User login
Bringing you the latest news, research and reviews, exclusive interviews, podcasts, quizzes, and more.
div[contains(@class, 'read-next-article')]
div[contains(@class, 'nav-primary')]
nav[contains(@class, 'nav-primary')]
section[contains(@class, 'footer-nav-section-wrapper')]
nav[contains(@class, 'nav-ce-stack nav-ce-stack__large-screen')]
header[@id='header']
div[contains(@class, 'header__large-screen')]
div[contains(@class, 'main-prefix')]
footer[@id='footer']
section[contains(@class, 'nav-hidden')]
div[contains(@class, 'ce-card-content')]
nav[contains(@class, 'nav-ce-stack')]
div[contains(@class, 'view-medstat-quiz-listing-panes')]
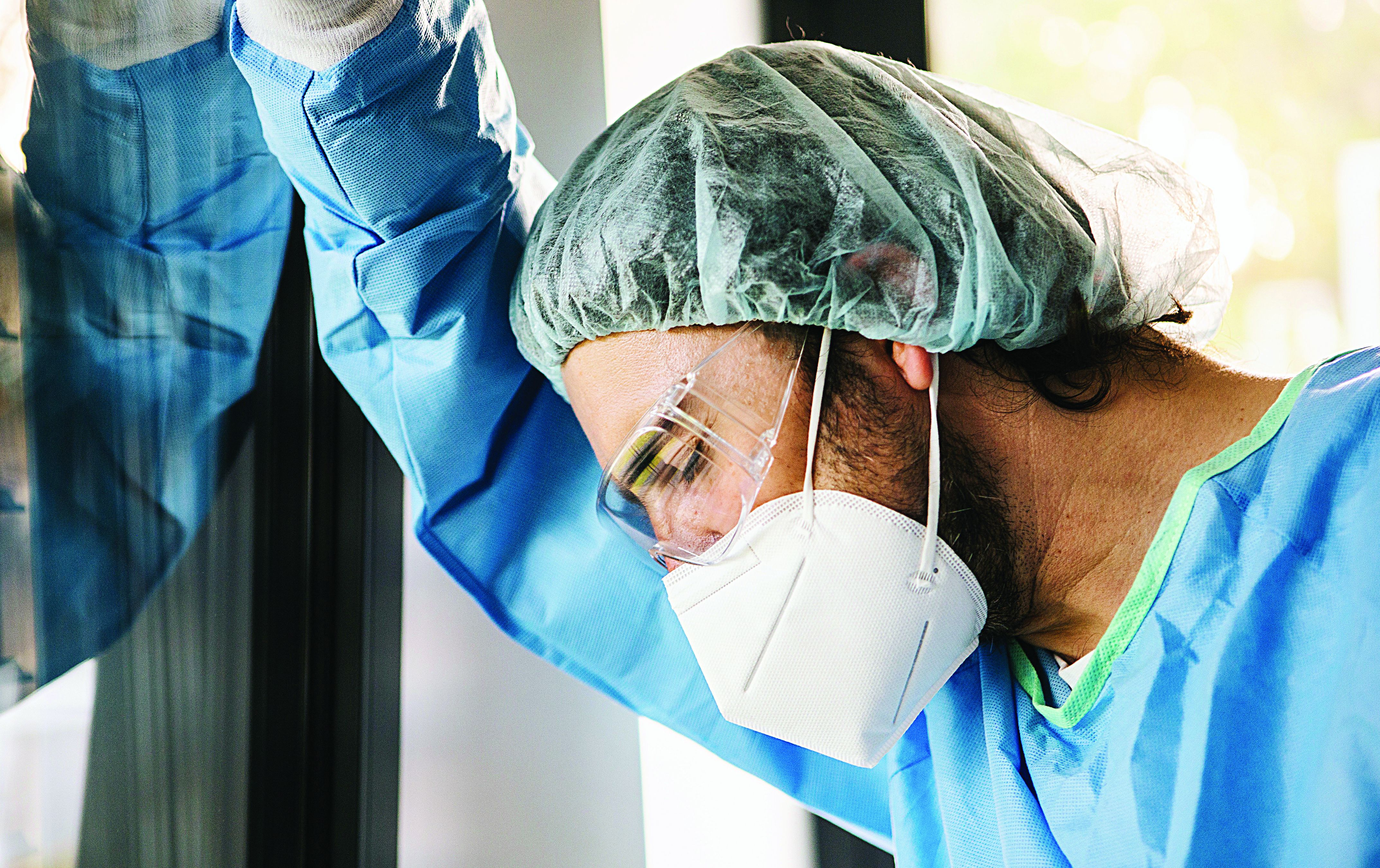
‘Empathy fatigue’ in clinicians rises with latest COVID-19 surge
Heidi Erickson, MD, is tired. As a pulmonary and critical care physician at Hennepin Healthcare in Minneapolis, she has been providing care for patients with COVID-19 since the start of the pandemic.
It was exhausting from the beginning, as she and her colleagues scrambled to understand how to deal with this new disease. But lately, she has noticed a different kind of exhaustion arising from the knowledge that with vaccines widely available, the latest surge was preventable.
Her intensive care unit is currently as full as it has ever been with COVID-19 patients, many of them young adults and most of them unvaccinated. After the recent death of one patient, an unvaccinated man with teenage children, she had to face his family’s questions about why ivermectin, an antiparasitic medication that was falsely promoted as a COVID-19 treatment, was not administered.
“I’m fatigued because I’m working more than ever, but more people don’t have to die,” Dr. Erickson said in an interview . “It’s been very hard physically, mentally, emotionally.”
Amid yet another surge in COVID-19 cases around the United States, clinicians are speaking out about their growing frustration with this preventable crisis.
Some are using the terms “empathy fatigue” and “compassion fatigue” – a sense that they are losing empathy for unvaccinated individuals who are fueling the pandemic.
Dr. Erickson says she is frustrated not by individual patients but by a system that has allowed disinformation to proliferate. Experts say these types of feelings fit into a widespread pattern of physician burnout that has taken a new turn at this stage of the pandemic.
Paradoxical choices
Empathy is a cornerstone of what clinicians do, and the ability to understand and share a patient’s feelings is an essential skill for providing effective care, says Kaz Nelson, MD, a psychiatrist at the University of Minnesota, Minneapolis.
Practitioners face paradoxical situations all the time, she notes. These include individuals who break bones and go skydiving again, people who have high cholesterol but continue to eat fried foods, and those with advanced lung cancer who continue to smoke.
To treat patients with compassion, practitioners learn to set aside judgment by acknowledging the complexity of human behavior. They may lament the addictive nature of nicotine and advertising that targets children, for example, while still listening and caring.
Empathy requires high-level brain function, but as stress levels rise, brain function that drives empathy tends to shut down. It’s a survival mechanism, Dr. Nelson says.
When health care workers feel overwhelmed, trapped, or threatened by patients demanding unproven treatments or by ICUs with more patients than ventilators, they may experience a fight-or-flight response that makes them defensive, frustrated, angry, or uncaring, notes Mona Masood, DO, a Philadelphia-area psychiatrist and founder of Physician Support Line, a free mental health hotline for doctors.
Some clinicians have taken to Twitter and other social media platforms to post about these types of experiences.
These feelings, which have been brewing for months, have been exacerbated by the complexity of the current situation. Clinicians see a disconnect between what is and what could be, Dr. Nelson notes.
“Prior to vaccines, there weren’t other options, and so we had toxic stress and we had fatigue, but we could still maintain little bits of empathy by saying, ‘You know, people didn’t choose to get infected, and we are in a pandemic.’ We could kind of hate the virus. Now with access to vaccines, that last connection to empathy is removed for many people,” she says.
Self-preservation vs. empathy
Compassion fatigue or empathy fatigue is just one reaction to feeling completely maxed out and overstressed, Dr. Nelson says. Anger at society, such as what Dr. Erickson experienced, is another response.
Practitioners may also feel as if they are just going through the motions of their job, or they might disassociate, ceasing to feel that their patients are human. Plenty of doctors and nurses have cried in their cars after shifts and have posted tearful videos on social media.
Early in the pandemic, Dr. Masood says, physicians who called the support hotline expressed sadness and grief. Now, she had her colleagues hear frustration and anger, along with guilt and shame for having feelings they believe they shouldn’t be having, especially toward patients. They may feel unprofessional or worse – unworthy of being physicians, she says.
One recent caller to the hotline was a long-time ICU physician who had been told so many times by patients that ivermectin was the only medicine that would cure them that he began to doubt himself, says Dr. Masood. This caller needed to be reassured by another physician that he was doing the right thing.
Another emergency department physician told Dr. Masood about a young child who had arrived at the hospital with COVID-19 symptoms. When asked whether the family had been exposed to anyone with COVID-19, the child’s parent lied so that they could be triaged faster.
The physician, who needed to step away from the situation, reached out to Dr. Masood to express her frustration so that she wouldn’t “let it out” on the patient.
“It’s hard to have empathy for people who, for all intents and purposes, are very self-centered,” Dr. Masood says. “We’re at a place where we’re having to choose between self-preservation and empathy.”
How to cope
To help practitioners cope, Dr. Masood offers words that describe what they’re experiencing. She often hears clinicians say things such as, “This is a type of burnout that I feel to my bones,” or “This makes me want to quit,” or “I feel like I’m at the end of my rope.”
She encourages them to consider the terms “empathy fatigue,” and “moral injury” in order to reconcile how their sense of responsibility to take care of people is compromised by factors outside of their control.
It is not shameful to acknowledge that they experience emotions, including difficult ones such as frustration, anger, sadness, and anxiety, Dr. Masood adds.
Being frustrated with a patient doesn’t make someone a bad doctor, and admitting those emotions is the first step toward dealing with them, she says.
before they cause a sense of callousness or other consequences that become harder to heal from as time goes on.
“We’re trained to just go, go, go and sometimes not pause and check in,” she says. Clinicians who open up are likely to find they are not the only ones feeling tired or frustrated right now, she adds.
“Connect with peers and colleagues, because chances are, they can relate,” Dr. Nelson says.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Heidi Erickson, MD, is tired. As a pulmonary and critical care physician at Hennepin Healthcare in Minneapolis, she has been providing care for patients with COVID-19 since the start of the pandemic.
It was exhausting from the beginning, as she and her colleagues scrambled to understand how to deal with this new disease. But lately, she has noticed a different kind of exhaustion arising from the knowledge that with vaccines widely available, the latest surge was preventable.
Her intensive care unit is currently as full as it has ever been with COVID-19 patients, many of them young adults and most of them unvaccinated. After the recent death of one patient, an unvaccinated man with teenage children, she had to face his family’s questions about why ivermectin, an antiparasitic medication that was falsely promoted as a COVID-19 treatment, was not administered.
“I’m fatigued because I’m working more than ever, but more people don’t have to die,” Dr. Erickson said in an interview . “It’s been very hard physically, mentally, emotionally.”
Amid yet another surge in COVID-19 cases around the United States, clinicians are speaking out about their growing frustration with this preventable crisis.
Some are using the terms “empathy fatigue” and “compassion fatigue” – a sense that they are losing empathy for unvaccinated individuals who are fueling the pandemic.
Dr. Erickson says she is frustrated not by individual patients but by a system that has allowed disinformation to proliferate. Experts say these types of feelings fit into a widespread pattern of physician burnout that has taken a new turn at this stage of the pandemic.
Paradoxical choices
Empathy is a cornerstone of what clinicians do, and the ability to understand and share a patient’s feelings is an essential skill for providing effective care, says Kaz Nelson, MD, a psychiatrist at the University of Minnesota, Minneapolis.
Practitioners face paradoxical situations all the time, she notes. These include individuals who break bones and go skydiving again, people who have high cholesterol but continue to eat fried foods, and those with advanced lung cancer who continue to smoke.
To treat patients with compassion, practitioners learn to set aside judgment by acknowledging the complexity of human behavior. They may lament the addictive nature of nicotine and advertising that targets children, for example, while still listening and caring.
Empathy requires high-level brain function, but as stress levels rise, brain function that drives empathy tends to shut down. It’s a survival mechanism, Dr. Nelson says.
When health care workers feel overwhelmed, trapped, or threatened by patients demanding unproven treatments or by ICUs with more patients than ventilators, they may experience a fight-or-flight response that makes them defensive, frustrated, angry, or uncaring, notes Mona Masood, DO, a Philadelphia-area psychiatrist and founder of Physician Support Line, a free mental health hotline for doctors.
Some clinicians have taken to Twitter and other social media platforms to post about these types of experiences.
These feelings, which have been brewing for months, have been exacerbated by the complexity of the current situation. Clinicians see a disconnect between what is and what could be, Dr. Nelson notes.
“Prior to vaccines, there weren’t other options, and so we had toxic stress and we had fatigue, but we could still maintain little bits of empathy by saying, ‘You know, people didn’t choose to get infected, and we are in a pandemic.’ We could kind of hate the virus. Now with access to vaccines, that last connection to empathy is removed for many people,” she says.
Self-preservation vs. empathy
Compassion fatigue or empathy fatigue is just one reaction to feeling completely maxed out and overstressed, Dr. Nelson says. Anger at society, such as what Dr. Erickson experienced, is another response.
Practitioners may also feel as if they are just going through the motions of their job, or they might disassociate, ceasing to feel that their patients are human. Plenty of doctors and nurses have cried in their cars after shifts and have posted tearful videos on social media.
Early in the pandemic, Dr. Masood says, physicians who called the support hotline expressed sadness and grief. Now, she had her colleagues hear frustration and anger, along with guilt and shame for having feelings they believe they shouldn’t be having, especially toward patients. They may feel unprofessional or worse – unworthy of being physicians, she says.
One recent caller to the hotline was a long-time ICU physician who had been told so many times by patients that ivermectin was the only medicine that would cure them that he began to doubt himself, says Dr. Masood. This caller needed to be reassured by another physician that he was doing the right thing.
Another emergency department physician told Dr. Masood about a young child who had arrived at the hospital with COVID-19 symptoms. When asked whether the family had been exposed to anyone with COVID-19, the child’s parent lied so that they could be triaged faster.
The physician, who needed to step away from the situation, reached out to Dr. Masood to express her frustration so that she wouldn’t “let it out” on the patient.
“It’s hard to have empathy for people who, for all intents and purposes, are very self-centered,” Dr. Masood says. “We’re at a place where we’re having to choose between self-preservation and empathy.”
How to cope
To help practitioners cope, Dr. Masood offers words that describe what they’re experiencing. She often hears clinicians say things such as, “This is a type of burnout that I feel to my bones,” or “This makes me want to quit,” or “I feel like I’m at the end of my rope.”
She encourages them to consider the terms “empathy fatigue,” and “moral injury” in order to reconcile how their sense of responsibility to take care of people is compromised by factors outside of their control.
It is not shameful to acknowledge that they experience emotions, including difficult ones such as frustration, anger, sadness, and anxiety, Dr. Masood adds.
Being frustrated with a patient doesn’t make someone a bad doctor, and admitting those emotions is the first step toward dealing with them, she says.
before they cause a sense of callousness or other consequences that become harder to heal from as time goes on.
“We’re trained to just go, go, go and sometimes not pause and check in,” she says. Clinicians who open up are likely to find they are not the only ones feeling tired or frustrated right now, she adds.
“Connect with peers and colleagues, because chances are, they can relate,” Dr. Nelson says.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Heidi Erickson, MD, is tired. As a pulmonary and critical care physician at Hennepin Healthcare in Minneapolis, she has been providing care for patients with COVID-19 since the start of the pandemic.
It was exhausting from the beginning, as she and her colleagues scrambled to understand how to deal with this new disease. But lately, she has noticed a different kind of exhaustion arising from the knowledge that with vaccines widely available, the latest surge was preventable.
Her intensive care unit is currently as full as it has ever been with COVID-19 patients, many of them young adults and most of them unvaccinated. After the recent death of one patient, an unvaccinated man with teenage children, she had to face his family’s questions about why ivermectin, an antiparasitic medication that was falsely promoted as a COVID-19 treatment, was not administered.
“I’m fatigued because I’m working more than ever, but more people don’t have to die,” Dr. Erickson said in an interview . “It’s been very hard physically, mentally, emotionally.”
Amid yet another surge in COVID-19 cases around the United States, clinicians are speaking out about their growing frustration with this preventable crisis.
Some are using the terms “empathy fatigue” and “compassion fatigue” – a sense that they are losing empathy for unvaccinated individuals who are fueling the pandemic.
Dr. Erickson says she is frustrated not by individual patients but by a system that has allowed disinformation to proliferate. Experts say these types of feelings fit into a widespread pattern of physician burnout that has taken a new turn at this stage of the pandemic.
Paradoxical choices
Empathy is a cornerstone of what clinicians do, and the ability to understand and share a patient’s feelings is an essential skill for providing effective care, says Kaz Nelson, MD, a psychiatrist at the University of Minnesota, Minneapolis.
Practitioners face paradoxical situations all the time, she notes. These include individuals who break bones and go skydiving again, people who have high cholesterol but continue to eat fried foods, and those with advanced lung cancer who continue to smoke.
To treat patients with compassion, practitioners learn to set aside judgment by acknowledging the complexity of human behavior. They may lament the addictive nature of nicotine and advertising that targets children, for example, while still listening and caring.
Empathy requires high-level brain function, but as stress levels rise, brain function that drives empathy tends to shut down. It’s a survival mechanism, Dr. Nelson says.
When health care workers feel overwhelmed, trapped, or threatened by patients demanding unproven treatments or by ICUs with more patients than ventilators, they may experience a fight-or-flight response that makes them defensive, frustrated, angry, or uncaring, notes Mona Masood, DO, a Philadelphia-area psychiatrist and founder of Physician Support Line, a free mental health hotline for doctors.
Some clinicians have taken to Twitter and other social media platforms to post about these types of experiences.
These feelings, which have been brewing for months, have been exacerbated by the complexity of the current situation. Clinicians see a disconnect between what is and what could be, Dr. Nelson notes.
“Prior to vaccines, there weren’t other options, and so we had toxic stress and we had fatigue, but we could still maintain little bits of empathy by saying, ‘You know, people didn’t choose to get infected, and we are in a pandemic.’ We could kind of hate the virus. Now with access to vaccines, that last connection to empathy is removed for many people,” she says.
