User login
The top pediatric articles of 2019
Updates in pediatric hospital medicine
The expansion of the field of pediatric hospital medicine in the past 30 years has resulted in improved health care outcomes for hospitalized children1,2 and has been accompanied by a robust increase in the amount of scholarly work related to the field.3 We performed a review of the literature published in 2019 to identify the 10 articles that had the most impact on pediatric hospital medicine, and presented the findings at HM20 Virtual, the 2020 annual conference of the Society of Hospital Medicine. Five of the selected articles are highlighted here.
STUDY 1
Wechsler ME et al. Step-up therapy in black children and adults with poorly controlled asthma. N Engl J Med. 2019 Sep 26;381(13):1227-39.
Background
Current pediatric asthma guidelines suggest adding a long-acting beta-agonist (LABA) to inhaled corticosteroid (ICS) therapy, rather than increasing the ICS dose, for children with poorly controlled asthma. However, these data are based on trials with disproportionately few Black subjects. This study aimed to determine the best step-up therapy for Black patients whose asthma was poorly controlled on ICS monotherapy.
Study overview and results
The authors reported two parallel double-blind, randomized, controlled trials, one in children and one in adolescents and adults. The study of children included 280 subjects ranging in age from 5 to 11, with at least one Black grandparent, and with poorly controlled asthma on low-dose ICS therapy. It used a four-way crossover design in which each subject was treated with four different 14-week treatment regimens: either double (medium-dose) or quintuple (high-dose) their baseline ICS dose, with or without the addition of a LABA. A superior response was defined by the composite outcome of at least one fewer asthma exacerbation, more asthma-control days, or a 5–percentage point difference in predicted FEV1. Forty-six percent of children had improved asthma outcomes when the ICS dose was increased rather than with the addition of a LABA. In contrast, Black adolescents and Black adults had superior responses to the addition of a LABA. There was no significant interaction between the percentage of African ancestry as determined by DNA genotyping and the primary composite outcome. High-dose ICS was associated with a decrease in the ratio of urinary cortisol to creatinine in children younger than 8 years.
Limitations
Approximately 25% of children dropped out of the study, with disproportionately more children dropping out while on a high-dose ICS regimen. Additionally, the difference in the composite outcome was primarily driven by differences in FEV1, with few subjects demonstrating a difference in asthma exacerbations or asthma-control days. Although a decrease in urinary cortisol to creatinine ratio was noted in children under 8 on high-dose ICS, the study period was not long enough to determine the clinical implications of this finding.
Important findings and implications
While studies with a majority of white children have suggested a superior response from adding a LABA compared to increasing the dose of an ICS, almost half of Black children showed a superior response when the dose of an ICS was increased rather than adding a LABA. It is important to note that current guidelines are based on studies with a disproportionate majority of white subjects and may not accurately reflect optimal care for patients in other racial groups. This study underscores the need to include a diverse patient population in research studies.
STUDY 2
Chang PW, Newman TB. A simpler prediction rule for rebound hyperbilirubinemia. Pediatrics. 2019 Jul;144(1):e20183712.
Background
Hyperbilirubinemia (jaundice) is estimated to affect 50%-60% of all newborns. Rebound hyperbilirubinemia – a rise in bilirubin after cessation of phototherapy – is common and can lead to recently discharged infants being readmitted for additional therapy. Lack of clear guidelines regarding when to discharge infants with hyperbilirubinemia has likely contributed to practice variation and some trepidation regarding whether a bilirubin level is “low enough” to discontinue therapy.
Study overview and results
The authors had previously proposed a three-factor hyperbilirubinemia risk model and sought to simplify their rule further.4 They examined a retrospective cohort of 7,048 infants greater than or equal to 35 weeks’ gestation using a random split sample. The authors derived a two-factor model using the same methods and compared its performance to the three-factor model. The two-factor formula was shown to be a good fit as a logistic regression model (Hosmer-Lemeshow test 9.21; P = .33), and the AUROC (area under the receiver operating characteristic) curves for the derivation and validation cohorts were similar between the two-factor (0.877 and 0.876, respectively) and three-factor risk models (0.887 and 0.881, respectively).
Limitations
These data are limited to infants receiving their first treatment of phototherapy and have not been externally validated. An important variable, serum bilirubin at phototherapy termination, was estimated in most subjects, which may have affected the accuracy of the prediction rule. Whether infants received home phototherapy was based only on equipment orders, and some infants may have received phototherapy unbeknownst to investigators. Last, infants with rebound hyperbilirubinemia at less than 72 hours after phototherapy discontinuation may have been missed.
Important findings and implications
This prediction model provides evidence-based, concrete data that can be used in making joint decisions with families regarding discharge timing of infants with hyperbilirubinemia. It also could be beneficial when deciding appropriate follow-up time after discharge.
STUDY 3
Ramgopal S et al. Risk of serious bacterial infection in infants aged ≤60 days presenting to emergency departments with a history of fever only. J Pediatr. 2019 Jan;204:191-195. doi: 10.1016/j.jpeds.2018.08.043.
Background
Febrile infants aged 60 days and younger are at risk for serious bacterial infections (SBI) including urinary tract infections (UTI), bacteremia, and meningitis. As physical exam is a poor discriminator of SBI in this age group, providers frequently rely on laboratory values and risk factors to guide management. Infants presenting with documented fevers by caregivers but found to have no fever in the emergency department are a challenge, and there are limited data regarding SBI frequency in this population.
Study overview and results
The authors performed a secondary analysis of a prospectively gathered cohort of infants aged 60 days and younger within the Pediatric Emergency Care Applied Research Network (PECARN) who had blood, urine, and CSF data available. Notable exclusions included infants who were premature, had a focal infection, were clinically ill, had recent antibiotic use, did not have blood, urine, and CSF data available, or were lost to telephone follow-up at 7 days to ensure wellness. The study cohort included 6,014 infants, 1,233 (32%) who were febrile by history alone. Rates of overall SBI were lower in the afebrile group (8.8% vs. 12.8%). For infants 0-28 days, rates of UTI were lower for the afebrile group (9.5% vs. 14.5%), but there was no difference in the rates of bacteremia or meningitis. For infants 29-60 days, rates of UTI (6.6% vs. 9.3%) and bacteremia (.5% vs. 1.7%) were lower in the afebrile group.
Limitations
Neither the use of home antipyretics nor the method of temperature taking at home were studied. Also, as this was a secondary analysis, it is possible that not all infants who presented with history of fever only were captured, as work-up was dictated by individual treating providers who may have chosen not to work up certain afebrile infants.
Important findings and implications
Nearly one-third of infants presenting for fever evaluation are afebrile on arrival. Although overall rates of SBI were lower in the group with fever by history only, this difference is largely accounted for by differing rates of UTI. Rates of bacteremia and meningitis remained substantial between groups, particularly for infants aged 0-28 days. Because of the significant morbidity associated with these infections, it is reasonable to suggest that absence of fever on presentation alone should not alter clinical or laboratory work-up, particularly in infants 0-28 days.
STUDY 4
Humphrey-Murto S et al. The influence of prior performance information on ratings of current performance and implications for learner handover: A scoping review. Acad Med. 2019 Jul;94(7):1050-7.
Background
Learner Handover (LH) or “forward feeding” occurs when information about trainees is shared between faculty supervisors. Although this can be helpful to tailor educational experiences and build upon previous assessments, it risks stigmatizing trainees and adding bias to future feedback and assessments as the trainee never really has a “clean slate.” In this study, the authors sought to uncover the key concepts of how prior performance information (PPI) influences assessments and any implications for medical education.
Study overview and results
The authors performed a cross-disciplinary scoping review looking at over 17,000 articles published between 1980 and 2017 across the domains of psychology, sports, business, and education. Seven themes were identified with the following notable findings. Raters exposed to positive PPI scored a learner’s performance higher, and vice versa. There was a dose-response relationship with more positive and more negative PPI resulting in higher and lower assessments, respectively. General standards, such as a direction to complete all work in a timely manner, caused an assimilation effect, while specific standards, such as a direction to complete a certain task by a certain day, did not. More motivated and more experienced raters are less affected by PPI, and those who believe that people can change (incremental theorists) are less affected by PPI while those who believe personal attributes are fixed (entity theorists) are more affected.
Limitations
The heterogeneity of the studies and the fact that they were largely conducted in experimental settings may limit generalizability to medical education. Slightly less than half of the studies included a control arm. Last, most of the studies looked at the ratings of only one target performance, not multiple performances over time.
Important findings and implications
Ratings of current performance displace toward PPI direction, with negative PPI more influential than positive PPI. In a formative setting, PPI may help the assessor focus on areas of possible weakness. In contrast, for a summative assessment, PPI may be prejudicial and have an impact on the rating given to the student. Clinicians should be mindful of the information they share with future raters about learners and the potential bias on future assessments that can manifest as a result.
STUDY 5
McCann ME et al. Neurodevelopmental outcome at 5 years of age after general anaesthesia or awake-regional anaesthesia in infancy (GAS): An international, multicentre, randomised, controlled equivalence trial. The Lancet. 2019 Feb;393:664-77.
Background
Animal models and observational studies have suggested a link between early anesthesia exposure and adverse neurocognitive outcomes; however, findings have been mixed and studies are prone to confounding. This study is the first randomized controlled trial to compare neurocognitive outcomes for infants exposed to general anesthesia versus awake-regional anesthesia.
Study overview and results
In this international, multicenter, assessor-masked trial, 722 infants undergoing inguinal hernia repair were randomized to awake-regional anesthesia or single-agent sevoflurane-based general anesthesia. Infants born at greater than 26 weeks’ gestational age were eligible, while those with prior anesthesia exposure or risks for neurocognitive delay were excluded. The primary outcome was full-scale intelligence quotient (FSIQ) testing at 5 years of age on the Wechsler Preschool and Primary Scale of Intelligence, third edition (WPPSI-III). Seven additional neurodevelopmental assessments and parental questionnaires regarding behavior were administered as secondary outcomes. Average anesthesia exposure was 54 minutes and no infant had exposure greater than 120 minutes. There was no significant difference in mean scores on WPPSI-III FSIQ testing, and no difference in the additional neurocognitive assessments or parent-reported outcomes used as secondary outcomes.
Limitations
This study was limited to single, short periods of single-agent anesthesia exposure in children with no additional neurologic risk factors, so caution should be used in extrapolating these data to children with medical complexity and children undergoing multiple procedures, longer surgeries, or multidrug anesthetic regimens. The study population was majority male because of the surgical pathology selected and included only children in the narrow range of postmenstrual age 60 weeks or less. While this population represents a suspected a period of high cerebral vulnerability based on animal models, the implications of anesthesia exposure at other ages are unclear.
Important findings and implications
An estimated 10% of children from developed countries are exposed to general anesthesia during the first 3 years of life. While hospitalists do not typically select the route of anesthesia, they frequently care for patients undergoing procedures and must address parental concerns regarding the safety of anesthesia exposure. Given the rigorous study methods and long-term follow up in the current study, these data should provide reassurance that, for healthy infants undergoing short, single-agent anesthetic exposure, there is no evidence of future adverse neurologic outcomes.
Dr. Russo is director of pediatrics, medical director for quality and innovation, at WellSpan Health, York, Pa. Dr. Money is a pediatric hospitalist at Primary Children’s Hospital, University of Utah School of Medicine, Salt Lake City. Dr. Steed is instructor of hospital medicine, Northwestern Memorial Hospital and Ann and Robert H. Lurie Children’s Hospital of Chicago, Northwestern University School of Medicine, Chicago. The authors would like to thank Dr. Klint M. Schwenk and the Society for Hospital Medicine Pediatric Special Interest Group Executive Council.
References
1. Roberts KB, Fisher ER, and Rauch DA. The history of pediatric hospital medicine in the United States, 1996-2019. J Hosp Med. 2020 Jul;15(7):424-7.
2. Mussman GM and Conway PH. Pediatric hospitalist systems versus traditional models of care: Effect on quality and cost outcomes. J Hosp Med. 2012 Apr;7(4):350-7.
3. Wang ME, Shaughnessy EE, and Leyenaar JK. The future of pediatric hospital medicine: Challenges and opportunities. J Hosp Med. 2020 Jul;15(7):428-30.
4. Chang PW et al. A clinical prediction rule for rebound hyperbilirubinemia following inpatient phototherapy. Pediatrics. 2017;139 Mar;139(3):e20162896.
Updates in pediatric hospital medicine
Updates in pediatric hospital medicine
The expansion of the field of pediatric hospital medicine in the past 30 years has resulted in improved health care outcomes for hospitalized children1,2 and has been accompanied by a robust increase in the amount of scholarly work related to the field.3 We performed a review of the literature published in 2019 to identify the 10 articles that had the most impact on pediatric hospital medicine, and presented the findings at HM20 Virtual, the 2020 annual conference of the Society of Hospital Medicine. Five of the selected articles are highlighted here.
STUDY 1
Wechsler ME et al. Step-up therapy in black children and adults with poorly controlled asthma. N Engl J Med. 2019 Sep 26;381(13):1227-39.
Background
Current pediatric asthma guidelines suggest adding a long-acting beta-agonist (LABA) to inhaled corticosteroid (ICS) therapy, rather than increasing the ICS dose, for children with poorly controlled asthma. However, these data are based on trials with disproportionately few Black subjects. This study aimed to determine the best step-up therapy for Black patients whose asthma was poorly controlled on ICS monotherapy.
Study overview and results
The authors reported two parallel double-blind, randomized, controlled trials, one in children and one in adolescents and adults. The study of children included 280 subjects ranging in age from 5 to 11, with at least one Black grandparent, and with poorly controlled asthma on low-dose ICS therapy. It used a four-way crossover design in which each subject was treated with four different 14-week treatment regimens: either double (medium-dose) or quintuple (high-dose) their baseline ICS dose, with or without the addition of a LABA. A superior response was defined by the composite outcome of at least one fewer asthma exacerbation, more asthma-control days, or a 5–percentage point difference in predicted FEV1. Forty-six percent of children had improved asthma outcomes when the ICS dose was increased rather than with the addition of a LABA. In contrast, Black adolescents and Black adults had superior responses to the addition of a LABA. There was no significant interaction between the percentage of African ancestry as determined by DNA genotyping and the primary composite outcome. High-dose ICS was associated with a decrease in the ratio of urinary cortisol to creatinine in children younger than 8 years.
Limitations
Approximately 25% of children dropped out of the study, with disproportionately more children dropping out while on a high-dose ICS regimen. Additionally, the difference in the composite outcome was primarily driven by differences in FEV1, with few subjects demonstrating a difference in asthma exacerbations or asthma-control days. Although a decrease in urinary cortisol to creatinine ratio was noted in children under 8 on high-dose ICS, the study period was not long enough to determine the clinical implications of this finding.
Important findings and implications
While studies with a majority of white children have suggested a superior response from adding a LABA compared to increasing the dose of an ICS, almost half of Black children showed a superior response when the dose of an ICS was increased rather than adding a LABA. It is important to note that current guidelines are based on studies with a disproportionate majority of white subjects and may not accurately reflect optimal care for patients in other racial groups. This study underscores the need to include a diverse patient population in research studies.
STUDY 2
Chang PW, Newman TB. A simpler prediction rule for rebound hyperbilirubinemia. Pediatrics. 2019 Jul;144(1):e20183712.
Background
Hyperbilirubinemia (jaundice) is estimated to affect 50%-60% of all newborns. Rebound hyperbilirubinemia – a rise in bilirubin after cessation of phototherapy – is common and can lead to recently discharged infants being readmitted for additional therapy. Lack of clear guidelines regarding when to discharge infants with hyperbilirubinemia has likely contributed to practice variation and some trepidation regarding whether a bilirubin level is “low enough” to discontinue therapy.
Study overview and results
The authors had previously proposed a three-factor hyperbilirubinemia risk model and sought to simplify their rule further.4 They examined a retrospective cohort of 7,048 infants greater than or equal to 35 weeks’ gestation using a random split sample. The authors derived a two-factor model using the same methods and compared its performance to the three-factor model. The two-factor formula was shown to be a good fit as a logistic regression model (Hosmer-Lemeshow test 9.21; P = .33), and the AUROC (area under the receiver operating characteristic) curves for the derivation and validation cohorts were similar between the two-factor (0.877 and 0.876, respectively) and three-factor risk models (0.887 and 0.881, respectively).
Limitations
These data are limited to infants receiving their first treatment of phototherapy and have not been externally validated. An important variable, serum bilirubin at phototherapy termination, was estimated in most subjects, which may have affected the accuracy of the prediction rule. Whether infants received home phototherapy was based only on equipment orders, and some infants may have received phototherapy unbeknownst to investigators. Last, infants with rebound hyperbilirubinemia at less than 72 hours after phototherapy discontinuation may have been missed.
Important findings and implications
This prediction model provides evidence-based, concrete data that can be used in making joint decisions with families regarding discharge timing of infants with hyperbilirubinemia. It also could be beneficial when deciding appropriate follow-up time after discharge.
STUDY 3
Ramgopal S et al. Risk of serious bacterial infection in infants aged ≤60 days presenting to emergency departments with a history of fever only. J Pediatr. 2019 Jan;204:191-195. doi: 10.1016/j.jpeds.2018.08.043.
Background
Febrile infants aged 60 days and younger are at risk for serious bacterial infections (SBI) including urinary tract infections (UTI), bacteremia, and meningitis. As physical exam is a poor discriminator of SBI in this age group, providers frequently rely on laboratory values and risk factors to guide management. Infants presenting with documented fevers by caregivers but found to have no fever in the emergency department are a challenge, and there are limited data regarding SBI frequency in this population.
Study overview and results
The authors performed a secondary analysis of a prospectively gathered cohort of infants aged 60 days and younger within the Pediatric Emergency Care Applied Research Network (PECARN) who had blood, urine, and CSF data available. Notable exclusions included infants who were premature, had a focal infection, were clinically ill, had recent antibiotic use, did not have blood, urine, and CSF data available, or were lost to telephone follow-up at 7 days to ensure wellness. The study cohort included 6,014 infants, 1,233 (32%) who were febrile by history alone. Rates of overall SBI were lower in the afebrile group (8.8% vs. 12.8%). For infants 0-28 days, rates of UTI were lower for the afebrile group (9.5% vs. 14.5%), but there was no difference in the rates of bacteremia or meningitis. For infants 29-60 days, rates of UTI (6.6% vs. 9.3%) and bacteremia (.5% vs. 1.7%) were lower in the afebrile group.
Limitations
Neither the use of home antipyretics nor the method of temperature taking at home were studied. Also, as this was a secondary analysis, it is possible that not all infants who presented with history of fever only were captured, as work-up was dictated by individual treating providers who may have chosen not to work up certain afebrile infants.
