User login
COVID-19: Hand sanitizer poisonings soar, psych patients at high risk
Cases of poisoning – intentional and unintentional – from ingestion of alcohol-based hand sanitizer have soared during the COVID-19 pandemic.
In the United Kingdom alone, alcohol-based hand sanitizer poisonings reported to the National Poisons Information Service jumped 157% – from 155 between January 1 and September 16, 2019, to 398 between Jan. 1 and Sept. 14, 2020, new research shows.
More needs to be done to protect those at risk of unintentional and intentional swallowing of alcohol-based hand sanitizer, including children, people with dementia/confusion, and those with mental health issues, according to Georgia Richards, DPhil student, Centre for Evidence-Based Medicine, Nuffield Department of Primary Care Health Sciences, University of Oxford (England).
“If providers are supplying alcohol-based hand sanitizers in the community to reduce the spread of SARS-CoV-2, Ms. Richards said in an interview.
The study was published online Dec. 1 in BMJ Evidence-Based Medicine.
European, U.S. poisoning rates soar
In the paper Ms. Richards described two deaths that occurred in hospitals in England.
In one case, a 30-year-old woman, detained in a psychiatric unit who received the antidepressant venlafaxine was found dead in her hospital bed with a container of hand-sanitizing gel beside her.
“The gel was readily accessible to patients on the ward from a communal dispenser, and patients were allowed to fill cups or other containers with it to keep in their rooms,” Ms. Richards reported.
A postmortem analysis found a high level of alcohol in her blood (214 mg of alcohol in 100 mL of blood). The medical cause of death was listed as “ingestion of alcohol and venlafaxine.” The coroner concluded that the combination of these substances suppressed the patient’s breathing, leading to her death.
The other case involved a 76-year-old man who unintentionally swallowed an unknown quantity of alcohol-based hand-sanitizing foam attached to the foot of his hospital bed.
The patient had a history of agitation and depression and was treated with antidepressants. He had become increasingly confused over the preceding 9 months, possibly because of vascular dementia.
His blood ethanol concentration was 463 mg/dL (100 mmol/L) initially and 354 mg/dL (77mmol/L) 10 hours later. He was admitted to the ICU, where he received lorazepam and haloperidol and treated with ventilation, with a plan to allow the alcohol to be naturally metabolized.
The patient developed complications and died 6 days later. The primary causes of death were bronchopneumonia and acute alcohol toxicity, secondary to acute delirium and coronary artery disease.
Since COVID-19 started, alcohol-based hand sanitizers are among the most sought-after commodities around the world. The volume of these products – now found in homes, hospitals, schools, workplaces, and elsewhere – “may be a cause for concern,” Ms. Richards wrote.
Yet, warnings about the toxicity and lethality of intentional or unintentional ingestion of these products have not been widely disseminated, she noted.
To reduce the risk of harm, Ms. Richards suggested educating the public and health care professionals, improving warning labels on products, and increasing the awareness and reporting of such exposures to public health authorities.
“While governments and public health authorities have successfully heightened our awareness of, and need for, better hand hygiene during the COVID-19 outbreak, they must also make the public aware of the potential harms and encourage the reporting of such harms to poisons information centers,” she noted.
Increases in alcohol-based hand sanitizer poisoning during the pandemic have also been reported in the United States.
The American Association of Poison Control Centers reports that data from the National Poison Data System show 32,892 hand sanitizer exposure cases reported to the 55 U.S. poison control centers from Jan. 1 to Nov. 15, 2020 – an increase of 73%, compared with the same time period during the previous year.
An increase in self-harm
Weighing in on this issue, Robert Bassett, DO, associate medical director of the Poison Control Center at Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia, said in an interview that “cleaning agents and disinfectants have been around for eons and their potential for toxicity hasn’t changed.
“Now with COVID, and this hypervigilance when it comes to cleanliness, there is increased access and the exposure risk has gone up,” he said.
“One of the sad casualties of an overstressed health care system and a globally depressed environment is worsening behavioral health emergencies and, as part of that, the risk of self-harm goes up,” Dr. Bassett added.
“The consensus is that there has been an exacerbation of behavioral health emergencies and behavioral health needs since COVID started and hand sanitizers are readily accessible to someone who may be looking to self-harm,” he said.
This research had no specific funding. Ms. Richards is the editorial registrar of BMJ Evidence Based Medicine and is developing a website to track preventable deaths. Dr. Bassett disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
Cases of poisoning – intentional and unintentional – from ingestion of alcohol-based hand sanitizer have soared during the COVID-19 pandemic.
In the United Kingdom alone, alcohol-based hand sanitizer poisonings reported to the National Poisons Information Service jumped 157% – from 155 between January 1 and September 16, 2019, to 398 between Jan. 1 and Sept. 14, 2020, new research shows.
More needs to be done to protect those at risk of unintentional and intentional swallowing of alcohol-based hand sanitizer, including children, people with dementia/confusion, and those with mental health issues, according to Georgia Richards, DPhil student, Centre for Evidence-Based Medicine, Nuffield Department of Primary Care Health Sciences, University of Oxford (England).
“If providers are supplying alcohol-based hand sanitizers in the community to reduce the spread of SARS-CoV-2, Ms. Richards said in an interview.
The study was published online Dec. 1 in BMJ Evidence-Based Medicine.
European, U.S. poisoning rates soar
In the paper Ms. Richards described two deaths that occurred in hospitals in England.
In one case, a 30-year-old woman, detained in a psychiatric unit who received the antidepressant venlafaxine was found dead in her hospital bed with a container of hand-sanitizing gel beside her.
“The gel was readily accessible to patients on the ward from a communal dispenser, and patients were allowed to fill cups or other containers with it to keep in their rooms,” Ms. Richards reported.
A postmortem analysis found a high level of alcohol in her blood (214 mg of alcohol in 100 mL of blood). The medical cause of death was listed as “ingestion of alcohol and venlafaxine.” The coroner concluded that the combination of these substances suppressed the patient’s breathing, leading to her death.
The other case involved a 76-year-old man who unintentionally swallowed an unknown quantity of alcohol-based hand-sanitizing foam attached to the foot of his hospital bed.
The patient had a history of agitation and depression and was treated with antidepressants. He had become increasingly confused over the preceding 9 months, possibly because of vascular dementia.
His blood ethanol concentration was 463 mg/dL (100 mmol/L) initially and 354 mg/dL (77mmol/L) 10 hours later. He was admitted to the ICU, where he received lorazepam and haloperidol and treated with ventilation, with a plan to allow the alcohol to be naturally metabolized.
The patient developed complications and died 6 days later. The primary causes of death were bronchopneumonia and acute alcohol toxicity, secondary to acute delirium and coronary artery disease.
Since COVID-19 started, alcohol-based hand sanitizers are among the most sought-after commodities around the world. The volume of these products – now found in homes, hospitals, schools, workplaces, and elsewhere – “may be a cause for concern,” Ms. Richards wrote.
Yet, warnings about the toxicity and lethality of intentional or unintentional ingestion of these products have not been widely disseminated, she noted.
To reduce the risk of harm, Ms. Richards suggested educating the public and health care professionals, improving warning labels on products, and increasing the awareness and reporting of such exposures to public health authorities.
“While governments and public health authorities have successfully heightened our awareness of, and need for, better hand hygiene during the COVID-19 outbreak, they must also make the public aware of the potential harms and encourage the reporting of such harms to poisons information centers,” she noted.
Increases in alcohol-based hand sanitizer poisoning during the pandemic have also been reported in the United States.
The American Association of Poison Control Centers reports that data from the National Poison Data System show 32,892 hand sanitizer exposure cases reported to the 55 U.S. poison control centers from Jan. 1 to Nov. 15, 2020 – an increase of 73%, compared with the same time period during the previous year.
An increase in self-harm
Weighing in on this issue, Robert Bassett, DO, associate medical director of the Poison Control Center at Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia, said in an interview that “cleaning agents and disinfectants have been around for eons and their potential for toxicity hasn’t changed.
“Now with COVID, and this hypervigilance when it comes to cleanliness, there is increased access and the exposure risk has gone up,” he said.
“One of the sad casualties of an overstressed health care system and a globally depressed environment is worsening behavioral health emergencies and, as part of that, the risk of self-harm goes up,” Dr. Bassett added.
“The consensus is that there has been an exacerbation of behavioral health emergencies and behavioral health needs since COVID started and hand sanitizers are readily accessible to someone who may be looking to self-harm,” he said.
This research had no specific funding. Ms. Richards is the editorial registrar of BMJ Evidence Based Medicine and is developing a website to track preventable deaths. Dr. Bassett disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
Cases of poisoning – intentional and unintentional – from ingestion of alcohol-based hand sanitizer have soared during the COVID-19 pandemic.
In the United Kingdom alone, alcohol-based hand sanitizer poisonings reported to the National Poisons Information Service jumped 157% – from 155 between January 1 and September 16, 2019, to 398 between Jan. 1 and Sept. 14, 2020, new research shows.
More needs to be done to protect those at risk of unintentional and intentional swallowing of alcohol-based hand sanitizer, including children, people with dementia/confusion, and those with mental health issues, according to Georgia Richards, DPhil student, Centre for Evidence-Based Medicine, Nuffield Department of Primary Care Health Sciences, University of Oxford (England).
“If providers are supplying alcohol-based hand sanitizers in the community to reduce the spread of SARS-CoV-2, Ms. Richards said in an interview.
The study was published online Dec. 1 in BMJ Evidence-Based Medicine.
European, U.S. poisoning rates soar
In the paper Ms. Richards described two deaths that occurred in hospitals in England.
In one case, a 30-year-old woman, detained in a psychiatric unit who received the antidepressant venlafaxine was found dead in her hospital bed with a container of hand-sanitizing gel beside her.
“The gel was readily accessible to patients on the ward from a communal dispenser, and patients were allowed to fill cups or other containers with it to keep in their rooms,” Ms. Richards reported.
A postmortem analysis found a high level of alcohol in her blood (214 mg of alcohol in 100 mL of blood). The medical cause of death was listed as “ingestion of alcohol and venlafaxine.” The coroner concluded that the combination of these substances suppressed the patient’s breathing, leading to her death.
The other case involved a 76-year-old man who unintentionally swallowed an unknown quantity of alcohol-based hand-sanitizing foam attached to the foot of his hospital bed.
The patient had a history of agitation and depression and was treated with antidepressants. He had become increasingly confused over the preceding 9 months, possibly because of vascular dementia.
His blood ethanol concentration was 463 mg/dL (100 mmol/L) initially and 354 mg/dL (77mmol/L) 10 hours later. He was admitted to the ICU, where he received lorazepam and haloperidol and treated with ventilation, with a plan to allow the alcohol to be naturally metabolized.
The patient developed complications and died 6 days later. The primary causes of death were bronchopneumonia and acute alcohol toxicity, secondary to acute delirium and coronary artery disease.
Since COVID-19 started, alcohol-based hand sanitizers are among the most sought-after commodities around the world. The volume of these products – now found in homes, hospitals, schools, workplaces, and elsewhere – “may be a cause for concern,” Ms. Richards wrote.
Yet, warnings about the toxicity and lethality of intentional or unintentional ingestion of these products have not been widely disseminated, she noted.
To reduce the risk of harm, Ms. Richards suggested educating the public and health care professionals, improving warning labels on products, and increasing the awareness and reporting of such exposures to public health authorities.
“While governments and public health authorities have successfully heightened our awareness of, and need for, better hand hygiene during the COVID-19 outbreak, they must also make the public aware of the potential harms and encourage the reporting of such harms to poisons information centers,” she noted.
Increases in alcohol-based hand sanitizer poisoning during the pandemic have also been reported in the United States.
The American Association of Poison Control Centers reports that data from the National Poison Data System show 32,892 hand sanitizer exposure cases reported to the 55 U.S. poison control centers from Jan. 1 to Nov. 15, 2020 – an increase of 73%, compared with the same time period during the previous year.
An increase in self-harm
Weighing in on this issue, Robert Bassett, DO, associate medical director of the Poison Control Center at Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia, said in an interview that “cleaning agents and disinfectants have been around for eons and their potential for toxicity hasn’t changed.
“Now with COVID, and this hypervigilance when it comes to cleanliness, there is increased access and the exposure risk has gone up,” he said.
“One of the sad casualties of an overstressed health care system and a globally depressed environment is worsening behavioral health emergencies and, as part of that, the risk of self-harm goes up,” Dr. Bassett added.
“The consensus is that there has been an exacerbation of behavioral health emergencies and behavioral health needs since COVID started and hand sanitizers are readily accessible to someone who may be looking to self-harm,” he said.
This research had no specific funding. Ms. Richards is the editorial registrar of BMJ Evidence Based Medicine and is developing a website to track preventable deaths. Dr. Bassett disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
Addressing Maternal Mortality Through Education: The Mommies Methadone Program
From the UT Health Long School of Medicine San Antonio, Texas.
Abstract
Objective: To educate pregnant patients with opioid use disorder (OUD) about the effects of opioids in order to improve understanding and help achieve sustained abstinence.
Methods: The Center for Health Care Services and University Hospital System (UHS) in San Antonio, TX, jointly o
Results: Of 68 women enrolled in the program, 33 completed both the pre-survey and the post-survey (48.5%). Nearly half (48%) were very motivated to quit before pregnancy, but 85% were very motivated to quit once pregnant. All participants said learning more about the effects of opiates would increase motivation for sobriety. Prior to the educational intervention, 39% of participants knew it was safe to breastfeed on methadone, which improved to 97% in the post-survey, and 76% incorrectly thought they would be reported to authorities by their health care providers if they used illegal drugs during pregnancy, while in the post-survey, 100% knew they would not be reported for doing so.
Conclusion: Pregnancy and education about opioids increased patients’ motivation to quit. Patients also advanced their breastfeeding knowledge and learned about patient-provider confidentiality. Our greatest challenge was participant follow-up; however, this improved with the help of a full-time Mommies Program nurse. Our future aim is to increase project awareness and extend the educational research.
Keywords: pregnancy; addiction; opioids; OUD; counseling.
In 2012 more than 259 million prescriptions for opioids were written in the United States, which was a 200% increase since 1998.1 Since the early 2000s, admissions to opioid substance abuse programs and the death rate from opioids have quadrupled.2-4 Specifically, the rate of heroin use increased more than 300% from 2010 to 2014.5 Opioid use in pregnancy has also escalated in recent years, with a 3- to 4-fold increase from 2000 to 2009 and with 4 in 1000 deliveries being complicated by opioid use disorder (OUD) in 2011.6-8
Between 2000 and 2014, the maternal mortality rate in the United States increased 24%, making it the only industrialized nation with a maternal mortality rate that is rising rather than falling.9 The Texas Maternal Mortality and Morbidity Task Force found that between 2012 and 2015 drug overdose was the leading cause of maternal death in the period from delivery to 365 days postpartum, and it has increased dramatically since 2010.10,11
In addition, maternal mortality reviews in several states have identified substance use as a major risk factor for pregnancy-associated deaths.12,13 In Texas between 2012 and 2015, opioids were found in 58% of maternal drug overdoses.10 In 2007, 22.8% of women who were enrolled in Medicaid programs in 46 states filled an opioid prescription during pregnancy.14 Additionally, the rising prevalence of opioid use in pregnancy has led to a sharp increase in neonatal abstinence syndrome (NAS), rising from 1.5 cases per 1000 hospital births in 1999 to 6.0 per 1000 hospital births in 2013.15 Unsurprisingly, states with the highest rates of opioid prescribing also have the highest rates of NAS.16
Methadone combined with counseling and behavioral therapy has been the standard of care for the treatment of OUD in pregnancy since the 1970s. Methadone treatment prevents opioid withdrawal symptoms and increases adherence to prenatal care.17 One of the largest methadone treatment clinics in the San Antonio, TX, area is the Center for Health Care Services (CHCS). University Health System in San Antonio (UHS) has established a clinic called The Mommies Program, where mothers addicted to opioids can receive prenatal care by a dedicated physician, registered nurse, and a certified nurse midwife, who work in collaboration with the CHCS methadone clinic. Pregnant patients with OUD in pregnancy are concurrently enrolled in the Mommies Program and receive prenatal care through UHS and methadone treatment and counseling through CHCS. The continuity effort aims to increase prenatal care rates and adherence to methadone treatment.
Once mothers are off illicit opioids and on methadone, it is essential to discuss breastfeeding with them, as many mothers addicted to illicit opioids may have been told that they should not be breastfeeding. However, breastfeeding should be encouraged in women who are stable on methadone if they are not using illicit drugs and do not have other contraindications, regardless of maternal methadone dose, since the transfer of methadone into breast milk is minimal.18-20 Breastfeeding is beneficial in women taking methadone and has been associated with decreased severity of NAS symptoms, decreased need for pharmacotherapy, and a shorter hospital stay for the baby.21 In addition, breastfeeding contributes to the development of an attachment between mother and infant, while also providing the infant with natural immunity. Women should be counseled about the need to stop breastfeeding in the event of a relapse.22
Finally, the postpartum period represents a time of increased stressors, such as loss of sleep, child protective services involvement, and frustration with constant demands from new baby. For mothers with addiction, this is an especially sensitive time, as the stressors may be exacerbated by their new sobriety and a sudden end to the motivation they experienced from pregnancy.23 Therefore, early and frequent postpartum care with methadone dose evaluation is essential in order to decrease drug relapse and screen for postpartum depression in detail, since patients with a history of drug use are at increased risk of postpartum depression.
In 2017 medical students at UT Health Long School of Medicine in San Antonio created a project to educate women about OUD in pregnancy and provide motivational incentives for sustained abstinence; this project has continued each year since. Students provide education about methadone treatment and the dangers of using illicit opioids during and after pregnancy. Students especially focus on educating patients on the key problem areas in the literature, such as overdose, NAS, breastfeeding, postpartum substance use, and postpartum depression.
Methods
From October 2018 to February 2020, a total of 15 medical students volunteered between 1 and 20 times at the Mommies Program clinic, which was held once or twice per week from 8
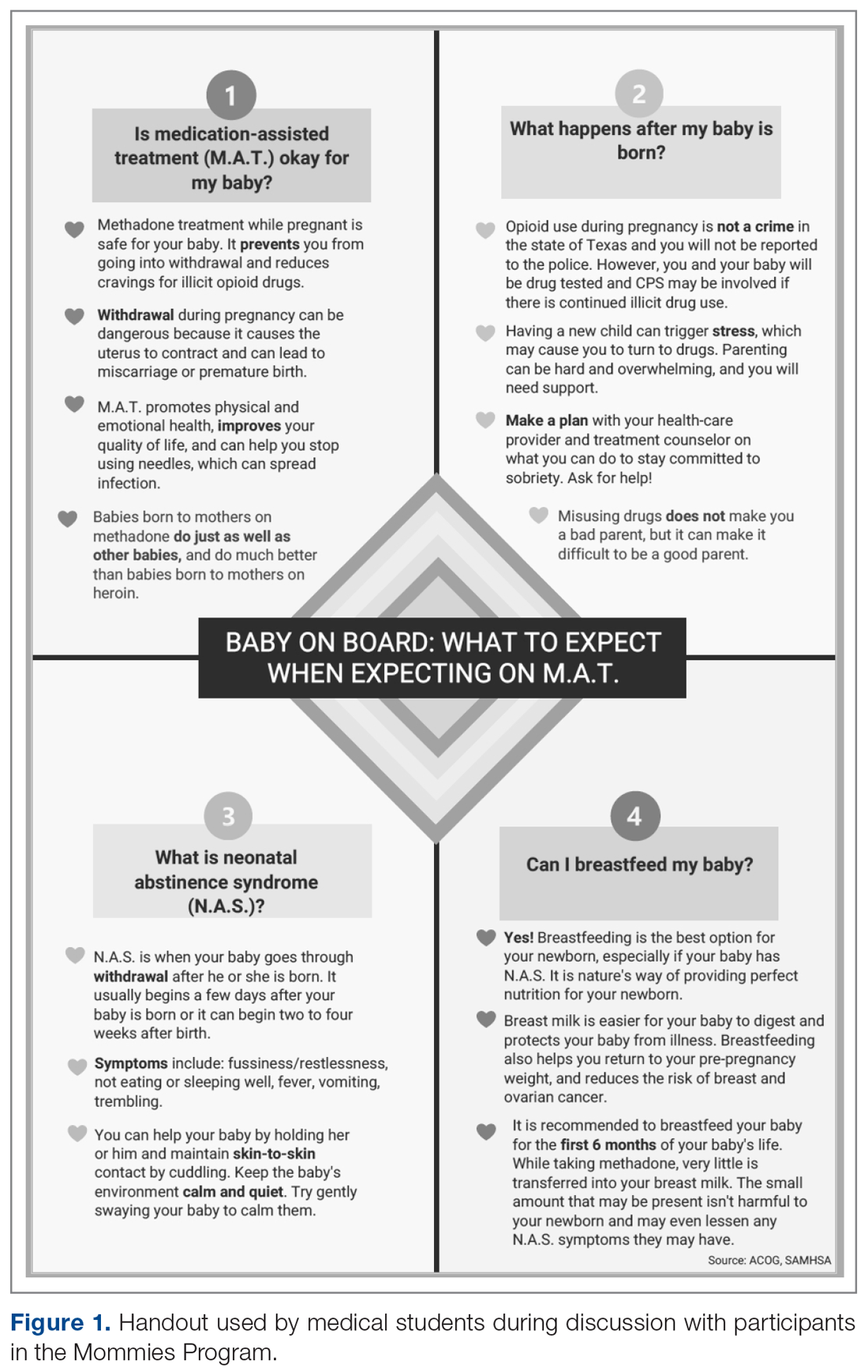
The only inclusion criteria for participating in the educational intervention and survey was participants had to be 18 years of age or older and enrolled in the Mommies Program. Patients who met the inclusion criteria and agreed to participate completed a pre-survey administered by the students during the patient’s initial prenatal visit (Figure 2). This survey collected baseline information about the patient’s history with opioid use and their current knowledge of methadone treatment, NAS, legal aspects of drug use disclosure, and drug testing prior to the education portion of the encounter. After the pre-survey was administered, students spent 30 minutes reviewing the correct answers of the survey with the patients by utilizing the standardized handout to help patients understand details of methadone and opioid use in pregnancy (Figure 1). The post-survey was administered by a student once patients entered the third trimester to assess whether the education session increased patients’ knowledge of these topics.

At the time patients completed the post-survey, they received a Baby Bag as well as education regarding each item in the bag. The aim of distributing Baby Bags was to relieve some possible postnatal stressors and educate the patients about infant care. Items included in the bag were diapers, wipes, bottles, clothes, and swaddles. Prenatal vitamins were added in January 2020, as many patients struggle to afford vitamins if they are not currently covered by Medicaid or have other barriers. The Baby Bag items were purchased through a Community Service Learning grant through UT Health San Antonio.
Results
Of 68 women enrolled in the Mommies Program during the intervention period, 33 completed the pre-survey and the post-survey (48.5%). Even though all patients enrolled in the program met the inclusion criteria, patients were not included in the educational program for multiple reasons, including refusal to participate, poor clinic follow-up, or lack of students to collect surveys. However, all patients who completed the pre-survey did complete the post-survey. In the pre-survey, only 39% of participants knew it was safe to breastfeed while on methadone. In the post-survey, 97% knew it safe to breastfeed. Nearly half (48%) reported being very motivated to quit opioids before pregnancy, but 85% were very motivated to quit once pregnant. In the pre-survey, 76% incorrectly thought they would be reported to authorities by their health providers if they used illegal drugs during pregnancy, while in the post-survey, 100% knew they would not be reported for doing so. Also, all participants said learning more about the effects of opiates would increase motivation for sobriety.
Discussion
Questions assessed during the educational surveys revolved around patients’ knowledge of the intricacies, legally and physiologically, of methadone treatment for OUD, as well as beneficial aspects for patients and future child health, such as breastfeeding and motivation to quit and stay sober.