Self-preservation vs. empathy
Compassion fatigue or empathy fatigue is just one reaction to feeling completely maxed out and overstressed, Dr. Nelson says. Anger at society, such as what Dr. Erickson experienced, is another response.
Practitioners may also feel as if they are just going through the motions of their job, or they might disassociate, ceasing to feel that their patients are human. Plenty of doctors and nurses have cried in their cars after shifts and have posted tearful videos on social media.
Early in the pandemic, Dr. Masood says, physicians who called the support hotline expressed sadness and grief. Now, she had her colleagues hear frustration and anger, along with guilt and shame for having feelings they believe they shouldn’t be having, especially toward patients. They may feel unprofessional or worse – unworthy of being physicians, she says.
One recent caller to the hotline was a long-time ICU physician who had been told so many times by patients that ivermectin was the only medicine that would cure them that he began to doubt himself, says Dr. Masood. This caller needed to be reassured by another physician that he was doing the right thing.
Another emergency department physician told Dr. Masood about a young child who had arrived at the hospital with COVID-19 symptoms. When asked whether the family had been exposed to anyone with COVID-19, the child’s parent lied so that they could be triaged faster.
The physician, who needed to step away from the situation, reached out to Dr. Masood to express her frustration so that she wouldn’t “let it out” on the patient.
“It’s hard to have empathy for people who, for all intents and purposes, are very self-centered,” Dr. Masood says. “We’re at a place where we’re having to choose between self-preservation and empathy.”
How to cope
To help practitioners cope, Dr. Masood offers words that describe what they’re experiencing. She often hears clinicians say things such as, “This is a type of burnout that I feel to my bones,” or “This makes me want to quit,” or “I feel like I’m at the end of my rope.”
She encourages them to consider the terms “empathy fatigue,” and “moral injury” in order to reconcile how their sense of responsibility to take care of people is compromised by factors outside of their control.
It is not shameful to acknowledge that they experience emotions, including difficult ones such as frustration, anger, sadness, and anxiety, Dr. Masood adds.
Being frustrated with a patient doesn’t make someone a bad doctor, and admitting those emotions is the first step toward dealing with them, she says.
before they cause a sense of callousness or other consequences that become harder to heal from as time goes on.
“We’re trained to just go, go, go and sometimes not pause and check in,” she says. Clinicians who open up are likely to find they are not the only ones feeling tired or frustrated right now, she adds.
“Connect with peers and colleagues, because chances are, they can relate,” Dr. Nelson says.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Online mental health treatment: Is this the answer we’ve been waiting for?
If you haven’t noticed yet, there has been an explosion of new online companies specializing in slicing off some little sliver of health care and leaving traditional medicine to take care of the rest of the patient. Lately, many of these startups involve mental health care, traditionally a difficult area to make profitable unless one caters just to the wealthy. Many pediatricians have been unsure exactly what to make of these new efforts. Are these the rescuers we’ve been waiting for to fill what seems like an enormous and growing unmet need? Are they just another means to extract money from desperate people and leave the real work to someone else? Something in-between? This article outlines some points to consider when evaluating this new frontier.
Case vignette
A 12-year-old girl presents with her parents for an annual exam. She has been struggling with her mood and anxiety over the past 2 years along with occasional superficial cutting. You have started treatment with a selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor and have recommended that she see a mental health professional but the parents report that one attempt with a therapist was a poor fit and nobody in the area seems to be accepting new patients. The parents state that they saw an advertisement on TV for a company that offers online psychotherapy by video appointments or text. They think this might be an option to pursue but are a little skeptical of the whole idea. They look for your opinion on this topic.
Most of these companies operate by having subscribers pay a monthly fee for different levels of services such as videoconference therapy sessions, supportive text messages, or even some psychopharmacological care. Many also offer the ability to switch rapidly between clinicians if you don’t like the one you have.
These arrangements sound great as the world grows increasingly comfortable with online communication and the mental health needs of children and adolescents increase with the seemingly endless COVID pandemic. Further, research generally finds that online mental health treatment is just as effective as services delivered in person, although the data on therapy by text are less robust.
Nevertheless, a lot of skepticism remains about online mental health treatment, particularly among those involved in more traditionally delivered mental health care. Some of the concerns that often get brought up include the following:
- Cost. Most of these online groups, especially the big national companies, don’t interact directly with insurance companies, leaving a lot of out-of-pocket expenses or the need for families to work things out directly with their insurance provider.
- Care fragmentation. In many ways, the online mental health care surge seems at odds with the growing “integrated care” movement that is trying to embed more behavioral care within primary care practices. From this lens, outsourcing someone’s mental health treatment to a therapist across the country that the patient has never actually met seems like a step in the wrong direction. Further, concerns arise about how much these folks will know about local resources in the community.
- The corporate model in mental health care. While being able to shop for a therapist like you would for a pillow sounds great on the surface, there are many times where a patient may need to be supportively confronted by their therapist or told no when asking about things like certain medications. The “customer is always right” principle often falls short when it comes to good mental health treatment.
- Depth and type of treatment. It is probably fair to say that most online therapy could be described as supportive psychotherapy. This type of therapy can be quite helpful for many but may lack the depth or specific techniques that some people need. For youth, some of the most effective types of psychotherapy, like cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT), can be harder to find, and implement, online.
- Emergencies. While many online companies claim to offer round-the-clock support for paying customers, they can quickly punt to “call your doctor” or even “call 911” if there is any real mental health crisis.
Balancing these potential benefits and pitfalls of online therapy, here are a few questions your patients may want to consider before signing onto a long-term contract with an online therapy company.
- Would the online clinician have any knowledge of my community? In some cases, this may not matter that much, while for others it could be quite important.
- What happens in an emergency? Would the regular online therapist be available to help through a crisis or would things revert back to local resources?
- What about privacy and collaboration? Effective communication between a patient’s primary care clinician and their therapist can be crucial to good care, and asking the patient always to be the intermediary can be fraught with difficulty.
- How long is the contract? Just like those gym memberships, these companies bank on individuals who sign up but then don’t really use the service.
- What kind of training do the therapists at the site have? Is it possible to receive specific types of therapy, like CBT or parent training? Otherwise, pediatricians might be quite likely to hear back from the family wondering about medications after therapy “isn’t helping.”
Overall, mental health treatment delivered by telehealth is here to stay whether we like it or not. For some families, it is likely to provide new access to services not easily obtainable locally, while for others it could end up being a costly and ineffective enterprise. For families who use these services, a key challenge for pediatricians that may be important to overcome is finding a way for these clinicians to integrate into the overall medical team rather than being a detached island unto themselves.
Dr. Rettew is a child and adolescent psychiatrist and associate professor of psychiatry and pediatrics at the University of Vermont Larner College of Medicine, Burlington. Follow him on Twitter @PediPsych. His book, “Parenting Made Complicated: What Science Really Knows About the Greatest Debates of Early Childhood” (New York: Oxford University Press, 2021). Email him at [email protected].
If you haven’t noticed yet, there has been an explosion of new online companies specializing in slicing off some little sliver of health care and leaving traditional medicine to take care of the rest of the patient. Lately, many of these startups involve mental health care, traditionally a difficult area to make profitable unless one caters just to the wealthy. Many pediatricians have been unsure exactly what to make of these new efforts. Are these the rescuers we’ve been waiting for to fill what seems like an enormous and growing unmet need? Are they just another means to extract money from desperate people and leave the real work to someone else? Something in-between? This article outlines some points to consider when evaluating this new frontier.
Case vignette
A 12-year-old girl presents with her parents for an annual exam. She has been struggling with her mood and anxiety over the past 2 years along with occasional superficial cutting. You have started treatment with a selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor and have recommended that she see a mental health professional but the parents report that one attempt with a therapist was a poor fit and nobody in the area seems to be accepting new patients. The parents state that they saw an advertisement on TV for a company that offers online psychotherapy by video appointments or text. They think this might be an option to pursue but are a little skeptical of the whole idea. They look for your opinion on this topic.
Most of these companies operate by having subscribers pay a monthly fee for different levels of services such as videoconference therapy sessions, supportive text messages, or even some psychopharmacological care. Many also offer the ability to switch rapidly between clinicians if you don’t like the one you have.
These arrangements sound great as the world grows increasingly comfortable with online communication and the mental health needs of children and adolescents increase with the seemingly endless COVID pandemic. Further, research generally finds that online mental health treatment is just as effective as services delivered in person, although the data on therapy by text are less robust.
Nevertheless, a lot of skepticism remains about online mental health treatment, particularly among those involved in more traditionally delivered mental health care. Some of the concerns that often get brought up include the following:
- Cost. Most of these online groups, especially the big national companies, don’t interact directly with insurance companies, leaving a lot of out-of-pocket expenses or the need for families to work things out directly with their insurance provider.
- Care fragmentation. In many ways, the online mental health care surge seems at odds with the growing “integrated care” movement that is trying to embed more behavioral care within primary care practices. From this lens, outsourcing someone’s mental health treatment to a therapist across the country that the patient has never actually met seems like a step in the wrong direction. Further, concerns arise about how much these folks will know about local resources in the community.
- The corporate model in mental health care. While being able to shop for a therapist like you would for a pillow sounds great on the surface, there are many times where a patient may need to be supportively confronted by their therapist or told no when asking about things like certain medications. The “customer is always right” principle often falls short when it comes to good mental health treatment.
- Depth and type of treatment. It is probably fair to say that most online therapy could be described as supportive psychotherapy. This type of therapy can be quite helpful for many but may lack the depth or specific techniques that some people need. For youth, some of the most effective types of psychotherapy, like cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT), can be harder to find, and implement, online.
- Emergencies. While many online companies claim to offer round-the-clock support for paying customers, they can quickly punt to “call your doctor” or even “call 911” if there is any real mental health crisis.
Balancing these potential benefits and pitfalls of online therapy, here are a few questions your patients may want to consider before signing onto a long-term contract with an online therapy company.
- Would the online clinician have any knowledge of my community? In some cases, this may not matter that much, while for others it could be quite important.
- What happens in an emergency? Would the regular online therapist be available to help through a crisis or would things revert back to local resources?
- What about privacy and collaboration? Effective communication between a patient’s primary care clinician and their therapist can be crucial to good care, and asking the patient always to be the intermediary can be fraught with difficulty.
- How long is the contract? Just like those gym memberships, these companies bank on individuals who sign up but then don’t really use the service.
- What kind of training do the therapists at the site have? Is it possible to receive specific types of therapy, like CBT or parent training? Otherwise, pediatricians might be quite likely to hear back from the family wondering about medications after therapy “isn’t helping.”
Overall, mental health treatment delivered by telehealth is here to stay whether we like it or not. For some families, it is likely to provide new access to services not easily obtainable locally, while for others it could end up being a costly and ineffective enterprise. For families who use these services, a key challenge for pediatricians that may be important to overcome is finding a way for these clinicians to integrate into the overall medical team rather than being a detached island unto themselves.
Dr. Rettew is a child and adolescent psychiatrist and associate professor of psychiatry and pediatrics at the University of Vermont Larner College of Medicine, Burlington. Follow him on Twitter @PediPsych. His book, “Parenting Made Complicated: What Science Really Knows About the Greatest Debates of Early Childhood” (New York: Oxford University Press, 2021). Email him at [email protected].
If you haven’t noticed yet, there has been an explosion of new online companies specializing in slicing off some little sliver of health care and leaving traditional medicine to take care of the rest of the patient. Lately, many of these startups involve mental health care, traditionally a difficult area to make profitable unless one caters just to the wealthy. Many pediatricians have been unsure exactly what to make of these new efforts. Are these the rescuers we’ve been waiting for to fill what seems like an enormous and growing unmet need? Are they just another means to extract money from desperate people and leave the real work to someone else? Something in-between? This article outlines some points to consider when evaluating this new frontier.
Case vignette
A 12-year-old girl presents with her parents for an annual exam. She has been struggling with her mood and anxiety over the past 2 years along with occasional superficial cutting. You have started treatment with a selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor and have recommended that she see a mental health professional but the parents report that one attempt with a therapist was a poor fit and nobody in the area seems to be accepting new patients. The parents state that they saw an advertisement on TV for a company that offers online psychotherapy by video appointments or text. They think this might be an option to pursue but are a little skeptical of the whole idea. They look for your opinion on this topic.
Most of these companies operate by having subscribers pay a monthly fee for different levels of services such as videoconference therapy sessions, supportive text messages, or even some psychopharmacological care. Many also offer the ability to switch rapidly between clinicians if you don’t like the one you have.
These arrangements sound great as the world grows increasingly comfortable with online communication and the mental health needs of children and adolescents increase with the seemingly endless COVID pandemic. Further, research generally finds that online mental health treatment is just as effective as services delivered in person, although the data on therapy by text are less robust.
Nevertheless, a lot of skepticism remains about online mental health treatment, particularly among those involved in more traditionally delivered mental health care. Some of the concerns that often get brought up include the following:
- Cost. Most of these online groups, especially the big national companies, don’t interact directly with insurance companies, leaving a lot of out-of-pocket expenses or the need for families to work things out directly with their insurance provider.
- Care fragmentation. In many ways, the online mental health care surge seems at odds with the growing “integrated care” movement that is trying to embed more behavioral care within primary care practices. From this lens, outsourcing someone’s mental health treatment to a therapist across the country that the patient has never actually met seems like a step in the wrong direction. Further, concerns arise about how much these folks will know about local resources in the community.
- The corporate model in mental health care. While being able to shop for a therapist like you would for a pillow sounds great on the surface, there are many times where a patient may need to be supportively confronted by their therapist or told no when asking about things like certain medications. The “customer is always right” principle often falls short when it comes to good mental health treatment.
- Depth and type of treatment. It is probably fair to say that most online therapy could be described as supportive psychotherapy. This type of therapy can be quite helpful for many but may lack the depth or specific techniques that some people need. For youth, some of the most effective types of psychotherapy, like cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT), can be harder to find, and implement, online.
- Emergencies. While many online companies claim to offer round-the-clock support for paying customers, they can quickly punt to “call your doctor” or even “call 911” if there is any real mental health crisis.
Balancing these potential benefits and pitfalls of online therapy, here are a few questions your patients may want to consider before signing onto a long-term contract with an online therapy company.
- Would the online clinician have any knowledge of my community? In some cases, this may not matter that much, while for others it could be quite important.
- What happens in an emergency? Would the regular online therapist be available to help through a crisis or would things revert back to local resources?
- What about privacy and collaboration? Effective communication between a patient’s primary care clinician and their therapist can be crucial to good care, and asking the patient always to be the intermediary can be fraught with difficulty.
- How long is the contract? Just like those gym memberships, these companies bank on individuals who sign up but then don’t really use the service.
- What kind of training do the therapists at the site have? Is it possible to receive specific types of therapy, like CBT or parent training? Otherwise, pediatricians might be quite likely to hear back from the family wondering about medications after therapy “isn’t helping.”
Overall, mental health treatment delivered by telehealth is here to stay whether we like it or not. For some families, it is likely to provide new access to services not easily obtainable locally, while for others it could end up being a costly and ineffective enterprise. For families who use these services, a key challenge for pediatricians that may be important to overcome is finding a way for these clinicians to integrate into the overall medical team rather than being a detached island unto themselves.
Dr. Rettew is a child and adolescent psychiatrist and associate professor of psychiatry and pediatrics at the University of Vermont Larner College of Medicine, Burlington. Follow him on Twitter @PediPsych. His book, “Parenting Made Complicated: What Science Really Knows About the Greatest Debates of Early Childhood” (New York: Oxford University Press, 2021). Email him at [email protected].
Opioid overdoses tied to lasting cognitive impairment
Opioid overdoses usually aren’t fatal, but a new review of numerous studies, mostly case reports and case series, suggests that they can have long-lasting effects on cognition, possibly because of hypoxia resulting from respiratory depression.
Erin L. Winstanley, PhD, MA, and associates noted in the review that opioids cause about 80% of worldwide deaths from illicit drug use, and the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention’s provisional August 2021 number of more than 88,000 opioid-caused deaths in the United States is the highest ever recorded – a 27% increase over what was reported last December. That number suggests that the opioid epidemic continues to rage, but the study results also show that the neurological consequences of nonfatal overdoses are an important public health problem.
And that’s something that may be overlooked, according to Mark S. Gold, MD, who was not involved with the study and was asked to comment on the review, which was published in the Journal of Addiction Science.
“Assuming that an overdose has no effect on the brain, mood, and behavior is not supported by experience or the literature. He is a University of Florida, Gainesville, Emeritus Eminent Scholar, adjunct professor of psychiatry at Washington University in St. Louis, and a member of the clinical council of Washington University’s Public Health Institute.
A common pattern among patients with opioid use disorder (OUD) is that they undergo treatment with medication-assisted therapy (MAT), only to drop out of treatment and then repeat the treatment at a later date. That suggests that physicians should take a harder look at the limitations of MAT and other treatments, Dr. Gold said.
Although the review found some associations between neurocognitive deficits and opioid overdose, the authors point out that it is difficult to make direct comparisons because of biases and differences in methodology among the included studies. They were not able to reach conclusions about the prevalence of brain injuries following nonfatal opioid overdoses. Few included studies controlled for confounding factors that might contribute to or explain neurocognitive impairments, reported Dr. Winstanley, associate professor in the department of behavioral medicine and psychiatry at the University of West Virginia, Morgantown, and associates.
Still, distinct patterns emerged from the analysis of almost 3,500 subjects in 79 studies in 21 countries. Twenty-nine studies reported diagnoses of leukoencephalopathy, which affects white matter. Spongiform leukoencephalopathy is known to occur secondarily after exposure to a variety of toxic agents, including carbon monoxide poisoning and drugs of abuse. The damage can lead to erosion of higher cerebral function. The condition can occur from 2 to 180 days after a hypoxic brain injury, potentially complicating efforts to attribute it specifically to an opioid overdose. Amnestic syndrome was also reported in some studies. One study found that about 39% of people seeking buprenorphine treatment suffered from neurocognitive impairment.
Dr. Gold called the study’s findings novel and of public health importance. “Each overdose takes a toll on the body, and especially the brain,” he said.
