User login
Long COVID Has Caused Thousands of US Deaths: New CDC Data
While COVID has now claimed more than 1 million lives in the United States alone, these aren’t the only fatalities caused at least in part by the virus. A small but growing number of Americans are surviving acute infections only to succumb months later to the lingering health problems caused by long COVID.
Much of the attention on long COVID has centered on the sometimes debilitating symptoms that strike people with the condition, with no formal diagnostic tests or standard treatments available, and the effect it has on quality of life. But new figures from the US Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) show that long COVID can also be deadly.
More than 5000 Americans have died from long COVID since the start of the pandemic, according to new estimates from the CDC.
This total, based on death certificate data collected by the CDC, includes a preliminary tally of 1491 long COVID deaths in 2023 in addition to 3544 fatalities previously reported from January 2020 through June 2022.
Guidance issued in 2023 on how to formally report long COVID as a cause of death on death certificates should help get a more accurate count of these fatalities going forward, said Robert Anderson, PhD, chief mortality statistician for the CDC, Atlanta, Georgia.
“We hope that the guidance will help cause of death certifiers be more aware of the impact of long COVID and more likely to report long COVID as a cause of death when appropriate,” Dr. Anderson said. “That said, we do not expect that this guidance will have a dramatic impact on the trend.”
There’s no standard definition or diagnostic test for long COVID. It’s typically diagnosed when people have symptoms at least 3 months after an acute infection that weren’t present before they got sick. As of the end of last year, about 7% of American adults had experienced long COVID at some point, the CDC estimated in September 2023.
The new death tally indicates long COVID remains a significant public health threat and is likely to grow in the years ahead, even though the pandemic may no longer be considered a global health crisis, experts said.
For example, the death certificate figures indicate:
COVID-19 was the third leading cause of American deaths in 2020 and 2021, and the fourth leading cause of death in the United States in 2023.
Nearly 1% of the more than one million deaths related to COVID-19 since the start of the pandemic have been attributed to long COVID, according to data released by the CDC.
The proportion of COVID-related deaths from long COVID peaked in June 2021 at 1.2% and again in April 2022 at 3.8%, according to the CDC. Both of these peaks coincided with periods of declining fatalities from acute infections.
“I do expect that deaths associated with long COVID will make up an increasingly larger proportion of total deaths associated with COVID-19,” said Mark Czeisler, PhD, a researcher at Harvard Medical School, Boston, Massachusetts, who has studied long COVID fatalities.
Months and even years after an acute infection, long COVID can contribute to serious and potentially life-threatening conditions that impact nearly every major system in the body, according to the CDC guidelines for identifying the condition on death certificates.
This means long COVID may often be listed as an underlying cause of death when people with this condition die of issues related to their heart, lungs, brain or kidneys, the CDC guidelines noted.
The risk for long COVID fatalities remains elevated for at least 6 months for people with milder acute infections and for at least 2 years in severe cases that require hospitalization, some previous research suggested.
As happens with other acute infections, certain people are more at risk for fatal case of long COVID. Age, race, and ethnicity have all been cited as risk factors by researchers who have been tracking the condition since the start of the pandemic.
Half of long COVID fatalities from July 2021 to June 2022 occurred in people aged 65 years and older, and another 23% were recorded among people aged 50-64 years old, according a report from CDC.
Long COVID death rates also varied by race and ethnicity, from a high of 14.1 cases per million among America Indian and Alaskan natives to a low of 1.5 cases per million among Asian people, the CDC found. Death rates per million were 6.7 for White individuals, 6.4 for Black people, and 4.7 for Hispanic people.
The disproportionate share of Black and Hispanic people who developed and died from severe acute infections may have left fewer survivors to develop long COVID, limiting long COVID fatalities among these groups, the CDC report concluded.
It’s also possible that long COVID fatalities were undercounted in these populations because they faced challenges accessing healthcare or seeing providers who could recognize the hallmark symptoms of long COVID.
It’s also difficult to distinguish between how many deaths related to the virus ultimately occur as a result of long COVID rather than acute infections. That’s because it may depend on a variety of factors, including how consistently medical examiners follow the CDC guidelines, said Ziyad Al-Aly, MD, chief of research at the Veterans Affairs, St. Louis Health Care System and a senior clinical epidemiologist at Washington University in St. Louis.
“Long COVID remains massively underdiagnosed, and death in people with long COVID is misattributed to other things,” Dr. Al-Aly said.
An accurate test for long COVID could help lead to a more accurate count of these fatalities, Dr. Czeisler said. Some preliminary research suggests that it might one day be possible to diagnose long COVID with a blood test.
“The timeline for such a test and the extent to which it would be widely applied is uncertain,” Dr. Czeisler noted, “though that would certainly be a gamechanger.”
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
While COVID has now claimed more than 1 million lives in the United States alone, these aren’t the only fatalities caused at least in part by the virus. A small but growing number of Americans are surviving acute infections only to succumb months later to the lingering health problems caused by long COVID.
Much of the attention on long COVID has centered on the sometimes debilitating symptoms that strike people with the condition, with no formal diagnostic tests or standard treatments available, and the effect it has on quality of life. But new figures from the US Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) show that long COVID can also be deadly.
More than 5000 Americans have died from long COVID since the start of the pandemic, according to new estimates from the CDC.
This total, based on death certificate data collected by the CDC, includes a preliminary tally of 1491 long COVID deaths in 2023 in addition to 3544 fatalities previously reported from January 2020 through June 2022.
Guidance issued in 2023 on how to formally report long COVID as a cause of death on death certificates should help get a more accurate count of these fatalities going forward, said Robert Anderson, PhD, chief mortality statistician for the CDC, Atlanta, Georgia.
“We hope that the guidance will help cause of death certifiers be more aware of the impact of long COVID and more likely to report long COVID as a cause of death when appropriate,” Dr. Anderson said. “That said, we do not expect that this guidance will have a dramatic impact on the trend.”
There’s no standard definition or diagnostic test for long COVID. It’s typically diagnosed when people have symptoms at least 3 months after an acute infection that weren’t present before they got sick. As of the end of last year, about 7% of American adults had experienced long COVID at some point, the CDC estimated in September 2023.
The new death tally indicates long COVID remains a significant public health threat and is likely to grow in the years ahead, even though the pandemic may no longer be considered a global health crisis, experts said.
For example, the death certificate figures indicate:
COVID-19 was the third leading cause of American deaths in 2020 and 2021, and the fourth leading cause of death in the United States in 2023.
Nearly 1% of the more than one million deaths related to COVID-19 since the start of the pandemic have been attributed to long COVID, according to data released by the CDC.
The proportion of COVID-related deaths from long COVID peaked in June 2021 at 1.2% and again in April 2022 at 3.8%, according to the CDC. Both of these peaks coincided with periods of declining fatalities from acute infections.
“I do expect that deaths associated with long COVID will make up an increasingly larger proportion of total deaths associated with COVID-19,” said Mark Czeisler, PhD, a researcher at Harvard Medical School, Boston, Massachusetts, who has studied long COVID fatalities.
Months and even years after an acute infection, long COVID can contribute to serious and potentially life-threatening conditions that impact nearly every major system in the body, according to the CDC guidelines for identifying the condition on death certificates.
This means long COVID may often be listed as an underlying cause of death when people with this condition die of issues related to their heart, lungs, brain or kidneys, the CDC guidelines noted.
The risk for long COVID fatalities remains elevated for at least 6 months for people with milder acute infections and for at least 2 years in severe cases that require hospitalization, some previous research suggested.
As happens with other acute infections, certain people are more at risk for fatal case of long COVID. Age, race, and ethnicity have all been cited as risk factors by researchers who have been tracking the condition since the start of the pandemic.
Half of long COVID fatalities from July 2021 to June 2022 occurred in people aged 65 years and older, and another 23% were recorded among people aged 50-64 years old, according a report from CDC.
Long COVID death rates also varied by race and ethnicity, from a high of 14.1 cases per million among America Indian and Alaskan natives to a low of 1.5 cases per million among Asian people, the CDC found. Death rates per million were 6.7 for White individuals, 6.4 for Black people, and 4.7 for Hispanic people.
The disproportionate share of Black and Hispanic people who developed and died from severe acute infections may have left fewer survivors to develop long COVID, limiting long COVID fatalities among these groups, the CDC report concluded.
It’s also possible that long COVID fatalities were undercounted in these populations because they faced challenges accessing healthcare or seeing providers who could recognize the hallmark symptoms of long COVID.
It’s also difficult to distinguish between how many deaths related to the virus ultimately occur as a result of long COVID rather than acute infections. That’s because it may depend on a variety of factors, including how consistently medical examiners follow the CDC guidelines, said Ziyad Al-Aly, MD, chief of research at the Veterans Affairs, St. Louis Health Care System and a senior clinical epidemiologist at Washington University in St. Louis.
“Long COVID remains massively underdiagnosed, and death in people with long COVID is misattributed to other things,” Dr. Al-Aly said.
An accurate test for long COVID could help lead to a more accurate count of these fatalities, Dr. Czeisler said. Some preliminary research suggests that it might one day be possible to diagnose long COVID with a blood test.
“The timeline for such a test and the extent to which it would be widely applied is uncertain,” Dr. Czeisler noted, “though that would certainly be a gamechanger.”
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
While COVID has now claimed more than 1 million lives in the United States alone, these aren’t the only fatalities caused at least in part by the virus. A small but growing number of Americans are surviving acute infections only to succumb months later to the lingering health problems caused by long COVID.
Much of the attention on long COVID has centered on the sometimes debilitating symptoms that strike people with the condition, with no formal diagnostic tests or standard treatments available, and the effect it has on quality of life. But new figures from the US Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) show that long COVID can also be deadly.
More than 5000 Americans have died from long COVID since the start of the pandemic, according to new estimates from the CDC.
This total, based on death certificate data collected by the CDC, includes a preliminary tally of 1491 long COVID deaths in 2023 in addition to 3544 fatalities previously reported from January 2020 through June 2022.
Guidance issued in 2023 on how to formally report long COVID as a cause of death on death certificates should help get a more accurate count of these fatalities going forward, said Robert Anderson, PhD, chief mortality statistician for the CDC, Atlanta, Georgia.
“We hope that the guidance will help cause of death certifiers be more aware of the impact of long COVID and more likely to report long COVID as a cause of death when appropriate,” Dr. Anderson said. “That said, we do not expect that this guidance will have a dramatic impact on the trend.”
There’s no standard definition or diagnostic test for long COVID. It’s typically diagnosed when people have symptoms at least 3 months after an acute infection that weren’t present before they got sick. As of the end of last year, about 7% of American adults had experienced long COVID at some point, the CDC estimated in September 2023.
The new death tally indicates long COVID remains a significant public health threat and is likely to grow in the years ahead, even though the pandemic may no longer be considered a global health crisis, experts said.
For example, the death certificate figures indicate:
COVID-19 was the third leading cause of American deaths in 2020 and 2021, and the fourth leading cause of death in the United States in 2023.
Nearly 1% of the more than one million deaths related to COVID-19 since the start of the pandemic have been attributed to long COVID, according to data released by the CDC.
The proportion of COVID-related deaths from long COVID peaked in June 2021 at 1.2% and again in April 2022 at 3.8%, according to the CDC. Both of these peaks coincided with periods of declining fatalities from acute infections.
“I do expect that deaths associated with long COVID will make up an increasingly larger proportion of total deaths associated with COVID-19,” said Mark Czeisler, PhD, a researcher at Harvard Medical School, Boston, Massachusetts, who has studied long COVID fatalities.
Months and even years after an acute infection, long COVID can contribute to serious and potentially life-threatening conditions that impact nearly every major system in the body, according to the CDC guidelines for identifying the condition on death certificates.
This means long COVID may often be listed as an underlying cause of death when people with this condition die of issues related to their heart, lungs, brain or kidneys, the CDC guidelines noted.
The risk for long COVID fatalities remains elevated for at least 6 months for people with milder acute infections and for at least 2 years in severe cases that require hospitalization, some previous research suggested.
As happens with other acute infections, certain people are more at risk for fatal case of long COVID. Age, race, and ethnicity have all been cited as risk factors by researchers who have been tracking the condition since the start of the pandemic.
Half of long COVID fatalities from July 2021 to June 2022 occurred in people aged 65 years and older, and another 23% were recorded among people aged 50-64 years old, according a report from CDC.
Long COVID death rates also varied by race and ethnicity, from a high of 14.1 cases per million among America Indian and Alaskan natives to a low of 1.5 cases per million among Asian people, the CDC found. Death rates per million were 6.7 for White individuals, 6.4 for Black people, and 4.7 for Hispanic people.
The disproportionate share of Black and Hispanic people who developed and died from severe acute infections may have left fewer survivors to develop long COVID, limiting long COVID fatalities among these groups, the CDC report concluded.
It’s also possible that long COVID fatalities were undercounted in these populations because they faced challenges accessing healthcare or seeing providers who could recognize the hallmark symptoms of long COVID.
It’s also difficult to distinguish between how many deaths related to the virus ultimately occur as a result of long COVID rather than acute infections. That’s because it may depend on a variety of factors, including how consistently medical examiners follow the CDC guidelines, said Ziyad Al-Aly, MD, chief of research at the Veterans Affairs, St. Louis Health Care System and a senior clinical epidemiologist at Washington University in St. Louis.
“Long COVID remains massively underdiagnosed, and death in people with long COVID is misattributed to other things,” Dr. Al-Aly said.
An accurate test for long COVID could help lead to a more accurate count of these fatalities, Dr. Czeisler said. Some preliminary research suggests that it might one day be possible to diagnose long COVID with a blood test.
“The timeline for such a test and the extent to which it would be widely applied is uncertain,” Dr. Czeisler noted, “though that would certainly be a gamechanger.”
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Why Do MDs Have Such a High Rate of Eating Disorders?
Ten years ago, Clare Gerada, FRCGP, an advocate for physician well-being and today president of the UK’s Royal College of General Practitioners, made a prediction to the audience at the International Conference on Physician Health.
“We have seen a massive increase in eating disorders [among doctors],” she said. “I’m not sure anybody is quite aware of the tsunami of eating disorders,” she believed would soon strike predominantly female physicians.
That was 2014. Did the tsunami hit?
Quite possibly. Data are limited on the prevalence of eating disorders (EDs) among healthcare workers, but studies do exist. A 2019 global review and meta-analysis determined “the summary prevalence of eating disorder (ED) risk among medical students was 10.4%.”
A 2022 update of that review boosted the estimate to 17.35%.
Tsunami or not, that’s nearly double the 9% rate within the US general public (from a 2020 report from STRIPED and the Academy of Eating Disorders). And while the following stat isn’t an indicator of EDs per se,
To her credit, Dr. Gerada, awarded a damehood in 2020, was in a position to know what was coming. Her statement was informed by research showing an increasing number of young doctors seeking treatment for mental health issues, including EDs, through the NHS Practitioner Health program, a mental health service she established in 2008.
So ... what puts doctors at such a high risk for EDs?
Be Careful of ‘Overlap Traits’
As with many mental health issues, EDs have no single cause. Researchers believe they stem from a complex interaction of genetic, biological, behavioral, psychological, and social factors. But the medical field should take note: Some personality traits commonly associated with EDs are often shared by successful physicians.
“I think some of the overlap traits would be being highly driven, goal-oriented and self-critical,” said Lesley Williams, MD, a family medicine physician at the Mayo Clinic in Phoenix, Arizona. “A lot of those traits can make you a very successful physician and physician-in-training but could also potentially spill over into body image and rigidity around food.”
Of course, we want physicians to strive for excellence, and the majority of diligent, driven doctors will not develop an ED.
But when pushed too far, those admirable qualities can easily become perfectionism — which has long been recognized as a risk factor for EDs, an association supported by decades of research.
Medical School: Where EDs Begin and Little Education About Them Happens
“I think medicine in general attracts people that often share similar characteristics to those who struggle with EDs — high-achieving, hardworking perfectionists who put a lot of pressure on themselves,” said Elizabeth McNaught, MD, a general practitioner and medical director at Family Mental Wealth.
Diagnosed with an ED at 14, Dr. McNaught has experienced this firsthand and shared her story in a 2020 memoir, Life Hurts: A Doctor’s Personal Journey Through Anorexia.
Competitive, high-stress environments can also be a trigger, Dr. McNaught explained. “The pressure of medical school,” for example, “can perpetuate an eating disorder if that’s something that you’re struggling with,” she said.
Pressure to perform may not be the only problem. Medical students are taught to view weight as a key indicator of health. Multiple studies suggested that not only does weight stigma exist in healthcare but also it has increased over time and negatively affects patients’ psychological well-being and physical health.
There is far less public discourse about how weight stigma can be harmful to medical students and physicians themselves. Dr. Williams believed the weight-centric paradigm was key.
“For so long, we believed that health presents itself within these confines on a BMI chart and anything outside of that is unhealthy and must be fixed,” she said. “I can say from having gone through medical education, having that continual messaging does make someone feel that if I myself am not within those confines, then I need to do something to fix that immediately if I’m going to continue to care for patients.”
In general, Dr. Williams, and Dr. McNaught agreed that medical training around EDs is lacking, producing doctors who are ill-equipped to diagnose, treat, or even discuss them with patients. Dr. Williams recalled only one lecture on the topic in med school.
“And yet, anorexia carries the second highest death rate of all mental illnesses after opioid-use disorders,” she said, “so it’s astonishing that that just wasn’t included.”
MDs Hiding Mental Health Issues
Claire Anderson, MD (a pseudonym), emphatically stated she would never tell anyone at the hospital where she works in the emergency department that she has an ED.
“There is still a lot of misunderstanding about mental health, and I never want people to doubt my ability to care for people,” Dr. Anderson said. “There’s so much stigma around eating disorders, and I also feel like once it’s out there, I can’t take it back, and I don’t want to feel like people are watching me.”
Melissa Klein, PhD, a clinical psychologist specializing in EDs, has more than 25 years of experience working the inpatient ED unit at New York Presbyterian. Having treated medical professionals, Dr. Klein said they have legitimate concerns about revealing their struggles.
“Sometimes, they do get reported to higher ups — the boards,” Dr. Klein said, “and they’re told that they have to get help in order for them to continue to work in their profession. I think people might be scared to ask for help because of that reason.”
Doctors Often Ignore EDs or Teach ‘Bad Habits’
Dr. Anderson firmly believed that if her early treatment from doctors had been better, she might not be struggling so much today.
The first time Dr. Anderson’s mother brought up her daughter’s sudden weight loss at 14, their family doctor conferred with a chart and said there was no reason to worry; Dr. Anderson’s weight was “normal.” “I was eating like 500 calories a day and swimming for 3 hours, and [by saying that], they assured me I was fine,” she recalls.
At 15, when Dr. Anderson went in for an initial assessment for an ED, she thought she’d be connected with a nutritionist and sent home. “I didn’t have a lot of classic thoughts of wanting to be thin or wanting to lose weight,” she said.
Instead, Dr. Anderson was sent to inpatient care, which she credits with escalating her ED. “I picked up on a lot of really bad habits when I went there — I sort of learned how to have an eating disorder,” she said. “When I left, it was very different than when I went in, which is kind of sad.”
Throughout high school, Dr. Anderson went in and out of so many hospitals and treatment programs that she’s lost track of them. Then, in 2008, she left formal treatment altogether. “I had been really angry with the treatment programs for trying to fit me into their box with a rigid schedule of inpatient and outpatient care,” she recalled. “I didn’t want to live in that world anymore.”
After working with a new psychiatrist, Dr. Anderson’s situation improved until a particularly stressful second year of residency. “That’s when I just tanked,” she said. “Residency, and especially being on my own and with COVID, things have not been great for me.”
Dr. Anderson now sees an eating disorder specialist, but she pays for this out-of-pocket. “I have terrible insurance,” she said with a laugh, aware of that irony.
If You Are Struggling, Don’t Be Ashamed
Some physicians who’ve experienced EDs firsthand are working to improve training on diagnosing and treating the conditions. Dr. McNaught has developed and launched a new eLearning program for healthcare workers on how to recognize the early signs and symptoms of an ED and provide support.
“It’s not only so they can recognize it in their patients but also if colleagues and family and friends are struggling,” she said.
In 2021, the American Psychiatric Association (APA) approved the APA Practice Guideline for the Treatment of Patients With Eating Disorders, which aims to improve patient care and treatment outcomes.
But Dr. Klein is concerned that increased stress since the COVID-19 pandemic may be putting healthcare workers at even greater risk.
“When people are under stress or when they feel like there are things in their life that maybe they can’t control, sometimes turning to an eating disorder is a way to cope,” she said, “In that sense, the stress on medical professionals is something that could lead to eating disorder behaviors.”
