User login
FDA advisors urge physician certification for flibanserin
Without the option of recommending physician certification as a condition for flibanserin approval, the Food and Drug Administration advisory panel vote might have shifted against approval of the drug for treating hypoactive sexual desire disorder in premenopausal women.
At a joint meeting of two FDA advisory panels in June, members of the Bone, Reproductive and Urologic Drugs Advisory Committee and the Drug Safety and Risk Management Advisory Committee voted 18-6 that the overall benefit-risk profile of flibanserin supported approval for treating hypoactive sexual desire disorder (HSDD) in premenopausal women, provided that certain risk management options beyond labeling were implemented. If approved by the FDA, flibanserin would be the first drug approved for treating HSDD.
Assurance that prescribers would be fully apprised of the serious risks of hypotension and syncope associated with the drug, exacerbation of those side effects when combined with alcohol or a CYP3A4 inhibitor – and the modest effects over placebo – was cited by several of the panelists who voted in favor of approval.
All of those voting in favor of approval chose the option of supporting approval “only if certain risk management options beyond labeling are implemented.” None of the panelists voted for the option of supporting approval with “labeling alone to manage the risks.”
The conditions include a risk management plan to address serious adverse effects associated with the drug, a requirement for physician certification, and postmarketing studies to further evaluate and monitor the drug’s safety and efficacy.
The risks of hypotension and syncope, and central nervous system depression are also exacerbated by moderate or strong CYP3A4 inhibitors, but the interaction with alcohol was raised as a particularly serious issue because of the high rate of alcohol use and binge drinking among women who would likely be treated with flibanserin, according to FDA reviewers.
The risk of drug interactions can be mitigated with drug interaction screening programs used in health care systems, such as in electronic medical records and pharmacies, while alcohol use is a patient-dependent behavior, is common among women, and therefore more difficult to control, Kimberly Lehrfeld, Pharm.D., a team leader in the division of risk management in the FDA’s office of medication error prevention and analysis, said at the meeting. Several panelists recommended that alcohol use be a contraindication.
Physician certification is among the Elements to Assure Safe Use or ETASU, which along with a medication guide and a communication plan for health care providers, are components of a Risk Evaluation and Mitigation Strategy (REMS), a way to help manage the risks of a drug or biologic while still making it available to patients who need it.
Physician certification is part of the REMS for drugs such as mifepristone (Mifeprex), thalidomide (Thalomid), and natalizumab (Tysabri).
“A risk strategy that gets physicians the information they need to use it properly is going to be key,” said Dr. Robert Silbergleit, who voted for approval.”A REMS strategy is going to be very important because I think that the most likely risks … are going to come from physicians who don’t use the drug properly because they’re not properly educated.”
Dr. Silbergleit, a professor in the department of emergency medicine at the University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, said he was also concerned about the marketing of the drug. “Clinicians may be in the situation where they have to counter direct-to-consumer marketing that could lead to misuse of the drug,” he said at the meeting.
Also voting for approval, Marjorie Shaw Phillips, R.Ph., pharmacy coordinator at Georgia Regents Medical Center in Augusta, said that everyone needs to be aware of the potential safety concerns. But while she does not think pharmacy registration would be beneficial, there is a role for the pharmacist to confirm that it’s an educated provider prescribing the drug and that they’ve discussed the risks with the patient.
She added that it will be important for physicians to set realistic expectations for patients.
“It’s not a magical little pink pill, and there are going to be a whole lot of women with sexual dysfunction for whom there’s no evidence that it’s going to benefit them,” she said at the meeting.
The panel did not specifically recommend pharmacy certification, but pharmacists would have to verify that the prescribing physicians are certified, if the drug is approved, an FDA official said at the meeting.
A decision from the FDA is expected in August. The FDA panelists reported having no relevant financial disclosures.
Sprout Pharmaceuticals, flibanserin’s manufacturer, said in a statement that the company looks forward “to continuing our work with the FDA as it completes its review of our new drug application, including the discussion of a Risks Evaluation and Mitigation Strategy.” If approved, the company plans to market flibanserin as “Addyi.”
Without the option of recommending physician certification as a condition for flibanserin approval, the Food and Drug Administration advisory panel vote might have shifted against approval of the drug for treating hypoactive sexual desire disorder in premenopausal women.
At a joint meeting of two FDA advisory panels in June, members of the Bone, Reproductive and Urologic Drugs Advisory Committee and the Drug Safety and Risk Management Advisory Committee voted 18-6 that the overall benefit-risk profile of flibanserin supported approval for treating hypoactive sexual desire disorder (HSDD) in premenopausal women, provided that certain risk management options beyond labeling were implemented. If approved by the FDA, flibanserin would be the first drug approved for treating HSDD.
Assurance that prescribers would be fully apprised of the serious risks of hypotension and syncope associated with the drug, exacerbation of those side effects when combined with alcohol or a CYP3A4 inhibitor – and the modest effects over placebo – was cited by several of the panelists who voted in favor of approval.
All of those voting in favor of approval chose the option of supporting approval “only if certain risk management options beyond labeling are implemented.” None of the panelists voted for the option of supporting approval with “labeling alone to manage the risks.”
The conditions include a risk management plan to address serious adverse effects associated with the drug, a requirement for physician certification, and postmarketing studies to further evaluate and monitor the drug’s safety and efficacy.
The risks of hypotension and syncope, and central nervous system depression are also exacerbated by moderate or strong CYP3A4 inhibitors, but the interaction with alcohol was raised as a particularly serious issue because of the high rate of alcohol use and binge drinking among women who would likely be treated with flibanserin, according to FDA reviewers.
The risk of drug interactions can be mitigated with drug interaction screening programs used in health care systems, such as in electronic medical records and pharmacies, while alcohol use is a patient-dependent behavior, is common among women, and therefore more difficult to control, Kimberly Lehrfeld, Pharm.D., a team leader in the division of risk management in the FDA’s office of medication error prevention and analysis, said at the meeting. Several panelists recommended that alcohol use be a contraindication.
Physician certification is among the Elements to Assure Safe Use or ETASU, which along with a medication guide and a communication plan for health care providers, are components of a Risk Evaluation and Mitigation Strategy (REMS), a way to help manage the risks of a drug or biologic while still making it available to patients who need it.
Physician certification is part of the REMS for drugs such as mifepristone (Mifeprex), thalidomide (Thalomid), and natalizumab (Tysabri).
“A risk strategy that gets physicians the information they need to use it properly is going to be key,” said Dr. Robert Silbergleit, who voted for approval.”A REMS strategy is going to be very important because I think that the most likely risks … are going to come from physicians who don’t use the drug properly because they’re not properly educated.”
Dr. Silbergleit, a professor in the department of emergency medicine at the University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, said he was also concerned about the marketing of the drug. “Clinicians may be in the situation where they have to counter direct-to-consumer marketing that could lead to misuse of the drug,” he said at the meeting.
Also voting for approval, Marjorie Shaw Phillips, R.Ph., pharmacy coordinator at Georgia Regents Medical Center in Augusta, said that everyone needs to be aware of the potential safety concerns. But while she does not think pharmacy registration would be beneficial, there is a role for the pharmacist to confirm that it’s an educated provider prescribing the drug and that they’ve discussed the risks with the patient.
She added that it will be important for physicians to set realistic expectations for patients.
“It’s not a magical little pink pill, and there are going to be a whole lot of women with sexual dysfunction for whom there’s no evidence that it’s going to benefit them,” she said at the meeting.
The panel did not specifically recommend pharmacy certification, but pharmacists would have to verify that the prescribing physicians are certified, if the drug is approved, an FDA official said at the meeting.
A decision from the FDA is expected in August. The FDA panelists reported having no relevant financial disclosures.
Sprout Pharmaceuticals, flibanserin’s manufacturer, said in a statement that the company looks forward “to continuing our work with the FDA as it completes its review of our new drug application, including the discussion of a Risks Evaluation and Mitigation Strategy.” If approved, the company plans to market flibanserin as “Addyi.”
Without the option of recommending physician certification as a condition for flibanserin approval, the Food and Drug Administration advisory panel vote might have shifted against approval of the drug for treating hypoactive sexual desire disorder in premenopausal women.
At a joint meeting of two FDA advisory panels in June, members of the Bone, Reproductive and Urologic Drugs Advisory Committee and the Drug Safety and Risk Management Advisory Committee voted 18-6 that the overall benefit-risk profile of flibanserin supported approval for treating hypoactive sexual desire disorder (HSDD) in premenopausal women, provided that certain risk management options beyond labeling were implemented. If approved by the FDA, flibanserin would be the first drug approved for treating HSDD.
Assurance that prescribers would be fully apprised of the serious risks of hypotension and syncope associated with the drug, exacerbation of those side effects when combined with alcohol or a CYP3A4 inhibitor – and the modest effects over placebo – was cited by several of the panelists who voted in favor of approval.
All of those voting in favor of approval chose the option of supporting approval “only if certain risk management options beyond labeling are implemented.” None of the panelists voted for the option of supporting approval with “labeling alone to manage the risks.”
The conditions include a risk management plan to address serious adverse effects associated with the drug, a requirement for physician certification, and postmarketing studies to further evaluate and monitor the drug’s safety and efficacy.
The risks of hypotension and syncope, and central nervous system depression are also exacerbated by moderate or strong CYP3A4 inhibitors, but the interaction with alcohol was raised as a particularly serious issue because of the high rate of alcohol use and binge drinking among women who would likely be treated with flibanserin, according to FDA reviewers.