Better documentation needed
The variability in symptoms, as well as their timing, present challenges to initial treatment, which often occur before a patient reaches the hospital. This is a vital window because the length of time of inadequate respiration because of opioid overdose is likely to predict the extent of brain injury. The duration of inadequate respiration may not be captured in electronic medical records, and emergency departments don’t typically collect toxicology information, which may lead health care providers to attribute neurocognitive impairments to ongoing drug use rather than an acute anoxic or hypoxic episode. Further neurocognitive damage may have a delayed onset, and better documentation of these events could help physicians determine whether those symptoms stem from the acute event.
Dr. Winstanley and associates called for more research, including prospective case-control studies to identify brain changes following opioid-related overdose.
The authors also suggested that physicians might want to consider screening patients who experience prolonged anoxia or hypoxia for neurocognitive impairments and brain injuries. Dr. Gold agreed.
“Clinicians working with OUD patients should take these data to heart and take a comprehensive history of previous overdoses, loss of consciousness, head trauma, and following up on the history with neuropsychological and other tests of brain function,” Dr. Gold said. “After an assessment, rehabilitation and treatment might then be more personalized and effective.”
Dr. Gold had no relevant financial disclosures.
Opioid overdoses usually aren’t fatal, but a new review of numerous studies, mostly case reports and case series, suggests that they can have long-lasting effects on cognition, possibly because of hypoxia resulting from respiratory depression.
Erin L. Winstanley, PhD, MA, and associates noted in the review that opioids cause about 80% of worldwide deaths from illicit drug use, and the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention’s provisional August 2021 number of more than 88,000 opioid-caused deaths in the United States is the highest ever recorded – a 27% increase over what was reported last December. That number suggests that the opioid epidemic continues to rage, but the study results also show that the neurological consequences of nonfatal overdoses are an important public health problem.
And that’s something that may be overlooked, according to Mark S. Gold, MD, who was not involved with the study and was asked to comment on the review, which was published in the Journal of Addiction Science.
“Assuming that an overdose has no effect on the brain, mood, and behavior is not supported by experience or the literature. He is a University of Florida, Gainesville, Emeritus Eminent Scholar, adjunct professor of psychiatry at Washington University in St. Louis, and a member of the clinical council of Washington University’s Public Health Institute.
A common pattern among patients with opioid use disorder (OUD) is that they undergo treatment with medication-assisted therapy (MAT), only to drop out of treatment and then repeat the treatment at a later date. That suggests that physicians should take a harder look at the limitations of MAT and other treatments, Dr. Gold said.
Although the review found some associations between neurocognitive deficits and opioid overdose, the authors point out that it is difficult to make direct comparisons because of biases and differences in methodology among the included studies. They were not able to reach conclusions about the prevalence of brain injuries following nonfatal opioid overdoses. Few included studies controlled for confounding factors that might contribute to or explain neurocognitive impairments, reported Dr. Winstanley, associate professor in the department of behavioral medicine and psychiatry at the University of West Virginia, Morgantown, and associates.
Still, distinct patterns emerged from the analysis of almost 3,500 subjects in 79 studies in 21 countries. Twenty-nine studies reported diagnoses of leukoencephalopathy, which affects white matter. Spongiform leukoencephalopathy is known to occur secondarily after exposure to a variety of toxic agents, including carbon monoxide poisoning and drugs of abuse. The damage can lead to erosion of higher cerebral function. The condition can occur from 2 to 180 days after a hypoxic brain injury, potentially complicating efforts to attribute it specifically to an opioid overdose. Amnestic syndrome was also reported in some studies. One study found that about 39% of people seeking buprenorphine treatment suffered from neurocognitive impairment.
Dr. Gold called the study’s findings novel and of public health importance. “Each overdose takes a toll on the body, and especially the brain,” he said.
Better documentation needed
The variability in symptoms, as well as their timing, present challenges to initial treatment, which often occur before a patient reaches the hospital. This is a vital window because the length of time of inadequate respiration because of opioid overdose is likely to predict the extent of brain injury. The duration of inadequate respiration may not be captured in electronic medical records, and emergency departments don’t typically collect toxicology information, which may lead health care providers to attribute neurocognitive impairments to ongoing drug use rather than an acute anoxic or hypoxic episode. Further neurocognitive damage may have a delayed onset, and better documentation of these events could help physicians determine whether those symptoms stem from the acute event.
Dr. Winstanley and associates called for more research, including prospective case-control studies to identify brain changes following opioid-related overdose.
The authors also suggested that physicians might want to consider screening patients who experience prolonged anoxia or hypoxia for neurocognitive impairments and brain injuries. Dr. Gold agreed.
“Clinicians working with OUD patients should take these data to heart and take a comprehensive history of previous overdoses, loss of consciousness, head trauma, and following up on the history with neuropsychological and other tests of brain function,” Dr. Gold said. “After an assessment, rehabilitation and treatment might then be more personalized and effective.”
Dr. Gold had no relevant financial disclosures.
Opioid overdoses usually aren’t fatal, but a new review of numerous studies, mostly case reports and case series, suggests that they can have long-lasting effects on cognition, possibly because of hypoxia resulting from respiratory depression.
Erin L. Winstanley, PhD, MA, and associates noted in the review that opioids cause about 80% of worldwide deaths from illicit drug use, and the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention’s provisional August 2021 number of more than 88,000 opioid-caused deaths in the United States is the highest ever recorded – a 27% increase over what was reported last December. That number suggests that the opioid epidemic continues to rage, but the study results also show that the neurological consequences of nonfatal overdoses are an important public health problem.
And that’s something that may be overlooked, according to Mark S. Gold, MD, who was not involved with the study and was asked to comment on the review, which was published in the Journal of Addiction Science.
“Assuming that an overdose has no effect on the brain, mood, and behavior is not supported by experience or the literature. He is a University of Florida, Gainesville, Emeritus Eminent Scholar, adjunct professor of psychiatry at Washington University in St. Louis, and a member of the clinical council of Washington University’s Public Health Institute.
A common pattern among patients with opioid use disorder (OUD) is that they undergo treatment with medication-assisted therapy (MAT), only to drop out of treatment and then repeat the treatment at a later date. That suggests that physicians should take a harder look at the limitations of MAT and other treatments, Dr. Gold said.
Although the review found some associations between neurocognitive deficits and opioid overdose, the authors point out that it is difficult to make direct comparisons because of biases and differences in methodology among the included studies. They were not able to reach conclusions about the prevalence of brain injuries following nonfatal opioid overdoses. Few included studies controlled for confounding factors that might contribute to or explain neurocognitive impairments, reported Dr. Winstanley, associate professor in the department of behavioral medicine and psychiatry at the University of West Virginia, Morgantown, and associates.
Still, distinct patterns emerged from the analysis of almost 3,500 subjects in 79 studies in 21 countries. Twenty-nine studies reported diagnoses of leukoencephalopathy, which affects white matter. Spongiform leukoencephalopathy is known to occur secondarily after exposure to a variety of toxic agents, including carbon monoxide poisoning and drugs of abuse. The damage can lead to erosion of higher cerebral function. The condition can occur from 2 to 180 days after a hypoxic brain injury, potentially complicating efforts to attribute it specifically to an opioid overdose. Amnestic syndrome was also reported in some studies. One study found that about 39% of people seeking buprenorphine treatment suffered from neurocognitive impairment.
Dr. Gold called the study’s findings novel and of public health importance. “Each overdose takes a toll on the body, and especially the brain,” he said.
Better documentation needed
The variability in symptoms, as well as their timing, present challenges to initial treatment, which often occur before a patient reaches the hospital. This is a vital window because the length of time of inadequate respiration because of opioid overdose is likely to predict the extent of brain injury. The duration of inadequate respiration may not be captured in electronic medical records, and emergency departments don’t typically collect toxicology information, which may lead health care providers to attribute neurocognitive impairments to ongoing drug use rather than an acute anoxic or hypoxic episode. Further neurocognitive damage may have a delayed onset, and better documentation of these events could help physicians determine whether those symptoms stem from the acute event.
Dr. Winstanley and associates called for more research, including prospective case-control studies to identify brain changes following opioid-related overdose.
The authors also suggested that physicians might want to consider screening patients who experience prolonged anoxia or hypoxia for neurocognitive impairments and brain injuries. Dr. Gold agreed.
“Clinicians working with OUD patients should take these data to heart and take a comprehensive history of previous overdoses, loss of consciousness, head trauma, and following up on the history with neuropsychological and other tests of brain function,” Dr. Gold said. “After an assessment, rehabilitation and treatment might then be more personalized and effective.”
Dr. Gold had no relevant financial disclosures.
FROM THE JOURNAL OF ADDICTION SCIENCE
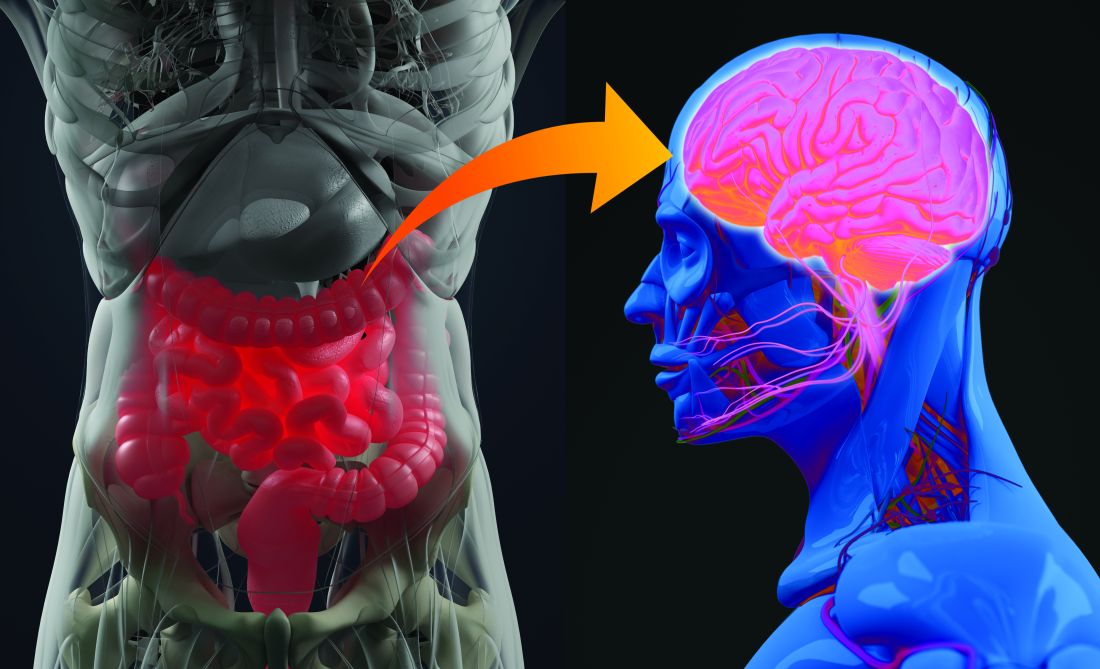
The role of probiotics in mental health
In 1950, at Staten Island’s Sea View Hospital, a group of patients with terminal tuberculosis were given a new antibiotic called isoniazid, which caused some unexpected side effects. The patients reported euphoria, mental stimulation, and improved sleep, and even began socializing with more vigor. The press was all over the case, writing about the sick “dancing in the halls tho’ they had holes in their lungs.” Soon doctors started prescribing isoniazid as the first-ever antidepressant.
The Sea View Hospital experiment was an early hint that changing the composition of the gut microbiome – in this case, via antibiotics – might affect our mental health. Yet only in the last 2 decades has research into connections between what we ingest and psychiatric disorders really taken off. In 2004, a landmark study showed that germ-free mice (born in such sterile conditions that they lacked a microbiome) had an exaggerated stress response. The effects were reversed, however, if the mice were fed a bacterial strain, Bifidobacterium infantis, a probiotic. This sparked academic interest, and thousands of research papers followed.
According to Stephen Ilardi, PhD, a clinical psychologist at the University of Kansas, Lawrence, focusing on the etiology and treatment of depression, now is the “time of exciting discovery” in the field of probiotics and psychiatric disorders, although, admittedly, a lot still remains unknown.
Gut microbiome profiles in mental health disorders
We humans have about 100 trillion microbes residing in our guts. Some of these are archaea, some fungi, some protozoans and even viruses, but most are bacteria. Things like diet, sleep, and stress can all impact the composition of our gut microbiome. When the microbiome differs considerably from the typical, doctors and researchers describe it as dysbiosis, or imbalance. Studies have uncovered dysbiosis in patients with depression, anxiety, schizophrenia, and bipolar disorder.
“I think there is now pretty good evidence that the gut microbiome is actually an important factor in a number of psychiatric disorders,” says Allan Young, MBChB, clinical psychiatrist at King’s College London. The gut microbiome composition does seem to differ between psychiatric patients and the healthy. In depression, for example, a recent review of nine studies found an increase on the genus level in Streptococcus and Oscillibacter and low abundance of Lactobacillus and Coprococcus, among others. In generalized anxiety disorder, meanwhile, there appears to be an increase in Fusobacteria and Escherichia/Shigella .
For Dr. Ilardi, the next important question is whether there are plausible mechanisms that could explain how gut microbiota may influence brain function. And, it appears there are.
“The microbes in the gut can release neurotransmitters into blood that cross into the brain and influence brain function. They can release hormones into the blood that again cross into the brain. They’ve got a lot of tricks up their sleeve,” he says.
One particularly important pathway runs through the vagus nerve – the longest nerve that emerges directly from the brain, connecting it to the gut. Another is the immune pathway. Gut bacteria can interact with immune cells and reduce cytokine production, which in turn can reduce systemic inflammation. Inflammatory processes have been implicated in both depression and bipolar disorder. What’s more, gut microbes can upregulate the expression of a protein called BDNF – brain-derived neurotrophic factor – which helps the development and survival of nerve cells in the brain.
Probiotics’ promise varies for different conditions
As the pathways by which gut dysbiosis may influence psychiatric disorders become clearer, the next logical step is to try to influence the composition of the microbiome to prevent and treat depression, anxiety, or schizophrenia. That’s where probiotics come in.
The evidence for the effects of probiotics – live microorganisms which, when ingested in adequate amounts, confer a health benefit – so far is the strongest for depression, says Viktoriya Nikolova, MRes, MSc, a PhD student and researcher at King’s College London. In their 2021 meta-analysis of seven trials, Mr. Nikolova and colleagues revealed that probiotics can significantly reduce depressive symptoms after just 8 weeks. There was a caveat, however – the probiotics only worked when used in addition to an approved antidepressant. Another meta-analysis, published in 2018, also showed that probiotics, when compared with placebo, improve mood in people with depressive symptoms (here, no antidepressant treatment was necessary).
Roumen Milev, MD, PhD, a neuroscientist at Queen’s University, Kingston, Ont., and coauthor of a review on probiotics and depression published in the Annals of General Psychiatry, warns, however, that the research is still in its infancy. “,” he says.
When it comes to using probiotics to relieve anxiety, “the evidence in the animal literature is really compelling,” says Dr. Ilardi. Human studies are less convincing, however, which Dr. Dr. Ilardi showed in his 2018 review and meta-analysis involving 743 animals and 1,527 humans. “Studies are small for the most part, and some of them aren’t terribly well conducted, and they often use very low doses of probiotics,” he says. One of the larger double-blind and placebo-controlled trials showed that supplementation with Lactobacillus plantarum helps reduce stress and anxiety, while the levels of proinflammatory cytokines go down. Another meta-analysis, published in June, revealed that, when it comes to reducing stress and anxiety in youth, the results are mixed.
Evidence of probiotics’ efficiency in schizophrenia is emerging, yet also limited. A 2019 review concluded that currently available results only “hint” at a possibility that probiotics could make a difference in schizophrenia. Similarly, a 2020 review summed up that the role of probiotics in bipolar disorder “remains unclear and underexplored.”
Better studies, remaining questions
Apart from small samples, one issue with research on probiotics is that they generally tend to use varied doses of different strains of bacteria, or even multistrain mixtures, making it tough to compare results. Although there are hundreds of species of bacteria in the human gut, only a few have been evaluated for their antidepressant or antianxiety effects.
“To make it even worse, it’s almost certainly the case that depending on a person’s actual genetics or maybe their epigenetics, a strain that is helpful for one person may not be helpful for another. There is almost certainly no one-size-fits-all probiotic formulation,” says Dr. Ilardi.
Another critical question that remains to be answered is that of potential side effects.
“Probiotics are often seen as food supplements, so they don’t follow under the same regulations as drugs would,” says Mr. Nikolova. “They don’t necessarily have to follow the pattern of drug trials in many countries, which means that the monitoring of side effects is not the requirement.”
That’s something that worries King’s College psychiatrist Young too. “If you are giving it to modulate how the brain works, you could potentially induce psychiatric symptoms or a psychiatric disorder. There could be allergic reactions. There could be lots of different things,” he says.
When you search the web for “probiotics,” chances are you will come across sites boasting amazing effects that such products can have on cardiovascular heath, the immune system, and yes, mental well-being. Many also sell various probiotic supplements “formulated” for your gut health or improved moods. However, many such commercially available strains have never been actually tested in clinical trials. What’s more, according to Kathrin Cohen Kadosh, PhD, a neuroscientist at University of Surrey (England), “it is not always clear whether the different strains actually reach the gut intact.”
For now, considering the limited research evidence, a safer bet is to try to improve gut health through consumption of fermented foods that naturally contain probiotics, such as miso, kefir, or sauerkraut. Alternatively, you could reach for prebiotics, such as foods containing fiber (prebiotics enhance the growth of beneficial gut microbes). This, Dr. Kadosh says, could be “a gentler way of improving gut health” than popping a pill. Whether an improved mental well-being might follow still remains to be seen.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
In 1950, at Staten Island’s Sea View Hospital, a group of patients with terminal tuberculosis were given a new antibiotic called isoniazid, which caused some unexpected side effects. The patients reported euphoria, mental stimulation, and improved sleep, and even began socializing with more vigor. The press was all over the case, writing about the sick “dancing in the halls tho’ they had holes in their lungs.” Soon doctors started prescribing isoniazid as the first-ever antidepressant.
The Sea View Hospital experiment was an early hint that changing the composition of the gut microbiome – in this case, via antibiotics – might affect our mental health. Yet only in the last 2 decades has research into connections between what we ingest and psychiatric disorders really taken off. In 2004, a landmark study showed that germ-free mice (born in such sterile conditions that they lacked a microbiome) had an exaggerated stress response. The effects were reversed, however, if the mice were fed a bacterial strain, Bifidobacterium infantis, a probiotic. This sparked academic interest, and thousands of research papers followed.
