User login
Tiny papules on trunk and genitals
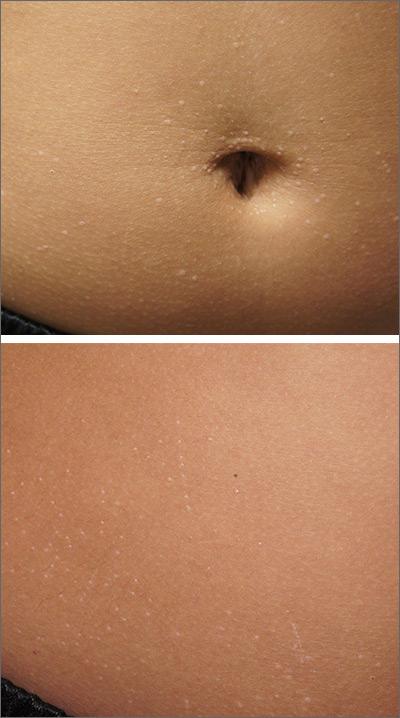
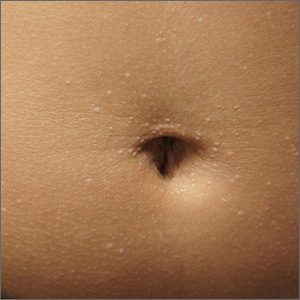
The miniscule papules arising suddenly on the trunk and genitals with linear arrays and clusters are clinically consistent with lichen nitidus, an uncommon eruption without a clear etiology.
Presentations may be focal or widespread and range from mildly itchy to asymptomatic. Children and young adults are most often affected. Linear arrays may appear in response to the trauma of scratching, which is termed the Koebner phenomenon. The differential diagnosis includes molluscum contagiosum, lichen planus, and lichen spinulosis. Usually these conditions can be distinguished clinically, but a biopsy would differentiate them, if needed. It’s worth noting, too, that lichen nitidus papules are monomorphic and lack the umbilication that is seen with molluscum contagiosum.
Cases of lichen nitidus clear up spontaneously, although usually months to years after diagnosis. Lichen nitidus is not contagious. Reassurance is, however, important as many patients may have experienced misdiagnosis and have concerns about sexual transmission because of the location of the papules on their genitals.
Treatment is often unnecessary. However, if itching is problematic, topical steroids and other topical antipruritics may be used. Topical hydrocortisone 2.5% cream or ointment for skin folds and genitals may be safely used, as well as topical triamcinolone 0.1% for the trunk and extremities. Pramoxine lotion (Sarna) is an over-the-counter nonsteroidal antipruritic. Oral nonsedating antihistamines can also be used as an adjunct.
This patient was reassured that the lesions were not contagious. Due to the itching, he was started on the pramoxine lotion twice daily, as needed, and the lesions cleared in about 6 months.
Text and photos courtesy of Jonathan Karnes, MD, medical director, MDFMR Dermatology Services, Augusta, ME. (Photo copyright retained.)
Al-Mutairi N, Hassanein A, Nour-Eldin O, et al. Generalized lichen nitidus. Pediatr Dermatol. 2005;22:158-160.

The miniscule papules arising suddenly on the trunk and genitals with linear arrays and clusters are clinically consistent with lichen nitidus, an uncommon eruption without a clear etiology.
Presentations may be focal or widespread and range from mildly itchy to asymptomatic. Children and young adults are most often affected. Linear arrays may appear in response to the trauma of scratching, which is termed the Koebner phenomenon. The differential diagnosis includes molluscum contagiosum, lichen planus, and lichen spinulosis. Usually these conditions can be distinguished clinically, but a biopsy would differentiate them, if needed. It’s worth noting, too, that lichen nitidus papules are monomorphic and lack the umbilication that is seen with molluscum contagiosum.
Cases of lichen nitidus clear up spontaneously, although usually months to years after diagnosis. Lichen nitidus is not contagious. Reassurance is, however, important as many patients may have experienced misdiagnosis and have concerns about sexual transmission because of the location of the papules on their genitals.
Treatment is often unnecessary. However, if itching is problematic, topical steroids and other topical antipruritics may be used. Topical hydrocortisone 2.5% cream or ointment for skin folds and genitals may be safely used, as well as topical triamcinolone 0.1% for the trunk and extremities. Pramoxine lotion (Sarna) is an over-the-counter nonsteroidal antipruritic. Oral nonsedating antihistamines can also be used as an adjunct.
This patient was reassured that the lesions were not contagious. Due to the itching, he was started on the pramoxine lotion twice daily, as needed, and the lesions cleared in about 6 months.
Text and photos courtesy of Jonathan Karnes, MD, medical director, MDFMR Dermatology Services, Augusta, ME. (Photo copyright retained.)

The miniscule papules arising suddenly on the trunk and genitals with linear arrays and clusters are clinically consistent with lichen nitidus, an uncommon eruption without a clear etiology.
Presentations may be focal or widespread and range from mildly itchy to asymptomatic. Children and young adults are most often affected. Linear arrays may appear in response to the trauma of scratching, which is termed the Koebner phenomenon. The differential diagnosis includes molluscum contagiosum, lichen planus, and lichen spinulosis. Usually these conditions can be distinguished clinically, but a biopsy would differentiate them, if needed. It’s worth noting, too, that lichen nitidus papules are monomorphic and lack the umbilication that is seen with molluscum contagiosum.
Cases of lichen nitidus clear up spontaneously, although usually months to years after diagnosis. Lichen nitidus is not contagious. Reassurance is, however, important as many patients may have experienced misdiagnosis and have concerns about sexual transmission because of the location of the papules on their genitals.
Treatment is often unnecessary. However, if itching is problematic, topical steroids and other topical antipruritics may be used. Topical hydrocortisone 2.5% cream or ointment for skin folds and genitals may be safely used, as well as topical triamcinolone 0.1% for the trunk and extremities. Pramoxine lotion (Sarna) is an over-the-counter nonsteroidal antipruritic. Oral nonsedating antihistamines can also be used as an adjunct.
This patient was reassured that the lesions were not contagious. Due to the itching, he was started on the pramoxine lotion twice daily, as needed, and the lesions cleared in about 6 months.
Text and photos courtesy of Jonathan Karnes, MD, medical director, MDFMR Dermatology Services, Augusta, ME. (Photo copyright retained.)
Al-Mutairi N, Hassanein A, Nour-Eldin O, et al. Generalized lichen nitidus. Pediatr Dermatol. 2005;22:158-160.
Al-Mutairi N, Hassanein A, Nour-Eldin O, et al. Generalized lichen nitidus. Pediatr Dermatol. 2005;22:158-160.
Home care for bortezomib safe and reduces hospital visits in myeloma patients
Home administration of bortezomib (Velcade), as a once or twice-weekly subcutaneous self-injection is safe in patients with myeloma, significantly reducing hospital visits, and likely improving quality of life, a study shows.
The majority (43 of 52 patients) successfully self-administered bortezomib and completed the course. Also, hospital visits for those on the so-called Homecare programme reduced by 50%, with most visits comprising a fortnightly drug pickup from the drive-through pharmacy.
The work was presented as a poster by lead author and researcher, Kanchana De Abrew, hematology consultant at University Hospital Southampton NHS Foundation Trust, at this year’s virtual British Society of Haematology (BSH) meeting. De Abrew conducted the study while at Queen Alexandra Hospital, Portsmouth.
“We wanted to minimize patient visits to hospital because with travel time and waiting time, patients can easily find a visit takes up a whole morning, so this relates to their quality of life as well as having financial implications for patients,” Dr. De Abrew said in an interview. It also reduced the impact on day units and improved capacity for other services.
Dr. De Abrew noted that the study was conducted in the pre-COVID-19 era, but that the current enhanced threat of infection only served to reinforce the benefits of self-administration at home and avoiding unnecessary hospital visits.
“This project could easily be set up in other hospitals and some other centers have already contacted us about this. It might suit rural areas,” she added.
‘Safe and effective’
Dr. Matthew Jenner, consultant hematologist for University Hospital Southampton NHS Foundation Trust, who was not involved in the study, remarked that the study demonstrated another way to deliver bortezomib outside of hospital in addition to home care services that require trained nurses to administer treatment. “With a modest amount of training of the patient and family, it is both a safe and effective way of delivering treatment. This reduces hospital visits for the patient and frees up much needed capacity for heavily stretched chemotherapy units, creating space for other newer treatments that require hospital attendance.
“It is of benefit all round to both the patients undertaking self-administration and those who benefit from improved capacity,” added Dr. Jenner.
Avoiding hospital visits
Myeloma patients are already immunosuppressed prior to treatment and then this worsens once on treatment. Once they are sitting in a clinic environment they are surrounded by similarly immunosuppressed patients, so their risk is heightened further.
Figures suggest myeloma cases are on the increase. Annually, the United Kingdom sees around 5,800 new cases of myeloma and incidence increased by a significant 32% between the periods of 1993-1995 and 2015-2017. These figures were reflected in the patient numbers at the Queen Alexandra Hospital where the study was carried out. Many patients receive bortezomib, which forms the backbone of four National Institute for Health and Care Excellence (NICE) approved regimens.
“Patients are living longer so in the early 2000s patients had a life expectancy of 2-3 years, whereas now patients live for around 5 years. Also, the scope and lines of treatments have increased a lot. Over 50% of patients are likely to have bortezomib at some point in their management,” explained Dr. De Abrew.
Bortezomib is given once or twice weekly as a subcutaneous injection, and this usually continues for approximately 6-8 months with four to six cycles. Administering the drug in hospital requires around a half-hour slot placing considerable burden on the hematology day unit resources, and this can adversely affect the patient experience with waiting times and the need for frequent hospital visits.
Patient or relatives taught to self-administer at home
In 2017, clinical nurse specialists taught suitable patients to self-administer bortezomib in the Homecare protocol. Patients collected a 2-week supply of the drug. The protocol aimed to improve patient quality of life by reducing hospital visits, and increasing capacity in the hematology day unit. Since the start of the programme in 2017, the majority (71) of myeloma patients at Portsmouth have been treated through the Homecare program.
Dr. De Abrew conducted a retrospective review of patients who received bortezomib between January and October 2019 aimed at determining the effectiveness of the Homecare programme. To this end, she measured the proportion able to commence the Homecare protocol; the proportion successful in completing treatment on the Homecare protocol; the amount of additional clinical nurse specialist time required to support the Homecare protocol; and the number of associated adverse incidents.
A total of 52 bortezomib-treated patients were included in the study. Patients were excluded if they were on a different combination of drugs that required hospital visits, or inpatient care for other reasons. Three patients ceased the drug – two because of toxicity, and one because of rapid progression. The average age of patients was 74 years, and 55.8% were using bortezomib as first-line, 36.5% second-line, and the remainder third-line or more.
The vast majority started the Homecare protocol (45/52), and 25 self-administered and 17 received a relative’s help. A total of 43 completed the self-administration protocol with two reverting to hospital assistance. Bortezomib was given for four to six cycles lasting around 6-8 months.
Clinical nurse specialists trained 38 patients for home care, with an average training time of 43 minutes. Two of these patients were considered unsuitable for self-administration. The remainder were trained by ward nurses or did not require training having received bortezomib previously.
A total of 20 patients required additional clinical nurse specialist time requiring an average of 55 minutes. Of those requiring additional support: Seven needed retraining; two needed the first dose delivered by a nurse specialist; two requested help from the hematology unit; and nine wanted general extra support – for example, help with injection site queries (usually administered to the abdominal area), reassurance during administration, syringe queries, administrative queries, and queries around spillages.
“Importantly, patients always have the phone number of the nurse specialist at hand. But most people managed okay, and even if they needed additional support they still got there,” remarked Dr. De Abrew.
In terms of adverse events, there were six in total. These included three reported spillages (with no harm caused), and three experienced injection site incidents (rash, pain). “We found a low number of reported adverse events,” she said.
Dr. De Abrew added that generally, many more medications were being converted to subcutaneous formulations in myeloma and other hematology conditions. “Perhaps these results could inform self-administration of other drugs. In hematology, we get so many new drugs come through every year, but we don’t get the increased resources to manage this in the day units. Broadening self-administration could really help with capacity as well as improve quality of life for the patients.
“These results show that it can be done!” she said.
Dr. De Abrew declared no relevant conflicts of interest. Dr. Jenner declared receiving honoraria from Janssen, which manufactures branded Velcade (bortezomib).
A version of this story originally appeared on Medscape.com.
Home administration of bortezomib (Velcade), as a once or twice-weekly subcutaneous self-injection is safe in patients with myeloma, significantly reducing hospital visits, and likely improving quality of life, a study shows.
The majority (43 of 52 patients) successfully self-administered bortezomib and completed the course. Also, hospital visits for those on the so-called Homecare programme reduced by 50%, with most visits comprising a fortnightly drug pickup from the drive-through pharmacy.
The work was presented as a poster by lead author and researcher, Kanchana De Abrew, hematology consultant at University Hospital Southampton NHS Foundation Trust, at this year’s virtual British Society of Haematology (BSH) meeting. De Abrew conducted the study while at Queen Alexandra Hospital, Portsmouth.
“We wanted to minimize patient visits to hospital because with travel time and waiting time, patients can easily find a visit takes up a whole morning, so this relates to their quality of life as well as having financial implications for patients,” Dr. De Abrew said in an interview. It also reduced the impact on day units and improved capacity for other services.
Dr. De Abrew noted that the study was conducted in the pre-COVID-19 era, but that the current enhanced threat of infection only served to reinforce the benefits of self-administration at home and avoiding unnecessary hospital visits.
“This project could easily be set up in other hospitals and some other centers have already contacted us about this. It might suit rural areas,” she added.
‘Safe and effective’
Dr. Matthew Jenner, consultant hematologist for University Hospital Southampton NHS Foundation Trust, who was not involved in the study, remarked that the study demonstrated another way to deliver bortezomib outside of hospital in addition to home care services that require trained nurses to administer treatment. “With a modest amount of training of the patient and family, it is both a safe and effective way of delivering treatment. This reduces hospital visits for the patient and frees up much needed capacity for heavily stretched chemotherapy units, creating space for other newer treatments that require hospital attendance.
“It is of benefit all round to both the patients undertaking self-administration and those who benefit from improved capacity,” added Dr. Jenner.
Avoiding hospital visits
Myeloma patients are already immunosuppressed prior to treatment and then this worsens once on treatment. Once they are sitting in a clinic environment they are surrounded by similarly immunosuppressed patients, so their risk is heightened further.
Figures suggest myeloma cases are on the increase. Annually, the United Kingdom sees around 5,800 new cases of myeloma and incidence increased by a significant 32% between the periods of 1993-1995 and 2015-2017. These figures were reflected in the patient numbers at the Queen Alexandra Hospital where the study was carried out. Many patients receive bortezomib, which forms the backbone of four National Institute for Health and Care Excellence (NICE) approved regimens.
“Patients are living longer so in the early 2000s patients had a life expectancy of 2-3 years, whereas now patients live for around 5 years. Also, the scope and lines of treatments have increased a lot. Over 50% of patients are likely to have bortezomib at some point in their management,” explained Dr. De Abrew.
Bortezomib is given once or twice weekly as a subcutaneous injection, and this usually continues for approximately 6-8 months with four to six cycles. Administering the drug in hospital requires around a half-hour slot placing considerable burden on the hematology day unit resources, and this can adversely affect the patient experience with waiting times and the need for frequent hospital visits.
Patient or relatives taught to self-administer at home
In 2017, clinical nurse specialists taught suitable patients to self-administer bortezomib in the Homecare protocol. Patients collected a 2-week supply of the drug. The protocol aimed to improve patient quality of life by reducing hospital visits, and increasing capacity in the hematology day unit. Since the start of the programme in 2017, the majority (71) of myeloma patients at Portsmouth have been treated through the Homecare program.
Dr. De Abrew conducted a retrospective review of patients who received bortezomib between January and October 2019 aimed at determining the effectiveness of the Homecare programme. To this end, she measured the proportion able to commence the Homecare protocol; the proportion successful in completing treatment on the Homecare protocol; the amount of additional clinical nurse specialist time required to support the Homecare protocol; and the number of associated adverse incidents.
A total of 52 bortezomib-treated patients were included in the study. Patients were excluded if they were on a different combination of drugs that required hospital visits, or inpatient care for other reasons. Three patients ceased the drug – two because of toxicity, and one because of rapid progression. The average age of patients was 74 years, and 55.8% were using bortezomib as first-line, 36.5% second-line, and the remainder third-line or more.
The vast majority started the Homecare protocol (45/52), and 25 self-administered and 17 received a relative’s help. A total of 43 completed the self-administration protocol with two reverting to hospital assistance. Bortezomib was given for four to six cycles lasting around 6-8 months.
Clinical nurse specialists trained 38 patients for home care, with an average training time of 43 minutes. Two of these patients were considered unsuitable for self-administration. The remainder were trained by ward nurses or did not require training having received bortezomib previously.
A total of 20 patients required additional clinical nurse specialist time requiring an average of 55 minutes. Of those requiring additional support: Seven needed retraining; two needed the first dose delivered by a nurse specialist; two requested help from the hematology unit; and nine wanted general extra support – for example, help with injection site queries (usually administered to the abdominal area), reassurance during administration, syringe queries, administrative queries, and queries around spillages.
“Importantly, patients always have the phone number of the nurse specialist at hand. But most people managed okay, and even if they needed additional support they still got there,” remarked Dr. De Abrew.
In terms of adverse events, there were six in total. These included three reported spillages (with no harm caused), and three experienced injection site incidents (rash, pain). “We found a low number of reported adverse events,” she said.
Dr. De Abrew added that generally, many more medications were being converted to subcutaneous formulations in myeloma and other hematology conditions. “Perhaps these results could inform self-administration of other drugs. In hematology, we get so many new drugs come through every year, but we don’t get the increased resources to manage this in the day units. Broadening self-administration could really help with capacity as well as improve quality of life for the patients.
“These results show that it can be done!” she said.
Dr. De Abrew declared no relevant conflicts of interest. Dr. Jenner declared receiving honoraria from Janssen, which manufactures branded Velcade (bortezomib).
A version of this story originally appeared on Medscape.com.
Home administration of bortezomib (Velcade), as a once or twice-weekly subcutaneous self-injection is safe in patients with myeloma, significantly reducing hospital visits, and likely improving quality of life, a study shows.
The majority (43 of 52 patients) successfully self-administered bortezomib and completed the course. Also, hospital visits for those on the so-called Homecare programme reduced by 50%, with most visits comprising a fortnightly drug pickup from the drive-through pharmacy.
The work was presented as a poster by lead author and researcher, Kanchana De Abrew, hematology consultant at University Hospital Southampton NHS Foundation Trust, at this year’s virtual British Society of Haematology (BSH) meeting. De Abrew conducted the study while at Queen Alexandra Hospital, Portsmouth.
“We wanted to minimize patient visits to hospital because with travel time and waiting time, patients can easily find a visit takes up a whole morning, so this relates to their quality of life as well as having financial implications for patients,” Dr. De Abrew said in an interview. It also reduced the impact on day units and improved capacity for other services.
Dr. De Abrew noted that the study was conducted in the pre-COVID-19 era, but that the current enhanced threat of infection only served to reinforce the benefits of self-administration at home and avoiding unnecessary hospital visits.