It was clear that there was a lack of knowledge and education about breastfeeding, as only 39% of the participants thought that it was safe to breastfeed while on methadone in the pre-survey; in the post survey, this improved to 97%. Students spent a large portion of the educational time going over the safety of breastfeeding for patients on methadone and the many benefits to mother and baby. Students also reviewed breastfeeding with patients every time patients came in for a visit and debunked any falsehoods about the negatives of breastfeeding while on methadone. This is another testament to the benefits of reinforcement around patient education.
The area of trust between provider and patient is essential in all provider-patient relationships. However, in the area of addiction, a trusting bond is especially important, as patients must feel confident and comfortable to disclose every aspect of their lives so the provider can give the best care. It was clear from our initial data that many patients did not feel this trust or understand the legal aspects regarding the provider-patient relationship in the terms of drug use, as the pre-survey shows 76% of patients originally thought they would be reported to authorities if they told their provider they used illegal drugs during pregnancy. This was an enormous issue in the clinic and something that needed to be addressed because, based on these data, we feared many patients would not be honest about using illegal drugs to supplement their methadone if they believed they would be reported to the authorities or even jailed. The medical student education team continually assured patients that their honesty about illegal drug use during pregnancy would not be revealed to the authorities, and also made it clear to patients that it was essential they were honest about illegal drug use so the optimal care could be provided by the team. These discussions were successful, as the post-survey showed that 100% of patients knew they would not be reported to the authorities if they used illegal drugs during the pregnancy. This showed an increase in knowledge, but also suggested an increase in confidence in the provider-patient relationship by patients, which we speculate allowed for a better patient experience, better patient outcomes, and less emotional stress for the patient and provider.
Last, we wanted to study and address the motivation to quit using drugs and stay sober through learning about the effects of opiates and how this motivation was related to pregnancy. A study by Mitchell et al makes clear that pregnancy is a motivation to seek treatment for drug use and to quit,24 and our survey data support these findings, with 48% of patients motivated to quit before they were pregnant and 85% motivated to quit once they knew they were pregnant. In addition, all patients attested on the pre- and post-survey that learning more about opioids would increase their motivation for sobriety. Therefore, we believe education about the use of opioids and other drugs is a strong motivation towards sobriety and should be further studied in methadone treatment and other drugs as well.
We will continue to focus on sobriety postpartum by using the education in pregnancy as a springboard to further postpartum education, as education seems to be very beneficial to future sobriety. In the future, we believe extending the educational program past pregnancy and discussing opioid use and addiction with patients at multiple follow-up visits will be beneficial to patients’ sobriety.
We faced 2 main challenges in implementing this intervention and survey: patients would often miss multiple appointments during their third trimester or would not attend their postpartum visit if they only had 1 prenatal visit; and many clinic sessions had low student attendance because students often had many other responsibilities in medical school and there were only 15 volunteers over the study time. These challenges decreased our post-survey completion rate. However, there has been improvement in follow-up as the project has continued. The Mommies Program now has a full-time registered nurse, and a larger number of medical student teachers have volunteered to attend the clinic. In the future, we aim to increase awareness of our project and the benefits of participation, expand advertising at our medical school to increase student participation, and increase follow-up education in the postpartum period.
Another future direction is to include local, free doula services, which are offered through Catholic Charities in San Antonio. Doulas provide antepartum, intrapartum, and postpartum services, which we believe will help our patients through advocacy and support for sobriety during this emotional and stressful time.
Conclusion
Counseled participants were receptive to learning about the effects of OUD and methadone on themselves and their newborn. Participants unanimously stated that learning more about OUD increased their motivation for sobriety. It was also clear that the increased motivation to be sober during pregnancy, as compared to before pregnancy, is an opportunity to help these women take steps to get sober. Patients also advanced their breastfeeding knowledge, as we helped debunk falsehoods surrounding breastfeeding while on methadone, and we anticipate this will lead to greater breastfeeding rates for our patients on methadone, although this was not specifically studied. Finally, patients learned about patient-provider confidentiality, which allowed for more open and clear communication with patients so they could be cared for to the greatest degree and trust could remain paramount.
Drug use is a common problem in the health care system, and exposure to patients with addiction is important for medical students in training. We believe that attending the Mommies Program allowed medical students to gain exposure and skills to better help patients with OUD.
Corresponding author: Nicholas Stansbury, MD, [email protected].
Financial disclosures: None.
1. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Opioid painkiller prescribing: where you live makes a difference. CDC website. www.cdc.gov/vitalsigns/opioid-prescribing. Accessed October 28, 2020.
2. Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration. Drug Abuse Warning Network, 2011: national estimates of drug-related emergency department visits. HHS Publication No. (SMA) 13-4760, DAWN Series D-39. Rockville (MD): SAMHSA; 2013. www.samhsa.gov/data/sites/default/files/DAWN2k11ED/DAWN2k11ED/DAWN2k11ED.pdf. Accessed October 28, 2020.
3. Compton WM, Jones CM, Baldwin GT. Relationship between nonmedical prescription-opioid use and heroin use. N Engl J Med. 2016;374:154-63.
4. National Center for Health Statistics. NCHS data on drug-poisoning deaths. NCHS Factsheet. https://www.cdc.gov/nchs/data/factsheets/factsheet-drug-poisoning-H.pdf. Accessed October 28, 2020.
5. National Institute on Drug Abuse. America’s addiction to opioids: heroin and prescription drug abuse. Bethesda (MD): NIDA; 2014. www.drugabuse.gov/about-nida/legislative-activities/testimony-to-congress/2016/americas-addiction-to-opioids-heroin-prescription-drug-abuse. Accessed October 28, 2020.
6. Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration (SAMHSA). Results from the 2010 National Survey on Drug Use and Health: Summary of National Findings. Rockville, MD: SAMHSA, 2011 Contract No.: HHS Publication no. (SMA) 11–4658.
7. Maeda A, Bateman BT, Clancy CR, et al. Opioid abuse and dependence during pregnancy: temporal trends and obstetrical outcomes. Anesthesiology. 2014;121:1158-1165.
8. Whiteman VE, Salemi JL, Mogos MF, et al. Maternal opioid drug use during pregnancy and its impact on perinatal morbidity, mortality, and the costs of medical care in the United States. J Pregnancy. 2014;2014:1-8
9. Pregnancy Mortality Surveillance System. www.cdc.gov/reproductivehealth/maternal-mortality/pregnancy-mortality-surveillance-system.htm#trends. Accessed February 4, 2020.
10. Macdorman MF, Declercq E, Cabral H, Morton C. Recent increases in the U.S. maternal mortality rate. Obstet Gynecol. 2016;128:447-455.
11. Texas Health and Human Services. Maternal Mortality and Morbidity Task Force and Department of State Health Services Joint Biennial Report, September 2018. www.dshs.texas.gov/legislative/2018-Reports/MMMTFJointReport2018.pdf
12. Virginia Department of Health. Pregnancy-associated deaths from drug overdose in Virginia, 1999-2007: a report from the Virginia Maternal Mortality Review Team. Richmond, VA: VDH; 2015. www.vdh.virginia.gov/content/uploads/sites/18/2016/04/Final-Pregnancy-Associated-Deaths-Due-to-Drug-Overdose.pdf. Accessed October 28, 2020.
13. Maryland Department of Health and Mental Hygiene. Maryland maternal mortality review 2016 annual report. Baltimore: DHMH; 2016. https://phpa.health.maryland.gov/Documents/Maryland-Maternal-Mortality-Review-2016-Report.pdf. Accessed October 28, 2020.
14. Desai RJ, Hernandez-Diaz S, Bateman BT, Huybrechts KF. Increase in prescription opioid use during pregnancy among Medicaid-enrolled women. Obstet Gynecol. 2014;123:997-1002.
15. Reddy UM, Davis JM, Ren Z, et al. Opioid use in pregnancy, neonatal abstinence syndrome, and childhood outcomes. Obstet Gynecol Survey. 2017;72:703-705.
16. Patrick SW, Davis MM, Lehmann CU, Cooper WO. Increasing incidence and geographic distribution of neonatal abstinence syndrome: United States 2009 to 2012. J Perinatol. 2015;35:650-655.
17. Center for Substance Abuse Treatment. Medication-assisted treatment for opioid addiction during pregnancy. In: Medication-assisted treatment for opioid addiction in opioid treatment programs. Treatment Improvement Protocol (TIP) Series, No. 43. Rockville, MD: Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration; 2005:211-224.
18. Wojnar-Horton RE, Kristensen JH, Yapp P, et al. Methadone distribution and excretion into breast milk of clients in a methadone maintenance programme. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 1997;44:543-547.
19. Reece-Stremtan S, Marinelli KA. ABM clinical protocol #21: guidelines for breastfeeding and substance use or substance use disorder, revised 2015. Breastfeed Med. 2015;10:135-141.
20. Sachs HC. The transfer of drugs and therapeutics into human breast milk: an update on selected topics. Committee on Drugs. Pediatrics. 2013;132:e796-809.
21. Bagley SM, Wachman EM, Holland E, Brogly SB. Review of the assessment and management of neonatal abstinence syndrome. Addict Sci Clin Pract. 2014;9:19.
22. Opioid use and opioid use disorder in pregnancy. Committee Opinion No. 711. Obstet Gynecol. 2017;130:488-489.
23. Gopman S. Prenatal and postpartum care of women with substance use disorders. Obstet Gynecol Clin North Am. 2014;41:213-228.
24. Mitchell M, Severtson S, Latimer W. Pregnancy and race/ethnicity as predictors of motivation for drug treatment. Am J Drug Alcohol Abuse. 2008;34:397-404.
From the UT Health Long School of Medicine San Antonio, Texas.
Abstract
Objective: To educate pregnant patients with opioid use disorder (OUD) about the effects of opioids in order to improve understanding and help achieve sustained abstinence.
Methods: The Center for Health Care Services and University Hospital System (UHS) in San Antonio, TX, jointly o
Results: Of 68 women enrolled in the program, 33 completed both the pre-survey and the post-survey (48.5%). Nearly half (48%) were very motivated to quit before pregnancy, but 85% were very motivated to quit once pregnant. All participants said learning more about the effects of opiates would increase motivation for sobriety. Prior to the educational intervention, 39% of participants knew it was safe to breastfeed on methadone, which improved to 97% in the post-survey, and 76% incorrectly thought they would be reported to authorities by their health care providers if they used illegal drugs during pregnancy, while in the post-survey, 100% knew they would not be reported for doing so.
Conclusion: Pregnancy and education about opioids increased patients’ motivation to quit. Patients also advanced their breastfeeding knowledge and learned about patient-provider confidentiality. Our greatest challenge was participant follow-up; however, this improved with the help of a full-time Mommies Program nurse. Our future aim is to increase project awareness and extend the educational research.
Keywords: pregnancy; addiction; opioids; OUD; counseling.
In 2012 more than 259 million prescriptions for opioids were written in the United States, which was a 200% increase since 1998.1 Since the early 2000s, admissions to opioid substance abuse programs and the death rate from opioids have quadrupled.2-4 Specifically, the rate of heroin use increased more than 300% from 2010 to 2014.5 Opioid use in pregnancy has also escalated in recent years, with a 3- to 4-fold increase from 2000 to 2009 and with 4 in 1000 deliveries being complicated by opioid use disorder (OUD) in 2011.6-8
Between 2000 and 2014, the maternal mortality rate in the United States increased 24%, making it the only industrialized nation with a maternal mortality rate that is rising rather than falling.9 The Texas Maternal Mortality and Morbidity Task Force found that between 2012 and 2015 drug overdose was the leading cause of maternal death in the period from delivery to 365 days postpartum, and it has increased dramatically since 2010.10,11
In addition, maternal mortality reviews in several states have identified substance use as a major risk factor for pregnancy-associated deaths.12,13 In Texas between 2012 and 2015, opioids were found in 58% of maternal drug overdoses.10 In 2007, 22.8% of women who were enrolled in Medicaid programs in 46 states filled an opioid prescription during pregnancy.14 Additionally, the rising prevalence of opioid use in pregnancy has led to a sharp increase in neonatal abstinence syndrome (NAS), rising from 1.5 cases per 1000 hospital births in 1999 to 6.0 per 1000 hospital births in 2013.15 Unsurprisingly, states with the highest rates of opioid prescribing also have the highest rates of NAS.16
Methadone combined with counseling and behavioral therapy has been the standard of care for the treatment of OUD in pregnancy since the 1970s. Methadone treatment prevents opioid withdrawal symptoms and increases adherence to prenatal care.17 One of the largest methadone treatment clinics in the San Antonio, TX, area is the Center for Health Care Services (CHCS). University Health System in San Antonio (UHS) has established a clinic called The Mommies Program, where mothers addicted to opioids can receive prenatal care by a dedicated physician, registered nurse, and a certified nurse midwife, who work in collaboration with the CHCS methadone clinic. Pregnant patients with OUD in pregnancy are concurrently enrolled in the Mommies Program and receive prenatal care through UHS and methadone treatment and counseling through CHCS. The continuity effort aims to increase prenatal care rates and adherence to methadone treatment.
Once mothers are off illicit opioids and on methadone, it is essential to discuss breastfeeding with them, as many mothers addicted to illicit opioids may have been told that they should not be breastfeeding. However, breastfeeding should be encouraged in women who are stable on methadone if they are not using illicit drugs and do not have other contraindications, regardless of maternal methadone dose, since the transfer of methadone into breast milk is minimal.18-20 Breastfeeding is beneficial in women taking methadone and has been associated with decreased severity of NAS symptoms, decreased need for pharmacotherapy, and a shorter hospital stay for the baby.21 In addition, breastfeeding contributes to the development of an attachment between mother and infant, while also providing the infant with natural immunity. Women should be counseled about the need to stop breastfeeding in the event of a relapse.22
Finally, the postpartum period represents a time of increased stressors, such as loss of sleep, child protective services involvement, and frustration with constant demands from new baby. For mothers with addiction, this is an especially sensitive time, as the stressors may be exacerbated by their new sobriety and a sudden end to the motivation they experienced from pregnancy.23 Therefore, early and frequent postpartum care with methadone dose evaluation is essential in order to decrease drug relapse and screen for postpartum depression in detail, since patients with a history of drug use are at increased risk of postpartum depression.
In 2017 medical students at UT Health Long School of Medicine in San Antonio created a project to educate women about OUD in pregnancy and provide motivational incentives for sustained abstinence; this project has continued each year since. Students provide education about methadone treatment and the dangers of using illicit opioids during and after pregnancy. Students especially focus on educating patients on the key problem areas in the literature, such as overdose, NAS, breastfeeding, postpartum substance use, and postpartum depression.
Methods
From October 2018 to February 2020, a total of 15 medical students volunteered between 1 and 20 times at the Mommies Program clinic, which was held once or twice per week from 8

The only inclusion criteria for participating in the educational intervention and survey was participants had to be 18 years of age or older and enrolled in the Mommies Program. Patients who met the inclusion criteria and agreed to participate completed a pre-survey administered by the students during the patient’s initial prenatal visit (Figure 2). This survey collected baseline information about the patient’s history with opioid use and their current knowledge of methadone treatment, NAS, legal aspects of drug use disclosure, and drug testing prior to the education portion of the encounter. After the pre-survey was administered, students spent 30 minutes reviewing the correct answers of the survey with the patients by utilizing the standardized handout to help patients understand details of methadone and opioid use in pregnancy (Figure 1). The post-survey was administered by a student once patients entered the third trimester to assess whether the education session increased patients’ knowledge of these topics.

At the time patients completed the post-survey, they received a Baby Bag as well as education regarding each item in the bag. The aim of distributing Baby Bags was to relieve some possible postnatal stressors and educate the patients about infant care. Items included in the bag were diapers, wipes, bottles, clothes, and swaddles. Prenatal vitamins were added in January 2020, as many patients struggle to afford vitamins if they are not currently covered by Medicaid or have other barriers. The Baby Bag items were purchased through a Community Service Learning grant through UT Health San Antonio.
Results
Of 68 women enrolled in the Mommies Program during the intervention period, 33 completed the pre-survey and the post-survey (48.5%). Even though all patients enrolled in the program met the inclusion criteria, patients were not included in the educational program for multiple reasons, including refusal to participate, poor clinic follow-up, or lack of students to collect surveys. However, all patients who completed the pre-survey did complete the post-survey. In the pre-survey, only 39% of participants knew it was safe to breastfeed while on methadone. In the post-survey, 97% knew it safe to breastfeed. Nearly half (48%) reported being very motivated to quit opioids before pregnancy, but 85% were very motivated to quit once pregnant. In the pre-survey, 76% incorrectly thought they would be reported to authorities by their health providers if they used illegal drugs during pregnancy, while in the post-survey, 100% knew they would not be reported for doing so. Also, all participants said learning more about the effects of opiates would increase motivation for sobriety.
Discussion
Questions assessed during the educational surveys revolved around patients’ knowledge of the intricacies, legally and physiologically, of methadone treatment for OUD, as well as beneficial aspects for patients and future child health, such as breastfeeding and motivation to quit and stay sober.
It was clear that there was a lack of knowledge and education about breastfeeding, as only 39% of the participants thought that it was safe to breastfeed while on methadone in the pre-survey; in the post survey, this improved to 97%. Students spent a large portion of the educational time going over the safety of breastfeeding for patients on methadone and the many benefits to mother and baby. Students also reviewed breastfeeding with patients every time patients came in for a visit and debunked any falsehoods about the negatives of breastfeeding while on methadone. This is another testament to the benefits of reinforcement around patient education.
The area of trust between provider and patient is essential in all provider-patient relationships. However, in the area of addiction, a trusting bond is especially important, as patients must feel confident and comfortable to disclose every aspect of their lives so the provider can give the best care. It was clear from our initial data that many patients did not feel this trust or understand the legal aspects regarding the provider-patient relationship in the terms of drug use, as the pre-survey shows 76% of patients originally thought they would be reported to authorities if they told their provider they used illegal drugs during pregnancy. This was an enormous issue in the clinic and something that needed to be addressed because, based on these data, we feared many patients would not be honest about using illegal drugs to supplement their methadone if they believed they would be reported to the authorities or even jailed. The medical student education team continually assured patients that their honesty about illegal drug use during pregnancy would not be revealed to the authorities, and also made it clear to patients that it was essential they were honest about illegal drug use so the optimal care could be provided by the team. These discussions were successful, as the post-survey showed that 100% of patients knew they would not be reported to the authorities if they used illegal drugs during the pregnancy. This showed an increase in knowledge, but also suggested an increase in confidence in the provider-patient relationship by patients, which we speculate allowed for a better patient experience, better patient outcomes, and less emotional stress for the patient and provider.
Last, we wanted to study and address the motivation to quit using drugs and stay sober through learning about the effects of opiates and how this motivation was related to pregnancy. A study by Mitchell et al makes clear that pregnancy is a motivation to seek treatment for drug use and to quit,24 and our survey data support these findings, with 48% of patients motivated to quit before they were pregnant and 85% motivated to quit once they knew they were pregnant. In addition, all patients attested on the pre- and post-survey that learning more about opioids would increase their motivation for sobriety. Therefore, we believe education about the use of opioids and other drugs is a strong motivation towards sobriety and should be further studied in methadone treatment and other drugs as well.
We will continue to focus on sobriety postpartum by using the education in pregnancy as a springboard to further postpartum education, as education seems to be very beneficial to future sobriety. In the future, we believe extending the educational program past pregnancy and discussing opioid use and addiction with patients at multiple follow-up visits will be beneficial to patients’ sobriety.
We faced 2 main challenges in implementing this intervention and survey: patients would often miss multiple appointments during their third trimester or would not attend their postpartum visit if they only had 1 prenatal visit; and many clinic sessions had low student attendance because students often had many other responsibilities in medical school and there were only 15 volunteers over the study time. These challenges decreased our post-survey completion rate. However, there has been improvement in follow-up as the project has continued. The Mommies Program now has a full-time registered nurse, and a larger number of medical student teachers have volunteered to attend the clinic. In the future, we aim to increase awareness of our project and the benefits of participation, expand advertising at our medical school to increase student participation, and increase follow-up education in the postpartum period.
Another future direction is to include local, free doula services, which are offered through Catholic Charities in San Antonio. Doulas provide antepartum, intrapartum, and postpartum services, which we believe will help our patients through advocacy and support for sobriety during this emotional and stressful time.
Conclusion
Counseled participants were receptive to learning about the effects of OUD and methadone on themselves and their newborn. Participants unanimously stated that learning more about OUD increased their motivation for sobriety. It was also clear that the increased motivation to be sober during pregnancy, as compared to before pregnancy, is an opportunity to help these women take steps to get sober. Patients also advanced their breastfeeding knowledge, as we helped debunk falsehoods surrounding breastfeeding while on methadone, and we anticipate this will lead to greater breastfeeding rates for our patients on methadone, although this was not specifically studied. Finally, patients learned about patient-provider confidentiality, which allowed for more open and clear communication with patients so they could be cared for to the greatest degree and trust could remain paramount.
Drug use is a common problem in the health care system, and exposure to patients with addiction is important for medical students in training. We believe that attending the Mommies Program allowed medical students to gain exposure and skills to better help patients with OUD.
Corresponding author: Nicholas Stansbury, MD, [email protected].
Financial disclosures: None.
From the UT Health Long School of Medicine San Antonio, Texas.
Abstract
Objective: To educate pregnant patients with opioid use disorder (OUD) about the effects of opioids in order to improve understanding and help achieve sustained abstinence.
Methods: The Center for Health Care Services and University Hospital System (UHS) in San Antonio, TX, jointly o
Results: Of 68 women enrolled in the program, 33 completed both the pre-survey and the post-survey (48.5%). Nearly half (48%) were very motivated to quit before pregnancy, but 85% were very motivated to quit once pregnant. All participants said learning more about the effects of opiates would increase motivation for sobriety. Prior to the educational intervention, 39% of participants knew it was safe to breastfeed on methadone, which improved to 97% in the post-survey, and 76% incorrectly thought they would be reported to authorities by their health care providers if they used illegal drugs during pregnancy, while in the post-survey, 100% knew they would not be reported for doing so.
Conclusion: Pregnancy and education about opioids increased patients’ motivation to quit. Patients also advanced their breastfeeding knowledge and learned about patient-provider confidentiality. Our greatest challenge was participant follow-up; however, this improved with the help of a full-time Mommies Program nurse. Our future aim is to increase project awareness and extend the educational research.
Keywords: pregnancy; addiction; opioids; OUD; counseling.
In 2012 more than 259 million prescriptions for opioids were written in the United States, which was a 200% increase since 1998.1 Since the early 2000s, admissions to opioid substance abuse programs and the death rate from opioids have quadrupled.2-4 Specifically, the rate of heroin use increased more than 300% from 2010 to 2014.5 Opioid use in pregnancy has also escalated in recent years, with a 3- to 4-fold increase from 2000 to 2009 and with 4 in 1000 deliveries being complicated by opioid use disorder (OUD) in 2011.6-8
Between 2000 and 2014, the maternal mortality rate in the United States increased 24%, making it the only industrialized nation with a maternal mortality rate that is rising rather than falling.9 The Texas Maternal Mortality and Morbidity Task Force found that between 2012 and 2015 drug overdose was the leading cause of maternal death in the period from delivery to 365 days postpartum, and it has increased dramatically since 2010.10,11
In addition, maternal mortality reviews in several states have identified substance use as a major risk factor for pregnancy-associated deaths.12,13 In Texas between 2012 and 2015, opioids were found in 58% of maternal drug overdoses.10 In 2007, 22.8% of women who were enrolled in Medicaid programs in 46 states filled an opioid prescription during pregnancy.14 Additionally, the rising prevalence of opioid use in pregnancy has led to a sharp increase in neonatal abstinence syndrome (NAS), rising from 1.5 cases per 1000 hospital births in 1999 to 6.0 per 1000 hospital births in 2013.15 Unsurprisingly, states with the highest rates of opioid prescribing also have the highest rates of NAS.16
Methadone combined with counseling and behavioral therapy has been the standard of care for the treatment of OUD in pregnancy since the 1970s. Methadone treatment prevents opioid withdrawal symptoms and increases adherence to prenatal care.17 One of the largest methadone treatment clinics in the San Antonio, TX, area is the Center for Health Care Services (CHCS). University Health System in San Antonio (UHS) has established a clinic called The Mommies Program, where mothers addicted to opioids can receive prenatal care by a dedicated physician, registered nurse, and a certified nurse midwife, who work in collaboration with the CHCS methadone clinic. Pregnant patients with OUD in pregnancy are concurrently enrolled in the Mommies Program and receive prenatal care through UHS and methadone treatment and counseling through CHCS. The continuity effort aims to increase prenatal care rates and adherence to methadone treatment.