According to Stephen Ilardi, PhD, a clinical psychologist at the University of Kansas, Lawrence, focusing on the etiology and treatment of depression, now is the “time of exciting discovery” in the field of probiotics and psychiatric disorders, although, admittedly, a lot still remains unknown.
Gut microbiome profiles in mental health disorders
We humans have about 100 trillion microbes residing in our guts. Some of these are archaea, some fungi, some protozoans and even viruses, but most are bacteria. Things like diet, sleep, and stress can all impact the composition of our gut microbiome. When the microbiome differs considerably from the typical, doctors and researchers describe it as dysbiosis, or imbalance. Studies have uncovered dysbiosis in patients with depression, anxiety, schizophrenia, and bipolar disorder.
“I think there is now pretty good evidence that the gut microbiome is actually an important factor in a number of psychiatric disorders,” says Allan Young, MBChB, clinical psychiatrist at King’s College London. The gut microbiome composition does seem to differ between psychiatric patients and the healthy. In depression, for example, a recent review of nine studies found an increase on the genus level in Streptococcus and Oscillibacter and low abundance of Lactobacillus and Coprococcus, among others. In generalized anxiety disorder, meanwhile, there appears to be an increase in Fusobacteria and Escherichia/Shigella .
For Dr. Ilardi, the next important question is whether there are plausible mechanisms that could explain how gut microbiota may influence brain function. And, it appears there are.
“The microbes in the gut can release neurotransmitters into blood that cross into the brain and influence brain function. They can release hormones into the blood that again cross into the brain. They’ve got a lot of tricks up their sleeve,” he says.
One particularly important pathway runs through the vagus nerve – the longest nerve that emerges directly from the brain, connecting it to the gut. Another is the immune pathway. Gut bacteria can interact with immune cells and reduce cytokine production, which in turn can reduce systemic inflammation. Inflammatory processes have been implicated in both depression and bipolar disorder. What’s more, gut microbes can upregulate the expression of a protein called BDNF – brain-derived neurotrophic factor – which helps the development and survival of nerve cells in the brain.
Probiotics’ promise varies for different conditions
As the pathways by which gut dysbiosis may influence psychiatric disorders become clearer, the next logical step is to try to influence the composition of the microbiome to prevent and treat depression, anxiety, or schizophrenia. That’s where probiotics come in.
The evidence for the effects of probiotics – live microorganisms which, when ingested in adequate amounts, confer a health benefit – so far is the strongest for depression, says Viktoriya Nikolova, MRes, MSc, a PhD student and researcher at King’s College London. In their 2021 meta-analysis of seven trials, Mr. Nikolova and colleagues revealed that probiotics can significantly reduce depressive symptoms after just 8 weeks. There was a caveat, however – the probiotics only worked when used in addition to an approved antidepressant. Another meta-analysis, published in 2018, also showed that probiotics, when compared with placebo, improve mood in people with depressive symptoms (here, no antidepressant treatment was necessary).
Roumen Milev, MD, PhD, a neuroscientist at Queen’s University, Kingston, Ont., and coauthor of a review on probiotics and depression published in the Annals of General Psychiatry, warns, however, that the research is still in its infancy. “,” he says.
When it comes to using probiotics to relieve anxiety, “the evidence in the animal literature is really compelling,” says Dr. Ilardi. Human studies are less convincing, however, which Dr. Dr. Ilardi showed in his 2018 review and meta-analysis involving 743 animals and 1,527 humans. “Studies are small for the most part, and some of them aren’t terribly well conducted, and they often use very low doses of probiotics,” he says. One of the larger double-blind and placebo-controlled trials showed that supplementation with Lactobacillus plantarum helps reduce stress and anxiety, while the levels of proinflammatory cytokines go down. Another meta-analysis, published in June, revealed that, when it comes to reducing stress and anxiety in youth, the results are mixed.
Evidence of probiotics’ efficiency in schizophrenia is emerging, yet also limited. A 2019 review concluded that currently available results only “hint” at a possibility that probiotics could make a difference in schizophrenia. Similarly, a 2020 review summed up that the role of probiotics in bipolar disorder “remains unclear and underexplored.”
Better studies, remaining questions
Apart from small samples, one issue with research on probiotics is that they generally tend to use varied doses of different strains of bacteria, or even multistrain mixtures, making it tough to compare results. Although there are hundreds of species of bacteria in the human gut, only a few have been evaluated for their antidepressant or antianxiety effects.
“To make it even worse, it’s almost certainly the case that depending on a person’s actual genetics or maybe their epigenetics, a strain that is helpful for one person may not be helpful for another. There is almost certainly no one-size-fits-all probiotic formulation,” says Dr. Ilardi.
Another critical question that remains to be answered is that of potential side effects.
“Probiotics are often seen as food supplements, so they don’t follow under the same regulations as drugs would,” says Mr. Nikolova. “They don’t necessarily have to follow the pattern of drug trials in many countries, which means that the monitoring of side effects is not the requirement.”
That’s something that worries King’s College psychiatrist Young too. “If you are giving it to modulate how the brain works, you could potentially induce psychiatric symptoms or a psychiatric disorder. There could be allergic reactions. There could be lots of different things,” he says.
When you search the web for “probiotics,” chances are you will come across sites boasting amazing effects that such products can have on cardiovascular heath, the immune system, and yes, mental well-being. Many also sell various probiotic supplements “formulated” for your gut health or improved moods. However, many such commercially available strains have never been actually tested in clinical trials. What’s more, according to Kathrin Cohen Kadosh, PhD, a neuroscientist at University of Surrey (England), “it is not always clear whether the different strains actually reach the gut intact.”
For now, considering the limited research evidence, a safer bet is to try to improve gut health through consumption of fermented foods that naturally contain probiotics, such as miso, kefir, or sauerkraut. Alternatively, you could reach for prebiotics, such as foods containing fiber (prebiotics enhance the growth of beneficial gut microbes). This, Dr. Kadosh says, could be “a gentler way of improving gut health” than popping a pill. Whether an improved mental well-being might follow still remains to be seen.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
In 1950, at Staten Island’s Sea View Hospital, a group of patients with terminal tuberculosis were given a new antibiotic called isoniazid, which caused some unexpected side effects. The patients reported euphoria, mental stimulation, and improved sleep, and even began socializing with more vigor. The press was all over the case, writing about the sick “dancing in the halls tho’ they had holes in their lungs.” Soon doctors started prescribing isoniazid as the first-ever antidepressant.
The Sea View Hospital experiment was an early hint that changing the composition of the gut microbiome – in this case, via antibiotics – might affect our mental health. Yet only in the last 2 decades has research into connections between what we ingest and psychiatric disorders really taken off. In 2004, a landmark study showed that germ-free mice (born in such sterile conditions that they lacked a microbiome) had an exaggerated stress response. The effects were reversed, however, if the mice were fed a bacterial strain, Bifidobacterium infantis, a probiotic. This sparked academic interest, and thousands of research papers followed.
According to Stephen Ilardi, PhD, a clinical psychologist at the University of Kansas, Lawrence, focusing on the etiology and treatment of depression, now is the “time of exciting discovery” in the field of probiotics and psychiatric disorders, although, admittedly, a lot still remains unknown.
Gut microbiome profiles in mental health disorders
We humans have about 100 trillion microbes residing in our guts. Some of these are archaea, some fungi, some protozoans and even viruses, but most are bacteria. Things like diet, sleep, and stress can all impact the composition of our gut microbiome. When the microbiome differs considerably from the typical, doctors and researchers describe it as dysbiosis, or imbalance. Studies have uncovered dysbiosis in patients with depression, anxiety, schizophrenia, and bipolar disorder.
“I think there is now pretty good evidence that the gut microbiome is actually an important factor in a number of psychiatric disorders,” says Allan Young, MBChB, clinical psychiatrist at King’s College London. The gut microbiome composition does seem to differ between psychiatric patients and the healthy. In depression, for example, a recent review of nine studies found an increase on the genus level in Streptococcus and Oscillibacter and low abundance of Lactobacillus and Coprococcus, among others. In generalized anxiety disorder, meanwhile, there appears to be an increase in Fusobacteria and Escherichia/Shigella .
For Dr. Ilardi, the next important question is whether there are plausible mechanisms that could explain how gut microbiota may influence brain function. And, it appears there are.
“The microbes in the gut can release neurotransmitters into blood that cross into the brain and influence brain function. They can release hormones into the blood that again cross into the brain. They’ve got a lot of tricks up their sleeve,” he says.
One particularly important pathway runs through the vagus nerve – the longest nerve that emerges directly from the brain, connecting it to the gut. Another is the immune pathway. Gut bacteria can interact with immune cells and reduce cytokine production, which in turn can reduce systemic inflammation. Inflammatory processes have been implicated in both depression and bipolar disorder. What’s more, gut microbes can upregulate the expression of a protein called BDNF – brain-derived neurotrophic factor – which helps the development and survival of nerve cells in the brain.
Probiotics’ promise varies for different conditions
As the pathways by which gut dysbiosis may influence psychiatric disorders become clearer, the next logical step is to try to influence the composition of the microbiome to prevent and treat depression, anxiety, or schizophrenia. That’s where probiotics come in.
The evidence for the effects of probiotics – live microorganisms which, when ingested in adequate amounts, confer a health benefit – so far is the strongest for depression, says Viktoriya Nikolova, MRes, MSc, a PhD student and researcher at King’s College London. In their 2021 meta-analysis of seven trials, Mr. Nikolova and colleagues revealed that probiotics can significantly reduce depressive symptoms after just 8 weeks. There was a caveat, however – the probiotics only worked when used in addition to an approved antidepressant. Another meta-analysis, published in 2018, also showed that probiotics, when compared with placebo, improve mood in people with depressive symptoms (here, no antidepressant treatment was necessary).
Roumen Milev, MD, PhD, a neuroscientist at Queen’s University, Kingston, Ont., and coauthor of a review on probiotics and depression published in the Annals of General Psychiatry, warns, however, that the research is still in its infancy. “,” he says.
When it comes to using probiotics to relieve anxiety, “the evidence in the animal literature is really compelling,” says Dr. Ilardi. Human studies are less convincing, however, which Dr. Dr. Ilardi showed in his 2018 review and meta-analysis involving 743 animals and 1,527 humans. “Studies are small for the most part, and some of them aren’t terribly well conducted, and they often use very low doses of probiotics,” he says. One of the larger double-blind and placebo-controlled trials showed that supplementation with Lactobacillus plantarum helps reduce stress and anxiety, while the levels of proinflammatory cytokines go down. Another meta-analysis, published in June, revealed that, when it comes to reducing stress and anxiety in youth, the results are mixed.
Evidence of probiotics’ efficiency in schizophrenia is emerging, yet also limited. A 2019 review concluded that currently available results only “hint” at a possibility that probiotics could make a difference in schizophrenia. Similarly, a 2020 review summed up that the role of probiotics in bipolar disorder “remains unclear and underexplored.”
Better studies, remaining questions
Apart from small samples, one issue with research on probiotics is that they generally tend to use varied doses of different strains of bacteria, or even multistrain mixtures, making it tough to compare results. Although there are hundreds of species of bacteria in the human gut, only a few have been evaluated for their antidepressant or antianxiety effects.
“To make it even worse, it’s almost certainly the case that depending on a person’s actual genetics or maybe their epigenetics, a strain that is helpful for one person may not be helpful for another. There is almost certainly no one-size-fits-all probiotic formulation,” says Dr. Ilardi.
Another critical question that remains to be answered is that of potential side effects.
“Probiotics are often seen as food supplements, so they don’t follow under the same regulations as drugs would,” says Mr. Nikolova. “They don’t necessarily have to follow the pattern of drug trials in many countries, which means that the monitoring of side effects is not the requirement.”
That’s something that worries King’s College psychiatrist Young too. “If you are giving it to modulate how the brain works, you could potentially induce psychiatric symptoms or a psychiatric disorder. There could be allergic reactions. There could be lots of different things,” he says.
When you search the web for “probiotics,” chances are you will come across sites boasting amazing effects that such products can have on cardiovascular heath, the immune system, and yes, mental well-being. Many also sell various probiotic supplements “formulated” for your gut health or improved moods. However, many such commercially available strains have never been actually tested in clinical trials. What’s more, according to Kathrin Cohen Kadosh, PhD, a neuroscientist at University of Surrey (England), “it is not always clear whether the different strains actually reach the gut intact.”
For now, considering the limited research evidence, a safer bet is to try to improve gut health through consumption of fermented foods that naturally contain probiotics, such as miso, kefir, or sauerkraut. Alternatively, you could reach for prebiotics, such as foods containing fiber (prebiotics enhance the growth of beneficial gut microbes). This, Dr. Kadosh says, could be “a gentler way of improving gut health” than popping a pill. Whether an improved mental well-being might follow still remains to be seen.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Nature versus nurture: Seasonal affective disorder
With summer coming to an end, and pumpkin spice lattes trending again, we might also expect to say hello to an old friend ... seasonal affective disorder (SAD).
Have you ever woken up one morning during the fall or winter and felt out of it for a prolonged period, not your regular self? I’m not referring to a day here and there, but consistently experiencing this “down mood” around the same time each year? At some point in their life, it is estimated that 2-3% of Canadians will experience SAD. To add to that, 15% of individuals will experience milder (and less impairing) SAD.
Seasonal affective disorder can be thought of as a type of depression that occurs during a specific time of the year, usually the winter or fall (with remission outside this period). It is typically characterized by symptoms of clinical depression such as low energy, difficulty with concentration, sleep problems, extreme fatigue, and agitation. While the evidence related to the risk factors for SAD are limited, it is suggested that a family history of SAD, female sex, location farther from the equator (that is, fewer days of sunlight), and being between the ages of 18-30 increase your risk for SAD.
The Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, 5th Edition (DSM-5) does not provide a separate and distinct categorization for SAD. Rather, SAD is categorized as a subtype of depression. However,
Nature versus nurture: An evolutionary perspective
The pathophysiology of SAD is not yet well understood. However, it is hypothesized that SAD is an adaptive response related to physiologic and behavioral patterns of reproduction and childrearing.
Historically, reproduction was closely linked to food and natural resource availability (for example, water, sunlight). Males primarily handled the hunting, while females were primarily responsible for agricultural work, a job closely tied to the seasons. With this in mind, it would logically follow that natural selection favored reproduction during times of food abundance and did not favor reproduction during times of food scarcity (that is, low energy).
Consequently, conception would occur when the growing season began (around the summer), giving females the chance to rest when heavily pregnant in the winter, and give birth in the spring. Accordingly, from an evolutionary perspective, greater seasonal variation in mood and behavior is a function of historic patterns of reproduction and food gathering.
An alternative hypothesis of SAD is the dual vulnerability hypothesis. This hypothesis posits that SAD is the result of seasonality and depression (or “vulnerability traits”). Seasonality refers to external environmental factors such as light availability.
It’s quite well known, and perhaps your personal experience can speak to this topic as well, that shorter days may trigger SAD because reduced light exposure is associated with phase-delayed circadian rhythms. As a result, less dopamine is produced, and relatively higher levels of melatonin are produced, compared to individuals without SAD. “Vulnerability traits” refer to a genetic predisposition, or external effects (for example, stress).
A disorder of the past?
By nature of natural selection, SAD is likely not to be considered an advantageous adaptive trait that would help with survival and reproduction. In fact, it could be considered a maladaptive trait. In that case, will SAD eventually fall to natural selection?
Leanna M.W. Lui, HBSc, completed an HBSc global health specialist degree at the University of Toronto, where she is now an MSc candidate.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
With summer coming to an end, and pumpkin spice lattes trending again, we might also expect to say hello to an old friend ... seasonal affective disorder (SAD).
Have you ever woken up one morning during the fall or winter and felt out of it for a prolonged period, not your regular self? I’m not referring to a day here and there, but consistently experiencing this “down mood” around the same time each year? At some point in their life, it is estimated that 2-3% of Canadians will experience SAD. To add to that, 15% of individuals will experience milder (and less impairing) SAD.
Seasonal affective disorder can be thought of as a type of depression that occurs during a specific time of the year, usually the winter or fall (with remission outside this period). It is typically characterized by symptoms of clinical depression such as low energy, difficulty with concentration, sleep problems, extreme fatigue, and agitation. While the evidence related to the risk factors for SAD are limited, it is suggested that a family history of SAD, female sex, location farther from the equator (that is, fewer days of sunlight), and being between the ages of 18-30 increase your risk for SAD.
The Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, 5th Edition (DSM-5) does not provide a separate and distinct categorization for SAD. Rather, SAD is categorized as a subtype of depression. However,
Nature versus nurture: An evolutionary perspective
The pathophysiology of SAD is not yet well understood. However, it is hypothesized that SAD is an adaptive response related to physiologic and behavioral patterns of reproduction and childrearing.
Historically, reproduction was closely linked to food and natural resource availability (for example, water, sunlight). Males primarily handled the hunting, while females were primarily responsible for agricultural work, a job closely tied to the seasons. With this in mind, it would logically follow that natural selection favored reproduction during times of food abundance and did not favor reproduction during times of food scarcity (that is, low energy).
Consequently, conception would occur when the growing season began (around the summer), giving females the chance to rest when heavily pregnant in the winter, and give birth in the spring. Accordingly, from an evolutionary perspective, greater seasonal variation in mood and behavior is a function of historic patterns of reproduction and food gathering.
An alternative hypothesis of SAD is the dual vulnerability hypothesis. This hypothesis posits that SAD is the result of seasonality and depression (or “vulnerability traits”). Seasonality refers to external environmental factors such as light availability.
It’s quite well known, and perhaps your personal experience can speak to this topic as well, that shorter days may trigger SAD because reduced light exposure is associated with phase-delayed circadian rhythms. As a result, less dopamine is produced, and relatively higher levels of melatonin are produced, compared to individuals without SAD. “Vulnerability traits” refer to a genetic predisposition, or external effects (for example, stress).
A disorder of the past?
By nature of natural selection, SAD is likely not to be considered an advantageous adaptive trait that would help with survival and reproduction. In fact, it could be considered a maladaptive trait. In that case, will SAD eventually fall to natural selection?