“This project could easily be set up in other hospitals and some other centers have already contacted us about this. It might suit rural areas,” she added.
‘Safe and effective’
Dr. Matthew Jenner, consultant hematologist for University Hospital Southampton NHS Foundation Trust, who was not involved in the study, remarked that the study demonstrated another way to deliver bortezomib outside of hospital in addition to home care services that require trained nurses to administer treatment. “With a modest amount of training of the patient and family, it is both a safe and effective way of delivering treatment. This reduces hospital visits for the patient and frees up much needed capacity for heavily stretched chemotherapy units, creating space for other newer treatments that require hospital attendance.
“It is of benefit all round to both the patients undertaking self-administration and those who benefit from improved capacity,” added Dr. Jenner.
Avoiding hospital visits
Myeloma patients are already immunosuppressed prior to treatment and then this worsens once on treatment. Once they are sitting in a clinic environment they are surrounded by similarly immunosuppressed patients, so their risk is heightened further.
Figures suggest myeloma cases are on the increase. Annually, the United Kingdom sees around 5,800 new cases of myeloma and incidence increased by a significant 32% between the periods of 1993-1995 and 2015-2017. These figures were reflected in the patient numbers at the Queen Alexandra Hospital where the study was carried out. Many patients receive bortezomib, which forms the backbone of four National Institute for Health and Care Excellence (NICE) approved regimens.
“Patients are living longer so in the early 2000s patients had a life expectancy of 2-3 years, whereas now patients live for around 5 years. Also, the scope and lines of treatments have increased a lot. Over 50% of patients are likely to have bortezomib at some point in their management,” explained Dr. De Abrew.
Bortezomib is given once or twice weekly as a subcutaneous injection, and this usually continues for approximately 6-8 months with four to six cycles. Administering the drug in hospital requires around a half-hour slot placing considerable burden on the hematology day unit resources, and this can adversely affect the patient experience with waiting times and the need for frequent hospital visits.
Patient or relatives taught to self-administer at home
In 2017, clinical nurse specialists taught suitable patients to self-administer bortezomib in the Homecare protocol. Patients collected a 2-week supply of the drug. The protocol aimed to improve patient quality of life by reducing hospital visits, and increasing capacity in the hematology day unit. Since the start of the programme in 2017, the majority (71) of myeloma patients at Portsmouth have been treated through the Homecare program.
Dr. De Abrew conducted a retrospective review of patients who received bortezomib between January and October 2019 aimed at determining the effectiveness of the Homecare programme. To this end, she measured the proportion able to commence the Homecare protocol; the proportion successful in completing treatment on the Homecare protocol; the amount of additional clinical nurse specialist time required to support the Homecare protocol; and the number of associated adverse incidents.
A total of 52 bortezomib-treated patients were included in the study. Patients were excluded if they were on a different combination of drugs that required hospital visits, or inpatient care for other reasons. Three patients ceased the drug – two because of toxicity, and one because of rapid progression. The average age of patients was 74 years, and 55.8% were using bortezomib as first-line, 36.5% second-line, and the remainder third-line or more.
The vast majority started the Homecare protocol (45/52), and 25 self-administered and 17 received a relative’s help. A total of 43 completed the self-administration protocol with two reverting to hospital assistance. Bortezomib was given for four to six cycles lasting around 6-8 months.
Clinical nurse specialists trained 38 patients for home care, with an average training time of 43 minutes. Two of these patients were considered unsuitable for self-administration. The remainder were trained by ward nurses or did not require training having received bortezomib previously.
A total of 20 patients required additional clinical nurse specialist time requiring an average of 55 minutes. Of those requiring additional support: Seven needed retraining; two needed the first dose delivered by a nurse specialist; two requested help from the hematology unit; and nine wanted general extra support – for example, help with injection site queries (usually administered to the abdominal area), reassurance during administration, syringe queries, administrative queries, and queries around spillages.
“Importantly, patients always have the phone number of the nurse specialist at hand. But most people managed okay, and even if they needed additional support they still got there,” remarked Dr. De Abrew.
In terms of adverse events, there were six in total. These included three reported spillages (with no harm caused), and three experienced injection site incidents (rash, pain). “We found a low number of reported adverse events,” she said.
Dr. De Abrew added that generally, many more medications were being converted to subcutaneous formulations in myeloma and other hematology conditions. “Perhaps these results could inform self-administration of other drugs. In hematology, we get so many new drugs come through every year, but we don’t get the increased resources to manage this in the day units. Broadening self-administration could really help with capacity as well as improve quality of life for the patients.
“These results show that it can be done!” she said.
Dr. De Abrew declared no relevant conflicts of interest. Dr. Jenner declared receiving honoraria from Janssen, which manufactures branded Velcade (bortezomib).
A version of this story originally appeared on Medscape.com.
Search for a snakebite drug might lead to a COVID treatment, too
Matthew Lewin, MD, PhD, founder of the Center for Exploration and Travel Health at the California Academy of Sciences, was researching snakebite treatments in rural locations in preparation for an expedition to the Philippines in 2011.
The story of a renowned herpetologist from the academy, Joseph Slowinski, who was bitten by a highly venomous krait in Myanmar and couldn’t get to a hospital in time to save his life a decade earlier, weighed on the emergency room doctor.
“I concluded that I needed something small and compact and that doesn’t care what kind of snake,” Dr. Lewin said.
It didn’t exist. That set Dr. Lewin in pursuit of a modern snakebite drug, a journey that finds his Corte Madera, Calif., company, Ophirex, nearing a promising oral treatment that fits in a pocket; is stable, easy to use, and affordable; and treats the venom from many species. “That’s the holy grail of snakebite treatment,” he said.
His work has gotten a boost with multimillion-dollar grants from a British charity and the U.S. Army. If it works – and it has been shown to work extremely well in mice and pigs – it could save tens of thousands of lives a year.
Dr. Lewin and Ophirex are not alone in their quest. Snakebites kill nearly 140,000 people a year, overwhelmingly in impoverished rural areas of Asia and Africa without adequate medical infrastructure and knowledge to administer antivenom. Though just a few people die each year in the United States from snakebites, the problem has risen to the top of the list of global health concerns in recent years. Funding has soared, and other research groups have also done promising work on new treatments. Herpetologists say deforestation and climate change are increasing human-snake encounters by forcing snakes to move to new habitats.
Dr. Lewin’s research is centered on a drug called varespladib. The enzyme inhibitor has proven itself in in-vitro lab studies and has effectively saved mice and pigs dosed with venom.
Along the way, Dr. Lewin and his team have come across another potential use for the drug. Varespladib has a positive effect on acute respiratory distress syndrome, associated with COVID-19. Next year, Ophirex will conduct human trials for the possible treatment of the condition funded with $9.9 million from the Army.
The link to a snakebite? The inflammation of the lungs caused by the coronavirus produces the sPLA2 enzyme. A more deadly version of the same enzyme is produced by snake venom.
The other companies that have come up with promising approaches to snakebite aren’t as far along as Ophirex. At the University of California-Irvine, chemist Ken Shea and his team created a nanogel – a kind of polymer used in medical applications – that blocks key proteins in the venom that cause cell destruction. At the Technical University of Denmark, Copenhagen, Andreas Laustsen is looking at engineering bacteria to manufacture anti-venom in fermentation tanks.
The days of incising a snakebite and sucking out the poison are long over, but the current treatment for venomous snakebites remains archaic.
Since the early 1900s, antivenom has been made by injecting horses or other animals with venom milked from snakes and diluted. The animals’ immune systems generate antibodies over several months, and blood plasma is taken from the animals and antibodies extracted from it.
It’s extremely expensive. Hospitals in the United States can charge as much as $15,000 a vial – and a single snakebite might require anywhere from 4 to 50 vials. Moreover, antivenom exists for little more than half the world’s species of venomous snakes.
A major problem is the roughly 2 hours it takes on average for a snakebite victim to reach a hospital and begin treatment. The chemical weapon that is venom starts immediately to destroy cells as it digests its next meal, making fast treatment essential to saving lives and preventing tissue loss.
“The two-hour window between fang and needle is where the most damage occurs,” said Leslie Boyer, director of the University of Arizona’s Venom Immunochemistry, Pharmacology and Emergency Response (VIPER) Institute. “We have a saying, ‘Time is tissue.’ ”
That’s why the search for a new snakebite drug has focused on an inexpensive treatment that can be taken into the field. Dr. Lewin’s drug wouldn’t replace antivenom. Instead, he thinks of it as the first line of defense until the victim can reach a hospital for antivenom treatment.
Dr. Lewin said he expects the drug to be inexpensive, so people in regions where snakebites are common can afford it.
Venom is extremely complicated chemically, and Dr. Lewin began his search by sussing out which of its myriad components to block. He zeroed in on the sPLA2 enzyme.
Surveying the literature about drugs that had been clinically tested for other conditions, he came across varespladib. It had been developed jointly by Eli Lilly and Shionogi, a Japanese pharmaceutical company, as a possible treatment for sepsis. They had never taken it to market.
If it worked, Dr. Lewin could license the right to produce the drug, which had already been thoroughly studied and was shown to be safe.
He placed venom in an array of test tubes. Varespladib and other drugs were added to the venom. He then added a reagent. If the venom was still active, the solution would turn yellow; if it was neutralized, it would remain clear.
The vials with varespladib “came up completely blank,” he said. “It was so stunning I said, ‘I must have made a mistake.’ ”
With a small grant, he sent the drug to the Yale Center for Molecular Discovery and found that varespladib effectively neutralized the venom of snakes found on six continents. The results were published in the journal Toxins and sent ripples through the small community of snakebite researchers.
Dr. Lewin then conducted tests on mice and pigs. Both were successful.
Human clinical trials are next, but they have been delayed by the pandemic. They are scheduled to get underway next spring.
Along the way, Dr. Lewin was fortunate enough to make some good connections that led to funding. In 2012, he attended a party at the Mill Valley, Calif., home of Jerry Harrison, the former guitarist and keyboardist for Talking Heads. Mr. Harrison had long been interested in business and start-ups – he said he was the most careful reader of the ’80s band’s contracts – and at the party he asked “if anyone had any ideas lying fallow,” Mr. Harrison said.
“And Matt pipes up and says, ‘I have this idea how to prevent people from dying from snakebites,’ ” Mr. Harrison said.
The musician said he was a bit taken aback by such an unusual and dire problem, but “I thought if it can save lives we have to do it,” he said. He became an investor and cofounder of Ophirex with Dr. Lewin.
Dr. Lewin met Lt. Col. Rebecca Carter, a biochemist who was assigned to lead the Medical Modernization Division of Air Force Special Operations Command, in 2016 when she attended a Venom Week conference in Greenville, N.C. He was presenting the results of his mouse studies. She told him about her first mission: to find a universal antivenom for medics on special operations teams in Africa. She persuaded the Special Operations Command Biomedical Research Advisory Group, which specializes in getting critical projects to production, to grant Ophirex $148,000 in 2017. She later retired from the Air Force and now works for Ophirex as vice president.
More multimillion-dollar grants followed, including the Army’s COVID grant. Clinical trials are scheduled to begin this winter.
Despite the progress and the sudden cash flow, Dr. Lewin tamps down talk of a universal snakebite cure. “There’s enough evidence to say the drug deserves to have its day in clinical trials,” he said.
KHN (Kaiser Health News) is a nonprofit news service covering health issues. It is an editorially independent program of KFF (Kaiser Family Foundation), which is not affiliated with Kaiser Permanente.
Matthew Lewin, MD, PhD, founder of the Center for Exploration and Travel Health at the California Academy of Sciences, was researching snakebite treatments in rural locations in preparation for an expedition to the Philippines in 2011.
The story of a renowned herpetologist from the academy, Joseph Slowinski, who was bitten by a highly venomous krait in Myanmar and couldn’t get to a hospital in time to save his life a decade earlier, weighed on the emergency room doctor.
“I concluded that I needed something small and compact and that doesn’t care what kind of snake,” Dr. Lewin said.
It didn’t exist. That set Dr. Lewin in pursuit of a modern snakebite drug, a journey that finds his Corte Madera, Calif., company, Ophirex, nearing a promising oral treatment that fits in a pocket; is stable, easy to use, and affordable; and treats the venom from many species. “That’s the holy grail of snakebite treatment,” he said.
His work has gotten a boost with multimillion-dollar grants from a British charity and the U.S. Army. If it works – and it has been shown to work extremely well in mice and pigs – it could save tens of thousands of lives a year.
Dr. Lewin and Ophirex are not alone in their quest. Snakebites kill nearly 140,000 people a year, overwhelmingly in impoverished rural areas of Asia and Africa without adequate medical infrastructure and knowledge to administer antivenom. Though just a few people die each year in the United States from snakebites, the problem has risen to the top of the list of global health concerns in recent years. Funding has soared, and other research groups have also done promising work on new treatments. Herpetologists say deforestation and climate change are increasing human-snake encounters by forcing snakes to move to new habitats.
Dr. Lewin’s research is centered on a drug called varespladib. The enzyme inhibitor has proven itself in in-vitro lab studies and has effectively saved mice and pigs dosed with venom.
Along the way, Dr. Lewin and his team have come across another potential use for the drug. Varespladib has a positive effect on acute respiratory distress syndrome, associated with COVID-19. Next year, Ophirex will conduct human trials for the possible treatment of the condition funded with $9.9 million from the Army.
The link to a snakebite? The inflammation of the lungs caused by the coronavirus produces the sPLA2 enzyme. A more deadly version of the same enzyme is produced by snake venom.
The other companies that have come up with promising approaches to snakebite aren’t as far along as Ophirex. At the University of California-Irvine, chemist Ken Shea and his team created a nanogel – a kind of polymer used in medical applications – that blocks key proteins in the venom that cause cell destruction. At the Technical University of Denmark, Copenhagen, Andreas Laustsen is looking at engineering bacteria to manufacture anti-venom in fermentation tanks.
The days of incising a snakebite and sucking out the poison are long over, but the current treatment for venomous snakebites remains archaic.
Since the early 1900s, antivenom has been made by injecting horses or other animals with venom milked from snakes and diluted. The animals’ immune systems generate antibodies over several months, and blood plasma is taken from the animals and antibodies extracted from it.
It’s extremely expensive. Hospitals in the United States can charge as much as $15,000 a vial – and a single snakebite might require anywhere from 4 to 50 vials. Moreover, antivenom exists for little more than half the world’s species of venomous snakes.
A major problem is the roughly 2 hours it takes on average for a snakebite victim to reach a hospital and begin treatment. The chemical weapon that is venom starts immediately to destroy cells as it digests its next meal, making fast treatment essential to saving lives and preventing tissue loss.
“The two-hour window between fang and needle is where the most damage occurs,” said Leslie Boyer, director of the University of Arizona’s Venom Immunochemistry, Pharmacology and Emergency Response (VIPER) Institute. “We have a saying, ‘Time is tissue.’ ”
That’s why the search for a new snakebite drug has focused on an inexpensive treatment that can be taken into the field. Dr. Lewin’s drug wouldn’t replace antivenom. Instead, he thinks of it as the first line of defense until the victim can reach a hospital for antivenom treatment.
Dr. Lewin said he expects the drug to be inexpensive, so people in regions where snakebites are common can afford it.
Venom is extremely complicated chemically, and Dr. Lewin began his search by sussing out which of its myriad components to block. He zeroed in on the sPLA2 enzyme.
Surveying the literature about drugs that had been clinically tested for other conditions, he came across varespladib. It had been developed jointly by Eli Lilly and Shionogi, a Japanese pharmaceutical company, as a possible treatment for sepsis. They had never taken it to market.
If it worked, Dr. Lewin could license the right to produce the drug, which had already been thoroughly studied and was shown to be safe.
He placed venom in an array of test tubes. Varespladib and other drugs were added to the venom. He then added a reagent. If the venom was still active, the solution would turn yellow; if it was neutralized, it would remain clear.
The vials with varespladib “came up completely blank,” he said. “It was so stunning I said, ‘I must have made a mistake.’ ”
With a small grant, he sent the drug to the Yale Center for Molecular Discovery and found that varespladib effectively neutralized the venom of snakes found on six continents. The results were published in the journal Toxins and sent ripples through the small community of snakebite researchers.
Dr. Lewin then conducted tests on mice and pigs. Both were successful.
Human clinical trials are next, but they have been delayed by the pandemic. They are scheduled to get underway next spring.
Along the way, Dr. Lewin was fortunate enough to make some good connections that led to funding. In 2012, he attended a party at the Mill Valley, Calif., home of Jerry Harrison, the former guitarist and keyboardist for Talking Heads. Mr. Harrison had long been interested in business and start-ups – he said he was the most careful reader of the ’80s band’s contracts – and at the party he asked “if anyone had any ideas lying fallow,” Mr. Harrison said.
“And Matt pipes up and says, ‘I have this idea how to prevent people from dying from snakebites,’ ” Mr. Harrison said.
The musician said he was a bit taken aback by such an unusual and dire problem, but “I thought if it can save lives we have to do it,” he said. He became an investor and cofounder of Ophirex with Dr. Lewin.
Dr. Lewin met Lt. Col. Rebecca Carter, a biochemist who was assigned to lead the Medical Modernization Division of Air Force Special Operations Command, in 2016 when she attended a Venom Week conference in Greenville, N.C. He was presenting the results of his mouse studies. She told him about her first mission: to find a universal antivenom for medics on special operations teams in Africa. She persuaded the Special Operations Command Biomedical Research Advisory Group, which specializes in getting critical projects to production, to grant Ophirex $148,000 in 2017. She later retired from the Air Force and now works for Ophirex as vice president.
More multimillion-dollar grants followed, including the Army’s COVID grant. Clinical trials are scheduled to begin this winter.
Despite the progress and the sudden cash flow, Dr. Lewin tamps down talk of a universal snakebite cure. “There’s enough evidence to say the drug deserves to have its day in clinical trials,” he said.
KHN (Kaiser Health News) is a nonprofit news service covering health issues. It is an editorially independent program of KFF (Kaiser Family Foundation), which is not affiliated with Kaiser Permanente.
Matthew Lewin, MD, PhD, founder of the Center for Exploration and Travel Health at the California Academy of Sciences, was researching snakebite treatments in rural locations in preparation for an expedition to the Philippines in 2011.
The story of a renowned herpetologist from the academy, Joseph Slowinski, who was bitten by a highly venomous krait in Myanmar and couldn’t get to a hospital in time to save his life a decade earlier, weighed on the emergency room doctor.
“I concluded that I needed something small and compact and that doesn’t care what kind of snake,” Dr. Lewin said.
It didn’t exist. That set Dr. Lewin in pursuit of a modern snakebite drug, a journey that finds his Corte Madera, Calif., company, Ophirex, nearing a promising oral treatment that fits in a pocket; is stable, easy to use, and affordable; and treats the venom from many species. “That’s the holy grail of snakebite treatment,” he said.
His work has gotten a boost with multimillion-dollar grants from a British charity and the U.S. Army. If it works – and it has been shown to work extremely well in mice and pigs – it could save tens of thousands of lives a year.