Dr. Klein’s message to healthcare workers: Don’t be ashamed. She described an ED as “a monster that takes over your brain. Once it starts, it’s very hard to turn it around on your own. So, I hope anyone who is suffering, in whatever field they’re in, that they are able to ask for help.”
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Ten years ago, Clare Gerada, FRCGP, an advocate for physician well-being and today president of the UK’s Royal College of General Practitioners, made a prediction to the audience at the International Conference on Physician Health.
“We have seen a massive increase in eating disorders [among doctors],” she said. “I’m not sure anybody is quite aware of the tsunami of eating disorders,” she believed would soon strike predominantly female physicians.
That was 2014. Did the tsunami hit?
Quite possibly. Data are limited on the prevalence of eating disorders (EDs) among healthcare workers, but studies do exist. A 2019 global review and meta-analysis determined “the summary prevalence of eating disorder (ED) risk among medical students was 10.4%.”
A 2022 update of that review boosted the estimate to 17.35%.
Tsunami or not, that’s nearly double the 9% rate within the US general public (from a 2020 report from STRIPED and the Academy of Eating Disorders). And while the following stat isn’t an indicator of EDs per se,
To her credit, Dr. Gerada, awarded a damehood in 2020, was in a position to know what was coming. Her statement was informed by research showing an increasing number of young doctors seeking treatment for mental health issues, including EDs, through the NHS Practitioner Health program, a mental health service she established in 2008.
So ... what puts doctors at such a high risk for EDs?
Be Careful of ‘Overlap Traits’
As with many mental health issues, EDs have no single cause. Researchers believe they stem from a complex interaction of genetic, biological, behavioral, psychological, and social factors. But the medical field should take note: Some personality traits commonly associated with EDs are often shared by successful physicians.
“I think some of the overlap traits would be being highly driven, goal-oriented and self-critical,” said Lesley Williams, MD, a family medicine physician at the Mayo Clinic in Phoenix, Arizona. “A lot of those traits can make you a very successful physician and physician-in-training but could also potentially spill over into body image and rigidity around food.”
Of course, we want physicians to strive for excellence, and the majority of diligent, driven doctors will not develop an ED.
But when pushed too far, those admirable qualities can easily become perfectionism — which has long been recognized as a risk factor for EDs, an association supported by decades of research.
Medical School: Where EDs Begin and Little Education About Them Happens
“I think medicine in general attracts people that often share similar characteristics to those who struggle with EDs — high-achieving, hardworking perfectionists who put a lot of pressure on themselves,” said Elizabeth McNaught, MD, a general practitioner and medical director at Family Mental Wealth.
Diagnosed with an ED at 14, Dr. McNaught has experienced this firsthand and shared her story in a 2020 memoir, Life Hurts: A Doctor’s Personal Journey Through Anorexia.
Competitive, high-stress environments can also be a trigger, Dr. McNaught explained. “The pressure of medical school,” for example, “can perpetuate an eating disorder if that’s something that you’re struggling with,” she said.
Pressure to perform may not be the only problem. Medical students are taught to view weight as a key indicator of health. Multiple studies suggested that not only does weight stigma exist in healthcare but also it has increased over time and negatively affects patients’ psychological well-being and physical health.
There is far less public discourse about how weight stigma can be harmful to medical students and physicians themselves. Dr. Williams believed the weight-centric paradigm was key.
“For so long, we believed that health presents itself within these confines on a BMI chart and anything outside of that is unhealthy and must be fixed,” she said. “I can say from having gone through medical education, having that continual messaging does make someone feel that if I myself am not within those confines, then I need to do something to fix that immediately if I’m going to continue to care for patients.”
In general, Dr. Williams, and Dr. McNaught agreed that medical training around EDs is lacking, producing doctors who are ill-equipped to diagnose, treat, or even discuss them with patients. Dr. Williams recalled only one lecture on the topic in med school.
“And yet, anorexia carries the second highest death rate of all mental illnesses after opioid-use disorders,” she said, “so it’s astonishing that that just wasn’t included.”
MDs Hiding Mental Health Issues
Claire Anderson, MD (a pseudonym), emphatically stated she would never tell anyone at the hospital where she works in the emergency department that she has an ED.
“There is still a lot of misunderstanding about mental health, and I never want people to doubt my ability to care for people,” Dr. Anderson said. “There’s so much stigma around eating disorders, and I also feel like once it’s out there, I can’t take it back, and I don’t want to feel like people are watching me.”
Melissa Klein, PhD, a clinical psychologist specializing in EDs, has more than 25 years of experience working the inpatient ED unit at New York Presbyterian. Having treated medical professionals, Dr. Klein said they have legitimate concerns about revealing their struggles.
“Sometimes, they do get reported to higher ups — the boards,” Dr. Klein said, “and they’re told that they have to get help in order for them to continue to work in their profession. I think people might be scared to ask for help because of that reason.”
Doctors Often Ignore EDs or Teach ‘Bad Habits’
Dr. Anderson firmly believed that if her early treatment from doctors had been better, she might not be struggling so much today.
The first time Dr. Anderson’s mother brought up her daughter’s sudden weight loss at 14, their family doctor conferred with a chart and said there was no reason to worry; Dr. Anderson’s weight was “normal.” “I was eating like 500 calories a day and swimming for 3 hours, and [by saying that], they assured me I was fine,” she recalls.
At 15, when Dr. Anderson went in for an initial assessment for an ED, she thought she’d be connected with a nutritionist and sent home. “I didn’t have a lot of classic thoughts of wanting to be thin or wanting to lose weight,” she said.
Instead, Dr. Anderson was sent to inpatient care, which she credits with escalating her ED. “I picked up on a lot of really bad habits when I went there — I sort of learned how to have an eating disorder,” she said. “When I left, it was very different than when I went in, which is kind of sad.”
Throughout high school, Dr. Anderson went in and out of so many hospitals and treatment programs that she’s lost track of them. Then, in 2008, she left formal treatment altogether. “I had been really angry with the treatment programs for trying to fit me into their box with a rigid schedule of inpatient and outpatient care,” she recalled. “I didn’t want to live in that world anymore.”
After working with a new psychiatrist, Dr. Anderson’s situation improved until a particularly stressful second year of residency. “That’s when I just tanked,” she said. “Residency, and especially being on my own and with COVID, things have not been great for me.”
Dr. Anderson now sees an eating disorder specialist, but she pays for this out-of-pocket. “I have terrible insurance,” she said with a laugh, aware of that irony.
If You Are Struggling, Don’t Be Ashamed
Some physicians who’ve experienced EDs firsthand are working to improve training on diagnosing and treating the conditions. Dr. McNaught has developed and launched a new eLearning program for healthcare workers on how to recognize the early signs and symptoms of an ED and provide support.
“It’s not only so they can recognize it in their patients but also if colleagues and family and friends are struggling,” she said.
In 2021, the American Psychiatric Association (APA) approved the APA Practice Guideline for the Treatment of Patients With Eating Disorders, which aims to improve patient care and treatment outcomes.
But Dr. Klein is concerned that increased stress since the COVID-19 pandemic may be putting healthcare workers at even greater risk.
“When people are under stress or when they feel like there are things in their life that maybe they can’t control, sometimes turning to an eating disorder is a way to cope,” she said, “In that sense, the stress on medical professionals is something that could lead to eating disorder behaviors.”
Dr. Klein’s message to healthcare workers: Don’t be ashamed. She described an ED as “a monster that takes over your brain. Once it starts, it’s very hard to turn it around on your own. So, I hope anyone who is suffering, in whatever field they’re in, that they are able to ask for help.”
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Ten years ago, Clare Gerada, FRCGP, an advocate for physician well-being and today president of the UK’s Royal College of General Practitioners, made a prediction to the audience at the International Conference on Physician Health.
“We have seen a massive increase in eating disorders [among doctors],” she said. “I’m not sure anybody is quite aware of the tsunami of eating disorders,” she believed would soon strike predominantly female physicians.
That was 2014. Did the tsunami hit?
Quite possibly. Data are limited on the prevalence of eating disorders (EDs) among healthcare workers, but studies do exist. A 2019 global review and meta-analysis determined “the summary prevalence of eating disorder (ED) risk among medical students was 10.4%.”
A 2022 update of that review boosted the estimate to 17.35%.
Tsunami or not, that’s nearly double the 9% rate within the US general public (from a 2020 report from STRIPED and the Academy of Eating Disorders). And while the following stat isn’t an indicator of EDs per se,
To her credit, Dr. Gerada, awarded a damehood in 2020, was in a position to know what was coming. Her statement was informed by research showing an increasing number of young doctors seeking treatment for mental health issues, including EDs, through the NHS Practitioner Health program, a mental health service she established in 2008.
So ... what puts doctors at such a high risk for EDs?
Be Careful of ‘Overlap Traits’
As with many mental health issues, EDs have no single cause. Researchers believe they stem from a complex interaction of genetic, biological, behavioral, psychological, and social factors. But the medical field should take note: Some personality traits commonly associated with EDs are often shared by successful physicians.
“I think some of the overlap traits would be being highly driven, goal-oriented and self-critical,” said Lesley Williams, MD, a family medicine physician at the Mayo Clinic in Phoenix, Arizona. “A lot of those traits can make you a very successful physician and physician-in-training but could also potentially spill over into body image and rigidity around food.”
Of course, we want physicians to strive for excellence, and the majority of diligent, driven doctors will not develop an ED.
But when pushed too far, those admirable qualities can easily become perfectionism — which has long been recognized as a risk factor for EDs, an association supported by decades of research.
Medical School: Where EDs Begin and Little Education About Them Happens
“I think medicine in general attracts people that often share similar characteristics to those who struggle with EDs — high-achieving, hardworking perfectionists who put a lot of pressure on themselves,” said Elizabeth McNaught, MD, a general practitioner and medical director at Family Mental Wealth.
Diagnosed with an ED at 14, Dr. McNaught has experienced this firsthand and shared her story in a 2020 memoir, Life Hurts: A Doctor’s Personal Journey Through Anorexia.
Competitive, high-stress environments can also be a trigger, Dr. McNaught explained. “The pressure of medical school,” for example, “can perpetuate an eating disorder if that’s something that you’re struggling with,” she said.
Pressure to perform may not be the only problem. Medical students are taught to view weight as a key indicator of health. Multiple studies suggested that not only does weight stigma exist in healthcare but also it has increased over time and negatively affects patients’ psychological well-being and physical health.
There is far less public discourse about how weight stigma can be harmful to medical students and physicians themselves. Dr. Williams believed the weight-centric paradigm was key.
“For so long, we believed that health presents itself within these confines on a BMI chart and anything outside of that is unhealthy and must be fixed,” she said. “I can say from having gone through medical education, having that continual messaging does make someone feel that if I myself am not within those confines, then I need to do something to fix that immediately if I’m going to continue to care for patients.”
In general, Dr. Williams, and Dr. McNaught agreed that medical training around EDs is lacking, producing doctors who are ill-equipped to diagnose, treat, or even discuss them with patients. Dr. Williams recalled only one lecture on the topic in med school.
“And yet, anorexia carries the second highest death rate of all mental illnesses after opioid-use disorders,” she said, “so it’s astonishing that that just wasn’t included.”
MDs Hiding Mental Health Issues
Claire Anderson, MD (a pseudonym), emphatically stated she would never tell anyone at the hospital where she works in the emergency department that she has an ED.
“There is still a lot of misunderstanding about mental health, and I never want people to doubt my ability to care for people,” Dr. Anderson said. “There’s so much stigma around eating disorders, and I also feel like once it’s out there, I can’t take it back, and I don’t want to feel like people are watching me.”
Melissa Klein, PhD, a clinical psychologist specializing in EDs, has more than 25 years of experience working the inpatient ED unit at New York Presbyterian. Having treated medical professionals, Dr. Klein said they have legitimate concerns about revealing their struggles.
“Sometimes, they do get reported to higher ups — the boards,” Dr. Klein said, “and they’re told that they have to get help in order for them to continue to work in their profession. I think people might be scared to ask for help because of that reason.”
Doctors Often Ignore EDs or Teach ‘Bad Habits’
Dr. Anderson firmly believed that if her early treatment from doctors had been better, she might not be struggling so much today.
The first time Dr. Anderson’s mother brought up her daughter’s sudden weight loss at 14, their family doctor conferred with a chart and said there was no reason to worry; Dr. Anderson’s weight was “normal.” “I was eating like 500 calories a day and swimming for 3 hours, and [by saying that], they assured me I was fine,” she recalls.
At 15, when Dr. Anderson went in for an initial assessment for an ED, she thought she’d be connected with a nutritionist and sent home. “I didn’t have a lot of classic thoughts of wanting to be thin or wanting to lose weight,” she said.
Instead, Dr. Anderson was sent to inpatient care, which she credits with escalating her ED. “I picked up on a lot of really bad habits when I went there — I sort of learned how to have an eating disorder,” she said. “When I left, it was very different than when I went in, which is kind of sad.”
Throughout high school, Dr. Anderson went in and out of so many hospitals and treatment programs that she’s lost track of them. Then, in 2008, she left formal treatment altogether. “I had been really angry with the treatment programs for trying to fit me into their box with a rigid schedule of inpatient and outpatient care,” she recalled. “I didn’t want to live in that world anymore.”
After working with a new psychiatrist, Dr. Anderson’s situation improved until a particularly stressful second year of residency. “That’s when I just tanked,” she said. “Residency, and especially being on my own and with COVID, things have not been great for me.”
Dr. Anderson now sees an eating disorder specialist, but she pays for this out-of-pocket. “I have terrible insurance,” she said with a laugh, aware of that irony.
If You Are Struggling, Don’t Be Ashamed
Some physicians who’ve experienced EDs firsthand are working to improve training on diagnosing and treating the conditions. Dr. McNaught has developed and launched a new eLearning program for healthcare workers on how to recognize the early signs and symptoms of an ED and provide support.
“It’s not only so they can recognize it in their patients but also if colleagues and family and friends are struggling,” she said.
In 2021, the American Psychiatric Association (APA) approved the APA Practice Guideline for the Treatment of Patients With Eating Disorders, which aims to improve patient care and treatment outcomes.
But Dr. Klein is concerned that increased stress since the COVID-19 pandemic may be putting healthcare workers at even greater risk.
“When people are under stress or when they feel like there are things in their life that maybe they can’t control, sometimes turning to an eating disorder is a way to cope,” she said, “In that sense, the stress on medical professionals is something that could lead to eating disorder behaviors.”
Dr. Klein’s message to healthcare workers: Don’t be ashamed. She described an ED as “a monster that takes over your brain. Once it starts, it’s very hard to turn it around on your own. So, I hope anyone who is suffering, in whatever field they’re in, that they are able to ask for help.”
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
New Stroke Prevention: Clopidogrel-Aspirin Within 72 Hours
TOPLINE:
Dual antiplatelet therapy (DAPT) with clopidogrel-aspirin given within 72 hours of a mild ischemic stroke or a high-risk transient ischemic attack (TIA) shows a greater risk reduction for new stroke than aspirin alone, although with a higher bleeding risk.
METHODOLOGY:
- The INSPIRES, a double-blind, placebo-controlled trial, involved patients with mild ischemic stroke or high-risk TIA of presumed atherosclerotic cause who had not undergone thrombolysis or thrombectomy.
- A total of 6100 patients were randomly assigned to receive clopidogrel plus aspirin or matching clopidogrel placebo plus aspirin within 72 hours after symptom onset.
- The occurrence of any new stroke (ischemic or hemorrhagic) within 90 days was the primary efficacy outcome.
- The primary safety outcome was moderate to severe bleeding, also assessed within 90 days.
TAKEAWAY:
- Within 24 hours of symptom onset, 12.8% of patients were assigned to each treatment group, and the remaining 87.2% were assigned within the time window of 24-72 hours.
- (7.3% vs 9.2%; marginal estimated hazard ratio [HR], 0.79; P =.008).
- The risk of a composite cardiovascular event and ischemic stroke were also 20%-25% lower with aspirin-clopidogrel combo vs aspirin alone.
- Moderate to severe bleeding was low in both groups (<1%), but the risk was double in patients who received DAPT vs aspirin alone (HR, 2.08; P =.03).
IN PRACTICE:
In an accompanying editorial, Anthony S. Kim, MD from the UCSF Weill Institute for Neurosciences, Department of Neurology, University of California, San Francisco, commented, “The current trial provides evidence to support expanding the time window for dual antiplatelet therapy to 72 hours.” He also warned against administering DAPT to “patients with heightened bleeding risks, such as those with a history of cerebral or systemic hemorrhage.”
SOURCE:
Yilong Wang, MD, PhD, who held positions in the Department of Neurology, Beijing Tiantan Hospital, and several other institutions, was the corresponding author of this study. This study was published online December 28 in the New England Journal of Medicine.
LIMITATIONS:
- Patients with stroke of presumed cardioembolic origin, those with moderate or severe stroke, and those who had undergone thrombolysis or thrombectomy were excluded from this study.
- Of the enrolled participants, 98.5% belonged to the Han Chinese ethnic group.
DISCLOSURES:
This study was supported by grants from the National Natural Science Foundation of China, the National Key R&D Program of China, and other sources. Some authors declared receiving grants or contracts or serving as consultants in various sources.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
Dual antiplatelet therapy (DAPT) with clopidogrel-aspirin given within 72 hours of a mild ischemic stroke or a high-risk transient ischemic attack (TIA) shows a greater risk reduction for new stroke than aspirin alone, although with a higher bleeding risk.
METHODOLOGY:
- The INSPIRES, a double-blind, placebo-controlled trial, involved patients with mild ischemic stroke or high-risk TIA of presumed atherosclerotic cause who had not undergone thrombolysis or thrombectomy.
- A total of 6100 patients were randomly assigned to receive clopidogrel plus aspirin or matching clopidogrel placebo plus aspirin within 72 hours after symptom onset.
- The occurrence of any new stroke (ischemic or hemorrhagic) within 90 days was the primary efficacy outcome.
- The primary safety outcome was moderate to severe bleeding, also assessed within 90 days.
TAKEAWAY:
- Within 24 hours of symptom onset, 12.8% of patients were assigned to each treatment group, and the remaining 87.2% were assigned within the time window of 24-72 hours.
- (7.3% vs 9.2%; marginal estimated hazard ratio [HR], 0.79; P =.008).
- The risk of a composite cardiovascular event and ischemic stroke were also 20%-25% lower with aspirin-clopidogrel combo vs aspirin alone.
- Moderate to severe bleeding was low in both groups (<1%), but the risk was double in patients who received DAPT vs aspirin alone (HR, 2.08; P =.03).
IN PRACTICE:
In an accompanying editorial, Anthony S. Kim, MD from the UCSF Weill Institute for Neurosciences, Department of Neurology, University of California, San Francisco, commented, “The current trial provides evidence to support expanding the time window for dual antiplatelet therapy to 72 hours.” He also warned against administering DAPT to “patients with heightened bleeding risks, such as those with a history of cerebral or systemic hemorrhage.”
SOURCE:
Yilong Wang, MD, PhD, who held positions in the Department of Neurology, Beijing Tiantan Hospital, and several other institutions, was the corresponding author of this study. This study was published online December 28 in the New England Journal of Medicine.
LIMITATIONS:
- Patients with stroke of presumed cardioembolic origin, those with moderate or severe stroke, and those who had undergone thrombolysis or thrombectomy were excluded from this study.
- Of the enrolled participants, 98.5% belonged to the Han Chinese ethnic group.
DISCLOSURES:
This study was supported by grants from the National Natural Science Foundation of China, the National Key R&D Program of China, and other sources. Some authors declared receiving grants or contracts or serving as consultants in various sources.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
Dual antiplatelet therapy (DAPT) with clopidogrel-aspirin given within 72 hours of a mild ischemic stroke or a high-risk transient ischemic attack (TIA) shows a greater risk reduction for new stroke than aspirin alone, although with a higher bleeding risk.
METHODOLOGY:
- The INSPIRES, a double-blind, placebo-controlled trial, involved patients with mild ischemic stroke or high-risk TIA of presumed atherosclerotic cause who had not undergone thrombolysis or thrombectomy.
- A total of 6100 patients were randomly assigned to receive clopidogrel plus aspirin or matching clopidogrel placebo plus aspirin within 72 hours after symptom onset.
- The occurrence of any new stroke (ischemic or hemorrhagic) within 90 days was the primary efficacy outcome.
- The primary safety outcome was moderate to severe bleeding, also assessed within 90 days.
TAKEAWAY:
- Within 24 hours of symptom onset, 12.8% of patients were assigned to each treatment group, and the remaining 87.2% were assigned within the time window of 24-72 hours.
- (7.3% vs 9.2%; marginal estimated hazard ratio [HR], 0.79; P =.008).
