User login
‘Striking’ increase in childhood obesity during pandemic
Obesity rates among children jumped substantially in the first months of the COVID-19 pandemic, according to a study published online in Pediatrics. Experts worry the excess weight will be a continuing problem for these children.
“Across the board in the span of a year, there has been a 2% increase in obesity, which is really striking,” lead author Brian P. Jenssen, MD, said in an interview.
The prevalence of obesity in a large pediatric primary care network increased from 13.7% to 15.4%.
Preexisting disparities by race or ethnicity and socioeconomic status worsened, noted Dr. Jenssen, a primary care pediatrician affiliated with Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia (CHOP) and the University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia.
Dr. Jenssen and colleagues compared the average obesity rate from June to December 2020 with the rate from June to December 2019 among patients in the CHOP Care Network, which includes 29 urban, suburban, and semirural clinics in the Philadelphia region. In June 2020, the volume of patient visits “returned to near-normal” after a dramatic decline in March 2020, the study authors wrote.
The investigators examined body mass index at all visits for patients aged 2-17 years for whom height and weight were documented. Patients with a BMI at or above the 95th percentile were classified as obese. The analysis included approximately 169,000 visits in 2019 and about 145,000 in 2020.
The average age of the patients was 9.2 years, and 48.9% were girls. In all, 21.4% were non-Hispanic Black, and about 30% were publicly insured.
Increases in obesity rates were more pronounced among patients aged 5-9 years and among patients who were Hispanic/Latino, non-Hispanic Black, publicly insured, or from lower-income neighborhoods.
Whereas the obesity rate increased 1% for patients aged 13-17 years, the rate increased 2.6% for patients aged 5-9 years.
Nearly 25% of Hispanic/Latino or non-Hispanic Black patients seen during the pandemic were obese, compared with 11.3% of non-Hispanic White patients. Before the pandemic, differences by race or ethnicity had been about 10%-11%.
Limiting the analysis to preventive visits did not meaningfully change the results, wrote Dr. Jenssen and colleagues.
“Having any increase in the obesity rates is alarming,” said Sandra Hassink, MD, medical director for the American Academy of Pediatrics’ (AAP’s) Institute for Healthy Childhood Weight. “I think what we’re seeing is what we feared.”
Before the pandemic, children received appropriately portioned breakfasts and lunches at school, but during the pandemic, they had less access to such meals, the academy noted. Disruptions to schooling, easier access to unhealthy snacks, increased screen time, and economic issues such as parents’ job losses were further factors, Hassink said.
Tackling the weight gain
In December 2020, the AAP issued two clinical guidance documents to highlight the importance of addressing obesity during the pandemic. Recommendations included physician counseling of families about maintaining healthy nutrition, minimizing sedentary time, and getting enough sleep and physical activity, as well as the assessment of all patients for onset of obesity and the maintenance of obesity treatment for patients with obesity.
In addition to clinical assessments and guidance, Dr. Jenssen emphasized that a return to routines may be crucial. Prepandemic studies have shown that many children, especially those insured by Medicaid, gain more weight during the summer when they are out of school, he noted. Many of the same factors are present during the pandemic, he said.
“One solution, and probably the most important solution, is getting kids back in school,” Dr. Jenssen said. School disruptions also have affected children’s learning and mental health, but those effects may be harder to quantify than BMI, he said.
Dr. Jenssen suggests that parents do their best to model good routines and habits. For example, they might decide that they and their children will stop drinking soda as a family, or opt for an apple instead of a bag of chips. They can walk around the house or up and down stairs when talking. “Those sorts of little things can make a big difference in the long run,” Dr. Jenssen said.
Clinicians should address obesity in a compassionate and caring way, be aware of community resources to help families adopt healthy lifestyles, and “look for the comorbidities of obesity,” such as type 2 diabetes, liver disease, sleep apnea, knee problems, and hypertension, Dr. Hassink said.
Policies that address other factors, such as the cost of healthy foods and the marketing of unhealthy foods, may also be needed, Dr. Hassink said.
“I’ve always thought of obesity as kind of the canary in the coal mine,” Dr. Hassink said. “It is important to keep our minds on the fact that it is a chronic disease. But it also indicates a lot of things about how we are able to support a healthy population.”
Potato chips, red meat, and sugary drinks
Other researchers have assessed how healthy behaviors tended to take a turn for the worse when routines were disrupted during the pandemic. Steven B. Heymsfield, MD, a professor in the metabolism and body composition laboratory at Pennington Biomedical Research Center, Louisiana State University System, Baton Rouge, and collaborators documented how diet and activity changed for children during the pandemic.
Dr. Heymsfield worked with researchers in Italy to examine changes in behavior among 41 children and adolescents with obesity in Verona, Italy, during an early lockdown.
As part of a longitudinal observational study, they had baseline data about diet and physical activity from interviews conducted from May to July 2019. They repeated the interviews 3 weeks after a mandatory quarantine.
Intake of potato chips, red meat, and sugary drinks had increased, time spent in sports activities had decreased by more than 2 hours per week, and screen time had increased by more than 4 hours per day, the researchers found. Their study was published in Obesity.
Unpublished follow-up data indicate that “there was further deterioration in the diets and activity patterns” for some but not all of the participants, Dr. Heymsfield said.
He said he was hopeful that children who experienced the onset of obesity during the pandemic may lose weight when routines return to normal, but added that it is unclear whether that will happen.
“My impression from the limited written literature on this question is that for some kids who gain weight during the lockdown or, by analogy, the summer months, the weight doesn’t go back down again. It is not universal, but it is a known phenomenon that it is a bit of a ratchet,” he said. “They just sort of slowly ratchet their weights up, up to adulthood.”
Recognizing weight gain during the pandemic may be an important first step.
“The first thing is not to ignore it,” Dr. Heymsfield said. “Anything that can be done to prevent excess weight gain during childhood – not to promote anorexia or anything like that, but just being careful – is very important, because these behaviors are formed early in life, and they persist.”
CHOP supported the research. Dr. Jenssen and Dr. Hassink have disclosed no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Heymsfield is a medical adviser for Medifast, a weight loss company.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Obesity rates among children jumped substantially in the first months of the COVID-19 pandemic, according to a study published online in Pediatrics. Experts worry the excess weight will be a continuing problem for these children.
“Across the board in the span of a year, there has been a 2% increase in obesity, which is really striking,” lead author Brian P. Jenssen, MD, said in an interview.
The prevalence of obesity in a large pediatric primary care network increased from 13.7% to 15.4%.
Preexisting disparities by race or ethnicity and socioeconomic status worsened, noted Dr. Jenssen, a primary care pediatrician affiliated with Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia (CHOP) and the University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia.
Dr. Jenssen and colleagues compared the average obesity rate from June to December 2020 with the rate from June to December 2019 among patients in the CHOP Care Network, which includes 29 urban, suburban, and semirural clinics in the Philadelphia region. In June 2020, the volume of patient visits “returned to near-normal” after a dramatic decline in March 2020, the study authors wrote.
The investigators examined body mass index at all visits for patients aged 2-17 years for whom height and weight were documented. Patients with a BMI at or above the 95th percentile were classified as obese. The analysis included approximately 169,000 visits in 2019 and about 145,000 in 2020.
The average age of the patients was 9.2 years, and 48.9% were girls. In all, 21.4% were non-Hispanic Black, and about 30% were publicly insured.
Increases in obesity rates were more pronounced among patients aged 5-9 years and among patients who were Hispanic/Latino, non-Hispanic Black, publicly insured, or from lower-income neighborhoods.
Whereas the obesity rate increased 1% for patients aged 13-17 years, the rate increased 2.6% for patients aged 5-9 years.
Nearly 25% of Hispanic/Latino or non-Hispanic Black patients seen during the pandemic were obese, compared with 11.3% of non-Hispanic White patients. Before the pandemic, differences by race or ethnicity had been about 10%-11%.
Limiting the analysis to preventive visits did not meaningfully change the results, wrote Dr. Jenssen and colleagues.
“Having any increase in the obesity rates is alarming,” said Sandra Hassink, MD, medical director for the American Academy of Pediatrics’ (AAP’s) Institute for Healthy Childhood Weight. “I think what we’re seeing is what we feared.”
Before the pandemic, children received appropriately portioned breakfasts and lunches at school, but during the pandemic, they had less access to such meals, the academy noted. Disruptions to schooling, easier access to unhealthy snacks, increased screen time, and economic issues such as parents’ job losses were further factors, Hassink said.
Tackling the weight gain
In December 2020, the AAP issued two clinical guidance documents to highlight the importance of addressing obesity during the pandemic. Recommendations included physician counseling of families about maintaining healthy nutrition, minimizing sedentary time, and getting enough sleep and physical activity, as well as the assessment of all patients for onset of obesity and the maintenance of obesity treatment for patients with obesity.
In addition to clinical assessments and guidance, Dr. Jenssen emphasized that a return to routines may be crucial. Prepandemic studies have shown that many children, especially those insured by Medicaid, gain more weight during the summer when they are out of school, he noted. Many of the same factors are present during the pandemic, he said.
“One solution, and probably the most important solution, is getting kids back in school,” Dr. Jenssen said. School disruptions also have affected children’s learning and mental health, but those effects may be harder to quantify than BMI, he said.
Dr. Jenssen suggests that parents do their best to model good routines and habits. For example, they might decide that they and their children will stop drinking soda as a family, or opt for an apple instead of a bag of chips. They can walk around the house or up and down stairs when talking. “Those sorts of little things can make a big difference in the long run,” Dr. Jenssen said.
Clinicians should address obesity in a compassionate and caring way, be aware of community resources to help families adopt healthy lifestyles, and “look for the comorbidities of obesity,” such as type 2 diabetes, liver disease, sleep apnea, knee problems, and hypertension, Dr. Hassink said.
Policies that address other factors, such as the cost of healthy foods and the marketing of unhealthy foods, may also be needed, Dr. Hassink said.
“I’ve always thought of obesity as kind of the canary in the coal mine,” Dr. Hassink said. “It is important to keep our minds on the fact that it is a chronic disease. But it also indicates a lot of things about how we are able to support a healthy population.”
Potato chips, red meat, and sugary drinks
Other researchers have assessed how healthy behaviors tended to take a turn for the worse when routines were disrupted during the pandemic. Steven B. Heymsfield, MD, a professor in the metabolism and body composition laboratory at Pennington Biomedical Research Center, Louisiana State University System, Baton Rouge, and collaborators documented how diet and activity changed for children during the pandemic.
Dr. Heymsfield worked with researchers in Italy to examine changes in behavior among 41 children and adolescents with obesity in Verona, Italy, during an early lockdown.
As part of a longitudinal observational study, they had baseline data about diet and physical activity from interviews conducted from May to July 2019. They repeated the interviews 3 weeks after a mandatory quarantine.
Intake of potato chips, red meat, and sugary drinks had increased, time spent in sports activities had decreased by more than 2 hours per week, and screen time had increased by more than 4 hours per day, the researchers found. Their study was published in Obesity.
Unpublished follow-up data indicate that “there was further deterioration in the diets and activity patterns” for some but not all of the participants, Dr. Heymsfield said.
He said he was hopeful that children who experienced the onset of obesity during the pandemic may lose weight when routines return to normal, but added that it is unclear whether that will happen.
“My impression from the limited written literature on this question is that for some kids who gain weight during the lockdown or, by analogy, the summer months, the weight doesn’t go back down again. It is not universal, but it is a known phenomenon that it is a bit of a ratchet,” he said. “They just sort of slowly ratchet their weights up, up to adulthood.”
Recognizing weight gain during the pandemic may be an important first step.
“The first thing is not to ignore it,” Dr. Heymsfield said. “Anything that can be done to prevent excess weight gain during childhood – not to promote anorexia or anything like that, but just being careful – is very important, because these behaviors are formed early in life, and they persist.”
CHOP supported the research. Dr. Jenssen and Dr. Hassink have disclosed no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Heymsfield is a medical adviser for Medifast, a weight loss company.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Obesity rates among children jumped substantially in the first months of the COVID-19 pandemic, according to a study published online in Pediatrics. Experts worry the excess weight will be a continuing problem for these children.
“Across the board in the span of a year, there has been a 2% increase in obesity, which is really striking,” lead author Brian P. Jenssen, MD, said in an interview.
The prevalence of obesity in a large pediatric primary care network increased from 13.7% to 15.4%.
Preexisting disparities by race or ethnicity and socioeconomic status worsened, noted Dr. Jenssen, a primary care pediatrician affiliated with Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia (CHOP) and the University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia.
Dr. Jenssen and colleagues compared the average obesity rate from June to December 2020 with the rate from June to December 2019 among patients in the CHOP Care Network, which includes 29 urban, suburban, and semirural clinics in the Philadelphia region. In June 2020, the volume of patient visits “returned to near-normal” after a dramatic decline in March 2020, the study authors wrote.
The investigators examined body mass index at all visits for patients aged 2-17 years for whom height and weight were documented. Patients with a BMI at or above the 95th percentile were classified as obese. The analysis included approximately 169,000 visits in 2019 and about 145,000 in 2020.
The average age of the patients was 9.2 years, and 48.9% were girls. In all, 21.4% were non-Hispanic Black, and about 30% were publicly insured.
Increases in obesity rates were more pronounced among patients aged 5-9 years and among patients who were Hispanic/Latino, non-Hispanic Black, publicly insured, or from lower-income neighborhoods.
Whereas the obesity rate increased 1% for patients aged 13-17 years, the rate increased 2.6% for patients aged 5-9 years.
Nearly 25% of Hispanic/Latino or non-Hispanic Black patients seen during the pandemic were obese, compared with 11.3% of non-Hispanic White patients. Before the pandemic, differences by race or ethnicity had been about 10%-11%.
Limiting the analysis to preventive visits did not meaningfully change the results, wrote Dr. Jenssen and colleagues.
“Having any increase in the obesity rates is alarming,” said Sandra Hassink, MD, medical director for the American Academy of Pediatrics’ (AAP’s) Institute for Healthy Childhood Weight. “I think what we’re seeing is what we feared.”
Before the pandemic, children received appropriately portioned breakfasts and lunches at school, but during the pandemic, they had less access to such meals, the academy noted. Disruptions to schooling, easier access to unhealthy snacks, increased screen time, and economic issues such as parents’ job losses were further factors, Hassink said.
Tackling the weight gain
In December 2020, the AAP issued two clinical guidance documents to highlight the importance of addressing obesity during the pandemic. Recommendations included physician counseling of families about maintaining healthy nutrition, minimizing sedentary time, and getting enough sleep and physical activity, as well as the assessment of all patients for onset of obesity and the maintenance of obesity treatment for patients with obesity.
In addition to clinical assessments and guidance, Dr. Jenssen emphasized that a return to routines may be crucial. Prepandemic studies have shown that many children, especially those insured by Medicaid, gain more weight during the summer when they are out of school, he noted. Many of the same factors are present during the pandemic, he said.
“One solution, and probably the most important solution, is getting kids back in school,” Dr. Jenssen said. School disruptions also have affected children’s learning and mental health, but those effects may be harder to quantify than BMI, he said.
Dr. Jenssen suggests that parents do their best to model good routines and habits. For example, they might decide that they and their children will stop drinking soda as a family, or opt for an apple instead of a bag of chips. They can walk around the house or up and down stairs when talking. “Those sorts of little things can make a big difference in the long run,” Dr. Jenssen said.
Clinicians should address obesity in a compassionate and caring way, be aware of community resources to help families adopt healthy lifestyles, and “look for the comorbidities of obesity,” such as type 2 diabetes, liver disease, sleep apnea, knee problems, and hypertension, Dr. Hassink said.
Policies that address other factors, such as the cost of healthy foods and the marketing of unhealthy foods, may also be needed, Dr. Hassink said.
“I’ve always thought of obesity as kind of the canary in the coal mine,” Dr. Hassink said. “It is important to keep our minds on the fact that it is a chronic disease. But it also indicates a lot of things about how we are able to support a healthy population.”
Potato chips, red meat, and sugary drinks
Other researchers have assessed how healthy behaviors tended to take a turn for the worse when routines were disrupted during the pandemic. Steven B. Heymsfield, MD, a professor in the metabolism and body composition laboratory at Pennington Biomedical Research Center, Louisiana State University System, Baton Rouge, and collaborators documented how diet and activity changed for children during the pandemic.
Dr. Heymsfield worked with researchers in Italy to examine changes in behavior among 41 children and adolescents with obesity in Verona, Italy, during an early lockdown.
As part of a longitudinal observational study, they had baseline data about diet and physical activity from interviews conducted from May to July 2019. They repeated the interviews 3 weeks after a mandatory quarantine.
Intake of potato chips, red meat, and sugary drinks had increased, time spent in sports activities had decreased by more than 2 hours per week, and screen time had increased by more than 4 hours per day, the researchers found. Their study was published in Obesity.
Unpublished follow-up data indicate that “there was further deterioration in the diets and activity patterns” for some but not all of the participants, Dr. Heymsfield said.
He said he was hopeful that children who experienced the onset of obesity during the pandemic may lose weight when routines return to normal, but added that it is unclear whether that will happen.
“My impression from the limited written literature on this question is that for some kids who gain weight during the lockdown or, by analogy, the summer months, the weight doesn’t go back down again. It is not universal, but it is a known phenomenon that it is a bit of a ratchet,” he said. “They just sort of slowly ratchet their weights up, up to adulthood.”
Recognizing weight gain during the pandemic may be an important first step.
“The first thing is not to ignore it,” Dr. Heymsfield said. “Anything that can be done to prevent excess weight gain during childhood – not to promote anorexia or anything like that, but just being careful – is very important, because these behaviors are formed early in life, and they persist.”
CHOP supported the research. Dr. Jenssen and Dr. Hassink have disclosed no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Heymsfield is a medical adviser for Medifast, a weight loss company.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
New guidelines on the diagnosis and treatment of adults with CAP
Background: More than a decade has passed since the last CAP guidelines. Since then there have been new trials and epidemiological studies. There have also been changes to the process for guideline development. This guideline has moved away from the narrative style of guidelines to the GRADE format and PICO framework with hopes of answering specific questions by looking at the quality of evidence.
Study design: Multidisciplinary panel conducted pragmatic systemic reviews of high-quality studies.
Setting: The panel revised and built upon the 2007 guidelines, addressing 16 clinical questions to be used in immunocompetent patients with radiographic evidence of CAP in the United States with no recent foreign travel.
Synopsis: Changes from the 2007 guidelines are as follows: Sputum and blood cultures, previously recommended only in patients with severe CAP, are now also recommended for inpatients being empirically treated for Pseudomonas or methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) and for those who have received IV antibiotics in the previous 90 days; use of procalcitonin is not recommended to decide whether to withhold antibiotics; steroids are not recommended unless being used for shock; HCAP categorization should be abandoned and need for empiric coverage of MRSA and Pseudomonas should be based on local epidemiology and local validated risk factors; B-lactam/macrolide is favored over fluoroquinolone for severe CAP therapy; and routine follow-up chest x-ray is not recommended.
Other recommendations include not routinely testing for urine pneumococcal or legionella antigens in nonsevere CAP; using PSI over CURB-65, in addition to clinical judgment, to determine need for inpatient care; using severe CAP criteria and clinical judgment for determining ICU need; not adding anaerobic coverage for aspiration pneumonia; and treating most cases of CAP that are clinically stable and uncomplicated for 5-7 days.
Bottom line: Given new data, updated recommendations have been made to help optimize CAP therapy.
Citation: Metlay JP et al. Diagnosis and treatment of adults with community-acquired pneumonia: An official clinical practice guideline of the American Thoracic Society and Infectious Diseases Society of America. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2019 Oct 1;200(7):e45-67.
Dr. Horton is a hospitalist and clinical instructor of medicine at the University of Utah, Salt Lake City.
Background: More than a decade has passed since the last CAP guidelines. Since then there have been new trials and epidemiological studies. There have also been changes to the process for guideline development. This guideline has moved away from the narrative style of guidelines to the GRADE format and PICO framework with hopes of answering specific questions by looking at the quality of evidence.
Study design: Multidisciplinary panel conducted pragmatic systemic reviews of high-quality studies.
Setting: The panel revised and built upon the 2007 guidelines, addressing 16 clinical questions to be used in immunocompetent patients with radiographic evidence of CAP in the United States with no recent foreign travel.
Synopsis: Changes from the 2007 guidelines are as follows: Sputum and blood cultures, previously recommended only in patients with severe CAP, are now also recommended for inpatients being empirically treated for Pseudomonas or methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) and for those who have received IV antibiotics in the previous 90 days; use of procalcitonin is not recommended to decide whether to withhold antibiotics; steroids are not recommended unless being used for shock; HCAP categorization should be abandoned and need for empiric coverage of MRSA and Pseudomonas should be based on local epidemiology and local validated risk factors; B-lactam/macrolide is favored over fluoroquinolone for severe CAP therapy; and routine follow-up chest x-ray is not recommended.
Other recommendations include not routinely testing for urine pneumococcal or legionella antigens in nonsevere CAP; using PSI over CURB-65, in addition to clinical judgment, to determine need for inpatient care; using severe CAP criteria and clinical judgment for determining ICU need; not adding anaerobic coverage for aspiration pneumonia; and treating most cases of CAP that are clinically stable and uncomplicated for 5-7 days.
Bottom line: Given new data, updated recommendations have been made to help optimize CAP therapy.
Citation: Metlay JP et al. Diagnosis and treatment of adults with community-acquired pneumonia: An official clinical practice guideline of the American Thoracic Society and Infectious Diseases Society of America. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2019 Oct 1;200(7):e45-67.
Dr. Horton is a hospitalist and clinical instructor of medicine at the University of Utah, Salt Lake City.
Background: More than a decade has passed since the last CAP guidelines. Since then there have been new trials and epidemiological studies. There have also been changes to the process for guideline development. This guideline has moved away from the narrative style of guidelines to the GRADE format and PICO framework with hopes of answering specific questions by looking at the quality of evidence.
Study design: Multidisciplinary panel conducted pragmatic systemic reviews of high-quality studies.
Setting: The panel revised and built upon the 2007 guidelines, addressing 16 clinical questions to be used in immunocompetent patients with radiographic evidence of CAP in the United States with no recent foreign travel.
Synopsis: Changes from the 2007 guidelines are as follows: Sputum and blood cultures, previously recommended only in patients with severe CAP, are now also recommended for inpatients being empirically treated for Pseudomonas or methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) and for those who have received IV antibiotics in the previous 90 days; use of procalcitonin is not recommended to decide whether to withhold antibiotics; steroids are not recommended unless being used for shock; HCAP categorization should be abandoned and need for empiric coverage of MRSA and Pseudomonas should be based on local epidemiology and local validated risk factors; B-lactam/macrolide is favored over fluoroquinolone for severe CAP therapy; and routine follow-up chest x-ray is not recommended.
Other recommendations include not routinely testing for urine pneumococcal or legionella antigens in nonsevere CAP; using PSI over CURB-65, in addition to clinical judgment, to determine need for inpatient care; using severe CAP criteria and clinical judgment for determining ICU need; not adding anaerobic coverage for aspiration pneumonia; and treating most cases of CAP that are clinically stable and uncomplicated for 5-7 days.
Bottom line: Given new data, updated recommendations have been made to help optimize CAP therapy.
Citation: Metlay JP et al. Diagnosis and treatment of adults with community-acquired pneumonia: An official clinical practice guideline of the American Thoracic Society and Infectious Diseases Society of America. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2019 Oct 1;200(7):e45-67.
Dr. Horton is a hospitalist and clinical instructor of medicine at the University of Utah, Salt Lake City.
Cutaneous Manifestation as Initial Presentation of Metastatic Breast Cancer: A Systematic Review
Breast cancer is the second most common malignancy in women (after primary skin cancer) and is the second leading cause of cancer-related death in this population. In 2020, the American Cancer Society reported an estimated 276,480 new breast cancer diagnoses and 42,170 breast cancer–related deaths.1 Despite the fact that routine screening with mammography and sonography is standard, the incidence of advanced breast cancer at the time of diagnosis has remained stable over time, suggesting that life-threatening breast cancers are not being caught at an earlier stage. The number of breast cancers with distant metastases at the time of diagnosis also has not decreased.2 Therefore, although screening tests are valuable, they are imperfect and not without limitations.
Cutaneous metastasis is defined as the spread of malignant cells from an internal neoplasm to the skin, which can occur either by contiguous invasion or by distant metastasis through hematogenous or lymphatic routes.3 The diagnosis of cutaneous metastasis requires a high index of suspicion on the part of the clinician.4 Of the various internal malignancies in women, breast cancer most frequently results in metastasis to the skin,5 with up to 24% of patients with metastatic breast cancer developing cutaneous lesions.6
In recent years, there have been multiple reports of skin lesions prompting the diagnosis of a previously unknown breast cancer. In a study by Lookingbill et al,6 6.3% of patients with breast cancer presented with cutaneous involvement at the time of diagnosis, with 3.5% having skin symptoms as the presenting sign. Although there have been studies analyzing cutaneous metastasis from various internal malignancies, none thus far have focused on cutaneous metastasis as a presenting sign of breast cancer. This systematic review aimed to highlight the diverse clinical presentations of cutaneous metastatic breast cancer and their clinical implications.
Methods
Study Selection
This study utilized the PRISMA guidelines for systematic reviews.7 A review of the literature was conducted using the following databases: MEDLINE/PubMed, EMBASE, Cochrane library, CINAHL, and EBSCO.
Search Strategy and Analysis
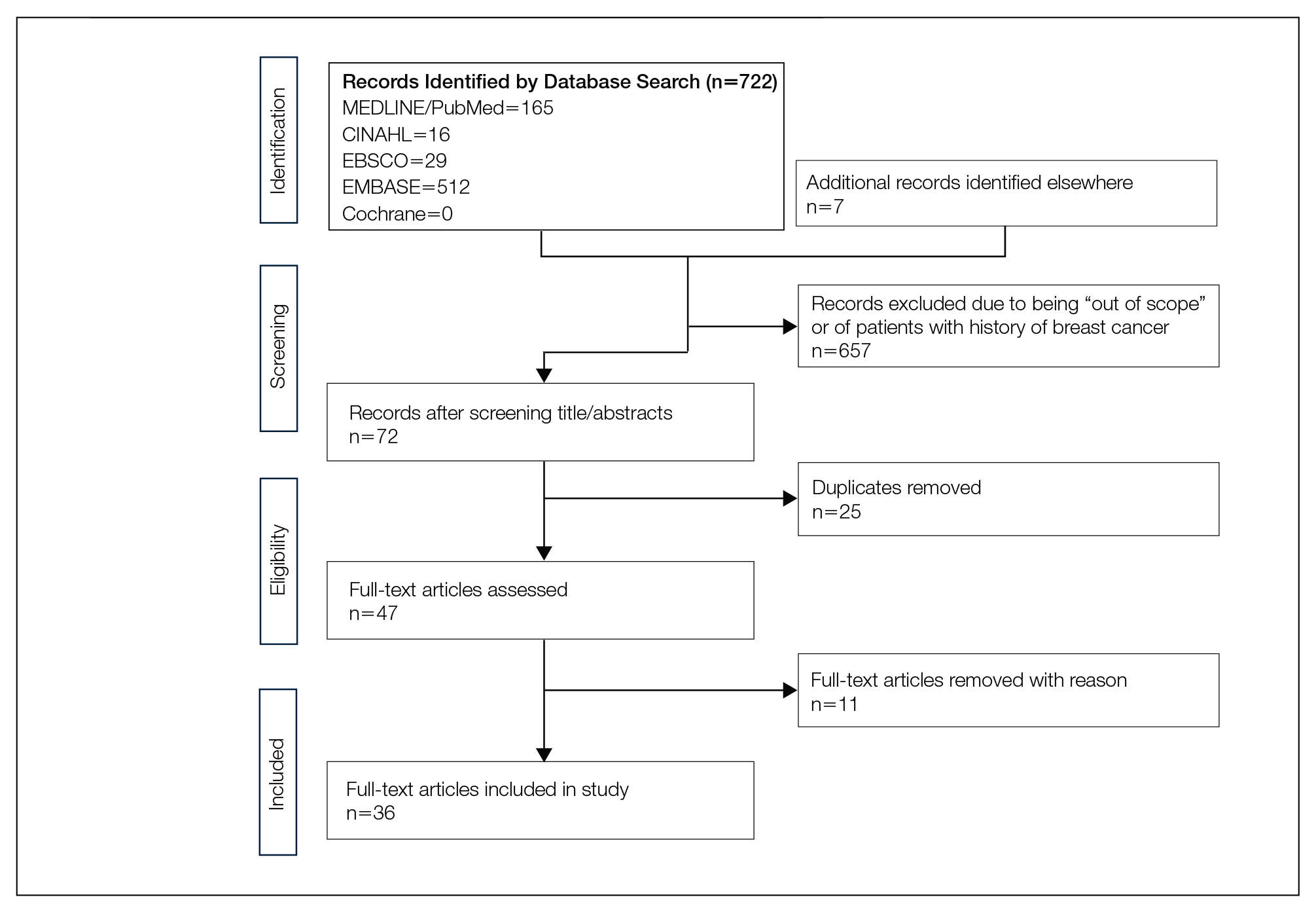
We completed our search of each of the databases on December 16, 2017, using the phrases cutaneous metastasis and breast cancer to find relevant case reports and retrospective studies. Three authors (C.J., S.R., and M.A.) manually reviewed the resulting abstracts. If an abstract did not include enough information to determine inclusion, the full-text version was reviewed by 2 of the authors (C.J. and S.R.). Two of the authors (C.J. and M.A.) also assessed each source for relevancy and included the articles deemed eligible (Figure 1).
Inclusion criteria were the following: case reports and retrospective studies published in the prior 10 years (January 1, 2007, to December 16, 2017) with human female patients who developed metastatic cutaneous lesions due to a previously unknown primary breast malignancy. Studies published in other languages were included; these articles were translated into English using a human translator or computer translation program (Google Translate). Exclusion criteria were the following: male patients, patients with a known diagnosis of primary breast malignancy prior to the appearance of a metastatic cutaneous lesion, articles focusing on the treatment of breast cancer, and articles without enough details to draw meaningful conclusions.
For a retrospective review to be included, it must have specified the number of breast cancer cases and the number of cutaneous metastases presenting initially or simultaneously to the breast cancer diagnosis. Bansal et al8 defined a simultaneous diagnosis as a skin lesion presenting with other concerns associated with the primary malignancy.
Results
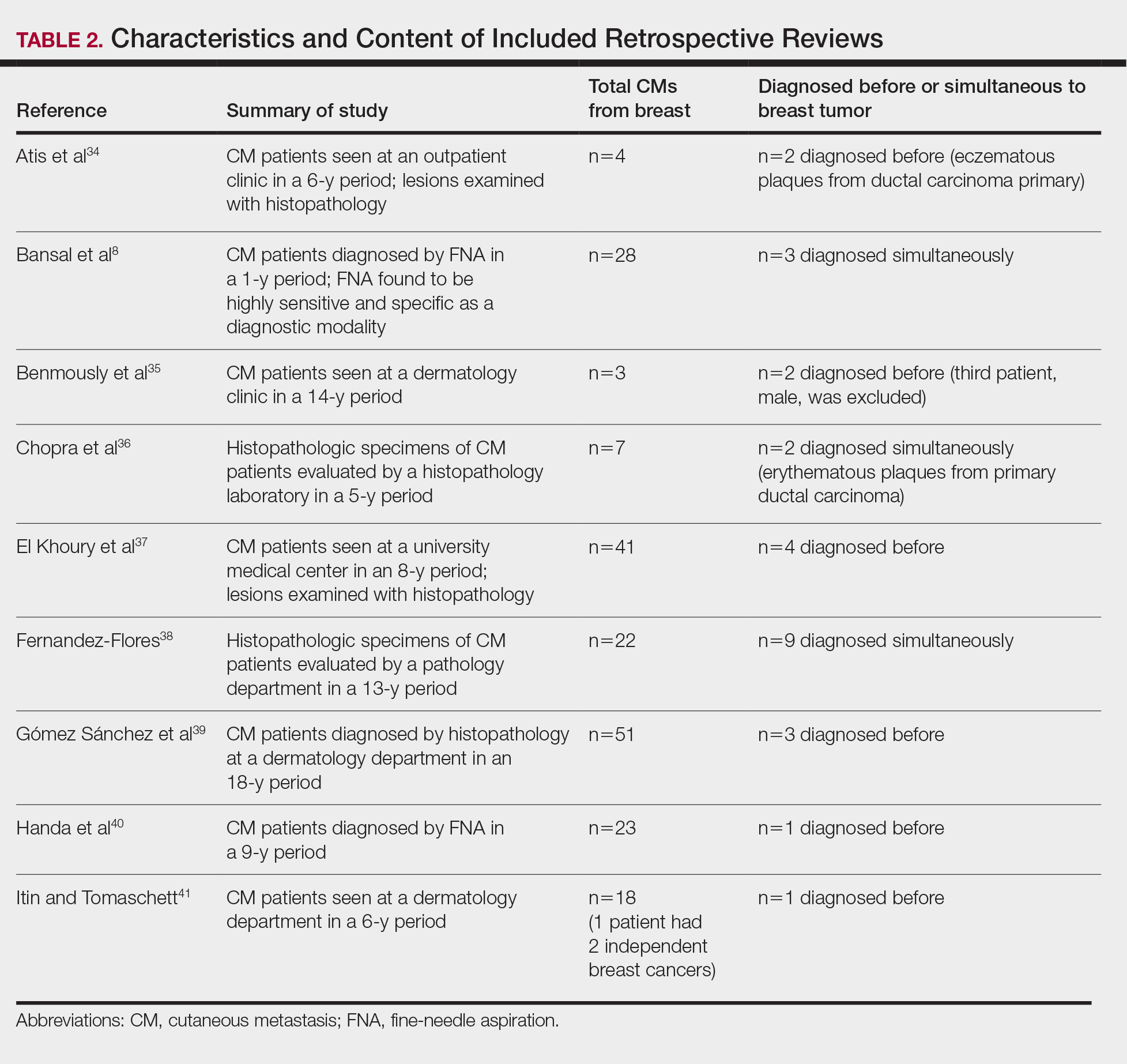
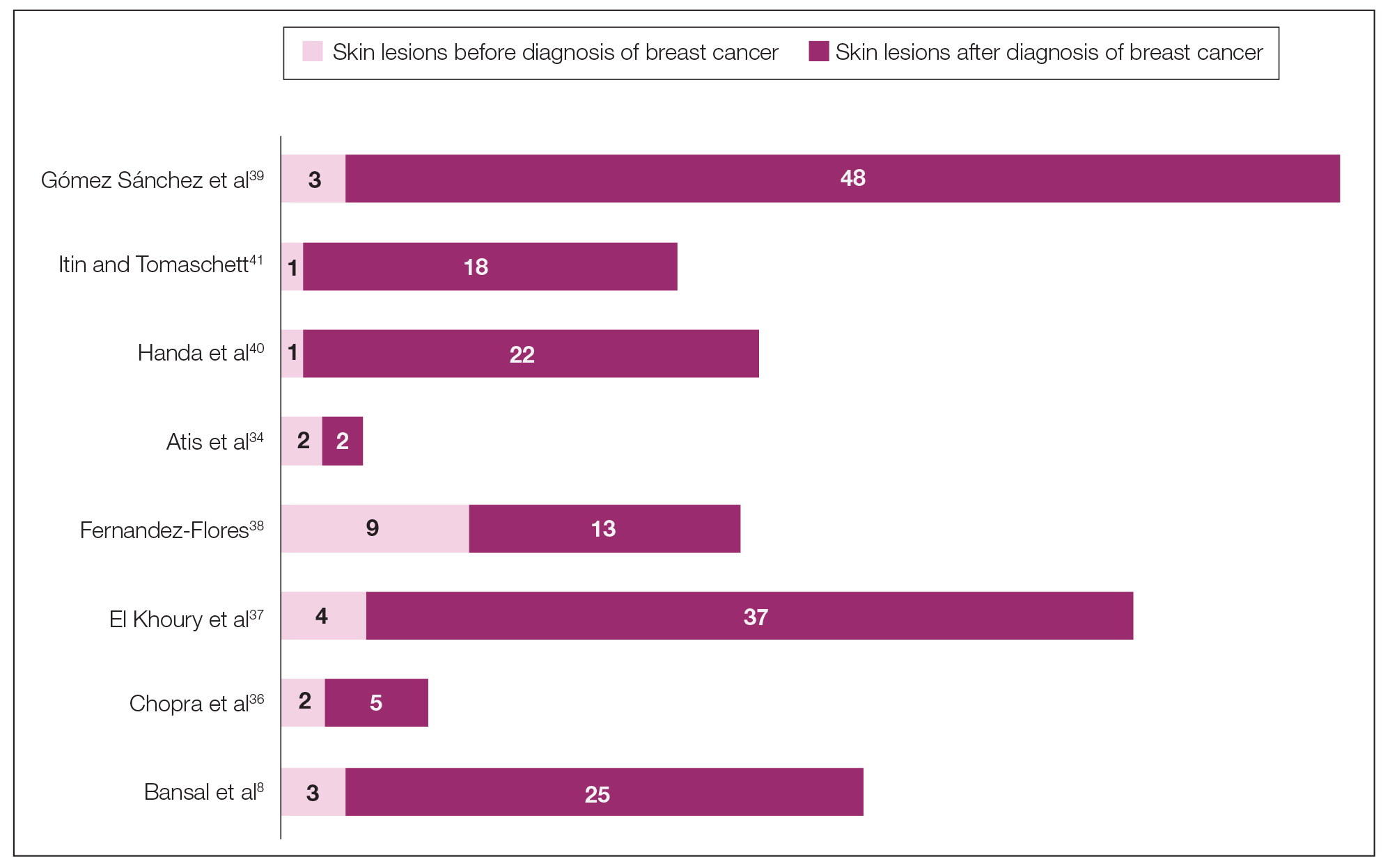
The initial search of MEDLINE/PubMed, EMBASE, Cochrane library, CINAHL, and EBSCO yielded a total of 722 articles. Seven other articles found separately while undergoing our initial research were added to this total. Abstracts were manually screened, with 657 articles discarded after failing to meet the predetermined inclusion criteria. After removal of 25 duplicate articles, the full text of the remaining 47 articles were reviewed, leading to the elimination of an additional 11 articles that did not meet the necessary criteria. This resulted in 36 articles (Figure 1), including 27 individual case reports (Table 1) and 9 retrospective reviews (Table 2). Approximately 13.7% of patients in the 9 retrospective reviews presented with a skin lesion before or simultaneous to the diagnosis of breast cancer (Figure 2).
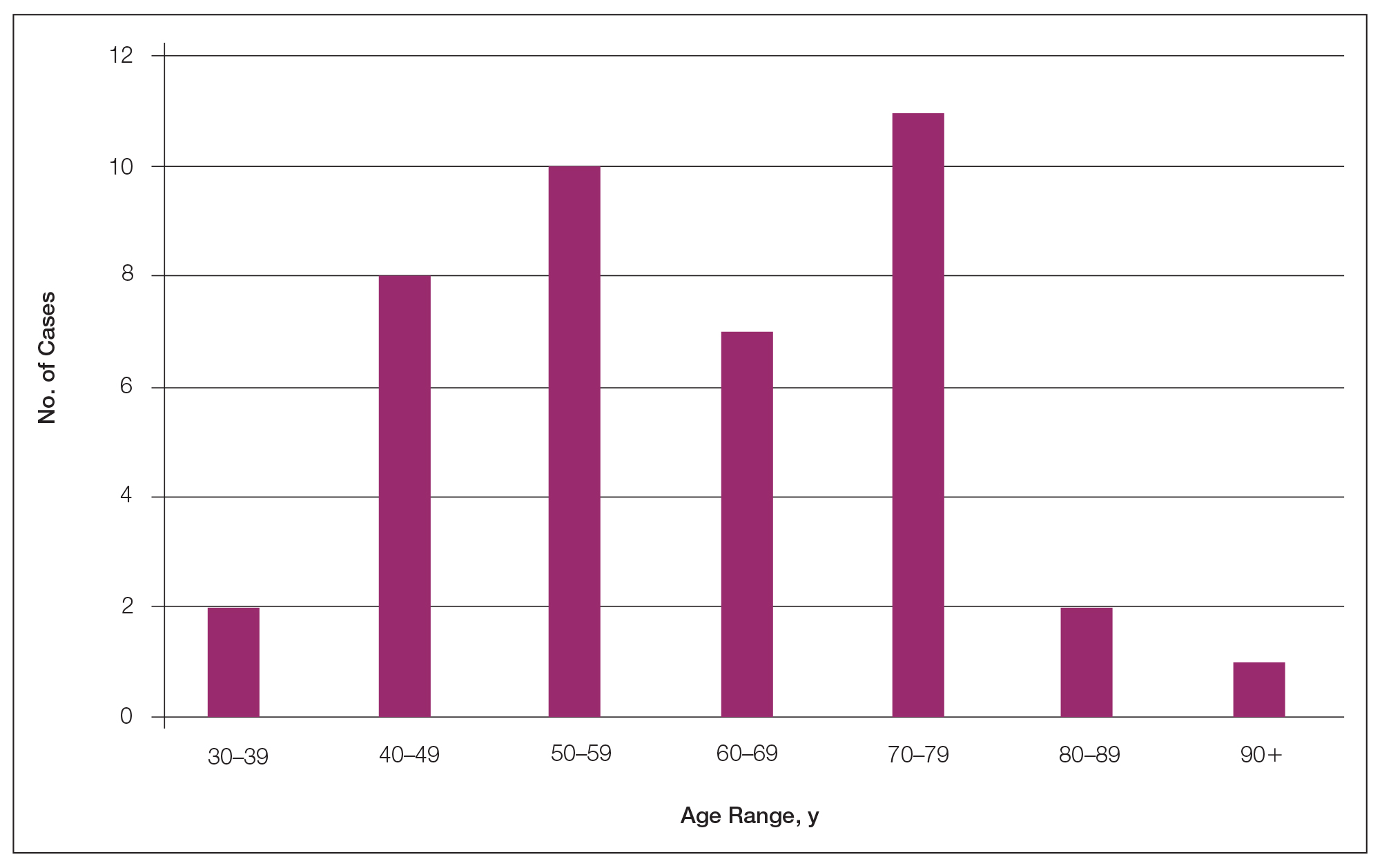
Forty-one percent (17/41) of the patients with cutaneous metastasis as a presenting feature of their breast cancer fell outside the age range for breast cancer screening recommended by the US Preventive Services Task Force,42 with 24% of the patients younger than 50 years and 17% older than 74 years (Figure 3).
Lesion Characteristics
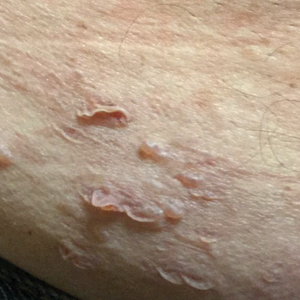
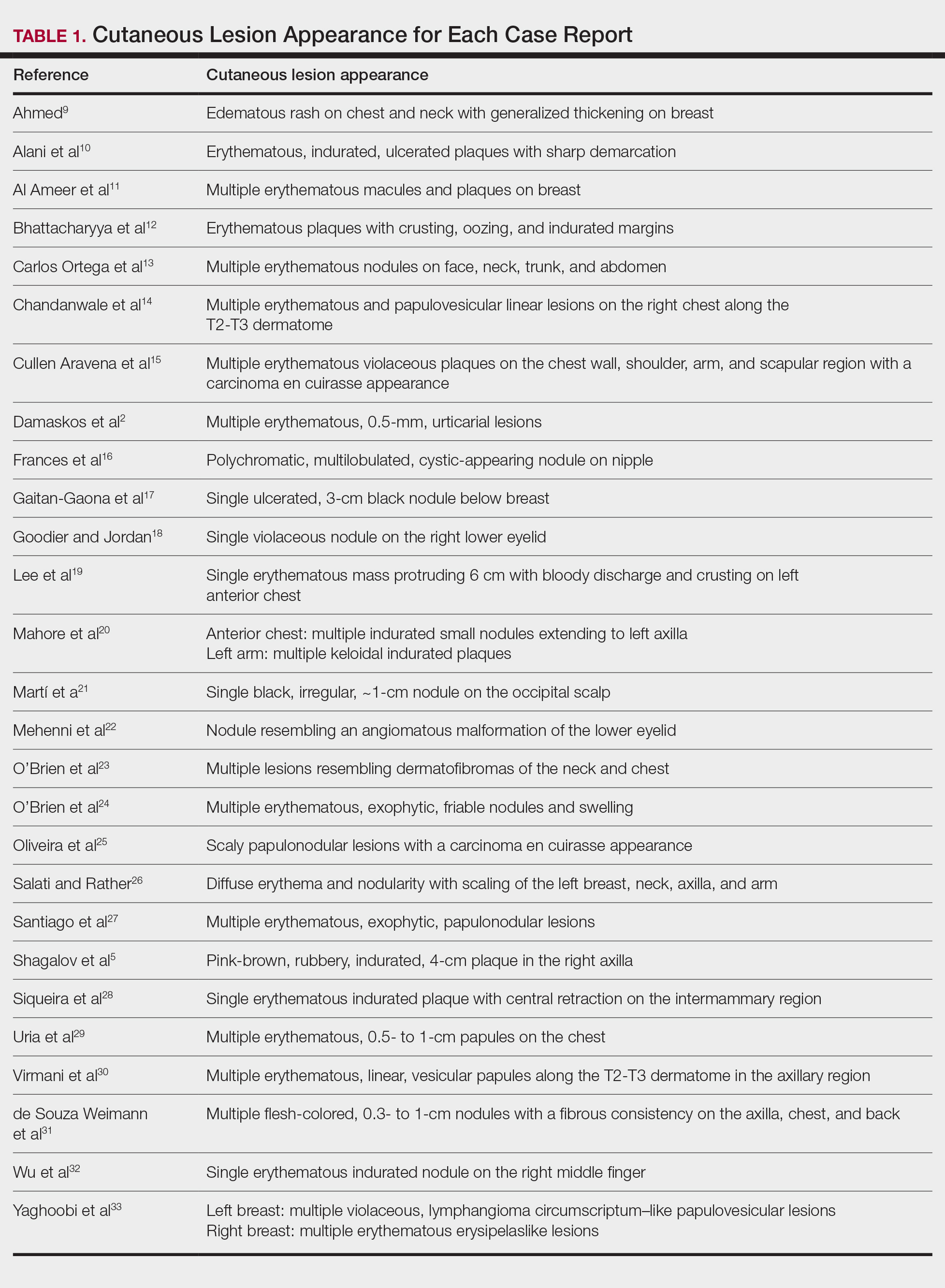
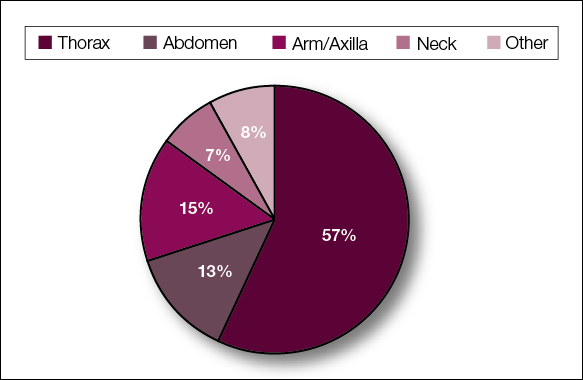
The most common cutaneous lesions were erythematous nodules and plaques, with a few reports of black17,21 or flesh-colored5,20,31 lesions, as well as ulceration.8,17,32 The most common location for skin lesions was on the thorax (chest or breast), accounting for 57% of the cutaneous metastases, with the arms and axillae being second most commonly involved (15%)(Figure 4). Some cases presented with skin lesions extending to multiple regions. In these cases, each location of the lesion was recorded separately when analyzing the data. An additional 5 cases, shown as “Other” in Figure 4, included the eyelids, occiput, and finger. Eight case reports described symptoms associated with the cutaneous lesions, with painful or tender lesions reported in 7 cases5,9,14,17,20,30,32 and pruritus in 2 cases.12,20 Moreover, 6 case reports presented patients denying any systemic or associated symptoms with their skin lesions.2,5,9,16,17,28 Multiple cases were initially treated as other conditions due to misdiagnosis, including herpes zoster14,30 and dermatitis.11,12
Diagnostic Data
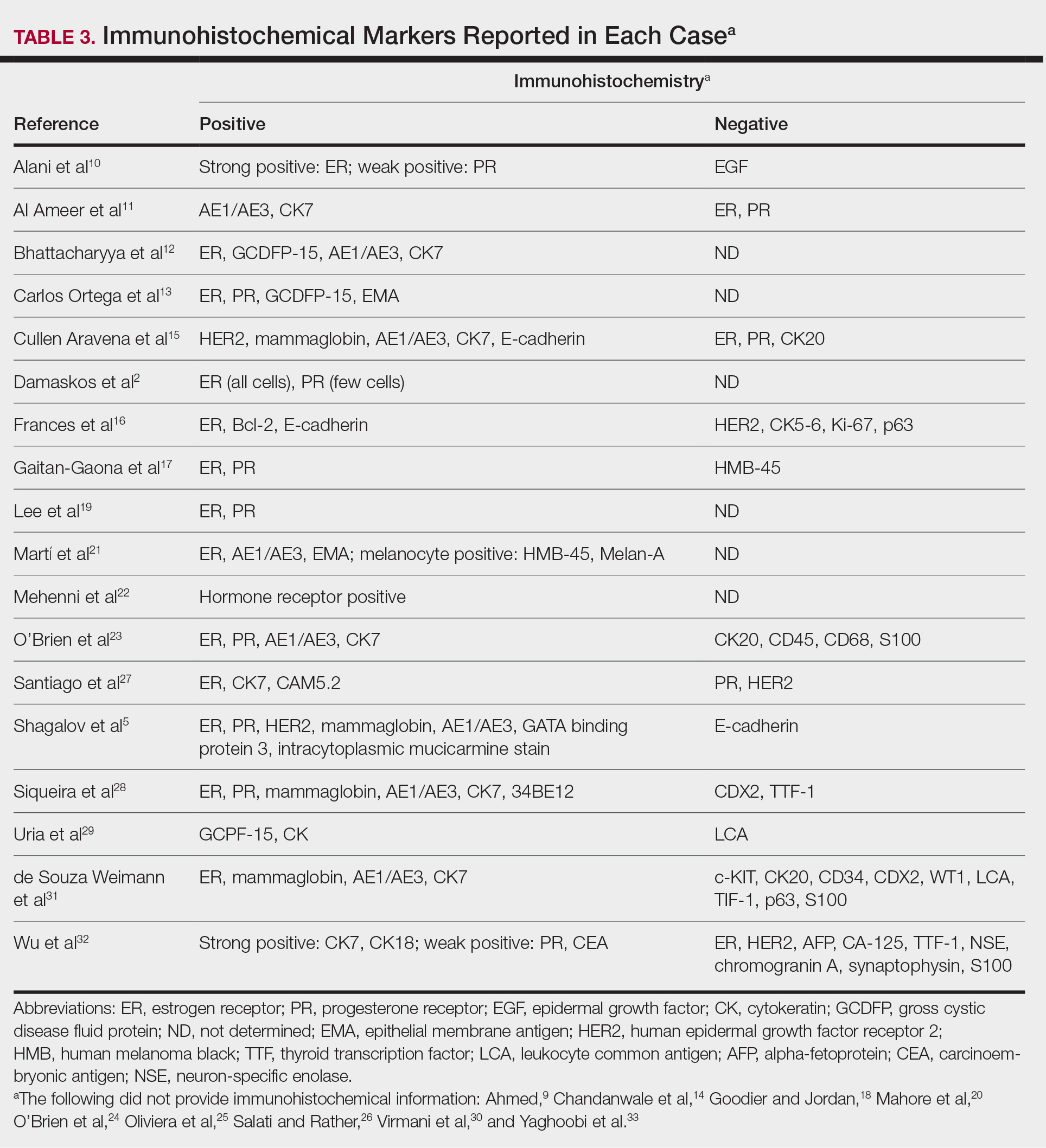
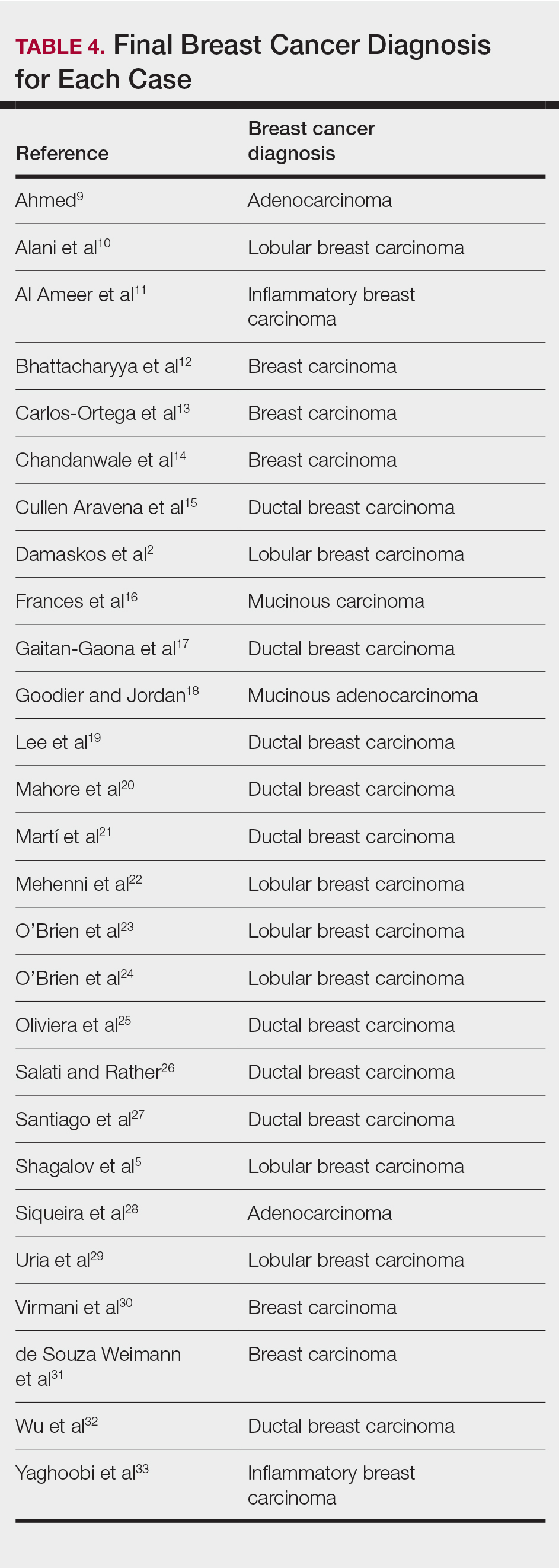
Eighteen cases reported positive immunohistochemistry from cutaneous biopsy (Table 3), given its high specificity in determining the origin of cutaneous metastases, while 8 case reports only performed hematoxylin and eosin staining. One case did not report hematoxylin and eosin or immunohistochemical staining. Table 4 lists the final breast cancer diagnosis for each case.
As per the standard of care, patients were evaluated with mammography or ultrasonography, combined with fine-needle aspiration of a suspected primary tumor, to give a definitive diagnosis of breast cancer. However, 4 cases reported negative mammography and ultrasonography.13,22,28,31 In 3 of these cases, no primary tumor was ever found.13,22,31
Comment
Our systematic review demonstrated that cutaneous lesions may be the first clinical manifestation of an undetected primary malignancy.40 These lesions often occur on the chest but may involve the face, abdomen, or extremities. Although asymptomatic erythematous nodules and plaques are the most common clinical presentations, lesions may be tender or pruritic or may even resemble benign skin conditions, including dermatitis, cellulitis, urticaria, and papulovesicular eruptions, causing them to go unrecognized.
Nevertheless, cutaneous metastasis of a visceral malignancy generally is observed late in the disease course, often following the diagnosis of a primary malignancy.14 Breast cancer is the most common internal malignancy to feature cutaneous spread, with the largest case series revealing a 23.9% rate of cutaneous metastases in females with breast carcinoma.6 Because of its proximity, the chest wall is the most common location for cutaneous lesions of metastatic breast cancer.
Malignant cells from a primary breast tumor may spread to the skin via lymphatic, hematogenous, or contiguous tissue dissemination, as well as iatrogenically through direct implantation during surgical procedures.3 The mechanism of neoplasm spread may likewise influence the clinical appearance of the resulting lesions. The localized lymphedema with a peau d’orange appearance of inflammatory metastatic breast carcinoma or the erythematous plaques of carcinoma erysipeloides are caused by embolized tumor cells obstructing dermal lymphatic vessels.3,11 On the other hand, the indurated erythematous plaques of carcinoma en cuirasse are caused by diffuse cutaneous and subcutaneous infiltration of tumor cells that also may be associated with marked reduction in breast volume.3
A primary breast cancer is classically diagnosed with a combination of clinical breast examination, radiologic imaging (ultrasound, mammogram, breast magnetic resonance imaging, or computed tomography), and fine-needle aspiration or lesional biopsy with histopathology.9 Given that in 20% of metastasized breast cancers the primary tumor may not be identified, a negative breast examination and imaging do not rule out breast cancer, especially if cutaneous biopsy reveals a primary malignancy.43 Histopathology and immunohistochemistry can thereby confirm the presence of metastatic cutaneous lesions and help characterize the breast cancer type involved, with adenocarcinomas being most commonly implicated.28 Although both ductal and lobular adenocarcinomas stain positive for cytokeratin 7, estrogen receptor, progesterone receptor, gross cystic disease fluid protein 15, carcinoembryonic antigen, and mammaglobin, only the former shows positivity for e-cadherin markers.3 Conversely, inflammatory carcinoma stains positive for CD31 and podoplanin, telangiectatic carcinoma stains positive for CD31, and mammary Paget disease stains positive for cytokeratin 7 and mucin 1, cell surface associated.3 Apart from cutaneous biopsy, fine-needle aspiration cytology can likewise provide a simple and rapid method of diagnosis with high sensitivity and specificity.14
Conclusion
Although cutaneous metastasis as the presenting sign of a breast malignancy is rare, a high index of suspicion should be exercised when encountering rapid-onset, out-of-place nodules or plaques in female patients, particularly nodules or plaques presenting on the chest.
- Siegel R, Miller K, Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2020 [published online January 8, 2020]. CA Cancer J Clin. 2020;70:7-30.
- Damaskos C, Dimitroulis D, Pergialiotis V, et al. An unexpected metastasis of breast cancer mimicking wheal rush. G Chir. 2016;37:136-138.
- Alcaraz I, Cerroni L, Rütten A, et al. Cutaneous metastases from internal malignancies: a clinicopathologic and immunohistochemical review. Am J Dermatopathol. 2012;34:347-393.
- Wong CYB, Helm MA, Kalb RE, et al. The presentation, pathology, and current management strategies of cutaneous metastasis. N Am J Med Sci. 2013;5:499-504.
- Shagalov D, Xu M, Liebman T, et al. Unilateral indurated plaque in the axilla: a case of metastatic breast carcinoma. Dermatol Online J. 2016;22:13030/qt8vw382nx.
- Lookingbill DP, Spangler N, Helm KF. Cutaneous metastases in patients with metastatic carcinoma: a retrospective study of 4020 patients. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1993;29:228-236.
- Liberati A, Altman DG, Tetzlaff J, et al. The PRISMA statement for reporting systematic reviews and meta-analyses of studies that evaluate health care interventions: explanation and elaboration. J Clin Epidemiol. 2009;62:e1-e34.
- Bansal R, Patel T, Sarin J, et al. Cutaneous and subcutaneous metastases from internal malignancies: an analysis of cases diagnosed by fine needle aspiration. Diagn Cytopathol. 2011;39:882-887.
- Ahmed M. Cutaneous metastases from breast carcinoma. BMJ Case Rep. 2011;2011:bcr0620114398.
- Alani A, Roberts G, Kerr O. Carcinoma en cuirasse. BMJ Case Rep. 2017;2017:bcr2017222121.
- Al Ameer A, Imran M, Kaliyadan F, et al. Carcinoma erysipeloides as a presenting feature of breast carcinoma: a case report and brief review of literature. Indian Dermatol Online J. 2015;6:396-398.
- Bhattacharyya A, Gangopadhyay M, Ghosh K, et al. Wolf in sheep’s clothing: a case of carcinoma erysipeloides. Oxf Med Case Rep. 2016;2016:97-100.
- Carlos Ortega B, Alfaro Mejia A, Gómez-Campos G, et al. Metástasis de carcinoma de mama que simula prototecosis. Dermatol Rev Mex. 2012;56:55-61.
- Chandanwale SS, Gore CR, Buch AC, et al. Zosteriform cutaneous metastasis: a primary manifestation of carcinoma breast, rare case report. Indian J Pathol Microbiol. 2011;54:863-864.
- Cullen Aravena R, Cullen Aravena D, Velasco MJ, et al. Carcinoma hemorrhagiectoides: case report of an uncommon presentation of cutaneous metastatic breast carcinoma. Dermatol Online J. 2017;23:13030/qt3hm3z850.
- Frances L, Cuesta L, Leiva-Salinas M, et al. Secondary mucinous carcinoma of the skin. Dermatol Online J. 2014;20:22361.
- Gaitan-Gaona F, Said MC, Valdes-Rodriguez R. Cutaneous metastatic pigmented breast carcinoma. Dermatol Online J. 2016;22:13030/qt0sv018ck.
- Goodier MA, Jordan JR. Metastatic breast cancer to the lower eyelid. Laryngoscope. 2010;120(suppl 4):S129.
- Lee H-J, Kim J-M, Kim G-W, et al. A unique cutaneous presentation of breast cancer: a red apple stuck in the breast. Ann Dermatol. 2016;28:499-501.
- Mahore SD, Bothale KA, Patrikar AD, et al. Carcinoma en cuirasse : a rare presentation of breast cancer. Indian J Pathol Microbiol. 2010;53:351-358.
- Martí N, Molina I, Monteagudo C, et al. Cutaneous metastasis of breast carcinoma mimicking malignant melanoma in scalp. Dermatol Online J. 2008;14:12.
- Mehenni NN, Gamaz-Bensaou M, Bouzid K. Metastatic breast carcinoma to the gallbladder and the lower eyelid with no malignant lesion in the breast: an unusual case report with a short review of the literature [abstract]. Ann Oncol. 2013;24(suppl 3):iii49.
- O’Brien OA, AboGhaly E, Heffron C. An unusual presentation of a common malignancy [abstract]. J Pathol. 2013;231:S33.
- O’Brien R, Porto DA, Friedman BJ, et al. Elderly female with swelling of the right breast. Ann Emerg Med. 2016;67:e25-e26.
- Oliveira GM de, Zachetti DBC, Barros HR, et al. Breast carcinoma en Cuirasse—case report. An Bras Dermatol. 2013;88:608-610.
- Salati SA, Rather AA. Carcinoma en cuirasse. J Pak Assoc Derma. 2013;23:452-454.
- Santiago F, Saleiro S, Brites MM, et al. A remarkable case of cutaneous metastatic breast carcinoma. Dermatol Online J. 2009;15:10.
- Siqueira VR, Frota AS, Maia IL, et al. Cutaneous involvement as the initial presentation of metastatic breast adenocarcinoma - case report. An Bras Dermatol. 2014;89:960-963.
- Uria M, Chirino C, Rivas D. Inusual clinical presentation of cutaneous metastasis from breast carcinoma. A case report. Rev Argent Dermatol. 2009;90:230-236.
- Virmani NC, Sharma YK, Panicker NK, et al. Zosteriform skin metastases: clue to an undiagnosed breast cancer. Indian J Dermatol. 2011;56:726-727.
- de Souza Weimann ET, Botero EB, Mendes C, et al. Cutaneous metastasis as the first manifestation of occult malignant breast neoplasia. An Bras Dermatol. 2016;91(5 suppl 1):105-107.
- Wu CY, Gao HW, Huang WH, et al. Infection-like acral cutaneous metastasis as the presenting sign of an occult breast cancer. Clin Exp Dermatol. 2009;34:e409-e410.
- Yaghoobi R, Talaizade A, Lal K, et al. Inflammatory breast carcinoma presenting with two different patterns of cutaneous metastases: carcinoma telangiectaticum and carcinoma erysipeloides. J Clin Aesthet Dermatol. 2015;8:47-51.
- Atis G, Demirci GT, Atunay IK, et al. The clinical characteristics and the frequency of metastatic cutaneous tumors among primary skin tumors. Turkderm. 2013;47:166-169.
- Benmously R, Souissi A, Badri T, et al. Cutaneous metastases from internal cancers. Acta Dermatovenerol Alp Pannonica Adriat. 2008;17:167-170.
- Chopra R, Chhabra S, Samra SG, et al. Cutaneous metastases of internal malignancies: a clinicopathologic study. Indian J Dermatol Venereol Leprol. 2010;76:125-131.
- El Khoury J, Khalifeh I, Kibbi AG, et al. Cutaneous metastasis: clinicopathological study of 72 patients from a tertiary care center in Lebanon. Int J Dermatol. 2014;53:147-158.
- Fernandez-Flores A. Cutaneous metastases: a study of 78 biopsies from 69 patients. Am J Dermatopathol. 2010;32:222-239.
- Gómez Sánchez ME, Martinez Martinez ML, Martín De Hijas MC, et al. Metástasis cutáneas de tumores sólidos. Estudio descriptivo retrospectivo. Piel. 2014;29:207-212
- Handa U, Kundu R, Dimri K. Cutaneous metastasis: a study of 138 cases diagnosed by fine-needle aspiration cytology. Acta Cytol. 2017;61:47-54.
- Itin P, Tomaschett S. Cutaneous metastases from malignancies which do not originate from the skin. An epidemiological study. Article in German. Internist (Berl). 2009;50:179-186.
- Siu AL, U.S. Preventive Services Task Force. Screening for breast cancer: U.S. Preventive Services Task Force recommendation statement. Ann Intern Med. 2016;164:279-296.
- Torres HA, Bodey GP, Tarrand JJ, et al. Protothecosis in patients with cancer: case series and literature review. Clin Microbiol Infect. 2003;9:786-792.
Breast cancer is the second most common malignancy in women (after primary skin cancer) and is the second leading cause of cancer-related death in this population. In 2020, the American Cancer Society reported an estimated 276,480 new breast cancer diagnoses and 42,170 breast cancer–related deaths.1 Despite the fact that routine screening with mammography and sonography is standard, the incidence of advanced breast cancer at the time of diagnosis has remained stable over time, suggesting that life-threatening breast cancers are not being caught at an earlier stage. The number of breast cancers with distant metastases at the time of diagnosis also has not decreased.2 Therefore, although screening tests are valuable, they are imperfect and not without limitations.
Cutaneous metastasis is defined as the spread of malignant cells from an internal neoplasm to the skin, which can occur either by contiguous invasion or by distant metastasis through hematogenous or lymphatic routes.3 The diagnosis of cutaneous metastasis requires a high index of suspicion on the part of the clinician.4 Of the various internal malignancies in women, breast cancer most frequently results in metastasis to the skin,5 with up to 24% of patients with metastatic breast cancer developing cutaneous lesions.6
In recent years, there have been multiple reports of skin lesions prompting the diagnosis of a previously unknown breast cancer. In a study by Lookingbill et al,6 6.3% of patients with breast cancer presented with cutaneous involvement at the time of diagnosis, with 3.5% having skin symptoms as the presenting sign. Although there have been studies analyzing cutaneous metastasis from various internal malignancies, none thus far have focused on cutaneous metastasis as a presenting sign of breast cancer. This systematic review aimed to highlight the diverse clinical presentations of cutaneous metastatic breast cancer and their clinical implications.
Methods
Study Selection
This study utilized the PRISMA guidelines for systematic reviews.7 A review of the literature was conducted using the following databases: MEDLINE/PubMed, EMBASE, Cochrane library, CINAHL, and EBSCO.
Search Strategy and Analysis
We completed our search of each of the databases on December 16, 2017, using the phrases cutaneous metastasis and breast cancer to find relevant case reports and retrospective studies. Three authors (C.J., S.R., and M.A.) manually reviewed the resulting abstracts. If an abstract did not include enough information to determine inclusion, the full-text version was reviewed by 2 of the authors (C.J. and S.R.). Two of the authors (C.J. and M.A.) also assessed each source for relevancy and included the articles deemed eligible (Figure 1).