Important findings and implications
Nearly one-third of infants presenting for fever evaluation are afebrile on arrival. Although overall rates of SBI were lower in the group with fever by history only, this difference is largely accounted for by differing rates of UTI. Rates of bacteremia and meningitis remained substantial between groups, particularly for infants aged 0-28 days. Because of the significant morbidity associated with these infections, it is reasonable to suggest that absence of fever on presentation alone should not alter clinical or laboratory work-up, particularly in infants 0-28 days.
STUDY 4
Humphrey-Murto S et al. The influence of prior performance information on ratings of current performance and implications for learner handover: A scoping review. Acad Med. 2019 Jul;94(7):1050-7.
Background
Learner Handover (LH) or “forward feeding” occurs when information about trainees is shared between faculty supervisors. Although this can be helpful to tailor educational experiences and build upon previous assessments, it risks stigmatizing trainees and adding bias to future feedback and assessments as the trainee never really has a “clean slate.” In this study, the authors sought to uncover the key concepts of how prior performance information (PPI) influences assessments and any implications for medical education.
Study overview and results
The authors performed a cross-disciplinary scoping review looking at over 17,000 articles published between 1980 and 2017 across the domains of psychology, sports, business, and education. Seven themes were identified with the following notable findings. Raters exposed to positive PPI scored a learner’s performance higher, and vice versa. There was a dose-response relationship with more positive and more negative PPI resulting in higher and lower assessments, respectively. General standards, such as a direction to complete all work in a timely manner, caused an assimilation effect, while specific standards, such as a direction to complete a certain task by a certain day, did not. More motivated and more experienced raters are less affected by PPI, and those who believe that people can change (incremental theorists) are less affected by PPI while those who believe personal attributes are fixed (entity theorists) are more affected.
Limitations
The heterogeneity of the studies and the fact that they were largely conducted in experimental settings may limit generalizability to medical education. Slightly less than half of the studies included a control arm. Last, most of the studies looked at the ratings of only one target performance, not multiple performances over time.
Important findings and implications
Ratings of current performance displace toward PPI direction, with negative PPI more influential than positive PPI. In a formative setting, PPI may help the assessor focus on areas of possible weakness. In contrast, for a summative assessment, PPI may be prejudicial and have an impact on the rating given to the student. Clinicians should be mindful of the information they share with future raters about learners and the potential bias on future assessments that can manifest as a result.
STUDY 5
McCann ME et al. Neurodevelopmental outcome at 5 years of age after general anaesthesia or awake-regional anaesthesia in infancy (GAS): An international, multicentre, randomised, controlled equivalence trial. The Lancet. 2019 Feb;393:664-77.
Background
Animal models and observational studies have suggested a link between early anesthesia exposure and adverse neurocognitive outcomes; however, findings have been mixed and studies are prone to confounding. This study is the first randomized controlled trial to compare neurocognitive outcomes for infants exposed to general anesthesia versus awake-regional anesthesia.
Study overview and results
In this international, multicenter, assessor-masked trial, 722 infants undergoing inguinal hernia repair were randomized to awake-regional anesthesia or single-agent sevoflurane-based general anesthesia. Infants born at greater than 26 weeks’ gestational age were eligible, while those with prior anesthesia exposure or risks for neurocognitive delay were excluded. The primary outcome was full-scale intelligence quotient (FSIQ) testing at 5 years of age on the Wechsler Preschool and Primary Scale of Intelligence, third edition (WPPSI-III). Seven additional neurodevelopmental assessments and parental questionnaires regarding behavior were administered as secondary outcomes. Average anesthesia exposure was 54 minutes and no infant had exposure greater than 120 minutes. There was no significant difference in mean scores on WPPSI-III FSIQ testing, and no difference in the additional neurocognitive assessments or parent-reported outcomes used as secondary outcomes.
Limitations
This study was limited to single, short periods of single-agent anesthesia exposure in children with no additional neurologic risk factors, so caution should be used in extrapolating these data to children with medical complexity and children undergoing multiple procedures, longer surgeries, or multidrug anesthetic regimens. The study population was majority male because of the surgical pathology selected and included only children in the narrow range of postmenstrual age 60 weeks or less. While this population represents a suspected a period of high cerebral vulnerability based on animal models, the implications of anesthesia exposure at other ages are unclear.
Important findings and implications
An estimated 10% of children from developed countries are exposed to general anesthesia during the first 3 years of life. While hospitalists do not typically select the route of anesthesia, they frequently care for patients undergoing procedures and must address parental concerns regarding the safety of anesthesia exposure. Given the rigorous study methods and long-term follow up in the current study, these data should provide reassurance that, for healthy infants undergoing short, single-agent anesthetic exposure, there is no evidence of future adverse neurologic outcomes.
Dr. Russo is director of pediatrics, medical director for quality and innovation, at WellSpan Health, York, Pa. Dr. Money is a pediatric hospitalist at Primary Children’s Hospital, University of Utah School of Medicine, Salt Lake City. Dr. Steed is instructor of hospital medicine, Northwestern Memorial Hospital and Ann and Robert H. Lurie Children’s Hospital of Chicago, Northwestern University School of Medicine, Chicago. The authors would like to thank Dr. Klint M. Schwenk and the Society for Hospital Medicine Pediatric Special Interest Group Executive Council.
References
1. Roberts KB, Fisher ER, and Rauch DA. The history of pediatric hospital medicine in the United States, 1996-2019. J Hosp Med. 2020 Jul;15(7):424-7.
2. Mussman GM and Conway PH. Pediatric hospitalist systems versus traditional models of care: Effect on quality and cost outcomes. J Hosp Med. 2012 Apr;7(4):350-7.
3. Wang ME, Shaughnessy EE, and Leyenaar JK. The future of pediatric hospital medicine: Challenges and opportunities. J Hosp Med. 2020 Jul;15(7):428-30.
4. Chang PW et al. A clinical prediction rule for rebound hyperbilirubinemia following inpatient phototherapy. Pediatrics. 2017;139 Mar;139(3):e20162896.
The expansion of the field of pediatric hospital medicine in the past 30 years has resulted in improved health care outcomes for hospitalized children1,2 and has been accompanied by a robust increase in the amount of scholarly work related to the field.3 We performed a review of the literature published in 2019 to identify the 10 articles that had the most impact on pediatric hospital medicine, and presented the findings at HM20 Virtual, the 2020 annual conference of the Society of Hospital Medicine. Five of the selected articles are highlighted here.
STUDY 1
Wechsler ME et al. Step-up therapy in black children and adults with poorly controlled asthma. N Engl J Med. 2019 Sep 26;381(13):1227-39.
Background
Current pediatric asthma guidelines suggest adding a long-acting beta-agonist (LABA) to inhaled corticosteroid (ICS) therapy, rather than increasing the ICS dose, for children with poorly controlled asthma. However, these data are based on trials with disproportionately few Black subjects. This study aimed to determine the best step-up therapy for Black patients whose asthma was poorly controlled on ICS monotherapy.
Study overview and results
The authors reported two parallel double-blind, randomized, controlled trials, one in children and one in adolescents and adults. The study of children included 280 subjects ranging in age from 5 to 11, with at least one Black grandparent, and with poorly controlled asthma on low-dose ICS therapy. It used a four-way crossover design in which each subject was treated with four different 14-week treatment regimens: either double (medium-dose) or quintuple (high-dose) their baseline ICS dose, with or without the addition of a LABA. A superior response was defined by the composite outcome of at least one fewer asthma exacerbation, more asthma-control days, or a 5–percentage point difference in predicted FEV1. Forty-six percent of children had improved asthma outcomes when the ICS dose was increased rather than with the addition of a LABA. In contrast, Black adolescents and Black adults had superior responses to the addition of a LABA. There was no significant interaction between the percentage of African ancestry as determined by DNA genotyping and the primary composite outcome. High-dose ICS was associated with a decrease in the ratio of urinary cortisol to creatinine in children younger than 8 years.
Limitations
Approximately 25% of children dropped out of the study, with disproportionately more children dropping out while on a high-dose ICS regimen. Additionally, the difference in the composite outcome was primarily driven by differences in FEV1, with few subjects demonstrating a difference in asthma exacerbations or asthma-control days. Although a decrease in urinary cortisol to creatinine ratio was noted in children under 8 on high-dose ICS, the study period was not long enough to determine the clinical implications of this finding.
Important findings and implications
While studies with a majority of white children have suggested a superior response from adding a LABA compared to increasing the dose of an ICS, almost half of Black children showed a superior response when the dose of an ICS was increased rather than adding a LABA. It is important to note that current guidelines are based on studies with a disproportionate majority of white subjects and may not accurately reflect optimal care for patients in other racial groups. This study underscores the need to include a diverse patient population in research studies.
STUDY 2
Chang PW, Newman TB. A simpler prediction rule for rebound hyperbilirubinemia. Pediatrics. 2019 Jul;144(1):e20183712.
Background
Hyperbilirubinemia (jaundice) is estimated to affect 50%-60% of all newborns. Rebound hyperbilirubinemia – a rise in bilirubin after cessation of phototherapy – is common and can lead to recently discharged infants being readmitted for additional therapy. Lack of clear guidelines regarding when to discharge infants with hyperbilirubinemia has likely contributed to practice variation and some trepidation regarding whether a bilirubin level is “low enough” to discontinue therapy.
Study overview and results
The authors had previously proposed a three-factor hyperbilirubinemia risk model and sought to simplify their rule further.4 They examined a retrospective cohort of 7,048 infants greater than or equal to 35 weeks’ gestation using a random split sample. The authors derived a two-factor model using the same methods and compared its performance to the three-factor model. The two-factor formula was shown to be a good fit as a logistic regression model (Hosmer-Lemeshow test 9.21; P = .33), and the AUROC (area under the receiver operating characteristic) curves for the derivation and validation cohorts were similar between the two-factor (0.877 and 0.876, respectively) and three-factor risk models (0.887 and 0.881, respectively).
Limitations
These data are limited to infants receiving their first treatment of phototherapy and have not been externally validated. An important variable, serum bilirubin at phototherapy termination, was estimated in most subjects, which may have affected the accuracy of the prediction rule. Whether infants received home phototherapy was based only on equipment orders, and some infants may have received phototherapy unbeknownst to investigators. Last, infants with rebound hyperbilirubinemia at less than 72 hours after phototherapy discontinuation may have been missed.
Important findings and implications
This prediction model provides evidence-based, concrete data that can be used in making joint decisions with families regarding discharge timing of infants with hyperbilirubinemia. It also could be beneficial when deciding appropriate follow-up time after discharge.
STUDY 3
Ramgopal S et al. Risk of serious bacterial infection in infants aged ≤60 days presenting to emergency departments with a history of fever only. J Pediatr. 2019 Jan;204:191-195. doi: 10.1016/j.jpeds.2018.08.043.
Background
Febrile infants aged 60 days and younger are at risk for serious bacterial infections (SBI) including urinary tract infections (UTI), bacteremia, and meningitis. As physical exam is a poor discriminator of SBI in this age group, providers frequently rely on laboratory values and risk factors to guide management. Infants presenting with documented fevers by caregivers but found to have no fever in the emergency department are a challenge, and there are limited data regarding SBI frequency in this population.
Study overview and results
The authors performed a secondary analysis of a prospectively gathered cohort of infants aged 60 days and younger within the Pediatric Emergency Care Applied Research Network (PECARN) who had blood, urine, and CSF data available. Notable exclusions included infants who were premature, had a focal infection, were clinically ill, had recent antibiotic use, did not have blood, urine, and CSF data available, or were lost to telephone follow-up at 7 days to ensure wellness. The study cohort included 6,014 infants, 1,233 (32%) who were febrile by history alone. Rates of overall SBI were lower in the afebrile group (8.8% vs. 12.8%). For infants 0-28 days, rates of UTI were lower for the afebrile group (9.5% vs. 14.5%), but there was no difference in the rates of bacteremia or meningitis. For infants 29-60 days, rates of UTI (6.6% vs. 9.3%) and bacteremia (.5% vs. 1.7%) were lower in the afebrile group.
Limitations
Neither the use of home antipyretics nor the method of temperature taking at home were studied. Also, as this was a secondary analysis, it is possible that not all infants who presented with history of fever only were captured, as work-up was dictated by individual treating providers who may have chosen not to work up certain afebrile infants.
Important findings and implications
Nearly one-third of infants presenting for fever evaluation are afebrile on arrival. Although overall rates of SBI were lower in the group with fever by history only, this difference is largely accounted for by differing rates of UTI. Rates of bacteremia and meningitis remained substantial between groups, particularly for infants aged 0-28 days. Because of the significant morbidity associated with these infections, it is reasonable to suggest that absence of fever on presentation alone should not alter clinical or laboratory work-up, particularly in infants 0-28 days.
STUDY 4
Humphrey-Murto S et al. The influence of prior performance information on ratings of current performance and implications for learner handover: A scoping review. Acad Med. 2019 Jul;94(7):1050-7.
Background
Learner Handover (LH) or “forward feeding” occurs when information about trainees is shared between faculty supervisors. Although this can be helpful to tailor educational experiences and build upon previous assessments, it risks stigmatizing trainees and adding bias to future feedback and assessments as the trainee never really has a “clean slate.” In this study, the authors sought to uncover the key concepts of how prior performance information (PPI) influences assessments and any implications for medical education.
Study overview and results
The authors performed a cross-disciplinary scoping review looking at over 17,000 articles published between 1980 and 2017 across the domains of psychology, sports, business, and education. Seven themes were identified with the following notable findings. Raters exposed to positive PPI scored a learner’s performance higher, and vice versa. There was a dose-response relationship with more positive and more negative PPI resulting in higher and lower assessments, respectively. General standards, such as a direction to complete all work in a timely manner, caused an assimilation effect, while specific standards, such as a direction to complete a certain task by a certain day, did not. More motivated and more experienced raters are less affected by PPI, and those who believe that people can change (incremental theorists) are less affected by PPI while those who believe personal attributes are fixed (entity theorists) are more affected.
Limitations
The heterogeneity of the studies and the fact that they were largely conducted in experimental settings may limit generalizability to medical education. Slightly less than half of the studies included a control arm. Last, most of the studies looked at the ratings of only one target performance, not multiple performances over time.
Important findings and implications
Ratings of current performance displace toward PPI direction, with negative PPI more influential than positive PPI. In a formative setting, PPI may help the assessor focus on areas of possible weakness. In contrast, for a summative assessment, PPI may be prejudicial and have an impact on the rating given to the student. Clinicians should be mindful of the information they share with future raters about learners and the potential bias on future assessments that can manifest as a result.
STUDY 5
McCann ME et al. Neurodevelopmental outcome at 5 years of age after general anaesthesia or awake-regional anaesthesia in infancy (GAS): An international, multicentre, randomised, controlled equivalence trial. The Lancet. 2019 Feb;393:664-77.
Background
Animal models and observational studies have suggested a link between early anesthesia exposure and adverse neurocognitive outcomes; however, findings have been mixed and studies are prone to confounding. This study is the first randomized controlled trial to compare neurocognitive outcomes for infants exposed to general anesthesia versus awake-regional anesthesia.
Study overview and results
In this international, multicenter, assessor-masked trial, 722 infants undergoing inguinal hernia repair were randomized to awake-regional anesthesia or single-agent sevoflurane-based general anesthesia. Infants born at greater than 26 weeks’ gestational age were eligible, while those with prior anesthesia exposure or risks for neurocognitive delay were excluded. The primary outcome was full-scale intelligence quotient (FSIQ) testing at 5 years of age on the Wechsler Preschool and Primary Scale of Intelligence, third edition (WPPSI-III). Seven additional neurodevelopmental assessments and parental questionnaires regarding behavior were administered as secondary outcomes. Average anesthesia exposure was 54 minutes and no infant had exposure greater than 120 minutes. There was no significant difference in mean scores on WPPSI-III FSIQ testing, and no difference in the additional neurocognitive assessments or parent-reported outcomes used as secondary outcomes.
Limitations
This study was limited to single, short periods of single-agent anesthesia exposure in children with no additional neurologic risk factors, so caution should be used in extrapolating these data to children with medical complexity and children undergoing multiple procedures, longer surgeries, or multidrug anesthetic regimens. The study population was majority male because of the surgical pathology selected and included only children in the narrow range of postmenstrual age 60 weeks or less. While this population represents a suspected a period of high cerebral vulnerability based on animal models, the implications of anesthesia exposure at other ages are unclear.
Important findings and implications
An estimated 10% of children from developed countries are exposed to general anesthesia during the first 3 years of life. While hospitalists do not typically select the route of anesthesia, they frequently care for patients undergoing procedures and must address parental concerns regarding the safety of anesthesia exposure. Given the rigorous study methods and long-term follow up in the current study, these data should provide reassurance that, for healthy infants undergoing short, single-agent anesthetic exposure, there is no evidence of future adverse neurologic outcomes.
Dr. Russo is director of pediatrics, medical director for quality and innovation, at WellSpan Health, York, Pa. Dr. Money is a pediatric hospitalist at Primary Children’s Hospital, University of Utah School of Medicine, Salt Lake City. Dr. Steed is instructor of hospital medicine, Northwestern Memorial Hospital and Ann and Robert H. Lurie Children’s Hospital of Chicago, Northwestern University School of Medicine, Chicago. The authors would like to thank Dr. Klint M. Schwenk and the Society for Hospital Medicine Pediatric Special Interest Group Executive Council.
References
1. Roberts KB, Fisher ER, and Rauch DA. The history of pediatric hospital medicine in the United States, 1996-2019. J Hosp Med. 2020 Jul;15(7):424-7.
2. Mussman GM and Conway PH. Pediatric hospitalist systems versus traditional models of care: Effect on quality and cost outcomes. J Hosp Med. 2012 Apr;7(4):350-7.
3. Wang ME, Shaughnessy EE, and Leyenaar JK. The future of pediatric hospital medicine: Challenges and opportunities. J Hosp Med. 2020 Jul;15(7):428-30.
4. Chang PW et al. A clinical prediction rule for rebound hyperbilirubinemia following inpatient phototherapy. Pediatrics. 2017;139 Mar;139(3):e20162896.
Weight loss may be paramount lifestyle change in preventing gout
A recent analysis of the incidence of gout in men, published in JAMA Network Open, offers new insights on the role of lifestyle changes in preventing gout, particularly the importance of obesity and its modification.
Prior gout research, although it addressed lifestyle issues, had not quantified the impact of obesity on incident gout cases, noted first author Natalie McCormick, PhD, and colleagues at Harvard Medical School and Massachusetts General Hospital in Boston. “To date the proportion of actual gout itself that could potentially be prevented by modifying such risk factors remains unknown.” To address that lack of data, they set out to estimate the proportion of avoidable incident gout in a large database in the Health Professionals Follow-up Study, initially of some 51,529 male health professionals who have completed a biannual personal health questionnaire since 1986. The follow-up rate for completing these questionnaires exceeds 90%.