- The risk of a composite cardiovascular event and ischemic stroke were also 20%-25% lower with aspirin-clopidogrel combo vs aspirin alone.
- Moderate to severe bleeding was low in both groups (<1%), but the risk was double in patients who received DAPT vs aspirin alone (HR, 2.08; P =.03).
IN PRACTICE:
In an accompanying editorial, Anthony S. Kim, MD from the UCSF Weill Institute for Neurosciences, Department of Neurology, University of California, San Francisco, commented, “The current trial provides evidence to support expanding the time window for dual antiplatelet therapy to 72 hours.” He also warned against administering DAPT to “patients with heightened bleeding risks, such as those with a history of cerebral or systemic hemorrhage.”
SOURCE:
Yilong Wang, MD, PhD, who held positions in the Department of Neurology, Beijing Tiantan Hospital, and several other institutions, was the corresponding author of this study. This study was published online December 28 in the New England Journal of Medicine.
LIMITATIONS:
- Patients with stroke of presumed cardioembolic origin, those with moderate or severe stroke, and those who had undergone thrombolysis or thrombectomy were excluded from this study.
- Of the enrolled participants, 98.5% belonged to the Han Chinese ethnic group.
DISCLOSURES:
This study was supported by grants from the National Natural Science Foundation of China, the National Key R&D Program of China, and other sources. Some authors declared receiving grants or contracts or serving as consultants in various sources.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Short Course of Amoxicillin Shows Effectiveness for Febrile UTIs
Use of oral amoxicillin-clavulanic acid for 5 days was noninferior to a 10-day course of treatment among children with noncomplicated febrile urinary tract infections (UTIs), according to new research.
Well-appearing children with febrile UTIs are generally treated with a 10-day course of oral antibiotics, but the effectiveness of a 5-day course has not been evaluated, wrote Giovanni Montini, MD, of the University of Milan, Milan, Italy, and colleagues.
Robert W. Frenck Jr, MD, a director of the Center for Vaccine Research at Cincinnati Children’s Hospital Medical Center, Ohio, said he was not surprised that the shorter course was sufficient to treat these cases. The antibiotic concentration in the urine often significantly exceeds the levels in the blood, he said.
Dr. Frenck, who was not involved in the study, said that he saw no real barriers to the use of a shorter course of therapy in clinical practice.
“I think both parents and the medical team would be happy to be able to use a shorter course of therapy,” he said.
In the study published in Pediatrics , researchers randomized 142 children aged 3 months to 5 years with uncomplicated febrile UTIs to 50 mg/kg/d of amoxicillin-clavulanate for either the short or standard period. The study took place at eight pediatric emergency departments in Italy between May 2020 and September 2022. All patients received prescriptions for 5 days of antibiotics, and those randomized to the standard course received a second prescription after randomization.
The primary endpoint was recurrence of the UTI within 30 days of completion of therapy. Secondary endpoints included clinical recovery at the end of treatment, adverse events related to the therapy, and signs of antibiotic resistance.
The UTI recurrence rate within 30 days of treatment completion was 2.8% in the short-course group and 14.3% in the standard group. A post hoc analysis excluding patients with vesicoureteral reflux and non–Escherichia coli UTIs further confirmed the noninferiority of short-course treatment.
“It is a bit surprising that the short-course group had fewer relapses within 30 days of discontinuing antibiotics,” Dr. Frenck said. “However, the differences may be due to small sample sizes and do not appear to be statistically significant differences in recurrence rates.”
Resolution of symptoms was similar between the short-course and standard groups (97.2% and 92.9%, respectively), and indications of antibiotic resistance were similar between the groups. No adverse events were reported in the standard group, and one case of diarrhea occurred in the short-course group.
The findings were limited by the study’s unblinded randomization, so parents were aware of the trial and were potentially sensitized to look for signs of infection. Researchers also relied on parent reports of adverse drug effects rather than through a standardized questionnaire, the researchers noted.
Dr. Frenck said a potential benefit to shortening treatment is that adherence usually increases.
“But you only want to decrease the length of a course of medicine if you can do so without compromising the effectiveness of the treatment,” Dr. Frenck said.
Dr. Frenck also noted a recent study, which demonstrated that 5 days of antibiotics had equivalent efficacy as 10 days for uncomplicated pneumonia.
“The current paper further demonstrates that shorter courses of antibiotics may be possible for other mild forms of infections.”
Looking ahead, researchers could evaluate the use of short-course antibiotics for other common infections such as otitis media, he noted.
The study was supported by the Ministry of Health, Rome, Italy, in collaboration with the Institute for Maternal and Child Health IRCCS Burlo Garofolo, Trieste, Italy. The researchers report no financial conflicts. Dr. Frenck disclosed conducting clinical trials for Pfizer, Moderna, AstraZeneca, Merck, and GSK; none of those trials were for antibiotics or urinary tract infections.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Use of oral amoxicillin-clavulanic acid for 5 days was noninferior to a 10-day course of treatment among children with noncomplicated febrile urinary tract infections (UTIs), according to new research.
Well-appearing children with febrile UTIs are generally treated with a 10-day course of oral antibiotics, but the effectiveness of a 5-day course has not been evaluated, wrote Giovanni Montini, MD, of the University of Milan, Milan, Italy, and colleagues.
Robert W. Frenck Jr, MD, a director of the Center for Vaccine Research at Cincinnati Children’s Hospital Medical Center, Ohio, said he was not surprised that the shorter course was sufficient to treat these cases. The antibiotic concentration in the urine often significantly exceeds the levels in the blood, he said.
Dr. Frenck, who was not involved in the study, said that he saw no real barriers to the use of a shorter course of therapy in clinical practice.
“I think both parents and the medical team would be happy to be able to use a shorter course of therapy,” he said.
In the study published in Pediatrics , researchers randomized 142 children aged 3 months to 5 years with uncomplicated febrile UTIs to 50 mg/kg/d of amoxicillin-clavulanate for either the short or standard period. The study took place at eight pediatric emergency departments in Italy between May 2020 and September 2022. All patients received prescriptions for 5 days of antibiotics, and those randomized to the standard course received a second prescription after randomization.
The primary endpoint was recurrence of the UTI within 30 days of completion of therapy. Secondary endpoints included clinical recovery at the end of treatment, adverse events related to the therapy, and signs of antibiotic resistance.
The UTI recurrence rate within 30 days of treatment completion was 2.8% in the short-course group and 14.3% in the standard group. A post hoc analysis excluding patients with vesicoureteral reflux and non–Escherichia coli UTIs further confirmed the noninferiority of short-course treatment.
“It is a bit surprising that the short-course group had fewer relapses within 30 days of discontinuing antibiotics,” Dr. Frenck said. “However, the differences may be due to small sample sizes and do not appear to be statistically significant differences in recurrence rates.”
Resolution of symptoms was similar between the short-course and standard groups (97.2% and 92.9%, respectively), and indications of antibiotic resistance were similar between the groups. No adverse events were reported in the standard group, and one case of diarrhea occurred in the short-course group.
The findings were limited by the study’s unblinded randomization, so parents were aware of the trial and were potentially sensitized to look for signs of infection. Researchers also relied on parent reports of adverse drug effects rather than through a standardized questionnaire, the researchers noted.
Dr. Frenck said a potential benefit to shortening treatment is that adherence usually increases.
“But you only want to decrease the length of a course of medicine if you can do so without compromising the effectiveness of the treatment,” Dr. Frenck said.
Dr. Frenck also noted a recent study, which demonstrated that 5 days of antibiotics had equivalent efficacy as 10 days for uncomplicated pneumonia.
“The current paper further demonstrates that shorter courses of antibiotics may be possible for other mild forms of infections.”
Looking ahead, researchers could evaluate the use of short-course antibiotics for other common infections such as otitis media, he noted.
The study was supported by the Ministry of Health, Rome, Italy, in collaboration with the Institute for Maternal and Child Health IRCCS Burlo Garofolo, Trieste, Italy. The researchers report no financial conflicts. Dr. Frenck disclosed conducting clinical trials for Pfizer, Moderna, AstraZeneca, Merck, and GSK; none of those trials were for antibiotics or urinary tract infections.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Use of oral amoxicillin-clavulanic acid for 5 days was noninferior to a 10-day course of treatment among children with noncomplicated febrile urinary tract infections (UTIs), according to new research.
Well-appearing children with febrile UTIs are generally treated with a 10-day course of oral antibiotics, but the effectiveness of a 5-day course has not been evaluated, wrote Giovanni Montini, MD, of the University of Milan, Milan, Italy, and colleagues.
Robert W. Frenck Jr, MD, a director of the Center for Vaccine Research at Cincinnati Children’s Hospital Medical Center, Ohio, said he was not surprised that the shorter course was sufficient to treat these cases. The antibiotic concentration in the urine often significantly exceeds the levels in the blood, he said.
Dr. Frenck, who was not involved in the study, said that he saw no real barriers to the use of a shorter course of therapy in clinical practice.
“I think both parents and the medical team would be happy to be able to use a shorter course of therapy,” he said.
In the study published in Pediatrics , researchers randomized 142 children aged 3 months to 5 years with uncomplicated febrile UTIs to 50 mg/kg/d of amoxicillin-clavulanate for either the short or standard period. The study took place at eight pediatric emergency departments in Italy between May 2020 and September 2022. All patients received prescriptions for 5 days of antibiotics, and those randomized to the standard course received a second prescription after randomization.
The primary endpoint was recurrence of the UTI within 30 days of completion of therapy. Secondary endpoints included clinical recovery at the end of treatment, adverse events related to the therapy, and signs of antibiotic resistance.
The UTI recurrence rate within 30 days of treatment completion was 2.8% in the short-course group and 14.3% in the standard group. A post hoc analysis excluding patients with vesicoureteral reflux and non–Escherichia coli UTIs further confirmed the noninferiority of short-course treatment.
“It is a bit surprising that the short-course group had fewer relapses within 30 days of discontinuing antibiotics,” Dr. Frenck said. “However, the differences may be due to small sample sizes and do not appear to be statistically significant differences in recurrence rates.”
Resolution of symptoms was similar between the short-course and standard groups (97.2% and 92.9%, respectively), and indications of antibiotic resistance were similar between the groups. No adverse events were reported in the standard group, and one case of diarrhea occurred in the short-course group.
The findings were limited by the study’s unblinded randomization, so parents were aware of the trial and were potentially sensitized to look for signs of infection. Researchers also relied on parent reports of adverse drug effects rather than through a standardized questionnaire, the researchers noted.
Dr. Frenck said a potential benefit to shortening treatment is that adherence usually increases.
“But you only want to decrease the length of a course of medicine if you can do so without compromising the effectiveness of the treatment,” Dr. Frenck said.
Dr. Frenck also noted a recent study, which demonstrated that 5 days of antibiotics had equivalent efficacy as 10 days for uncomplicated pneumonia.
“The current paper further demonstrates that shorter courses of antibiotics may be possible for other mild forms of infections.”
Looking ahead, researchers could evaluate the use of short-course antibiotics for other common infections such as otitis media, he noted.
The study was supported by the Ministry of Health, Rome, Italy, in collaboration with the Institute for Maternal and Child Health IRCCS Burlo Garofolo, Trieste, Italy. The researchers report no financial conflicts. Dr. Frenck disclosed conducting clinical trials for Pfizer, Moderna, AstraZeneca, Merck, and GSK; none of those trials were for antibiotics or urinary tract infections.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM PEDIATRICS
Light Activity in Childhood May Lower Cholesterol
TOPLINE:
Light physical activity during childhood may lower blood cholesterol levels more effectively than moderate to vigorous physical activity, regardless of body fat mass.
METHODOLOGY:
- Researchers analyzed the data of 792 children (58% females) from the Avon Longitudinal Study of Parents and Children (ALSPAC) UK birth cohort.
- The measures included accelerometer-based sedentary time, light physical activity, and moderate to vigorous physical activity at ages 11, 15, and 24 years.
- The children had complete measurements of fasting high-density lipoprotein cholesterol, low-density lipoprotein cholesterol, triglyceride, and total cholesterol levels at ages 15 , 17, and 24 years.
- Data also included measures of body mass, composition (fat and lean mass), insulin resistance, inflammation, and other cardiometabolic, socioeconomic, and lifestyle factors.
- The researchers conducted two types of analyses: Mediation path, to examine how fat and lean body mass affected longitudinal associations of activity level with blood lipids over 13 years, and temporal path, to look at temporal relationships between activity and lipid levels at ages 15 and 24 years only.
TAKEAWAY:
- Higher cumulative light physical activity from childhood through young adulthood was associated with a fivefold to eightfold decrease in total cholesterol, while total body fat mass decreased the impact of light physical activity on total cholesterol by 6%.
- Higher cumulative moderate to vigorous physical activity over 13 years led to a modest decrease in total cholesterol, an effect reduced to nonsignificance by the presence of higher fat mass.
- More cumulative sedentary time was associated with increasing total cholesterol.
IN PRACTICE:
“Light physical activity provides an opportunity for persons with obesity to follow a path to potentially benefit from the lipid-lowering effect of mild exercise,» wrote the author.
SOURCE:
Andrew O. Agbaje, from the Institute of Public Health and Clinical Nutrition, School of Medicine, University of Eastern Finland, Kuopio, Finland, conducted this study. It was published online December 14, 2023, in the Journal of Clinical Endocrinology and Metabolism.
LIMITATIONS:
The study included mostly White participants, so the findings might not apply to diverse racial and ethnic groups. The accelerometer data were gathered using a 60-second epoch, a duration known to underestimate moderate to vigorous physical activity in pediatric populations. There were no measures of fasting plasma lipids at age 11 years. The study also lacked data on participants’ dietary habits, alcohol intake, and menstrual cycle.
DISCLOSURES:
The ALSPAC UK birth cohort is funded by the UK Medical Research Council, the Wellcome Trust, and the University of Bristol. The author is funded by multiple foundations. No conflicts of interest were reported.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
Light physical activity during childhood may lower blood cholesterol levels more effectively than moderate to vigorous physical activity, regardless of body fat mass.
METHODOLOGY:
- Researchers analyzed the data of 792 children (58% females) from the Avon Longitudinal Study of Parents and Children (ALSPAC) UK birth cohort.
- The measures included accelerometer-based sedentary time, light physical activity, and moderate to vigorous physical activity at ages 11, 15, and 24 years.
- The children had complete measurements of fasting high-density lipoprotein cholesterol, low-density lipoprotein cholesterol, triglyceride, and total cholesterol levels at ages 15 , 17, and 24 years.
- Data also included measures of body mass, composition (fat and lean mass), insulin resistance, inflammation, and other cardiometabolic, socioeconomic, and lifestyle factors.
- The researchers conducted two types of analyses: Mediation path, to examine how fat and lean body mass affected longitudinal associations of activity level with blood lipids over 13 years, and temporal path, to look at temporal relationships between activity and lipid levels at ages 15 and 24 years only.
TAKEAWAY:
- Higher cumulative light physical activity from childhood through young adulthood was associated with a fivefold to eightfold decrease in total cholesterol, while total body fat mass decreased the impact of light physical activity on total cholesterol by 6%.
- Higher cumulative moderate to vigorous physical activity over 13 years led to a modest decrease in total cholesterol, an effect reduced to nonsignificance by the presence of higher fat mass.
- More cumulative sedentary time was associated with increasing total cholesterol.
IN PRACTICE:
“Light physical activity provides an opportunity for persons with obesity to follow a path to potentially benefit from the lipid-lowering effect of mild exercise,» wrote the author.
SOURCE:
Andrew O. Agbaje, from the Institute of Public Health and Clinical Nutrition, School of Medicine, University of Eastern Finland, Kuopio, Finland, conducted this study. It was published online December 14, 2023, in the Journal of Clinical Endocrinology and Metabolism.
LIMITATIONS:
The study included mostly White participants, so the findings might not apply to diverse racial and ethnic groups. The accelerometer data were gathered using a 60-second epoch, a duration known to underestimate moderate to vigorous physical activity in pediatric populations. There were no measures of fasting plasma lipids at age 11 years. The study also lacked data on participants’ dietary habits, alcohol intake, and menstrual cycle.
DISCLOSURES:
The ALSPAC UK birth cohort is funded by the UK Medical Research Council, the Wellcome Trust, and the University of Bristol. The author is funded by multiple foundations. No conflicts of interest were reported.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
Light physical activity during childhood may lower blood cholesterol levels more effectively than moderate to vigorous physical activity, regardless of body fat mass.
METHODOLOGY:
- Researchers analyzed the data of 792 children (58% females) from the Avon Longitudinal Study of Parents and Children (ALSPAC) UK birth cohort.
- The measures included accelerometer-based sedentary time, light physical activity, and moderate to vigorous physical activity at ages 11, 15, and 24 years.
- The children had complete measurements of fasting high-density lipoprotein cholesterol, low-density lipoprotein cholesterol, triglyceride, and total cholesterol levels at ages 15 , 17, and 24 years.
- Data also included measures of body mass, composition (fat and lean mass), insulin resistance, inflammation, and other cardiometabolic, socioeconomic, and lifestyle factors.
- The researchers conducted two types of analyses: Mediation path, to examine how fat and lean body mass affected longitudinal associations of activity level with blood lipids over 13 years, and temporal path, to look at temporal relationships between activity and lipid levels at ages 15 and 24 years only.
TAKEAWAY:
- Higher cumulative light physical activity from childhood through young adulthood was associated with a fivefold to eightfold decrease in total cholesterol, while total body fat mass decreased the impact of light physical activity on total cholesterol by 6%.
- Higher cumulative moderate to vigorous physical activity over 13 years led to a modest decrease in total cholesterol, an effect reduced to nonsignificance by the presence of higher fat mass.
- More cumulative sedentary time was associated with increasing total cholesterol.
IN PRACTICE:
“Light physical activity provides an opportunity for persons with obesity to follow a path to potentially benefit from the lipid-lowering effect of mild exercise,» wrote the author.
SOURCE:
Andrew O. Agbaje, from the Institute of Public Health and Clinical Nutrition, School of Medicine, University of Eastern Finland, Kuopio, Finland, conducted this study. It was published online December 14, 2023, in the Journal of Clinical Endocrinology and Metabolism.
LIMITATIONS:
The study included mostly White participants, so the findings might not apply to diverse racial and ethnic groups. The accelerometer data were gathered using a 60-second epoch, a duration known to underestimate moderate to vigorous physical activity in pediatric populations. There were no measures of fasting plasma lipids at age 11 years. The study also lacked data on participants’ dietary habits, alcohol intake, and menstrual cycle.
DISCLOSURES:
The ALSPAC UK birth cohort is funded by the UK Medical Research Council, the Wellcome Trust, and the University of Bristol. The author is funded by multiple foundations. No conflicts of interest were reported.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Cemiplimab-Associated Eruption of Generalized Eruptive Keratoacanthoma of Grzybowski
To the Editor:
Treatment of cancer, including cutaneous malignancy, has been transformed by the use of immunotherapeutic agents such as immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICIs) that target cytotoxic T lymphocyte-associated antigen 4, programmed cell-death protein 1 (PD-1), or programmed cell-death ligand 1 (PD-L1). However, these drugs are associated with a distinct set of immune-related adverse events (IRAEs). We present a case of generalized eruptive keratoacanthoma of Grzybowski associated with the ICI cemiplimab.
A 94-year-old White woman presented to the dermatology clinic with acute onset of extensive, locally advanced cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma (cSCC) of the upper right posterolateral calf as well as multiple noninvasive cSCCs of the arms and legs. Her medical history was remarkable for widespread actinic keratoses and numerous cSCCs. The patient had no personal or family history of melanoma. Various cSCCs had required treatment with electrodesiccation and curettage, topical or intralesional 5-fluorouracil, and Mohs micrographic surgery. Approximately 1 year prior to presentation, oral acitretin was initiated to help control the cSCC. Given the extent of locally advanced disease, which was considered unresectable, she was referred to oncology but continued to follow up with dermatology. Positron emission tomography was remarkable for hypermetabolic cutaneous thickening in the upper right posterolateral calf with no evidence of visceral disease.