Inclusion criteria were the following: case reports and retrospective studies published in the prior 10 years (January 1, 2007, to December 16, 2017) with human female patients who developed metastatic cutaneous lesions due to a previously unknown primary breast malignancy. Studies published in other languages were included; these articles were translated into English using a human translator or computer translation program (Google Translate). Exclusion criteria were the following: male patients, patients with a known diagnosis of primary breast malignancy prior to the appearance of a metastatic cutaneous lesion, articles focusing on the treatment of breast cancer, and articles without enough details to draw meaningful conclusions.
For a retrospective review to be included, it must have specified the number of breast cancer cases and the number of cutaneous metastases presenting initially or simultaneously to the breast cancer diagnosis. Bansal et al8 defined a simultaneous diagnosis as a skin lesion presenting with other concerns associated with the primary malignancy.
Results
The initial search of MEDLINE/PubMed, EMBASE, Cochrane library, CINAHL, and EBSCO yielded a total of 722 articles. Seven other articles found separately while undergoing our initial research were added to this total. Abstracts were manually screened, with 657 articles discarded after failing to meet the predetermined inclusion criteria. After removal of 25 duplicate articles, the full text of the remaining 47 articles were reviewed, leading to the elimination of an additional 11 articles that did not meet the necessary criteria. This resulted in 36 articles (Figure 1), including 27 individual case reports (Table 1) and 9 retrospective reviews (Table 2). Approximately 13.7% of patients in the 9 retrospective reviews presented with a skin lesion before or simultaneous to the diagnosis of breast cancer (Figure 2).