Once mothers are off illicit opioids and on methadone, it is essential to discuss breastfeeding with them, as many mothers addicted to illicit opioids may have been told that they should not be breastfeeding. However, breastfeeding should be encouraged in women who are stable on methadone if they are not using illicit drugs and do not have other contraindications, regardless of maternal methadone dose, since the transfer of methadone into breast milk is minimal.18-20 Breastfeeding is beneficial in women taking methadone and has been associated with decreased severity of NAS symptoms, decreased need for pharmacotherapy, and a shorter hospital stay for the baby.21 In addition, breastfeeding contributes to the development of an attachment between mother and infant, while also providing the infant with natural immunity. Women should be counseled about the need to stop breastfeeding in the event of a relapse.22
Finally, the postpartum period represents a time of increased stressors, such as loss of sleep, child protective services involvement, and frustration with constant demands from new baby. For mothers with addiction, this is an especially sensitive time, as the stressors may be exacerbated by their new sobriety and a sudden end to the motivation they experienced from pregnancy.23 Therefore, early and frequent postpartum care with methadone dose evaluation is essential in order to decrease drug relapse and screen for postpartum depression in detail, since patients with a history of drug use are at increased risk of postpartum depression.
In 2017 medical students at UT Health Long School of Medicine in San Antonio created a project to educate women about OUD in pregnancy and provide motivational incentives for sustained abstinence; this project has continued each year since. Students provide education about methadone treatment and the dangers of using illicit opioids during and after pregnancy. Students especially focus on educating patients on the key problem areas in the literature, such as overdose, NAS, breastfeeding, postpartum substance use, and postpartum depression.
Methods
From October 2018 to February 2020, a total of 15 medical students volunteered between 1 and 20 times at the Mommies Program clinic, which was held once or twice per week from 8

The only inclusion criteria for participating in the educational intervention and survey was participants had to be 18 years of age or older and enrolled in the Mommies Program. Patients who met the inclusion criteria and agreed to participate completed a pre-survey administered by the students during the patient’s initial prenatal visit (Figure 2). This survey collected baseline information about the patient’s history with opioid use and their current knowledge of methadone treatment, NAS, legal aspects of drug use disclosure, and drug testing prior to the education portion of the encounter. After the pre-survey was administered, students spent 30 minutes reviewing the correct answers of the survey with the patients by utilizing the standardized handout to help patients understand details of methadone and opioid use in pregnancy (Figure 1). The post-survey was administered by a student once patients entered the third trimester to assess whether the education session increased patients’ knowledge of these topics.

At the time patients completed the post-survey, they received a Baby Bag as well as education regarding each item in the bag. The aim of distributing Baby Bags was to relieve some possible postnatal stressors and educate the patients about infant care. Items included in the bag were diapers, wipes, bottles, clothes, and swaddles. Prenatal vitamins were added in January 2020, as many patients struggle to afford vitamins if they are not currently covered by Medicaid or have other barriers. The Baby Bag items were purchased through a Community Service Learning grant through UT Health San Antonio.
Results
Of 68 women enrolled in the Mommies Program during the intervention period, 33 completed the pre-survey and the post-survey (48.5%). Even though all patients enrolled in the program met the inclusion criteria, patients were not included in the educational program for multiple reasons, including refusal to participate, poor clinic follow-up, or lack of students to collect surveys. However, all patients who completed the pre-survey did complete the post-survey. In the pre-survey, only 39% of participants knew it was safe to breastfeed while on methadone. In the post-survey, 97% knew it safe to breastfeed. Nearly half (48%) reported being very motivated to quit opioids before pregnancy, but 85% were very motivated to quit once pregnant. In the pre-survey, 76% incorrectly thought they would be reported to authorities by their health providers if they used illegal drugs during pregnancy, while in the post-survey, 100% knew they would not be reported for doing so. Also, all participants said learning more about the effects of opiates would increase motivation for sobriety.
Discussion
Questions assessed during the educational surveys revolved around patients’ knowledge of the intricacies, legally and physiologically, of methadone treatment for OUD, as well as beneficial aspects for patients and future child health, such as breastfeeding and motivation to quit and stay sober.
It was clear that there was a lack of knowledge and education about breastfeeding, as only 39% of the participants thought that it was safe to breastfeed while on methadone in the pre-survey; in the post survey, this improved to 97%. Students spent a large portion of the educational time going over the safety of breastfeeding for patients on methadone and the many benefits to mother and baby. Students also reviewed breastfeeding with patients every time patients came in for a visit and debunked any falsehoods about the negatives of breastfeeding while on methadone. This is another testament to the benefits of reinforcement around patient education.
The area of trust between provider and patient is essential in all provider-patient relationships. However, in the area of addiction, a trusting bond is especially important, as patients must feel confident and comfortable to disclose every aspect of their lives so the provider can give the best care. It was clear from our initial data that many patients did not feel this trust or understand the legal aspects regarding the provider-patient relationship in the terms of drug use, as the pre-survey shows 76% of patients originally thought they would be reported to authorities if they told their provider they used illegal drugs during pregnancy. This was an enormous issue in the clinic and something that needed to be addressed because, based on these data, we feared many patients would not be honest about using illegal drugs to supplement their methadone if they believed they would be reported to the authorities or even jailed. The medical student education team continually assured patients that their honesty about illegal drug use during pregnancy would not be revealed to the authorities, and also made it clear to patients that it was essential they were honest about illegal drug use so the optimal care could be provided by the team. These discussions were successful, as the post-survey showed that 100% of patients knew they would not be reported to the authorities if they used illegal drugs during the pregnancy. This showed an increase in knowledge, but also suggested an increase in confidence in the provider-patient relationship by patients, which we speculate allowed for a better patient experience, better patient outcomes, and less emotional stress for the patient and provider.
Last, we wanted to study and address the motivation to quit using drugs and stay sober through learning about the effects of opiates and how this motivation was related to pregnancy. A study by Mitchell et al makes clear that pregnancy is a motivation to seek treatment for drug use and to quit,24 and our survey data support these findings, with 48% of patients motivated to quit before they were pregnant and 85% motivated to quit once they knew they were pregnant. In addition, all patients attested on the pre- and post-survey that learning more about opioids would increase their motivation for sobriety. Therefore, we believe education about the use of opioids and other drugs is a strong motivation towards sobriety and should be further studied in methadone treatment and other drugs as well.
We will continue to focus on sobriety postpartum by using the education in pregnancy as a springboard to further postpartum education, as education seems to be very beneficial to future sobriety. In the future, we believe extending the educational program past pregnancy and discussing opioid use and addiction with patients at multiple follow-up visits will be beneficial to patients’ sobriety.
We faced 2 main challenges in implementing this intervention and survey: patients would often miss multiple appointments during their third trimester or would not attend their postpartum visit if they only had 1 prenatal visit; and many clinic sessions had low student attendance because students often had many other responsibilities in medical school and there were only 15 volunteers over the study time. These challenges decreased our post-survey completion rate. However, there has been improvement in follow-up as the project has continued. The Mommies Program now has a full-time registered nurse, and a larger number of medical student teachers have volunteered to attend the clinic. In the future, we aim to increase awareness of our project and the benefits of participation, expand advertising at our medical school to increase student participation, and increase follow-up education in the postpartum period.
Another future direction is to include local, free doula services, which are offered through Catholic Charities in San Antonio. Doulas provide antepartum, intrapartum, and postpartum services, which we believe will help our patients through advocacy and support for sobriety during this emotional and stressful time.
Conclusion
Counseled participants were receptive to learning about the effects of OUD and methadone on themselves and their newborn. Participants unanimously stated that learning more about OUD increased their motivation for sobriety. It was also clear that the increased motivation to be sober during pregnancy, as compared to before pregnancy, is an opportunity to help these women take steps to get sober. Patients also advanced their breastfeeding knowledge, as we helped debunk falsehoods surrounding breastfeeding while on methadone, and we anticipate this will lead to greater breastfeeding rates for our patients on methadone, although this was not specifically studied. Finally, patients learned about patient-provider confidentiality, which allowed for more open and clear communication with patients so they could be cared for to the greatest degree and trust could remain paramount.
Drug use is a common problem in the health care system, and exposure to patients with addiction is important for medical students in training. We believe that attending the Mommies Program allowed medical students to gain exposure and skills to better help patients with OUD.
Corresponding author: Nicholas Stansbury, MD, [email protected].
Financial disclosures: None.
1. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Opioid painkiller prescribing: where you live makes a difference. CDC website. www.cdc.gov/vitalsigns/opioid-prescribing. Accessed October 28, 2020.
2. Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration. Drug Abuse Warning Network, 2011: national estimates of drug-related emergency department visits. HHS Publication No. (SMA) 13-4760, DAWN Series D-39. Rockville (MD): SAMHSA; 2013. www.samhsa.gov/data/sites/default/files/DAWN2k11ED/DAWN2k11ED/DAWN2k11ED.pdf. Accessed October 28, 2020.
3. Compton WM, Jones CM, Baldwin GT. Relationship between nonmedical prescription-opioid use and heroin use. N Engl J Med. 2016;374:154-63.
4. National Center for Health Statistics. NCHS data on drug-poisoning deaths. NCHS Factsheet. https://www.cdc.gov/nchs/data/factsheets/factsheet-drug-poisoning-H.pdf. Accessed October 28, 2020.
5. National Institute on Drug Abuse. America’s addiction to opioids: heroin and prescription drug abuse. Bethesda (MD): NIDA; 2014. www.drugabuse.gov/about-nida/legislative-activities/testimony-to-congress/2016/americas-addiction-to-opioids-heroin-prescription-drug-abuse. Accessed October 28, 2020.
6. Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration (SAMHSA). Results from the 2010 National Survey on Drug Use and Health: Summary of National Findings. Rockville, MD: SAMHSA, 2011 Contract No.: HHS Publication no. (SMA) 11–4658.
7. Maeda A, Bateman BT, Clancy CR, et al. Opioid abuse and dependence during pregnancy: temporal trends and obstetrical outcomes. Anesthesiology. 2014;121:1158-1165.
8. Whiteman VE, Salemi JL, Mogos MF, et al. Maternal opioid drug use during pregnancy and its impact on perinatal morbidity, mortality, and the costs of medical care in the United States. J Pregnancy. 2014;2014:1-8
9. Pregnancy Mortality Surveillance System. www.cdc.gov/reproductivehealth/maternal-mortality/pregnancy-mortality-surveillance-system.htm#trends. Accessed February 4, 2020.
10. Macdorman MF, Declercq E, Cabral H, Morton C. Recent increases in the U.S. maternal mortality rate. Obstet Gynecol. 2016;128:447-455.
11. Texas Health and Human Services. Maternal Mortality and Morbidity Task Force and Department of State Health Services Joint Biennial Report, September 2018. www.dshs.texas.gov/legislative/2018-Reports/MMMTFJointReport2018.pdf
12. Virginia Department of Health. Pregnancy-associated deaths from drug overdose in Virginia, 1999-2007: a report from the Virginia Maternal Mortality Review Team. Richmond, VA: VDH; 2015. www.vdh.virginia.gov/content/uploads/sites/18/2016/04/Final-Pregnancy-Associated-Deaths-Due-to-Drug-Overdose.pdf. Accessed October 28, 2020.
13. Maryland Department of Health and Mental Hygiene. Maryland maternal mortality review 2016 annual report. Baltimore: DHMH; 2016. https://phpa.health.maryland.gov/Documents/Maryland-Maternal-Mortality-Review-2016-Report.pdf. Accessed October 28, 2020.
14. Desai RJ, Hernandez-Diaz S, Bateman BT, Huybrechts KF. Increase in prescription opioid use during pregnancy among Medicaid-enrolled women. Obstet Gynecol. 2014;123:997-1002.
15. Reddy UM, Davis JM, Ren Z, et al. Opioid use in pregnancy, neonatal abstinence syndrome, and childhood outcomes. Obstet Gynecol Survey. 2017;72:703-705.
16. Patrick SW, Davis MM, Lehmann CU, Cooper WO. Increasing incidence and geographic distribution of neonatal abstinence syndrome: United States 2009 to 2012. J Perinatol. 2015;35:650-655.
17. Center for Substance Abuse Treatment. Medication-assisted treatment for opioid addiction during pregnancy. In: Medication-assisted treatment for opioid addiction in opioid treatment programs. Treatment Improvement Protocol (TIP) Series, No. 43. Rockville, MD: Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration; 2005:211-224.
18. Wojnar-Horton RE, Kristensen JH, Yapp P, et al. Methadone distribution and excretion into breast milk of clients in a methadone maintenance programme. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 1997;44:543-547.
19. Reece-Stremtan S, Marinelli KA. ABM clinical protocol #21: guidelines for breastfeeding and substance use or substance use disorder, revised 2015. Breastfeed Med. 2015;10:135-141.
20. Sachs HC. The transfer of drugs and therapeutics into human breast milk: an update on selected topics. Committee on Drugs. Pediatrics. 2013;132:e796-809.
21. Bagley SM, Wachman EM, Holland E, Brogly SB. Review of the assessment and management of neonatal abstinence syndrome. Addict Sci Clin Pract. 2014;9:19.
22. Opioid use and opioid use disorder in pregnancy. Committee Opinion No. 711. Obstet Gynecol. 2017;130:488-489.
23. Gopman S. Prenatal and postpartum care of women with substance use disorders. Obstet Gynecol Clin North Am. 2014;41:213-228.
24. Mitchell M, Severtson S, Latimer W. Pregnancy and race/ethnicity as predictors of motivation for drug treatment. Am J Drug Alcohol Abuse. 2008;34:397-404.
1. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Opioid painkiller prescribing: where you live makes a difference. CDC website. www.cdc.gov/vitalsigns/opioid-prescribing. Accessed October 28, 2020.
2. Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration. Drug Abuse Warning Network, 2011: national estimates of drug-related emergency department visits. HHS Publication No. (SMA) 13-4760, DAWN Series D-39. Rockville (MD): SAMHSA; 2013. www.samhsa.gov/data/sites/default/files/DAWN2k11ED/DAWN2k11ED/DAWN2k11ED.pdf. Accessed October 28, 2020.
3. Compton WM, Jones CM, Baldwin GT. Relationship between nonmedical prescription-opioid use and heroin use. N Engl J Med. 2016;374:154-63.
4. National Center for Health Statistics. NCHS data on drug-poisoning deaths. NCHS Factsheet. https://www.cdc.gov/nchs/data/factsheets/factsheet-drug-poisoning-H.pdf. Accessed October 28, 2020.
5. National Institute on Drug Abuse. America’s addiction to opioids: heroin and prescription drug abuse. Bethesda (MD): NIDA; 2014. www.drugabuse.gov/about-nida/legislative-activities/testimony-to-congress/2016/americas-addiction-to-opioids-heroin-prescription-drug-abuse. Accessed October 28, 2020.
6. Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration (SAMHSA). Results from the 2010 National Survey on Drug Use and Health: Summary of National Findings. Rockville, MD: SAMHSA, 2011 Contract No.: HHS Publication no. (SMA) 11–4658.
7. Maeda A, Bateman BT, Clancy CR, et al. Opioid abuse and dependence during pregnancy: temporal trends and obstetrical outcomes. Anesthesiology. 2014;121:1158-1165.
8. Whiteman VE, Salemi JL, Mogos MF, et al. Maternal opioid drug use during pregnancy and its impact on perinatal morbidity, mortality, and the costs of medical care in the United States. J Pregnancy. 2014;2014:1-8
9. Pregnancy Mortality Surveillance System. www.cdc.gov/reproductivehealth/maternal-mortality/pregnancy-mortality-surveillance-system.htm#trends. Accessed February 4, 2020.
10. Macdorman MF, Declercq E, Cabral H, Morton C. Recent increases in the U.S. maternal mortality rate. Obstet Gynecol. 2016;128:447-455.
11. Texas Health and Human Services. Maternal Mortality and Morbidity Task Force and Department of State Health Services Joint Biennial Report, September 2018. www.dshs.texas.gov/legislative/2018-Reports/MMMTFJointReport2018.pdf
12. Virginia Department of Health. Pregnancy-associated deaths from drug overdose in Virginia, 1999-2007: a report from the Virginia Maternal Mortality Review Team. Richmond, VA: VDH; 2015. www.vdh.virginia.gov/content/uploads/sites/18/2016/04/Final-Pregnancy-Associated-Deaths-Due-to-Drug-Overdose.pdf. Accessed October 28, 2020.
13. Maryland Department of Health and Mental Hygiene. Maryland maternal mortality review 2016 annual report. Baltimore: DHMH; 2016. https://phpa.health.maryland.gov/Documents/Maryland-Maternal-Mortality-Review-2016-Report.pdf. Accessed October 28, 2020.
14. Desai RJ, Hernandez-Diaz S, Bateman BT, Huybrechts KF. Increase in prescription opioid use during pregnancy among Medicaid-enrolled women. Obstet Gynecol. 2014;123:997-1002.
15. Reddy UM, Davis JM, Ren Z, et al. Opioid use in pregnancy, neonatal abstinence syndrome, and childhood outcomes. Obstet Gynecol Survey. 2017;72:703-705.
16. Patrick SW, Davis MM, Lehmann CU, Cooper WO. Increasing incidence and geographic distribution of neonatal abstinence syndrome: United States 2009 to 2012. J Perinatol. 2015;35:650-655.
17. Center for Substance Abuse Treatment. Medication-assisted treatment for opioid addiction during pregnancy. In: Medication-assisted treatment for opioid addiction in opioid treatment programs. Treatment Improvement Protocol (TIP) Series, No. 43. Rockville, MD: Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration; 2005:211-224.
18. Wojnar-Horton RE, Kristensen JH, Yapp P, et al. Methadone distribution and excretion into breast milk of clients in a methadone maintenance programme. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 1997;44:543-547.
19. Reece-Stremtan S, Marinelli KA. ABM clinical protocol #21: guidelines for breastfeeding and substance use or substance use disorder, revised 2015. Breastfeed Med. 2015;10:135-141.
20. Sachs HC. The transfer of drugs and therapeutics into human breast milk: an update on selected topics. Committee on Drugs. Pediatrics. 2013;132:e796-809.
21. Bagley SM, Wachman EM, Holland E, Brogly SB. Review of the assessment and management of neonatal abstinence syndrome. Addict Sci Clin Pract. 2014;9:19.
22. Opioid use and opioid use disorder in pregnancy. Committee Opinion No. 711. Obstet Gynecol. 2017;130:488-489.
23. Gopman S. Prenatal and postpartum care of women with substance use disorders. Obstet Gynecol Clin North Am. 2014;41:213-228.
24. Mitchell M, Severtson S, Latimer W. Pregnancy and race/ethnicity as predictors of motivation for drug treatment. Am J Drug Alcohol Abuse. 2008;34:397-404.
‘Impressive’ results with neoadjuvant T-VEC in advanced melanoma
T-VEC is a modified virus that lyses tumor cells locally and induces a systemic immune response. In the phase 2 trial, neoadjuvant T-VEC plus surgery improved 3-year recurrence-free survival, when compared with immediate surgery, in patients with resectable melanoma.
“This is the first neoadjuvant trial for an approved oncolytic virus in melanoma and the largest randomized prospectively controlled neoadjuvant melanoma trial completed to date,” said investigator Reinhard Dummer, MD, of University Hospital Zürich.
The multicenter trial enrolled 150 patients with resectable stage IIIB–IV M1a melanoma (thereby including many with in-transit metastasis) who had at least one injectable lesion.
“This patient population is typically excluded from the trials that are published. Those trials typically focus on lymph node metastasis only,” Dr. Dummer noted.
The patients were randomized evenly to receive six doses over 12 weeks of intralesional T-VEC followed by surgical resection, or to the conventional approach of immediate surgical resection.
Survival results
The median follow-up for this interim analysis was 41.3 months.
The 3-year rate of recurrence-free survival, the trial’s primary endpoint, was 46.5% with T-VEC plus surgery and 31.0% with immediate surgery (hazard ratio, 0.67; P = .043). The median duration of recurrence-free survival was 27.5 months and 5.4 months, respectively.
These results were comparable with results seen at 2 years, which were published in Annals of Oncology in 2019. The 2-year rate of recurrence-free survival was 50.5% with T-VEC plus surgery and 31.0% with immediate surgery (HR, 0.66; P = .038).
“These patients appear to be in a plateau phase now,” Dr. Dummer remarked.
The 3-year rate of event-free survival, which excluded any events related to a delay of surgery, was 50.3% for T-VEC and 32.7% for immediate surgery (HR, 0.58, P = .015).
Findings for both outcomes were similar when analyses were repeated after removing events that occurred after receipt of therapy in the adjuvant or metastatic setting.
Finally, the 3-year rate of overall survival was 83.2% with T-VEC plus surgery and 71.6% with immediate surgery (HR, 0.54; P = .061). Respective 2-year values were 88.9% and 77.4% (HR, 0.49; P = .050).
In all, 50.7% of patients in the T-VEC group received subsequent anticancer therapy, compared with 76.8% in the immediate-surgery group. Respective values specifically for subsequent immunotherapy – usually immune checkpoint inhibitors – were 32.9% and 46.4%.
“I think this is a good argument that the effects we see on overall survival and recurrence-free survival are not caused by improved second-line treatments,” Dr. Dummer said.
No new safety signals emerged during the additional year of follow-up. The trial’s final analysis will be conducted after 5 years of follow-up.
“These results build upon the prior 2-year results to support the potential beneficial effect of neoadjuvant T-VEC on advanced resectable melanoma,” Dr. Dummer said.
“In general, if you compare this to the objective outcomes that we see with neoadjuvant ipilimumab-nivolumab, for example, the results do not look very attractive,” he acknowledged.
“However, we have to keep in mind that this is a difficult patient population,” he added, noting that many patients have in-transit metastases that would disqualify them from conventional neoadjuvant therapy. Also, cross-trial comparisons are complicated by the need to allow adjuvant therapy in patients who receive neoadjuvant therapy.
“I would say the combination of ipilimumab-nivolumab should be more powerful, but T-VEC has some impact, and from my understanding, T-VEC would be a perfect partner for a combination, for example, with an anti–[programmed death 1] agent,” Dr. Dummer concluded.
‘Impressive’ data support more research
“Neoadjuvant approaches are gaining enthusiasm for patients with locally advanced disease that may not be amenable to simple excision or may require large disfiguring procedures,” said Howard L. Kaufman, MD, of Massachusetts General Hospital and Dana Farber/Harvard Cancer Center, both in Boston, who was not involved in this study.
“A treatment option that could induce tumor regression while also promoting immune responses against the tumor is attractive,” Dr. Kaufman added.
“I continue to be impressed with this clinical trial as it demonstrates a consistent improvement in recurrence-free survival, event-free survival, and overall survival for patients treated with neoadjuvant T-VEC and surgery, compared to those who undergo surgery alone,” he said in an interview. “Confirmation that the responses are now maintained for another year is an important milestone.”
Given the study’s fairly small size, large treatment differences would be needed to attain the observed statistical significance, and “this is why the data at 3 years of follow-up is so impressive,” Dr. Kaufman said.