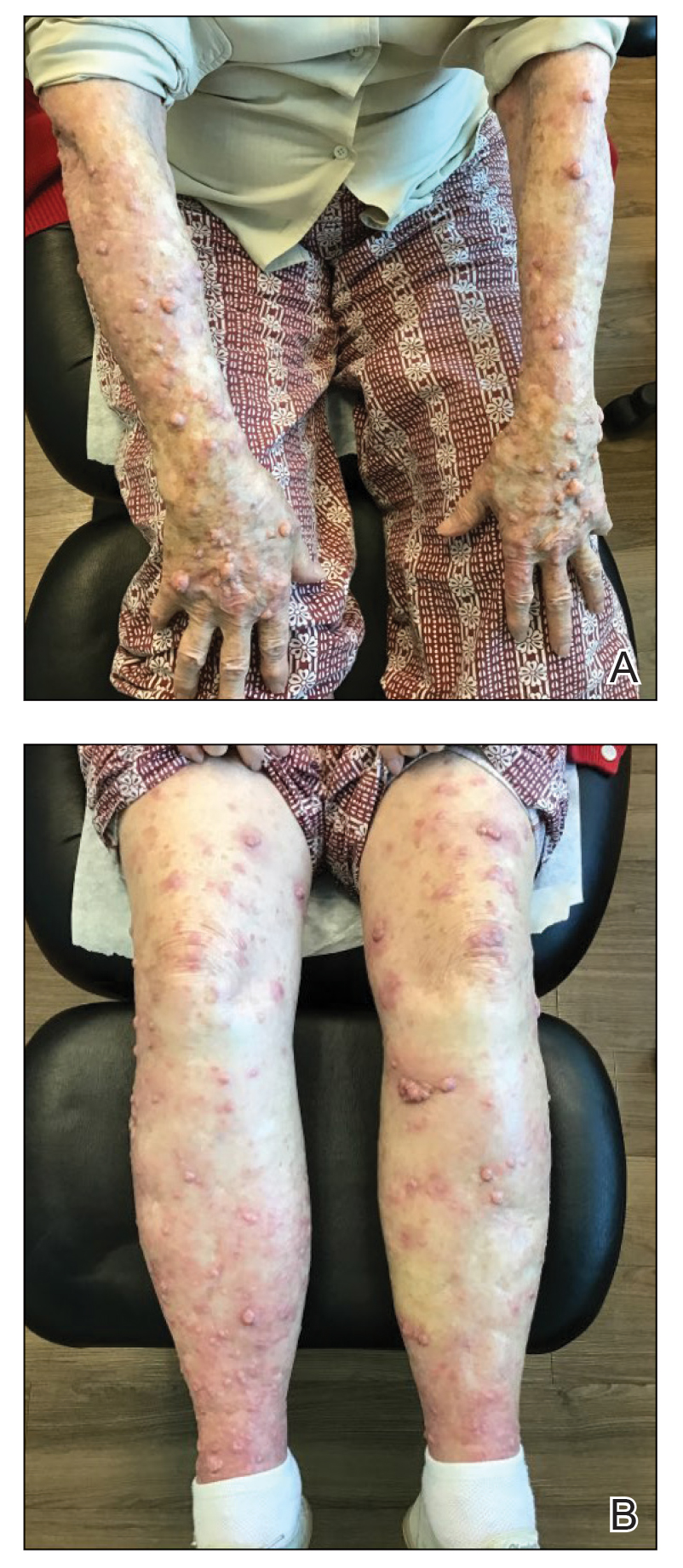
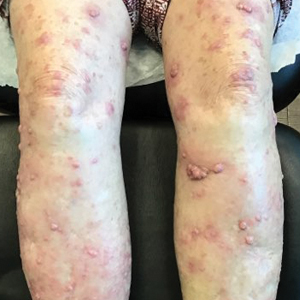
The patient was started on cemiplimab, an anti-PD-1 monoclonal antibody ICI indicated for the treatment of both metastatic and advanced cSCC. After 4 cycles of intravenous cemiplimab, the patient developed widespread nodules covering the arms and legs (Figure 1) as well as associated tenderness and pruritus. Biopsies of nodules revealed superficially invasive, well-differentiated cSCC consistent with keratoacanthoma. Although a lymphocytic infiltrate was present, no other specific reaction pattern, such as a lichenoid infiltrate, was present (Figure 2).

Positron emission tomography was repeated, demonstrating resolution of the right calf lesion; however, new diffuse cutaneous lesions and inguinal lymph node involvement were present, again without evidence of visceral disease. Given the clinical and histologic findings, a diagnosis of generalized eruptive keratoacanthoma of Grzybowski was made. Cemiplimab was discontinued after the fifth cycle. The patient declined further systemic treatment, instead choosing a regimen of topical steroids and an emollient.
Immunotherapeutics have transformed cancer therapy, which includes ICIs that target cytotoxic T lymphocyte-associated antigen 4, PD-1, or PD-L1. Increased activity of these checkpoints allows tumor cells to downregulate T-cell activation, thereby evading immune destruction. When PD-1 on T cells binds PD-L1 on tumor cells, T lymphocytes are inhibited from cytotoxic-mediated killing. Therefore, anti-PD-1 ICIs such as cemiplimab permit T-lymphocyte activation and destruction of malignant cells. However, this unique mechanism of immunotherapy is associated with an array of IRAEs, which often manifest in a delayed and prolonged fashion.1 Immune-related adverse events most commonly affect the gastrointestinal tract as well as the endocrine and dermatologic systems.2 Notably, patients with certain tumors who experience these adverse effects might be more likely to have superior overall survival; therefore, IRAEs are sometimes used as an indicator of favorable treatment response.2,3
Dermatologic IRAEs associated with the use of a PD-1 inhibitor include lichenoid reactions, pruritus, morbilliform eruptions, vitiligo, and bullous pemphigoid.4,5 Eruptions of keratoacanthoma rarely have been reported following treatment with the PD-1 inhibitors nivolumab and pembrolizumab.3,6,7 In our patient, we believe the profound and generalized eruptive keratoacanthoma—a well-differentiated cSCC variant—was related to treatment of locally advanced cSCC with cemiplimab. The mechanism underlying the formation of anti-PD-1 eruptive keratoacanthoma is not well understood. In susceptible patients, it is plausible that the inflammatory environment permitted by ICIs paradoxically induces regression of tumors such as locally invasive cSCC and simultaneously promotes formation of keratoacanthoma.
The role of inflammation in the pathogenesis and progression of cSCC is complex and possibly involves contrasting roles of leukocyte subpopulations.8 The increased incidence of cSCC in the immunocompromised population,8 PD-L1 overexpression in cSCC,9,10 and successful treatment of cSCC with PD-1 inhibition10 all suggest that inhibition of specific inflammatory pathways is pivotal in tumor pathogenesis. However, increased inflammation, particularly inflammation driven by T lymphocytes and Langerhans cells, also is believed to play a key role in the formation of cSCCs, including the degeneration of actinic keratosis into cSCC. Moreover, because keratoacanthomas are believed to be a cSCC variant and also are associated with PD-L1 overexpression,9 it is perplexing that PD-1 blockade may result in eruptive keratoacanthoma in some patients while also treating locally advanced cSCC, as seen in our patient. Successful treatment of keratoacanthoma with anti-inflammatory intralesional or topical corticosteroids adds to this complicated picture.3
We hypothesize that the pathogenesis of invasive cSCC and keratoacanthoma shares certain immune-mediated mechanisms but also differs in distinct manners. To understand the relationship between systemic treatment of cSCC and eruptive keratoacanthoma, further research is required.
In addition, the RAS/BRAF/MEK oncogenic pathway may be involved in the development of cSCCs associated with anti-PD-1. It is hypothesized that BRAF and MEK inhibition increases T-cell infiltration and increases PD-L1 expression on tumor cells,11 thus increasing the susceptibility of those cells to PD-1 blockade. Further supporting a relationship between the RAS/BRAF/MEK and PD-1 pathways, BRAF inhibitors are associated with development of SCCs and verrucal keratosis by upregulation of the RAS pathway.12,13 Perhaps a common mechanism underlying these pathways results in their shared association for an increased risk for cSCC upon blockade. More research is needed to fully elucidate the underlying biochemical mechanism of immunotherapy and formation of SCCs, such as keratoacanthoma.
Treatment of solitary keratoacanthoma often involves surgical excision; however, the sheer number of lesions in eruptive keratoacanthoma presents a larger dilemma. Because oral systemic retinoids have been shown to be most effective for treating eruptive keratoacanthoma, they are considered first-line therapy as monotherapy or in combination with surgical excision.3 Other treatment options include intralesional or topical corticosteroids, cyclosporine, 5-fluorouracil, imiquimod, and cryotherapy.3,6
The development of ICIs has revolutionized the treatment of cutaneous malignancy, yet we have a great deal more to comprehend on the systemic effects of these medications. Although IRAEs may signal a better response to therapy, some of these effects regrettably can be dose limiting. In our patient, cemiplimab was successful in treating locally advanced cSCC, but treatment also resulted in devastating widespread eruptive keratoacanthoma. The mechanism of this kind of eruption has yet to be understood; we hypothesize that it likely involves T lymphocyte–driven inflammation and the interplay of molecular and immune-mediated pathways.
- Ramos-Casals M, Brahmer JR, Callahan MK, et al. Immune-related adverse events of checkpoint inhibitors. Nat Rev Dis Primers. 2020;6:38. doi:10.1038/s41572-020-0160-6
- Das S, Johnson DB. Immune-related adverse events and anti-tumor efficacy of immune checkpoint inhibitors. J Immunother Cancer. 2019;7:306. doi:10.1186/s40425-019-0805-8
- Freites-Martinez A, Kwong BY, Rieger KE, et al. Eruptive keratoacanthomas associated with pembrolizumab therapy. JAMA Dermatol. 2017;153:694-697. doi:10.1001/jamadermatol.2017.0989
- Shen J, Chang J, Mendenhall M, et al. Diverse cutaneous adverse eruptions caused by anti-programmed cell death-1 (PD-1) and anti-programmed cell death ligand-1 (PD-L1) immunotherapies: clinicalfeatures and management. Ther Adv Med Oncol. 2018;10:1758834017751634. doi:10.1177/1758834017751634
- Bandino JP, Perry DM, Clarke CE, et al. Two cases of anti-programmed cell death 1-associated bullous pemphigoid-like disease and eruptive keratoacanthomas featuring combined histopathology. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2017;31:E378-E380. doi:10.1111/jdv.14179
- Marsh RL, Kolodney JA, Iyengar S, et al. Formation of eruptive cutaneous squamous cell carcinomas after programmed cell death protein-1 blockade. JAAD Case Rep. 2020;6:390-393. doi:10.1016/j.jdcr.2020.02.024
- Antonov NK, Nair KG, Halasz CL. Transient eruptive keratoacanthomas associated with nivolumab. JAAD Case Rep. 2019;5:342-345. doi:10.1016/j.jdcr.2019.01.025
- Bottomley MJ, Thomson J, Harwood C, et al. The role of the immune system in cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma. Int J Mol Sci. 2019;20:2009. doi:10.3390/ijms20082009
- Gambichler T, Gnielka M, Rüddel I, et al. Expression of PD-L1 in keratoacanthoma and different stages of progression in cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma. Cancer Immunol Immunother. 2017;66:1199-1204. doi:10.1007/s00262-017-2015-x
- Patel R, Chang ALS. Immune checkpoint inhibitors for treating advanced cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma. Am J Clin Dermatol. 2019;20:477-482. doi:10.1007/s40257-019-00426-w
- Rozeman EA, Blank CU. Combining checkpoint inhibition and targeted therapy in melanoma. Nat Med. 2019;25:879-882. doi:10.1038/s41591-019-0482-7
- Dubauskas Z, Kunishige J, Prieto VG, Jonasch E, Hwu P, Tannir NM. Cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma and inflammation of actinic keratoses associated with sorafenib. Clin Genitourin Cancer. 2009;7:20-23. doi:10.3816/CGC.2009.n.003
- Chen P, Chen F, Zhou B. Systematic review and meta-analysis of prevalence of dermatological toxicities associated with vemurafenib treatment in patients with melanoma. Clin Exp Dermatol. 2019;44:243-251. doi:10.1111/ced.13751
To the Editor:
Treatment of cancer, including cutaneous malignancy, has been transformed by the use of immunotherapeutic agents such as immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICIs) that target cytotoxic T lymphocyte-associated antigen 4, programmed cell-death protein 1 (PD-1), or programmed cell-death ligand 1 (PD-L1). However, these drugs are associated with a distinct set of immune-related adverse events (IRAEs). We present a case of generalized eruptive keratoacanthoma of Grzybowski associated with the ICI cemiplimab.
A 94-year-old White woman presented to the dermatology clinic with acute onset of extensive, locally advanced cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma (cSCC) of the upper right posterolateral calf as well as multiple noninvasive cSCCs of the arms and legs. Her medical history was remarkable for widespread actinic keratoses and numerous cSCCs. The patient had no personal or family history of melanoma. Various cSCCs had required treatment with electrodesiccation and curettage, topical or intralesional 5-fluorouracil, and Mohs micrographic surgery. Approximately 1 year prior to presentation, oral acitretin was initiated to help control the cSCC. Given the extent of locally advanced disease, which was considered unresectable, she was referred to oncology but continued to follow up with dermatology. Positron emission tomography was remarkable for hypermetabolic cutaneous thickening in the upper right posterolateral calf with no evidence of visceral disease.

The patient was started on cemiplimab, an anti-PD-1 monoclonal antibody ICI indicated for the treatment of both metastatic and advanced cSCC. After 4 cycles of intravenous cemiplimab, the patient developed widespread nodules covering the arms and legs (Figure 1) as well as associated tenderness and pruritus. Biopsies of nodules revealed superficially invasive, well-differentiated cSCC consistent with keratoacanthoma. Although a lymphocytic infiltrate was present, no other specific reaction pattern, such as a lichenoid infiltrate, was present (Figure 2).

Positron emission tomography was repeated, demonstrating resolution of the right calf lesion; however, new diffuse cutaneous lesions and inguinal lymph node involvement were present, again without evidence of visceral disease. Given the clinical and histologic findings, a diagnosis of generalized eruptive keratoacanthoma of Grzybowski was made. Cemiplimab was discontinued after the fifth cycle. The patient declined further systemic treatment, instead choosing a regimen of topical steroids and an emollient.
Immunotherapeutics have transformed cancer therapy, which includes ICIs that target cytotoxic T lymphocyte-associated antigen 4, PD-1, or PD-L1. Increased activity of these checkpoints allows tumor cells to downregulate T-cell activation, thereby evading immune destruction. When PD-1 on T cells binds PD-L1 on tumor cells, T lymphocytes are inhibited from cytotoxic-mediated killing. Therefore, anti-PD-1 ICIs such as cemiplimab permit T-lymphocyte activation and destruction of malignant cells. However, this unique mechanism of immunotherapy is associated with an array of IRAEs, which often manifest in a delayed and prolonged fashion.1 Immune-related adverse events most commonly affect the gastrointestinal tract as well as the endocrine and dermatologic systems.2 Notably, patients with certain tumors who experience these adverse effects might be more likely to have superior overall survival; therefore, IRAEs are sometimes used as an indicator of favorable treatment response.2,3
Dermatologic IRAEs associated with the use of a PD-1 inhibitor include lichenoid reactions, pruritus, morbilliform eruptions, vitiligo, and bullous pemphigoid.4,5 Eruptions of keratoacanthoma rarely have been reported following treatment with the PD-1 inhibitors nivolumab and pembrolizumab.3,6,7 In our patient, we believe the profound and generalized eruptive keratoacanthoma—a well-differentiated cSCC variant—was related to treatment of locally advanced cSCC with cemiplimab. The mechanism underlying the formation of anti-PD-1 eruptive keratoacanthoma is not well understood. In susceptible patients, it is plausible that the inflammatory environment permitted by ICIs paradoxically induces regression of tumors such as locally invasive cSCC and simultaneously promotes formation of keratoacanthoma.
The role of inflammation in the pathogenesis and progression of cSCC is complex and possibly involves contrasting roles of leukocyte subpopulations.8 The increased incidence of cSCC in the immunocompromised population,8 PD-L1 overexpression in cSCC,9,10 and successful treatment of cSCC with PD-1 inhibition10 all suggest that inhibition of specific inflammatory pathways is pivotal in tumor pathogenesis. However, increased inflammation, particularly inflammation driven by T lymphocytes and Langerhans cells, also is believed to play a key role in the formation of cSCCs, including the degeneration of actinic keratosis into cSCC. Moreover, because keratoacanthomas are believed to be a cSCC variant and also are associated with PD-L1 overexpression,9 it is perplexing that PD-1 blockade may result in eruptive keratoacanthoma in some patients while also treating locally advanced cSCC, as seen in our patient. Successful treatment of keratoacanthoma with anti-inflammatory intralesional or topical corticosteroids adds to this complicated picture.3
We hypothesize that the pathogenesis of invasive cSCC and keratoacanthoma shares certain immune-mediated mechanisms but also differs in distinct manners. To understand the relationship between systemic treatment of cSCC and eruptive keratoacanthoma, further research is required.
In addition, the RAS/BRAF/MEK oncogenic pathway may be involved in the development of cSCCs associated with anti-PD-1. It is hypothesized that BRAF and MEK inhibition increases T-cell infiltration and increases PD-L1 expression on tumor cells,11 thus increasing the susceptibility of those cells to PD-1 blockade. Further supporting a relationship between the RAS/BRAF/MEK and PD-1 pathways, BRAF inhibitors are associated with development of SCCs and verrucal keratosis by upregulation of the RAS pathway.12,13 Perhaps a common mechanism underlying these pathways results in their shared association for an increased risk for cSCC upon blockade. More research is needed to fully elucidate the underlying biochemical mechanism of immunotherapy and formation of SCCs, such as keratoacanthoma.
Treatment of solitary keratoacanthoma often involves surgical excision; however, the sheer number of lesions in eruptive keratoacanthoma presents a larger dilemma. Because oral systemic retinoids have been shown to be most effective for treating eruptive keratoacanthoma, they are considered first-line therapy as monotherapy or in combination with surgical excision.3 Other treatment options include intralesional or topical corticosteroids, cyclosporine, 5-fluorouracil, imiquimod, and cryotherapy.3,6
The development of ICIs has revolutionized the treatment of cutaneous malignancy, yet we have a great deal more to comprehend on the systemic effects of these medications. Although IRAEs may signal a better response to therapy, some of these effects regrettably can be dose limiting. In our patient, cemiplimab was successful in treating locally advanced cSCC, but treatment also resulted in devastating widespread eruptive keratoacanthoma. The mechanism of this kind of eruption has yet to be understood; we hypothesize that it likely involves T lymphocyte–driven inflammation and the interplay of molecular and immune-mediated pathways.
To the Editor:
Treatment of cancer, including cutaneous malignancy, has been transformed by the use of immunotherapeutic agents such as immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICIs) that target cytotoxic T lymphocyte-associated antigen 4, programmed cell-death protein 1 (PD-1), or programmed cell-death ligand 1 (PD-L1). However, these drugs are associated with a distinct set of immune-related adverse events (IRAEs). We present a case of generalized eruptive keratoacanthoma of Grzybowski associated with the ICI cemiplimab.
A 94-year-old White woman presented to the dermatology clinic with acute onset of extensive, locally advanced cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma (cSCC) of the upper right posterolateral calf as well as multiple noninvasive cSCCs of the arms and legs. Her medical history was remarkable for widespread actinic keratoses and numerous cSCCs. The patient had no personal or family history of melanoma. Various cSCCs had required treatment with electrodesiccation and curettage, topical or intralesional 5-fluorouracil, and Mohs micrographic surgery. Approximately 1 year prior to presentation, oral acitretin was initiated to help control the cSCC. Given the extent of locally advanced disease, which was considered unresectable, she was referred to oncology but continued to follow up with dermatology. Positron emission tomography was remarkable for hypermetabolic cutaneous thickening in the upper right posterolateral calf with no evidence of visceral disease.

The patient was started on cemiplimab, an anti-PD-1 monoclonal antibody ICI indicated for the treatment of both metastatic and advanced cSCC. After 4 cycles of intravenous cemiplimab, the patient developed widespread nodules covering the arms and legs (Figure 1) as well as associated tenderness and pruritus. Biopsies of nodules revealed superficially invasive, well-differentiated cSCC consistent with keratoacanthoma. Although a lymphocytic infiltrate was present, no other specific reaction pattern, such as a lichenoid infiltrate, was present (Figure 2).

Positron emission tomography was repeated, demonstrating resolution of the right calf lesion; however, new diffuse cutaneous lesions and inguinal lymph node involvement were present, again without evidence of visceral disease. Given the clinical and histologic findings, a diagnosis of generalized eruptive keratoacanthoma of Grzybowski was made. Cemiplimab was discontinued after the fifth cycle. The patient declined further systemic treatment, instead choosing a regimen of topical steroids and an emollient.
