User login
Domperidone appears safe galactagogue for mothers and infants
Denver – Prescribing domperidone to support breastfeeding effectively reduced the use of infant formula without significant adverse effects in mothers and infants in a large retrospective study, Mitko Madjunkov, MD, reported at the annual meeting of the Teratology Society.
His study included 985 mothers who began taking domperidone to initiate and support breastfeeding after a visit to the International Breastfeeding Centre in Toronto. Collectively, the women had 1,005 infants.
The study was undertaken because few data exist on the dosing and safety of domperidone during lactation. Additionally, the Food and Drug Administration issued a warning in 2004 regarding the use of domperidone as a galactagogue in response to reports of cardiac arrhythmias and sudden deaths when the drug was prescribed as an antiemetic, explained Dr. Madjunkov of the Hospital for Sick Children in Toronto.
The FDA has not approved domperidone for any indication in the United States, though it is available in Canada and other countries.
Domperidone was used by the Toronto women for a median of 20 days. The maximum daily dose was 107 mg. The infants were an average of 38 days old at the time of the visit when domperidone was prescribed and 72 days of age at their last follow-up visit related to the study.
The drug was effective as a galactagogue: 63% of women were using infant formula before going on domperidone; after using the drug, 41% were still using formula, for an absolute 22% reduction. The drug was similarly effective in promoting breastfeeding in infants with or without tongue-tie/lip-tie defects.
In total, 18% of mothers reported minor side effects. Headaches were the most common, reported by 9.2% of domperidone users. Dose reduction was employed in just 0.6% of women in the study; 0.4% of participants discontinued treatment. Rapid heart rate and other minor cardiac side effects were reported by 0.7% of women, uniformly in conjunction with trigger factors such as anxiety or caffeine use, but none of these women discontinued treatment. No treatment-associated adverse effects occurred in the infants.
Dr. Madjunkov reported having no financial conflicts related to his study.
Denver – Prescribing domperidone to support breastfeeding effectively reduced the use of infant formula without significant adverse effects in mothers and infants in a large retrospective study, Mitko Madjunkov, MD, reported at the annual meeting of the Teratology Society.
His study included 985 mothers who began taking domperidone to initiate and support breastfeeding after a visit to the International Breastfeeding Centre in Toronto. Collectively, the women had 1,005 infants.
The study was undertaken because few data exist on the dosing and safety of domperidone during lactation. Additionally, the Food and Drug Administration issued a warning in 2004 regarding the use of domperidone as a galactagogue in response to reports of cardiac arrhythmias and sudden deaths when the drug was prescribed as an antiemetic, explained Dr. Madjunkov of the Hospital for Sick Children in Toronto.
The FDA has not approved domperidone for any indication in the United States, though it is available in Canada and other countries.
Domperidone was used by the Toronto women for a median of 20 days. The maximum daily dose was 107 mg. The infants were an average of 38 days old at the time of the visit when domperidone was prescribed and 72 days of age at their last follow-up visit related to the study.
The drug was effective as a galactagogue: 63% of women were using infant formula before going on domperidone; after using the drug, 41% were still using formula, for an absolute 22% reduction. The drug was similarly effective in promoting breastfeeding in infants with or without tongue-tie/lip-tie defects.
In total, 18% of mothers reported minor side effects. Headaches were the most common, reported by 9.2% of domperidone users. Dose reduction was employed in just 0.6% of women in the study; 0.4% of participants discontinued treatment. Rapid heart rate and other minor cardiac side effects were reported by 0.7% of women, uniformly in conjunction with trigger factors such as anxiety or caffeine use, but none of these women discontinued treatment. No treatment-associated adverse effects occurred in the infants.
Dr. Madjunkov reported having no financial conflicts related to his study.
Denver – Prescribing domperidone to support breastfeeding effectively reduced the use of infant formula without significant adverse effects in mothers and infants in a large retrospective study, Mitko Madjunkov, MD, reported at the annual meeting of the Teratology Society.
His study included 985 mothers who began taking domperidone to initiate and support breastfeeding after a visit to the International Breastfeeding Centre in Toronto. Collectively, the women had 1,005 infants.
The study was undertaken because few data exist on the dosing and safety of domperidone during lactation. Additionally, the Food and Drug Administration issued a warning in 2004 regarding the use of domperidone as a galactagogue in response to reports of cardiac arrhythmias and sudden deaths when the drug was prescribed as an antiemetic, explained Dr. Madjunkov of the Hospital for Sick Children in Toronto.
The FDA has not approved domperidone for any indication in the United States, though it is available in Canada and other countries.
Domperidone was used by the Toronto women for a median of 20 days. The maximum daily dose was 107 mg. The infants were an average of 38 days old at the time of the visit when domperidone was prescribed and 72 days of age at their last follow-up visit related to the study.
The drug was effective as a galactagogue: 63% of women were using infant formula before going on domperidone; after using the drug, 41% were still using formula, for an absolute 22% reduction. The drug was similarly effective in promoting breastfeeding in infants with or without tongue-tie/lip-tie defects.
In total, 18% of mothers reported minor side effects. Headaches were the most common, reported by 9.2% of domperidone users. Dose reduction was employed in just 0.6% of women in the study; 0.4% of participants discontinued treatment. Rapid heart rate and other minor cardiac side effects were reported by 0.7% of women, uniformly in conjunction with trigger factors such as anxiety or caffeine use, but none of these women discontinued treatment. No treatment-associated adverse effects occurred in the infants.
Dr. Madjunkov reported having no financial conflicts related to his study.
EXPERT ANALYSIS FROM TERATOLOGY SOCIETY 2017
Key clinical point:
Major finding: The use of the domperidone reduced the proportion of women using infant formula by an absolute 22%.
Data source: A retrospective study of 985 women who were prescribed domperidone as a galactagogue at the International Breastfeeding Centre in Toronto.
Disclosures: Dr. Madjunkov reported having no financial conflicts of interest related to the study.
Development and Implementation of a Homeless Mobile Medical/Mental Veteran Intervention
Research has consistently identified remarkably high rates of addiction, mental illness, and health problems in the homeless population.1-9 Yet in spite of extensive service needs for these problems, abundant evidence exists of consistent underuse of health care services by homeless populations.10-12 Most of the homeless population reside in emergency shelters or in transitional or supportive housing, but many remain in places not meant for human habitation.
Homelessness is significantly overrepresented among military veterans.13 The January 2016 national point-in-time count identified 39,471 veterans experiencing homelessness.13 Iraq and Afghanistan veterans seem to have an especially high risk for homelessness.13-15 Disheartening statistics such as these prompted former VA Secretary Eric Shinseki to pledge to end veteran homelessness by December 2015.16 He argued in support of this mission that 85% of veteran homeless resources go to health care—implying that homelessness among veterans is primarily a health care issue, which is heavily burdened by substance abuse and other psychiatric and medical illnesses.17
Health care service use has been associated with improved health, mental health, and outcomes among homeless populations.12,18 Unfortunately, access to these services is limited by barriers associated with homelessness, such as transportation or lack of proper identification.19,20 Veterans experiencing homelessness also face these common barriers to health care, and unsheltered veterans especially underutilize VA health care services.21
Housing First—a successful model that places individuals into housing without prerequisites for sobriety, active participation in treatment, or other behavioral accomplishments, such as gainful employment—has not managed yet to place all the disengaged homeless veteran population into stable housing.22 However, the Housing First model, which is based on the individual’s priorities, is consistent with the approach of a new program at the VA North Texas Health Care System (VANTHCS).
The VHA, similar to other health care systems, is engaged in a cultural transformation to convert its health care approach from a traditional medical model to patient-centered care (PCC).23 In this priority area, a strategic objective is for the VHA to partner with each veteran to create a personalized, proactive strategy to optimize health and well-being and when needed provide state-of-the-art disease management. Patient-centered care is designed to address veterans’ specific needs in spiritual, environmental, physical, mental, and social domains and empower veterans to become active participants in their care. Patient-centered care differs from the traditional medical model in that patients are active participants in their treatment, partnering and collaborating with their providers on care that is quality-of-life centered instead of disease centered.23 This model is based on both respect for patients as unique individuals and on the obligation to care for them on their own terms, focused on their self-identified goals and aspirations.24
At VANTHCS, the Homeless Mobile Medical/Mental Veteran (HMMM-V) pilot program was designed to deliver effective health care services to a homeless subpopulation of veterans who historically have been the most difficult to serve—those living in unsheltered environments, such as under bridges and in encampments. The purpose of the HMMM-V program was to contact and serve veterans not currently being reached by the VA system of care, using a PCC model.
This pilot program was initially funded in January 2013 by a 2-year grant from the Office of Patient Centered Care and Cultural Transformation to apply the PCC approach to engage veteran participation. For this project, the VA Personal Health Inventory tool—originally designed for use with the general veteran population—was adapted for use with the homeless veteran population. The grant funding period covered the design, development, and implementation of the HMMM-V program; thereafter, VANTHCS provided resources through its Comprehensive Homeless Center Programs to assure its sustainability and continued use of the clinical assessment tool created for this project.
This article describes the development and implementation of this novel program with sufficient detail to inform the development of similar programs in other sites. Descriptions of the program and staffing, creation of community partnerships, and modification of an assessment instrument are provided. It also illustrates the original implementation period of the HMMM-V program through presentation of self-reported data on the first homeless veterans it served.
Equipment and Staffing
A custom 28-foot mobile outreach vehicle was assembled according to specifications identified by the HMMM-V team as necessary to conduct the program’s interventions. The van became fully operational on April 8, 2015, after it underwent all the required reviews and inspections (eg, safety, infection control, etc) and was accredited in 2015 by the Commission on Accreditation of Rehabilitation Facilities.
The HMMM-V van has a driver compartment that is separate from its services rooms, which include a patient registration area, a fully equipped examination room, a laboratory area, and a bathroom. The vehicle is equipped with a wheelchair lift and an awning to shade outdoor areas where tables and chairs are set up for patient/staff waiting and rest areas. The vehicle is stocked with essential equipment and supplies needed to conduct work in off-street locations, vacant lots, under bridges, fields, unpaved paths, etc. It also is equipped with telemedicine capabilities to provide clinical supervision and access to attending physicians and specialists at VANTHCS. Personnel carry cell phones and laptop computers with secure Internet connections using a commercially available mobile wireless Wi-Fi hotspot to facilitate documentation of medical records and communication from the field.
This reliable type of equipment is routine for use in VA field operations; the only hurdle using these technologies for the program was acquiring funding and purchasing the equipment. The vehicle is further equipped with a refrigerator solely for secure storage of pharmaceutical supplies, a second refrigerator for specimens, and wall-mounted blood pressure and otoscope/ophthalmoscope units. The vehicle is supplied with thermometers, scales, phlebotomy supplies, and first-aid kits and is stocked with vaccines and medications, including antibiotic, hypertensive, diabetic, allergy, and over-the-counter pain medications. A more comprehensive list of supplies for the vehicle is available from the authors on request.
Medication provisions supplied to the HMMM-V mobile clinic conform to the Texas State Board of Pharmacy compliance regulations. Because the vehicle is designated as federal property and has U.S. government license plates, it is considered an extension of VANTHCS Pharmacy Service and falls under its pharmacy license. A medication formulary was created with input from HMMM-V prescribers and Dallas VAMC Pharmacy Service pharmacists. To safeguard the integrity of these pharmaceutical agents, the HMMM-V physician assistant picks up the medications before field deployment and returns the unused medications to the Dallas VAMC at the end of the day. The medications are transported in locked containers and placed either in a locked medication refrigerator or cabinet on the mobile unit.
For medication prescriptions that need laboratory testing before prescribing them, HMMM-V prescribers can check the VA electronic medical record from the field to determine whether these tests have been completed recently. If not, then HMMM-V team has an agreement with Dallas VA Pathology and Laboratory Medicine Service for testing samples obtained in the field.
The program was designed for staffing of the vehicle by 2 professional teams, each includes medical (physician’s assistant or registered nurse), mental health (psychiatrist, residents), and social work providers (licensed social workers, clinical social workers); trainees of these disciplines; a peer support specialist; and an administrative clerk. The staffing varies daily, depending on available personnel. When personnel deploy to the field, they go in pairs or groups to address potential safety issues. Cell phones are available to summon police or ambulance services in an emergency. Systematic safety training was conducted with all field personnel before their first deployment to guard against vulnerability to danger in these settings.
Once in the field, personnel engage unsheltered homeless individuals to assess eligibility for VA services. Veterans found ineligible are assisted with application for military discharge upgrade, service-connected compensation, or appeal for health care coverage. Veterans eligible for VA care receive physical examinations, vital and glucose checks, influenza and pneumonia vaccinations, first-aid skin and wound care, medication management with limited medications provided at point of care, blood and urine testing, peer support services, suicide assessments, clinical mental health evaluations, and social work services through the HMMM-V program.
Social work assistance provided includes psychosocial assessment and care coordination for psychosocial needs such as mental health, substance abuse, vision, dental, housing, employment, legal aid, transportation, food, income, hygiene, and weather-appropriate provision needs.
Community Partnerships
The HMMM-V program benefitted from a number of partnerships with community agencies. During development of the program, HMMM-V personnel accompanied the Dallas Police Department’s Crisis Intervention Unit on typical homeless crisis services deployments into the field to learn about the locations and nature of encampments and homeless peregrination patterns in the Dallas area.
To aid in the design and selection of features for the mobile outreach vehicle, team members toured Homeless Outreach Medical Service mobile clinics from 2 local county hospitals, Parkland Hospital and John Peter Smith Hospital. The staff for these mobile clinics were interviewed about their experience with various components of their programs and their recommendations for optimal design of the mobile medical clinic for service delivery.
Numerous agencies in the Dallas area that serve the homeless population assisted with locating and connecting homeless veterans to HMMM-V programs. These partnering agencies also serve homeless individuals who do not qualify for the HMMM-V program, such as veterans with other-than-honorable military discharges.
The HMMM-V mobile outreach vehicle travels to partnering agencies and provides services on a recurring basis. These agencies are the Dallas International Street Church, a church and faith-based agency aiding the recovery of people with “broken lives”; Cornerstone Ministries, a church-based ministry serving people with adverse circumstances; and City Square’s Opportunity Center, human services and community development programs for low-income city residents. The mobile clinic also travels regularly to other areas to serve homeless veterans residing in unsheltered locations, such as homeless encampments and under bridges.
Clinical Assessment
The project used a modification of the VA Personalized Health Inventory (PHI) for general veteran populations, which assesses 8 areas of self-identified needs to address the specific concerns of homeless veterans served by a mobile clinic.25 Version 19 of the PHI (revised September 18, 2012), the version of the instrument available to the team at the inception of the project, was deployed with the HMMM-V personnel into the field. It imposed a heavy interview time burden (several hours), and its content areas did not seem appropriate to address the immediate concerns of homeless populations (eg, sections pertaining to personal development through hobbies, recreation, or volunteering; healthy living spaces with plenty of lighting and color; “eating healthy, balanced meals with plenty of fruits and vegetables each day”).25
Based on HMMM-V personnel feedback, the team modified this tool and developed a patient-centered health inventory (P-CHI) for homeless veterans that was acceptable in length and applicable to the situational characteristics of homeless existence. The tool’s 10 “current and desired states” were revised to remove domains of exercise and flexibility, sleep and relaxation, and mind-body techniques. The intervention and prevention domains were combined. A material needs (clothing, furniture, transportation, financial benefits) domain was added, and a new domain on reducing alcohol/drug use was created by moving this material from the food and drink domain.
The remaining domains were modified to fit the homeless living situation (Food and Drink = Nutrition; Personal Development = Employment/Vocation; Family, Friends, and Co-Workers = Family/Social/Legal Support; Spirit and Soul = Personal/Spiritual Fulfillment; Surroundings = Housing). Current state ratings were revised to reflect level of satisfaction, and ratings of Desired State were replaced with level of importance.
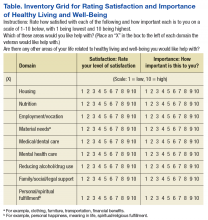
The modifications resulted in 9 domains, which were assembled into a grid for efficient rating of both satisfaction and importance for each domain (rated 1 to 10, lowest to highest, respectively), followed by an instruction to mark an X in a designated space in all the domains with which the individual would like help (Table). The intent was to reduce the burden of the instrument by having the participant complete sections providing detailed information about only the domains selected by the participant.
The details of each domain in the original VA PHI tool were captured through open-ended questions in text responses provided by the veteran. Because open-ended text responses are not conducive for summarizing characteristics of the population served or for evaluating program activities, the detailed sections covering the domains were revised completely to capture data within categoric and numeric variables. Items from the validated Homeless Supplement Interview were added to collect information not provided in the Homeless Operations Management and Evaluation System interview that is routinely administered to all veterans accessing homeless VA services.26-28
The information collected in these domains cover duration of current homeless episode, lifetime number of homeless episodes, current living arrangements and dissatisfactions with these arrangements, frequency and source of meals, employment history and current work status, sources of income, special material needs, medical and dental problems and sources of care, current medications, mental health problems and sources of care, urgent mental health concerns, current amount and frequency of alcohol and drug use, substance abuse treatment history, relationships with family and intimate partners, legal assistance needs, and self-identified needs for spiritual and personal fulfillment. This instrument is available on request to the authors.
Veterans Served
The project began with 1 team of professionals deploying with the HMMM-V vehicle while a second team was being assembled. Currently, the 2 HMMM-V teams deploy the mobile clinic 4 days per week. The mobile clinic visits agencies that serve the homeless, including emergency shelters and food ministries, as well as homeless encampments. To date, 195 homeless veterans have been served by the mobile clinic, 111 were currently enrolled with the VA, 8 were not enrolled but eligible for services, and 77 were not eligible for VA services. Of the unenrolled veterans, those eligible for services were offered VA enrollment assistance; those ineligible for VA services were offered a community referral.
For the veterans encountered in the field, the following interventions were provided: 49 housing placement referrals, 4 rental assistance referrals, 4 legal referrals, 27 medical care interventions, 13 dental referrals, 11 vision/hearing referrals, 12 mental health interventions, 9 substance abuse treatment referrals, 14 employment assistance referrals, 13 disability benefit applications, 18 transportation assists, 23 goods delivered, and 159 information assists. The HMMM-V mobile clinic also is deployed to participate in various educational and outreach events. At the time this article was written, the mobile clinic has reached nearly 2,000 veterans and community partners in at least 25 such events.