Dr. Lewin and Ophirex are not alone in their quest. Snakebites kill nearly 140,000 people a year, overwhelmingly in impoverished rural areas of Asia and Africa without adequate medical infrastructure and knowledge to administer antivenom. Though just a few people die each year in the United States from snakebites, the problem has risen to the top of the list of global health concerns in recent years. Funding has soared, and other research groups have also done promising work on new treatments. Herpetologists say deforestation and climate change are increasing human-snake encounters by forcing snakes to move to new habitats.
Dr. Lewin’s research is centered on a drug called varespladib. The enzyme inhibitor has proven itself in in-vitro lab studies and has effectively saved mice and pigs dosed with venom.
Along the way, Dr. Lewin and his team have come across another potential use for the drug. Varespladib has a positive effect on acute respiratory distress syndrome, associated with COVID-19. Next year, Ophirex will conduct human trials for the possible treatment of the condition funded with $9.9 million from the Army.
The link to a snakebite? The inflammation of the lungs caused by the coronavirus produces the sPLA2 enzyme. A more deadly version of the same enzyme is produced by snake venom.
The other companies that have come up with promising approaches to snakebite aren’t as far along as Ophirex. At the University of California-Irvine, chemist Ken Shea and his team created a nanogel – a kind of polymer used in medical applications – that blocks key proteins in the venom that cause cell destruction. At the Technical University of Denmark, Copenhagen, Andreas Laustsen is looking at engineering bacteria to manufacture anti-venom in fermentation tanks.
The days of incising a snakebite and sucking out the poison are long over, but the current treatment for venomous snakebites remains archaic.
Since the early 1900s, antivenom has been made by injecting horses or other animals with venom milked from snakes and diluted. The animals’ immune systems generate antibodies over several months, and blood plasma is taken from the animals and antibodies extracted from it.
It’s extremely expensive. Hospitals in the United States can charge as much as $15,000 a vial – and a single snakebite might require anywhere from 4 to 50 vials. Moreover, antivenom exists for little more than half the world’s species of venomous snakes.
A major problem is the roughly 2 hours it takes on average for a snakebite victim to reach a hospital and begin treatment. The chemical weapon that is venom starts immediately to destroy cells as it digests its next meal, making fast treatment essential to saving lives and preventing tissue loss.
“The two-hour window between fang and needle is where the most damage occurs,” said Leslie Boyer, director of the University of Arizona’s Venom Immunochemistry, Pharmacology and Emergency Response (VIPER) Institute. “We have a saying, ‘Time is tissue.’ ”
That’s why the search for a new snakebite drug has focused on an inexpensive treatment that can be taken into the field. Dr. Lewin’s drug wouldn’t replace antivenom. Instead, he thinks of it as the first line of defense until the victim can reach a hospital for antivenom treatment.
Dr. Lewin said he expects the drug to be inexpensive, so people in regions where snakebites are common can afford it.
Venom is extremely complicated chemically, and Dr. Lewin began his search by sussing out which of its myriad components to block. He zeroed in on the sPLA2 enzyme.
Surveying the literature about drugs that had been clinically tested for other conditions, he came across varespladib. It had been developed jointly by Eli Lilly and Shionogi, a Japanese pharmaceutical company, as a possible treatment for sepsis. They had never taken it to market.
If it worked, Dr. Lewin could license the right to produce the drug, which had already been thoroughly studied and was shown to be safe.
He placed venom in an array of test tubes. Varespladib and other drugs were added to the venom. He then added a reagent. If the venom was still active, the solution would turn yellow; if it was neutralized, it would remain clear.
The vials with varespladib “came up completely blank,” he said. “It was so stunning I said, ‘I must have made a mistake.’ ”
With a small grant, he sent the drug to the Yale Center for Molecular Discovery and found that varespladib effectively neutralized the venom of snakes found on six continents. The results were published in the journal Toxins and sent ripples through the small community of snakebite researchers.
Dr. Lewin then conducted tests on mice and pigs. Both were successful.
Human clinical trials are next, but they have been delayed by the pandemic. They are scheduled to get underway next spring.
Along the way, Dr. Lewin was fortunate enough to make some good connections that led to funding. In 2012, he attended a party at the Mill Valley, Calif., home of Jerry Harrison, the former guitarist and keyboardist for Talking Heads. Mr. Harrison had long been interested in business and start-ups – he said he was the most careful reader of the ’80s band’s contracts – and at the party he asked “if anyone had any ideas lying fallow,” Mr. Harrison said.
“And Matt pipes up and says, ‘I have this idea how to prevent people from dying from snakebites,’ ” Mr. Harrison said.
The musician said he was a bit taken aback by such an unusual and dire problem, but “I thought if it can save lives we have to do it,” he said. He became an investor and cofounder of Ophirex with Dr. Lewin.
Dr. Lewin met Lt. Col. Rebecca Carter, a biochemist who was assigned to lead the Medical Modernization Division of Air Force Special Operations Command, in 2016 when she attended a Venom Week conference in Greenville, N.C. He was presenting the results of his mouse studies. She told him about her first mission: to find a universal antivenom for medics on special operations teams in Africa. She persuaded the Special Operations Command Biomedical Research Advisory Group, which specializes in getting critical projects to production, to grant Ophirex $148,000 in 2017. She later retired from the Air Force and now works for Ophirex as vice president.
More multimillion-dollar grants followed, including the Army’s COVID grant. Clinical trials are scheduled to begin this winter.
Despite the progress and the sudden cash flow, Dr. Lewin tamps down talk of a universal snakebite cure. “There’s enough evidence to say the drug deserves to have its day in clinical trials,” he said.
KHN (Kaiser Health News) is a nonprofit news service covering health issues. It is an editorially independent program of KFF (Kaiser Family Foundation), which is not affiliated with Kaiser Permanente.
Moral distress: COVID-19 shortages prompt tough decisions at bedside
Choosing which hospitalized COVID-19 patients receive potentially lifesaving care, making urgent calls for ventilators and other equipment, and triaging care based on patient age and comorbidities were among the challenges revealed in new feedback from health care leaders and frontline workers.
Even though many hospitals have contingency plans for how to allocate resources and triage patient care during crisis capacity, for many providers during the real-world COVID-19 trial of these protocols, they fell short.
Many hospital crisis capacity plans, for example, were too general to address all the specific challenges arising during the pandemic, investigators report in a study published online Nov. 6 in JAMA Network Open.
“Our research shows that the types of challenges and approach to resource limitation in real-world clinical settings during the pandemic differed in practice from how we had prepared in theory,” lead author Catherine Butler, MD, told Medscape Medical News. Insufficient dialysis treatment time, staff shortages, and routine supply scarcity are examples “for which there was not an established plan or approach for appropriate allocation.”
“This left frontline clinicians to determine what constituted an acceptable standard of care and to make difficult allocation decisions at the bedside,” added Butler, acting instructor in the Division of Nephrology at the University of Washington in Seattle and a research fellow at the VA Health Services Research and Development Seattle-Denver Center of Innovation.
The investigators conducted semistructured interviews in April and May with 61 clinicians and health leaders. Mean age was 46 years, 63% were women, and participants practiced in 15 states. Most participants hailed from locations hard-hit by the pandemic at the time, including Seattle, New York City, and New Orleans.
Triage tribulations
The qualitative study included comments from respondents on three major themes that emerged: planning for crisis capacity, adapting to resource limitation, and the multiple unprecedented barriers to care delivery.
Overall, planning and support from institutional leaders varied. One provider said, “Talking to administration, and they just seemed really disengaged with the problem. We asked multiple times if there was a triage command center or a plan for what would occur if we got to the point where we had to triage resources. They said there was, but they wouldn’t provide it to us.”
Another had a more positive experience. “The biggest deal in the ethics world in the last 2 months has been preparing in case we need to triage. So, we have a very detailed, elaborate, well thought-out triage policy … that was done at the highest levels of the system.”
Clinicians said they participate on triage teams – despite the moral weight and likely emotional burden – out of a sense of duty.
Interestingly, some providers on these teams also reported a reluctance to reveal their participation to colleagues. “I didn’t feel like I should tell anybody … even some of my close friends who are physicians and nurses here … that I’ve been asked to be on this [triage team],” one respondent said. “I didn’t feel like I should make it known.”
Adapting to scarce resources
Multiple providers said they faced difficult care decisions because of limited dialysis or supply shortages. “They felt that this patient had the greatest likelihood of benefiting from most aggressive therapy. … I think there was probably like 5 or 6 patients in the ICU … and then you had this 35-year-old with no comorbidities,” one respondent said. “That’s who the ICU dialyzed, and I couldn’t really disagree.”
“I emailed all of [my colleagues], and I said ‘Help! We need X, we need CRRT [continuous renal replacement therapy] machines, we need dialysates,’ “ another responded.
“One of the attendings had a tweet when we were running out of CRRT. He had a tweet about, ‘Can anybody give us supplies for CRRT?’ So, it got to that. You do anything. You get really desperate,” the clinician said.
Other providers reported getting innovative under the circumstances. “My partner’s son, he actually borrowed a couple of 3D printers. He printed some of these face shields, and then they got the formula, or the specifics as to how to make this particular connection to connect to a dialysis machine to generate dialysate. So, he also printed some of those from the 3D printer.”
Dire situations with dialysis
Another respondent understood the focus on ventilators and ICU beds throughout the crisis, but said “no one has acknowledged that dialysis has been one of the most, if not the most, limited resources.”
Another clinician expressed surprise at a decision made in the face of limited availability of traditional dialysis. “A month ago, people said we were going to do acute peritoneal dialysis [PD]. And I said, ‘No, we’re not going to do acute PD. PD, it’s not that great for acute patients, sick people in the ICUs. I don’t think we’re going to do PD.’
“Three days later we were doing acute PD. I mean, that was unbelievable!”
Some institutions rationed dialysis therapy. “We went through the entire list at the beginning of the week and [said], this person has to dialyze these days, this person would probably benefit from a dialysis session, a third group person we could probably just string along and medically manage if we needed to,” one provider said.
Another respondent reported a different strategy. “No one was not getting dialysis, but there were a lot of people getting minimal dialysis. Even though people were getting treated, resources were very stretched.”
Changing family dynamics
COVID-19 has naturally changed how clinicians speak with families. One respondent recalled looking at the ICU physician and being like, ‘Have you talked to the son this week?’ And she’s like, ‘Oh my God, no. … Did you talk to the son?’ I’m like, ‘Oh my God, no.’ “
They realized, the respondent added, “that none of us had called the family because it’s just not in your workflow. You’re so used to the family being there.”
Multiple providers also feared a conversation with family regarding necessary changes to care given the limitation of resources during the pandemic.
“Most families have been actually very understanding. This is a crisis, and we’re in a pandemic, and we’re all doing things we wouldn’t normally do.”
Another respondent said, “We were pretty honest about how resources were limited and how we were doing with this COVID-19 surge. And I think we talked about how the usual ability to provide aggressive dialysis was not the case with COVID-19. There was a lot of understanding, sometimes to my surprise. I would think people would be more upset when hearing something like that.”
Many clinicians facing these challenges experience moral distress, the researchers noted.
“Early in the pandemic, it became quickly apparent that possible resource limitation, such as scarce ventilators, was a major ethical concern. There was robust debate and discussion published in medical journals and the popular press about how to appropriately allocate health care resources,” the University of Washington’s Butler said.
“Transparency, accountability, and standardized processes for rationing these resources in ‘crisis capacity’ settings were seen as key to avoiding the impact of implicit bias and moral distress for clinicians,” she added.
Lessons learned
In terms of potential solutions that could mitigate these challenges in the future, health care leaders “could develop standardized protocols or guidelines for allocating a broader range of potentially scarce health care resources even before ‘crisis capacity’ is declared,” Butler said.
Furthermore, no frontline worker should have to go it alone. “Medical ethicists and/or other clinicians familiar with ethical considerations in settings of scarce health care resources might provide bedside consultation and collaborate with frontline providers who must grapple with the impact of more subtle forms of resource limitation on clinical decision-making.”
The study was partially funded by grants from the National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases and a COVID-19 Research Award from the University of Washington Institute of Translational Health Sciences given to Butler.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Choosing which hospitalized COVID-19 patients receive potentially lifesaving care, making urgent calls for ventilators and other equipment, and triaging care based on patient age and comorbidities were among the challenges revealed in new feedback from health care leaders and frontline workers.
Even though many hospitals have contingency plans for how to allocate resources and triage patient care during crisis capacity, for many providers during the real-world COVID-19 trial of these protocols, they fell short.
Many hospital crisis capacity plans, for example, were too general to address all the specific challenges arising during the pandemic, investigators report in a study published online Nov. 6 in JAMA Network Open.
“Our research shows that the types of challenges and approach to resource limitation in real-world clinical settings during the pandemic differed in practice from how we had prepared in theory,” lead author Catherine Butler, MD, told Medscape Medical News. Insufficient dialysis treatment time, staff shortages, and routine supply scarcity are examples “for which there was not an established plan or approach for appropriate allocation.”
“This left frontline clinicians to determine what constituted an acceptable standard of care and to make difficult allocation decisions at the bedside,” added Butler, acting instructor in the Division of Nephrology at the University of Washington in Seattle and a research fellow at the VA Health Services Research and Development Seattle-Denver Center of Innovation.
The investigators conducted semistructured interviews in April and May with 61 clinicians and health leaders. Mean age was 46 years, 63% were women, and participants practiced in 15 states. Most participants hailed from locations hard-hit by the pandemic at the time, including Seattle, New York City, and New Orleans.
Triage tribulations
The qualitative study included comments from respondents on three major themes that emerged: planning for crisis capacity, adapting to resource limitation, and the multiple unprecedented barriers to care delivery.
Overall, planning and support from institutional leaders varied. One provider said, “Talking to administration, and they just seemed really disengaged with the problem. We asked multiple times if there was a triage command center or a plan for what would occur if we got to the point where we had to triage resources. They said there was, but they wouldn’t provide it to us.”
Another had a more positive experience. “The biggest deal in the ethics world in the last 2 months has been preparing in case we need to triage. So, we have a very detailed, elaborate, well thought-out triage policy … that was done at the highest levels of the system.”
Clinicians said they participate on triage teams – despite the moral weight and likely emotional burden – out of a sense of duty.
Interestingly, some providers on these teams also reported a reluctance to reveal their participation to colleagues. “I didn’t feel like I should tell anybody … even some of my close friends who are physicians and nurses here … that I’ve been asked to be on this [triage team],” one respondent said. “I didn’t feel like I should make it known.”
Adapting to scarce resources
Multiple providers said they faced difficult care decisions because of limited dialysis or supply shortages. “They felt that this patient had the greatest likelihood of benefiting from most aggressive therapy. … I think there was probably like 5 or 6 patients in the ICU … and then you had this 35-year-old with no comorbidities,” one respondent said. “That’s who the ICU dialyzed, and I couldn’t really disagree.”
“I emailed all of [my colleagues], and I said ‘Help! We need X, we need CRRT [continuous renal replacement therapy] machines, we need dialysates,’ “ another responded.
“One of the attendings had a tweet when we were running out of CRRT. He had a tweet about, ‘Can anybody give us supplies for CRRT?’ So, it got to that. You do anything. You get really desperate,” the clinician said.
Other providers reported getting innovative under the circumstances. “My partner’s son, he actually borrowed a couple of 3D printers. He printed some of these face shields, and then they got the formula, or the specifics as to how to make this particular connection to connect to a dialysis machine to generate dialysate. So, he also printed some of those from the 3D printer.”
Dire situations with dialysis
Another respondent understood the focus on ventilators and ICU beds throughout the crisis, but said “no one has acknowledged that dialysis has been one of the most, if not the most, limited resources.”
Another clinician expressed surprise at a decision made in the face of limited availability of traditional dialysis. “A month ago, people said we were going to do acute peritoneal dialysis [PD]. And I said, ‘No, we’re not going to do acute PD. PD, it’s not that great for acute patients, sick people in the ICUs. I don’t think we’re going to do PD.’
“Three days later we were doing acute PD. I mean, that was unbelievable!”
Some institutions rationed dialysis therapy. “We went through the entire list at the beginning of the week and [said], this person has to dialyze these days, this person would probably benefit from a dialysis session, a third group person we could probably just string along and medically manage if we needed to,” one provider said.
Another respondent reported a different strategy. “No one was not getting dialysis, but there were a lot of people getting minimal dialysis. Even though people were getting treated, resources were very stretched.”
Changing family dynamics
COVID-19 has naturally changed how clinicians speak with families. One respondent recalled looking at the ICU physician and being like, ‘Have you talked to the son this week?’ And she’s like, ‘Oh my God, no. … Did you talk to the son?’ I’m like, ‘Oh my God, no.’ “
They realized, the respondent added, “that none of us had called the family because it’s just not in your workflow. You’re so used to the family being there.”
Multiple providers also feared a conversation with family regarding necessary changes to care given the limitation of resources during the pandemic.
“Most families have been actually very understanding. This is a crisis, and we’re in a pandemic, and we’re all doing things we wouldn’t normally do.”
Another respondent said, “We were pretty honest about how resources were limited and how we were doing with this COVID-19 surge. And I think we talked about how the usual ability to provide aggressive dialysis was not the case with COVID-19. There was a lot of understanding, sometimes to my surprise. I would think people would be more upset when hearing something like that.”
Many clinicians facing these challenges experience moral distress, the researchers noted.
“Early in the pandemic, it became quickly apparent that possible resource limitation, such as scarce ventilators, was a major ethical concern. There was robust debate and discussion published in medical journals and the popular press about how to appropriately allocate health care resources,” the University of Washington’s Butler said.
“Transparency, accountability, and standardized processes for rationing these resources in ‘crisis capacity’ settings were seen as key to avoiding the impact of implicit bias and moral distress for clinicians,” she added.
Lessons learned
In terms of potential solutions that could mitigate these challenges in the future, health care leaders “could develop standardized protocols or guidelines for allocating a broader range of potentially scarce health care resources even before ‘crisis capacity’ is declared,” Butler said.
Furthermore, no frontline worker should have to go it alone. “Medical ethicists and/or other clinicians familiar with ethical considerations in settings of scarce health care resources might provide bedside consultation and collaborate with frontline providers who must grapple with the impact of more subtle forms of resource limitation on clinical decision-making.”
The study was partially funded by grants from the National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases and a COVID-19 Research Award from the University of Washington Institute of Translational Health Sciences given to Butler.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Choosing which hospitalized COVID-19 patients receive potentially lifesaving care, making urgent calls for ventilators and other equipment, and triaging care based on patient age and comorbidities were among the challenges revealed in new feedback from health care leaders and frontline workers.
Even though many hospitals have contingency plans for how to allocate resources and triage patient care during crisis capacity, for many providers during the real-world COVID-19 trial of these protocols, they fell short.
Many hospital crisis capacity plans, for example, were too general to address all the specific challenges arising during the pandemic, investigators report in a study published online Nov. 6 in JAMA Network Open.
“Our research shows that the types of challenges and approach to resource limitation in real-world clinical settings during the pandemic differed in practice from how we had prepared in theory,” lead author Catherine Butler, MD, told Medscape Medical News. Insufficient dialysis treatment time, staff shortages, and routine supply scarcity are examples “for which there was not an established plan or approach for appropriate allocation.”
“This left frontline clinicians to determine what constituted an acceptable standard of care and to make difficult allocation decisions at the bedside,” added Butler, acting instructor in the Division of Nephrology at the University of Washington in Seattle and a research fellow at the VA Health Services Research and Development Seattle-Denver Center of Innovation.
