User login
A Joint Effort to Save the Joints: What Dermatologists Need to Know About Psoriatic Arthritis
Nearly all dermatologists are aware that psoriatic arthritis (PsA) is one of the most prevalent comorbidities associated with psoriasis, yet we may lack the insight regarding how to utilize this information. After all, we specialize in the skin, not the joints, right?
When I graduated from residency in 2014, I began staffing our psoriasis clinic, where we care for the toughest, most complicated psoriasis patients, many of them struggling with both severe recalcitrant psoriasis as well as debilitating PsA. In 2016, we partnered with rheumatology to open a multidisciplinary psoriasis and PsA clinic, and I quickly began to appreciate how much PsA was being overlooked simply because patients with psoriasis were not being asked about their joints.
To start, let’s look at several facts:
- One quarter of patients with psoriasis also have PsA.1
- Skin disease most commonly develops before PsA.1
- Fifteen percent of PsA cases go undiagnosed, which dramatically increases the risk for deformed joints, erosions, osteolysis, sacroiliitis, and arthritis mutilans2 and also increases the cost of health care.3
- Everyone is crazy busy—rheumatology wait lists often are months long.
Given that dermatologists are the ones who already are seeing the majority of patients who develop PsA, we play a key role in screening for this debilitating comorbidity and starting therapy for patients with both psoriasis and PsA. We, too, are crazy busy; therefore, we need to make this process quick and efficient but also reliable. Fortunately, the Psoriasis Epidemiology Screening Tool (PEST) is effective, fast, and very easy. With only 5 questions and a sensitivity and specificity of around 70%,4 this short and simple questionnaire can be incorporated into an intake form or rooming note or can just be asked during the visit. The questions include whether the patient currently has or has had a swollen joint, nail pits, heel pain, and/or dactylitis, as well as if they have been told by a physician that they have arthritis. A score of 3 or higher is considered positive and a referral to rheumatology should be considered. At the bare minimum, I highly encourage all dermatologists to incorporate the PEST screening tool into their practice.
During the physical examination itself, be sure to look at the patient’s nails and also look for joint swelling and redness, especially in the hands. When palpating a swollen joint, the presence of inflammatory arthritis will feel spongy or boggy, while the osteophytes associated with osteoarthritis will feel hard. Radiography of the affected joint may be helpful, but keep in mind that bone changes are latter sequelae of PsA, and negative radiographs do not rule out PsA.
If you highly suspect PsA after using the PEST screening tool and palpating any swollen joints, then a rheumatology referral certainly is warranted. Medication that covers both psoriasis and PsA also can be initiated. Although methotrexate often is used for joints, higher doses (ie, >15 mg/wk) usually are needed. A 2019 Cochrane review found that low-dose methotrexate (ie, ≤15 mg/wk) may be only slightly more effective then placebo5—certainly not a ringing endorsement for its use in PsA. Additionally, quality data demonstrating methotrexate’s efficacy for enthesitis or axial spondyloarthritis is lacking, and methotrexate has not demonstrated an ability to slow the radiographic progression of joints. In contrast, the anti–tumor necrosis factor agents, including adalimumab, infliximab, etanercept, and certolizumab, as well as ustekinumab and the anti–IL-17 biologics secukinumab and ixekizumab have demonstrated efficacy in American College of Rheumatology (ACR) scores, enthesitis, dactylitis, and prevention of radiographic progression of joints.6,7 Although brodalumab, an anti–IL-17 receptor inhibitor, demonstrated improvement in ACR scores, enthesitis, and dactylitis, data on its effects on radiographic progression of joints were inconclusive given the phase III trial’s premature ending due to suicidal ideation and behavior in participants.8 Several of the anti–IL-23 agents also may help PsA, with trials demonstrating improvements in ACR scores, enthesitis, and dactylitis; however, only guselkumab 100 mg every 4 weeks decreased radiographic progression of joints.9 Additionally, with the age of the Janus kinase (JAK) inhibitor upon us, there are several JAK/TYK2 inhibitors that are approved by the US Food and Drug Administration for psoriasis (deucravacitinib) as well as for PsA (tofacitinib, upadacitinib), and there are more JAK inhibitors in the pipeline. These medications are effective; however, I do encourage caution and careful consideration in selecting the appropriate patient, as data demonstrated an increased risk for major adverse cardiovascular events and cancer in older (>50 years) rheumatoid arthritis patients who had at least 1 cardiovascular risk factor and were treated with tofacitinib.10 Although several other trials have not demonstrated this increased risk, further data are needed to determine risk for both pan-JAK inhibitors as well as selective JAK inhibitors and TYK2 inhibitors. Additionally, given psoriasis already is closely linked with many cardiovascular risk factors including heart disease, obesity, hypertension, hyperlipidemia, and diabetes mellitus,11 it will be important to have long-term safety information for JAK inhibitors in the psoriasis and PsA population.
Dermatologists are in a pivotal position to identify patients affected by PsA and start an appropriate systemic medication. We can help make an enormous impact on our patients’ lives as well as help decrease the economic impact of untreated disease. Let’s join the effort to save the joints!
- Alinaghi F, Calov M, Kristensen L, et al. Prevalence of psoriatic arthritis in patients with psoriasis: a systematic review and meta-analysis of observational and clinical studies. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2019;80:251-265.
- Villani A, Zouzaud M, Sevrain M, et al. Prevalence of undiagnosed psoriatic arthritis among psoriasis patients: systematic review and meta-analysis. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2015;73:242-248.
- Iragorri N, Hazlewood G, Manns B, et al. Model to determine the cost-effectiveness of screening psoriasis patients for psoriatic arthritis. Arth Car Res. 2021;73:266-274.
- Karreman M, Weel A, Van der Ven M, et al. Performance of screening tools for psoriatic arthritis: a cross-sectional study in primary care. Rheumatology. 2017;56:597-602.
- Wilsdon TD, Whittle SL, Thynne TR, et al. Methotrexate for psoriatic arthritis. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2019;1:CD012722. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD012722.pub2
- Mourad A, Gniadecki R. Treatment of dactylitis and enthesitis in psoriatic arthritis with biologic agents: a systematic review and metaanalysis. J Rheum. 2020;47:59-65.
- Wu D, Li C, Zhang S, et al. Effect of biologics on radiographic progression of peripheral joint in patients with psoriatic arthritis: meta-analysis. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2020;59:3172-3180.
- Mease P, Helliwell P, Fjellhaugen Hjuler K, et al. Brodalumab in psoriatic arthritis: results from the randomised phase III AMVISION-1 and AMVISION-2 trials. Ann Rheum Dis. 2021;80:185-193.
- McInnes I, Rahman P, Gottlieb A, et al. Long-term efficacy and safety of guselkumab, a monoclonal antibody specific to the p19 subunit of interleukin-23, through two years: results from a phase III, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study conducted in biologic-naïve patients with active psoriatic arthritis. Arth Rheum. 2022;74:475-485.
- Ytterberg S, Bhatt D, Mikuls T, et al. Cardiovascular and cancer risk with tofacitinib in rheumatoid arthritis. N Engl J Med. 2022;386:316-326.
- Miller I, Ellervik C, Yazdanyar S, et al. Meta-analysis of psoriasis, cardiovascular disease, and associated risk factors. JAAD. 2013;69:1014-1024.
Nearly all dermatologists are aware that psoriatic arthritis (PsA) is one of the most prevalent comorbidities associated with psoriasis, yet we may lack the insight regarding how to utilize this information. After all, we specialize in the skin, not the joints, right?
When I graduated from residency in 2014, I began staffing our psoriasis clinic, where we care for the toughest, most complicated psoriasis patients, many of them struggling with both severe recalcitrant psoriasis as well as debilitating PsA. In 2016, we partnered with rheumatology to open a multidisciplinary psoriasis and PsA clinic, and I quickly began to appreciate how much PsA was being overlooked simply because patients with psoriasis were not being asked about their joints.
To start, let’s look at several facts:
- One quarter of patients with psoriasis also have PsA.1
- Skin disease most commonly develops before PsA.1
- Fifteen percent of PsA cases go undiagnosed, which dramatically increases the risk for deformed joints, erosions, osteolysis, sacroiliitis, and arthritis mutilans2 and also increases the cost of health care.3
- Everyone is crazy busy—rheumatology wait lists often are months long.
Given that dermatologists are the ones who already are seeing the majority of patients who develop PsA, we play a key role in screening for this debilitating comorbidity and starting therapy for patients with both psoriasis and PsA. We, too, are crazy busy; therefore, we need to make this process quick and efficient but also reliable. Fortunately, the Psoriasis Epidemiology Screening Tool (PEST) is effective, fast, and very easy. With only 5 questions and a sensitivity and specificity of around 70%,4 this short and simple questionnaire can be incorporated into an intake form or rooming note or can just be asked during the visit. The questions include whether the patient currently has or has had a swollen joint, nail pits, heel pain, and/or dactylitis, as well as if they have been told by a physician that they have arthritis. A score of 3 or higher is considered positive and a referral to rheumatology should be considered. At the bare minimum, I highly encourage all dermatologists to incorporate the PEST screening tool into their practice.
During the physical examination itself, be sure to look at the patient’s nails and also look for joint swelling and redness, especially in the hands. When palpating a swollen joint, the presence of inflammatory arthritis will feel spongy or boggy, while the osteophytes associated with osteoarthritis will feel hard. Radiography of the affected joint may be helpful, but keep in mind that bone changes are latter sequelae of PsA, and negative radiographs do not rule out PsA.
If you highly suspect PsA after using the PEST screening tool and palpating any swollen joints, then a rheumatology referral certainly is warranted. Medication that covers both psoriasis and PsA also can be initiated. Although methotrexate often is used for joints, higher doses (ie, >15 mg/wk) usually are needed. A 2019 Cochrane review found that low-dose methotrexate (ie, ≤15 mg/wk) may be only slightly more effective then placebo5—certainly not a ringing endorsement for its use in PsA. Additionally, quality data demonstrating methotrexate’s efficacy for enthesitis or axial spondyloarthritis is lacking, and methotrexate has not demonstrated an ability to slow the radiographic progression of joints. In contrast, the anti–tumor necrosis factor agents, including adalimumab, infliximab, etanercept, and certolizumab, as well as ustekinumab and the anti–IL-17 biologics secukinumab and ixekizumab have demonstrated efficacy in American College of Rheumatology (ACR) scores, enthesitis, dactylitis, and prevention of radiographic progression of joints.6,7 Although brodalumab, an anti–IL-17 receptor inhibitor, demonstrated improvement in ACR scores, enthesitis, and dactylitis, data on its effects on radiographic progression of joints were inconclusive given the phase III trial’s premature ending due to suicidal ideation and behavior in participants.8 Several of the anti–IL-23 agents also may help PsA, with trials demonstrating improvements in ACR scores, enthesitis, and dactylitis; however, only guselkumab 100 mg every 4 weeks decreased radiographic progression of joints.9 Additionally, with the age of the Janus kinase (JAK) inhibitor upon us, there are several JAK/TYK2 inhibitors that are approved by the US Food and Drug Administration for psoriasis (deucravacitinib) as well as for PsA (tofacitinib, upadacitinib), and there are more JAK inhibitors in the pipeline. These medications are effective; however, I do encourage caution and careful consideration in selecting the appropriate patient, as data demonstrated an increased risk for major adverse cardiovascular events and cancer in older (>50 years) rheumatoid arthritis patients who had at least 1 cardiovascular risk factor and were treated with tofacitinib.10 Although several other trials have not demonstrated this increased risk, further data are needed to determine risk for both pan-JAK inhibitors as well as selective JAK inhibitors and TYK2 inhibitors. Additionally, given psoriasis already is closely linked with many cardiovascular risk factors including heart disease, obesity, hypertension, hyperlipidemia, and diabetes mellitus,11 it will be important to have long-term safety information for JAK inhibitors in the psoriasis and PsA population.
Dermatologists are in a pivotal position to identify patients affected by PsA and start an appropriate systemic medication. We can help make an enormous impact on our patients’ lives as well as help decrease the economic impact of untreated disease. Let’s join the effort to save the joints!
Nearly all dermatologists are aware that psoriatic arthritis (PsA) is one of the most prevalent comorbidities associated with psoriasis, yet we may lack the insight regarding how to utilize this information. After all, we specialize in the skin, not the joints, right?
When I graduated from residency in 2014, I began staffing our psoriasis clinic, where we care for the toughest, most complicated psoriasis patients, many of them struggling with both severe recalcitrant psoriasis as well as debilitating PsA. In 2016, we partnered with rheumatology to open a multidisciplinary psoriasis and PsA clinic, and I quickly began to appreciate how much PsA was being overlooked simply because patients with psoriasis were not being asked about their joints.
To start, let’s look at several facts:
- One quarter of patients with psoriasis also have PsA.1
- Skin disease most commonly develops before PsA.1
- Fifteen percent of PsA cases go undiagnosed, which dramatically increases the risk for deformed joints, erosions, osteolysis, sacroiliitis, and arthritis mutilans2 and also increases the cost of health care.3
- Everyone is crazy busy—rheumatology wait lists often are months long.
Given that dermatologists are the ones who already are seeing the majority of patients who develop PsA, we play a key role in screening for this debilitating comorbidity and starting therapy for patients with both psoriasis and PsA. We, too, are crazy busy; therefore, we need to make this process quick and efficient but also reliable. Fortunately, the Psoriasis Epidemiology Screening Tool (PEST) is effective, fast, and very easy. With only 5 questions and a sensitivity and specificity of around 70%,4 this short and simple questionnaire can be incorporated into an intake form or rooming note or can just be asked during the visit. The questions include whether the patient currently has or has had a swollen joint, nail pits, heel pain, and/or dactylitis, as well as if they have been told by a physician that they have arthritis. A score of 3 or higher is considered positive and a referral to rheumatology should be considered. At the bare minimum, I highly encourage all dermatologists to incorporate the PEST screening tool into their practice.
During the physical examination itself, be sure to look at the patient’s nails and also look for joint swelling and redness, especially in the hands. When palpating a swollen joint, the presence of inflammatory arthritis will feel spongy or boggy, while the osteophytes associated with osteoarthritis will feel hard. Radiography of the affected joint may be helpful, but keep in mind that bone changes are latter sequelae of PsA, and negative radiographs do not rule out PsA.
If you highly suspect PsA after using the PEST screening tool and palpating any swollen joints, then a rheumatology referral certainly is warranted. Medication that covers both psoriasis and PsA also can be initiated. Although methotrexate often is used for joints, higher doses (ie, >15 mg/wk) usually are needed. A 2019 Cochrane review found that low-dose methotrexate (ie, ≤15 mg/wk) may be only slightly more effective then placebo5—certainly not a ringing endorsement for its use in PsA. Additionally, quality data demonstrating methotrexate’s efficacy for enthesitis or axial spondyloarthritis is lacking, and methotrexate has not demonstrated an ability to slow the radiographic progression of joints. In contrast, the anti–tumor necrosis factor agents, including adalimumab, infliximab, etanercept, and certolizumab, as well as ustekinumab and the anti–IL-17 biologics secukinumab and ixekizumab have demonstrated efficacy in American College of Rheumatology (ACR) scores, enthesitis, dactylitis, and prevention of radiographic progression of joints.6,7 Although brodalumab, an anti–IL-17 receptor inhibitor, demonstrated improvement in ACR scores, enthesitis, and dactylitis, data on its effects on radiographic progression of joints were inconclusive given the phase III trial’s premature ending due to suicidal ideation and behavior in participants.8 Several of the anti–IL-23 agents also may help PsA, with trials demonstrating improvements in ACR scores, enthesitis, and dactylitis; however, only guselkumab 100 mg every 4 weeks decreased radiographic progression of joints.9 Additionally, with the age of the Janus kinase (JAK) inhibitor upon us, there are several JAK/TYK2 inhibitors that are approved by the US Food and Drug Administration for psoriasis (deucravacitinib) as well as for PsA (tofacitinib, upadacitinib), and there are more JAK inhibitors in the pipeline. These medications are effective; however, I do encourage caution and careful consideration in selecting the appropriate patient, as data demonstrated an increased risk for major adverse cardiovascular events and cancer in older (>50 years) rheumatoid arthritis patients who had at least 1 cardiovascular risk factor and were treated with tofacitinib.10 Although several other trials have not demonstrated this increased risk, further data are needed to determine risk for both pan-JAK inhibitors as well as selective JAK inhibitors and TYK2 inhibitors. Additionally, given psoriasis already is closely linked with many cardiovascular risk factors including heart disease, obesity, hypertension, hyperlipidemia, and diabetes mellitus,11 it will be important to have long-term safety information for JAK inhibitors in the psoriasis and PsA population.
Dermatologists are in a pivotal position to identify patients affected by PsA and start an appropriate systemic medication. We can help make an enormous impact on our patients’ lives as well as help decrease the economic impact of untreated disease. Let’s join the effort to save the joints!
- Alinaghi F, Calov M, Kristensen L, et al. Prevalence of psoriatic arthritis in patients with psoriasis: a systematic review and meta-analysis of observational and clinical studies. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2019;80:251-265.
- Villani A, Zouzaud M, Sevrain M, et al. Prevalence of undiagnosed psoriatic arthritis among psoriasis patients: systematic review and meta-analysis. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2015;73:242-248.
- Iragorri N, Hazlewood G, Manns B, et al. Model to determine the cost-effectiveness of screening psoriasis patients for psoriatic arthritis. Arth Car Res. 2021;73:266-274.
- Karreman M, Weel A, Van der Ven M, et al. Performance of screening tools for psoriatic arthritis: a cross-sectional study in primary care. Rheumatology. 2017;56:597-602.
- Wilsdon TD, Whittle SL, Thynne TR, et al. Methotrexate for psoriatic arthritis. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2019;1:CD012722. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD012722.pub2
- Mourad A, Gniadecki R. Treatment of dactylitis and enthesitis in psoriatic arthritis with biologic agents: a systematic review and metaanalysis. J Rheum. 2020;47:59-65.
- Wu D, Li C, Zhang S, et al. Effect of biologics on radiographic progression of peripheral joint in patients with psoriatic arthritis: meta-analysis. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2020;59:3172-3180.
- Mease P, Helliwell P, Fjellhaugen Hjuler K, et al. Brodalumab in psoriatic arthritis: results from the randomised phase III AMVISION-1 and AMVISION-2 trials. Ann Rheum Dis. 2021;80:185-193.
- McInnes I, Rahman P, Gottlieb A, et al. Long-term efficacy and safety of guselkumab, a monoclonal antibody specific to the p19 subunit of interleukin-23, through two years: results from a phase III, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study conducted in biologic-naïve patients with active psoriatic arthritis. Arth Rheum. 2022;74:475-485.
- Ytterberg S, Bhatt D, Mikuls T, et al. Cardiovascular and cancer risk with tofacitinib in rheumatoid arthritis. N Engl J Med. 2022;386:316-326.
- Miller I, Ellervik C, Yazdanyar S, et al. Meta-analysis of psoriasis, cardiovascular disease, and associated risk factors. JAAD. 2013;69:1014-1024.
- Alinaghi F, Calov M, Kristensen L, et al. Prevalence of psoriatic arthritis in patients with psoriasis: a systematic review and meta-analysis of observational and clinical studies. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2019;80:251-265.
- Villani A, Zouzaud M, Sevrain M, et al. Prevalence of undiagnosed psoriatic arthritis among psoriasis patients: systematic review and meta-analysis. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2015;73:242-248.
- Iragorri N, Hazlewood G, Manns B, et al. Model to determine the cost-effectiveness of screening psoriasis patients for psoriatic arthritis. Arth Car Res. 2021;73:266-274.
- Karreman M, Weel A, Van der Ven M, et al. Performance of screening tools for psoriatic arthritis: a cross-sectional study in primary care. Rheumatology. 2017;56:597-602.
- Wilsdon TD, Whittle SL, Thynne TR, et al. Methotrexate for psoriatic arthritis. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2019;1:CD012722. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD012722.pub2
- Mourad A, Gniadecki R. Treatment of dactylitis and enthesitis in psoriatic arthritis with biologic agents: a systematic review and metaanalysis. J Rheum. 2020;47:59-65.
- Wu D, Li C, Zhang S, et al. Effect of biologics on radiographic progression of peripheral joint in patients with psoriatic arthritis: meta-analysis. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2020;59:3172-3180.
- Mease P, Helliwell P, Fjellhaugen Hjuler K, et al. Brodalumab in psoriatic arthritis: results from the randomised phase III AMVISION-1 and AMVISION-2 trials. Ann Rheum Dis. 2021;80:185-193.
- McInnes I, Rahman P, Gottlieb A, et al. Long-term efficacy and safety of guselkumab, a monoclonal antibody specific to the p19 subunit of interleukin-23, through two years: results from a phase III, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study conducted in biologic-naïve patients with active psoriatic arthritis. Arth Rheum. 2022;74:475-485.
- Ytterberg S, Bhatt D, Mikuls T, et al. Cardiovascular and cancer risk with tofacitinib in rheumatoid arthritis. N Engl J Med. 2022;386:316-326.
- Miller I, Ellervik C, Yazdanyar S, et al. Meta-analysis of psoriasis, cardiovascular disease, and associated risk factors. JAAD. 2013;69:1014-1024.
Interacting With Dermatology Patients Online: Private Practice vs Academic Institute Website Content
Patients are finding it easier to use online resources to discover health care providers who fit their personalized needs. In the United States, approximately 70% of individuals use the internet to find health care information, and 80% are influenced by the information presented to them on health care websites.1 Patients utilize the internet to better understand treatments offered by providers and their prices as well as how other patients have rated their experience. Providers in private practice also have noticed that many patients are referring themselves vs obtaining a referral from another provider.2 As a result, it is critical for practice websites to have information that is of value to their patients, including the unique qualities and treatments offered. The purpose of this study was to analyze the differences between the content presented on dermatology private practice websites and academic institutional websites.
Methods
Websites Searched —All 140 academic dermatology programs, including both allopathic and osteopathic programs, were queried from the Association of American Medical Colleges (AAMC) database in March 2022. 3 First, the dermatology departmental websites for each program were analyzed to see if they contained information pertinent to patients. Any website that lacked this information or only had information relevant to the dermatology residency program was excluded from the study. After exclusion, a total of 113 websites were used in the academic website cohort. The private practices were found through an incognito Google search with the search term dermatologist and matched to be within 5 miles of each academic institution. The private practices that included at least one board-certified dermatologist and received the highest number of reviews on Google compared to other practices in the same region—a measure of online reputation—were selected to be in the private practice cohort (N = 113). Any duplicate practices, practices belonging to the same conglomerate company, or multispecialty clinics were excluded from the study. Board-certified dermatologists were confirmed using the Find a Dermatologist tool on the American Academy of Dermatology (AAD) website. 4
Website Assessments —Each website was assessed using 23 criteria divided into 4 categories: practice, physician(s), patient, and treatment/procedure (Table). Criteria for social media and publicity were further assessed. Criteria for social media included links on the website to a Facebook page, an Instagram account, a Twitter account, a Pinterest account, a LinkedIn account, a blog, a Yelp page, a YouTube channel, and/or any other social media. Criteria for publicity included links on the website to local television news, national news, newspapers, and/or magazines. 5-8 Ease of site access was determined if the website was the first search result found on Google when searching for each website. Nondermatology professionals included listing of mid-level providers or researchers.
Four individuals (V.S.J., A.C.B., M.E.O., and M.B.B.) independently assessed each of the websites using the established criteria. Each criterion was defined and discussed prior to data collection to maintain consistency. The criteria were determined as being present if the website clearly displayed, stated, explained, or linked to the relevant content. If the website did not directly contain the content, it was determined that the criteria were absent. One other individual (J.P.) independently cross-examined the data for consistency and evaluated for any discrepancies. 8
A raw analysis was done between each cohort. Another analysis was done that controlled for population density and the proportionate population age in each city 9 in which an academic institution/private practice was located. We proposed that more densely populated cities naturally may have more competition between practices, which may result in more optimized websites. 10 We also anticipated similar findings in cities with younger populations, as the younger demographic may be more likely to utilize and value online information when compared to older populations. 11 The websites for each cohort were equally divided into 3 tiers of population density (not shown) and population age (not shown).
