User login
FDA OKs Tremfya for Ulcerative Colitis
Guselkumab is the first and only interleukin-23 (IL-23) inhibitor available as both SC and intravenous (IV) induction options for the treatment of UC and Crohn’s disease (CD), the company noted in a news release.
The approval of SC guselkumab induction in UC was based on results from the phase 3 ASTRO trial, which randomly allocated 418 patients with moderately to severely active UC to receive either induction with 400 mg SC guselkumab at weeks 0, 4, and 8 or placebo.
Following induction, the treatment group either received a maintenance dose of 200 mg SC guselkumab at week 12 and then every 4 weeks or 100 mg every 8 weeks (starting at 16 weeks).
All patients had had an inadequate response or intolerance to conventional therapy.
All primary and secondary endpoints demonstrated statistically significant and clinically meaningful improvements with SC guselkumab compared to placebo across all clinical and endoscopic measures, the company said.
At 12 weeks, a significantly greater proportion of patients treated with 400 mg SC guselkumab every 4 weeks achieved clinical remission (26% vs 7% with placebo; P < .001) and endoscopic improvement (36% vs 12%; P < .001).
The results were consistent with the FDA-approved 200 mg IV induction regimen, which previously achieved clinical remission (23% vs 8% with placebo; P < .001) and endoscopic improvement (27% vs 11%; P < .001).
The efficacy of SC and IV induction was comparable across subgroups with severe or refractory disease and both routes demonstrated a similar time to onset of efficacy.
SC guselkumab induction followed by SC guselkumab maintenance therapy also demonstrated statistically significant and clinically meaningful improvements in clinical remission and endoscopic improvement compared to placebo.
“Historically, IL-23 inhibitors have required IV infusions at the start of therapy, which can create barriers to starting treatment or be burdensome for some patients and clinicians,” study investigator David T. Rubin, MD, AGAF, director of the Inflammatory Bowel Disease Center at University of Chicago Medicine, said in the news release.
“UC patients and providers now have the choice of starting Tremfya with a self-administered subcutaneous injection, with the same efficacy and safety that were established with IV induction in the prior clinical trials and subsequently seen in our real-world practice,” Rubin said.
Full prescribing information and medication guide are available online.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Guselkumab is the first and only interleukin-23 (IL-23) inhibitor available as both SC and intravenous (IV) induction options for the treatment of UC and Crohn’s disease (CD), the company noted in a news release.
The approval of SC guselkumab induction in UC was based on results from the phase 3 ASTRO trial, which randomly allocated 418 patients with moderately to severely active UC to receive either induction with 400 mg SC guselkumab at weeks 0, 4, and 8 or placebo.
Following induction, the treatment group either received a maintenance dose of 200 mg SC guselkumab at week 12 and then every 4 weeks or 100 mg every 8 weeks (starting at 16 weeks).
All patients had had an inadequate response or intolerance to conventional therapy.
All primary and secondary endpoints demonstrated statistically significant and clinically meaningful improvements with SC guselkumab compared to placebo across all clinical and endoscopic measures, the company said.
At 12 weeks, a significantly greater proportion of patients treated with 400 mg SC guselkumab every 4 weeks achieved clinical remission (26% vs 7% with placebo; P < .001) and endoscopic improvement (36% vs 12%; P < .001).
The results were consistent with the FDA-approved 200 mg IV induction regimen, which previously achieved clinical remission (23% vs 8% with placebo; P < .001) and endoscopic improvement (27% vs 11%; P < .001).
The efficacy of SC and IV induction was comparable across subgroups with severe or refractory disease and both routes demonstrated a similar time to onset of efficacy.
SC guselkumab induction followed by SC guselkumab maintenance therapy also demonstrated statistically significant and clinically meaningful improvements in clinical remission and endoscopic improvement compared to placebo.
“Historically, IL-23 inhibitors have required IV infusions at the start of therapy, which can create barriers to starting treatment or be burdensome for some patients and clinicians,” study investigator David T. Rubin, MD, AGAF, director of the Inflammatory Bowel Disease Center at University of Chicago Medicine, said in the news release.
“UC patients and providers now have the choice of starting Tremfya with a self-administered subcutaneous injection, with the same efficacy and safety that were established with IV induction in the prior clinical trials and subsequently seen in our real-world practice,” Rubin said.
Full prescribing information and medication guide are available online.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Guselkumab is the first and only interleukin-23 (IL-23) inhibitor available as both SC and intravenous (IV) induction options for the treatment of UC and Crohn’s disease (CD), the company noted in a news release.
The approval of SC guselkumab induction in UC was based on results from the phase 3 ASTRO trial, which randomly allocated 418 patients with moderately to severely active UC to receive either induction with 400 mg SC guselkumab at weeks 0, 4, and 8 or placebo.
Following induction, the treatment group either received a maintenance dose of 200 mg SC guselkumab at week 12 and then every 4 weeks or 100 mg every 8 weeks (starting at 16 weeks).
All patients had had an inadequate response or intolerance to conventional therapy.
All primary and secondary endpoints demonstrated statistically significant and clinically meaningful improvements with SC guselkumab compared to placebo across all clinical and endoscopic measures, the company said.
At 12 weeks, a significantly greater proportion of patients treated with 400 mg SC guselkumab every 4 weeks achieved clinical remission (26% vs 7% with placebo; P < .001) and endoscopic improvement (36% vs 12%; P < .001).
The results were consistent with the FDA-approved 200 mg IV induction regimen, which previously achieved clinical remission (23% vs 8% with placebo; P < .001) and endoscopic improvement (27% vs 11%; P < .001).
The efficacy of SC and IV induction was comparable across subgroups with severe or refractory disease and both routes demonstrated a similar time to onset of efficacy.
SC guselkumab induction followed by SC guselkumab maintenance therapy also demonstrated statistically significant and clinically meaningful improvements in clinical remission and endoscopic improvement compared to placebo.
“Historically, IL-23 inhibitors have required IV infusions at the start of therapy, which can create barriers to starting treatment or be burdensome for some patients and clinicians,” study investigator David T. Rubin, MD, AGAF, director of the Inflammatory Bowel Disease Center at University of Chicago Medicine, said in the news release.
“UC patients and providers now have the choice of starting Tremfya with a self-administered subcutaneous injection, with the same efficacy and safety that were established with IV induction in the prior clinical trials and subsequently seen in our real-world practice,” Rubin said.
Full prescribing information and medication guide are available online.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Are Probiotics for Pouchitis Prevention Worth the Cost?
, but its cost-effectiveness depends on relapse risk and may only be justified in patients who experience frequent relapses of pouchitis, a new analysis showed.
“Our findings highlight that while probiotic treatments can reduce the risk of this complication, their high costs limit their overall value for most patients,” lead author Gaurav Syal, MD, a gastroenterologist at UCLA Health, said in a statement.
“Our analysis can help guide shared decision-making between patients, clinicians, and payers to ensure resources are used where they can provide the most benefit,” Syal added.
The study was published online in Gastro Hep Advances.
Common Complication After Ulcerative Colitis Surgery
Pouchitis is a common complication in patients with ulcerative colitis who undergo restorative proctocolectomy with IPAA, with a cumulative incidence of around 48% at 2 years and 80% at 30 years.
Many patients who experience pouchitis have a single episode and respond well to short antibiotic courses. However, others develop recurrent or relapsing pouchitis, and 17% progress to a chronic form that can become dependent on antibiotics or refractory to antibiotics.
An eight-strain probiotic was shown to be effective in primary and secondary prevention of pouchitis in randomized, placebo-controlled trials.
Syal and colleagues sought to determine whether it’s worth the cost.
They constructed decision-tree models with Markov simulations to compare the risk for initial development and recurrence of pouchitis over a 2-year period between no prophylaxis and daily use of the eight-strain probiotic.
In the primary prophylaxis model, the cycle length was 2 weeks and pouchitis treatment sequence was ciprofloxacin, metronidazole and ciprofloxacin-tinidazole. In the secondary prophylaxis model, the cycle length was 4 weeks and pouchitis treatment sequence was initially the same as the primary prophylaxis model with the addition of vedolizumab and infliximab.
Costs were calculated from a US third-party payer perspective, using a willingness-to-pay threshold of $100,000 per quality-adjusted life year (QALY).
For primary prevention, the probiotic slightly increased QALYs compared with no probiotic (0.927 vs 0.918) but at a far higher cost ($2223 vs $299), resulting in an incremental cost-effectiveness ratio (ICER) of $236,076 per QALY — well above the accepted threshold.
In patients with infrequent relapses, probiotic use was slightly more effective than no use of probiotic (cumulative QALYs, 1.26 vs 1.24) but more expensive ($3370 vs $557), yielding an ICER of $153,011 per QALY — again above the accepted threshold.
However, sensitivity analyses revealed that the probiotic was cost-effective in patients with frequent relapsing pouchitis — defined as two or more episodes per year.
In this subgroup, the ICER dropped below the willingness-to-pay threshold of $100,000 per QALY, and in some scenarios, the probiotic even became the dominant strategy, meaning it was both more effective and less costly than no prophylaxis, the researchers noted.
Current guidelines from AGA on managing pouchitis suggest using probiotics to prevent recurrent episodes of pouchitis with a caveat that those who experience infrequent episodes may choose to avoid secondary prevention strategies.
“Our findings supplement the guidelines by confirming that the eight-strain probiotics can be cost-effective in frequent relapsing not in infrequent relapsing pouchitis,” the authors wrote.
They also noted that the probiotic cost itself was the biggest driver of results, accounting for 95% of the total cost in the primary prevention model. According to their analysis, reducing its price by half could make it a cost-effective option more broadly.
They also noted that probiotic prophylaxis could be cost-effective for patients at higher-than-average risk, such as those with primary sclerosing cholangitis (PSC), who have 4.2 times higher odds of developing pouchitis than peers without PSC.
But they cautioned that “further research is warranted on the effectiveness of the eight-strain probiotic for primary prevention of pouchitis in patients with ulcerative colitis and IPAA and PSC.”
The study had no financial support. Syal reported receiving research support from Pfizer.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
, but its cost-effectiveness depends on relapse risk and may only be justified in patients who experience frequent relapses of pouchitis, a new analysis showed.
“Our findings highlight that while probiotic treatments can reduce the risk of this complication, their high costs limit their overall value for most patients,” lead author Gaurav Syal, MD, a gastroenterologist at UCLA Health, said in a statement.
“Our analysis can help guide shared decision-making between patients, clinicians, and payers to ensure resources are used where they can provide the most benefit,” Syal added.
The study was published online in Gastro Hep Advances.
Common Complication After Ulcerative Colitis Surgery
Pouchitis is a common complication in patients with ulcerative colitis who undergo restorative proctocolectomy with IPAA, with a cumulative incidence of around 48% at 2 years and 80% at 30 years.
Many patients who experience pouchitis have a single episode and respond well to short antibiotic courses. However, others develop recurrent or relapsing pouchitis, and 17% progress to a chronic form that can become dependent on antibiotics or refractory to antibiotics.
An eight-strain probiotic was shown to be effective in primary and secondary prevention of pouchitis in randomized, placebo-controlled trials.
Syal and colleagues sought to determine whether it’s worth the cost.
They constructed decision-tree models with Markov simulations to compare the risk for initial development and recurrence of pouchitis over a 2-year period between no prophylaxis and daily use of the eight-strain probiotic.
In the primary prophylaxis model, the cycle length was 2 weeks and pouchitis treatment sequence was ciprofloxacin, metronidazole and ciprofloxacin-tinidazole. In the secondary prophylaxis model, the cycle length was 4 weeks and pouchitis treatment sequence was initially the same as the primary prophylaxis model with the addition of vedolizumab and infliximab.
Costs were calculated from a US third-party payer perspective, using a willingness-to-pay threshold of $100,000 per quality-adjusted life year (QALY).
For primary prevention, the probiotic slightly increased QALYs compared with no probiotic (0.927 vs 0.918) but at a far higher cost ($2223 vs $299), resulting in an incremental cost-effectiveness ratio (ICER) of $236,076 per QALY — well above the accepted threshold.
In patients with infrequent relapses, probiotic use was slightly more effective than no use of probiotic (cumulative QALYs, 1.26 vs 1.24) but more expensive ($3370 vs $557), yielding an ICER of $153,011 per QALY — again above the accepted threshold.
However, sensitivity analyses revealed that the probiotic was cost-effective in patients with frequent relapsing pouchitis — defined as two or more episodes per year.
In this subgroup, the ICER dropped below the willingness-to-pay threshold of $100,000 per QALY, and in some scenarios, the probiotic even became the dominant strategy, meaning it was both more effective and less costly than no prophylaxis, the researchers noted.
Current guidelines from AGA on managing pouchitis suggest using probiotics to prevent recurrent episodes of pouchitis with a caveat that those who experience infrequent episodes may choose to avoid secondary prevention strategies.
“Our findings supplement the guidelines by confirming that the eight-strain probiotics can be cost-effective in frequent relapsing not in infrequent relapsing pouchitis,” the authors wrote.
They also noted that the probiotic cost itself was the biggest driver of results, accounting for 95% of the total cost in the primary prevention model. According to their analysis, reducing its price by half could make it a cost-effective option more broadly.
They also noted that probiotic prophylaxis could be cost-effective for patients at higher-than-average risk, such as those with primary sclerosing cholangitis (PSC), who have 4.2 times higher odds of developing pouchitis than peers without PSC.
But they cautioned that “further research is warranted on the effectiveness of the eight-strain probiotic for primary prevention of pouchitis in patients with ulcerative colitis and IPAA and PSC.”
The study had no financial support. Syal reported receiving research support from Pfizer.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
, but its cost-effectiveness depends on relapse risk and may only be justified in patients who experience frequent relapses of pouchitis, a new analysis showed.
“Our findings highlight that while probiotic treatments can reduce the risk of this complication, their high costs limit their overall value for most patients,” lead author Gaurav Syal, MD, a gastroenterologist at UCLA Health, said in a statement.
“Our analysis can help guide shared decision-making between patients, clinicians, and payers to ensure resources are used where they can provide the most benefit,” Syal added.
The study was published online in Gastro Hep Advances.
Common Complication After Ulcerative Colitis Surgery
Pouchitis is a common complication in patients with ulcerative colitis who undergo restorative proctocolectomy with IPAA, with a cumulative incidence of around 48% at 2 years and 80% at 30 years.
Many patients who experience pouchitis have a single episode and respond well to short antibiotic courses. However, others develop recurrent or relapsing pouchitis, and 17% progress to a chronic form that can become dependent on antibiotics or refractory to antibiotics.
An eight-strain probiotic was shown to be effective in primary and secondary prevention of pouchitis in randomized, placebo-controlled trials.
Syal and colleagues sought to determine whether it’s worth the cost.
They constructed decision-tree models with Markov simulations to compare the risk for initial development and recurrence of pouchitis over a 2-year period between no prophylaxis and daily use of the eight-strain probiotic.
In the primary prophylaxis model, the cycle length was 2 weeks and pouchitis treatment sequence was ciprofloxacin, metronidazole and ciprofloxacin-tinidazole. In the secondary prophylaxis model, the cycle length was 4 weeks and pouchitis treatment sequence was initially the same as the primary prophylaxis model with the addition of vedolizumab and infliximab.
Costs were calculated from a US third-party payer perspective, using a willingness-to-pay threshold of $100,000 per quality-adjusted life year (QALY).
For primary prevention, the probiotic slightly increased QALYs compared with no probiotic (0.927 vs 0.918) but at a far higher cost ($2223 vs $299), resulting in an incremental cost-effectiveness ratio (ICER) of $236,076 per QALY — well above the accepted threshold.
In patients with infrequent relapses, probiotic use was slightly more effective than no use of probiotic (cumulative QALYs, 1.26 vs 1.24) but more expensive ($3370 vs $557), yielding an ICER of $153,011 per QALY — again above the accepted threshold.
However, sensitivity analyses revealed that the probiotic was cost-effective in patients with frequent relapsing pouchitis — defined as two or more episodes per year.
In this subgroup, the ICER dropped below the willingness-to-pay threshold of $100,000 per QALY, and in some scenarios, the probiotic even became the dominant strategy, meaning it was both more effective and less costly than no prophylaxis, the researchers noted.
Current guidelines from AGA on managing pouchitis suggest using probiotics to prevent recurrent episodes of pouchitis with a caveat that those who experience infrequent episodes may choose to avoid secondary prevention strategies.
“Our findings supplement the guidelines by confirming that the eight-strain probiotics can be cost-effective in frequent relapsing not in infrequent relapsing pouchitis,” the authors wrote.
They also noted that the probiotic cost itself was the biggest driver of results, accounting for 95% of the total cost in the primary prevention model. According to their analysis, reducing its price by half could make it a cost-effective option more broadly.
They also noted that probiotic prophylaxis could be cost-effective for patients at higher-than-average risk, such as those with primary sclerosing cholangitis (PSC), who have 4.2 times higher odds of developing pouchitis than peers without PSC.
But they cautioned that “further research is warranted on the effectiveness of the eight-strain probiotic for primary prevention of pouchitis in patients with ulcerative colitis and IPAA and PSC.”
The study had no financial support. Syal reported receiving research support from Pfizer.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM GASTRO HEP ADVANCES
Military Background Shapes Eating Disorders in VA Oncology
Military Background Shapes Eating Disorders in VA Oncology
PHOENIX – Veterans are especially vulnerable to disordered eating because of their military backgrounds, a dietician warned US Department of Veterans Affairs (VA) oncology clinicians at the annual meeting of the Association of VA Hematology/Oncology. In fact, an estimated 15% to 25% of veterans meet diagnostic criteria for eating disorders.
“Their experience in the military probably has really shaped the way that they see weight and the stigma behind it,” said Emily Fasciana, MS, RDN, LDN, a registered dietician with the VA based in Wilkes-Barre, Pennsylvania.
When cancer appears, the risk of eating disorders goes up even more, she said. “If we don’t catch eating disorders early on, severe medical problems can occur. In the cancer population, they’re going through enough medical problems as it is.”
Here are things to know about eating disorders in oncology.
Military Life Can Produce a ‘Perfect Storm’ of Risk Factors
Tightly controlled eating environments and food deprivation are often routine in military life. Along with trauma, these can create a “perfect storm of risk factors for eating disorders,” Fasciana said.
During service, for example, “people often will eat as much as they can when they can, sometimes followed by days of not being able to eat,” she said. These are very much like disordered eating behaviors such as binge eating and restricting, and they can place veterans at greater risk.”
She described how service members can develop specific eating patterns during service, such as “midrats” – midnight rations – “meals served during midnight shifts that were the best meal served all day long that they had access to.”
“When I hear veterans who wake up in the middle of the night, and they’re eating, I ask: ‘Did they practice something similar during their military experience?’ They associate that time of the day with enjoyable comfort foods, and that’s what they go to now.”
Vets Can be Haunted by Stigma of Excess Weight
“Making weight” – meeting weight standards – is routine in the military. The pressure to remain under a certain level can have lasting effects on how veterans think about extra pounds, said Kaitlin Ohde, PhD, a clinical health psychologist with the VA Puget Sound Health Care System in Seattle.
“I’ve heard some veterans tell me about getting kicked out of positions because of not being able to make weight. Then they carry this throughout their life, which is really sad,” Ohde said. “When they gain weight during treatment, sometimes it can be really bothersome for them.”
Regular weigh-ins can trouble patients, she said, so it’s important to explain to them why they’re getting on scales: “I’m getting your weight today because I want to see if this medication is doing XYZ.”
