User login
Suicide attempts in kids ages 10-12 quadrupled over 20 years
Suicide attempts spurring calls to poison control centers more than quadrupled among U.S. children aged 10-12 years from 2000 to 2020, according to research published in JAMA Pediatrics.
The reasons for the increase in suicide attempts isn’t clear from the new study, but the researchers note that popular social media networks launched during the 20-year period, and other studies have linked spending time on social media with depression in adolescence. The COVID-19 pandemic, which began in the last year the researchers looked at, also disrupted normal life and routines for children.
For all children older than age 9, the proportion of incidents in which kids ate or drank something harmful that were deemed suicide attempts increased, while those classified as misuse or abuse of potentially poisonous substances declined. Children aged 6-9 did not have an increase in suicide attempts, the study found.
“It’s a huge problem we’re seeing in [ERs]. It’s exponentially blowing up numbers across the nation,” says David Sheridan, MD, an ER pediatric doctor at the Oregon Health and Science University, Portland, who led the study.
Adolescents or preteens who have attempted suicide can sit in ERs “for days or weeks” as they wait to be moved elsewhere in the hospital or to an outpatient facility for treatment, Dr. Sheridan says. The delays are not only unpleasant for the children, he says, but they also strain hospitals by leaving less space available for other patients coming to the ER.
“It’s really tough on the entire health care system, and most importantly, it’s really rough on the families who are going through a crisis,” Dr. Sheridan says. He noted that young people often attempt suicide by taking excessive quantities of common over-the-counter products found in many medicine cabinets – acetaminophen, ibuprofen, diphenhydramine – not items marked “poison.”
Twenty-year trend
The researchers examined phone calls to poison control centers about kids age 6 and up taking in potentially harmful substances from 2000-2020 recorded in the National Poison Data System, which is maintained by the American Association of Poison Control Centers.
Of more than 1.2 million total calls, 854,000 involved girls. A poison control data analyst determined if the call involved attempted suicide or the deliberate misuse or abuse of a potentially poisonous substance.
The researchers identified 1,005 deaths. About 70% of the total cases had either no effect or a minor effect on the child’s health.
Over the 20-year period, more than 90% of the calls involved children aged at least 13 years, with approximately 72,000 (5.7%) about children aged 10-12. Most calls for children 13 and older were for suicide attempts.
Suspected suicide attempts accounted for about 50% of the total calls to poison control centers among children aged 10-12 in 2000 – a figure that ballooned to 80% in 2020, the researchers found.
Both the number of calls and the proportion related to suicide attempts increased among children aged 10-12, Dr. Sheridan says. By 2020, the researchers found, poison control centers were fielding 4.5 times as many suicide-related calls among kids of this age group as they had in 2000. This jump was the largest such increase for any age group in the study, he says.
The reasons for such a large increase of suicide-related calls among preadolescents are unclear, the researchers note.
The increase became apparent around 2013, at the time many popular social media networks launched. Dr. Sheridan and his colleagues cite studies showing an association between spending more time on social media or watching television and depression in adolescence but said further research is needed to understand the root causes of this increase.
The latest study did not look specifically at the effect of the COVID-19 pandemic on suicide among young people. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention earlier reported a sharp rise in suicide attempts among youth during the early months of the pandemic, especially among girls aged 12-17 years. By February 2021, suicide attempts within this group had climbed by 50%, compared with 2 years earlier.
Although suicide attempts are concerning enough, deaths by suicide are even more worrisome, experts said.
The researchers’ findings are consistent with overall recent trends in youth suicide deaths, says Jeff Bridge, PhD, an epidemiologist at Nationwide Children’s Hospital, Columbus. From 2010-2020, suicide rates increased by 50% among 13- to 18-year-olds, Dr. Bridge said, and more than doubled in children aged 10-12.
The latest study captured only calls to poison control centers, so it did not count suicide attempts that did not result in a call for help. Another limitation of the study is that poison control data are not categorized by race or ethnicity, prompting Dr. Bridge to urge researchers to look specifically at the effect of race and ethnicity on these trends.
“This study supports screening for suicide risk as young as 10 years old,” Dr. Bridge says.
Dr. Sheridan agrees that prevention is essential: “The ER is where kids come when they’re in crisis. Trying to be more preventative by diagnosing or picking up on this earlier, I think, is really important.”
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
Suicide attempts spurring calls to poison control centers more than quadrupled among U.S. children aged 10-12 years from 2000 to 2020, according to research published in JAMA Pediatrics.
The reasons for the increase in suicide attempts isn’t clear from the new study, but the researchers note that popular social media networks launched during the 20-year period, and other studies have linked spending time on social media with depression in adolescence. The COVID-19 pandemic, which began in the last year the researchers looked at, also disrupted normal life and routines for children.
For all children older than age 9, the proportion of incidents in which kids ate or drank something harmful that were deemed suicide attempts increased, while those classified as misuse or abuse of potentially poisonous substances declined. Children aged 6-9 did not have an increase in suicide attempts, the study found.
“It’s a huge problem we’re seeing in [ERs]. It’s exponentially blowing up numbers across the nation,” says David Sheridan, MD, an ER pediatric doctor at the Oregon Health and Science University, Portland, who led the study.
Adolescents or preteens who have attempted suicide can sit in ERs “for days or weeks” as they wait to be moved elsewhere in the hospital or to an outpatient facility for treatment, Dr. Sheridan says. The delays are not only unpleasant for the children, he says, but they also strain hospitals by leaving less space available for other patients coming to the ER.
“It’s really tough on the entire health care system, and most importantly, it’s really rough on the families who are going through a crisis,” Dr. Sheridan says. He noted that young people often attempt suicide by taking excessive quantities of common over-the-counter products found in many medicine cabinets – acetaminophen, ibuprofen, diphenhydramine – not items marked “poison.”
Twenty-year trend
The researchers examined phone calls to poison control centers about kids age 6 and up taking in potentially harmful substances from 2000-2020 recorded in the National Poison Data System, which is maintained by the American Association of Poison Control Centers.
Of more than 1.2 million total calls, 854,000 involved girls. A poison control data analyst determined if the call involved attempted suicide or the deliberate misuse or abuse of a potentially poisonous substance.
The researchers identified 1,005 deaths. About 70% of the total cases had either no effect or a minor effect on the child’s health.
Over the 20-year period, more than 90% of the calls involved children aged at least 13 years, with approximately 72,000 (5.7%) about children aged 10-12. Most calls for children 13 and older were for suicide attempts.
Suspected suicide attempts accounted for about 50% of the total calls to poison control centers among children aged 10-12 in 2000 – a figure that ballooned to 80% in 2020, the researchers found.
Both the number of calls and the proportion related to suicide attempts increased among children aged 10-12, Dr. Sheridan says. By 2020, the researchers found, poison control centers were fielding 4.5 times as many suicide-related calls among kids of this age group as they had in 2000. This jump was the largest such increase for any age group in the study, he says.
The reasons for such a large increase of suicide-related calls among preadolescents are unclear, the researchers note.
The increase became apparent around 2013, at the time many popular social media networks launched. Dr. Sheridan and his colleagues cite studies showing an association between spending more time on social media or watching television and depression in adolescence but said further research is needed to understand the root causes of this increase.
The latest study did not look specifically at the effect of the COVID-19 pandemic on suicide among young people. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention earlier reported a sharp rise in suicide attempts among youth during the early months of the pandemic, especially among girls aged 12-17 years. By February 2021, suicide attempts within this group had climbed by 50%, compared with 2 years earlier.
Although suicide attempts are concerning enough, deaths by suicide are even more worrisome, experts said.
The researchers’ findings are consistent with overall recent trends in youth suicide deaths, says Jeff Bridge, PhD, an epidemiologist at Nationwide Children’s Hospital, Columbus. From 2010-2020, suicide rates increased by 50% among 13- to 18-year-olds, Dr. Bridge said, and more than doubled in children aged 10-12.
The latest study captured only calls to poison control centers, so it did not count suicide attempts that did not result in a call for help. Another limitation of the study is that poison control data are not categorized by race or ethnicity, prompting Dr. Bridge to urge researchers to look specifically at the effect of race and ethnicity on these trends.
“This study supports screening for suicide risk as young as 10 years old,” Dr. Bridge says.
Dr. Sheridan agrees that prevention is essential: “The ER is where kids come when they’re in crisis. Trying to be more preventative by diagnosing or picking up on this earlier, I think, is really important.”
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
Suicide attempts spurring calls to poison control centers more than quadrupled among U.S. children aged 10-12 years from 2000 to 2020, according to research published in JAMA Pediatrics.
The reasons for the increase in suicide attempts isn’t clear from the new study, but the researchers note that popular social media networks launched during the 20-year period, and other studies have linked spending time on social media with depression in adolescence. The COVID-19 pandemic, which began in the last year the researchers looked at, also disrupted normal life and routines for children.
For all children older than age 9, the proportion of incidents in which kids ate or drank something harmful that were deemed suicide attempts increased, while those classified as misuse or abuse of potentially poisonous substances declined. Children aged 6-9 did not have an increase in suicide attempts, the study found.
“It’s a huge problem we’re seeing in [ERs]. It’s exponentially blowing up numbers across the nation,” says David Sheridan, MD, an ER pediatric doctor at the Oregon Health and Science University, Portland, who led the study.
Adolescents or preteens who have attempted suicide can sit in ERs “for days or weeks” as they wait to be moved elsewhere in the hospital or to an outpatient facility for treatment, Dr. Sheridan says. The delays are not only unpleasant for the children, he says, but they also strain hospitals by leaving less space available for other patients coming to the ER.
“It’s really tough on the entire health care system, and most importantly, it’s really rough on the families who are going through a crisis,” Dr. Sheridan says. He noted that young people often attempt suicide by taking excessive quantities of common over-the-counter products found in many medicine cabinets – acetaminophen, ibuprofen, diphenhydramine – not items marked “poison.”
Twenty-year trend
The researchers examined phone calls to poison control centers about kids age 6 and up taking in potentially harmful substances from 2000-2020 recorded in the National Poison Data System, which is maintained by the American Association of Poison Control Centers.
Of more than 1.2 million total calls, 854,000 involved girls. A poison control data analyst determined if the call involved attempted suicide or the deliberate misuse or abuse of a potentially poisonous substance.
The researchers identified 1,005 deaths. About 70% of the total cases had either no effect or a minor effect on the child’s health.
Over the 20-year period, more than 90% of the calls involved children aged at least 13 years, with approximately 72,000 (5.7%) about children aged 10-12. Most calls for children 13 and older were for suicide attempts.
Suspected suicide attempts accounted for about 50% of the total calls to poison control centers among children aged 10-12 in 2000 – a figure that ballooned to 80% in 2020, the researchers found.
Both the number of calls and the proportion related to suicide attempts increased among children aged 10-12, Dr. Sheridan says. By 2020, the researchers found, poison control centers were fielding 4.5 times as many suicide-related calls among kids of this age group as they had in 2000. This jump was the largest such increase for any age group in the study, he says.
The reasons for such a large increase of suicide-related calls among preadolescents are unclear, the researchers note.
The increase became apparent around 2013, at the time many popular social media networks launched. Dr. Sheridan and his colleagues cite studies showing an association between spending more time on social media or watching television and depression in adolescence but said further research is needed to understand the root causes of this increase.
The latest study did not look specifically at the effect of the COVID-19 pandemic on suicide among young people. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention earlier reported a sharp rise in suicide attempts among youth during the early months of the pandemic, especially among girls aged 12-17 years. By February 2021, suicide attempts within this group had climbed by 50%, compared with 2 years earlier.
Although suicide attempts are concerning enough, deaths by suicide are even more worrisome, experts said.
The researchers’ findings are consistent with overall recent trends in youth suicide deaths, says Jeff Bridge, PhD, an epidemiologist at Nationwide Children’s Hospital, Columbus. From 2010-2020, suicide rates increased by 50% among 13- to 18-year-olds, Dr. Bridge said, and more than doubled in children aged 10-12.