Forty-one percent (17/41) of the patients with cutaneous metastasis as a presenting feature of their breast cancer fell outside the age range for breast cancer screening recommended by the US Preventive Services Task Force,42 with 24% of the patients younger than 50 years and 17% older than 74 years (Figure 3).

Lesion Characteristics
The most common cutaneous lesions were erythematous nodules and plaques, with a few reports of black17,21 or flesh-colored5,20,31 lesions, as well as ulceration.8,17,32 The most common location for skin lesions was on the thorax (chest or breast), accounting for 57% of the cutaneous metastases, with the arms and axillae being second most commonly involved (15%)(Figure 4). Some cases presented with skin lesions extending to multiple regions. In these cases, each location of the lesion was recorded separately when analyzing the data. An additional 5 cases, shown as “Other” in Figure 4, included the eyelids, occiput, and finger. Eight case reports described symptoms associated with the cutaneous lesions, with painful or tender lesions reported in 7 cases5,9,14,17,20,30,32 and pruritus in 2 cases.12,20 Moreover, 6 case reports presented patients denying any systemic or associated symptoms with their skin lesions.2,5,9,16,17,28 Multiple cases were initially treated as other conditions due to misdiagnosis, including herpes zoster14,30 and dermatitis.11,12

Diagnostic Data
Eighteen cases reported positive immunohistochemistry from cutaneous biopsy (Table 3), given its high specificity in determining the origin of cutaneous metastases, while 8 case reports only performed hematoxylin and eosin staining. One case did not report hematoxylin and eosin or immunohistochemical staining. Table 4 lists the final breast cancer diagnosis for each case.


As per the standard of care, patients were evaluated with mammography or ultrasonography, combined with fine-needle aspiration of a suspected primary tumor, to give a definitive diagnosis of breast cancer. However, 4 cases reported negative mammography and ultrasonography.13,22,28,31 In 3 of these cases, no primary tumor was ever found.13,22,31
Comment
Our systematic review demonstrated that cutaneous lesions may be the first clinical manifestation of an undetected primary malignancy.40 These lesions often occur on the chest but may involve the face, abdomen, or extremities. Although asymptomatic erythematous nodules and plaques are the most common clinical presentations, lesions may be tender or pruritic or may even resemble benign skin conditions, including dermatitis, cellulitis, urticaria, and papulovesicular eruptions, causing them to go unrecognized.
Nevertheless, cutaneous metastasis of a visceral malignancy generally is observed late in the disease course, often following the diagnosis of a primary malignancy.14 Breast cancer is the most common internal malignancy to feature cutaneous spread, with the largest case series revealing a 23.9% rate of cutaneous metastases in females with breast carcinoma.6 Because of its proximity, the chest wall is the most common location for cutaneous lesions of metastatic breast cancer.
Malignant cells from a primary breast tumor may spread to the skin via lymphatic, hematogenous, or contiguous tissue dissemination, as well as iatrogenically through direct implantation during surgical procedures.3 The mechanism of neoplasm spread may likewise influence the clinical appearance of the resulting lesions. The localized lymphedema with a peau d’orange appearance of inflammatory metastatic breast carcinoma or the erythematous plaques of carcinoma erysipeloides are caused by embolized tumor cells obstructing dermal lymphatic vessels.3,11 On the other hand, the indurated erythematous plaques of carcinoma en cuirasse are caused by diffuse cutaneous and subcutaneous infiltration of tumor cells that also may be associated with marked reduction in breast volume.3
A primary breast cancer is classically diagnosed with a combination of clinical breast examination, radiologic imaging (ultrasound, mammogram, breast magnetic resonance imaging, or computed tomography), and fine-needle aspiration or lesional biopsy with histopathology.9 Given that in 20% of metastasized breast cancers the primary tumor may not be identified, a negative breast examination and imaging do not rule out breast cancer, especially if cutaneous biopsy reveals a primary malignancy.43 Histopathology and immunohistochemistry can thereby confirm the presence of metastatic cutaneous lesions and help characterize the breast cancer type involved, with adenocarcinomas being most commonly implicated.28 Although both ductal and lobular adenocarcinomas stain positive for cytokeratin 7, estrogen receptor, progesterone receptor, gross cystic disease fluid protein 15, carcinoembryonic antigen, and mammaglobin, only the former shows positivity for e-cadherin markers.3 Conversely, inflammatory carcinoma stains positive for CD31 and podoplanin, telangiectatic carcinoma stains positive for CD31, and mammary Paget disease stains positive for cytokeratin 7 and mucin 1, cell surface associated.3 Apart from cutaneous biopsy, fine-needle aspiration cytology can likewise provide a simple and rapid method of diagnosis with high sensitivity and specificity.14
Conclusion
Although cutaneous metastasis as the presenting sign of a breast malignancy is rare, a high index of suspicion should be exercised when encountering rapid-onset, out-of-place nodules or plaques in female patients, particularly nodules or plaques presenting on the chest.
Breast cancer is the second most common malignancy in women (after primary skin cancer) and is the second leading cause of cancer-related death in this population. In 2020, the American Cancer Society reported an estimated 276,480 new breast cancer diagnoses and 42,170 breast cancer–related deaths.1 Despite the fact that routine screening with mammography and sonography is standard, the incidence of advanced breast cancer at the time of diagnosis has remained stable over time, suggesting that life-threatening breast cancers are not being caught at an earlier stage. The number of breast cancers with distant metastases at the time of diagnosis also has not decreased.2 Therefore, although screening tests are valuable, they are imperfect and not without limitations.
Cutaneous metastasis is defined as the spread of malignant cells from an internal neoplasm to the skin, which can occur either by contiguous invasion or by distant metastasis through hematogenous or lymphatic routes.3 The diagnosis of cutaneous metastasis requires a high index of suspicion on the part of the clinician.4 Of the various internal malignancies in women, breast cancer most frequently results in metastasis to the skin,5 with up to 24% of patients with metastatic breast cancer developing cutaneous lesions.6
In recent years, there have been multiple reports of skin lesions prompting the diagnosis of a previously unknown breast cancer. In a study by Lookingbill et al,6 6.3% of patients with breast cancer presented with cutaneous involvement at the time of diagnosis, with 3.5% having skin symptoms as the presenting sign. Although there have been studies analyzing cutaneous metastasis from various internal malignancies, none thus far have focused on cutaneous metastasis as a presenting sign of breast cancer. This systematic review aimed to highlight the diverse clinical presentations of cutaneous metastatic breast cancer and their clinical implications.
Methods
Study Selection
This study utilized the PRISMA guidelines for systematic reviews.7 A review of the literature was conducted using the following databases: MEDLINE/PubMed, EMBASE, Cochrane library, CINAHL, and EBSCO.
Search Strategy and Analysis
We completed our search of each of the databases on December 16, 2017, using the phrases cutaneous metastasis and breast cancer to find relevant case reports and retrospective studies. Three authors (C.J., S.R., and M.A.) manually reviewed the resulting abstracts. If an abstract did not include enough information to determine inclusion, the full-text version was reviewed by 2 of the authors (C.J. and S.R.). Two of the authors (C.J. and M.A.) also assessed each source for relevancy and included the articles deemed eligible (Figure 1).

Inclusion criteria were the following: case reports and retrospective studies published in the prior 10 years (January 1, 2007, to December 16, 2017) with human female patients who developed metastatic cutaneous lesions due to a previously unknown primary breast malignancy. Studies published in other languages were included; these articles were translated into English using a human translator or computer translation program (Google Translate). Exclusion criteria were the following: male patients, patients with a known diagnosis of primary breast malignancy prior to the appearance of a metastatic cutaneous lesion, articles focusing on the treatment of breast cancer, and articles without enough details to draw meaningful conclusions.
For a retrospective review to be included, it must have specified the number of breast cancer cases and the number of cutaneous metastases presenting initially or simultaneously to the breast cancer diagnosis. Bansal et al8 defined a simultaneous diagnosis as a skin lesion presenting with other concerns associated with the primary malignancy.
Results
The initial search of MEDLINE/PubMed, EMBASE, Cochrane library, CINAHL, and EBSCO yielded a total of 722 articles. Seven other articles found separately while undergoing our initial research were added to this total. Abstracts were manually screened, with 657 articles discarded after failing to meet the predetermined inclusion criteria. After removal of 25 duplicate articles, the full text of the remaining 47 articles were reviewed, leading to the elimination of an additional 11 articles that did not meet the necessary criteria. This resulted in 36 articles (Figure 1), including 27 individual case reports (Table 1) and 9 retrospective reviews (Table 2). Approximately 13.7% of patients in the 9 retrospective reviews presented with a skin lesion before or simultaneous to the diagnosis of breast cancer (Figure 2).



Forty-one percent (17/41) of the patients with cutaneous metastasis as a presenting feature of their breast cancer fell outside the age range for breast cancer screening recommended by the US Preventive Services Task Force,42 with 24% of the patients younger than 50 years and 17% older than 74 years (Figure 3).

Lesion Characteristics
The most common cutaneous lesions were erythematous nodules and plaques, with a few reports of black17,21 or flesh-colored5,20,31 lesions, as well as ulceration.8,17,32 The most common location for skin lesions was on the thorax (chest or breast), accounting for 57% of the cutaneous metastases, with the arms and axillae being second most commonly involved (15%)(Figure 4). Some cases presented with skin lesions extending to multiple regions. In these cases, each location of the lesion was recorded separately when analyzing the data. An additional 5 cases, shown as “Other” in Figure 4, included the eyelids, occiput, and finger. Eight case reports described symptoms associated with the cutaneous lesions, with painful or tender lesions reported in 7 cases5,9,14,17,20,30,32 and pruritus in 2 cases.12,20 Moreover, 6 case reports presented patients denying any systemic or associated symptoms with their skin lesions.2,5,9,16,17,28 Multiple cases were initially treated as other conditions due to misdiagnosis, including herpes zoster14,30 and dermatitis.11,12

Diagnostic Data
Eighteen cases reported positive immunohistochemistry from cutaneous biopsy (Table 3), given its high specificity in determining the origin of cutaneous metastases, while 8 case reports only performed hematoxylin and eosin staining. One case did not report hematoxylin and eosin or immunohistochemical staining. Table 4 lists the final breast cancer diagnosis for each case.