For their analysis, the researchers tracked 44,654 of these men, with an average age of 54 at the 1986 baseline and no history of gout, through the year 2012. They looked at four lifestyle risk factors attributed to gout: body mass index; alcohol intake; adherence to a Dietary Approach to Stop Hypertension (DASH)-style diet, which recommends less red meat and sweetened beverages and more fruits, vegetables, and low-fat dairy products; and the absence of diuretic drugs, which are used to treat blood pressure or heart failure, in order to observe and compare their effects on new reports of gout. Over the subsequent 26 years, nearly 4% of the men developed gout, the most common inflammatory arthritis. Obese men had 2.65 times greater risk for developing gout than did those with a normal body mass index.
If one addressed all four risk factors – modifying obesity, having no alcohol intake, not taking diuretic drugs, and following a DASH-style, lower-fat diet – 77% of new gout cases would disappear, the study’s corresponding author, Hyon K. Choi, MD, DrPH, of the division of rheumatology, allergy, and immunology at Massachusetts General Hospital, said in an interview. “But we learned that if you don’t include modifying obesity as a targetable risk factor, none of the other factors alone reaches significance. We can’t make firm conclusions about cause and effect, but modifying obesity seems to be a prerequisite to preventing gout through lifestyle. It’s a very interesting finding that needs to be confirmed in further research,” he said.
Of course, identifying the importance of lifestyle risk factors is not the same as actually achieving modifications of those factors. Changing lifestyle is difficult, Dr. Choi acknowledged. “But there’s not much potential for achieving the goal if the clinician doesn’t understand the target. Now we know obesity has a lot to do with gout. We can see it as a public health issue, especially since gout increases risks for comorbidities and mortality. All of these risk factors deserve intervention by the physician.”
A worldwide gout epidemic
Currently, there is a kind of worldwide gout epidemic linked to obesity, Dr. Choi said. The disease burden of gout is increasing worldwide. “This may be more of an issue for family practice or primary care physicians, who see 80%-90% of gout cases, rather than for rheumatologists, who are more likely to see advanced cases in need of drug therapy. But we would say: Don’t lose sight of the lifestyle risk factors, which are interrelated. This is not only the responsibility of one doctor or the other.”
The new findings should give practicing rheumatologists more confidence in addressing lifestyle issues, particularly weight loss, with their patients, said Angelo Gaffo, MD, section chief of rheumatology at the Birmingham VA Medical Center and associate professor of medicine in the division of rheumatology at the University of Alabama at Birmingham.
“Our patients with gout are interested in what they can do in their lives that might help with their gout. In the past, we’ve had generic advice about changing their diet. But in general, the evidence for the impact of dietary changes has not been strong.”
Doctors can now recommend a DASH-style diet, allowing room for moderate consumption of red meat, so long as patients are working on their weight loss – and showing results. “Now we have the information to give advice that’s more evidence-based,” Dr. Gaffo said. “You can ask the question whether this study is applicable to patients who already have gout. It doesn’t directly address them. But it mainly builds on the narrative that weight loss is important.”
Other studies have also looked at how weight loss led to serum urate reduction. This study adds to a growing body of literature emphasizing that the most important lifestyle factor relative to gout risk is weight gain, and the simplest, most effective intervention is counseling patients about weight loss, he said.
This research was supported by grants from the National Institutes of Health. Dr. Choi reported receiving research support from Ironwood and Horizon and consulting fees from Ironwood, Selecta, Horizon, Takeda, Kowa, and Vaxart. No other relevant financial disclosures were reported.
SOURCE: McCormick N et al. JAMA Netw Open. 2020;3(11):e2027421. doi: 10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2020.27421.
A recent analysis of the incidence of gout in men, published in JAMA Network Open, offers new insights on the role of lifestyle changes in preventing gout, particularly the importance of obesity and its modification.
Prior gout research, although it addressed lifestyle issues, had not quantified the impact of obesity on incident gout cases, noted first author Natalie McCormick, PhD, and colleagues at Harvard Medical School and Massachusetts General Hospital in Boston. “To date the proportion of actual gout itself that could potentially be prevented by modifying such risk factors remains unknown.” To address that lack of data, they set out to estimate the proportion of avoidable incident gout in a large database in the Health Professionals Follow-up Study, initially of some 51,529 male health professionals who have completed a biannual personal health questionnaire since 1986. The follow-up rate for completing these questionnaires exceeds 90%.
For their analysis, the researchers tracked 44,654 of these men, with an average age of 54 at the 1986 baseline and no history of gout, through the year 2012. They looked at four lifestyle risk factors attributed to gout: body mass index; alcohol intake; adherence to a Dietary Approach to Stop Hypertension (DASH)-style diet, which recommends less red meat and sweetened beverages and more fruits, vegetables, and low-fat dairy products; and the absence of diuretic drugs, which are used to treat blood pressure or heart failure, in order to observe and compare their effects on new reports of gout. Over the subsequent 26 years, nearly 4% of the men developed gout, the most common inflammatory arthritis. Obese men had 2.65 times greater risk for developing gout than did those with a normal body mass index.
If one addressed all four risk factors – modifying obesity, having no alcohol intake, not taking diuretic drugs, and following a DASH-style, lower-fat diet – 77% of new gout cases would disappear, the study’s corresponding author, Hyon K. Choi, MD, DrPH, of the division of rheumatology, allergy, and immunology at Massachusetts General Hospital, said in an interview. “But we learned that if you don’t include modifying obesity as a targetable risk factor, none of the other factors alone reaches significance. We can’t make firm conclusions about cause and effect, but modifying obesity seems to be a prerequisite to preventing gout through lifestyle. It’s a very interesting finding that needs to be confirmed in further research,” he said.
Of course, identifying the importance of lifestyle risk factors is not the same as actually achieving modifications of those factors. Changing lifestyle is difficult, Dr. Choi acknowledged. “But there’s not much potential for achieving the goal if the clinician doesn’t understand the target. Now we know obesity has a lot to do with gout. We can see it as a public health issue, especially since gout increases risks for comorbidities and mortality. All of these risk factors deserve intervention by the physician.”
A worldwide gout epidemic
Currently, there is a kind of worldwide gout epidemic linked to obesity, Dr. Choi said. The disease burden of gout is increasing worldwide. “This may be more of an issue for family practice or primary care physicians, who see 80%-90% of gout cases, rather than for rheumatologists, who are more likely to see advanced cases in need of drug therapy. But we would say: Don’t lose sight of the lifestyle risk factors, which are interrelated. This is not only the responsibility of one doctor or the other.”
The new findings should give practicing rheumatologists more confidence in addressing lifestyle issues, particularly weight loss, with their patients, said Angelo Gaffo, MD, section chief of rheumatology at the Birmingham VA Medical Center and associate professor of medicine in the division of rheumatology at the University of Alabama at Birmingham.
“Our patients with gout are interested in what they can do in their lives that might help with their gout. In the past, we’ve had generic advice about changing their diet. But in general, the evidence for the impact of dietary changes has not been strong.”
Doctors can now recommend a DASH-style diet, allowing room for moderate consumption of red meat, so long as patients are working on their weight loss – and showing results. “Now we have the information to give advice that’s more evidence-based,” Dr. Gaffo said. “You can ask the question whether this study is applicable to patients who already have gout. It doesn’t directly address them. But it mainly builds on the narrative that weight loss is important.”
Other studies have also looked at how weight loss led to serum urate reduction. This study adds to a growing body of literature emphasizing that the most important lifestyle factor relative to gout risk is weight gain, and the simplest, most effective intervention is counseling patients about weight loss, he said.
This research was supported by grants from the National Institutes of Health. Dr. Choi reported receiving research support from Ironwood and Horizon and consulting fees from Ironwood, Selecta, Horizon, Takeda, Kowa, and Vaxart. No other relevant financial disclosures were reported.
SOURCE: McCormick N et al. JAMA Netw Open. 2020;3(11):e2027421. doi: 10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2020.27421.
A recent analysis of the incidence of gout in men, published in JAMA Network Open, offers new insights on the role of lifestyle changes in preventing gout, particularly the importance of obesity and its modification.
Prior gout research, although it addressed lifestyle issues, had not quantified the impact of obesity on incident gout cases, noted first author Natalie McCormick, PhD, and colleagues at Harvard Medical School and Massachusetts General Hospital in Boston. “To date the proportion of actual gout itself that could potentially be prevented by modifying such risk factors remains unknown.” To address that lack of data, they set out to estimate the proportion of avoidable incident gout in a large database in the Health Professionals Follow-up Study, initially of some 51,529 male health professionals who have completed a biannual personal health questionnaire since 1986. The follow-up rate for completing these questionnaires exceeds 90%.
For their analysis, the researchers tracked 44,654 of these men, with an average age of 54 at the 1986 baseline and no history of gout, through the year 2012. They looked at four lifestyle risk factors attributed to gout: body mass index; alcohol intake; adherence to a Dietary Approach to Stop Hypertension (DASH)-style diet, which recommends less red meat and sweetened beverages and more fruits, vegetables, and low-fat dairy products; and the absence of diuretic drugs, which are used to treat blood pressure or heart failure, in order to observe and compare their effects on new reports of gout. Over the subsequent 26 years, nearly 4% of the men developed gout, the most common inflammatory arthritis. Obese men had 2.65 times greater risk for developing gout than did those with a normal body mass index.
If one addressed all four risk factors – modifying obesity, having no alcohol intake, not taking diuretic drugs, and following a DASH-style, lower-fat diet – 77% of new gout cases would disappear, the study’s corresponding author, Hyon K. Choi, MD, DrPH, of the division of rheumatology, allergy, and immunology at Massachusetts General Hospital, said in an interview. “But we learned that if you don’t include modifying obesity as a targetable risk factor, none of the other factors alone reaches significance. We can’t make firm conclusions about cause and effect, but modifying obesity seems to be a prerequisite to preventing gout through lifestyle. It’s a very interesting finding that needs to be confirmed in further research,” he said.
Of course, identifying the importance of lifestyle risk factors is not the same as actually achieving modifications of those factors. Changing lifestyle is difficult, Dr. Choi acknowledged. “But there’s not much potential for achieving the goal if the clinician doesn’t understand the target. Now we know obesity has a lot to do with gout. We can see it as a public health issue, especially since gout increases risks for comorbidities and mortality. All of these risk factors deserve intervention by the physician.”
A worldwide gout epidemic
Currently, there is a kind of worldwide gout epidemic linked to obesity, Dr. Choi said. The disease burden of gout is increasing worldwide. “This may be more of an issue for family practice or primary care physicians, who see 80%-90% of gout cases, rather than for rheumatologists, who are more likely to see advanced cases in need of drug therapy. But we would say: Don’t lose sight of the lifestyle risk factors, which are interrelated. This is not only the responsibility of one doctor or the other.”
The new findings should give practicing rheumatologists more confidence in addressing lifestyle issues, particularly weight loss, with their patients, said Angelo Gaffo, MD, section chief of rheumatology at the Birmingham VA Medical Center and associate professor of medicine in the division of rheumatology at the University of Alabama at Birmingham.
“Our patients with gout are interested in what they can do in their lives that might help with their gout. In the past, we’ve had generic advice about changing their diet. But in general, the evidence for the impact of dietary changes has not been strong.”
Doctors can now recommend a DASH-style diet, allowing room for moderate consumption of red meat, so long as patients are working on their weight loss – and showing results. “Now we have the information to give advice that’s more evidence-based,” Dr. Gaffo said. “You can ask the question whether this study is applicable to patients who already have gout. It doesn’t directly address them. But it mainly builds on the narrative that weight loss is important.”
Other studies have also looked at how weight loss led to serum urate reduction. This study adds to a growing body of literature emphasizing that the most important lifestyle factor relative to gout risk is weight gain, and the simplest, most effective intervention is counseling patients about weight loss, he said.
This research was supported by grants from the National Institutes of Health. Dr. Choi reported receiving research support from Ironwood and Horizon and consulting fees from Ironwood, Selecta, Horizon, Takeda, Kowa, and Vaxart. No other relevant financial disclosures were reported.
SOURCE: McCormick N et al. JAMA Netw Open. 2020;3(11):e2027421. doi: 10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2020.27421.
FROM JAMA NETWORK OPEN
Gender surgical outcomes differ following puberty suppression
Puberty suppression (PS) not only successfully reduces the physical development of sex characteristics, giving transgender youth the opportunity to qualify “for different gender-affirming surgical techniques, it also gives adolescents the time needed to explore their gender identity prior to beginning irreversible cross-sex hormone (CSH) treatment,” Tim C. van de Grift, MD, PhD, of the Vrije Universiteit Medical Center, Amsterdam, and colleagues reported in a retrospective single-center cohort study published in Pediatrics.
Dr. van de Grift and his colleagues evaluated the development of sex characteristics in 184 (61%) transgender men and 116 (39%) transgender women aged an average of 23 years at follow-up; a total of 50 men and 50 women served as controls within the total patient pool. The patients, identified from local registries, were adolescents at the time who had applied for gender-affirming medical interventions between 2006 and 2013.
In order to be included in the analysis, patients were required to 1) have a confirmed gender dysphoria diagnosis, 2) be at least 18 years of age at the point of data collection, 3) be less than 18 years of age when PS was initiated, 4) have initiated and continued PS treatment, and 5) not be lost to follow-up.
Clinical controls were identified by random sample using hospital records. Unlike patients in the PS cohort, the controls received CSH instead of PS, but they otherwise applied for gender-affirming surgery during the same years and met all other non-PS inclusion criteria.
PS offers more favorable, less invasive outcomes for transgender men than women
The researchers found no statistically significant impact of PS on height, weight, and body mass index preoperatively in either transgender men or women.
In transgender men, breast development differed the most, with the least development in the Tanner 2/3 puberty scale group, intermediate development in Tanner 4/5 patients, and the most development in controls who did not have PS. As a result, fewer mastectomies were required after PS, and those that were performed were less invasive, compared with controls. Dr. van de Grift and colleagues noted that these findings were in line with surgical guidelines that advise which mastectomy technique is appropriate based on breast size, elasticity, and ptosis grade. They cautioned that, while PS improves the odds of not needing a mastectomy, it is not a guaranteed outcome.
In transgender women, PS had a significant effect on penile development, which was less in Tanner 2/3 patients, compared with the other groups and less in Tanner 4/5 patients, compared with controls. As the researchers explained, penile length is key to vaginoplasty surgery since the penile skin is what is used to create the vaginal lining. For patients lacking sufficient skin, an alternative vaginoplasty technique using intestinal tissue or full-thickness graft is necessary. In this group, surgical options depended upon the onset of PS. In the control group, standard penile-inversion vaginoplasty was more probable, but it was less so in the Tanner 4/5 patients and only infrequently probable in Tanner 2/3 patients. Most transgender women who started PS in Tanner 2/3 underwent intestinal vaginoplasty.
Before PS is initiated much dialog and planning is warranted
“Clinicians should counsel transgender youth and their parents in making informed decisions when starting PS. Counseling consists of informing about the possible surgical consequences when puberty is suppressed and that these techniques may not be available in general transgender care facilities,” advised Dr. van de Grift and his colleagues. Specifically, when pediatricians prescribe PS, they need to be cognizant of the consequences down the line regarding the demand for “technically complex gender-affirming surgery,” performed by, for example, plastic surgeons, who will need to be “skilled in minimally invasive mastectomy techniques and more extensive vaginoplasty approaches.” Therefore, it is key for referring physicians to be sensitive to the need for early referral to specialized care in order to maximize positive outcomes, they added.
The study was limited by the sample size of some subgroups. Only two-thirds of eligible candidates were included in the sample size because follow-up data were not available for the remaining patients. Future studies should include multicenter standardized prospective data collection that provides patient-reported outcomes to enhance the perspective of the clinical findings, the researchers observed.
In a separate interview with Pediatric News, M. Brett Cooper, MD, of the department of pediatrics at University of Texas, Dallas, and an adolescent medicine physician at Children’s Medical Center in Dallas, noted that “Initiation of puberty suppression can be lifesaving for many gender-diverse youth, preventing the development of secondary sex characteristics. However, this can have effects later if these youth choose to pursue gender-affirming surgeries. This study is important for helping to frame the conversation for youth and their parents when doing consent to start puberty-blocking medications, as well as around optimal timing for each individual.”
Dr. Cooper is a paid MDedge consultant for the LGBTQ Youth Consult in Pediatric News. He had no other disclosures to report.
SOURCE: van de Grift T et al. Pediatrics. 2020;146(5):e20193653.
Puberty suppression (PS) not only successfully reduces the physical development of sex characteristics, giving transgender youth the opportunity to qualify “for different gender-affirming surgical techniques, it also gives adolescents the time needed to explore their gender identity prior to beginning irreversible cross-sex hormone (CSH) treatment,” Tim C. van de Grift, MD, PhD, of the Vrije Universiteit Medical Center, Amsterdam, and colleagues reported in a retrospective single-center cohort study published in Pediatrics.
Dr. van de Grift and his colleagues evaluated the development of sex characteristics in 184 (61%) transgender men and 116 (39%) transgender women aged an average of 23 years at follow-up; a total of 50 men and 50 women served as controls within the total patient pool. The patients, identified from local registries, were adolescents at the time who had applied for gender-affirming medical interventions between 2006 and 2013.
In order to be included in the analysis, patients were required to 1) have a confirmed gender dysphoria diagnosis, 2) be at least 18 years of age at the point of data collection, 3) be less than 18 years of age when PS was initiated, 4) have initiated and continued PS treatment, and 5) not be lost to follow-up.
Clinical controls were identified by random sample using hospital records. Unlike patients in the PS cohort, the controls received CSH instead of PS, but they otherwise applied for gender-affirming surgery during the same years and met all other non-PS inclusion criteria.
PS offers more favorable, less invasive outcomes for transgender men than women
The researchers found no statistically significant impact of PS on height, weight, and body mass index preoperatively in either transgender men or women.
In transgender men, breast development differed the most, with the least development in the Tanner 2/3 puberty scale group, intermediate development in Tanner 4/5 patients, and the most development in controls who did not have PS. As a result, fewer mastectomies were required after PS, and those that were performed were less invasive, compared with controls. Dr. van de Grift and colleagues noted that these findings were in line with surgical guidelines that advise which mastectomy technique is appropriate based on breast size, elasticity, and ptosis grade. They cautioned that, while PS improves the odds of not needing a mastectomy, it is not a guaranteed outcome.