She advised colleagues to “make sure they explicitly know why we’re doing it [measuring weight], and how the things we’re using to treat them can impact their weight. This piece of the puzzle sometimes falls off the radar.”
Eating Disorders Can be Catastrophic in Cancer
Untreated eating disorders cause severe medical complications such as malnutrition, hormone dysregulation, low bone density or fractures, bradycardia, gastroparesis, and even anemia, Fasciana said.
There’s a New Category of Eating Disorder
Fasciana highlighted a condition that is underrecognized in oncology: Avoidant/restrictive food intake disorder (ARFID), which refers to patients who stay away from certain foods but not because they’re worried about body image or weight gain. “Patients with ARFID are clinically distinct from those who have anorexia, bulimia, and binge eating disorder,” she noted.
ARFID diagnosis requires food avoidance that leads to at least 1 of these consequences: significant weight loss, nutritional deficiencies, dependence on supplements or tube feeding, or psychosocial impairment.
“Veterans might have a gagging or retching reflex at the sight or smell of certain foods,” Fasciana explained. “They might have difficulty being in the presence of another person eating a nonpreferred food.”
Some cancer patients may be averse to foods of certain temperatures. “You might need to assess why they don’t like the temperature of that food. Why are those foods something that you can’t go to? Are they hurting your teeth? What are they doing to you?”
ARFID patients may also experience social withdrawal around eating. “With a lot of our head and neck cancer patients, especially those with oral cancers and those on feeding tubes, they might feel embarrassed to be around people while eating,” Fasciana said.
She highlighted a 2021 report about 4 cancer survivors with upper abdominal cancers who developed new-onset eating disorders with malnutrition resembling ARFID.
The patients experienced malabsorption, dumping syndrome, and excessive weight loss for 12 months postoperatively without classic body-image concerns. “This is a case example of how eating disorders can evolve in the oncology population,” Fasciana said.
The report said that none of the patients “returned to a healthy weight and/or healthy eating despite extensive team input… The outcomes were poor; 1 patient died, another required admission to a specialist eating disorder admission with a subsequent relapsing-remitting course, and the remaining 2 had complicated chronic courses.”
Treatment: Start With Screening, Then Reframe Thinking
Fasciana highlighted several screening tools, such as SCOFF, BREDS, and one for ARFID.
“Any screen is going to be better than no screen at all, and any question is going to be better than no question at all,” Fasciana said.
She cautioned that “veterans are not going to be so forthcoming about some of their struggles due to stigma and shame because of their past experiences in the military.”
As for therapy, psychological care may not be required, Ohde said. And it’s especially important to “listen to your patients about what they’re going through, and give them space to share.”
For those who could be helped by psychotherapy, she said, “sometimes I introduce it as therapy that can be really brief. Maybe you just need to talk to someone for a few sessions or just get some support around coping with this.”
One strategy is to focus on bringing enjoyment back to eating, she said. For some patients, “eating becomes a chore,” a task performed without joy, alone in a hospital room.
Fasciana emphasized asking questions over time, perhaps through multiple follow-ups, without expecting answers immediately. And she coaxes patients to consider what they hold dear. “I try to get them to think about the meaning that losing or gaining weight has for them, what their values are, and what really matters to them. I link it back to health, healing, and longevity of life.”
Fasciana and Ohde reported they had no disclosures.
PHOENIX – Veterans are especially vulnerable to disordered eating because of their military backgrounds, a dietician warned US Department of Veterans Affairs (VA) oncology clinicians at the annual meeting of the Association of VA Hematology/Oncology. In fact, an estimated 15% to 25% of veterans meet diagnostic criteria for eating disorders.
“Their experience in the military probably has really shaped the way that they see weight and the stigma behind it,” said Emily Fasciana, MS, RDN, LDN, a registered dietician with the VA based in Wilkes-Barre, Pennsylvania.
When cancer appears, the risk of eating disorders goes up even more, she said. “If we don’t catch eating disorders early on, severe medical problems can occur. In the cancer population, they’re going through enough medical problems as it is.”
Here are things to know about eating disorders in oncology.
Military Life Can Produce a ‘Perfect Storm’ of Risk Factors
Tightly controlled eating environments and food deprivation are often routine in military life. Along with trauma, these can create a “perfect storm of risk factors for eating disorders,” Fasciana said.
During service, for example, “people often will eat as much as they can when they can, sometimes followed by days of not being able to eat,” she said. These are very much like disordered eating behaviors such as binge eating and restricting, and they can place veterans at greater risk.”
She described how service members can develop specific eating patterns during service, such as “midrats” – midnight rations – “meals served during midnight shifts that were the best meal served all day long that they had access to.”
“When I hear veterans who wake up in the middle of the night, and they’re eating, I ask: ‘Did they practice something similar during their military experience?’ They associate that time of the day with enjoyable comfort foods, and that’s what they go to now.”
Vets Can be Haunted by Stigma of Excess Weight
“Making weight” – meeting weight standards – is routine in the military. The pressure to remain under a certain level can have lasting effects on how veterans think about extra pounds, said Kaitlin Ohde, PhD, a clinical health psychologist with the VA Puget Sound Health Care System in Seattle.
“I’ve heard some veterans tell me about getting kicked out of positions because of not being able to make weight. Then they carry this throughout their life, which is really sad,” Ohde said. “When they gain weight during treatment, sometimes it can be really bothersome for them.”
Regular weigh-ins can trouble patients, she said, so it’s important to explain to them why they’re getting on scales: “I’m getting your weight today because I want to see if this medication is doing XYZ.”
She advised colleagues to “make sure they explicitly know why we’re doing it [measuring weight], and how the things we’re using to treat them can impact their weight. This piece of the puzzle sometimes falls off the radar.”
Eating Disorders Can be Catastrophic in Cancer
Untreated eating disorders cause severe medical complications such as malnutrition, hormone dysregulation, low bone density or fractures, bradycardia, gastroparesis, and even anemia, Fasciana said.
There’s a New Category of Eating Disorder
Fasciana highlighted a condition that is underrecognized in oncology: Avoidant/restrictive food intake disorder (ARFID), which refers to patients who stay away from certain foods but not because they’re worried about body image or weight gain. “Patients with ARFID are clinically distinct from those who have anorexia, bulimia, and binge eating disorder,” she noted.
ARFID diagnosis requires food avoidance that leads to at least 1 of these consequences: significant weight loss, nutritional deficiencies, dependence on supplements or tube feeding, or psychosocial impairment.
“Veterans might have a gagging or retching reflex at the sight or smell of certain foods,” Fasciana explained. “They might have difficulty being in the presence of another person eating a nonpreferred food.”
Some cancer patients may be averse to foods of certain temperatures. “You might need to assess why they don’t like the temperature of that food. Why are those foods something that you can’t go to? Are they hurting your teeth? What are they doing to you?”
ARFID patients may also experience social withdrawal around eating. “With a lot of our head and neck cancer patients, especially those with oral cancers and those on feeding tubes, they might feel embarrassed to be around people while eating,” Fasciana said.
She highlighted a 2021 report about 4 cancer survivors with upper abdominal cancers who developed new-onset eating disorders with malnutrition resembling ARFID.
The patients experienced malabsorption, dumping syndrome, and excessive weight loss for 12 months postoperatively without classic body-image concerns. “This is a case example of how eating disorders can evolve in the oncology population,” Fasciana said.
The report said that none of the patients “returned to a healthy weight and/or healthy eating despite extensive team input… The outcomes were poor; 1 patient died, another required admission to a specialist eating disorder admission with a subsequent relapsing-remitting course, and the remaining 2 had complicated chronic courses.”
Treatment: Start With Screening, Then Reframe Thinking
Fasciana highlighted several screening tools, such as SCOFF, BREDS, and one for ARFID.
“Any screen is going to be better than no screen at all, and any question is going to be better than no question at all,” Fasciana said.
She cautioned that “veterans are not going to be so forthcoming about some of their struggles due to stigma and shame because of their past experiences in the military.”
As for therapy, psychological care may not be required, Ohde said. And it’s especially important to “listen to your patients about what they’re going through, and give them space to share.”
For those who could be helped by psychotherapy, she said, “sometimes I introduce it as therapy that can be really brief. Maybe you just need to talk to someone for a few sessions or just get some support around coping with this.”
One strategy is to focus on bringing enjoyment back to eating, she said. For some patients, “eating becomes a chore,” a task performed without joy, alone in a hospital room.
Fasciana emphasized asking questions over time, perhaps through multiple follow-ups, without expecting answers immediately. And she coaxes patients to consider what they hold dear. “I try to get them to think about the meaning that losing or gaining weight has for them, what their values are, and what really matters to them. I link it back to health, healing, and longevity of life.”
Fasciana and Ohde reported they had no disclosures.
PHOENIX – Veterans are especially vulnerable to disordered eating because of their military backgrounds, a dietician warned US Department of Veterans Affairs (VA) oncology clinicians at the annual meeting of the Association of VA Hematology/Oncology. In fact, an estimated 15% to 25% of veterans meet diagnostic criteria for eating disorders.
“Their experience in the military probably has really shaped the way that they see weight and the stigma behind it,” said Emily Fasciana, MS, RDN, LDN, a registered dietician with the VA based in Wilkes-Barre, Pennsylvania.
When cancer appears, the risk of eating disorders goes up even more, she said. “If we don’t catch eating disorders early on, severe medical problems can occur. In the cancer population, they’re going through enough medical problems as it is.”
Here are things to know about eating disorders in oncology.
Military Life Can Produce a ‘Perfect Storm’ of Risk Factors
Tightly controlled eating environments and food deprivation are often routine in military life. Along with trauma, these can create a “perfect storm of risk factors for eating disorders,” Fasciana said.
During service, for example, “people often will eat as much as they can when they can, sometimes followed by days of not being able to eat,” she said. These are very much like disordered eating behaviors such as binge eating and restricting, and they can place veterans at greater risk.”
She described how service members can develop specific eating patterns during service, such as “midrats” – midnight rations – “meals served during midnight shifts that were the best meal served all day long that they had access to.”
“When I hear veterans who wake up in the middle of the night, and they’re eating, I ask: ‘Did they practice something similar during their military experience?’ They associate that time of the day with enjoyable comfort foods, and that’s what they go to now.”
Vets Can be Haunted by Stigma of Excess Weight
“Making weight” – meeting weight standards – is routine in the military. The pressure to remain under a certain level can have lasting effects on how veterans think about extra pounds, said Kaitlin Ohde, PhD, a clinical health psychologist with the VA Puget Sound Health Care System in Seattle.
“I’ve heard some veterans tell me about getting kicked out of positions because of not being able to make weight. Then they carry this throughout their life, which is really sad,” Ohde said. “When they gain weight during treatment, sometimes it can be really bothersome for them.”
Regular weigh-ins can trouble patients, she said, so it’s important to explain to them why they’re getting on scales: “I’m getting your weight today because I want to see if this medication is doing XYZ.”
She advised colleagues to “make sure they explicitly know why we’re doing it [measuring weight], and how the things we’re using to treat them can impact their weight. This piece of the puzzle sometimes falls off the radar.”
Eating Disorders Can be Catastrophic in Cancer
Untreated eating disorders cause severe medical complications such as malnutrition, hormone dysregulation, low bone density or fractures, bradycardia, gastroparesis, and even anemia, Fasciana said.
There’s a New Category of Eating Disorder
Fasciana highlighted a condition that is underrecognized in oncology: Avoidant/restrictive food intake disorder (ARFID), which refers to patients who stay away from certain foods but not because they’re worried about body image or weight gain. “Patients with ARFID are clinically distinct from those who have anorexia, bulimia, and binge eating disorder,” she noted.
ARFID diagnosis requires food avoidance that leads to at least 1 of these consequences: significant weight loss, nutritional deficiencies, dependence on supplements or tube feeding, or psychosocial impairment.
“Veterans might have a gagging or retching reflex at the sight or smell of certain foods,” Fasciana explained. “They might have difficulty being in the presence of another person eating a nonpreferred food.”
Some cancer patients may be averse to foods of certain temperatures. “You might need to assess why they don’t like the temperature of that food. Why are those foods something that you can’t go to? Are they hurting your teeth? What are they doing to you?”
ARFID patients may also experience social withdrawal around eating. “With a lot of our head and neck cancer patients, especially those with oral cancers and those on feeding tubes, they might feel embarrassed to be around people while eating,” Fasciana said.
She highlighted a 2021 report about 4 cancer survivors with upper abdominal cancers who developed new-onset eating disorders with malnutrition resembling ARFID.
The patients experienced malabsorption, dumping syndrome, and excessive weight loss for 12 months postoperatively without classic body-image concerns. “This is a case example of how eating disorders can evolve in the oncology population,” Fasciana said.
The report said that none of the patients “returned to a healthy weight and/or healthy eating despite extensive team input… The outcomes were poor; 1 patient died, another required admission to a specialist eating disorder admission with a subsequent relapsing-remitting course, and the remaining 2 had complicated chronic courses.”
Treatment: Start With Screening, Then Reframe Thinking
Fasciana highlighted several screening tools, such as SCOFF, BREDS, and one for ARFID.
“Any screen is going to be better than no screen at all, and any question is going to be better than no question at all,” Fasciana said.
She cautioned that “veterans are not going to be so forthcoming about some of their struggles due to stigma and shame because of their past experiences in the military.”
As for therapy, psychological care may not be required, Ohde said. And it’s especially important to “listen to your patients about what they’re going through, and give them space to share.”
For those who could be helped by psychotherapy, she said, “sometimes I introduce it as therapy that can be really brief. Maybe you just need to talk to someone for a few sessions or just get some support around coping with this.”
One strategy is to focus on bringing enjoyment back to eating, she said. For some patients, “eating becomes a chore,” a task performed without joy, alone in a hospital room.
Fasciana emphasized asking questions over time, perhaps through multiple follow-ups, without expecting answers immediately. And she coaxes patients to consider what they hold dear. “I try to get them to think about the meaning that losing or gaining weight has for them, what their values are, and what really matters to them. I link it back to health, healing, and longevity of life.”
Fasciana and Ohde reported they had no disclosures.
Military Background Shapes Eating Disorders in VA Oncology
Military Background Shapes Eating Disorders in VA Oncology
Helicobacter pylori May Shift Gastric Cancer Earlier
Helicobacter pylori May Shift Gastric Cancer Earlier
ORLANDO, Fl — , new data suggested.
H pylori infection is a leading risk factor for gastric carcinoma, accounting for as many as 90% of cases. As the new data show, failure to screen routinely for the bacteria could be leading to younger people developing easily preventable forms of gastric cancer, experts said.
“The most concerning and the most interesting finding for us was we found higher prevalence” of gastric cancer linked to H pylori in the younger group, Neel Patel, MD, MPH, with the Department of Pathology at Staten Island University Hospital in Staten Island, New York, told GI & Hepatology News.
“This does not mean most patients are young. Rather, it means H pylori increases the likelihood of gastric cancer appearing earlier in life compared with non-H pylori cases.”
For the study, Patel and his colleagues, who presented their findings at the annual meeting of the College of American Pathologists (CAP) 2025, used 2016-2020 data from the Nationwide Inpatient Sample, which included records for adults with primary diagnoses of gastric cancer. They looked at outcomes of those whose cancer was associated with H pylori compared with the non-H pylori group.
Among 91,670 adult hospitalizations, 1830 (2%) had gastric cancer linked to H pylori (2016-2020). Patel said the low percentage resulted from focusing solely on diagnostic codes for primary diagnoses of gastric cancer and excluding secondary diagnoses.
These cancers were twice as prevalent in patients aged 18-49 years (3.97%) as in those older than 65 years (1.65%).
Septicemia Odds Higher in H pylori Group
Patients in the H pylori group also had a higher burden of comorbidities such as anemia, chronic blood loss, and metastatic cancer, according to the data. The researcher found these patients also had significantly higher odds of septicemia (odds ratio, 1.62; 95% CI, 1.17-2.24; P = .003) and spent an average of 8 days in the hospital — two more than those with cancers not associated with the infection.
Dipti M. Karamchandani, MD, a professor of pathology at the University of Texas Southwestern Medical Center in Dallas, who was not part of the study, said the longer hospital stays and greater risk for septicemia may be related to increased comorbidities among people who get H pylori infection in general. The infection often is caused by unsanitary conditions, and the groups infected may also be more likely to experience malnutrition, anemia, or lower body reserves, for example, she said.
“Also, H pylori often causes gastric ulcers, even before causing cancer, and those patients may be prone to chronic blood loss,” Karamchandani said. “These are all reasons that these patients may be more prone to longer hospital stay.”
US Guidelines Lacking
H pylori infection is a strong predictor of gastric cancer, but it often goes undetected. “Sometimes we ignore the symptoms,” Patel said.
“There are no standard guidelines for screening for H pylori,” he added. “We need to stop the transition from H pylori to gastric cancer.”
“This abstract highlights an important issue: Gastric cancer is rising among younger adults in the US, particularly in noncardia gastric cancer, which is most often associated with Helicobacter pylori infection,” said Chul S. Hyun, MD, PhD, MPH, director of the Gastric Cancer Prevention and Screening Program at Yale School of Medicine in New Haven, Connecticut.
Hyun said the 2% of patients in the study diagnosed with gastric cancer associated with H pylori likely reflected undercoding and “incomplete capture” in the database and noted that subgroup comparisons “become difficult to interpret reliably.” By extension, the findings also underscore, “We are not adequately capturing H pylori in routine US coding and claims.”
“What we do know is that H pylori is the central, modifiable driver of risk, and that prevention efforts should focus on high prevalence populations — including Asian, Hispanic, and immigrant communities — where systematic H pylori screening remains a major unmet need,” said Hyun, who was not involved in the new research.
Currently no US society guideline recommends systematic screening, Hyun said. “Other high-incidence countries, such as Japan and Korea, already incorporate H pylori and gastroscopy screening into national policy,” he said. “For these reasons, guidelines urgently need to evolve to recommend targeted H pylori screening in high prevalence groups.”
Patel, Karamchandani, and Hyun reported having no relevant financial conflicts of interest.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
ORLANDO, Fl — , new data suggested.
H pylori infection is a leading risk factor for gastric carcinoma, accounting for as many as 90% of cases. As the new data show, failure to screen routinely for the bacteria could be leading to younger people developing easily preventable forms of gastric cancer, experts said.
“The most concerning and the most interesting finding for us was we found higher prevalence” of gastric cancer linked to H pylori in the younger group, Neel Patel, MD, MPH, with the Department of Pathology at Staten Island University Hospital in Staten Island, New York, told GI & Hepatology News.
“This does not mean most patients are young. Rather, it means H pylori increases the likelihood of gastric cancer appearing earlier in life compared with non-H pylori cases.”
For the study, Patel and his colleagues, who presented their findings at the annual meeting of the College of American Pathologists (CAP) 2025, used 2016-2020 data from the Nationwide Inpatient Sample, which included records for adults with primary diagnoses of gastric cancer. They looked at outcomes of those whose cancer was associated with H pylori compared with the non-H pylori group.
Among 91,670 adult hospitalizations, 1830 (2%) had gastric cancer linked to H pylori (2016-2020). Patel said the low percentage resulted from focusing solely on diagnostic codes for primary diagnoses of gastric cancer and excluding secondary diagnoses.
These cancers were twice as prevalent in patients aged 18-49 years (3.97%) as in those older than 65 years (1.65%).