Statistical Analysis —Statistical analysis was completed using descriptive statistics, χ 2 testing, and Fisher exact tests where appropriate with a predetermined level of significance of P < .05 in Microsoft Excel.
Results
Demographics —A total of 226 websites from both private practices and academic institutions were evaluated. Of them, only 108 private practices and 108 academic institutions listed practicing dermatologists on their site. Of 108 private practices, 76 (70.4%) had more than one practicing board-certified dermatologist. Of 108 academic institutions, all 108 (100%) institutions had more than one practicing board-certified dermatologist.
Of the dermatologists who practiced at academic institutions (n=2014) and private practices (n=817), 1157 (57.4%) and 419 (51.2%) were females, respectively. The population density of the cities with each of these practices/institutions ranged from 137 individuals per square kilometer to 11,232 individuals per square kilometer (mean [SD] population density, 2579 [2485] individuals per square kilometer). Densely populated, moderately populated, and sparsely populated cities had a median population density of 4618, 1708, and 760 individuals per square kilometer, respectively. The data also were divided into 3 age groups. In the older population tier, the median percentage of individuals older than 64 years was 14.2%, the median percentage of individuals aged 18 to 64 years was 63.8%, and the median percentage of individuals aged 5 to 17 years was 14.9%. In the moderately aged population tier, the median percentage of individuals older than 64 years was 10.2%, the median percentage of individuals aged 18 to 64 years was 70.3%, and the median percentage of individuals aged 5 to 17 years was 13.6%. In the younger population tier, the median percentage of individuals older than 64 years was 12%, the median percentage of individuals aged 18 to 64 years was 66.8%, and the median percentage of individuals aged 5 to 17 years was 15%.
Practice and Physician Content—In the raw analysis (Figure), the most commonly listed types of content (>90% of websites) in both private practice and academic sites was address (range, 95% to 100%), telephone number (range, 97% to 100%), and dermatologist profiles (both 92%). The least commonly listed types of content in both cohorts was publicity (range, 20% to 23%). Private practices were more likely to list profiles of nondermatology professionals (73% vs 56%; P<.02), email (47% vs 17%; P<.0001), and social media (29% vs 8%; P<.0001) compared with academic institution websites. Although Facebook was the most-linked social media account for both groups, 75% of private practice sites included the link compared with 16% of academic institutions. Academic institutions were more likely to list fellowship availability (66% vs 1%; P<.0001). Accessing each website was significantly easier in the private practice cohort (99% vs 61%; P<.0001).
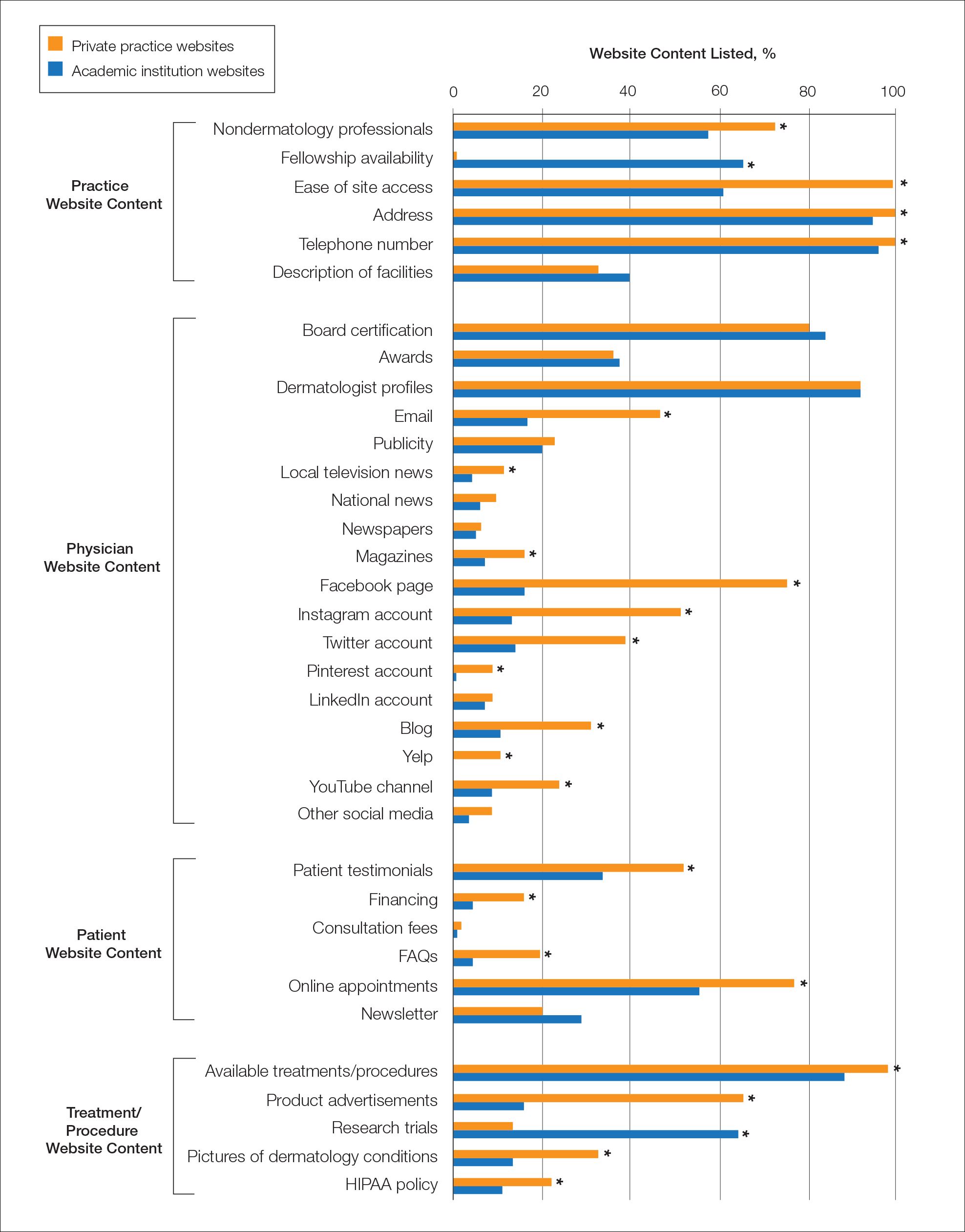
When controlling for population density, private practices were only more likely to list nondermatology professionals’ profiles in densely populated cities when compared with academic institutions (73% vs 41%; P<.01). Academic institutions continued to list fellowship availability more often than private practices regardless of population density. The same trend was observed for private practices with ease of site access and listing of social media.
When controlling for population age, similar trends were seen as when controlling for population density. However, private practices listing nondermatology professionals’ profiles was only more likely in the cities with a proportionately younger population when compared with academic institutions (74% vs 47%; P<.04).
Patient and Treatment/Procedure—The most commonly listed content types on both private practice websites and academic institution websites were available treatments/procedures (range, 89% to 98%). The least commonly listed content included financing for elective procedures (range, 4% to 16%), consultation fees (range, 1% to 2%), FAQs (frequently asked questions)(range, 4% to 20%), and HIPAA (Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act) policy (range, 12% to 22%). Private practices were more likely to list patient testimonials (52% vs 35%; P<.005), financing (16% vs 4%; P<.005), FAQs (20% vs 4%; P<.001), online appointments (77% vs 56%; P<.001), available treatments/procedures (98% vs 86%; P<.004), product advertisements (66% vs 16%; P<.0001), pictures of dermatology conditions (33% vs 13%; P<.001), and HIPAA policy (22% vs 12%; P<.04). Academic institutions were more likely to list research trials (65% vs 13%; P<.0001).
When controlling for population density, private practices were only more likely to list patient testimonials in densely populated (P=.035) and moderately populated cities (P=.019). The same trend was observed for online appointments in densely populated (P=.0023) and moderately populated cities (P=.037). Private practices continued to list product availability more often than academic institutions regardless of population density or population age. Academic institutions also continued to list research trials more often than private practices regardless of population density or population age.
Comment
Our study uniquely analyzed the differences in website content between private practices and academic institutions in dermatology. Of the 140 academic institutions accredited by the Accreditation Council for Graduate Medical Education (ACGME), only 113 had patient-pertinent websites.
Access to Websites —There was a significant difference in many website content criteria between the 2 groups. Private practice sites were easier to access via a Google search when compared with academic sites, which likely is influenced by the Google search algorithm that ranks websites higher based on several criteria including but not limited to keyword use in the title tag, link popularity of the site, and historic ranking. 12,13 Academic sites often were only accessible through portals found on their main institutional site or institution’s residency site.
Role of Social Media —Social media has been found to assist in educating patients on medical practices as well as selecting a physician. 14,15 Our study found that private practice websites listed links to social media more often than their academic counterparts. Social media consumption is increasing, in part due to the COVID-19 pandemic, and it may be optimal for patients and practices alike to include links on their websites. 16 Facebook and Instagram were listed more often on private practice sites when compared with academic institution sites, which was similar to a recent study analyzing the websites of plastic surgery private practices (N = 310) in which 90% of private practices included some type of social media, with Instagram and Facebook being the most used. 8 Social networking accounts can act as convenient platforms for marketing, providing patient education, and generating referrals, which suggests that the prominence of their usage in private practice poses benefits in patient decision-making when seeking care. 17-19 A study analyzing the impact of Facebook in medicine concluded that a Facebook page can serve as an effective vehicle for medical education, particularly in younger generations that favor technology-oriented teaching methods. 20 A survey on trends in cosmetic facial procedures in plastic surgery found that the most influential online methods patients used for choosing their providers were social media platforms and practice websites. Front-page placement on Google also was commonly associated with the number of social media followers. 21,22 A lack of social media prominence could hinder a website’s potential to reach patients.
Communication With Practices —Our study also found significant differences in other metrics related to a patient’s ability to directly communicate with a practice, such as physical addresses, telephone numbers, products available for direct purchase, and online appointment booking, all of which were listed more often on private practice websites compared with academic institution websites. Online appointment booking also was found more frequently on private practice websites. Although physical addresses and telephone numbers were listed significantly more often on private practice sites, this information was ubiquitous and easily accessible elsewhere. Academic institution websites listed research trials and fellowship training significantly more often than private practices. These differences imply a divergence in focus between private practices and academic institutions, likely because academic institutions are funded in large part from research grants, begetting a cycle of academic contribution. 23 In contrast, private practices may not rely as heavily on academic revenue and may be more likely to prioritize other revenue streams such as product sales. 24
HIPAA Policy —Surprisingly, HIPAA policy rarely was listed on any private (22%) or academic site (12%). Conversely, in the plastic surgery study, HIPAA policy was listed much more often, with more than half of private practices with board-certified plastic surgeons accredited in the year 2015 including it on their website, 8 which may suggest that surgically oriented specialties, particularly cosmetic subspecialties, aim to more noticeably display their privacy policies for patient reassurance.
Study Limitations —There are several limitations of our study. First, it is common for a conglomerate company to own multiple private practices in different specialties. As with academic sites, private practice sites may be limited by the hosting platforms, which often are tedious to navigate. Also noteworthy is the emergence of designated social media management positions—both by practice employees and by third-party firms 25 —but the impact of these positions in private practices and academic institutions has not been fully explored. Finally, inclusion criteria and standardized criteria definitions were chosen based on the precedent established by the authors of similar analyses in plastic surgery and radiology. 5-8 Further investigation into the most valued aspects of care by patients within the context of the type of practice chosen would be valuable in refining inclusion criteria. Additionally, this study did not stratify the data collected based on factors such as gender, race, and geographical location; studies conducted on website traffic analysis patterns that focus on these aspects likely would further explain the significance of these findings. Differences in the length of time to the next available appointment between private practices and academic institutions also may help support our findings. Finally, there is a need for further investigation into the preferences of patients themselves garnered from website traffic alone.
Conclusion
Our study examined a diverse compilation of private practice and academic institution websites and uncovered numerous differences in content. As technology and health care continuously evolve, it is imperative that both private practices and academic institutions are actively adapting to optimize their online presence. In doing so, patients will be better equipped at accessing provider information, gaining familiarity with the practice, and understanding treatment options.
- Gentry ZL, Ananthasekar S, Yeatts M, et al. Can patients find an endocrine surgeon? how hospital websites hide the expertise of these medical professionals. Am J Surg . 2021;221:101-105.
- Pollack CE, Rastegar A, Keating NL, et al. Is self-referral associated with higher quality care? Health Serv Res . 2015;50:1472-1490.
- Association of American Medical Colleges. Residency Explorer TM tool. Accessed May 15, 2023. https://students-residents.aamc.org/apply-smart-residency/residency-explorer-tool
- Find a dermatologist. American Academy of Dermatology website. Accessed May 15, 2023. https://find-a-derm.aad.org/
- Johnson EJ, Doshi AM, Rosenkrantz AB. Strengths and deficiencies in the content of US radiology private practices’ websites. J Am Coll Radiol. 2017;14:431-435.
- Brunk D. Medical website expert shares design tips. Dermatology News . February 9, 2012. Accessed May 15, 2023. https://www.mdedge.com/dermatology/article/47413/health-policy/medical-website-expert-shares-design-tips
- Kuhnigk O, Ramuschkat M, Schreiner J, et al. Internet presence of neurologists, psychiatrists and medical psychotherapists in private practice [in German]. Psychiatr Prax . 2013;41:142-147.
- Ananthasekar S, Patel JJ, Patel NJ, et al. The content of US plastic surgery private practices’ websites. Ann Plast Surg . 2021;86(6S suppl 5):S578-S584.
- US Census Bureau. Age and Sex: 2021. Updated December 2, 2021. Accessed March 15, 2023. https://www.census.gov/topics/population/age-and-sex/data/tables.2021.List_897222059.html#list-tab-List_897222059
- Porter ME. The competitive advantage of the inner city. Harvard Business Review . Published August 1, 2014. https://hbr.org/1995/05/the-competitive-advantage-of-the-inner-city
- Clark PG. The social allocation of health care resources: ethical dilemmas in age-group competition. Gerontologist. 1985;25:119-125.
- Su A-J, Hu YC, Kuzmanovic A, et al. How to improve your Google ranking: myths and reality. ACM Transactions on the Web . 2014;8. https://dl.acm.org/doi/abs/10.1145/2579990
- McCormick K. 39 ways to increase traffic to your website. WordStream website. Published March 28, 2023. Accessed May 22, 2023. https://www.wordstream.com/blog/ws/2014/08/14/increase-traffic-to-my-website
- Montemurro P, Porcnik A, Hedén P, et al. The influence of social media and easily accessible online information on the aesthetic plastic surgery practice: literature review and our own experience. Aesthetic Plast Surg . 2015;39:270-277.
- Steehler KR, Steehler MK, Pierce ML, et al. Social media’s role in otolaryngology–head and neck surgery. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg . 2013;149:521-524.
- Tsao S-F, Chen H, Tisseverasinghe T, et al. What social media told us in the time of COVID-19: a scoping review. Lancet Digit Health . 2021;3:E175-E194.
- Geist R, Militello M, Albrecht JM, et al. Social media and clinical research in dermatology. Curr Dermatol Rep . 2021;10:105-111.
- McLawhorn AS, De Martino I, Fehring KA, et al. Social media and your practice: navigating the surgeon-patient relationship. Curr Rev Musculoskelet Med . 2016;9:487-495.
- Thomas RB, Johnson PT, Fishman EK. Social media for global education: pearls and pitfalls of using Facebook, Twitter, and Instagram. J Am Coll Radiol . 2018;15:1513-1516.
- Lugo-Fagundo C, Johnson MB, Thomas RB, et al. New frontiers in education: Facebook as a vehicle for medical information delivery. J Am Coll Radiol . 2016;13:316-319.
- Ho T-VT, Dayan SH. How to leverage social media in private practice. Facial Plast Surg Clin North Am . 2020;28:515-522.
- Fan KL, Graziano F, Economides JM, et al. The public’s preferences on plastic surgery social media engagement and professionalism. Plast Reconstr Surg . 2019;143:619-630.
- Jacob BA, Lefgren L. The impact of research grant funding on scientific productivity. J Public Econ. 2011;95:1168-1177.
- Baumann L. Ethics in cosmetic dermatology. Clin Dermatol. 2012;30:522-527.
- Miller AR, Tucker C. Active social media management: the case of health care. Info Sys Res . 2013;24:52-70.
Patients are finding it easier to use online resources to discover health care providers who fit their personalized needs. In the United States, approximately 70% of individuals use the internet to find health care information, and 80% are influenced by the information presented to them on health care websites.1 Patients utilize the internet to better understand treatments offered by providers and their prices as well as how other patients have rated their experience. Providers in private practice also have noticed that many patients are referring themselves vs obtaining a referral from another provider.2 As a result, it is critical for practice websites to have information that is of value to their patients, including the unique qualities and treatments offered. The purpose of this study was to analyze the differences between the content presented on dermatology private practice websites and academic institutional websites.
Methods
Websites Searched —All 140 academic dermatology programs, including both allopathic and osteopathic programs, were queried from the Association of American Medical Colleges (AAMC) database in March 2022. 3 First, the dermatology departmental websites for each program were analyzed to see if they contained information pertinent to patients. Any website that lacked this information or only had information relevant to the dermatology residency program was excluded from the study. After exclusion, a total of 113 websites were used in the academic website cohort. The private practices were found through an incognito Google search with the search term dermatologist and matched to be within 5 miles of each academic institution. The private practices that included at least one board-certified dermatologist and received the highest number of reviews on Google compared to other practices in the same region—a measure of online reputation—were selected to be in the private practice cohort (N = 113). Any duplicate practices, practices belonging to the same conglomerate company, or multispecialty clinics were excluded from the study. Board-certified dermatologists were confirmed using the Find a Dermatologist tool on the American Academy of Dermatology (AAD) website. 4
Website Assessments —Each website was assessed using 23 criteria divided into 4 categories: practice, physician(s), patient, and treatment/procedure (Table). Criteria for social media and publicity were further assessed. Criteria for social media included links on the website to a Facebook page, an Instagram account, a Twitter account, a Pinterest account, a LinkedIn account, a blog, a Yelp page, a YouTube channel, and/or any other social media. Criteria for publicity included links on the website to local television news, national news, newspapers, and/or magazines. 5-8 Ease of site access was determined if the website was the first search result found on Google when searching for each website. Nondermatology professionals included listing of mid-level providers or researchers.

Four individuals (V.S.J., A.C.B., M.E.O., and M.B.B.) independently assessed each of the websites using the established criteria. Each criterion was defined and discussed prior to data collection to maintain consistency. The criteria were determined as being present if the website clearly displayed, stated, explained, or linked to the relevant content. If the website did not directly contain the content, it was determined that the criteria were absent. One other individual (J.P.) independently cross-examined the data for consistency and evaluated for any discrepancies. 8
A raw analysis was done between each cohort. Another analysis was done that controlled for population density and the proportionate population age in each city 9 in which an academic institution/private practice was located. We proposed that more densely populated cities naturally may have more competition between practices, which may result in more optimized websites. 10 We also anticipated similar findings in cities with younger populations, as the younger demographic may be more likely to utilize and value online information when compared to older populations. 11 The websites for each cohort were equally divided into 3 tiers of population density (not shown) and population age (not shown).
Statistical Analysis —Statistical analysis was completed using descriptive statistics, χ 2 testing, and Fisher exact tests where appropriate with a predetermined level of significance of P < .05 in Microsoft Excel.
Results
Demographics —A total of 226 websites from both private practices and academic institutions were evaluated. Of them, only 108 private practices and 108 academic institutions listed practicing dermatologists on their site. Of 108 private practices, 76 (70.4%) had more than one practicing board-certified dermatologist. Of 108 academic institutions, all 108 (100%) institutions had more than one practicing board-certified dermatologist.
Of the dermatologists who practiced at academic institutions (n=2014) and private practices (n=817), 1157 (57.4%) and 419 (51.2%) were females, respectively. The population density of the cities with each of these practices/institutions ranged from 137 individuals per square kilometer to 11,232 individuals per square kilometer (mean [SD] population density, 2579 [2485] individuals per square kilometer). Densely populated, moderately populated, and sparsely populated cities had a median population density of 4618, 1708, and 760 individuals per square kilometer, respectively. The data also were divided into 3 age groups. In the older population tier, the median percentage of individuals older than 64 years was 14.2%, the median percentage of individuals aged 18 to 64 years was 63.8%, and the median percentage of individuals aged 5 to 17 years was 14.9%. In the moderately aged population tier, the median percentage of individuals older than 64 years was 10.2%, the median percentage of individuals aged 18 to 64 years was 70.3%, and the median percentage of individuals aged 5 to 17 years was 13.6%. In the younger population tier, the median percentage of individuals older than 64 years was 12%, the median percentage of individuals aged 18 to 64 years was 66.8%, and the median percentage of individuals aged 5 to 17 years was 15%.
Practice and Physician Content—In the raw analysis (Figure), the most commonly listed types of content (>90% of websites) in both private practice and academic sites was address (range, 95% to 100%), telephone number (range, 97% to 100%), and dermatologist profiles (both 92%). The least commonly listed types of content in both cohorts was publicity (range, 20% to 23%). Private practices were more likely to list profiles of nondermatology professionals (73% vs 56%; P<.02), email (47% vs 17%; P<.0001), and social media (29% vs 8%; P<.0001) compared with academic institution websites. Although Facebook was the most-linked social media account for both groups, 75% of private practice sites included the link compared with 16% of academic institutions. Academic institutions were more likely to list fellowship availability (66% vs 1%; P<.0001). Accessing each website was significantly easier in the private practice cohort (99% vs 61%; P<.0001).

When controlling for population density, private practices were only more likely to list nondermatology professionals’ profiles in densely populated cities when compared with academic institutions (73% vs 41%; P<.01). Academic institutions continued to list fellowship availability more often than private practices regardless of population density. The same trend was observed for private practices with ease of site access and listing of social media.
When controlling for population age, similar trends were seen as when controlling for population density. However, private practices listing nondermatology professionals’ profiles was only more likely in the cities with a proportionately younger population when compared with academic institutions (74% vs 47%; P<.04).
Patient and Treatment/Procedure—The most commonly listed content types on both private practice websites and academic institution websites were available treatments/procedures (range, 89% to 98%). The least commonly listed content included financing for elective procedures (range, 4% to 16%), consultation fees (range, 1% to 2%), FAQs (frequently asked questions)(range, 4% to 20%), and HIPAA (Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act) policy (range, 12% to 22%). Private practices were more likely to list patient testimonials (52% vs 35%; P<.005), financing (16% vs 4%; P<.005), FAQs (20% vs 4%; P<.001), online appointments (77% vs 56%; P<.001), available treatments/procedures (98% vs 86%; P<.004), product advertisements (66% vs 16%; P<.0001), pictures of dermatology conditions (33% vs 13%; P<.001), and HIPAA policy (22% vs 12%; P<.04). Academic institutions were more likely to list research trials (65% vs 13%; P<.0001).
When controlling for population density, private practices were only more likely to list patient testimonials in densely populated (P=.035) and moderately populated cities (P=.019). The same trend was observed for online appointments in densely populated (P=.0023) and moderately populated cities (P=.037). Private practices continued to list product availability more often than academic institutions regardless of population density or population age. Academic institutions also continued to list research trials more often than private practices regardless of population density or population age.
Comment
Our study uniquely analyzed the differences in website content between private practices and academic institutions in dermatology. Of the 140 academic institutions accredited by the Accreditation Council for Graduate Medical Education (ACGME), only 113 had patient-pertinent websites.
Access to Websites —There was a significant difference in many website content criteria between the 2 groups. Private practice sites were easier to access via a Google search when compared with academic sites, which likely is influenced by the Google search algorithm that ranks websites higher based on several criteria including but not limited to keyword use in the title tag, link popularity of the site, and historic ranking. 12,13 Academic sites often were only accessible through portals found on their main institutional site or institution’s residency site.