In transgender women, PS had a significant effect on penile development, which was less in Tanner 2/3 patients, compared with the other groups and less in Tanner 4/5 patients, compared with controls. As the researchers explained, penile length is key to vaginoplasty surgery since the penile skin is what is used to create the vaginal lining. For patients lacking sufficient skin, an alternative vaginoplasty technique using intestinal tissue or full-thickness graft is necessary. In this group, surgical options depended upon the onset of PS. In the control group, standard penile-inversion vaginoplasty was more probable, but it was less so in the Tanner 4/5 patients and only infrequently probable in Tanner 2/3 patients. Most transgender women who started PS in Tanner 2/3 underwent intestinal vaginoplasty.
Before PS is initiated much dialog and planning is warranted
“Clinicians should counsel transgender youth and their parents in making informed decisions when starting PS. Counseling consists of informing about the possible surgical consequences when puberty is suppressed and that these techniques may not be available in general transgender care facilities,” advised Dr. van de Grift and his colleagues. Specifically, when pediatricians prescribe PS, they need to be cognizant of the consequences down the line regarding the demand for “technically complex gender-affirming surgery,” performed by, for example, plastic surgeons, who will need to be “skilled in minimally invasive mastectomy techniques and more extensive vaginoplasty approaches.” Therefore, it is key for referring physicians to be sensitive to the need for early referral to specialized care in order to maximize positive outcomes, they added.
The study was limited by the sample size of some subgroups. Only two-thirds of eligible candidates were included in the sample size because follow-up data were not available for the remaining patients. Future studies should include multicenter standardized prospective data collection that provides patient-reported outcomes to enhance the perspective of the clinical findings, the researchers observed.
In a separate interview with Pediatric News, M. Brett Cooper, MD, of the department of pediatrics at University of Texas, Dallas, and an adolescent medicine physician at Children’s Medical Center in Dallas, noted that “Initiation of puberty suppression can be lifesaving for many gender-diverse youth, preventing the development of secondary sex characteristics. However, this can have effects later if these youth choose to pursue gender-affirming surgeries. This study is important for helping to frame the conversation for youth and their parents when doing consent to start puberty-blocking medications, as well as around optimal timing for each individual.”
Dr. Cooper is a paid MDedge consultant for the LGBTQ Youth Consult in Pediatric News. He had no other disclosures to report.
SOURCE: van de Grift T et al. Pediatrics. 2020;146(5):e20193653.
Puberty suppression (PS) not only successfully reduces the physical development of sex characteristics, giving transgender youth the opportunity to qualify “for different gender-affirming surgical techniques, it also gives adolescents the time needed to explore their gender identity prior to beginning irreversible cross-sex hormone (CSH) treatment,” Tim C. van de Grift, MD, PhD, of the Vrije Universiteit Medical Center, Amsterdam, and colleagues reported in a retrospective single-center cohort study published in Pediatrics.
Dr. van de Grift and his colleagues evaluated the development of sex characteristics in 184 (61%) transgender men and 116 (39%) transgender women aged an average of 23 years at follow-up; a total of 50 men and 50 women served as controls within the total patient pool. The patients, identified from local registries, were adolescents at the time who had applied for gender-affirming medical interventions between 2006 and 2013.
In order to be included in the analysis, patients were required to 1) have a confirmed gender dysphoria diagnosis, 2) be at least 18 years of age at the point of data collection, 3) be less than 18 years of age when PS was initiated, 4) have initiated and continued PS treatment, and 5) not be lost to follow-up.
Clinical controls were identified by random sample using hospital records. Unlike patients in the PS cohort, the controls received CSH instead of PS, but they otherwise applied for gender-affirming surgery during the same years and met all other non-PS inclusion criteria.
PS offers more favorable, less invasive outcomes for transgender men than women
The researchers found no statistically significant impact of PS on height, weight, and body mass index preoperatively in either transgender men or women.
In transgender men, breast development differed the most, with the least development in the Tanner 2/3 puberty scale group, intermediate development in Tanner 4/5 patients, and the most development in controls who did not have PS. As a result, fewer mastectomies were required after PS, and those that were performed were less invasive, compared with controls. Dr. van de Grift and colleagues noted that these findings were in line with surgical guidelines that advise which mastectomy technique is appropriate based on breast size, elasticity, and ptosis grade. They cautioned that, while PS improves the odds of not needing a mastectomy, it is not a guaranteed outcome.
In transgender women, PS had a significant effect on penile development, which was less in Tanner 2/3 patients, compared with the other groups and less in Tanner 4/5 patients, compared with controls. As the researchers explained, penile length is key to vaginoplasty surgery since the penile skin is what is used to create the vaginal lining. For patients lacking sufficient skin, an alternative vaginoplasty technique using intestinal tissue or full-thickness graft is necessary. In this group, surgical options depended upon the onset of PS. In the control group, standard penile-inversion vaginoplasty was more probable, but it was less so in the Tanner 4/5 patients and only infrequently probable in Tanner 2/3 patients. Most transgender women who started PS in Tanner 2/3 underwent intestinal vaginoplasty.
Before PS is initiated much dialog and planning is warranted
“Clinicians should counsel transgender youth and their parents in making informed decisions when starting PS. Counseling consists of informing about the possible surgical consequences when puberty is suppressed and that these techniques may not be available in general transgender care facilities,” advised Dr. van de Grift and his colleagues. Specifically, when pediatricians prescribe PS, they need to be cognizant of the consequences down the line regarding the demand for “technically complex gender-affirming surgery,” performed by, for example, plastic surgeons, who will need to be “skilled in minimally invasive mastectomy techniques and more extensive vaginoplasty approaches.” Therefore, it is key for referring physicians to be sensitive to the need for early referral to specialized care in order to maximize positive outcomes, they added.
The study was limited by the sample size of some subgroups. Only two-thirds of eligible candidates were included in the sample size because follow-up data were not available for the remaining patients. Future studies should include multicenter standardized prospective data collection that provides patient-reported outcomes to enhance the perspective of the clinical findings, the researchers observed.
In a separate interview with Pediatric News, M. Brett Cooper, MD, of the department of pediatrics at University of Texas, Dallas, and an adolescent medicine physician at Children’s Medical Center in Dallas, noted that “Initiation of puberty suppression can be lifesaving for many gender-diverse youth, preventing the development of secondary sex characteristics. However, this can have effects later if these youth choose to pursue gender-affirming surgeries. This study is important for helping to frame the conversation for youth and their parents when doing consent to start puberty-blocking medications, as well as around optimal timing for each individual.”
Dr. Cooper is a paid MDedge consultant for the LGBTQ Youth Consult in Pediatric News. He had no other disclosures to report.
SOURCE: van de Grift T et al. Pediatrics. 2020;146(5):e20193653.
FROM PEDIATRICS
Choosing civility
I am reading an excellent book called “Choosing Civility,” by P. M. Forni, cofounder of the John Hopkins Civility Project. It is a quick read and is a book that, in particular, all politicians, reporters, and political pundits should read. Most of it deals with common-sense good manners – things your mother taught you. The chapter that has been the most difficult for me to read (and to apply in practice) was the one on listening. I must admit I have been, or am guilty of being, a poor listener. I often try to expedite things by jumping ahead of where the speaker is going, my logic being that I am saving everyone time. In reality, I am probably distorting what the speaker intends to say and certainly not endearing myself to the speaker.
This is, of course, a classic example of attention deficit disorder with which I am certain I am afflicted. I have to make a deliberate effort to pause in my responses to speakers so that they can finish what they have to say. This is extremely hard for those of us who have this problem. I have made progress over the years and can attend committee meetings and say very little, except an occasional clarification query. I make a deliberate attempt to be civil and respect other’s comments. I have learned to let meetings reach their natural conclusion, which takes great patience when we could have arrived there hours earlier if I had interrupted and been less civil. If that course is taken, you will not have the buy in from all participants, and any decision made might not stick.
Luckily, almost all our discussions in organized medicine are civil, and our behavior has improved. The attending surgeon throwing instruments at the nurse or hitting the resident with a retractor – incidents that I have personally witnessed – would not be tolerated today. Our medical meetings are usually civil, if not downright boring.
Of course, patients who are ill or anxious are exempt from any civility requirement. They need comfort and reassurance, as much as a discussion of their diagnosis and treatment plan. They are allowed to be uncivil in their questions and responses.
A few years ago, when I was training a fellow who was Black, I was horrified when one of my patients treated him with disdain and a gross racist attitude. This patient was uncivil, which of course had nothing to do with his diagnosis or treatment. I excused the fellow, discussed this with the patient, and tried to explain that the doctor’s skin color had nothing to do with his training or competence. I went further and told him that if this continued, he would be excused from my practice, which he eventually was. I apologized to the fellow, who, after living in his skin his whole life, had already shaken it off, having heard it all before. Living in my bubble I had thought this type of uncivil behavior was long gone, but not so.
This topic has received discussion and policy action at the American Medical Association. The AMA has adopted a new policy that “recognizes racism as a public health threat and commits to actively work on dismantling racist policies and practices across all of health care,” according to an AMA press release. This includes a recommendation to “clearly and openly support physicians, trainees, and facility personnel who experience prejudiced behavior and discrimination by patients, including allowing physicians, trainees, and facility personnel to decline to care for those patients, without penalty, who have exhibited discriminatory behavior specifically toward them,” according to the AMA report.
As far as I go, not to worry; I still have personal issues to work on. My wife’s favorite song is by Alison Krauss when she sings, “you say it best when you say nothing at all.”
Dr. Coldiron is in private practice but maintains a clinical assistant professorship at the University of Cincinnati. He cares for patients, teaches medical students and residents, and has several active clinical research projects. Dr. Coldiron is the author of more than 80 scientific letters, papers, and several book chapters, and he speaks frequently on a variety of topics. He is a past president of the American Academy of Dermatology. Write to him at [email protected].
I am reading an excellent book called “Choosing Civility,” by P. M. Forni, cofounder of the John Hopkins Civility Project. It is a quick read and is a book that, in particular, all politicians, reporters, and political pundits should read. Most of it deals with common-sense good manners – things your mother taught you. The chapter that has been the most difficult for me to read (and to apply in practice) was the one on listening. I must admit I have been, or am guilty of being, a poor listener. I often try to expedite things by jumping ahead of where the speaker is going, my logic being that I am saving everyone time. In reality, I am probably distorting what the speaker intends to say and certainly not endearing myself to the speaker.
This is, of course, a classic example of attention deficit disorder with which I am certain I am afflicted. I have to make a deliberate effort to pause in my responses to speakers so that they can finish what they have to say. This is extremely hard for those of us who have this problem. I have made progress over the years and can attend committee meetings and say very little, except an occasional clarification query. I make a deliberate attempt to be civil and respect other’s comments. I have learned to let meetings reach their natural conclusion, which takes great patience when we could have arrived there hours earlier if I had interrupted and been less civil. If that course is taken, you will not have the buy in from all participants, and any decision made might not stick.
Luckily, almost all our discussions in organized medicine are civil, and our behavior has improved. The attending surgeon throwing instruments at the nurse or hitting the resident with a retractor – incidents that I have personally witnessed – would not be tolerated today. Our medical meetings are usually civil, if not downright boring.
Of course, patients who are ill or anxious are exempt from any civility requirement. They need comfort and reassurance, as much as a discussion of their diagnosis and treatment plan. They are allowed to be uncivil in their questions and responses.
A few years ago, when I was training a fellow who was Black, I was horrified when one of my patients treated him with disdain and a gross racist attitude. This patient was uncivil, which of course had nothing to do with his diagnosis or treatment. I excused the fellow, discussed this with the patient, and tried to explain that the doctor’s skin color had nothing to do with his training or competence. I went further and told him that if this continued, he would be excused from my practice, which he eventually was. I apologized to the fellow, who, after living in his skin his whole life, had already shaken it off, having heard it all before. Living in my bubble I had thought this type of uncivil behavior was long gone, but not so.
This topic has received discussion and policy action at the American Medical Association. The AMA has adopted a new policy that “recognizes racism as a public health threat and commits to actively work on dismantling racist policies and practices across all of health care,” according to an AMA press release. This includes a recommendation to “clearly and openly support physicians, trainees, and facility personnel who experience prejudiced behavior and discrimination by patients, including allowing physicians, trainees, and facility personnel to decline to care for those patients, without penalty, who have exhibited discriminatory behavior specifically toward them,” according to the AMA report.
As far as I go, not to worry; I still have personal issues to work on. My wife’s favorite song is by Alison Krauss when she sings, “you say it best when you say nothing at all.”
Dr. Coldiron is in private practice but maintains a clinical assistant professorship at the University of Cincinnati. He cares for patients, teaches medical students and residents, and has several active clinical research projects. Dr. Coldiron is the author of more than 80 scientific letters, papers, and several book chapters, and he speaks frequently on a variety of topics. He is a past president of the American Academy of Dermatology. Write to him at [email protected].
I am reading an excellent book called “Choosing Civility,” by P. M. Forni, cofounder of the John Hopkins Civility Project. It is a quick read and is a book that, in particular, all politicians, reporters, and political pundits should read. Most of it deals with common-sense good manners – things your mother taught you. The chapter that has been the most difficult for me to read (and to apply in practice) was the one on listening. I must admit I have been, or am guilty of being, a poor listener. I often try to expedite things by jumping ahead of where the speaker is going, my logic being that I am saving everyone time. In reality, I am probably distorting what the speaker intends to say and certainly not endearing myself to the speaker.
This is, of course, a classic example of attention deficit disorder with which I am certain I am afflicted. I have to make a deliberate effort to pause in my responses to speakers so that they can finish what they have to say. This is extremely hard for those of us who have this problem. I have made progress over the years and can attend committee meetings and say very little, except an occasional clarification query. I make a deliberate attempt to be civil and respect other’s comments. I have learned to let meetings reach their natural conclusion, which takes great patience when we could have arrived there hours earlier if I had interrupted and been less civil. If that course is taken, you will not have the buy in from all participants, and any decision made might not stick.
Luckily, almost all our discussions in organized medicine are civil, and our behavior has improved. The attending surgeon throwing instruments at the nurse or hitting the resident with a retractor – incidents that I have personally witnessed – would not be tolerated today. Our medical meetings are usually civil, if not downright boring.
Of course, patients who are ill or anxious are exempt from any civility requirement. They need comfort and reassurance, as much as a discussion of their diagnosis and treatment plan. They are allowed to be uncivil in their questions and responses.
A few years ago, when I was training a fellow who was Black, I was horrified when one of my patients treated him with disdain and a gross racist attitude. This patient was uncivil, which of course had nothing to do with his diagnosis or treatment. I excused the fellow, discussed this with the patient, and tried to explain that the doctor’s skin color had nothing to do with his training or competence. I went further and told him that if this continued, he would be excused from my practice, which he eventually was. I apologized to the fellow, who, after living in his skin his whole life, had already shaken it off, having heard it all before. Living in my bubble I had thought this type of uncivil behavior was long gone, but not so.
This topic has received discussion and policy action at the American Medical Association. The AMA has adopted a new policy that “recognizes racism as a public health threat and commits to actively work on dismantling racist policies and practices across all of health care,” according to an AMA press release. This includes a recommendation to “clearly and openly support physicians, trainees, and facility personnel who experience prejudiced behavior and discrimination by patients, including allowing physicians, trainees, and facility personnel to decline to care for those patients, without penalty, who have exhibited discriminatory behavior specifically toward them,” according to the AMA report.
As far as I go, not to worry; I still have personal issues to work on. My wife’s favorite song is by Alison Krauss when she sings, “you say it best when you say nothing at all.”
Dr. Coldiron is in private practice but maintains a clinical assistant professorship at the University of Cincinnati. He cares for patients, teaches medical students and residents, and has several active clinical research projects. Dr. Coldiron is the author of more than 80 scientific letters, papers, and several book chapters, and he speaks frequently on a variety of topics. He is a past president of the American Academy of Dermatology. Write to him at [email protected].
FDA OKs osimertinib as first adjuvant drug for NSCLC
Osimertinib was first approved in the US in 2018 for the first-line treatment of patients with metastatic EGFR-mutated NSCLC.
With this new indication, “patients may be treated with this targeted therapy in an earlier and potentially more curative stage of non-small cell lung cancer,” Richard Pazdur, MD, director of the FDA’s Oncology Center of Excellence and acting director of the Office of Oncologic Diseases in the FDA’s Center for Drug Evaluation and Research, said in a news release.
The expanded indication is based on results of the ADAURA clinical trial, which compared osimertinib with placebo following complete resection of localized or locally advanced NSCLC with negative margins.
In the trial, adjuvant osimertinib reduced the relative risk of disease recurrence or death by 83% in patients with stage II and IIIA disease (hazard ratio [HR], 0.17; 95% CI, 0.12 - 0.23; P < .0001).
Disease-free survival (DFS) in the overall trial population of patients with stage IB-IIIA disease showed osimertinib reduced the risk of disease recurrence or death by 80% (HR, 0.20; 95% CI, 0.15 - 0.27; P < .0001).
At 2 years, 89% of patients treated with the targeted agent remained alive and disease free vs 52% on placebo after surgery. The safety and tolerability of osimertinib in the adjuvant setting was consistent with previous trials in the metastatic setting.
The trial of 682 patients was unblinded early and halted on the recommendation of the independent data-monitoring committee, because of the efficacy of osimertinib.
“If I were on the committee, I would have done the same thing. These are extraordinary results,” study investigator Roy S. Herbst, MD, PhD, chief of medical oncology at the Yale Cancer Center, New Haven, Connecticut, said at a press briefing prior to the study presentation at the American Society of Clinical Oncology’s (ASCO) virtual scientific program last spring.
In a Medscape commentary, Mark Kris, MD, of Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center in New York City, said the data with osimertinib in the adjuvant setting are “important and practice-changing.”
“The potential for this drug to improve outcomes has been there for a long time. This phase 3 randomized trial presented at the plenary session of ASCO showed a more than doubling of disease-free survival at 2 years. It shows that we can use therapies in the earlier stages of disease,” Kris noted.
“This approval dispels the notion that treatment is over after surgery and chemotherapy, as the ADAURA results show that Tagrisso can dramatically change the course of this disease,” Dave Fredrickson, executive vice president, AstraZeneca oncology business unit, said in a news release.
Osimertinib had orphan drug status and breakthrough therapy designation for treatment of EGFR mutation-positive NSCLC.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Osimertinib was first approved in the US in 2018 for the first-line treatment of patients with metastatic EGFR-mutated NSCLC.
With this new indication, “patients may be treated with this targeted therapy in an earlier and potentially more curative stage of non-small cell lung cancer,” Richard Pazdur, MD, director of the FDA’s Oncology Center of Excellence and acting director of the Office of Oncologic Diseases in the FDA’s Center for Drug Evaluation and Research, said in a news release.
The expanded indication is based on results of the ADAURA clinical trial, which compared osimertinib with placebo following complete resection of localized or locally advanced NSCLC with negative margins.