However, benefit of T-VEC’s activity in inducing a systemic immune response may not become fully evident until the end of the trial.
“Overall survival at 5 years is the most relevant endpoint,” Dr. Kaufman maintained.
An important aspect of the study is that it enrolled patients with a range of melanoma stages, including about 18% with stage IV M1a disease, he added.
“This could potentially influence the results, where earlier-stage patients may have a more durable response, compared to higher-stage patients and, thus, the data may be further diluted by the small sample size,” he proposed. “Given this possibility, my sense is that the data is even more impressive since there still appears to be a significant clinical benefit at 3 years, and I would recommend larger studies in patients with earlier-stage melanoma as fertile ground for further oncolytic virus drug development.”
The current trial was funded by Amgen. Dr. Dummer disclosed relationships with Amgen, Novartis, Merck Sharp & Dohme, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Roche, Takeda, Pierre Fabre, Sun Pharma, Sanofi, and CatalYm. Dr. Kaufman disclosed employment by Immuneering.
SOURCE: Dummer R et al. SITC 2020, Abstract 432.
T-VEC is a modified virus that lyses tumor cells locally and induces a systemic immune response. In the phase 2 trial, neoadjuvant T-VEC plus surgery improved 3-year recurrence-free survival, when compared with immediate surgery, in patients with resectable melanoma.
“This is the first neoadjuvant trial for an approved oncolytic virus in melanoma and the largest randomized prospectively controlled neoadjuvant melanoma trial completed to date,” said investigator Reinhard Dummer, MD, of University Hospital Zürich.
The multicenter trial enrolled 150 patients with resectable stage IIIB–IV M1a melanoma (thereby including many with in-transit metastasis) who had at least one injectable lesion.
“This patient population is typically excluded from the trials that are published. Those trials typically focus on lymph node metastasis only,” Dr. Dummer noted.
The patients were randomized evenly to receive six doses over 12 weeks of intralesional T-VEC followed by surgical resection, or to the conventional approach of immediate surgical resection.
Survival results
The median follow-up for this interim analysis was 41.3 months.
The 3-year rate of recurrence-free survival, the trial’s primary endpoint, was 46.5% with T-VEC plus surgery and 31.0% with immediate surgery (hazard ratio, 0.67; P = .043). The median duration of recurrence-free survival was 27.5 months and 5.4 months, respectively.
These results were comparable with results seen at 2 years, which were published in Annals of Oncology in 2019. The 2-year rate of recurrence-free survival was 50.5% with T-VEC plus surgery and 31.0% with immediate surgery (HR, 0.66; P = .038).
“These patients appear to be in a plateau phase now,” Dr. Dummer remarked.
The 3-year rate of event-free survival, which excluded any events related to a delay of surgery, was 50.3% for T-VEC and 32.7% for immediate surgery (HR, 0.58, P = .015).
Findings for both outcomes were similar when analyses were repeated after removing events that occurred after receipt of therapy in the adjuvant or metastatic setting.
Finally, the 3-year rate of overall survival was 83.2% with T-VEC plus surgery and 71.6% with immediate surgery (HR, 0.54; P = .061). Respective 2-year values were 88.9% and 77.4% (HR, 0.49; P = .050).
In all, 50.7% of patients in the T-VEC group received subsequent anticancer therapy, compared with 76.8% in the immediate-surgery group. Respective values specifically for subsequent immunotherapy – usually immune checkpoint inhibitors – were 32.9% and 46.4%.
“I think this is a good argument that the effects we see on overall survival and recurrence-free survival are not caused by improved second-line treatments,” Dr. Dummer said.
No new safety signals emerged during the additional year of follow-up. The trial’s final analysis will be conducted after 5 years of follow-up.
“These results build upon the prior 2-year results to support the potential beneficial effect of neoadjuvant T-VEC on advanced resectable melanoma,” Dr. Dummer said.
“In general, if you compare this to the objective outcomes that we see with neoadjuvant ipilimumab-nivolumab, for example, the results do not look very attractive,” he acknowledged.
“However, we have to keep in mind that this is a difficult patient population,” he added, noting that many patients have in-transit metastases that would disqualify them from conventional neoadjuvant therapy. Also, cross-trial comparisons are complicated by the need to allow adjuvant therapy in patients who receive neoadjuvant therapy.
“I would say the combination of ipilimumab-nivolumab should be more powerful, but T-VEC has some impact, and from my understanding, T-VEC would be a perfect partner for a combination, for example, with an anti–[programmed death 1] agent,” Dr. Dummer concluded.
‘Impressive’ data support more research
“Neoadjuvant approaches are gaining enthusiasm for patients with locally advanced disease that may not be amenable to simple excision or may require large disfiguring procedures,” said Howard L. Kaufman, MD, of Massachusetts General Hospital and Dana Farber/Harvard Cancer Center, both in Boston, who was not involved in this study.
“A treatment option that could induce tumor regression while also promoting immune responses against the tumor is attractive,” Dr. Kaufman added.
“I continue to be impressed with this clinical trial as it demonstrates a consistent improvement in recurrence-free survival, event-free survival, and overall survival for patients treated with neoadjuvant T-VEC and surgery, compared to those who undergo surgery alone,” he said in an interview. “Confirmation that the responses are now maintained for another year is an important milestone.”
Given the study’s fairly small size, large treatment differences would be needed to attain the observed statistical significance, and “this is why the data at 3 years of follow-up is so impressive,” Dr. Kaufman said.
However, benefit of T-VEC’s activity in inducing a systemic immune response may not become fully evident until the end of the trial.
“Overall survival at 5 years is the most relevant endpoint,” Dr. Kaufman maintained.
An important aspect of the study is that it enrolled patients with a range of melanoma stages, including about 18% with stage IV M1a disease, he added.
“This could potentially influence the results, where earlier-stage patients may have a more durable response, compared to higher-stage patients and, thus, the data may be further diluted by the small sample size,” he proposed. “Given this possibility, my sense is that the data is even more impressive since there still appears to be a significant clinical benefit at 3 years, and I would recommend larger studies in patients with earlier-stage melanoma as fertile ground for further oncolytic virus drug development.”
The current trial was funded by Amgen. Dr. Dummer disclosed relationships with Amgen, Novartis, Merck Sharp & Dohme, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Roche, Takeda, Pierre Fabre, Sun Pharma, Sanofi, and CatalYm. Dr. Kaufman disclosed employment by Immuneering.
SOURCE: Dummer R et al. SITC 2020, Abstract 432.
T-VEC is a modified virus that lyses tumor cells locally and induces a systemic immune response. In the phase 2 trial, neoadjuvant T-VEC plus surgery improved 3-year recurrence-free survival, when compared with immediate surgery, in patients with resectable melanoma.
“This is the first neoadjuvant trial for an approved oncolytic virus in melanoma and the largest randomized prospectively controlled neoadjuvant melanoma trial completed to date,” said investigator Reinhard Dummer, MD, of University Hospital Zürich.
The multicenter trial enrolled 150 patients with resectable stage IIIB–IV M1a melanoma (thereby including many with in-transit metastasis) who had at least one injectable lesion.
“This patient population is typically excluded from the trials that are published. Those trials typically focus on lymph node metastasis only,” Dr. Dummer noted.
The patients were randomized evenly to receive six doses over 12 weeks of intralesional T-VEC followed by surgical resection, or to the conventional approach of immediate surgical resection.
Survival results
The median follow-up for this interim analysis was 41.3 months.
The 3-year rate of recurrence-free survival, the trial’s primary endpoint, was 46.5% with T-VEC plus surgery and 31.0% with immediate surgery (hazard ratio, 0.67; P = .043). The median duration of recurrence-free survival was 27.5 months and 5.4 months, respectively.
These results were comparable with results seen at 2 years, which were published in Annals of Oncology in 2019. The 2-year rate of recurrence-free survival was 50.5% with T-VEC plus surgery and 31.0% with immediate surgery (HR, 0.66; P = .038).
“These patients appear to be in a plateau phase now,” Dr. Dummer remarked.
The 3-year rate of event-free survival, which excluded any events related to a delay of surgery, was 50.3% for T-VEC and 32.7% for immediate surgery (HR, 0.58, P = .015).
Findings for both outcomes were similar when analyses were repeated after removing events that occurred after receipt of therapy in the adjuvant or metastatic setting.
Finally, the 3-year rate of overall survival was 83.2% with T-VEC plus surgery and 71.6% with immediate surgery (HR, 0.54; P = .061). Respective 2-year values were 88.9% and 77.4% (HR, 0.49; P = .050).
In all, 50.7% of patients in the T-VEC group received subsequent anticancer therapy, compared with 76.8% in the immediate-surgery group. Respective values specifically for subsequent immunotherapy – usually immune checkpoint inhibitors – were 32.9% and 46.4%.
“I think this is a good argument that the effects we see on overall survival and recurrence-free survival are not caused by improved second-line treatments,” Dr. Dummer said.
No new safety signals emerged during the additional year of follow-up. The trial’s final analysis will be conducted after 5 years of follow-up.
“These results build upon the prior 2-year results to support the potential beneficial effect of neoadjuvant T-VEC on advanced resectable melanoma,” Dr. Dummer said.
“In general, if you compare this to the objective outcomes that we see with neoadjuvant ipilimumab-nivolumab, for example, the results do not look very attractive,” he acknowledged.
“However, we have to keep in mind that this is a difficult patient population,” he added, noting that many patients have in-transit metastases that would disqualify them from conventional neoadjuvant therapy. Also, cross-trial comparisons are complicated by the need to allow adjuvant therapy in patients who receive neoadjuvant therapy.
“I would say the combination of ipilimumab-nivolumab should be more powerful, but T-VEC has some impact, and from my understanding, T-VEC would be a perfect partner for a combination, for example, with an anti–[programmed death 1] agent,” Dr. Dummer concluded.
‘Impressive’ data support more research
“Neoadjuvant approaches are gaining enthusiasm for patients with locally advanced disease that may not be amenable to simple excision or may require large disfiguring procedures,” said Howard L. Kaufman, MD, of Massachusetts General Hospital and Dana Farber/Harvard Cancer Center, both in Boston, who was not involved in this study.
“A treatment option that could induce tumor regression while also promoting immune responses against the tumor is attractive,” Dr. Kaufman added.
“I continue to be impressed with this clinical trial as it demonstrates a consistent improvement in recurrence-free survival, event-free survival, and overall survival for patients treated with neoadjuvant T-VEC and surgery, compared to those who undergo surgery alone,” he said in an interview. “Confirmation that the responses are now maintained for another year is an important milestone.”
Given the study’s fairly small size, large treatment differences would be needed to attain the observed statistical significance, and “this is why the data at 3 years of follow-up is so impressive,” Dr. Kaufman said.
However, benefit of T-VEC’s activity in inducing a systemic immune response may not become fully evident until the end of the trial.
“Overall survival at 5 years is the most relevant endpoint,” Dr. Kaufman maintained.
An important aspect of the study is that it enrolled patients with a range of melanoma stages, including about 18% with stage IV M1a disease, he added.
“This could potentially influence the results, where earlier-stage patients may have a more durable response, compared to higher-stage patients and, thus, the data may be further diluted by the small sample size,” he proposed. “Given this possibility, my sense is that the data is even more impressive since there still appears to be a significant clinical benefit at 3 years, and I would recommend larger studies in patients with earlier-stage melanoma as fertile ground for further oncolytic virus drug development.”
The current trial was funded by Amgen. Dr. Dummer disclosed relationships with Amgen, Novartis, Merck Sharp & Dohme, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Roche, Takeda, Pierre Fabre, Sun Pharma, Sanofi, and CatalYm. Dr. Kaufman disclosed employment by Immuneering.
SOURCE: Dummer R et al. SITC 2020, Abstract 432.
FROM SITC 2020
SABCS 2020: What’s hot, including a major chemotherapy trial
That’s the word from Virginia Kaklamani, MD, from the University of Texas Health Sciences Center San Antonio. Dr. Kaklamani, a professor of medicine in the division of hematology/oncology, is codirector of the meeting that runs online Dec. 8-11.
If the new trial sounds familiar, that’s because it’s a lot like the TAILORx trial, the results of which were first presented in 2018 and have changed practice in women with early-stage disease and no lymph node involvement.
“This is the lymph-node positive TAILORx. It’s extremely important,” Dr. Kaklamani said in an interview, adding that both trials involved women with hormone receptor (HR)–positive, HER2-negative disease.
If the RxPONDER trial shows similar outcomes between women randomized to adjuvant endocrine therapy alone versus endocrine therapy plus chemotherapy, then clinicians “can potentially avoid giving chemotherapy to a large number of women who are currently receiving it,” she explained.
Because women with nodal involvement (one to three positive axillary nodes) are at a higher risk of recurrence, RxPONDER may provide needed insight on the management of these types of breast cancers, Dr. Kaklamani suggested.
Both trials have used the 21-tumor gene expression assay (Oncotype Dx) to determine recurrence-risk status.
Dr. Kaklamani also spotlighted the phase 3 CONTESSA trial (abstract GS4-01) in 600+ patients with locally advanced or metastatic breast cancer that is HR positive and HER2 negative and has been previously treated with a taxane.
The trial features an experimental oral taxane, tesetaxel. The primary objective is to compare the efficacy of tesetaxel plus a reduced dose of capecitabine (Xeloda) versus the approved dose of capecitabine alone. Presented data will include progression-free survival results, indicating about a 3-month PFS advantage with tesetaxel, which is taken once every 3 weeks.
“Oral drugs are convenient for patients and, despite limitations, they are, all in all, a revolution in cancer treatment,” noted Dr. Kaklamani, adding that they beneficially eliminate the need for time-consuming infusions and related clinic visits as well as drug ports.
It will be interesting to see what Steven Vogl, MD, a private practitioner in New Yorky, has to say about CONTESSA and the rest of the SABCS.
He is usually a commentator from the meeting floor, whose self-introduction, “Vogl, New York,” is well known to perennial meeting attendees, according to a profile piece published some years ago.
This year the medical oncologist will also serve as the chair of the “View from the Trenches” session, which is devoted to summarizing the meeting’s most important findings for everyday practitioners.
A number of years ago, Dr. Vogl proposed the idea of this where-the-rubber-meets-the-road session to SABCS meeting planners, which they then adopted. This year, Dr. Kaklamani invited Dr. Vogl to run the session and he accepted.
Dr. Vogl is a “really smart guy who is always right on” with his comments and questions, and he will be the first-ever independent, community-based oncologist to chair a meeting session, said Dr. Kaklamani.
Other hot topics
Another hot topic featured at the meeting will be the use of CDK4/6 inhibitors in the adjuvant treatment of HR-positive and HER2-negative disease that has a high risk of recurrence, Dr. Kaklamani said. New data from two trials, monarchE and PENELOPE-B, will be presented.
First, there will be an update from the monarchE trial (abstract GS1-01). The first results from this trial were reported in September at the European Society for Medical Oncology Virtual Congress 2020. They showed that adding abemaciclib (Verzenio) to endocrine therapy reduced the risk of early recurrence. The positive outcome represented the first treatment improvement in this high-risk setting in more than 20 years, according to experts.
A similar trial, PENELOPE-B (abstract GS1-02), looks at palbociclib (Ibrance) in a somewhat different population – those patients with high relapse risk after neoadjuvant chemotherapy. “These are even higher risk ER+ patients [than those in monarchE], which is why they received chemotherapy before surgery,” commented Dr. Kaklamani.
In triple-negative disease, there will be overall survival (OS) results from the phase 3 KEYNOTE-355 study (abstract GS3-01) of pembrolizumab (Keytruda) versus placebo (plus chemotherapy for all patients) as first-line therapy for locally recurrent inoperable or metastatic triple-negative breast cancer. “It’s potentially a huge deal,” said Dr. Kaklamani about the OS data, if they are statistically significant.
A meta-analysis (abstract GS4-08) of data on circulating tumor cells (CTCs), which are shed from the primary tumor into the bloodstream, may point to their value as a tool to determine whether or not a breast cancer treatment is effective. “CTCs allow you to assess how a treatment is doing before you do scans, which typically occur 3 months or so later,” explained Dr. Kaklamani.
CTC results can be assessed in 3-4 weeks and allow clinicians to change treatments if CTC volume increases. However, a previous study of CTCs did not show a clinical benefit with the tool among patients treated mainly with chemotherapies. What’s different about the new study, which is from an international group of investigators, is in the treatments patients with metastatic breast cancer received. “This study is from a different era – with targeted therapies,” said Dr. Kaklamani.
In the new study, changes in CTC levels (with a reduction being a good result) between baseline (pretreatment) and follow-up were analyzed to determine whether they were associated with overall survival.
COVID sessions
On the meeting’s first day, SABCS will feature a special session on COVID-19 and breast cancer. The meeting organizers sought to separate the wheat from the chaff in this subject, as much has already been written, published, or presented.
“We received a lot of abstracts on COVID that were studies that were poorly done. We tried to tease through them and select the well-researched ones,” acknowledged Dr. Kaklamani.
The organizers included two patient advocates who have had COVID-19, including during treatment for breast cancer, as participants in the meeting session. The session will also feature global perspectives, with presenters from Brazil, Italy, and the Netherlands.
Plenary lectures
The meeting’s two plenary lectures will focus, respectively, on the increasingly used clinical approach of neoadjuvant therapy in breast cancer, and research in the time of a pandemic.
Elizabeth Mittendorf, MD, PhD, a surgical oncologist and director of the Breast lmmuno-Oncology program and co-director of the Breast Cancer Clinical Research Program at the Dana-Farber/Brigham and Women’s Cancer Center, Boston, will present “Local regional management following neoadjuvant therapy: Minding the knowledge gaps.”
Ned Sharpless, MD, director of the National Cancer Institute, will present “Advancing cancer research during challenging times.”
Dr. Kaklamani disclosed recieving consulting fees with Amgen, Eisai, Puma, Celldex, AstraZeneca, and Athenex; receiving fees for non-CME services received directly from commercial interest or their agents from Pfizer, Celgene, Genentech, Genomic Health, Puma, Eisai, and Novartis; and contracted research with Eisai.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
That’s the word from Virginia Kaklamani, MD, from the University of Texas Health Sciences Center San Antonio. Dr. Kaklamani, a professor of medicine in the division of hematology/oncology, is codirector of the meeting that runs online Dec. 8-11.
If the new trial sounds familiar, that’s because it’s a lot like the TAILORx trial, the results of which were first presented in 2018 and have changed practice in women with early-stage disease and no lymph node involvement.
“This is the lymph-node positive TAILORx. It’s extremely important,” Dr. Kaklamani said in an interview, adding that both trials involved women with hormone receptor (HR)–positive, HER2-negative disease.
If the RxPONDER trial shows similar outcomes between women randomized to adjuvant endocrine therapy alone versus endocrine therapy plus chemotherapy, then clinicians “can potentially avoid giving chemotherapy to a large number of women who are currently receiving it,” she explained.
Because women with nodal involvement (one to three positive axillary nodes) are at a higher risk of recurrence, RxPONDER may provide needed insight on the management of these types of breast cancers, Dr. Kaklamani suggested.
Both trials have used the 21-tumor gene expression assay (Oncotype Dx) to determine recurrence-risk status.
Dr. Kaklamani also spotlighted the phase 3 CONTESSA trial (abstract GS4-01) in 600+ patients with locally advanced or metastatic breast cancer that is HR positive and HER2 negative and has been previously treated with a taxane.
The trial features an experimental oral taxane, tesetaxel. The primary objective is to compare the efficacy of tesetaxel plus a reduced dose of capecitabine (Xeloda) versus the approved dose of capecitabine alone. Presented data will include progression-free survival results, indicating about a 3-month PFS advantage with tesetaxel, which is taken once every 3 weeks.
“Oral drugs are convenient for patients and, despite limitations, they are, all in all, a revolution in cancer treatment,” noted Dr. Kaklamani, adding that they beneficially eliminate the need for time-consuming infusions and related clinic visits as well as drug ports.
It will be interesting to see what Steven Vogl, MD, a private practitioner in New Yorky, has to say about CONTESSA and the rest of the SABCS.
He is usually a commentator from the meeting floor, whose self-introduction, “Vogl, New York,” is well known to perennial meeting attendees, according to a profile piece published some years ago.
This year the medical oncologist will also serve as the chair of the “View from the Trenches” session, which is devoted to summarizing the meeting’s most important findings for everyday practitioners.
A number of years ago, Dr. Vogl proposed the idea of this where-the-rubber-meets-the-road session to SABCS meeting planners, which they then adopted. This year, Dr. Kaklamani invited Dr. Vogl to run the session and he accepted.
Dr. Vogl is a “really smart guy who is always right on” with his comments and questions, and he will be the first-ever independent, community-based oncologist to chair a meeting session, said Dr. Kaklamani.
Other hot topics
Another hot topic featured at the meeting will be the use of CDK4/6 inhibitors in the adjuvant treatment of HR-positive and HER2-negative disease that has a high risk of recurrence, Dr. Kaklamani said. New data from two trials, monarchE and PENELOPE-B, will be presented.
First, there will be an update from the monarchE trial (abstract GS1-01). The first results from this trial were reported in September at the European Society for Medical Oncology Virtual Congress 2020. They showed that adding abemaciclib (Verzenio) to endocrine therapy reduced the risk of early recurrence. The positive outcome represented the first treatment improvement in this high-risk setting in more than 20 years, according to experts.
A similar trial, PENELOPE-B (abstract GS1-02), looks at palbociclib (Ibrance) in a somewhat different population – those patients with high relapse risk after neoadjuvant chemotherapy. “These are even higher risk ER+ patients [than those in monarchE], which is why they received chemotherapy before surgery,” commented Dr. Kaklamani.
In triple-negative disease, there will be overall survival (OS) results from the phase 3 KEYNOTE-355 study (abstract GS3-01) of pembrolizumab (Keytruda) versus placebo (plus chemotherapy for all patients) as first-line therapy for locally recurrent inoperable or metastatic triple-negative breast cancer. “It’s potentially a huge deal,” said Dr. Kaklamani about the OS data, if they are statistically significant.
A meta-analysis (abstract GS4-08) of data on circulating tumor cells (CTCs), which are shed from the primary tumor into the bloodstream, may point to their value as a tool to determine whether or not a breast cancer treatment is effective. “CTCs allow you to assess how a treatment is doing before you do scans, which typically occur 3 months or so later,” explained Dr. Kaklamani.
CTC results can be assessed in 3-4 weeks and allow clinicians to change treatments if CTC volume increases. However, a previous study of CTCs did not show a clinical benefit with the tool among patients treated mainly with chemotherapies. What’s different about the new study, which is from an international group of investigators, is in the treatments patients with metastatic breast cancer received. “This study is from a different era – with targeted therapies,” said Dr. Kaklamani.
In the new study, changes in CTC levels (with a reduction being a good result) between baseline (pretreatment) and follow-up were analyzed to determine whether they were associated with overall survival.
COVID sessions
On the meeting’s first day, SABCS will feature a special session on COVID-19 and breast cancer. The meeting organizers sought to separate the wheat from the chaff in this subject, as much has already been written, published, or presented.
“We received a lot of abstracts on COVID that were studies that were poorly done. We tried to tease through them and select the well-researched ones,” acknowledged Dr. Kaklamani.
The organizers included two patient advocates who have had COVID-19, including during treatment for breast cancer, as participants in the meeting session. The session will also feature global perspectives, with presenters from Brazil, Italy, and the Netherlands.
Plenary lectures
The meeting’s two plenary lectures will focus, respectively, on the increasingly used clinical approach of neoadjuvant therapy in breast cancer, and research in the time of a pandemic.
Elizabeth Mittendorf, MD, PhD, a surgical oncologist and director of the Breast lmmuno-Oncology program and co-director of the Breast Cancer Clinical Research Program at the Dana-Farber/Brigham and Women’s Cancer Center, Boston, will present “Local regional management following neoadjuvant therapy: Minding the knowledge gaps.”