Septicemia Odds Higher in H pylori Group
Patients in the H pylori group also had a higher burden of comorbidities such as anemia, chronic blood loss, and metastatic cancer, according to the data. The researcher found these patients also had significantly higher odds of septicemia (odds ratio, 1.62; 95% CI, 1.17-2.24; P = .003) and spent an average of 8 days in the hospital — two more than those with cancers not associated with the infection.
Dipti M. Karamchandani, MD, a professor of pathology at the University of Texas Southwestern Medical Center in Dallas, who was not part of the study, said the longer hospital stays and greater risk for septicemia may be related to increased comorbidities among people who get H pylori infection in general. The infection often is caused by unsanitary conditions, and the groups infected may also be more likely to experience malnutrition, anemia, or lower body reserves, for example, she said.
“Also, H pylori often causes gastric ulcers, even before causing cancer, and those patients may be prone to chronic blood loss,” Karamchandani said. “These are all reasons that these patients may be more prone to longer hospital stay.”
US Guidelines Lacking
H pylori infection is a strong predictor of gastric cancer, but it often goes undetected. “Sometimes we ignore the symptoms,” Patel said.
“There are no standard guidelines for screening for H pylori,” he added. “We need to stop the transition from H pylori to gastric cancer.”
“This abstract highlights an important issue: Gastric cancer is rising among younger adults in the US, particularly in noncardia gastric cancer, which is most often associated with Helicobacter pylori infection,” said Chul S. Hyun, MD, PhD, MPH, director of the Gastric Cancer Prevention and Screening Program at Yale School of Medicine in New Haven, Connecticut.
Hyun said the 2% of patients in the study diagnosed with gastric cancer associated with H pylori likely reflected undercoding and “incomplete capture” in the database and noted that subgroup comparisons “become difficult to interpret reliably.” By extension, the findings also underscore, “We are not adequately capturing H pylori in routine US coding and claims.”
“What we do know is that H pylori is the central, modifiable driver of risk, and that prevention efforts should focus on high prevalence populations — including Asian, Hispanic, and immigrant communities — where systematic H pylori screening remains a major unmet need,” said Hyun, who was not involved in the new research.
Currently no US society guideline recommends systematic screening, Hyun said. “Other high-incidence countries, such as Japan and Korea, already incorporate H pylori and gastroscopy screening into national policy,” he said. “For these reasons, guidelines urgently need to evolve to recommend targeted H pylori screening in high prevalence groups.”
Patel, Karamchandani, and Hyun reported having no relevant financial conflicts of interest.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
ORLANDO, Fl — , new data suggested.
H pylori infection is a leading risk factor for gastric carcinoma, accounting for as many as 90% of cases. As the new data show, failure to screen routinely for the bacteria could be leading to younger people developing easily preventable forms of gastric cancer, experts said.
“The most concerning and the most interesting finding for us was we found higher prevalence” of gastric cancer linked to H pylori in the younger group, Neel Patel, MD, MPH, with the Department of Pathology at Staten Island University Hospital in Staten Island, New York, told GI & Hepatology News.
“This does not mean most patients are young. Rather, it means H pylori increases the likelihood of gastric cancer appearing earlier in life compared with non-H pylori cases.”
For the study, Patel and his colleagues, who presented their findings at the annual meeting of the College of American Pathologists (CAP) 2025, used 2016-2020 data from the Nationwide Inpatient Sample, which included records for adults with primary diagnoses of gastric cancer. They looked at outcomes of those whose cancer was associated with H pylori compared with the non-H pylori group.
Among 91,670 adult hospitalizations, 1830 (2%) had gastric cancer linked to H pylori (2016-2020). Patel said the low percentage resulted from focusing solely on diagnostic codes for primary diagnoses of gastric cancer and excluding secondary diagnoses.
These cancers were twice as prevalent in patients aged 18-49 years (3.97%) as in those older than 65 years (1.65%).
Septicemia Odds Higher in H pylori Group
Patients in the H pylori group also had a higher burden of comorbidities such as anemia, chronic blood loss, and metastatic cancer, according to the data. The researcher found these patients also had significantly higher odds of septicemia (odds ratio, 1.62; 95% CI, 1.17-2.24; P = .003) and spent an average of 8 days in the hospital — two more than those with cancers not associated with the infection.
Dipti M. Karamchandani, MD, a professor of pathology at the University of Texas Southwestern Medical Center in Dallas, who was not part of the study, said the longer hospital stays and greater risk for septicemia may be related to increased comorbidities among people who get H pylori infection in general. The infection often is caused by unsanitary conditions, and the groups infected may also be more likely to experience malnutrition, anemia, or lower body reserves, for example, she said.
“Also, H pylori often causes gastric ulcers, even before causing cancer, and those patients may be prone to chronic blood loss,” Karamchandani said. “These are all reasons that these patients may be more prone to longer hospital stay.”
US Guidelines Lacking
H pylori infection is a strong predictor of gastric cancer, but it often goes undetected. “Sometimes we ignore the symptoms,” Patel said.
“There are no standard guidelines for screening for H pylori,” he added. “We need to stop the transition from H pylori to gastric cancer.”
“This abstract highlights an important issue: Gastric cancer is rising among younger adults in the US, particularly in noncardia gastric cancer, which is most often associated with Helicobacter pylori infection,” said Chul S. Hyun, MD, PhD, MPH, director of the Gastric Cancer Prevention and Screening Program at Yale School of Medicine in New Haven, Connecticut.
Hyun said the 2% of patients in the study diagnosed with gastric cancer associated with H pylori likely reflected undercoding and “incomplete capture” in the database and noted that subgroup comparisons “become difficult to interpret reliably.” By extension, the findings also underscore, “We are not adequately capturing H pylori in routine US coding and claims.”
“What we do know is that H pylori is the central, modifiable driver of risk, and that prevention efforts should focus on high prevalence populations — including Asian, Hispanic, and immigrant communities — where systematic H pylori screening remains a major unmet need,” said Hyun, who was not involved in the new research.
Currently no US society guideline recommends systematic screening, Hyun said. “Other high-incidence countries, such as Japan and Korea, already incorporate H pylori and gastroscopy screening into national policy,” he said. “For these reasons, guidelines urgently need to evolve to recommend targeted H pylori screening in high prevalence groups.”
Patel, Karamchandani, and Hyun reported having no relevant financial conflicts of interest.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Helicobacter pylori May Shift Gastric Cancer Earlier
Helicobacter pylori May Shift Gastric Cancer Earlier
VIP Boot Camp: Expanding the Impact of VA Primary Care Mental Health With a Transdiagnostic Modular Group Program
VIP Boot Camp: Expanding the Impact of VA Primary Care Mental Health With a Transdiagnostic Modular Group Program
Since 2007, Primary Care Mental Health Integration (PCMHI) at the Veterans Health Administration (VHA) has improved access to mental health care services for veterans by directly embedding mental health care professionals (HCPs) within primary care teams.1 Veterans referred to PCMHI often have co-occurring physical and mental health disorders.2 Untreated chronic physical and mental comorbidities can diminish the effectiveness of medical and mental health interventions. Growing evidence suggests that treatment of mental health conditions can improve physical health outcomes and management of physical conditions can improve mental health outcomes.2,3
Chronic pain and sleep disorders are common reasons patients present to primary care, and often coexist together with mental health comorbidities.4 Sleep disorders affect 50% to 88% of patients with chronic pain, and 40% of patients with sleep disorders report chronic pain.4 Research has found that chronic pain and sleep disorders increase the risk of suicide attempts and deaths by suicide. Addressing suicide prevention simultaneously with treating chronic pain and insomnia is encouraged.5
Background
PCMHI treats physical and mental health comorbidities with a collaborative framework and a biopsychosocial integrative model.6 PCMHI staff provide mental health services as members of primary care teams. An interdisciplinary PCMHI team can include, but is not limited to, psychologists, mental health social workers, psychiatrists, nurse practitioners, clinical pharmacists, and mental health nurses. Quality of care within this model is elevated, as mental and physical health are recognized as interconnected. Collaboration between primary care and mental health benefits veterans and the VHA by increasing access to mental health care, decreasing stigma associated with mental health treatment, improving health outcomes, and enhancing the likelihood of recovery, resulting in high patient satisfaction.6-8
In the existing PCMHI model, HCPs are encouraged to use short-term, evidence-based psychotherapies (EBPs).9 Veterans referred to PCMHI from primary care are typically able to attend 1 to 6 brief sessions of mental health treatment, often 20 to 30 minutes long. Most EBPs in PCMHI are disorder- specific, providing interventions focused on a single presenting problem (eg, insomnia, chronic pain, or posttraumatic stress disorder [PTSD]). For veterans with a single issue, this model can be very effective. 1,10 However, the high rate of co-occurrence of mental and physical health issues can make it difficult to fully treat interrelated problems if the focus is on 1 specific diagnosis. Veterans with a need for additional (more comprehensive or intensive) mental health treatment are frequently referred to a higher, more resource-intensive level of mental health care, either in the VHA or the community. Examples of higher levels of mental health care include the longer term behavioral health interdisciplinary program (BHIP), sometimes called a mental health clinic (MHC), or a specialty mental health program such as a PTSD clinic.
As PCMHI continues to grow, new challenges have emerged related to staffing shortages and gaps in the clinical delivery of mental health treatment within the VHA. At the same time, demand for VHA mental health treatment has increased. However, a mental health professional shortage severely limits the ability of the VHA to meet this demand. In many systems, this shortage may result in more referrals being made to a higher level of mental health care because of fewer resources to provide comprehensive treatment in a less intensive PCMHI setting.8,10,11 This referral pattern can overburden higher level care, often with long wait times for treatment and lengthy lag times between appointments. Furthermore, these gaps in the clinical delivery of care cannot be effectively addressed by hiring additional mental health professionals. This strain on resources can impede access to care and negatively affect outcomes.10
Recent congressional reports highlight these issues, noting that demand for mental health services continues to outpace the capacity of both PCMHI and higher levels of mental health care, leading to delays in treatment that may negatively affect outcomes.8,10,11 These delays can be particularly detrimental for individuals with conditions requiring timely intervention.8,11 Some veterans are willing to engage with PCMHI in a primary care setting but may be reluctant to engage in general mental health treatment. These veterans might not receive the mental health care they need without PCMHI.
Group Psychotherapy
A group psychotherapy format can address gaps in care delivery and provide advantages for patients, mental health professionals, and the VHA. Group psychotherapy aligns with the US Department of Veterans Affairs (VA) 2018 Blueprint for Excellence and 2018 to 2024 strategic plan, underscoring the need for more timely and efficient mental health services.12,13
Benefits of group psychotherapy include reductions in symptoms, decreased feelings of isolation, increased social support, decreased emotional suppression, and enhanced satisfaction with overall quality of life.14-17 Studies of veterans with PTSD have found less attrition among those who chose group therapy compared with individual therapy.14,18 Group psychotherapy improves access to care by enabling delivery to more patients.14 When compared with individual therapy, the group format allows for a large number of patients to be treated simultaneously, maximizing resources and reducing costs.3,19-21
VISN 9 CRH Innovation
The VA provides care to veterans through regionally distinct administrative systems known as Veterans Integrated Service Networks (VISNs). Clinical resource hubs (CRH) are VISN-based programs created to cover VA staffing shortages by virtually deploying HCPs into local VA systems until vacancies are filled. The national CRH vision of effectively using resources and innovative technologies to meet veterans’ health care needs, along with the above-referenced clinical gaps in the delivery of care, inspired the development of VIP Boot Camp within the VISN 9 CRH.22
Program Description
VIP Boot Camp is an evidence-informed group psychotherapy program designed to provide timely, brief, and comprehensive mental health treatment for veterans. VIP Boot Camp was developed to address the needs of veterans accessing PCMHI services who experience ≥ 1 of the often overlapping problems of anxiety/emotion regulation/stress, sleep difficulties, and chronic pain (Figure). VIP Boot Camp uses an integrative approach to highlight interconnections and similarities among these difficulties and their treatment. A primary vision of the program is to provide this comprehensive treatment within PCMHI (upstream) so additional referrals to higher levels of mental health care (downstream) may not be needed.
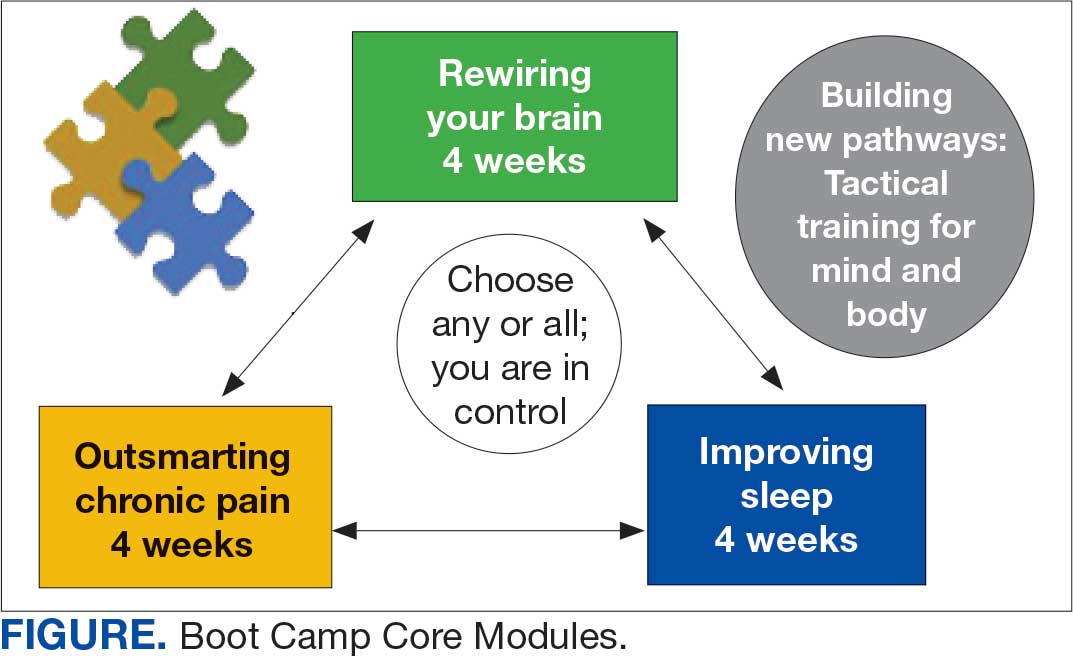
This design is intentional because it increases the number of individuals who can be treated upstream with comprehensive, preventive, and proactive care within PCMHI which, over time, frees up resources in the BHIP for individuals requiring higher levels of care. This approach also aligns with the importance of early treatment for chronic pain and sleep disturbances, which are linked to increased risk of suicide attempts and deaths by suicide for veterans.5 National interest for VIP Boot Camp grew during fiscal year 2024 after it received the Gold Medal Recognition for Most Adoptable and Greatest Potential for Impact during VHA National Access Sprint Wave 3—Mental Health Call of Champions.
History
VIP Boot Camp began in August 2021 at VISN 9 as a 6-week virtual group for veterans with chronic pain. It was established to assist a large VA medical center experiencing PCMHI staffing shortages and lacking available PCMHI groups. Many veterans in the chronic pain group discussed co-occurring issues such as sleep disturbances, anxiety, and stress. The CRH team considered launching 2 separate groups to address these additional PCMHI-level issues; however, in developing the group material which drew from multiple clinical approaches, the team recognized significant overlapping and interconnected themes.
The team discussed EBPs within the VHA and how certain interventions within these treatments could be helpful across many other co-occurring disorders. Integrated tactics (clinical interventions) were drawn from cognitive-behavioral therapy (for depression, insomnia, or chronic pain), acceptance and commitment therapy, prolonged exposure, cognitive processing therapy, dialectical behavior therapy, unified protocol, pain reprocessing therapy, emotional awareness and expression therapy, interpersonal neurobiology, and mindfulness. We collaborated with veterans during VIP Boot Camp groups to determine how to present and discuss complex interventions in ways that were clinically accurate, understandable, relatable, and relevant to their experiences.
To address accessibility issues, the chronic pain group was reduced to 4 weeks. A second 4-week module for anxiety, emotion regulation, and stress was developed, mirroring the tactics, language, and integrative approach of the revised chronic pain module. A similar integrative approach led to the development of the third and final 4-week module for sleep disturbances.
Current Program
The VIP Boot Camp consists of three 4-week integrated modules, each highlighting a critical area: sleep disturbances (Improving Sleep), chronic pain difficulties (Outsmarting Chronic Pain), and emotion regulation difficulties (Rewiring Your Brain). VIP Boot Camp is designed for veterans who are at the PCMHI level of care. Referrals are accepted for patients receiving treatment from primary care or PCMHI.
Guidelines for participation in VIP Boot Camp may differ across sites or VISNs. For example, a veteran who has been referred to the BHIP for medication management only or to a specialty MHC such as a pain clinic or PTSD clinic might also be appropriate and eligible for VIP Boot Camp.
Given the interconnectedness of foundational themes, elements, and practices across the VIP Boot Camp modules, the modules are offered in a rolling format with a veteran-centric “choose your own adventure” approach. Tactics are presented in the modules in a way that allows patients to begin with any 1 of the 3 modules and receive treatment that will help in the other areas. Participants choose their core module and initial treatment focus based on their values, needs, and goals. Individuals who complete a core module can end their VIP Boot Camp experience or continue to the next 4-week module for up to 3 modules.
The group is open to new individuals at the start of any 4-week module and closed for the remainder of its 4-week duration. This innovative rolling modular approach combines elements of open- and closed-group format, allowing for the flexibility and accessibility of an open group with the stability and peer support of a closed group.
Given the complicated and overlapping nature of chronic pain, emotion regulation/ stress, and sleep disturbances, VIP Boot Camp acknowledges that everything is interconnected and difficulties in 1 area may impact other areas. The 3 interconnected modules with repeating themes provide coherence and consistency. Veterans learn how interconnections across difficulties can be leveraged so that tactics learned and practiced in 1 area can assist in other areas, changing the cycle of suffering into a cycle of growth.
VIP Boot Camp sessions are 90 minutes long, once weekly for 4 weeks, with 2 mental health professionals trained to lead a dynamic group psychotherapy experience that aims to be fun for participants. VIP Boot Camp synthesizes evidence-based and evidence-informed interventions, as well as techniques from VHA complementary and integrative health programs, psychoeducation, and interpersonal interventions that model connection, playfulness, and healthy boundaries. These varied strategies combine to equip veterans with practical tactics for self-management outside of sessions, a process described as “finding puzzle pieces.” VIP Boot Camp is built on the idea that people are more likely to adopt and practice any tactic after being taught why that tactic is important, and how it fits into their larger interconnected puzzle. After each session, participants are provided with additional asynchronous educational material to help reinforce their learnings and practices.
Although individuals may hesitate to participate in a group setting, they often find the experience of community enhances and accelerates their treatment and gains. This involvement is highlighted in a core aspect of a VIP Boot Camp session called wins, during which participants learn how others on their Boot Camp team are implementing new skills and moving toward their personal values and objectives in a stepwise manner. Through these shared experiences, veterans discover how tactics working for others may serve as a model for their own personal objectives and plans for practice. The sense of relief described by many upon realizing they are not alone in their experiences, along with the satisfaction felt in discovering their ability to support others in Boot Camp, is described by many participants as deeply meaningful and in line with their personal values.