In the trial, adjuvant osimertinib reduced the relative risk of disease recurrence or death by 83% in patients with stage II and IIIA disease (hazard ratio [HR], 0.17; 95% CI, 0.12 - 0.23; P < .0001).
Disease-free survival (DFS) in the overall trial population of patients with stage IB-IIIA disease showed osimertinib reduced the risk of disease recurrence or death by 80% (HR, 0.20; 95% CI, 0.15 - 0.27; P < .0001).
At 2 years, 89% of patients treated with the targeted agent remained alive and disease free vs 52% on placebo after surgery. The safety and tolerability of osimertinib in the adjuvant setting was consistent with previous trials in the metastatic setting.
The trial of 682 patients was unblinded early and halted on the recommendation of the independent data-monitoring committee, because of the efficacy of osimertinib.
“If I were on the committee, I would have done the same thing. These are extraordinary results,” study investigator Roy S. Herbst, MD, PhD, chief of medical oncology at the Yale Cancer Center, New Haven, Connecticut, said at a press briefing prior to the study presentation at the American Society of Clinical Oncology’s (ASCO) virtual scientific program last spring.
In a Medscape commentary, Mark Kris, MD, of Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center in New York City, said the data with osimertinib in the adjuvant setting are “important and practice-changing.”
“The potential for this drug to improve outcomes has been there for a long time. This phase 3 randomized trial presented at the plenary session of ASCO showed a more than doubling of disease-free survival at 2 years. It shows that we can use therapies in the earlier stages of disease,” Kris noted.
“This approval dispels the notion that treatment is over after surgery and chemotherapy, as the ADAURA results show that Tagrisso can dramatically change the course of this disease,” Dave Fredrickson, executive vice president, AstraZeneca oncology business unit, said in a news release.
Osimertinib had orphan drug status and breakthrough therapy designation for treatment of EGFR mutation-positive NSCLC.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Osimertinib was first approved in the US in 2018 for the first-line treatment of patients with metastatic EGFR-mutated NSCLC.
With this new indication, “patients may be treated with this targeted therapy in an earlier and potentially more curative stage of non-small cell lung cancer,” Richard Pazdur, MD, director of the FDA’s Oncology Center of Excellence and acting director of the Office of Oncologic Diseases in the FDA’s Center for Drug Evaluation and Research, said in a news release.
The expanded indication is based on results of the ADAURA clinical trial, which compared osimertinib with placebo following complete resection of localized or locally advanced NSCLC with negative margins.
In the trial, adjuvant osimertinib reduced the relative risk of disease recurrence or death by 83% in patients with stage II and IIIA disease (hazard ratio [HR], 0.17; 95% CI, 0.12 - 0.23; P < .0001).
Disease-free survival (DFS) in the overall trial population of patients with stage IB-IIIA disease showed osimertinib reduced the risk of disease recurrence or death by 80% (HR, 0.20; 95% CI, 0.15 - 0.27; P < .0001).
At 2 years, 89% of patients treated with the targeted agent remained alive and disease free vs 52% on placebo after surgery. The safety and tolerability of osimertinib in the adjuvant setting was consistent with previous trials in the metastatic setting.
The trial of 682 patients was unblinded early and halted on the recommendation of the independent data-monitoring committee, because of the efficacy of osimertinib.
“If I were on the committee, I would have done the same thing. These are extraordinary results,” study investigator Roy S. Herbst, MD, PhD, chief of medical oncology at the Yale Cancer Center, New Haven, Connecticut, said at a press briefing prior to the study presentation at the American Society of Clinical Oncology’s (ASCO) virtual scientific program last spring.
In a Medscape commentary, Mark Kris, MD, of Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center in New York City, said the data with osimertinib in the adjuvant setting are “important and practice-changing.”
“The potential for this drug to improve outcomes has been there for a long time. This phase 3 randomized trial presented at the plenary session of ASCO showed a more than doubling of disease-free survival at 2 years. It shows that we can use therapies in the earlier stages of disease,” Kris noted.
“This approval dispels the notion that treatment is over after surgery and chemotherapy, as the ADAURA results show that Tagrisso can dramatically change the course of this disease,” Dave Fredrickson, executive vice president, AstraZeneca oncology business unit, said in a news release.
Osimertinib had orphan drug status and breakthrough therapy designation for treatment of EGFR mutation-positive NSCLC.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
No benefit of cannabis on depression in pregnant women with OUD
Cannabis is ineffective at alleviating depression in pregnant women undergoing opioid agonist therapy (OAT), new research shows.
A study of more than 120 pregnant women undergoing treatment of opioid use disorder (OUD) showed that those who used cannabis to alleviate their depressive symptoms while undergoing OAT continued to have high depression scores at the end of opioid treatment.
In addition, depression scores improved for those who abstained from cannabis use after their first positive screen. Interestingly, cannabis use did not affect patient retention in treatment for OUD, the investigators note.
“To our knowledge, this is the first time looking at the impact of cannabis on the specific population of pregnant women with opioid use disorder, who are very vulnerable to depression,” lead author Abigail Richison, MD, University of Arkansas for Medical Sciences, Little Rock, said in an interview.
The findings were presented at the American Academy of Addiction Psychiatry (AAAP) 31st Annual Meeting, which was held online this year because of the COVID-19 pandemic.
A safer alternative?
Data from the National Survey on Drug Use and Health show that perinatal cannabis use increased by 62% between 2002 and 2014. Many women try to ameliorate their depression symptoms by using cannabis in the mistaken belief that it will help their depression, the investigators noted.
In addition, many women consider cannabis safer during pregnancy than prescribed medications for improving mood, said Dr. Richison. She said that cannabis does not alleviate depression and may even worsen it.
Dr. Richison noted that at her center, which has a women’s health program that treats pregnant women with OUDs, she was seeing a lot of patients who reported using cannabis to improve their mood.
“However, it didn’t seem like it was really helping, so I started researching about cannabis and depression,” Dr. Richison said.
“ and can be accused of perinatal substance use. I think it is very important to screen for depression as well as cannabis use in this population,” she added.
To shed some light on the impact of cannabis use by pregnant patients with OUD, the investigators conducted a retrospective chart review of 121 pregnant women with OUD who attended outpatient OAT. All were prescribed buprenorphine.
At each visit, Beck Depression Inventory (BDI) scores were obtained and urine drug screens were administered. The primary outcome was BDI score. Other measures included retention, urinary drug screen results, and antidepressant use.
The women were divided into two groups. The first comprised cannabis users, defined as having more than one urine drug screen that was positive for cannabis (n = 35). The other group comprised nonusers, defined as having urine drug screens that were negative for cannabis (n = 86).
Cannabis users were a little younger (mean age, 27 years) than non–cannabis users (mean age, 29.5 years; P = .006). Most of the participants were White (80.2%). Roughly half were on Medicaid, and most of the other participants had private insurance; a small number of women had no insurance.
Results showed that cannabis users had significantly higher BDI scores than non–cannabis users (mean scores, 16 vs. 9.3; P < .001).
Cannabis use continued to be associated with elevated scores for depression when controlling for opioid misuse and antidepressant use. There were no significant differences in retention or lapse to opioid misuse between the two groups.
More evidence of risk
Commenting on the findings in an interview, Carla Marienfeld, MD, professor of psychiatry at the University of California, San Diego, said there is a growing body of evidence about risks from cannabis use during pregnancy, “a time where we already know the endocannabinoid system is very active in the developing fetus.”
She noted that the current study’s design makes it hard to know whether marijuana use causes worse depression.
However, “it clearly is not associated with helping to improve mood the way people who are using it believe or hope for,” said Dr. Marienfeld, who was not part of the research.
“The risk for harm in terms of worse mood for the pregnant woman or risks for harm to the developing fetus are being better understood with many new studies,” she added.
Yet as more and more states legalize medical marijuana, cannabis use during pregnancy is only going to rise, experts fear.
Cornel Stanciu, MD, of Dartmouth-Hitchcock Medical Center, Lebanon, N.H., who was asked for comment, noted that public endorsement for potential benefits of the marijuana plant is at an all-time high.
“To date, 33 states and the District of Columbia have responded by legalizing medical marijuana, with 10 states also having legalized recreational use of marijuana. The current practice is said to be ahead of science, as robust research has been hindered by strict regulations – and most epidemiological studies point toward harmful associations,” Dr. Stanciu said in an interview.
“Given the decreased perception of harm by the general public, women are certainly compelled to seek what they perceive as more natural self-management remedies,” he said.
A harmful habit
Dr. Stanciu cited a recent study conducted in Colorado in which researchers contacted cannabis dispensaries, identified themselves as being pregnant, and asked for guidance in managing pregnancy-related symptoms.
Almost 70% of dispensaries recommended products to treat symptoms, particularly in the vulnerable first trimester; 36% of them also provided reassurance of the safety profile. Very few encouraged a discussion with the physician.
“Consumption of cannabis during pregnancy results in cannabinoid placental crossing and accumulation in the fetal brain, as well as other organs, where it interferes with neurodevelopment and the endocannabinoid system,” he said.
In addition, retrospective studies have shown an association between prenatal cannabis ingestion and anemia in the mothers, low birth weight, greater risk for preterm and stillbirths, and increased need for neonatal ICU admissions.
“Children born to mothers who used cannabis during pregnancy have higher rates of impulsivity, delinquency, learning and memory impairment, as well as executive function deficits. There is also an increased association with proneness to psychosis during middle childhood,” Dr. Stanciu said.
When used during pregnancy, cannabis has been associated with increased anxiety in mothers, as well as increased risk for depressive disorders, incidence of suicidal ideations and behavior, and symptoms of mania and psychosis among those with bipolar and schizophrenia spectrum conditions. Cannabis has also been linked to coingestion of other substances and with alcohol use.
“So cannabis can pose harm, especially when used by those with affective disorders,” Dr. Stanciu said.
The study was funded by the National Institute on Drug Abuse. Dr. Richison, Dr. Marienfeld, and Dr. Stanciu have reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com
Cannabis is ineffective at alleviating depression in pregnant women undergoing opioid agonist therapy (OAT), new research shows.
A study of more than 120 pregnant women undergoing treatment of opioid use disorder (OUD) showed that those who used cannabis to alleviate their depressive symptoms while undergoing OAT continued to have high depression scores at the end of opioid treatment.
In addition, depression scores improved for those who abstained from cannabis use after their first positive screen. Interestingly, cannabis use did not affect patient retention in treatment for OUD, the investigators note.
“To our knowledge, this is the first time looking at the impact of cannabis on the specific population of pregnant women with opioid use disorder, who are very vulnerable to depression,” lead author Abigail Richison, MD, University of Arkansas for Medical Sciences, Little Rock, said in an interview.
The findings were presented at the American Academy of Addiction Psychiatry (AAAP) 31st Annual Meeting, which was held online this year because of the COVID-19 pandemic.
A safer alternative?
Data from the National Survey on Drug Use and Health show that perinatal cannabis use increased by 62% between 2002 and 2014. Many women try to ameliorate their depression symptoms by using cannabis in the mistaken belief that it will help their depression, the investigators noted.
In addition, many women consider cannabis safer during pregnancy than prescribed medications for improving mood, said Dr. Richison. She said that cannabis does not alleviate depression and may even worsen it.
Dr. Richison noted that at her center, which has a women’s health program that treats pregnant women with OUDs, she was seeing a lot of patients who reported using cannabis to improve their mood.
“However, it didn’t seem like it was really helping, so I started researching about cannabis and depression,” Dr. Richison said.
“ and can be accused of perinatal substance use. I think it is very important to screen for depression as well as cannabis use in this population,” she added.
To shed some light on the impact of cannabis use by pregnant patients with OUD, the investigators conducted a retrospective chart review of 121 pregnant women with OUD who attended outpatient OAT. All were prescribed buprenorphine.
At each visit, Beck Depression Inventory (BDI) scores were obtained and urine drug screens were administered. The primary outcome was BDI score. Other measures included retention, urinary drug screen results, and antidepressant use.
The women were divided into two groups. The first comprised cannabis users, defined as having more than one urine drug screen that was positive for cannabis (n = 35). The other group comprised nonusers, defined as having urine drug screens that were negative for cannabis (n = 86).
Cannabis users were a little younger (mean age, 27 years) than non–cannabis users (mean age, 29.5 years; P = .006). Most of the participants were White (80.2%). Roughly half were on Medicaid, and most of the other participants had private insurance; a small number of women had no insurance.
Results showed that cannabis users had significantly higher BDI scores than non–cannabis users (mean scores, 16 vs. 9.3; P < .001).
Cannabis use continued to be associated with elevated scores for depression when controlling for opioid misuse and antidepressant use. There were no significant differences in retention or lapse to opioid misuse between the two groups.
More evidence of risk
Commenting on the findings in an interview, Carla Marienfeld, MD, professor of psychiatry at the University of California, San Diego, said there is a growing body of evidence about risks from cannabis use during pregnancy, “a time where we already know the endocannabinoid system is very active in the developing fetus.”
She noted that the current study’s design makes it hard to know whether marijuana use causes worse depression.
However, “it clearly is not associated with helping to improve mood the way people who are using it believe or hope for,” said Dr. Marienfeld, who was not part of the research.
“The risk for harm in terms of worse mood for the pregnant woman or risks for harm to the developing fetus are being better understood with many new studies,” she added.
Yet as more and more states legalize medical marijuana, cannabis use during pregnancy is only going to rise, experts fear.
Cornel Stanciu, MD, of Dartmouth-Hitchcock Medical Center, Lebanon, N.H., who was asked for comment, noted that public endorsement for potential benefits of the marijuana plant is at an all-time high.
“To date, 33 states and the District of Columbia have responded by legalizing medical marijuana, with 10 states also having legalized recreational use of marijuana. The current practice is said to be ahead of science, as robust research has been hindered by strict regulations – and most epidemiological studies point toward harmful associations,” Dr. Stanciu said in an interview.
“Given the decreased perception of harm by the general public, women are certainly compelled to seek what they perceive as more natural self-management remedies,” he said.
A harmful habit
Dr. Stanciu cited a recent study conducted in Colorado in which researchers contacted cannabis dispensaries, identified themselves as being pregnant, and asked for guidance in managing pregnancy-related symptoms.
Almost 70% of dispensaries recommended products to treat symptoms, particularly in the vulnerable first trimester; 36% of them also provided reassurance of the safety profile. Very few encouraged a discussion with the physician.
“Consumption of cannabis during pregnancy results in cannabinoid placental crossing and accumulation in the fetal brain, as well as other organs, where it interferes with neurodevelopment and the endocannabinoid system,” he said.
In addition, retrospective studies have shown an association between prenatal cannabis ingestion and anemia in the mothers, low birth weight, greater risk for preterm and stillbirths, and increased need for neonatal ICU admissions.
“Children born to mothers who used cannabis during pregnancy have higher rates of impulsivity, delinquency, learning and memory impairment, as well as executive function deficits. There is also an increased association with proneness to psychosis during middle childhood,” Dr. Stanciu said.
When used during pregnancy, cannabis has been associated with increased anxiety in mothers, as well as increased risk for depressive disorders, incidence of suicidal ideations and behavior, and symptoms of mania and psychosis among those with bipolar and schizophrenia spectrum conditions. Cannabis has also been linked to coingestion of other substances and with alcohol use.
“So cannabis can pose harm, especially when used by those with affective disorders,” Dr. Stanciu said.
The study was funded by the National Institute on Drug Abuse. Dr. Richison, Dr. Marienfeld, and Dr. Stanciu have reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com
Cannabis is ineffective at alleviating depression in pregnant women undergoing opioid agonist therapy (OAT), new research shows.
A study of more than 120 pregnant women undergoing treatment of opioid use disorder (OUD) showed that those who used cannabis to alleviate their depressive symptoms while undergoing OAT continued to have high depression scores at the end of opioid treatment.
In addition, depression scores improved for those who abstained from cannabis use after their first positive screen. Interestingly, cannabis use did not affect patient retention in treatment for OUD, the investigators note.
“To our knowledge, this is the first time looking at the impact of cannabis on the specific population of pregnant women with opioid use disorder, who are very vulnerable to depression,” lead author Abigail Richison, MD, University of Arkansas for Medical Sciences, Little Rock, said in an interview.
The findings were presented at the American Academy of Addiction Psychiatry (AAAP) 31st Annual Meeting, which was held online this year because of the COVID-19 pandemic.
A safer alternative?
Data from the National Survey on Drug Use and Health show that perinatal cannabis use increased by 62% between 2002 and 2014. Many women try to ameliorate their depression symptoms by using cannabis in the mistaken belief that it will help their depression, the investigators noted.
In addition, many women consider cannabis safer during pregnancy than prescribed medications for improving mood, said Dr. Richison. She said that cannabis does not alleviate depression and may even worsen it.
Dr. Richison noted that at her center, which has a women’s health program that treats pregnant women with OUDs, she was seeing a lot of patients who reported using cannabis to improve their mood.
“However, it didn’t seem like it was really helping, so I started researching about cannabis and depression,” Dr. Richison said.
“ and can be accused of perinatal substance use. I think it is very important to screen for depression as well as cannabis use in this population,” she added.
To shed some light on the impact of cannabis use by pregnant patients with OUD, the investigators conducted a retrospective chart review of 121 pregnant women with OUD who attended outpatient OAT. All were prescribed buprenorphine.
At each visit, Beck Depression Inventory (BDI) scores were obtained and urine drug screens were administered. The primary outcome was BDI score. Other measures included retention, urinary drug screen results, and antidepressant use.
The women were divided into two groups. The first comprised cannabis users, defined as having more than one urine drug screen that was positive for cannabis (n = 35). The other group comprised nonusers, defined as having urine drug screens that were negative for cannabis (n = 86).
Cannabis users were a little younger (mean age, 27 years) than non–cannabis users (mean age, 29.5 years; P = .006). Most of the participants were White (80.2%). Roughly half were on Medicaid, and most of the other participants had private insurance; a small number of women had no insurance.
Results showed that cannabis users had significantly higher BDI scores than non–cannabis users (mean scores, 16 vs. 9.3; P < .001).
Cannabis use continued to be associated with elevated scores for depression when controlling for opioid misuse and antidepressant use. There were no significant differences in retention or lapse to opioid misuse between the two groups.
More evidence of risk
Commenting on the findings in an interview, Carla Marienfeld, MD, professor of psychiatry at the University of California, San Diego, said there is a growing body of evidence about risks from cannabis use during pregnancy, “a time where we already know the endocannabinoid system is very active in the developing fetus.”
She noted that the current study’s design makes it hard to know whether marijuana use causes worse depression.
However, “it clearly is not associated with helping to improve mood the way people who are using it believe or hope for,” said Dr. Marienfeld, who was not part of the research.
“The risk for harm in terms of worse mood for the pregnant woman or risks for harm to the developing fetus are being better understood with many new studies,” she added.