Role of Social Media —Social media has been found to assist in educating patients on medical practices as well as selecting a physician. 14,15 Our study found that private practice websites listed links to social media more often than their academic counterparts. Social media consumption is increasing, in part due to the COVID-19 pandemic, and it may be optimal for patients and practices alike to include links on their websites. 16 Facebook and Instagram were listed more often on private practice sites when compared with academic institution sites, which was similar to a recent study analyzing the websites of plastic surgery private practices (N = 310) in which 90% of private practices included some type of social media, with Instagram and Facebook being the most used. 8 Social networking accounts can act as convenient platforms for marketing, providing patient education, and generating referrals, which suggests that the prominence of their usage in private practice poses benefits in patient decision-making when seeking care. 17-19 A study analyzing the impact of Facebook in medicine concluded that a Facebook page can serve as an effective vehicle for medical education, particularly in younger generations that favor technology-oriented teaching methods. 20 A survey on trends in cosmetic facial procedures in plastic surgery found that the most influential online methods patients used for choosing their providers were social media platforms and practice websites. Front-page placement on Google also was commonly associated with the number of social media followers. 21,22 A lack of social media prominence could hinder a website’s potential to reach patients.
Communication With Practices —Our study also found significant differences in other metrics related to a patient’s ability to directly communicate with a practice, such as physical addresses, telephone numbers, products available for direct purchase, and online appointment booking, all of which were listed more often on private practice websites compared with academic institution websites. Online appointment booking also was found more frequently on private practice websites. Although physical addresses and telephone numbers were listed significantly more often on private practice sites, this information was ubiquitous and easily accessible elsewhere. Academic institution websites listed research trials and fellowship training significantly more often than private practices. These differences imply a divergence in focus between private practices and academic institutions, likely because academic institutions are funded in large part from research grants, begetting a cycle of academic contribution. 23 In contrast, private practices may not rely as heavily on academic revenue and may be more likely to prioritize other revenue streams such as product sales. 24
HIPAA Policy —Surprisingly, HIPAA policy rarely was listed on any private (22%) or academic site (12%). Conversely, in the plastic surgery study, HIPAA policy was listed much more often, with more than half of private practices with board-certified plastic surgeons accredited in the year 2015 including it on their website, 8 which may suggest that surgically oriented specialties, particularly cosmetic subspecialties, aim to more noticeably display their privacy policies for patient reassurance.
Study Limitations —There are several limitations of our study. First, it is common for a conglomerate company to own multiple private practices in different specialties. As with academic sites, private practice sites may be limited by the hosting platforms, which often are tedious to navigate. Also noteworthy is the emergence of designated social media management positions—both by practice employees and by third-party firms 25 —but the impact of these positions in private practices and academic institutions has not been fully explored. Finally, inclusion criteria and standardized criteria definitions were chosen based on the precedent established by the authors of similar analyses in plastic surgery and radiology. 5-8 Further investigation into the most valued aspects of care by patients within the context of the type of practice chosen would be valuable in refining inclusion criteria. Additionally, this study did not stratify the data collected based on factors such as gender, race, and geographical location; studies conducted on website traffic analysis patterns that focus on these aspects likely would further explain the significance of these findings. Differences in the length of time to the next available appointment between private practices and academic institutions also may help support our findings. Finally, there is a need for further investigation into the preferences of patients themselves garnered from website traffic alone.
Conclusion
Our study examined a diverse compilation of private practice and academic institution websites and uncovered numerous differences in content. As technology and health care continuously evolve, it is imperative that both private practices and academic institutions are actively adapting to optimize their online presence. In doing so, patients will be better equipped at accessing provider information, gaining familiarity with the practice, and understanding treatment options.
Patients are finding it easier to use online resources to discover health care providers who fit their personalized needs. In the United States, approximately 70% of individuals use the internet to find health care information, and 80% are influenced by the information presented to them on health care websites.1 Patients utilize the internet to better understand treatments offered by providers and their prices as well as how other patients have rated their experience. Providers in private practice also have noticed that many patients are referring themselves vs obtaining a referral from another provider.2 As a result, it is critical for practice websites to have information that is of value to their patients, including the unique qualities and treatments offered. The purpose of this study was to analyze the differences between the content presented on dermatology private practice websites and academic institutional websites.
Methods
Websites Searched —All 140 academic dermatology programs, including both allopathic and osteopathic programs, were queried from the Association of American Medical Colleges (AAMC) database in March 2022. 3 First, the dermatology departmental websites for each program were analyzed to see if they contained information pertinent to patients. Any website that lacked this information or only had information relevant to the dermatology residency program was excluded from the study. After exclusion, a total of 113 websites were used in the academic website cohort. The private practices were found through an incognito Google search with the search term dermatologist and matched to be within 5 miles of each academic institution. The private practices that included at least one board-certified dermatologist and received the highest number of reviews on Google compared to other practices in the same region—a measure of online reputation—were selected to be in the private practice cohort (N = 113). Any duplicate practices, practices belonging to the same conglomerate company, or multispecialty clinics were excluded from the study. Board-certified dermatologists were confirmed using the Find a Dermatologist tool on the American Academy of Dermatology (AAD) website. 4
Website Assessments —Each website was assessed using 23 criteria divided into 4 categories: practice, physician(s), patient, and treatment/procedure (Table). Criteria for social media and publicity were further assessed. Criteria for social media included links on the website to a Facebook page, an Instagram account, a Twitter account, a Pinterest account, a LinkedIn account, a blog, a Yelp page, a YouTube channel, and/or any other social media. Criteria for publicity included links on the website to local television news, national news, newspapers, and/or magazines. 5-8 Ease of site access was determined if the website was the first search result found on Google when searching for each website. Nondermatology professionals included listing of mid-level providers or researchers.

Four individuals (V.S.J., A.C.B., M.E.O., and M.B.B.) independently assessed each of the websites using the established criteria. Each criterion was defined and discussed prior to data collection to maintain consistency. The criteria were determined as being present if the website clearly displayed, stated, explained, or linked to the relevant content. If the website did not directly contain the content, it was determined that the criteria were absent. One other individual (J.P.) independently cross-examined the data for consistency and evaluated for any discrepancies. 8
A raw analysis was done between each cohort. Another analysis was done that controlled for population density and the proportionate population age in each city 9 in which an academic institution/private practice was located. We proposed that more densely populated cities naturally may have more competition between practices, which may result in more optimized websites. 10 We also anticipated similar findings in cities with younger populations, as the younger demographic may be more likely to utilize and value online information when compared to older populations. 11 The websites for each cohort were equally divided into 3 tiers of population density (not shown) and population age (not shown).
Statistical Analysis —Statistical analysis was completed using descriptive statistics, χ 2 testing, and Fisher exact tests where appropriate with a predetermined level of significance of P < .05 in Microsoft Excel.
Results
Demographics —A total of 226 websites from both private practices and academic institutions were evaluated. Of them, only 108 private practices and 108 academic institutions listed practicing dermatologists on their site. Of 108 private practices, 76 (70.4%) had more than one practicing board-certified dermatologist. Of 108 academic institutions, all 108 (100%) institutions had more than one practicing board-certified dermatologist.
Of the dermatologists who practiced at academic institutions (n=2014) and private practices (n=817), 1157 (57.4%) and 419 (51.2%) were females, respectively. The population density of the cities with each of these practices/institutions ranged from 137 individuals per square kilometer to 11,232 individuals per square kilometer (mean [SD] population density, 2579 [2485] individuals per square kilometer). Densely populated, moderately populated, and sparsely populated cities had a median population density of 4618, 1708, and 760 individuals per square kilometer, respectively. The data also were divided into 3 age groups. In the older population tier, the median percentage of individuals older than 64 years was 14.2%, the median percentage of individuals aged 18 to 64 years was 63.8%, and the median percentage of individuals aged 5 to 17 years was 14.9%. In the moderately aged population tier, the median percentage of individuals older than 64 years was 10.2%, the median percentage of individuals aged 18 to 64 years was 70.3%, and the median percentage of individuals aged 5 to 17 years was 13.6%. In the younger population tier, the median percentage of individuals older than 64 years was 12%, the median percentage of individuals aged 18 to 64 years was 66.8%, and the median percentage of individuals aged 5 to 17 years was 15%.
Practice and Physician Content—In the raw analysis (Figure), the most commonly listed types of content (>90% of websites) in both private practice and academic sites was address (range, 95% to 100%), telephone number (range, 97% to 100%), and dermatologist profiles (both 92%). The least commonly listed types of content in both cohorts was publicity (range, 20% to 23%). Private practices were more likely to list profiles of nondermatology professionals (73% vs 56%; P<.02), email (47% vs 17%; P<.0001), and social media (29% vs 8%; P<.0001) compared with academic institution websites. Although Facebook was the most-linked social media account for both groups, 75% of private practice sites included the link compared with 16% of academic institutions. Academic institutions were more likely to list fellowship availability (66% vs 1%; P<.0001). Accessing each website was significantly easier in the private practice cohort (99% vs 61%; P<.0001).

When controlling for population density, private practices were only more likely to list nondermatology professionals’ profiles in densely populated cities when compared with academic institutions (73% vs 41%; P<.01). Academic institutions continued to list fellowship availability more often than private practices regardless of population density. The same trend was observed for private practices with ease of site access and listing of social media.
When controlling for population age, similar trends were seen as when controlling for population density. However, private practices listing nondermatology professionals’ profiles was only more likely in the cities with a proportionately younger population when compared with academic institutions (74% vs 47%; P<.04).
Patient and Treatment/Procedure—The most commonly listed content types on both private practice websites and academic institution websites were available treatments/procedures (range, 89% to 98%). The least commonly listed content included financing for elective procedures (range, 4% to 16%), consultation fees (range, 1% to 2%), FAQs (frequently asked questions)(range, 4% to 20%), and HIPAA (Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act) policy (range, 12% to 22%). Private practices were more likely to list patient testimonials (52% vs 35%; P<.005), financing (16% vs 4%; P<.005), FAQs (20% vs 4%; P<.001), online appointments (77% vs 56%; P<.001), available treatments/procedures (98% vs 86%; P<.004), product advertisements (66% vs 16%; P<.0001), pictures of dermatology conditions (33% vs 13%; P<.001), and HIPAA policy (22% vs 12%; P<.04). Academic institutions were more likely to list research trials (65% vs 13%; P<.0001).
When controlling for population density, private practices were only more likely to list patient testimonials in densely populated (P=.035) and moderately populated cities (P=.019). The same trend was observed for online appointments in densely populated (P=.0023) and moderately populated cities (P=.037). Private practices continued to list product availability more often than academic institutions regardless of population density or population age. Academic institutions also continued to list research trials more often than private practices regardless of population density or population age.
Comment
Our study uniquely analyzed the differences in website content between private practices and academic institutions in dermatology. Of the 140 academic institutions accredited by the Accreditation Council for Graduate Medical Education (ACGME), only 113 had patient-pertinent websites.
Access to Websites —There was a significant difference in many website content criteria between the 2 groups. Private practice sites were easier to access via a Google search when compared with academic sites, which likely is influenced by the Google search algorithm that ranks websites higher based on several criteria including but not limited to keyword use in the title tag, link popularity of the site, and historic ranking. 12,13 Academic sites often were only accessible through portals found on their main institutional site or institution’s residency site.
Role of Social Media —Social media has been found to assist in educating patients on medical practices as well as selecting a physician. 14,15 Our study found that private practice websites listed links to social media more often than their academic counterparts. Social media consumption is increasing, in part due to the COVID-19 pandemic, and it may be optimal for patients and practices alike to include links on their websites. 16 Facebook and Instagram were listed more often on private practice sites when compared with academic institution sites, which was similar to a recent study analyzing the websites of plastic surgery private practices (N = 310) in which 90% of private practices included some type of social media, with Instagram and Facebook being the most used. 8 Social networking accounts can act as convenient platforms for marketing, providing patient education, and generating referrals, which suggests that the prominence of their usage in private practice poses benefits in patient decision-making when seeking care. 17-19 A study analyzing the impact of Facebook in medicine concluded that a Facebook page can serve as an effective vehicle for medical education, particularly in younger generations that favor technology-oriented teaching methods. 20 A survey on trends in cosmetic facial procedures in plastic surgery found that the most influential online methods patients used for choosing their providers were social media platforms and practice websites. Front-page placement on Google also was commonly associated with the number of social media followers. 21,22 A lack of social media prominence could hinder a website’s potential to reach patients.
Communication With Practices —Our study also found significant differences in other metrics related to a patient’s ability to directly communicate with a practice, such as physical addresses, telephone numbers, products available for direct purchase, and online appointment booking, all of which were listed more often on private practice websites compared with academic institution websites. Online appointment booking also was found more frequently on private practice websites. Although physical addresses and telephone numbers were listed significantly more often on private practice sites, this information was ubiquitous and easily accessible elsewhere. Academic institution websites listed research trials and fellowship training significantly more often than private practices. These differences imply a divergence in focus between private practices and academic institutions, likely because academic institutions are funded in large part from research grants, begetting a cycle of academic contribution. 23 In contrast, private practices may not rely as heavily on academic revenue and may be more likely to prioritize other revenue streams such as product sales. 24
HIPAA Policy —Surprisingly, HIPAA policy rarely was listed on any private (22%) or academic site (12%). Conversely, in the plastic surgery study, HIPAA policy was listed much more often, with more than half of private practices with board-certified plastic surgeons accredited in the year 2015 including it on their website, 8 which may suggest that surgically oriented specialties, particularly cosmetic subspecialties, aim to more noticeably display their privacy policies for patient reassurance.
Study Limitations —There are several limitations of our study. First, it is common for a conglomerate company to own multiple private practices in different specialties. As with academic sites, private practice sites may be limited by the hosting platforms, which often are tedious to navigate. Also noteworthy is the emergence of designated social media management positions—both by practice employees and by third-party firms 25 —but the impact of these positions in private practices and academic institutions has not been fully explored. Finally, inclusion criteria and standardized criteria definitions were chosen based on the precedent established by the authors of similar analyses in plastic surgery and radiology. 5-8 Further investigation into the most valued aspects of care by patients within the context of the type of practice chosen would be valuable in refining inclusion criteria. Additionally, this study did not stratify the data collected based on factors such as gender, race, and geographical location; studies conducted on website traffic analysis patterns that focus on these aspects likely would further explain the significance of these findings. Differences in the length of time to the next available appointment between private practices and academic institutions also may help support our findings. Finally, there is a need for further investigation into the preferences of patients themselves garnered from website traffic alone.
Conclusion
Our study examined a diverse compilation of private practice and academic institution websites and uncovered numerous differences in content. As technology and health care continuously evolve, it is imperative that both private practices and academic institutions are actively adapting to optimize their online presence. In doing so, patients will be better equipped at accessing provider information, gaining familiarity with the practice, and understanding treatment options.
- Gentry ZL, Ananthasekar S, Yeatts M, et al. Can patients find an endocrine surgeon? how hospital websites hide the expertise of these medical professionals. Am J Surg . 2021;221:101-105.
- Pollack CE, Rastegar A, Keating NL, et al. Is self-referral associated with higher quality care? Health Serv Res . 2015;50:1472-1490.
- Association of American Medical Colleges. Residency Explorer TM tool. Accessed May 15, 2023. https://students-residents.aamc.org/apply-smart-residency/residency-explorer-tool
- Find a dermatologist. American Academy of Dermatology website. Accessed May 15, 2023. https://find-a-derm.aad.org/
- Johnson EJ, Doshi AM, Rosenkrantz AB. Strengths and deficiencies in the content of US radiology private practices’ websites. J Am Coll Radiol. 2017;14:431-435.
- Brunk D. Medical website expert shares design tips. Dermatology News . February 9, 2012. Accessed May 15, 2023. https://www.mdedge.com/dermatology/article/47413/health-policy/medical-website-expert-shares-design-tips
- Kuhnigk O, Ramuschkat M, Schreiner J, et al. Internet presence of neurologists, psychiatrists and medical psychotherapists in private practice [in German]. Psychiatr Prax . 2013;41:142-147.
- Ananthasekar S, Patel JJ, Patel NJ, et al. The content of US plastic surgery private practices’ websites. Ann Plast Surg . 2021;86(6S suppl 5):S578-S584.
- US Census Bureau. Age and Sex: 2021. Updated December 2, 2021. Accessed March 15, 2023. https://www.census.gov/topics/population/age-and-sex/data/tables.2021.List_897222059.html#list-tab-List_897222059
- Porter ME. The competitive advantage of the inner city. Harvard Business Review . Published August 1, 2014. https://hbr.org/1995/05/the-competitive-advantage-of-the-inner-city
- Clark PG. The social allocation of health care resources: ethical dilemmas in age-group competition. Gerontologist. 1985;25:119-125.
- Su A-J, Hu YC, Kuzmanovic A, et al. How to improve your Google ranking: myths and reality. ACM Transactions on the Web . 2014;8. https://dl.acm.org/doi/abs/10.1145/2579990
- McCormick K. 39 ways to increase traffic to your website. WordStream website. Published March 28, 2023. Accessed May 22, 2023. https://www.wordstream.com/blog/ws/2014/08/14/increase-traffic-to-my-website
- Montemurro P, Porcnik A, Hedén P, et al. The influence of social media and easily accessible online information on the aesthetic plastic surgery practice: literature review and our own experience. Aesthetic Plast Surg . 2015;39:270-277.
- Steehler KR, Steehler MK, Pierce ML, et al. Social media’s role in otolaryngology–head and neck surgery. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg . 2013;149:521-524.
- Tsao S-F, Chen H, Tisseverasinghe T, et al. What social media told us in the time of COVID-19: a scoping review. Lancet Digit Health . 2021;3:E175-E194.
- Geist R, Militello M, Albrecht JM, et al. Social media and clinical research in dermatology. Curr Dermatol Rep . 2021;10:105-111.
- McLawhorn AS, De Martino I, Fehring KA, et al. Social media and your practice: navigating the surgeon-patient relationship. Curr Rev Musculoskelet Med . 2016;9:487-495.
- Thomas RB, Johnson PT, Fishman EK. Social media for global education: pearls and pitfalls of using Facebook, Twitter, and Instagram. J Am Coll Radiol . 2018;15:1513-1516.
- Lugo-Fagundo C, Johnson MB, Thomas RB, et al. New frontiers in education: Facebook as a vehicle for medical information delivery. J Am Coll Radiol . 2016;13:316-319.
- Ho T-VT, Dayan SH. How to leverage social media in private practice. Facial Plast Surg Clin North Am . 2020;28:515-522.
- Fan KL, Graziano F, Economides JM, et al. The public’s preferences on plastic surgery social media engagement and professionalism. Plast Reconstr Surg . 2019;143:619-630.
- Jacob BA, Lefgren L. The impact of research grant funding on scientific productivity. J Public Econ. 2011;95:1168-1177.
- Baumann L. Ethics in cosmetic dermatology. Clin Dermatol. 2012;30:522-527.
- Miller AR, Tucker C. Active social media management: the case of health care. Info Sys Res . 2013;24:52-70.
- Gentry ZL, Ananthasekar S, Yeatts M, et al. Can patients find an endocrine surgeon? how hospital websites hide the expertise of these medical professionals. Am J Surg . 2021;221:101-105.
- Pollack CE, Rastegar A, Keating NL, et al. Is self-referral associated with higher quality care? Health Serv Res . 2015;50:1472-1490.
- Association of American Medical Colleges. Residency Explorer TM tool. Accessed May 15, 2023. https://students-residents.aamc.org/apply-smart-residency/residency-explorer-tool
- Find a dermatologist. American Academy of Dermatology website. Accessed May 15, 2023. https://find-a-derm.aad.org/
- Johnson EJ, Doshi AM, Rosenkrantz AB. Strengths and deficiencies in the content of US radiology private practices’ websites. J Am Coll Radiol. 2017;14:431-435.
- Brunk D. Medical website expert shares design tips. Dermatology News . February 9, 2012. Accessed May 15, 2023. https://www.mdedge.com/dermatology/article/47413/health-policy/medical-website-expert-shares-design-tips
- Kuhnigk O, Ramuschkat M, Schreiner J, et al. Internet presence of neurologists, psychiatrists and medical psychotherapists in private practice [in German]. Psychiatr Prax . 2013;41:142-147.
- Ananthasekar S, Patel JJ, Patel NJ, et al. The content of US plastic surgery private practices’ websites. Ann Plast Surg . 2021;86(6S suppl 5):S578-S584.
- US Census Bureau. Age and Sex: 2021. Updated December 2, 2021. Accessed March 15, 2023. https://www.census.gov/topics/population/age-and-sex/data/tables.2021.List_897222059.html#list-tab-List_897222059
- Porter ME. The competitive advantage of the inner city. Harvard Business Review . Published August 1, 2014. https://hbr.org/1995/05/the-competitive-advantage-of-the-inner-city
- Clark PG. The social allocation of health care resources: ethical dilemmas in age-group competition. Gerontologist. 1985;25:119-125.
- Su A-J, Hu YC, Kuzmanovic A, et al. How to improve your Google ranking: myths and reality. ACM Transactions on the Web . 2014;8. https://dl.acm.org/doi/abs/10.1145/2579990
- McCormick K. 39 ways to increase traffic to your website. WordStream website. Published March 28, 2023. Accessed May 22, 2023. https://www.wordstream.com/blog/ws/2014/08/14/increase-traffic-to-my-website
- Montemurro P, Porcnik A, Hedén P, et al. The influence of social media and easily accessible online information on the aesthetic plastic surgery practice: literature review and our own experience. Aesthetic Plast Surg . 2015;39:270-277.
- Steehler KR, Steehler MK, Pierce ML, et al. Social media’s role in otolaryngology–head and neck surgery. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg . 2013;149:521-524.
- Tsao S-F, Chen H, Tisseverasinghe T, et al. What social media told us in the time of COVID-19: a scoping review. Lancet Digit Health . 2021;3:E175-E194.
- Geist R, Militello M, Albrecht JM, et al. Social media and clinical research in dermatology. Curr Dermatol Rep . 2021;10:105-111.
- McLawhorn AS, De Martino I, Fehring KA, et al. Social media and your practice: navigating the surgeon-patient relationship. Curr Rev Musculoskelet Med . 2016;9:487-495.
- Thomas RB, Johnson PT, Fishman EK. Social media for global education: pearls and pitfalls of using Facebook, Twitter, and Instagram. J Am Coll Radiol . 2018;15:1513-1516.
- Lugo-Fagundo C, Johnson MB, Thomas RB, et al. New frontiers in education: Facebook as a vehicle for medical information delivery. J Am Coll Radiol . 2016;13:316-319.
- Ho T-VT, Dayan SH. How to leverage social media in private practice. Facial Plast Surg Clin North Am . 2020;28:515-522.
- Fan KL, Graziano F, Economides JM, et al. The public’s preferences on plastic surgery social media engagement and professionalism. Plast Reconstr Surg . 2019;143:619-630.
- Jacob BA, Lefgren L. The impact of research grant funding on scientific productivity. J Public Econ. 2011;95:1168-1177.
- Baumann L. Ethics in cosmetic dermatology. Clin Dermatol. 2012;30:522-527.
- Miller AR, Tucker C. Active social media management: the case of health care. Info Sys Res . 2013;24:52-70.
Practice Points
- Dermatologists at both private practices and academic institutions should understand that website content often may be the most accessible source of information about the practice available to patients and should be as specific and detailed as possible.
- When compared to private practices, academic institutions largely fail to have a social media presence, which may limit patient interaction with their websites.
