User login
Defining Skin of Color (See Letter to the Editor. 2003;71:141-143)
Antidepressants for fibromyalgia: Latest word on the link to depression and anxiety
Patients with fibromyalgia often resist being referred to a psychiatrist because they fear being told their pain and other somatic symptoms are “all in their heads.” Evidence is mounting that they may be literally correct—the symptoms of fibromyalgia appear to have a physiologic connection with the central nervous system. Abnormal CNS activity, including sleep patterns, response to stress, pain processing, and neurotransmitter levels, has been documented in patients with fibromyalgia.
As psychiatrists, we can reassure these patients—and their primary care physicians and rheumatologists—that we are in a position to help because we:
- have expertise in assessing mood and anxiety disorders and in managing antidepressants, the medication physicians most commonly prescribe for fibromyalgia;
- are skilled in the use of the anticonvulsant gabapentin, which is being used in fibromyalgia for its analgesic and sedative effects;
- can offer much-needed support through psychotherapy, as chronic pain and other fibromyalgia-related symptoms create great stress in these patients’ lives.
Antidepressants are showing promise as an effective treatment for pain, fatigue, and depression in patients with fibromyalgia in studies by our group and others. The following information can help you stay current with the newest understandings of this ailment.
Table 1
CRITERIA FOR DIAGNOSING FIBROMYALGIA
| 1. | History of widespread pain |
| Definition Pain in the right and left side of the body, pain above and below the waist, axial skeletal pain (cervical spine or anterior chest or thoracic spine or low back). In this definition, shoulder and buttock pain is considered as pain for each involved side. “Low back” pain is considered lower segment pain. | |
| 2. | Pain in 11 of 18 tender point sites on digital palpation |
| Definition Pain, on digital palpation, must be present in at least 11 of the following 18 tender points: | |
| Occiput Bilateral, at the suboccipital muscle insertion | |
| Low cervical Bilateral, at the anterior aspects of the intertransverse spaces at C5-C7 | |
| Trapezius Bilateral, at the midpoint of the upper border | |
| Supraspinatus Bilateral, at origins, above the scapula spine near the medial border | |
| Second rib Bilateral, at the second costochondral junctions, just lateral to the junctions on upper surfaces | |
| Lateral epicondyle Bilateral, 2 cm distal to the epicondyles | |
| Gluteal Bilateral, in upper outer quadrants of buttocks in anterior fold of muscle | |
| Greater trochanter Bilateral, posterior to the trochanteric prominence | |
| Knee Bilateral, at the medial fat pad proximal to the joint line | |
| Digital palpation should be performed with an approximate force of 4 kg. For a tender point to be considered “positive” the patient must state that the palpation was painful. “Tender” is not to be considered “painful” Source: American College of Rheumatology1 | |
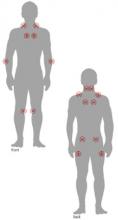
Figure 1 LOCATION OF FIBROMYALGIA TENDER POINTS
To palpate tender point sites, pressure is applied with the thumb pad perpendicularly to each site and the force increased by 1 kg per second until 4 kg of pressure is achieved. Whitening of the thumbnail bed usually occurs when applying the 4-kg force.
Mood disorders in fibromyalgia
A diagnosis of fibromyalgia requires the finding of widespread pain and tenderness at specific anatomic points (Table 1, Figure 1).1 Most patients also report fatigue, sleep disturbance, and morning stiffness (Box 1).2-5 American College of Rheumatology criteria do not require exclusionary tests such as radiographs and blood tests for the diagnosis.
Primary care physicians are increasingly making the diagnosis themselves and referring patients to rheumatologists only when conditions other than fibromyalgia are suspected. The differential diagnosis is broad, and other rheumatic and nonrheumatic disorders have similar symptoms, require different treatment, and affect fibromyalgia management (Table 2).6
Patients with fibromyalgia often report symptoms of major depressive disorder, such as depressed mood, anxiety, fatigue, and insomnia.7 Many psychological studies of such patients have documented increased rates of depressive symptoms.8 Depression and anxiety symptoms are common and frequently severe, even among individuals with fibromyalgia in the general population.9
Patients’ mood and anxiety disorders correlate highly with the number of medically unexplained symptoms and are associated with functional disability.10 The presence of psychological symptoms predicts persistent fibromyalgia symptoms,11 and psychological distress is strongly associated with symptom severity.12
Evidence for a CNS link
CNS mechanisms appear to contribute to the development of clinical findings in fibromyalgia.
Abnormal sleep A qualitative defect in sleep has been identified in patients with fibromyalgia.13 This sleep abnormality consists of inappropriate intrusion of alpha waves (normally seen during wakefulness or REM sleep) into deep sleep (usually characterized by delta waves).13 Some researchers believe alpha-delta sleep intrusion is associated with the chronic musculoskeletal pain and fatigue of fibromyalgia and, in turn, is mediated by an abnormality in central serotonergic neurotransmission.14 This sleep abnormality is not specific to fibromyalgia and can be found in other conditions, however.15 Debate continues regarding the role of sleep dysregulation in the pathophysiology of fibromyalgia.
Fibromyalgia is more common in women than men, with an estimated prevalence of 2% in the general population (3.4% in women and 0.5% in men). Its prevalence increases with age, rising sharply in middle age and then dropping off after age 80.2
Fibromyalgia is seen most often in women ages 50 and older.2 It occurs in 5% to 6% of patients presenting to general medical and family practice clinics and in 15% to 20% of patients presenting to rheumatologists, making it one of the most common diagnoses in office-based rheumatology practices.
American College of Rheumatology criteria may require only widespread pain and tenderness for a diagnosis of fibromyalgia, but most patients (73% to 85%) also report fatigue, sleep disturbance, and morning stiffness. Many (45% to 69%) report “pain all over,” paresthesias, headache, and anxiety. Co-occurring irritable bowel syndrome, sicca symptoms, and Raynaud’s phenomenon are less common (<35%).1 Patients with fibromyalgia also have high lifetime rates of other comorbid disorders, including migraine, chronic fatigue syndrome, and mood and anxiety disorders. Some patients report weakness, forgetfulness, difficulties in concentration, urinary frequency, history of dysmenorrhea, and restless legs.
Fibromyalgia is chronic, debilitating, and often leads to substantial functional impairment.3 Most patients with fibromyalgia do not display significant improvement over an average of 7 years of treatment.4 Patients with fibromyalgia report lower quality of well-being than patients with diagnoses of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, rheumatoid arthritis, atrial fibrillation, advanced cancer, and several other chronic diseases.5
Stress response Stress appears to precipitate or exacerbate fibromyalgia symptoms in many patients.16 For example, fibromyalgia appears to be associated with victimization (adult and childhood sexual, physical, and emotional trauma), and this stress may trigger the development of fibromyalgia in some patients.17
Patients with fibromyalgia appear to develop disturbances in the two major stress-response systems: the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal (HPA) axis and the sympathetic nervous system.16 Although the interpretation of these disturbances is still debated, some researchers suggest that the available data point to reduction in CNS corticotropin releasing hormone (CRH), the key mediator in the HPA axis.18,19 CRH is also a behaviorally active peptide that leads to physiologic and behavioral arousal when administered centrally to animals.18 CRH reduction could contribute to the clinical features of fibromyalgia (e.g., fatigue) either directly or indirectly by causing a relative glucocorticoid deficiency.18,19
Table 2
DIFFERENTIAL DIAGNOSIS OF FIBROMYALGIA
| Rheumatic disorders | Nonrheumatic disorders |
|---|---|
| Rheumatoid arthritis | Hypothyroidism |
| Systemic lupus erythematosus | Sleep apnea |
| Polyarticular osteoarthritis | Hepatitis |
| Polymyalgia rheumatica | Cushing’s syndrome |
| Addison’s disease | |
| Hyperparathyroidism | |
| Adapted from Clauw DJ. Fibromyalgia syndrome: an update on current understanding and medical management. Rheumatol Grand Rds 2000;3:1-9. | |
Fibromyalgia is also associated with moderate basal hypocortisolism.18,19 A relative glucocorticoid deficiency could contribute to fibromyalgia’s characteristic fatigue, arthralgias, myalgias, and disturbances in mood and sleep.18 This deficiency may also cause some of the immunologic disturbances seen with fibromyalgia.18,19
Atypical depression, which shares such features of fibromyalgia as profound lethargy, is also associated with inappropriately normal or reduced activation of the HPA axis and a functional deficit in the release of hypothalamic CRH.18 The unifying feature of HPA axis activity in both atypical depression and fibromyalgia may be a shared hypofunctioning.18 A more complete understanding of the neuroendocrine changes in fibromyalgia awaits further study.
Pain processing Aberrant CNS processing of pain may also play a role in fibromyalgia.16,20 Fibromyalgia is sometimes precipitated by physical trauma.21 A traumatic injury may start a process in susceptible individuals that leads to an enhanced central processing of painful stimuli characteristic of central sensitization.22 Patients with fibromyalgia often develop an increased response to painful stimuli (hyeralgesia) and experience pain from normally nonnoxious stimuli (allodynia).20
Substance P, an important nociceptive neurotransmitter, may have a role in generating central sensitization.23 Elevated concentrations of substance P have been found in the cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) of individuals with fibromyalgia.24 Substance P also inhibits CRH release and may contribute to low CRH activity in fibromyalgia.16
Neurotransmitter defects A functional reduction in serotonergic activity has been demonstrated in patients with fibromyalgia. Schwarz et al25 found a strong negative correlation between serum concentrations of the primary serotonin metabolite, 5-hydroxyindoleacetic acid (5-HIAA), and substance P, pain, and insomnia. Evidence also exists of reduced concentrations of the primary norepinephrine metabolite, 3-methoxy-4-hydroxyphenethylene (MHPG), in the CSF of patients with fibromyalgia.26 Reduced serotonin and norepinephrine levels in descending pain-inhibitory pathways may cause the allodynia and hyperalgesia of fibromyalgia.
Pharmacologic treatment
Most studies of pharmacologic treatment of fibromyalgia have examined antidepressants for three reasons:
- There is evidence of the successful use of antidepressants in other chronic pain conditions.27
- These agents are effective for treating mood and anxiety disorders, which frequently occur in patients with fibromyalgia and may share a common physiologic abnormality.28
- Antidepressants might enhance the activity of neurotransmitters such as serotonin and norepinephrine in the descending inhibitory pain pathways, leading to reduced pain perception.29
Tricyclics In randomized, controlled trials, tricyclic medications (including the muscle relaxant cyclobenzaprine) appear to be moderately effective in improving fibromyalgia symptoms. Two meta-analyses of trials of tricyclic medications (amitriptyline, dothiepin, cyclobenzaprine, clomipramine, and maprotiline) have found similar results.30,31 Our group found the greatest effect on measures of sleep improvement, which may be due in part to tricyclics’ sedative properties.30 Many patients with fibromyalgia, however, cannot tolerate the sedative and other side effects associated with tricyclic agents, even though low dosages (e.g., 25 mg/d of amitriptyline) have typically been used in clinical trials.
SSRIs. Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors, although likely to be better tolerated than tricyclics, have been examined in only five placebo-controlled trials in fibromyalgia: two with citalopram, and three with fluoxetine. One citalopram study found no significant differences in efficacy between citalopram and a placebo,32 but the other reported significant improvement in one measure of pain and a significant decrease in depressive symptoms compared with the placebo group.33 No significant differences were found between groups in the global assessment of improvement.
The initial fluoxetine trial in fibromyalgia treatment did not reveal a significant therapeutic effect over a placebo,34 although the study was limited by a high (57%) placebo dropout rate, small sample size (42 subjects), brief duration (3 to 6 weeks after treatment), and restriction of fluoxetine dosage to 20 mg/d. In the two other controlled trials, including one which we recently conducted, fluoxetine was superior to a placebo in reducing pain and other fibromyalgia-associated symptoms.35,36
In our 12-week investigation (a randomized, placebocontrolled, parallel-group, flexible-dose trial), 60 subjects with fibromyalgia received fluoxetine 20 to 80 mg/d or a placebo.36 Those receiving fluoxetine (mean dosage 45 ±25 mg/d) displayed significantly greater reduction in pain, fatigue, and depression compared with those receiving the placebo. The effect of fluoxetine on pain remained significant after we adjusted for change in depression.
Sertraline was evaluated in an open study of 47 fibromyalgia patients at dosages of 25 to 200 mg/d for 6 weeks. Nearly two-thirds (63%) assessed the efficacy of sertraline as good or very good in the treatment of their symptoms.37 Paroxetine effectively reduced fibromyalgia symptoms in a single-blind study at dosages of 20 mg/d for 3 months.38
SNRIs Venlafaxine, a dual serotonin and norepinephrine reuptake inhibitor, has shown promise in the treatment of fibromyalgia in a preliminary open trial conducted by our group.39 Venlafaxine at a mean dosage of 167 mg/d resulted in significant improvement in fibromyalgia symptoms and quality of life compared with baseline. Notably, lifetime comorbid depressive and anxiety disorders were common in this sample, and their presence predicted response of fibromyalgia symptoms to venlafaxine.
Gabapentin Although no studies have been published on fibromyalgia treatment with this anticonvulsant, gabapentin has been found to exert substantial analgesic effects in controlled studies of other kinds of pain, including diabetic neuropathy, post-herpetic neuralgia, and migraines.40-42 There are also anecdotal reports of its successful use in fibromyalgia.2
Nonpharmacologic treatment
Cardiovascular fitness training, regional sympathetic block, electromyographic biofeedback, hypnotherapy, and electroacupuncture have been reported to have modest efficacy for fibromyalgia symptoms in short-term, randomized controlled trials.43-46 Other studies, however, have not replicated the efficacy of these treatments.
Cognitive-behavioral therapy has shown promise in preliminary studies.47,48 Cognitive restructuring techniques that challenge negative thoughts and promote an active, positive, problem-solving approach to pain were found to be important components of fibromyalgia therapy, as were relaxation training, aerobic exercise and stretching, pacing of activities, and family education.47
Recommendations
Based on our group’s experience and the limited data available, the following are recommendations for the pharmacologic treatment of fibromyalgia:
- Consider a trial of antidepressant medication for patients with a history of mood (unipolar) or anxiety disorders. First try an SSRI or an SNRI because many patients do not tolerate tricyclics. Use antidepressant therapeutic dosages and an adequate duration of treatment (at least 6 weeks).
- If symptoms do not respond to an adequate trial of first-line medications, treatment with tricyclics appears warranted. Although studies have focused mostly on tertiary amine tricyclics (e.g., amitriptyline), secondary amine agents (e.g., nortriptyline) may be just as effective and better tolerated, allowing for titration to higher dosages.
- Consider combination therapy when needed. For example, in patients who experience relief of pain, fatigue, and depressed mood with fluoxetine but continue to have insomnia, gabapentin can be added at night. Begin with 100 mg/d and increase by 100 mg/d until you see improvement or intolerance. Another option is trazodone, beginning with 50 mg hs. If you add a low-dose tricyclic to an SSRI, be aware of pharmacokinetic interaction and monitor tricyclic levels.
- Gabapentin alone, although it has not been studied in controlled trials of fibromyalgia, may be an option for patients who do not respond to antidepressants. Other pain conditions treated with gabapentin have required dosages of 1,600 to 2,400 mg/d to achieve substantial analgesic effects.
Cardiovascular fitness training is a potentially important component of fibromyalgia treatment. Many patients, however, have difficulty getting started because of increased pain after exercise and disabling fatigue. Treatment with medications as recommended may provide enough relief for patients to start an exercise program. Remind patients to start slowly, increasing the frequency and intensity of exercise as their endurance improves.
Because stress and a history of psychological trauma contribute to the onset and exacerbation of symptoms in some patients, cognitive-behavioral therapy is recommended as an adjunctive treatment as appropriate.
Related resources
- American Fibromyalgia Syndrome Association, Inc. www.afsafund.org
- Arnold LM, et al. Antidepressant treatment of fibromyalgia. A metaanalysis and review. Psychosomatics 2000;41:104-13.
- Kranzler JD, Gendreau JF, Rao SG. The psychopharmacology of fibromyalgia: a drug development perspective. Psychopharmacol Bull 2002;36:165-213.
Drug brand names
- Amitriptyline • Elavil
- Citalopram • Celexa
- Clomipramine • Anafranil
- Cyclobenzaprine • Flexeril
- Fluoxetine • Prozac
- Gabapentin • Neurontin
- Maprotiline • Ludiomil
- Nortriptyline • Pamelor
- Paroxetine • Paxil
- Sertraline • Zoloft
- Trazodone • Desyrel
- Venlafaxine • Effexor
Disclosure
The author reports that she receives research support from Eli Lilly & Co. and Pfizer Inc. and serves as a consultant and member of the speakers’ bureaus for both of those companies.
1. Wolfe F, Smythe HA, Yunus MB, et al. The American College of Rheumatology 1990 criteria for the classification of fibromyalgia. Arthritis Rheum 1990;33:160-72.
2. Wolfe F, Ross K, Anderson J, et al. The prevalence and characteristics of fibromyalgia in the general population. Arthritis Rheum 1995;38:19-28.
3. White KP, Speechley M, Harth M, et al. Comparing self-reported function and work disability in 100 community cases of fibromyalgia syndrome versus controls in London, Ontario. The London fibromyalgia epidemiology study. Arthritis Rheum 1999;42:76-83.
4. Wolfe F, Anderson J, Harkness D, et al. Health status and disease severity in fibromyalgia. Arthritis Rheum 1997;40:1571-9.
5. Kaplan RM, Schmidt SM, Cronan TA. Quality of well being in patients with fibromyalgia. J Rheumatol 2000;27:785-9.
6. Clauw DJ. Fibromyalgia syndrome: an update on current understanding and medical management. Rheumatol Grand Rds 2000;3:1-9.
7. Yunus MB, Masi AT, Aldag JC. A controlled study of primary fibromyalgia syndrome: Clinical features and association with other functional syndromes. J Rheumatol 1989;16:62-71.