Of the veterans served to date, 73 completed the P-CHI. These veterans were predominantly male (77%), and the majority (60%) were black. The median age of the sample was 58 years, and typically they had a high school level of education (12.7; SD, 2.1 mean years of education). About half (49%) the sample were separated or divorced, and only a minority were currently married (8%). Half (50%) the sample served in the U.S. Army, with the post-Vietnam era being the era of service most represented (19%). Few (21%) veterans reported exposure to hostile or friendly fire during their service. More than three-fourths (80%) of the sample had experienced a homeless episode prior to their current one. On average, members of the sample had experienced a median of 3 lifetime homeless episodes. They had a mean 4.1 (SD, 5.8) lifetime number of years of homelessness, and 3.0 (SD, 5.2) years in their current homeless episode. Nearly one-third (31%) reported that they were currently staying in a homeless shelter, and nearly one-sixth (16%) were currently unsheltered in street settings, such as under bridges or in outdoor encampments at the time of the initial visit.
The mean number of minutes spent completing the P-CHI was 18.5 (SD, 9.4). The veterans indicated that they would like assistance with a mean 3.2 (SD, 2.2) number of domains. The domains with the highest average importance ratings were housing (mean, 9.4; SD, 1.7) and medical/dental care (mean, 8.9; SD, 2.2); the domains with the lowest average importance rating were reducing alcohol/drug use (mean, 6.4; SD, 4.1) and employment/vocation (mean, 6.3; SD, 4.2). The domains with the highest average satisfaction ratings were personal/spiritual fulfillment (mean, 7.3; SD, 2.9) and reducing substance use (mean, 5.9; SD, 4.0), and the domains with the lowest average satisfaction ratings were housing (mean, 2.9; SD, 2.9), material needs (mean, 4.2; SD, 3.3), and employment/vocation (mean, 4.2; SD, 3.2). The domain with the greatest indication of desire for help was housing, endorsed by more than four-fifths (84%) of the sample. This highly endorsed housing domain also was one of the lowest in satisfaction. The domains with the least expressed interest in obtaining help were reducing substance use (18%) and personal/spiritual fulfillment (15%).Reducing substance abuse also was one of the lowest domains of importance and the least for dissatisfaction.
Challenges and Barriers
As anticipated from its inception, this project encountered many challenges and barriers. The first was with the design, construction, and delivery of the mobile clinic unit. The vehicle took more than 2 years to be delivered. There were delays in progress necessitated by required selection of an approved vendor to build the vehicle, extensive specification of details and features, and stocking it with equipment and supplies. The weight of the unit had to be < 26,000 pounds to avoid the requirement of a commercial driver’s license, which limited the size of the vehicle to 28 feet. Stocking the unit with equipment and supplies required attention to a myriad of specifications and decisions. For example, separate refrigerators were needed for specimens, medications, and food; pharmaceutical regulations governing medications in mobile clinics required strict adherence; and difficulties were encountered in attempting to establish adequate and secure connectivity for communications devices in the field.
Once the mobile unit was delivered and prepared for deployment, the next set of challenges pertained to learning all of the instructions required to operate and drive the vehicle and learning how to maneuver the vehicle in the field. Specific challenges for driving the vehicle encountered included unexpectedly low overpasses that prohibited passage, narrow spaces for passage, rough and uneven terrain in off-road settings, and lateral and vertical tilt of roads creating potential for sideswipes and undercarriage scrapes. Maintenance schedules needed to be developed and implemented for cleaning the unit, inspection compliance, repairs, refueling, and emptying waste materials.
Staffing the vehicle required the development of unique job specifications addressing special expertise in accessing VA databases for veteran verification and registration and for driving the mobile clinic vehicle. Schedules and deployment plans for 2 teams that shared the same vehicle had to be established and followed. Locating veterans in unsheltered settings, such as under bridges and in encampments, required community intelligence facilitated through partnerships with knowledgeable members of the Dallas police crisis unit and by gaining field experience to locate where the usual homeless gathering places are, especially those inhabited by veterans. Safety of team members and equipment/supplies in the field was paramount from the start, and additional steps beyond safety training required extra measures, such as special care in navigating known dangerous areas. Provision of services necessitated completion of everything needed in a single visit due to the likelihood of loss to follow-up and acceptance of the limited types of service that could be provided in a mobile clinic. Special procedures were needed to provide referrals to sources of available care for non-VA-qualifying veterans.
Discussion
The HMMM-V program for delivery of PCC to homeless veterans is an innovative pilot program designed to connect with difficult-to-reach homeless veterans and engage them in care. The deliverables provided by this project are (1) A mobile outreach vehicle to deliver care to homeless veterans and outreach to other veterans and community agencies in North Texas; (2) The P-CHI assessment tool for homeless veterans modified and adapted for use with this special population; and (3) pilot data on its first cohort of homeless veterans served, describing their baseline characteristics and their stated satisfaction and preferences about their goals and aspirations for their physical, emotional, and mental health and well-being.
The HMMM-V program successfully identified homeless veterans in need of services, and more than one-third of these veterans were not previously engaged in VA services. Compared with the “typical” veterans served at VANTHCS homeless programs, veterans served by the HMMM-V comprised a greater proportion of minorities and a higher proportion who had been exposed to combat.29 Age and gender characteristics were similar.29 When compared with veterans who access care at VANTHCS and have not experienced homelessness, those served by the HMMM-V were younger and more likely to belong to a minority group; however, they were similar in combat exposure and gender.1 The veterans served by the HMMM-V program also were considerably older and had more homeless chronicity than did nonveteran homeless populations, consistent with other research.4,29,30
The veterans served by the HMMM-V program not surprisingly made housing their top priority in need of help, consistent with the Housing First model.22,31 They also indicated that employment/vocation and reducing substance use were of lower importance. Need for assistance with reducing substance use and social support were the domains least often identified as areas where help was needed, which seems inconsistent with the higher established rates of substance abuse problems among homeless veterans.1
With additional fieldwork, the HMMM-V program is expected to allow refinement of procedures for identifying and serving veterans from a patient-centered care perspective. The P-CHI will be further tested and developed, and the next step will be to create and pilot intervention templates for a Patient-Centered Health Improvement Plan, based on the P-CHI results. This process parallels the original development treatment plans for the VA’s Personalized Health Plan based on the PHI.25 Once the HMMM-V program is fully established in Dallas, the plans are for an expansion that will cover a broader geographic area in North Texas that includes rural areas.
The HMMM-V program was designed to address the barriers to health care that are encountered by homeless veterans. It is unique in homeless veteran care due to its patient-centered approach that partners with homeless veterans to prioritize their needs as determined by them rather than based solely on policies or provider conceptualizations of their needs. Access to services, engagement in care, and successful utilization of needed services may lead to measurable improvements in health care outcomes among homeless populations of veterans. Desired goals include remission of illness through appropriate medical intervention, preventing morbidity, achieving healthy lifestyles, recovery from addiction, stabilization of psychiatric illness, and attainment of stable housing.
The first hurdle for implementing this type of program in other settings is the identification of resources needed for these efforts. Need of additional staffing resources, however, may be circumvented by allowing employees working in other areas to rotate in community outreach shifts in the mobile unit. Another hurdle encountered in implementation of the HMMM-V initiative was the initial difficulty finding homeless veterans in community settings, especially those in unsheltered locations. The HMMM-V program addressed this issue by partnering with other agencies serving the homeless in the community. Therefore, a general recommendation for other entities seeking to implement this type of program is to reach out to these community partners from the outset.
Conclusion
The HMMM-V has the potential to engage the most difficult-to-reach homeless veterans in need of health services by delivering care and providing resources in challenging environments. Further work is needed to validate the P-CHI for use with this program and to conduct well-designed and implemented research to demonstrate effectiveness of this intervention on veteran outcomes, especially quality of life. Once this additional work is accomplished, this innovative program can potentially be implemented by VAMCs across the nation, and potentially in more general community care settings, to more effectively reach out and deliver services to homeless members of the community.
Acknowledgments
Grant support was received from the Department of Veterans Affairs, Office of Patient Centered Care. The authors would like to acknowledge all the clinicians, trainees, and support staff who have contributed to the success of the HMMM-V program: Tara Ayala, Jose Cabrera, Tony Castillo, Rachael Lynn David, Teresa DeShazo, Sylvia Figueroa, Steven Fisher, Eric Gary, Evelyn Gibbs, Kevin Hosey, JoAnn Joseph, Taly Drimer Kagan, Miranda Kelly, Michelle King-Thompson, Sharon Marcus, Shiji Mathew, Moneeza Matin, John Moreno, Joseph Neifert, Joel Price, Tiffany Price, Natalie Qualls, Reginald Robertson, Kristine Rodrigues, Jon Saffelder, Jill Stokes, Scott Stone, and John Smith.
1. LePage JP, Bradshaw LD, Cipher DJ, Crawford AM, Hooshyar D. The effects of homelessness on veterans’ health care service use: an evaluation of independence from comorbidities. Public Health. 2014;128(11):985-992.
2. Fischer PJ, Breakey WR. The epidemiology of alcohol, drug, and mental disorders among homeless persons. Am Psychol. 1991;46(11):1115-1128.
3. Robertson MJ, Zlotnick C, Westerfelt A. Drug use disorders and treatment contact among homeless adults in Alameda County, California. Am J Public Health. 1997;87(2):221-228.
4. North CS, Eyrich KM, Pollio DE, Spitznagel EL. Are rates of psychiatric disorders in the homeless population changing? Am J Public Health. 2004;94(1):103-108.
5. Fazel S, Khosla V, Doll H, Geddes J. The prevalence of mental disorders among the homeless in western countries: systematic review and meta-regression analysis. PLoS Med. 2008;5(12):e225.
6. Harpaz-Rotem I, Rosenheck RA, Desai R. The mental health of children exposed to maternal mental illness and homelessness. Community Ment Health J. 2006;42(5):437-448.
7. Pollio DE, Eyrich-Garg KM, North CS. The homeless. In: Johnson BA, ed. Addiction Medicine: Science and Practice. New York, NY: Springer; 2011:1487-1504.
8. Padgett D, Struening EL, Andrews H. Factors affecting the use of medical, mental health, alcohol, and drug treatment services by homeless adults. Med Care. 1990;28(9):805-821.
9. Baggett TP, Singer DE, Rao SR, O’Connell JJ, Bharel M, Rigotti NA. Food insufficiency and health services utilization in a national sample of homeless adults. J Gen Intern Med. 2011;26(6):627-634.
10. Folsom DP, Hawthorne W, Lindamer L, et al. Prevalence and risk factors for homelessness and utilization of mental health services among 10,340 patients with serious mental illness in a large public mental health system. Am J Psychiatry. 2005;162(2):370-376.
11. Fuehrlein BS, Cowell AJ, Pollio D, Cupps L, Balfour ME, North CS. A prospective study of the associations among housing status and costs of services in a homeless population. Psychiatr Serv. 2015;66(1):27-32.
12. Pollio DE, North CS, Eyrich KM, Foster DA, Spitznagel E. Modeling service access in a homeless population. J Psychoactive Drugs. 2003;35(4):487-495.
13. U.S. Department of Housing and Urban Development Office of Community Planning and Development. The 2016 Annual Homeless Assessment Report (AHAR) to Congress. Part 1: point-in-time estimates of homelessness. https://www.hudexchange.info/resources/documents/2016-AHAR-Part-1.pdf. Published 2016. Accessed August 7, 2017.
14. Tsai J, Rosenheck RA. Risk factors for homelessness among U.S. veterans. Epidemiol Rev. 2015;37:177-195.
15. Williamson V, Mulhall E. Coming home: the housing crisis and homelessness threaten new veterans. Iraq and Afghanistan Veterans of America, January, 2009. http://media.iava.org/IAVA_coming_home_2009%20The%20Housing%20Crisis%20and%20Homelessness%20Threaten%20New%20Veterans.pdf. Accessed August 10, 2017
16. Shinseki EK. Remarks by Secretary Eric K. Shinseki. National Summit on Homeless Veterans; November 3, 2009; Washington, DC. https://www.va.gov/opa/speeches/2009/09_1103.asp. Updated August 8, 2016. Accessed August 7, 2017.
17. Shinseki EK. Remarks by Secretary Eric K. Shinseki. 2014 National Coalition for Homeless Veterans Annual Meeting; May 30, 2014; Arlington, VA. https://www.va.gov/opa/speeches/2014/05_30_2014.asp. Updated April 21, 2015. Accessed August 7, 2017.
18. Pollio DE, Spitznagel EL, North CS, Thompson S, Foster DA. Service use over time and achievement of stable housing in a mentally ill homeless population. Psychiatr Serv. 2000;51(12):1536-1543.
19. Page J. Barriers to transferring care of homeless people with serious mental illnesses to community mental health organizations: perspectives of street-based programs. Best Practices in Mental Health: An International Journal. 2007;3(1):26.
20. Young AS, Chinman MJ, Cradock-O’Leary JA, et al. Characteristics of individuals with severe mental illness who use emergency services. Community Ment Health J. 2005;41(2):159-168.
21. Gabrielian S, Yuan AH, Andersen RM, Rubenstein LV, Gelberg L. VA health service utilization for homeless and low-income veterans: a spotlight on the VA Supportive Housing (VASH) program in greater Los Angeles. Med Care. 2014;52(5):454-461.
22. Tsemberis S, Gulcur L, Nakae M. Housing First, consumer choice, and harm reduction for homeless individuals with a dual diagnosis. Am J Public Health. 2004;94(4):651-656.
23. U.S. Department of Veterans Affairs, Veterans Health Administration. VA Patient Centered Care. http://www.va.gov/patientcenteredcare. Updated July 24,2017. Accessed August 7, 2017.
24. Epstein RM, Street RL Jr. The values and value of patient-centered care. Ann Fam Med. 2011;9(2):100-103.
25. U.S. Department of Veterans Affairs, Office of Patient Centered Care and Cultural Transformation. My story: personal health inventory. https://www.va.gov/PATIENTCENTEREDCARE/docs/VA-OPCC-Personal-Health-Inventory-final-508.pdf. Published October 7, 2013. Accessed August 7, 2017
26. North CS, Smith EM, Pollio DE. The Homeless Supplement to the Diagnostic Interview Schedule (DIS/HS). St. Louis: Washington University, 2004.
27. North CS, Eyrich KM, Pollio DE, Foster DA, Cottler LB, Spitznagel EL. The homeless supplement to the diagnostic interview schedule: test-retest analyses. Int J Methods Psychiatr Res. 2004;13(3):184-191.
28. LaSalle JL. Homeless Operations Management and Evaluation System (HOMES) user manual-phase 1. http://www.vfwsc.org/homes.pdf. Published April 19, 2011. Accessed August 7, 2017.
29. Petrovich JC, Pollio DE, North CS. Characteristics and service use of homeless veterans and nonveterans residing in a low-demand emergency shelter. Psychiatr Serv. 2014;65(6):751-757.
30. North CS, Smith EM. A comparison of homeless men and women: different populations, different needs. Community Ment Health J. 1993;29(5):423-431.
31. Kertesz SG, Austin EL, Holmes SK, et al. Making housing first happen: organizational leadership in VA’s expansion of permanent supportive housing. J Gen Intern Med. 2014;29(suppl 4):835-844.
Research has consistently identified remarkably high rates of addiction, mental illness, and health problems in the homeless population.1-9 Yet in spite of extensive service needs for these problems, abundant evidence exists of consistent underuse of health care services by homeless populations.10-12 Most of the homeless population reside in emergency shelters or in transitional or supportive housing, but many remain in places not meant for human habitation.
Homelessness is significantly overrepresented among military veterans.13 The January 2016 national point-in-time count identified 39,471 veterans experiencing homelessness.13 Iraq and Afghanistan veterans seem to have an especially high risk for homelessness.13-15 Disheartening statistics such as these prompted former VA Secretary Eric Shinseki to pledge to end veteran homelessness by December 2015.16 He argued in support of this mission that 85% of veteran homeless resources go to health care—implying that homelessness among veterans is primarily a health care issue, which is heavily burdened by substance abuse and other psychiatric and medical illnesses.17
Health care service use has been associated with improved health, mental health, and outcomes among homeless populations.12,18 Unfortunately, access to these services is limited by barriers associated with homelessness, such as transportation or lack of proper identification.19,20 Veterans experiencing homelessness also face these common barriers to health care, and unsheltered veterans especially underutilize VA health care services.21
Housing First—a successful model that places individuals into housing without prerequisites for sobriety, active participation in treatment, or other behavioral accomplishments, such as gainful employment—has not managed yet to place all the disengaged homeless veteran population into stable housing.22 However, the Housing First model, which is based on the individual’s priorities, is consistent with the approach of a new program at the VA North Texas Health Care System (VANTHCS).
The VHA, similar to other health care systems, is engaged in a cultural transformation to convert its health care approach from a traditional medical model to patient-centered care (PCC).23 In this priority area, a strategic objective is for the VHA to partner with each veteran to create a personalized, proactive strategy to optimize health and well-being and when needed provide state-of-the-art disease management. Patient-centered care is designed to address veterans’ specific needs in spiritual, environmental, physical, mental, and social domains and empower veterans to become active participants in their care. Patient-centered care differs from the traditional medical model in that patients are active participants in their treatment, partnering and collaborating with their providers on care that is quality-of-life centered instead of disease centered.23 This model is based on both respect for patients as unique individuals and on the obligation to care for them on their own terms, focused on their self-identified goals and aspirations.24
At VANTHCS, the Homeless Mobile Medical/Mental Veteran (HMMM-V) pilot program was designed to deliver effective health care services to a homeless subpopulation of veterans who historically have been the most difficult to serve—those living in unsheltered environments, such as under bridges and in encampments. The purpose of the HMMM-V program was to contact and serve veterans not currently being reached by the VA system of care, using a PCC model.
This pilot program was initially funded in January 2013 by a 2-year grant from the Office of Patient Centered Care and Cultural Transformation to apply the PCC approach to engage veteran participation. For this project, the VA Personal Health Inventory tool—originally designed for use with the general veteran population—was adapted for use with the homeless veteran population. The grant funding period covered the design, development, and implementation of the HMMM-V program; thereafter, VANTHCS provided resources through its Comprehensive Homeless Center Programs to assure its sustainability and continued use of the clinical assessment tool created for this project.
This article describes the development and implementation of this novel program with sufficient detail to inform the development of similar programs in other sites. Descriptions of the program and staffing, creation of community partnerships, and modification of an assessment instrument are provided. It also illustrates the original implementation period of the HMMM-V program through presentation of self-reported data on the first homeless veterans it served.
Equipment and Staffing
A custom 28-foot mobile outreach vehicle was assembled according to specifications identified by the HMMM-V team as necessary to conduct the program’s interventions. The van became fully operational on April 8, 2015, after it underwent all the required reviews and inspections (eg, safety, infection control, etc) and was accredited in 2015 by the Commission on Accreditation of Rehabilitation Facilities.