Glitter Effects of Nail Art on Optical Coherence Tomography
Practice Gap
Nail art can skew the results of optical coherence tomography (OCT), a noninvasive imaging technology that is used to visualize nail morphology in diseases such as psoriatic arthritis and onychomycosis, with a penetration depth of 2 mm and high-resolution images.1 Few studies have evaluated the effects of nail art on OCT. Saleah and colleagues1 found that clear, semitransparent, and red nail polishes do not interfere with visualization of the nail plate, whereas nontransparent gel polish and art stones obscure the image. They did not comment on the effect of glitter nail art in their study, though they did test 1 nail that contained glitter.1 Monpeurt et al2 compared matte and glossy nail polishes. They found that matte polish was readily identifiable from the nail plate, whereas glossy polish presented a greater number of artifacts.2
The Solution
We looked at 3 glitter nail polishes—gold, pink, and silver—that were scanned by OCT to assess the effect of the polish on the resulting image. We determined that glitter particles completely obscured the nail bed and nail plate, regardless of color (Figure 1). Glossy clear polish imparted a distinct film on the top of the nail plate that did not obscure the nail plate or the nail bed (Figure 2).
We conclude that glitter nail polish contains numerous reflective solid particles that interfere with OCT imaging of the nail plate and nail bed. As a result, we recommend removal of nail art to properly assess nail pathology. Because removal may need to be conducted by a nail technician, the treating clinician should inform the patient ahead of time to come to the appointment with bare (ie, unpolished) nails.
Practice Implications
Bringing awareness to the necessity of removing nail art prior to OCT imaging is crucial because many patients partake in its application, and removal may require the involvement of a professional nail technician. If a patient can be made aware that they should remove all nail art in advance, they will be better prepared for an OCT imaging session. Such a protocol increases efficiency, decreases diagnostic delay, and reduces cost associated with multiple office visits.
- Saleah S, Kim P, Seong D, et al. A preliminary study of post-progressive nail-art effects on in vivo nail plate using optical coherence tomography-based intensity profiling assessment. Sci Rep. 2021;11:666. doi:10.1038/s41598-020-79497-3
- Monpeurt C, Cinotti E, Hebert M, et al. Thickness and morphology assessment of nail polishes applied on nails by high-definition optical coherence tomography. Skin Res Technol. 2018;24:156-157. doi:10.1111/srt.12406
Practice Gap
Nail art can skew the results of optical coherence tomography (OCT), a noninvasive imaging technology that is used to visualize nail morphology in diseases such as psoriatic arthritis and onychomycosis, with a penetration depth of 2 mm and high-resolution images.1 Few studies have evaluated the effects of nail art on OCT. Saleah and colleagues1 found that clear, semitransparent, and red nail polishes do not interfere with visualization of the nail plate, whereas nontransparent gel polish and art stones obscure the image. They did not comment on the effect of glitter nail art in their study, though they did test 1 nail that contained glitter.1 Monpeurt et al2 compared matte and glossy nail polishes. They found that matte polish was readily identifiable from the nail plate, whereas glossy polish presented a greater number of artifacts.2
The Solution
We looked at 3 glitter nail polishes—gold, pink, and silver—that were scanned by OCT to assess the effect of the polish on the resulting image. We determined that glitter particles completely obscured the nail bed and nail plate, regardless of color (Figure 1). Glossy clear polish imparted a distinct film on the top of the nail plate that did not obscure the nail plate or the nail bed (Figure 2).

We conclude that glitter nail polish contains numerous reflective solid particles that interfere with OCT imaging of the nail plate and nail bed. As a result, we recommend removal of nail art to properly assess nail pathology. Because removal may need to be conducted by a nail technician, the treating clinician should inform the patient ahead of time to come to the appointment with bare (ie, unpolished) nails.

Practice Implications
Bringing awareness to the necessity of removing nail art prior to OCT imaging is crucial because many patients partake in its application, and removal may require the involvement of a professional nail technician. If a patient can be made aware that they should remove all nail art in advance, they will be better prepared for an OCT imaging session. Such a protocol increases efficiency, decreases diagnostic delay, and reduces cost associated with multiple office visits.
Practice Gap
Nail art can skew the results of optical coherence tomography (OCT), a noninvasive imaging technology that is used to visualize nail morphology in diseases such as psoriatic arthritis and onychomycosis, with a penetration depth of 2 mm and high-resolution images.1 Few studies have evaluated the effects of nail art on OCT. Saleah and colleagues1 found that clear, semitransparent, and red nail polishes do not interfere with visualization of the nail plate, whereas nontransparent gel polish and art stones obscure the image. They did not comment on the effect of glitter nail art in their study, though they did test 1 nail that contained glitter.1 Monpeurt et al2 compared matte and glossy nail polishes. They found that matte polish was readily identifiable from the nail plate, whereas glossy polish presented a greater number of artifacts.2
The Solution
We looked at 3 glitter nail polishes—gold, pink, and silver—that were scanned by OCT to assess the effect of the polish on the resulting image. We determined that glitter particles completely obscured the nail bed and nail plate, regardless of color (Figure 1). Glossy clear polish imparted a distinct film on the top of the nail plate that did not obscure the nail plate or the nail bed (Figure 2).

We conclude that glitter nail polish contains numerous reflective solid particles that interfere with OCT imaging of the nail plate and nail bed. As a result, we recommend removal of nail art to properly assess nail pathology. Because removal may need to be conducted by a nail technician, the treating clinician should inform the patient ahead of time to come to the appointment with bare (ie, unpolished) nails.

Practice Implications
Bringing awareness to the necessity of removing nail art prior to OCT imaging is crucial because many patients partake in its application, and removal may require the involvement of a professional nail technician. If a patient can be made aware that they should remove all nail art in advance, they will be better prepared for an OCT imaging session. Such a protocol increases efficiency, decreases diagnostic delay, and reduces cost associated with multiple office visits.
- Saleah S, Kim P, Seong D, et al. A preliminary study of post-progressive nail-art effects on in vivo nail plate using optical coherence tomography-based intensity profiling assessment. Sci Rep. 2021;11:666. doi:10.1038/s41598-020-79497-3
- Monpeurt C, Cinotti E, Hebert M, et al. Thickness and morphology assessment of nail polishes applied on nails by high-definition optical coherence tomography. Skin Res Technol. 2018;24:156-157. doi:10.1111/srt.12406
- Saleah S, Kim P, Seong D, et al. A preliminary study of post-progressive nail-art effects on in vivo nail plate using optical coherence tomography-based intensity profiling assessment. Sci Rep. 2021;11:666. doi:10.1038/s41598-020-79497-3
- Monpeurt C, Cinotti E, Hebert M, et al. Thickness and morphology assessment of nail polishes applied on nails by high-definition optical coherence tomography. Skin Res Technol. 2018;24:156-157. doi:10.1111/srt.12406
Lower racial disparity in melanoma diagnoses in vets than U.S. men overall, study finds
a new analysis shows.
“The trend of a lower racial disparity in the VA in the proportion of melanomas with local disease and in the proportion of distant metastasis at presentation was observed across age groups,” wrote Martin A. Weinstock MD, PhD, and Rachel K. Lim, of the department of dermatology at Brown University, Providence, R.I., and the Center for Dermatoepidemiology at the VA Providence Healthcare System. The study was published online in the Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology.
“Melanoma was the fourth-most common cancer [diagnosed] in male VA patients in 2010,” wrote the authors, who also pointed out that “prior surveys found that 11%-13% of U.S. active-duty personnel routinely use sunscreen despite significant occupational sun exposure. Racial disparities are important concerns in the VA and elsewhere.”
To compare the stage of melanoma at presentation among White and non-Whites patients in the VA and in the general U.S. population, the researchers identified invasive cutaneous melanoma cases from 2000 to 2019 in the VA Corporate Data Warehouse and the Surveillance, Epidemiology and End Results Program (SEER).
They restricted the analysis to men because of the small proportion of women in the at-risk veteran population and excluded cases with an age younger than 20, those with unknown histology, and melanoma in situ. The researchers performed two-tailed z-tests to evaluate the difference in proportions of melanoma stages between the veteran population and the general population.
The analysis included 44,077 cases of invasive melanoma in the VA and 217,030 in SEER. Racial disparities in melanoma staging were substantially less pronounced in the VA than in SEER.
In the VA, localized disease represented 77.9% of melanomas among Whites versus 71.0% among non-Whites. But in SEER, localized disease represented 80.7% of melanomas among Whites versus 61.5% in non-Whites – over double the VA disparity (P < .0001).
Likewise, the disparity between Whites and nonwhites observed for regional or distant metastatic disease at presentation in the VA was lower than the disparity observed in SEER. For example, in the VA, distant metastatic disease at presentation represented 6.1% of melanomas among Whites versus 8.6% among non-Whites, while in SEER it represented 4.8% of melanomas among Whites versus 11.3% in non-Whites – again, more than double the VA disparity (P < .0001).
“These differences between the VA and SEER were less marked” among those older than 65 years, the researchers wrote. “Notably, the differences between VA and SEER in racial disparities among those greater than 65 in age were still significant for localized disease and for distant metastasis.”
The findings suggest that the VA “may be more effective in reducing racial disparities in melanoma stage at diagnosis, potentially due to all patients in the VA dataset having insured access to health care, regardless of socioeconomic status,” the researchers concluded. Similarly, the decreased difference in racial disparities observed in patients older than 65 across systems “may be related to the availability of Medicare to the older general populations. The authors acknowledged several study limitations, such as the predominantly elderly and male VA population, potentially underreported utilization of non-VA dermatologic care, and variation in geographic regions covered by each database.
Travis W. Blalock, MD, director of dermatologic surgery, Mohs micrographic surgery, and cutaneous oncology at Emory University, Atlanta, who was asked to comment on the work, said in an interview he would have liked to see a more detailed breakdown of the younger patients, “for those in their 30s and 40s, to see if this trend held up.”
He would have also liked to see how the data trended over time, adding, “while this, broadly, may be good news for our veterans, attributing this finding to a reduction in access disparity or some other organizational intervention seems a little premature. Regardless, Dr. Weinstock has given us, once again, information from our veterans to probe for the betterment of all patients.”
The researchers reported having no relevant disclosures and the study had no funding. Dr. Blalock disclosed that he has served as a principal investigator for Castle Biosciences.
a new analysis shows.
“The trend of a lower racial disparity in the VA in the proportion of melanomas with local disease and in the proportion of distant metastasis at presentation was observed across age groups,” wrote Martin A. Weinstock MD, PhD, and Rachel K. Lim, of the department of dermatology at Brown University, Providence, R.I., and the Center for Dermatoepidemiology at the VA Providence Healthcare System. The study was published online in the Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology.
“Melanoma was the fourth-most common cancer [diagnosed] in male VA patients in 2010,” wrote the authors, who also pointed out that “prior surveys found that 11%-13% of U.S. active-duty personnel routinely use sunscreen despite significant occupational sun exposure. Racial disparities are important concerns in the VA and elsewhere.”
To compare the stage of melanoma at presentation among White and non-Whites patients in the VA and in the general U.S. population, the researchers identified invasive cutaneous melanoma cases from 2000 to 2019 in the VA Corporate Data Warehouse and the Surveillance, Epidemiology and End Results Program (SEER).
They restricted the analysis to men because of the small proportion of women in the at-risk veteran population and excluded cases with an age younger than 20, those with unknown histology, and melanoma in situ. The researchers performed two-tailed z-tests to evaluate the difference in proportions of melanoma stages between the veteran population and the general population.
The analysis included 44,077 cases of invasive melanoma in the VA and 217,030 in SEER. Racial disparities in melanoma staging were substantially less pronounced in the VA than in SEER.
In the VA, localized disease represented 77.9% of melanomas among Whites versus 71.0% among non-Whites. But in SEER, localized disease represented 80.7% of melanomas among Whites versus 61.5% in non-Whites – over double the VA disparity (P < .0001).
Likewise, the disparity between Whites and nonwhites observed for regional or distant metastatic disease at presentation in the VA was lower than the disparity observed in SEER. For example, in the VA, distant metastatic disease at presentation represented 6.1% of melanomas among Whites versus 8.6% among non-Whites, while in SEER it represented 4.8% of melanomas among Whites versus 11.3% in non-Whites – again, more than double the VA disparity (P < .0001).
“These differences between the VA and SEER were less marked” among those older than 65 years, the researchers wrote. “Notably, the differences between VA and SEER in racial disparities among those greater than 65 in age were still significant for localized disease and for distant metastasis.”
The findings suggest that the VA “may be more effective in reducing racial disparities in melanoma stage at diagnosis, potentially due to all patients in the VA dataset having insured access to health care, regardless of socioeconomic status,” the researchers concluded. Similarly, the decreased difference in racial disparities observed in patients older than 65 across systems “may be related to the availability of Medicare to the older general populations. The authors acknowledged several study limitations, such as the predominantly elderly and male VA population, potentially underreported utilization of non-VA dermatologic care, and variation in geographic regions covered by each database.
Travis W. Blalock, MD, director of dermatologic surgery, Mohs micrographic surgery, and cutaneous oncology at Emory University, Atlanta, who was asked to comment on the work, said in an interview he would have liked to see a more detailed breakdown of the younger patients, “for those in their 30s and 40s, to see if this trend held up.”
He would have also liked to see how the data trended over time, adding, “while this, broadly, may be good news for our veterans, attributing this finding to a reduction in access disparity or some other organizational intervention seems a little premature. Regardless, Dr. Weinstock has given us, once again, information from our veterans to probe for the betterment of all patients.”
The researchers reported having no relevant disclosures and the study had no funding. Dr. Blalock disclosed that he has served as a principal investigator for Castle Biosciences.
a new analysis shows.
“The trend of a lower racial disparity in the VA in the proportion of melanomas with local disease and in the proportion of distant metastasis at presentation was observed across age groups,” wrote Martin A. Weinstock MD, PhD, and Rachel K. Lim, of the department of dermatology at Brown University, Providence, R.I., and the Center for Dermatoepidemiology at the VA Providence Healthcare System. The study was published online in the Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology.
“Melanoma was the fourth-most common cancer [diagnosed] in male VA patients in 2010,” wrote the authors, who also pointed out that “prior surveys found that 11%-13% of U.S. active-duty personnel routinely use sunscreen despite significant occupational sun exposure. Racial disparities are important concerns in the VA and elsewhere.”
To compare the stage of melanoma at presentation among White and non-Whites patients in the VA and in the general U.S. population, the researchers identified invasive cutaneous melanoma cases from 2000 to 2019 in the VA Corporate Data Warehouse and the Surveillance, Epidemiology and End Results Program (SEER).
They restricted the analysis to men because of the small proportion of women in the at-risk veteran population and excluded cases with an age younger than 20, those with unknown histology, and melanoma in situ. The researchers performed two-tailed z-tests to evaluate the difference in proportions of melanoma stages between the veteran population and the general population.
The analysis included 44,077 cases of invasive melanoma in the VA and 217,030 in SEER. Racial disparities in melanoma staging were substantially less pronounced in the VA than in SEER.
In the VA, localized disease represented 77.9% of melanomas among Whites versus 71.0% among non-Whites. But in SEER, localized disease represented 80.7% of melanomas among Whites versus 61.5% in non-Whites – over double the VA disparity (P < .0001).
Likewise, the disparity between Whites and nonwhites observed for regional or distant metastatic disease at presentation in the VA was lower than the disparity observed in SEER. For example, in the VA, distant metastatic disease at presentation represented 6.1% of melanomas among Whites versus 8.6% among non-Whites, while in SEER it represented 4.8% of melanomas among Whites versus 11.3% in non-Whites – again, more than double the VA disparity (P < .0001).
“These differences between the VA and SEER were less marked” among those older than 65 years, the researchers wrote. “Notably, the differences between VA and SEER in racial disparities among those greater than 65 in age were still significant for localized disease and for distant metastasis.”
The findings suggest that the VA “may be more effective in reducing racial disparities in melanoma stage at diagnosis, potentially due to all patients in the VA dataset having insured access to health care, regardless of socioeconomic status,” the researchers concluded. Similarly, the decreased difference in racial disparities observed in patients older than 65 across systems “may be related to the availability of Medicare to the older general populations. The authors acknowledged several study limitations, such as the predominantly elderly and male VA population, potentially underreported utilization of non-VA dermatologic care, and variation in geographic regions covered by each database.
Travis W. Blalock, MD, director of dermatologic surgery, Mohs micrographic surgery, and cutaneous oncology at Emory University, Atlanta, who was asked to comment on the work, said in an interview he would have liked to see a more detailed breakdown of the younger patients, “for those in their 30s and 40s, to see if this trend held up.”
He would have also liked to see how the data trended over time, adding, “while this, broadly, may be good news for our veterans, attributing this finding to a reduction in access disparity or some other organizational intervention seems a little premature. Regardless, Dr. Weinstock has given us, once again, information from our veterans to probe for the betterment of all patients.”
The researchers reported having no relevant disclosures and the study had no funding. Dr. Blalock disclosed that he has served as a principal investigator for Castle Biosciences.
FROM THE JOURNAL OF THE AMERICAN ACADEMY OF DERMATOLOGY
Continuous glucose monitors come to hospitals
But that technological future will require ensuring that the monitoring devices are as accurate as the conventional method, experts told this news organization.
In 2020, the U.S. Food and Drug Administration enabled in-hospital use of CGMs to reduce contact between patients and health care providers during the COVID-19 pandemic. Diabetes is a risk factor for more severe COVID, meaning that many patients with the infection also required ongoing care for their blood sugar problems.
Prior to the pandemic, in-person finger-stick tests were the primary means of measuring glucose for hospitalized patients with diabetes.
The trouble is that finger-stick measurements quickly become inaccurate.
“Glucose is a measurement that changes pretty rapidly,” said Eileen Faulds, RN, PhD, an endocrinology nurse and health services researcher at the Ohio State University, Columbus. Finger sticks might occur only four or five times per day, Dr. Faulds noted, or as often as every hour for people who receive insulin intravenously. But even that more frequent pace is far from continuous.
“With CGM we can get the glucose level in real time,” Dr. Faulds said.
Dr. Faulds is lead author of a new study in the Journal of Diabetes Science and Technology, which shows that nurses in the ICU believe that using continuous monitors, subcutaneous filaments connected to sensors that regularly report glucose levels, enables better patient care than does relying on periodic glucose tests alone. Nurses still used traditional finger sticks, which Dr. Faulds notes are highly accurate at the time of the reading.
In a 2022 study, glucose levels generated by CGM and those measured by finger sticks varied by up to 14%. A hybrid care model combining CGMs and finger stick tests may emerge, Dr. Faulds said.
A gusher of glucose data
People with diabetes have long been able to use CGMs in their daily lives, which typically report the glucose value to a smartphone or watch. The devices are now part of hospital care as well. In 2022, the Food and Drug Administration granted a breakthrough therapy designation to the company Dexcom for use of its CGMs to manage care of people with diabetes in hospitals.
One open question is how often CGMs should report glucose readings for optimum patient health. Dexcom’s G6 CGM reports glucose levels every five minutes, for example, whereas Abbott’s FreeStyle Libre 2 delivers glucose values every minute.
“We wouldn’t look at each value, we would look at the big picture,” to determine if a patient is at risk of becoming hyper- or hypoglycemic, said Lizda Guerrero-Arroyo, MD, a postdoctoral fellow in endocrinology at the Emory University School of Medicine, Atlanta. Dr. Guerrero-Arroyo recently reported that clinicians in multiple ICUs began to use CGMs in conjunction with finger sticks during the pandemic and felt the devices could reduce patient discomfort.
“A finger stick is very painful,” Dr. Guerrero-Arroyo said, and a bottleneck for nursing staff who administer these tests. In contrast, Dr. Faulds said, CGM placement is essentially painless and requires less labor on the ward to manage.
Beyond use in the ICU, clinicians are also experimenting with use of CGMs to monitor blood sugar levels in people with diabetes who are undergoing general surgery. And other researchers are describing how to integrate data from CGMs into patient care tools such as the electronic health record, although a standard way to do this does not yet exist.
Assuming CGMs remain part of the mix for in-hospital care of people with diabetes, clinicians may mainly need trend summaries of how glucose levels rise and fall over time, said data scientist Samantha Spierling Bagsic, PhD, of the Scripps Whittier Diabetes Institute, San Diego. Dr. Guerrero-Arroyo said that she shares that vision. But a minute-by-minute analysis of glucose levels also may be necessary to get a granular sense of how changing a patient’s insulin level affects their blood sugar, Dr. Spierling Bagsic said.
“We need to figure out what data different audiences need, how often we need to measure glucose, and how to present that information to different audiences in different ways,” said Dr. Spierling Bagsic, a co-author of the study about integrating CGM data into patient care tools.
The wider use of CGMs in hospitals may be one silver lining of the COVID-19 pandemic. As an inpatient endocrinology nurse, Dr. Faulds said that she wanted to use CGMs prior to the outbreak, but at that point, a critical mass of studies about their benefits was missing.
“We all know the terrible things that happened during the pandemic,” Dr. Faulds said. “But it gave us the allowance to use CGMs, and we saw that nurses loved them.”
Dr. Faulds reports relationships with Dexcom and Insulet and has received an honorarium from Medscape. Dr. Guerrero-Arroyo and Dr. Spierling Bagsic reported no financial conflicts of interest.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
But that technological future will require ensuring that the monitoring devices are as accurate as the conventional method, experts told this news organization.
In 2020, the U.S. Food and Drug Administration enabled in-hospital use of CGMs to reduce contact between patients and health care providers during the COVID-19 pandemic. Diabetes is a risk factor for more severe COVID, meaning that many patients with the infection also required ongoing care for their blood sugar problems.
Prior to the pandemic, in-person finger-stick tests were the primary means of measuring glucose for hospitalized patients with diabetes.
The trouble is that finger-stick measurements quickly become inaccurate.
“Glucose is a measurement that changes pretty rapidly,” said Eileen Faulds, RN, PhD, an endocrinology nurse and health services researcher at the Ohio State University, Columbus. Finger sticks might occur only four or five times per day, Dr. Faulds noted, or as often as every hour for people who receive insulin intravenously. But even that more frequent pace is far from continuous.
“With CGM we can get the glucose level in real time,” Dr. Faulds said.
Dr. Faulds is lead author of a new study in the Journal of Diabetes Science and Technology, which shows that nurses in the ICU believe that using continuous monitors, subcutaneous filaments connected to sensors that regularly report glucose levels, enables better patient care than does relying on periodic glucose tests alone. Nurses still used traditional finger sticks, which Dr. Faulds notes are highly accurate at the time of the reading.
In a 2022 study, glucose levels generated by CGM and those measured by finger sticks varied by up to 14%. A hybrid care model combining CGMs and finger stick tests may emerge, Dr. Faulds said.
A gusher of glucose data
People with diabetes have long been able to use CGMs in their daily lives, which typically report the glucose value to a smartphone or watch. The devices are now part of hospital care as well. In 2022, the Food and Drug Administration granted a breakthrough therapy designation to the company Dexcom for use of its CGMs to manage care of people with diabetes in hospitals.
One open question is how often CGMs should report glucose readings for optimum patient health. Dexcom’s G6 CGM reports glucose levels every five minutes, for example, whereas Abbott’s FreeStyle Libre 2 delivers glucose values every minute.
“We wouldn’t look at each value, we would look at the big picture,” to determine if a patient is at risk of becoming hyper- or hypoglycemic, said Lizda Guerrero-Arroyo, MD, a postdoctoral fellow in endocrinology at the Emory University School of Medicine, Atlanta. Dr. Guerrero-Arroyo recently reported that clinicians in multiple ICUs began to use CGMs in conjunction with finger sticks during the pandemic and felt the devices could reduce patient discomfort.
“A finger stick is very painful,” Dr. Guerrero-Arroyo said, and a bottleneck for nursing staff who administer these tests. In contrast, Dr. Faulds said, CGM placement is essentially painless and requires less labor on the ward to manage.
Beyond use in the ICU, clinicians are also experimenting with use of CGMs to monitor blood sugar levels in people with diabetes who are undergoing general surgery. And other researchers are describing how to integrate data from CGMs into patient care tools such as the electronic health record, although a standard way to do this does not yet exist.