The latest study captured only calls to poison control centers, so it did not count suicide attempts that did not result in a call for help. Another limitation of the study is that poison control data are not categorized by race or ethnicity, prompting Dr. Bridge to urge researchers to look specifically at the effect of race and ethnicity on these trends.
“This study supports screening for suicide risk as young as 10 years old,” Dr. Bridge says.
Dr. Sheridan agrees that prevention is essential: “The ER is where kids come when they’re in crisis. Trying to be more preventative by diagnosing or picking up on this earlier, I think, is really important.”
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
FROM JAMA PEDIATRICS
Virtual and in-person pediatric visits get similar family ratings
CHICAGO – Satisfaction ratings for virtual outpatient visits for pediatric orthopedic patients were similar to those for in-person office visits across most categories in an analysis of postencounter surveys completed by patients at the Cleveland Clinic.
Satisfaction ratings for both virtual and office visits were consistently higher than 85% across all measured parameters, according to the data presented at the annual meeting of the American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons.
Ahmed Emara, MD, a clinical research fellow in adult joint reconstruction at the Cleveland Clinic, led the study, which included data from all patients or guardians at the clinic who experienced such visits from March 2020 to March 2021.
A total of 1,686 responses were received, of which 226 (13.4%) involved virtual visits and 1,460 (86.6%) involved in-office visits. The primary endpoint was a patient-reported satisfaction score of good or excellent.
Analysis included ratings for access, care provider, telemedicine technology, and overall assessment/perception of satisfaction.
Target areas for improvement
In some areas, the virtual visits were less satisfactory than the in-office visits.
Patients had lower odds of reporting good/excellent satisfaction regarding their ability to schedule at a particularly convenient time (odds ratio, 0.1; 95% confidence interval, 0.08-0.18; P < .001). The study authors said scheduling more virtual time slots may help increase satisfaction in that area.
Satisfaction was also lower than with in-office visits with respect to providers’ explanations of patients’ conditions (OR, 0.4; 95% CI, 0.17-0.91; P = .03). Providers may need to find ways to better provide educational material in addition to the virtual consultation, the authors wrote.
No significant differences in categories of satisfaction
The researchers accounted for age, sex, traumatic etiology, and anatomic location of the complaint in multivariate regression analysis and found no significant differences between the two types of visits in the odds of getting a good/excellent rating for the following areas: patient inclusion in treatment decision (P = .562), discussion of proposed treatment (P = .222), concern by the provider (P = .189), degree of care for the patient as a person (P = .208), adequacy of teamwork in care provision (P = .053), likelihood of recommending the practice to others (P = .108), ease of receiving care at a particular practice (P = .109), ease of contacting the clinic (P = .177), and likelihood of recommending a particular provider (P = .218).
Anna Dimitriovna Vergun, MD, a pediatric orthopedist at the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill, who was not involved in the study, said in an interview she had been conducting virtual visits even before the pandemic, when she worked for several years at a Shriner’s children’s hospital in Los Angeles, before coming to UNC. The virtual visits were necessary because the hospital offered charity care and covered an area that included several states.
She said that during the height of the pandemic, 80% of her visits at UNC were virtual; it is down to about 5% now.
Some consultations don’t need physical visits at all, Dr. Vergun noted. For example, UNC is starting a clinic for prenatal counseling in cases in which ultrasound detects a limb deformity. Without a virtual option, she said, pregnant mothers in all parts of the state may have to drive long distances when no physical exam is necessary.
And sometimes, a visit simply involves checking in with families to see whether pain is being controlled, which is done well virtually.
“Those are particularly useful for telemedicine,” Dr. Vergun said. “There’s a lot of space for this to be useful. You sometimes don’t realize it until you start doing it and getting feedback from the families that they like it.”
Other exams may be better suited to office visits, she said. These include spine and hip exams and exams in which providers need to check reflexes.
She said she sees many cases of club feet, for which an in-person exam is needed to determine flexibility.
Expert says virtual misses nuances
Ryan Fitzgerald, MD, an orthopedic expert with Children’s Orthopaedic and Scoliosis Surgery Associates in St. Petersburg, Fla., who also was not involved in the study, said in an interview he doesn’t offer the virtual option now because he thinks those visits usually miss too much.
COSSA is a private practice that provides orthopedic services for Johns Hopkins All Children’s Hospital.
“I think physicians’ perspective versus the families’ perspective may be quite a bit different,” he said.
While families like the convenience, “a lot of what we do is watching the patient walk, looking at their hip range of motion, and virtually, that’s a really difficult thing to do,” he said.
You can instruct a family on how to turn a camera on the patient, but “it doesn’t always translate,” he said.
He said virtual visits also highlight disparities in access, because many families don’t own the hardware needed for such visits, and internet connections can be spotty or images pixelated.
Dr. Fitzgerald said virtual visits were helpful during the pandemic and would be beneficial for yearly checkups “if you know [the patient] well and it’s a fairly run-of-the-mill thing.”
However, he said, “everything we do is about human interaction, and I think that’s a downfall of the virtual platform right now. While it is helpful in situations like COVID and where it is a very basic follow-up, it still has a ways to go.”
Dr. Fitzgerald is a consultant for OrthoPediatrics, Medtronic, and Depuy Synthes. Dr. Vergun disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
CHICAGO – Satisfaction ratings for virtual outpatient visits for pediatric orthopedic patients were similar to those for in-person office visits across most categories in an analysis of postencounter surveys completed by patients at the Cleveland Clinic.
Satisfaction ratings for both virtual and office visits were consistently higher than 85% across all measured parameters, according to the data presented at the annual meeting of the American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons.
Ahmed Emara, MD, a clinical research fellow in adult joint reconstruction at the Cleveland Clinic, led the study, which included data from all patients or guardians at the clinic who experienced such visits from March 2020 to March 2021.
A total of 1,686 responses were received, of which 226 (13.4%) involved virtual visits and 1,460 (86.6%) involved in-office visits. The primary endpoint was a patient-reported satisfaction score of good or excellent.
Analysis included ratings for access, care provider, telemedicine technology, and overall assessment/perception of satisfaction.
Target areas for improvement
In some areas, the virtual visits were less satisfactory than the in-office visits.
Patients had lower odds of reporting good/excellent satisfaction regarding their ability to schedule at a particularly convenient time (odds ratio, 0.1; 95% confidence interval, 0.08-0.18; P < .001). The study authors said scheduling more virtual time slots may help increase satisfaction in that area.
Satisfaction was also lower than with in-office visits with respect to providers’ explanations of patients’ conditions (OR, 0.4; 95% CI, 0.17-0.91; P = .03). Providers may need to find ways to better provide educational material in addition to the virtual consultation, the authors wrote.
No significant differences in categories of satisfaction
The researchers accounted for age, sex, traumatic etiology, and anatomic location of the complaint in multivariate regression analysis and found no significant differences between the two types of visits in the odds of getting a good/excellent rating for the following areas: patient inclusion in treatment decision (P = .562), discussion of proposed treatment (P = .222), concern by the provider (P = .189), degree of care for the patient as a person (P = .208), adequacy of teamwork in care provision (P = .053), likelihood of recommending the practice to others (P = .108), ease of receiving care at a particular practice (P = .109), ease of contacting the clinic (P = .177), and likelihood of recommending a particular provider (P = .218).
Anna Dimitriovna Vergun, MD, a pediatric orthopedist at the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill, who was not involved in the study, said in an interview she had been conducting virtual visits even before the pandemic, when she worked for several years at a Shriner’s children’s hospital in Los Angeles, before coming to UNC. The virtual visits were necessary because the hospital offered charity care and covered an area that included several states.
She said that during the height of the pandemic, 80% of her visits at UNC were virtual; it is down to about 5% now.
Some consultations don’t need physical visits at all, Dr. Vergun noted. For example, UNC is starting a clinic for prenatal counseling in cases in which ultrasound detects a limb deformity. Without a virtual option, she said, pregnant mothers in all parts of the state may have to drive long distances when no physical exam is necessary.
And sometimes, a visit simply involves checking in with families to see whether pain is being controlled, which is done well virtually.
“Those are particularly useful for telemedicine,” Dr. Vergun said. “There’s a lot of space for this to be useful. You sometimes don’t realize it until you start doing it and getting feedback from the families that they like it.”
Other exams may be better suited to office visits, she said. These include spine and hip exams and exams in which providers need to check reflexes.
She said she sees many cases of club feet, for which an in-person exam is needed to determine flexibility.
Expert says virtual misses nuances
Ryan Fitzgerald, MD, an orthopedic expert with Children’s Orthopaedic and Scoliosis Surgery Associates in St. Petersburg, Fla., who also was not involved in the study, said in an interview he doesn’t offer the virtual option now because he thinks those visits usually miss too much.
COSSA is a private practice that provides orthopedic services for Johns Hopkins All Children’s Hospital.
“I think physicians’ perspective versus the families’ perspective may be quite a bit different,” he said.
While families like the convenience, “a lot of what we do is watching the patient walk, looking at their hip range of motion, and virtually, that’s a really difficult thing to do,” he said.
You can instruct a family on how to turn a camera on the patient, but “it doesn’t always translate,” he said.
He said virtual visits also highlight disparities in access, because many families don’t own the hardware needed for such visits, and internet connections can be spotty or images pixelated.
Dr. Fitzgerald said virtual visits were helpful during the pandemic and would be beneficial for yearly checkups “if you know [the patient] well and it’s a fairly run-of-the-mill thing.”
However, he said, “everything we do is about human interaction, and I think that’s a downfall of the virtual platform right now. While it is helpful in situations like COVID and where it is a very basic follow-up, it still has a ways to go.”
Dr. Fitzgerald is a consultant for OrthoPediatrics, Medtronic, and Depuy Synthes. Dr. Vergun disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
CHICAGO – Satisfaction ratings for virtual outpatient visits for pediatric orthopedic patients were similar to those for in-person office visits across most categories in an analysis of postencounter surveys completed by patients at the Cleveland Clinic.
Satisfaction ratings for both virtual and office visits were consistently higher than 85% across all measured parameters, according to the data presented at the annual meeting of the American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons.
Ahmed Emara, MD, a clinical research fellow in adult joint reconstruction at the Cleveland Clinic, led the study, which included data from all patients or guardians at the clinic who experienced such visits from March 2020 to March 2021.
A total of 1,686 responses were received, of which 226 (13.4%) involved virtual visits and 1,460 (86.6%) involved in-office visits. The primary endpoint was a patient-reported satisfaction score of good or excellent.
Analysis included ratings for access, care provider, telemedicine technology, and overall assessment/perception of satisfaction.
Target areas for improvement
In some areas, the virtual visits were less satisfactory than the in-office visits.
Patients had lower odds of reporting good/excellent satisfaction regarding their ability to schedule at a particularly convenient time (odds ratio, 0.1; 95% confidence interval, 0.08-0.18; P < .001). The study authors said scheduling more virtual time slots may help increase satisfaction in that area.
Satisfaction was also lower than with in-office visits with respect to providers’ explanations of patients’ conditions (OR, 0.4; 95% CI, 0.17-0.91; P = .03). Providers may need to find ways to better provide educational material in addition to the virtual consultation, the authors wrote.
No significant differences in categories of satisfaction
The researchers accounted for age, sex, traumatic etiology, and anatomic location of the complaint in multivariate regression analysis and found no significant differences between the two types of visits in the odds of getting a good/excellent rating for the following areas: patient inclusion in treatment decision (P = .562), discussion of proposed treatment (P = .222), concern by the provider (P = .189), degree of care for the patient as a person (P = .208), adequacy of teamwork in care provision (P = .053), likelihood of recommending the practice to others (P = .108), ease of receiving care at a particular practice (P = .109), ease of contacting the clinic (P = .177), and likelihood of recommending a particular provider (P = .218).
Anna Dimitriovna Vergun, MD, a pediatric orthopedist at the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill, who was not involved in the study, said in an interview she had been conducting virtual visits even before the pandemic, when she worked for several years at a Shriner’s children’s hospital in Los Angeles, before coming to UNC. The virtual visits were necessary because the hospital offered charity care and covered an area that included several states.
She said that during the height of the pandemic, 80% of her visits at UNC were virtual; it is down to about 5% now.