8. Wolfe F, Cathey MA, Kleinheksel SM, et al. Psychological status in primary fibrositis and fibrositis associated with rheumatoid arthritis. J Rheumatol 1984;11:500-6.
9. White KP, Nielson WR, Harth M, et al. Chronic widespread musculoskeletal pain with or without fibromyalgia: Psychological distress in a representative community adult sample. J Rheumatol 2002;29:588-94.
10. Walker EA, Keegan D, Gardner G, et al. Psychosocial factors in fibromyalgia and rheumatoid arthritis: I. Psychiatric diagnoses and functional disability. Psychosomatic Med 1997;59:565-71.
11. MacFarlane GJ, Thomas E, Papageorgiou AC, et al. The natural history of chroninc pain in the community: A better prognosis than in the clinic? J Rheumatol 1996;23:1617-20.
12. Aaron LA, Bradley LA, Alarcón GS, et al. Psychiatric diagnoses in patients with fibromyalgia are related to health care-seeking behavior rather than to illness. Arthritis Rheum 1996;39:436-45.
13. Moldofsky H, Scarisbrick P, England R, et al. Musculoskeletal symptoms and non-REM sleep disturbance in patients with “fibrositis syndrome” and healthy subjects. Psychosom Med 1975;37:341-5.
14. Moldofsky H, Scarisbrick P. Induction of neurasthenic musculoskeletal pain syndrome by selective sleep stage deprivation. Psychosom Med 1975;38:35-44.
15. Schneider-Helmert D, Whitehouse I, Kumar A, et al. Insomnia and alpha sleep in chronic non-organic pain as compared to primary insomnia. Neuropsychobiology 2001;43:54-8.
16. Pillemer SR, Bradley LA, Crofford LJ, et al. The neuroscience and endocrinology of fibromyalgia. Arthritis Rheum 1997;40:1928-39.
17. Walker EA, Keegan D, Gardner G, et al. Psychosocial factors in fibromyalgia and rheumatoid arthritis: II. Sexual, physical, and emotional abuse and neglect. Psychosomatic Med 1997;59:572-7.
18. Demitrack MA, Crofford LJ. Hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis dysregulation in fibromyalgia and chronic fatigue syndrome: An overview and hypothesis. J Musculoskeletal Pain 1995;3:67-73.
19. Heim C, Ehlert U, Hellhammer DH. The potential role of hypocortisolism in the pathophysiology of stress-related bodily disorders. Psychoneuroendocrinology 2000;25:1-35.
20. Bennett RM. Emerging concepts in the neurobiology of chronic pain: Evidence of abnormal sensory processing in fibromyalgia. Mayo Clin Proc 1999;74:385-98.
21. Weigent DA, Bradley LA, Blalock JE, et al. Current concepts in the pathophysiology of abnormal pain perception in fibromyalgia. Am J Med Sci 1998;315:405-12.
22. Baranauskas G, Nistri A. Sensitization of pain pathways in the spinal cord: cellular mechanisms. Prog Neurobiol 1998;7:309-38.
23. Watkins LR, Wiertelak EP, Furness LE, et al. Illness-induced hyperalgesia is mediated by spinal neuropeptides and excitatory amino acids. Brain Res 1994;664:17-24.
24. Russell IJ, Orr MD, Littman B, et al. Elevated cerebrospinal fluid levels of substance P in patients with fibromyalgia syndrome. Arthritis Rheum 1994;37:1593-1601.
25. Schwarz MJ, Spath M, Muller-Bardorff H, et al. Relationship of substance P, 5-hydroxyindole acetic acid and tryptophan in serum of fibromyalgia patients. Neurosci Lett 1999;259:196-8.
26. Russell IJ, Vaeroy H, Javors M, Nyberg F. Cerebrospinal fluid biogenic amine metabolites in fibromyalgia/fibrositis syndrome and rheumatoid arthritis. Arthrits Rheum 1993;35(5):550-6.
27. Fishbain D. Evidence-based data on pain relief with antidepressants. Ann Med 2000;32:305-16.
28. Hudson JI, Goldenberg DL, Pope HG, et al. Comorbidity of fibromyalgia with medical and psychiatric disorders. Am J Med 1992;92:363-7.
29. Basbaum AI, Fields HL. Endogenous pain control systems: Brainstem pathways and endorphin circuitry. Ann Rev Neurosci 1984;7:309-38.
30. Arnold LM, Keck PE, Jr, Welge JA. Antidepressant treatment of fibromyalgia. A meta-analysis and review. Psychosomatics 2000;41:104-13.
31. O’Malley PG, Balden E, Tomkins G, et al. Treatment of fibromyalgia with antidepressants. A meta-analysis. J Gen Intern Med 2000;15:659-66.
32. Nørregaard J, Volkmann H, Danneskiold-Samsø B. A randomized controlled trial of citalopram in the treatment of fibromyalgia. Pain 1995;61:445-9.
33. Anderberg UM, Marteinsdottir I, von Knokrring L. Citalopram in patients with fibromyalgia-A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study. Eur J Pain 2000;4:27-35.
34. Wolfe F, Cathey MA, Hawley DJ. A double-blind placebo controlled trial of fluoxetine in fibromyalgia. Scand J Rheumatol 1994;23(5):255-9.
35. Goldenberg DL, Mayskiy M, Mossey C, et al. A randomized, double-blind crossover trial of fluoxetine and amitriptyline in the treatment of fibromyalgia. Arthritis Rheum 1996;39:1852-9.
36. Arnold LM, Hess EV, Hudson JI, et al. A randomized, placebo-controlled, double-blind, flexible-dose study of fluoxetine in the treatment of women with fibromyalgia. Am J Med 2002;112:191-7.
37. Syuertsen JO, Smedsrud T, Lane RM. An open study of sertraline in fibromyalgia syndrome. Eur Neuropsychopharmacol 1995;5:315.-
38. Giordano N, Geraci S, et al. Efficacy and tolerability of paroxetine in patients with fibromyalgia syndrome: A single blind study. Curr Ther Res 1999;60:696-702.
39. Dwight MM, Arnold LM, O’Brien H, et al. An open clinical trial of venlafaxine treatment of fibromyalgia. Psychosomatics 1998;39:14-17.
40. Backonja M, Beydoun A, Edwards KR, et al. Gabapentin for the symptomatic treatment of painful neuropathy in patients with diabetes mellitus: A randomized controlled trial. JAMA 1998;280:1831-6.
41. Rice AS, Maton S. Gabapentin in postherpetic neuralgia: A randomized, doubleblind, placebo controlled study. Pain 2001;94:215-24.
42. Mathew NT, Rapoport A, Saper J, et al. Efficacy of gabapentin in migraine prophylaxis. Headache 2001;41:119-28.
43. Ferraccioli G, Ghirelli L, Scita F, et al. EMG-biofeedback training in fibromyalgia syndrome. J Rheumatol 1987;14:820-5.
44. McCain GA, Bell DA, Mai FM, et al. A controlled study of the effects of a supervised cardiovascular fitness training program on the manifestations of primary fibromyalgia. Arthritis Rheum 1988;31:1135-41.
45. Haanen HCM, Hoenderdos HTW, van Romande LKJ, et al. Controlled trial of hypnotherapy in the treatment of refractory fibromyalgia. J Rheumatol 1991;18:72-5.
46. Deluze C, Bosia L, Irbs A, et al. Electroacupuncture in fibromyalgia: Results of a controlled trial. BMJ 1992;1249-52.
47. Nielson WR, Walker C, McCain GA. Cognitive behavioral treatment of fibromyalgia syndrome preliminary findings. J Rheumatol 1992;19:98-103.
Patients with fibromyalgia often resist being referred to a psychiatrist because they fear being told their pain and other somatic symptoms are “all in their heads.” Evidence is mounting that they may be literally correct—the symptoms of fibromyalgia appear to have a physiologic connection with the central nervous system. Abnormal CNS activity, including sleep patterns, response to stress, pain processing, and neurotransmitter levels, has been documented in patients with fibromyalgia.
As psychiatrists, we can reassure these patients—and their primary care physicians and rheumatologists—that we are in a position to help because we:
- have expertise in assessing mood and anxiety disorders and in managing antidepressants, the medication physicians most commonly prescribe for fibromyalgia;
- are skilled in the use of the anticonvulsant gabapentin, which is being used in fibromyalgia for its analgesic and sedative effects;
- can offer much-needed support through psychotherapy, as chronic pain and other fibromyalgia-related symptoms create great stress in these patients’ lives.
Antidepressants are showing promise as an effective treatment for pain, fatigue, and depression in patients with fibromyalgia in studies by our group and others. The following information can help you stay current with the newest understandings of this ailment.
Table 1
CRITERIA FOR DIAGNOSING FIBROMYALGIA
| 1. | History of widespread pain |
| Definition Pain in the right and left side of the body, pain above and below the waist, axial skeletal pain (cervical spine or anterior chest or thoracic spine or low back). In this definition, shoulder and buttock pain is considered as pain for each involved side. “Low back” pain is considered lower segment pain. | |
| 2. | Pain in 11 of 18 tender point sites on digital palpation |
| Definition Pain, on digital palpation, must be present in at least 11 of the following 18 tender points: | |
| Occiput Bilateral, at the suboccipital muscle insertion | |
| Low cervical Bilateral, at the anterior aspects of the intertransverse spaces at C5-C7 | |
| Trapezius Bilateral, at the midpoint of the upper border | |
| Supraspinatus Bilateral, at origins, above the scapula spine near the medial border | |
| Second rib Bilateral, at the second costochondral junctions, just lateral to the junctions on upper surfaces | |
| Lateral epicondyle Bilateral, 2 cm distal to the epicondyles | |
| Gluteal Bilateral, in upper outer quadrants of buttocks in anterior fold of muscle | |
| Greater trochanter Bilateral, posterior to the trochanteric prominence | |
| Knee Bilateral, at the medial fat pad proximal to the joint line | |
| Digital palpation should be performed with an approximate force of 4 kg. For a tender point to be considered “positive” the patient must state that the palpation was painful. “Tender” is not to be considered “painful” Source: American College of Rheumatology1 | |
Figure 1 LOCATION OF FIBROMYALGIA TENDER POINTS
To palpate tender point sites, pressure is applied with the thumb pad perpendicularly to each site and the force increased by 1 kg per second until 4 kg of pressure is achieved. Whitening of the thumbnail bed usually occurs when applying the 4-kg force.
Mood disorders in fibromyalgia
A diagnosis of fibromyalgia requires the finding of widespread pain and tenderness at specific anatomic points (Table 1, Figure 1).1 Most patients also report fatigue, sleep disturbance, and morning stiffness (Box 1).2-5 American College of Rheumatology criteria do not require exclusionary tests such as radiographs and blood tests for the diagnosis.
Primary care physicians are increasingly making the diagnosis themselves and referring patients to rheumatologists only when conditions other than fibromyalgia are suspected. The differential diagnosis is broad, and other rheumatic and nonrheumatic disorders have similar symptoms, require different treatment, and affect fibromyalgia management (Table 2).6
Patients with fibromyalgia often report symptoms of major depressive disorder, such as depressed mood, anxiety, fatigue, and insomnia.7 Many psychological studies of such patients have documented increased rates of depressive symptoms.8 Depression and anxiety symptoms are common and frequently severe, even among individuals with fibromyalgia in the general population.9
Patients’ mood and anxiety disorders correlate highly with the number of medically unexplained symptoms and are associated with functional disability.10 The presence of psychological symptoms predicts persistent fibromyalgia symptoms,11 and psychological distress is strongly associated with symptom severity.12
Evidence for a CNS link
CNS mechanisms appear to contribute to the development of clinical findings in fibromyalgia.
Abnormal sleep A qualitative defect in sleep has been identified in patients with fibromyalgia.13 This sleep abnormality consists of inappropriate intrusion of alpha waves (normally seen during wakefulness or REM sleep) into deep sleep (usually characterized by delta waves).13 Some researchers believe alpha-delta sleep intrusion is associated with the chronic musculoskeletal pain and fatigue of fibromyalgia and, in turn, is mediated by an abnormality in central serotonergic neurotransmission.14 This sleep abnormality is not specific to fibromyalgia and can be found in other conditions, however.15 Debate continues regarding the role of sleep dysregulation in the pathophysiology of fibromyalgia.
Fibromyalgia is more common in women than men, with an estimated prevalence of 2% in the general population (3.4% in women and 0.5% in men). Its prevalence increases with age, rising sharply in middle age and then dropping off after age 80.2
Fibromyalgia is seen most often in women ages 50 and older.2 It occurs in 5% to 6% of patients presenting to general medical and family practice clinics and in 15% to 20% of patients presenting to rheumatologists, making it one of the most common diagnoses in office-based rheumatology practices.
American College of Rheumatology criteria may require only widespread pain and tenderness for a diagnosis of fibromyalgia, but most patients (73% to 85%) also report fatigue, sleep disturbance, and morning stiffness. Many (45% to 69%) report “pain all over,” paresthesias, headache, and anxiety. Co-occurring irritable bowel syndrome, sicca symptoms, and Raynaud’s phenomenon are less common (<35%).1 Patients with fibromyalgia also have high lifetime rates of other comorbid disorders, including migraine, chronic fatigue syndrome, and mood and anxiety disorders. Some patients report weakness, forgetfulness, difficulties in concentration, urinary frequency, history of dysmenorrhea, and restless legs.
Fibromyalgia is chronic, debilitating, and often leads to substantial functional impairment.3 Most patients with fibromyalgia do not display significant improvement over an average of 7 years of treatment.4 Patients with fibromyalgia report lower quality of well-being than patients with diagnoses of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, rheumatoid arthritis, atrial fibrillation, advanced cancer, and several other chronic diseases.5
Stress response Stress appears to precipitate or exacerbate fibromyalgia symptoms in many patients.16 For example, fibromyalgia appears to be associated with victimization (adult and childhood sexual, physical, and emotional trauma), and this stress may trigger the development of fibromyalgia in some patients.17
Patients with fibromyalgia appear to develop disturbances in the two major stress-response systems: the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal (HPA) axis and the sympathetic nervous system.16 Although the interpretation of these disturbances is still debated, some researchers suggest that the available data point to reduction in CNS corticotropin releasing hormone (CRH), the key mediator in the HPA axis.18,19 CRH is also a behaviorally active peptide that leads to physiologic and behavioral arousal when administered centrally to animals.18 CRH reduction could contribute to the clinical features of fibromyalgia (e.g., fatigue) either directly or indirectly by causing a relative glucocorticoid deficiency.18,19
Table 2
DIFFERENTIAL DIAGNOSIS OF FIBROMYALGIA
| Rheumatic disorders | Nonrheumatic disorders |
|---|---|
| Rheumatoid arthritis | Hypothyroidism |
| Systemic lupus erythematosus | Sleep apnea |
| Polyarticular osteoarthritis | Hepatitis |
| Polymyalgia rheumatica | Cushing’s syndrome |
| Addison’s disease | |
| Hyperparathyroidism | |
| Adapted from Clauw DJ. Fibromyalgia syndrome: an update on current understanding and medical management. Rheumatol Grand Rds 2000;3:1-9. | |
Fibromyalgia is also associated with moderate basal hypocortisolism.18,19 A relative glucocorticoid deficiency could contribute to fibromyalgia’s characteristic fatigue, arthralgias, myalgias, and disturbances in mood and sleep.18 This deficiency may also cause some of the immunologic disturbances seen with fibromyalgia.18,19
Atypical depression, which shares such features of fibromyalgia as profound lethargy, is also associated with inappropriately normal or reduced activation of the HPA axis and a functional deficit in the release of hypothalamic CRH.18 The unifying feature of HPA axis activity in both atypical depression and fibromyalgia may be a shared hypofunctioning.18 A more complete understanding of the neuroendocrine changes in fibromyalgia awaits further study.
Pain processing Aberrant CNS processing of pain may also play a role in fibromyalgia.16,20 Fibromyalgia is sometimes precipitated by physical trauma.21 A traumatic injury may start a process in susceptible individuals that leads to an enhanced central processing of painful stimuli characteristic of central sensitization.22 Patients with fibromyalgia often develop an increased response to painful stimuli (hyeralgesia) and experience pain from normally nonnoxious stimuli (allodynia).20
Substance P, an important nociceptive neurotransmitter, may have a role in generating central sensitization.23 Elevated concentrations of substance P have been found in the cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) of individuals with fibromyalgia.24 Substance P also inhibits CRH release and may contribute to low CRH activity in fibromyalgia.16
Neurotransmitter defects A functional reduction in serotonergic activity has been demonstrated in patients with fibromyalgia. Schwarz et al25 found a strong negative correlation between serum concentrations of the primary serotonin metabolite, 5-hydroxyindoleacetic acid (5-HIAA), and substance P, pain, and insomnia. Evidence also exists of reduced concentrations of the primary norepinephrine metabolite, 3-methoxy-4-hydroxyphenethylene (MHPG), in the CSF of patients with fibromyalgia.26 Reduced serotonin and norepinephrine levels in descending pain-inhibitory pathways may cause the allodynia and hyperalgesia of fibromyalgia.
Pharmacologic treatment
Most studies of pharmacologic treatment of fibromyalgia have examined antidepressants for three reasons:
- There is evidence of the successful use of antidepressants in other chronic pain conditions.27
- These agents are effective for treating mood and anxiety disorders, which frequently occur in patients with fibromyalgia and may share a common physiologic abnormality.28
- Antidepressants might enhance the activity of neurotransmitters such as serotonin and norepinephrine in the descending inhibitory pain pathways, leading to reduced pain perception.29
Tricyclics In randomized, controlled trials, tricyclic medications (including the muscle relaxant cyclobenzaprine) appear to be moderately effective in improving fibromyalgia symptoms. Two meta-analyses of trials of tricyclic medications (amitriptyline, dothiepin, cyclobenzaprine, clomipramine, and maprotiline) have found similar results.30,31 Our group found the greatest effect on measures of sleep improvement, which may be due in part to tricyclics’ sedative properties.30 Many patients with fibromyalgia, however, cannot tolerate the sedative and other side effects associated with tricyclic agents, even though low dosages (e.g., 25 mg/d of amitriptyline) have typically been used in clinical trials.