Assuming CGMs remain part of the mix for in-hospital care of people with diabetes, clinicians may mainly need trend summaries of how glucose levels rise and fall over time, said data scientist Samantha Spierling Bagsic, PhD, of the Scripps Whittier Diabetes Institute, San Diego. Dr. Guerrero-Arroyo said that she shares that vision. But a minute-by-minute analysis of glucose levels also may be necessary to get a granular sense of how changing a patient’s insulin level affects their blood sugar, Dr. Spierling Bagsic said.
“We need to figure out what data different audiences need, how often we need to measure glucose, and how to present that information to different audiences in different ways,” said Dr. Spierling Bagsic, a co-author of the study about integrating CGM data into patient care tools.
The wider use of CGMs in hospitals may be one silver lining of the COVID-19 pandemic. As an inpatient endocrinology nurse, Dr. Faulds said that she wanted to use CGMs prior to the outbreak, but at that point, a critical mass of studies about their benefits was missing.
“We all know the terrible things that happened during the pandemic,” Dr. Faulds said. “But it gave us the allowance to use CGMs, and we saw that nurses loved them.”
Dr. Faulds reports relationships with Dexcom and Insulet and has received an honorarium from Medscape. Dr. Guerrero-Arroyo and Dr. Spierling Bagsic reported no financial conflicts of interest.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
But that technological future will require ensuring that the monitoring devices are as accurate as the conventional method, experts told this news organization.
In 2020, the U.S. Food and Drug Administration enabled in-hospital use of CGMs to reduce contact between patients and health care providers during the COVID-19 pandemic. Diabetes is a risk factor for more severe COVID, meaning that many patients with the infection also required ongoing care for their blood sugar problems.
Prior to the pandemic, in-person finger-stick tests were the primary means of measuring glucose for hospitalized patients with diabetes.
The trouble is that finger-stick measurements quickly become inaccurate.
“Glucose is a measurement that changes pretty rapidly,” said Eileen Faulds, RN, PhD, an endocrinology nurse and health services researcher at the Ohio State University, Columbus. Finger sticks might occur only four or five times per day, Dr. Faulds noted, or as often as every hour for people who receive insulin intravenously. But even that more frequent pace is far from continuous.
“With CGM we can get the glucose level in real time,” Dr. Faulds said.
Dr. Faulds is lead author of a new study in the Journal of Diabetes Science and Technology, which shows that nurses in the ICU believe that using continuous monitors, subcutaneous filaments connected to sensors that regularly report glucose levels, enables better patient care than does relying on periodic glucose tests alone. Nurses still used traditional finger sticks, which Dr. Faulds notes are highly accurate at the time of the reading.
In a 2022 study, glucose levels generated by CGM and those measured by finger sticks varied by up to 14%. A hybrid care model combining CGMs and finger stick tests may emerge, Dr. Faulds said.
A gusher of glucose data
People with diabetes have long been able to use CGMs in their daily lives, which typically report the glucose value to a smartphone or watch. The devices are now part of hospital care as well. In 2022, the Food and Drug Administration granted a breakthrough therapy designation to the company Dexcom for use of its CGMs to manage care of people with diabetes in hospitals.
One open question is how often CGMs should report glucose readings for optimum patient health. Dexcom’s G6 CGM reports glucose levels every five minutes, for example, whereas Abbott’s FreeStyle Libre 2 delivers glucose values every minute.
“We wouldn’t look at each value, we would look at the big picture,” to determine if a patient is at risk of becoming hyper- or hypoglycemic, said Lizda Guerrero-Arroyo, MD, a postdoctoral fellow in endocrinology at the Emory University School of Medicine, Atlanta. Dr. Guerrero-Arroyo recently reported that clinicians in multiple ICUs began to use CGMs in conjunction with finger sticks during the pandemic and felt the devices could reduce patient discomfort.
“A finger stick is very painful,” Dr. Guerrero-Arroyo said, and a bottleneck for nursing staff who administer these tests. In contrast, Dr. Faulds said, CGM placement is essentially painless and requires less labor on the ward to manage.
Beyond use in the ICU, clinicians are also experimenting with use of CGMs to monitor blood sugar levels in people with diabetes who are undergoing general surgery. And other researchers are describing how to integrate data from CGMs into patient care tools such as the electronic health record, although a standard way to do this does not yet exist.
Assuming CGMs remain part of the mix for in-hospital care of people with diabetes, clinicians may mainly need trend summaries of how glucose levels rise and fall over time, said data scientist Samantha Spierling Bagsic, PhD, of the Scripps Whittier Diabetes Institute, San Diego. Dr. Guerrero-Arroyo said that she shares that vision. But a minute-by-minute analysis of glucose levels also may be necessary to get a granular sense of how changing a patient’s insulin level affects their blood sugar, Dr. Spierling Bagsic said.
“We need to figure out what data different audiences need, how often we need to measure glucose, and how to present that information to different audiences in different ways,” said Dr. Spierling Bagsic, a co-author of the study about integrating CGM data into patient care tools.
The wider use of CGMs in hospitals may be one silver lining of the COVID-19 pandemic. As an inpatient endocrinology nurse, Dr. Faulds said that she wanted to use CGMs prior to the outbreak, but at that point, a critical mass of studies about their benefits was missing.
“We all know the terrible things that happened during the pandemic,” Dr. Faulds said. “But it gave us the allowance to use CGMs, and we saw that nurses loved them.”
Dr. Faulds reports relationships with Dexcom and Insulet and has received an honorarium from Medscape. Dr. Guerrero-Arroyo and Dr. Spierling Bagsic reported no financial conflicts of interest.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
Oval Brown Plaque on the Palm
The Diagnosis: Poroma
Histopathology showed an endophytic expansion of the epidermis by bland, uniform, basaloid epithelial cells with focal ductal differentiation and an abrupt transition with surrounding epidermal keratinocytes (Figure), consistent with a diagnosis of poroma. The patient elected to monitor the lesion rather than to have it excised.
Eccrine poroma, used interchangeably with the term poroma, is a rare benign adnexal tumor of the eccrine sweat glands resulting from proliferation of the acrosyringium.1,2 It often occurs on the palms or soles, though it also can arise anywhere sweat glands are present.1 Eccrine poromas often appear in middle-aged individuals as singular, well-circumscribed, red-brown papules or nodules.3 A characteristic feature is a shallow, cup-shaped depression within the larger papule or nodule.1
Because the condition is benign and often asymptomatic, it can be safely monitored for progression.1 However, if the lesion is symptomatic or located in a sensitive area, complete excision is curative.4 Eccrine poromas can recur, making close monitoring following excision important.5 The development of bleeding, itching, or pain in a previously asymptomatic lesion may indicate possible malignant transformation, which occurs in only 18% of cases.6
The differential diagnosis includes basal cell carcinoma, circumscribed acral hypokeratosis, Kaposi sarcoma, and pyogenic granuloma. Basal cell carcinoma is the most common type of skin cancer.7 In rare cases it has been shown to present on the palms or soles as a slowgrowing, reddish-pink papule or plaque with central ulceration. It typically is asymptomatic. Histopathology shows dermal nests of basaloid cells with peripheral palisading, stromal mucin, and peritumoral clefts. Treatment is surgical excision.7
Circumscribed acral hypokeratosis presents on the palms or soles as a solitary, shallow, well-defined lesion with a flat base and raised border.8 It often is red-pink in color and most frequently occurs in middle-aged women. Although the cause of the condition is unknown, it is thought to be the result of trauma or human papillomavirus infection.8 Biopsy results characteristically show hypokeratosis demarcated by a sharp and frayed cutoff from uninvolved acral skin with discrete hypogranulosis, dilated blood vessels in the papillary dermis, and slightly thickened collagen fibers in the reticular dermis.9 Surgical excision is a potential treatment option, as topical corticosteroids, retinoids, and calcipotriene have not been shown to be effective; spontaneous resolution has been reported.8
Kaposi sarcoma is a vascular neoplasm that is associated with human herpesvirus 8 infection.10 It typically presents on mucocutaneous sites and the lower extremities. Palmar involvement has been reported in rare cases, occurring as a solitary, well-demarcated, violaceous macule or patch that may be painful.10-12 Characteristic histopathologic features include a proliferation in the dermis of slitlike vascular spaces and spindle cell proliferation.13 Treatment options include cryosurgery; pulsed dye laser; and topical, intralesional, or systemic chemotherapy agents, depending on the stage of the patient’s disease. Antiretroviral therapy is indicated for patients with Kaposi sarcoma secondary to AIDS.14
Pyogenic granuloma presents as a solitary red-brown or bluish-black papule or nodule that bleeds easily when manipulated.15 It commonly occurs following trauma, typically on the fingers, feet, and lips.6 Although benign, potential complications include ulceration and blood loss. Pyogenic granulomas can be treated via curettage and cautery, excision, cryosurgery, or pulsed dye laser.15
- Wankhade V, Singh R, Sadhwani V, et al. Eccrine poroma. Indian Dermatol Online J. 2015;6:304-305.
- Yorulmaz A, Aksoy GG, Ozhamam EU. A growing mass under the nail: subungual eccrine poroma. Skin Appendage Disord. 2020;6:254-257.
- Wang Y, Liu M, Zheng Y, et al. Eccrine poroma presented as spindleshaped plaque: a case report. Medicine (Baltimore). 2021;100:E25971. doi:10.1097/MD.0000000000025971
- Sharma M, Singh M, Gupta K, et al. Eccrine poroma of the eyelid. Indian J Ophthalmol. 2020;68:2522.
- Rasool MN, Hawary MB. Benign eccrine poroma in the palm of the hand. Ann Saudi Med. 2004;24:46-47.
- Sawaya JL, Khachemoune A. Poroma: a review of eccrine, apocrine, and malignant forms [published online April 2, 2014]. Int J Dermatol. 2014;53:1053-1061. doi:10.1111/ijd.12448
- López-Sánchez C, Ferguson P, Collgros H. Basal cell carcinoma of the palm: an unusual presentation of a common tumour [published online August 6, 2019]. Australas J Dermatol. 2020;61:69-70. doi:10.1111/ajd.13129
- Berk DR, Böer A, Bauschard FD, et al. Circumscribed acral hypokeratosis [published online April 6, 2007]. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2007;57:292-296. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2007.02.022
- Majluf-Cáceres P, Vera-Kellet C, González-Bombardiere S. New dermoscopic keys for circumscribed acral hypokeratosis: report of four cases. Dermatol Pract Concept. 2021;11:E2021010. doi:10.5826/dpc.1102a10
- Simonart T, De Dobbeleer G, Stallenberg B. Classic Kaposi’s sarcoma of the palm in a metallurgist: role of iron filings in its development? Br J Dermatol. 2003;148:1061-1063. doi:10.1046/j.1365-2133.2003.05331.x
- Radu O, Pantanowitz L. Kaposi sarcoma. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 2013;137:289-294. doi:10.5858/arpa.2012-0101-RS
- Al Zolibani AA, Al Robaee AA. Primary palmoplantar Kaposi’s sarcoma: an unusual presentation. Skinmed. 2006;5:248-249. doi:10.1111/j.1540-9740.2006.04662.x
- Cesarman E, Damania B, Krown SE, et al. Kaposi sarcoma. Nat Rev Dis Primers. 2019;5:9. doi:10.1038/s41572-019-0060-9
- Etemad SA, Dewan AK. Kaposi sarcoma updates [published online July 10, 2019]. Dermatol Clin. 2019;37:505-517. doi:10.1016/j. det.2019.05.008
- Murthy SC, Nagaraj A. Pyogenic granuloma. Indian Pediatr. 2012;49:855. doi:10.1007/s13312-012-0184-4
The Diagnosis: Poroma
Histopathology showed an endophytic expansion of the epidermis by bland, uniform, basaloid epithelial cells with focal ductal differentiation and an abrupt transition with surrounding epidermal keratinocytes (Figure), consistent with a diagnosis of poroma. The patient elected to monitor the lesion rather than to have it excised.

Eccrine poroma, used interchangeably with the term poroma, is a rare benign adnexal tumor of the eccrine sweat glands resulting from proliferation of the acrosyringium.1,2 It often occurs on the palms or soles, though it also can arise anywhere sweat glands are present.1 Eccrine poromas often appear in middle-aged individuals as singular, well-circumscribed, red-brown papules or nodules.3 A characteristic feature is a shallow, cup-shaped depression within the larger papule or nodule.1
Because the condition is benign and often asymptomatic, it can be safely monitored for progression.1 However, if the lesion is symptomatic or located in a sensitive area, complete excision is curative.4 Eccrine poromas can recur, making close monitoring following excision important.5 The development of bleeding, itching, or pain in a previously asymptomatic lesion may indicate possible malignant transformation, which occurs in only 18% of cases.6
The differential diagnosis includes basal cell carcinoma, circumscribed acral hypokeratosis, Kaposi sarcoma, and pyogenic granuloma. Basal cell carcinoma is the most common type of skin cancer.7 In rare cases it has been shown to present on the palms or soles as a slowgrowing, reddish-pink papule or plaque with central ulceration. It typically is asymptomatic. Histopathology shows dermal nests of basaloid cells with peripheral palisading, stromal mucin, and peritumoral clefts. Treatment is surgical excision.7
Circumscribed acral hypokeratosis presents on the palms or soles as a solitary, shallow, well-defined lesion with a flat base and raised border.8 It often is red-pink in color and most frequently occurs in middle-aged women. Although the cause of the condition is unknown, it is thought to be the result of trauma or human papillomavirus infection.8 Biopsy results characteristically show hypokeratosis demarcated by a sharp and frayed cutoff from uninvolved acral skin with discrete hypogranulosis, dilated blood vessels in the papillary dermis, and slightly thickened collagen fibers in the reticular dermis.9 Surgical excision is a potential treatment option, as topical corticosteroids, retinoids, and calcipotriene have not been shown to be effective; spontaneous resolution has been reported.8
Kaposi sarcoma is a vascular neoplasm that is associated with human herpesvirus 8 infection.10 It typically presents on mucocutaneous sites and the lower extremities. Palmar involvement has been reported in rare cases, occurring as a solitary, well-demarcated, violaceous macule or patch that may be painful.10-12 Characteristic histopathologic features include a proliferation in the dermis of slitlike vascular spaces and spindle cell proliferation.13 Treatment options include cryosurgery; pulsed dye laser; and topical, intralesional, or systemic chemotherapy agents, depending on the stage of the patient’s disease. Antiretroviral therapy is indicated for patients with Kaposi sarcoma secondary to AIDS.14
Pyogenic granuloma presents as a solitary red-brown or bluish-black papule or nodule that bleeds easily when manipulated.15 It commonly occurs following trauma, typically on the fingers, feet, and lips.6 Although benign, potential complications include ulceration and blood loss. Pyogenic granulomas can be treated via curettage and cautery, excision, cryosurgery, or pulsed dye laser.15
The Diagnosis: Poroma
Histopathology showed an endophytic expansion of the epidermis by bland, uniform, basaloid epithelial cells with focal ductal differentiation and an abrupt transition with surrounding epidermal keratinocytes (Figure), consistent with a diagnosis of poroma. The patient elected to monitor the lesion rather than to have it excised.

Eccrine poroma, used interchangeably with the term poroma, is a rare benign adnexal tumor of the eccrine sweat glands resulting from proliferation of the acrosyringium.1,2 It often occurs on the palms or soles, though it also can arise anywhere sweat glands are present.1 Eccrine poromas often appear in middle-aged individuals as singular, well-circumscribed, red-brown papules or nodules.3 A characteristic feature is a shallow, cup-shaped depression within the larger papule or nodule.1
Because the condition is benign and often asymptomatic, it can be safely monitored for progression.1 However, if the lesion is symptomatic or located in a sensitive area, complete excision is curative.4 Eccrine poromas can recur, making close monitoring following excision important.5 The development of bleeding, itching, or pain in a previously asymptomatic lesion may indicate possible malignant transformation, which occurs in only 18% of cases.6
The differential diagnosis includes basal cell carcinoma, circumscribed acral hypokeratosis, Kaposi sarcoma, and pyogenic granuloma. Basal cell carcinoma is the most common type of skin cancer.7 In rare cases it has been shown to present on the palms or soles as a slowgrowing, reddish-pink papule or plaque with central ulceration. It typically is asymptomatic. Histopathology shows dermal nests of basaloid cells with peripheral palisading, stromal mucin, and peritumoral clefts. Treatment is surgical excision.7
Circumscribed acral hypokeratosis presents on the palms or soles as a solitary, shallow, well-defined lesion with a flat base and raised border.8 It often is red-pink in color and most frequently occurs in middle-aged women. Although the cause of the condition is unknown, it is thought to be the result of trauma or human papillomavirus infection.8 Biopsy results characteristically show hypokeratosis demarcated by a sharp and frayed cutoff from uninvolved acral skin with discrete hypogranulosis, dilated blood vessels in the papillary dermis, and slightly thickened collagen fibers in the reticular dermis.9 Surgical excision is a potential treatment option, as topical corticosteroids, retinoids, and calcipotriene have not been shown to be effective; spontaneous resolution has been reported.8
Kaposi sarcoma is a vascular neoplasm that is associated with human herpesvirus 8 infection.10 It typically presents on mucocutaneous sites and the lower extremities. Palmar involvement has been reported in rare cases, occurring as a solitary, well-demarcated, violaceous macule or patch that may be painful.10-12 Characteristic histopathologic features include a proliferation in the dermis of slitlike vascular spaces and spindle cell proliferation.13 Treatment options include cryosurgery; pulsed dye laser; and topical, intralesional, or systemic chemotherapy agents, depending on the stage of the patient’s disease. Antiretroviral therapy is indicated for patients with Kaposi sarcoma secondary to AIDS.14
Pyogenic granuloma presents as a solitary red-brown or bluish-black papule or nodule that bleeds easily when manipulated.15 It commonly occurs following trauma, typically on the fingers, feet, and lips.6 Although benign, potential complications include ulceration and blood loss. Pyogenic granulomas can be treated via curettage and cautery, excision, cryosurgery, or pulsed dye laser.15
- Wankhade V, Singh R, Sadhwani V, et al. Eccrine poroma. Indian Dermatol Online J. 2015;6:304-305.
- Yorulmaz A, Aksoy GG, Ozhamam EU. A growing mass under the nail: subungual eccrine poroma. Skin Appendage Disord. 2020;6:254-257.
- Wang Y, Liu M, Zheng Y, et al. Eccrine poroma presented as spindleshaped plaque: a case report. Medicine (Baltimore). 2021;100:E25971. doi:10.1097/MD.0000000000025971
- Sharma M, Singh M, Gupta K, et al. Eccrine poroma of the eyelid. Indian J Ophthalmol. 2020;68:2522.
- Rasool MN, Hawary MB. Benign eccrine poroma in the palm of the hand. Ann Saudi Med. 2004;24:46-47.
- Sawaya JL, Khachemoune A. Poroma: a review of eccrine, apocrine, and malignant forms [published online April 2, 2014]. Int J Dermatol. 2014;53:1053-1061. doi:10.1111/ijd.12448
- López-Sánchez C, Ferguson P, Collgros H. Basal cell carcinoma of the palm: an unusual presentation of a common tumour [published online August 6, 2019]. Australas J Dermatol. 2020;61:69-70. doi:10.1111/ajd.13129
- Berk DR, Böer A, Bauschard FD, et al. Circumscribed acral hypokeratosis [published online April 6, 2007]. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2007;57:292-296. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2007.02.022
- Majluf-Cáceres P, Vera-Kellet C, González-Bombardiere S. New dermoscopic keys for circumscribed acral hypokeratosis: report of four cases. Dermatol Pract Concept. 2021;11:E2021010. doi:10.5826/dpc.1102a10
- Simonart T, De Dobbeleer G, Stallenberg B. Classic Kaposi’s sarcoma of the palm in a metallurgist: role of iron filings in its development? Br J Dermatol. 2003;148:1061-1063. doi:10.1046/j.1365-2133.2003.05331.x
- Radu O, Pantanowitz L. Kaposi sarcoma. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 2013;137:289-294. doi:10.5858/arpa.2012-0101-RS
- Al Zolibani AA, Al Robaee AA. Primary palmoplantar Kaposi’s sarcoma: an unusual presentation. Skinmed. 2006;5:248-249. doi:10.1111/j.1540-9740.2006.04662.x
- Cesarman E, Damania B, Krown SE, et al. Kaposi sarcoma. Nat Rev Dis Primers. 2019;5:9. doi:10.1038/s41572-019-0060-9
- Etemad SA, Dewan AK. Kaposi sarcoma updates [published online July 10, 2019]. Dermatol Clin. 2019;37:505-517. doi:10.1016/j. det.2019.05.008
- Murthy SC, Nagaraj A. Pyogenic granuloma. Indian Pediatr. 2012;49:855. doi:10.1007/s13312-012-0184-4
- Wankhade V, Singh R, Sadhwani V, et al. Eccrine poroma. Indian Dermatol Online J. 2015;6:304-305.
- Yorulmaz A, Aksoy GG, Ozhamam EU. A growing mass under the nail: subungual eccrine poroma. Skin Appendage Disord. 2020;6:254-257.
- Wang Y, Liu M, Zheng Y, et al. Eccrine poroma presented as spindleshaped plaque: a case report. Medicine (Baltimore). 2021;100:E25971. doi:10.1097/MD.0000000000025971
- Sharma M, Singh M, Gupta K, et al. Eccrine poroma of the eyelid. Indian J Ophthalmol. 2020;68:2522.
- Rasool MN, Hawary MB. Benign eccrine poroma in the palm of the hand. Ann Saudi Med. 2004;24:46-47.
- Sawaya JL, Khachemoune A. Poroma: a review of eccrine, apocrine, and malignant forms [published online April 2, 2014]. Int J Dermatol. 2014;53:1053-1061. doi:10.1111/ijd.12448
- López-Sánchez C, Ferguson P, Collgros H. Basal cell carcinoma of the palm: an unusual presentation of a common tumour [published online August 6, 2019]. Australas J Dermatol. 2020;61:69-70. doi:10.1111/ajd.13129
- Berk DR, Böer A, Bauschard FD, et al. Circumscribed acral hypokeratosis [published online April 6, 2007]. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2007;57:292-296. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2007.02.022
- Majluf-Cáceres P, Vera-Kellet C, González-Bombardiere S. New dermoscopic keys for circumscribed acral hypokeratosis: report of four cases. Dermatol Pract Concept. 2021;11:E2021010. doi:10.5826/dpc.1102a10
- Simonart T, De Dobbeleer G, Stallenberg B. Classic Kaposi’s sarcoma of the palm in a metallurgist: role of iron filings in its development? Br J Dermatol. 2003;148:1061-1063. doi:10.1046/j.1365-2133.2003.05331.x
- Radu O, Pantanowitz L. Kaposi sarcoma. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 2013;137:289-294. doi:10.5858/arpa.2012-0101-RS
- Al Zolibani AA, Al Robaee AA. Primary palmoplantar Kaposi’s sarcoma: an unusual presentation. Skinmed. 2006;5:248-249. doi:10.1111/j.1540-9740.2006.04662.x
- Cesarman E, Damania B, Krown SE, et al. Kaposi sarcoma. Nat Rev Dis Primers. 2019;5:9. doi:10.1038/s41572-019-0060-9
- Etemad SA, Dewan AK. Kaposi sarcoma updates [published online July 10, 2019]. Dermatol Clin. 2019;37:505-517. doi:10.1016/j. det.2019.05.008
- Murthy SC, Nagaraj A. Pyogenic granuloma. Indian Pediatr. 2012;49:855. doi:10.1007/s13312-012-0184-4
A 43-year-old woman presented with a painful lesion on the palm of 30 years’ duration that had grown in size. Physical examination revealed an oval, brown, lobulated plaque with a hyperkeratotic rim on the left palm. She reported bleeding and pain. A shallow cup-shaped depression was noted within the plaque. A 4-mm punch biopsy was performed.
Long-term freedom from NMOSD relapse with satralizumab
DENVER – , new research shows.