The HMMM-V van has a driver compartment that is separate from its services rooms, which include a patient registration area, a fully equipped examination room, a laboratory area, and a bathroom. The vehicle is equipped with a wheelchair lift and an awning to shade outdoor areas where tables and chairs are set up for patient/staff waiting and rest areas. The vehicle is stocked with essential equipment and supplies needed to conduct work in off-street locations, vacant lots, under bridges, fields, unpaved paths, etc. It also is equipped with telemedicine capabilities to provide clinical supervision and access to attending physicians and specialists at VANTHCS. Personnel carry cell phones and laptop computers with secure Internet connections using a commercially available mobile wireless Wi-Fi hotspot to facilitate documentation of medical records and communication from the field.
This reliable type of equipment is routine for use in VA field operations; the only hurdle using these technologies for the program was acquiring funding and purchasing the equipment. The vehicle is further equipped with a refrigerator solely for secure storage of pharmaceutical supplies, a second refrigerator for specimens, and wall-mounted blood pressure and otoscope/ophthalmoscope units. The vehicle is supplied with thermometers, scales, phlebotomy supplies, and first-aid kits and is stocked with vaccines and medications, including antibiotic, hypertensive, diabetic, allergy, and over-the-counter pain medications. A more comprehensive list of supplies for the vehicle is available from the authors on request.
Medication provisions supplied to the HMMM-V mobile clinic conform to the Texas State Board of Pharmacy compliance regulations. Because the vehicle is designated as federal property and has U.S. government license plates, it is considered an extension of VANTHCS Pharmacy Service and falls under its pharmacy license. A medication formulary was created with input from HMMM-V prescribers and Dallas VAMC Pharmacy Service pharmacists. To safeguard the integrity of these pharmaceutical agents, the HMMM-V physician assistant picks up the medications before field deployment and returns the unused medications to the Dallas VAMC at the end of the day. The medications are transported in locked containers and placed either in a locked medication refrigerator or cabinet on the mobile unit.
For medication prescriptions that need laboratory testing before prescribing them, HMMM-V prescribers can check the VA electronic medical record from the field to determine whether these tests have been completed recently. If not, then HMMM-V team has an agreement with Dallas VA Pathology and Laboratory Medicine Service for testing samples obtained in the field.
The program was designed for staffing of the vehicle by 2 professional teams, each includes medical (physician’s assistant or registered nurse), mental health (psychiatrist, residents), and social work providers (licensed social workers, clinical social workers); trainees of these disciplines; a peer support specialist; and an administrative clerk. The staffing varies daily, depending on available personnel. When personnel deploy to the field, they go in pairs or groups to address potential safety issues. Cell phones are available to summon police or ambulance services in an emergency. Systematic safety training was conducted with all field personnel before their first deployment to guard against vulnerability to danger in these settings.
Once in the field, personnel engage unsheltered homeless individuals to assess eligibility for VA services. Veterans found ineligible are assisted with application for military discharge upgrade, service-connected compensation, or appeal for health care coverage. Veterans eligible for VA care receive physical examinations, vital and glucose checks, influenza and pneumonia vaccinations, first-aid skin and wound care, medication management with limited medications provided at point of care, blood and urine testing, peer support services, suicide assessments, clinical mental health evaluations, and social work services through the HMMM-V program.
Social work assistance provided includes psychosocial assessment and care coordination for psychosocial needs such as mental health, substance abuse, vision, dental, housing, employment, legal aid, transportation, food, income, hygiene, and weather-appropriate provision needs.
Community Partnerships
The HMMM-V program benefitted from a number of partnerships with community agencies. During development of the program, HMMM-V personnel accompanied the Dallas Police Department’s Crisis Intervention Unit on typical homeless crisis services deployments into the field to learn about the locations and nature of encampments and homeless peregrination patterns in the Dallas area.
To aid in the design and selection of features for the mobile outreach vehicle, team members toured Homeless Outreach Medical Service mobile clinics from 2 local county hospitals, Parkland Hospital and John Peter Smith Hospital. The staff for these mobile clinics were interviewed about their experience with various components of their programs and their recommendations for optimal design of the mobile medical clinic for service delivery.
Numerous agencies in the Dallas area that serve the homeless population assisted with locating and connecting homeless veterans to HMMM-V programs. These partnering agencies also serve homeless individuals who do not qualify for the HMMM-V program, such as veterans with other-than-honorable military discharges.
The HMMM-V mobile outreach vehicle travels to partnering agencies and provides services on a recurring basis. These agencies are the Dallas International Street Church, a church and faith-based agency aiding the recovery of people with “broken lives”; Cornerstone Ministries, a church-based ministry serving people with adverse circumstances; and City Square’s Opportunity Center, human services and community development programs for low-income city residents. The mobile clinic also travels regularly to other areas to serve homeless veterans residing in unsheltered locations, such as homeless encampments and under bridges.
Clinical Assessment
The project used a modification of the VA Personalized Health Inventory (PHI) for general veteran populations, which assesses 8 areas of self-identified needs to address the specific concerns of homeless veterans served by a mobile clinic.25 Version 19 of the PHI (revised September 18, 2012), the version of the instrument available to the team at the inception of the project, was deployed with the HMMM-V personnel into the field. It imposed a heavy interview time burden (several hours), and its content areas did not seem appropriate to address the immediate concerns of homeless populations (eg, sections pertaining to personal development through hobbies, recreation, or volunteering; healthy living spaces with plenty of lighting and color; “eating healthy, balanced meals with plenty of fruits and vegetables each day”).25
Based on HMMM-V personnel feedback, the team modified this tool and developed a patient-centered health inventory (P-CHI) for homeless veterans that was acceptable in length and applicable to the situational characteristics of homeless existence. The tool’s 10 “current and desired states” were revised to remove domains of exercise and flexibility, sleep and relaxation, and mind-body techniques. The intervention and prevention domains were combined. A material needs (clothing, furniture, transportation, financial benefits) domain was added, and a new domain on reducing alcohol/drug use was created by moving this material from the food and drink domain.
The remaining domains were modified to fit the homeless living situation (Food and Drink = Nutrition; Personal Development = Employment/Vocation; Family, Friends, and Co-Workers = Family/Social/Legal Support; Spirit and Soul = Personal/Spiritual Fulfillment; Surroundings = Housing). Current state ratings were revised to reflect level of satisfaction, and ratings of Desired State were replaced with level of importance.
The modifications resulted in 9 domains, which were assembled into a grid for efficient rating of both satisfaction and importance for each domain (rated 1 to 10, lowest to highest, respectively), followed by an instruction to mark an X in a designated space in all the domains with which the individual would like help (Table). The intent was to reduce the burden of the instrument by having the participant complete sections providing detailed information about only the domains selected by the participant.
The details of each domain in the original VA PHI tool were captured through open-ended questions in text responses provided by the veteran. Because open-ended text responses are not conducive for summarizing characteristics of the population served or for evaluating program activities, the detailed sections covering the domains were revised completely to capture data within categoric and numeric variables. Items from the validated Homeless Supplement Interview were added to collect information not provided in the Homeless Operations Management and Evaluation System interview that is routinely administered to all veterans accessing homeless VA services.26-28
The information collected in these domains cover duration of current homeless episode, lifetime number of homeless episodes, current living arrangements and dissatisfactions with these arrangements, frequency and source of meals, employment history and current work status, sources of income, special material needs, medical and dental problems and sources of care, current medications, mental health problems and sources of care, urgent mental health concerns, current amount and frequency of alcohol and drug use, substance abuse treatment history, relationships with family and intimate partners, legal assistance needs, and self-identified needs for spiritual and personal fulfillment. This instrument is available on request to the authors.
Veterans Served
The project began with 1 team of professionals deploying with the HMMM-V vehicle while a second team was being assembled. Currently, the 2 HMMM-V teams deploy the mobile clinic 4 days per week. The mobile clinic visits agencies that serve the homeless, including emergency shelters and food ministries, as well as homeless encampments. To date, 195 homeless veterans have been served by the mobile clinic, 111 were currently enrolled with the VA, 8 were not enrolled but eligible for services, and 77 were not eligible for VA services. Of the unenrolled veterans, those eligible for services were offered VA enrollment assistance; those ineligible for VA services were offered a community referral.
For the veterans encountered in the field, the following interventions were provided: 49 housing placement referrals, 4 rental assistance referrals, 4 legal referrals, 27 medical care interventions, 13 dental referrals, 11 vision/hearing referrals, 12 mental health interventions, 9 substance abuse treatment referrals, 14 employment assistance referrals, 13 disability benefit applications, 18 transportation assists, 23 goods delivered, and 159 information assists. The HMMM-V mobile clinic also is deployed to participate in various educational and outreach events. At the time this article was written, the mobile clinic has reached nearly 2,000 veterans and community partners in at least 25 such events.
Of the veterans served to date, 73 completed the P-CHI. These veterans were predominantly male (77%), and the majority (60%) were black. The median age of the sample was 58 years, and typically they had a high school level of education (12.7; SD, 2.1 mean years of education). About half (49%) the sample were separated or divorced, and only a minority were currently married (8%). Half (50%) the sample served in the U.S. Army, with the post-Vietnam era being the era of service most represented (19%). Few (21%) veterans reported exposure to hostile or friendly fire during their service. More than three-fourths (80%) of the sample had experienced a homeless episode prior to their current one. On average, members of the sample had experienced a median of 3 lifetime homeless episodes. They had a mean 4.1 (SD, 5.8) lifetime number of years of homelessness, and 3.0 (SD, 5.2) years in their current homeless episode. Nearly one-third (31%) reported that they were currently staying in a homeless shelter, and nearly one-sixth (16%) were currently unsheltered in street settings, such as under bridges or in outdoor encampments at the time of the initial visit.
The mean number of minutes spent completing the P-CHI was 18.5 (SD, 9.4). The veterans indicated that they would like assistance with a mean 3.2 (SD, 2.2) number of domains. The domains with the highest average importance ratings were housing (mean, 9.4; SD, 1.7) and medical/dental care (mean, 8.9; SD, 2.2); the domains with the lowest average importance rating were reducing alcohol/drug use (mean, 6.4; SD, 4.1) and employment/vocation (mean, 6.3; SD, 4.2). The domains with the highest average satisfaction ratings were personal/spiritual fulfillment (mean, 7.3; SD, 2.9) and reducing substance use (mean, 5.9; SD, 4.0), and the domains with the lowest average satisfaction ratings were housing (mean, 2.9; SD, 2.9), material needs (mean, 4.2; SD, 3.3), and employment/vocation (mean, 4.2; SD, 3.2). The domain with the greatest indication of desire for help was housing, endorsed by more than four-fifths (84%) of the sample. This highly endorsed housing domain also was one of the lowest in satisfaction. The domains with the least expressed interest in obtaining help were reducing substance use (18%) and personal/spiritual fulfillment (15%).Reducing substance abuse also was one of the lowest domains of importance and the least for dissatisfaction.
Challenges and Barriers
As anticipated from its inception, this project encountered many challenges and barriers. The first was with the design, construction, and delivery of the mobile clinic unit. The vehicle took more than 2 years to be delivered. There were delays in progress necessitated by required selection of an approved vendor to build the vehicle, extensive specification of details and features, and stocking it with equipment and supplies. The weight of the unit had to be < 26,000 pounds to avoid the requirement of a commercial driver’s license, which limited the size of the vehicle to 28 feet. Stocking the unit with equipment and supplies required attention to a myriad of specifications and decisions. For example, separate refrigerators were needed for specimens, medications, and food; pharmaceutical regulations governing medications in mobile clinics required strict adherence; and difficulties were encountered in attempting to establish adequate and secure connectivity for communications devices in the field.
Once the mobile unit was delivered and prepared for deployment, the next set of challenges pertained to learning all of the instructions required to operate and drive the vehicle and learning how to maneuver the vehicle in the field. Specific challenges for driving the vehicle encountered included unexpectedly low overpasses that prohibited passage, narrow spaces for passage, rough and uneven terrain in off-road settings, and lateral and vertical tilt of roads creating potential for sideswipes and undercarriage scrapes. Maintenance schedules needed to be developed and implemented for cleaning the unit, inspection compliance, repairs, refueling, and emptying waste materials.
Staffing the vehicle required the development of unique job specifications addressing special expertise in accessing VA databases for veteran verification and registration and for driving the mobile clinic vehicle. Schedules and deployment plans for 2 teams that shared the same vehicle had to be established and followed. Locating veterans in unsheltered settings, such as under bridges and in encampments, required community intelligence facilitated through partnerships with knowledgeable members of the Dallas police crisis unit and by gaining field experience to locate where the usual homeless gathering places are, especially those inhabited by veterans. Safety of team members and equipment/supplies in the field was paramount from the start, and additional steps beyond safety training required extra measures, such as special care in navigating known dangerous areas. Provision of services necessitated completion of everything needed in a single visit due to the likelihood of loss to follow-up and acceptance of the limited types of service that could be provided in a mobile clinic. Special procedures were needed to provide referrals to sources of available care for non-VA-qualifying veterans.
Discussion
The HMMM-V program for delivery of PCC to homeless veterans is an innovative pilot program designed to connect with difficult-to-reach homeless veterans and engage them in care. The deliverables provided by this project are (1) A mobile outreach vehicle to deliver care to homeless veterans and outreach to other veterans and community agencies in North Texas; (2) The P-CHI assessment tool for homeless veterans modified and adapted for use with this special population; and (3) pilot data on its first cohort of homeless veterans served, describing their baseline characteristics and their stated satisfaction and preferences about their goals and aspirations for their physical, emotional, and mental health and well-being.
The HMMM-V program successfully identified homeless veterans in need of services, and more than one-third of these veterans were not previously engaged in VA services. Compared with the “typical” veterans served at VANTHCS homeless programs, veterans served by the HMMM-V comprised a greater proportion of minorities and a higher proportion who had been exposed to combat.29 Age and gender characteristics were similar.29 When compared with veterans who access care at VANTHCS and have not experienced homelessness, those served by the HMMM-V were younger and more likely to belong to a minority group; however, they were similar in combat exposure and gender.1 The veterans served by the HMMM-V program also were considerably older and had more homeless chronicity than did nonveteran homeless populations, consistent with other research.4,29,30
The veterans served by the HMMM-V program not surprisingly made housing their top priority in need of help, consistent with the Housing First model.22,31 They also indicated that employment/vocation and reducing substance use were of lower importance. Need for assistance with reducing substance use and social support were the domains least often identified as areas where help was needed, which seems inconsistent with the higher established rates of substance abuse problems among homeless veterans.1
With additional fieldwork, the HMMM-V program is expected to allow refinement of procedures for identifying and serving veterans from a patient-centered care perspective. The P-CHI will be further tested and developed, and the next step will be to create and pilot intervention templates for a Patient-Centered Health Improvement Plan, based on the P-CHI results. This process parallels the original development treatment plans for the VA’s Personalized Health Plan based on the PHI.25 Once the HMMM-V program is fully established in Dallas, the plans are for an expansion that will cover a broader geographic area in North Texas that includes rural areas.
The HMMM-V program was designed to address the barriers to health care that are encountered by homeless veterans. It is unique in homeless veteran care due to its patient-centered approach that partners with homeless veterans to prioritize their needs as determined by them rather than based solely on policies or provider conceptualizations of their needs. Access to services, engagement in care, and successful utilization of needed services may lead to measurable improvements in health care outcomes among homeless populations of veterans. Desired goals include remission of illness through appropriate medical intervention, preventing morbidity, achieving healthy lifestyles, recovery from addiction, stabilization of psychiatric illness, and attainment of stable housing.
The first hurdle for implementing this type of program in other settings is the identification of resources needed for these efforts. Need of additional staffing resources, however, may be circumvented by allowing employees working in other areas to rotate in community outreach shifts in the mobile unit. Another hurdle encountered in implementation of the HMMM-V initiative was the initial difficulty finding homeless veterans in community settings, especially those in unsheltered locations. The HMMM-V program addressed this issue by partnering with other agencies serving the homeless in the community. Therefore, a general recommendation for other entities seeking to implement this type of program is to reach out to these community partners from the outset.
Conclusion
The HMMM-V has the potential to engage the most difficult-to-reach homeless veterans in need of health services by delivering care and providing resources in challenging environments. Further work is needed to validate the P-CHI for use with this program and to conduct well-designed and implemented research to demonstrate effectiveness of this intervention on veteran outcomes, especially quality of life. Once this additional work is accomplished, this innovative program can potentially be implemented by VAMCs across the nation, and potentially in more general community care settings, to more effectively reach out and deliver services to homeless members of the community.
Acknowledgments
Grant support was received from the Department of Veterans Affairs, Office of Patient Centered Care. The authors would like to acknowledge all the clinicians, trainees, and support staff who have contributed to the success of the HMMM-V program: Tara Ayala, Jose Cabrera, Tony Castillo, Rachael Lynn David, Teresa DeShazo, Sylvia Figueroa, Steven Fisher, Eric Gary, Evelyn Gibbs, Kevin Hosey, JoAnn Joseph, Taly Drimer Kagan, Miranda Kelly, Michelle King-Thompson, Sharon Marcus, Shiji Mathew, Moneeza Matin, John Moreno, Joseph Neifert, Joel Price, Tiffany Price, Natalie Qualls, Reginald Robertson, Kristine Rodrigues, Jon Saffelder, Jill Stokes, Scott Stone, and John Smith.
Research has consistently identified remarkably high rates of addiction, mental illness, and health problems in the homeless population.1-9 Yet in spite of extensive service needs for these problems, abundant evidence exists of consistent underuse of health care services by homeless populations.10-12 Most of the homeless population reside in emergency shelters or in transitional or supportive housing, but many remain in places not meant for human habitation.
Homelessness is significantly overrepresented among military veterans.13 The January 2016 national point-in-time count identified 39,471 veterans experiencing homelessness.13 Iraq and Afghanistan veterans seem to have an especially high risk for homelessness.13-15 Disheartening statistics such as these prompted former VA Secretary Eric Shinseki to pledge to end veteran homelessness by December 2015.16 He argued in support of this mission that 85% of veteran homeless resources go to health care—implying that homelessness among veterans is primarily a health care issue, which is heavily burdened by substance abuse and other psychiatric and medical illnesses.17
Health care service use has been associated with improved health, mental health, and outcomes among homeless populations.12,18 Unfortunately, access to these services is limited by barriers associated with homelessness, such as transportation or lack of proper identification.19,20 Veterans experiencing homelessness also face these common barriers to health care, and unsheltered veterans especially underutilize VA health care services.21
Housing First—a successful model that places individuals into housing without prerequisites for sobriety, active participation in treatment, or other behavioral accomplishments, such as gainful employment—has not managed yet to place all the disengaged homeless veteran population into stable housing.22 However, the Housing First model, which is based on the individual’s priorities, is consistent with the approach of a new program at the VA North Texas Health Care System (VANTHCS).