SSRIs. Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors, although likely to be better tolerated than tricyclics, have been examined in only five placebo-controlled trials in fibromyalgia: two with citalopram, and three with fluoxetine. One citalopram study found no significant differences in efficacy between citalopram and a placebo,32 but the other reported significant improvement in one measure of pain and a significant decrease in depressive symptoms compared with the placebo group.33 No significant differences were found between groups in the global assessment of improvement.
The initial fluoxetine trial in fibromyalgia treatment did not reveal a significant therapeutic effect over a placebo,34 although the study was limited by a high (57%) placebo dropout rate, small sample size (42 subjects), brief duration (3 to 6 weeks after treatment), and restriction of fluoxetine dosage to 20 mg/d. In the two other controlled trials, including one which we recently conducted, fluoxetine was superior to a placebo in reducing pain and other fibromyalgia-associated symptoms.35,36
In our 12-week investigation (a randomized, placebocontrolled, parallel-group, flexible-dose trial), 60 subjects with fibromyalgia received fluoxetine 20 to 80 mg/d or a placebo.36 Those receiving fluoxetine (mean dosage 45 ±25 mg/d) displayed significantly greater reduction in pain, fatigue, and depression compared with those receiving the placebo. The effect of fluoxetine on pain remained significant after we adjusted for change in depression.
Sertraline was evaluated in an open study of 47 fibromyalgia patients at dosages of 25 to 200 mg/d for 6 weeks. Nearly two-thirds (63%) assessed the efficacy of sertraline as good or very good in the treatment of their symptoms.37 Paroxetine effectively reduced fibromyalgia symptoms in a single-blind study at dosages of 20 mg/d for 3 months.38
SNRIs Venlafaxine, a dual serotonin and norepinephrine reuptake inhibitor, has shown promise in the treatment of fibromyalgia in a preliminary open trial conducted by our group.39 Venlafaxine at a mean dosage of 167 mg/d resulted in significant improvement in fibromyalgia symptoms and quality of life compared with baseline. Notably, lifetime comorbid depressive and anxiety disorders were common in this sample, and their presence predicted response of fibromyalgia symptoms to venlafaxine.
Gabapentin Although no studies have been published on fibromyalgia treatment with this anticonvulsant, gabapentin has been found to exert substantial analgesic effects in controlled studies of other kinds of pain, including diabetic neuropathy, post-herpetic neuralgia, and migraines.40-42 There are also anecdotal reports of its successful use in fibromyalgia.2
Nonpharmacologic treatment
Cardiovascular fitness training, regional sympathetic block, electromyographic biofeedback, hypnotherapy, and electroacupuncture have been reported to have modest efficacy for fibromyalgia symptoms in short-term, randomized controlled trials.43-46 Other studies, however, have not replicated the efficacy of these treatments.
Cognitive-behavioral therapy has shown promise in preliminary studies.47,48 Cognitive restructuring techniques that challenge negative thoughts and promote an active, positive, problem-solving approach to pain were found to be important components of fibromyalgia therapy, as were relaxation training, aerobic exercise and stretching, pacing of activities, and family education.47
Recommendations
Based on our group’s experience and the limited data available, the following are recommendations for the pharmacologic treatment of fibromyalgia:
- Consider a trial of antidepressant medication for patients with a history of mood (unipolar) or anxiety disorders. First try an SSRI or an SNRI because many patients do not tolerate tricyclics. Use antidepressant therapeutic dosages and an adequate duration of treatment (at least 6 weeks).
- If symptoms do not respond to an adequate trial of first-line medications, treatment with tricyclics appears warranted. Although studies have focused mostly on tertiary amine tricyclics (e.g., amitriptyline), secondary amine agents (e.g., nortriptyline) may be just as effective and better tolerated, allowing for titration to higher dosages.
- Consider combination therapy when needed. For example, in patients who experience relief of pain, fatigue, and depressed mood with fluoxetine but continue to have insomnia, gabapentin can be added at night. Begin with 100 mg/d and increase by 100 mg/d until you see improvement or intolerance. Another option is trazodone, beginning with 50 mg hs. If you add a low-dose tricyclic to an SSRI, be aware of pharmacokinetic interaction and monitor tricyclic levels.
- Gabapentin alone, although it has not been studied in controlled trials of fibromyalgia, may be an option for patients who do not respond to antidepressants. Other pain conditions treated with gabapentin have required dosages of 1,600 to 2,400 mg/d to achieve substantial analgesic effects.
Cardiovascular fitness training is a potentially important component of fibromyalgia treatment. Many patients, however, have difficulty getting started because of increased pain after exercise and disabling fatigue. Treatment with medications as recommended may provide enough relief for patients to start an exercise program. Remind patients to start slowly, increasing the frequency and intensity of exercise as their endurance improves.
Because stress and a history of psychological trauma contribute to the onset and exacerbation of symptoms in some patients, cognitive-behavioral therapy is recommended as an adjunctive treatment as appropriate.
Related resources
- American Fibromyalgia Syndrome Association, Inc. www.afsafund.org
- Arnold LM, et al. Antidepressant treatment of fibromyalgia. A metaanalysis and review. Psychosomatics 2000;41:104-13.
- Kranzler JD, Gendreau JF, Rao SG. The psychopharmacology of fibromyalgia: a drug development perspective. Psychopharmacol Bull 2002;36:165-213.
Drug brand names
- Amitriptyline • Elavil
- Citalopram • Celexa
- Clomipramine • Anafranil
- Cyclobenzaprine • Flexeril
- Fluoxetine • Prozac
- Gabapentin • Neurontin
- Maprotiline • Ludiomil
- Nortriptyline • Pamelor
- Paroxetine • Paxil
- Sertraline • Zoloft
- Trazodone • Desyrel
- Venlafaxine • Effexor
Disclosure
The author reports that she receives research support from Eli Lilly & Co. and Pfizer Inc. and serves as a consultant and member of the speakers’ bureaus for both of those companies.
Patients with fibromyalgia often resist being referred to a psychiatrist because they fear being told their pain and other somatic symptoms are “all in their heads.” Evidence is mounting that they may be literally correct—the symptoms of fibromyalgia appear to have a physiologic connection with the central nervous system. Abnormal CNS activity, including sleep patterns, response to stress, pain processing, and neurotransmitter levels, has been documented in patients with fibromyalgia.
As psychiatrists, we can reassure these patients—and their primary care physicians and rheumatologists—that we are in a position to help because we:
- have expertise in assessing mood and anxiety disorders and in managing antidepressants, the medication physicians most commonly prescribe for fibromyalgia;
- are skilled in the use of the anticonvulsant gabapentin, which is being used in fibromyalgia for its analgesic and sedative effects;
- can offer much-needed support through psychotherapy, as chronic pain and other fibromyalgia-related symptoms create great stress in these patients’ lives.
Antidepressants are showing promise as an effective treatment for pain, fatigue, and depression in patients with fibromyalgia in studies by our group and others. The following information can help you stay current with the newest understandings of this ailment.
Table 1
CRITERIA FOR DIAGNOSING FIBROMYALGIA
| 1. | History of widespread pain |
| Definition Pain in the right and left side of the body, pain above and below the waist, axial skeletal pain (cervical spine or anterior chest or thoracic spine or low back). In this definition, shoulder and buttock pain is considered as pain for each involved side. “Low back” pain is considered lower segment pain. | |
| 2. | Pain in 11 of 18 tender point sites on digital palpation |
| Definition Pain, on digital palpation, must be present in at least 11 of the following 18 tender points: | |
| Occiput Bilateral, at the suboccipital muscle insertion | |
| Low cervical Bilateral, at the anterior aspects of the intertransverse spaces at C5-C7 | |
| Trapezius Bilateral, at the midpoint of the upper border | |
| Supraspinatus Bilateral, at origins, above the scapula spine near the medial border | |
| Second rib Bilateral, at the second costochondral junctions, just lateral to the junctions on upper surfaces | |
| Lateral epicondyle Bilateral, 2 cm distal to the epicondyles | |
| Gluteal Bilateral, in upper outer quadrants of buttocks in anterior fold of muscle | |
| Greater trochanter Bilateral, posterior to the trochanteric prominence | |
| Knee Bilateral, at the medial fat pad proximal to the joint line | |
| Digital palpation should be performed with an approximate force of 4 kg. For a tender point to be considered “positive” the patient must state that the palpation was painful. “Tender” is not to be considered “painful” Source: American College of Rheumatology1 | |
Figure 1 LOCATION OF FIBROMYALGIA TENDER POINTS
To palpate tender point sites, pressure is applied with the thumb pad perpendicularly to each site and the force increased by 1 kg per second until 4 kg of pressure is achieved. Whitening of the thumbnail bed usually occurs when applying the 4-kg force.
Mood disorders in fibromyalgia
A diagnosis of fibromyalgia requires the finding of widespread pain and tenderness at specific anatomic points (Table 1, Figure 1).1 Most patients also report fatigue, sleep disturbance, and morning stiffness (Box 1).2-5 American College of Rheumatology criteria do not require exclusionary tests such as radiographs and blood tests for the diagnosis.
Primary care physicians are increasingly making the diagnosis themselves and referring patients to rheumatologists only when conditions other than fibromyalgia are suspected. The differential diagnosis is broad, and other rheumatic and nonrheumatic disorders have similar symptoms, require different treatment, and affect fibromyalgia management (Table 2).6
Patients with fibromyalgia often report symptoms of major depressive disorder, such as depressed mood, anxiety, fatigue, and insomnia.7 Many psychological studies of such patients have documented increased rates of depressive symptoms.8 Depression and anxiety symptoms are common and frequently severe, even among individuals with fibromyalgia in the general population.9
Patients’ mood and anxiety disorders correlate highly with the number of medically unexplained symptoms and are associated with functional disability.10 The presence of psychological symptoms predicts persistent fibromyalgia symptoms,11 and psychological distress is strongly associated with symptom severity.12
Evidence for a CNS link
CNS mechanisms appear to contribute to the development of clinical findings in fibromyalgia.
Abnormal sleep A qualitative defect in sleep has been identified in patients with fibromyalgia.13 This sleep abnormality consists of inappropriate intrusion of alpha waves (normally seen during wakefulness or REM sleep) into deep sleep (usually characterized by delta waves).13 Some researchers believe alpha-delta sleep intrusion is associated with the chronic musculoskeletal pain and fatigue of fibromyalgia and, in turn, is mediated by an abnormality in central serotonergic neurotransmission.14 This sleep abnormality is not specific to fibromyalgia and can be found in other conditions, however.15 Debate continues regarding the role of sleep dysregulation in the pathophysiology of fibromyalgia.
Fibromyalgia is more common in women than men, with an estimated prevalence of 2% in the general population (3.4% in women and 0.5% in men). Its prevalence increases with age, rising sharply in middle age and then dropping off after age 80.2
Fibromyalgia is seen most often in women ages 50 and older.2 It occurs in 5% to 6% of patients presenting to general medical and family practice clinics and in 15% to 20% of patients presenting to rheumatologists, making it one of the most common diagnoses in office-based rheumatology practices.
American College of Rheumatology criteria may require only widespread pain and tenderness for a diagnosis of fibromyalgia, but most patients (73% to 85%) also report fatigue, sleep disturbance, and morning stiffness. Many (45% to 69%) report “pain all over,” paresthesias, headache, and anxiety. Co-occurring irritable bowel syndrome, sicca symptoms, and Raynaud’s phenomenon are less common (<35%).1 Patients with fibromyalgia also have high lifetime rates of other comorbid disorders, including migraine, chronic fatigue syndrome, and mood and anxiety disorders. Some patients report weakness, forgetfulness, difficulties in concentration, urinary frequency, history of dysmenorrhea, and restless legs.
Fibromyalgia is chronic, debilitating, and often leads to substantial functional impairment.3 Most patients with fibromyalgia do not display significant improvement over an average of 7 years of treatment.4 Patients with fibromyalgia report lower quality of well-being than patients with diagnoses of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, rheumatoid arthritis, atrial fibrillation, advanced cancer, and several other chronic diseases.5
Stress response Stress appears to precipitate or exacerbate fibromyalgia symptoms in many patients.16 For example, fibromyalgia appears to be associated with victimization (adult and childhood sexual, physical, and emotional trauma), and this stress may trigger the development of fibromyalgia in some patients.17
Patients with fibromyalgia appear to develop disturbances in the two major stress-response systems: the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal (HPA) axis and the sympathetic nervous system.16 Although the interpretation of these disturbances is still debated, some researchers suggest that the available data point to reduction in CNS corticotropin releasing hormone (CRH), the key mediator in the HPA axis.18,19 CRH is also a behaviorally active peptide that leads to physiologic and behavioral arousal when administered centrally to animals.18 CRH reduction could contribute to the clinical features of fibromyalgia (e.g., fatigue) either directly or indirectly by causing a relative glucocorticoid deficiency.18,19
Table 2
DIFFERENTIAL DIAGNOSIS OF FIBROMYALGIA
| Rheumatic disorders | Nonrheumatic disorders |
|---|---|
| Rheumatoid arthritis | Hypothyroidism |
| Systemic lupus erythematosus | Sleep apnea |
| Polyarticular osteoarthritis | Hepatitis |
| Polymyalgia rheumatica | Cushing’s syndrome |
| Addison’s disease | |
| Hyperparathyroidism | |
| Adapted from Clauw DJ. Fibromyalgia syndrome: an update on current understanding and medical management. Rheumatol Grand Rds 2000;3:1-9. | |
Fibromyalgia is also associated with moderate basal hypocortisolism.18,19 A relative glucocorticoid deficiency could contribute to fibromyalgia’s characteristic fatigue, arthralgias, myalgias, and disturbances in mood and sleep.18 This deficiency may also cause some of the immunologic disturbances seen with fibromyalgia.18,19
Atypical depression, which shares such features of fibromyalgia as profound lethargy, is also associated with inappropriately normal or reduced activation of the HPA axis and a functional deficit in the release of hypothalamic CRH.18 The unifying feature of HPA axis activity in both atypical depression and fibromyalgia may be a shared hypofunctioning.18 A more complete understanding of the neuroendocrine changes in fibromyalgia awaits further study.
Pain processing Aberrant CNS processing of pain may also play a role in fibromyalgia.16,20 Fibromyalgia is sometimes precipitated by physical trauma.21 A traumatic injury may start a process in susceptible individuals that leads to an enhanced central processing of painful stimuli characteristic of central sensitization.22 Patients with fibromyalgia often develop an increased response to painful stimuli (hyeralgesia) and experience pain from normally nonnoxious stimuli (allodynia).20
Substance P, an important nociceptive neurotransmitter, may have a role in generating central sensitization.23 Elevated concentrations of substance P have been found in the cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) of individuals with fibromyalgia.24 Substance P also inhibits CRH release and may contribute to low CRH activity in fibromyalgia.16
Neurotransmitter defects A functional reduction in serotonergic activity has been demonstrated in patients with fibromyalgia. Schwarz et al25 found a strong negative correlation between serum concentrations of the primary serotonin metabolite, 5-hydroxyindoleacetic acid (5-HIAA), and substance P, pain, and insomnia. Evidence also exists of reduced concentrations of the primary norepinephrine metabolite, 3-methoxy-4-hydroxyphenethylene (MHPG), in the CSF of patients with fibromyalgia.26 Reduced serotonin and norepinephrine levels in descending pain-inhibitory pathways may cause the allodynia and hyperalgesia of fibromyalgia.
Pharmacologic treatment
Most studies of pharmacologic treatment of fibromyalgia have examined antidepressants for three reasons:
- There is evidence of the successful use of antidepressants in other chronic pain conditions.27
- These agents are effective for treating mood and anxiety disorders, which frequently occur in patients with fibromyalgia and may share a common physiologic abnormality.28
- Antidepressants might enhance the activity of neurotransmitters such as serotonin and norepinephrine in the descending inhibitory pain pathways, leading to reduced pain perception.29
Tricyclics In randomized, controlled trials, tricyclic medications (including the muscle relaxant cyclobenzaprine) appear to be moderately effective in improving fibromyalgia symptoms. Two meta-analyses of trials of tricyclic medications (amitriptyline, dothiepin, cyclobenzaprine, clomipramine, and maprotiline) have found similar results.30,31 Our group found the greatest effect on measures of sleep improvement, which may be due in part to tricyclics’ sedative properties.30 Many patients with fibromyalgia, however, cannot tolerate the sedative and other side effects associated with tricyclic agents, even though low dosages (e.g., 25 mg/d of amitriptyline) have typically been used in clinical trials.
SSRIs. Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors, although likely to be better tolerated than tricyclics, have been examined in only five placebo-controlled trials in fibromyalgia: two with citalopram, and three with fluoxetine. One citalopram study found no significant differences in efficacy between citalopram and a placebo,32 but the other reported significant improvement in one measure of pain and a significant decrease in depressive symptoms compared with the placebo group.33 No significant differences were found between groups in the global assessment of improvement.
The initial fluoxetine trial in fibromyalgia treatment did not reveal a significant therapeutic effect over a placebo,34 although the study was limited by a high (57%) placebo dropout rate, small sample size (42 subjects), brief duration (3 to 6 weeks after treatment), and restriction of fluoxetine dosage to 20 mg/d. In the two other controlled trials, including one which we recently conducted, fluoxetine was superior to a placebo in reducing pain and other fibromyalgia-associated symptoms.35,36
In our 12-week investigation (a randomized, placebocontrolled, parallel-group, flexible-dose trial), 60 subjects with fibromyalgia received fluoxetine 20 to 80 mg/d or a placebo.36 Those receiving fluoxetine (mean dosage 45 ±25 mg/d) displayed significantly greater reduction in pain, fatigue, and depression compared with those receiving the placebo. The effect of fluoxetine on pain remained significant after we adjusted for change in depression.
