory cytokine IL-10 by antigen-presenting cells. 2-4
Suboptimal VD levels have been associated with numerous health consequences including malignancy, prompting interest in VD supplementation for improving cancer-related outcomes.5 Beyond disease prognosis, high-dose VD supplementation has been suggested as a potential therapy for adverse events (AEs) related to cancer treatments. In one study, mice that received oral vitamin D3 supplementation of 11,500 IU/kg daily had fewer doxorubicin-induced cardiotoxic effects on ejection fraction (P<.0001) and stroke volume (P<.01) than mice that received VD supplementation of 1500 IU/kg daily.6
In this review, we examine the impact of chemoradiation on 25(OH)D levels—which more accurately reflects VD stores than 1,25(OH)2D levels—and the impact of suboptimal VD on cutaneous toxicities related to chemoradiation. To define the suboptimal VD threshold, we used the Endocrine Society’s clinical practice guidelines, which characterize suboptimal 25(OH)D levels as insufficiency (21–29 ng/mL [52.5–72.5 nmol/L]) or deficiency (<20 ng/mL [50 nmol/L])7; deficiency can be further categorized as severe deficiency (<12 ng/mL [30 nmol/L]).8 This review also evaluates the evidence for vitamin D3 supplementation to alleviate the cutaneous AEs of chemotherapy and radiation treatments.
Effects of Chemotherapy on Vitamin D Levels
A high prevalence of VD deficiency is seen in various cancers. In a retrospective review of 25(OH)D levels in 2098 adults with solid tumors of any stage (6% had metastatic disease [n=124]), suboptimal levels were found in 69% of patients with breast cancer (n=617), 75% with colorectal cancer (n=84), 72% with gynecologic cancer (n=65), 79% with kidney and bladder cancer (n=145), 83% with pancreatic and upper gastrointestinal tract cancer (n=178), 73% with lung cancer (n=73), 69% with prostate cancer (n=225), 61% with skin cancer (n=399), and 63% with thyroid cancer (n=172).5 Suboptimal VD also has been found in hematologic malignancies. In a prospective cohort study, mean serum 25(OH)D levels in 23 patients with recently diagnosed acute myeloid leukemia demonstrated VD deficiency (mean [SD], 18.6 [6.6] nmol/L).9 Given that many patients already exhibit a baseline VD deficiency at cancer diagnosis, it is important to understand the relationship between VD and cancer treatment modalities.5
In the United States, breast and colorectal cancers were estimated to be the first and fourth most common cancers, with 313,510 and 152,810 predicted new cases in 2024, respectively.10 This review will focus on breast and colorectal cancer when describing VD variation associated with chemotherapy exposure due to their high prevalence.
Effects of Chemotherapy on Vitamin D Levels in Breast Cancer—Breast cancer studies have shown suboptimal VD levels in 76% of females 75 years or younger with any T1, T2, or T3; N0 or N1; and M0 breast cancer, in which 38.5% (n=197) had insufficient and 37.5% (n=192) had deficient 25(OH)D levels.11 In a study of female patients with primary breast cancer (stage I, II, or III and T1 with high Ki67 expression [≥30%], T2, or T3), VD deficiency was seen in 60% of patients not receiving VD supplementation.12,13 A systematic review that included 7 studies of different types of breast cancer suggested that circulating 25(OH)D may be associated with improved prognosis.14 Thus, studies have investigated risk factors associated with poor or worsening VD status in individuals with breast cancer, including exposure to chemotherapy and/or radiation treatment.12,15-18
A prospective cohort study assessed 25(OH)D levels in 95 patients with any breast cancer (stages I, II, IIIA, IIIB) before and after initiating chemotherapy with docetaxel, doxorubicin, epirubicin, 5-fluorouracil, or cyclophosphamide, compared with a group of 52 females without cancer.17 In the breast cancer group, approximately 80% (76/95) had suboptimal and 50% (47/95) had deficient VD levels before chemotherapy initiation (mean [SD], 54.1 [22.8] nmol/L). In the comparison group, 60% (31/52) had suboptimal and 30% (15/52) had deficient VD at baseline (mean [SD], 66.1 [23.5] nmol/L), which was higher than the breast cancer group (P=.03). A subgroup analysis excluded participants who started, stopped, or lacked data on dietary supplements containing VD (n=39); in the remaining 56 participants, a significant decrease in 25(OH)D levels was observed shortly after finishing chemotherapy compared with the prechemotherapy baseline value (mean, −7.9 nmol/L; P=.004). Notably, 6 months after chemotherapy completion, 25(OH)D levels increased (mean, +12.8 nmol/L; P<.001). Vitamin D levels remained stable in the comparison group (P=.987).17
Consistent with these findings, a cross-sectional study assessing VD status in 394 female patients with primary breast cancer (stage I, II, or III and T1 with high Ki67 expression [≥30%], T2, or T3), found that a history of chemotherapy was associated with increased odds of 25(OH)D levels less than 20 ng/mL compared with breast cancer patients with no prior chemotherapy (odds ratio, 1.86; 95% CI, 1.03-3.38).12 Although the study data included chemotherapy history, no information was provided on specific chemotherapy agents or regimens used in this cohort, limiting the ability to detect the drugs most often implicated.
Both studies indicated a complex interplay between chemotherapy and VD levels in breast cancer patients. Although Kok et al17 suggested a transient decrease in VD levels during chemotherapy with a subsequent recovery after cessation, Fassio et al12 highlighted the increased odds of VD deficiency associated with chemotherapy. Ultimately, larger randomized controlled trials are needed to better understand the relationship between chemotherapy and VD status in breast cancer patients.
Effects of Chemotherapy on Vitamin D Levels in Colorectal Cancer—Similar to patterns seen in breast cancer, a systematic review with 6 studies of different types of colorectal cancer suggested that circulating 25(OH)D levels may be associated with prognosis.14 Studies also have investigated the relationship between colorectal chemotherapy regimens and VD status.15,16,18,19
A retrospective study assessed 25(OH)D levels in 315 patients with any colorectal cancer (stage I–IV).15 Patients were included in the analysis if they received less than 400 IU daily of VD supplementation at baseline. For the whole study sample, the mean (SD) VD level was 23.7 (13.71) ng/mL. Patients who had not received chemotherapy within 3 months of the VD level assessment were categorized as the no chemotherapy group, and the others were designated as the chemotherapy group; the latter group was exposed to various chemotherapy regimens, including combinations of irinotecan, oxaliplatin, 5-fluorouracil, leucovorin, bevacizumab, or cetuximab. Multivariate analysis showed that the chemotherapy group was 3.7 times more likely to have very low VD levels (≤15 ng/mL) compared with those in the no chemotherapy group (P<.0001).15
A separate cross-sectional study examined serum 25(OH)D concentrations in 1201 patients with any newly diagnosed colorectal carcinoma (stage I–III); 91% of cases were adenocarcinoma.18 In a multivariate analysis, chemotherapy plus surgery was associated with lower VD levels than surgery alone 6 months after diagnosis (mean, −8.74 nmol/L; 95% CI, −11.30 to −6.18 nmol/L), specifically decreasing by a mean of 6.7 nmol/L (95% CI, −9.8 to −3.8 nmol/L) after adjusting for demographic and lifestyle factors.18 However, a prospective cohort study demonstrated different findings.19 Comparing 58 patients with newly diagnosed colorectal adenocarcinoma (stages I–IV) who underwent chemotherapy and 36 patients who did not receive chemotherapy, there was no significant change in 25(OH)D levels from the time of diagnosis to 6 months later. Median VD levels decreased by 0.7 ng/mL in those who received chemotherapy, while a minimal (and not significant) increase of 1.6 ng/mL was observed in those without chemotherapy intervention (P=.26). Notably, supplementation was not restricted in this cohort, which may have resulted in higher VD levels in those taking supplements.19
Since time of year and geographic location can influence VD levels, one prospective cohort study controlled for differential sun exposure due to these factors in their analysis.16 Assessment of 25(OH)D levels was completed in 81 chemotherapy-naïve cancer patients immediately before beginning chemotherapy as well as 6 and 12 weeks into treatment. More than 8 primary cancer types were represented in this study, with breast (34% [29/81]) and colorectal (14% [12/81]) cancer being the most common, but the cancer stages of the participants were not detailed. Vitamin D levels decreased after commencing chemotherapy, with the largest drop occurring 6 weeks into treatment. From the 6- to 12-week end points, VD increased but remained below the original baseline level (baseline: mean [SD], 49.2 [22.3] nmol/L; 6 weeks: mean [SD], 40.9 [19.0] nmol/L; 12 weeks: mean [SD], 45.9 [19.7] nmol/L; P=.05).16
Although focused on breast and colorectal cancers, these studies suggest that various chemotherapy regimens may confer a higher risk for VD deficiency compared with VD status at diagnosis and/or prior to chemotherapy treatment. However, most of these studies only discussed stage-based differences, excluding analysis of the variety of cancer subtypes that comprise breast and colorectal malignancies, which may limit our ability to extrapolate from these data. Ultimately, larger randomized controlled trials are needed to better understand the relationship between chemotherapy and VD status across various primary cancer types.
Effects of Radiation Therapy on Vitamin D Levels
Unlike chemotherapy, studies on the association between radiation therapy and VD levels are minimal, with most reports in the literature discussing the use of VD to potentiate the effects of radiation therapy. In one cross-sectional analysis of 1201 patients with newly diagnosed stage I, II, or III colorectal cancer of any type (94% were adenocarcinoma), radiation plus surgery was associated with slightly lower 25(OH)D levels than surgery alone for tumor treatment 6 months after diagnosis (mean, −3.17; 95% CI, −6.07 to −0.28 nmol/L). However, after adjustment for demographic and lifestyle factors, this decrease in VD levels attributable to radiotherapy was not statistically significant compared with the surgery-only cohort (mean, −1.78; 95% CI, −5.07 to 1.52 nmol/L).18
Similarly, a cross-sectional study assessing VD status in 394 female patients with primary breast cancer (stage I, II, or III and T1 with high Ki67 expression [≥30%], T2, or T3), found that a history of radiotherapy was not associated with a difference in serum 25(OH)D levels compared with those with breast cancer without prior radiotherapy (odds ratio, 0.90; 95% CI, 0.52-1.54).12 From the limited existing literature specifically addressing variations of VD levels with radiation, radiation therapy does not appear to significantly impact VD levels.
Vitamin D Levels and the Severity of Chemotherapy- or Radiation Therapy–Induced AEs
A prospective cohort of 241 patients did not find an increase in the incidence or severity of chemotherapy-induced cutaneous toxicities in those with suboptimal 1,25(OH)2D3 levels (≤75 nmol/L).20 Eight different primary cancer types were represented, including breast and colorectal cancer; the tumor stages of the participants were not detailed. Forty-one patients had normal 1,25(OH)2D3 levels, while the remaining 200 had suboptimal levels. There was no significant association between serum VD levels and the following dermatologic toxicities: desquamation (P=.26), xerosis (P=.15), mucositis (P=.30), or painful rash (P=.87). Surprisingly, nail changes and hand-foot reactions occurred with greater frequency in patients with normal VD levels (P=.01 and P=.03, respectively).20 Hand-foot reaction is part of the toxic erythema of chemotherapy (TEC) spectrum, which is comprised of a range of cytotoxic skin injuries that typically manifest within 2 to 3 weeks of exposure to the offending chemotherapeutic agents, often characterized by erythema, pain, swelling, and blistering, particularly in intertriginous and acral areas.21-23 Recovery from TEC generally takes at least 2 to 4 weeks and may necessitate cessation of the offending chemotherapeutic agent.21,24 Notably, this study measured 1,25(OH)2D3 levels instead of 25(OH)D levels, which may not reliably indicate body stores of VD.7,20 These results underscore the complex nature between chemotherapy and VD; however, VD levels alone do not appear to be a sufficient biomarker for predicting chemotherapy-associated cutaneous AEs.
Interestingly, radiation therapy–induced AEs may be associated with VD levels. A prospective cohort study of 98 patients with prostate, bladder, or gynecologic cancers (tumor stages were not detailed) undergoing pelvic radiotherapy found that females and males with 25(OH)D levels below a threshold of 35 and 40 nmol/L, respectively, were more likely to experience higher Radiation Therapy Oncology Group (RTOG) grade acute proctitis compared with those with VD above these thresholds.25 Specifically, VD below these thresholds was associated with increased odds of RTOG grade 2 or higher radiation-induced proctitis (OR, 3.07; 95% CI, 1.27-7.50 [P=.013]). Additionally, a weak correlation was noted between VD below these thresholds and the RTOG grade, with a Spearman correlation value of −0.189 (P=.031).25
One prospective cohort study included 28 patients with any cancer of the oral cavity, oropharynx, hypopharynx, or larynx stages II, III, or IVA; 93% (26/28) were stage III or IVA.26 The 20 (71%) patients with suboptimal 25(OH)D levels (≤75 nmol/L) experienced a higher prevalence of grade II radiation dermatitis compared with the 8 (29%) patients with optimal VD levels (χ22 =5.973; P=.0505). This pattern persisted with the severity of mucositis; patients from the suboptimal VD group presented with higher rates of grades II and III mucositis compared with the VD optimal group (χ22 =13.627; P=.0011).26 Recognizing the small cohort evaluated in the study, we highlight the importance of further studies to clarify these associations.
Chemotherapy-Induced Cutaneous Events Treated with High-Dose Vitamin D
Chemotherapeutic agents are known to induce cellular damage, resulting in a range of cutaneous AEs that can invoke discontinuation of otherwise effective chemotherapeutic interventions.27,28 Recent research has explored the potential of high-dose vitamin D3 as a therapeutic agent to mitigate cutaneous reactions.29,30
A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial investigated the use of a single high dose of oral 25(OH)D to treat topical nitrogen mustard (NM)–induced rash.29 To characterize baseline inflammatory responses from NM injury without intervention, clinical measures, serum studies, and tissue analyses from skin biopsies were performed on 28 healthy adults after exposure to topical NM—a chemotherapeutic agent classified as a DNA alkylator. Two weeks later, participants were exposed to topical NM a second time and were split into 2 groups: 14 patients received a single 200,000-IU dose of oral 25(OH)D while the other 14 participants were given a placebo. Using the inflammatory markers induced from baseline exposure to NM alone, posttreatment analysis revealed that the punch biopsies from
Although Ernst et al29 did not observe any clinically significant improvements with VD treatment, a case series of 6 patients with either glioblastoma multiforme, acute myeloid leukemia, or aplastic anemia did demonstrate clinical improvement of TEC after receiving high-dose vitamin D3.30 The mean time to onset of TEC was noted at 8.5 days following administration of the inciting chemotherapeutic agent, which included combinations of anthracycline, antimetabolite, kinase inhibitor, B-cell lymphoma 2 inhibitor, purine analogue, and alkylating agents. A combination of clinical and histologic findings was used to diagnose TEC. Baseline 25(OH)D levels were not established prior to treatment. The treatment regimen for 1 patient included 2 doses of 50,000 IU of VD spaced 1 week apart, totaling 100,000 IU, while the remaining 5 patients received a total of 200,000 IU, also split into 2 doses given 1 week apart. All patients received their first dose of VD within a week of the cutaneous eruption. Following the initial VD dose, there was a notable improvement in pain, pruritus, or swelling by the next day. Reduction in erythema also was observed within 1 to 4 days.30
No AEs associated with VD supplementation were reported, suggesting a potential beneficial role of high-dose VD in accelerating recovery from chemotherapy-induced rashes without evident safety concerns.
Radiation Therapy–Induced Cutaneous Events Treated with High-Dose Vitamin D
Radiation dermatitis is a common and often severe complication of radiation therapy that affects more than 90% of patients undergoing treatment, with half of these individuals experiencing grade 2 toxicity, according to the National Cancer Institute’s Common Terminology Criteria for Adverse Events.31,32 Radiation damage to basal keratinocytes and hair follicle stem cells disrupts the renewal of the skin’s outer layer, while a surge of free radicals causes irreversible DNA damage.33 Symptoms of radiation dermatitis can vary from mild pink erythema to tissue ulceration and necrosis, typically within 1 to 4 weeks of radiation exposure.34 The resulting dermatitis can take 2 to 4 weeks to heal, notably impacting patient quality of life and often necessitating modifications or interruptions in cancer therapy.33
Prior studies have demonstrated the use of high-dose VD to improve the healing of UV-irradiated skin. A randomized controlled trial investigated high-dose vitamin D3 to treat experimentally induced sunburn in 20 healthy adults. Compared with those who received a placebo, participants receiving the oral dose of 200,000 IU of vitamin D3 demonstrated suppression of the pro-inflammatory mediators tumor necrosis factor α (P=.04) and inducible nitric oxide synthase (P=.02), while expression of tissue repair enhancer arginase 1 was increased (P<.005).35 The mechanism of this enhanced tissue repair was investigated using a mouse model, in which intraperitoneal 25(OH)D was administered following severe UV-induced skin injury. On immunofluorescence microscopy, mice treated with VD showed enhanced autophagy within the macrophages infiltrating UV-irradiated skin.36 The use of high-dose VD to treat UV-irradiated skin in these studies established a precedent for using VD to heal cutaneous injury caused by ionizing radiation therapy.