The VHA, similar to other health care systems, is engaged in a cultural transformation to convert its health care approach from a traditional medical model to patient-centered care (PCC).23 In this priority area, a strategic objective is for the VHA to partner with each veteran to create a personalized, proactive strategy to optimize health and well-being and when needed provide state-of-the-art disease management. Patient-centered care is designed to address veterans’ specific needs in spiritual, environmental, physical, mental, and social domains and empower veterans to become active participants in their care. Patient-centered care differs from the traditional medical model in that patients are active participants in their treatment, partnering and collaborating with their providers on care that is quality-of-life centered instead of disease centered.23 This model is based on both respect for patients as unique individuals and on the obligation to care for them on their own terms, focused on their self-identified goals and aspirations.24
At VANTHCS, the Homeless Mobile Medical/Mental Veteran (HMMM-V) pilot program was designed to deliver effective health care services to a homeless subpopulation of veterans who historically have been the most difficult to serve—those living in unsheltered environments, such as under bridges and in encampments. The purpose of the HMMM-V program was to contact and serve veterans not currently being reached by the VA system of care, using a PCC model.
This pilot program was initially funded in January 2013 by a 2-year grant from the Office of Patient Centered Care and Cultural Transformation to apply the PCC approach to engage veteran participation. For this project, the VA Personal Health Inventory tool—originally designed for use with the general veteran population—was adapted for use with the homeless veteran population. The grant funding period covered the design, development, and implementation of the HMMM-V program; thereafter, VANTHCS provided resources through its Comprehensive Homeless Center Programs to assure its sustainability and continued use of the clinical assessment tool created for this project.
This article describes the development and implementation of this novel program with sufficient detail to inform the development of similar programs in other sites. Descriptions of the program and staffing, creation of community partnerships, and modification of an assessment instrument are provided. It also illustrates the original implementation period of the HMMM-V program through presentation of self-reported data on the first homeless veterans it served.
Equipment and Staffing
A custom 28-foot mobile outreach vehicle was assembled according to specifications identified by the HMMM-V team as necessary to conduct the program’s interventions. The van became fully operational on April 8, 2015, after it underwent all the required reviews and inspections (eg, safety, infection control, etc) and was accredited in 2015 by the Commission on Accreditation of Rehabilitation Facilities.
The HMMM-V van has a driver compartment that is separate from its services rooms, which include a patient registration area, a fully equipped examination room, a laboratory area, and a bathroom. The vehicle is equipped with a wheelchair lift and an awning to shade outdoor areas where tables and chairs are set up for patient/staff waiting and rest areas. The vehicle is stocked with essential equipment and supplies needed to conduct work in off-street locations, vacant lots, under bridges, fields, unpaved paths, etc. It also is equipped with telemedicine capabilities to provide clinical supervision and access to attending physicians and specialists at VANTHCS. Personnel carry cell phones and laptop computers with secure Internet connections using a commercially available mobile wireless Wi-Fi hotspot to facilitate documentation of medical records and communication from the field.
This reliable type of equipment is routine for use in VA field operations; the only hurdle using these technologies for the program was acquiring funding and purchasing the equipment. The vehicle is further equipped with a refrigerator solely for secure storage of pharmaceutical supplies, a second refrigerator for specimens, and wall-mounted blood pressure and otoscope/ophthalmoscope units. The vehicle is supplied with thermometers, scales, phlebotomy supplies, and first-aid kits and is stocked with vaccines and medications, including antibiotic, hypertensive, diabetic, allergy, and over-the-counter pain medications. A more comprehensive list of supplies for the vehicle is available from the authors on request.
Medication provisions supplied to the HMMM-V mobile clinic conform to the Texas State Board of Pharmacy compliance regulations. Because the vehicle is designated as federal property and has U.S. government license plates, it is considered an extension of VANTHCS Pharmacy Service and falls under its pharmacy license. A medication formulary was created with input from HMMM-V prescribers and Dallas VAMC Pharmacy Service pharmacists. To safeguard the integrity of these pharmaceutical agents, the HMMM-V physician assistant picks up the medications before field deployment and returns the unused medications to the Dallas VAMC at the end of the day. The medications are transported in locked containers and placed either in a locked medication refrigerator or cabinet on the mobile unit.
For medication prescriptions that need laboratory testing before prescribing them, HMMM-V prescribers can check the VA electronic medical record from the field to determine whether these tests have been completed recently. If not, then HMMM-V team has an agreement with Dallas VA Pathology and Laboratory Medicine Service for testing samples obtained in the field.
The program was designed for staffing of the vehicle by 2 professional teams, each includes medical (physician’s assistant or registered nurse), mental health (psychiatrist, residents), and social work providers (licensed social workers, clinical social workers); trainees of these disciplines; a peer support specialist; and an administrative clerk. The staffing varies daily, depending on available personnel. When personnel deploy to the field, they go in pairs or groups to address potential safety issues. Cell phones are available to summon police or ambulance services in an emergency. Systematic safety training was conducted with all field personnel before their first deployment to guard against vulnerability to danger in these settings.
Once in the field, personnel engage unsheltered homeless individuals to assess eligibility for VA services. Veterans found ineligible are assisted with application for military discharge upgrade, service-connected compensation, or appeal for health care coverage. Veterans eligible for VA care receive physical examinations, vital and glucose checks, influenza and pneumonia vaccinations, first-aid skin and wound care, medication management with limited medications provided at point of care, blood and urine testing, peer support services, suicide assessments, clinical mental health evaluations, and social work services through the HMMM-V program.
Social work assistance provided includes psychosocial assessment and care coordination for psychosocial needs such as mental health, substance abuse, vision, dental, housing, employment, legal aid, transportation, food, income, hygiene, and weather-appropriate provision needs.
Community Partnerships
The HMMM-V program benefitted from a number of partnerships with community agencies. During development of the program, HMMM-V personnel accompanied the Dallas Police Department’s Crisis Intervention Unit on typical homeless crisis services deployments into the field to learn about the locations and nature of encampments and homeless peregrination patterns in the Dallas area.
To aid in the design and selection of features for the mobile outreach vehicle, team members toured Homeless Outreach Medical Service mobile clinics from 2 local county hospitals, Parkland Hospital and John Peter Smith Hospital. The staff for these mobile clinics were interviewed about their experience with various components of their programs and their recommendations for optimal design of the mobile medical clinic for service delivery.
Numerous agencies in the Dallas area that serve the homeless population assisted with locating and connecting homeless veterans to HMMM-V programs. These partnering agencies also serve homeless individuals who do not qualify for the HMMM-V program, such as veterans with other-than-honorable military discharges.
The HMMM-V mobile outreach vehicle travels to partnering agencies and provides services on a recurring basis. These agencies are the Dallas International Street Church, a church and faith-based agency aiding the recovery of people with “broken lives”; Cornerstone Ministries, a church-based ministry serving people with adverse circumstances; and City Square’s Opportunity Center, human services and community development programs for low-income city residents. The mobile clinic also travels regularly to other areas to serve homeless veterans residing in unsheltered locations, such as homeless encampments and under bridges.
Clinical Assessment
The project used a modification of the VA Personalized Health Inventory (PHI) for general veteran populations, which assesses 8 areas of self-identified needs to address the specific concerns of homeless veterans served by a mobile clinic.25 Version 19 of the PHI (revised September 18, 2012), the version of the instrument available to the team at the inception of the project, was deployed with the HMMM-V personnel into the field. It imposed a heavy interview time burden (several hours), and its content areas did not seem appropriate to address the immediate concerns of homeless populations (eg, sections pertaining to personal development through hobbies, recreation, or volunteering; healthy living spaces with plenty of lighting and color; “eating healthy, balanced meals with plenty of fruits and vegetables each day”).25
Based on HMMM-V personnel feedback, the team modified this tool and developed a patient-centered health inventory (P-CHI) for homeless veterans that was acceptable in length and applicable to the situational characteristics of homeless existence. The tool’s 10 “current and desired states” were revised to remove domains of exercise and flexibility, sleep and relaxation, and mind-body techniques. The intervention and prevention domains were combined. A material needs (clothing, furniture, transportation, financial benefits) domain was added, and a new domain on reducing alcohol/drug use was created by moving this material from the food and drink domain.
The remaining domains were modified to fit the homeless living situation (Food and Drink = Nutrition; Personal Development = Employment/Vocation; Family, Friends, and Co-Workers = Family/Social/Legal Support; Spirit and Soul = Personal/Spiritual Fulfillment; Surroundings = Housing). Current state ratings were revised to reflect level of satisfaction, and ratings of Desired State were replaced with level of importance.
The modifications resulted in 9 domains, which were assembled into a grid for efficient rating of both satisfaction and importance for each domain (rated 1 to 10, lowest to highest, respectively), followed by an instruction to mark an X in a designated space in all the domains with which the individual would like help (Table). The intent was to reduce the burden of the instrument by having the participant complete sections providing detailed information about only the domains selected by the participant.
The details of each domain in the original VA PHI tool were captured through open-ended questions in text responses provided by the veteran. Because open-ended text responses are not conducive for summarizing characteristics of the population served or for evaluating program activities, the detailed sections covering the domains were revised completely to capture data within categoric and numeric variables. Items from the validated Homeless Supplement Interview were added to collect information not provided in the Homeless Operations Management and Evaluation System interview that is routinely administered to all veterans accessing homeless VA services.26-28
The information collected in these domains cover duration of current homeless episode, lifetime number of homeless episodes, current living arrangements and dissatisfactions with these arrangements, frequency and source of meals, employment history and current work status, sources of income, special material needs, medical and dental problems and sources of care, current medications, mental health problems and sources of care, urgent mental health concerns, current amount and frequency of alcohol and drug use, substance abuse treatment history, relationships with family and intimate partners, legal assistance needs, and self-identified needs for spiritual and personal fulfillment. This instrument is available on request to the authors.
Veterans Served
The project began with 1 team of professionals deploying with the HMMM-V vehicle while a second team was being assembled. Currently, the 2 HMMM-V teams deploy the mobile clinic 4 days per week. The mobile clinic visits agencies that serve the homeless, including emergency shelters and food ministries, as well as homeless encampments. To date, 195 homeless veterans have been served by the mobile clinic, 111 were currently enrolled with the VA, 8 were not enrolled but eligible for services, and 77 were not eligible for VA services. Of the unenrolled veterans, those eligible for services were offered VA enrollment assistance; those ineligible for VA services were offered a community referral.
For the veterans encountered in the field, the following interventions were provided: 49 housing placement referrals, 4 rental assistance referrals, 4 legal referrals, 27 medical care interventions, 13 dental referrals, 11 vision/hearing referrals, 12 mental health interventions, 9 substance abuse treatment referrals, 14 employment assistance referrals, 13 disability benefit applications, 18 transportation assists, 23 goods delivered, and 159 information assists. The HMMM-V mobile clinic also is deployed to participate in various educational and outreach events. At the time this article was written, the mobile clinic has reached nearly 2,000 veterans and community partners in at least 25 such events.
Of the veterans served to date, 73 completed the P-CHI. These veterans were predominantly male (77%), and the majority (60%) were black. The median age of the sample was 58 years, and typically they had a high school level of education (12.7; SD, 2.1 mean years of education). About half (49%) the sample were separated or divorced, and only a minority were currently married (8%). Half (50%) the sample served in the U.S. Army, with the post-Vietnam era being the era of service most represented (19%). Few (21%) veterans reported exposure to hostile or friendly fire during their service. More than three-fourths (80%) of the sample had experienced a homeless episode prior to their current one. On average, members of the sample had experienced a median of 3 lifetime homeless episodes. They had a mean 4.1 (SD, 5.8) lifetime number of years of homelessness, and 3.0 (SD, 5.2) years in their current homeless episode. Nearly one-third (31%) reported that they were currently staying in a homeless shelter, and nearly one-sixth (16%) were currently unsheltered in street settings, such as under bridges or in outdoor encampments at the time of the initial visit.
The mean number of minutes spent completing the P-CHI was 18.5 (SD, 9.4). The veterans indicated that they would like assistance with a mean 3.2 (SD, 2.2) number of domains. The domains with the highest average importance ratings were housing (mean, 9.4; SD, 1.7) and medical/dental care (mean, 8.9; SD, 2.2); the domains with the lowest average importance rating were reducing alcohol/drug use (mean, 6.4; SD, 4.1) and employment/vocation (mean, 6.3; SD, 4.2). The domains with the highest average satisfaction ratings were personal/spiritual fulfillment (mean, 7.3; SD, 2.9) and reducing substance use (mean, 5.9; SD, 4.0), and the domains with the lowest average satisfaction ratings were housing (mean, 2.9; SD, 2.9), material needs (mean, 4.2; SD, 3.3), and employment/vocation (mean, 4.2; SD, 3.2). The domain with the greatest indication of desire for help was housing, endorsed by more than four-fifths (84%) of the sample. This highly endorsed housing domain also was one of the lowest in satisfaction. The domains with the least expressed interest in obtaining help were reducing substance use (18%) and personal/spiritual fulfillment (15%).Reducing substance abuse also was one of the lowest domains of importance and the least for dissatisfaction.
Challenges and Barriers
As anticipated from its inception, this project encountered many challenges and barriers. The first was with the design, construction, and delivery of the mobile clinic unit. The vehicle took more than 2 years to be delivered. There were delays in progress necessitated by required selection of an approved vendor to build the vehicle, extensive specification of details and features, and stocking it with equipment and supplies. The weight of the unit had to be < 26,000 pounds to avoid the requirement of a commercial driver’s license, which limited the size of the vehicle to 28 feet. Stocking the unit with equipment and supplies required attention to a myriad of specifications and decisions. For example, separate refrigerators were needed for specimens, medications, and food; pharmaceutical regulations governing medications in mobile clinics required strict adherence; and difficulties were encountered in attempting to establish adequate and secure connectivity for communications devices in the field.
Once the mobile unit was delivered and prepared for deployment, the next set of challenges pertained to learning all of the instructions required to operate and drive the vehicle and learning how to maneuver the vehicle in the field. Specific challenges for driving the vehicle encountered included unexpectedly low overpasses that prohibited passage, narrow spaces for passage, rough and uneven terrain in off-road settings, and lateral and vertical tilt of roads creating potential for sideswipes and undercarriage scrapes. Maintenance schedules needed to be developed and implemented for cleaning the unit, inspection compliance, repairs, refueling, and emptying waste materials.
Staffing the vehicle required the development of unique job specifications addressing special expertise in accessing VA databases for veteran verification and registration and for driving the mobile clinic vehicle. Schedules and deployment plans for 2 teams that shared the same vehicle had to be established and followed. Locating veterans in unsheltered settings, such as under bridges and in encampments, required community intelligence facilitated through partnerships with knowledgeable members of the Dallas police crisis unit and by gaining field experience to locate where the usual homeless gathering places are, especially those inhabited by veterans. Safety of team members and equipment/supplies in the field was paramount from the start, and additional steps beyond safety training required extra measures, such as special care in navigating known dangerous areas. Provision of services necessitated completion of everything needed in a single visit due to the likelihood of loss to follow-up and acceptance of the limited types of service that could be provided in a mobile clinic. Special procedures were needed to provide referrals to sources of available care for non-VA-qualifying veterans.
Discussion
The HMMM-V program for delivery of PCC to homeless veterans is an innovative pilot program designed to connect with difficult-to-reach homeless veterans and engage them in care. The deliverables provided by this project are (1) A mobile outreach vehicle to deliver care to homeless veterans and outreach to other veterans and community agencies in North Texas; (2) The P-CHI assessment tool for homeless veterans modified and adapted for use with this special population; and (3) pilot data on its first cohort of homeless veterans served, describing their baseline characteristics and their stated satisfaction and preferences about their goals and aspirations for their physical, emotional, and mental health and well-being.
The HMMM-V program successfully identified homeless veterans in need of services, and more than one-third of these veterans were not previously engaged in VA services. Compared with the “typical” veterans served at VANTHCS homeless programs, veterans served by the HMMM-V comprised a greater proportion of minorities and a higher proportion who had been exposed to combat.29 Age and gender characteristics were similar.29 When compared with veterans who access care at VANTHCS and have not experienced homelessness, those served by the HMMM-V were younger and more likely to belong to a minority group; however, they were similar in combat exposure and gender.1 The veterans served by the HMMM-V program also were considerably older and had more homeless chronicity than did nonveteran homeless populations, consistent with other research.4,29,30
The veterans served by the HMMM-V program not surprisingly made housing their top priority in need of help, consistent with the Housing First model.22,31 They also indicated that employment/vocation and reducing substance use were of lower importance. Need for assistance with reducing substance use and social support were the domains least often identified as areas where help was needed, which seems inconsistent with the higher established rates of substance abuse problems among homeless veterans.1
With additional fieldwork, the HMMM-V program is expected to allow refinement of procedures for identifying and serving veterans from a patient-centered care perspective. The P-CHI will be further tested and developed, and the next step will be to create and pilot intervention templates for a Patient-Centered Health Improvement Plan, based on the P-CHI results. This process parallels the original development treatment plans for the VA’s Personalized Health Plan based on the PHI.25 Once the HMMM-V program is fully established in Dallas, the plans are for an expansion that will cover a broader geographic area in North Texas that includes rural areas.
The HMMM-V program was designed to address the barriers to health care that are encountered by homeless veterans. It is unique in homeless veteran care due to its patient-centered approach that partners with homeless veterans to prioritize their needs as determined by them rather than based solely on policies or provider conceptualizations of their needs. Access to services, engagement in care, and successful utilization of needed services may lead to measurable improvements in health care outcomes among homeless populations of veterans. Desired goals include remission of illness through appropriate medical intervention, preventing morbidity, achieving healthy lifestyles, recovery from addiction, stabilization of psychiatric illness, and attainment of stable housing.
The first hurdle for implementing this type of program in other settings is the identification of resources needed for these efforts. Need of additional staffing resources, however, may be circumvented by allowing employees working in other areas to rotate in community outreach shifts in the mobile unit. Another hurdle encountered in implementation of the HMMM-V initiative was the initial difficulty finding homeless veterans in community settings, especially those in unsheltered locations. The HMMM-V program addressed this issue by partnering with other agencies serving the homeless in the community. Therefore, a general recommendation for other entities seeking to implement this type of program is to reach out to these community partners from the outset.
Conclusion
The HMMM-V has the potential to engage the most difficult-to-reach homeless veterans in need of health services by delivering care and providing resources in challenging environments. Further work is needed to validate the P-CHI for use with this program and to conduct well-designed and implemented research to demonstrate effectiveness of this intervention on veteran outcomes, especially quality of life. Once this additional work is accomplished, this innovative program can potentially be implemented by VAMCs across the nation, and potentially in more general community care settings, to more effectively reach out and deliver services to homeless members of the community.