Sertraline was evaluated in an open study of 47 fibromyalgia patients at dosages of 25 to 200 mg/d for 6 weeks. Nearly two-thirds (63%) assessed the efficacy of sertraline as good or very good in the treatment of their symptoms.37 Paroxetine effectively reduced fibromyalgia symptoms in a single-blind study at dosages of 20 mg/d for 3 months.38
SNRIs Venlafaxine, a dual serotonin and norepinephrine reuptake inhibitor, has shown promise in the treatment of fibromyalgia in a preliminary open trial conducted by our group.39 Venlafaxine at a mean dosage of 167 mg/d resulted in significant improvement in fibromyalgia symptoms and quality of life compared with baseline. Notably, lifetime comorbid depressive and anxiety disorders were common in this sample, and their presence predicted response of fibromyalgia symptoms to venlafaxine.
Gabapentin Although no studies have been published on fibromyalgia treatment with this anticonvulsant, gabapentin has been found to exert substantial analgesic effects in controlled studies of other kinds of pain, including diabetic neuropathy, post-herpetic neuralgia, and migraines.40-42 There are also anecdotal reports of its successful use in fibromyalgia.2
Nonpharmacologic treatment
Cardiovascular fitness training, regional sympathetic block, electromyographic biofeedback, hypnotherapy, and electroacupuncture have been reported to have modest efficacy for fibromyalgia symptoms in short-term, randomized controlled trials.43-46 Other studies, however, have not replicated the efficacy of these treatments.
Cognitive-behavioral therapy has shown promise in preliminary studies.47,48 Cognitive restructuring techniques that challenge negative thoughts and promote an active, positive, problem-solving approach to pain were found to be important components of fibromyalgia therapy, as were relaxation training, aerobic exercise and stretching, pacing of activities, and family education.47
Recommendations
Based on our group’s experience and the limited data available, the following are recommendations for the pharmacologic treatment of fibromyalgia:
- Consider a trial of antidepressant medication for patients with a history of mood (unipolar) or anxiety disorders. First try an SSRI or an SNRI because many patients do not tolerate tricyclics. Use antidepressant therapeutic dosages and an adequate duration of treatment (at least 6 weeks).
- If symptoms do not respond to an adequate trial of first-line medications, treatment with tricyclics appears warranted. Although studies have focused mostly on tertiary amine tricyclics (e.g., amitriptyline), secondary amine agents (e.g., nortriptyline) may be just as effective and better tolerated, allowing for titration to higher dosages.
- Consider combination therapy when needed. For example, in patients who experience relief of pain, fatigue, and depressed mood with fluoxetine but continue to have insomnia, gabapentin can be added at night. Begin with 100 mg/d and increase by 100 mg/d until you see improvement or intolerance. Another option is trazodone, beginning with 50 mg hs. If you add a low-dose tricyclic to an SSRI, be aware of pharmacokinetic interaction and monitor tricyclic levels.
- Gabapentin alone, although it has not been studied in controlled trials of fibromyalgia, may be an option for patients who do not respond to antidepressants. Other pain conditions treated with gabapentin have required dosages of 1,600 to 2,400 mg/d to achieve substantial analgesic effects.
Cardiovascular fitness training is a potentially important component of fibromyalgia treatment. Many patients, however, have difficulty getting started because of increased pain after exercise and disabling fatigue. Treatment with medications as recommended may provide enough relief for patients to start an exercise program. Remind patients to start slowly, increasing the frequency and intensity of exercise as their endurance improves.
Because stress and a history of psychological trauma contribute to the onset and exacerbation of symptoms in some patients, cognitive-behavioral therapy is recommended as an adjunctive treatment as appropriate.
Related resources
- American Fibromyalgia Syndrome Association, Inc. www.afsafund.org
- Arnold LM, et al. Antidepressant treatment of fibromyalgia. A metaanalysis and review. Psychosomatics 2000;41:104-13.
- Kranzler JD, Gendreau JF, Rao SG. The psychopharmacology of fibromyalgia: a drug development perspective. Psychopharmacol Bull 2002;36:165-213.
Drug brand names
- Amitriptyline • Elavil
- Citalopram • Celexa
- Clomipramine • Anafranil
- Cyclobenzaprine • Flexeril
- Fluoxetine • Prozac
- Gabapentin • Neurontin
- Maprotiline • Ludiomil
- Nortriptyline • Pamelor
- Paroxetine • Paxil
- Sertraline • Zoloft
- Trazodone • Desyrel
- Venlafaxine • Effexor
Disclosure
The author reports that she receives research support from Eli Lilly & Co. and Pfizer Inc. and serves as a consultant and member of the speakers’ bureaus for both of those companies.
1. Wolfe F, Smythe HA, Yunus MB, et al. The American College of Rheumatology 1990 criteria for the classification of fibromyalgia. Arthritis Rheum 1990;33:160-72.
2. Wolfe F, Ross K, Anderson J, et al. The prevalence and characteristics of fibromyalgia in the general population. Arthritis Rheum 1995;38:19-28.
3. White KP, Speechley M, Harth M, et al. Comparing self-reported function and work disability in 100 community cases of fibromyalgia syndrome versus controls in London, Ontario. The London fibromyalgia epidemiology study. Arthritis Rheum 1999;42:76-83.
4. Wolfe F, Anderson J, Harkness D, et al. Health status and disease severity in fibromyalgia. Arthritis Rheum 1997;40:1571-9.
5. Kaplan RM, Schmidt SM, Cronan TA. Quality of well being in patients with fibromyalgia. J Rheumatol 2000;27:785-9.
6. Clauw DJ. Fibromyalgia syndrome: an update on current understanding and medical management. Rheumatol Grand Rds 2000;3:1-9.
7. Yunus MB, Masi AT, Aldag JC. A controlled study of primary fibromyalgia syndrome: Clinical features and association with other functional syndromes. J Rheumatol 1989;16:62-71.
8. Wolfe F, Cathey MA, Kleinheksel SM, et al. Psychological status in primary fibrositis and fibrositis associated with rheumatoid arthritis. J Rheumatol 1984;11:500-6.
9. White KP, Nielson WR, Harth M, et al. Chronic widespread musculoskeletal pain with or without fibromyalgia: Psychological distress in a representative community adult sample. J Rheumatol 2002;29:588-94.
10. Walker EA, Keegan D, Gardner G, et al. Psychosocial factors in fibromyalgia and rheumatoid arthritis: I. Psychiatric diagnoses and functional disability. Psychosomatic Med 1997;59:565-71.
11. MacFarlane GJ, Thomas E, Papageorgiou AC, et al. The natural history of chroninc pain in the community: A better prognosis than in the clinic? J Rheumatol 1996;23:1617-20.
12. Aaron LA, Bradley LA, Alarcón GS, et al. Psychiatric diagnoses in patients with fibromyalgia are related to health care-seeking behavior rather than to illness. Arthritis Rheum 1996;39:436-45.
13. Moldofsky H, Scarisbrick P, England R, et al. Musculoskeletal symptoms and non-REM sleep disturbance in patients with “fibrositis syndrome” and healthy subjects. Psychosom Med 1975;37:341-5.
14. Moldofsky H, Scarisbrick P. Induction of neurasthenic musculoskeletal pain syndrome by selective sleep stage deprivation. Psychosom Med 1975;38:35-44.
15. Schneider-Helmert D, Whitehouse I, Kumar A, et al. Insomnia and alpha sleep in chronic non-organic pain as compared to primary insomnia. Neuropsychobiology 2001;43:54-8.
16. Pillemer SR, Bradley LA, Crofford LJ, et al. The neuroscience and endocrinology of fibromyalgia. Arthritis Rheum 1997;40:1928-39.
17. Walker EA, Keegan D, Gardner G, et al. Psychosocial factors in fibromyalgia and rheumatoid arthritis: II. Sexual, physical, and emotional abuse and neglect. Psychosomatic Med 1997;59:572-7.
18. Demitrack MA, Crofford LJ. Hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis dysregulation in fibromyalgia and chronic fatigue syndrome: An overview and hypothesis. J Musculoskeletal Pain 1995;3:67-73.
19. Heim C, Ehlert U, Hellhammer DH. The potential role of hypocortisolism in the pathophysiology of stress-related bodily disorders. Psychoneuroendocrinology 2000;25:1-35.
20. Bennett RM. Emerging concepts in the neurobiology of chronic pain: Evidence of abnormal sensory processing in fibromyalgia. Mayo Clin Proc 1999;74:385-98.
21. Weigent DA, Bradley LA, Blalock JE, et al. Current concepts in the pathophysiology of abnormal pain perception in fibromyalgia. Am J Med Sci 1998;315:405-12.
22. Baranauskas G, Nistri A. Sensitization of pain pathways in the spinal cord: cellular mechanisms. Prog Neurobiol 1998;7:309-38.
23. Watkins LR, Wiertelak EP, Furness LE, et al. Illness-induced hyperalgesia is mediated by spinal neuropeptides and excitatory amino acids. Brain Res 1994;664:17-24.
24. Russell IJ, Orr MD, Littman B, et al. Elevated cerebrospinal fluid levels of substance P in patients with fibromyalgia syndrome. Arthritis Rheum 1994;37:1593-1601.
25. Schwarz MJ, Spath M, Muller-Bardorff H, et al. Relationship of substance P, 5-hydroxyindole acetic acid and tryptophan in serum of fibromyalgia patients. Neurosci Lett 1999;259:196-8.
26. Russell IJ, Vaeroy H, Javors M, Nyberg F. Cerebrospinal fluid biogenic amine metabolites in fibromyalgia/fibrositis syndrome and rheumatoid arthritis. Arthrits Rheum 1993;35(5):550-6.
27. Fishbain D. Evidence-based data on pain relief with antidepressants. Ann Med 2000;32:305-16.
28. Hudson JI, Goldenberg DL, Pope HG, et al. Comorbidity of fibromyalgia with medical and psychiatric disorders. Am J Med 1992;92:363-7.
29. Basbaum AI, Fields HL. Endogenous pain control systems: Brainstem pathways and endorphin circuitry. Ann Rev Neurosci 1984;7:309-38.
30. Arnold LM, Keck PE, Jr, Welge JA. Antidepressant treatment of fibromyalgia. A meta-analysis and review. Psychosomatics 2000;41:104-13.
31. O’Malley PG, Balden E, Tomkins G, et al. Treatment of fibromyalgia with antidepressants. A meta-analysis. J Gen Intern Med 2000;15:659-66.
32. Nørregaard J, Volkmann H, Danneskiold-Samsø B. A randomized controlled trial of citalopram in the treatment of fibromyalgia. Pain 1995;61:445-9.
33. Anderberg UM, Marteinsdottir I, von Knokrring L. Citalopram in patients with fibromyalgia-A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study. Eur J Pain 2000;4:27-35.
34. Wolfe F, Cathey MA, Hawley DJ. A double-blind placebo controlled trial of fluoxetine in fibromyalgia. Scand J Rheumatol 1994;23(5):255-9.
35. Goldenberg DL, Mayskiy M, Mossey C, et al. A randomized, double-blind crossover trial of fluoxetine and amitriptyline in the treatment of fibromyalgia. Arthritis Rheum 1996;39:1852-9.
36. Arnold LM, Hess EV, Hudson JI, et al. A randomized, placebo-controlled, double-blind, flexible-dose study of fluoxetine in the treatment of women with fibromyalgia. Am J Med 2002;112:191-7.
37. Syuertsen JO, Smedsrud T, Lane RM. An open study of sertraline in fibromyalgia syndrome. Eur Neuropsychopharmacol 1995;5:315.-
38. Giordano N, Geraci S, et al. Efficacy and tolerability of paroxetine in patients with fibromyalgia syndrome: A single blind study. Curr Ther Res 1999;60:696-702.
39. Dwight MM, Arnold LM, O’Brien H, et al. An open clinical trial of venlafaxine treatment of fibromyalgia. Psychosomatics 1998;39:14-17.
40. Backonja M, Beydoun A, Edwards KR, et al. Gabapentin for the symptomatic treatment of painful neuropathy in patients with diabetes mellitus: A randomized controlled trial. JAMA 1998;280:1831-6.
41. Rice AS, Maton S. Gabapentin in postherpetic neuralgia: A randomized, doubleblind, placebo controlled study. Pain 2001;94:215-24.
42. Mathew NT, Rapoport A, Saper J, et al. Efficacy of gabapentin in migraine prophylaxis. Headache 2001;41:119-28.
43. Ferraccioli G, Ghirelli L, Scita F, et al. EMG-biofeedback training in fibromyalgia syndrome. J Rheumatol 1987;14:820-5.
44. McCain GA, Bell DA, Mai FM, et al. A controlled study of the effects of a supervised cardiovascular fitness training program on the manifestations of primary fibromyalgia. Arthritis Rheum 1988;31:1135-41.
45. Haanen HCM, Hoenderdos HTW, van Romande LKJ, et al. Controlled trial of hypnotherapy in the treatment of refractory fibromyalgia. J Rheumatol 1991;18:72-5.
46. Deluze C, Bosia L, Irbs A, et al. Electroacupuncture in fibromyalgia: Results of a controlled trial. BMJ 1992;1249-52.
47. Nielson WR, Walker C, McCain GA. Cognitive behavioral treatment of fibromyalgia syndrome preliminary findings. J Rheumatol 1992;19:98-103.
1. Wolfe F, Smythe HA, Yunus MB, et al. The American College of Rheumatology 1990 criteria for the classification of fibromyalgia. Arthritis Rheum 1990;33:160-72.
2. Wolfe F, Ross K, Anderson J, et al. The prevalence and characteristics of fibromyalgia in the general population. Arthritis Rheum 1995;38:19-28.
3. White KP, Speechley M, Harth M, et al. Comparing self-reported function and work disability in 100 community cases of fibromyalgia syndrome versus controls in London, Ontario. The London fibromyalgia epidemiology study. Arthritis Rheum 1999;42:76-83.
4. Wolfe F, Anderson J, Harkness D, et al. Health status and disease severity in fibromyalgia. Arthritis Rheum 1997;40:1571-9.
5. Kaplan RM, Schmidt SM, Cronan TA. Quality of well being in patients with fibromyalgia. J Rheumatol 2000;27:785-9.
6. Clauw DJ. Fibromyalgia syndrome: an update on current understanding and medical management. Rheumatol Grand Rds 2000;3:1-9.
7. Yunus MB, Masi AT, Aldag JC. A controlled study of primary fibromyalgia syndrome: Clinical features and association with other functional syndromes. J Rheumatol 1989;16:62-71.
8. Wolfe F, Cathey MA, Kleinheksel SM, et al. Psychological status in primary fibrositis and fibrositis associated with rheumatoid arthritis. J Rheumatol 1984;11:500-6.
9. White KP, Nielson WR, Harth M, et al. Chronic widespread musculoskeletal pain with or without fibromyalgia: Psychological distress in a representative community adult sample. J Rheumatol 2002;29:588-94.
10. Walker EA, Keegan D, Gardner G, et al. Psychosocial factors in fibromyalgia and rheumatoid arthritis: I. Psychiatric diagnoses and functional disability. Psychosomatic Med 1997;59:565-71.
11. MacFarlane GJ, Thomas E, Papageorgiou AC, et al. The natural history of chroninc pain in the community: A better prognosis than in the clinic? J Rheumatol 1996;23:1617-20.
12. Aaron LA, Bradley LA, Alarcón GS, et al. Psychiatric diagnoses in patients with fibromyalgia are related to health care-seeking behavior rather than to illness. Arthritis Rheum 1996;39:436-45.
13. Moldofsky H, Scarisbrick P, England R, et al. Musculoskeletal symptoms and non-REM sleep disturbance in patients with “fibrositis syndrome” and healthy subjects. Psychosom Med 1975;37:341-5.
14. Moldofsky H, Scarisbrick P. Induction of neurasthenic musculoskeletal pain syndrome by selective sleep stage deprivation. Psychosom Med 1975;38:35-44.
15. Schneider-Helmert D, Whitehouse I, Kumar A, et al. Insomnia and alpha sleep in chronic non-organic pain as compared to primary insomnia. Neuropsychobiology 2001;43:54-8.
16. Pillemer SR, Bradley LA, Crofford LJ, et al. The neuroscience and endocrinology of fibromyalgia. Arthritis Rheum 1997;40:1928-39.
17. Walker EA, Keegan D, Gardner G, et al. Psychosocial factors in fibromyalgia and rheumatoid arthritis: II. Sexual, physical, and emotional abuse and neglect. Psychosomatic Med 1997;59:572-7.
18. Demitrack MA, Crofford LJ. Hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis dysregulation in fibromyalgia and chronic fatigue syndrome: An overview and hypothesis. J Musculoskeletal Pain 1995;3:67-73.
19. Heim C, Ehlert U, Hellhammer DH. The potential role of hypocortisolism in the pathophysiology of stress-related bodily disorders. Psychoneuroendocrinology 2000;25:1-35.
20. Bennett RM. Emerging concepts in the neurobiology of chronic pain: Evidence of abnormal sensory processing in fibromyalgia. Mayo Clin Proc 1999;74:385-98.
21. Weigent DA, Bradley LA, Blalock JE, et al. Current concepts in the pathophysiology of abnormal pain perception in fibromyalgia. Am J Med Sci 1998;315:405-12.
22. Baranauskas G, Nistri A. Sensitization of pain pathways in the spinal cord: cellular mechanisms. Prog Neurobiol 1998;7:309-38.
23. Watkins LR, Wiertelak EP, Furness LE, et al. Illness-induced hyperalgesia is mediated by spinal neuropeptides and excitatory amino acids. Brain Res 1994;664:17-24.
24. Russell IJ, Orr MD, Littman B, et al. Elevated cerebrospinal fluid levels of substance P in patients with fibromyalgia syndrome. Arthritis Rheum 1994;37:1593-1601.