Some studies have focused on the role of VD for treating acute radiation dermatitis. A study of 23 patients with ductal carcinoma in situ or localized invasive ductal carcinoma breast cancer compared the effectiveness of topical calcipotriol to that of a standard hydrating ointment.37 Participants were randomized to 1 of 2 treatments before starting adjuvant radiotherapy to evaluate their potential in preventing radiation dermatitis. In 87% (20/23) of these patients, no difference in skin reaction was observed between the 2 treatments, suggesting that topical VD application may not offer any advantage over the standard hydrating ointment for the prevention of radiation dermatitis.37
Benefits of high-dose oral VD for treating radiation dermatitis also have been reported. Nguyen et al38 documented 3 cases in which patients with neuroendocrine carcinoma of the pancreas, tonsillar carcinoma, and breast cancer received 200,000 IU of oral ergocalciferol distributed over 2 doses given 7 days apart for radiation dermatitis. These patients experienced substantial improvements in pain, swelling, and redness within a week of the initial dose. Additionally, a case of radiation recall dermatitis, which occurred a week after vinorelbine chemotherapy, was treated with 2 doses totaling 100,000 IU of oral ergocalciferol. This patient also had improvement in pain and swelling but continued to have tumor-related induration and ulceration.39
Although topical VD did not show significant benefits over standard treatments for radiation dermatitis, high-dose oral VD appears promising in improving patient outcomes of pain and swelling more rapidly than current practices. Further research is needed to confirm these findings and establish standardized treatment protocols.
Final Thoughts
Suboptimal VD levels are prevalent in numerous cancer types. Chemotherapy often is associated with acute, potentially transient worsening of VD status in patients with breast and colorectal cancer. Although 25(OH)D levels have not corresponded with increased frequency of chemotherapy-related dermatologic AEs, suboptimal 25(OH)D levels appear to be associated with increased severity of radiation-induced mucositis and dermatitis.20,25,26 The use of high-dose VD as a therapeutic agent shows promise in mitigating chemotherapy-induced and radiation therapy–induced rashes in multiple cancer types with reduction of inflammatory markers and a durable anti-inflammatory impact. Although the mechanisms of cellular injury vary among chemotherapeutic agents, the anti-inflammatory and tissue repair properties of VD may make it an effective treatment for chemotherapy-induced cutaneous damage regardless of injury mechanism.2-4,35 However, reports of clinical improvement vary, and further objective studies to classify optimal dosing, administration, and outcome measures are needed. The absence of reported AEs associated with high-dose VD supplementation is encouraging, but selection of a safe and optimal dosing regimen can only occur with dedicated clinical trials.
- Bikle DD. Vitamin D and the skin: physiology and pathophysiology. Rev Endocr Metab Disord. 2012;13:3-19. doi:10.1007/s11154-011-9194-0
- Penna G, Adorini L. 1α,25-Dihydroxyvitamin D3 inhibits differentiation, maturation, activation, and survival of dendritic cells leading to impaired alloreactive T cell activation. J Immunol. 2000;164:2405-2411. doi:10.4049/jimmunol.164.5.2405
- Penna G, Amuchastegui S, Cossetti C, et al. Treatment of experimental autoimmune prostatitis in nonobese diabetic mice by the vitamin D receptor agonist elocalcitol. J Immunol. 2006;177:8504-8511. doi:10.4049/jimmunol.177.12.8504
- Heine G, Niesner U, Chang HD, et al. 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3 promotes IL-10 production in human B cells. Eur J Immunol. 2008;38:2210-2218. doi:10.1002/eji.200838216
- Hauser K, Walsh D, Shrotriya S, et al. Low 25-hydroxyvitamin D levels in people with a solid tumor cancer diagnosis: the tip of the iceberg? Support Care Cancer. 2014;22:1931-1939. doi:10.1007/s00520-014-2154-y
- Lee KJ, Wright G, Bryant H, et al. Cytoprotective effect of vitamin D on doxorubicin-induced cardiac toxicity in triple negative breast cancer. Int J Mol Sci. 2021;22:7439. doi:10.3390/ijms22147439
- Holick MF, Binkley NC, Bischoff-Ferrari HA, et al. Evaluation, treatment, and prevention of vitamin D deficiency: an Endocrine Society clinical practice guideline. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2011;96:1911-1930. doi:10.1210/jc.2011-0385
- Amrein K, Scherkl M, Hoffmann M, et al. Vitamin D deficiency 2.0: an update on the current status worldwide. Eur J Clin Nutr. 2020;74:1498-1513. doi:10.1038/s41430-020-0558-y
- Thomas X, Chelghoum Y, Fanari N, et al. Serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D levels are associated with prognosis in hematological malignancies. Hematology. 2011;16:278-283. doi:10.1179/102453311X13085644679908
- Siegel RL, Giaquinto AN, Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2024. CA Cancer J Clin. 2024;74:12-49. doi:10.3322/caac.21820
- Goodwin PJ, Ennis M, Pritchard KI, et al. Prognostic effects of 25-hydroxyvitamin D levels in early breast cancer. J Clin Oncol. 2009;27:3757-3763. doi:10.1200/JCO.2008.20.0725
- Fassio A, Porciello G, Carioli G, et al. Post-diagnosis serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D concentrations in women treated for breast cancer participating in a lifestyle trial in Italy. Reumatismo. 2024;76:21-34.
- Augustin LSA, Libra M, Crispo A, et al. Low glycemic index diet, exercise and vitamin D to reduce breast cancer recurrence (DEDiCa): design of a clinical trial. BMC Cancer. 2017;17:69. doi:10.1186/s12885-017-3064-4
- Toriola AT, Nguyen N, Scheitler-Ring K, et al. Circulating 25-hydroxyvitamin D levels and prognosis among cancer patients: a systematic review. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 2014;23:917-933. doi:10.1158/1055-9965.EPI-14-0053
- Fakih MG, Trump DL, Johnson CS, et al. Chemotherapy is linked to severe vitamin D deficiency in patients with colorectal cancer. Int J Colorectal Dis. 2009;24:219-224. doi:10.1007/s00384-008-0593-y
- Isenring EA, Teleni L, Woodman RJ, et al. Serum vitamin D decreases during chemotherapy: an Australian prospective cohort study. Asia Pac J Clin Nutr. 2018;27:962-967. doi:10.6133/apjcn.042018.01
- Kok DE, van den Berg MMGA, Posthuma L, et al. Changes in circulating levels of 25-hydroxyvitamin D3 in breast cancer patients receiving chemotherapy. Nutr Cancer. 2019;71:756-766. doi:10.1080/01635581.2018.1559938
- Wesselink E, Bours MJL, de Wilt JHW, et al. Chemotherapy and vitamin D supplement use are determinants of serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D levels during the first six months after colorectal cancer diagnosis. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 2020;199:105577. doi:10.1016/j.jsbmb.2020.105577
- Savoie MB, Paciorek A, Zhang L, et al. Vitamin D levels in patients with colorectal cancer before and after treatment initiation. J Gastrointest Cancer. 2019;50:769-779. doi:10.1007/s12029-018-0147-7
- Kitchen D, Hughes B, Gill I, et al. The relationship between vitamin D and chemotherapy-induced toxicity—a pilot study. Br J Cancer. 2012;107:158-160. doi:10.1038/bjc.2012.194
- Demircay Z, Gürbüz O, Alpdogan TB, et al. Chemotherapy-induced acral erythema in leukemic patients: a report of 15 cases. Int J Dermatol. 1997;36:593-598. doi:10.1046/j.1365-4362.1997.00040.x
- Valks R, Fraga J, Porras-Luque J, et al. Chemotherapy-induced eccrine squamous syringometaplasia. a distinctive eruption in patients receiving hematopoietic progenitor cells. Arch Dermatol. 1997;133;873-878. doi:10.1001/archderm.133.7.873
- Webber KA, Kos L, Holland KE, et al. Intertriginous eruption associated with chemotherapy in pediatric patients. Arch Dermatol. 2007;143:67-71. doi:10.1001/archderm.143.1.67
- Hunjan MK, Nowsheen S, Ramos-Rodriguez AJ, et al. Clinical and histopathological spectrum of toxic erythema of chemotherapy in patients who have undergone allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation. Hematol Oncol Stem Cell Ther. 2019;12:19-25. doi:10.1016/j.hemonc.2018.09.001
- Ghorbanzadeh-Moghaddam A, Gholamrezaei A, Hemati S. Vitamin D deficiency is associated with the severity of radiation-induced proctitis in cancer patients. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2015;92:613-618. doi:10.1016/j.ijrobp.2015.02.011
- Bhanu A, Waghmare CM, Jain VS, et al. Serum 25-hydroxy vitamin-D levels in head and neck cancer chemoradiation therapy: potential in cancer therapeutics. Indian J Cancer. Published online February 27, 2003. doi:10.4103/ijc.ijc_358_20
- Yang B, Xie X, Wu Z, et al. DNA damage-mediated cellular senescence promotes hand-foot syndrome that can be relieved by thymidine prodrug. Genes Dis. 2022;10:2557-2571. doi:10.1016/j.gendis.2022.10.004
- Lassere Y, Hoff P. Management of hand-foot syndrome in patients treated with capecitabine (Xeloda®). Eur J Oncol Nurs. 2004;8(suppl 1):S31-S40. doi:10.1016/j.ejon.2004.06.007
- Ernst MK, Evans ST, Techner JM, et al. Vitamin D3 and deconvoluting a rash. JCI Insight. 2023;8:E163789.
- Nguyen CV, Zheng L, Zhou XA, et al. High-dose vitamin d for the management of toxic erythema of chemotherapy in hospitalized patients. JAMA Dermatol. 2023;159:219-221. doi:10.1001/jamadermatol.2022.5397
- Fisher J, Scott C, Stevens R, et al. Randomized phase III study comparing best supportive care to biafine as a prophylactic agent for radiation-induced skin toxicity for women undergoing breast irradiation: Radiation Therapy Oncology Group (RTOG) 97-13. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2000;48:1307-1310. doi:10.1016/s0360-3016(00)00782-3
- Pignol JP, Olivotto I, Rakovitch E, et al. A multicenter randomized trial of breast intensity-modulated radiation therapy to reduce acute radiation dermatitis. J Clin Oncol. 2008;26:2085-2092. doi:10.1200/JCO.2007.15.2488
- Hymes SR, Strom EA, Fife C. Radiation dermatitis: clinical presentation, pathophysiology, and treatment 2006. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2006;54:28-46. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2005.08.054
- Ryan JL. Ionizing radiation: the good, the bad, and the ugly. J Invest Dermatol. 2012;132(3 pt 2):985-993. doi:10.1038/jid.2011.411
- Scott JF, Das LM, Ahsanuddin S, et al. Oral vitamin D rapidly attenuates inflammation from sunburn: an interventional study. J Invest Dermatol. 2017;137:2078-2086. doi:10.1016/j.jid.2017.04.040
- Das LM, Binko AM, Traylor ZP, et al. Vitamin D improves sunburns by increasing autophagy in M2 macrophages. Autophagy. 2019;15:813-826. doi:10.1080/15548627.2019.1569298
- Nasser NJ, Fenig S, Ravid A, et al. Vitamin D ointment for prevention of radiation dermatitis in breast cancer patients. NPJ Breast Cancer. 2017;3:10. doi:10.1038/s41523-017-0006-x
- Nguyen CV, Zheng L, Lu KQ. High-dose vitamin D for the management acute radiation dermatitis. JAAD Case Rep. 2023;39:47-50. doi:10.1016/j.jdcr.2023.07.001
- Nguyen CV, Lu KQ. Vitamin D3 and its potential to ameliorate chemical and radiation-induced skin injury during cancer therapy. Disaster Med Public Health Prep. 2024;18:E4. doi:10.1017/dmp.2023.211
- Bikle DD. Vitamin D and the skin: physiology and pathophysiology. Rev Endocr Metab Disord. 2012;13:3-19. doi:10.1007/s11154-011-9194-0
- Penna G, Adorini L. 1α,25-Dihydroxyvitamin D3 inhibits differentiation, maturation, activation, and survival of dendritic cells leading to impaired alloreactive T cell activation. J Immunol. 2000;164:2405-2411. doi:10.4049/jimmunol.164.5.2405
- Penna G, Amuchastegui S, Cossetti C, et al. Treatment of experimental autoimmune prostatitis in nonobese diabetic mice by the vitamin D receptor agonist elocalcitol. J Immunol. 2006;177:8504-8511. doi:10.4049/jimmunol.177.12.8504
- Heine G, Niesner U, Chang HD, et al. 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3 promotes IL-10 production in human B cells. Eur J Immunol. 2008;38:2210-2218. doi:10.1002/eji.200838216
- Hauser K, Walsh D, Shrotriya S, et al. Low 25-hydroxyvitamin D levels in people with a solid tumor cancer diagnosis: the tip of the iceberg? Support Care Cancer. 2014;22:1931-1939. doi:10.1007/s00520-014-2154-y
- Lee KJ, Wright G, Bryant H, et al. Cytoprotective effect of vitamin D on doxorubicin-induced cardiac toxicity in triple negative breast cancer. Int J Mol Sci. 2021;22:7439. doi:10.3390/ijms22147439
- Holick MF, Binkley NC, Bischoff-Ferrari HA, et al. Evaluation, treatment, and prevention of vitamin D deficiency: an Endocrine Society clinical practice guideline. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2011;96:1911-1930. doi:10.1210/jc.2011-0385
- Amrein K, Scherkl M, Hoffmann M, et al. Vitamin D deficiency 2.0: an update on the current status worldwide. Eur J Clin Nutr. 2020;74:1498-1513. doi:10.1038/s41430-020-0558-y
- Thomas X, Chelghoum Y, Fanari N, et al. Serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D levels are associated with prognosis in hematological malignancies. Hematology. 2011;16:278-283. doi:10.1179/102453311X13085644679908
- Siegel RL, Giaquinto AN, Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2024. CA Cancer J Clin. 2024;74:12-49. doi:10.3322/caac.21820
- Goodwin PJ, Ennis M, Pritchard KI, et al. Prognostic effects of 25-hydroxyvitamin D levels in early breast cancer. J Clin Oncol. 2009;27:3757-3763. doi:10.1200/JCO.2008.20.0725
- Fassio A, Porciello G, Carioli G, et al. Post-diagnosis serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D concentrations in women treated for breast cancer participating in a lifestyle trial in Italy. Reumatismo. 2024;76:21-34.
- Augustin LSA, Libra M, Crispo A, et al. Low glycemic index diet, exercise and vitamin D to reduce breast cancer recurrence (DEDiCa): design of a clinical trial. BMC Cancer. 2017;17:69. doi:10.1186/s12885-017-3064-4
- Toriola AT, Nguyen N, Scheitler-Ring K, et al. Circulating 25-hydroxyvitamin D levels and prognosis among cancer patients: a systematic review. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 2014;23:917-933. doi:10.1158/1055-9965.EPI-14-0053
- Fakih MG, Trump DL, Johnson CS, et al. Chemotherapy is linked to severe vitamin D deficiency in patients with colorectal cancer. Int J Colorectal Dis. 2009;24:219-224. doi:10.1007/s00384-008-0593-y
- Isenring EA, Teleni L, Woodman RJ, et al. Serum vitamin D decreases during chemotherapy: an Australian prospective cohort study. Asia Pac J Clin Nutr. 2018;27:962-967. doi:10.6133/apjcn.042018.01
- Kok DE, van den Berg MMGA, Posthuma L, et al. Changes in circulating levels of 25-hydroxyvitamin D3 in breast cancer patients receiving chemotherapy. Nutr Cancer. 2019;71:756-766. doi:10.1080/01635581.2018.1559938
- Wesselink E, Bours MJL, de Wilt JHW, et al. Chemotherapy and vitamin D supplement use are determinants of serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D levels during the first six months after colorectal cancer diagnosis. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 2020;199:105577. doi:10.1016/j.jsbmb.2020.105577
- Savoie MB, Paciorek A, Zhang L, et al. Vitamin D levels in patients with colorectal cancer before and after treatment initiation. J Gastrointest Cancer. 2019;50:769-779. doi:10.1007/s12029-018-0147-7
- Kitchen D, Hughes B, Gill I, et al. The relationship between vitamin D and chemotherapy-induced toxicity—a pilot study. Br J Cancer. 2012;107:158-160. doi:10.1038/bjc.2012.194
- Demircay Z, Gürbüz O, Alpdogan TB, et al. Chemotherapy-induced acral erythema in leukemic patients: a report of 15 cases. Int J Dermatol. 1997;36:593-598. doi:10.1046/j.1365-4362.1997.00040.x
- Valks R, Fraga J, Porras-Luque J, et al. Chemotherapy-induced eccrine squamous syringometaplasia. a distinctive eruption in patients receiving hematopoietic progenitor cells. Arch Dermatol. 1997;133;873-878. doi:10.1001/archderm.133.7.873
- Webber KA, Kos L, Holland KE, et al. Intertriginous eruption associated with chemotherapy in pediatric patients. Arch Dermatol. 2007;143:67-71. doi:10.1001/archderm.143.1.67
- Hunjan MK, Nowsheen S, Ramos-Rodriguez AJ, et al. Clinical and histopathological spectrum of toxic erythema of chemotherapy in patients who have undergone allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation. Hematol Oncol Stem Cell Ther. 2019;12:19-25. doi:10.1016/j.hemonc.2018.09.001
- Ghorbanzadeh-Moghaddam A, Gholamrezaei A, Hemati S. Vitamin D deficiency is associated with the severity of radiation-induced proctitis in cancer patients. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2015;92:613-618. doi:10.1016/j.ijrobp.2015.02.011
- Bhanu A, Waghmare CM, Jain VS, et al. Serum 25-hydroxy vitamin-D levels in head and neck cancer chemoradiation therapy: potential in cancer therapeutics. Indian J Cancer. Published online February 27, 2003. doi:10.4103/ijc.ijc_358_20
- Yang B, Xie X, Wu Z, et al. DNA damage-mediated cellular senescence promotes hand-foot syndrome that can be relieved by thymidine prodrug. Genes Dis. 2022;10:2557-2571. doi:10.1016/j.gendis.2022.10.004
- Lassere Y, Hoff P. Management of hand-foot syndrome in patients treated with capecitabine (Xeloda®). Eur J Oncol Nurs. 2004;8(suppl 1):S31-S40. doi:10.1016/j.ejon.2004.06.007
- Ernst MK, Evans ST, Techner JM, et al. Vitamin D3 and deconvoluting a rash. JCI Insight. 2023;8:E163789.