The investigators conducted semistructured interviews in April and May with 61 clinicians and health leaders. Mean age was 46 years, 63% were women, and participants practiced in 15 states. Most participants hailed from locations hard-hit by the pandemic at the time, including Seattle, New York City, and New Orleans.
Triage tribulations
The qualitative study included comments from respondents on three major themes that emerged: planning for crisis capacity, adapting to resource limitation, and the multiple unprecedented barriers to care delivery.
Overall, planning and support from institutional leaders varied. One provider said, “Talking to administration, and they just seemed really disengaged with the problem. We asked multiple times if there was a triage command center or a plan for what would occur if we got to the point where we had to triage resources. They said there was, but they wouldn’t provide it to us.”
Another had a more positive experience. “The biggest deal in the ethics world in the last 2 months has been preparing in case we need to triage. So, we have a very detailed, elaborate, well thought-out triage policy … that was done at the highest levels of the system.”
Clinicians said they participate on triage teams – despite the moral weight and likely emotional burden – out of a sense of duty.
Interestingly, some providers on these teams also reported a reluctance to reveal their participation to colleagues. “I didn’t feel like I should tell anybody … even some of my close friends who are physicians and nurses here … that I’ve been asked to be on this [triage team],” one respondent said. “I didn’t feel like I should make it known.”
Adapting to scarce resources
Multiple providers said they faced difficult care decisions because of limited dialysis or supply shortages. “They felt that this patient had the greatest likelihood of benefiting from most aggressive therapy. … I think there was probably like 5 or 6 patients in the ICU … and then you had this 35-year-old with no comorbidities,” one respondent said. “That’s who the ICU dialyzed, and I couldn’t really disagree.”
“I emailed all of [my colleagues], and I said ‘Help! We need X, we need CRRT [continuous renal replacement therapy] machines, we need dialysates,’ “ another responded.
“One of the attendings had a tweet when we were running out of CRRT. He had a tweet about, ‘Can anybody give us supplies for CRRT?’ So, it got to that. You do anything. You get really desperate,” the clinician said.
Other providers reported getting innovative under the circumstances. “My partner’s son, he actually borrowed a couple of 3D printers. He printed some of these face shields, and then they got the formula, or the specifics as to how to make this particular connection to connect to a dialysis machine to generate dialysate. So, he also printed some of those from the 3D printer.”
Dire situations with dialysis
Another respondent understood the focus on ventilators and ICU beds throughout the crisis, but said “no one has acknowledged that dialysis has been one of the most, if not the most, limited resources.”
Another clinician expressed surprise at a decision made in the face of limited availability of traditional dialysis. “A month ago, people said we were going to do acute peritoneal dialysis [PD]. And I said, ‘No, we’re not going to do acute PD. PD, it’s not that great for acute patients, sick people in the ICUs. I don’t think we’re going to do PD.’
“Three days later we were doing acute PD. I mean, that was unbelievable!”
Some institutions rationed dialysis therapy. “We went through the entire list at the beginning of the week and [said], this person has to dialyze these days, this person would probably benefit from a dialysis session, a third group person we could probably just string along and medically manage if we needed to,” one provider said.
Another respondent reported a different strategy. “No one was not getting dialysis, but there were a lot of people getting minimal dialysis. Even though people were getting treated, resources were very stretched.”
Changing family dynamics
COVID-19 has naturally changed how clinicians speak with families. One respondent recalled looking at the ICU physician and being like, ‘Have you talked to the son this week?’ And she’s like, ‘Oh my God, no. … Did you talk to the son?’ I’m like, ‘Oh my God, no.’ “
They realized, the respondent added, “that none of us had called the family because it’s just not in your workflow. You’re so used to the family being there.”
Multiple providers also feared a conversation with family regarding necessary changes to care given the limitation of resources during the pandemic.
“Most families have been actually very understanding. This is a crisis, and we’re in a pandemic, and we’re all doing things we wouldn’t normally do.”
Another respondent said, “We were pretty honest about how resources were limited and how we were doing with this COVID-19 surge. And I think we talked about how the usual ability to provide aggressive dialysis was not the case with COVID-19. There was a lot of understanding, sometimes to my surprise. I would think people would be more upset when hearing something like that.”
Many clinicians facing these challenges experience moral distress, the researchers noted.
“Early in the pandemic, it became quickly apparent that possible resource limitation, such as scarce ventilators, was a major ethical concern. There was robust debate and discussion published in medical journals and the popular press about how to appropriately allocate health care resources,” the University of Washington’s Butler said.
“Transparency, accountability, and standardized processes for rationing these resources in ‘crisis capacity’ settings were seen as key to avoiding the impact of implicit bias and moral distress for clinicians,” she added.
Lessons learned
In terms of potential solutions that could mitigate these challenges in the future, health care leaders “could develop standardized protocols or guidelines for allocating a broader range of potentially scarce health care resources even before ‘crisis capacity’ is declared,” Butler said.
Furthermore, no frontline worker should have to go it alone. “Medical ethicists and/or other clinicians familiar with ethical considerations in settings of scarce health care resources might provide bedside consultation and collaborate with frontline providers who must grapple with the impact of more subtle forms of resource limitation on clinical decision-making.”
The study was partially funded by grants from the National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases and a COVID-19 Research Award from the University of Washington Institute of Translational Health Sciences given to Butler.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
What happened to melanoma care during COVID-19 sequestration
Initial evidence suggests that the , Rebecca I. Hartman, MD, MPH, said at a virtual forum on cutaneous malignancies jointly presented by Postgraduate Institute for Medicine and Global Academy for Medication Education.
This is not what National Comprehensive Cancer Network officials expected when they issued short-term recommendations on how to manage cutaneous melanoma during the first wave of the COVID-19 pandemic. Those recommendations for restriction of care, which Dr. Hartman characterized as “pretty significant changes from how we typically practice melanoma care in the U.S.,” came at a time when there was justifiable concern that the first COVID-19 surge would strain the U.S. health care system beyond the breaking point.
The rationale given for the NCCN recommendations was that most time-to-treat studies have shown no adverse patient outcomes for 90-day delays in treatment, even for thicker melanomas. But those studies, all retrospective, have been called into question. And the first real-world data on the impact of care restrictions during the lockdown, reported by Italian dermatologists, highlights adverse effects with potentially far-reaching consequences, noted Dr. Hartman, director of melanoma epidemiology at Brigham and Women’s Hospital and a dermatologist, Harvard University, Boston.
Analysis of the impact of lockdown-induced delays in melanoma care is not merely an academic exercise, she added. While everyone hopes that the spring 2020 COVID-19 shelter-in-place was a once-in-a-lifetime event, there’s no guarantee that will be the case. Moreover, the lockdown provides a natural experiment addressing the possible consequences of melanoma care delays on patient outcomes, a topic that for ethical reasons could never be addressed in a randomized trial.
The short-term NCCN recommendations included the use of excisional biopsies for melanoma diagnosis whenever possible; and delay of up to 3 months for wide local excision of in situ melanoma, any invasive melanoma with negative margins, and even T1 melanomas with positive margins provided the bulk of the lesion had been excised. The guidance also suggested delaying sentinel lymph node biopsy (SLNB), along with increased use of neoadjuvant therapy in patients with clinically palpable regional lymph nodes in order to delay surgery for up to 8 weeks. Single-agent systemic therapy at the least-frequent dosing was advised in order to minimize toxicity and reduce the need for additional health care resources: for example, nivolumab (Opdivo) at 480 mg every 4 weeks instead of every 2 weeks, and pembrolizumab (Keytruda) at 400 mg every 6 weeks, rather than every 3 weeks.
So, that’s what the NCCN recommended. Here’s what actually happened during shelter-in-place as captured in Dr. Hartman’s survey of 18 U.S. members of the Melanoma Prevention Working Group, all practicing dermatology in centers particularly hard-hit in the first wave of the pandemic: In-person new melanoma patient visits plunged from an average of 4.83 per week per provider to 0.83 per week. Telemedicine visits with new melanoma patients went from zero prepandemic to 0.67 visits per week per provider, which doesn’t come close to making up for the drop in in-person visits. Interestingly, two respondents reported turning to gene-expression profile testing for patient prognostication because of delays in SLNB.
Wide local excision was delayed by an average of 6 weeks in roughly one-third of melanoma patients with early tumor stage disease, regardless of margin status. For patients with stage T1b disease, wide local excision was typically performed on time during shelter-in-place; however, SLNB was delayed by an average of 5 weeks in 22% of patients with positive margins and 28% of those with negative margins. In contrast, 80% of patients with more advanced T2-T4 melanoma underwent on-schedule definitive management with wide local excision and SLNB, Dr. Hartman reported.
Critics have taken issue with the NCCN’s conclusion that most time-to-treatment studies show no harm arising from 90-day treatment delays. A review of the relevant published literature by Dr. Hartman’s Harvard colleagues, published in July, found that the evidence is mixed. “There is insufficient evidence to definitively conclude that delayed wide resection after gross removal of the primary melanoma is without harm,” they concluded in the review.
Spanish dermatologists performed a modeling study in order to estimate the potential impact of COVID-19 lockdowns on 5- and 10-year survival of melanoma patients. Using the growth rate of a random sample of 1,000 melanomas to model estimates of tumor thickness after various delays, coupled with American Joint Committee on Cancer survival data for different T stages, they estimated that 5-year survival would be reduced from 94.2% to 92.3% with a 90-day delay in diagnosis, and that 10-year survival would drop from 90.0% to 87.6%.
But that’s merely modeling. Francesco Ricci, MD, PhD, and colleagues from the melanoma unit at the Istituto Dermopatico dell’Immacolata, Rome, have provided a first look at the real-world impact of the lockdown. In the prelockdown period of January through March 9th, 2020, the referral center averaged 2.3 new melanoma diagnoses per day. During the Rome lockdown, from March 10th through May 3rd, this figure dropped to a mean of 0.6 melanoma diagnoses per day. Postlockdown, from May 4th to June 6th, the average climbed to 1.3 per day. The rate of newly diagnosed nodular melanoma was 5.5-fold greater postlockdown, compared with prelockdown; the rate of ulcerated melanoma was 4.9-fold greater.
“We can hypothesize that this may have been due to delays in diagnosis and care,” Dr. Hartman commented. “This is important because we know that nodular melanoma as well as ulceration tend to have a worse prognosis in terms of mortality.”
The mean Breslow thickness of newly diagnosed melanomas was 0.88 mm prelockdown, 0.66 mm during lockdown, and 1.96 mm postlockdown. The investigators speculated that the reduced Breslow thickness of melanomas diagnosed during lockdown might be explained by a greater willingness of more health-conscious people to defy the shelter-in-place instructions because of their concern about a suspicious skin lesion. “Though it is way too early to gauge the consequences of such diagnostic delay, should this issue be neglected, dermatologists and their patients may pay a higher price later with increased morbidity, mortality, and financial burden,” according to the investigators.
Dr. Hartman observed that it will be important to learn whether similar experiences occurred elsewhere during lockdown.
Another speaker, John M. Kirkwood, MD, said he has seen several melanoma patients referred from outside centers who had delays of up to 3 months in sentinel lymph node management of T2 and T3 tumors during lockdown who now have widespread metastatic disease.
“Now, is that anecdotal? I don’t know, it’s just worrisome to me,” commented Dr. Kirkwood, professor of medicine, dermatology, and translational science at the University of Pittsburgh.
Merrick Ross, MD, professor of surgical oncology at M.D. Anderson Cancer Center, Houston, recalled, “There was a period of time [during the lockdown] when we weren’t allowed to do certain elective procedures, if you want to call cancer surgery elective.”
“It’s too soon to talk about outcomes because a lot of patients are still in the process of being treated after what I would consider a significant delay in diagnosis,” the surgeon added.
An audience member asked if there will be an opportunity to see data on the damage done by delaying melanoma management as compared to lives saved through the lockdown for COVID-19. Dr. Ross replied that M.D. Anderson is in the midst of an institution-wide study analyzing the delay in diagnosis of a range of cancers.
“In our melanoma center it is absolutely clear, although we’re still collecting data, that the median tumor thickness is much higher since the lockdown,” Dr. Ross commented.
Dr. Hartman said she and her coinvestigators in the Melanoma Prevention Working Group are attempting to tally up the damage done via the lockdown by delaying melanoma diagnosis and treatment. But she agreed with the questioner that the most important thing is overall net lives saved through shelter-in-place.
“I’m sure that, separately, nondermatologists – perhaps infectious disease doctors and internists – are looking at how many lives were saved by the lockdown policy. So I do think all that data will come out,” Dr. Hartman predicted.
She reported having no financial conflicts regarding her presentation.
Global Academy for Medical Education and this news organization are owned by the same company.
SOURCE: Hartman, R. Cutaneous malignancies forum.
Initial evidence suggests that the , Rebecca I. Hartman, MD, MPH, said at a virtual forum on cutaneous malignancies jointly presented by Postgraduate Institute for Medicine and Global Academy for Medication Education.
This is not what National Comprehensive Cancer Network officials expected when they issued short-term recommendations on how to manage cutaneous melanoma during the first wave of the COVID-19 pandemic. Those recommendations for restriction of care, which Dr. Hartman characterized as “pretty significant changes from how we typically practice melanoma care in the U.S.,” came at a time when there was justifiable concern that the first COVID-19 surge would strain the U.S. health care system beyond the breaking point.
The rationale given for the NCCN recommendations was that most time-to-treat studies have shown no adverse patient outcomes for 90-day delays in treatment, even for thicker melanomas. But those studies, all retrospective, have been called into question. And the first real-world data on the impact of care restrictions during the lockdown, reported by Italian dermatologists, highlights adverse effects with potentially far-reaching consequences, noted Dr. Hartman, director of melanoma epidemiology at Brigham and Women’s Hospital and a dermatologist, Harvard University, Boston.
Analysis of the impact of lockdown-induced delays in melanoma care is not merely an academic exercise, she added. While everyone hopes that the spring 2020 COVID-19 shelter-in-place was a once-in-a-lifetime event, there’s no guarantee that will be the case. Moreover, the lockdown provides a natural experiment addressing the possible consequences of melanoma care delays on patient outcomes, a topic that for ethical reasons could never be addressed in a randomized trial.
The short-term NCCN recommendations included the use of excisional biopsies for melanoma diagnosis whenever possible; and delay of up to 3 months for wide local excision of in situ melanoma, any invasive melanoma with negative margins, and even T1 melanomas with positive margins provided the bulk of the lesion had been excised. The guidance also suggested delaying sentinel lymph node biopsy (SLNB), along with increased use of neoadjuvant therapy in patients with clinically palpable regional lymph nodes in order to delay surgery for up to 8 weeks. Single-agent systemic therapy at the least-frequent dosing was advised in order to minimize toxicity and reduce the need for additional health care resources: for example, nivolumab (Opdivo) at 480 mg every 4 weeks instead of every 2 weeks, and pembrolizumab (Keytruda) at 400 mg every 6 weeks, rather than every 3 weeks.
So, that’s what the NCCN recommended. Here’s what actually happened during shelter-in-place as captured in Dr. Hartman’s survey of 18 U.S. members of the Melanoma Prevention Working Group, all practicing dermatology in centers particularly hard-hit in the first wave of the pandemic: In-person new melanoma patient visits plunged from an average of 4.83 per week per provider to 0.83 per week. Telemedicine visits with new melanoma patients went from zero prepandemic to 0.67 visits per week per provider, which doesn’t come close to making up for the drop in in-person visits. Interestingly, two respondents reported turning to gene-expression profile testing for patient prognostication because of delays in SLNB.
Wide local excision was delayed by an average of 6 weeks in roughly one-third of melanoma patients with early tumor stage disease, regardless of margin status. For patients with stage T1b disease, wide local excision was typically performed on time during shelter-in-place; however, SLNB was delayed by an average of 5 weeks in 22% of patients with positive margins and 28% of those with negative margins. In contrast, 80% of patients with more advanced T2-T4 melanoma underwent on-schedule definitive management with wide local excision and SLNB, Dr. Hartman reported.
Critics have taken issue with the NCCN’s conclusion that most time-to-treatment studies show no harm arising from 90-day treatment delays. A review of the relevant published literature by Dr. Hartman’s Harvard colleagues, published in July, found that the evidence is mixed. “There is insufficient evidence to definitively conclude that delayed wide resection after gross removal of the primary melanoma is without harm,” they concluded in the review.
Spanish dermatologists performed a modeling study in order to estimate the potential impact of COVID-19 lockdowns on 5- and 10-year survival of melanoma patients. Using the growth rate of a random sample of 1,000 melanomas to model estimates of tumor thickness after various delays, coupled with American Joint Committee on Cancer survival data for different T stages, they estimated that 5-year survival would be reduced from 94.2% to 92.3% with a 90-day delay in diagnosis, and that 10-year survival would drop from 90.0% to 87.6%.
But that’s merely modeling. Francesco Ricci, MD, PhD, and colleagues from the melanoma unit at the Istituto Dermopatico dell’Immacolata, Rome, have provided a first look at the real-world impact of the lockdown. In the prelockdown period of January through March 9th, 2020, the referral center averaged 2.3 new melanoma diagnoses per day. During the Rome lockdown, from March 10th through May 3rd, this figure dropped to a mean of 0.6 melanoma diagnoses per day. Postlockdown, from May 4th to June 6th, the average climbed to 1.3 per day. The rate of newly diagnosed nodular melanoma was 5.5-fold greater postlockdown, compared with prelockdown; the rate of ulcerated melanoma was 4.9-fold greater.
“We can hypothesize that this may have been due to delays in diagnosis and care,” Dr. Hartman commented. “This is important because we know that nodular melanoma as well as ulceration tend to have a worse prognosis in terms of mortality.”
The mean Breslow thickness of newly diagnosed melanomas was 0.88 mm prelockdown, 0.66 mm during lockdown, and 1.96 mm postlockdown. The investigators speculated that the reduced Breslow thickness of melanomas diagnosed during lockdown might be explained by a greater willingness of more health-conscious people to defy the shelter-in-place instructions because of their concern about a suspicious skin lesion. “Though it is way too early to gauge the consequences of such diagnostic delay, should this issue be neglected, dermatologists and their patients may pay a higher price later with increased morbidity, mortality, and financial burden,” according to the investigators.
Dr. Hartman observed that it will be important to learn whether similar experiences occurred elsewhere during lockdown.
Another speaker, John M. Kirkwood, MD, said he has seen several melanoma patients referred from outside centers who had delays of up to 3 months in sentinel lymph node management of T2 and T3 tumors during lockdown who now have widespread metastatic disease.
“Now, is that anecdotal? I don’t know, it’s just worrisome to me,” commented Dr. Kirkwood, professor of medicine, dermatology, and translational science at the University of Pittsburgh.
Merrick Ross, MD, professor of surgical oncology at M.D. Anderson Cancer Center, Houston, recalled, “There was a period of time [during the lockdown] when we weren’t allowed to do certain elective procedures, if you want to call cancer surgery elective.”
“It’s too soon to talk about outcomes because a lot of patients are still in the process of being treated after what I would consider a significant delay in diagnosis,” the surgeon added.