As per the standard of care, patients were evaluated with mammography or ultrasonography, combined with fine-needle aspiration of a suspected primary tumor, to give a definitive diagnosis of breast cancer. However, 4 cases reported negative mammography and ultrasonography.13,22,28,31 In 3 of these cases, no primary tumor was ever found.13,22,31
Comment
Our systematic review demonstrated that cutaneous lesions may be the first clinical manifestation of an undetected primary malignancy.40 These lesions often occur on the chest but may involve the face, abdomen, or extremities. Although asymptomatic erythematous nodules and plaques are the most common clinical presentations, lesions may be tender or pruritic or may even resemble benign skin conditions, including dermatitis, cellulitis, urticaria, and papulovesicular eruptions, causing them to go unrecognized.
Nevertheless, cutaneous metastasis of a visceral malignancy generally is observed late in the disease course, often following the diagnosis of a primary malignancy.14 Breast cancer is the most common internal malignancy to feature cutaneous spread, with the largest case series revealing a 23.9% rate of cutaneous metastases in females with breast carcinoma.6 Because of its proximity, the chest wall is the most common location for cutaneous lesions of metastatic breast cancer.
Malignant cells from a primary breast tumor may spread to the skin via lymphatic, hematogenous, or contiguous tissue dissemination, as well as iatrogenically through direct implantation during surgical procedures.3 The mechanism of neoplasm spread may likewise influence the clinical appearance of the resulting lesions. The localized lymphedema with a peau d’orange appearance of inflammatory metastatic breast carcinoma or the erythematous plaques of carcinoma erysipeloides are caused by embolized tumor cells obstructing dermal lymphatic vessels.3,11 On the other hand, the indurated erythematous plaques of carcinoma en cuirasse are caused by diffuse cutaneous and subcutaneous infiltration of tumor cells that also may be associated with marked reduction in breast volume.3
A primary breast cancer is classically diagnosed with a combination of clinical breast examination, radiologic imaging (ultrasound, mammogram, breast magnetic resonance imaging, or computed tomography), and fine-needle aspiration or lesional biopsy with histopathology.9 Given that in 20% of metastasized breast cancers the primary tumor may not be identified, a negative breast examination and imaging do not rule out breast cancer, especially if cutaneous biopsy reveals a primary malignancy.43 Histopathology and immunohistochemistry can thereby confirm the presence of metastatic cutaneous lesions and help characterize the breast cancer type involved, with adenocarcinomas being most commonly implicated.28 Although both ductal and lobular adenocarcinomas stain positive for cytokeratin 7, estrogen receptor, progesterone receptor, gross cystic disease fluid protein 15, carcinoembryonic antigen, and mammaglobin, only the former shows positivity for e-cadherin markers.3 Conversely, inflammatory carcinoma stains positive for CD31 and podoplanin, telangiectatic carcinoma stains positive for CD31, and mammary Paget disease stains positive for cytokeratin 7 and mucin 1, cell surface associated.3 Apart from cutaneous biopsy, fine-needle aspiration cytology can likewise provide a simple and rapid method of diagnosis with high sensitivity and specificity.14
Conclusion
Although cutaneous metastasis as the presenting sign of a breast malignancy is rare, a high index of suspicion should be exercised when encountering rapid-onset, out-of-place nodules or plaques in female patients, particularly nodules or plaques presenting on the chest.
- Siegel R, Miller K, Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2020 [published online January 8, 2020]. CA Cancer J Clin. 2020;70:7-30.
- Damaskos C, Dimitroulis D, Pergialiotis V, et al. An unexpected metastasis of breast cancer mimicking wheal rush. G Chir. 2016;37:136-138.
- Alcaraz I, Cerroni L, Rütten A, et al. Cutaneous metastases from internal malignancies: a clinicopathologic and immunohistochemical review. Am J Dermatopathol. 2012;34:347-393.
- Wong CYB, Helm MA, Kalb RE, et al. The presentation, pathology, and current management strategies of cutaneous metastasis. N Am J Med Sci. 2013;5:499-504.
- Shagalov D, Xu M, Liebman T, et al. Unilateral indurated plaque in the axilla: a case of metastatic breast carcinoma. Dermatol Online J. 2016;22:13030/qt8vw382nx.
- Lookingbill DP, Spangler N, Helm KF. Cutaneous metastases in patients with metastatic carcinoma: a retrospective study of 4020 patients. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1993;29:228-236.
- Liberati A, Altman DG, Tetzlaff J, et al. The PRISMA statement for reporting systematic reviews and meta-analyses of studies that evaluate health care interventions: explanation and elaboration. J Clin Epidemiol. 2009;62:e1-e34.
- Bansal R, Patel T, Sarin J, et al. Cutaneous and subcutaneous metastases from internal malignancies: an analysis of cases diagnosed by fine needle aspiration. Diagn Cytopathol. 2011;39:882-887.
- Ahmed M. Cutaneous metastases from breast carcinoma. BMJ Case Rep. 2011;2011:bcr0620114398.
- Alani A, Roberts G, Kerr O. Carcinoma en cuirasse. BMJ Case Rep. 2017;2017:bcr2017222121.
- Al Ameer A, Imran M, Kaliyadan F, et al. Carcinoma erysipeloides as a presenting feature of breast carcinoma: a case report and brief review of literature. Indian Dermatol Online J. 2015;6:396-398.
- Bhattacharyya A, Gangopadhyay M, Ghosh K, et al. Wolf in sheep’s clothing: a case of carcinoma erysipeloides. Oxf Med Case Rep. 2016;2016:97-100.
- Carlos Ortega B, Alfaro Mejia A, Gómez-Campos G, et al. Metástasis de carcinoma de mama que simula prototecosis. Dermatol Rev Mex. 2012;56:55-61.
- Chandanwale SS, Gore CR, Buch AC, et al. Zosteriform cutaneous metastasis: a primary manifestation of carcinoma breast, rare case report. Indian J Pathol Microbiol. 2011;54:863-864.
- Cullen Aravena R, Cullen Aravena D, Velasco MJ, et al. Carcinoma hemorrhagiectoides: case report of an uncommon presentation of cutaneous metastatic breast carcinoma. Dermatol Online J. 2017;23:13030/qt3hm3z850.
- Frances L, Cuesta L, Leiva-Salinas M, et al. Secondary mucinous carcinoma of the skin. Dermatol Online J. 2014;20:22361.
- Gaitan-Gaona F, Said MC, Valdes-Rodriguez R. Cutaneous metastatic pigmented breast carcinoma. Dermatol Online J. 2016;22:13030/qt0sv018ck.
- Goodier MA, Jordan JR. Metastatic breast cancer to the lower eyelid. Laryngoscope. 2010;120(suppl 4):S129.
- Lee H-J, Kim J-M, Kim G-W, et al. A unique cutaneous presentation of breast cancer: a red apple stuck in the breast. Ann Dermatol. 2016;28:499-501.
- Mahore SD, Bothale KA, Patrikar AD, et al. Carcinoma en cuirasse : a rare presentation of breast cancer. Indian J Pathol Microbiol. 2010;53:351-358.
- Martí N, Molina I, Monteagudo C, et al. Cutaneous metastasis of breast carcinoma mimicking malignant melanoma in scalp. Dermatol Online J. 2008;14:12.
- Mehenni NN, Gamaz-Bensaou M, Bouzid K. Metastatic breast carcinoma to the gallbladder and the lower eyelid with no malignant lesion in the breast: an unusual case report with a short review of the literature [abstract]. Ann Oncol. 2013;24(suppl 3):iii49.
- O’Brien OA, AboGhaly E, Heffron C. An unusual presentation of a common malignancy [abstract]. J Pathol. 2013;231:S33.
- O’Brien R, Porto DA, Friedman BJ, et al. Elderly female with swelling of the right breast. Ann Emerg Med. 2016;67:e25-e26.
- Oliveira GM de, Zachetti DBC, Barros HR, et al. Breast carcinoma en Cuirasse—case report. An Bras Dermatol. 2013;88:608-610.
- Salati SA, Rather AA. Carcinoma en cuirasse. J Pak Assoc Derma. 2013;23:452-454.
- Santiago F, Saleiro S, Brites MM, et al. A remarkable case of cutaneous metastatic breast carcinoma. Dermatol Online J. 2009;15:10.
- Siqueira VR, Frota AS, Maia IL, et al. Cutaneous involvement as the initial presentation of metastatic breast adenocarcinoma - case report. An Bras Dermatol. 2014;89:960-963.
- Uria M, Chirino C, Rivas D. Inusual clinical presentation of cutaneous metastasis from breast carcinoma. A case report. Rev Argent Dermatol. 2009;90:230-236.
- Virmani NC, Sharma YK, Panicker NK, et al. Zosteriform skin metastases: clue to an undiagnosed breast cancer. Indian J Dermatol. 2011;56:726-727.
- de Souza Weimann ET, Botero EB, Mendes C, et al. Cutaneous metastasis as the first manifestation of occult malignant breast neoplasia. An Bras Dermatol. 2016;91(5 suppl 1):105-107.
- Wu CY, Gao HW, Huang WH, et al. Infection-like acral cutaneous metastasis as the presenting sign of an occult breast cancer. Clin Exp Dermatol. 2009;34:e409-e410.
- Yaghoobi R, Talaizade A, Lal K, et al. Inflammatory breast carcinoma presenting with two different patterns of cutaneous metastases: carcinoma telangiectaticum and carcinoma erysipeloides. J Clin Aesthet Dermatol. 2015;8:47-51.
- Atis G, Demirci GT, Atunay IK, et al. The clinical characteristics and the frequency of metastatic cutaneous tumors among primary skin tumors. Turkderm. 2013;47:166-169.
- Benmously R, Souissi A, Badri T, et al. Cutaneous metastases from internal cancers. Acta Dermatovenerol Alp Pannonica Adriat. 2008;17:167-170.
- Chopra R, Chhabra S, Samra SG, et al. Cutaneous metastases of internal malignancies: a clinicopathologic study. Indian J Dermatol Venereol Leprol. 2010;76:125-131.
- El Khoury J, Khalifeh I, Kibbi AG, et al. Cutaneous metastasis: clinicopathological study of 72 patients from a tertiary care center in Lebanon. Int J Dermatol. 2014;53:147-158.
- Fernandez-Flores A. Cutaneous metastases: a study of 78 biopsies from 69 patients. Am J Dermatopathol. 2010;32:222-239.
- Gómez Sánchez ME, Martinez Martinez ML, Martín De Hijas MC, et al. Metástasis cutáneas de tumores sólidos. Estudio descriptivo retrospectivo. Piel. 2014;29:207-212
- Handa U, Kundu R, Dimri K. Cutaneous metastasis: a study of 138 cases diagnosed by fine-needle aspiration cytology. Acta Cytol. 2017;61:47-54.
- Itin P, Tomaschett S. Cutaneous metastases from malignancies which do not originate from the skin. An epidemiological study. Article in German. Internist (Berl). 2009;50:179-186.
- Siu AL, U.S. Preventive Services Task Force. Screening for breast cancer: U.S. Preventive Services Task Force recommendation statement. Ann Intern Med. 2016;164:279-296.
- Torres HA, Bodey GP, Tarrand JJ, et al. Protothecosis in patients with cancer: case series and literature review. Clin Microbiol Infect. 2003;9:786-792.
- Siegel R, Miller K, Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2020 [published online January 8, 2020]. CA Cancer J Clin. 2020;70:7-30.
- Damaskos C, Dimitroulis D, Pergialiotis V, et al. An unexpected metastasis of breast cancer mimicking wheal rush. G Chir. 2016;37:136-138.
- Alcaraz I, Cerroni L, Rütten A, et al. Cutaneous metastases from internal malignancies: a clinicopathologic and immunohistochemical review. Am J Dermatopathol. 2012;34:347-393.
- Wong CYB, Helm MA, Kalb RE, et al. The presentation, pathology, and current management strategies of cutaneous metastasis. N Am J Med Sci. 2013;5:499-504.
- Shagalov D, Xu M, Liebman T, et al. Unilateral indurated plaque in the axilla: a case of metastatic breast carcinoma. Dermatol Online J. 2016;22:13030/qt8vw382nx.
- Lookingbill DP, Spangler N, Helm KF. Cutaneous metastases in patients with metastatic carcinoma: a retrospective study of 4020 patients. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1993;29:228-236.
- Liberati A, Altman DG, Tetzlaff J, et al. The PRISMA statement for reporting systematic reviews and meta-analyses of studies that evaluate health care interventions: explanation and elaboration. J Clin Epidemiol. 2009;62:e1-e34.
- Bansal R, Patel T, Sarin J, et al. Cutaneous and subcutaneous metastases from internal malignancies: an analysis of cases diagnosed by fine needle aspiration. Diagn Cytopathol. 2011;39:882-887.
- Ahmed M. Cutaneous metastases from breast carcinoma. BMJ Case Rep. 2011;2011:bcr0620114398.
- Alani A, Roberts G, Kerr O. Carcinoma en cuirasse. BMJ Case Rep. 2017;2017:bcr2017222121.
- Al Ameer A, Imran M, Kaliyadan F, et al. Carcinoma erysipeloides as a presenting feature of breast carcinoma: a case report and brief review of literature. Indian Dermatol Online J. 2015;6:396-398.
- Bhattacharyya A, Gangopadhyay M, Ghosh K, et al. Wolf in sheep’s clothing: a case of carcinoma erysipeloides. Oxf Med Case Rep. 2016;2016:97-100.
- Carlos Ortega B, Alfaro Mejia A, Gómez-Campos G, et al. Metástasis de carcinoma de mama que simula prototecosis. Dermatol Rev Mex. 2012;56:55-61.
- Chandanwale SS, Gore CR, Buch AC, et al. Zosteriform cutaneous metastasis: a primary manifestation of carcinoma breast, rare case report. Indian J Pathol Microbiol. 2011;54:863-864.
- Cullen Aravena R, Cullen Aravena D, Velasco MJ, et al. Carcinoma hemorrhagiectoides: case report of an uncommon presentation of cutaneous metastatic breast carcinoma. Dermatol Online J. 2017;23:13030/qt3hm3z850.
- Frances L, Cuesta L, Leiva-Salinas M, et al. Secondary mucinous carcinoma of the skin. Dermatol Online J. 2014;20:22361.
- Gaitan-Gaona F, Said MC, Valdes-Rodriguez R. Cutaneous metastatic pigmented breast carcinoma. Dermatol Online J. 2016;22:13030/qt0sv018ck.
- Goodier MA, Jordan JR. Metastatic breast cancer to the lower eyelid. Laryngoscope. 2010;120(suppl 4):S129.
- Lee H-J, Kim J-M, Kim G-W, et al. A unique cutaneous presentation of breast cancer: a red apple stuck in the breast. Ann Dermatol. 2016;28:499-501.
- Mahore SD, Bothale KA, Patrikar AD, et al. Carcinoma en cuirasse : a rare presentation of breast cancer. Indian J Pathol Microbiol. 2010;53:351-358.
- Martí N, Molina I, Monteagudo C, et al. Cutaneous metastasis of breast carcinoma mimicking malignant melanoma in scalp. Dermatol Online J. 2008;14:12.
- Mehenni NN, Gamaz-Bensaou M, Bouzid K. Metastatic breast carcinoma to the gallbladder and the lower eyelid with no malignant lesion in the breast: an unusual case report with a short review of the literature [abstract]. Ann Oncol. 2013;24(suppl 3):iii49.
- O’Brien OA, AboGhaly E, Heffron C. An unusual presentation of a common malignancy [abstract]. J Pathol. 2013;231:S33.
- O’Brien R, Porto DA, Friedman BJ, et al. Elderly female with swelling of the right breast. Ann Emerg Med. 2016;67:e25-e26.
- Oliveira GM de, Zachetti DBC, Barros HR, et al. Breast carcinoma en Cuirasse—case report. An Bras Dermatol. 2013;88:608-610.
- Salati SA, Rather AA. Carcinoma en cuirasse. J Pak Assoc Derma. 2013;23:452-454.
- Santiago F, Saleiro S, Brites MM, et al. A remarkable case of cutaneous metastatic breast carcinoma. Dermatol Online J. 2009;15:10.
- Siqueira VR, Frota AS, Maia IL, et al. Cutaneous involvement as the initial presentation of metastatic breast adenocarcinoma - case report. An Bras Dermatol. 2014;89:960-963.
- Uria M, Chirino C, Rivas D. Inusual clinical presentation of cutaneous metastasis from breast carcinoma. A case report. Rev Argent Dermatol. 2009;90:230-236.
- Virmani NC, Sharma YK, Panicker NK, et al. Zosteriform skin metastases: clue to an undiagnosed breast cancer. Indian J Dermatol. 2011;56:726-727.
- de Souza Weimann ET, Botero EB, Mendes C, et al. Cutaneous metastasis as the first manifestation of occult malignant breast neoplasia. An Bras Dermatol. 2016;91(5 suppl 1):105-107.
- Wu CY, Gao HW, Huang WH, et al. Infection-like acral cutaneous metastasis as the presenting sign of an occult breast cancer. Clin Exp Dermatol. 2009;34:e409-e410.
- Yaghoobi R, Talaizade A, Lal K, et al. Inflammatory breast carcinoma presenting with two different patterns of cutaneous metastases: carcinoma telangiectaticum and carcinoma erysipeloides. J Clin Aesthet Dermatol. 2015;8:47-51.
- Atis G, Demirci GT, Atunay IK, et al. The clinical characteristics and the frequency of metastatic cutaneous tumors among primary skin tumors. Turkderm. 2013;47:166-169.
- Benmously R, Souissi A, Badri T, et al. Cutaneous metastases from internal cancers. Acta Dermatovenerol Alp Pannonica Adriat. 2008;17:167-170.
- Chopra R, Chhabra S, Samra SG, et al. Cutaneous metastases of internal malignancies: a clinicopathologic study. Indian J Dermatol Venereol Leprol. 2010;76:125-131.
- El Khoury J, Khalifeh I, Kibbi AG, et al. Cutaneous metastasis: clinicopathological study of 72 patients from a tertiary care center in Lebanon. Int J Dermatol. 2014;53:147-158.
- Fernandez-Flores A. Cutaneous metastases: a study of 78 biopsies from 69 patients. Am J Dermatopathol. 2010;32:222-239.
- Gómez Sánchez ME, Martinez Martinez ML, Martín De Hijas MC, et al. Metástasis cutáneas de tumores sólidos. Estudio descriptivo retrospectivo. Piel. 2014;29:207-212
- Handa U, Kundu R, Dimri K. Cutaneous metastasis: a study of 138 cases diagnosed by fine-needle aspiration cytology. Acta Cytol. 2017;61:47-54.
- Itin P, Tomaschett S. Cutaneous metastases from malignancies which do not originate from the skin. An epidemiological study. Article in German. Internist (Berl). 2009;50:179-186.
- Siu AL, U.S. Preventive Services Task Force. Screening for breast cancer: U.S. Preventive Services Task Force recommendation statement. Ann Intern Med. 2016;164:279-296.
- Torres HA, Bodey GP, Tarrand JJ, et al. Protothecosis in patients with cancer: case series and literature review. Clin Microbiol Infect. 2003;9:786-792.
PRACTICE POINTS
- Dermatologists may play a role in diagnosing breast cancer through cutaneous metastasis, even in patients without a history of breast cancer.
- Clinicians should consider breast cancer metastasis in the differential for any erythematous lesion on the trunk.
Contact dermatitis content varies among social media sites
on YouTube, Facebook, Instagram, Google, Twitter, and Reddit.
Data on social media use suggest that approximately 65% of U.S. adults regularly use social media, and 40% of individuals use it in making medical decisions, Morgan Nguyen, a medical student at Northwestern University, Chicago, said at the annual meeting of the American Contact Dermatitis Society, held virtually this year.
“Dermatologists’ awareness of social media discussions can further their understanding of where patients go for information and what they might encounter,” she said. In particular, “contact dermatitis practitioners can tailor their counseling by knowing what their patients are seeing online.”
To characterize the social media landscape for content related to allergic contact dermatitis (ACD), Ms. Nguyen and colleagues assessed metrics on content and authorship on six different platforms.
For YouTube, the authors reviewed 15 videos related to ACD with views ranging from 24,262 to 232,300. Of these videos, two were produced as medical education, four were produced by patients, and nine were produced by physicians. The content of many videos was poor quality, with an average QUEST score of 7.4/28 overall and 8.7 for physician videos. Video quality was not associated with increased views. Video titles included “What to do if you have a rash on your face,” and “Contact dermatitis on lips!”
Overall, Instagram was more popular than Twitter, particularly among patients. The investigators searched using the hashtags #ContactDermatitis, #AllergicContactDermatitis, and #ContactDerm and reviewed the 100 most recent posts for authorship. The most recent 100 posts occurred over 16 days; physicians, patients, and companies each contributed approximately one-third of the content, but patient content was more focused on symptoms, treatment progress, and advice.
For Instagram, the hashtag search phrase made a notable difference in authorship, Ms. Nguyen said. Physicians were disproportionately more likely to use #AllergicContactDermatitis (43%) compared with patients (22%).
On Twitter, the most recent 100 posts were spread over 152 days, and professional organizations and companies generated approximately two-thirds of the posts. The #ContactDermatitis hashtag was the most common, and accounted for 94% of tweets.
Although patient support groups specific to ACD exist on Facebook, the researchers found none on Reddit. These two venues are designed for creating online communities, rather than simply providing information, and the researchers searched for support groups related to contact dermatitis. One of the main differences between the two is that Facebook allows for the creation of private groups, while Reddit is an open forum.
The largest contact dermatitis Facebook group, the “Eczema, Contact Dermatitis and Patch Testing Alliance,” had 4,665 members at the time of the study, and most groups were private. Although no support groups existed on Reddit, titles of Reddit forums discussing ACD included allergies, askdoctors, fragrance, haircarescience, legaladvice, skincareaddicts, beauty, dermatologyquestions, medical_advice, skincare_addiction, tretinoin, and vulvodynia.
For Google, the researchers used terms similar to “contact dermatitis” as generated by the Google Keyword Planner tool, and used Google Adwords data to estimate monthly searches. The top estimated term was “contact dermatitis,” with 8,322 searches, followed by “contact dermatitis pictures,” with 1,666 searches, and “contact dermatitis treatment” with 595 searches. By contrast, “allergic dermatitis” had an estimated 346 monthly searches, and “allergic contact dermatitis” had 194.
Overall, approximately 9,000 searches each month involve “contact dermatitis,” “allergic contact dermatitis,” or “allergic dermatitis,” said Ms. Nguyen. However, these estimated searches seemed comparatively low, given the high burden of ACD, she said. Although ACD ranks eighth among skin diseases based on health care costs, psoriasis (fourteenth based on health care costs) shows an estimated monthly Google search volume of 600,462, she pointed out.
The study findings were limited by several factors including the potential impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on social media use, and by the lack of specificity associated with the search term “contact dermatitis,” which is not unique to ACD, Ms. Nguyen said.
Although more research on quality assessment is needed, the results suggest that social media is a popular venue for ACD patients to seek and share information, Ms. Nguyen emphasized. There is an opportunity for patch testing physicians to create and disperse educational content for patients using these sites, she concluded.
Study highlights education opportunities
“Due to the pandemic, patients have been increasingly interacting with online resources in lieu of coming to a physician’s office,” corresponding author Walter J. Liszewski, MD, of the department of dermatology, Northwestern University, Chicago, said in an interview. “As social media is increasingly used by patients and physicians, it is important to get a sense of its footprint,” he said.
He and Ms. Nguyen were surprised by several of their findings: First, searches for ACD on Google were not particularly common given its relatively high prevalence and economic cost to society. In addition, they found that physicians often used different language than that of patients to describe ACD on Twitter and Instagram. They were also surprised at how often ACD appeared in Reddit posts, which they noted highlights that ACD impacts multiple sections of society.
The greatest challenge in studying social media and medicine is the quality of material available, Dr. Liszewski and Ms. Nguyen observed, emphasizing that while there are numerous videos on ACD on YouTube, the quality is highly variable, and there is a need for more patient-centered, educational materials. However, the results of their study highlight the opportunity for physicians and industry to create medically-accurate educational materials, they added.
Ms. Nguyen and Dr. Liszewski had no financial conflicts to disclose.
on YouTube, Facebook, Instagram, Google, Twitter, and Reddit.
Data on social media use suggest that approximately 65% of U.S. adults regularly use social media, and 40% of individuals use it in making medical decisions, Morgan Nguyen, a medical student at Northwestern University, Chicago, said at the annual meeting of the American Contact Dermatitis Society, held virtually this year.
“Dermatologists’ awareness of social media discussions can further their understanding of where patients go for information and what they might encounter,” she said. In particular, “contact dermatitis practitioners can tailor their counseling by knowing what their patients are seeing online.”
To characterize the social media landscape for content related to allergic contact dermatitis (ACD), Ms. Nguyen and colleagues assessed metrics on content and authorship on six different platforms.
For YouTube, the authors reviewed 15 videos related to ACD with views ranging from 24,262 to 232,300. Of these videos, two were produced as medical education, four were produced by patients, and nine were produced by physicians. The content of many videos was poor quality, with an average QUEST score of 7.4/28 overall and 8.7 for physician videos. Video quality was not associated with increased views. Video titles included “What to do if you have a rash on your face,” and “Contact dermatitis on lips!”
Overall, Instagram was more popular than Twitter, particularly among patients. The investigators searched using the hashtags #ContactDermatitis, #AllergicContactDermatitis, and #ContactDerm and reviewed the 100 most recent posts for authorship. The most recent 100 posts occurred over 16 days; physicians, patients, and companies each contributed approximately one-third of the content, but patient content was more focused on symptoms, treatment progress, and advice.
For Instagram, the hashtag search phrase made a notable difference in authorship, Ms. Nguyen said. Physicians were disproportionately more likely to use #AllergicContactDermatitis (43%) compared with patients (22%).
On Twitter, the most recent 100 posts were spread over 152 days, and professional organizations and companies generated approximately two-thirds of the posts. The #ContactDermatitis hashtag was the most common, and accounted for 94% of tweets.
Although patient support groups specific to ACD exist on Facebook, the researchers found none on Reddit. These two venues are designed for creating online communities, rather than simply providing information, and the researchers searched for support groups related to contact dermatitis. One of the main differences between the two is that Facebook allows for the creation of private groups, while Reddit is an open forum.
The largest contact dermatitis Facebook group, the “Eczema, Contact Dermatitis and Patch Testing Alliance,” had 4,665 members at the time of the study, and most groups were private. Although no support groups existed on Reddit, titles of Reddit forums discussing ACD included allergies, askdoctors, fragrance, haircarescience, legaladvice, skincareaddicts, beauty, dermatologyquestions, medical_advice, skincare_addiction, tretinoin, and vulvodynia.
For Google, the researchers used terms similar to “contact dermatitis” as generated by the Google Keyword Planner tool, and used Google Adwords data to estimate monthly searches. The top estimated term was “contact dermatitis,” with 8,322 searches, followed by “contact dermatitis pictures,” with 1,666 searches, and “contact dermatitis treatment” with 595 searches. By contrast, “allergic dermatitis” had an estimated 346 monthly searches, and “allergic contact dermatitis” had 194.
Overall, approximately 9,000 searches each month involve “contact dermatitis,” “allergic contact dermatitis,” or “allergic dermatitis,” said Ms. Nguyen. However, these estimated searches seemed comparatively low, given the high burden of ACD, she said. Although ACD ranks eighth among skin diseases based on health care costs, psoriasis (fourteenth based on health care costs) shows an estimated monthly Google search volume of 600,462, she pointed out.
The study findings were limited by several factors including the potential impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on social media use, and by the lack of specificity associated with the search term “contact dermatitis,” which is not unique to ACD, Ms. Nguyen said.
Although more research on quality assessment is needed, the results suggest that social media is a popular venue for ACD patients to seek and share information, Ms. Nguyen emphasized. There is an opportunity for patch testing physicians to create and disperse educational content for patients using these sites, she concluded.
Study highlights education opportunities
“Due to the pandemic, patients have been increasingly interacting with online resources in lieu of coming to a physician’s office,” corresponding author Walter J. Liszewski, MD, of the department of dermatology, Northwestern University, Chicago, said in an interview. “As social media is increasingly used by patients and physicians, it is important to get a sense of its footprint,” he said.
He and Ms. Nguyen were surprised by several of their findings: First, searches for ACD on Google were not particularly common given its relatively high prevalence and economic cost to society. In addition, they found that physicians often used different language than that of patients to describe ACD on Twitter and Instagram. They were also surprised at how often ACD appeared in Reddit posts, which they noted highlights that ACD impacts multiple sections of society.
The greatest challenge in studying social media and medicine is the quality of material available, Dr. Liszewski and Ms. Nguyen observed, emphasizing that while there are numerous videos on ACD on YouTube, the quality is highly variable, and there is a need for more patient-centered, educational materials. However, the results of their study highlight the opportunity for physicians and industry to create medically-accurate educational materials, they added.
Ms. Nguyen and Dr. Liszewski had no financial conflicts to disclose.
on YouTube, Facebook, Instagram, Google, Twitter, and Reddit.
Data on social media use suggest that approximately 65% of U.S. adults regularly use social media, and 40% of individuals use it in making medical decisions, Morgan Nguyen, a medical student at Northwestern University, Chicago, said at the annual meeting of the American Contact Dermatitis Society, held virtually this year.
“Dermatologists’ awareness of social media discussions can further their understanding of where patients go for information and what they might encounter,” she said. In particular, “contact dermatitis practitioners can tailor their counseling by knowing what their patients are seeing online.”
To characterize the social media landscape for content related to allergic contact dermatitis (ACD), Ms. Nguyen and colleagues assessed metrics on content and authorship on six different platforms.
For YouTube, the authors reviewed 15 videos related to ACD with views ranging from 24,262 to 232,300. Of these videos, two were produced as medical education, four were produced by patients, and nine were produced by physicians. The content of many videos was poor quality, with an average QUEST score of 7.4/28 overall and 8.7 for physician videos. Video quality was not associated with increased views. Video titles included “What to do if you have a rash on your face,” and “Contact dermatitis on lips!”
Overall, Instagram was more popular than Twitter, particularly among patients. The investigators searched using the hashtags #ContactDermatitis, #AllergicContactDermatitis, and #ContactDerm and reviewed the 100 most recent posts for authorship. The most recent 100 posts occurred over 16 days; physicians, patients, and companies each contributed approximately one-third of the content, but patient content was more focused on symptoms, treatment progress, and advice.
For Instagram, the hashtag search phrase made a notable difference in authorship, Ms. Nguyen said. Physicians were disproportionately more likely to use #AllergicContactDermatitis (43%) compared with patients (22%).
On Twitter, the most recent 100 posts were spread over 152 days, and professional organizations and companies generated approximately two-thirds of the posts. The #ContactDermatitis hashtag was the most common, and accounted for 94% of tweets.
Although patient support groups specific to ACD exist on Facebook, the researchers found none on Reddit. These two venues are designed for creating online communities, rather than simply providing information, and the researchers searched for support groups related to contact dermatitis. One of the main differences between the two is that Facebook allows for the creation of private groups, while Reddit is an open forum.
The largest contact dermatitis Facebook group, the “Eczema, Contact Dermatitis and Patch Testing Alliance,” had 4,665 members at the time of the study, and most groups were private. Although no support groups existed on Reddit, titles of Reddit forums discussing ACD included allergies, askdoctors, fragrance, haircarescience, legaladvice, skincareaddicts, beauty, dermatologyquestions, medical_advice, skincare_addiction, tretinoin, and vulvodynia.
For Google, the researchers used terms similar to “contact dermatitis” as generated by the Google Keyword Planner tool, and used Google Adwords data to estimate monthly searches. The top estimated term was “contact dermatitis,” with 8,322 searches, followed by “contact dermatitis pictures,” with 1,666 searches, and “contact dermatitis treatment” with 595 searches. By contrast, “allergic dermatitis” had an estimated 346 monthly searches, and “allergic contact dermatitis” had 194.
Overall, approximately 9,000 searches each month involve “contact dermatitis,” “allergic contact dermatitis,” or “allergic dermatitis,” said Ms. Nguyen. However, these estimated searches seemed comparatively low, given the high burden of ACD, she said. Although ACD ranks eighth among skin diseases based on health care costs, psoriasis (fourteenth based on health care costs) shows an estimated monthly Google search volume of 600,462, she pointed out.
The study findings were limited by several factors including the potential impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on social media use, and by the lack of specificity associated with the search term “contact dermatitis,” which is not unique to ACD, Ms. Nguyen said.
Although more research on quality assessment is needed, the results suggest that social media is a popular venue for ACD patients to seek and share information, Ms. Nguyen emphasized. There is an opportunity for patch testing physicians to create and disperse educational content for patients using these sites, she concluded.
Study highlights education opportunities
“Due to the pandemic, patients have been increasingly interacting with online resources in lieu of coming to a physician’s office,” corresponding author Walter J. Liszewski, MD, of the department of dermatology, Northwestern University, Chicago, said in an interview. “As social media is increasingly used by patients and physicians, it is important to get a sense of its footprint,” he said.
He and Ms. Nguyen were surprised by several of their findings: First, searches for ACD on Google were not particularly common given its relatively high prevalence and economic cost to society. In addition, they found that physicians often used different language than that of patients to describe ACD on Twitter and Instagram. They were also surprised at how often ACD appeared in Reddit posts, which they noted highlights that ACD impacts multiple sections of society.
The greatest challenge in studying social media and medicine is the quality of material available, Dr. Liszewski and Ms. Nguyen observed, emphasizing that while there are numerous videos on ACD on YouTube, the quality is highly variable, and there is a need for more patient-centered, educational materials. However, the results of their study highlight the opportunity for physicians and industry to create medically-accurate educational materials, they added.
Ms. Nguyen and Dr. Liszewski had no financial conflicts to disclose.
FROM ACDS 2021
New COVID-19 cases rise again in children
The number of new COVID-19 cases in children increased for the second consecutive week in the United States, according to a report from the American Academy of Pediatrics and the Children’s Hospital Association.
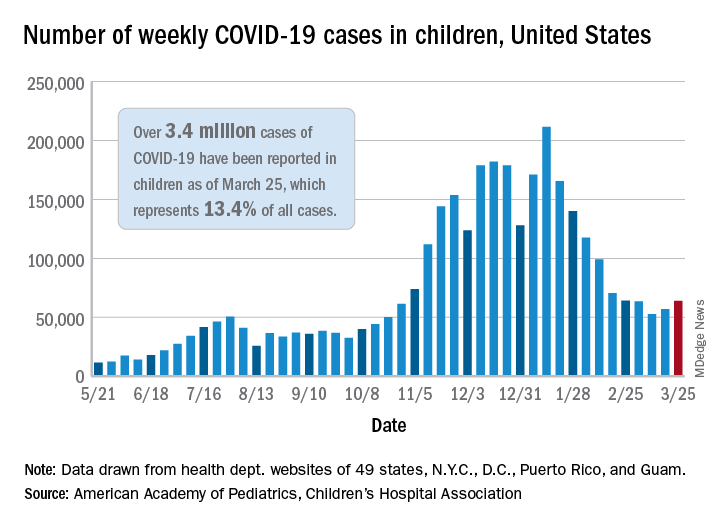
That brings the number of children infected with the coronavirus to over 3.4 million since the beginning of the pandemic, or 13.4% of all reported cases, the AAP and CHA said in their weekly COVID-19 report.
For just the week of March 19-25, however, the proportion of all cases occurring in children was quite a bit higher, 19.1%. That’s higher than at any other point during the pandemic, passing the previous high of 18.7% set just a week earlier, based on the data collected by AAP/CHA from 49 states (excluding New York), the District of Columbia, New York City, Puerto Rico, and Guam.
The national infection rate was 4,525 cases per 100,000 children for the week of March 19-25, compared with 4,440 per 100,000 the previous week. States falling the farthest from that national mark were Hawaii at 1,101 per 100,000 and North Dakota at 8,848, the AAP and CHA said.
There was double-digit increase, 11, in the number of child deaths, as the total went from 268 to 279 despite Virginia’s revising its mortality data downward. The mortality rate for children remains 0.01%, and children represent only 0.06% of all COVID-19–related deaths in the 43 states, along with New York City, Puerto Rico, and Guam, that are reporting deaths by age, the report shows.
The state/local-level data show that Texas has the highest number of child deaths (48), followed by Arizona (26), New York City (22), California (16), and Illinois (16), while nine states and the District of Columbia have not yet reported a death, the AAP and CHA said.
The number of new COVID-19 cases in children increased for the second consecutive week in the United States, according to a report from the American Academy of Pediatrics and the Children’s Hospital Association.