- Nguyen CV, Zheng L, Zhou XA, et al. High-dose vitamin d for the management of toxic erythema of chemotherapy in hospitalized patients. JAMA Dermatol. 2023;159:219-221. doi:10.1001/jamadermatol.2022.5397
- Fisher J, Scott C, Stevens R, et al. Randomized phase III study comparing best supportive care to biafine as a prophylactic agent for radiation-induced skin toxicity for women undergoing breast irradiation: Radiation Therapy Oncology Group (RTOG) 97-13. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2000;48:1307-1310. doi:10.1016/s0360-3016(00)00782-3
- Pignol JP, Olivotto I, Rakovitch E, et al. A multicenter randomized trial of breast intensity-modulated radiation therapy to reduce acute radiation dermatitis. J Clin Oncol. 2008;26:2085-2092. doi:10.1200/JCO.2007.15.2488
- Hymes SR, Strom EA, Fife C. Radiation dermatitis: clinical presentation, pathophysiology, and treatment 2006. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2006;54:28-46. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2005.08.054
- Ryan JL. Ionizing radiation: the good, the bad, and the ugly. J Invest Dermatol. 2012;132(3 pt 2):985-993. doi:10.1038/jid.2011.411
- Scott JF, Das LM, Ahsanuddin S, et al. Oral vitamin D rapidly attenuates inflammation from sunburn: an interventional study. J Invest Dermatol. 2017;137:2078-2086. doi:10.1016/j.jid.2017.04.040
- Das LM, Binko AM, Traylor ZP, et al. Vitamin D improves sunburns by increasing autophagy in M2 macrophages. Autophagy. 2019;15:813-826. doi:10.1080/15548627.2019.1569298
- Nasser NJ, Fenig S, Ravid A, et al. Vitamin D ointment for prevention of radiation dermatitis in breast cancer patients. NPJ Breast Cancer. 2017;3:10. doi:10.1038/s41523-017-0006-x
- Nguyen CV, Zheng L, Lu KQ. High-dose vitamin D for the management acute radiation dermatitis. JAAD Case Rep. 2023;39:47-50. doi:10.1016/j.jdcr.2023.07.001
- Nguyen CV, Lu KQ. Vitamin D3 and its potential to ameliorate chemical and radiation-induced skin injury during cancer therapy. Disaster Med Public Health Prep. 2024;18:E4. doi:10.1017/dmp.2023.211
Practice Points
- High-dose vitamin D supplementation may be considered in the management of cutaneous injury from chemotherapy or ionizing radiation.
- Optimal dosing has not been established, so patients given high-dose vitamin D supplementation should have close clinical follow-up; however, adverse events from high-dose vitamin D supplementation have not been reported.
Can Antihistamines Trigger Seizures in Young Kids?
TOPLINE:
new research shows. The risk appears to be most pronounced in children aged 6-24 months.
METHODOLOGY:
- Researchers in Korea used a self-controlled case-crossover design to assess the risk for seizures associated with prescriptions of first-generation antihistamines.
- They analyzed data from 11,729 children who had a seizure event (an emergency department visit with a diagnosis of epilepsy, status epilepticus, or convulsion) and had previously received a prescription for a first-generation antihistamine, including chlorpheniramine maleate, mequitazine, oxatomide, piprinhydrinate, or hydroxyzine hydrochloride.
- Prescriptions during the 15 days before a seizure were considered to have been received during a hazard period, whereas earlier prescriptions were considered to have been received during a control period.
- The researchers excluded patients with febrile seizures.
TAKEAWAY:
- In an adjusted analysis, a prescription for an antihistamine during the hazard period was associated with a 22% higher risk for seizures in children (adjusted odds ratio, 1.22; 95% CI, 1.13-1.31).
- The seizure risk was significant in children aged 6-24 months, with an adjusted odds ratio of 1.49 (95% CI, 1.31-1.70).
- For older children, the risk was not statistically significant.
IN PRACTICE:
“The study underscores a substantial increase in seizure risk associated with antihistamine prescription among children aged 6-24 months,” the authors of the study wrote. “We are not aware of any other studies that have pointed out the increased risk of seizures with first-generation antihistamines in this particular age group. ... The benefits and risks of antihistamine use should always be carefully considered, especially when prescribing H1 antihistamines to vulnerable infants.”
The findings raise a host of questions for clinicians, including how a “relatively small risk” should translate into practice, and whether the risk may be attenuated with newer antihistamines, wrote Frank Max Charles Besag, MB, ChB, with East London NHS Foundation Trust in England, in an editorial accompanying the study. “It would be reasonable to inform families that at least one study has suggested a relatively small increase in the risk of seizures with first-generation antihistamines, adding that there are still too few data to draw any firm conclusions and also providing families with the information on what to do if the child were to have a seizure.”
SOURCE:
Seonkyeong Rhie, MD, and Man Yong Han, MD, both with the Department of Pediatrics at CHA University School of Medicine, in Seongnam, South Korea, were the corresponding authors on the study. The research was published online in JAMA Network Open.
LIMITATIONS:
The researchers did not have details about seizure symptoms, did not include children seen in outpatient clinics, and were unable to verify the actual intake of the prescribed antihistamines. Although second-generation antihistamines may be less likely to cross the blood-brain barrier, one newer medication, desloratadine, has been associated with seizures.
DISCLOSURES:
The study was supported by grants from the Korea Health Technology R&D Project through the Korea Health Industry Development Institute, the Ministry of Health and Welfare, Republic of Korea.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
new research shows. The risk appears to be most pronounced in children aged 6-24 months.
METHODOLOGY:
- Researchers in Korea used a self-controlled case-crossover design to assess the risk for seizures associated with prescriptions of first-generation antihistamines.
- They analyzed data from 11,729 children who had a seizure event (an emergency department visit with a diagnosis of epilepsy, status epilepticus, or convulsion) and had previously received a prescription for a first-generation antihistamine, including chlorpheniramine maleate, mequitazine, oxatomide, piprinhydrinate, or hydroxyzine hydrochloride.
- Prescriptions during the 15 days before a seizure were considered to have been received during a hazard period, whereas earlier prescriptions were considered to have been received during a control period.
- The researchers excluded patients with febrile seizures.
TAKEAWAY:
- In an adjusted analysis, a prescription for an antihistamine during the hazard period was associated with a 22% higher risk for seizures in children (adjusted odds ratio, 1.22; 95% CI, 1.13-1.31).
- The seizure risk was significant in children aged 6-24 months, with an adjusted odds ratio of 1.49 (95% CI, 1.31-1.70).
- For older children, the risk was not statistically significant.
IN PRACTICE:
“The study underscores a substantial increase in seizure risk associated with antihistamine prescription among children aged 6-24 months,” the authors of the study wrote. “We are not aware of any other studies that have pointed out the increased risk of seizures with first-generation antihistamines in this particular age group. ... The benefits and risks of antihistamine use should always be carefully considered, especially when prescribing H1 antihistamines to vulnerable infants.”
The findings raise a host of questions for clinicians, including how a “relatively small risk” should translate into practice, and whether the risk may be attenuated with newer antihistamines, wrote Frank Max Charles Besag, MB, ChB, with East London NHS Foundation Trust in England, in an editorial accompanying the study. “It would be reasonable to inform families that at least one study has suggested a relatively small increase in the risk of seizures with first-generation antihistamines, adding that there are still too few data to draw any firm conclusions and also providing families with the information on what to do if the child were to have a seizure.”
SOURCE:
Seonkyeong Rhie, MD, and Man Yong Han, MD, both with the Department of Pediatrics at CHA University School of Medicine, in Seongnam, South Korea, were the corresponding authors on the study. The research was published online in JAMA Network Open.
LIMITATIONS:
The researchers did not have details about seizure symptoms, did not include children seen in outpatient clinics, and were unable to verify the actual intake of the prescribed antihistamines. Although second-generation antihistamines may be less likely to cross the blood-brain barrier, one newer medication, desloratadine, has been associated with seizures.
DISCLOSURES:
The study was supported by grants from the Korea Health Technology R&D Project through the Korea Health Industry Development Institute, the Ministry of Health and Welfare, Republic of Korea.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
new research shows. The risk appears to be most pronounced in children aged 6-24 months.
METHODOLOGY:
- Researchers in Korea used a self-controlled case-crossover design to assess the risk for seizures associated with prescriptions of first-generation antihistamines.
- They analyzed data from 11,729 children who had a seizure event (an emergency department visit with a diagnosis of epilepsy, status epilepticus, or convulsion) and had previously received a prescription for a first-generation antihistamine, including chlorpheniramine maleate, mequitazine, oxatomide, piprinhydrinate, or hydroxyzine hydrochloride.
- Prescriptions during the 15 days before a seizure were considered to have been received during a hazard period, whereas earlier prescriptions were considered to have been received during a control period.
- The researchers excluded patients with febrile seizures.
TAKEAWAY:
- In an adjusted analysis, a prescription for an antihistamine during the hazard period was associated with a 22% higher risk for seizures in children (adjusted odds ratio, 1.22; 95% CI, 1.13-1.31).
- The seizure risk was significant in children aged 6-24 months, with an adjusted odds ratio of 1.49 (95% CI, 1.31-1.70).
- For older children, the risk was not statistically significant.
IN PRACTICE:
“The study underscores a substantial increase in seizure risk associated with antihistamine prescription among children aged 6-24 months,” the authors of the study wrote. “We are not aware of any other studies that have pointed out the increased risk of seizures with first-generation antihistamines in this particular age group. ... The benefits and risks of antihistamine use should always be carefully considered, especially when prescribing H1 antihistamines to vulnerable infants.”
The findings raise a host of questions for clinicians, including how a “relatively small risk” should translate into practice, and whether the risk may be attenuated with newer antihistamines, wrote Frank Max Charles Besag, MB, ChB, with East London NHS Foundation Trust in England, in an editorial accompanying the study. “It would be reasonable to inform families that at least one study has suggested a relatively small increase in the risk of seizures with first-generation antihistamines, adding that there are still too few data to draw any firm conclusions and also providing families with the information on what to do if the child were to have a seizure.”
SOURCE:
Seonkyeong Rhie, MD, and Man Yong Han, MD, both with the Department of Pediatrics at CHA University School of Medicine, in Seongnam, South Korea, were the corresponding authors on the study. The research was published online in JAMA Network Open.
LIMITATIONS:
The researchers did not have details about seizure symptoms, did not include children seen in outpatient clinics, and were unable to verify the actual intake of the prescribed antihistamines. Although second-generation antihistamines may be less likely to cross the blood-brain barrier, one newer medication, desloratadine, has been associated with seizures.
DISCLOSURES:
The study was supported by grants from the Korea Health Technology R&D Project through the Korea Health Industry Development Institute, the Ministry of Health and Welfare, Republic of Korea.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Genetic Testing and Novel Biomarkers Important in Cystic Fibrosis Diagnosis and Monitoring
VIENNA — Advances in genetic testing and newly discovered biomarkers can help screen newborns and monitor inflammation and pulmonary exacerbations in patients diagnosed with cystic fibrosis.
At the European Respiratory Society (ERS) 2024 International Congress, clinical researchers presented results from the Turkish context.
Cystic fibrosis is the most common genetic disorder among Caucasians. The average prevalence at birth in Europe is 1 in 5000, whereas the overall population averages 1 in 9000. Both rates vary significantly based on geographic area. In the central Anatolia region, one study found that the incidence of cystic fibrosis is 1 in 3400 live births.
Çigdem Korkmaz, a researcher at the Department of Pediatric Pulmonology at the Istanbul University-Cerrahpasa in Istanbul, Turkey, said that diagnosis in Turkey is especially challenging because of the genetic diversity of cystic fibrosis within the population. She said genetic testing might be necessary to catch missed cases by traditional screening methods.
Genetic Testing Picks Up Missed Cases
In 2022, 30 European countries run newborn bloodspot screening for cystic fibrosis, with 26 national programs. Screening protocols vary between countries but generally involve initial screening using an immunoreactive trypsinogen (IRT) blood test. Follow-up testing may include a second IRT test, DNA analysis for common CFTR mutations, and sweat chloride test (SCT).
Turkey introduced newborn screening for cystic fibrosis in 2015. Newborns with an elevated IRT and confirmatory SCT undergo genetic testing. However, in a retrospective study, researchers found that IRT tests turn many false-positive results, and some patients who turn a normal SCT are diagnosed with the disease through genetic testing.
The study included 205 infants referred to a tertiary care center in Istanbul between January 2015 and January 2023 following an elevator IRT result. The researchers analyzed the clinical and sociodemographic data, IRT and SCT values, and genetic analysis results.
“The high false-positive rate of the current screening strategy suggests that the IRT thresholds used in Turkey may be too low,” said Ms. Korkmaz, who presented the study at the ERS Congress. She added that genetic testing might be important, especially in patients with normal SCT results. “Early diagnosis means these patients avoid missing or delaying treatments.”
Biomarkers for Monitoring Cystic Fibrosis Exacerbations
C-reactive protein (CRP) blood testing is typically used in monitoring inflammation and pulmonary exacerbations in patients who have already been diagnosed with cystic fibrosis. CRP is an inflammatory biomarker that increases in patients with cystic fibrosis during pulmonary exacerbations and settles with treatment.
Researchers at Gazi University in Ankara, Turkey, found other biomarkers to identify inflammation and pulmonary exacerbations with great sensitivity and specificity in patients with cystic fibrosis.
Over 3 years, from 2021 to 2024, the researchers analyzed blood samples from 54 children aged 1-18 years during exacerbation and non-exacerbation periods. Besides CRP, they tested CRP/albumin (ALB) ratio, neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio (NLR), delivered NLR (dNLR), and systemic immune inflammation (SII).
All biomarkers increased during exacerbation episodes. All showed high specificity and sensitivity:
- CPR/ALB had a specificity of 81% and a sensitivity of 90% at a cutoff of 1.7 mg/dL.
- SII had a specificity of 86% and a sensitivity of 67% at a cutoff of 426 mg/dL.
- NLR had a specificity of 62% and a sensitivity of 79% at a cutoff of 2.2 mg/dL.
- SII had a specificity of 86% and a sensitivity of 67% at a cutoff of 426 mg/dL.
- dNLR had a specificity of 71% and a sensitivity of 66% at a cutoff of 1.15 mg/dL.
- In comparison, CPR had a specificity of 85% and a sensitivity of 84% at a cutoff of 6.2 mg/dL.
Ayse Tana Aslan, a professor at the Department of Pediatric Pulmonology, Faculty of Medicine, at Gazi University in Ankara, Turkey, who presented the results at the ERS Congress, said that these biomarkers can be easily and quickly identified with a blood test while waiting on phlegm culture results, which can take days. “It is important to predict inflammation and exacerbation quickly so that patients can start a course of antibiotics as soon as possible,” she said.
Ms. Korkmaz and Ms. Aslan reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
VIENNA — Advances in genetic testing and newly discovered biomarkers can help screen newborns and monitor inflammation and pulmonary exacerbations in patients diagnosed with cystic fibrosis.
At the European Respiratory Society (ERS) 2024 International Congress, clinical researchers presented results from the Turkish context.
Cystic fibrosis is the most common genetic disorder among Caucasians. The average prevalence at birth in Europe is 1 in 5000, whereas the overall population averages 1 in 9000. Both rates vary significantly based on geographic area. In the central Anatolia region, one study found that the incidence of cystic fibrosis is 1 in 3400 live births.