The risk of drug interactions can be mitigated with drug interaction screening programs used in health care systems, such as in electronic medical records and pharmacies, while alcohol use is a patient-dependent behavior, is common among women, and therefore more difficult to control, Kimberly Lehrfeld, Pharm.D., a team leader in the division of risk management in the FDA’s office of medication error prevention and analysis, said at the meeting. Several panelists recommended that alcohol use be a contraindication.
Physician certification is among the Elements to Assure Safe Use or ETASU, which along with a medication guide and a communication plan for health care providers, are components of a Risk Evaluation and Mitigation Strategy (REMS), a way to help manage the risks of a drug or biologic while still making it available to patients who need it.
Physician certification is part of the REMS for drugs such as mifepristone (Mifeprex), thalidomide (Thalomid), and natalizumab (Tysabri).
“A risk strategy that gets physicians the information they need to use it properly is going to be key,” said Dr. Robert Silbergleit, who voted for approval.”A REMS strategy is going to be very important because I think that the most likely risks … are going to come from physicians who don’t use the drug properly because they’re not properly educated.”
Dr. Silbergleit, a professor in the department of emergency medicine at the University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, said he was also concerned about the marketing of the drug. “Clinicians may be in the situation where they have to counter direct-to-consumer marketing that could lead to misuse of the drug,” he said at the meeting.
Also voting for approval, Marjorie Shaw Phillips, R.Ph., pharmacy coordinator at Georgia Regents Medical Center in Augusta, said that everyone needs to be aware of the potential safety concerns. But while she does not think pharmacy registration would be beneficial, there is a role for the pharmacist to confirm that it’s an educated provider prescribing the drug and that they’ve discussed the risks with the patient.
She added that it will be important for physicians to set realistic expectations for patients.
“It’s not a magical little pink pill, and there are going to be a whole lot of women with sexual dysfunction for whom there’s no evidence that it’s going to benefit them,” she said at the meeting.
The panel did not specifically recommend pharmacy certification, but pharmacists would have to verify that the prescribing physicians are certified, if the drug is approved, an FDA official said at the meeting.
A decision from the FDA is expected in August. The FDA panelists reported having no relevant financial disclosures.
Sprout Pharmaceuticals, flibanserin’s manufacturer, said in a statement that the company looks forward “to continuing our work with the FDA as it completes its review of our new drug application, including the discussion of a Risks Evaluation and Mitigation Strategy.” If approved, the company plans to market flibanserin as “Addyi.”
Cardiovascular disease in oncology
Click on the PDF icon at the top of this introduction to read the full article.
Click on the PDF icon at the top of this introduction to read the full article.
Click on the PDF icon at the top of this introduction to read the full article.
Measuring end-of-life care in oncology practices: learning from the care of the dying
Background There is increased interest among oncology and palliative professionals in providing appropriately timed hospice services for cancer patients. End of life (EoL) metrics have been included in oncology quality programs, but accurate EoL data and benchmarks are hard to obtain.
Objective To improve EoL care by measuring patterns of care among recently deceased patients.
Methods Care utilization among deceased patients was analyzed by using software integrated with patient electronic health records. The data was verified by chart review.
Results Of 179 cancer deaths, tumor registry data differed from chart review in 7% of cases with regard to dates and/or location of death. Institutional EoL metrics were significantly affected by a large number of patients (37%) with advanced illnesses who had clinical diagnoses of cancer made at the end of life, but who had not been managed by oncologists. This population of patients who had not been managed by oncologists was older, less likely to use hospice, and more likely to use the intensive care unit than were oncologist-managed cancer patients. Among the patients of individual oncologists, the median stay in hospice ranged from 6-28 days. Data collection and chart review took an average of 27 minutes per case with combined efforts by a data analyst and oncology practitioner.
Limitations Single institution with comprehensive electronic medical record; some patients were treated outside of the system.
Conclusion Acquiring accurate data on EoL metrics is time consuming. Compared with chart review, other data sources have inaccuracies and include some patients who have not been managed by oncologists. Accurate attribution to individual physicians requires chart review by an experienced clinician.
Click on the PDF icon at the top of this introduction to read the full article.
Background There is increased interest among oncology and palliative professionals in providing appropriately timed hospice services for cancer patients. End of life (EoL) metrics have been included in oncology quality programs, but accurate EoL data and benchmarks are hard to obtain.
Objective To improve EoL care by measuring patterns of care among recently deceased patients.
Methods Care utilization among deceased patients was analyzed by using software integrated with patient electronic health records. The data was verified by chart review.
Results Of 179 cancer deaths, tumor registry data differed from chart review in 7% of cases with regard to dates and/or location of death. Institutional EoL metrics were significantly affected by a large number of patients (37%) with advanced illnesses who had clinical diagnoses of cancer made at the end of life, but who had not been managed by oncologists. This population of patients who had not been managed by oncologists was older, less likely to use hospice, and more likely to use the intensive care unit than were oncologist-managed cancer patients. Among the patients of individual oncologists, the median stay in hospice ranged from 6-28 days. Data collection and chart review took an average of 27 minutes per case with combined efforts by a data analyst and oncology practitioner.
Limitations Single institution with comprehensive electronic medical record; some patients were treated outside of the system.
Conclusion Acquiring accurate data on EoL metrics is time consuming. Compared with chart review, other data sources have inaccuracies and include some patients who have not been managed by oncologists. Accurate attribution to individual physicians requires chart review by an experienced clinician.
Click on the PDF icon at the top of this introduction to read the full article.
Background There is increased interest among oncology and palliative professionals in providing appropriately timed hospice services for cancer patients. End of life (EoL) metrics have been included in oncology quality programs, but accurate EoL data and benchmarks are hard to obtain.
Objective To improve EoL care by measuring patterns of care among recently deceased patients.
Methods Care utilization among deceased patients was analyzed by using software integrated with patient electronic health records. The data was verified by chart review.
Results Of 179 cancer deaths, tumor registry data differed from chart review in 7% of cases with regard to dates and/or location of death. Institutional EoL metrics were significantly affected by a large number of patients (37%) with advanced illnesses who had clinical diagnoses of cancer made at the end of life, but who had not been managed by oncologists. This population of patients who had not been managed by oncologists was older, less likely to use hospice, and more likely to use the intensive care unit than were oncologist-managed cancer patients. Among the patients of individual oncologists, the median stay in hospice ranged from 6-28 days. Data collection and chart review took an average of 27 minutes per case with combined efforts by a data analyst and oncology practitioner.
Limitations Single institution with comprehensive electronic medical record; some patients were treated outside of the system.
Conclusion Acquiring accurate data on EoL metrics is time consuming. Compared with chart review, other data sources have inaccuracies and include some patients who have not been managed by oncologists. Accurate attribution to individual physicians requires chart review by an experienced clinician.
Click on the PDF icon at the top of this introduction to read the full article.
Impact of nurse navigation on timeliness of diagnostic medical services in patients with newly diagnosed lung cancer
Background The Summa Cancer Institute in Akron, Ohio, sought to improve access to and the timeliness of lung cancer care by hiring an oncology-certified nurse navigator. The nurse navigator was charged with coordinating diagnostic procedures and specialty oncology consultations, and with facilitating a multidisciplinary thoracic oncology tumor board.
Objective To test the hypothesis that nurse navigation would improve the timeliness of and access to diagnostic medical services among men and women with newly diagnosed lung cancer.
Methods A conducted a retrospective review of 460 patients with lung cancer to evaluate access to care and the timeliness of the care received in the non-navigated and nurse-navigated cohorts.
Results During December 2009-September 2013, the time between the suspicion of cancer on chest X-ray to treatment was 64 days. During October 2013-March 2014, the nurse navigator helped reduce that timespan to 45 days (P < .001).
Limitations Long-term follow-up on clinical outcomes remains premature.
Conclusion This finding attests to the successful implementation of nurse navigation to improve access and timeliness of lung cancer care in a community oncology practice.
Click on the PDF icon at the top of this introduction to read the full article.
Background The Summa Cancer Institute in Akron, Ohio, sought to improve access to and the timeliness of lung cancer care by hiring an oncology-certified nurse navigator. The nurse navigator was charged with coordinating diagnostic procedures and specialty oncology consultations, and with facilitating a multidisciplinary thoracic oncology tumor board.
Objective To test the hypothesis that nurse navigation would improve the timeliness of and access to diagnostic medical services among men and women with newly diagnosed lung cancer.
Methods A conducted a retrospective review of 460 patients with lung cancer to evaluate access to care and the timeliness of the care received in the non-navigated and nurse-navigated cohorts.
Results During December 2009-September 2013, the time between the suspicion of cancer on chest X-ray to treatment was 64 days. During October 2013-March 2014, the nurse navigator helped reduce that timespan to 45 days (P < .001).
Limitations Long-term follow-up on clinical outcomes remains premature.
Conclusion This finding attests to the successful implementation of nurse navigation to improve access and timeliness of lung cancer care in a community oncology practice.
Click on the PDF icon at the top of this introduction to read the full article.
Background The Summa Cancer Institute in Akron, Ohio, sought to improve access to and the timeliness of lung cancer care by hiring an oncology-certified nurse navigator. The nurse navigator was charged with coordinating diagnostic procedures and specialty oncology consultations, and with facilitating a multidisciplinary thoracic oncology tumor board.
Objective To test the hypothesis that nurse navigation would improve the timeliness of and access to diagnostic medical services among men and women with newly diagnosed lung cancer.
Methods A conducted a retrospective review of 460 patients with lung cancer to evaluate access to care and the timeliness of the care received in the non-navigated and nurse-navigated cohorts.