Leanna M.W. Lui, HBSc, completed an HBSc global health specialist degree at the University of Toronto, where she is now an MSc candidate.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
With summer coming to an end, and pumpkin spice lattes trending again, we might also expect to say hello to an old friend ... seasonal affective disorder (SAD).
Have you ever woken up one morning during the fall or winter and felt out of it for a prolonged period, not your regular self? I’m not referring to a day here and there, but consistently experiencing this “down mood” around the same time each year? At some point in their life, it is estimated that 2-3% of Canadians will experience SAD. To add to that, 15% of individuals will experience milder (and less impairing) SAD.
Seasonal affective disorder can be thought of as a type of depression that occurs during a specific time of the year, usually the winter or fall (with remission outside this period). It is typically characterized by symptoms of clinical depression such as low energy, difficulty with concentration, sleep problems, extreme fatigue, and agitation. While the evidence related to the risk factors for SAD are limited, it is suggested that a family history of SAD, female sex, location farther from the equator (that is, fewer days of sunlight), and being between the ages of 18-30 increase your risk for SAD.
The Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, 5th Edition (DSM-5) does not provide a separate and distinct categorization for SAD. Rather, SAD is categorized as a subtype of depression. However,
Nature versus nurture: An evolutionary perspective
The pathophysiology of SAD is not yet well understood. However, it is hypothesized that SAD is an adaptive response related to physiologic and behavioral patterns of reproduction and childrearing.
Historically, reproduction was closely linked to food and natural resource availability (for example, water, sunlight). Males primarily handled the hunting, while females were primarily responsible for agricultural work, a job closely tied to the seasons. With this in mind, it would logically follow that natural selection favored reproduction during times of food abundance and did not favor reproduction during times of food scarcity (that is, low energy).
Consequently, conception would occur when the growing season began (around the summer), giving females the chance to rest when heavily pregnant in the winter, and give birth in the spring. Accordingly, from an evolutionary perspective, greater seasonal variation in mood and behavior is a function of historic patterns of reproduction and food gathering.
An alternative hypothesis of SAD is the dual vulnerability hypothesis. This hypothesis posits that SAD is the result of seasonality and depression (or “vulnerability traits”). Seasonality refers to external environmental factors such as light availability.
It’s quite well known, and perhaps your personal experience can speak to this topic as well, that shorter days may trigger SAD because reduced light exposure is associated with phase-delayed circadian rhythms. As a result, less dopamine is produced, and relatively higher levels of melatonin are produced, compared to individuals without SAD. “Vulnerability traits” refer to a genetic predisposition, or external effects (for example, stress).
A disorder of the past?
By nature of natural selection, SAD is likely not to be considered an advantageous adaptive trait that would help with survival and reproduction. In fact, it could be considered a maladaptive trait. In that case, will SAD eventually fall to natural selection?
Leanna M.W. Lui, HBSc, completed an HBSc global health specialist degree at the University of Toronto, where she is now an MSc candidate.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Is social media worsening our social fears?
Ping. Here’s a picture of your friends on a trip without you.
Ding. In your inbox, you find an email from your attending dismissing you from a very important project or patient.
Ring. There’s that call from your colleague telling you all about the incredible dinner with some other residents, which you weren’t invited to.
FoMO. Fear of missing out.
FoMO refers to a social anxiety phenomenon fueled by the need or desire to participate in an experience, event, interaction, or investment. It can be conceptualized in two parts: (1) social ostracism and (2) the need to maintain social connectedness through a sense of belonging and/or strong relationships. It is generally characterized by episodic feelings of regret, discontent, social inferiority, and/or loneliness.
Social networking sites and FoMO
Social networking sites (SNS) are a great way for people to connect instantaneously and without borders. However, they may also decrease the quality of intimate connections and relationships. In the current COVID-19 era of Zoom, most of us could agree that face-to-face and in-person communication triumphs over Internet-based interactions. I can attest that Zoom university, endless FaceTime calls, and late-night Netflix parties are not fulfilling my desire for in-person interactions. That is to say, SNS cannot fully compensate for our unmet social needs.
In fact, achieving social compensation through SNS may exacerbate social fears and anxiety disorders, and encourage rumination. For example, a recent systematic review investigating social media use among individuals who are socially anxious and lonely found that both of the foregoing factors may lead to greater negative and inhibitory behavior as a result of social media use. Feelings of inadequacy can lead to a distorted sense of oneself.
Ping. Ding. Ring. In 2021, almost half of people in the United States spend 5-6 hours on their phones daily.
Most of us are one click away from what essentially is a “live stream” of continuous updates on peoples’ lives. With these constant updates, we often start to imagine what we’re missing out on: trips, dinners, parties, and everything under the sun. However, in reality, what we see on social media is only a fraction of true reality. For example, that 10-second video of your friend going hiking cannot begin to sum up the entire day. The 24/7 nature of SNS can often lead to a perversion of the truth and unhealthy self-comparisons.
In this vicious cycle of notifications and constant entertainment, unreasonable expectations are created that adversely impact self-confidence and self-esteem, and may even lead to the emergence of depressive symptoms.
FoMO and negative associations of SNS go hand in hand. While SNS are a powerful tool for connection and information, they have also been reported to negatively impact quality of interactions.
Next time you see a picture, video, or post of a missed event, perhaps it’s best to stop thinking of the “what ifs” and start crafting your own narrative.
Ms Lui completed an HBSc global health specialist degree at the University of Toronto, where she is now an MSc candidate. She has received income from Braxia Scientific Corp. A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Ping. Here’s a picture of your friends on a trip without you.
Ding. In your inbox, you find an email from your attending dismissing you from a very important project or patient.
Ring. There’s that call from your colleague telling you all about the incredible dinner with some other residents, which you weren’t invited to.
FoMO. Fear of missing out.
FoMO refers to a social anxiety phenomenon fueled by the need or desire to participate in an experience, event, interaction, or investment. It can be conceptualized in two parts: (1) social ostracism and (2) the need to maintain social connectedness through a sense of belonging and/or strong relationships. It is generally characterized by episodic feelings of regret, discontent, social inferiority, and/or loneliness.
Social networking sites and FoMO
Social networking sites (SNS) are a great way for people to connect instantaneously and without borders. However, they may also decrease the quality of intimate connections and relationships. In the current COVID-19 era of Zoom, most of us could agree that face-to-face and in-person communication triumphs over Internet-based interactions. I can attest that Zoom university, endless FaceTime calls, and late-night Netflix parties are not fulfilling my desire for in-person interactions. That is to say, SNS cannot fully compensate for our unmet social needs.
In fact, achieving social compensation through SNS may exacerbate social fears and anxiety disorders, and encourage rumination. For example, a recent systematic review investigating social media use among individuals who are socially anxious and lonely found that both of the foregoing factors may lead to greater negative and inhibitory behavior as a result of social media use. Feelings of inadequacy can lead to a distorted sense of oneself.
Ping. Ding. Ring. In 2021, almost half of people in the United States spend 5-6 hours on their phones daily.
Most of us are one click away from what essentially is a “live stream” of continuous updates on peoples’ lives. With these constant updates, we often start to imagine what we’re missing out on: trips, dinners, parties, and everything under the sun. However, in reality, what we see on social media is only a fraction of true reality. For example, that 10-second video of your friend going hiking cannot begin to sum up the entire day. The 24/7 nature of SNS can often lead to a perversion of the truth and unhealthy self-comparisons.
In this vicious cycle of notifications and constant entertainment, unreasonable expectations are created that adversely impact self-confidence and self-esteem, and may even lead to the emergence of depressive symptoms.
FoMO and negative associations of SNS go hand in hand. While SNS are a powerful tool for connection and information, they have also been reported to negatively impact quality of interactions.
Next time you see a picture, video, or post of a missed event, perhaps it’s best to stop thinking of the “what ifs” and start crafting your own narrative.
Ms Lui completed an HBSc global health specialist degree at the University of Toronto, where she is now an MSc candidate. She has received income from Braxia Scientific Corp. A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Ping. Here’s a picture of your friends on a trip without you.
Ding. In your inbox, you find an email from your attending dismissing you from a very important project or patient.
Ring. There’s that call from your colleague telling you all about the incredible dinner with some other residents, which you weren’t invited to.
FoMO. Fear of missing out.
FoMO refers to a social anxiety phenomenon fueled by the need or desire to participate in an experience, event, interaction, or investment. It can be conceptualized in two parts: (1) social ostracism and (2) the need to maintain social connectedness through a sense of belonging and/or strong relationships. It is generally characterized by episodic feelings of regret, discontent, social inferiority, and/or loneliness.
Social networking sites and FoMO
Social networking sites (SNS) are a great way for people to connect instantaneously and without borders. However, they may also decrease the quality of intimate connections and relationships. In the current COVID-19 era of Zoom, most of us could agree that face-to-face and in-person communication triumphs over Internet-based interactions. I can attest that Zoom university, endless FaceTime calls, and late-night Netflix parties are not fulfilling my desire for in-person interactions. That is to say, SNS cannot fully compensate for our unmet social needs.
In fact, achieving social compensation through SNS may exacerbate social fears and anxiety disorders, and encourage rumination. For example, a recent systematic review investigating social media use among individuals who are socially anxious and lonely found that both of the foregoing factors may lead to greater negative and inhibitory behavior as a result of social media use. Feelings of inadequacy can lead to a distorted sense of oneself.
Ping. Ding. Ring. In 2021, almost half of people in the United States spend 5-6 hours on their phones daily.
Most of us are one click away from what essentially is a “live stream” of continuous updates on peoples’ lives. With these constant updates, we often start to imagine what we’re missing out on: trips, dinners, parties, and everything under the sun. However, in reality, what we see on social media is only a fraction of true reality. For example, that 10-second video of your friend going hiking cannot begin to sum up the entire day. The 24/7 nature of SNS can often lead to a perversion of the truth and unhealthy self-comparisons.
In this vicious cycle of notifications and constant entertainment, unreasonable expectations are created that adversely impact self-confidence and self-esteem, and may even lead to the emergence of depressive symptoms.
FoMO and negative associations of SNS go hand in hand. While SNS are a powerful tool for connection and information, they have also been reported to negatively impact quality of interactions.
Next time you see a picture, video, or post of a missed event, perhaps it’s best to stop thinking of the “what ifs” and start crafting your own narrative.
Ms Lui completed an HBSc global health specialist degree at the University of Toronto, where she is now an MSc candidate. She has received income from Braxia Scientific Corp. A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Three ‘bad news’ payment changes coming soon for physicians
Physicians are bracing for upcoming changes in reimbursement that may start within a few months. As doctors gear up for another wave of COVID, payment trends may not be the top priority, but some “uh oh” announcements in the fall of 2021 could have far-reaching implications that could affect your future.
The Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services issued a proposed rule in the summer covering key aspects of physician payment. Although the rule contained some small bright lights, the most important changes proposed were far from welcome.
Here’s what could be in store:
1. The highly anticipated Medicare Physician Fee Schedule ruling confirmed a sweeping payment cut. The drive to maintain budget neutrality forced the federal agency to reduce Medicare payments, on average, by nearly 4%. Many physicians are outraged at the proposed cut.
2. More bad news for 2022: Sequestration will be back. Sequestration is the mandatory, pesky, negative 2% adjustment on all Medicare payments. It had been put on hold and is set to return at the beginning of 2022.
Essentially, sequestration reduces what Medicare pays its providers for health services, but Medicare beneficiaries bear no responsibility for the cost difference. To prevent further debt, CMS imposes financially on hospitals, physicians, and other health care providers.
The Health Resources and Services Administration has funds remaining to reimburse for all COVID-related testing, treatment, and vaccines provided to uninsured individuals. You can apply and be reimbursed at Medicare rates for these services when COVID is the primary diagnosis (or secondary in the case of pregnancy). Patients need not be American citizens for you to get paid.
3. Down to a nail-biter: The final ruling is expected in early November. The situation smacks of earlier days when physicians clung to a precipice, waiting in anticipation for a legislative body to save them from the dreaded income plunge. Indeed, we are slipping back to the decade-long period when Congress kept coming to the rescue simply to maintain the status quo.
Many anticipate a last-minute Congressional intervention to save the day, particularly in the midst of another COVID spike. The promises of a stable reimbursement system made possible by the Medicare Access and CHIP Reauthorization Act have been far from realized, and there are signs that the payment landscape is in the midst of a fundamental transformation.
Other changes proposed in the 1,747-page ruling include:
Positive:
- More telehealth services will be covered by Medicare, including home visits.
- Tele–mental health services got a big boost; many restrictions were removed so that now the patient’s home is considered a permissible originating site. It also allows for audio-only (no visual required) encounters; the audio-only allowance will extend to opioid use disorder treatment services. Phone treatment is covered.
- Permanent adoption of G2252: The 11- to 20-minute virtual check-in code wasn’t just a one-time payment but will be reimbursed in perpetuity.
- Boosts in reimbursement for chronic care and principal care management codes, which range on the basis of service but indicate a commitment to pay for care coordination.
- Clarification of roles and billing opportunities for split/shared visits, which occur if a physician and advanced practice provider see the same patient on a particular day. Prepare for new coding rules to include a modifier. Previously, the rules for billing were muddled, so transparency helps guide payment opportunities.
- Delay of the appropriate use criteria for advanced imaging for 1 (more) year, a welcome postponement of the ruling that carries a significant administrative burden.
- Physician assistants will be able to bill Medicare directly, and referrals to be made to medical nutrition therapy by a nontreating physician.
- A new approach to patient cost-sharing for colorectal cancer screenings will be phased in. This area has caused problems in the past when the physician identifies a need for additional services (for example, polyp removal by a gastroenterologist during routine colonoscopy).
Not positive:
- Which specialties benefit and which get zapped? The anticipated impact by specialty ranges from hits to interventional radiologists (–9%) and vascular surgeons (–8%), to increases for family practitioners, hand surgeons, endocrinologists, and geriatricians, each estimated to gain a modest 2%. (The exception is portable x-ray supplier, with an estimated increase of 10%.) All other specialties fall in between.
- The proposed conversion factor for 2022 is $33.58, a 3.75% drop from the 2021 conversion factor of $34.89.
The proposed ruling also covered the Quality Payment Program, the overarching program of which the Merit-based Incentive Payment System (MIPS) is the main track for participation. The proposal incorporates additional episode-based cost measures as well as updates to quality indicators and improvement activities.
MIPS penalties. The stakes are higher now, with 9% penalties on the table for nonparticipants. The government offers physicians the ability to officially get out of the program in 2021 because of the COVID-19 pandemic, thereby staving off the steep penalty. The option, which is available through the end of the year, requires a simple application that can be completed on behalf of the entire practice. If you want out, now is the time to find and fill out that application.
Exempt from technology requirements. If the proposal is accepted, small practices – defined by CMS as 15 eligible clinicians or fewer – won’t have to file an annual application to reweight the “promoting interoperability” portion of the program. If acknowledged, small practices will automatically be exempt from the program’s technology section. That’s a big plus, as one of the many chief complaints from small practices is the onus of meeting the technology requirements, which include a security risk analysis, bi-directional health information exchange, public health reporting, and patient access to health information. Meeting the requirements is no small feat. That will only affect future years, so be sure to apply in 2021 if applicable for your practice.
Changes in MIPS. MIPS Value Pathways (MVPs) are anticipated for 2023, with the government releasing details about proposed models for heart disease, rheumatology, joint repair, and more. The MVPs are slated to take over the traditional MIPS by 2027.
The program will shift to 30% of your score coming from the “cost” category, which is based on the government’s analysis of a physician’s claims – and, if attributed, the claims of the patients for whom you care. This area is tricky to manage, but recognize that the costs under scrutiny are the expenses paid by Medicare on behalf of its patients.
In essence, Medicare is measuring the cost of your patients as compared with your colleagues’ costs (in the form of specialty-based benchmarks). Therefore, if you’re referring, or ordering, a more costly set of diagnostic tests, assessments, or interventions than your peers, you’ll be dinged.
However, physicians are more likely this year to flat out reject participation in the federal payment program. Payouts have been paltry and dismal to date, and the buzz is that physicians just don’t consider it worth the effort. Of course, clearing the threshold (which is proposed at 70 points next year) is a must to avoid the penalty, but don’t go crazy to get a perfect score as it won’t count for much. 2022 is the final year that there are any monies for exceptional performance.
Considering that the payouts for exceptional performance have been less than 2% for several years now, it’s hard to justify dedicating resources to achieve perfection. Experts believe that even exceptional performance will only be worth pennies in bonus payments.
The fear of the stick, therefore, may be the only motivation. And that is subjective, as physicians weigh the effort required versus just taking the hit on the penalty. But the penalty is substantial, and so even without the incentive, it’s important to participate at least at the threshold.
Fewer cost-sharing waivers. While the federal government’s payment policies have a major impact on reimbursement, other forces may have broader implications. Commercial payers have rolled back cost-sharing waivers, bringing to light the significant financial responsibility that patients have for their health care in the form of deductibles, coinsurance, and so forth.
More than a third of Americans had trouble paying their health care bills before the pandemic; as patients catch up with services that were postponed or delayed because of the pandemic, this may expose challenges for you. Patients with unpaid bills translate into your financial burden.
Virtual-first health plans. Patients may be seeking alternatives to avoid the frustrating cycle of unpaid medical bills. This may be a factor propelling another trend: Lower-cost virtual-first health plans such as Alignment Health have taken hold in the market. As the name implies, insurance coverage features telehealth that extends to in-person services if necessary.
These disruptors may have their hands at least somewhat tied, however. The market may not be able to fully embrace telemedicine until state licensure is addressed. Despite the federal regulatory relaxations, states still control the distribution of medical care through licensure requirements. Many are rolling back their pandemic-based emergency orders and only allowing licensed physicians to see patients in their state, even over telemedicine.
While seemingly frustrating for physicians who want to see patients over state lines, the delays imposed by states may actually have a welcome effect. If licensure migrates to the federal level, there are many implications. For the purposes of this article, the competitive landscape will become incredibly aggressive. You will need to compete with Amazon Care, Walmart, Cigna, and many other well-funded national players that would love nothing more than to launch a campaign to target the entire nation. Investors are eager to capture part of the nearly quarter-trillion-dollar market, with telemedicine at 38 times prepandemic levels and no signs of abating.
Increased competition for insurers. While the proposed drop in Medicare reimbursement is frustrating, keep a pulse on the fact that your patients may soon be lured by vendors like Amazon and others eager to gain access to physician payments. Instead of analyzing Federal Registers in the future, we may be assessing stock prices.