An audience member asked if there will be an opportunity to see data on the damage done by delaying melanoma management as compared to lives saved through the lockdown for COVID-19. Dr. Ross replied that M.D. Anderson is in the midst of an institution-wide study analyzing the delay in diagnosis of a range of cancers.
“In our melanoma center it is absolutely clear, although we’re still collecting data, that the median tumor thickness is much higher since the lockdown,” Dr. Ross commented.
Dr. Hartman said she and her coinvestigators in the Melanoma Prevention Working Group are attempting to tally up the damage done via the lockdown by delaying melanoma diagnosis and treatment. But she agreed with the questioner that the most important thing is overall net lives saved through shelter-in-place.
“I’m sure that, separately, nondermatologists – perhaps infectious disease doctors and internists – are looking at how many lives were saved by the lockdown policy. So I do think all that data will come out,” Dr. Hartman predicted.
She reported having no financial conflicts regarding her presentation.
Global Academy for Medical Education and this news organization are owned by the same company.
SOURCE: Hartman, R. Cutaneous malignancies forum.
Initial evidence suggests that the , Rebecca I. Hartman, MD, MPH, said at a virtual forum on cutaneous malignancies jointly presented by Postgraduate Institute for Medicine and Global Academy for Medication Education.
This is not what National Comprehensive Cancer Network officials expected when they issued short-term recommendations on how to manage cutaneous melanoma during the first wave of the COVID-19 pandemic. Those recommendations for restriction of care, which Dr. Hartman characterized as “pretty significant changes from how we typically practice melanoma care in the U.S.,” came at a time when there was justifiable concern that the first COVID-19 surge would strain the U.S. health care system beyond the breaking point.
The rationale given for the NCCN recommendations was that most time-to-treat studies have shown no adverse patient outcomes for 90-day delays in treatment, even for thicker melanomas. But those studies, all retrospective, have been called into question. And the first real-world data on the impact of care restrictions during the lockdown, reported by Italian dermatologists, highlights adverse effects with potentially far-reaching consequences, noted Dr. Hartman, director of melanoma epidemiology at Brigham and Women’s Hospital and a dermatologist, Harvard University, Boston.
Analysis of the impact of lockdown-induced delays in melanoma care is not merely an academic exercise, she added. While everyone hopes that the spring 2020 COVID-19 shelter-in-place was a once-in-a-lifetime event, there’s no guarantee that will be the case. Moreover, the lockdown provides a natural experiment addressing the possible consequences of melanoma care delays on patient outcomes, a topic that for ethical reasons could never be addressed in a randomized trial.
The short-term NCCN recommendations included the use of excisional biopsies for melanoma diagnosis whenever possible; and delay of up to 3 months for wide local excision of in situ melanoma, any invasive melanoma with negative margins, and even T1 melanomas with positive margins provided the bulk of the lesion had been excised. The guidance also suggested delaying sentinel lymph node biopsy (SLNB), along with increased use of neoadjuvant therapy in patients with clinically palpable regional lymph nodes in order to delay surgery for up to 8 weeks. Single-agent systemic therapy at the least-frequent dosing was advised in order to minimize toxicity and reduce the need for additional health care resources: for example, nivolumab (Opdivo) at 480 mg every 4 weeks instead of every 2 weeks, and pembrolizumab (Keytruda) at 400 mg every 6 weeks, rather than every 3 weeks.
So, that’s what the NCCN recommended. Here’s what actually happened during shelter-in-place as captured in Dr. Hartman’s survey of 18 U.S. members of the Melanoma Prevention Working Group, all practicing dermatology in centers particularly hard-hit in the first wave of the pandemic: In-person new melanoma patient visits plunged from an average of 4.83 per week per provider to 0.83 per week. Telemedicine visits with new melanoma patients went from zero prepandemic to 0.67 visits per week per provider, which doesn’t come close to making up for the drop in in-person visits. Interestingly, two respondents reported turning to gene-expression profile testing for patient prognostication because of delays in SLNB.
Wide local excision was delayed by an average of 6 weeks in roughly one-third of melanoma patients with early tumor stage disease, regardless of margin status. For patients with stage T1b disease, wide local excision was typically performed on time during shelter-in-place; however, SLNB was delayed by an average of 5 weeks in 22% of patients with positive margins and 28% of those with negative margins. In contrast, 80% of patients with more advanced T2-T4 melanoma underwent on-schedule definitive management with wide local excision and SLNB, Dr. Hartman reported.
Critics have taken issue with the NCCN’s conclusion that most time-to-treatment studies show no harm arising from 90-day treatment delays. A review of the relevant published literature by Dr. Hartman’s Harvard colleagues, published in July, found that the evidence is mixed. “There is insufficient evidence to definitively conclude that delayed wide resection after gross removal of the primary melanoma is without harm,” they concluded in the review.
Spanish dermatologists performed a modeling study in order to estimate the potential impact of COVID-19 lockdowns on 5- and 10-year survival of melanoma patients. Using the growth rate of a random sample of 1,000 melanomas to model estimates of tumor thickness after various delays, coupled with American Joint Committee on Cancer survival data for different T stages, they estimated that 5-year survival would be reduced from 94.2% to 92.3% with a 90-day delay in diagnosis, and that 10-year survival would drop from 90.0% to 87.6%.
But that’s merely modeling. Francesco Ricci, MD, PhD, and colleagues from the melanoma unit at the Istituto Dermopatico dell’Immacolata, Rome, have provided a first look at the real-world impact of the lockdown. In the prelockdown period of January through March 9th, 2020, the referral center averaged 2.3 new melanoma diagnoses per day. During the Rome lockdown, from March 10th through May 3rd, this figure dropped to a mean of 0.6 melanoma diagnoses per day. Postlockdown, from May 4th to June 6th, the average climbed to 1.3 per day. The rate of newly diagnosed nodular melanoma was 5.5-fold greater postlockdown, compared with prelockdown; the rate of ulcerated melanoma was 4.9-fold greater.
“We can hypothesize that this may have been due to delays in diagnosis and care,” Dr. Hartman commented. “This is important because we know that nodular melanoma as well as ulceration tend to have a worse prognosis in terms of mortality.”
The mean Breslow thickness of newly diagnosed melanomas was 0.88 mm prelockdown, 0.66 mm during lockdown, and 1.96 mm postlockdown. The investigators speculated that the reduced Breslow thickness of melanomas diagnosed during lockdown might be explained by a greater willingness of more health-conscious people to defy the shelter-in-place instructions because of their concern about a suspicious skin lesion. “Though it is way too early to gauge the consequences of such diagnostic delay, should this issue be neglected, dermatologists and their patients may pay a higher price later with increased morbidity, mortality, and financial burden,” according to the investigators.
Dr. Hartman observed that it will be important to learn whether similar experiences occurred elsewhere during lockdown.
Another speaker, John M. Kirkwood, MD, said he has seen several melanoma patients referred from outside centers who had delays of up to 3 months in sentinel lymph node management of T2 and T3 tumors during lockdown who now have widespread metastatic disease.
“Now, is that anecdotal? I don’t know, it’s just worrisome to me,” commented Dr. Kirkwood, professor of medicine, dermatology, and translational science at the University of Pittsburgh.
Merrick Ross, MD, professor of surgical oncology at M.D. Anderson Cancer Center, Houston, recalled, “There was a period of time [during the lockdown] when we weren’t allowed to do certain elective procedures, if you want to call cancer surgery elective.”
“It’s too soon to talk about outcomes because a lot of patients are still in the process of being treated after what I would consider a significant delay in diagnosis,” the surgeon added.
An audience member asked if there will be an opportunity to see data on the damage done by delaying melanoma management as compared to lives saved through the lockdown for COVID-19. Dr. Ross replied that M.D. Anderson is in the midst of an institution-wide study analyzing the delay in diagnosis of a range of cancers.
“In our melanoma center it is absolutely clear, although we’re still collecting data, that the median tumor thickness is much higher since the lockdown,” Dr. Ross commented.
Dr. Hartman said she and her coinvestigators in the Melanoma Prevention Working Group are attempting to tally up the damage done via the lockdown by delaying melanoma diagnosis and treatment. But she agreed with the questioner that the most important thing is overall net lives saved through shelter-in-place.
“I’m sure that, separately, nondermatologists – perhaps infectious disease doctors and internists – are looking at how many lives were saved by the lockdown policy. So I do think all that data will come out,” Dr. Hartman predicted.
She reported having no financial conflicts regarding her presentation.
Global Academy for Medical Education and this news organization are owned by the same company.
SOURCE: Hartman, R. Cutaneous malignancies forum.
REPORTING FROM THE CUTANEOUS MALIGNANCIES FORUM
Task force recommends best practices for malignant colorectal polyps
For patients with malignant colorectal polyps, endoscopists should look for features of deep submucosal invasion and should retrieve, handle, and submit specimens in ways that support thorough and accurate pathologic assessment, according to new recommendations from the US Multi-Society Task Force on Colorectal Cancer.
“In nonpedunculated lesions with features of deep submucosal invasion, endoscopic biopsy is followed by surgical resection. In cases without features of deep submucosal invasion, en bloc resection and proper specimen handling should be considered (if feasible) for lesions with a high risk of superficial submucosal invasion,” wrote Aasma Shaukat, MD, MPH, of the Minneapolis Veterans Affairs Health Care System and her fellow experts. The recommendations were published in Gastroenterology.
Malignant colorectal polyps invade the submucosa but do not extend into the muscularis propria. Pedunculated and nonpedunculated polyps should be considered to invade the deep submucosa if they are classified as NICE (NBI International Colorectal Endoscopic) type 3, Kudo type VN (neoplastic and invasive, with an irregular arrangement), or Kudo type VI (an amorphous structure, with a loss of or decrease in pits). “Nonpedunculated lesions with these features should be biopsied (in the area of surface feature disruption), tattooed (unless in or near the cecum), and referred to surgery. Pedunculated polyps with features of deep submucosal invasion should undergo endoscopic polypectomy,” according to the MSTFCC recommendations.
Moderate-quality evidence links submucosal invasion with two types of polyp morphology: LST-NG (laterally spreading tumor, nongranular type) showing a depression or sessile shape and LST-G (laterally spreading tumor, granular type) that includes a dominant nodule. According to low-quality evidence, these lesions should be managed with en bloc rather than piecemeal resection. En bloc resection is important for all pedunculated polyps (even if large) and should be considered for LST-G lesions with a dominant nodule. Resected pedunculated polyps should be retrieved through the suction channel – if doing so does not require them to be cut – or with a net or snare during scope withdrawal. Nonpedunculated lesions with suspected submucosal invasion that are removed en bloc should be pinned peripherally around the entire circumference to a hard surface and fixed in 10% formalin. This practice helps pathologists orient specimens to correctly assess depth of invasion and margin involvement.
For both pedunculated and nonpedunculated polyps, features denoting a high risk for residual or recurrent malignancy are poor tumor differentiation, lymphovascular invasion, or more than 1 mm of submucosal invasion. For nonpedunculated polyps, additional high-risk features include tumor budding and tumor involvement of the cautery margin. The MSTFCC recommends that, when reporting on a malignant colorectal polyp, pathologists follow the structured template of the College of American Pathologists and note the lesion’s histologic type, grade of differentiation, extent of tumor extension or invasion, stalk and mucosal margin, and presence or absence of lymphovascular invasion. Specimen integrity, polyp size and morphology, and tumor budding are also useful. To reduce miscommunication and facilitate appropriate management, pathologists should avoid using the terms carcinoma and cancer when describing malignant colorectal polyps, according to the MSTFCC.
The decision to recommend adjuvant surgery “is based on polyp shape, whether there was en bloc resection and adequate histologic assessment, the presence or absence of unfavorable histologic features, the patient’s risk for surgical mortality and morbidity, and patient preferences,” the recommendations state. Because multidisciplinary management can optimize clinical outcomes for patients with malignant polyps, gastroenterologists, pathologists, oncologists, and surgeons should identify best ways to communicate with each other and share decision-making conjointly and with patients. “Patient values are important in cases where the risk of residual cancer and the risk of surgical mortality are similar,” the MSTFCC notes. “In these latter cases, shared decision-making is emphasized.”
The authors of the task force recommendations reported having no relevant conflicts of interest since 2016.
SOURCE: Shaukat A et al. Gastroenterology. 2020 Nov 4. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2020.08.050
For patients with malignant colorectal polyps, endoscopists should look for features of deep submucosal invasion and should retrieve, handle, and submit specimens in ways that support thorough and accurate pathologic assessment, according to new recommendations from the US Multi-Society Task Force on Colorectal Cancer.
“In nonpedunculated lesions with features of deep submucosal invasion, endoscopic biopsy is followed by surgical resection. In cases without features of deep submucosal invasion, en bloc resection and proper specimen handling should be considered (if feasible) for lesions with a high risk of superficial submucosal invasion,” wrote Aasma Shaukat, MD, MPH, of the Minneapolis Veterans Affairs Health Care System and her fellow experts. The recommendations were published in Gastroenterology.
Malignant colorectal polyps invade the submucosa but do not extend into the muscularis propria. Pedunculated and nonpedunculated polyps should be considered to invade the deep submucosa if they are classified as NICE (NBI International Colorectal Endoscopic) type 3, Kudo type VN (neoplastic and invasive, with an irregular arrangement), or Kudo type VI (an amorphous structure, with a loss of or decrease in pits). “Nonpedunculated lesions with these features should be biopsied (in the area of surface feature disruption), tattooed (unless in or near the cecum), and referred to surgery. Pedunculated polyps with features of deep submucosal invasion should undergo endoscopic polypectomy,” according to the MSTFCC recommendations.
Moderate-quality evidence links submucosal invasion with two types of polyp morphology: LST-NG (laterally spreading tumor, nongranular type) showing a depression or sessile shape and LST-G (laterally spreading tumor, granular type) that includes a dominant nodule. According to low-quality evidence, these lesions should be managed with en bloc rather than piecemeal resection. En bloc resection is important for all pedunculated polyps (even if large) and should be considered for LST-G lesions with a dominant nodule. Resected pedunculated polyps should be retrieved through the suction channel – if doing so does not require them to be cut – or with a net or snare during scope withdrawal. Nonpedunculated lesions with suspected submucosal invasion that are removed en bloc should be pinned peripherally around the entire circumference to a hard surface and fixed in 10% formalin. This practice helps pathologists orient specimens to correctly assess depth of invasion and margin involvement.
For both pedunculated and nonpedunculated polyps, features denoting a high risk for residual or recurrent malignancy are poor tumor differentiation, lymphovascular invasion, or more than 1 mm of submucosal invasion. For nonpedunculated polyps, additional high-risk features include tumor budding and tumor involvement of the cautery margin. The MSTFCC recommends that, when reporting on a malignant colorectal polyp, pathologists follow the structured template of the College of American Pathologists and note the lesion’s histologic type, grade of differentiation, extent of tumor extension or invasion, stalk and mucosal margin, and presence or absence of lymphovascular invasion. Specimen integrity, polyp size and morphology, and tumor budding are also useful. To reduce miscommunication and facilitate appropriate management, pathologists should avoid using the terms carcinoma and cancer when describing malignant colorectal polyps, according to the MSTFCC.
The decision to recommend adjuvant surgery “is based on polyp shape, whether there was en bloc resection and adequate histologic assessment, the presence or absence of unfavorable histologic features, the patient’s risk for surgical mortality and morbidity, and patient preferences,” the recommendations state. Because multidisciplinary management can optimize clinical outcomes for patients with malignant polyps, gastroenterologists, pathologists, oncologists, and surgeons should identify best ways to communicate with each other and share decision-making conjointly and with patients. “Patient values are important in cases where the risk of residual cancer and the risk of surgical mortality are similar,” the MSTFCC notes. “In these latter cases, shared decision-making is emphasized.”
The authors of the task force recommendations reported having no relevant conflicts of interest since 2016.
SOURCE: Shaukat A et al. Gastroenterology. 2020 Nov 4. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2020.08.050
For patients with malignant colorectal polyps, endoscopists should look for features of deep submucosal invasion and should retrieve, handle, and submit specimens in ways that support thorough and accurate pathologic assessment, according to new recommendations from the US Multi-Society Task Force on Colorectal Cancer.
“In nonpedunculated lesions with features of deep submucosal invasion, endoscopic biopsy is followed by surgical resection. In cases without features of deep submucosal invasion, en bloc resection and proper specimen handling should be considered (if feasible) for lesions with a high risk of superficial submucosal invasion,” wrote Aasma Shaukat, MD, MPH, of the Minneapolis Veterans Affairs Health Care System and her fellow experts. The recommendations were published in Gastroenterology.
Malignant colorectal polyps invade the submucosa but do not extend into the muscularis propria. Pedunculated and nonpedunculated polyps should be considered to invade the deep submucosa if they are classified as NICE (NBI International Colorectal Endoscopic) type 3, Kudo type VN (neoplastic and invasive, with an irregular arrangement), or Kudo type VI (an amorphous structure, with a loss of or decrease in pits). “Nonpedunculated lesions with these features should be biopsied (in the area of surface feature disruption), tattooed (unless in or near the cecum), and referred to surgery. Pedunculated polyps with features of deep submucosal invasion should undergo endoscopic polypectomy,” according to the MSTFCC recommendations.
Moderate-quality evidence links submucosal invasion with two types of polyp morphology: LST-NG (laterally spreading tumor, nongranular type) showing a depression or sessile shape and LST-G (laterally spreading tumor, granular type) that includes a dominant nodule. According to low-quality evidence, these lesions should be managed with en bloc rather than piecemeal resection. En bloc resection is important for all pedunculated polyps (even if large) and should be considered for LST-G lesions with a dominant nodule. Resected pedunculated polyps should be retrieved through the suction channel – if doing so does not require them to be cut – or with a net or snare during scope withdrawal. Nonpedunculated lesions with suspected submucosal invasion that are removed en bloc should be pinned peripherally around the entire circumference to a hard surface and fixed in 10% formalin. This practice helps pathologists orient specimens to correctly assess depth of invasion and margin involvement.
For both pedunculated and nonpedunculated polyps, features denoting a high risk for residual or recurrent malignancy are poor tumor differentiation, lymphovascular invasion, or more than 1 mm of submucosal invasion. For nonpedunculated polyps, additional high-risk features include tumor budding and tumor involvement of the cautery margin. The MSTFCC recommends that, when reporting on a malignant colorectal polyp, pathologists follow the structured template of the College of American Pathologists and note the lesion’s histologic type, grade of differentiation, extent of tumor extension or invasion, stalk and mucosal margin, and presence or absence of lymphovascular invasion. Specimen integrity, polyp size and morphology, and tumor budding are also useful. To reduce miscommunication and facilitate appropriate management, pathologists should avoid using the terms carcinoma and cancer when describing malignant colorectal polyps, according to the MSTFCC.
The decision to recommend adjuvant surgery “is based on polyp shape, whether there was en bloc resection and adequate histologic assessment, the presence or absence of unfavorable histologic features, the patient’s risk for surgical mortality and morbidity, and patient preferences,” the recommendations state. Because multidisciplinary management can optimize clinical outcomes for patients with malignant polyps, gastroenterologists, pathologists, oncologists, and surgeons should identify best ways to communicate with each other and share decision-making conjointly and with patients. “Patient values are important in cases where the risk of residual cancer and the risk of surgical mortality are similar,” the MSTFCC notes. “In these latter cases, shared decision-making is emphasized.”