Some consultations don’t need physical visits at all, Dr. Vergun noted. For example, UNC is starting a clinic for prenatal counseling in cases in which ultrasound detects a limb deformity. Without a virtual option, she said, pregnant mothers in all parts of the state may have to drive long distances when no physical exam is necessary.
And sometimes, a visit simply involves checking in with families to see whether pain is being controlled, which is done well virtually.
“Those are particularly useful for telemedicine,” Dr. Vergun said. “There’s a lot of space for this to be useful. You sometimes don’t realize it until you start doing it and getting feedback from the families that they like it.”
Other exams may be better suited to office visits, she said. These include spine and hip exams and exams in which providers need to check reflexes.
She said she sees many cases of club feet, for which an in-person exam is needed to determine flexibility.
Expert says virtual misses nuances
Ryan Fitzgerald, MD, an orthopedic expert with Children’s Orthopaedic and Scoliosis Surgery Associates in St. Petersburg, Fla., who also was not involved in the study, said in an interview he doesn’t offer the virtual option now because he thinks those visits usually miss too much.
COSSA is a private practice that provides orthopedic services for Johns Hopkins All Children’s Hospital.
“I think physicians’ perspective versus the families’ perspective may be quite a bit different,” he said.
While families like the convenience, “a lot of what we do is watching the patient walk, looking at their hip range of motion, and virtually, that’s a really difficult thing to do,” he said.
You can instruct a family on how to turn a camera on the patient, but “it doesn’t always translate,” he said.
He said virtual visits also highlight disparities in access, because many families don’t own the hardware needed for such visits, and internet connections can be spotty or images pixelated.
Dr. Fitzgerald said virtual visits were helpful during the pandemic and would be beneficial for yearly checkups “if you know [the patient] well and it’s a fairly run-of-the-mill thing.”
However, he said, “everything we do is about human interaction, and I think that’s a downfall of the virtual platform right now. While it is helpful in situations like COVID and where it is a very basic follow-up, it still has a ways to go.”
Dr. Fitzgerald is a consultant for OrthoPediatrics, Medtronic, and Depuy Synthes. Dr. Vergun disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
AT AAOS 2022
Medical cannabis may cut opioid use for back pain, OA
CHICAGO – Access to medical cannabis (MC) cut opioid prescriptions for patients with chronic noncancer back pain and patients with osteoarthritis, according to preliminary data presented at the annual meeting of the American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons.
For those with chronic back pain, the average morphine milligram equivalents (MME) per day dropped from 15.1 to 11.0 (n = 186; P < .01). More than one-third of the patients (38.7%) stopped taking morphine after they filled prescriptions for medical cannabis.
Opioid prescriptions were filled 6 months before access to MC and then were compared with 6 months after access to MC.
In analyzing subgroups, the researchers found that patients who started at less than 15 MME/day and more than 15 MME/day showed significant decreases after filling the MC prescription.
Almost half (48.5%) of the patients in the group that started at less than 15 MME daily dropped to 0 MME/day, and 13.5% of patients who were getting more than 15 MME/day stopped using opioids.
Data on filled opioid prescriptions were gathered from a Prescription Drug Monitoring Program (PDMP) system for patients diagnosed with chronic musculoskeletal noncancer back pain who were eligible for MC access between February 2018 and July 2019.
Medical cannabis has shown benefit in treating chronic pain, but evidence has been limited on whether it can reduce opioid use, which can lead to substance abuse, addiction, overdose, and death, the researchers noted.
Researchers found that using MC via multiple routes of administration seemed to be important.
Patients who used only a single administration route showed a statistically insignificant decrease in MME/day from 20.0 to 15.1 (n = 68; P = .054), whereas patients who used two or more routes showed a significant decrease from 13.2 to 9.5 (n = 76; P < .01).
“We have many patients who are benefiting from a single route of delivery for chronic orthopedic pain,” Ari Greis, DO, a physical medicine and rehabilitation specialist in Bryn Mawr, Pa., and a coauthor of the MC studies for both back pain and OA, said in an interview. “However, our data shows a greater reduction in opioid consumption in patients using more than one route of delivery.”
He said delivery modes in the studies included vaporized cannabis oil or flower; sublingual tinctures; capsules or tablets; and topical lotions, creams, and salves.
Dr. Greis is the director of the medical cannabis department at Rothman Orthopaedic Institute in Bryn Mawr, and is a senior fellow in the Institute of Emerging Health Professions and the Lambert Center for the Study of Medicinal Cannabis and Hemp, both in Philadelphia.
Medical cannabis also reduces opioids for OA
The same team of researchers, using the data from the PDMP system, showed that medical cannabis also helped reduce opioid use for osteoarthritis.
For patients using opioids for OA, there was a significant decrease in average MME/day of prescriptions filled by patients following MC access – from 18.2 to 9.8 (n = 40; P < .05). The average drop in MME/day was 46.3%. The percentage of patients who stopped using opioids was 37.5%. Pain score on a 0-10 visual analog scale decreased significantly from 6.6 (n = 36) to 5.0 (n = 26; P < .01) at 3 months and 5.4 (n = 16; P < .05) at 6 months.
Gary Stewart, MD, an orthopedic surgeon in Morrow, Ga., who was not part of the studies, told this news organization that the studies offer good preliminary data to offer help with the opioid issue.
“I sometimes feel that we, as orthopedic surgeons and physicians in general, are working with one hand behind our back. We’re taking something that is a heroin or morphine derivative and giving it to our patients when we know it has a high risk of building tolerance and addiction. But at the same time, we have no alternative,” he said.
He said it’s important to remember the results from the relatively small study are preliminary and observational. People used different forms and amounts of MC and the data show only that prescriptions were filled, but not whether the cannabis was used. Prospective, controlled studies where opioids go head-to-head with MC are needed, he said.
“Still, this can lead us to more studies to give us an option [apart from] an opioid that we know is highly addictive,” he said.
Dr. Stewart is a member of the AAOS Opioid Task Force. Dr. Greis and several coauthors have disclosed no relevant financial relationships, and other coauthors report financial ties to companies unrelated to the research presented.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
CHICAGO – Access to medical cannabis (MC) cut opioid prescriptions for patients with chronic noncancer back pain and patients with osteoarthritis, according to preliminary data presented at the annual meeting of the American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons.
For those with chronic back pain, the average morphine milligram equivalents (MME) per day dropped from 15.1 to 11.0 (n = 186; P < .01). More than one-third of the patients (38.7%) stopped taking morphine after they filled prescriptions for medical cannabis.
Opioid prescriptions were filled 6 months before access to MC and then were compared with 6 months after access to MC.
In analyzing subgroups, the researchers found that patients who started at less than 15 MME/day and more than 15 MME/day showed significant decreases after filling the MC prescription.
Almost half (48.5%) of the patients in the group that started at less than 15 MME daily dropped to 0 MME/day, and 13.5% of patients who were getting more than 15 MME/day stopped using opioids.
Data on filled opioid prescriptions were gathered from a Prescription Drug Monitoring Program (PDMP) system for patients diagnosed with chronic musculoskeletal noncancer back pain who were eligible for MC access between February 2018 and July 2019.
Medical cannabis has shown benefit in treating chronic pain, but evidence has been limited on whether it can reduce opioid use, which can lead to substance abuse, addiction, overdose, and death, the researchers noted.
Researchers found that using MC via multiple routes of administration seemed to be important.
Patients who used only a single administration route showed a statistically insignificant decrease in MME/day from 20.0 to 15.1 (n = 68; P = .054), whereas patients who used two or more routes showed a significant decrease from 13.2 to 9.5 (n = 76; P < .01).
“We have many patients who are benefiting from a single route of delivery for chronic orthopedic pain,” Ari Greis, DO, a physical medicine and rehabilitation specialist in Bryn Mawr, Pa., and a coauthor of the MC studies for both back pain and OA, said in an interview. “However, our data shows a greater reduction in opioid consumption in patients using more than one route of delivery.”
He said delivery modes in the studies included vaporized cannabis oil or flower; sublingual tinctures; capsules or tablets; and topical lotions, creams, and salves.
Dr. Greis is the director of the medical cannabis department at Rothman Orthopaedic Institute in Bryn Mawr, and is a senior fellow in the Institute of Emerging Health Professions and the Lambert Center for the Study of Medicinal Cannabis and Hemp, both in Philadelphia.
Medical cannabis also reduces opioids for OA
The same team of researchers, using the data from the PDMP system, showed that medical cannabis also helped reduce opioid use for osteoarthritis.
For patients using opioids for OA, there was a significant decrease in average MME/day of prescriptions filled by patients following MC access – from 18.2 to 9.8 (n = 40; P < .05). The average drop in MME/day was 46.3%. The percentage of patients who stopped using opioids was 37.5%. Pain score on a 0-10 visual analog scale decreased significantly from 6.6 (n = 36) to 5.0 (n = 26; P < .01) at 3 months and 5.4 (n = 16; P < .05) at 6 months.
Gary Stewart, MD, an orthopedic surgeon in Morrow, Ga., who was not part of the studies, told this news organization that the studies offer good preliminary data to offer help with the opioid issue.
“I sometimes feel that we, as orthopedic surgeons and physicians in general, are working with one hand behind our back. We’re taking something that is a heroin or morphine derivative and giving it to our patients when we know it has a high risk of building tolerance and addiction. But at the same time, we have no alternative,” he said.
He said it’s important to remember the results from the relatively small study are preliminary and observational. People used different forms and amounts of MC and the data show only that prescriptions were filled, but not whether the cannabis was used. Prospective, controlled studies where opioids go head-to-head with MC are needed, he said.
“Still, this can lead us to more studies to give us an option [apart from] an opioid that we know is highly addictive,” he said.
Dr. Stewart is a member of the AAOS Opioid Task Force. Dr. Greis and several coauthors have disclosed no relevant financial relationships, and other coauthors report financial ties to companies unrelated to the research presented.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
CHICAGO – Access to medical cannabis (MC) cut opioid prescriptions for patients with chronic noncancer back pain and patients with osteoarthritis, according to preliminary data presented at the annual meeting of the American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons.
For those with chronic back pain, the average morphine milligram equivalents (MME) per day dropped from 15.1 to 11.0 (n = 186; P < .01). More than one-third of the patients (38.7%) stopped taking morphine after they filled prescriptions for medical cannabis.
Opioid prescriptions were filled 6 months before access to MC and then were compared with 6 months after access to MC.
In analyzing subgroups, the researchers found that patients who started at less than 15 MME/day and more than 15 MME/day showed significant decreases after filling the MC prescription.
Almost half (48.5%) of the patients in the group that started at less than 15 MME daily dropped to 0 MME/day, and 13.5% of patients who were getting more than 15 MME/day stopped using opioids.
Data on filled opioid prescriptions were gathered from a Prescription Drug Monitoring Program (PDMP) system for patients diagnosed with chronic musculoskeletal noncancer back pain who were eligible for MC access between February 2018 and July 2019.
Medical cannabis has shown benefit in treating chronic pain, but evidence has been limited on whether it can reduce opioid use, which can lead to substance abuse, addiction, overdose, and death, the researchers noted.
Researchers found that using MC via multiple routes of administration seemed to be important.
Patients who used only a single administration route showed a statistically insignificant decrease in MME/day from 20.0 to 15.1 (n = 68; P = .054), whereas patients who used two or more routes showed a significant decrease from 13.2 to 9.5 (n = 76; P < .01).
“We have many patients who are benefiting from a single route of delivery for chronic orthopedic pain,” Ari Greis, DO, a physical medicine and rehabilitation specialist in Bryn Mawr, Pa., and a coauthor of the MC studies for both back pain and OA, said in an interview. “However, our data shows a greater reduction in opioid consumption in patients using more than one route of delivery.”
He said delivery modes in the studies included vaporized cannabis oil or flower; sublingual tinctures; capsules or tablets; and topical lotions, creams, and salves.
Dr. Greis is the director of the medical cannabis department at Rothman Orthopaedic Institute in Bryn Mawr, and is a senior fellow in the Institute of Emerging Health Professions and the Lambert Center for the Study of Medicinal Cannabis and Hemp, both in Philadelphia.