25. Schwarz MJ, Spath M, Muller-Bardorff H, et al. Relationship of substance P, 5-hydroxyindole acetic acid and tryptophan in serum of fibromyalgia patients. Neurosci Lett 1999;259:196-8.
26. Russell IJ, Vaeroy H, Javors M, Nyberg F. Cerebrospinal fluid biogenic amine metabolites in fibromyalgia/fibrositis syndrome and rheumatoid arthritis. Arthrits Rheum 1993;35(5):550-6.
27. Fishbain D. Evidence-based data on pain relief with antidepressants. Ann Med 2000;32:305-16.
28. Hudson JI, Goldenberg DL, Pope HG, et al. Comorbidity of fibromyalgia with medical and psychiatric disorders. Am J Med 1992;92:363-7.
29. Basbaum AI, Fields HL. Endogenous pain control systems: Brainstem pathways and endorphin circuitry. Ann Rev Neurosci 1984;7:309-38.
30. Arnold LM, Keck PE, Jr, Welge JA. Antidepressant treatment of fibromyalgia. A meta-analysis and review. Psychosomatics 2000;41:104-13.
31. O’Malley PG, Balden E, Tomkins G, et al. Treatment of fibromyalgia with antidepressants. A meta-analysis. J Gen Intern Med 2000;15:659-66.
32. Nørregaard J, Volkmann H, Danneskiold-Samsø B. A randomized controlled trial of citalopram in the treatment of fibromyalgia. Pain 1995;61:445-9.
33. Anderberg UM, Marteinsdottir I, von Knokrring L. Citalopram in patients with fibromyalgia-A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study. Eur J Pain 2000;4:27-35.
34. Wolfe F, Cathey MA, Hawley DJ. A double-blind placebo controlled trial of fluoxetine in fibromyalgia. Scand J Rheumatol 1994;23(5):255-9.
35. Goldenberg DL, Mayskiy M, Mossey C, et al. A randomized, double-blind crossover trial of fluoxetine and amitriptyline in the treatment of fibromyalgia. Arthritis Rheum 1996;39:1852-9.
36. Arnold LM, Hess EV, Hudson JI, et al. A randomized, placebo-controlled, double-blind, flexible-dose study of fluoxetine in the treatment of women with fibromyalgia. Am J Med 2002;112:191-7.
37. Syuertsen JO, Smedsrud T, Lane RM. An open study of sertraline in fibromyalgia syndrome. Eur Neuropsychopharmacol 1995;5:315.-
38. Giordano N, Geraci S, et al. Efficacy and tolerability of paroxetine in patients with fibromyalgia syndrome: A single blind study. Curr Ther Res 1999;60:696-702.
39. Dwight MM, Arnold LM, O’Brien H, et al. An open clinical trial of venlafaxine treatment of fibromyalgia. Psychosomatics 1998;39:14-17.
40. Backonja M, Beydoun A, Edwards KR, et al. Gabapentin for the symptomatic treatment of painful neuropathy in patients with diabetes mellitus: A randomized controlled trial. JAMA 1998;280:1831-6.
41. Rice AS, Maton S. Gabapentin in postherpetic neuralgia: A randomized, doubleblind, placebo controlled study. Pain 2001;94:215-24.
42. Mathew NT, Rapoport A, Saper J, et al. Efficacy of gabapentin in migraine prophylaxis. Headache 2001;41:119-28.
43. Ferraccioli G, Ghirelli L, Scita F, et al. EMG-biofeedback training in fibromyalgia syndrome. J Rheumatol 1987;14:820-5.
44. McCain GA, Bell DA, Mai FM, et al. A controlled study of the effects of a supervised cardiovascular fitness training program on the manifestations of primary fibromyalgia. Arthritis Rheum 1988;31:1135-41.
45. Haanen HCM, Hoenderdos HTW, van Romande LKJ, et al. Controlled trial of hypnotherapy in the treatment of refractory fibromyalgia. J Rheumatol 1991;18:72-5.
46. Deluze C, Bosia L, Irbs A, et al. Electroacupuncture in fibromyalgia: Results of a controlled trial. BMJ 1992;1249-52.
47. Nielson WR, Walker C, McCain GA. Cognitive behavioral treatment of fibromyalgia syndrome preliminary findings. J Rheumatol 1992;19:98-103.
Eating baby powder controls her urge to purge
History: An inpatient discovery
Ms. A, 20, presented to the emergency room with an exacerbation of asthma due to noncompliance with medications. A review of her systems and a physical exam revealed significant bilateral shortness of breath, wheezes, and rhonchi.
A single mother who lives with her two daughters, ages 5 and 2, Ms. A is 28 weeks pregnant with her third child. After receiving albuterol nebulizers for her asthma, she was admitted to the obstetrics and gynecology floor for monitoring of maternal and fetal status. There, a nursing staff member observed her eating baby powder.
The psychiatric team evaluated Ms. A and learned that, during her first pregnancy at age 15, she grew uncomfortable with her increased weight and started purging. Standing at 5 feet, 6 inches, Ms. A weighed as much as 220 during the pregnancy; her weight fell to 170 pounds after delivery. When she presented to us she lamented, “All of my friends are still thin.”
The stress of being a single teenage mother and going to school, combined with disgust over her physical appearance, provoked her purging. She did not think purging would help her lose weight but would prevent her from gaining more even as she ate as much as she wanted.
For 11 months after the birth of her first child, she purged three to four times daily. She could eat as many as five “value meals” within 2 to 3 hours at fast-food restaurants. Eating relaxed her and made her feel comfortable, but the frequency of purging escalated to five to six times daily and the vomiting was physically exhausting, painful, and caused esophageal damage.
At age 17, Ms. A became pregnant with her second child. In the first 2 to 3 months, she continued to eat large quantities of food but purged less often (two to three times daily).
One day in the third month of this pregnancy, Ms. A watched as her mother used medicated powder on her own child, and the powder's scent stimulated within Ms. A an urge to taste it. Before long Ms. A was eating the powder regularly and had stopped purging. She recalled purging only three times during the remaining 6 months of the pregnancy. The craving for powder replaced both her desire to vomit and the need to binge on food. She returned to regular binging and purging (once or twice weekly) after her second child was born, however.
In your view, which should be addressed first, the bulimia or the obsession with baby powder? Or should both be addressed in tandem?
Commentary
This case displays a form of adult pica for baby powder, which has only been described in the literature for pediatric pica.1,2 She displays no cognitive deficits or psychological disorders (e.g., mental retardation, schizophrenia) that are commonly associated with pica.3-6 Pregnancy, which is also common in pica, did exist in this patient and may provide some physiologic or psychological insight into the patient’s disorder.7 The patient’s bulimia nervosa, however, gives an unusual twist to this case.
In the 18th century, pica was classified together with bulimia simply as an erroneous or aberrant appetite (Box 1).8 Pica has been known to occur with—and can be a symptom of—bulimia and anorexia, but it is rarely cited.8,10 As in other eating disorders, affected individuals are ashamed of their weight, body shape, and body image.13
The term pica has evolved over centuries to describe the compulsive ingestion of non-nutritive substances or unusual food cravings. Its etymology stems from the Latin word for magpie (genus Pica), a bird said to pick up, carry away, and presumably eat a myriad of objects.
The word was first used in 1563 by Thomas Gale, who noted this consumption of unusual foodstuffs in pregnant women and children.8 In contemporary literature, the word “craving” is often used instead of pica to minimize social judgment toward practices that deviate from “normal.”
An estimated 20% of pregnant women are believed to have a history of pica, but the documented prevalence of these cravings may be underestimated because women often are embarrassed to disclose the behavior.9
Pica has been speculated to be a form of aggression, a result of compulsive neuroses, or a manifestation of oral fixation because of its association with thumb sucking.1 In the end, pica is a poorly understood disorder.
Scientists question the etiology of pica. Early psychiatric hypotheses focused on societal expectations of women’s outward beauty. A higher prevalence of pica has been recognized in mentally retarded persons and patients with schizophrenia.3-6
Pica is most frequently observed in children, pregnant women, and patients from a low socioeconomic background.10,11 More comprehensive studies have explored geophagia (a craving to eat chalk, clay, or dirt) in Africa and the southern United States.12
Comorbid bulimia and pica disorders tend to work together to accomplish a similar task: weight loss/control. Eating non-nutritive substances occupies space in the stomach, creating a sense of satiety without taking in calories. Therefore, this behavior acts as a substitute for binging in the patient with bulimia.14
One study identified eight themes associated with pica during pregnancy: keeping practices secret, singularity of the experience, extravagant means for obtaining the craved substance, fears for the effects on the fetus, yielding or not yielding to the cravings, use of the substances as medication, pica and lack of food intake, and sensory experiences other than taste.2 All eight of these themes were present in Ms. A.
Evaluation: Needing more and more
By her third pregnancy, Ms. A’s obsession with powder started to take hold. She found it easier to conceal the purging from her partner, so she began purging more often (twice daily) to offset her cravings for the baby powder. Purging was a last resort for the patient and her only means of off-setting her desire for the powder, which relieved her urge to vomit. She ate baby powder throughout the day, even awaking two to three times at night to ingest a few spoonfuls.
Until she presented to us, Ms. A had followed a daily ritual. At 10:30 a.m., when the local drug store opens, she superficially tested the consistency of a certain brand of powder available on the shelves. She then purchased one case (six 14-ounce containers) of powder, went home and sampled each container, and rated them in quality from 1 to 6, with 1 being the bottle of powder she ate that day. The next morning, regardless of how many cases of powder were piled in her closet, she went to the drug store and repeated the process.
Ms. A felt comfortable eating the talc-based powder in her apartment and her mother’s house. She kept some baby powder in her desk at work, but she regularly took an hour-long lunch break to drive back to her apartment and satisfy her craving. She also carried powder in the car, tasting it while driving.
When asked how the powder made her feel, Ms. A replied: “Powder is like nothing else. It makes me feel content and at ease.” Whenever she was irritated, or if the children were frustrating her, she would take a spoonful of powder.
In the beginning, she consumed approximately one 14-ounce bottle per month. When she presented 28 weeks pregnant with her third child, she could not imagine life without baby powder. A spoonful satisfied her for only 5 to 10 minutes before she would desire more. No other substance quelled the cravings. She had tried edible substitutes such as confectioners sugar, cornstarch, and ice chips, but nothing offered the satisfaction she got from powder.
When she is unable to ingest powder, she develops a headache, begins to sweat, gets extremely anxious and irritable, cries profusely, and becomes depressed. If she is abstinent more than 2 days she is unable to sleep and becomes preoccupied with the powder. If powder is not available, she binges and induces vomiting to stifle her craving.
In the hospital she craved powder 2 days after it was removed from her access. She became extremely anxious and distressed. She then ordered as much food as possible so she could purge and forget about the powder.
How would you explain the patient’s psychopathological attraction to baby powder?
Commentary
Patients with pica typically express satisfaction from consuming non-nutrient substances (Box 2). Ms. A’s motive for eating the powder stemmed from what she perceived as its soothing properties.
Other reported cases have alluded to the sensation generated by the texture of soil or chalk in the mouth. Some of these patients also described the importance of the soil’s taste—i.e., particle size—as being second to its texture.12 The desire to experience a certain texture, color, odor, and taste are important components in pica cravings.10
| Object | Specific disorder |
|---|---|
| Burnt matches | Cautopyreiophagia |
| Earth (chalk, clay, dirt) | Geophagia |
| Feces | Coprophagia |
| Hair | Tricophagia |
| Ice | Pagophagia |
| Laundry starch, cornstarch | Amylophagia |
| Lead paint chips | Plumbophagia |
| Raw potatoes | Geomelophagia |
| Stones | Lithophagia |
Other known objects of pica—Ashes, baking soda, balloons, carrots, celery, chewing gum, cigarette butts, cloth, coal, coca leaf, coffee grounds/beans, cotton balls, concrete, crayons, croutons, detergent, grass, hard candy, insects, lavatory fresheners, latex gloves, licorice, lint, metal, milk, newsprint, oats, oyster shells, paper, parsley, plant leaves, pencil erasers, plastic, popcorn, powder puffs, salt, soap, string, thread, toilet tissue, tomato seeds, twigs, vinegar, wood.
Pica appears to meet the individual’s need for mental relaxation and sensory pleasure15 in much the same way that alcohol or drug abusers satisfy their intense desire for euphoria and relaxation. Scientists theorize that alcohol and drug abuse may be exacerbated by or result from a neurochemical imbalance. A similar hypothesis may explain this “variant” in pica patients.
Pregnant women often develop taste aversions for items that are potentially harmful to the developing fetus, such as alcohol and coffee. Expectant mothers may develop utter disgust and provocation of nausea toward items they enjoyed while not gravid. Aversions to foods and other items during pregnancy might be the consequence of homeostatic factors that have evolved as general feto-protective mechanisms.16,17 The metabolic changes that accompany the gravid state might alter olfactory and taste sensitivity.17
If a pregnancy-related change in chemical balance can cause taste aversion, certainly a similar situation could evolve into pica. In laboratory rats, intraventricular injection of exogenous neuropeptide Y, a hormone with documented CNS activity, caused taste aversions and elicited geophagia.18
Ms. A’s ingestion of baby powder itself did not harm the fetus. Stephen Emery, MD, director of perinatal ultrasound at the Cleveland Clinic, notes that talc is inert and the powder’s perfumes probably are benign. He adds, however, that because the powder often has replaced real food, Ms. A placed her unborn child at risk via malnourishment.
Further evaluation: A ‘pleasant’ appearance
Ms. A’s medical history revealed chronic asthma since childhood and gastroesophageal reflux disease. According to her social history, she is dating the father of her expectant child. She has been smoking one pack of cigarettes per day for 2 years but says she does not drink alcohol and has never abused illicit drugs.
Her lab values were as follows (with normal ranges in parentheses): blood urea, 4 mg/dl (9-23); serum iron, 69 mg/dl (42-135); calcium 8.7 mg/dl (8.5-10.5); magnesium, 1.6 mg/dl (1.8-2.4); phosphate, 2.4 mg/dl (2.7-4.6); hemoglobin, 10.0 g/dl (12.0-14.0); hematocrit, 31.1% (37.0-47.0); mean corpuscular volume, 86.4 fl (81-99).
Ms. A appeared well-nourished, appropriately dressed, and well-groomed during our examination. She was alert, oriented and cooperative, and held a pleasant conversation with good eye contact. Her mood was depressed and anxious, and her affect was congruent. Speech was normal in rate, tone, and volume. Her thoughts were well organized and goal-directed. She denied suicidal ideation but had thoughts of harming her fetus. She denied any perceptual disturbances. No intellectual impairment was evident, and her insight and judgment were preserved.
What is the psychiatric diagnosis for this patient? Also, in your view, how likely is she to harm her fetus or her two children? How would you assess and manage that risk?
Commentary
The physiologic cause of pica may be metabolic disturbances in iron, zinc, calcium, potassium, lead, and magnesium.10,19-22 Ice pica typically is associated with iron deficiency and low hemoglobin levels,14,20,23,24 although other forms of pica have been linked to iron deficiency.12,25 Some studies show iron deficiency in nearly half of patients who display ice pica;20,26 correcting the iron deficiency relieves the cravings for the desired substances.7,14 Scientists are split as to whether pica results in the deficiency of certain minerals or whether mineral deficiencies cause pica. Mineral deficiencies may alter appetite-regulating brain enzymes that can lead to these cravings.7,10,11,23
Ms. A’s laboratory values demonstrated decreased hemoglobin, hematocrit, and magnesium levels. Magnesium replacement did not change her eating behavior. Her mild anemia may simply have been an effect of pregnancy.
Treatment: Confronting comorbid depression
Ms. A’s diagnosis was pica, bulimia nervosa-purging type, with comorbid depressive disorder NOS.
She was placed on the selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor sertraline, 12.5 mg/d. The dosage was increased gradually to 50 mg qd. Supportive psychotherapy was provided during the patient’s hospital course.
After her discharge, cognitive therapy was initiated. Ms. A was asked to keep a journal utilizing the “triple column technique,” through which she described a situation in one column, explained the symptoms or unwanted behaviors and emotions evoked by that situation in the second, and wrote down her thoughts in the third.
Ms. A was monitored for signs and symptoms of postpartum depression. After this careful assessment, in which two psychiatrists and the ob/gyn team participated, we concluded that the patient’s transient thoughts of harming her fetus had fully resolved.
Ms. A was educated about nutrition and healthy exercise, as well as birth control options. We also asked to see her as an outpatient.
In the ensuing months, Ms. A reported moderate depressive symptoms but described a significant decrease in her craving for, and consumption of, powder. She continued follow-up treatment with her physician at the women’s care center. Ms. A decided to stop taking sertraline after 2 months because she felt it was not helping her depression and was causing fatigue.
When we followed up after 6 months, Ms. A reported that she and her baby were doing well. She told us that her powder cravings had decreased markedly.
Related resources
- Alliance for Eating Disorders Awareness. www.eatingdisorderinfo.org
- Stein DJ, Bouwer C, van Heerden B. Pica and the obsessive spectrum disorders. S Afr Med J 1996; 86(12 suppl):1586-8, 1591-2.
Drug brand names
- Sertraline • Zoloft
Disclosure
The authors report no financial relationship with any company whose products are mentioned in this article.
1. Robischon P. Pica practice and other hand-mouth behavior and children’s development level. Nurs Res 1971;20(1):4-16.
2. Cooksey NR. Pica and olfactory craving of pregnancy: How deep are the secrets? Birth 1995;22(3):129-37.
3. Danford DE, Smith JC, Huber AM. Pica and mineral status in the mentally retarded. Am J Clin Nutr 1982;35(5):958-67.
4. Jawed SH, Krishnan VH, et al. Worsening of pica as a symptom of Depressive illness in a person with severe mental handicap. Br J Psychiatry 1993;162:835-7.
5. Sturmey P. Pica and developmental disability. J Am Board Fam Pract 2001;14(1):80-1.
6. Tracy JI, de Leon J, Qureshi G, et al. Repetitive behaviors in schizophrenia: a single disturbance or discrete symptoms? Schizophr Res 1996;20(1-2):221-9.