Acknowledgments
Grant support was received from the Department of Veterans Affairs, Office of Patient Centered Care. The authors would like to acknowledge all the clinicians, trainees, and support staff who have contributed to the success of the HMMM-V program: Tara Ayala, Jose Cabrera, Tony Castillo, Rachael Lynn David, Teresa DeShazo, Sylvia Figueroa, Steven Fisher, Eric Gary, Evelyn Gibbs, Kevin Hosey, JoAnn Joseph, Taly Drimer Kagan, Miranda Kelly, Michelle King-Thompson, Sharon Marcus, Shiji Mathew, Moneeza Matin, John Moreno, Joseph Neifert, Joel Price, Tiffany Price, Natalie Qualls, Reginald Robertson, Kristine Rodrigues, Jon Saffelder, Jill Stokes, Scott Stone, and John Smith.
1. LePage JP, Bradshaw LD, Cipher DJ, Crawford AM, Hooshyar D. The effects of homelessness on veterans’ health care service use: an evaluation of independence from comorbidities. Public Health. 2014;128(11):985-992.
2. Fischer PJ, Breakey WR. The epidemiology of alcohol, drug, and mental disorders among homeless persons. Am Psychol. 1991;46(11):1115-1128.
3. Robertson MJ, Zlotnick C, Westerfelt A. Drug use disorders and treatment contact among homeless adults in Alameda County, California. Am J Public Health. 1997;87(2):221-228.
4. North CS, Eyrich KM, Pollio DE, Spitznagel EL. Are rates of psychiatric disorders in the homeless population changing? Am J Public Health. 2004;94(1):103-108.
5. Fazel S, Khosla V, Doll H, Geddes J. The prevalence of mental disorders among the homeless in western countries: systematic review and meta-regression analysis. PLoS Med. 2008;5(12):e225.
6. Harpaz-Rotem I, Rosenheck RA, Desai R. The mental health of children exposed to maternal mental illness and homelessness. Community Ment Health J. 2006;42(5):437-448.
7. Pollio DE, Eyrich-Garg KM, North CS. The homeless. In: Johnson BA, ed. Addiction Medicine: Science and Practice. New York, NY: Springer; 2011:1487-1504.
8. Padgett D, Struening EL, Andrews H. Factors affecting the use of medical, mental health, alcohol, and drug treatment services by homeless adults. Med Care. 1990;28(9):805-821.
9. Baggett TP, Singer DE, Rao SR, O’Connell JJ, Bharel M, Rigotti NA. Food insufficiency and health services utilization in a national sample of homeless adults. J Gen Intern Med. 2011;26(6):627-634.
10. Folsom DP, Hawthorne W, Lindamer L, et al. Prevalence and risk factors for homelessness and utilization of mental health services among 10,340 patients with serious mental illness in a large public mental health system. Am J Psychiatry. 2005;162(2):370-376.
11. Fuehrlein BS, Cowell AJ, Pollio D, Cupps L, Balfour ME, North CS. A prospective study of the associations among housing status and costs of services in a homeless population. Psychiatr Serv. 2015;66(1):27-32.
12. Pollio DE, North CS, Eyrich KM, Foster DA, Spitznagel E. Modeling service access in a homeless population. J Psychoactive Drugs. 2003;35(4):487-495.
13. U.S. Department of Housing and Urban Development Office of Community Planning and Development. The 2016 Annual Homeless Assessment Report (AHAR) to Congress. Part 1: point-in-time estimates of homelessness. https://www.hudexchange.info/resources/documents/2016-AHAR-Part-1.pdf. Published 2016. Accessed August 7, 2017.
14. Tsai J, Rosenheck RA. Risk factors for homelessness among U.S. veterans. Epidemiol Rev. 2015;37:177-195.
15. Williamson V, Mulhall E. Coming home: the housing crisis and homelessness threaten new veterans. Iraq and Afghanistan Veterans of America, January, 2009. http://media.iava.org/IAVA_coming_home_2009%20The%20Housing%20Crisis%20and%20Homelessness%20Threaten%20New%20Veterans.pdf. Accessed August 10, 2017
16. Shinseki EK. Remarks by Secretary Eric K. Shinseki. National Summit on Homeless Veterans; November 3, 2009; Washington, DC. https://www.va.gov/opa/speeches/2009/09_1103.asp. Updated August 8, 2016. Accessed August 7, 2017.
17. Shinseki EK. Remarks by Secretary Eric K. Shinseki. 2014 National Coalition for Homeless Veterans Annual Meeting; May 30, 2014; Arlington, VA. https://www.va.gov/opa/speeches/2014/05_30_2014.asp. Updated April 21, 2015. Accessed August 7, 2017.
18. Pollio DE, Spitznagel EL, North CS, Thompson S, Foster DA. Service use over time and achievement of stable housing in a mentally ill homeless population. Psychiatr Serv. 2000;51(12):1536-1543.
19. Page J. Barriers to transferring care of homeless people with serious mental illnesses to community mental health organizations: perspectives of street-based programs. Best Practices in Mental Health: An International Journal. 2007;3(1):26.
20. Young AS, Chinman MJ, Cradock-O’Leary JA, et al. Characteristics of individuals with severe mental illness who use emergency services. Community Ment Health J. 2005;41(2):159-168.
21. Gabrielian S, Yuan AH, Andersen RM, Rubenstein LV, Gelberg L. VA health service utilization for homeless and low-income veterans: a spotlight on the VA Supportive Housing (VASH) program in greater Los Angeles. Med Care. 2014;52(5):454-461.
22. Tsemberis S, Gulcur L, Nakae M. Housing First, consumer choice, and harm reduction for homeless individuals with a dual diagnosis. Am J Public Health. 2004;94(4):651-656.
23. U.S. Department of Veterans Affairs, Veterans Health Administration. VA Patient Centered Care. http://www.va.gov/patientcenteredcare. Updated July 24,2017. Accessed August 7, 2017.
24. Epstein RM, Street RL Jr. The values and value of patient-centered care. Ann Fam Med. 2011;9(2):100-103.
25. U.S. Department of Veterans Affairs, Office of Patient Centered Care and Cultural Transformation. My story: personal health inventory. https://www.va.gov/PATIENTCENTEREDCARE/docs/VA-OPCC-Personal-Health-Inventory-final-508.pdf. Published October 7, 2013. Accessed August 7, 2017
26. North CS, Smith EM, Pollio DE. The Homeless Supplement to the Diagnostic Interview Schedule (DIS/HS). St. Louis: Washington University, 2004.
27. North CS, Eyrich KM, Pollio DE, Foster DA, Cottler LB, Spitznagel EL. The homeless supplement to the diagnostic interview schedule: test-retest analyses. Int J Methods Psychiatr Res. 2004;13(3):184-191.
28. LaSalle JL. Homeless Operations Management and Evaluation System (HOMES) user manual-phase 1. http://www.vfwsc.org/homes.pdf. Published April 19, 2011. Accessed August 7, 2017.
29. Petrovich JC, Pollio DE, North CS. Characteristics and service use of homeless veterans and nonveterans residing in a low-demand emergency shelter. Psychiatr Serv. 2014;65(6):751-757.
30. North CS, Smith EM. A comparison of homeless men and women: different populations, different needs. Community Ment Health J. 1993;29(5):423-431.
31. Kertesz SG, Austin EL, Holmes SK, et al. Making housing first happen: organizational leadership in VA’s expansion of permanent supportive housing. J Gen Intern Med. 2014;29(suppl 4):835-844.
1. LePage JP, Bradshaw LD, Cipher DJ, Crawford AM, Hooshyar D. The effects of homelessness on veterans’ health care service use: an evaluation of independence from comorbidities. Public Health. 2014;128(11):985-992.
2. Fischer PJ, Breakey WR. The epidemiology of alcohol, drug, and mental disorders among homeless persons. Am Psychol. 1991;46(11):1115-1128.
3. Robertson MJ, Zlotnick C, Westerfelt A. Drug use disorders and treatment contact among homeless adults in Alameda County, California. Am J Public Health. 1997;87(2):221-228.
4. North CS, Eyrich KM, Pollio DE, Spitznagel EL. Are rates of psychiatric disorders in the homeless population changing? Am J Public Health. 2004;94(1):103-108.
5. Fazel S, Khosla V, Doll H, Geddes J. The prevalence of mental disorders among the homeless in western countries: systematic review and meta-regression analysis. PLoS Med. 2008;5(12):e225.
6. Harpaz-Rotem I, Rosenheck RA, Desai R. The mental health of children exposed to maternal mental illness and homelessness. Community Ment Health J. 2006;42(5):437-448.
7. Pollio DE, Eyrich-Garg KM, North CS. The homeless. In: Johnson BA, ed. Addiction Medicine: Science and Practice. New York, NY: Springer; 2011:1487-1504.
8. Padgett D, Struening EL, Andrews H. Factors affecting the use of medical, mental health, alcohol, and drug treatment services by homeless adults. Med Care. 1990;28(9):805-821.
9. Baggett TP, Singer DE, Rao SR, O’Connell JJ, Bharel M, Rigotti NA. Food insufficiency and health services utilization in a national sample of homeless adults. J Gen Intern Med. 2011;26(6):627-634.
10. Folsom DP, Hawthorne W, Lindamer L, et al. Prevalence and risk factors for homelessness and utilization of mental health services among 10,340 patients with serious mental illness in a large public mental health system. Am J Psychiatry. 2005;162(2):370-376.
11. Fuehrlein BS, Cowell AJ, Pollio D, Cupps L, Balfour ME, North CS. A prospective study of the associations among housing status and costs of services in a homeless population. Psychiatr Serv. 2015;66(1):27-32.
12. Pollio DE, North CS, Eyrich KM, Foster DA, Spitznagel E. Modeling service access in a homeless population. J Psychoactive Drugs. 2003;35(4):487-495.
13. U.S. Department of Housing and Urban Development Office of Community Planning and Development. The 2016 Annual Homeless Assessment Report (AHAR) to Congress. Part 1: point-in-time estimates of homelessness. https://www.hudexchange.info/resources/documents/2016-AHAR-Part-1.pdf. Published 2016. Accessed August 7, 2017.
14. Tsai J, Rosenheck RA. Risk factors for homelessness among U.S. veterans. Epidemiol Rev. 2015;37:177-195.
15. Williamson V, Mulhall E. Coming home: the housing crisis and homelessness threaten new veterans. Iraq and Afghanistan Veterans of America, January, 2009. http://media.iava.org/IAVA_coming_home_2009%20The%20Housing%20Crisis%20and%20Homelessness%20Threaten%20New%20Veterans.pdf. Accessed August 10, 2017
16. Shinseki EK. Remarks by Secretary Eric K. Shinseki. National Summit on Homeless Veterans; November 3, 2009; Washington, DC. https://www.va.gov/opa/speeches/2009/09_1103.asp. Updated August 8, 2016. Accessed August 7, 2017.
17. Shinseki EK. Remarks by Secretary Eric K. Shinseki. 2014 National Coalition for Homeless Veterans Annual Meeting; May 30, 2014; Arlington, VA. https://www.va.gov/opa/speeches/2014/05_30_2014.asp. Updated April 21, 2015. Accessed August 7, 2017.
18. Pollio DE, Spitznagel EL, North CS, Thompson S, Foster DA. Service use over time and achievement of stable housing in a mentally ill homeless population. Psychiatr Serv. 2000;51(12):1536-1543.
19. Page J. Barriers to transferring care of homeless people with serious mental illnesses to community mental health organizations: perspectives of street-based programs. Best Practices in Mental Health: An International Journal. 2007;3(1):26.
20. Young AS, Chinman MJ, Cradock-O’Leary JA, et al. Characteristics of individuals with severe mental illness who use emergency services. Community Ment Health J. 2005;41(2):159-168.
21. Gabrielian S, Yuan AH, Andersen RM, Rubenstein LV, Gelberg L. VA health service utilization for homeless and low-income veterans: a spotlight on the VA Supportive Housing (VASH) program in greater Los Angeles. Med Care. 2014;52(5):454-461.
22. Tsemberis S, Gulcur L, Nakae M. Housing First, consumer choice, and harm reduction for homeless individuals with a dual diagnosis. Am J Public Health. 2004;94(4):651-656.
23. U.S. Department of Veterans Affairs, Veterans Health Administration. VA Patient Centered Care. http://www.va.gov/patientcenteredcare. Updated July 24,2017. Accessed August 7, 2017.
24. Epstein RM, Street RL Jr. The values and value of patient-centered care. Ann Fam Med. 2011;9(2):100-103.
25. U.S. Department of Veterans Affairs, Office of Patient Centered Care and Cultural Transformation. My story: personal health inventory. https://www.va.gov/PATIENTCENTEREDCARE/docs/VA-OPCC-Personal-Health-Inventory-final-508.pdf. Published October 7, 2013. Accessed August 7, 2017
26. North CS, Smith EM, Pollio DE. The Homeless Supplement to the Diagnostic Interview Schedule (DIS/HS). St. Louis: Washington University, 2004.
27. North CS, Eyrich KM, Pollio DE, Foster DA, Cottler LB, Spitznagel EL. The homeless supplement to the diagnostic interview schedule: test-retest analyses. Int J Methods Psychiatr Res. 2004;13(3):184-191.
28. LaSalle JL. Homeless Operations Management and Evaluation System (HOMES) user manual-phase 1. http://www.vfwsc.org/homes.pdf. Published April 19, 2011. Accessed August 7, 2017.
29. Petrovich JC, Pollio DE, North CS. Characteristics and service use of homeless veterans and nonveterans residing in a low-demand emergency shelter. Psychiatr Serv. 2014;65(6):751-757.
30. North CS, Smith EM. A comparison of homeless men and women: different populations, different needs. Community Ment Health J. 1993;29(5):423-431.
31. Kertesz SG, Austin EL, Holmes SK, et al. Making housing first happen: organizational leadership in VA’s expansion of permanent supportive housing. J Gen Intern Med. 2014;29(suppl 4):835-844.
Checkmate 238: Nivolumab bests ipilimumab for resectable stage III or IV melanoma
MADRID – For patients with resectable stage III melanoma, adjuvant therapy with the programmed death 1 (PD-1) immune checkpoint inhibitor nivolumab (Opdivo) was associated with significantly longer relapse-free survival compared with the cytotoxic T-lymphocyte antigen 4 (CTLA-4) inhibitor ipilimumab (Yervoy), results of a randomized phase 3 trial show.
Among 906 patients who underwent complete resection of stage IIIB, IIIC, or stage IV melanoma in the Checkmate 238 trial, the rates of relapse-free survival (RFS), the primary endpoint, were 71% at 12 months for patients assigned to adjuvant nivolumab, compared with 61% for adjuvant ipilimumab. At 18 months, the respective RFS rates were 66% and 53%, reported Jeffrey Weber, MD, PhD, of NYU Langone Health’s Perlmutter Cancer Center in New York City.
However, longer follow-up will be needed to see whether the RFS advantage of nivolumab translates into an overall survival advantage, he acknowledged.
In the trial, patients with high-risk, completely resected stage IIIB, IIIC, or IV melanoma were stratified by disease stage and PD-L1 status at baseline and randomly assigned in cohorts of 453 patients each to receive either nivolumab 3 mg/kg intravenously every 2 weeks and ipilimumab placebo every 3 weeks for four doses, or to ipilimumab 10 mg/kg IV every 3 weeks for four doses, then every 12 weeks from week 24, and nivolumab placebo IV every 2 weeks.
The maximum duration of therapy was 1 year.
For the primary RFS endpoint, the hazard ratio (HR) favoring nivolumab was 0.65 (P less than .0001).
The benefit for nivolumab was observed across the majority of prespecified subgroups tested, including PD-L1 and BRAF mutational status, Dr. Weber said.
Nivolumab also had a better safety profile, with a 14.4% incidence of grade 3 or 4 treatment-related adverse events, compared with 45.9% for ipilimumab. Grade 3 or 4 treatment-related adverse events leading to discontinuation of therapy occurred in 4.6% of patients on nivolumab, compared with 30.9% of those on ipilimumab.
Two patients in the ipilimumab arm died from toxicities related to therapy, one from marrow aplasia, and one from colitis. Both of these deaths occurred more than 100 days after the patients received their last dose of ipilimumab. There were no treatment-related deaths in the nivolumab arm.
Commenting on both the Checkmate 238 trial and a second trial reported at ESMO (COMBI-AD) looking at a combination of dabrafenib and trametinib for patients with stage III melanoma with a BRAF V600 mutation, Olivier Michielin, MD, PhD, said that “we now have, with the data, two fantastic new options. We couldn’t dream those studies to be so positive. This is really something that will open new futures for our patients.”
Dr. Michielin and Dr. Dummer were invited commentators at the briefing. Dr. Michielin was not involved in either trial. Dr. Dummer was a coinvestigator for the COMBI-AD trial.
The study was published simultaneously online by the New England Journal of Medicine.
Checkmate 238 was funded by Bristol-Myers Squibb and Ono Pharmaceutical. Dr. Weber disclosed honoraria, consulting fees, and travel accommodations/expenses from BMS and multiple other companies. Dr. Michielin disclosed consulting and/or honoraria from Amgen, BMS, Roche, MSD, Novartis, and GSK. Dr. Dummer reported advising/consulting roles with BMS and others.
MADRID – For patients with resectable stage III melanoma, adjuvant therapy with the programmed death 1 (PD-1) immune checkpoint inhibitor nivolumab (Opdivo) was associated with significantly longer relapse-free survival compared with the cytotoxic T-lymphocyte antigen 4 (CTLA-4) inhibitor ipilimumab (Yervoy), results of a randomized phase 3 trial show.
Among 906 patients who underwent complete resection of stage IIIB, IIIC, or stage IV melanoma in the Checkmate 238 trial, the rates of relapse-free survival (RFS), the primary endpoint, were 71% at 12 months for patients assigned to adjuvant nivolumab, compared with 61% for adjuvant ipilimumab. At 18 months, the respective RFS rates were 66% and 53%, reported Jeffrey Weber, MD, PhD, of NYU Langone Health’s Perlmutter Cancer Center in New York City.
However, longer follow-up will be needed to see whether the RFS advantage of nivolumab translates into an overall survival advantage, he acknowledged.
In the trial, patients with high-risk, completely resected stage IIIB, IIIC, or IV melanoma were stratified by disease stage and PD-L1 status at baseline and randomly assigned in cohorts of 453 patients each to receive either nivolumab 3 mg/kg intravenously every 2 weeks and ipilimumab placebo every 3 weeks for four doses, or to ipilimumab 10 mg/kg IV every 3 weeks for four doses, then every 12 weeks from week 24, and nivolumab placebo IV every 2 weeks.
The maximum duration of therapy was 1 year.
For the primary RFS endpoint, the hazard ratio (HR) favoring nivolumab was 0.65 (P less than .0001).
The benefit for nivolumab was observed across the majority of prespecified subgroups tested, including PD-L1 and BRAF mutational status, Dr. Weber said.