That brings the number of children infected with the coronavirus to over 3.4 million since the beginning of the pandemic, or 13.4% of all reported cases, the AAP and CHA said in their weekly COVID-19 report.
For just the week of March 19-25, however, the proportion of all cases occurring in children was quite a bit higher, 19.1%. That’s higher than at any other point during the pandemic, passing the previous high of 18.7% set just a week earlier, based on the data collected by AAP/CHA from 49 states (excluding New York), the District of Columbia, New York City, Puerto Rico, and Guam.
The national infection rate was 4,525 cases per 100,000 children for the week of March 19-25, compared with 4,440 per 100,000 the previous week. States falling the farthest from that national mark were Hawaii at 1,101 per 100,000 and North Dakota at 8,848, the AAP and CHA said.
There was double-digit increase, 11, in the number of child deaths, as the total went from 268 to 279 despite Virginia’s revising its mortality data downward. The mortality rate for children remains 0.01%, and children represent only 0.06% of all COVID-19–related deaths in the 43 states, along with New York City, Puerto Rico, and Guam, that are reporting deaths by age, the report shows.
The state/local-level data show that Texas has the highest number of child deaths (48), followed by Arizona (26), New York City (22), California (16), and Illinois (16), while nine states and the District of Columbia have not yet reported a death, the AAP and CHA said.
The number of new COVID-19 cases in children increased for the second consecutive week in the United States, according to a report from the American Academy of Pediatrics and the Children’s Hospital Association.