While developed as a fully virtual group program, VIP Boot Camp can also be conducted in person. The virtual program has been successful and continues to spread across VISN 9. There are 8 virtual VIP Boot Camps running in VISN 9, with plans for continued expansion. In the VISN 9 CRH, Boot Camps typically have 10 to 12 participants. Additionally, as VIP Boot Camp grows within a location there are frequently sufficient referrals to support a second rolling group, which enables staggering of the module offerings to allow for even more timely treatment.
Training Program
VISN 9 CRH also developed a VIP Boot Camp 3-day intensive training program for PCMHI HCPs that consists of learning and practicing VIP Boot Camp material for chronic pain, emotion regulation/ stress, sleep disturbances, mindfulness, and guided imagery, along with gaining experience as a VIP Boot Camp coleader. Feedback received from PCMHI HCPs who completed training has been positive. There is also a private Microsoft Teams channel for HCPs, which allows for resource sharing and community building among coleaders. More than 75 PCMHI HCPs have completed VIP Boot Camp training and > 25 VIP Boot Camps have been established at 4 additional VISNs.
The VISN 9 CRH VIP Boot Camp program initiated an implementation and effectiveness project with the Michael E. DeBakey VA Medical Center and the South Central Mental Illness Research, Education and Clinical Center. The focus of this collaboration is support for implementation and treatment effectiveness research with reports, articles, and a white paper on findings and best practices, alongside continued dissemination of the VIP Boot Camp program and training.
Conclusions
VIP Boot Camp is a PCMHI group program offering readily available, comprehensive, and integrative group psychotherapy services to veterans experiencing . 1 of the following: chronic pain, emotion regulation/ stress, and sleep disturbances. It was launched at the VISN 9 CRH with a goal of addressing clinical gaps in the delivery of mental health care, by increasing the number of patients treated within PCMHI. The VIP Boot Camp model provides veterans the opportunity to transform cycles of suffering into cycles of growth through a single approach that can address multiple presenting and interconnected issues.
A 3-day VIP Boot Camp training program provides a quick and effective path for a PCMHI program to train HCPs to launch a VIP Boot Camp. The VISN 9 CRH will continue to champion VIP Boot Camp as a model for the successful provision of comprehensive and integrative mental health treatment within PCMHI at the VA. Through readily available access to comprehensive mental health treatment in an environment that promotes participant empowerment and social engagement, VIP Boot Camp represents an integrative and innovative model of mental health treatment that offers benefits to veteran participants, HCPs, and the VHA.
- Leung LB, Yoon J, Escarce JJ, et al. Primary care-mental health integration in the VA: shifting mental health services for common mental illnesses to primary care. Psychiatr Serv. 2018;69:403-409. doi:10.1176/appi.ps.201700190
- Zhang A, Park S, Sullivan JE, et al. The effectiveness of problem-solving therapy for primary care patients’ depressive and/or anxiety disorders: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Am Board Fam Med. 2018;31:139-150. doi:10.3122/jabfm.2018.01.170270
- Hundt NE, Barrera TL, Robinson A, et al. A systematic review of cognitive behavioral therapy for depression in veterans. Mil Med. 2014;179:942-949. doi:10.7205/milmed-d-14-00128
- Jank R, Gallee A, Boeckle M, et al. Chronic pain and sleep disorders in primary care. Pain Res Treat. 2017;2017:1-9. doi:10.1155/2017/9081802
- Ashrafioun L, Bishop TM, Pigeon WR. The relationship between pain severity, insomnia, and suicide attempts among a national veteran sample initiating pain care. Psychosom Med. 2021;83:733- 738. doi:10.1097/psy.0000000000000975
- Ramanuj P, Ferenchik E, Docherty M, et al. Evolving models of integrated behavioral health and primary care. Curr Psychiatry Rep. 2019;21:1. doi:10.1007/s11920-019-0985-4
- Post EP, Metzger M, Dumas P, et al. Integrating mental health into primary care within the Veterans Health Administration. Fam Syst Health. 2010;28:83-90. doi:10.1037/a0020130
- Smith TL, Kim B, Benzer JK, et al. FLOW: early results from a clinical demonstration project to improve the transition of patients with mental health disorders back to primary care. Psychol Serv. 2021;18:23-32. doi:10.1037/ser0000336
- Kearney LK, Post EP, Pomerantz AS, et al. Applying the interprofessional patient aligned care team in the department of veterans affairs transforming primary care. Am Psychol. 2014;69(4):399-408. doi:10.1037/a0035909
- US Government Accountability Office. Veterans health care: staffing challenges persist for fully integrating mental health and primary care services. December 15, 2022. Accessed July 9, 2025. https://www.gao.gov/products/gao-23-105372
- National Academies of Science and Engineering. Evaluation of the Department of Veterans Affairs Mental Health Services. National Academies Press; 2018. Accessed July 9, 2025. https://nap.nationalacademies.org/catalog/24915/evaluation-of-the-department-of-veterans-affairs-mental-health-services
- US Department of Veterans Affairs. Blueprint for excellence: achieving veterans’ excellence. October 6, 2014. Accessed July 9, 2025. https://www.volunteer.va.gov/docs/blueprintforexcellence_factsheet.PDF
- US Department of Veterans Affairs. Department of Veterans Affairs FY 2018-2024 strategic plan. Accessed July 9, 2025. https://www.calvet.ca.gov/Regulations/USDVA%20Strategic%20Plan%202018-2024.pdf
- Sripada RK, Bohnert KM, Ganoczy D, et al. Initial group versus individual therapy for posttraumatic stress disorder and subsequent follow-up treatment adequacy. Psychol Serv. 2016;13:349-355. doi:10.1037/ser0000077
- Burnett-Zeigler IE, Pfeiffer P, Zivin K, et al. Psychotherapy utilization for acute depression within the Veterans Affairs health care system. Psychol Serv. 2012;9:325-335. doi:10.1037/a0027957
- Kim JS, Prins A, Hirschhorn EW, et al. Preliminary investigation into the effectiveness of group webSTAIR for trauma-exposed veterans in primary care. Mil Med. 2024;189:e1403-e1408. doi:10.1093/milmed/usae052
- Jakupcak M, Blais RK, Grossbard J, et al. “Toughness” in association with mental health symptoms among Iraq and Afghanistan war veterans seeking Veterans Affairs health care. Psychol Men Masc. 2014;15:100-104. doi:10.1037/a0031508
- Stoycos SA, Berzenski SR, Beck JG, et al. Predictors of treatment completion in group psychotherapy for male veterans with posttraumatic stress disorder. J Trauma Stress. 2023;36:346-358. doi:10.1002/jts.22915
- Possemato K. The current state of intervention research for posttraumatic stress disorder within the primary care setting. J Clin Psychol Med Settings. 2011;18:268-280. doi:10.1007/s10880-011-9237-4
- Hunt MG, Rosenheck RA. Psychotherapy in mental health clinics of the Department of Veterans Affairs. J Clin Psychol. 2011;67:561-573. doi:10.1002/jclp.20788
- Khatri N, Marziali E, Tchernikov I, et al. Comparing telehealth-based and clinic-based group cognitive behavioral therapy for adults with depression and anxiety: a pilot study. Clin Interv Aging. 2014;9:765. doi:10.2147/cia.s57832
- Dangel J. Clinical resource hub increases veterans' access to care. VA News. January 12, 2025. Accessed September 3, 2025. https://news.va.gov/137439/clinical-resource-hub-increases-access-to-care/
Since 2007, Primary Care Mental Health Integration (PCMHI) at the Veterans Health Administration (VHA) has improved access to mental health care services for veterans by directly embedding mental health care professionals (HCPs) within primary care teams.1 Veterans referred to PCMHI often have co-occurring physical and mental health disorders.2 Untreated chronic physical and mental comorbidities can diminish the effectiveness of medical and mental health interventions. Growing evidence suggests that treatment of mental health conditions can improve physical health outcomes and management of physical conditions can improve mental health outcomes.2,3
Chronic pain and sleep disorders are common reasons patients present to primary care, and often coexist together with mental health comorbidities.4 Sleep disorders affect 50% to 88% of patients with chronic pain, and 40% of patients with sleep disorders report chronic pain.4 Research has found that chronic pain and sleep disorders increase the risk of suicide attempts and deaths by suicide. Addressing suicide prevention simultaneously with treating chronic pain and insomnia is encouraged.5
Background
PCMHI treats physical and mental health comorbidities with a collaborative framework and a biopsychosocial integrative model.6 PCMHI staff provide mental health services as members of primary care teams. An interdisciplinary PCMHI team can include, but is not limited to, psychologists, mental health social workers, psychiatrists, nurse practitioners, clinical pharmacists, and mental health nurses. Quality of care within this model is elevated, as mental and physical health are recognized as interconnected. Collaboration between primary care and mental health benefits veterans and the VHA by increasing access to mental health care, decreasing stigma associated with mental health treatment, improving health outcomes, and enhancing the likelihood of recovery, resulting in high patient satisfaction.6-8
In the existing PCMHI model, HCPs are encouraged to use short-term, evidence-based psychotherapies (EBPs).9 Veterans referred to PCMHI from primary care are typically able to attend 1 to 6 brief sessions of mental health treatment, often 20 to 30 minutes long. Most EBPs in PCMHI are disorder- specific, providing interventions focused on a single presenting problem (eg, insomnia, chronic pain, or posttraumatic stress disorder [PTSD]). For veterans with a single issue, this model can be very effective. 1,10 However, the high rate of co-occurrence of mental and physical health issues can make it difficult to fully treat interrelated problems if the focus is on 1 specific diagnosis. Veterans with a need for additional (more comprehensive or intensive) mental health treatment are frequently referred to a higher, more resource-intensive level of mental health care, either in the VHA or the community. Examples of higher levels of mental health care include the longer term behavioral health interdisciplinary program (BHIP), sometimes called a mental health clinic (MHC), or a specialty mental health program such as a PTSD clinic.
As PCMHI continues to grow, new challenges have emerged related to staffing shortages and gaps in the clinical delivery of mental health treatment within the VHA. At the same time, demand for VHA mental health treatment has increased. However, a mental health professional shortage severely limits the ability of the VHA to meet this demand. In many systems, this shortage may result in more referrals being made to a higher level of mental health care because of fewer resources to provide comprehensive treatment in a less intensive PCMHI setting.8,10,11 This referral pattern can overburden higher level care, often with long wait times for treatment and lengthy lag times between appointments. Furthermore, these gaps in the clinical delivery of care cannot be effectively addressed by hiring additional mental health professionals. This strain on resources can impede access to care and negatively affect outcomes.10
Recent congressional reports highlight these issues, noting that demand for mental health services continues to outpace the capacity of both PCMHI and higher levels of mental health care, leading to delays in treatment that may negatively affect outcomes.8,10,11 These delays can be particularly detrimental for individuals with conditions requiring timely intervention.8,11 Some veterans are willing to engage with PCMHI in a primary care setting but may be reluctant to engage in general mental health treatment. These veterans might not receive the mental health care they need without PCMHI.
Group Psychotherapy
A group psychotherapy format can address gaps in care delivery and provide advantages for patients, mental health professionals, and the VHA. Group psychotherapy aligns with the US Department of Veterans Affairs (VA) 2018 Blueprint for Excellence and 2018 to 2024 strategic plan, underscoring the need for more timely and efficient mental health services.12,13
Benefits of group psychotherapy include reductions in symptoms, decreased feelings of isolation, increased social support, decreased emotional suppression, and enhanced satisfaction with overall quality of life.14-17 Studies of veterans with PTSD have found less attrition among those who chose group therapy compared with individual therapy.14,18 Group psychotherapy improves access to care by enabling delivery to more patients.14 When compared with individual therapy, the group format allows for a large number of patients to be treated simultaneously, maximizing resources and reducing costs.3,19-21
VISN 9 CRH Innovation
The VA provides care to veterans through regionally distinct administrative systems known as Veterans Integrated Service Networks (VISNs). Clinical resource hubs (CRH) are VISN-based programs created to cover VA staffing shortages by virtually deploying HCPs into local VA systems until vacancies are filled. The national CRH vision of effectively using resources and innovative technologies to meet veterans’ health care needs, along with the above-referenced clinical gaps in the delivery of care, inspired the development of VIP Boot Camp within the VISN 9 CRH.22
Program Description
VIP Boot Camp is an evidence-informed group psychotherapy program designed to provide timely, brief, and comprehensive mental health treatment for veterans. VIP Boot Camp was developed to address the needs of veterans accessing PCMHI services who experience ≥ 1 of the often overlapping problems of anxiety/emotion regulation/stress, sleep difficulties, and chronic pain (Figure). VIP Boot Camp uses an integrative approach to highlight interconnections and similarities among these difficulties and their treatment. A primary vision of the program is to provide this comprehensive treatment within PCMHI (upstream) so additional referrals to higher levels of mental health care (downstream) may not be needed.

This design is intentional because it increases the number of individuals who can be treated upstream with comprehensive, preventive, and proactive care within PCMHI which, over time, frees up resources in the BHIP for individuals requiring higher levels of care. This approach also aligns with the importance of early treatment for chronic pain and sleep disturbances, which are linked to increased risk of suicide attempts and deaths by suicide for veterans.5 National interest for VIP Boot Camp grew during fiscal year 2024 after it received the Gold Medal Recognition for Most Adoptable and Greatest Potential for Impact during VHA National Access Sprint Wave 3—Mental Health Call of Champions.
History
VIP Boot Camp began in August 2021 at VISN 9 as a 6-week virtual group for veterans with chronic pain. It was established to assist a large VA medical center experiencing PCMHI staffing shortages and lacking available PCMHI groups. Many veterans in the chronic pain group discussed co-occurring issues such as sleep disturbances, anxiety, and stress. The CRH team considered launching 2 separate groups to address these additional PCMHI-level issues; however, in developing the group material which drew from multiple clinical approaches, the team recognized significant overlapping and interconnected themes.
The team discussed EBPs within the VHA and how certain interventions within these treatments could be helpful across many other co-occurring disorders. Integrated tactics (clinical interventions) were drawn from cognitive-behavioral therapy (for depression, insomnia, or chronic pain), acceptance and commitment therapy, prolonged exposure, cognitive processing therapy, dialectical behavior therapy, unified protocol, pain reprocessing therapy, emotional awareness and expression therapy, interpersonal neurobiology, and mindfulness. We collaborated with veterans during VIP Boot Camp groups to determine how to present and discuss complex interventions in ways that were clinically accurate, understandable, relatable, and relevant to their experiences.
To address accessibility issues, the chronic pain group was reduced to 4 weeks. A second 4-week module for anxiety, emotion regulation, and stress was developed, mirroring the tactics, language, and integrative approach of the revised chronic pain module. A similar integrative approach led to the development of the third and final 4-week module for sleep disturbances.
Current Program
The VIP Boot Camp consists of three 4-week integrated modules, each highlighting a critical area: sleep disturbances (Improving Sleep), chronic pain difficulties (Outsmarting Chronic Pain), and emotion regulation difficulties (Rewiring Your Brain). VIP Boot Camp is designed for veterans who are at the PCMHI level of care. Referrals are accepted for patients receiving treatment from primary care or PCMHI.
Guidelines for participation in VIP Boot Camp may differ across sites or VISNs. For example, a veteran who has been referred to the BHIP for medication management only or to a specialty MHC such as a pain clinic or PTSD clinic might also be appropriate and eligible for VIP Boot Camp.
Given the interconnectedness of foundational themes, elements, and practices across the VIP Boot Camp modules, the modules are offered in a rolling format with a veteran-centric “choose your own adventure” approach. Tactics are presented in the modules in a way that allows patients to begin with any 1 of the 3 modules and receive treatment that will help in the other areas. Participants choose their core module and initial treatment focus based on their values, needs, and goals. Individuals who complete a core module can end their VIP Boot Camp experience or continue to the next 4-week module for up to 3 modules.
The group is open to new individuals at the start of any 4-week module and closed for the remainder of its 4-week duration. This innovative rolling modular approach combines elements of open- and closed-group format, allowing for the flexibility and accessibility of an open group with the stability and peer support of a closed group.
Given the complicated and overlapping nature of chronic pain, emotion regulation/ stress, and sleep disturbances, VIP Boot Camp acknowledges that everything is interconnected and difficulties in 1 area may impact other areas. The 3 interconnected modules with repeating themes provide coherence and consistency. Veterans learn how interconnections across difficulties can be leveraged so that tactics learned and practiced in 1 area can assist in other areas, changing the cycle of suffering into a cycle of growth.
VIP Boot Camp sessions are 90 minutes long, once weekly for 4 weeks, with 2 mental health professionals trained to lead a dynamic group psychotherapy experience that aims to be fun for participants. VIP Boot Camp synthesizes evidence-based and evidence-informed interventions, as well as techniques from VHA complementary and integrative health programs, psychoeducation, and interpersonal interventions that model connection, playfulness, and healthy boundaries. These varied strategies combine to equip veterans with practical tactics for self-management outside of sessions, a process described as “finding puzzle pieces.” VIP Boot Camp is built on the idea that people are more likely to adopt and practice any tactic after being taught why that tactic is important, and how it fits into their larger interconnected puzzle. After each session, participants are provided with additional asynchronous educational material to help reinforce their learnings and practices.
Although individuals may hesitate to participate in a group setting, they often find the experience of community enhances and accelerates their treatment and gains. This involvement is highlighted in a core aspect of a VIP Boot Camp session called wins, during which participants learn how others on their Boot Camp team are implementing new skills and moving toward their personal values and objectives in a stepwise manner. Through these shared experiences, veterans discover how tactics working for others may serve as a model for their own personal objectives and plans for practice. The sense of relief described by many upon realizing they are not alone in their experiences, along with the satisfaction felt in discovering their ability to support others in Boot Camp, is described by many participants as deeply meaningful and in line with their personal values.
While developed as a fully virtual group program, VIP Boot Camp can also be conducted in person. The virtual program has been successful and continues to spread across VISN 9. There are 8 virtual VIP Boot Camps running in VISN 9, with plans for continued expansion. In the VISN 9 CRH, Boot Camps typically have 10 to 12 participants. Additionally, as VIP Boot Camp grows within a location there are frequently sufficient referrals to support a second rolling group, which enables staggering of the module offerings to allow for even more timely treatment.
Training Program
VISN 9 CRH also developed a VIP Boot Camp 3-day intensive training program for PCMHI HCPs that consists of learning and practicing VIP Boot Camp material for chronic pain, emotion regulation/ stress, sleep disturbances, mindfulness, and guided imagery, along with gaining experience as a VIP Boot Camp coleader. Feedback received from PCMHI HCPs who completed training has been positive. There is also a private Microsoft Teams channel for HCPs, which allows for resource sharing and community building among coleaders. More than 75 PCMHI HCPs have completed VIP Boot Camp training and > 25 VIP Boot Camps have been established at 4 additional VISNs.
The VISN 9 CRH VIP Boot Camp program initiated an implementation and effectiveness project with the Michael E. DeBakey VA Medical Center and the South Central Mental Illness Research, Education and Clinical Center. The focus of this collaboration is support for implementation and treatment effectiveness research with reports, articles, and a white paper on findings and best practices, alongside continued dissemination of the VIP Boot Camp program and training.
Conclusions
VIP Boot Camp is a PCMHI group program offering readily available, comprehensive, and integrative group psychotherapy services to veterans experiencing . 1 of the following: chronic pain, emotion regulation/ stress, and sleep disturbances. It was launched at the VISN 9 CRH with a goal of addressing clinical gaps in the delivery of mental health care, by increasing the number of patients treated within PCMHI. The VIP Boot Camp model provides veterans the opportunity to transform cycles of suffering into cycles of growth through a single approach that can address multiple presenting and interconnected issues.