Çigdem Korkmaz, a researcher at the Department of Pediatric Pulmonology at the Istanbul University-Cerrahpasa in Istanbul, Turkey, said that diagnosis in Turkey is especially challenging because of the genetic diversity of cystic fibrosis within the population. She said genetic testing might be necessary to catch missed cases by traditional screening methods.
Genetic Testing Picks Up Missed Cases
In 2022, 30 European countries run newborn bloodspot screening for cystic fibrosis, with 26 national programs. Screening protocols vary between countries but generally involve initial screening using an immunoreactive trypsinogen (IRT) blood test. Follow-up testing may include a second IRT test, DNA analysis for common CFTR mutations, and sweat chloride test (SCT).
Turkey introduced newborn screening for cystic fibrosis in 2015. Newborns with an elevated IRT and confirmatory SCT undergo genetic testing. However, in a retrospective study, researchers found that IRT tests turn many false-positive results, and some patients who turn a normal SCT are diagnosed with the disease through genetic testing.
The study included 205 infants referred to a tertiary care center in Istanbul between January 2015 and January 2023 following an elevator IRT result. The researchers analyzed the clinical and sociodemographic data, IRT and SCT values, and genetic analysis results.
“The high false-positive rate of the current screening strategy suggests that the IRT thresholds used in Turkey may be too low,” said Ms. Korkmaz, who presented the study at the ERS Congress. She added that genetic testing might be important, especially in patients with normal SCT results. “Early diagnosis means these patients avoid missing or delaying treatments.”
Biomarkers for Monitoring Cystic Fibrosis Exacerbations
C-reactive protein (CRP) blood testing is typically used in monitoring inflammation and pulmonary exacerbations in patients who have already been diagnosed with cystic fibrosis. CRP is an inflammatory biomarker that increases in patients with cystic fibrosis during pulmonary exacerbations and settles with treatment.
Researchers at Gazi University in Ankara, Turkey, found other biomarkers to identify inflammation and pulmonary exacerbations with great sensitivity and specificity in patients with cystic fibrosis.
Over 3 years, from 2021 to 2024, the researchers analyzed blood samples from 54 children aged 1-18 years during exacerbation and non-exacerbation periods. Besides CRP, they tested CRP/albumin (ALB) ratio, neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio (NLR), delivered NLR (dNLR), and systemic immune inflammation (SII).
All biomarkers increased during exacerbation episodes. All showed high specificity and sensitivity:
- CPR/ALB had a specificity of 81% and a sensitivity of 90% at a cutoff of 1.7 mg/dL.
- SII had a specificity of 86% and a sensitivity of 67% at a cutoff of 426 mg/dL.
- NLR had a specificity of 62% and a sensitivity of 79% at a cutoff of 2.2 mg/dL.
- SII had a specificity of 86% and a sensitivity of 67% at a cutoff of 426 mg/dL.
- dNLR had a specificity of 71% and a sensitivity of 66% at a cutoff of 1.15 mg/dL.
- In comparison, CPR had a specificity of 85% and a sensitivity of 84% at a cutoff of 6.2 mg/dL.
Ayse Tana Aslan, a professor at the Department of Pediatric Pulmonology, Faculty of Medicine, at Gazi University in Ankara, Turkey, who presented the results at the ERS Congress, said that these biomarkers can be easily and quickly identified with a blood test while waiting on phlegm culture results, which can take days. “It is important to predict inflammation and exacerbation quickly so that patients can start a course of antibiotics as soon as possible,” she said.
Ms. Korkmaz and Ms. Aslan reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
VIENNA — Advances in genetic testing and newly discovered biomarkers can help screen newborns and monitor inflammation and pulmonary exacerbations in patients diagnosed with cystic fibrosis.
At the European Respiratory Society (ERS) 2024 International Congress, clinical researchers presented results from the Turkish context.
Cystic fibrosis is the most common genetic disorder among Caucasians. The average prevalence at birth in Europe is 1 in 5000, whereas the overall population averages 1 in 9000. Both rates vary significantly based on geographic area. In the central Anatolia region, one study found that the incidence of cystic fibrosis is 1 in 3400 live births.
Çigdem Korkmaz, a researcher at the Department of Pediatric Pulmonology at the Istanbul University-Cerrahpasa in Istanbul, Turkey, said that diagnosis in Turkey is especially challenging because of the genetic diversity of cystic fibrosis within the population. She said genetic testing might be necessary to catch missed cases by traditional screening methods.
Genetic Testing Picks Up Missed Cases
In 2022, 30 European countries run newborn bloodspot screening for cystic fibrosis, with 26 national programs. Screening protocols vary between countries but generally involve initial screening using an immunoreactive trypsinogen (IRT) blood test. Follow-up testing may include a second IRT test, DNA analysis for common CFTR mutations, and sweat chloride test (SCT).
Turkey introduced newborn screening for cystic fibrosis in 2015. Newborns with an elevated IRT and confirmatory SCT undergo genetic testing. However, in a retrospective study, researchers found that IRT tests turn many false-positive results, and some patients who turn a normal SCT are diagnosed with the disease through genetic testing.
The study included 205 infants referred to a tertiary care center in Istanbul between January 2015 and January 2023 following an elevator IRT result. The researchers analyzed the clinical and sociodemographic data, IRT and SCT values, and genetic analysis results.
“The high false-positive rate of the current screening strategy suggests that the IRT thresholds used in Turkey may be too low,” said Ms. Korkmaz, who presented the study at the ERS Congress. She added that genetic testing might be important, especially in patients with normal SCT results. “Early diagnosis means these patients avoid missing or delaying treatments.”
Biomarkers for Monitoring Cystic Fibrosis Exacerbations
C-reactive protein (CRP) blood testing is typically used in monitoring inflammation and pulmonary exacerbations in patients who have already been diagnosed with cystic fibrosis. CRP is an inflammatory biomarker that increases in patients with cystic fibrosis during pulmonary exacerbations and settles with treatment.
Researchers at Gazi University in Ankara, Turkey, found other biomarkers to identify inflammation and pulmonary exacerbations with great sensitivity and specificity in patients with cystic fibrosis.
Over 3 years, from 2021 to 2024, the researchers analyzed blood samples from 54 children aged 1-18 years during exacerbation and non-exacerbation periods. Besides CRP, they tested CRP/albumin (ALB) ratio, neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio (NLR), delivered NLR (dNLR), and systemic immune inflammation (SII).
All biomarkers increased during exacerbation episodes. All showed high specificity and sensitivity:
- CPR/ALB had a specificity of 81% and a sensitivity of 90% at a cutoff of 1.7 mg/dL.
- SII had a specificity of 86% and a sensitivity of 67% at a cutoff of 426 mg/dL.
- NLR had a specificity of 62% and a sensitivity of 79% at a cutoff of 2.2 mg/dL.
- SII had a specificity of 86% and a sensitivity of 67% at a cutoff of 426 mg/dL.
- dNLR had a specificity of 71% and a sensitivity of 66% at a cutoff of 1.15 mg/dL.
- In comparison, CPR had a specificity of 85% and a sensitivity of 84% at a cutoff of 6.2 mg/dL.
Ayse Tana Aslan, a professor at the Department of Pediatric Pulmonology, Faculty of Medicine, at Gazi University in Ankara, Turkey, who presented the results at the ERS Congress, said that these biomarkers can be easily and quickly identified with a blood test while waiting on phlegm culture results, which can take days. “It is important to predict inflammation and exacerbation quickly so that patients can start a course of antibiotics as soon as possible,” she said.
Ms. Korkmaz and Ms. Aslan reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Is Frontal Fibrosing Alopecia Connected to Sunscreen Usage?
Frontal fibrosing alopecia (FFA) has become increasingly common since it was first described in 1994.1 A positive correlation between FFA and the use of sunscreens was reported in an observational study.2 The geographic distribution of this association has spanned the United Kingdom (UK), Europe, and Asia, though data from the United States are lacking. Various international studies have demonstrated an association between FFA and sunscreen use, further exemplifying this stark contrast.
In the United Kingdom (UK), Aldoori et al2 found that women who used sunscreen at least twice weekly had 2 times the likelihood of developing FFA compared with women who did not use sunscreen regularly. Kidambi et al3 found similar results in UK men with FFA who had higher rates of primary sunscreen use and higher rates of at least twice-weekly use of facial moisturizer with unspecified sunscreen content.
These associations between FFA and sunscreen use are not unique to the UK. A study conducted in Spain identified a statistical association between FFA and use of facial sunscreen in women (odds ratio, 1.6 [95% CI, 1.06-2.41]) and men (odds ratio, 1.84 [95% CI, 1.04-3.23]).4 In Thailand, FFA was nearly twice as likely to be present in patients with regular sunscreen use compared to controls who did not apply sunscreen regularly.5 Interestingly, a Brazilian study showed no connection between sunscreen use and FFA. Instead, FFA was associated with hair straightening with formalin or use of facial soap orfacial moisturizer.6 An international systematic review of 1248 patients with FFA and 1459 controls determined that sunscreen users were 2.21 times more likely to develop FFA than their counterparts who did not use sunscreen regularly.7
Quite glaring is the lack of data from the United States, which could be used to compare FFA and sunscreen associations to other nations. It is possible that certain regions of the world such as the United States may not have an increased risk for FFA in sunscreen users due to other environmental factors, differing sunscreen application practices, or differing chemical ingredients. At the same time, many other countries cannot afford or lack access to sunscreens or facial moisturizers, which is an additional variable that may complicate this association. These populations need to be studied to determine whether they are as susceptible to FFA as those who use sunscreen regularly around the world.
Another underlying factor supporting this association is the inherent need for sunscreen use. For instance, research has shown that patients with FFA had higher rates of actinic skin damage, which could explain increased sunscreen use.8
To make more clear and distinct claims, further studies are needed in regions that are known to use sunscreen extensively (eg, United States) to compare with their European, Asian, and South American counterparts. Moreover, it also is important to study regions where sunscreen access is limited and whether there is FFA development in these populations.
Given the potential association between sunscreen use and FFA, dermatologists can take a cautious approach tailored to the patient by recommending noncomedogenic mineral sunscreens with zinc or titanium oxide, which are less irritating than chemical sunscreens. Avoidance of sunscreen application to the hairline and use of additional sun-protection methods such as broad-brimmed hats also should be emphasized.
- Kossard S. Postmenopausal frontal fibrosing alopecia: scarring alopecia in a pattern distribution. Arch Dermatol. 1994;130:770-774. doi:10.1001/archderm.1994.01690060100013
- Aldoori N, Dobson K, Holden CR, et al. Frontal fibrosing alopecia: possible association with leave-on facial skin care products and sunscreens: a questionnaire study. Br J Dermatol. 2016;175:762-767.
- Kidambi AD, Dobson K, Holmes S, et al. Frontal fibrosing alopecia in men: an association with leave-on facial cosmetics and sunscreens. Br J Dermatol. 2020;175:61-67.
- Moreno-Arrones OM, Saceda-Corralo D, Rodrigues-Barata AR, et al. Risk factors associated with frontal fibrosing alopecia: a multicentre case-control study. Clin Exp Dermatol. 2019;44:404-410. doi:10.1111/ced.13785
- Leecharoen W, Thanomkitti K, Thuangtong R, et al. Use of facial care products and frontal fibrosing alopecia: coincidence or true association? J Dermatol. 2021;48:1557-1563.
- Müller Ramos P, Anzai A, Duque-Estrada B, et al. Risk factors for frontal fibrosing alopecia: a case-control study in a multiracial population. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2021;84:712-718. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2020.08.07
- Kam O, Na S, Guo W, et al. Frontal fibrosing alopecia and personal care product use: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Arch Dermatol Res. 2023;315:2313-2331. doi:10.1007/s00403-023-02604-7
- Porriño-Bustamante ML, Montero-Vílchez T, Pinedo-Moraleda FJ, et al. Frontal fibrosing alopecia and sunscreen use: a cross-sectionalstudy of actinic damage. Acta Derm Venereol. Published online August 11, 2022. doi:10.2340/actadv.v102.306
Frontal fibrosing alopecia (FFA) has become increasingly common since it was first described in 1994.1 A positive correlation between FFA and the use of sunscreens was reported in an observational study.2 The geographic distribution of this association has spanned the United Kingdom (UK), Europe, and Asia, though data from the United States are lacking. Various international studies have demonstrated an association between FFA and sunscreen use, further exemplifying this stark contrast.
In the United Kingdom (UK), Aldoori et al2 found that women who used sunscreen at least twice weekly had 2 times the likelihood of developing FFA compared with women who did not use sunscreen regularly. Kidambi et al3 found similar results in UK men with FFA who had higher rates of primary sunscreen use and higher rates of at least twice-weekly use of facial moisturizer with unspecified sunscreen content.
These associations between FFA and sunscreen use are not unique to the UK. A study conducted in Spain identified a statistical association between FFA and use of facial sunscreen in women (odds ratio, 1.6 [95% CI, 1.06-2.41]) and men (odds ratio, 1.84 [95% CI, 1.04-3.23]).4 In Thailand, FFA was nearly twice as likely to be present in patients with regular sunscreen use compared to controls who did not apply sunscreen regularly.5 Interestingly, a Brazilian study showed no connection between sunscreen use and FFA. Instead, FFA was associated with hair straightening with formalin or use of facial soap orfacial moisturizer.6 An international systematic review of 1248 patients with FFA and 1459 controls determined that sunscreen users were 2.21 times more likely to develop FFA than their counterparts who did not use sunscreen regularly.7
Quite glaring is the lack of data from the United States, which could be used to compare FFA and sunscreen associations to other nations. It is possible that certain regions of the world such as the United States may not have an increased risk for FFA in sunscreen users due to other environmental factors, differing sunscreen application practices, or differing chemical ingredients. At the same time, many other countries cannot afford or lack access to sunscreens or facial moisturizers, which is an additional variable that may complicate this association. These populations need to be studied to determine whether they are as susceptible to FFA as those who use sunscreen regularly around the world.
Another underlying factor supporting this association is the inherent need for sunscreen use. For instance, research has shown that patients with FFA had higher rates of actinic skin damage, which could explain increased sunscreen use.8
To make more clear and distinct claims, further studies are needed in regions that are known to use sunscreen extensively (eg, United States) to compare with their European, Asian, and South American counterparts. Moreover, it also is important to study regions where sunscreen access is limited and whether there is FFA development in these populations.
Given the potential association between sunscreen use and FFA, dermatologists can take a cautious approach tailored to the patient by recommending noncomedogenic mineral sunscreens with zinc or titanium oxide, which are less irritating than chemical sunscreens. Avoidance of sunscreen application to the hairline and use of additional sun-protection methods such as broad-brimmed hats also should be emphasized.
Frontal fibrosing alopecia (FFA) has become increasingly common since it was first described in 1994.1 A positive correlation between FFA and the use of sunscreens was reported in an observational study.2 The geographic distribution of this association has spanned the United Kingdom (UK), Europe, and Asia, though data from the United States are lacking. Various international studies have demonstrated an association between FFA and sunscreen use, further exemplifying this stark contrast.
In the United Kingdom (UK), Aldoori et al2 found that women who used sunscreen at least twice weekly had 2 times the likelihood of developing FFA compared with women who did not use sunscreen regularly. Kidambi et al3 found similar results in UK men with FFA who had higher rates of primary sunscreen use and higher rates of at least twice-weekly use of facial moisturizer with unspecified sunscreen content.
These associations between FFA and sunscreen use are not unique to the UK. A study conducted in Spain identified a statistical association between FFA and use of facial sunscreen in women (odds ratio, 1.6 [95% CI, 1.06-2.41]) and men (odds ratio, 1.84 [95% CI, 1.04-3.23]).4 In Thailand, FFA was nearly twice as likely to be present in patients with regular sunscreen use compared to controls who did not apply sunscreen regularly.5 Interestingly, a Brazilian study showed no connection between sunscreen use and FFA. Instead, FFA was associated with hair straightening with formalin or use of facial soap orfacial moisturizer.6 An international systematic review of 1248 patients with FFA and 1459 controls determined that sunscreen users were 2.21 times more likely to develop FFA than their counterparts who did not use sunscreen regularly.7
Quite glaring is the lack of data from the United States, which could be used to compare FFA and sunscreen associations to other nations. It is possible that certain regions of the world such as the United States may not have an increased risk for FFA in sunscreen users due to other environmental factors, differing sunscreen application practices, or differing chemical ingredients. At the same time, many other countries cannot afford or lack access to sunscreens or facial moisturizers, which is an additional variable that may complicate this association. These populations need to be studied to determine whether they are as susceptible to FFA as those who use sunscreen regularly around the world.
Another underlying factor supporting this association is the inherent need for sunscreen use. For instance, research has shown that patients with FFA had higher rates of actinic skin damage, which could explain increased sunscreen use.8
To make more clear and distinct claims, further studies are needed in regions that are known to use sunscreen extensively (eg, United States) to compare with their European, Asian, and South American counterparts. Moreover, it also is important to study regions where sunscreen access is limited and whether there is FFA development in these populations.