“In long-term observations, we are seeing a nice, sustained suppression of relapses early, as well as late, in treatment,” said study investigator Anthony Traboulsee, MD, University of British Columbia, Vancouver, in presenting the findings at the annual meeting of the Consortium of Multiple Sclerosis Centers.
“It remains very tolerable with no participants discontinuing because of side effects,” he said. “And importantly, [there are] no signs of a delayed risk of infections for both monotherapy and combination therapy.”
Satralizumab, a monoclonal recycling antibody, targets the interleukin (IL)–6 receptor, which is elevated in the serum and cerebrospinal fluid of patients in NMOSD.
The drug was approved by the Food and Drug Administration in 2020 for the treatment of AQP4 antibody–positive NMOSD after favorable results from two key trials: SAkuraSky and SAkuraStar.
The FDA approval marked satralizumab as the third therapy for NMOSD, following eculizumab (Soliris) and inebilizumab (Uplizna).
Satralizumab is administered in subcutaneous injections every 4 weeks after a run-in period of injections at weeks 0, 2, and 4.
Longest trial to date
To evaluate the drug’s long-term efficacy in the treatment of AQP4 IgG–positive NMOSD, patients from the two previous phase 3 trials were entered into the single arm, open-label SAkuraMoon study and continued treatment with the satralizumab 120 mg injections once monthly, with or without immunosuppressive therapy.
The study included 106 patients (mean age 44 years, 89.6% women), all of whom had received one or more doses of satralizumab by the data cutoff of January 2022.
With a median duration of satralizumab exposure of 5 years, the overall adjusted annualized rate of investigator protocol-defined relapse (ARR) was 0.09.
Longitudinal assessment further showed no significant increase in the relapse rate over the course of the study, with an ARR rate of 0.16 at year 1; 0.10 at year 2; 0.05 at year 3; and 0.07 at year 4.
At week 240 (4.6 years), 72% of satralizumab-treated patients were relapse-free, with 91% free from severe relapse.
In addition, 85% of patients had no sustained disability, as measured by Expanded Disability Status Scale (EDSS) worsening, over the study period.
Asked if there are potential subgroups of patients who may be more susceptible to the worsening of disability, Dr. Traboulsee responded “not that we can tell as of yet.”
“I would like to explore this further as this is a relatively new observation, and, as far as I know, this is the longest follow-up for an NMO treatment trial cohort,” he said.
Favorable safety profile
The safety profile was also favorable, consistent with results in the earlier trials. The longer exposure to satralizumab was not associated with a higher risk of severe (grade 3 or higher) laboratory changes versus the double-blind studies. “Rates of adverse events and serious adverse events with overall satralizumab treatment were comparable with the double-blind periods,” said Dr. Traboulsee.
“With satralizumab combined with immunosuppressant therapy, we’re not seeing an increased rate of infections, because it’s not an immune suppressant – it doesn’t suppress lymphocytes or lower immunoglobulin,” he added.
While the use of combination therapy has been an important clinical concern, Dr. Traboulsee noted that “this does not appear to be the case with satralizumab when combined with daily prednisone or daily azathioprine.”
“There is no increased risk of infections, compared with placebo, and it interestingly appears lower than patients on prednisone or azathioprine alone,” he said.
While the median follow-up was 5 years, some in the clinical trial population have been on treatment for up to 7.9 years.
“Based on the current safety and efficacy data, they could stay on this therapy indefinitely, in my opinion,” Dr. Traboulsee said.
In addition to its long-term safety and efficacy, satralizumab “is easy for patients to take and does not require access to an infusion center. It’s easy for physicians to monitor safety, especially since no additional vaccinations or precautions are required beyond what is done in routine care.”
“What I conclude from that clinically is that this is a highly effective and safe therapy by itself or in combination with another agent,” Dr. Traboulsee said.
He noted that the lack of a bump in infections is “really encouraging and very important with a chronic disease that affects elderly patients. So far, so good,” he added.
‘A good first-line therapy’
Commenting on the study, Shailee Shah, MD, an assistant professor in the neuroimmunology division at Vanderbilt University Medical Center, Nashville, Tenn., agreed that the findings bode well for satralizumab’s long-term benefits.
“These are promising results and suggest that satralizumab is very effective in the long term, and even when patients relapse, those relapses are less severe than they would likely be if the patient were off therapy,” she said.
She noted that, while the ability to self-administer injections with satralizumab is convenient, preferences vary.
“This is patient dependent,” Dr. Shah said. “For some patients an injectable medication is ideal but for others an infusion medication [such as eculizumab] is preferred.”
Overall, however, Dr. Shah described satralizumab as “a good first-line therapy for patients with NMOSD in addition to eculizumab/ravulizumab and inebilizumab.”
“It is reasonable to consider this medication in isolation or with concomitant immunosuppressive therapy,” she said.
Dr. Traboulsee’s disclosures include relationships with Novartis, Roche, Sanofi (Genzyme), Ingo Kleiter, Alexion, Almirall, Bayer, Biogen, Celgene, Genentech, Hexal, Horizon, Merck, and Sanofi. Dr. Shah reports that she has served on advisory boards for Horizon, Alexion, and Genentech.
DENVER – , new research shows.
“In long-term observations, we are seeing a nice, sustained suppression of relapses early, as well as late, in treatment,” said study investigator Anthony Traboulsee, MD, University of British Columbia, Vancouver, in presenting the findings at the annual meeting of the Consortium of Multiple Sclerosis Centers.
“It remains very tolerable with no participants discontinuing because of side effects,” he said. “And importantly, [there are] no signs of a delayed risk of infections for both monotherapy and combination therapy.”
Satralizumab, a monoclonal recycling antibody, targets the interleukin (IL)–6 receptor, which is elevated in the serum and cerebrospinal fluid of patients in NMOSD.
The drug was approved by the Food and Drug Administration in 2020 for the treatment of AQP4 antibody–positive NMOSD after favorable results from two key trials: SAkuraSky and SAkuraStar.
The FDA approval marked satralizumab as the third therapy for NMOSD, following eculizumab (Soliris) and inebilizumab (Uplizna).
Satralizumab is administered in subcutaneous injections every 4 weeks after a run-in period of injections at weeks 0, 2, and 4.
Longest trial to date
To evaluate the drug’s long-term efficacy in the treatment of AQP4 IgG–positive NMOSD, patients from the two previous phase 3 trials were entered into the single arm, open-label SAkuraMoon study and continued treatment with the satralizumab 120 mg injections once monthly, with or without immunosuppressive therapy.
The study included 106 patients (mean age 44 years, 89.6% women), all of whom had received one or more doses of satralizumab by the data cutoff of January 2022.
With a median duration of satralizumab exposure of 5 years, the overall adjusted annualized rate of investigator protocol-defined relapse (ARR) was 0.09.
Longitudinal assessment further showed no significant increase in the relapse rate over the course of the study, with an ARR rate of 0.16 at year 1; 0.10 at year 2; 0.05 at year 3; and 0.07 at year 4.
At week 240 (4.6 years), 72% of satralizumab-treated patients were relapse-free, with 91% free from severe relapse.
In addition, 85% of patients had no sustained disability, as measured by Expanded Disability Status Scale (EDSS) worsening, over the study period.
Asked if there are potential subgroups of patients who may be more susceptible to the worsening of disability, Dr. Traboulsee responded “not that we can tell as of yet.”
“I would like to explore this further as this is a relatively new observation, and, as far as I know, this is the longest follow-up for an NMO treatment trial cohort,” he said.
Favorable safety profile
The safety profile was also favorable, consistent with results in the earlier trials. The longer exposure to satralizumab was not associated with a higher risk of severe (grade 3 or higher) laboratory changes versus the double-blind studies. “Rates of adverse events and serious adverse events with overall satralizumab treatment were comparable with the double-blind periods,” said Dr. Traboulsee.
“With satralizumab combined with immunosuppressant therapy, we’re not seeing an increased rate of infections, because it’s not an immune suppressant – it doesn’t suppress lymphocytes or lower immunoglobulin,” he added.
While the use of combination therapy has been an important clinical concern, Dr. Traboulsee noted that “this does not appear to be the case with satralizumab when combined with daily prednisone or daily azathioprine.”
“There is no increased risk of infections, compared with placebo, and it interestingly appears lower than patients on prednisone or azathioprine alone,” he said.
While the median follow-up was 5 years, some in the clinical trial population have been on treatment for up to 7.9 years.
“Based on the current safety and efficacy data, they could stay on this therapy indefinitely, in my opinion,” Dr. Traboulsee said.
In addition to its long-term safety and efficacy, satralizumab “is easy for patients to take and does not require access to an infusion center. It’s easy for physicians to monitor safety, especially since no additional vaccinations or precautions are required beyond what is done in routine care.”
“What I conclude from that clinically is that this is a highly effective and safe therapy by itself or in combination with another agent,” Dr. Traboulsee said.
He noted that the lack of a bump in infections is “really encouraging and very important with a chronic disease that affects elderly patients. So far, so good,” he added.
‘A good first-line therapy’
Commenting on the study, Shailee Shah, MD, an assistant professor in the neuroimmunology division at Vanderbilt University Medical Center, Nashville, Tenn., agreed that the findings bode well for satralizumab’s long-term benefits.
“These are promising results and suggest that satralizumab is very effective in the long term, and even when patients relapse, those relapses are less severe than they would likely be if the patient were off therapy,” she said.
She noted that, while the ability to self-administer injections with satralizumab is convenient, preferences vary.
“This is patient dependent,” Dr. Shah said. “For some patients an injectable medication is ideal but for others an infusion medication [such as eculizumab] is preferred.”
Overall, however, Dr. Shah described satralizumab as “a good first-line therapy for patients with NMOSD in addition to eculizumab/ravulizumab and inebilizumab.”
“It is reasonable to consider this medication in isolation or with concomitant immunosuppressive therapy,” she said.
Dr. Traboulsee’s disclosures include relationships with Novartis, Roche, Sanofi (Genzyme), Ingo Kleiter, Alexion, Almirall, Bayer, Biogen, Celgene, Genentech, Hexal, Horizon, Merck, and Sanofi. Dr. Shah reports that she has served on advisory boards for Horizon, Alexion, and Genentech.
DENVER – , new research shows.
“In long-term observations, we are seeing a nice, sustained suppression of relapses early, as well as late, in treatment,” said study investigator Anthony Traboulsee, MD, University of British Columbia, Vancouver, in presenting the findings at the annual meeting of the Consortium of Multiple Sclerosis Centers.
“It remains very tolerable with no participants discontinuing because of side effects,” he said. “And importantly, [there are] no signs of a delayed risk of infections for both monotherapy and combination therapy.”
Satralizumab, a monoclonal recycling antibody, targets the interleukin (IL)–6 receptor, which is elevated in the serum and cerebrospinal fluid of patients in NMOSD.
The drug was approved by the Food and Drug Administration in 2020 for the treatment of AQP4 antibody–positive NMOSD after favorable results from two key trials: SAkuraSky and SAkuraStar.
The FDA approval marked satralizumab as the third therapy for NMOSD, following eculizumab (Soliris) and inebilizumab (Uplizna).
Satralizumab is administered in subcutaneous injections every 4 weeks after a run-in period of injections at weeks 0, 2, and 4.
Longest trial to date
To evaluate the drug’s long-term efficacy in the treatment of AQP4 IgG–positive NMOSD, patients from the two previous phase 3 trials were entered into the single arm, open-label SAkuraMoon study and continued treatment with the satralizumab 120 mg injections once monthly, with or without immunosuppressive therapy.
The study included 106 patients (mean age 44 years, 89.6% women), all of whom had received one or more doses of satralizumab by the data cutoff of January 2022.
With a median duration of satralizumab exposure of 5 years, the overall adjusted annualized rate of investigator protocol-defined relapse (ARR) was 0.09.
Longitudinal assessment further showed no significant increase in the relapse rate over the course of the study, with an ARR rate of 0.16 at year 1; 0.10 at year 2; 0.05 at year 3; and 0.07 at year 4.
At week 240 (4.6 years), 72% of satralizumab-treated patients were relapse-free, with 91% free from severe relapse.
In addition, 85% of patients had no sustained disability, as measured by Expanded Disability Status Scale (EDSS) worsening, over the study period.
Asked if there are potential subgroups of patients who may be more susceptible to the worsening of disability, Dr. Traboulsee responded “not that we can tell as of yet.”
“I would like to explore this further as this is a relatively new observation, and, as far as I know, this is the longest follow-up for an NMO treatment trial cohort,” he said.
Favorable safety profile
The safety profile was also favorable, consistent with results in the earlier trials. The longer exposure to satralizumab was not associated with a higher risk of severe (grade 3 or higher) laboratory changes versus the double-blind studies. “Rates of adverse events and serious adverse events with overall satralizumab treatment were comparable with the double-blind periods,” said Dr. Traboulsee.
“With satralizumab combined with immunosuppressant therapy, we’re not seeing an increased rate of infections, because it’s not an immune suppressant – it doesn’t suppress lymphocytes or lower immunoglobulin,” he added.
While the use of combination therapy has been an important clinical concern, Dr. Traboulsee noted that “this does not appear to be the case with satralizumab when combined with daily prednisone or daily azathioprine.”
“There is no increased risk of infections, compared with placebo, and it interestingly appears lower than patients on prednisone or azathioprine alone,” he said.
While the median follow-up was 5 years, some in the clinical trial population have been on treatment for up to 7.9 years.
“Based on the current safety and efficacy data, they could stay on this therapy indefinitely, in my opinion,” Dr. Traboulsee said.
In addition to its long-term safety and efficacy, satralizumab “is easy for patients to take and does not require access to an infusion center. It’s easy for physicians to monitor safety, especially since no additional vaccinations or precautions are required beyond what is done in routine care.”
“What I conclude from that clinically is that this is a highly effective and safe therapy by itself or in combination with another agent,” Dr. Traboulsee said.
He noted that the lack of a bump in infections is “really encouraging and very important with a chronic disease that affects elderly patients. So far, so good,” he added.
‘A good first-line therapy’
Commenting on the study, Shailee Shah, MD, an assistant professor in the neuroimmunology division at Vanderbilt University Medical Center, Nashville, Tenn., agreed that the findings bode well for satralizumab’s long-term benefits.
“These are promising results and suggest that satralizumab is very effective in the long term, and even when patients relapse, those relapses are less severe than they would likely be if the patient were off therapy,” she said.
She noted that, while the ability to self-administer injections with satralizumab is convenient, preferences vary.
“This is patient dependent,” Dr. Shah said. “For some patients an injectable medication is ideal but for others an infusion medication [such as eculizumab] is preferred.”
Overall, however, Dr. Shah described satralizumab as “a good first-line therapy for patients with NMOSD in addition to eculizumab/ravulizumab and inebilizumab.”
“It is reasonable to consider this medication in isolation or with concomitant immunosuppressive therapy,” she said.
Dr. Traboulsee’s disclosures include relationships with Novartis, Roche, Sanofi (Genzyme), Ingo Kleiter, Alexion, Almirall, Bayer, Biogen, Celgene, Genentech, Hexal, Horizon, Merck, and Sanofi. Dr. Shah reports that she has served on advisory boards for Horizon, Alexion, and Genentech.
AT CMSC 2023
MDs with chronic illness live in a different medical world
Linda Bluestein remembers all the doctors who missed, ignored, or incompletely diagnosed her chronic illness.
There was the orthopedic surgeon who noted her hyperextended elbows but failed to check any of her other joints. The gastroenterologist who insisted on performing multiple scoping procedures but wouldn’t discuss how to manage her symptoms. The other surgeon who, after performing arthroscopy on her injured knee, yelled at her: “There is nothing wrong with your knee! You’re fine!” in a room full of people.
And then there was the rheumatologist who said: “Oh, you want something to be wrong with you?”
“No,” she replied, “I want an explanation. I want to keep working. I just want to know why these things keep happening to me.”
The medical frustration she experienced was especially difficult because, like her health care providers, Linda Bluestein has an MD after her name. She is a board-certified anesthesiologist and integrative medicine physician.
Along with the physically demanding schedule of medical practice, they must cope with what many call a “culture of invincibility” within medicine. Doctors are not supposed to get sick. In fact, the unwritten rule is presenteeism – to function without adequate food or sleep and to never prioritize their own self-care over their dedication to their patients.
Whether their conditions are visible, such as muscular dystrophy and multiple sclerosis, or invisible, such as fibromyalgia and mental illnesses – and now, long COVID – these doctors often meet significant stigma. They fight the assumption that they are less capable than their colleagues.
But they also experience an invaluable benefit: They gain firsthand knowledge of the patient experience, a profound understanding which, they say, enhances how they care for their own patients.
What it takes to become a doctor when you have a chronic condition
In short, it’s not easy.
Data from the 2018 National Health Interview Survey show that more than half of U.S. adults had at least one of several chronic conditions, including rheumatoid arthritis, asthma, diabetes, hypertension, and kidney problems. Nearly a third of respondents had more than one condition. But fewer than 5% of medical students and 3% of practicing physicians report having a chronic illness or disability, according to studies from 2019 and 2021.
While that could mean that fewer people with chronic illness enter medicine, cases also exist in which aspiring physicians with conditions were dissuaded from pursuing a career in medicine at all.
Amy Stenehjem, MD, a physical medicine and rehabilitation physician, is one of the exceptions. Diagnosed with several autoimmune-related conditions as a teenager and young adult, Dr. Stenehjem was determined to become a doctor. In her 20s, her health was relatively stable, and she was able to manage medical school and residency. Her training institutions agreed to provide some accommodations that helped her succeed.
“They let me build some flexibility into the training,” Dr. Stenehjem said. “In medical school, when I knew I wasn’t going to be able to do a particular specialty as a career, they let me work with an attending doctor that did not require a lot of on-call time during that particular rotation.”
Dr. Stenehjem specialized in chronic neck and back disorders, fibromyalgia, chronic fatigue syndrome (myalgic encephalomyelitis), and autoimmune-related diseases. She practiced for more than a decade. But in 2011, her condition spiraled. She couldn’t walk a few steps or even sit upright without experiencing dizziness and shortness of breath. She had debilitating fatigue and episodes of fever, rash, headaches, and joint pain.
It would take 7 years and more than 20 doctors to determine Dr. Stenehjem’s multiple diagnoses. In addition to her autoimmune diseases, she was diagnosed with postural orthostatic tachycardia syndrome, autoinflammatory periodic fever syndrome, Lyme disease, and reactivated Epstein-Barr infection.
While she suspects that her providers gave her more “leeway” because she was a physician, many did not show a deep understanding of the severity of her symptoms and the impact those symptoms had.
“When I was practicing, I really didn’t fully understand the impact chronic illness had on my patients,” Dr. Stenehjem said. “Things like chronic dizziness, headaches, fatigue, pain, or brain fog can be really hard to understand unless you’ve experienced these symptoms. When I got sick, I finally realized, ‘Oh my goodness, when a patient says they’re dealing with fatigue, this is not your normal, I’m-super-tired-from-being-on-call fatigue. This is I-can’t-get-out-of-bed fatigue.’ That’s what people with chronic illness often deal with on a daily basis.”
Treating the individual
Dr. Stenehjem was aware that her chronic illness would affect her medical career. For Jason Baker, MD, an endocrinologist at Weill Cornell Medicine, New York, it came as a shock. Dr. Baker was a third-year medical student when he experienced increased urination and rapid weight loss. It was only when friends pressed him to visit student health that a blood test revealed type 1 diabetes. Dr. Baker suddenly found himself lying in a hospital bed.
He remembers an attending physician who simply handed him a textbook on diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA) and a resident who informed him that he had kidney damage, which turned out to be untrue. Neither discussed the psychological issues from a frightening diagnosis that would require lifelong, daily management.
“There certainly could have been a bit more empathy from some of the people I dealt with early on,” he said.
Although his training gave him a stark picture of worst-case scenarios, Dr. Baker found that knowledge motivating. “I’d already seen patients come in who had diabetes complications,” Dr. Baker says. “I vowed to never ever get those complications. It was a good balance of fear and motivation.”
Dr. Baker had not planned to specialize in endocrinology, but he quickly realized that his personal diagnosis could help others. Now he often shares his experience with his patients who have diabetes, which he says makes them more comfortable discussing their own problems.
His approach, Dr. Baker explained, is to treat everyone as an individual. Trying to neatly classify patients with chronic illness is a common mistake he notices among physicians.
“There’s a lot of misunderstanding about type 1 versus type 2 [diabetes],” Dr. Baker said, “and trying to categorize people when sometimes people can’t be categorized. That’s really with any chronic condition; there’s no one size fits all.”
Managing his health is still a time-consuming task. At work, he needs breaks to eat, check his blood sugar, or take insulin. “During the workday seeing patients, I have to also remember that I’m a patient,” Dr. Baker said. “I have to be okay with prioritizing my own health. Otherwise I can’t help anybody.”
‘I am not the doctor for you’
Chronic diseases such as diabetes or hypertension are familiar to most doctors, and with good management, patients can usually function normally. When chronic conditions become disabling, however, attitudes in the medical field can change.
According to data from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention and from studies, people with disabilities experience significant disparities and barriers to care. Some of this can be linked to social determinants of health. People with disabilities are more likely to be poor and to rely on Medicare and Medicaid for insurance coverage. But lack of training, unwillingness to provide accommodations, ignorance of legal requirements, and inaccurate assumptions among physicians also play a role.
These are themes that Lisa Iezzoni, MD, a professor of medicine at Harvard Medical School, Boston, has heard from hundreds of patients with disabilities during the more than 25 years that she has conducted research.
In late 2019, Dr. Iezzoni and coinvestigators fielded a national survey of 714 practicing physicians. Only 40.7% reported they were “very confident” that they could provide the same quality of care to patients with disabilities as they do for other patients. And only 56.5% “strongly agreed” that they welcomed these patients into their practices.
The survey was conducted through a series of small focus groups that Dr. Iezzoni held with physicians in 2018. These yielded views that were startling, and in some cases, overtly discriminatory:
- Doctors complained about the “burden” of caring for a patient with a disability.
- They lacked the time or equipment, such as accessible exam tables or weight scales.
- They admitted to inventing excuses for why appointments were not available or routine diagnostic tests were not performed.
- They described being fearful of lawsuits under the Americans with Disabilities Act.
The overall message was summed up in one doctor’s statement: “I am not the doctor for you.”
“Doctors are people too,” Dr. Iezzoni pointed out. “And so they reflect the same prejudices and stigmatized attitudes of the rest of the population. It might be implicit, so they might not be aware of it. [But] it might be explicit.”
Ableism in the medical field is all too familiar to Dr. Iezzoni. She was diagnosed with multiple sclerosis at age 26 during her first year at Harvard Medical School in the early 1980s. Despite symptom flare-ups, Dr. Iezzoni was able to graduate with her class, but many instructors and administrators had little interest in accommodating her physical limitations. In fact, several physicians discouraged her from continuing to train.
Unable to take call, run up flights of stairs, or stand for hours at a time, Dr. Iezzoni remembers being told by a senior surgeon that she shouldn’t become a doctor since she lacked the “most important quality,” which was “24/7 availability.” A hospital CEO informed her: “There are too many doctors in the country right now for us to worry about training a handicapped physician. If that means that some people get left by the wayside, so be it.”
Ultimately, Harvard Medical School declined to write Dr. Iezzoni a letter of recommendation for an internship. She would never practice medicine. “My career was just truncated from the start,” Dr. Iezzoni said. “It never happened because of discrimination.”
She later learned the legal term for her treatment: constructive dismissal.
“The medical school didn’t outright say, ‘Go away. We’re not allowing you to graduate.’ ” Dr. Iezzoni explained. “But they made my life so difficult that I did so voluntarily.”
Dr. Iezzoni graduated in 1984, before the passage of the ADA in 1990, and she refers to her experience as a “ghost from the past,” a historical reminder of how the legal landscape has changed – even though the tendency toward bias may not have.