Yet as more and more states legalize medical marijuana, cannabis use during pregnancy is only going to rise, experts fear.
Cornel Stanciu, MD, of Dartmouth-Hitchcock Medical Center, Lebanon, N.H., who was asked for comment, noted that public endorsement for potential benefits of the marijuana plant is at an all-time high.
“To date, 33 states and the District of Columbia have responded by legalizing medical marijuana, with 10 states also having legalized recreational use of marijuana. The current practice is said to be ahead of science, as robust research has been hindered by strict regulations – and most epidemiological studies point toward harmful associations,” Dr. Stanciu said in an interview.
“Given the decreased perception of harm by the general public, women are certainly compelled to seek what they perceive as more natural self-management remedies,” he said.
A harmful habit
Dr. Stanciu cited a recent study conducted in Colorado in which researchers contacted cannabis dispensaries, identified themselves as being pregnant, and asked for guidance in managing pregnancy-related symptoms.
Almost 70% of dispensaries recommended products to treat symptoms, particularly in the vulnerable first trimester; 36% of them also provided reassurance of the safety profile. Very few encouraged a discussion with the physician.
“Consumption of cannabis during pregnancy results in cannabinoid placental crossing and accumulation in the fetal brain, as well as other organs, where it interferes with neurodevelopment and the endocannabinoid system,” he said.
In addition, retrospective studies have shown an association between prenatal cannabis ingestion and anemia in the mothers, low birth weight, greater risk for preterm and stillbirths, and increased need for neonatal ICU admissions.
“Children born to mothers who used cannabis during pregnancy have higher rates of impulsivity, delinquency, learning and memory impairment, as well as executive function deficits. There is also an increased association with proneness to psychosis during middle childhood,” Dr. Stanciu said.
When used during pregnancy, cannabis has been associated with increased anxiety in mothers, as well as increased risk for depressive disorders, incidence of suicidal ideations and behavior, and symptoms of mania and psychosis among those with bipolar and schizophrenia spectrum conditions. Cannabis has also been linked to coingestion of other substances and with alcohol use.
“So cannabis can pose harm, especially when used by those with affective disorders,” Dr. Stanciu said.
The study was funded by the National Institute on Drug Abuse. Dr. Richison, Dr. Marienfeld, and Dr. Stanciu have reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com
Give psych patients the COVID vaccination now, experts say
With COVID-19 vaccinations now underway, mental health experts around the world continue to push for patients with serious mental illness (SMI) to be considered a high-priority group for the vaccine.
Research shows that patients with SMI are at increased risk of being infected with SARS-CoV-2 and have higher rates of hospitalization and poor outcomes, Nicola Warren, MBBS, University of Queensland, Brisbane, Australia, and coauthors write in a viewpoint published online Dec. 15 in JAMA Psychiatry
Factors behind the worse outcomes in individuals with SMI include concomitant medications, poorer premorbid general health, physical comorbidity, reduced access to medical care, and environmental and lifestyle factors such as lower socioeconomic status, overcrowding, smoking, and obesity.
“In light of these vulnerabilities, it is important that people with SMI are a priority group to receive a vaccination,” Dr. Warren and colleagues say.
Yet there are challenges at the individual and public health level in getting people with SMI vaccinated against COVID-19, they point out.
Challenges at the individual level include getting people with SMI to recognize the importance of the vaccine and combating negative beliefs about safety and misconceptions that the vaccine itself can make them sick with COVID-19.
Mental health professionals are “uniquely skilled” to deliver vaccine education, “being able to adapt for those with communication difficulties and balance factors influencing decision-making,” Dr. Warren and colleagues write.
, like getting to a vaccination clinic.
Research has shown that running vaccination clinics parallel to mental health services can boost vaccination rates by 25%, the authors note. Therefore, one solution may be to embed vaccination clinics within mental health services, Dr. Warren and colleagues suggest.
Join the chorus
Plans and policies to ensure rapid delivery of the COVID-19 vaccine are “vital,” they conclude. “Mental health clinicians have a key role in advocating for priority access to a COVID-19 vaccination for those with SMI, as well as facilitating its uptake,” they add.
Dr. Warren and her colleagues join a chorus of other mental health care providers who have sounded the alarm on the risks of COVID-19 for patients with SMI and the need to get them vaccinated early.
In a perspective article published last month in World Psychiatry, Marc De Hert, MD, PhD, professor of psychiatry at KU Leuven (Belgium), and coauthors called for individuals with SMI to have priority status for any COVID-19 vaccine, as reported by this news organization.
Dr. De Hert and colleagues noted that there is an ethical duty to prioritize vaccination for people with SMI given their increased risk of worse outcomes following COVID-19 infection and the structural barriers faced by people with SMI in accessing a vaccine.
Joining the chorus, Benjamin Druss, MD, MPH, from Emory University, Atlanta, Georgia, warned in a JAMA Psychiatry viewpoint in April that the COVID-19 pandemic represents a looming crisis for patients with SMI and the health care systems that serve them.
“Careful planning and execution at multiple levels will be essential for minimizing the adverse outcomes of this pandemic for this vulnerable population,” Dr. Druss wrote.
The authors have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
With COVID-19 vaccinations now underway, mental health experts around the world continue to push for patients with serious mental illness (SMI) to be considered a high-priority group for the vaccine.
Research shows that patients with SMI are at increased risk of being infected with SARS-CoV-2 and have higher rates of hospitalization and poor outcomes, Nicola Warren, MBBS, University of Queensland, Brisbane, Australia, and coauthors write in a viewpoint published online Dec. 15 in JAMA Psychiatry
Factors behind the worse outcomes in individuals with SMI include concomitant medications, poorer premorbid general health, physical comorbidity, reduced access to medical care, and environmental and lifestyle factors such as lower socioeconomic status, overcrowding, smoking, and obesity.
“In light of these vulnerabilities, it is important that people with SMI are a priority group to receive a vaccination,” Dr. Warren and colleagues say.
Yet there are challenges at the individual and public health level in getting people with SMI vaccinated against COVID-19, they point out.
Challenges at the individual level include getting people with SMI to recognize the importance of the vaccine and combating negative beliefs about safety and misconceptions that the vaccine itself can make them sick with COVID-19.
Mental health professionals are “uniquely skilled” to deliver vaccine education, “being able to adapt for those with communication difficulties and balance factors influencing decision-making,” Dr. Warren and colleagues write.
, like getting to a vaccination clinic.
Research has shown that running vaccination clinics parallel to mental health services can boost vaccination rates by 25%, the authors note. Therefore, one solution may be to embed vaccination clinics within mental health services, Dr. Warren and colleagues suggest.
Join the chorus
Plans and policies to ensure rapid delivery of the COVID-19 vaccine are “vital,” they conclude. “Mental health clinicians have a key role in advocating for priority access to a COVID-19 vaccination for those with SMI, as well as facilitating its uptake,” they add.
Dr. Warren and her colleagues join a chorus of other mental health care providers who have sounded the alarm on the risks of COVID-19 for patients with SMI and the need to get them vaccinated early.
In a perspective article published last month in World Psychiatry, Marc De Hert, MD, PhD, professor of psychiatry at KU Leuven (Belgium), and coauthors called for individuals with SMI to have priority status for any COVID-19 vaccine, as reported by this news organization.
Dr. De Hert and colleagues noted that there is an ethical duty to prioritize vaccination for people with SMI given their increased risk of worse outcomes following COVID-19 infection and the structural barriers faced by people with SMI in accessing a vaccine.
Joining the chorus, Benjamin Druss, MD, MPH, from Emory University, Atlanta, Georgia, warned in a JAMA Psychiatry viewpoint in April that the COVID-19 pandemic represents a looming crisis for patients with SMI and the health care systems that serve them.
“Careful planning and execution at multiple levels will be essential for minimizing the adverse outcomes of this pandemic for this vulnerable population,” Dr. Druss wrote.
The authors have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
With COVID-19 vaccinations now underway, mental health experts around the world continue to push for patients with serious mental illness (SMI) to be considered a high-priority group for the vaccine.
Research shows that patients with SMI are at increased risk of being infected with SARS-CoV-2 and have higher rates of hospitalization and poor outcomes, Nicola Warren, MBBS, University of Queensland, Brisbane, Australia, and coauthors write in a viewpoint published online Dec. 15 in JAMA Psychiatry
Factors behind the worse outcomes in individuals with SMI include concomitant medications, poorer premorbid general health, physical comorbidity, reduced access to medical care, and environmental and lifestyle factors such as lower socioeconomic status, overcrowding, smoking, and obesity.
“In light of these vulnerabilities, it is important that people with SMI are a priority group to receive a vaccination,” Dr. Warren and colleagues say.
Yet there are challenges at the individual and public health level in getting people with SMI vaccinated against COVID-19, they point out.
Challenges at the individual level include getting people with SMI to recognize the importance of the vaccine and combating negative beliefs about safety and misconceptions that the vaccine itself can make them sick with COVID-19.
Mental health professionals are “uniquely skilled” to deliver vaccine education, “being able to adapt for those with communication difficulties and balance factors influencing decision-making,” Dr. Warren and colleagues write.
, like getting to a vaccination clinic.
Research has shown that running vaccination clinics parallel to mental health services can boost vaccination rates by 25%, the authors note. Therefore, one solution may be to embed vaccination clinics within mental health services, Dr. Warren and colleagues suggest.
Join the chorus
Plans and policies to ensure rapid delivery of the COVID-19 vaccine are “vital,” they conclude. “Mental health clinicians have a key role in advocating for priority access to a COVID-19 vaccination for those with SMI, as well as facilitating its uptake,” they add.
Dr. Warren and her colleagues join a chorus of other mental health care providers who have sounded the alarm on the risks of COVID-19 for patients with SMI and the need to get them vaccinated early.
In a perspective article published last month in World Psychiatry, Marc De Hert, MD, PhD, professor of psychiatry at KU Leuven (Belgium), and coauthors called for individuals with SMI to have priority status for any COVID-19 vaccine, as reported by this news organization.
Dr. De Hert and colleagues noted that there is an ethical duty to prioritize vaccination for people with SMI given their increased risk of worse outcomes following COVID-19 infection and the structural barriers faced by people with SMI in accessing a vaccine.
Joining the chorus, Benjamin Druss, MD, MPH, from Emory University, Atlanta, Georgia, warned in a JAMA Psychiatry viewpoint in April that the COVID-19 pandemic represents a looming crisis for patients with SMI and the health care systems that serve them.
“Careful planning and execution at multiple levels will be essential for minimizing the adverse outcomes of this pandemic for this vulnerable population,” Dr. Druss wrote.
The authors have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Global experts map the latest in bipolar management
A new monograph offers a far-reaching update on research and clinical management of bipolar disorders (BDs), including epidemiology, genetics, pathogenesis, psychosocial aspects, and current and investigational therapies.
“I regard this as a ‘global state-of-the-union’ type of paper designed to bring the world up to speed regarding where we’re at and where we’re going in terms of bipolar disorder, to present the changes on the scientific and clinical fronts, and to open up a global conversation about bipolar disorder,” lead author Roger S. McIntyre, MD, professor of psychiatry and pharmacology, University of Toronto, Ontario, Canada, told Medscape Medical News.
“The paper is oriented toward multidisciplinary care, with particular emphasis on primary care, as well as people in healthcare administration and policy, who want a snapshot of where we’re at,” said McIntyre, who is also the head of the Mood Disorders Psychopharmacology Unit and director of the Depression and Bipolar Support Alliance in Chicago, Illinois.
The article was published online December 5 in The Lancet.
Severe, complex
The authors call BPs “a complex group of severe and chronic disorders” that include both BP I and BP II disorders.
“These disorders continue to be the world’s leading causes of disability, morbidity, and mortality, which are significant and getting worse, with studies indicating that bipolar disorders are associated with a loss of roughly 10 to 20 potential years of life,” McIntyre said.
Cardiovascular disease is the most common cause of premature death in people with BD. The second is suicide, the authors state, noting that patients with BDs are roughly 20-30 times more likely to die by suicide compared with the general population. In addition, 30%-50% have a lifetime history of suicide attempts.
BP I is “defined by the presence of a syndromal manic episode,” while BP II is “defined by the presence of a syndromal hypomanic episode and a major depressive episode,” the authors state.
Unlike the DSM-IV-TR, the DSM-5 includes “persistently increased energy or activity, along with elevated, expansive, or irritable mood” in the diagnostic criteria for mania and hypomania, “so diagnosing mania on mood instability alone is no longer sufficient,” the authors note.
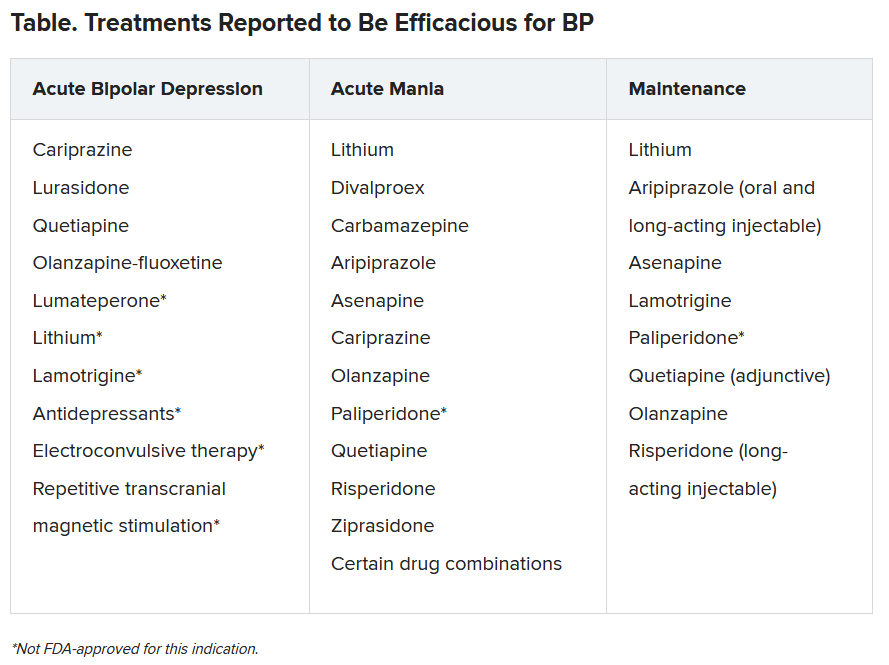
In addition, clinicians “should be aware that individuals with BDs presenting with depression will often manifest symptoms of anxiety, agitation, anger-irritability, and attentional disturbance-distractibility (the four A’s), all of which are highly suggestive of mixed features,” they write.
Depression is the “predominant index presentation of BD” and “differentiating BD from major depressive disorder (MDD) is the most common clinical challenge for most clinicians.”
Features suggesting a diagnosis of BD rather than MDD include earlier age of onset, phenomenology (e.g., hyperphagia, hypersomnia, psychosis), higher frequency of affective episodes, comorbidities (e.g., substance use disorders, anxiety disorders, binge eating disorders, and migraines), family history of psychopathology, nonresponse to antidepressants or induction of hypomania, mixed features, and comorbidities
The authors advise “routine and systematic screening for BDs in all patients presenting with depressive symptomatology” and recommend using the Mood Disorders Questionnaire and the Hypomania Checklist.
Additional differential diagnoses include psychiatric disorders involving impulsivity, affective instability, anxiety, cognitive disorganization, depression, and psychosis.
“Futuristic” technology
“Although the pathogenesis of BDs is unknown, approximately 70% of the risk for BDs is heritable,” the authors note. They review recent research into genetic loci associated with BDs, based on genome-wide association studies, and the role of genetics not only in BDs but also in overlapping neurologic and psychiatric conditions, insulin resistance, and endocannabinoid signaling.
Inflammatory disturbances may also be implicated, in part related to “lifestyle and environment exposures” common in BDs such as smoking, poor diet, physical inactivity, and trauma, they suggest.
An “exciting new technology” analyzing “pluripotent” stem cells might illuminate the pathogenesis of BDs and mechanism of action of treatments by shedding light on mitochondrial dysfunction, McIntyre said.
“This interest in stem cells might almost be seen as futuristic. It is currently being used in the laboratory to understand the biology of BD, and it may eventually lead to the development of new therapeutics,” he added.
“Exciting” treatments
“Our expansive list of treatments and soon-to-be new treatments is very exciting,” said McIntyre.
The authors highlight “ongoing controversy regarding the safe and appropriate use of antidepressants in BD,” cautioning against potential treatment-emergent hypomania and suggesting limited circumstances when antidepressants might be administered.
Lithium remains the “gold standard mood-stabilizing agent” and is “capable of reducing suicidality,” they note.
Nonpharmacologic interventions include patient self-management, compliance, and cognitive enhancement strategies, primary prevention for psychiatric and medical comorbidity, psychosocial treatments and lifestyle interventions during maintenance, as well as surveillance for suicidality during both acute and maintenance phases.
Novel potential treatments include coenzyme Q10, N-acetyl cysteine, statins, nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, omega-3 fatty acids, incretin-based therapies, insulin, nitrous oxide, ketamine, prebiotics, probiotics, antibiotics, and adjunctive bright light therapy.
The authors caution that these investigational agents “cannot be considered efficacious or safe” in the treatment of BDs at present.
Call to action
Commenting for Medscape Medical News, Michael Thase, MD, professor of psychiatry, Perelman School of Medicine, University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, said he is glad that this “stellar group of authors” with “worldwide psychiatric expertise” wrote the article and he hopes it “gets the readership it deserves.”
Thase, who was not an author, said, “One takeaway is that BDs together comprise one of the world’s great public health problems — probably within the top 10.”
Another “has to do with our ability to do more with the tools we have — ie, ensuring diagnosis, implementing treatment, engaging social support, and using proven therapies from both psychopharmacologic and psychosocial domains.”
McIntyre characterized the article as a “public health call to action, incorporating screening, interesting neurobiological insights, an extensive set of treatments, and cool technological capabilities for the future.”
McIntyre has reported receiving grant support from the Stanley Medical Research Institute and the Canadian Institutes of Health Research/Global Alliance for Chronic Disease/Chinese National Natural Research Foundation, and speaker fees from Lundbeck, Janssen, Shire, Purdue, Pfizer, Otsuka, Allergan, Takeda, Neurocrine, Sunovion, Intra-Cellular, Alkermes, and Minerva, and is chief executive officer of Champignon. Disclosures for the other authors are listed in the article. Thase has reported consulting with and receiving research funding from many of the companies that manufacture/sell antidepressants and antipsychotics. He also has reported receiving royalties from the American Psychiatric Press Incorporated, Guilford Publications, Herald House, and W.W. Norton & Company.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
A new monograph offers a far-reaching update on research and clinical management of bipolar disorders (BDs), including epidemiology, genetics, pathogenesis, psychosocial aspects, and current and investigational therapies.