A 3-day VIP Boot Camp training program provides a quick and effective path for a PCMHI program to train HCPs to launch a VIP Boot Camp. The VISN 9 CRH will continue to champion VIP Boot Camp as a model for the successful provision of comprehensive and integrative mental health treatment within PCMHI at the VA. Through readily available access to comprehensive mental health treatment in an environment that promotes participant empowerment and social engagement, VIP Boot Camp represents an integrative and innovative model of mental health treatment that offers benefits to veteran participants, HCPs, and the VHA.
Since 2007, Primary Care Mental Health Integration (PCMHI) at the Veterans Health Administration (VHA) has improved access to mental health care services for veterans by directly embedding mental health care professionals (HCPs) within primary care teams.1 Veterans referred to PCMHI often have co-occurring physical and mental health disorders.2 Untreated chronic physical and mental comorbidities can diminish the effectiveness of medical and mental health interventions. Growing evidence suggests that treatment of mental health conditions can improve physical health outcomes and management of physical conditions can improve mental health outcomes.2,3
Chronic pain and sleep disorders are common reasons patients present to primary care, and often coexist together with mental health comorbidities.4 Sleep disorders affect 50% to 88% of patients with chronic pain, and 40% of patients with sleep disorders report chronic pain.4 Research has found that chronic pain and sleep disorders increase the risk of suicide attempts and deaths by suicide. Addressing suicide prevention simultaneously with treating chronic pain and insomnia is encouraged.5
Background
PCMHI treats physical and mental health comorbidities with a collaborative framework and a biopsychosocial integrative model.6 PCMHI staff provide mental health services as members of primary care teams. An interdisciplinary PCMHI team can include, but is not limited to, psychologists, mental health social workers, psychiatrists, nurse practitioners, clinical pharmacists, and mental health nurses. Quality of care within this model is elevated, as mental and physical health are recognized as interconnected. Collaboration between primary care and mental health benefits veterans and the VHA by increasing access to mental health care, decreasing stigma associated with mental health treatment, improving health outcomes, and enhancing the likelihood of recovery, resulting in high patient satisfaction.6-8
In the existing PCMHI model, HCPs are encouraged to use short-term, evidence-based psychotherapies (EBPs).9 Veterans referred to PCMHI from primary care are typically able to attend 1 to 6 brief sessions of mental health treatment, often 20 to 30 minutes long. Most EBPs in PCMHI are disorder- specific, providing interventions focused on a single presenting problem (eg, insomnia, chronic pain, or posttraumatic stress disorder [PTSD]). For veterans with a single issue, this model can be very effective. 1,10 However, the high rate of co-occurrence of mental and physical health issues can make it difficult to fully treat interrelated problems if the focus is on 1 specific diagnosis. Veterans with a need for additional (more comprehensive or intensive) mental health treatment are frequently referred to a higher, more resource-intensive level of mental health care, either in the VHA or the community. Examples of higher levels of mental health care include the longer term behavioral health interdisciplinary program (BHIP), sometimes called a mental health clinic (MHC), or a specialty mental health program such as a PTSD clinic.
As PCMHI continues to grow, new challenges have emerged related to staffing shortages and gaps in the clinical delivery of mental health treatment within the VHA. At the same time, demand for VHA mental health treatment has increased. However, a mental health professional shortage severely limits the ability of the VHA to meet this demand. In many systems, this shortage may result in more referrals being made to a higher level of mental health care because of fewer resources to provide comprehensive treatment in a less intensive PCMHI setting.8,10,11 This referral pattern can overburden higher level care, often with long wait times for treatment and lengthy lag times between appointments. Furthermore, these gaps in the clinical delivery of care cannot be effectively addressed by hiring additional mental health professionals. This strain on resources can impede access to care and negatively affect outcomes.10
Recent congressional reports highlight these issues, noting that demand for mental health services continues to outpace the capacity of both PCMHI and higher levels of mental health care, leading to delays in treatment that may negatively affect outcomes.8,10,11 These delays can be particularly detrimental for individuals with conditions requiring timely intervention.8,11 Some veterans are willing to engage with PCMHI in a primary care setting but may be reluctant to engage in general mental health treatment. These veterans might not receive the mental health care they need without PCMHI.
Group Psychotherapy
A group psychotherapy format can address gaps in care delivery and provide advantages for patients, mental health professionals, and the VHA. Group psychotherapy aligns with the US Department of Veterans Affairs (VA) 2018 Blueprint for Excellence and 2018 to 2024 strategic plan, underscoring the need for more timely and efficient mental health services.12,13
Benefits of group psychotherapy include reductions in symptoms, decreased feelings of isolation, increased social support, decreased emotional suppression, and enhanced satisfaction with overall quality of life.14-17 Studies of veterans with PTSD have found less attrition among those who chose group therapy compared with individual therapy.14,18 Group psychotherapy improves access to care by enabling delivery to more patients.14 When compared with individual therapy, the group format allows for a large number of patients to be treated simultaneously, maximizing resources and reducing costs.3,19-21
VISN 9 CRH Innovation
The VA provides care to veterans through regionally distinct administrative systems known as Veterans Integrated Service Networks (VISNs). Clinical resource hubs (CRH) are VISN-based programs created to cover VA staffing shortages by virtually deploying HCPs into local VA systems until vacancies are filled. The national CRH vision of effectively using resources and innovative technologies to meet veterans’ health care needs, along with the above-referenced clinical gaps in the delivery of care, inspired the development of VIP Boot Camp within the VISN 9 CRH.22
Program Description
VIP Boot Camp is an evidence-informed group psychotherapy program designed to provide timely, brief, and comprehensive mental health treatment for veterans. VIP Boot Camp was developed to address the needs of veterans accessing PCMHI services who experience ≥ 1 of the often overlapping problems of anxiety/emotion regulation/stress, sleep difficulties, and chronic pain (Figure). VIP Boot Camp uses an integrative approach to highlight interconnections and similarities among these difficulties and their treatment. A primary vision of the program is to provide this comprehensive treatment within PCMHI (upstream) so additional referrals to higher levels of mental health care (downstream) may not be needed.

This design is intentional because it increases the number of individuals who can be treated upstream with comprehensive, preventive, and proactive care within PCMHI which, over time, frees up resources in the BHIP for individuals requiring higher levels of care. This approach also aligns with the importance of early treatment for chronic pain and sleep disturbances, which are linked to increased risk of suicide attempts and deaths by suicide for veterans.5 National interest for VIP Boot Camp grew during fiscal year 2024 after it received the Gold Medal Recognition for Most Adoptable and Greatest Potential for Impact during VHA National Access Sprint Wave 3—Mental Health Call of Champions.
History
VIP Boot Camp began in August 2021 at VISN 9 as a 6-week virtual group for veterans with chronic pain. It was established to assist a large VA medical center experiencing PCMHI staffing shortages and lacking available PCMHI groups. Many veterans in the chronic pain group discussed co-occurring issues such as sleep disturbances, anxiety, and stress. The CRH team considered launching 2 separate groups to address these additional PCMHI-level issues; however, in developing the group material which drew from multiple clinical approaches, the team recognized significant overlapping and interconnected themes.
The team discussed EBPs within the VHA and how certain interventions within these treatments could be helpful across many other co-occurring disorders. Integrated tactics (clinical interventions) were drawn from cognitive-behavioral therapy (for depression, insomnia, or chronic pain), acceptance and commitment therapy, prolonged exposure, cognitive processing therapy, dialectical behavior therapy, unified protocol, pain reprocessing therapy, emotional awareness and expression therapy, interpersonal neurobiology, and mindfulness. We collaborated with veterans during VIP Boot Camp groups to determine how to present and discuss complex interventions in ways that were clinically accurate, understandable, relatable, and relevant to their experiences.
To address accessibility issues, the chronic pain group was reduced to 4 weeks. A second 4-week module for anxiety, emotion regulation, and stress was developed, mirroring the tactics, language, and integrative approach of the revised chronic pain module. A similar integrative approach led to the development of the third and final 4-week module for sleep disturbances.
Current Program
The VIP Boot Camp consists of three 4-week integrated modules, each highlighting a critical area: sleep disturbances (Improving Sleep), chronic pain difficulties (Outsmarting Chronic Pain), and emotion regulation difficulties (Rewiring Your Brain). VIP Boot Camp is designed for veterans who are at the PCMHI level of care. Referrals are accepted for patients receiving treatment from primary care or PCMHI.
Guidelines for participation in VIP Boot Camp may differ across sites or VISNs. For example, a veteran who has been referred to the BHIP for medication management only or to a specialty MHC such as a pain clinic or PTSD clinic might also be appropriate and eligible for VIP Boot Camp.
Given the interconnectedness of foundational themes, elements, and practices across the VIP Boot Camp modules, the modules are offered in a rolling format with a veteran-centric “choose your own adventure” approach. Tactics are presented in the modules in a way that allows patients to begin with any 1 of the 3 modules and receive treatment that will help in the other areas. Participants choose their core module and initial treatment focus based on their values, needs, and goals. Individuals who complete a core module can end their VIP Boot Camp experience or continue to the next 4-week module for up to 3 modules.
The group is open to new individuals at the start of any 4-week module and closed for the remainder of its 4-week duration. This innovative rolling modular approach combines elements of open- and closed-group format, allowing for the flexibility and accessibility of an open group with the stability and peer support of a closed group.
Given the complicated and overlapping nature of chronic pain, emotion regulation/ stress, and sleep disturbances, VIP Boot Camp acknowledges that everything is interconnected and difficulties in 1 area may impact other areas. The 3 interconnected modules with repeating themes provide coherence and consistency. Veterans learn how interconnections across difficulties can be leveraged so that tactics learned and practiced in 1 area can assist in other areas, changing the cycle of suffering into a cycle of growth.
VIP Boot Camp sessions are 90 minutes long, once weekly for 4 weeks, with 2 mental health professionals trained to lead a dynamic group psychotherapy experience that aims to be fun for participants. VIP Boot Camp synthesizes evidence-based and evidence-informed interventions, as well as techniques from VHA complementary and integrative health programs, psychoeducation, and interpersonal interventions that model connection, playfulness, and healthy boundaries. These varied strategies combine to equip veterans with practical tactics for self-management outside of sessions, a process described as “finding puzzle pieces.” VIP Boot Camp is built on the idea that people are more likely to adopt and practice any tactic after being taught why that tactic is important, and how it fits into their larger interconnected puzzle. After each session, participants are provided with additional asynchronous educational material to help reinforce their learnings and practices.
Although individuals may hesitate to participate in a group setting, they often find the experience of community enhances and accelerates their treatment and gains. This involvement is highlighted in a core aspect of a VIP Boot Camp session called wins, during which participants learn how others on their Boot Camp team are implementing new skills and moving toward their personal values and objectives in a stepwise manner. Through these shared experiences, veterans discover how tactics working for others may serve as a model for their own personal objectives and plans for practice. The sense of relief described by many upon realizing they are not alone in their experiences, along with the satisfaction felt in discovering their ability to support others in Boot Camp, is described by many participants as deeply meaningful and in line with their personal values.
While developed as a fully virtual group program, VIP Boot Camp can also be conducted in person. The virtual program has been successful and continues to spread across VISN 9. There are 8 virtual VIP Boot Camps running in VISN 9, with plans for continued expansion. In the VISN 9 CRH, Boot Camps typically have 10 to 12 participants. Additionally, as VIP Boot Camp grows within a location there are frequently sufficient referrals to support a second rolling group, which enables staggering of the module offerings to allow for even more timely treatment.
Training Program
VISN 9 CRH also developed a VIP Boot Camp 3-day intensive training program for PCMHI HCPs that consists of learning and practicing VIP Boot Camp material for chronic pain, emotion regulation/ stress, sleep disturbances, mindfulness, and guided imagery, along with gaining experience as a VIP Boot Camp coleader. Feedback received from PCMHI HCPs who completed training has been positive. There is also a private Microsoft Teams channel for HCPs, which allows for resource sharing and community building among coleaders. More than 75 PCMHI HCPs have completed VIP Boot Camp training and > 25 VIP Boot Camps have been established at 4 additional VISNs.
The VISN 9 CRH VIP Boot Camp program initiated an implementation and effectiveness project with the Michael E. DeBakey VA Medical Center and the South Central Mental Illness Research, Education and Clinical Center. The focus of this collaboration is support for implementation and treatment effectiveness research with reports, articles, and a white paper on findings and best practices, alongside continued dissemination of the VIP Boot Camp program and training.
Conclusions
VIP Boot Camp is a PCMHI group program offering readily available, comprehensive, and integrative group psychotherapy services to veterans experiencing . 1 of the following: chronic pain, emotion regulation/ stress, and sleep disturbances. It was launched at the VISN 9 CRH with a goal of addressing clinical gaps in the delivery of mental health care, by increasing the number of patients treated within PCMHI. The VIP Boot Camp model provides veterans the opportunity to transform cycles of suffering into cycles of growth through a single approach that can address multiple presenting and interconnected issues.
A 3-day VIP Boot Camp training program provides a quick and effective path for a PCMHI program to train HCPs to launch a VIP Boot Camp. The VISN 9 CRH will continue to champion VIP Boot Camp as a model for the successful provision of comprehensive and integrative mental health treatment within PCMHI at the VA. Through readily available access to comprehensive mental health treatment in an environment that promotes participant empowerment and social engagement, VIP Boot Camp represents an integrative and innovative model of mental health treatment that offers benefits to veteran participants, HCPs, and the VHA.
- Leung LB, Yoon J, Escarce JJ, et al. Primary care-mental health integration in the VA: shifting mental health services for common mental illnesses to primary care. Psychiatr Serv. 2018;69:403-409. doi:10.1176/appi.ps.201700190
- Zhang A, Park S, Sullivan JE, et al. The effectiveness of problem-solving therapy for primary care patients’ depressive and/or anxiety disorders: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Am Board Fam Med. 2018;31:139-150. doi:10.3122/jabfm.2018.01.170270
- Hundt NE, Barrera TL, Robinson A, et al. A systematic review of cognitive behavioral therapy for depression in veterans. Mil Med. 2014;179:942-949. doi:10.7205/milmed-d-14-00128
- Jank R, Gallee A, Boeckle M, et al. Chronic pain and sleep disorders in primary care. Pain Res Treat. 2017;2017:1-9. doi:10.1155/2017/9081802
- Ashrafioun L, Bishop TM, Pigeon WR. The relationship between pain severity, insomnia, and suicide attempts among a national veteran sample initiating pain care. Psychosom Med. 2021;83:733- 738. doi:10.1097/psy.0000000000000975
- Ramanuj P, Ferenchik E, Docherty M, et al. Evolving models of integrated behavioral health and primary care. Curr Psychiatry Rep. 2019;21:1. doi:10.1007/s11920-019-0985-4
- Post EP, Metzger M, Dumas P, et al. Integrating mental health into primary care within the Veterans Health Administration. Fam Syst Health. 2010;28:83-90. doi:10.1037/a0020130
- Smith TL, Kim B, Benzer JK, et al. FLOW: early results from a clinical demonstration project to improve the transition of patients with mental health disorders back to primary care. Psychol Serv. 2021;18:23-32. doi:10.1037/ser0000336
- Kearney LK, Post EP, Pomerantz AS, et al. Applying the interprofessional patient aligned care team in the department of veterans affairs transforming primary care. Am Psychol. 2014;69(4):399-408. doi:10.1037/a0035909
- US Government Accountability Office. Veterans health care: staffing challenges persist for fully integrating mental health and primary care services. December 15, 2022. Accessed July 9, 2025. https://www.gao.gov/products/gao-23-105372
- National Academies of Science and Engineering. Evaluation of the Department of Veterans Affairs Mental Health Services. National Academies Press; 2018. Accessed July 9, 2025. https://nap.nationalacademies.org/catalog/24915/evaluation-of-the-department-of-veterans-affairs-mental-health-services
- US Department of Veterans Affairs. Blueprint for excellence: achieving veterans’ excellence. October 6, 2014. Accessed July 9, 2025. https://www.volunteer.va.gov/docs/blueprintforexcellence_factsheet.PDF
- US Department of Veterans Affairs. Department of Veterans Affairs FY 2018-2024 strategic plan. Accessed July 9, 2025. https://www.calvet.ca.gov/Regulations/USDVA%20Strategic%20Plan%202018-2024.pdf
- Sripada RK, Bohnert KM, Ganoczy D, et al. Initial group versus individual therapy for posttraumatic stress disorder and subsequent follow-up treatment adequacy. Psychol Serv. 2016;13:349-355. doi:10.1037/ser0000077
- Burnett-Zeigler IE, Pfeiffer P, Zivin K, et al. Psychotherapy utilization for acute depression within the Veterans Affairs health care system. Psychol Serv. 2012;9:325-335. doi:10.1037/a0027957
- Kim JS, Prins A, Hirschhorn EW, et al. Preliminary investigation into the effectiveness of group webSTAIR for trauma-exposed veterans in primary care. Mil Med. 2024;189:e1403-e1408. doi:10.1093/milmed/usae052
- Jakupcak M, Blais RK, Grossbard J, et al. “Toughness” in association with mental health symptoms among Iraq and Afghanistan war veterans seeking Veterans Affairs health care. Psychol Men Masc. 2014;15:100-104. doi:10.1037/a0031508
- Stoycos SA, Berzenski SR, Beck JG, et al. Predictors of treatment completion in group psychotherapy for male veterans with posttraumatic stress disorder. J Trauma Stress. 2023;36:346-358. doi:10.1002/jts.22915
- Possemato K. The current state of intervention research for posttraumatic stress disorder within the primary care setting. J Clin Psychol Med Settings. 2011;18:268-280. doi:10.1007/s10880-011-9237-4
- Hunt MG, Rosenheck RA. Psychotherapy in mental health clinics of the Department of Veterans Affairs. J Clin Psychol. 2011;67:561-573. doi:10.1002/jclp.20788
- Khatri N, Marziali E, Tchernikov I, et al. Comparing telehealth-based and clinic-based group cognitive behavioral therapy for adults with depression and anxiety: a pilot study. Clin Interv Aging. 2014;9:765. doi:10.2147/cia.s57832
- Dangel J. Clinical resource hub increases veterans' access to care. VA News. January 12, 2025. Accessed September 3, 2025. https://news.va.gov/137439/clinical-resource-hub-increases-access-to-care/
- Leung LB, Yoon J, Escarce JJ, et al. Primary care-mental health integration in the VA: shifting mental health services for common mental illnesses to primary care. Psychiatr Serv. 2018;69:403-409. doi:10.1176/appi.ps.201700190
- Zhang A, Park S, Sullivan JE, et al. The effectiveness of problem-solving therapy for primary care patients’ depressive and/or anxiety disorders: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Am Board Fam Med. 2018;31:139-150. doi:10.3122/jabfm.2018.01.170270
- Hundt NE, Barrera TL, Robinson A, et al. A systematic review of cognitive behavioral therapy for depression in veterans. Mil Med. 2014;179:942-949. doi:10.7205/milmed-d-14-00128
- Jank R, Gallee A, Boeckle M, et al. Chronic pain and sleep disorders in primary care. Pain Res Treat. 2017;2017:1-9. doi:10.1155/2017/9081802
- Ashrafioun L, Bishop TM, Pigeon WR. The relationship between pain severity, insomnia, and suicide attempts among a national veteran sample initiating pain care. Psychosom Med. 2021;83:733- 738. doi:10.1097/psy.0000000000000975
- Ramanuj P, Ferenchik E, Docherty M, et al. Evolving models of integrated behavioral health and primary care. Curr Psychiatry Rep. 2019;21:1. doi:10.1007/s11920-019-0985-4
- Post EP, Metzger M, Dumas P, et al. Integrating mental health into primary care within the Veterans Health Administration. Fam Syst Health. 2010;28:83-90. doi:10.1037/a0020130
- Smith TL, Kim B, Benzer JK, et al. FLOW: early results from a clinical demonstration project to improve the transition of patients with mental health disorders back to primary care. Psychol Serv. 2021;18:23-32. doi:10.1037/ser0000336
- Kearney LK, Post EP, Pomerantz AS, et al. Applying the interprofessional patient aligned care team in the department of veterans affairs transforming primary care. Am Psychol. 2014;69(4):399-408. doi:10.1037/a0035909
- US Government Accountability Office. Veterans health care: staffing challenges persist for fully integrating mental health and primary care services. December 15, 2022. Accessed July 9, 2025. https://www.gao.gov/products/gao-23-105372
- National Academies of Science and Engineering. Evaluation of the Department of Veterans Affairs Mental Health Services. National Academies Press; 2018. Accessed July 9, 2025. https://nap.nationalacademies.org/catalog/24915/evaluation-of-the-department-of-veterans-affairs-mental-health-services
- US Department of Veterans Affairs. Blueprint for excellence: achieving veterans’ excellence. October 6, 2014. Accessed July 9, 2025. https://www.volunteer.va.gov/docs/blueprintforexcellence_factsheet.PDF
- US Department of Veterans Affairs. Department of Veterans Affairs FY 2018-2024 strategic plan. Accessed July 9, 2025. https://www.calvet.ca.gov/Regulations/USDVA%20Strategic%20Plan%202018-2024.pdf
- Sripada RK, Bohnert KM, Ganoczy D, et al. Initial group versus individual therapy for posttraumatic stress disorder and subsequent follow-up treatment adequacy. Psychol Serv. 2016;13:349-355. doi:10.1037/ser0000077
- Burnett-Zeigler IE, Pfeiffer P, Zivin K, et al. Psychotherapy utilization for acute depression within the Veterans Affairs health care system. Psychol Serv. 2012;9:325-335. doi:10.1037/a0027957
- Kim JS, Prins A, Hirschhorn EW, et al. Preliminary investigation into the effectiveness of group webSTAIR for trauma-exposed veterans in primary care. Mil Med. 2024;189:e1403-e1408. doi:10.1093/milmed/usae052
- Jakupcak M, Blais RK, Grossbard J, et al. “Toughness” in association with mental health symptoms among Iraq and Afghanistan war veterans seeking Veterans Affairs health care. Psychol Men Masc. 2014;15:100-104. doi:10.1037/a0031508
- Stoycos SA, Berzenski SR, Beck JG, et al. Predictors of treatment completion in group psychotherapy for male veterans with posttraumatic stress disorder. J Trauma Stress. 2023;36:346-358. doi:10.1002/jts.22915
- Possemato K. The current state of intervention research for posttraumatic stress disorder within the primary care setting. J Clin Psychol Med Settings. 2011;18:268-280. doi:10.1007/s10880-011-9237-4
- Hunt MG, Rosenheck RA. Psychotherapy in mental health clinics of the Department of Veterans Affairs. J Clin Psychol. 2011;67:561-573. doi:10.1002/jclp.20788
- Khatri N, Marziali E, Tchernikov I, et al. Comparing telehealth-based and clinic-based group cognitive behavioral therapy for adults with depression and anxiety: a pilot study. Clin Interv Aging. 2014;9:765. doi:10.2147/cia.s57832
- Dangel J. Clinical resource hub increases veterans' access to care. VA News. January 12, 2025. Accessed September 3, 2025. https://news.va.gov/137439/clinical-resource-hub-increases-access-to-care/
VIP Boot Camp: Expanding the Impact of VA Primary Care Mental Health With a Transdiagnostic Modular Group Program
VIP Boot Camp: Expanding the Impact of VA Primary Care Mental Health With a Transdiagnostic Modular Group Program
Healthy Diet, Exercise Cut Liver Death Risk in Drinkers
Following a healthy diet and engaging in a high level of physical activity can significantly lower the risk for alcohol-related liver mortality, even among all drinking patterns, including heavy and binge drinking, according to a new study from Indiana University researchers.