Consider, therefore, how to ensure that your digital front door is at least available, if not wide open, in the meantime. The nature of physician payments is surely changing.
Ms. Woodcock is president of Woodcock & Associates, Atlanta. She has disclosed no relevant financial relationships. A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Physicians are bracing for upcoming changes in reimbursement that may start within a few months. As doctors gear up for another wave of COVID, payment trends may not be the top priority, but some “uh oh” announcements in the fall of 2021 could have far-reaching implications that could affect your future.
The Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services issued a proposed rule in the summer covering key aspects of physician payment. Although the rule contained some small bright lights, the most important changes proposed were far from welcome.
Here’s what could be in store:
1. The highly anticipated Medicare Physician Fee Schedule ruling confirmed a sweeping payment cut. The drive to maintain budget neutrality forced the federal agency to reduce Medicare payments, on average, by nearly 4%. Many physicians are outraged at the proposed cut.
2. More bad news for 2022: Sequestration will be back. Sequestration is the mandatory, pesky, negative 2% adjustment on all Medicare payments. It had been put on hold and is set to return at the beginning of 2022.
Essentially, sequestration reduces what Medicare pays its providers for health services, but Medicare beneficiaries bear no responsibility for the cost difference. To prevent further debt, CMS imposes financially on hospitals, physicians, and other health care providers.
The Health Resources and Services Administration has funds remaining to reimburse for all COVID-related testing, treatment, and vaccines provided to uninsured individuals. You can apply and be reimbursed at Medicare rates for these services when COVID is the primary diagnosis (or secondary in the case of pregnancy). Patients need not be American citizens for you to get paid.
3. Down to a nail-biter: The final ruling is expected in early November. The situation smacks of earlier days when physicians clung to a precipice, waiting in anticipation for a legislative body to save them from the dreaded income plunge. Indeed, we are slipping back to the decade-long period when Congress kept coming to the rescue simply to maintain the status quo.
Many anticipate a last-minute Congressional intervention to save the day, particularly in the midst of another COVID spike. The promises of a stable reimbursement system made possible by the Medicare Access and CHIP Reauthorization Act have been far from realized, and there are signs that the payment landscape is in the midst of a fundamental transformation.
Other changes proposed in the 1,747-page ruling include:
Positive:
- More telehealth services will be covered by Medicare, including home visits.
- Tele–mental health services got a big boost; many restrictions were removed so that now the patient’s home is considered a permissible originating site. It also allows for audio-only (no visual required) encounters; the audio-only allowance will extend to opioid use disorder treatment services. Phone treatment is covered.
- Permanent adoption of G2252: The 11- to 20-minute virtual check-in code wasn’t just a one-time payment but will be reimbursed in perpetuity.
- Boosts in reimbursement for chronic care and principal care management codes, which range on the basis of service but indicate a commitment to pay for care coordination.
- Clarification of roles and billing opportunities for split/shared visits, which occur if a physician and advanced practice provider see the same patient on a particular day. Prepare for new coding rules to include a modifier. Previously, the rules for billing were muddled, so transparency helps guide payment opportunities.
- Delay of the appropriate use criteria for advanced imaging for 1 (more) year, a welcome postponement of the ruling that carries a significant administrative burden.
- Physician assistants will be able to bill Medicare directly, and referrals to be made to medical nutrition therapy by a nontreating physician.
- A new approach to patient cost-sharing for colorectal cancer screenings will be phased in. This area has caused problems in the past when the physician identifies a need for additional services (for example, polyp removal by a gastroenterologist during routine colonoscopy).
Not positive:
- Which specialties benefit and which get zapped? The anticipated impact by specialty ranges from hits to interventional radiologists (–9%) and vascular surgeons (–8%), to increases for family practitioners, hand surgeons, endocrinologists, and geriatricians, each estimated to gain a modest 2%. (The exception is portable x-ray supplier, with an estimated increase of 10%.) All other specialties fall in between.
- The proposed conversion factor for 2022 is $33.58, a 3.75% drop from the 2021 conversion factor of $34.89.
The proposed ruling also covered the Quality Payment Program, the overarching program of which the Merit-based Incentive Payment System (MIPS) is the main track for participation. The proposal incorporates additional episode-based cost measures as well as updates to quality indicators and improvement activities.
MIPS penalties. The stakes are higher now, with 9% penalties on the table for nonparticipants. The government offers physicians the ability to officially get out of the program in 2021 because of the COVID-19 pandemic, thereby staving off the steep penalty. The option, which is available through the end of the year, requires a simple application that can be completed on behalf of the entire practice. If you want out, now is the time to find and fill out that application.
Exempt from technology requirements. If the proposal is accepted, small practices – defined by CMS as 15 eligible clinicians or fewer – won’t have to file an annual application to reweight the “promoting interoperability” portion of the program. If acknowledged, small practices will automatically be exempt from the program’s technology section. That’s a big plus, as one of the many chief complaints from small practices is the onus of meeting the technology requirements, which include a security risk analysis, bi-directional health information exchange, public health reporting, and patient access to health information. Meeting the requirements is no small feat. That will only affect future years, so be sure to apply in 2021 if applicable for your practice.
Changes in MIPS. MIPS Value Pathways (MVPs) are anticipated for 2023, with the government releasing details about proposed models for heart disease, rheumatology, joint repair, and more. The MVPs are slated to take over the traditional MIPS by 2027.
The program will shift to 30% of your score coming from the “cost” category, which is based on the government’s analysis of a physician’s claims – and, if attributed, the claims of the patients for whom you care. This area is tricky to manage, but recognize that the costs under scrutiny are the expenses paid by Medicare on behalf of its patients.
In essence, Medicare is measuring the cost of your patients as compared with your colleagues’ costs (in the form of specialty-based benchmarks). Therefore, if you’re referring, or ordering, a more costly set of diagnostic tests, assessments, or interventions than your peers, you’ll be dinged.
However, physicians are more likely this year to flat out reject participation in the federal payment program. Payouts have been paltry and dismal to date, and the buzz is that physicians just don’t consider it worth the effort. Of course, clearing the threshold (which is proposed at 70 points next year) is a must to avoid the penalty, but don’t go crazy to get a perfect score as it won’t count for much. 2022 is the final year that there are any monies for exceptional performance.
Considering that the payouts for exceptional performance have been less than 2% for several years now, it’s hard to justify dedicating resources to achieve perfection. Experts believe that even exceptional performance will only be worth pennies in bonus payments.
The fear of the stick, therefore, may be the only motivation. And that is subjective, as physicians weigh the effort required versus just taking the hit on the penalty. But the penalty is substantial, and so even without the incentive, it’s important to participate at least at the threshold.
Fewer cost-sharing waivers. While the federal government’s payment policies have a major impact on reimbursement, other forces may have broader implications. Commercial payers have rolled back cost-sharing waivers, bringing to light the significant financial responsibility that patients have for their health care in the form of deductibles, coinsurance, and so forth.
More than a third of Americans had trouble paying their health care bills before the pandemic; as patients catch up with services that were postponed or delayed because of the pandemic, this may expose challenges for you. Patients with unpaid bills translate into your financial burden.
Virtual-first health plans. Patients may be seeking alternatives to avoid the frustrating cycle of unpaid medical bills. This may be a factor propelling another trend: Lower-cost virtual-first health plans such as Alignment Health have taken hold in the market. As the name implies, insurance coverage features telehealth that extends to in-person services if necessary.
These disruptors may have their hands at least somewhat tied, however. The market may not be able to fully embrace telemedicine until state licensure is addressed. Despite the federal regulatory relaxations, states still control the distribution of medical care through licensure requirements. Many are rolling back their pandemic-based emergency orders and only allowing licensed physicians to see patients in their state, even over telemedicine.
While seemingly frustrating for physicians who want to see patients over state lines, the delays imposed by states may actually have a welcome effect. If licensure migrates to the federal level, there are many implications. For the purposes of this article, the competitive landscape will become incredibly aggressive. You will need to compete with Amazon Care, Walmart, Cigna, and many other well-funded national players that would love nothing more than to launch a campaign to target the entire nation. Investors are eager to capture part of the nearly quarter-trillion-dollar market, with telemedicine at 38 times prepandemic levels and no signs of abating.
Increased competition for insurers. While the proposed drop in Medicare reimbursement is frustrating, keep a pulse on the fact that your patients may soon be lured by vendors like Amazon and others eager to gain access to physician payments. Instead of analyzing Federal Registers in the future, we may be assessing stock prices.
Consider, therefore, how to ensure that your digital front door is at least available, if not wide open, in the meantime. The nature of physician payments is surely changing.
Ms. Woodcock is president of Woodcock & Associates, Atlanta. She has disclosed no relevant financial relationships. A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Physicians are bracing for upcoming changes in reimbursement that may start within a few months. As doctors gear up for another wave of COVID, payment trends may not be the top priority, but some “uh oh” announcements in the fall of 2021 could have far-reaching implications that could affect your future.
The Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services issued a proposed rule in the summer covering key aspects of physician payment. Although the rule contained some small bright lights, the most important changes proposed were far from welcome.
Here’s what could be in store:
1. The highly anticipated Medicare Physician Fee Schedule ruling confirmed a sweeping payment cut. The drive to maintain budget neutrality forced the federal agency to reduce Medicare payments, on average, by nearly 4%. Many physicians are outraged at the proposed cut.
2. More bad news for 2022: Sequestration will be back. Sequestration is the mandatory, pesky, negative 2% adjustment on all Medicare payments. It had been put on hold and is set to return at the beginning of 2022.
Essentially, sequestration reduces what Medicare pays its providers for health services, but Medicare beneficiaries bear no responsibility for the cost difference. To prevent further debt, CMS imposes financially on hospitals, physicians, and other health care providers.
The Health Resources and Services Administration has funds remaining to reimburse for all COVID-related testing, treatment, and vaccines provided to uninsured individuals. You can apply and be reimbursed at Medicare rates for these services when COVID is the primary diagnosis (or secondary in the case of pregnancy). Patients need not be American citizens for you to get paid.
3. Down to a nail-biter: The final ruling is expected in early November. The situation smacks of earlier days when physicians clung to a precipice, waiting in anticipation for a legislative body to save them from the dreaded income plunge. Indeed, we are slipping back to the decade-long period when Congress kept coming to the rescue simply to maintain the status quo.
Many anticipate a last-minute Congressional intervention to save the day, particularly in the midst of another COVID spike. The promises of a stable reimbursement system made possible by the Medicare Access and CHIP Reauthorization Act have been far from realized, and there are signs that the payment landscape is in the midst of a fundamental transformation.
Other changes proposed in the 1,747-page ruling include:
Positive:
- More telehealth services will be covered by Medicare, including home visits.
- Tele–mental health services got a big boost; many restrictions were removed so that now the patient’s home is considered a permissible originating site. It also allows for audio-only (no visual required) encounters; the audio-only allowance will extend to opioid use disorder treatment services. Phone treatment is covered.
- Permanent adoption of G2252: The 11- to 20-minute virtual check-in code wasn’t just a one-time payment but will be reimbursed in perpetuity.
- Boosts in reimbursement for chronic care and principal care management codes, which range on the basis of service but indicate a commitment to pay for care coordination.
- Clarification of roles and billing opportunities for split/shared visits, which occur if a physician and advanced practice provider see the same patient on a particular day. Prepare for new coding rules to include a modifier. Previously, the rules for billing were muddled, so transparency helps guide payment opportunities.
- Delay of the appropriate use criteria for advanced imaging for 1 (more) year, a welcome postponement of the ruling that carries a significant administrative burden.
- Physician assistants will be able to bill Medicare directly, and referrals to be made to medical nutrition therapy by a nontreating physician.
- A new approach to patient cost-sharing for colorectal cancer screenings will be phased in. This area has caused problems in the past when the physician identifies a need for additional services (for example, polyp removal by a gastroenterologist during routine colonoscopy).
Not positive:
- Which specialties benefit and which get zapped? The anticipated impact by specialty ranges from hits to interventional radiologists (–9%) and vascular surgeons (–8%), to increases for family practitioners, hand surgeons, endocrinologists, and geriatricians, each estimated to gain a modest 2%. (The exception is portable x-ray supplier, with an estimated increase of 10%.) All other specialties fall in between.
- The proposed conversion factor for 2022 is $33.58, a 3.75% drop from the 2021 conversion factor of $34.89.
The proposed ruling also covered the Quality Payment Program, the overarching program of which the Merit-based Incentive Payment System (MIPS) is the main track for participation. The proposal incorporates additional episode-based cost measures as well as updates to quality indicators and improvement activities.
MIPS penalties. The stakes are higher now, with 9% penalties on the table for nonparticipants. The government offers physicians the ability to officially get out of the program in 2021 because of the COVID-19 pandemic, thereby staving off the steep penalty. The option, which is available through the end of the year, requires a simple application that can be completed on behalf of the entire practice. If you want out, now is the time to find and fill out that application.
Exempt from technology requirements. If the proposal is accepted, small practices – defined by CMS as 15 eligible clinicians or fewer – won’t have to file an annual application to reweight the “promoting interoperability” portion of the program. If acknowledged, small practices will automatically be exempt from the program’s technology section. That’s a big plus, as one of the many chief complaints from small practices is the onus of meeting the technology requirements, which include a security risk analysis, bi-directional health information exchange, public health reporting, and patient access to health information. Meeting the requirements is no small feat. That will only affect future years, so be sure to apply in 2021 if applicable for your practice.
Changes in MIPS. MIPS Value Pathways (MVPs) are anticipated for 2023, with the government releasing details about proposed models for heart disease, rheumatology, joint repair, and more. The MVPs are slated to take over the traditional MIPS by 2027.
The program will shift to 30% of your score coming from the “cost” category, which is based on the government’s analysis of a physician’s claims – and, if attributed, the claims of the patients for whom you care. This area is tricky to manage, but recognize that the costs under scrutiny are the expenses paid by Medicare on behalf of its patients.
In essence, Medicare is measuring the cost of your patients as compared with your colleagues’ costs (in the form of specialty-based benchmarks). Therefore, if you’re referring, or ordering, a more costly set of diagnostic tests, assessments, or interventions than your peers, you’ll be dinged.
However, physicians are more likely this year to flat out reject participation in the federal payment program. Payouts have been paltry and dismal to date, and the buzz is that physicians just don’t consider it worth the effort. Of course, clearing the threshold (which is proposed at 70 points next year) is a must to avoid the penalty, but don’t go crazy to get a perfect score as it won’t count for much. 2022 is the final year that there are any monies for exceptional performance.
Considering that the payouts for exceptional performance have been less than 2% for several years now, it’s hard to justify dedicating resources to achieve perfection. Experts believe that even exceptional performance will only be worth pennies in bonus payments.
The fear of the stick, therefore, may be the only motivation. And that is subjective, as physicians weigh the effort required versus just taking the hit on the penalty. But the penalty is substantial, and so even without the incentive, it’s important to participate at least at the threshold.
Fewer cost-sharing waivers. While the federal government’s payment policies have a major impact on reimbursement, other forces may have broader implications. Commercial payers have rolled back cost-sharing waivers, bringing to light the significant financial responsibility that patients have for their health care in the form of deductibles, coinsurance, and so forth.
More than a third of Americans had trouble paying their health care bills before the pandemic; as patients catch up with services that were postponed or delayed because of the pandemic, this may expose challenges for you. Patients with unpaid bills translate into your financial burden.
Virtual-first health plans. Patients may be seeking alternatives to avoid the frustrating cycle of unpaid medical bills. This may be a factor propelling another trend: Lower-cost virtual-first health plans such as Alignment Health have taken hold in the market. As the name implies, insurance coverage features telehealth that extends to in-person services if necessary.
These disruptors may have their hands at least somewhat tied, however. The market may not be able to fully embrace telemedicine until state licensure is addressed. Despite the federal regulatory relaxations, states still control the distribution of medical care through licensure requirements. Many are rolling back their pandemic-based emergency orders and only allowing licensed physicians to see patients in their state, even over telemedicine.
While seemingly frustrating for physicians who want to see patients over state lines, the delays imposed by states may actually have a welcome effect. If licensure migrates to the federal level, there are many implications. For the purposes of this article, the competitive landscape will become incredibly aggressive. You will need to compete with Amazon Care, Walmart, Cigna, and many other well-funded national players that would love nothing more than to launch a campaign to target the entire nation. Investors are eager to capture part of the nearly quarter-trillion-dollar market, with telemedicine at 38 times prepandemic levels and no signs of abating.
Increased competition for insurers. While the proposed drop in Medicare reimbursement is frustrating, keep a pulse on the fact that your patients may soon be lured by vendors like Amazon and others eager to gain access to physician payments. Instead of analyzing Federal Registers in the future, we may be assessing stock prices.
Consider, therefore, how to ensure that your digital front door is at least available, if not wide open, in the meantime. The nature of physician payments is surely changing.
Ms. Woodcock is president of Woodcock & Associates, Atlanta. She has disclosed no relevant financial relationships. A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
COVID wars, part nine: The rise of iodine
Onions and iodine and COVID, oh my!
As surely as the sun rises, anti-vaxxers will come up with some wacky and dangerous new idea to prevent COVID. While perhaps nothing will top horse medication, gargling iodine (or spraying it into the nose) is also not a great idea.
Multiple social media posts have extolled the virtues of gargling Betadine (povidone iodine), which is a TOPICAL disinfectant commonly used in EDs and operating rooms. One post cited a paper by a Bangladeshi plastic surgeon who hypothesized on the subject, and if that’s not a peer-reviewed, rigorously researched source, we don’t know what is.
Perhaps unsurprisingly, actual medical experts do not recommend using Betadine to prevent COVID. Ingesting it can cause iodine poisoning and plenty of nasty GI side effects; while Betadine does make a diluted product safe for gargling use (used for the treatment of sore throats), it has not shown any effectiveness against viruses or COVID in particular.
A New York ED doctor summed it up best in the Rolling Stone article when he was told anti-vaxxers were gargling iodine: He offered a choice four-letter expletive, then said, “Of course they are.”
But wait! We’ve got a two-for-one deal on dubious COVID cures this week. Health experts in Myanmar (Burma to all the “Seinfeld” fans) and Thailand have been combating social media posts claiming that onion fumes will cure COVID. All you need to do is slice an onion in half, sniff it for a while, then chew on a second onion, and your COVID will be cured!