That brings the number of children infected with the coronavirus to over 3.4 million since the beginning of the pandemic, or 13.4% of all reported cases, the AAP and CHA said in their weekly COVID-19 report.
For just the week of March 19-25, however, the proportion of all cases occurring in children was quite a bit higher, 19.1%. That’s higher than at any other point during the pandemic, passing the previous high of 18.7% set just a week earlier, based on the data collected by AAP/CHA from 49 states (excluding New York), the District of Columbia, New York City, Puerto Rico, and Guam.
The national infection rate was 4,525 cases per 100,000 children for the week of March 19-25, compared with 4,440 per 100,000 the previous week. States falling the farthest from that national mark were Hawaii at 1,101 per 100,000 and North Dakota at 8,848, the AAP and CHA said.
There was double-digit increase, 11, in the number of child deaths, as the total went from 268 to 279 despite Virginia’s revising its mortality data downward. The mortality rate for children remains 0.01%, and children represent only 0.06% of all COVID-19–related deaths in the 43 states, along with New York City, Puerto Rico, and Guam, that are reporting deaths by age, the report shows.
The state/local-level data show that Texas has the highest number of child deaths (48), followed by Arizona (26), New York City (22), California (16), and Illinois (16), while nine states and the District of Columbia have not yet reported a death, the AAP and CHA said.
Combo shows efficacy in platinum-resistant ovarian cancer
The median progression-free survival (PFS) was 5.5 months for patients randomized to receive ixabepilone and bevacizumab, versus 2.2 months for patients assigned to ixabepilone alone (P < .001). The median overall survival (OS) was 10 months and 6 months, respectively (P = .006), although the trial was underpowered to detect OS differences.
These results were presented in a late-breaking abstract session at the Society of Gynecologic Oncology’s Virtual Annual Meeting on Women’s Cancer (Abstract 11570).
“Therapeutic options for platinum- and taxane-resistant ovarian cancer are limited, and, unfortunately, median overall survival in this population is only approximately 12 months. It’s obvious that additional treatment strategies are warranted,” Dana M. Roque, MD, of the University of Maryland in Baltimore, said when presenting the results.
Study rationale and details
Dr. Roque explained that ixabepilone is an epothilone B analog that may retain activity in patients with taxane-resistant disease. She and her colleagues previously found, in a retrospective study, that ixabepilone, with or without bevacizumab, showed “promising” activity with acceptable toxicity in patients with recurrent uterine or ovarian/primary peritoneal/fallopian tube cancers.
At SGO 2021, Dr. Roque reported results of a prospective, phase 2 trial of 76 patients randomized to ixabepilone alone or in combination with bevacizumab.
Patients with measurable recurrent or persistent platinum-resistant or refractory epithelial nonmucinous ovarian, fallopian tube, or primary peritoneal cancers were enrolled. The patients had to have received at least three prior cycles of paclitaxel, but there was no upper limit on prior lines of therapy, including bevacizumab.
After stratification by prior bevacizumab and study site, the patients were randomly assigned to either ixabepilone monotherapy at a dose of 20 mg/m2 on days 1, 8, and 15 of every 28-day cycle (n = 37), or the same dose of ixabepilone plus bevacizumab at 10 mg/kg on days 1 and 15 every 28 days (n = 39).
Most patients in each arm – 78% in the monotherapy arm and 87% in the combination arm – had serous tumors, with the remaining patients having carcinosarcomas or other, unspecified histologies.
Efficacy and safety
The overall response rate was 33% with the combination and 8% with ixabepilone monotherapy. There were no correlations between TUBB3 staining and either responses or durable disease control.
As noted before, PFS and OS were significantly better with the combination. Neither PFS nor OS were influenced by prior bevacizumab use, heavy pretreatment, poor performance status, nonserous histology, or age.
Dose-limiting toxicities with the combination included peripheral neuropathy, neutropenia, and fatigue. There was one bowel perforation in a patient on the combination.
Patients assigned to the combination were significantly more likely to experience hypertension (36% vs. 8%, P = .005) and peripheral neuropathy (51% vs. 19%, P = .004). However, there were no differences in serious adverse events between the treatment arms.
Dr. Roque acknowledged that this study was limited by incomplete immunohistochemistry data, a lack of stratification by extent of prior taxane exposure in the recurrent setting, a lack of a bevacizumab control arm, and underpowering to detect OS differences.
Comparison with AURELIA
Dr. Roque and the invited discussant, Thomas J. Herzog, MD, of the University of Cincinnati Cancer Center in Ohio, both compared results of the current trial to results from the AURELIA trial, in which patients with platinum-resistant ovarian cancers were randomized to chemotherapy with or without bevacizumab.
According to AURELIA data published in 2014, the ORR with the bevacizumab-chemotherapy combination was 27%, compared with 33% with ixabepilone-bevacizumab in the current trial. The median PFS was 6.7 months and 5.5 months, respectively, and the median OS was 16.6 months and 10 months, respectively.
An analysis of AURELIA data published in 2015 suggested that outcomes were even better for patients who received paclitaxel plus bevacizumab. This group had an ORR of 53.3%, a median PFS of 10.4 months, and a median OS of 22.4 months.
Though the current study’s results don’t appear to measure up to results from AURELIA, Dr. Herzog called the current study “very exciting.”
“The efficacy looks very promising,” he said. “They even showed efficacy for OS that looked very interesting, even though that was underpowered.”
Dr. Herzog did note the lack of a companion diagnostic because the TUBB3 staining did not correlate with response. He also said the trial was limited by the lack of a bevacizumab control arm. Furthermore, because of the relatively small sample size in the combination group (n = 39), the lower bound of the confidence interval for ORR includes response rates typically seen with conventional therapies.
“I do think that the combination does make sense biologically, so I’d like to see more data on that,” he concluded.
The trial was sponsored by Yale University, with study drug supplied by R-Pharm-US. Dr. Roque reported no conflicts of interest. Dr. Herzog disclosed serving as a scientific advisor to several companies, including Genentech, maker of bevacizumab.
The median progression-free survival (PFS) was 5.5 months for patients randomized to receive ixabepilone and bevacizumab, versus 2.2 months for patients assigned to ixabepilone alone (P < .001). The median overall survival (OS) was 10 months and 6 months, respectively (P = .006), although the trial was underpowered to detect OS differences.
These results were presented in a late-breaking abstract session at the Society of Gynecologic Oncology’s Virtual Annual Meeting on Women’s Cancer (Abstract 11570).
“Therapeutic options for platinum- and taxane-resistant ovarian cancer are limited, and, unfortunately, median overall survival in this population is only approximately 12 months. It’s obvious that additional treatment strategies are warranted,” Dana M. Roque, MD, of the University of Maryland in Baltimore, said when presenting the results.
Study rationale and details
Dr. Roque explained that ixabepilone is an epothilone B analog that may retain activity in patients with taxane-resistant disease. She and her colleagues previously found, in a retrospective study, that ixabepilone, with or without bevacizumab, showed “promising” activity with acceptable toxicity in patients with recurrent uterine or ovarian/primary peritoneal/fallopian tube cancers.
At SGO 2021, Dr. Roque reported results of a prospective, phase 2 trial of 76 patients randomized to ixabepilone alone or in combination with bevacizumab.
Patients with measurable recurrent or persistent platinum-resistant or refractory epithelial nonmucinous ovarian, fallopian tube, or primary peritoneal cancers were enrolled. The patients had to have received at least three prior cycles of paclitaxel, but there was no upper limit on prior lines of therapy, including bevacizumab.
After stratification by prior bevacizumab and study site, the patients were randomly assigned to either ixabepilone monotherapy at a dose of 20 mg/m2 on days 1, 8, and 15 of every 28-day cycle (n = 37), or the same dose of ixabepilone plus bevacizumab at 10 mg/kg on days 1 and 15 every 28 days (n = 39).
Most patients in each arm – 78% in the monotherapy arm and 87% in the combination arm – had serous tumors, with the remaining patients having carcinosarcomas or other, unspecified histologies.
Efficacy and safety
The overall response rate was 33% with the combination and 8% with ixabepilone monotherapy. There were no correlations between TUBB3 staining and either responses or durable disease control.
As noted before, PFS and OS were significantly better with the combination. Neither PFS nor OS were influenced by prior bevacizumab use, heavy pretreatment, poor performance status, nonserous histology, or age.
Dose-limiting toxicities with the combination included peripheral neuropathy, neutropenia, and fatigue. There was one bowel perforation in a patient on the combination.
Patients assigned to the combination were significantly more likely to experience hypertension (36% vs. 8%, P = .005) and peripheral neuropathy (51% vs. 19%, P = .004). However, there were no differences in serious adverse events between the treatment arms.
Dr. Roque acknowledged that this study was limited by incomplete immunohistochemistry data, a lack of stratification by extent of prior taxane exposure in the recurrent setting, a lack of a bevacizumab control arm, and underpowering to detect OS differences.
Comparison with AURELIA
Dr. Roque and the invited discussant, Thomas J. Herzog, MD, of the University of Cincinnati Cancer Center in Ohio, both compared results of the current trial to results from the AURELIA trial, in which patients with platinum-resistant ovarian cancers were randomized to chemotherapy with or without bevacizumab.
According to AURELIA data published in 2014, the ORR with the bevacizumab-chemotherapy combination was 27%, compared with 33% with ixabepilone-bevacizumab in the current trial. The median PFS was 6.7 months and 5.5 months, respectively, and the median OS was 16.6 months and 10 months, respectively.
An analysis of AURELIA data published in 2015 suggested that outcomes were even better for patients who received paclitaxel plus bevacizumab. This group had an ORR of 53.3%, a median PFS of 10.4 months, and a median OS of 22.4 months.
Though the current study’s results don’t appear to measure up to results from AURELIA, Dr. Herzog called the current study “very exciting.”
“The efficacy looks very promising,” he said. “They even showed efficacy for OS that looked very interesting, even though that was underpowered.”
Dr. Herzog did note the lack of a companion diagnostic because the TUBB3 staining did not correlate with response. He also said the trial was limited by the lack of a bevacizumab control arm. Furthermore, because of the relatively small sample size in the combination group (n = 39), the lower bound of the confidence interval for ORR includes response rates typically seen with conventional therapies.
“I do think that the combination does make sense biologically, so I’d like to see more data on that,” he concluded.
The trial was sponsored by Yale University, with study drug supplied by R-Pharm-US. Dr. Roque reported no conflicts of interest. Dr. Herzog disclosed serving as a scientific advisor to several companies, including Genentech, maker of bevacizumab.
The median progression-free survival (PFS) was 5.5 months for patients randomized to receive ixabepilone and bevacizumab, versus 2.2 months for patients assigned to ixabepilone alone (P < .001). The median overall survival (OS) was 10 months and 6 months, respectively (P = .006), although the trial was underpowered to detect OS differences.
These results were presented in a late-breaking abstract session at the Society of Gynecologic Oncology’s Virtual Annual Meeting on Women’s Cancer (Abstract 11570).
“Therapeutic options for platinum- and taxane-resistant ovarian cancer are limited, and, unfortunately, median overall survival in this population is only approximately 12 months. It’s obvious that additional treatment strategies are warranted,” Dana M. Roque, MD, of the University of Maryland in Baltimore, said when presenting the results.
Study rationale and details
Dr. Roque explained that ixabepilone is an epothilone B analog that may retain activity in patients with taxane-resistant disease. She and her colleagues previously found, in a retrospective study, that ixabepilone, with or without bevacizumab, showed “promising” activity with acceptable toxicity in patients with recurrent uterine or ovarian/primary peritoneal/fallopian tube cancers.
At SGO 2021, Dr. Roque reported results of a prospective, phase 2 trial of 76 patients randomized to ixabepilone alone or in combination with bevacizumab.
Patients with measurable recurrent or persistent platinum-resistant or refractory epithelial nonmucinous ovarian, fallopian tube, or primary peritoneal cancers were enrolled. The patients had to have received at least three prior cycles of paclitaxel, but there was no upper limit on prior lines of therapy, including bevacizumab.
After stratification by prior bevacizumab and study site, the patients were randomly assigned to either ixabepilone monotherapy at a dose of 20 mg/m2 on days 1, 8, and 15 of every 28-day cycle (n = 37), or the same dose of ixabepilone plus bevacizumab at 10 mg/kg on days 1 and 15 every 28 days (n = 39).
Most patients in each arm – 78% in the monotherapy arm and 87% in the combination arm – had serous tumors, with the remaining patients having carcinosarcomas or other, unspecified histologies.
Efficacy and safety
The overall response rate was 33% with the combination and 8% with ixabepilone monotherapy. There were no correlations between TUBB3 staining and either responses or durable disease control.
As noted before, PFS and OS were significantly better with the combination. Neither PFS nor OS were influenced by prior bevacizumab use, heavy pretreatment, poor performance status, nonserous histology, or age.
Dose-limiting toxicities with the combination included peripheral neuropathy, neutropenia, and fatigue. There was one bowel perforation in a patient on the combination.
Patients assigned to the combination were significantly more likely to experience hypertension (36% vs. 8%, P = .005) and peripheral neuropathy (51% vs. 19%, P = .004). However, there were no differences in serious adverse events between the treatment arms.
Dr. Roque acknowledged that this study was limited by incomplete immunohistochemistry data, a lack of stratification by extent of prior taxane exposure in the recurrent setting, a lack of a bevacizumab control arm, and underpowering to detect OS differences.
Comparison with AURELIA
Dr. Roque and the invited discussant, Thomas J. Herzog, MD, of the University of Cincinnati Cancer Center in Ohio, both compared results of the current trial to results from the AURELIA trial, in which patients with platinum-resistant ovarian cancers were randomized to chemotherapy with or without bevacizumab.
According to AURELIA data published in 2014, the ORR with the bevacizumab-chemotherapy combination was 27%, compared with 33% with ixabepilone-bevacizumab in the current trial. The median PFS was 6.7 months and 5.5 months, respectively, and the median OS was 16.6 months and 10 months, respectively.
An analysis of AURELIA data published in 2015 suggested that outcomes were even better for patients who received paclitaxel plus bevacizumab. This group had an ORR of 53.3%, a median PFS of 10.4 months, and a median OS of 22.4 months.
Though the current study’s results don’t appear to measure up to results from AURELIA, Dr. Herzog called the current study “very exciting.”
“The efficacy looks very promising,” he said. “They even showed efficacy for OS that looked very interesting, even though that was underpowered.”
Dr. Herzog did note the lack of a companion diagnostic because the TUBB3 staining did not correlate with response. He also said the trial was limited by the lack of a bevacizumab control arm. Furthermore, because of the relatively small sample size in the combination group (n = 39), the lower bound of the confidence interval for ORR includes response rates typically seen with conventional therapies.
“I do think that the combination does make sense biologically, so I’d like to see more data on that,” he concluded.
The trial was sponsored by Yale University, with study drug supplied by R-Pharm-US. Dr. Roque reported no conflicts of interest. Dr. Herzog disclosed serving as a scientific advisor to several companies, including Genentech, maker of bevacizumab.
FROM SGO 2021
The best exercises for BP control? European statement sorts it out
Recommendations for prescribing exercise to control high blood pressure have been put forward by various medical organizations and expert panels, but finding the bandwidth to craft personalized exercise training for their patients poses a challenge for clinicians.
Now, European cardiology societies have issued a consensus statement that offers an algorithm of sorts for developing personalized exercise programs as part of overall management approach for patients with or at risk of high BP.
The statement, published in the European Journal of Preventive Cardiology and issued by the European Association of Preventive Cardiology and the European Society of Cardiology Council on Hypertension, claims to be the first document to focus on personalized exercise for BP.
The statement draws on a systematic review, including meta-analyses, to produce guidance on how to lower BP in three specific types of patients: Those with hypertension (>140/90 mm Hg), high-normal blood pressure (130-139/85-89 mm Hg), and normal blood pressure (<130/84 mm Hg).
By making recommendations for these three specific groups, along with providing guidance for combined exercise – that is, blending aerobic exercise with resistance training (RT) – the consensus statement goes one step further than recommendations other organizations have issued, Matthew W. Martinez, MD, said in an interview.
“What it adds is an algorithmic approach, if you will,” said Dr. Martinez, a sports medicine cardiologist at Morristown (N.J.) Medical Center. “There are some recommendations to help the clinicians to decide what they’re going to offer individuals, but what’s a challenge for us when seeing patients is finding the time to deliver the message and explain how valuable nutrition and exercise are.”
Guidelines, updates, and statements that include the role of exercise in BP control have been issued by the European Society of Cardiology, American Heart Association, and American College of Sports Medicine (Med Sci Sports Exercise. 2019;51:1314-23).
The European consensus statement includes the expected range of BP lowering for each activity. For example, aerobic exercise for patients with hypertension should lead to a reduction from –4.9 to –12 mm Hg systolic and –3.4 to –5.8 mm Hg diastolic.
The consensus statement recommends the following exercise priorities based on a patient’s blood pressure:
- Hypertension: Aerobic training (AT) as a first-line exercise therapy; and low- to moderate-intensity RT – equally using dynamic and isometric RT – as second-line therapy. In non-White patients, dynamic RT should be considered as a first-line therapy. RT can be combined with aerobic exercise on an individual basis if the clinician determines either form of RT would provide a metabolic benefit.
- High-to-normal BP: Dynamic RT as a first-line exercise, which the systematic review determined led to greater BP reduction than that of aerobic training. “Isometric RT is likely to elicit similar if not superior BP-lowering effects as [dynamic RT], but the level of evidence is low and the available data are scarce,” wrote first author Henner Hanssen, MD, of the University of Basel, Switzerland, and coauthors. Combining dynamic resistance training with aerobic training “may be preferable” to dynamic RT alone in patients with a combination of cardiovascular risk factors.
- Normal BP: Isometric RT may be indicated as a first-line intervention in individuals with a family or gestational history or obese or overweight people currently with normal BP. This advice includes a caveat: “The number of studies is limited and the 95% confidence intervals are large,” Dr. Hanssen and coauthors noted. AT is also an option in these patients, with more high-quality meta-analyses than the recommendation for isometric RT. “Hence, the BP-lowering effects of [isometric RT] as compared to AT may be overestimated and both exercise modalities may have similar BP-lowering effects in individuals with normotension,” wrote the consensus statement authors.
They note that more research is needed to validate the BP-lowering effects of combined exercise.
The statement acknowledges the difficulty clinicians face in managing patients with high blood pressure. “From a socioeconomic health perspective, it is a major challenge to develop, promote, and implement individually tailored exercise programs for patients with hypertension under consideration of sustainable costs,” wrote Dr. Hanssen and coauthors.
Dr. Martinez noted that one strength of the consensus statement is that it addresses the impact exercise can have on vascular health and metabolic function. And, it points out existing knowledge gaps.
“Are we going to see greater applicability of this as we use IT health technology?” he asked. “Are wearables and telehealth going to help deliver this message more easily, more frequently? Is there work to be done in terms of differences in gender? Do men and women respond differently, and is there a different exercise prescription based on that as well as ethnicity? We well know there’s a different treatment for African Americans compared to other ethnic groups.”
The statement also raises the stakes for using exercise as part of a multifaceted, integrated approach to hypertension management, he said.
“It’s not enough to talk just about exercise or nutrition, or to just give an antihypertension medicine,” Dr. Martinez said. “Perhaps the sweet spot is in integrating an approach that includes all three.”
Consensus statement coauthor Antonio Coca, MD, reported financial relationships with Abbott, Berlin-Chemie, Biolab, Boehringer-Ingelheim, Ferrer, Menarini, Merck, Novartis and Sanofi-Aventis. Coauthor Maria Simonenko, MD, reported financial relationships with Novartis and Sanofi-Aventis. Linda Pescatello, PhD, is lead author of the American College of Sports Medicine 2019 statement. Dr. Hanssen and all other authors have no disclosures. Dr. Martinez has no relevant relationships to disclose.
Recommendations for prescribing exercise to control high blood pressure have been put forward by various medical organizations and expert panels, but finding the bandwidth to craft personalized exercise training for their patients poses a challenge for clinicians.
Now, European cardiology societies have issued a consensus statement that offers an algorithm of sorts for developing personalized exercise programs as part of overall management approach for patients with or at risk of high BP.
The statement, published in the European Journal of Preventive Cardiology and issued by the European Association of Preventive Cardiology and the European Society of Cardiology Council on Hypertension, claims to be the first document to focus on personalized exercise for BP.
The statement draws on a systematic review, including meta-analyses, to produce guidance on how to lower BP in three specific types of patients: Those with hypertension (>140/90 mm Hg), high-normal blood pressure (130-139/85-89 mm Hg), and normal blood pressure (<130/84 mm Hg).
By making recommendations for these three specific groups, along with providing guidance for combined exercise – that is, blending aerobic exercise with resistance training (RT) – the consensus statement goes one step further than recommendations other organizations have issued, Matthew W. Martinez, MD, said in an interview.
“What it adds is an algorithmic approach, if you will,” said Dr. Martinez, a sports medicine cardiologist at Morristown (N.J.) Medical Center. “There are some recommendations to help the clinicians to decide what they’re going to offer individuals, but what’s a challenge for us when seeing patients is finding the time to deliver the message and explain how valuable nutrition and exercise are.”
Guidelines, updates, and statements that include the role of exercise in BP control have been issued by the European Society of Cardiology, American Heart Association, and American College of Sports Medicine (Med Sci Sports Exercise. 2019;51:1314-23).
The European consensus statement includes the expected range of BP lowering for each activity. For example, aerobic exercise for patients with hypertension should lead to a reduction from –4.9 to –12 mm Hg systolic and –3.4 to –5.8 mm Hg diastolic.
The consensus statement recommends the following exercise priorities based on a patient’s blood pressure:
- Hypertension: Aerobic training (AT) as a first-line exercise therapy; and low- to moderate-intensity RT – equally using dynamic and isometric RT – as second-line therapy. In non-White patients, dynamic RT should be considered as a first-line therapy. RT can be combined with aerobic exercise on an individual basis if the clinician determines either form of RT would provide a metabolic benefit.
- High-to-normal BP: Dynamic RT as a first-line exercise, which the systematic review determined led to greater BP reduction than that of aerobic training. “Isometric RT is likely to elicit similar if not superior BP-lowering effects as [dynamic RT], but the level of evidence is low and the available data are scarce,” wrote first author Henner Hanssen, MD, of the University of Basel, Switzerland, and coauthors. Combining dynamic resistance training with aerobic training “may be preferable” to dynamic RT alone in patients with a combination of cardiovascular risk factors.
- Normal BP: Isometric RT may be indicated as a first-line intervention in individuals with a family or gestational history or obese or overweight people currently with normal BP. This advice includes a caveat: “The number of studies is limited and the 95% confidence intervals are large,” Dr. Hanssen and coauthors noted. AT is also an option in these patients, with more high-quality meta-analyses than the recommendation for isometric RT. “Hence, the BP-lowering effects of [isometric RT] as compared to AT may be overestimated and both exercise modalities may have similar BP-lowering effects in individuals with normotension,” wrote the consensus statement authors.
They note that more research is needed to validate the BP-lowering effects of combined exercise.
The statement acknowledges the difficulty clinicians face in managing patients with high blood pressure. “From a socioeconomic health perspective, it is a major challenge to develop, promote, and implement individually tailored exercise programs for patients with hypertension under consideration of sustainable costs,” wrote Dr. Hanssen and coauthors.
Dr. Martinez noted that one strength of the consensus statement is that it addresses the impact exercise can have on vascular health and metabolic function. And, it points out existing knowledge gaps.
“Are we going to see greater applicability of this as we use IT health technology?” he asked. “Are wearables and telehealth going to help deliver this message more easily, more frequently? Is there work to be done in terms of differences in gender? Do men and women respond differently, and is there a different exercise prescription based on that as well as ethnicity? We well know there’s a different treatment for African Americans compared to other ethnic groups.”
The statement also raises the stakes for using exercise as part of a multifaceted, integrated approach to hypertension management, he said.
“It’s not enough to talk just about exercise or nutrition, or to just give an antihypertension medicine,” Dr. Martinez said. “Perhaps the sweet spot is in integrating an approach that includes all three.”
Consensus statement coauthor Antonio Coca, MD, reported financial relationships with Abbott, Berlin-Chemie, Biolab, Boehringer-Ingelheim, Ferrer, Menarini, Merck, Novartis and Sanofi-Aventis. Coauthor Maria Simonenko, MD, reported financial relationships with Novartis and Sanofi-Aventis. Linda Pescatello, PhD, is lead author of the American College of Sports Medicine 2019 statement. Dr. Hanssen and all other authors have no disclosures. Dr. Martinez has no relevant relationships to disclose.
Recommendations for prescribing exercise to control high blood pressure have been put forward by various medical organizations and expert panels, but finding the bandwidth to craft personalized exercise training for their patients poses a challenge for clinicians.
Now, European cardiology societies have issued a consensus statement that offers an algorithm of sorts for developing personalized exercise programs as part of overall management approach for patients with or at risk of high BP.
The statement, published in the European Journal of Preventive Cardiology and issued by the European Association of Preventive Cardiology and the European Society of Cardiology Council on Hypertension, claims to be the first document to focus on personalized exercise for BP.
The statement draws on a systematic review, including meta-analyses, to produce guidance on how to lower BP in three specific types of patients: Those with hypertension (>140/90 mm Hg), high-normal blood pressure (130-139/85-89 mm Hg), and normal blood pressure (<130/84 mm Hg).
By making recommendations for these three specific groups, along with providing guidance for combined exercise – that is, blending aerobic exercise with resistance training (RT) – the consensus statement goes one step further than recommendations other organizations have issued, Matthew W. Martinez, MD, said in an interview.
“What it adds is an algorithmic approach, if you will,” said Dr. Martinez, a sports medicine cardiologist at Morristown (N.J.) Medical Center. “There are some recommendations to help the clinicians to decide what they’re going to offer individuals, but what’s a challenge for us when seeing patients is finding the time to deliver the message and explain how valuable nutrition and exercise are.”
Guidelines, updates, and statements that include the role of exercise in BP control have been issued by the European Society of Cardiology, American Heart Association, and American College of Sports Medicine (Med Sci Sports Exercise. 2019;51:1314-23).
The European consensus statement includes the expected range of BP lowering for each activity. For example, aerobic exercise for patients with hypertension should lead to a reduction from –4.9 to –12 mm Hg systolic and –3.4 to –5.8 mm Hg diastolic.
The consensus statement recommends the following exercise priorities based on a patient’s blood pressure:
- Hypertension: Aerobic training (AT) as a first-line exercise therapy; and low- to moderate-intensity RT – equally using dynamic and isometric RT – as second-line therapy. In non-White patients, dynamic RT should be considered as a first-line therapy. RT can be combined with aerobic exercise on an individual basis if the clinician determines either form of RT would provide a metabolic benefit.
- High-to-normal BP: Dynamic RT as a first-line exercise, which the systematic review determined led to greater BP reduction than that of aerobic training. “Isometric RT is likely to elicit similar if not superior BP-lowering effects as [dynamic RT], but the level of evidence is low and the available data are scarce,” wrote first author Henner Hanssen, MD, of the University of Basel, Switzerland, and coauthors. Combining dynamic resistance training with aerobic training “may be preferable” to dynamic RT alone in patients with a combination of cardiovascular risk factors.
- Normal BP: Isometric RT may be indicated as a first-line intervention in individuals with a family or gestational history or obese or overweight people currently with normal BP. This advice includes a caveat: “The number of studies is limited and the 95% confidence intervals are large,” Dr. Hanssen and coauthors noted. AT is also an option in these patients, with more high-quality meta-analyses than the recommendation for isometric RT. “Hence, the BP-lowering effects of [isometric RT] as compared to AT may be overestimated and both exercise modalities may have similar BP-lowering effects in individuals with normotension,” wrote the consensus statement authors.
They note that more research is needed to validate the BP-lowering effects of combined exercise.
The statement acknowledges the difficulty clinicians face in managing patients with high blood pressure. “From a socioeconomic health perspective, it is a major challenge to develop, promote, and implement individually tailored exercise programs for patients with hypertension under consideration of sustainable costs,” wrote Dr. Hanssen and coauthors.
Dr. Martinez noted that one strength of the consensus statement is that it addresses the impact exercise can have on vascular health and metabolic function. And, it points out existing knowledge gaps.
“Are we going to see greater applicability of this as we use IT health technology?” he asked. “Are wearables and telehealth going to help deliver this message more easily, more frequently? Is there work to be done in terms of differences in gender? Do men and women respond differently, and is there a different exercise prescription based on that as well as ethnicity? We well know there’s a different treatment for African Americans compared to other ethnic groups.”
The statement also raises the stakes for using exercise as part of a multifaceted, integrated approach to hypertension management, he said.
“It’s not enough to talk just about exercise or nutrition, or to just give an antihypertension medicine,” Dr. Martinez said. “Perhaps the sweet spot is in integrating an approach that includes all three.”
Consensus statement coauthor Antonio Coca, MD, reported financial relationships with Abbott, Berlin-Chemie, Biolab, Boehringer-Ingelheim, Ferrer, Menarini, Merck, Novartis and Sanofi-Aventis. Coauthor Maria Simonenko, MD, reported financial relationships with Novartis and Sanofi-Aventis. Linda Pescatello, PhD, is lead author of the American College of Sports Medicine 2019 statement. Dr. Hanssen and all other authors have no disclosures. Dr. Martinez has no relevant relationships to disclose.
FROM THE EUROPEAN JOURNAL OF PREVENTIVE CARDIOLOGY
Changes required for gynecologic surgeons to achieve greater pay equity
In a recent commentary published in Obstetrics & Gynecology, Katie L. Watson, JD, and Louise P. King, MD, JD, describe the issue of “double discrimination” in gynecologic surgery. The authors outlined how lower pay in a specialty where a majority of the surgeons and all of the patients are women may impact quality of care.
The commentary raises a number of concerns in gynecologic surgery that are important to discuss. Ob.gyn. as a whole is underpaid, as are many nonprocedural specialties such as family medicine and internal medicine. When ob.gyns. were predominantly men, the same situation existed – ob.gyns. were paid less than many other procedural specialties. While we’ve come a long way from the relative value unit (RVU) originally determined from the Harvard studies 30 years ago, there is room for additional improvement.
Several rationales were proposed by the authors to explain the disparities in pay between gynecologic surgery and those in urology: patient gender, surgeon gender, and length of training for gynecologic surgeons. The authors cited comparisons between urology and gynecology regarding “anatomically similar, sex-specific procedures” which require closer examination. Many of the code pairs selected were not actually comparable services. For example, management of Peyronie’s disease is a highly complex treatment performed by urologists that is not comparable with vaginectomy, yet this is an example of two codes used in the reference cited by the authors to conclude that surgeries on women are undervalued.
The overall RVUs for a procedure are also dependent upon the global period. The Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services designated RVUs as the total amount of work before, during, and after a procedure. If a surgery has a 90-day global period, all the work for 90 days thereafter is bundled into the value, whereas if something is a zero-day global, only that day’s work is counted. A gynecologic surgeon who sees a patient back two or three times is coding and billing for those encounters in addition to that initial procedure.
Many of the code comparisons used in the analysis of gender in RVUs compared services with different global periods. Finally, some of the services that were compared had vastly different utilization. Some of the services and codes that were compared are performed extremely rarely and for that reason have not had their values reassessed over the years. There may be inequities in the RVUs for these services, but they will account for extremely little in overall compensation.
As a former chair of the American Medical Association’s RVS Update Committee (RUC), I spent years attempting to revalue ob.gyn. procedures. CMS assigns work RVUs based on physician work, practice expense, and professional liability insurance. The work is calculated using total physician time and intensity based on surveys completed by the specialty. The American College of Obstetrician and Gynecologist’s Committee on Health Economics and Coding, and the AMA RUC have worked diligently over many years to reassess potentially misvalued services. The ultimate RVUs assigned by CMS for gynecologic surgery are determined by the surveys completed by ACOG members. One issue we encountered with reexamining some procedures under RBRVS is that they have become so low volume that it has been difficult to justify the cost and effort to revalue them.
Lack of ob.gyn. training isn’t the full story
On average, ob.gyns. have between 18 and 24 months of surgical training, which is significantly less than other specialties. Lack of training in gynecologic surgery was proposed as another explanation for reduced compensation among female gynecologic surgeons. This is a complex issue not adequately explained by training time for gynecologic surgeons alone. While the number of trained ob.gyns. has increased in recent decades, the surgical volume has diminished and the workload of gynecologic surgery is far lower than it used to be. Surgical volume during and after training was much higher 35 years ago, prior to the advancements of procedures like endometrial ablation or tubal ligation. Women who had finished childbearing often underwent vaginal hysterectomies to manage contraception along with various other conditions.
With the advent of minimally invasive surgery, laparoscopic sterilization became possible, which has reduced the number of hysterectomies performed. Endometrial ablation is an office-based, noninvasive procedure. The development of the levonorgestrel IUD has helped manage abnormal bleeding, further reducing the need for hysterectomy.
This reduction in surgical volume does have an impact on quality of care. The model of tracking surgical outcomes at Kaiser Health System, as mentioned by the authors, could work well in some, but not all centers. A more approachable solution to address surgical volume for the average ob.gyn. would be to implement a mentoring and coaching process whereby recently trained ob.gyns. assist their senior partner(s) in surgery. This was the model years ago: I was trained by an ob.gyn. who was trained as a general surgeon. It was through the experience of assisting on each one of his cases – and him assisting on each one of my cases – that I received incredibly thorough surgical training.
These changes in practice, however, do not impact reimbursement. Rather than discrimination based on the gender of the surgeon, lower salaries in ob.gyn. are more likely to be the result of these and other factors.
The wage and quality gap in ob.gyn.
As a predominantly female surgical specialty, some of the disparity between gynecology and urology could be explained by how each specialty values its work. Here, gender plays a role in that when ob.gyns. are surveyed during the RUC process they may undervalue their work by reporting they can perform a procedure (and the before and after care) faster than what a urologist reports. The survey results may then result in lower RVUs.
Ob.gyn. is an overpopulated specialty for the number of surgeons needed to manage the volume of gynecologic surgery. When a health system wants to hire a general ob.gyn., it doesn’t have trouble finding one, while urologists are more challenging to recruit. This is not because of the structure of resource-based relative value scale (RBRVS) – despite the overall RVUs for gynecologic surgery, gynecologic oncologists are often paid well because health systems need them – but rather to the market economy of hiring physicians in specialty areas where there is demand.
Women are also chronically undervalued for the hours that we spend with patients. Data show that we spend more time with patients, which does not generate as many RVUs, but it generates better outcomes for patients. Evidence shows that women doctors in internal medicine and family medicine have better outcomes than doctors who are men.
On Jan. 1, 2021, Medicare and other payers implemented a new structure to reporting the level of office visit based on either medical decision-making or time spent on the date of encounter. Time spent with patients will now be rewarded – increased RVUs for increased time.
Part of the solution is value-based medicine and moving away from counting RVUs. This is also an opportunity to look at where time is spent in general ob.gyn. training and redistribute it, focusing on what trainees need for their education and not what hospitals need to service labor and delivery. We should step back and look creatively at optimizing the education and the training of ob.gyns., and where possible utilize other health care professionals such as nurse practitioners and midwives to address the uncomplicated obstetric needs of the hospital which could free up ob.gyn. trainees to obtain further surgical education.
To be clear, gender discrimination in compensation is prevalent and a persistent problem in medicine – ob.gyn. is no exception. Many ob.gyns. are employed by large health systems with payment structures and incentives that don’t align with those of the physician or the patient. There is definite misalignment in the way salaries are determined. Transparency on salaries is a critical component of addressing the pay gap that exists between women and men in medicine and in other industries.
The pay gap as it relates to reimbursement for gynecologic surgery, however, is a more complex matter that relates to how the RBRVS system was developed nearly 30 years ago when gynecologic surgery was not predominantly performed by women.
Dr. Levy is a voluntary clinical professor in the department of obstetrics, gynecology, and reproductive sciences at University of California San Diego Health, the former vice president of health policy at ACOG, past chair of the AMA/RUC, and current voting member of the AMA CPT editorial panel. She reported no relevant financial disclosures.
In a recent commentary published in Obstetrics & Gynecology, Katie L. Watson, JD, and Louise P. King, MD, JD, describe the issue of “double discrimination” in gynecologic surgery. The authors outlined how lower pay in a specialty where a majority of the surgeons and all of the patients are women may impact quality of care.
The commentary raises a number of concerns in gynecologic surgery that are important to discuss. Ob.gyn. as a whole is underpaid, as are many nonprocedural specialties such as family medicine and internal medicine. When ob.gyns. were predominantly men, the same situation existed – ob.gyns. were paid less than many other procedural specialties. While we’ve come a long way from the relative value unit (RVU) originally determined from the Harvard studies 30 years ago, there is room for additional improvement.
Several rationales were proposed by the authors to explain the disparities in pay between gynecologic surgery and those in urology: patient gender, surgeon gender, and length of training for gynecologic surgeons. The authors cited comparisons between urology and gynecology regarding “anatomically similar, sex-specific procedures” which require closer examination. Many of the code pairs selected were not actually comparable services. For example, management of Peyronie’s disease is a highly complex treatment performed by urologists that is not comparable with vaginectomy, yet this is an example of two codes used in the reference cited by the authors to conclude that surgeries on women are undervalued.
The overall RVUs for a procedure are also dependent upon the global period. The Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services designated RVUs as the total amount of work before, during, and after a procedure. If a surgery has a 90-day global period, all the work for 90 days thereafter is bundled into the value, whereas if something is a zero-day global, only that day’s work is counted. A gynecologic surgeon who sees a patient back two or three times is coding and billing for those encounters in addition to that initial procedure.
Many of the code comparisons used in the analysis of gender in RVUs compared services with different global periods. Finally, some of the services that were compared had vastly different utilization. Some of the services and codes that were compared are performed extremely rarely and for that reason have not had their values reassessed over the years. There may be inequities in the RVUs for these services, but they will account for extremely little in overall compensation.
As a former chair of the American Medical Association’s RVS Update Committee (RUC), I spent years attempting to revalue ob.gyn. procedures. CMS assigns work RVUs based on physician work, practice expense, and professional liability insurance. The work is calculated using total physician time and intensity based on surveys completed by the specialty. The American College of Obstetrician and Gynecologist’s Committee on Health Economics and Coding, and the AMA RUC have worked diligently over many years to reassess potentially misvalued services. The ultimate RVUs assigned by CMS for gynecologic surgery are determined by the surveys completed by ACOG members. One issue we encountered with reexamining some procedures under RBRVS is that they have become so low volume that it has been difficult to justify the cost and effort to revalue them.