Ned Sharpless, MD, director of the National Cancer Institute, will present “Advancing cancer research during challenging times.”
Dr. Kaklamani disclosed recieving consulting fees with Amgen, Eisai, Puma, Celldex, AstraZeneca, and Athenex; receiving fees for non-CME services received directly from commercial interest or their agents from Pfizer, Celgene, Genentech, Genomic Health, Puma, Eisai, and Novartis; and contracted research with Eisai.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
That’s the word from Virginia Kaklamani, MD, from the University of Texas Health Sciences Center San Antonio. Dr. Kaklamani, a professor of medicine in the division of hematology/oncology, is codirector of the meeting that runs online Dec. 8-11.
If the new trial sounds familiar, that’s because it’s a lot like the TAILORx trial, the results of which were first presented in 2018 and have changed practice in women with early-stage disease and no lymph node involvement.
“This is the lymph-node positive TAILORx. It’s extremely important,” Dr. Kaklamani said in an interview, adding that both trials involved women with hormone receptor (HR)–positive, HER2-negative disease.
If the RxPONDER trial shows similar outcomes between women randomized to adjuvant endocrine therapy alone versus endocrine therapy plus chemotherapy, then clinicians “can potentially avoid giving chemotherapy to a large number of women who are currently receiving it,” she explained.
Because women with nodal involvement (one to three positive axillary nodes) are at a higher risk of recurrence, RxPONDER may provide needed insight on the management of these types of breast cancers, Dr. Kaklamani suggested.
Both trials have used the 21-tumor gene expression assay (Oncotype Dx) to determine recurrence-risk status.
Dr. Kaklamani also spotlighted the phase 3 CONTESSA trial (abstract GS4-01) in 600+ patients with locally advanced or metastatic breast cancer that is HR positive and HER2 negative and has been previously treated with a taxane.
The trial features an experimental oral taxane, tesetaxel. The primary objective is to compare the efficacy of tesetaxel plus a reduced dose of capecitabine (Xeloda) versus the approved dose of capecitabine alone. Presented data will include progression-free survival results, indicating about a 3-month PFS advantage with tesetaxel, which is taken once every 3 weeks.
“Oral drugs are convenient for patients and, despite limitations, they are, all in all, a revolution in cancer treatment,” noted Dr. Kaklamani, adding that they beneficially eliminate the need for time-consuming infusions and related clinic visits as well as drug ports.
It will be interesting to see what Steven Vogl, MD, a private practitioner in New Yorky, has to say about CONTESSA and the rest of the SABCS.
He is usually a commentator from the meeting floor, whose self-introduction, “Vogl, New York,” is well known to perennial meeting attendees, according to a profile piece published some years ago.
This year the medical oncologist will also serve as the chair of the “View from the Trenches” session, which is devoted to summarizing the meeting’s most important findings for everyday practitioners.
A number of years ago, Dr. Vogl proposed the idea of this where-the-rubber-meets-the-road session to SABCS meeting planners, which they then adopted. This year, Dr. Kaklamani invited Dr. Vogl to run the session and he accepted.
Dr. Vogl is a “really smart guy who is always right on” with his comments and questions, and he will be the first-ever independent, community-based oncologist to chair a meeting session, said Dr. Kaklamani.
Other hot topics
Another hot topic featured at the meeting will be the use of CDK4/6 inhibitors in the adjuvant treatment of HR-positive and HER2-negative disease that has a high risk of recurrence, Dr. Kaklamani said. New data from two trials, monarchE and PENELOPE-B, will be presented.
First, there will be an update from the monarchE trial (abstract GS1-01). The first results from this trial were reported in September at the European Society for Medical Oncology Virtual Congress 2020. They showed that adding abemaciclib (Verzenio) to endocrine therapy reduced the risk of early recurrence. The positive outcome represented the first treatment improvement in this high-risk setting in more than 20 years, according to experts.
A similar trial, PENELOPE-B (abstract GS1-02), looks at palbociclib (Ibrance) in a somewhat different population – those patients with high relapse risk after neoadjuvant chemotherapy. “These are even higher risk ER+ patients [than those in monarchE], which is why they received chemotherapy before surgery,” commented Dr. Kaklamani.
In triple-negative disease, there will be overall survival (OS) results from the phase 3 KEYNOTE-355 study (abstract GS3-01) of pembrolizumab (Keytruda) versus placebo (plus chemotherapy for all patients) as first-line therapy for locally recurrent inoperable or metastatic triple-negative breast cancer. “It’s potentially a huge deal,” said Dr. Kaklamani about the OS data, if they are statistically significant.
A meta-analysis (abstract GS4-08) of data on circulating tumor cells (CTCs), which are shed from the primary tumor into the bloodstream, may point to their value as a tool to determine whether or not a breast cancer treatment is effective. “CTCs allow you to assess how a treatment is doing before you do scans, which typically occur 3 months or so later,” explained Dr. Kaklamani.
CTC results can be assessed in 3-4 weeks and allow clinicians to change treatments if CTC volume increases. However, a previous study of CTCs did not show a clinical benefit with the tool among patients treated mainly with chemotherapies. What’s different about the new study, which is from an international group of investigators, is in the treatments patients with metastatic breast cancer received. “This study is from a different era – with targeted therapies,” said Dr. Kaklamani.
In the new study, changes in CTC levels (with a reduction being a good result) between baseline (pretreatment) and follow-up were analyzed to determine whether they were associated with overall survival.
COVID sessions
On the meeting’s first day, SABCS will feature a special session on COVID-19 and breast cancer. The meeting organizers sought to separate the wheat from the chaff in this subject, as much has already been written, published, or presented.
“We received a lot of abstracts on COVID that were studies that were poorly done. We tried to tease through them and select the well-researched ones,” acknowledged Dr. Kaklamani.
The organizers included two patient advocates who have had COVID-19, including during treatment for breast cancer, as participants in the meeting session. The session will also feature global perspectives, with presenters from Brazil, Italy, and the Netherlands.
Plenary lectures
The meeting’s two plenary lectures will focus, respectively, on the increasingly used clinical approach of neoadjuvant therapy in breast cancer, and research in the time of a pandemic.
Elizabeth Mittendorf, MD, PhD, a surgical oncologist and director of the Breast lmmuno-Oncology program and co-director of the Breast Cancer Clinical Research Program at the Dana-Farber/Brigham and Women’s Cancer Center, Boston, will present “Local regional management following neoadjuvant therapy: Minding the knowledge gaps.”
Ned Sharpless, MD, director of the National Cancer Institute, will present “Advancing cancer research during challenging times.”
Dr. Kaklamani disclosed recieving consulting fees with Amgen, Eisai, Puma, Celldex, AstraZeneca, and Athenex; receiving fees for non-CME services received directly from commercial interest or their agents from Pfizer, Celgene, Genentech, Genomic Health, Puma, Eisai, and Novartis; and contracted research with Eisai.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM SABCS 2020
Impostor syndrome: Implications for medical professionals
A few years ago, I was asked to give a talk on impostor syndrome at a national conference. My initial thought was “I am not even remotely qualified to give this talk.” Upon reflection, I think that was the first time I acknowledged that I, too, suffer from this syndrome.
There are many definitions and designations (e.g., impostor phenomenon or fraud syndrome), but the one I use most often is high-achieving individuals who are marked by an inability to internalize their accomplishments and a persistent fear of being exposed as a fraud. They live in fear that their incompetence will be exposed and they will be revealed as a fraud both intellectually and within their job or role. First described by Clance and Imes in 1978,1 the original authors observed that many highly respected and accomplished women did not experience an internal sense of success despite their education and evidence of academic achievement. Based in part on previous observations regarding the differential attribution of success in men and women,2 the authors suggested that two general principles were found to be at the heart of this syndrome. The first was that an unexpected performance outcome will be attributed to a temporary cause. The second was that an expected performance outcome will be attributed to a stable cause. As such, the authors originally suggested that women tended to explain failure with lack of ability, whereas men attributed failure to luck or task difficulty. Furthermore, the authors emphasized environmental factors – such as mentorship, competition, and isolation – as the primary influence in the development of these tendencies.
Although originally described in women, this phenomenon can also affect men, as well as a wide variety of people from different occupations and cultures.3-6 Furthermore, although environmental factors were originally linked as the primary driver of these tendencies, further research has suggested that personality factors play a larger role, and that up to 70% of people may experience this phenomenon in their lifetime.7 Personality traits such as perfectionism and neuroticism may be linked to the development of this phenomenon.3,8
There are several online screening questionnaires that can be used to gauge whether individuals experience some or most of these traits. On one such questionnaire, the Clance IP Scale,9 poses such questions as: “I have often succeeded on a test or task even though I was afraid that I would not do well before I undertook the task” and “I am afraid people important to me may find out that I am not as capable as they think I am.” There are 20 questions scored from 1 to 5 and a score of 40 or below suggests few impostor tendencies, while a score of 80 or above suggests the respondent often has intense IP experiences. The higher the score, the more frequently and seriously the impostor syndrome interferes in a person’s life. What is unclear is whether this worsens, improves, or stays the same throughout one’s career. Of interest is that my personal score at this time is 43; however, it would have been 89 had I taken the test during college and medical school. What is unclear to me from the literature is what factors may play a role in a person’s perception of their abilities and their personal confidence over time.
Why is this important? Given that we are all professionals, impostor tendencies appear to have significant impact in the context of our work. This may have impact on us both as employers and as employees.10 Individuals with impostor syndrome tendencies often characterize themselves negatively and perform poorly on self-appraisals.11 In a study of 201 Belgian white-collar workers, Vergauwe and colleagues found that impostor syndrome tendencies were negatively related to job satisfaction and organizational citizenship behavior; both of which could be influenced by a high degree of social support.10 Individuals with impostor syndrome tendencies do less career planning, explore career options less frequently, and are less inclined to lead.12,13 These tendencies can be detrimental as the most qualified people for a position or opportunity may not step forward for consideration. Employers may tend to overlook these individuals for promotions or for pay raises which could negatively influence future earnings. Furthermore, a person may experience increased burnout as they continuously try to overcompensate for what they perceive as their shortcomings. They may feel concerned they are letting others down or not performing to standards. They may derive less enjoyment from life because of the constant focus on feelings of inadequacy.14 Research along these lines suggest impostor syndrome tendencies can have adverse personal and health-related consequences and may increase social anxiety, depression, and overall psychological distress.15,16
What can we do about it? In a very interesting study by Zanchetta and colleagues, the authors studied 103 young employees and randomized them to receive coaching, training, or no intervention.17 Their findings showed that coaching was an effective mindset intervention which resulted in reduced impostor syndrome scores. Furthermore, fear of negative evaluation and the effect of coaching appeared to be significantly associated with a reduction in the impostor syndrome scores. Coaching appeared to improve self-enhancing attributions and self-efficacy with a reduction in the tendency of subjects to fear negative evaluation. The authors concluded that fostering a mindset shift by reducing the fear of negative evaluations through coaching demonstrated measurable and sustained improvements in overall impostor syndrome scores for participants.17
What do I suggest? It is clear this affects a significant percentage of physicians, health care professionals, and professionals in general. Harboring these tendencies can have a negative impact on health, professional achievement, income, and happiness. It is important to self-reflect, identify if you are at risk, and if so, take the opportunity to explore solutions. My recommendations are:
- Name it: Take the test and see how you score.
- Be mindful: Self-reflection will help you identify the behaviors that are interfering with your happiness and success.
- Write it down: Be strategic and document your plan for success to reinforce your accomplishments.
- Create a feedback group: Friends and colleagues can help to mitigate the negative effects of impostor syndrome tendencies.
- Speak up: Ask for help; coaching has been documented to reduce impostor syndrome scores and help lessen the burden of these tendencies.
- Step out of your comfort zone: Develop a mantra, break bigger challenges into smaller pieces, and acknowledge little wins along the way.
In conclusion, impostor syndrome appears to be highly prevalent in professionals including those of us in medicine. The experience can adversely affect our careers and ability to secure key leadership positions. As managers, we also must keep in mind our role in mentoring others and recognizing the potential impact of impostor syndrome on those who report to us. Recognition of this phenomenon – and understanding of the effects on oneself – is the first step in overcoming the negative effects and moving toward realization of one’s potential.
Dr. Brown is a professor of medicine at Wayne State University, division chief of gastroenterology and hepatology at Henry Ford Hospital, and associate medical director at the Henry Ford Hospital Transplant Institute, all in Detroit.
References
1. Clance PR, Imes S. Psychother Theory Res Pract. 1978 Fall;15(3):1-7.
2. Deaux D. In J.H.Harvey, W.J.Ickes and R.F. Kidd (Eds). New directions in attribution research. Vol. 1. New York: Halsted Press Division, Wiley. 1976; p 335-42.
3. Bernard NS et al. J Pers Assess. 2002;78(2):321-33.
4. Topping ME et al. Acad Psychol Bull. 1985;(7):213-26.
5. Langford J et al. Psychotherapy. 1993;30(3):495-501.
6. Chae JH et al. J Pers Assess. 1995;65(3):468-85.
7. Harvey JC et al. If I’m successful, why do I feel like a fake? New York: Random House, 1985.
8. Ross SR et al. Pers Individ Diff. 2001;31:1347-55.
9. Clance PR. The impostor phenomenon: When success makes you feel like a fake. Toronto: Bantam Books, 1985; p 20-2.
10. Vergauwe J et al. J Bus Psychol. 2015;30:565-81.
11. Leary MR et al. J Pers. 2000;68(4):725-56.
12. Neureiter M et al. Front Psychol. 2016;7:48.
13. Neureiter M et al. J Vocat Behav. 2017;98:56-69.
14. Duhigg C. The power of habit: Why we do what we do in life and business. New York: Random House, 2012.
15. Henning K et al. Med Educ. 1998 Sep;32(5):456-64.
16. Oriel K et al. Fam Med. 2004 Apr;36(4):248-52.
17. Zanchetta M et al. Front Psychol. 2020 May 15;11:405.
A few years ago, I was asked to give a talk on impostor syndrome at a national conference. My initial thought was “I am not even remotely qualified to give this talk.” Upon reflection, I think that was the first time I acknowledged that I, too, suffer from this syndrome.
There are many definitions and designations (e.g., impostor phenomenon or fraud syndrome), but the one I use most often is high-achieving individuals who are marked by an inability to internalize their accomplishments and a persistent fear of being exposed as a fraud. They live in fear that their incompetence will be exposed and they will be revealed as a fraud both intellectually and within their job or role. First described by Clance and Imes in 1978,1 the original authors observed that many highly respected and accomplished women did not experience an internal sense of success despite their education and evidence of academic achievement. Based in part on previous observations regarding the differential attribution of success in men and women,2 the authors suggested that two general principles were found to be at the heart of this syndrome. The first was that an unexpected performance outcome will be attributed to a temporary cause. The second was that an expected performance outcome will be attributed to a stable cause. As such, the authors originally suggested that women tended to explain failure with lack of ability, whereas men attributed failure to luck or task difficulty. Furthermore, the authors emphasized environmental factors – such as mentorship, competition, and isolation – as the primary influence in the development of these tendencies.
Although originally described in women, this phenomenon can also affect men, as well as a wide variety of people from different occupations and cultures.3-6 Furthermore, although environmental factors were originally linked as the primary driver of these tendencies, further research has suggested that personality factors play a larger role, and that up to 70% of people may experience this phenomenon in their lifetime.7 Personality traits such as perfectionism and neuroticism may be linked to the development of this phenomenon.3,8
There are several online screening questionnaires that can be used to gauge whether individuals experience some or most of these traits. On one such questionnaire, the Clance IP Scale,9 poses such questions as: “I have often succeeded on a test or task even though I was afraid that I would not do well before I undertook the task” and “I am afraid people important to me may find out that I am not as capable as they think I am.” There are 20 questions scored from 1 to 5 and a score of 40 or below suggests few impostor tendencies, while a score of 80 or above suggests the respondent often has intense IP experiences. The higher the score, the more frequently and seriously the impostor syndrome interferes in a person’s life. What is unclear is whether this worsens, improves, or stays the same throughout one’s career. Of interest is that my personal score at this time is 43; however, it would have been 89 had I taken the test during college and medical school. What is unclear to me from the literature is what factors may play a role in a person’s perception of their abilities and their personal confidence over time.
Why is this important? Given that we are all professionals, impostor tendencies appear to have significant impact in the context of our work. This may have impact on us both as employers and as employees.10 Individuals with impostor syndrome tendencies often characterize themselves negatively and perform poorly on self-appraisals.11 In a study of 201 Belgian white-collar workers, Vergauwe and colleagues found that impostor syndrome tendencies were negatively related to job satisfaction and organizational citizenship behavior; both of which could be influenced by a high degree of social support.10 Individuals with impostor syndrome tendencies do less career planning, explore career options less frequently, and are less inclined to lead.12,13 These tendencies can be detrimental as the most qualified people for a position or opportunity may not step forward for consideration. Employers may tend to overlook these individuals for promotions or for pay raises which could negatively influence future earnings. Furthermore, a person may experience increased burnout as they continuously try to overcompensate for what they perceive as their shortcomings. They may feel concerned they are letting others down or not performing to standards. They may derive less enjoyment from life because of the constant focus on feelings of inadequacy.14 Research along these lines suggest impostor syndrome tendencies can have adverse personal and health-related consequences and may increase social anxiety, depression, and overall psychological distress.15,16
What can we do about it? In a very interesting study by Zanchetta and colleagues, the authors studied 103 young employees and randomized them to receive coaching, training, or no intervention.17 Their findings showed that coaching was an effective mindset intervention which resulted in reduced impostor syndrome scores. Furthermore, fear of negative evaluation and the effect of coaching appeared to be significantly associated with a reduction in the impostor syndrome scores. Coaching appeared to improve self-enhancing attributions and self-efficacy with a reduction in the tendency of subjects to fear negative evaluation. The authors concluded that fostering a mindset shift by reducing the fear of negative evaluations through coaching demonstrated measurable and sustained improvements in overall impostor syndrome scores for participants.17
What do I suggest? It is clear this affects a significant percentage of physicians, health care professionals, and professionals in general. Harboring these tendencies can have a negative impact on health, professional achievement, income, and happiness. It is important to self-reflect, identify if you are at risk, and if so, take the opportunity to explore solutions. My recommendations are:
- Name it: Take the test and see how you score.
- Be mindful: Self-reflection will help you identify the behaviors that are interfering with your happiness and success.
- Write it down: Be strategic and document your plan for success to reinforce your accomplishments.
- Create a feedback group: Friends and colleagues can help to mitigate the negative effects of impostor syndrome tendencies.
- Speak up: Ask for help; coaching has been documented to reduce impostor syndrome scores and help lessen the burden of these tendencies.
- Step out of your comfort zone: Develop a mantra, break bigger challenges into smaller pieces, and acknowledge little wins along the way.
In conclusion, impostor syndrome appears to be highly prevalent in professionals including those of us in medicine. The experience can adversely affect our careers and ability to secure key leadership positions. As managers, we also must keep in mind our role in mentoring others and recognizing the potential impact of impostor syndrome on those who report to us. Recognition of this phenomenon – and understanding of the effects on oneself – is the first step in overcoming the negative effects and moving toward realization of one’s potential.
Dr. Brown is a professor of medicine at Wayne State University, division chief of gastroenterology and hepatology at Henry Ford Hospital, and associate medical director at the Henry Ford Hospital Transplant Institute, all in Detroit.
References
1. Clance PR, Imes S. Psychother Theory Res Pract. 1978 Fall;15(3):1-7.
2. Deaux D. In J.H.Harvey, W.J.Ickes and R.F. Kidd (Eds). New directions in attribution research. Vol. 1. New York: Halsted Press Division, Wiley. 1976; p 335-42.
3. Bernard NS et al. J Pers Assess. 2002;78(2):321-33.
4. Topping ME et al. Acad Psychol Bull. 1985;(7):213-26.
5. Langford J et al. Psychotherapy. 1993;30(3):495-501.
6. Chae JH et al. J Pers Assess. 1995;65(3):468-85.
7. Harvey JC et al. If I’m successful, why do I feel like a fake? New York: Random House, 1985.
8. Ross SR et al. Pers Individ Diff. 2001;31:1347-55.
9. Clance PR. The impostor phenomenon: When success makes you feel like a fake. Toronto: Bantam Books, 1985; p 20-2.
10. Vergauwe J et al. J Bus Psychol. 2015;30:565-81.
11. Leary MR et al. J Pers. 2000;68(4):725-56.
12. Neureiter M et al. Front Psychol. 2016;7:48.
13. Neureiter M et al. J Vocat Behav. 2017;98:56-69.
14. Duhigg C. The power of habit: Why we do what we do in life and business. New York: Random House, 2012.
15. Henning K et al. Med Educ. 1998 Sep;32(5):456-64.
16. Oriel K et al. Fam Med. 2004 Apr;36(4):248-52.
17. Zanchetta M et al. Front Psychol. 2020 May 15;11:405.
A few years ago, I was asked to give a talk on impostor syndrome at a national conference. My initial thought was “I am not even remotely qualified to give this talk.” Upon reflection, I think that was the first time I acknowledged that I, too, suffer from this syndrome.
There are many definitions and designations (e.g., impostor phenomenon or fraud syndrome), but the one I use most often is high-achieving individuals who are marked by an inability to internalize their accomplishments and a persistent fear of being exposed as a fraud. They live in fear that their incompetence will be exposed and they will be revealed as a fraud both intellectually and within their job or role. First described by Clance and Imes in 1978,1 the original authors observed that many highly respected and accomplished women did not experience an internal sense of success despite their education and evidence of academic achievement. Based in part on previous observations regarding the differential attribution of success in men and women,2 the authors suggested that two general principles were found to be at the heart of this syndrome. The first was that an unexpected performance outcome will be attributed to a temporary cause. The second was that an expected performance outcome will be attributed to a stable cause. As such, the authors originally suggested that women tended to explain failure with lack of ability, whereas men attributed failure to luck or task difficulty. Furthermore, the authors emphasized environmental factors – such as mentorship, competition, and isolation – as the primary influence in the development of these tendencies.
Although originally described in women, this phenomenon can also affect men, as well as a wide variety of people from different occupations and cultures.3-6 Furthermore, although environmental factors were originally linked as the primary driver of these tendencies, further research has suggested that personality factors play a larger role, and that up to 70% of people may experience this phenomenon in their lifetime.7 Personality traits such as perfectionism and neuroticism may be linked to the development of this phenomenon.3,8
There are several online screening questionnaires that can be used to gauge whether individuals experience some or most of these traits. On one such questionnaire, the Clance IP Scale,9 poses such questions as: “I have often succeeded on a test or task even though I was afraid that I would not do well before I undertook the task” and “I am afraid people important to me may find out that I am not as capable as they think I am.” There are 20 questions scored from 1 to 5 and a score of 40 or below suggests few impostor tendencies, while a score of 80 or above suggests the respondent often has intense IP experiences. The higher the score, the more frequently and seriously the impostor syndrome interferes in a person’s life. What is unclear is whether this worsens, improves, or stays the same throughout one’s career. Of interest is that my personal score at this time is 43; however, it would have been 89 had I taken the test during college and medical school. What is unclear to me from the literature is what factors may play a role in a person’s perception of their abilities and their personal confidence over time.