Results During December 2009-September 2013, the time between the suspicion of cancer on chest X-ray to treatment was 64 days. During October 2013-March 2014, the nurse navigator helped reduce that timespan to 45 days (P < .001).
Limitations Long-term follow-up on clinical outcomes remains premature.
Conclusion This finding attests to the successful implementation of nurse navigation to improve access and timeliness of lung cancer care in a community oncology practice.
Click on the PDF icon at the top of this introduction to read the full article.
Only moderate-quality evidence supports medical cannabinoids
At best, only moderate-quality evidence supports the use of medical cannabinoids, and for only two conditions. And low-quality evidence only “suggests” that these agents may improve other medical conditions, but that limited effectiveness applies only to the four conditions that have been studied, according to a report published online June 23 in JAMA.
This doesn’t necessarily mean that cannabinoids have poor efficacy but instead likely reflects the dearth of high-quality research into their medical usefulness.
In what they described as the first comprehensive review to evaluate the efficacy of numerous cannabinoids across a broad range of indications, researchers analyzed data from 79 studies involving 6,462 participants performed from 1975 to early 2015. The studies assessed nabilone, dronabinol, nabiximols, levonantradol, THC, THC/CBD, and ajuvenic acid, delivered via oral capsules, cigarettes, vaporizers, oromucosal sprays, or intramuscular injection, said Penny F. Whiting, Ph.D., of University Hospitals Bristol (England) and her associates.
Most of the studies suggested that cannabinoids improved symptoms for nearly all the 10 medical conditions included in this meta-analysis, but most of the studies were of poor quality so their conclusions were questionable. These agents’ efficacy did not vary according to the type of cannabinoid assessed or the mode of delivery.
Moderate-quality evidence indicated that cannabinoids may be beneficial for chronic neuropathic or cancer pain, and moderate-quality evidence indicated that they may also be beneficial for spasticity due to multiple sclerosis or traumatic paraplegia. Low-quality evidence suggested that cannabinoids may improve nausea and vomiting due to chemotherapy, may improve appetite and induce weight gain in HIV infection, and may improve sleep in primary sleep disorders as well as in conditions that disrupt sleep such as fibromyalgia, multiple sclerosis, and chronic pain. Very low-quality evidence (due to extremely small sample sizes) suggested that cannabinoids may greatly improve tic severity in Tourette’s syndrome, Dr. Whiting and her associates said (JAMA 2015 June 23 [doi:10.1001/jama.2015.6358]).
Otherwise, the evidence did not support cannabinoids’ efficacy in anxiety, depression, psychosis, or glaucoma. Adverse events included asthenia, problems with balance, confusion, dizziness, disorientation, dry mouth, fatigue, and somnolence.
It is unclear why medical marijuana has averted the usual Food and Drug Administration approval process required of other medications.
Adequately powered, double-blind, randomized, placebo- or treatment-controlled clinical trials are critical to establish cannabinoids’ short- and long-term efficacy and safety. Yet they already qualify by state law for use in conditions as varied as hepatitis C, Crohn’s disease, Parkinson’s disease, psoriasis, sickle cell disease, and posttraumatic stress disorder.
In particular, the risks of repeated exposure to cannabinoids needs further study. Addiction, tolerance, and a distinct withdrawal syndrome have been documented, and there is also a small but definite risk of psychotic disorder.
Dr. Deepak Cyril D’Souza and Dr. Mohini Ranganathan are in the department of psychiatry at Yale University, New Haven; in the psychiatry service at Veterans Affairs Connecticut Healthcare System, West Haven; and at Abraham Ribicoff Research Facilities at the Connecticut Mental Health Center, New Haven. Dr. D’Souza reported receiving grants from AbbVie and Pfizer, and serves on the Connecticut Board of Physicians that advises the Commissioner of Consumer Protection about the Act Concerning the Palliative Use of Marijuana. Dr. Ranganathan reported receiving grants from Insys Therapeutics. Dr. D’Souza and Dr. Ranganathan made these remarks in an editorial accompanying Dr. Whiting’s report (JAMA 2015;313:2431-2).
It is unclear why medical marijuana has averted the usual Food and Drug Administration approval process required of other medications.
Adequately powered, double-blind, randomized, placebo- or treatment-controlled clinical trials are critical to establish cannabinoids’ short- and long-term efficacy and safety. Yet they already qualify by state law for use in conditions as varied as hepatitis C, Crohn’s disease, Parkinson’s disease, psoriasis, sickle cell disease, and posttraumatic stress disorder.
In particular, the risks of repeated exposure to cannabinoids needs further study. Addiction, tolerance, and a distinct withdrawal syndrome have been documented, and there is also a small but definite risk of psychotic disorder.
Dr. Deepak Cyril D’Souza and Dr. Mohini Ranganathan are in the department of psychiatry at Yale University, New Haven; in the psychiatry service at Veterans Affairs Connecticut Healthcare System, West Haven; and at Abraham Ribicoff Research Facilities at the Connecticut Mental Health Center, New Haven. Dr. D’Souza reported receiving grants from AbbVie and Pfizer, and serves on the Connecticut Board of Physicians that advises the Commissioner of Consumer Protection about the Act Concerning the Palliative Use of Marijuana. Dr. Ranganathan reported receiving grants from Insys Therapeutics. Dr. D’Souza and Dr. Ranganathan made these remarks in an editorial accompanying Dr. Whiting’s report (JAMA 2015;313:2431-2).
It is unclear why medical marijuana has averted the usual Food and Drug Administration approval process required of other medications.
Adequately powered, double-blind, randomized, placebo- or treatment-controlled clinical trials are critical to establish cannabinoids’ short- and long-term efficacy and safety. Yet they already qualify by state law for use in conditions as varied as hepatitis C, Crohn’s disease, Parkinson’s disease, psoriasis, sickle cell disease, and posttraumatic stress disorder.
In particular, the risks of repeated exposure to cannabinoids needs further study. Addiction, tolerance, and a distinct withdrawal syndrome have been documented, and there is also a small but definite risk of psychotic disorder.
Dr. Deepak Cyril D’Souza and Dr. Mohini Ranganathan are in the department of psychiatry at Yale University, New Haven; in the psychiatry service at Veterans Affairs Connecticut Healthcare System, West Haven; and at Abraham Ribicoff Research Facilities at the Connecticut Mental Health Center, New Haven. Dr. D’Souza reported receiving grants from AbbVie and Pfizer, and serves on the Connecticut Board of Physicians that advises the Commissioner of Consumer Protection about the Act Concerning the Palliative Use of Marijuana. Dr. Ranganathan reported receiving grants from Insys Therapeutics. Dr. D’Souza and Dr. Ranganathan made these remarks in an editorial accompanying Dr. Whiting’s report (JAMA 2015;313:2431-2).
At best, only moderate-quality evidence supports the use of medical cannabinoids, and for only two conditions. And low-quality evidence only “suggests” that these agents may improve other medical conditions, but that limited effectiveness applies only to the four conditions that have been studied, according to a report published online June 23 in JAMA.
This doesn’t necessarily mean that cannabinoids have poor efficacy but instead likely reflects the dearth of high-quality research into their medical usefulness.
In what they described as the first comprehensive review to evaluate the efficacy of numerous cannabinoids across a broad range of indications, researchers analyzed data from 79 studies involving 6,462 participants performed from 1975 to early 2015. The studies assessed nabilone, dronabinol, nabiximols, levonantradol, THC, THC/CBD, and ajuvenic acid, delivered via oral capsules, cigarettes, vaporizers, oromucosal sprays, or intramuscular injection, said Penny F. Whiting, Ph.D., of University Hospitals Bristol (England) and her associates.
Most of the studies suggested that cannabinoids improved symptoms for nearly all the 10 medical conditions included in this meta-analysis, but most of the studies were of poor quality so their conclusions were questionable. These agents’ efficacy did not vary according to the type of cannabinoid assessed or the mode of delivery.
Moderate-quality evidence indicated that cannabinoids may be beneficial for chronic neuropathic or cancer pain, and moderate-quality evidence indicated that they may also be beneficial for spasticity due to multiple sclerosis or traumatic paraplegia. Low-quality evidence suggested that cannabinoids may improve nausea and vomiting due to chemotherapy, may improve appetite and induce weight gain in HIV infection, and may improve sleep in primary sleep disorders as well as in conditions that disrupt sleep such as fibromyalgia, multiple sclerosis, and chronic pain. Very low-quality evidence (due to extremely small sample sizes) suggested that cannabinoids may greatly improve tic severity in Tourette’s syndrome, Dr. Whiting and her associates said (JAMA 2015 June 23 [doi:10.1001/jama.2015.6358]).
Otherwise, the evidence did not support cannabinoids’ efficacy in anxiety, depression, psychosis, or glaucoma. Adverse events included asthenia, problems with balance, confusion, dizziness, disorientation, dry mouth, fatigue, and somnolence.
At best, only moderate-quality evidence supports the use of medical cannabinoids, and for only two conditions. And low-quality evidence only “suggests” that these agents may improve other medical conditions, but that limited effectiveness applies only to the four conditions that have been studied, according to a report published online June 23 in JAMA.
This doesn’t necessarily mean that cannabinoids have poor efficacy but instead likely reflects the dearth of high-quality research into their medical usefulness.
In what they described as the first comprehensive review to evaluate the efficacy of numerous cannabinoids across a broad range of indications, researchers analyzed data from 79 studies involving 6,462 participants performed from 1975 to early 2015. The studies assessed nabilone, dronabinol, nabiximols, levonantradol, THC, THC/CBD, and ajuvenic acid, delivered via oral capsules, cigarettes, vaporizers, oromucosal sprays, or intramuscular injection, said Penny F. Whiting, Ph.D., of University Hospitals Bristol (England) and her associates.