Lack of ob.gyn. training isn’t the full story
On average, ob.gyns. have between 18 and 24 months of surgical training, which is significantly less than other specialties. Lack of training in gynecologic surgery was proposed as another explanation for reduced compensation among female gynecologic surgeons. This is a complex issue not adequately explained by training time for gynecologic surgeons alone. While the number of trained ob.gyns. has increased in recent decades, the surgical volume has diminished and the workload of gynecologic surgery is far lower than it used to be. Surgical volume during and after training was much higher 35 years ago, prior to the advancements of procedures like endometrial ablation or tubal ligation. Women who had finished childbearing often underwent vaginal hysterectomies to manage contraception along with various other conditions.
With the advent of minimally invasive surgery, laparoscopic sterilization became possible, which has reduced the number of hysterectomies performed. Endometrial ablation is an office-based, noninvasive procedure. The development of the levonorgestrel IUD has helped manage abnormal bleeding, further reducing the need for hysterectomy.
This reduction in surgical volume does have an impact on quality of care. The model of tracking surgical outcomes at Kaiser Health System, as mentioned by the authors, could work well in some, but not all centers. A more approachable solution to address surgical volume for the average ob.gyn. would be to implement a mentoring and coaching process whereby recently trained ob.gyns. assist their senior partner(s) in surgery. This was the model years ago: I was trained by an ob.gyn. who was trained as a general surgeon. It was through the experience of assisting on each one of his cases – and him assisting on each one of my cases – that I received incredibly thorough surgical training.
These changes in practice, however, do not impact reimbursement. Rather than discrimination based on the gender of the surgeon, lower salaries in ob.gyn. are more likely to be the result of these and other factors.
The wage and quality gap in ob.gyn.
As a predominantly female surgical specialty, some of the disparity between gynecology and urology could be explained by how each specialty values its work. Here, gender plays a role in that when ob.gyns. are surveyed during the RUC process they may undervalue their work by reporting they can perform a procedure (and the before and after care) faster than what a urologist reports. The survey results may then result in lower RVUs.
Ob.gyn. is an overpopulated specialty for the number of surgeons needed to manage the volume of gynecologic surgery. When a health system wants to hire a general ob.gyn., it doesn’t have trouble finding one, while urologists are more challenging to recruit. This is not because of the structure of resource-based relative value scale (RBRVS) – despite the overall RVUs for gynecologic surgery, gynecologic oncologists are often paid well because health systems need them – but rather to the market economy of hiring physicians in specialty areas where there is demand.
Women are also chronically undervalued for the hours that we spend with patients. Data show that we spend more time with patients, which does not generate as many RVUs, but it generates better outcomes for patients. Evidence shows that women doctors in internal medicine and family medicine have better outcomes than doctors who are men.
On Jan. 1, 2021, Medicare and other payers implemented a new structure to reporting the level of office visit based on either medical decision-making or time spent on the date of encounter. Time spent with patients will now be rewarded – increased RVUs for increased time.
Part of the solution is value-based medicine and moving away from counting RVUs. This is also an opportunity to look at where time is spent in general ob.gyn. training and redistribute it, focusing on what trainees need for their education and not what hospitals need to service labor and delivery. We should step back and look creatively at optimizing the education and the training of ob.gyns., and where possible utilize other health care professionals such as nurse practitioners and midwives to address the uncomplicated obstetric needs of the hospital which could free up ob.gyn. trainees to obtain further surgical education.
To be clear, gender discrimination in compensation is prevalent and a persistent problem in medicine – ob.gyn. is no exception. Many ob.gyns. are employed by large health systems with payment structures and incentives that don’t align with those of the physician or the patient. There is definite misalignment in the way salaries are determined. Transparency on salaries is a critical component of addressing the pay gap that exists between women and men in medicine and in other industries.
The pay gap as it relates to reimbursement for gynecologic surgery, however, is a more complex matter that relates to how the RBRVS system was developed nearly 30 years ago when gynecologic surgery was not predominantly performed by women.
Dr. Levy is a voluntary clinical professor in the department of obstetrics, gynecology, and reproductive sciences at University of California San Diego Health, the former vice president of health policy at ACOG, past chair of the AMA/RUC, and current voting member of the AMA CPT editorial panel. She reported no relevant financial disclosures.
In a recent commentary published in Obstetrics & Gynecology, Katie L. Watson, JD, and Louise P. King, MD, JD, describe the issue of “double discrimination” in gynecologic surgery. The authors outlined how lower pay in a specialty where a majority of the surgeons and all of the patients are women may impact quality of care.
The commentary raises a number of concerns in gynecologic surgery that are important to discuss. Ob.gyn. as a whole is underpaid, as are many nonprocedural specialties such as family medicine and internal medicine. When ob.gyns. were predominantly men, the same situation existed – ob.gyns. were paid less than many other procedural specialties. While we’ve come a long way from the relative value unit (RVU) originally determined from the Harvard studies 30 years ago, there is room for additional improvement.
Several rationales were proposed by the authors to explain the disparities in pay between gynecologic surgery and those in urology: patient gender, surgeon gender, and length of training for gynecologic surgeons. The authors cited comparisons between urology and gynecology regarding “anatomically similar, sex-specific procedures” which require closer examination. Many of the code pairs selected were not actually comparable services. For example, management of Peyronie’s disease is a highly complex treatment performed by urologists that is not comparable with vaginectomy, yet this is an example of two codes used in the reference cited by the authors to conclude that surgeries on women are undervalued.
The overall RVUs for a procedure are also dependent upon the global period. The Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services designated RVUs as the total amount of work before, during, and after a procedure. If a surgery has a 90-day global period, all the work for 90 days thereafter is bundled into the value, whereas if something is a zero-day global, only that day’s work is counted. A gynecologic surgeon who sees a patient back two or three times is coding and billing for those encounters in addition to that initial procedure.
Many of the code comparisons used in the analysis of gender in RVUs compared services with different global periods. Finally, some of the services that were compared had vastly different utilization. Some of the services and codes that were compared are performed extremely rarely and for that reason have not had their values reassessed over the years. There may be inequities in the RVUs for these services, but they will account for extremely little in overall compensation.
As a former chair of the American Medical Association’s RVS Update Committee (RUC), I spent years attempting to revalue ob.gyn. procedures. CMS assigns work RVUs based on physician work, practice expense, and professional liability insurance. The work is calculated using total physician time and intensity based on surveys completed by the specialty. The American College of Obstetrician and Gynecologist’s Committee on Health Economics and Coding, and the AMA RUC have worked diligently over many years to reassess potentially misvalued services. The ultimate RVUs assigned by CMS for gynecologic surgery are determined by the surveys completed by ACOG members. One issue we encountered with reexamining some procedures under RBRVS is that they have become so low volume that it has been difficult to justify the cost and effort to revalue them.
Lack of ob.gyn. training isn’t the full story
On average, ob.gyns. have between 18 and 24 months of surgical training, which is significantly less than other specialties. Lack of training in gynecologic surgery was proposed as another explanation for reduced compensation among female gynecologic surgeons. This is a complex issue not adequately explained by training time for gynecologic surgeons alone. While the number of trained ob.gyns. has increased in recent decades, the surgical volume has diminished and the workload of gynecologic surgery is far lower than it used to be. Surgical volume during and after training was much higher 35 years ago, prior to the advancements of procedures like endometrial ablation or tubal ligation. Women who had finished childbearing often underwent vaginal hysterectomies to manage contraception along with various other conditions.
With the advent of minimally invasive surgery, laparoscopic sterilization became possible, which has reduced the number of hysterectomies performed. Endometrial ablation is an office-based, noninvasive procedure. The development of the levonorgestrel IUD has helped manage abnormal bleeding, further reducing the need for hysterectomy.
This reduction in surgical volume does have an impact on quality of care. The model of tracking surgical outcomes at Kaiser Health System, as mentioned by the authors, could work well in some, but not all centers. A more approachable solution to address surgical volume for the average ob.gyn. would be to implement a mentoring and coaching process whereby recently trained ob.gyns. assist their senior partner(s) in surgery. This was the model years ago: I was trained by an ob.gyn. who was trained as a general surgeon. It was through the experience of assisting on each one of his cases – and him assisting on each one of my cases – that I received incredibly thorough surgical training.
These changes in practice, however, do not impact reimbursement. Rather than discrimination based on the gender of the surgeon, lower salaries in ob.gyn. are more likely to be the result of these and other factors.
The wage and quality gap in ob.gyn.
As a predominantly female surgical specialty, some of the disparity between gynecology and urology could be explained by how each specialty values its work. Here, gender plays a role in that when ob.gyns. are surveyed during the RUC process they may undervalue their work by reporting they can perform a procedure (and the before and after care) faster than what a urologist reports. The survey results may then result in lower RVUs.
Ob.gyn. is an overpopulated specialty for the number of surgeons needed to manage the volume of gynecologic surgery. When a health system wants to hire a general ob.gyn., it doesn’t have trouble finding one, while urologists are more challenging to recruit. This is not because of the structure of resource-based relative value scale (RBRVS) – despite the overall RVUs for gynecologic surgery, gynecologic oncologists are often paid well because health systems need them – but rather to the market economy of hiring physicians in specialty areas where there is demand.
Women are also chronically undervalued for the hours that we spend with patients. Data show that we spend more time with patients, which does not generate as many RVUs, but it generates better outcomes for patients. Evidence shows that women doctors in internal medicine and family medicine have better outcomes than doctors who are men.
On Jan. 1, 2021, Medicare and other payers implemented a new structure to reporting the level of office visit based on either medical decision-making or time spent on the date of encounter. Time spent with patients will now be rewarded – increased RVUs for increased time.
Part of the solution is value-based medicine and moving away from counting RVUs. This is also an opportunity to look at where time is spent in general ob.gyn. training and redistribute it, focusing on what trainees need for their education and not what hospitals need to service labor and delivery. We should step back and look creatively at optimizing the education and the training of ob.gyns., and where possible utilize other health care professionals such as nurse practitioners and midwives to address the uncomplicated obstetric needs of the hospital which could free up ob.gyn. trainees to obtain further surgical education.
To be clear, gender discrimination in compensation is prevalent and a persistent problem in medicine – ob.gyn. is no exception. Many ob.gyns. are employed by large health systems with payment structures and incentives that don’t align with those of the physician or the patient. There is definite misalignment in the way salaries are determined. Transparency on salaries is a critical component of addressing the pay gap that exists between women and men in medicine and in other industries.
The pay gap as it relates to reimbursement for gynecologic surgery, however, is a more complex matter that relates to how the RBRVS system was developed nearly 30 years ago when gynecologic surgery was not predominantly performed by women.
Dr. Levy is a voluntary clinical professor in the department of obstetrics, gynecology, and reproductive sciences at University of California San Diego Health, the former vice president of health policy at ACOG, past chair of the AMA/RUC, and current voting member of the AMA CPT editorial panel. She reported no relevant financial disclosures.
Long-haul COVID-19 brings welcome attention to POTS
Before COVID-19, postural orthostatic tachycardia syndrome (POTS) was one of those diseases that many people, including physicians, dismissed.
“They thought it was just anxious, crazy young women,” said Pam R. Taub, MD, who runs the cardiac rehabilitation program at the University of California, San Diego.
The cryptic autonomic condition was estimated to affect 1-3 million Americans before the pandemic hit. Now case reports confirm that it is a manifestation of postacute sequelae of SARS-CoV-2 infection (PASC), or so-called long-haul COVID-19.
“I’m excited that this condition that has been so often the ugly stepchild of both cardiology and neurology is getting some attention,” said Dr. Taub. She said she is hopeful that the National Institutes of Health’s commitment to PASC research will benefit patients affected by the cardiovascular dysautonomia characterized by orthostatic intolerance in the absence of orthostatic hypotension.
Postinfection POTS is not exclusive to SARS-CoV-2. It has been reported after Lyme disease and Epstein-Barr virus infections, for example. One theory is that some of the antibodies generated against the virus cross react and damage the autonomic nervous system, which regulates heart rate and blood pressure, Dr. Taub explained.
It is not known whether COVID-19 is more likely to trigger POTS than are other infections or whether the rise in cases merely reflects the fact that more than 115 million people worldwide have been infected with the novel coronavirus.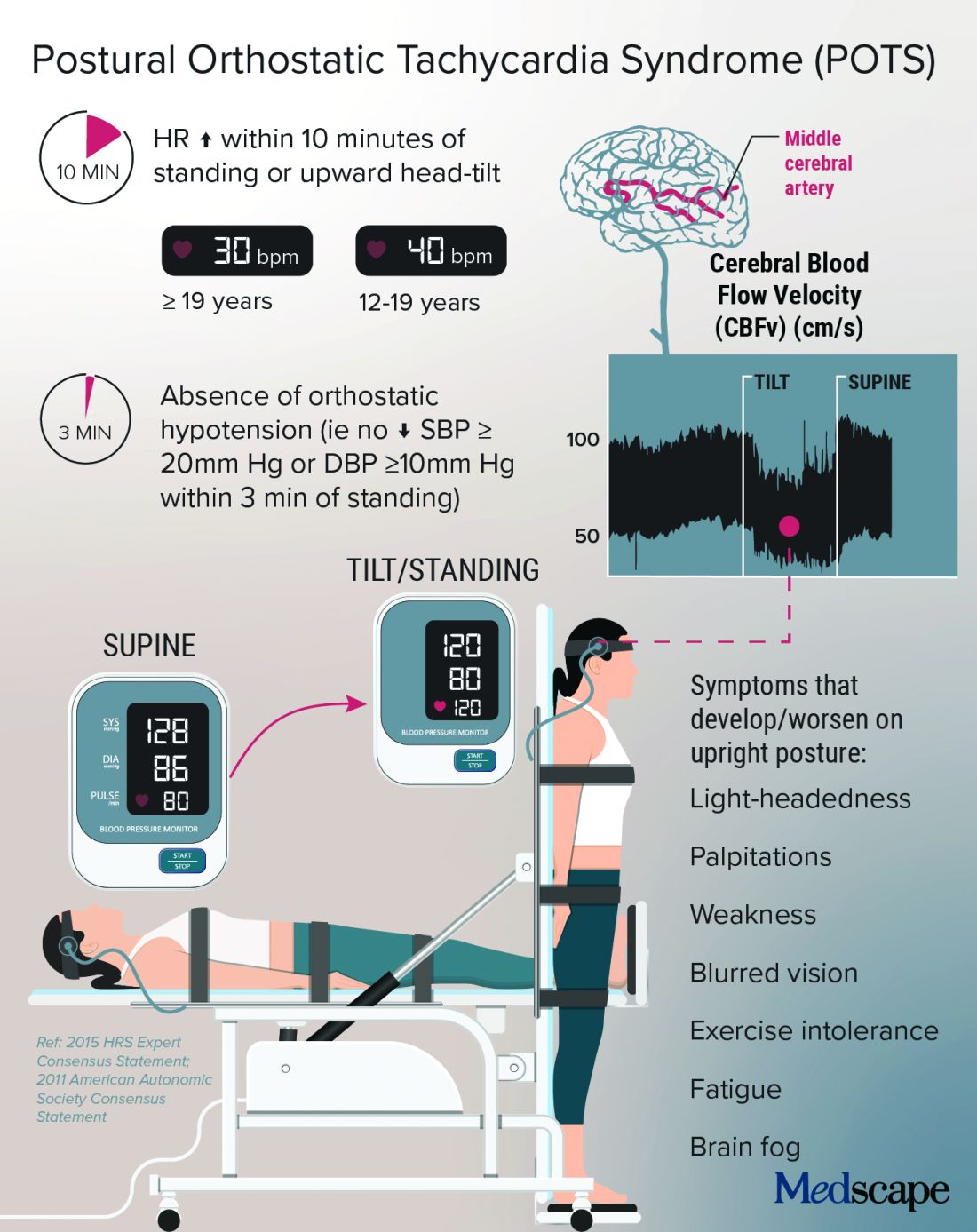
Low blood volume, dysregulation of the autonomic nervous system, and autoimmunity may all play a role in POTS, perhaps leading to distinct subtypes, according to a State of the Science document from the NIH; the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute; and the National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke.
In Dr. Taub’s experience, “The truth is that patients actually have a mix of the subtypes.”
Kamal Shouman, MD, an autonomic neurologist at Mayo Clinic, Rochester, Minn., said in an interview that he has seen patients present with post–COVID-19 POTS in “all flavors,” including “neuropathic POTS, which is thought of as the classic postinfectious phenomenon.”
Why does it mostly affect athletic women?
The condition, which can be the result of dehydration or prolonged bed rest, leading to deconditioning, affects women disproportionately.
According to Manesh Patel, MD, if a patient with POTS who is not a young woman is presented on medical rounds, the response is, “Tell me again why you think this patient has POTS.”
Dr. Patel, chief of the division of cardiology at Duke University, Durham, N.C., has a theory for why many of the women who have POTS are athletes or are highly active: They likely have an underlying predisposition, compounded by a smaller body volume, leaving less margin for error. “If they decondition and lose 500 cc’s, it makes a bigger difference to them than, say, a 300-pound offensive lineman,” Dr. Patel explained.
That hypothesis makes sense to Dr. Taub, who added, “There are just some people metabolically that are more hyperadrenergic,” and it may be that “all their activity really helps tone down that sympathetic output,” but the infection affects these regulatory processes, and deconditioning disrupts things further.
Women also have more autoimmune disorders than do men. The driving force of the dysregulation of the autonomic nervous system is thought to be “immune mediated; we think it’s triggered by a response to a virus,” she said.
Dr. Shouman said the underlying susceptibility may predispose toward orthostatic intolerance. For example, patients will tell him, “Well, many years ago, I was prone to fainting.” He emphasized that POTS is not exclusive to women – he sees men with POTS, and one of the three recent case reports of post–COVID-19 POTS involved a 37-year-old man. So far, the male POTS patients that Dr. Patel has encountered have been deconditioned athletes.
Poor (wo)man’s tilt test and treatment options
POTS is typically diagnosed with a tilt test and transcranial Doppler. Dr. Taub described her “poor man’s tilt test” of asking the patient to lie down for 5-10 minutes and then having the patient stand up.
She likes the fact that transcranial Doppler helps validate the brain fog that patients report, which can be dismissed as “just your excuse for not wanting to work.” If blood perfusion to the brain is cut by 40%-50%, “how are you going to think clearly?” she said.
Dr. Shouman noted that overall volume expansion with salt water, compression garments, and a graduated exercise program play a major role in the rehabilitation of all POTS patients.
He likes to tailor treatments to the most likely underlying cause. But patients should first undergo a medical assessment by their internists to make sure there isn’t a primary lung or heart problem.
“Once the decision is made for them to be evaluated in the autonomic practice and [a] POTS diagnosis is made, I think it is very useful to determine what type of POTS,” he said.
With hyperadrenergic POTS, “you are looking at a standing norepinephrine level of over 600 pg/mL or so.” For these patients, drugs such as ivabradine or beta-blockers can help, he noted.
Dr. Taub recently conducted a small study that showed a benefit with the selective If channel blocker ivabradine for patients with hyperadrenergic POTS unrelated to COVID-19. She tends to favor ivabradine over beta-blockers because it lowers heart rate but not blood pressure. In addition, beta-blockers can exacerbate fatigue and brain fog.
A small crossover study will compare propranolol and ivabradine in POTS. For someone who is very hypovolemic, “you might try a salt tablet or a prescription drug like fludrocortisone,” Dr. Taub explained.
Another problem that patients with POTS experience is an inability to exercise because of orthostatic intolerance. Recumbent exercise targets deconditioning and can tamp down the hyperadrenergic effect. Dr. Shouman’s approach is to start gradually with swimming or the use of a recumbent bike or a rowing machine.
Dr. Taub recommends wearables to patients because POTS is “a very dynamic condition” that is easy to overmedicate or undermedicate. If it’s a good day, the patients are well hydrated, and the standing heart rate is only 80 bpm, she tells them they could titrate down their second dose of ivabradine, for example. The feedback from wearables also helps patients manage their exercise response.
For Dr. Shouman, wearables are not always as accurate as he would like. He tells his patients that it’s okay to use one as long as it doesn’t become a source of anxiety such that they’re constantly checking it.
POTS hope: A COVID-19 silver lining?
With increasing attention being paid to long-haul COVID-19, are there any concerns that POTS will get lost among the myriad symptoms connected to PASC?
Dr. Shouman cautioned, “Not all long COVID is POTS,” and said that clinicians at long-haul clinics should be able to recognize the different conditions “when POTS is suspected. I think it is useful for those providers to make the appropriate referral for POTS clinic autonomic assessment.”
He and his colleagues at Mayo have seen quite a few patients who have post–COVID-19 autonomic dysfunction, such as vasodepressor syncope, not just POTS. They plan to write about this soon.
“Of all the things I treat in cardiology, this is the most complex, because there’s so many different systems involved,” said Dr. Taub, who has seen patients recover fully from POTS. “There’s a spectrum, and there’s people that are definitely on one end of the spectrum where they have very severe diseases.”
For her, the important message is, “No matter where you are on the spectrum, there are things we can do to make your symptoms better.” And with grant funding for PASC research, “hopefully we will address the mechanisms of disease, and we’ll be able to cure this,” she said.
Dr. Patel has served as a consultant for Bayer, Janssen, AstraZeneca, and Heartflow and has received research grants from Bayer, Janssen, AstraZeneca, and the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute. Dr. Shouman reports no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Taub has served as a consultant for Amgen, Bayer, Esperion, Boehringer Ingelheim, Novo Nordisk, and Sanofi; is a shareholder in Epirium Bio; and has received research grants from the National Institutes of Health, the American Heart Association, and the Department of Homeland Security/FEMA.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Before COVID-19, postural orthostatic tachycardia syndrome (POTS) was one of those diseases that many people, including physicians, dismissed.
“They thought it was just anxious, crazy young women,” said Pam R. Taub, MD, who runs the cardiac rehabilitation program at the University of California, San Diego.
The cryptic autonomic condition was estimated to affect 1-3 million Americans before the pandemic hit. Now case reports confirm that it is a manifestation of postacute sequelae of SARS-CoV-2 infection (PASC), or so-called long-haul COVID-19.
“I’m excited that this condition that has been so often the ugly stepchild of both cardiology and neurology is getting some attention,” said Dr. Taub. She said she is hopeful that the National Institutes of Health’s commitment to PASC research will benefit patients affected by the cardiovascular dysautonomia characterized by orthostatic intolerance in the absence of orthostatic hypotension.
Postinfection POTS is not exclusive to SARS-CoV-2. It has been reported after Lyme disease and Epstein-Barr virus infections, for example. One theory is that some of the antibodies generated against the virus cross react and damage the autonomic nervous system, which regulates heart rate and blood pressure, Dr. Taub explained.
It is not known whether COVID-19 is more likely to trigger POTS than are other infections or whether the rise in cases merely reflects the fact that more than 115 million people worldwide have been infected with the novel coronavirus.
Low blood volume, dysregulation of the autonomic nervous system, and autoimmunity may all play a role in POTS, perhaps leading to distinct subtypes, according to a State of the Science document from the NIH; the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute; and the National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke.
In Dr. Taub’s experience, “The truth is that patients actually have a mix of the subtypes.”
Kamal Shouman, MD, an autonomic neurologist at Mayo Clinic, Rochester, Minn., said in an interview that he has seen patients present with post–COVID-19 POTS in “all flavors,” including “neuropathic POTS, which is thought of as the classic postinfectious phenomenon.”
Why does it mostly affect athletic women?
The condition, which can be the result of dehydration or prolonged bed rest, leading to deconditioning, affects women disproportionately.
According to Manesh Patel, MD, if a patient with POTS who is not a young woman is presented on medical rounds, the response is, “Tell me again why you think this patient has POTS.”
Dr. Patel, chief of the division of cardiology at Duke University, Durham, N.C., has a theory for why many of the women who have POTS are athletes or are highly active: They likely have an underlying predisposition, compounded by a smaller body volume, leaving less margin for error. “If they decondition and lose 500 cc’s, it makes a bigger difference to them than, say, a 300-pound offensive lineman,” Dr. Patel explained.
That hypothesis makes sense to Dr. Taub, who added, “There are just some people metabolically that are more hyperadrenergic,” and it may be that “all their activity really helps tone down that sympathetic output,” but the infection affects these regulatory processes, and deconditioning disrupts things further.
Women also have more autoimmune disorders than do men. The driving force of the dysregulation of the autonomic nervous system is thought to be “immune mediated; we think it’s triggered by a response to a virus,” she said.
Dr. Shouman said the underlying susceptibility may predispose toward orthostatic intolerance. For example, patients will tell him, “Well, many years ago, I was prone to fainting.” He emphasized that POTS is not exclusive to women – he sees men with POTS, and one of the three recent case reports of post–COVID-19 POTS involved a 37-year-old man. So far, the male POTS patients that Dr. Patel has encountered have been deconditioned athletes.
Poor (wo)man’s tilt test and treatment options
POTS is typically diagnosed with a tilt test and transcranial Doppler. Dr. Taub described her “poor man’s tilt test” of asking the patient to lie down for 5-10 minutes and then having the patient stand up.
She likes the fact that transcranial Doppler helps validate the brain fog that patients report, which can be dismissed as “just your excuse for not wanting to work.” If blood perfusion to the brain is cut by 40%-50%, “how are you going to think clearly?” she said.
Dr. Shouman noted that overall volume expansion with salt water, compression garments, and a graduated exercise program play a major role in the rehabilitation of all POTS patients.
He likes to tailor treatments to the most likely underlying cause. But patients should first undergo a medical assessment by their internists to make sure there isn’t a primary lung or heart problem.
“Once the decision is made for them to be evaluated in the autonomic practice and [a] POTS diagnosis is made, I think it is very useful to determine what type of POTS,” he said.
With hyperadrenergic POTS, “you are looking at a standing norepinephrine level of over 600 pg/mL or so.” For these patients, drugs such as ivabradine or beta-blockers can help, he noted.
Dr. Taub recently conducted a small study that showed a benefit with the selective If channel blocker ivabradine for patients with hyperadrenergic POTS unrelated to COVID-19. She tends to favor ivabradine over beta-blockers because it lowers heart rate but not blood pressure. In addition, beta-blockers can exacerbate fatigue and brain fog.
A small crossover study will compare propranolol and ivabradine in POTS. For someone who is very hypovolemic, “you might try a salt tablet or a prescription drug like fludrocortisone,” Dr. Taub explained.
Another problem that patients with POTS experience is an inability to exercise because of orthostatic intolerance. Recumbent exercise targets deconditioning and can tamp down the hyperadrenergic effect. Dr. Shouman’s approach is to start gradually with swimming or the use of a recumbent bike or a rowing machine.
Dr. Taub recommends wearables to patients because POTS is “a very dynamic condition” that is easy to overmedicate or undermedicate. If it’s a good day, the patients are well hydrated, and the standing heart rate is only 80 bpm, she tells them they could titrate down their second dose of ivabradine, for example. The feedback from wearables also helps patients manage their exercise response.
For Dr. Shouman, wearables are not always as accurate as he would like. He tells his patients that it’s okay to use one as long as it doesn’t become a source of anxiety such that they’re constantly checking it.
POTS hope: A COVID-19 silver lining?
With increasing attention being paid to long-haul COVID-19, are there any concerns that POTS will get lost among the myriad symptoms connected to PASC?
Dr. Shouman cautioned, “Not all long COVID is POTS,” and said that clinicians at long-haul clinics should be able to recognize the different conditions “when POTS is suspected. I think it is useful for those providers to make the appropriate referral for POTS clinic autonomic assessment.”
He and his colleagues at Mayo have seen quite a few patients who have post–COVID-19 autonomic dysfunction, such as vasodepressor syncope, not just POTS. They plan to write about this soon.
“Of all the things I treat in cardiology, this is the most complex, because there’s so many different systems involved,” said Dr. Taub, who has seen patients recover fully from POTS. “There’s a spectrum, and there’s people that are definitely on one end of the spectrum where they have very severe diseases.”
For her, the important message is, “No matter where you are on the spectrum, there are things we can do to make your symptoms better.” And with grant funding for PASC research, “hopefully we will address the mechanisms of disease, and we’ll be able to cure this,” she said.
Dr. Patel has served as a consultant for Bayer, Janssen, AstraZeneca, and Heartflow and has received research grants from Bayer, Janssen, AstraZeneca, and the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute. Dr. Shouman reports no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Taub has served as a consultant for Amgen, Bayer, Esperion, Boehringer Ingelheim, Novo Nordisk, and Sanofi; is a shareholder in Epirium Bio; and has received research grants from the National Institutes of Health, the American Heart Association, and the Department of Homeland Security/FEMA.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Before COVID-19, postural orthostatic tachycardia syndrome (POTS) was one of those diseases that many people, including physicians, dismissed.
“They thought it was just anxious, crazy young women,” said Pam R. Taub, MD, who runs the cardiac rehabilitation program at the University of California, San Diego.
The cryptic autonomic condition was estimated to affect 1-3 million Americans before the pandemic hit. Now case reports confirm that it is a manifestation of postacute sequelae of SARS-CoV-2 infection (PASC), or so-called long-haul COVID-19.
“I’m excited that this condition that has been so often the ugly stepchild of both cardiology and neurology is getting some attention,” said Dr. Taub. She said she is hopeful that the National Institutes of Health’s commitment to PASC research will benefit patients affected by the cardiovascular dysautonomia characterized by orthostatic intolerance in the absence of orthostatic hypotension.
Postinfection POTS is not exclusive to SARS-CoV-2. It has been reported after Lyme disease and Epstein-Barr virus infections, for example. One theory is that some of the antibodies generated against the virus cross react and damage the autonomic nervous system, which regulates heart rate and blood pressure, Dr. Taub explained.
It is not known whether COVID-19 is more likely to trigger POTS than are other infections or whether the rise in cases merely reflects the fact that more than 115 million people worldwide have been infected with the novel coronavirus.
Low blood volume, dysregulation of the autonomic nervous system, and autoimmunity may all play a role in POTS, perhaps leading to distinct subtypes, according to a State of the Science document from the NIH; the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute; and the National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke.
In Dr. Taub’s experience, “The truth is that patients actually have a mix of the subtypes.”
Kamal Shouman, MD, an autonomic neurologist at Mayo Clinic, Rochester, Minn., said in an interview that he has seen patients present with post–COVID-19 POTS in “all flavors,” including “neuropathic POTS, which is thought of as the classic postinfectious phenomenon.”
Why does it mostly affect athletic women?
The condition, which can be the result of dehydration or prolonged bed rest, leading to deconditioning, affects women disproportionately.
According to Manesh Patel, MD, if a patient with POTS who is not a young woman is presented on medical rounds, the response is, “Tell me again why you think this patient has POTS.”
Dr. Patel, chief of the division of cardiology at Duke University, Durham, N.C., has a theory for why many of the women who have POTS are athletes or are highly active: They likely have an underlying predisposition, compounded by a smaller body volume, leaving less margin for error. “If they decondition and lose 500 cc’s, it makes a bigger difference to them than, say, a 300-pound offensive lineman,” Dr. Patel explained.
That hypothesis makes sense to Dr. Taub, who added, “There are just some people metabolically that are more hyperadrenergic,” and it may be that “all their activity really helps tone down that sympathetic output,” but the infection affects these regulatory processes, and deconditioning disrupts things further.
Women also have more autoimmune disorders than do men. The driving force of the dysregulation of the autonomic nervous system is thought to be “immune mediated; we think it’s triggered by a response to a virus,” she said.
Dr. Shouman said the underlying susceptibility may predispose toward orthostatic intolerance. For example, patients will tell him, “Well, many years ago, I was prone to fainting.” He emphasized that POTS is not exclusive to women – he sees men with POTS, and one of the three recent case reports of post–COVID-19 POTS involved a 37-year-old man. So far, the male POTS patients that Dr. Patel has encountered have been deconditioned athletes.
Poor (wo)man’s tilt test and treatment options
POTS is typically diagnosed with a tilt test and transcranial Doppler. Dr. Taub described her “poor man’s tilt test” of asking the patient to lie down for 5-10 minutes and then having the patient stand up.
She likes the fact that transcranial Doppler helps validate the brain fog that patients report, which can be dismissed as “just your excuse for not wanting to work.” If blood perfusion to the brain is cut by 40%-50%, “how are you going to think clearly?” she said.
Dr. Shouman noted that overall volume expansion with salt water, compression garments, and a graduated exercise program play a major role in the rehabilitation of all POTS patients.
He likes to tailor treatments to the most likely underlying cause. But patients should first undergo a medical assessment by their internists to make sure there isn’t a primary lung or heart problem.
“Once the decision is made for them to be evaluated in the autonomic practice and [a] POTS diagnosis is made, I think it is very useful to determine what type of POTS,” he said.
With hyperadrenergic POTS, “you are looking at a standing norepinephrine level of over 600 pg/mL or so.” For these patients, drugs such as ivabradine or beta-blockers can help, he noted.
Dr. Taub recently conducted a small study that showed a benefit with the selective If channel blocker ivabradine for patients with hyperadrenergic POTS unrelated to COVID-19. She tends to favor ivabradine over beta-blockers because it lowers heart rate but not blood pressure. In addition, beta-blockers can exacerbate fatigue and brain fog.
A small crossover study will compare propranolol and ivabradine in POTS. For someone who is very hypovolemic, “you might try a salt tablet or a prescription drug like fludrocortisone,” Dr. Taub explained.
Another problem that patients with POTS experience is an inability to exercise because of orthostatic intolerance. Recumbent exercise targets deconditioning and can tamp down the hyperadrenergic effect. Dr. Shouman’s approach is to start gradually with swimming or the use of a recumbent bike or a rowing machine.
Dr. Taub recommends wearables to patients because POTS is “a very dynamic condition” that is easy to overmedicate or undermedicate. If it’s a good day, the patients are well hydrated, and the standing heart rate is only 80 bpm, she tells them they could titrate down their second dose of ivabradine, for example. The feedback from wearables also helps patients manage their exercise response.
For Dr. Shouman, wearables are not always as accurate as he would like. He tells his patients that it’s okay to use one as long as it doesn’t become a source of anxiety such that they’re constantly checking it.
POTS hope: A COVID-19 silver lining?
With increasing attention being paid to long-haul COVID-19, are there any concerns that POTS will get lost among the myriad symptoms connected to PASC?
Dr. Shouman cautioned, “Not all long COVID is POTS,” and said that clinicians at long-haul clinics should be able to recognize the different conditions “when POTS is suspected. I think it is useful for those providers to make the appropriate referral for POTS clinic autonomic assessment.”
He and his colleagues at Mayo have seen quite a few patients who have post–COVID-19 autonomic dysfunction, such as vasodepressor syncope, not just POTS. They plan to write about this soon.
“Of all the things I treat in cardiology, this is the most complex, because there’s so many different systems involved,” said Dr. Taub, who has seen patients recover fully from POTS. “There’s a spectrum, and there’s people that are definitely on one end of the spectrum where they have very severe diseases.”
For her, the important message is, “No matter where you are on the spectrum, there are things we can do to make your symptoms better.” And with grant funding for PASC research, “hopefully we will address the mechanisms of disease, and we’ll be able to cure this,” she said.
Dr. Patel has served as a consultant for Bayer, Janssen, AstraZeneca, and Heartflow and has received research grants from Bayer, Janssen, AstraZeneca, and the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute. Dr. Shouman reports no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Taub has served as a consultant for Amgen, Bayer, Esperion, Boehringer Ingelheim, Novo Nordisk, and Sanofi; is a shareholder in Epirium Bio; and has received research grants from the National Institutes of Health, the American Heart Association, and the Department of Homeland Security/FEMA.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Enfuvirtide-Induced Cutaneous Amyloidosis
To the Editor:
Cutaneous amyloidosis can be secondary to many causes. We describe a case of amyloidosis that was secondary to the deposition of an antiretroviral drug enfuvirtide and clinically presented as bullae over the anterior abdominal wall.
A 65-year-old man with HIV presented with pink vesicles and flaccid bullae on the anterolateral aspect of the lower abdomen (Figure 1) in areas of self-administered subcutaneous injections of enfuvirtide. He reported tissue swelling with a yellow discoloration immediately after injections that would spontaneously subside after a few minutes.
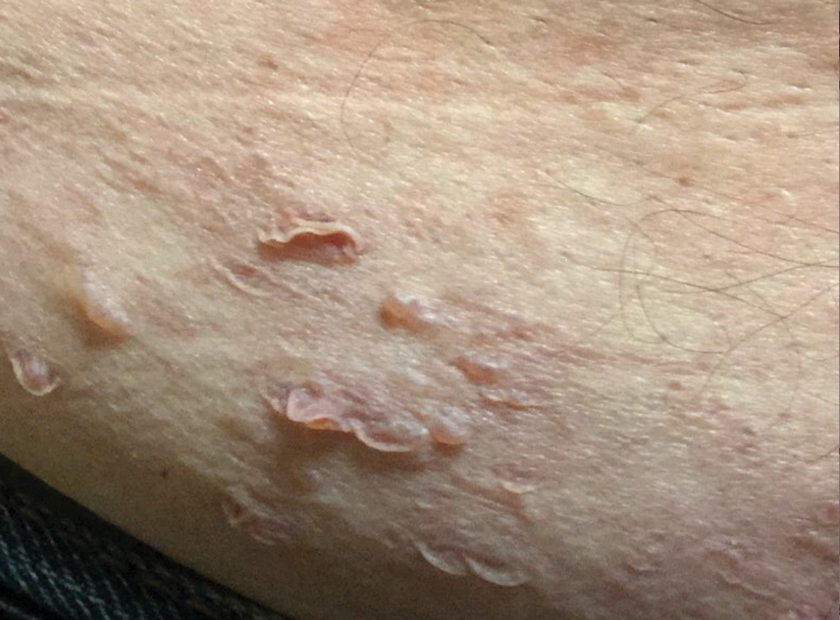
A biopsy from the left lateral abdomen revealed dilated vessels concentrically encompassed by pink globular material and nodular collections of the pink amorphous substance in the upper dermis (Figure 2), which was accompanied by a sparse, perivascular, lymphohistiocytic inflammatory infiltrate; scattered plasma cells; and rare eosinophils in a background of dermal edema. Although Congo red stain was negative, crystal violet revealed metachromatic staining of the globular material that was highlighted as dark violet against a blue background. Given these clinical and histopathologic findings, a diagnosis of drug-induced amyloidosis was made.
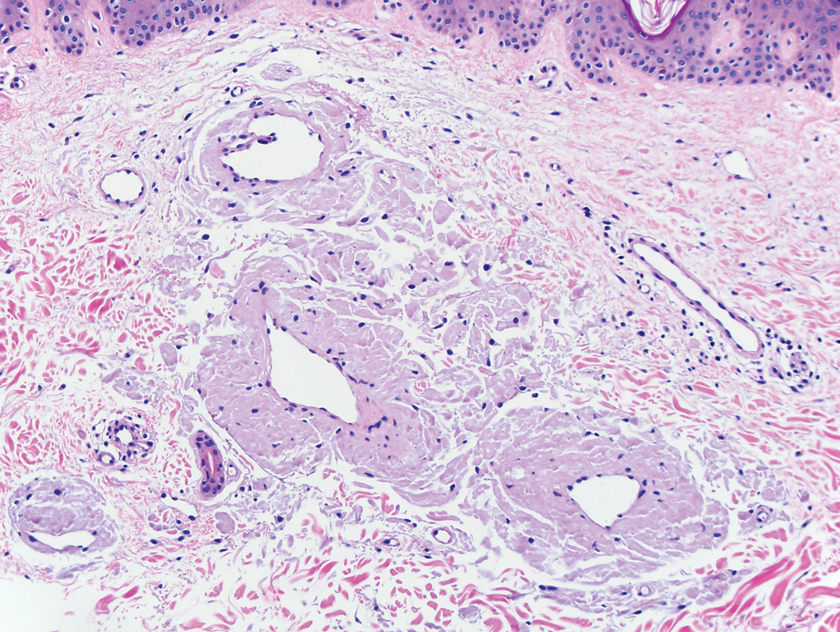
Amyloidosis refers to a group of disorders that result from misfolding of proteins in the characteristic beta-pleated sheet structure that can accumulate in various tissues. There are different subtypes of amyloidosis based on the type of protein deposited: immunoglobulin light chain protein (AL); serum amyloid A (AA), an acute-phase reactant accumulating in those with long-standing inflammatory conditions; beta-2 microglobulin (Ab2M) in patients with renal failure; keratin in macular and lichen amyloidosis; pharmaceutical-derived amyloid (eg, enfuvirtide, injectable insulin); and mutated proteins in hereditary amyloidosis such as transthyretin.1 Other familial forms include genetic variants of apolipolipoprotein AII (AApoAI, AApoAII), fibrinogen A alpha chain (AFib), lysozyme (ALys), cystatin C (ACys), and gelsolin (AGel).2
Cutaneous amyloidosis can stem from a systemic disease or arise as a localized phenomenon. Primary cutaneous amyloidosis can present as either macular, lichen, or nodular forms. The pathogenesis of cutaneous nodular amyloidosis differs from that of lichen and macular types and results from deposition of light chain–derived amyloid protein. In contrast, lichen and macular subtypes have keratin-derived amyloid deposits in the papillary dermis and stain positive for keratin antibodies, especially cytokeratins 5 and 6. Primary nodular amyloidosis has a 7% to 50% risk for developing systemic amyloidosis and a 9% risk for local recurrence, hence the necessity to assess for monoclonal gammopathy with urine light chains and serum immunoelectrophoresis.3
Drug-induced amyloidosis is a distinct type of cutaneous amyloidosis that histopathologically resembles nodular amyloidosis. Multiple drugs have been reported in this setting: insulin,4,5 enfuvirtide injections, and liraglutide.6 Enfuvirtide belongs to a class of antiretroviral agents and is a synthetic peptide composed of 36 amino acids. It inhibits the fusion of HIV with the host helper T cell by binding to glycoprotein 41.7 Enfuvirtide-related amyloidosis was described in 3 case reports, 2 that confirmed enfuvirtide as the amyloid constituent by protein analysis.8-10 One study analyzed the amyloid proteome in 50 cases of insulin-derived amyloidosis and 2 cases of enfuvirtide-derived amyloidosis. Laser microdissection–tandem microscopy revealed that the amyloid in such cases was composed of the drug enfuvirtide itself along with deposits of apolipoproteins (E, A-I, A-IV) and serum amyloid P component.4 Additional complications can occur at the site of enfuvirtide injections. A retrospective review of 7 patients with injection-site reactions to enfuvirtide described erythema, induration, and nodules, with histopathologic findings including hypersensitivity reactions and palisaded granulomas resembling granuloma annulare. Amorphous material was noted within histiocytes and in the surrounding connective tissue that was confirmed as enfuvirtide by immunoperoxidase staining.11
In summary, several types of cutaneous amyloidosis occur, including secondary cutaneous involvement by systemic amyloidosis and drug-induced amyloidosis, and notable histopathologic overlap exists between these types. Given the differing treatment requirements depending on the type of cutaneous amyloidosis, obtaining an appropriate clinical history, including the patient’s medication list, is important to ensure the correct diagnosis is reached. Protein analysis with mass spectrometry can be used if the nature of the amyloid remains indeterminate.
- Merlini G, Bellotti V. Molecular mechanisms of amyloidosis. N Engl J Med. 2003;349:583-596.
- Ferri FF. Amyloidosis. In: Ferri F. Ferri’s Clinical Advisor 2016: 5 Books in 1. Elsevier; 2016.
- Kaltoft B, Schmidt G, Lauritzen AF, et al. Primary localised cutaneous amyloidosis—a systematic review. Dan Med J. 2013;60:A4727.
- D’Souza A, Theis JD, Vrana JA, et al. Pharmaceutical amyloidosis associated with subcutaneous insulin and enfuvirtide administration. Amyloid. 2014;21:71-75.
- Sie MP, van der Wiel HE, Smedts FM, et al. Human recombinant insulin and amyloidosis: an unexpected association. Neth J Med. 2010;68:138-140.
- Martins CO, Lezcano C, Yi SS, et al. Novel iatrogenic amyloidosis caused by peptide drug liraglutide: a clinical mimic of AL amyloidosis. Haematologica. 2018;103:E610-E612.
- Lazzarin A, Clotet B, Cooper D, et al. Efficacy of enfuvirtide in patients infected with drug-resistant HIV-1 in Europe and Australia. N Engl J Med. 2003;348:2186-2195.
- Naujokas A, Vidal CI, Mercer SE, et al. A novel form of amyloid deposited at the site of enfuvirtide injection. J Cutan Pathol. 2012;39:220-221; quiz 219.
- Mercer S, Whang T, Vidal C, et al. Massive amyloidosis at the site of enfuvirtide (Fuzeon) injection. J Cutan Pathol. 2011;38:93.
- Morilla ME, Kocher J, Harmaty M. Localized amyloidosis at the site of enfuvirtide injection. Ann Intern Med. 2009;151:515-516.
- Ball RA, Kinchelow T; ISR Substudy Group. Injection site reactions with the HIV-1 fusion inhibitor enfuvirtide. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2003;49:826-831.
To the Editor:
Cutaneous amyloidosis can be secondary to many causes. We describe a case of amyloidosis that was secondary to the deposition of an antiretroviral drug enfuvirtide and clinically presented as bullae over the anterior abdominal wall.
A 65-year-old man with HIV presented with pink vesicles and flaccid bullae on the anterolateral aspect of the lower abdomen (Figure 1) in areas of self-administered subcutaneous injections of enfuvirtide. He reported tissue swelling with a yellow discoloration immediately after injections that would spontaneously subside after a few minutes.