Immunotherapeutics have transformed cancer therapy, which includes ICIs that target cytotoxic T lymphocyte-associated antigen 4, PD-1, or PD-L1. Increased activity of these checkpoints allows tumor cells to downregulate T-cell activation, thereby evading immune destruction. When PD-1 on T cells binds PD-L1 on tumor cells, T lymphocytes are inhibited from cytotoxic-mediated killing. Therefore, anti-PD-1 ICIs such as cemiplimab permit T-lymphocyte activation and destruction of malignant cells. However, this unique mechanism of immunotherapy is associated with an array of IRAEs, which often manifest in a delayed and prolonged fashion.1 Immune-related adverse events most commonly affect the gastrointestinal tract as well as the endocrine and dermatologic systems.2 Notably, patients with certain tumors who experience these adverse effects might be more likely to have superior overall survival; therefore, IRAEs are sometimes used as an indicator of favorable treatment response.2,3
Dermatologic IRAEs associated with the use of a PD-1 inhibitor include lichenoid reactions, pruritus, morbilliform eruptions, vitiligo, and bullous pemphigoid.4,5 Eruptions of keratoacanthoma rarely have been reported following treatment with the PD-1 inhibitors nivolumab and pembrolizumab.3,6,7 In our patient, we believe the profound and generalized eruptive keratoacanthoma—a well-differentiated cSCC variant—was related to treatment of locally advanced cSCC with cemiplimab. The mechanism underlying the formation of anti-PD-1 eruptive keratoacanthoma is not well understood. In susceptible patients, it is plausible that the inflammatory environment permitted by ICIs paradoxically induces regression of tumors such as locally invasive cSCC and simultaneously promotes formation of keratoacanthoma.
The role of inflammation in the pathogenesis and progression of cSCC is complex and possibly involves contrasting roles of leukocyte subpopulations.8 The increased incidence of cSCC in the immunocompromised population,8 PD-L1 overexpression in cSCC,9,10 and successful treatment of cSCC with PD-1 inhibition10 all suggest that inhibition of specific inflammatory pathways is pivotal in tumor pathogenesis. However, increased inflammation, particularly inflammation driven by T lymphocytes and Langerhans cells, also is believed to play a key role in the formation of cSCCs, including the degeneration of actinic keratosis into cSCC. Moreover, because keratoacanthomas are believed to be a cSCC variant and also are associated with PD-L1 overexpression,9 it is perplexing that PD-1 blockade may result in eruptive keratoacanthoma in some patients while also treating locally advanced cSCC, as seen in our patient. Successful treatment of keratoacanthoma with anti-inflammatory intralesional or topical corticosteroids adds to this complicated picture.3
We hypothesize that the pathogenesis of invasive cSCC and keratoacanthoma shares certain immune-mediated mechanisms but also differs in distinct manners. To understand the relationship between systemic treatment of cSCC and eruptive keratoacanthoma, further research is required.
In addition, the RAS/BRAF/MEK oncogenic pathway may be involved in the development of cSCCs associated with anti-PD-1. It is hypothesized that BRAF and MEK inhibition increases T-cell infiltration and increases PD-L1 expression on tumor cells,11 thus increasing the susceptibility of those cells to PD-1 blockade. Further supporting a relationship between the RAS/BRAF/MEK and PD-1 pathways, BRAF inhibitors are associated with development of SCCs and verrucal keratosis by upregulation of the RAS pathway.12,13 Perhaps a common mechanism underlying these pathways results in their shared association for an increased risk for cSCC upon blockade. More research is needed to fully elucidate the underlying biochemical mechanism of immunotherapy and formation of SCCs, such as keratoacanthoma.
Treatment of solitary keratoacanthoma often involves surgical excision; however, the sheer number of lesions in eruptive keratoacanthoma presents a larger dilemma. Because oral systemic retinoids have been shown to be most effective for treating eruptive keratoacanthoma, they are considered first-line therapy as monotherapy or in combination with surgical excision.3 Other treatment options include intralesional or topical corticosteroids, cyclosporine, 5-fluorouracil, imiquimod, and cryotherapy.3,6
The development of ICIs has revolutionized the treatment of cutaneous malignancy, yet we have a great deal more to comprehend on the systemic effects of these medications. Although IRAEs may signal a better response to therapy, some of these effects regrettably can be dose limiting. In our patient, cemiplimab was successful in treating locally advanced cSCC, but treatment also resulted in devastating widespread eruptive keratoacanthoma. The mechanism of this kind of eruption has yet to be understood; we hypothesize that it likely involves T lymphocyte–driven inflammation and the interplay of molecular and immune-mediated pathways.
- Ramos-Casals M, Brahmer JR, Callahan MK, et al. Immune-related adverse events of checkpoint inhibitors. Nat Rev Dis Primers. 2020;6:38. doi:10.1038/s41572-020-0160-6
- Das S, Johnson DB. Immune-related adverse events and anti-tumor efficacy of immune checkpoint inhibitors. J Immunother Cancer. 2019;7:306. doi:10.1186/s40425-019-0805-8
- Freites-Martinez A, Kwong BY, Rieger KE, et al. Eruptive keratoacanthomas associated with pembrolizumab therapy. JAMA Dermatol. 2017;153:694-697. doi:10.1001/jamadermatol.2017.0989
- Shen J, Chang J, Mendenhall M, et al. Diverse cutaneous adverse eruptions caused by anti-programmed cell death-1 (PD-1) and anti-programmed cell death ligand-1 (PD-L1) immunotherapies: clinicalfeatures and management. Ther Adv Med Oncol. 2018;10:1758834017751634. doi:10.1177/1758834017751634
- Bandino JP, Perry DM, Clarke CE, et al. Two cases of anti-programmed cell death 1-associated bullous pemphigoid-like disease and eruptive keratoacanthomas featuring combined histopathology. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2017;31:E378-E380. doi:10.1111/jdv.14179
- Marsh RL, Kolodney JA, Iyengar S, et al. Formation of eruptive cutaneous squamous cell carcinomas after programmed cell death protein-1 blockade. JAAD Case Rep. 2020;6:390-393. doi:10.1016/j.jdcr.2020.02.024
- Antonov NK, Nair KG, Halasz CL. Transient eruptive keratoacanthomas associated with nivolumab. JAAD Case Rep. 2019;5:342-345. doi:10.1016/j.jdcr.2019.01.025
- Bottomley MJ, Thomson J, Harwood C, et al. The role of the immune system in cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma. Int J Mol Sci. 2019;20:2009. doi:10.3390/ijms20082009
- Gambichler T, Gnielka M, Rüddel I, et al. Expression of PD-L1 in keratoacanthoma and different stages of progression in cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma. Cancer Immunol Immunother. 2017;66:1199-1204. doi:10.1007/s00262-017-2015-x
- Patel R, Chang ALS. Immune checkpoint inhibitors for treating advanced cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma. Am J Clin Dermatol. 2019;20:477-482. doi:10.1007/s40257-019-00426-w
- Rozeman EA, Blank CU. Combining checkpoint inhibition and targeted therapy in melanoma. Nat Med. 2019;25:879-882. doi:10.1038/s41591-019-0482-7
- Dubauskas Z, Kunishige J, Prieto VG, Jonasch E, Hwu P, Tannir NM. Cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma and inflammation of actinic keratoses associated with sorafenib. Clin Genitourin Cancer. 2009;7:20-23. doi:10.3816/CGC.2009.n.003
- Chen P, Chen F, Zhou B. Systematic review and meta-analysis of prevalence of dermatological toxicities associated with vemurafenib treatment in patients with melanoma. Clin Exp Dermatol. 2019;44:243-251. doi:10.1111/ced.13751
- Ramos-Casals M, Brahmer JR, Callahan MK, et al. Immune-related adverse events of checkpoint inhibitors. Nat Rev Dis Primers. 2020;6:38. doi:10.1038/s41572-020-0160-6
- Das S, Johnson DB. Immune-related adverse events and anti-tumor efficacy of immune checkpoint inhibitors. J Immunother Cancer. 2019;7:306. doi:10.1186/s40425-019-0805-8
- Freites-Martinez A, Kwong BY, Rieger KE, et al. Eruptive keratoacanthomas associated with pembrolizumab therapy. JAMA Dermatol. 2017;153:694-697. doi:10.1001/jamadermatol.2017.0989
- Shen J, Chang J, Mendenhall M, et al. Diverse cutaneous adverse eruptions caused by anti-programmed cell death-1 (PD-1) and anti-programmed cell death ligand-1 (PD-L1) immunotherapies: clinicalfeatures and management. Ther Adv Med Oncol. 2018;10:1758834017751634. doi:10.1177/1758834017751634
- Bandino JP, Perry DM, Clarke CE, et al. Two cases of anti-programmed cell death 1-associated bullous pemphigoid-like disease and eruptive keratoacanthomas featuring combined histopathology. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2017;31:E378-E380. doi:10.1111/jdv.14179
- Marsh RL, Kolodney JA, Iyengar S, et al. Formation of eruptive cutaneous squamous cell carcinomas after programmed cell death protein-1 blockade. JAAD Case Rep. 2020;6:390-393. doi:10.1016/j.jdcr.2020.02.024
- Antonov NK, Nair KG, Halasz CL. Transient eruptive keratoacanthomas associated with nivolumab. JAAD Case Rep. 2019;5:342-345. doi:10.1016/j.jdcr.2019.01.025
- Bottomley MJ, Thomson J, Harwood C, et al. The role of the immune system in cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma. Int J Mol Sci. 2019;20:2009. doi:10.3390/ijms20082009
- Gambichler T, Gnielka M, Rüddel I, et al. Expression of PD-L1 in keratoacanthoma and different stages of progression in cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma. Cancer Immunol Immunother. 2017;66:1199-1204. doi:10.1007/s00262-017-2015-x
- Patel R, Chang ALS. Immune checkpoint inhibitors for treating advanced cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma. Am J Clin Dermatol. 2019;20:477-482. doi:10.1007/s40257-019-00426-w
- Rozeman EA, Blank CU. Combining checkpoint inhibition and targeted therapy in melanoma. Nat Med. 2019;25:879-882. doi:10.1038/s41591-019-0482-7
- Dubauskas Z, Kunishige J, Prieto VG, Jonasch E, Hwu P, Tannir NM. Cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma and inflammation of actinic keratoses associated with sorafenib. Clin Genitourin Cancer. 2009;7:20-23. doi:10.3816/CGC.2009.n.003
- Chen P, Chen F, Zhou B. Systematic review and meta-analysis of prevalence of dermatological toxicities associated with vemurafenib treatment in patients with melanoma. Clin Exp Dermatol. 2019;44:243-251. doi:10.1111/ced.13751
Practice Points
- Immunotherapy, including immune checkpoint inhibitors such as programmed cell-death protein 1 (PD-1) inhibitors, is associated with an array of immune-related adverse events that often manifest in a delayed and prolonged manner. They most commonly affect the gastrointestinal tract as well as the endocrine and dermatologic systems.
- Dermatologic adverse effects associated with PD-1 inhibitors include lichenoid reactions, pruritus, morbilliform eruptions, vitiligo, and bullous pemphigoid.
- Eruptions of keratoacanthoma rarely have been reported following treatment with PD-1 inhibitors such as cemiplimab, nivolumab, and pembrolizumab.
Pediatric Obesity Specialists Struggle to Get GLP-1s
While adults, many of whom don’t meet the clinical definition of obesity, scramble to procure glucagon-like peptide 1 (GLP-1) agonists for weight loss, pediatric obesity specialists said their young patients who could benefit more over the long term often are unable to access the potentially life-altering medications.
The US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approved two GLP-1 agonists — both marketed by Novo Nordisk — for use in adolescents aged ≥ 12 years: Wegovy (semaglutide) in December 2022 and Saxenda (liraglutide) in December 2020. Novo Nordisk and Eli Lilly — which makes the dual glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypetide/GLP-1 agonist tirzepatide (Zepbound) — are also investigating the drugs for obesity in children as young as age 6 years. The crushing demand for semaglutide in the last year — driving a thriving market in compounded versions and online prescriptions — has made it increasingly difficult to find pharmacies that can fill prescriptions, pediatricians told this news organization.
“It’s been more difficult to get people initiated now than it was a year ago,” said Brooke Sweeney, MD, medical director of weight management services at Children’s Mercy in Kansas City, Missouri. “Because of the supply issues, for the most part we›re not starting anyone new because I don›t have enough medication to keep my patients on it who are already on it,” she said.
Sarah Raatz, MD, a pediatrician at the University of Minnesota’s Center for Pediatric Obesity Medicine, said, “I actually haven’t really been prescribing many of these medications as of late.” Both liraglutide and semaglutide “are largely unavailable or quite hard to get a hold of,” Dr. Raatz told this news organization.
Susma Shanti Vaidya, MPH, MD, associate medical director of the IDEAL pediatric obesity clinic at Children›s National Hospital in Washington, DC, said that patients taking GLP-1 agonists in her practice have reduced their body mass index and have seen resolution of prediabetes, diabetes, and fatty liver disease. «I had one patient who had severe obstructive sleep apnea which resolved with semaglutide.»
But when they can’t find the medications, it can lead to a plateauing of weight loss and a reversal of hard-won victories, Dr. Vaidya said.
Insurance Denials Also Growing
In January 2023, the American Academy of Pediatrics urged aggressive treatment of childhood obesity, including using FDA-approved medications such as GLP-1 agonists combined with lifestyle and dietary modifications.
The US Preventive Services Task Force, however, has issued a draft proposal that recommends a variety of lifestyle and behavior modification interventions for children and adolescents but says the evidence does not yet support recommending bariatric surgery or medications.
Insurance coverage for children — even for FDA-approved indications and the age 12-and-over population — has become increasingly difficult, said the pediatric obesity specialists. Insurers are also creating hurdles that make getting coverage more difficult, they said.
Some insurers track an adolescent’s weight trajectory, “and if they’re not meeting a certain response threshold set by the insurance company, then they can pull coverage and then we have to try to advocate for why continued coverage might be beneficial and necessary,” Dr. Raatz said.
Insurers in the region around Children’s Mercy are erecting similar barriers, said Sweeney. Interim weight loss goals are challenging in pediatrics — given that adolescents are constantly changing and growing, she said.
Dr. Vaidya said she’s had success with commercial insurers but that the Washington, DC, and Maryland Medicaid programs have been stingier.
All the pediatricians said they expect greater restrictions in 2024.
Dr. Vaidya said some patients told her they had been notified that prior authorization will be required for new prescriptions for a GLP-1 agonist.
“We will just kind of be forced to see what happens when these medications are taken away from patients who have benefited from them,” Dr. Raatz said.
Some Parents Asking for GLP-1 Agonists
Pediatric obesity specialists said more parents are asking if a GLP-1 agonist might be appropriate for their children this year than in 2022.
Dr. Sweeney said parents ask for the medications when they feel they have exhausted all other options for their children. “These parents are not coming because they are concerned about the cosmetic effects of the weight,” she said. In most cases, children she sees have been struggling for years with extreme hunger and lack of satiety and may have prediabetes or diabetes. Many are being bullied in school because of their weight. They have only marginally been helped by interventions suggested by primary care or dietitians or other specialists, Dr. Sweeney said.
“Starting semaglutide really is life-changing for some of these patients,” Dr. Vaidya said. One patient said, “it just stopped the food chatter,” she added, noting that the adolescent no longer felt ruled by cravings.
In a recent poll by Morning Consult, 65% of parents of children with weight-related issues said they would be interested in GLP-1 agonists for their kids. A third of all parents said they would be interested in having their children use the drugs if they were available.
Lifelong Medication?
Parents — and adolescents — are generally counseled that obesity is a chronic disease and GLP-1 agonists are likely a lifelong treatment.
With the medications, “our first step is to get induction of weight loss and get your set point decreased enough that we can get you to a healthier weight for your body,” Dr. Sweeney said.
She tells patients and families, “I can’t tell you that you’re necessarily going to be on this medication at this dose for the rest of your life, but you will need treatment for life.”
Based on current knowledge, the risks for lifelong obesity outweigh the risk for the medications. Dr. Sweeney said she would like to see more data. “There absolutely is an evidence gap, and we need more information on the long-term effectiveness and safety.”
“When we start kids on this medication, I’m very clear that we are going to try to get to the lowest effective dose,” Dr. Vaidya said. She also emphasizes to parents that the medications must be used in conjunction with continued lifestyle modifications. She expressed hope that as clinicians gain more experience, and patients’ comorbidities resolve, perhaps it will be possible in some cases to take individuals “off for a period of time, with the understanding that they might have to go back on in a few months.”
“We’re weighing the pros and cons of being on a medication long term but we’re also weighing the pros and cons of weight-related health complications long term,” Dr. Raatz said.
Dr. Raatz also said clinicians have much to learn about the long-term safety of GLP-1 agonists in their pediatric patients.
She tells parents and families, “we expect that this is going to be a long-term medication, and this is going to be something that we’re going to continue to monitor.”
Dr. Sweeney reports that she is a speaker and unpaid consultant on Rhythm Pharmaceuticals’ Imcivree (setmelanotide) medication and that she consults for Eli Lilly. Dr. Raatz is a coprincipal investigator for a Novo Nordisk trial of semaglutide in young children and will be a co-PI for a similar trial for Eli Lilly’s tirzepatide but receives no consulting fees or honoraria. Dr. Vaidya reported no conflicts.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
While adults, many of whom don’t meet the clinical definition of obesity, scramble to procure glucagon-like peptide 1 (GLP-1) agonists for weight loss, pediatric obesity specialists said their young patients who could benefit more over the long term often are unable to access the potentially life-altering medications.
The US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approved two GLP-1 agonists — both marketed by Novo Nordisk — for use in adolescents aged ≥ 12 years: Wegovy (semaglutide) in December 2022 and Saxenda (liraglutide) in December 2020. Novo Nordisk and Eli Lilly — which makes the dual glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypetide/GLP-1 agonist tirzepatide (Zepbound) — are also investigating the drugs for obesity in children as young as age 6 years. The crushing demand for semaglutide in the last year — driving a thriving market in compounded versions and online prescriptions — has made it increasingly difficult to find pharmacies that can fill prescriptions, pediatricians told this news organization.
“It’s been more difficult to get people initiated now than it was a year ago,” said Brooke Sweeney, MD, medical director of weight management services at Children’s Mercy in Kansas City, Missouri. “Because of the supply issues, for the most part we›re not starting anyone new because I don›t have enough medication to keep my patients on it who are already on it,” she said.
Sarah Raatz, MD, a pediatrician at the University of Minnesota’s Center for Pediatric Obesity Medicine, said, “I actually haven’t really been prescribing many of these medications as of late.” Both liraglutide and semaglutide “are largely unavailable or quite hard to get a hold of,” Dr. Raatz told this news organization.
Susma Shanti Vaidya, MPH, MD, associate medical director of the IDEAL pediatric obesity clinic at Children›s National Hospital in Washington, DC, said that patients taking GLP-1 agonists in her practice have reduced their body mass index and have seen resolution of prediabetes, diabetes, and fatty liver disease. «I had one patient who had severe obstructive sleep apnea which resolved with semaglutide.»
But when they can’t find the medications, it can lead to a plateauing of weight loss and a reversal of hard-won victories, Dr. Vaidya said.
Insurance Denials Also Growing
In January 2023, the American Academy of Pediatrics urged aggressive treatment of childhood obesity, including using FDA-approved medications such as GLP-1 agonists combined with lifestyle and dietary modifications.
The US Preventive Services Task Force, however, has issued a draft proposal that recommends a variety of lifestyle and behavior modification interventions for children and adolescents but says the evidence does not yet support recommending bariatric surgery or medications.
Insurance coverage for children — even for FDA-approved indications and the age 12-and-over population — has become increasingly difficult, said the pediatric obesity specialists. Insurers are also creating hurdles that make getting coverage more difficult, they said.
Some insurers track an adolescent’s weight trajectory, “and if they’re not meeting a certain response threshold set by the insurance company, then they can pull coverage and then we have to try to advocate for why continued coverage might be beneficial and necessary,” Dr. Raatz said.
Insurers in the region around Children’s Mercy are erecting similar barriers, said Sweeney. Interim weight loss goals are challenging in pediatrics — given that adolescents are constantly changing and growing, she said.
Dr. Vaidya said she’s had success with commercial insurers but that the Washington, DC, and Maryland Medicaid programs have been stingier.
All the pediatricians said they expect greater restrictions in 2024.
Dr. Vaidya said some patients told her they had been notified that prior authorization will be required for new prescriptions for a GLP-1 agonist.
“We will just kind of be forced to see what happens when these medications are taken away from patients who have benefited from them,” Dr. Raatz said.
Some Parents Asking for GLP-1 Agonists
Pediatric obesity specialists said more parents are asking if a GLP-1 agonist might be appropriate for their children this year than in 2022.