In what is surely the most radical understatement of the year, a professor in the department of preventive and social medicine at Chulalongkorn University, Bangkok, said in the AFP article that there is “no solid evidence” to support onion sniffing from “any clinical research.”
We’re just going to assume the expletives that surely followed were kept off the record.
Pro-Trump state governor encourages vaccination
Clearly, the politics of COVID-19 have been working against the science of COVID-19. Politicians can’t, or won’t, agree on what to do about it, and many prominent Republicans have been actively resisting vaccine and mask mandates.
There is at least one Republican governor who has wholeheartedly encouraged vaccination in his pro-Trump state. We’re talking about Gov. Jim Justice of West Virginia, and not for the first time.
The Washington Post has detailed his efforts to promote the COVID vaccine, and we would like to share a couple of examples.
In June he suggested that people who didn’t get vaccinated were “entering the death drawing.” He followed that by saying, “If I knew for certain that there was going to be eight or nine people die by next Tuesday, and I could be one of them if I don’t take the vaccine ... What in the world do you think I would do? I mean, I would run over top of somebody.”
More recently, Gov. Justice took on vaccine conspiracy theories.
“For God’s sakes a livin’, how difficult is this to understand? Why in the world do we have to come up with these crazy ideas – and they’re crazy ideas – that the vaccine’s got something in it and it’s tracing people wherever they go? And the very same people that are saying that are carrying their cellphones around. I mean, come on. Come on.”
Nuff said.
Jet lag may be a gut feeling
After a week-long vacation halfway around the world, it’s time to go back to your usual routine and time zone. But don’t forget about that free souvenir, jet lag. A disrupted circadian rhythm can be a real bummer, but researchers may have found the fix in your belly.
In a study funded by the U.S. Navy, researchers at the University of Colorado, Boulder, looked into how the presence of a prebiotic in one’s diet can have on the disrupted biological clocks. They’re not the same as probiotics, which help you stay regular in another way. Prebiotics work as food to help the good gut bacteria you already have. An earlier study had suggested that prebiotics may have a positive effect on the brain.
To test the theory, the researchers gave one group of rats their regular food while another group received food with two different prebiotics. After manipulating the rats’ light-dark cycle for 8 weeks to give the illusion of traveling to a time zone 12 hours ahead every week, they found that the rats who ate the prebiotics were able to bounce back faster.
The possibility of ingesting something to keep your body clock regular sounds like a dream, but the researchers don’t really advise you to snatch all the supplements you can at your local pharmacy just yet.
“If you know you are going to come into a challenge, you could take a look at some of the prebiotics that are available. Just realize that they are not customized yet, so it might work for you but it won’t work for your neighbor,” said senior author Monika Fleshner.
Until there’s more conclusive research, just be good to your bacteria.
How to make stuff up and influence people
You’ve probably heard that we use only 10% of our brain. It’s right up there with “the Earth is flat” and “an apple a day keeps the doctor away.”
The idea that we use only 10% of our brains can probably be traced back to the early 1900s, suggests Discover magazine, when psychologist William James wrote, “Compared with what we ought to be, we are only half awake. Our fires are damped, our drafts are checked. We are making use of only a small part of our possible mental and physical resources.”
There are many different takes on it, but it is indeed a myth that we use only 10% of our brains. Dale Carnegie, the public speaking teacher, seems to be the one who put the specific number of 10% on James’ idea in his 1936 book, “How to Win Friends and Influence People.”
“We think that people are excited by this pseudo fact because it’s very optimistic,” neuroscientist Sandra Aamodt told Discover. “Wouldn’t we all love to think our brains had some giant pool of untapped potential that we’re not using?”
The reality is, we do use our whole brain. Functional MRI shows that different parts of the brain are used for different things such as language and memories. “Not all at the same time, of course. But every part of the brain has a job to do,” the Discover article explained.
There are many things we don’t know about how the brain works, but at least you know you use more than 10%. After all, a brain just told you so.
Onions and iodine and COVID, oh my!
As surely as the sun rises, anti-vaxxers will come up with some wacky and dangerous new idea to prevent COVID. While perhaps nothing will top horse medication, gargling iodine (or spraying it into the nose) is also not a great idea.
Multiple social media posts have extolled the virtues of gargling Betadine (povidone iodine), which is a TOPICAL disinfectant commonly used in EDs and operating rooms. One post cited a paper by a Bangladeshi plastic surgeon who hypothesized on the subject, and if that’s not a peer-reviewed, rigorously researched source, we don’t know what is.
Perhaps unsurprisingly, actual medical experts do not recommend using Betadine to prevent COVID. Ingesting it can cause iodine poisoning and plenty of nasty GI side effects; while Betadine does make a diluted product safe for gargling use (used for the treatment of sore throats), it has not shown any effectiveness against viruses or COVID in particular.
A New York ED doctor summed it up best in the Rolling Stone article when he was told anti-vaxxers were gargling iodine: He offered a choice four-letter expletive, then said, “Of course they are.”
But wait! We’ve got a two-for-one deal on dubious COVID cures this week. Health experts in Myanmar (Burma to all the “Seinfeld” fans) and Thailand have been combating social media posts claiming that onion fumes will cure COVID. All you need to do is slice an onion in half, sniff it for a while, then chew on a second onion, and your COVID will be cured!
In what is surely the most radical understatement of the year, a professor in the department of preventive and social medicine at Chulalongkorn University, Bangkok, said in the AFP article that there is “no solid evidence” to support onion sniffing from “any clinical research.”
We’re just going to assume the expletives that surely followed were kept off the record.
Pro-Trump state governor encourages vaccination
Clearly, the politics of COVID-19 have been working against the science of COVID-19. Politicians can’t, or won’t, agree on what to do about it, and many prominent Republicans have been actively resisting vaccine and mask mandates.
There is at least one Republican governor who has wholeheartedly encouraged vaccination in his pro-Trump state. We’re talking about Gov. Jim Justice of West Virginia, and not for the first time.
The Washington Post has detailed his efforts to promote the COVID vaccine, and we would like to share a couple of examples.
In June he suggested that people who didn’t get vaccinated were “entering the death drawing.” He followed that by saying, “If I knew for certain that there was going to be eight or nine people die by next Tuesday, and I could be one of them if I don’t take the vaccine ... What in the world do you think I would do? I mean, I would run over top of somebody.”
More recently, Gov. Justice took on vaccine conspiracy theories.
“For God’s sakes a livin’, how difficult is this to understand? Why in the world do we have to come up with these crazy ideas – and they’re crazy ideas – that the vaccine’s got something in it and it’s tracing people wherever they go? And the very same people that are saying that are carrying their cellphones around. I mean, come on. Come on.”
Nuff said.
Jet lag may be a gut feeling
After a week-long vacation halfway around the world, it’s time to go back to your usual routine and time zone. But don’t forget about that free souvenir, jet lag. A disrupted circadian rhythm can be a real bummer, but researchers may have found the fix in your belly.
In a study funded by the U.S. Navy, researchers at the University of Colorado, Boulder, looked into how the presence of a prebiotic in one’s diet can have on the disrupted biological clocks. They’re not the same as probiotics, which help you stay regular in another way. Prebiotics work as food to help the good gut bacteria you already have. An earlier study had suggested that prebiotics may have a positive effect on the brain.
To test the theory, the researchers gave one group of rats their regular food while another group received food with two different prebiotics. After manipulating the rats’ light-dark cycle for 8 weeks to give the illusion of traveling to a time zone 12 hours ahead every week, they found that the rats who ate the prebiotics were able to bounce back faster.
The possibility of ingesting something to keep your body clock regular sounds like a dream, but the researchers don’t really advise you to snatch all the supplements you can at your local pharmacy just yet.
“If you know you are going to come into a challenge, you could take a look at some of the prebiotics that are available. Just realize that they are not customized yet, so it might work for you but it won’t work for your neighbor,” said senior author Monika Fleshner.
Until there’s more conclusive research, just be good to your bacteria.
How to make stuff up and influence people
You’ve probably heard that we use only 10% of our brain. It’s right up there with “the Earth is flat” and “an apple a day keeps the doctor away.”
The idea that we use only 10% of our brains can probably be traced back to the early 1900s, suggests Discover magazine, when psychologist William James wrote, “Compared with what we ought to be, we are only half awake. Our fires are damped, our drafts are checked. We are making use of only a small part of our possible mental and physical resources.”
There are many different takes on it, but it is indeed a myth that we use only 10% of our brains. Dale Carnegie, the public speaking teacher, seems to be the one who put the specific number of 10% on James’ idea in his 1936 book, “How to Win Friends and Influence People.”
“We think that people are excited by this pseudo fact because it’s very optimistic,” neuroscientist Sandra Aamodt told Discover. “Wouldn’t we all love to think our brains had some giant pool of untapped potential that we’re not using?”
The reality is, we do use our whole brain. Functional MRI shows that different parts of the brain are used for different things such as language and memories. “Not all at the same time, of course. But every part of the brain has a job to do,” the Discover article explained.
There are many things we don’t know about how the brain works, but at least you know you use more than 10%. After all, a brain just told you so.
Onions and iodine and COVID, oh my!
As surely as the sun rises, anti-vaxxers will come up with some wacky and dangerous new idea to prevent COVID. While perhaps nothing will top horse medication, gargling iodine (or spraying it into the nose) is also not a great idea.
Multiple social media posts have extolled the virtues of gargling Betadine (povidone iodine), which is a TOPICAL disinfectant commonly used in EDs and operating rooms. One post cited a paper by a Bangladeshi plastic surgeon who hypothesized on the subject, and if that’s not a peer-reviewed, rigorously researched source, we don’t know what is.
Perhaps unsurprisingly, actual medical experts do not recommend using Betadine to prevent COVID. Ingesting it can cause iodine poisoning and plenty of nasty GI side effects; while Betadine does make a diluted product safe for gargling use (used for the treatment of sore throats), it has not shown any effectiveness against viruses or COVID in particular.
A New York ED doctor summed it up best in the Rolling Stone article when he was told anti-vaxxers were gargling iodine: He offered a choice four-letter expletive, then said, “Of course they are.”
But wait! We’ve got a two-for-one deal on dubious COVID cures this week. Health experts in Myanmar (Burma to all the “Seinfeld” fans) and Thailand have been combating social media posts claiming that onion fumes will cure COVID. All you need to do is slice an onion in half, sniff it for a while, then chew on a second onion, and your COVID will be cured!
In what is surely the most radical understatement of the year, a professor in the department of preventive and social medicine at Chulalongkorn University, Bangkok, said in the AFP article that there is “no solid evidence” to support onion sniffing from “any clinical research.”
We’re just going to assume the expletives that surely followed were kept off the record.
Pro-Trump state governor encourages vaccination
Clearly, the politics of COVID-19 have been working against the science of COVID-19. Politicians can’t, or won’t, agree on what to do about it, and many prominent Republicans have been actively resisting vaccine and mask mandates.
There is at least one Republican governor who has wholeheartedly encouraged vaccination in his pro-Trump state. We’re talking about Gov. Jim Justice of West Virginia, and not for the first time.
The Washington Post has detailed his efforts to promote the COVID vaccine, and we would like to share a couple of examples.
In June he suggested that people who didn’t get vaccinated were “entering the death drawing.” He followed that by saying, “If I knew for certain that there was going to be eight or nine people die by next Tuesday, and I could be one of them if I don’t take the vaccine ... What in the world do you think I would do? I mean, I would run over top of somebody.”
More recently, Gov. Justice took on vaccine conspiracy theories.
“For God’s sakes a livin’, how difficult is this to understand? Why in the world do we have to come up with these crazy ideas – and they’re crazy ideas – that the vaccine’s got something in it and it’s tracing people wherever they go? And the very same people that are saying that are carrying their cellphones around. I mean, come on. Come on.”
Nuff said.
Jet lag may be a gut feeling
After a week-long vacation halfway around the world, it’s time to go back to your usual routine and time zone. But don’t forget about that free souvenir, jet lag. A disrupted circadian rhythm can be a real bummer, but researchers may have found the fix in your belly.
In a study funded by the U.S. Navy, researchers at the University of Colorado, Boulder, looked into how the presence of a prebiotic in one’s diet can have on the disrupted biological clocks. They’re not the same as probiotics, which help you stay regular in another way. Prebiotics work as food to help the good gut bacteria you already have. An earlier study had suggested that prebiotics may have a positive effect on the brain.
To test the theory, the researchers gave one group of rats their regular food while another group received food with two different prebiotics. After manipulating the rats’ light-dark cycle for 8 weeks to give the illusion of traveling to a time zone 12 hours ahead every week, they found that the rats who ate the prebiotics were able to bounce back faster.
The possibility of ingesting something to keep your body clock regular sounds like a dream, but the researchers don’t really advise you to snatch all the supplements you can at your local pharmacy just yet.
“If you know you are going to come into a challenge, you could take a look at some of the prebiotics that are available. Just realize that they are not customized yet, so it might work for you but it won’t work for your neighbor,” said senior author Monika Fleshner.
Until there’s more conclusive research, just be good to your bacteria.
How to make stuff up and influence people
You’ve probably heard that we use only 10% of our brain. It’s right up there with “the Earth is flat” and “an apple a day keeps the doctor away.”
The idea that we use only 10% of our brains can probably be traced back to the early 1900s, suggests Discover magazine, when psychologist William James wrote, “Compared with what we ought to be, we are only half awake. Our fires are damped, our drafts are checked. We are making use of only a small part of our possible mental and physical resources.”
There are many different takes on it, but it is indeed a myth that we use only 10% of our brains. Dale Carnegie, the public speaking teacher, seems to be the one who put the specific number of 10% on James’ idea in his 1936 book, “How to Win Friends and Influence People.”
“We think that people are excited by this pseudo fact because it’s very optimistic,” neuroscientist Sandra Aamodt told Discover. “Wouldn’t we all love to think our brains had some giant pool of untapped potential that we’re not using?”
The reality is, we do use our whole brain. Functional MRI shows that different parts of the brain are used for different things such as language and memories. “Not all at the same time, of course. But every part of the brain has a job to do,” the Discover article explained.
There are many things we don’t know about how the brain works, but at least you know you use more than 10%. After all, a brain just told you so.
Why misinformation spreads
Over the past 16 months, the COVID-19 pandemic has highlighted not only our vulnerability to disease outbreaks but also our susceptibility to misinformation and the dangers of “fake news.”
In fact, COVID-19 is not a pandemic but rather a syndemic of viral disease and misinformation. In the current digital age, there is an abundance of information at our fingertips. This has resulted in a surplus of accurate as well as inaccurate information – information that is subject to the various biases we humans are subject to.
Our decision making and cognition are colored by our internal and external environmental biases, whether through our emotions, societal influences, or cues from the “machines” that are now such an omnipresent part of our lives.
Let’s break them down:
- Emotional bias: We’re only human, and our emotions often overwhelm objective judgment. Even when the evidence is of low quality, emotional attachments can deter us from rational thinking. This kind of bias can be rooted in personal experiences.
- Societal bias: Thoughts, opinions, or perspectives of peers are powerful forces that may influence our decisions and viewpoints. We can conceptualize our social networks as partisan circles and “echo chambers.” This bias is perhaps most evident in various online social media platforms.
- Machine bias: Our online platforms are laced with algorithms that tailor the content we see. Accordingly, the curated content we see (and, by extension, the less diverse content we view) may reinforce existing biases, such as confirmation bias.
- Although bias plays a significant role in decision making, we should also consider intuition versus deliberation – and whether the “gut” is a reliable source of information.
Intuition versus deliberation: The power of reasoning
The dual process theory suggests that thought may be categorized in two ways: System 1, referred to as rapid, intuitive, or automatic thinking (which may be a result of personal experience); and system 2, referred to as deliberate or controlled thinking (for example, reasoned thinking). System 1 versus system 2 may be conceptualized as fast versus slow thinking.
Let’s use the Cognitive Reflection Test to illustrate the dual process theory. This test measures the ability to reflect and deliberate on a question and to forgo an intuitive, rapid response. One of the questions asks: “A bat and a ball cost $1.10 in total. The bat costs $1.00 more than the ball. How much does the ball cost?” A common answer is that the ball costs $0.10. However, the ball actually costs $0.05. The common response is a “gut” response, rather than an analytic or deliberate response.
This example can be extrapolated to social media behavior, such as when individuals endorse beliefs and behaviors that may be far from the truth (for example, conspiracy ideation). It is not uncommon for individuals to rely on intuition, which may be incorrect, as a driving source of truth. Although one’s intuition can be correct, it’s important to be careful and to deliberate.
But would deliberate engagement lead to more politically valenced perspectives? One hypothesis posits that system 2 can lead to false claims and worsening discernment of truth. Another, and more popular, account of classical reasoning says that more thoughtful engagement (regardless of one’s political beliefs) is less susceptible to false news (for example, hyperpartisan news).
Additionally, having good literacy (political, scientific, or general) is important for discerning the truth, especially regarding events in which the information and/or claims of knowledge have been heavily manipulated.
Are believing and sharing the same?
Interestingly, believing in a headline and sharing it are not the same. A study that investigated the difference between the two found that although individuals were able to discern the validity of headlines, the veracity of those headlines was not a determining factor in sharing the story on social media.
It has been suggested that social media context may distract individuals from engaging in deliberate thinking that would enhance their ability to determine the accuracy of the content. The dissociation between truthfulness and sharing may be a result of the “attention economy,” which refers to user engagement of likes, comments, shares, and so forth. As such, social media behavior and content consumption may not necessarily reflect one’s beliefs and may be influenced by what others value.
To combat the spread of misinformation, it has been suggested that proactive interventions – “prebunking” or “inoculation” – are necessary. This idea is in accordance with the inoculation theory, which suggests that pre-exposure can confer resistance to challenge. This line of thinking is aligned with the use of vaccines to counter medical illnesses. Increasing awareness of individual vulnerability to manipulation and misinformation has also been proposed as a strategy to resist persuasion.
The age old tale of what others think of us versus what we believe to be true has existed long before the viral overtake of social media. The main difference today is that social media acts as a catalyst for pockets of misinformation. Although social media outlets are cracking down on “false news,” we must consider what criteria should be employed to identify false information. Should external bodies regulate our content consumption? We are certainly entering a gray zone of “wrong” versus “right.” With the overabundance of information available online, it may be the case of “them” versus “us” – that is, those who do not believe in the existence of misinformation versus those who do.