A biopsy from the left lateral abdomen revealed dilated vessels concentrically encompassed by pink globular material and nodular collections of the pink amorphous substance in the upper dermis (Figure 2), which was accompanied by a sparse, perivascular, lymphohistiocytic inflammatory infiltrate; scattered plasma cells; and rare eosinophils in a background of dermal edema. Although Congo red stain was negative, crystal violet revealed metachromatic staining of the globular material that was highlighted as dark violet against a blue background. Given these clinical and histopathologic findings, a diagnosis of drug-induced amyloidosis was made.

Amyloidosis refers to a group of disorders that result from misfolding of proteins in the characteristic beta-pleated sheet structure that can accumulate in various tissues. There are different subtypes of amyloidosis based on the type of protein deposited: immunoglobulin light chain protein (AL); serum amyloid A (AA), an acute-phase reactant accumulating in those with long-standing inflammatory conditions; beta-2 microglobulin (Ab2M) in patients with renal failure; keratin in macular and lichen amyloidosis; pharmaceutical-derived amyloid (eg, enfuvirtide, injectable insulin); and mutated proteins in hereditary amyloidosis such as transthyretin.1 Other familial forms include genetic variants of apolipolipoprotein AII (AApoAI, AApoAII), fibrinogen A alpha chain (AFib), lysozyme (ALys), cystatin C (ACys), and gelsolin (AGel).2
Cutaneous amyloidosis can stem from a systemic disease or arise as a localized phenomenon. Primary cutaneous amyloidosis can present as either macular, lichen, or nodular forms. The pathogenesis of cutaneous nodular amyloidosis differs from that of lichen and macular types and results from deposition of light chain–derived amyloid protein. In contrast, lichen and macular subtypes have keratin-derived amyloid deposits in the papillary dermis and stain positive for keratin antibodies, especially cytokeratins 5 and 6. Primary nodular amyloidosis has a 7% to 50% risk for developing systemic amyloidosis and a 9% risk for local recurrence, hence the necessity to assess for monoclonal gammopathy with urine light chains and serum immunoelectrophoresis.3
Drug-induced amyloidosis is a distinct type of cutaneous amyloidosis that histopathologically resembles nodular amyloidosis. Multiple drugs have been reported in this setting: insulin,4,5 enfuvirtide injections, and liraglutide.6 Enfuvirtide belongs to a class of antiretroviral agents and is a synthetic peptide composed of 36 amino acids. It inhibits the fusion of HIV with the host helper T cell by binding to glycoprotein 41.7 Enfuvirtide-related amyloidosis was described in 3 case reports, 2 that confirmed enfuvirtide as the amyloid constituent by protein analysis.8-10 One study analyzed the amyloid proteome in 50 cases of insulin-derived amyloidosis and 2 cases of enfuvirtide-derived amyloidosis. Laser microdissection–tandem microscopy revealed that the amyloid in such cases was composed of the drug enfuvirtide itself along with deposits of apolipoproteins (E, A-I, A-IV) and serum amyloid P component.4 Additional complications can occur at the site of enfuvirtide injections. A retrospective review of 7 patients with injection-site reactions to enfuvirtide described erythema, induration, and nodules, with histopathologic findings including hypersensitivity reactions and palisaded granulomas resembling granuloma annulare. Amorphous material was noted within histiocytes and in the surrounding connective tissue that was confirmed as enfuvirtide by immunoperoxidase staining.11
In summary, several types of cutaneous amyloidosis occur, including secondary cutaneous involvement by systemic amyloidosis and drug-induced amyloidosis, and notable histopathologic overlap exists between these types. Given the differing treatment requirements depending on the type of cutaneous amyloidosis, obtaining an appropriate clinical history, including the patient’s medication list, is important to ensure the correct diagnosis is reached. Protein analysis with mass spectrometry can be used if the nature of the amyloid remains indeterminate.
To the Editor:
Cutaneous amyloidosis can be secondary to many causes. We describe a case of amyloidosis that was secondary to the deposition of an antiretroviral drug enfuvirtide and clinically presented as bullae over the anterior abdominal wall.
A 65-year-old man with HIV presented with pink vesicles and flaccid bullae on the anterolateral aspect of the lower abdomen (Figure 1) in areas of self-administered subcutaneous injections of enfuvirtide. He reported tissue swelling with a yellow discoloration immediately after injections that would spontaneously subside after a few minutes.

A biopsy from the left lateral abdomen revealed dilated vessels concentrically encompassed by pink globular material and nodular collections of the pink amorphous substance in the upper dermis (Figure 2), which was accompanied by a sparse, perivascular, lymphohistiocytic inflammatory infiltrate; scattered plasma cells; and rare eosinophils in a background of dermal edema. Although Congo red stain was negative, crystal violet revealed metachromatic staining of the globular material that was highlighted as dark violet against a blue background. Given these clinical and histopathologic findings, a diagnosis of drug-induced amyloidosis was made.

Amyloidosis refers to a group of disorders that result from misfolding of proteins in the characteristic beta-pleated sheet structure that can accumulate in various tissues. There are different subtypes of amyloidosis based on the type of protein deposited: immunoglobulin light chain protein (AL); serum amyloid A (AA), an acute-phase reactant accumulating in those with long-standing inflammatory conditions; beta-2 microglobulin (Ab2M) in patients with renal failure; keratin in macular and lichen amyloidosis; pharmaceutical-derived amyloid (eg, enfuvirtide, injectable insulin); and mutated proteins in hereditary amyloidosis such as transthyretin.1 Other familial forms include genetic variants of apolipolipoprotein AII (AApoAI, AApoAII), fibrinogen A alpha chain (AFib), lysozyme (ALys), cystatin C (ACys), and gelsolin (AGel).2
Cutaneous amyloidosis can stem from a systemic disease or arise as a localized phenomenon. Primary cutaneous amyloidosis can present as either macular, lichen, or nodular forms. The pathogenesis of cutaneous nodular amyloidosis differs from that of lichen and macular types and results from deposition of light chain–derived amyloid protein. In contrast, lichen and macular subtypes have keratin-derived amyloid deposits in the papillary dermis and stain positive for keratin antibodies, especially cytokeratins 5 and 6. Primary nodular amyloidosis has a 7% to 50% risk for developing systemic amyloidosis and a 9% risk for local recurrence, hence the necessity to assess for monoclonal gammopathy with urine light chains and serum immunoelectrophoresis.3
Drug-induced amyloidosis is a distinct type of cutaneous amyloidosis that histopathologically resembles nodular amyloidosis. Multiple drugs have been reported in this setting: insulin,4,5 enfuvirtide injections, and liraglutide.6 Enfuvirtide belongs to a class of antiretroviral agents and is a synthetic peptide composed of 36 amino acids. It inhibits the fusion of HIV with the host helper T cell by binding to glycoprotein 41.7 Enfuvirtide-related amyloidosis was described in 3 case reports, 2 that confirmed enfuvirtide as the amyloid constituent by protein analysis.8-10 One study analyzed the amyloid proteome in 50 cases of insulin-derived amyloidosis and 2 cases of enfuvirtide-derived amyloidosis. Laser microdissection–tandem microscopy revealed that the amyloid in such cases was composed of the drug enfuvirtide itself along with deposits of apolipoproteins (E, A-I, A-IV) and serum amyloid P component.4 Additional complications can occur at the site of enfuvirtide injections. A retrospective review of 7 patients with injection-site reactions to enfuvirtide described erythema, induration, and nodules, with histopathologic findings including hypersensitivity reactions and palisaded granulomas resembling granuloma annulare. Amorphous material was noted within histiocytes and in the surrounding connective tissue that was confirmed as enfuvirtide by immunoperoxidase staining.11
In summary, several types of cutaneous amyloidosis occur, including secondary cutaneous involvement by systemic amyloidosis and drug-induced amyloidosis, and notable histopathologic overlap exists between these types. Given the differing treatment requirements depending on the type of cutaneous amyloidosis, obtaining an appropriate clinical history, including the patient’s medication list, is important to ensure the correct diagnosis is reached. Protein analysis with mass spectrometry can be used if the nature of the amyloid remains indeterminate.
- Merlini G, Bellotti V. Molecular mechanisms of amyloidosis. N Engl J Med. 2003;349:583-596.
- Ferri FF. Amyloidosis. In: Ferri F. Ferri’s Clinical Advisor 2016: 5 Books in 1. Elsevier; 2016.
- Kaltoft B, Schmidt G, Lauritzen AF, et al. Primary localised cutaneous amyloidosis—a systematic review. Dan Med J. 2013;60:A4727.
- D’Souza A, Theis JD, Vrana JA, et al. Pharmaceutical amyloidosis associated with subcutaneous insulin and enfuvirtide administration. Amyloid. 2014;21:71-75.
- Sie MP, van der Wiel HE, Smedts FM, et al. Human recombinant insulin and amyloidosis: an unexpected association. Neth J Med. 2010;68:138-140.
- Martins CO, Lezcano C, Yi SS, et al. Novel iatrogenic amyloidosis caused by peptide drug liraglutide: a clinical mimic of AL amyloidosis. Haematologica. 2018;103:E610-E612.
- Lazzarin A, Clotet B, Cooper D, et al. Efficacy of enfuvirtide in patients infected with drug-resistant HIV-1 in Europe and Australia. N Engl J Med. 2003;348:2186-2195.
- Naujokas A, Vidal CI, Mercer SE, et al. A novel form of amyloid deposited at the site of enfuvirtide injection. J Cutan Pathol. 2012;39:220-221; quiz 219.
- Mercer S, Whang T, Vidal C, et al. Massive amyloidosis at the site of enfuvirtide (Fuzeon) injection. J Cutan Pathol. 2011;38:93.
- Morilla ME, Kocher J, Harmaty M. Localized amyloidosis at the site of enfuvirtide injection. Ann Intern Med. 2009;151:515-516.
- Ball RA, Kinchelow T; ISR Substudy Group. Injection site reactions with the HIV-1 fusion inhibitor enfuvirtide. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2003;49:826-831.
- Merlini G, Bellotti V. Molecular mechanisms of amyloidosis. N Engl J Med. 2003;349:583-596.
- Ferri FF. Amyloidosis. In: Ferri F. Ferri’s Clinical Advisor 2016: 5 Books in 1. Elsevier; 2016.
- Kaltoft B, Schmidt G, Lauritzen AF, et al. Primary localised cutaneous amyloidosis—a systematic review. Dan Med J. 2013;60:A4727.
- D’Souza A, Theis JD, Vrana JA, et al. Pharmaceutical amyloidosis associated with subcutaneous insulin and enfuvirtide administration. Amyloid. 2014;21:71-75.
- Sie MP, van der Wiel HE, Smedts FM, et al. Human recombinant insulin and amyloidosis: an unexpected association. Neth J Med. 2010;68:138-140.
- Martins CO, Lezcano C, Yi SS, et al. Novel iatrogenic amyloidosis caused by peptide drug liraglutide: a clinical mimic of AL amyloidosis. Haematologica. 2018;103:E610-E612.
- Lazzarin A, Clotet B, Cooper D, et al. Efficacy of enfuvirtide in patients infected with drug-resistant HIV-1 in Europe and Australia. N Engl J Med. 2003;348:2186-2195.
- Naujokas A, Vidal CI, Mercer SE, et al. A novel form of amyloid deposited at the site of enfuvirtide injection. J Cutan Pathol. 2012;39:220-221; quiz 219.
- Mercer S, Whang T, Vidal C, et al. Massive amyloidosis at the site of enfuvirtide (Fuzeon) injection. J Cutan Pathol. 2011;38:93.
- Morilla ME, Kocher J, Harmaty M. Localized amyloidosis at the site of enfuvirtide injection. Ann Intern Med. 2009;151:515-516.
- Ball RA, Kinchelow T; ISR Substudy Group. Injection site reactions with the HIV-1 fusion inhibitor enfuvirtide. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2003;49:826-831.
Practice Points
- There are multiple types of cutaneous amyloidosis, and proper diagnosis is essential to direct treatment and follow-up care.
- Medication-associated amyloidosis is a rare type of amyloidosis that is not associated with systemic amyloidosis and is treated by switching to alternative medicines.