Dr. Sweeney said parents ask for the medications when they feel they have exhausted all other options for their children. “These parents are not coming because they are concerned about the cosmetic effects of the weight,” she said. In most cases, children she sees have been struggling for years with extreme hunger and lack of satiety and may have prediabetes or diabetes. Many are being bullied in school because of their weight. They have only marginally been helped by interventions suggested by primary care or dietitians or other specialists, Dr. Sweeney said.
“Starting semaglutide really is life-changing for some of these patients,” Dr. Vaidya said. One patient said, “it just stopped the food chatter,” she added, noting that the adolescent no longer felt ruled by cravings.
In a recent poll by Morning Consult, 65% of parents of children with weight-related issues said they would be interested in GLP-1 agonists for their kids. A third of all parents said they would be interested in having their children use the drugs if they were available.
Lifelong Medication?
Parents — and adolescents — are generally counseled that obesity is a chronic disease and GLP-1 agonists are likely a lifelong treatment.
With the medications, “our first step is to get induction of weight loss and get your set point decreased enough that we can get you to a healthier weight for your body,” Dr. Sweeney said.
She tells patients and families, “I can’t tell you that you’re necessarily going to be on this medication at this dose for the rest of your life, but you will need treatment for life.”
Based on current knowledge, the risks for lifelong obesity outweigh the risk for the medications. Dr. Sweeney said she would like to see more data. “There absolutely is an evidence gap, and we need more information on the long-term effectiveness and safety.”
“When we start kids on this medication, I’m very clear that we are going to try to get to the lowest effective dose,” Dr. Vaidya said. She also emphasizes to parents that the medications must be used in conjunction with continued lifestyle modifications. She expressed hope that as clinicians gain more experience, and patients’ comorbidities resolve, perhaps it will be possible in some cases to take individuals “off for a period of time, with the understanding that they might have to go back on in a few months.”
“We’re weighing the pros and cons of being on a medication long term but we’re also weighing the pros and cons of weight-related health complications long term,” Dr. Raatz said.
Dr. Raatz also said clinicians have much to learn about the long-term safety of GLP-1 agonists in their pediatric patients.
She tells parents and families, “we expect that this is going to be a long-term medication, and this is going to be something that we’re going to continue to monitor.”
Dr. Sweeney reports that she is a speaker and unpaid consultant on Rhythm Pharmaceuticals’ Imcivree (setmelanotide) medication and that she consults for Eli Lilly. Dr. Raatz is a coprincipal investigator for a Novo Nordisk trial of semaglutide in young children and will be a co-PI for a similar trial for Eli Lilly’s tirzepatide but receives no consulting fees or honoraria. Dr. Vaidya reported no conflicts.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
While adults, many of whom don’t meet the clinical definition of obesity, scramble to procure glucagon-like peptide 1 (GLP-1) agonists for weight loss, pediatric obesity specialists said their young patients who could benefit more over the long term often are unable to access the potentially life-altering medications.
The US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approved two GLP-1 agonists — both marketed by Novo Nordisk — for use in adolescents aged ≥ 12 years: Wegovy (semaglutide) in December 2022 and Saxenda (liraglutide) in December 2020. Novo Nordisk and Eli Lilly — which makes the dual glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypetide/GLP-1 agonist tirzepatide (Zepbound) — are also investigating the drugs for obesity in children as young as age 6 years. The crushing demand for semaglutide in the last year — driving a thriving market in compounded versions and online prescriptions — has made it increasingly difficult to find pharmacies that can fill prescriptions, pediatricians told this news organization.
“It’s been more difficult to get people initiated now than it was a year ago,” said Brooke Sweeney, MD, medical director of weight management services at Children’s Mercy in Kansas City, Missouri. “Because of the supply issues, for the most part we›re not starting anyone new because I don›t have enough medication to keep my patients on it who are already on it,” she said.
Sarah Raatz, MD, a pediatrician at the University of Minnesota’s Center for Pediatric Obesity Medicine, said, “I actually haven’t really been prescribing many of these medications as of late.” Both liraglutide and semaglutide “are largely unavailable or quite hard to get a hold of,” Dr. Raatz told this news organization.
Susma Shanti Vaidya, MPH, MD, associate medical director of the IDEAL pediatric obesity clinic at Children›s National Hospital in Washington, DC, said that patients taking GLP-1 agonists in her practice have reduced their body mass index and have seen resolution of prediabetes, diabetes, and fatty liver disease. «I had one patient who had severe obstructive sleep apnea which resolved with semaglutide.»
But when they can’t find the medications, it can lead to a plateauing of weight loss and a reversal of hard-won victories, Dr. Vaidya said.
Insurance Denials Also Growing
In January 2023, the American Academy of Pediatrics urged aggressive treatment of childhood obesity, including using FDA-approved medications such as GLP-1 agonists combined with lifestyle and dietary modifications.
The US Preventive Services Task Force, however, has issued a draft proposal that recommends a variety of lifestyle and behavior modification interventions for children and adolescents but says the evidence does not yet support recommending bariatric surgery or medications.
Insurance coverage for children — even for FDA-approved indications and the age 12-and-over population — has become increasingly difficult, said the pediatric obesity specialists. Insurers are also creating hurdles that make getting coverage more difficult, they said.
Some insurers track an adolescent’s weight trajectory, “and if they’re not meeting a certain response threshold set by the insurance company, then they can pull coverage and then we have to try to advocate for why continued coverage might be beneficial and necessary,” Dr. Raatz said.
Insurers in the region around Children’s Mercy are erecting similar barriers, said Sweeney. Interim weight loss goals are challenging in pediatrics — given that adolescents are constantly changing and growing, she said.
Dr. Vaidya said she’s had success with commercial insurers but that the Washington, DC, and Maryland Medicaid programs have been stingier.
All the pediatricians said they expect greater restrictions in 2024.
Dr. Vaidya said some patients told her they had been notified that prior authorization will be required for new prescriptions for a GLP-1 agonist.
“We will just kind of be forced to see what happens when these medications are taken away from patients who have benefited from them,” Dr. Raatz said.
Some Parents Asking for GLP-1 Agonists
Pediatric obesity specialists said more parents are asking if a GLP-1 agonist might be appropriate for their children this year than in 2022.
Dr. Sweeney said parents ask for the medications when they feel they have exhausted all other options for their children. “These parents are not coming because they are concerned about the cosmetic effects of the weight,” she said. In most cases, children she sees have been struggling for years with extreme hunger and lack of satiety and may have prediabetes or diabetes. Many are being bullied in school because of their weight. They have only marginally been helped by interventions suggested by primary care or dietitians or other specialists, Dr. Sweeney said.
“Starting semaglutide really is life-changing for some of these patients,” Dr. Vaidya said. One patient said, “it just stopped the food chatter,” she added, noting that the adolescent no longer felt ruled by cravings.
In a recent poll by Morning Consult, 65% of parents of children with weight-related issues said they would be interested in GLP-1 agonists for their kids. A third of all parents said they would be interested in having their children use the drugs if they were available.
Lifelong Medication?
Parents — and adolescents — are generally counseled that obesity is a chronic disease and GLP-1 agonists are likely a lifelong treatment.
With the medications, “our first step is to get induction of weight loss and get your set point decreased enough that we can get you to a healthier weight for your body,” Dr. Sweeney said.
She tells patients and families, “I can’t tell you that you’re necessarily going to be on this medication at this dose for the rest of your life, but you will need treatment for life.”
Based on current knowledge, the risks for lifelong obesity outweigh the risk for the medications. Dr. Sweeney said she would like to see more data. “There absolutely is an evidence gap, and we need more information on the long-term effectiveness and safety.”
“When we start kids on this medication, I’m very clear that we are going to try to get to the lowest effective dose,” Dr. Vaidya said. She also emphasizes to parents that the medications must be used in conjunction with continued lifestyle modifications. She expressed hope that as clinicians gain more experience, and patients’ comorbidities resolve, perhaps it will be possible in some cases to take individuals “off for a period of time, with the understanding that they might have to go back on in a few months.”
“We’re weighing the pros and cons of being on a medication long term but we’re also weighing the pros and cons of weight-related health complications long term,” Dr. Raatz said.
Dr. Raatz also said clinicians have much to learn about the long-term safety of GLP-1 agonists in their pediatric patients.
She tells parents and families, “we expect that this is going to be a long-term medication, and this is going to be something that we’re going to continue to monitor.”
Dr. Sweeney reports that she is a speaker and unpaid consultant on Rhythm Pharmaceuticals’ Imcivree (setmelanotide) medication and that she consults for Eli Lilly. Dr. Raatz is a coprincipal investigator for a Novo Nordisk trial of semaglutide in young children and will be a co-PI for a similar trial for Eli Lilly’s tirzepatide but receives no consulting fees or honoraria. Dr. Vaidya reported no conflicts.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Hospital Adverse Events Rise After Private Equity Acquisition
Hospital-acquired adverse events or conditions including falls and infections increased by approximately 25% after hospitals’ acquisition by private equity compared with control hospitals, on the basis of a study of Medicare claims for more than 4,500,000 hospitalizations.
“Prior research on private equity in health care showed that acquisition is associated with higher charges, prices, and spending; however, the implications for quality of care and patient outcomes remained less understood,” corresponding author Zirui Song, MD, of Harvard Medical School, Boston, said in an interview. “This was particularly true for measures of clinical quality that were less susceptible to changes in patient mix or coding behavior, such as hospital-acquired adverse events.”
In the study, published in JAMA, the researchers compared data from 100% Medicare Part A claims for 662,095 hospitalizations at 51 hospitals acquired by private equities and 4,160,720 hospitalizations at 259 control hospitals. The hospitalizations occurred between 2009 and 2019. The researchers also used a difference-in-differences design to evaluate hospitalizations from 3 years before to 3 years after acquisition, controlling for patient and hospital attributes.
Hospital-acquired adverse events as defined by the US Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services included falls, infections, stage III or IV pressure ulcers, foreign objects retained after surgery, air embolism, and blood incompatibility.
Overall, Medicare patients in private equity hospitals experienced a 25.4% increase in hospital-acquired conditions compared with those in control hospitals through a period of up to 3 years after acquisition, with a difference of 4.6 additional hospital-acquired conditions per 10,000 hospitalizations (P = .004). Central line-associated bloodstream infections accounted for 37.7% of the increase (P = .04), despite a 16.2% decrease in placement of central lines, and falls accounted for 27.3% (P = .02).
Notably, the incidence of surgical site infections increased from 10.8 per 10,000 hospitalizations before acquisition to 21.6 per 10,000 hospitalizations after acquisition, despite a reduction of 8.1% in surgical volume. By contrast, surgical site infections decreased at control hospitals over the study period.
In-hospital mortality decreased slightly at private equity hospitals compared with the control hospitals, but there was no differential change in mortality by 30 days after hospital discharge. The slight difference might be caused by the trend in slightly younger Medicare beneficiaries treated at private equity hospitals; these patients were less likely to be eligible for both Medicaid and Medicare and were more likely to be transferred to other hospitals, the researchers noted.
The findings were limited by several factors including the lack of generalizability to all private equity-acquired hospitals and to non-Medicare patients, the researchers noted. Other limitations include the use of the International Classification of Diseases, Ninth Revision (ICD-9) and Tenth Revision (ICD-10) codes that might have failed to capture all hospital-acquired conditions and the inability to account for all confounding factors.
However, the results suggest that private equity acquisition was associated with increased hospital-acquired adverse events and highlight concerns about the impact of private equity ownership on healthcare delivery, the researchers concluded.
In a related story published in July 2023, this news organization described a report showing an association between private equity ownership of medical practices and increased consumer prices for multiple medical specialties.
“Medicare patients admitted to private equity-owned hospitals experienced, on average, an 25% increase in hospital-acquired adverse events after the hospital was bought compared to similar patients at hospitals not acquired by private equity firms. We were surprised by the extent of this change relative to the comparison (non-private equity) hospitals, including the sizable increase in central line-associated bloodstream infections and the doubling of surgical site infections at private equity hospitals — both of which went down at the comparison hospitals during the same period,” Dr. Song said in an interview.
“A key implication is that patients, providers, and policymakers might be more attuned to the potential clinical impact of private equity ownership in the delivery system. Given that a plausible explanation for these findings is reductions in clinician staffing, clinical organizations and policymakers might also be more aware of cost-cutting strategies after acquisition,” Dr. Song said. “Prior research has shown that hospitals, nursing homes, and physician practices experience staffing cuts after private equity acquisition, which is a common way to reduce operating costs and boost the profitability of acquired entities,” he noted.
“More research is needed to understand the impact of private equity acquisitions across health care settings and the potential effects of policy levers that aim to protect patients and societal resources,” said Dr. Song, who coauthored an article outlining a policy framework for addressing private equity in healthcare, published in JAMA in April 2023. “Potential regulatory remedies include minimum staffing ratios, antitrust enforcement, mitigating the financial risk of such acquisitions, increasing the transparency of these acquisitions, and protecting patients and society from the higher prices of care attributed to this model of provider ownership,” he said.
Patients Pay the Price of Private Equity Acquisition
“The exponential growth in private equity ownership in hospital and physician practices in the past few decades has left a majority of health care providers disillusioned with cost-cutting practices resulting in staffing reductions and ratios that sacrifice patient care as part of their approach to running clinical operations ‘lean,’ ” Robert Glatter, MD, an emergency medicine physician at Lenox Hill Hospital, New York, NY, said in an interview.
“While private equity companies argue that such practices are essential to meet their bottom line and increase operating margins, it doesn’t translate into ideal care for patients; lean practices in staffing which focus on profits at the expense of patient safety and quality of care.
“When you look at patient outcomes, it is the patients who ultimately pay the price — not the shareholders,” Dr. Glatter said. “This translates to higher risks of hospital-acquired complications including falls and blood-borne infections, including surgical site infections, as noted by the authors of the current study when private equity took over operations in hospitals.
Dr. Glatter said he was not surprised by the findings. “In my world, patient care and safety come first. Period,” he said. “Would you want your family’s health and well-being sacrificed in the name of company profits? I think it’s a rhetorical question, but one that every health care provider who works in a hospital or practice run by private equity must consider.”
Despite a decline in utilization at private equity hospitals as noted in the current study, hospital-acquired infections and adverse outcomes still increased, illustrating a decline in quality of care, said Dr. Glatter. “While these disparities were not evident when looking at 30-day outcomes, they demonstrate how operational changes impact patient outcomes in the near term. Having younger and healthier patients, and fewer Medicare and Medicaid patients combined with more hospital transfers to non–private equity run hospitals, resulted in lower in-hospital mortality in the near term, which was not apparent at 30 days post discharge,” he said.
“The explosion of hospital mergers and consolidation in the past several decades has led to skyrocketing health care costs at the expense of patient satisfaction, but also health care providers’ autonomy to manage and maintain quality care for their patients,” Dr. Glatter said.
“It’s important to understand that private equity’s interests are primarily aligned with their shareholder’s interests, as opposed to patients’ outcomes and interests,” Dr. Glatter told this news organization. “Within 5-7 years, the goal is to increase operating margins and profits and then sell a practice or hospital, which is ultimately part of a ‘health care portfolio,’ ” he said.
Additional research is needed to examine whether other hospital-acquired conditions including pressure sores, catheter-associated UTIs, methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus infections, Clostridium difficile infections, and nosocomial pneumonia have increased in hospitals following private equity acquisition, given the overall national decline in these events, he said.
“At the same time, it is vital to also look at management and readmission rates for patients with strokes, heart attacks, and congestive heart failure in hospitals that are run by private equity,” Dr. Glatter noted. “These are important benchmarks of care monitored by CMS that reflect the quality of care that payers ultimately factor into reimbursement.”
Examining the metrics associated with these diagnoses will help in understanding whether private equity-managed facilities are leading to adverse outcomes and mortality, increased length of stay, hospital readmissions, and increased nosocomial infections, apart from other aspects of patient experience, Dr. Glatter added.
The study was supported by the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute, the National Institute on Aging, and Arnold Ventures. The researchers had no financial conflicts to disclose. Dr. Glatter had no financial conflicts to disclose and serves on the Medscape Emergency Medicine Editorial Board.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Hospital-acquired adverse events or conditions including falls and infections increased by approximately 25% after hospitals’ acquisition by private equity compared with control hospitals, on the basis of a study of Medicare claims for more than 4,500,000 hospitalizations.
“Prior research on private equity in health care showed that acquisition is associated with higher charges, prices, and spending; however, the implications for quality of care and patient outcomes remained less understood,” corresponding author Zirui Song, MD, of Harvard Medical School, Boston, said in an interview. “This was particularly true for measures of clinical quality that were less susceptible to changes in patient mix or coding behavior, such as hospital-acquired adverse events.”
In the study, published in JAMA, the researchers compared data from 100% Medicare Part A claims for 662,095 hospitalizations at 51 hospitals acquired by private equities and 4,160,720 hospitalizations at 259 control hospitals. The hospitalizations occurred between 2009 and 2019. The researchers also used a difference-in-differences design to evaluate hospitalizations from 3 years before to 3 years after acquisition, controlling for patient and hospital attributes.
Hospital-acquired adverse events as defined by the US Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services included falls, infections, stage III or IV pressure ulcers, foreign objects retained after surgery, air embolism, and blood incompatibility.
Overall, Medicare patients in private equity hospitals experienced a 25.4% increase in hospital-acquired conditions compared with those in control hospitals through a period of up to 3 years after acquisition, with a difference of 4.6 additional hospital-acquired conditions per 10,000 hospitalizations (P = .004). Central line-associated bloodstream infections accounted for 37.7% of the increase (P = .04), despite a 16.2% decrease in placement of central lines, and falls accounted for 27.3% (P = .02).
Notably, the incidence of surgical site infections increased from 10.8 per 10,000 hospitalizations before acquisition to 21.6 per 10,000 hospitalizations after acquisition, despite a reduction of 8.1% in surgical volume. By contrast, surgical site infections decreased at control hospitals over the study period.
In-hospital mortality decreased slightly at private equity hospitals compared with the control hospitals, but there was no differential change in mortality by 30 days after hospital discharge. The slight difference might be caused by the trend in slightly younger Medicare beneficiaries treated at private equity hospitals; these patients were less likely to be eligible for both Medicaid and Medicare and were more likely to be transferred to other hospitals, the researchers noted.
The findings were limited by several factors including the lack of generalizability to all private equity-acquired hospitals and to non-Medicare patients, the researchers noted. Other limitations include the use of the International Classification of Diseases, Ninth Revision (ICD-9) and Tenth Revision (ICD-10) codes that might have failed to capture all hospital-acquired conditions and the inability to account for all confounding factors.
However, the results suggest that private equity acquisition was associated with increased hospital-acquired adverse events and highlight concerns about the impact of private equity ownership on healthcare delivery, the researchers concluded.
In a related story published in July 2023, this news organization described a report showing an association between private equity ownership of medical practices and increased consumer prices for multiple medical specialties.
“Medicare patients admitted to private equity-owned hospitals experienced, on average, an 25% increase in hospital-acquired adverse events after the hospital was bought compared to similar patients at hospitals not acquired by private equity firms. We were surprised by the extent of this change relative to the comparison (non-private equity) hospitals, including the sizable increase in central line-associated bloodstream infections and the doubling of surgical site infections at private equity hospitals — both of which went down at the comparison hospitals during the same period,” Dr. Song said in an interview.
“A key implication is that patients, providers, and policymakers might be more attuned to the potential clinical impact of private equity ownership in the delivery system. Given that a plausible explanation for these findings is reductions in clinician staffing, clinical organizations and policymakers might also be more aware of cost-cutting strategies after acquisition,” Dr. Song said. “Prior research has shown that hospitals, nursing homes, and physician practices experience staffing cuts after private equity acquisition, which is a common way to reduce operating costs and boost the profitability of acquired entities,” he noted.
“More research is needed to understand the impact of private equity acquisitions across health care settings and the potential effects of policy levers that aim to protect patients and societal resources,” said Dr. Song, who coauthored an article outlining a policy framework for addressing private equity in healthcare, published in JAMA in April 2023. “Potential regulatory remedies include minimum staffing ratios, antitrust enforcement, mitigating the financial risk of such acquisitions, increasing the transparency of these acquisitions, and protecting patients and society from the higher prices of care attributed to this model of provider ownership,” he said.
Patients Pay the Price of Private Equity Acquisition
“The exponential growth in private equity ownership in hospital and physician practices in the past few decades has left a majority of health care providers disillusioned with cost-cutting practices resulting in staffing reductions and ratios that sacrifice patient care as part of their approach to running clinical operations ‘lean,’ ” Robert Glatter, MD, an emergency medicine physician at Lenox Hill Hospital, New York, NY, said in an interview.