Given the potential association between sunscreen use and FFA, dermatologists can take a cautious approach tailored to the patient by recommending noncomedogenic mineral sunscreens with zinc or titanium oxide, which are less irritating than chemical sunscreens. Avoidance of sunscreen application to the hairline and use of additional sun-protection methods such as broad-brimmed hats also should be emphasized.
- Kossard S. Postmenopausal frontal fibrosing alopecia: scarring alopecia in a pattern distribution. Arch Dermatol. 1994;130:770-774. doi:10.1001/archderm.1994.01690060100013
- Aldoori N, Dobson K, Holden CR, et al. Frontal fibrosing alopecia: possible association with leave-on facial skin care products and sunscreens: a questionnaire study. Br J Dermatol. 2016;175:762-767.
- Kidambi AD, Dobson K, Holmes S, et al. Frontal fibrosing alopecia in men: an association with leave-on facial cosmetics and sunscreens. Br J Dermatol. 2020;175:61-67.
- Moreno-Arrones OM, Saceda-Corralo D, Rodrigues-Barata AR, et al. Risk factors associated with frontal fibrosing alopecia: a multicentre case-control study. Clin Exp Dermatol. 2019;44:404-410. doi:10.1111/ced.13785
- Leecharoen W, Thanomkitti K, Thuangtong R, et al. Use of facial care products and frontal fibrosing alopecia: coincidence or true association? J Dermatol. 2021;48:1557-1563.
- Müller Ramos P, Anzai A, Duque-Estrada B, et al. Risk factors for frontal fibrosing alopecia: a case-control study in a multiracial population. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2021;84:712-718. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2020.08.07
- Kam O, Na S, Guo W, et al. Frontal fibrosing alopecia and personal care product use: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Arch Dermatol Res. 2023;315:2313-2331. doi:10.1007/s00403-023-02604-7
- Porriño-Bustamante ML, Montero-Vílchez T, Pinedo-Moraleda FJ, et al. Frontal fibrosing alopecia and sunscreen use: a cross-sectionalstudy of actinic damage. Acta Derm Venereol. Published online August 11, 2022. doi:10.2340/actadv.v102.306
- Kossard S. Postmenopausal frontal fibrosing alopecia: scarring alopecia in a pattern distribution. Arch Dermatol. 1994;130:770-774. doi:10.1001/archderm.1994.01690060100013
- Aldoori N, Dobson K, Holden CR, et al. Frontal fibrosing alopecia: possible association with leave-on facial skin care products and sunscreens: a questionnaire study. Br J Dermatol. 2016;175:762-767.
- Kidambi AD, Dobson K, Holmes S, et al. Frontal fibrosing alopecia in men: an association with leave-on facial cosmetics and sunscreens. Br J Dermatol. 2020;175:61-67.
- Moreno-Arrones OM, Saceda-Corralo D, Rodrigues-Barata AR, et al. Risk factors associated with frontal fibrosing alopecia: a multicentre case-control study. Clin Exp Dermatol. 2019;44:404-410. doi:10.1111/ced.13785
- Leecharoen W, Thanomkitti K, Thuangtong R, et al. Use of facial care products and frontal fibrosing alopecia: coincidence or true association? J Dermatol. 2021;48:1557-1563.
- Müller Ramos P, Anzai A, Duque-Estrada B, et al. Risk factors for frontal fibrosing alopecia: a case-control study in a multiracial population. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2021;84:712-718. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2020.08.07
- Kam O, Na S, Guo W, et al. Frontal fibrosing alopecia and personal care product use: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Arch Dermatol Res. 2023;315:2313-2331. doi:10.1007/s00403-023-02604-7
- Porriño-Bustamante ML, Montero-Vílchez T, Pinedo-Moraleda FJ, et al. Frontal fibrosing alopecia and sunscreen use: a cross-sectionalstudy of actinic damage. Acta Derm Venereol. Published online August 11, 2022. doi:10.2340/actadv.v102.306
Blood Eosinophil Counts Might Predict Childhood Asthma, Treatment Response
VIENNA — Simply relying on clinical symptoms is insufficient to predict which children with wheezing will develop asthma and respond to treatments.
Sejal Saglani, MD, PhD, a professor of pediatric respiratory medicine at the National Heart and Lung Institute, Imperial College, London, England, said that preschool wheezing has long-term adverse consequences through to adulthood. “We need to prevent that downward trajectory of low lung function,” she said, presenting the latest research in the field at the annual European Respiratory Society International Congress.
Wheezing affects up to one third of all infants and preschool children, with one third developing asthma later in life. “It’s important to identify those kids because then we can treat them with the right medication,” said Mariëlle W.H. Pijnenburg, MD, PhD, a pulmonary specialist at Erasmus University Rotterdam in the Netherlands.
“We cannot just use clinical phenotype to decide what treatment a child should get. We need to run tests to identify the endotype of preschool wheeze and intervene appropriately,” Dr. Saglani added.
Eosinophilia as a Biomarker for Predicting Exacerbations and Steroid Responsiveness
In a cluster analysis, Dr. Saglani and colleagues classified preschool children with wheezing into two main subgroups: Those who experience frequent exacerbations and those who experience sporadic attacks. Frequent exacerbators were more likely to develop asthma, use asthma medications, and show signs of reduced lung function and airway inflammation, such as higher fractional exhaled nitric oxide and allergic sensitization. “Severe and frequent exacerbators are the kids that get in trouble,” she said. “They’re the ones we must identify at preschool age and really try to minimize their exacerbations.”
Research has shown that eosinophilia is a valuable biomarker in predicting both asthma exacerbations and responsiveness to inhaled corticosteroids. Children with elevated blood eosinophils are more likely to experience frequent and severe exacerbations. These children often demonstrate an inflammatory profile more responsive to corticosteroids, making eosinophilia a predictor of treatment success. Children with eosinophilia are also more likely to have underlying allergic sensitizations, which further supports the use of corticosteroids as part of their management strategy.
Dr. Saglani said a simple blood test can provide a window into the child’s inflammatory status, allowing physicians to make more targeted and personalized treatment plans.
Traditionally, identifying eosinophilia required venipuncture and laboratory analysis, which can be time consuming and impractical in a busy clinical setting. Dr. Saglani’s research group is developing a point-of-care test designed to quickly and efficiently measure blood eosinophil levels in children with asthma or wheezing symptoms from a finger-prick test. Preliminary data presented at the congress show that children with higher eosinophil counts in the clinic were more likely to experience an asthma attack within 3 months.
“The problem is the majority of the children we see are either not atopic or do not have high blood eosinophils. What are we going to do with those?”
How to Treat Those Who Don’t Have Eosinophilia
Most children with wheezing are not atopic and do not exhibit eosinophilic inflammation, and these children may not respond as effectively to corticosteroids. How to treat them remains the “1-billion-dollar question,” Dr. Saglani said.
Respiratory syncytial virus and rhinovirus play a crucial role in triggering wheezing episodes in these children. Research has shown that viral-induced wheezing is a common feature in this phenotype, and repeated viral infections can lead to an increased severity and frequency of exacerbations. However, there are currently no effective antiviral therapies or vaccines for rhinovirus, which limits the ability to address the viral component of the disease directly.
Up to 50% of children with severe, recurrent wheezing also have bacterial pathogens like Moraxella catarrhalis and Haemophilus influenzae in their lower airways. For these children, addressing the bacterial infection is the best treatment option to mitigate the wheezing. “We now have something that we can target with antibiotics for those who don’t respond to corticosteroids,” Dr. Saglani said.
Dr. Pijnenburg said that this body of research is helping pulmonary specialists and general pediatricians navigate the complexity of childhood wheezing beyond phenotyping and symptoms. “We need to dive more deeply into those kids with preschool wheezing to see what’s happening in their lungs.”
Dr. Pijnenburg and Dr. Saglani reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
VIENNA — Simply relying on clinical symptoms is insufficient to predict which children with wheezing will develop asthma and respond to treatments.
Sejal Saglani, MD, PhD, a professor of pediatric respiratory medicine at the National Heart and Lung Institute, Imperial College, London, England, said that preschool wheezing has long-term adverse consequences through to adulthood. “We need to prevent that downward trajectory of low lung function,” she said, presenting the latest research in the field at the annual European Respiratory Society International Congress.
Wheezing affects up to one third of all infants and preschool children, with one third developing asthma later in life. “It’s important to identify those kids because then we can treat them with the right medication,” said Mariëlle W.H. Pijnenburg, MD, PhD, a pulmonary specialist at Erasmus University Rotterdam in the Netherlands.
“We cannot just use clinical phenotype to decide what treatment a child should get. We need to run tests to identify the endotype of preschool wheeze and intervene appropriately,” Dr. Saglani added.
Eosinophilia as a Biomarker for Predicting Exacerbations and Steroid Responsiveness
In a cluster analysis, Dr. Saglani and colleagues classified preschool children with wheezing into two main subgroups: Those who experience frequent exacerbations and those who experience sporadic attacks. Frequent exacerbators were more likely to develop asthma, use asthma medications, and show signs of reduced lung function and airway inflammation, such as higher fractional exhaled nitric oxide and allergic sensitization. “Severe and frequent exacerbators are the kids that get in trouble,” she said. “They’re the ones we must identify at preschool age and really try to minimize their exacerbations.”
Research has shown that eosinophilia is a valuable biomarker in predicting both asthma exacerbations and responsiveness to inhaled corticosteroids. Children with elevated blood eosinophils are more likely to experience frequent and severe exacerbations. These children often demonstrate an inflammatory profile more responsive to corticosteroids, making eosinophilia a predictor of treatment success. Children with eosinophilia are also more likely to have underlying allergic sensitizations, which further supports the use of corticosteroids as part of their management strategy.
Dr. Saglani said a simple blood test can provide a window into the child’s inflammatory status, allowing physicians to make more targeted and personalized treatment plans.
Traditionally, identifying eosinophilia required venipuncture and laboratory analysis, which can be time consuming and impractical in a busy clinical setting. Dr. Saglani’s research group is developing a point-of-care test designed to quickly and efficiently measure blood eosinophil levels in children with asthma or wheezing symptoms from a finger-prick test. Preliminary data presented at the congress show that children with higher eosinophil counts in the clinic were more likely to experience an asthma attack within 3 months.
“The problem is the majority of the children we see are either not atopic or do not have high blood eosinophils. What are we going to do with those?”
How to Treat Those Who Don’t Have Eosinophilia
Most children with wheezing are not atopic and do not exhibit eosinophilic inflammation, and these children may not respond as effectively to corticosteroids. How to treat them remains the “1-billion-dollar question,” Dr. Saglani said.
Respiratory syncytial virus and rhinovirus play a crucial role in triggering wheezing episodes in these children. Research has shown that viral-induced wheezing is a common feature in this phenotype, and repeated viral infections can lead to an increased severity and frequency of exacerbations. However, there are currently no effective antiviral therapies or vaccines for rhinovirus, which limits the ability to address the viral component of the disease directly.
Up to 50% of children with severe, recurrent wheezing also have bacterial pathogens like Moraxella catarrhalis and Haemophilus influenzae in their lower airways. For these children, addressing the bacterial infection is the best treatment option to mitigate the wheezing. “We now have something that we can target with antibiotics for those who don’t respond to corticosteroids,” Dr. Saglani said.
Dr. Pijnenburg said that this body of research is helping pulmonary specialists and general pediatricians navigate the complexity of childhood wheezing beyond phenotyping and symptoms. “We need to dive more deeply into those kids with preschool wheezing to see what’s happening in their lungs.”
Dr. Pijnenburg and Dr. Saglani reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
VIENNA — Simply relying on clinical symptoms is insufficient to predict which children with wheezing will develop asthma and respond to treatments.
Sejal Saglani, MD, PhD, a professor of pediatric respiratory medicine at the National Heart and Lung Institute, Imperial College, London, England, said that preschool wheezing has long-term adverse consequences through to adulthood. “We need to prevent that downward trajectory of low lung function,” she said, presenting the latest research in the field at the annual European Respiratory Society International Congress.
Wheezing affects up to one third of all infants and preschool children, with one third developing asthma later in life. “It’s important to identify those kids because then we can treat them with the right medication,” said Mariëlle W.H. Pijnenburg, MD, PhD, a pulmonary specialist at Erasmus University Rotterdam in the Netherlands.
“We cannot just use clinical phenotype to decide what treatment a child should get. We need to run tests to identify the endotype of preschool wheeze and intervene appropriately,” Dr. Saglani added.
Eosinophilia as a Biomarker for Predicting Exacerbations and Steroid Responsiveness
In a cluster analysis, Dr. Saglani and colleagues classified preschool children with wheezing into two main subgroups: Those who experience frequent exacerbations and those who experience sporadic attacks. Frequent exacerbators were more likely to develop asthma, use asthma medications, and show signs of reduced lung function and airway inflammation, such as higher fractional exhaled nitric oxide and allergic sensitization. “Severe and frequent exacerbators are the kids that get in trouble,” she said. “They’re the ones we must identify at preschool age and really try to minimize their exacerbations.”
Research has shown that eosinophilia is a valuable biomarker in predicting both asthma exacerbations and responsiveness to inhaled corticosteroids. Children with elevated blood eosinophils are more likely to experience frequent and severe exacerbations. These children often demonstrate an inflammatory profile more responsive to corticosteroids, making eosinophilia a predictor of treatment success. Children with eosinophilia are also more likely to have underlying allergic sensitizations, which further supports the use of corticosteroids as part of their management strategy.
Dr. Saglani said a simple blood test can provide a window into the child’s inflammatory status, allowing physicians to make more targeted and personalized treatment plans.
Traditionally, identifying eosinophilia required venipuncture and laboratory analysis, which can be time consuming and impractical in a busy clinical setting. Dr. Saglani’s research group is developing a point-of-care test designed to quickly and efficiently measure blood eosinophil levels in children with asthma or wheezing symptoms from a finger-prick test. Preliminary data presented at the congress show that children with higher eosinophil counts in the clinic were more likely to experience an asthma attack within 3 months.
“The problem is the majority of the children we see are either not atopic or do not have high blood eosinophils. What are we going to do with those?”
How to Treat Those Who Don’t Have Eosinophilia
Most children with wheezing are not atopic and do not exhibit eosinophilic inflammation, and these children may not respond as effectively to corticosteroids. How to treat them remains the “1-billion-dollar question,” Dr. Saglani said.
Respiratory syncytial virus and rhinovirus play a crucial role in triggering wheezing episodes in these children. Research has shown that viral-induced wheezing is a common feature in this phenotype, and repeated viral infections can lead to an increased severity and frequency of exacerbations. However, there are currently no effective antiviral therapies or vaccines for rhinovirus, which limits the ability to address the viral component of the disease directly.
Up to 50% of children with severe, recurrent wheezing also have bacterial pathogens like Moraxella catarrhalis and Haemophilus influenzae in their lower airways. For these children, addressing the bacterial infection is the best treatment option to mitigate the wheezing. “We now have something that we can target with antibiotics for those who don’t respond to corticosteroids,” Dr. Saglani said.
Dr. Pijnenburg said that this body of research is helping pulmonary specialists and general pediatricians navigate the complexity of childhood wheezing beyond phenotyping and symptoms. “We need to dive more deeply into those kids with preschool wheezing to see what’s happening in their lungs.”
Dr. Pijnenburg and Dr. Saglani reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Does Omalizumab Cause Atopic Dermatitis Flare-Ups?
To the Editor:
We read with interest the case reported by Yanovsky et al1 (Cutis. 2023;112:E23-E25). We thank the authors for updating our knowledge about atopic dermatitis (AD) and omalizumab and improving our understanding of the various wanted and unwanted effects that may manifest with omalizumab. We wish to clarify a few points on omalizumab use.
First, Yanovsky et al1 reported that their patient’s AD flares occurred within a few days after omalizumab injections to control asthma, possibly because omalizumab may have caused a paradoxical increase in sensitivity to other cytokines such as IL-33 in basophils and increased IL-4/IL-13 production in the skin. The authors cited Imai2 to explain that IL-33 plays a role in the pathogenesis of AD, increases itching, and disrupts the skin barrier. However, Imai2 did not discuss a relationship with omalizumab. As a recombinant humanized IgG1 monoclonal anti-IgE antibody, omalizumab works by interacting with the high-affinity receptor Fc epsilon RI that typically is found on eosinophils, mast cells, and basophils and plays a critical role in preventing the allergic cascade.3 We could not find any studies in the literature regarding omalizumab having a specific effect on the skin, causing cytokine imbalance, or increasing IL-4/IL-13 levels.
Second, the case report indicated that AD lesions improved with the biologic dupilumab,1 which seems amazing. Dupilumab is a monoclonal antibody used in patients with moderate to severe AD that blocks IL-4/IL-13 signaling and thus inhibits receptor signaling downstream of the Janus kinase signal transducer and activator of transcription protein pathway.4 It also has been shown to be beneficial in children with moderate to severe uncontrolled asthma.5 In vivo studies are needed to learn about the effects of these biologics on asthma and AD, whose complex immunologic effects are increasingly well understood by real patient experience.