Notably, any amount of daily alcohol intake or binge drinking increases the liver mortality risk, the researchers found. However, that risk can be reduced somewhat with healthy dietary patterns and increased physical activity.
Although previous studies suggested that one or two drinks per day could be associated with lower risks for cardiovascular disease, cancer, or liver-related outcomes, other confounders and unmeasured lifestyle behaviors could vary significantly between consumers and influence their health risks, the researchers said.
“A significant knowledge gap exists regarding the interplay of dietary patterns and physical activity with alcohol-attributable liver-specific mortality,” said senior author Naga Chalasani, MD, AGAF, professor of gastroenterology and hepatology at the Indiana University School of Medicine in Indianapolis.
“It is not well understood whether healthy diets or increased physical activity levels explain differences in liver-specific mortality risks between lifetime abstainers and light-to-moderate alcohol consumers,” he said. “More importantly, it remains unclear whether a healthy diet and physical activity can lower liver-specific mortality in individuals engaging in high-risk alcohol consumption, such as heavy or binge drinking.”
The study was published online in the Journal of Hepatology.
Analyzing Alcohol-Related Effects
Chalasani and colleagues analyzed data from more than 60,000 adults in the National Health and Nutrition Examination Surveys for 1984-2018 and linked data in the National Death Index through December 2019.
The research team looked at self-reported alcohol use, diet quality based on the Healthy Eating Index, and physical activity levels. Heavy drinking was defined as more than three drinks per day for women and more than four drinks per day for men, while binge drinking was defined as four or more drinks per day for women and five or more drinks per day for men.
Physically active participants had at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity physical activity or 75 minutes of vigorous-intensity physical activity per week. Participants with healthier diets were in the top quartile of the Healthy Eating Index, which included diets high in vegetables, fruits, whole grains, seafood, plant-based proteins, and unsaturated fats, as well as diets low in solid fats, alcohol, and added sugars.
During a 12-year follow-up period, 12,881 deaths were reported, including 252 related to liver disease. An increased risk for liver-related death was associated with older age, smoking, diabetes, higher BMI, waist circumference, average daily alcohol intake, and binge drinking.
Compared to nondrinkers, those with daily alcohol intake had an increased liver-specific mortality risk, with an adjusted subdistribution hazard ratio (aSHR) of 1.04 for men and 1.08 for women.
Binge drinking had an even greater liver mortality risk, with an aSHR of 1.52 for men and 2.52 for women, than nonbinge drinking.
In contrast, a healthier diet — among those at the top quartile of the Healthy Eating Index — had a lower liver mortality risk in nonheavy drinkers (aSHR, 0.35), heavy drinkers (aSHR, 0.14), and binge drinkers (aSHR, 0.16).
In addition, physically active participants had a lower liver mortality risk for nonheavy drinkers (aSHR, 0.52), heavy drinkers (aSHR, 0.64), and binge drinkers (aSHR, 0.31).
Overall, the benefits of higher diet quality and physical activity were substantially greater in women than in men, the researchers found.
“The uniqueness of our study lies in its ability to simultaneously assess the moderating effects of two important lifestyle behaviors on liver mortality risk across different levels and patterns of alcohol consumption in a representative US population, offering a more nuanced and complete view of the risks of drinking,” Chalasani said.
Messaging From Clinicians to Patients
Despite some attenuation from a healthy diet and physical activity, alcohol consumption still carries an increased liver mortality risk, the researchers noted. Economically disadvantaged groups face higher exposure to high-risk alcohol use, unhealthy diets, and physical activity — and as a result, increased liver mortality.
“This study challenges the long-held belief that light-to-moderate drinking might be safe for the liver. It shows that any level of alcohol raises risk, but healthy diet and exercise can meaningfully reduce that harm,” said Joseph Ahn, MD, AGAF, assistant professor of medicine in the Division of Gastroenterology and Hepatology at the Mayo Clinic in Rochester, Minnesota.
“The results should change how we think about alcohol — not as something potentially protective, but as a risk factor that can be partly mitigated by lifestyle,” he said.
“The key takeaway is that there is no safe level of alcohol for liver health. Clinicians should move away from reassuring patients about ‘moderate’ drinking and instead stress both alcohol reduction and the protective role of diet and physical activity,” Ahn added. “The next step is bringing these insights into guidelines and patient counseling, especially for populations at higher risk.”
The study was funded by departmental internal funding. Chalasani declared having no conflicts of interest for this paper, but he disclosed paid consulting agreements with numerous pharmaceutical companies. Ahn reported having no disclosures.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Following a healthy diet and engaging in a high level of physical activity can significantly lower the risk for alcohol-related liver mortality, even among all drinking patterns, including heavy and binge drinking, according to a new study from Indiana University researchers.
Notably, any amount of daily alcohol intake or binge drinking increases the liver mortality risk, the researchers found. However, that risk can be reduced somewhat with healthy dietary patterns and increased physical activity.
Although previous studies suggested that one or two drinks per day could be associated with lower risks for cardiovascular disease, cancer, or liver-related outcomes, other confounders and unmeasured lifestyle behaviors could vary significantly between consumers and influence their health risks, the researchers said.
“A significant knowledge gap exists regarding the interplay of dietary patterns and physical activity with alcohol-attributable liver-specific mortality,” said senior author Naga Chalasani, MD, AGAF, professor of gastroenterology and hepatology at the Indiana University School of Medicine in Indianapolis.
“It is not well understood whether healthy diets or increased physical activity levels explain differences in liver-specific mortality risks between lifetime abstainers and light-to-moderate alcohol consumers,” he said. “More importantly, it remains unclear whether a healthy diet and physical activity can lower liver-specific mortality in individuals engaging in high-risk alcohol consumption, such as heavy or binge drinking.”
The study was published online in the Journal of Hepatology.
Analyzing Alcohol-Related Effects
Chalasani and colleagues analyzed data from more than 60,000 adults in the National Health and Nutrition Examination Surveys for 1984-2018 and linked data in the National Death Index through December 2019.
The research team looked at self-reported alcohol use, diet quality based on the Healthy Eating Index, and physical activity levels. Heavy drinking was defined as more than three drinks per day for women and more than four drinks per day for men, while binge drinking was defined as four or more drinks per day for women and five or more drinks per day for men.
Physically active participants had at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity physical activity or 75 minutes of vigorous-intensity physical activity per week. Participants with healthier diets were in the top quartile of the Healthy Eating Index, which included diets high in vegetables, fruits, whole grains, seafood, plant-based proteins, and unsaturated fats, as well as diets low in solid fats, alcohol, and added sugars.
During a 12-year follow-up period, 12,881 deaths were reported, including 252 related to liver disease. An increased risk for liver-related death was associated with older age, smoking, diabetes, higher BMI, waist circumference, average daily alcohol intake, and binge drinking.
Compared to nondrinkers, those with daily alcohol intake had an increased liver-specific mortality risk, with an adjusted subdistribution hazard ratio (aSHR) of 1.04 for men and 1.08 for women.
Binge drinking had an even greater liver mortality risk, with an aSHR of 1.52 for men and 2.52 for women, than nonbinge drinking.
In contrast, a healthier diet — among those at the top quartile of the Healthy Eating Index — had a lower liver mortality risk in nonheavy drinkers (aSHR, 0.35), heavy drinkers (aSHR, 0.14), and binge drinkers (aSHR, 0.16).
In addition, physically active participants had a lower liver mortality risk for nonheavy drinkers (aSHR, 0.52), heavy drinkers (aSHR, 0.64), and binge drinkers (aSHR, 0.31).
Overall, the benefits of higher diet quality and physical activity were substantially greater in women than in men, the researchers found.
“The uniqueness of our study lies in its ability to simultaneously assess the moderating effects of two important lifestyle behaviors on liver mortality risk across different levels and patterns of alcohol consumption in a representative US population, offering a more nuanced and complete view of the risks of drinking,” Chalasani said.
Messaging From Clinicians to Patients
Despite some attenuation from a healthy diet and physical activity, alcohol consumption still carries an increased liver mortality risk, the researchers noted. Economically disadvantaged groups face higher exposure to high-risk alcohol use, unhealthy diets, and physical activity — and as a result, increased liver mortality.
“This study challenges the long-held belief that light-to-moderate drinking might be safe for the liver. It shows that any level of alcohol raises risk, but healthy diet and exercise can meaningfully reduce that harm,” said Joseph Ahn, MD, AGAF, assistant professor of medicine in the Division of Gastroenterology and Hepatology at the Mayo Clinic in Rochester, Minnesota.
“The results should change how we think about alcohol — not as something potentially protective, but as a risk factor that can be partly mitigated by lifestyle,” he said.
“The key takeaway is that there is no safe level of alcohol for liver health. Clinicians should move away from reassuring patients about ‘moderate’ drinking and instead stress both alcohol reduction and the protective role of diet and physical activity,” Ahn added. “The next step is bringing these insights into guidelines and patient counseling, especially for populations at higher risk.”
The study was funded by departmental internal funding. Chalasani declared having no conflicts of interest for this paper, but he disclosed paid consulting agreements with numerous pharmaceutical companies. Ahn reported having no disclosures.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Following a healthy diet and engaging in a high level of physical activity can significantly lower the risk for alcohol-related liver mortality, even among all drinking patterns, including heavy and binge drinking, according to a new study from Indiana University researchers.
Notably, any amount of daily alcohol intake or binge drinking increases the liver mortality risk, the researchers found. However, that risk can be reduced somewhat with healthy dietary patterns and increased physical activity.
Although previous studies suggested that one or two drinks per day could be associated with lower risks for cardiovascular disease, cancer, or liver-related outcomes, other confounders and unmeasured lifestyle behaviors could vary significantly between consumers and influence their health risks, the researchers said.
“A significant knowledge gap exists regarding the interplay of dietary patterns and physical activity with alcohol-attributable liver-specific mortality,” said senior author Naga Chalasani, MD, AGAF, professor of gastroenterology and hepatology at the Indiana University School of Medicine in Indianapolis.
“It is not well understood whether healthy diets or increased physical activity levels explain differences in liver-specific mortality risks between lifetime abstainers and light-to-moderate alcohol consumers,” he said. “More importantly, it remains unclear whether a healthy diet and physical activity can lower liver-specific mortality in individuals engaging in high-risk alcohol consumption, such as heavy or binge drinking.”
The study was published online in the Journal of Hepatology.
Analyzing Alcohol-Related Effects
Chalasani and colleagues analyzed data from more than 60,000 adults in the National Health and Nutrition Examination Surveys for 1984-2018 and linked data in the National Death Index through December 2019.
The research team looked at self-reported alcohol use, diet quality based on the Healthy Eating Index, and physical activity levels. Heavy drinking was defined as more than three drinks per day for women and more than four drinks per day for men, while binge drinking was defined as four or more drinks per day for women and five or more drinks per day for men.
Physically active participants had at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity physical activity or 75 minutes of vigorous-intensity physical activity per week. Participants with healthier diets were in the top quartile of the Healthy Eating Index, which included diets high in vegetables, fruits, whole grains, seafood, plant-based proteins, and unsaturated fats, as well as diets low in solid fats, alcohol, and added sugars.
During a 12-year follow-up period, 12,881 deaths were reported, including 252 related to liver disease. An increased risk for liver-related death was associated with older age, smoking, diabetes, higher BMI, waist circumference, average daily alcohol intake, and binge drinking.
Compared to nondrinkers, those with daily alcohol intake had an increased liver-specific mortality risk, with an adjusted subdistribution hazard ratio (aSHR) of 1.04 for men and 1.08 for women.
Binge drinking had an even greater liver mortality risk, with an aSHR of 1.52 for men and 2.52 for women, than nonbinge drinking.
In contrast, a healthier diet — among those at the top quartile of the Healthy Eating Index — had a lower liver mortality risk in nonheavy drinkers (aSHR, 0.35), heavy drinkers (aSHR, 0.14), and binge drinkers (aSHR, 0.16).
In addition, physically active participants had a lower liver mortality risk for nonheavy drinkers (aSHR, 0.52), heavy drinkers (aSHR, 0.64), and binge drinkers (aSHR, 0.31).
Overall, the benefits of higher diet quality and physical activity were substantially greater in women than in men, the researchers found.
“The uniqueness of our study lies in its ability to simultaneously assess the moderating effects of two important lifestyle behaviors on liver mortality risk across different levels and patterns of alcohol consumption in a representative US population, offering a more nuanced and complete view of the risks of drinking,” Chalasani said.
Messaging From Clinicians to Patients
Despite some attenuation from a healthy diet and physical activity, alcohol consumption still carries an increased liver mortality risk, the researchers noted. Economically disadvantaged groups face higher exposure to high-risk alcohol use, unhealthy diets, and physical activity — and as a result, increased liver mortality.
“This study challenges the long-held belief that light-to-moderate drinking might be safe for the liver. It shows that any level of alcohol raises risk, but healthy diet and exercise can meaningfully reduce that harm,” said Joseph Ahn, MD, AGAF, assistant professor of medicine in the Division of Gastroenterology and Hepatology at the Mayo Clinic in Rochester, Minnesota.
“The results should change how we think about alcohol — not as something potentially protective, but as a risk factor that can be partly mitigated by lifestyle,” he said.
“The key takeaway is that there is no safe level of alcohol for liver health. Clinicians should move away from reassuring patients about ‘moderate’ drinking and instead stress both alcohol reduction and the protective role of diet and physical activity,” Ahn added. “The next step is bringing these insights into guidelines and patient counseling, especially for populations at higher risk.”
The study was funded by departmental internal funding. Chalasani declared having no conflicts of interest for this paper, but he disclosed paid consulting agreements with numerous pharmaceutical companies. Ahn reported having no disclosures.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Repeat Intubation of the Sigmoid Colon Improves Adenoma Detection
, new research showed.
“After eliminating the impact of time, the adenoma-detection rate [with a second intubation vs standard withdrawal] was still significantly increased, indicating that the second intubation technique could enhance the visualization of the sigmoid colon mucosa and reduce the rate of missed lesions,” reported the authors of the study, published in The American Journal of Gastroenterology.
When precancerous polyps are removed during standard colonoscopies, as many as 70%-90% of colorectal cancers can be prevented; however, rates of missed polyps during colonoscopy are notoriously high.
Recent studies have shown improved adenoma-detection rates with the use of Endocuff, water-assisted colonoscopy, full-spectrum endoscopy, and repeat withdrawal examinations, which include retroflexion and forward-viewing methods.
The repeat colonoscopy examinations may represent “the easiest and most practical option for endoscopists as they do not require additional tools, staff, or funding,” the authors explained.
However, most studies on the issue have focused mainly on the right colon and forward-viewing examinations, whereas the sigmoid colon, which has the most turns and is the most easily compressed, can be easily missed during withdrawal observation.