“While private equity companies argue that such practices are essential to meet their bottom line and increase operating margins, it doesn’t translate into ideal care for patients; lean practices in staffing which focus on profits at the expense of patient safety and quality of care.
“When you look at patient outcomes, it is the patients who ultimately pay the price — not the shareholders,” Dr. Glatter said. “This translates to higher risks of hospital-acquired complications including falls and blood-borne infections, including surgical site infections, as noted by the authors of the current study when private equity took over operations in hospitals.
Dr. Glatter said he was not surprised by the findings. “In my world, patient care and safety come first. Period,” he said. “Would you want your family’s health and well-being sacrificed in the name of company profits? I think it’s a rhetorical question, but one that every health care provider who works in a hospital or practice run by private equity must consider.”
Despite a decline in utilization at private equity hospitals as noted in the current study, hospital-acquired infections and adverse outcomes still increased, illustrating a decline in quality of care, said Dr. Glatter. “While these disparities were not evident when looking at 30-day outcomes, they demonstrate how operational changes impact patient outcomes in the near term. Having younger and healthier patients, and fewer Medicare and Medicaid patients combined with more hospital transfers to non–private equity run hospitals, resulted in lower in-hospital mortality in the near term, which was not apparent at 30 days post discharge,” he said.
“The explosion of hospital mergers and consolidation in the past several decades has led to skyrocketing health care costs at the expense of patient satisfaction, but also health care providers’ autonomy to manage and maintain quality care for their patients,” Dr. Glatter said.
“It’s important to understand that private equity’s interests are primarily aligned with their shareholder’s interests, as opposed to patients’ outcomes and interests,” Dr. Glatter told this news organization. “Within 5-7 years, the goal is to increase operating margins and profits and then sell a practice or hospital, which is ultimately part of a ‘health care portfolio,’ ” he said.
Additional research is needed to examine whether other hospital-acquired conditions including pressure sores, catheter-associated UTIs, methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus infections, Clostridium difficile infections, and nosocomial pneumonia have increased in hospitals following private equity acquisition, given the overall national decline in these events, he said.
“At the same time, it is vital to also look at management and readmission rates for patients with strokes, heart attacks, and congestive heart failure in hospitals that are run by private equity,” Dr. Glatter noted. “These are important benchmarks of care monitored by CMS that reflect the quality of care that payers ultimately factor into reimbursement.”
Examining the metrics associated with these diagnoses will help in understanding whether private equity-managed facilities are leading to adverse outcomes and mortality, increased length of stay, hospital readmissions, and increased nosocomial infections, apart from other aspects of patient experience, Dr. Glatter added.
The study was supported by the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute, the National Institute on Aging, and Arnold Ventures. The researchers had no financial conflicts to disclose. Dr. Glatter had no financial conflicts to disclose and serves on the Medscape Emergency Medicine Editorial Board.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Hospital-acquired adverse events or conditions including falls and infections increased by approximately 25% after hospitals’ acquisition by private equity compared with control hospitals, on the basis of a study of Medicare claims for more than 4,500,000 hospitalizations.
“Prior research on private equity in health care showed that acquisition is associated with higher charges, prices, and spending; however, the implications for quality of care and patient outcomes remained less understood,” corresponding author Zirui Song, MD, of Harvard Medical School, Boston, said in an interview. “This was particularly true for measures of clinical quality that were less susceptible to changes in patient mix or coding behavior, such as hospital-acquired adverse events.”
In the study, published in JAMA, the researchers compared data from 100% Medicare Part A claims for 662,095 hospitalizations at 51 hospitals acquired by private equities and 4,160,720 hospitalizations at 259 control hospitals. The hospitalizations occurred between 2009 and 2019. The researchers also used a difference-in-differences design to evaluate hospitalizations from 3 years before to 3 years after acquisition, controlling for patient and hospital attributes.
Hospital-acquired adverse events as defined by the US Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services included falls, infections, stage III or IV pressure ulcers, foreign objects retained after surgery, air embolism, and blood incompatibility.
Overall, Medicare patients in private equity hospitals experienced a 25.4% increase in hospital-acquired conditions compared with those in control hospitals through a period of up to 3 years after acquisition, with a difference of 4.6 additional hospital-acquired conditions per 10,000 hospitalizations (P = .004). Central line-associated bloodstream infections accounted for 37.7% of the increase (P = .04), despite a 16.2% decrease in placement of central lines, and falls accounted for 27.3% (P = .02).
Notably, the incidence of surgical site infections increased from 10.8 per 10,000 hospitalizations before acquisition to 21.6 per 10,000 hospitalizations after acquisition, despite a reduction of 8.1% in surgical volume. By contrast, surgical site infections decreased at control hospitals over the study period.
In-hospital mortality decreased slightly at private equity hospitals compared with the control hospitals, but there was no differential change in mortality by 30 days after hospital discharge. The slight difference might be caused by the trend in slightly younger Medicare beneficiaries treated at private equity hospitals; these patients were less likely to be eligible for both Medicaid and Medicare and were more likely to be transferred to other hospitals, the researchers noted.
The findings were limited by several factors including the lack of generalizability to all private equity-acquired hospitals and to non-Medicare patients, the researchers noted. Other limitations include the use of the International Classification of Diseases, Ninth Revision (ICD-9) and Tenth Revision (ICD-10) codes that might have failed to capture all hospital-acquired conditions and the inability to account for all confounding factors.
However, the results suggest that private equity acquisition was associated with increased hospital-acquired adverse events and highlight concerns about the impact of private equity ownership on healthcare delivery, the researchers concluded.
In a related story published in July 2023, this news organization described a report showing an association between private equity ownership of medical practices and increased consumer prices for multiple medical specialties.
“Medicare patients admitted to private equity-owned hospitals experienced, on average, an 25% increase in hospital-acquired adverse events after the hospital was bought compared to similar patients at hospitals not acquired by private equity firms. We were surprised by the extent of this change relative to the comparison (non-private equity) hospitals, including the sizable increase in central line-associated bloodstream infections and the doubling of surgical site infections at private equity hospitals — both of which went down at the comparison hospitals during the same period,” Dr. Song said in an interview.
“A key implication is that patients, providers, and policymakers might be more attuned to the potential clinical impact of private equity ownership in the delivery system. Given that a plausible explanation for these findings is reductions in clinician staffing, clinical organizations and policymakers might also be more aware of cost-cutting strategies after acquisition,” Dr. Song said. “Prior research has shown that hospitals, nursing homes, and physician practices experience staffing cuts after private equity acquisition, which is a common way to reduce operating costs and boost the profitability of acquired entities,” he noted.
“More research is needed to understand the impact of private equity acquisitions across health care settings and the potential effects of policy levers that aim to protect patients and societal resources,” said Dr. Song, who coauthored an article outlining a policy framework for addressing private equity in healthcare, published in JAMA in April 2023. “Potential regulatory remedies include minimum staffing ratios, antitrust enforcement, mitigating the financial risk of such acquisitions, increasing the transparency of these acquisitions, and protecting patients and society from the higher prices of care attributed to this model of provider ownership,” he said.
Patients Pay the Price of Private Equity Acquisition
“The exponential growth in private equity ownership in hospital and physician practices in the past few decades has left a majority of health care providers disillusioned with cost-cutting practices resulting in staffing reductions and ratios that sacrifice patient care as part of their approach to running clinical operations ‘lean,’ ” Robert Glatter, MD, an emergency medicine physician at Lenox Hill Hospital, New York, NY, said in an interview.
“While private equity companies argue that such practices are essential to meet their bottom line and increase operating margins, it doesn’t translate into ideal care for patients; lean practices in staffing which focus on profits at the expense of patient safety and quality of care.
“When you look at patient outcomes, it is the patients who ultimately pay the price — not the shareholders,” Dr. Glatter said. “This translates to higher risks of hospital-acquired complications including falls and blood-borne infections, including surgical site infections, as noted by the authors of the current study when private equity took over operations in hospitals.
Dr. Glatter said he was not surprised by the findings. “In my world, patient care and safety come first. Period,” he said. “Would you want your family’s health and well-being sacrificed in the name of company profits? I think it’s a rhetorical question, but one that every health care provider who works in a hospital or practice run by private equity must consider.”
Despite a decline in utilization at private equity hospitals as noted in the current study, hospital-acquired infections and adverse outcomes still increased, illustrating a decline in quality of care, said Dr. Glatter. “While these disparities were not evident when looking at 30-day outcomes, they demonstrate how operational changes impact patient outcomes in the near term. Having younger and healthier patients, and fewer Medicare and Medicaid patients combined with more hospital transfers to non–private equity run hospitals, resulted in lower in-hospital mortality in the near term, which was not apparent at 30 days post discharge,” he said.
“The explosion of hospital mergers and consolidation in the past several decades has led to skyrocketing health care costs at the expense of patient satisfaction, but also health care providers’ autonomy to manage and maintain quality care for their patients,” Dr. Glatter said.
“It’s important to understand that private equity’s interests are primarily aligned with their shareholder’s interests, as opposed to patients’ outcomes and interests,” Dr. Glatter told this news organization. “Within 5-7 years, the goal is to increase operating margins and profits and then sell a practice or hospital, which is ultimately part of a ‘health care portfolio,’ ” he said.
Additional research is needed to examine whether other hospital-acquired conditions including pressure sores, catheter-associated UTIs, methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus infections, Clostridium difficile infections, and nosocomial pneumonia have increased in hospitals following private equity acquisition, given the overall national decline in these events, he said.
“At the same time, it is vital to also look at management and readmission rates for patients with strokes, heart attacks, and congestive heart failure in hospitals that are run by private equity,” Dr. Glatter noted. “These are important benchmarks of care monitored by CMS that reflect the quality of care that payers ultimately factor into reimbursement.”
Examining the metrics associated with these diagnoses will help in understanding whether private equity-managed facilities are leading to adverse outcomes and mortality, increased length of stay, hospital readmissions, and increased nosocomial infections, apart from other aspects of patient experience, Dr. Glatter added.
The study was supported by the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute, the National Institute on Aging, and Arnold Ventures. The researchers had no financial conflicts to disclose. Dr. Glatter had no financial conflicts to disclose and serves on the Medscape Emergency Medicine Editorial Board.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Perinatal Psychiatry in 2024: Helping More Patients Access Care
The past year has been a challenging time for many, both at the local level and globally, with divisive undercurrents across many communities. Many times, the end of the year is an opportunity for reflection. As I reflect on the state of perinatal psychiatry in the new year, I see several evolving issues that I’d like to share in this first column of 2024.
In 2023, the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists published new recommendations meant to enhance the well-being of pregnant and postpartum women and families. A main message from discussion papers borne out of these recommendations was that as a field, we should be doing more than identifying perinatal illness. We should be screening women at risk for postpartum psychiatric illness and see that those suffering from posttraumatic stress disorder (PTSD) have access to care and “wrap-around services” from clinicians with varying expertise.
Screening is a primary way we identify patients at risk for psychiatric illness and also those who are suffering at the time of a screen. One problem I see in the near future is our disparate collection and management of data. When we look closely across health care systems, it’s not clear how screening data are captured, let alone managed. What is being done in one hospital system may be very different from what is being done elsewhere. Some clinicians are adopting digital platforms to identify those with postpartum depression, while others are practicing as they always have, either through a paper screening process or with queries as part of a clinical encounter.
Given this amalgam of methods for collecting and storing information, there does not appear to be a systematic way clinicians and researchers are recording whether women are meeting criteria for significant depressive symptoms or frank postpartum psychiatric illness. It is clear a more cohesive method for collection and management is needed to optimize the likelihood that next steps can be taken to get patients the care they need.
However, screening is only one part of the story. Certainly, in our own center, one of our greatest interests, both clinically and on the research side, is what happens after screening. Through our center’s initiation of the Screening and Treatment Enhancement for Postpartum Depression (STEPS for PPD) project funded by the Marriott Foundation, we are evaluating the outcomes of women who are screened at 6 weeks postpartum with significant depressive symptoms, and who are then given an opportunity to engage with a perinatal social worker who can assist with direct psychotherapy, arranging for referrals, and navigating care for a new mother.
What we are learning as we enroll women through the initial stages of STEPS for PPD is that screening and identifying women who likely suffer from PPD simply is not enough. In fact, once identified with a depression screening tool, women who are suffering from postpartum depression can be very challenging to engage clinically. What I am learning decades after starting to work with perinatal patients is that even with a screening system and effective tools for treatment of PPD, optimizing engagement with these depressed women seems a critical and understudied step on the road to optimizing positive clinical outcomes.
A recent study published in the Journal of Women’s Health explored gaps in care for perinatal depression and found that patients without a history of psychiatric illness prior to pregnancy were less likely to be screened for depression and 80% less likely to receive care if they developed depression compared with women with a previous history of psychiatric illness (J Womens Health (Larchmt). 2023 Oct;32[10]:1111-9).
That history may help women navigate to care, while women for whom psychiatric illness is a new experience may be less likely to engage, be referred for care, and receive appropriate treatment. The study indicates that, as a field, we must strive to ensure universal screening for depression in perinatal populations.
While we have always been particularly interested in populations of patients at highest risk for PPD, helping women at risk for PPD in the general population without a history of psychiatric illness is a large public health issue and will be an even larger undertaking. As women’s mental health is gaining more appropriate focus, both at the local level and even in the recent White House Initiative on Women’s Health Research, the focus has been on screening and developing new treatments.
We are not lacking in pharmacologic agents nor nonpharmacologic options as treatments for women experiencing PPD. Newer alternative treatments are being explored, such as transcranial magnetic stimulation (TMS) and even psychedelics as a potential therapy for PPD. But perhaps what we’ve learned in 2023 and as we move into a new year, is that the problem of tackling PPD is not only about having the right tools, but is about helping women navigate to the care that they need.
The COVID-19 pandemic brought with it an explosion of telehealth options that have enhanced the odds women can find support during such a challenging time; as society has returned to some semblance of normal, nearly all support groups for postpartum women have remained online.
When we set up Virtual Rounds at the Center for Women’s Mental Health at the beginning of the pandemic, I was struck by the community of colleagues at various stages of their careers dedicated to mitigating the suffering associated with perinatal psychiatric illness. As I’ve often said, it takes a village to care for these patients. We need help from colleagues with varying expertise — from lactation consultants, psychiatrists, psychologists, obstetricians, nurse practitioners, support group leaders, and a host of others — who can help reach these women.
At the end of the day, helping depressed women find resources is a challenge that we have not met in this country. We should be excited that we have so many treatment options to offer patients — whether it be a new first-in-class medication, TMS, or digital apps to ensure patients are receiving effective treatment. But there should also be a focus on reaching women who still need treatment, particularly in underserved communities where resources are sparse or nonexistent. Identifying the path to reaching these women where they are and getting them well should be a top priority in 2024.
Dr. Cohen is the director of the Ammon-Pinizzotto Center for Women’s Mental Health at Massachusetts General Hospital (MGH) in Boston, which provides information resources and conducts clinical care and research in reproductive mental health. He has been a consultant to manufacturers of psychiatric medications. STEPS for PPD is funded by the Marriott Foundation. Full disclosure information for Dr. Cohen is available at womensmentalhealth.org. Email Dr. Cohen at [email protected].
The past year has been a challenging time for many, both at the local level and globally, with divisive undercurrents across many communities. Many times, the end of the year is an opportunity for reflection. As I reflect on the state of perinatal psychiatry in the new year, I see several evolving issues that I’d like to share in this first column of 2024.
In 2023, the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists published new recommendations meant to enhance the well-being of pregnant and postpartum women and families. A main message from discussion papers borne out of these recommendations was that as a field, we should be doing more than identifying perinatal illness. We should be screening women at risk for postpartum psychiatric illness and see that those suffering from posttraumatic stress disorder (PTSD) have access to care and “wrap-around services” from clinicians with varying expertise.
Screening is a primary way we identify patients at risk for psychiatric illness and also those who are suffering at the time of a screen. One problem I see in the near future is our disparate collection and management of data. When we look closely across health care systems, it’s not clear how screening data are captured, let alone managed. What is being done in one hospital system may be very different from what is being done elsewhere. Some clinicians are adopting digital platforms to identify those with postpartum depression, while others are practicing as they always have, either through a paper screening process or with queries as part of a clinical encounter.
Given this amalgam of methods for collecting and storing information, there does not appear to be a systematic way clinicians and researchers are recording whether women are meeting criteria for significant depressive symptoms or frank postpartum psychiatric illness. It is clear a more cohesive method for collection and management is needed to optimize the likelihood that next steps can be taken to get patients the care they need.
However, screening is only one part of the story. Certainly, in our own center, one of our greatest interests, both clinically and on the research side, is what happens after screening. Through our center’s initiation of the Screening and Treatment Enhancement for Postpartum Depression (STEPS for PPD) project funded by the Marriott Foundation, we are evaluating the outcomes of women who are screened at 6 weeks postpartum with significant depressive symptoms, and who are then given an opportunity to engage with a perinatal social worker who can assist with direct psychotherapy, arranging for referrals, and navigating care for a new mother.
What we are learning as we enroll women through the initial stages of STEPS for PPD is that screening and identifying women who likely suffer from PPD simply is not enough. In fact, once identified with a depression screening tool, women who are suffering from postpartum depression can be very challenging to engage clinically. What I am learning decades after starting to work with perinatal patients is that even with a screening system and effective tools for treatment of PPD, optimizing engagement with these depressed women seems a critical and understudied step on the road to optimizing positive clinical outcomes.
A recent study published in the Journal of Women’s Health explored gaps in care for perinatal depression and found that patients without a history of psychiatric illness prior to pregnancy were less likely to be screened for depression and 80% less likely to receive care if they developed depression compared with women with a previous history of psychiatric illness (J Womens Health (Larchmt). 2023 Oct;32[10]:1111-9).
That history may help women navigate to care, while women for whom psychiatric illness is a new experience may be less likely to engage, be referred for care, and receive appropriate treatment. The study indicates that, as a field, we must strive to ensure universal screening for depression in perinatal populations.
While we have always been particularly interested in populations of patients at highest risk for PPD, helping women at risk for PPD in the general population without a history of psychiatric illness is a large public health issue and will be an even larger undertaking. As women’s mental health is gaining more appropriate focus, both at the local level and even in the recent White House Initiative on Women’s Health Research, the focus has been on screening and developing new treatments.
We are not lacking in pharmacologic agents nor nonpharmacologic options as treatments for women experiencing PPD. Newer alternative treatments are being explored, such as transcranial magnetic stimulation (TMS) and even psychedelics as a potential therapy for PPD. But perhaps what we’ve learned in 2023 and as we move into a new year, is that the problem of tackling PPD is not only about having the right tools, but is about helping women navigate to the care that they need.
The COVID-19 pandemic brought with it an explosion of telehealth options that have enhanced the odds women can find support during such a challenging time; as society has returned to some semblance of normal, nearly all support groups for postpartum women have remained online.
When we set up Virtual Rounds at the Center for Women’s Mental Health at the beginning of the pandemic, I was struck by the community of colleagues at various stages of their careers dedicated to mitigating the suffering associated with perinatal psychiatric illness. As I’ve often said, it takes a village to care for these patients. We need help from colleagues with varying expertise — from lactation consultants, psychiatrists, psychologists, obstetricians, nurse practitioners, support group leaders, and a host of others — who can help reach these women.
At the end of the day, helping depressed women find resources is a challenge that we have not met in this country. We should be excited that we have so many treatment options to offer patients — whether it be a new first-in-class medication, TMS, or digital apps to ensure patients are receiving effective treatment. But there should also be a focus on reaching women who still need treatment, particularly in underserved communities where resources are sparse or nonexistent. Identifying the path to reaching these women where they are and getting them well should be a top priority in 2024.
Dr. Cohen is the director of the Ammon-Pinizzotto Center for Women’s Mental Health at Massachusetts General Hospital (MGH) in Boston, which provides information resources and conducts clinical care and research in reproductive mental health. He has been a consultant to manufacturers of psychiatric medications. STEPS for PPD is funded by the Marriott Foundation. Full disclosure information for Dr. Cohen is available at womensmentalhealth.org. Email Dr. Cohen at [email protected].
The past year has been a challenging time for many, both at the local level and globally, with divisive undercurrents across many communities. Many times, the end of the year is an opportunity for reflection. As I reflect on the state of perinatal psychiatry in the new year, I see several evolving issues that I’d like to share in this first column of 2024.
In 2023, the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists published new recommendations meant to enhance the well-being of pregnant and postpartum women and families. A main message from discussion papers borne out of these recommendations was that as a field, we should be doing more than identifying perinatal illness. We should be screening women at risk for postpartum psychiatric illness and see that those suffering from posttraumatic stress disorder (PTSD) have access to care and “wrap-around services” from clinicians with varying expertise.