Medical cannabis also reduces opioids for OA
The same team of researchers, using the data from the PDMP system, showed that medical cannabis also helped reduce opioid use for osteoarthritis.
For patients using opioids for OA, there was a significant decrease in average MME/day of prescriptions filled by patients following MC access – from 18.2 to 9.8 (n = 40; P < .05). The average drop in MME/day was 46.3%. The percentage of patients who stopped using opioids was 37.5%. Pain score on a 0-10 visual analog scale decreased significantly from 6.6 (n = 36) to 5.0 (n = 26; P < .01) at 3 months and 5.4 (n = 16; P < .05) at 6 months.
Gary Stewart, MD, an orthopedic surgeon in Morrow, Ga., who was not part of the studies, told this news organization that the studies offer good preliminary data to offer help with the opioid issue.
“I sometimes feel that we, as orthopedic surgeons and physicians in general, are working with one hand behind our back. We’re taking something that is a heroin or morphine derivative and giving it to our patients when we know it has a high risk of building tolerance and addiction. But at the same time, we have no alternative,” he said.
He said it’s important to remember the results from the relatively small study are preliminary and observational. People used different forms and amounts of MC and the data show only that prescriptions were filled, but not whether the cannabis was used. Prospective, controlled studies where opioids go head-to-head with MC are needed, he said.
“Still, this can lead us to more studies to give us an option [apart from] an opioid that we know is highly addictive,” he said.
Dr. Stewart is a member of the AAOS Opioid Task Force. Dr. Greis and several coauthors have disclosed no relevant financial relationships, and other coauthors report financial ties to companies unrelated to the research presented.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
AT AAOS 2022
Metformin use linked to birth defects in boys
researchers have found.
The association appears to involve the effects of metformin on the development of sperm during a critical window prior to conception. Female offspring were not affected. Although previous studies have linked diabetes with fertility problems in men, the latest study is the first to show that these problems can result from treatment rather than the disease itself, according to the researchers, whose findings appear in Annals of Internal Medicine.
“This is the first data to suggest that paternal metformin [use] may be associated with birth defects in children. As such, it would be early to begin to alter clinical practice,” Michael Eisenberg, MD, director of male reproductive medicine and surgery, department of urology, Stanford (Calif.) University, who is a coauthor of the study, said in an interview. “However, if it is confirmed in other populations, then it may begin to enter counseling discussions.”
Dr. Eisenberg added that eating a nutritious diet, exercising, and maintaining a healthy body weight “can improve a man’s health and likely his fertility as well.”
For the new study, Dr. Eisenberg and colleagues analyzed records in a registry of all 1.25 million births that occurred in Denmark between 1997 and 2016. The registry included information on birth defects and parental drug prescriptions.
Offspring were considered exposed to a diabetes drug if a father had filled one or more prescriptions for the medications during the 3 months prior to conception, when the fertilizing sperm would have been produced.
The final analysis included 1,116,779 offspring – all singleton births to women without a history of diabetes or essential hypertension – of whom 7,029 were exposed to diabetes drugs via the father, and 3.3% (n = 36,585) had one or more major birth defects.
Among male offspring whose fathers had taken metformin (n = 1,451), there was a 3.4-fold greater incidence of major genitourinary birth defects, according to the researchers. The study failed to find associations between birth defects and the use of insulin. Although a signal did emerge for sulfonylurea-based drugs, it did not reach statistical significance.
The risk associated with metformin did not appear for men who were prescribed the drug in the year before or after sperm development. Nor was it evident in siblings of the boys with birth defects who were not considered to have been exposed to the medication, the researchers reported.
In an editorial accompanying the journal article, Germaine Buck Louis, PhD, a reproductive and perinatal epidemiologist, wrote: “Given the prevalence of metformin use as first-line therapy for type 2 diabetes, corroboration of these findings is urgently needed.”
Dr. Louis, dean of the College of Health and Human Services at George Mason University, Washington, said a key limitation of the research is the lack of data on how well men in the study adhered to their diabetes treatment. Nevertheless, “clinical guidance is needed to help couples planning pregnancy weigh the risks and benefits of paternal metformin use relative to other medications.”
The researchers received funding from the National Institutes of Health and the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
researchers have found.
The association appears to involve the effects of metformin on the development of sperm during a critical window prior to conception. Female offspring were not affected. Although previous studies have linked diabetes with fertility problems in men, the latest study is the first to show that these problems can result from treatment rather than the disease itself, according to the researchers, whose findings appear in Annals of Internal Medicine.
“This is the first data to suggest that paternal metformin [use] may be associated with birth defects in children. As such, it would be early to begin to alter clinical practice,” Michael Eisenberg, MD, director of male reproductive medicine and surgery, department of urology, Stanford (Calif.) University, who is a coauthor of the study, said in an interview. “However, if it is confirmed in other populations, then it may begin to enter counseling discussions.”
Dr. Eisenberg added that eating a nutritious diet, exercising, and maintaining a healthy body weight “can improve a man’s health and likely his fertility as well.”
For the new study, Dr. Eisenberg and colleagues analyzed records in a registry of all 1.25 million births that occurred in Denmark between 1997 and 2016. The registry included information on birth defects and parental drug prescriptions.
Offspring were considered exposed to a diabetes drug if a father had filled one or more prescriptions for the medications during the 3 months prior to conception, when the fertilizing sperm would have been produced.
The final analysis included 1,116,779 offspring – all singleton births to women without a history of diabetes or essential hypertension – of whom 7,029 were exposed to diabetes drugs via the father, and 3.3% (n = 36,585) had one or more major birth defects.
Among male offspring whose fathers had taken metformin (n = 1,451), there was a 3.4-fold greater incidence of major genitourinary birth defects, according to the researchers. The study failed to find associations between birth defects and the use of insulin. Although a signal did emerge for sulfonylurea-based drugs, it did not reach statistical significance.
The risk associated with metformin did not appear for men who were prescribed the drug in the year before or after sperm development. Nor was it evident in siblings of the boys with birth defects who were not considered to have been exposed to the medication, the researchers reported.
In an editorial accompanying the journal article, Germaine Buck Louis, PhD, a reproductive and perinatal epidemiologist, wrote: “Given the prevalence of metformin use as first-line therapy for type 2 diabetes, corroboration of these findings is urgently needed.”
Dr. Louis, dean of the College of Health and Human Services at George Mason University, Washington, said a key limitation of the research is the lack of data on how well men in the study adhered to their diabetes treatment. Nevertheless, “clinical guidance is needed to help couples planning pregnancy weigh the risks and benefits of paternal metformin use relative to other medications.”
The researchers received funding from the National Institutes of Health and the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
researchers have found.
The association appears to involve the effects of metformin on the development of sperm during a critical window prior to conception. Female offspring were not affected. Although previous studies have linked diabetes with fertility problems in men, the latest study is the first to show that these problems can result from treatment rather than the disease itself, according to the researchers, whose findings appear in Annals of Internal Medicine.
“This is the first data to suggest that paternal metformin [use] may be associated with birth defects in children. As such, it would be early to begin to alter clinical practice,” Michael Eisenberg, MD, director of male reproductive medicine and surgery, department of urology, Stanford (Calif.) University, who is a coauthor of the study, said in an interview. “However, if it is confirmed in other populations, then it may begin to enter counseling discussions.”
Dr. Eisenberg added that eating a nutritious diet, exercising, and maintaining a healthy body weight “can improve a man’s health and likely his fertility as well.”
For the new study, Dr. Eisenberg and colleagues analyzed records in a registry of all 1.25 million births that occurred in Denmark between 1997 and 2016. The registry included information on birth defects and parental drug prescriptions.
Offspring were considered exposed to a diabetes drug if a father had filled one or more prescriptions for the medications during the 3 months prior to conception, when the fertilizing sperm would have been produced.
The final analysis included 1,116,779 offspring – all singleton births to women without a history of diabetes or essential hypertension – of whom 7,029 were exposed to diabetes drugs via the father, and 3.3% (n = 36,585) had one or more major birth defects.
Among male offspring whose fathers had taken metformin (n = 1,451), there was a 3.4-fold greater incidence of major genitourinary birth defects, according to the researchers. The study failed to find associations between birth defects and the use of insulin. Although a signal did emerge for sulfonylurea-based drugs, it did not reach statistical significance.
The risk associated with metformin did not appear for men who were prescribed the drug in the year before or after sperm development. Nor was it evident in siblings of the boys with birth defects who were not considered to have been exposed to the medication, the researchers reported.
In an editorial accompanying the journal article, Germaine Buck Louis, PhD, a reproductive and perinatal epidemiologist, wrote: “Given the prevalence of metformin use as first-line therapy for type 2 diabetes, corroboration of these findings is urgently needed.”
Dr. Louis, dean of the College of Health and Human Services at George Mason University, Washington, said a key limitation of the research is the lack of data on how well men in the study adhered to their diabetes treatment. Nevertheless, “clinical guidance is needed to help couples planning pregnancy weigh the risks and benefits of paternal metformin use relative to other medications.”
The researchers received funding from the National Institutes of Health and the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM ANNALS OF INTERNAL MEDICINE
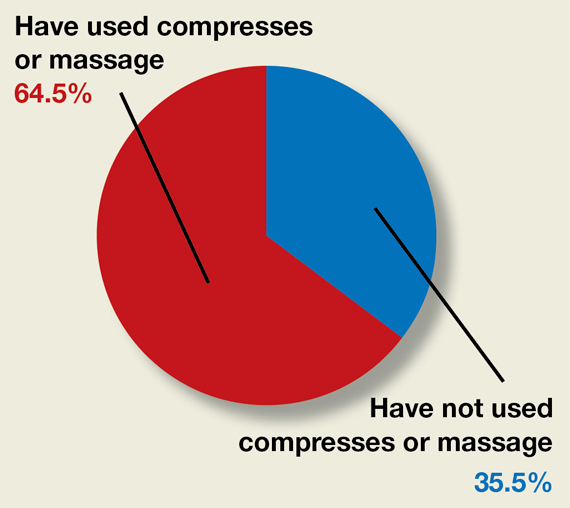
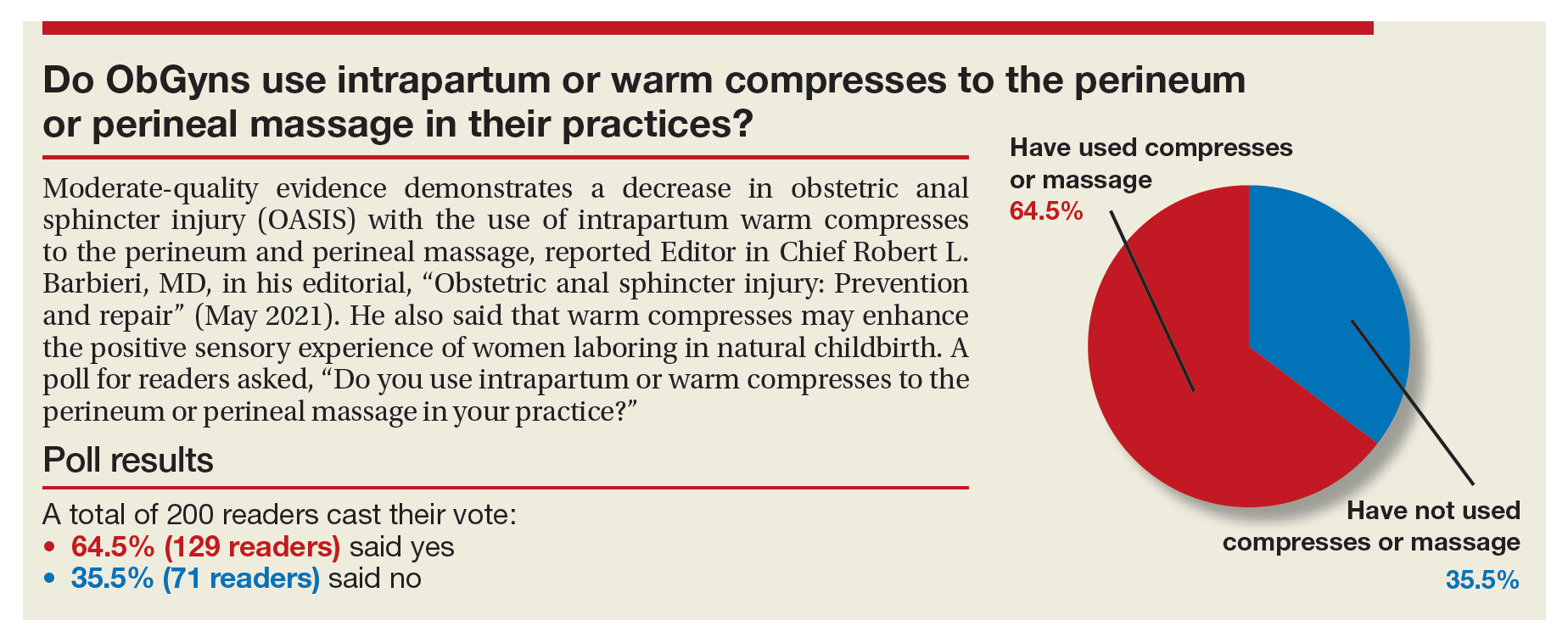
Do ObGyns use intrapartum warm compresses to the perineum or perineal massage in their practices?