7. Federman DG, Kirsner RS, Federman GS. Pica: Are you hungry for the facts? Conn Med 1997;61(4):207-9.
8. Parry-Jones B, Parry-Jones WL. Pica: symptom or eating disorder? A historical perspective. Br J Psychiatry. 1992;160:341-54.
9. Goldstein M. Adult pica: A clinical nexus of physiology and psychodynamics. Psychosom 1998;39:465-9.
10. Danford DE. Pica and nutrition. Annu Rev Nutr 1982;2:303-22.
11. Jackson WC, Martin JP. Amylophagia presenting as gestational diabetes. Arch Fam Med 2000;9(7):649-52.
12. Geissler PW, Prince RJ, Levene M, et al. Perceptions of soil-eating and anemia among pregnant women on the Kenyan coast. Soc Sci Med 1999;48(8):1069-79.
13. Parry-Jones B. Historical terminology of eating disorders. Psychol Med 1991;21:21-8.
14. Rose EA, Porcerelli JH, Neale AV. Pica: common but commonly missed. J Am Board Fam Pract 2000;13(5):353-8.
15. Castiglia PT. Pica. J Pediatr Health Care 1993;7(4):174-5.
16. Fairburn CG, Stein A, Jones R. Eating habits and eating disorders during pregnancy. Psychosom Med 1992;54(6):665-72.
17. Hook EB. Dietary cravings and aversions during pregnancy. Am J Clin Nutr 1978;31(8):1355-62.
18. Madden LJ, Seeley RJ, Woods SC. Intraventricular neuropeptide Y decreases need induced sodium appetite and increases pica in rats. Behav Neurosci 1999;113:826-32.
19. Appel RG, Bleyer AJ. Pica associated with renal and electrolyte disorders. Int J Artif Organs 1999;22(11):726-9.
20. Crosby WH. Pica. JAMA 1976;235(25):2765.-
21. Lofts RH, Schroeder SR, Maier RH. Effects of serum zinc supplementation on pica behavior of persons with mental retardation. Am J Ment Retard 1990;95(1):103-9.
22. Siklar Z, Gulten T, Dallor Y, Gunay S. Pica and intoxication in childhood. Clin Pediatr (Phila) 2000;39(10):624-5.
23. Rainville AJ. Pica practices of pregnant women are associated with lower maternal hemoglobin level at delivery. J Am Diet Assoc 1998;98(3):293-6.
24. Rothenberg SJ, Manalo M, Jiang J, et al. Maternal blood lead level during pregnancy in South Central Los Angeles. Arch Environ Health 1999;54(3):151-7.
25. Marinella MA. “Tomatophagia” and iron-deficiency anemia. N Engl J Med 1999;341(1):60-1.
26. Crosby WH. Pica: A compulsion caused by iron deficiency. Br J Haematol 1976;34(2):341-2.
History: An inpatient discovery
Ms. A, 20, presented to the emergency room with an exacerbation of asthma due to noncompliance with medications. A review of her systems and a physical exam revealed significant bilateral shortness of breath, wheezes, and rhonchi.
A single mother who lives with her two daughters, ages 5 and 2, Ms. A is 28 weeks pregnant with her third child. After receiving albuterol nebulizers for her asthma, she was admitted to the obstetrics and gynecology floor for monitoring of maternal and fetal status. There, a nursing staff member observed her eating baby powder.
The psychiatric team evaluated Ms. A and learned that, during her first pregnancy at age 15, she grew uncomfortable with her increased weight and started purging. Standing at 5 feet, 6 inches, Ms. A weighed as much as 220 during the pregnancy; her weight fell to 170 pounds after delivery. When she presented to us she lamented, “All of my friends are still thin.”
The stress of being a single teenage mother and going to school, combined with disgust over her physical appearance, provoked her purging. She did not think purging would help her lose weight but would prevent her from gaining more even as she ate as much as she wanted.
For 11 months after the birth of her first child, she purged three to four times daily. She could eat as many as five “value meals” within 2 to 3 hours at fast-food restaurants. Eating relaxed her and made her feel comfortable, but the frequency of purging escalated to five to six times daily and the vomiting was physically exhausting, painful, and caused esophageal damage.
At age 17, Ms. A became pregnant with her second child. In the first 2 to 3 months, she continued to eat large quantities of food but purged less often (two to three times daily).
One day in the third month of this pregnancy, Ms. A watched as her mother used medicated powder on her own child, and the powder's scent stimulated within Ms. A an urge to taste it. Before long Ms. A was eating the powder regularly and had stopped purging. She recalled purging only three times during the remaining 6 months of the pregnancy. The craving for powder replaced both her desire to vomit and the need to binge on food. She returned to regular binging and purging (once or twice weekly) after her second child was born, however.
In your view, which should be addressed first, the bulimia or the obsession with baby powder? Or should both be addressed in tandem?
Commentary
This case displays a form of adult pica for baby powder, which has only been described in the literature for pediatric pica.1,2 She displays no cognitive deficits or psychological disorders (e.g., mental retardation, schizophrenia) that are commonly associated with pica.3-6 Pregnancy, which is also common in pica, did exist in this patient and may provide some physiologic or psychological insight into the patient’s disorder.7 The patient’s bulimia nervosa, however, gives an unusual twist to this case.
In the 18th century, pica was classified together with bulimia simply as an erroneous or aberrant appetite (Box 1).8 Pica has been known to occur with—and can be a symptom of—bulimia and anorexia, but it is rarely cited.8,10 As in other eating disorders, affected individuals are ashamed of their weight, body shape, and body image.13
The term pica has evolved over centuries to describe the compulsive ingestion of non-nutritive substances or unusual food cravings. Its etymology stems from the Latin word for magpie (genus Pica), a bird said to pick up, carry away, and presumably eat a myriad of objects.
The word was first used in 1563 by Thomas Gale, who noted this consumption of unusual foodstuffs in pregnant women and children.8 In contemporary literature, the word “craving” is often used instead of pica to minimize social judgment toward practices that deviate from “normal.”
An estimated 20% of pregnant women are believed to have a history of pica, but the documented prevalence of these cravings may be underestimated because women often are embarrassed to disclose the behavior.9
Pica has been speculated to be a form of aggression, a result of compulsive neuroses, or a manifestation of oral fixation because of its association with thumb sucking.1 In the end, pica is a poorly understood disorder.
Scientists question the etiology of pica. Early psychiatric hypotheses focused on societal expectations of women’s outward beauty. A higher prevalence of pica has been recognized in mentally retarded persons and patients with schizophrenia.3-6
Pica is most frequently observed in children, pregnant women, and patients from a low socioeconomic background.10,11 More comprehensive studies have explored geophagia (a craving to eat chalk, clay, or dirt) in Africa and the southern United States.12
Comorbid bulimia and pica disorders tend to work together to accomplish a similar task: weight loss/control. Eating non-nutritive substances occupies space in the stomach, creating a sense of satiety without taking in calories. Therefore, this behavior acts as a substitute for binging in the patient with bulimia.14
One study identified eight themes associated with pica during pregnancy: keeping practices secret, singularity of the experience, extravagant means for obtaining the craved substance, fears for the effects on the fetus, yielding or not yielding to the cravings, use of the substances as medication, pica and lack of food intake, and sensory experiences other than taste.2 All eight of these themes were present in Ms. A.
Evaluation: Needing more and more
By her third pregnancy, Ms. A’s obsession with powder started to take hold. She found it easier to conceal the purging from her partner, so she began purging more often (twice daily) to offset her cravings for the baby powder. Purging was a last resort for the patient and her only means of off-setting her desire for the powder, which relieved her urge to vomit. She ate baby powder throughout the day, even awaking two to three times at night to ingest a few spoonfuls.
Until she presented to us, Ms. A had followed a daily ritual. At 10:30 a.m., when the local drug store opens, she superficially tested the consistency of a certain brand of powder available on the shelves. She then purchased one case (six 14-ounce containers) of powder, went home and sampled each container, and rated them in quality from 1 to 6, with 1 being the bottle of powder she ate that day. The next morning, regardless of how many cases of powder were piled in her closet, she went to the drug store and repeated the process.
Ms. A felt comfortable eating the talc-based powder in her apartment and her mother’s house. She kept some baby powder in her desk at work, but she regularly took an hour-long lunch break to drive back to her apartment and satisfy her craving. She also carried powder in the car, tasting it while driving.
When asked how the powder made her feel, Ms. A replied: “Powder is like nothing else. It makes me feel content and at ease.” Whenever she was irritated, or if the children were frustrating her, she would take a spoonful of powder.
In the beginning, she consumed approximately one 14-ounce bottle per month. When she presented 28 weeks pregnant with her third child, she could not imagine life without baby powder. A spoonful satisfied her for only 5 to 10 minutes before she would desire more. No other substance quelled the cravings. She had tried edible substitutes such as confectioners sugar, cornstarch, and ice chips, but nothing offered the satisfaction she got from powder.
When she is unable to ingest powder, she develops a headache, begins to sweat, gets extremely anxious and irritable, cries profusely, and becomes depressed. If she is abstinent more than 2 days she is unable to sleep and becomes preoccupied with the powder. If powder is not available, she binges and induces vomiting to stifle her craving.
In the hospital she craved powder 2 days after it was removed from her access. She became extremely anxious and distressed. She then ordered as much food as possible so she could purge and forget about the powder.
How would you explain the patient’s psychopathological attraction to baby powder?
Commentary
Patients with pica typically express satisfaction from consuming non-nutrient substances (Box 2). Ms. A’s motive for eating the powder stemmed from what she perceived as its soothing properties.
Other reported cases have alluded to the sensation generated by the texture of soil or chalk in the mouth. Some of these patients also described the importance of the soil’s taste—i.e., particle size—as being second to its texture.12 The desire to experience a certain texture, color, odor, and taste are important components in pica cravings.10
| Object | Specific disorder |
|---|---|
| Burnt matches | Cautopyreiophagia |
| Earth (chalk, clay, dirt) | Geophagia |
| Feces | Coprophagia |
| Hair | Tricophagia |
| Ice | Pagophagia |
| Laundry starch, cornstarch | Amylophagia |
| Lead paint chips | Plumbophagia |
| Raw potatoes | Geomelophagia |
| Stones | Lithophagia |
Other known objects of pica—Ashes, baking soda, balloons, carrots, celery, chewing gum, cigarette butts, cloth, coal, coca leaf, coffee grounds/beans, cotton balls, concrete, crayons, croutons, detergent, grass, hard candy, insects, lavatory fresheners, latex gloves, licorice, lint, metal, milk, newsprint, oats, oyster shells, paper, parsley, plant leaves, pencil erasers, plastic, popcorn, powder puffs, salt, soap, string, thread, toilet tissue, tomato seeds, twigs, vinegar, wood.
Pica appears to meet the individual’s need for mental relaxation and sensory pleasure15 in much the same way that alcohol or drug abusers satisfy their intense desire for euphoria and relaxation. Scientists theorize that alcohol and drug abuse may be exacerbated by or result from a neurochemical imbalance. A similar hypothesis may explain this “variant” in pica patients.
Pregnant women often develop taste aversions for items that are potentially harmful to the developing fetus, such as alcohol and coffee. Expectant mothers may develop utter disgust and provocation of nausea toward items they enjoyed while not gravid. Aversions to foods and other items during pregnancy might be the consequence of homeostatic factors that have evolved as general feto-protective mechanisms.16,17 The metabolic changes that accompany the gravid state might alter olfactory and taste sensitivity.17
If a pregnancy-related change in chemical balance can cause taste aversion, certainly a similar situation could evolve into pica. In laboratory rats, intraventricular injection of exogenous neuropeptide Y, a hormone with documented CNS activity, caused taste aversions and elicited geophagia.18
Ms. A’s ingestion of baby powder itself did not harm the fetus. Stephen Emery, MD, director of perinatal ultrasound at the Cleveland Clinic, notes that talc is inert and the powder’s perfumes probably are benign. He adds, however, that because the powder often has replaced real food, Ms. A placed her unborn child at risk via malnourishment.
Further evaluation: A ‘pleasant’ appearance
Ms. A’s medical history revealed chronic asthma since childhood and gastroesophageal reflux disease. According to her social history, she is dating the father of her expectant child. She has been smoking one pack of cigarettes per day for 2 years but says she does not drink alcohol and has never abused illicit drugs.
Her lab values were as follows (with normal ranges in parentheses): blood urea, 4 mg/dl (9-23); serum iron, 69 mg/dl (42-135); calcium 8.7 mg/dl (8.5-10.5); magnesium, 1.6 mg/dl (1.8-2.4); phosphate, 2.4 mg/dl (2.7-4.6); hemoglobin, 10.0 g/dl (12.0-14.0); hematocrit, 31.1% (37.0-47.0); mean corpuscular volume, 86.4 fl (81-99).
Ms. A appeared well-nourished, appropriately dressed, and well-groomed during our examination. She was alert, oriented and cooperative, and held a pleasant conversation with good eye contact. Her mood was depressed and anxious, and her affect was congruent. Speech was normal in rate, tone, and volume. Her thoughts were well organized and goal-directed. She denied suicidal ideation but had thoughts of harming her fetus. She denied any perceptual disturbances. No intellectual impairment was evident, and her insight and judgment were preserved.
What is the psychiatric diagnosis for this patient? Also, in your view, how likely is she to harm her fetus or her two children? How would you assess and manage that risk?
Commentary
The physiologic cause of pica may be metabolic disturbances in iron, zinc, calcium, potassium, lead, and magnesium.10,19-22 Ice pica typically is associated with iron deficiency and low hemoglobin levels,14,20,23,24 although other forms of pica have been linked to iron deficiency.12,25 Some studies show iron deficiency in nearly half of patients who display ice pica;20,26 correcting the iron deficiency relieves the cravings for the desired substances.7,14 Scientists are split as to whether pica results in the deficiency of certain minerals or whether mineral deficiencies cause pica. Mineral deficiencies may alter appetite-regulating brain enzymes that can lead to these cravings.7,10,11,23
Ms. A’s laboratory values demonstrated decreased hemoglobin, hematocrit, and magnesium levels. Magnesium replacement did not change her eating behavior. Her mild anemia may simply have been an effect of pregnancy.
Treatment: Confronting comorbid depression
Ms. A’s diagnosis was pica, bulimia nervosa-purging type, with comorbid depressive disorder NOS.
She was placed on the selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor sertraline, 12.5 mg/d. The dosage was increased gradually to 50 mg qd. Supportive psychotherapy was provided during the patient’s hospital course.
After her discharge, cognitive therapy was initiated. Ms. A was asked to keep a journal utilizing the “triple column technique,” through which she described a situation in one column, explained the symptoms or unwanted behaviors and emotions evoked by that situation in the second, and wrote down her thoughts in the third.
Ms. A was monitored for signs and symptoms of postpartum depression. After this careful assessment, in which two psychiatrists and the ob/gyn team participated, we concluded that the patient’s transient thoughts of harming her fetus had fully resolved.
Ms. A was educated about nutrition and healthy exercise, as well as birth control options. We also asked to see her as an outpatient.
In the ensuing months, Ms. A reported moderate depressive symptoms but described a significant decrease in her craving for, and consumption of, powder. She continued follow-up treatment with her physician at the women’s care center. Ms. A decided to stop taking sertraline after 2 months because she felt it was not helping her depression and was causing fatigue.
When we followed up after 6 months, Ms. A reported that she and her baby were doing well. She told us that her powder cravings had decreased markedly.
Related resources
- Alliance for Eating Disorders Awareness. www.eatingdisorderinfo.org
- Stein DJ, Bouwer C, van Heerden B. Pica and the obsessive spectrum disorders. S Afr Med J 1996; 86(12 suppl):1586-8, 1591-2.
Drug brand names
- Sertraline • Zoloft
Disclosure
The authors report no financial relationship with any company whose products are mentioned in this article.
History: An inpatient discovery
Ms. A, 20, presented to the emergency room with an exacerbation of asthma due to noncompliance with medications. A review of her systems and a physical exam revealed significant bilateral shortness of breath, wheezes, and rhonchi.
A single mother who lives with her two daughters, ages 5 and 2, Ms. A is 28 weeks pregnant with her third child. After receiving albuterol nebulizers for her asthma, she was admitted to the obstetrics and gynecology floor for monitoring of maternal and fetal status. There, a nursing staff member observed her eating baby powder.
The psychiatric team evaluated Ms. A and learned that, during her first pregnancy at age 15, she grew uncomfortable with her increased weight and started purging. Standing at 5 feet, 6 inches, Ms. A weighed as much as 220 during the pregnancy; her weight fell to 170 pounds after delivery. When she presented to us she lamented, “All of my friends are still thin.”
The stress of being a single teenage mother and going to school, combined with disgust over her physical appearance, provoked her purging. She did not think purging would help her lose weight but would prevent her from gaining more even as she ate as much as she wanted.
For 11 months after the birth of her first child, she purged three to four times daily. She could eat as many as five “value meals” within 2 to 3 hours at fast-food restaurants. Eating relaxed her and made her feel comfortable, but the frequency of purging escalated to five to six times daily and the vomiting was physically exhausting, painful, and caused esophageal damage.
At age 17, Ms. A became pregnant with her second child. In the first 2 to 3 months, she continued to eat large quantities of food but purged less often (two to three times daily).
One day in the third month of this pregnancy, Ms. A watched as her mother used medicated powder on her own child, and the powder's scent stimulated within Ms. A an urge to taste it. Before long Ms. A was eating the powder regularly and had stopped purging. She recalled purging only three times during the remaining 6 months of the pregnancy. The craving for powder replaced both her desire to vomit and the need to binge on food. She returned to regular binging and purging (once or twice weekly) after her second child was born, however.
In your view, which should be addressed first, the bulimia or the obsession with baby powder? Or should both be addressed in tandem?