The fight for inclusion
Zainub Dhanani, a fifth-year medical student at Stanford (Calif.) University, won’t forget an interview at one of the other schools to which she applied. The interviewer asked how she expected to be in a hospital all day if she had a chronic illness.
“Does it really make sense?” he wanted to know.
The question shocked her in the moment, but now she sees this type of bias as linked to the inequalities that many marginalized groups face in health care and beyond. That’s also why she believes physician-patients are crucial to improve the quality of care for people with chronic illness and other groups that face discrimination.
Who else, she wonders, could provide that “reaffirming” experience for patients or have that “unique edge” other than a provider who has navigated the same world?
Ms. Dhanani is the executive director and founder of Medical Students With Disability and Chronic Illness, an organization dedicated to empowering these students through advocacy, education, accessibility, and community. The group now has 19 chapters at medical schools across the country.
Ms. Dhanani said she has received excellent accommodations from Stanford for her own condition (which she prefers not to disclose), but all medical schools are not as responsive to students with various physical needs. Her organization offers support and resources to inform these future physicians about their options and rights.
“Disability justice is also racial justice,” Ms. Dhanani stressed. “It’s also environmental justice. It’s also gender and sexuality-based justice. Those compounded layers of biases lead to worse and worse levels of care. As a patient, it’s terrifying. And as a future physician, it’s tragic to know that this is something so pervasive and yet so under-addressed in medicine.”
Soldiering on
Unfortunately, for some physicians with chronic illness, there are no practical accommodations that could save their careers in clinical practice.
Dr. Stenehjem now works part-time as a health consultant, helping those with chronic illnesses navigate their health care systems.
Dr. Bluestein offers a similar coaching service to patients with Ehlers-Danlos syndrome (EDS) and other connective tissue and hypermobility disorders. Because of her own EDS, she can no longer practice as an anesthesiologist but instead opened an integrative pain management practice for patients with complex pain conditions..
She believes the idea that doctors are “invincible” needs to change. She recalls the time her former group practice told her in no uncertain terms to “never call in sick.”
The stories she hears from her current clients are similar to her own. She can empathize, knowing firsthand the physical and psychological damage these attitudes can cause.
“When I was at my worst physically, I was also at my worst psychologically,” said Dr. Bluestein. “We tend to think of them as separate, but they go hand in hand. If we can validate people’s experiences rather than disregard them, it has a positive forward cycle, as opposed to the reverse, which is what usually happens.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Linda Bluestein remembers all the doctors who missed, ignored, or incompletely diagnosed her chronic illness.
There was the orthopedic surgeon who noted her hyperextended elbows but failed to check any of her other joints. The gastroenterologist who insisted on performing multiple scoping procedures but wouldn’t discuss how to manage her symptoms. The other surgeon who, after performing arthroscopy on her injured knee, yelled at her: “There is nothing wrong with your knee! You’re fine!” in a room full of people.
And then there was the rheumatologist who said: “Oh, you want something to be wrong with you?”
“No,” she replied, “I want an explanation. I want to keep working. I just want to know why these things keep happening to me.”
The medical frustration she experienced was especially difficult because, like her health care providers, Linda Bluestein has an MD after her name. She is a board-certified anesthesiologist and integrative medicine physician.
Along with the physically demanding schedule of medical practice, they must cope with what many call a “culture of invincibility” within medicine. Doctors are not supposed to get sick. In fact, the unwritten rule is presenteeism – to function without adequate food or sleep and to never prioritize their own self-care over their dedication to their patients.
Whether their conditions are visible, such as muscular dystrophy and multiple sclerosis, or invisible, such as fibromyalgia and mental illnesses – and now, long COVID – these doctors often meet significant stigma. They fight the assumption that they are less capable than their colleagues.
But they also experience an invaluable benefit: They gain firsthand knowledge of the patient experience, a profound understanding which, they say, enhances how they care for their own patients.
What it takes to become a doctor when you have a chronic condition
In short, it’s not easy.
Data from the 2018 National Health Interview Survey show that more than half of U.S. adults had at least one of several chronic conditions, including rheumatoid arthritis, asthma, diabetes, hypertension, and kidney problems. Nearly a third of respondents had more than one condition. But fewer than 5% of medical students and 3% of practicing physicians report having a chronic illness or disability, according to studies from 2019 and 2021.
While that could mean that fewer people with chronic illness enter medicine, cases also exist in which aspiring physicians with conditions were dissuaded from pursuing a career in medicine at all.
Amy Stenehjem, MD, a physical medicine and rehabilitation physician, is one of the exceptions. Diagnosed with several autoimmune-related conditions as a teenager and young adult, Dr. Stenehjem was determined to become a doctor. In her 20s, her health was relatively stable, and she was able to manage medical school and residency. Her training institutions agreed to provide some accommodations that helped her succeed.
“They let me build some flexibility into the training,” Dr. Stenehjem said. “In medical school, when I knew I wasn’t going to be able to do a particular specialty as a career, they let me work with an attending doctor that did not require a lot of on-call time during that particular rotation.”
Dr. Stenehjem specialized in chronic neck and back disorders, fibromyalgia, chronic fatigue syndrome (myalgic encephalomyelitis), and autoimmune-related diseases. She practiced for more than a decade. But in 2011, her condition spiraled. She couldn’t walk a few steps or even sit upright without experiencing dizziness and shortness of breath. She had debilitating fatigue and episodes of fever, rash, headaches, and joint pain.
It would take 7 years and more than 20 doctors to determine Dr. Stenehjem’s multiple diagnoses. In addition to her autoimmune diseases, she was diagnosed with postural orthostatic tachycardia syndrome, autoinflammatory periodic fever syndrome, Lyme disease, and reactivated Epstein-Barr infection.
While she suspects that her providers gave her more “leeway” because she was a physician, many did not show a deep understanding of the severity of her symptoms and the impact those symptoms had.
“When I was practicing, I really didn’t fully understand the impact chronic illness had on my patients,” Dr. Stenehjem said. “Things like chronic dizziness, headaches, fatigue, pain, or brain fog can be really hard to understand unless you’ve experienced these symptoms. When I got sick, I finally realized, ‘Oh my goodness, when a patient says they’re dealing with fatigue, this is not your normal, I’m-super-tired-from-being-on-call fatigue. This is I-can’t-get-out-of-bed fatigue.’ That’s what people with chronic illness often deal with on a daily basis.”
Treating the individual
Dr. Stenehjem was aware that her chronic illness would affect her medical career. For Jason Baker, MD, an endocrinologist at Weill Cornell Medicine, New York, it came as a shock. Dr. Baker was a third-year medical student when he experienced increased urination and rapid weight loss. It was only when friends pressed him to visit student health that a blood test revealed type 1 diabetes. Dr. Baker suddenly found himself lying in a hospital bed.
He remembers an attending physician who simply handed him a textbook on diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA) and a resident who informed him that he had kidney damage, which turned out to be untrue. Neither discussed the psychological issues from a frightening diagnosis that would require lifelong, daily management.
“There certainly could have been a bit more empathy from some of the people I dealt with early on,” he said.
Although his training gave him a stark picture of worst-case scenarios, Dr. Baker found that knowledge motivating. “I’d already seen patients come in who had diabetes complications,” Dr. Baker says. “I vowed to never ever get those complications. It was a good balance of fear and motivation.”
Dr. Baker had not planned to specialize in endocrinology, but he quickly realized that his personal diagnosis could help others. Now he often shares his experience with his patients who have diabetes, which he says makes them more comfortable discussing their own problems.
His approach, Dr. Baker explained, is to treat everyone as an individual. Trying to neatly classify patients with chronic illness is a common mistake he notices among physicians.
“There’s a lot of misunderstanding about type 1 versus type 2 [diabetes],” Dr. Baker said, “and trying to categorize people when sometimes people can’t be categorized. That’s really with any chronic condition; there’s no one size fits all.”
Managing his health is still a time-consuming task. At work, he needs breaks to eat, check his blood sugar, or take insulin. “During the workday seeing patients, I have to also remember that I’m a patient,” Dr. Baker said. “I have to be okay with prioritizing my own health. Otherwise I can’t help anybody.”
‘I am not the doctor for you’
Chronic diseases such as diabetes or hypertension are familiar to most doctors, and with good management, patients can usually function normally. When chronic conditions become disabling, however, attitudes in the medical field can change.
According to data from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention and from studies, people with disabilities experience significant disparities and barriers to care. Some of this can be linked to social determinants of health. People with disabilities are more likely to be poor and to rely on Medicare and Medicaid for insurance coverage. But lack of training, unwillingness to provide accommodations, ignorance of legal requirements, and inaccurate assumptions among physicians also play a role.
These are themes that Lisa Iezzoni, MD, a professor of medicine at Harvard Medical School, Boston, has heard from hundreds of patients with disabilities during the more than 25 years that she has conducted research.
In late 2019, Dr. Iezzoni and coinvestigators fielded a national survey of 714 practicing physicians. Only 40.7% reported they were “very confident” that they could provide the same quality of care to patients with disabilities as they do for other patients. And only 56.5% “strongly agreed” that they welcomed these patients into their practices.
The survey was conducted through a series of small focus groups that Dr. Iezzoni held with physicians in 2018. These yielded views that were startling, and in some cases, overtly discriminatory:
- Doctors complained about the “burden” of caring for a patient with a disability.
- They lacked the time or equipment, such as accessible exam tables or weight scales.
- They admitted to inventing excuses for why appointments were not available or routine diagnostic tests were not performed.
- They described being fearful of lawsuits under the Americans with Disabilities Act.
The overall message was summed up in one doctor’s statement: “I am not the doctor for you.”
“Doctors are people too,” Dr. Iezzoni pointed out. “And so they reflect the same prejudices and stigmatized attitudes of the rest of the population. It might be implicit, so they might not be aware of it. [But] it might be explicit.”
Ableism in the medical field is all too familiar to Dr. Iezzoni. She was diagnosed with multiple sclerosis at age 26 during her first year at Harvard Medical School in the early 1980s. Despite symptom flare-ups, Dr. Iezzoni was able to graduate with her class, but many instructors and administrators had little interest in accommodating her physical limitations. In fact, several physicians discouraged her from continuing to train.
Unable to take call, run up flights of stairs, or stand for hours at a time, Dr. Iezzoni remembers being told by a senior surgeon that she shouldn’t become a doctor since she lacked the “most important quality,” which was “24/7 availability.” A hospital CEO informed her: “There are too many doctors in the country right now for us to worry about training a handicapped physician. If that means that some people get left by the wayside, so be it.”
Ultimately, Harvard Medical School declined to write Dr. Iezzoni a letter of recommendation for an internship. She would never practice medicine. “My career was just truncated from the start,” Dr. Iezzoni said. “It never happened because of discrimination.”
She later learned the legal term for her treatment: constructive dismissal.
“The medical school didn’t outright say, ‘Go away. We’re not allowing you to graduate.’ ” Dr. Iezzoni explained. “But they made my life so difficult that I did so voluntarily.”
Dr. Iezzoni graduated in 1984, before the passage of the ADA in 1990, and she refers to her experience as a “ghost from the past,” a historical reminder of how the legal landscape has changed – even though the tendency toward bias may not have.
The fight for inclusion
Zainub Dhanani, a fifth-year medical student at Stanford (Calif.) University, won’t forget an interview at one of the other schools to which she applied. The interviewer asked how she expected to be in a hospital all day if she had a chronic illness.
“Does it really make sense?” he wanted to know.
The question shocked her in the moment, but now she sees this type of bias as linked to the inequalities that many marginalized groups face in health care and beyond. That’s also why she believes physician-patients are crucial to improve the quality of care for people with chronic illness and other groups that face discrimination.
Who else, she wonders, could provide that “reaffirming” experience for patients or have that “unique edge” other than a provider who has navigated the same world?
Ms. Dhanani is the executive director and founder of Medical Students With Disability and Chronic Illness, an organization dedicated to empowering these students through advocacy, education, accessibility, and community. The group now has 19 chapters at medical schools across the country.
Ms. Dhanani said she has received excellent accommodations from Stanford for her own condition (which she prefers not to disclose), but all medical schools are not as responsive to students with various physical needs. Her organization offers support and resources to inform these future physicians about their options and rights.
“Disability justice is also racial justice,” Ms. Dhanani stressed. “It’s also environmental justice. It’s also gender and sexuality-based justice. Those compounded layers of biases lead to worse and worse levels of care. As a patient, it’s terrifying. And as a future physician, it’s tragic to know that this is something so pervasive and yet so under-addressed in medicine.”
Soldiering on
Unfortunately, for some physicians with chronic illness, there are no practical accommodations that could save their careers in clinical practice.
Dr. Stenehjem now works part-time as a health consultant, helping those with chronic illnesses navigate their health care systems.
Dr. Bluestein offers a similar coaching service to patients with Ehlers-Danlos syndrome (EDS) and other connective tissue and hypermobility disorders. Because of her own EDS, she can no longer practice as an anesthesiologist but instead opened an integrative pain management practice for patients with complex pain conditions..
She believes the idea that doctors are “invincible” needs to change. She recalls the time her former group practice told her in no uncertain terms to “never call in sick.”
The stories she hears from her current clients are similar to her own. She can empathize, knowing firsthand the physical and psychological damage these attitudes can cause.
“When I was at my worst physically, I was also at my worst psychologically,” said Dr. Bluestein. “We tend to think of them as separate, but they go hand in hand. If we can validate people’s experiences rather than disregard them, it has a positive forward cycle, as opposed to the reverse, which is what usually happens.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Linda Bluestein remembers all the doctors who missed, ignored, or incompletely diagnosed her chronic illness.
There was the orthopedic surgeon who noted her hyperextended elbows but failed to check any of her other joints. The gastroenterologist who insisted on performing multiple scoping procedures but wouldn’t discuss how to manage her symptoms. The other surgeon who, after performing arthroscopy on her injured knee, yelled at her: “There is nothing wrong with your knee! You’re fine!” in a room full of people.
And then there was the rheumatologist who said: “Oh, you want something to be wrong with you?”
“No,” she replied, “I want an explanation. I want to keep working. I just want to know why these things keep happening to me.”
The medical frustration she experienced was especially difficult because, like her health care providers, Linda Bluestein has an MD after her name. She is a board-certified anesthesiologist and integrative medicine physician.
Along with the physically demanding schedule of medical practice, they must cope with what many call a “culture of invincibility” within medicine. Doctors are not supposed to get sick. In fact, the unwritten rule is presenteeism – to function without adequate food or sleep and to never prioritize their own self-care over their dedication to their patients.
Whether their conditions are visible, such as muscular dystrophy and multiple sclerosis, or invisible, such as fibromyalgia and mental illnesses – and now, long COVID – these doctors often meet significant stigma. They fight the assumption that they are less capable than their colleagues.
But they also experience an invaluable benefit: They gain firsthand knowledge of the patient experience, a profound understanding which, they say, enhances how they care for their own patients.
What it takes to become a doctor when you have a chronic condition
In short, it’s not easy.
Data from the 2018 National Health Interview Survey show that more than half of U.S. adults had at least one of several chronic conditions, including rheumatoid arthritis, asthma, diabetes, hypertension, and kidney problems. Nearly a third of respondents had more than one condition. But fewer than 5% of medical students and 3% of practicing physicians report having a chronic illness or disability, according to studies from 2019 and 2021.
While that could mean that fewer people with chronic illness enter medicine, cases also exist in which aspiring physicians with conditions were dissuaded from pursuing a career in medicine at all.
Amy Stenehjem, MD, a physical medicine and rehabilitation physician, is one of the exceptions. Diagnosed with several autoimmune-related conditions as a teenager and young adult, Dr. Stenehjem was determined to become a doctor. In her 20s, her health was relatively stable, and she was able to manage medical school and residency. Her training institutions agreed to provide some accommodations that helped her succeed.
“They let me build some flexibility into the training,” Dr. Stenehjem said. “In medical school, when I knew I wasn’t going to be able to do a particular specialty as a career, they let me work with an attending doctor that did not require a lot of on-call time during that particular rotation.”
Dr. Stenehjem specialized in chronic neck and back disorders, fibromyalgia, chronic fatigue syndrome (myalgic encephalomyelitis), and autoimmune-related diseases. She practiced for more than a decade. But in 2011, her condition spiraled. She couldn’t walk a few steps or even sit upright without experiencing dizziness and shortness of breath. She had debilitating fatigue and episodes of fever, rash, headaches, and joint pain.
It would take 7 years and more than 20 doctors to determine Dr. Stenehjem’s multiple diagnoses. In addition to her autoimmune diseases, she was diagnosed with postural orthostatic tachycardia syndrome, autoinflammatory periodic fever syndrome, Lyme disease, and reactivated Epstein-Barr infection.
While she suspects that her providers gave her more “leeway” because she was a physician, many did not show a deep understanding of the severity of her symptoms and the impact those symptoms had.
“When I was practicing, I really didn’t fully understand the impact chronic illness had on my patients,” Dr. Stenehjem said. “Things like chronic dizziness, headaches, fatigue, pain, or brain fog can be really hard to understand unless you’ve experienced these symptoms. When I got sick, I finally realized, ‘Oh my goodness, when a patient says they’re dealing with fatigue, this is not your normal, I’m-super-tired-from-being-on-call fatigue. This is I-can’t-get-out-of-bed fatigue.’ That’s what people with chronic illness often deal with on a daily basis.”
Treating the individual
Dr. Stenehjem was aware that her chronic illness would affect her medical career. For Jason Baker, MD, an endocrinologist at Weill Cornell Medicine, New York, it came as a shock. Dr. Baker was a third-year medical student when he experienced increased urination and rapid weight loss. It was only when friends pressed him to visit student health that a blood test revealed type 1 diabetes. Dr. Baker suddenly found himself lying in a hospital bed.
He remembers an attending physician who simply handed him a textbook on diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA) and a resident who informed him that he had kidney damage, which turned out to be untrue. Neither discussed the psychological issues from a frightening diagnosis that would require lifelong, daily management.
“There certainly could have been a bit more empathy from some of the people I dealt with early on,” he said.
Although his training gave him a stark picture of worst-case scenarios, Dr. Baker found that knowledge motivating. “I’d already seen patients come in who had diabetes complications,” Dr. Baker says. “I vowed to never ever get those complications. It was a good balance of fear and motivation.”
Dr. Baker had not planned to specialize in endocrinology, but he quickly realized that his personal diagnosis could help others. Now he often shares his experience with his patients who have diabetes, which he says makes them more comfortable discussing their own problems.
His approach, Dr. Baker explained, is to treat everyone as an individual. Trying to neatly classify patients with chronic illness is a common mistake he notices among physicians.
“There’s a lot of misunderstanding about type 1 versus type 2 [diabetes],” Dr. Baker said, “and trying to categorize people when sometimes people can’t be categorized. That’s really with any chronic condition; there’s no one size fits all.”
Managing his health is still a time-consuming task. At work, he needs breaks to eat, check his blood sugar, or take insulin. “During the workday seeing patients, I have to also remember that I’m a patient,” Dr. Baker said. “I have to be okay with prioritizing my own health. Otherwise I can’t help anybody.”
‘I am not the doctor for you’
Chronic diseases such as diabetes or hypertension are familiar to most doctors, and with good management, patients can usually function normally. When chronic conditions become disabling, however, attitudes in the medical field can change.
According to data from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention and from studies, people with disabilities experience significant disparities and barriers to care. Some of this can be linked to social determinants of health. People with disabilities are more likely to be poor and to rely on Medicare and Medicaid for insurance coverage. But lack of training, unwillingness to provide accommodations, ignorance of legal requirements, and inaccurate assumptions among physicians also play a role.
These are themes that Lisa Iezzoni, MD, a professor of medicine at Harvard Medical School, Boston, has heard from hundreds of patients with disabilities during the more than 25 years that she has conducted research.
In late 2019, Dr. Iezzoni and coinvestigators fielded a national survey of 714 practicing physicians. Only 40.7% reported they were “very confident” that they could provide the same quality of care to patients with disabilities as they do for other patients. And only 56.5% “strongly agreed” that they welcomed these patients into their practices.
The survey was conducted through a series of small focus groups that Dr. Iezzoni held with physicians in 2018. These yielded views that were startling, and in some cases, overtly discriminatory:
- Doctors complained about the “burden” of caring for a patient with a disability.
- They lacked the time or equipment, such as accessible exam tables or weight scales.
- They admitted to inventing excuses for why appointments were not available or routine diagnostic tests were not performed.
- They described being fearful of lawsuits under the Americans with Disabilities Act.
The overall message was summed up in one doctor’s statement: “I am not the doctor for you.”
“Doctors are people too,” Dr. Iezzoni pointed out. “And so they reflect the same prejudices and stigmatized attitudes of the rest of the population. It might be implicit, so they might not be aware of it. [But] it might be explicit.”
Ableism in the medical field is all too familiar to Dr. Iezzoni. She was diagnosed with multiple sclerosis at age 26 during her first year at Harvard Medical School in the early 1980s. Despite symptom flare-ups, Dr. Iezzoni was able to graduate with her class, but many instructors and administrators had little interest in accommodating her physical limitations. In fact, several physicians discouraged her from continuing to train.
Unable to take call, run up flights of stairs, or stand for hours at a time, Dr. Iezzoni remembers being told by a senior surgeon that she shouldn’t become a doctor since she lacked the “most important quality,” which was “24/7 availability.” A hospital CEO informed her: “There are too many doctors in the country right now for us to worry about training a handicapped physician. If that means that some people get left by the wayside, so be it.”
Ultimately, Harvard Medical School declined to write Dr. Iezzoni a letter of recommendation for an internship. She would never practice medicine. “My career was just truncated from the start,” Dr. Iezzoni said. “It never happened because of discrimination.”
She later learned the legal term for her treatment: constructive dismissal.
“The medical school didn’t outright say, ‘Go away. We’re not allowing you to graduate.’ ” Dr. Iezzoni explained. “But they made my life so difficult that I did so voluntarily.”
Dr. Iezzoni graduated in 1984, before the passage of the ADA in 1990, and she refers to her experience as a “ghost from the past,” a historical reminder of how the legal landscape has changed – even though the tendency toward bias may not have.
The fight for inclusion
Zainub Dhanani, a fifth-year medical student at Stanford (Calif.) University, won’t forget an interview at one of the other schools to which she applied. The interviewer asked how she expected to be in a hospital all day if she had a chronic illness.
“Does it really make sense?” he wanted to know.
The question shocked her in the moment, but now she sees this type of bias as linked to the inequalities that many marginalized groups face in health care and beyond. That’s also why she believes physician-patients are crucial to improve the quality of care for people with chronic illness and other groups that face discrimination.
Who else, she wonders, could provide that “reaffirming” experience for patients or have that “unique edge” other than a provider who has navigated the same world?
Ms. Dhanani is the executive director and founder of Medical Students With Disability and Chronic Illness, an organization dedicated to empowering these students through advocacy, education, accessibility, and community. The group now has 19 chapters at medical schools across the country.
Ms. Dhanani said she has received excellent accommodations from Stanford for her own condition (which she prefers not to disclose), but all medical schools are not as responsive to students with various physical needs. Her organization offers support and resources to inform these future physicians about their options and rights.
“Disability justice is also racial justice,” Ms. Dhanani stressed. “It’s also environmental justice. It’s also gender and sexuality-based justice. Those compounded layers of biases lead to worse and worse levels of care. As a patient, it’s terrifying. And as a future physician, it’s tragic to know that this is something so pervasive and yet so under-addressed in medicine.”
Soldiering on
Unfortunately, for some physicians with chronic illness, there are no practical accommodations that could save their careers in clinical practice.
Dr. Stenehjem now works part-time as a health consultant, helping those with chronic illnesses navigate their health care systems.
Dr. Bluestein offers a similar coaching service to patients with Ehlers-Danlos syndrome (EDS) and other connective tissue and hypermobility disorders. Because of her own EDS, she can no longer practice as an anesthesiologist but instead opened an integrative pain management practice for patients with complex pain conditions..
She believes the idea that doctors are “invincible” needs to change. She recalls the time her former group practice told her in no uncertain terms to “never call in sick.”