Moderate-quality evidence demonstrates a decrease in obstetric anal sphincter injury (OASIS) with the use of intrapartum warm compresses to the perineum and perineal massage, reported Editor in Chief Robert L. Barbieri, MD, in his editorial, “Obstetric anal sphincter injury: Prevention and repair” (May 2021). He also said that warm compresses may enhance the positive sensory experience of women laboring in natural childbirth. A poll for readers asked, “Do you use intrapartum or warm compresses to the perineum or perineal massage in your practice?”
A total of 200 readers cast their vote:
65.4% (129 readers)said yes
35.5% (71 readers)said no
Moderate-quality evidence demonstrates a decrease in obstetric anal sphincter injury (OASIS) with the use of intrapartum warm compresses to the perineum and perineal massage, reported Editor in Chief Robert L. Barbieri, MD, in his editorial, “Obstetric anal sphincter injury: Prevention and repair” (May 2021). He also said that warm compresses may enhance the positive sensory experience of women laboring in natural childbirth. A poll for readers asked, “Do you use intrapartum or warm compresses to the perineum or perineal massage in your practice?”
A total of 200 readers cast their vote:
65.4% (129 readers)said yes
35.5% (71 readers)said no


Moderate-quality evidence demonstrates a decrease in obstetric anal sphincter injury (OASIS) with the use of intrapartum warm compresses to the perineum and perineal massage, reported Editor in Chief Robert L. Barbieri, MD, in his editorial, “Obstetric anal sphincter injury: Prevention and repair” (May 2021). He also said that warm compresses may enhance the positive sensory experience of women laboring in natural childbirth. A poll for readers asked, “Do you use intrapartum or warm compresses to the perineum or perineal massage in your practice?”
A total of 200 readers cast their vote:
65.4% (129 readers)said yes
35.5% (71 readers)said no


FDA approves HIV injectable Cabenuva initiation without oral lead-in
Initiating treatment may become easier for adults living with HIV. a combination injectable, without a lead-in period of oral tablets, according to a press release from Janssen Pharmaceuticals.
Cabenuva combines rilpivirine (Janssen) and cabotegravir (ViiV Healthcare). The change offers patients and clinicians an option for a streamlined entry to treatment without the burden of daily pill taking, according to the release.
Cabenuva injections may be given as few as six times a year to manage HIV, according to Janssen. HIV patients with viral suppression previously had to complete an oral treatment regimen before starting monthly or bimonthly injections.
The injectable combination of cabotegravir, an HIV-1 integrase strand transfer inhibitor, and rilpivirine, an HIV-1 nonnucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitor, is currently indicated as a complete treatment regimen to replace the current antiretroviral regimen for adults with HIV who are virologically suppressed,” according to the press release.
“Janssen and ViiV are exploring the future possibility of an ultra–long-acting version of Cabenuva, which could reduce the frequency of injections even further, according to the press release.
Access may improve, but barriers persist
“Despite advances in HIV care, many barriers remain, particularly for the most vulnerable populations,” Lina Rosengren-Hovee, MD, of the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill, said in an interview.
“Care engagement has improved with the use of bridge counselors, rapid ART [antiretroviral therapy] initiation policies, and contact tracing,” she said. “Similarly, increasing access to multiple modalities of HIV treatment is critical to increase engagement in care.
“For patients, removing the oral lead-in primarily reduces the number of clinical visits to start injectable ART,” Dr. Rosengren-Hovee added. “It may also remove adherence barriers for patients who have difficulty taking a daily oral medication.”
But Dr. Rosengren-Hovee (who has no financial connection to the manufacturers) pointed out that access to Cabenuva may not be seamless. “Unless the medication is stocked in clinics, patients are not likely to receive their first injection during the initial visit. Labs are also required prior to initiation to ensure there is no contraindication to the medication, such as viral resistance to one of its components. Cost and insurance coverage are also likely to remain major obstacles.”
Dr. Rosengren-Hovee has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Initiating treatment may become easier for adults living with HIV. a combination injectable, without a lead-in period of oral tablets, according to a press release from Janssen Pharmaceuticals.
Cabenuva combines rilpivirine (Janssen) and cabotegravir (ViiV Healthcare). The change offers patients and clinicians an option for a streamlined entry to treatment without the burden of daily pill taking, according to the release.
Cabenuva injections may be given as few as six times a year to manage HIV, according to Janssen. HIV patients with viral suppression previously had to complete an oral treatment regimen before starting monthly or bimonthly injections.
The injectable combination of cabotegravir, an HIV-1 integrase strand transfer inhibitor, and rilpivirine, an HIV-1 nonnucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitor, is currently indicated as a complete treatment regimen to replace the current antiretroviral regimen for adults with HIV who are virologically suppressed,” according to the press release.
“Janssen and ViiV are exploring the future possibility of an ultra–long-acting version of Cabenuva, which could reduce the frequency of injections even further, according to the press release.
Access may improve, but barriers persist
“Despite advances in HIV care, many barriers remain, particularly for the most vulnerable populations,” Lina Rosengren-Hovee, MD, of the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill, said in an interview.
“Care engagement has improved with the use of bridge counselors, rapid ART [antiretroviral therapy] initiation policies, and contact tracing,” she said. “Similarly, increasing access to multiple modalities of HIV treatment is critical to increase engagement in care.
“For patients, removing the oral lead-in primarily reduces the number of clinical visits to start injectable ART,” Dr. Rosengren-Hovee added. “It may also remove adherence barriers for patients who have difficulty taking a daily oral medication.”
But Dr. Rosengren-Hovee (who has no financial connection to the manufacturers) pointed out that access to Cabenuva may not be seamless. “Unless the medication is stocked in clinics, patients are not likely to receive their first injection during the initial visit. Labs are also required prior to initiation to ensure there is no contraindication to the medication, such as viral resistance to one of its components. Cost and insurance coverage are also likely to remain major obstacles.”
Dr. Rosengren-Hovee has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Initiating treatment may become easier for adults living with HIV. a combination injectable, without a lead-in period of oral tablets, according to a press release from Janssen Pharmaceuticals.
Cabenuva combines rilpivirine (Janssen) and cabotegravir (ViiV Healthcare). The change offers patients and clinicians an option for a streamlined entry to treatment without the burden of daily pill taking, according to the release.
Cabenuva injections may be given as few as six times a year to manage HIV, according to Janssen. HIV patients with viral suppression previously had to complete an oral treatment regimen before starting monthly or bimonthly injections.
The injectable combination of cabotegravir, an HIV-1 integrase strand transfer inhibitor, and rilpivirine, an HIV-1 nonnucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitor, is currently indicated as a complete treatment regimen to replace the current antiretroviral regimen for adults with HIV who are virologically suppressed,” according to the press release.
“Janssen and ViiV are exploring the future possibility of an ultra–long-acting version of Cabenuva, which could reduce the frequency of injections even further, according to the press release.
Access may improve, but barriers persist
“Despite advances in HIV care, many barriers remain, particularly for the most vulnerable populations,” Lina Rosengren-Hovee, MD, of the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill, said in an interview.
“Care engagement has improved with the use of bridge counselors, rapid ART [antiretroviral therapy] initiation policies, and contact tracing,” she said. “Similarly, increasing access to multiple modalities of HIV treatment is critical to increase engagement in care.
“For patients, removing the oral lead-in primarily reduces the number of clinical visits to start injectable ART,” Dr. Rosengren-Hovee added. “It may also remove adherence barriers for patients who have difficulty taking a daily oral medication.”
But Dr. Rosengren-Hovee (who has no financial connection to the manufacturers) pointed out that access to Cabenuva may not be seamless. “Unless the medication is stocked in clinics, patients are not likely to receive their first injection during the initial visit. Labs are also required prior to initiation to ensure there is no contraindication to the medication, such as viral resistance to one of its components. Cost and insurance coverage are also likely to remain major obstacles.”
Dr. Rosengren-Hovee has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Psychedelics’ interaction with psych meds: More questions than answers
“Despite prolific psychedelic research and public interest, I was surprised to see little clinical research on how psilocybin and common psychiatric treatments interact,” study investigator Aryan Sarparast, MD, department of psychiatry, Oregon Health and Science University, Portland, told this news organization.
The review was published online March 7, 2022, in Psychopharmacology.
Need for RCTs
The Food and Drug Administration recently granted breakthrough therapy designation to psilocybin-assisted psychotherapy for major depression and treatment-resistant depression and to MDMA-assisted psychotherapy for PTSD.
The investigators assessed the volume of available research on interactions between psychedelics and traditional psychiatric medications, such as antidepressants.
They found 40 studies dating back to 1958, including 26 randomized controlled trials, 11 case reports, and 3 epidemiologic studies.
Only one randomized clinical trial evaluated the interaction between psilocybin and the most common psychiatric treatment, SSRIs, said Dr. Sarparast.
However, this study is “reassuring and overlaps with our hypothesis that there is a low risk of psilocybin and most psychiatric drugs causing harm when combined,” he noted.
Yet all of the clinical trials exclusively included young healthy adults, who were often recruited from university campuses. “We don’t have data on what happens when a depressed person on an SSRI takes psilocybin,” said Dr. Sarparast.
He added that he is concerned that the lack of evidence on drug-drug interactions will lead some providers to require patients to be tapered off existing traditional psychiatric medications before initiation of psilocybin therapy.
This may force vulnerable patients to choose between their existing therapy and psilocybin.
In addition, patients who opt for the “DIY method” of tapering risk mental health relapse and medication withdrawal effects. “That’s a very, very tough place to be,” Dr. Sarparast said.
Ideally, Dr. Sarparast would like to see a study in which depressed patients who have been receiving long-term antidepressant treatment are randomly assigned to received low, medium, and high doses of psilocybin. “This would clarify a lot of question marks.”
Evidence gap
In a comment, Roger McIntyre, MD, professor of psychiatry and pharmacology, University of Toronto, said: “The point in this article is very well taken. Indeed, more research is needed” on potential interactions between psychedelics and traditional psychiatric medications.
“Before we embark on completing research and development for psychedelics – or, for that matter, any psychoactive substance – we should endeavor to identify what the potential safety and toxicity concerns are when they are coprescribed with other prescribed medications, over-the-counter medications, and other substances (e.g., marijuana) that people take,” Dr. McIntyre said.
A case in point – a 2017 study conducted by McIntyre and colleagues revealed “significant drug-drug interactions with cannabis, which never receives that much attention.”
Also weighing in, Albert Garcia-Romeu, PhD, assistant professor of psychiatry and behavioral sciences, Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore, confirmed that there is “an evidence gap” on psilocybin’s and other psychedelic drugs’ interactions with other medications.
“This has not been formally studied for a number of reasons, but mainly because psilocybin has primarily been considered a drug of abuse. Psilocybin has only recently started to be looked at as a potential medication, and as such, research on drug-drug interactions is still limited, but growing,” Dr. Garcia-Romeu told this news organization.