Third, omalizumab has been found to relieve AD, not exacerbate it, in our own experience with 7 patients (unpublished data, 2024) and randomized controlled trials.6
Fourth, Yanovsky et al1 reported that the patient’s lesions flared up within a few days after taking omalizumab, which suggests a non-IgE delayed reaction. Could this reaction be related to polysorbate 20 used as an excipient in the commercial preparation? When we examined both preparations, the presence of polysorbate 80 in dupilumab was noteworthy,7 unlike omalizumab. We suggest the authors perform a patch test including polysorbate 20 and polysorbate 80.
Finally, the authors mentioned that omalizumab may cause a paradoxical exacerbation of AD in certain patients, as in tumor necrosis factor α inhibitor–induced psoriasis.8 This has been reported,8 but tumor necrosis factor α inhibitors are cytokine inhibitors and can lead to cytokine imbalance, while omalizumab is an IgE inhibitor.
Yanovsky et al1 described AD flares as “triggered by omalizumab,” which we believe was not the case. Because this patient had chronic AD, other causes of AD exacerbation in this patient could include stress or infection. Also, when they say that AD is triggered or induced, it implies that they are attributing the occurrence/development of AD in this patient to omalizumab. Of course, this also is not true.
Author’s Response
Thank you for your thoughtful comments. Although we agree that we cannot prove omalizumab was the cause of our patient’s AD flares, the new onset of severely worsening disease that was exacerbated by each dose of omalizumab as well as subsequent resolution upon switching to dupilumab was highly suggestive for a causal relationship. Our goal was to alert physicians to the possibility of this phenomenon and to encourage further study.
Karen A. Chernoff, MD
From the Department of Dermatology, Weill Cornell Medical College, New York, New York.
The author has no relevant financial disclosures to report.
- Yanovsky RL, Mitre M, Chernoff KA. Atopic dermatitis triggered by omalizumab and treated with dupilumab. Cutis. 2023;112:E23-E25. 2. Imai Y. Interleukin-33 in atopic dermatitis. J Dermatol Sci. 2019;96:2-7.
- Kumar C, Zito PM. Omalizumab. In: StatPearls [internet]. StatPearls Publishing; 2024.
- Seegräber M, Srour J, Walter A, et al. Dupilumab for treatment of atopic dermatitis. Expert Rev Clin Pharmacol. 2018;11:467-474.
- Bacharier LB, Maspero JF, Katelaris CH, et al. Dupilumab in children with uncontrolled moderate-to-severe asthma. N Engl J Med. 2021;385:2230-2240.
- Chan SMH, Cro S, Cornelius V, et al. Omalizumab for severe atopic dermatitis in 4- to 19-year-olds: the ADAPT RCT. National Institute for Health and Care Research; May 2022.
- Sumi T, Nagahisa Y, Matsuura K, et al. Delayed local reaction at a previous injection site reaction with dupilumab. Respirol Case Rep. 2021;9:E0852.
- Lian N, Zhang L, Chen M. Tumor necrosis factors-α inhibition-induced paradoxical psoriasis: a case series and literature review. Dermatol Ther. 2020;33:e14225.
To the Editor:
We read with interest the case reported by Yanovsky et al1 (Cutis. 2023;112:E23-E25). We thank the authors for updating our knowledge about atopic dermatitis (AD) and omalizumab and improving our understanding of the various wanted and unwanted effects that may manifest with omalizumab. We wish to clarify a few points on omalizumab use.
First, Yanovsky et al1 reported that their patient’s AD flares occurred within a few days after omalizumab injections to control asthma, possibly because omalizumab may have caused a paradoxical increase in sensitivity to other cytokines such as IL-33 in basophils and increased IL-4/IL-13 production in the skin. The authors cited Imai2 to explain that IL-33 plays a role in the pathogenesis of AD, increases itching, and disrupts the skin barrier. However, Imai2 did not discuss a relationship with omalizumab. As a recombinant humanized IgG1 monoclonal anti-IgE antibody, omalizumab works by interacting with the high-affinity receptor Fc epsilon RI that typically is found on eosinophils, mast cells, and basophils and plays a critical role in preventing the allergic cascade.3 We could not find any studies in the literature regarding omalizumab having a specific effect on the skin, causing cytokine imbalance, or increasing IL-4/IL-13 levels.
Second, the case report indicated that AD lesions improved with the biologic dupilumab,1 which seems amazing. Dupilumab is a monoclonal antibody used in patients with moderate to severe AD that blocks IL-4/IL-13 signaling and thus inhibits receptor signaling downstream of the Janus kinase signal transducer and activator of transcription protein pathway.4 It also has been shown to be beneficial in children with moderate to severe uncontrolled asthma.5 In vivo studies are needed to learn about the effects of these biologics on asthma and AD, whose complex immunologic effects are increasingly well understood by real patient experience.
Third, omalizumab has been found to relieve AD, not exacerbate it, in our own experience with 7 patients (unpublished data, 2024) and randomized controlled trials.6
Fourth, Yanovsky et al1 reported that the patient’s lesions flared up within a few days after taking omalizumab, which suggests a non-IgE delayed reaction. Could this reaction be related to polysorbate 20 used as an excipient in the commercial preparation? When we examined both preparations, the presence of polysorbate 80 in dupilumab was noteworthy,7 unlike omalizumab. We suggest the authors perform a patch test including polysorbate 20 and polysorbate 80.
Finally, the authors mentioned that omalizumab may cause a paradoxical exacerbation of AD in certain patients, as in tumor necrosis factor α inhibitor–induced psoriasis.8 This has been reported,8 but tumor necrosis factor α inhibitors are cytokine inhibitors and can lead to cytokine imbalance, while omalizumab is an IgE inhibitor.
Yanovsky et al1 described AD flares as “triggered by omalizumab,” which we believe was not the case. Because this patient had chronic AD, other causes of AD exacerbation in this patient could include stress or infection. Also, when they say that AD is triggered or induced, it implies that they are attributing the occurrence/development of AD in this patient to omalizumab. Of course, this also is not true.
Author’s Response
Thank you for your thoughtful comments. Although we agree that we cannot prove omalizumab was the cause of our patient’s AD flares, the new onset of severely worsening disease that was exacerbated by each dose of omalizumab as well as subsequent resolution upon switching to dupilumab was highly suggestive for a causal relationship. Our goal was to alert physicians to the possibility of this phenomenon and to encourage further study.
Karen A. Chernoff, MD
From the Department of Dermatology, Weill Cornell Medical College, New York, New York.
The author has no relevant financial disclosures to report.
To the Editor:
We read with interest the case reported by Yanovsky et al1 (Cutis. 2023;112:E23-E25). We thank the authors for updating our knowledge about atopic dermatitis (AD) and omalizumab and improving our understanding of the various wanted and unwanted effects that may manifest with omalizumab. We wish to clarify a few points on omalizumab use.
First, Yanovsky et al1 reported that their patient’s AD flares occurred within a few days after omalizumab injections to control asthma, possibly because omalizumab may have caused a paradoxical increase in sensitivity to other cytokines such as IL-33 in basophils and increased IL-4/IL-13 production in the skin. The authors cited Imai2 to explain that IL-33 plays a role in the pathogenesis of AD, increases itching, and disrupts the skin barrier. However, Imai2 did not discuss a relationship with omalizumab. As a recombinant humanized IgG1 monoclonal anti-IgE antibody, omalizumab works by interacting with the high-affinity receptor Fc epsilon RI that typically is found on eosinophils, mast cells, and basophils and plays a critical role in preventing the allergic cascade.3 We could not find any studies in the literature regarding omalizumab having a specific effect on the skin, causing cytokine imbalance, or increasing IL-4/IL-13 levels.
Second, the case report indicated that AD lesions improved with the biologic dupilumab,1 which seems amazing. Dupilumab is a monoclonal antibody used in patients with moderate to severe AD that blocks IL-4/IL-13 signaling and thus inhibits receptor signaling downstream of the Janus kinase signal transducer and activator of transcription protein pathway.4 It also has been shown to be beneficial in children with moderate to severe uncontrolled asthma.5 In vivo studies are needed to learn about the effects of these biologics on asthma and AD, whose complex immunologic effects are increasingly well understood by real patient experience.
Third, omalizumab has been found to relieve AD, not exacerbate it, in our own experience with 7 patients (unpublished data, 2024) and randomized controlled trials.6
Fourth, Yanovsky et al1 reported that the patient’s lesions flared up within a few days after taking omalizumab, which suggests a non-IgE delayed reaction. Could this reaction be related to polysorbate 20 used as an excipient in the commercial preparation? When we examined both preparations, the presence of polysorbate 80 in dupilumab was noteworthy,7 unlike omalizumab. We suggest the authors perform a patch test including polysorbate 20 and polysorbate 80.
Finally, the authors mentioned that omalizumab may cause a paradoxical exacerbation of AD in certain patients, as in tumor necrosis factor α inhibitor–induced psoriasis.8 This has been reported,8 but tumor necrosis factor α inhibitors are cytokine inhibitors and can lead to cytokine imbalance, while omalizumab is an IgE inhibitor.
Yanovsky et al1 described AD flares as “triggered by omalizumab,” which we believe was not the case. Because this patient had chronic AD, other causes of AD exacerbation in this patient could include stress or infection. Also, when they say that AD is triggered or induced, it implies that they are attributing the occurrence/development of AD in this patient to omalizumab. Of course, this also is not true.
Author’s Response
Thank you for your thoughtful comments. Although we agree that we cannot prove omalizumab was the cause of our patient’s AD flares, the new onset of severely worsening disease that was exacerbated by each dose of omalizumab as well as subsequent resolution upon switching to dupilumab was highly suggestive for a causal relationship. Our goal was to alert physicians to the possibility of this phenomenon and to encourage further study.
Karen A. Chernoff, MD
From the Department of Dermatology, Weill Cornell Medical College, New York, New York.
The author has no relevant financial disclosures to report.
- Yanovsky RL, Mitre M, Chernoff KA. Atopic dermatitis triggered by omalizumab and treated with dupilumab. Cutis. 2023;112:E23-E25. 2. Imai Y. Interleukin-33 in atopic dermatitis. J Dermatol Sci. 2019;96:2-7.
- Kumar C, Zito PM. Omalizumab. In: StatPearls [internet]. StatPearls Publishing; 2024.
- Seegräber M, Srour J, Walter A, et al. Dupilumab for treatment of atopic dermatitis. Expert Rev Clin Pharmacol. 2018;11:467-474.
- Bacharier LB, Maspero JF, Katelaris CH, et al. Dupilumab in children with uncontrolled moderate-to-severe asthma. N Engl J Med. 2021;385:2230-2240.
- Chan SMH, Cro S, Cornelius V, et al. Omalizumab for severe atopic dermatitis in 4- to 19-year-olds: the ADAPT RCT. National Institute for Health and Care Research; May 2022.
- Sumi T, Nagahisa Y, Matsuura K, et al. Delayed local reaction at a previous injection site reaction with dupilumab. Respirol Case Rep. 2021;9:E0852.
- Lian N, Zhang L, Chen M. Tumor necrosis factors-α inhibition-induced paradoxical psoriasis: a case series and literature review. Dermatol Ther. 2020;33:e14225.
- Yanovsky RL, Mitre M, Chernoff KA. Atopic dermatitis triggered by omalizumab and treated with dupilumab. Cutis. 2023;112:E23-E25. 2. Imai Y. Interleukin-33 in atopic dermatitis. J Dermatol Sci. 2019;96:2-7.
- Kumar C, Zito PM. Omalizumab. In: StatPearls [internet]. StatPearls Publishing; 2024.
- Seegräber M, Srour J, Walter A, et al. Dupilumab for treatment of atopic dermatitis. Expert Rev Clin Pharmacol. 2018;11:467-474.
- Bacharier LB, Maspero JF, Katelaris CH, et al. Dupilumab in children with uncontrolled moderate-to-severe asthma. N Engl J Med. 2021;385:2230-2240.
- Chan SMH, Cro S, Cornelius V, et al. Omalizumab for severe atopic dermatitis in 4- to 19-year-olds: the ADAPT RCT. National Institute for Health and Care Research; May 2022.
- Sumi T, Nagahisa Y, Matsuura K, et al. Delayed local reaction at a previous injection site reaction with dupilumab. Respirol Case Rep. 2021;9:E0852.
- Lian N, Zhang L, Chen M. Tumor necrosis factors-α inhibition-induced paradoxical psoriasis: a case series and literature review. Dermatol Ther. 2020;33:e14225.
The Link Between Vision Impairment and Dementia in Older Adults
TOPLINE:
METHODOLOGY:
- Researchers conducted a cross-sectional analysis using data from the National Health and Aging Trends Study (NHATS).
- The analysis included 2767 US adults aged 71 years or older (54.7% female and 45.3% male).
- Vision impairments were defined using 2019 World Health Organization criteria. Near and distance vision impairments were defined as greater than 0.30 logMAR, and contrast sensitivity impairment was identified by scores below 1.55 logCS.
- Dementia was classified using a standardized algorithm developed in NHATS, which incorporated a series of tests measuring cognition, memory and orientation, reports of Alzheimer’s disease, or a dementia diagnosis from the patient or a proxy, and an informant questionnaire (Ascertain Dementia-8 Dementia Screening Interview).
- The study analyzed data from 2021, with the primary outcome being the population attributable fraction (PAF) of dementia from vision impairment.
TAKEAWAY:
- The PAF of dementia associated with at least one vision impairment was 19% (95% CI, 8.2-29.7).
- Impairment in contrast sensitivity had the highest PAF among all other vision issues, at 15% (95% CI, 6.6-23.6). This figure was higher than that for impairment of near acuity, at 9.7% (95% CI, 2.6-17.0), or distance acuity, at 4.9% (95% CI, 0.1-9.9).
- The highest PAFs for dementia due to vision impairment was among participants aged 71-79 years (24.3%; 95% CI, 6.6-41.8), women (26.8%; 95% CI, 12.2-39.9), and non-Hispanic White participants (22.3%; 95% CI, 9.6-34.5).
IN PRACTICE:
“While not proving a cause-and-effect relationship, these findings support inclusion of multiple objective measures of vision impairments, including contrast sensitivity and visual acuity, to capture the total potential impact of addressing vision impairment on dementia,” study authors wrote.
SOURCE:
This study was led by Jason R. Smith, ScM, of the Department of Epidemiology at the Johns Hopkins Bloomberg School of Public Health in Baltimore. It was published online in JAMA Ophthalmology.
LIMITATIONS:
The limited sample sizes for American Indian, Alaska Native, Asian, and Hispanic groups prevented researchers from calculating PAFs for these populations. The cross-sectional design prevented the researchers from examining the timing of vision impairment in relation to a diagnosis of dementia. The study did not explore links between other measures of vision and dementia. Those with early cognitive impairment may not have updated glasses, affecting visual performance. The findings from the study may not apply to institutionalized older adults.
DISCLOSURES:
Jennifer A. Deal, PhD, MHS, reported receiving personal fees from Frontiers in Epidemiology, Velux Stiftung, and Medical Education Speakers Network outside the submitted work. Nicholas S. Reed, AuD, PhD, reported receiving stock options from Neosensory outside the submitted work. No other disclosures were reported.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication.A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
METHODOLOGY:
- Researchers conducted a cross-sectional analysis using data from the National Health and Aging Trends Study (NHATS).
- The analysis included 2767 US adults aged 71 years or older (54.7% female and 45.3% male).
- Vision impairments were defined using 2019 World Health Organization criteria. Near and distance vision impairments were defined as greater than 0.30 logMAR, and contrast sensitivity impairment was identified by scores below 1.55 logCS.
- Dementia was classified using a standardized algorithm developed in NHATS, which incorporated a series of tests measuring cognition, memory and orientation, reports of Alzheimer’s disease, or a dementia diagnosis from the patient or a proxy, and an informant questionnaire (Ascertain Dementia-8 Dementia Screening Interview).
- The study analyzed data from 2021, with the primary outcome being the population attributable fraction (PAF) of dementia from vision impairment.
TAKEAWAY:
- The PAF of dementia associated with at least one vision impairment was 19% (95% CI, 8.2-29.7).
- Impairment in contrast sensitivity had the highest PAF among all other vision issues, at 15% (95% CI, 6.6-23.6). This figure was higher than that for impairment of near acuity, at 9.7% (95% CI, 2.6-17.0), or distance acuity, at 4.9% (95% CI, 0.1-9.9).
- The highest PAFs for dementia due to vision impairment was among participants aged 71-79 years (24.3%; 95% CI, 6.6-41.8), women (26.8%; 95% CI, 12.2-39.9), and non-Hispanic White participants (22.3%; 95% CI, 9.6-34.5).
IN PRACTICE:
“While not proving a cause-and-effect relationship, these findings support inclusion of multiple objective measures of vision impairments, including contrast sensitivity and visual acuity, to capture the total potential impact of addressing vision impairment on dementia,” study authors wrote.
SOURCE:
This study was led by Jason R. Smith, ScM, of the Department of Epidemiology at the Johns Hopkins Bloomberg School of Public Health in Baltimore. It was published online in JAMA Ophthalmology.