The authors of the task force recommendations reported having no relevant conflicts of interest since 2016.
SOURCE: Shaukat A et al. Gastroenterology. 2020 Nov 4. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2020.08.050
FROM GASTROENTEROLOGY
Do electronic reminder systems help patients with T2DM to lose weight?
EVIDENCE SUMMARY
A meta-analysis of 6 RCTs studied the effect of smartphone self-care applications on A1C, weight, blood pressure, and lipids in adult patients with T2DM. All the interventions comprised 4 components: electronic self-management prompts and reminders, personal measuring devices, patient-driven data upload, and remote analysis of the data with feedback. The review excluded studies that used phone calls or lasted fewer than 3 months.
Some improvement in A1C found, but no effect on weight
Telehealth interventions improved A1C more than usual care (6 trials, 884 patients; mean difference = –0.40%; 95% CI, –0.69% to –0.11%).1 A subset of 4 studies with 560 patients evaluated changes in weight. Patients had a mean age of 61 years and average weight of 84 kg (in 3 of 4 studies reporting baseline weight). Aggregate weight loss was insignificant after 3 to 12 months (mean difference = –0.84 kg; 95% CI, –2.04 kg to 0.36 kg, P = .17). Investigators reported no harms. Limitations of the analysis included high heterogeneity in the main outcome of A1C (I2 = 70%) but low heterogeneity within the 4 studies assessing weight (I2 = 30%).
Other, small studies found no change in A1C
Two subsequent small RCTs came to different conclusions than the meta-analysis. One compared the impact of individualized physical activity–based text messages in response to pedometer readings with pedometer use alone.2 It included 126 adult patients (mean age, 50.5 years) with T2DM who had an A1C > 7% and access to an Internet-connected computer. Researchers excluded patients who were unable to perform moderate physical activity or who had cognitive deficits.
At enrollment, researchers supplied all patients with a pedometer and an appointment with a counselor to set goals for physical activity. They sent 2 text messages daily to the intervention group (and none to the control group) based on uploaded pedometer data. One message detailed physical activity progress and the second encouraged increased physical activity. The primary outcome was mean step counts per month; secondary outcomes included A1C and weight measured at 6 months.
The groups showed no significant difference in A1C (mean difference = 0.07%; 95% CI, –0.47% to 0.34%, P = .75) or weight loss (mean difference = 3.1 lb; 95% CI, –24.5 lb to 18.3 lb, P = .77). Many patients (43%) reported difficulty uploading step counts, receiving texts, and responding to texts. The dropout rate was 24%.
A second RCT with 150 patients, using a less elaborate protocol, assessed the effectiveness of tailored text-message reminders compared with nontailored text messages to improve A1C and body mass index (BMI).3 Patients were adult Iranians (mean age, 52.5 years) with T2DM who owned a cell phone and could receive and read text messages.
Patients filled out a diabetic self-care assessment to identify barriers to improving care and were randomized into 3 groups. The first group received tailored text messages (75% addressing the patient’s top 2 barriers to self-care and 25% general messages). The second group received nontailored text messages of encouragement. The control group received no text messages.
Continue to: After 3 months...
After 3 months, BMI was reduced in both messaging groups but not the control group (tailored text = –0.6 kg/m2, nontailored text = –0.5 kg/m2, controls = 0.7 kg/m2; P < .05). A1C levels didn’t change significantly. One limitation of the study was that 30% to 35% of the patients in the intervention group had a university-level education, compared with 12% in the control group.
Recommendations
The Department of Veterans Affairs issued guidelines in 2017 regarding management of patients with T2DM in primary care.4 The guidelines state that all patients should receive individualized self-management education using “modalities tailored to their preferences” (strong recommendation). They further recommend “offering one or more bidirectional telehealth interventions” in coordination with patients’ health care providers (weak recommendation).
The 2017 diabetes self-management recommendations endorsed by the American Diabetes Association state that “strong evidence” shows that incorporating text messaging into diabetes care improves outcomes, enhances feedback loops, and empowers patients.5
Editor’s takeaway
Telehealth offers mechanisms for patients and physicians to enhance communication about health behaviors and health status. But does it alter outcomes? The cited literature suggests that benefits aren’t a forgone conclusion and that acceptability, ease of use, cost, and individualization are critical issues in telehealth design.
1. Cui M, Wu X, Mao J, et al. T2DM self-management via smartphone applications: a systematic review and meta-analysis. PLoS ONE. 2016;11:e0166718.
2. Agboola S, Jethwani K, Lopez L, et al. Text to Move: A randomized controlled trial of a text-messaging program to improve physical activity behaviors in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. J Med Internet Res. 2016;18:e307.
3. Peimani M, Rambod C, Omidvar M, et al. Effectiveness of short message service-based intervention (SMS) on self-care in type 2 diabetes: a feasibility study. Prim Care Diabetes. 2016;10:251-258.
4. Guideline summary: VA/DoD clinical practice guideline for the management of type 2 diabetes mellitus in primary care. Rockville, MD: Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality; 2017. www.innovations.ahrq.gov/qualitytools/department-veterans-affairsdepartment-defense-vadod-clinical-practice-guideline-4. Accessed October 26, 2020.
5. Beck J, Greenwood DA, Blanton L, et al. 2017 National Standards for Diabetes Self-Management, Education and Support. Diabetes Care. 2017;40:1409-1419.
EVIDENCE SUMMARY
A meta-analysis of 6 RCTs studied the effect of smartphone self-care applications on A1C, weight, blood pressure, and lipids in adult patients with T2DM. All the interventions comprised 4 components: electronic self-management prompts and reminders, personal measuring devices, patient-driven data upload, and remote analysis of the data with feedback. The review excluded studies that used phone calls or lasted fewer than 3 months.
Some improvement in A1C found, but no effect on weight
Telehealth interventions improved A1C more than usual care (6 trials, 884 patients; mean difference = –0.40%; 95% CI, –0.69% to –0.11%).1 A subset of 4 studies with 560 patients evaluated changes in weight. Patients had a mean age of 61 years and average weight of 84 kg (in 3 of 4 studies reporting baseline weight). Aggregate weight loss was insignificant after 3 to 12 months (mean difference = –0.84 kg; 95% CI, –2.04 kg to 0.36 kg, P = .17). Investigators reported no harms. Limitations of the analysis included high heterogeneity in the main outcome of A1C (I2 = 70%) but low heterogeneity within the 4 studies assessing weight (I2 = 30%).
Other, small studies found no change in A1C
Two subsequent small RCTs came to different conclusions than the meta-analysis. One compared the impact of individualized physical activity–based text messages in response to pedometer readings with pedometer use alone.2 It included 126 adult patients (mean age, 50.5 years) with T2DM who had an A1C > 7% and access to an Internet-connected computer. Researchers excluded patients who were unable to perform moderate physical activity or who had cognitive deficits.
At enrollment, researchers supplied all patients with a pedometer and an appointment with a counselor to set goals for physical activity. They sent 2 text messages daily to the intervention group (and none to the control group) based on uploaded pedometer data. One message detailed physical activity progress and the second encouraged increased physical activity. The primary outcome was mean step counts per month; secondary outcomes included A1C and weight measured at 6 months.
The groups showed no significant difference in A1C (mean difference = 0.07%; 95% CI, –0.47% to 0.34%, P = .75) or weight loss (mean difference = 3.1 lb; 95% CI, –24.5 lb to 18.3 lb, P = .77). Many patients (43%) reported difficulty uploading step counts, receiving texts, and responding to texts. The dropout rate was 24%.
A second RCT with 150 patients, using a less elaborate protocol, assessed the effectiveness of tailored text-message reminders compared with nontailored text messages to improve A1C and body mass index (BMI).3 Patients were adult Iranians (mean age, 52.5 years) with T2DM who owned a cell phone and could receive and read text messages.
Patients filled out a diabetic self-care assessment to identify barriers to improving care and were randomized into 3 groups. The first group received tailored text messages (75% addressing the patient’s top 2 barriers to self-care and 25% general messages). The second group received nontailored text messages of encouragement. The control group received no text messages.
Continue to: After 3 months...
After 3 months, BMI was reduced in both messaging groups but not the control group (tailored text = –0.6 kg/m2, nontailored text = –0.5 kg/m2, controls = 0.7 kg/m2; P < .05). A1C levels didn’t change significantly. One limitation of the study was that 30% to 35% of the patients in the intervention group had a university-level education, compared with 12% in the control group.
Recommendations
The Department of Veterans Affairs issued guidelines in 2017 regarding management of patients with T2DM in primary care.4 The guidelines state that all patients should receive individualized self-management education using “modalities tailored to their preferences” (strong recommendation). They further recommend “offering one or more bidirectional telehealth interventions” in coordination with patients’ health care providers (weak recommendation).
The 2017 diabetes self-management recommendations endorsed by the American Diabetes Association state that “strong evidence” shows that incorporating text messaging into diabetes care improves outcomes, enhances feedback loops, and empowers patients.5
Editor’s takeaway
Telehealth offers mechanisms for patients and physicians to enhance communication about health behaviors and health status. But does it alter outcomes? The cited literature suggests that benefits aren’t a forgone conclusion and that acceptability, ease of use, cost, and individualization are critical issues in telehealth design.
EVIDENCE SUMMARY
A meta-analysis of 6 RCTs studied the effect of smartphone self-care applications on A1C, weight, blood pressure, and lipids in adult patients with T2DM. All the interventions comprised 4 components: electronic self-management prompts and reminders, personal measuring devices, patient-driven data upload, and remote analysis of the data with feedback. The review excluded studies that used phone calls or lasted fewer than 3 months.
Some improvement in A1C found, but no effect on weight
Telehealth interventions improved A1C more than usual care (6 trials, 884 patients; mean difference = –0.40%; 95% CI, –0.69% to –0.11%).1 A subset of 4 studies with 560 patients evaluated changes in weight. Patients had a mean age of 61 years and average weight of 84 kg (in 3 of 4 studies reporting baseline weight). Aggregate weight loss was insignificant after 3 to 12 months (mean difference = –0.84 kg; 95% CI, –2.04 kg to 0.36 kg, P = .17). Investigators reported no harms. Limitations of the analysis included high heterogeneity in the main outcome of A1C (I2 = 70%) but low heterogeneity within the 4 studies assessing weight (I2 = 30%).
Other, small studies found no change in A1C
Two subsequent small RCTs came to different conclusions than the meta-analysis. One compared the impact of individualized physical activity–based text messages in response to pedometer readings with pedometer use alone.2 It included 126 adult patients (mean age, 50.5 years) with T2DM who had an A1C > 7% and access to an Internet-connected computer. Researchers excluded patients who were unable to perform moderate physical activity or who had cognitive deficits.
At enrollment, researchers supplied all patients with a pedometer and an appointment with a counselor to set goals for physical activity. They sent 2 text messages daily to the intervention group (and none to the control group) based on uploaded pedometer data. One message detailed physical activity progress and the second encouraged increased physical activity. The primary outcome was mean step counts per month; secondary outcomes included A1C and weight measured at 6 months.
The groups showed no significant difference in A1C (mean difference = 0.07%; 95% CI, –0.47% to 0.34%, P = .75) or weight loss (mean difference = 3.1 lb; 95% CI, –24.5 lb to 18.3 lb, P = .77). Many patients (43%) reported difficulty uploading step counts, receiving texts, and responding to texts. The dropout rate was 24%.
A second RCT with 150 patients, using a less elaborate protocol, assessed the effectiveness of tailored text-message reminders compared with nontailored text messages to improve A1C and body mass index (BMI).3 Patients were adult Iranians (mean age, 52.5 years) with T2DM who owned a cell phone and could receive and read text messages.
Patients filled out a diabetic self-care assessment to identify barriers to improving care and were randomized into 3 groups. The first group received tailored text messages (75% addressing the patient’s top 2 barriers to self-care and 25% general messages). The second group received nontailored text messages of encouragement. The control group received no text messages.
Continue to: After 3 months...
After 3 months, BMI was reduced in both messaging groups but not the control group (tailored text = –0.6 kg/m2, nontailored text = –0.5 kg/m2, controls = 0.7 kg/m2; P < .05). A1C levels didn’t change significantly. One limitation of the study was that 30% to 35% of the patients in the intervention group had a university-level education, compared with 12% in the control group.
Recommendations
The Department of Veterans Affairs issued guidelines in 2017 regarding management of patients with T2DM in primary care.4 The guidelines state that all patients should receive individualized self-management education using “modalities tailored to their preferences” (strong recommendation). They further recommend “offering one or more bidirectional telehealth interventions” in coordination with patients’ health care providers (weak recommendation).
The 2017 diabetes self-management recommendations endorsed by the American Diabetes Association state that “strong evidence” shows that incorporating text messaging into diabetes care improves outcomes, enhances feedback loops, and empowers patients.5
Editor’s takeaway
Telehealth offers mechanisms for patients and physicians to enhance communication about health behaviors and health status. But does it alter outcomes? The cited literature suggests that benefits aren’t a forgone conclusion and that acceptability, ease of use, cost, and individualization are critical issues in telehealth design.
1. Cui M, Wu X, Mao J, et al. T2DM self-management via smartphone applications: a systematic review and meta-analysis. PLoS ONE. 2016;11:e0166718.
2. Agboola S, Jethwani K, Lopez L, et al. Text to Move: A randomized controlled trial of a text-messaging program to improve physical activity behaviors in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. J Med Internet Res. 2016;18:e307.
3. Peimani M, Rambod C, Omidvar M, et al. Effectiveness of short message service-based intervention (SMS) on self-care in type 2 diabetes: a feasibility study. Prim Care Diabetes. 2016;10:251-258.
4. Guideline summary: VA/DoD clinical practice guideline for the management of type 2 diabetes mellitus in primary care. Rockville, MD: Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality; 2017. www.innovations.ahrq.gov/qualitytools/department-veterans-affairsdepartment-defense-vadod-clinical-practice-guideline-4. Accessed October 26, 2020.
5. Beck J, Greenwood DA, Blanton L, et al. 2017 National Standards for Diabetes Self-Management, Education and Support. Diabetes Care. 2017;40:1409-1419.
1. Cui M, Wu X, Mao J, et al. T2DM self-management via smartphone applications: a systematic review and meta-analysis. PLoS ONE. 2016;11:e0166718.
2. Agboola S, Jethwani K, Lopez L, et al. Text to Move: A randomized controlled trial of a text-messaging program to improve physical activity behaviors in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. J Med Internet Res. 2016;18:e307.
3. Peimani M, Rambod C, Omidvar M, et al. Effectiveness of short message service-based intervention (SMS) on self-care in type 2 diabetes: a feasibility study. Prim Care Diabetes. 2016;10:251-258.
4. Guideline summary: VA/DoD clinical practice guideline for the management of type 2 diabetes mellitus in primary care. Rockville, MD: Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality; 2017. www.innovations.ahrq.gov/qualitytools/department-veterans-affairsdepartment-defense-vadod-clinical-practice-guideline-4. Accessed October 26, 2020.
5. Beck J, Greenwood DA, Blanton L, et al. 2017 National Standards for Diabetes Self-Management, Education and Support. Diabetes Care. 2017;40:1409-1419.
EVIDENCE-BASED ANSWER:
PROBABLY NOT—but they may augment self-management. Four-component telehealth systems—including electronic reminders, measuring devices, patient-driven data upload, and remote data analysis—likely don’t result in significant weight reductions in adults with type 2 diabetes (T2DM). However, their use may be associated with a decrease in hemoglobin A1C of about 0.4% (strength of recommendation [SOR]: B, meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials [RCTs] and conflicting smaller subsequent RCTs).
Telehealth is considered a reasonable option for augmenting diabetes self-management in patients who are facile with the technology (SOR: C, expert opinion).
Use long-acting second-generation antipsychotics ‘as early as possible’ in psychosis
Don’t wait to give patients with first-episode psychosis long-acting injectable formulations of second-generation antipsychotics, according to Henry A. Nasrallah, MD.
Many clinicians wait to use long-acting injectables (LAIs) until the patient has experienced multiple relapses, but using them after the first discharge may help prevent future relapse, Dr. Nasrallah, professor of psychiatry, neurology, and neuroscience at the University of Cincinnati, said at the virtual Psychopharmacology Update presented by Current Psychiatry and Global Academy for Medical Education.
LAIs and clozapine are “vastly underutilized” after the first discharge, he noted. “I really encourage everybody to use them without hesitation as early as possible.”
In patients with first-episode psychosis, “the most important thing, in my opinion, is to start establishing a therapeutic alliance with the patient from day one,” Dr. Nasrallah said. “It’s always important in psychiatry, but it’s particularly important for first-episode psychosis.”
These patients respond to low doses of antipsychotics and should not be given first-generation antipsychotics because of a risk for acute extrapyramidal symptoms, tardive dyskinesia, and neurotoxicity.
“I usually select an antipsychotic that is extended release and also available as a long-acting injectable formulation,” Dr. Nasrallah said, noting that it helps when he gives a patient a long-acting injectable right after discharge. During hospitalization, Dr. Nasrallah said, he educates the patient and their family about psychosis, treatment, how psychosis affects the brain, and adherence to treatment.
“The primary goal, of course, is to achieve remission and very importantly, to prevent a second episode,” he said. “This is the golden opportunity for us psychiatrists to prevent the patient from relapsing again and again. That is the reason for disability and for brain damage, because every psychotic episode destroys brain tissue. That is why I am very eager to not only achieve a remission in the first episode but also to position the patient to be protected after discharge by giving them long-acting injectable.”
After a clinician performs a full workup to rule out substance use or a general medical condition inducing first-episode psychosis, Dr. Nasrallah recommends paliperidone extended-release (ER), given to patients in the morning because of its tolerability and the availability of an LAI version of the drug. “If the patient is very sick and agitated, I might go to 6 mg a day, which is actually a very good dose for first-episode patients, and it’s still quite well tolerated.”
Oral or injectable lorazepam taken as needed may be given to a patient with first-episode psychosis with agitation. For patients who manifest akathisia, twice or thrice daily propranolol at dose of 10-20 mg can be used off label, he said. Dr. Nasrallah also recommended twice-daily omega 3 at a dose of 1,000 mg or N-acetylcysteine at a dose of 600 mg per day as supplements.
“They’re not approved by the [Food and Drug Administration] for first-episode psychosis, but there are numerous publications in the literature by academic psychiatrists showing that they are quite beneficial, and they reduce the two destructive processes during psychosis, which are neuroinflammation and oxidative stress, or free radicals,” he said. “Those two supplements can help in the acute phase of the illness.”
Another option for clinicians is to begin a patient with first-episode psychosis on oral aripiprazole at a dose of 5 mg per day for 2 days, increasing the dose to 7.5 mg per day for 2 days, then increasing to 10 mg per day. “It is not extended-release, so you have to start with low doses to protect the patient from side effects,” Dr. Nasrallah explained. “Some patients may need 15 or 20 [mg], but most first-episode patients may do well on 10 [mg] without risking side effects.”
Planning for discharge
Patients who tolerate aripiprazole can start the long-acting aripiprazole lauroxil at discharge, and clinicians have two options to choose from. One formulation “requires 2 weeks of oral supplementation, which you can do in the hospital if you start the patient on oral aripiprazole, and then you can give that injection prior to discharge.” Another option involves giving the patient “any antipsychotic you like and then switch[ing] the patient to aripiprazole lauroxil. The full dose can be given without oral supplementation on the day of discharge.”