Most of the studies suggested that cannabinoids improved symptoms for nearly all the 10 medical conditions included in this meta-analysis, but most of the studies were of poor quality so their conclusions were questionable. These agents’ efficacy did not vary according to the type of cannabinoid assessed or the mode of delivery.
Moderate-quality evidence indicated that cannabinoids may be beneficial for chronic neuropathic or cancer pain, and moderate-quality evidence indicated that they may also be beneficial for spasticity due to multiple sclerosis or traumatic paraplegia. Low-quality evidence suggested that cannabinoids may improve nausea and vomiting due to chemotherapy, may improve appetite and induce weight gain in HIV infection, and may improve sleep in primary sleep disorders as well as in conditions that disrupt sleep such as fibromyalgia, multiple sclerosis, and chronic pain. Very low-quality evidence (due to extremely small sample sizes) suggested that cannabinoids may greatly improve tic severity in Tourette’s syndrome, Dr. Whiting and her associates said (JAMA 2015 June 23 [doi:10.1001/jama.2015.6358]).
Otherwise, the evidence did not support cannabinoids’ efficacy in anxiety, depression, psychosis, or glaucoma. Adverse events included asthenia, problems with balance, confusion, dizziness, disorientation, dry mouth, fatigue, and somnolence.
FROM JAMA
Key clinical point: Only moderate-quality evidence supports the use of medical cannabinoids, and only for two conditions.
Major finding: Moderate-quality evidence indicated that cannabinoids may be beneficial for chronic neuropathic or cancer pain and for spasticity due to multiple sclerosis or traumatic paraplegia.
Data source: A comprehensive review of the literature since 1975 and a meta-analysis of 79 clinical trials involving 6,462 participants.
Disclosures: This study was funded by the Swiss Federal Office of Public Health. Dr. Whiting and her associates reported having no relevant financial conflicts of interest.
Simultaneous integrated boost using stereotactic radiosurgery for resected brain metastases: rationale, dosimetric parameters, and preliminary clinical outcomes
Click on the PDF icon at the top of this introduction to read the full article.
Click on the PDF icon at the top of this introduction to read the full article.
Click on the PDF icon at the top of this introduction to read the full article.
Comparison of antiemetic efficacy and safety of palonosetron vs ondansetron in the prevention of chemotherapy-induced nausea and vomiting in children
Background Chemotherapy-induced nausea and vomiting (CINV) in children is a major side effect despite the use of combination antiemetic drugs.
Objective To compare the efficacy and safety profile of palonosetron, a second-generation 5-hydroxytryptamine-3 (5-HT3) receptor antagonist, with ondansetron in the prevention of CINV in children.
Methods A prospective, randomized, crossover study was conducted in patients aged 2-18 years. 160 chemotherapy cycles, consisting of chemotherapy drugs with moderate- and high-emetogenic potential, were studied. The study group received a single dose of intravenous (IV) palonosetron 5 mcg/kg, and the standard group received IV ondansetron 5 mg/m2 every 8 hours while receiving chemotherapy. The patients were observed for vomiting, use of rescue antiemetic medications, and nausea from Day 1 0-72 hours after completion of each chemotherapy cycle. All adverse events during the study period were recorded.
Results The overall percentage of patients with complete response (CR) in the palonosetron and ondansetron groups were 60% and 56.2%, respectively (P = .631). The CR rates in the palonosetron and ondansetron groups were 75% and 70%, respectively, in the acute phase (P = .479), and 68.8% and 65%, respectively, in the delayed phase (P = .614). There was no statistically significant difference in the CR rates cross both groups.
Conclusion A single dose of palonosetron is noninferior to ondansetron in the prevention of CINV in children and can be considered as an alternative antiemetic drug. There was no significant difference in adverse effects between the palonosetron and ondansetron group.
Click on the PDF icon at the top of this introduction to read the full article.
Background Chemotherapy-induced nausea and vomiting (CINV) in children is a major side effect despite the use of combination antiemetic drugs.
Objective To compare the efficacy and safety profile of palonosetron, a second-generation 5-hydroxytryptamine-3 (5-HT3) receptor antagonist, with ondansetron in the prevention of CINV in children.
Methods A prospective, randomized, crossover study was conducted in patients aged 2-18 years. 160 chemotherapy cycles, consisting of chemotherapy drugs with moderate- and high-emetogenic potential, were studied. The study group received a single dose of intravenous (IV) palonosetron 5 mcg/kg, and the standard group received IV ondansetron 5 mg/m2 every 8 hours while receiving chemotherapy. The patients were observed for vomiting, use of rescue antiemetic medications, and nausea from Day 1 0-72 hours after completion of each chemotherapy cycle. All adverse events during the study period were recorded.
Results The overall percentage of patients with complete response (CR) in the palonosetron and ondansetron groups were 60% and 56.2%, respectively (P = .631). The CR rates in the palonosetron and ondansetron groups were 75% and 70%, respectively, in the acute phase (P = .479), and 68.8% and 65%, respectively, in the delayed phase (P = .614). There was no statistically significant difference in the CR rates cross both groups.
Conclusion A single dose of palonosetron is noninferior to ondansetron in the prevention of CINV in children and can be considered as an alternative antiemetic drug. There was no significant difference in adverse effects between the palonosetron and ondansetron group.
Click on the PDF icon at the top of this introduction to read the full article.
Background Chemotherapy-induced nausea and vomiting (CINV) in children is a major side effect despite the use of combination antiemetic drugs.
Objective To compare the efficacy and safety profile of palonosetron, a second-generation 5-hydroxytryptamine-3 (5-HT3) receptor antagonist, with ondansetron in the prevention of CINV in children.
Methods A prospective, randomized, crossover study was conducted in patients aged 2-18 years. 160 chemotherapy cycles, consisting of chemotherapy drugs with moderate- and high-emetogenic potential, were studied. The study group received a single dose of intravenous (IV) palonosetron 5 mcg/kg, and the standard group received IV ondansetron 5 mg/m2 every 8 hours while receiving chemotherapy. The patients were observed for vomiting, use of rescue antiemetic medications, and nausea from Day 1 0-72 hours after completion of each chemotherapy cycle. All adverse events during the study period were recorded.
Results The overall percentage of patients with complete response (CR) in the palonosetron and ondansetron groups were 60% and 56.2%, respectively (P = .631). The CR rates in the palonosetron and ondansetron groups were 75% and 70%, respectively, in the acute phase (P = .479), and 68.8% and 65%, respectively, in the delayed phase (P = .614). There was no statistically significant difference in the CR rates cross both groups.
Conclusion A single dose of palonosetron is noninferior to ondansetron in the prevention of CINV in children and can be considered as an alternative antiemetic drug. There was no significant difference in adverse effects between the palonosetron and ondansetron group.
Click on the PDF icon at the top of this introduction to read the full article.
DDW: New scale measures impact of IBD on sexual function in men
WASHINGTON – Almost 40% of men with inflammatory bowel disease said the disease had a negative effect on their libido and almost 30% said that the disease had prevented them from having sex, in a study that used a new scale designed to evaluate sexual dysfunction in men with IBD, Dr. Aoibhlinn O’Toole reported at the annual Digestive Disease Week.
Dr. O’Toole, an IBD fellow at Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center, Boston, developed the IBD Sexual Dysfunction Scale (IBDSDS) with her associates at Beth Israel Deaconess and Brigham and Women’s Hospital. The results of the study were based on 175 responses to the IBDSDS questionnaire, which were sent to all the adult male patients treated at the IBD clinics at both medical centers. The IBD-specific tool is now being validated.
Because there has been no IBD-specific scale to measure sexual dysfunction in this group of patients, they developed the IBDSDS and conducted the study to evaluate the prevalence of sexual dysfunction in male patients with IBD and identify factors associated with sexual dysfunction. The process of designing the scale included a literature search of generic questionnaires to identify relevant domains of sexual function and the addition of IBD-specific questions related to the effects of symptoms, medications, and surgery on sexual function.
Despite significant issues that can clearly affect sexuality in this group of patients – including perianal disease and the effect of treatment and symptoms on body image, intimacy, and sexual function – the extent and effects of sexual dysfunction in men with IBD is not well known, Dr. O’Toole pointed out.
The 43 questions in the scale include those that pertain to libido, ejaculation, satisfaction, and body image, as well as elements of two validated screening tools, the International Index of Erectile Function (IIEF), the gold standard screening tool for erectile dysfunction; and the Patient Health Questionnaire 9 (PHQ-9), for depression.
The average age of the 175 respondents was 43 years and the average duration of IBD was 14 years; 57% had Crohn’s disease, 33% had had surgery, 6% had chronic pain, 2% used narcotics, 12% had hypertension, and 4% had diabetes. Almost 90% were in a relationship that “could involve sexual activity” and 2% had not been sexually active in the previous year. In addition, 14% said that they felt that IBD had caused a breakup in an existing relationship, and 21% said they had felt hesitant about starting a new relationship because of IBD.
As for the effects of IBD on sexual function, in the last year, 38% felt that IBD had a negative effect on their libido, 27% said IBD prevented them from having sex, and 18% said that IBD caused problems during sex. In addition, 20% said that IBD made them feel guilty about having sex and 30% said they feared having sex; 2% reported having erectile dysfunction.