He noted that studies are underway to better understand potential interactions between psilocybin and other medications.
“This will allow us to better understand how psilocybin should be used medically and what types of interactions could occur with other drugs or medications,” Dr. Garcia-Romeu added.
The study had no specific funding. Dr. Sarparast, Dr. McIntyre, and Dr. Garcia-Romeu reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
“Despite prolific psychedelic research and public interest, I was surprised to see little clinical research on how psilocybin and common psychiatric treatments interact,” study investigator Aryan Sarparast, MD, department of psychiatry, Oregon Health and Science University, Portland, told this news organization.
The review was published online March 7, 2022, in Psychopharmacology.
Need for RCTs
The Food and Drug Administration recently granted breakthrough therapy designation to psilocybin-assisted psychotherapy for major depression and treatment-resistant depression and to MDMA-assisted psychotherapy for PTSD.
The investigators assessed the volume of available research on interactions between psychedelics and traditional psychiatric medications, such as antidepressants.
They found 40 studies dating back to 1958, including 26 randomized controlled trials, 11 case reports, and 3 epidemiologic studies.
Only one randomized clinical trial evaluated the interaction between psilocybin and the most common psychiatric treatment, SSRIs, said Dr. Sarparast.
However, this study is “reassuring and overlaps with our hypothesis that there is a low risk of psilocybin and most psychiatric drugs causing harm when combined,” he noted.
Yet all of the clinical trials exclusively included young healthy adults, who were often recruited from university campuses. “We don’t have data on what happens when a depressed person on an SSRI takes psilocybin,” said Dr. Sarparast.
He added that he is concerned that the lack of evidence on drug-drug interactions will lead some providers to require patients to be tapered off existing traditional psychiatric medications before initiation of psilocybin therapy.
This may force vulnerable patients to choose between their existing therapy and psilocybin.
In addition, patients who opt for the “DIY method” of tapering risk mental health relapse and medication withdrawal effects. “That’s a very, very tough place to be,” Dr. Sarparast said.
Ideally, Dr. Sarparast would like to see a study in which depressed patients who have been receiving long-term antidepressant treatment are randomly assigned to received low, medium, and high doses of psilocybin. “This would clarify a lot of question marks.”
Evidence gap
In a comment, Roger McIntyre, MD, professor of psychiatry and pharmacology, University of Toronto, said: “The point in this article is very well taken. Indeed, more research is needed” on potential interactions between psychedelics and traditional psychiatric medications.
“Before we embark on completing research and development for psychedelics – or, for that matter, any psychoactive substance – we should endeavor to identify what the potential safety and toxicity concerns are when they are coprescribed with other prescribed medications, over-the-counter medications, and other substances (e.g., marijuana) that people take,” Dr. McIntyre said.
A case in point – a 2017 study conducted by McIntyre and colleagues revealed “significant drug-drug interactions with cannabis, which never receives that much attention.”
Also weighing in, Albert Garcia-Romeu, PhD, assistant professor of psychiatry and behavioral sciences, Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore, confirmed that there is “an evidence gap” on psilocybin’s and other psychedelic drugs’ interactions with other medications.
“This has not been formally studied for a number of reasons, but mainly because psilocybin has primarily been considered a drug of abuse. Psilocybin has only recently started to be looked at as a potential medication, and as such, research on drug-drug interactions is still limited, but growing,” Dr. Garcia-Romeu told this news organization.
He noted that studies are underway to better understand potential interactions between psilocybin and other medications.
“This will allow us to better understand how psilocybin should be used medically and what types of interactions could occur with other drugs or medications,” Dr. Garcia-Romeu added.
The study had no specific funding. Dr. Sarparast, Dr. McIntyre, and Dr. Garcia-Romeu reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
“Despite prolific psychedelic research and public interest, I was surprised to see little clinical research on how psilocybin and common psychiatric treatments interact,” study investigator Aryan Sarparast, MD, department of psychiatry, Oregon Health and Science University, Portland, told this news organization.
The review was published online March 7, 2022, in Psychopharmacology.
Need for RCTs
The Food and Drug Administration recently granted breakthrough therapy designation to psilocybin-assisted psychotherapy for major depression and treatment-resistant depression and to MDMA-assisted psychotherapy for PTSD.
The investigators assessed the volume of available research on interactions between psychedelics and traditional psychiatric medications, such as antidepressants.
They found 40 studies dating back to 1958, including 26 randomized controlled trials, 11 case reports, and 3 epidemiologic studies.
Only one randomized clinical trial evaluated the interaction between psilocybin and the most common psychiatric treatment, SSRIs, said Dr. Sarparast.
However, this study is “reassuring and overlaps with our hypothesis that there is a low risk of psilocybin and most psychiatric drugs causing harm when combined,” he noted.
Yet all of the clinical trials exclusively included young healthy adults, who were often recruited from university campuses. “We don’t have data on what happens when a depressed person on an SSRI takes psilocybin,” said Dr. Sarparast.
He added that he is concerned that the lack of evidence on drug-drug interactions will lead some providers to require patients to be tapered off existing traditional psychiatric medications before initiation of psilocybin therapy.
This may force vulnerable patients to choose between their existing therapy and psilocybin.
In addition, patients who opt for the “DIY method” of tapering risk mental health relapse and medication withdrawal effects. “That’s a very, very tough place to be,” Dr. Sarparast said.
Ideally, Dr. Sarparast would like to see a study in which depressed patients who have been receiving long-term antidepressant treatment are randomly assigned to received low, medium, and high doses of psilocybin. “This would clarify a lot of question marks.”
Evidence gap
In a comment, Roger McIntyre, MD, professor of psychiatry and pharmacology, University of Toronto, said: “The point in this article is very well taken. Indeed, more research is needed” on potential interactions between psychedelics and traditional psychiatric medications.
“Before we embark on completing research and development for psychedelics – or, for that matter, any psychoactive substance – we should endeavor to identify what the potential safety and toxicity concerns are when they are coprescribed with other prescribed medications, over-the-counter medications, and other substances (e.g., marijuana) that people take,” Dr. McIntyre said.
A case in point – a 2017 study conducted by McIntyre and colleagues revealed “significant drug-drug interactions with cannabis, which never receives that much attention.”
Also weighing in, Albert Garcia-Romeu, PhD, assistant professor of psychiatry and behavioral sciences, Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore, confirmed that there is “an evidence gap” on psilocybin’s and other psychedelic drugs’ interactions with other medications.
“This has not been formally studied for a number of reasons, but mainly because psilocybin has primarily been considered a drug of abuse. Psilocybin has only recently started to be looked at as a potential medication, and as such, research on drug-drug interactions is still limited, but growing,” Dr. Garcia-Romeu told this news organization.
He noted that studies are underway to better understand potential interactions between psilocybin and other medications.
“This will allow us to better understand how psilocybin should be used medically and what types of interactions could occur with other drugs or medications,” Dr. Garcia-Romeu added.
The study had no specific funding. Dr. Sarparast, Dr. McIntyre, and Dr. Garcia-Romeu reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM PSYCHOPHARMACOLOGY
Going digital won’t fully fix prior authorizations, say medical groups
That was the message from groups representing physicians, medical practices, and hospitals in response to a request for input from the Office of the National Coordinator for Health Information Technology (ONC). In January, ONC requested public feedback on how making the process for insurer approvals digital can “ease the burden of prior authorization tasks on patients, providers, and payers.”
According to a study conducted by America’s Health Insurance Plans, 71% of providers who implemented electronic prior authorization experienced “faster time to patient care.” The organization, which represents many of the nation’s health insurers, also reported that electronic prior authorization reduced the time it took to receive a decision by a health plan by 69%.
In its response to ONC, the American Association of Family Physicians (AAFP) called out prior authorization as a “leading cause of physician burden” and wrote that the organization is “strongly supportive of efforts to reform and streamline the prior authorization process.”
AAFP, which represents 127,600 family physicians, residents, and students, cited in its comments an AMA survey in which 88% of physicians said that prior authorization “generates high or extremely high administrative burden” for their practices. Practices are responsible for an average of 41 prior authorizations per physician each week, which can take almost 2 days of a physician’s time each week, according to the AAFP.
Delayed care, increased confusion, reduced treatment adherence, and even discontinuation of treatment are some of the harms prior authorization causes patients, wrote AAFP board chair Ada D. Stewart, MD.
Electronic prior authorization is “just one step in addressing the flaws of utilization management practices, and comprehensive reform is needed to reduce the volume of prior authorizations and ensure patients’ timely access to care,” wrote Dr. Stewart.
AHA: Most common prior auth means are phones, fax
The American Hospital Association (AHA) highlighted the variety of prior authorization requests from different payers, writing, “While some plans accept electronic means, the most common method remains using fax machines and contacting call centers, with regular hold times of 20 to 30 minutes.”
The AHA’s Senior Vice President Ashley Thompson wrote that the various prior authorization processes required by payers take up staff time and increase the chance of data entry errors.
To fix this, the AHA calls for an “end-to-end automated prior authorization process that integrates with clinicians’ EHR workflow.” According to the AHA, this approach can help physicians have access to the required prior authorization information during treatment planning.
In response to the federal agency’s question about the functional capabilities for certified health IT modules to facilitate electronic prior authorization, the AAFP wrote that the standards should include communicating to providers the expected timeline from a payer on a response, the ability to access payers’ reasoning for denials, and the creation of a process for appealing decisions.
The ONC also asked for input on the use of three fast health care interoperability resources (FHIR)–based Da Vinci implementation guides in electronic prior authorization.
Developed by the Da Vinci Project in coordination with the HL7 Clinical Decision Support Workgroup, the FHIR-based implementation guides create a mechanism for reducing the burden on provider organizations and simplifying processes by establishing electronic versions of administrative and clinical requirements that are a part of providers’ workflow.
In its response, the AHA requested that prior authorization solutions “be fully developed and tested prior to wide scale industry rollout.”
The AAFP largely agreed with the AHA in its response, writing, “Only standards and [implementation guides] that have been proven effective and adoptable in real world testing should be candidates for mandatory certification and utilization, including the Da Vinci standards.”
The Medical Group Management Association (MGMA), which represents more than 60,000 medical practice administrators, executives, and leaders, supports the idea that electronic prior authorization “has the potential to decrease administrative burden through automation but only if implemented properly.”
In its comments, the MGMA called for broader reform of prior authorization. One way to accomplish that goal is by aligning electronic prior authorization standards “with payment and quality reporting programs, as well as care delivery models, to minimize burden and overhead costs.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
That was the message from groups representing physicians, medical practices, and hospitals in response to a request for input from the Office of the National Coordinator for Health Information Technology (ONC). In January, ONC requested public feedback on how making the process for insurer approvals digital can “ease the burden of prior authorization tasks on patients, providers, and payers.”
According to a study conducted by America’s Health Insurance Plans, 71% of providers who implemented electronic prior authorization experienced “faster time to patient care.” The organization, which represents many of the nation’s health insurers, also reported that electronic prior authorization reduced the time it took to receive a decision by a health plan by 69%.
In its response to ONC, the American Association of Family Physicians (AAFP) called out prior authorization as a “leading cause of physician burden” and wrote that the organization is “strongly supportive of efforts to reform and streamline the prior authorization process.”
AAFP, which represents 127,600 family physicians, residents, and students, cited in its comments an AMA survey in which 88% of physicians said that prior authorization “generates high or extremely high administrative burden” for their practices. Practices are responsible for an average of 41 prior authorizations per physician each week, which can take almost 2 days of a physician’s time each week, according to the AAFP.
Delayed care, increased confusion, reduced treatment adherence, and even discontinuation of treatment are some of the harms prior authorization causes patients, wrote AAFP board chair Ada D. Stewart, MD.
Electronic prior authorization is “just one step in addressing the flaws of utilization management practices, and comprehensive reform is needed to reduce the volume of prior authorizations and ensure patients’ timely access to care,” wrote Dr. Stewart.
AHA: Most common prior auth means are phones, fax
The American Hospital Association (AHA) highlighted the variety of prior authorization requests from different payers, writing, “While some plans accept electronic means, the most common method remains using fax machines and contacting call centers, with regular hold times of 20 to 30 minutes.”