Nivolumab also had a better safety profile, with a 14.4% incidence of grade 3 or 4 treatment-related adverse events, compared with 45.9% for ipilimumab. Grade 3 or 4 treatment-related adverse events leading to discontinuation of therapy occurred in 4.6% of patients on nivolumab, compared with 30.9% of those on ipilimumab.
Two patients in the ipilimumab arm died from toxicities related to therapy, one from marrow aplasia, and one from colitis. Both of these deaths occurred more than 100 days after the patients received their last dose of ipilimumab. There were no treatment-related deaths in the nivolumab arm.
Commenting on both the Checkmate 238 trial and a second trial reported at ESMO (COMBI-AD) looking at a combination of dabrafenib and trametinib for patients with stage III melanoma with a BRAF V600 mutation, Olivier Michielin, MD, PhD, said that “we now have, with the data, two fantastic new options. We couldn’t dream those studies to be so positive. This is really something that will open new futures for our patients.”
Dr. Michielin and Dr. Dummer were invited commentators at the briefing. Dr. Michielin was not involved in either trial. Dr. Dummer was a coinvestigator for the COMBI-AD trial.
The study was published simultaneously online by the New England Journal of Medicine.
Checkmate 238 was funded by Bristol-Myers Squibb and Ono Pharmaceutical. Dr. Weber disclosed honoraria, consulting fees, and travel accommodations/expenses from BMS and multiple other companies. Dr. Michielin disclosed consulting and/or honoraria from Amgen, BMS, Roche, MSD, Novartis, and GSK. Dr. Dummer reported advising/consulting roles with BMS and others.
MADRID – For patients with resectable stage III melanoma, adjuvant therapy with the programmed death 1 (PD-1) immune checkpoint inhibitor nivolumab (Opdivo) was associated with significantly longer relapse-free survival compared with the cytotoxic T-lymphocyte antigen 4 (CTLA-4) inhibitor ipilimumab (Yervoy), results of a randomized phase 3 trial show.
Among 906 patients who underwent complete resection of stage IIIB, IIIC, or stage IV melanoma in the Checkmate 238 trial, the rates of relapse-free survival (RFS), the primary endpoint, were 71% at 12 months for patients assigned to adjuvant nivolumab, compared with 61% for adjuvant ipilimumab. At 18 months, the respective RFS rates were 66% and 53%, reported Jeffrey Weber, MD, PhD, of NYU Langone Health’s Perlmutter Cancer Center in New York City.
However, longer follow-up will be needed to see whether the RFS advantage of nivolumab translates into an overall survival advantage, he acknowledged.
In the trial, patients with high-risk, completely resected stage IIIB, IIIC, or IV melanoma were stratified by disease stage and PD-L1 status at baseline and randomly assigned in cohorts of 453 patients each to receive either nivolumab 3 mg/kg intravenously every 2 weeks and ipilimumab placebo every 3 weeks for four doses, or to ipilimumab 10 mg/kg IV every 3 weeks for four doses, then every 12 weeks from week 24, and nivolumab placebo IV every 2 weeks.
The maximum duration of therapy was 1 year.
For the primary RFS endpoint, the hazard ratio (HR) favoring nivolumab was 0.65 (P less than .0001).
The benefit for nivolumab was observed across the majority of prespecified subgroups tested, including PD-L1 and BRAF mutational status, Dr. Weber said.
Nivolumab also had a better safety profile, with a 14.4% incidence of grade 3 or 4 treatment-related adverse events, compared with 45.9% for ipilimumab. Grade 3 or 4 treatment-related adverse events leading to discontinuation of therapy occurred in 4.6% of patients on nivolumab, compared with 30.9% of those on ipilimumab.
Two patients in the ipilimumab arm died from toxicities related to therapy, one from marrow aplasia, and one from colitis. Both of these deaths occurred more than 100 days after the patients received their last dose of ipilimumab. There were no treatment-related deaths in the nivolumab arm.
Commenting on both the Checkmate 238 trial and a second trial reported at ESMO (COMBI-AD) looking at a combination of dabrafenib and trametinib for patients with stage III melanoma with a BRAF V600 mutation, Olivier Michielin, MD, PhD, said that “we now have, with the data, two fantastic new options. We couldn’t dream those studies to be so positive. This is really something that will open new futures for our patients.”
Dr. Michielin and Dr. Dummer were invited commentators at the briefing. Dr. Michielin was not involved in either trial. Dr. Dummer was a coinvestigator for the COMBI-AD trial.
The study was published simultaneously online by the New England Journal of Medicine.
Checkmate 238 was funded by Bristol-Myers Squibb and Ono Pharmaceutical. Dr. Weber disclosed honoraria, consulting fees, and travel accommodations/expenses from BMS and multiple other companies. Dr. Michielin disclosed consulting and/or honoraria from Amgen, BMS, Roche, MSD, Novartis, and GSK. Dr. Dummer reported advising/consulting roles with BMS and others.
AT ESMO 2017
Key clinical point: Nivolumab improved relapse-free survival over ipilimumab in patients with stage III or IV resectable melanoma.
Major finding: The rates of relapse-free survival were 71% at 12 months for patients assigned to adjuvant nivolumab, compared with 61% for adjuvant ipilimumab.
Data source: Randomized clinical trial in 906 patients with completely resectable stage III melanoma.
Disclosures: Checkmate 238 was funded by Bristol-Myers Squibb and Ono Pharmaceutical. Dr. Weber disclosed honoraria, consulting fees, and travel accommodations/expenses from BMS and other companies. Dr. Michielin disclosed consulting and/or honoraria from Amgen, BMS, Roche, MSD, Novartis, and GSK.. Dr. Dummer reported advising/consulting roles with BMS and others.
News Flash! Nocturnists are in high demand
Over 70% of all hospitalist programs have nocturnists, according to the 2016 State of Hospital Medicine Report. For adult-only practices, this has increased to 72.3% from 46.1% in the 2012 State of Hospital Medicine Report.
While one can assert that most hospital medicine practices have nocturnists, not all nights are covered by nocturnists. Thirty-nine percent (39%) of adult practices report that nocturnists cover 100% of nights, and 9.2% report that less than 25% of nights are covered by nocturnists. So, there remains a great deal of variability in the widespread use of nocturnists for nighttime coverage.
Categorically, nocturnists are hospitalists who work primarily at night, providing in-house coverage for hospitalist admissions and coverage for patients cared for by the hospitalist group.
Other clinicians, such as nurses, patient care technicians, medical technologists, and radiology technologists, have worked night shifts for many, many years. The phenomenon of hospital-based physicians and advanced practice clinicians working only at night is reflective of the needs in an acute care environment.
There are many lifestyle benefits to being a nocturnist – raising a family during the day while working at night, working fewer hours for more pay, and being in high demand.
Nocturnists can also allow a hospitalist group to offer more flexible scheduling options and create career longevity within the group. Having a nocturnist can allow a group to offer other hospitalists a “day shift only” option and other flexible scheduling options that many seasoned hospitalists are looking for.
Demand
Because of the increasing demand, it’s becoming more difficult to find long-term nocturnists, and therefore permanent nocturnists are expensive to hire. As reported in the 2016 State of Hospital Medicine Report, groups with nocturnists may offer either a differential in the hours or shifts worked, or compensation, or a combination of both.
About half of nocturnists work fewer shifts, compared with non-nocturnists. Equally stated, about half of nocturnists work the same number of shifts as their day-only counterparts. Of those groups whose nocturnists work fewer shifts than their daytime counterparts, about 60% work 1%-20% fewer shifts.
Nearly 70% of groups with nocturnists pay nocturnists differently. The median pay differential is 15%. While this compensation differential is an increase since the 2014 report, it is on par with the 2012 report.
It should not be construed that every practice with hospitalists offers both fewer shifts and more compensation. In fact, there are many who may offer neither and develop other, more creative ways of recognizing the nocturnist differently, such as evaluating scheduled hours per shift (e.g., 8 vs. 10 vs. 12).
Responsibility
With more adaptation and remuneration for nocturnists comes more responsibility.
Working as a nocturnist can be grueling work. Many times nocturnists may be working alone, and with less support from consultants and fewer hospital resources at night. On the other hand, it’s quieter at night and there can be a strong camaraderie from the smaller team at the hospital at night.
Nocturnists, many times, must be comfortable working alone; they must have strong clinical skills, and may need to seek extra training. In fact, in some hospitals the nocturnists may be the primary, or only, physician covering in-house codes.
Nocturnists must also take responsibility to remain abreast of the quality initiatives of the hospitalist group and hospital, since many of the quality committee meetings and hospitalist group meetings typically occur during daytime hours. Nocturnists may need to make an extra effort to feel a part of the group by voluntarily participating in daytime group activities, so that they don’t feel like an outsider.
Nocturnists should take the lead in receiving hand-off each evening, and handing off each morning to the day shift. This will likely mean handing off valuable patient care information with more than a few of their hospitalist colleagues. This is so immensely important that national patient safety-focused organizations have emphasized it for many years.
Since four out of five hospitalist programs have a hospitalist on site at night, and the majority of those programs have at least some nocturnist coverage, designing hospitalist programs and staffing models that meet the patient care need of 24/7 in-house coverage is a necessity. Also, given the strong demand for nocturnists, more and more program leaders are being challenged to evaluate creative alternatives to provide sustainable hospitalist services.
Some examples of creative solutions for in-house night coverage are implementing telemedicine for admissions, cross cover, or both; expanding coverage by advanced practice clinicians; and staggering shifts to cover late evenings and early mornings.
Perhaps we’ll see more questions about how hospitalist groups are addressing this need in future surveys?
Amanda Trask, MBA, MHA, FACHE, CMPE, SFHM, is national vice president, Hospital Medicine Service Line, at Catholic Health Initiatives, Englewood, Colo.
Over 70% of all hospitalist programs have nocturnists, according to the 2016 State of Hospital Medicine Report. For adult-only practices, this has increased to 72.3% from 46.1% in the 2012 State of Hospital Medicine Report.
While one can assert that most hospital medicine practices have nocturnists, not all nights are covered by nocturnists. Thirty-nine percent (39%) of adult practices report that nocturnists cover 100% of nights, and 9.2% report that less than 25% of nights are covered by nocturnists. So, there remains a great deal of variability in the widespread use of nocturnists for nighttime coverage.
Categorically, nocturnists are hospitalists who work primarily at night, providing in-house coverage for hospitalist admissions and coverage for patients cared for by the hospitalist group.
Other clinicians, such as nurses, patient care technicians, medical technologists, and radiology technologists, have worked night shifts for many, many years. The phenomenon of hospital-based physicians and advanced practice clinicians working only at night is reflective of the needs in an acute care environment.
There are many lifestyle benefits to being a nocturnist – raising a family during the day while working at night, working fewer hours for more pay, and being in high demand.
Nocturnists can also allow a hospitalist group to offer more flexible scheduling options and create career longevity within the group. Having a nocturnist can allow a group to offer other hospitalists a “day shift only” option and other flexible scheduling options that many seasoned hospitalists are looking for.
Demand
Because of the increasing demand, it’s becoming more difficult to find long-term nocturnists, and therefore permanent nocturnists are expensive to hire. As reported in the 2016 State of Hospital Medicine Report, groups with nocturnists may offer either a differential in the hours or shifts worked, or compensation, or a combination of both.
About half of nocturnists work fewer shifts, compared with non-nocturnists. Equally stated, about half of nocturnists work the same number of shifts as their day-only counterparts. Of those groups whose nocturnists work fewer shifts than their daytime counterparts, about 60% work 1%-20% fewer shifts.
Nearly 70% of groups with nocturnists pay nocturnists differently. The median pay differential is 15%. While this compensation differential is an increase since the 2014 report, it is on par with the 2012 report.
It should not be construed that every practice with hospitalists offers both fewer shifts and more compensation. In fact, there are many who may offer neither and develop other, more creative ways of recognizing the nocturnist differently, such as evaluating scheduled hours per shift (e.g., 8 vs. 10 vs. 12).
Responsibility
With more adaptation and remuneration for nocturnists comes more responsibility.
Working as a nocturnist can be grueling work. Many times nocturnists may be working alone, and with less support from consultants and fewer hospital resources at night. On the other hand, it’s quieter at night and there can be a strong camaraderie from the smaller team at the hospital at night.
Nocturnists, many times, must be comfortable working alone; they must have strong clinical skills, and may need to seek extra training. In fact, in some hospitals the nocturnists may be the primary, or only, physician covering in-house codes.
Nocturnists must also take responsibility to remain abreast of the quality initiatives of the hospitalist group and hospital, since many of the quality committee meetings and hospitalist group meetings typically occur during daytime hours. Nocturnists may need to make an extra effort to feel a part of the group by voluntarily participating in daytime group activities, so that they don’t feel like an outsider.
Nocturnists should take the lead in receiving hand-off each evening, and handing off each morning to the day shift. This will likely mean handing off valuable patient care information with more than a few of their hospitalist colleagues. This is so immensely important that national patient safety-focused organizations have emphasized it for many years.
Since four out of five hospitalist programs have a hospitalist on site at night, and the majority of those programs have at least some nocturnist coverage, designing hospitalist programs and staffing models that meet the patient care need of 24/7 in-house coverage is a necessity. Also, given the strong demand for nocturnists, more and more program leaders are being challenged to evaluate creative alternatives to provide sustainable hospitalist services.
Some examples of creative solutions for in-house night coverage are implementing telemedicine for admissions, cross cover, or both; expanding coverage by advanced practice clinicians; and staggering shifts to cover late evenings and early mornings.
Perhaps we’ll see more questions about how hospitalist groups are addressing this need in future surveys?
Amanda Trask, MBA, MHA, FACHE, CMPE, SFHM, is national vice president, Hospital Medicine Service Line, at Catholic Health Initiatives, Englewood, Colo.
Over 70% of all hospitalist programs have nocturnists, according to the 2016 State of Hospital Medicine Report. For adult-only practices, this has increased to 72.3% from 46.1% in the 2012 State of Hospital Medicine Report.
While one can assert that most hospital medicine practices have nocturnists, not all nights are covered by nocturnists. Thirty-nine percent (39%) of adult practices report that nocturnists cover 100% of nights, and 9.2% report that less than 25% of nights are covered by nocturnists. So, there remains a great deal of variability in the widespread use of nocturnists for nighttime coverage.
Categorically, nocturnists are hospitalists who work primarily at night, providing in-house coverage for hospitalist admissions and coverage for patients cared for by the hospitalist group.
Other clinicians, such as nurses, patient care technicians, medical technologists, and radiology technologists, have worked night shifts for many, many years. The phenomenon of hospital-based physicians and advanced practice clinicians working only at night is reflective of the needs in an acute care environment.
There are many lifestyle benefits to being a nocturnist – raising a family during the day while working at night, working fewer hours for more pay, and being in high demand.
Nocturnists can also allow a hospitalist group to offer more flexible scheduling options and create career longevity within the group. Having a nocturnist can allow a group to offer other hospitalists a “day shift only” option and other flexible scheduling options that many seasoned hospitalists are looking for.
Demand
Because of the increasing demand, it’s becoming more difficult to find long-term nocturnists, and therefore permanent nocturnists are expensive to hire. As reported in the 2016 State of Hospital Medicine Report, groups with nocturnists may offer either a differential in the hours or shifts worked, or compensation, or a combination of both.
About half of nocturnists work fewer shifts, compared with non-nocturnists. Equally stated, about half of nocturnists work the same number of shifts as their day-only counterparts. Of those groups whose nocturnists work fewer shifts than their daytime counterparts, about 60% work 1%-20% fewer shifts.
Nearly 70% of groups with nocturnists pay nocturnists differently. The median pay differential is 15%. While this compensation differential is an increase since the 2014 report, it is on par with the 2012 report.
It should not be construed that every practice with hospitalists offers both fewer shifts and more compensation. In fact, there are many who may offer neither and develop other, more creative ways of recognizing the nocturnist differently, such as evaluating scheduled hours per shift (e.g., 8 vs. 10 vs. 12).
Responsibility
With more adaptation and remuneration for nocturnists comes more responsibility.
Working as a nocturnist can be grueling work. Many times nocturnists may be working alone, and with less support from consultants and fewer hospital resources at night. On the other hand, it’s quieter at night and there can be a strong camaraderie from the smaller team at the hospital at night.
Nocturnists, many times, must be comfortable working alone; they must have strong clinical skills, and may need to seek extra training. In fact, in some hospitals the nocturnists may be the primary, or only, physician covering in-house codes.
Nocturnists must also take responsibility to remain abreast of the quality initiatives of the hospitalist group and hospital, since many of the quality committee meetings and hospitalist group meetings typically occur during daytime hours. Nocturnists may need to make an extra effort to feel a part of the group by voluntarily participating in daytime group activities, so that they don’t feel like an outsider.
Nocturnists should take the lead in receiving hand-off each evening, and handing off each morning to the day shift. This will likely mean handing off valuable patient care information with more than a few of their hospitalist colleagues. This is so immensely important that national patient safety-focused organizations have emphasized it for many years.
Since four out of five hospitalist programs have a hospitalist on site at night, and the majority of those programs have at least some nocturnist coverage, designing hospitalist programs and staffing models that meet the patient care need of 24/7 in-house coverage is a necessity. Also, given the strong demand for nocturnists, more and more program leaders are being challenged to evaluate creative alternatives to provide sustainable hospitalist services.
Some examples of creative solutions for in-house night coverage are implementing telemedicine for admissions, cross cover, or both; expanding coverage by advanced practice clinicians; and staggering shifts to cover late evenings and early mornings.
Perhaps we’ll see more questions about how hospitalist groups are addressing this need in future surveys?
Amanda Trask, MBA, MHA, FACHE, CMPE, SFHM, is national vice president, Hospital Medicine Service Line, at Catholic Health Initiatives, Englewood, Colo.
Diagnosing high-risk keratinocyte carcinomas in the dermatology clinic
SAN FRANCISCO – Patients with high-risk keratinocyte carcinomas sometimes present with neurologic symptoms mimicking Bell’s palsy or trigeminal neuralgia, making the diagnosis of these perineural tumors challenging, Siegrid Yu, MD, said at the annual meeting of the Pacific Dermatologic Association.
Eventually, skin manifestations can land them in a dermatologist’s office. “There is a high incidence of delayed diagnosis and misdiagnosis, which affects the outcome of these patients,” said Dr. Yu of the department of dermatology, University of California, San Francisco.
She presented several cases illustrating the central role that dermatologists can play in the diagnosis and management of high-risk keratinocyte carcinomas. “All of these patients were seen by various doctors, sometimes multiple times, without a diagnosis,” she said.
Perineural invasion occurs in 2.6%-6% of squamous cell carcinoma (SCC) cases and 2% of basal cell carcinoma (BCC) cases. “Perineural invasion presenting with neurologic symptoms is not that common, which is part of why I think it’s easy to misdiagnose these patients,” said Dr. Yu, director of the Mohs Micrographic Surgery and Cutaneous Oncology Fellowship at the UCSF Dermatologic Surgery and Laser Center. In many cases, patients were diagnosed as having Bell’s palsy or trigeminal neuralgia for years before being diagnosed with skin cancer.