Screening is a primary way we identify patients at risk for psychiatric illness and also those who are suffering at the time of a screen. One problem I see in the near future is our disparate collection and management of data. When we look closely across health care systems, it’s not clear how screening data are captured, let alone managed. What is being done in one hospital system may be very different from what is being done elsewhere. Some clinicians are adopting digital platforms to identify those with postpartum depression, while others are practicing as they always have, either through a paper screening process or with queries as part of a clinical encounter.
Given this amalgam of methods for collecting and storing information, there does not appear to be a systematic way clinicians and researchers are recording whether women are meeting criteria for significant depressive symptoms or frank postpartum psychiatric illness. It is clear a more cohesive method for collection and management is needed to optimize the likelihood that next steps can be taken to get patients the care they need.
However, screening is only one part of the story. Certainly, in our own center, one of our greatest interests, both clinically and on the research side, is what happens after screening. Through our center’s initiation of the Screening and Treatment Enhancement for Postpartum Depression (STEPS for PPD) project funded by the Marriott Foundation, we are evaluating the outcomes of women who are screened at 6 weeks postpartum with significant depressive symptoms, and who are then given an opportunity to engage with a perinatal social worker who can assist with direct psychotherapy, arranging for referrals, and navigating care for a new mother.
What we are learning as we enroll women through the initial stages of STEPS for PPD is that screening and identifying women who likely suffer from PPD simply is not enough. In fact, once identified with a depression screening tool, women who are suffering from postpartum depression can be very challenging to engage clinically. What I am learning decades after starting to work with perinatal patients is that even with a screening system and effective tools for treatment of PPD, optimizing engagement with these depressed women seems a critical and understudied step on the road to optimizing positive clinical outcomes.
A recent study published in the Journal of Women’s Health explored gaps in care for perinatal depression and found that patients without a history of psychiatric illness prior to pregnancy were less likely to be screened for depression and 80% less likely to receive care if they developed depression compared with women with a previous history of psychiatric illness (J Womens Health (Larchmt). 2023 Oct;32[10]:1111-9).
That history may help women navigate to care, while women for whom psychiatric illness is a new experience may be less likely to engage, be referred for care, and receive appropriate treatment. The study indicates that, as a field, we must strive to ensure universal screening for depression in perinatal populations.
While we have always been particularly interested in populations of patients at highest risk for PPD, helping women at risk for PPD in the general population without a history of psychiatric illness is a large public health issue and will be an even larger undertaking. As women’s mental health is gaining more appropriate focus, both at the local level and even in the recent White House Initiative on Women’s Health Research, the focus has been on screening and developing new treatments.
We are not lacking in pharmacologic agents nor nonpharmacologic options as treatments for women experiencing PPD. Newer alternative treatments are being explored, such as transcranial magnetic stimulation (TMS) and even psychedelics as a potential therapy for PPD. But perhaps what we’ve learned in 2023 and as we move into a new year, is that the problem of tackling PPD is not only about having the right tools, but is about helping women navigate to the care that they need.
The COVID-19 pandemic brought with it an explosion of telehealth options that have enhanced the odds women can find support during such a challenging time; as society has returned to some semblance of normal, nearly all support groups for postpartum women have remained online.
When we set up Virtual Rounds at the Center for Women’s Mental Health at the beginning of the pandemic, I was struck by the community of colleagues at various stages of their careers dedicated to mitigating the suffering associated with perinatal psychiatric illness. As I’ve often said, it takes a village to care for these patients. We need help from colleagues with varying expertise — from lactation consultants, psychiatrists, psychologists, obstetricians, nurse practitioners, support group leaders, and a host of others — who can help reach these women.
At the end of the day, helping depressed women find resources is a challenge that we have not met in this country. We should be excited that we have so many treatment options to offer patients — whether it be a new first-in-class medication, TMS, or digital apps to ensure patients are receiving effective treatment. But there should also be a focus on reaching women who still need treatment, particularly in underserved communities where resources are sparse or nonexistent. Identifying the path to reaching these women where they are and getting them well should be a top priority in 2024.
Dr. Cohen is the director of the Ammon-Pinizzotto Center for Women’s Mental Health at Massachusetts General Hospital (MGH) in Boston, which provides information resources and conducts clinical care and research in reproductive mental health. He has been a consultant to manufacturers of psychiatric medications. STEPS for PPD is funded by the Marriott Foundation. Full disclosure information for Dr. Cohen is available at womensmentalhealth.org. Email Dr. Cohen at [email protected].
Nasal Tanning Sprays: Illuminating the Risks of a Popular TikTok Trend
Nasal tanning spray is a recent phenomenon that has been gaining popularity among consumers on TikTok and other social media platforms. The active ingredient in the tanning spray is melanotan II—a synthetic analog of α‒melanocyte-stimulating hormone,1,2 a naturally occurring hormone responsible for skin pigmentation. α‒Melanocyte-stimulating hormone is a derivative of the precursor proopiomelanocortin, an agonist on the melanocortin-1 receptor that promotes formation of eumelanin.1,3 Eumelanin then provides pigmentation to the skin.3 Apart from its use for tanning, melanotan II has been reported to increase sexual function and aid in weight loss.1
Melanotan II is not approved by the US Food and Drug Administration; however, injectable formulations can be obtained illegally on the Internet as well as at some tanning salons and beauty parlors.4 Although injectable forms of melanotan II have been used for years to artificially increase skin pigmentation, the newly hyped nasal tanning sprays are drawing the attention of consumers. The synthetic chemical spray is inhaled into the nasal mucosae, where it is readily absorbed into the bloodstream to act on melanocortin receptors throughout the body, thus enhancing skin pigmentation.2 Because melanotan II is not approved, there is no guarantee that the product purchased from those sources is pure; therefore, consumers risk inhaling or injecting contaminated chemicals.5
In a 2017 study, Kirk and Greenfield6 cited self-image as a common concern among participants who expressed a preference for appearing tanned.6 Societal influence and standards to which young adults, particularly young women, often are accustomed drive some to take steps to achieve tanned skin, which they view as more attractive and healthier than untanned skin.7,8
Social media consumption is a significant risk factor for developing or exacerbating body dissatisfaction among impressionable teenagers and young adults, who may be less risk averse and therefore choose to embrace trends such as nasal tanning sprays to enhance their appearance, without considering possible consequences. Most young adults, and even teens, are aware of the risks associated with tanning beds, which may propel them to seek out what they perceive as a less-risky tanning alternative such as a tanner delivered via a nasal route, but it is unlikely that this group is fully informed about the possible dangers of nasal tanning sprays.
It is crucial for dermatologists and other clinicians to provide awareness and education about the potential harm of nasal tanning sprays. Along with the general risks of using an unregulated substance, common adverse effects include acne, facial flushing, gastrointestinal tract upset, and sensitivity to sunlight (Table).1,9,10 Several case reports have linked melanotan II to cutaneous changes, including dysplastic nevi and even melanoma.1 Less common complications, such as renal infarction and priapism, also have been observed with melanotan II use.9,10
Even with the known risks involving tanning beds and skin cancer, an analysis by Kream et al11 in 2020 showed that 90% (441/488) of tanning-related videos on TikTok promoted a positive view of tanning. Of these TikTok videos involving pro-tanning trends, 3% (12/441) were specifically about melanotan II nasal spray, injection, or both, which has only become more popular since this study was published.11
Dermatologists should be aware of the impact that tanning trends, such as nasal tanning spray, can have on all patients and initiate discussions regarding the risks of using these products with patients as appropriate. Alternatives to nasal tanning sprays such as spray-on tans and self-tanning lotions are safer ways for patients to achieve a tanned look without the health risks associated with melanotan II.
- Habbema L, Halk AB, Neumann M, et al. Risks of unregulated use of alpha-melanocyte-stimulating hormone analogues: a review. Int J Dermatol. 2017;56:975-980. doi:10.1111/ijd.13585
- Why you should never use nasal tanning spray. Cleveland Clinic Health Essentials [Internet]. November 1, 2022. Accessed December 18, 2023. https://health.clevelandclinic.org/nasal-tanning-spray
- Hjuler KF, Lorentzen HF. Melanoma associated with the use of melanotan-II. Dermatology. 2014;228:34-36. doi:10.1159/000356389
- Evans-Brown M, Dawson RT, Chandler M, et al. Use of melanotan I and II in the general population. BMJ. 2009;338:b566. doi:10.116/bmj.b566
- Callaghan DJ III. A glimpse into the underground market of melanotan. Dermatol Online J. 2018;24:1-5. doi:10.5070/D3245040036
- Kirk L, Greenfield S. Knowledge and attitudes of UK university students in relation to ultraviolet radiation (UVR) exposure and their sun-related behaviours: a qualitative study. BMJ Open. 2017;7:e014388. doi:10.1136/bmjopen-2016-014388
- Hay JL, Geller AC, Schoenhammer M, et al. Tanning and beauty: mother and teenage daughters in discussion. J Health Psychol. 2016;21:1261-1270. doi:10.1177/1359105314551621
- Gillen MM, Markey CN. The role of body image and depression in tanning behaviors and attitudes. Behav Med. 2017;38:74-82.
- Peters B, Hadimeri H, Wahlberg R, et al. Melanotan II: a possible cause of renal infarction: review of the literature and case report. CEN Case Rep. 2020;9:159-161. doi:10.1007/s13730-020-00447-z
- Mallory CW, Lopategui DM, Cordon BH. Melanotan tanning injection: a rare cause of priapism. Sex Med. 2021;9:100298. doi:10.1016/j.esxm.2020.100298
- Kream E, Watchmaker JD, Dover JS. TikTok sheds light on tanning: tanning is still popular and emerging trends pose new risks. Dermatol Surg. 2022;48:1018-1021. doi:10.1097/DSS.0000000000003549
Nasal tanning spray is a recent phenomenon that has been gaining popularity among consumers on TikTok and other social media platforms. The active ingredient in the tanning spray is melanotan II—a synthetic analog of α‒melanocyte-stimulating hormone,1,2 a naturally occurring hormone responsible for skin pigmentation. α‒Melanocyte-stimulating hormone is a derivative of the precursor proopiomelanocortin, an agonist on the melanocortin-1 receptor that promotes formation of eumelanin.1,3 Eumelanin then provides pigmentation to the skin.3 Apart from its use for tanning, melanotan II has been reported to increase sexual function and aid in weight loss.1
Melanotan II is not approved by the US Food and Drug Administration; however, injectable formulations can be obtained illegally on the Internet as well as at some tanning salons and beauty parlors.4 Although injectable forms of melanotan II have been used for years to artificially increase skin pigmentation, the newly hyped nasal tanning sprays are drawing the attention of consumers. The synthetic chemical spray is inhaled into the nasal mucosae, where it is readily absorbed into the bloodstream to act on melanocortin receptors throughout the body, thus enhancing skin pigmentation.2 Because melanotan II is not approved, there is no guarantee that the product purchased from those sources is pure; therefore, consumers risk inhaling or injecting contaminated chemicals.5
In a 2017 study, Kirk and Greenfield6 cited self-image as a common concern among participants who expressed a preference for appearing tanned.6 Societal influence and standards to which young adults, particularly young women, often are accustomed drive some to take steps to achieve tanned skin, which they view as more attractive and healthier than untanned skin.7,8
Social media consumption is a significant risk factor for developing or exacerbating body dissatisfaction among impressionable teenagers and young adults, who may be less risk averse and therefore choose to embrace trends such as nasal tanning sprays to enhance their appearance, without considering possible consequences. Most young adults, and even teens, are aware of the risks associated with tanning beds, which may propel them to seek out what they perceive as a less-risky tanning alternative such as a tanner delivered via a nasal route, but it is unlikely that this group is fully informed about the possible dangers of nasal tanning sprays.
It is crucial for dermatologists and other clinicians to provide awareness and education about the potential harm of nasal tanning sprays. Along with the general risks of using an unregulated substance, common adverse effects include acne, facial flushing, gastrointestinal tract upset, and sensitivity to sunlight (Table).1,9,10 Several case reports have linked melanotan II to cutaneous changes, including dysplastic nevi and even melanoma.1 Less common complications, such as renal infarction and priapism, also have been observed with melanotan II use.9,10

Even with the known risks involving tanning beds and skin cancer, an analysis by Kream et al11 in 2020 showed that 90% (441/488) of tanning-related videos on TikTok promoted a positive view of tanning. Of these TikTok videos involving pro-tanning trends, 3% (12/441) were specifically about melanotan II nasal spray, injection, or both, which has only become more popular since this study was published.11
Dermatologists should be aware of the impact that tanning trends, such as nasal tanning spray, can have on all patients and initiate discussions regarding the risks of using these products with patients as appropriate. Alternatives to nasal tanning sprays such as spray-on tans and self-tanning lotions are safer ways for patients to achieve a tanned look without the health risks associated with melanotan II.
Nasal tanning spray is a recent phenomenon that has been gaining popularity among consumers on TikTok and other social media platforms. The active ingredient in the tanning spray is melanotan II—a synthetic analog of α‒melanocyte-stimulating hormone,1,2 a naturally occurring hormone responsible for skin pigmentation. α‒Melanocyte-stimulating hormone is a derivative of the precursor proopiomelanocortin, an agonist on the melanocortin-1 receptor that promotes formation of eumelanin.1,3 Eumelanin then provides pigmentation to the skin.3 Apart from its use for tanning, melanotan II has been reported to increase sexual function and aid in weight loss.1
Melanotan II is not approved by the US Food and Drug Administration; however, injectable formulations can be obtained illegally on the Internet as well as at some tanning salons and beauty parlors.4 Although injectable forms of melanotan II have been used for years to artificially increase skin pigmentation, the newly hyped nasal tanning sprays are drawing the attention of consumers. The synthetic chemical spray is inhaled into the nasal mucosae, where it is readily absorbed into the bloodstream to act on melanocortin receptors throughout the body, thus enhancing skin pigmentation.2 Because melanotan II is not approved, there is no guarantee that the product purchased from those sources is pure; therefore, consumers risk inhaling or injecting contaminated chemicals.5
In a 2017 study, Kirk and Greenfield6 cited self-image as a common concern among participants who expressed a preference for appearing tanned.6 Societal influence and standards to which young adults, particularly young women, often are accustomed drive some to take steps to achieve tanned skin, which they view as more attractive and healthier than untanned skin.7,8
Social media consumption is a significant risk factor for developing or exacerbating body dissatisfaction among impressionable teenagers and young adults, who may be less risk averse and therefore choose to embrace trends such as nasal tanning sprays to enhance their appearance, without considering possible consequences. Most young adults, and even teens, are aware of the risks associated with tanning beds, which may propel them to seek out what they perceive as a less-risky tanning alternative such as a tanner delivered via a nasal route, but it is unlikely that this group is fully informed about the possible dangers of nasal tanning sprays.
It is crucial for dermatologists and other clinicians to provide awareness and education about the potential harm of nasal tanning sprays. Along with the general risks of using an unregulated substance, common adverse effects include acne, facial flushing, gastrointestinal tract upset, and sensitivity to sunlight (Table).1,9,10 Several case reports have linked melanotan II to cutaneous changes, including dysplastic nevi and even melanoma.1 Less common complications, such as renal infarction and priapism, also have been observed with melanotan II use.9,10

Even with the known risks involving tanning beds and skin cancer, an analysis by Kream et al11 in 2020 showed that 90% (441/488) of tanning-related videos on TikTok promoted a positive view of tanning. Of these TikTok videos involving pro-tanning trends, 3% (12/441) were specifically about melanotan II nasal spray, injection, or both, which has only become more popular since this study was published.11
Dermatologists should be aware of the impact that tanning trends, such as nasal tanning spray, can have on all patients and initiate discussions regarding the risks of using these products with patients as appropriate. Alternatives to nasal tanning sprays such as spray-on tans and self-tanning lotions are safer ways for patients to achieve a tanned look without the health risks associated with melanotan II.
- Habbema L, Halk AB, Neumann M, et al. Risks of unregulated use of alpha-melanocyte-stimulating hormone analogues: a review. Int J Dermatol. 2017;56:975-980. doi:10.1111/ijd.13585
- Why you should never use nasal tanning spray. Cleveland Clinic Health Essentials [Internet]. November 1, 2022. Accessed December 18, 2023. https://health.clevelandclinic.org/nasal-tanning-spray
- Hjuler KF, Lorentzen HF. Melanoma associated with the use of melanotan-II. Dermatology. 2014;228:34-36. doi:10.1159/000356389
- Evans-Brown M, Dawson RT, Chandler M, et al. Use of melanotan I and II in the general population. BMJ. 2009;338:b566. doi:10.116/bmj.b566
- Callaghan DJ III. A glimpse into the underground market of melanotan. Dermatol Online J. 2018;24:1-5. doi:10.5070/D3245040036
- Kirk L, Greenfield S. Knowledge and attitudes of UK university students in relation to ultraviolet radiation (UVR) exposure and their sun-related behaviours: a qualitative study. BMJ Open. 2017;7:e014388. doi:10.1136/bmjopen-2016-014388
- Hay JL, Geller AC, Schoenhammer M, et al. Tanning and beauty: mother and teenage daughters in discussion. J Health Psychol. 2016;21:1261-1270. doi:10.1177/1359105314551621
- Gillen MM, Markey CN. The role of body image and depression in tanning behaviors and attitudes. Behav Med. 2017;38:74-82.
- Peters B, Hadimeri H, Wahlberg R, et al. Melanotan II: a possible cause of renal infarction: review of the literature and case report. CEN Case Rep. 2020;9:159-161. doi:10.1007/s13730-020-00447-z
- Mallory CW, Lopategui DM, Cordon BH. Melanotan tanning injection: a rare cause of priapism. Sex Med. 2021;9:100298. doi:10.1016/j.esxm.2020.100298
- Kream E, Watchmaker JD, Dover JS. TikTok sheds light on tanning: tanning is still popular and emerging trends pose new risks. Dermatol Surg. 2022;48:1018-1021. doi:10.1097/DSS.0000000000003549
- Habbema L, Halk AB, Neumann M, et al. Risks of unregulated use of alpha-melanocyte-stimulating hormone analogues: a review. Int J Dermatol. 2017;56:975-980. doi:10.1111/ijd.13585
- Why you should never use nasal tanning spray. Cleveland Clinic Health Essentials [Internet]. November 1, 2022. Accessed December 18, 2023. https://health.clevelandclinic.org/nasal-tanning-spray
- Hjuler KF, Lorentzen HF. Melanoma associated with the use of melanotan-II. Dermatology. 2014;228:34-36. doi:10.1159/000356389
- Evans-Brown M, Dawson RT, Chandler M, et al. Use of melanotan I and II in the general population. BMJ. 2009;338:b566. doi:10.116/bmj.b566
- Callaghan DJ III. A glimpse into the underground market of melanotan. Dermatol Online J. 2018;24:1-5. doi:10.5070/D3245040036
- Kirk L, Greenfield S. Knowledge and attitudes of UK university students in relation to ultraviolet radiation (UVR) exposure and their sun-related behaviours: a qualitative study. BMJ Open. 2017;7:e014388. doi:10.1136/bmjopen-2016-014388
- Hay JL, Geller AC, Schoenhammer M, et al. Tanning and beauty: mother and teenage daughters in discussion. J Health Psychol. 2016;21:1261-1270. doi:10.1177/1359105314551621
- Gillen MM, Markey CN. The role of body image and depression in tanning behaviors and attitudes. Behav Med. 2017;38:74-82.
- Peters B, Hadimeri H, Wahlberg R, et al. Melanotan II: a possible cause of renal infarction: review of the literature and case report. CEN Case Rep. 2020;9:159-161. doi:10.1007/s13730-020-00447-z
- Mallory CW, Lopategui DM, Cordon BH. Melanotan tanning injection: a rare cause of priapism. Sex Med. 2021;9:100298. doi:10.1016/j.esxm.2020.100298
- Kream E, Watchmaker JD, Dover JS. TikTok sheds light on tanning: tanning is still popular and emerging trends pose new risks. Dermatol Surg. 2022;48:1018-1021. doi:10.1097/DSS.0000000000003549
PRACTICE POINTS
- Although tanning beds are arguably the most common and dangerous method used by patients to tan their skin, dermatologists should be aware of the other means by which patients may artificially increase skin pigmentation and the risks imposed by undertaking such practices.
- We challenge dermatologists to note the influence of social media on tanning trends and consider creating a platform on these mediums to combat misinformation and promote sun safety and skin health.
- We encourage dermatologists to diligently stay informed about the popular societal trends related to the skin such as the use of nasal tanning products (eg, melanotan I and II) and be proactive in discussing their risks with patients as deemed appropriate.