To investigate if use of a second colon intubation of the sigmoid colon could improve detection rates, senior author Jianning Yao, MD, of the Department of Gastroenterology, The First Affiliated Hospital of Zhengzhou University, Zhengzhou, China, conducted a randomized trial, enrolling 650 patients between December 2023 and April 2024 who were aged 45 or older and had overweight or obesity (BMI ≥ 24).
At the time of the first withdrawal during the colonoscopy, the patients were randomized 1:1 to groups of 325 each to either receive standard withdrawal, with withdrawal to the anus, or to receive a second intubation, with reinsertion into the sigmoid colon.
In the second intubation, the colonoscope was pushed forward without straightening, “allowing for slight looping that could be used to flatten the colonic folds as the tip of the instrument was advanced,” they explained.
The patients had a mean age of 55; about 25% had a smoking habit, and the mean BMI was about 28. There were no significant differences in other baseline characteristics.
The results showed that patients in the second-intubation group vs standard-withdrawal group had a substantially higher adenoma-detection rate (24.3% vs 14.5%) and polyp-detection rate (29.2% vs 17.8%, P = .001 for both) in the sigmoid colon.
In the second-intubation group, 85% of the adenomas discovered throughout the second inspection in the sigmoid colon were 5 mm or smaller in size. In addition, 90% of the 40 adenomas were somewhat raised or pedunculated, and all were tubular adenomas.
No high-grade dysplasia adenomas were discovered.
Of note, the colonoscopy in the second-intubation group’s colonoscopic examinations took just 1.47 minute longer overall than the standard-withdrawal group’s examinations.
Factors that were determined in a multivariate analysis to be independent predictors of higher adenoma detection in the second-intubation group included older age, smoking habit, longer duration of the second inspection, and the identification of lesions during the initial withdrawal from the sigmoid colon.
Patients’ vital signs were monitored at intervals of 3 minutes throughout the colonoscopy procedure, and patients were followed up to monitor for any adverse events occurring within 2 weeks after the examination, with no notable disparities observed between the two groups.
Alternative to AKS Approach in Second Intubation
The authors explained that, in their approach in the second intubation, the common axis-keeping shortening (AKS) was not utilized, and instead they pushed the colonoscope forward without straightening it, which offers important advantages.
“In this way, slight looping of the colonoscope can be used to flatten the colonic folds as the tip of the instrument is advanced, thereby achieving an observation effect that cannot be reached by any number of withdrawal examinations.”
In general, the stimulation of peristalsis during a second examination allows for the observation of the colonic mucosa from different angles, thereby reducing the rate of missed lesions, the authors added.
“Although the detection of these lesions may not significantly affect clinical outcomes, it serves as a reminder for patients regarding regular follow-ups and lifestyle adjustments,” they explained. “Additionally, it may reduce the likelihood of missing some smaller lesions that progress rapidly, such as de novo cancer.”
Based on the results, the authors concluded that older patients, patients who smoke, or those with lesions found on the first sigmoid inspection have a higher chance of having missed adenomas discovered in the sigmoid colon during the second intubation examination.
“If one of these risk factors is present, a second examination of the sigmoid colon may be considered to detect missed lesions,” they said.
The added time commitment of just 1.47 minutes can be a worthwhile tradeoff, they added.
“Considering the improvements in the adenoma-detection rate provided by the second intubation, this modest time increase may be acceptable.”
The authors had no disclosures to report.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
, new research showed.
“After eliminating the impact of time, the adenoma-detection rate [with a second intubation vs standard withdrawal] was still significantly increased, indicating that the second intubation technique could enhance the visualization of the sigmoid colon mucosa and reduce the rate of missed lesions,” reported the authors of the study, published in The American Journal of Gastroenterology.
When precancerous polyps are removed during standard colonoscopies, as many as 70%-90% of colorectal cancers can be prevented; however, rates of missed polyps during colonoscopy are notoriously high.
Recent studies have shown improved adenoma-detection rates with the use of Endocuff, water-assisted colonoscopy, full-spectrum endoscopy, and repeat withdrawal examinations, which include retroflexion and forward-viewing methods.
The repeat colonoscopy examinations may represent “the easiest and most practical option for endoscopists as they do not require additional tools, staff, or funding,” the authors explained.
However, most studies on the issue have focused mainly on the right colon and forward-viewing examinations, whereas the sigmoid colon, which has the most turns and is the most easily compressed, can be easily missed during withdrawal observation.
To investigate if use of a second colon intubation of the sigmoid colon could improve detection rates, senior author Jianning Yao, MD, of the Department of Gastroenterology, The First Affiliated Hospital of Zhengzhou University, Zhengzhou, China, conducted a randomized trial, enrolling 650 patients between December 2023 and April 2024 who were aged 45 or older and had overweight or obesity (BMI ≥ 24).
At the time of the first withdrawal during the colonoscopy, the patients were randomized 1:1 to groups of 325 each to either receive standard withdrawal, with withdrawal to the anus, or to receive a second intubation, with reinsertion into the sigmoid colon.
In the second intubation, the colonoscope was pushed forward without straightening, “allowing for slight looping that could be used to flatten the colonic folds as the tip of the instrument was advanced,” they explained.
The patients had a mean age of 55; about 25% had a smoking habit, and the mean BMI was about 28. There were no significant differences in other baseline characteristics.
The results showed that patients in the second-intubation group vs standard-withdrawal group had a substantially higher adenoma-detection rate (24.3% vs 14.5%) and polyp-detection rate (29.2% vs 17.8%, P = .001 for both) in the sigmoid colon.
In the second-intubation group, 85% of the adenomas discovered throughout the second inspection in the sigmoid colon were 5 mm or smaller in size. In addition, 90% of the 40 adenomas were somewhat raised or pedunculated, and all were tubular adenomas.
No high-grade dysplasia adenomas were discovered.
Of note, the colonoscopy in the second-intubation group’s colonoscopic examinations took just 1.47 minute longer overall than the standard-withdrawal group’s examinations.
Factors that were determined in a multivariate analysis to be independent predictors of higher adenoma detection in the second-intubation group included older age, smoking habit, longer duration of the second inspection, and the identification of lesions during the initial withdrawal from the sigmoid colon.
Patients’ vital signs were monitored at intervals of 3 minutes throughout the colonoscopy procedure, and patients were followed up to monitor for any adverse events occurring within 2 weeks after the examination, with no notable disparities observed between the two groups.
Alternative to AKS Approach in Second Intubation
The authors explained that, in their approach in the second intubation, the common axis-keeping shortening (AKS) was not utilized, and instead they pushed the colonoscope forward without straightening it, which offers important advantages.
“In this way, slight looping of the colonoscope can be used to flatten the colonic folds as the tip of the instrument is advanced, thereby achieving an observation effect that cannot be reached by any number of withdrawal examinations.”
In general, the stimulation of peristalsis during a second examination allows for the observation of the colonic mucosa from different angles, thereby reducing the rate of missed lesions, the authors added.
“Although the detection of these lesions may not significantly affect clinical outcomes, it serves as a reminder for patients regarding regular follow-ups and lifestyle adjustments,” they explained. “Additionally, it may reduce the likelihood of missing some smaller lesions that progress rapidly, such as de novo cancer.”
Based on the results, the authors concluded that older patients, patients who smoke, or those with lesions found on the first sigmoid inspection have a higher chance of having missed adenomas discovered in the sigmoid colon during the second intubation examination.
“If one of these risk factors is present, a second examination of the sigmoid colon may be considered to detect missed lesions,” they said.
The added time commitment of just 1.47 minutes can be a worthwhile tradeoff, they added.
“Considering the improvements in the adenoma-detection rate provided by the second intubation, this modest time increase may be acceptable.”
The authors had no disclosures to report.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
, new research showed.
“After eliminating the impact of time, the adenoma-detection rate [with a second intubation vs standard withdrawal] was still significantly increased, indicating that the second intubation technique could enhance the visualization of the sigmoid colon mucosa and reduce the rate of missed lesions,” reported the authors of the study, published in The American Journal of Gastroenterology.
When precancerous polyps are removed during standard colonoscopies, as many as 70%-90% of colorectal cancers can be prevented; however, rates of missed polyps during colonoscopy are notoriously high.
Recent studies have shown improved adenoma-detection rates with the use of Endocuff, water-assisted colonoscopy, full-spectrum endoscopy, and repeat withdrawal examinations, which include retroflexion and forward-viewing methods.
The repeat colonoscopy examinations may represent “the easiest and most practical option for endoscopists as they do not require additional tools, staff, or funding,” the authors explained.
However, most studies on the issue have focused mainly on the right colon and forward-viewing examinations, whereas the sigmoid colon, which has the most turns and is the most easily compressed, can be easily missed during withdrawal observation.
To investigate if use of a second colon intubation of the sigmoid colon could improve detection rates, senior author Jianning Yao, MD, of the Department of Gastroenterology, The First Affiliated Hospital of Zhengzhou University, Zhengzhou, China, conducted a randomized trial, enrolling 650 patients between December 2023 and April 2024 who were aged 45 or older and had overweight or obesity (BMI ≥ 24).
At the time of the first withdrawal during the colonoscopy, the patients were randomized 1:1 to groups of 325 each to either receive standard withdrawal, with withdrawal to the anus, or to receive a second intubation, with reinsertion into the sigmoid colon.
In the second intubation, the colonoscope was pushed forward without straightening, “allowing for slight looping that could be used to flatten the colonic folds as the tip of the instrument was advanced,” they explained.
The patients had a mean age of 55; about 25% had a smoking habit, and the mean BMI was about 28. There were no significant differences in other baseline characteristics.
The results showed that patients in the second-intubation group vs standard-withdrawal group had a substantially higher adenoma-detection rate (24.3% vs 14.5%) and polyp-detection rate (29.2% vs 17.8%, P = .001 for both) in the sigmoid colon.
In the second-intubation group, 85% of the adenomas discovered throughout the second inspection in the sigmoid colon were 5 mm or smaller in size. In addition, 90% of the 40 adenomas were somewhat raised or pedunculated, and all were tubular adenomas.
No high-grade dysplasia adenomas were discovered.
Of note, the colonoscopy in the second-intubation group’s colonoscopic examinations took just 1.47 minute longer overall than the standard-withdrawal group’s examinations.
Factors that were determined in a multivariate analysis to be independent predictors of higher adenoma detection in the second-intubation group included older age, smoking habit, longer duration of the second inspection, and the identification of lesions during the initial withdrawal from the sigmoid colon.
Patients’ vital signs were monitored at intervals of 3 minutes throughout the colonoscopy procedure, and patients were followed up to monitor for any adverse events occurring within 2 weeks after the examination, with no notable disparities observed between the two groups.
Alternative to AKS Approach in Second Intubation
The authors explained that, in their approach in the second intubation, the common axis-keeping shortening (AKS) was not utilized, and instead they pushed the colonoscope forward without straightening it, which offers important advantages.
“In this way, slight looping of the colonoscope can be used to flatten the colonic folds as the tip of the instrument is advanced, thereby achieving an observation effect that cannot be reached by any number of withdrawal examinations.”
In general, the stimulation of peristalsis during a second examination allows for the observation of the colonic mucosa from different angles, thereby reducing the rate of missed lesions, the authors added.
“Although the detection of these lesions may not significantly affect clinical outcomes, it serves as a reminder for patients regarding regular follow-ups and lifestyle adjustments,” they explained. “Additionally, it may reduce the likelihood of missing some smaller lesions that progress rapidly, such as de novo cancer.”
Based on the results, the authors concluded that older patients, patients who smoke, or those with lesions found on the first sigmoid inspection have a higher chance of having missed adenomas discovered in the sigmoid colon during the second intubation examination.
“If one of these risk factors is present, a second examination of the sigmoid colon may be considered to detect missed lesions,” they said.
The added time commitment of just 1.47 minutes can be a worthwhile tradeoff, they added.
“Considering the improvements in the adenoma-detection rate provided by the second intubation, this modest time increase may be acceptable.”
The authors had no disclosures to report.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Ocaliva for Primary Biliary Cholangitis Withdrawn From US Market
The decision follows a request from the FDA. The FDA has also placed a clinical hold on all of Intercept’s clinical trials involving obeticholic acid.
PBC is a rare, progressive, and chronic autoimmune disease that affects the bile ducts in the liver and is most prevalent in women older than 40 years of age. PBC causes a buildup of bile acid in the liver, resulting in inflammation and fibrosis, which — if not treated — can lead to cirrhosis, a liver transplant, or death.
Ocaliva, a farnesoid X receptor agonist, received accelerated FDA approval in 2016 for the treatment of PBC in adults with an inadequate response to or intolerance of ursodeoxycholic acid.
Yet, in September 2024, staff reviewers at the FDA said a confirmatory trial did not show that the drug was effective for PBC.
Ocaliva has also been linked to an increased risk of serious liver injury in patients with PBC with and without cirrhosis.
The company has advised patients currently taking Ocaliva for PBC to consult their healthcare provider before making any changes.
Intercept will provide additional information to support healthcare professionals and patients as it works with the FDA on the transition process.
Healthcare professionals who have questions about this development can contact Intercept Medical Information at [email protected] or call 1-844-782-4278.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
The decision follows a request from the FDA. The FDA has also placed a clinical hold on all of Intercept’s clinical trials involving obeticholic acid.
PBC is a rare, progressive, and chronic autoimmune disease that affects the bile ducts in the liver and is most prevalent in women older than 40 years of age. PBC causes a buildup of bile acid in the liver, resulting in inflammation and fibrosis, which — if not treated — can lead to cirrhosis, a liver transplant, or death.
Ocaliva, a farnesoid X receptor agonist, received accelerated FDA approval in 2016 for the treatment of PBC in adults with an inadequate response to or intolerance of ursodeoxycholic acid.
Yet, in September 2024, staff reviewers at the FDA said a confirmatory trial did not show that the drug was effective for PBC.
Ocaliva has also been linked to an increased risk of serious liver injury in patients with PBC with and without cirrhosis.
The company has advised patients currently taking Ocaliva for PBC to consult their healthcare provider before making any changes.
Intercept will provide additional information to support healthcare professionals and patients as it works with the FDA on the transition process.
Healthcare professionals who have questions about this development can contact Intercept Medical Information at [email protected] or call 1-844-782-4278.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
The decision follows a request from the FDA. The FDA has also placed a clinical hold on all of Intercept’s clinical trials involving obeticholic acid.
PBC is a rare, progressive, and chronic autoimmune disease that affects the bile ducts in the liver and is most prevalent in women older than 40 years of age. PBC causes a buildup of bile acid in the liver, resulting in inflammation and fibrosis, which — if not treated — can lead to cirrhosis, a liver transplant, or death.
Ocaliva, a farnesoid X receptor agonist, received accelerated FDA approval in 2016 for the treatment of PBC in adults with an inadequate response to or intolerance of ursodeoxycholic acid.
Yet, in September 2024, staff reviewers at the FDA said a confirmatory trial did not show that the drug was effective for PBC.
Ocaliva has also been linked to an increased risk of serious liver injury in patients with PBC with and without cirrhosis.
The company has advised patients currently taking Ocaliva for PBC to consult their healthcare provider before making any changes.
Intercept will provide additional information to support healthcare professionals and patients as it works with the FDA on the transition process.
Healthcare professionals who have questions about this development can contact Intercept Medical Information at [email protected] or call 1-844-782-4278.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Screening for H. pylori May Reduce Bleeding in Some Patients With MI
Screening for H. pylori May Reduce Bleeding in Some Patients With MI
, according to the HELP-MI SWEDEHEART trial published in JAMA and presented at the European Society of Cardiology (ESC) Congress 2025.
Bleeding in the upper gastrointestinal tract is a common complication after MI. It increases morbidity and mortality itself but can also reduce the effectiveness of antithrombotic treatments and lead to new cardiovascular events. It is often related to infection with H. pylori, the bacterium that can cause stomach inflammation, ulcers, and cancer, said Robin Hofmann, MD, PhD, a cardiologist at the Karolinska Institute in Stockholm, Sweden, who presented the trial results.Hofmann and his colleagues wondered whether screening for the bacterium using a simple urea breath test would help reduce the risk for bleeds. Using Sweden’s national SWEDEHEART registry, researchers performed a cluster-randomized crossover trial of more than 18,000 patients with MI at 35 Swedish hospitals. They found that screening for H. pylori reduced the risk for upper gastrointestinal bleeding by 10%, but the results were not statistically significant.
Several factors may have contributed to the neutral result, noted Hofmann. Just 70% of the people in the screening population were actually screened — though he said that is a fairly good number for a diagnostic test. A relatively small number, around 23%, were positive for H. pylori, a much lower rate than in many other parts of the world, and about 25% of participants in both arms of the trial were already taking proton pump inhibitors to reduce the risk for bleeding.
Signals of Benefit in High-Risk Patients
But in some high-risk subgroups, there was a clearer signal of benefit. Patients with anemia or kidney failure, for example, who are at higher risk for bleeding, saw a relative risk reduction of around 50% in the screening group — though the numbers were too small for formal statistical analysis.
“In unselected patients with myocardial infarction we could not show a significant reduction in bleeding,” said Hofmann. “But it’s very likely that there is a clinical effect, at least in those individuals at increased risk of bleeding.”
Discussant Paul Ridker, MD, a cardiologist at Harvard Medical School, Boston, said he agreed that the trial was technically neutral but clinically positive. He noted that in every subgroup, the trend was in the direction of benefit, with only the top end of the cardiac indices crossing over into no benefit. And the benefit appeared larger among high-risk patients with anemia or kidney failure.
“These are the very patients I’m most concerned about and don’t want to bleed,” he said.Because the urea breath test and eradication therapy are simple, safe, and inexpensive, Hofmann said he thinks there is “good evidence to recommend H. pylori screening in patients at higher risk of bleeding.”
“I’m very sure from a clinical perspective that we will be able to identify the groups that are low-hanging fruit,” he said. “But the guideline committees will have to decide if this evidence is enough.”
Hofmann and Ridker reported having no financial conflicts of interest.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
, according to the HELP-MI SWEDEHEART trial published in JAMA and presented at the European Society of Cardiology (ESC) Congress 2025.
Bleeding in the upper gastrointestinal tract is a common complication after MI. It increases morbidity and mortality itself but can also reduce the effectiveness of antithrombotic treatments and lead to new cardiovascular events. It is often related to infection with H. pylori, the bacterium that can cause stomach inflammation, ulcers, and cancer, said Robin Hofmann, MD, PhD, a cardiologist at the Karolinska Institute in Stockholm, Sweden, who presented the trial results.Hofmann and his colleagues wondered whether screening for the bacterium using a simple urea breath test would help reduce the risk for bleeds. Using Sweden’s national SWEDEHEART registry, researchers performed a cluster-randomized crossover trial of more than 18,000 patients with MI at 35 Swedish hospitals. They found that screening for H. pylori reduced the risk for upper gastrointestinal bleeding by 10%, but the results were not statistically significant.
Several factors may have contributed to the neutral result, noted Hofmann. Just 70% of the people in the screening population were actually screened — though he said that is a fairly good number for a diagnostic test. A relatively small number, around 23%, were positive for H. pylori, a much lower rate than in many other parts of the world, and about 25% of participants in both arms of the trial were already taking proton pump inhibitors to reduce the risk for bleeding.
Signals of Benefit in High-Risk Patients
But in some high-risk subgroups, there was a clearer signal of benefit. Patients with anemia or kidney failure, for example, who are at higher risk for bleeding, saw a relative risk reduction of around 50% in the screening group — though the numbers were too small for formal statistical analysis.