Common features of perineural invasion cases include midface location of the tumor, male gender, tumor size larger than 2 cm, recurrence, and poor histologic differentiation. Symptoms often include formication, pain, numbness, and facial weakness. Diagnosis is often delayed by 6 months to 2 years.
One case she described involved a 57-year-old immunosuppressed man who had previously undergone Mohs micrographic surgery for a primary SCC of the nasal sidewall. He experienced delayed numbness and pain of the upper lip and cheek near the surgical site 1 year later. There was no sign of cutaneous recurrence, and MRIs of the head and neck were normal. Examinations by dermatologists, neurologists, and otorhinolaryngologists yielded no diagnosis.
Two years after his initial surgery, the patient developed thickening of the scar from the Mohs surgery, without any overlying skin change. A punch biopsy showed only scar tissue, but a deeper incisional biopsy revealed a recurrence of the SCC. A second head/neck MRI, using a perineural protocol, showed abnormal enhancement at the V2 branch of the trigeminal nerve leading to the foramen rotundum. The patient underwent intensity-modulated radiation, which relies on computer-modeling to deliver doses to the precise location of the tumor. An MRI 2 months later showed a reduction in tumor size and radiographic resolution of trigeminal nerve involvement.
Another case involved a 75-year-old man with progressive right facial droop, who had experienced neurologic symptoms on the right side of his face, including numbness, tingling, oculomotor dysfunction, and radiating pain. He had been diagnosed with shingles on the right side of his face more than 20 years previously, but there was no history of postherpetic neuralgia. He also had hypertension and hypothyroidism, and had been prescribed levothyroxine, amlodipine, losartan, and gabapentin.
He had been evaluated by primary care, dermatology, and ophthalmology with no diagnosis. He then sequentially sought the opinion of four neurologists, and underwent lumbar puncture, serologic evaluation, head CT, and MRI with no findings that correlated with his symptoms. The patient’s neurological symptoms improved transiently with prednisone, and his pain improved slightly with gabapentin.
Finally, a skin biopsy of an ill-defined firmness in the right temple revealed infiltrative SCC. A repeat MRI, this time with perineural protocol, showed perineural spread along the trigeminal nerve, with involvement of the V2 and V3 branches, and possibly the V1 branch.
In another case, complete hemifacial palsy due to perineural spread of SCC was overlooked as having been related to the patient’s history of stroke. However, upon further questioning, the facial palsy involved all branches of the facial nerve, while the patient’s residual stroke symptoms of expressive aphasia and dysphagia were improving. “If you think about head and neck anatomy, an upper motor neuron lesion would not lead to complete facial nerve palsy. It could lead to palsy of the lower two-thirds of the face, sparing the temporal nerve due to cross innervation of the forehead. Only a lower motor neuron can result in progressive palsy of all branches of the facial nerve,” Dr. Yu said. In this case, the facial palsy was due to a large SCC of the external auditory canal.
Dr. Yu highlighted several considerations to keep in mind when examining these patients, including vigilance around prior skin cancer surgeries in cases with neurologic symptoms, the potential need for repeated imaging along with communication with the radiologist regarding suspicion of perineural spread, consideration of anatomy during the clinical exam, and correlation of clinical exam, histopathology, and radiographic findings.
When it comes to imaging, MRI is the most sensitive technique, she noted. It can show increase in nerve diameter, destruction of the nerve-blood barrier, obliteration of the fat below a foramen, nerve enhancement, and denervation atrophy.
Dr. Yu reported having no financial disclosures.
SAN FRANCISCO – Patients with high-risk keratinocyte carcinomas sometimes present with neurologic symptoms mimicking Bell’s palsy or trigeminal neuralgia, making the diagnosis of these perineural tumors challenging, Siegrid Yu, MD, said at the annual meeting of the Pacific Dermatologic Association.
Eventually, skin manifestations can land them in a dermatologist’s office. “There is a high incidence of delayed diagnosis and misdiagnosis, which affects the outcome of these patients,” said Dr. Yu of the department of dermatology, University of California, San Francisco.
She presented several cases illustrating the central role that dermatologists can play in the diagnosis and management of high-risk keratinocyte carcinomas. “All of these patients were seen by various doctors, sometimes multiple times, without a diagnosis,” she said.
Perineural invasion occurs in 2.6%-6% of squamous cell carcinoma (SCC) cases and 2% of basal cell carcinoma (BCC) cases. “Perineural invasion presenting with neurologic symptoms is not that common, which is part of why I think it’s easy to misdiagnose these patients,” said Dr. Yu, director of the Mohs Micrographic Surgery and Cutaneous Oncology Fellowship at the UCSF Dermatologic Surgery and Laser Center. In many cases, patients were diagnosed as having Bell’s palsy or trigeminal neuralgia for years before being diagnosed with skin cancer.
Common features of perineural invasion cases include midface location of the tumor, male gender, tumor size larger than 2 cm, recurrence, and poor histologic differentiation. Symptoms often include formication, pain, numbness, and facial weakness. Diagnosis is often delayed by 6 months to 2 years.
One case she described involved a 57-year-old immunosuppressed man who had previously undergone Mohs micrographic surgery for a primary SCC of the nasal sidewall. He experienced delayed numbness and pain of the upper lip and cheek near the surgical site 1 year later. There was no sign of cutaneous recurrence, and MRIs of the head and neck were normal. Examinations by dermatologists, neurologists, and otorhinolaryngologists yielded no diagnosis.
Two years after his initial surgery, the patient developed thickening of the scar from the Mohs surgery, without any overlying skin change. A punch biopsy showed only scar tissue, but a deeper incisional biopsy revealed a recurrence of the SCC. A second head/neck MRI, using a perineural protocol, showed abnormal enhancement at the V2 branch of the trigeminal nerve leading to the foramen rotundum. The patient underwent intensity-modulated radiation, which relies on computer-modeling to deliver doses to the precise location of the tumor. An MRI 2 months later showed a reduction in tumor size and radiographic resolution of trigeminal nerve involvement.
Another case involved a 75-year-old man with progressive right facial droop, who had experienced neurologic symptoms on the right side of his face, including numbness, tingling, oculomotor dysfunction, and radiating pain. He had been diagnosed with shingles on the right side of his face more than 20 years previously, but there was no history of postherpetic neuralgia. He also had hypertension and hypothyroidism, and had been prescribed levothyroxine, amlodipine, losartan, and gabapentin.
He had been evaluated by primary care, dermatology, and ophthalmology with no diagnosis. He then sequentially sought the opinion of four neurologists, and underwent lumbar puncture, serologic evaluation, head CT, and MRI with no findings that correlated with his symptoms. The patient’s neurological symptoms improved transiently with prednisone, and his pain improved slightly with gabapentin.
Finally, a skin biopsy of an ill-defined firmness in the right temple revealed infiltrative SCC. A repeat MRI, this time with perineural protocol, showed perineural spread along the trigeminal nerve, with involvement of the V2 and V3 branches, and possibly the V1 branch.
In another case, complete hemifacial palsy due to perineural spread of SCC was overlooked as having been related to the patient’s history of stroke. However, upon further questioning, the facial palsy involved all branches of the facial nerve, while the patient’s residual stroke symptoms of expressive aphasia and dysphagia were improving. “If you think about head and neck anatomy, an upper motor neuron lesion would not lead to complete facial nerve palsy. It could lead to palsy of the lower two-thirds of the face, sparing the temporal nerve due to cross innervation of the forehead. Only a lower motor neuron can result in progressive palsy of all branches of the facial nerve,” Dr. Yu said. In this case, the facial palsy was due to a large SCC of the external auditory canal.
Dr. Yu highlighted several considerations to keep in mind when examining these patients, including vigilance around prior skin cancer surgeries in cases with neurologic symptoms, the potential need for repeated imaging along with communication with the radiologist regarding suspicion of perineural spread, consideration of anatomy during the clinical exam, and correlation of clinical exam, histopathology, and radiographic findings.
When it comes to imaging, MRI is the most sensitive technique, she noted. It can show increase in nerve diameter, destruction of the nerve-blood barrier, obliteration of the fat below a foramen, nerve enhancement, and denervation atrophy.
Dr. Yu reported having no financial disclosures.
SAN FRANCISCO – Patients with high-risk keratinocyte carcinomas sometimes present with neurologic symptoms mimicking Bell’s palsy or trigeminal neuralgia, making the diagnosis of these perineural tumors challenging, Siegrid Yu, MD, said at the annual meeting of the Pacific Dermatologic Association.
Eventually, skin manifestations can land them in a dermatologist’s office. “There is a high incidence of delayed diagnosis and misdiagnosis, which affects the outcome of these patients,” said Dr. Yu of the department of dermatology, University of California, San Francisco.
She presented several cases illustrating the central role that dermatologists can play in the diagnosis and management of high-risk keratinocyte carcinomas. “All of these patients were seen by various doctors, sometimes multiple times, without a diagnosis,” she said.
Perineural invasion occurs in 2.6%-6% of squamous cell carcinoma (SCC) cases and 2% of basal cell carcinoma (BCC) cases. “Perineural invasion presenting with neurologic symptoms is not that common, which is part of why I think it’s easy to misdiagnose these patients,” said Dr. Yu, director of the Mohs Micrographic Surgery and Cutaneous Oncology Fellowship at the UCSF Dermatologic Surgery and Laser Center. In many cases, patients were diagnosed as having Bell’s palsy or trigeminal neuralgia for years before being diagnosed with skin cancer.
Common features of perineural invasion cases include midface location of the tumor, male gender, tumor size larger than 2 cm, recurrence, and poor histologic differentiation. Symptoms often include formication, pain, numbness, and facial weakness. Diagnosis is often delayed by 6 months to 2 years.
One case she described involved a 57-year-old immunosuppressed man who had previously undergone Mohs micrographic surgery for a primary SCC of the nasal sidewall. He experienced delayed numbness and pain of the upper lip and cheek near the surgical site 1 year later. There was no sign of cutaneous recurrence, and MRIs of the head and neck were normal. Examinations by dermatologists, neurologists, and otorhinolaryngologists yielded no diagnosis.
Two years after his initial surgery, the patient developed thickening of the scar from the Mohs surgery, without any overlying skin change. A punch biopsy showed only scar tissue, but a deeper incisional biopsy revealed a recurrence of the SCC. A second head/neck MRI, using a perineural protocol, showed abnormal enhancement at the V2 branch of the trigeminal nerve leading to the foramen rotundum. The patient underwent intensity-modulated radiation, which relies on computer-modeling to deliver doses to the precise location of the tumor. An MRI 2 months later showed a reduction in tumor size and radiographic resolution of trigeminal nerve involvement.
Another case involved a 75-year-old man with progressive right facial droop, who had experienced neurologic symptoms on the right side of his face, including numbness, tingling, oculomotor dysfunction, and radiating pain. He had been diagnosed with shingles on the right side of his face more than 20 years previously, but there was no history of postherpetic neuralgia. He also had hypertension and hypothyroidism, and had been prescribed levothyroxine, amlodipine, losartan, and gabapentin.
He had been evaluated by primary care, dermatology, and ophthalmology with no diagnosis. He then sequentially sought the opinion of four neurologists, and underwent lumbar puncture, serologic evaluation, head CT, and MRI with no findings that correlated with his symptoms. The patient’s neurological symptoms improved transiently with prednisone, and his pain improved slightly with gabapentin.
Finally, a skin biopsy of an ill-defined firmness in the right temple revealed infiltrative SCC. A repeat MRI, this time with perineural protocol, showed perineural spread along the trigeminal nerve, with involvement of the V2 and V3 branches, and possibly the V1 branch.
In another case, complete hemifacial palsy due to perineural spread of SCC was overlooked as having been related to the patient’s history of stroke. However, upon further questioning, the facial palsy involved all branches of the facial nerve, while the patient’s residual stroke symptoms of expressive aphasia and dysphagia were improving. “If you think about head and neck anatomy, an upper motor neuron lesion would not lead to complete facial nerve palsy. It could lead to palsy of the lower two-thirds of the face, sparing the temporal nerve due to cross innervation of the forehead. Only a lower motor neuron can result in progressive palsy of all branches of the facial nerve,” Dr. Yu said. In this case, the facial palsy was due to a large SCC of the external auditory canal.
Dr. Yu highlighted several considerations to keep in mind when examining these patients, including vigilance around prior skin cancer surgeries in cases with neurologic symptoms, the potential need for repeated imaging along with communication with the radiologist regarding suspicion of perineural spread, consideration of anatomy during the clinical exam, and correlation of clinical exam, histopathology, and radiographic findings.
When it comes to imaging, MRI is the most sensitive technique, she noted. It can show increase in nerve diameter, destruction of the nerve-blood barrier, obliteration of the fat below a foramen, nerve enhancement, and denervation atrophy.
Dr. Yu reported having no financial disclosures.
AT PDA 2017
Submit VAM Session Topic Proposals
SVS is seeking proposals for invited sessions from internal committees and members alike for the 2018 Vascular Annual Meeting, June 20-23 (exhibits: June 21 to 22; plenaries: June 21 to 23) in Boston, Mass.
Invited sessions consist of postgraduate courses, breakfast sessions, concurrent sessions and workshops/small-group sessions. Submitters will be asked to address educational needs, provide objectives, indicate proposed formats and identify target audiences.
The deadline is 3 p.m. Central Daylight Time, Friday, Sept. 15. Submitters will be notified the week of Sept. 25 if their proposals have been selected for further development. Contact [email protected] or call 312-334-2327 with questions.
SVS is seeking proposals for invited sessions from internal committees and members alike for the 2018 Vascular Annual Meeting, June 20-23 (exhibits: June 21 to 22; plenaries: June 21 to 23) in Boston, Mass.
Invited sessions consist of postgraduate courses, breakfast sessions, concurrent sessions and workshops/small-group sessions. Submitters will be asked to address educational needs, provide objectives, indicate proposed formats and identify target audiences.
The deadline is 3 p.m. Central Daylight Time, Friday, Sept. 15. Submitters will be notified the week of Sept. 25 if their proposals have been selected for further development. Contact [email protected] or call 312-334-2327 with questions.
SVS is seeking proposals for invited sessions from internal committees and members alike for the 2018 Vascular Annual Meeting, June 20-23 (exhibits: June 21 to 22; plenaries: June 21 to 23) in Boston, Mass.
Invited sessions consist of postgraduate courses, breakfast sessions, concurrent sessions and workshops/small-group sessions. Submitters will be asked to address educational needs, provide objectives, indicate proposed formats and identify target audiences.
The deadline is 3 p.m. Central Daylight Time, Friday, Sept. 15. Submitters will be notified the week of Sept. 25 if their proposals have been selected for further development. Contact [email protected] or call 312-334-2327 with questions.
PAD Resources for SVS Members
September is Peripheral Artery Disease Awareness Month. To help SVS members educate patients and to spread awareness about vascular surgeons, we have prepared several things you can share.
1. An infographic for patients and their families. We urge you to print it and post around the office or your institution.
2. A quick resource web page for patients, offering patients a PAD video playlist and links to articles and information on PAD.
3. The latest PAD research information for physicians, along with clinical practice guideline links. If you have contacts among primary care physicians or other referrers, please feel free to send them this link.
4. Two press releases on PAD, to share with your communications people, public relations departments and/or patients
September is Peripheral Artery Disease Awareness Month. To help SVS members educate patients and to spread awareness about vascular surgeons, we have prepared several things you can share.
1. An infographic for patients and their families. We urge you to print it and post around the office or your institution.
2. A quick resource web page for patients, offering patients a PAD video playlist and links to articles and information on PAD.
3. The latest PAD research information for physicians, along with clinical practice guideline links. If you have contacts among primary care physicians or other referrers, please feel free to send them this link.
4. Two press releases on PAD, to share with your communications people, public relations departments and/or patients
September is Peripheral Artery Disease Awareness Month. To help SVS members educate patients and to spread awareness about vascular surgeons, we have prepared several things you can share.
1. An infographic for patients and their families. We urge you to print it and post around the office or your institution.
2. A quick resource web page for patients, offering patients a PAD video playlist and links to articles and information on PAD.
3. The latest PAD research information for physicians, along with clinical practice guideline links. If you have contacts among primary care physicians or other referrers, please feel free to send them this link.
4. Two press releases on PAD, to share with your communications people, public relations departments and/or patients
Three percent of high school seniors report using synthetic cannabinoids
, according to data from the national Monitoring the Future survey.
SCs are more potent than marijuana (as much as 100 times stronger); do not contain the anti-anxiety and antipsychotic constituent of marijuana, cannabidiol; and have a greater risk of a range of adverse effects, such as tachycardia, agitation, nausea, generalized tonic-clonic seizures, psychiatric problems, and death.
Joseph J. Palamar, PhD, MPH, of New York University, and his colleagues set out to examine data about current use of SCs, as previous studies had focused on lifetime or past-year use. Monitoring the Future surveys approximately 15,000 high school seniors annually in the United States. Of the six survey forms (which are distributed randomly), only two asked seniors about their current use of SCs, limiting the current study to a third of the survey sample.
The researchers found that, while 81% of current SC users also reported current use of marijuana, only 9% of current marijuana users reported current use of SCs. SC use was correlated much more highly than marijuana use with the current use of other drugs such as LSD (15% vs. 3%), opioids (14% vs. 6%), cocaine (11% vs. 3%), and heroin (6% vs. 0.1%).
“Current SC use appears to be part of a more extensive polydrug use repertoire involving other illegal drugs that are less prevalent among marijuana-only users. ... These associations suggest the need to target marijuana users who also use other drugs to help prevent initiation of SCs,” concluded Dr. Palamar and his associates.
Read more at (Pediatrics. 2017 Oct;140[4]:e20171330).
, according to data from the national Monitoring the Future survey.
SCs are more potent than marijuana (as much as 100 times stronger); do not contain the anti-anxiety and antipsychotic constituent of marijuana, cannabidiol; and have a greater risk of a range of adverse effects, such as tachycardia, agitation, nausea, generalized tonic-clonic seizures, psychiatric problems, and death.
Joseph J. Palamar, PhD, MPH, of New York University, and his colleagues set out to examine data about current use of SCs, as previous studies had focused on lifetime or past-year use. Monitoring the Future surveys approximately 15,000 high school seniors annually in the United States. Of the six survey forms (which are distributed randomly), only two asked seniors about their current use of SCs, limiting the current study to a third of the survey sample.
The researchers found that, while 81% of current SC users also reported current use of marijuana, only 9% of current marijuana users reported current use of SCs. SC use was correlated much more highly than marijuana use with the current use of other drugs such as LSD (15% vs. 3%), opioids (14% vs. 6%), cocaine (11% vs. 3%), and heroin (6% vs. 0.1%).