The stories she hears from her current clients are similar to her own. She can empathize, knowing firsthand the physical and psychological damage these attitudes can cause.
“When I was at my worst physically, I was also at my worst psychologically,” said Dr. Bluestein. “We tend to think of them as separate, but they go hand in hand. If we can validate people’s experiences rather than disregard them, it has a positive forward cycle, as opposed to the reverse, which is what usually happens.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Community workers may address psychiatrist shortage
SAN FRANCISCO – promises to bring timely, evidence-based health services to those with little to no access to effective care.
The current shortage of mental health clinicians is driven by increased demand from a population more willing to seek psychiatric help and clinicians leaving the workforce. Both factors were exacerbated by the COVID-19 pandemic.
“It would be costly to address the problem through additional specialist training, and doing so would take decades to see any changes,” project director Milton L. Wainberg, MD, professor of clinical psychiatry at Columbia University, New York, and New York State Psychiatric Institute, said in an interview.
A better solution is to train members of the community to be the entry point to the mental health care system, a strategy that has been proven effective.
Details of the project were discussed at the annual meeting of the American Psychiatric Association.
Half of the United States population will be diagnosed with a mental or substance use disorder in their lifetime, but only about half of those will receive proper treatment. That percentage is even greater among lower-income groups and minorities, said Dr. Wainberg.
Despite the availability of multiple evidence-based therapies, there has been no reduction in the global prevalence of psychiatric illness since 1990 – the first time this burden was determined, he said.
Unfeasible model
“The historic paradigm of ongoing long-term care is costly and not a feasible public mental health model. There is no evidence that it works, and there is increasing demand for brief interventions,” said Dr. Wainberg.
The new initiative – called ENGAGE – has its origins in parts of Africa, where nurses had to be trained during the AIDS crisis as there weren’t enough doctors to roll out antiretroviral therapy.
In the United States, the program trains and certifies community workers who are passionate about their community. “Members of the community want to learn how to help their neighbors,” said Dr. Wainberg. “When we give them the opportunity to learn skills that can actually change community members’ symptoms, they are excited.”
The training involves a didactic component and an experiential component, in which trainees work with at least three cases under supervision to demonstrate competency. Technical assistance and other supports, such as refresher training, are offered for a year after training.
Workers ask three initial questions to quickly determine if a person has a mental health disorder. Asking 10 additional questions tells the worker if the person has a common mental health disorder like depression, anxiety, or posttraumatic stress disorder (PTSD), a substance use disorder involving alcohol or drugs, suicide risk, or a severe disorder requiring referral to a mental health specialist.
Those who do not require a referral are offered an intervention personalized to their need.
The training costs $5,000 per person. “We calculated for New York State it would cost only $18 million to train everybody we need,” said Dr. Wainberg.
Cost effective
He stressed the program, which is funded by the New York Office of Mental Health, is cost effective. Just like patients don’t need to see a plastic surgeon to have a small mole removed, they don’t always need to see a psychiatrist for run-of-the-mill mild depression, he said.
To date, 20 workers have been trained and have started to meet with clients in clinics in four New York City neighborhoods/boroughs (Harlem, Brooklyn, the Bronx, and Washington Heights). Additional clinics in West Harlem and Staten Island are expected to begin training soon.
Dr. Wainberg has been inundated with interest in the initiative. “Over the last 3 months I have been having 15 meetings a day” with parties interested in getting more information or wanting to know how to start such a program.
He plans to examine the program’s effectiveness in a number of areas, including patient symptoms, timeliness of services, access, sustainability, and cost. And he aims to expand the project beyond New York.
Mental health specialists shouldn’t worry about becoming irrelevant with the addition of community workers, as the demand is so great, said Dr. Wainberg. “There will always be a need for the kind of care mental health specialists are trained for. This initiative aims to expand capacity for those with less severe symptoms, who might not need an intensive level of intervention.”
Unique program
In a comment, Jonathan E. Alpert, MD, PhD, chair of the department of psychiatry and behavioral sciences, Montefiore Medical Center and Albert Einstein College of Medicine, New York, said the project is “unique” and an “excellent” idea.
“This is one of the first pilots that I know of in this country to train lay-members of the community to screen for mental illness and substance use disorders and even to provide evidence-based treatment for people who may have more mild symptoms and might not yet need to see a professional but otherwise would not have access to care.”
Dr. Alpert noted the current challenges of accessing care for a mental health or substance abuse disorder. “Many clinics have wait lists of 3-6 months.”
Another issue is the “stigma and lack of trust” among minority communities when it comes to formal mental health treatments. “Having lay-members who know the community, who look like the community, who understand the community, and who are available for screening and treatment is exceptionally important.”
Although this pilot program will have to be assessed for effectiveness, “the concept behind it is very important,” said Dr. Alpert. “If you’re relying on MDs and PhDs to provide mental health services, there just aren’t enough of us to go around.”
Dr. Wainberg and Dr. Alpert report no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
SAN FRANCISCO – promises to bring timely, evidence-based health services to those with little to no access to effective care.
The current shortage of mental health clinicians is driven by increased demand from a population more willing to seek psychiatric help and clinicians leaving the workforce. Both factors were exacerbated by the COVID-19 pandemic.
“It would be costly to address the problem through additional specialist training, and doing so would take decades to see any changes,” project director Milton L. Wainberg, MD, professor of clinical psychiatry at Columbia University, New York, and New York State Psychiatric Institute, said in an interview.
A better solution is to train members of the community to be the entry point to the mental health care system, a strategy that has been proven effective.
Details of the project were discussed at the annual meeting of the American Psychiatric Association.
Half of the United States population will be diagnosed with a mental or substance use disorder in their lifetime, but only about half of those will receive proper treatment. That percentage is even greater among lower-income groups and minorities, said Dr. Wainberg.
Despite the availability of multiple evidence-based therapies, there has been no reduction in the global prevalence of psychiatric illness since 1990 – the first time this burden was determined, he said.
Unfeasible model
“The historic paradigm of ongoing long-term care is costly and not a feasible public mental health model. There is no evidence that it works, and there is increasing demand for brief interventions,” said Dr. Wainberg.
The new initiative – called ENGAGE – has its origins in parts of Africa, where nurses had to be trained during the AIDS crisis as there weren’t enough doctors to roll out antiretroviral therapy.
In the United States, the program trains and certifies community workers who are passionate about their community. “Members of the community want to learn how to help their neighbors,” said Dr. Wainberg. “When we give them the opportunity to learn skills that can actually change community members’ symptoms, they are excited.”
The training involves a didactic component and an experiential component, in which trainees work with at least three cases under supervision to demonstrate competency. Technical assistance and other supports, such as refresher training, are offered for a year after training.
Workers ask three initial questions to quickly determine if a person has a mental health disorder. Asking 10 additional questions tells the worker if the person has a common mental health disorder like depression, anxiety, or posttraumatic stress disorder (PTSD), a substance use disorder involving alcohol or drugs, suicide risk, or a severe disorder requiring referral to a mental health specialist.
Those who do not require a referral are offered an intervention personalized to their need.
The training costs $5,000 per person. “We calculated for New York State it would cost only $18 million to train everybody we need,” said Dr. Wainberg.
Cost effective
He stressed the program, which is funded by the New York Office of Mental Health, is cost effective. Just like patients don’t need to see a plastic surgeon to have a small mole removed, they don’t always need to see a psychiatrist for run-of-the-mill mild depression, he said.
To date, 20 workers have been trained and have started to meet with clients in clinics in four New York City neighborhoods/boroughs (Harlem, Brooklyn, the Bronx, and Washington Heights). Additional clinics in West Harlem and Staten Island are expected to begin training soon.
Dr. Wainberg has been inundated with interest in the initiative. “Over the last 3 months I have been having 15 meetings a day” with parties interested in getting more information or wanting to know how to start such a program.
He plans to examine the program’s effectiveness in a number of areas, including patient symptoms, timeliness of services, access, sustainability, and cost. And he aims to expand the project beyond New York.
Mental health specialists shouldn’t worry about becoming irrelevant with the addition of community workers, as the demand is so great, said Dr. Wainberg. “There will always be a need for the kind of care mental health specialists are trained for. This initiative aims to expand capacity for those with less severe symptoms, who might not need an intensive level of intervention.”
Unique program
In a comment, Jonathan E. Alpert, MD, PhD, chair of the department of psychiatry and behavioral sciences, Montefiore Medical Center and Albert Einstein College of Medicine, New York, said the project is “unique” and an “excellent” idea.
“This is one of the first pilots that I know of in this country to train lay-members of the community to screen for mental illness and substance use disorders and even to provide evidence-based treatment for people who may have more mild symptoms and might not yet need to see a professional but otherwise would not have access to care.”
Dr. Alpert noted the current challenges of accessing care for a mental health or substance abuse disorder. “Many clinics have wait lists of 3-6 months.”
Another issue is the “stigma and lack of trust” among minority communities when it comes to formal mental health treatments. “Having lay-members who know the community, who look like the community, who understand the community, and who are available for screening and treatment is exceptionally important.”
Although this pilot program will have to be assessed for effectiveness, “the concept behind it is very important,” said Dr. Alpert. “If you’re relying on MDs and PhDs to provide mental health services, there just aren’t enough of us to go around.”
Dr. Wainberg and Dr. Alpert report no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
SAN FRANCISCO – promises to bring timely, evidence-based health services to those with little to no access to effective care.
The current shortage of mental health clinicians is driven by increased demand from a population more willing to seek psychiatric help and clinicians leaving the workforce. Both factors were exacerbated by the COVID-19 pandemic.
“It would be costly to address the problem through additional specialist training, and doing so would take decades to see any changes,” project director Milton L. Wainberg, MD, professor of clinical psychiatry at Columbia University, New York, and New York State Psychiatric Institute, said in an interview.
A better solution is to train members of the community to be the entry point to the mental health care system, a strategy that has been proven effective.
Details of the project were discussed at the annual meeting of the American Psychiatric Association.
Half of the United States population will be diagnosed with a mental or substance use disorder in their lifetime, but only about half of those will receive proper treatment. That percentage is even greater among lower-income groups and minorities, said Dr. Wainberg.
Despite the availability of multiple evidence-based therapies, there has been no reduction in the global prevalence of psychiatric illness since 1990 – the first time this burden was determined, he said.
Unfeasible model
“The historic paradigm of ongoing long-term care is costly and not a feasible public mental health model. There is no evidence that it works, and there is increasing demand for brief interventions,” said Dr. Wainberg.
The new initiative – called ENGAGE – has its origins in parts of Africa, where nurses had to be trained during the AIDS crisis as there weren’t enough doctors to roll out antiretroviral therapy.
In the United States, the program trains and certifies community workers who are passionate about their community. “Members of the community want to learn how to help their neighbors,” said Dr. Wainberg. “When we give them the opportunity to learn skills that can actually change community members’ symptoms, they are excited.”
The training involves a didactic component and an experiential component, in which trainees work with at least three cases under supervision to demonstrate competency. Technical assistance and other supports, such as refresher training, are offered for a year after training.
Workers ask three initial questions to quickly determine if a person has a mental health disorder. Asking 10 additional questions tells the worker if the person has a common mental health disorder like depression, anxiety, or posttraumatic stress disorder (PTSD), a substance use disorder involving alcohol or drugs, suicide risk, or a severe disorder requiring referral to a mental health specialist.
Those who do not require a referral are offered an intervention personalized to their need.
The training costs $5,000 per person. “We calculated for New York State it would cost only $18 million to train everybody we need,” said Dr. Wainberg.
Cost effective
He stressed the program, which is funded by the New York Office of Mental Health, is cost effective. Just like patients don’t need to see a plastic surgeon to have a small mole removed, they don’t always need to see a psychiatrist for run-of-the-mill mild depression, he said.
To date, 20 workers have been trained and have started to meet with clients in clinics in four New York City neighborhoods/boroughs (Harlem, Brooklyn, the Bronx, and Washington Heights). Additional clinics in West Harlem and Staten Island are expected to begin training soon.
Dr. Wainberg has been inundated with interest in the initiative. “Over the last 3 months I have been having 15 meetings a day” with parties interested in getting more information or wanting to know how to start such a program.
He plans to examine the program’s effectiveness in a number of areas, including patient symptoms, timeliness of services, access, sustainability, and cost. And he aims to expand the project beyond New York.
Mental health specialists shouldn’t worry about becoming irrelevant with the addition of community workers, as the demand is so great, said Dr. Wainberg. “There will always be a need for the kind of care mental health specialists are trained for. This initiative aims to expand capacity for those with less severe symptoms, who might not need an intensive level of intervention.”
Unique program
In a comment, Jonathan E. Alpert, MD, PhD, chair of the department of psychiatry and behavioral sciences, Montefiore Medical Center and Albert Einstein College of Medicine, New York, said the project is “unique” and an “excellent” idea.
“This is one of the first pilots that I know of in this country to train lay-members of the community to screen for mental illness and substance use disorders and even to provide evidence-based treatment for people who may have more mild symptoms and might not yet need to see a professional but otherwise would not have access to care.”
Dr. Alpert noted the current challenges of accessing care for a mental health or substance abuse disorder. “Many clinics have wait lists of 3-6 months.”
Another issue is the “stigma and lack of trust” among minority communities when it comes to formal mental health treatments. “Having lay-members who know the community, who look like the community, who understand the community, and who are available for screening and treatment is exceptionally important.”
Although this pilot program will have to be assessed for effectiveness, “the concept behind it is very important,” said Dr. Alpert. “If you’re relying on MDs and PhDs to provide mental health services, there just aren’t enough of us to go around.”
Dr. Wainberg and Dr. Alpert report no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM APA 2023
U.S. psychiatrist shortage causing months-long wait times
SAN FRANCISCO –
“Long wait times for mental health care were a huge problem even before the pandemic but especially during the pandemic,” study investigator Erin McDaid, BS, Virginia Tech Carilion School of Medicine, Roanoke, said in an interview.
“It’s not like you have a cold or a virus and maybe you wait a little bit and it goes away. Mental health problems can completely impact your life; you can’t do anything, you can’t go to work, you can’t build relationships, you can’t take care of your kids. It’s a really big issue,” Ms. McDaid said.
The study was presented at the annual meeting of the American Psychiatric Association.
Few psychiatrists taking new patients
To find out just how big an issue wait times are, the researchers examined general psychiatry outpatient availability during the COVID-19 pandemic in five states – New York, California, North Dakota, Virginia, and Wyoming.
Altogether, 948 psychiatrists were sampled. Simulated adult patients made 864 calls seeking an initial psychiatric evaluation for general mental health care. The calls were made late in the pandemic, between May and July 2022.
Only 18.5% of psychiatrists were available to see new patients. The median wait time was 67 days for in-person appointments and 43 days for telepsychiatry appointments (P < .001).
More than half of psychiatrists who were contacted said they were not taking new patients, which was the most common reason given for unavailability.
“This is happening at the worst time, when we are seeing mental health issues spike,” Ms. McDaid said.
Telepsychiatry helpful but no panacea
The fact that wait times were a bit shorter for telepsychiatry is encouraging, Ms. McDaid said.
Telepsychiatry is a potential solution to provider shortages and geographic barriers, but it does not resolve the concerning shortage of psychiatric outpatient care, she noted.
“Psychiatrists adapted very well to telepsychiatry during COVID,” Saul Levin, MD, MPA, chief executive officer and medical director of the APA, noted during a preconference briefing with reporters.
“Before COVID, we always thought that the psychiatrist had to be with the patient in the room,” said Dr. Levin. But now we see that either “sitting inside the room with your psychiatrist or mental health specialist or [being there virtually] has the same effect. The patient is concentrating and working out their problems with you. I think that’s one of the positives – if anything coming out of COVID is positive.”
In an interview, Robert Trestman, MD, chair of the APA Council on Healthcare Systems and Financing, said telepsychiatry “will help, but there is not one simple solution that will fix the problem” regarding access to mental health care.
One promising approach is the collaborative care model, which enlists primary care physicians to provide mental health care in consultation with psychiatry and case management, Dr. Trestman said.
“There’s no question that there aren’t enough providers. There aren’t enough primary care doctors, and there certainly aren’t enough psychiatrists,” Dr. Trestman noted.
Encouragingly, however, the past few years have seen a steady increase in medical students choosing psychiatry.
“Psychiatry is now being thought of as a branch of neuroscience. We are understanding so much more about the field and about the brain. So that’s intriguing and intellectually challenging to many,” Dr. Trestman said.
He also noted that the pandemic has helped to “break down stigma. More people acknowledge and talk about mental health, and when an area is destigmatized, it’s so much easier for people to consider.”
Jack Resneck, Jr., MD, president of the American Medical Association, acknowledged that there is a “severe workforce shortage in health care right now.”
“I’m a physician and the president of the AMA, and it took me way too long to be able to find a primary care physician for myself,” he said.
“I also am a physician who refers patients to rheumatology and endocrinology, psychiatry, and other areas of medicine, and it is, in many geographic areas both rural and urban, a huge struggle right now,” said Dr. Resneck.
The study had no specific funding. Ms. McDaid, Dr. Levin, and Dr. Trestman have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
SAN FRANCISCO –
“Long wait times for mental health care were a huge problem even before the pandemic but especially during the pandemic,” study investigator Erin McDaid, BS, Virginia Tech Carilion School of Medicine, Roanoke, said in an interview.
“It’s not like you have a cold or a virus and maybe you wait a little bit and it goes away. Mental health problems can completely impact your life; you can’t do anything, you can’t go to work, you can’t build relationships, you can’t take care of your kids. It’s a really big issue,” Ms. McDaid said.
The study was presented at the annual meeting of the American Psychiatric Association.
Few psychiatrists taking new patients
To find out just how big an issue wait times are, the researchers examined general psychiatry outpatient availability during the COVID-19 pandemic in five states – New York, California, North Dakota, Virginia, and Wyoming.
Altogether, 948 psychiatrists were sampled. Simulated adult patients made 864 calls seeking an initial psychiatric evaluation for general mental health care. The calls were made late in the pandemic, between May and July 2022.
Only 18.5% of psychiatrists were available to see new patients. The median wait time was 67 days for in-person appointments and 43 days for telepsychiatry appointments (P < .001).
More than half of psychiatrists who were contacted said they were not taking new patients, which was the most common reason given for unavailability.
“This is happening at the worst time, when we are seeing mental health issues spike,” Ms. McDaid said.
Telepsychiatry helpful but no panacea
The fact that wait times were a bit shorter for telepsychiatry is encouraging, Ms. McDaid said.
Telepsychiatry is a potential solution to provider shortages and geographic barriers, but it does not resolve the concerning shortage of psychiatric outpatient care, she noted.
“Psychiatrists adapted very well to telepsychiatry during COVID,” Saul Levin, MD, MPA, chief executive officer and medical director of the APA, noted during a preconference briefing with reporters.
“Before COVID, we always thought that the psychiatrist had to be with the patient in the room,” said Dr. Levin. But now we see that either “sitting inside the room with your psychiatrist or mental health specialist or [being there virtually] has the same effect. The patient is concentrating and working out their problems with you. I think that’s one of the positives – if anything coming out of COVID is positive.”
In an interview, Robert Trestman, MD, chair of the APA Council on Healthcare Systems and Financing, said telepsychiatry “will help, but there is not one simple solution that will fix the problem” regarding access to mental health care.
One promising approach is the collaborative care model, which enlists primary care physicians to provide mental health care in consultation with psychiatry and case management, Dr. Trestman said.
“There’s no question that there aren’t enough providers. There aren’t enough primary care doctors, and there certainly aren’t enough psychiatrists,” Dr. Trestman noted.
Encouragingly, however, the past few years have seen a steady increase in medical students choosing psychiatry.
“Psychiatry is now being thought of as a branch of neuroscience. We are understanding so much more about the field and about the brain. So that’s intriguing and intellectually challenging to many,” Dr. Trestman said.
He also noted that the pandemic has helped to “break down stigma. More people acknowledge and talk about mental health, and when an area is destigmatized, it’s so much easier for people to consider.”
Jack Resneck, Jr., MD, president of the American Medical Association, acknowledged that there is a “severe workforce shortage in health care right now.”
“I’m a physician and the president of the AMA, and it took me way too long to be able to find a primary care physician for myself,” he said.
“I also am a physician who refers patients to rheumatology and endocrinology, psychiatry, and other areas of medicine, and it is, in many geographic areas both rural and urban, a huge struggle right now,” said Dr. Resneck.
The study had no specific funding. Ms. McDaid, Dr. Levin, and Dr. Trestman have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
SAN FRANCISCO –
“Long wait times for mental health care were a huge problem even before the pandemic but especially during the pandemic,” study investigator Erin McDaid, BS, Virginia Tech Carilion School of Medicine, Roanoke, said in an interview.
“It’s not like you have a cold or a virus and maybe you wait a little bit and it goes away. Mental health problems can completely impact your life; you can’t do anything, you can’t go to work, you can’t build relationships, you can’t take care of your kids. It’s a really big issue,” Ms. McDaid said.
The study was presented at the annual meeting of the American Psychiatric Association.
Few psychiatrists taking new patients
To find out just how big an issue wait times are, the researchers examined general psychiatry outpatient availability during the COVID-19 pandemic in five states – New York, California, North Dakota, Virginia, and Wyoming.
Altogether, 948 psychiatrists were sampled. Simulated adult patients made 864 calls seeking an initial psychiatric evaluation for general mental health care. The calls were made late in the pandemic, between May and July 2022.
Only 18.5% of psychiatrists were available to see new patients. The median wait time was 67 days for in-person appointments and 43 days for telepsychiatry appointments (P < .001).
More than half of psychiatrists who were contacted said they were not taking new patients, which was the most common reason given for unavailability.
“This is happening at the worst time, when we are seeing mental health issues spike,” Ms. McDaid said.
Telepsychiatry helpful but no panacea
The fact that wait times were a bit shorter for telepsychiatry is encouraging, Ms. McDaid said.
Telepsychiatry is a potential solution to provider shortages and geographic barriers, but it does not resolve the concerning shortage of psychiatric outpatient care, she noted.
“Psychiatrists adapted very well to telepsychiatry during COVID,” Saul Levin, MD, MPA, chief executive officer and medical director of the APA, noted during a preconference briefing with reporters.
“Before COVID, we always thought that the psychiatrist had to be with the patient in the room,” said Dr. Levin. But now we see that either “sitting inside the room with your psychiatrist or mental health specialist or [being there virtually] has the same effect. The patient is concentrating and working out their problems with you. I think that’s one of the positives – if anything coming out of COVID is positive.”
In an interview, Robert Trestman, MD, chair of the APA Council on Healthcare Systems and Financing, said telepsychiatry “will help, but there is not one simple solution that will fix the problem” regarding access to mental health care.
One promising approach is the collaborative care model, which enlists primary care physicians to provide mental health care in consultation with psychiatry and case management, Dr. Trestman said.
“There’s no question that there aren’t enough providers. There aren’t enough primary care doctors, and there certainly aren’t enough psychiatrists,” Dr. Trestman noted.
Encouragingly, however, the past few years have seen a steady increase in medical students choosing psychiatry.
“Psychiatry is now being thought of as a branch of neuroscience. We are understanding so much more about the field and about the brain. So that’s intriguing and intellectually challenging to many,” Dr. Trestman said.
He also noted that the pandemic has helped to “break down stigma. More people acknowledge and talk about mental health, and when an area is destigmatized, it’s so much easier for people to consider.”
Jack Resneck, Jr., MD, president of the American Medical Association, acknowledged that there is a “severe workforce shortage in health care right now.”
“I’m a physician and the president of the AMA, and it took me way too long to be able to find a primary care physician for myself,” he said.
“I also am a physician who refers patients to rheumatology and endocrinology, psychiatry, and other areas of medicine, and it is, in many geographic areas both rural and urban, a huge struggle right now,” said Dr. Resneck.
The study had no specific funding. Ms. McDaid, Dr. Levin, and Dr. Trestman have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
AT APA 2023