“In unselected patients with myocardial infarction we could not show a significant reduction in bleeding,” said Hofmann. “But it’s very likely that there is a clinical effect, at least in those individuals at increased risk of bleeding.”
Discussant Paul Ridker, MD, a cardiologist at Harvard Medical School, Boston, said he agreed that the trial was technically neutral but clinically positive. He noted that in every subgroup, the trend was in the direction of benefit, with only the top end of the cardiac indices crossing over into no benefit. And the benefit appeared larger among high-risk patients with anemia or kidney failure.
“These are the very patients I’m most concerned about and don’t want to bleed,” he said.Because the urea breath test and eradication therapy are simple, safe, and inexpensive, Hofmann said he thinks there is “good evidence to recommend H. pylori screening in patients at higher risk of bleeding.”
“I’m very sure from a clinical perspective that we will be able to identify the groups that are low-hanging fruit,” he said. “But the guideline committees will have to decide if this evidence is enough.”
Hofmann and Ridker reported having no financial conflicts of interest.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
, according to the HELP-MI SWEDEHEART trial published in JAMA and presented at the European Society of Cardiology (ESC) Congress 2025.
Bleeding in the upper gastrointestinal tract is a common complication after MI. It increases morbidity and mortality itself but can also reduce the effectiveness of antithrombotic treatments and lead to new cardiovascular events. It is often related to infection with H. pylori, the bacterium that can cause stomach inflammation, ulcers, and cancer, said Robin Hofmann, MD, PhD, a cardiologist at the Karolinska Institute in Stockholm, Sweden, who presented the trial results.Hofmann and his colleagues wondered whether screening for the bacterium using a simple urea breath test would help reduce the risk for bleeds. Using Sweden’s national SWEDEHEART registry, researchers performed a cluster-randomized crossover trial of more than 18,000 patients with MI at 35 Swedish hospitals. They found that screening for H. pylori reduced the risk for upper gastrointestinal bleeding by 10%, but the results were not statistically significant.
Several factors may have contributed to the neutral result, noted Hofmann. Just 70% of the people in the screening population were actually screened — though he said that is a fairly good number for a diagnostic test. A relatively small number, around 23%, were positive for H. pylori, a much lower rate than in many other parts of the world, and about 25% of participants in both arms of the trial were already taking proton pump inhibitors to reduce the risk for bleeding.
Signals of Benefit in High-Risk Patients
But in some high-risk subgroups, there was a clearer signal of benefit. Patients with anemia or kidney failure, for example, who are at higher risk for bleeding, saw a relative risk reduction of around 50% in the screening group — though the numbers were too small for formal statistical analysis.
“In unselected patients with myocardial infarction we could not show a significant reduction in bleeding,” said Hofmann. “But it’s very likely that there is a clinical effect, at least in those individuals at increased risk of bleeding.”
Discussant Paul Ridker, MD, a cardiologist at Harvard Medical School, Boston, said he agreed that the trial was technically neutral but clinically positive. He noted that in every subgroup, the trend was in the direction of benefit, with only the top end of the cardiac indices crossing over into no benefit. And the benefit appeared larger among high-risk patients with anemia or kidney failure.
“These are the very patients I’m most concerned about and don’t want to bleed,” he said.Because the urea breath test and eradication therapy are simple, safe, and inexpensive, Hofmann said he thinks there is “good evidence to recommend H. pylori screening in patients at higher risk of bleeding.”
“I’m very sure from a clinical perspective that we will be able to identify the groups that are low-hanging fruit,” he said. “But the guideline committees will have to decide if this evidence is enough.”
Hofmann and Ridker reported having no financial conflicts of interest.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Screening for H. pylori May Reduce Bleeding in Some Patients With MI
Screening for H. pylori May Reduce Bleeding in Some Patients With MI
Architect of VA Transformation Urges Innovation Amid Uncertainty
Architect of VA Transformation Urges Innovation Amid Uncertainty
PHOENIX – Three decades after he initiated the transformation of the Veterans Health Administration (VHA) into a model research and clinical health care system, former US Department of Veterans Affairs (VA) Under Secretary of Health Kenneth W. Kizer, MD, MPH, urged cancer specialists to embrace this challenging moment as an opportunity for bold innovation.
At the annual meeting of the Association of VA Hematology/Oncology (AVAHO), Kizer acknowledged that the VA faces an “uncertain and turbulent time” in areas such as funding, staffing, community care implementation, and the rollout of a new electronic health record system.
He also noted the grim rise of global instability, economic turmoil, climate change, infectious diseases, political violence, and mass shootings.
“This can be stressful. It can create negative energy. But this uncertainty can also be liberating, and it can prompt positive energy and innovation, depending on choices that we make,” said Kizer, who also has served as California’s top health official prior to leading the VHA from 1994 to 1999.
From “Bloated Bureaucracy’ to High-Quality Health Care System
Kizer has been credited with revitalizing VHA care through a greater commitment to quality, and harkened to his work with the VA as an example of how bold goals can lead to bold innovation.
“What were the perceptions of VA health care in 1994? Well, they weren’t very good, frankly,” Kizer recalled. He described the VA as having a reputation at that time as “highly dysfunctional” with “a very bloated and entrenched bureaucracy.” As for quality of care, it “wasn’t viewed as very good.”
The system’s problems were so severe that patients would park motorhomes in VA medical center parking lots as they waited for care. “While they might have an appointment for one day, they may not be seen for 3 or 4 or 5 days. So they would stay in their motorhome until they finally got into their clinic appointment,” Kizer said.
Overall, “the public viewed the VA as this bleak backwater of incompetence and difference and inefficiency, and there were very strong calls to privatize the VA,” Kizer said.
Kizer asked colleagues about what he should do after he was asked to take the under secretary job. “With one exception, they all said, don’t go near it. Don’t touch it. Walk away. That it’s impossible to change the organization.
“I looked at the VA and I saw an opportunity. When I told [members of the President Bill] Clinton [Administration] yes, my bold aim was that I would like to pursue this was to make VHA a model of excellent health care, an exemplary health care system. Most everyone else thought that I was totally delusional, but sometimes it’s good to be delusional.”
Revolutionary Changes Despite Opposition
Kizer sought reforms in 5 major strategic objectives, all without explicit congressional approval: creating an accountable management structure, decentralizing decision-making, integrating care, implementing universal primary care, and pursuing eligibility reform to create the current 8-tier VA system.
One major innovation was the implementation of community-based outpatient clinics (CBOCs): “Those were strongly opposed initially,” Kizer said. “Everyone, the veteran community in particular, had been led to believe that the only good care was in the hospital.”
The resistance was substantial. “There was a lot of opposition when we said we’re going to move out into the community where you live to make [care] easier to access,” Kizer said.
To make things more difficult, Congress wouldn’t fund the project: “For the first 3 years, every CBOC had to be funded by redirected savings from other things that we could do within the system,” he said. “All of this was through redirected savings and finding ways to save and reinvest.”
Innovation From the Ground Up
Kizer emphasized that many breakthrough innovations came from frontline staff rather than executive mandates. He cited the example of Barcode Medication Administration, which originated from a nurse in Topeka, Kan.
The nurse saw a barcode scanner put to work at a rental car company where it was used to check cars in and out. She wondered, “Why can’t we do this with medications when they’re given on the floor? We followed up on it, pursued those things, tested it out, it worked.”
The results were dramatic. “I was told at a meeting that they had achieved close to 80% reduction in medication errors,” Kizer said. After verifying the results personally, he “authorized $20 million, and we moved forward with it systemwide.”
This experience reinforced his belief in harvesting ideas from staff at all levels.
Innovation remains part of the VA’s culture “despite what some people would have you believe,” Kizer said. Recently, the VA has made major advances in areas such as patient transportation and the climate crisis, he said.
Inside the Recipe for Innovation
Boldness, persistence, adaptability, and tolerance for risk are necessary ingredients for high-risk goals, Kizer said. Ambition is also part of the picture.
He highlighted examples such as the Apollo moon landing, the first sub-4-minute mile, and the first swim across the English Channel by a woman.
In medicine, Kizer pointed to a national patient safety campaign that saved an estimated 122,000 lives. He also mentioned recent progress in organ transplantation such as recommendations from the National Academies of Sciences, Engineering, and Medicine to establish national performance goals and the Organ Procurement and Transplantation Network’s target of 60,000 deceased donor transplants by 2026.
Bold doesn’t mean being reckless or careless, Kizer said. “But it does require innovation. And it does require that you try some new things, some of which aren’t going to work out.”
The key mindset, he explained, is to “embrace the unknown” because “you often really don’t know how you will accomplish the aim when you start. But you’ll figure it out as you go.”
Kizer highlighted 2 opposing strategies to handling challenging times.
According to him, the “negative energy” approach focuses on frustrations, limitations, and asking “Why is this happening to me?”
In contrast, a “positive energy” approach expects problems, focuses on available resources and capabilities, and asks, “What are the opportunities that these changes are creating for me?”
Kizer made it crystal clear which option he prefers.
Dr. Kizer disclosed that his comments represent his opinions only, and he noted his ongoing connections to the VA.
PHOENIX – Three decades after he initiated the transformation of the Veterans Health Administration (VHA) into a model research and clinical health care system, former US Department of Veterans Affairs (VA) Under Secretary of Health Kenneth W. Kizer, MD, MPH, urged cancer specialists to embrace this challenging moment as an opportunity for bold innovation.
At the annual meeting of the Association of VA Hematology/Oncology (AVAHO), Kizer acknowledged that the VA faces an “uncertain and turbulent time” in areas such as funding, staffing, community care implementation, and the rollout of a new electronic health record system.
He also noted the grim rise of global instability, economic turmoil, climate change, infectious diseases, political violence, and mass shootings.
“This can be stressful. It can create negative energy. But this uncertainty can also be liberating, and it can prompt positive energy and innovation, depending on choices that we make,” said Kizer, who also has served as California’s top health official prior to leading the VHA from 1994 to 1999.
From “Bloated Bureaucracy’ to High-Quality Health Care System
Kizer has been credited with revitalizing VHA care through a greater commitment to quality, and harkened to his work with the VA as an example of how bold goals can lead to bold innovation.
“What were the perceptions of VA health care in 1994? Well, they weren’t very good, frankly,” Kizer recalled. He described the VA as having a reputation at that time as “highly dysfunctional” with “a very bloated and entrenched bureaucracy.” As for quality of care, it “wasn’t viewed as very good.”
The system’s problems were so severe that patients would park motorhomes in VA medical center parking lots as they waited for care. “While they might have an appointment for one day, they may not be seen for 3 or 4 or 5 days. So they would stay in their motorhome until they finally got into their clinic appointment,” Kizer said.
Overall, “the public viewed the VA as this bleak backwater of incompetence and difference and inefficiency, and there were very strong calls to privatize the VA,” Kizer said.
Kizer asked colleagues about what he should do after he was asked to take the under secretary job. “With one exception, they all said, don’t go near it. Don’t touch it. Walk away. That it’s impossible to change the organization.
“I looked at the VA and I saw an opportunity. When I told [members of the President Bill] Clinton [Administration] yes, my bold aim was that I would like to pursue this was to make VHA a model of excellent health care, an exemplary health care system. Most everyone else thought that I was totally delusional, but sometimes it’s good to be delusional.”
Revolutionary Changes Despite Opposition
Kizer sought reforms in 5 major strategic objectives, all without explicit congressional approval: creating an accountable management structure, decentralizing decision-making, integrating care, implementing universal primary care, and pursuing eligibility reform to create the current 8-tier VA system.
One major innovation was the implementation of community-based outpatient clinics (CBOCs): “Those were strongly opposed initially,” Kizer said. “Everyone, the veteran community in particular, had been led to believe that the only good care was in the hospital.”
The resistance was substantial. “There was a lot of opposition when we said we’re going to move out into the community where you live to make [care] easier to access,” Kizer said.
To make things more difficult, Congress wouldn’t fund the project: “For the first 3 years, every CBOC had to be funded by redirected savings from other things that we could do within the system,” he said. “All of this was through redirected savings and finding ways to save and reinvest.”
Innovation From the Ground Up
Kizer emphasized that many breakthrough innovations came from frontline staff rather than executive mandates. He cited the example of Barcode Medication Administration, which originated from a nurse in Topeka, Kan.
The nurse saw a barcode scanner put to work at a rental car company where it was used to check cars in and out. She wondered, “Why can’t we do this with medications when they’re given on the floor? We followed up on it, pursued those things, tested it out, it worked.”
The results were dramatic. “I was told at a meeting that they had achieved close to 80% reduction in medication errors,” Kizer said. After verifying the results personally, he “authorized $20 million, and we moved forward with it systemwide.”
This experience reinforced his belief in harvesting ideas from staff at all levels.
Innovation remains part of the VA’s culture “despite what some people would have you believe,” Kizer said. Recently, the VA has made major advances in areas such as patient transportation and the climate crisis, he said.
Inside the Recipe for Innovation
Boldness, persistence, adaptability, and tolerance for risk are necessary ingredients for high-risk goals, Kizer said. Ambition is also part of the picture.
He highlighted examples such as the Apollo moon landing, the first sub-4-minute mile, and the first swim across the English Channel by a woman.
In medicine, Kizer pointed to a national patient safety campaign that saved an estimated 122,000 lives. He also mentioned recent progress in organ transplantation such as recommendations from the National Academies of Sciences, Engineering, and Medicine to establish national performance goals and the Organ Procurement and Transplantation Network’s target of 60,000 deceased donor transplants by 2026.
Bold doesn’t mean being reckless or careless, Kizer said. “But it does require innovation. And it does require that you try some new things, some of which aren’t going to work out.”
The key mindset, he explained, is to “embrace the unknown” because “you often really don’t know how you will accomplish the aim when you start. But you’ll figure it out as you go.”
Kizer highlighted 2 opposing strategies to handling challenging times.
According to him, the “negative energy” approach focuses on frustrations, limitations, and asking “Why is this happening to me?”
In contrast, a “positive energy” approach expects problems, focuses on available resources and capabilities, and asks, “What are the opportunities that these changes are creating for me?”
Kizer made it crystal clear which option he prefers.
Dr. Kizer disclosed that his comments represent his opinions only, and he noted his ongoing connections to the VA.
PHOENIX – Three decades after he initiated the transformation of the Veterans Health Administration (VHA) into a model research and clinical health care system, former US Department of Veterans Affairs (VA) Under Secretary of Health Kenneth W. Kizer, MD, MPH, urged cancer specialists to embrace this challenging moment as an opportunity for bold innovation.
At the annual meeting of the Association of VA Hematology/Oncology (AVAHO), Kizer acknowledged that the VA faces an “uncertain and turbulent time” in areas such as funding, staffing, community care implementation, and the rollout of a new electronic health record system.
He also noted the grim rise of global instability, economic turmoil, climate change, infectious diseases, political violence, and mass shootings.
“This can be stressful. It can create negative energy. But this uncertainty can also be liberating, and it can prompt positive energy and innovation, depending on choices that we make,” said Kizer, who also has served as California’s top health official prior to leading the VHA from 1994 to 1999.
From “Bloated Bureaucracy’ to High-Quality Health Care System
Kizer has been credited with revitalizing VHA care through a greater commitment to quality, and harkened to his work with the VA as an example of how bold goals can lead to bold innovation.
“What were the perceptions of VA health care in 1994? Well, they weren’t very good, frankly,” Kizer recalled. He described the VA as having a reputation at that time as “highly dysfunctional” with “a very bloated and entrenched bureaucracy.” As for quality of care, it “wasn’t viewed as very good.”
The system’s problems were so severe that patients would park motorhomes in VA medical center parking lots as they waited for care. “While they might have an appointment for one day, they may not be seen for 3 or 4 or 5 days. So they would stay in their motorhome until they finally got into their clinic appointment,” Kizer said.
Overall, “the public viewed the VA as this bleak backwater of incompetence and difference and inefficiency, and there were very strong calls to privatize the VA,” Kizer said.
Kizer asked colleagues about what he should do after he was asked to take the under secretary job. “With one exception, they all said, don’t go near it. Don’t touch it. Walk away. That it’s impossible to change the organization.
“I looked at the VA and I saw an opportunity. When I told [members of the President Bill] Clinton [Administration] yes, my bold aim was that I would like to pursue this was to make VHA a model of excellent health care, an exemplary health care system. Most everyone else thought that I was totally delusional, but sometimes it’s good to be delusional.”
Revolutionary Changes Despite Opposition
Kizer sought reforms in 5 major strategic objectives, all without explicit congressional approval: creating an accountable management structure, decentralizing decision-making, integrating care, implementing universal primary care, and pursuing eligibility reform to create the current 8-tier VA system.
One major innovation was the implementation of community-based outpatient clinics (CBOCs): “Those were strongly opposed initially,” Kizer said. “Everyone, the veteran community in particular, had been led to believe that the only good care was in the hospital.”
The resistance was substantial. “There was a lot of opposition when we said we’re going to move out into the community where you live to make [care] easier to access,” Kizer said.
To make things more difficult, Congress wouldn’t fund the project: “For the first 3 years, every CBOC had to be funded by redirected savings from other things that we could do within the system,” he said. “All of this was through redirected savings and finding ways to save and reinvest.”
Innovation From the Ground Up
Kizer emphasized that many breakthrough innovations came from frontline staff rather than executive mandates. He cited the example of Barcode Medication Administration, which originated from a nurse in Topeka, Kan.
The nurse saw a barcode scanner put to work at a rental car company where it was used to check cars in and out. She wondered, “Why can’t we do this with medications when they’re given on the floor? We followed up on it, pursued those things, tested it out, it worked.”
The results were dramatic. “I was told at a meeting that they had achieved close to 80% reduction in medication errors,” Kizer said. After verifying the results personally, he “authorized $20 million, and we moved forward with it systemwide.”
This experience reinforced his belief in harvesting ideas from staff at all levels.
Innovation remains part of the VA’s culture “despite what some people would have you believe,” Kizer said. Recently, the VA has made major advances in areas such as patient transportation and the climate crisis, he said.
Inside the Recipe for Innovation
Boldness, persistence, adaptability, and tolerance for risk are necessary ingredients for high-risk goals, Kizer said. Ambition is also part of the picture.
He highlighted examples such as the Apollo moon landing, the first sub-4-minute mile, and the first swim across the English Channel by a woman.
In medicine, Kizer pointed to a national patient safety campaign that saved an estimated 122,000 lives. He also mentioned recent progress in organ transplantation such as recommendations from the National Academies of Sciences, Engineering, and Medicine to establish national performance goals and the Organ Procurement and Transplantation Network’s target of 60,000 deceased donor transplants by 2026.
Bold doesn’t mean being reckless or careless, Kizer said. “But it does require innovation. And it does require that you try some new things, some of which aren’t going to work out.”
The key mindset, he explained, is to “embrace the unknown” because “you often really don’t know how you will accomplish the aim when you start. But you’ll figure it out as you go.”
Kizer highlighted 2 opposing strategies to handling challenging times.
According to him, the “negative energy” approach focuses on frustrations, limitations, and asking “Why is this happening to me?”
In contrast, a “positive energy” approach expects problems, focuses on available resources and capabilities, and asks, “What are the opportunities that these changes are creating for me?”
Kizer made it crystal clear which option he prefers.
Dr. Kizer disclosed that his comments represent his opinions only, and he noted his ongoing connections to the VA.
Architect of VA Transformation Urges Innovation Amid Uncertainty
Architect of VA Transformation Urges Innovation Amid Uncertainty