The use of erectile-enhancing medications were reported by 23% (prescribed mostly by doctors other than the physician treating the IBD) and 5% were taking testosterone to enhance sexual function. While 78% said they were comfortable speaking about sexual function with their gastroenterologist, only 10% said that their gastroenterologist had initiated a discussion about this topic, Dr. O’Toole said.
Based on other analyses of the results, “we found that impaired sexual function was associated with older age, longer duration of disease, active disease, comorbid depression, presence of an ostomy, and diabetes,” she added.
While the thrombotic risks of testosterone are clear, Dr. O’Toole noted that in patients with IBD, the effects of phosphodiesterase-5 (PDE5) inhibitors like sildenafil (Viagra) on the microcirculation within the gastrointestinal tract and whether the effects of these drugs contribute to microscopic ischemia in the GI tract is unclear, she said. Dr. O’Toole had no relevant financial disclosures.
WASHINGTON – Almost 40% of men with inflammatory bowel disease said the disease had a negative effect on their libido and almost 30% said that the disease had prevented them from having sex, in a study that used a new scale designed to evaluate sexual dysfunction in men with IBD, Dr. Aoibhlinn O’Toole reported at the annual Digestive Disease Week.
Dr. O’Toole, an IBD fellow at Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center, Boston, developed the IBD Sexual Dysfunction Scale (IBDSDS) with her associates at Beth Israel Deaconess and Brigham and Women’s Hospital. The results of the study were based on 175 responses to the IBDSDS questionnaire, which were sent to all the adult male patients treated at the IBD clinics at both medical centers. The IBD-specific tool is now being validated.
Because there has been no IBD-specific scale to measure sexual dysfunction in this group of patients, they developed the IBDSDS and conducted the study to evaluate the prevalence of sexual dysfunction in male patients with IBD and identify factors associated with sexual dysfunction. The process of designing the scale included a literature search of generic questionnaires to identify relevant domains of sexual function and the addition of IBD-specific questions related to the effects of symptoms, medications, and surgery on sexual function.
Despite significant issues that can clearly affect sexuality in this group of patients – including perianal disease and the effect of treatment and symptoms on body image, intimacy, and sexual function – the extent and effects of sexual dysfunction in men with IBD is not well known, Dr. O’Toole pointed out.
The 43 questions in the scale include those that pertain to libido, ejaculation, satisfaction, and body image, as well as elements of two validated screening tools, the International Index of Erectile Function (IIEF), the gold standard screening tool for erectile dysfunction; and the Patient Health Questionnaire 9 (PHQ-9), for depression.
The average age of the 175 respondents was 43 years and the average duration of IBD was 14 years; 57% had Crohn’s disease, 33% had had surgery, 6% had chronic pain, 2% used narcotics, 12% had hypertension, and 4% had diabetes. Almost 90% were in a relationship that “could involve sexual activity” and 2% had not been sexually active in the previous year. In addition, 14% said that they felt that IBD had caused a breakup in an existing relationship, and 21% said they had felt hesitant about starting a new relationship because of IBD.
As for the effects of IBD on sexual function, in the last year, 38% felt that IBD had a negative effect on their libido, 27% said IBD prevented them from having sex, and 18% said that IBD caused problems during sex. In addition, 20% said that IBD made them feel guilty about having sex and 30% said they feared having sex; 2% reported having erectile dysfunction.
The use of erectile-enhancing medications were reported by 23% (prescribed mostly by doctors other than the physician treating the IBD) and 5% were taking testosterone to enhance sexual function. While 78% said they were comfortable speaking about sexual function with their gastroenterologist, only 10% said that their gastroenterologist had initiated a discussion about this topic, Dr. O’Toole said.
Based on other analyses of the results, “we found that impaired sexual function was associated with older age, longer duration of disease, active disease, comorbid depression, presence of an ostomy, and diabetes,” she added.
While the thrombotic risks of testosterone are clear, Dr. O’Toole noted that in patients with IBD, the effects of phosphodiesterase-5 (PDE5) inhibitors like sildenafil (Viagra) on the microcirculation within the gastrointestinal tract and whether the effects of these drugs contribute to microscopic ischemia in the GI tract is unclear, she said. Dr. O’Toole had no relevant financial disclosures.
WASHINGTON – Almost 40% of men with inflammatory bowel disease said the disease had a negative effect on their libido and almost 30% said that the disease had prevented them from having sex, in a study that used a new scale designed to evaluate sexual dysfunction in men with IBD, Dr. Aoibhlinn O’Toole reported at the annual Digestive Disease Week.
Dr. O’Toole, an IBD fellow at Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center, Boston, developed the IBD Sexual Dysfunction Scale (IBDSDS) with her associates at Beth Israel Deaconess and Brigham and Women’s Hospital. The results of the study were based on 175 responses to the IBDSDS questionnaire, which were sent to all the adult male patients treated at the IBD clinics at both medical centers. The IBD-specific tool is now being validated.
Because there has been no IBD-specific scale to measure sexual dysfunction in this group of patients, they developed the IBDSDS and conducted the study to evaluate the prevalence of sexual dysfunction in male patients with IBD and identify factors associated with sexual dysfunction. The process of designing the scale included a literature search of generic questionnaires to identify relevant domains of sexual function and the addition of IBD-specific questions related to the effects of symptoms, medications, and surgery on sexual function.
Despite significant issues that can clearly affect sexuality in this group of patients – including perianal disease and the effect of treatment and symptoms on body image, intimacy, and sexual function – the extent and effects of sexual dysfunction in men with IBD is not well known, Dr. O’Toole pointed out.
The 43 questions in the scale include those that pertain to libido, ejaculation, satisfaction, and body image, as well as elements of two validated screening tools, the International Index of Erectile Function (IIEF), the gold standard screening tool for erectile dysfunction; and the Patient Health Questionnaire 9 (PHQ-9), for depression.
The average age of the 175 respondents was 43 years and the average duration of IBD was 14 years; 57% had Crohn’s disease, 33% had had surgery, 6% had chronic pain, 2% used narcotics, 12% had hypertension, and 4% had diabetes. Almost 90% were in a relationship that “could involve sexual activity” and 2% had not been sexually active in the previous year. In addition, 14% said that they felt that IBD had caused a breakup in an existing relationship, and 21% said they had felt hesitant about starting a new relationship because of IBD.
As for the effects of IBD on sexual function, in the last year, 38% felt that IBD had a negative effect on their libido, 27% said IBD prevented them from having sex, and 18% said that IBD caused problems during sex. In addition, 20% said that IBD made them feel guilty about having sex and 30% said they feared having sex; 2% reported having erectile dysfunction.
The use of erectile-enhancing medications were reported by 23% (prescribed mostly by doctors other than the physician treating the IBD) and 5% were taking testosterone to enhance sexual function. While 78% said they were comfortable speaking about sexual function with their gastroenterologist, only 10% said that their gastroenterologist had initiated a discussion about this topic, Dr. O’Toole said.
Based on other analyses of the results, “we found that impaired sexual function was associated with older age, longer duration of disease, active disease, comorbid depression, presence of an ostomy, and diabetes,” she added.
While the thrombotic risks of testosterone are clear, Dr. O’Toole noted that in patients with IBD, the effects of phosphodiesterase-5 (PDE5) inhibitors like sildenafil (Viagra) on the microcirculation within the gastrointestinal tract and whether the effects of these drugs contribute to microscopic ischemia in the GI tract is unclear, she said. Dr. O’Toole had no relevant financial disclosures.
AT DDW 2015
Key clinical point: Once validated, a new scale designed to evaluate sexual dysfunction in men with inflammatory bowel disease could provide a useful tool to evaluate the impact the disease has on sexual function in male patients.
Major finding: The negative effects of IBD on sexual dysfunction in men with the disease, reflected in the responses to the IBD-specific questionnaire, included negative effects on libido in 38% and fear of having sex in 30%.
Data source: Results were based on the responses to the questionnaire from 175 male patients treated at the IBD clinics at two Boston medical centers.
Disclosures: Dr. O’Toole had no relevant financial disclosures.
DDW: Budesonide improves dysphagia, histology, and endoscopic findings in EoE
WASHINGTON – Treatment with an oral formulation of budesonide was associated with significant improvements in dysphagia and esophageal eosinophil counts in adolescents and adults with eosinophilic esophagitis, in a study that is also the first to use a recently validated scoring instrument to evaluate medical therapy for this disorder in a randomized trial.
Results of the multicenter, double-blind, randomized study comparing treatment with an oral budesonide suspension to placebo for 12 weeks in almost 100 patients with eosinophilic esophagitis (EoE) were reported in two separate presentations at the annual Digestive Disease Week. One of the investigators, Dr. Evan Dellon of the Center for Gastrointestinal Biology and Disease, at the University of North Carolina, Chapel Hill, said that treatment with this “mucoadherent” formulation of the topical steroid was associated with significant improvements in dysphagia symptoms, as measured with the Dysphagia Symptom Questionnaire (DSQ), and a histologic response rate of 39%, vs. 3% among those on placebo.
“The study not only adds to the evidence that topical budesonide is effective for inducing histologic response in subjects with active EoE, but [also] shows for the first time that symptoms of dysphagia, as measured with a validated symptom instrument, improve concordantly with the histologic and endoscopic findings,” Dr. Dellon said in an interview after the meeting. “Moreover, this study shows that a topical steroid formulation designed specifically for EoE, rather than an asthma formulation that is adapted for esophageal use, will likely be a beneficial and potentially preferred clinical treatment option.”