“Current SC use appears to be part of a more extensive polydrug use repertoire involving other illegal drugs that are less prevalent among marijuana-only users. ... These associations suggest the need to target marijuana users who also use other drugs to help prevent initiation of SCs,” concluded Dr. Palamar and his associates.
Read more at (Pediatrics. 2017 Oct;140[4]:e20171330).
, according to data from the national Monitoring the Future survey.
SCs are more potent than marijuana (as much as 100 times stronger); do not contain the anti-anxiety and antipsychotic constituent of marijuana, cannabidiol; and have a greater risk of a range of adverse effects, such as tachycardia, agitation, nausea, generalized tonic-clonic seizures, psychiatric problems, and death.
Joseph J. Palamar, PhD, MPH, of New York University, and his colleagues set out to examine data about current use of SCs, as previous studies had focused on lifetime or past-year use. Monitoring the Future surveys approximately 15,000 high school seniors annually in the United States. Of the six survey forms (which are distributed randomly), only two asked seniors about their current use of SCs, limiting the current study to a third of the survey sample.
The researchers found that, while 81% of current SC users also reported current use of marijuana, only 9% of current marijuana users reported current use of SCs. SC use was correlated much more highly than marijuana use with the current use of other drugs such as LSD (15% vs. 3%), opioids (14% vs. 6%), cocaine (11% vs. 3%), and heroin (6% vs. 0.1%).
“Current SC use appears to be part of a more extensive polydrug use repertoire involving other illegal drugs that are less prevalent among marijuana-only users. ... These associations suggest the need to target marijuana users who also use other drugs to help prevent initiation of SCs,” concluded Dr. Palamar and his associates.
Read more at (Pediatrics. 2017 Oct;140[4]:e20171330).
FROM PEDIATRICS
Reduced fracture risk maintained in abaloparatide extension study
denver – Sequential treatment with abaloparatide and alendronate was associated with reduced vertebral and non-vertebral fractures compared to placebo and alendronate among high-risk women with osteoporosis in a 3.5 year extension study of the ACTIVE trial.
The ACTIVExtend trial included 558 women in the abaloparatide group and 581 women in the placebo group of the original ACTIVE study (NCT01343004). In that double-blind trial, 2,463 postmenopausal women with osteoporosis were randomized to receive daily injections of abaloparatide (80 µg) or placebo, or open-label teriparatide (20 µg). After 18 months of treatment, patients in the placebo and abaloparatide groups were switched to alendronate 70 mg weekly for two years, Henry Bone, MD, director of the Michigan Bone and Mineral Clinic in Detroit, said at the annual meeting of the American Society for Bone and Mineral Research.
The abaloparatide-alendronate group had a 34% relative risk reduction for all clinical fractures compared to the placebo-alendronate group (P = .045). For major osteoporotic fractures, the abaloparatide-alendronate group had a 50% relative risk reduction compared to the placebo-alendronate group (P = .011).
Among women who had no new vertebral fractures during the first 18 months of the ACTIVE study, 2 women in the abaloparatide-alendronate group and 13 in the placebo-alendronate group had new vertebral fractures during ACTIVExtend.
Adverse events were similar in both arms of the study. There were no cases of atypical femur fracture or osteonecrosis of the jaw.The anabolic agent abaloparatide was approved by the Food and Drug Administration in April for the treatment of osteoporosis in women at high risk of fracture. Sequential treatment with the anti-resorptive agent alendronate aims to preserve the bone density gains from abaloparatide, as previous research has shown that improvements with anabolic agents can be lost once the drug is stopped.
denver – Sequential treatment with abaloparatide and alendronate was associated with reduced vertebral and non-vertebral fractures compared to placebo and alendronate among high-risk women with osteoporosis in a 3.5 year extension study of the ACTIVE trial.
The ACTIVExtend trial included 558 women in the abaloparatide group and 581 women in the placebo group of the original ACTIVE study (NCT01343004). In that double-blind trial, 2,463 postmenopausal women with osteoporosis were randomized to receive daily injections of abaloparatide (80 µg) or placebo, or open-label teriparatide (20 µg). After 18 months of treatment, patients in the placebo and abaloparatide groups were switched to alendronate 70 mg weekly for two years, Henry Bone, MD, director of the Michigan Bone and Mineral Clinic in Detroit, said at the annual meeting of the American Society for Bone and Mineral Research.
The abaloparatide-alendronate group had a 34% relative risk reduction for all clinical fractures compared to the placebo-alendronate group (P = .045). For major osteoporotic fractures, the abaloparatide-alendronate group had a 50% relative risk reduction compared to the placebo-alendronate group (P = .011).
Among women who had no new vertebral fractures during the first 18 months of the ACTIVE study, 2 women in the abaloparatide-alendronate group and 13 in the placebo-alendronate group had new vertebral fractures during ACTIVExtend.
Adverse events were similar in both arms of the study. There were no cases of atypical femur fracture or osteonecrosis of the jaw.The anabolic agent abaloparatide was approved by the Food and Drug Administration in April for the treatment of osteoporosis in women at high risk of fracture. Sequential treatment with the anti-resorptive agent alendronate aims to preserve the bone density gains from abaloparatide, as previous research has shown that improvements with anabolic agents can be lost once the drug is stopped.
denver – Sequential treatment with abaloparatide and alendronate was associated with reduced vertebral and non-vertebral fractures compared to placebo and alendronate among high-risk women with osteoporosis in a 3.5 year extension study of the ACTIVE trial.
The ACTIVExtend trial included 558 women in the abaloparatide group and 581 women in the placebo group of the original ACTIVE study (NCT01343004). In that double-blind trial, 2,463 postmenopausal women with osteoporosis were randomized to receive daily injections of abaloparatide (80 µg) or placebo, or open-label teriparatide (20 µg). After 18 months of treatment, patients in the placebo and abaloparatide groups were switched to alendronate 70 mg weekly for two years, Henry Bone, MD, director of the Michigan Bone and Mineral Clinic in Detroit, said at the annual meeting of the American Society for Bone and Mineral Research.
The abaloparatide-alendronate group had a 34% relative risk reduction for all clinical fractures compared to the placebo-alendronate group (P = .045). For major osteoporotic fractures, the abaloparatide-alendronate group had a 50% relative risk reduction compared to the placebo-alendronate group (P = .011).
Among women who had no new vertebral fractures during the first 18 months of the ACTIVE study, 2 women in the abaloparatide-alendronate group and 13 in the placebo-alendronate group had new vertebral fractures during ACTIVExtend.
Adverse events were similar in both arms of the study. There were no cases of atypical femur fracture or osteonecrosis of the jaw.The anabolic agent abaloparatide was approved by the Food and Drug Administration in April for the treatment of osteoporosis in women at high risk of fracture. Sequential treatment with the anti-resorptive agent alendronate aims to preserve the bone density gains from abaloparatide, as previous research has shown that improvements with anabolic agents can be lost once the drug is stopped.
REPORTING FROM ASBMR 2017
Key clinical point: The reduced fracture risk seen after 18 months of abaloparatide therapy persisted at 43 months with follow up alendronate therapy, and was superior to the results seen in women who received placebo for 18 months followed by alendronate.
Major finding: 0.9% of women who started on abaloparatide experienced at least 1 new vertebral fracture, compared to 5.6% of those who started on placebo.
Data source: The ACTIVExtend trial included 558 women in the abaloparatide group and 581 women in the placebo group.
Disclosures: The study was funded by Radius Health, the maker of abaloparatide. Dr. Bone is a consultant and investigator for Radius Health and Amgen.
Osimertinib bests PFS achieved with standard care for EGFR-mutated NSCLC
MADRID – The EGFR inhibitor osimertinib (Tagrisso) is being hailed as a new standard of care for first-line therapy of advanced, treatment naïve non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) with mutations in the epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR).
Osimertinib cut the risk of disease progression in these patients by 54% compared gefitinib (Iressa) or erlotinib (Tarceva).
Among 279 patients with EGFR-mutated locally advanced or metastatic NSCLC treated with osemirtinib, the median progression-free survival (PFS) was 18.9 months, compared with 10.2 months for 277 patients treated with the standard of care, which translates into a hazard ratio (HR) of 0.46 (P less than .0001).
“We wanted to see if by shutting down a major escape pathway by giving osemirtinib upfront, whether we would be able to improve patient outcomes,” he said at a briefing at the European Society of Medical Oncology (ESMO) Congress.
Osimertinib is a third-generation EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitor (TKI) selective for EGFR mutations, including the T790M resistance mutation. It is currently approved in the US for the treatment of patients with EGFR T790M mutation-positive NSCLC whose disease has progressed on or after EGFR TKI therapy.
In the FLAURA trial (NCT02296125) investigators stratified patients with previously untreated NSCLC positive for EGFR resistance mutations according to mutation status (exon 19 deletion or the L858R amino acid substitution in exon 21) and race (Asian or non-Asian).
Patients were randomly assigned to treatment with either oral osimertinib 80 mg daily or an EGFR TKI, either oral gefitinib 250 mg or erlotinib 150 mg daily.
The patients were assessed by Response Evaluation Criteria in Solid Tumors (RECIST) every 6 weeks until objective disease progression.
Patients assigned to the standard-of-care arm who had central confirmation of progression and T790M positivity were allowed to cross over to open-label osimertinib.
PFS, the primary endpoint, was also significantly better with osimertinib than with either of the comparator TKIs in patients with and without central nervous system metastases at study entry (HR 0.47, P = .0009 for patients with CNS metastases, HR 0.46, P less than .0001 for patients with no CNS metastases).
For this interim analysis, with OS data at only 25% maturity, median OS had not been reached in either trial arm. The HR for OS with osimertinib was 0.63, with a P value of .0068, but this was not statistically significant, as the statistical method used required a P of less than .0015 for significance, Dr. Ramalingam explained.
The safety profile of osimertinib was comparable to that of the standard of care, with lower rates of grade 3 or greater adverse events, and a lower discontinuation rate, than with either gefitinib or erlotinib.
Enriqueta Felip, MD, the invited commentator at the briefing, said that “based on these results, osimertinib should be considered a new first-line treatment option for patients with EGFR mutations.”
Tony Mok, MD, from the Chinese University of Hong Kong, the invited discussant at the presidential symposium where Dr. Ramalingam presented the study, commented that “there is little doubt that FLAURA is a positive study demonstrating superiority in PFS with first-line osimertinib.”
He questioned, however whether all patients with EGFR mutation-positve NSCLC should receive osimertinib up front.
“I have confidence that patients with CNS metastases at presentation would benefit the most considering osimertinib’s higher CNS penetration, but the optimal sequence for overall survival benefit is controversial,” he said.
Dr. Mok said that he was reserving judgment about elevating osimertinib to standard-of-care status until there were more answers about the final number of patients who are able to crossover to osimertinib, and about the “mechanism and management of osimertinib resistance upon disease progression.”
The study was funded by AstraZeneca, the maker of osimertinib. Dr Ramalingam is on the advisory boards of AstraZeneca and other companies. Dr Mok disclosed honoraria, fees, and research funding from Astra-Zeneca. Dr. Felip disclosed financial relationships with multiple companies not including AstraZeneca.
MADRID – The EGFR inhibitor osimertinib (Tagrisso) is being hailed as a new standard of care for first-line therapy of advanced, treatment naïve non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) with mutations in the epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR).
Osimertinib cut the risk of disease progression in these patients by 54% compared gefitinib (Iressa) or erlotinib (Tarceva).
Among 279 patients with EGFR-mutated locally advanced or metastatic NSCLC treated with osemirtinib, the median progression-free survival (PFS) was 18.9 months, compared with 10.2 months for 277 patients treated with the standard of care, which translates into a hazard ratio (HR) of 0.46 (P less than .0001).
“We wanted to see if by shutting down a major escape pathway by giving osemirtinib upfront, whether we would be able to improve patient outcomes,” he said at a briefing at the European Society of Medical Oncology (ESMO) Congress.
Osimertinib is a third-generation EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitor (TKI) selective for EGFR mutations, including the T790M resistance mutation. It is currently approved in the US for the treatment of patients with EGFR T790M mutation-positive NSCLC whose disease has progressed on or after EGFR TKI therapy.
In the FLAURA trial (NCT02296125) investigators stratified patients with previously untreated NSCLC positive for EGFR resistance mutations according to mutation status (exon 19 deletion or the L858R amino acid substitution in exon 21) and race (Asian or non-Asian).
Patients were randomly assigned to treatment with either oral osimertinib 80 mg daily or an EGFR TKI, either oral gefitinib 250 mg or erlotinib 150 mg daily.
The patients were assessed by Response Evaluation Criteria in Solid Tumors (RECIST) every 6 weeks until objective disease progression.
Patients assigned to the standard-of-care arm who had central confirmation of progression and T790M positivity were allowed to cross over to open-label osimertinib.
PFS, the primary endpoint, was also significantly better with osimertinib than with either of the comparator TKIs in patients with and without central nervous system metastases at study entry (HR 0.47, P = .0009 for patients with CNS metastases, HR 0.46, P less than .0001 for patients with no CNS metastases).
For this interim analysis, with OS data at only 25% maturity, median OS had not been reached in either trial arm. The HR for OS with osimertinib was 0.63, with a P value of .0068, but this was not statistically significant, as the statistical method used required a P of less than .0015 for significance, Dr. Ramalingam explained.
The safety profile of osimertinib was comparable to that of the standard of care, with lower rates of grade 3 or greater adverse events, and a lower discontinuation rate, than with either gefitinib or erlotinib.
Enriqueta Felip, MD, the invited commentator at the briefing, said that “based on these results, osimertinib should be considered a new first-line treatment option for patients with EGFR mutations.”
Tony Mok, MD, from the Chinese University of Hong Kong, the invited discussant at the presidential symposium where Dr. Ramalingam presented the study, commented that “there is little doubt that FLAURA is a positive study demonstrating superiority in PFS with first-line osimertinib.”
He questioned, however whether all patients with EGFR mutation-positve NSCLC should receive osimertinib up front.
“I have confidence that patients with CNS metastases at presentation would benefit the most considering osimertinib’s higher CNS penetration, but the optimal sequence for overall survival benefit is controversial,” he said.
Dr. Mok said that he was reserving judgment about elevating osimertinib to standard-of-care status until there were more answers about the final number of patients who are able to crossover to osimertinib, and about the “mechanism and management of osimertinib resistance upon disease progression.”
The study was funded by AstraZeneca, the maker of osimertinib. Dr Ramalingam is on the advisory boards of AstraZeneca and other companies. Dr Mok disclosed honoraria, fees, and research funding from Astra-Zeneca. Dr. Felip disclosed financial relationships with multiple companies not including AstraZeneca.
MADRID – The EGFR inhibitor osimertinib (Tagrisso) is being hailed as a new standard of care for first-line therapy of advanced, treatment naïve non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) with mutations in the epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR).
Osimertinib cut the risk of disease progression in these patients by 54% compared gefitinib (Iressa) or erlotinib (Tarceva).
Among 279 patients with EGFR-mutated locally advanced or metastatic NSCLC treated with osemirtinib, the median progression-free survival (PFS) was 18.9 months, compared with 10.2 months for 277 patients treated with the standard of care, which translates into a hazard ratio (HR) of 0.46 (P less than .0001).
“We wanted to see if by shutting down a major escape pathway by giving osemirtinib upfront, whether we would be able to improve patient outcomes,” he said at a briefing at the European Society of Medical Oncology (ESMO) Congress.
Osimertinib is a third-generation EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitor (TKI) selective for EGFR mutations, including the T790M resistance mutation. It is currently approved in the US for the treatment of patients with EGFR T790M mutation-positive NSCLC whose disease has progressed on or after EGFR TKI therapy.
In the FLAURA trial (NCT02296125) investigators stratified patients with previously untreated NSCLC positive for EGFR resistance mutations according to mutation status (exon 19 deletion or the L858R amino acid substitution in exon 21) and race (Asian or non-Asian).
Patients were randomly assigned to treatment with either oral osimertinib 80 mg daily or an EGFR TKI, either oral gefitinib 250 mg or erlotinib 150 mg daily.
The patients were assessed by Response Evaluation Criteria in Solid Tumors (RECIST) every 6 weeks until objective disease progression.
Patients assigned to the standard-of-care arm who had central confirmation of progression and T790M positivity were allowed to cross over to open-label osimertinib.
PFS, the primary endpoint, was also significantly better with osimertinib than with either of the comparator TKIs in patients with and without central nervous system metastases at study entry (HR 0.47, P = .0009 for patients with CNS metastases, HR 0.46, P less than .0001 for patients with no CNS metastases).
For this interim analysis, with OS data at only 25% maturity, median OS had not been reached in either trial arm. The HR for OS with osimertinib was 0.63, with a P value of .0068, but this was not statistically significant, as the statistical method used required a P of less than .0015 for significance, Dr. Ramalingam explained.
The safety profile of osimertinib was comparable to that of the standard of care, with lower rates of grade 3 or greater adverse events, and a lower discontinuation rate, than with either gefitinib or erlotinib.
Enriqueta Felip, MD, the invited commentator at the briefing, said that “based on these results, osimertinib should be considered a new first-line treatment option for patients with EGFR mutations.”
Tony Mok, MD, from the Chinese University of Hong Kong, the invited discussant at the presidential symposium where Dr. Ramalingam presented the study, commented that “there is little doubt that FLAURA is a positive study demonstrating superiority in PFS with first-line osimertinib.”
He questioned, however whether all patients with EGFR mutation-positve NSCLC should receive osimertinib up front.
“I have confidence that patients with CNS metastases at presentation would benefit the most considering osimertinib’s higher CNS penetration, but the optimal sequence for overall survival benefit is controversial,” he said.
Dr. Mok said that he was reserving judgment about elevating osimertinib to standard-of-care status until there were more answers about the final number of patients who are able to crossover to osimertinib, and about the “mechanism and management of osimertinib resistance upon disease progression.”
The study was funded by AstraZeneca, the maker of osimertinib. Dr Ramalingam is on the advisory boards of AstraZeneca and other companies. Dr Mok disclosed honoraria, fees, and research funding from Astra-Zeneca. Dr. Felip disclosed financial relationships with multiple companies not including AstraZeneca.
AT ESMO 2017
Key clinical point:
Major finding: The median PFS with osimertinib was 18.9 months, compared with 10.2 months for the standard of care (gefitinib or erlotinib).
Data source: Randomized double-blind study of 556 patients with EGFR-mutated NSCLC.
Disclosures: The study was funded by AstraZeneca. Dr Ramalingam is on the advisory boards of AstraZeneca and other companies. Dr Mok disclosed honoraria, fees, and research funding from Astra-Zeneca. Dr. Felip disclosed financial relationships with multiple companies not including AstraZeneca.