Why is this important? Given that we are all professionals, impostor tendencies appear to have significant impact in the context of our work. This may have impact on us both as employers and as employees.10 Individuals with impostor syndrome tendencies often characterize themselves negatively and perform poorly on self-appraisals.11 In a study of 201 Belgian white-collar workers, Vergauwe and colleagues found that impostor syndrome tendencies were negatively related to job satisfaction and organizational citizenship behavior; both of which could be influenced by a high degree of social support.10 Individuals with impostor syndrome tendencies do less career planning, explore career options less frequently, and are less inclined to lead.12,13 These tendencies can be detrimental as the most qualified people for a position or opportunity may not step forward for consideration. Employers may tend to overlook these individuals for promotions or for pay raises which could negatively influence future earnings. Furthermore, a person may experience increased burnout as they continuously try to overcompensate for what they perceive as their shortcomings. They may feel concerned they are letting others down or not performing to standards. They may derive less enjoyment from life because of the constant focus on feelings of inadequacy.14 Research along these lines suggest impostor syndrome tendencies can have adverse personal and health-related consequences and may increase social anxiety, depression, and overall psychological distress.15,16
What can we do about it? In a very interesting study by Zanchetta and colleagues, the authors studied 103 young employees and randomized them to receive coaching, training, or no intervention.17 Their findings showed that coaching was an effective mindset intervention which resulted in reduced impostor syndrome scores. Furthermore, fear of negative evaluation and the effect of coaching appeared to be significantly associated with a reduction in the impostor syndrome scores. Coaching appeared to improve self-enhancing attributions and self-efficacy with a reduction in the tendency of subjects to fear negative evaluation. The authors concluded that fostering a mindset shift by reducing the fear of negative evaluations through coaching demonstrated measurable and sustained improvements in overall impostor syndrome scores for participants.17
What do I suggest? It is clear this affects a significant percentage of physicians, health care professionals, and professionals in general. Harboring these tendencies can have a negative impact on health, professional achievement, income, and happiness. It is important to self-reflect, identify if you are at risk, and if so, take the opportunity to explore solutions. My recommendations are:
- Name it: Take the test and see how you score.
- Be mindful: Self-reflection will help you identify the behaviors that are interfering with your happiness and success.
- Write it down: Be strategic and document your plan for success to reinforce your accomplishments.
- Create a feedback group: Friends and colleagues can help to mitigate the negative effects of impostor syndrome tendencies.
- Speak up: Ask for help; coaching has been documented to reduce impostor syndrome scores and help lessen the burden of these tendencies.
- Step out of your comfort zone: Develop a mantra, break bigger challenges into smaller pieces, and acknowledge little wins along the way.
In conclusion, impostor syndrome appears to be highly prevalent in professionals including those of us in medicine. The experience can adversely affect our careers and ability to secure key leadership positions. As managers, we also must keep in mind our role in mentoring others and recognizing the potential impact of impostor syndrome on those who report to us. Recognition of this phenomenon – and understanding of the effects on oneself – is the first step in overcoming the negative effects and moving toward realization of one’s potential.
Dr. Brown is a professor of medicine at Wayne State University, division chief of gastroenterology and hepatology at Henry Ford Hospital, and associate medical director at the Henry Ford Hospital Transplant Institute, all in Detroit.
References
1. Clance PR, Imes S. Psychother Theory Res Pract. 1978 Fall;15(3):1-7.
2. Deaux D. In J.H.Harvey, W.J.Ickes and R.F. Kidd (Eds). New directions in attribution research. Vol. 1. New York: Halsted Press Division, Wiley. 1976; p 335-42.
3. Bernard NS et al. J Pers Assess. 2002;78(2):321-33.
4. Topping ME et al. Acad Psychol Bull. 1985;(7):213-26.
5. Langford J et al. Psychotherapy. 1993;30(3):495-501.
6. Chae JH et al. J Pers Assess. 1995;65(3):468-85.
7. Harvey JC et al. If I’m successful, why do I feel like a fake? New York: Random House, 1985.
8. Ross SR et al. Pers Individ Diff. 2001;31:1347-55.
9. Clance PR. The impostor phenomenon: When success makes you feel like a fake. Toronto: Bantam Books, 1985; p 20-2.
10. Vergauwe J et al. J Bus Psychol. 2015;30:565-81.
11. Leary MR et al. J Pers. 2000;68(4):725-56.
12. Neureiter M et al. Front Psychol. 2016;7:48.
13. Neureiter M et al. J Vocat Behav. 2017;98:56-69.
14. Duhigg C. The power of habit: Why we do what we do in life and business. New York: Random House, 2012.
15. Henning K et al. Med Educ. 1998 Sep;32(5):456-64.
16. Oriel K et al. Fam Med. 2004 Apr;36(4):248-52.
17. Zanchetta M et al. Front Psychol. 2020 May 15;11:405.
Fixed duration ibrutinib/venetoclax appears feasible for some CLL/SLL patients
Among chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL)/small lymphocytic lymphoma (SLL) patients in the minimal residual disease (MRD) cohort of the phase 2 CAPTIVATE trial, a 1-year disease-free survival (DFS) rate of 95% in those randomized to placebo after 12 cycles of combined ibrutinib plus venetoclax supports a fixed-duration treatment approach, according to William G. Wierda, MD, PhD, University of Texas, MD Anderson Cancer Center, Houston.
Ibrutinib, a once-daily Bruton kinase inhibitor, is the only targeted therapy for first-line treatment of CLL that has demonstrated significant overall survival benefit in randomized phase 3 studies, Dr. Wierda said at the American Society of Hematology annual meeting, held virtually.
Ibrutinib and venetoclax have synergistic and complementary antitumor activity, he noted, through mobilizing and clearing CLL cells from protective niches and disease compartments beyond blood and bone marrow.
Fixed-duration study
CAPTIVATE (PCYC-1142), an international phase 2 study, evaluated first-line treatment with 12 cycles of the ibrutinib/venetoclax combination in MRD and fixed-duration cohorts. The current primary analysis of 1-year DFS from the MRD cohort tested whether the regimen allows for treatment-free remission in the setting of confirmed undetectable MRD (uMRD).
Patients (n = 164, median age 58 years) in the CAPTIVATE study MRD cohort had previously untreated active CLL/SLL requiring treatment per International Workshop on Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia criteria.
They received 3 cycles of lead-in ibrutinib (420 mg once daily) followed by 12 cycles of ibrutinib (420 mg once daily plus venetoclax ramp-up to 400 mg once daily). Thereafter, in an MRD-guided 1:1 randomization stratified by immunoglobulin heavy chain (IGHV) mutational status, those with confirmed uMRD received either placebo or ibrutinib, and those with uMRD not confirmed received either ibrutinib or ibrutinib plus venetoclax (both open-label).
Among high-risk features in CAPTIVATE subjects, 60% of patients had unmutated IGHV, with del(17p)/TP53 mutation in 20%, del(11Q) in 17%, complex karyotype in 19%, cytopenias in 36%, bulky lymph nodes in 32%, and absolute neutrophil count ≥25x109/L in 76%.
Response findings
The ibrutinib lead-in, Dr. Wierda said, reduced tumor lysis syndrome (TLS) risk, shifting 90% of patients with high baseline TLS risk to medium or low-risk categories (from 77 to 51 patients), precluding need for hospitalization with venetoclax initiation.
The rate for best response of uMRD (defined as uMRD over at least 3 cycles in both peripheral blood and bone marrow) in evaluable patients was 75% in peripheral blood (n = 163) and 72% in bone marrow (n = 155).
Confirmed uMRD was achieved in 86/149 (58%), with uMRD not confirmed in 63/149 (uMRD 32% in bone marrow and 48% in peripheral blood). One-year DFS after the further randomization to placebo or ibrutinib in the confirmed uMRD group was 95.3% in the placebo group and 100% in the ibrutinib group (P = .1475). In the uMRD not confirmed group, 30-month progression-free survival (PFS) was 95.2% and 96.7% in the ibrutinib and ibrutinib plus venetoclax groups, respectively. Thirty-month PFS rates in the confirmed uMRD placebo and ibrutinib arms were 95.3% and 100%. “Thirty-month PFS rates were greater than 95% across all randomized arms,” Dr. Wierda stated.
In patients without confirmed uMRD after 12 cycles of combined ibrutinib plus venetoclax, additional randomized treatment led to greater increases in uMRD in the ibrutinib plus venetoclax group than in the ibrutinib alone group (bone marrow additional 10% ibrutinib alone, 34% ibrutinib plus venetoclax; peripheral blood 0% ibrutinib, 19% ibrutinib plus venetoclax).
Adverse events generally decreased after the first 6 months of ibrutinib plus venetoclax treatment, with no new safety signals emerging over time. “There were no safety concerns with this highly active combination of first-line ibrutinib plus venetoclax. It’s an oral, once-daily fixed duration regimen that achieves undetectable MRD in blood or bone marrow in three-fourths of patients after 12 cycles of combined treatment.”
When asked, in a question-and-answer session after his presentation, if the findings were “practice changing,” Dr. Wierda responded: “We need additional data from ongoing studies looking at various combinations of targeted therapy. But this study does clearly show efficacy in terms of depth of remission, and it supports the concept of fixed duration treatment, particularly for those patients who achieved undetectable MRD status.”
SOURCE: William G. Wierda, MD, PhD. ASH 2020, Abstract 123.
Among chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL)/small lymphocytic lymphoma (SLL) patients in the minimal residual disease (MRD) cohort of the phase 2 CAPTIVATE trial, a 1-year disease-free survival (DFS) rate of 95% in those randomized to placebo after 12 cycles of combined ibrutinib plus venetoclax supports a fixed-duration treatment approach, according to William G. Wierda, MD, PhD, University of Texas, MD Anderson Cancer Center, Houston.
Ibrutinib, a once-daily Bruton kinase inhibitor, is the only targeted therapy for first-line treatment of CLL that has demonstrated significant overall survival benefit in randomized phase 3 studies, Dr. Wierda said at the American Society of Hematology annual meeting, held virtually.
Ibrutinib and venetoclax have synergistic and complementary antitumor activity, he noted, through mobilizing and clearing CLL cells from protective niches and disease compartments beyond blood and bone marrow.
Fixed-duration study
CAPTIVATE (PCYC-1142), an international phase 2 study, evaluated first-line treatment with 12 cycles of the ibrutinib/venetoclax combination in MRD and fixed-duration cohorts. The current primary analysis of 1-year DFS from the MRD cohort tested whether the regimen allows for treatment-free remission in the setting of confirmed undetectable MRD (uMRD).
Patients (n = 164, median age 58 years) in the CAPTIVATE study MRD cohort had previously untreated active CLL/SLL requiring treatment per International Workshop on Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia criteria.
They received 3 cycles of lead-in ibrutinib (420 mg once daily) followed by 12 cycles of ibrutinib (420 mg once daily plus venetoclax ramp-up to 400 mg once daily). Thereafter, in an MRD-guided 1:1 randomization stratified by immunoglobulin heavy chain (IGHV) mutational status, those with confirmed uMRD received either placebo or ibrutinib, and those with uMRD not confirmed received either ibrutinib or ibrutinib plus venetoclax (both open-label).
Among high-risk features in CAPTIVATE subjects, 60% of patients had unmutated IGHV, with del(17p)/TP53 mutation in 20%, del(11Q) in 17%, complex karyotype in 19%, cytopenias in 36%, bulky lymph nodes in 32%, and absolute neutrophil count ≥25x109/L in 76%.
Response findings
The ibrutinib lead-in, Dr. Wierda said, reduced tumor lysis syndrome (TLS) risk, shifting 90% of patients with high baseline TLS risk to medium or low-risk categories (from 77 to 51 patients), precluding need for hospitalization with venetoclax initiation.
The rate for best response of uMRD (defined as uMRD over at least 3 cycles in both peripheral blood and bone marrow) in evaluable patients was 75% in peripheral blood (n = 163) and 72% in bone marrow (n = 155).
Confirmed uMRD was achieved in 86/149 (58%), with uMRD not confirmed in 63/149 (uMRD 32% in bone marrow and 48% in peripheral blood). One-year DFS after the further randomization to placebo or ibrutinib in the confirmed uMRD group was 95.3% in the placebo group and 100% in the ibrutinib group (P = .1475). In the uMRD not confirmed group, 30-month progression-free survival (PFS) was 95.2% and 96.7% in the ibrutinib and ibrutinib plus venetoclax groups, respectively. Thirty-month PFS rates in the confirmed uMRD placebo and ibrutinib arms were 95.3% and 100%. “Thirty-month PFS rates were greater than 95% across all randomized arms,” Dr. Wierda stated.
In patients without confirmed uMRD after 12 cycles of combined ibrutinib plus venetoclax, additional randomized treatment led to greater increases in uMRD in the ibrutinib plus venetoclax group than in the ibrutinib alone group (bone marrow additional 10% ibrutinib alone, 34% ibrutinib plus venetoclax; peripheral blood 0% ibrutinib, 19% ibrutinib plus venetoclax).
Adverse events generally decreased after the first 6 months of ibrutinib plus venetoclax treatment, with no new safety signals emerging over time. “There were no safety concerns with this highly active combination of first-line ibrutinib plus venetoclax. It’s an oral, once-daily fixed duration regimen that achieves undetectable MRD in blood or bone marrow in three-fourths of patients after 12 cycles of combined treatment.”
When asked, in a question-and-answer session after his presentation, if the findings were “practice changing,” Dr. Wierda responded: “We need additional data from ongoing studies looking at various combinations of targeted therapy. But this study does clearly show efficacy in terms of depth of remission, and it supports the concept of fixed duration treatment, particularly for those patients who achieved undetectable MRD status.”
SOURCE: William G. Wierda, MD, PhD. ASH 2020, Abstract 123.
Among chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL)/small lymphocytic lymphoma (SLL) patients in the minimal residual disease (MRD) cohort of the phase 2 CAPTIVATE trial, a 1-year disease-free survival (DFS) rate of 95% in those randomized to placebo after 12 cycles of combined ibrutinib plus venetoclax supports a fixed-duration treatment approach, according to William G. Wierda, MD, PhD, University of Texas, MD Anderson Cancer Center, Houston.
Ibrutinib, a once-daily Bruton kinase inhibitor, is the only targeted therapy for first-line treatment of CLL that has demonstrated significant overall survival benefit in randomized phase 3 studies, Dr. Wierda said at the American Society of Hematology annual meeting, held virtually.
Ibrutinib and venetoclax have synergistic and complementary antitumor activity, he noted, through mobilizing and clearing CLL cells from protective niches and disease compartments beyond blood and bone marrow.
Fixed-duration study
CAPTIVATE (PCYC-1142), an international phase 2 study, evaluated first-line treatment with 12 cycles of the ibrutinib/venetoclax combination in MRD and fixed-duration cohorts. The current primary analysis of 1-year DFS from the MRD cohort tested whether the regimen allows for treatment-free remission in the setting of confirmed undetectable MRD (uMRD).
Patients (n = 164, median age 58 years) in the CAPTIVATE study MRD cohort had previously untreated active CLL/SLL requiring treatment per International Workshop on Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia criteria.
They received 3 cycles of lead-in ibrutinib (420 mg once daily) followed by 12 cycles of ibrutinib (420 mg once daily plus venetoclax ramp-up to 400 mg once daily). Thereafter, in an MRD-guided 1:1 randomization stratified by immunoglobulin heavy chain (IGHV) mutational status, those with confirmed uMRD received either placebo or ibrutinib, and those with uMRD not confirmed received either ibrutinib or ibrutinib plus venetoclax (both open-label).
Among high-risk features in CAPTIVATE subjects, 60% of patients had unmutated IGHV, with del(17p)/TP53 mutation in 20%, del(11Q) in 17%, complex karyotype in 19%, cytopenias in 36%, bulky lymph nodes in 32%, and absolute neutrophil count ≥25x109/L in 76%.
Response findings
The ibrutinib lead-in, Dr. Wierda said, reduced tumor lysis syndrome (TLS) risk, shifting 90% of patients with high baseline TLS risk to medium or low-risk categories (from 77 to 51 patients), precluding need for hospitalization with venetoclax initiation.
The rate for best response of uMRD (defined as uMRD over at least 3 cycles in both peripheral blood and bone marrow) in evaluable patients was 75% in peripheral blood (n = 163) and 72% in bone marrow (n = 155).
Confirmed uMRD was achieved in 86/149 (58%), with uMRD not confirmed in 63/149 (uMRD 32% in bone marrow and 48% in peripheral blood). One-year DFS after the further randomization to placebo or ibrutinib in the confirmed uMRD group was 95.3% in the placebo group and 100% in the ibrutinib group (P = .1475). In the uMRD not confirmed group, 30-month progression-free survival (PFS) was 95.2% and 96.7% in the ibrutinib and ibrutinib plus venetoclax groups, respectively. Thirty-month PFS rates in the confirmed uMRD placebo and ibrutinib arms were 95.3% and 100%. “Thirty-month PFS rates were greater than 95% across all randomized arms,” Dr. Wierda stated.
In patients without confirmed uMRD after 12 cycles of combined ibrutinib plus venetoclax, additional randomized treatment led to greater increases in uMRD in the ibrutinib plus venetoclax group than in the ibrutinib alone group (bone marrow additional 10% ibrutinib alone, 34% ibrutinib plus venetoclax; peripheral blood 0% ibrutinib, 19% ibrutinib plus venetoclax).
Adverse events generally decreased after the first 6 months of ibrutinib plus venetoclax treatment, with no new safety signals emerging over time. “There were no safety concerns with this highly active combination of first-line ibrutinib plus venetoclax. It’s an oral, once-daily fixed duration regimen that achieves undetectable MRD in blood or bone marrow in three-fourths of patients after 12 cycles of combined treatment.”
When asked, in a question-and-answer session after his presentation, if the findings were “practice changing,” Dr. Wierda responded: “We need additional data from ongoing studies looking at various combinations of targeted therapy. But this study does clearly show efficacy in terms of depth of remission, and it supports the concept of fixed duration treatment, particularly for those patients who achieved undetectable MRD status.”
SOURCE: William G. Wierda, MD, PhD. ASH 2020, Abstract 123.
FROM ASH 2020
Key clinical point: A favorable 1-year DFS in patients after 12 cycles of ibrutinib plus venetoclax in the MRD cohort of the phase 2 CAPTIVATE trial supports fixed-duration treatment for chronic lymphocytic leukemia/small lymphocytic lymphoma.
Major finding: One-year DFS after randomization to placebo or ibrutinib in the confirmed undetectable MRD group was 95.3% in the placebo group and 100.0 percent in the ibrutinib group (P = .1475).
Study details: The phase 2 CAPTIVATE study included 164 patients with previously untreated active chronic lymphocytic leukemia/small lymphocytic lymphoma requiring treatment per International Workshop on Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia criteria.
Disclosures: Dr. Wierda disclosed consultancy and research funding with multiple pharmaceutical companies.
Source: William G. Wierda, MD, PhD. ASH 2020 Abstract 123.
Durable responses with anti-BCMA CAR T-cell for multiple myeloma
For patients with heavily-pretreated multiple myeloma, the early and deep responses seen with the novel chimeric antigen receptor T-cell (CAR T-cell) construct ciltacabtagene autoleucel (cilta-cel) have also been durable, according to investigators in the CARTITUDE-1 trial.
Among 97 patients with multiple myeloma that had progressed on three or more prior lines of therapy or following treatment with at least two lines of therapy with a proteasome inhibitor and immunomodulating agent, the overall response rate (ORR) was 96.9%, with a median duration of response not reached after a median of 12.4 months of follow-up, reported Deepu Madduri, MD of Mount Sinai Medical Center in New York, and colleagues.
“We saw how heavily pretreated these patients were, and to see a one-time treatment get these kind of response rates is quite exceptional. What’s even more impressive is that 72% of these patients were still maintaining their response at the time of data cutoff,“ she said in an oral abstract presented during the virtual American Society of Hematology annual meeting.
Cilta-cel is a second-generation CAR T containing two single-domain antibodies targeted against B-cell maturation protein (BCMA). BCMA was first described in myeloma in 2004 as a mechanism for the growth and survival of malignant plasma cells.
As previously reported, the same CAR T-cell construct showed a high overall response with manageable toxicities in 74 patients with relapsed/refractory multiple myeloma.
Ciltacabtagene autoleucel was granted a breakthrough therapy designation for relapsed/refractory multiple myeloma by the Food and Drug Administration in December 2019, a priority medicines (PRIME) designation by the European Medicines Agency in April 2019, and breakthrough designation in China in September 2020.
At the 2019 ASH annual meeting, Dr. Madduri reported phase 1b results from the trial, which showed that for 29 patients with heavily pretreated, relapsed/refractory multiple myeloma, the ORR at 6 months median follow-up was 100%, including 69% complete responses, with 27 patients remaining free of disease progression.
Combined data
For the 2020 ASH annual meeting, Dr. Madduri reported combined results from phases 1b and 2 of the CARTITUDE-1 study.
The investigators enrolled patients with multiple myeloma with measurable diseases as assessed by M-protein or serum free light chain levels who had experienced disease progression on at least three prior lines of therapy, or whose disease was refractory to at least two lines of therapy with a proteasome inhibitor, immunomodulatory drug, and an anti-CD38 antibody.
Patients underwent apheresis for T-cell collection, with bridging therapy allowed until the expanded T cells could be delivered.
Following T-cell depletion with cyclophosphamide 300 mg/m2 and fludarabine 30 mg/m2 over 3 days, patients received a single weight-based infusion (compared with fixed-dose infusions used with other CAR T-cell constructs).
The dose was targeted at 0.75x106 CAR-positive cells/kg, with a target range of 0.5–1.0x106, administered 5-7 days after the start of the conditioning regimen.
Of the 101 patients who underwent lymphodepletion, 97 (29 in phase 1b and 68 in phase 2) were treated with cilta-cel. Five of the patients in phase 1b and nine in phase 2 died on study, five of whom succumbed to progressive disease, and three due to adverse events unrelated to treatment. The remaining six patients died from treatment-related causes, including two patients from sepsis or septic shock, and one each from the cytokine release syndrome (CRS)/hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis (HLH), lung abscess, respiratory failure, and neurotoxicity.
At the time of data cutoff, 83 patients remained on study.
High ORR
The ORR was 96.9% (94 of 97 patients), comprising 67% stringent complete responses (sCR), 25.8% very good partial responses (VGPR), and 4.1% partial responses (PR).
Among 57 patients evaluable for minimal residual disease (MRD), 53 (93%) were MRD negative. Of this group, 49 had a VGPR or better.
The median time to first response was 1 month (range 0.9 to 8.5 months). At the time of data cutoff 70 patients had an ongoing response.
Among patients followed for a minimum of 6 months, most had cilta-cel CAR T-cells below the level of quantification (2 cells per microliter) in peripheral blood.
At a median follow-up of 12.4 months, 12-month overall progression-free survival rate was 76%, with the median PFS not reached. The 12-month overall survival rate was 88.5%, with the median OS not reached.
Safety data
All patients had at least one hematologic adverse event, 96 of which were grade 3 or 4 in severity. The events include neutropenia, anemia, thrombocytopenia, leukopenia, and lymphopenia. The median time to recovery was 2 weeks for grade 3 or 4 neutropenia and 4 weeks for thrombocytopenia.
Infections of any grade occurred in 57.7% of patients, including grade 3/4 pneumonia in 8.2% and grade 3/4 sepsis in 4.1%.
Grade 3 or 4 nonhematologic toxicities were uncommon, Dr. Madduri noted.
CRS of any grade occurred in 92 patients, but only 4 had grade 3 or 4 CRS.
Neurotoxicities occurred in 20 patients, of whom 10 had grade 3 or 4 neurotoxicity.
Immune effector cell-associated neurotoxicity syndrome (ICANS) occurred in 16 patients, with 2 having grade 3 or greater ICANS. Other neurotoxicities of any grade, many which overlapped with ICANS, occurred in 12 patients, with 9 having grade 3 or 4 neurotoxicity.
The median time to ICANS onset was 8 days, with a median time to recovery of 4 days. Other neurotoxicities took longer to manifest and disappear, however, with a median time to onset of 27 days, and median time to recovery of 75 days.
Neurotoxicity mechanism questioned
In the question-and-answer session following her presentation, an audience member asked whether the investigators had any insights into the mechanism underlying the non-ICANS neurotoxicities they saw.
“We saw no clear etiology in the other neurotoxicities, but we saw that maybe there could be some mild associations with high tumor burden, prior CRS, ICANS, or even the higher expansion and persistence of these cells,” Dr. Madduri replied.