“I regard this as a ‘global state-of-the-union’ type of paper designed to bring the world up to speed regarding where we’re at and where we’re going in terms of bipolar disorder, to present the changes on the scientific and clinical fronts, and to open up a global conversation about bipolar disorder,” lead author Roger S. McIntyre, MD, professor of psychiatry and pharmacology, University of Toronto, Ontario, Canada, told Medscape Medical News.
“The paper is oriented toward multidisciplinary care, with particular emphasis on primary care, as well as people in healthcare administration and policy, who want a snapshot of where we’re at,” said McIntyre, who is also the head of the Mood Disorders Psychopharmacology Unit and director of the Depression and Bipolar Support Alliance in Chicago, Illinois.
The article was published online December 5 in The Lancet.
Severe, complex
The authors call BPs “a complex group of severe and chronic disorders” that include both BP I and BP II disorders.
“These disorders continue to be the world’s leading causes of disability, morbidity, and mortality, which are significant and getting worse, with studies indicating that bipolar disorders are associated with a loss of roughly 10 to 20 potential years of life,” McIntyre said.
Cardiovascular disease is the most common cause of premature death in people with BD. The second is suicide, the authors state, noting that patients with BDs are roughly 20-30 times more likely to die by suicide compared with the general population. In addition, 30%-50% have a lifetime history of suicide attempts.
BP I is “defined by the presence of a syndromal manic episode,” while BP II is “defined by the presence of a syndromal hypomanic episode and a major depressive episode,” the authors state.
Unlike the DSM-IV-TR, the DSM-5 includes “persistently increased energy or activity, along with elevated, expansive, or irritable mood” in the diagnostic criteria for mania and hypomania, “so diagnosing mania on mood instability alone is no longer sufficient,” the authors note.

In addition, clinicians “should be aware that individuals with BDs presenting with depression will often manifest symptoms of anxiety, agitation, anger-irritability, and attentional disturbance-distractibility (the four A’s), all of which are highly suggestive of mixed features,” they write.
Depression is the “predominant index presentation of BD” and “differentiating BD from major depressive disorder (MDD) is the most common clinical challenge for most clinicians.”
Features suggesting a diagnosis of BD rather than MDD include earlier age of onset, phenomenology (e.g., hyperphagia, hypersomnia, psychosis), higher frequency of affective episodes, comorbidities (e.g., substance use disorders, anxiety disorders, binge eating disorders, and migraines), family history of psychopathology, nonresponse to antidepressants or induction of hypomania, mixed features, and comorbidities
The authors advise “routine and systematic screening for BDs in all patients presenting with depressive symptomatology” and recommend using the Mood Disorders Questionnaire and the Hypomania Checklist.
Additional differential diagnoses include psychiatric disorders involving impulsivity, affective instability, anxiety, cognitive disorganization, depression, and psychosis.
“Futuristic” technology
“Although the pathogenesis of BDs is unknown, approximately 70% of the risk for BDs is heritable,” the authors note. They review recent research into genetic loci associated with BDs, based on genome-wide association studies, and the role of genetics not only in BDs but also in overlapping neurologic and psychiatric conditions, insulin resistance, and endocannabinoid signaling.
Inflammatory disturbances may also be implicated, in part related to “lifestyle and environment exposures” common in BDs such as smoking, poor diet, physical inactivity, and trauma, they suggest.
An “exciting new technology” analyzing “pluripotent” stem cells might illuminate the pathogenesis of BDs and mechanism of action of treatments by shedding light on mitochondrial dysfunction, McIntyre said.
“This interest in stem cells might almost be seen as futuristic. It is currently being used in the laboratory to understand the biology of BD, and it may eventually lead to the development of new therapeutics,” he added.
“Exciting” treatments
“Our expansive list of treatments and soon-to-be new treatments is very exciting,” said McIntyre.
The authors highlight “ongoing controversy regarding the safe and appropriate use of antidepressants in BD,” cautioning against potential treatment-emergent hypomania and suggesting limited circumstances when antidepressants might be administered.
Lithium remains the “gold standard mood-stabilizing agent” and is “capable of reducing suicidality,” they note.
Nonpharmacologic interventions include patient self-management, compliance, and cognitive enhancement strategies, primary prevention for psychiatric and medical comorbidity, psychosocial treatments and lifestyle interventions during maintenance, as well as surveillance for suicidality during both acute and maintenance phases.
Novel potential treatments include coenzyme Q10, N-acetyl cysteine, statins, nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, omega-3 fatty acids, incretin-based therapies, insulin, nitrous oxide, ketamine, prebiotics, probiotics, antibiotics, and adjunctive bright light therapy.
The authors caution that these investigational agents “cannot be considered efficacious or safe” in the treatment of BDs at present.
Call to action
Commenting for Medscape Medical News, Michael Thase, MD, professor of psychiatry, Perelman School of Medicine, University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, said he is glad that this “stellar group of authors” with “worldwide psychiatric expertise” wrote the article and he hopes it “gets the readership it deserves.”
Thase, who was not an author, said, “One takeaway is that BDs together comprise one of the world’s great public health problems — probably within the top 10.”
Another “has to do with our ability to do more with the tools we have — ie, ensuring diagnosis, implementing treatment, engaging social support, and using proven therapies from both psychopharmacologic and psychosocial domains.”
McIntyre characterized the article as a “public health call to action, incorporating screening, interesting neurobiological insights, an extensive set of treatments, and cool technological capabilities for the future.”
McIntyre has reported receiving grant support from the Stanley Medical Research Institute and the Canadian Institutes of Health Research/Global Alliance for Chronic Disease/Chinese National Natural Research Foundation, and speaker fees from Lundbeck, Janssen, Shire, Purdue, Pfizer, Otsuka, Allergan, Takeda, Neurocrine, Sunovion, Intra-Cellular, Alkermes, and Minerva, and is chief executive officer of Champignon. Disclosures for the other authors are listed in the article. Thase has reported consulting with and receiving research funding from many of the companies that manufacture/sell antidepressants and antipsychotics. He also has reported receiving royalties from the American Psychiatric Press Incorporated, Guilford Publications, Herald House, and W.W. Norton & Company.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
A new monograph offers a far-reaching update on research and clinical management of bipolar disorders (BDs), including epidemiology, genetics, pathogenesis, psychosocial aspects, and current and investigational therapies.
“I regard this as a ‘global state-of-the-union’ type of paper designed to bring the world up to speed regarding where we’re at and where we’re going in terms of bipolar disorder, to present the changes on the scientific and clinical fronts, and to open up a global conversation about bipolar disorder,” lead author Roger S. McIntyre, MD, professor of psychiatry and pharmacology, University of Toronto, Ontario, Canada, told Medscape Medical News.
“The paper is oriented toward multidisciplinary care, with particular emphasis on primary care, as well as people in healthcare administration and policy, who want a snapshot of where we’re at,” said McIntyre, who is also the head of the Mood Disorders Psychopharmacology Unit and director of the Depression and Bipolar Support Alliance in Chicago, Illinois.
The article was published online December 5 in The Lancet.
Severe, complex
The authors call BPs “a complex group of severe and chronic disorders” that include both BP I and BP II disorders.
“These disorders continue to be the world’s leading causes of disability, morbidity, and mortality, which are significant and getting worse, with studies indicating that bipolar disorders are associated with a loss of roughly 10 to 20 potential years of life,” McIntyre said.
Cardiovascular disease is the most common cause of premature death in people with BD. The second is suicide, the authors state, noting that patients with BDs are roughly 20-30 times more likely to die by suicide compared with the general population. In addition, 30%-50% have a lifetime history of suicide attempts.
BP I is “defined by the presence of a syndromal manic episode,” while BP II is “defined by the presence of a syndromal hypomanic episode and a major depressive episode,” the authors state.
Unlike the DSM-IV-TR, the DSM-5 includes “persistently increased energy or activity, along with elevated, expansive, or irritable mood” in the diagnostic criteria for mania and hypomania, “so diagnosing mania on mood instability alone is no longer sufficient,” the authors note.

In addition, clinicians “should be aware that individuals with BDs presenting with depression will often manifest symptoms of anxiety, agitation, anger-irritability, and attentional disturbance-distractibility (the four A’s), all of which are highly suggestive of mixed features,” they write.
Depression is the “predominant index presentation of BD” and “differentiating BD from major depressive disorder (MDD) is the most common clinical challenge for most clinicians.”
Features suggesting a diagnosis of BD rather than MDD include earlier age of onset, phenomenology (e.g., hyperphagia, hypersomnia, psychosis), higher frequency of affective episodes, comorbidities (e.g., substance use disorders, anxiety disorders, binge eating disorders, and migraines), family history of psychopathology, nonresponse to antidepressants or induction of hypomania, mixed features, and comorbidities
The authors advise “routine and systematic screening for BDs in all patients presenting with depressive symptomatology” and recommend using the Mood Disorders Questionnaire and the Hypomania Checklist.
Additional differential diagnoses include psychiatric disorders involving impulsivity, affective instability, anxiety, cognitive disorganization, depression, and psychosis.
“Futuristic” technology
“Although the pathogenesis of BDs is unknown, approximately 70% of the risk for BDs is heritable,” the authors note. They review recent research into genetic loci associated with BDs, based on genome-wide association studies, and the role of genetics not only in BDs but also in overlapping neurologic and psychiatric conditions, insulin resistance, and endocannabinoid signaling.
Inflammatory disturbances may also be implicated, in part related to “lifestyle and environment exposures” common in BDs such as smoking, poor diet, physical inactivity, and trauma, they suggest.
An “exciting new technology” analyzing “pluripotent” stem cells might illuminate the pathogenesis of BDs and mechanism of action of treatments by shedding light on mitochondrial dysfunction, McIntyre said.
“This interest in stem cells might almost be seen as futuristic. It is currently being used in the laboratory to understand the biology of BD, and it may eventually lead to the development of new therapeutics,” he added.
“Exciting” treatments
“Our expansive list of treatments and soon-to-be new treatments is very exciting,” said McIntyre.
The authors highlight “ongoing controversy regarding the safe and appropriate use of antidepressants in BD,” cautioning against potential treatment-emergent hypomania and suggesting limited circumstances when antidepressants might be administered.
Lithium remains the “gold standard mood-stabilizing agent” and is “capable of reducing suicidality,” they note.
Nonpharmacologic interventions include patient self-management, compliance, and cognitive enhancement strategies, primary prevention for psychiatric and medical comorbidity, psychosocial treatments and lifestyle interventions during maintenance, as well as surveillance for suicidality during both acute and maintenance phases.
Novel potential treatments include coenzyme Q10, N-acetyl cysteine, statins, nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, omega-3 fatty acids, incretin-based therapies, insulin, nitrous oxide, ketamine, prebiotics, probiotics, antibiotics, and adjunctive bright light therapy.
The authors caution that these investigational agents “cannot be considered efficacious or safe” in the treatment of BDs at present.
Call to action
Commenting for Medscape Medical News, Michael Thase, MD, professor of psychiatry, Perelman School of Medicine, University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, said he is glad that this “stellar group of authors” with “worldwide psychiatric expertise” wrote the article and he hopes it “gets the readership it deserves.”
Thase, who was not an author, said, “One takeaway is that BDs together comprise one of the world’s great public health problems — probably within the top 10.”
Another “has to do with our ability to do more with the tools we have — ie, ensuring diagnosis, implementing treatment, engaging social support, and using proven therapies from both psychopharmacologic and psychosocial domains.”
McIntyre characterized the article as a “public health call to action, incorporating screening, interesting neurobiological insights, an extensive set of treatments, and cool technological capabilities for the future.”
McIntyre has reported receiving grant support from the Stanley Medical Research Institute and the Canadian Institutes of Health Research/Global Alliance for Chronic Disease/Chinese National Natural Research Foundation, and speaker fees from Lundbeck, Janssen, Shire, Purdue, Pfizer, Otsuka, Allergan, Takeda, Neurocrine, Sunovion, Intra-Cellular, Alkermes, and Minerva, and is chief executive officer of Champignon. Disclosures for the other authors are listed in the article. Thase has reported consulting with and receiving research funding from many of the companies that manufacture/sell antidepressants and antipsychotics. He also has reported receiving royalties from the American Psychiatric Press Incorporated, Guilford Publications, Herald House, and W.W. Norton & Company.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
COVID-19 variant sparks U.K. travel restrictions
Researchers have detected a highly contagious coronavirus variant in the United Kingdom, leading Prime Minister Boris Johnson to shut down parts of the country and triggering other nations to impose travel and shipping restrictions on England.
Mr. Johnson held a crisis meeting with ministers Monday after Saturday’s shutdown announcement. The prime minister said in a nationally televised address that this coronavirus variant may be “up to 70% more transmissible than the old variant” and was probably responsible for an increase in cases in southeastern England.
“There is still much we don’t know. While we are fairly certain the variant is transmitted more quickly, there is no evidence to suggest that it is more lethal or causes more severe illness. Equally there is no evidence to suggest the vaccine will be any less effective against the new variant,” he said.
Public Health England says it is working to learn as much about the variant as possible. “We know that mortality is a lagging indicator, and we will need to continually monitor this over the coming weeks,” the agency says.
That scientific uncertainty about the variant’s threat shook European nations that were rushing to ship goods to England in advance of a Dec. 31 Brexit deadline. Under Brexit, which is short for “British exit,” the United Kingdom will leave the European Union on Jan. 31, 2020. Until then, the two sides will come up with new trade and security relationships.
European Union members Austria, Belgium, Bulgaria, France, Germany, Ireland, Italy, and the Netherlands announced travel restrictions hours after Johnson’s speech.
Those restrictions created food uncertainty across the U.K., which imports about a quarter of its food from the EU, according to The New York Times. Long lines of trucks heading to ports in the U.K. came to a standstill on major roads such as the M20 near Kent and the Port of Dover.
Outside Europe, Canada, India, Iran, Israel, Hong Kong, Saudi Arabia, and Turkey banned all incoming flights from the U.K. And more bans could come.
The U.S. reaction
The United States has not imposed any new limits on travel with the United Kingdom, although New York Gov. Andrew Cuomo (D) has requested all passengers bound for John F. Kennedy International Airport from the U.K. be tested before boarding and a new travel ban be placed for Europe. He says the federal government must take action now to avoid a crisis situation like the one New York experienced in March and April.
“The United States has a number of flights coming in from the U.K. each day, and we have done absolutely nothing,” Mr. Cuomo said in a statement on the governor’s webpage. “To me, this is reprehensible because this is what happened in the spring. How many times in life do you have to make the same mistake before you learn?”
Leading U.S. health officials have downplayed the dangers of the virus.
“We don’t know that it’s more dangerous, and very importantly, we have not seen a single mutation yet that would make it evade the vaccine,” U.S. Assistant Secretary of Health and Human Services Adm. Brett Giroir, MD, said Sunday on ABC’s This Week with George Stephanopoulos. “I can’t say that won’t happen in the future, but right now it looks like the vaccine will cover everything that we see.”
Dr. Giroir said the HHS and other U.S. government agencies will monitor the variant.
“Viruses mutate,” he said. “We’ve seen almost 4,000 different mutations among this virus. There is no indication that the mutation right now that they’re talking about is overcoming England.”
Where did the variant come from?
Public Health England says the coronavirus variant had existed in the U.K. since September and circulated at very low levels until mid-November.
“The increase in cases linked to the new variant first came to light in late November when PHE was investigating why infection rates in Kent were not falling despite national restrictions. We then discovered a cluster linked to this variant spreading rapidly into London and Essex,” the agency said.
Public Health England says there’s no evidence the new variant is resistant to the Pfizer-BioNTech vaccine, which is now being given across the country to high-priority groups such as health care workers.
An article in The BMJ, a British medical journal, says the variant was first detected by Covid-19 Genomics UK, a consortium that tests the random genetic sequencing of positive COVID-19 samples around the U.K. The variant cases were mostly in the southeast of England.
A University of Birmingham professor said in a Dec. 15 briefing that the variant accounts for 20% of viruses sequenced in Norfolk, 10% in Essex, and 3% in Suffolk. “There are no data to suggest it had been imported from abroad, so it is likely to have evolved in the U.K.,” he said.
The variant is named VUI-202012/01, for the first “variant under investigation” in December 2020, BMJ says. It’s defined by a set of 17 mutations, with the most significant mutation in the spike protein the virus uses to bind to the human ACE2 receptor.
“Changes in this part of spike protein may, in theory, result in the virus becoming more infectious and spreading more easily between people,” the article says.
The European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control says the variant emerged during the time of year when people usually socialize more.
“There is no indication at this point of increased infection severity associated with the new variant,” the agency said. “A few cases with the new variant have to date been reported by Denmark and the Netherlands and, according to media reports, in Belgium.”
Mr. Johnson announced tighter restrictions on England’s hardest-hit areas, such as the southeast and east of England, where new coronavirus cases have continued to rise. And he said people must cut back on their Christmas socializing.
“In England, those living in tier 4 areas should not mix with anyone outside their own household at Christmas, though support bubbles will remain in place for those at particular risk of loneliness or isolation,” he said.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
Researchers have detected a highly contagious coronavirus variant in the United Kingdom, leading Prime Minister Boris Johnson to shut down parts of the country and triggering other nations to impose travel and shipping restrictions on England.
Mr. Johnson held a crisis meeting with ministers Monday after Saturday’s shutdown announcement. The prime minister said in a nationally televised address that this coronavirus variant may be “up to 70% more transmissible than the old variant” and was probably responsible for an increase in cases in southeastern England.
“There is still much we don’t know. While we are fairly certain the variant is transmitted more quickly, there is no evidence to suggest that it is more lethal or causes more severe illness. Equally there is no evidence to suggest the vaccine will be any less effective against the new variant,” he said.
Public Health England says it is working to learn as much about the variant as possible. “We know that mortality is a lagging indicator, and we will need to continually monitor this over the coming weeks,” the agency says.
That scientific uncertainty about the variant’s threat shook European nations that were rushing to ship goods to England in advance of a Dec. 31 Brexit deadline. Under Brexit, which is short for “British exit,” the United Kingdom will leave the European Union on Jan. 31, 2020. Until then, the two sides will come up with new trade and security relationships.
European Union members Austria, Belgium, Bulgaria, France, Germany, Ireland, Italy, and the Netherlands announced travel restrictions hours after Johnson’s speech.
Those restrictions created food uncertainty across the U.K., which imports about a quarter of its food from the EU, according to The New York Times. Long lines of trucks heading to ports in the U.K. came to a standstill on major roads such as the M20 near Kent and the Port of Dover.
Outside Europe, Canada, India, Iran, Israel, Hong Kong, Saudi Arabia, and Turkey banned all incoming flights from the U.K. And more bans could come.