Commentary
This case displays a form of adult pica for baby powder, which has only been described in the literature for pediatric pica.1,2 She displays no cognitive deficits or psychological disorders (e.g., mental retardation, schizophrenia) that are commonly associated with pica.3-6 Pregnancy, which is also common in pica, did exist in this patient and may provide some physiologic or psychological insight into the patient’s disorder.7 The patient’s bulimia nervosa, however, gives an unusual twist to this case.
In the 18th century, pica was classified together with bulimia simply as an erroneous or aberrant appetite (Box 1).8 Pica has been known to occur with—and can be a symptom of—bulimia and anorexia, but it is rarely cited.8,10 As in other eating disorders, affected individuals are ashamed of their weight, body shape, and body image.13
The term pica has evolved over centuries to describe the compulsive ingestion of non-nutritive substances or unusual food cravings. Its etymology stems from the Latin word for magpie (genus Pica), a bird said to pick up, carry away, and presumably eat a myriad of objects.
The word was first used in 1563 by Thomas Gale, who noted this consumption of unusual foodstuffs in pregnant women and children.8 In contemporary literature, the word “craving” is often used instead of pica to minimize social judgment toward practices that deviate from “normal.”
An estimated 20% of pregnant women are believed to have a history of pica, but the documented prevalence of these cravings may be underestimated because women often are embarrassed to disclose the behavior.9
Pica has been speculated to be a form of aggression, a result of compulsive neuroses, or a manifestation of oral fixation because of its association with thumb sucking.1 In the end, pica is a poorly understood disorder.
Scientists question the etiology of pica. Early psychiatric hypotheses focused on societal expectations of women’s outward beauty. A higher prevalence of pica has been recognized in mentally retarded persons and patients with schizophrenia.3-6
Pica is most frequently observed in children, pregnant women, and patients from a low socioeconomic background.10,11 More comprehensive studies have explored geophagia (a craving to eat chalk, clay, or dirt) in Africa and the southern United States.12
Comorbid bulimia and pica disorders tend to work together to accomplish a similar task: weight loss/control. Eating non-nutritive substances occupies space in the stomach, creating a sense of satiety without taking in calories. Therefore, this behavior acts as a substitute for binging in the patient with bulimia.14
One study identified eight themes associated with pica during pregnancy: keeping practices secret, singularity of the experience, extravagant means for obtaining the craved substance, fears for the effects on the fetus, yielding or not yielding to the cravings, use of the substances as medication, pica and lack of food intake, and sensory experiences other than taste.2 All eight of these themes were present in Ms. A.
Evaluation: Needing more and more
By her third pregnancy, Ms. A’s obsession with powder started to take hold. She found it easier to conceal the purging from her partner, so she began purging more often (twice daily) to offset her cravings for the baby powder. Purging was a last resort for the patient and her only means of off-setting her desire for the powder, which relieved her urge to vomit. She ate baby powder throughout the day, even awaking two to three times at night to ingest a few spoonfuls.
Until she presented to us, Ms. A had followed a daily ritual. At 10:30 a.m., when the local drug store opens, she superficially tested the consistency of a certain brand of powder available on the shelves. She then purchased one case (six 14-ounce containers) of powder, went home and sampled each container, and rated them in quality from 1 to 6, with 1 being the bottle of powder she ate that day. The next morning, regardless of how many cases of powder were piled in her closet, she went to the drug store and repeated the process.
Ms. A felt comfortable eating the talc-based powder in her apartment and her mother’s house. She kept some baby powder in her desk at work, but she regularly took an hour-long lunch break to drive back to her apartment and satisfy her craving. She also carried powder in the car, tasting it while driving.
When asked how the powder made her feel, Ms. A replied: “Powder is like nothing else. It makes me feel content and at ease.” Whenever she was irritated, or if the children were frustrating her, she would take a spoonful of powder.
In the beginning, she consumed approximately one 14-ounce bottle per month. When she presented 28 weeks pregnant with her third child, she could not imagine life without baby powder. A spoonful satisfied her for only 5 to 10 minutes before she would desire more. No other substance quelled the cravings. She had tried edible substitutes such as confectioners sugar, cornstarch, and ice chips, but nothing offered the satisfaction she got from powder.
When she is unable to ingest powder, she develops a headache, begins to sweat, gets extremely anxious and irritable, cries profusely, and becomes depressed. If she is abstinent more than 2 days she is unable to sleep and becomes preoccupied with the powder. If powder is not available, she binges and induces vomiting to stifle her craving.
In the hospital she craved powder 2 days after it was removed from her access. She became extremely anxious and distressed. She then ordered as much food as possible so she could purge and forget about the powder.
How would you explain the patient’s psychopathological attraction to baby powder?
Commentary
Patients with pica typically express satisfaction from consuming non-nutrient substances (Box 2). Ms. A’s motive for eating the powder stemmed from what she perceived as its soothing properties.
Other reported cases have alluded to the sensation generated by the texture of soil or chalk in the mouth. Some of these patients also described the importance of the soil’s taste—i.e., particle size—as being second to its texture.12 The desire to experience a certain texture, color, odor, and taste are important components in pica cravings.10
| Object | Specific disorder |
|---|---|
| Burnt matches | Cautopyreiophagia |
| Earth (chalk, clay, dirt) | Geophagia |
| Feces | Coprophagia |
| Hair | Tricophagia |
| Ice | Pagophagia |
| Laundry starch, cornstarch | Amylophagia |
| Lead paint chips | Plumbophagia |
| Raw potatoes | Geomelophagia |
| Stones | Lithophagia |
Other known objects of pica—Ashes, baking soda, balloons, carrots, celery, chewing gum, cigarette butts, cloth, coal, coca leaf, coffee grounds/beans, cotton balls, concrete, crayons, croutons, detergent, grass, hard candy, insects, lavatory fresheners, latex gloves, licorice, lint, metal, milk, newsprint, oats, oyster shells, paper, parsley, plant leaves, pencil erasers, plastic, popcorn, powder puffs, salt, soap, string, thread, toilet tissue, tomato seeds, twigs, vinegar, wood.
Pica appears to meet the individual’s need for mental relaxation and sensory pleasure15 in much the same way that alcohol or drug abusers satisfy their intense desire for euphoria and relaxation. Scientists theorize that alcohol and drug abuse may be exacerbated by or result from a neurochemical imbalance. A similar hypothesis may explain this “variant” in pica patients.
Pregnant women often develop taste aversions for items that are potentially harmful to the developing fetus, such as alcohol and coffee. Expectant mothers may develop utter disgust and provocation of nausea toward items they enjoyed while not gravid. Aversions to foods and other items during pregnancy might be the consequence of homeostatic factors that have evolved as general feto-protective mechanisms.16,17 The metabolic changes that accompany the gravid state might alter olfactory and taste sensitivity.17
If a pregnancy-related change in chemical balance can cause taste aversion, certainly a similar situation could evolve into pica. In laboratory rats, intraventricular injection of exogenous neuropeptide Y, a hormone with documented CNS activity, caused taste aversions and elicited geophagia.18
Ms. A’s ingestion of baby powder itself did not harm the fetus. Stephen Emery, MD, director of perinatal ultrasound at the Cleveland Clinic, notes that talc is inert and the powder’s perfumes probably are benign. He adds, however, that because the powder often has replaced real food, Ms. A placed her unborn child at risk via malnourishment.
Further evaluation: A ‘pleasant’ appearance
Ms. A’s medical history revealed chronic asthma since childhood and gastroesophageal reflux disease. According to her social history, she is dating the father of her expectant child. She has been smoking one pack of cigarettes per day for 2 years but says she does not drink alcohol and has never abused illicit drugs.
Her lab values were as follows (with normal ranges in parentheses): blood urea, 4 mg/dl (9-23); serum iron, 69 mg/dl (42-135); calcium 8.7 mg/dl (8.5-10.5); magnesium, 1.6 mg/dl (1.8-2.4); phosphate, 2.4 mg/dl (2.7-4.6); hemoglobin, 10.0 g/dl (12.0-14.0); hematocrit, 31.1% (37.0-47.0); mean corpuscular volume, 86.4 fl (81-99).
Ms. A appeared well-nourished, appropriately dressed, and well-groomed during our examination. She was alert, oriented and cooperative, and held a pleasant conversation with good eye contact. Her mood was depressed and anxious, and her affect was congruent. Speech was normal in rate, tone, and volume. Her thoughts were well organized and goal-directed. She denied suicidal ideation but had thoughts of harming her fetus. She denied any perceptual disturbances. No intellectual impairment was evident, and her insight and judgment were preserved.
What is the psychiatric diagnosis for this patient? Also, in your view, how likely is she to harm her fetus or her two children? How would you assess and manage that risk?
Commentary
The physiologic cause of pica may be metabolic disturbances in iron, zinc, calcium, potassium, lead, and magnesium.10,19-22 Ice pica typically is associated with iron deficiency and low hemoglobin levels,14,20,23,24 although other forms of pica have been linked to iron deficiency.12,25 Some studies show iron deficiency in nearly half of patients who display ice pica;20,26 correcting the iron deficiency relieves the cravings for the desired substances.7,14 Scientists are split as to whether pica results in the deficiency of certain minerals or whether mineral deficiencies cause pica. Mineral deficiencies may alter appetite-regulating brain enzymes that can lead to these cravings.7,10,11,23
Ms. A’s laboratory values demonstrated decreased hemoglobin, hematocrit, and magnesium levels. Magnesium replacement did not change her eating behavior. Her mild anemia may simply have been an effect of pregnancy.
Treatment: Confronting comorbid depression
Ms. A’s diagnosis was pica, bulimia nervosa-purging type, with comorbid depressive disorder NOS.
She was placed on the selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor sertraline, 12.5 mg/d. The dosage was increased gradually to 50 mg qd. Supportive psychotherapy was provided during the patient’s hospital course.
After her discharge, cognitive therapy was initiated. Ms. A was asked to keep a journal utilizing the “triple column technique,” through which she described a situation in one column, explained the symptoms or unwanted behaviors and emotions evoked by that situation in the second, and wrote down her thoughts in the third.
Ms. A was monitored for signs and symptoms of postpartum depression. After this careful assessment, in which two psychiatrists and the ob/gyn team participated, we concluded that the patient’s transient thoughts of harming her fetus had fully resolved.
Ms. A was educated about nutrition and healthy exercise, as well as birth control options. We also asked to see her as an outpatient.
In the ensuing months, Ms. A reported moderate depressive symptoms but described a significant decrease in her craving for, and consumption of, powder. She continued follow-up treatment with her physician at the women’s care center. Ms. A decided to stop taking sertraline after 2 months because she felt it was not helping her depression and was causing fatigue.
When we followed up after 6 months, Ms. A reported that she and her baby were doing well. She told us that her powder cravings had decreased markedly.
Related resources
- Alliance for Eating Disorders Awareness. www.eatingdisorderinfo.org
- Stein DJ, Bouwer C, van Heerden B. Pica and the obsessive spectrum disorders. S Afr Med J 1996; 86(12 suppl):1586-8, 1591-2.
Drug brand names
- Sertraline • Zoloft
Disclosure
The authors report no financial relationship with any company whose products are mentioned in this article.
1. Robischon P. Pica practice and other hand-mouth behavior and children’s development level. Nurs Res 1971;20(1):4-16.
2. Cooksey NR. Pica and olfactory craving of pregnancy: How deep are the secrets? Birth 1995;22(3):129-37.
3. Danford DE, Smith JC, Huber AM. Pica and mineral status in the mentally retarded. Am J Clin Nutr 1982;35(5):958-67.
4. Jawed SH, Krishnan VH, et al. Worsening of pica as a symptom of Depressive illness in a person with severe mental handicap. Br J Psychiatry 1993;162:835-7.
5. Sturmey P. Pica and developmental disability. J Am Board Fam Pract 2001;14(1):80-1.
6. Tracy JI, de Leon J, Qureshi G, et al. Repetitive behaviors in schizophrenia: a single disturbance or discrete symptoms? Schizophr Res 1996;20(1-2):221-9.
7. Federman DG, Kirsner RS, Federman GS. Pica: Are you hungry for the facts? Conn Med 1997;61(4):207-9.
8. Parry-Jones B, Parry-Jones WL. Pica: symptom or eating disorder? A historical perspective. Br J Psychiatry. 1992;160:341-54.
9. Goldstein M. Adult pica: A clinical nexus of physiology and psychodynamics. Psychosom 1998;39:465-9.
10. Danford DE. Pica and nutrition. Annu Rev Nutr 1982;2:303-22.
11. Jackson WC, Martin JP. Amylophagia presenting as gestational diabetes. Arch Fam Med 2000;9(7):649-52.
12. Geissler PW, Prince RJ, Levene M, et al. Perceptions of soil-eating and anemia among pregnant women on the Kenyan coast. Soc Sci Med 1999;48(8):1069-79.
13. Parry-Jones B. Historical terminology of eating disorders. Psychol Med 1991;21:21-8.
14. Rose EA, Porcerelli JH, Neale AV. Pica: common but commonly missed. J Am Board Fam Pract 2000;13(5):353-8.
15. Castiglia PT. Pica. J Pediatr Health Care 1993;7(4):174-5.
16. Fairburn CG, Stein A, Jones R. Eating habits and eating disorders during pregnancy. Psychosom Med 1992;54(6):665-72.
17. Hook EB. Dietary cravings and aversions during pregnancy. Am J Clin Nutr 1978;31(8):1355-62.
18. Madden LJ, Seeley RJ, Woods SC. Intraventricular neuropeptide Y decreases need induced sodium appetite and increases pica in rats. Behav Neurosci 1999;113:826-32.
19. Appel RG, Bleyer AJ. Pica associated with renal and electrolyte disorders. Int J Artif Organs 1999;22(11):726-9.
20. Crosby WH. Pica. JAMA 1976;235(25):2765.-
21. Lofts RH, Schroeder SR, Maier RH. Effects of serum zinc supplementation on pica behavior of persons with mental retardation. Am J Ment Retard 1990;95(1):103-9.
22. Siklar Z, Gulten T, Dallor Y, Gunay S. Pica and intoxication in childhood. Clin Pediatr (Phila) 2000;39(10):624-5.
23. Rainville AJ. Pica practices of pregnant women are associated with lower maternal hemoglobin level at delivery. J Am Diet Assoc 1998;98(3):293-6.
24. Rothenberg SJ, Manalo M, Jiang J, et al. Maternal blood lead level during pregnancy in South Central Los Angeles. Arch Environ Health 1999;54(3):151-7.
25. Marinella MA. “Tomatophagia” and iron-deficiency anemia. N Engl J Med 1999;341(1):60-1.
26. Crosby WH. Pica: A compulsion caused by iron deficiency. Br J Haematol 1976;34(2):341-2.
1. Robischon P. Pica practice and other hand-mouth behavior and children’s development level. Nurs Res 1971;20(1):4-16.
2. Cooksey NR. Pica and olfactory craving of pregnancy: How deep are the secrets? Birth 1995;22(3):129-37.
3. Danford DE, Smith JC, Huber AM. Pica and mineral status in the mentally retarded. Am J Clin Nutr 1982;35(5):958-67.
4. Jawed SH, Krishnan VH, et al. Worsening of pica as a symptom of Depressive illness in a person with severe mental handicap. Br J Psychiatry 1993;162:835-7.
5. Sturmey P. Pica and developmental disability. J Am Board Fam Pract 2001;14(1):80-1.
6. Tracy JI, de Leon J, Qureshi G, et al. Repetitive behaviors in schizophrenia: a single disturbance or discrete symptoms? Schizophr Res 1996;20(1-2):221-9.
7. Federman DG, Kirsner RS, Federman GS. Pica: Are you hungry for the facts? Conn Med 1997;61(4):207-9.
8. Parry-Jones B, Parry-Jones WL. Pica: symptom or eating disorder? A historical perspective. Br J Psychiatry. 1992;160:341-54.
9. Goldstein M. Adult pica: A clinical nexus of physiology and psychodynamics. Psychosom 1998;39:465-9.
10. Danford DE. Pica and nutrition. Annu Rev Nutr 1982;2:303-22.
11. Jackson WC, Martin JP. Amylophagia presenting as gestational diabetes. Arch Fam Med 2000;9(7):649-52.
12. Geissler PW, Prince RJ, Levene M, et al. Perceptions of soil-eating and anemia among pregnant women on the Kenyan coast. Soc Sci Med 1999;48(8):1069-79.
13. Parry-Jones B. Historical terminology of eating disorders. Psychol Med 1991;21:21-8.
14. Rose EA, Porcerelli JH, Neale AV. Pica: common but commonly missed. J Am Board Fam Pract 2000;13(5):353-8.
15. Castiglia PT. Pica. J Pediatr Health Care 1993;7(4):174-5.
16. Fairburn CG, Stein A, Jones R. Eating habits and eating disorders during pregnancy. Psychosom Med 1992;54(6):665-72.
17. Hook EB. Dietary cravings and aversions during pregnancy. Am J Clin Nutr 1978;31(8):1355-62.
18. Madden LJ, Seeley RJ, Woods SC. Intraventricular neuropeptide Y decreases need induced sodium appetite and increases pica in rats. Behav Neurosci 1999;113:826-32.
19. Appel RG, Bleyer AJ. Pica associated with renal and electrolyte disorders. Int J Artif Organs 1999;22(11):726-9.
20. Crosby WH. Pica. JAMA 1976;235(25):2765.-
21. Lofts RH, Schroeder SR, Maier RH. Effects of serum zinc supplementation on pica behavior of persons with mental retardation. Am J Ment Retard 1990;95(1):103-9.
22. Siklar Z, Gulten T, Dallor Y, Gunay S. Pica and intoxication in childhood. Clin Pediatr (Phila) 2000;39(10):624-5.
23. Rainville AJ. Pica practices of pregnant women are associated with lower maternal hemoglobin level at delivery. J Am Diet Assoc 1998;98(3):293-6.