She noted that subsequent to these findings, the investigators have implemented mitigation strategies including allowing patients to have more bridging chemotherapy, more aggressive steroid use for early ICANS, and extensive monitoring.
Eric Smith, MD, PhD, of Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center in New York, said that the non-ICANS neurotoxicity profile of cilta-cel was different from that seen in other CAR T-cell trials, and asked how it compared to that of bi-specific BCMA/CD3 CAR T constructs.
“We did see some nerve palsies and peripheral motor neuropathy, but it wasn’t that many patients, and it’s really hard to compare what happened here with the bi-specifics, as every product is very different,” she said.
The study was sponsored by Janssen Research & Development and Legend Biotech. Dr. Madduri disclosed honoraria, consultancy, and speakers bureau activities for those companies and others.
SOURCE: Madduri D et al. ASH 2020. Abstract 177.
For patients with heavily-pretreated multiple myeloma, the early and deep responses seen with the novel chimeric antigen receptor T-cell (CAR T-cell) construct ciltacabtagene autoleucel (cilta-cel) have also been durable, according to investigators in the CARTITUDE-1 trial.
Among 97 patients with multiple myeloma that had progressed on three or more prior lines of therapy or following treatment with at least two lines of therapy with a proteasome inhibitor and immunomodulating agent, the overall response rate (ORR) was 96.9%, with a median duration of response not reached after a median of 12.4 months of follow-up, reported Deepu Madduri, MD of Mount Sinai Medical Center in New York, and colleagues.
“We saw how heavily pretreated these patients were, and to see a one-time treatment get these kind of response rates is quite exceptional. What’s even more impressive is that 72% of these patients were still maintaining their response at the time of data cutoff,“ she said in an oral abstract presented during the virtual American Society of Hematology annual meeting.
Cilta-cel is a second-generation CAR T containing two single-domain antibodies targeted against B-cell maturation protein (BCMA). BCMA was first described in myeloma in 2004 as a mechanism for the growth and survival of malignant plasma cells.
As previously reported, the same CAR T-cell construct showed a high overall response with manageable toxicities in 74 patients with relapsed/refractory multiple myeloma.
Ciltacabtagene autoleucel was granted a breakthrough therapy designation for relapsed/refractory multiple myeloma by the Food and Drug Administration in December 2019, a priority medicines (PRIME) designation by the European Medicines Agency in April 2019, and breakthrough designation in China in September 2020.
At the 2019 ASH annual meeting, Dr. Madduri reported phase 1b results from the trial, which showed that for 29 patients with heavily pretreated, relapsed/refractory multiple myeloma, the ORR at 6 months median follow-up was 100%, including 69% complete responses, with 27 patients remaining free of disease progression.
Combined data
For the 2020 ASH annual meeting, Dr. Madduri reported combined results from phases 1b and 2 of the CARTITUDE-1 study.
The investigators enrolled patients with multiple myeloma with measurable diseases as assessed by M-protein or serum free light chain levels who had experienced disease progression on at least three prior lines of therapy, or whose disease was refractory to at least two lines of therapy with a proteasome inhibitor, immunomodulatory drug, and an anti-CD38 antibody.
Patients underwent apheresis for T-cell collection, with bridging therapy allowed until the expanded T cells could be delivered.
Following T-cell depletion with cyclophosphamide 300 mg/m2 and fludarabine 30 mg/m2 over 3 days, patients received a single weight-based infusion (compared with fixed-dose infusions used with other CAR T-cell constructs).
The dose was targeted at 0.75x106 CAR-positive cells/kg, with a target range of 0.5–1.0x106, administered 5-7 days after the start of the conditioning regimen.
Of the 101 patients who underwent lymphodepletion, 97 (29 in phase 1b and 68 in phase 2) were treated with cilta-cel. Five of the patients in phase 1b and nine in phase 2 died on study, five of whom succumbed to progressive disease, and three due to adverse events unrelated to treatment. The remaining six patients died from treatment-related causes, including two patients from sepsis or septic shock, and one each from the cytokine release syndrome (CRS)/hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis (HLH), lung abscess, respiratory failure, and neurotoxicity.
At the time of data cutoff, 83 patients remained on study.
High ORR
The ORR was 96.9% (94 of 97 patients), comprising 67% stringent complete responses (sCR), 25.8% very good partial responses (VGPR), and 4.1% partial responses (PR).
Among 57 patients evaluable for minimal residual disease (MRD), 53 (93%) were MRD negative. Of this group, 49 had a VGPR or better.
The median time to first response was 1 month (range 0.9 to 8.5 months). At the time of data cutoff 70 patients had an ongoing response.
Among patients followed for a minimum of 6 months, most had cilta-cel CAR T-cells below the level of quantification (2 cells per microliter) in peripheral blood.
At a median follow-up of 12.4 months, 12-month overall progression-free survival rate was 76%, with the median PFS not reached. The 12-month overall survival rate was 88.5%, with the median OS not reached.
Safety data
All patients had at least one hematologic adverse event, 96 of which were grade 3 or 4 in severity. The events include neutropenia, anemia, thrombocytopenia, leukopenia, and lymphopenia. The median time to recovery was 2 weeks for grade 3 or 4 neutropenia and 4 weeks for thrombocytopenia.
Infections of any grade occurred in 57.7% of patients, including grade 3/4 pneumonia in 8.2% and grade 3/4 sepsis in 4.1%.
Grade 3 or 4 nonhematologic toxicities were uncommon, Dr. Madduri noted.
CRS of any grade occurred in 92 patients, but only 4 had grade 3 or 4 CRS.
Neurotoxicities occurred in 20 patients, of whom 10 had grade 3 or 4 neurotoxicity.
Immune effector cell-associated neurotoxicity syndrome (ICANS) occurred in 16 patients, with 2 having grade 3 or greater ICANS. Other neurotoxicities of any grade, many which overlapped with ICANS, occurred in 12 patients, with 9 having grade 3 or 4 neurotoxicity.
The median time to ICANS onset was 8 days, with a median time to recovery of 4 days. Other neurotoxicities took longer to manifest and disappear, however, with a median time to onset of 27 days, and median time to recovery of 75 days.
Neurotoxicity mechanism questioned
In the question-and-answer session following her presentation, an audience member asked whether the investigators had any insights into the mechanism underlying the non-ICANS neurotoxicities they saw.
“We saw no clear etiology in the other neurotoxicities, but we saw that maybe there could be some mild associations with high tumor burden, prior CRS, ICANS, or even the higher expansion and persistence of these cells,” Dr. Madduri replied.
She noted that subsequent to these findings, the investigators have implemented mitigation strategies including allowing patients to have more bridging chemotherapy, more aggressive steroid use for early ICANS, and extensive monitoring.
Eric Smith, MD, PhD, of Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center in New York, said that the non-ICANS neurotoxicity profile of cilta-cel was different from that seen in other CAR T-cell trials, and asked how it compared to that of bi-specific BCMA/CD3 CAR T constructs.
“We did see some nerve palsies and peripheral motor neuropathy, but it wasn’t that many patients, and it’s really hard to compare what happened here with the bi-specifics, as every product is very different,” she said.
The study was sponsored by Janssen Research & Development and Legend Biotech. Dr. Madduri disclosed honoraria, consultancy, and speakers bureau activities for those companies and others.
SOURCE: Madduri D et al. ASH 2020. Abstract 177.
For patients with heavily-pretreated multiple myeloma, the early and deep responses seen with the novel chimeric antigen receptor T-cell (CAR T-cell) construct ciltacabtagene autoleucel (cilta-cel) have also been durable, according to investigators in the CARTITUDE-1 trial.
Among 97 patients with multiple myeloma that had progressed on three or more prior lines of therapy or following treatment with at least two lines of therapy with a proteasome inhibitor and immunomodulating agent, the overall response rate (ORR) was 96.9%, with a median duration of response not reached after a median of 12.4 months of follow-up, reported Deepu Madduri, MD of Mount Sinai Medical Center in New York, and colleagues.
“We saw how heavily pretreated these patients were, and to see a one-time treatment get these kind of response rates is quite exceptional. What’s even more impressive is that 72% of these patients were still maintaining their response at the time of data cutoff,“ she said in an oral abstract presented during the virtual American Society of Hematology annual meeting.
Cilta-cel is a second-generation CAR T containing two single-domain antibodies targeted against B-cell maturation protein (BCMA). BCMA was first described in myeloma in 2004 as a mechanism for the growth and survival of malignant plasma cells.
As previously reported, the same CAR T-cell construct showed a high overall response with manageable toxicities in 74 patients with relapsed/refractory multiple myeloma.
Ciltacabtagene autoleucel was granted a breakthrough therapy designation for relapsed/refractory multiple myeloma by the Food and Drug Administration in December 2019, a priority medicines (PRIME) designation by the European Medicines Agency in April 2019, and breakthrough designation in China in September 2020.
At the 2019 ASH annual meeting, Dr. Madduri reported phase 1b results from the trial, which showed that for 29 patients with heavily pretreated, relapsed/refractory multiple myeloma, the ORR at 6 months median follow-up was 100%, including 69% complete responses, with 27 patients remaining free of disease progression.
Combined data
For the 2020 ASH annual meeting, Dr. Madduri reported combined results from phases 1b and 2 of the CARTITUDE-1 study.
The investigators enrolled patients with multiple myeloma with measurable diseases as assessed by M-protein or serum free light chain levels who had experienced disease progression on at least three prior lines of therapy, or whose disease was refractory to at least two lines of therapy with a proteasome inhibitor, immunomodulatory drug, and an anti-CD38 antibody.
Patients underwent apheresis for T-cell collection, with bridging therapy allowed until the expanded T cells could be delivered.
Following T-cell depletion with cyclophosphamide 300 mg/m2 and fludarabine 30 mg/m2 over 3 days, patients received a single weight-based infusion (compared with fixed-dose infusions used with other CAR T-cell constructs).
The dose was targeted at 0.75x106 CAR-positive cells/kg, with a target range of 0.5–1.0x106, administered 5-7 days after the start of the conditioning regimen.
Of the 101 patients who underwent lymphodepletion, 97 (29 in phase 1b and 68 in phase 2) were treated with cilta-cel. Five of the patients in phase 1b and nine in phase 2 died on study, five of whom succumbed to progressive disease, and three due to adverse events unrelated to treatment. The remaining six patients died from treatment-related causes, including two patients from sepsis or septic shock, and one each from the cytokine release syndrome (CRS)/hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis (HLH), lung abscess, respiratory failure, and neurotoxicity.
At the time of data cutoff, 83 patients remained on study.
High ORR
The ORR was 96.9% (94 of 97 patients), comprising 67% stringent complete responses (sCR), 25.8% very good partial responses (VGPR), and 4.1% partial responses (PR).
Among 57 patients evaluable for minimal residual disease (MRD), 53 (93%) were MRD negative. Of this group, 49 had a VGPR or better.
The median time to first response was 1 month (range 0.9 to 8.5 months). At the time of data cutoff 70 patients had an ongoing response.
Among patients followed for a minimum of 6 months, most had cilta-cel CAR T-cells below the level of quantification (2 cells per microliter) in peripheral blood.
At a median follow-up of 12.4 months, 12-month overall progression-free survival rate was 76%, with the median PFS not reached. The 12-month overall survival rate was 88.5%, with the median OS not reached.
Safety data
All patients had at least one hematologic adverse event, 96 of which were grade 3 or 4 in severity. The events include neutropenia, anemia, thrombocytopenia, leukopenia, and lymphopenia. The median time to recovery was 2 weeks for grade 3 or 4 neutropenia and 4 weeks for thrombocytopenia.
Infections of any grade occurred in 57.7% of patients, including grade 3/4 pneumonia in 8.2% and grade 3/4 sepsis in 4.1%.
Grade 3 or 4 nonhematologic toxicities were uncommon, Dr. Madduri noted.
CRS of any grade occurred in 92 patients, but only 4 had grade 3 or 4 CRS.
Neurotoxicities occurred in 20 patients, of whom 10 had grade 3 or 4 neurotoxicity.
Immune effector cell-associated neurotoxicity syndrome (ICANS) occurred in 16 patients, with 2 having grade 3 or greater ICANS. Other neurotoxicities of any grade, many which overlapped with ICANS, occurred in 12 patients, with 9 having grade 3 or 4 neurotoxicity.
The median time to ICANS onset was 8 days, with a median time to recovery of 4 days. Other neurotoxicities took longer to manifest and disappear, however, with a median time to onset of 27 days, and median time to recovery of 75 days.
Neurotoxicity mechanism questioned
In the question-and-answer session following her presentation, an audience member asked whether the investigators had any insights into the mechanism underlying the non-ICANS neurotoxicities they saw.
“We saw no clear etiology in the other neurotoxicities, but we saw that maybe there could be some mild associations with high tumor burden, prior CRS, ICANS, or even the higher expansion and persistence of these cells,” Dr. Madduri replied.
She noted that subsequent to these findings, the investigators have implemented mitigation strategies including allowing patients to have more bridging chemotherapy, more aggressive steroid use for early ICANS, and extensive monitoring.
Eric Smith, MD, PhD, of Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center in New York, said that the non-ICANS neurotoxicity profile of cilta-cel was different from that seen in other CAR T-cell trials, and asked how it compared to that of bi-specific BCMA/CD3 CAR T constructs.
“We did see some nerve palsies and peripheral motor neuropathy, but it wasn’t that many patients, and it’s really hard to compare what happened here with the bi-specifics, as every product is very different,” she said.
The study was sponsored by Janssen Research & Development and Legend Biotech. Dr. Madduri disclosed honoraria, consultancy, and speakers bureau activities for those companies and others.
SOURCE: Madduri D et al. ASH 2020. Abstract 177.
FROM ASH 2020
Allogeneic transplant leads to durable remissions in T-cell lymphomas
, results of a large retrospective observational study suggest.
Five-year progression-free survival (PFS) approached 40% and 5-year overall survival (OS) was over 50% in the study, which according to an investigator is the largest-ever reported patient series of allogeneic stem cell transplantation in T-cell lymphomas.
“We believe that eligible patients with relapsed/refractory T-cell lymphomas should be considered for consultation for allogeneic transplant by an expert clinician,” said investigator Neha Mehta-Shah, MD, of Washington University in St. Louis.
“These decisions should occur on a patient by patient level – but it’s important to consider this,” Dr. Mehta-Shah said at the annual meeting of the American Society of Hematology, held virtually this year.
Notably, patients with cutaneous T-cell lymphoma (CTCL) had a higher rate of relapse yet similar overall survival (OS) compared to patients with common peripheral T-cell lymphoma (PTCL) subtypes, according to Dr. Mehta-Shah.
Among PTCL subtypes, there was a trend toward improved PFS and OS for angioimmunoblastic T-cell lymphoma (AITL), compared with PTCL not otherwise specified (PTCL-NOS) and anaplastic large-cell lymphoma (ALCL), she added.
Catherine M. Diefenbach, MD, director of the clinical lymphoma program at NYU Langone’s Perlmutter Cancer Center, said the results of this retrospective study need to considered in light of the treatment-related risks associated with allogeneic transplantation.
Treatment-related mortality in the study ranged from about 8% to 24%, depending on the donor type, while acute and chronic graft-versus-host-disease (GvHD) was seen in more than 40% of patients, the reported data show.
“If I have a relapsed patient with AITL, I would look to this data and say that patients with AITL appear in a retrospective study to have a strong benefit,” Dr. Diefenbach said in an interview.
“For the other patients, you would describe both potential benefits and also discuss the treatment-associated risks – both the chronic GvHD and transplant-related mortality – and you’d have to balance the risk with the benefits for each individual case,” Dr. Diefenbach added.
The retrospective analysis by Dr. Mehta-Shah and colleagues included 508 consecutive T-cell lymphoma patients receiving allogeneic transplants at 12 academic centers between 2000 and 2019. The most common subtypes were PTCL-NOS in 26%, AITL in 16%, CTCL in 13%, and hepatosplenic T-cell lymphoma (HSTCL) in 7%. About 40% had a matched related donor (MRD) and 39% had a matched unrelated donor (MUD). The conditioning regimen was myeloablative in about a third of patients and nonmyeloablative in two-thirds.
At 5 years, PFS was 39.4% and OS was 50.8% for the overall study cohort, Dr. Mehta-Shah reported, noting that the median time from relapse to death post allogeneic transplant was 10.2 months.
Patients in complete remission at the time of transplant fared better than others, with a median PFS of 44.6 months vs. 8.5 months for those in partial remission, 21.0 months in those with stable disease, and 3.5 months for those with progressive disease at time of transplant, data show.
Patients with common PTCL subtypes had better PFS compared to patients with CTCL, yet OS was similar, according to the investigator. At 5 years, PFS was 43.7% and 18.6%, respectively, for PTCL and CTCL, while OS was 53.1% and 44.0%, respectively.
There was a trend toward improved outcomes for AITL relative to PTCL-NOS and ALCL, with a median PFS of 51.4 months for AITL versus 18.3 months those other subtypes. Similarly, median OS was not reached for AITL versus 73.1 months in the other subtypes.
Treatment-related mortality was lowest for patients with MRDs, or 8.2% at 12 months, Dr. Mehta-Shah reported, while patients with MUDs, mismatched donors, or haploidentical donors had treatment-related mortality of 13% to 16% at 12 months, and those with cord blood donors had treatment-related mortality of nearly 24% at 12 months.
Acute GvHD was observed in 46% of patients and chronic GvHD was seen in nearly 41%, the investigator added.
While these findings are important to consider in individual patient consultations, the study is nevertheless subject to limitations including patient selection and referral bias, according to Dr. Mehta-Shah.
“This was a retrospective analysis of patients who underwent transplant,” she said in a question-and-answer period. “Of course, that is heavily biased by who got to a transplant center, who was well enough to achieve transplant, and who had a donor or donor options, as well as their overall health and depth of remission,” the researcher said.
“I think this just represents what we could tell patients about what may happen to them once they embark on a transplant,” she added, “but really, there would be more prospective work needed to be done for what happens to patients overarching, and how many of them even get to a transplant consultation.”
Further studies should be done to develop predictive tools or biomarkers to determine who benefits from an allogeneic transplant, if there are predictors of relapse following allogeneic transplant, and what are the mechanisms of relapse following allogeneic transplant, according to Dr. Mehta-Shah.
Dr. Mehta-Shah reported research funding from Bristol Myers-Squibb, Celgene, Verastem, Corvus, Innate Pharmaceuticals, and Genentech/Roche. She reported consultancy with Kyowa Hakko Kirin, C4 Therapeutics, and Karyopharm Therapeutics.
SOURCE: Mehta-Shah N et al. ASH 2020, Abstract 41.
, results of a large retrospective observational study suggest.
Five-year progression-free survival (PFS) approached 40% and 5-year overall survival (OS) was over 50% in the study, which according to an investigator is the largest-ever reported patient series of allogeneic stem cell transplantation in T-cell lymphomas.
“We believe that eligible patients with relapsed/refractory T-cell lymphomas should be considered for consultation for allogeneic transplant by an expert clinician,” said investigator Neha Mehta-Shah, MD, of Washington University in St. Louis.
“These decisions should occur on a patient by patient level – but it’s important to consider this,” Dr. Mehta-Shah said at the annual meeting of the American Society of Hematology, held virtually this year.
Notably, patients with cutaneous T-cell lymphoma (CTCL) had a higher rate of relapse yet similar overall survival (OS) compared to patients with common peripheral T-cell lymphoma (PTCL) subtypes, according to Dr. Mehta-Shah.
Among PTCL subtypes, there was a trend toward improved PFS and OS for angioimmunoblastic T-cell lymphoma (AITL), compared with PTCL not otherwise specified (PTCL-NOS) and anaplastic large-cell lymphoma (ALCL), she added.
Catherine M. Diefenbach, MD, director of the clinical lymphoma program at NYU Langone’s Perlmutter Cancer Center, said the results of this retrospective study need to considered in light of the treatment-related risks associated with allogeneic transplantation.
Treatment-related mortality in the study ranged from about 8% to 24%, depending on the donor type, while acute and chronic graft-versus-host-disease (GvHD) was seen in more than 40% of patients, the reported data show.
“If I have a relapsed patient with AITL, I would look to this data and say that patients with AITL appear in a retrospective study to have a strong benefit,” Dr. Diefenbach said in an interview.
“For the other patients, you would describe both potential benefits and also discuss the treatment-associated risks – both the chronic GvHD and transplant-related mortality – and you’d have to balance the risk with the benefits for each individual case,” Dr. Diefenbach added.
The retrospective analysis by Dr. Mehta-Shah and colleagues included 508 consecutive T-cell lymphoma patients receiving allogeneic transplants at 12 academic centers between 2000 and 2019. The most common subtypes were PTCL-NOS in 26%, AITL in 16%, CTCL in 13%, and hepatosplenic T-cell lymphoma (HSTCL) in 7%. About 40% had a matched related donor (MRD) and 39% had a matched unrelated donor (MUD). The conditioning regimen was myeloablative in about a third of patients and nonmyeloablative in two-thirds.
At 5 years, PFS was 39.4% and OS was 50.8% for the overall study cohort, Dr. Mehta-Shah reported, noting that the median time from relapse to death post allogeneic transplant was 10.2 months.
Patients in complete remission at the time of transplant fared better than others, with a median PFS of 44.6 months vs. 8.5 months for those in partial remission, 21.0 months in those with stable disease, and 3.5 months for those with progressive disease at time of transplant, data show.
Patients with common PTCL subtypes had better PFS compared to patients with CTCL, yet OS was similar, according to the investigator. At 5 years, PFS was 43.7% and 18.6%, respectively, for PTCL and CTCL, while OS was 53.1% and 44.0%, respectively.
There was a trend toward improved outcomes for AITL relative to PTCL-NOS and ALCL, with a median PFS of 51.4 months for AITL versus 18.3 months those other subtypes. Similarly, median OS was not reached for AITL versus 73.1 months in the other subtypes.
Treatment-related mortality was lowest for patients with MRDs, or 8.2% at 12 months, Dr. Mehta-Shah reported, while patients with MUDs, mismatched donors, or haploidentical donors had treatment-related mortality of 13% to 16% at 12 months, and those with cord blood donors had treatment-related mortality of nearly 24% at 12 months.
Acute GvHD was observed in 46% of patients and chronic GvHD was seen in nearly 41%, the investigator added.
While these findings are important to consider in individual patient consultations, the study is nevertheless subject to limitations including patient selection and referral bias, according to Dr. Mehta-Shah.
“This was a retrospective analysis of patients who underwent transplant,” she said in a question-and-answer period. “Of course, that is heavily biased by who got to a transplant center, who was well enough to achieve transplant, and who had a donor or donor options, as well as their overall health and depth of remission,” the researcher said.
“I think this just represents what we could tell patients about what may happen to them once they embark on a transplant,” she added, “but really, there would be more prospective work needed to be done for what happens to patients overarching, and how many of them even get to a transplant consultation.”
Further studies should be done to develop predictive tools or biomarkers to determine who benefits from an allogeneic transplant, if there are predictors of relapse following allogeneic transplant, and what are the mechanisms of relapse following allogeneic transplant, according to Dr. Mehta-Shah.
Dr. Mehta-Shah reported research funding from Bristol Myers-Squibb, Celgene, Verastem, Corvus, Innate Pharmaceuticals, and Genentech/Roche. She reported consultancy with Kyowa Hakko Kirin, C4 Therapeutics, and Karyopharm Therapeutics.
SOURCE: Mehta-Shah N et al. ASH 2020, Abstract 41.
, results of a large retrospective observational study suggest.
Five-year progression-free survival (PFS) approached 40% and 5-year overall survival (OS) was over 50% in the study, which according to an investigator is the largest-ever reported patient series of allogeneic stem cell transplantation in T-cell lymphomas.
“We believe that eligible patients with relapsed/refractory T-cell lymphomas should be considered for consultation for allogeneic transplant by an expert clinician,” said investigator Neha Mehta-Shah, MD, of Washington University in St. Louis.