LIMITATIONS:
The limited sample sizes for American Indian, Alaska Native, Asian, and Hispanic groups prevented researchers from calculating PAFs for these populations. The cross-sectional design prevented the researchers from examining the timing of vision impairment in relation to a diagnosis of dementia. The study did not explore links between other measures of vision and dementia. Those with early cognitive impairment may not have updated glasses, affecting visual performance. The findings from the study may not apply to institutionalized older adults.
DISCLOSURES:
Jennifer A. Deal, PhD, MHS, reported receiving personal fees from Frontiers in Epidemiology, Velux Stiftung, and Medical Education Speakers Network outside the submitted work. Nicholas S. Reed, AuD, PhD, reported receiving stock options from Neosensory outside the submitted work. No other disclosures were reported.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication.A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
METHODOLOGY:
- Researchers conducted a cross-sectional analysis using data from the National Health and Aging Trends Study (NHATS).
- The analysis included 2767 US adults aged 71 years or older (54.7% female and 45.3% male).
- Vision impairments were defined using 2019 World Health Organization criteria. Near and distance vision impairments were defined as greater than 0.30 logMAR, and contrast sensitivity impairment was identified by scores below 1.55 logCS.
- Dementia was classified using a standardized algorithm developed in NHATS, which incorporated a series of tests measuring cognition, memory and orientation, reports of Alzheimer’s disease, or a dementia diagnosis from the patient or a proxy, and an informant questionnaire (Ascertain Dementia-8 Dementia Screening Interview).
- The study analyzed data from 2021, with the primary outcome being the population attributable fraction (PAF) of dementia from vision impairment.
TAKEAWAY:
- The PAF of dementia associated with at least one vision impairment was 19% (95% CI, 8.2-29.7).
- Impairment in contrast sensitivity had the highest PAF among all other vision issues, at 15% (95% CI, 6.6-23.6). This figure was higher than that for impairment of near acuity, at 9.7% (95% CI, 2.6-17.0), or distance acuity, at 4.9% (95% CI, 0.1-9.9).
- The highest PAFs for dementia due to vision impairment was among participants aged 71-79 years (24.3%; 95% CI, 6.6-41.8), women (26.8%; 95% CI, 12.2-39.9), and non-Hispanic White participants (22.3%; 95% CI, 9.6-34.5).
IN PRACTICE:
“While not proving a cause-and-effect relationship, these findings support inclusion of multiple objective measures of vision impairments, including contrast sensitivity and visual acuity, to capture the total potential impact of addressing vision impairment on dementia,” study authors wrote.
SOURCE:
This study was led by Jason R. Smith, ScM, of the Department of Epidemiology at the Johns Hopkins Bloomberg School of Public Health in Baltimore. It was published online in JAMA Ophthalmology.
LIMITATIONS:
The limited sample sizes for American Indian, Alaska Native, Asian, and Hispanic groups prevented researchers from calculating PAFs for these populations. The cross-sectional design prevented the researchers from examining the timing of vision impairment in relation to a diagnosis of dementia. The study did not explore links between other measures of vision and dementia. Those with early cognitive impairment may not have updated glasses, affecting visual performance. The findings from the study may not apply to institutionalized older adults.
DISCLOSURES:
Jennifer A. Deal, PhD, MHS, reported receiving personal fees from Frontiers in Epidemiology, Velux Stiftung, and Medical Education Speakers Network outside the submitted work. Nicholas S. Reed, AuD, PhD, reported receiving stock options from Neosensory outside the submitted work. No other disclosures were reported.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication.A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Mental Health Services: The Missing Piece or Missing Peace for Patients With Atopic Dermatitis
There is a well-established connection between the mind and the skin, and it is clear that this relationship is bidirectional—not only does skin disease increase the risk for depression, anxiety, sleep disturbance, and suicidality, but psychologic stress actually can worsen skin disease through multiple mechanisms, including direct damage to the skin barrier.1,2 Psychologic stress also impacts the microbiome, another critical driver of skin disease.3,4 The concept of the itch-scratch cycle vividly illustrates the vicious interplay between the mind and body in atopic dermatitis (AD).
However, patients with AD are not the only ones impacted—caregivers also experience psychologic stress. Remarkably, one study of patients with AD and their caregivers found that the caregivers actually reported significantly worse mental health and anxiety (P=.01 and P=.03, respectively) than patients themselves, even when controlling for the severity of disease.5
Thus, it would seem obvious for mental health to be a central component of AD care—to improve patient and caregiver quality of life while also improving symptoms. Research has actually borne this out, with one systematic review and meta-analysis concluding that psychological intervention has a beneficial effect on AD,6 and another that the addition of psychological and educational interventions to conventional treatment provided better therapeutic results in alleviating eczema severity and psychological symptoms.7 One study demonstrated that patients with AD who received cognitive behavioral therapy via the internet displayed a statistically significant improvement in their disease (P<.001) as measured by the Patient-Oriented Eczema Measure compared with those in the control group who received standard care alone. They also reported improvements in perceived stress, sleep problems, and depression in the intervention group that were sustained at 1-year follow-up.8 These findings are particularly impactful because clinical results were achieved while leveraging an internet-based approach to therapy.
Regrettably, despite the preponderance of evidence supporting the connection between mental health and AD, there remain considerable unmet needs. A recent cross-sectional survey of 954 adults with AD and caregivers of children with AD (N=954) conducted by the National Eczema Association found that half of patients were never asked about mental health during any of their visits, and of those referred for mental health resources, only 57% utilized the recommended services.9 Importantly, patients aged 18 to 34 years reported wanting to be asked about mental health. Of those who did receive referrals, most were for counseling services (23%), followed by alternative mental health therapy such as music or art therapy (15%), cognitive behavioral therapy (13%), or peer/social support groups (12%). Approximately 10% reported receiving a pamphlet or a brochure only.9
Physicians who treat patients with AD can and must do better, but first we must explore why these referral rates are so low. As with many complex problems, there is unlikely to be one simple unifying reason. As expected, the answer is nuanced and multifaceted, and—most importantly—staggeringly incomplete.
For starters, mental health interventions rarely are as easy as applying a cream or taking a pill. Hedman-Lagerlöf et al8 specifically pointed out that although their approach—using internet-based cognitive behavioral therapy—was explicitly designed to be more accessible with fewer resources, it required approximately 35 hours of treatment over 12 weeks, requiring both substantial time and commitment from patients who often are already burned out and exhausted due to AD. They even underscored that the most commonly reported adverse effect of therapy was increased stress or worry, making it a difficult sell.8
Even before most patients have a chance to consider the time required and the potential adverse effects of mental health interventions for AD, greater hurdles exist. Finances, medical insurance, and wait times were highlighted as barriers to care in a systematic review.10 These are deep-seated problems in the United States; while they may be surmountable in certain geographic areas, the frequency with which these concerns arise means that it does not take too many failed attempts at referring patients for mental health services before clinicians just give up—similar to any form of operant conditioning.
A more elusive concept is stigmatization. Although it may not be quantifiable, the idea is that patients may encounter additional challenges when seeking mental health care, either because the interactions themselves may worsen their symptoms (eg, increased anxiety) or they may be more likely to have a negative perception of the experience.11 A 2020 systematic review of barriers to addressing common mental health problems found that stigma was the most prominent barrier in adolescents, with the second most prominent being negative attitudes and beliefs about mental health services and professionals.12 As a clinician, I can attest that I have sometimes detected skepticism when I have suggested mental health services to patients and have even been asked outright if I thought the problem was all in their head. My patients with AD generally have been much more open to the idea of mental health support, especially after I explain the powerful mind-body connection, than patients with other conditions—most notably delusions of parasitosis—who have been much more dismissive of such overtures. An oft-cited paper from 1976 frames the problem perfectly, describing what can happen after a referral for mental health services.13 The authors stated that the suggestion of mental health makes patients feel that the dermatologist does not believe them in the first place. Beyond this, the authors pointed out that referring the patient elsewhere reduces their hopes for dermatologic treatment.13
Knowing now—perhaps more than ever before—that the mind and skin are intimately connected compels us to solve these problems and find ways around these obstacles. Selecting the optimal forms of mental health services for each patient, having the structural support of the health care system, and winning the trust of patients and caregivers while combating stigma are undoubtedly tall orders; however, understanding the stakes for patients with AD, their caregivers, and society as a whole should inspire us to keep pushing forward.
- Nicholas MN, Gooderham MJ. Atopic dermatitis, depression, and suicidality. J Cutan Med Surg. 2017;21:237-242. doi:10.1177/1203475416685078
- aarouf M, Maarouf CL, Yosipovitch G, et al. The impact of stress on epidermal barrier function: an evidence‐based review. Br J Dermatol. 2019;181:1129-1137.
- Prescott SL, Larcombe DL, Logan AC, et al. The skin microbiome: impact of modern environments on skin ecology, barrier integrity, and systemic immune programming. World Allergy Organ J. 2017;10:29.
- Zhang XE, Zheng P, Ye SZ, et al. Microbiome: role in inflammatory skin diseases. J Inflamm Res. 2024;17:1057-1082.
- Chong AC, Schwartz A, Lang J, et al. Patients’ and caregivers’ preferences for mental health care and support in atopic dermatitis. Dermatitis. 2024;35(suppl 1):S70-S76.
- Chida Y, Steptoe A, Hirakawa N, et al. The effects of psychological intervention on atopic dermatitis. a systematic review and meta-analysis. Int Arch Allergy Immunol. 2007;144:1-9.
- Hashimoto K, Ogawa Y, Takeshima N, et al. Psychological and educational interventions for atopic dermatitis in adults: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Behav Change. 2017;34:48-65.
- Hedman-Lagerlöf E, Fust J, Axelsson E, et al. Internet-delivered cognitive behavior therapy for atopic dermatitis: a randomized clinical trial. JAMA Dermatol. 2021;157:796-804. doi:10.1001/jamadermatol.2021.1450
- Chatrath S, Loiselle AR, Johnson JK, et al. Evaluating mental health support by healthcare providers for patients with atopic dermatitis: a cross‐sectional survey. Skin Health Dis. Published online June 15, 2024. doi:10.1002/ski2.408
- Toy J, Gregory A, Rehmus W. Barriers to healthcare access in pediatric dermatology: a systematic review. Pediatr Dermatol. 2021;38(suppl 2):13-19.
- Borba CPC, DePadilla L, McCarty FA, et al. A qualitative study examining the perceived barriers and facilitators to medical healthcare services among women with a serious mental illness. Womens Health Issues. 2012;22:E217-E224.
- Aguirre Velasco A, Cruz ISS, Billings J, et al. What are the barriers, facilitators and interventions targeting help-seeking behaviours for common mental health problems in adolescents? a systematic review. BMC Psychiatry. 2020;20:293.
- Gould WM, Gragg TM. Delusions of parasitosis. an approach to the problem. Arch Dermatol. 1976;112:1745-1748.
There is a well-established connection between the mind and the skin, and it is clear that this relationship is bidirectional—not only does skin disease increase the risk for depression, anxiety, sleep disturbance, and suicidality, but psychologic stress actually can worsen skin disease through multiple mechanisms, including direct damage to the skin barrier.1,2 Psychologic stress also impacts the microbiome, another critical driver of skin disease.3,4 The concept of the itch-scratch cycle vividly illustrates the vicious interplay between the mind and body in atopic dermatitis (AD).
However, patients with AD are not the only ones impacted—caregivers also experience psychologic stress. Remarkably, one study of patients with AD and their caregivers found that the caregivers actually reported significantly worse mental health and anxiety (P=.01 and P=.03, respectively) than patients themselves, even when controlling for the severity of disease.5
Thus, it would seem obvious for mental health to be a central component of AD care—to improve patient and caregiver quality of life while also improving symptoms. Research has actually borne this out, with one systematic review and meta-analysis concluding that psychological intervention has a beneficial effect on AD,6 and another that the addition of psychological and educational interventions to conventional treatment provided better therapeutic results in alleviating eczema severity and psychological symptoms.7 One study demonstrated that patients with AD who received cognitive behavioral therapy via the internet displayed a statistically significant improvement in their disease (P<.001) as measured by the Patient-Oriented Eczema Measure compared with those in the control group who received standard care alone. They also reported improvements in perceived stress, sleep problems, and depression in the intervention group that were sustained at 1-year follow-up.8 These findings are particularly impactful because clinical results were achieved while leveraging an internet-based approach to therapy.
Regrettably, despite the preponderance of evidence supporting the connection between mental health and AD, there remain considerable unmet needs. A recent cross-sectional survey of 954 adults with AD and caregivers of children with AD (N=954) conducted by the National Eczema Association found that half of patients were never asked about mental health during any of their visits, and of those referred for mental health resources, only 57% utilized the recommended services.9 Importantly, patients aged 18 to 34 years reported wanting to be asked about mental health. Of those who did receive referrals, most were for counseling services (23%), followed by alternative mental health therapy such as music or art therapy (15%), cognitive behavioral therapy (13%), or peer/social support groups (12%). Approximately 10% reported receiving a pamphlet or a brochure only.9
Physicians who treat patients with AD can and must do better, but first we must explore why these referral rates are so low. As with many complex problems, there is unlikely to be one simple unifying reason. As expected, the answer is nuanced and multifaceted, and—most importantly—staggeringly incomplete.
For starters, mental health interventions rarely are as easy as applying a cream or taking a pill. Hedman-Lagerlöf et al8 specifically pointed out that although their approach—using internet-based cognitive behavioral therapy—was explicitly designed to be more accessible with fewer resources, it required approximately 35 hours of treatment over 12 weeks, requiring both substantial time and commitment from patients who often are already burned out and exhausted due to AD. They even underscored that the most commonly reported adverse effect of therapy was increased stress or worry, making it a difficult sell.8
Even before most patients have a chance to consider the time required and the potential adverse effects of mental health interventions for AD, greater hurdles exist. Finances, medical insurance, and wait times were highlighted as barriers to care in a systematic review.10 These are deep-seated problems in the United States; while they may be surmountable in certain geographic areas, the frequency with which these concerns arise means that it does not take too many failed attempts at referring patients for mental health services before clinicians just give up—similar to any form of operant conditioning.
A more elusive concept is stigmatization. Although it may not be quantifiable, the idea is that patients may encounter additional challenges when seeking mental health care, either because the interactions themselves may worsen their symptoms (eg, increased anxiety) or they may be more likely to have a negative perception of the experience.11 A 2020 systematic review of barriers to addressing common mental health problems found that stigma was the most prominent barrier in adolescents, with the second most prominent being negative attitudes and beliefs about mental health services and professionals.12 As a clinician, I can attest that I have sometimes detected skepticism when I have suggested mental health services to patients and have even been asked outright if I thought the problem was all in their head. My patients with AD generally have been much more open to the idea of mental health support, especially after I explain the powerful mind-body connection, than patients with other conditions—most notably delusions of parasitosis—who have been much more dismissive of such overtures. An oft-cited paper from 1976 frames the problem perfectly, describing what can happen after a referral for mental health services.13 The authors stated that the suggestion of mental health makes patients feel that the dermatologist does not believe them in the first place. Beyond this, the authors pointed out that referring the patient elsewhere reduces their hopes for dermatologic treatment.13
Knowing now—perhaps more than ever before—that the mind and skin are intimately connected compels us to solve these problems and find ways around these obstacles. Selecting the optimal forms of mental health services for each patient, having the structural support of the health care system, and winning the trust of patients and caregivers while combating stigma are undoubtedly tall orders; however, understanding the stakes for patients with AD, their caregivers, and society as a whole should inspire us to keep pushing forward.
There is a well-established connection between the mind and the skin, and it is clear that this relationship is bidirectional—not only does skin disease increase the risk for depression, anxiety, sleep disturbance, and suicidality, but psychologic stress actually can worsen skin disease through multiple mechanisms, including direct damage to the skin barrier.1,2 Psychologic stress also impacts the microbiome, another critical driver of skin disease.3,4 The concept of the itch-scratch cycle vividly illustrates the vicious interplay between the mind and body in atopic dermatitis (AD).
However, patients with AD are not the only ones impacted—caregivers also experience psychologic stress. Remarkably, one study of patients with AD and their caregivers found that the caregivers actually reported significantly worse mental health and anxiety (P=.01 and P=.03, respectively) than patients themselves, even when controlling for the severity of disease.5
Thus, it would seem obvious for mental health to be a central component of AD care—to improve patient and caregiver quality of life while also improving symptoms. Research has actually borne this out, with one systematic review and meta-analysis concluding that psychological intervention has a beneficial effect on AD,6 and another that the addition of psychological and educational interventions to conventional treatment provided better therapeutic results in alleviating eczema severity and psychological symptoms.7 One study demonstrated that patients with AD who received cognitive behavioral therapy via the internet displayed a statistically significant improvement in their disease (P<.001) as measured by the Patient-Oriented Eczema Measure compared with those in the control group who received standard care alone. They also reported improvements in perceived stress, sleep problems, and depression in the intervention group that were sustained at 1-year follow-up.8 These findings are particularly impactful because clinical results were achieved while leveraging an internet-based approach to therapy.