The AHA’s Senior Vice President Ashley Thompson wrote that the various prior authorization processes required by payers take up staff time and increase the chance of data entry errors.
To fix this, the AHA calls for an “end-to-end automated prior authorization process that integrates with clinicians’ EHR workflow.” According to the AHA, this approach can help physicians have access to the required prior authorization information during treatment planning.
In response to the federal agency’s question about the functional capabilities for certified health IT modules to facilitate electronic prior authorization, the AAFP wrote that the standards should include communicating to providers the expected timeline from a payer on a response, the ability to access payers’ reasoning for denials, and the creation of a process for appealing decisions.
The ONC also asked for input on the use of three fast health care interoperability resources (FHIR)–based Da Vinci implementation guides in electronic prior authorization.
Developed by the Da Vinci Project in coordination with the HL7 Clinical Decision Support Workgroup, the FHIR-based implementation guides create a mechanism for reducing the burden on provider organizations and simplifying processes by establishing electronic versions of administrative and clinical requirements that are a part of providers’ workflow.
In its response, the AHA requested that prior authorization solutions “be fully developed and tested prior to wide scale industry rollout.”
The AAFP largely agreed with the AHA in its response, writing, “Only standards and [implementation guides] that have been proven effective and adoptable in real world testing should be candidates for mandatory certification and utilization, including the Da Vinci standards.”
The Medical Group Management Association (MGMA), which represents more than 60,000 medical practice administrators, executives, and leaders, supports the idea that electronic prior authorization “has the potential to decrease administrative burden through automation but only if implemented properly.”
In its comments, the MGMA called for broader reform of prior authorization. One way to accomplish that goal is by aligning electronic prior authorization standards “with payment and quality reporting programs, as well as care delivery models, to minimize burden and overhead costs.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
That was the message from groups representing physicians, medical practices, and hospitals in response to a request for input from the Office of the National Coordinator for Health Information Technology (ONC). In January, ONC requested public feedback on how making the process for insurer approvals digital can “ease the burden of prior authorization tasks on patients, providers, and payers.”
According to a study conducted by America’s Health Insurance Plans, 71% of providers who implemented electronic prior authorization experienced “faster time to patient care.” The organization, which represents many of the nation’s health insurers, also reported that electronic prior authorization reduced the time it took to receive a decision by a health plan by 69%.
In its response to ONC, the American Association of Family Physicians (AAFP) called out prior authorization as a “leading cause of physician burden” and wrote that the organization is “strongly supportive of efforts to reform and streamline the prior authorization process.”
AAFP, which represents 127,600 family physicians, residents, and students, cited in its comments an AMA survey in which 88% of physicians said that prior authorization “generates high or extremely high administrative burden” for their practices. Practices are responsible for an average of 41 prior authorizations per physician each week, which can take almost 2 days of a physician’s time each week, according to the AAFP.
Delayed care, increased confusion, reduced treatment adherence, and even discontinuation of treatment are some of the harms prior authorization causes patients, wrote AAFP board chair Ada D. Stewart, MD.
Electronic prior authorization is “just one step in addressing the flaws of utilization management practices, and comprehensive reform is needed to reduce the volume of prior authorizations and ensure patients’ timely access to care,” wrote Dr. Stewart.
AHA: Most common prior auth means are phones, fax
The American Hospital Association (AHA) highlighted the variety of prior authorization requests from different payers, writing, “While some plans accept electronic means, the most common method remains using fax machines and contacting call centers, with regular hold times of 20 to 30 minutes.”
The AHA’s Senior Vice President Ashley Thompson wrote that the various prior authorization processes required by payers take up staff time and increase the chance of data entry errors.
To fix this, the AHA calls for an “end-to-end automated prior authorization process that integrates with clinicians’ EHR workflow.” According to the AHA, this approach can help physicians have access to the required prior authorization information during treatment planning.
In response to the federal agency’s question about the functional capabilities for certified health IT modules to facilitate electronic prior authorization, the AAFP wrote that the standards should include communicating to providers the expected timeline from a payer on a response, the ability to access payers’ reasoning for denials, and the creation of a process for appealing decisions.
The ONC also asked for input on the use of three fast health care interoperability resources (FHIR)–based Da Vinci implementation guides in electronic prior authorization.
Developed by the Da Vinci Project in coordination with the HL7 Clinical Decision Support Workgroup, the FHIR-based implementation guides create a mechanism for reducing the burden on provider organizations and simplifying processes by establishing electronic versions of administrative and clinical requirements that are a part of providers’ workflow.
In its response, the AHA requested that prior authorization solutions “be fully developed and tested prior to wide scale industry rollout.”
The AAFP largely agreed with the AHA in its response, writing, “Only standards and [implementation guides] that have been proven effective and adoptable in real world testing should be candidates for mandatory certification and utilization, including the Da Vinci standards.”
The Medical Group Management Association (MGMA), which represents more than 60,000 medical practice administrators, executives, and leaders, supports the idea that electronic prior authorization “has the potential to decrease administrative burden through automation but only if implemented properly.”
In its comments, the MGMA called for broader reform of prior authorization. One way to accomplish that goal is by aligning electronic prior authorization standards “with payment and quality reporting programs, as well as care delivery models, to minimize burden and overhead costs.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Courtesy: It’s not so common anymore
Earlier this month one of our dogs needed surgery. Early one morning I dropped her off at the veterinarian’s office.
About 10 minutes after leaving, they called and asked me to come back and get her. The vet had called in sick, so all her surgeries for the day had to be rescheduled.
It’s a pain in the rear, but what can you do? It happens to the best of us. My staff has had their share of times where they had to frantically call and reschedule patients when I was too sick to work.
So I drove back and waited in line. Most people were understanding, but some less so. The lady in front of me was demanding her dog’s surgery (which hadn’t happened yet) be free due to her being inconvenienced. A staff member at another desk was dealing with an angry man who was demanding the veterinarian’s home phone number.
When I got up to the front I picked up my dog and rescheduled the surgery for 2 weeks later. The young lady at the desk handed me a reminder card and said “Thank you for not yelling at me.”
How sad is that? Is this what our society has come to, where people feel obliged to thank you for not being an ass?
Common courtesy should be the rule rather than the exception, right? What’s wrong with politeness?
Yeah, going back to have to get my dog and reschedule her surgery is an inconvenience, but that’s about it. Certainly not something to get worked up over, or to scream at another person who’s just doing their job. Getting sick is part of life. It’s happened to me, it’s happened to you, and on this day it happened to our veterinarian.
Although we all went through it together, for some it’s removed the thin veneer of civilization, leaving them angry, bitter, and hostile over things that are beyond the control of mortals.
Whatever happened to the Golden Rule? It takes less effort to be nice than nasty, and it’s definitely better for your blood pressure.
I really don’t understand this. What’s to be gained by going through the world angry at things you can’t control? Especially when they’re so minor, like having to reschedule a veterinarian’s appointment.
It just ain’t worth it to be like that. For you, or the innocent person you’re abusing.
Dr. Block has a solo neurology practice in Scottsdale, Ariz.
Earlier this month one of our dogs needed surgery. Early one morning I dropped her off at the veterinarian’s office.
About 10 minutes after leaving, they called and asked me to come back and get her. The vet had called in sick, so all her surgeries for the day had to be rescheduled.
It’s a pain in the rear, but what can you do? It happens to the best of us. My staff has had their share of times where they had to frantically call and reschedule patients when I was too sick to work.
So I drove back and waited in line. Most people were understanding, but some less so. The lady in front of me was demanding her dog’s surgery (which hadn’t happened yet) be free due to her being inconvenienced. A staff member at another desk was dealing with an angry man who was demanding the veterinarian’s home phone number.
When I got up to the front I picked up my dog and rescheduled the surgery for 2 weeks later. The young lady at the desk handed me a reminder card and said “Thank you for not yelling at me.”
How sad is that? Is this what our society has come to, where people feel obliged to thank you for not being an ass?
Common courtesy should be the rule rather than the exception, right? What’s wrong with politeness?
Yeah, going back to have to get my dog and reschedule her surgery is an inconvenience, but that’s about it. Certainly not something to get worked up over, or to scream at another person who’s just doing their job. Getting sick is part of life. It’s happened to me, it’s happened to you, and on this day it happened to our veterinarian.
Although we all went through it together, for some it’s removed the thin veneer of civilization, leaving them angry, bitter, and hostile over things that are beyond the control of mortals.
Whatever happened to the Golden Rule? It takes less effort to be nice than nasty, and it’s definitely better for your blood pressure.
I really don’t understand this. What’s to be gained by going through the world angry at things you can’t control? Especially when they’re so minor, like having to reschedule a veterinarian’s appointment.
It just ain’t worth it to be like that. For you, or the innocent person you’re abusing.
Dr. Block has a solo neurology practice in Scottsdale, Ariz.
Earlier this month one of our dogs needed surgery. Early one morning I dropped her off at the veterinarian’s office.
About 10 minutes after leaving, they called and asked me to come back and get her. The vet had called in sick, so all her surgeries for the day had to be rescheduled.
It’s a pain in the rear, but what can you do? It happens to the best of us. My staff has had their share of times where they had to frantically call and reschedule patients when I was too sick to work.
So I drove back and waited in line. Most people were understanding, but some less so. The lady in front of me was demanding her dog’s surgery (which hadn’t happened yet) be free due to her being inconvenienced. A staff member at another desk was dealing with an angry man who was demanding the veterinarian’s home phone number.
When I got up to the front I picked up my dog and rescheduled the surgery for 2 weeks later. The young lady at the desk handed me a reminder card and said “Thank you for not yelling at me.”
How sad is that? Is this what our society has come to, where people feel obliged to thank you for not being an ass?
Common courtesy should be the rule rather than the exception, right? What’s wrong with politeness?
Yeah, going back to have to get my dog and reschedule her surgery is an inconvenience, but that’s about it. Certainly not something to get worked up over, or to scream at another person who’s just doing their job. Getting sick is part of life. It’s happened to me, it’s happened to you, and on this day it happened to our veterinarian.
Although we all went through it together, for some it’s removed the thin veneer of civilization, leaving them angry, bitter, and hostile over things that are beyond the control of mortals.
Whatever happened to the Golden Rule? It takes less effort to be nice than nasty, and it’s definitely better for your blood pressure.
I really don’t understand this. What’s to be gained by going through the world angry at things you can’t control? Especially when they’re so minor, like having to reschedule a veterinarian’s appointment.
It just ain’t worth it to be like that. For you, or the innocent person you’re abusing.
Dr. Block has a solo neurology practice in Scottsdale, Ariz.
ADHD link to prenatal opioid exposure shifts with other substances
Children prenatally exposed to opioids alone have an increased risk of attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD), but interactions between opioids and both cannabis use and alcohol use were linked to varying levels of ADHD risk as well, according to findings published March 11 in JAMA Network Open.
While many prenatal exposure studies examine associations with one substance, the results of this case-control study “suggest that it is important to consider prenatal exposure to multiple substances and the interactions between these substances when counseling women regarding substance use during pregnancy,” wrote Henri M. Garrison-Desany of the Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore, and colleagues.
Using data from children in the prospective Boston Birth Cohort between 1998 and 2019, the researchers did a secondary analysis on the 3,138 children (50.4% of whom were male) with at least 2 years of follow-up, excluding children from multiple-gestation pregnancies, in vitro fertilization pregnancies, and deliveries involving major maternal trauma or major chromosomal anomalies. Mothers answered a questionnaire within 24-72 hours of delivery regarding their demographics, substance use, pregnancy history, and health status. Among the mothers, 58.6% were Black, 22.3% were Hispanic, 7.2% were White, 1.5% were Asian, and 10.4% were other races/ethnicities.
The children’s electronic medical records were used to identify those with ADHD diagnoses. The researchers did not assess prescription opioid exposure during pregnancy, but they based opioid exposure on mothers’ reports of recreationally using heroin or oxycodone, mothers’ reports of receiving methadone treatment, or a newborn diagnosis of neonatal abstinence syndrome or neonatal opioid withdrawal syndrome.