Dr. Nasrallah emphasized the use of LAIs in patients discharged for first-episode psychosis. In a study published in JAMA Psychiatry, researchers found use of LAI risperidone in patients with first-episode psychosis significantly reduced the risk of psychotic exacerbation and relapse compared with patients who were given oral risperidone (JAMA Psychiatry. 2015;72:822-9).
“This kind of well-done study shows you that you can do a great job protecting your patient from the very beginning by giving long-acting injectables,” Dr. Nasrallah explained. “That’s why you have to develop rapport with the patient. That’s why you have to convince the patient to take the injectable, and that’s why you have to educate the patient about the hazards of psychosis to the brain, and the fact that it’s very hard to remember to take the pills, because the illness itself can interfere with that due to cognitive impairment [and] negative symptoms.” Another reason for nonadherence is that the patients might not believe they are sick, he added.
After 2 or 3 weeks, if a patient with first-episode psychosis has a minimal response or does not response at all to an LAI, clozapine is an “aggressive” option that may help nonresponders. For patients with schizophrenia, “about 65%-70% would respond to a dopamine antagonist and the remaining 30% are going to need clozapine sooner or later,” Dr. Nasrallah said. “For clozapine after one or two failures [on LAIs] with an adequate dose and adequate duration, don’t wait. Give the patient clozapine, give them an opportunity to regain their life. I’ve seen some very gratifying results with clozapine in those who respond to it.
“The outcome of schizophrenia may be far less malignant than the perception out there if we actually ensure adherence very early and manage the first-episode aggressively, like cardiologists manage the first heart attack,” he said. “[Cardiologists] do everything in their power to protect the patient from a second heart attack, and I regard psychosis as a ‘brain attack.’ ”
Global Academy and this news organization are owned by the same parent company. Dr. Nasrallah reported that he has received research grants from Acadia; served as a consultant for Acadia, Alkermes, Allergan, Janssen, Otsuka, Indivior, Intracellular, Neurocrine, Sunovion, Teva, and Boehringer-Ingelheim; and is on the speakers bureau for Acadia, Alkermes, Allergan, Janssen, Otsuka, Indivior, Intracellular, Neurocrine, Noven, Sunovion, and Teva.
Don’t wait to give patients with first-episode psychosis long-acting injectable formulations of second-generation antipsychotics, according to Henry A. Nasrallah, MD.
Many clinicians wait to use long-acting injectables (LAIs) until the patient has experienced multiple relapses, but using them after the first discharge may help prevent future relapse, Dr. Nasrallah, professor of psychiatry, neurology, and neuroscience at the University of Cincinnati, said at the virtual Psychopharmacology Update presented by Current Psychiatry and Global Academy for Medical Education.
LAIs and clozapine are “vastly underutilized” after the first discharge, he noted. “I really encourage everybody to use them without hesitation as early as possible.”
In patients with first-episode psychosis, “the most important thing, in my opinion, is to start establishing a therapeutic alliance with the patient from day one,” Dr. Nasrallah said. “It’s always important in psychiatry, but it’s particularly important for first-episode psychosis.”
These patients respond to low doses of antipsychotics and should not be given first-generation antipsychotics because of a risk for acute extrapyramidal symptoms, tardive dyskinesia, and neurotoxicity.
“I usually select an antipsychotic that is extended release and also available as a long-acting injectable formulation,” Dr. Nasrallah said, noting that it helps when he gives a patient a long-acting injectable right after discharge. During hospitalization, Dr. Nasrallah said, he educates the patient and their family about psychosis, treatment, how psychosis affects the brain, and adherence to treatment.
“The primary goal, of course, is to achieve remission and very importantly, to prevent a second episode,” he said. “This is the golden opportunity for us psychiatrists to prevent the patient from relapsing again and again. That is the reason for disability and for brain damage, because every psychotic episode destroys brain tissue. That is why I am very eager to not only achieve a remission in the first episode but also to position the patient to be protected after discharge by giving them long-acting injectable.”
After a clinician performs a full workup to rule out substance use or a general medical condition inducing first-episode psychosis, Dr. Nasrallah recommends paliperidone extended-release (ER), given to patients in the morning because of its tolerability and the availability of an LAI version of the drug. “If the patient is very sick and agitated, I might go to 6 mg a day, which is actually a very good dose for first-episode patients, and it’s still quite well tolerated.”
Oral or injectable lorazepam taken as needed may be given to a patient with first-episode psychosis with agitation. For patients who manifest akathisia, twice or thrice daily propranolol at dose of 10-20 mg can be used off label, he said. Dr. Nasrallah also recommended twice-daily omega 3 at a dose of 1,000 mg or N-acetylcysteine at a dose of 600 mg per day as supplements.
“They’re not approved by the [Food and Drug Administration] for first-episode psychosis, but there are numerous publications in the literature by academic psychiatrists showing that they are quite beneficial, and they reduce the two destructive processes during psychosis, which are neuroinflammation and oxidative stress, or free radicals,” he said. “Those two supplements can help in the acute phase of the illness.”
Another option for clinicians is to begin a patient with first-episode psychosis on oral aripiprazole at a dose of 5 mg per day for 2 days, increasing the dose to 7.5 mg per day for 2 days, then increasing to 10 mg per day. “It is not extended-release, so you have to start with low doses to protect the patient from side effects,” Dr. Nasrallah explained. “Some patients may need 15 or 20 [mg], but most first-episode patients may do well on 10 [mg] without risking side effects.”
Planning for discharge
Patients who tolerate aripiprazole can start the long-acting aripiprazole lauroxil at discharge, and clinicians have two options to choose from. One formulation “requires 2 weeks of oral supplementation, which you can do in the hospital if you start the patient on oral aripiprazole, and then you can give that injection prior to discharge.” Another option involves giving the patient “any antipsychotic you like and then switch[ing] the patient to aripiprazole lauroxil. The full dose can be given without oral supplementation on the day of discharge.”
Dr. Nasrallah emphasized the use of LAIs in patients discharged for first-episode psychosis. In a study published in JAMA Psychiatry, researchers found use of LAI risperidone in patients with first-episode psychosis significantly reduced the risk of psychotic exacerbation and relapse compared with patients who were given oral risperidone (JAMA Psychiatry. 2015;72:822-9).
“This kind of well-done study shows you that you can do a great job protecting your patient from the very beginning by giving long-acting injectables,” Dr. Nasrallah explained. “That’s why you have to develop rapport with the patient. That’s why you have to convince the patient to take the injectable, and that’s why you have to educate the patient about the hazards of psychosis to the brain, and the fact that it’s very hard to remember to take the pills, because the illness itself can interfere with that due to cognitive impairment [and] negative symptoms.” Another reason for nonadherence is that the patients might not believe they are sick, he added.
After 2 or 3 weeks, if a patient with first-episode psychosis has a minimal response or does not response at all to an LAI, clozapine is an “aggressive” option that may help nonresponders. For patients with schizophrenia, “about 65%-70% would respond to a dopamine antagonist and the remaining 30% are going to need clozapine sooner or later,” Dr. Nasrallah said. “For clozapine after one or two failures [on LAIs] with an adequate dose and adequate duration, don’t wait. Give the patient clozapine, give them an opportunity to regain their life. I’ve seen some very gratifying results with clozapine in those who respond to it.
“The outcome of schizophrenia may be far less malignant than the perception out there if we actually ensure adherence very early and manage the first-episode aggressively, like cardiologists manage the first heart attack,” he said. “[Cardiologists] do everything in their power to protect the patient from a second heart attack, and I regard psychosis as a ‘brain attack.’ ”
Global Academy and this news organization are owned by the same parent company. Dr. Nasrallah reported that he has received research grants from Acadia; served as a consultant for Acadia, Alkermes, Allergan, Janssen, Otsuka, Indivior, Intracellular, Neurocrine, Sunovion, Teva, and Boehringer-Ingelheim; and is on the speakers bureau for Acadia, Alkermes, Allergan, Janssen, Otsuka, Indivior, Intracellular, Neurocrine, Noven, Sunovion, and Teva.
Don’t wait to give patients with first-episode psychosis long-acting injectable formulations of second-generation antipsychotics, according to Henry A. Nasrallah, MD.
Many clinicians wait to use long-acting injectables (LAIs) until the patient has experienced multiple relapses, but using them after the first discharge may help prevent future relapse, Dr. Nasrallah, professor of psychiatry, neurology, and neuroscience at the University of Cincinnati, said at the virtual Psychopharmacology Update presented by Current Psychiatry and Global Academy for Medical Education.
LAIs and clozapine are “vastly underutilized” after the first discharge, he noted. “I really encourage everybody to use them without hesitation as early as possible.”
In patients with first-episode psychosis, “the most important thing, in my opinion, is to start establishing a therapeutic alliance with the patient from day one,” Dr. Nasrallah said. “It’s always important in psychiatry, but it’s particularly important for first-episode psychosis.”
These patients respond to low doses of antipsychotics and should not be given first-generation antipsychotics because of a risk for acute extrapyramidal symptoms, tardive dyskinesia, and neurotoxicity.
“I usually select an antipsychotic that is extended release and also available as a long-acting injectable formulation,” Dr. Nasrallah said, noting that it helps when he gives a patient a long-acting injectable right after discharge. During hospitalization, Dr. Nasrallah said, he educates the patient and their family about psychosis, treatment, how psychosis affects the brain, and adherence to treatment.
“The primary goal, of course, is to achieve remission and very importantly, to prevent a second episode,” he said. “This is the golden opportunity for us psychiatrists to prevent the patient from relapsing again and again. That is the reason for disability and for brain damage, because every psychotic episode destroys brain tissue. That is why I am very eager to not only achieve a remission in the first episode but also to position the patient to be protected after discharge by giving them long-acting injectable.”
After a clinician performs a full workup to rule out substance use or a general medical condition inducing first-episode psychosis, Dr. Nasrallah recommends paliperidone extended-release (ER), given to patients in the morning because of its tolerability and the availability of an LAI version of the drug. “If the patient is very sick and agitated, I might go to 6 mg a day, which is actually a very good dose for first-episode patients, and it’s still quite well tolerated.”
Oral or injectable lorazepam taken as needed may be given to a patient with first-episode psychosis with agitation. For patients who manifest akathisia, twice or thrice daily propranolol at dose of 10-20 mg can be used off label, he said. Dr. Nasrallah also recommended twice-daily omega 3 at a dose of 1,000 mg or N-acetylcysteine at a dose of 600 mg per day as supplements.
“They’re not approved by the [Food and Drug Administration] for first-episode psychosis, but there are numerous publications in the literature by academic psychiatrists showing that they are quite beneficial, and they reduce the two destructive processes during psychosis, which are neuroinflammation and oxidative stress, or free radicals,” he said. “Those two supplements can help in the acute phase of the illness.”
Another option for clinicians is to begin a patient with first-episode psychosis on oral aripiprazole at a dose of 5 mg per day for 2 days, increasing the dose to 7.5 mg per day for 2 days, then increasing to 10 mg per day. “It is not extended-release, so you have to start with low doses to protect the patient from side effects,” Dr. Nasrallah explained. “Some patients may need 15 or 20 [mg], but most first-episode patients may do well on 10 [mg] without risking side effects.”
Planning for discharge
Patients who tolerate aripiprazole can start the long-acting aripiprazole lauroxil at discharge, and clinicians have two options to choose from. One formulation “requires 2 weeks of oral supplementation, which you can do in the hospital if you start the patient on oral aripiprazole, and then you can give that injection prior to discharge.” Another option involves giving the patient “any antipsychotic you like and then switch[ing] the patient to aripiprazole lauroxil. The full dose can be given without oral supplementation on the day of discharge.”
Dr. Nasrallah emphasized the use of LAIs in patients discharged for first-episode psychosis. In a study published in JAMA Psychiatry, researchers found use of LAI risperidone in patients with first-episode psychosis significantly reduced the risk of psychotic exacerbation and relapse compared with patients who were given oral risperidone (JAMA Psychiatry. 2015;72:822-9).
“This kind of well-done study shows you that you can do a great job protecting your patient from the very beginning by giving long-acting injectables,” Dr. Nasrallah explained. “That’s why you have to develop rapport with the patient. That’s why you have to convince the patient to take the injectable, and that’s why you have to educate the patient about the hazards of psychosis to the brain, and the fact that it’s very hard to remember to take the pills, because the illness itself can interfere with that due to cognitive impairment [and] negative symptoms.” Another reason for nonadherence is that the patients might not believe they are sick, he added.
After 2 or 3 weeks, if a patient with first-episode psychosis has a minimal response or does not response at all to an LAI, clozapine is an “aggressive” option that may help nonresponders. For patients with schizophrenia, “about 65%-70% would respond to a dopamine antagonist and the remaining 30% are going to need clozapine sooner or later,” Dr. Nasrallah said. “For clozapine after one or two failures [on LAIs] with an adequate dose and adequate duration, don’t wait. Give the patient clozapine, give them an opportunity to regain their life. I’ve seen some very gratifying results with clozapine in those who respond to it.
“The outcome of schizophrenia may be far less malignant than the perception out there if we actually ensure adherence very early and manage the first-episode aggressively, like cardiologists manage the first heart attack,” he said. “[Cardiologists] do everything in their power to protect the patient from a second heart attack, and I regard psychosis as a ‘brain attack.’ ”
Global Academy and this news organization are owned by the same parent company. Dr. Nasrallah reported that he has received research grants from Acadia; served as a consultant for Acadia, Alkermes, Allergan, Janssen, Otsuka, Indivior, Intracellular, Neurocrine, Sunovion, Teva, and Boehringer-Ingelheim; and is on the speakers bureau for Acadia, Alkermes, Allergan, Janssen, Otsuka, Indivior, Intracellular, Neurocrine, Noven, Sunovion, and Teva.
FROM PSYCHOPHARMACOLOGY UPDATE
When patients don’t get the care they should
During the COVID-19 pandemic, nearly all primary care clinicians have been engaged in telemedicine. Telemedicine visits have certain advantages—especially convenience to patients. But there are dangers, as well. The following true story illustrates one of the important dangers.
“I had an interesting experience late last week that reminded me how important it is to be one’s own advocate in health care. I cut my foot going for an outdoor swim. It got infected so I had a telehealth visit with a physician assistant. She prescribed an antibiotic. The next day, Friday, the swelling and redness were rapidly moving up my foot. I called the office twice. I sent a picture of my foot. No call-back.
I texted my podiatrist the same photo with the question: Do I sit tight or go to the ED? A half hour later, he called me: Go to the hospital. I did. I got IV antibiotics and a tetanus shot. I was also told by the ED doc that my itchy palms were a reaction to the antibiotic I’d been prescribed, and that the physician assistant shouldn’t have prescribed a sulfa drug, given that my chart listed a past reaction to sulfa eye drops.”
The patient is a top-flight triathlete and the editor of JFP, Marya Ostrowski. She was gracious to share her story with us, and she did recover uneventfully, although the outcome might have been much different if there had been further delay.
Her story has 3 important teaching points:
- We must ensure that our office phone system prioritizes calls from patients. If there is any hint that the problem is urgent, it must be handled immediately.a
- CAREFULLY check for allergies before prescribing medication. Perhaps the physician assistant did check the medication list and noted an allergy to eye drops but did not zero in on the fact that they were sulfa. Medication allergy lists can be misleading because they can be too specific. Had her medication allergy been listed as “sulfa medications,” rather than the specific eye drop, the physician assistant may have recognized the allergy correctly.
- Finally, and most important in my estimation: Patients must act as their own health advocates. Patients are the final common barrier against medical errors and we must learn to listen to them carefully. We should encourage our patients to report problems and irregularities in care.
a The physician assistant returned Marya’s calls at 4:30 that Friday afternoon—8 hours after her first outreach. Marya was already in an ED bed and the nursing staff was starting her IV.
During the COVID-19 pandemic, nearly all primary care clinicians have been engaged in telemedicine. Telemedicine visits have certain advantages—especially convenience to patients. But there are dangers, as well. The following true story illustrates one of the important dangers.
“I had an interesting experience late last week that reminded me how important it is to be one’s own advocate in health care. I cut my foot going for an outdoor swim. It got infected so I had a telehealth visit with a physician assistant. She prescribed an antibiotic. The next day, Friday, the swelling and redness were rapidly moving up my foot. I called the office twice. I sent a picture of my foot. No call-back.
I texted my podiatrist the same photo with the question: Do I sit tight or go to the ED? A half hour later, he called me: Go to the hospital. I did. I got IV antibiotics and a tetanus shot. I was also told by the ED doc that my itchy palms were a reaction to the antibiotic I’d been prescribed, and that the physician assistant shouldn’t have prescribed a sulfa drug, given that my chart listed a past reaction to sulfa eye drops.”
The patient is a top-flight triathlete and the editor of JFP, Marya Ostrowski. She was gracious to share her story with us, and she did recover uneventfully, although the outcome might have been much different if there had been further delay.
Her story has 3 important teaching points:
- We must ensure that our office phone system prioritizes calls from patients. If there is any hint that the problem is urgent, it must be handled immediately.a
- CAREFULLY check for allergies before prescribing medication. Perhaps the physician assistant did check the medication list and noted an allergy to eye drops but did not zero in on the fact that they were sulfa. Medication allergy lists can be misleading because they can be too specific. Had her medication allergy been listed as “sulfa medications,” rather than the specific eye drop, the physician assistant may have recognized the allergy correctly.
- Finally, and most important in my estimation: Patients must act as their own health advocates. Patients are the final common barrier against medical errors and we must learn to listen to them carefully. We should encourage our patients to report problems and irregularities in care.
a The physician assistant returned Marya’s calls at 4:30 that Friday afternoon—8 hours after her first outreach. Marya was already in an ED bed and the nursing staff was starting her IV.
During the COVID-19 pandemic, nearly all primary care clinicians have been engaged in telemedicine. Telemedicine visits have certain advantages—especially convenience to patients. But there are dangers, as well. The following true story illustrates one of the important dangers.
“I had an interesting experience late last week that reminded me how important it is to be one’s own advocate in health care. I cut my foot going for an outdoor swim. It got infected so I had a telehealth visit with a physician assistant. She prescribed an antibiotic. The next day, Friday, the swelling and redness were rapidly moving up my foot. I called the office twice. I sent a picture of my foot. No call-back.
I texted my podiatrist the same photo with the question: Do I sit tight or go to the ED? A half hour later, he called me: Go to the hospital. I did. I got IV antibiotics and a tetanus shot. I was also told by the ED doc that my itchy palms were a reaction to the antibiotic I’d been prescribed, and that the physician assistant shouldn’t have prescribed a sulfa drug, given that my chart listed a past reaction to sulfa eye drops.”
The patient is a top-flight triathlete and the editor of JFP, Marya Ostrowski. She was gracious to share her story with us, and she did recover uneventfully, although the outcome might have been much different if there had been further delay.
Her story has 3 important teaching points:
- We must ensure that our office phone system prioritizes calls from patients. If there is any hint that the problem is urgent, it must be handled immediately.a
- CAREFULLY check for allergies before prescribing medication. Perhaps the physician assistant did check the medication list and noted an allergy to eye drops but did not zero in on the fact that they were sulfa. Medication allergy lists can be misleading because they can be too specific. Had her medication allergy been listed as “sulfa medications,” rather than the specific eye drop, the physician assistant may have recognized the allergy correctly.