Another study investigator, Dr. Ikuo Hirano, professor of medicine and director of the gastroenterology and hepatology fellowship program at Northwestern University, Chicago, reported that treatment was also associated with significant improvements in the EoE Endoscopic Reference Score, EREFS, which was designed to classify and grade the severity of five major endoscopic features of EoE: edema, rings, exudates, furrows, and stricture formation. This was the first study to use this validated endoscopic scoring instrument in a randomized controlled trial of a medical therapy in patients with EoE, he said at the meeting.
The study was conducted between 2012 and 2014 at 25 U.S. sites, in patients aged 11-40 years with EoE. Baseline demographic and endoscopic characteristics were similar in the two groups. Their mean age was 21-22 years (41% of those on placebo and 35% of those on budesonide were younger than age 18 years) and 69% were male; most patients had edema, all had dysphagia, and 39%-41% had heartburn. Patients were excluded if they had esophageal stricture on screening endoscopy that did not allow passage of a standard adult diagnostic endoscope.
Patients were randomized to treatment with budesonide suspension, at a dose of 2 mg twice a day (51 patients) or a placebo suspension (42 patients). The primary outcomes were a change in the DSQ score from baseline, and the proportion of patients with a histologic response, defined as at least 6 eosinophils per high-power field (eos/hpf) from all biopsies. The final analysis included 87 patients.
At baseline, the mean peak eosinophil counts were 156/hpf among those on budesonide and 130/hpf among those on placebo; after treatment, the mean peak counts dropped to 39/hpf among those on budesonide (a 65% reduction) and to 113/hpf among those on placebo (a 10% reduction), a statistically significant difference (P < .05), said Dr. Dellon, also with the department of medicine at UNC.
From a mean of about 29 in both groups at baseline, DSQ scores dropped by a mean of 14.3 among the treated patients, vs. 7.5 among those on placebo, which was a statistically significant difference (P = .0096). The other primary endpoint, the histologic response rate, was 39% among treated patients, vs. 3% among those on placebo, also a significant difference (P < .0001).
Adverse events were not different between the two groups, and growth velocity among those under age 18 years and cortisol levels were not different between the two groups, he added. There was one case of esophageal candidiasis in a patient on budesonide.
During his presentation, Dr. Hirano said that there were also significant improvements in EREFS scores from baseline in the proximal and distal esophagus among those treated with budesonide, but not among those on placebo. Based on EREFS scores, oral budesonide “resulted in significant improvement in endoscopic features of edema, exudate, rings, [and] furrows, compared to placebo,” but there was no significant change in strictures, another component of the EREFS, in either the treatment or placebo groups. However, patients with high-grade strictures were not enrolled in the study, he added.
After treatment, proximal, distal, and total EREFS scores correlated with peak eosinophil counts, a highly statistically significant finding.
Dr. Hirano said that the primary endpoints used in most EoE clinical trials to date have focused mostly on assessments of symptoms and histopathology, which have limitations. “Symptoms are difficult to quantify and often intermittent [and] they may improve as a result of changes in eating behavior and food avoidance,” he said. Patient-reported outcome instruments have been recently validated, “but have questionable utility in clinical practice” and histology “has shown limited correlation between degree of esophageal eosinophilia and symptom severity [and does not] assess for modeling, an important determinant of overall disease complications,” he added.
The utility of endoscopy in EoE includes the features that are present in vast majority of patients with EoE, and provides a gross assessment of overall disease activity, “both in terms of inflammatory and fibrostenotic features,” he said.
“Endoscopic outcomes are now emerging as clinically relevant endpoints of therapy of trials of eosinophilic esophagitis that supports and complements” symptom and histologic assessments, Dr. Hirano commented, adding that more studies are need to determine the “relative importance of these individual endoscopic features as well as the appropriate utilization of endoscopic parameters in disease management.”
The study was funded by Meritage Pharma, recently acquired by the Shire group of companies. All authors received research funds to conduct the study, and Dr. Hirano disclosed having worked as a consultant for Meritage. Dr. Dellon’s disclosures included receiving grant and research support from Meritage. Shire is developing the oral budesonide suspension formulation as a treatment for adolescents and adults with EoE.
WASHINGTON – Treatment with an oral formulation of budesonide was associated with significant improvements in dysphagia and esophageal eosinophil counts in adolescents and adults with eosinophilic esophagitis, in a study that is also the first to use a recently validated scoring instrument to evaluate medical therapy for this disorder in a randomized trial.
Results of the multicenter, double-blind, randomized study comparing treatment with an oral budesonide suspension to placebo for 12 weeks in almost 100 patients with eosinophilic esophagitis (EoE) were reported in two separate presentations at the annual Digestive Disease Week. One of the investigators, Dr. Evan Dellon of the Center for Gastrointestinal Biology and Disease, at the University of North Carolina, Chapel Hill, said that treatment with this “mucoadherent” formulation of the topical steroid was associated with significant improvements in dysphagia symptoms, as measured with the Dysphagia Symptom Questionnaire (DSQ), and a histologic response rate of 39%, vs. 3% among those on placebo.
“The study not only adds to the evidence that topical budesonide is effective for inducing histologic response in subjects with active EoE, but [also] shows for the first time that symptoms of dysphagia, as measured with a validated symptom instrument, improve concordantly with the histologic and endoscopic findings,” Dr. Dellon said in an interview after the meeting. “Moreover, this study shows that a topical steroid formulation designed specifically for EoE, rather than an asthma formulation that is adapted for esophageal use, will likely be a beneficial and potentially preferred clinical treatment option.”
Another study investigator, Dr. Ikuo Hirano, professor of medicine and director of the gastroenterology and hepatology fellowship program at Northwestern University, Chicago, reported that treatment was also associated with significant improvements in the EoE Endoscopic Reference Score, EREFS, which was designed to classify and grade the severity of five major endoscopic features of EoE: edema, rings, exudates, furrows, and stricture formation. This was the first study to use this validated endoscopic scoring instrument in a randomized controlled trial of a medical therapy in patients with EoE, he said at the meeting.
The study was conducted between 2012 and 2014 at 25 U.S. sites, in patients aged 11-40 years with EoE. Baseline demographic and endoscopic characteristics were similar in the two groups. Their mean age was 21-22 years (41% of those on placebo and 35% of those on budesonide were younger than age 18 years) and 69% were male; most patients had edema, all had dysphagia, and 39%-41% had heartburn. Patients were excluded if they had esophageal stricture on screening endoscopy that did not allow passage of a standard adult diagnostic endoscope.
Patients were randomized to treatment with budesonide suspension, at a dose of 2 mg twice a day (51 patients) or a placebo suspension (42 patients). The primary outcomes were a change in the DSQ score from baseline, and the proportion of patients with a histologic response, defined as at least 6 eosinophils per high-power field (eos/hpf) from all biopsies. The final analysis included 87 patients.
At baseline, the mean peak eosinophil counts were 156/hpf among those on budesonide and 130/hpf among those on placebo; after treatment, the mean peak counts dropped to 39/hpf among those on budesonide (a 65% reduction) and to 113/hpf among those on placebo (a 10% reduction), a statistically significant difference (P < .05), said Dr. Dellon, also with the department of medicine at UNC.
From a mean of about 29 in both groups at baseline, DSQ scores dropped by a mean of 14.3 among the treated patients, vs. 7.5 among those on placebo, which was a statistically significant difference (P = .0096). The other primary endpoint, the histologic response rate, was 39% among treated patients, vs. 3% among those on placebo, also a significant difference (P < .0001).
Adverse events were not different between the two groups, and growth velocity among those under age 18 years and cortisol levels were not different between the two groups, he added. There was one case of esophageal candidiasis in a patient on budesonide.
During his presentation, Dr. Hirano said that there were also significant improvements in EREFS scores from baseline in the proximal and distal esophagus among those treated with budesonide, but not among those on placebo. Based on EREFS scores, oral budesonide “resulted in significant improvement in endoscopic features of edema, exudate, rings, [and] furrows, compared to placebo,” but there was no significant change in strictures, another component of the EREFS, in either the treatment or placebo groups. However, patients with high-grade strictures were not enrolled in the study, he added.
After treatment, proximal, distal, and total EREFS scores correlated with peak eosinophil counts, a highly statistically significant finding.
Dr. Hirano said that the primary endpoints used in most EoE clinical trials to date have focused mostly on assessments of symptoms and histopathology, which have limitations. “Symptoms are difficult to quantify and often intermittent [and] they may improve as a result of changes in eating behavior and food avoidance,” he said. Patient-reported outcome instruments have been recently validated, “but have questionable utility in clinical practice” and histology “has shown limited correlation between degree of esophageal eosinophilia and symptom severity [and does not] assess for modeling, an important determinant of overall disease complications,” he added.
The utility of endoscopy in EoE includes the features that are present in vast majority of patients with EoE, and provides a gross assessment of overall disease activity, “both in terms of inflammatory and fibrostenotic features,” he said.
“Endoscopic outcomes are now emerging as clinically relevant endpoints of therapy of trials of eosinophilic esophagitis that supports and complements” symptom and histologic assessments, Dr. Hirano commented, adding that more studies are need to determine the “relative importance of these individual endoscopic features as well as the appropriate utilization of endoscopic parameters in disease management.”
The study was funded by Meritage Pharma, recently acquired by the Shire group of companies. All authors received research funds to conduct the study, and Dr. Hirano disclosed having worked as a consultant for Meritage. Dr. Dellon’s disclosures included receiving grant and research support from Meritage. Shire is developing the oral budesonide suspension formulation as a treatment for adolescents and adults with EoE.