Leanna M. W. Lui, HBSc, completed an HBSc global health specialist degree at the University of Toronto, where she is now an MSc candidate.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Over the past 16 months, the COVID-19 pandemic has highlighted not only our vulnerability to disease outbreaks but also our susceptibility to misinformation and the dangers of “fake news.”
In fact, COVID-19 is not a pandemic but rather a syndemic of viral disease and misinformation. In the current digital age, there is an abundance of information at our fingertips. This has resulted in a surplus of accurate as well as inaccurate information – information that is subject to the various biases we humans are subject to.
Our decision making and cognition are colored by our internal and external environmental biases, whether through our emotions, societal influences, or cues from the “machines” that are now such an omnipresent part of our lives.
Let’s break them down:
- Emotional bias: We’re only human, and our emotions often overwhelm objective judgment. Even when the evidence is of low quality, emotional attachments can deter us from rational thinking. This kind of bias can be rooted in personal experiences.
- Societal bias: Thoughts, opinions, or perspectives of peers are powerful forces that may influence our decisions and viewpoints. We can conceptualize our social networks as partisan circles and “echo chambers.” This bias is perhaps most evident in various online social media platforms.
- Machine bias: Our online platforms are laced with algorithms that tailor the content we see. Accordingly, the curated content we see (and, by extension, the less diverse content we view) may reinforce existing biases, such as confirmation bias.
- Although bias plays a significant role in decision making, we should also consider intuition versus deliberation – and whether the “gut” is a reliable source of information.
Intuition versus deliberation: The power of reasoning
The dual process theory suggests that thought may be categorized in two ways: System 1, referred to as rapid, intuitive, or automatic thinking (which may be a result of personal experience); and system 2, referred to as deliberate or controlled thinking (for example, reasoned thinking). System 1 versus system 2 may be conceptualized as fast versus slow thinking.
Let’s use the Cognitive Reflection Test to illustrate the dual process theory. This test measures the ability to reflect and deliberate on a question and to forgo an intuitive, rapid response. One of the questions asks: “A bat and a ball cost $1.10 in total. The bat costs $1.00 more than the ball. How much does the ball cost?” A common answer is that the ball costs $0.10. However, the ball actually costs $0.05. The common response is a “gut” response, rather than an analytic or deliberate response.
This example can be extrapolated to social media behavior, such as when individuals endorse beliefs and behaviors that may be far from the truth (for example, conspiracy ideation). It is not uncommon for individuals to rely on intuition, which may be incorrect, as a driving source of truth. Although one’s intuition can be correct, it’s important to be careful and to deliberate.
But would deliberate engagement lead to more politically valenced perspectives? One hypothesis posits that system 2 can lead to false claims and worsening discernment of truth. Another, and more popular, account of classical reasoning says that more thoughtful engagement (regardless of one’s political beliefs) is less susceptible to false news (for example, hyperpartisan news).
Additionally, having good literacy (political, scientific, or general) is important for discerning the truth, especially regarding events in which the information and/or claims of knowledge have been heavily manipulated.
Are believing and sharing the same?
Interestingly, believing in a headline and sharing it are not the same. A study that investigated the difference between the two found that although individuals were able to discern the validity of headlines, the veracity of those headlines was not a determining factor in sharing the story on social media.
It has been suggested that social media context may distract individuals from engaging in deliberate thinking that would enhance their ability to determine the accuracy of the content. The dissociation between truthfulness and sharing may be a result of the “attention economy,” which refers to user engagement of likes, comments, shares, and so forth. As such, social media behavior and content consumption may not necessarily reflect one’s beliefs and may be influenced by what others value.
To combat the spread of misinformation, it has been suggested that proactive interventions – “prebunking” or “inoculation” – are necessary. This idea is in accordance with the inoculation theory, which suggests that pre-exposure can confer resistance to challenge. This line of thinking is aligned with the use of vaccines to counter medical illnesses. Increasing awareness of individual vulnerability to manipulation and misinformation has also been proposed as a strategy to resist persuasion.
The age old tale of what others think of us versus what we believe to be true has existed long before the viral overtake of social media. The main difference today is that social media acts as a catalyst for pockets of misinformation. Although social media outlets are cracking down on “false news,” we must consider what criteria should be employed to identify false information. Should external bodies regulate our content consumption? We are certainly entering a gray zone of “wrong” versus “right.” With the overabundance of information available online, it may be the case of “them” versus “us” – that is, those who do not believe in the existence of misinformation versus those who do.
Leanna M. W. Lui, HBSc, completed an HBSc global health specialist degree at the University of Toronto, where she is now an MSc candidate.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Over the past 16 months, the COVID-19 pandemic has highlighted not only our vulnerability to disease outbreaks but also our susceptibility to misinformation and the dangers of “fake news.”
In fact, COVID-19 is not a pandemic but rather a syndemic of viral disease and misinformation. In the current digital age, there is an abundance of information at our fingertips. This has resulted in a surplus of accurate as well as inaccurate information – information that is subject to the various biases we humans are subject to.
Our decision making and cognition are colored by our internal and external environmental biases, whether through our emotions, societal influences, or cues from the “machines” that are now such an omnipresent part of our lives.
Let’s break them down:
- Emotional bias: We’re only human, and our emotions often overwhelm objective judgment. Even when the evidence is of low quality, emotional attachments can deter us from rational thinking. This kind of bias can be rooted in personal experiences.
- Societal bias: Thoughts, opinions, or perspectives of peers are powerful forces that may influence our decisions and viewpoints. We can conceptualize our social networks as partisan circles and “echo chambers.” This bias is perhaps most evident in various online social media platforms.
- Machine bias: Our online platforms are laced with algorithms that tailor the content we see. Accordingly, the curated content we see (and, by extension, the less diverse content we view) may reinforce existing biases, such as confirmation bias.
- Although bias plays a significant role in decision making, we should also consider intuition versus deliberation – and whether the “gut” is a reliable source of information.
Intuition versus deliberation: The power of reasoning
The dual process theory suggests that thought may be categorized in two ways: System 1, referred to as rapid, intuitive, or automatic thinking (which may be a result of personal experience); and system 2, referred to as deliberate or controlled thinking (for example, reasoned thinking). System 1 versus system 2 may be conceptualized as fast versus slow thinking.
Let’s use the Cognitive Reflection Test to illustrate the dual process theory. This test measures the ability to reflect and deliberate on a question and to forgo an intuitive, rapid response. One of the questions asks: “A bat and a ball cost $1.10 in total. The bat costs $1.00 more than the ball. How much does the ball cost?” A common answer is that the ball costs $0.10. However, the ball actually costs $0.05. The common response is a “gut” response, rather than an analytic or deliberate response.
This example can be extrapolated to social media behavior, such as when individuals endorse beliefs and behaviors that may be far from the truth (for example, conspiracy ideation). It is not uncommon for individuals to rely on intuition, which may be incorrect, as a driving source of truth. Although one’s intuition can be correct, it’s important to be careful and to deliberate.
But would deliberate engagement lead to more politically valenced perspectives? One hypothesis posits that system 2 can lead to false claims and worsening discernment of truth. Another, and more popular, account of classical reasoning says that more thoughtful engagement (regardless of one’s political beliefs) is less susceptible to false news (for example, hyperpartisan news).
Additionally, having good literacy (political, scientific, or general) is important for discerning the truth, especially regarding events in which the information and/or claims of knowledge have been heavily manipulated.
Are believing and sharing the same?
Interestingly, believing in a headline and sharing it are not the same. A study that investigated the difference between the two found that although individuals were able to discern the validity of headlines, the veracity of those headlines was not a determining factor in sharing the story on social media.
It has been suggested that social media context may distract individuals from engaging in deliberate thinking that would enhance their ability to determine the accuracy of the content. The dissociation between truthfulness and sharing may be a result of the “attention economy,” which refers to user engagement of likes, comments, shares, and so forth. As such, social media behavior and content consumption may not necessarily reflect one’s beliefs and may be influenced by what others value.
To combat the spread of misinformation, it has been suggested that proactive interventions – “prebunking” or “inoculation” – are necessary. This idea is in accordance with the inoculation theory, which suggests that pre-exposure can confer resistance to challenge. This line of thinking is aligned with the use of vaccines to counter medical illnesses. Increasing awareness of individual vulnerability to manipulation and misinformation has also been proposed as a strategy to resist persuasion.
The age old tale of what others think of us versus what we believe to be true has existed long before the viral overtake of social media. The main difference today is that social media acts as a catalyst for pockets of misinformation. Although social media outlets are cracking down on “false news,” we must consider what criteria should be employed to identify false information. Should external bodies regulate our content consumption? We are certainly entering a gray zone of “wrong” versus “right.” With the overabundance of information available online, it may be the case of “them” versus “us” – that is, those who do not believe in the existence of misinformation versus those who do.
Leanna M. W. Lui, HBSc, completed an HBSc global health specialist degree at the University of Toronto, where she is now an MSc candidate.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
ADHD a new risk factor for Alzheimer’s?
results from a large, multigenerational study show.
“The findings suggest there are common genetic and/or environmental contributions to the association between ADHD and dementia,” study investigator Zheng Chang, PhD, from the department of medical epidemiology and biostatistics at Karolinska Institute, Stockholm, said in a statement.
“There have been few studies previously on the link between ADHD and dementia, all with limited sample size,” Dr. Chang said in an interview.
“This is the first study to look at ADHD and dementia within extended families. It’s a large population-based study including over 2 million individuals and their over 5 million biological relatives,” he noted.
The study was published online Sept. 9, 2021, in the journal Alzheimer’s & Dementia.
Shared familial risk
The researchers identified roughly 2.1 million people born in Sweden between 1980 and 2001. Overall, 3.2% of the cohort had a diagnosis of ADHD.
Using national registries, they linked these individuals to more than 5 million of their biological relatives including parents, grandparents, uncles, and aunts and determined which of these relatives developed dementia over time.
In adjusted analyses, parents of individuals with ADHD had 34% higher risk for any dementia than parents of those without ADHD (hazard ratio, 1.34; 95% CI, 1.11-1.63).
The risk for AD, the most common type of dementia, was 55% higher in parents of individuals with ADHD (HR, 1.55; 95% CI, 1.26-1.89).
Individuals with ADHD were more likely to have parents with early-onset dementia rather than late-onset dementia. However, the absolute risk for dementia was low for the parent cohort: Only 0.17% of the parents were diagnosed with dementia during follow-up.
The association between ADHD and dementia was not as strong for second-degree relatives of individuals with ADHD. For example, grandparents of individuals with ADHD had a 10% increased risk for dementia, compared with grandparents of individuals without ADHD.
The finding of attenuated associations with decreasing genetic relatedness (parents > grandparents and uncles/aunts), points to shared familial risk between ADHD and AD, the researchers said.
There could be “undiscovered genetic variants that contribute to either traits or family-wide environmental risk factors, such as socioeconomic status, that may have an impact on the association,” Dr. Chang said in the news release.
“There are no direct clinical implications from this study, but research like this could lead to further research with goals for improved detection, prevention, and treatment,” he said in an interview.
More questions than answers
Heather Snyder, PhD, vice president of medical and scientific relations for the Alzheimer’s Association that the way different brain diseases are linked “is a question the Alzheimer’s Association is often asked, and it is a part of our funding portfolio to get that question answered.”
This study looking at ADHD and dementia is “intriguing,” Dr. Snyder said, “because, right now, there is limited information available. That said, this is an association study; it shows that two things are somehow connected. Because of how the study was conducted, it does not – and cannot – prove causation,” Dr. Snyder said. “But it is interesting all the same. More research is needed to uncover specifically why and how these two diseases are related. That might eventually give us insight into how to manage risk or even improve treatment.”
The study was supported by grants from the Swedish Council for Health, Working Life and Welfare, the Swedish Research Council, the Swedish Brain Foundation, the European Union’s Horizon 2020 research and innovation program under the Marie Skłodowska-Curie, the Fredrik & Ingrid Thurings Stiftelse, and the Karolinska Institutet Research Foundation. Dr. Chang and Dr. Snyder disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
results from a large, multigenerational study show.
“The findings suggest there are common genetic and/or environmental contributions to the association between ADHD and dementia,” study investigator Zheng Chang, PhD, from the department of medical epidemiology and biostatistics at Karolinska Institute, Stockholm, said in a statement.
“There have been few studies previously on the link between ADHD and dementia, all with limited sample size,” Dr. Chang said in an interview.
“This is the first study to look at ADHD and dementia within extended families. It’s a large population-based study including over 2 million individuals and their over 5 million biological relatives,” he noted.
The study was published online Sept. 9, 2021, in the journal Alzheimer’s & Dementia.
Shared familial risk
The researchers identified roughly 2.1 million people born in Sweden between 1980 and 2001. Overall, 3.2% of the cohort had a diagnosis of ADHD.
Using national registries, they linked these individuals to more than 5 million of their biological relatives including parents, grandparents, uncles, and aunts and determined which of these relatives developed dementia over time.
In adjusted analyses, parents of individuals with ADHD had 34% higher risk for any dementia than parents of those without ADHD (hazard ratio, 1.34; 95% CI, 1.11-1.63).
The risk for AD, the most common type of dementia, was 55% higher in parents of individuals with ADHD (HR, 1.55; 95% CI, 1.26-1.89).
Individuals with ADHD were more likely to have parents with early-onset dementia rather than late-onset dementia. However, the absolute risk for dementia was low for the parent cohort: Only 0.17% of the parents were diagnosed with dementia during follow-up.
The association between ADHD and dementia was not as strong for second-degree relatives of individuals with ADHD. For example, grandparents of individuals with ADHD had a 10% increased risk for dementia, compared with grandparents of individuals without ADHD.
The finding of attenuated associations with decreasing genetic relatedness (parents > grandparents and uncles/aunts), points to shared familial risk between ADHD and AD, the researchers said.
There could be “undiscovered genetic variants that contribute to either traits or family-wide environmental risk factors, such as socioeconomic status, that may have an impact on the association,” Dr. Chang said in the news release.
“There are no direct clinical implications from this study, but research like this could lead to further research with goals for improved detection, prevention, and treatment,” he said in an interview.
More questions than answers
Heather Snyder, PhD, vice president of medical and scientific relations for the Alzheimer’s Association that the way different brain diseases are linked “is a question the Alzheimer’s Association is often asked, and it is a part of our funding portfolio to get that question answered.”
This study looking at ADHD and dementia is “intriguing,” Dr. Snyder said, “because, right now, there is limited information available. That said, this is an association study; it shows that two things are somehow connected. Because of how the study was conducted, it does not – and cannot – prove causation,” Dr. Snyder said. “But it is interesting all the same. More research is needed to uncover specifically why and how these two diseases are related. That might eventually give us insight into how to manage risk or even improve treatment.”
The study was supported by grants from the Swedish Council for Health, Working Life and Welfare, the Swedish Research Council, the Swedish Brain Foundation, the European Union’s Horizon 2020 research and innovation program under the Marie Skłodowska-Curie, the Fredrik & Ingrid Thurings Stiftelse, and the Karolinska Institutet Research Foundation. Dr. Chang and Dr. Snyder disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
results from a large, multigenerational study show.
“The findings suggest there are common genetic and/or environmental contributions to the association between ADHD and dementia,” study investigator Zheng Chang, PhD, from the department of medical epidemiology and biostatistics at Karolinska Institute, Stockholm, said in a statement.
“There have been few studies previously on the link between ADHD and dementia, all with limited sample size,” Dr. Chang said in an interview.
“This is the first study to look at ADHD and dementia within extended families. It’s a large population-based study including over 2 million individuals and their over 5 million biological relatives,” he noted.
The study was published online Sept. 9, 2021, in the journal Alzheimer’s & Dementia.
Shared familial risk
The researchers identified roughly 2.1 million people born in Sweden between 1980 and 2001. Overall, 3.2% of the cohort had a diagnosis of ADHD.
Using national registries, they linked these individuals to more than 5 million of their biological relatives including parents, grandparents, uncles, and aunts and determined which of these relatives developed dementia over time.
In adjusted analyses, parents of individuals with ADHD had 34% higher risk for any dementia than parents of those without ADHD (hazard ratio, 1.34; 95% CI, 1.11-1.63).
The risk for AD, the most common type of dementia, was 55% higher in parents of individuals with ADHD (HR, 1.55; 95% CI, 1.26-1.89).
Individuals with ADHD were more likely to have parents with early-onset dementia rather than late-onset dementia. However, the absolute risk for dementia was low for the parent cohort: Only 0.17% of the parents were diagnosed with dementia during follow-up.
The association between ADHD and dementia was not as strong for second-degree relatives of individuals with ADHD. For example, grandparents of individuals with ADHD had a 10% increased risk for dementia, compared with grandparents of individuals without ADHD.
The finding of attenuated associations with decreasing genetic relatedness (parents > grandparents and uncles/aunts), points to shared familial risk between ADHD and AD, the researchers said.
There could be “undiscovered genetic variants that contribute to either traits or family-wide environmental risk factors, such as socioeconomic status, that may have an impact on the association,” Dr. Chang said in the news release.
“There are no direct clinical implications from this study, but research like this could lead to further research with goals for improved detection, prevention, and treatment,” he said in an interview.
More questions than answers
Heather Snyder, PhD, vice president of medical and scientific relations for the Alzheimer’s Association that the way different brain diseases are linked “is a question the Alzheimer’s Association is often asked, and it is a part of our funding portfolio to get that question answered.”
This study looking at ADHD and dementia is “intriguing,” Dr. Snyder said, “because, right now, there is limited information available. That said, this is an association study; it shows that two things are somehow connected. Because of how the study was conducted, it does not – and cannot – prove causation,” Dr. Snyder said. “But it is interesting all the same. More research is needed to uncover specifically why and how these two diseases are related. That might eventually give us insight into how to manage risk or even improve treatment.”
The study was supported by grants from the Swedish Council for Health, Working Life and Welfare, the Swedish Research Council, the Swedish Brain Foundation, the European Union’s Horizon 2020 research and innovation program under the Marie Skłodowska-Curie, the Fredrik & Ingrid Thurings Stiftelse, and the Karolinska Institutet Research Foundation. Dr. Chang and Dr. Snyder disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.