- Finally, and most important in my estimation: Patients must act as their own health advocates. Patients are the final common barrier against medical errors and we must learn to listen to them carefully. We should encourage our patients to report problems and irregularities in care.
a The physician assistant returned Marya’s calls at 4:30 that Friday afternoon—8 hours after her first outreach. Marya was already in an ED bed and the nursing staff was starting her IV.
JIA guideline calls for earlier use of targeted therapies
A draft guideline for the management of patients with juvenile idiopathic arthritis reflects changes in therapy away from reliance on NSAIDs and glucocorticoids and toward earlier introduction of biologic disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (DMARDs).
The guideline, described in an oral session during the virtual annual meeting of the American College of Rheumatology, contains weighted recommendations for the treatment of JIA, including therapeutic approaches for oligoarthritis, tempromandibular joint (TMJ) arthritis, and systemic JIA (sJIA). The recommendations were the result of expert consensus and literature review using GRADE methodology, with input from clinicians, as well as patients and parents.
“Although evidence remains very low and many recommendations are conditional, the inclusion of parents and patients in the decision-making process strengthens their validity,” said project principal investigator Karen Onel, MD, of the Hospital for Special Surgery and Weill Cornell Medicine, both in New York.
She added that “it’s important to remember that these guidelines are meant to be guidelines; clinical care remains in the hands of the provider and the patient, and we endorse the importance of shared decision-making in coming to these agreements.”
Dr. Onel outlined key recommendations for patients for whom a diagnosis of JIA has already been made and who have no contraindications to recommended therapies. The strength of the recommendations (strong or conditional) and evidence levels (high, moderate, low, very low) were also reported.
Oligoarthritis with fewer than five involved joints
For these patients, intra-articular glucocorticoids (IAGC) are recommended as a part of initial therapy (strong, very low evidence).
Triamcinolone acetonide is the preferred agent in this situation (strong, low evidence).
The guideline also has a conditional recommendation (very low evidence) for a trial of consistent NSAIDS as part of initial therapy and a conditional recommendation against oral glucocorticoids for initial therapy (very low evidence).
Patients with no or incomplete responses or intolerance to NSAIDS and/or IAGC may be tried on a nonbiologic DMARD (strong, very low evidence), with methotrexate as the preferred agent (conditional, low evidence).
If the patient has no response or an inadequate response to at least one nonbiologic DMARD, biologic DMARDs are recommended (strong, very low evidence), with no preferred agent.
The guideline also conditionally recommends (all with very low evidence) using risk factors and validated disease activity measures to guide treatment decisions, as well as imaging guidance of joints that are difficult to access or to localize the distribution of inflammation.
TMJ arthritis
For patients with temporomandibular joint arthritis, isolated or not, IAGCs are conditionally recommended as part of initial therapy (very low evidence) with no preferred agents. The guideline also conditionally recommends in favor of a trial of consistent NSAIDs, and against oral glucocorticoids in initial therapy (evidence for both very low).
Recommendations for patients with TMJ with no or an incomplete response to the initial therapy are the same as for patients with oligoarthritis, with no preferred agent.
sJIA without macrophage activation syndrome
For patients with sJIA without macrophage activation syndrome (MAS), NSAIDS are conditionally recommended as initial monotherapy (very low evidence). Biologic DMARDS (including interleukin-1 and IL-6 inhibitors) are also recommended, conditionally, as initial monotherapy, with no preferred agent.
If the patient has an inadequate response or intolerance to NSAIDS and at least one nonbiologic DMARD, a single biologic DMARD is recommended over a combination of nonbiologic therapies (strong, very low evidence).
“However, there have been reports of emergent, highly severe lung disease associated with the use of biologics in children with systemic JIA, especially in those who are young, with chronic macrophage activation syndrome, and those with trisomy 21. More information is needed to clarify the safety of these agents,” Dr. Onel said.
There is a conditional recommendation against oral glucocorticoids as initial monotherapy, and strong recommendation against nonbiologic DMARDs as initial monotherapy (both very low evidence).
sJIA with MAS
“Macrophage activation syndrome is a major cause of morbidity and mortality for children with sJIA. Cytokine storm and secondary hemophagocytic syndrome can be seen with any rheumatic disease, but are most commonly seen with sJIA,” she said.
The features of MAS include fever, high ferritin levels, cytopenias, elevated liver-function test results, and high triglyceride levels.
For these patients, glucocorticoids are recommended as initial monotherapy (conditional, very low evidence). Biologic DMARDs (IL-1 and IL-6 inhibitors) are recommended over calcineurin inhibitors for achieving inactive disease and resolution of MAS (conditional, very low evidence). There is no preferred agent.
For patients with residual arthritis and an incomplete response to IL-1 or IL-6 inhibitors, biologic and nonbiologic DMARDs are recommended over chronic glucocorticoids (strong, very low evidence). There is no preferred agent.
After an MAS inactive disease state has been attained, the guideline recommends tapering and discontinuing glucocorticoids (strong, very low evidence) and the same for biologic DMARDs (conditional, very low evidence).
All children with JIA
In addition to the recommendations on specific clinical situations, the guideline includes recommendations for all children with JIA on medication monitoring, laboratory testing, and infection screening, as well as immunization and nonpharmacologic management.
A rheumatologist who was not involved in development of the guidelines commented on the importance of optimal management of JIA.
“Children are not immune from devastating rheumatic diseases, and the largest group is juvenile idiopathic arthritis. In my clinic, I have patients in their 30s, 40s, and 50s who have adult persistence of their arthritis from JIA who have permanent joint damage and even ongoing hard-to-control disease, and it has to do with the lack of therapies in the 1990s,” said Donald Thomas, MD, from Arthritis and Pain Associates of Prince George’s County (Md.).
“Today when we get a young adult transitioned from the pediatric clinic they’re usually in remission or have low disease activity because these treatments have paralleled those of our adult RA patients. Yet they do [provide clinicians with] unique challenges, with stunting of growth, macrophage activiation syndrome, and having to work with family members of the patient,” he said at a press briefing he moderated following the presentation of RA and JIA guidelines.
Eyal Muscal, MD, associate professor of pediatrics and rheumatology at Baylor College of Medicine, Houston, said in an interview that the guidelines clarify recommendations about earlier use of targeted therapies, primarily biologics.
“This will not change care, but hopefully remind all to adopt such strategies. Yet earlier utilization of often expensive biologic agents is delayed by administrative and insurance hurdles in the U.S. and access to these medications globally. I hope the guidelines will enhance advocacy on a state, national, and global stage,” he said when asked for comment.
The guideline development process is supported by ACR. Dr. Onel, Dr. Thomas, and Dr. Muscal reported no relevant conflicts of interest.
SOURCE: Onel K et al. ACR 2020, Presented November 8.
A draft guideline for the management of patients with juvenile idiopathic arthritis reflects changes in therapy away from reliance on NSAIDs and glucocorticoids and toward earlier introduction of biologic disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (DMARDs).
The guideline, described in an oral session during the virtual annual meeting of the American College of Rheumatology, contains weighted recommendations for the treatment of JIA, including therapeutic approaches for oligoarthritis, tempromandibular joint (TMJ) arthritis, and systemic JIA (sJIA). The recommendations were the result of expert consensus and literature review using GRADE methodology, with input from clinicians, as well as patients and parents.
“Although evidence remains very low and many recommendations are conditional, the inclusion of parents and patients in the decision-making process strengthens their validity,” said project principal investigator Karen Onel, MD, of the Hospital for Special Surgery and Weill Cornell Medicine, both in New York.
She added that “it’s important to remember that these guidelines are meant to be guidelines; clinical care remains in the hands of the provider and the patient, and we endorse the importance of shared decision-making in coming to these agreements.”
Dr. Onel outlined key recommendations for patients for whom a diagnosis of JIA has already been made and who have no contraindications to recommended therapies. The strength of the recommendations (strong or conditional) and evidence levels (high, moderate, low, very low) were also reported.
Oligoarthritis with fewer than five involved joints
For these patients, intra-articular glucocorticoids (IAGC) are recommended as a part of initial therapy (strong, very low evidence).
Triamcinolone acetonide is the preferred agent in this situation (strong, low evidence).
The guideline also has a conditional recommendation (very low evidence) for a trial of consistent NSAIDS as part of initial therapy and a conditional recommendation against oral glucocorticoids for initial therapy (very low evidence).
Patients with no or incomplete responses or intolerance to NSAIDS and/or IAGC may be tried on a nonbiologic DMARD (strong, very low evidence), with methotrexate as the preferred agent (conditional, low evidence).
If the patient has no response or an inadequate response to at least one nonbiologic DMARD, biologic DMARDs are recommended (strong, very low evidence), with no preferred agent.
The guideline also conditionally recommends (all with very low evidence) using risk factors and validated disease activity measures to guide treatment decisions, as well as imaging guidance of joints that are difficult to access or to localize the distribution of inflammation.
TMJ arthritis
For patients with temporomandibular joint arthritis, isolated or not, IAGCs are conditionally recommended as part of initial therapy (very low evidence) with no preferred agents. The guideline also conditionally recommends in favor of a trial of consistent NSAIDs, and against oral glucocorticoids in initial therapy (evidence for both very low).
Recommendations for patients with TMJ with no or an incomplete response to the initial therapy are the same as for patients with oligoarthritis, with no preferred agent.
sJIA without macrophage activation syndrome
For patients with sJIA without macrophage activation syndrome (MAS), NSAIDS are conditionally recommended as initial monotherapy (very low evidence). Biologic DMARDS (including interleukin-1 and IL-6 inhibitors) are also recommended, conditionally, as initial monotherapy, with no preferred agent.
If the patient has an inadequate response or intolerance to NSAIDS and at least one nonbiologic DMARD, a single biologic DMARD is recommended over a combination of nonbiologic therapies (strong, very low evidence).
“However, there have been reports of emergent, highly severe lung disease associated with the use of biologics in children with systemic JIA, especially in those who are young, with chronic macrophage activation syndrome, and those with trisomy 21. More information is needed to clarify the safety of these agents,” Dr. Onel said.
There is a conditional recommendation against oral glucocorticoids as initial monotherapy, and strong recommendation against nonbiologic DMARDs as initial monotherapy (both very low evidence).
sJIA with MAS
“Macrophage activation syndrome is a major cause of morbidity and mortality for children with sJIA. Cytokine storm and secondary hemophagocytic syndrome can be seen with any rheumatic disease, but are most commonly seen with sJIA,” she said.
The features of MAS include fever, high ferritin levels, cytopenias, elevated liver-function test results, and high triglyceride levels.
For these patients, glucocorticoids are recommended as initial monotherapy (conditional, very low evidence). Biologic DMARDs (IL-1 and IL-6 inhibitors) are recommended over calcineurin inhibitors for achieving inactive disease and resolution of MAS (conditional, very low evidence). There is no preferred agent.
For patients with residual arthritis and an incomplete response to IL-1 or IL-6 inhibitors, biologic and nonbiologic DMARDs are recommended over chronic glucocorticoids (strong, very low evidence). There is no preferred agent.
After an MAS inactive disease state has been attained, the guideline recommends tapering and discontinuing glucocorticoids (strong, very low evidence) and the same for biologic DMARDs (conditional, very low evidence).
All children with JIA
In addition to the recommendations on specific clinical situations, the guideline includes recommendations for all children with JIA on medication monitoring, laboratory testing, and infection screening, as well as immunization and nonpharmacologic management.
A rheumatologist who was not involved in development of the guidelines commented on the importance of optimal management of JIA.
“Children are not immune from devastating rheumatic diseases, and the largest group is juvenile idiopathic arthritis. In my clinic, I have patients in their 30s, 40s, and 50s who have adult persistence of their arthritis from JIA who have permanent joint damage and even ongoing hard-to-control disease, and it has to do with the lack of therapies in the 1990s,” said Donald Thomas, MD, from Arthritis and Pain Associates of Prince George’s County (Md.).
“Today when we get a young adult transitioned from the pediatric clinic they’re usually in remission or have low disease activity because these treatments have paralleled those of our adult RA patients. Yet they do [provide clinicians with] unique challenges, with stunting of growth, macrophage activiation syndrome, and having to work with family members of the patient,” he said at a press briefing he moderated following the presentation of RA and JIA guidelines.
Eyal Muscal, MD, associate professor of pediatrics and rheumatology at Baylor College of Medicine, Houston, said in an interview that the guidelines clarify recommendations about earlier use of targeted therapies, primarily biologics.
“This will not change care, but hopefully remind all to adopt such strategies. Yet earlier utilization of often expensive biologic agents is delayed by administrative and insurance hurdles in the U.S. and access to these medications globally. I hope the guidelines will enhance advocacy on a state, national, and global stage,” he said when asked for comment.
The guideline development process is supported by ACR. Dr. Onel, Dr. Thomas, and Dr. Muscal reported no relevant conflicts of interest.
SOURCE: Onel K et al. ACR 2020, Presented November 8.
A draft guideline for the management of patients with juvenile idiopathic arthritis reflects changes in therapy away from reliance on NSAIDs and glucocorticoids and toward earlier introduction of biologic disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (DMARDs).
The guideline, described in an oral session during the virtual annual meeting of the American College of Rheumatology, contains weighted recommendations for the treatment of JIA, including therapeutic approaches for oligoarthritis, tempromandibular joint (TMJ) arthritis, and systemic JIA (sJIA). The recommendations were the result of expert consensus and literature review using GRADE methodology, with input from clinicians, as well as patients and parents.
“Although evidence remains very low and many recommendations are conditional, the inclusion of parents and patients in the decision-making process strengthens their validity,” said project principal investigator Karen Onel, MD, of the Hospital for Special Surgery and Weill Cornell Medicine, both in New York.
She added that “it’s important to remember that these guidelines are meant to be guidelines; clinical care remains in the hands of the provider and the patient, and we endorse the importance of shared decision-making in coming to these agreements.”
Dr. Onel outlined key recommendations for patients for whom a diagnosis of JIA has already been made and who have no contraindications to recommended therapies. The strength of the recommendations (strong or conditional) and evidence levels (high, moderate, low, very low) were also reported.
Oligoarthritis with fewer than five involved joints
For these patients, intra-articular glucocorticoids (IAGC) are recommended as a part of initial therapy (strong, very low evidence).
Triamcinolone acetonide is the preferred agent in this situation (strong, low evidence).
The guideline also has a conditional recommendation (very low evidence) for a trial of consistent NSAIDS as part of initial therapy and a conditional recommendation against oral glucocorticoids for initial therapy (very low evidence).
Patients with no or incomplete responses or intolerance to NSAIDS and/or IAGC may be tried on a nonbiologic DMARD (strong, very low evidence), with methotrexate as the preferred agent (conditional, low evidence).
If the patient has no response or an inadequate response to at least one nonbiologic DMARD, biologic DMARDs are recommended (strong, very low evidence), with no preferred agent.
The guideline also conditionally recommends (all with very low evidence) using risk factors and validated disease activity measures to guide treatment decisions, as well as imaging guidance of joints that are difficult to access or to localize the distribution of inflammation.
TMJ arthritis
For patients with temporomandibular joint arthritis, isolated or not, IAGCs are conditionally recommended as part of initial therapy (very low evidence) with no preferred agents. The guideline also conditionally recommends in favor of a trial of consistent NSAIDs, and against oral glucocorticoids in initial therapy (evidence for both very low).
Recommendations for patients with TMJ with no or an incomplete response to the initial therapy are the same as for patients with oligoarthritis, with no preferred agent.
sJIA without macrophage activation syndrome
For patients with sJIA without macrophage activation syndrome (MAS), NSAIDS are conditionally recommended as initial monotherapy (very low evidence). Biologic DMARDS (including interleukin-1 and IL-6 inhibitors) are also recommended, conditionally, as initial monotherapy, with no preferred agent.
If the patient has an inadequate response or intolerance to NSAIDS and at least one nonbiologic DMARD, a single biologic DMARD is recommended over a combination of nonbiologic therapies (strong, very low evidence).
“However, there have been reports of emergent, highly severe lung disease associated with the use of biologics in children with systemic JIA, especially in those who are young, with chronic macrophage activation syndrome, and those with trisomy 21. More information is needed to clarify the safety of these agents,” Dr. Onel said.
There is a conditional recommendation against oral glucocorticoids as initial monotherapy, and strong recommendation against nonbiologic DMARDs as initial monotherapy (both very low evidence).
sJIA with MAS
“Macrophage activation syndrome is a major cause of morbidity and mortality for children with sJIA. Cytokine storm and secondary hemophagocytic syndrome can be seen with any rheumatic disease, but are most commonly seen with sJIA,” she said.
The features of MAS include fever, high ferritin levels, cytopenias, elevated liver-function test results, and high triglyceride levels.
For these patients, glucocorticoids are recommended as initial monotherapy (conditional, very low evidence). Biologic DMARDs (IL-1 and IL-6 inhibitors) are recommended over calcineurin inhibitors for achieving inactive disease and resolution of MAS (conditional, very low evidence). There is no preferred agent.
For patients with residual arthritis and an incomplete response to IL-1 or IL-6 inhibitors, biologic and nonbiologic DMARDs are recommended over chronic glucocorticoids (strong, very low evidence). There is no preferred agent.
After an MAS inactive disease state has been attained, the guideline recommends tapering and discontinuing glucocorticoids (strong, very low evidence) and the same for biologic DMARDs (conditional, very low evidence).
All children with JIA
In addition to the recommendations on specific clinical situations, the guideline includes recommendations for all children with JIA on medication monitoring, laboratory testing, and infection screening, as well as immunization and nonpharmacologic management.
A rheumatologist who was not involved in development of the guidelines commented on the importance of optimal management of JIA.
“Children are not immune from devastating rheumatic diseases, and the largest group is juvenile idiopathic arthritis. In my clinic, I have patients in their 30s, 40s, and 50s who have adult persistence of their arthritis from JIA who have permanent joint damage and even ongoing hard-to-control disease, and it has to do with the lack of therapies in the 1990s,” said Donald Thomas, MD, from Arthritis and Pain Associates of Prince George’s County (Md.).
“Today when we get a young adult transitioned from the pediatric clinic they’re usually in remission or have low disease activity because these treatments have paralleled those of our adult RA patients. Yet they do [provide clinicians with] unique challenges, with stunting of growth, macrophage activiation syndrome, and having to work with family members of the patient,” he said at a press briefing he moderated following the presentation of RA and JIA guidelines.
Eyal Muscal, MD, associate professor of pediatrics and rheumatology at Baylor College of Medicine, Houston, said in an interview that the guidelines clarify recommendations about earlier use of targeted therapies, primarily biologics.
“This will not change care, but hopefully remind all to adopt such strategies. Yet earlier utilization of often expensive biologic agents is delayed by administrative and insurance hurdles in the U.S. and access to these medications globally. I hope the guidelines will enhance advocacy on a state, national, and global stage,” he said when asked for comment.
The guideline development process is supported by ACR. Dr. Onel, Dr. Thomas, and Dr. Muscal reported no relevant conflicts of interest.
SOURCE: Onel K et al. ACR 2020, Presented November 8.
FROM ACR 2020