WASHINGTON – Treatment with an oral formulation of budesonide was associated with significant improvements in dysphagia and esophageal eosinophil counts in adolescents and adults with eosinophilic esophagitis, in a study that is also the first to use a recently validated scoring instrument to evaluate medical therapy for this disorder in a randomized trial.
Results of the multicenter, double-blind, randomized study comparing treatment with an oral budesonide suspension to placebo for 12 weeks in almost 100 patients with eosinophilic esophagitis (EoE) were reported in two separate presentations at the annual Digestive Disease Week. One of the investigators, Dr. Evan Dellon of the Center for Gastrointestinal Biology and Disease, at the University of North Carolina, Chapel Hill, said that treatment with this “mucoadherent” formulation of the topical steroid was associated with significant improvements in dysphagia symptoms, as measured with the Dysphagia Symptom Questionnaire (DSQ), and a histologic response rate of 39%, vs. 3% among those on placebo.
“The study not only adds to the evidence that topical budesonide is effective for inducing histologic response in subjects with active EoE, but [also] shows for the first time that symptoms of dysphagia, as measured with a validated symptom instrument, improve concordantly with the histologic and endoscopic findings,” Dr. Dellon said in an interview after the meeting. “Moreover, this study shows that a topical steroid formulation designed specifically for EoE, rather than an asthma formulation that is adapted for esophageal use, will likely be a beneficial and potentially preferred clinical treatment option.”
Another study investigator, Dr. Ikuo Hirano, professor of medicine and director of the gastroenterology and hepatology fellowship program at Northwestern University, Chicago, reported that treatment was also associated with significant improvements in the EoE Endoscopic Reference Score, EREFS, which was designed to classify and grade the severity of five major endoscopic features of EoE: edema, rings, exudates, furrows, and stricture formation. This was the first study to use this validated endoscopic scoring instrument in a randomized controlled trial of a medical therapy in patients with EoE, he said at the meeting.
The study was conducted between 2012 and 2014 at 25 U.S. sites, in patients aged 11-40 years with EoE. Baseline demographic and endoscopic characteristics were similar in the two groups. Their mean age was 21-22 years (41% of those on placebo and 35% of those on budesonide were younger than age 18 years) and 69% were male; most patients had edema, all had dysphagia, and 39%-41% had heartburn. Patients were excluded if they had esophageal stricture on screening endoscopy that did not allow passage of a standard adult diagnostic endoscope.
Patients were randomized to treatment with budesonide suspension, at a dose of 2 mg twice a day (51 patients) or a placebo suspension (42 patients). The primary outcomes were a change in the DSQ score from baseline, and the proportion of patients with a histologic response, defined as at least 6 eosinophils per high-power field (eos/hpf) from all biopsies. The final analysis included 87 patients.
At baseline, the mean peak eosinophil counts were 156/hpf among those on budesonide and 130/hpf among those on placebo; after treatment, the mean peak counts dropped to 39/hpf among those on budesonide (a 65% reduction) and to 113/hpf among those on placebo (a 10% reduction), a statistically significant difference (P < .05), said Dr. Dellon, also with the department of medicine at UNC.
From a mean of about 29 in both groups at baseline, DSQ scores dropped by a mean of 14.3 among the treated patients, vs. 7.5 among those on placebo, which was a statistically significant difference (P = .0096). The other primary endpoint, the histologic response rate, was 39% among treated patients, vs. 3% among those on placebo, also a significant difference (P < .0001).
Adverse events were not different between the two groups, and growth velocity among those under age 18 years and cortisol levels were not different between the two groups, he added. There was one case of esophageal candidiasis in a patient on budesonide.
During his presentation, Dr. Hirano said that there were also significant improvements in EREFS scores from baseline in the proximal and distal esophagus among those treated with budesonide, but not among those on placebo. Based on EREFS scores, oral budesonide “resulted in significant improvement in endoscopic features of edema, exudate, rings, [and] furrows, compared to placebo,” but there was no significant change in strictures, another component of the EREFS, in either the treatment or placebo groups. However, patients with high-grade strictures were not enrolled in the study, he added.
After treatment, proximal, distal, and total EREFS scores correlated with peak eosinophil counts, a highly statistically significant finding.
Dr. Hirano said that the primary endpoints used in most EoE clinical trials to date have focused mostly on assessments of symptoms and histopathology, which have limitations. “Symptoms are difficult to quantify and often intermittent [and] they may improve as a result of changes in eating behavior and food avoidance,” he said. Patient-reported outcome instruments have been recently validated, “but have questionable utility in clinical practice” and histology “has shown limited correlation between degree of esophageal eosinophilia and symptom severity [and does not] assess for modeling, an important determinant of overall disease complications,” he added.
The utility of endoscopy in EoE includes the features that are present in vast majority of patients with EoE, and provides a gross assessment of overall disease activity, “both in terms of inflammatory and fibrostenotic features,” he said.
“Endoscopic outcomes are now emerging as clinically relevant endpoints of therapy of trials of eosinophilic esophagitis that supports and complements” symptom and histologic assessments, Dr. Hirano commented, adding that more studies are need to determine the “relative importance of these individual endoscopic features as well as the appropriate utilization of endoscopic parameters in disease management.”
The study was funded by Meritage Pharma, recently acquired by the Shire group of companies. All authors received research funds to conduct the study, and Dr. Hirano disclosed having worked as a consultant for Meritage. Dr. Dellon’s disclosures included receiving grant and research support from Meritage. Shire is developing the oral budesonide suspension formulation as a treatment for adolescents and adults with EoE.
AT DDW 2015
Key clinical point: A mucoadherent oral formulation of budesonide shows promise as an effective treatment for eosinophilic esophagitis (EoE), with a favorable safety profile.
Major finding: Beneficial effects of oral budesonide in a study of adolescents and adults with EoE included a histologic response rate of 39% and significantly improved dysphagia symptoms.
Data source: A randomized, double-blind multicenter U.S. study evaluated the healing effects and response to of oral budesonide vs. placebo in 93 patients with EoE, aged 11-40 years.
Disclosures: The study was funded by Meritage Pharma, recently acquired by the Shire group of companies. All authors received research funds to conduct the study. Dr. Dellon’s disclosures included receiving grant and research support from Meritage. Dr. Hirano disclosed having worked as a consultant for Meritage.
EZH2 inhibitor proves active in rel/ref NHL
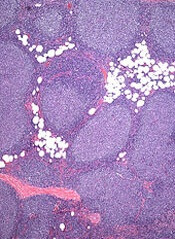
LUGANO—The EZH2 inhibitor tazemetostat (EPZ-6438) has shown “meaningful clinical activity” as monotherapy in patients with advanced non-Hodgkin lymphoma (NHL), according to researchers.
In a phase 1 trial, 9 of the 15 evaluable NHL patients achieved an objective response to tazemetostat.
This included 2 ongoing complete responses (CRs), 1 in a patient with diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL) and 1 in a patient with follicular lymphoma (FL).
It also included a partial response (PR) in the first treated patient with an EZH2 mutation.
And researchers said the drug was largely well-tolerated, as most adverse events were grade 1 or 2.
“The breadth, depth, and durability of responses seen in NHL patients among multiple histologies continue to impress, as does the safety and tolerability of tazemetostat in this phase 1 study,” said Vincent Ribrag, MD, of Institut Gustave Roussy in Villejuif, France.
“Among the patients in the dose-escalation cohorts, we have seen a noteworthy deepening of responses over time, and, in the first treated patient with an EZH2 tumor mutation, we have seen a partial response, which is very encouraging.”
Dr Ribrag presented these results at the 13th International Conference on Malignant Lymphoma (abstract 145*). The study, which was previously presented at the 26th EORTC-NCI-AACR Symposium on Molecular Targets and Cancer Therapeutics, was sponsored by Epizyme, Inc., the company developing tazemetostat.
The phase 1 trial has enrolled 19 patients with relapsed or refractory B-cell NHL and 26 patients with advanced solid tumors.
Researchers have evaluated 5 cohorts of patients in the dose-escalation portion of the study—100 mg, 200 mg, 400 mg, 800 mg, and 1600 mg—and 2 cohorts—800 mg and 1600 mg—in the dose-expansion phase. All doses of tazemetostat were given twice daily.
The 19 NHL patients had a median age of 61 (range, 24-84) and were heavily pretreated. Eighty-five percent had received 3 or more prior therapies, and 37% had received 5 or more prior therapies.
Thirty-seven percent of patients were refractory to their last prior regimen, and 26% had received a prior autologous hematopoietic stem cell transplant.
Dosing and efficacy
As of June 8, 2015, 15 NHL patients were evaluable for efficacy. Nine had achieved an objective response, including 2 patients with an ongoing CR. All responses were observed between 2 and 10 months on therapy.
Five of the 9 evaluable patients with DLBCL achieved an objective response. One DLBCL patient with a CR remains on study at 18 months of treatment.
Three of 5 evaluable patients with follicular lymphoma (FL) achieved an objective response. One FL patient with a CR remains on study at 13 months, and 1 FL patient with a PR remains on study at 13 months.
The only patient with marginal zone lymphoma achieved a PR and continues on study at 11 months.
One of the 14 patients evaluated for EZH2 status has a specific EZH2 tumor mutation (Y646H). This patient, who had DLBCL that relapsed or was refractory to 6 previous treatment regimens, achieved a PR after 16 weeks of therapy and remains on study.
The recommended phase 2 dose of tazemetostat is 800 mg twice daily.