Regrettably, despite the preponderance of evidence supporting the connection between mental health and AD, there remain considerable unmet needs. A recent cross-sectional survey of 954 adults with AD and caregivers of children with AD (N=954) conducted by the National Eczema Association found that half of patients were never asked about mental health during any of their visits, and of those referred for mental health resources, only 57% utilized the recommended services.9 Importantly, patients aged 18 to 34 years reported wanting to be asked about mental health. Of those who did receive referrals, most were for counseling services (23%), followed by alternative mental health therapy such as music or art therapy (15%), cognitive behavioral therapy (13%), or peer/social support groups (12%). Approximately 10% reported receiving a pamphlet or a brochure only.9
Physicians who treat patients with AD can and must do better, but first we must explore why these referral rates are so low. As with many complex problems, there is unlikely to be one simple unifying reason. As expected, the answer is nuanced and multifaceted, and—most importantly—staggeringly incomplete.
For starters, mental health interventions rarely are as easy as applying a cream or taking a pill. Hedman-Lagerlöf et al8 specifically pointed out that although their approach—using internet-based cognitive behavioral therapy—was explicitly designed to be more accessible with fewer resources, it required approximately 35 hours of treatment over 12 weeks, requiring both substantial time and commitment from patients who often are already burned out and exhausted due to AD. They even underscored that the most commonly reported adverse effect of therapy was increased stress or worry, making it a difficult sell.8
Even before most patients have a chance to consider the time required and the potential adverse effects of mental health interventions for AD, greater hurdles exist. Finances, medical insurance, and wait times were highlighted as barriers to care in a systematic review.10 These are deep-seated problems in the United States; while they may be surmountable in certain geographic areas, the frequency with which these concerns arise means that it does not take too many failed attempts at referring patients for mental health services before clinicians just give up—similar to any form of operant conditioning.
A more elusive concept is stigmatization. Although it may not be quantifiable, the idea is that patients may encounter additional challenges when seeking mental health care, either because the interactions themselves may worsen their symptoms (eg, increased anxiety) or they may be more likely to have a negative perception of the experience.11 A 2020 systematic review of barriers to addressing common mental health problems found that stigma was the most prominent barrier in adolescents, with the second most prominent being negative attitudes and beliefs about mental health services and professionals.12 As a clinician, I can attest that I have sometimes detected skepticism when I have suggested mental health services to patients and have even been asked outright if I thought the problem was all in their head. My patients with AD generally have been much more open to the idea of mental health support, especially after I explain the powerful mind-body connection, than patients with other conditions—most notably delusions of parasitosis—who have been much more dismissive of such overtures. An oft-cited paper from 1976 frames the problem perfectly, describing what can happen after a referral for mental health services.13 The authors stated that the suggestion of mental health makes patients feel that the dermatologist does not believe them in the first place. Beyond this, the authors pointed out that referring the patient elsewhere reduces their hopes for dermatologic treatment.13
Knowing now—perhaps more than ever before—that the mind and skin are intimately connected compels us to solve these problems and find ways around these obstacles. Selecting the optimal forms of mental health services for each patient, having the structural support of the health care system, and winning the trust of patients and caregivers while combating stigma are undoubtedly tall orders; however, understanding the stakes for patients with AD, their caregivers, and society as a whole should inspire us to keep pushing forward.
- Nicholas MN, Gooderham MJ. Atopic dermatitis, depression, and suicidality. J Cutan Med Surg. 2017;21:237-242. doi:10.1177/1203475416685078
- aarouf M, Maarouf CL, Yosipovitch G, et al. The impact of stress on epidermal barrier function: an evidence‐based review. Br J Dermatol. 2019;181:1129-1137.
- Prescott SL, Larcombe DL, Logan AC, et al. The skin microbiome: impact of modern environments on skin ecology, barrier integrity, and systemic immune programming. World Allergy Organ J. 2017;10:29.
- Zhang XE, Zheng P, Ye SZ, et al. Microbiome: role in inflammatory skin diseases. J Inflamm Res. 2024;17:1057-1082.
- Chong AC, Schwartz A, Lang J, et al. Patients’ and caregivers’ preferences for mental health care and support in atopic dermatitis. Dermatitis. 2024;35(suppl 1):S70-S76.
- Chida Y, Steptoe A, Hirakawa N, et al. The effects of psychological intervention on atopic dermatitis. a systematic review and meta-analysis. Int Arch Allergy Immunol. 2007;144:1-9.
- Hashimoto K, Ogawa Y, Takeshima N, et al. Psychological and educational interventions for atopic dermatitis in adults: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Behav Change. 2017;34:48-65.
- Hedman-Lagerlöf E, Fust J, Axelsson E, et al. Internet-delivered cognitive behavior therapy for atopic dermatitis: a randomized clinical trial. JAMA Dermatol. 2021;157:796-804. doi:10.1001/jamadermatol.2021.1450
- Chatrath S, Loiselle AR, Johnson JK, et al. Evaluating mental health support by healthcare providers for patients with atopic dermatitis: a cross‐sectional survey. Skin Health Dis. Published online June 15, 2024. doi:10.1002/ski2.408
- Toy J, Gregory A, Rehmus W. Barriers to healthcare access in pediatric dermatology: a systematic review. Pediatr Dermatol. 2021;38(suppl 2):13-19.
- Borba CPC, DePadilla L, McCarty FA, et al. A qualitative study examining the perceived barriers and facilitators to medical healthcare services among women with a serious mental illness. Womens Health Issues. 2012;22:E217-E224.
- Aguirre Velasco A, Cruz ISS, Billings J, et al. What are the barriers, facilitators and interventions targeting help-seeking behaviours for common mental health problems in adolescents? a systematic review. BMC Psychiatry. 2020;20:293.
- Gould WM, Gragg TM. Delusions of parasitosis. an approach to the problem. Arch Dermatol. 1976;112:1745-1748.
- Nicholas MN, Gooderham MJ. Atopic dermatitis, depression, and suicidality. J Cutan Med Surg. 2017;21:237-242. doi:10.1177/1203475416685078
- aarouf M, Maarouf CL, Yosipovitch G, et al. The impact of stress on epidermal barrier function: an evidence‐based review. Br J Dermatol. 2019;181:1129-1137.
- Prescott SL, Larcombe DL, Logan AC, et al. The skin microbiome: impact of modern environments on skin ecology, barrier integrity, and systemic immune programming. World Allergy Organ J. 2017;10:29.
- Zhang XE, Zheng P, Ye SZ, et al. Microbiome: role in inflammatory skin diseases. J Inflamm Res. 2024;17:1057-1082.
- Chong AC, Schwartz A, Lang J, et al. Patients’ and caregivers’ preferences for mental health care and support in atopic dermatitis. Dermatitis. 2024;35(suppl 1):S70-S76.
- Chida Y, Steptoe A, Hirakawa N, et al. The effects of psychological intervention on atopic dermatitis. a systematic review and meta-analysis. Int Arch Allergy Immunol. 2007;144:1-9.
- Hashimoto K, Ogawa Y, Takeshima N, et al. Psychological and educational interventions for atopic dermatitis in adults: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Behav Change. 2017;34:48-65.
- Hedman-Lagerlöf E, Fust J, Axelsson E, et al. Internet-delivered cognitive behavior therapy for atopic dermatitis: a randomized clinical trial. JAMA Dermatol. 2021;157:796-804. doi:10.1001/jamadermatol.2021.1450
- Chatrath S, Loiselle AR, Johnson JK, et al. Evaluating mental health support by healthcare providers for patients with atopic dermatitis: a cross‐sectional survey. Skin Health Dis. Published online June 15, 2024. doi:10.1002/ski2.408
- Toy J, Gregory A, Rehmus W. Barriers to healthcare access in pediatric dermatology: a systematic review. Pediatr Dermatol. 2021;38(suppl 2):13-19.
- Borba CPC, DePadilla L, McCarty FA, et al. A qualitative study examining the perceived barriers and facilitators to medical healthcare services among women with a serious mental illness. Womens Health Issues. 2012;22:E217-E224.
- Aguirre Velasco A, Cruz ISS, Billings J, et al. What are the barriers, facilitators and interventions targeting help-seeking behaviours for common mental health problems in adolescents? a systematic review. BMC Psychiatry. 2020;20:293.
- Gould WM, Gragg TM. Delusions of parasitosis. an approach to the problem. Arch Dermatol. 1976;112:1745-1748.
Practice Points
- The mind-body connection plays a role in many conditions, including atopic dermatitis.
- Atopic dermatitis can make patients feel anxious, stressed, and depressed; at the same time, those feelings can lead to worsening of the condition.
- There are many barriers to getting mental health care in the United States, from financial constraints to stigmatization.
- Mental health is part of overall health and should be more highly prioritized by all physicians.
Alcohol’s Effect on Gout Risk Strongest in Men But Present in Both Sexes
TOPLINE:
A higher alcohol consumption is associated with an increased risk for gout, more strongly in men than in women. This sex-specific difference may be attributed to the different types of alcohol consumed by men and women, rather than biologic variations.
METHODOLOGY:
- This prospective cohort study investigated the association between total and specific alcohol consumption and the long-term risk for incident gout in 179,828 men (mean age, 56.0 years) and 221,300 women (mean age, 56.0 years) from the UK Biobank who did not have gout at baseline.
- Alcohol consumption was assessed using a computer-assisted touch screen system. Among men, 2.9%, 3.6%, and 93.6% were identified as never, former, and current drinkers, respectively. Among women, 5.9%, 3.6%, and 90.5% were identified as never, former, and current drinkers, respectively.
- Participants were also required to share details about their weekly alcohol intake and the types of alcoholic beverages they consumed (red wine, champagne or white wine, beer or cider, spirits, or fortified wine).
- The median follow-up duration of this study was 12.7 years.
- Cases of incident gout during the follow-up period were identified using hospital records and the International Classification of Diseases codes.
TAKEAWAY:
- The risk for gout was 69% higher in men who were current drinkers than in those who were never drinkers (hazard ratio [HR], 1.69; 95% CI, 1.30-2.18), while an inverse association was observed in women who were current drinkers, although it was not statistically significant. A significant interaction was observed between drinking status and sex (P < .001 for interaction).
- Among current drinkers, more frequent alcohol consumption was associated with a higher risk for gout among both sexes, with the association being stronger in men (HR, 2.05; 95% CI, 1.84-2.30) than in women (HR, 1.34; 95% CI, 1.12-1.61).
- The consumption of beer or cider was higher in men than in women (4.2 vs 0.4 pints/wk).
- Among all alcoholic beverages, the consumption of beer or cider (per 1 pint/d) showed the strongest association with the risk for gout in both men (HR, 1.60; 95% CI, 1.53-1.67) and women (HR, 1.62; 95% CI, 1.02-2.57).
IN PRACTICE:
“The observed sex-specific difference in the association of total alcohol consumption with incident gout may be owing to differences between men and women in the types of alcohol consumed rather than biological differences,” the authors wrote.
SOURCE:
The study was led by Jie-Qiong Lyu, MPH, Department of Nutrition and Food Hygiene, School of Public Health, Suzhou Medical College of Soochow University in China. It was published online in JAMA Network Open.
LIMITATIONS:
The frequency of alcohol consumption was self-reported, leading to potential misclassification. Incident cases of gout were identified from hospital records, which may have caused some undiagnosed cases or those diagnosed only in primary care settings to be missed. Most participants were of European descent and relatively healthier than the general population, limiting generalizability.
DISCLOSURES:
This work was supported by the Gusu Leading Talent Plan for Scientific and Technological Innovation and Entrepreneurship. The authors declared no conflicts of interest.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
A higher alcohol consumption is associated with an increased risk for gout, more strongly in men than in women. This sex-specific difference may be attributed to the different types of alcohol consumed by men and women, rather than biologic variations.
METHODOLOGY:
- This prospective cohort study investigated the association between total and specific alcohol consumption and the long-term risk for incident gout in 179,828 men (mean age, 56.0 years) and 221,300 women (mean age, 56.0 years) from the UK Biobank who did not have gout at baseline.
- Alcohol consumption was assessed using a computer-assisted touch screen system. Among men, 2.9%, 3.6%, and 93.6% were identified as never, former, and current drinkers, respectively. Among women, 5.9%, 3.6%, and 90.5% were identified as never, former, and current drinkers, respectively.
- Participants were also required to share details about their weekly alcohol intake and the types of alcoholic beverages they consumed (red wine, champagne or white wine, beer or cider, spirits, or fortified wine).
- The median follow-up duration of this study was 12.7 years.
- Cases of incident gout during the follow-up period were identified using hospital records and the International Classification of Diseases codes.
TAKEAWAY:
- The risk for gout was 69% higher in men who were current drinkers than in those who were never drinkers (hazard ratio [HR], 1.69; 95% CI, 1.30-2.18), while an inverse association was observed in women who were current drinkers, although it was not statistically significant. A significant interaction was observed between drinking status and sex (P < .001 for interaction).
- Among current drinkers, more frequent alcohol consumption was associated with a higher risk for gout among both sexes, with the association being stronger in men (HR, 2.05; 95% CI, 1.84-2.30) than in women (HR, 1.34; 95% CI, 1.12-1.61).
- The consumption of beer or cider was higher in men than in women (4.2 vs 0.4 pints/wk).
- Among all alcoholic beverages, the consumption of beer or cider (per 1 pint/d) showed the strongest association with the risk for gout in both men (HR, 1.60; 95% CI, 1.53-1.67) and women (HR, 1.62; 95% CI, 1.02-2.57).
IN PRACTICE:
“The observed sex-specific difference in the association of total alcohol consumption with incident gout may be owing to differences between men and women in the types of alcohol consumed rather than biological differences,” the authors wrote.
SOURCE:
The study was led by Jie-Qiong Lyu, MPH, Department of Nutrition and Food Hygiene, School of Public Health, Suzhou Medical College of Soochow University in China. It was published online in JAMA Network Open.
LIMITATIONS:
The frequency of alcohol consumption was self-reported, leading to potential misclassification. Incident cases of gout were identified from hospital records, which may have caused some undiagnosed cases or those diagnosed only in primary care settings to be missed. Most participants were of European descent and relatively healthier than the general population, limiting generalizability.
DISCLOSURES:
This work was supported by the Gusu Leading Talent Plan for Scientific and Technological Innovation and Entrepreneurship. The authors declared no conflicts of interest.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
A higher alcohol consumption is associated with an increased risk for gout, more strongly in men than in women. This sex-specific difference may be attributed to the different types of alcohol consumed by men and women, rather than biologic variations.
METHODOLOGY:
- This prospective cohort study investigated the association between total and specific alcohol consumption and the long-term risk for incident gout in 179,828 men (mean age, 56.0 years) and 221,300 women (mean age, 56.0 years) from the UK Biobank who did not have gout at baseline.
- Alcohol consumption was assessed using a computer-assisted touch screen system. Among men, 2.9%, 3.6%, and 93.6% were identified as never, former, and current drinkers, respectively. Among women, 5.9%, 3.6%, and 90.5% were identified as never, former, and current drinkers, respectively.
- Participants were also required to share details about their weekly alcohol intake and the types of alcoholic beverages they consumed (red wine, champagne or white wine, beer or cider, spirits, or fortified wine).
- The median follow-up duration of this study was 12.7 years.
- Cases of incident gout during the follow-up period were identified using hospital records and the International Classification of Diseases codes.
TAKEAWAY:
- The risk for gout was 69% higher in men who were current drinkers than in those who were never drinkers (hazard ratio [HR], 1.69; 95% CI, 1.30-2.18), while an inverse association was observed in women who were current drinkers, although it was not statistically significant. A significant interaction was observed between drinking status and sex (P < .001 for interaction).
- Among current drinkers, more frequent alcohol consumption was associated with a higher risk for gout among both sexes, with the association being stronger in men (HR, 2.05; 95% CI, 1.84-2.30) than in women (HR, 1.34; 95% CI, 1.12-1.61).
- The consumption of beer or cider was higher in men than in women (4.2 vs 0.4 pints/wk).
- Among all alcoholic beverages, the consumption of beer or cider (per 1 pint/d) showed the strongest association with the risk for gout in both men (HR, 1.60; 95% CI, 1.53-1.67) and women (HR, 1.62; 95% CI, 1.02-2.57).
IN PRACTICE:
“The observed sex-specific difference in the association of total alcohol consumption with incident gout may be owing to differences between men and women in the types of alcohol consumed rather than biological differences,” the authors wrote.
SOURCE:
The study was led by Jie-Qiong Lyu, MPH, Department of Nutrition and Food Hygiene, School of Public Health, Suzhou Medical College of Soochow University in China. It was published online in JAMA Network Open.
LIMITATIONS:
The frequency of alcohol consumption was self-reported, leading to potential misclassification. Incident cases of gout were identified from hospital records, which may have caused some undiagnosed cases or those diagnosed only in primary care settings to be missed. Most participants were of European descent and relatively healthier than the general population, limiting generalizability.
DISCLOSURES:
This work was supported by the Gusu Leading Talent Plan for Scientific and Technological Innovation and Entrepreneurship. The authors declared no conflicts of interest.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.