24. Rothenberg SJ, Manalo M, Jiang J, et al. Maternal blood lead level during pregnancy in South Central Los Angeles. Arch Environ Health 1999;54(3):151-7.
25. Marinella MA. “Tomatophagia” and iron-deficiency anemia. N Engl J Med 1999;341(1):60-1.
26. Crosby WH. Pica: A compulsion caused by iron deficiency. Br J Haematol 1976;34(2):341-2.
Questioning ADHD red flags
Dr. Manuel Mota-Castillo’s description of “Five red flags that rule out ADHD in children” (Pearls, April) is remarkably at variance with current research and clinical practice in the diagnosis and treatment of children with attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder.
Mood disorders are well-known comorbidities of ADHD and, unfortunately, numerous young adults with a childhood history of ADHD do “get high on” and become addicted to cocaine and other street drugs. Further, impairing, problematic symptoms often are not noted until the second grade or later in the elementary school years, especially in children who have the inattentive type of ADHD. Absence of a history of symptoms in kindergarten certainly does not contradict a diagnosis of ADHD.
The Multimodal Treatment Study for ADHD, or MTA study, among others, found that about 40% of carefully diagnosed children with ADHD also had oppositional-defiant disorder (ODD), and that 10% to 20% had conduct disorder (CD). These are common ADHD comorbidities.
Finally, a child’s response to initial medication treatment never confirms nor refutes this diagnosis. This point has been emphasized in every major publication in our field for a decade.
Corydon G. Clark, MD
Medical Director,
ADD Clinic Inc Las Vegas, Nev.
I have several problems with Dr. Mota-Castillo’s comments:
First, moodiness can be a part of ADHD. Also, some unfortunate children have ADHD with comorbid bipolar or mood disorders.
Second, depending on the demands of the child, the environment, and the response to the child’s behavior (among other things), ADHD can appear to be intermittent.
Third, ADHD symptoms are present in kindergarten. Some kids do not get diagnosed that early, especially those with ADHD, inattentive type, but they still meet the criteria for ADHD.
Fourth, comorbidity is usually the rule with ADHD. Fifth, response to a stimulant does not make a diagnosis of ADHD. I do not have ADHD, but I would likely “think better” on a stimulant!
Finally, a follow-up appointment at 2 weeks does not confirm a diagnosis of ADHD. The diagnosis is made only after a thorough review of the child's history, a review of the pediatric record, a physical examination by the pediatrician, a clinical interview with the parents or primary caregiver, an interview and examination of the child, a review of school records, and input from current and previous teachers as well as all others who provide care for the child in structured and unstructured settings.
Lori W. Bekenstein, MD
Child and Adolescent Psychiatrist,
Richmond, Va
Dr. Mota-Castillo responds:
Dr. Clark’s letter is not surprising; his statements echo other ADHD experts and the ADHD clinics around the country. Let me clarify several misconceptions around this illness, however.
I don’t blame people who follow dictates from the MTA study, considering the high academic level of the researchers involved. Still, their findings are not immune to further investigation and clinical testing. In fact, other prominent investigators such as Charles Huffine, MD, and Andres Pumariega, MD, have requested the deletion of the CD diagnosis from DSM-IV. Several others have questioned ODD as a valid entity.
I am not a famous scholar from a prestigious school, but I can point to hundreds of children previously diagnosed with ODD who became “non-oppositional” after treatment for their real conditions—either a mood, anxiety, or psychotic disorder.
Other prominent researchers, including Kay Redfield-Jamison, have refuted the assumption that all children diagnosed historically with ADHD were correctly differentiated from other disorders that may display some similar symptoms. Jamison recently cited a tragic patient outcome: A young boy was misdiagnosed with ADHD, placed on stimulants, and ultimately hanged himself.
Most studies on ADHD, including the MTA, are statistically irrelevant because they are based on samples that include many wrongly diagnosed children. I can prove that the combination of ADHD, CD, and ODD really means that these diagnoses are erroneous. The same rationale also explains why statistics about the alleged lack of diagnostic relevance of medication trials are unreliable: Many patients who “failed” did not really have ADHD.
Major published papers do not carry an imprimatur. Remember that several decades ago, experts said that because of lack of ego development, children could not get depressed. Also remember the many papers that acknowledged that bipolar patients were being wrongly diagnosed with schizophrenia.
In regard to labeling with ADD people who abuse illegal stimulants such cocaine or “speed,” I want to emphasize that it is chemically absurd to believe that somebody can get “high” on cocaine and also respond focused and calm on Ritalin. Multiple psychopharmacological and addiction studies have demonstrated that these two substances are identical twins both chemically and in brain responses.
Finally, my clinical findings, described as “remarkably at variance with current research and practice” are based on my research of the files of hundreds of youths in the correctional system. These youths’ attitudes, behavior, and lives completely changed when stimulants were replaced with mood stabilizers or antipsychotics. Many of them stayed on stimulant medications despite overly elevated mood, hallucinations, and aggressive behavior. Aggravated assault charges landed them behind bars.
With regard to Dr. Bekenstein’s comments, I can only say that if she thoughtfully rereads my article, she will realize that I did not say some of the things she perceived.
In the end, I have hundreds of former “treatment failures” to corroborate my statements. I am not alone either in my perspectives on these ADHD issues if all research and practice are considered, or in the conviction that science and patient treatment is advanced by divergent research that tests current views.
Editor’s note:
Thanks to Drs. Clark, Bekenstein, and Mota-Castillo.
The concept of publishing clinical “Pearls” is to allow experienced clinicians to share what they have learned in practice. The somewhat sad truth is that a lot of what we do in practice every day is not “evidence-based.” As Dr. Mota-Castillo points out, much of what was generally accepted not long ago has turned out not to be true.
For the purpose of determining whether a clinician has met “the standard of care” in a professional liability case, the standard is not that what they did would be agreed to by all clinicians, or even by a majority of clinicians. The standard is whether a “reasonable minority” of clinicians would agree. In the case of “Pearls,” we are willing to print recommendations that are endorsed by a reasonable minority, even if they do not represent the majority opinion.
In our regular articles, we are careful to differentiate majority from minority opinion. We have not done that so far in the “Pearls” section. In the future, we will make sure to include an editorial comment in cases like this where most practitioners probably would not endorse the author’s opinion.
To be honest, I am pretty sure that I have seen patients who had ADHD who also became cocaine abusers.
J. Randolph Hillard, MD
Editor-in-chief
Dr. Manuel Mota-Castillo’s description of “Five red flags that rule out ADHD in children” (Pearls, April) is remarkably at variance with current research and clinical practice in the diagnosis and treatment of children with attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder.
Mood disorders are well-known comorbidities of ADHD and, unfortunately, numerous young adults with a childhood history of ADHD do “get high on” and become addicted to cocaine and other street drugs. Further, impairing, problematic symptoms often are not noted until the second grade or later in the elementary school years, especially in children who have the inattentive type of ADHD. Absence of a history of symptoms in kindergarten certainly does not contradict a diagnosis of ADHD.
The Multimodal Treatment Study for ADHD, or MTA study, among others, found that about 40% of carefully diagnosed children with ADHD also had oppositional-defiant disorder (ODD), and that 10% to 20% had conduct disorder (CD). These are common ADHD comorbidities.
Finally, a child’s response to initial medication treatment never confirms nor refutes this diagnosis. This point has been emphasized in every major publication in our field for a decade.
Corydon G. Clark, MD
Medical Director,
ADD Clinic Inc Las Vegas, Nev.
I have several problems with Dr. Mota-Castillo’s comments:
First, moodiness can be a part of ADHD. Also, some unfortunate children have ADHD with comorbid bipolar or mood disorders.
Second, depending on the demands of the child, the environment, and the response to the child’s behavior (among other things), ADHD can appear to be intermittent.
Third, ADHD symptoms are present in kindergarten. Some kids do not get diagnosed that early, especially those with ADHD, inattentive type, but they still meet the criteria for ADHD.
Fourth, comorbidity is usually the rule with ADHD. Fifth, response to a stimulant does not make a diagnosis of ADHD. I do not have ADHD, but I would likely “think better” on a stimulant!
Finally, a follow-up appointment at 2 weeks does not confirm a diagnosis of ADHD. The diagnosis is made only after a thorough review of the child's history, a review of the pediatric record, a physical examination by the pediatrician, a clinical interview with the parents or primary caregiver, an interview and examination of the child, a review of school records, and input from current and previous teachers as well as all others who provide care for the child in structured and unstructured settings.
Lori W. Bekenstein, MD
Child and Adolescent Psychiatrist,
Richmond, Va
Dr. Mota-Castillo responds:
Dr. Clark’s letter is not surprising; his statements echo other ADHD experts and the ADHD clinics around the country. Let me clarify several misconceptions around this illness, however.
I don’t blame people who follow dictates from the MTA study, considering the high academic level of the researchers involved. Still, their findings are not immune to further investigation and clinical testing. In fact, other prominent investigators such as Charles Huffine, MD, and Andres Pumariega, MD, have requested the deletion of the CD diagnosis from DSM-IV. Several others have questioned ODD as a valid entity.
I am not a famous scholar from a prestigious school, but I can point to hundreds of children previously diagnosed with ODD who became “non-oppositional” after treatment for their real conditions—either a mood, anxiety, or psychotic disorder.
Other prominent researchers, including Kay Redfield-Jamison, have refuted the assumption that all children diagnosed historically with ADHD were correctly differentiated from other disorders that may display some similar symptoms. Jamison recently cited a tragic patient outcome: A young boy was misdiagnosed with ADHD, placed on stimulants, and ultimately hanged himself.
Most studies on ADHD, including the MTA, are statistically irrelevant because they are based on samples that include many wrongly diagnosed children. I can prove that the combination of ADHD, CD, and ODD really means that these diagnoses are erroneous. The same rationale also explains why statistics about the alleged lack of diagnostic relevance of medication trials are unreliable: Many patients who “failed” did not really have ADHD.
Major published papers do not carry an imprimatur. Remember that several decades ago, experts said that because of lack of ego development, children could not get depressed. Also remember the many papers that acknowledged that bipolar patients were being wrongly diagnosed with schizophrenia.
In regard to labeling with ADD people who abuse illegal stimulants such cocaine or “speed,” I want to emphasize that it is chemically absurd to believe that somebody can get “high” on cocaine and also respond focused and calm on Ritalin. Multiple psychopharmacological and addiction studies have demonstrated that these two substances are identical twins both chemically and in brain responses.
Finally, my clinical findings, described as “remarkably at variance with current research and practice” are based on my research of the files of hundreds of youths in the correctional system. These youths’ attitudes, behavior, and lives completely changed when stimulants were replaced with mood stabilizers or antipsychotics. Many of them stayed on stimulant medications despite overly elevated mood, hallucinations, and aggressive behavior. Aggravated assault charges landed them behind bars.
With regard to Dr. Bekenstein’s comments, I can only say that if she thoughtfully rereads my article, she will realize that I did not say some of the things she perceived.
In the end, I have hundreds of former “treatment failures” to corroborate my statements. I am not alone either in my perspectives on these ADHD issues if all research and practice are considered, or in the conviction that science and patient treatment is advanced by divergent research that tests current views.
Editor’s note:
Thanks to Drs. Clark, Bekenstein, and Mota-Castillo.
The concept of publishing clinical “Pearls” is to allow experienced clinicians to share what they have learned in practice. The somewhat sad truth is that a lot of what we do in practice every day is not “evidence-based.” As Dr. Mota-Castillo points out, much of what was generally accepted not long ago has turned out not to be true.
For the purpose of determining whether a clinician has met “the standard of care” in a professional liability case, the standard is not that what they did would be agreed to by all clinicians, or even by a majority of clinicians. The standard is whether a “reasonable minority” of clinicians would agree. In the case of “Pearls,” we are willing to print recommendations that are endorsed by a reasonable minority, even if they do not represent the majority opinion.
In our regular articles, we are careful to differentiate majority from minority opinion. We have not done that so far in the “Pearls” section. In the future, we will make sure to include an editorial comment in cases like this where most practitioners probably would not endorse the author’s opinion.
To be honest, I am pretty sure that I have seen patients who had ADHD who also became cocaine abusers.
J. Randolph Hillard, MD
Editor-in-chief
Dr. Manuel Mota-Castillo’s description of “Five red flags that rule out ADHD in children” (Pearls, April) is remarkably at variance with current research and clinical practice in the diagnosis and treatment of children with attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder.
Mood disorders are well-known comorbidities of ADHD and, unfortunately, numerous young adults with a childhood history of ADHD do “get high on” and become addicted to cocaine and other street drugs. Further, impairing, problematic symptoms often are not noted until the second grade or later in the elementary school years, especially in children who have the inattentive type of ADHD. Absence of a history of symptoms in kindergarten certainly does not contradict a diagnosis of ADHD.
The Multimodal Treatment Study for ADHD, or MTA study, among others, found that about 40% of carefully diagnosed children with ADHD also had oppositional-defiant disorder (ODD), and that 10% to 20% had conduct disorder (CD). These are common ADHD comorbidities.
Finally, a child’s response to initial medication treatment never confirms nor refutes this diagnosis. This point has been emphasized in every major publication in our field for a decade.
Corydon G. Clark, MD
Medical Director,
ADD Clinic Inc Las Vegas, Nev.
I have several problems with Dr. Mota-Castillo’s comments:
First, moodiness can be a part of ADHD. Also, some unfortunate children have ADHD with comorbid bipolar or mood disorders.
Second, depending on the demands of the child, the environment, and the response to the child’s behavior (among other things), ADHD can appear to be intermittent.
Third, ADHD symptoms are present in kindergarten. Some kids do not get diagnosed that early, especially those with ADHD, inattentive type, but they still meet the criteria for ADHD.
Fourth, comorbidity is usually the rule with ADHD. Fifth, response to a stimulant does not make a diagnosis of ADHD. I do not have ADHD, but I would likely “think better” on a stimulant!
Finally, a follow-up appointment at 2 weeks does not confirm a diagnosis of ADHD. The diagnosis is made only after a thorough review of the child's history, a review of the pediatric record, a physical examination by the pediatrician, a clinical interview with the parents or primary caregiver, an interview and examination of the child, a review of school records, and input from current and previous teachers as well as all others who provide care for the child in structured and unstructured settings.
Lori W. Bekenstein, MD
Child and Adolescent Psychiatrist,
Richmond, Va
Dr. Mota-Castillo responds:
Dr. Clark’s letter is not surprising; his statements echo other ADHD experts and the ADHD clinics around the country. Let me clarify several misconceptions around this illness, however.
I don’t blame people who follow dictates from the MTA study, considering the high academic level of the researchers involved. Still, their findings are not immune to further investigation and clinical testing. In fact, other prominent investigators such as Charles Huffine, MD, and Andres Pumariega, MD, have requested the deletion of the CD diagnosis from DSM-IV. Several others have questioned ODD as a valid entity.
I am not a famous scholar from a prestigious school, but I can point to hundreds of children previously diagnosed with ODD who became “non-oppositional” after treatment for their real conditions—either a mood, anxiety, or psychotic disorder.
Other prominent researchers, including Kay Redfield-Jamison, have refuted the assumption that all children diagnosed historically with ADHD were correctly differentiated from other disorders that may display some similar symptoms. Jamison recently cited a tragic patient outcome: A young boy was misdiagnosed with ADHD, placed on stimulants, and ultimately hanged himself.
Most studies on ADHD, including the MTA, are statistically irrelevant because they are based on samples that include many wrongly diagnosed children. I can prove that the combination of ADHD, CD, and ODD really means that these diagnoses are erroneous. The same rationale also explains why statistics about the alleged lack of diagnostic relevance of medication trials are unreliable: Many patients who “failed” did not really have ADHD.
Major published papers do not carry an imprimatur. Remember that several decades ago, experts said that because of lack of ego development, children could not get depressed. Also remember the many papers that acknowledged that bipolar patients were being wrongly diagnosed with schizophrenia.
In regard to labeling with ADD people who abuse illegal stimulants such cocaine or “speed,” I want to emphasize that it is chemically absurd to believe that somebody can get “high” on cocaine and also respond focused and calm on Ritalin. Multiple psychopharmacological and addiction studies have demonstrated that these two substances are identical twins both chemically and in brain responses.
Finally, my clinical findings, described as “remarkably at variance with current research and practice” are based on my research of the files of hundreds of youths in the correctional system. These youths’ attitudes, behavior, and lives completely changed when stimulants were replaced with mood stabilizers or antipsychotics. Many of them stayed on stimulant medications despite overly elevated mood, hallucinations, and aggressive behavior. Aggravated assault charges landed them behind bars.
With regard to Dr. Bekenstein’s comments, I can only say that if she thoughtfully rereads my article, she will realize that I did not say some of the things she perceived.
In the end, I have hundreds of former “treatment failures” to corroborate my statements. I am not alone either in my perspectives on these ADHD issues if all research and practice are considered, or in the conviction that science and patient treatment is advanced by divergent research that tests current views.
Editor’s note:
Thanks to Drs. Clark, Bekenstein, and Mota-Castillo.
The concept of publishing clinical “Pearls” is to allow experienced clinicians to share what they have learned in practice. The somewhat sad truth is that a lot of what we do in practice every day is not “evidence-based.” As Dr. Mota-Castillo points out, much of what was generally accepted not long ago has turned out not to be true.
For the purpose of determining whether a clinician has met “the standard of care” in a professional liability case, the standard is not that what they did would be agreed to by all clinicians, or even by a majority of clinicians. The standard is whether a “reasonable minority” of clinicians would agree. In the case of “Pearls,” we are willing to print recommendations that are endorsed by a reasonable minority, even if they do not represent the majority opinion.
In our regular articles, we are careful to differentiate majority from minority opinion. We have not done that so far in the “Pearls” section. In the future, we will make sure to include an editorial comment in cases like this where most practitioners probably would not endorse the author’s opinion.
To be honest, I am pretty sure that I have seen patients who had ADHD who also became cocaine abusers.
J. Randolph Hillard, MD
Editor-in-chief