Adverse events and next steps
All of the 45 enrolled patients were evaluable for safety. Treatment-related adverse events included asthenia (n=10), nausea (n=6), dyspepsia (n=5), thrombocytopenia (n=4), anorexia (n=4), anemia (n=4), vomiting (n=3), constipation (n=2), muscle spasm (n=2), hypertension (n=2), neutropenia (n=2), and elevated transaminase (n=1).
There were 5 grade 3 or higher adverse events related to treatment, including grade 3 anorexia, grade 3 hypertension, grade 3 transaminase elevation, grade 4 thrombocytopenia, and grade 4 neutropenia.
Epizyme plans to report a further update from this trial by the end of this year. The company is now enrolling patients in a phase 2 study of tazemetostat monotherapy in patients with relapsed or refractory NHL, stratified by cell of origin and EZH2 mutation status.
Epizyme is also planning a phase 2 trial of tazemetostat in adults with INI1-deficient solid tumors, a phase 1 study of pediatric patients with INI1-deficient solid tumors, a combination study of tazemetostat with R-CHOP in patients with DLBCL, and a combination study of tazemetostat with a B-cell signaling agent or other emerging targeted therapies for B-cell lymphomas. ![]()
*Information in the abstract differs from that presented at the meeting.

LUGANO—The EZH2 inhibitor tazemetostat (EPZ-6438) has shown “meaningful clinical activity” as monotherapy in patients with advanced non-Hodgkin lymphoma (NHL), according to researchers.
In a phase 1 trial, 9 of the 15 evaluable NHL patients achieved an objective response to tazemetostat.
This included 2 ongoing complete responses (CRs), 1 in a patient with diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL) and 1 in a patient with follicular lymphoma (FL).
It also included a partial response (PR) in the first treated patient with an EZH2 mutation.
And researchers said the drug was largely well-tolerated, as most adverse events were grade 1 or 2.
“The breadth, depth, and durability of responses seen in NHL patients among multiple histologies continue to impress, as does the safety and tolerability of tazemetostat in this phase 1 study,” said Vincent Ribrag, MD, of Institut Gustave Roussy in Villejuif, France.
“Among the patients in the dose-escalation cohorts, we have seen a noteworthy deepening of responses over time, and, in the first treated patient with an EZH2 tumor mutation, we have seen a partial response, which is very encouraging.”
Dr Ribrag presented these results at the 13th International Conference on Malignant Lymphoma (abstract 145*). The study, which was previously presented at the 26th EORTC-NCI-AACR Symposium on Molecular Targets and Cancer Therapeutics, was sponsored by Epizyme, Inc., the company developing tazemetostat.
The phase 1 trial has enrolled 19 patients with relapsed or refractory B-cell NHL and 26 patients with advanced solid tumors.
Researchers have evaluated 5 cohorts of patients in the dose-escalation portion of the study—100 mg, 200 mg, 400 mg, 800 mg, and 1600 mg—and 2 cohorts—800 mg and 1600 mg—in the dose-expansion phase. All doses of tazemetostat were given twice daily.
The 19 NHL patients had a median age of 61 (range, 24-84) and were heavily pretreated. Eighty-five percent had received 3 or more prior therapies, and 37% had received 5 or more prior therapies.
Thirty-seven percent of patients were refractory to their last prior regimen, and 26% had received a prior autologous hematopoietic stem cell transplant.
Dosing and efficacy
As of June 8, 2015, 15 NHL patients were evaluable for efficacy. Nine had achieved an objective response, including 2 patients with an ongoing CR. All responses were observed between 2 and 10 months on therapy.
Five of the 9 evaluable patients with DLBCL achieved an objective response. One DLBCL patient with a CR remains on study at 18 months of treatment.
Three of 5 evaluable patients with follicular lymphoma (FL) achieved an objective response. One FL patient with a CR remains on study at 13 months, and 1 FL patient with a PR remains on study at 13 months.
The only patient with marginal zone lymphoma achieved a PR and continues on study at 11 months.
One of the 14 patients evaluated for EZH2 status has a specific EZH2 tumor mutation (Y646H). This patient, who had DLBCL that relapsed or was refractory to 6 previous treatment regimens, achieved a PR after 16 weeks of therapy and remains on study.
The recommended phase 2 dose of tazemetostat is 800 mg twice daily.
Adverse events and next steps
All of the 45 enrolled patients were evaluable for safety. Treatment-related adverse events included asthenia (n=10), nausea (n=6), dyspepsia (n=5), thrombocytopenia (n=4), anorexia (n=4), anemia (n=4), vomiting (n=3), constipation (n=2), muscle spasm (n=2), hypertension (n=2), neutropenia (n=2), and elevated transaminase (n=1).
There were 5 grade 3 or higher adverse events related to treatment, including grade 3 anorexia, grade 3 hypertension, grade 3 transaminase elevation, grade 4 thrombocytopenia, and grade 4 neutropenia.
Epizyme plans to report a further update from this trial by the end of this year. The company is now enrolling patients in a phase 2 study of tazemetostat monotherapy in patients with relapsed or refractory NHL, stratified by cell of origin and EZH2 mutation status.
Epizyme is also planning a phase 2 trial of tazemetostat in adults with INI1-deficient solid tumors, a phase 1 study of pediatric patients with INI1-deficient solid tumors, a combination study of tazemetostat with R-CHOP in patients with DLBCL, and a combination study of tazemetostat with a B-cell signaling agent or other emerging targeted therapies for B-cell lymphomas. ![]()
*Information in the abstract differs from that presented at the meeting.

LUGANO—The EZH2 inhibitor tazemetostat (EPZ-6438) has shown “meaningful clinical activity” as monotherapy in patients with advanced non-Hodgkin lymphoma (NHL), according to researchers.
In a phase 1 trial, 9 of the 15 evaluable NHL patients achieved an objective response to tazemetostat.
This included 2 ongoing complete responses (CRs), 1 in a patient with diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL) and 1 in a patient with follicular lymphoma (FL).
It also included a partial response (PR) in the first treated patient with an EZH2 mutation.
And researchers said the drug was largely well-tolerated, as most adverse events were grade 1 or 2.
“The breadth, depth, and durability of responses seen in NHL patients among multiple histologies continue to impress, as does the safety and tolerability of tazemetostat in this phase 1 study,” said Vincent Ribrag, MD, of Institut Gustave Roussy in Villejuif, France.
“Among the patients in the dose-escalation cohorts, we have seen a noteworthy deepening of responses over time, and, in the first treated patient with an EZH2 tumor mutation, we have seen a partial response, which is very encouraging.”
Dr Ribrag presented these results at the 13th International Conference on Malignant Lymphoma (abstract 145*). The study, which was previously presented at the 26th EORTC-NCI-AACR Symposium on Molecular Targets and Cancer Therapeutics, was sponsored by Epizyme, Inc., the company developing tazemetostat.
The phase 1 trial has enrolled 19 patients with relapsed or refractory B-cell NHL and 26 patients with advanced solid tumors.
Researchers have evaluated 5 cohorts of patients in the dose-escalation portion of the study—100 mg, 200 mg, 400 mg, 800 mg, and 1600 mg—and 2 cohorts—800 mg and 1600 mg—in the dose-expansion phase. All doses of tazemetostat were given twice daily.
The 19 NHL patients had a median age of 61 (range, 24-84) and were heavily pretreated. Eighty-five percent had received 3 or more prior therapies, and 37% had received 5 or more prior therapies.
Thirty-seven percent of patients were refractory to their last prior regimen, and 26% had received a prior autologous hematopoietic stem cell transplant.
Dosing and efficacy
As of June 8, 2015, 15 NHL patients were evaluable for efficacy. Nine had achieved an objective response, including 2 patients with an ongoing CR. All responses were observed between 2 and 10 months on therapy.
Five of the 9 evaluable patients with DLBCL achieved an objective response. One DLBCL patient with a CR remains on study at 18 months of treatment.
Three of 5 evaluable patients with follicular lymphoma (FL) achieved an objective response. One FL patient with a CR remains on study at 13 months, and 1 FL patient with a PR remains on study at 13 months.
The only patient with marginal zone lymphoma achieved a PR and continues on study at 11 months.
One of the 14 patients evaluated for EZH2 status has a specific EZH2 tumor mutation (Y646H). This patient, who had DLBCL that relapsed or was refractory to 6 previous treatment regimens, achieved a PR after 16 weeks of therapy and remains on study.
The recommended phase 2 dose of tazemetostat is 800 mg twice daily.
Adverse events and next steps
All of the 45 enrolled patients were evaluable for safety. Treatment-related adverse events included asthenia (n=10), nausea (n=6), dyspepsia (n=5), thrombocytopenia (n=4), anorexia (n=4), anemia (n=4), vomiting (n=3), constipation (n=2), muscle spasm (n=2), hypertension (n=2), neutropenia (n=2), and elevated transaminase (n=1).
There were 5 grade 3 or higher adverse events related to treatment, including grade 3 anorexia, grade 3 hypertension, grade 3 transaminase elevation, grade 4 thrombocytopenia, and grade 4 neutropenia.
Epizyme plans to report a further update from this trial by the end of this year. The company is now enrolling patients in a phase 2 study of tazemetostat monotherapy in patients with relapsed or refractory NHL, stratified by cell of origin and EZH2 mutation status.
Epizyme is also planning a phase 2 trial of tazemetostat in adults with INI1-deficient solid tumors, a phase 1 study of pediatric patients with INI1-deficient solid tumors, a combination study of tazemetostat with R-CHOP in patients with DLBCL, and a combination study of tazemetostat with a B-cell signaling agent or other emerging targeted therapies for B-cell lymphomas. ![]()
*Information in the abstract differs from that presented at the meeting.