“These decisions should occur on a patient by patient level – but it’s important to consider this,” Dr. Mehta-Shah said at the annual meeting of the American Society of Hematology, held virtually this year.
Notably, patients with cutaneous T-cell lymphoma (CTCL) had a higher rate of relapse yet similar overall survival (OS) compared to patients with common peripheral T-cell lymphoma (PTCL) subtypes, according to Dr. Mehta-Shah.
Among PTCL subtypes, there was a trend toward improved PFS and OS for angioimmunoblastic T-cell lymphoma (AITL), compared with PTCL not otherwise specified (PTCL-NOS) and anaplastic large-cell lymphoma (ALCL), she added.
Catherine M. Diefenbach, MD, director of the clinical lymphoma program at NYU Langone’s Perlmutter Cancer Center, said the results of this retrospective study need to considered in light of the treatment-related risks associated with allogeneic transplantation.
Treatment-related mortality in the study ranged from about 8% to 24%, depending on the donor type, while acute and chronic graft-versus-host-disease (GvHD) was seen in more than 40% of patients, the reported data show.
“If I have a relapsed patient with AITL, I would look to this data and say that patients with AITL appear in a retrospective study to have a strong benefit,” Dr. Diefenbach said in an interview.
“For the other patients, you would describe both potential benefits and also discuss the treatment-associated risks – both the chronic GvHD and transplant-related mortality – and you’d have to balance the risk with the benefits for each individual case,” Dr. Diefenbach added.
The retrospective analysis by Dr. Mehta-Shah and colleagues included 508 consecutive T-cell lymphoma patients receiving allogeneic transplants at 12 academic centers between 2000 and 2019. The most common subtypes were PTCL-NOS in 26%, AITL in 16%, CTCL in 13%, and hepatosplenic T-cell lymphoma (HSTCL) in 7%. About 40% had a matched related donor (MRD) and 39% had a matched unrelated donor (MUD). The conditioning regimen was myeloablative in about a third of patients and nonmyeloablative in two-thirds.
At 5 years, PFS was 39.4% and OS was 50.8% for the overall study cohort, Dr. Mehta-Shah reported, noting that the median time from relapse to death post allogeneic transplant was 10.2 months.
Patients in complete remission at the time of transplant fared better than others, with a median PFS of 44.6 months vs. 8.5 months for those in partial remission, 21.0 months in those with stable disease, and 3.5 months for those with progressive disease at time of transplant, data show.
Patients with common PTCL subtypes had better PFS compared to patients with CTCL, yet OS was similar, according to the investigator. At 5 years, PFS was 43.7% and 18.6%, respectively, for PTCL and CTCL, while OS was 53.1% and 44.0%, respectively.
There was a trend toward improved outcomes for AITL relative to PTCL-NOS and ALCL, with a median PFS of 51.4 months for AITL versus 18.3 months those other subtypes. Similarly, median OS was not reached for AITL versus 73.1 months in the other subtypes.
Treatment-related mortality was lowest for patients with MRDs, or 8.2% at 12 months, Dr. Mehta-Shah reported, while patients with MUDs, mismatched donors, or haploidentical donors had treatment-related mortality of 13% to 16% at 12 months, and those with cord blood donors had treatment-related mortality of nearly 24% at 12 months.
Acute GvHD was observed in 46% of patients and chronic GvHD was seen in nearly 41%, the investigator added.
While these findings are important to consider in individual patient consultations, the study is nevertheless subject to limitations including patient selection and referral bias, according to Dr. Mehta-Shah.
“This was a retrospective analysis of patients who underwent transplant,” she said in a question-and-answer period. “Of course, that is heavily biased by who got to a transplant center, who was well enough to achieve transplant, and who had a donor or donor options, as well as their overall health and depth of remission,” the researcher said.
“I think this just represents what we could tell patients about what may happen to them once they embark on a transplant,” she added, “but really, there would be more prospective work needed to be done for what happens to patients overarching, and how many of them even get to a transplant consultation.”
Further studies should be done to develop predictive tools or biomarkers to determine who benefits from an allogeneic transplant, if there are predictors of relapse following allogeneic transplant, and what are the mechanisms of relapse following allogeneic transplant, according to Dr. Mehta-Shah.
Dr. Mehta-Shah reported research funding from Bristol Myers-Squibb, Celgene, Verastem, Corvus, Innate Pharmaceuticals, and Genentech/Roche. She reported consultancy with Kyowa Hakko Kirin, C4 Therapeutics, and Karyopharm Therapeutics.
SOURCE: Mehta-Shah N et al. ASH 2020, Abstract 41.
FROM ASH 2020
COVID-19–related outcomes poor for patients with hematologic disease in ASH registry
Patients with hematologic disease who develop COVID-19 may experience substantial morbidity and mortality related to SARS-CoV-2 infection, according to recent registry data reported at the all-virtual annual meeting of the American Society of Hematology.
Overall mortality was 28% for the first 250 patients entered into the ASH Research Collaborative COVID-19 Registry for Hematology, researchers reported in an abstract of their study findings.
However, the burden of death and moderate-to-severe COVID-19 outcomes was highest in patients with poorer prognosis and those with relapsed/refractory hematological disease, they added.
The most commonly represented malignancies were acute leukemia, non-Hodgkin lymphoma, and myeloma or amyloidosis, according to the report.
Taken together, the findings do support an “emerging consensus” that COVID-19 related morbidity and mortality is significant in these patients, authors said – however, the current findings may not be reason enough to support a change in treatment course for the underlying disease.
“We see no reason, based on our data, to withhold intensive therapies from patients with underlying hematologic malignancies and favorable prognoses, if aggressive supportive care is consistent with patient preferences,” wrote the researchers.
ASH President Stephanie Lee, MD, MPH, said these registry findings are important to better understand how SARS-CoV-2 is affecting not only patients with hematologic diseases, but also individuals who experience COVID-19-related hematologic complications.
However, the findings are limited due to the heterogeneity of diseases, symptoms, and treatments represented in the registry, said Dr. Lee, associate director of the clinical research division at Fred Hutchinson Cancer Center in Seattle.
“More data will be coming in, but I think this is an example of trying to harness real-world information to try to learn things until we get more controlled studies,” Dr. Lee said in a media briefing held in advance of the ASH meeting.
Comorbidities and more
Patients with blood cancers are often older and may have comorbidities such as diabetes or hypertension that have been linked to poor COVID-19 outcomes, according to the authors of the report, led by William A. Wood, MD, MPH, associate professor of medicine with the UNC Lineberger Comprehensive Cancer Center in Chapel Hill, N.C.
Moreover, these patients may have underlying immune dysfunction and may receive chemotherapy or immunotherapy that is “profoundly immunosuppressive,” Dr. Wood and coauthors said in their report.
To date, however, risks of morbidity and mortality related to SARS-CoV-2 infection have not been well defined in this patient population, authors said.
More data is emerging now from the ASH Research Collaborative COVID-19 Registry for Hematology, which includes data on patients positive for COVID-19 who have a past or present hematologic condition or have experienced a hematologic complication related to COVID-19.
All data from the registry is being made available through a dashboard on the ASH Research Collaborative website, which as of Dec. 1, 2020, included 693 complete cases.
The data cut in the ASH abstract includes the first 250 patients enrolled at 74 sites around the world, the authors said. The most common malignancies included acute leukemia in 33%, non-Hodgkin lymphoma in 27%, and myeloma or amyloidosis in 16%.
The most frequently reported symptoms included fever in 73%, cough in 67%, dyspnea in 50%, and fatigue in 40%, according to that report.
At the time of this data snapshot, treatment with COVID-19-directed therapies including hydroxychloroquine or azithromycin were common, reported in 76 and 59 patients, respectively, in the cohort.
Batch submissions from sites with high incidence of COVID-19 infection are ongoing. The registry has been expanded to include nonmalignant hematologic diseases, and the registry will continue to accumulate data as a resource for the hematology community.
Overall mortality was 28% at the time, according to the abstract, with nearly all of the deaths occurring in patients classified as having COVID-19 that was moderate (i.e., requiring hospitalization) or severe (i.e., requiring ICU admission).
“In some instances, death occurred after a decision was made to forgo ICU admission in favor of a palliative approach,” said Dr. Wood and coauthors in their report.
Dr. Wood reported research funding from Pfizer, consultancy with Teladoc/Best Doctors, and honoraria from the ASH Research Collaborative. Coauthors provided disclosures related to Celgene, Madrigal Pharmaceuticals, Pharmacyclics, and Amgen, among others.
SOURCE: Wood WA et al. ASH 2020, Abstract 215.
Patients with hematologic disease who develop COVID-19 may experience substantial morbidity and mortality related to SARS-CoV-2 infection, according to recent registry data reported at the all-virtual annual meeting of the American Society of Hematology.
Overall mortality was 28% for the first 250 patients entered into the ASH Research Collaborative COVID-19 Registry for Hematology, researchers reported in an abstract of their study findings.
However, the burden of death and moderate-to-severe COVID-19 outcomes was highest in patients with poorer prognosis and those with relapsed/refractory hematological disease, they added.
The most commonly represented malignancies were acute leukemia, non-Hodgkin lymphoma, and myeloma or amyloidosis, according to the report.
Taken together, the findings do support an “emerging consensus” that COVID-19 related morbidity and mortality is significant in these patients, authors said – however, the current findings may not be reason enough to support a change in treatment course for the underlying disease.
“We see no reason, based on our data, to withhold intensive therapies from patients with underlying hematologic malignancies and favorable prognoses, if aggressive supportive care is consistent with patient preferences,” wrote the researchers.
ASH President Stephanie Lee, MD, MPH, said these registry findings are important to better understand how SARS-CoV-2 is affecting not only patients with hematologic diseases, but also individuals who experience COVID-19-related hematologic complications.
However, the findings are limited due to the heterogeneity of diseases, symptoms, and treatments represented in the registry, said Dr. Lee, associate director of the clinical research division at Fred Hutchinson Cancer Center in Seattle.
“More data will be coming in, but I think this is an example of trying to harness real-world information to try to learn things until we get more controlled studies,” Dr. Lee said in a media briefing held in advance of the ASH meeting.
Comorbidities and more
Patients with blood cancers are often older and may have comorbidities such as diabetes or hypertension that have been linked to poor COVID-19 outcomes, according to the authors of the report, led by William A. Wood, MD, MPH, associate professor of medicine with the UNC Lineberger Comprehensive Cancer Center in Chapel Hill, N.C.
Moreover, these patients may have underlying immune dysfunction and may receive chemotherapy or immunotherapy that is “profoundly immunosuppressive,” Dr. Wood and coauthors said in their report.
To date, however, risks of morbidity and mortality related to SARS-CoV-2 infection have not been well defined in this patient population, authors said.
More data is emerging now from the ASH Research Collaborative COVID-19 Registry for Hematology, which includes data on patients positive for COVID-19 who have a past or present hematologic condition or have experienced a hematologic complication related to COVID-19.
All data from the registry is being made available through a dashboard on the ASH Research Collaborative website, which as of Dec. 1, 2020, included 693 complete cases.
The data cut in the ASH abstract includes the first 250 patients enrolled at 74 sites around the world, the authors said. The most common malignancies included acute leukemia in 33%, non-Hodgkin lymphoma in 27%, and myeloma or amyloidosis in 16%.
The most frequently reported symptoms included fever in 73%, cough in 67%, dyspnea in 50%, and fatigue in 40%, according to that report.
At the time of this data snapshot, treatment with COVID-19-directed therapies including hydroxychloroquine or azithromycin were common, reported in 76 and 59 patients, respectively, in the cohort.
Batch submissions from sites with high incidence of COVID-19 infection are ongoing. The registry has been expanded to include nonmalignant hematologic diseases, and the registry will continue to accumulate data as a resource for the hematology community.
Overall mortality was 28% at the time, according to the abstract, with nearly all of the deaths occurring in patients classified as having COVID-19 that was moderate (i.e., requiring hospitalization) or severe (i.e., requiring ICU admission).
“In some instances, death occurred after a decision was made to forgo ICU admission in favor of a palliative approach,” said Dr. Wood and coauthors in their report.
Dr. Wood reported research funding from Pfizer, consultancy with Teladoc/Best Doctors, and honoraria from the ASH Research Collaborative. Coauthors provided disclosures related to Celgene, Madrigal Pharmaceuticals, Pharmacyclics, and Amgen, among others.
SOURCE: Wood WA et al. ASH 2020, Abstract 215.
Patients with hematologic disease who develop COVID-19 may experience substantial morbidity and mortality related to SARS-CoV-2 infection, according to recent registry data reported at the all-virtual annual meeting of the American Society of Hematology.
Overall mortality was 28% for the first 250 patients entered into the ASH Research Collaborative COVID-19 Registry for Hematology, researchers reported in an abstract of their study findings.
However, the burden of death and moderate-to-severe COVID-19 outcomes was highest in patients with poorer prognosis and those with relapsed/refractory hematological disease, they added.
The most commonly represented malignancies were acute leukemia, non-Hodgkin lymphoma, and myeloma or amyloidosis, according to the report.
Taken together, the findings do support an “emerging consensus” that COVID-19 related morbidity and mortality is significant in these patients, authors said – however, the current findings may not be reason enough to support a change in treatment course for the underlying disease.
“We see no reason, based on our data, to withhold intensive therapies from patients with underlying hematologic malignancies and favorable prognoses, if aggressive supportive care is consistent with patient preferences,” wrote the researchers.
ASH President Stephanie Lee, MD, MPH, said these registry findings are important to better understand how SARS-CoV-2 is affecting not only patients with hematologic diseases, but also individuals who experience COVID-19-related hematologic complications.
However, the findings are limited due to the heterogeneity of diseases, symptoms, and treatments represented in the registry, said Dr. Lee, associate director of the clinical research division at Fred Hutchinson Cancer Center in Seattle.
“More data will be coming in, but I think this is an example of trying to harness real-world information to try to learn things until we get more controlled studies,” Dr. Lee said in a media briefing held in advance of the ASH meeting.
Comorbidities and more
Patients with blood cancers are often older and may have comorbidities such as diabetes or hypertension that have been linked to poor COVID-19 outcomes, according to the authors of the report, led by William A. Wood, MD, MPH, associate professor of medicine with the UNC Lineberger Comprehensive Cancer Center in Chapel Hill, N.C.
Moreover, these patients may have underlying immune dysfunction and may receive chemotherapy or immunotherapy that is “profoundly immunosuppressive,” Dr. Wood and coauthors said in their report.
To date, however, risks of morbidity and mortality related to SARS-CoV-2 infection have not been well defined in this patient population, authors said.
More data is emerging now from the ASH Research Collaborative COVID-19 Registry for Hematology, which includes data on patients positive for COVID-19 who have a past or present hematologic condition or have experienced a hematologic complication related to COVID-19.
All data from the registry is being made available through a dashboard on the ASH Research Collaborative website, which as of Dec. 1, 2020, included 693 complete cases.
The data cut in the ASH abstract includes the first 250 patients enrolled at 74 sites around the world, the authors said. The most common malignancies included acute leukemia in 33%, non-Hodgkin lymphoma in 27%, and myeloma or amyloidosis in 16%.
The most frequently reported symptoms included fever in 73%, cough in 67%, dyspnea in 50%, and fatigue in 40%, according to that report.
At the time of this data snapshot, treatment with COVID-19-directed therapies including hydroxychloroquine or azithromycin were common, reported in 76 and 59 patients, respectively, in the cohort.
Batch submissions from sites with high incidence of COVID-19 infection are ongoing. The registry has been expanded to include nonmalignant hematologic diseases, and the registry will continue to accumulate data as a resource for the hematology community.
Overall mortality was 28% at the time, according to the abstract, with nearly all of the deaths occurring in patients classified as having COVID-19 that was moderate (i.e., requiring hospitalization) or severe (i.e., requiring ICU admission).
“In some instances, death occurred after a decision was made to forgo ICU admission in favor of a palliative approach,” said Dr. Wood and coauthors in their report.
Dr. Wood reported research funding from Pfizer, consultancy with Teladoc/Best Doctors, and honoraria from the ASH Research Collaborative. Coauthors provided disclosures related to Celgene, Madrigal Pharmaceuticals, Pharmacyclics, and Amgen, among others.
SOURCE: Wood WA et al. ASH 2020, Abstract 215.
FROM ASH 2020
Infant’s COVID-19–related myocardial injury reversed
Reports of signs of heart failure in adults with COVID-19 have been rare – just four such cases have been published since the outbreak started in China – and now a team of pediatric cardiologists in New York have reported a case of acute but reversible myocardial injury in an infant with COVID-19.
and right upper lobe atelectasis.
The 2-month-old infant went home after more than 2 weeks in the hospital with no apparent lingering cardiac effects of the illness and not needing any oral heart failure medications, Madhu Sharma, MD, of the Children’s Hospital and Montefiore in New York and colleagues reported in JACC Case Reports. With close follow-up, the child’s left ventricle size and systolic function have remained normal and mitral regurgitation resolved. The case report didn’t mention the infant’s gender.
But before the straightforward postdischarge course emerged, the infant was in a precarious state, and Dr. Sharma and her team were challenged to diagnose the underlying causes.
The child, who was born about 7 weeks premature, first came to the hospital having turned blue after choking on food. Nonrebreather mask ventilation was initiated in the ED, and an examination detected a holosystolic murmur. A test for COVID-19 was negative, but a later test was positive, and a chest x-ray exhibited cardiomegaly and signs of fluid and inflammation in the lungs.
An electrocardiogram detected sinus tachycardia, ST-segment depression and other anomalies in cardiac function. Further investigation with a transthoracic ECG showed severely depressed left ventricle systolic function with an ejection fraction of 30%, severe mitral regurgitation, and normal right ventricular systolic function.
Treatment included remdesivir and intravenous antibiotics. Through the hospital course, the patient was extubated to noninvasive ventilation, reintubated, put on intravenous steroid (methylprednisolone) and low-molecular-weight heparin, extubated, and tested throughout for cardiac function.
By day 14, left ventricle size and function normalized, and while the mitral regurgitation remained severe, it improved later without HF therapies. Left ventricle ejection fraction had recovered to 60%, and key cardiac biomarkers had normalized. On day 16, milrinone was discontinued, and the care team determined the patient no longer needed oral heart failure therapies.
“Most children with COVID-19 are either asymptomatic or have mild symptoms, but our case shows the potential for reversible myocardial injury in infants with COVID-19,” said Dr. Sharma. “Testing for COVID-19 in children presenting with signs and symptoms of heart failure is very important as we learn more about the impact of this virus.”
Dr. Sharma and coauthors have no relevant financial relationships to disclose.
SOURCE: Sharma M et al. JACC Case Rep. 2020. doi: 10.1016/j.jaccas.2020.09.031.
Reports of signs of heart failure in adults with COVID-19 have been rare – just four such cases have been published since the outbreak started in China – and now a team of pediatric cardiologists in New York have reported a case of acute but reversible myocardial injury in an infant with COVID-19.
and right upper lobe atelectasis.
The 2-month-old infant went home after more than 2 weeks in the hospital with no apparent lingering cardiac effects of the illness and not needing any oral heart failure medications, Madhu Sharma, MD, of the Children’s Hospital and Montefiore in New York and colleagues reported in JACC Case Reports. With close follow-up, the child’s left ventricle size and systolic function have remained normal and mitral regurgitation resolved. The case report didn’t mention the infant’s gender.
But before the straightforward postdischarge course emerged, the infant was in a precarious state, and Dr. Sharma and her team were challenged to diagnose the underlying causes.
The child, who was born about 7 weeks premature, first came to the hospital having turned blue after choking on food. Nonrebreather mask ventilation was initiated in the ED, and an examination detected a holosystolic murmur. A test for COVID-19 was negative, but a later test was positive, and a chest x-ray exhibited cardiomegaly and signs of fluid and inflammation in the lungs.
An electrocardiogram detected sinus tachycardia, ST-segment depression and other anomalies in cardiac function. Further investigation with a transthoracic ECG showed severely depressed left ventricle systolic function with an ejection fraction of 30%, severe mitral regurgitation, and normal right ventricular systolic function.
Treatment included remdesivir and intravenous antibiotics. Through the hospital course, the patient was extubated to noninvasive ventilation, reintubated, put on intravenous steroid (methylprednisolone) and low-molecular-weight heparin, extubated, and tested throughout for cardiac function.
By day 14, left ventricle size and function normalized, and while the mitral regurgitation remained severe, it improved later without HF therapies. Left ventricle ejection fraction had recovered to 60%, and key cardiac biomarkers had normalized. On day 16, milrinone was discontinued, and the care team determined the patient no longer needed oral heart failure therapies.
“Most children with COVID-19 are either asymptomatic or have mild symptoms, but our case shows the potential for reversible myocardial injury in infants with COVID-19,” said Dr. Sharma. “Testing for COVID-19 in children presenting with signs and symptoms of heart failure is very important as we learn more about the impact of this virus.”
Dr. Sharma and coauthors have no relevant financial relationships to disclose.
SOURCE: Sharma M et al. JACC Case Rep. 2020. doi: 10.1016/j.jaccas.2020.09.031.
Reports of signs of heart failure in adults with COVID-19 have been rare – just four such cases have been published since the outbreak started in China – and now a team of pediatric cardiologists in New York have reported a case of acute but reversible myocardial injury in an infant with COVID-19.
and right upper lobe atelectasis.
The 2-month-old infant went home after more than 2 weeks in the hospital with no apparent lingering cardiac effects of the illness and not needing any oral heart failure medications, Madhu Sharma, MD, of the Children’s Hospital and Montefiore in New York and colleagues reported in JACC Case Reports. With close follow-up, the child’s left ventricle size and systolic function have remained normal and mitral regurgitation resolved. The case report didn’t mention the infant’s gender.
But before the straightforward postdischarge course emerged, the infant was in a precarious state, and Dr. Sharma and her team were challenged to diagnose the underlying causes.
The child, who was born about 7 weeks premature, first came to the hospital having turned blue after choking on food. Nonrebreather mask ventilation was initiated in the ED, and an examination detected a holosystolic murmur. A test for COVID-19 was negative, but a later test was positive, and a chest x-ray exhibited cardiomegaly and signs of fluid and inflammation in the lungs.
An electrocardiogram detected sinus tachycardia, ST-segment depression and other anomalies in cardiac function. Further investigation with a transthoracic ECG showed severely depressed left ventricle systolic function with an ejection fraction of 30%, severe mitral regurgitation, and normal right ventricular systolic function.
Treatment included remdesivir and intravenous antibiotics. Through the hospital course, the patient was extubated to noninvasive ventilation, reintubated, put on intravenous steroid (methylprednisolone) and low-molecular-weight heparin, extubated, and tested throughout for cardiac function.
By day 14, left ventricle size and function normalized, and while the mitral regurgitation remained severe, it improved later without HF therapies. Left ventricle ejection fraction had recovered to 60%, and key cardiac biomarkers had normalized. On day 16, milrinone was discontinued, and the care team determined the patient no longer needed oral heart failure therapies.
“Most children with COVID-19 are either asymptomatic or have mild symptoms, but our case shows the potential for reversible myocardial injury in infants with COVID-19,” said Dr. Sharma. “Testing for COVID-19 in children presenting with signs and symptoms of heart failure is very important as we learn more about the impact of this virus.”
Dr. Sharma and coauthors have no relevant financial relationships to disclose.
SOURCE: Sharma M et al. JACC Case Rep. 2020. doi: 10.1016/j.jaccas.2020.09.031.
FROM JACC CASE REPORTS
Key clinical point: Children presenting with COVID-19 should be tested for heart failure.
Major finding: A 2-month-old infant with COVID-19 had acute but reversible myocardial injury.
Study details: Single case report.
Disclosures: Dr. Sharma, MD, has no relevant financial relationships to disclose.
Source: Sharma M et al. JACC Case Rep. 2020. doi: 10.1016/j.jaccas.2020.09.031.