Just under a quarter of the women (24.2%) reported using at least one substance during pregnancy. After tobacco smoking (18.5%), the next most reported substances were alcohol (8.1%), cannabis (3.9%), and opioids (1.9%). With a median 12 years of follow-up, 15.5% of the children had been diagnosed with ADHD, most of whom (71.6%) were male.
Before considering interaction of different substances, children exposed to opioids had a little over twice the risk of ADHD (hazard ratio [HR], 2.19) compared to those with no prenatal substance exposure. Although neither cannabis nor alcohol was independently associated with ADHD, smoking had a 40% increased risk, and researchers found a 21% increase in risk of ADHD with each additional substance mothers used during pregnancy. The researchers had adjusted these findings for maternal age, race/ethnicity, marital status, educational level, annual household income, parity, number of perinatal visits, and general stress during pregnancy, based on a structured interview.
When the researchers considered all the substances together, opioid exposure increased risk of ADHD by 60% (HR, 1.6), opioids with cannabis increased risk by 42%, opioids with alcohol increased risk by 15%, and opioids with smoking increased risk by 17%.
”Our findings suggest opioids may interact with other substances (including cannabis), which may be particularly deleterious,” the researchers reported. “It is not clear whether this interaction is owing to biological or environmental factors, such as whether individuals with illicit polysubstance use are more likely to use more substances or whether they have other characteristics that may impact child development.”
The authors noted that cannabis exposure has been linked to other neurodevelopmental outcomes, including reduced executive and motor function in infants. ”Notably, although we did not find a significant independent association between cannabis exposure and ADHD, children exposed to both cannabis and opioids had a 23% greater risk than expected from either exposure individually,” they reported.
The researchers suggest that their findings provide data for considering harm reduction approaches that reduce use of any single substance during pregnancy. “Focusing on the most obviously harmful exposures may be a useful way to reduce the risk of ADHD,” they wrote. “Further work is needed to directly investigate this hypothesis and examine whether reduction in the use of any substance among those with polysubstance use could be acceptable compared with abstinence.”
In an invited commentary, Angela Lupattelli, PhD, and Nhung T. H. Trinh, PhD, both of the department of pharmacy at the University of Oslo, noted the methodological challenges of assessing exposures and associations from multiple different substances during pregnancy.
“First, how can we disentangle the consequences of individual and/or combined substance exposures during pregnancy from the underlying risks?” they asked. In addition to differences in baseline characteristic between those who use opioids or cannabis, Dr. Lupattelli and Dr. Trinh noted that other important unmeasured factors, such as genetics and family environment, may confound the effect size estimates for ADHD.
They also noted the need to consider intensity, dose, duration, and timing of substance use during pregnancy.
“Understanding the longer-term safety of substance use during pregnancy is paramount to inform prevention policy and shape counseling strategies. Observational studies, despite their limitations, are a necessary piece of the puzzle,” they wrote. “However, the study findings should be interpreted with caution, as the use of advanced analytical methods cannot overcome the unavailability of some important confounding factors and exposure information.”
The research was funded by the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services and the National Institutes of Health. The authors had no industry-related disclosures.
Children prenatally exposed to opioids alone have an increased risk of attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD), but interactions between opioids and both cannabis use and alcohol use were linked to varying levels of ADHD risk as well, according to findings published March 11 in JAMA Network Open.
While many prenatal exposure studies examine associations with one substance, the results of this case-control study “suggest that it is important to consider prenatal exposure to multiple substances and the interactions between these substances when counseling women regarding substance use during pregnancy,” wrote Henri M. Garrison-Desany of the Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore, and colleagues.
Using data from children in the prospective Boston Birth Cohort between 1998 and 2019, the researchers did a secondary analysis on the 3,138 children (50.4% of whom were male) with at least 2 years of follow-up, excluding children from multiple-gestation pregnancies, in vitro fertilization pregnancies, and deliveries involving major maternal trauma or major chromosomal anomalies. Mothers answered a questionnaire within 24-72 hours of delivery regarding their demographics, substance use, pregnancy history, and health status. Among the mothers, 58.6% were Black, 22.3% were Hispanic, 7.2% were White, 1.5% were Asian, and 10.4% were other races/ethnicities.
The children’s electronic medical records were used to identify those with ADHD diagnoses. The researchers did not assess prescription opioid exposure during pregnancy, but they based opioid exposure on mothers’ reports of recreationally using heroin or oxycodone, mothers’ reports of receiving methadone treatment, or a newborn diagnosis of neonatal abstinence syndrome or neonatal opioid withdrawal syndrome.
Just under a quarter of the women (24.2%) reported using at least one substance during pregnancy. After tobacco smoking (18.5%), the next most reported substances were alcohol (8.1%), cannabis (3.9%), and opioids (1.9%). With a median 12 years of follow-up, 15.5% of the children had been diagnosed with ADHD, most of whom (71.6%) were male.
Before considering interaction of different substances, children exposed to opioids had a little over twice the risk of ADHD (hazard ratio [HR], 2.19) compared to those with no prenatal substance exposure. Although neither cannabis nor alcohol was independently associated with ADHD, smoking had a 40% increased risk, and researchers found a 21% increase in risk of ADHD with each additional substance mothers used during pregnancy. The researchers had adjusted these findings for maternal age, race/ethnicity, marital status, educational level, annual household income, parity, number of perinatal visits, and general stress during pregnancy, based on a structured interview.
When the researchers considered all the substances together, opioid exposure increased risk of ADHD by 60% (HR, 1.6), opioids with cannabis increased risk by 42%, opioids with alcohol increased risk by 15%, and opioids with smoking increased risk by 17%.
”Our findings suggest opioids may interact with other substances (including cannabis), which may be particularly deleterious,” the researchers reported. “It is not clear whether this interaction is owing to biological or environmental factors, such as whether individuals with illicit polysubstance use are more likely to use more substances or whether they have other characteristics that may impact child development.”
The authors noted that cannabis exposure has been linked to other neurodevelopmental outcomes, including reduced executive and motor function in infants. ”Notably, although we did not find a significant independent association between cannabis exposure and ADHD, children exposed to both cannabis and opioids had a 23% greater risk than expected from either exposure individually,” they reported.
The researchers suggest that their findings provide data for considering harm reduction approaches that reduce use of any single substance during pregnancy. “Focusing on the most obviously harmful exposures may be a useful way to reduce the risk of ADHD,” they wrote. “Further work is needed to directly investigate this hypothesis and examine whether reduction in the use of any substance among those with polysubstance use could be acceptable compared with abstinence.”
In an invited commentary, Angela Lupattelli, PhD, and Nhung T. H. Trinh, PhD, both of the department of pharmacy at the University of Oslo, noted the methodological challenges of assessing exposures and associations from multiple different substances during pregnancy.
“First, how can we disentangle the consequences of individual and/or combined substance exposures during pregnancy from the underlying risks?” they asked. In addition to differences in baseline characteristic between those who use opioids or cannabis, Dr. Lupattelli and Dr. Trinh noted that other important unmeasured factors, such as genetics and family environment, may confound the effect size estimates for ADHD.
They also noted the need to consider intensity, dose, duration, and timing of substance use during pregnancy.
“Understanding the longer-term safety of substance use during pregnancy is paramount to inform prevention policy and shape counseling strategies. Observational studies, despite their limitations, are a necessary piece of the puzzle,” they wrote. “However, the study findings should be interpreted with caution, as the use of advanced analytical methods cannot overcome the unavailability of some important confounding factors and exposure information.”
The research was funded by the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services and the National Institutes of Health. The authors had no industry-related disclosures.
Children prenatally exposed to opioids alone have an increased risk of attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD), but interactions between opioids and both cannabis use and alcohol use were linked to varying levels of ADHD risk as well, according to findings published March 11 in JAMA Network Open.
While many prenatal exposure studies examine associations with one substance, the results of this case-control study “suggest that it is important to consider prenatal exposure to multiple substances and the interactions between these substances when counseling women regarding substance use during pregnancy,” wrote Henri M. Garrison-Desany of the Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore, and colleagues.
Using data from children in the prospective Boston Birth Cohort between 1998 and 2019, the researchers did a secondary analysis on the 3,138 children (50.4% of whom were male) with at least 2 years of follow-up, excluding children from multiple-gestation pregnancies, in vitro fertilization pregnancies, and deliveries involving major maternal trauma or major chromosomal anomalies. Mothers answered a questionnaire within 24-72 hours of delivery regarding their demographics, substance use, pregnancy history, and health status. Among the mothers, 58.6% were Black, 22.3% were Hispanic, 7.2% were White, 1.5% were Asian, and 10.4% were other races/ethnicities.
The children’s electronic medical records were used to identify those with ADHD diagnoses. The researchers did not assess prescription opioid exposure during pregnancy, but they based opioid exposure on mothers’ reports of recreationally using heroin or oxycodone, mothers’ reports of receiving methadone treatment, or a newborn diagnosis of neonatal abstinence syndrome or neonatal opioid withdrawal syndrome.
Just under a quarter of the women (24.2%) reported using at least one substance during pregnancy. After tobacco smoking (18.5%), the next most reported substances were alcohol (8.1%), cannabis (3.9%), and opioids (1.9%). With a median 12 years of follow-up, 15.5% of the children had been diagnosed with ADHD, most of whom (71.6%) were male.
Before considering interaction of different substances, children exposed to opioids had a little over twice the risk of ADHD (hazard ratio [HR], 2.19) compared to those with no prenatal substance exposure. Although neither cannabis nor alcohol was independently associated with ADHD, smoking had a 40% increased risk, and researchers found a 21% increase in risk of ADHD with each additional substance mothers used during pregnancy. The researchers had adjusted these findings for maternal age, race/ethnicity, marital status, educational level, annual household income, parity, number of perinatal visits, and general stress during pregnancy, based on a structured interview.
When the researchers considered all the substances together, opioid exposure increased risk of ADHD by 60% (HR, 1.6), opioids with cannabis increased risk by 42%, opioids with alcohol increased risk by 15%, and opioids with smoking increased risk by 17%.
”Our findings suggest opioids may interact with other substances (including cannabis), which may be particularly deleterious,” the researchers reported. “It is not clear whether this interaction is owing to biological or environmental factors, such as whether individuals with illicit polysubstance use are more likely to use more substances or whether they have other characteristics that may impact child development.”
The authors noted that cannabis exposure has been linked to other neurodevelopmental outcomes, including reduced executive and motor function in infants. ”Notably, although we did not find a significant independent association between cannabis exposure and ADHD, children exposed to both cannabis and opioids had a 23% greater risk than expected from either exposure individually,” they reported.
The researchers suggest that their findings provide data for considering harm reduction approaches that reduce use of any single substance during pregnancy. “Focusing on the most obviously harmful exposures may be a useful way to reduce the risk of ADHD,” they wrote. “Further work is needed to directly investigate this hypothesis and examine whether reduction in the use of any substance among those with polysubstance use could be acceptable compared with abstinence.”
In an invited commentary, Angela Lupattelli, PhD, and Nhung T. H. Trinh, PhD, both of the department of pharmacy at the University of Oslo, noted the methodological challenges of assessing exposures and associations from multiple different substances during pregnancy.
“First, how can we disentangle the consequences of individual and/or combined substance exposures during pregnancy from the underlying risks?” they asked. In addition to differences in baseline characteristic between those who use opioids or cannabis, Dr. Lupattelli and Dr. Trinh noted that other important unmeasured factors, such as genetics and family environment, may confound the effect size estimates for ADHD.
They also noted the need to consider intensity, dose, duration, and timing of substance use during pregnancy.
“Understanding the longer-term safety of substance use during pregnancy is paramount to inform prevention policy and shape counseling strategies. Observational studies, despite their limitations, are a necessary piece of the puzzle,” they wrote. “However, the study findings should be interpreted with caution, as the use of advanced analytical methods cannot overcome the unavailability of some important confounding factors and exposure information.”
The research was funded by the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services and the National Institutes of Health. The authors had no industry-related disclosures.
FROM JAMA NETWORK OPEN