The U.S. reaction
The United States has not imposed any new limits on travel with the United Kingdom, although New York Gov. Andrew Cuomo (D) has requested all passengers bound for John F. Kennedy International Airport from the U.K. be tested before boarding and a new travel ban be placed for Europe. He says the federal government must take action now to avoid a crisis situation like the one New York experienced in March and April.
“The United States has a number of flights coming in from the U.K. each day, and we have done absolutely nothing,” Mr. Cuomo said in a statement on the governor’s webpage. “To me, this is reprehensible because this is what happened in the spring. How many times in life do you have to make the same mistake before you learn?”
Leading U.S. health officials have downplayed the dangers of the virus.
“We don’t know that it’s more dangerous, and very importantly, we have not seen a single mutation yet that would make it evade the vaccine,” U.S. Assistant Secretary of Health and Human Services Adm. Brett Giroir, MD, said Sunday on ABC’s This Week with George Stephanopoulos. “I can’t say that won’t happen in the future, but right now it looks like the vaccine will cover everything that we see.”
Dr. Giroir said the HHS and other U.S. government agencies will monitor the variant.
“Viruses mutate,” he said. “We’ve seen almost 4,000 different mutations among this virus. There is no indication that the mutation right now that they’re talking about is overcoming England.”
Where did the variant come from?
Public Health England says the coronavirus variant had existed in the U.K. since September and circulated at very low levels until mid-November.
“The increase in cases linked to the new variant first came to light in late November when PHE was investigating why infection rates in Kent were not falling despite national restrictions. We then discovered a cluster linked to this variant spreading rapidly into London and Essex,” the agency said.
Public Health England says there’s no evidence the new variant is resistant to the Pfizer-BioNTech vaccine, which is now being given across the country to high-priority groups such as health care workers.
An article in The BMJ, a British medical journal, says the variant was first detected by Covid-19 Genomics UK, a consortium that tests the random genetic sequencing of positive COVID-19 samples around the U.K. The variant cases were mostly in the southeast of England.
A University of Birmingham professor said in a Dec. 15 briefing that the variant accounts for 20% of viruses sequenced in Norfolk, 10% in Essex, and 3% in Suffolk. “There are no data to suggest it had been imported from abroad, so it is likely to have evolved in the U.K.,” he said.
The variant is named VUI-202012/01, for the first “variant under investigation” in December 2020, BMJ says. It’s defined by a set of 17 mutations, with the most significant mutation in the spike protein the virus uses to bind to the human ACE2 receptor.
“Changes in this part of spike protein may, in theory, result in the virus becoming more infectious and spreading more easily between people,” the article says.
The European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control says the variant emerged during the time of year when people usually socialize more.
“There is no indication at this point of increased infection severity associated with the new variant,” the agency said. “A few cases with the new variant have to date been reported by Denmark and the Netherlands and, according to media reports, in Belgium.”
Mr. Johnson announced tighter restrictions on England’s hardest-hit areas, such as the southeast and east of England, where new coronavirus cases have continued to rise. And he said people must cut back on their Christmas socializing.
“In England, those living in tier 4 areas should not mix with anyone outside their own household at Christmas, though support bubbles will remain in place for those at particular risk of loneliness or isolation,” he said.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
Researchers have detected a highly contagious coronavirus variant in the United Kingdom, leading Prime Minister Boris Johnson to shut down parts of the country and triggering other nations to impose travel and shipping restrictions on England.
Mr. Johnson held a crisis meeting with ministers Monday after Saturday’s shutdown announcement. The prime minister said in a nationally televised address that this coronavirus variant may be “up to 70% more transmissible than the old variant” and was probably responsible for an increase in cases in southeastern England.
“There is still much we don’t know. While we are fairly certain the variant is transmitted more quickly, there is no evidence to suggest that it is more lethal or causes more severe illness. Equally there is no evidence to suggest the vaccine will be any less effective against the new variant,” he said.
Public Health England says it is working to learn as much about the variant as possible. “We know that mortality is a lagging indicator, and we will need to continually monitor this over the coming weeks,” the agency says.
That scientific uncertainty about the variant’s threat shook European nations that were rushing to ship goods to England in advance of a Dec. 31 Brexit deadline. Under Brexit, which is short for “British exit,” the United Kingdom will leave the European Union on Jan. 31, 2020. Until then, the two sides will come up with new trade and security relationships.
European Union members Austria, Belgium, Bulgaria, France, Germany, Ireland, Italy, and the Netherlands announced travel restrictions hours after Johnson’s speech.
Those restrictions created food uncertainty across the U.K., which imports about a quarter of its food from the EU, according to The New York Times. Long lines of trucks heading to ports in the U.K. came to a standstill on major roads such as the M20 near Kent and the Port of Dover.
Outside Europe, Canada, India, Iran, Israel, Hong Kong, Saudi Arabia, and Turkey banned all incoming flights from the U.K. And more bans could come.
The U.S. reaction
The United States has not imposed any new limits on travel with the United Kingdom, although New York Gov. Andrew Cuomo (D) has requested all passengers bound for John F. Kennedy International Airport from the U.K. be tested before boarding and a new travel ban be placed for Europe. He says the federal government must take action now to avoid a crisis situation like the one New York experienced in March and April.
“The United States has a number of flights coming in from the U.K. each day, and we have done absolutely nothing,” Mr. Cuomo said in a statement on the governor’s webpage. “To me, this is reprehensible because this is what happened in the spring. How many times in life do you have to make the same mistake before you learn?”
Leading U.S. health officials have downplayed the dangers of the virus.
“We don’t know that it’s more dangerous, and very importantly, we have not seen a single mutation yet that would make it evade the vaccine,” U.S. Assistant Secretary of Health and Human Services Adm. Brett Giroir, MD, said Sunday on ABC’s This Week with George Stephanopoulos. “I can’t say that won’t happen in the future, but right now it looks like the vaccine will cover everything that we see.”
Dr. Giroir said the HHS and other U.S. government agencies will monitor the variant.
“Viruses mutate,” he said. “We’ve seen almost 4,000 different mutations among this virus. There is no indication that the mutation right now that they’re talking about is overcoming England.”
Where did the variant come from?
Public Health England says the coronavirus variant had existed in the U.K. since September and circulated at very low levels until mid-November.
“The increase in cases linked to the new variant first came to light in late November when PHE was investigating why infection rates in Kent were not falling despite national restrictions. We then discovered a cluster linked to this variant spreading rapidly into London and Essex,” the agency said.
Public Health England says there’s no evidence the new variant is resistant to the Pfizer-BioNTech vaccine, which is now being given across the country to high-priority groups such as health care workers.
An article in The BMJ, a British medical journal, says the variant was first detected by Covid-19 Genomics UK, a consortium that tests the random genetic sequencing of positive COVID-19 samples around the U.K. The variant cases were mostly in the southeast of England.
A University of Birmingham professor said in a Dec. 15 briefing that the variant accounts for 20% of viruses sequenced in Norfolk, 10% in Essex, and 3% in Suffolk. “There are no data to suggest it had been imported from abroad, so it is likely to have evolved in the U.K.,” he said.
The variant is named VUI-202012/01, for the first “variant under investigation” in December 2020, BMJ says. It’s defined by a set of 17 mutations, with the most significant mutation in the spike protein the virus uses to bind to the human ACE2 receptor.
“Changes in this part of spike protein may, in theory, result in the virus becoming more infectious and spreading more easily between people,” the article says.
The European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control says the variant emerged during the time of year when people usually socialize more.
“There is no indication at this point of increased infection severity associated with the new variant,” the agency said. “A few cases with the new variant have to date been reported by Denmark and the Netherlands and, according to media reports, in Belgium.”
Mr. Johnson announced tighter restrictions on England’s hardest-hit areas, such as the southeast and east of England, where new coronavirus cases have continued to rise. And he said people must cut back on their Christmas socializing.
“In England, those living in tier 4 areas should not mix with anyone outside their own household at Christmas, though support bubbles will remain in place for those at particular risk of loneliness or isolation,” he said.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
Food allergy testing for eczema in kids varies by specialty
Specialists vary on their opinion about the ordering of food allergy tests for children with eczema, a recent survey reveals.
A child with eczema is more likely to be given food allergy tests if seen by an allergist or a pediatrician and less likely to be given these tests if seen by a general practitioner or dermatologist.
“In our survey, we found evidence of variation in practice and a spectrum of opinion on what to do to treat eczema in children,” Matthew Ridd, MD, University of Bristol (England) said in an interview.
His clinician survey was sent to 155 health care providers. Findings were presented at the Food Allergy and Anaphylaxis Meeting–European Consortium on Application of Flow Cytometry in Allergy Congress, held virtually. They revealed big differences in the way physicians follow up on eczema. For a child with eczema with reported reactions to food, 20 of 22 (91%) allergists and 22 of 30 (73%) pediatricians always order food allergy tests.
But only 16 of 65 (25%) general practitioners and 3 of 12 (25%) dermatologists always order tests in the same situation.
A total of 155 health care practitioners responded to the survey, sent by a U.K. research team. Of those, 26 were unable to order allergy tests. Of the remaining 129, 65 (50%) specialized in general practice, 30 (23%) in pediatrics, 22 (17%) in the treatment of allergies, and 12 (9%) in dermatology.
Their opinions varied on when to order food allergy tests. For children with severe eczema who had no prior reaction to food, 8 of 22 (36%) practitioners specializing in allergy said they would order food allergy tests, as did 9 of 30 (30%) in pediatrics.
Of those surveyed, only 6 of 65 in general practice (9%) said they would request an allergy test for severe eczema for a patient with no allergy history, and no dermatologists (0%) would order the tests.
Only if a parent specifically requested a food allergy test would practitioners respond in a similar way. About two-thirds of all respondents said they would sometimes order the test if a parent asked (general practice, 75%; pediatrics, 63%; allergy, 68%; dermatology, 75%).
Dr. Ridd said in an interview that it’s not surprising there’s a wide variation in practice, inasmuch as the guidelines are quite convoluted and complex. “Eczema is a common problem, but we don’t have any good evidence to guide clinicians on when to consider food allergy as a possible cause.”
Current guidelines advise calling for allergy tests only when eczema is difficult to treat. “But this is a complex decision. We know that a third of children with eczema are at higher risk for food allergy,” Dr. Ridd said. A 2014 study published in Clinical and Experimental Allergy showed that infants with eczema are six times more likely to have egg allergy and 11 times more likely to have peanut allergy by 12 months than infants without eczema (Clin Exp Allergy. 2014;45:255-64).
Food allergy is a sticky subject, he said. “So we have to wonder, are general practitioners frightened to raise the question?
“We definitely see uncertainty around it.”
He suspects that parents may also be hesitant to bring it up. “They are likely thinking about it even if they don’t ask,” Dr. Ridd said. “I think it’s important to test for food allergy, to provide reassurance. Once we show it’s not an allergy, we can focus on topical treatment.”
Treating eczema with emollients may increase likelihood of food allergy
In a separate presentation at the FAAM-EUROBAT congress, Maeve Kelleher, MD, Imperial College London, said that, rather than help reduce eczema, emollients in infants probably cause an increase in the risk for skin infection and food allergy. Her research team performed a systematic review of 25,827 participants in randomized controlled trials of the use of skin care interventions in term infants for primary prevention of eczema and food allergy. The study focused especially on topical creams.
Dr. Kelleher reported that skin care interventions “probably don’t prevent eczema. They probably increase local skin infections and may increase food allergy.”
Other interventions need to be explored, she said. “Maybe prevention should be along the line of looking at the microbiome, or exposures on the skin when you’re younger.”
Dr. Ridd and Dr. Kelleher have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Specialists vary on their opinion about the ordering of food allergy tests for children with eczema, a recent survey reveals.
A child with eczema is more likely to be given food allergy tests if seen by an allergist or a pediatrician and less likely to be given these tests if seen by a general practitioner or dermatologist.
“In our survey, we found evidence of variation in practice and a spectrum of opinion on what to do to treat eczema in children,” Matthew Ridd, MD, University of Bristol (England) said in an interview.
His clinician survey was sent to 155 health care providers. Findings were presented at the Food Allergy and Anaphylaxis Meeting–European Consortium on Application of Flow Cytometry in Allergy Congress, held virtually. They revealed big differences in the way physicians follow up on eczema. For a child with eczema with reported reactions to food, 20 of 22 (91%) allergists and 22 of 30 (73%) pediatricians always order food allergy tests.
But only 16 of 65 (25%) general practitioners and 3 of 12 (25%) dermatologists always order tests in the same situation.
A total of 155 health care practitioners responded to the survey, sent by a U.K. research team. Of those, 26 were unable to order allergy tests. Of the remaining 129, 65 (50%) specialized in general practice, 30 (23%) in pediatrics, 22 (17%) in the treatment of allergies, and 12 (9%) in dermatology.
Their opinions varied on when to order food allergy tests. For children with severe eczema who had no prior reaction to food, 8 of 22 (36%) practitioners specializing in allergy said they would order food allergy tests, as did 9 of 30 (30%) in pediatrics.
Of those surveyed, only 6 of 65 in general practice (9%) said they would request an allergy test for severe eczema for a patient with no allergy history, and no dermatologists (0%) would order the tests.
Only if a parent specifically requested a food allergy test would practitioners respond in a similar way. About two-thirds of all respondents said they would sometimes order the test if a parent asked (general practice, 75%; pediatrics, 63%; allergy, 68%; dermatology, 75%).
Dr. Ridd said in an interview that it’s not surprising there’s a wide variation in practice, inasmuch as the guidelines are quite convoluted and complex. “Eczema is a common problem, but we don’t have any good evidence to guide clinicians on when to consider food allergy as a possible cause.”
Current guidelines advise calling for allergy tests only when eczema is difficult to treat. “But this is a complex decision. We know that a third of children with eczema are at higher risk for food allergy,” Dr. Ridd said. A 2014 study published in Clinical and Experimental Allergy showed that infants with eczema are six times more likely to have egg allergy and 11 times more likely to have peanut allergy by 12 months than infants without eczema (Clin Exp Allergy. 2014;45:255-64).
Food allergy is a sticky subject, he said. “So we have to wonder, are general practitioners frightened to raise the question?
“We definitely see uncertainty around it.”
He suspects that parents may also be hesitant to bring it up. “They are likely thinking about it even if they don’t ask,” Dr. Ridd said. “I think it’s important to test for food allergy, to provide reassurance. Once we show it’s not an allergy, we can focus on topical treatment.”
Treating eczema with emollients may increase likelihood of food allergy
In a separate presentation at the FAAM-EUROBAT congress, Maeve Kelleher, MD, Imperial College London, said that, rather than help reduce eczema, emollients in infants probably cause an increase in the risk for skin infection and food allergy. Her research team performed a systematic review of 25,827 participants in randomized controlled trials of the use of skin care interventions in term infants for primary prevention of eczema and food allergy. The study focused especially on topical creams.
Dr. Kelleher reported that skin care interventions “probably don’t prevent eczema. They probably increase local skin infections and may increase food allergy.”
Other interventions need to be explored, she said. “Maybe prevention should be along the line of looking at the microbiome, or exposures on the skin when you’re younger.”
Dr. Ridd and Dr. Kelleher have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Specialists vary on their opinion about the ordering of food allergy tests for children with eczema, a recent survey reveals.
A child with eczema is more likely to be given food allergy tests if seen by an allergist or a pediatrician and less likely to be given these tests if seen by a general practitioner or dermatologist.
“In our survey, we found evidence of variation in practice and a spectrum of opinion on what to do to treat eczema in children,” Matthew Ridd, MD, University of Bristol (England) said in an interview.
His clinician survey was sent to 155 health care providers. Findings were presented at the Food Allergy and Anaphylaxis Meeting–European Consortium on Application of Flow Cytometry in Allergy Congress, held virtually. They revealed big differences in the way physicians follow up on eczema. For a child with eczema with reported reactions to food, 20 of 22 (91%) allergists and 22 of 30 (73%) pediatricians always order food allergy tests.
But only 16 of 65 (25%) general practitioners and 3 of 12 (25%) dermatologists always order tests in the same situation.
A total of 155 health care practitioners responded to the survey, sent by a U.K. research team. Of those, 26 were unable to order allergy tests. Of the remaining 129, 65 (50%) specialized in general practice, 30 (23%) in pediatrics, 22 (17%) in the treatment of allergies, and 12 (9%) in dermatology.
Their opinions varied on when to order food allergy tests. For children with severe eczema who had no prior reaction to food, 8 of 22 (36%) practitioners specializing in allergy said they would order food allergy tests, as did 9 of 30 (30%) in pediatrics.
Of those surveyed, only 6 of 65 in general practice (9%) said they would request an allergy test for severe eczema for a patient with no allergy history, and no dermatologists (0%) would order the tests.
Only if a parent specifically requested a food allergy test would practitioners respond in a similar way. About two-thirds of all respondents said they would sometimes order the test if a parent asked (general practice, 75%; pediatrics, 63%; allergy, 68%; dermatology, 75%).
Dr. Ridd said in an interview that it’s not surprising there’s a wide variation in practice, inasmuch as the guidelines are quite convoluted and complex. “Eczema is a common problem, but we don’t have any good evidence to guide clinicians on when to consider food allergy as a possible cause.”
Current guidelines advise calling for allergy tests only when eczema is difficult to treat. “But this is a complex decision. We know that a third of children with eczema are at higher risk for food allergy,” Dr. Ridd said. A 2014 study published in Clinical and Experimental Allergy showed that infants with eczema are six times more likely to have egg allergy and 11 times more likely to have peanut allergy by 12 months than infants without eczema (Clin Exp Allergy. 2014;45:255-64).
Food allergy is a sticky subject, he said. “So we have to wonder, are general practitioners frightened to raise the question?
“We definitely see uncertainty around it.”
He suspects that parents may also be hesitant to bring it up. “They are likely thinking about it even if they don’t ask,” Dr. Ridd said. “I think it’s important to test for food allergy, to provide reassurance. Once we show it’s not an allergy, we can focus on topical treatment.”
Treating eczema with emollients may increase likelihood of food allergy
In a separate presentation at the FAAM-EUROBAT congress, Maeve Kelleher, MD, Imperial College London, said that, rather than help reduce eczema, emollients in infants probably cause an increase in the risk for skin infection and food allergy. Her research team performed a systematic review of 25,827 participants in randomized controlled trials of the use of skin care interventions in term infants for primary prevention of eczema and food allergy. The study focused especially on topical creams.
Dr. Kelleher reported that skin care interventions “probably don’t prevent eczema. They probably increase local skin infections and may increase food allergy.”
Other interventions need to be explored, she said. “Maybe prevention should be along the line of looking at the microbiome, or exposures on the skin when you’re younger.”
Dr. Ridd and Dr. Kelleher have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.















